Patents
Literature
29207 results about "Time domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
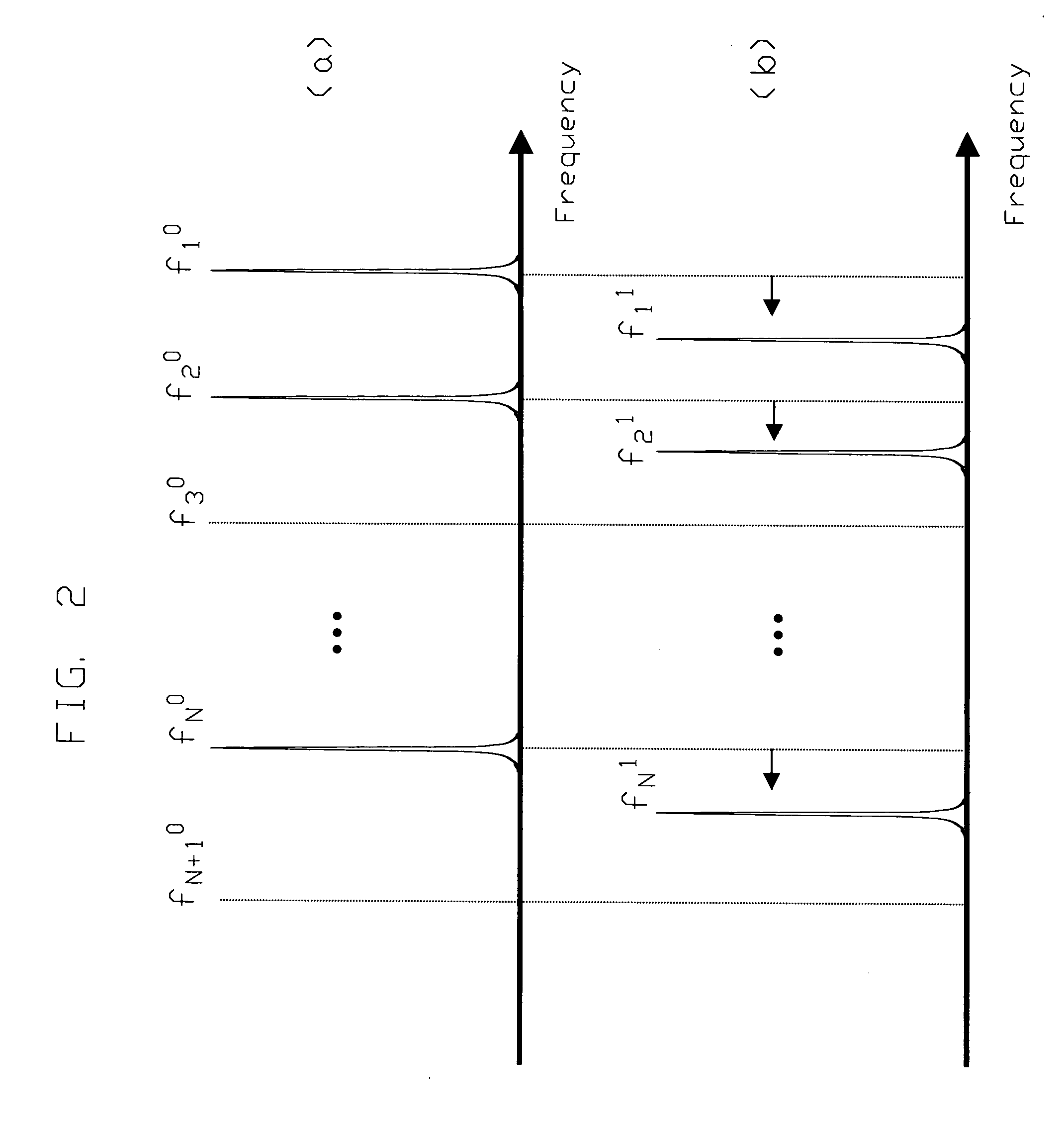
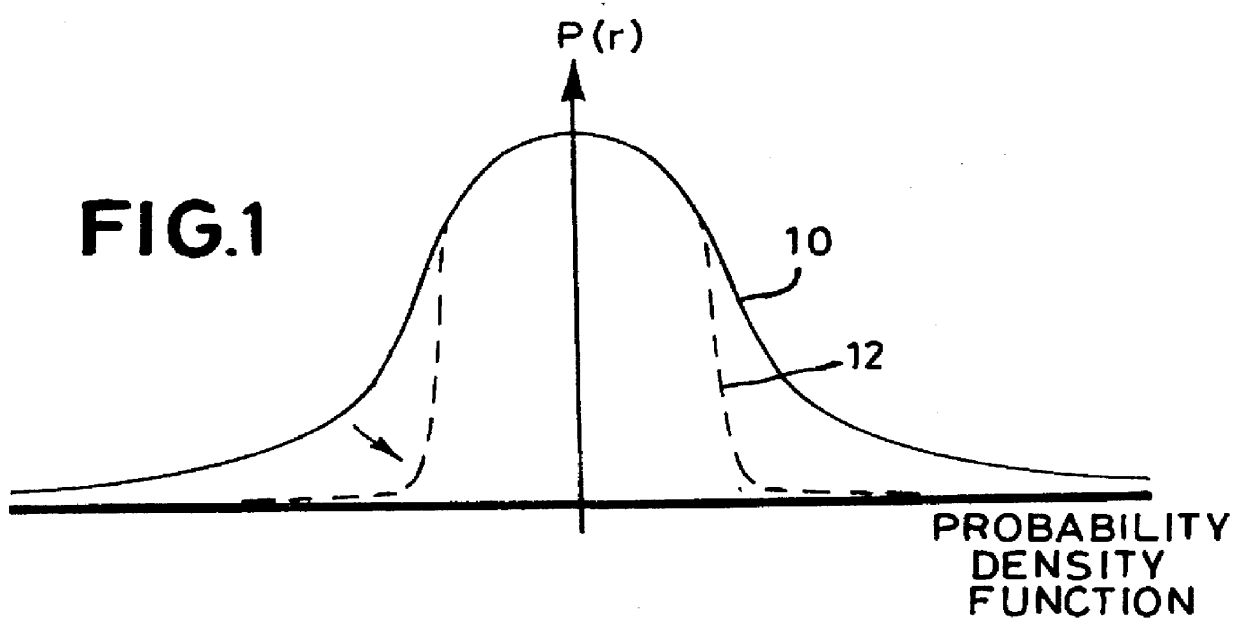
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various separate instants in the case of discrete time. An oscilloscope is a tool commonly used to visualize real-world signals in the time domain. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes with time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies.
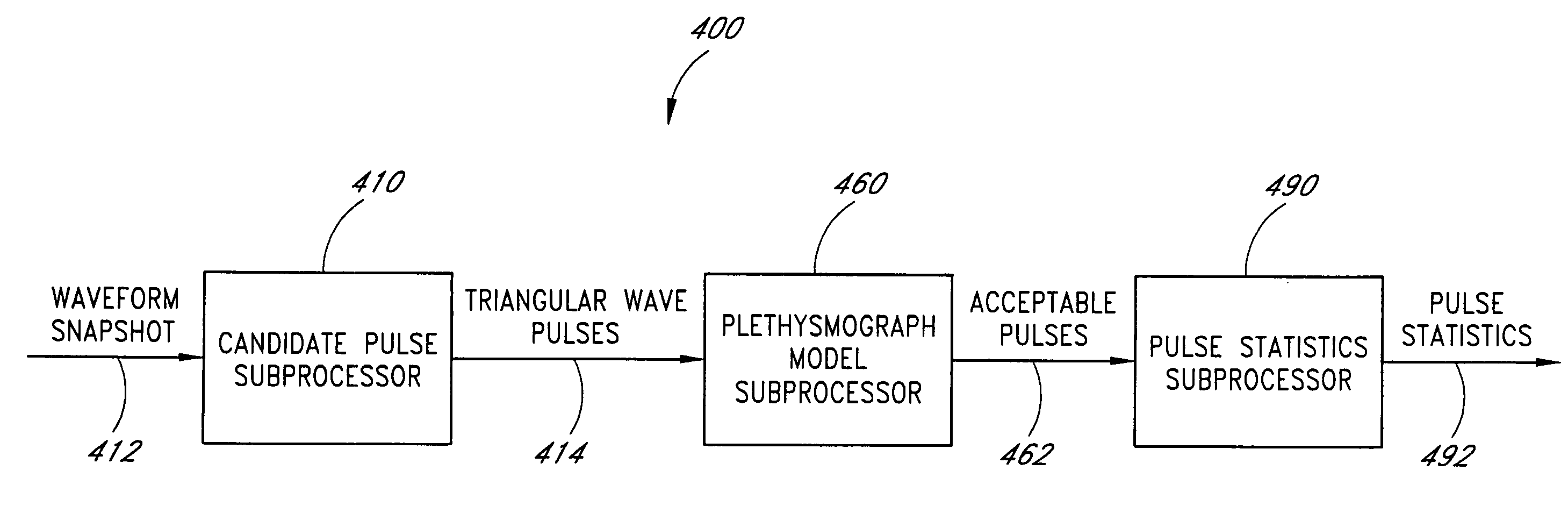
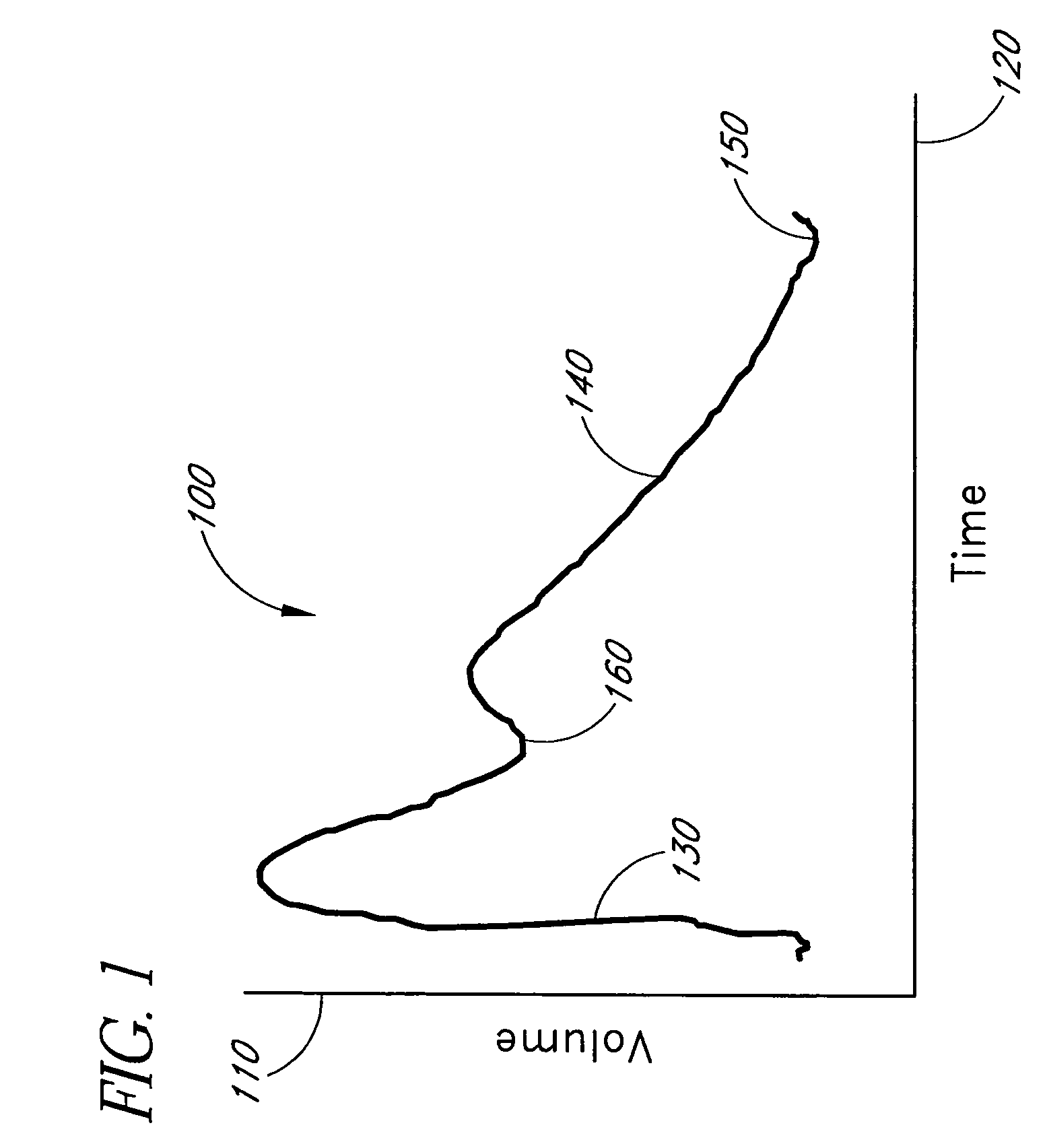
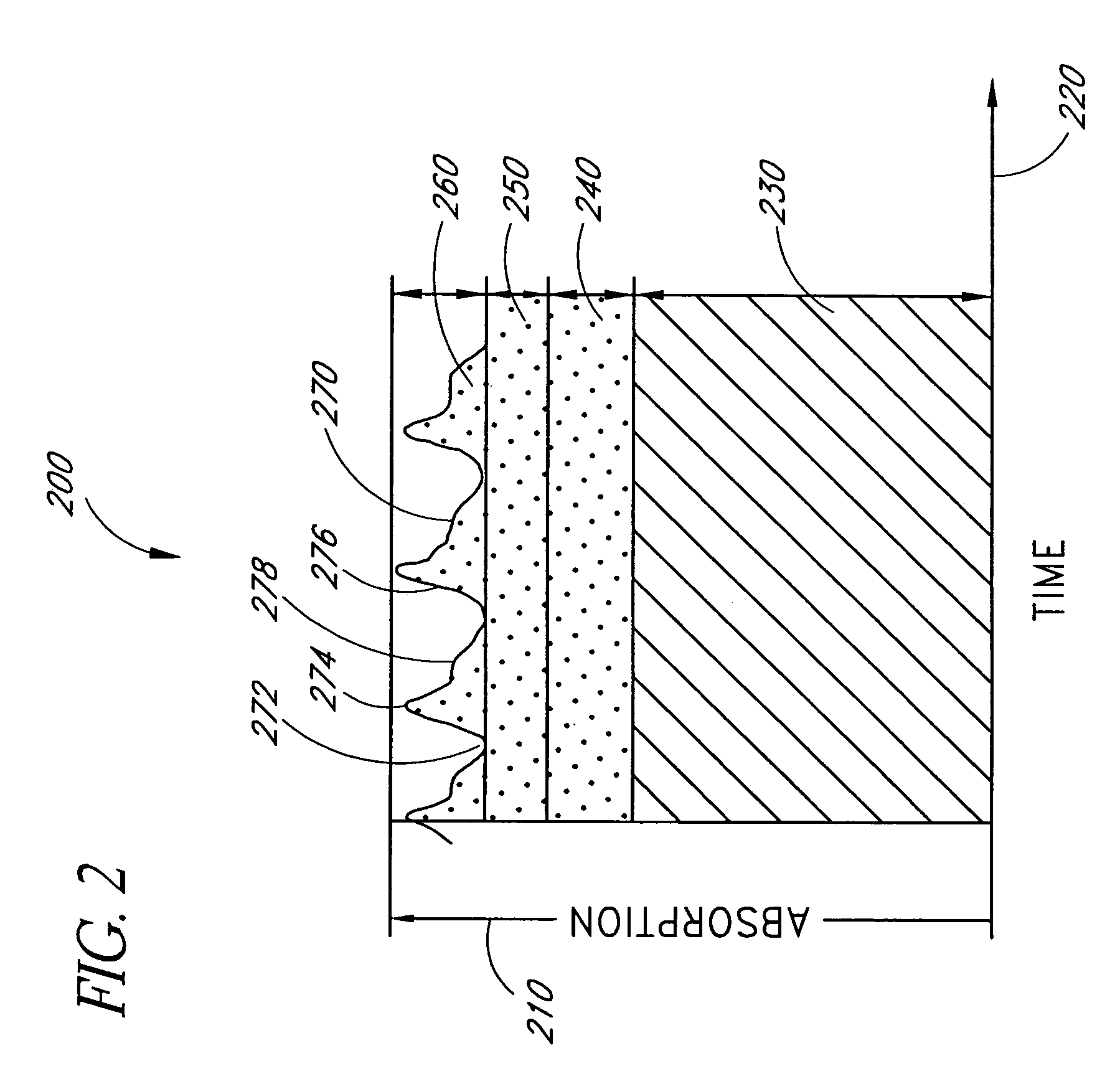
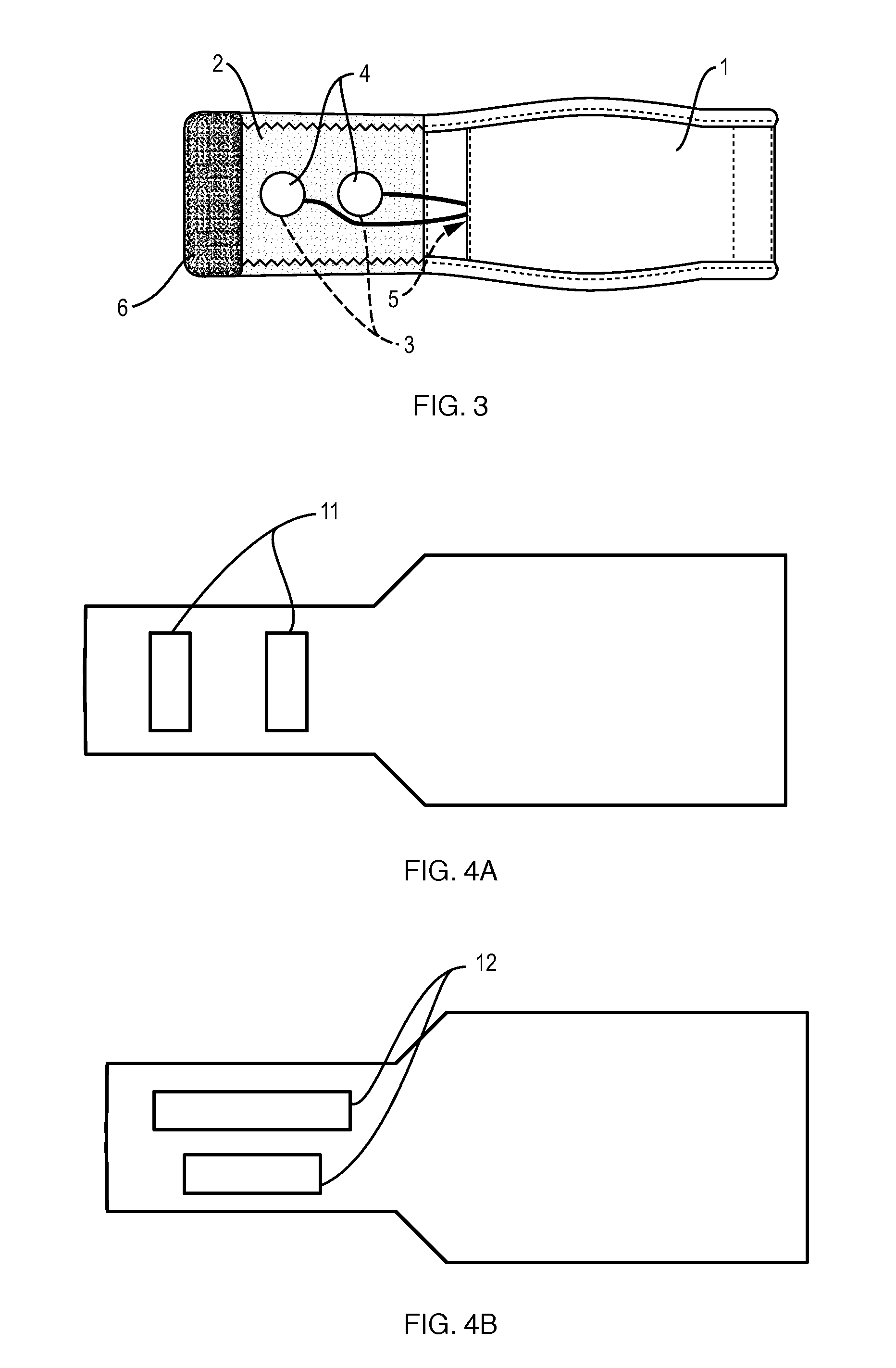
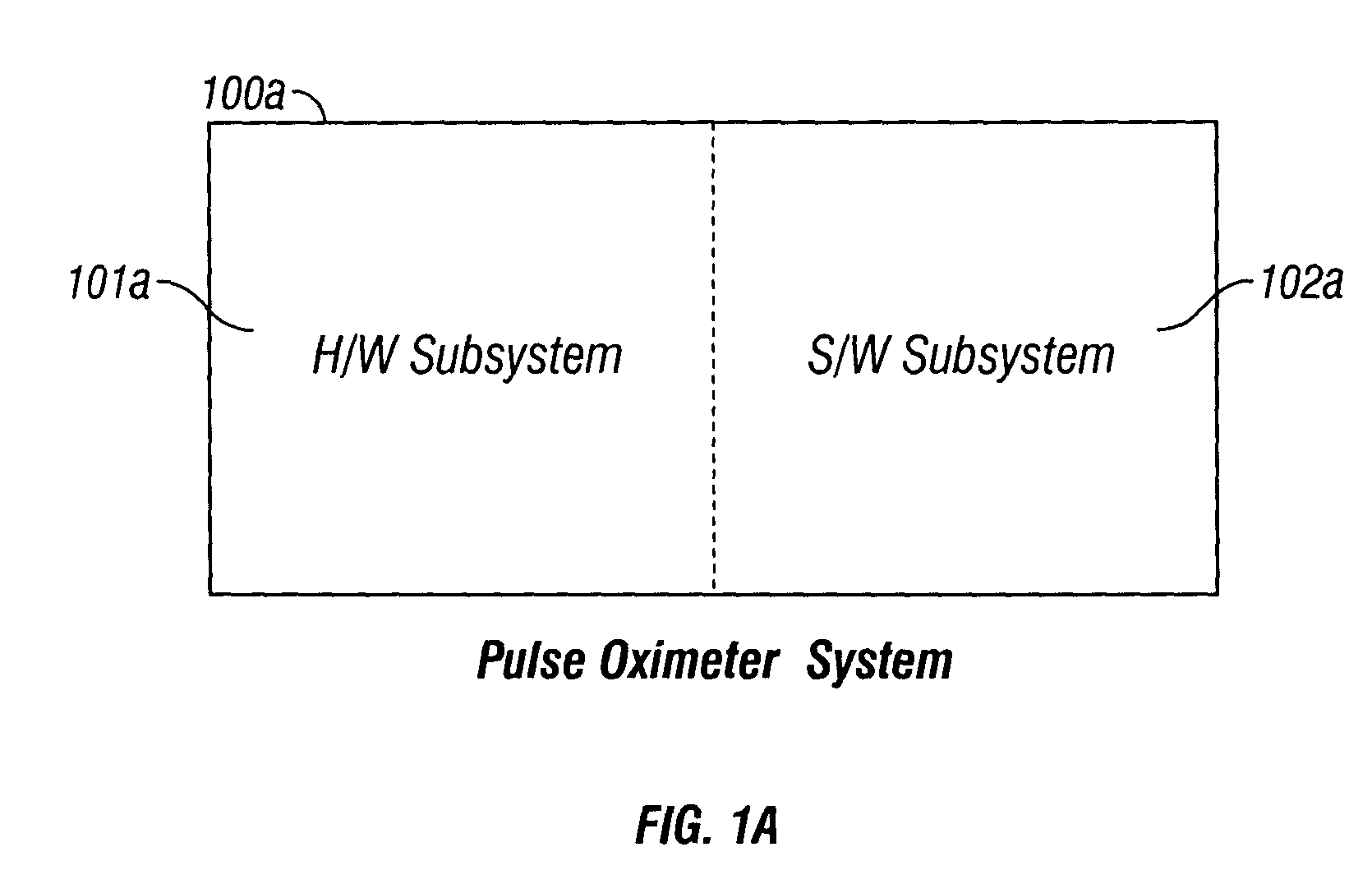
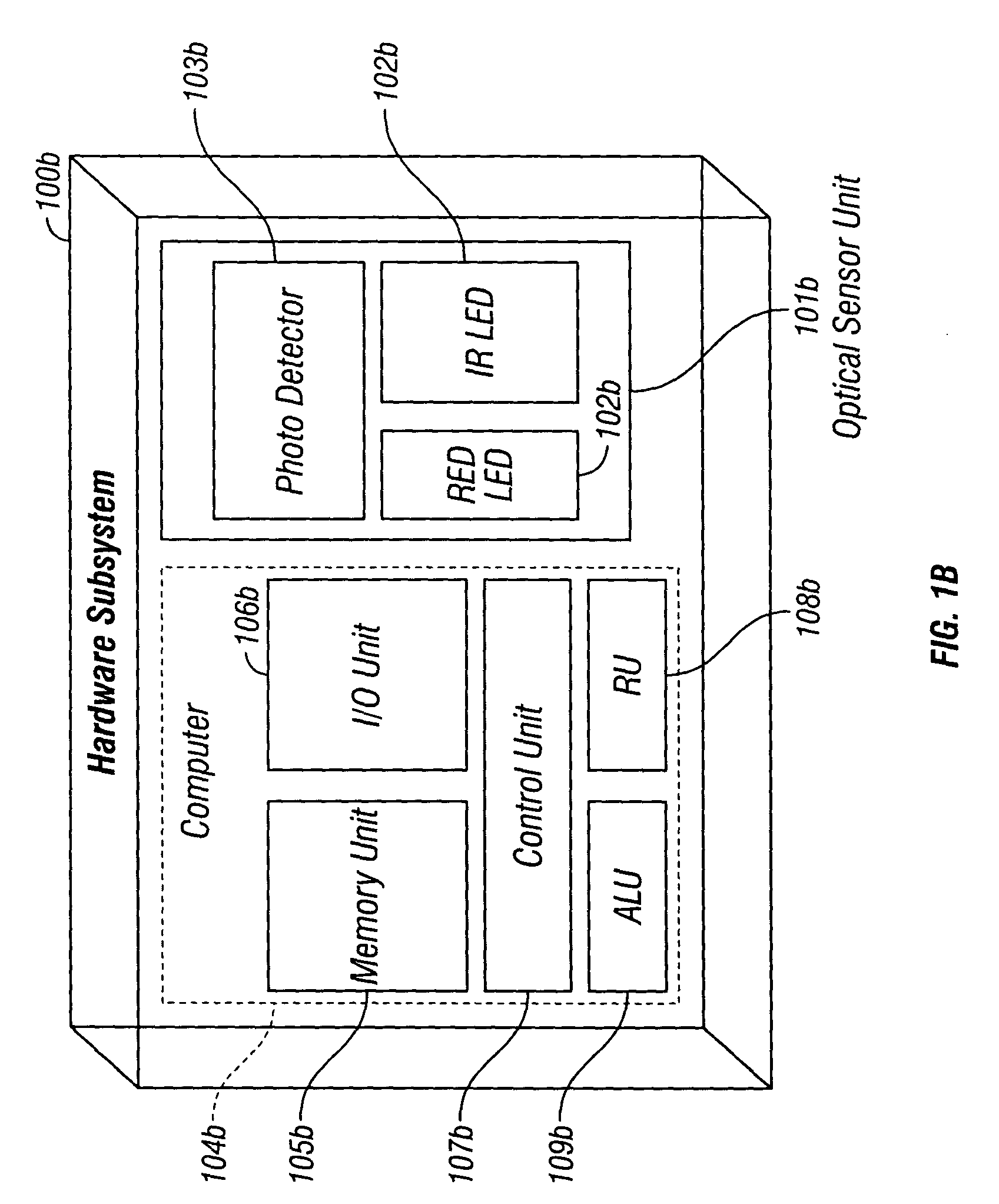
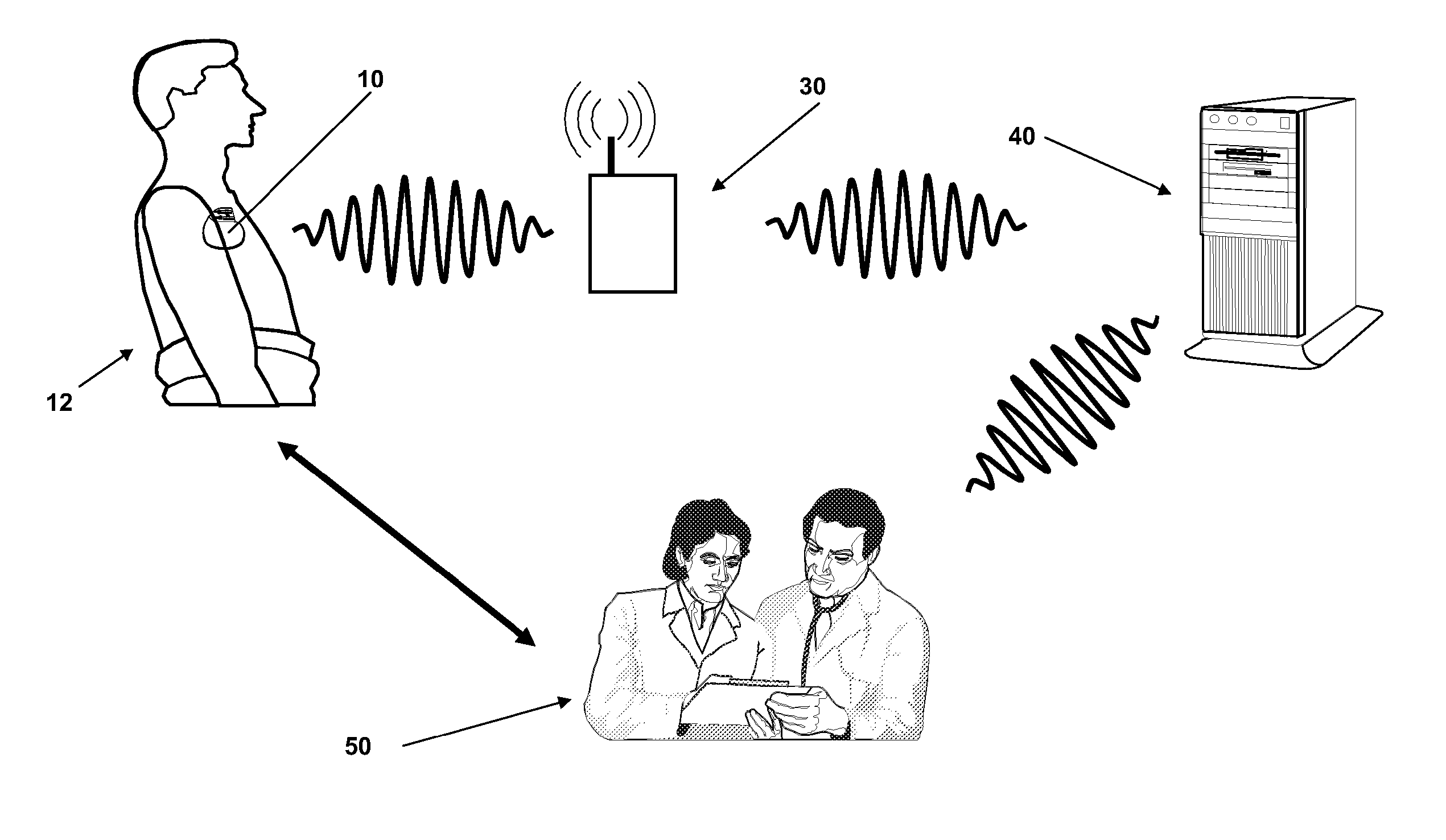
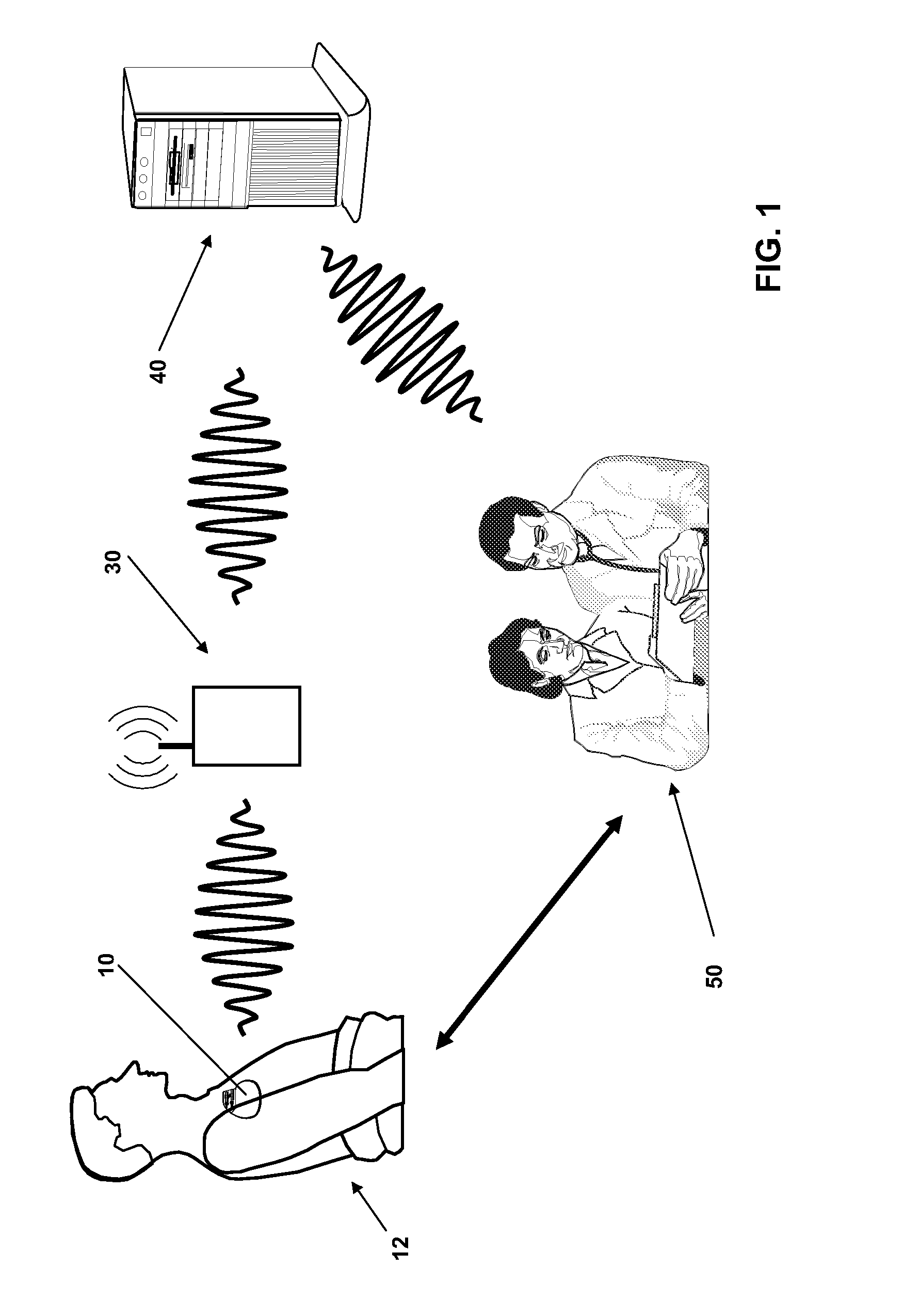
Plethysmograph pulse recognition processor
A time domain rule-based processor provides recognition of individual pulses in a pulse oximeter-derived photo-plethysmograph waveform.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
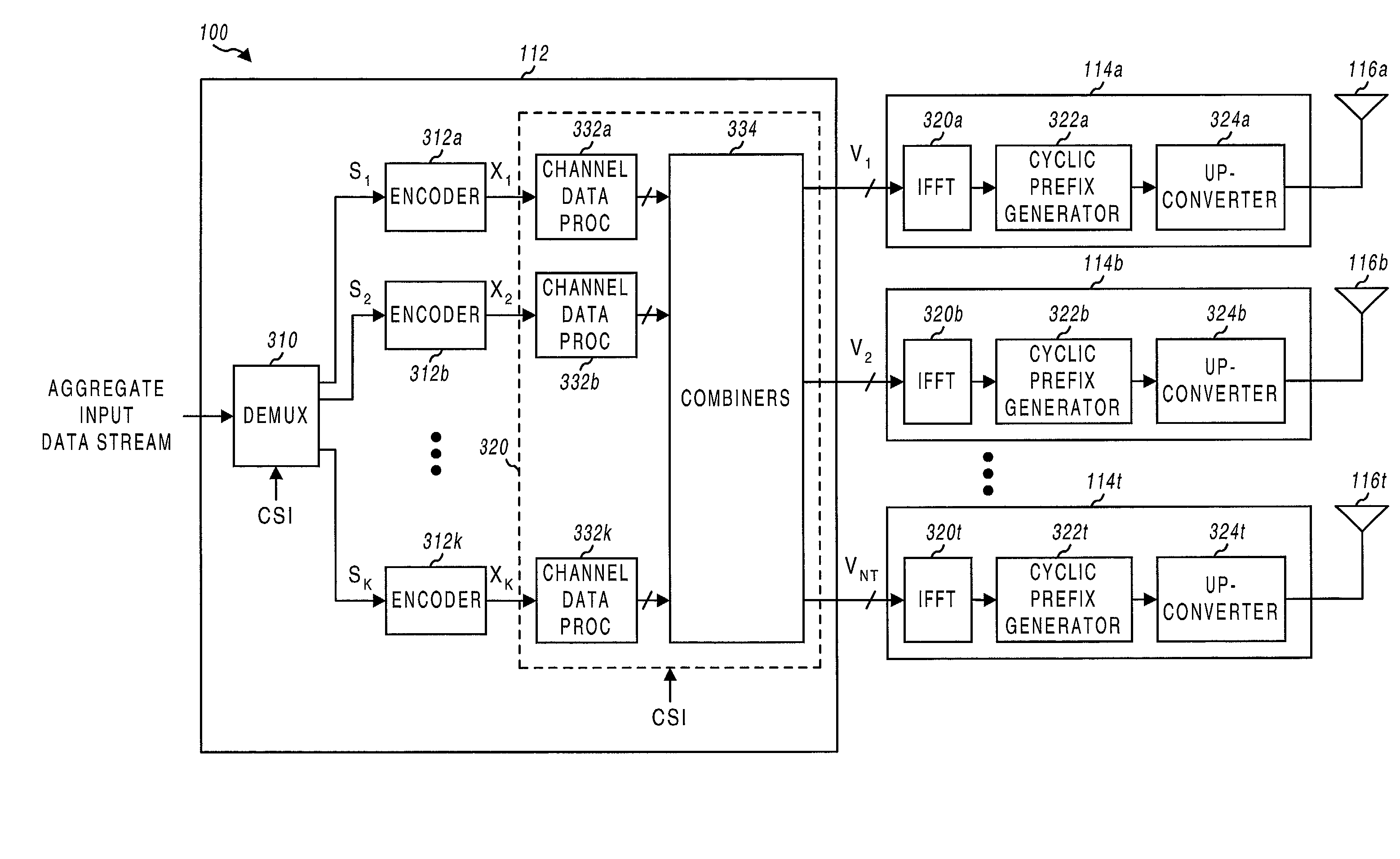
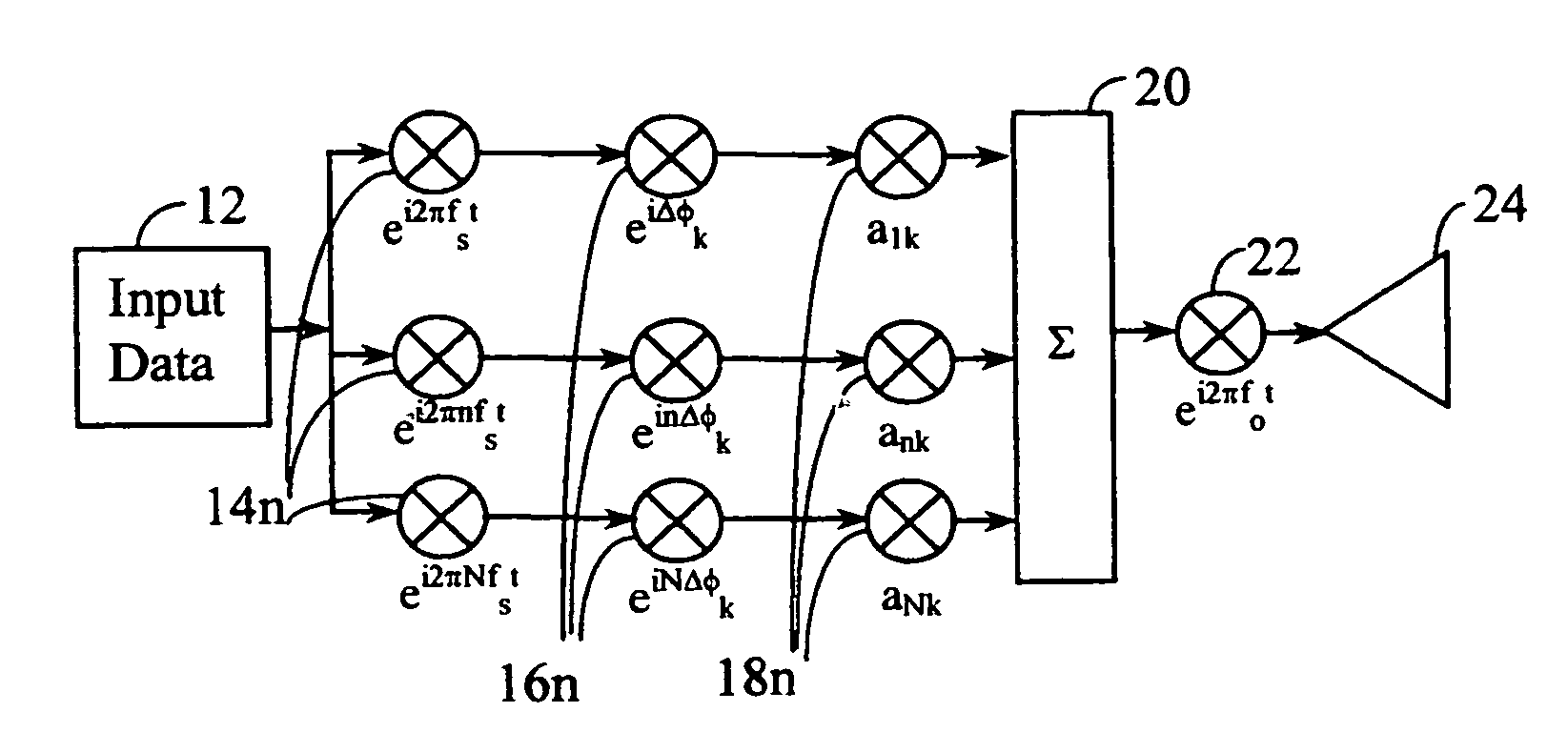
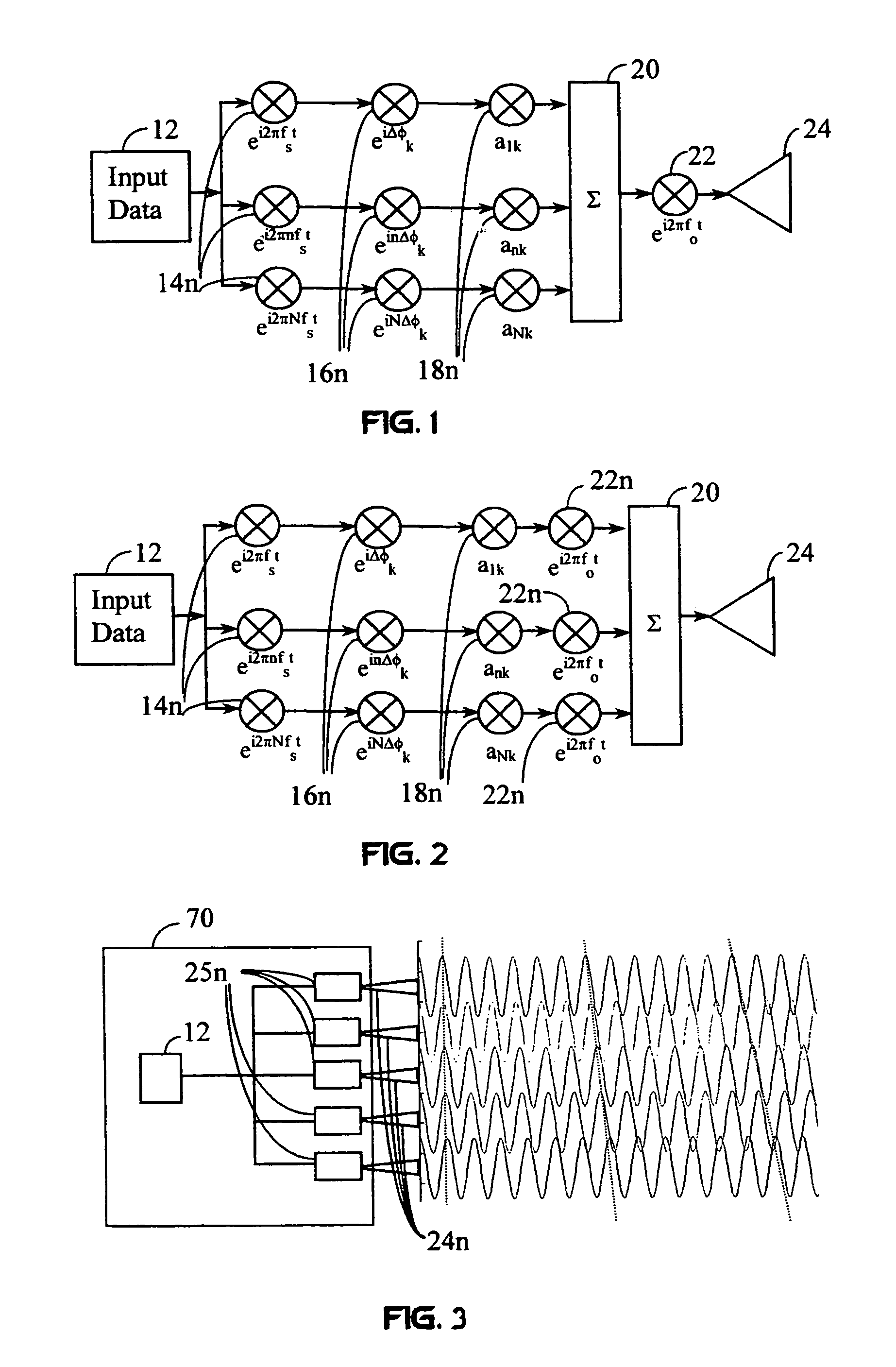
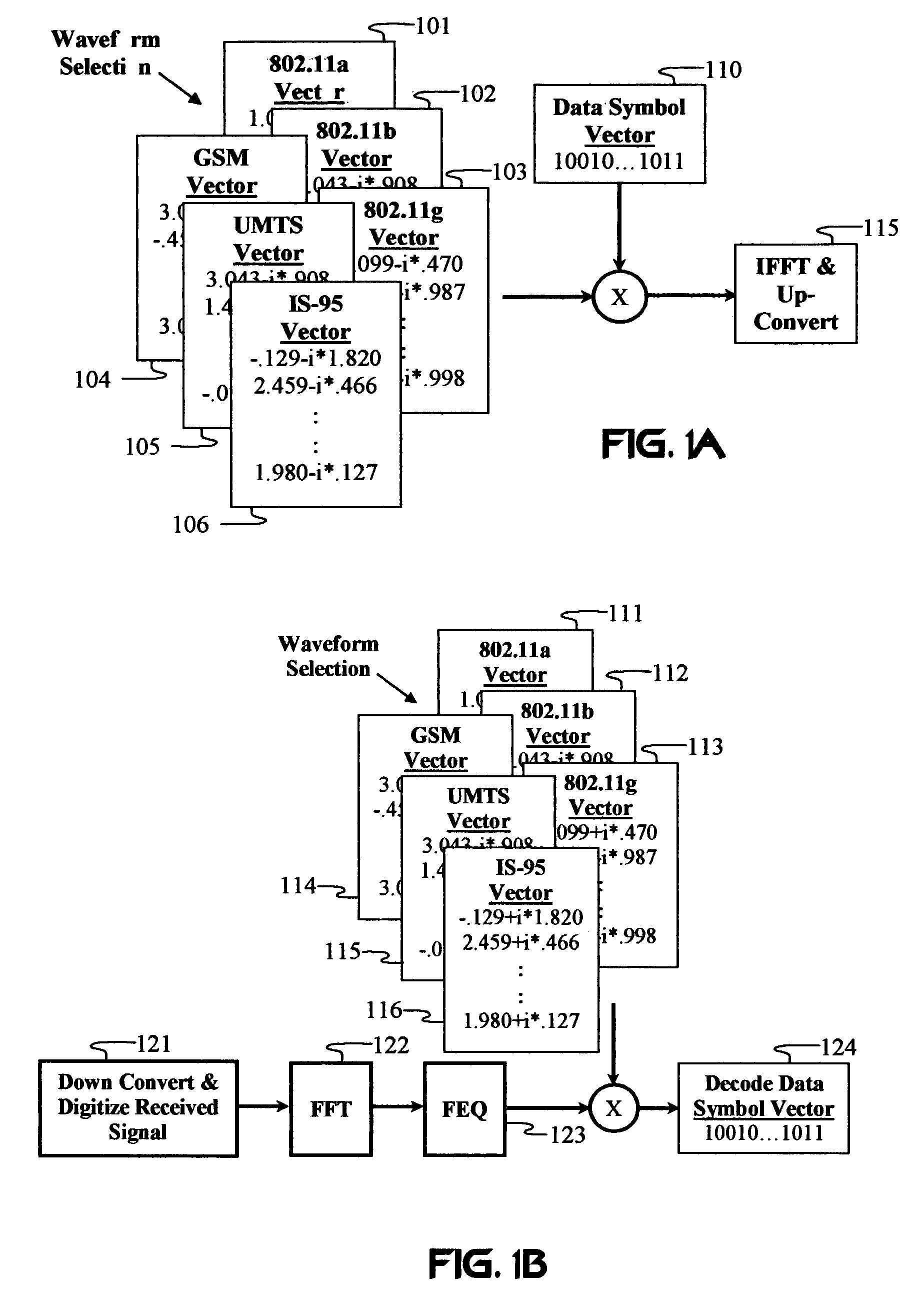
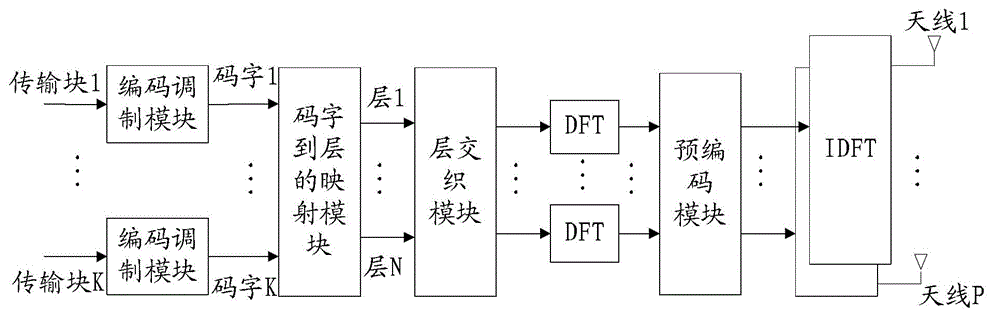
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
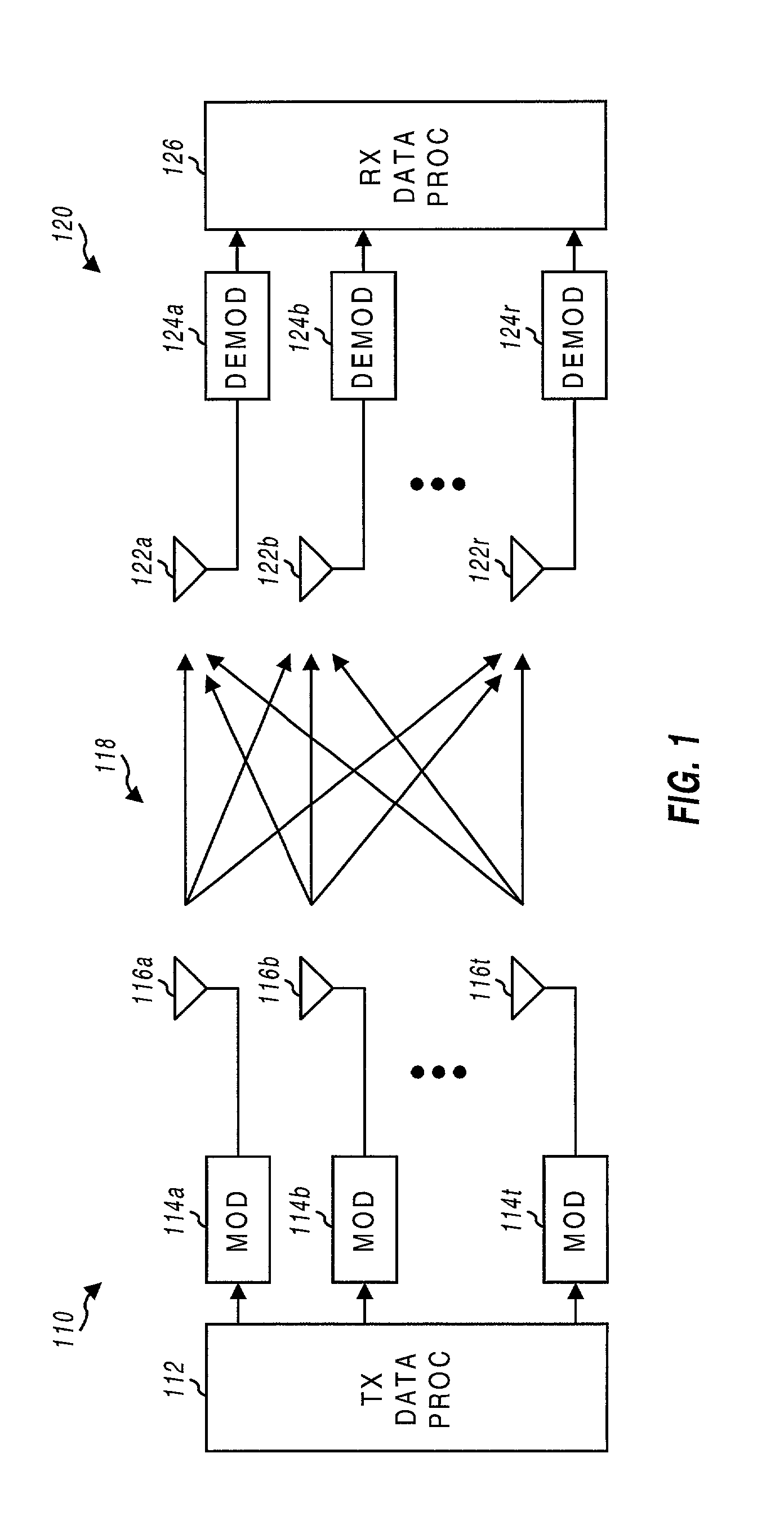
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
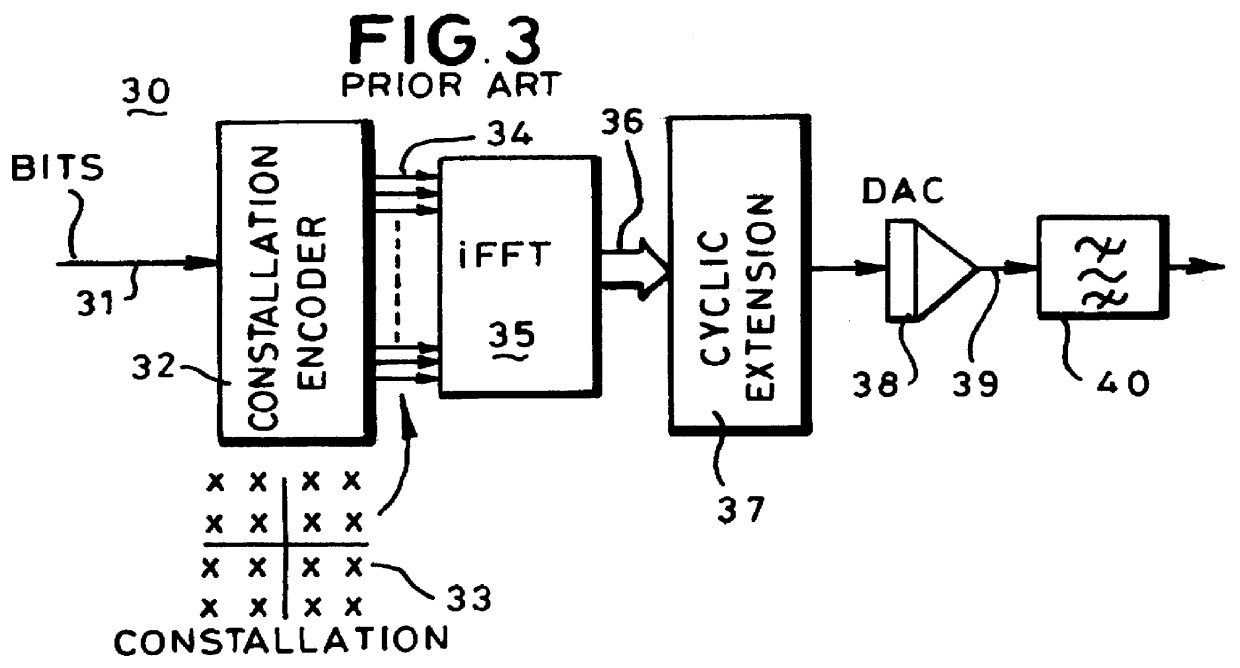
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
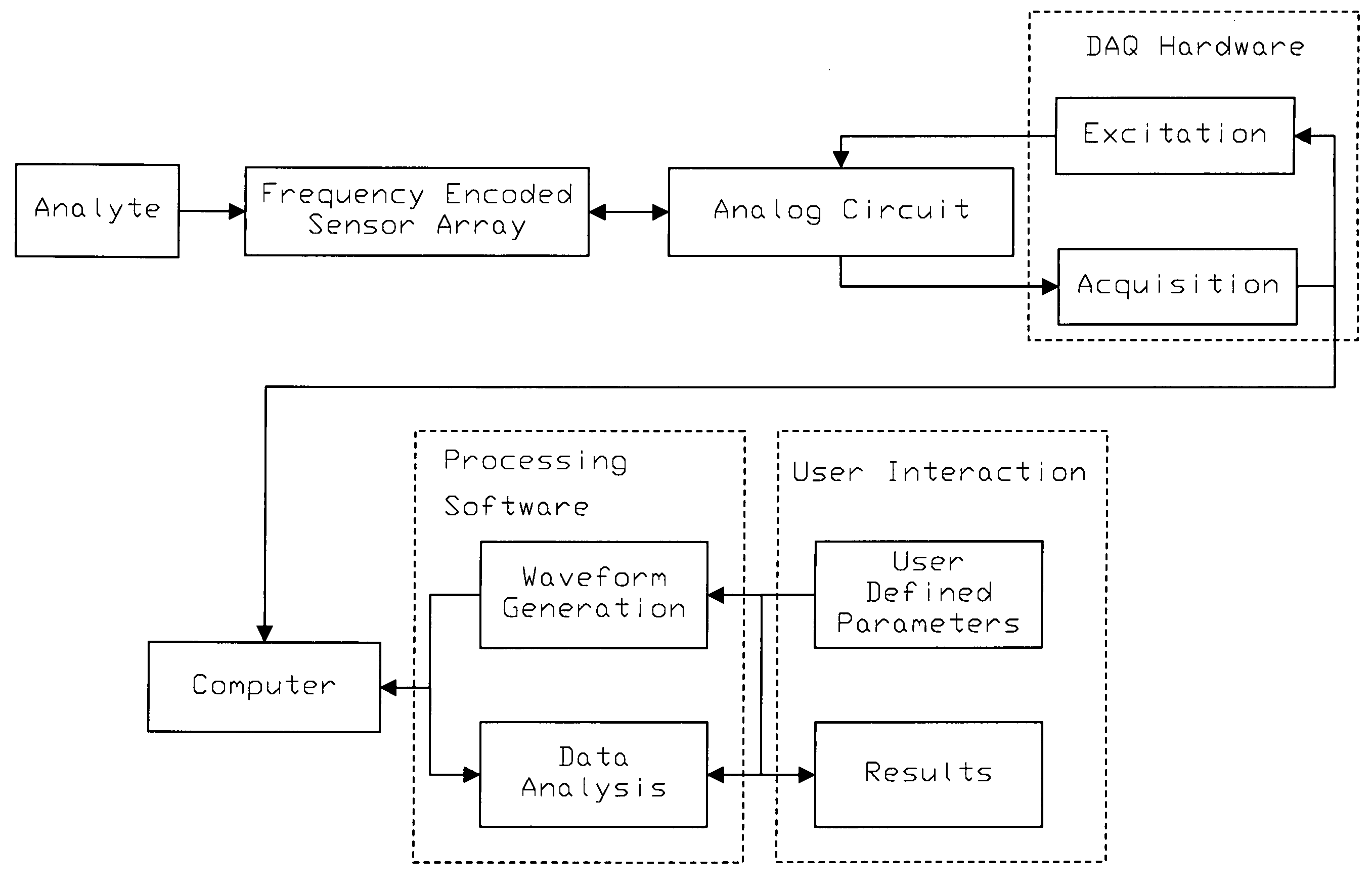
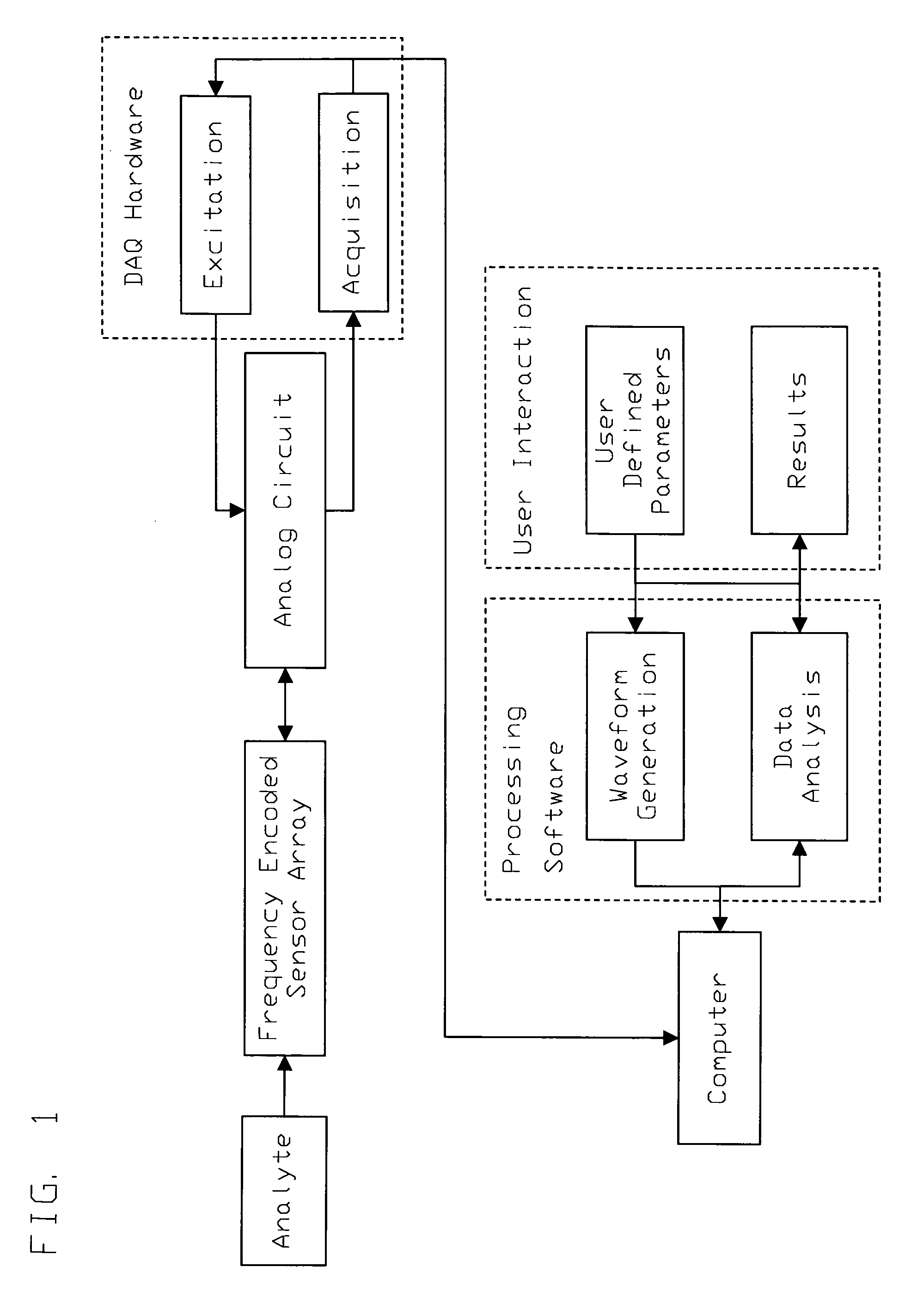
Frequency encoding of resonant mass sensors
InactiveUS20050016276A1Sufficient ring timeImprove stabilityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayFrequency spectrum
A method for the detection of analytes using resonant mass sensors or sensor arrays comprises frequency encoding each sensor element, acquiring a time-domain resonance signal from the sensor or sensor array as it is exposed to analyte, detecting change in the frequency or resonant properties of each sensor element using a Fourier transform or other spectral analysis method, and classifying, identifying, and / or quantifying analyte using an appropriate data analysis procedure. Frequency encoded sensors or sensor arrays comprise sensor elements with frequency domain resonance signals that can be uniquely identified under a defined range of operating conditions. Frequency encoding can be realized either by fabricating individual sensor elements with unique resonant frequencies or by tuning or modifying identical resonant devices to unique frequencies by adding or removing mass from individual sensor elements. The array of sensor elements comprises multiple resonant structures that may have identical or unique sensing layers. The sensing layers influence the sensor elements' response to analyte. Time-domain signal is acquired, typically in a single data acquisition channel, and typically using either (1) a pulsed excitation followed by acquisition of the free oscillatory decay of the entire array or (2) a rapid scan acquisition of signal from the entire array in a direct or heterodyne configuration. Spectrum analysis of the time domain data is typically accomplished with Fourier transform analysis. The methods and sensor arrays of the invention enable rapid and sensitive analyte detection, classification and / or identification of complex mixtures and unknown compounds, and quantification of known analytes, using sensor element design and signal detection hardware that are robust, simple and low cost.
Owner:PALO ALTO SENSOR TECH INNOVATION
Systems and methods for the prevention of unauthorized use and manipulation of digital content
InactiveUS7328453B2Overwhelm usefulnessHigh normal sclerosisMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsTime domainThird party
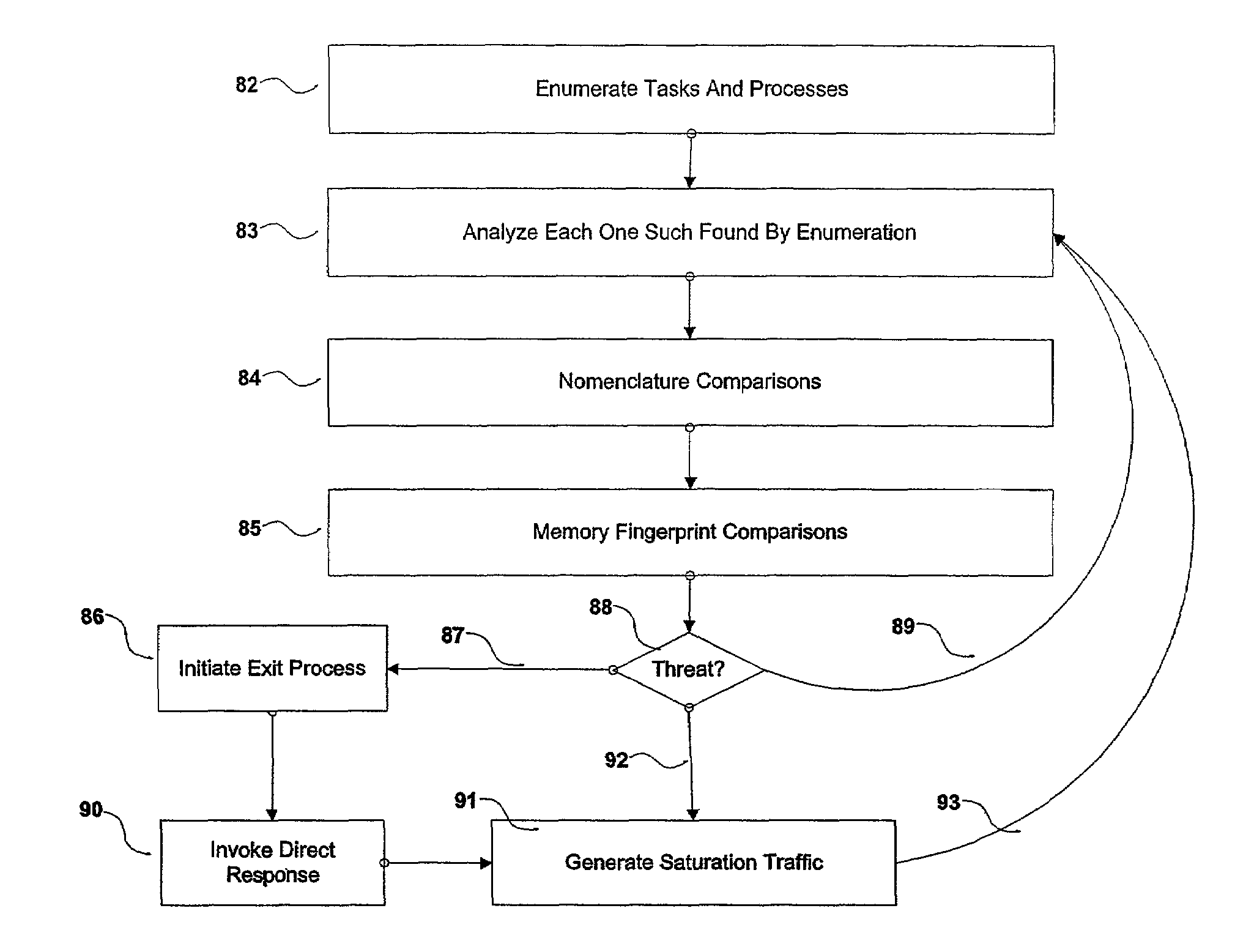
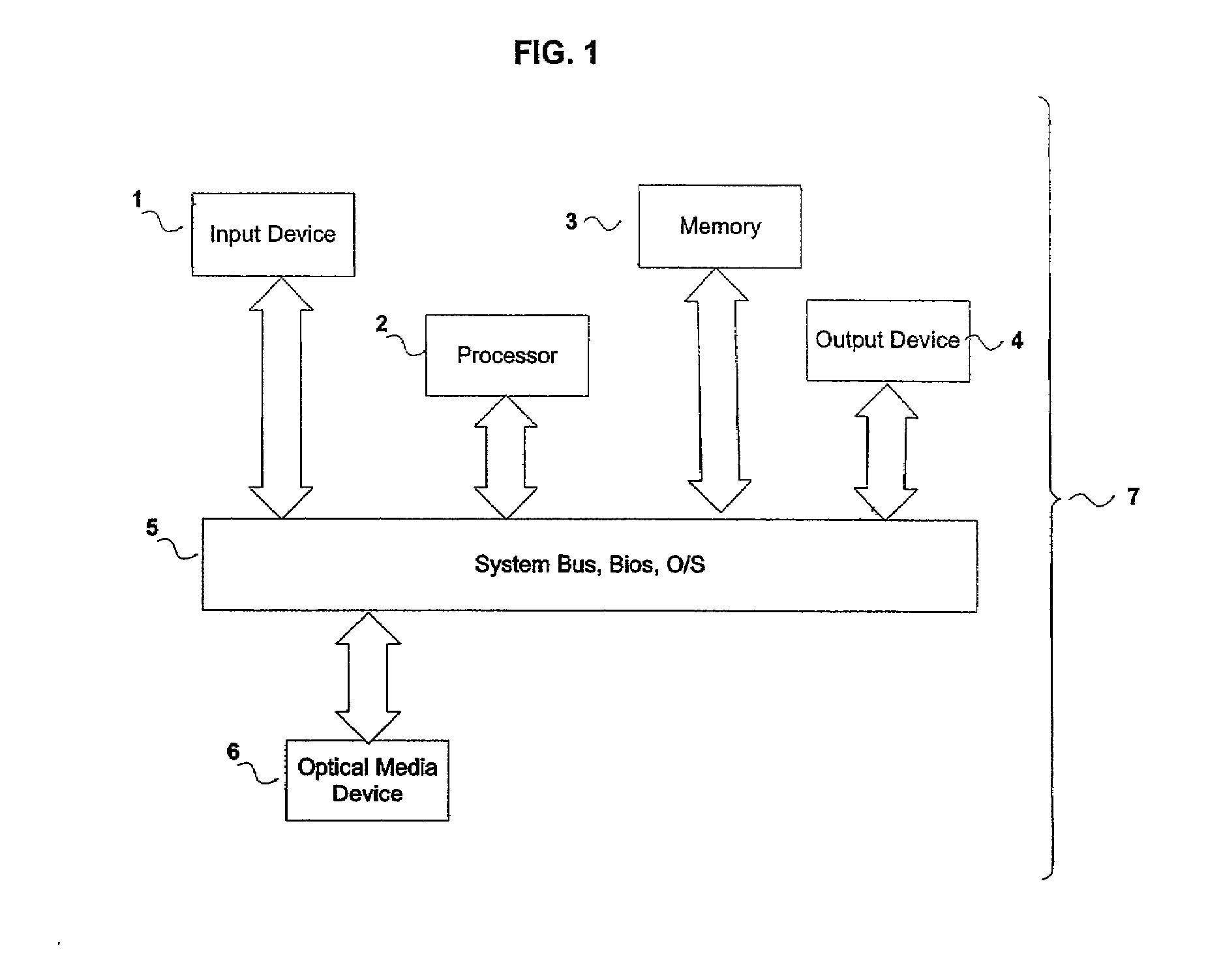
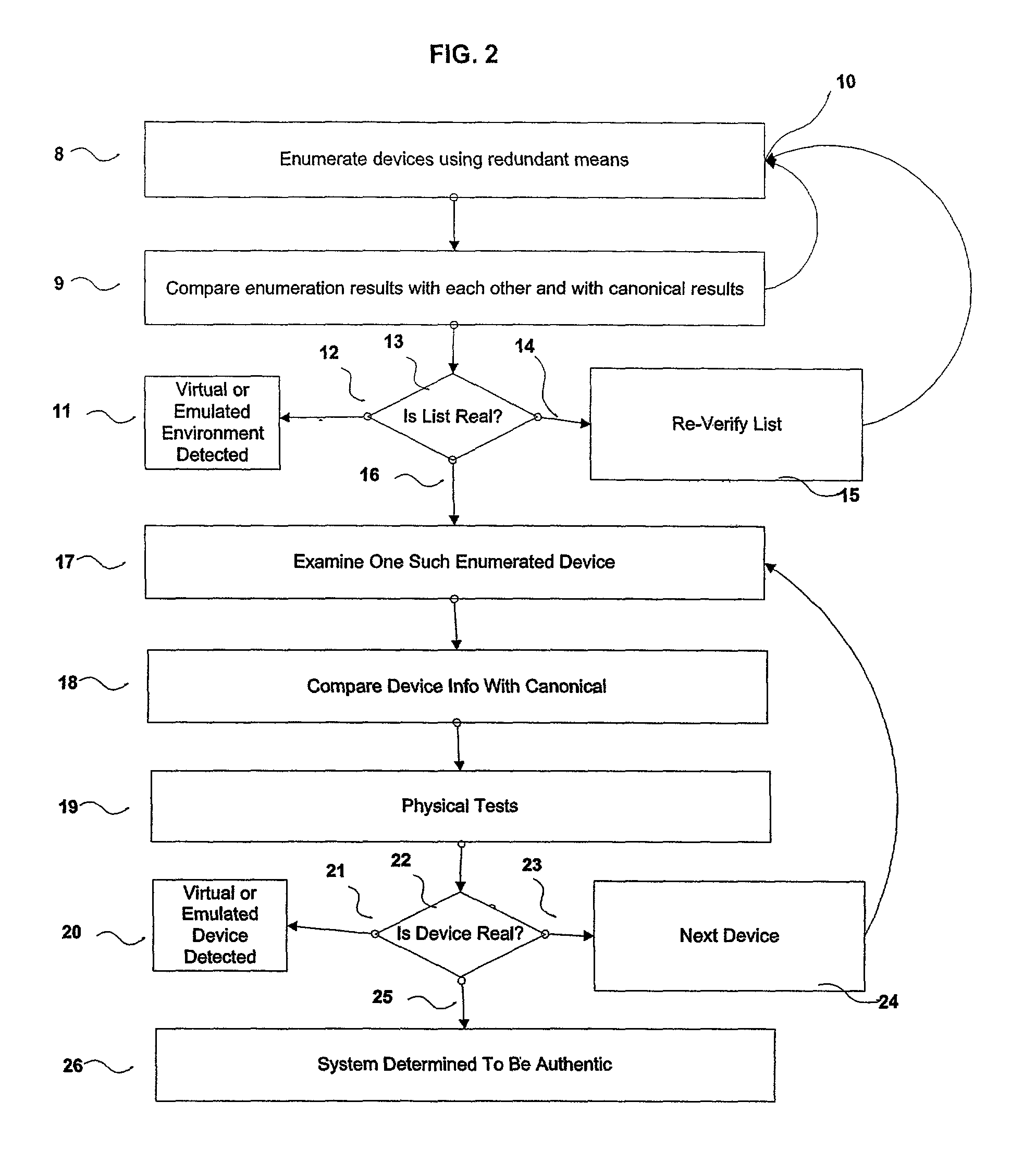
A number of systems and methods, alone, or in combination, achieve various levels of protection against unauthorized modification and distribution of digital content. This encompasses at least unauthorized study, modification, monitoring, reconstruction, and any other means for subversion from the originally intended purpose and license model of the digital content. The invention combines a number of techniques that in whole, or in part, serve to protect such content from unauthorized modification, reconstructive engineering, or monitoring by third parties. This is accomplished by means of methods which protect against subversion by specific tools operating on specific platforms as well as general tools operating on general platforms. Specific time domain attacks are identified, code modification can be identified and reversed, and virtual and emulated systems are identified. In addition, identification of in-circuit emulator tools (both software and hardware), debuggers, and security threats to running programs can be achieved.
Owner:IPLA HLDG
Data framing for adaptive-block-length coding system
InactiveUS6226608B1Easily maintain video/audio synchronizationMinimize artifactElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsColor television signals processingTime domainControl signal
An audio encoder applies an adaptive block-encoding process to segments of audio information to generate frames of encoded information that are aligned with a reference signal conveying the alignment of a sequence of video information frames. The audio information is analyzed to determine various characteristics of the audio signal such as the occurrence and location of a transient, and a control signal is generated that causes the adaptive block-encoding process to encode segments of varying length. A complementary decoder applies an adaptive block-decoding process to recover the segments of audio information from the frames of encoded information. In embodiments that apply time-domain aliasing cancellation (TDAC) transforms, window functions and transforms are applied according to one of a plurality of segment patterns that define window functions and transform parameters for each segment in a sequence of segments. The segments in each frame of a sequence of overlapping frames may be recovered without aliasing artifacts independently from the recovery of segments in other frames. Window functions are adapted to provide preferred frequency-domain responses and time-domain gain profiles.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for configuring control channel in OFDM system
InactiveUS20110044391A1Increasing control channel efficiencyIncreasing system coverageNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionTime domainCommunications system
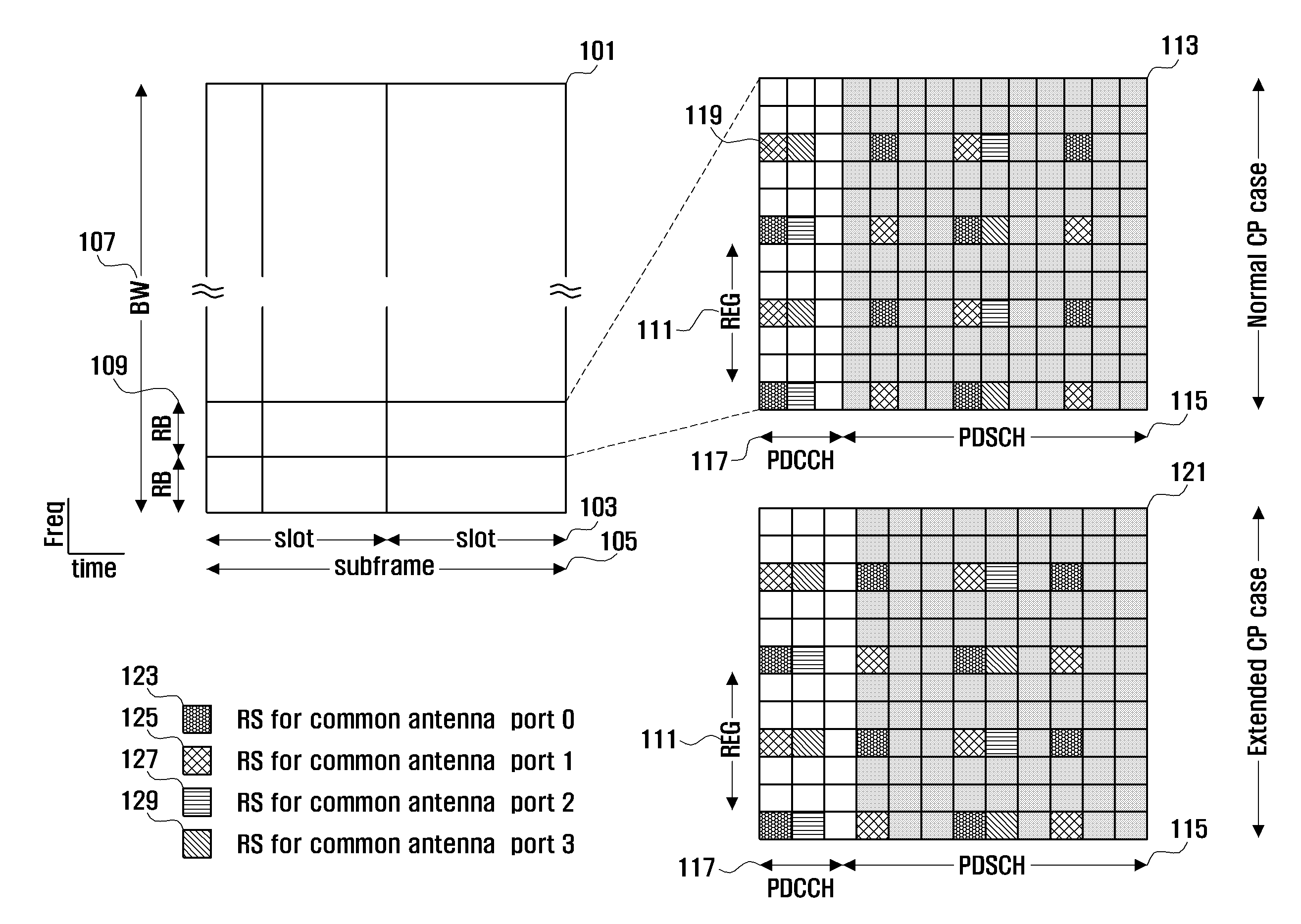
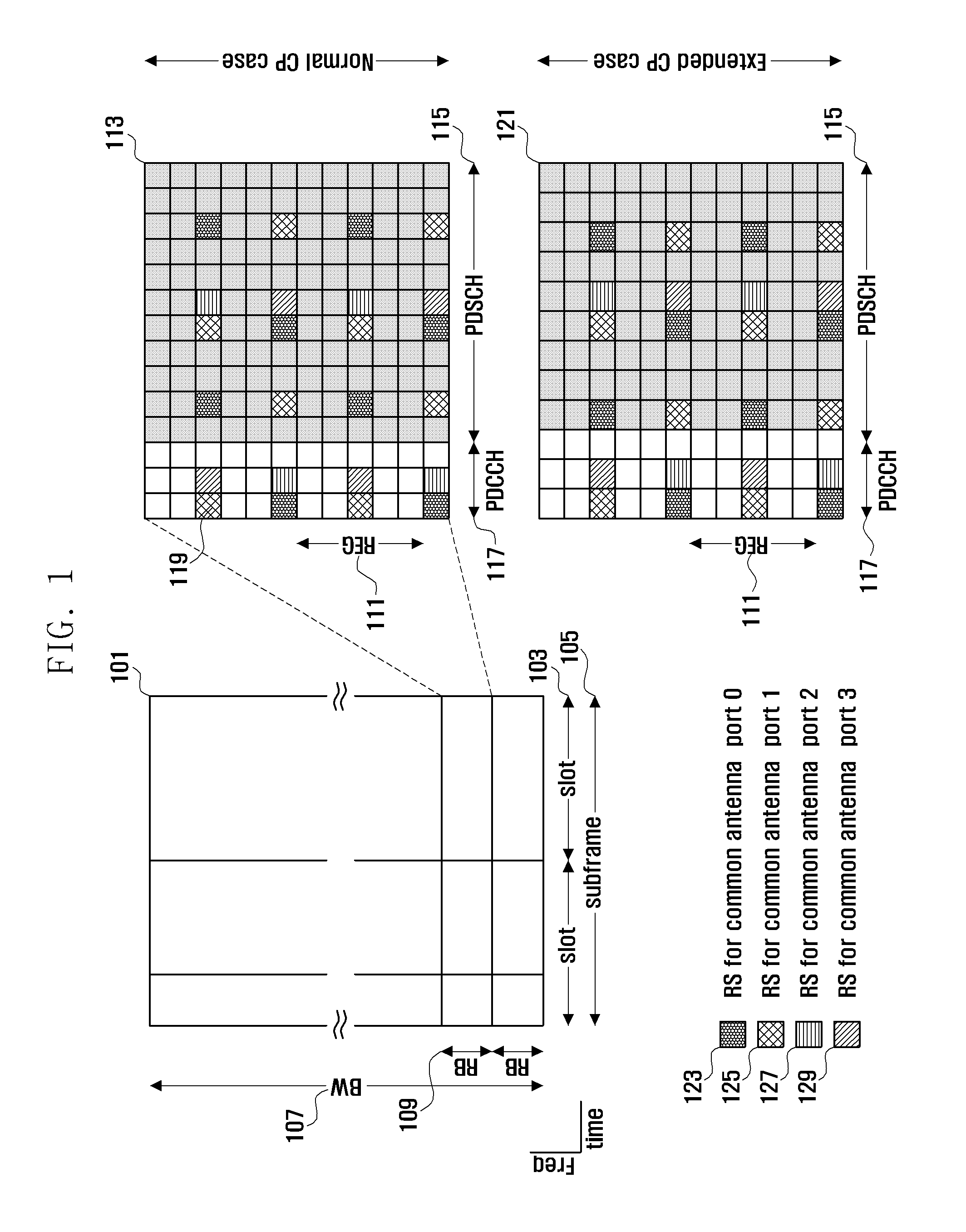
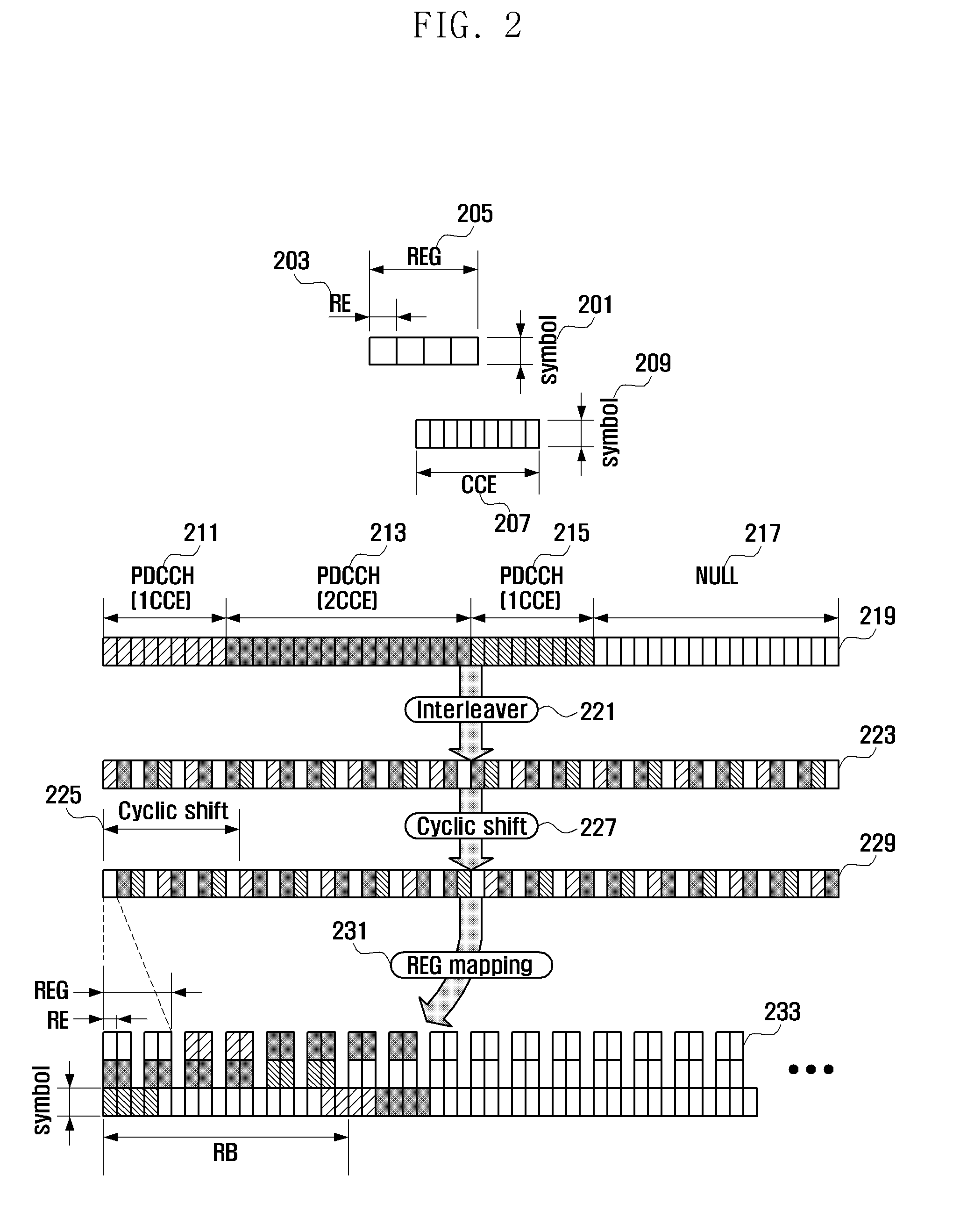
A control channel configuration method and apparatus is provided for supporting Inter-Cell Interference Coordination (ICIC) in an OFDM-based communication system. The control channel configuration method includes determining a Resource Block (RB) to be used for configuring control channels; configuring the control channels by mapping the control channels in a data channel region within the RB; and transmitting the configured control channels, wherein configuring the control channels includes mapping the control channels in units of Resource Element Groups (REGs) formed by binding one or more Resource Elements (REs) in a time domain-preferred allocation manner within the same RB.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Washable wearable biosensor
ActiveUS20100268056A1Level of comfortAvoid overwritingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAdhesiveMultiple sensor
A washable, wearable biosensor that can gather sensor data, communicate the sensed data by wireless protocols, and permits the analysis of sensed data in real-time as a person goes about their normal lifestyle activities. The biosensor can be worn in multiple positions, can be put on or removed quickly without having to apply or remove gels and adhesives, and provides a snug, comfortable fit to gather data with minimal motion artifacts. The textile, wearable device can support integrated photoplethysmography, skin conductance, motion, and temperature sensors in a small wearable package. The supported sensors may be coupled to utilization devices by channel-sharing wireless protocols to enable the transmission of data from multiple users and multiple sensors (e.g. both sides of body, wrists or hands and feet, or multiple people). An on-board processor, or the receiving utilization device, can map patterns of the physiological and motion data to signals or alerts such as a likely seizure, drug craving, or other states that the wearer may exhibit or experience. The sensor data may be sent by wireless transmission and received by a mobile phone or other personal digital device, a computer, a favorite toy, or another wearable device. The sensors may include multiple photoplethysmographs and / or one or more EDAs which perform a time-domain measurement of skin conductance
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Global boundary-centric feature extraction and associated discontinuity metrics
Portions from time-domain speech segments are extracted. Feature vectors that represent the portions in a vector space are created. The feature vectors incorporate phase information of the portions. A distance between the feature vectors in the vector space is determined. In one aspect, the feature vectors are created by constructing a matrix W from the portions and decomposing the matrix W. In one aspect, decomposing the matrix W comprises extracting global boundary-centric features from the portions. In one aspect, the portions include at least one pitch period. In another aspect, the portions include centered pitch periods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Separating motion from cardiac signals using second order derivative of the photo-plethysmogram and fast fourier transforms
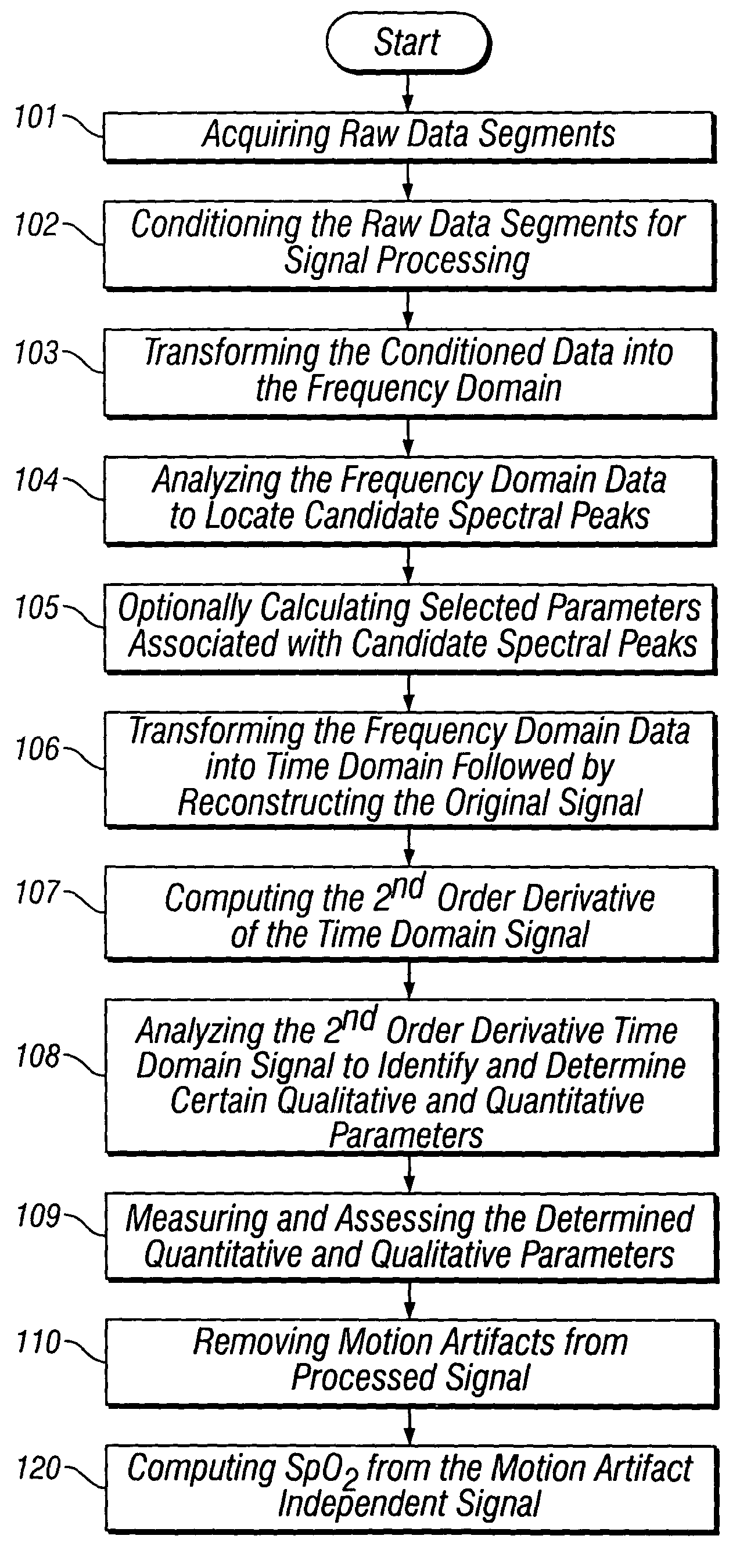
The present invention is directed toward a pulse oximetry system for the determination of a physiological parameter capable of removing motion artifacts from physiological signals comprises a hardware subsystem and a software subsystem. The software subsystem is used in conjunction with the hardware subsystem to perform a method for removing a plurality of motion artifacts from the photo-plethysmographic data and for obtaining a measure of at least one physiological parameter from the data. The method comprises acquiring the raw photo-plethysmographic data, transforming the data into the frequency domain, analyzing the transformed data to locate a series of candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), reconstructing a photo-plethysmographic signal in the time domain with only the candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), computing the second order derivative of the reconstructed photo-plethysmographic signal, analyzing the candidate second order derivative photo-plethysmographic signal to determine the absence or presence of cardiac physiologic signal characteristics, and finally selecting the best physiologic candidate from the series of potential cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics) based upon a second derivative scoring system. This scoring system is preferentially based upon second derivative processing analysis, but can be equally applied using the first, third, fourth or other similar derivative processing analysis.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
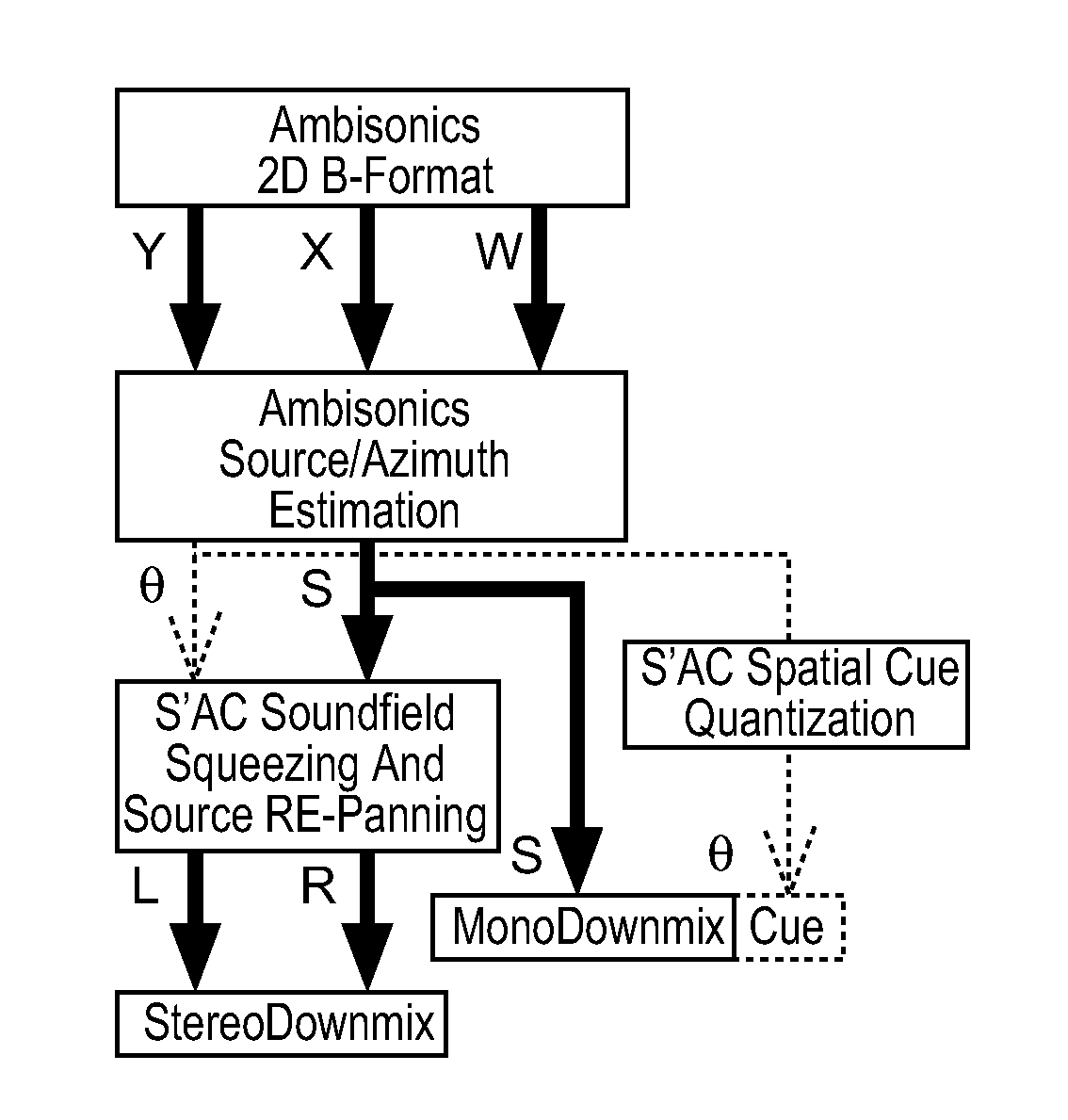
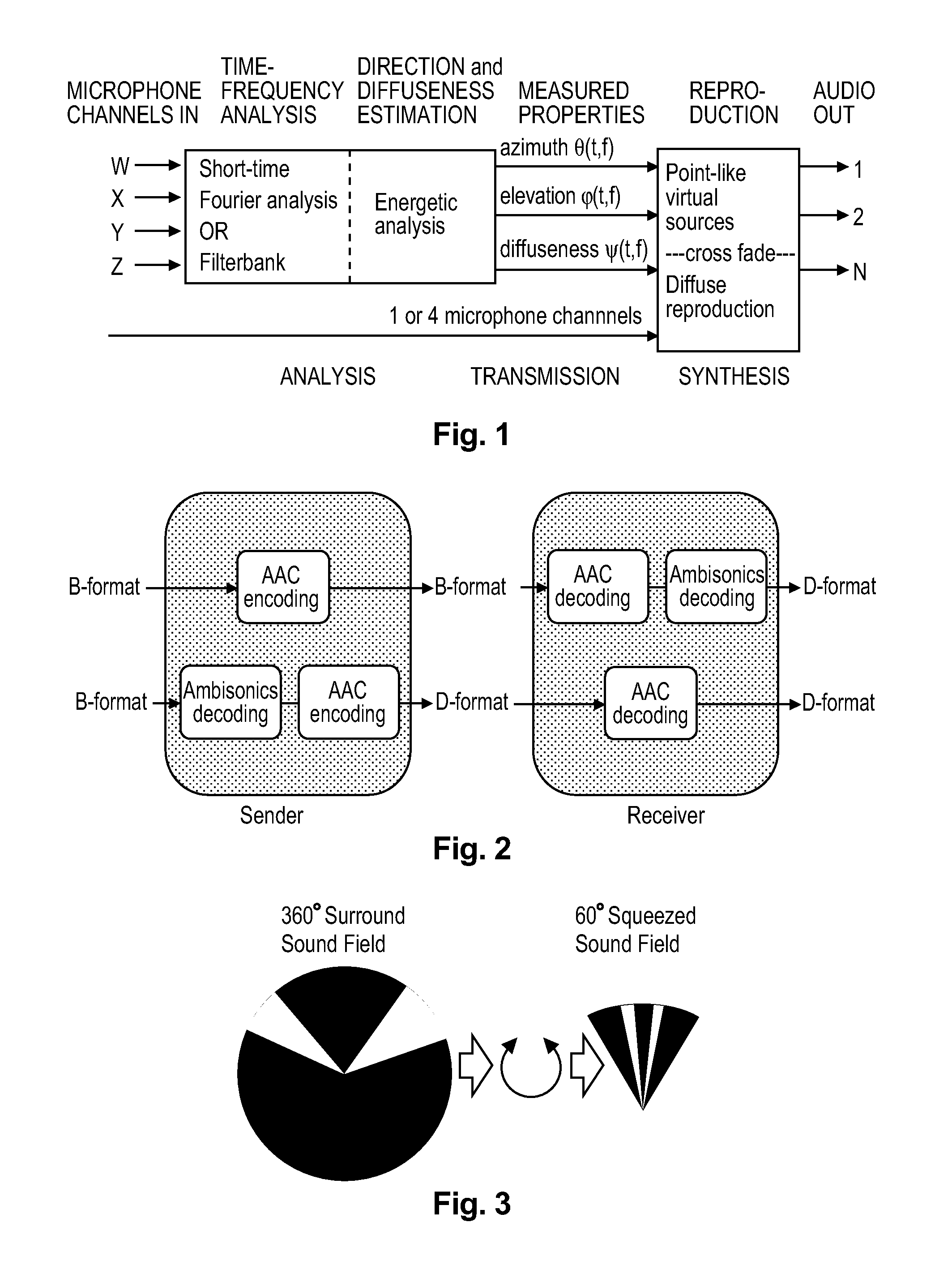
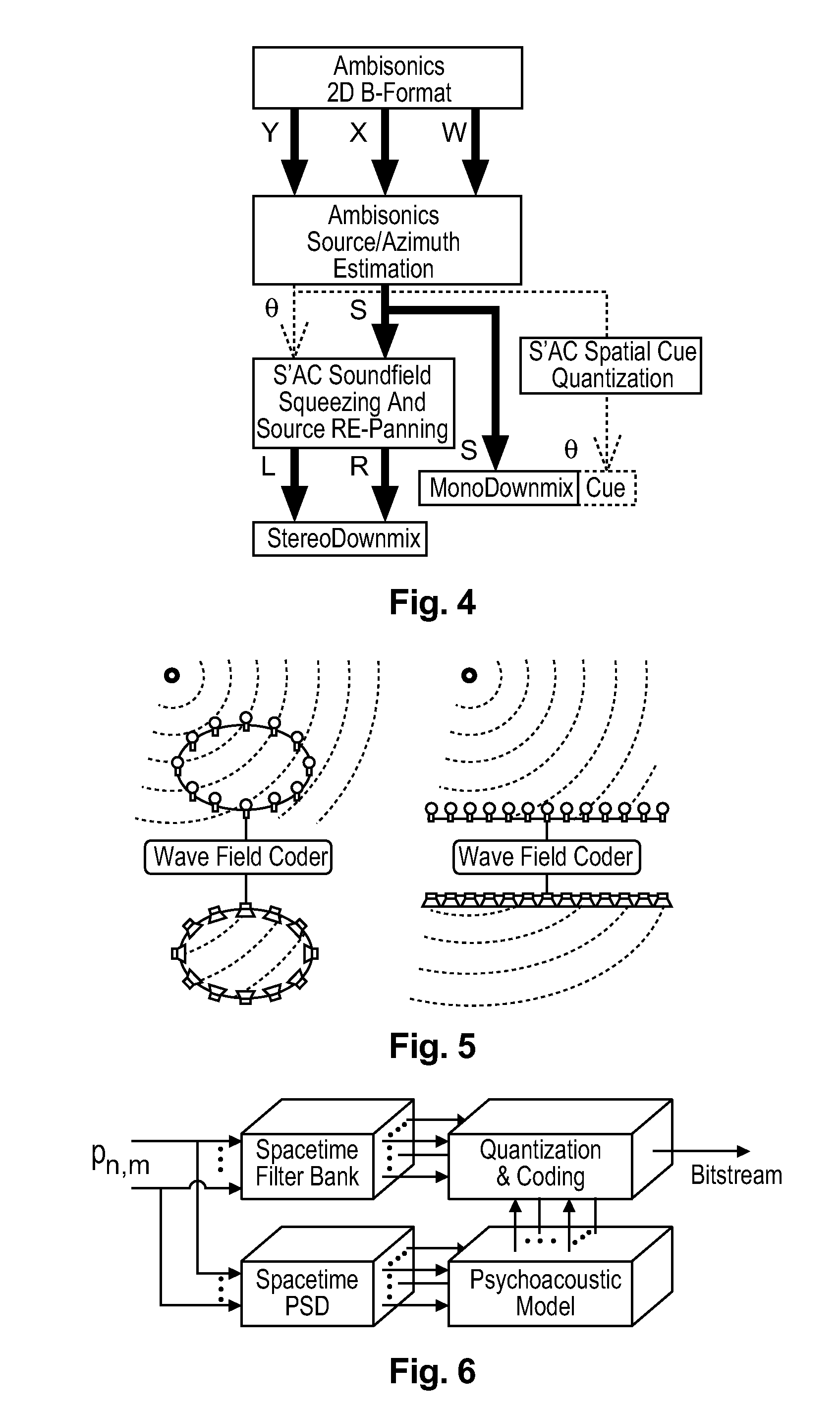
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding successive frames of an ambisonics representation of a 2- or 3-dimensional sound field
ActiveUS20120155653A1Easy accessThe result is reasonableBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainData rate
Representations of spatial audio scenes using higher-order Ambisonics HOA technology typically require a large number of coefficients per time instant. This data rate is too high for most practical applications that require real-time transmission of audio signals. According to the invention, the compression is carried out in spatial domain instead of HOA domain. The (N+1)2 input HOA coefficients are transformed into (N+1)2 equivalent signals in spatial domain, and the resulting (N+1)2 time-domain signals are input to a bank of parallel perceptual codecs. At decoder side, the individual spatial-domain signals are decoded, and the spatial-domain coefficients are transformed back into HOA domain in order to recover the original HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
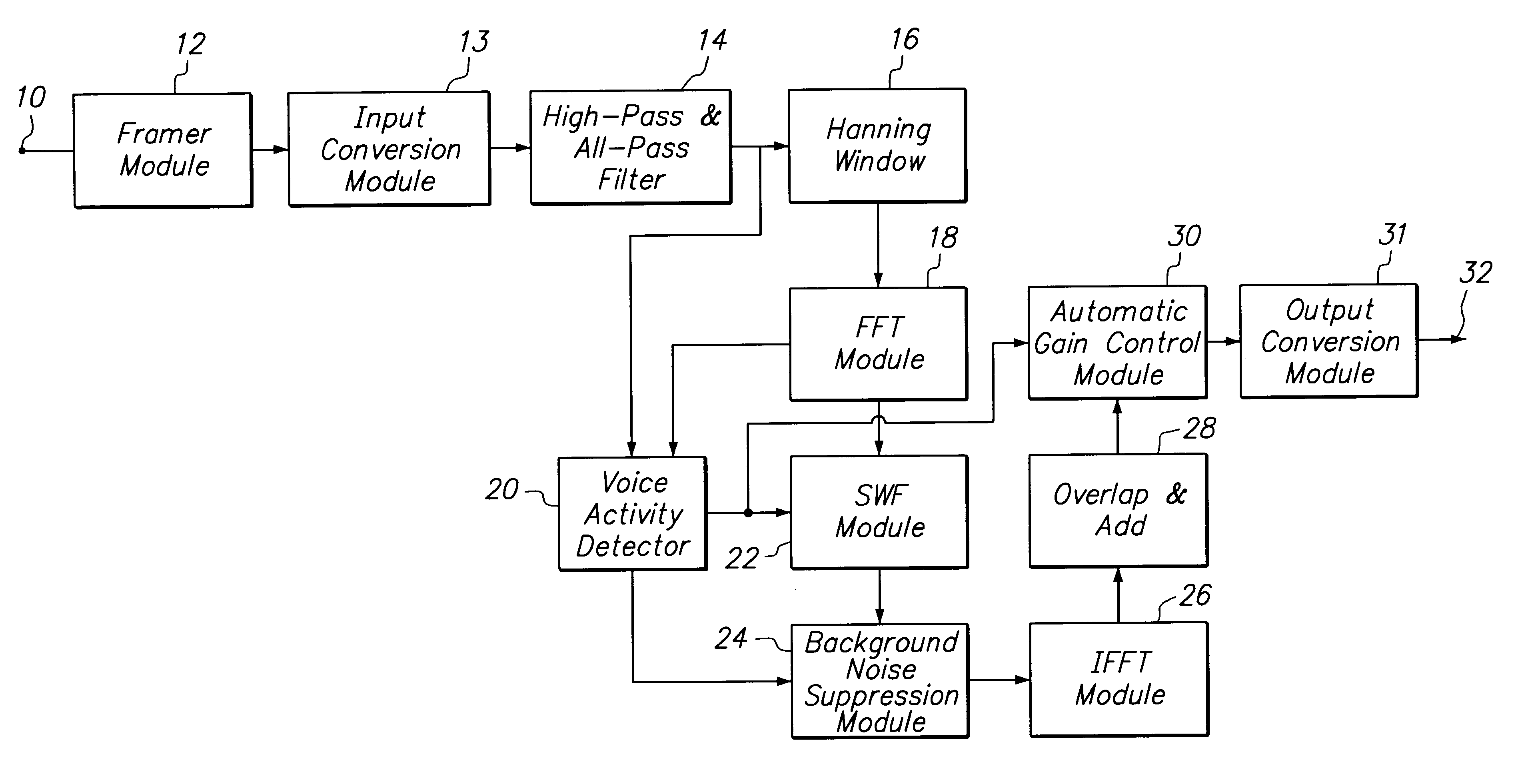
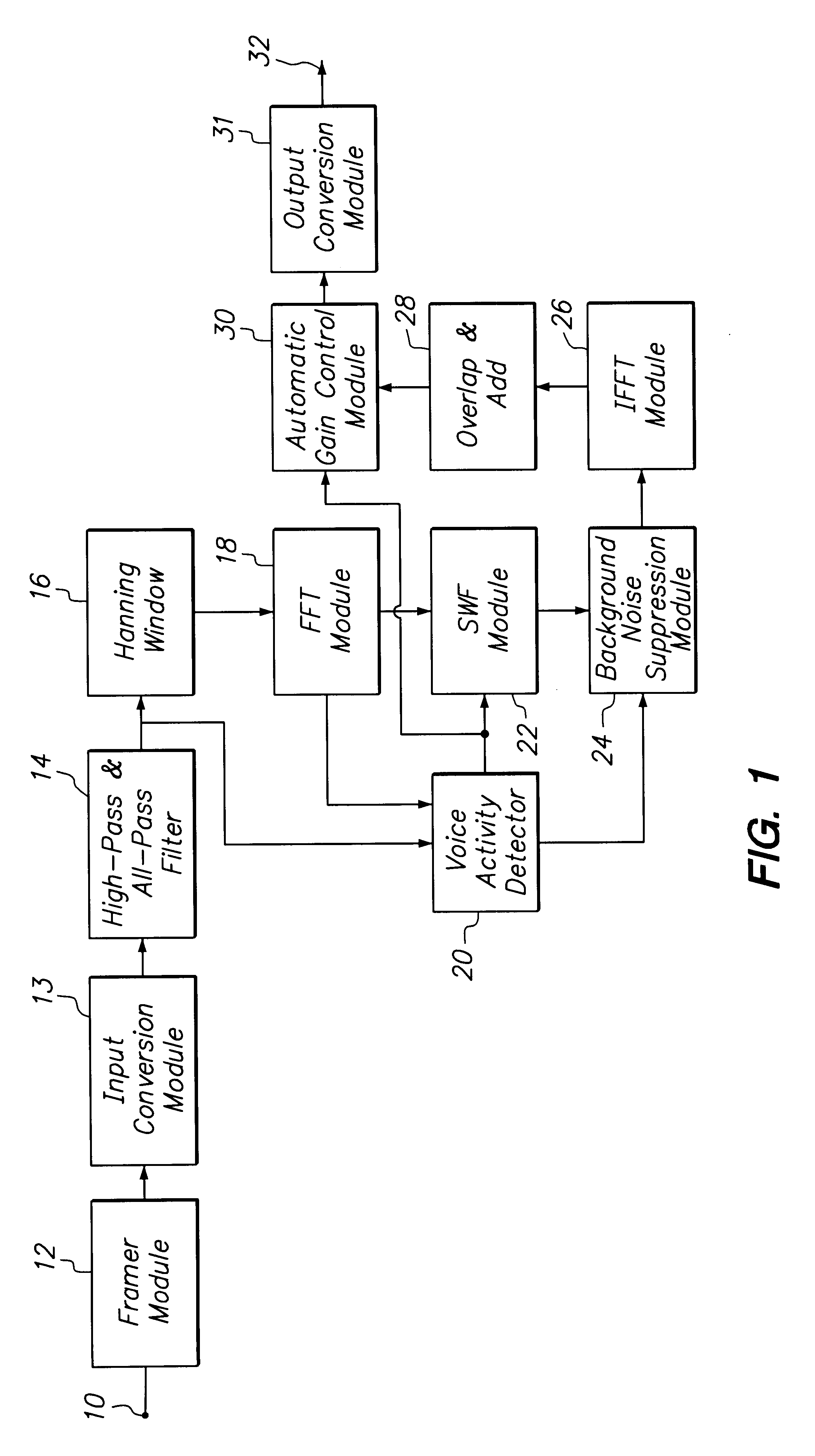
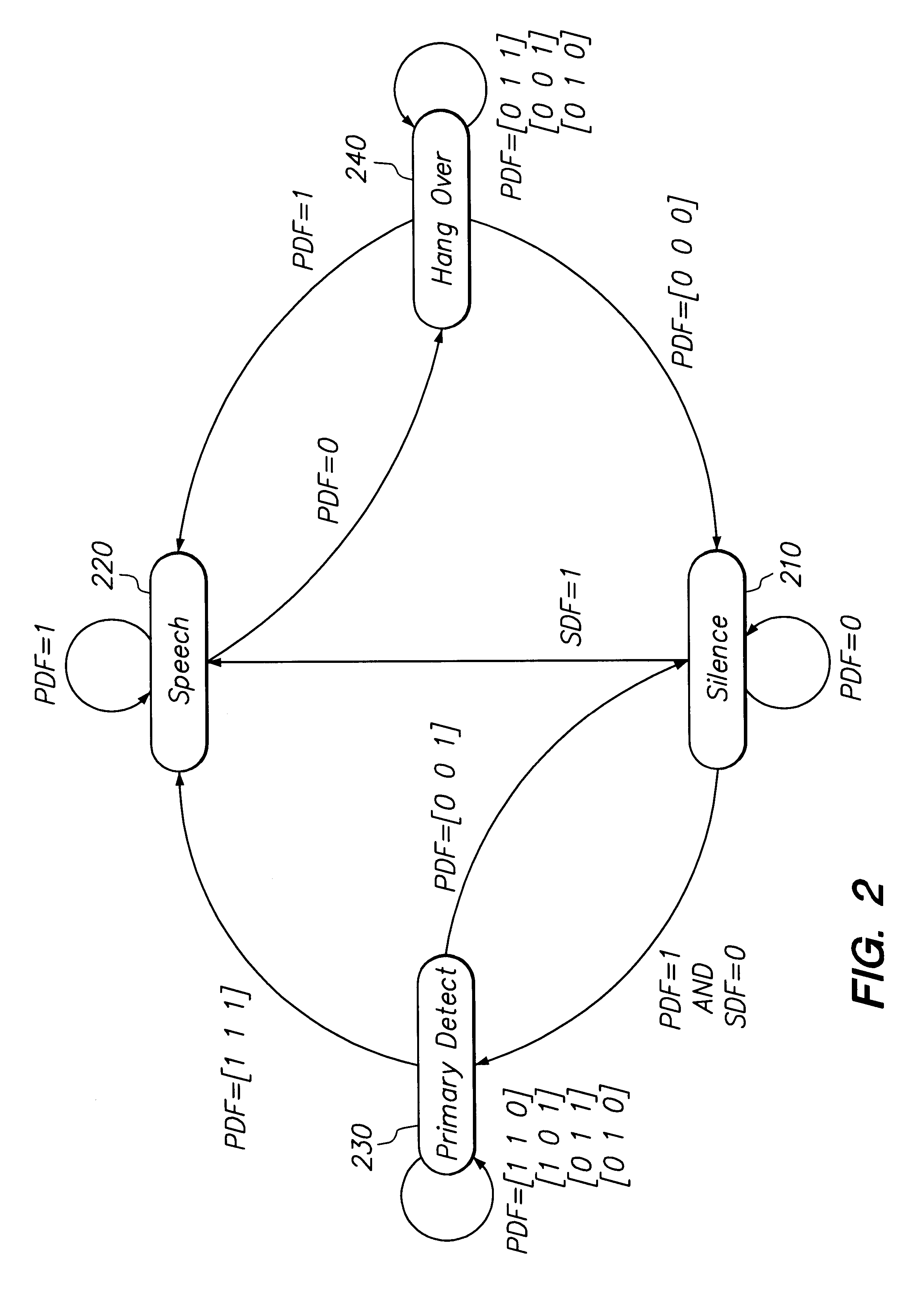
Method and apparatus for enhancing noise-corrupted speech
InactiveUS6415253B1Reduce peakImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionTime domainFast Fourier transform
A noise suppression device receives data representative of a noise-corrupted signal which contains a speech signal and a noise signal, divides the received data into data frames, and then passes the data frames through a pre-filter to remove a dc-component and the minimum phase aspect of the noise-corrupted signal. The noise suppression device appends adjacent data frames to eliminate boundary discontinuities, and applies fast Fourier transform to the appended data frames. A voice activity detector of the noise suppression device determines if the noise-corrupted signal contains the speech signal based on components in the time domain and the frequency domain. A smoothed Wiener filter of the noise suppression device filters the data frames in the frequency domain using different sizes of a window based on the existence of the speech signal. Filter coefficients used for Wiener filter are smoothed before filtering. The noise suppression device modifies magnitude of the time domain data based on the voicing information outputted from the voice activity detector.
Owner:META C CORP
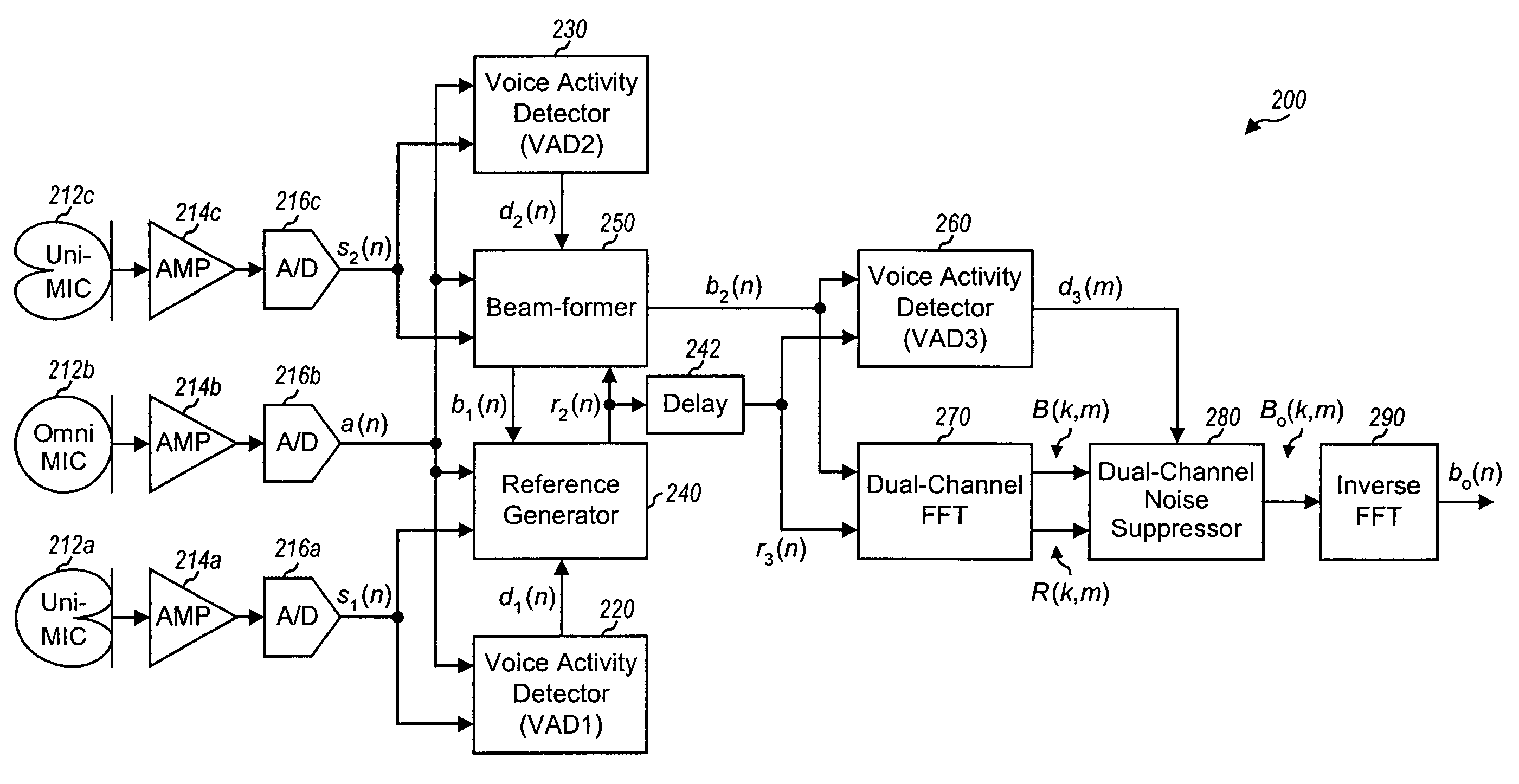
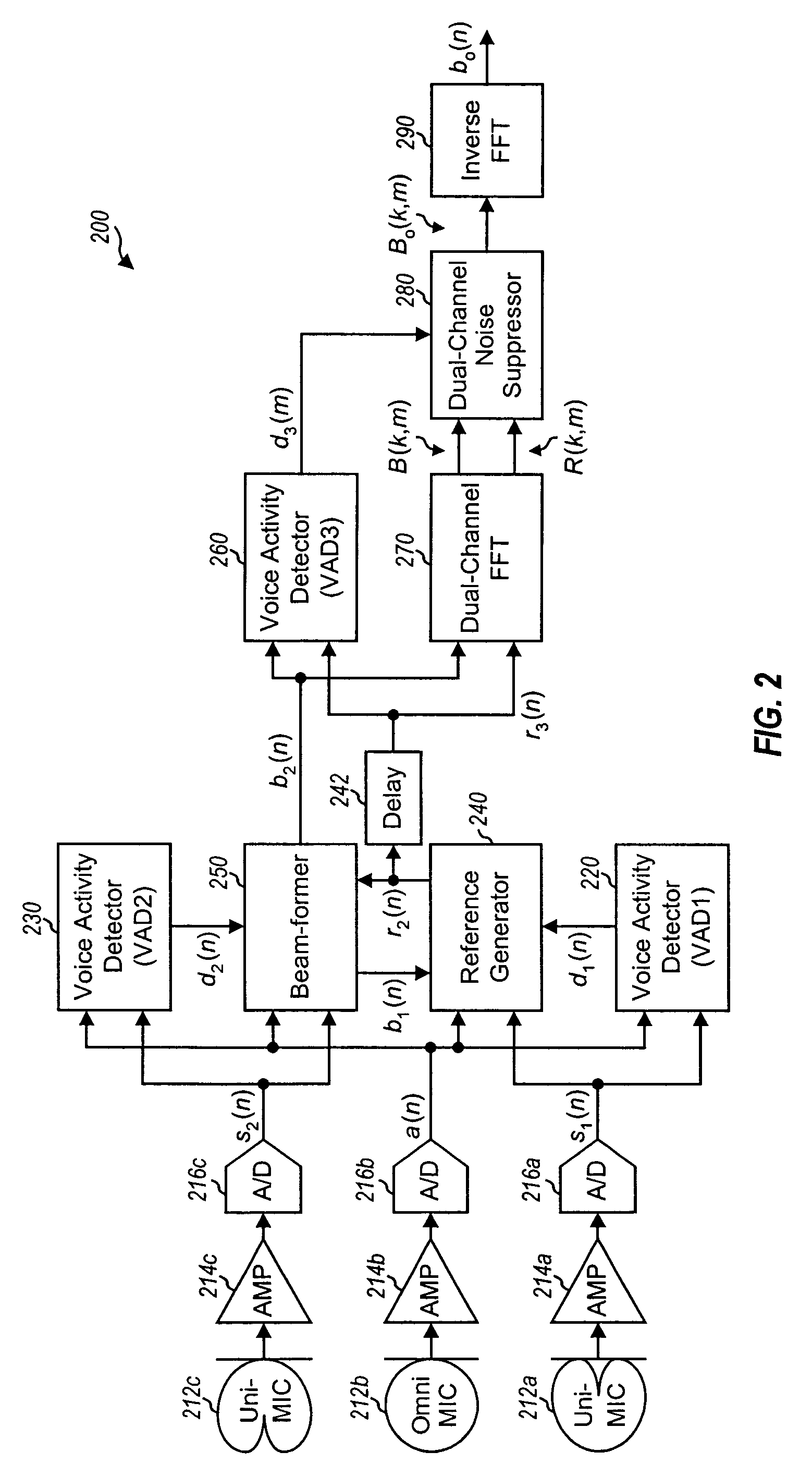
Small array microphone for beam-forming and noise suppression
ActiveUS7174022B1Suppress interferenceSuppress noiseSpeech analysisMicrophones signal combinationTime domainEngineering
Techniques are provided to suppress noise and interference using an array microphone and a combination of time-domain and frequency-domain signal processing. In one design, a noise suppression system includes an array microphone, at least one voice activity detector (VAD), a reference generator, a beam-former, and a multi-channel noise suppressor. The array microphone includes multiple microphones—at least one omni-directional microphone and at least one uni-directional microphone. Each microphone provides a respective received signal. The VAD provides at least one voice detection signal used to control the operation of the reference generator, beam-former, and noise suppressor. The reference generator provides a reference signal based on a first set of received signals and having desired voice signal suppressed. The beam-former provides a beam-formed signal based on a second set of received signals and having noise and interference suppressed. The noise suppressor further suppresses noise and interference in the beam-formed signal.
Owner:FORTEMEDIA
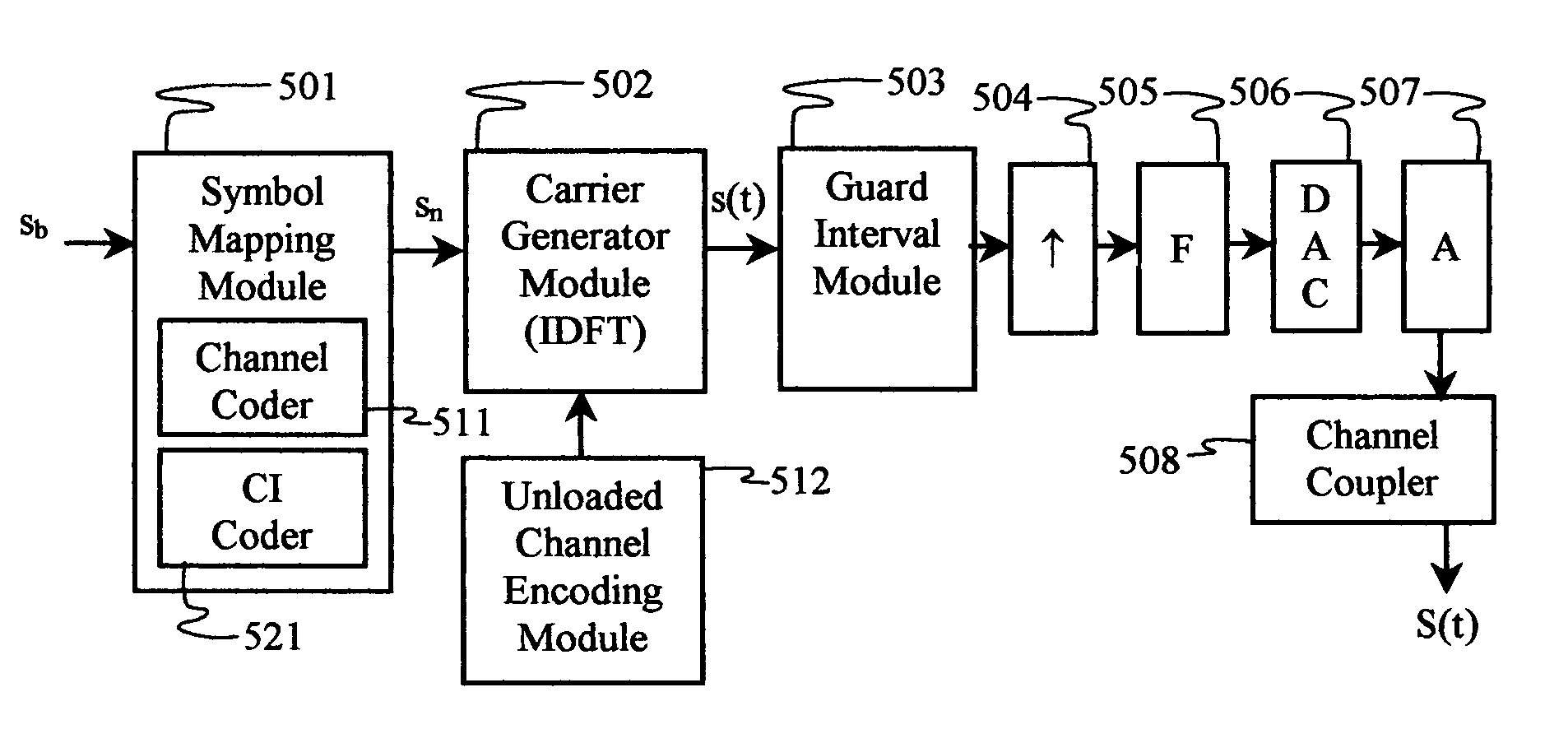
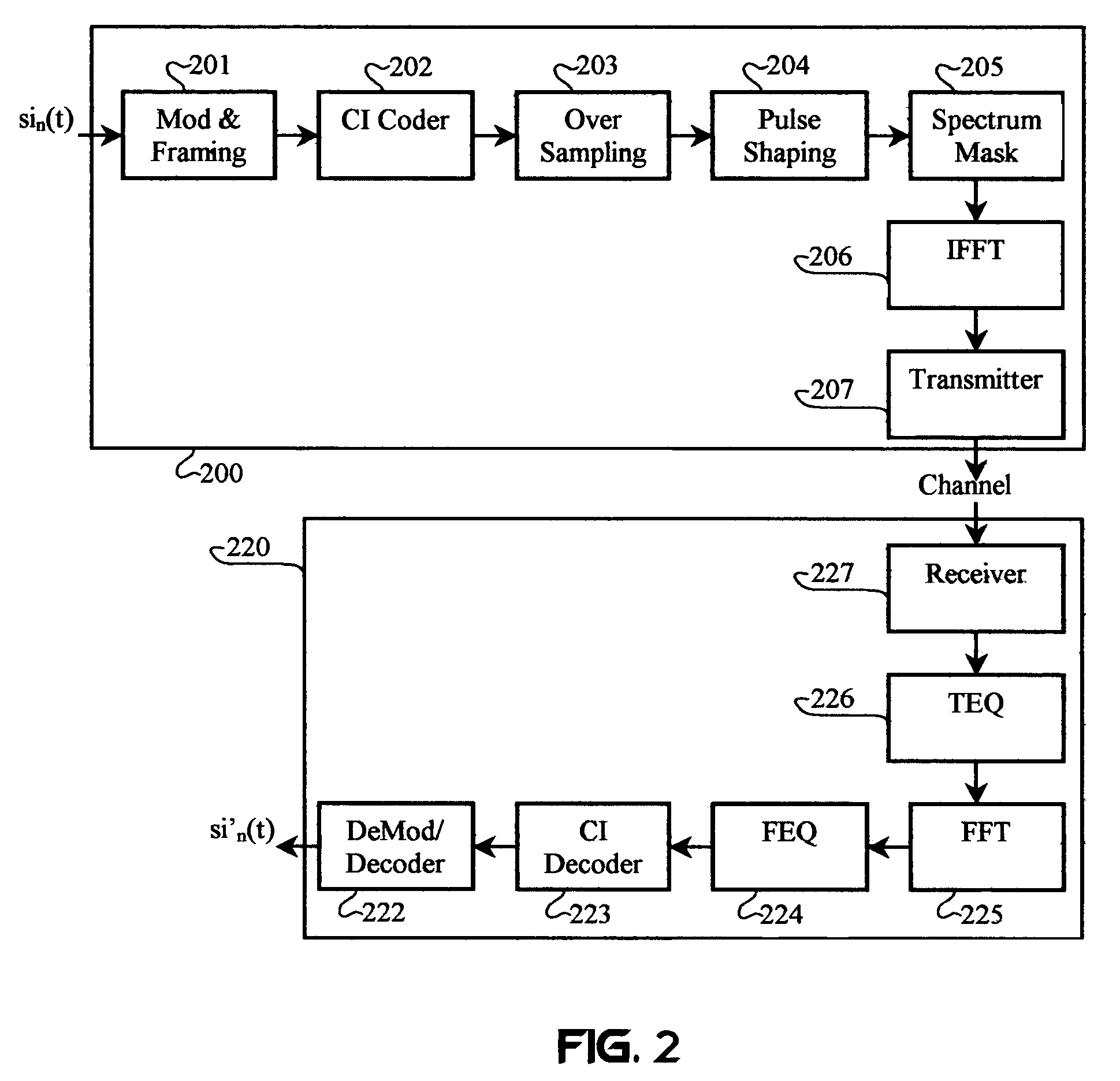
Software adaptable high performance multicarrier transmission protocol
InactiveUS7418043B2Reduce PAPREnhance other technique used for PAPR mitigationModulated carrier system with waveletsSecret communicationTransmission protocolTime domain
Techniques for reducing peak-to-average power in multicarrier transmitters employ peak cancellation with subcarriers that are impaired by existing channel conditions. The use of Carrier Interferometry (CI) coding further improves the effectiveness of peak reduction. CI coding can also be impressed onto pulse sequences in the time domain, which enhances spectral selection and facilitates peak-power control.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Data compression method for use in wellbore and formation characterization
A method is disclosed for compressing a frame of data representing parameter values, a time at which each parameter value was recorded, and an orientation of a sensor at the time each parameter value was recorded. Generally the method includes performing a two-dimensional transform on the data in the orientation domain and in a domain related to the recording time. In one embodiment, the method includes calculating a logarithm of each parameter value. In one embodiment, the 2-D transform includes generating a Fourier transform of the logarithm of the parameter values in the azimuthal domain, generating a discrete cosine transform of the transform coefficients in the time domain. This embodiment includes quantizing the coefficients of the Fourier transform and the discrete cosine transform. One embodiment of the method is adapted to transmit resistivity measurements made by an LWD instrument in pressure modulation telemetry so that while-drilling images of a wellbore can be generated. The one embodiment includes encoding the quantized coefficients, error encoding the encoded coefficients, and applying the error encoded coefficients to the pressure modulation telemetry.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and method for interference mitigation for wireless communication
InactiveUS20050122999A1Facilitate interference mitigationEnables utilization of spectrumFrequency-division multiplexDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTime domainFrequency spectrum
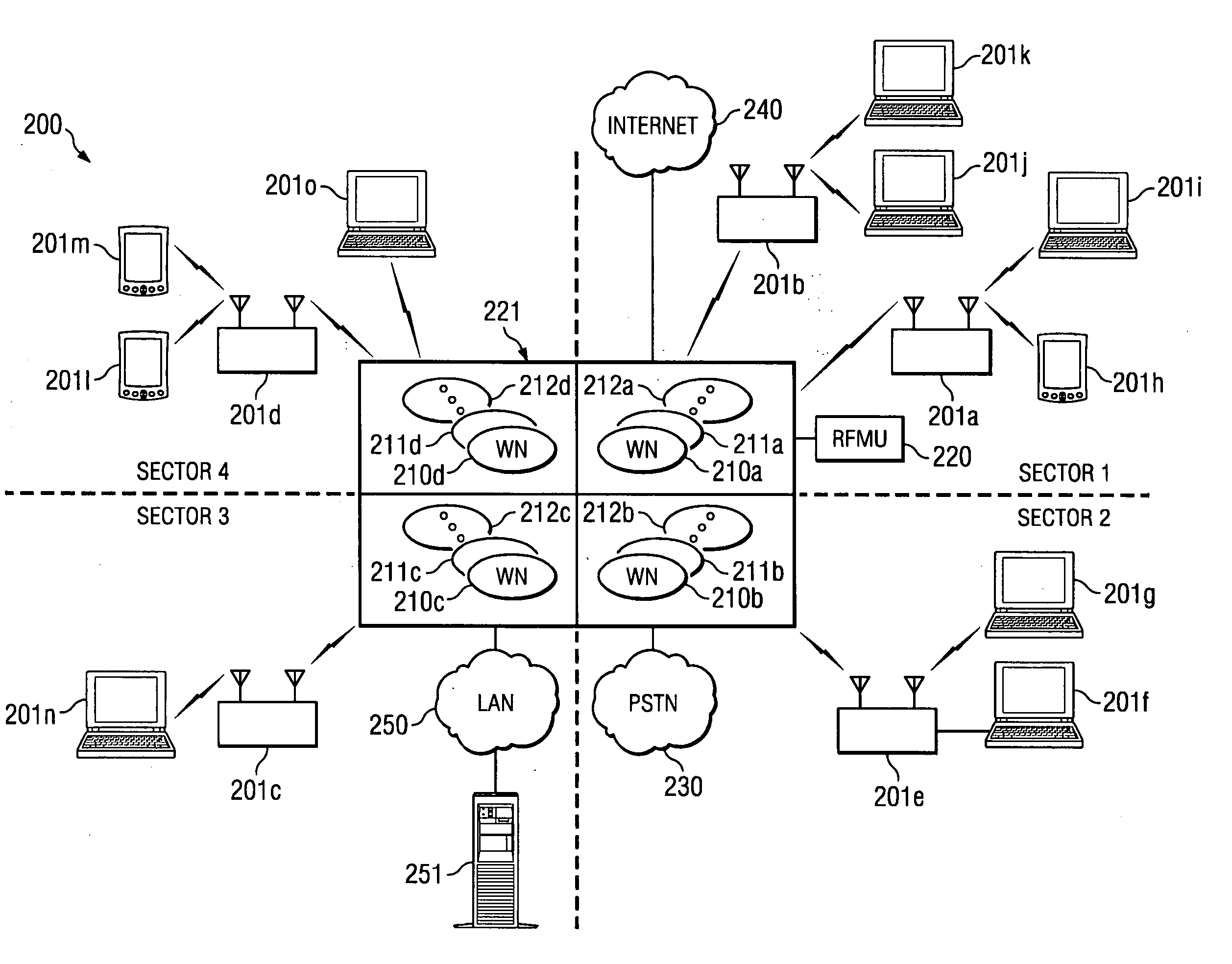
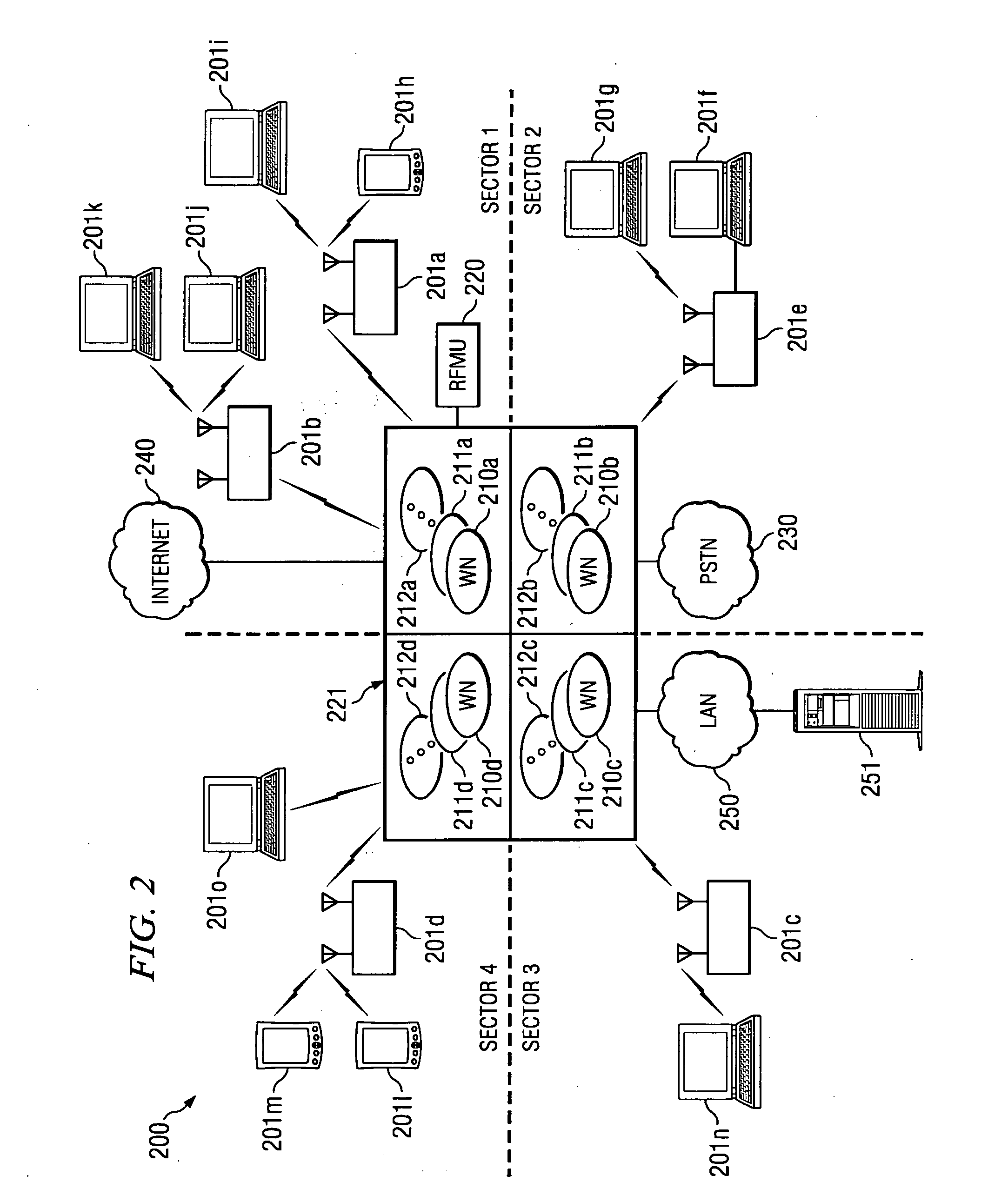
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide interference mitigation by making alternative resources available within areas served by wireless communication links. Embodiments provide multiple channel availability in establishing wireless communication links to facilitate interference mitigation. Time domain techniques, spatial processing techniques, and / or frequency domain techniques may be implemented for spectrum management. Embodiments provide wireless base station configurations in which all or a plurality of base station sectors use a same frequency channel and / or in which each sector or a plurality of sectors use all frequency channels. Multi-channel strategies may be implemented such as to provide dynamic selection of a “best” frequency channel, to provide transmission of identical data on multiple channels for combining / selection at the receiver, and / or to provide for dividing the data for transmission on multiple channels.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
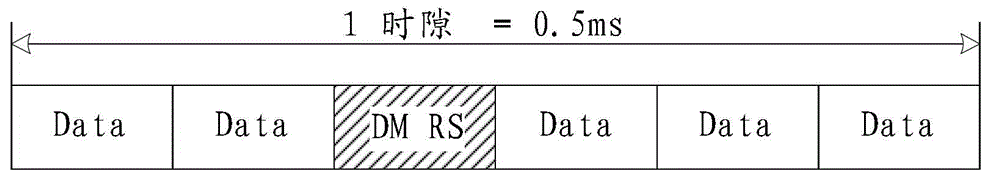
Uplink DMRS transmitting method, device and system/ Transmitting method, device and system used for uplink DMRS
ActiveCN103944665ASolve excessive overheadTransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainDemodulation
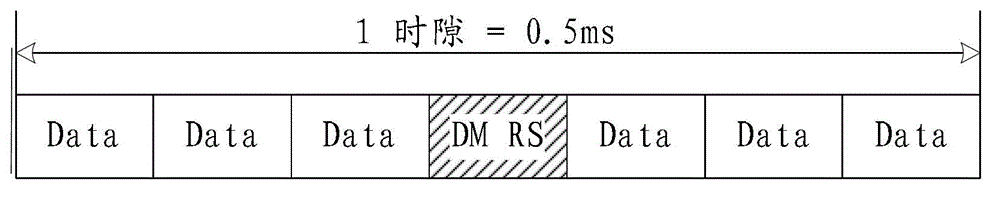
The invention relates to the field of communication, provides an uplink DMRS (Demodulation Reference Signal) transmitting method, device and system and solves the problem that the time-frequency resource overhead of the uplink demodulation reference signal is excessive. The method comprises the steps that a base station configures a resource, a pattern or a parameter set required for transmitting the uplink DMRS for a user terminal; and the base station transmits or indicates the resource, the pattern or the parameter set required for transmitting the uplink DMRS to the user terminal via a bit domain or a high-level signaling of downlink control information. The resource, the pattern or the parameter set comprises a time domain position, a frequency domain position, a subframe configuration or a cycle, and a hopping mode. The technical scheme is applicable to a long term evolution system, and an uplink DMRS transmitting mechanism with the low time-frequency resource overhead is realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
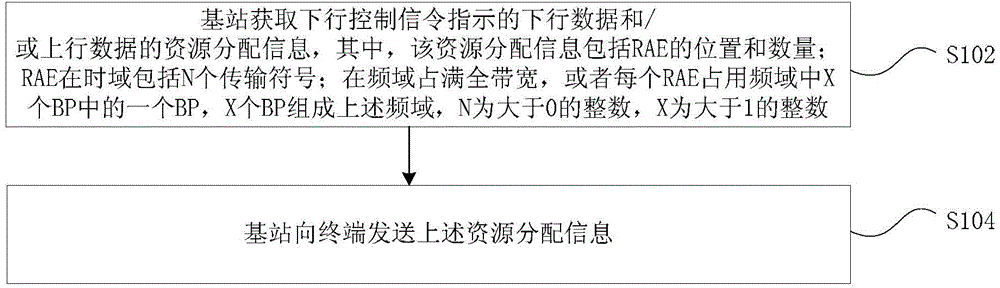
Dynamic resource allocating method and apparatus, base station, terminal
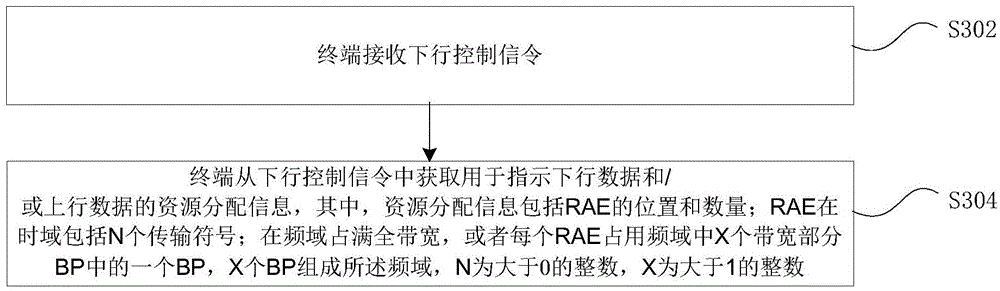
ActiveCN105099634ASolve problems such as high costReduce overheadTransmission path divisionSignal allocationTime domainDynamic resource
Provided are a dynamic resource allocation method and device, a base station and a terminal. The method comprises: a base station acquiring resource allocation information about downlink data and / or uplink data indicated by downlink control signalling, wherein the resource allocation information comprises the location and number of resource allocation elements (RAEs); the RAEs comprise N transmission symbols in a time domain; and the RAEs completely occupy the full bandwidth in a frequency domain, or each RAE occupies one BP among X bandwidth parts (BPs) in the frequency domain, the X BPs forming the frequency domain, where N is an integer greater than 0, and X is an integer greater than 1; and the base station sending the resource allocation information to a terminal. By means of the technical solution provided in the present invention, the problems in the related art that it is not possible to use an LTE control channel to schedule uplink and downlink services of a plurality of transmission symbols on a high-frequency carrier and the transmission of uplink services, and that the overhead of control signalling is relatively high in a network independently networked by an LTE carrier and the high-frequency carrier and the like are solved, thus achieving that the LTE carrier schedules the high-frequency carrier across carriers.
Owner:ZTE CORP
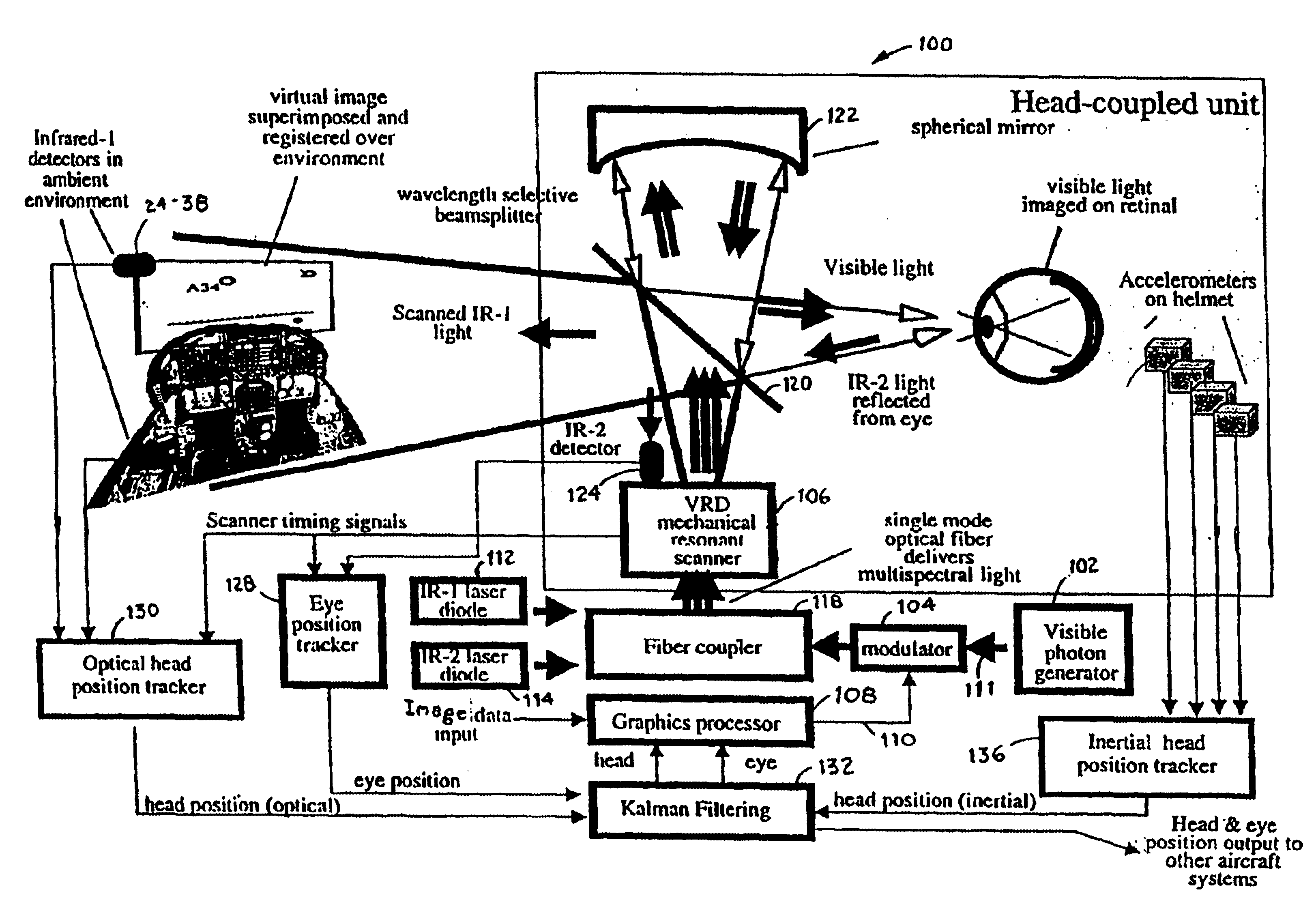
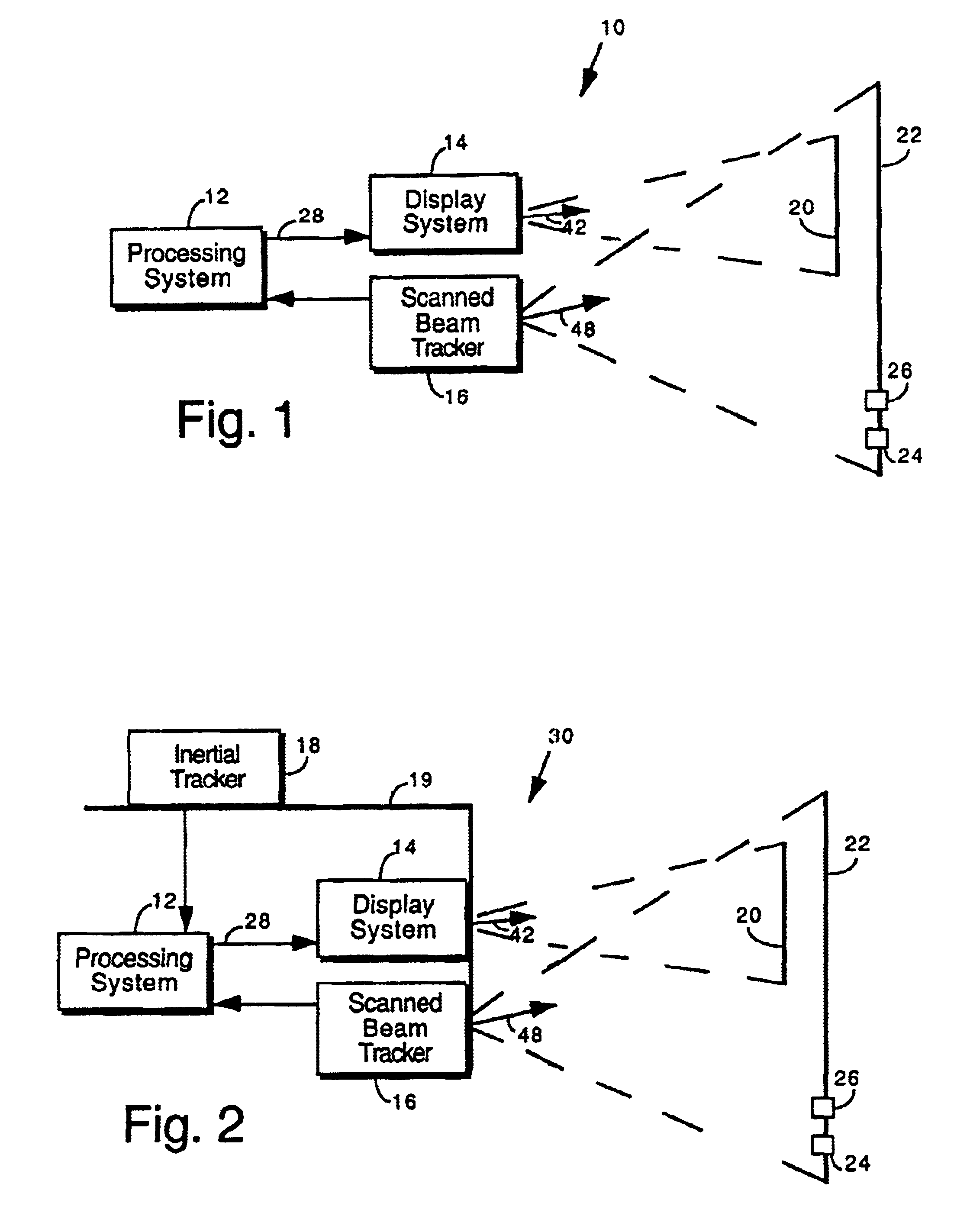
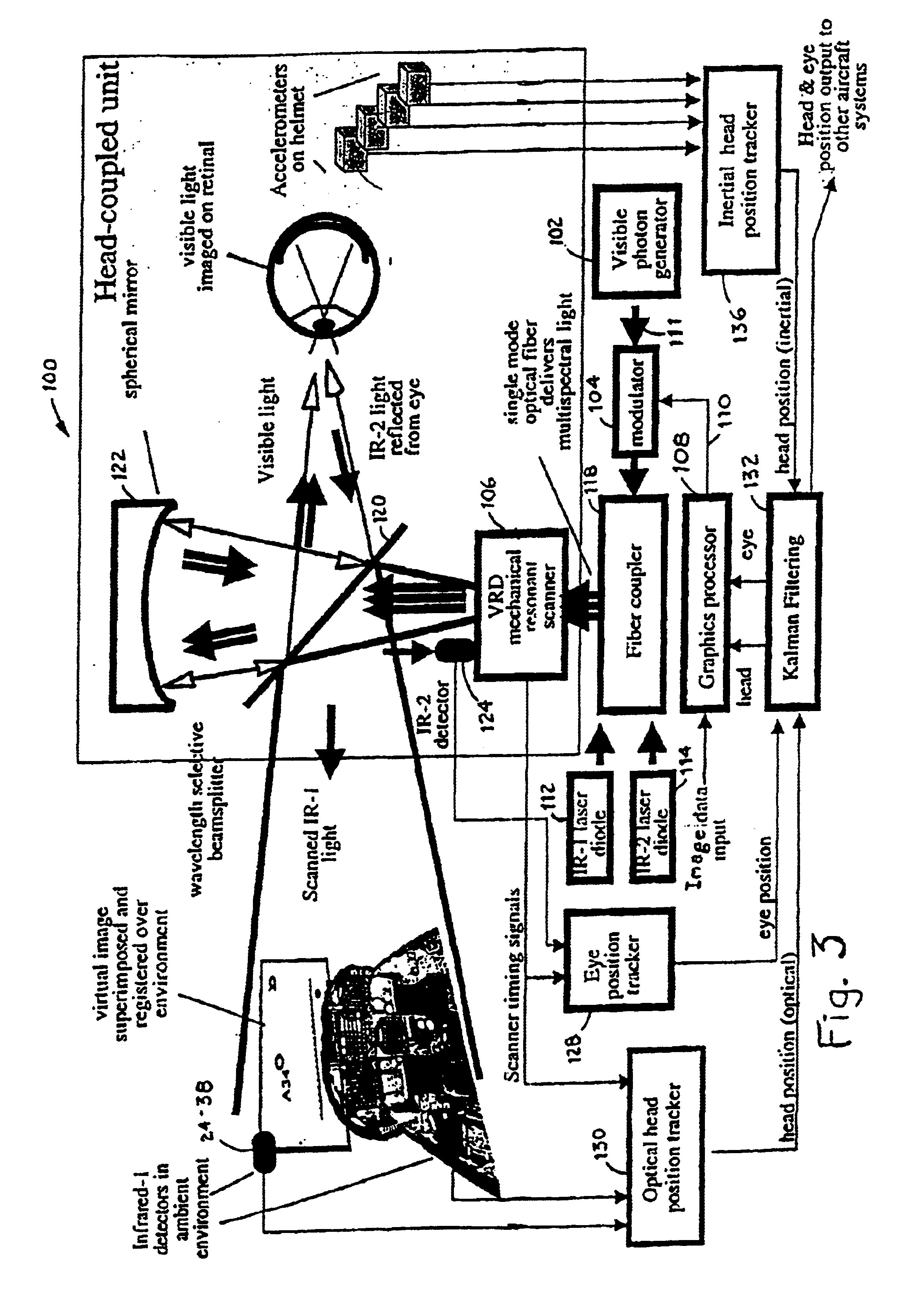
Virtual image registration in augmented display field
InactiveUS6867753B2Accurate locationAccurate predictionInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainTemporal resolution
A virtual image is registered among a perceived real world background. Tracking light is scanned into the real world environment, which includes at least one detector pair. A first time and a second time at which the tracking light impinges on the first detector is detected, in which the first time and second time occurs within adjacent scan lines. A time at which a horizontal scan line edge (e.g., beginning of scan line or end of scan line) is encountered is derived as occurring one half way between the first time and the second time. The horizontal location of the first detector then is determined within a specific scan line inferring the scan line edge time. The vertical location of the detector is determined within a scan frame by measuring time duration using the beginning of the frame. By determining a location independently from the temporal resolution of the augmented imaging system, the temporal location of the detector is identified to a sub-pixel / sub-line precision. The augmented image is registered either to a 3D real world spatial coordinate system or to a time domain coordinate system based upon tracked position and orientation of the user.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Scattered pilot pattern and channel estimation method for MIMO-OFDM systems
ActiveUS7248559B2Reduced scattered pilot overheadLess computationally complexPower managementSpatial transmit diversityTime domainCommunications system
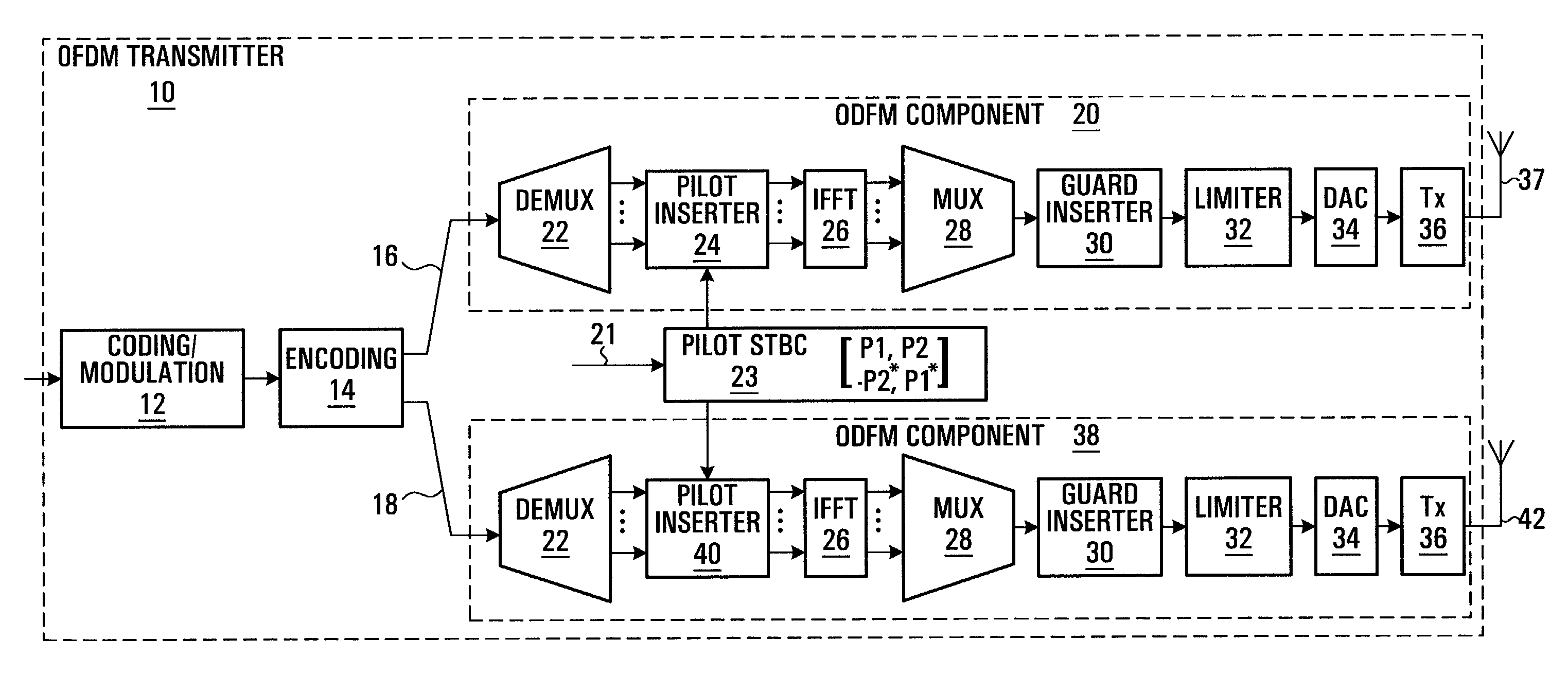
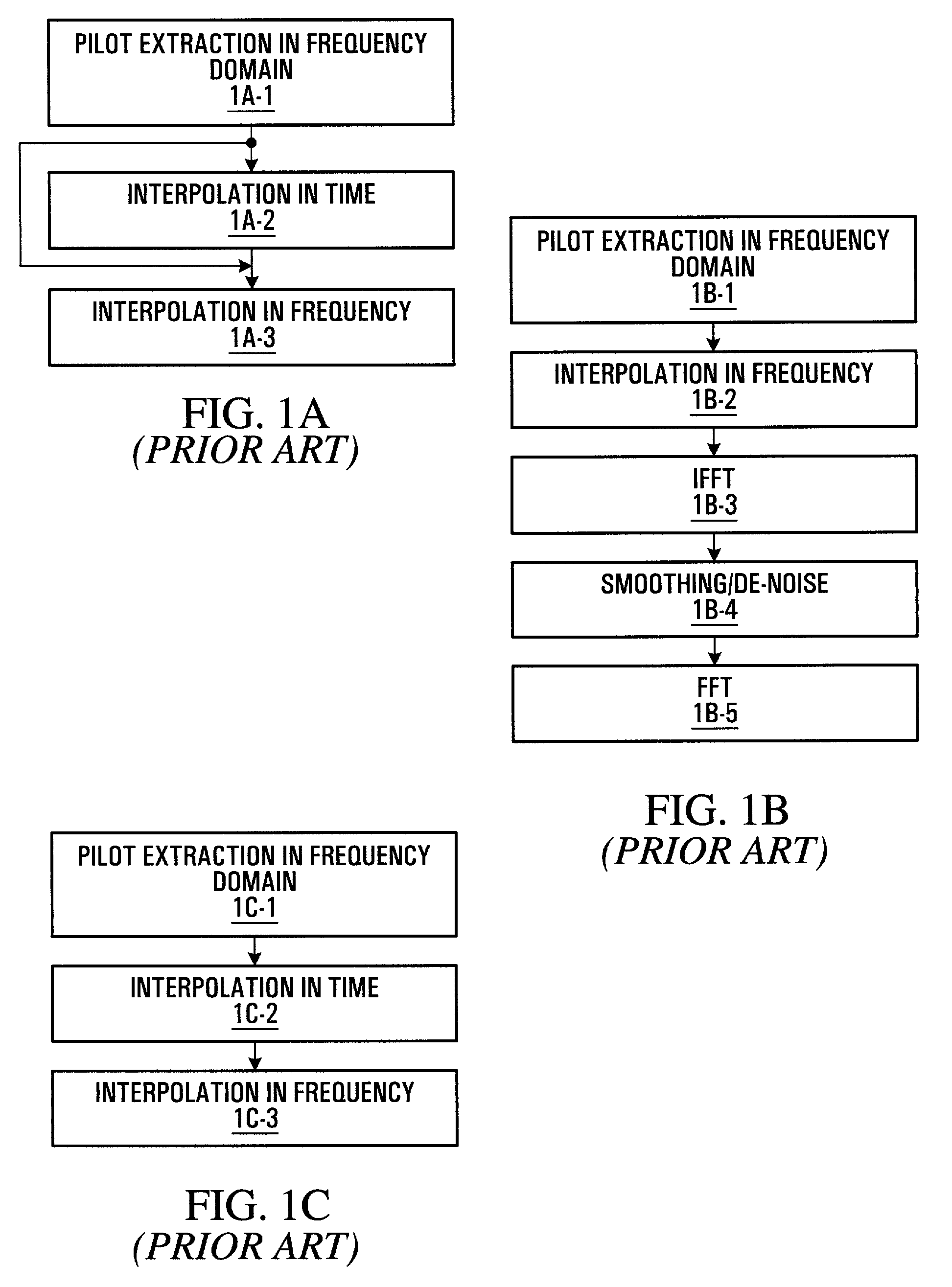
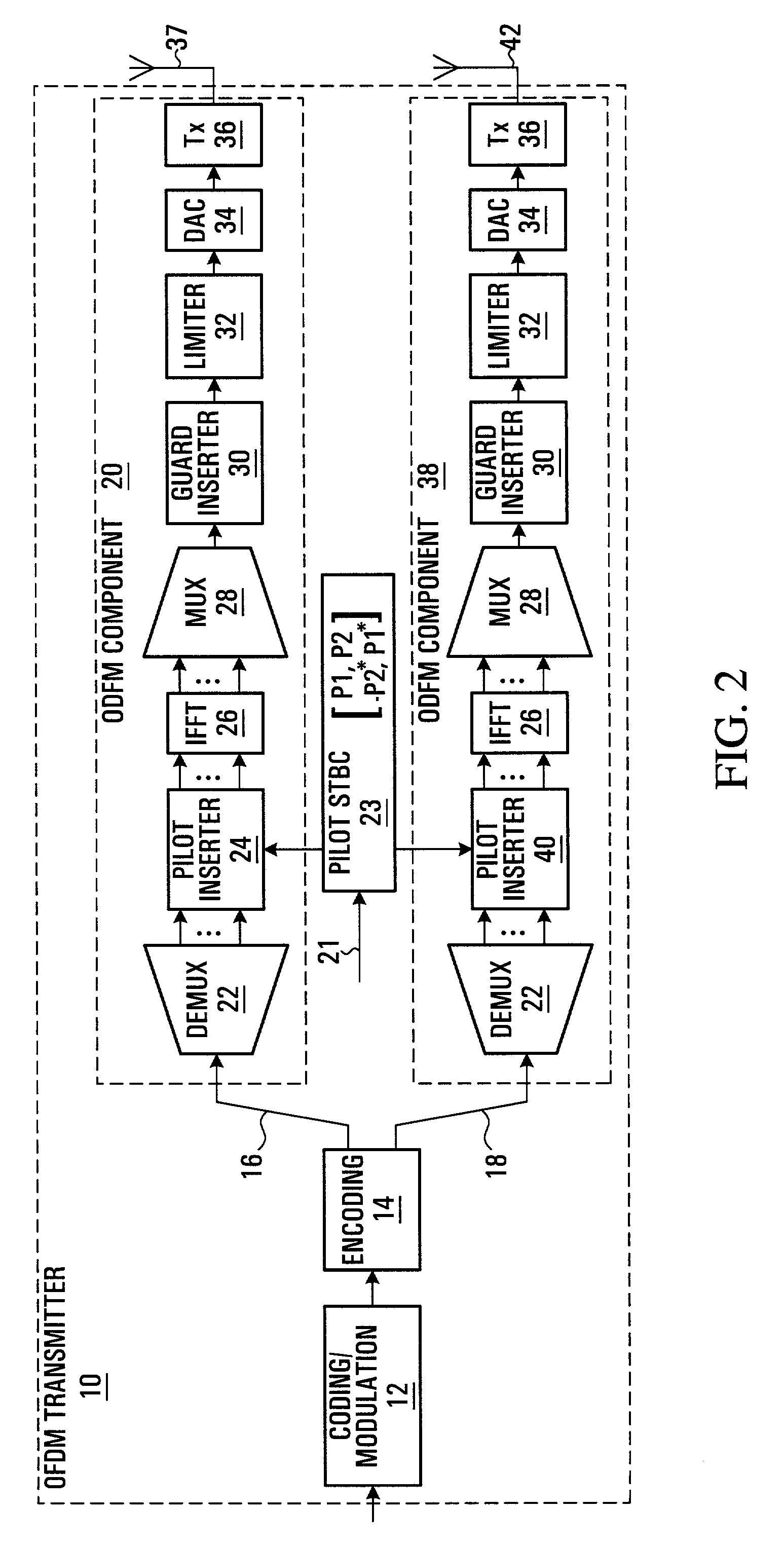
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing the number of pilot symbols within a MIMO-OFDM communication system, and for improving channel estimation within such a system. For each transmitting antenna in an OFDM transmitter, pilot symbols are encoded so as to be unique to the transmitting antenna. The encoded pilot symbols are then inserted into an OFDM frame to form a diamond lattice, the diamond lattices for the different transmitting antennae using the same frequencies but being offset from each other by a single symbol in the time domain. At the OFDM receiver, a channel response is estimated for a symbol central to each diamond of the diamond lattice using a two-dimensional interpolation. The estimated channel responses are smoothed in the frequency domain. The channel responses of remaining symbols are then estimated by interpolation in the frequency domain.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Binaural synthesis, head-related transfer functions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6118875AReduce the differenceFunction increaseTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsTime domainSound sources
PCT No. PCT / DK95 / 00089 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 27, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 27, 1996 PCT Filed Feb. 27, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 23493 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 31, 1995A method and apparatus for simulating the transmission of sound from sound sources to the ear canals of a listener encompasses novel head-related transfer functions (HTFs), novel methods of measuring and processing HTFs, and novel methods of changing or maintaining the directions of the sound sources as perceived by the listener. The measurement methods enable the measurement and construction of HTFs for which the time domain descriptions are surprisingly short, and for which the differences between listeners are surprisingly small. The novel HTFs can be exploited in any application concerning the simulation of sound transmission, measurement, simulation, or reproduction. The invention is particularly advantageous in the field of binaural synthesis, specifically, the creation, by means of two sound sources, of the perception in the listener of listening to sound generated by a multichannel sound system. It is also particularly useful in the designing of electronic filters used, for example, in virtual reality systems, and in the designing of an "artificial head" having HTFs that approximate the HTFs of the invention as closely as possible in order to make the best possible representation of humans by the artificial head, thereby making artificial head recordings of optimal quality.
Owner:M O SLASHED LLER HENRIK +3
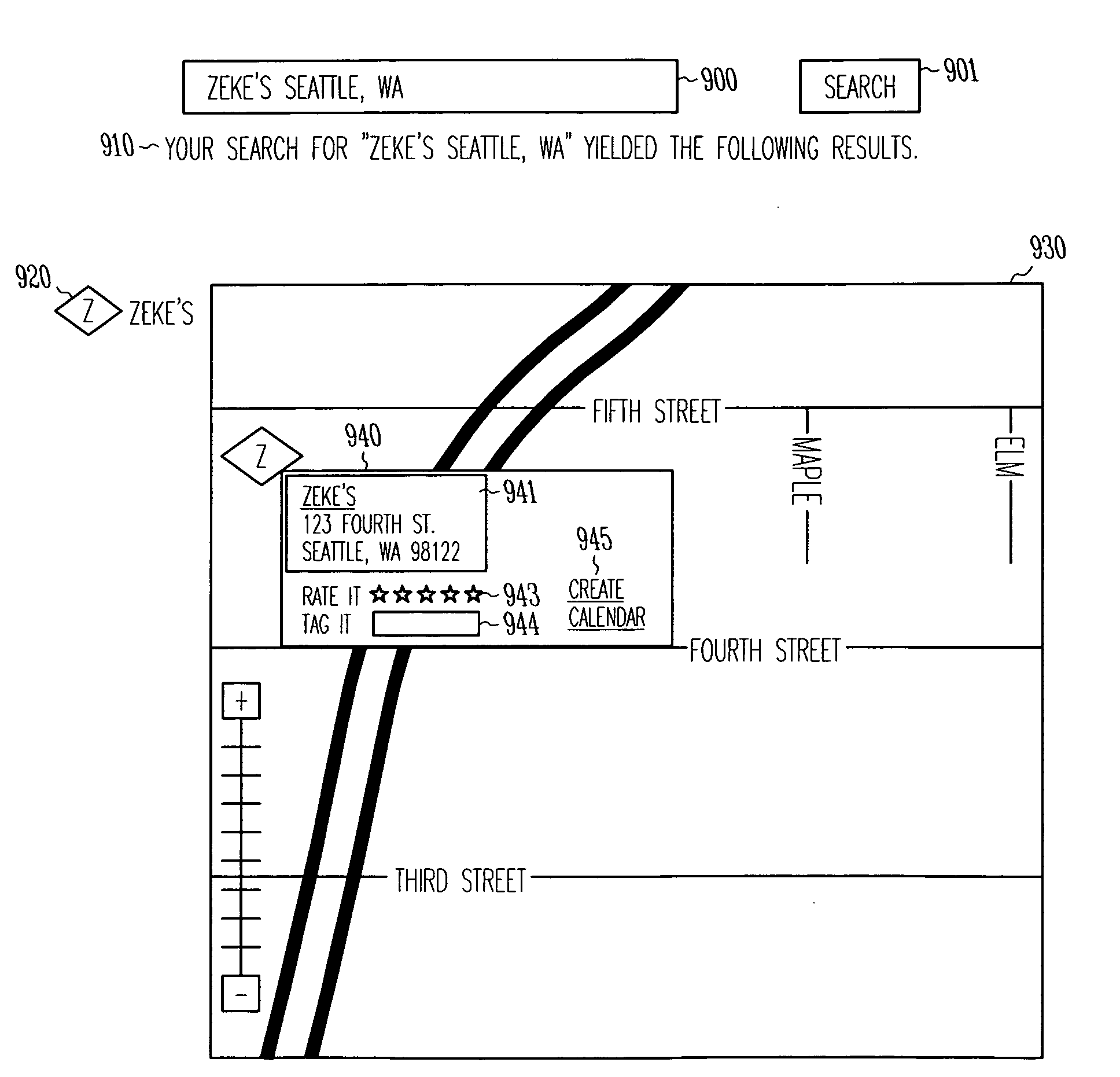
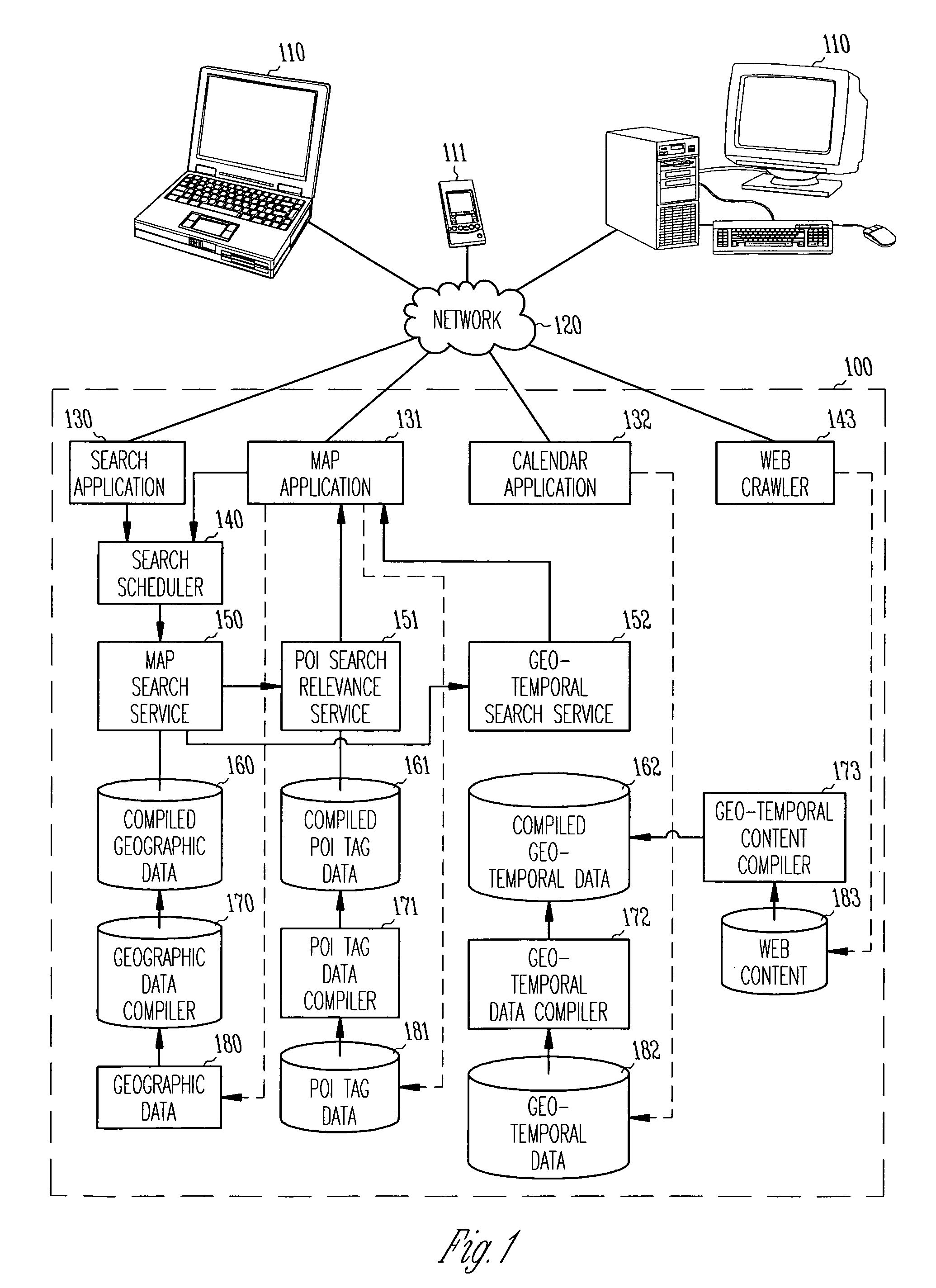
System and method for capturing, integrating, discovering, and using geo-temporal data
Various embodiments relate to the systems and methods for creating events, creating points of interest, associating points of interest with geographic locations, associating events with points of interest or with geographic locations, discovering events in a geographic area given a time frame, tagging and rating events and points of interest and sharing events among users. A particular embodiment includes a computer-implemented method including associating geographical locations or points of interest with events having geographical and temporal attributes in a geo-temporal data store, receiving a geo-temporal search query specified by a user, and producing search results including items from the geo-temporal data store having a pre-determined degree of relevance to the geo-temporal search query in both a geographical and temporal domain.
Owner:ROBERTS JONATHAN
Washable wearable biosensor
ActiveUS8140143B2Level of comfortAvoid overwritingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAdhesiveOn board
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
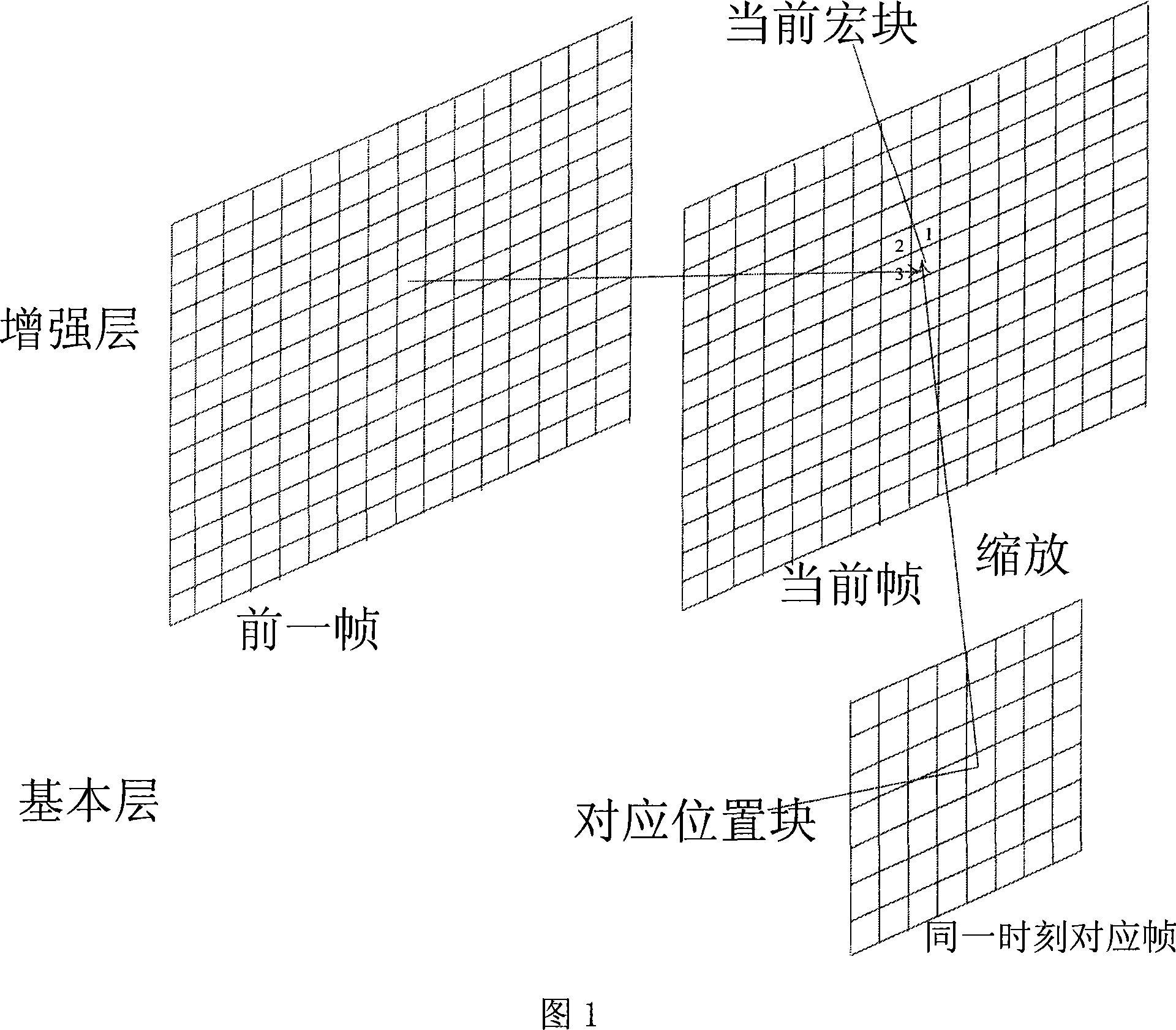
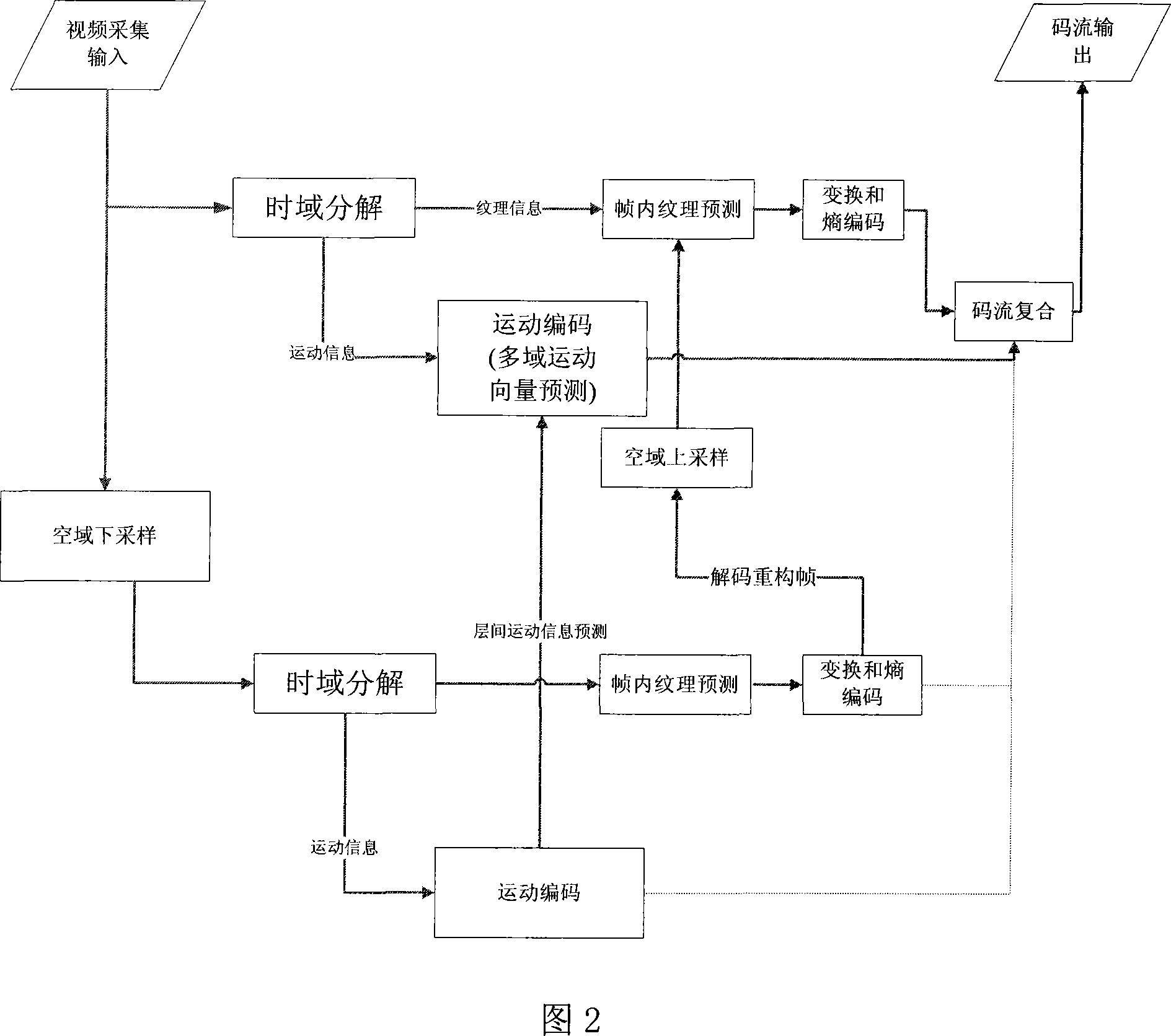
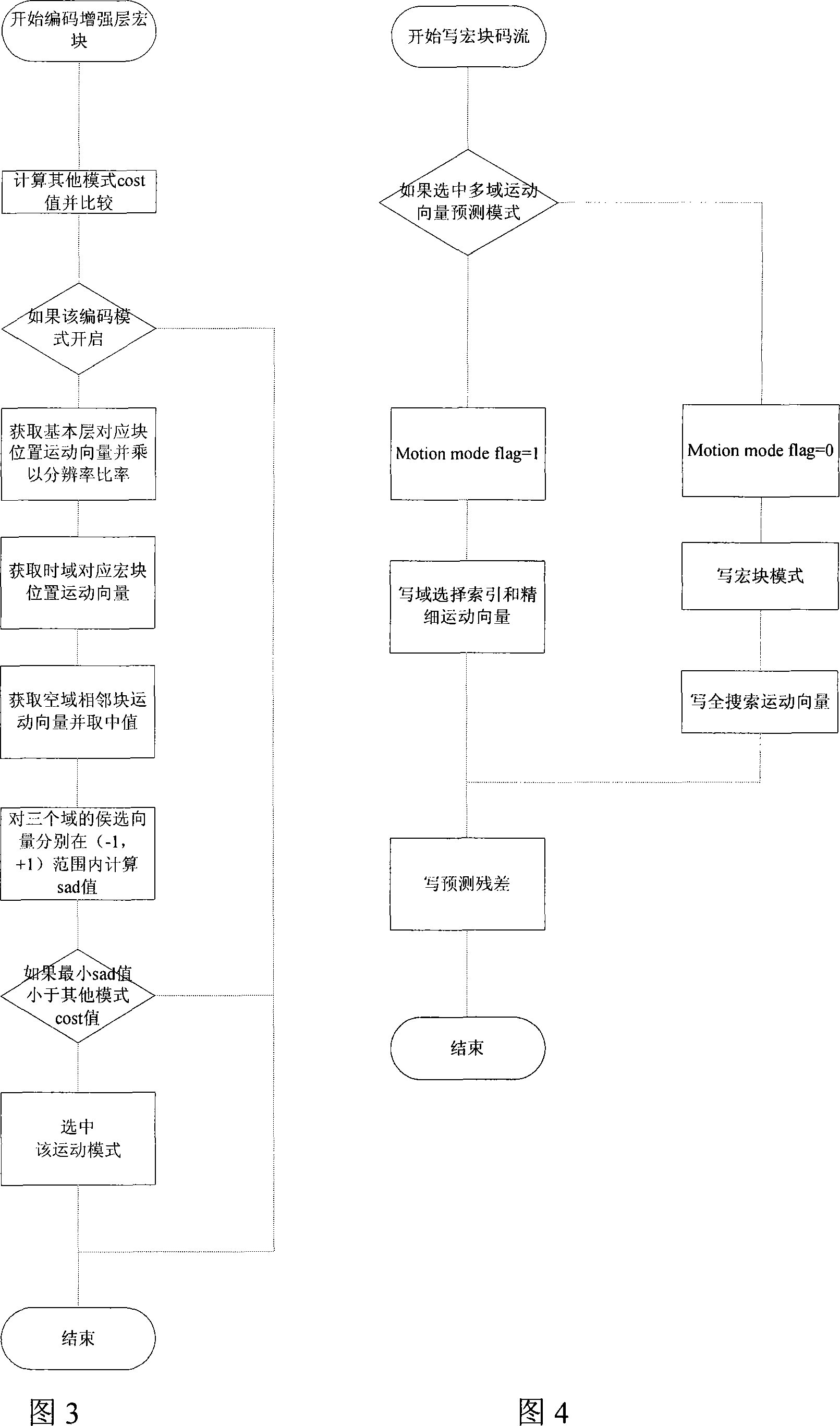
Movement vector prediction method in resolution demixing technology
InactiveCN101198064AReduce bit rateHigh gain performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationTime domainMotion vector
The invention discloses a motion vector forecasting method in a resolution quantizing structure, wherein, forecasting motion vectors of macro blocks in enhancement layers are acquired by utilization of relativity of motion vectors of a time domain, a space domain and an interlayer domain. The realization process is that: on the time domain, candidate motion vectors of the time domain are acquired from motion vectors of macro blocks with the same position with the prior frame; on the space domain, candidate motion vectors of the space domain are acquired from motion vectors of adjacent blocks; on the interlayer domain, candidate motion vectors of the interlayer domain are acquired from corresponding motion vectors with low space domain resolution hierarchy; candidate motion vectors with minimum motion estimation cost are selected to be forecasting motion vectors by selection among the candidate motion vectors of the time domain, the space domain and the interlayer domain. The invention has the advantages of capability of acquiring more accurate forecasting motion vectors, capability of compressing code rate of motion vectors, and obtaining of performance gain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for reducing the peak-to-average ratio in a multicarrier communication system
InactiveUS6130918AReduce impactGood dispersionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainData set
A reduction in a peak-to-mean envelope power ratio of a multicarrier signal, represented as a time domain signal, is achieved by applying (76) an offset, indicative of a difference (74) between a mean signal level and a midpoint level of the time domain signal, to the time domain signal. Alternatively, constellation values of positive and negative frequency components are modified by differing functions to produce a modified data set. Preferably, the negative frequency components are set to a predetermined value (namely zero (124)) to provide an alternate coding scheme Once the multicarrier signal has been converted into a time domain representation, real and imaginary parts (126-128) of the modified data set that consequently only contain positive frequency components and zeros are compared with one another to identify (130) which of the real and imaginary parts has a lower peak-to-average signal ratio (134) for the time domain representation. Then, based upon which of the peak-to-average signal ratios is lowest (136), either the real and imaginary part of the time domain signal is selected for subsequent transmission (138).
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
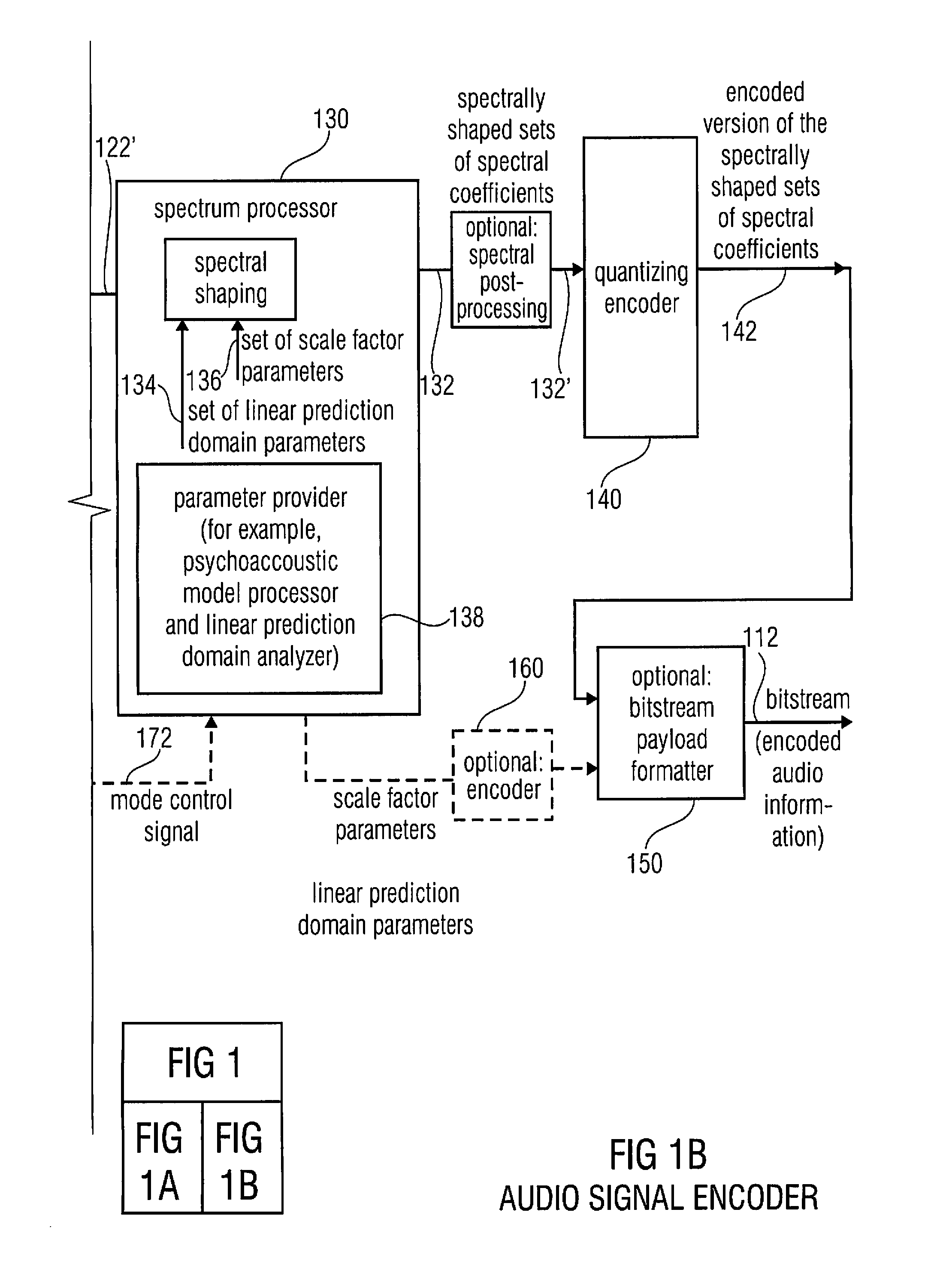
Multi-mode audio signal decoder, multi-mode audio signal encoder, methods and computer program using a linear-prediction-coding based noise shaping
ActiveUS20120245947A1Without inacceptable artifactEasy transitionSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
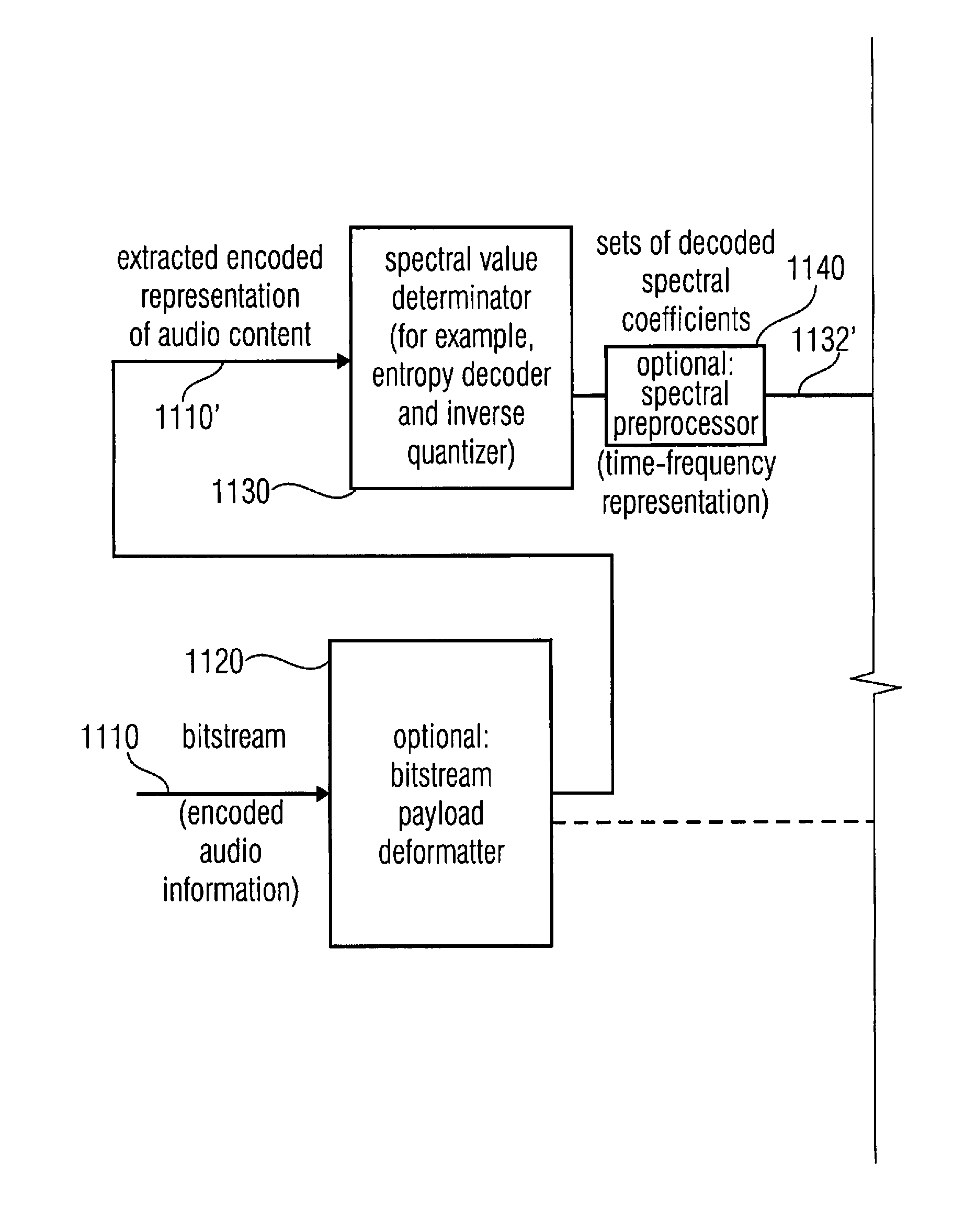
A multi-mode audio signal decoder has a spectral value determinator to obtain sets of decoded spectral coefficients for a plurality of portions of an audio content and a spectrum processor configured to apply a spectral shaping to a set of spectral coefficients in dependence on a set of linear-prediction-domain parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a linear-prediction mode, and in dependence on a set of scale factor parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a frequency-domain mode. The audio signal decoder has a frequency-domain-to-time-domain converter configured to obtain a time-domain audio representation on the basis of a spectrally-shaped set of decoded spectral coefficients for a portion of the audio content encoded in the linear-prediction mode and for a portion of the audio content encoded in the frequency domain mode. An audio signal encoder is also described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
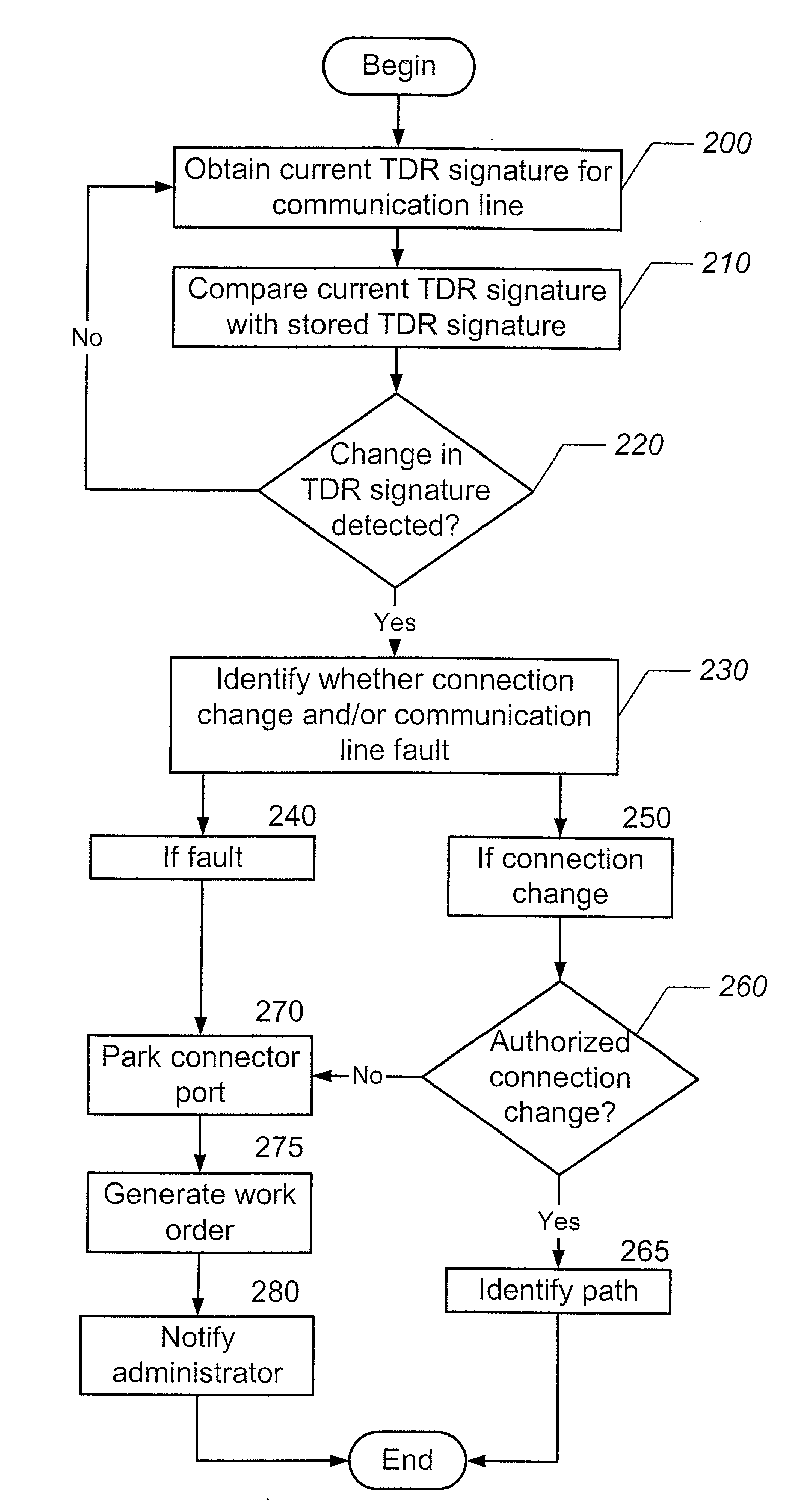
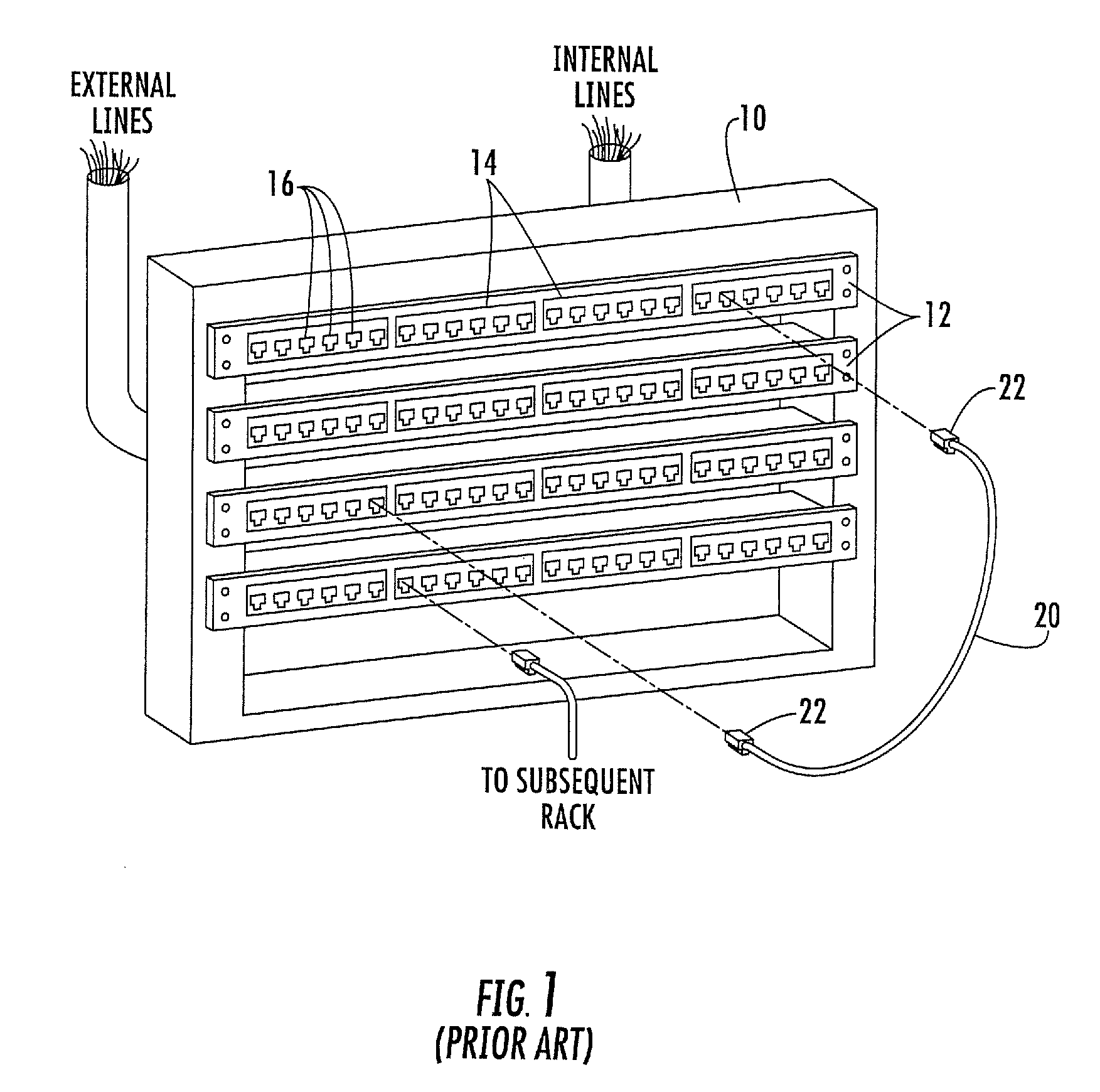
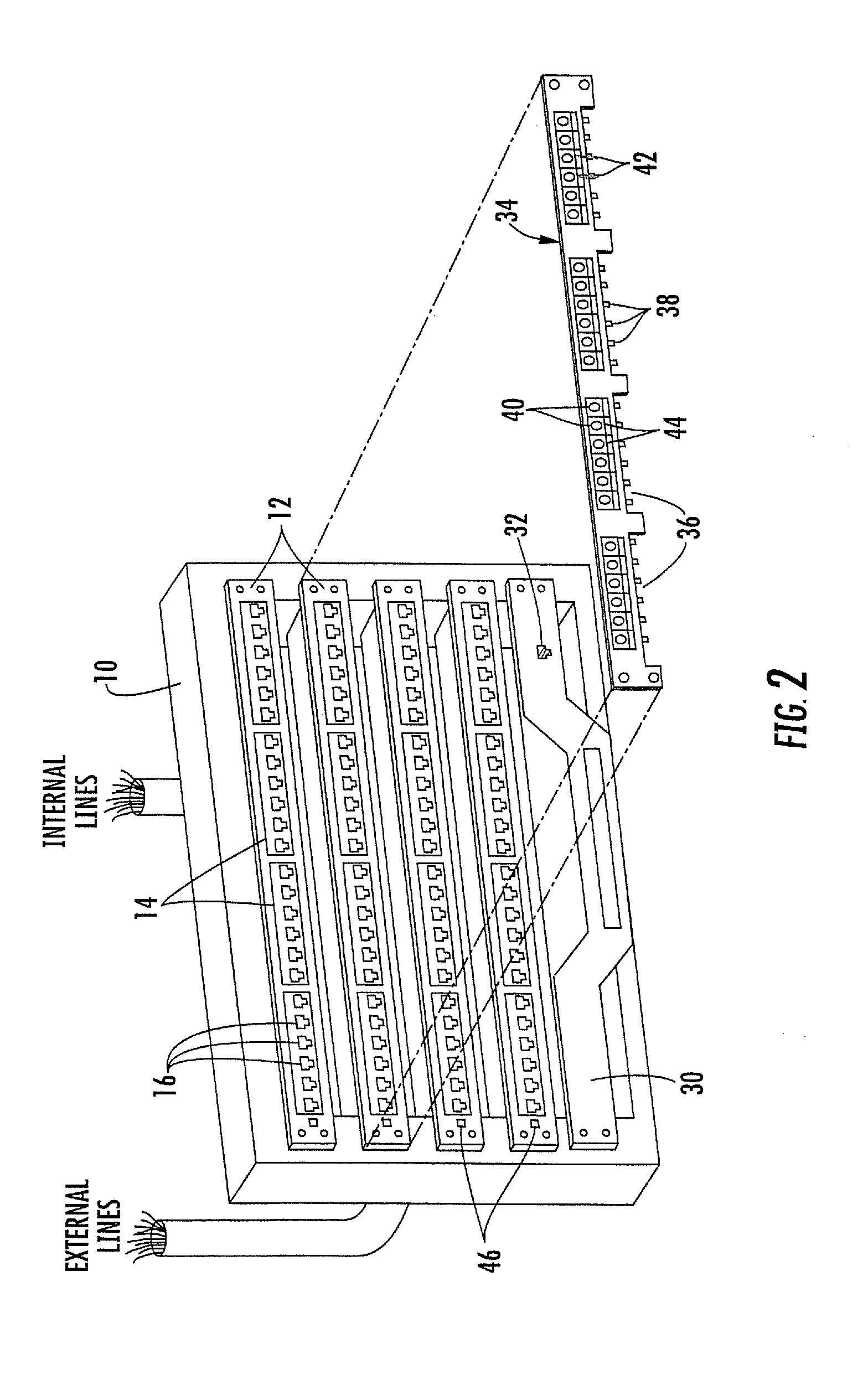
Methods, systems and computer program products for using time domain reflectometry signatures to monitor network communication lines
InactiveUS20090175195A1Data switching by path configurationFault location by pulse reflection methodsTime domainPatch panel
Methods, systems and computer program products for uniquely identifying communication lines in a network via time domain reflectometry (TDR) signatures are provided. A pulsed signal is sent into a communication line through a patch panel connector port and a reflection of the pulsed signal through the patch panel connector port is received to obtain a TDR signature for each communication line. The pulsed signal is sent and received by a controller operatively associated with the patch panel and / or by a network switch in communication with the patch panel. Connection changes and / or communication line faults at a network patch panel are detected by comparing current and stored TDR signatures.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
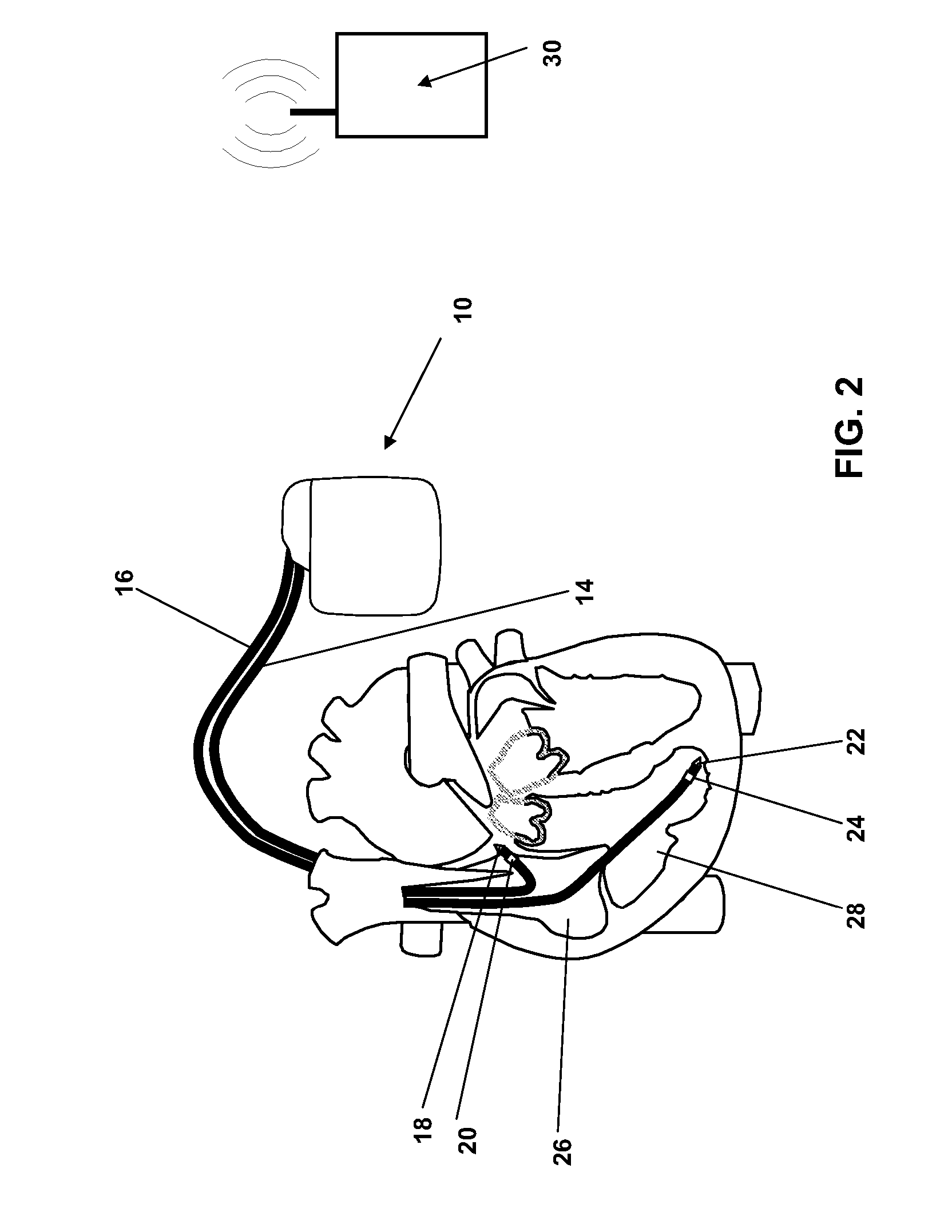
Wavelet based feature extraction and dimension reduction for the classification of human cardiac electrogram depolarization waveforms
ActiveUS20080109041A1Improve accuracyPrecise processElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisCardiac pacemaker electrodeClassification methods
A depolarization waveform classifier based on the Modified lifting line wavelet Transform is described. Overcomes problems in existing rate-based event classifiers. A task for pacemaker / defibrillators is the accurate identification of rhythm categories so correct electrotherapy can be administered. Because some rhythms cause rapid dangerous drop in cardiac output, it's desirable to categorize depolarization waveforms on a beat-to-beat basis to accomplish rhythm classification as rapidly as possible. Although rate based methods of event categorization have served well in implanted devices, these methods suffer in sensitivity and specificity when atrial / ventricular rates are similar. Human experts differentiate rhythms by morphological features of strip chart electrocardiograms. The wavelet transform approximates human expert analysis function because it correlates distinct morphological features at multiple scales. The accuracy of implanted rhythm determination can then be improved by using human-appreciable time domain features enhanced by time scale decomposition of depolarization waveforms.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
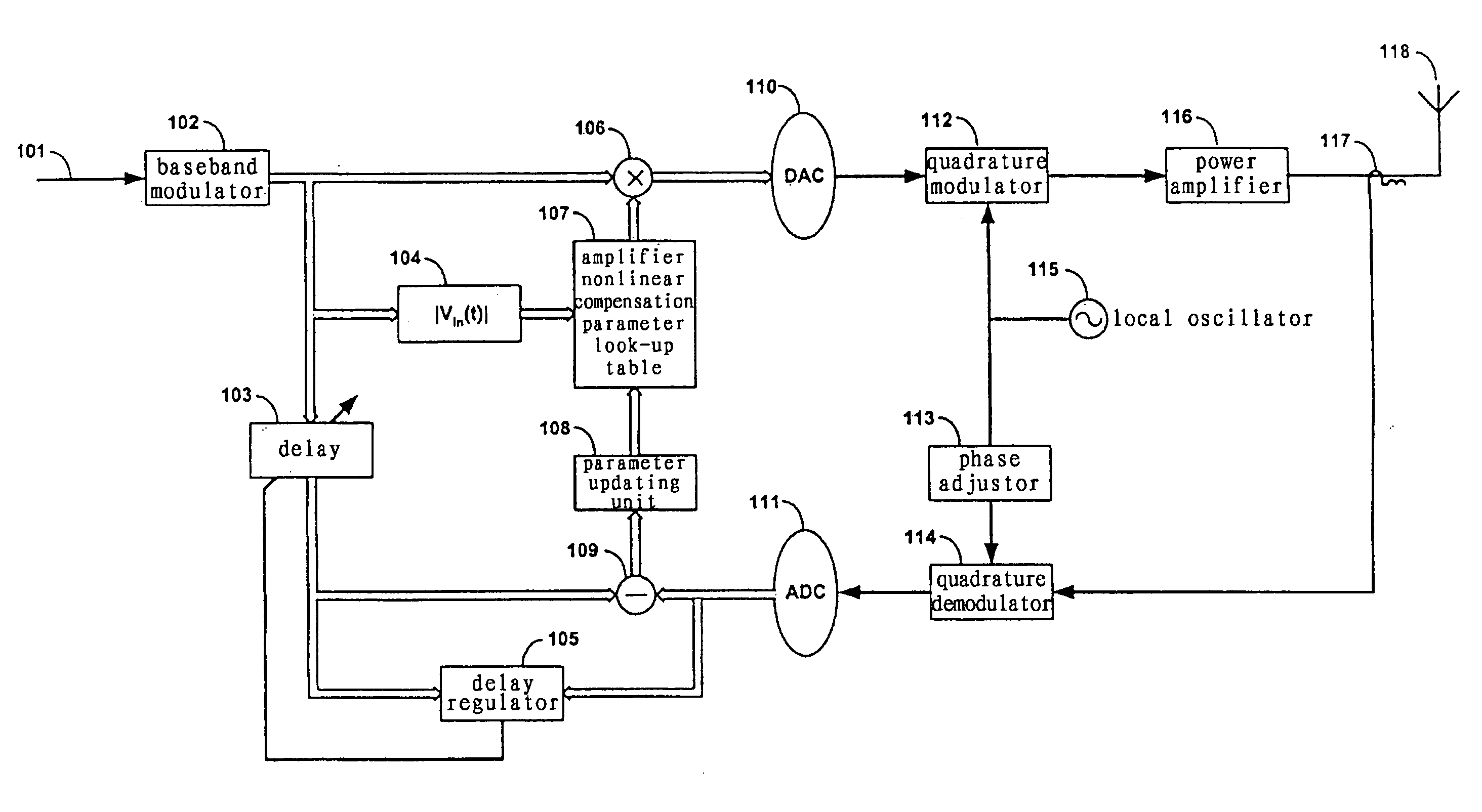
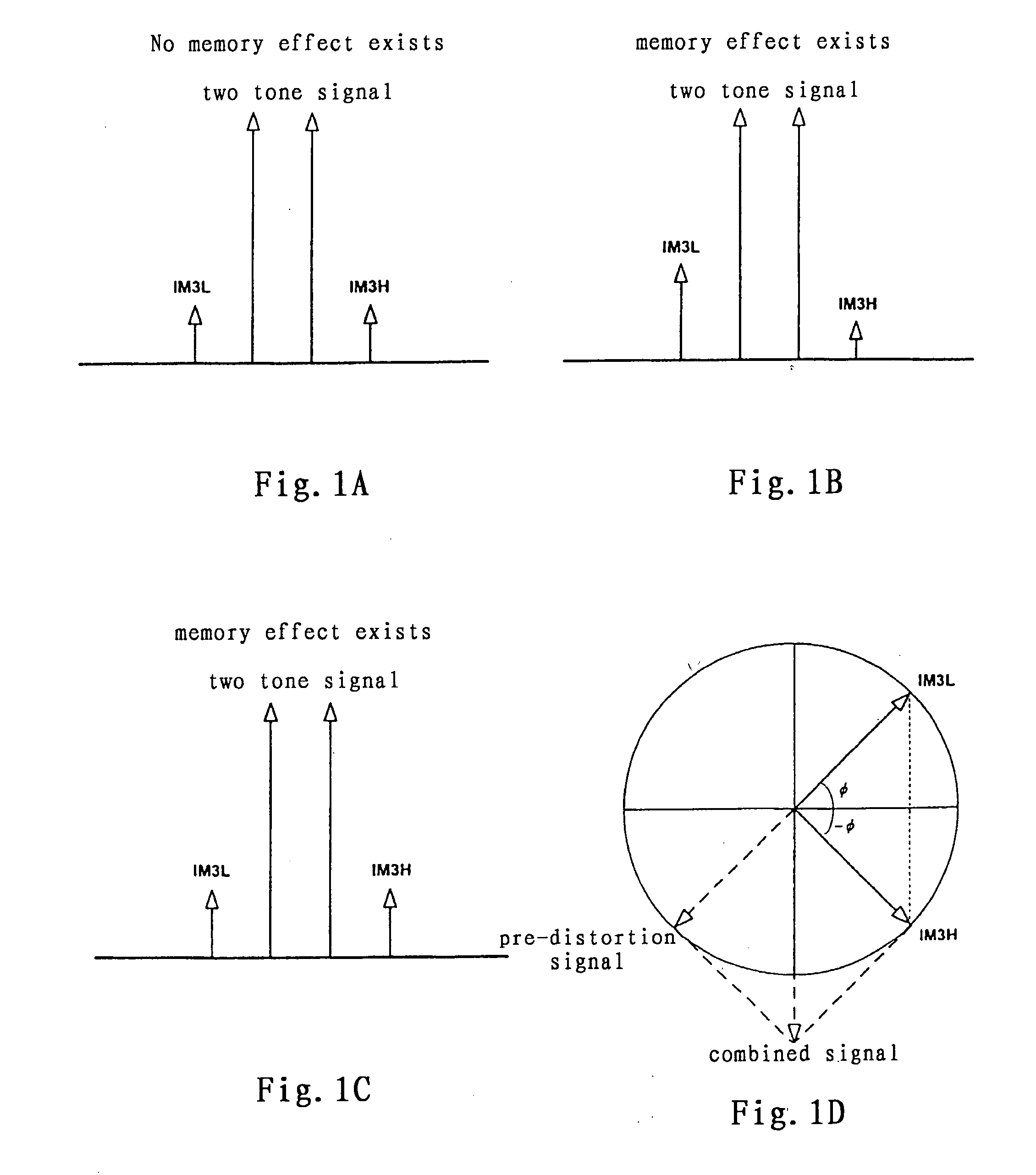
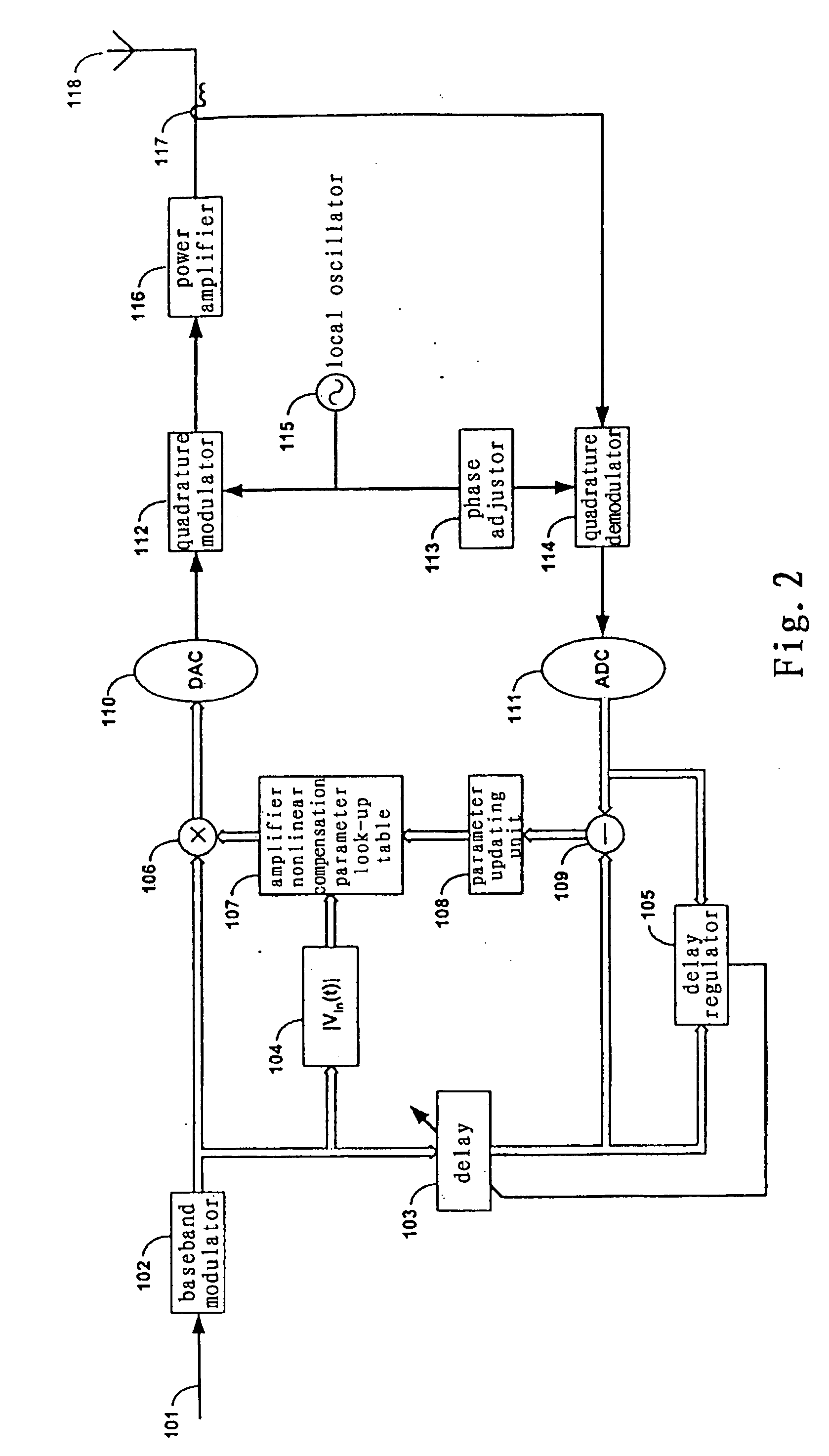
Method and system for broadband predistortion linearization
InactiveUS20060240786A1Improve linearization performanceExtends linearization bandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationTime domainRadio frequency
The invention relates to a method and system for wideband digital pre-distortion linearization, which is used to overcome the influence of memory effect in radio frequency power amplifier, to expand digital pre-distortion linearization bandwidth, and to improve digital pre-distortion linearization performance. The method and system can get an in-band pre-distortion signal and an out-of-band pre-distortion signal according to the characteristic parameter of the amplifier; the in-band pre-distortion signal is up-converted and the up-converted signal is added to the out-of-band pre-distortion signal, which is not up-converted, then the combined signal is inputted to the power amplifier as an input signal; a part of the output signal from the power amplifier, serving as a feedback signal, can be compared with the original input signal, and the characteristic parameter of the amplifier for generating the in-band pre-distortion signal and the out-of-band pre-distortion signal is adaptively regulated according to the comparison result, so that the waveform of time domain or the frequency domain of the feedback signal can be close to that of the original input signal as much as possible.
Owner:ZTE CORP
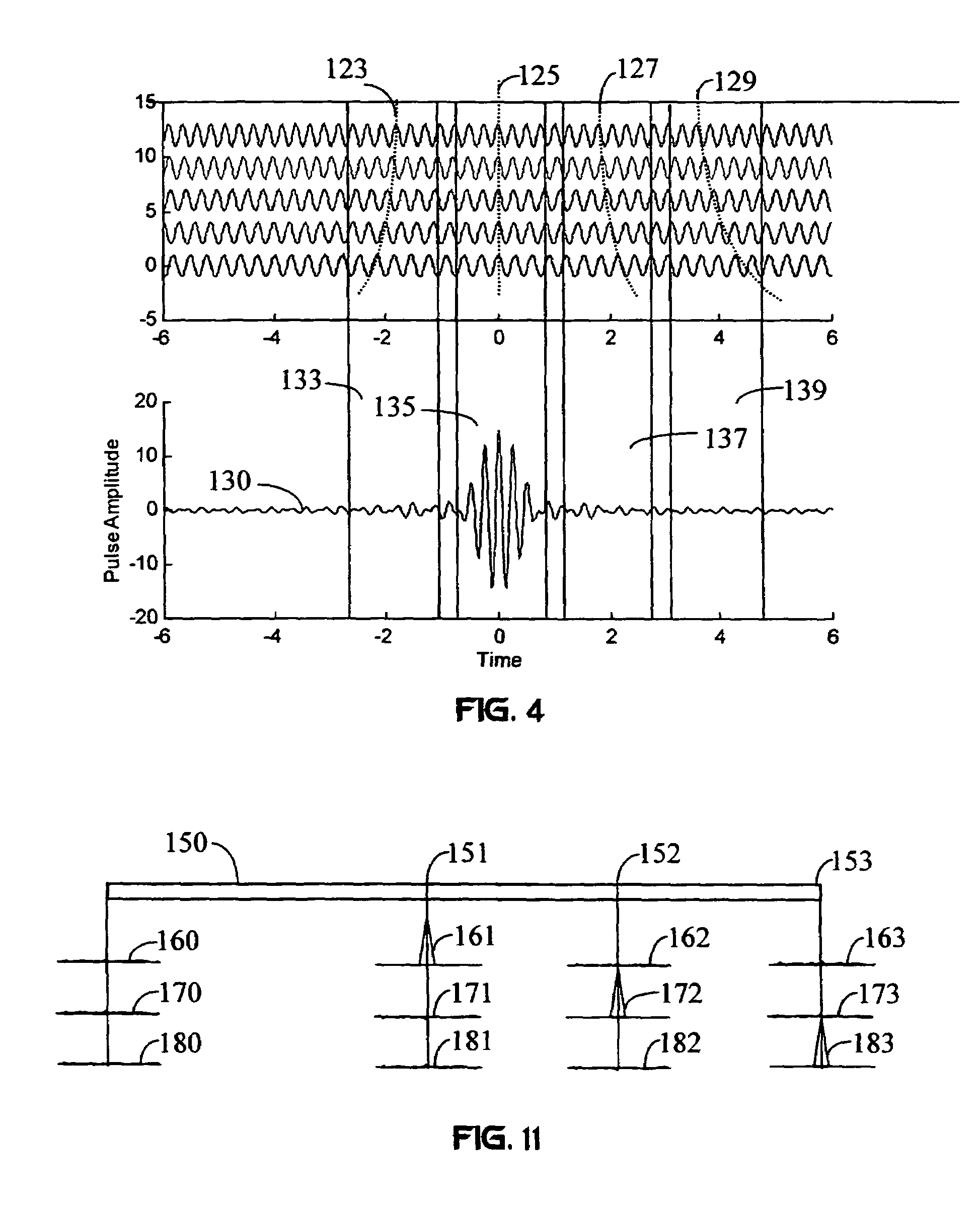
Time domain symbols
ActiveUS8848808B2Modulated-carrier systemsDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationTime domainElectrical and Electronics engineering
Methods and apparatus are described for time domain signals. A method includes creating a bipolar pulse whose high (up) and low (down) periods are separately and precisely controllable.
Owner:LIGHTFLEET CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com