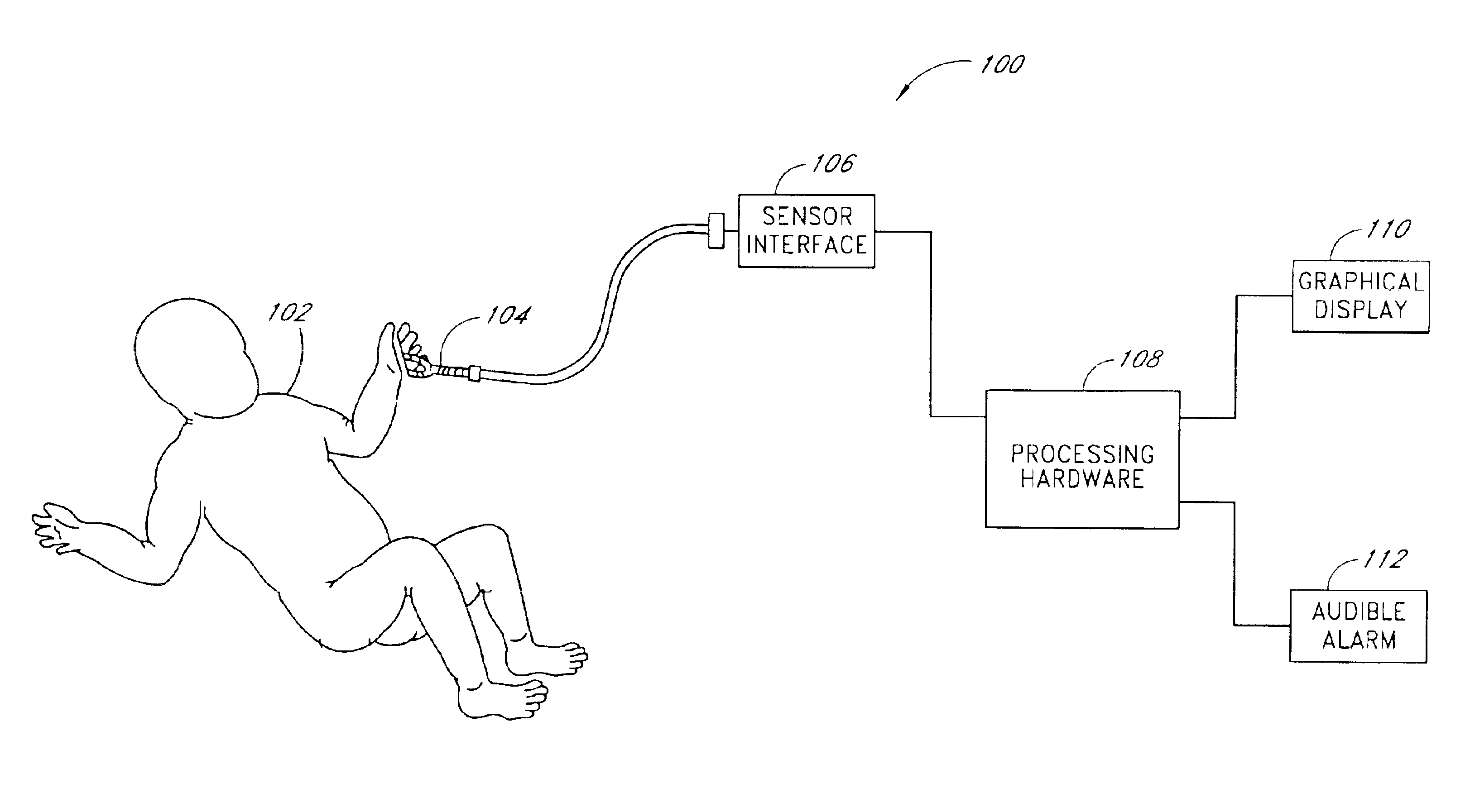
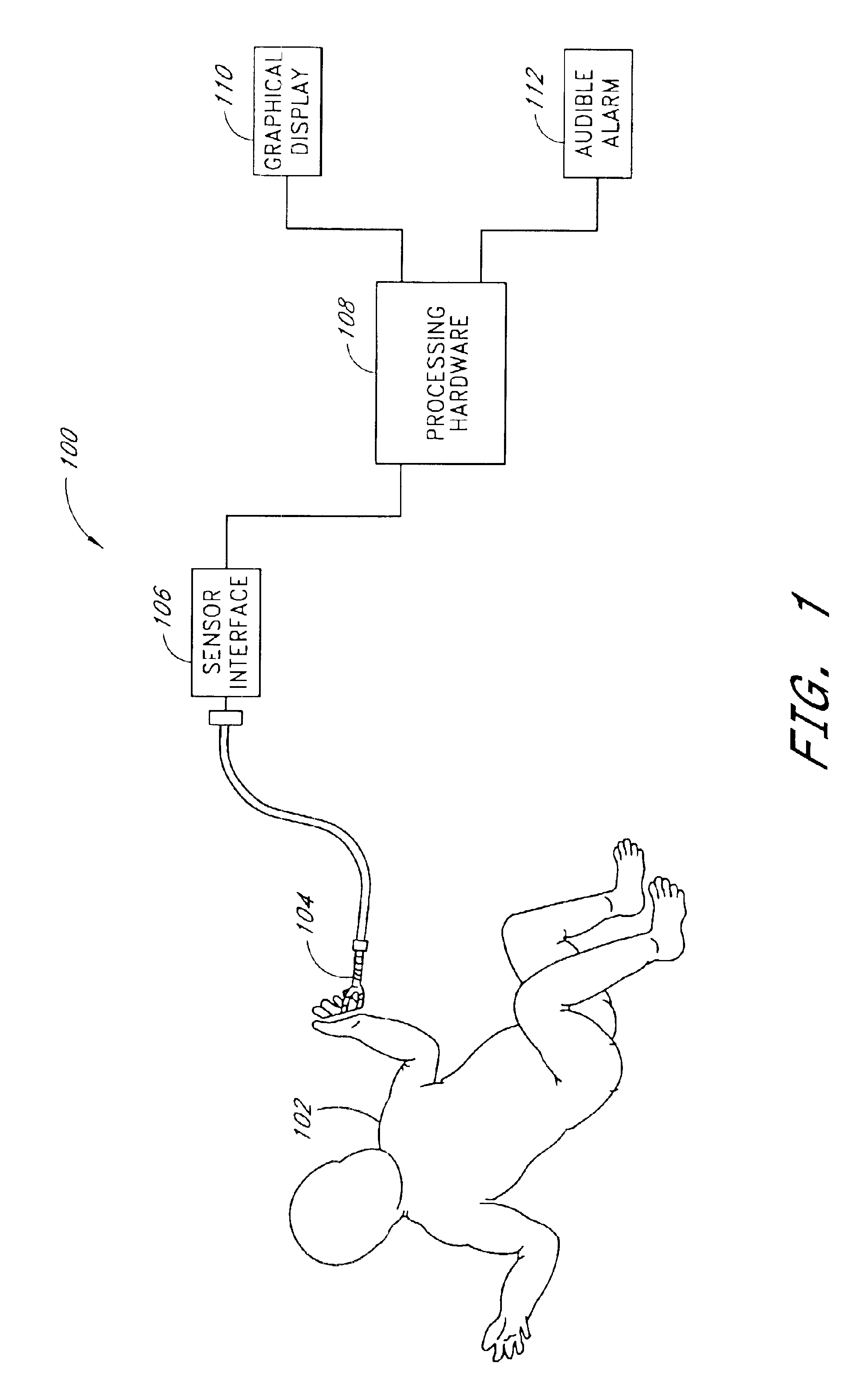
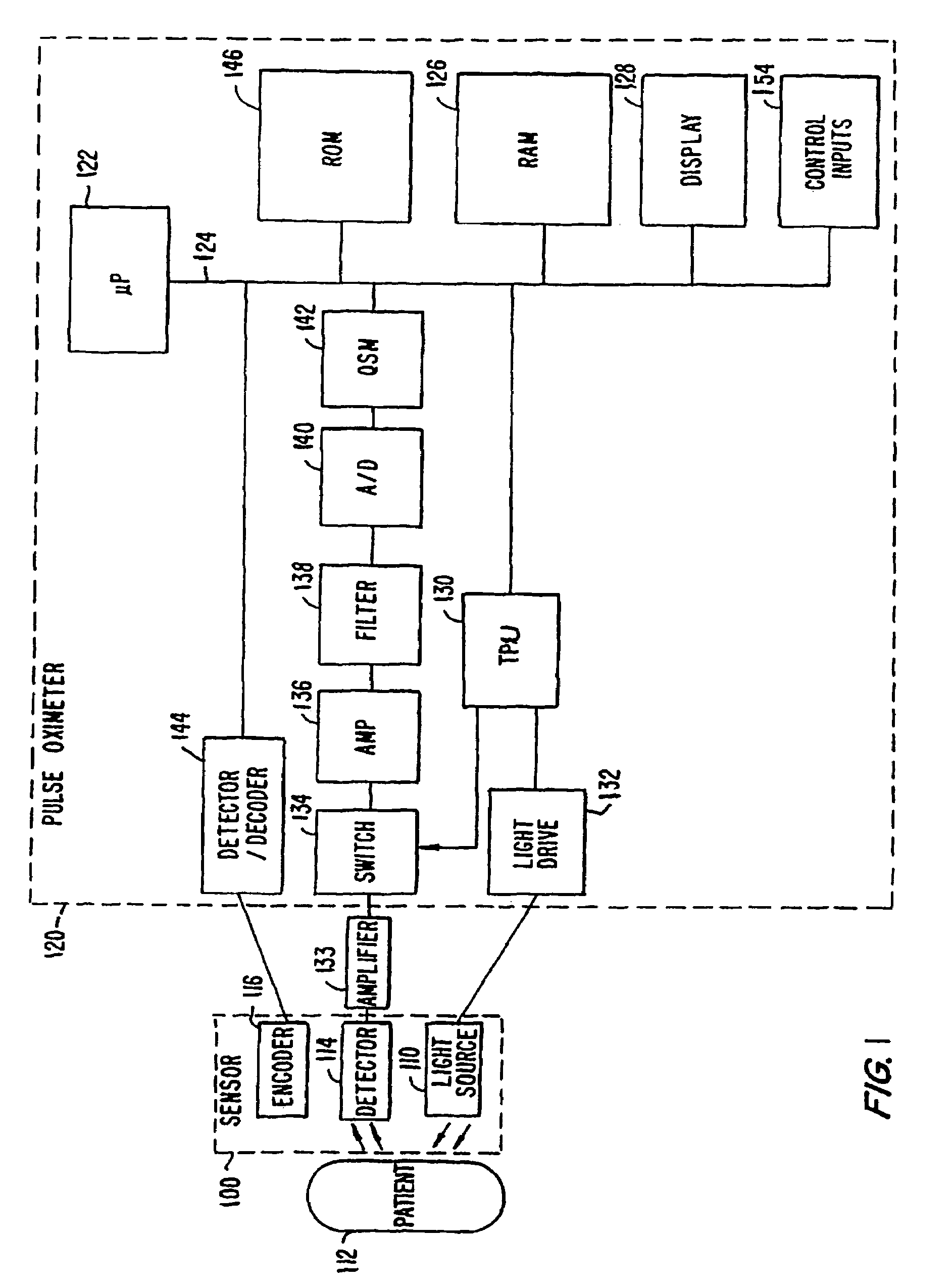
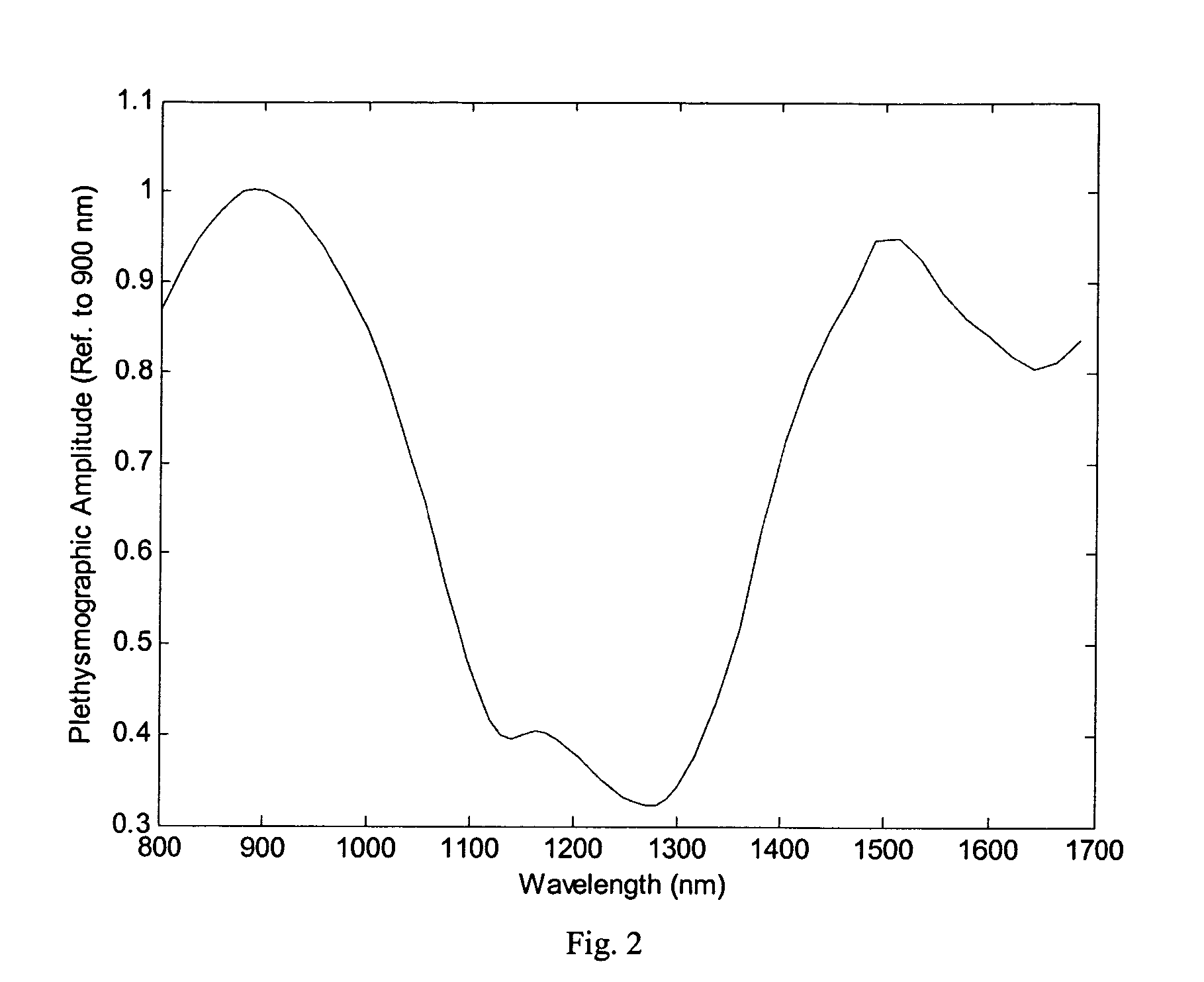
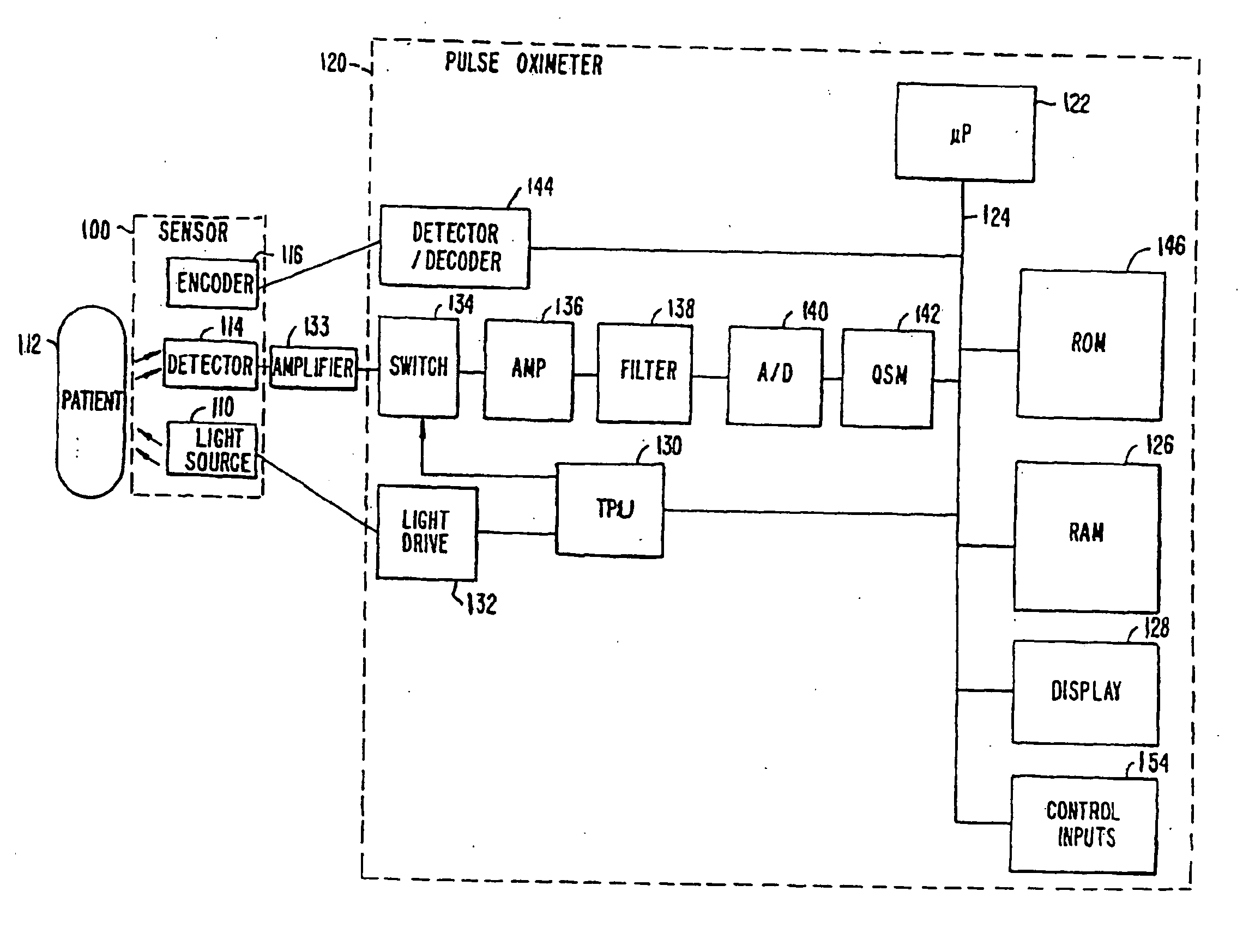
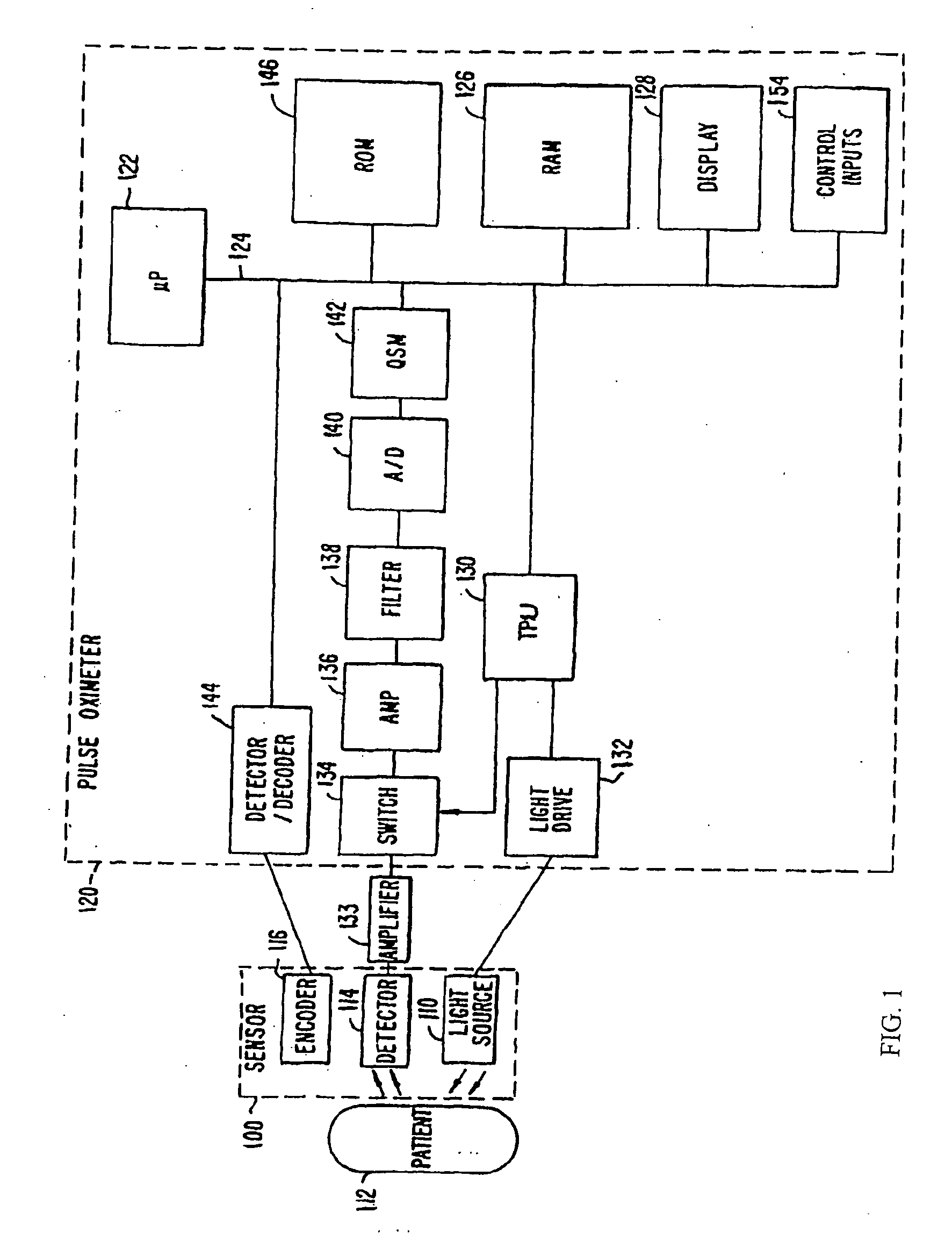
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Plethysmograph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A plethysmograph is an instrument for measuring changes in volume within an organ or whole body (usually resulting from fluctuations in the amount of blood or air it contains). The word is derived from the Greek "plethysmos" (increasing, enlarging, becoming full), and "graphos" (to write).
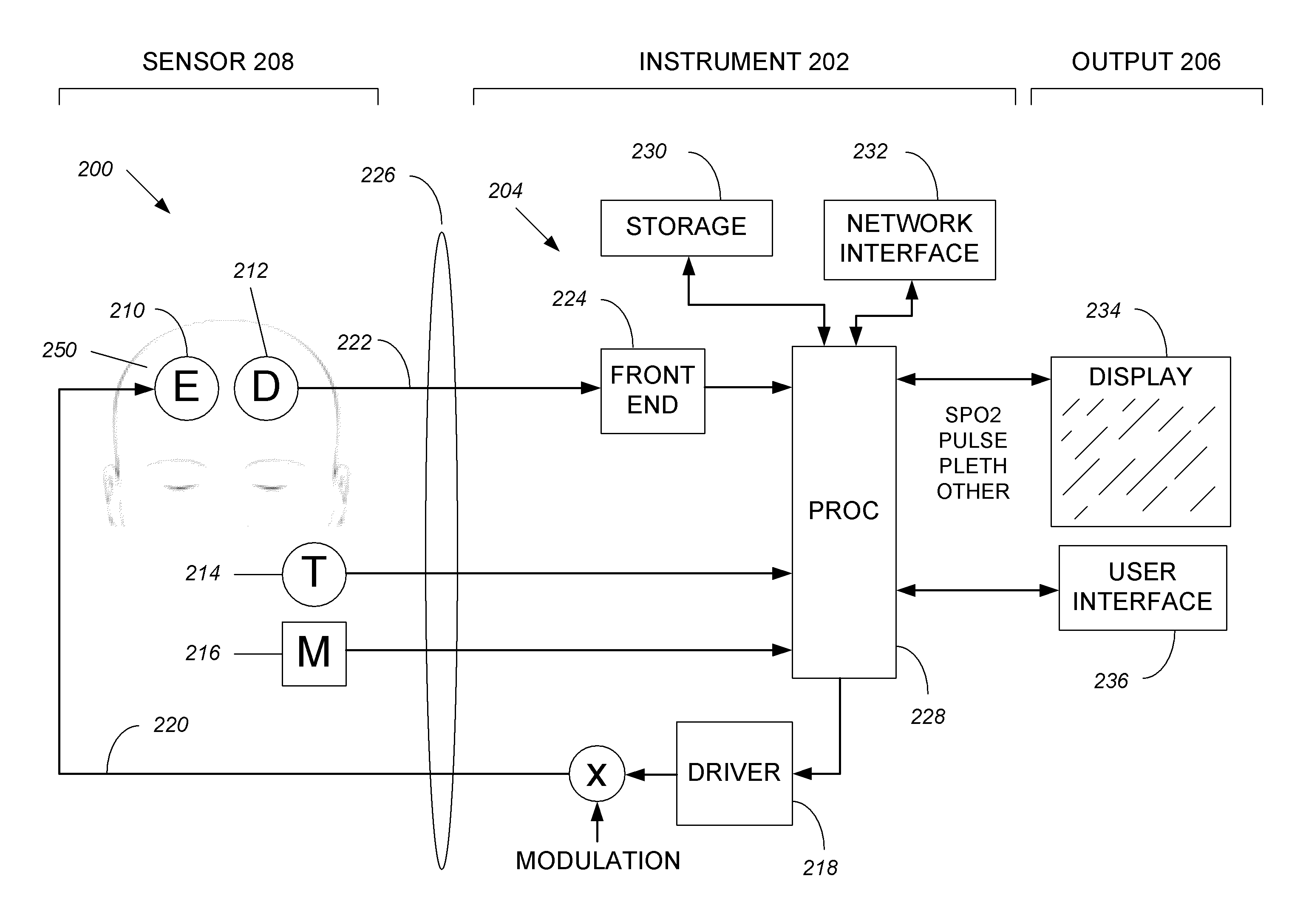
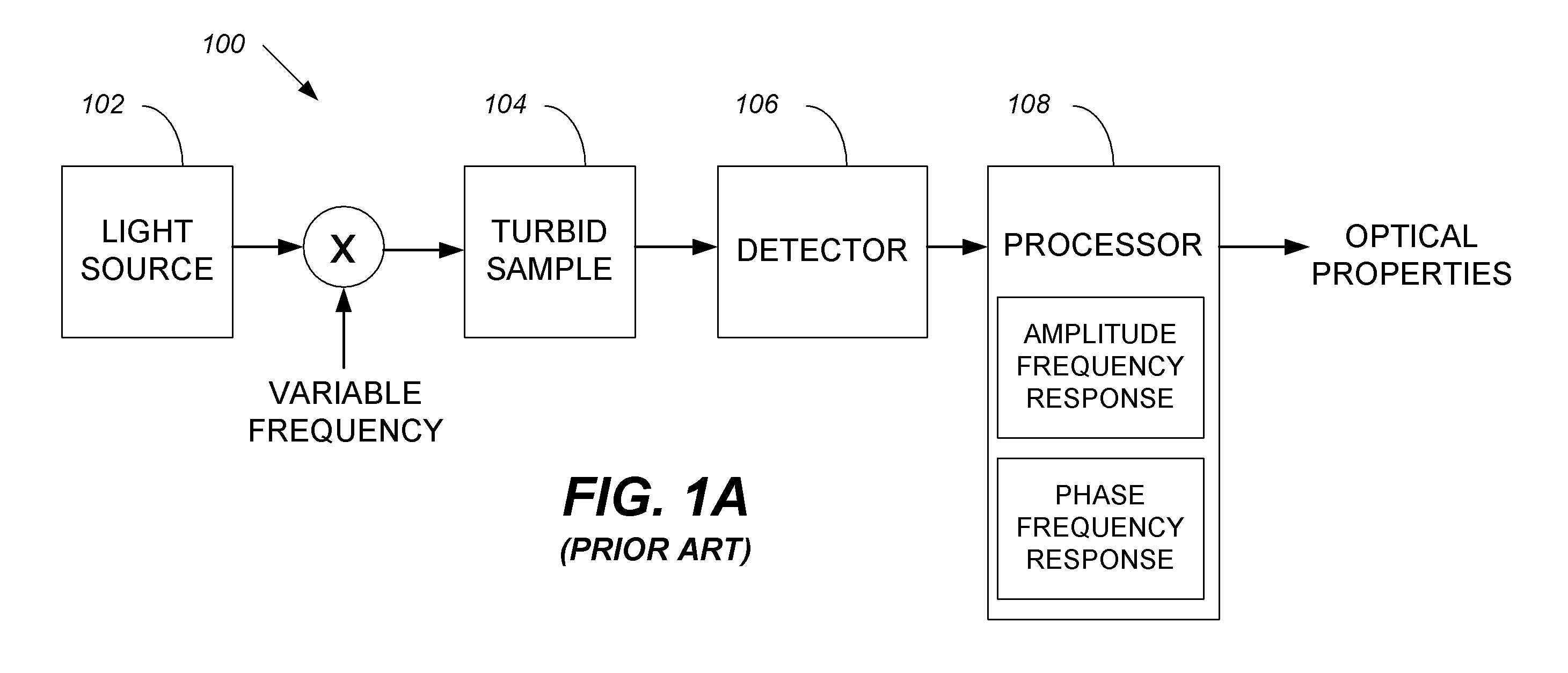
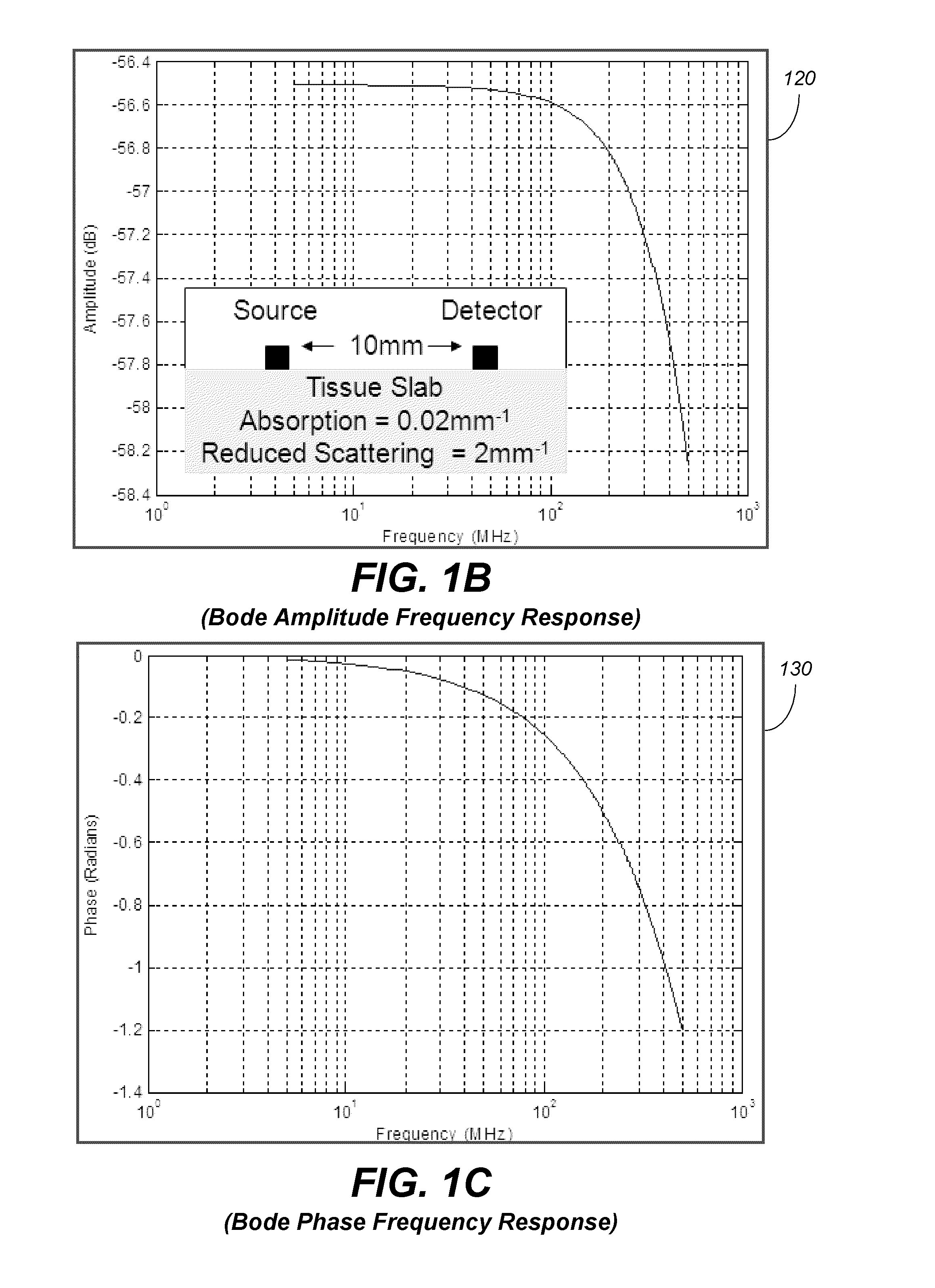
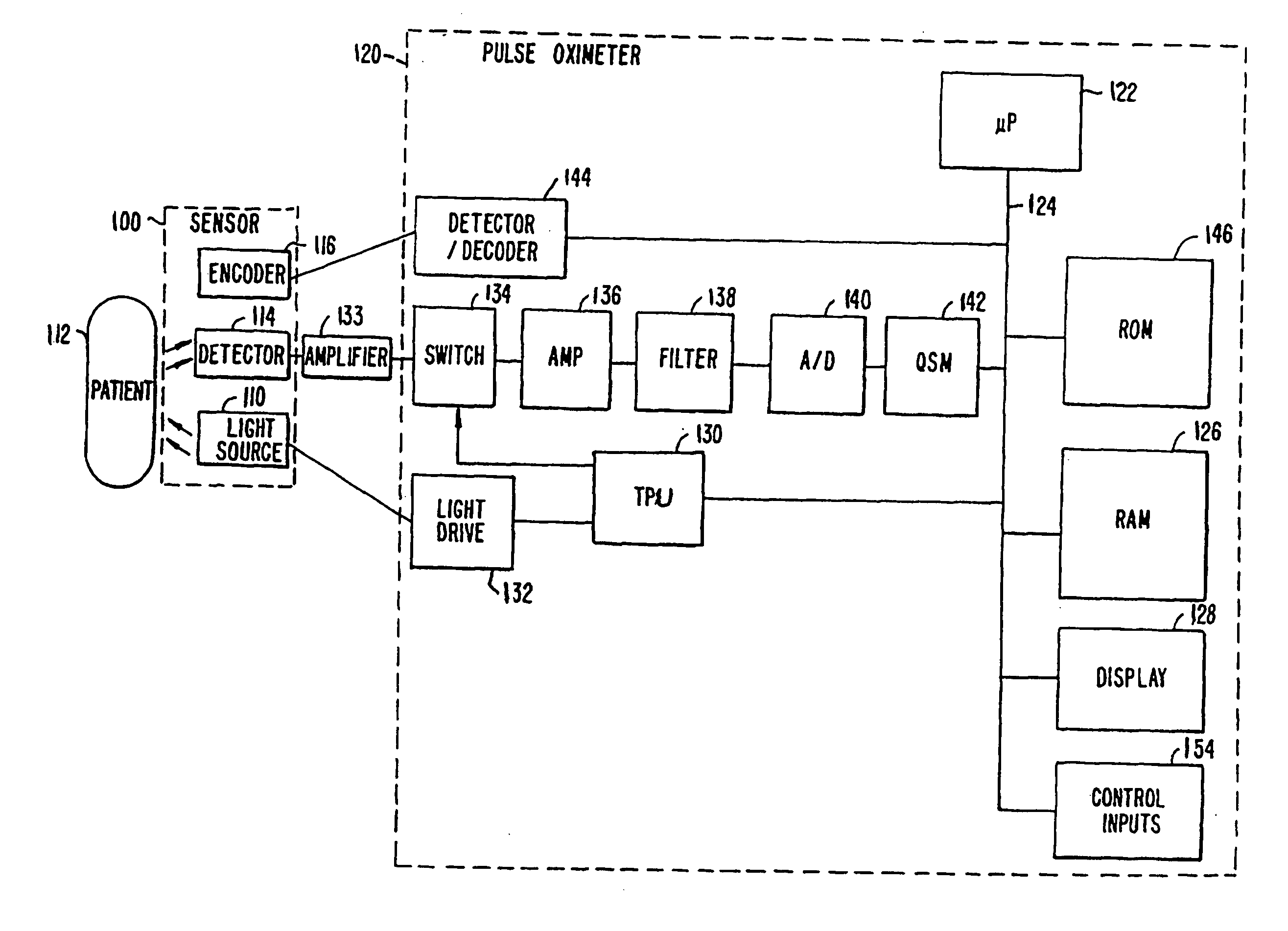
Systems and methods of monitoring a patient through frequency-domain photo migration spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120165629A1Reduce signalingReduce dependenceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSpectroscopyClinical tests
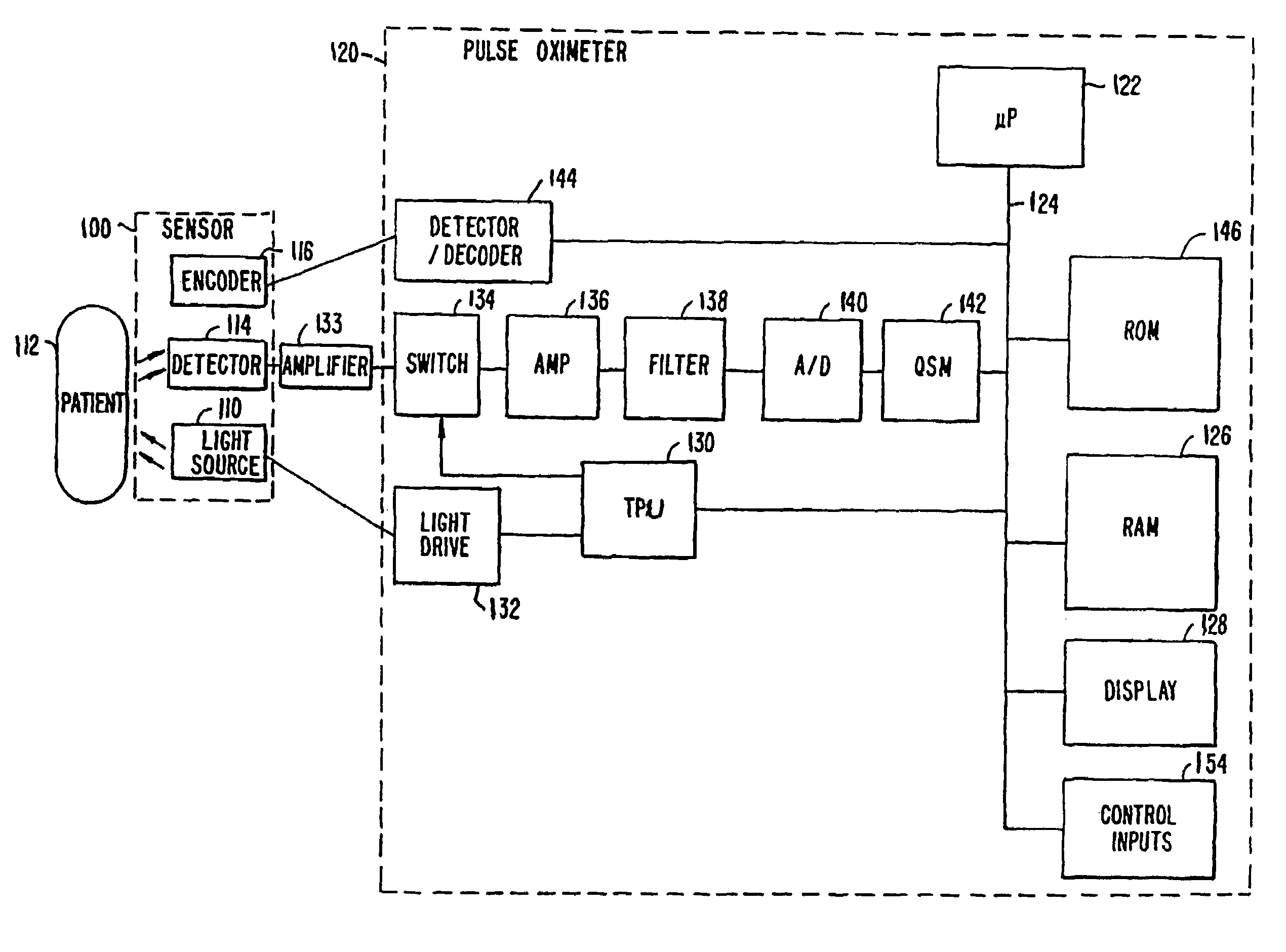
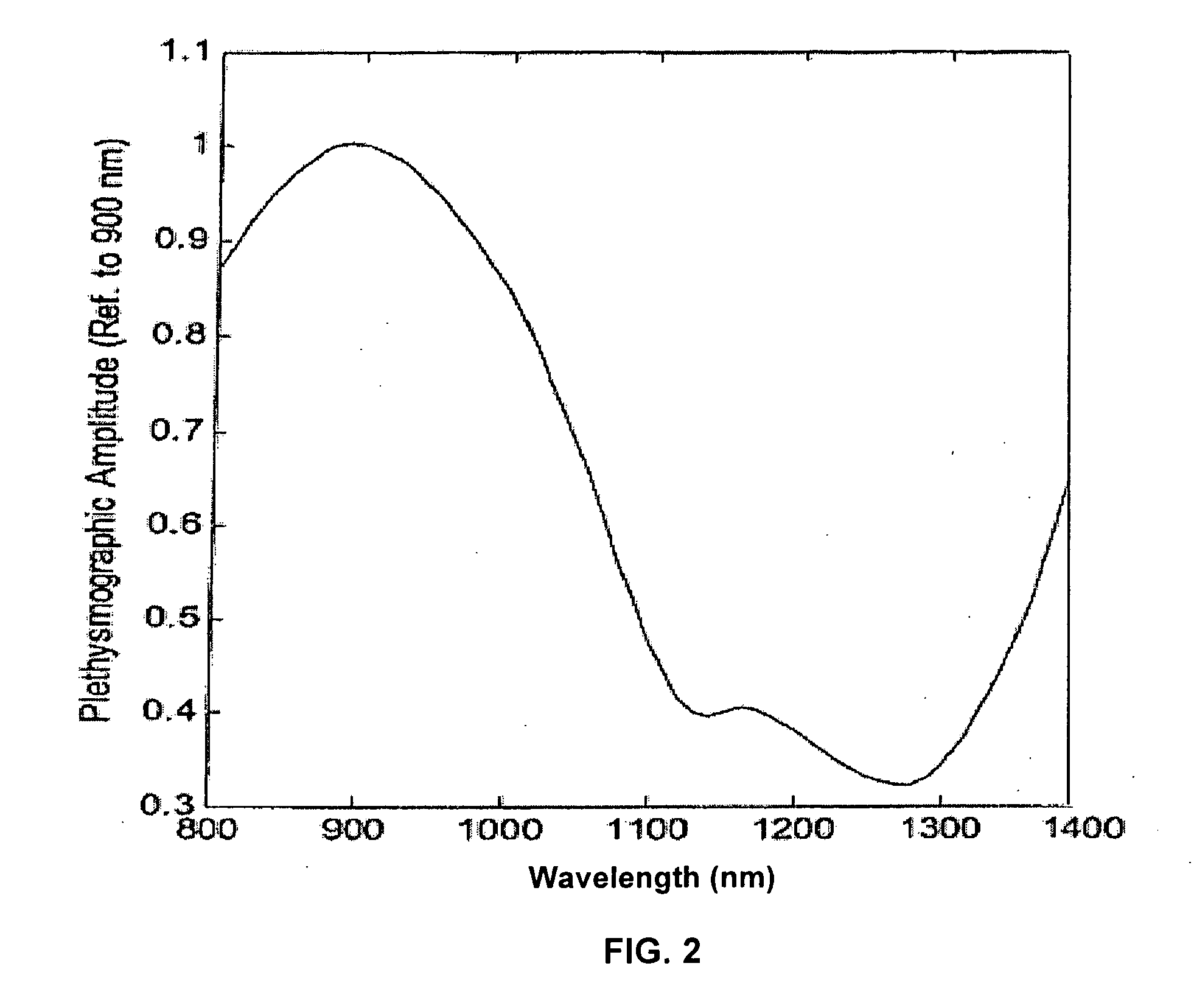
FDPM processing provides an amplitude signal and a phase signal at a modulation frequency to improve measurement fidelity during measurement of one or more blood parameters. In an embodiment, a light source modulates light at a modulation frequency around 200 MHz to produce an amplitude and phase plethysmograph, usable to access clinical test data.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Pulse oximetry motion artifact rejection using near infrared absorption by water
ActiveUS20050203357A1Signals is relatively smallSeparating signalCatheterSensorsNear infrared absorptionPulse oximetry
A method and an apparatus for measuring a physiological parameter, functioning based on obtaining a first signal derived from electromagnetic energy transmitted through a tissue portion at a first wavelength, the first signal including a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events and a signal portion corresponding with arterial pulsation events, where at the first wavelength water is a dominant absorber of electromagnetic energy in the tissue portion; obtaining a second signal derived from electromagnetic energy transmitted through a tissue portion at a second wavelength, the second signal including a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events and a signal portion corresponding with arterial pulsation events, where at the second wavelength hemoglobin is a dominant absorber of electromagnetic energy in the tissue portion; and combining the first signal and the second signal to generate a combined plethysmograph signal, such that the combined signal has a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events that is smaller than that present in the first signal or the second signal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
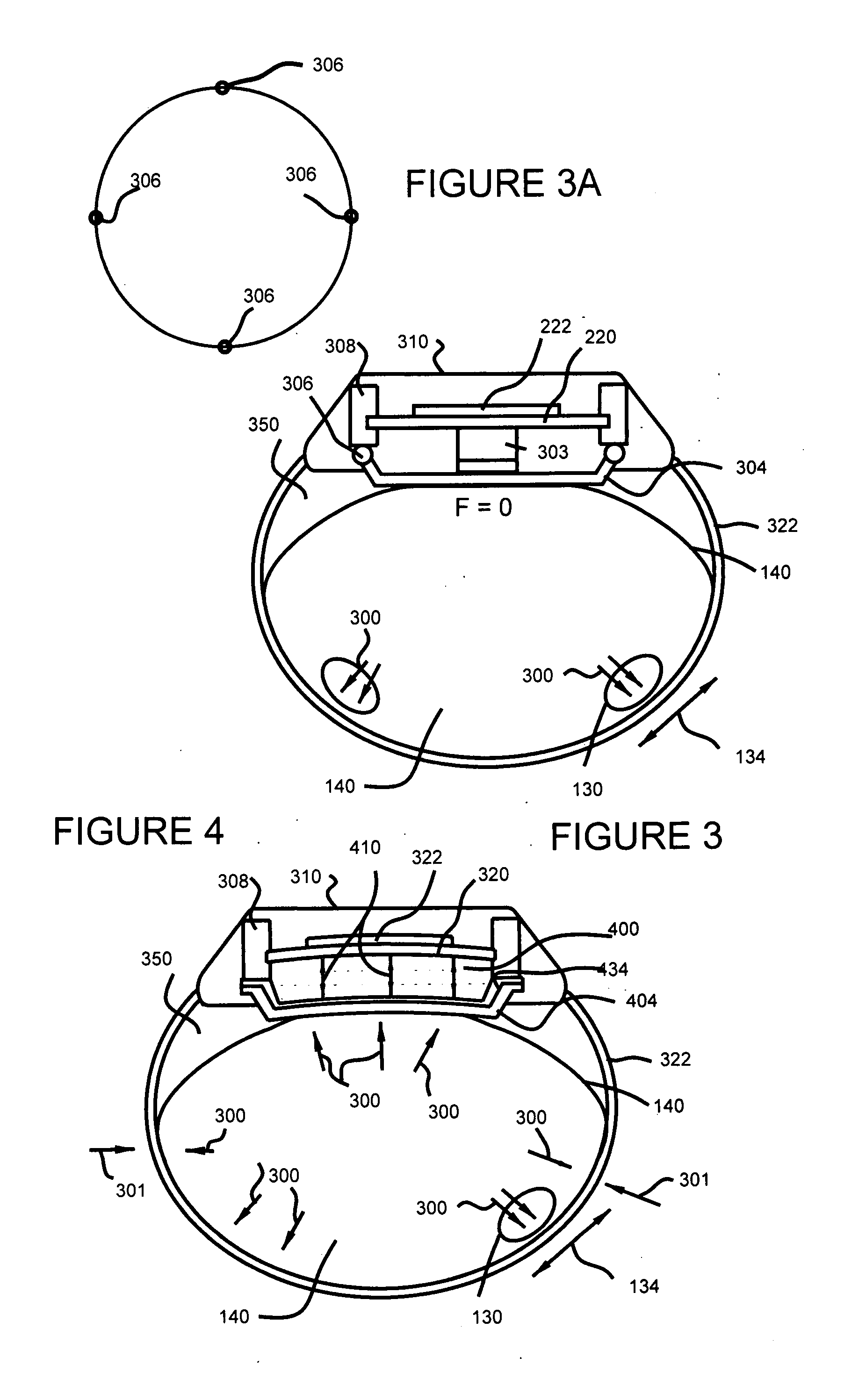
Wrist plethysmograph
A pulse monitoring plethysmograph system for establishing a history of the pulses of the user over an extended period of time, comprises a housing, a piezoelectric sensing element mounted within said housing, and fixed to the housing, a force transmitting member positioned to cause said piezoelectric sensing element to flex in response to an external force and to generate a current, and a transimpedance amplifier. The transimpedance amplifier converts the current generated by the flexing of the piezoelectric element into a voltage signal and an analog to digital converter converts the voltage signal into digital data. A digital memory storing member is provided for storing the digital data and establishing a history of data over an extended period of time.
Owner:ADKINS CHARLES +2
Method and apparatus for measuring pulsus paradoxus
InactiveUS6869402B2Accurate measurementReliable measurementCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainPulsus paradoxus
A method and apparatus are disclosed of utilizing a source of arterial and / or arteriolar pulse waveform data from a patient for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus. The arterial pulse waveform data source described is a pulse oximeter plethysmograph but can be any similar waveform data source, including intra-arterial transducer, blood pressure transducer, or plethysmograph. Through incorporation of the measurements of values, such as the area under the pulse waveform curve, that are time-domain functions of a change in height of the pulse waveform over at least a partial duration of the waveform, embodiments of the present invention represent a significant improvement upon previously described methods of measuring pulsus paradoxus and, further, produce improved accuracy in measurement of the multiple contributing variables generating pulsus paradoxus, in particular the contribution of diastolic events, to the extent that the physical signs so measured can be regarded as “Revised Pulsus Paradoxus.”
Owner:PRECISION PULSUS
System for measuring respiratory function
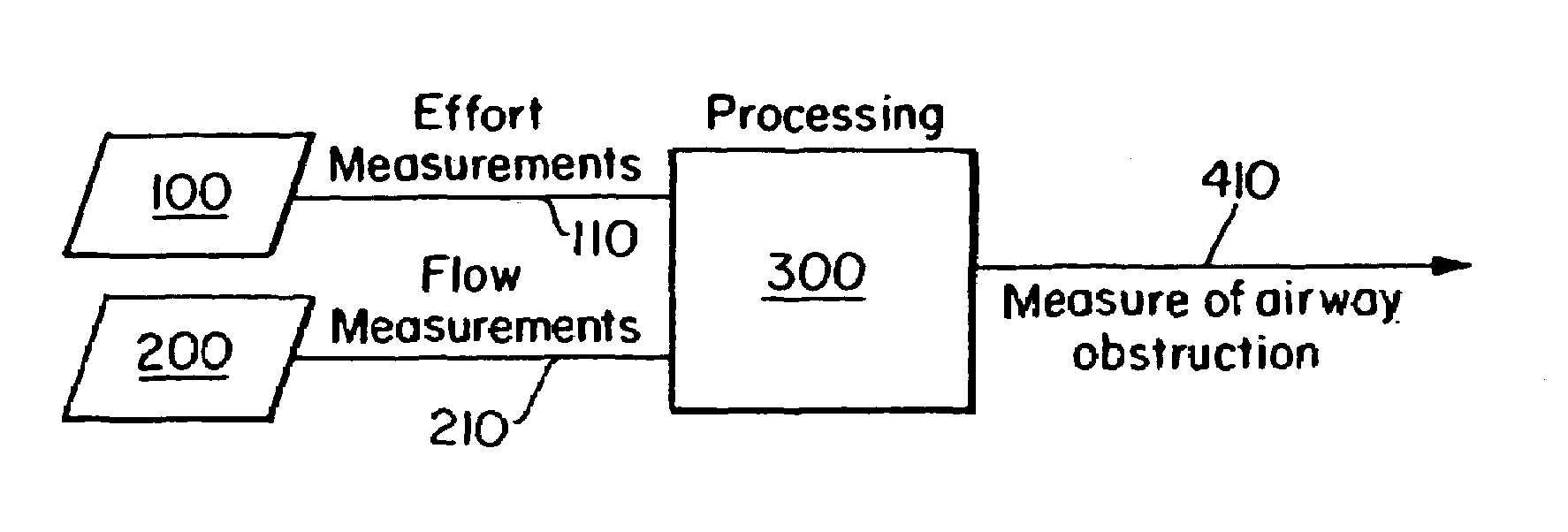
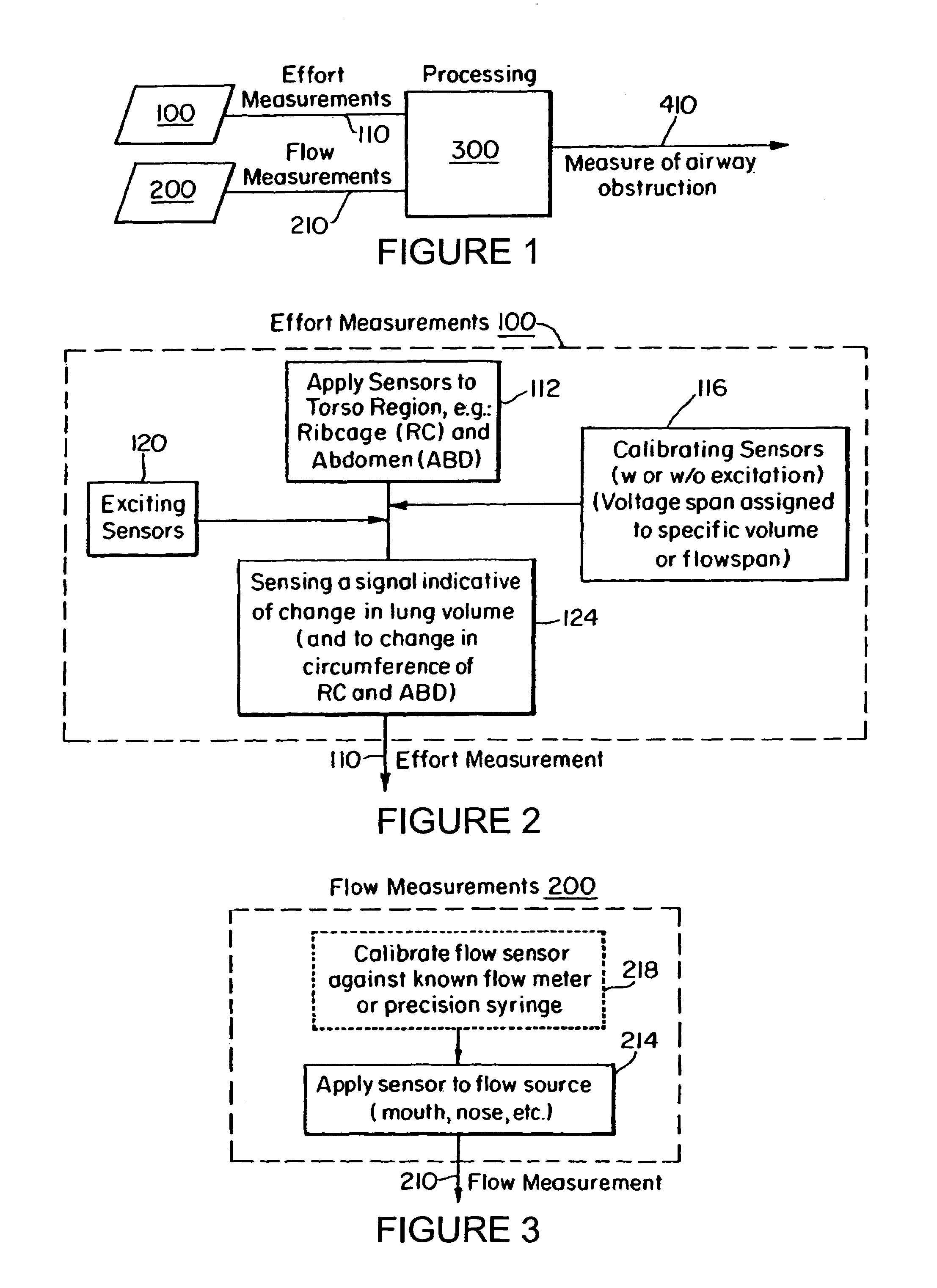
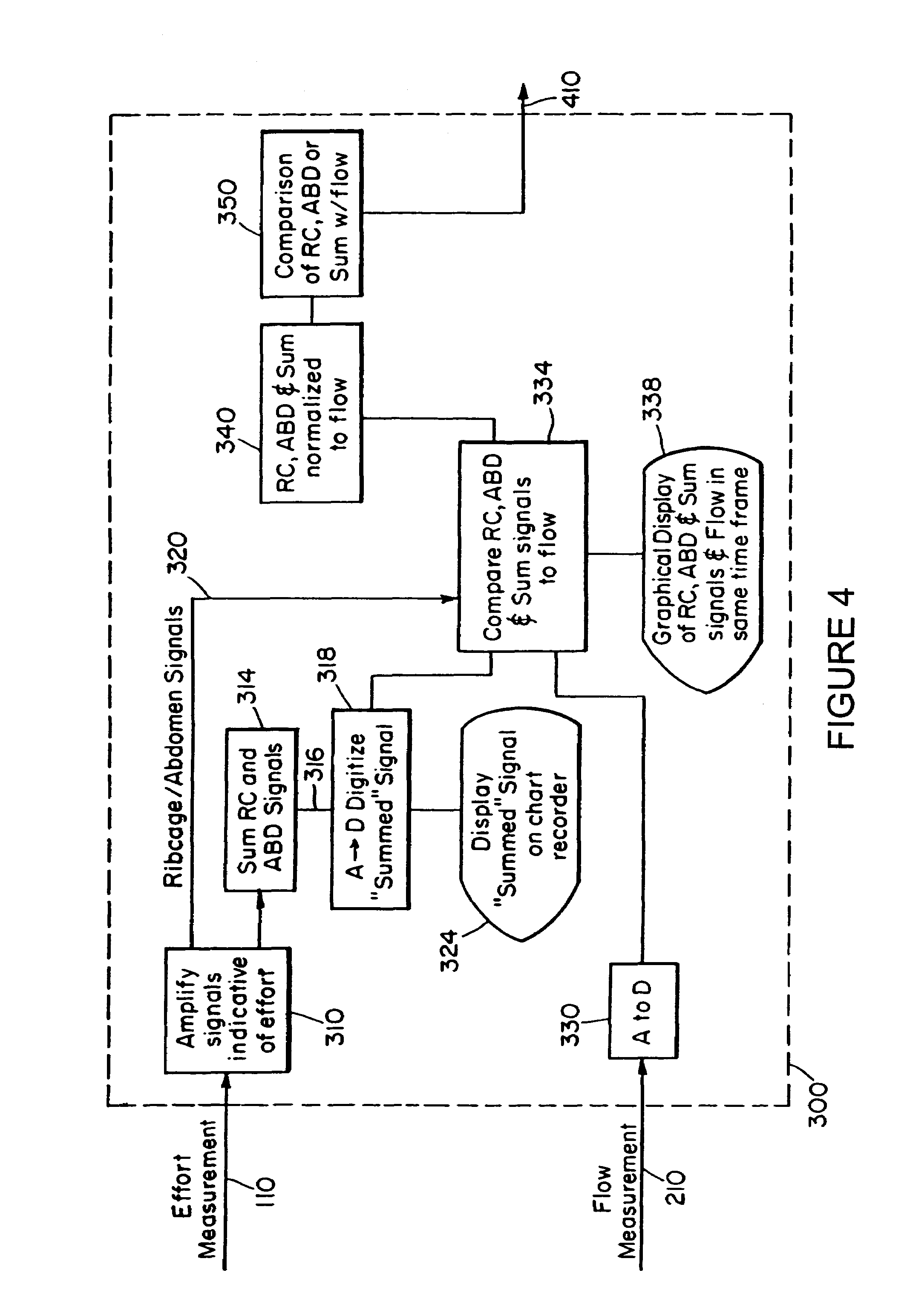
InactiveUS7094206B2Easy to carryEasy to transportMedical automated diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationBiological bodyAirway responsiveness
The present invention relates to a system for measuring respiratory function of living organisms. More particularly, signals indicative of the change in lung volume, defined as active and passive work, required to breathe and the airflow through the respiratory system of the living organism are obtained and processed as waveforms to provide a signal indicative of the respiratory restriction. The methods of the present invention measure clinical forms of airway obstruction, airway reactivity and lung volume and may be used to continuously or intermittently monitor patients with compromised respiratory function. In a preferred embodiment, a head-out, breath in respiratory plethysmograph system provides the signals indicative of change in lung volume as related to pressure changes in a chamber. Further, flowmetric variables are generated that provide a characterization of airway obstructions.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
Pulse oximetry motion artifact rejection using near infrared absorption by water
A method and an apparatus for measuring a physiological parameter, functioning based on obtaining a first signal derived from electromagnetic energy transmitted through a tissue portion at a first wavelength, the first signal including a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events and a signal portion corresponding with arterial pulsation events, where at the first wavelength water is a dominant absorber of electromagnetic energy in the tissue portion; obtaining a second signal derived from electromagnetic energy transmitted through a tissue portion at a second wavelength, the second signal including a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events and a signal portion corresponding with arterial pulsation events, where at the second wavelength hemoglobin is a dominant absorber of electromagnetic energy in the tissue portion; and combining the first signal and the second signal to generate a combined plethysmograph signal, such that the combined signal has a signal portion corresponding with motion-related events that is smaller than that present in the first signal or the second signal.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Pulse oximetry signal correction using near infrared absorption by water
ActiveUS20070106137A1Minimize artifactSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateSignal correctionNear infrared absorption
A method and system for measuring a physiological parameter, comprising collecting a first absorbance at a first wavelength, chosen to be primarily absorbed by water; collecting a second absorbance at a second wavelength, chosen to be primarily absorbed by hemoglobin; and combining the first signal and the second signal to generate a combined plethysmograph signal which is proportionate lower in noise caused by motion-related interference.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methods and Devices for Central Photoplethysmographic Monitoring Methods
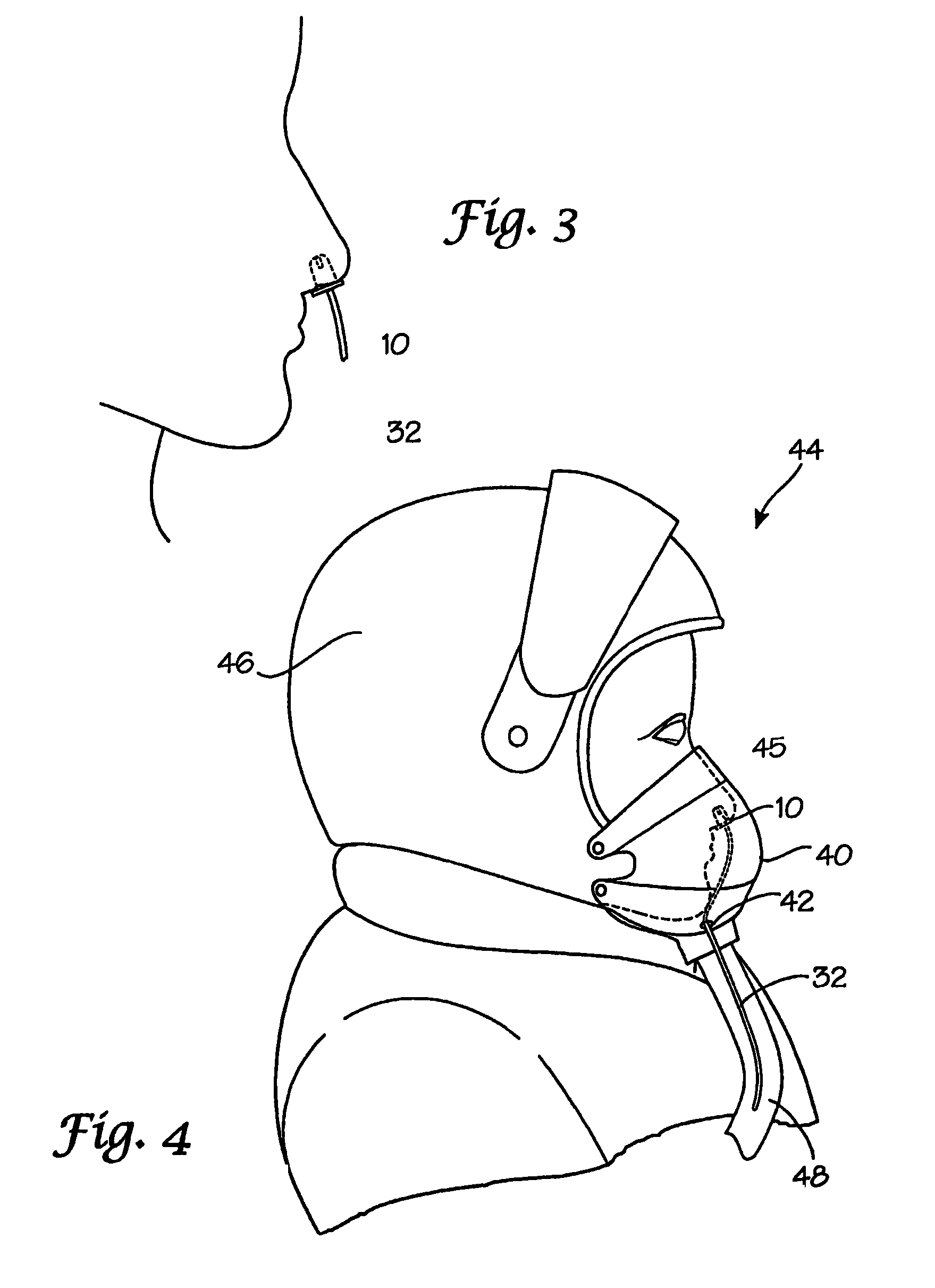
ActiveUS20100192952A1Decreasing cerebral blood flowHigh trafficOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksPulse oximetersEmergency medicine
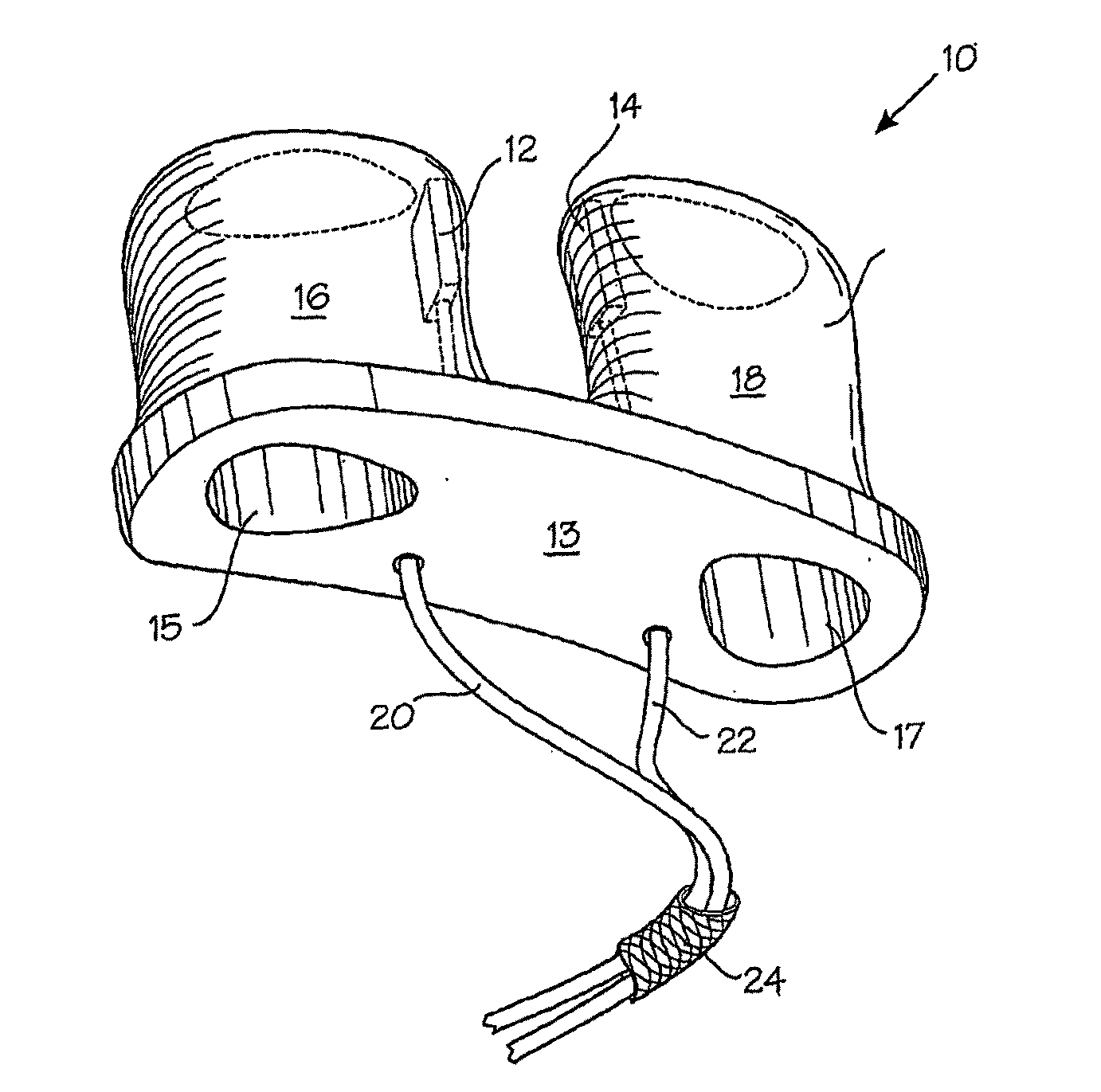
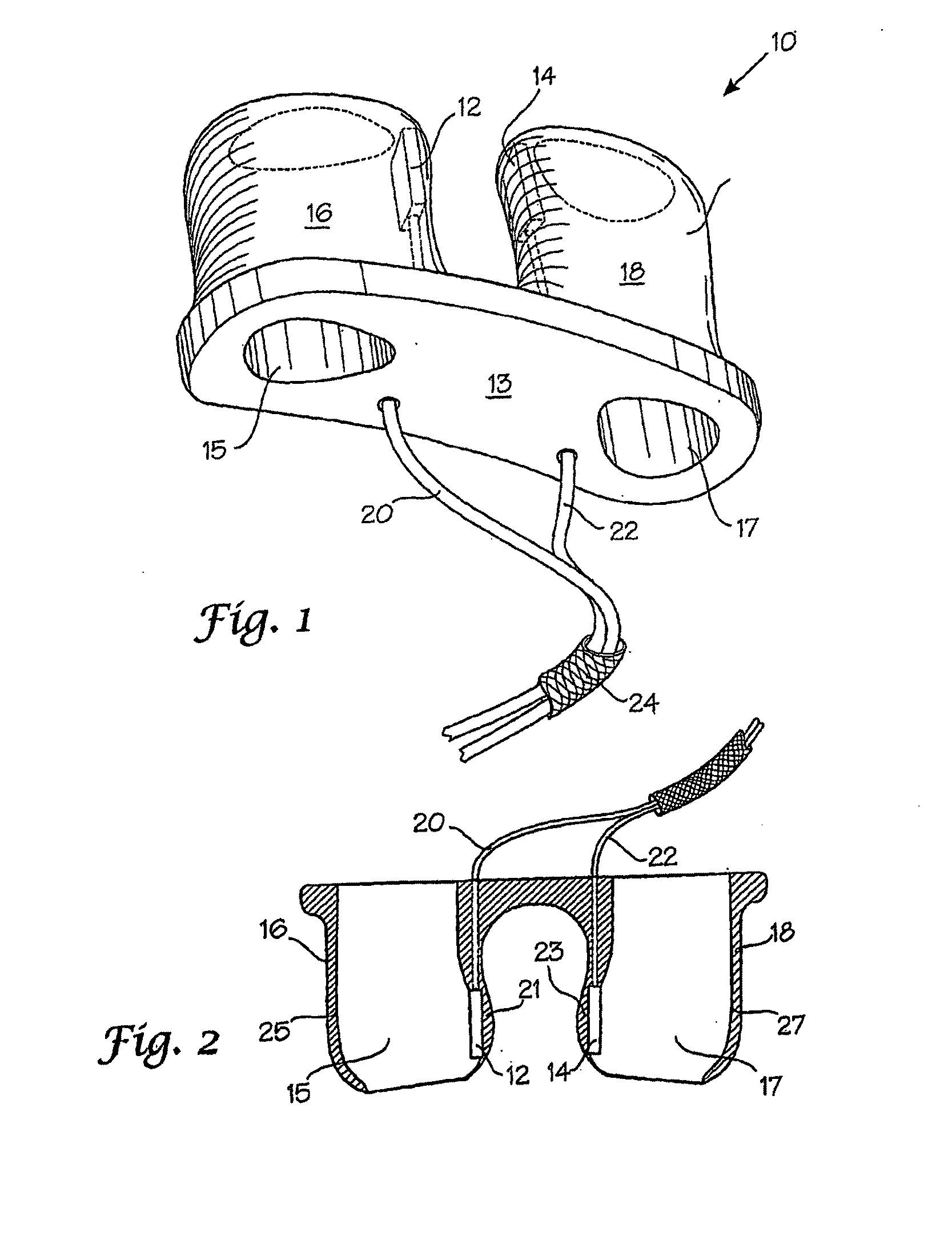
Disclosed herein are methods and devices for delivering gas to a subject and obtaining plethysmograph readings from a subject. Specifically disclosed herein are masks and helmets which comprise one or more pulse oximeter probes associated therewith. The masks and helmets may be used in particular contexts, including, but not limited to, emergency responder personnel, pilots or subjects of medical attention.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +2
Cough/sneeze analyzer and method
ActiveUS7104962B2Improve analysis accuracyImprove accuracyAuscultation instrumentsRespiratory organ evaluationAir compressionMedicine
A cough event is differentiated from a sneeze event of a test subject enclosed within a plethysmograph test chamber by measuring air pressure changes during the event, and comparing the pressure changes against criteria indicative of a cough to determine the likelihood that the event is a cough. Air pressure changes are recorded as pressure and / or sound values. A graphical record of a waveform of changes in the air pressure during an event relative to a baseline value is recorded, and a value is calculated that is indicative of the likelihood that the event is a cough based on the sizes of areas between the waveform and baseline during the event, said areas including a first area indicative of the change in air pressure during air inspiration, a second area indicative of the change in air pressure during air compression, and a third area indicative of the change in air pressure during expiration.
Owner:DATA SCI INT
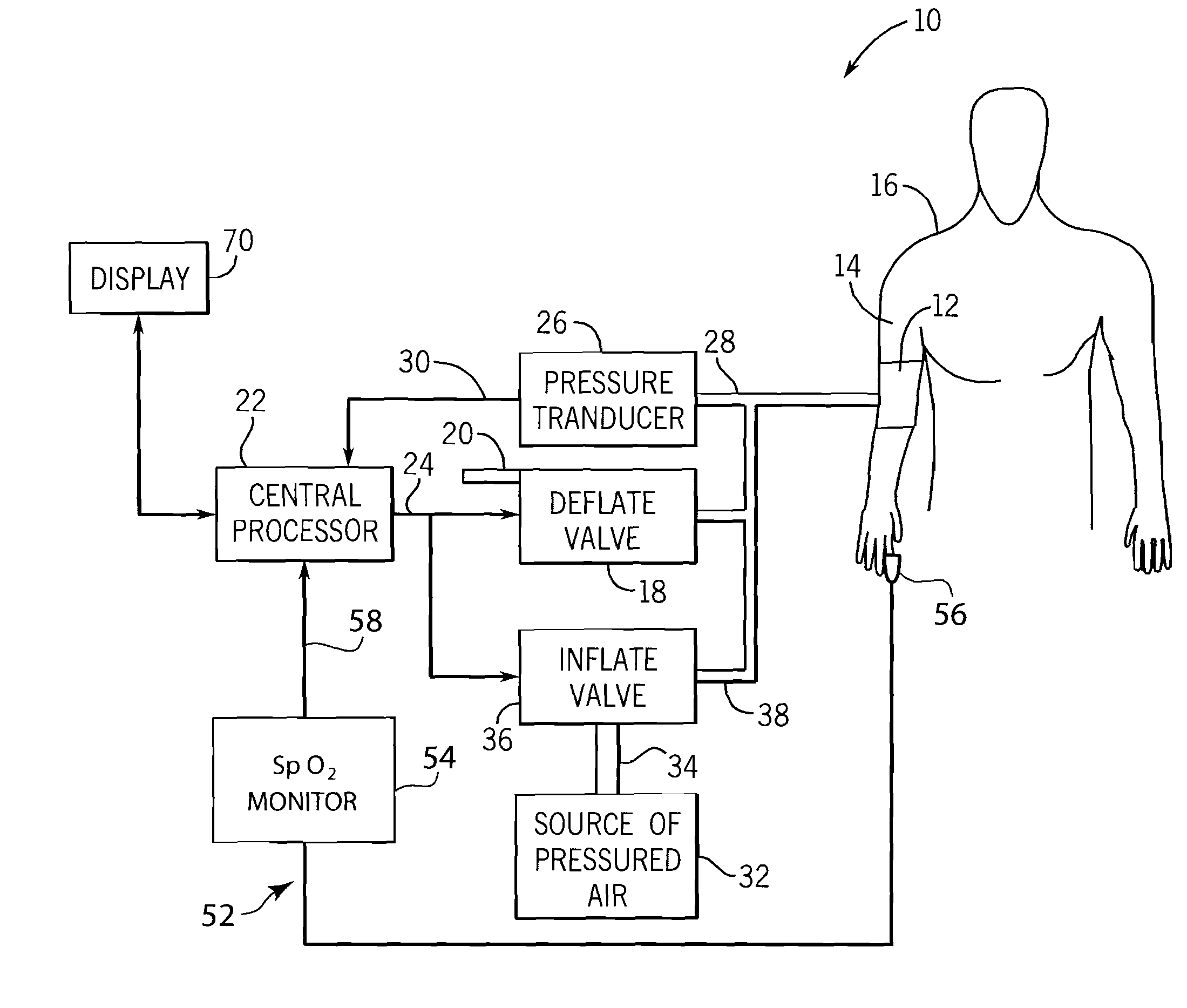
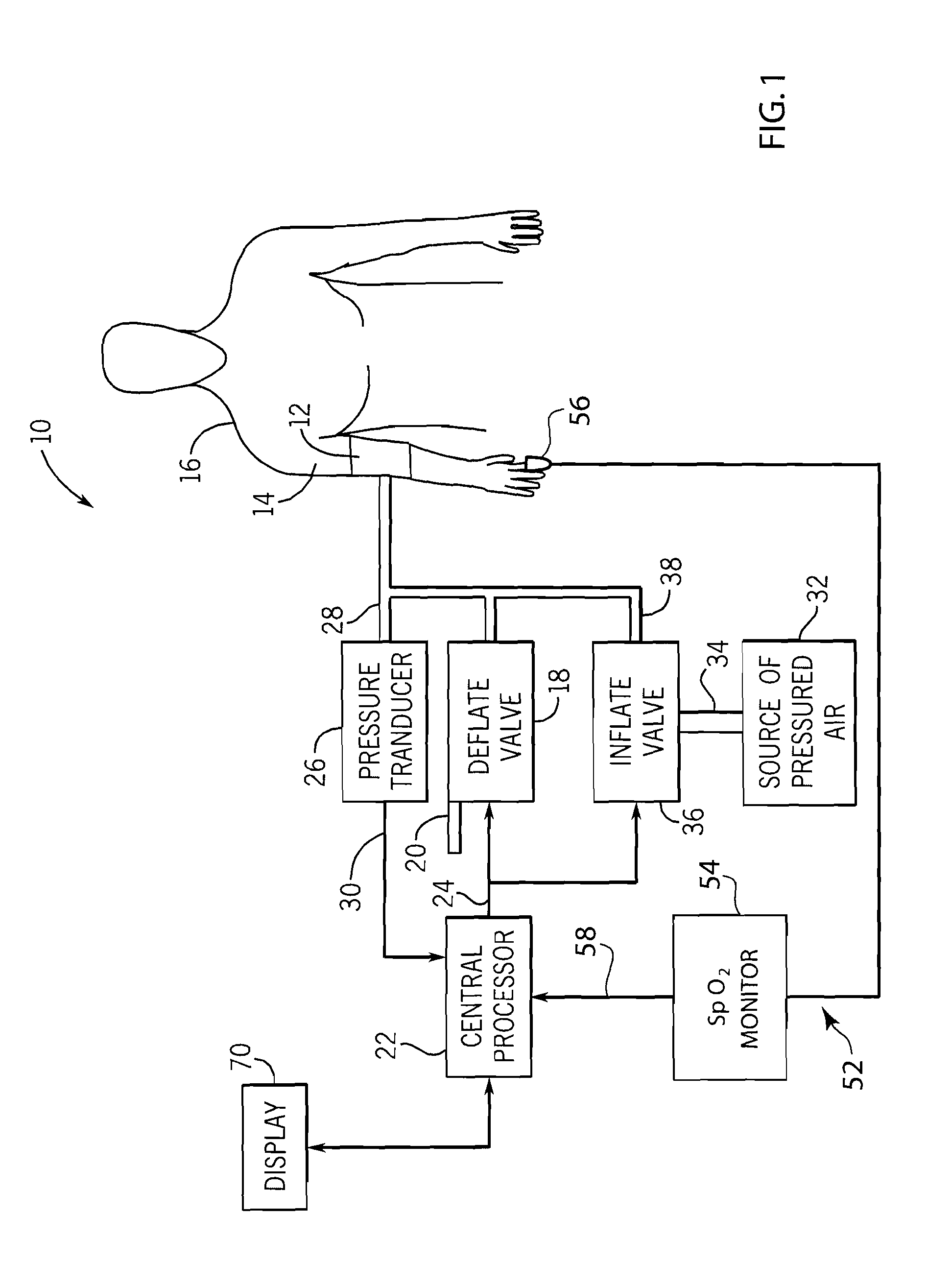
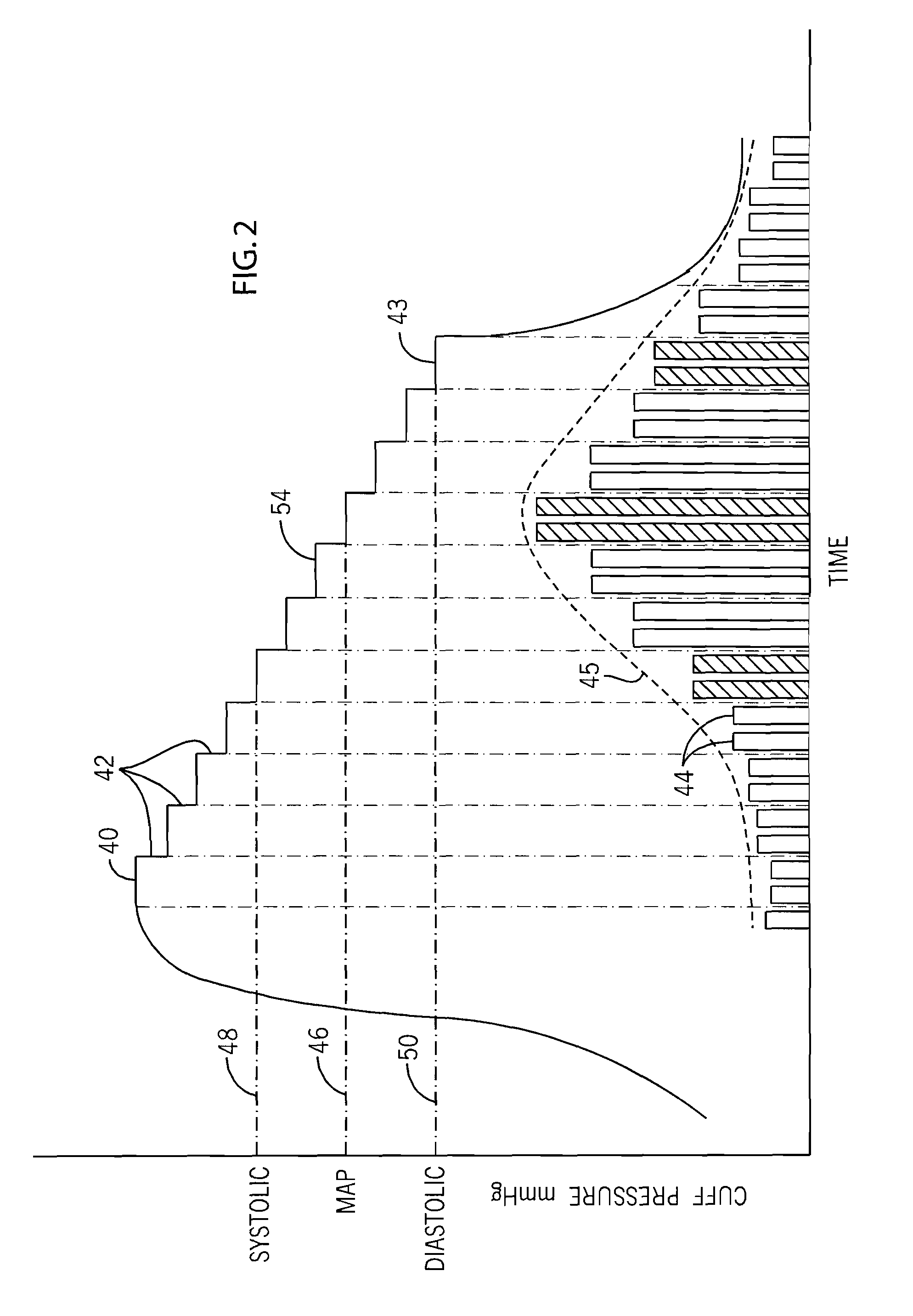
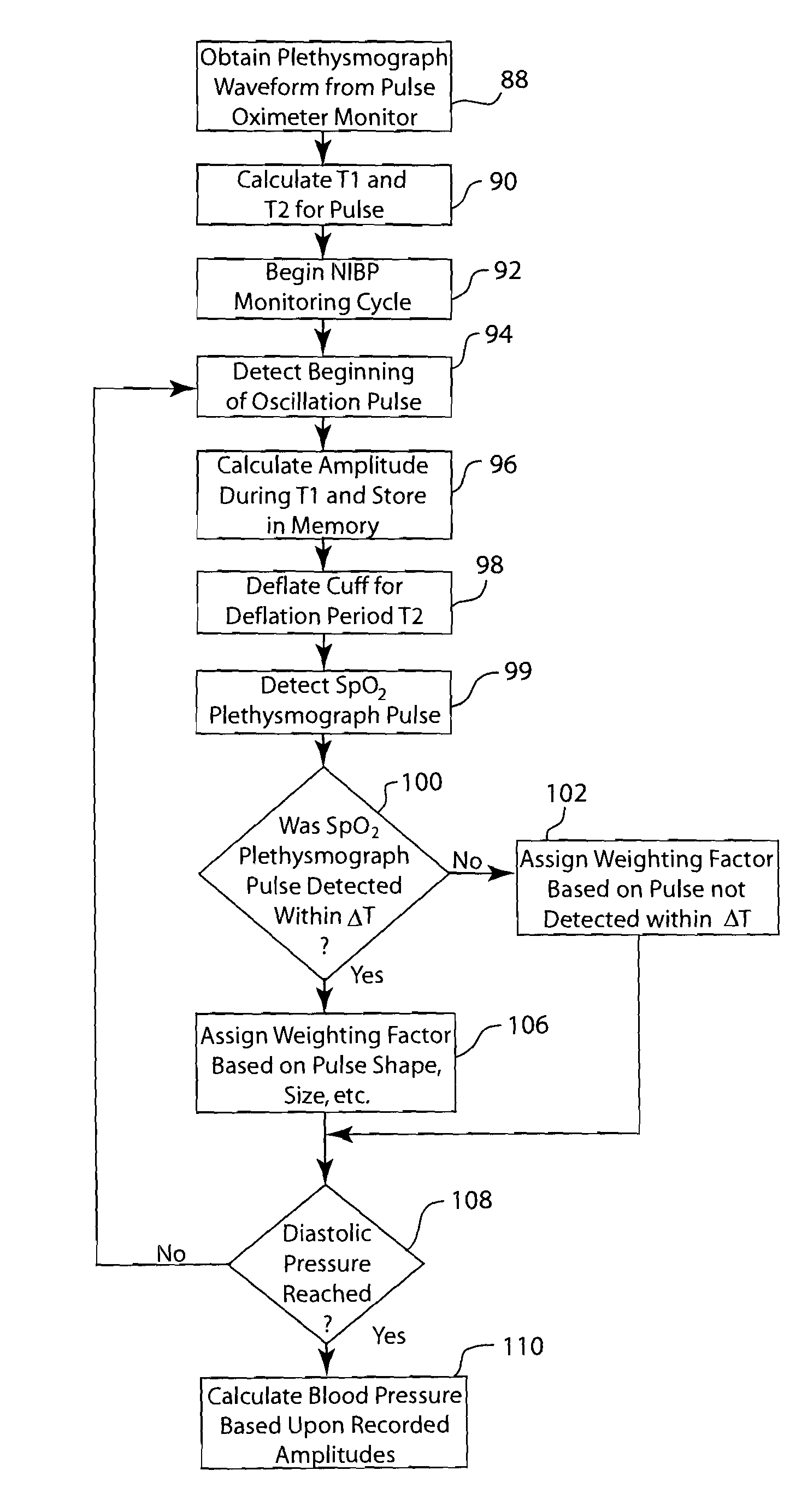
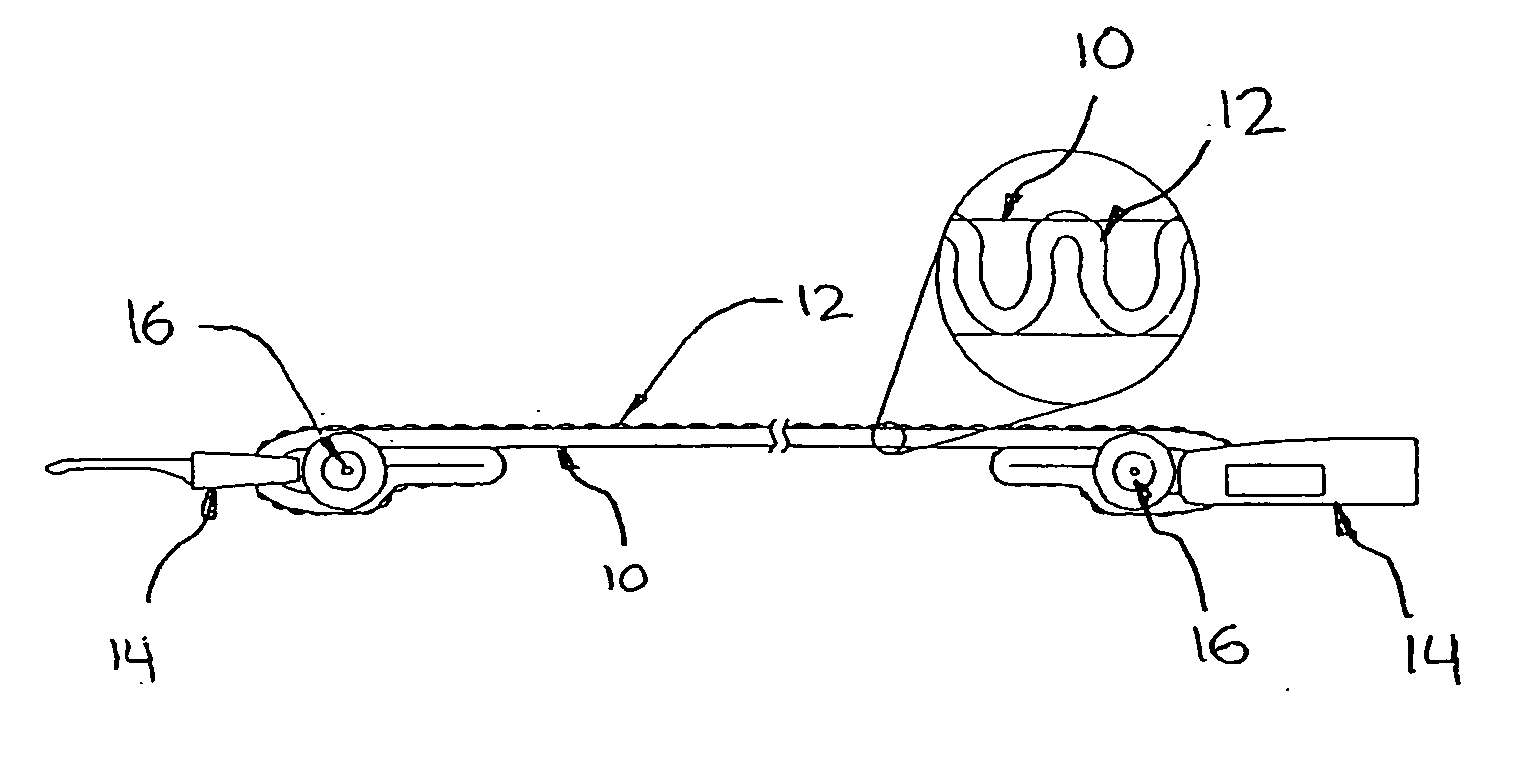
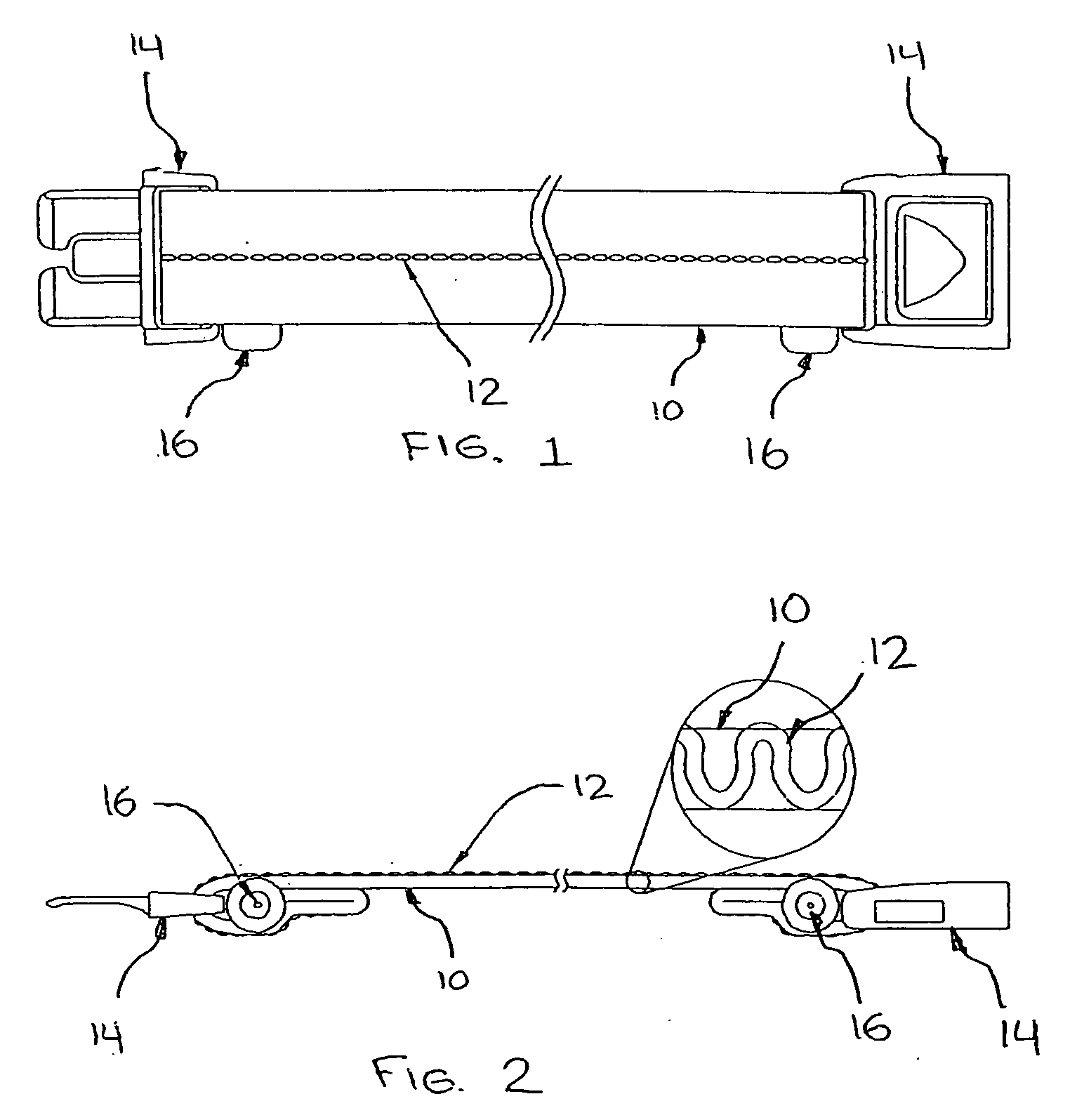
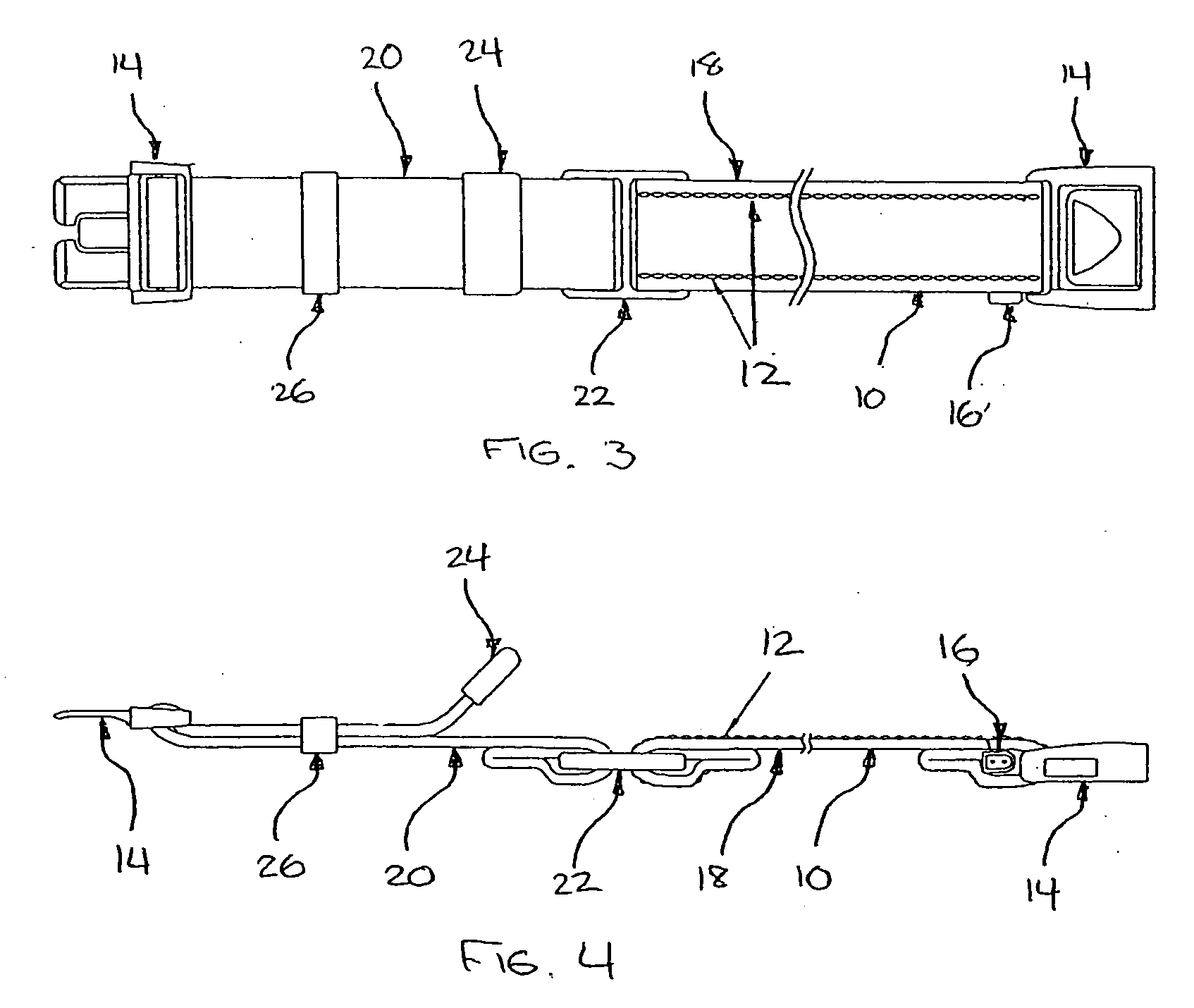
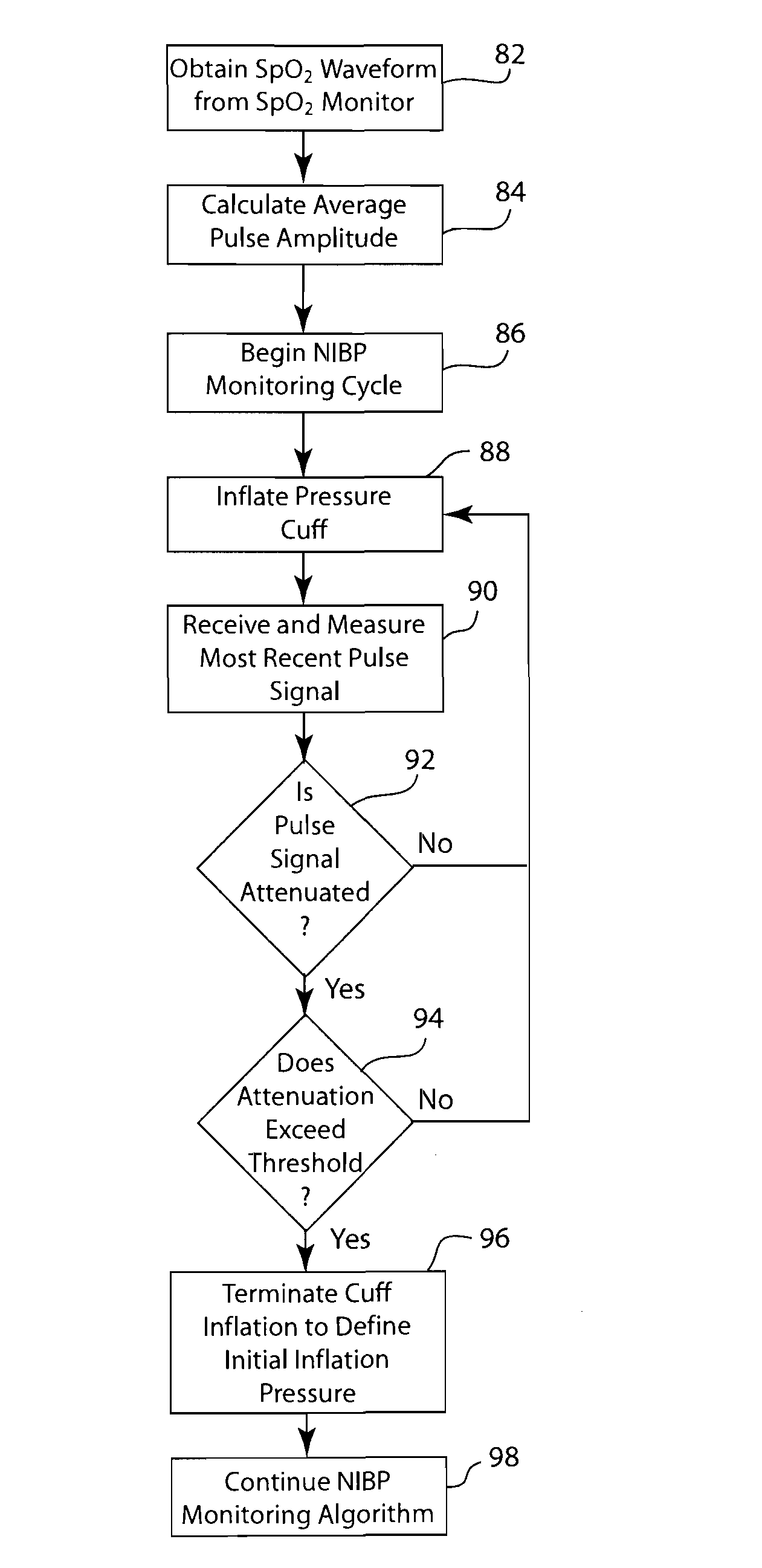
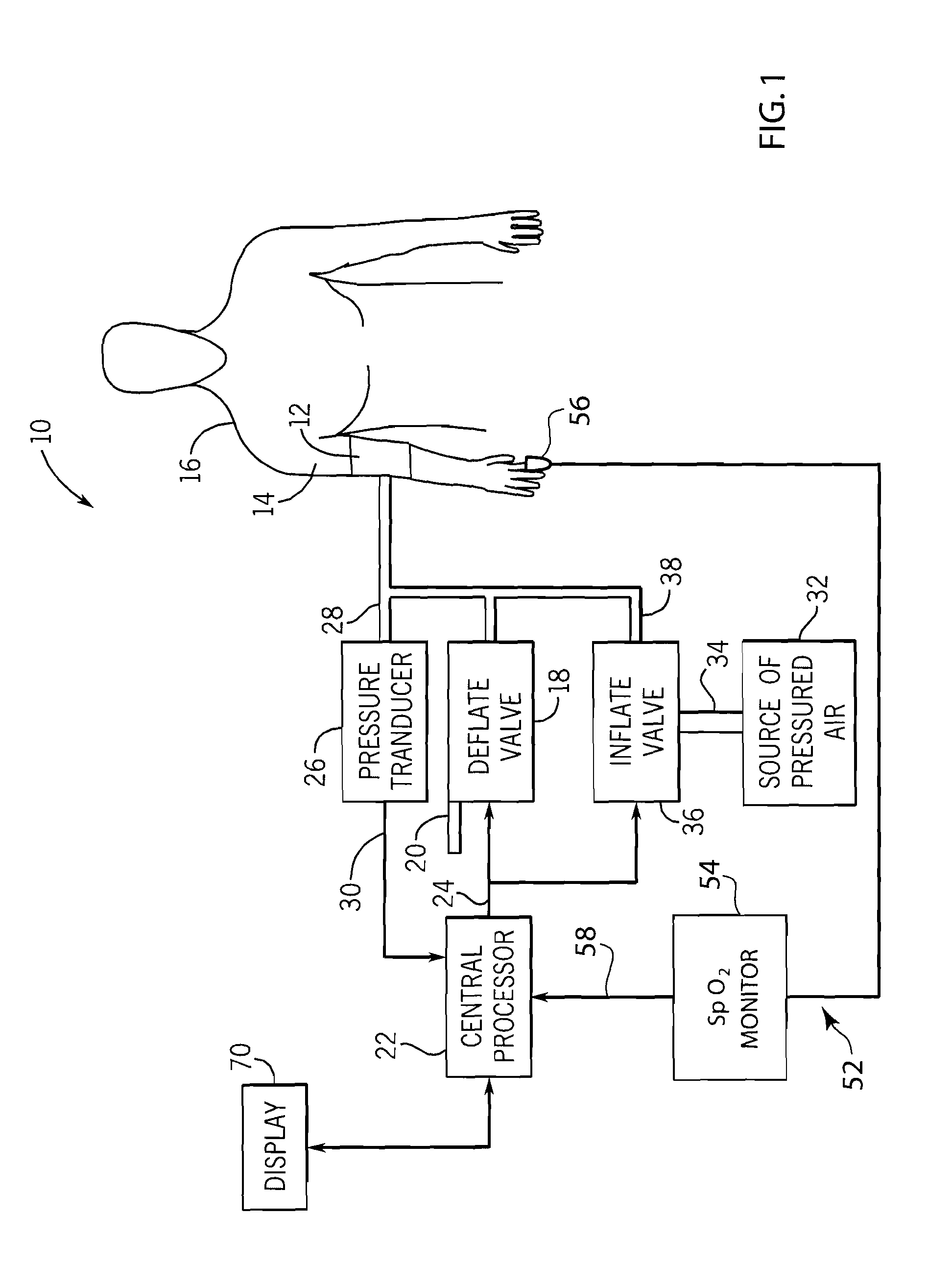
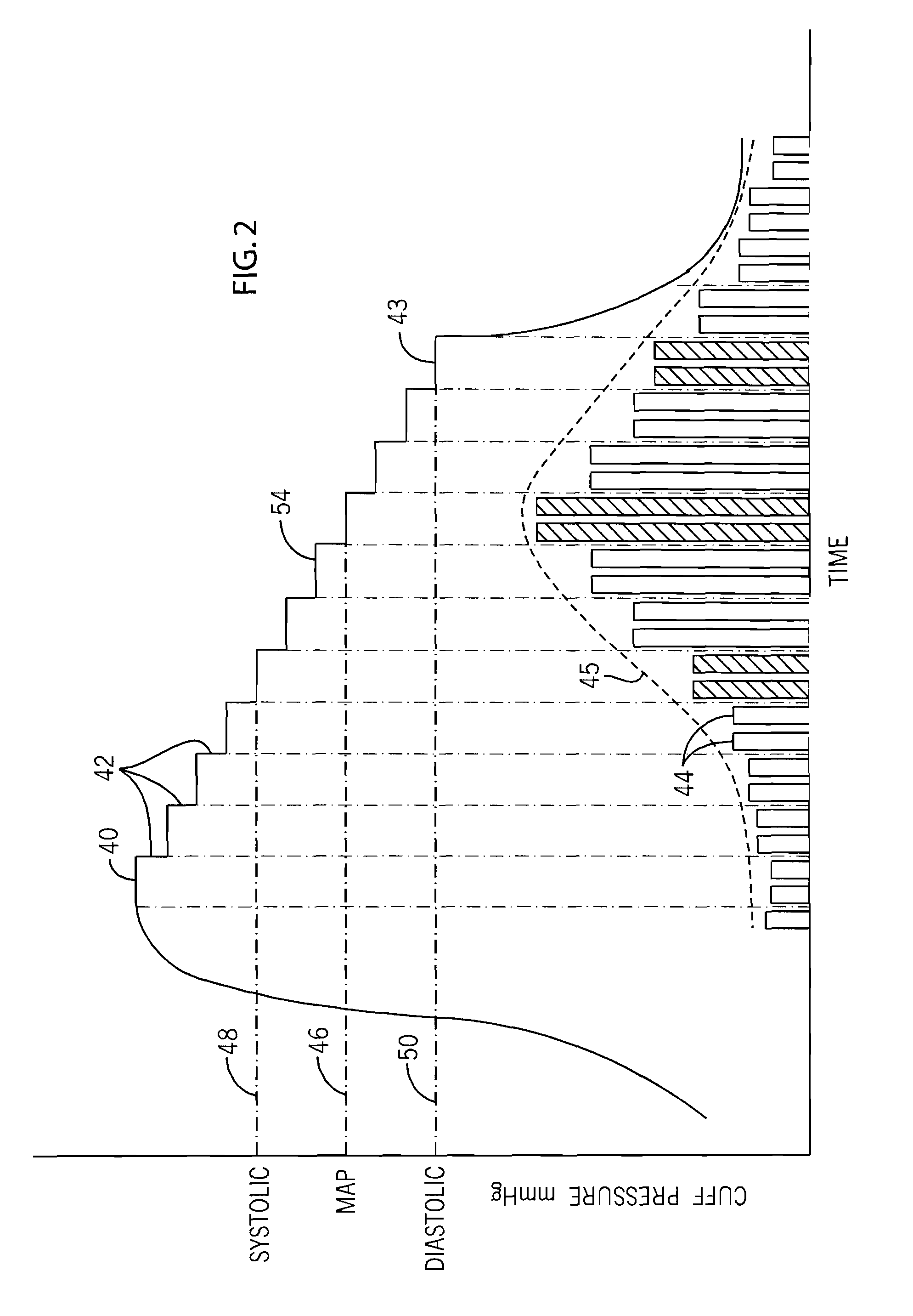
Method and system of determining nibp target inflation pressure using an sp02 plethysmograph signal
InactiveUS20080045846A1Improve performanceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationBlood pressure cuffs
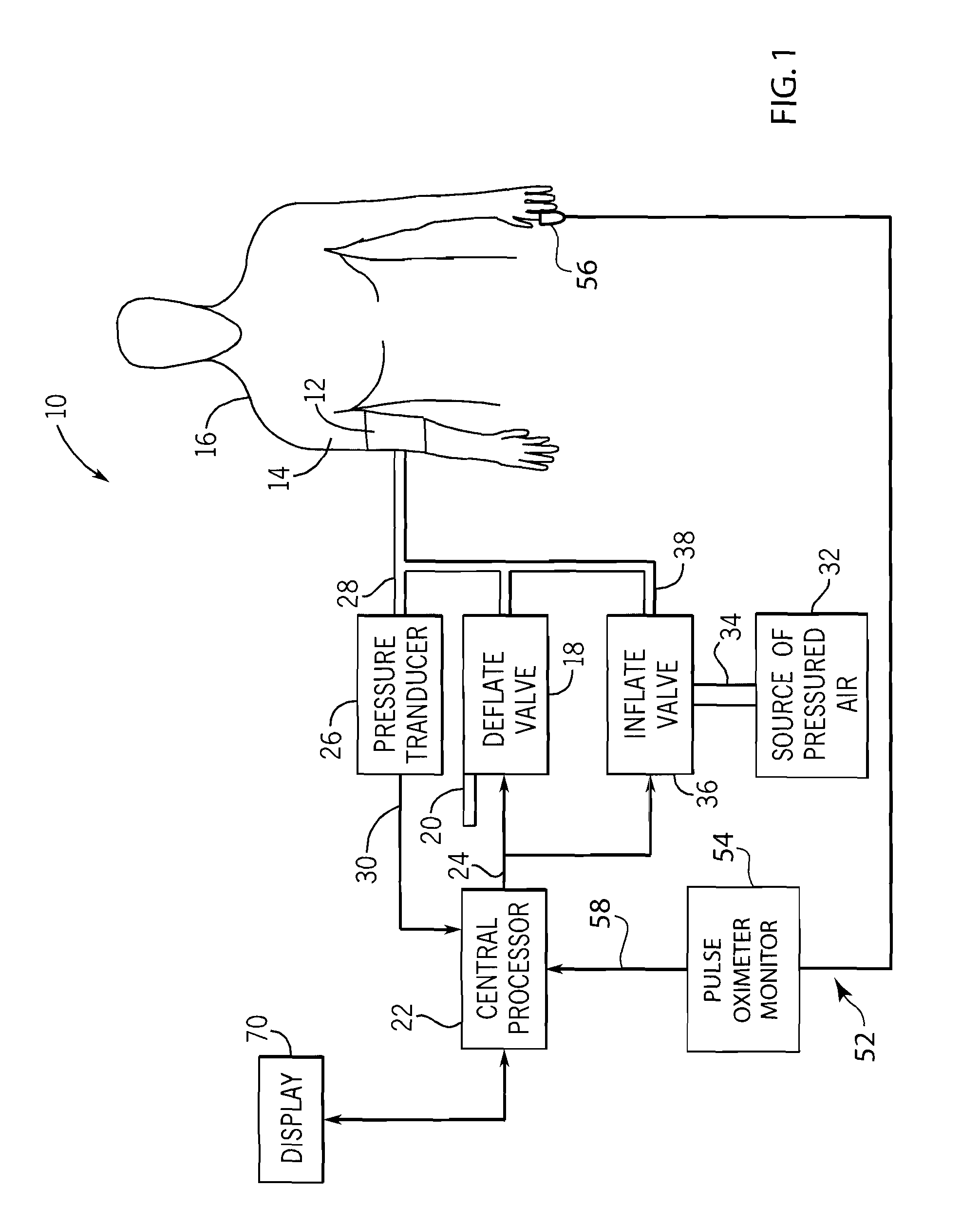
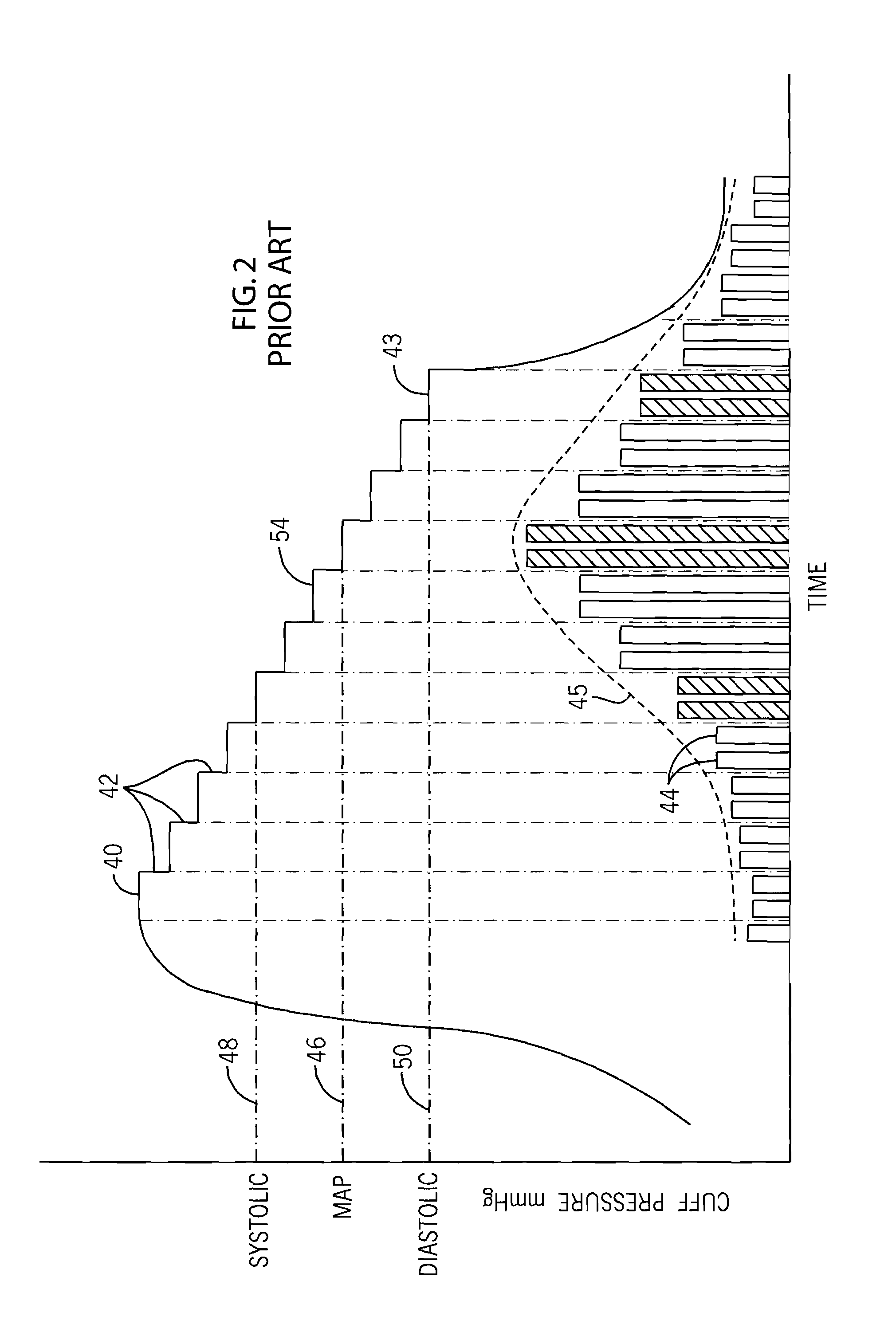
A method and system for operating a non-invasive blood pressure monitor that utilizes an SpO2 plethysmograph signal to determine the initial inflation pressure for the blood pressure cuff of the NIBP monitor. A pulse sensor is placed on the patient's limb distal to the blood pressure cuff such that as the blood pressure cuff is inflated, the pulse signals from the pulse sensor will be reduced. When the blood pressure cuff reaches systolic pressure, the pulse signals from the pulse sensor will be initially attenuated and eventually eliminated, thus providing an indication that the cuff pressure has reached systolic pressure for the patient. The central processor of the NIBP monitor compares the pulse signals during cuff inflation to an average pulse signal and terminates the inflation of the blood pressure cuff upon sufficient attenuation. The use of the SpO2 plethysmograph signal to determine the initial inflation pressure reduces both the over-inflation of the blood pressure cuff and the under-inflation of the blood pressure cuff which increases the rate at which the blood pressure measurement can be made while increasing patient comfort.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and devices for central photoplethysmographic monitoring methods
ActiveUS8641635B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksPulse oximetersEmergency medicine
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +2
Apnea detection system
A method and apparatus are described for utilizing a source of vascular pulse waveform data from a patient for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus. The arterial pulse waveform data source described is a pulse oximeter plethysmograph but can be any similar waveform data source, including an intra-arterial transducer, external blood pressure transducer, or plethysmograph. Through incorporation of measurements of values, such as an area under a pulse waveform curve, that are time-domain functions of a change in amplitude of the pulse waveform over a duration of the waveform, embodiments of the present invention represent a significant improvement upon previously described methods of measuring pulsus paradoxus.
Owner:PRECISION PULSUS
Method and system utilizing SpO2 plethysmograph signal to reduce NIBP determination time
ActiveUS7462152B2Improve performanceShorten the timeCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringBlood pressure cuffsEmergency medicine
A method and system for operating a non-invasive blood pressure monitor that utilizes an SpO2 plethysmographic signal to reduce the time required to obtain an estimation of a patient's blood pressure. During operation of the NIBP monitor, the NIBP monitor utilizes the SpO2 plethysmographic signal to determine a timing period and a deflation period for each pulse associated with the patient's heartbeat. Upon receiving an oscillation pulse, the NIBP monitor determines the oscillation amplitude during the timing period and deflates the blood pressure cuff during the deflation period immediately following the timing period. Preferably, the deflation period occurs during the same oscillation pulse used to calculate the oscillation pulse amplitude to decrease the amount of time required to obtain a blood pressure estimate from the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
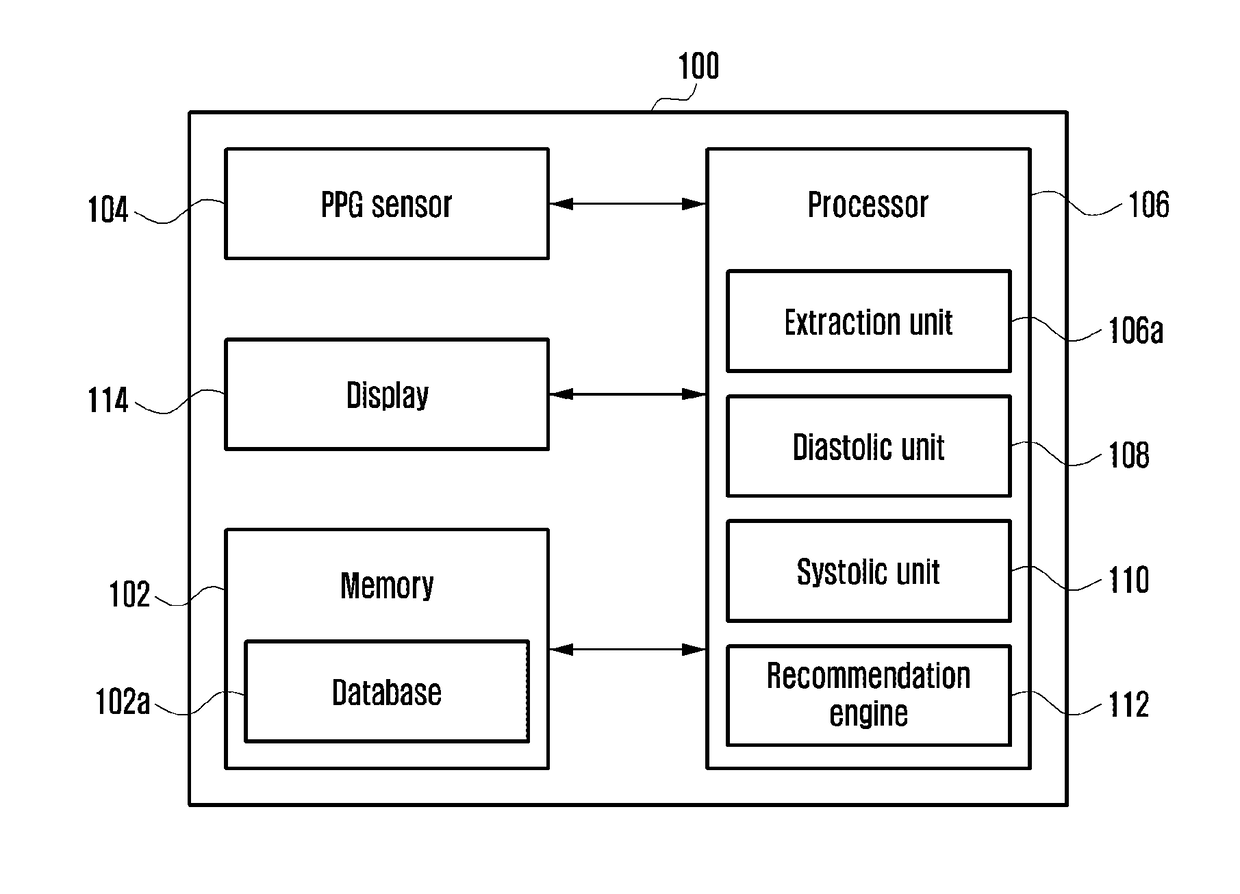
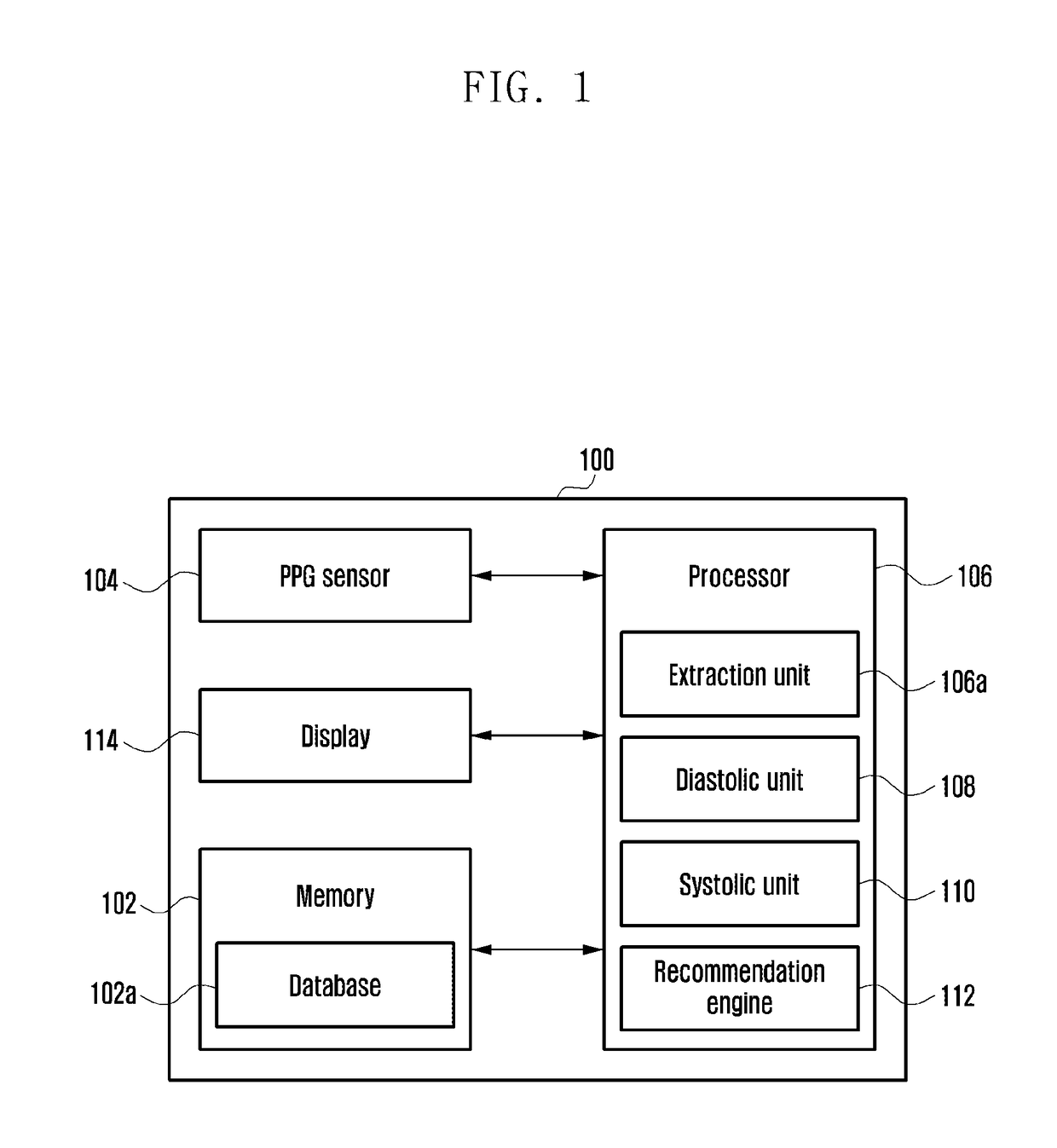
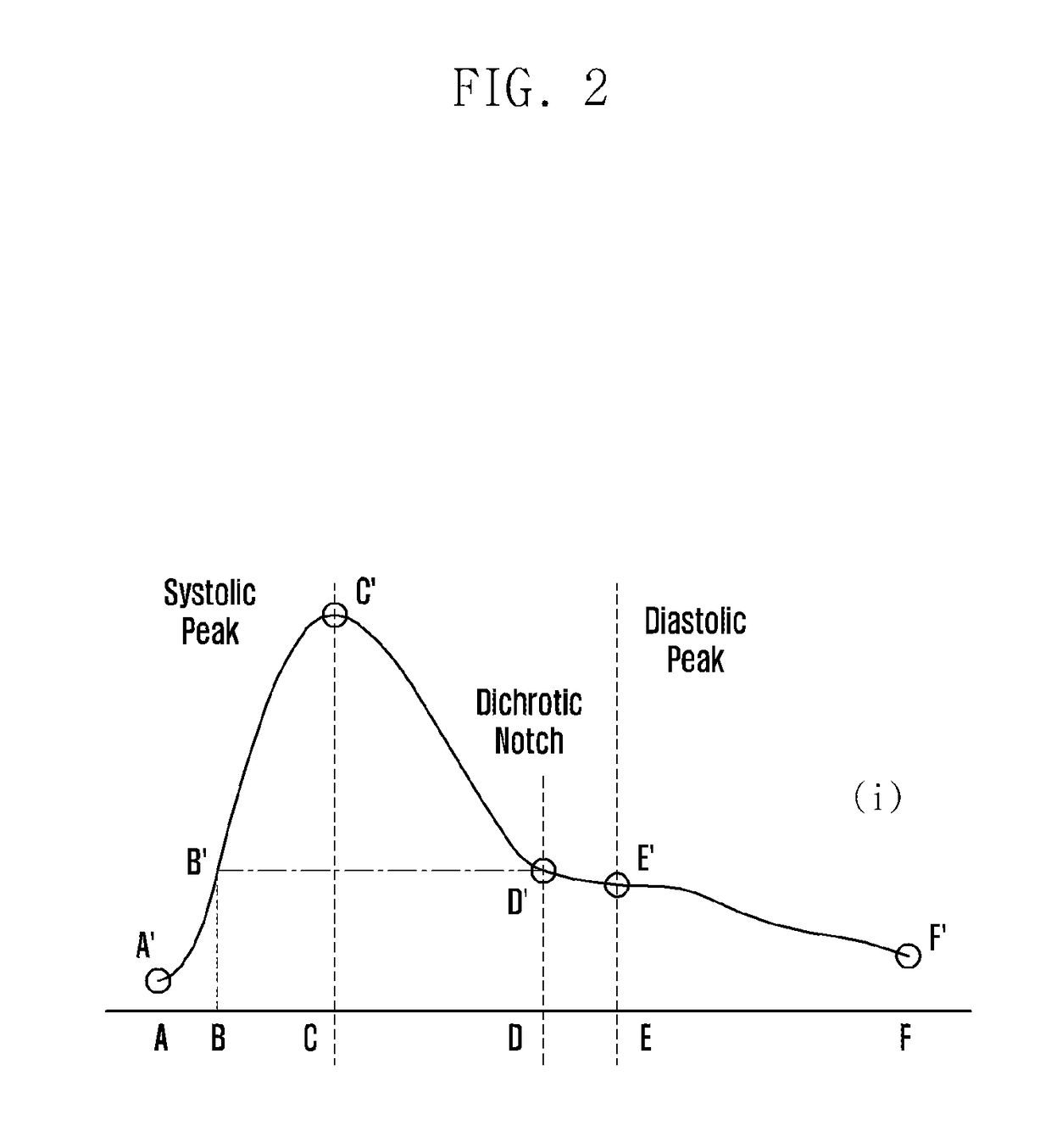
Method and electronic device for cuff-less blood pressure (BP) measurement
A method and an electronic device for measuring blood pressure are provided. The method includes illuminating, by a PPG sensor included in the electronic device, skin of a user and measuring a PPG signal based on an illumination absorption by the skin. Further, the method also includes extracting, by the electronic device, a plurality of parameters from the PPG signal, wherein the parameters may comprise PPG features, Heart Rate Variability (HRV) features, Acceleration Plethysmograph (APG) features, and non-linear features. The method also includes estimating, by the electronic device, the BP based on the extracted plurality of parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
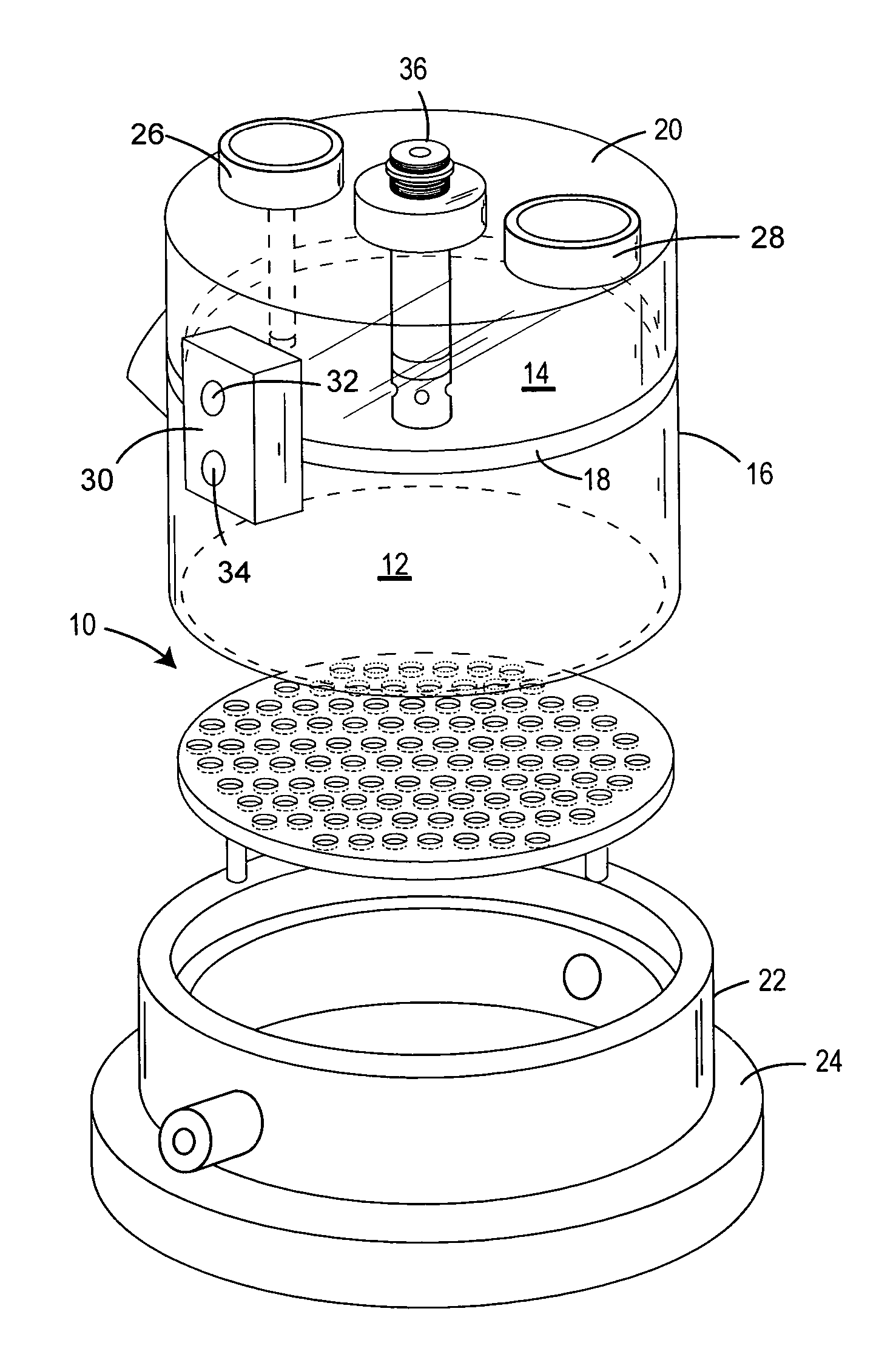
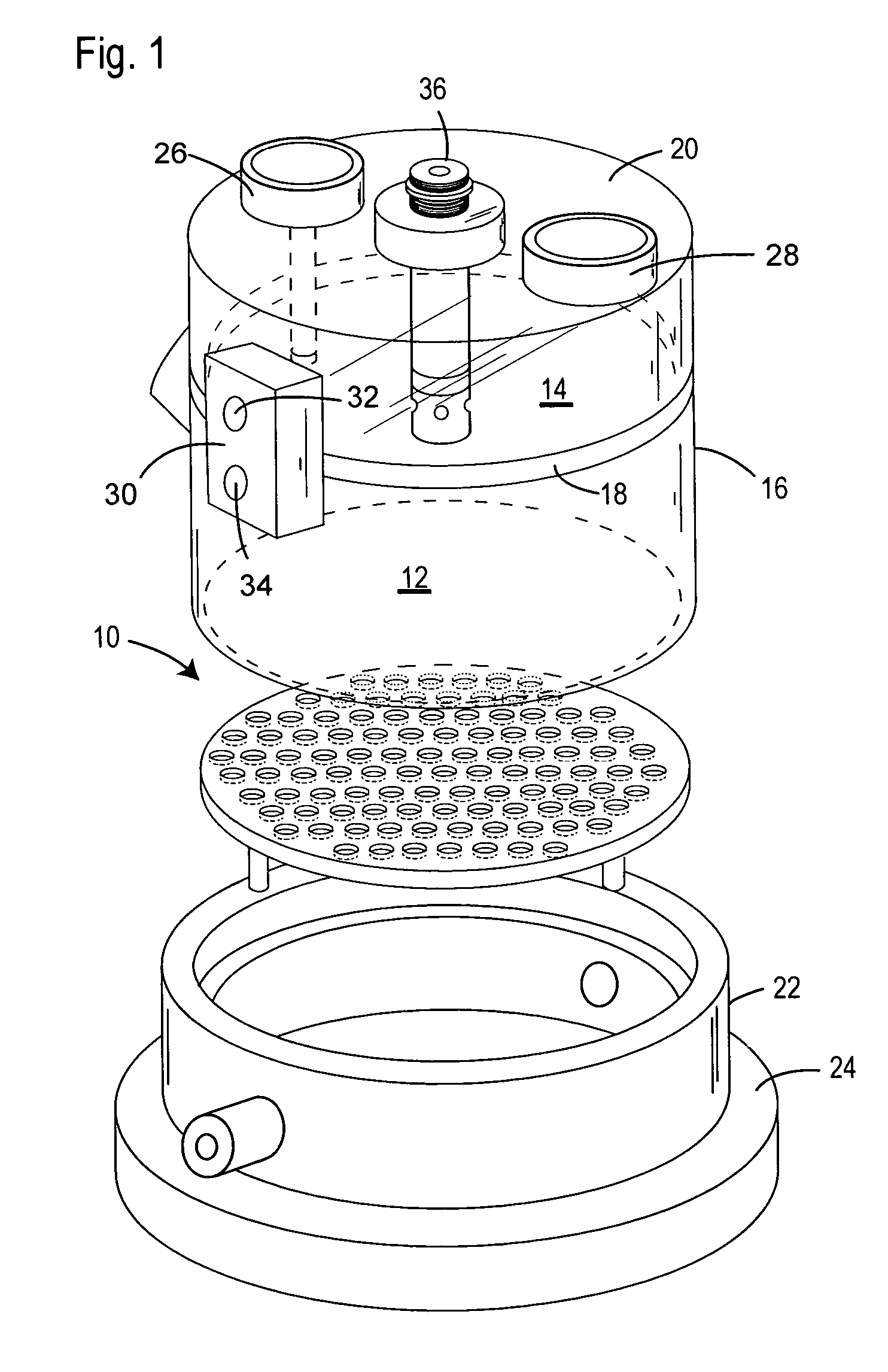
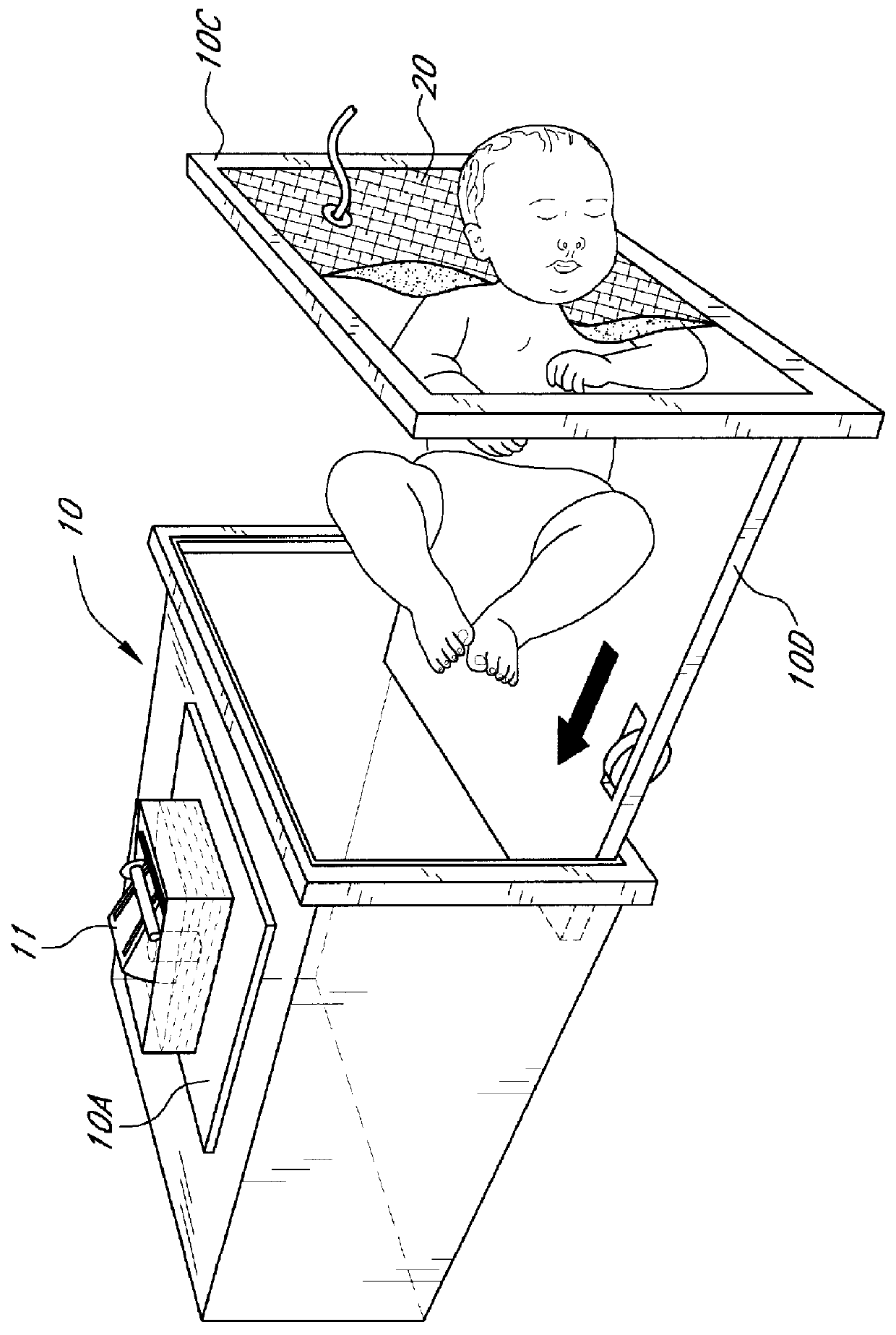
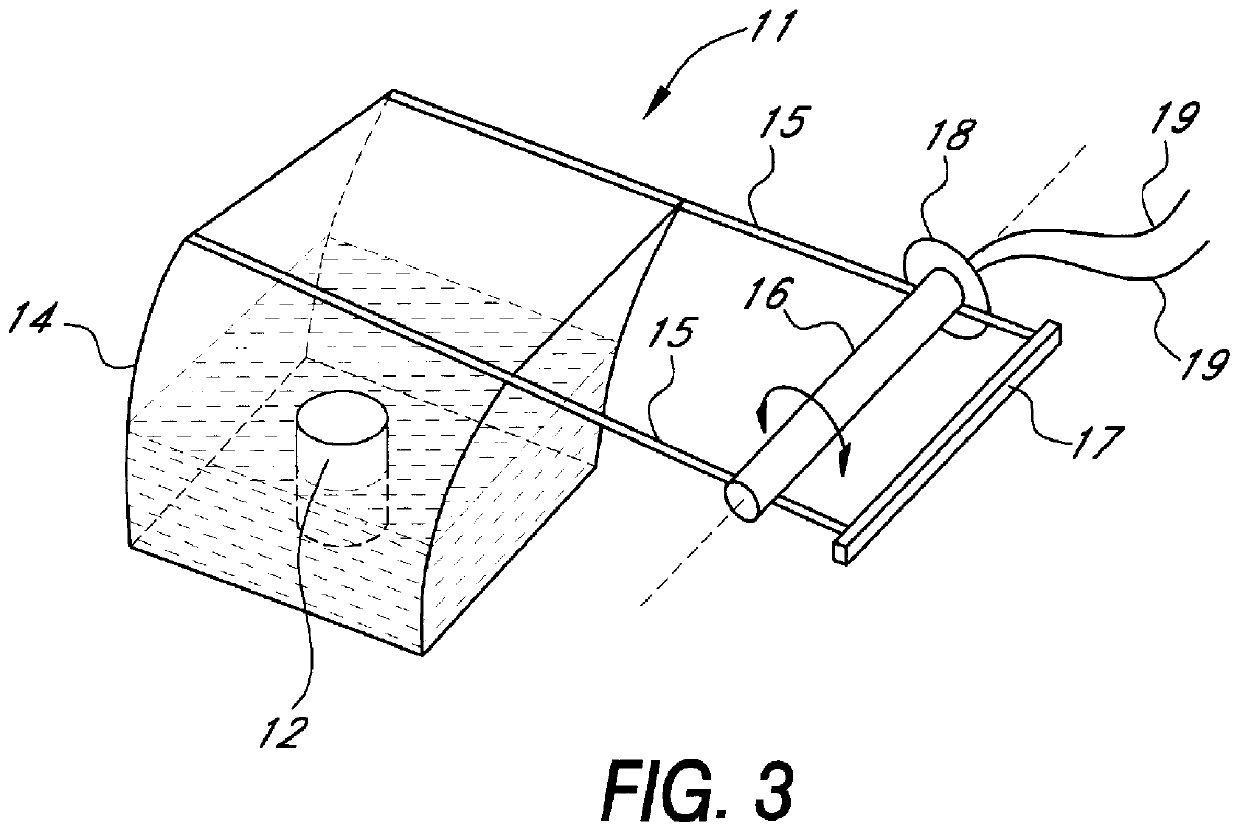
Plethysmograph
InactiveUS6113550ACheap constructionBreathe freelyBaby-incubatorsRespiratory organ evaluationTidal volumeNon invasive
Non invasive measurement of infant lung function during unsedated sleep is achieved by a plethysmograph which comprises of a rigid acrylic box (10) with integral water sealed spirometer (11) and a vacuum-actuated neck seal (20) allowing "head out" monitoring. The neck seal comprises particulate material entrapped in the space between two layers of rubber, which become rigid when a vacuum is applied to the space. Tidal volume, respiratory rate and changes in functional residual capacity (FRC) are able to be recorded during unsedated REM and NREM sleep whilst monitoring with conventional polysomnographic methods. The head out configuration allows additional instrumentation to be used, avoids facial stimulation and allows unimpeded access to the upper airway.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
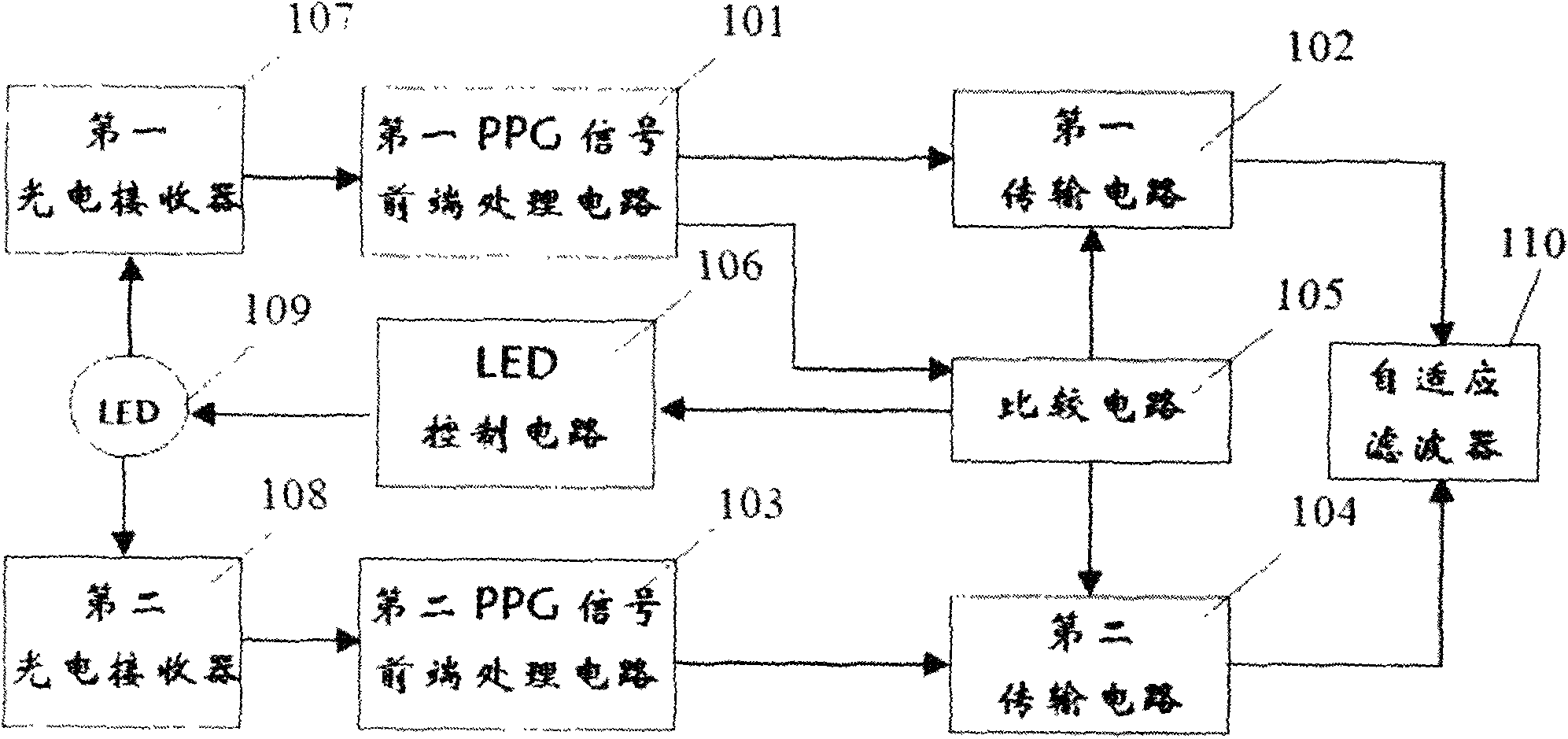
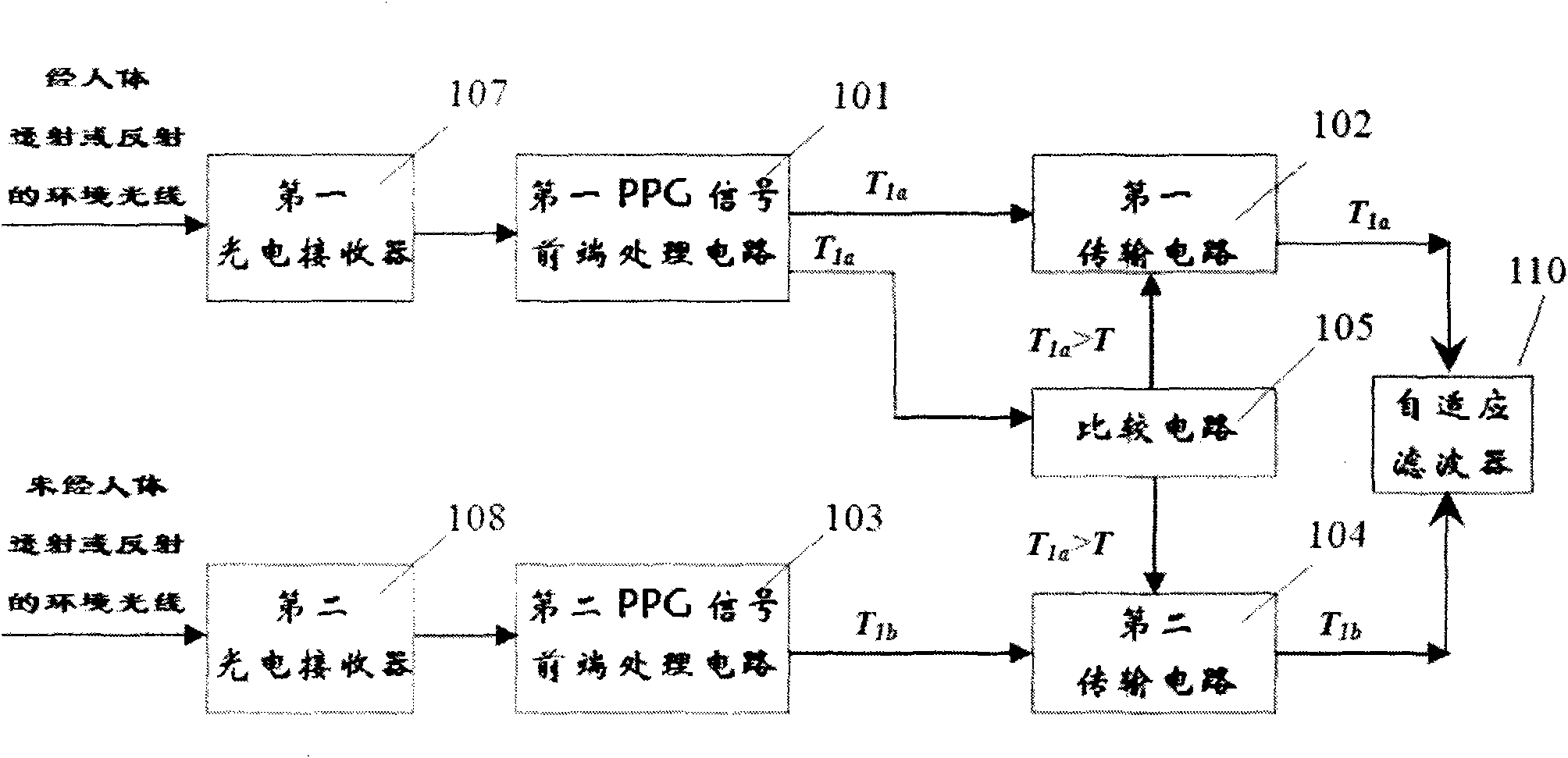
Low-power consumption and high-precision front processing module of photoelectric plethysmograph signal based on ambient light
ActiveCN101627902AReduce power consumptionEliminate errorsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal qualityComputer module
The invention relates to a front processing module of a photoelectric plethysmograph signal, which comprises a first photoelectric receiver, a second photoelectric receiver, a first front processing circuit of the photoelectric plethysmograph signal, a second front processing circuit of the photoelectric plethysmograph signal, a first transmission circuit, a second transmission circuit, a comparison circuit, an LED control circuit and an LED. When ambient light is enough and the signal quality is good, the ambient light is utilized as a light source, and the LED is turned off. When the ambient light is not enough and the signal quality is poor, the ambient light and the LED are used as the light source. The output of the front processing circuit of the photoelectric plethysmograph signal can provide an input for adaptive filtering. The front processing module of the photoelectric plethysmograph signal has the advantages of low power consumption and high precision.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
Reusable inductive transducer for measuring respiration
InactiveUS20060258948A1Improve electrical performanceLow costRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsElectrical conductorSignal-to-noise ratio
The present invention is an inductance plethysmograph transducer particularly suited for use in respiratory monitoring. The transducer is in the form of a woven fabric providing a substantially flat extensible belt for encircling a portion of a patient for a wide range of patient sizes. The transducer is used for monitoring changes in cross-sectional area corresponding to changes in volume of an expandable organ such as the patient's chest or abdomen. At least one electrical conductor is woven directly into the fabric in a manner that improves the electrical performance of the transducer over the prior art in two ways. First, a high-density weave is used for the fabric that produces many more inductive turns of the embedded conductor(s), thereby increasing the overall inductance change, hence improving the signal to noise ratio, and increasing the expandability of the effective length of the transducer. Secondly, the conductor(s) are oriented within the weave perpendicular to the surface or the torso of a patient being monitored, thus reducing artifact due to body capacitance. In addition to improvements in the electrical performance, the manufacture of the inductance sensor is a single step process that can be carried out on existing looms, reducing the overall cost while improving the flexibility, durability, and ease of use. The present invention is also machine washable making reuse much less labor intensive and therefor much less expensive.
Owner:PRO TECH SERVICES A WASHINGTON CORP
Method and system of determining NIBP target inflation pressure using an SpO2 plethysmograph signal
InactiveUS7390302B2Improve performanceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound attenuationBlood pressure cuffs
A method and system for operating a non-invasive blood pressure monitor that utilizes an SpO2 plethysmograph signal to determine the initial inflation pressure for the blood pressure cuff of the NIBP monitor. A pulse sensor is placed on the patient's limb distal to the blood pressure cuff such that as the blood pressure cuff is inflated, the pulse signals from the pulse sensor will be reduced. When the blood pressure cuff reaches systolic pressure, the pulse signals from the pulse sensor will be initially attenuated and eventually eliminated, thus providing an indication that the cuff pressure has reached systolic pressure for the patient. The central processor of the NIBP monitor compares the pulse signals during cuff inflation to an average pulse signal and terminates the inflation of the blood pressure cuff upon sufficient attenuation. The use of the SpO2 plethysmograph signal to determine the initial inflation pressure reduces both the over-inflation of the blood pressure cuff and the under-inflation of the blood pressure cuff which increases the rate at which the blood pressure measurement can be made while increasing patient comfort.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
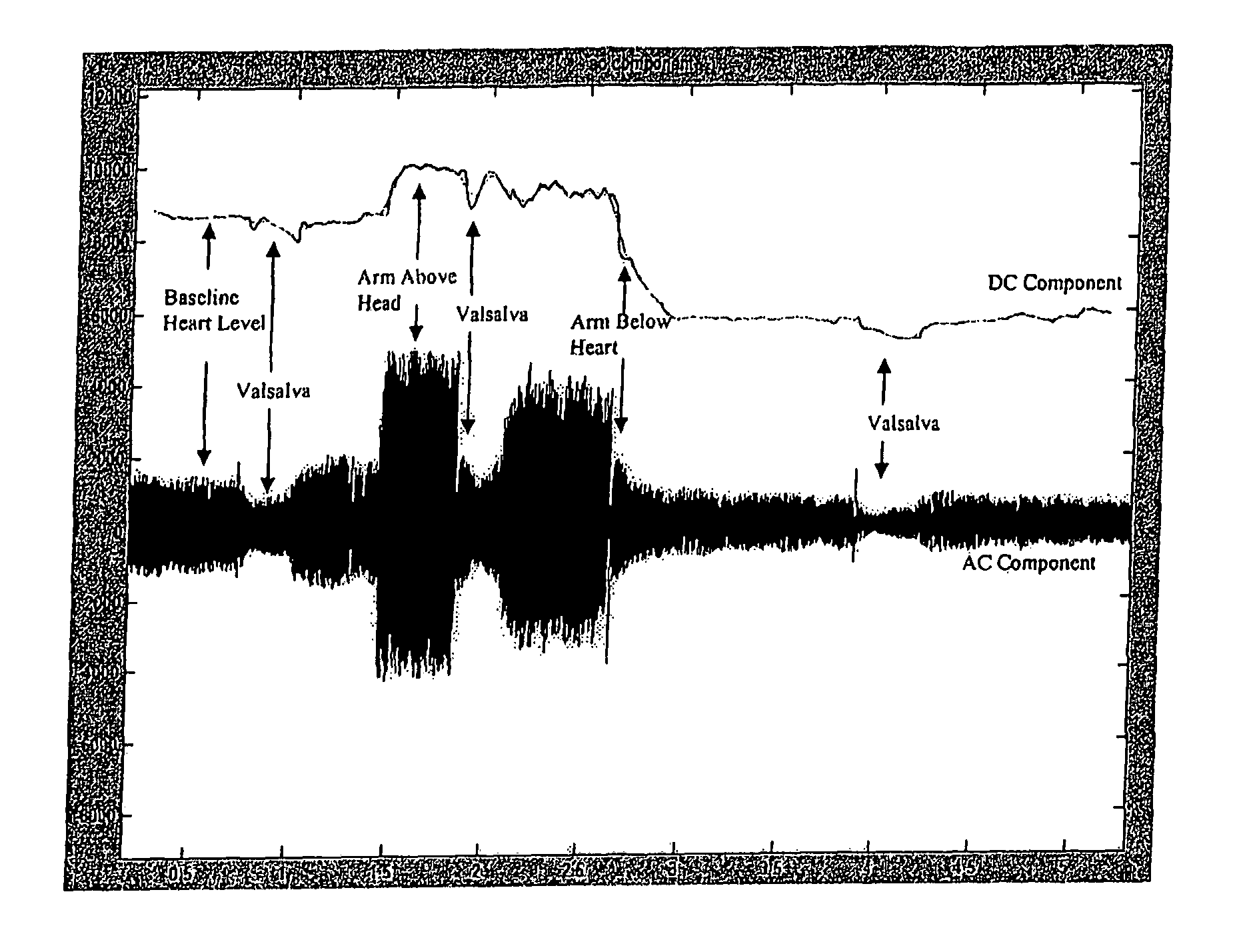
Methods and devices for countering grativity induced loss of consciousness and novel pulse oximeter probes
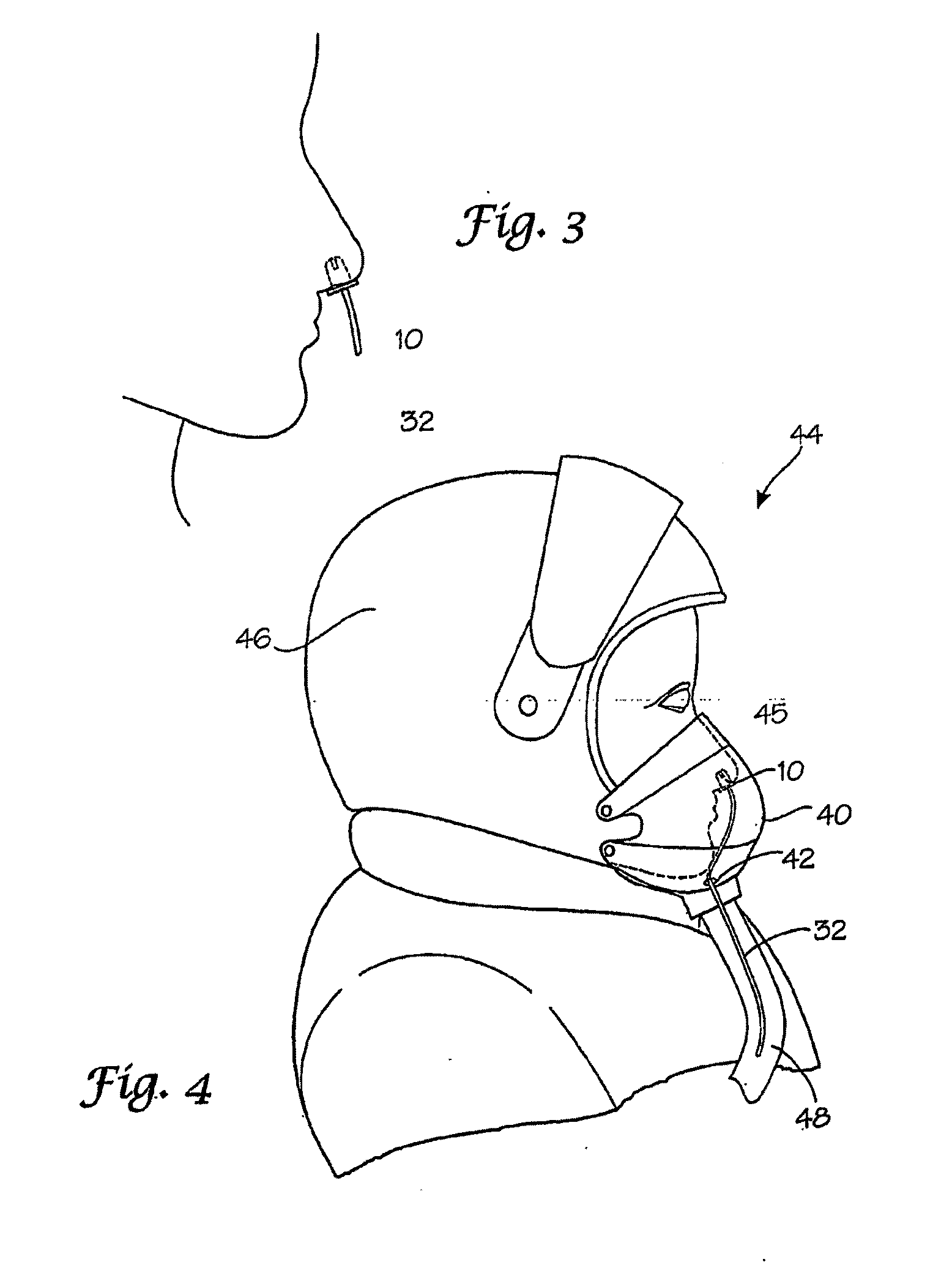
Disclosed herein are methods and devices of obtaining plethysmograph readings and utilizing plethysomography to identify when pilots are about to experience GLOC. Furthermore, in other embodiments, the invention pertains to methods and devices designed to warn a pilot that he / she is about to enter GLOC and / or automatically averting catastrophic damage or injuries by directing a plane being piloted to take predetermined corrective actions. Specifically disclosed is a system embodiment for assisting in the prevention of gravity induced loss of consciousness. The system comprises at least one pulse oximeter probe 10 configured for securing to a central source site of a pilot and to generate signals indicative of blood flow at said central source site, an analyzer unit 58 communicatingly connected to said at least one pulse oximeter probe 10, said analyzer unit comprising at least one processing module 56 configured to determine whether said blood flow is approaching a predefined level, and an aircraft computer 51 communicatingly connected to said analyzer unit 58, said aircraft computer 51 comprising at least one processing module 59 configured to effect a predetermined reaction responsive to said blood flow falling below a predetermined level.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +2
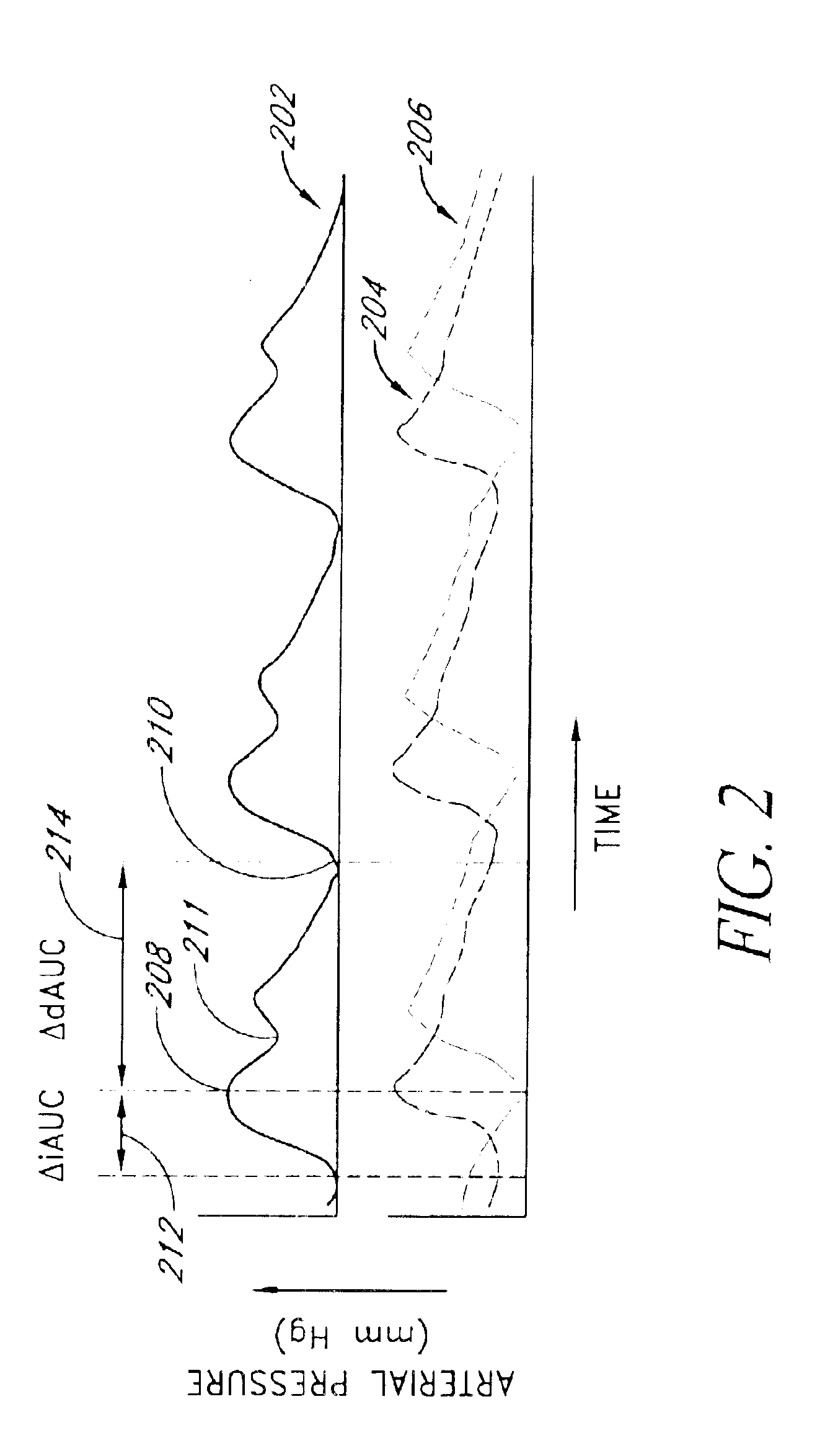
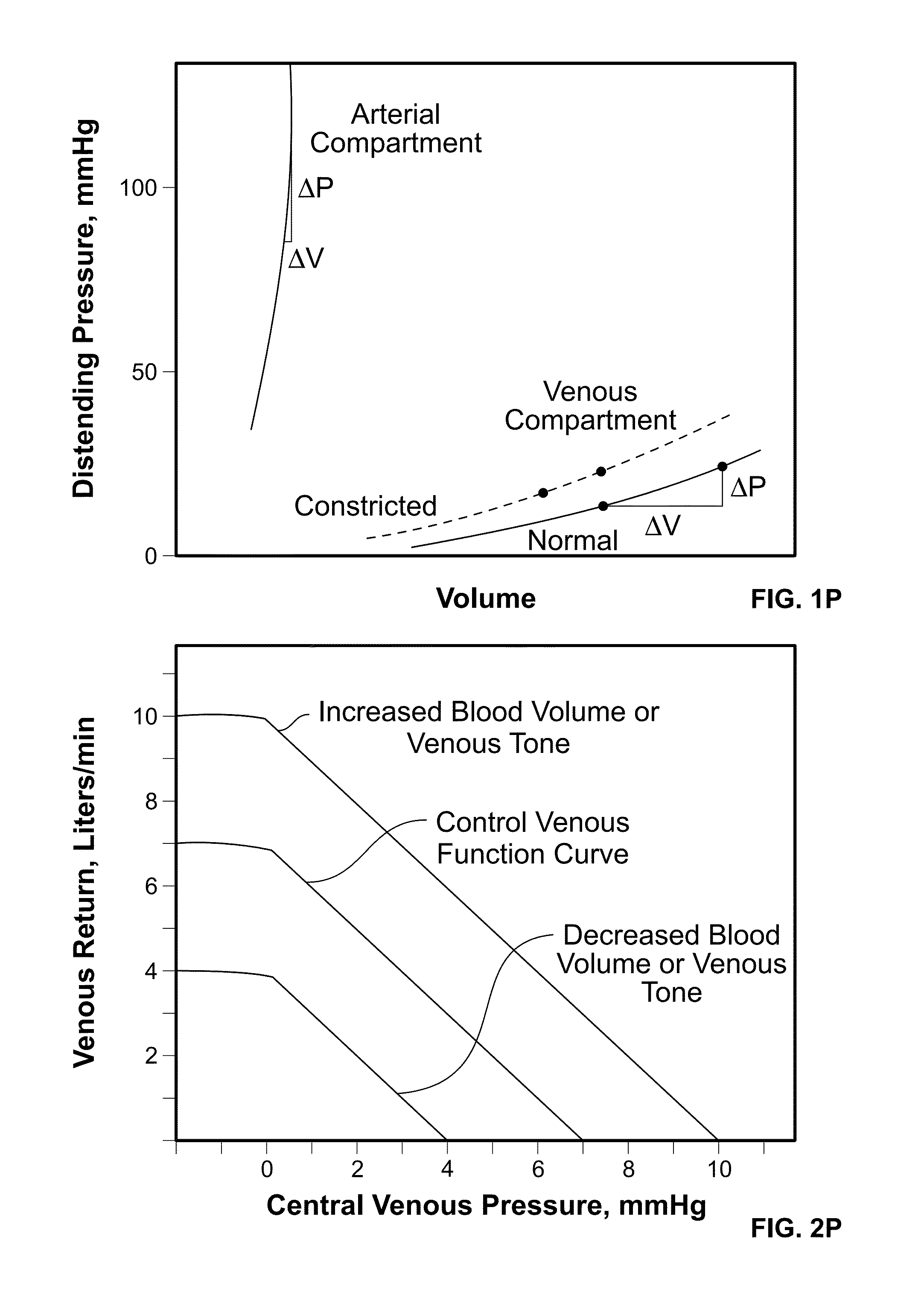
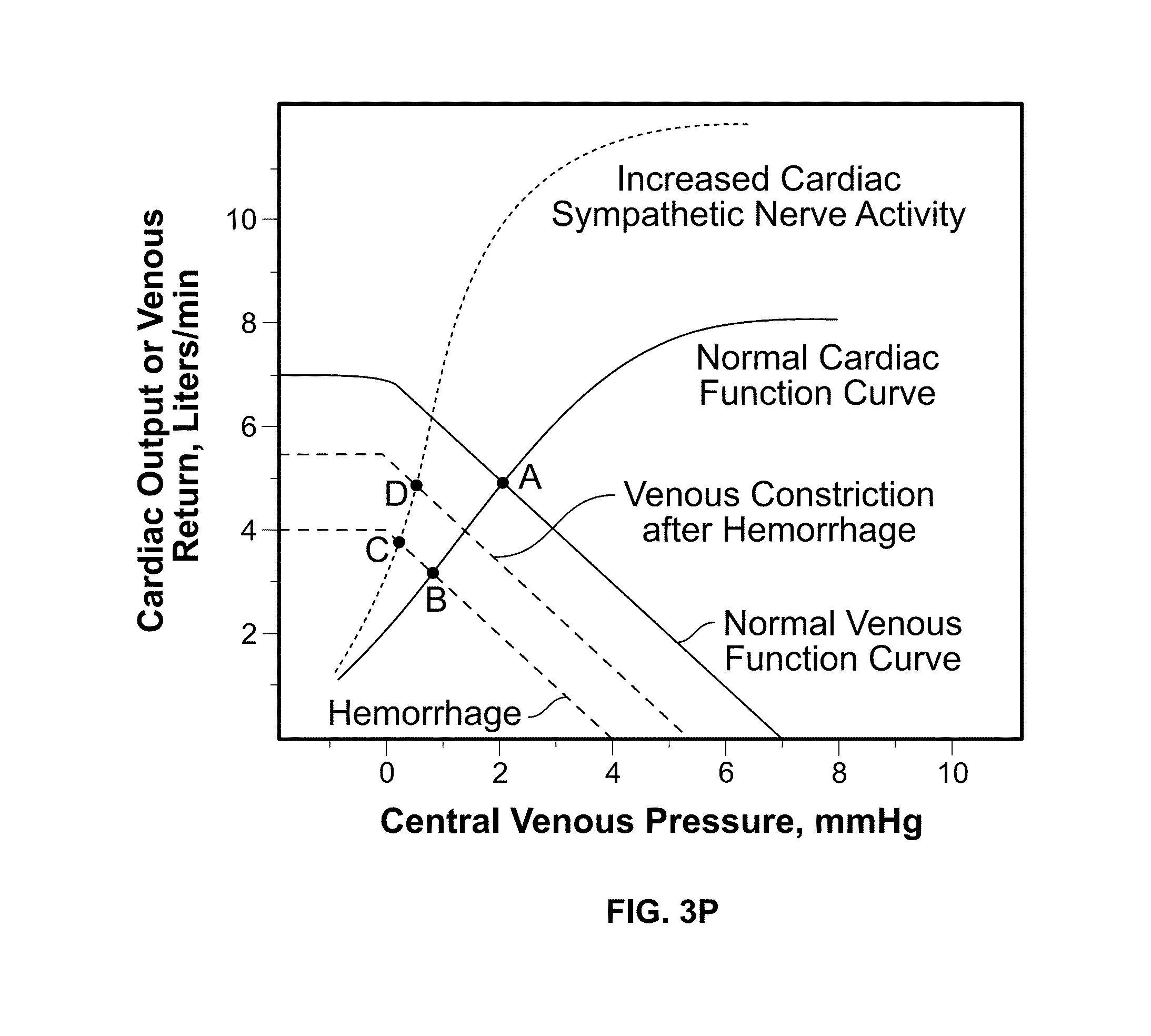
Apparatus, Systems and Methods Analyzing Pressure and Volume Waveforms in the Vasculature
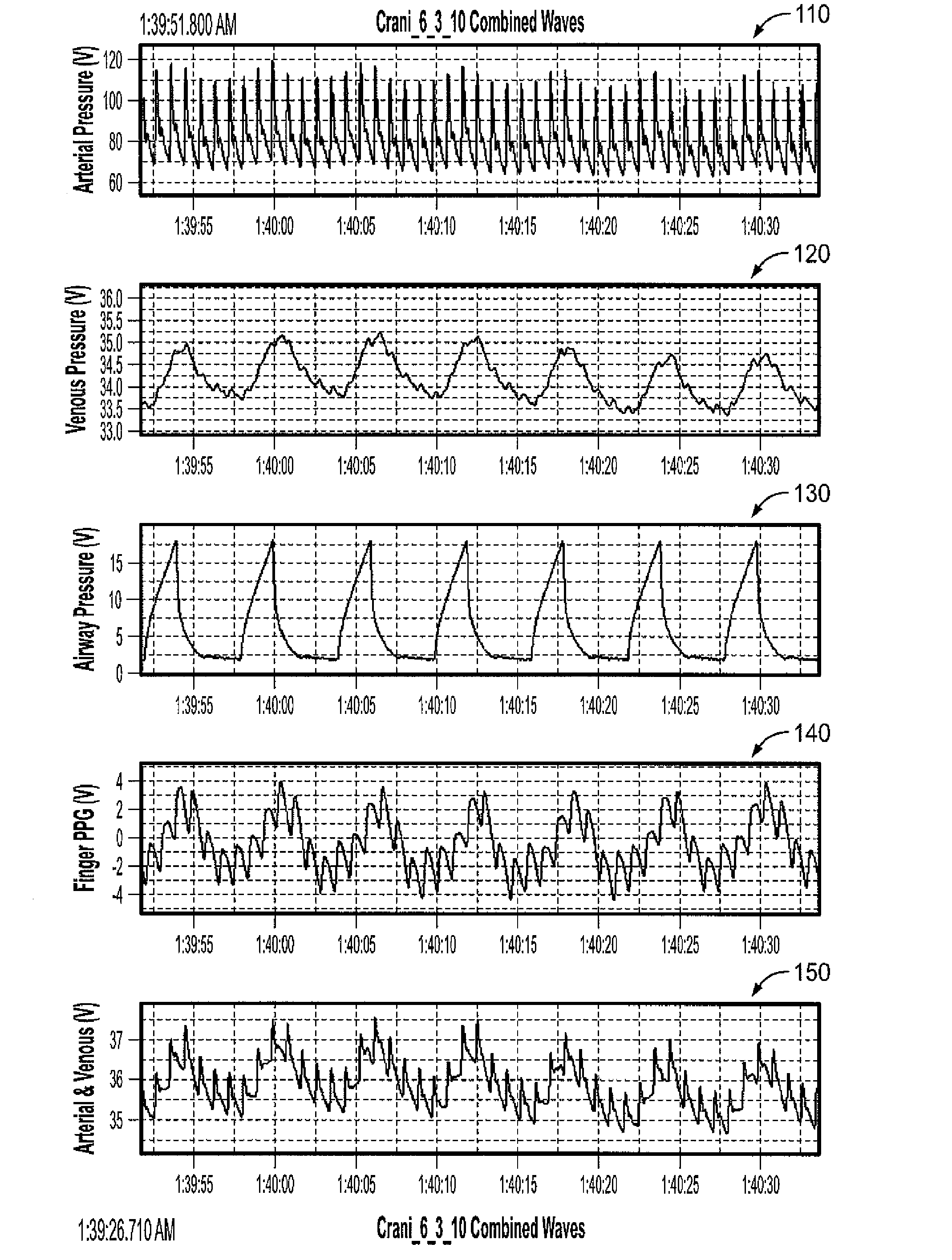
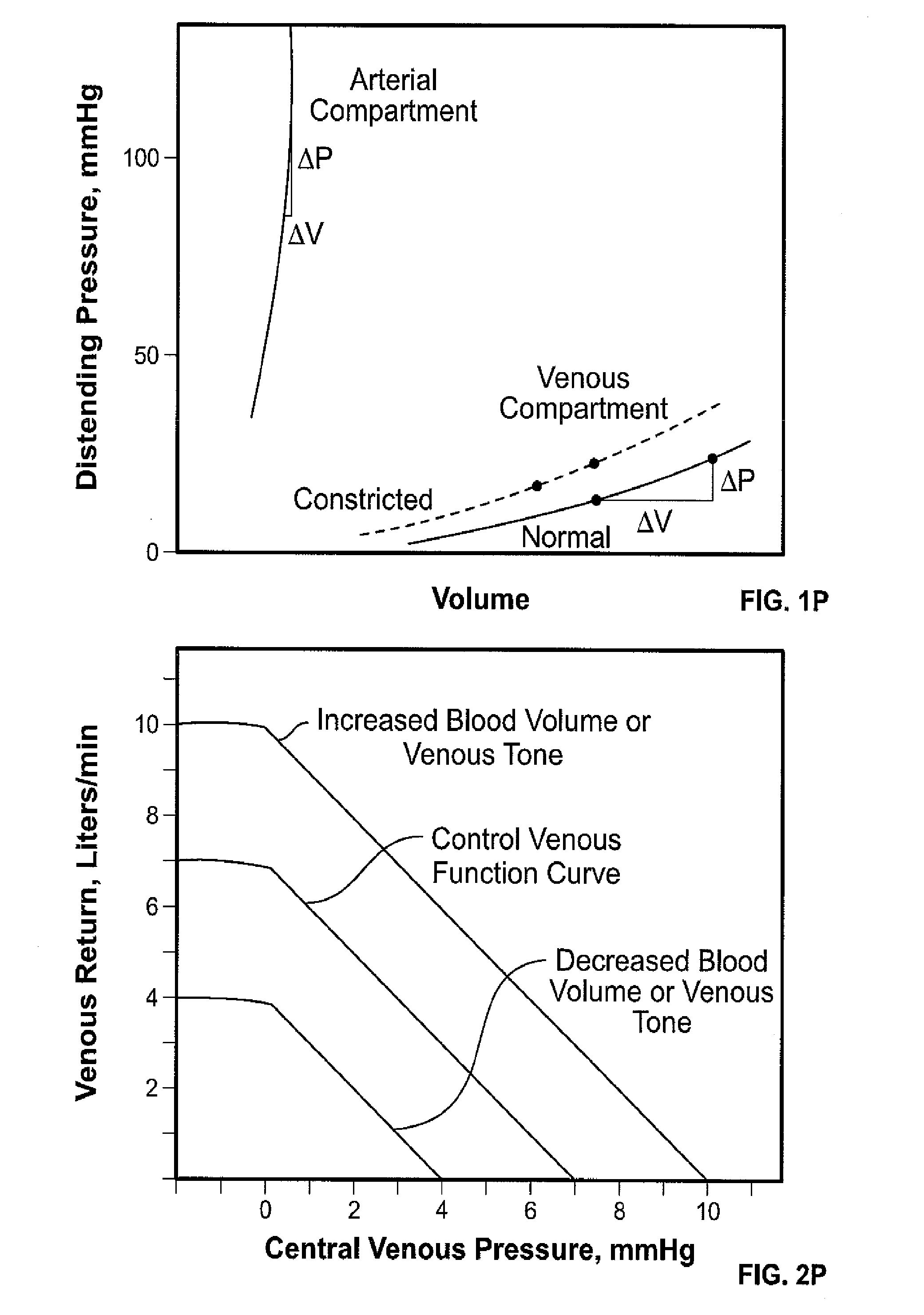
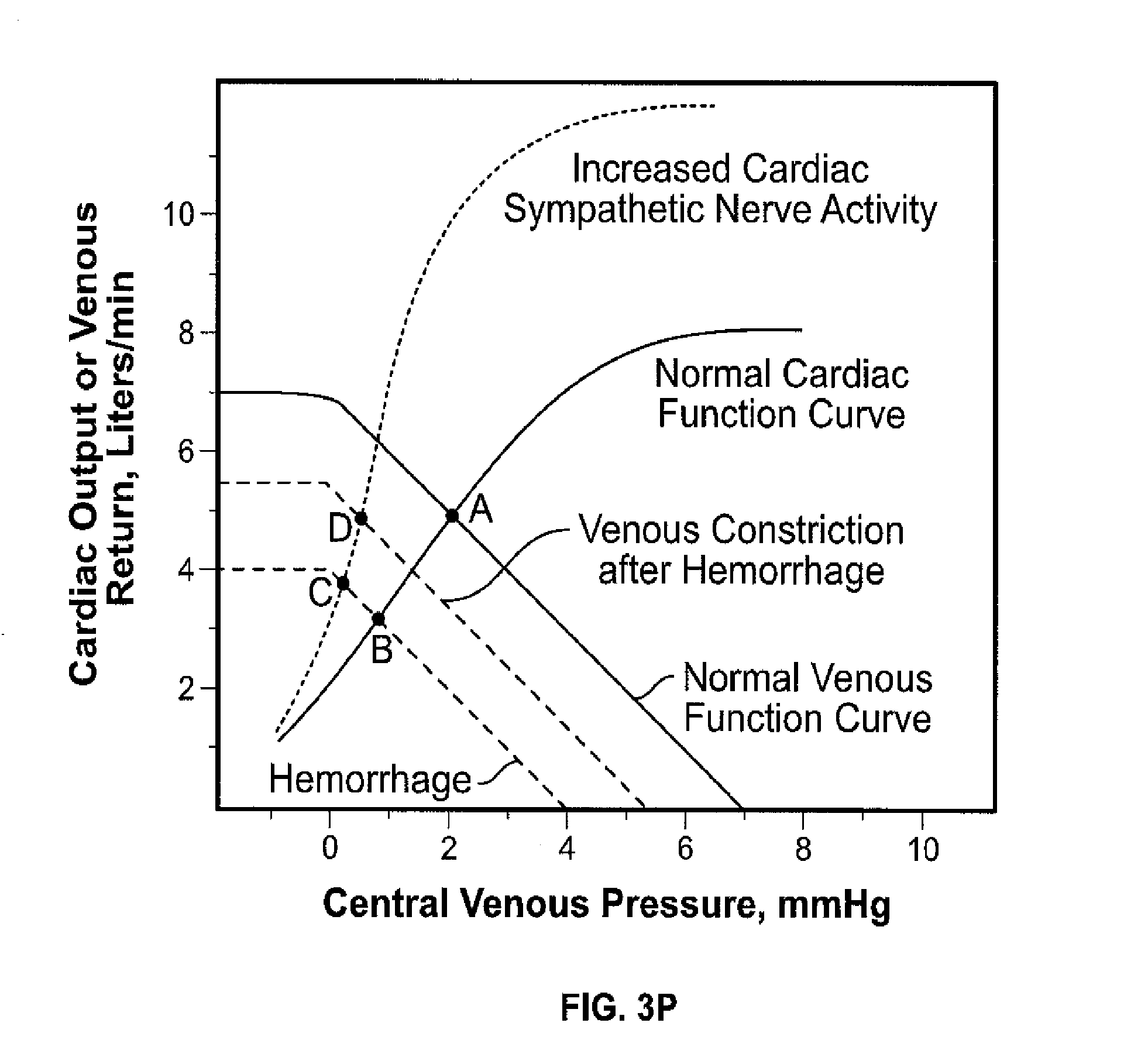
Apparatus, systems and methods are provided for analyzing relative compliance in the peripheral vasculature that generally involve generating a plethysmograph (PG) signal, generating one or more pressure waveforms and comparing the pressure waveform(s) relative to the PG signal to determine compliance indexes associated particular regions of the vasculature. A relative compliance ratio may also be determined by comparing arterial and venous relative compliance indexes. Apparatus, systems and methods are also provided for analyzing a PG waveform that generally involve generating a plethysmograph (PG) signal and comparing amplitude modulation of the PG signal relative to baseline modulation of the PG signal to estimate a relationship between left ventricular end diastolic pressure and stroke volume. The estimated relationship may account for a phase offset for the time between when changes in venous return affect left ventricular end diastolic pressure and stroke volume.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for measuring pulsus paradoxus
A method and apparatus are disclosed of utilizing a source of arterial and / or arteriolar pulse waveform data from a patient for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus. The arterial pulse waveform data source described is a pulse oximeter plethysmograph but can be any similar waveform data source, including intra-arterial transducer, blood pressure transducer, or plethysmograph. Through incorporation of the measurements of values, such as the area under the pulse waveform curve, that are time-domain functions of a change in height of the pulse waveform over at least a partial duration of the waveform, embodiments of the present invention represent a significant improvement upon previously described methods of measuring pulsus paradoxus and, further, produce improved accuracy in measurement of the multiple contributing variables generating pulsus paradoxus, in particular the contribution of diastolic events, to the extent that the physical signs so measured can be regarded as “Revised Pulsus Paradoxus.”
Owner:PRECISION PULSUS
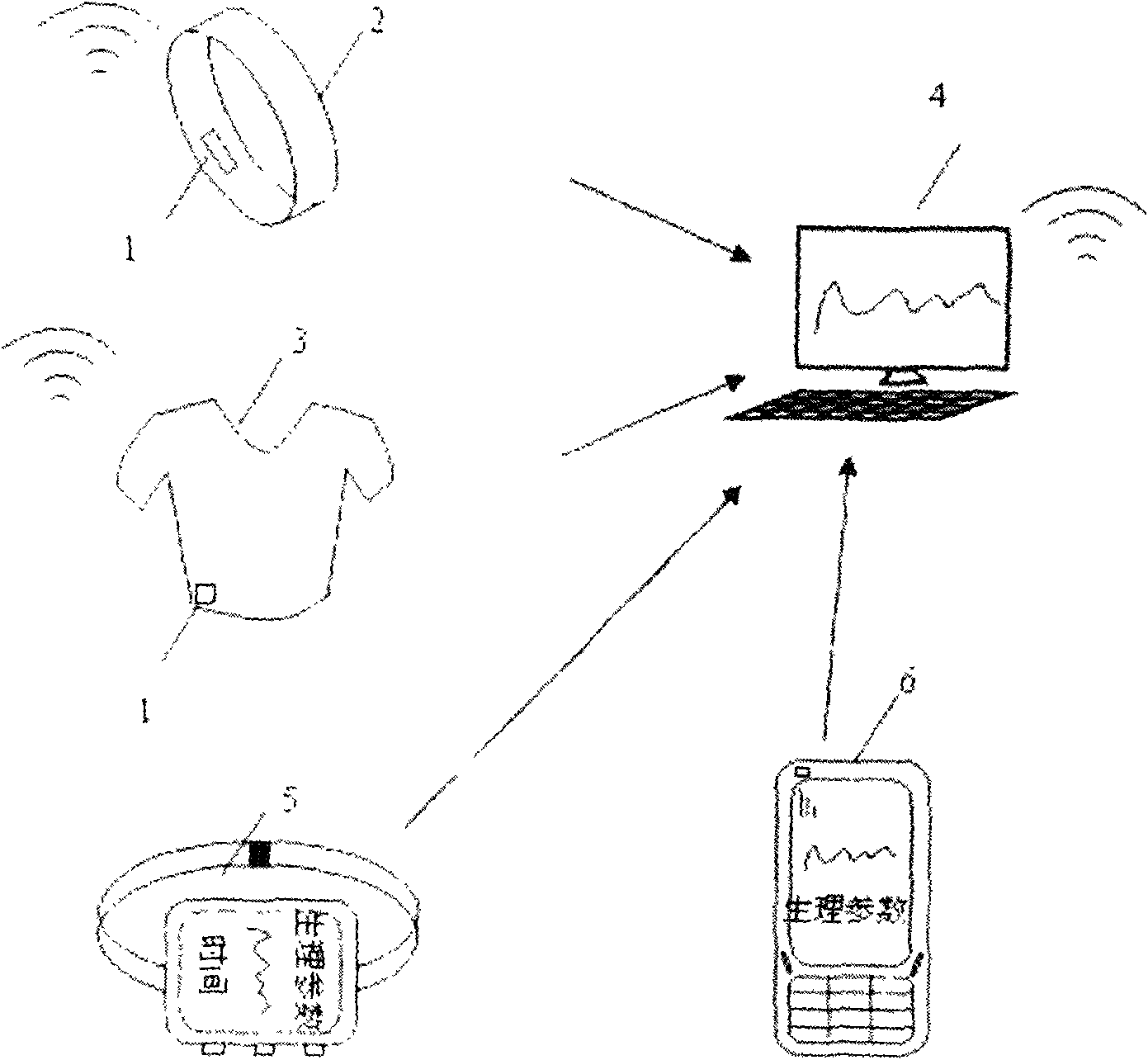
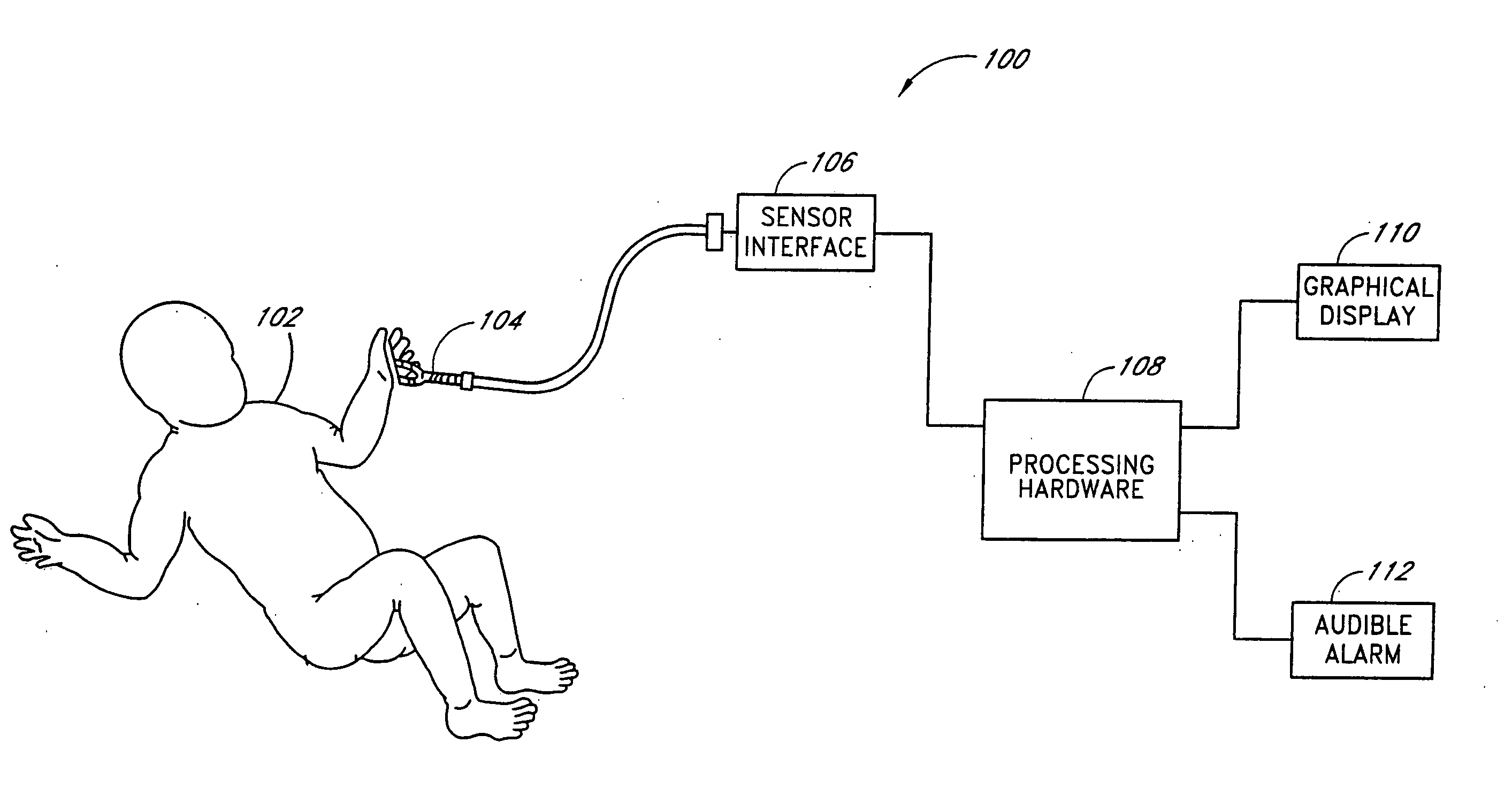
Wearable physiological measuring device
A wearable physiological measuring device has a torso-worn module and a limb-worn module configured to communicate in a wireless way with each other. The torso-worn module is configured to be coupled with a torso of a user to obtain an R-peak from an electrocardiac signal. The limb-worn module is configured to be coupled with at least one limb of four limbs of the user to obtain a pulse wave peak from a plethysmograph signal. There are no physical connections (neither wire nor cable) between the torso-worn module and the limb-worn module. The wearable physiological measuring device is configured to use the R-peak time and the pulse wave peak time to generate a pulse transit time data.
Owner:HONG YUE TECH CORP
Reduced-noise plethysmograph
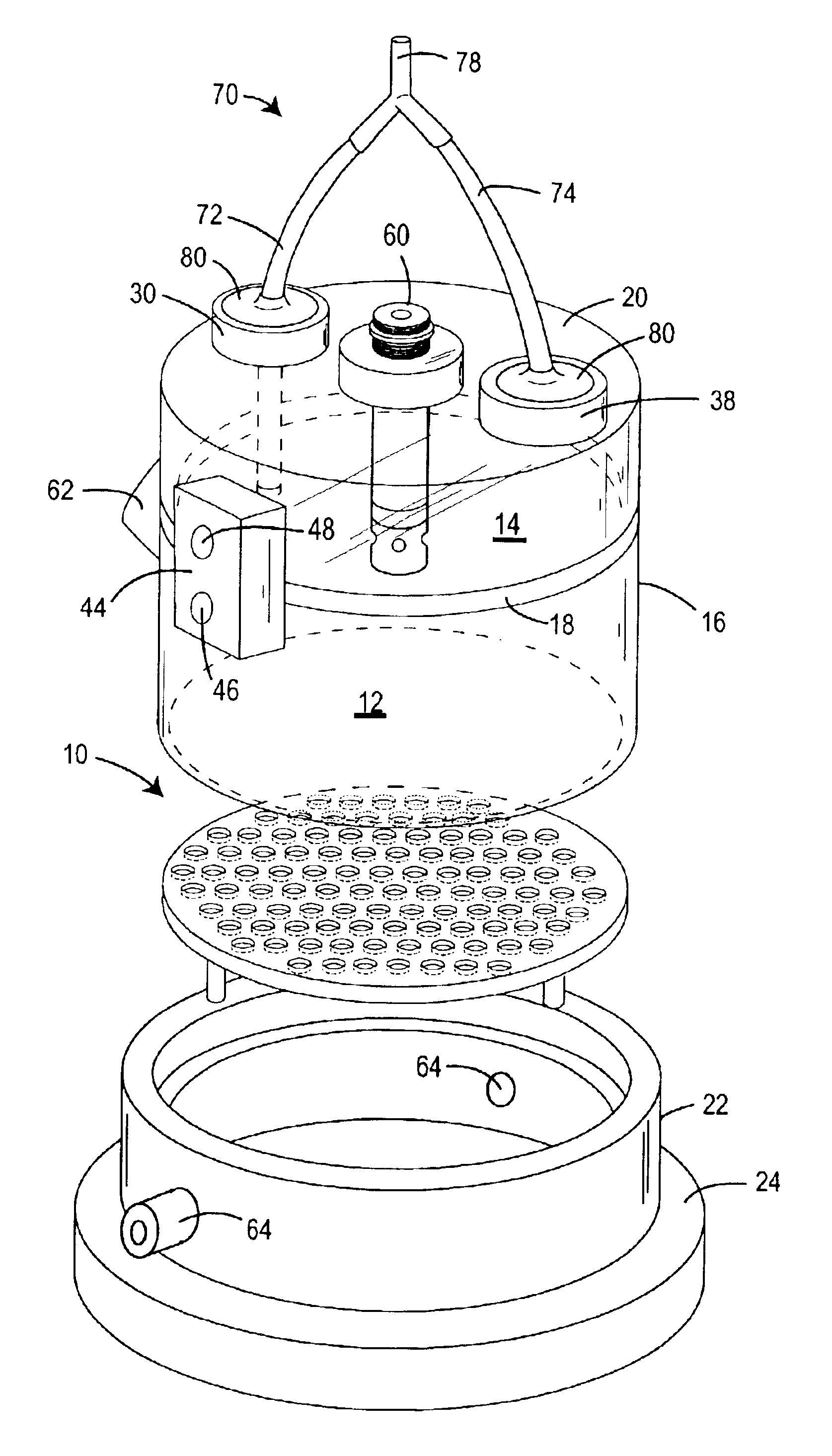
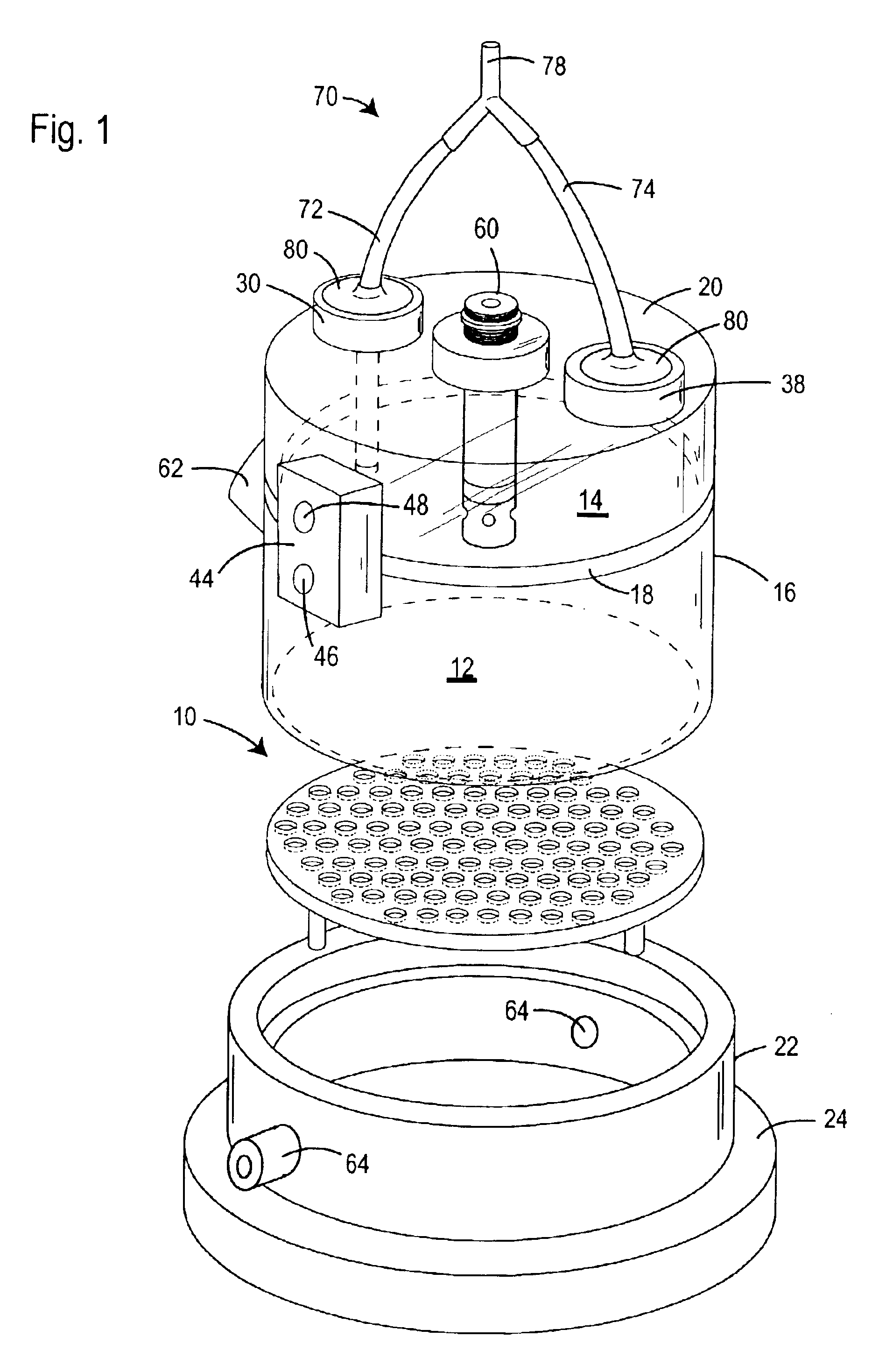
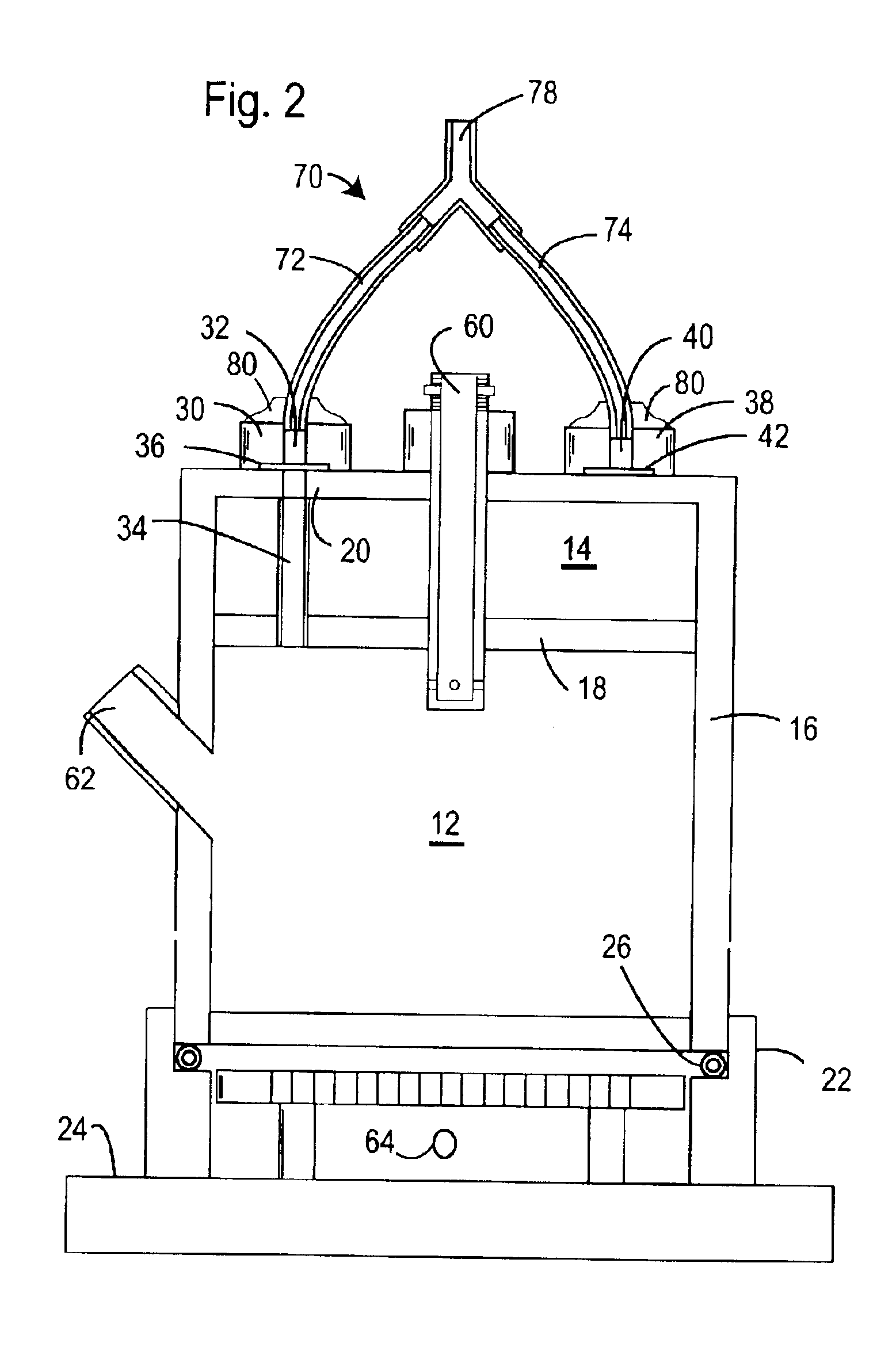
ActiveUS6902532B2Change noiseReduce noiseWeather/light/corrosion resistanceRespiratory organ evaluationAir volumeDifferential pressure
The accuracy of measurements of changes in air volumes within a plethysmograph is improved by addition of a manifold to provide a common source of exterior air to the plethysmograph test and reference chamber. The preferred plethysmograph includes test and reference chambers divided by a common separator wall, pneumotachs in communication with the chambers, and a differential pressure transducer having a first inlet in communication with the test chamber and a second inlet in communication with the reference chamber. The manifold includes an exterior air inlet and a passageway extending between the two pneumotachs and the air inlet. The passageway may be in the form of separate tubes or conduits, or a common housing covering the pneumotachs. Preferably, the distances from the exterior air inlets to the two pneumotachs are approximately the same.
Owner:DATA SCI INT
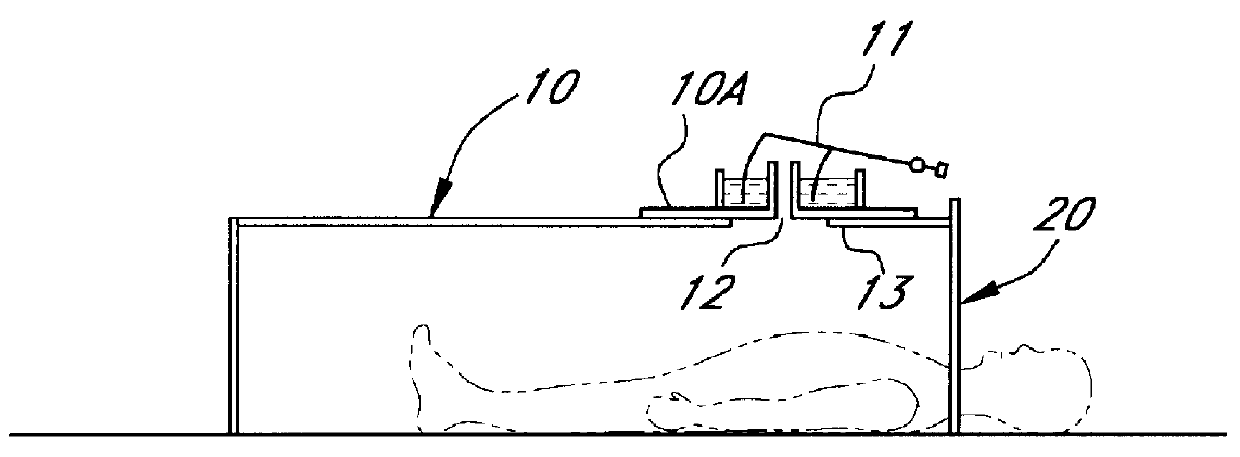
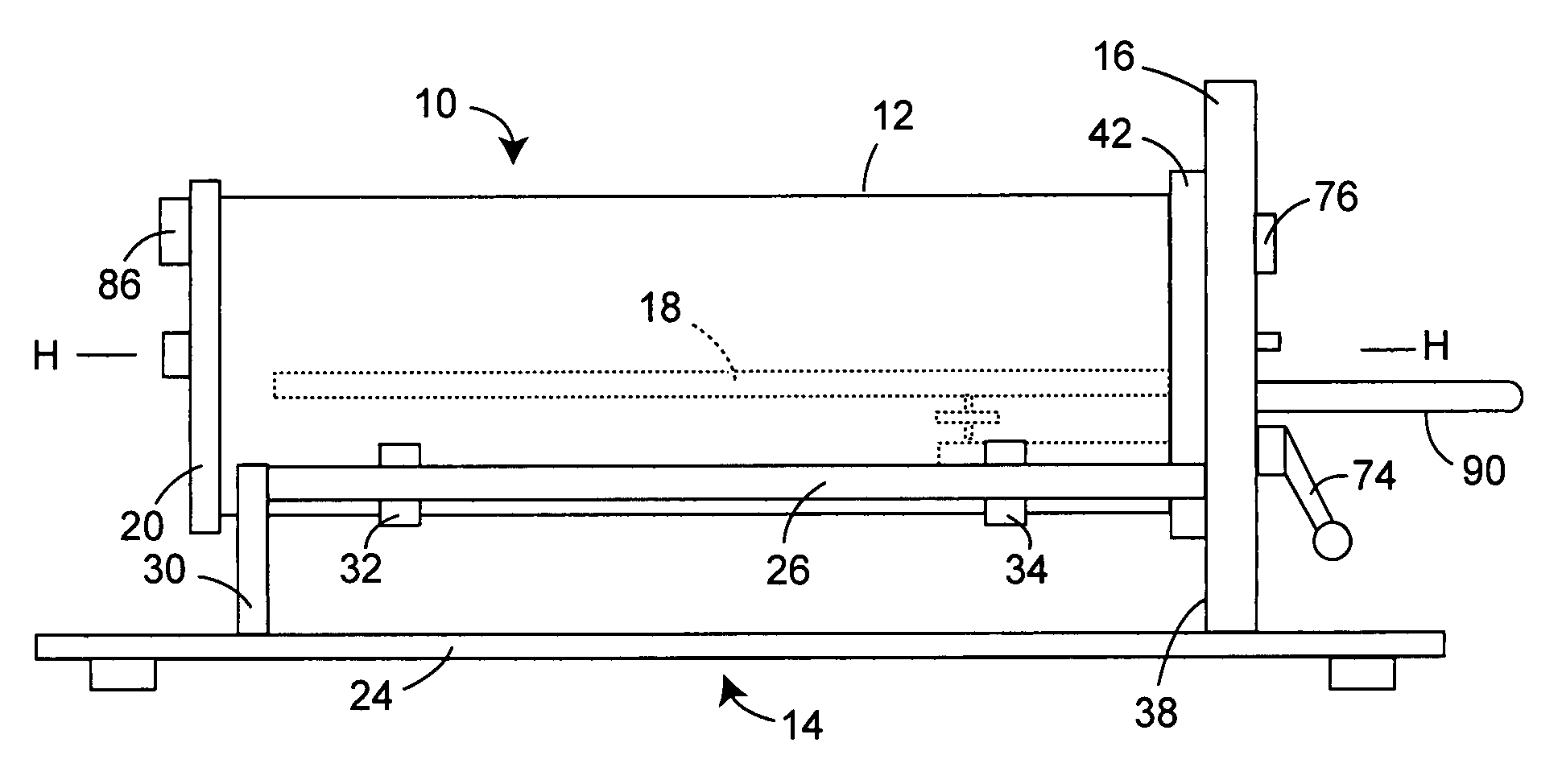
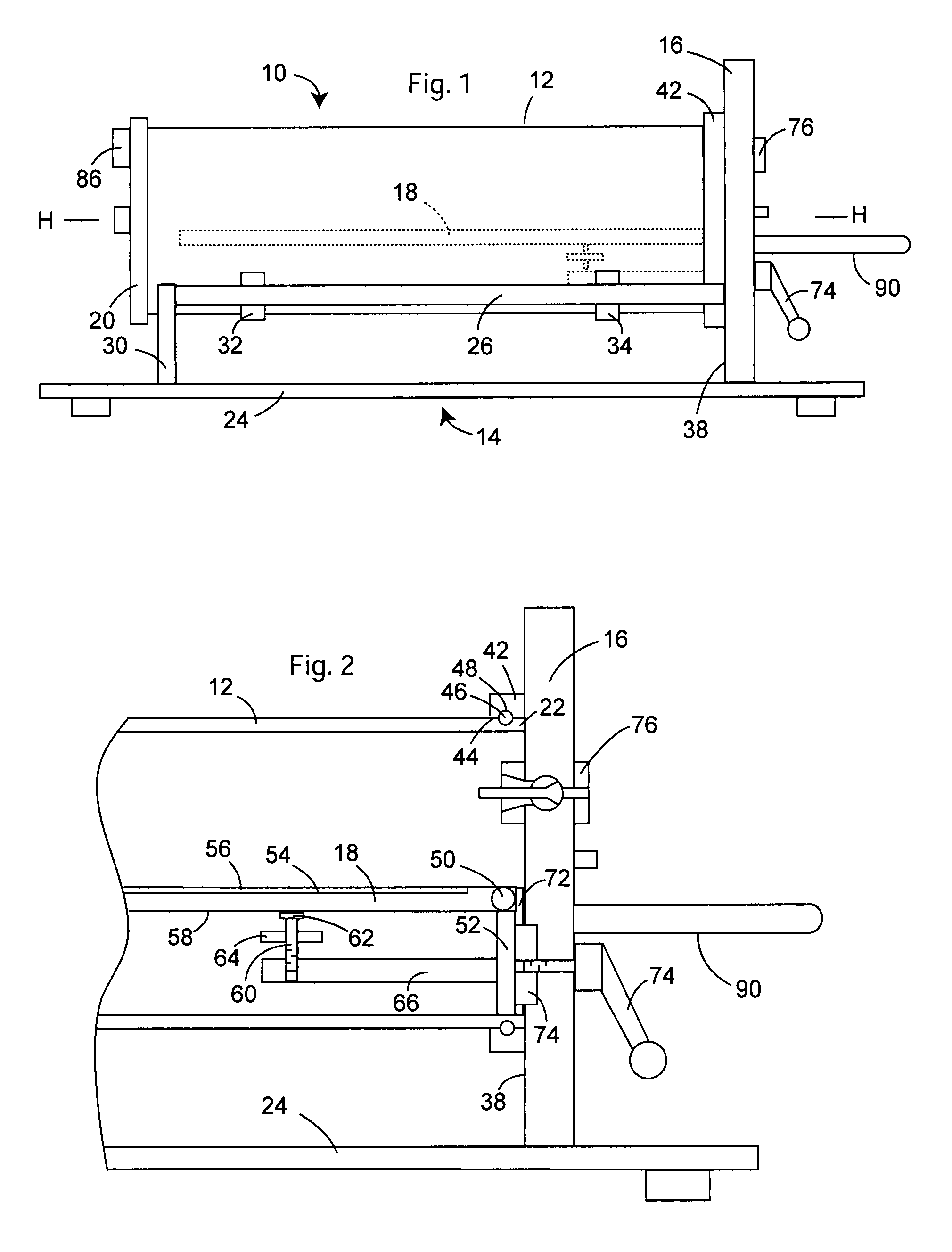
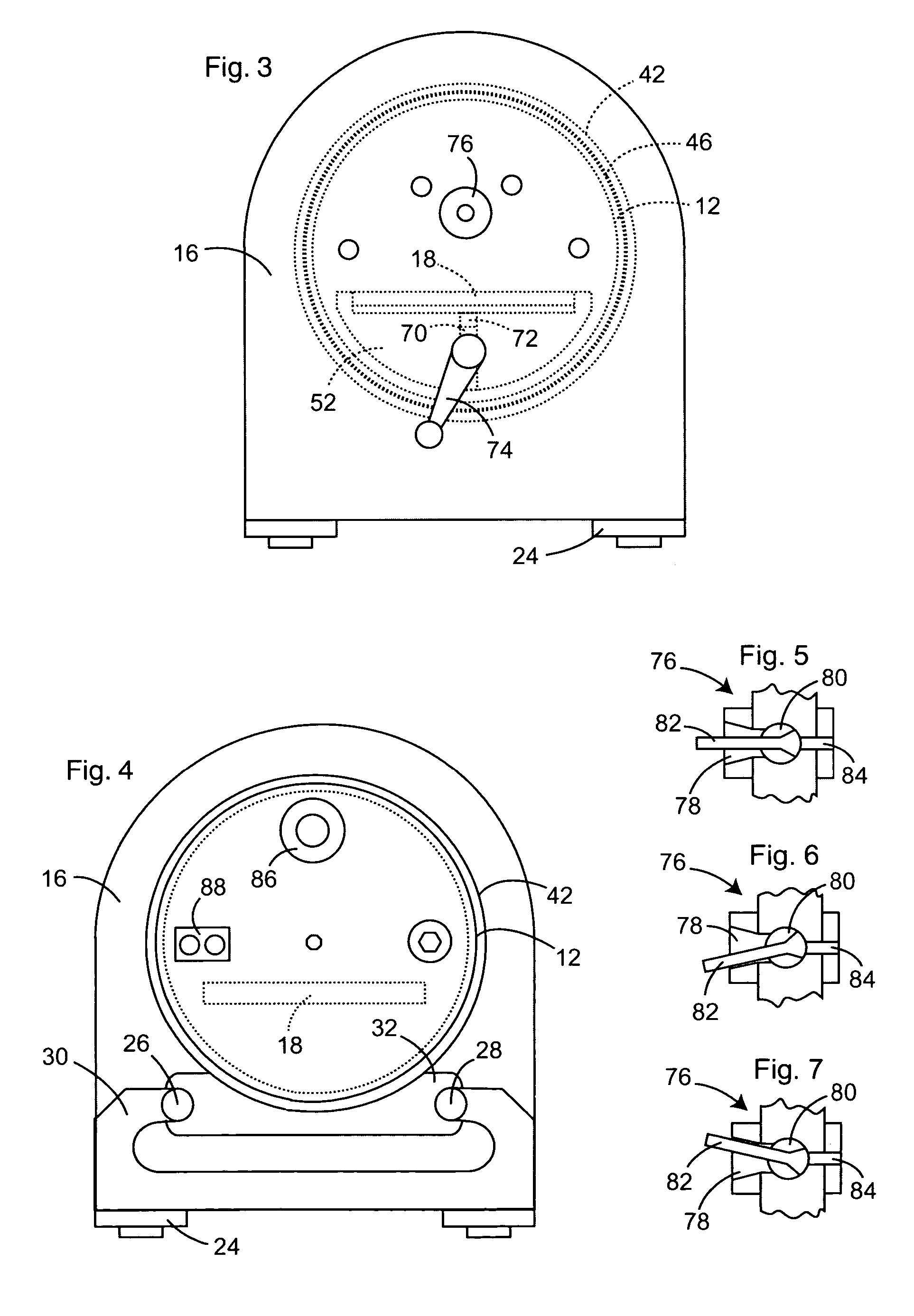
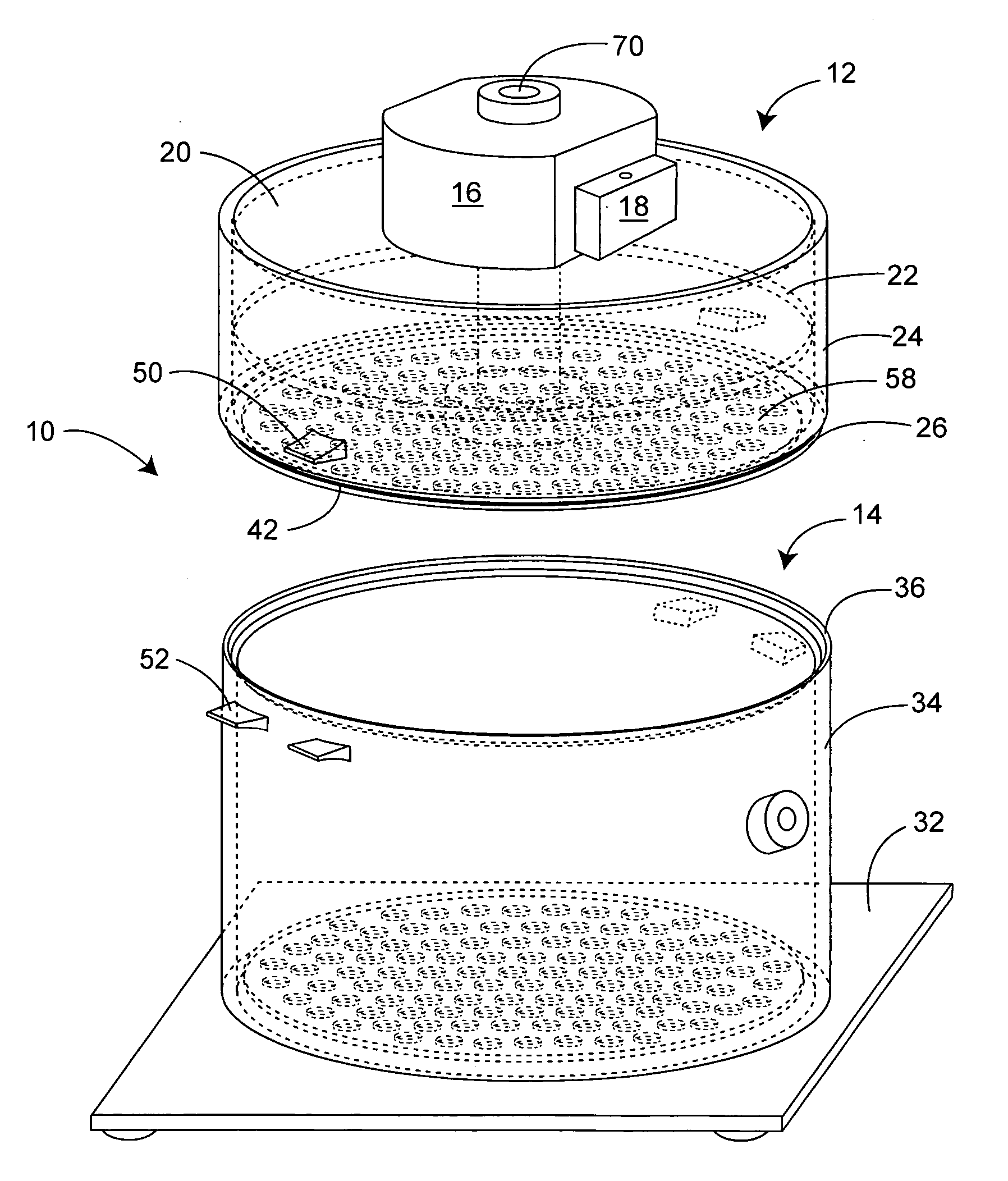
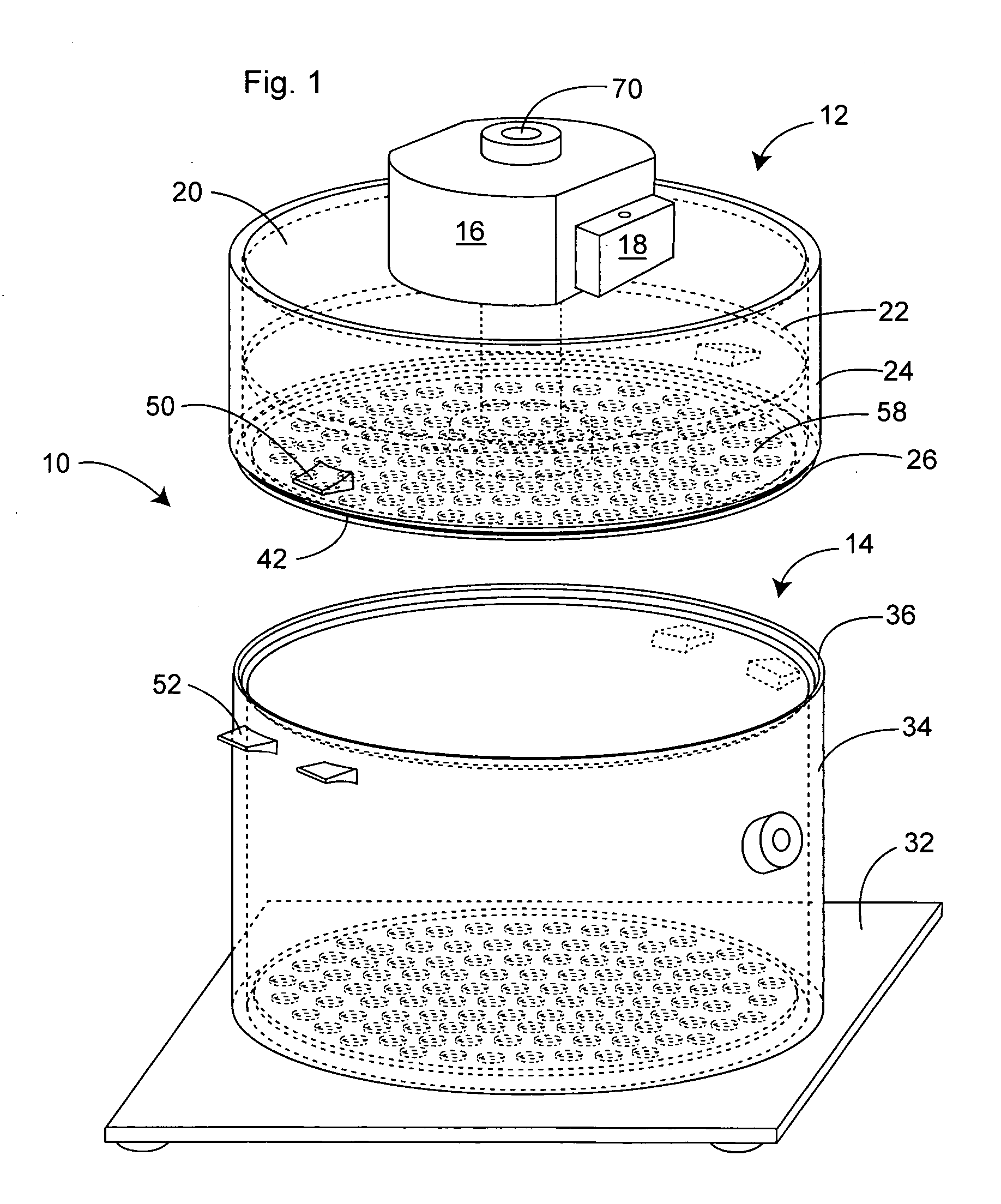
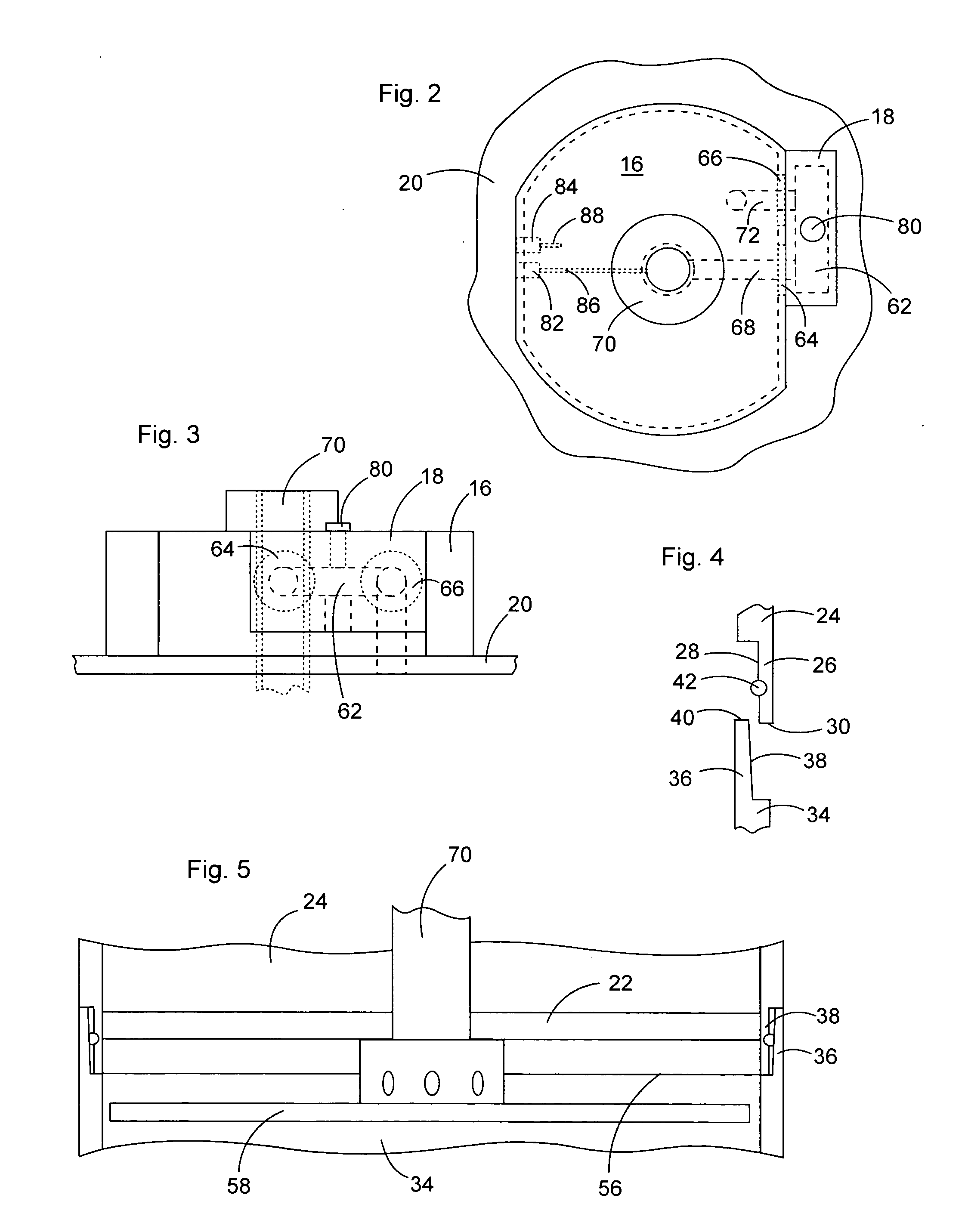
Adjustable table plethysmograph
ActiveUS7402137B2Precise positioningQuick and accurate joinderBreathing protectionTreatment roomsEngineeringPlethysmograph
A plethysmograph is constructed with a base including parallel, horizontal guide rails; an open-ended, moveable enclosure section having a horizontal central axis slidable on the guide rails between open and closed positions; a fixed enclosure section mounted on the base transverse to the horizontal pathway, the fixed enclosure section including an inner face toward the open end of the enclosure section adapted for sealing engagement with the open end of the moveable enclosure section when the moveable enclosure section is in its closed position; and a support table attached to the fixed section, the table projecting into the moveable enclosure section when the moveable enclosure section is in the closed position, the table being vertically adjustable and having an angularly adjustable longitudinal axis.
Owner:DATA SCI INT
Photoplethysmograph (PPG) and terminal
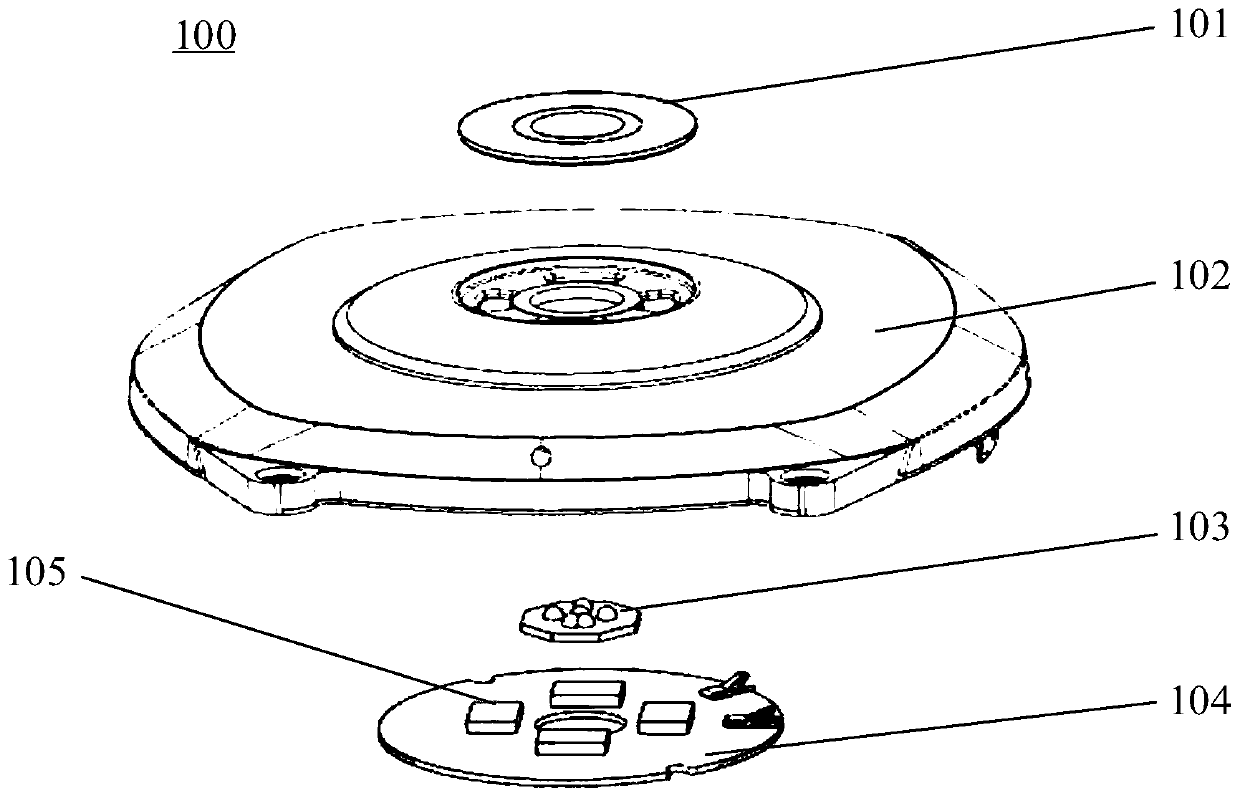
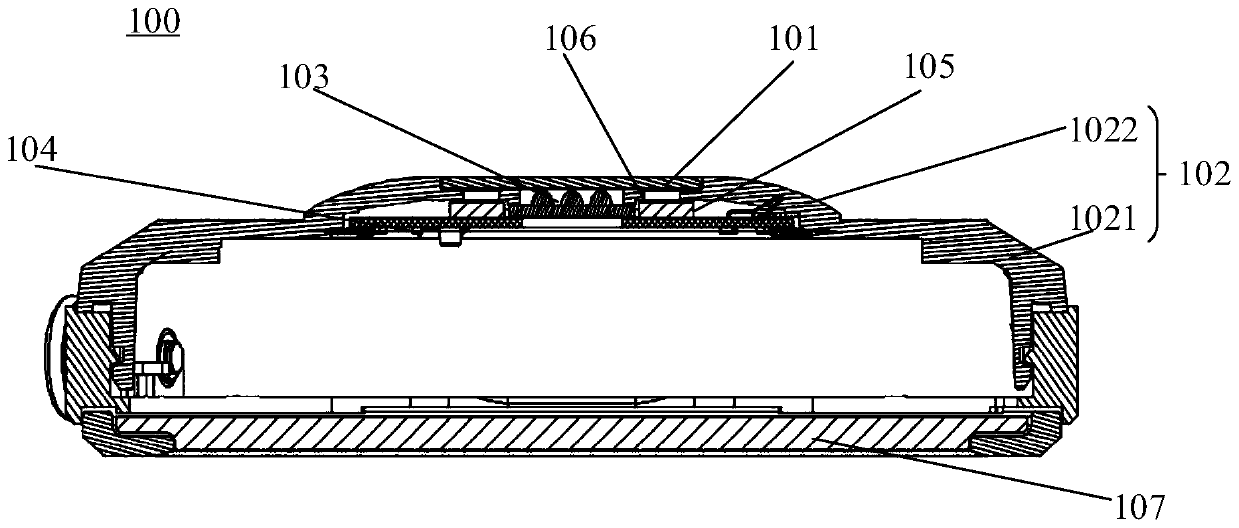
ActiveCN110432883AImprove experienceSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateEngineeringPlethysmograph
An embodiment of the invention discloses a photoplethysmograph (PPG) and a terminal. The PPG comprises a shell, a cover plate, an optical device for emitting light rays outwards as well as photoelectric sensors for receiving external optical signals; the shell and the cover plate define a closed space, and the optical device and the photoelectric sensors are accommodated in the closed space; the cover plate comprises a first area for the optical device to emit light rays outwards and a second area for the photoelectric sensors to receive external optical signals; and the cover plate further comprises a third area, and a shielding structure is arranged on the third area and used for isolating light rays between the optical device and the photoelectric sensors. By arrangement of the shielding structure in the third area, the PPG improves the isolation between the optical device and the photoelectric sensors, avoids light leakage between the optical device and the photoelectric sensors, improves measurement accuracy of the photoelectric sensors and improves user experience.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
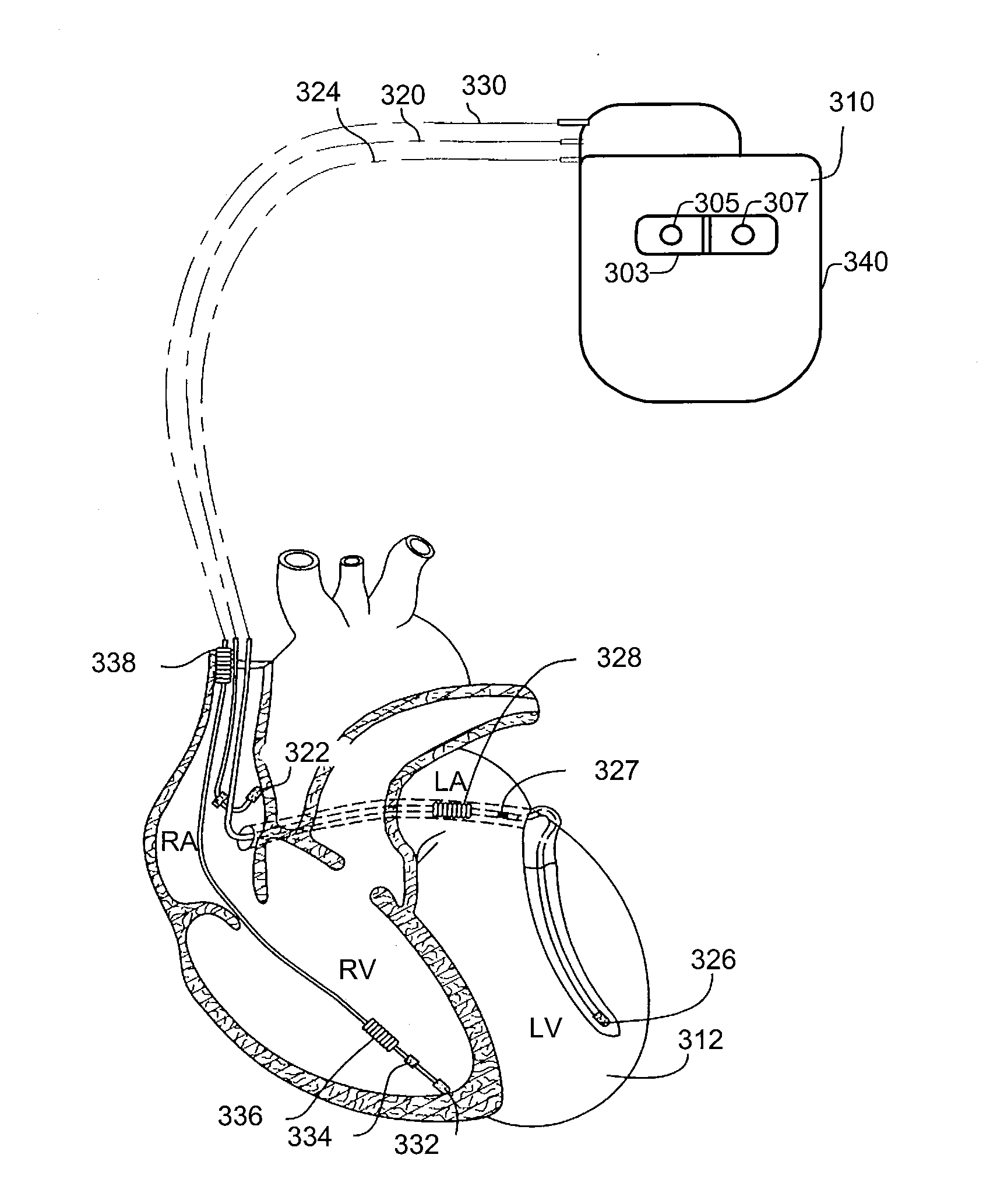
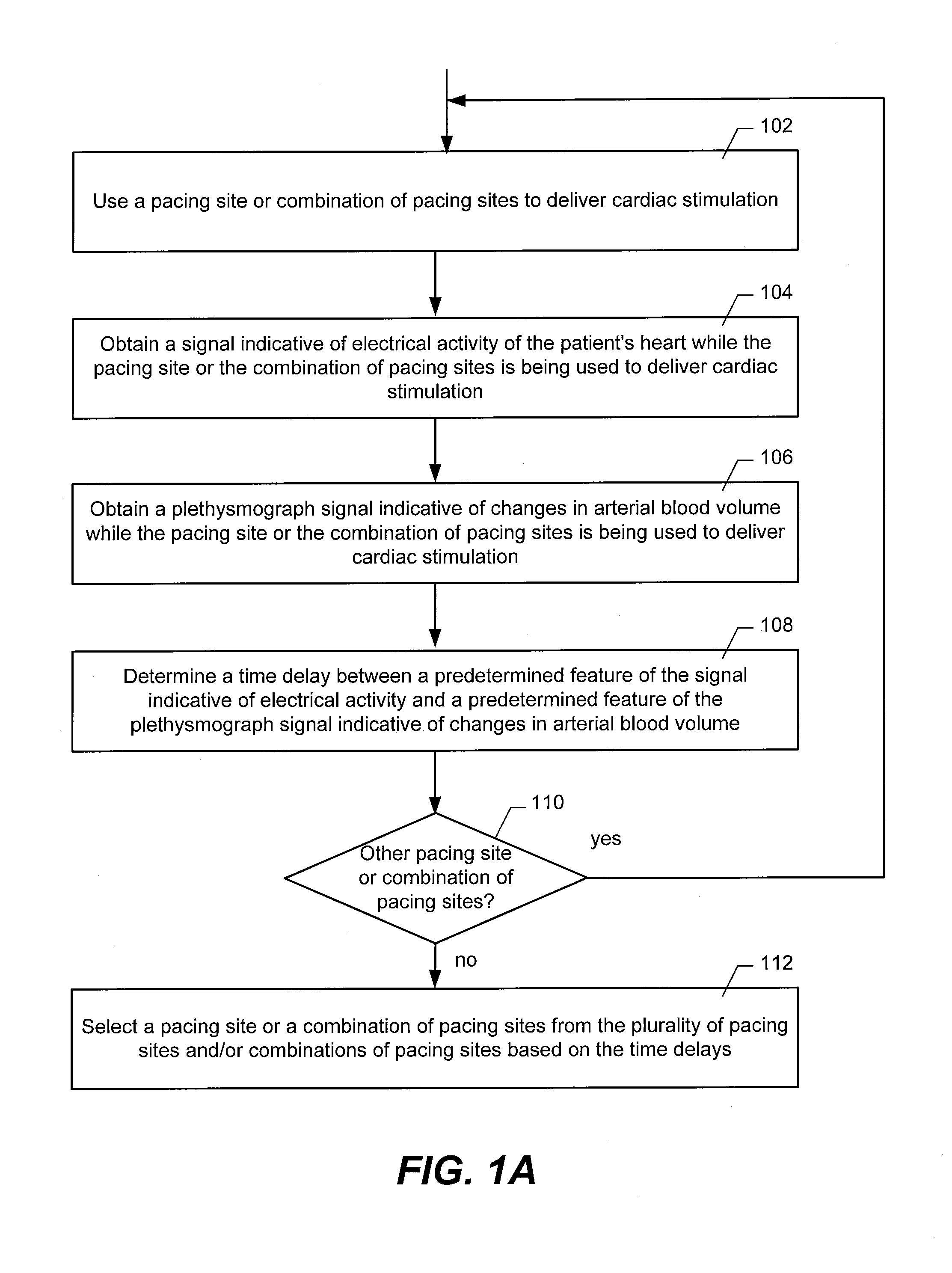
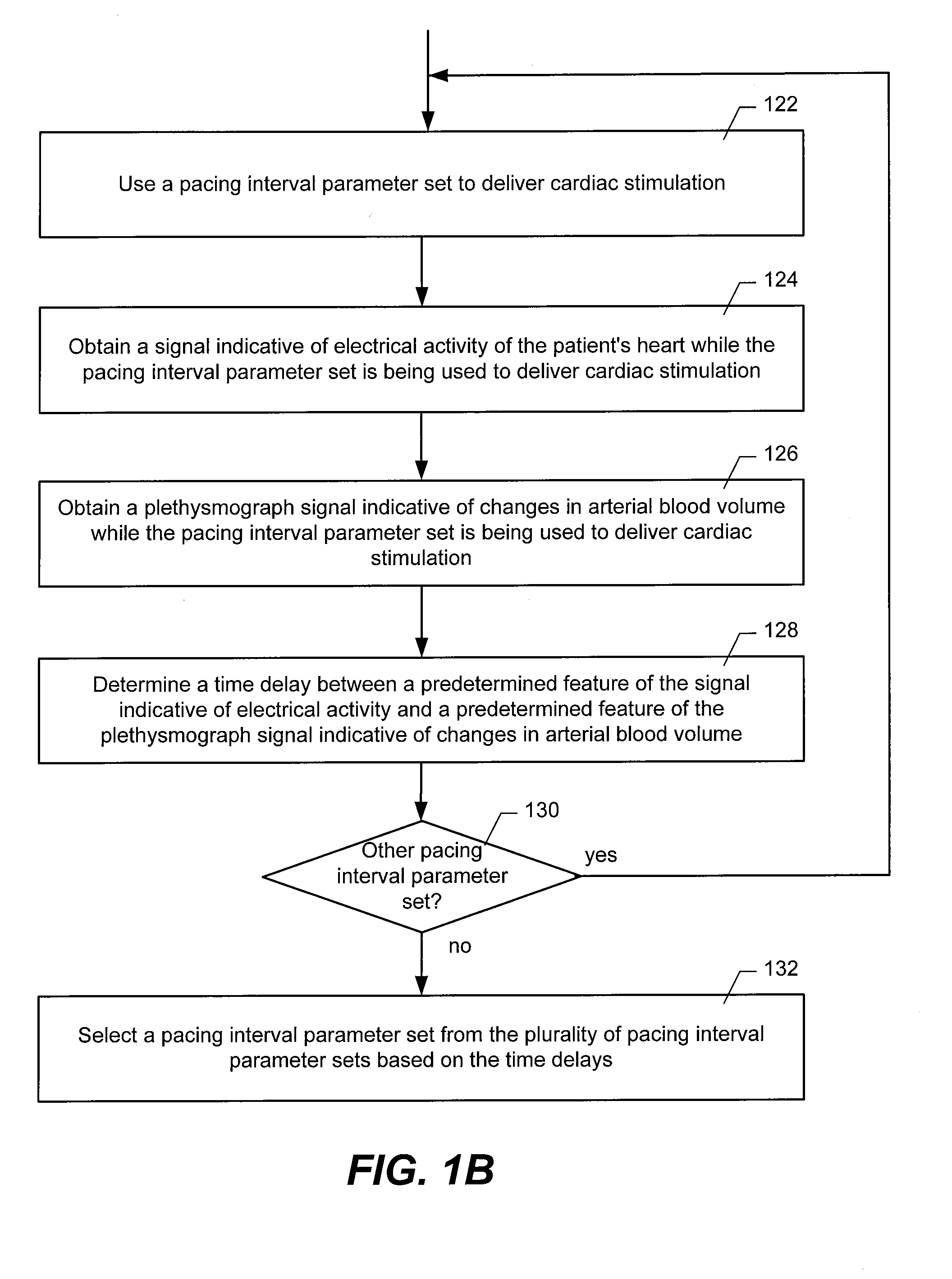
Method and System for Hemodynamic Optimization Using Plethysmography
ActiveUS20110144711A1Short delayLarge stroke volumeElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringPacing intervalBlood flow
Time delays between a feature of a signal indicative of electrical activity of a patient's heart and a feature of a plethysmograph signal indicative of changes in arterial blood volume are used to arrange the operation of an implantable device, such as a pacemaker. Shorter time delays between the feature of the signal indicative of electrical activity of a patient's heart and the feature of the plethysmograph signal indicative of changes in arterial blood volume are indicative of larger cardiac stroke volumes. The time delay can be used to select a pacing site or combination of pacing sites and / or to select a pacing interval set.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
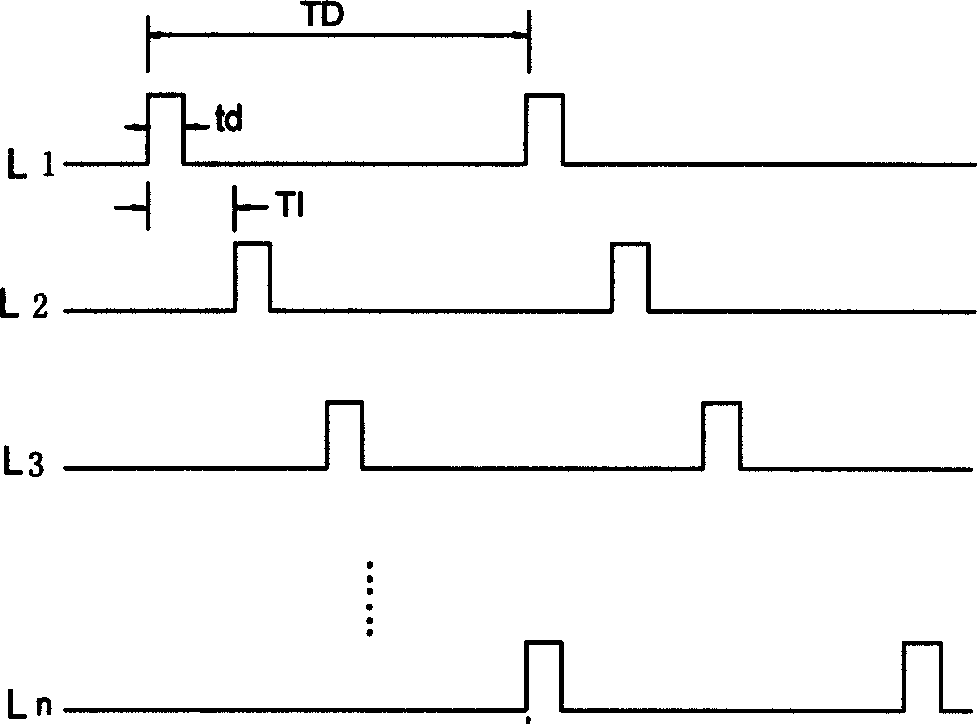
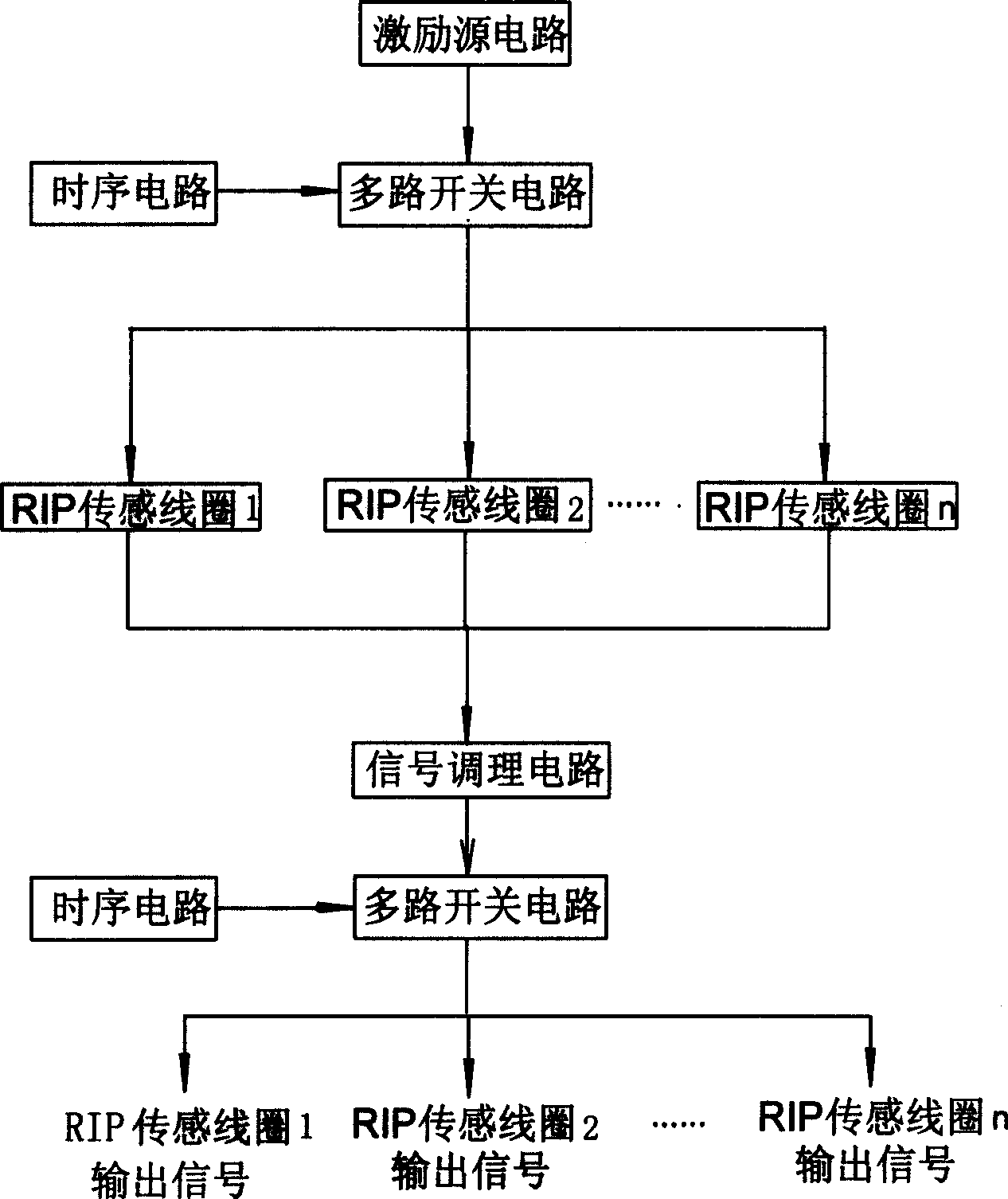
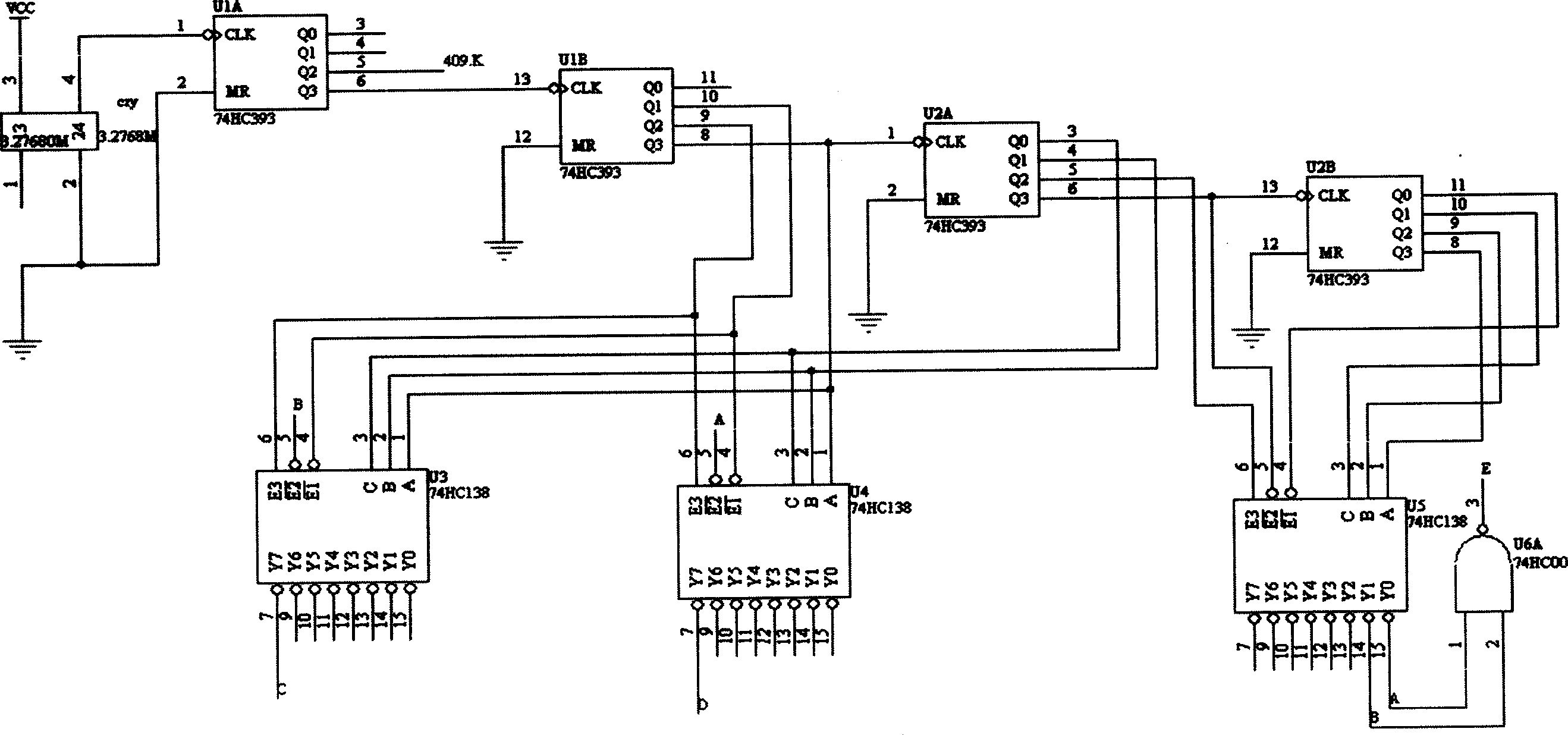
Method and apparatus for exciting sensing coiles of multi-channel breathing sensitive volume discribing device
InactiveCN1745708ASolve mutual interferenceLow average power consumptionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsSignal conditioning circuitsMultiway switching
A method for exciting the sensing coils of multi-channel respiration volume tracer is disclosed, which features that a HF signal exciting source is used to periodically apply the HF exciting pulses to the sensing coils of all channels in time-sharing mode. Its apparatus is composed of an exciting source, timing circuit, multi-channel pulse switch circuit controlled by timing signals and connected to the said sensing coils, and signal conditioning circuit connected to the outputs of sensing coils and the multi-channel switch circuit. Its advantages are low electric consumption, high exciting power and low interference.
Owner:AVIATION MEDICINE INST AIR FORCE PLA +2
Apparatus, Systems and Methods Analyzing Pressure and Volume Waveforms in the Vasculature
Apparatus, systems and methods are provided for analyzing relative compliance in the peripheral vasculature. Such apparatus, systems and methods generally involve generating a plethysmograph (PG) signal, generating one or more pressure waveforms and comparing the pressure waveform(s) relative to the PG signal to determine compliance indexes associated particular regions of the vasculature. A relative compliance ratio may also be determined by comparing arterial and venous relative compliance indexes. Apparatus, systems and methods are also provided for analyzing a PG waveform. Such apparatus, systems and methods generally involve generating a plethysmograph (PG) signal and comparing amplitude modulation of the PG signal relative to baseline modulation of the PG signal to estimate a relationship between left ventricular end diastolic pressure and stroke volume. The estimated relationship may account for a phase offset for the time between when changes in venous return affect left ventricular end diastolic pressure and stroke volume.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Large diameter plethysmograph
ActiveUS20070179394A1Reduce background noiseEfficient productionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEngineeringTest chamber
A plethysmograph is described that includes a reference chamber having a top wall, a bottom wall, a barrier wall spaced beneath the bottom wall, a continuous side wall having a lower edge, and a first continuous flange with a lower edge below the bottom wall and above the barrier wall; a test chamber having a bottom wall, a continuous side wall with an upper edge, and a second continuous flange extending upwardly from the upper edge, the interior face of one of the flanges including an annular groove with an O-ring in the groove, and the interior face of the other flange being tapered from vertical by up to about 1°; and a manifold having airflow openings in communication with the reference and test chamber and a common exterior airflow opening through a passageway, and a sampling port in communication with the passageway.
Owner:DATA SCI INT
Wearable smart T-shirt capable of detecting health data in real time
The invention discloses a wearable smart T-shirt capable of detecting health data in real time. The wearable smart T-shirt is characterized in that electro-conductive fibers are sewn on the T-shirt; electrocardio inductive sensors, respiratory inductive plethysmograph sensors, elastic gloves, oxyhemoglobin saturation monitors, T-shirt and glove connecting interfaces and a portable compressed oxygen and face mask are connected with a main unit and power supply through the electro-conductive fibers; the electrocardio inductive sensors, the respiratory inductive plethysmograph sensors, an elastic chest band and an elastic bellyband are sewn on the body-fitting face of the T-shirt; the elastic gloves are connected with the T-shirt through the T-shirt and glove connecting interfaces; the main unit and power supply, the portable compressed oxygen and face mask and a first-aid health package are integrated; the first-aid health package is arranged at the waist part of the T-shirt. The wearable smart T-shirt can realize real-time health data monitoring, data integration and wireless transmission, provide acousto-optic and vibrating alarms after data exceeds the early-warning value, and further provide first-aid treatment through the first-aid health package, the portable compressed oxygen and face mask at the first moment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com