Patents
Literature
734 results about "Oversampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
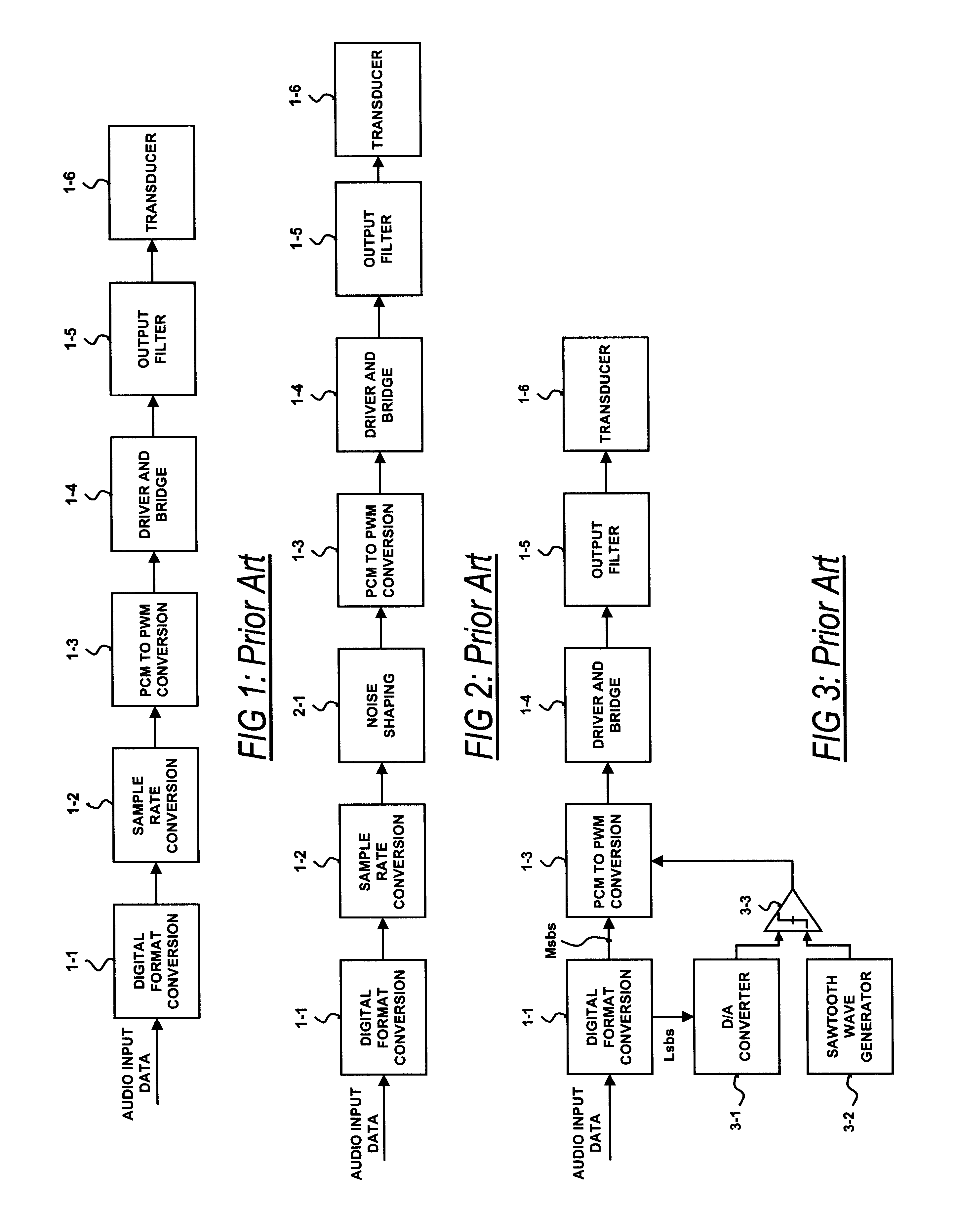
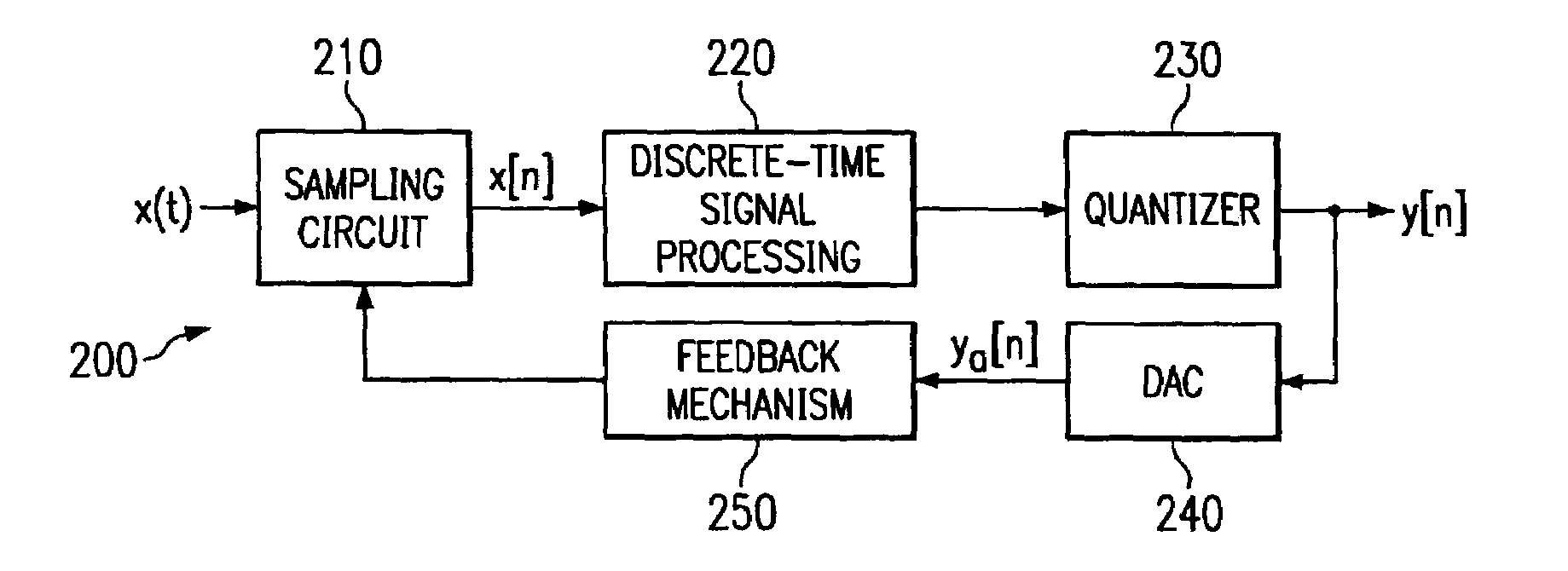
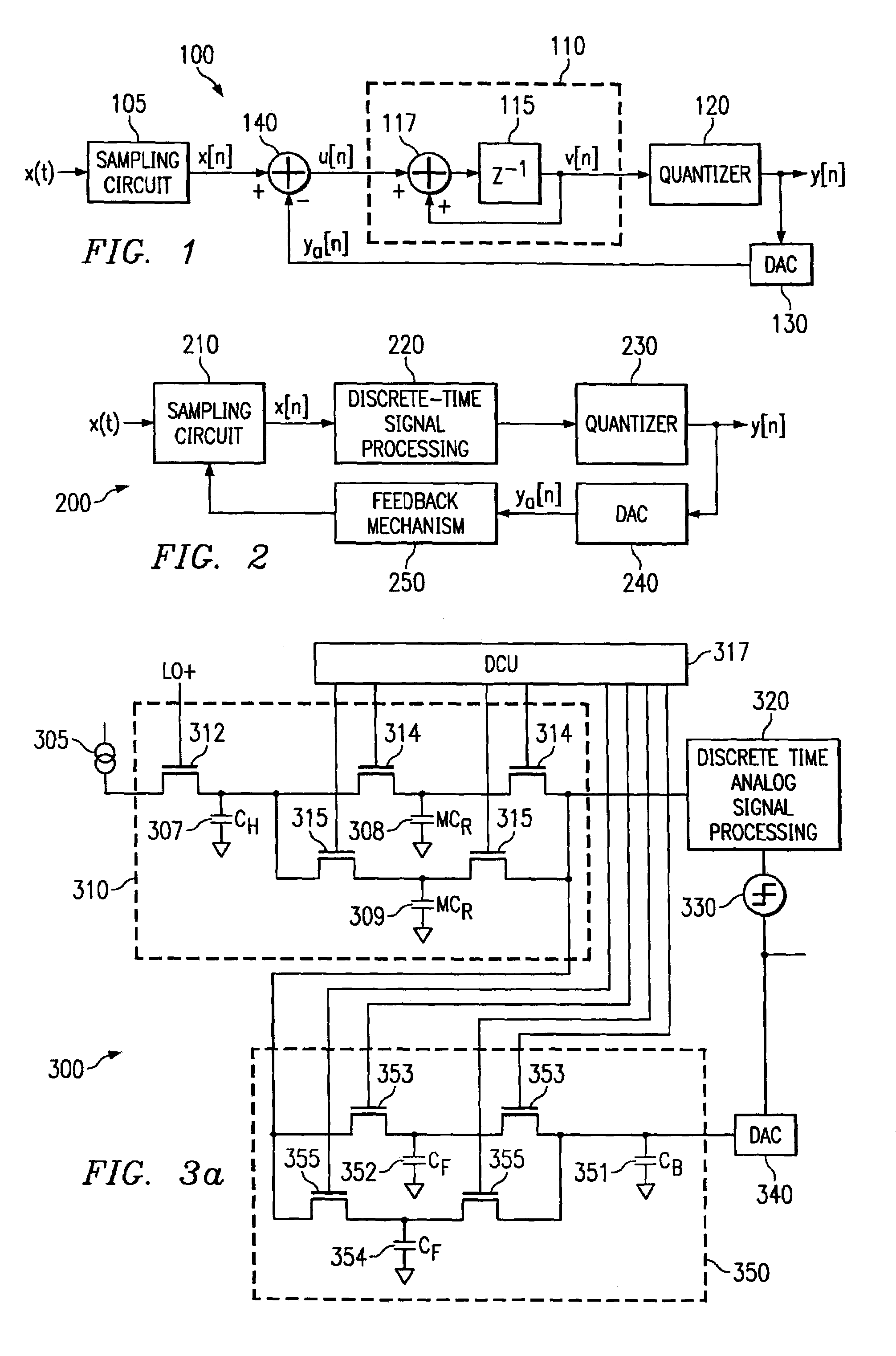
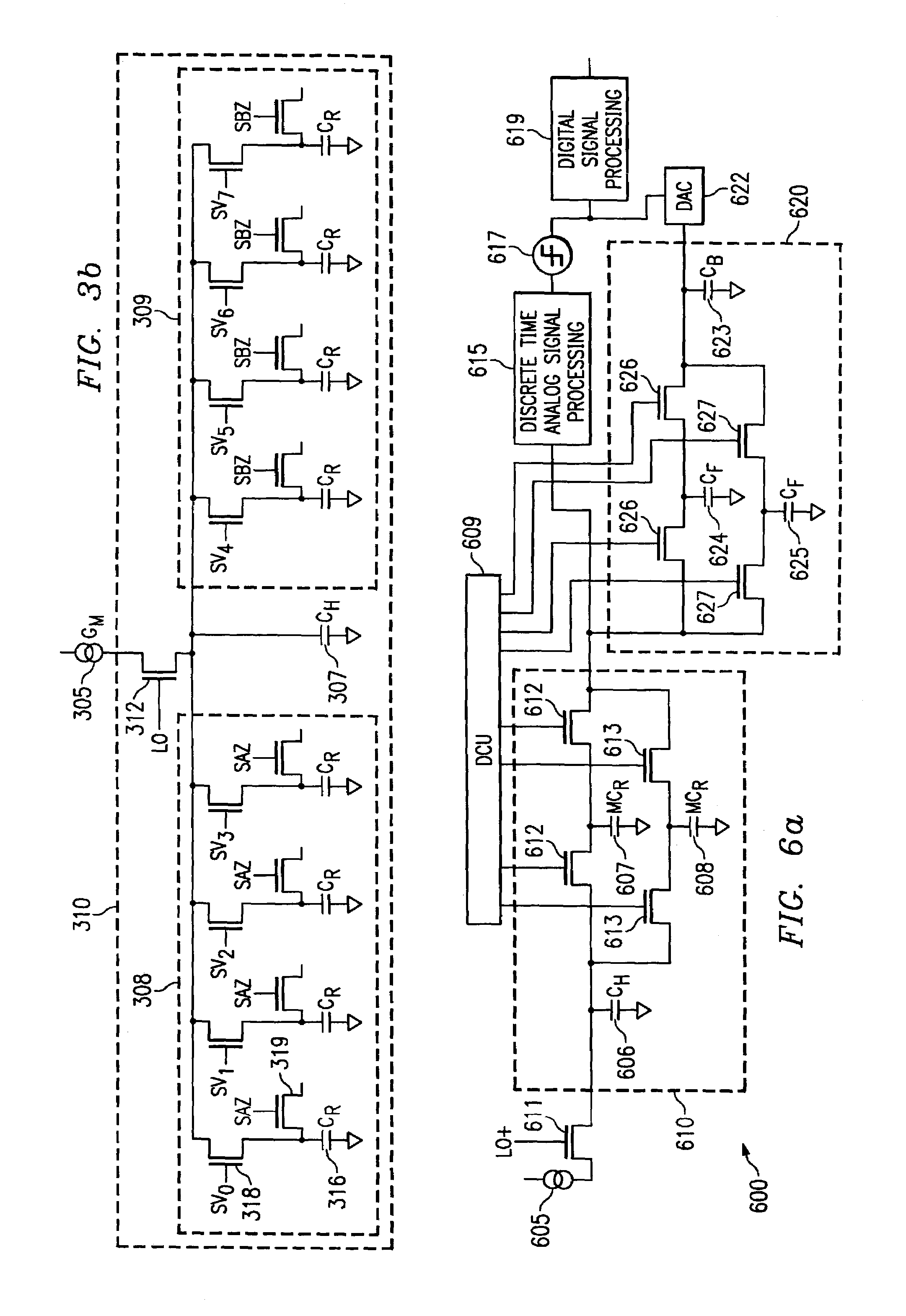
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal at a sampling frequency significantly higher than the Nyquist rate. Theoretically, a bandwidth-limited signal can be perfectly reconstructed if sampled at the Nyquist rate or above it. The Nyquist rate is defined as twice the highest frequency component in the signal. Oversampling is capable of improving resolution and signal-to-noise ratio, and can be helpful in avoiding aliasing and phase distortion by relaxing anti-aliasing filter performance requirements.
Methods apparatus and data structures for enhancing the resolution of images to be rendered on patterned display devices
InactiveUS6393145B2Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementSub-pixel resolutionArray data structure
Techniques for improving the resolution of images (either analog images, analytic images, or images having a higher resolution than that of a display device) to be rendered on patterned displays. In one aspect of the present invention, an overscaling or oversampling process may accept analytic character information, such as contours for example, and a scale factor or grid and overscale or oversample the analytic character information to produce an overscaled or oversampled image. The overscaled or oversampled image generated has a higher resolution than the display upon which the character is to be rendered. Displaced samples of the overscaled or oversampled image are then combined (or filtered). An analytic image, such as a line drawing for example, may be applied to the oversampling / overscaling process as was the case with the character analytic image. However, since the analytic image may have different units than that of the character analytic image, the scale factor applied may be different. Since an ultra resolution image is already "digitized", that is, not merely mathematically expressed contours or lines between points, it may be applied directly to a process for combining displaced samples of the ultra-resolution image to generate another ultra-resolution image (or an image with sub-pixel information). The functionality of the overscaling / oversampling process and the processes for combining displaced samples may be combined into a single step analytic to digital sub-pixel resolution conversion process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Methods apparatus and data structures for enhancing the resolution of images to be rendered on patterned display devices
InactiveUS20010048764A1Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSub-pixel resolutionArray data structure
Techniques for improving the resolution of images (either analog images, analytic images, or images having a higher resolution than that of a display device) to be rendered on patterned displays. In one aspect of the present invention, an overscaling or oversampling process may accept analytic character information, such as contours for example, and a scale factor or grid and overscale or oversample the analytic character information to produce an overscaled or oversampled image. The overscaled or oversampled image generated has a higher resolution than the display upon which the character is to be rendered. Displaced samples of the overscaled or oversampled image are then combined (or filtered). An analytic image, such as a line drawing for example, may be applied to the oversampling / overscaling process as was the case with the character analytic image. However, since the analytic image may have different units than that of the character analytic image, the scale factor applied may be different. Since an ultra resolution image is already "digitized", that is, not merely mathematically expressed contours or lines between points, it may be applied directly to a process for combining displaced samples of the ultra-resolution image to generate another ultra-resolution image (or an image with sub-pixel information). The functionality of the overscaling / oversampling process and the processes for combining displaced samples may be combined into a single step analytic to digital sub-pixel resolution conversion process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
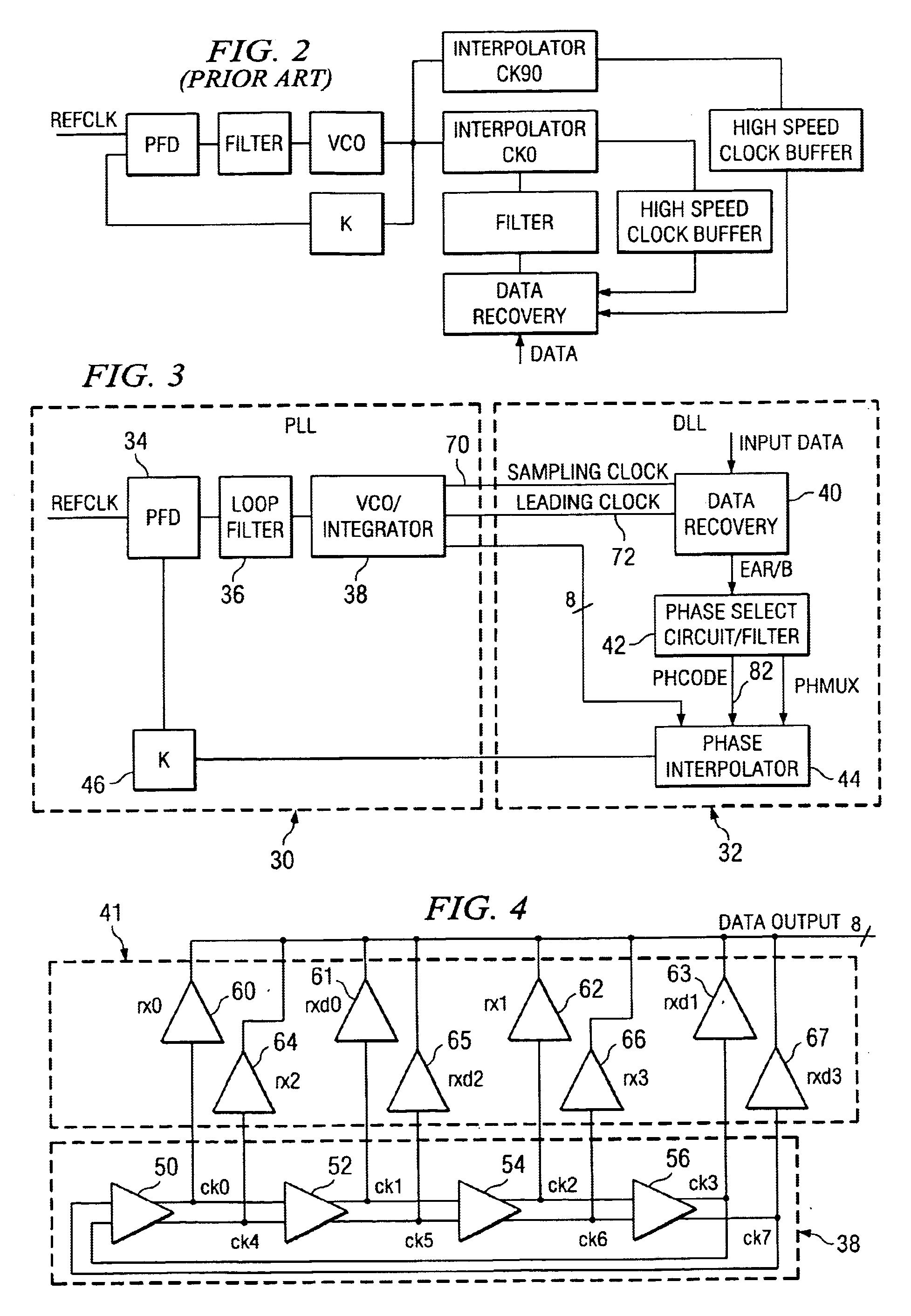
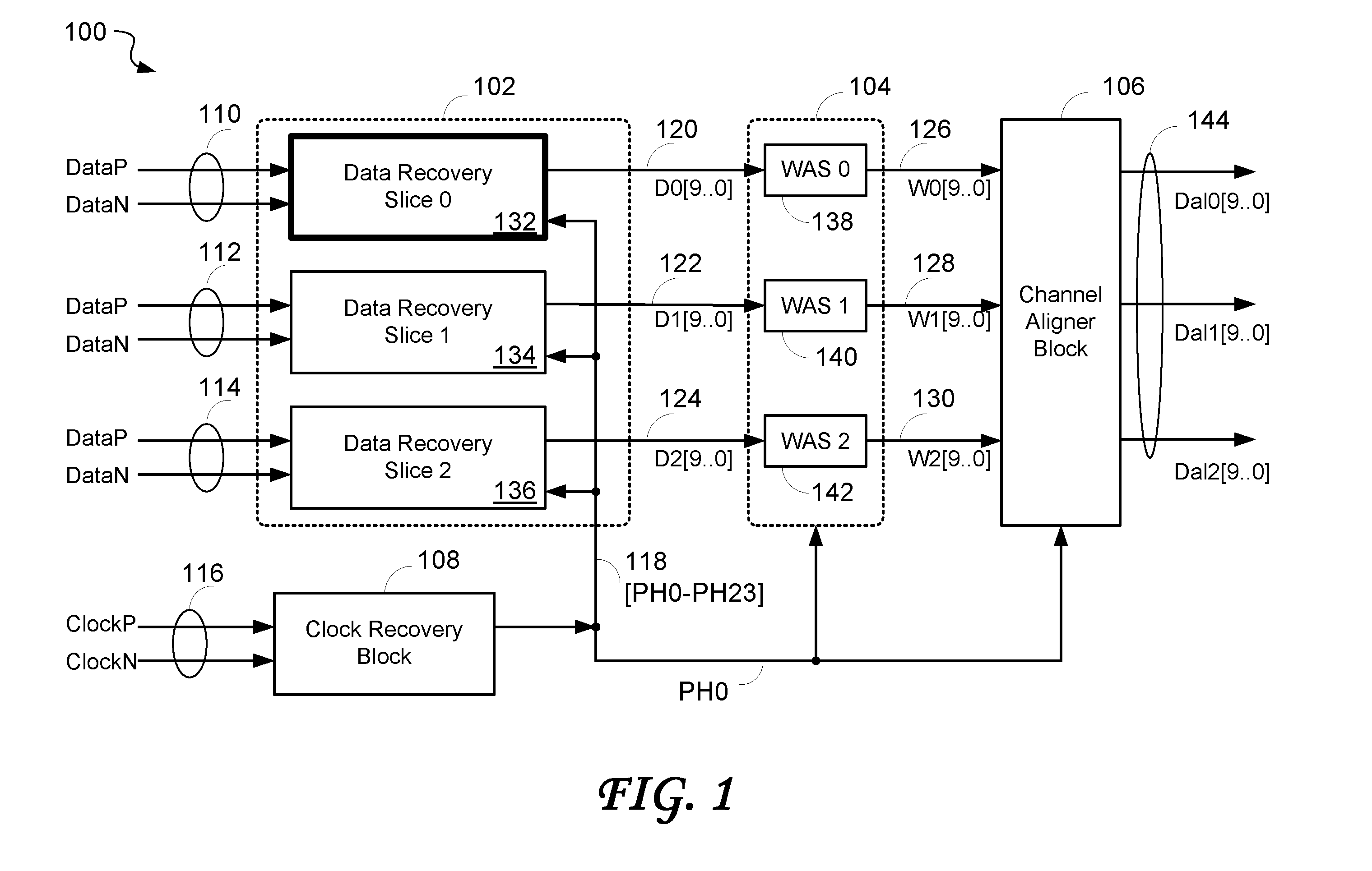
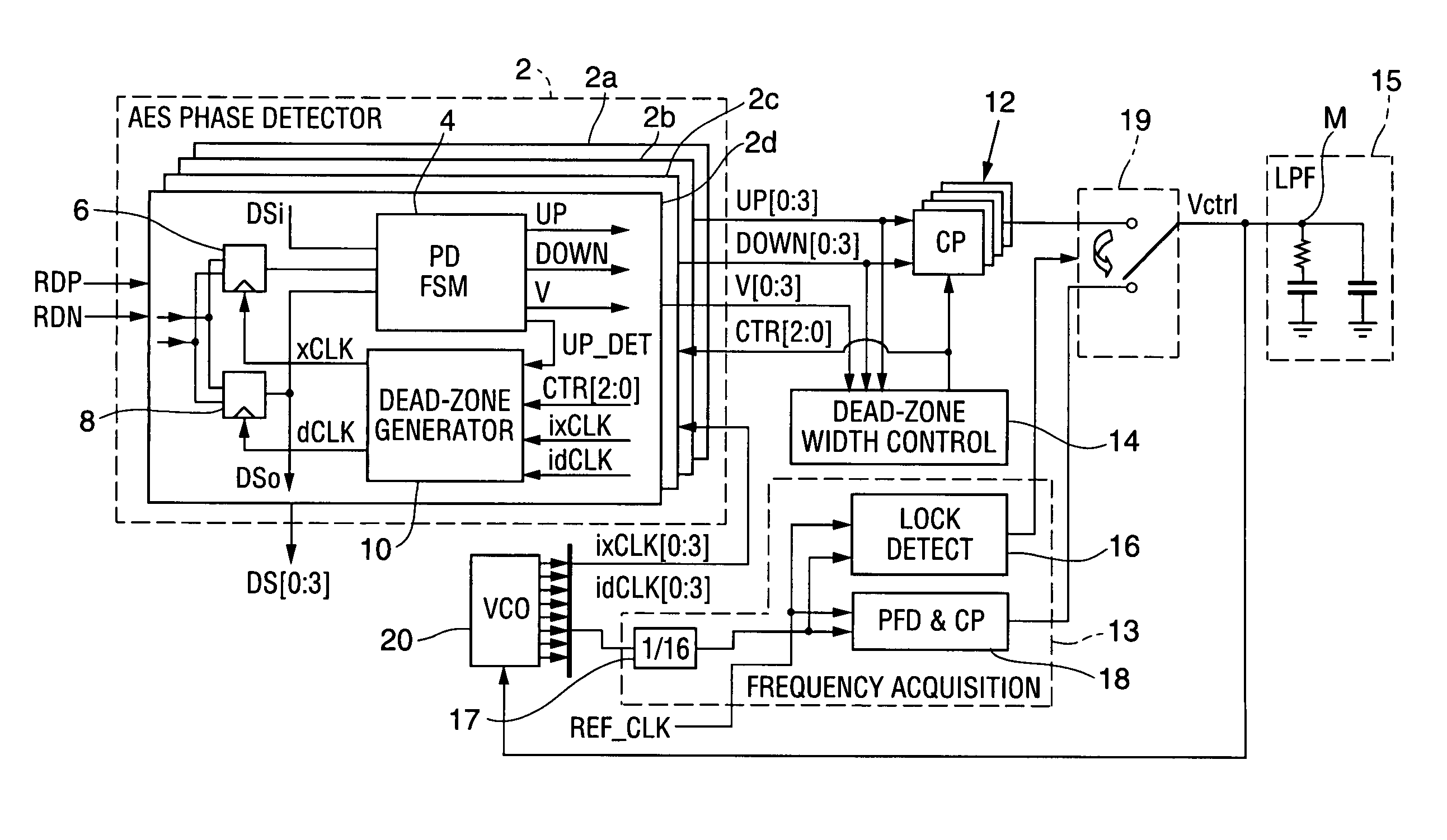
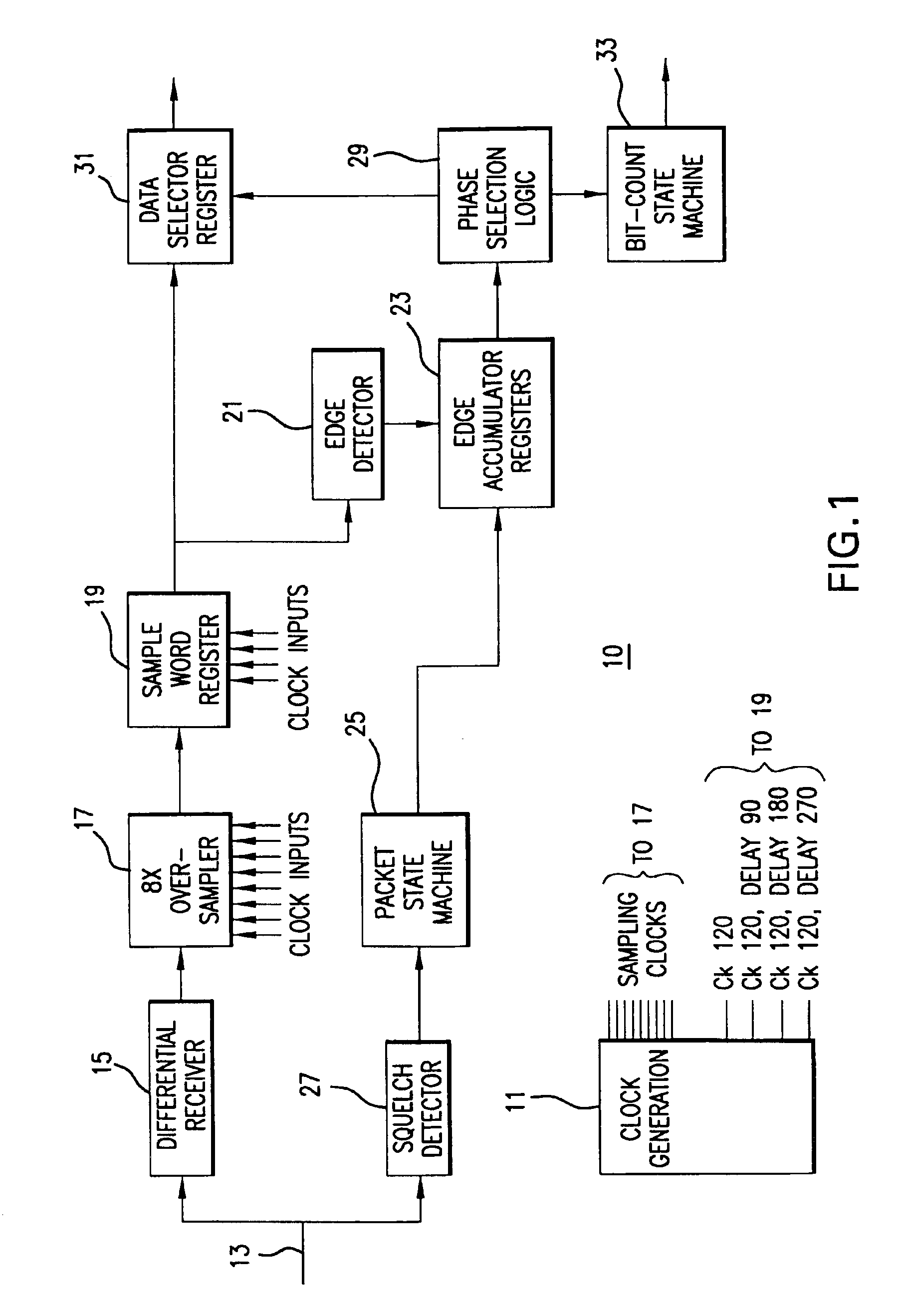
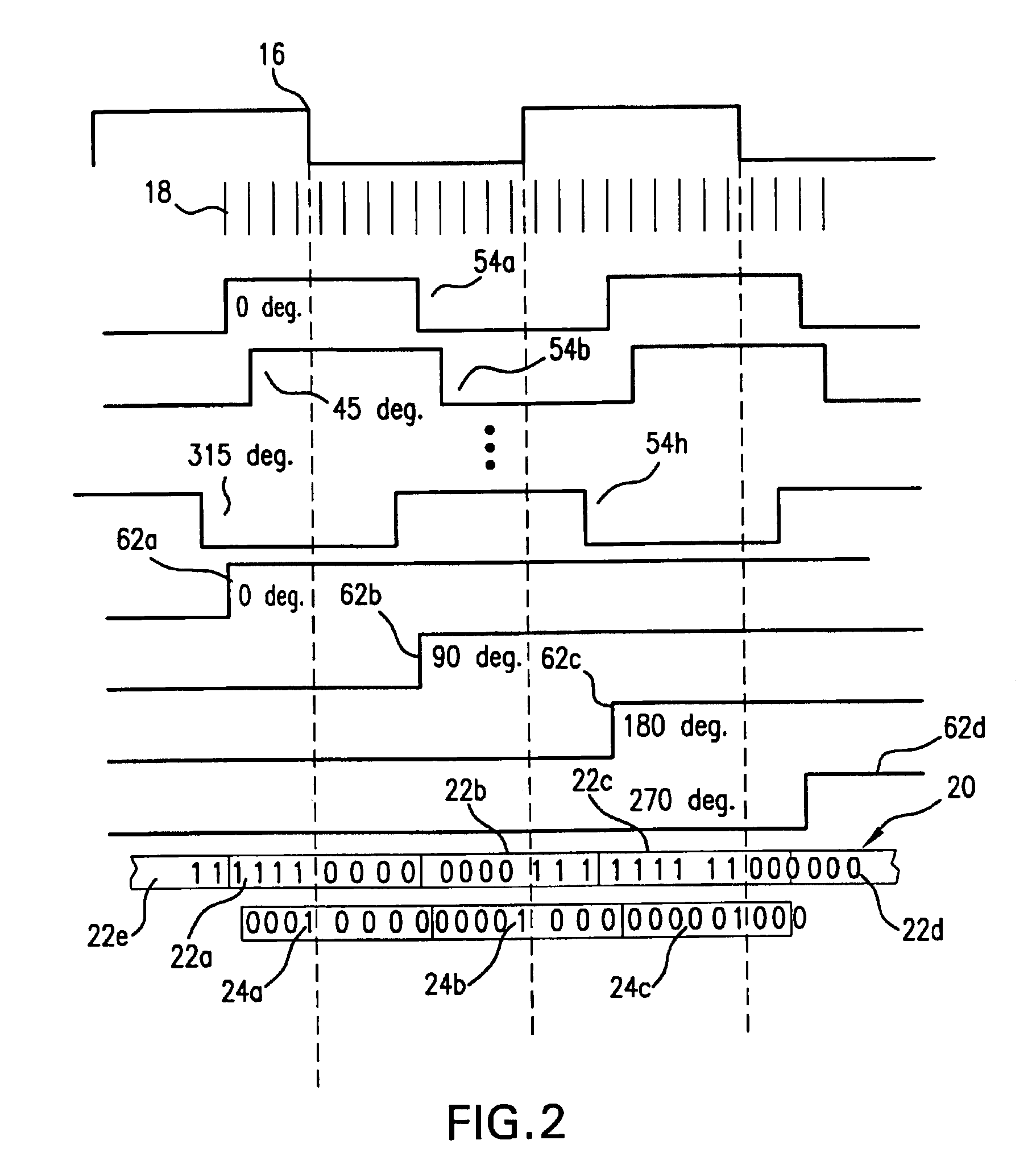
Time division multiplex data recovery system using close loop phase and delay locked loop
InactiveUS6901126B1Alleviate duty cycle issuesHigh bandwidthPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDelay-locked loopClosed loop
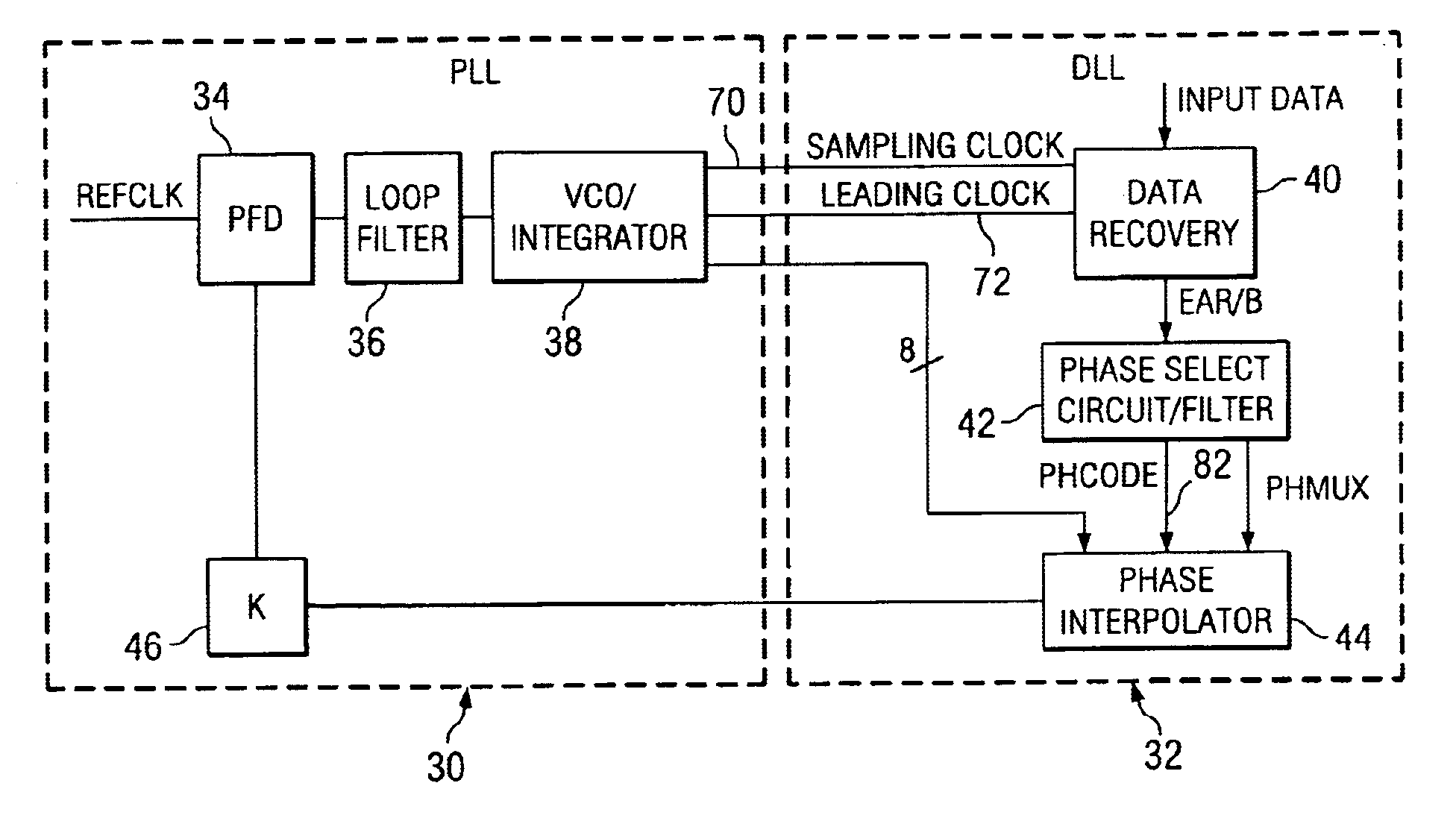
A time division multiplex data recovery system using a closed-loop phase lock loop (PLL) and delay locked loop (DLL) is disclosed. In other words, one closed loop comprises both a phase locked loop (PLL) and a delay locked loop (DLL) in a novel time division multiplex data recovery system. This new architecture comprises a 4 stage Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) used to generate 8 clock signals, 45 degrees phase shifted from one another, for 8 receivers to do the oversampling. An interpolator tracks the received data signal and feeds it back to the Phase / Frequency Detector (PFD). The PFD has a second input of the reference clock which the PFD uses along with the interpolator input to correct the frequency of the PLL. The PLL operates at a high bandwidth. The DLL's bandwidth is several orders lower than the PLL. The DLL activates only a multiplexer and an interpolator continuously, thereby drawing a minimum amount of power.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
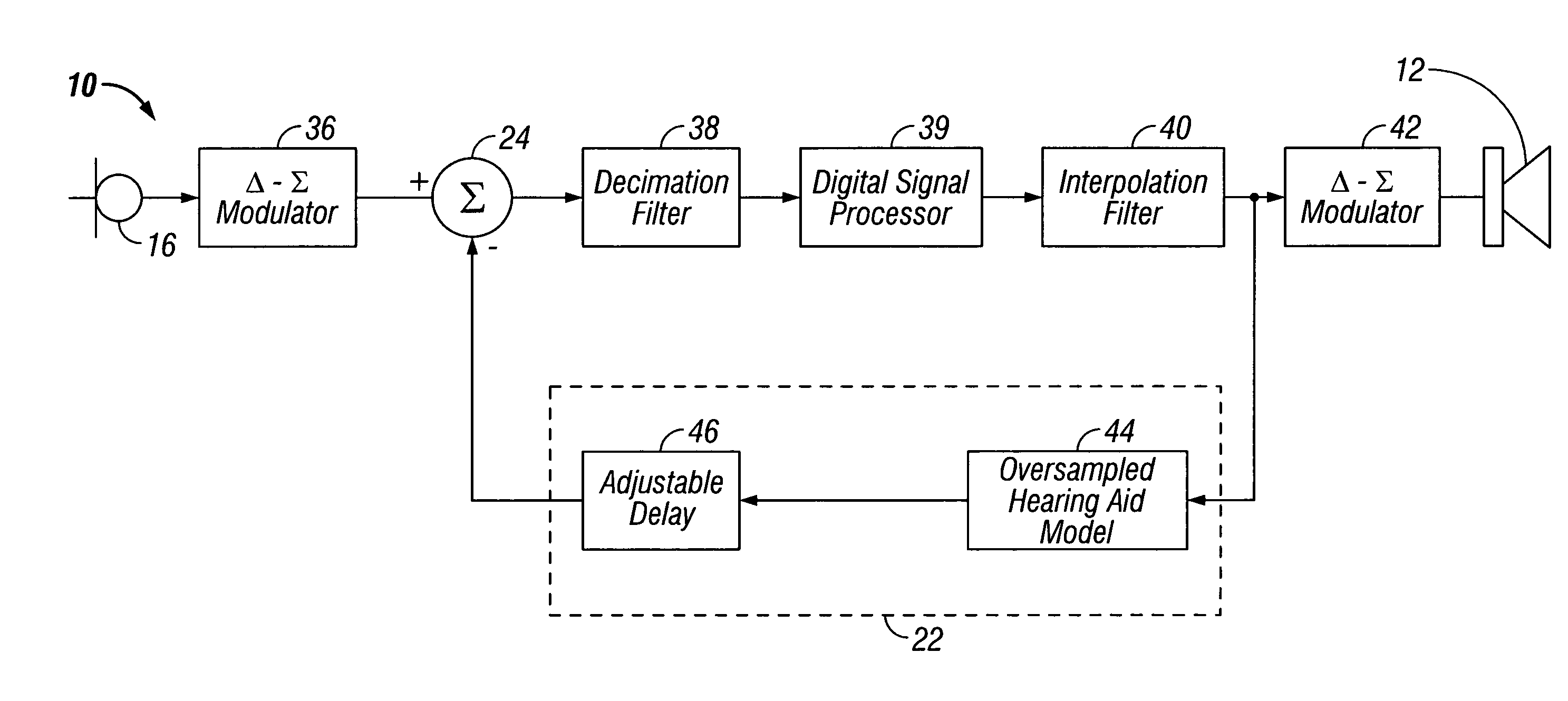
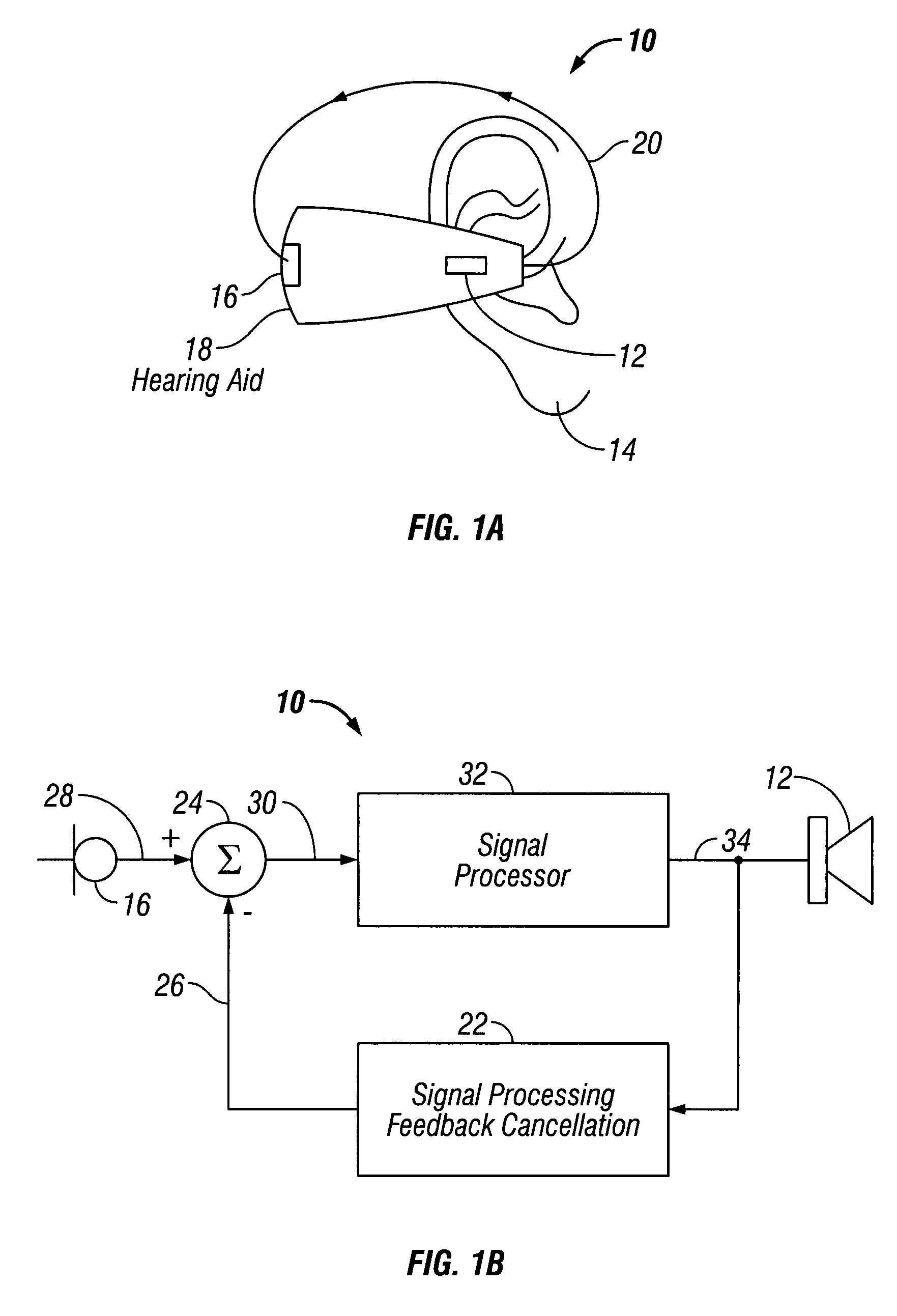
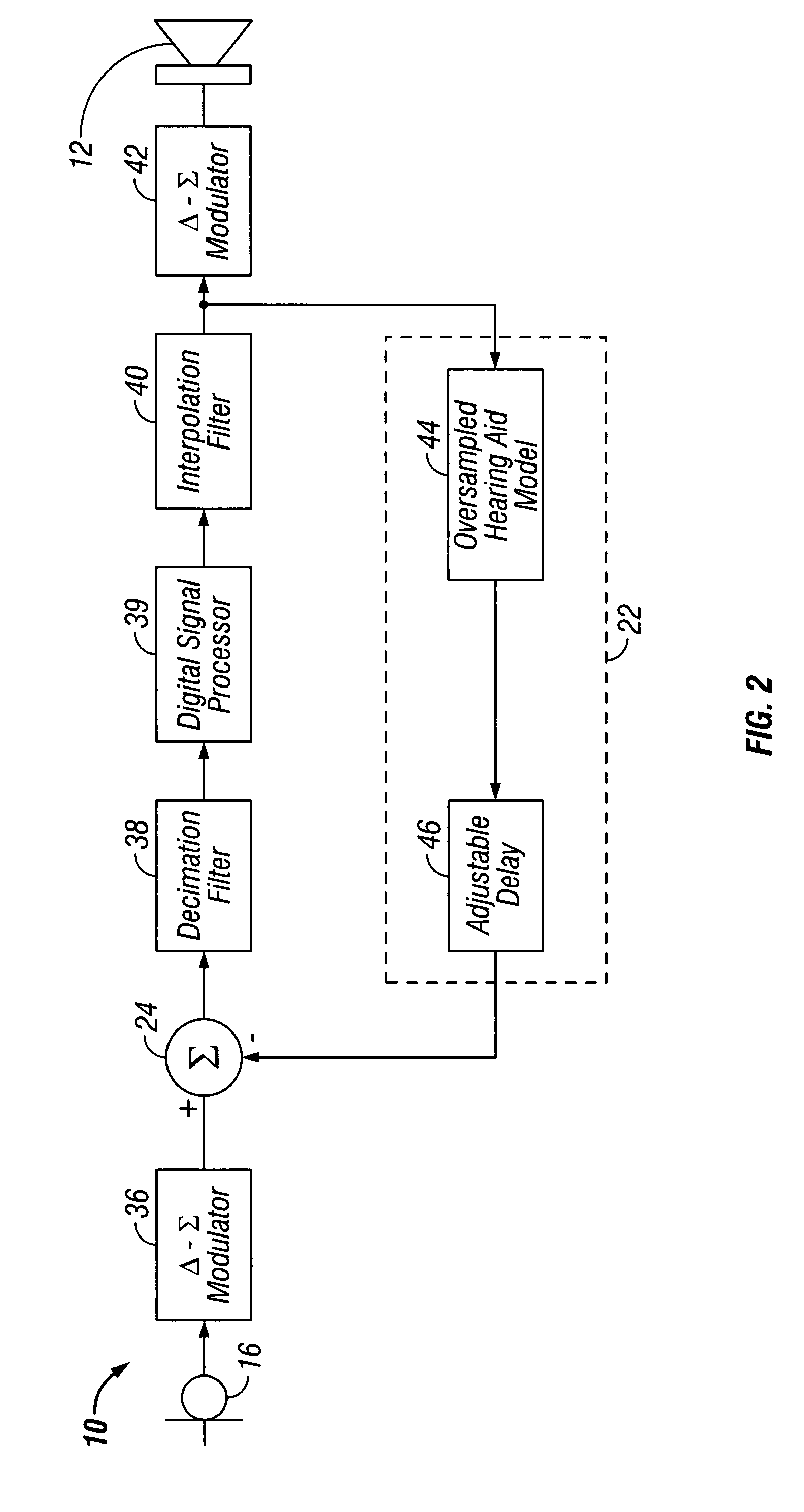
Low-delay signal processing based on highly oversampled digital processing
ActiveUS7365669B1High oversampling rateLower latencyAnalogue conversionSpeech analysisAnalog signalOversampling
A low-delay signal processing system and method are provided which includes a delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter, an oversampling processor, and a delta-sigma digital-to-analog converter. The delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter receives an input or audio signal and generates a digital sample signal at a high oversampling rate. The oversampling processor is connected to the analog-to-digital converter for processing the digital sample signal at the high oversampling rate with low-delay. The delta-sigma digital-to-analog converter is connected to the oversampling processor for receiving the digital sample signal at the high oversampling rate with low-delay for generating an analog signal. The oversampling processor includes a low-delay filter and a programmable delay element. In this manner, the analog signal is produced with a low delay and high accuracy.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
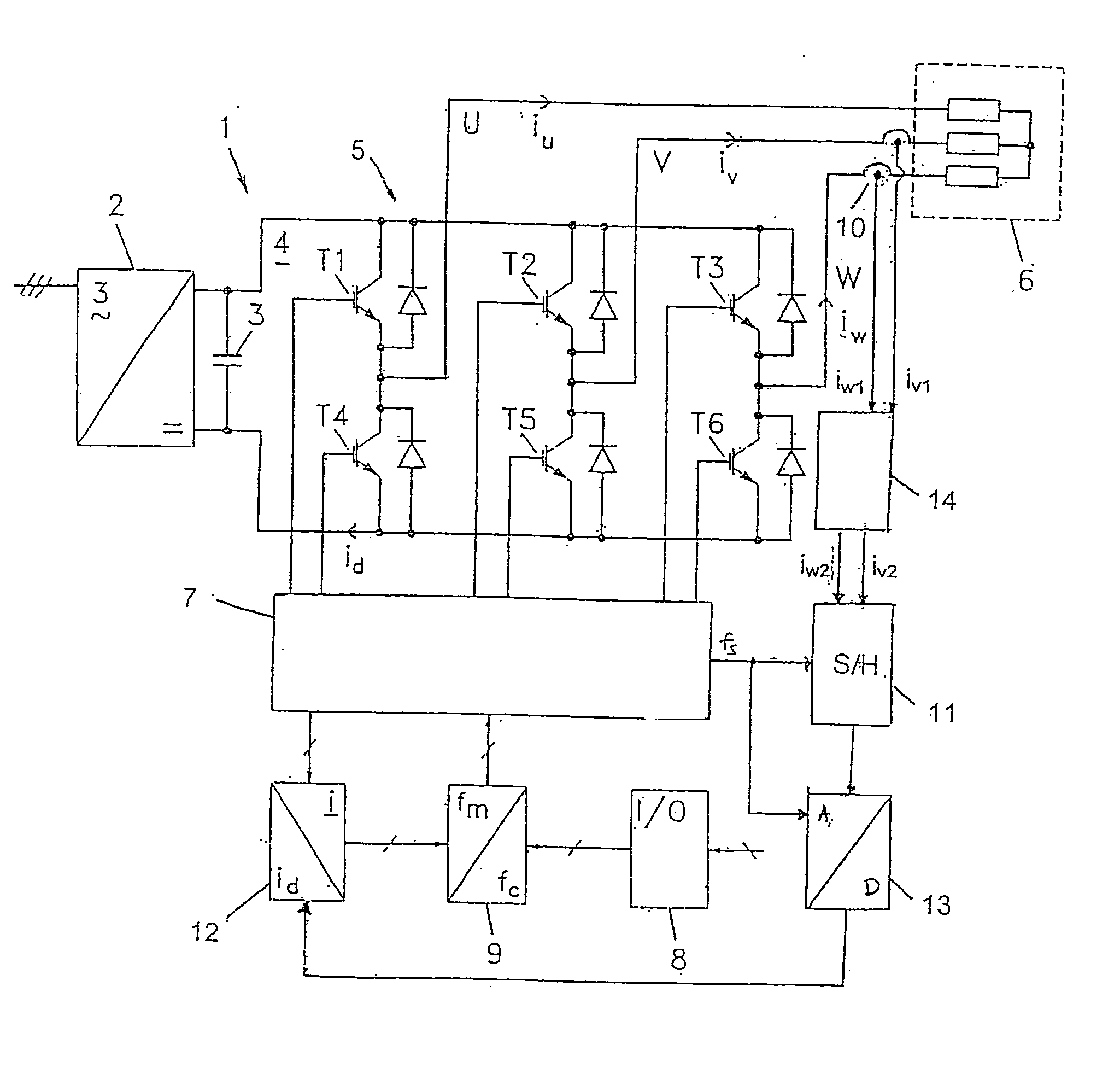
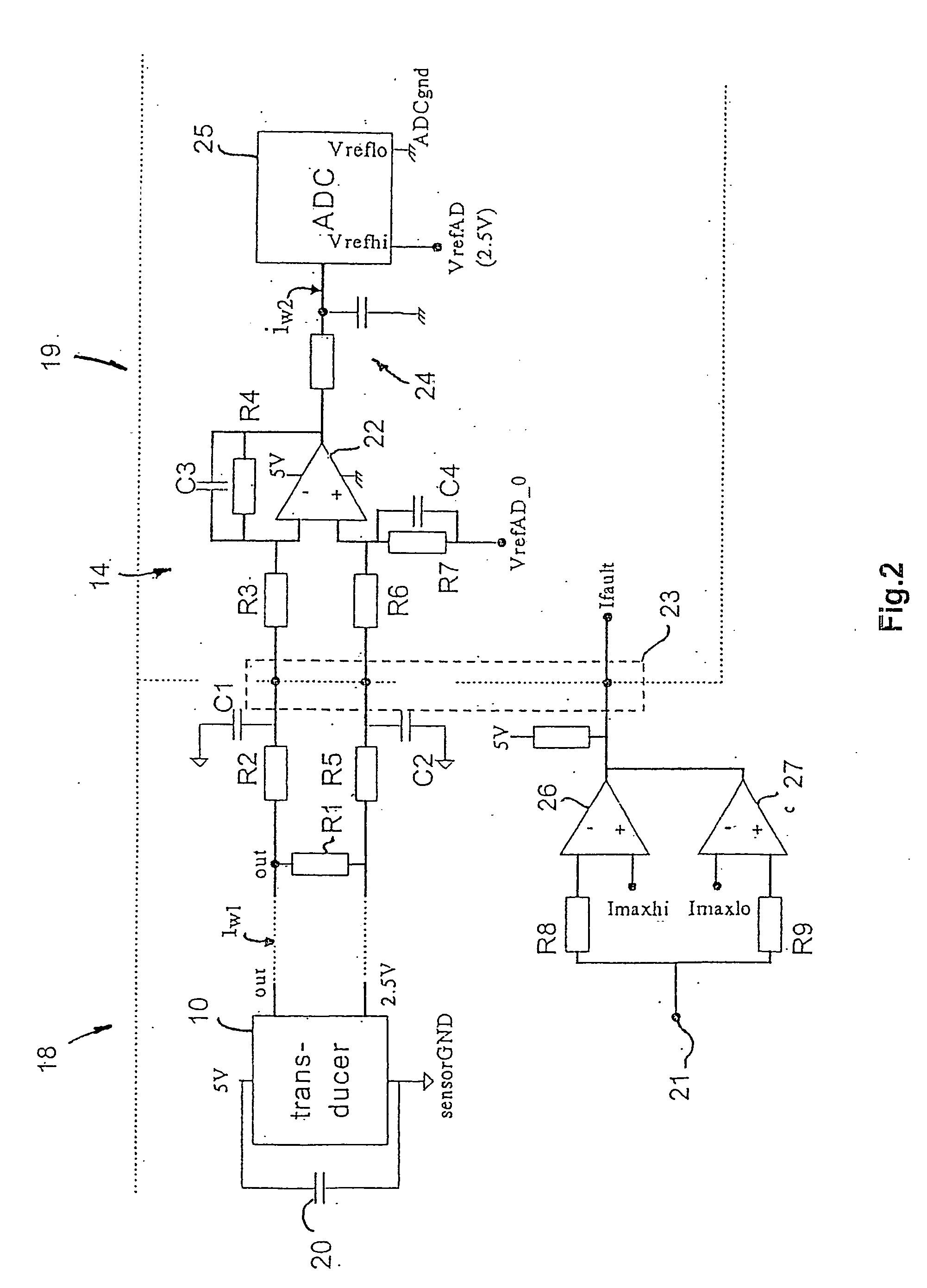
Method for measuring currents in a motor controller and motor controller using such method
InactiveUS20050190094A1Increase heightReduce random noiseElectric signal transmission systemsField or armature current controlSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Differential transmission
The invention relates to a method for measuring currents in a motor controller. Some current sensing devices placed on the motor wires or inside the motor controller provide low amplitude output signals thus complicating sampling and data processing. In order to improve the signal / noise ratio, an oversampling technique is disclosed which makes used of a differential transmission of the output signal. Further, by applying intelligent sorting techniques on the sampled data, a substantial improvement in the signal / noise ratio can be obtained. The invention also concerns a motor controller using this method, and discloses the use of a power card and a control card, where the current sensing device is placed on the power card and a differential amplifier is placed on the control card. The gain of the differential amplifier is controlled by components placed on the power card as well as on the control card.
Owner:DANFOSS DRIVES
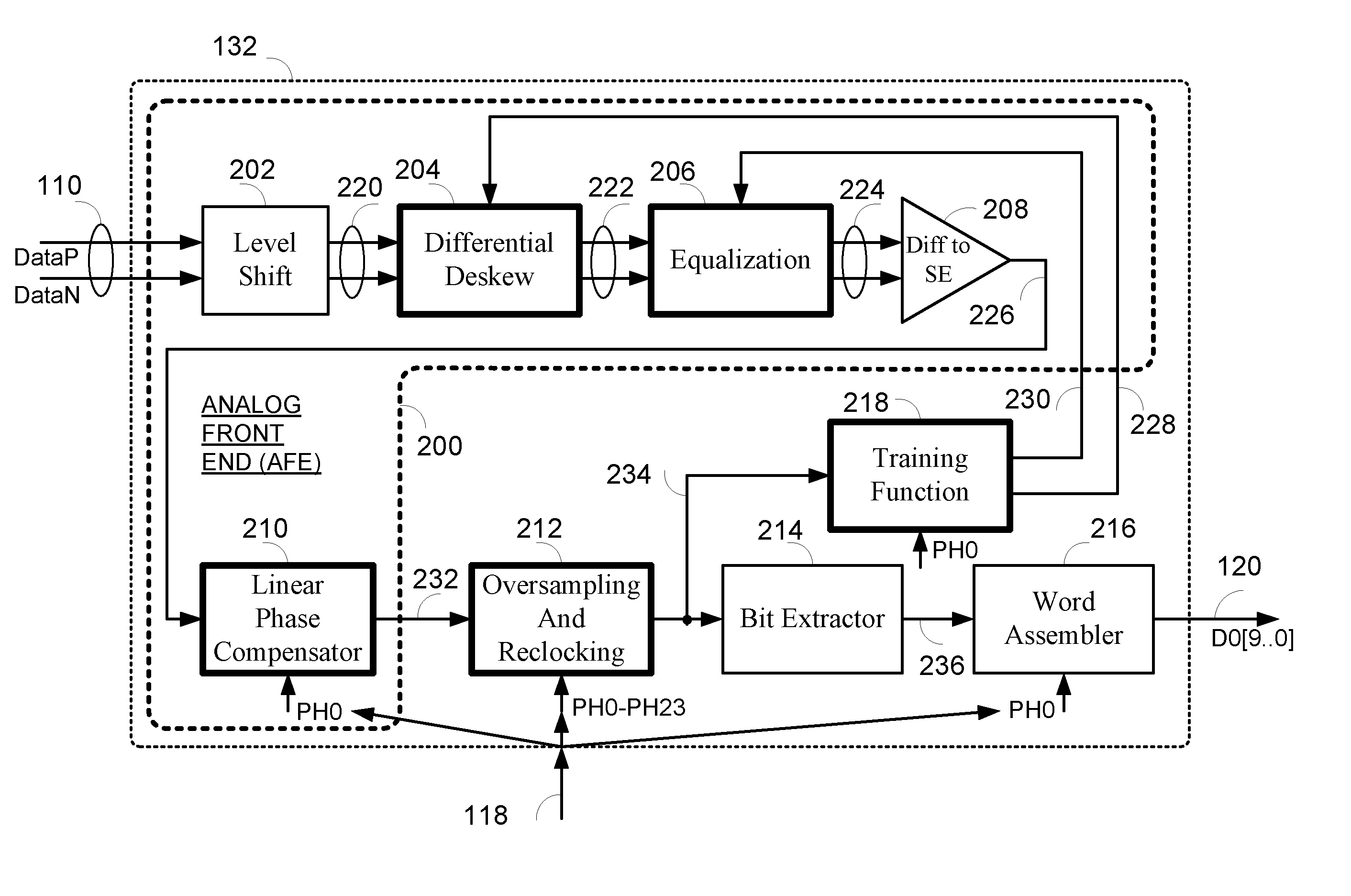
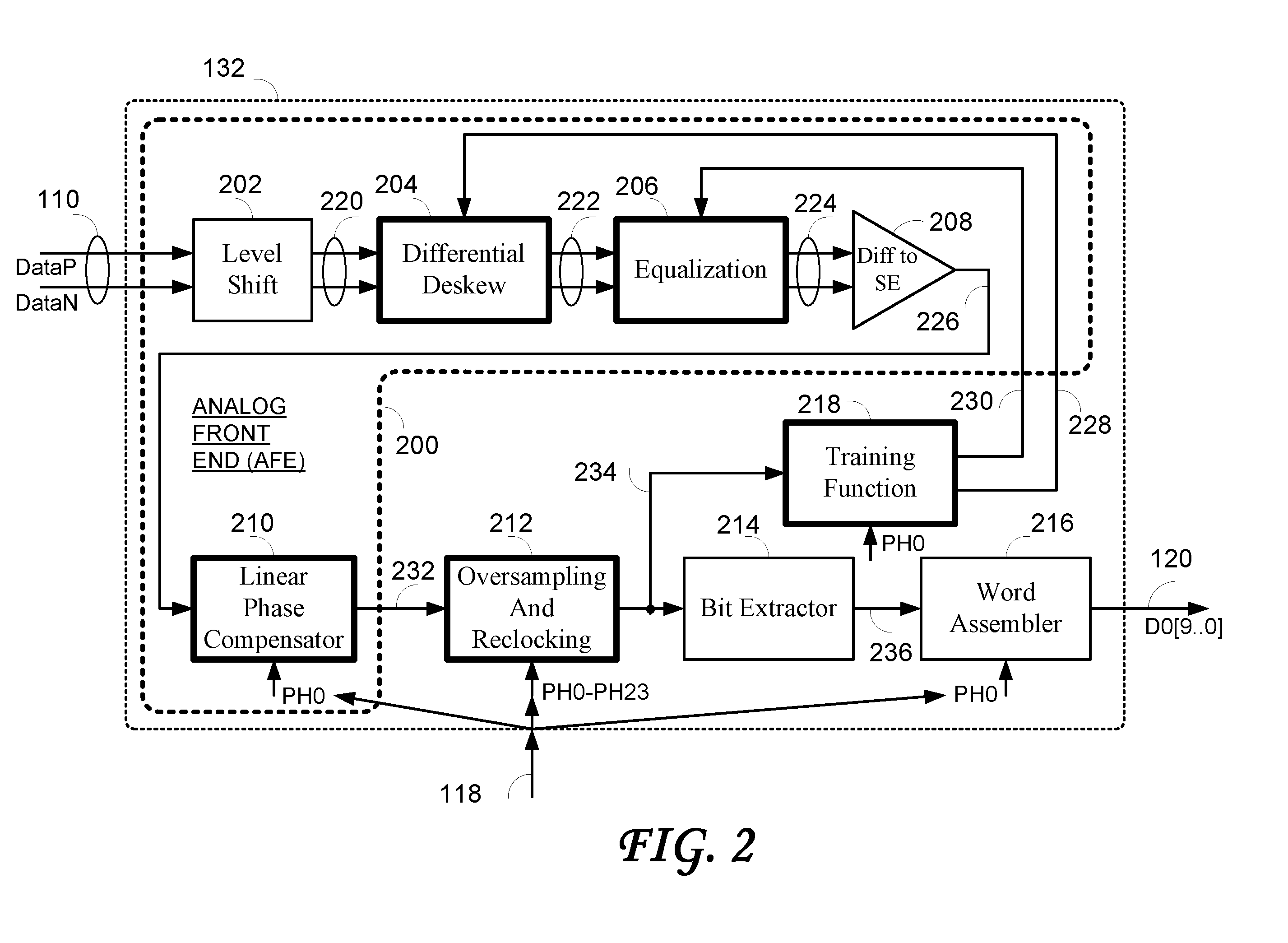
Data recovery system for source synchronous data channels
ActiveUS20070164802A1Easy Data RecoveryReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulator24-bitAnalog signal
A high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) receiver recovers high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels of a lossy cable, along with a clock. Inter symbol interference, high-frequency loss, skew between the clock and data channels, and differential skew within a differential signal are compensated by analog circuits which are automatically tuned for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. Oversampling is used to provide a 24-bit digital representation of the analog signal for determining the quality of the signal. A corresponding method of deskewing a differential signal and a system and circuit therefor are also provided.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
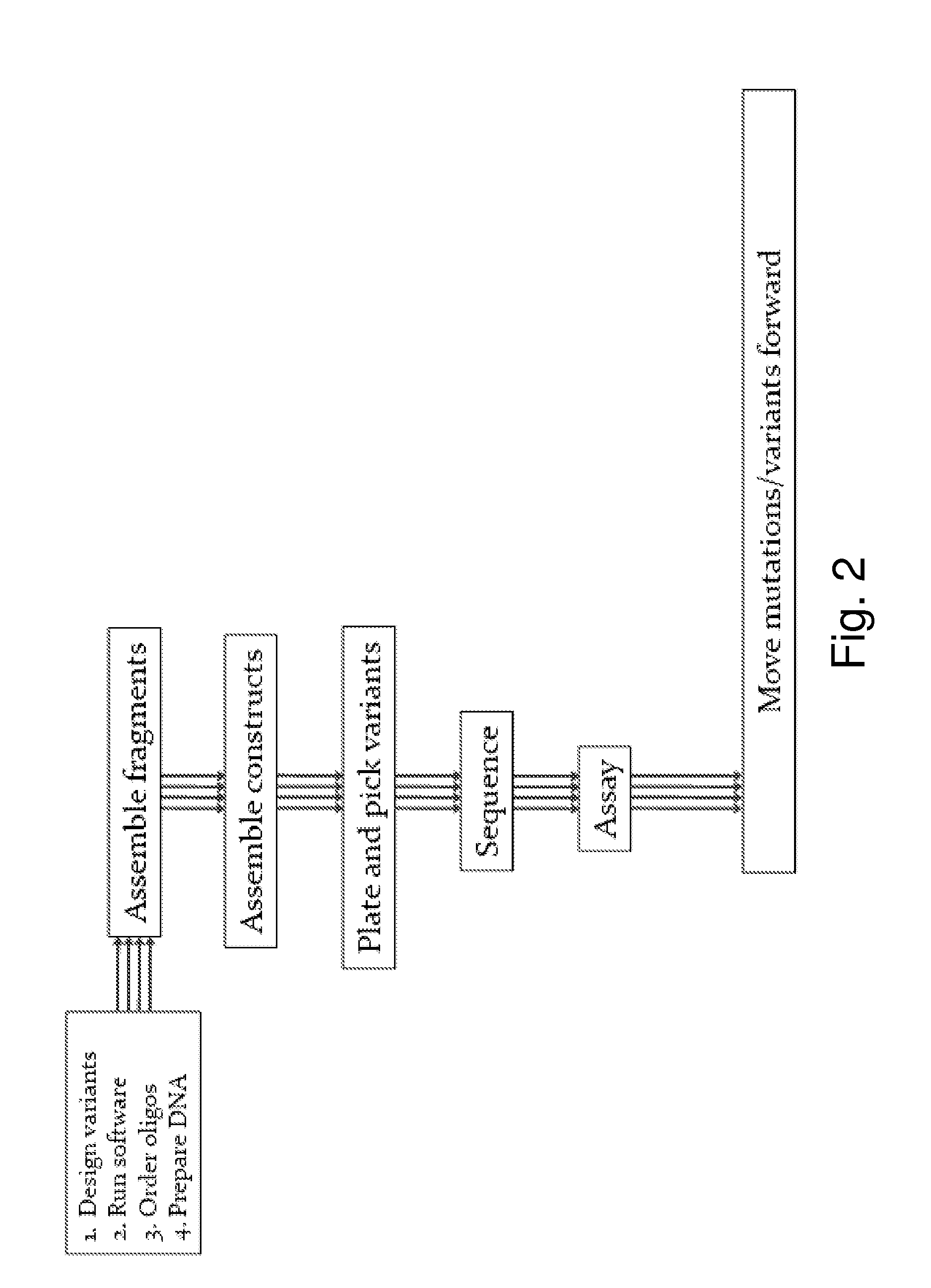
Reduced codon mutagenesis
InactiveUS20110082055A1Reduce complexityImprove screening efficiencyLibrary creationProtein nucleotide librariesOversamplingDegenerate oligonucleotide
Methods and compositions that reduce complexity of libraries of variant biological molecules, that reduce oversampling of these libraries during screening and that improve screening efficiency are provided. Sets of efficient degenerate codon sets are provided that efficiently encode all, or nearly all canonical amino acids. Degenerate oligonucleotides comprising these codons are provided, as are polynucleotide variants. Variant pooling strategies are used during library construction. Logical filtering is applied to select codon sites for mutagenesis, or to select amino acid sets to be incorporated at such sites. Methods for reducing non-optimal oversampling during screening are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Method and circuit arrangement for improving carrier separation for the transmission of OFDM signals
InactiveUS6088327AEasy to receiveEasy to separateMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 02209 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 17, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 17, 1997 PCT Filed May 23, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 41458 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 19, 1996In the case of the OFDM method, a large number of modulated carriers are transmitted using frequency division multiplexing, a spectrum having a virtually rectangular shape being produced as a result of the large number of carriers. In order to separate the carriers from one another again in the receiver, a Fast-Fourier-Transformation is carried out, it then being possible to separate each carrier cleanly from the others provided the carriers are exactly orthogonal with respect to one another. The carrier orthogonality can, however, be disturbed by various causes. Furthermore, the wanted signal must be separated from the undesired adjacent channel signals by analog or digital filtering in the receiver. In order to improve carrier and channel separation, the selectivity of the FFT filtering can be increased by enlarging the number of FFT components. However, this normally leads to an undesirably sharp increase in the computation complexity. The refinement according to the invention of the time window which is used for the FFT and the oversampling before the FFT make it possible, however, to dispense with calculation of some of the coefficients.
Owner:DEUTSCHE THOMSON-BRANDT GMBH
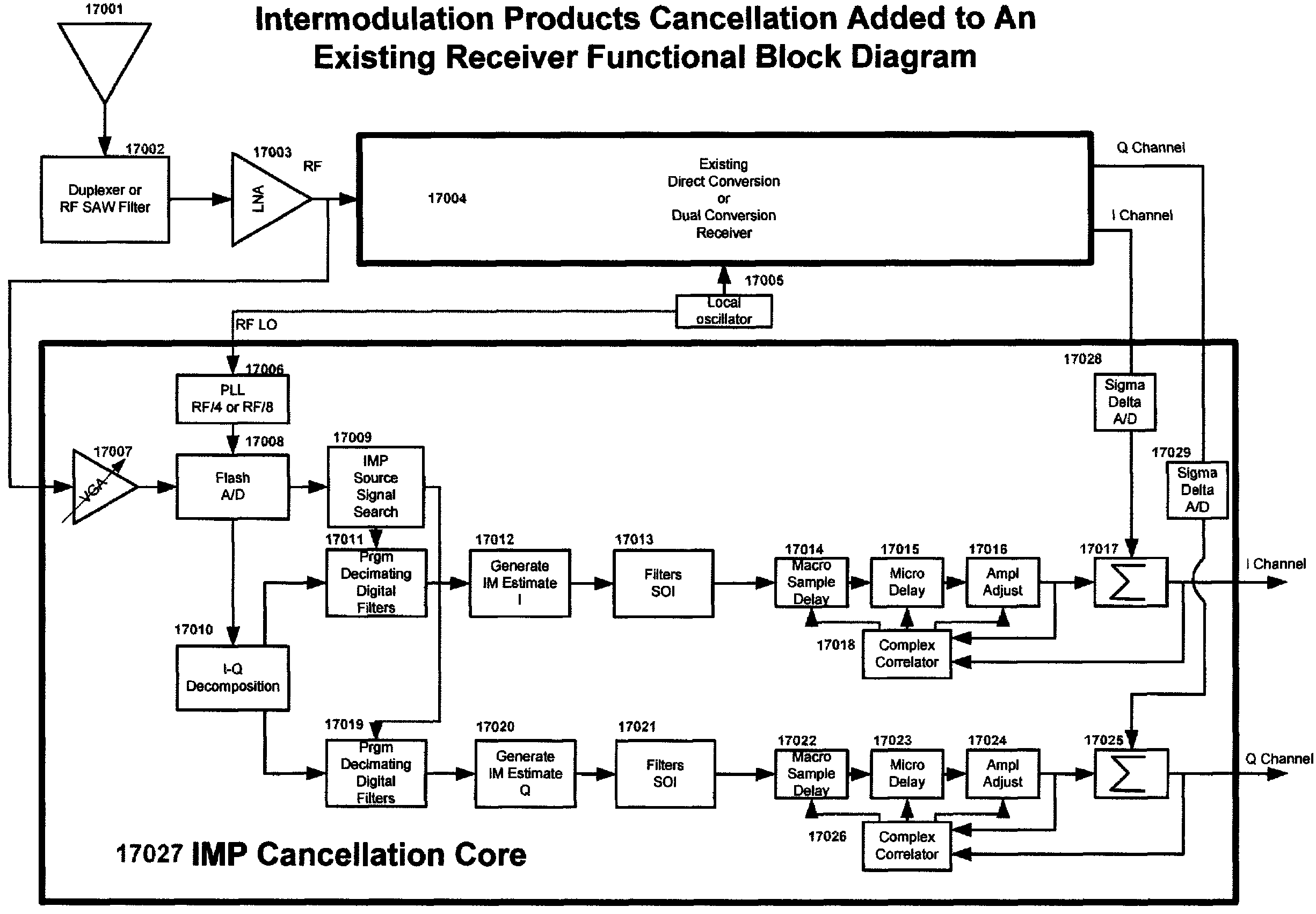
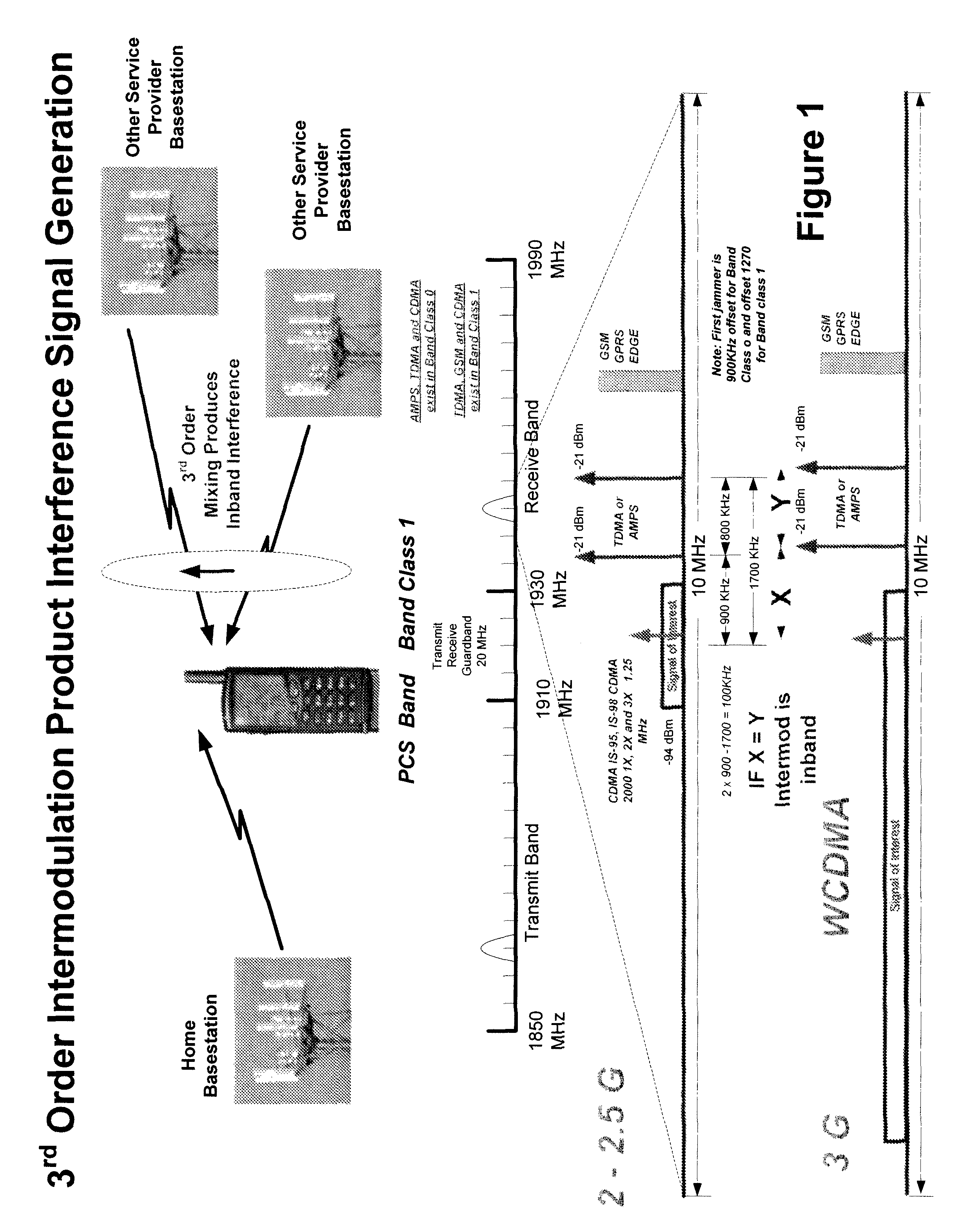
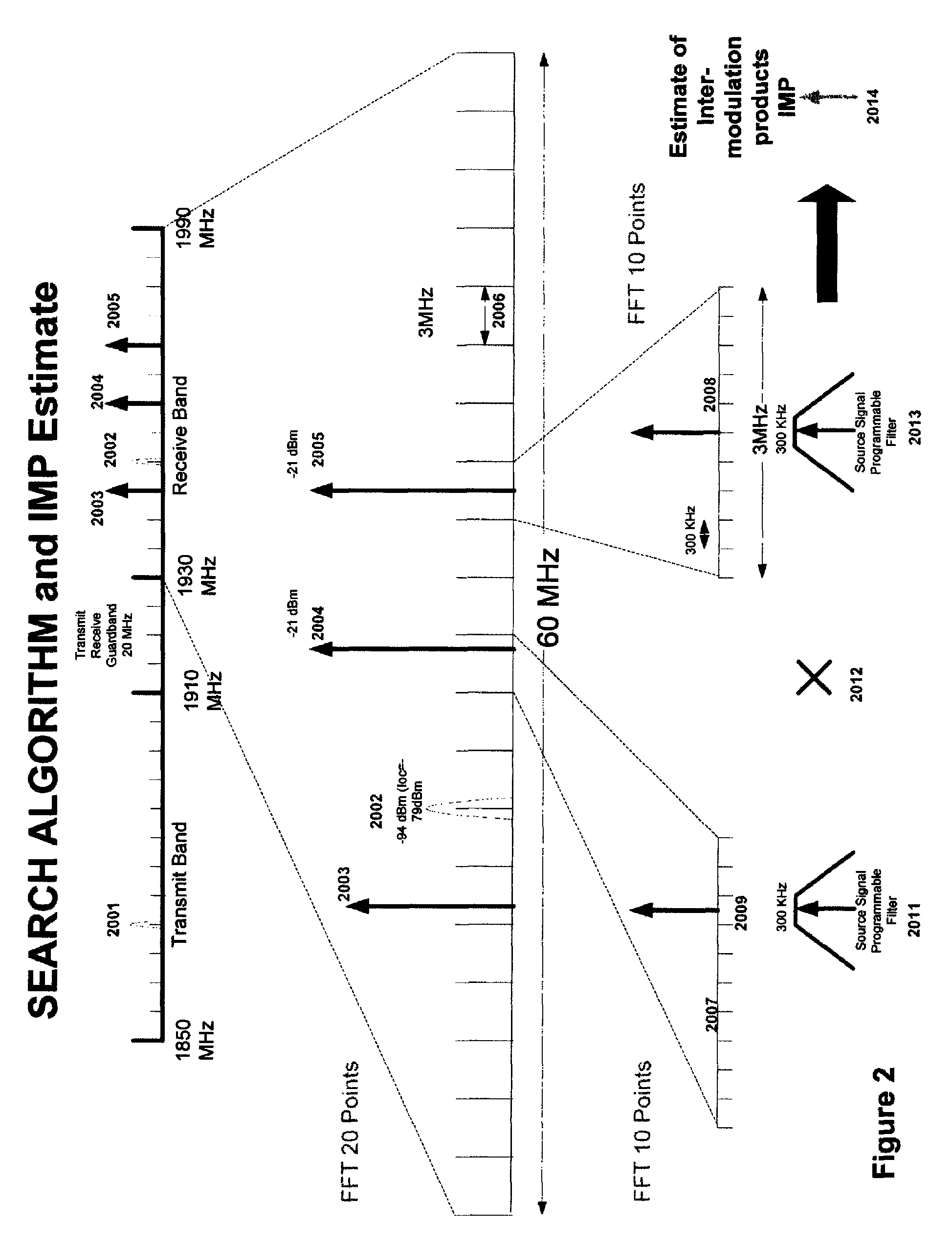
Multi-mode—multi-band direct conversion receiver with complex I and Q channel interference mitigation processing for cancellation of intermodulation products
Owner:SMITH FRANCIS J
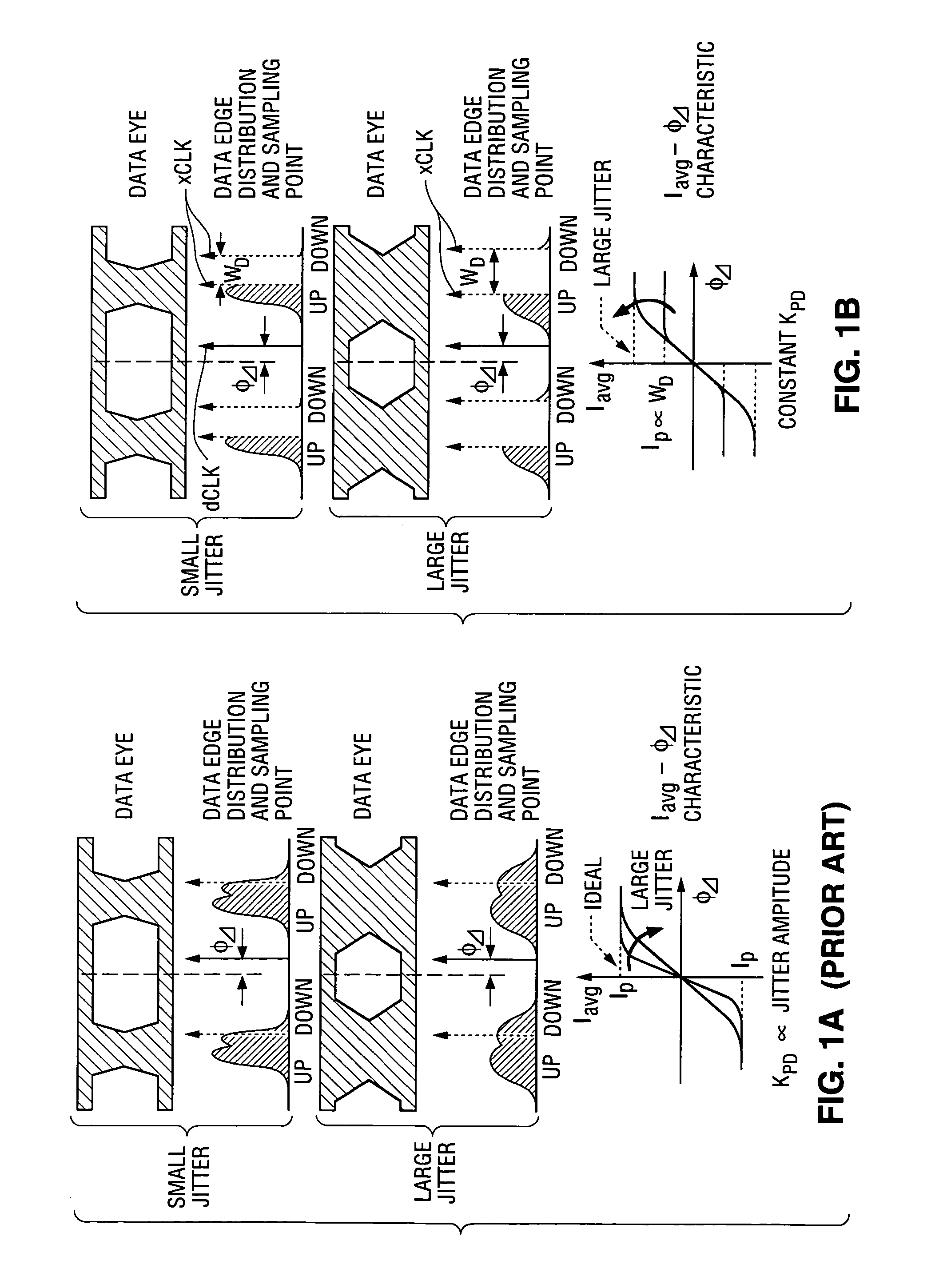
Data sampling method and apparatus with alternating edge sampling phase detection for loop characteristic stabilization
ActiveUS7409031B1Reduce phase differenceIncrease widthPulse automatic controlSynchronisation transmittersPhase detectorData rate
A method and apparatus for 2× oversampling of data having jitter. In some embodiments, the invention is a clock and data recovery device including an alternating edge sampling binary phase detector, and which is configured to stabilize loop characteristics in various jitter environments and can be implemented with small hardware overhead. A transceiver that embodies the invention can be implemented as a CMOS integrated circuit using a 0.18 μm CMOS process, with the transceiver chip being capable of recovering data having a data rate of up to 11.5 Gbps from a signal received over a serial link, while consuming no more than 540 mW from 1.8V supply, and with a bit error rate of less than 10−12.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
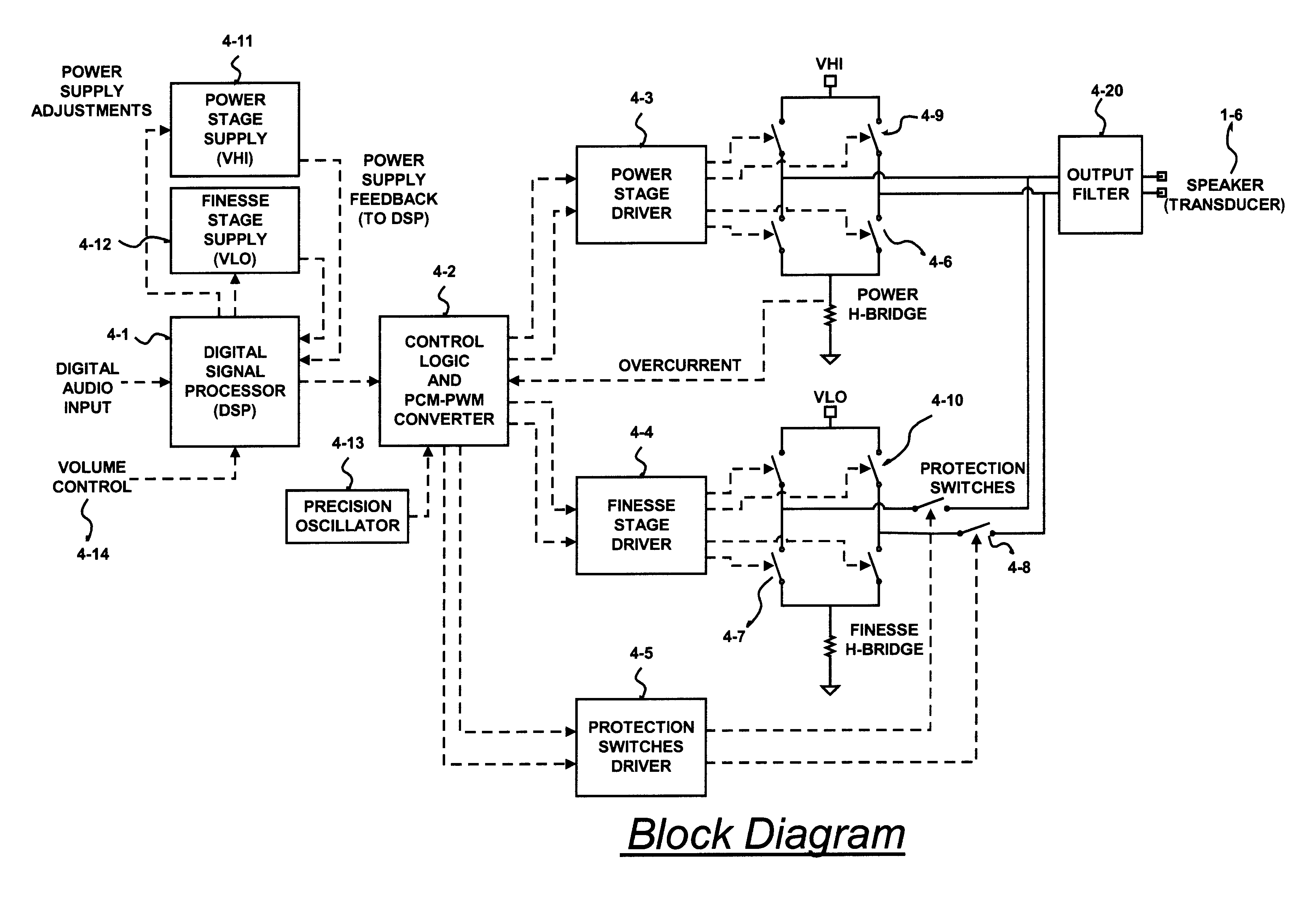
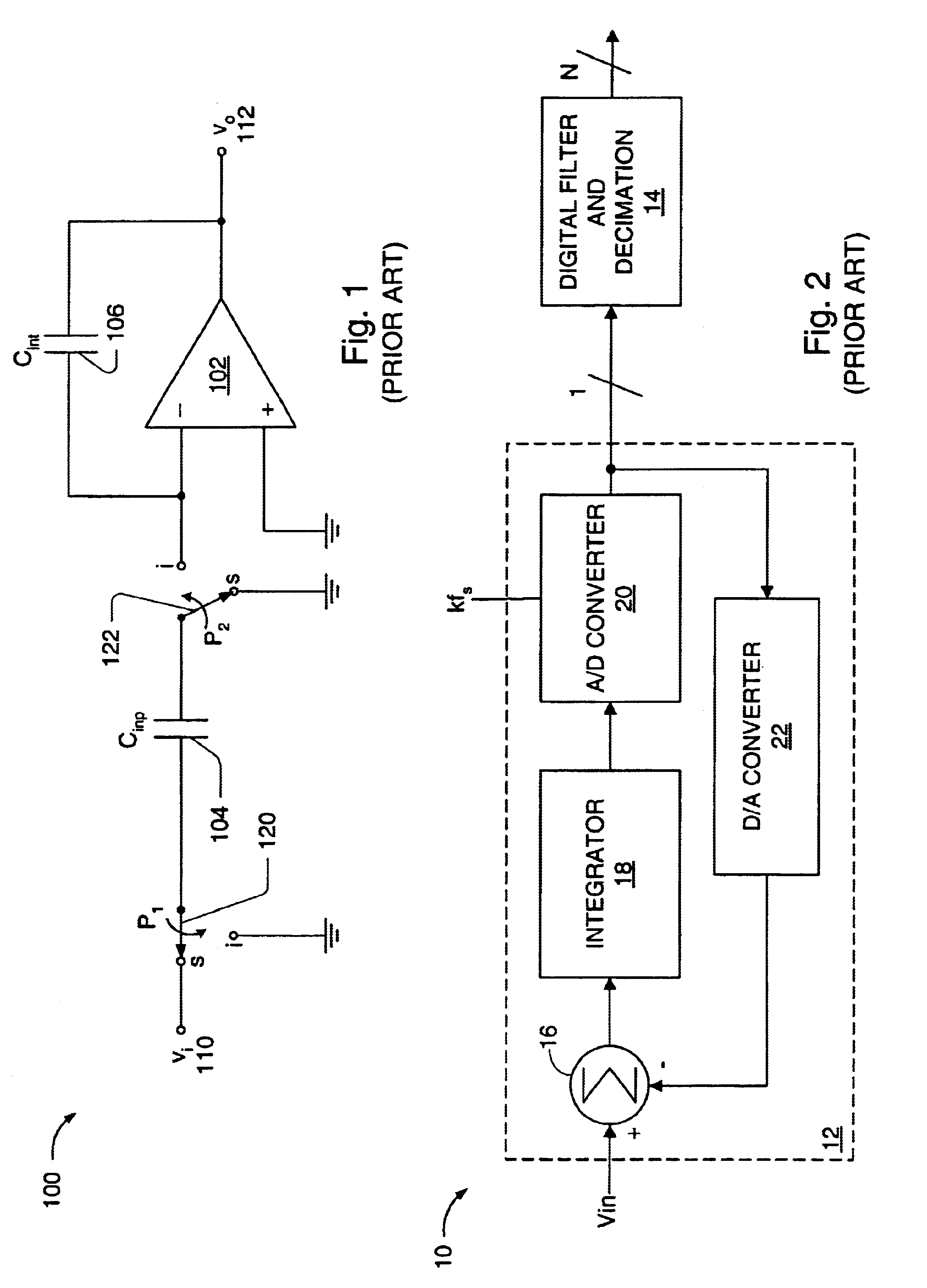
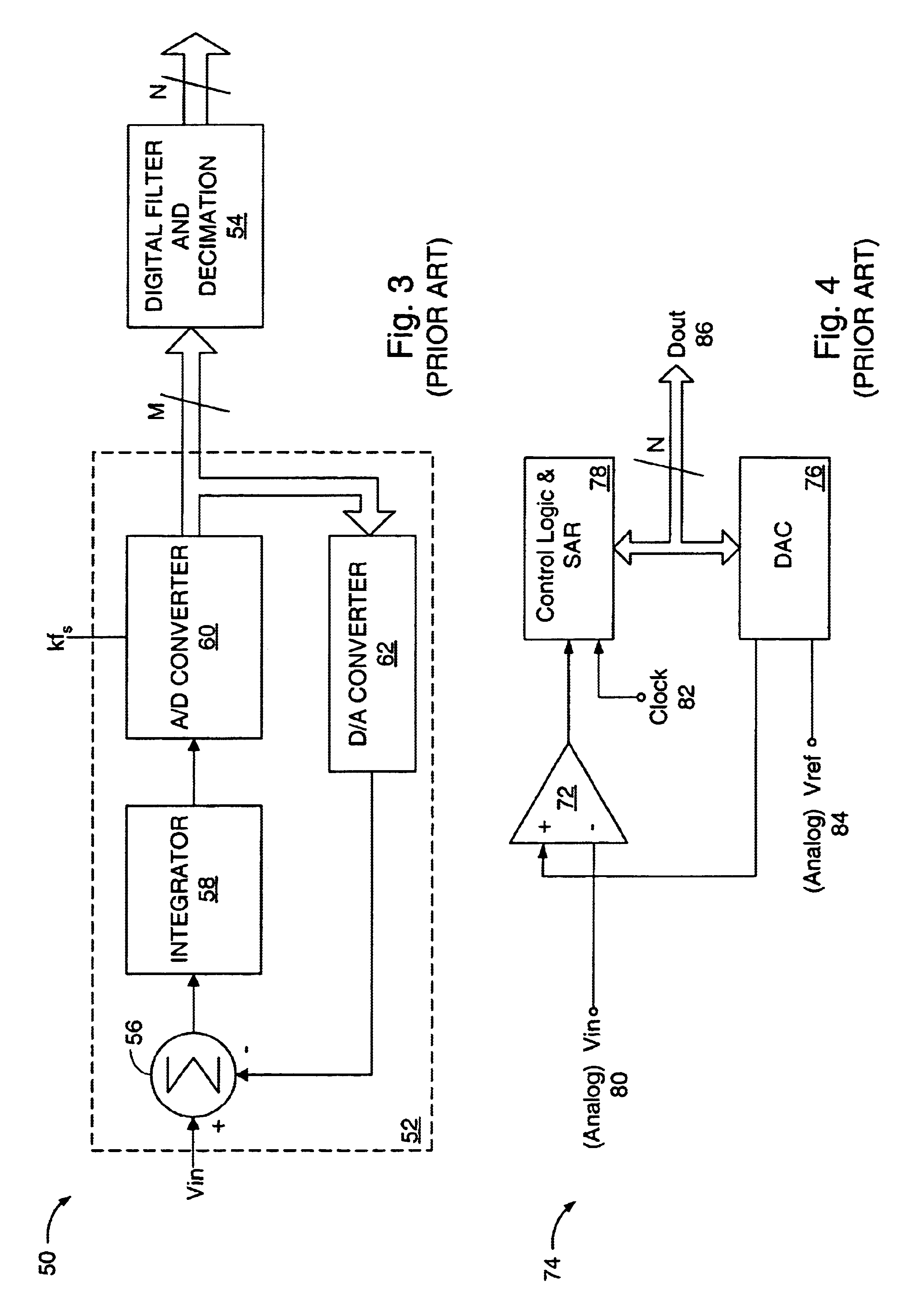
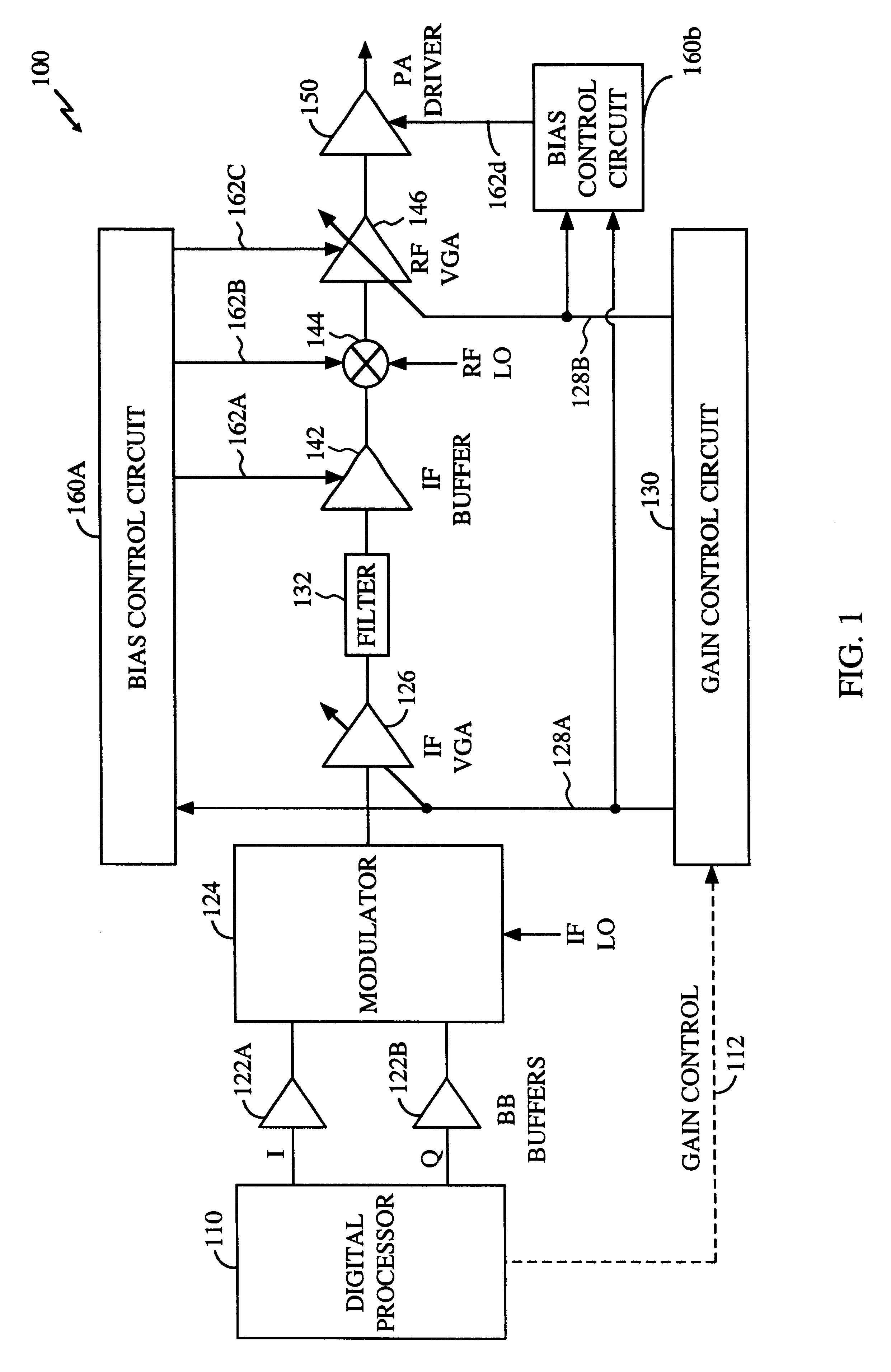
Digital amplifier with improved performance
InactiveUS6593807B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersDigital dataLow-pass filter
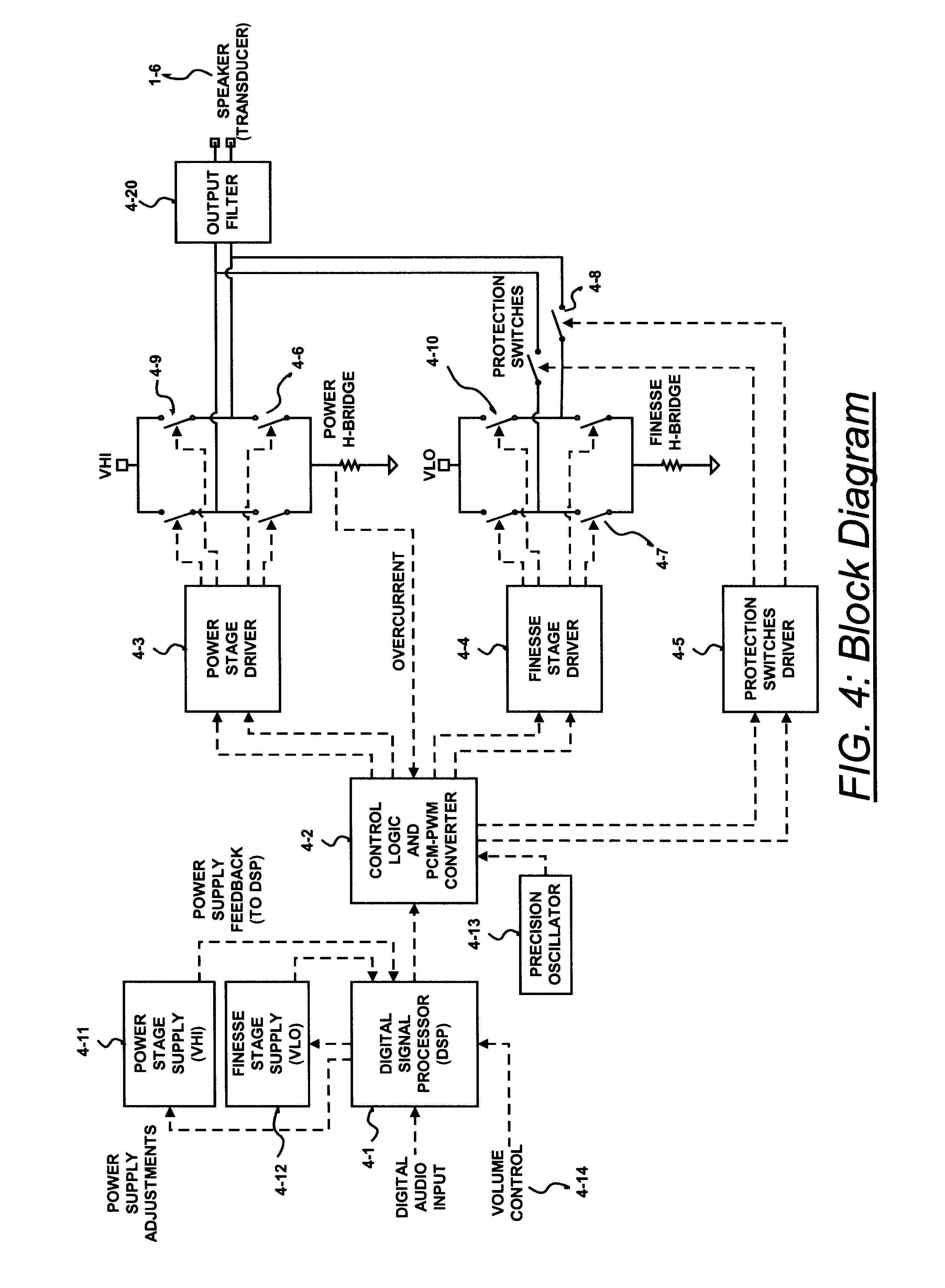
A class D amplifier uses a summation of two or more PWM output stages to achieve an increased dynamic range and improved linearity for any given clock operating speed. The amplifier accepts a digital data stream as its input, such as from a compact disk, or other compatible media, at a data rate, Fa, that could be 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz, or any other rate appropriate for audio data. In the preferred embodiment, the input audio data resolution, N bits, would be split into two data samples, of J and K.Internal switching frequency, Fs, switches the PWM with an over sampling factor M, where Fs=M*Fa. The time resolution of the PWM is determined by a precision oscillator that operates at Fc=Fs*(max(J,K)-log2(M)+1).The J most significant bits would be routed to a power PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VHI. The K least significant bits are routed to a finesse PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VLO.The ratio of VLO to VHI will be appropriate for the ratio of K and J so the summation of the power PWM stage and the finesse PWM stage will provide the full range of N bits. This summation is accomplished with a low pass filter and time-division multiplexing of the two PWM stages.A micro controller (MCU) is used to apply a sample packet distribution algorithm to provide more resolution by reducing quantization noise in the audio band of interest. The MCU is also used to calibrate the VLO or VHI, or to calibrate the PWM timing of the two PWM stages to achieve appropriate performance.
Owner:GROVES JR WILLIAM HARRIS +1
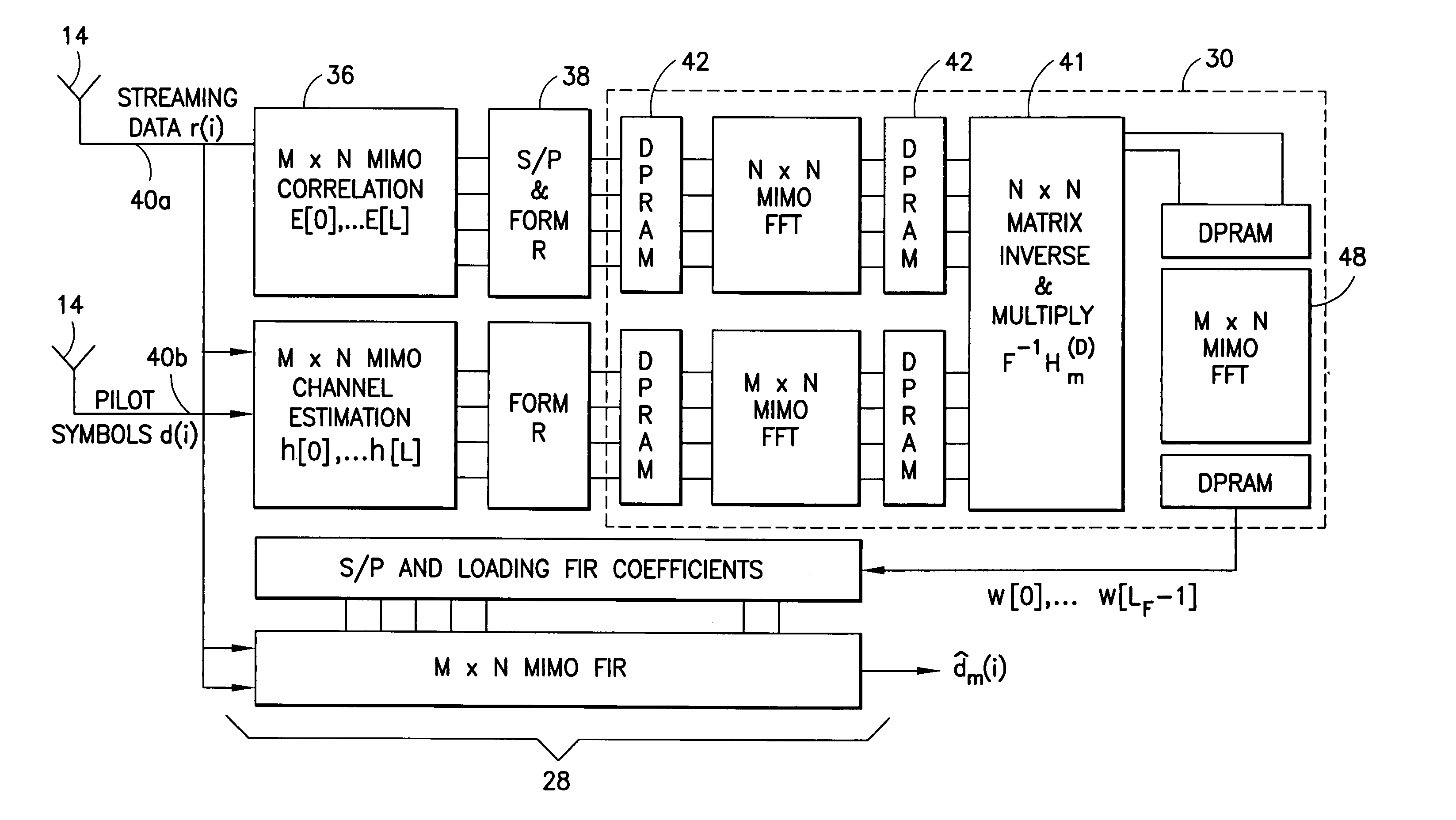
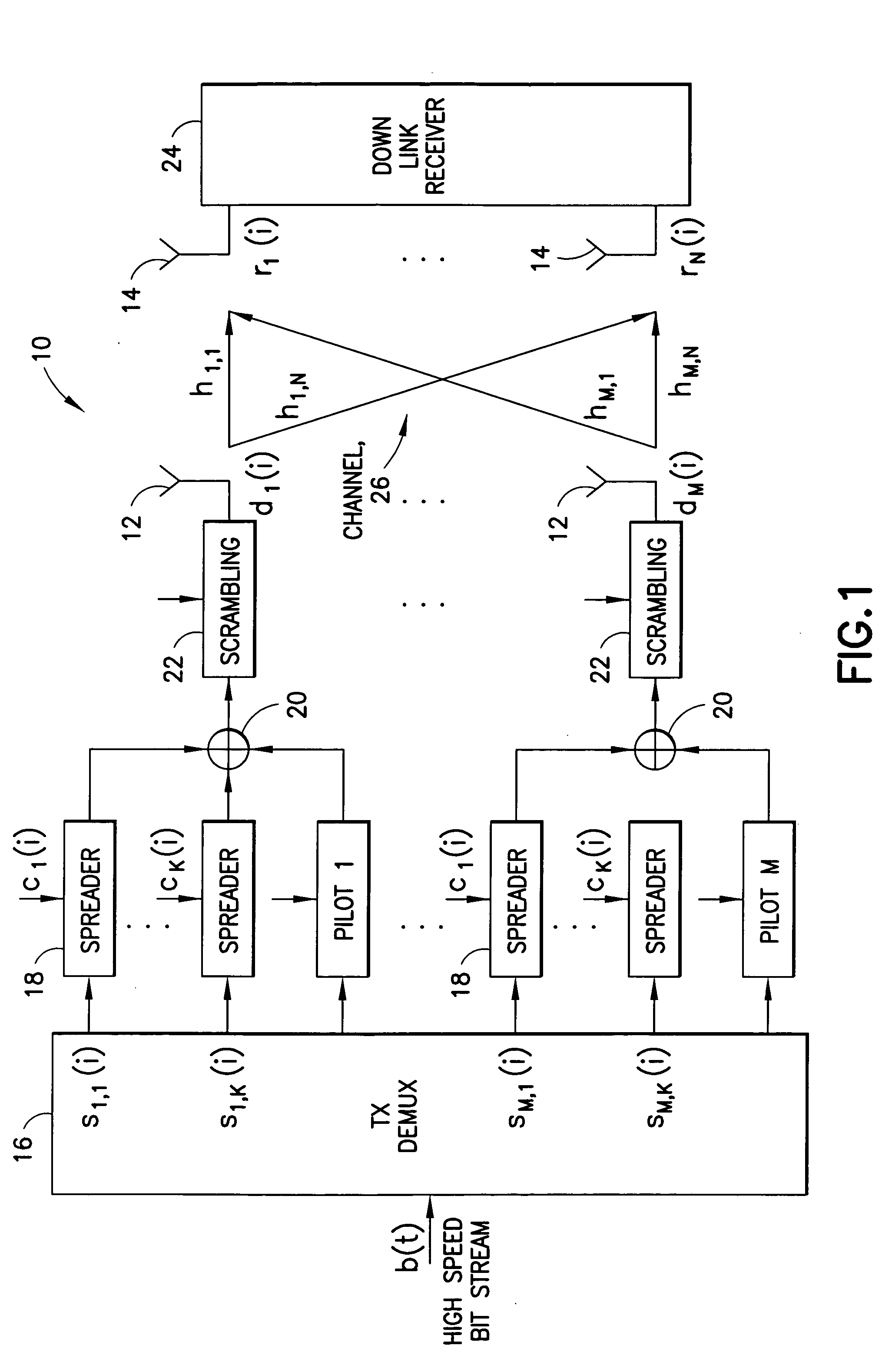
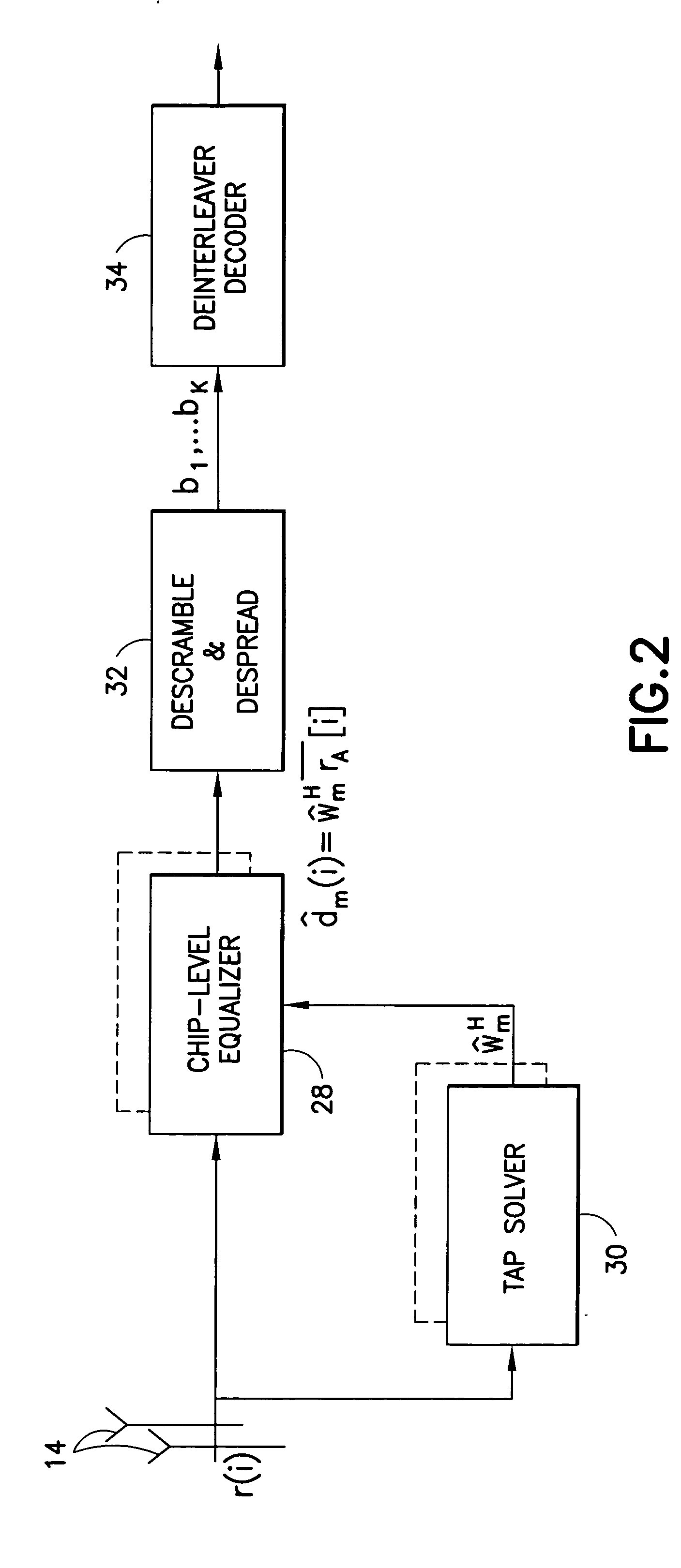
Reduced parallel and pipelined high-order MIMO LMMSE receiver architecture
ActiveUS20060109891A1Reduce complexityReduce the numberMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFast Fourier transformRound complexity
Disclosed is a LMMSE receiver that restores orthogonality of spreading codes in the downlink channel for a spread spectrum signal received over N receive antennas. The FFT-based chip equalizer tap solver reduces the direct matrix inverse of the prior art to the inverse of some submatrices of size N×N with the dimension of the receive antennas, and most efficiently reduces matrix inverses to no larger than 2×2. Complexity is further reduced over a conventional Fast Fourier Transform approach by Hermitian optimization to the inverse of submatrices and tree pruning. For a receiver with N=4 or N=2 with double oversampling, the resulting 4×4 matrices are partitioned into 2×2 block sub-matrices, inverted, and rebuilt into a 4×4 matrix. Common computations are found and repeated computations are eliminated to improve efficiency. Generic design architecture is derived from the special design blocks to eliminate redundancies in complex operations. Optimally, the architecture is parallel and pipelined.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
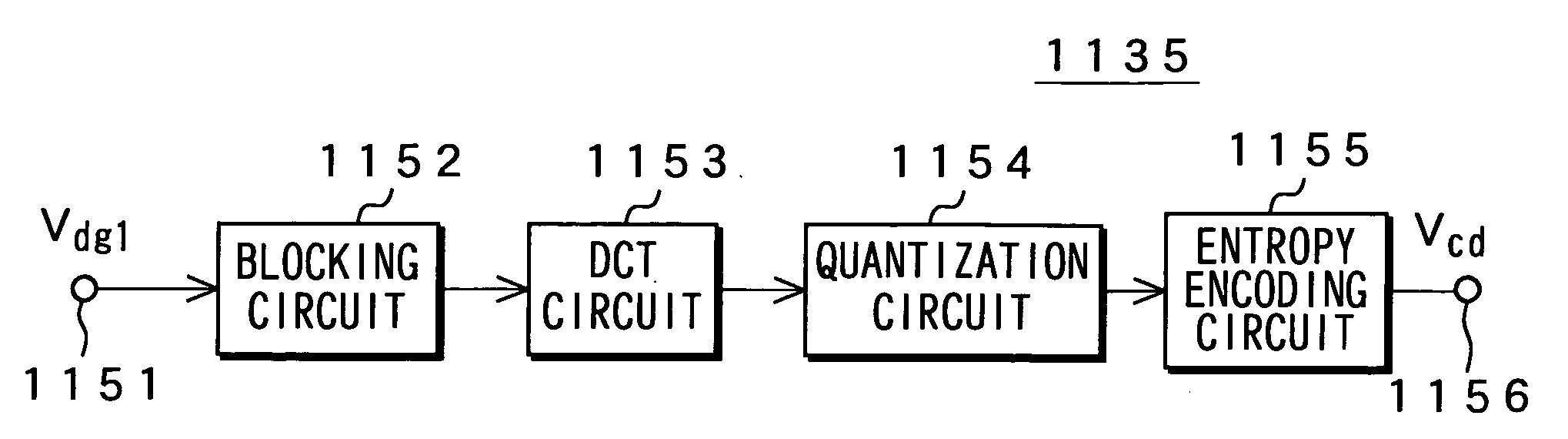
Data encoding apparatus, data encoding method, data output apparatus, data output method, signal processing system, signal processing apparatus, signal processing method, data decoding apparatus, and data decoding method
InactiveUS20060188012A1Quality improvementPreventing illegal copyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData encodingComputer science
This invention relates to an apparatus for encoding data or the like, which disables the data to be copied in a condition where its good quality is maintained without deteriorating a quality of an output owing to the data before being copied. Synchronization signals VD and HD separated from the analog image data Van are delayed and supplied to a clock generation circuit 1133 where a clock CLK is generated in a range of an effective screen based on the synchronization signals. This clock signal CLK is shifted vertically and horizontally so that a phase of image data Vdg1 output from A / D converter 1134 is also shifted. In this image data Vdg1, a signal-deteriorating factor is generated. Encoding section 1135 performs encoding by sampling, conversion encoding, and the like. By shifting the phase of the image data Vdg1, a sampling position and / or a block position are caused to be shifted from a position where obtaining original encoding data relative to the image data Van1, thereby generating significant deterioration in the encoding section 1135.
Owner:SONY CORP
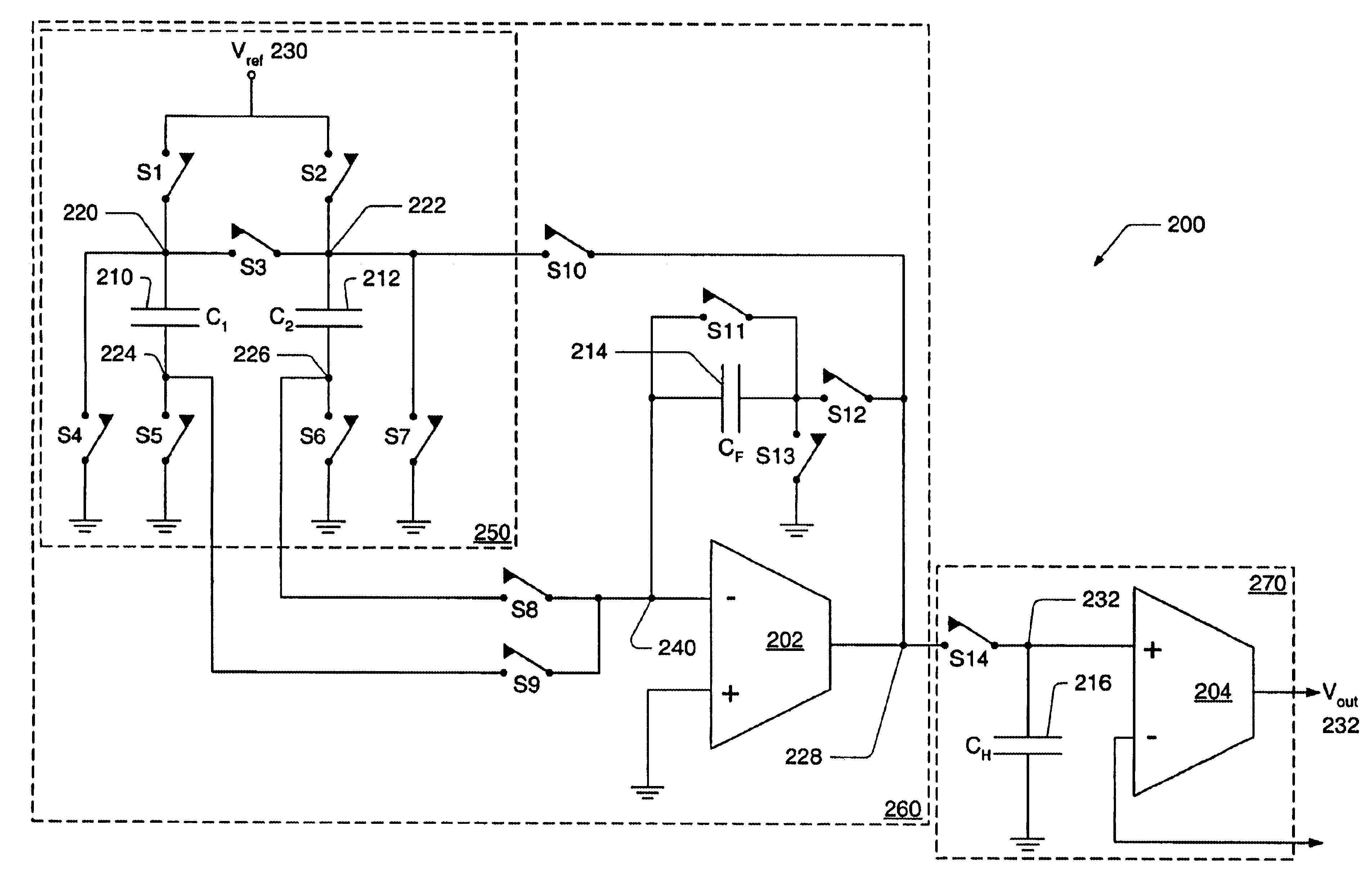
Highly accurate switched capacitor DAC
ActiveUS6924760B1Minimize even-order errorReducing even-order errorElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationCompact dimensionCapacitance
In one set of embodiments the invention comprises a highly accurate, low-power, compact size DAC utilizing charge redistribution techniques. Two complementary conversions may be performed and added together to form a final DAC output voltage by performing charge redistribution a first time, and again a second time in a complementary fashion, followed by a summing of the two charge distributions, in effect canceling the odd order capacitor mismatch errors. By canceling all odd order mismatch errors the accuracy of the DAC may become a function of the square of the mismatch of the two capacitors, resulting in greatly increased accuracy. When performing the complementary conversions for multiple bits, the sequence in which each of the two capacitors is charged may be determined to minimize the even-order errors, especially second-order errors. The DEM technique may be applied, in conjunction with the complementary conversions, with less oversampling than required by current DEM implementations, resulting in even-order errors being substantially reduced in addition to all odd-order errors being eliminated.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Sigma-delta (SigmaDelta) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) structure incorporating a direct sampling mixer
InactiveUS7057540B2Simple to fabricateHigh sampling rateElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationFrequency mixerHigh frequency
A sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter-offers advantages such as noise shaping and high frequency operation. However, a sampling circuit needed to provide a highly oversampled discrete-time sample stream with low noise characteristics is difficult to design and implement. The present invention provides a sigma-delta mixer 300 with such a sampling circuit 310. The present invention discloses a sampling circuit using switched capacitors 307, 308, and 309 with low noise characteristics and at the same time is capable of providing a highly oversampled discrete-time sample stream.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
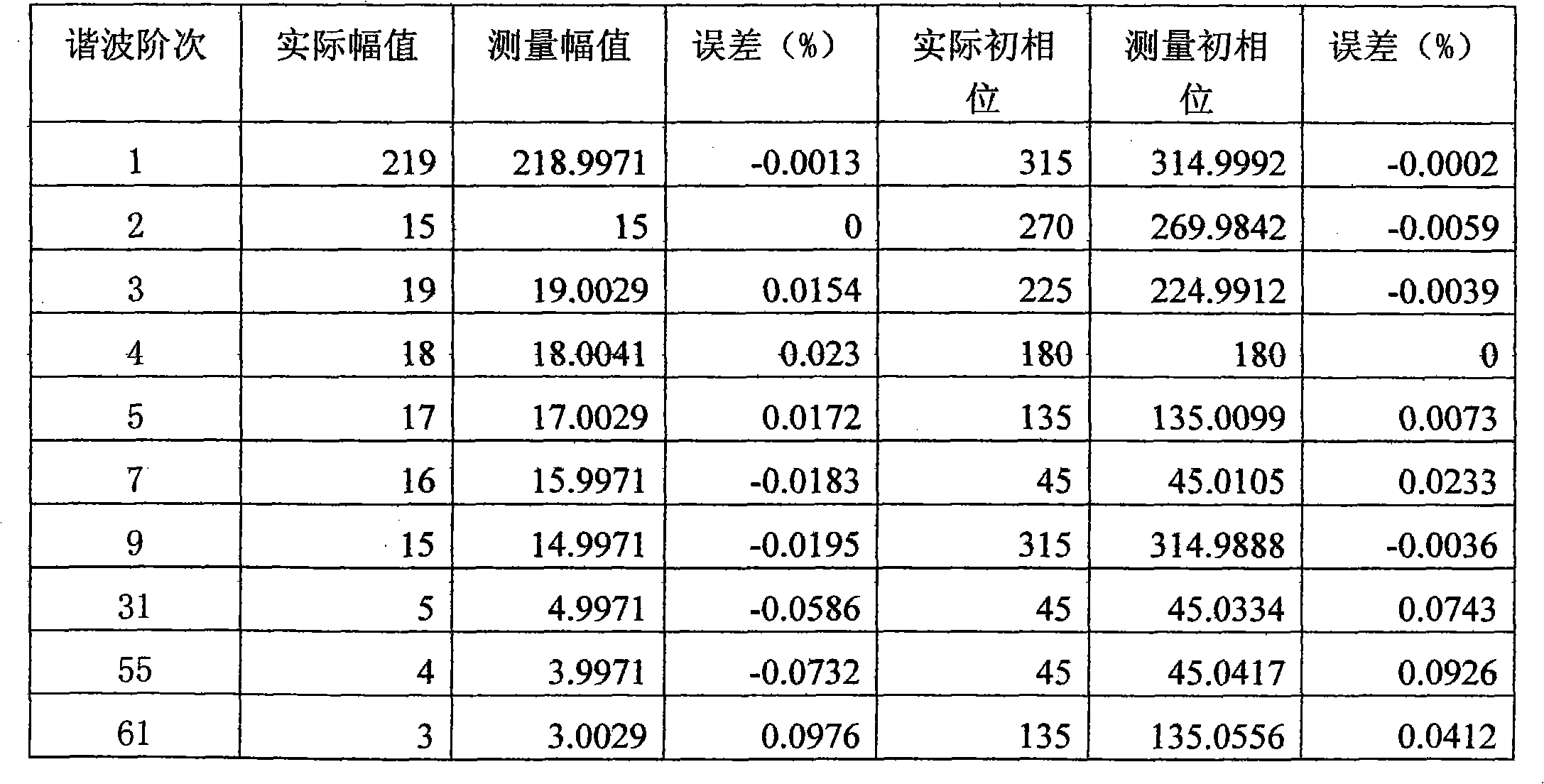
Harmonic wave detection method based on Fourier transformation
ActiveCN101915874AThe need for increased precisionImprove real-time performanceFrequency analysisFrequency spectrumWave detection
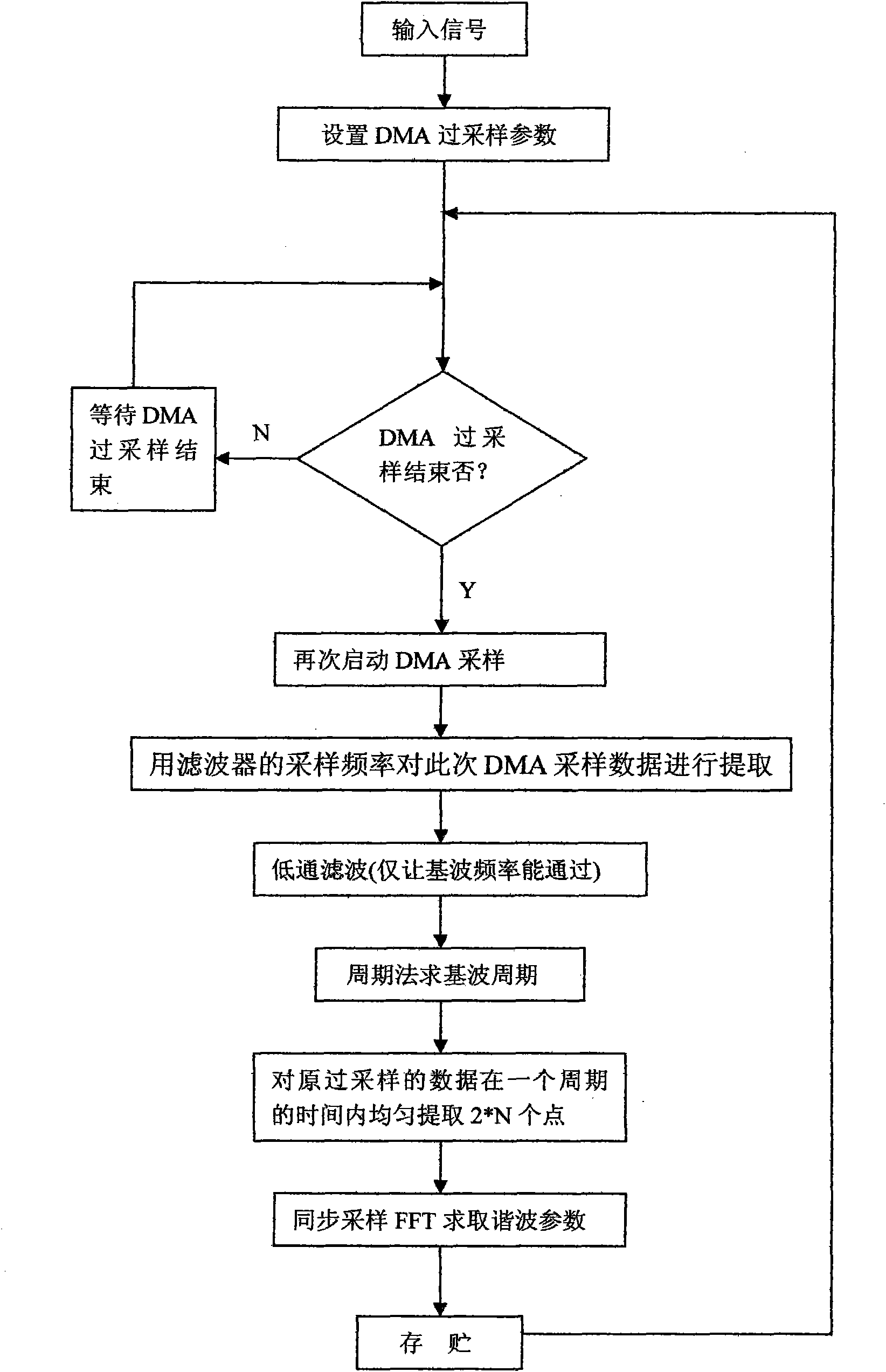
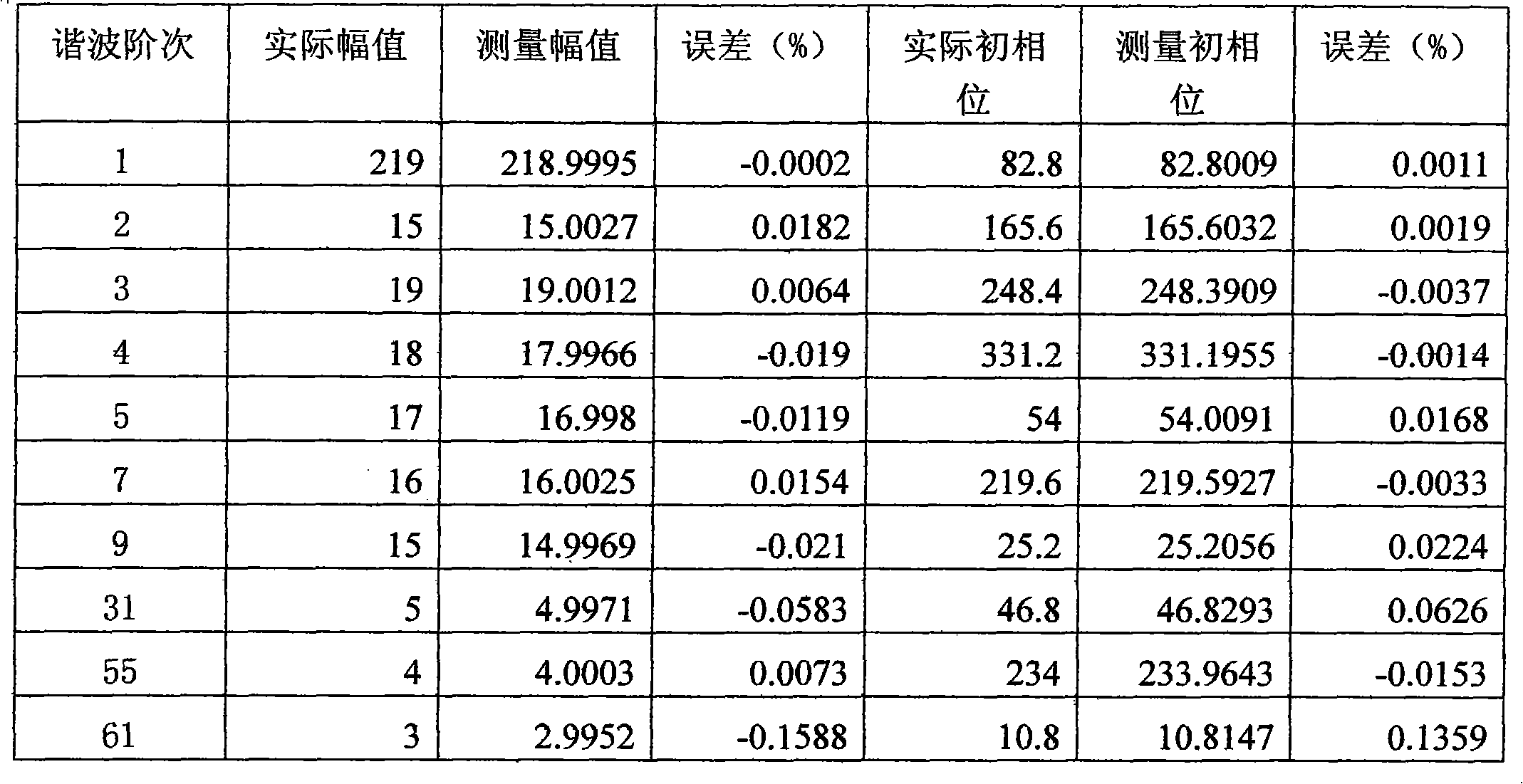
The invention discloses a harmonic wave detection method based on Fourier transformation, comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out oversampling and analog-to-digital conversion on a measured signal, and ensuring that data of two signal periods can be sampled from each group of data according to the maximum periodic value estimated by the measured signal; (2) filtering harmonic wave components outside fundamental waves by a digital low pass filter; (3) calculating a fundamental wave period by a periodic method; (4) extracting 2*N numbered data points within one period, wherein, N-1 is the highest harmonic order number; and (5) calculating the parameter of each harmonic wave component by utilizing a synchronous sample FFT. The method of the invention belongs to the signal processingtechnical field, and also can be used for spectrum analysis of other signals. Very high harmonic wave detection accuracy can be obtained by the method; the instantaneity can be doubled compared with three to five signal periods of a quasi-synchronizing method; and the time of two signal periods are only needed, and the fundamental wave frequency also can be accurately measured.
Owner:BEIHAI SHENLAN SCI & TECH DEV
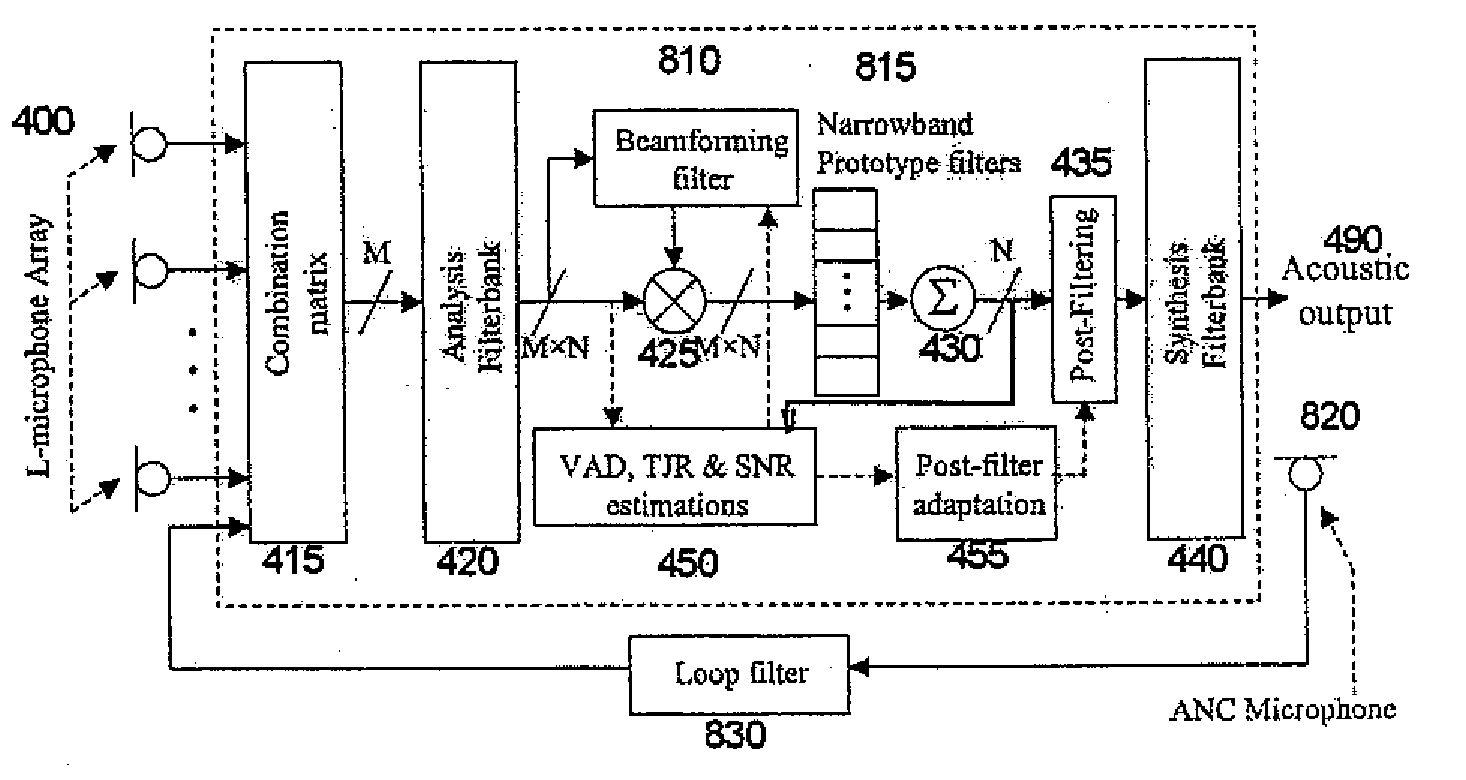
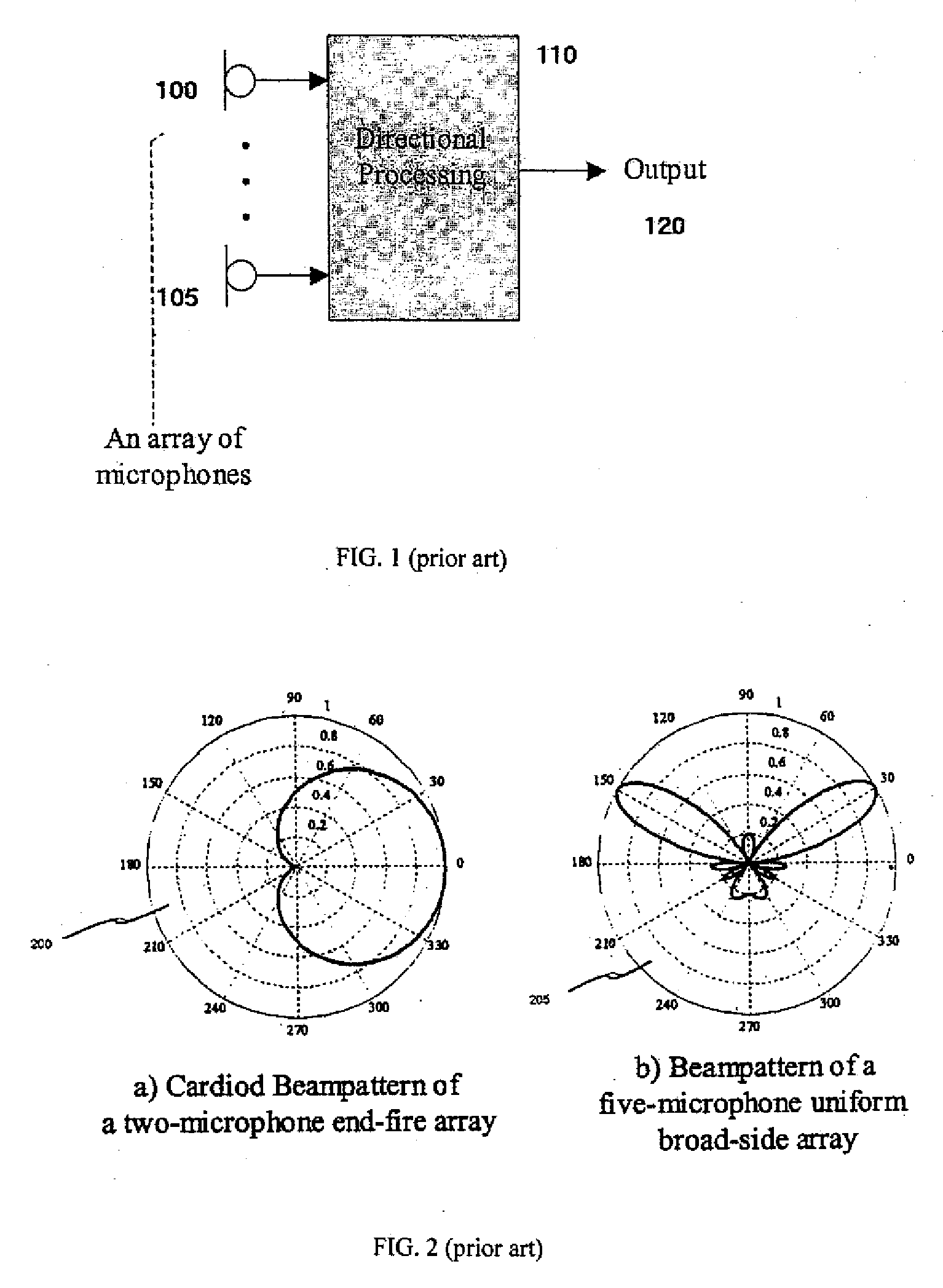
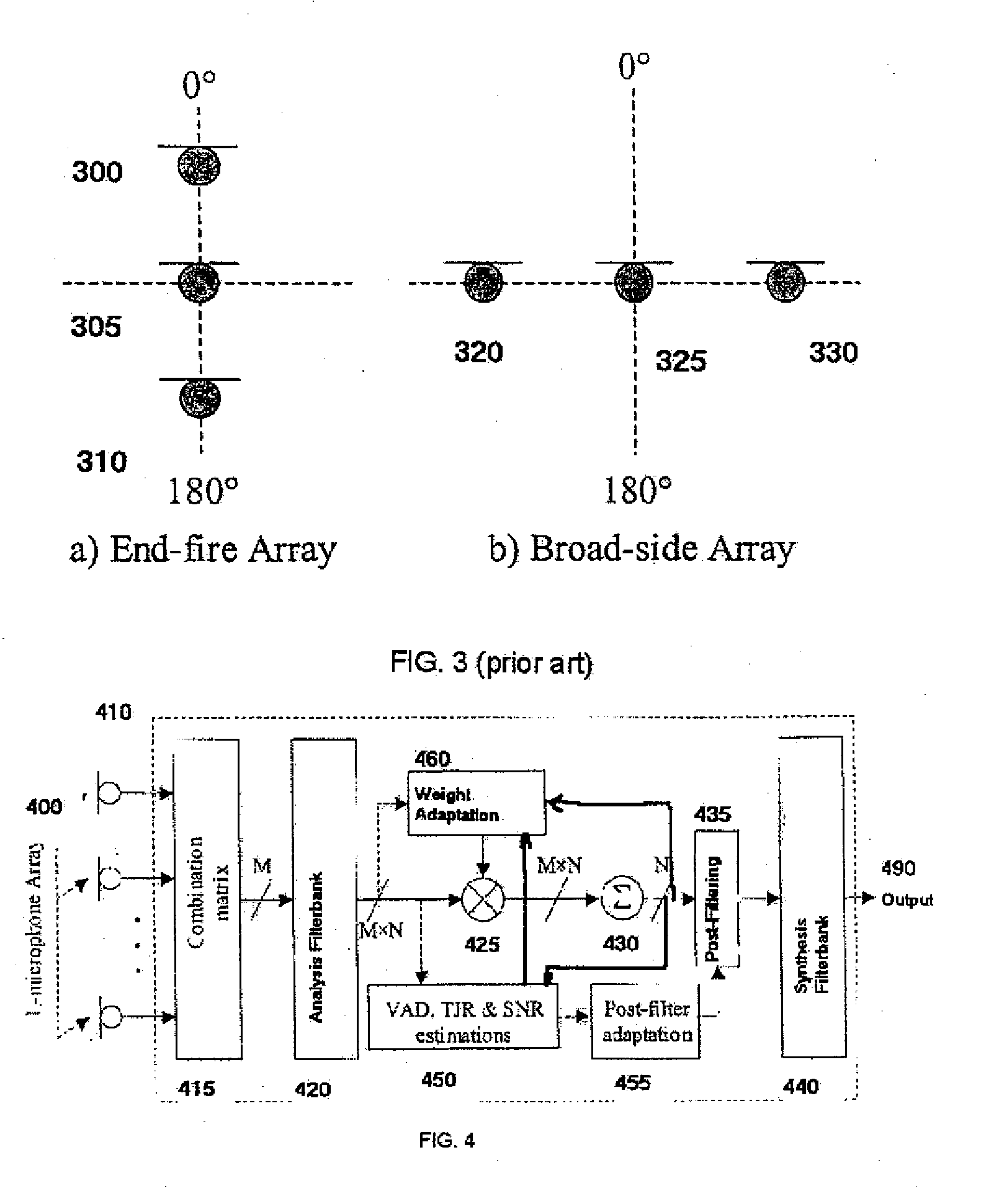
Directional audio signal processing using an oversampled filterbank
InactiveUS20080112574A1Improve abilitiesHigh resolutionMicrophones signal combinationSpeech recognitionTime domainHandling system
A directional signal processing system for beamforming information signals. The system includes an oversampled filterbank, which has an analysis filterbank for transforming the information signals in time domain into channel signals in transform domain, a synthesis filterbank and a signal processor. The signal processor processes the outputs of the analysis filterbank for beamforming the information signals. The synthesis filterbank transforms the outputs of the signal processor to a single information signal in time domain.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Apparatus and method for generating a high frequency audio signal using adaptive oversampling
ActiveUS20120281859A1Reduce complexityImprove transient performanceSpeech analysisTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency spectrumOversampling
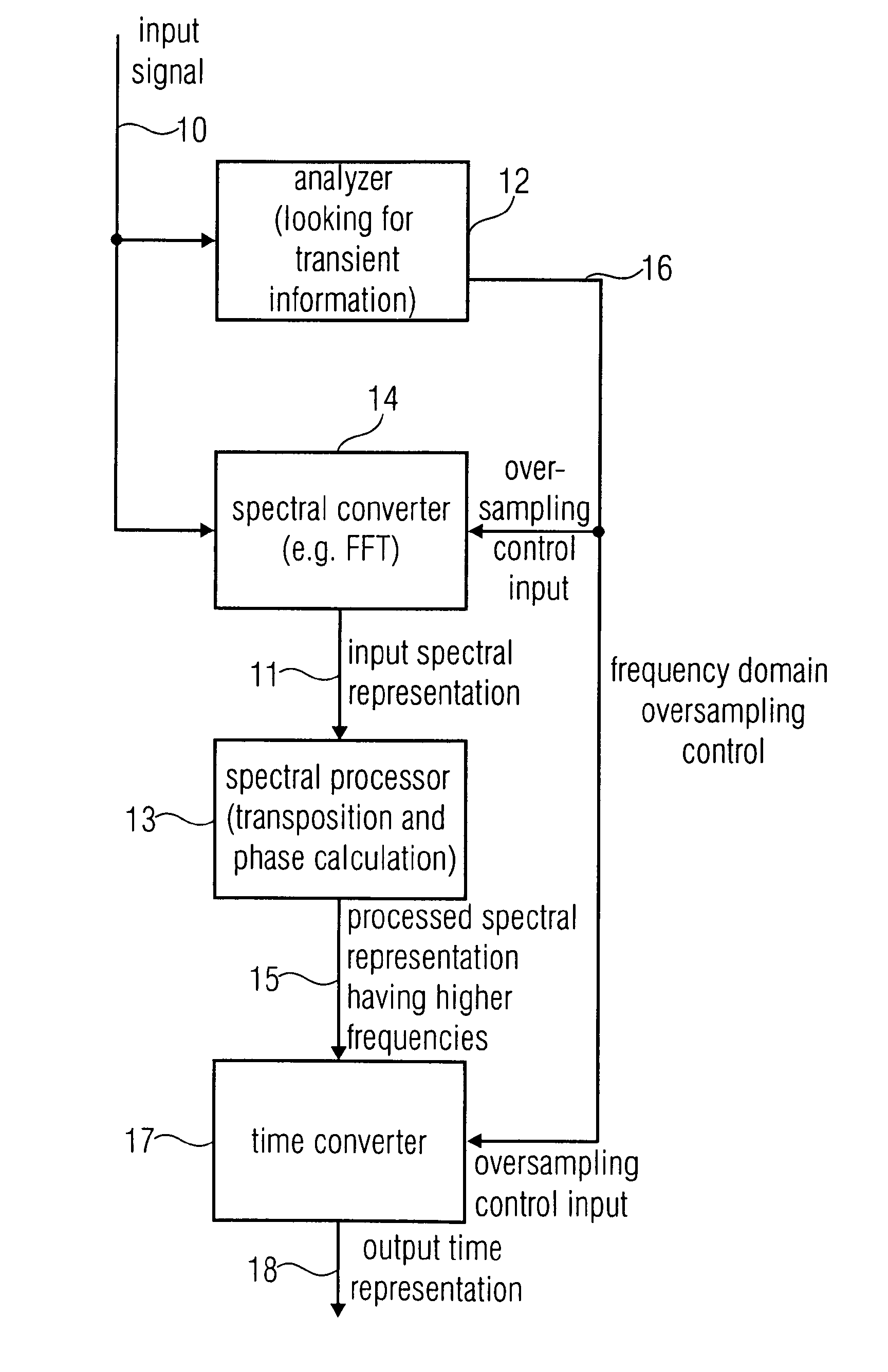
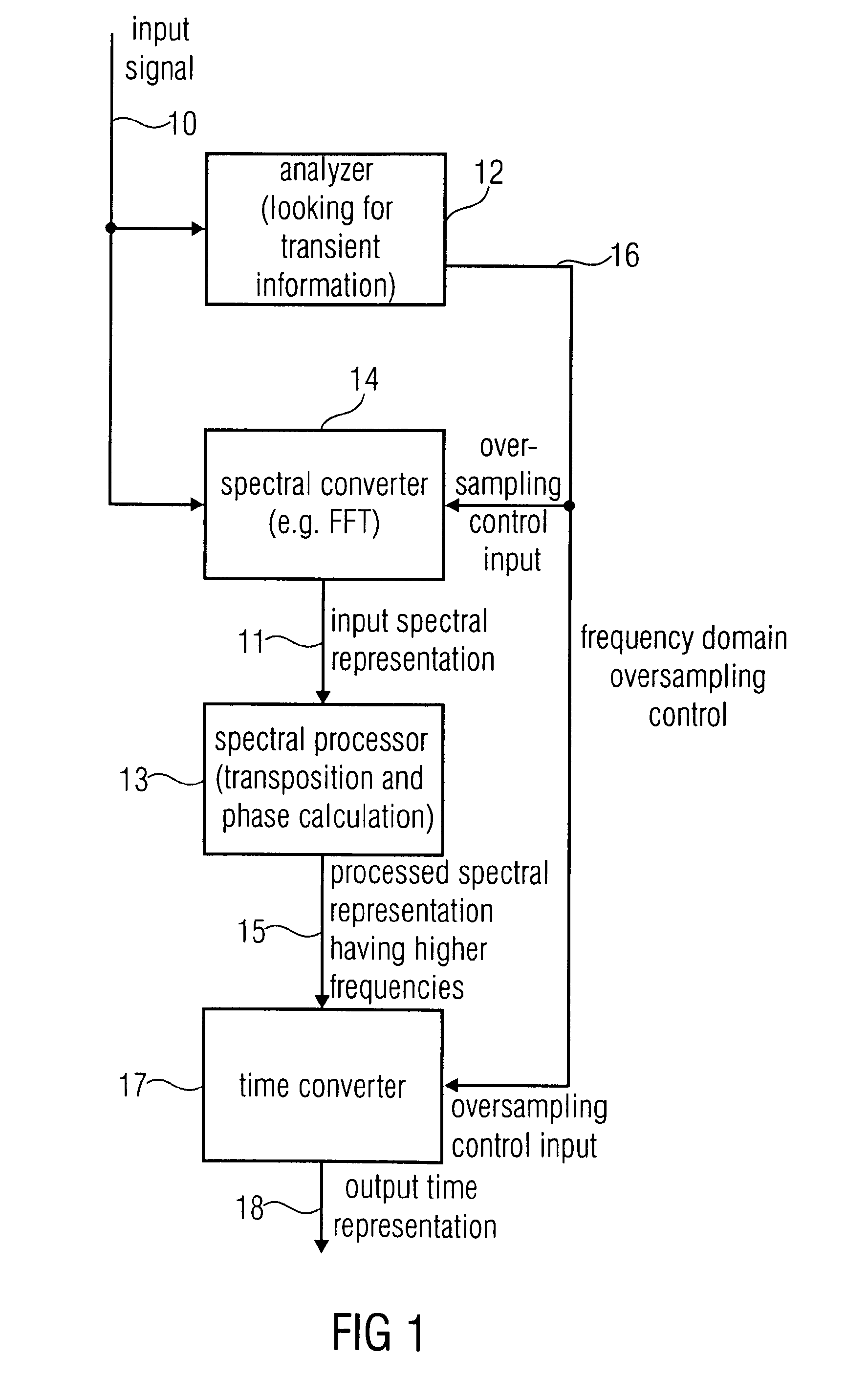
An apparatus for generating a high frequency audio signal that includes an analyzer for analyzing an input signal to determine a transient information adaptively. Additionally a spectral converter is provided for converting the input signal into an input spectral representation. A spectral processor processes the input spectral representation to generate a processed spectral representation including values for higher frequencies than the input spectral representation. A time converter is configured for converting the processed spectral representation to a time representation, wherein the spectral converter or the time converter are controllable to perform a frequency domain oversampling for the first portion of the input signal having the transient information associated and to not perform the frequency domain oversampling for the second portion of the input signal not having the associated transient information.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +1
Data recovery method and apparatus
InactiveUS6907096B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRecovery methodClock rate
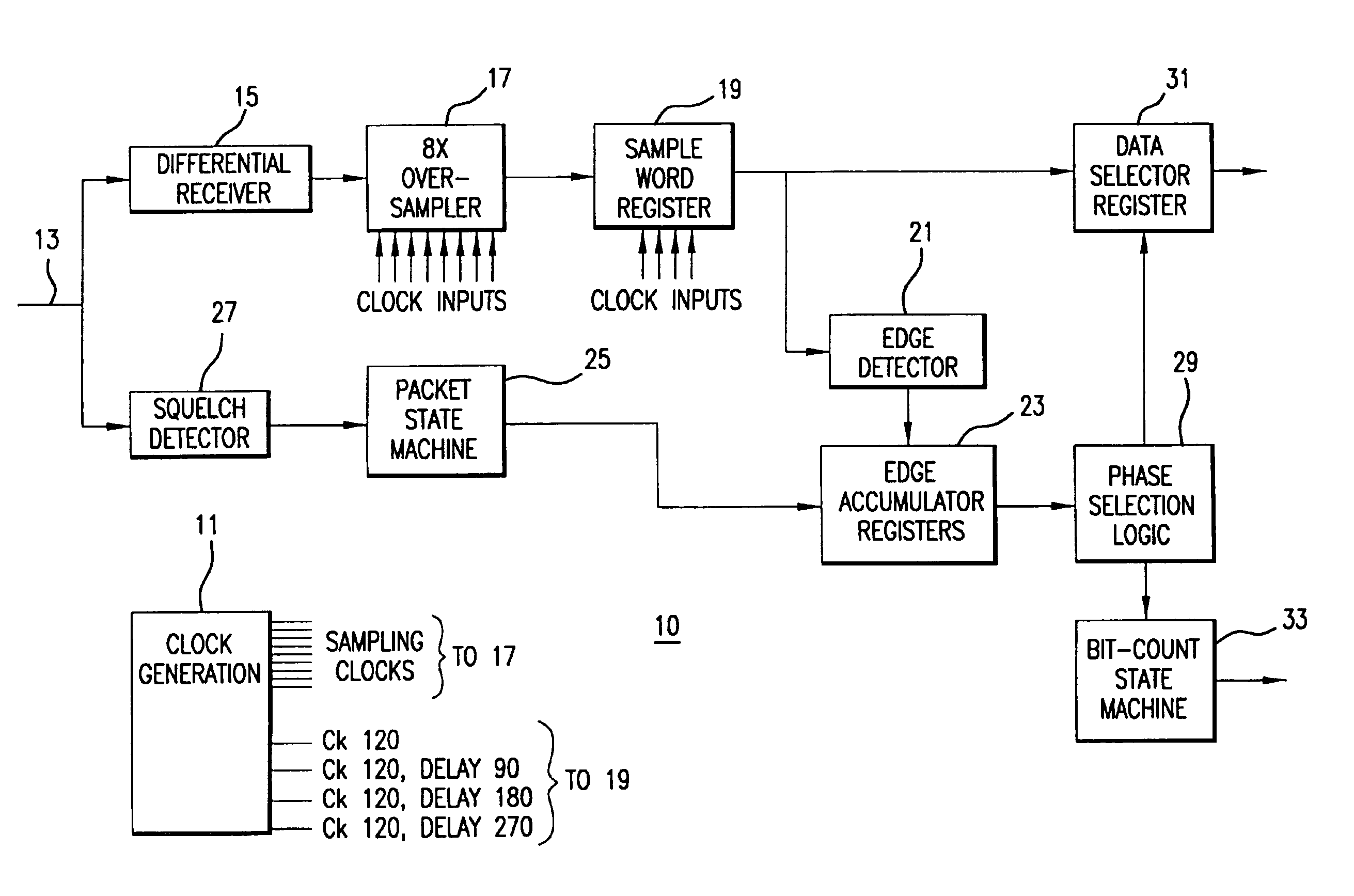
In order to recover phase information, data transmitted at a first frequency is over-sampled using a clock at a second frequency, n times per bit time to obtain n samples. The n samples are used to detect the transitions between two logic levels in said transmitted data which are stored in groups of m sets of said n edge results which are, in turn output at a clock frequency which is the second frequency divided by m, for further processing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
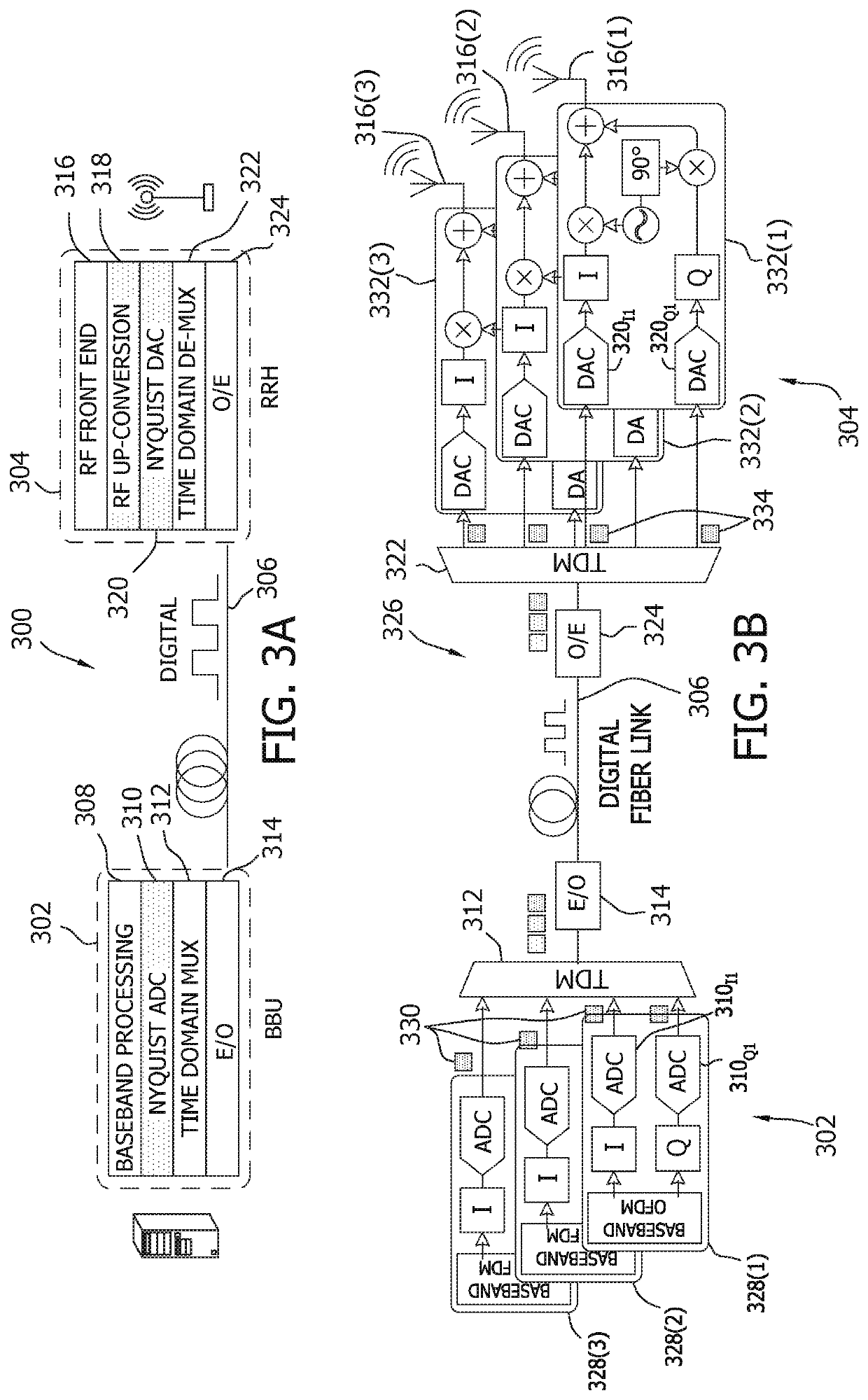
Systems and methods for delta-sigma digitization
ActiveUS20190379455A1Analogue conversionDistortion/dispersion eliminationRadio access technologyTransport medium
A baseband processing unit includes a baseband processor configured to receive a plurality of component carriers of a radio access technology wireless service, and a delta-sigma digitization interface configured to digitize at least one carrier signal of the plurality of component carriers into a digitized bit stream, for transport over a transport medium, by (i) oversampling the at least one carrier signal, (ii) quantizing the oversampled carrier signal into the digitized bit stream using two or fewer quantization bits.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
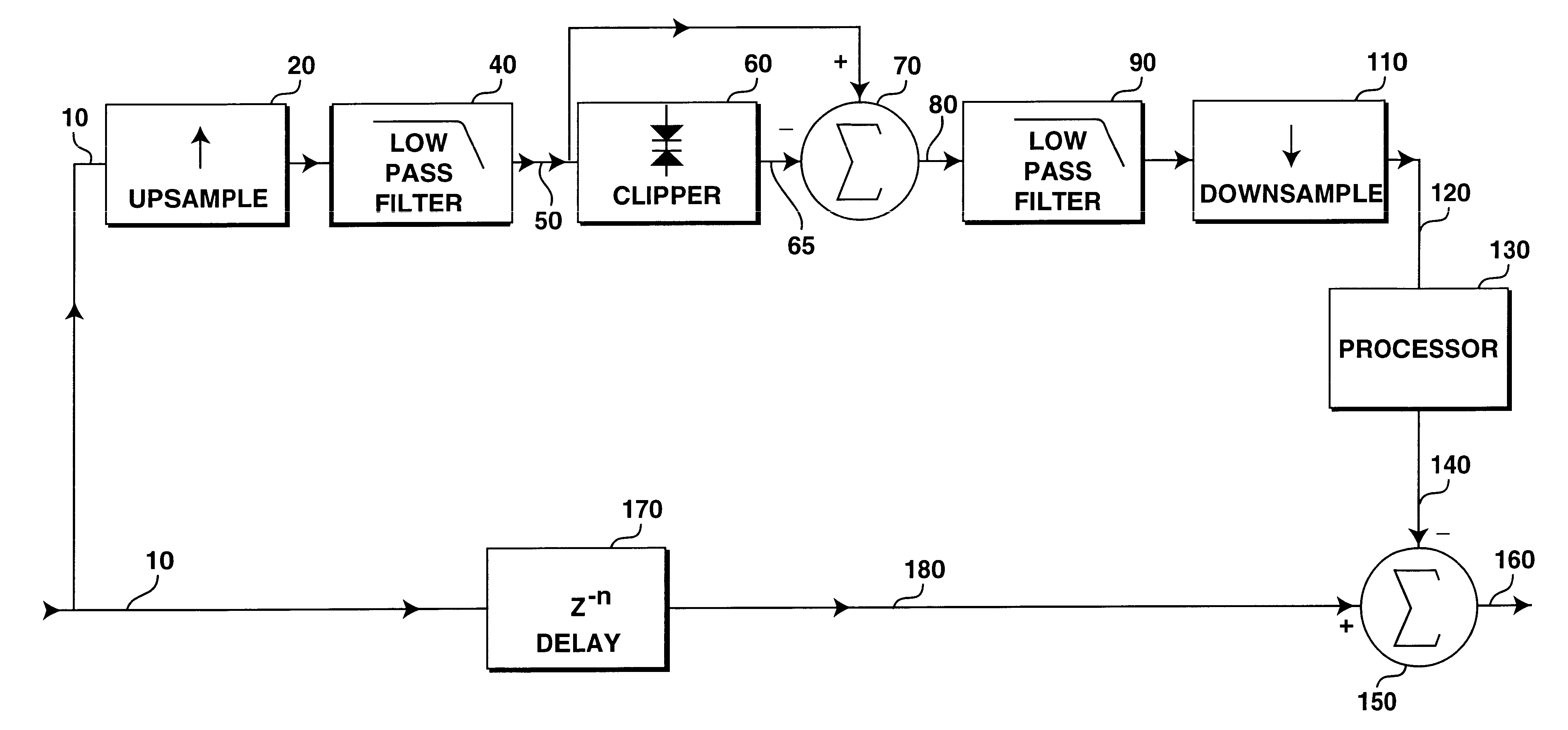
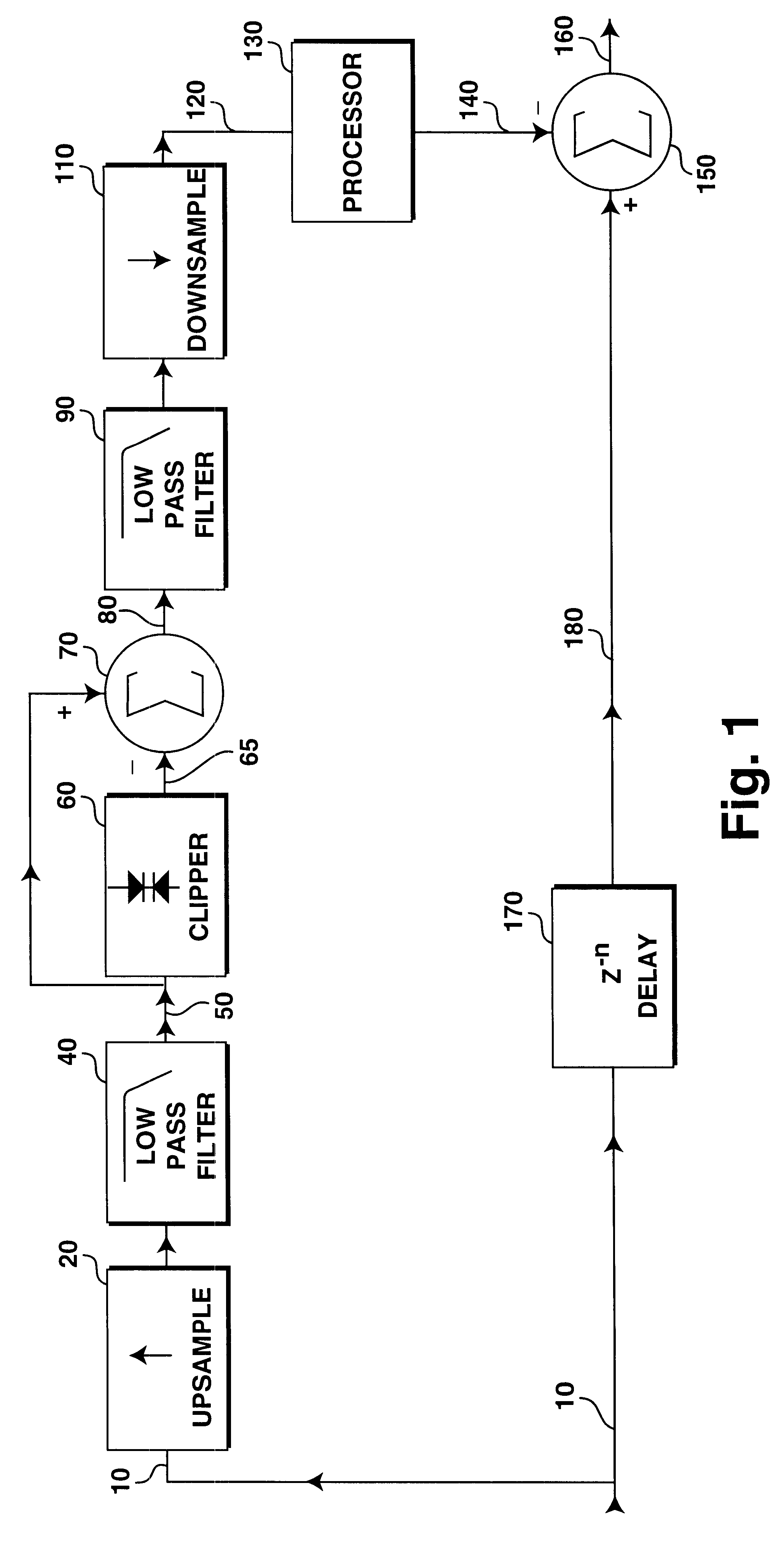
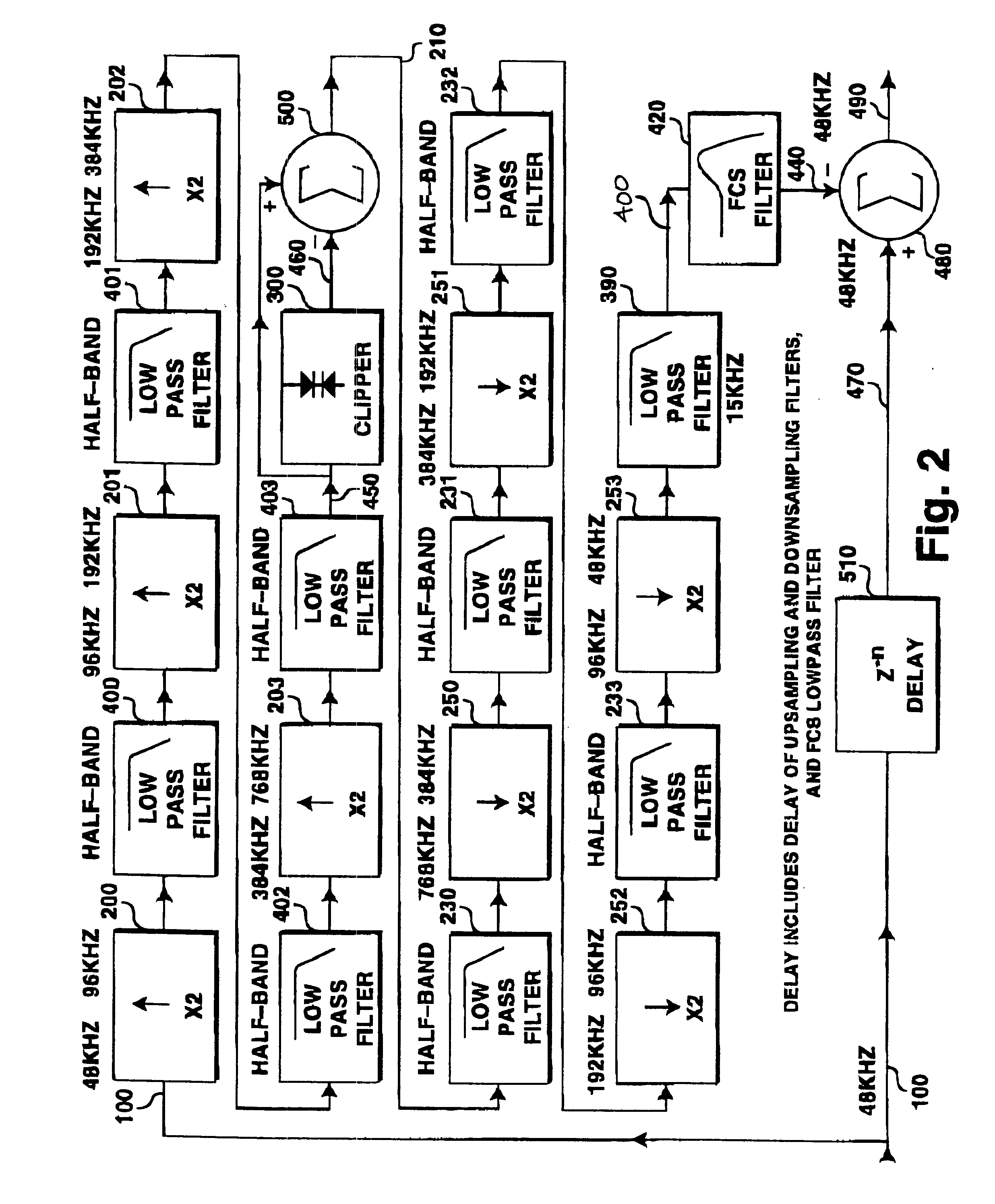
Oversampled differential clipper
InactiveUS6337999B1Improve the level ofVolume compression/expansionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsOversampling
A digital clipper is highly oversampled to decrease aliasing and increase accuracy. The difference between the clipper's input and output is then downsampled and added to the delayed, unclipped signal at 1x sample rate to achieve clipping. Filters operating at 1x can be placed in series with the downsampled differentially-clipped signal to achieve overshoot compensation, bandlimiting of the clipped signal, and other goals.
Owner:ORBAN ASSOCS
Cross product enhanced subband block based harmonic transposition
ActiveUS20130182870A1Promote resultsLow intermodulationGain controlSpeech analysisHarmonicImage resolution
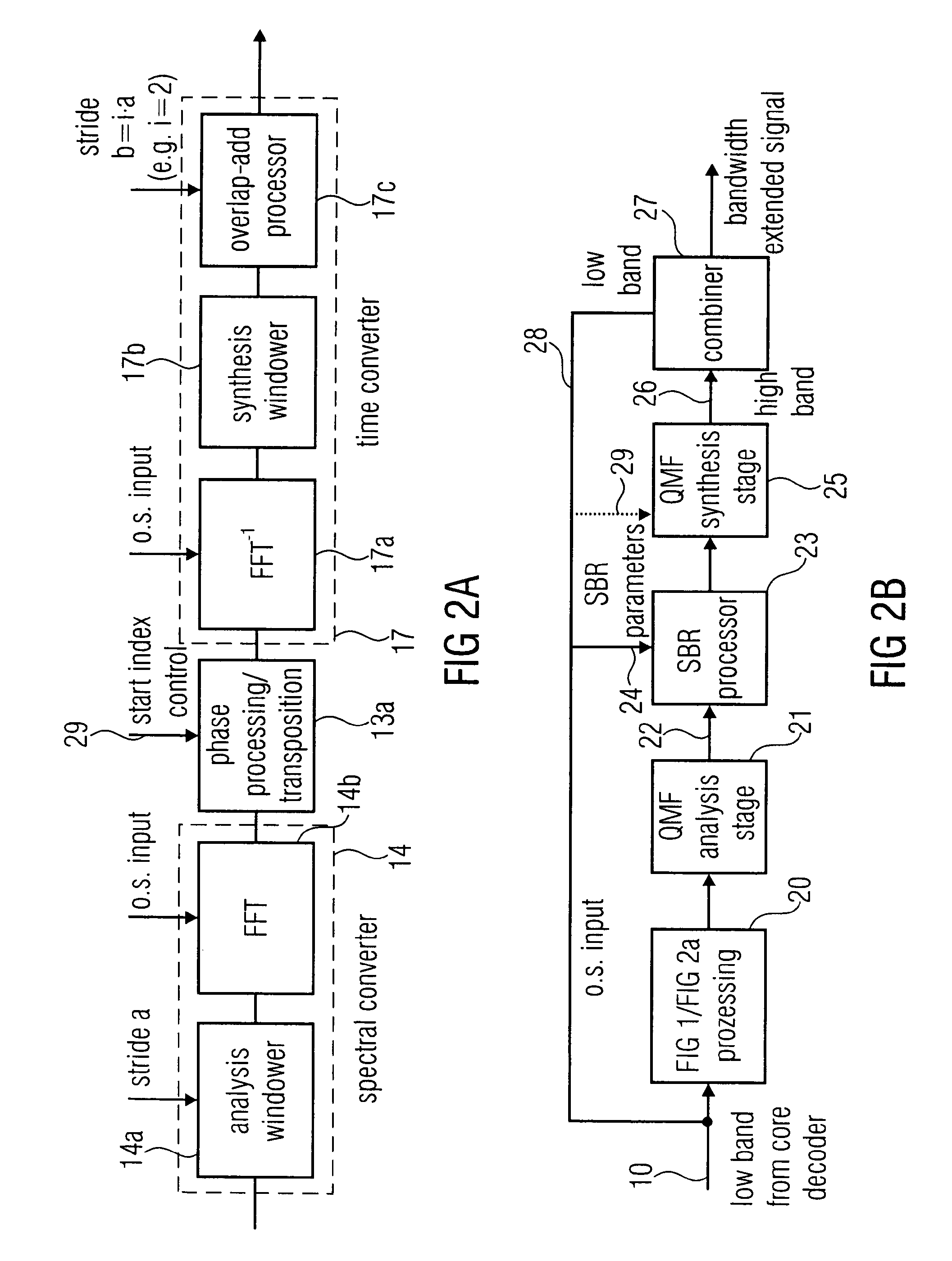
The invention provides an efficient implementation of cross-product enhanced high-frequency reconstruction (HFR), wherein a new component at frequency QΩ+Ωq is generated on the basis of existing components at Ω and QΩ+Ωq. The invention provides a block-based harmonic transposition, wherein a time block of complex subband samples is processed with a common phase modification. Superposition of several modified samples has the net effect of limiting undesirable intermodulation products, thereby enabling a coarser frequency resolution and / or lower degree of oversampling to be used. In one embodiment, the invention further includes a window function suitable for use with block-based cross-product enhanced HFR. A hardware embodiment of the invention may include an analysis filter bank (101), a subband processing unit (102) configurable by control data (104) and a synthesis filter bank (103).
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
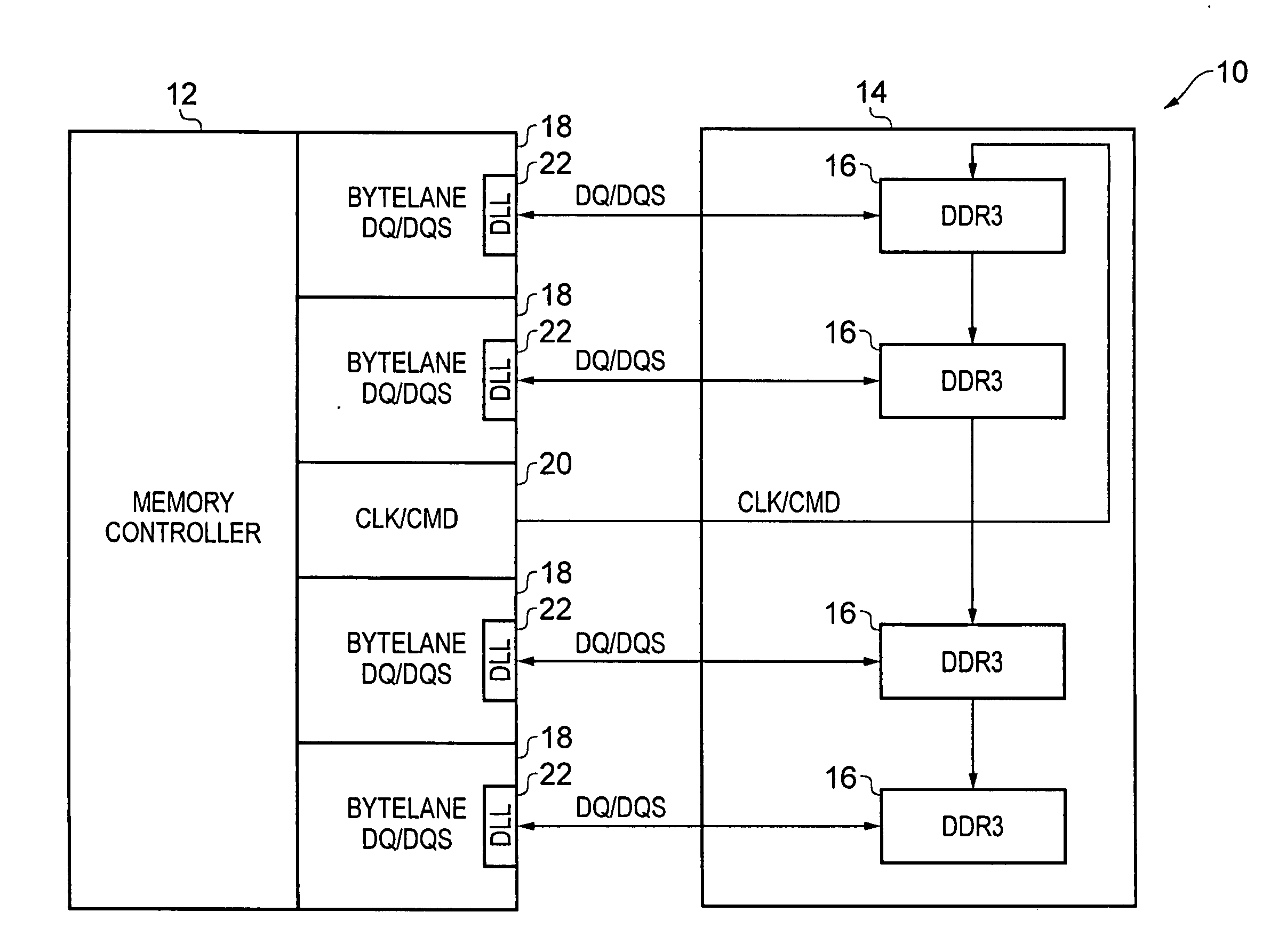
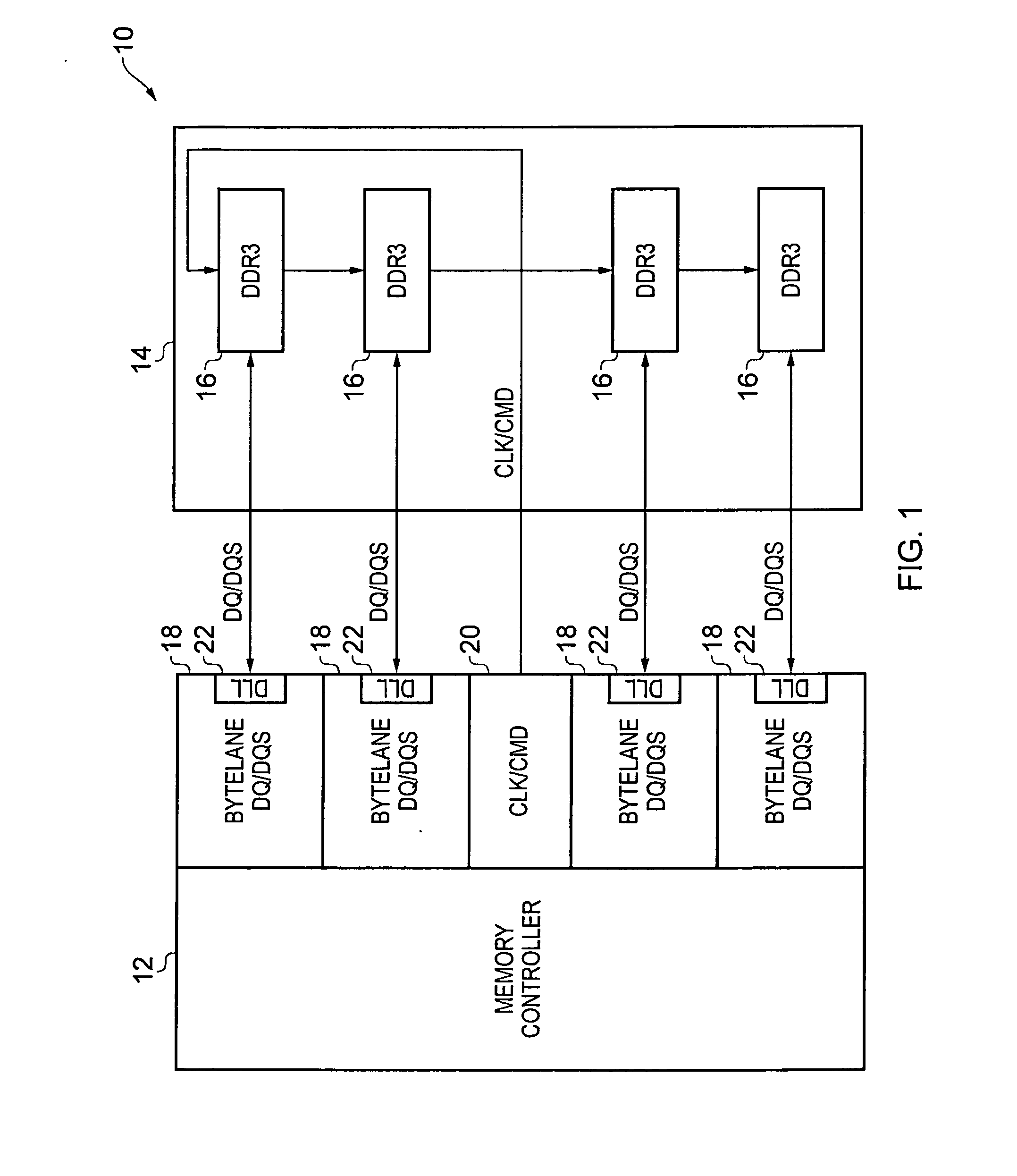
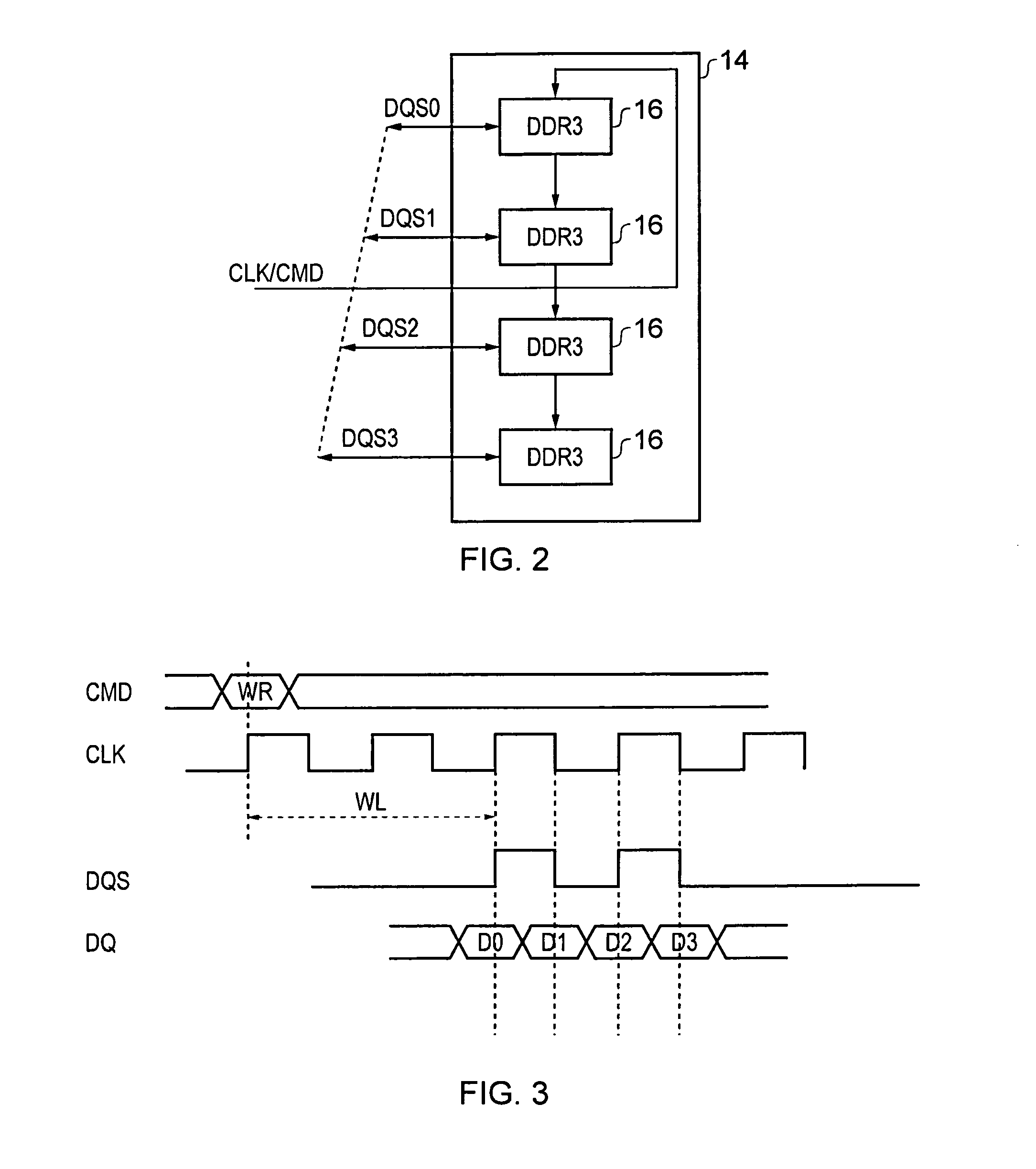
Method and apparatus for aligning a clock signal and a data strobe signal in a memory system
ActiveUS20140177359A1Simple technologyDigital storageElectric digital data processingOversamplingMemory controller
A method of aligning a clock signal and a data strobe signal in a system comprising a memory controller and a memory, and a corresponding memory system are provided. The method comprising the steps of: putting the memory into a write levelling mode; incrementing an alignment delay applied to the data strobe signal until a transition point occurs at which a response of the memory to issuance of the data strobe signal transitions to an inverse state; performing an oversampling of the response of the memory over a selected interval following said transition point; repeating the steps of incrementing and performing an oversampling until, for a selected alignment delay, a majority of results of the oversampling is in the inverse state; performing a cycle alignment detection procedure to determine an identified clock cycle of a plurality of adjacent cycles of the clock signal, the identified clock cycle responsible for the transition point; and applying the selected alignment delay to the data strobe signal and applying a clock cycle selection to a data path in the system to match the identified clock cycle.
Owner:ARM LTD
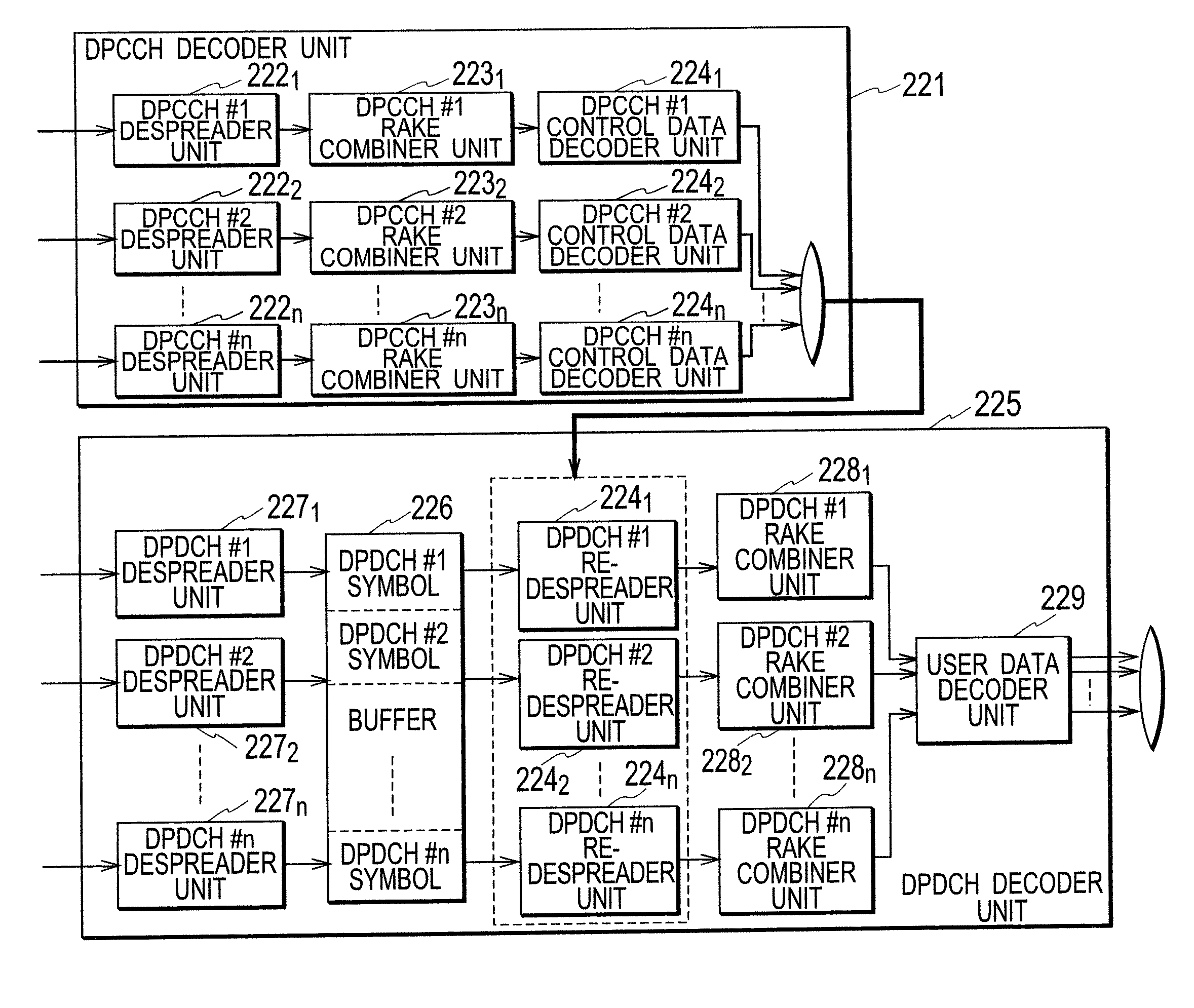
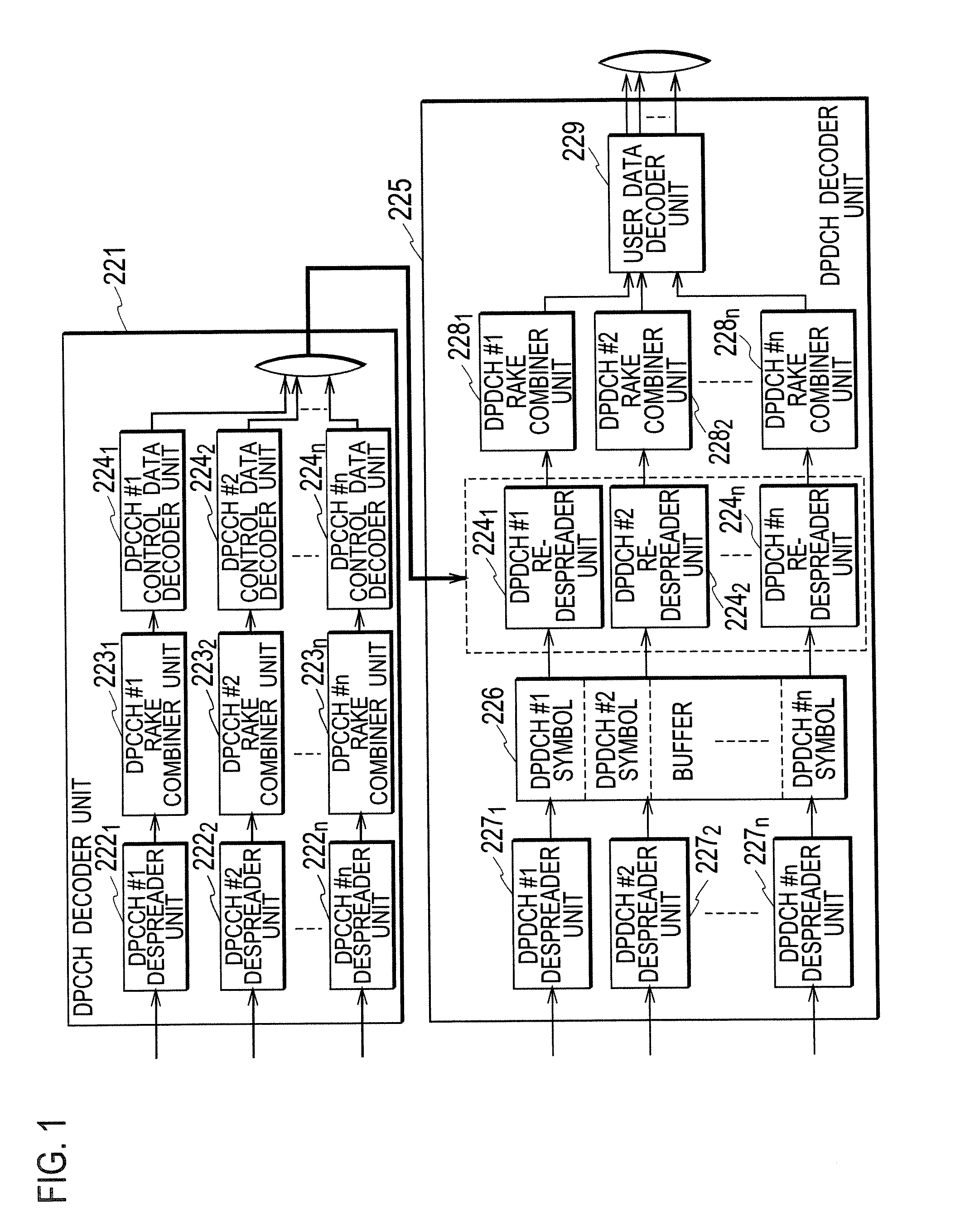
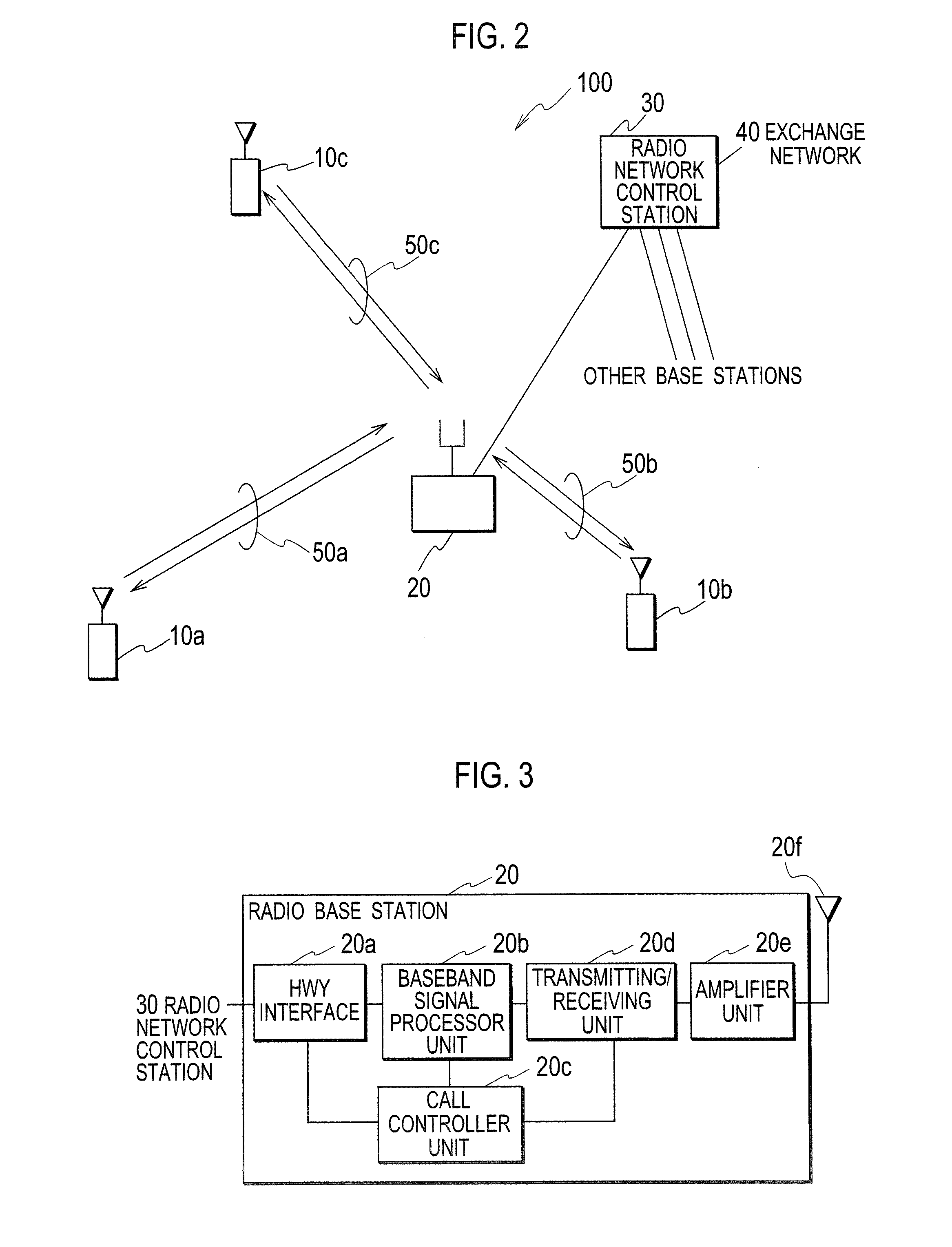
Radio Base Station, Radio Line Control Station, And Mobile Communication System, And Mobile Communication Method
InactiveUS20080089447A1Increase the number of connectionsReceiver specific arrangementsInformation formatOversamplingMobile communication systems
A radio base station related to the present invention includes: a signal storing unit configured to store baseband signals received and over-sampled; a format determining unit configured to determine transport formats of the baseband signals; and a despreader unit configured to despread the baseband signals stored in the signal storing unit, in accordance with the transport formats determined by the format determining unit, after the determination by the format determining unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Classification method based on improved DBSCAN-SMOTE algorithm
InactiveCN105930856AEasy to handleSolve for uniformityCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmClassification methods
The invention relates to a classification method based on an improved DBSCAN-SMOTE algorithm for an intra-class unbalanced condition in data sample space processing, firstly, in a data sample set, which are belongs to boundary samples is judged, the boundary samples are divided into majority boundary samples and minority boundary samples, and cluster is performed on the boundary samples in a majority boundary sample space; a PSO algorithm is adopted to optimize oversampling rate of the boundary samples and safe samples in cluster, oversampling with different sampling rates is performed on minority boundary samples through an SMOTE algorithm; wherein the cluster is based on the improved DBSCAN algorithm, the algorithm can generate cluster of minority, perform oversampling in the sample cluster, and can fully resolve the problem of uneven distribution and data fragment or small disjunct in intra-class unbalance.
Owner:SHENZHEN ETTOM TECH CO LTD
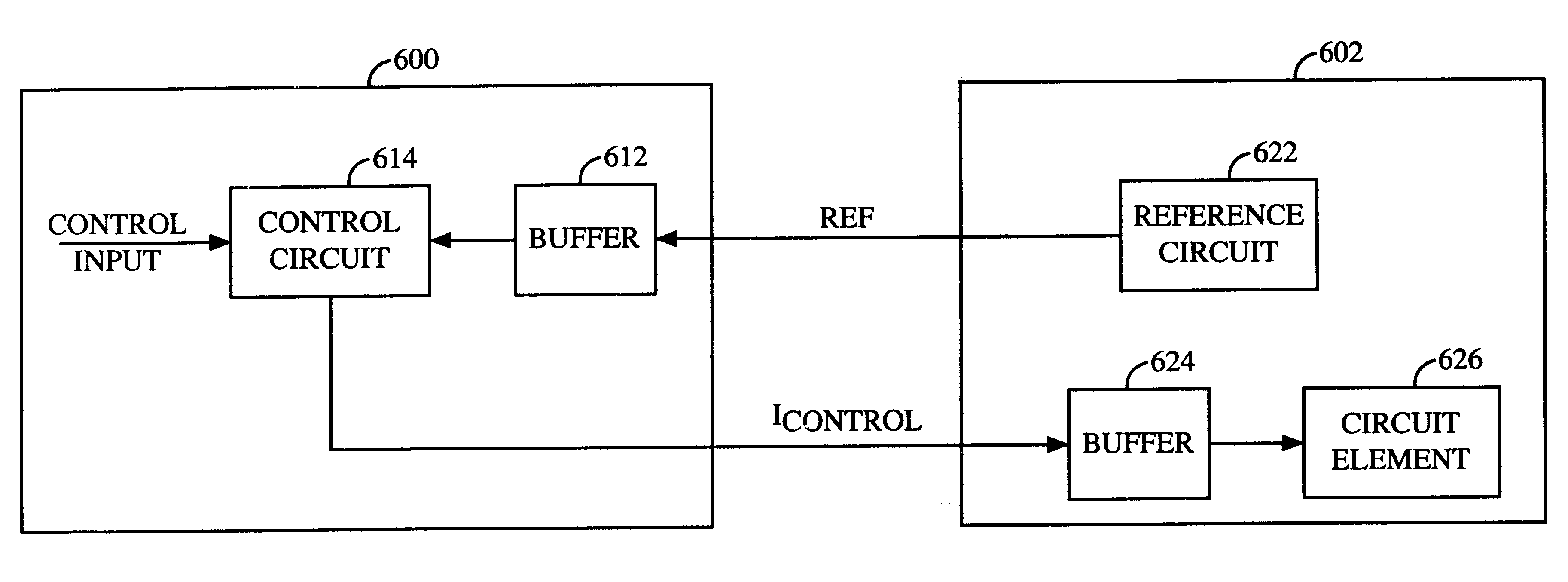
Method and circuit for providing interface signals between integrated circuits
InactiveUS6615027B1Electric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsImage resolutionControl circuit
Circuitry that generates an interface signal between a first and a second integrated circuit (IC). The circuitry includes a reference circuit that provides a reference signal, an interface circuit, and a circuit element. The interface circuit is implemented on the first IC, operatively couples to the reference circuit, receives the reference signal and a data input, and generates the interface signal. The circuit element is implemented on the second IC, operatively couples to the control circuit, receives the interface signal, and provides an output signal. The reference signal can be a voltage or a current signal, and can be generated in the first or second IC. The interface circuit can be implemented with a current mirror coupled to a switch array, and can be oversampled to ease the filtering requirement. The interface signal can be a differential current signal having multiple (e.g., four, eight, or more) bits of resolution. The circuit element can be, for example, a VGA, a modulator, or other circuits.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Reduced complexity sliding window based equalizer
The present invention has many aspects. One aspect of the invention is to perform equalization using a sliding window approach. A second aspect reuses information derived for each window for use by a subsequent window. A third aspect utilizes a discrete Fourier transform based approach for the equalization. A fourth aspect relates to handling oversampling of the received signals and channel responses. A fifth aspect relates to handling multiple reception antennas. A sixth embodiment relates to handling both oversampling and multiple reception antennas.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
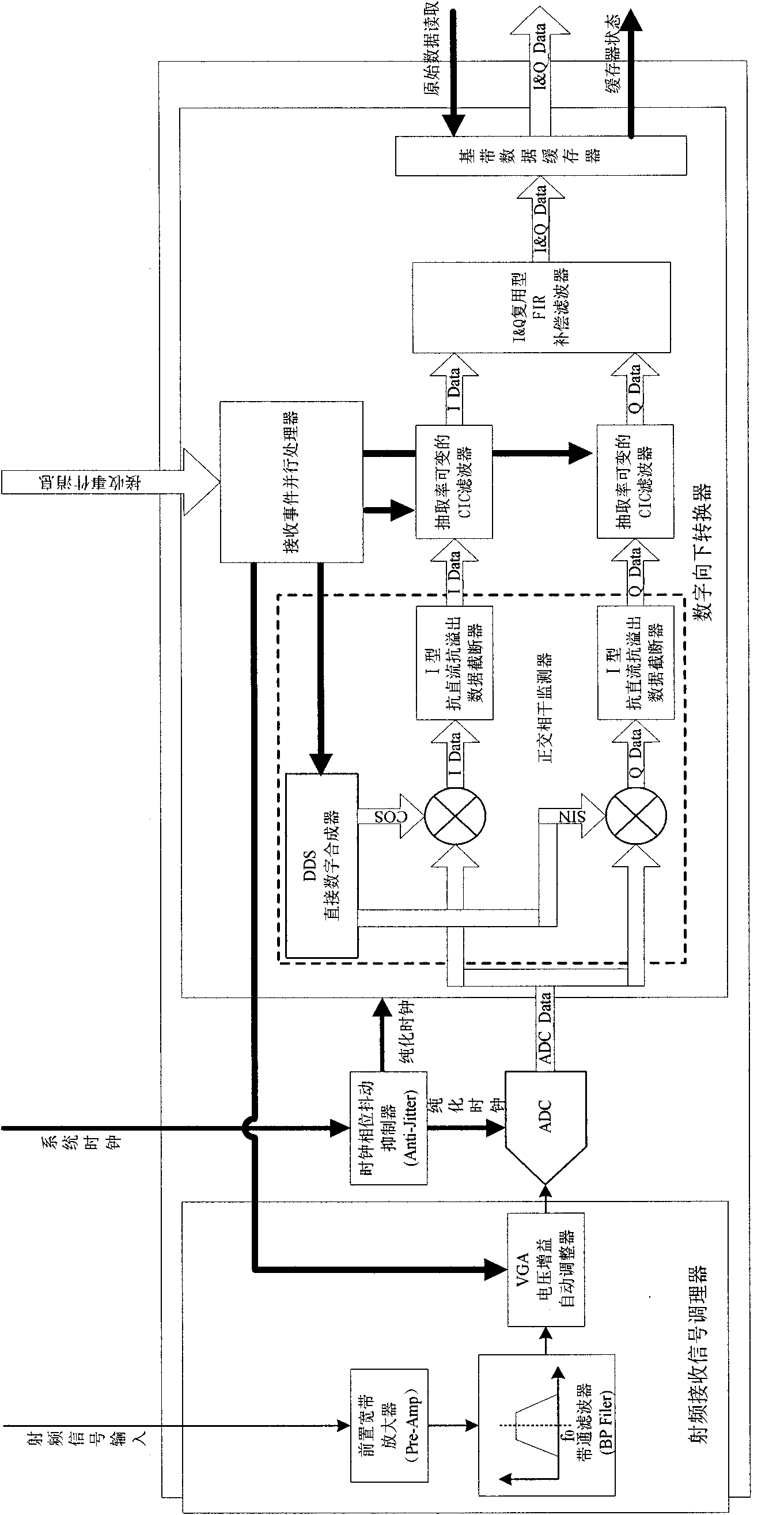
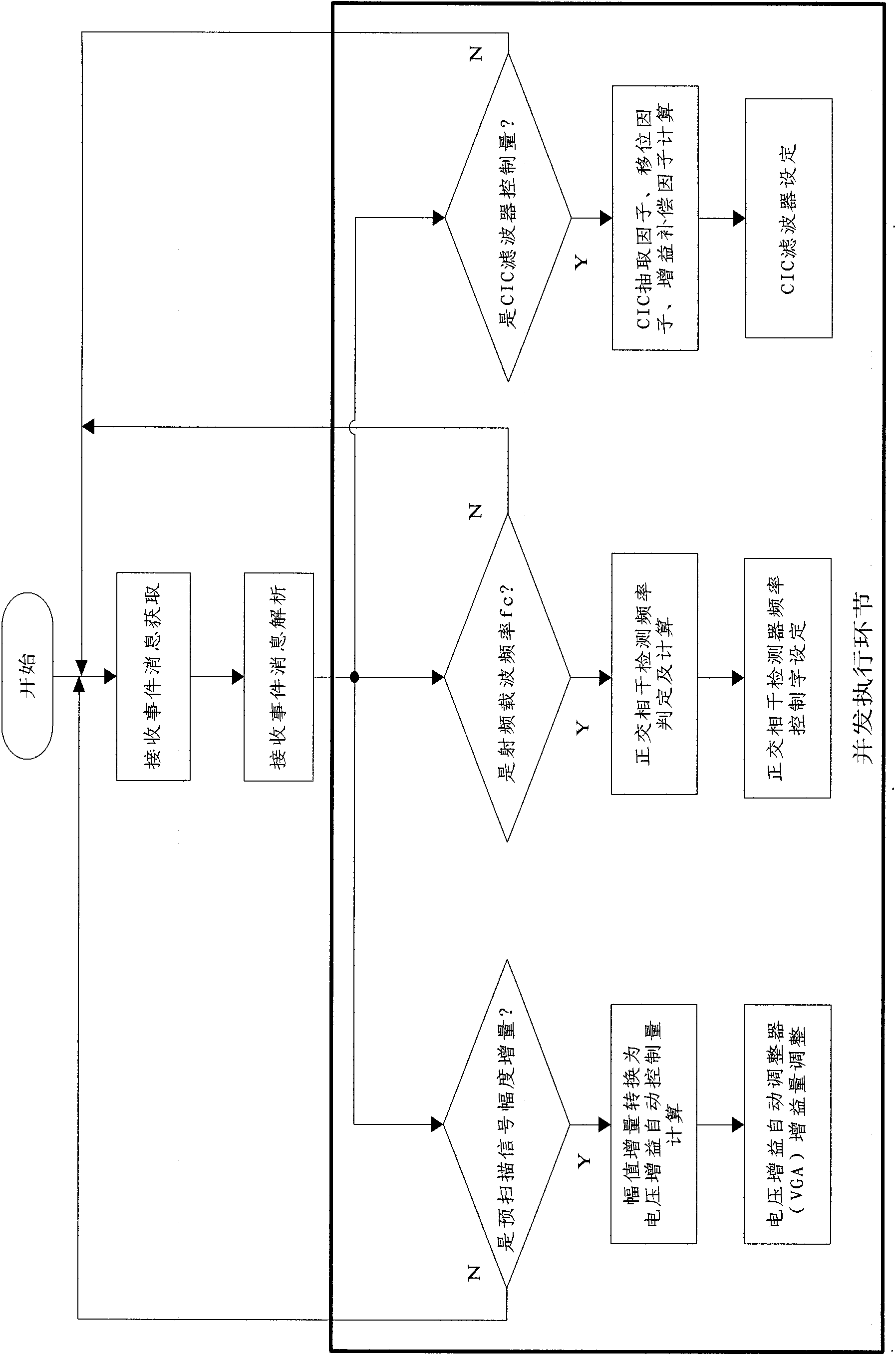
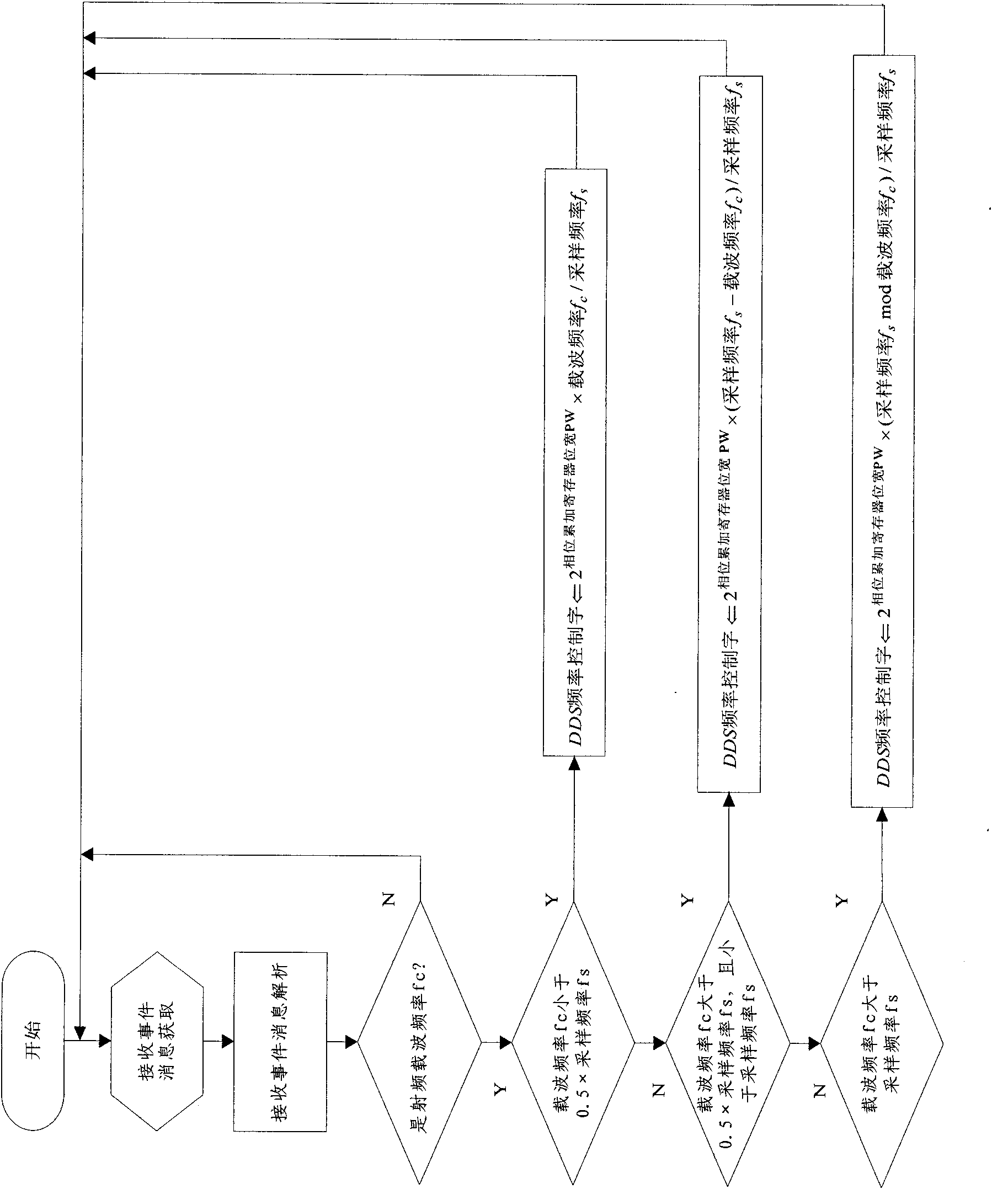
Device and method for realizing broadband digital magnetic resonance radio frequency receiving
ActiveCN102103195AImprove signal-to-noise ratioDigital receptionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAnti-aliasingDigital down converter
The invention relates to a device and method for realizing broadband digital magnetic resonance radio frequency receiving. The device comprises a radio frequency receiving signal conditioner, a clock phase jitter suppressor, a high-speed analog to digital converter and a digital down converter, wherein the radio frequency receiving signal conditioner conducts front-end voltage amplification and anti-aliasing filtering for a magnetic resonance signal received by an external device; the clock phase jitter suppressor is used for suppressing phase jitter of a system clock and providing a high-stability clock source in a picosecond or femtosecond order of magnitude for the high-speed analog to digital converter and the digital down converter; the high-speed analog to digital converter is used for realizing digitalized conversion of the radio frequency receiving signal; and the digital down converter is used for conducting orthogonal coherent detection, filtering and frequency down conversion for data output by the high-speed analog to digital converter to obtain broadband data, of a real part and an imaginary part, to be output to the external device. The device can ensure higher channel signal to noise ratio, realizes orthogonal coherent detection and conducts accurate control for nuclear magnetic resonance signal receiving phases. In the process of applying a direct oversampling or undersampling technology, the device can ensure good receiving channel signal to noise ratio and has good instantaneity.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
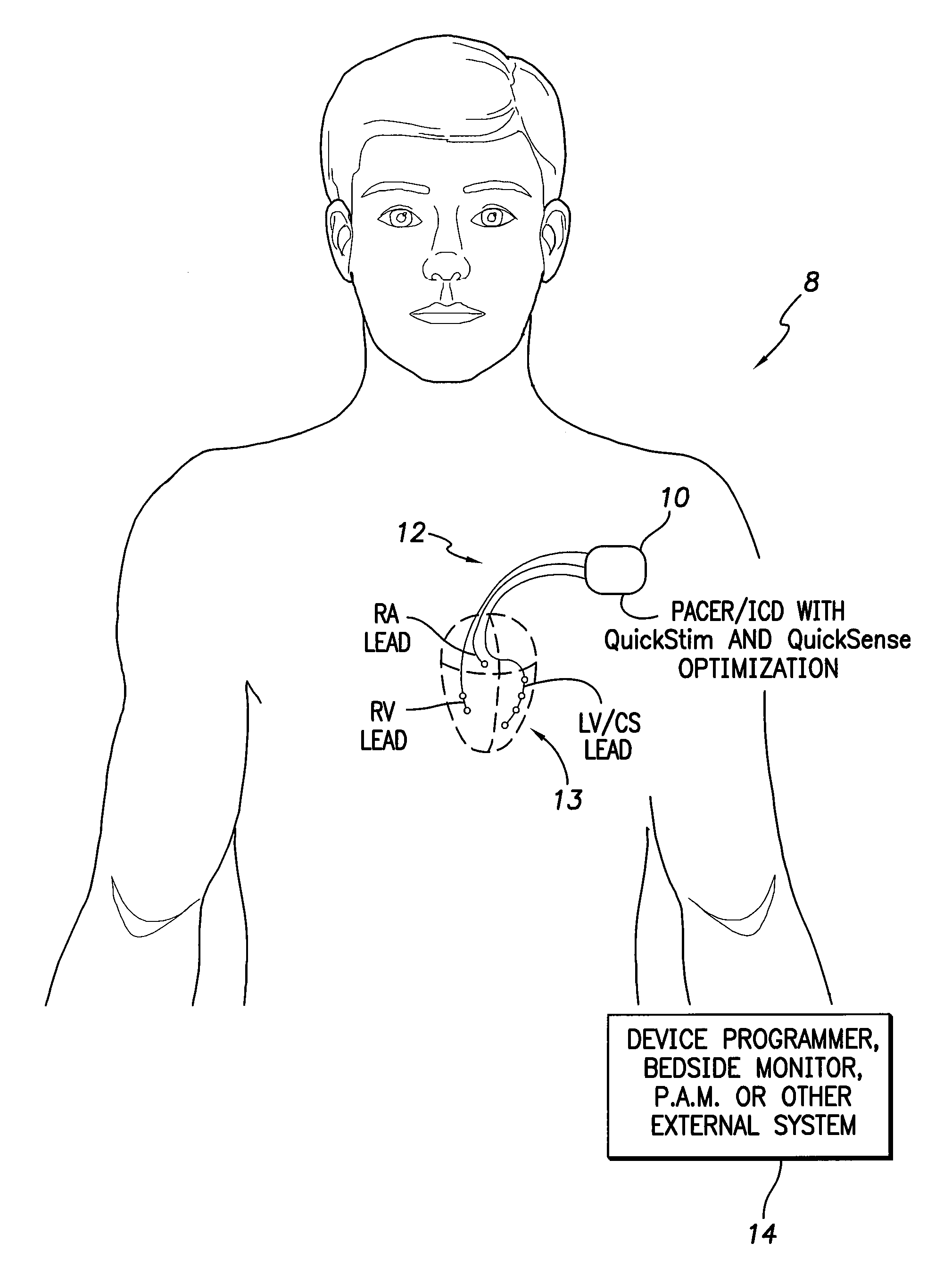
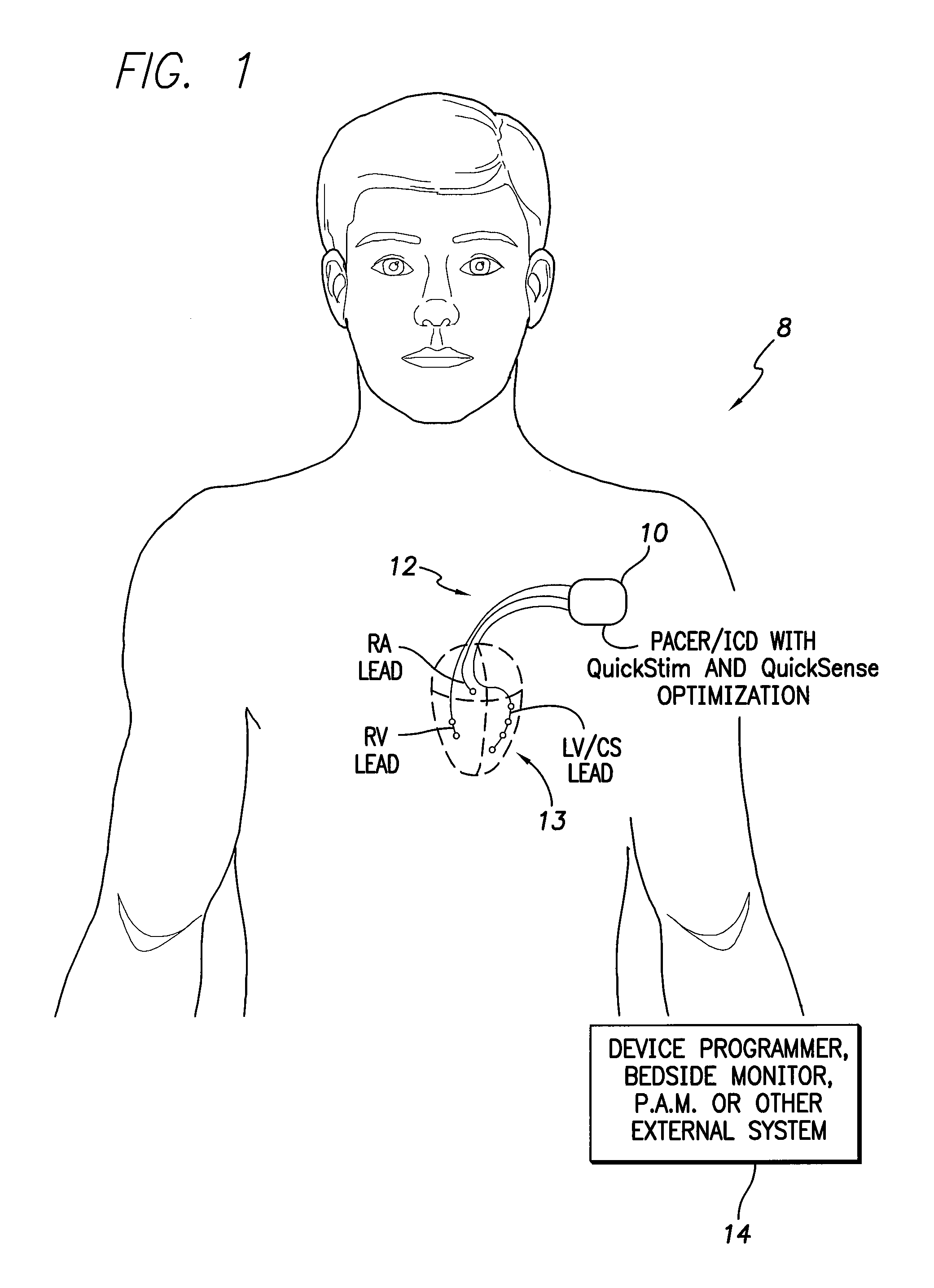
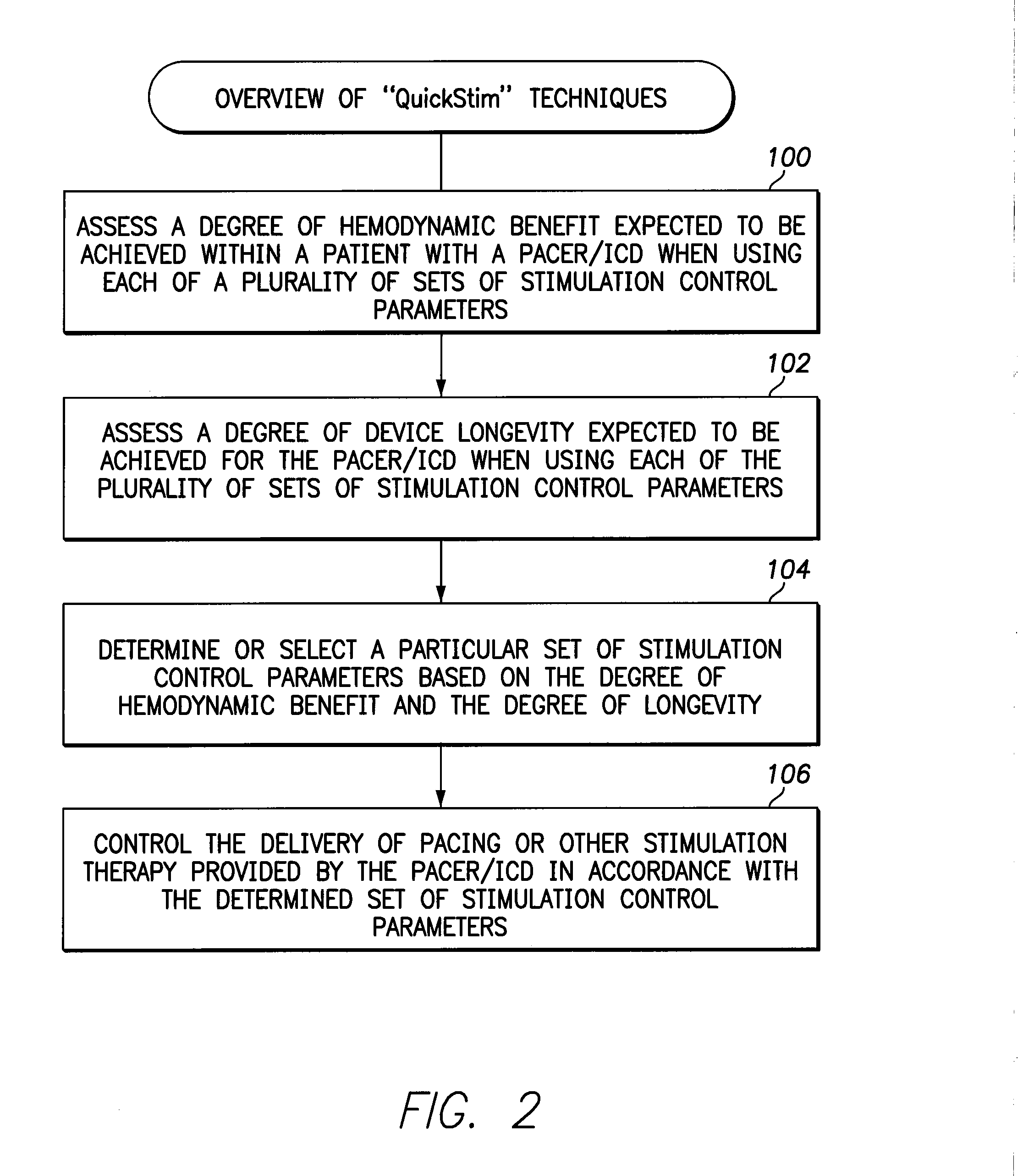
Systems and methods for optimizing multi-site cardiac pacing and sensing configurations for use with an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for use with an implantable cardiac stimulation device equipped for multi-site left ventricular (MSLV) pacing using a multi-pole LV lead. In one example, referred to herein as QuickStim, cardiac pacing configurations are optimized based on an assessment of hemodynamic benefit and device longevity. In another example, referred to herein as QuickSense, cardiac sensing configurations are optimized based on sensing profiles input by a clinician. Various virtual sensing channels are also described that provide for the multiplexing or gating of sensed signals. Anisotropic oversampling is also described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and circuit for recovering a data signal from a stream of binary data
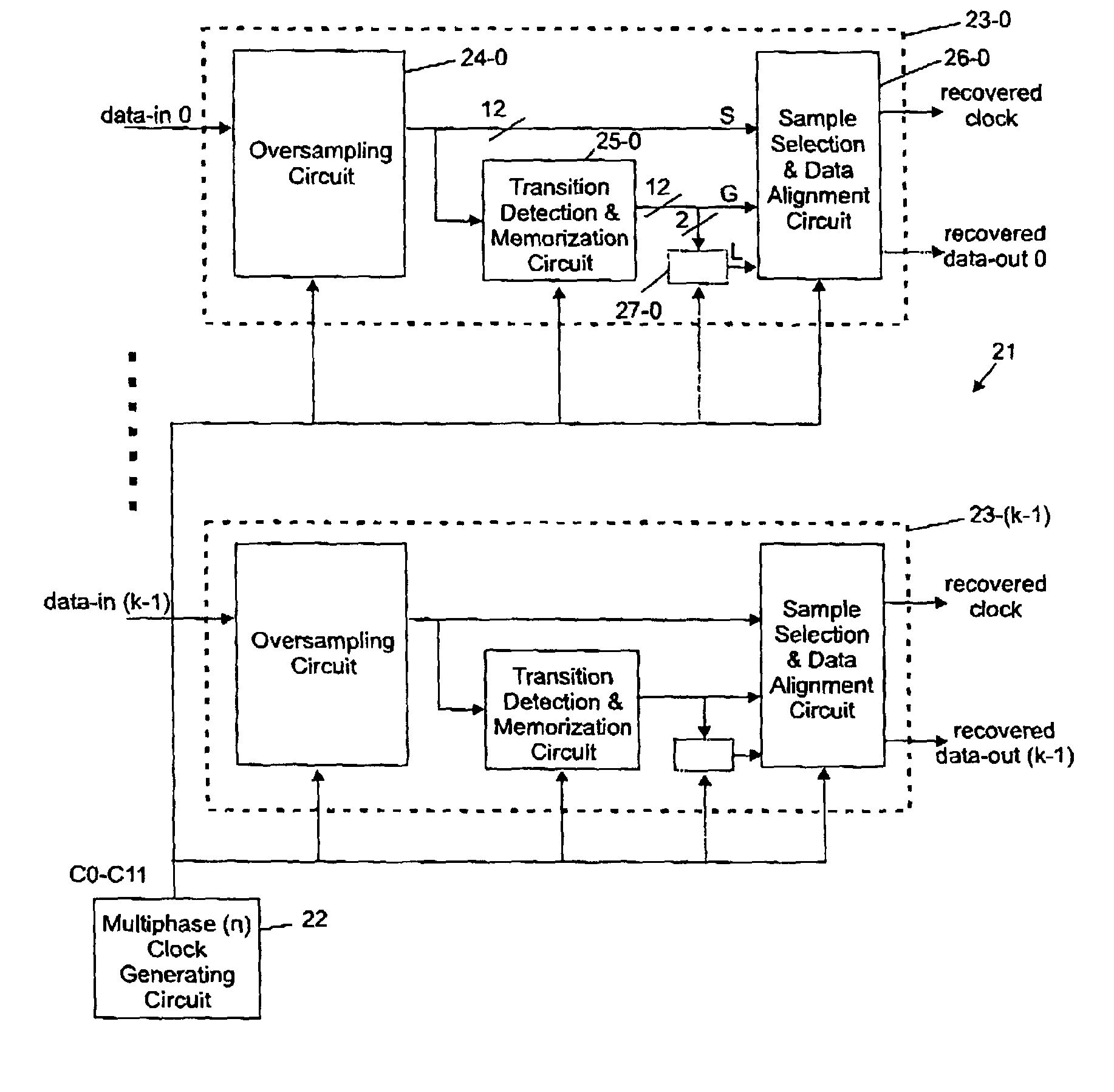
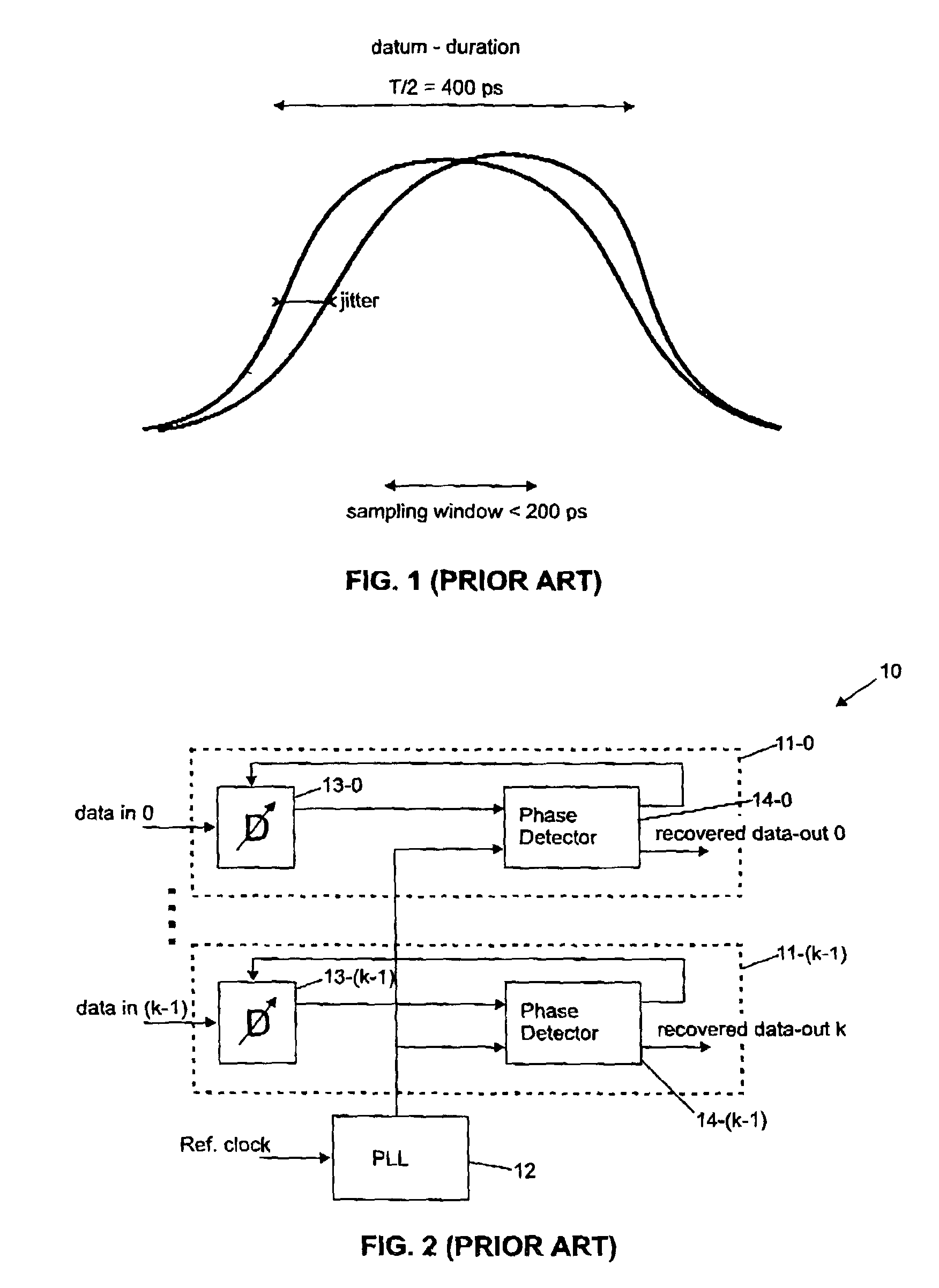
InactiveUS7142621B2Simple methodQuick checkModulated-carrier systemsPulse automatic controlDigital dataData transformation
There is disclosed a data recovery (DR) circuit including an over sampling (OS) circuit, a transition detection (TD) circuit and a sample selection / data alignment (SSDA) circuit. A multiphase clock generating circuit delivering n phases is coupled to each of these circuits. The OS circuit over samples the received digital data stream and produces n sampled signals at each clock period. The TD circuit is configured to detect a data transition (if any) and to generate n select signals, only one of which is active and represents a determined delay with respect to the transition position, indicating thereby which over sampled signal is the best to be retained. The SSDA circuit is configured to generate the recovered (retimed) data signal that is aligned with a predefined phase of the multiphase clock signal. The data recovery circuit is well adapted to high speed serial data communications between integrated circuits / systems on digital networks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com