Patents
Literature
4172 results about "Cuff" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cuff is a layer of fabric at the lower edge of the sleeve of a garment (shirt, coat, jacket, etc.) at the wrist, or at the ankle end of a trouser leg. The function of turned-back cuffs is to protect the cloth of the garment from fraying, and, when frayed, to allow the cuffs to be readily repaired or replaced, without changing the garment. Cuffs are made by turning back (folding) the material, or a separate band of material can be sewn on, or worn separately, attached either by buttons or studs. A cuff may display an ornamental border or have lace or some other trimming. In US usage, the word trouser cuffs refers to the folded, finished bottoms of the legs of a pair of trousers.
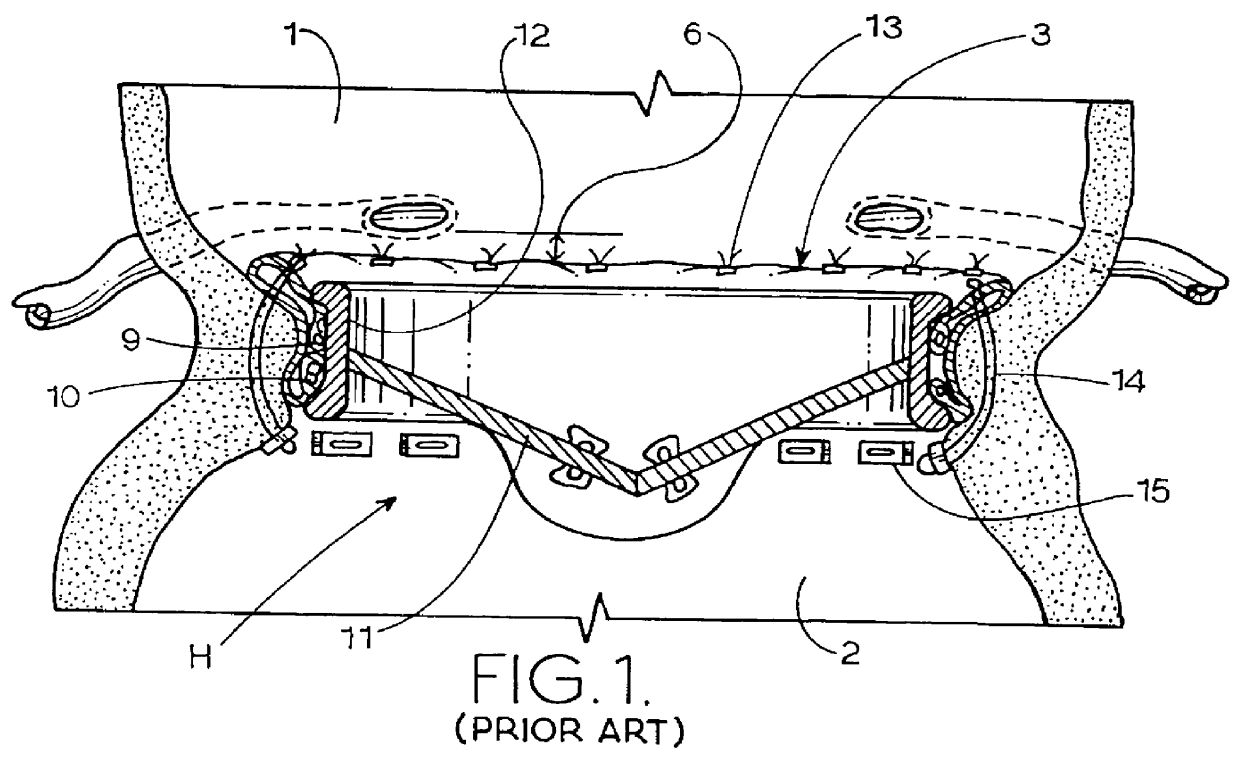
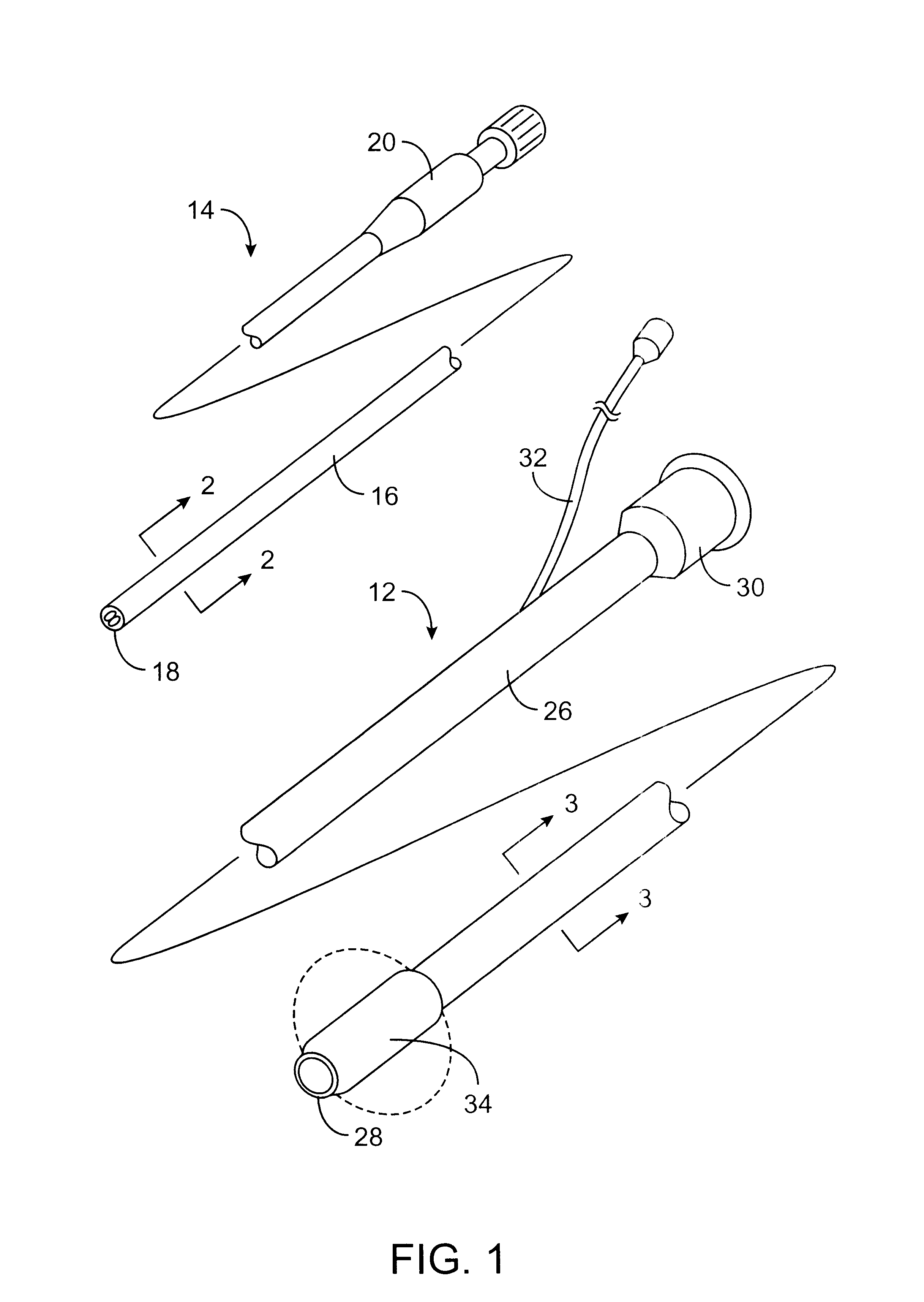
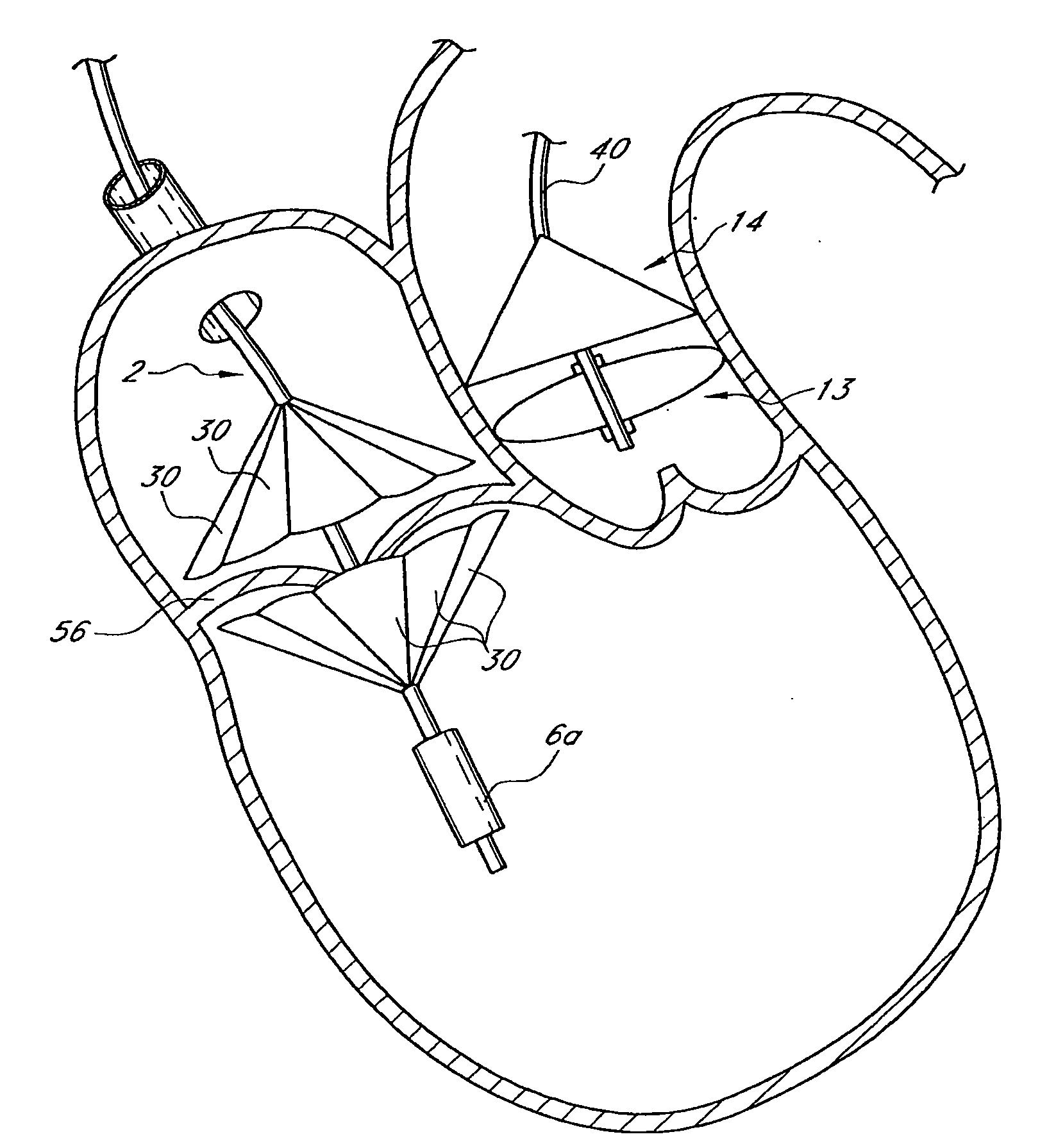
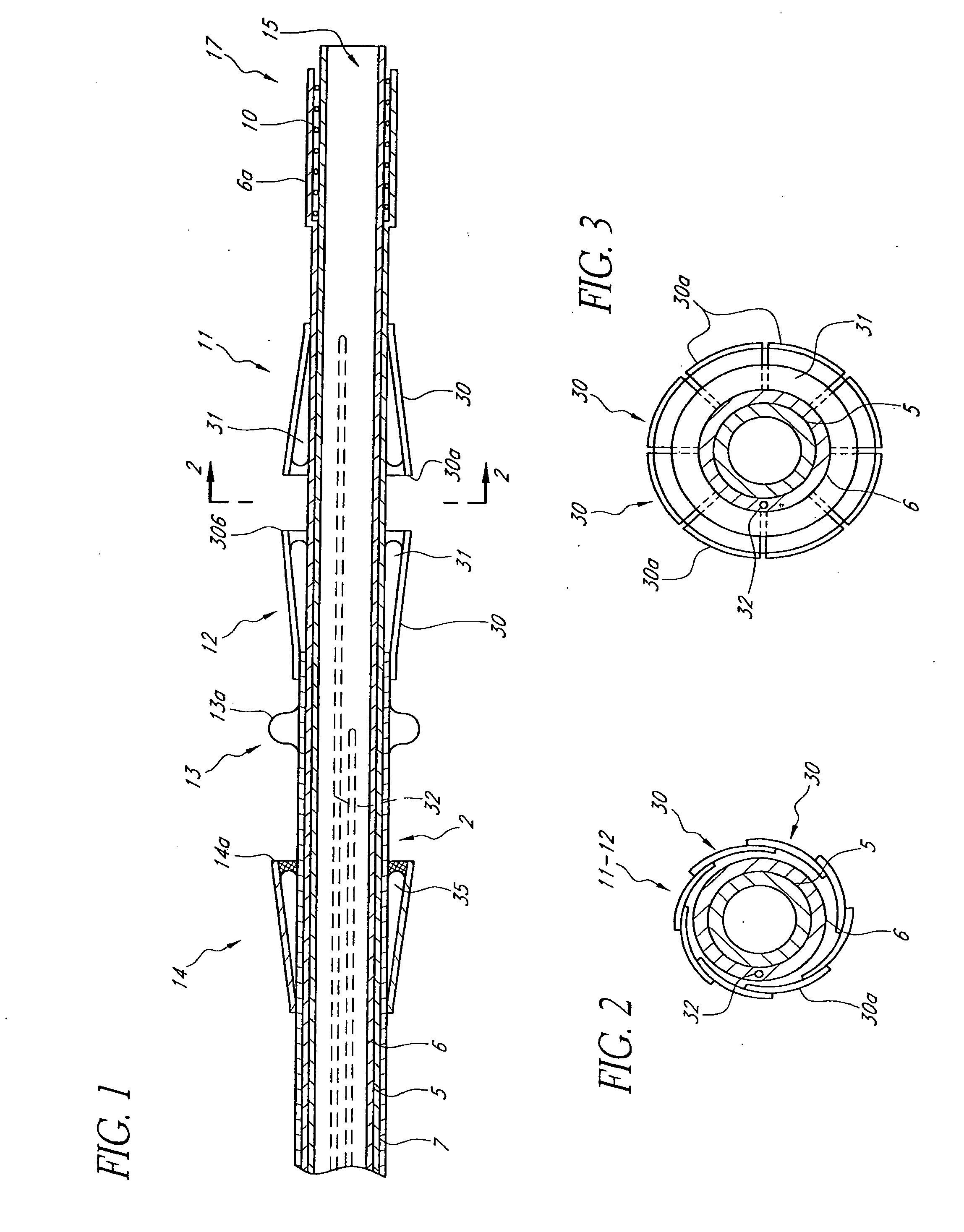
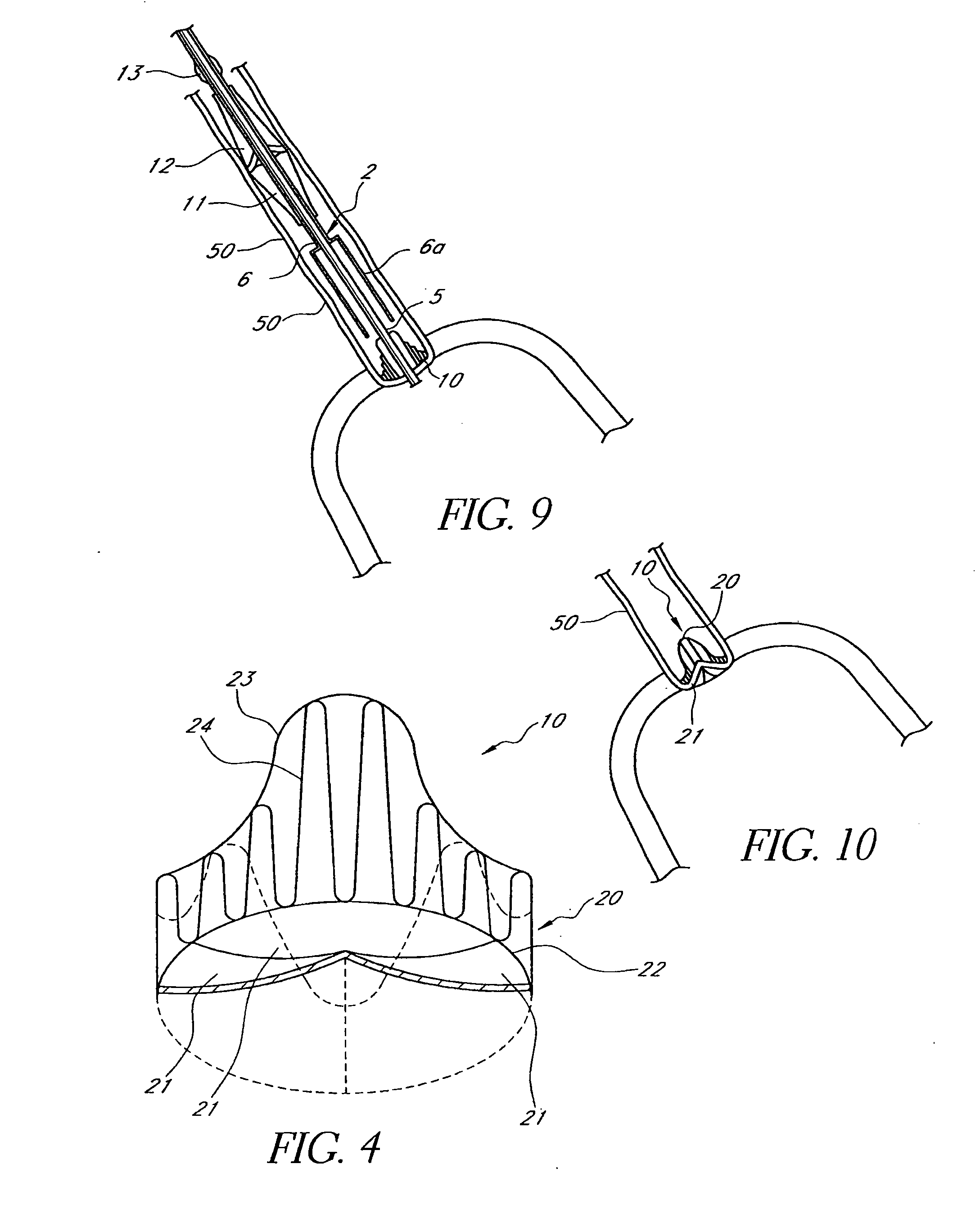
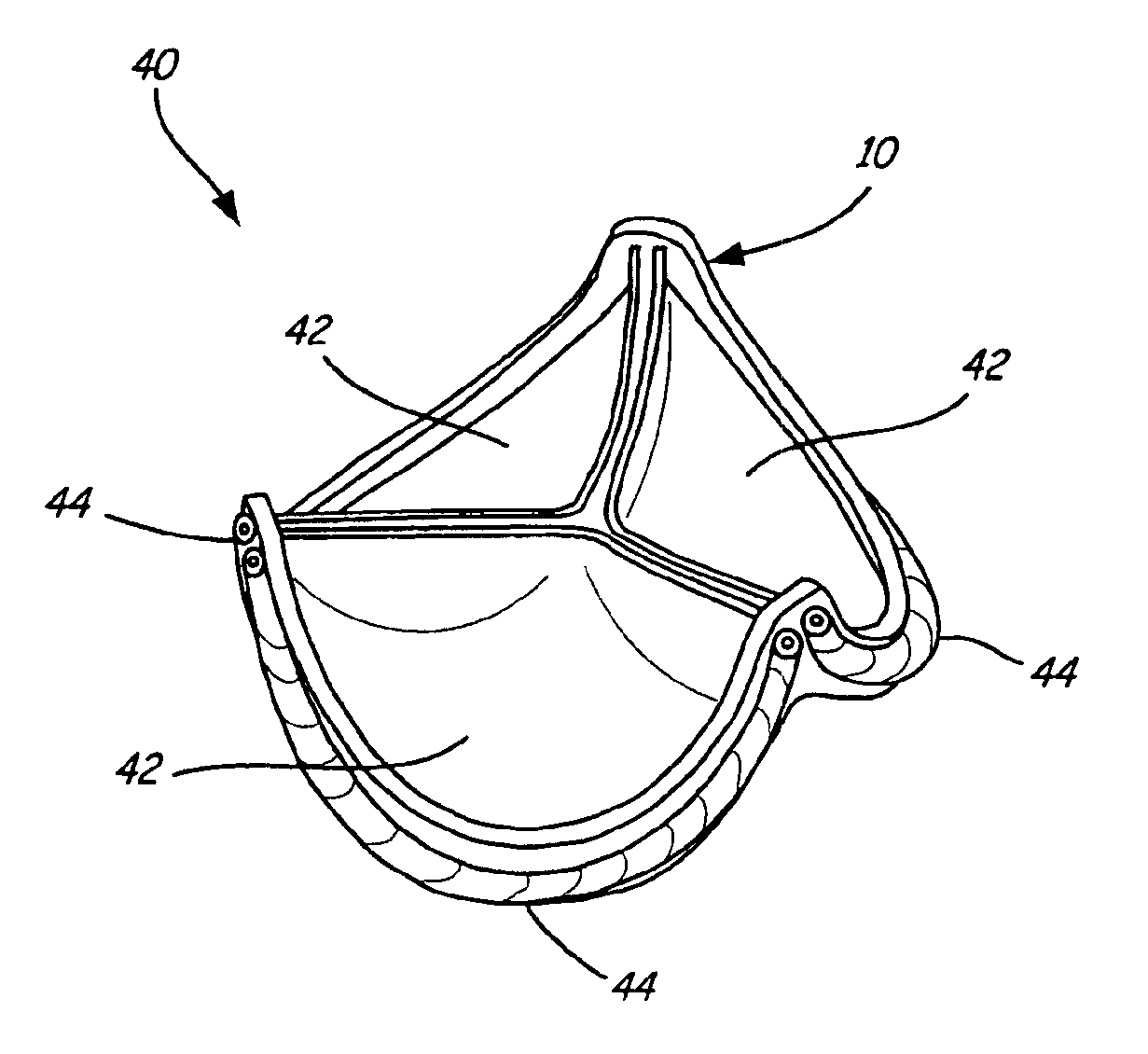
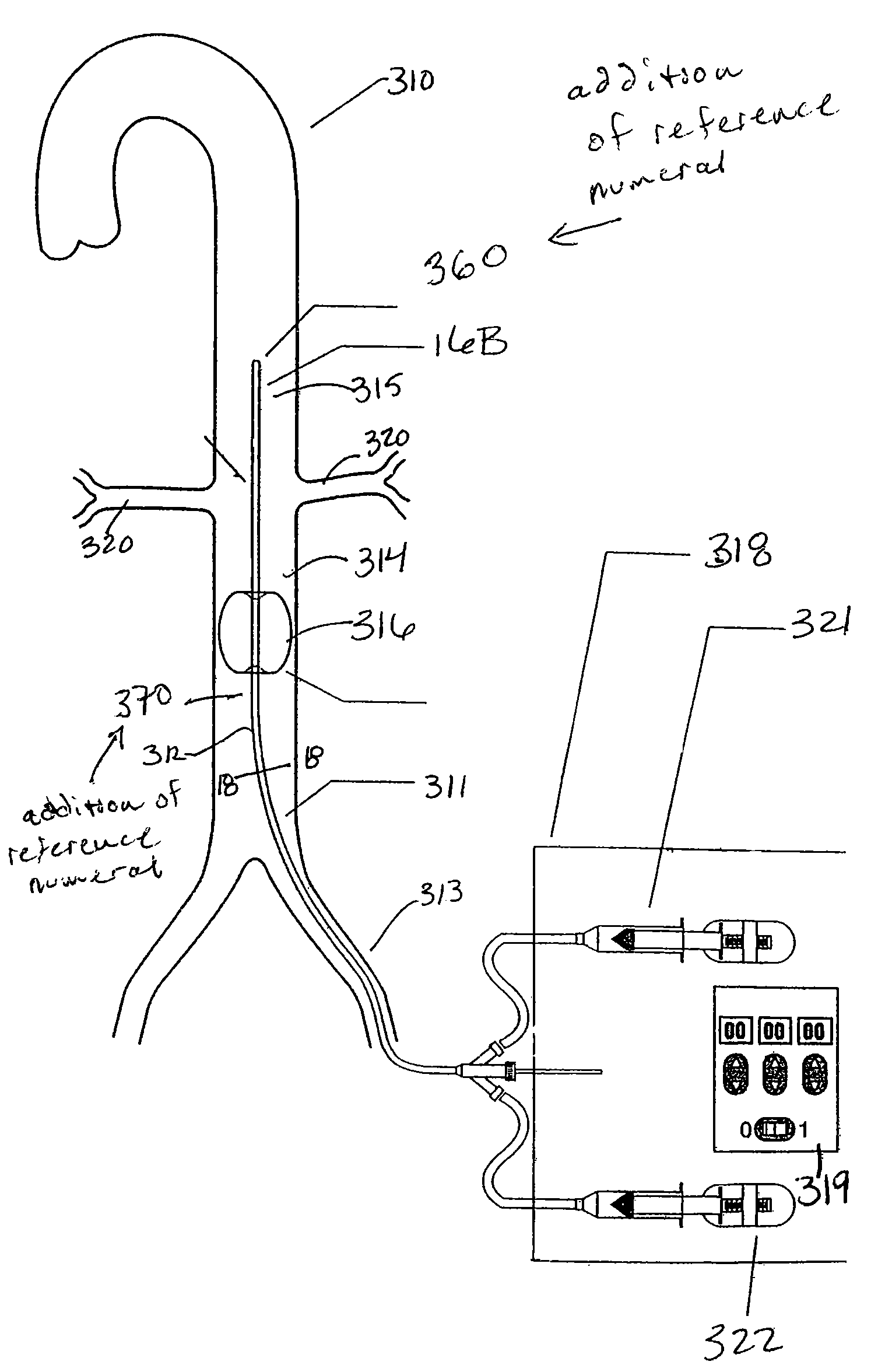
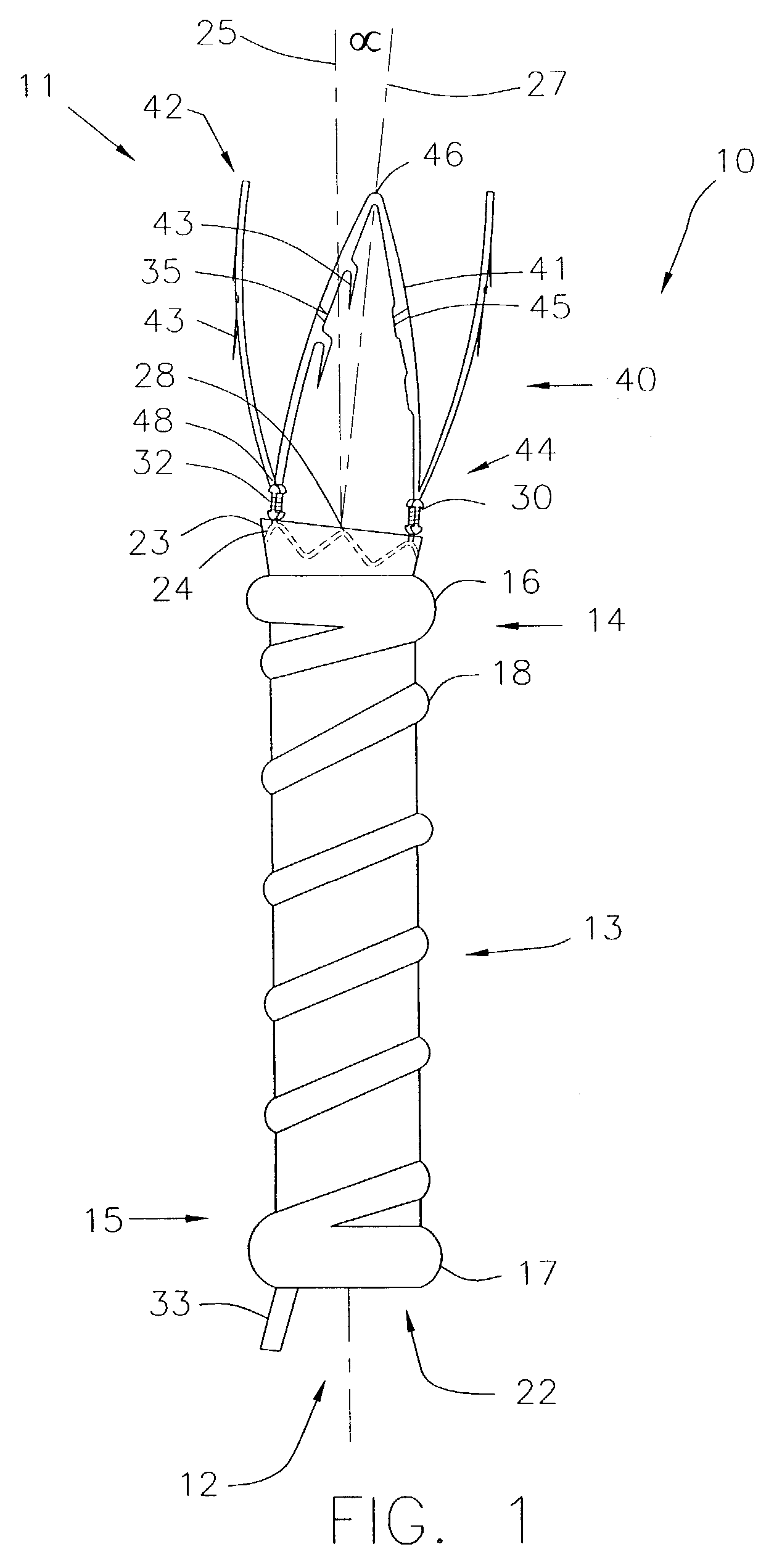
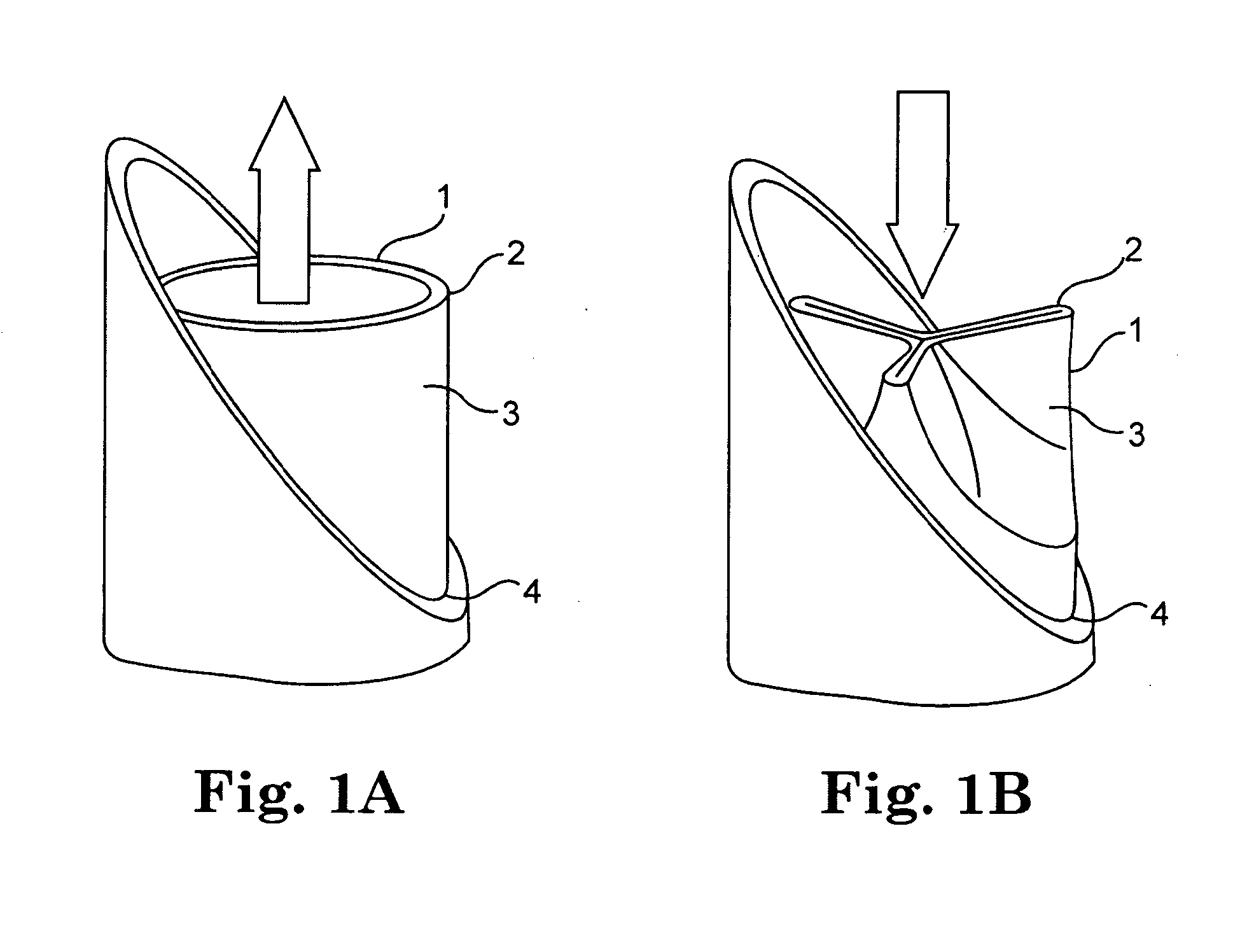
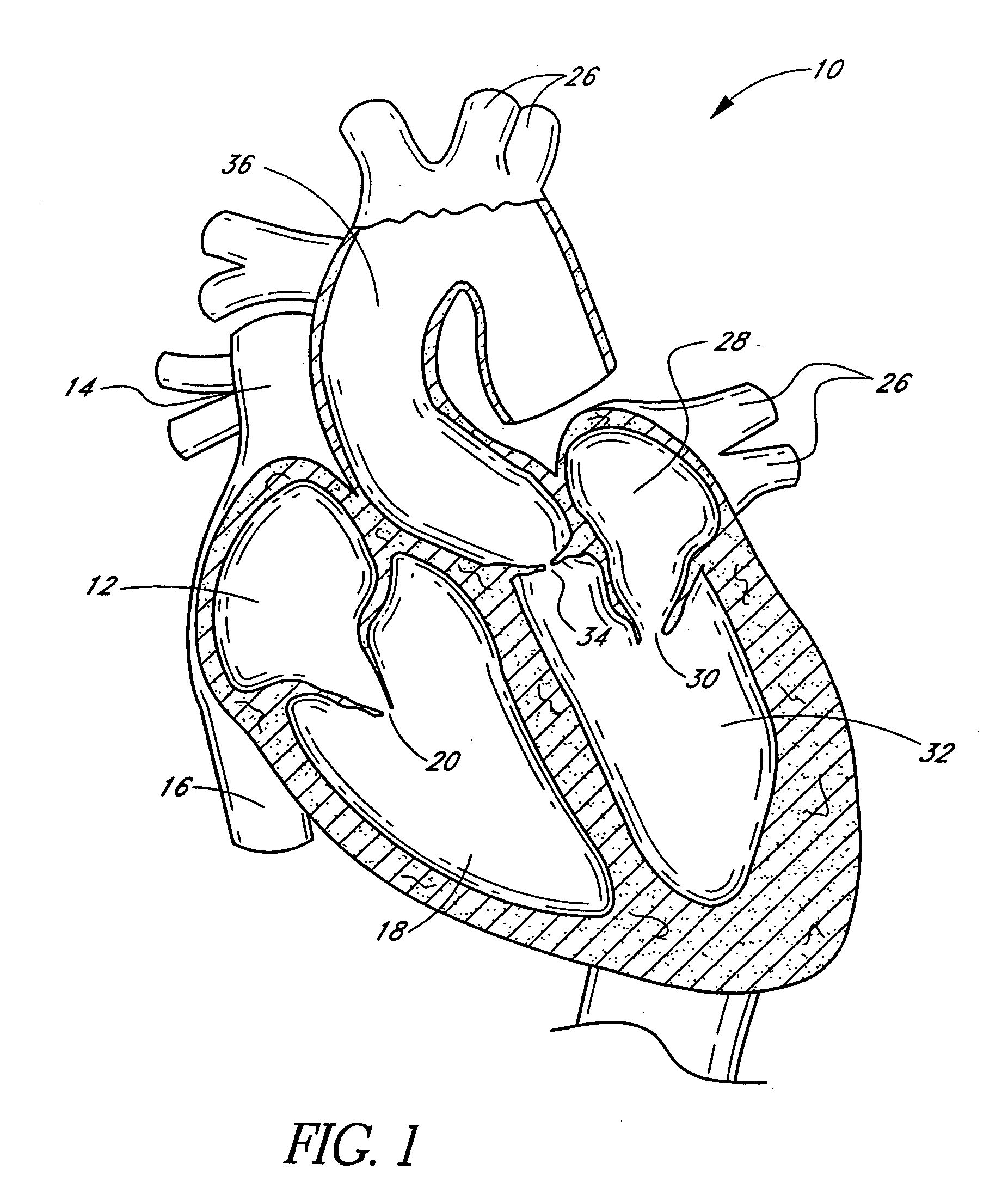
Means and method of replacing a heart valve in a minimally invasive manner
InactiveUS6042607AMinimally invasiveEfficient and effectiveSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLess invasive surgeryCuff
A heart valve can be replaced using minimally invasive methods which include a sutureless sewing cuff that and a fastener delivery tool that holds the cuff against the patient's tissue while delivering fasteners, two at a time to attach the cuff to the tissue from the inside out. The tool stores a plurality of fasteners. Drawstrings are operated from outside the patient's body and cinch the sewing cuff to the valve body. The cuff is releasably mounted on the tool and the tool holds the cuff against tissue and drives the fastener through the cuff and the tissue before folding over the legs of the fastener whereby secure securement between the cuff and the tissue is assured. At least two rows of staggered fasteners are formed whereby fasteners are located continuously throughout the entire circumference of the cuff. A minimally invasive surgical method is disclosed, and a method and tool are disclosed for repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in a minimally invasive manner.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
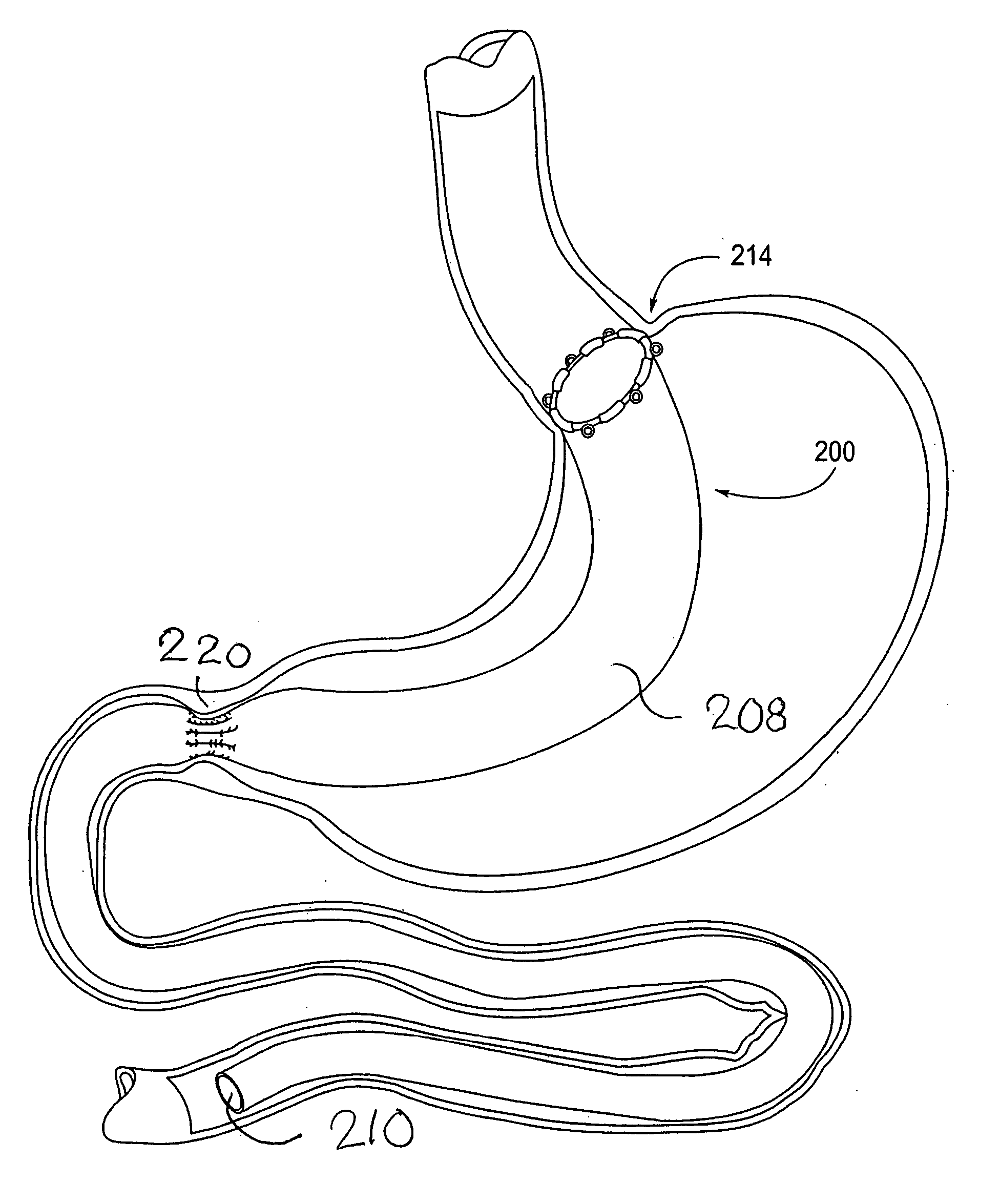
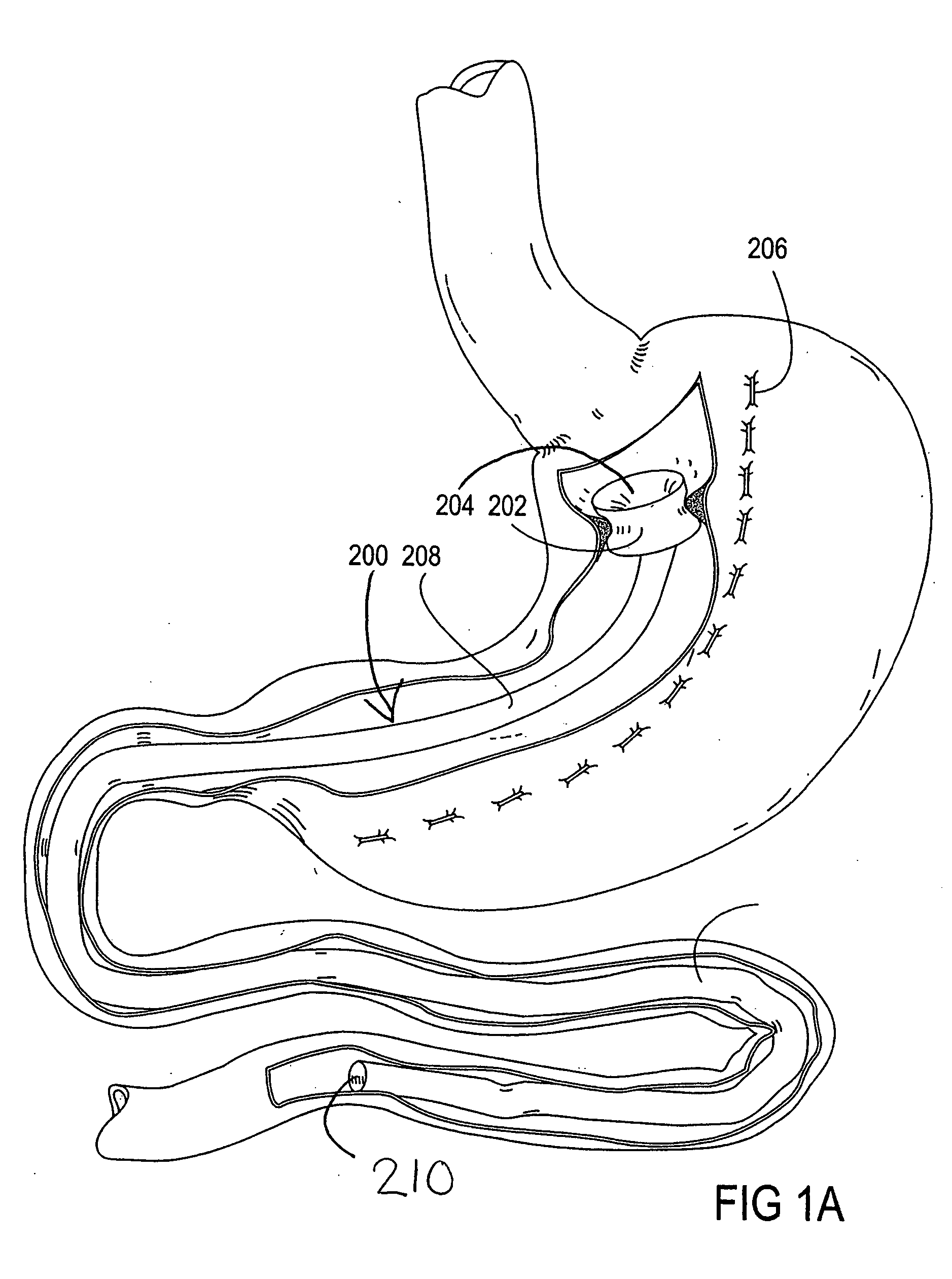
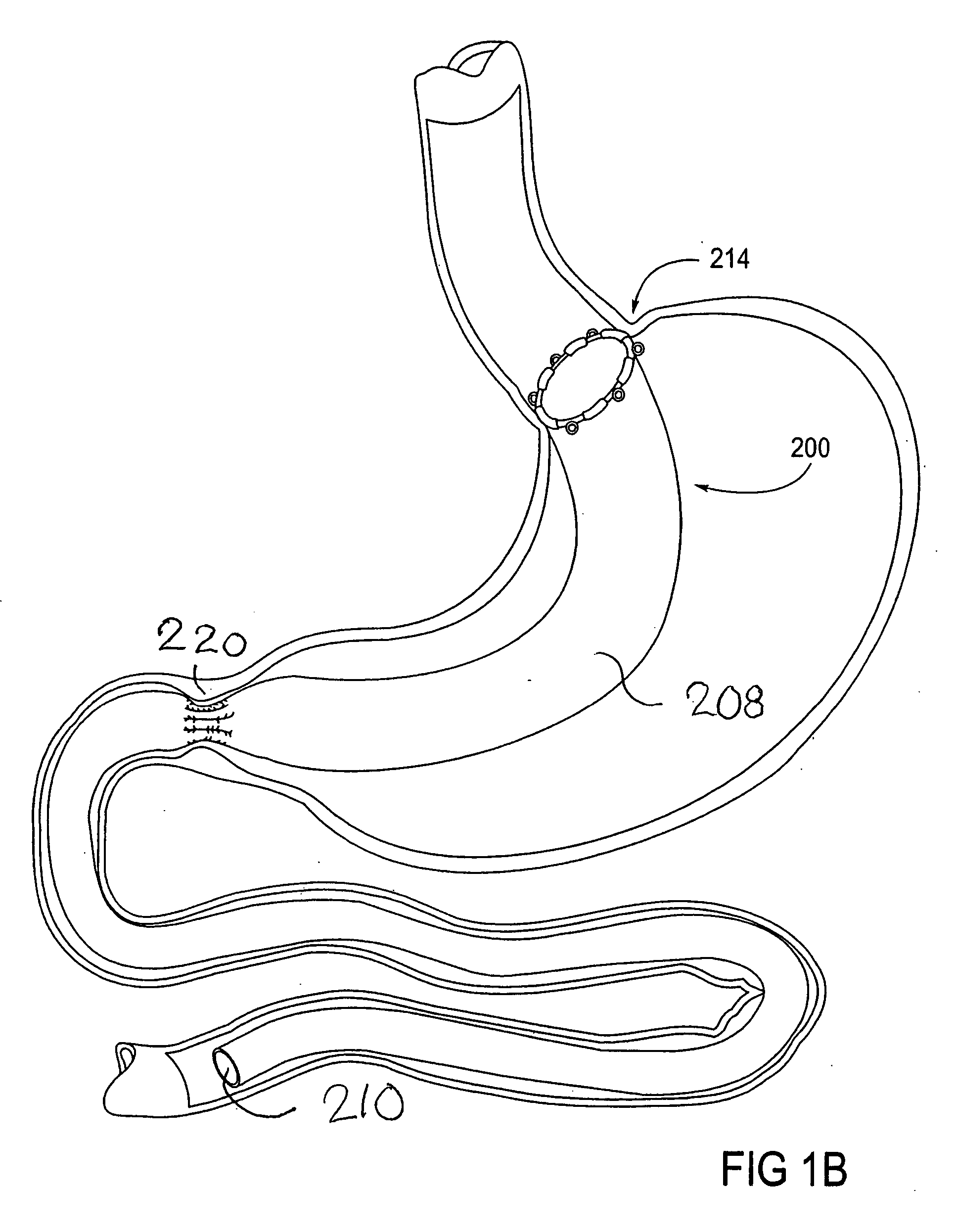
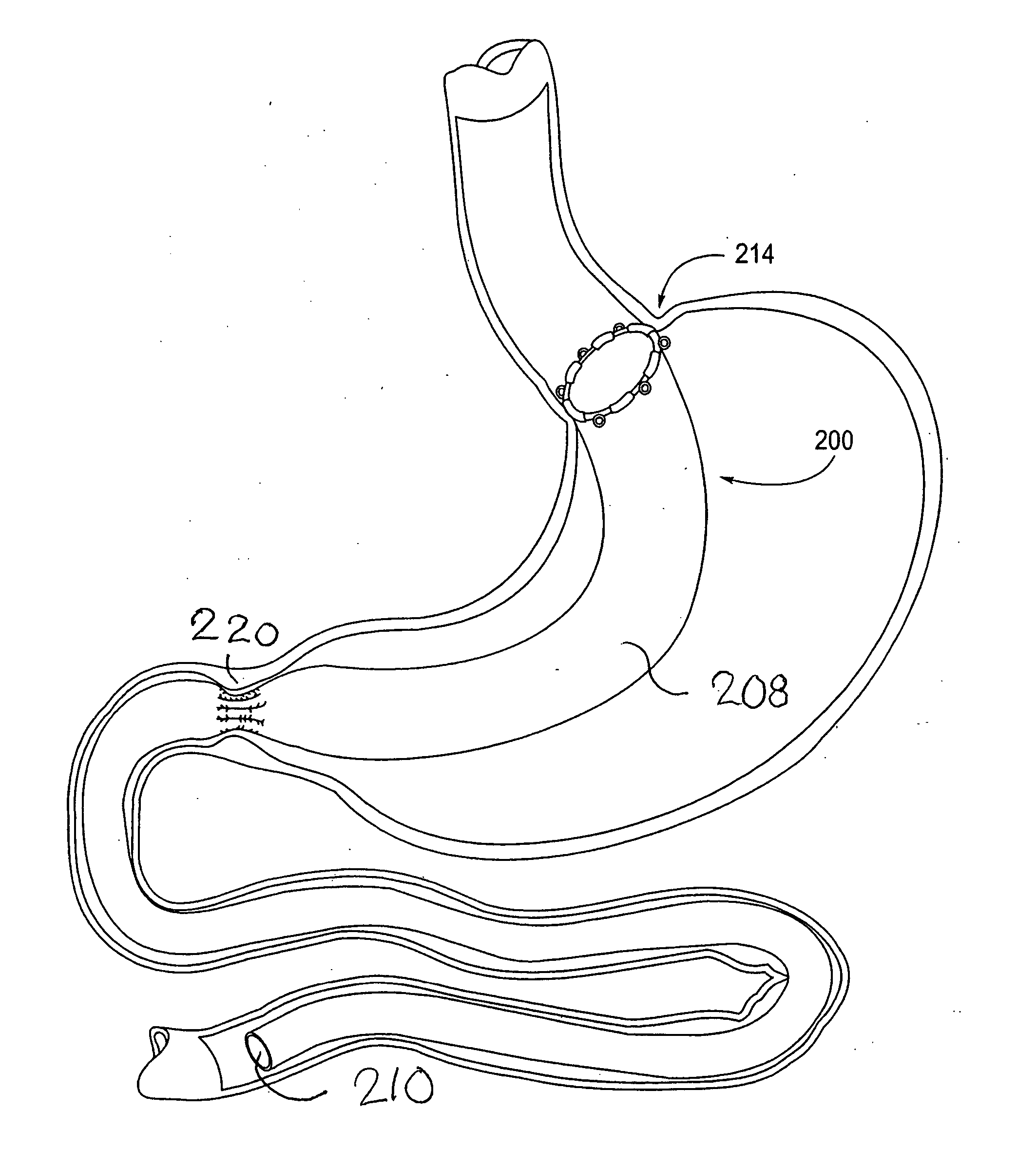
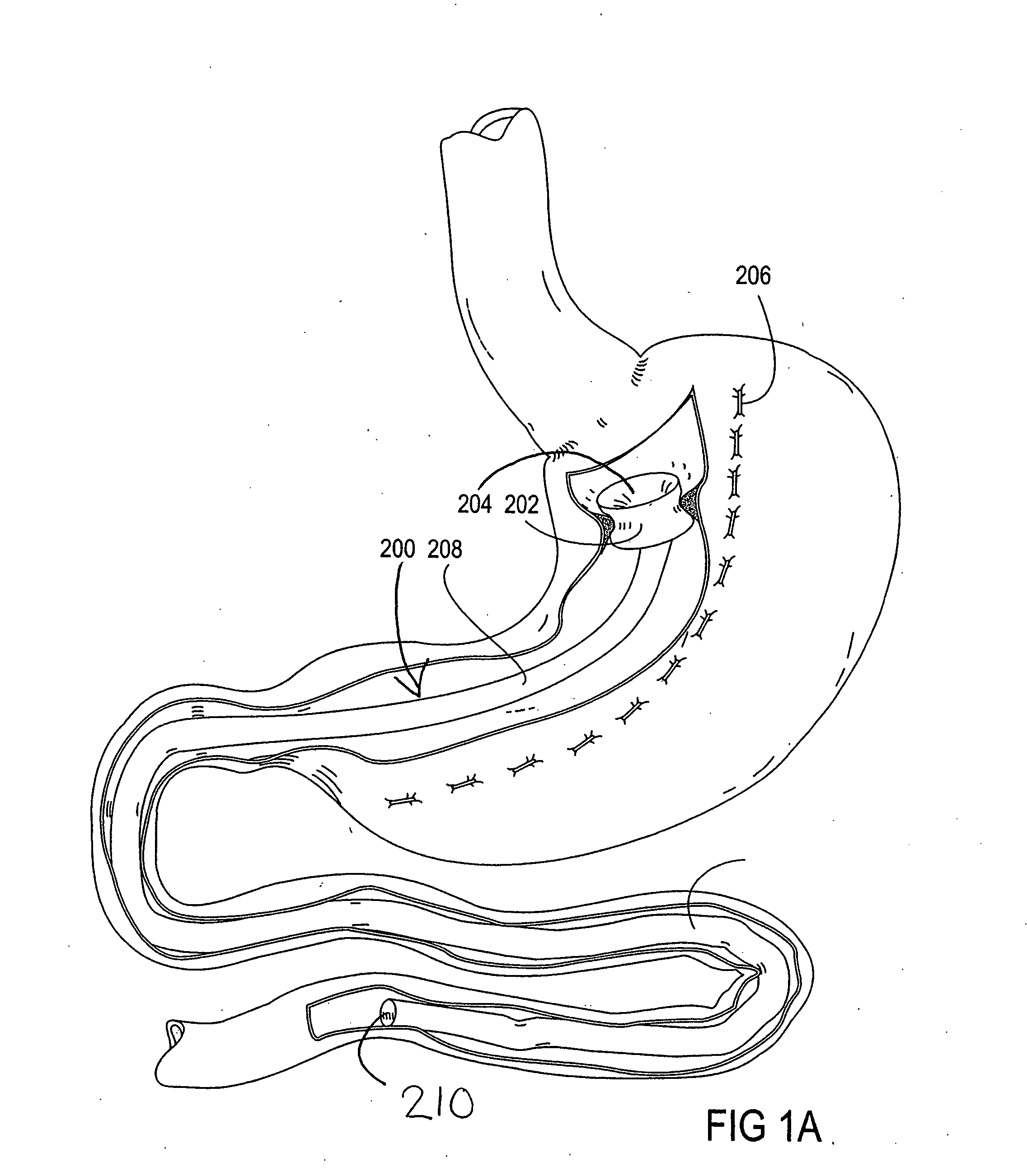
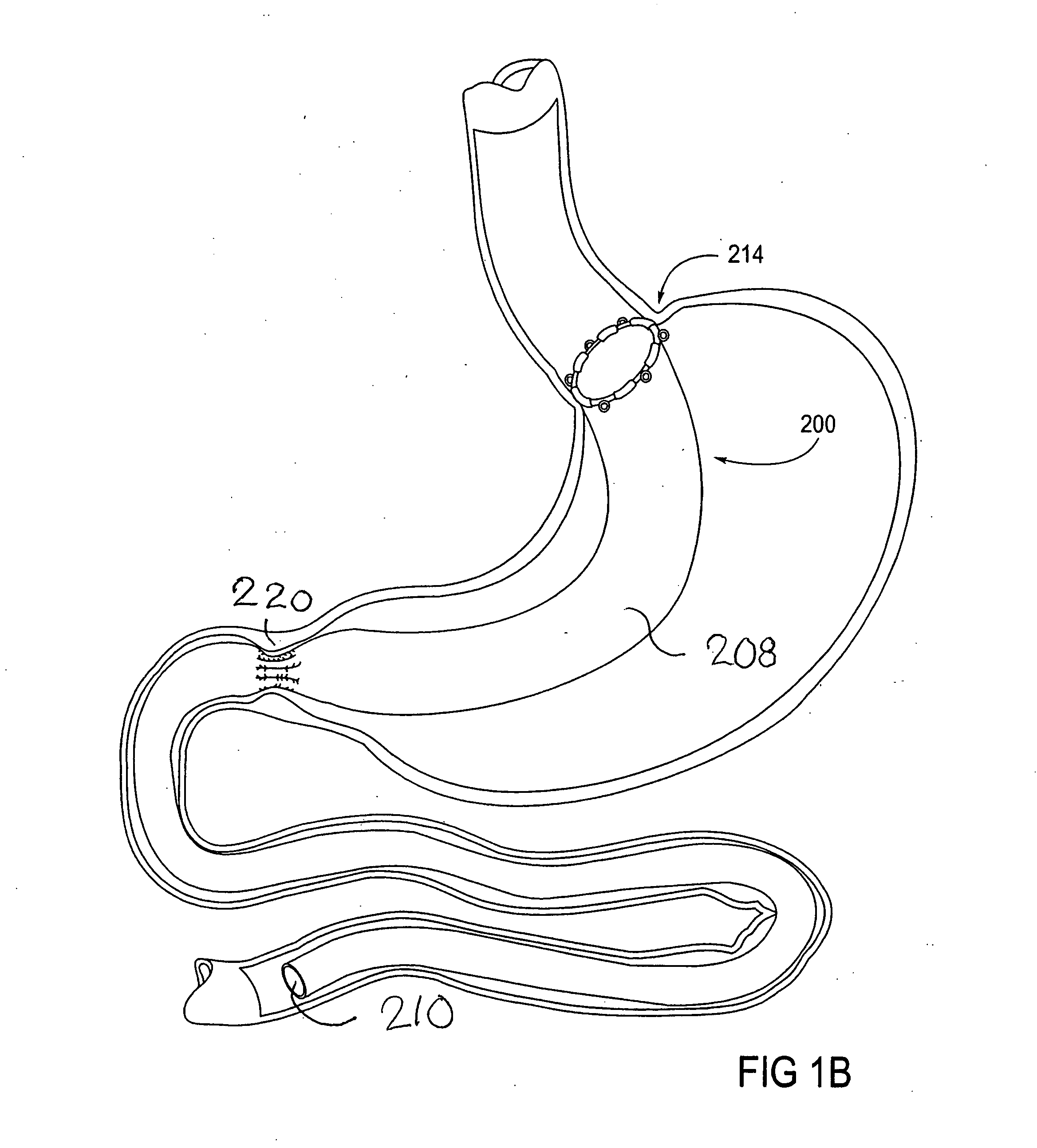
Devices and methods for treating morbid obesity
The present invention provides devices and methods for attachment of an implanted device, such as an artificial stoma device, a gastrointestinal sleeve device or an attachment cuff, within a patient's digestive tract for treatment of obesity. Special surgical fasteners provide a lasting and durable attachment to the gastrointestinal tissue without causing excessive pressure that could result in tissue erosion and detachment of the implanted device. Fastener delivery devices that facilitate peroral placement and deployment of fasteners and secondary devices are also provided. Also described are implantable devices and attachment means that avoid causing excessive pressure within the tissue by having compliance that is compatible with the gastrointestinal tissues where it is attached.
Owner:VALENTX
Devices and methods for treating morbid obesity
The present invention provides devices and methods for attachment of an implanted device, such as an artificial stoma device, a gastrointestinal sleeve device or an attachment cuff, within a patient's digestive tract for treatment of obesity. Special surgical fasteners provide a lasting and durable attachment to the gastrointestinal tissue without causing excessive pressure that could result in tissue erosion and detachment of the implanted device. Fastener delivery devices that facilitate peroral placement and deployment of fasteners and secondary devices are also provided. Also described are implantable devices and attachment means that avoid causing excessive pressure within the tissue by having compliance that is compatible with the gastrointestinal tissues where it is attached.
Owner:VALENTX
Electrosurgical system and method
InactiveUS7001380B2Lower impedanceMinimizing char formationCannulasDiagnosticsBenign conditionEnlarged tonsils
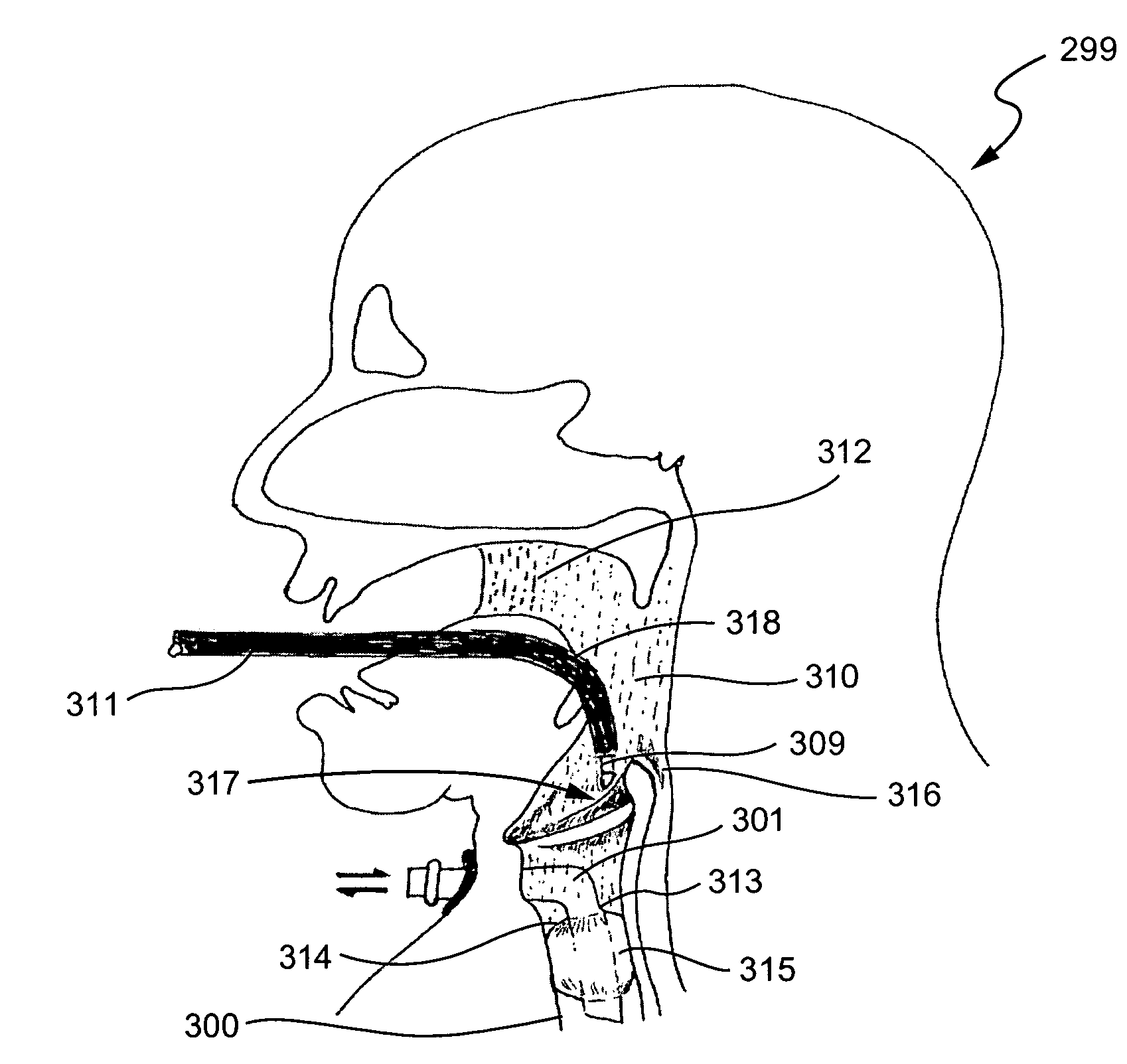
A method is disclosed for treating benign conditions, such as enlarged tonsils and / or adenoids located in a patient's throat or nasopharynx, or soft tissue lesions located in a patient's oropharynx or larynx. According to the method, a space containing the patient's nasopharynx, oropharynx or pharynx and larynx is isolated from the patient's trachea and lungs using an inflatable cuff tracheostomy tube or nasotracheal tube inserted in the patient's trachea. The cuff is inflated to occlude the trachea. The patient is placed in a supine position, whereupon at least a portion of the space containing the nasopharynx and / or oropharynx and larynx is filled with saline. An endoscope is then inserted into the space to view the operative site in which the tonsils or tissue lesion are to be treated. An electrosurgical instrument having an active tissue treatment electrode and a return electrode connected to an electrosurgical generator is then inserted into the space, either along side the endoscope or through the endoscope's working channel. The generator is then operated to apply a radio frequency voltage between the active and return electrodes of the electrosurgical instrument, whereby a conduction path is formed between the active and return electrodes, at least partially through the saline, whereupon the active electrode is manipulated to debulk or otherwise treat the soft tissue lesion or enlarged tonsils and / or adenoids.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
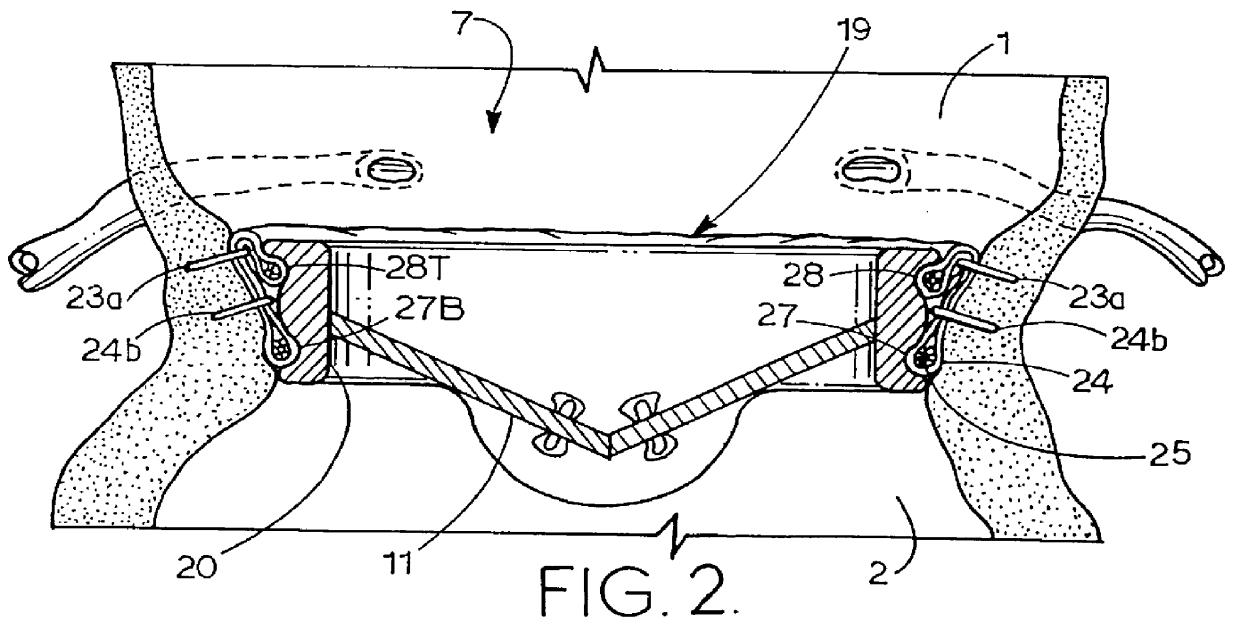
Means and method of replacing a heart valve in a minimally invasive manner
A heart valve can be replaced using minimally invasive methods which include a sutureless sewing cuff that and a fastener delivery tool that holds the cuff against the patient's tissue while delivering fasteners to attach the cuff to the tissue from the inside out. The tool stores a plurality of fasteners and is self-contained whereby a fastener is delivered and placed all from inside a vessel. The fasteners are self-forming whereby they do not need an anvil to be formed. Anchor elements are operated from outside the patient's body to cinch a prosthesis to an anchoring cuff of the valve body. The cuff is releasably mounted on the tool and the tool holds the cuff against tissue and drives the fastener through the cuff and the tissue before folding over the legs of the fastener whereby secure securement between the cuff and the tissue is assured. Fasteners are placed and formed whereby fasteners are located continuously throughout the entire circumference of the cuff. A minimally invasive surgical method is disclosed, and a method and tool are disclosed for repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in a minimally invasive manner. Fasteners that are permanently deformed during the process of attaching the cuff are disclosed as are fasteners that are not permanently deformed during the attaching process.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
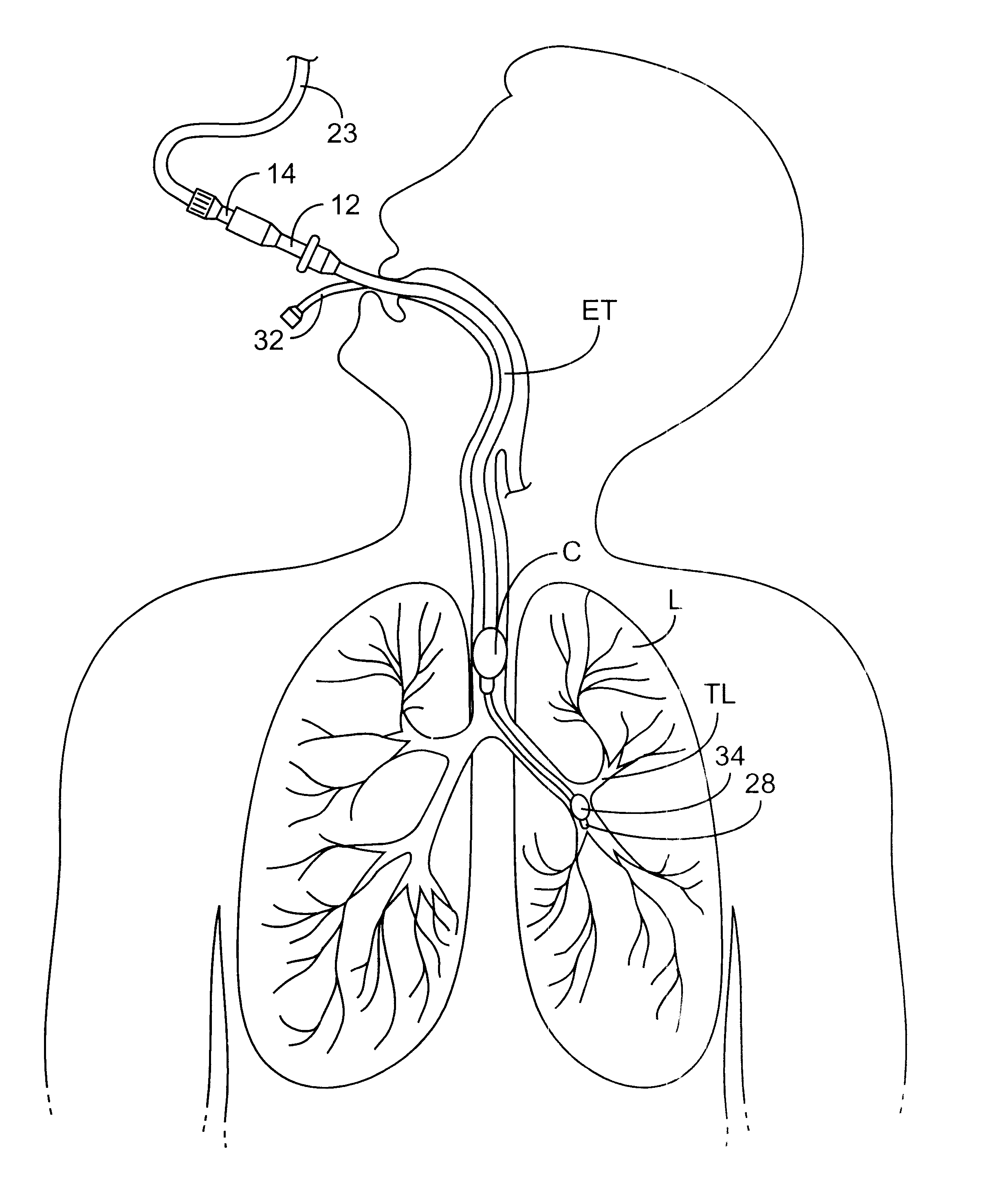
Sheath and method for reconfiguring lung viewing scope
Apparatus, methods, and kits, are provided for use in combination with a conventional bronchoscope or other lung viewing scope. In particular, sheaths having an inflatable cuff at their distal end are provided to receive a viewing scope through a lumen thereof. The sheaths thus provide an inflatable cuff on a viewing scope assembly so that the scope can be used in procedures which require selective isolation of regions of a patient's lungs. In particular embodiments, the sheaths may include stop elements for properly positioning a viewing scope therein, pressure transducers for providing accurate lung pressure information during procedures, and the like. Methods for using and forming sheaths having inflatable cuffs are also described.
Owner:PULMONX
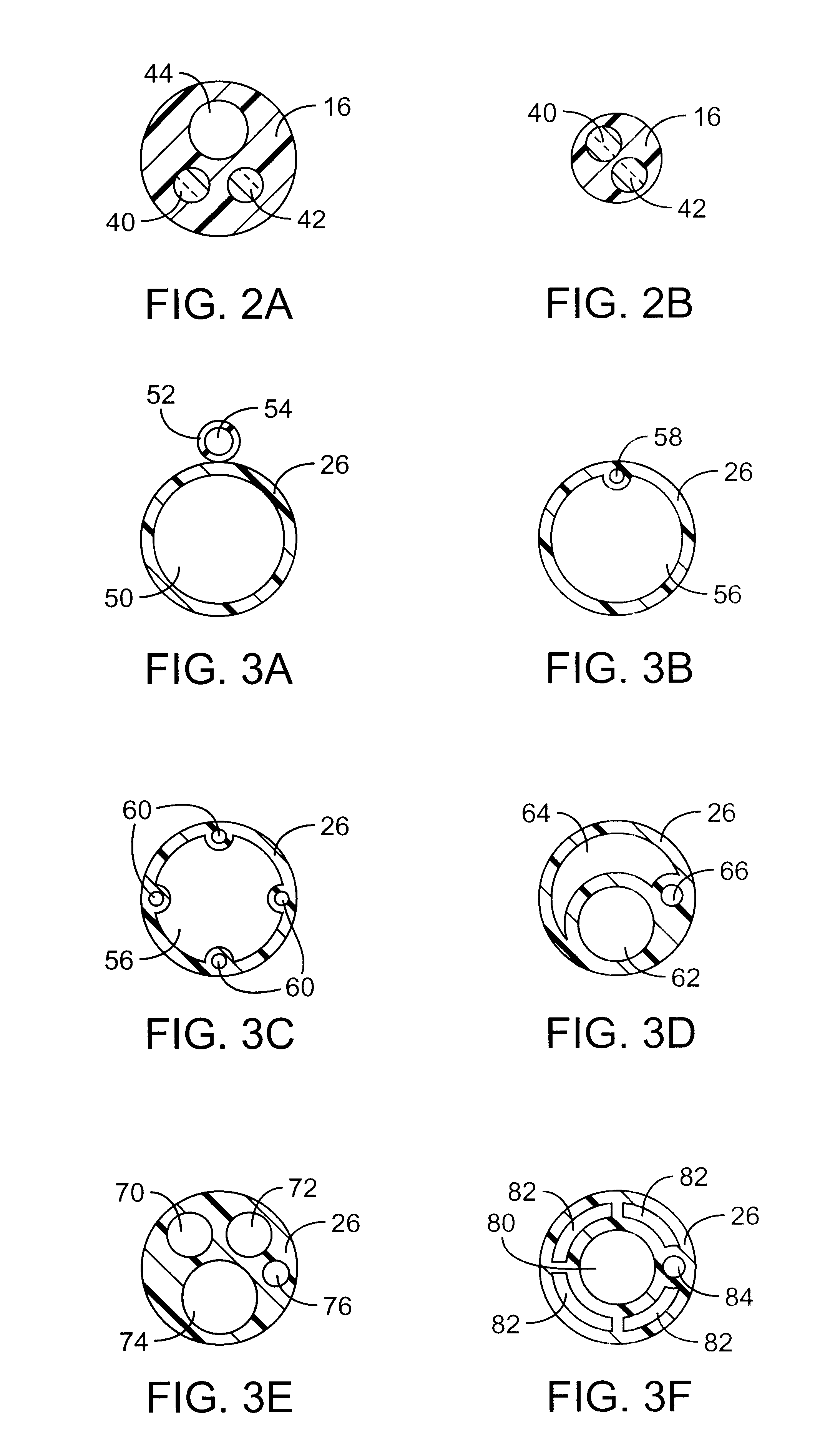
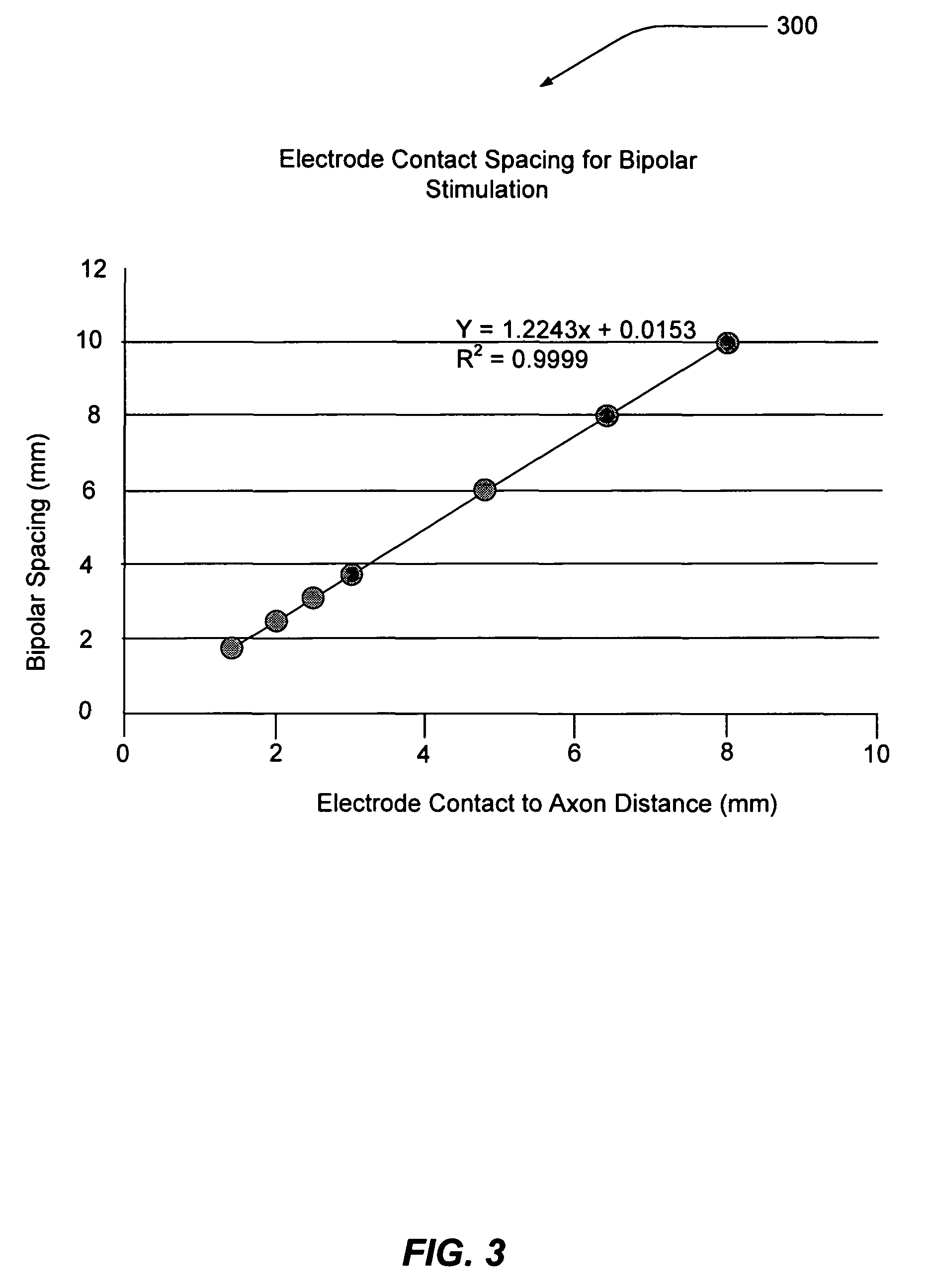
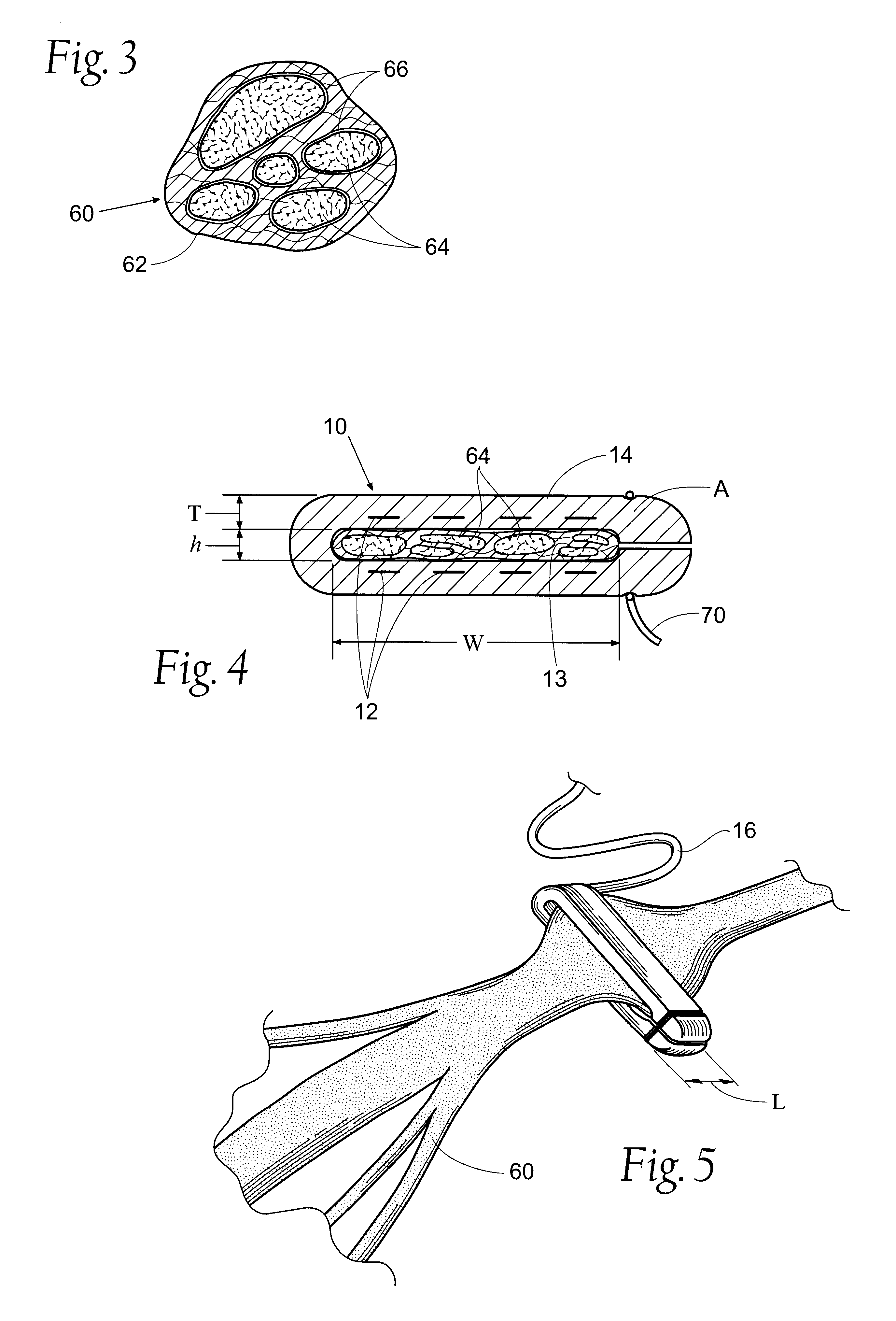
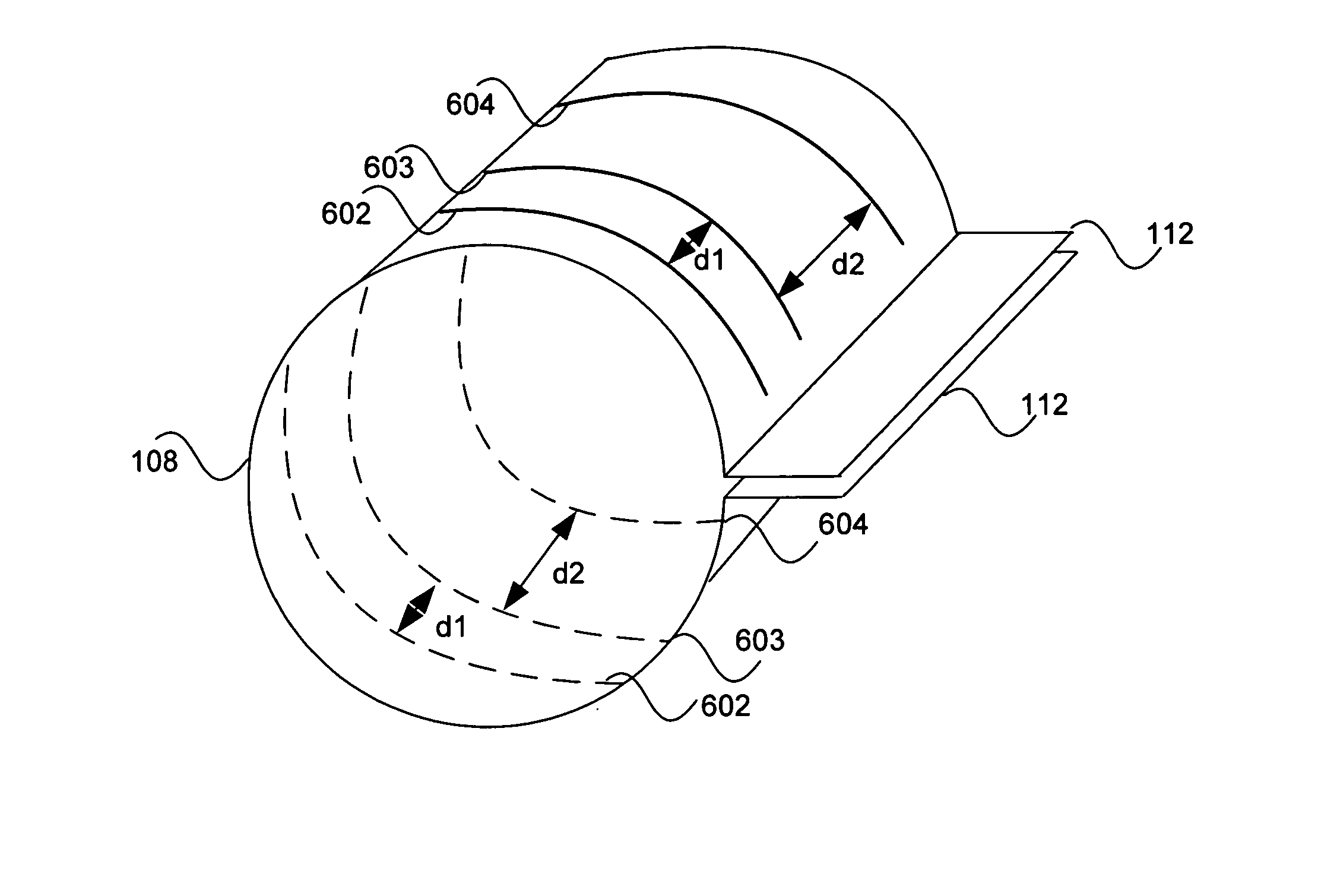
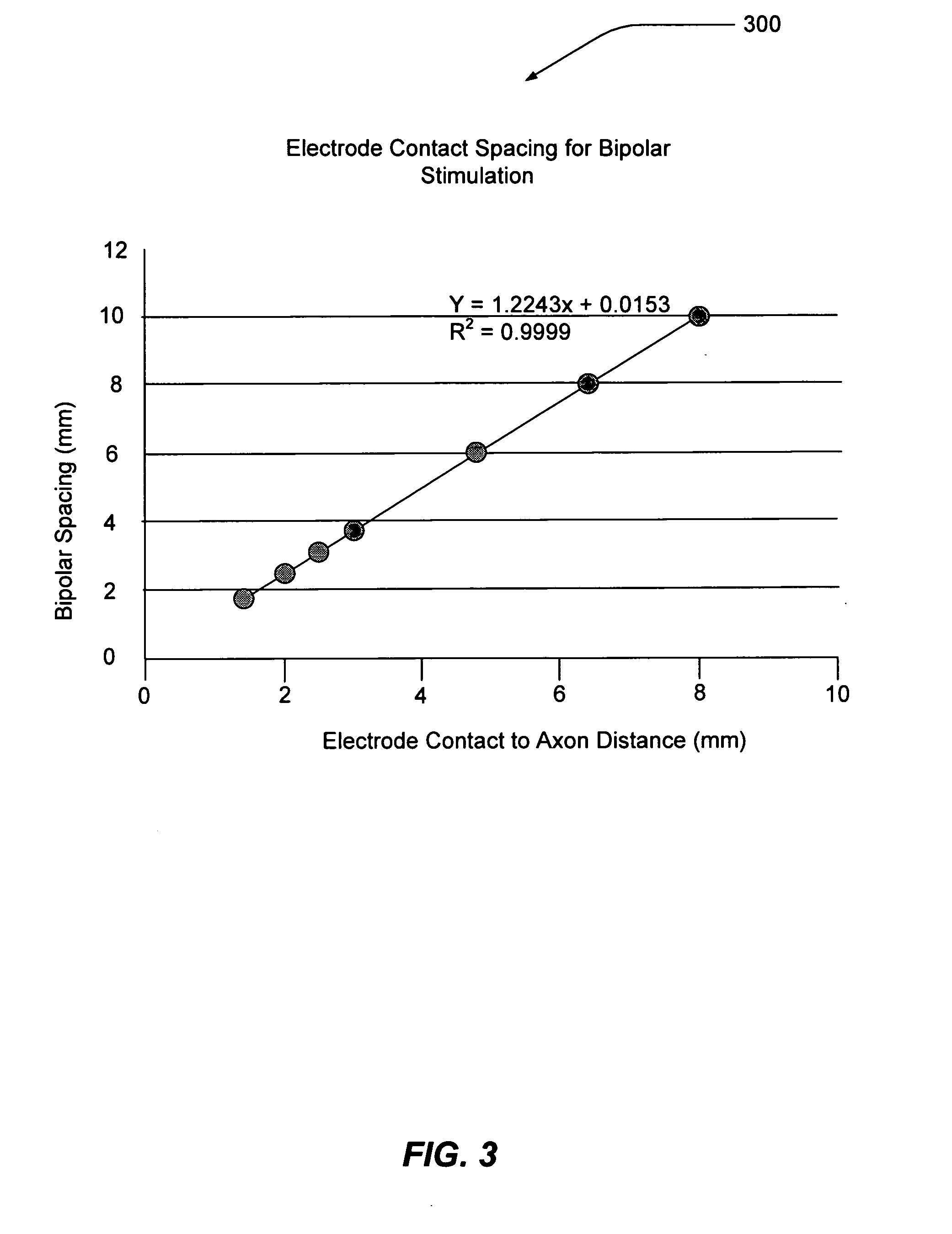
Electrode contact configurations for cuff leads
A stimulation system is disclosed that may include a stimulator unit coupled to electrode contacts on a cuff. In one embodiment, the cuff may be placed at least partially around a nerve. The stimulation system may include at least two electrode contacts disposed on the cuff such that a distance between the at least two electrode contacts various along a length of the electrode contacts. In another embodiment, a plurality of electrode contacts are disposed on the cuff such that distances between at least one electrode contact within the plurality of electrode contacts and each electrode contact immediately adjacent to the at least one electrode contact are different. The stimulator unit may also be implantable.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Stapling apparatus and method for heart valve replacement
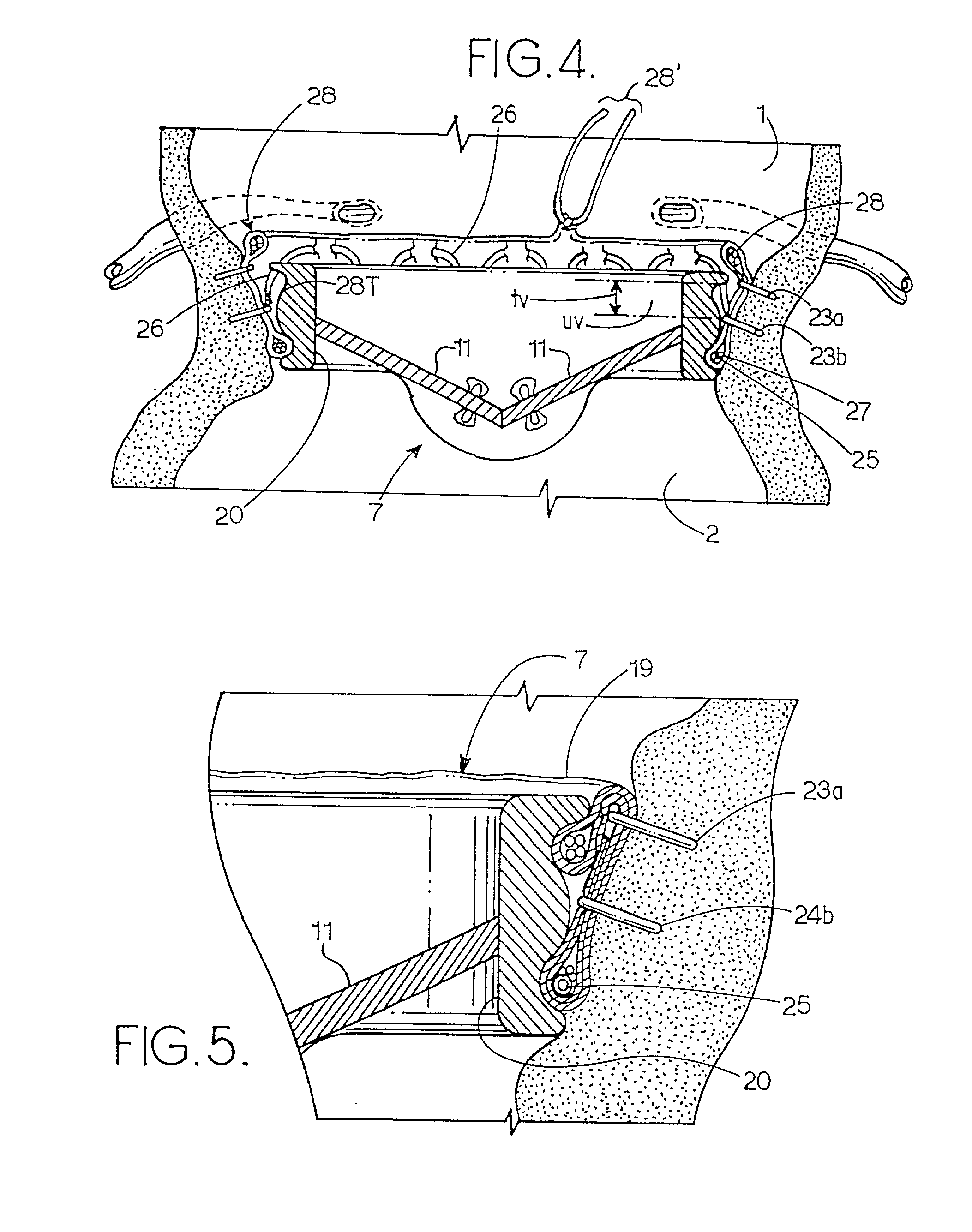
A surgical stapler for securing a prosthetic heart valve within a patient generally includes a first cylindrical portion for carrying at least one staple assembly on a distal end thereof; a second cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the first cylindrical portion and having a camming arm on a distal end thereof, the camming arm configured to cam the at least one staple assembly radially outward and drive the at least one staple assembly distally such that a first leg of the at least one staple assembly penetrates a cuff of the prosthetic heart valve and a second leg of the at least one staple assembly pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, as the second cylindrical portion is moved distally relative to the first cylindrical portion; and a third cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the second cylindrical portion and having an anvil flange on a distal end thereof, the anvil flange configured to crimp the second leg of the at least one staple assembly toward the first leg of the at least one staple assembly to secure the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue as the third cylindrical portion is moved relative to the second cylindrical portion. A method of installing a heart valve within a patient which includes the steps of accessing a site within a heart from which a natural heart valve has been removed; lowering a prosthetic heart valve into position within the site in the heart; positioning a surgical stapler having at least one staple assembly removably held on a distal end thereof adjacent the prosthetic heart valve within the site in the heart; driving a first leg of the at least one staple assembly through a peripheral cuff of the prosthetic heart valve; and crimping a second leg of the at least one staple assembly in a direction toward the first leg such that the second leg pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, thereby securing the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
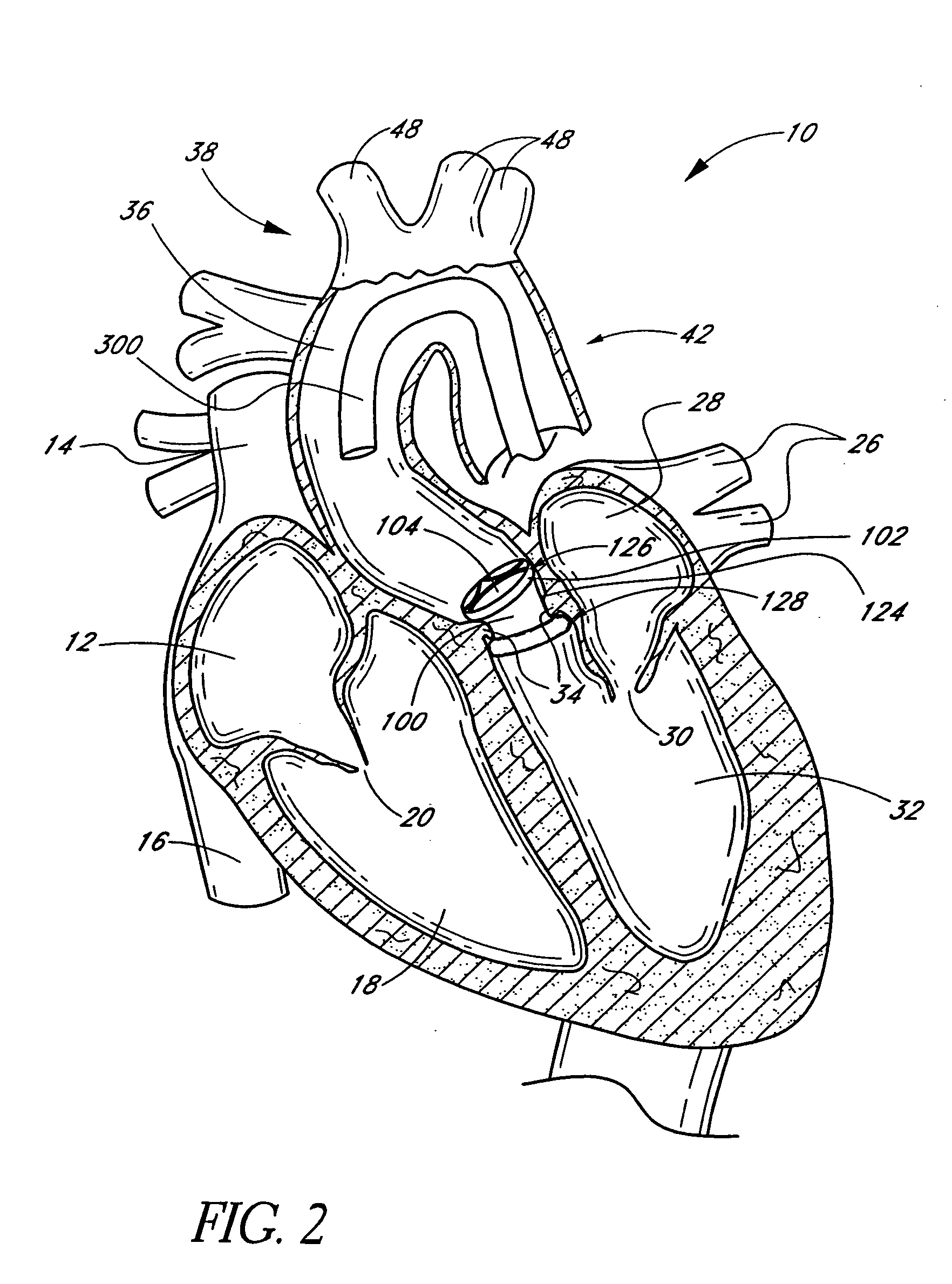
Prosthetic Valve for Transluminal Delivery
InactiveUS20100004740A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesVenous accessImplantation Site
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchors may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. A radial restraint, comprising a wire, thread or cuff, may be used to ensure expansion does not exceed the preset diameter. The valve support may optionally comprise a drug elution component. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. A blood pump may be inserted into the catheter to ensure continued blood flow across the implantation site during implantation procedure. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. Insertion of the catheter may optionally be performed over a transseptally delivered guidewire that has been externalized through the arterial vasculature. Such a guidewire provide dual venous and arterial access to the implantation site and allows additional manipulation of the implantation site after arterial implantation of the prosthetic valve. Additional expansion stents may be delivered by venous access to the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
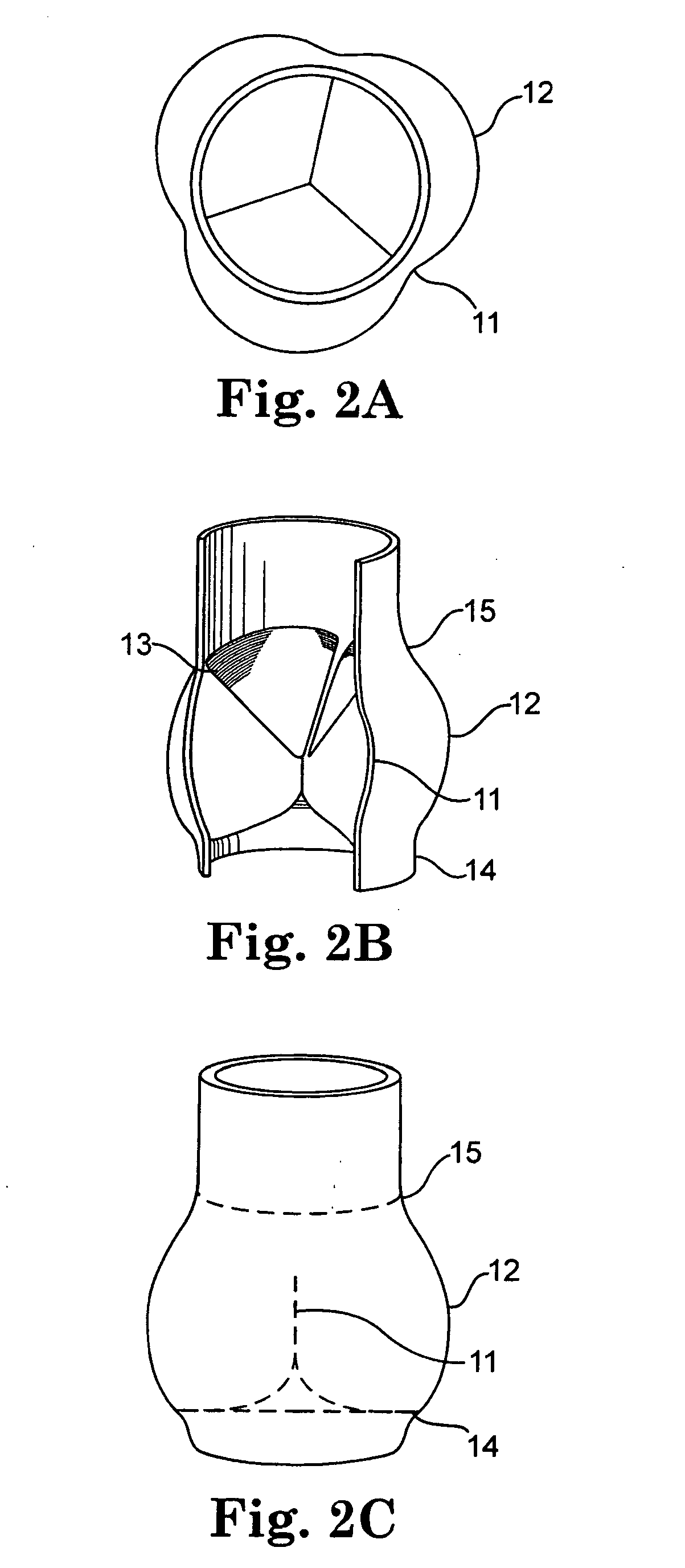
Prosthetic heart valve with slit stent
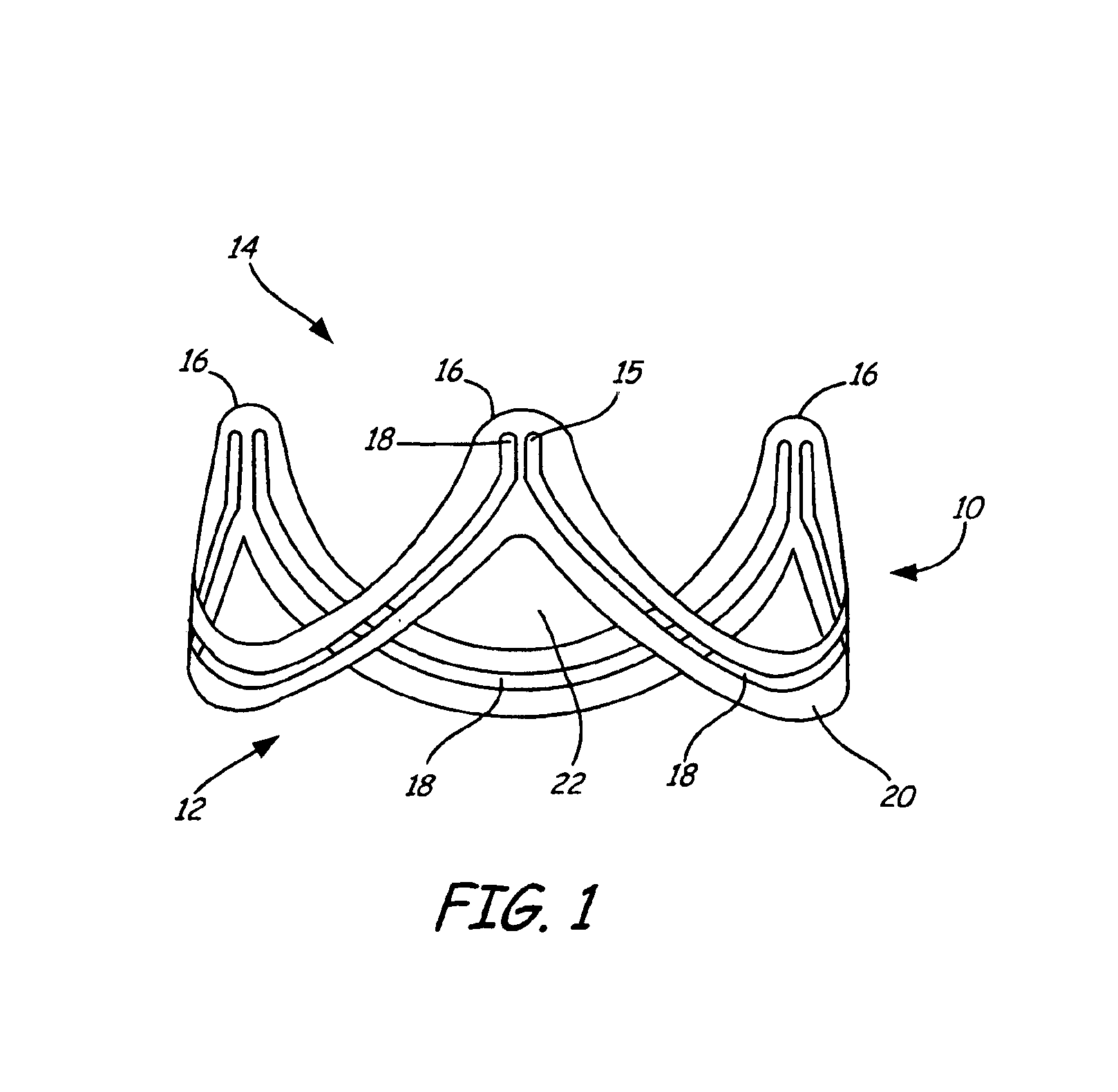
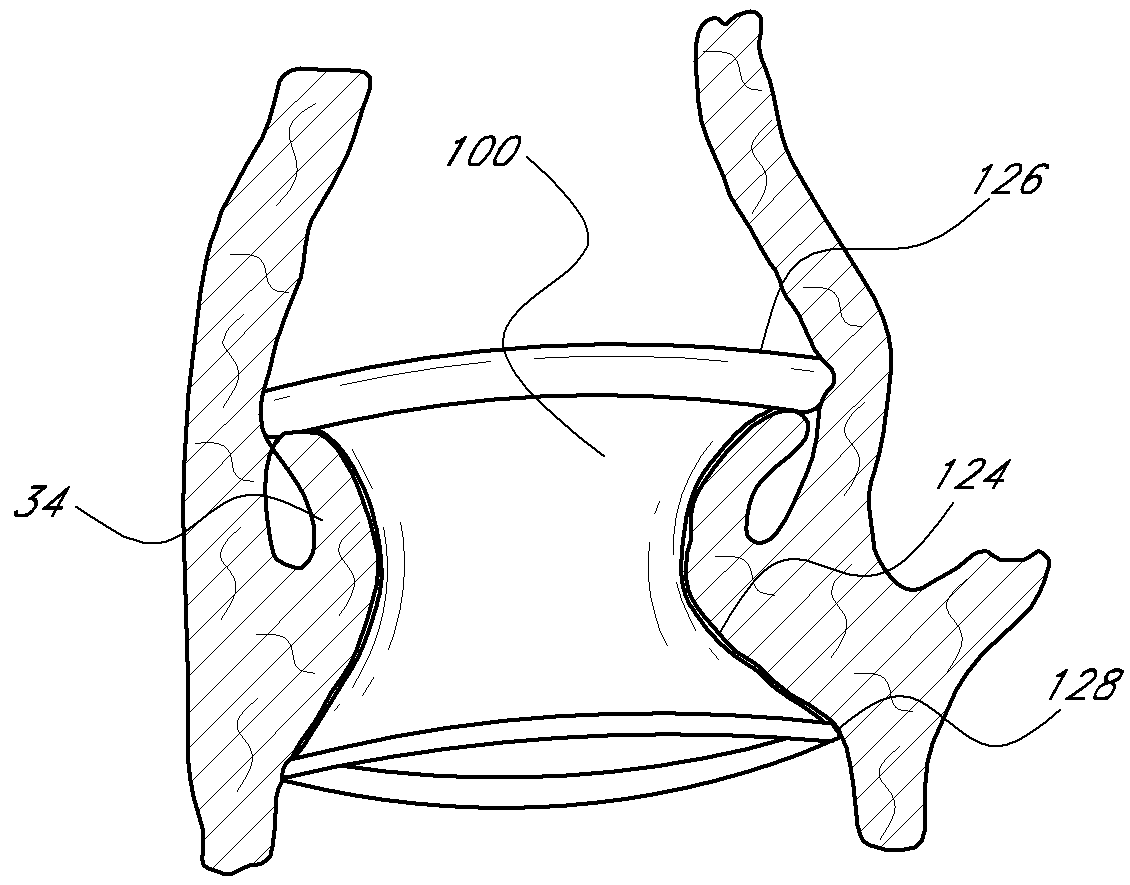
A valve prosthesis includes a plurality of flexible leaflets and a stent having a central lumen. A slit in the stent extends from the central lumen to an outer surface. An occluding portion of the flexible leaflets extends across the central lumen and an attachment portion extends from the central lumen through the slit and forms a sewing cuff for attachment to a patient's tissue. The attachment portion forms a sewing cuff for attachment to native heart tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Intravascular cuff
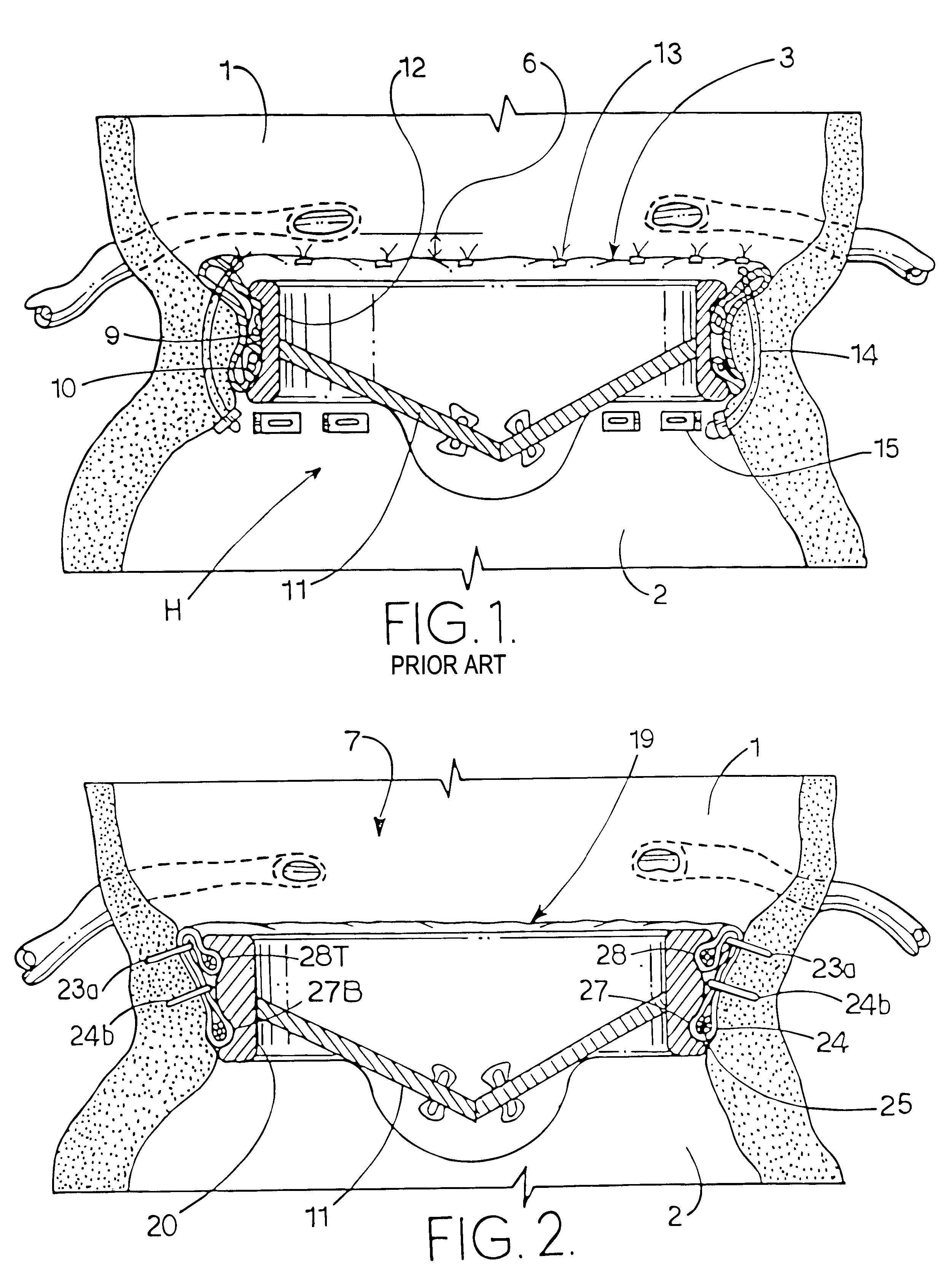
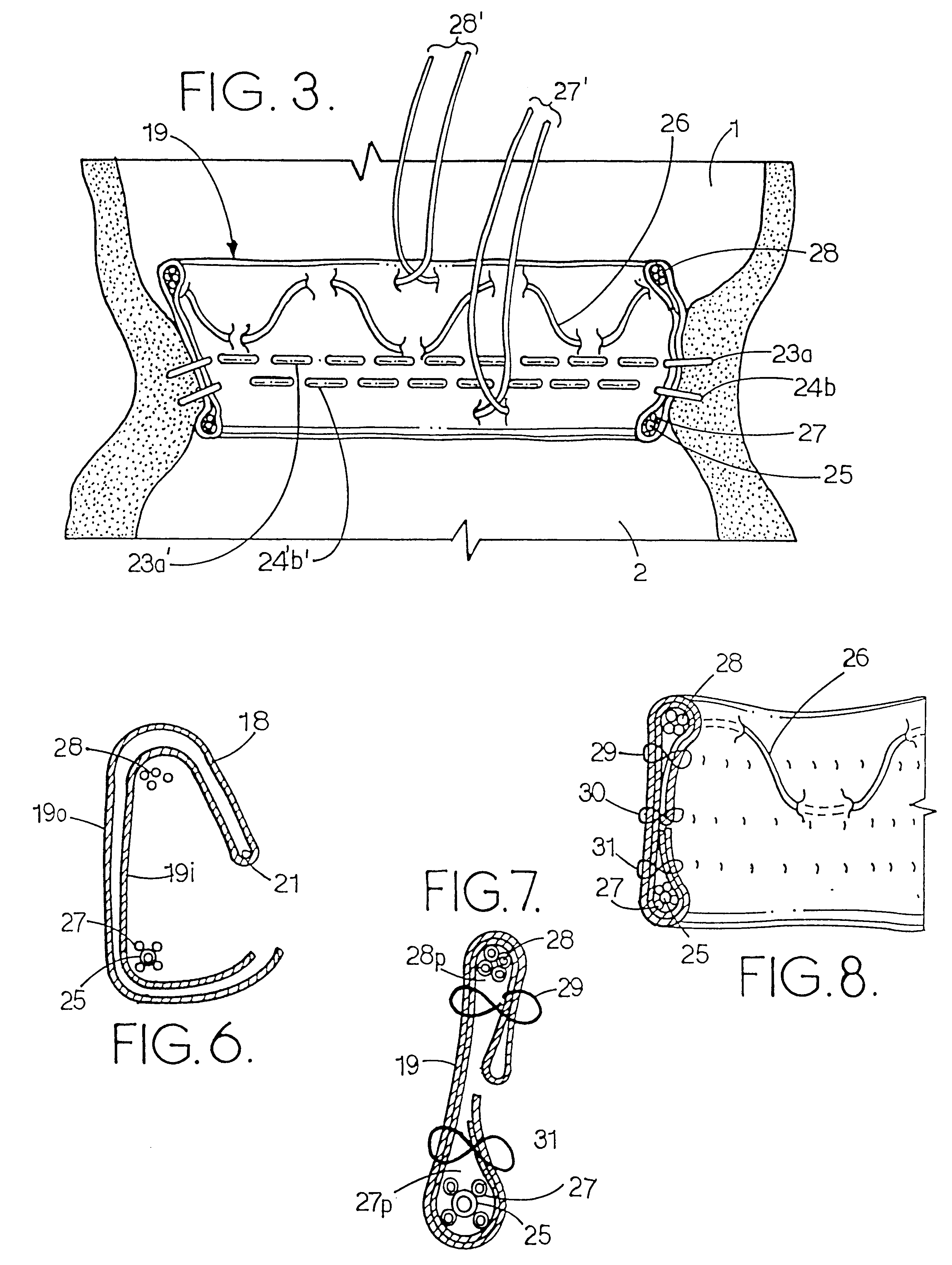
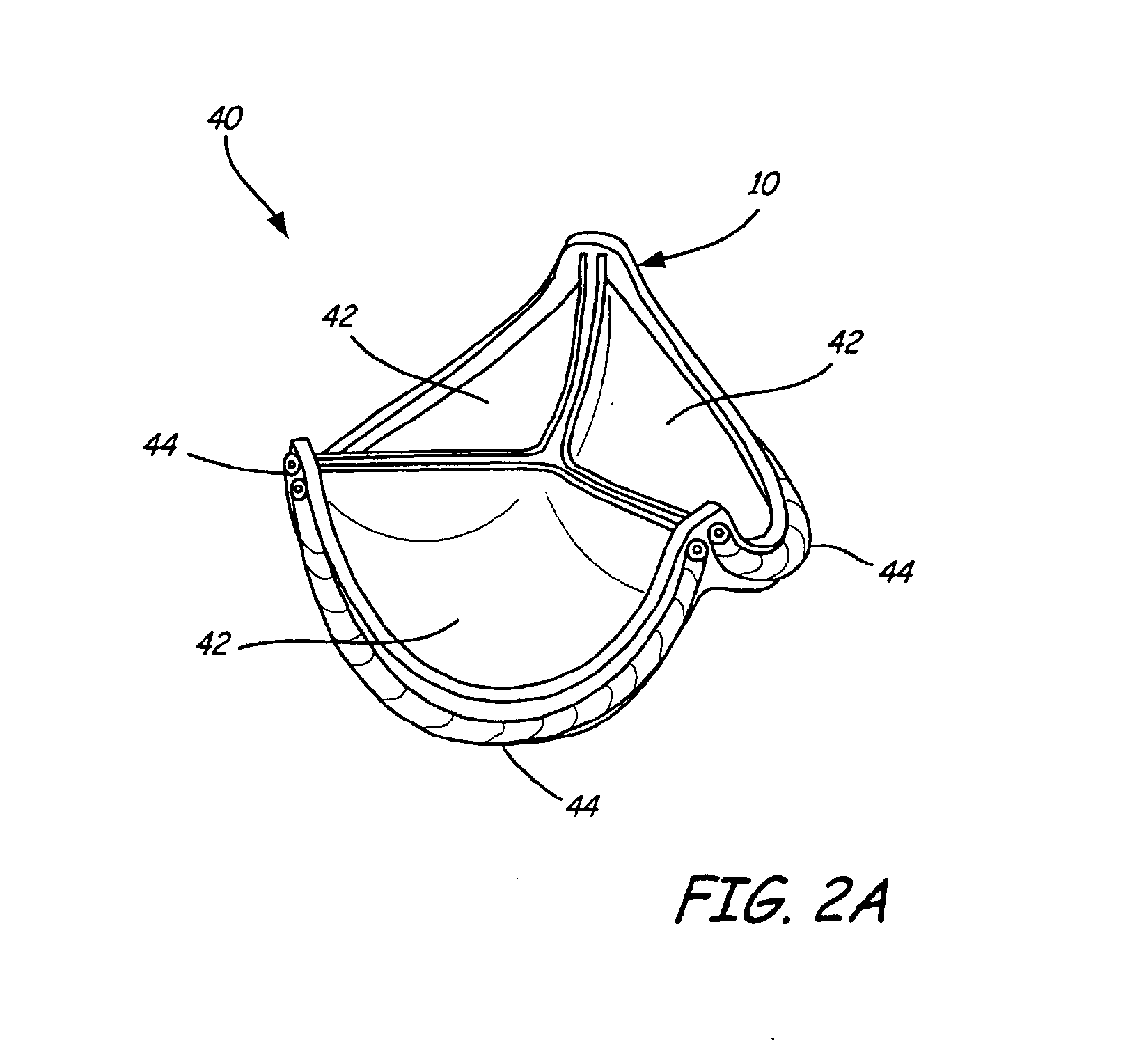
An intravascular cuff acts as a lining between a native vessel and an intravascular prosthetic device. During deployment, the ends of the cuff curl back upon themselves and are capable of trapping native tissue, such as valve leaflet tissue, between the ends. The cuff creates a seal between the vessel and the prosthetic, thereby preventing leakage around the prosthetic. The cuff also traps any embolic material dislodged from the vessel during expansion of the prosthetic.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
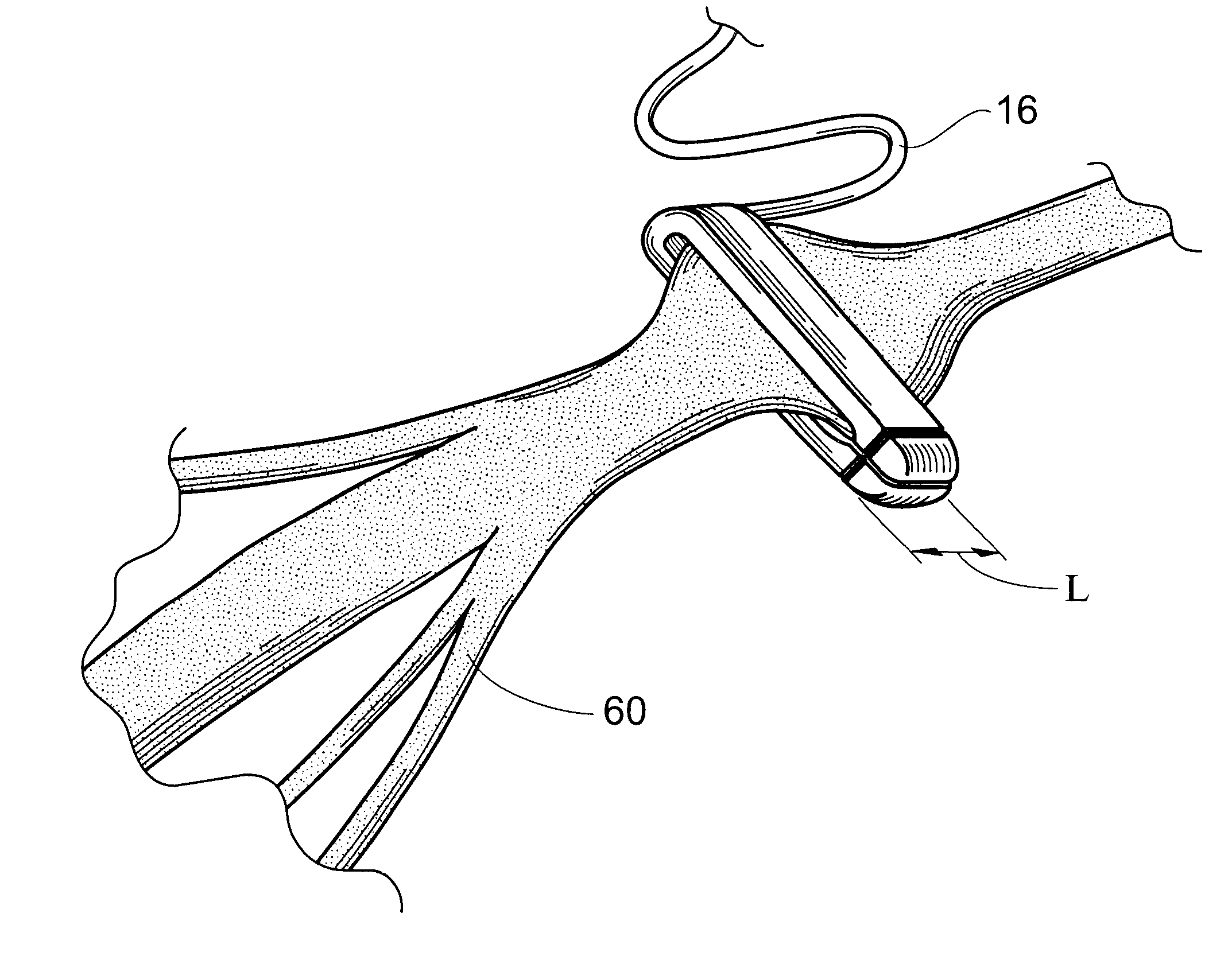
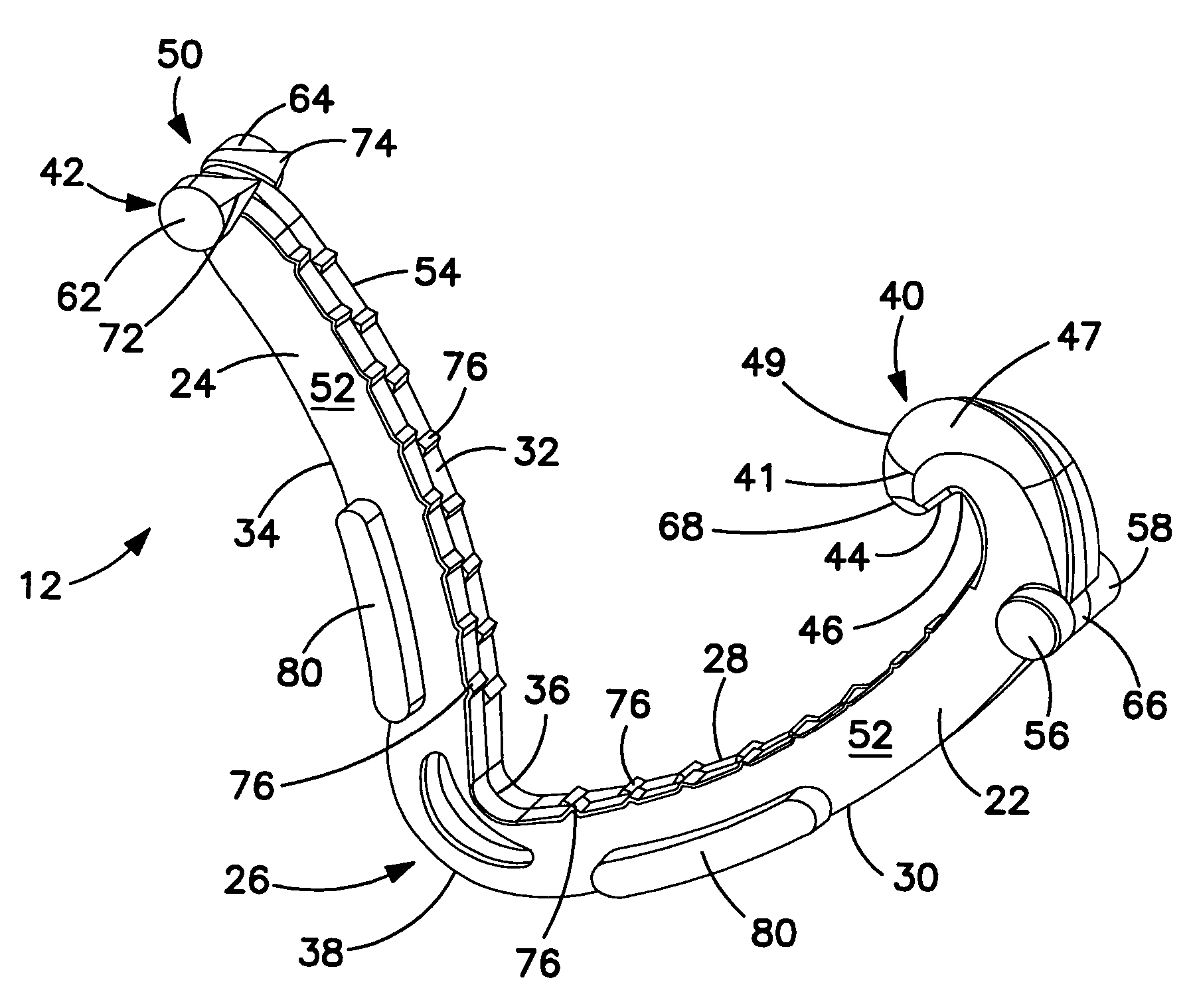
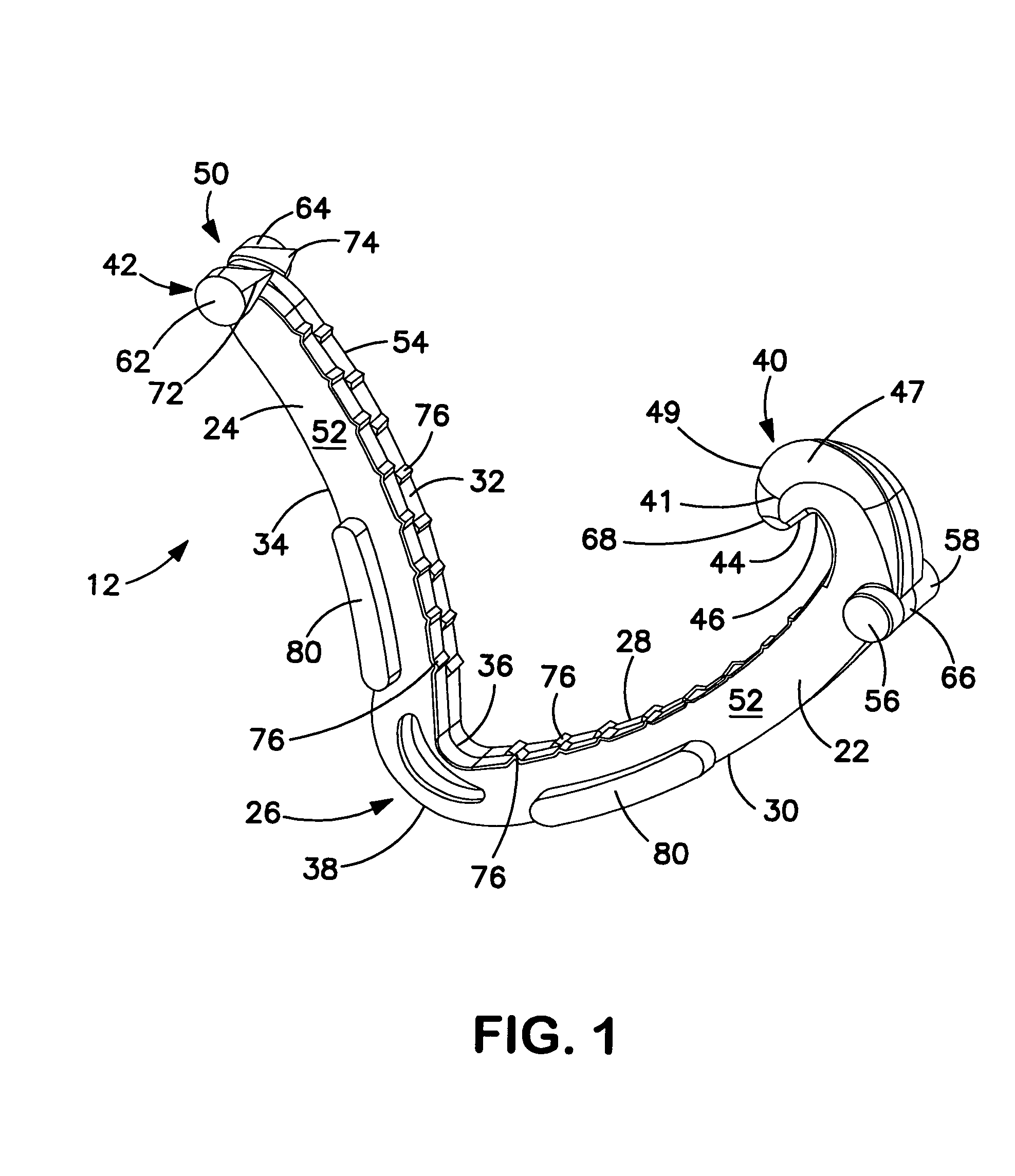
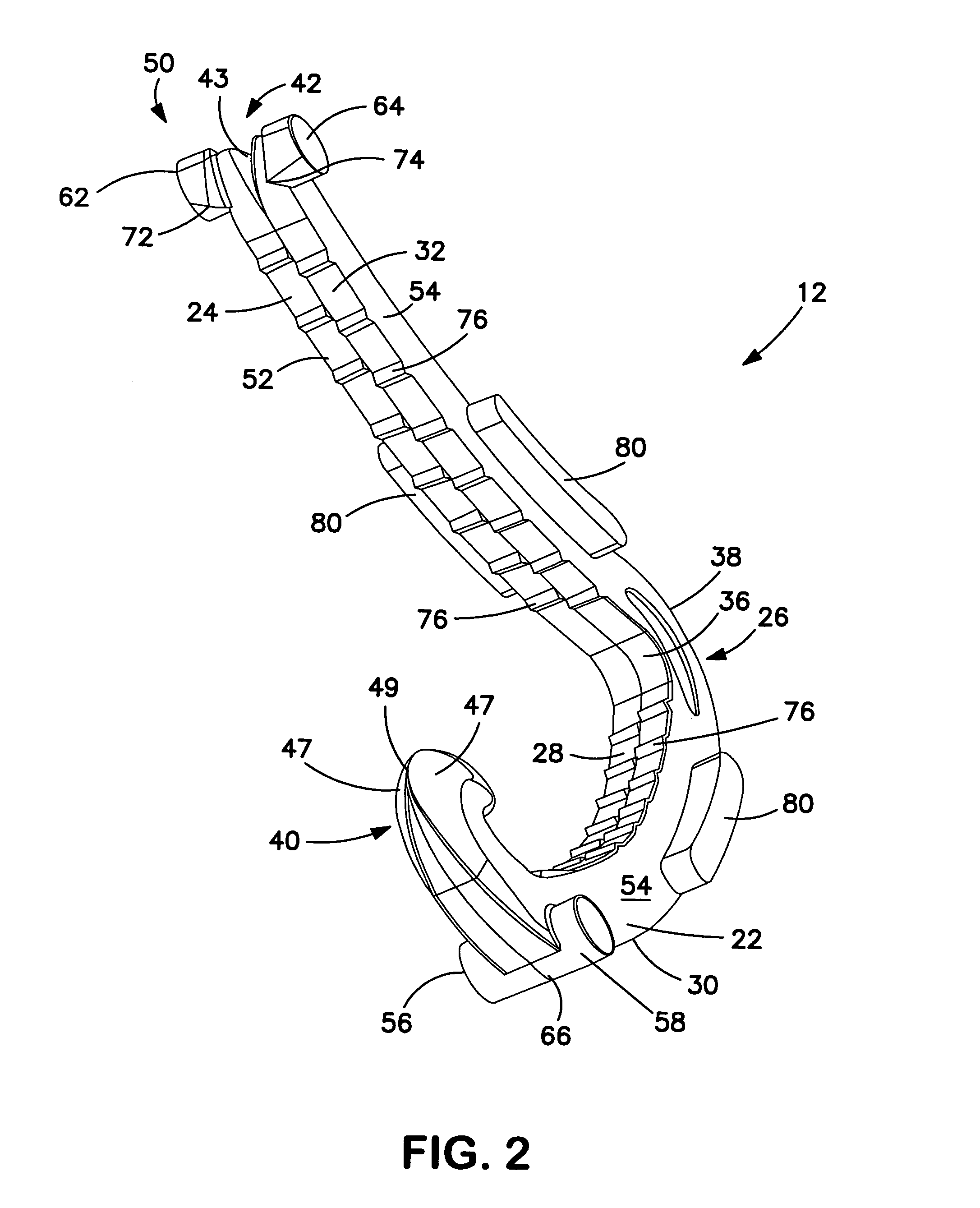
Fixation band for affixing a prosthetic heart valve to tissue
InactiveUS6846325B2Quickly and easily and conveniently affixingHeart valvesProsthetic valveProsthesis
A prosthetic heart value assembly comprising a prosthetic heart valve and a fixation band. The fixation band comprises a tubular frame and a tube. The tubular frame comprises longitudinally-extending members having hooks on their distal ends and fixation means on proximal ends, and a stabilizing laterally-extending member. The tube is positioned inside the longitudinally-extending members, a distal end of the tube being everted over the hooks. A sewing cuff is formed in the tube. The prosthetic valve is secured to the fixation band by suturing a prosthetic valve sewing cuff to a fixation band sewing cuff. The prosthetic valve and fixation band are advanced to the valve's seat. The fixation band's hooks are passed through the wall of the everted tube and into surrounding tissue and the fixation band's fixation means are deployed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Conformable prosthesis for implanting two-piece heart valves and methods for using them
A heart valve assembly includes an annular prosthesis and a valve prosthesis. The annular prosthesis includes an annular ring for dilating tissue within a biological annulus and a conformable sewing cuff extending radially from the annular member. The valve prosthesis includes a frame and a valve component. The annular ring is introduced into the biological annulus to dilate tissue surrounding the biological annulus and the sewing cuff conforms to tissue above the biological annulus. Fasteners are directed through the sewing cuff to secure the annular prosthesis to the biological annulus. The annular prosthesis may include a baleen element for biasing fabric on the annular ring outwardly to enhance sealing against the biological annulus. A valve prosthesis is then advanced into the sinus cavity, and secured relative to the annular prosthesis. The sewing cuff may enhance a seal between the valve prosthesis and annular prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
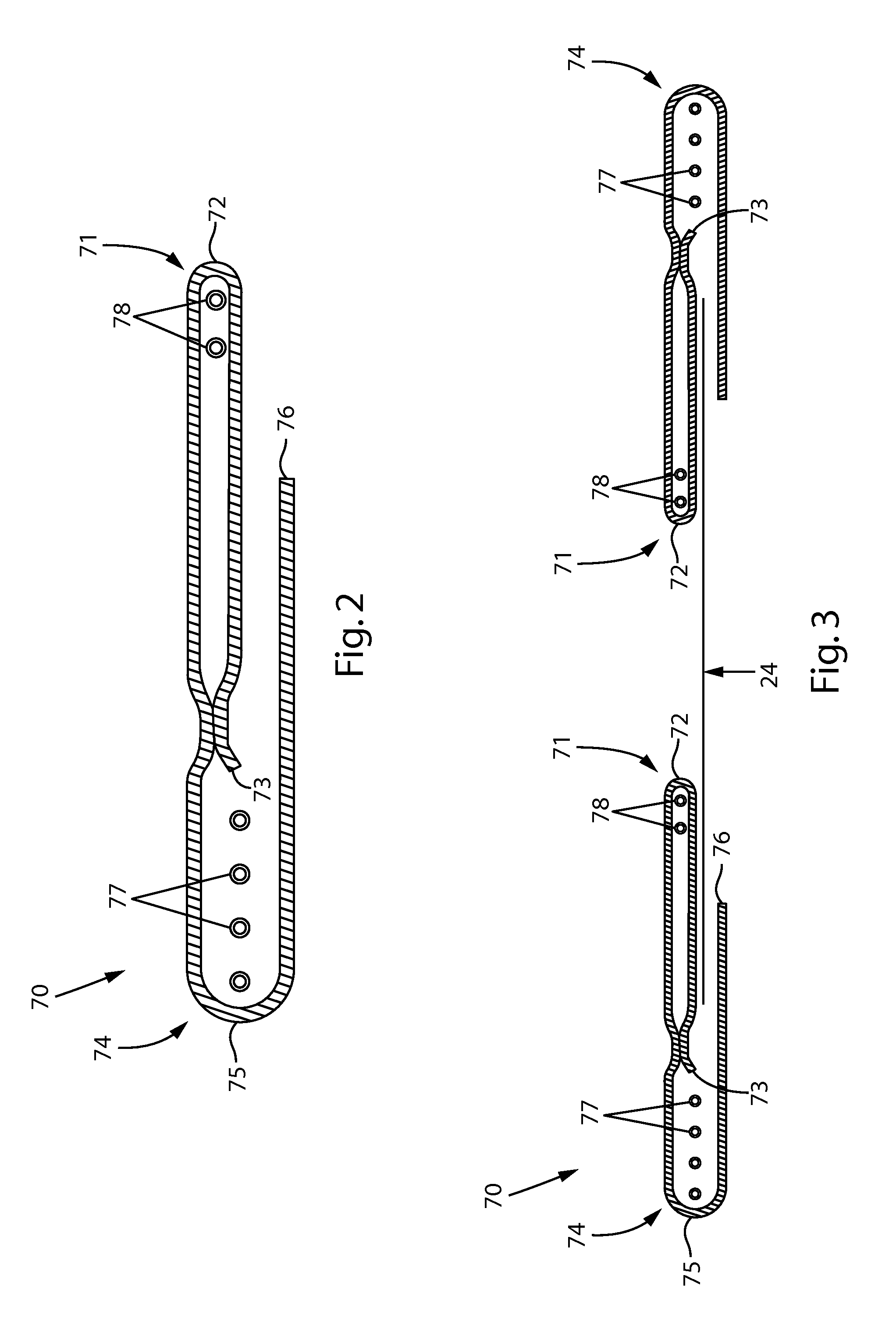
Methods and Apparatuses for Making Leg Cuffs for Absorbent Articles
The present disclosure relates to methods and apparatuses for assembling absorbent articles that include leg cuff gasketing assemblies. As discussed in more detail below, each leg gasketing assembly may be formed from elastic laminates having stretched elastic strands intermittently bonded thereto. As such, the elastic laminate includes bonded regions and non-bonded regions intermittently spaced along the machine direction. The elastic strands are then intermittently deactivated by severing the strands in the non-bonded regions of the continuous elastic laminate to form continuous lengths of leg gasketing assemblies having elastic regions and deactivated regions. The continuous lengths of leg gasketing assemblies may then bonded to a continuous topsheet substrate. In some embodiments, the elastic laminate may be combined with the topsheet substrate before severing the strands in the non-bonded regions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
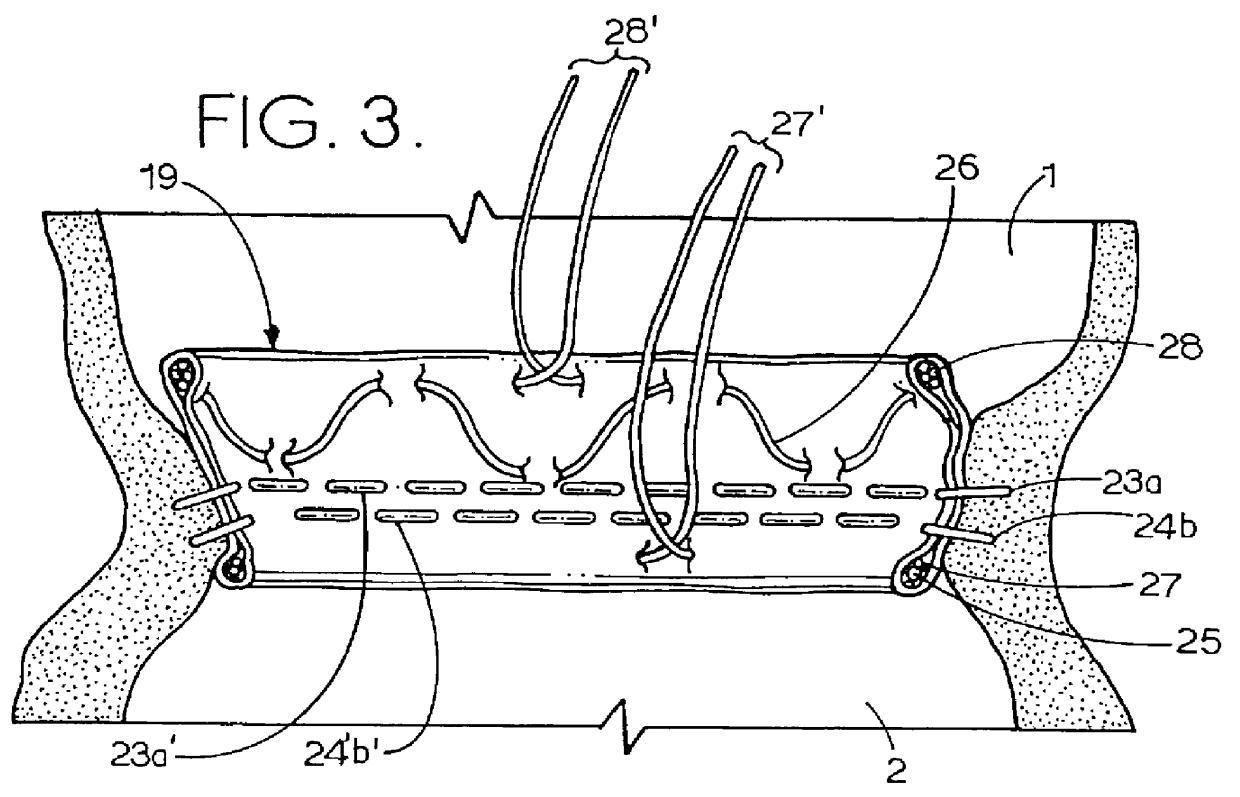
Means and method of replacing a heart valve in a minimally invasive manner
InactiveUS20010044656A1Minimally invasiveLarge flow areaSuture equipmentsStentsLess invasive surgerySelf forming
A heart valve can be replaced using minimally invasive methods which include a sutureless sewing cuff that and a fastener delivery tool that holds the cuff against the patient's tissue while delivering fasteners to attach the cuff to the tissue from the inside out. The tool stores a plurality of fasteners and is self-contained whereby a fastener is delivered and placed all from inside a vessel. The fasteners are self-forming whereby they do not need an anvil to be formed. Anchor elements are operated from outside the patient's body to cinch a prosthesis to an anchoring cuff of the valve body. The cuff is releasably mounted on the tool and the tool holds the cuff against tissue and drives the fastener through the cuff and the tissue before folding over the legs of the fastener whereby secure securement between the cuff and the tissue is assured. Fasteners are placed and formed whereby fasteners are located continuously throughout the entire circumference of the cuff. A minimally invasive surgical method is disclosed, and a method and tool are disclosed for repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in a minimally invasive manner. Fasteners that are permanently deformed during the process of attaching the cuff are disclosed as are fasteners that are not permanently deformed during the attaching process.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
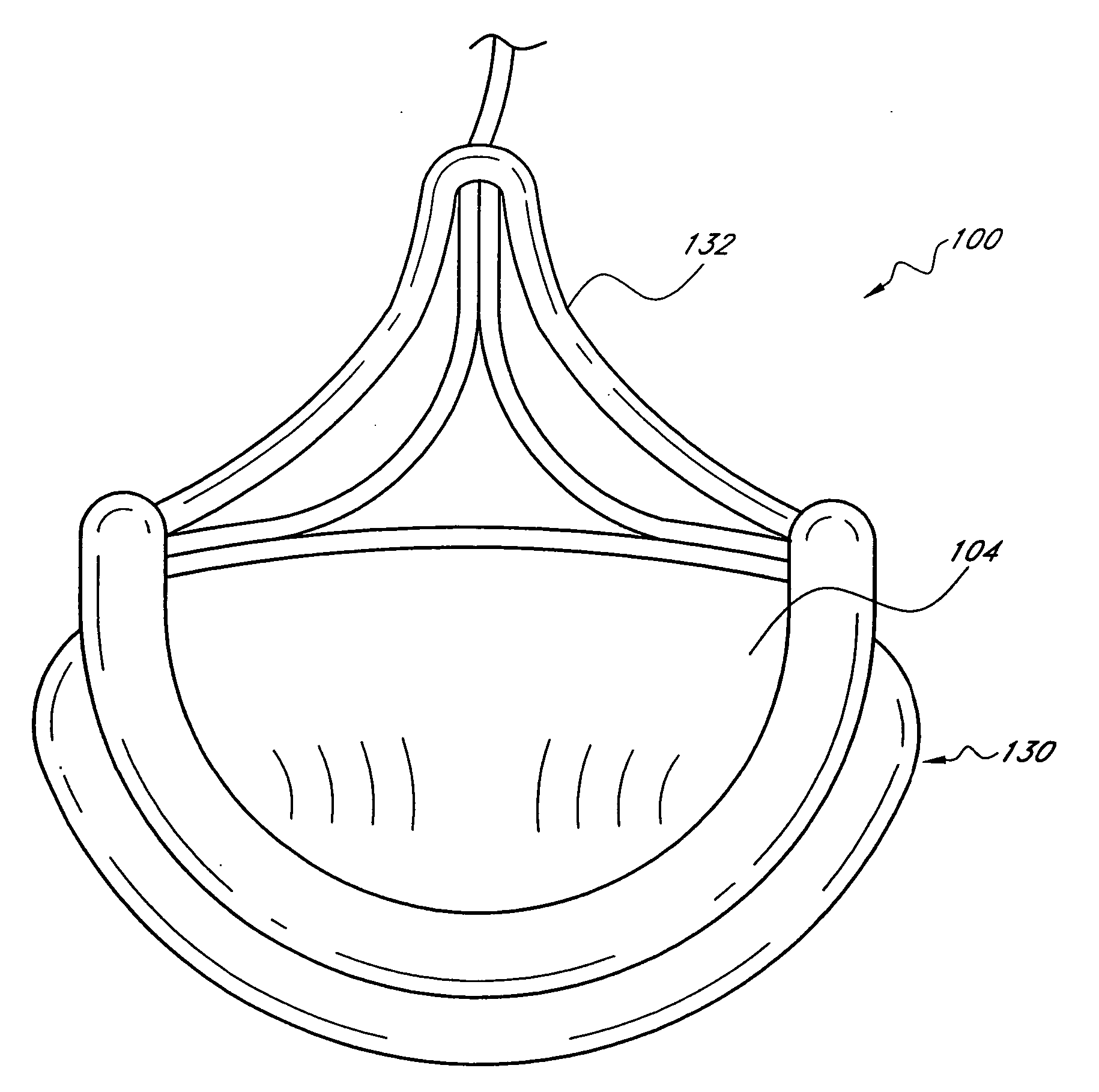
Annuloplasty rings for repair of abnormal mitral valves
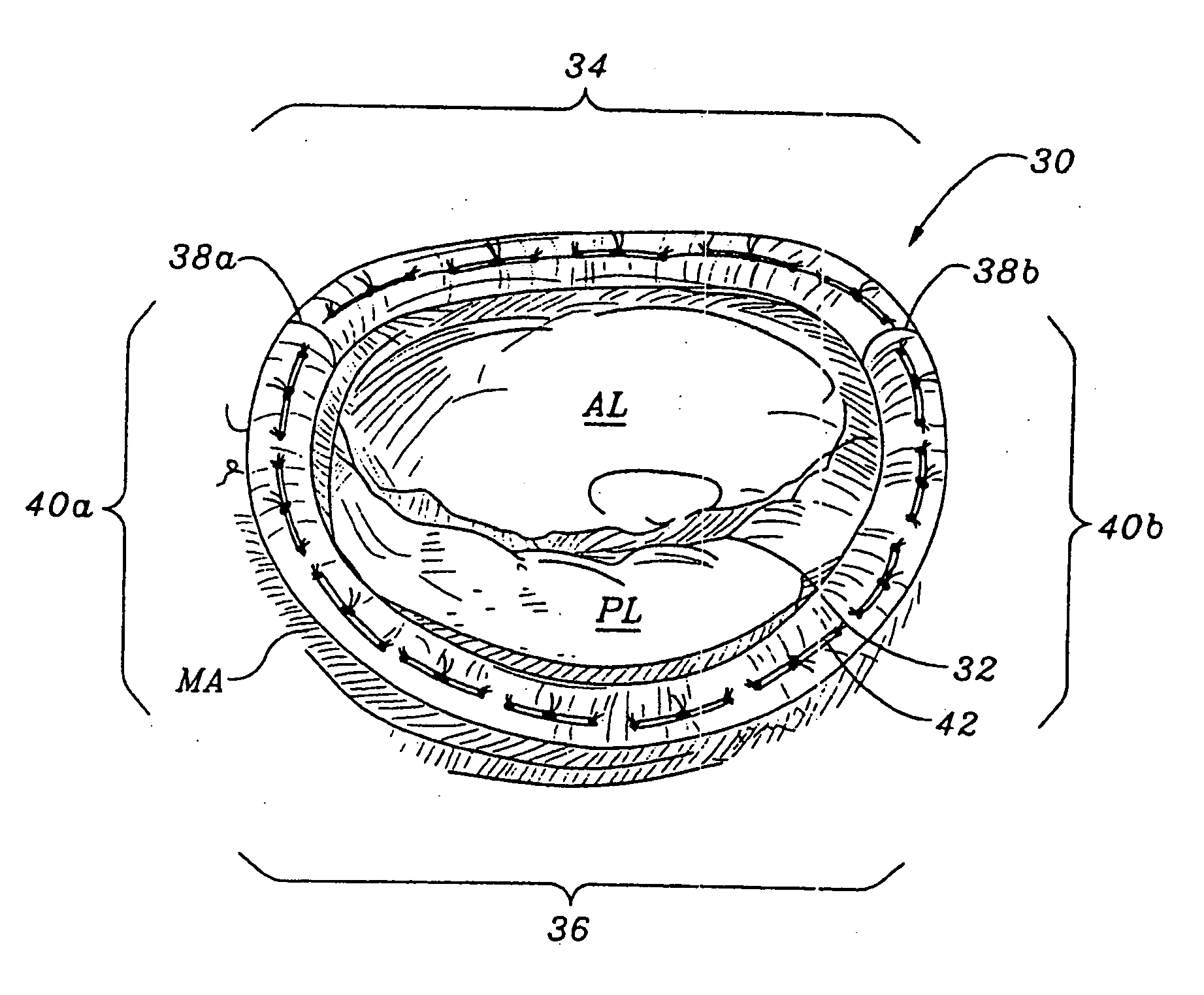
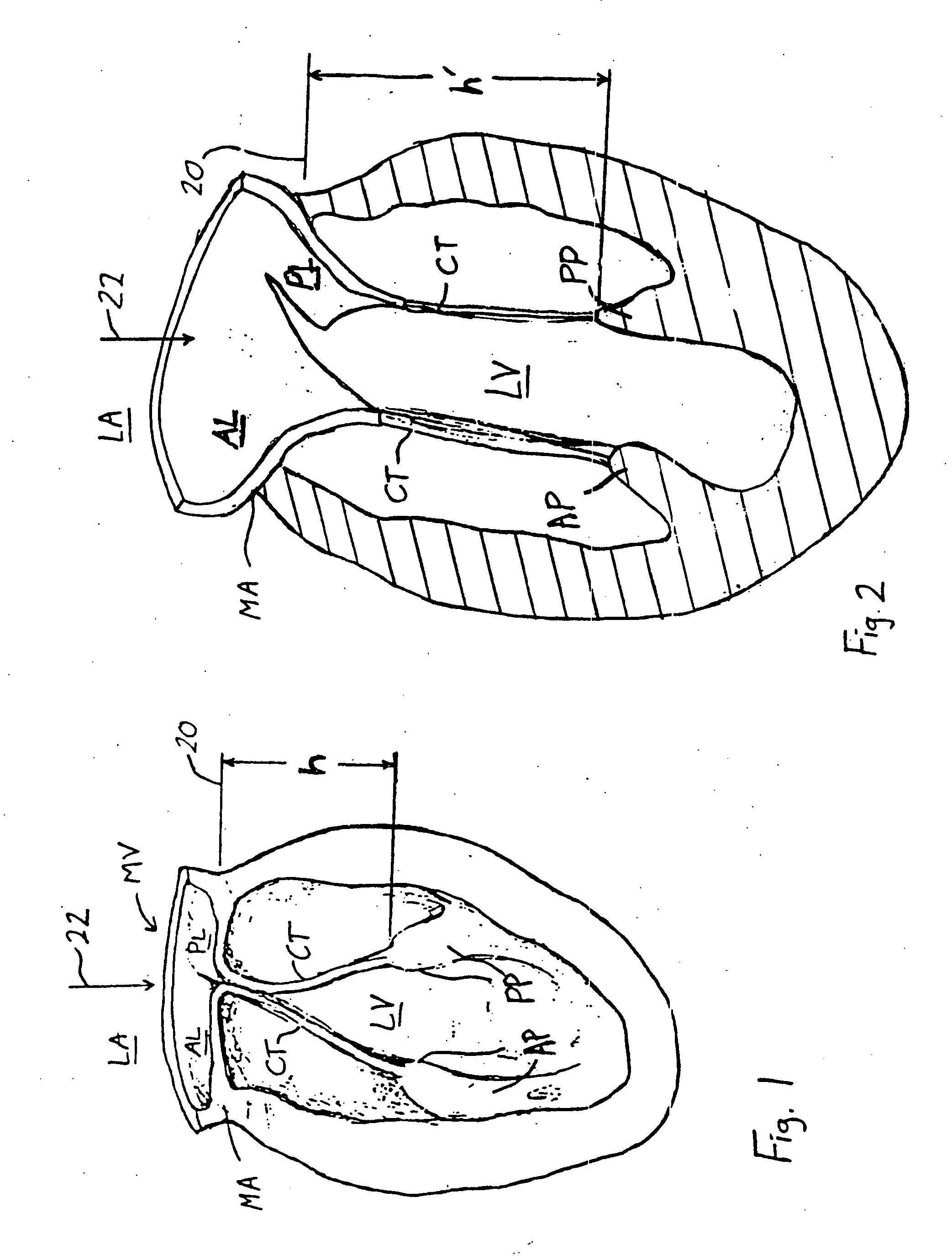
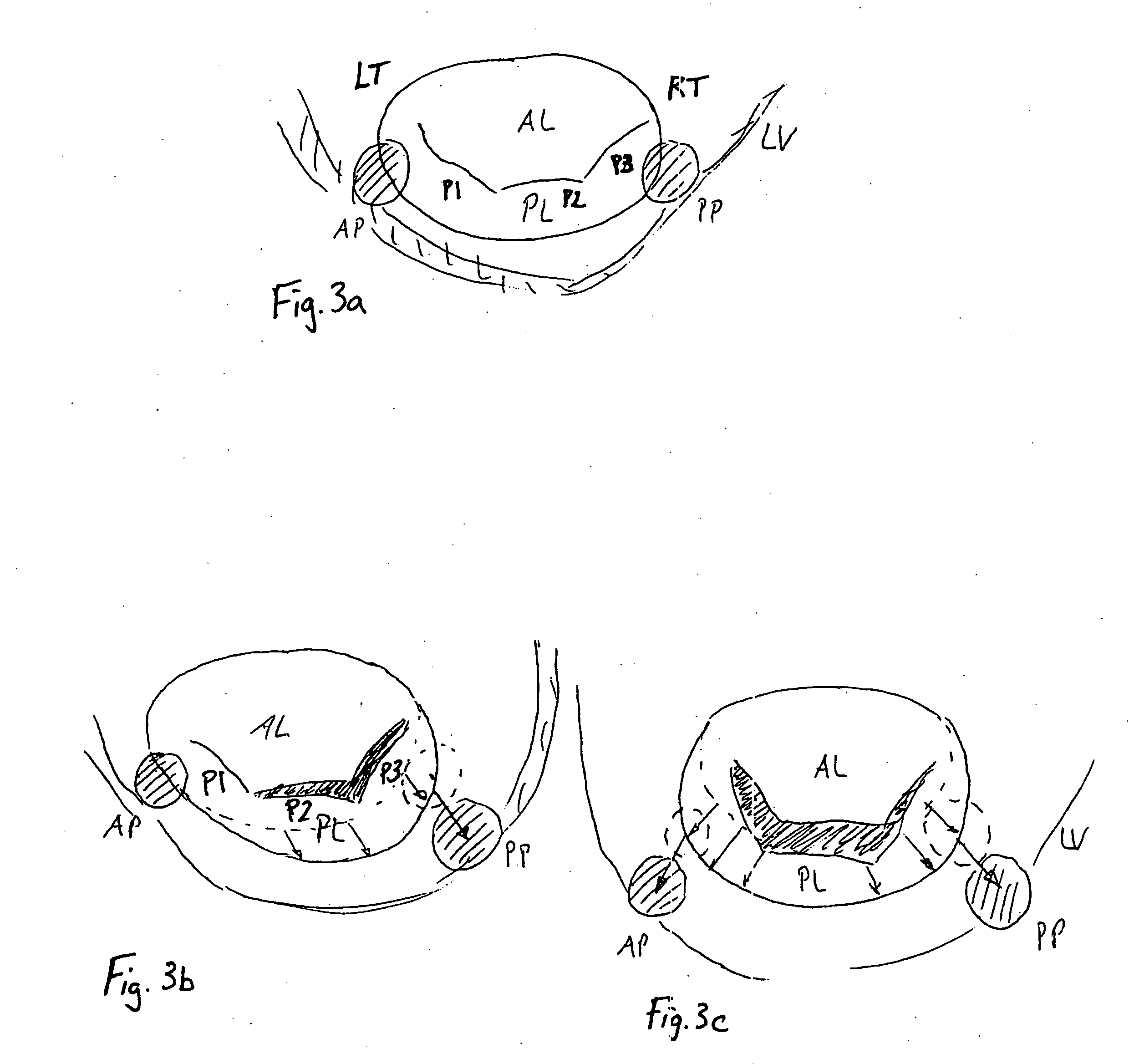
InactiveUS20050131533A1Reduced orifice areaReduce the overall diameterAnnuloplasty ringsPosterior leafletBlood flow
A remodeling mitral annuloplasty ring with a reduced anterior-to-posterior dimension to restore coaptation between the mitral leaflets in mitral valve insufficiency (IMVI). The ring has a generally oval shaped body with a major axis perpendicular to a minor axis, both perpendicular to a blood flow axis. An anterior section lies between anteriolateral and posteriomedial trigones, while a posterior section defines the remaining ring body and is divided into P1, P2, and P3 segments corresponding to the three scallops of the same nomenclature in the posterior leaflet of the mitral valve. The anterior-to-posterior dimension of the ring body is reduced from conventional rings; such as by providing, in atrial plan view, a pulled-in P3 segment. Viewed another way, the convexity of the P3 segment is less pronounced than the convexity of the P1 segment. In addition, the ring body may have a downwardly deflected portion in the posterior section, preferably within the P2 and P3 segments. The downwardly deflected portion may have an apex which is the lowest elevation of the ring body and may be offset with respect to the center of the downwardly deflected portion toward the P1 segment. A sewing cuff may have an enlarged radial dimension of between 5-10 cm, or only a portion of the sewing cuff may be enlarged.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
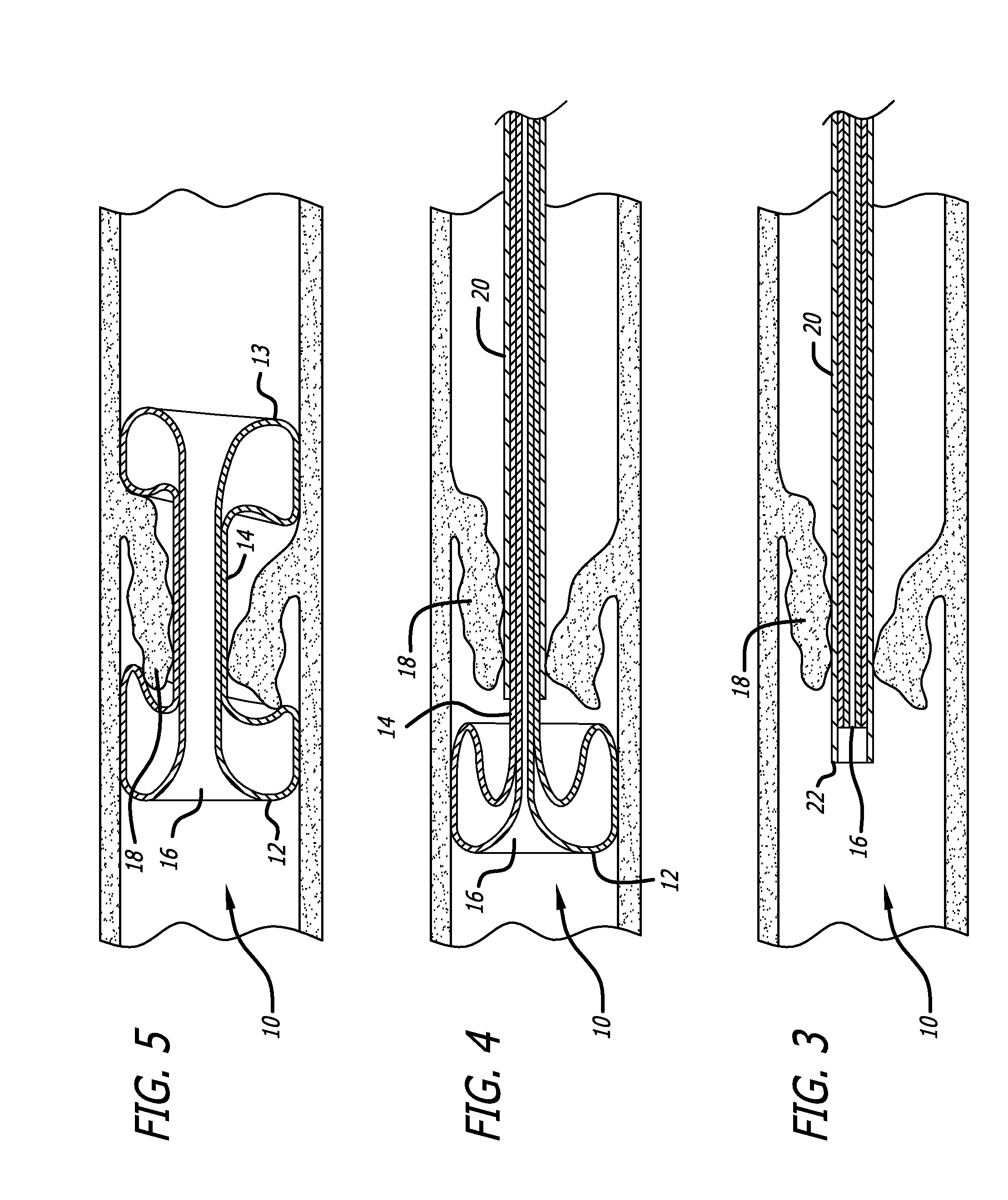
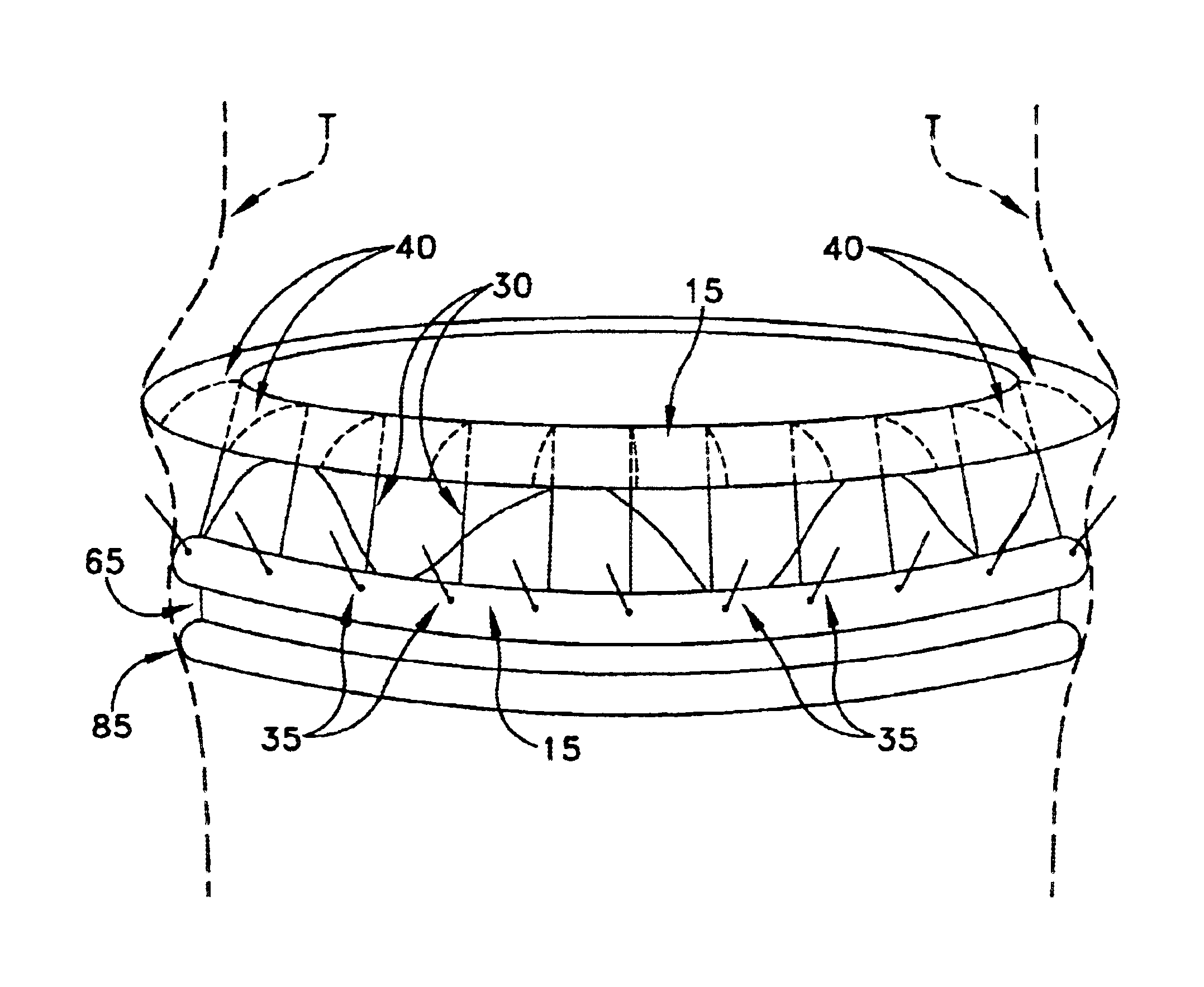
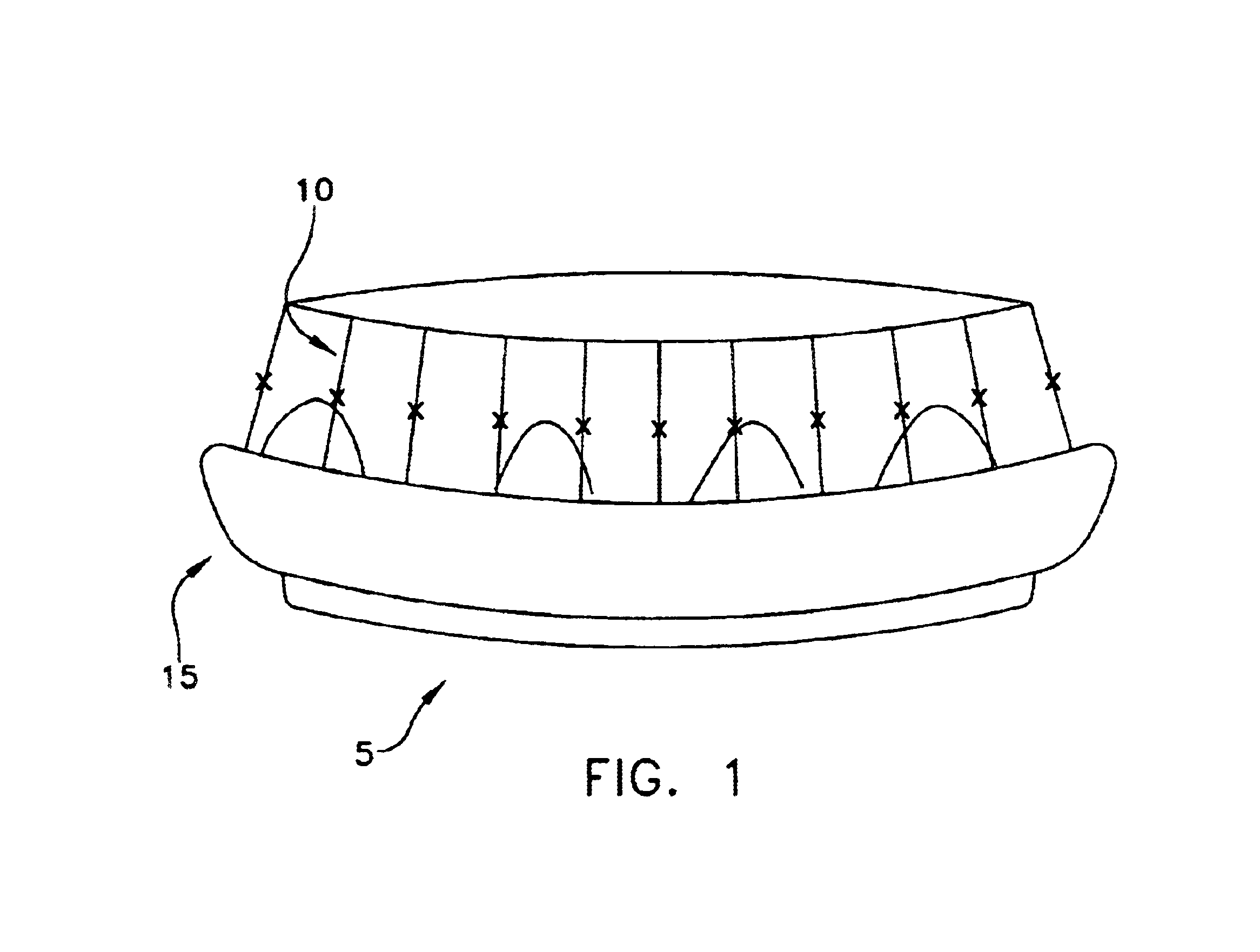
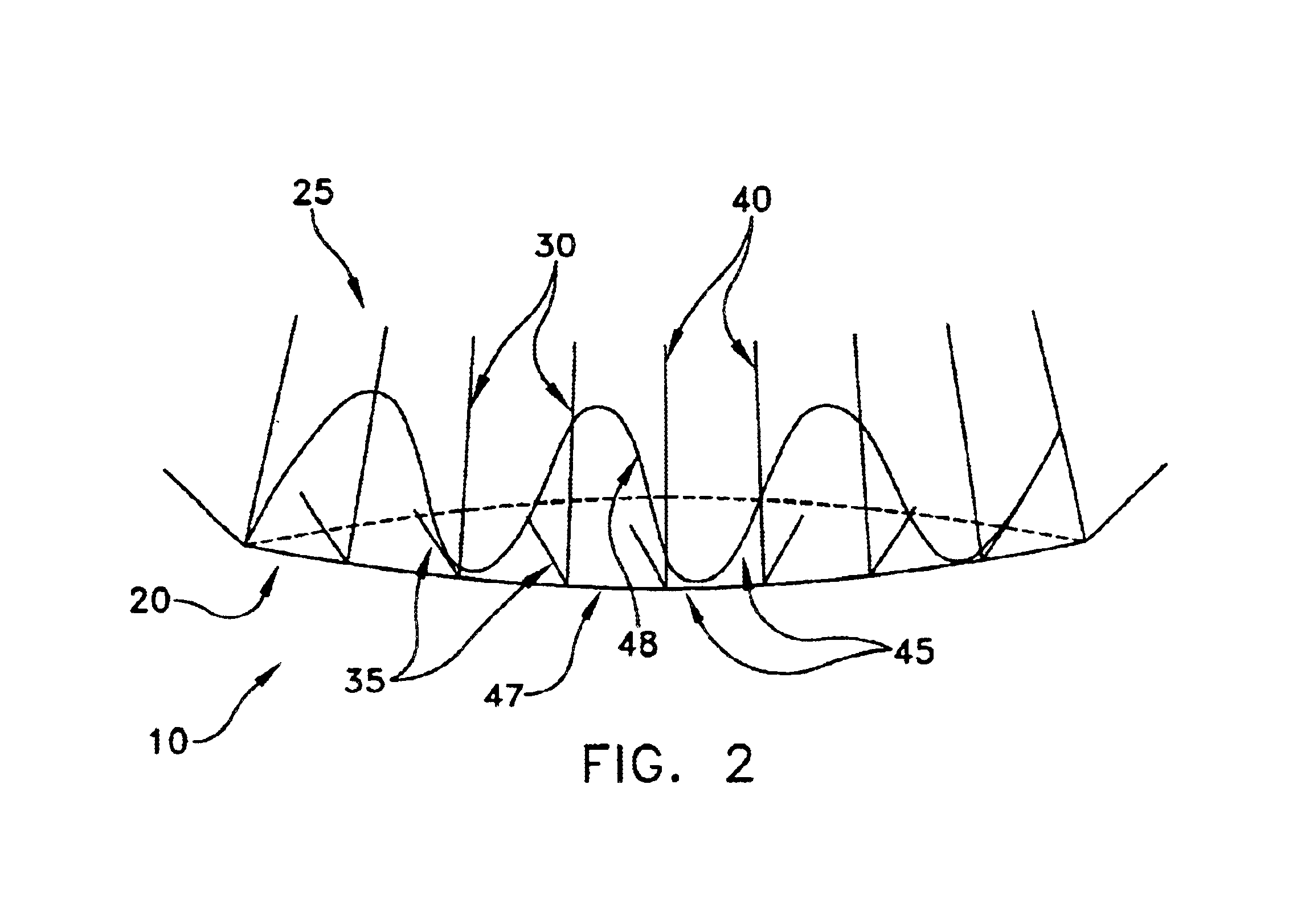
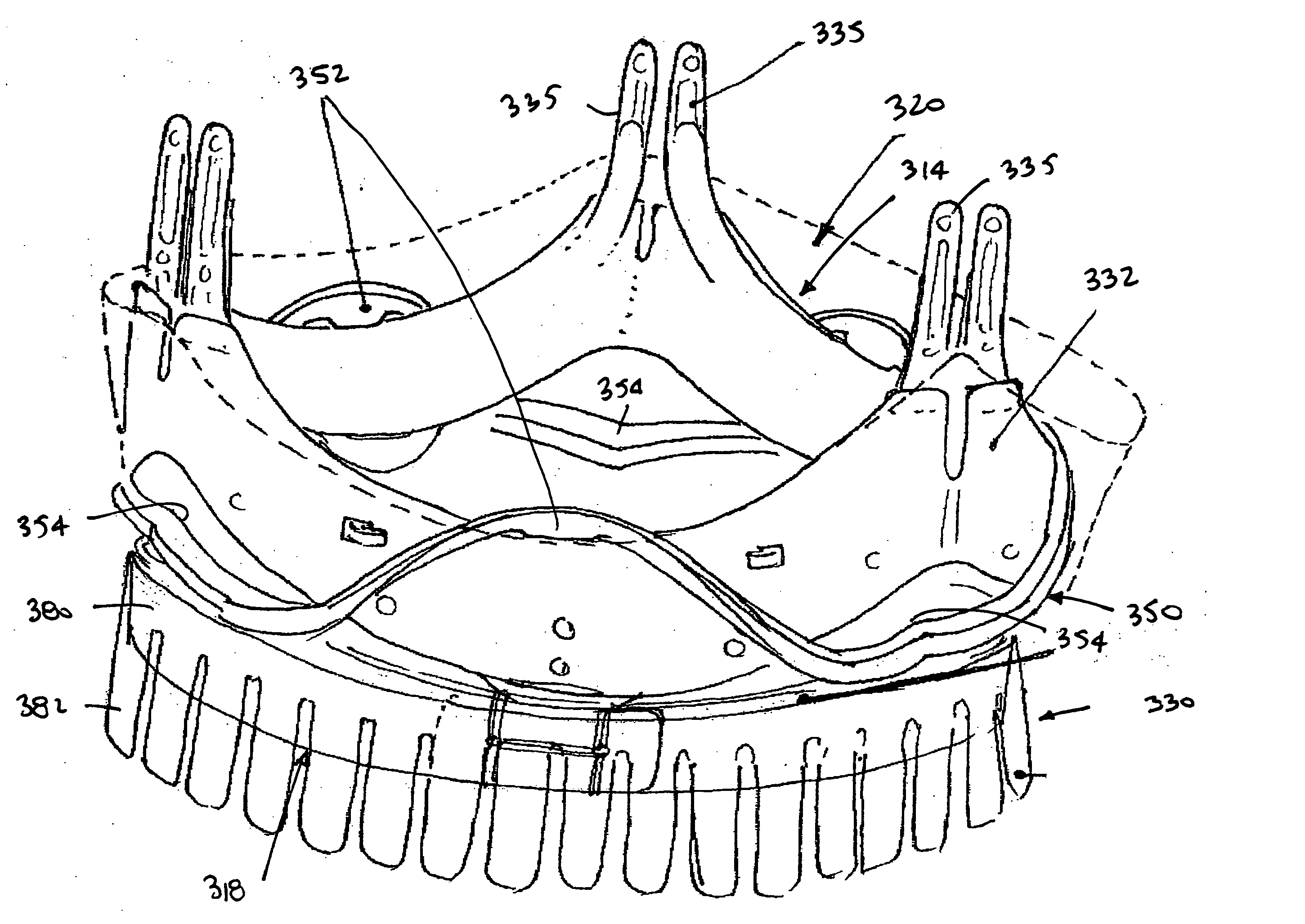
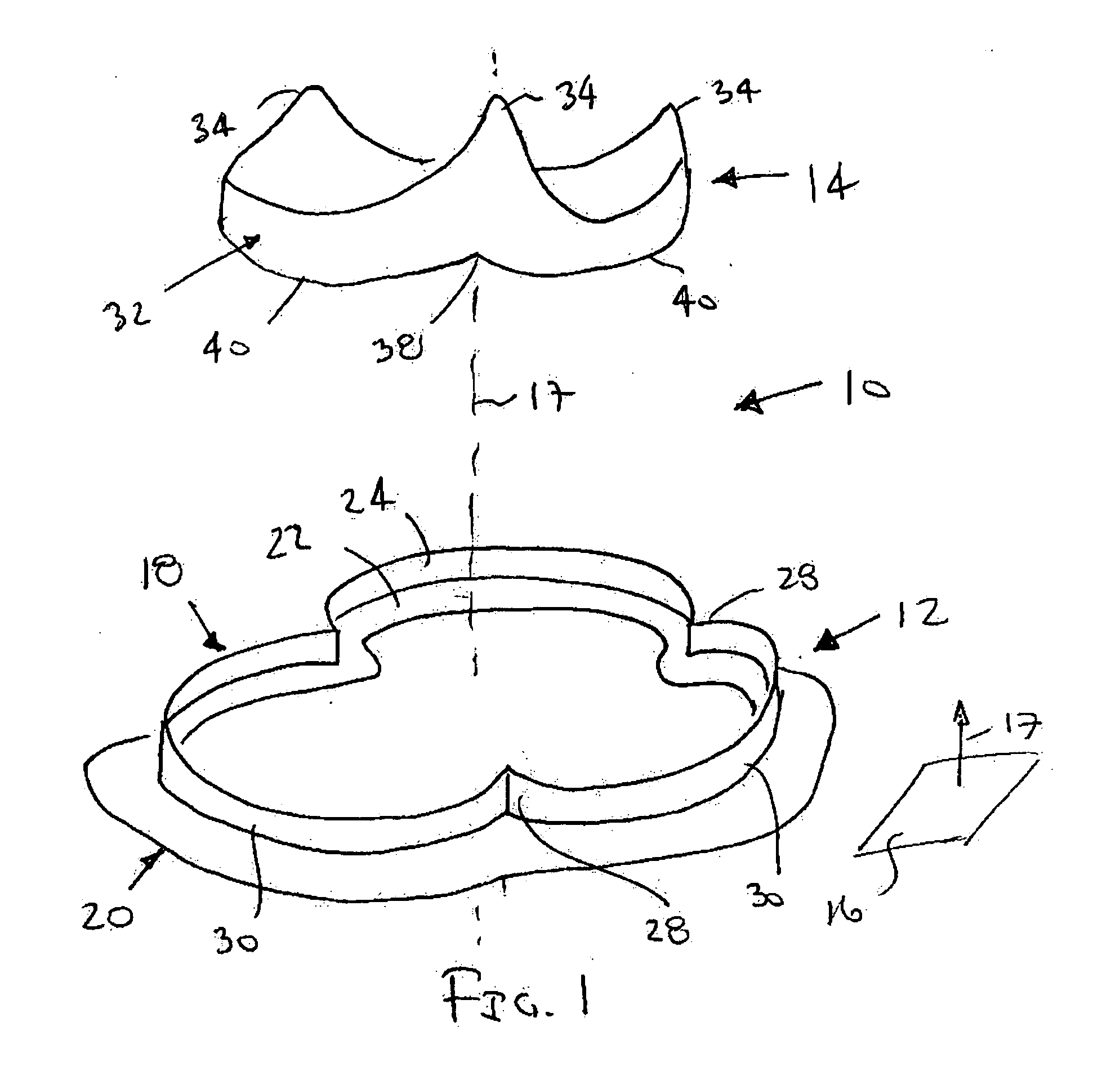
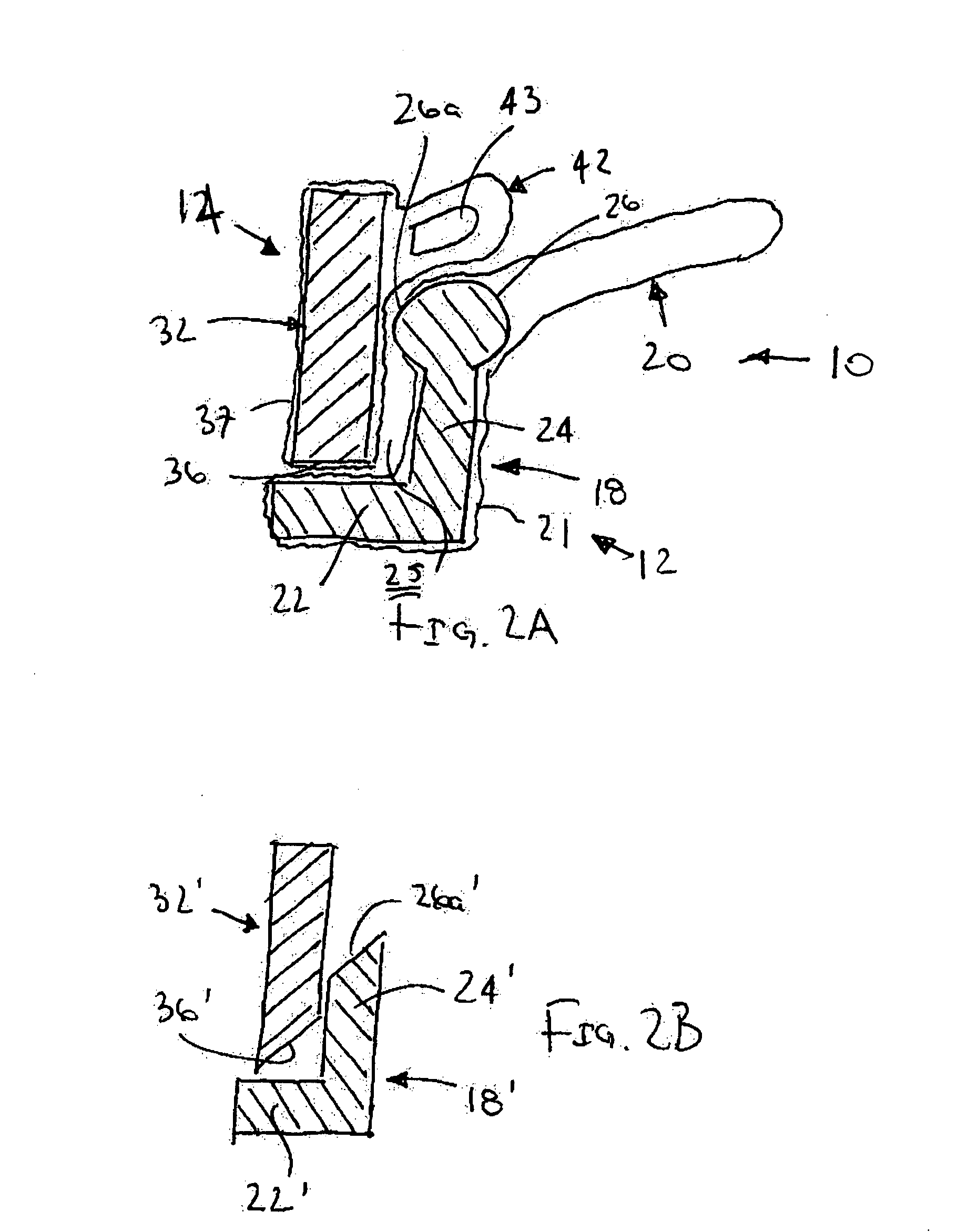
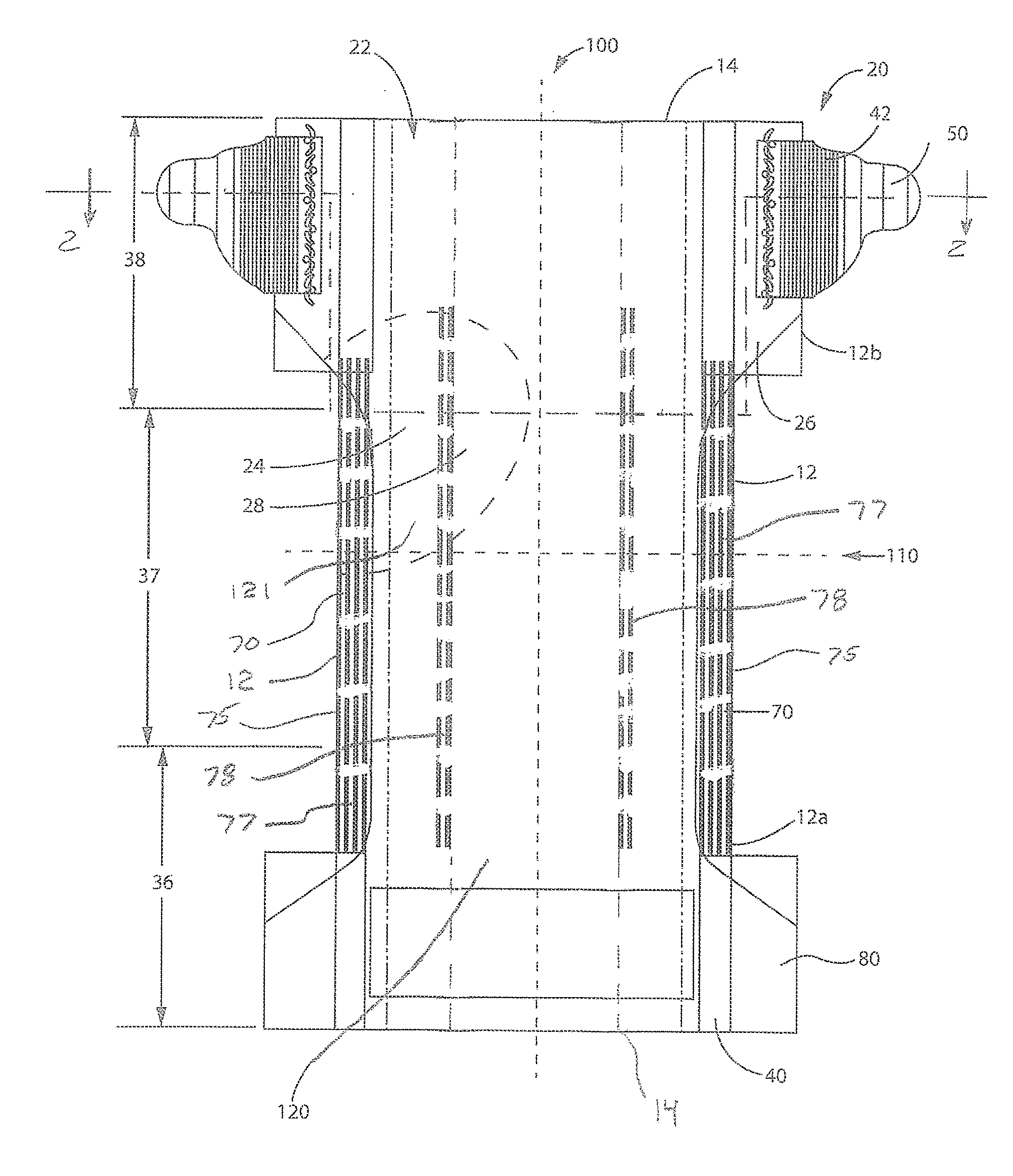
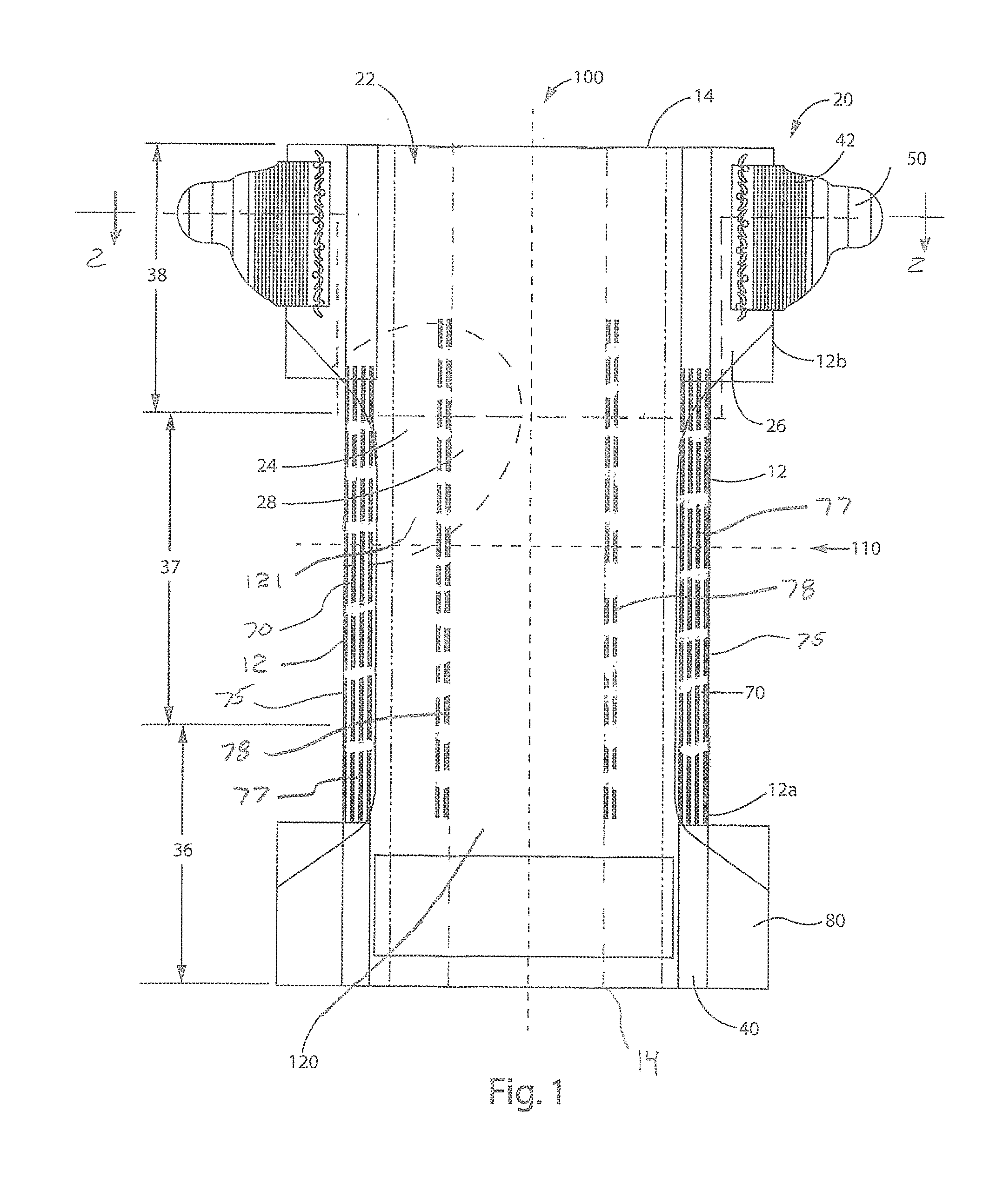
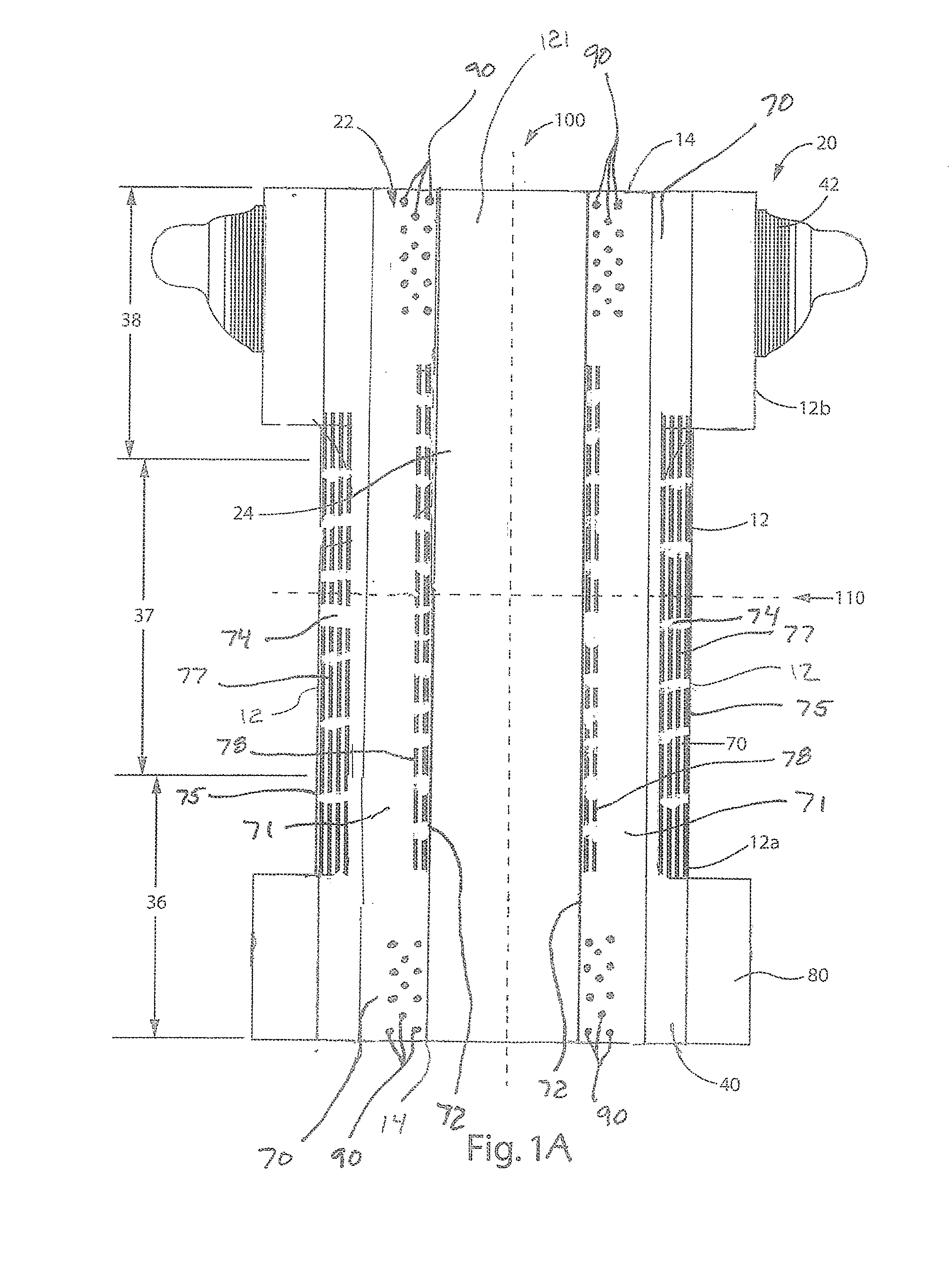
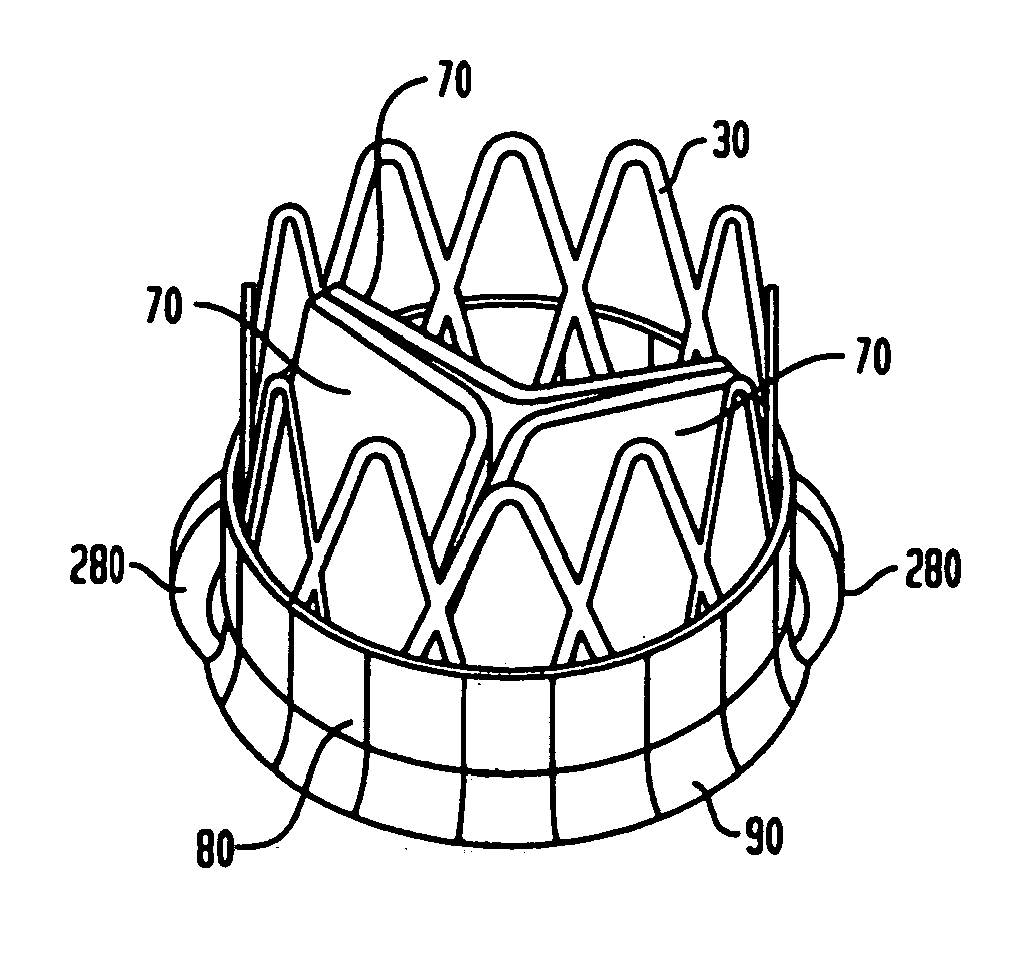
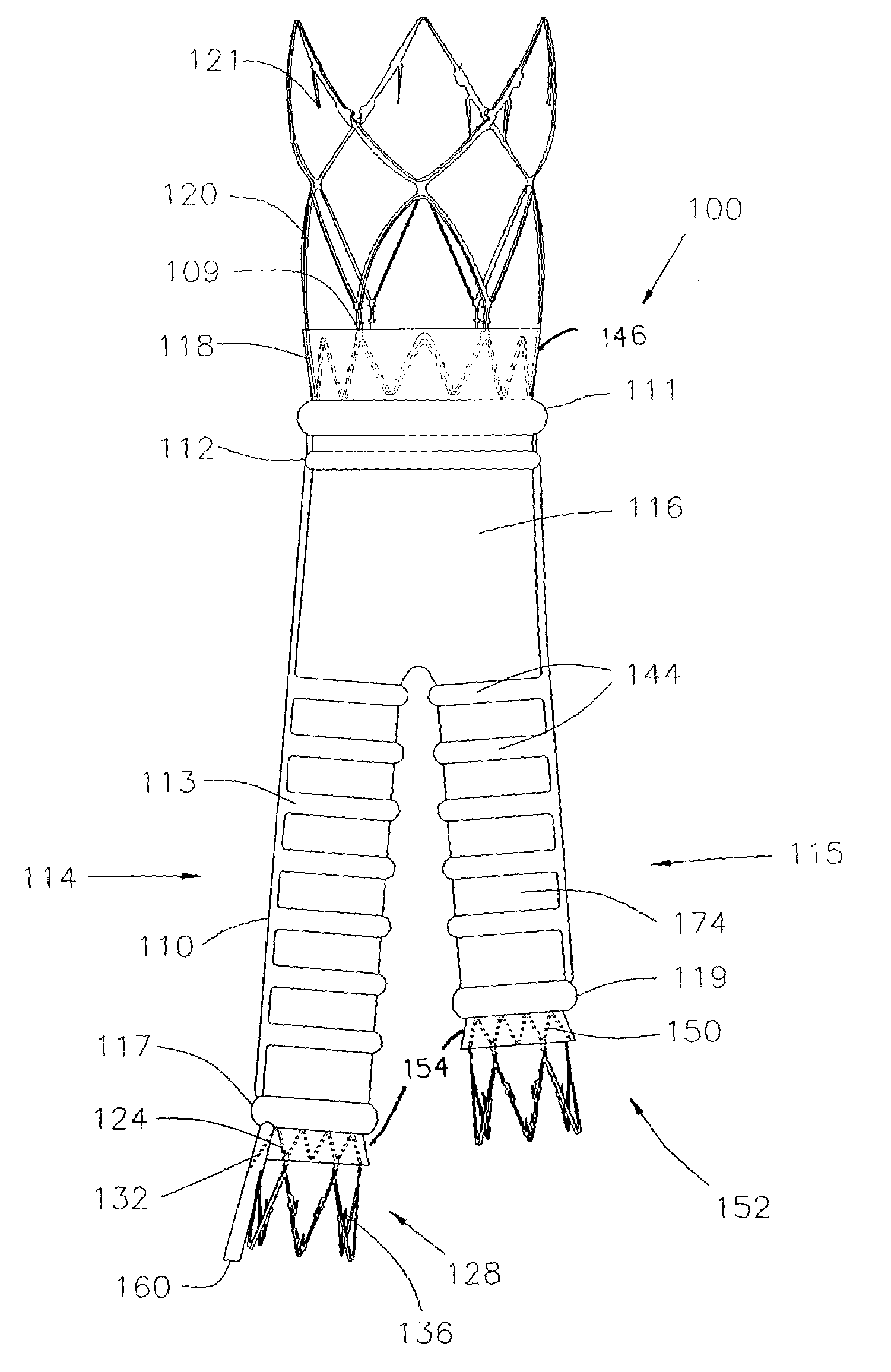
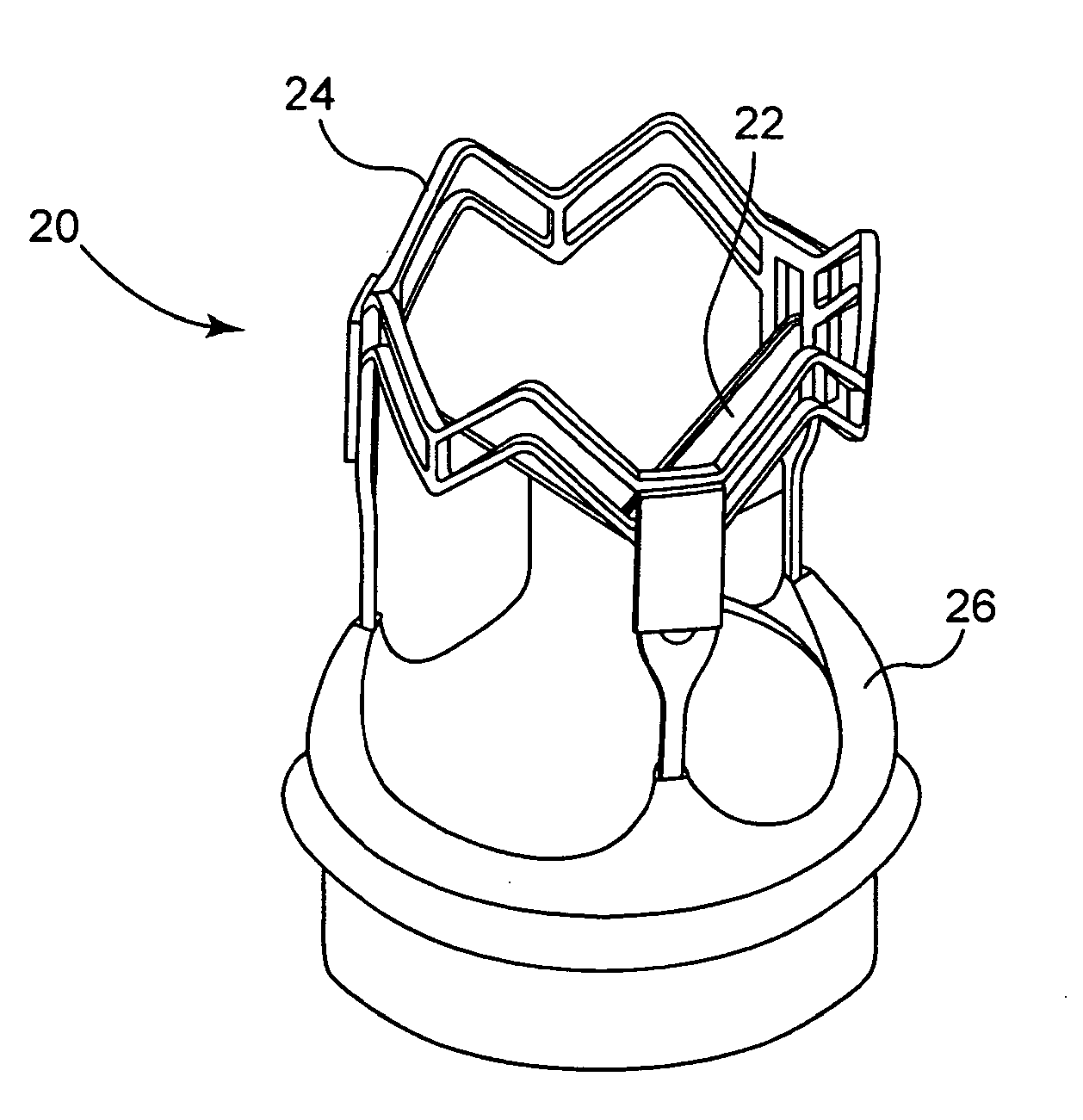
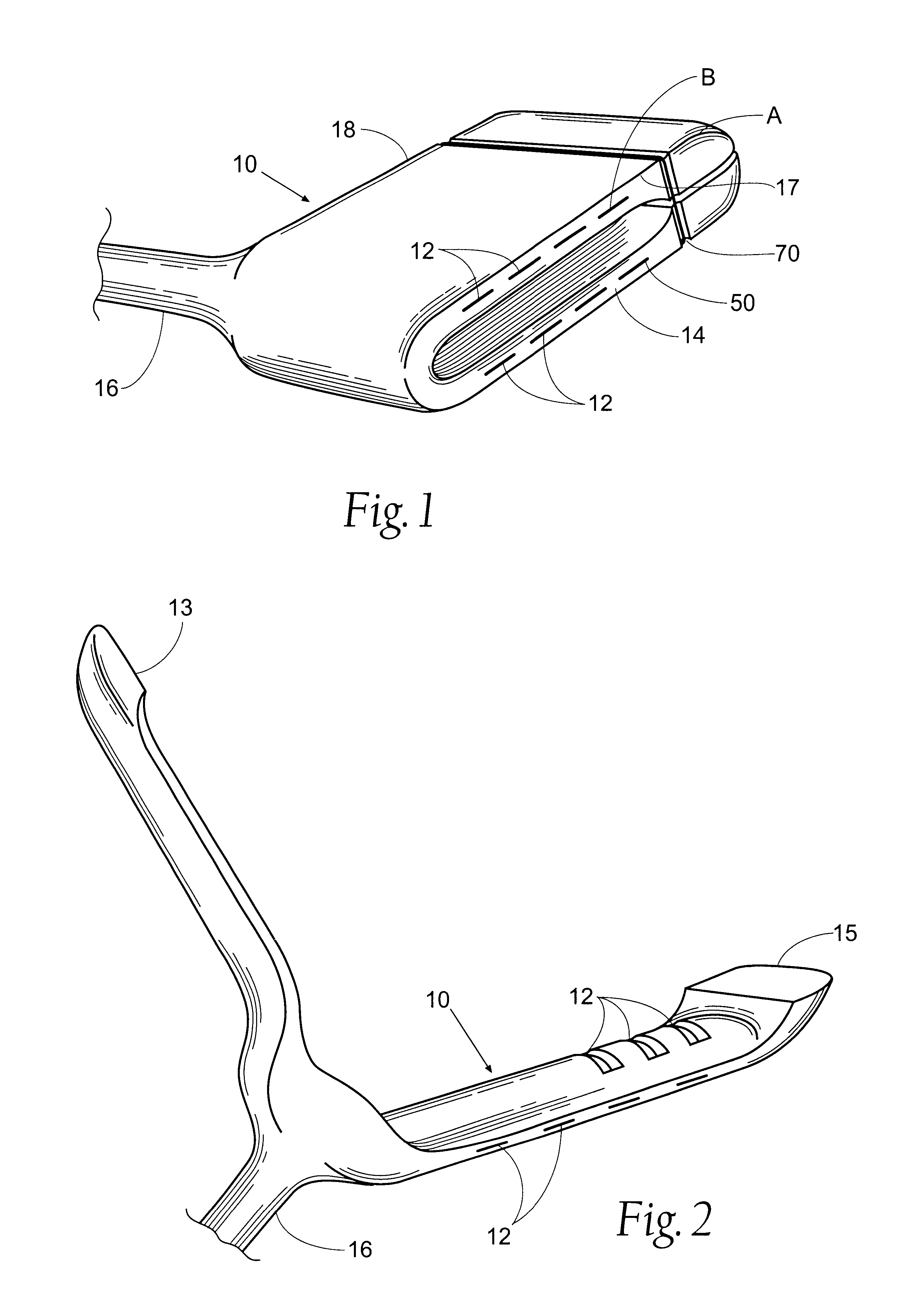
Collapsible and re-expandable prosthetic heart valve cuff designs and complementary technological applications
ActiveUS20110098802A1Improve sealingPromote intimate engagementStentsBalloon catheterInsertion stentPattern matching
A prosthetic heart valve is provided with a cuff (85, 285, 400) having features which promote sealing with the native tissues even where the native tissues are irregular. The cuff may include a portion (90) adapted to bear native aortic valve. The valve may include elements (210, 211, 230, 252, 253) for biasing the cuff outwardly with respect to the stent body when the stent body is in an expanded condition. The cuff may have portions of different thickness (280) distributed around the circumference of the valve in a pattern matching the shape of the opening defined by the native tissue. All or part (402) of the cuff may be movable relative to the stent during implantation.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LLC
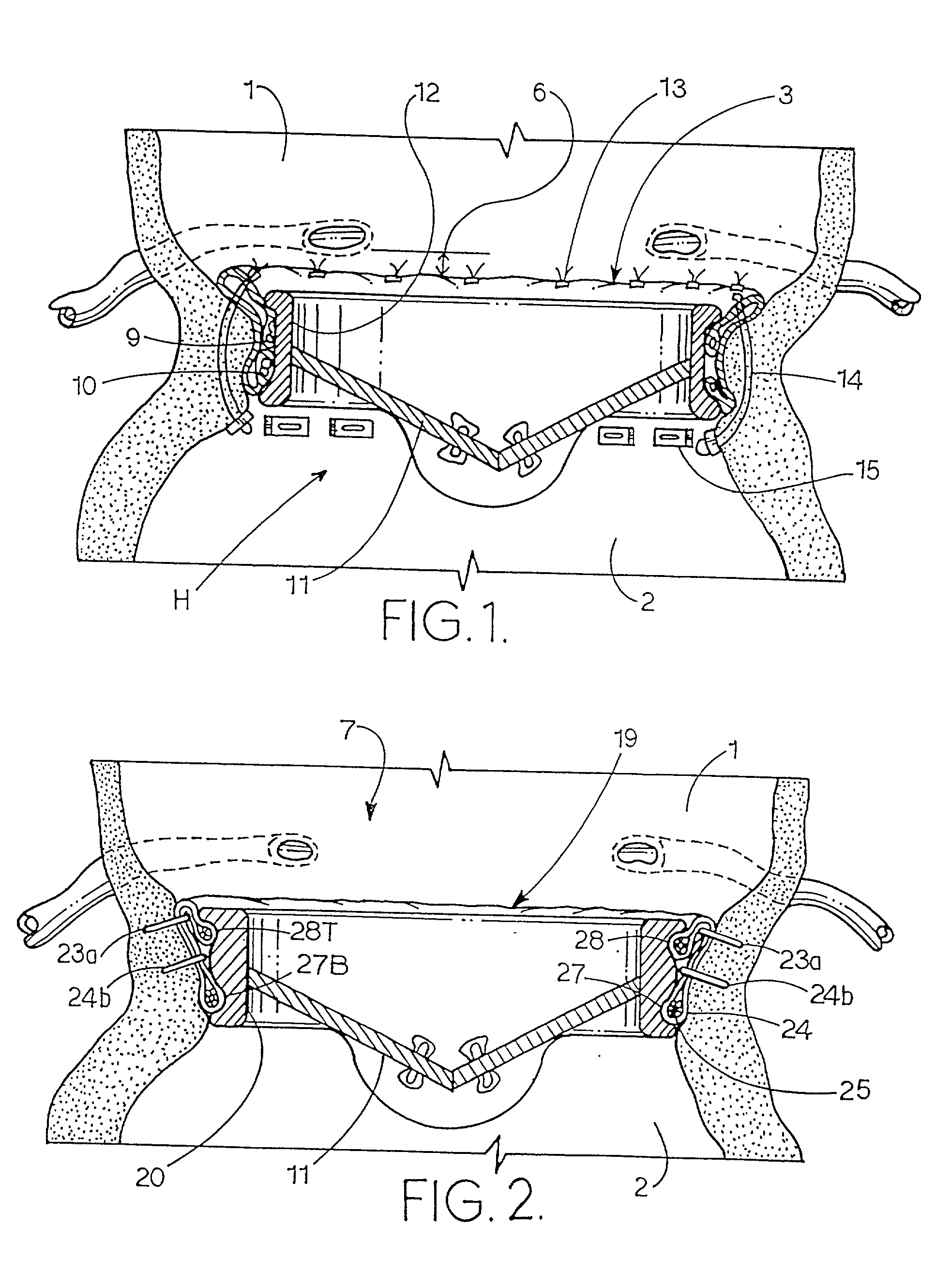
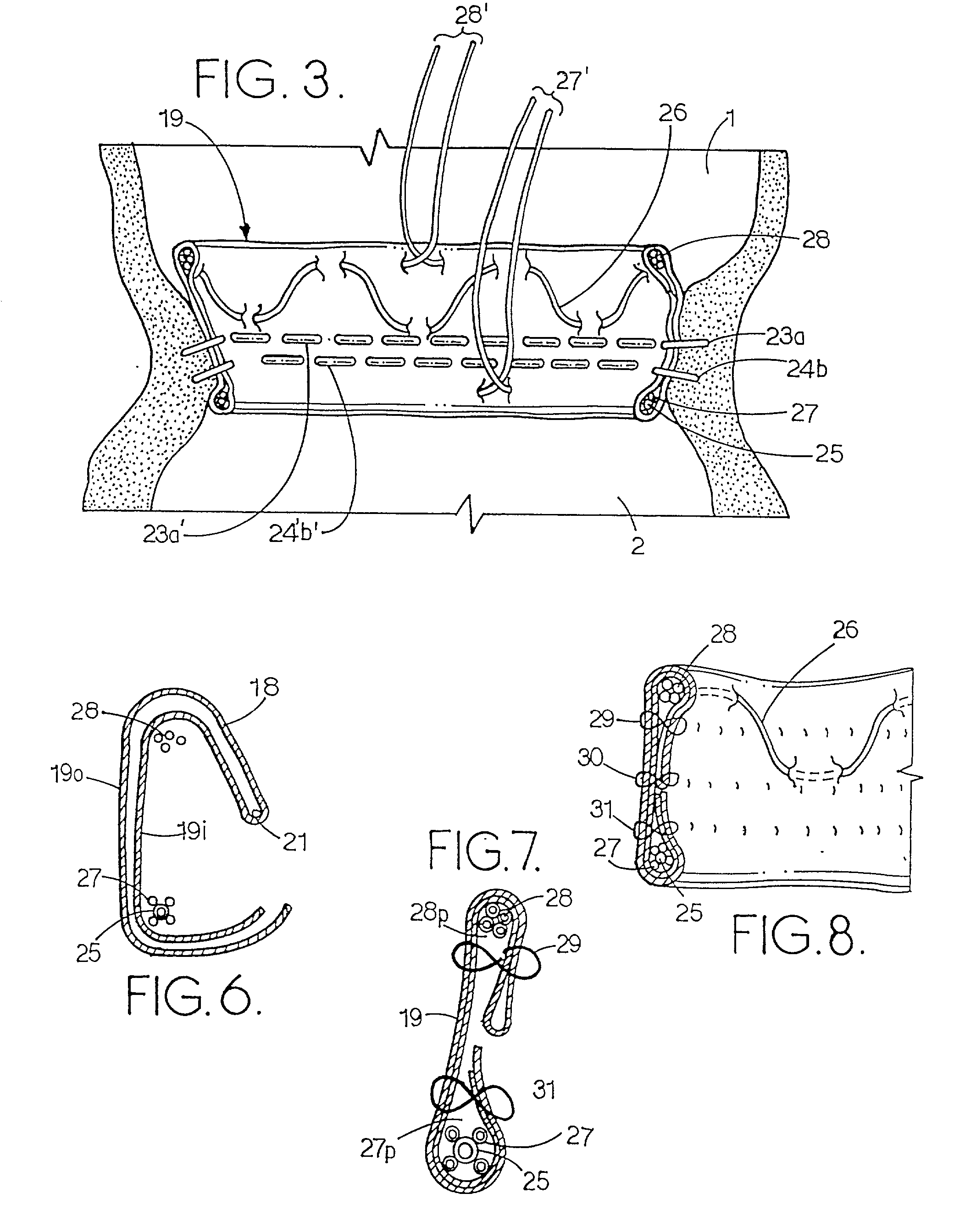
Heart valve assembly and methods for using them
A heart valve assembly includes a base including a multi-lobular annular shape within a plane, a valve member or other annular body including a multi-lobular shape complementary to the shape of the base, and cooperating connectors on the base and the annular body for connecting the annular body to the base. The base includes an anchoring ring, and a flexible cuff for attaching the base to a biological annulus. The base and the annular body include guides for aligning their multi-lobular shapes, e.g., visual, tactile, or other markers, or tethers that extend from the base that are slidable through the annular body. During use, the base is attached to a biological annulus, the annular body is directed adjacent the annulus, oriented such that the multi-lobular shape of the annular body valve member is aligned with the base, and the annular body is attached to the base.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Absorbent Article With Leg Gasketing Cuff
A disposable absorbent article may include a topsheet, a backsheet, an absorbent core disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet, and a leg gasketing system. The leg gasketing system may include an inner cuff and an outer cuff; the inner cuff may include an inner cuff folded edge and an inner cuff material edge and the outer cuff may include an outer cuff folded edge and an outer cuff material edge such that the web of material is folded laterally inward to form the outer cuff folded edge and folded laterally outward to form the inner cuff material edge.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Translumenally implantable heart valve with formed in place support
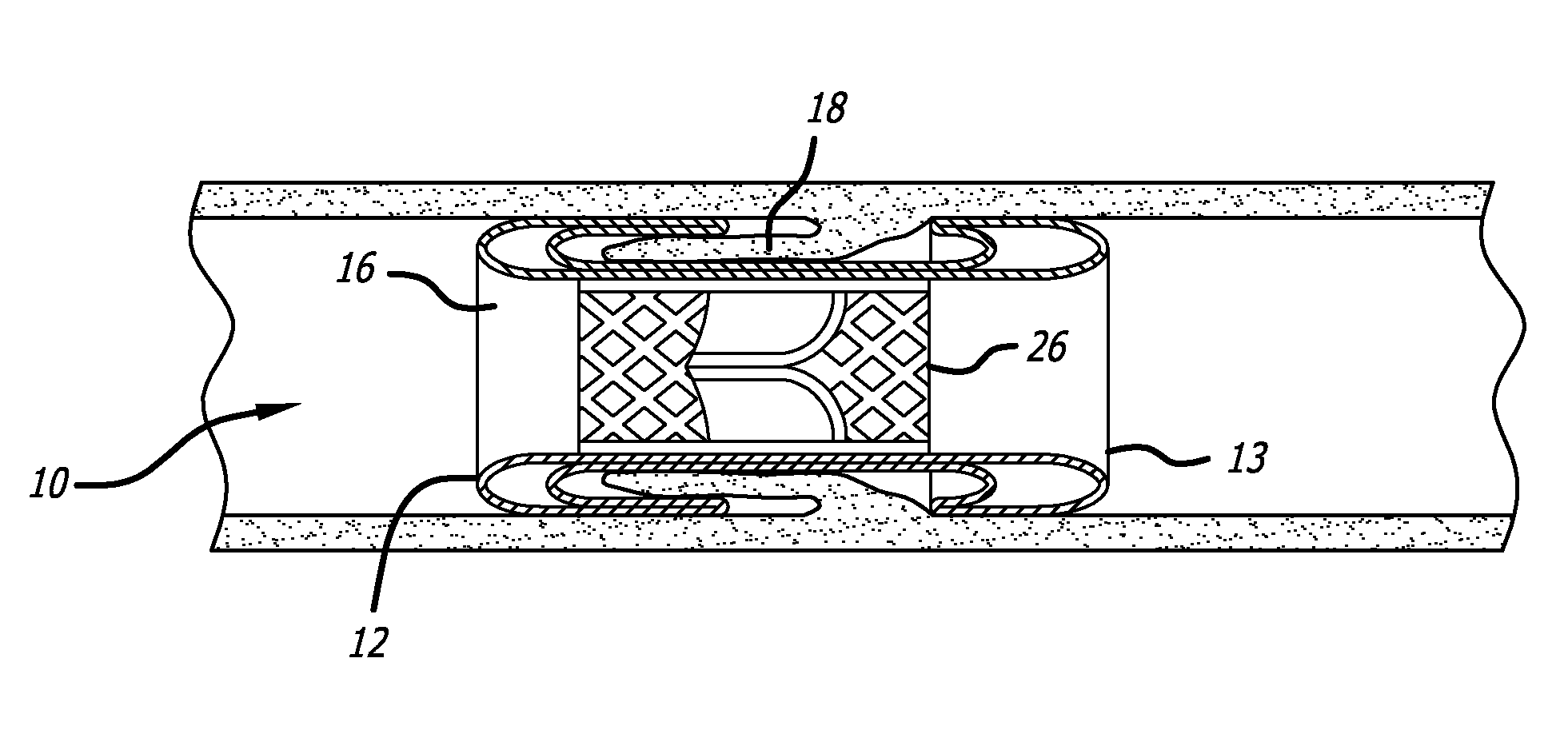
A cardiovascular prosthetic valve, the valve comprising an inflatable cuff comprising at least one inflatable channel that forms, at least in part, an inflatable structure, and a valve coupled to the inflatable cuff, the valve configured to permit flow in a first axial direction and to inhibit flow in a second axial direction opposite to the first axial direction, the valve comprising a plurality of tissue supports that extend generally in the axial direction and that are flexible and / or movable throughout a range in a radial direction.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
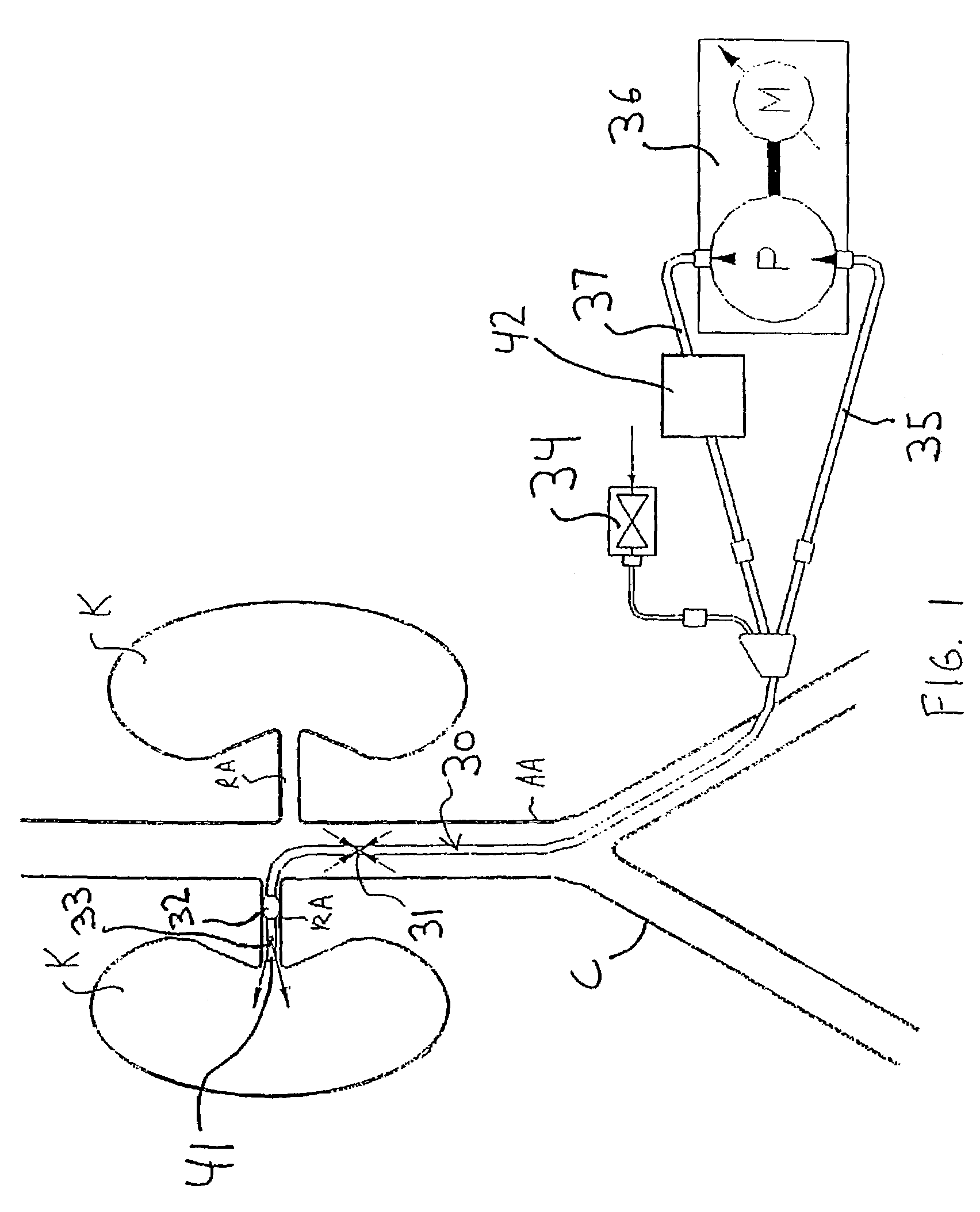
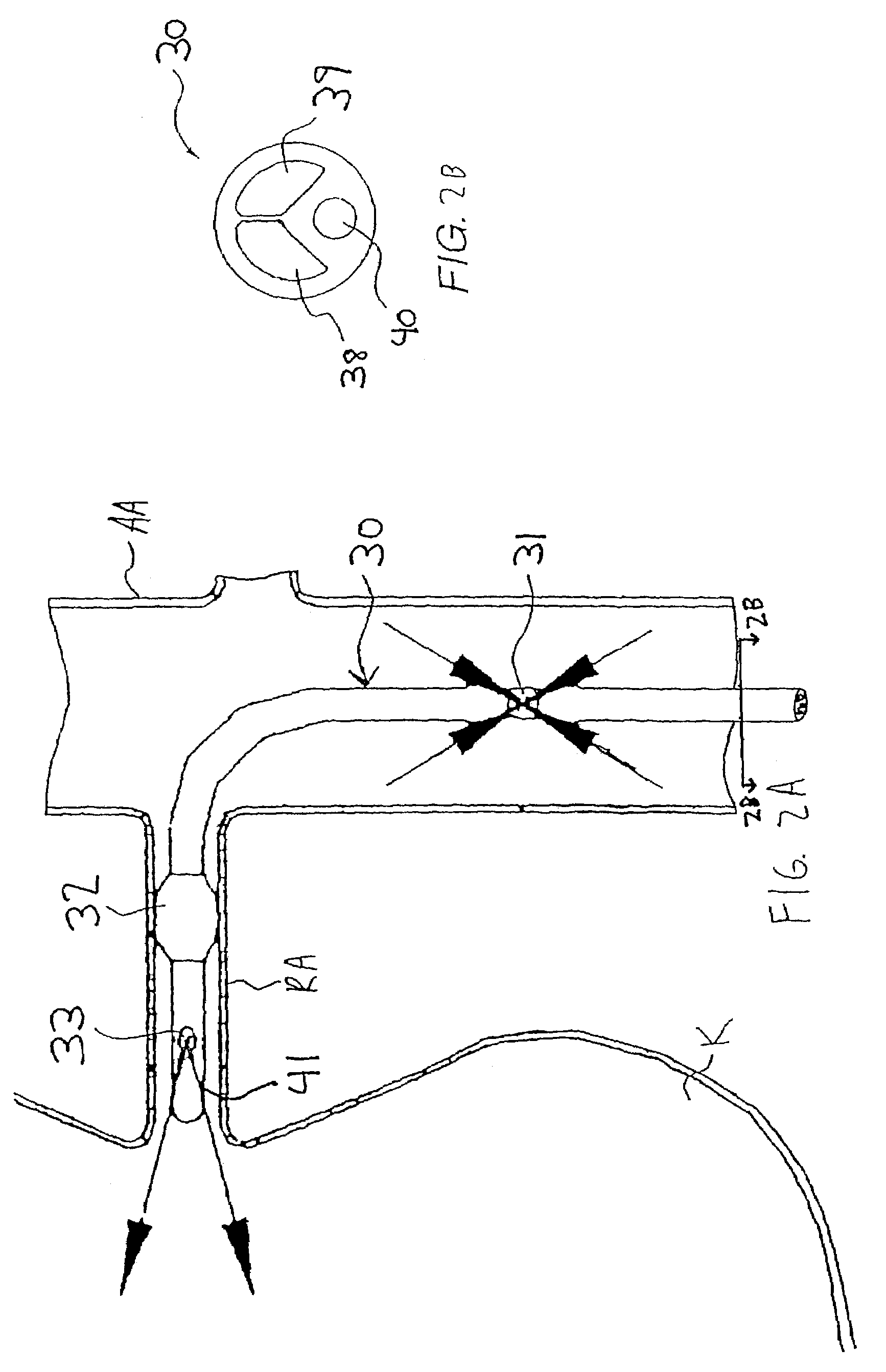
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart disease
InactiveUS7335192B2Increase blood flowImprove kidney functionBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesInsertion stentPeri-aortic
Methods and apparatus are provided for treating congestive heart by actively or passively enhancing perfusion to the renal arteries. A first embodiment comprises a specially configured balloon catheter and extracorporeal pump, wherein the pump operates in a “once-through” fashion or alternating volume displacement mode. In another embodiment the catheter includes a pair of balloons to isolate a region of the aorta, and a third balloon that directs flow into the renal arteries. In still further embodiments, a stent or cuff having a constricted region is deployed in or around the aorta, respectively, to create a backpressure upstream of the stent or cuff. Methods of enhancing renal perfusion also are provided.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Advanced endovascular graft
This invention is a system for the treatment of body passageways; in particular, vessels with vascular disease. The system includes an endovascular graft with a low-profile delivery configuration and a deployed configuration in which it conforms to the morphology of the vessel or body passageway to be treated as well as various connector members and stents. The graft is made from an inflatable graft body section and may be bifurcated. One or more inflatable cuffs may be disposed at either end of the graft body section. At least one inflatable channel is disposed between and in fluid communication with the inflatable cuffs.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart failure
InactiveUS6076013AImprove efficiencyImproved ventricular functionEpicardial electrodesHeart valvesCardiac muscleVentricular function
Apparatus and method for the treatment of congestive heart failure are disclosed that utilize a cuff that surrounds the heart and constrains cardiac dilation, while electrodes embedded in the cuff stimulate the myocardium to contractile function. An EKG signal can be processed to create an optimal pattern of selective stimulation of different areas of the heart at different times. An implantable circuit contains a power source and stimulation circuits. In some embodiments, a telemetry unit and an EKG collection circuit are also included. In accordance with the present disclosure, cuff limits the dilation of the heart and the stimulation electrodes enhance ventricular function by optimizing ventricular contractility.
Owner:BRENNAN EDWARD F +1
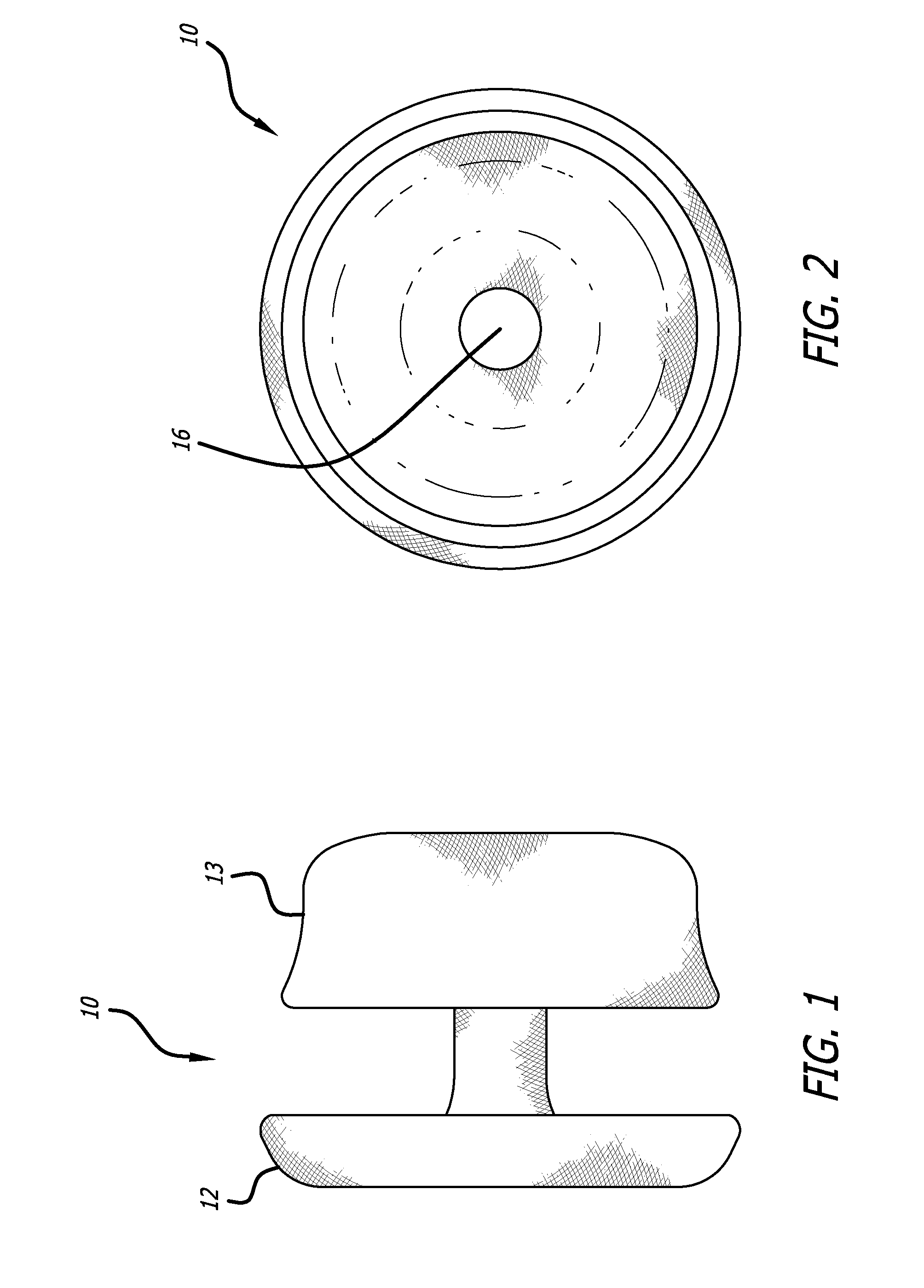
Cushion for a respiratory mask assembly
ActiveUS7523754B2More comfortableAvoid Sealing ProblemsChemical protectionHeat protectionChinRespirator
A respiratory mark assembly for delivering breathable gas to a patient includes a frame and a cushion. The cushion has a non-face contacting portion structured to be connected to the frame, a face-contacting portion structured to engage the patient's face, and an intermediate portion that interconnects the non-face contacting portion and the face-contacting portion. The intermediate portion includes a gusset portion that applies a first component of force to the patient's face through the face-contacting portion. A spring structure is coupled with the face-contacting portion of the cushion. The spring structure applies a second component of force to the patient's face through the face-contacting portion. The first and second components of force applied by the gusset portion and spring structure, respectively, determine a contact force of the cushion applied to the patient's face through the face-contacting portion. The intermediate portion may also include an elastic cuff portion. Further, in the case of an oral mask, the sealing section may include a portion that is designed to promote a better seal in the chin region of the mask.
Owner:RESMED LTD
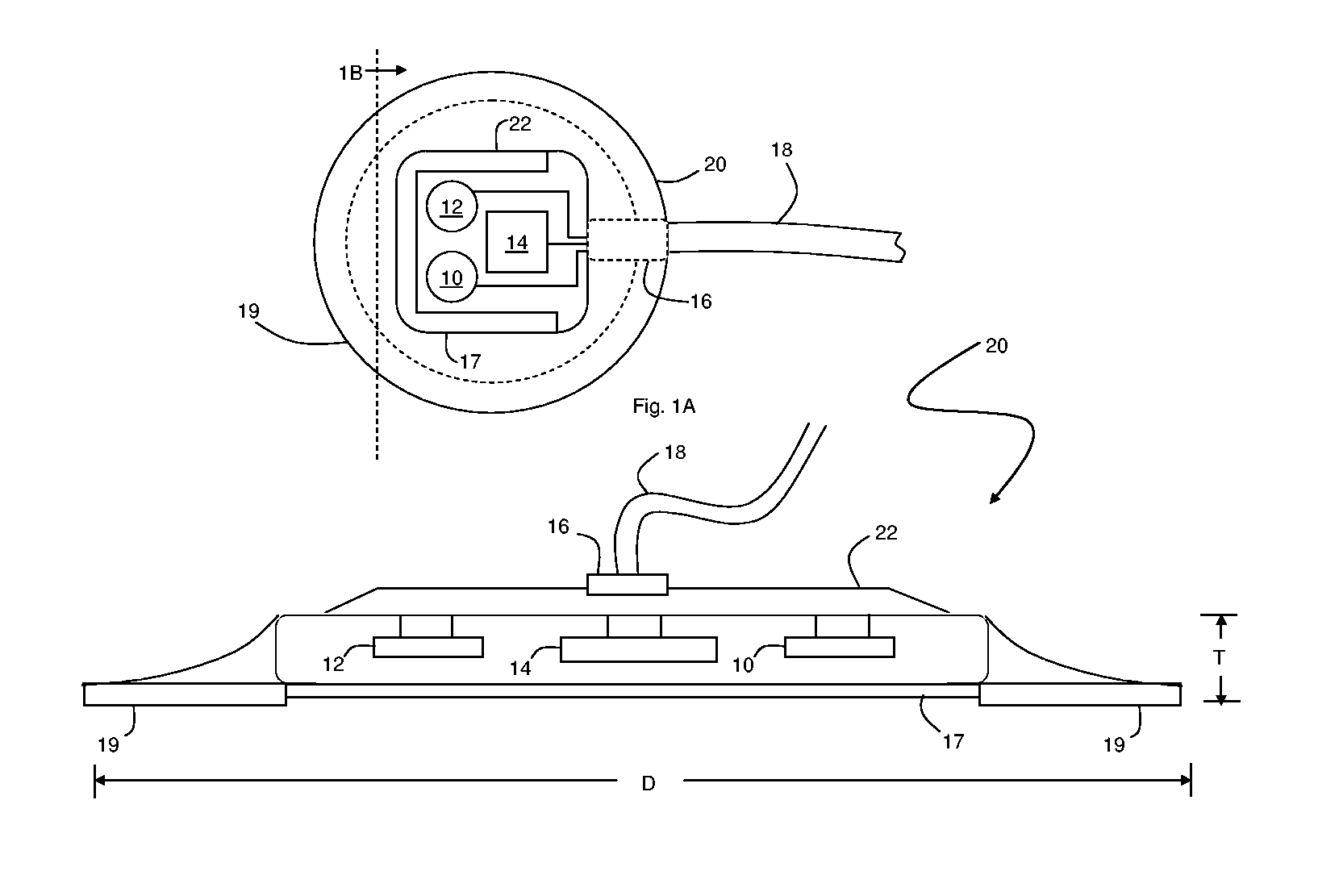
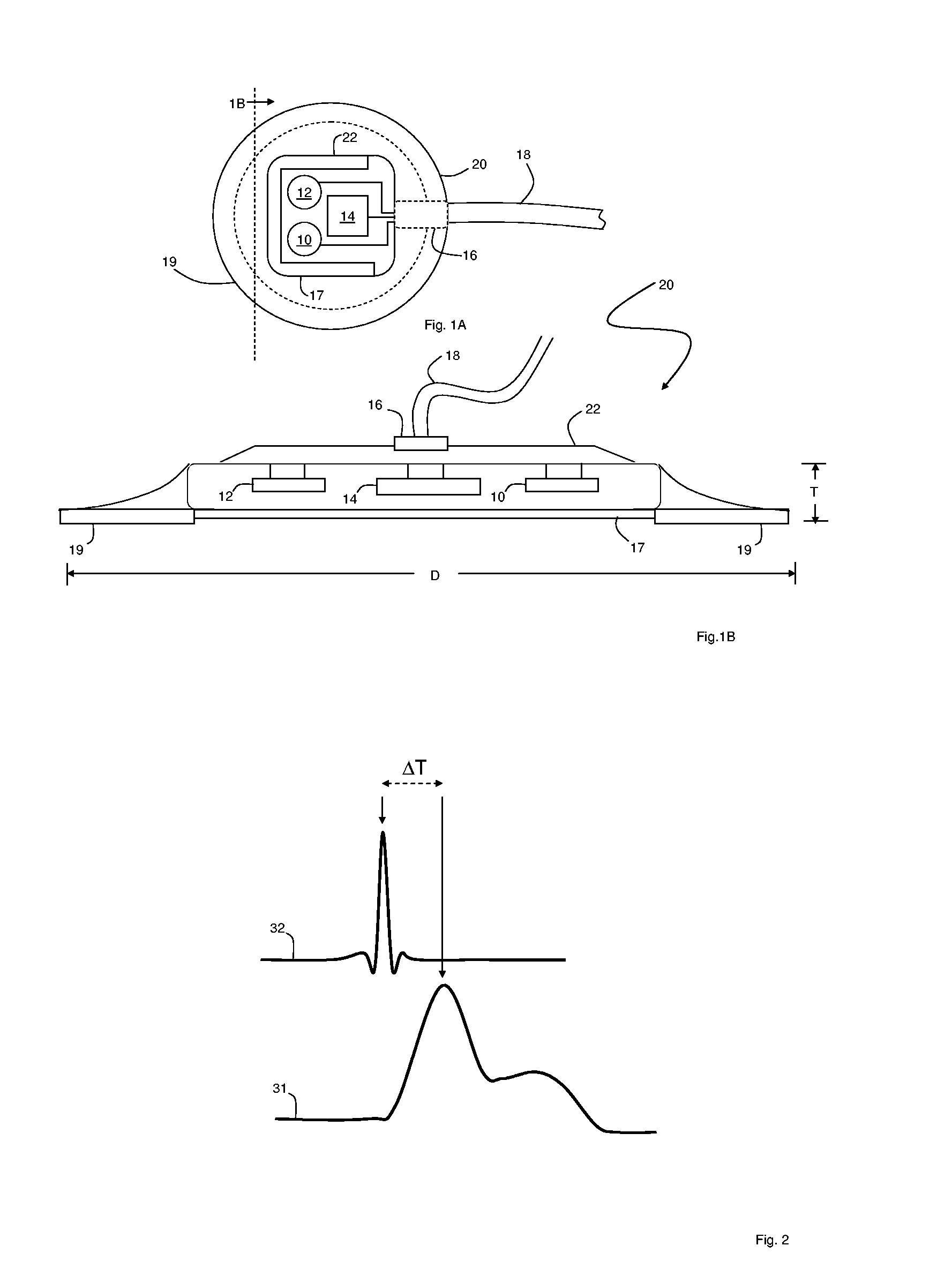
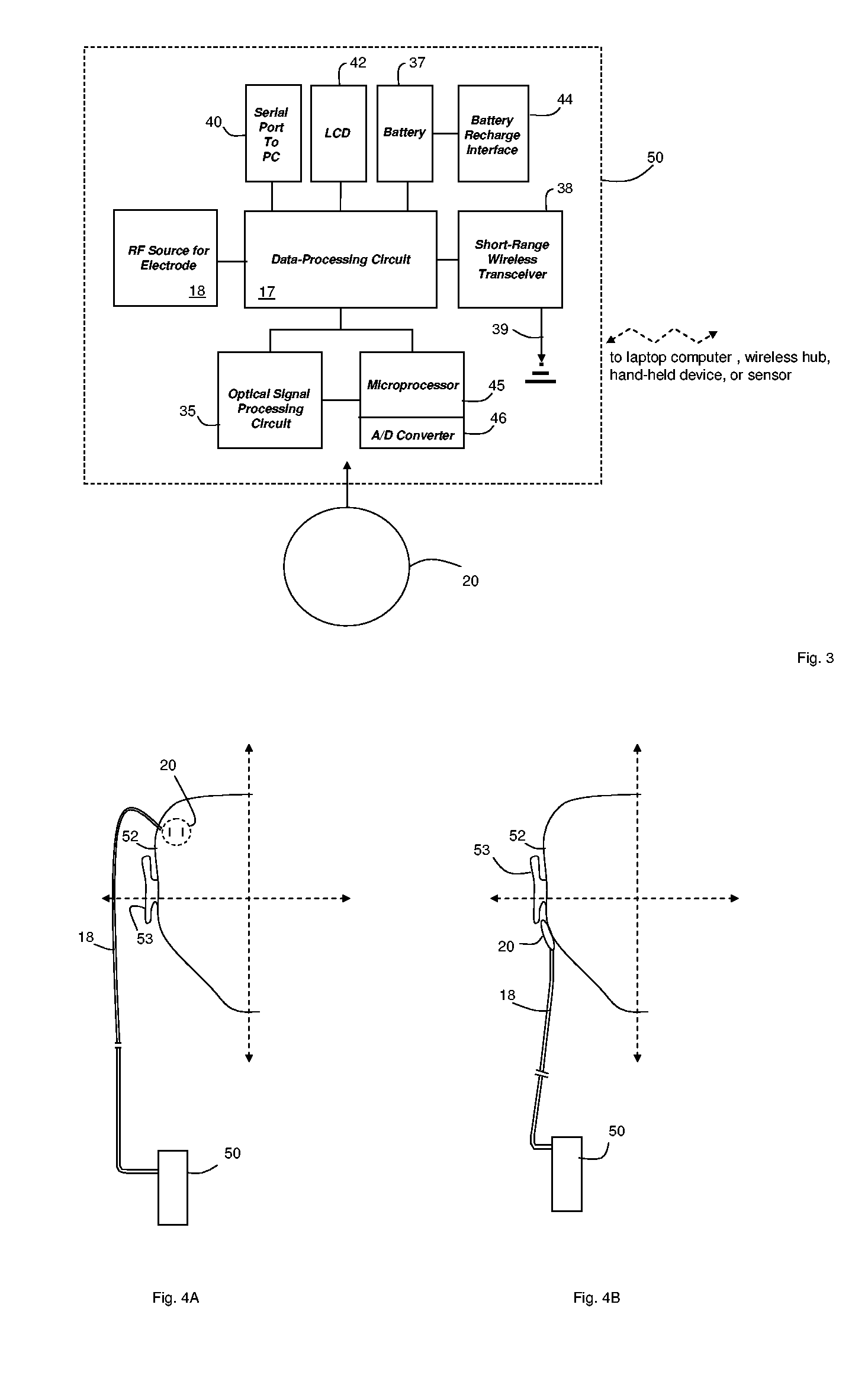
Patch sensor for measuring blood pressure without a cuff
InactiveUS20050228299A1Easy can be wornNon-invasive measurementElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood pressureEngineering
A monitoring device, method and system for monitoring vital signs of a patient over a wireless network are disclosed herein. The monitoring device includes an adhesive patch sensor, typically mounted on a patient's head, and a processing component. The adhesive patch sensor typically includes an optical system that generates an optical waveform, and an electrode that generates an electrical waveform. The processing component processes the optical and electrical waveforms, along with a calibration table, to determine the patient's vital signs.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
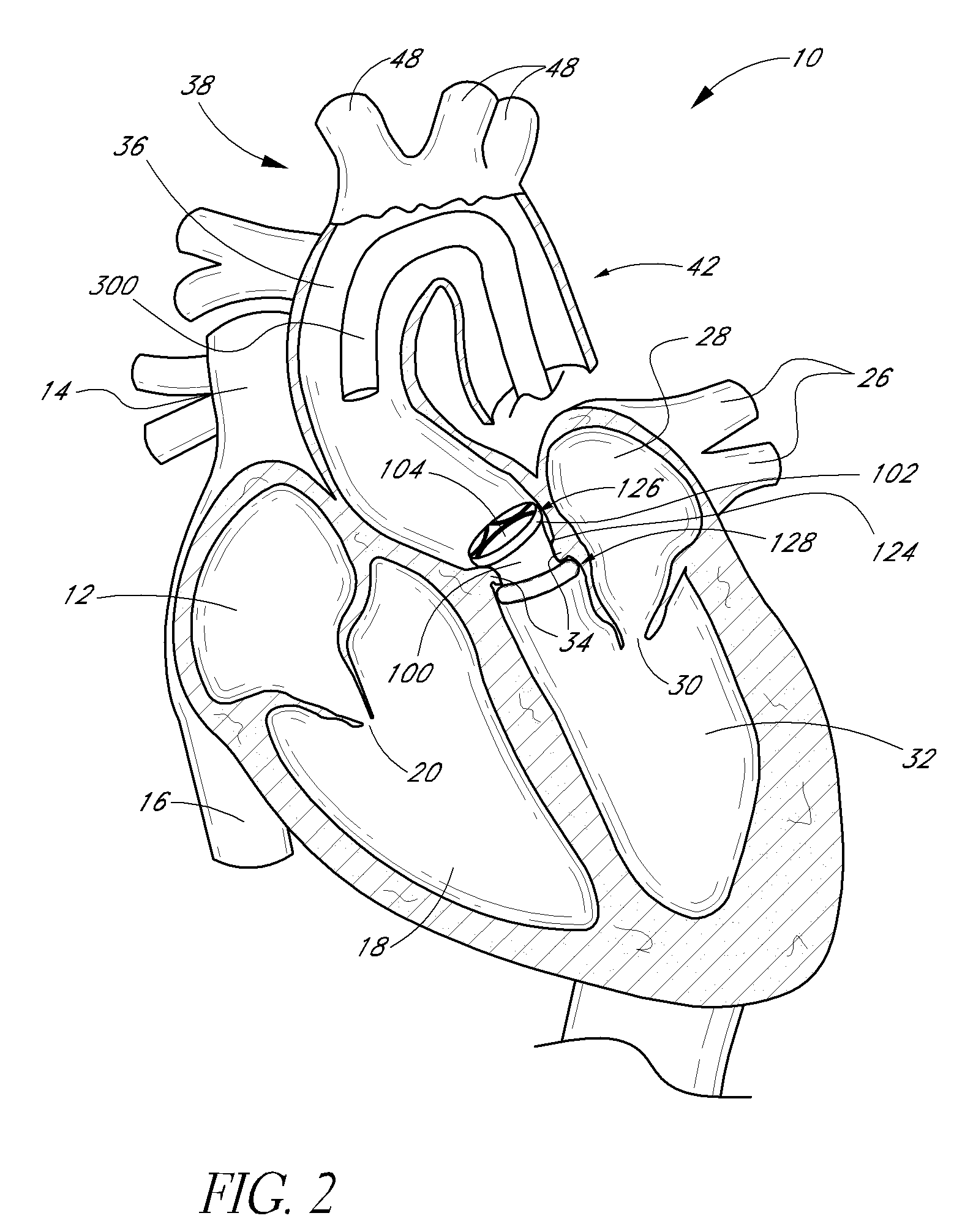
Methods and systems for reducing paravalvular leakage in heart valves
InactiveUS20100168844A1Reducing paravalvular leakageIncrease opportunitiesHeart valvesParavalvular leakageCuff
A replacement valve comprises a valve body having an inflow end, an outflow end, and a valve support structure, and a valve cuff surrounding the inflow end of the valve body. The valve support structure surrounds the valve body, and the valve cuff is coupled to the valve support structure. The valve cuff includes a skirt portion and at least one flange coupled to and protruding from the skirt portion, the at least one flange forming a seal around the inflow end of the valve body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Flat interface nerve electrode and a method for use
A flat interface nerve electrode is provided along with a method for its use. The electrode provides a plurality of conductive elements embedded in a non-conductive cuff structure, which acts to gently and non-evasively redefine the geometry of a nerve through the application of a force so as to apply pressure to a nerve in a defined range, namely from 2 to 40 mmHG and more preferably from 15 to 30 mmHG and most preferably from 15 mmHG to 20 MMHG. This range is selected to minimize the reduction of blood flow within the tissue, which preferably is at least 70% of the initial value, more preferably 90% of the initial value. The cuff has an opening, which is elongated relative to the diameter of the nerve to which it is applied. Preferably, the cuff is constructed from an elastic bio-compatible material having top and bottom beam members configured to define a nerve opening. The cuff is open at one side and has a connection at the other side which results in a spring force being applied through the surfaces of the nerve opening to the subject nerve. During implantation the open sides of the cuff are closed so as to capture the nerve in the cuff. As the nerve is reshaped, specific nerve axons become more easily addressed through the epineurium by the embedded conductive elements.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Electrode contact configurations for cuff leads
A stimulation system is disclosed that may include a stimulator unit coupled to electrode contacts on a cuff. In one embodiment, the cuff may be placed at least partially around a nerve. The stimulation system may include at least two electrode contacts disposed on the cuff such that a distance between the at least two electrode contacts various along a length of the electrode contacts. In another embodiment, a plurality of electrode contacts are disposed on the cuff such that distances between at least one electrode contact within the plurality of electrode contacts and each electrode contact immediately adjacent to the at least one electrode contact are different. The stimulator unit may also be implantable.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Ligating clip with integral cutting guide
InactiveUS7326223B2Removably lock the clipHigh retention rateCurling devicesHair dryingEngineeringLigating clips
A polymeric, surgical clip having first and second curved legs with each having a pair of opposing side surfaces joined at their proximal ends by a flexible hinge section and movable from an open position to a closed position for clamping a vessel between curved opposing inner surfaces. The first leg terminates at its distal end in a female locking member, and the second leg member terminates in a male locking member complimentary to the female locking member such that when the first and second leg members are moved from an open position to a closed position about the hinge section the male member is lockingly engaged in the female locking member. The clip has at least one cutting guide extending outward from and disposed along at least a portion of the length of at least one of the side surfaces of at least one of the first and second legs. The cutting guide aids in cutting the ligated tissue a safe distance from the clip such that a tissue cuff is formed.
Owner:TECH HLDG CO II
Translumenally implantable heart valve with formed in place support
InactiveUS20060025854A1Minimally invasive procedurePrevent disengagementSuture equipmentsHeart valvesProsthetic valveCuff
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com