Codebook constraint, codebook parameter determination method and device
A technology of codebooks and codebook subsets, which is applied in the codebook parameter determination method and device, and in the field of codebook constraints, and can solve problems such as inability to directly use codebooks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
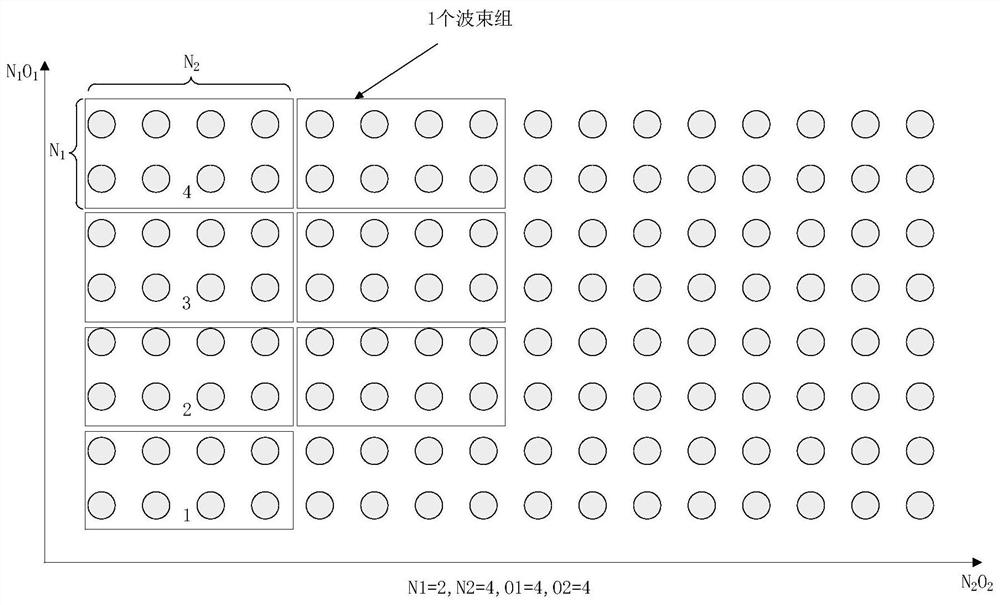
[0145] Assume that the numbers of antenna ports are N1 and N2, where N1 represents the number of antenna ports in the first dimension, and N2 represents the number of antenna ports in the second dimension. The oversampling factors of the beams in the codebook are O1 and O2. In this way, the candidate combined beam set contains N1O1N2O2 beams, and each beam is expressed as The system agrees to divide adjacent N1N2 beams into one group, and there are O1O2 groups in total, such as figure 1 shown.
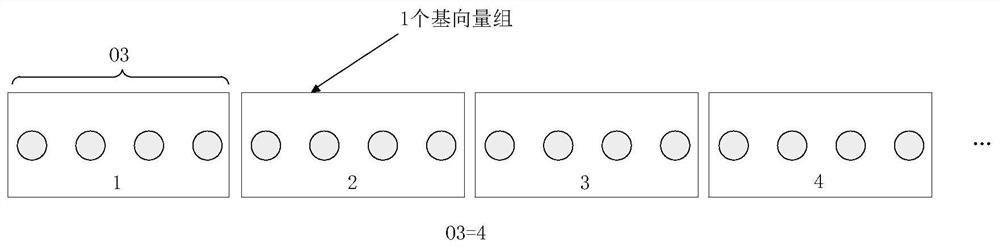
[0146] Assume that the length of the candidate base vector is N, and the number of vectors in the candidate base vector set is N*O3, where O3 represents an oversampling factor. Then each candidate basis vector can be expressed as [f i,0 f i,1 … f i,N-1 ] H ,i=0,1,...,N·O 3 -1. The system predefines that the adjacent O3 beams in the N*O3 candidate beam vector sets are divided into one group, and there are N groups in total, such as figure 2 shown.
[0147] When Rank=1, the...
Embodiment 2
[0159] The system stipulates that the coefficients in the coefficient set corresponding to each beam are restricted to the value of the sum of all amplitude coefficients in the restricted set; at the same time, the system stipulates that each constrained basis vector cannot be used in the codebook.
[0160] The base station indicates through high-level signaling that the two beam groups in the candidate beam set are constrained (such as figure 1 Beamgroups 1 and 2 in beamgroup 1 and 2), and high-level signaling indicates that the amplitude constraints of the 8 beams in beamgroup 1 and the 8 beams in beamgroup 2 are {P max1 P max2 …P max16}, whose value can be selected from the quantized value of the amplitude coefficient of the Type II codebook. The terminal determines W according to the channel estimation result 1 When the second beam among the L beams is the third among the 16 constrained beams, the constraint The coefficients in satisfy:
[0161] as well as,
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0166] If W 1 The basis vectors corresponding to each beam in can be different, at this time The value of M in each row of can be different, assuming that the value of the i-th row is denoted as Mi.
[0167] In this case, in addition to the above constraint indication, the set of candidate basis vectors for each beam, or the value of the number of basis vectors corresponding to each beam may also be indicated through high-layer signaling. For example using 2L x NO 3 The bitmap of indicates the candidate basis vectors that each beam can choose, as shown in the following table. Alternatively, 2L×N positions are used to indicate the candidate basis vector groups that can be selected by each beam.
[0168]
[0169] As shown in the table, a bit value of 1 indicates that the base vector can be used, otherwise, the base vector cannot be used.
[0170] In addition, the value of the number of basis vectors corresponding to each beam can also be constrained, that is, the constra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com