Patents
Literature
1087 results about "Saline" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Saline, also known as saline solution, is a mixture of sodium chloride in water and has a number of uses in medicine. Applied to the affected area it is used to clean wounds, help remove contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. It is also used to dilute other medications to be given by injection.
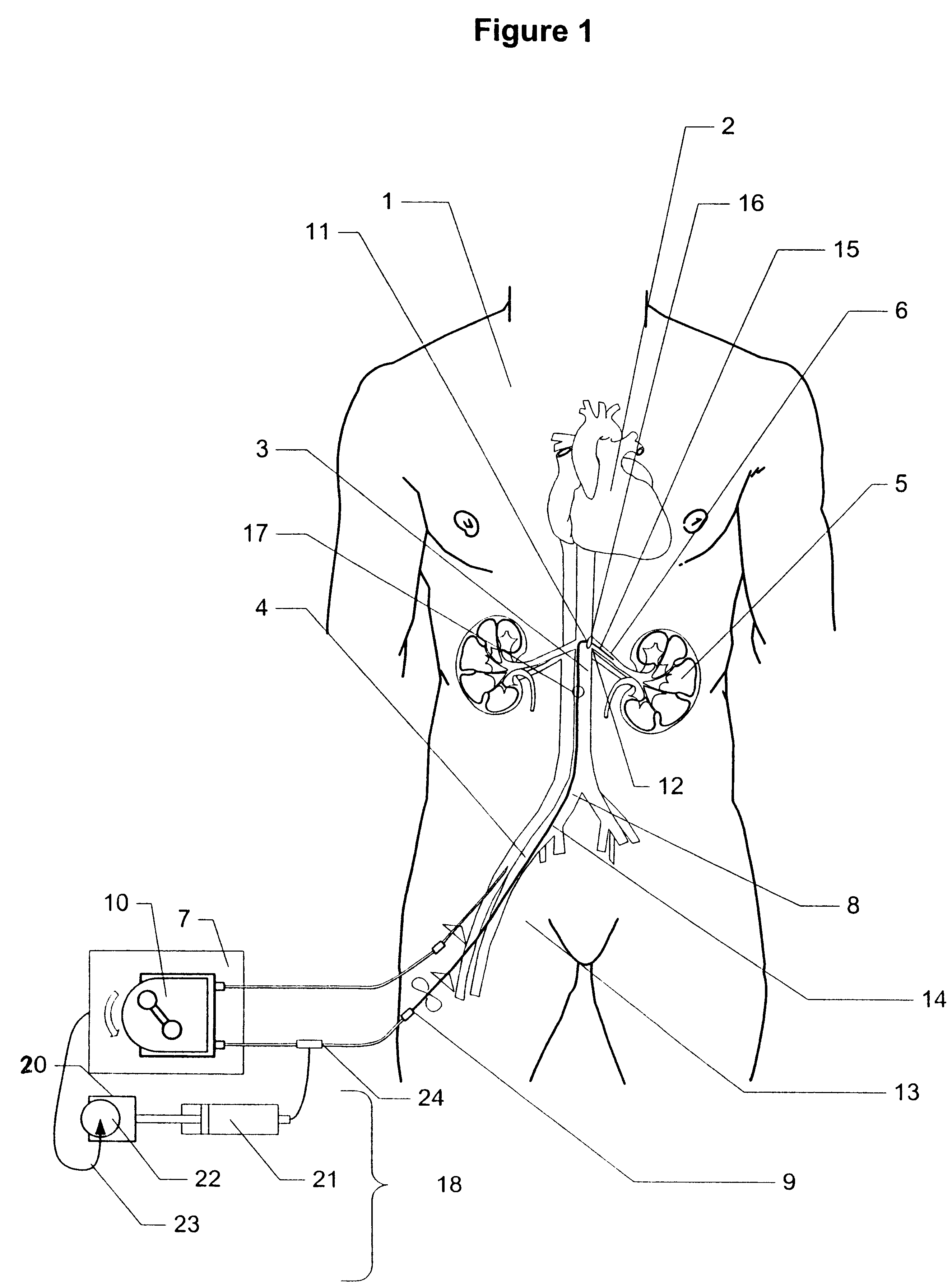
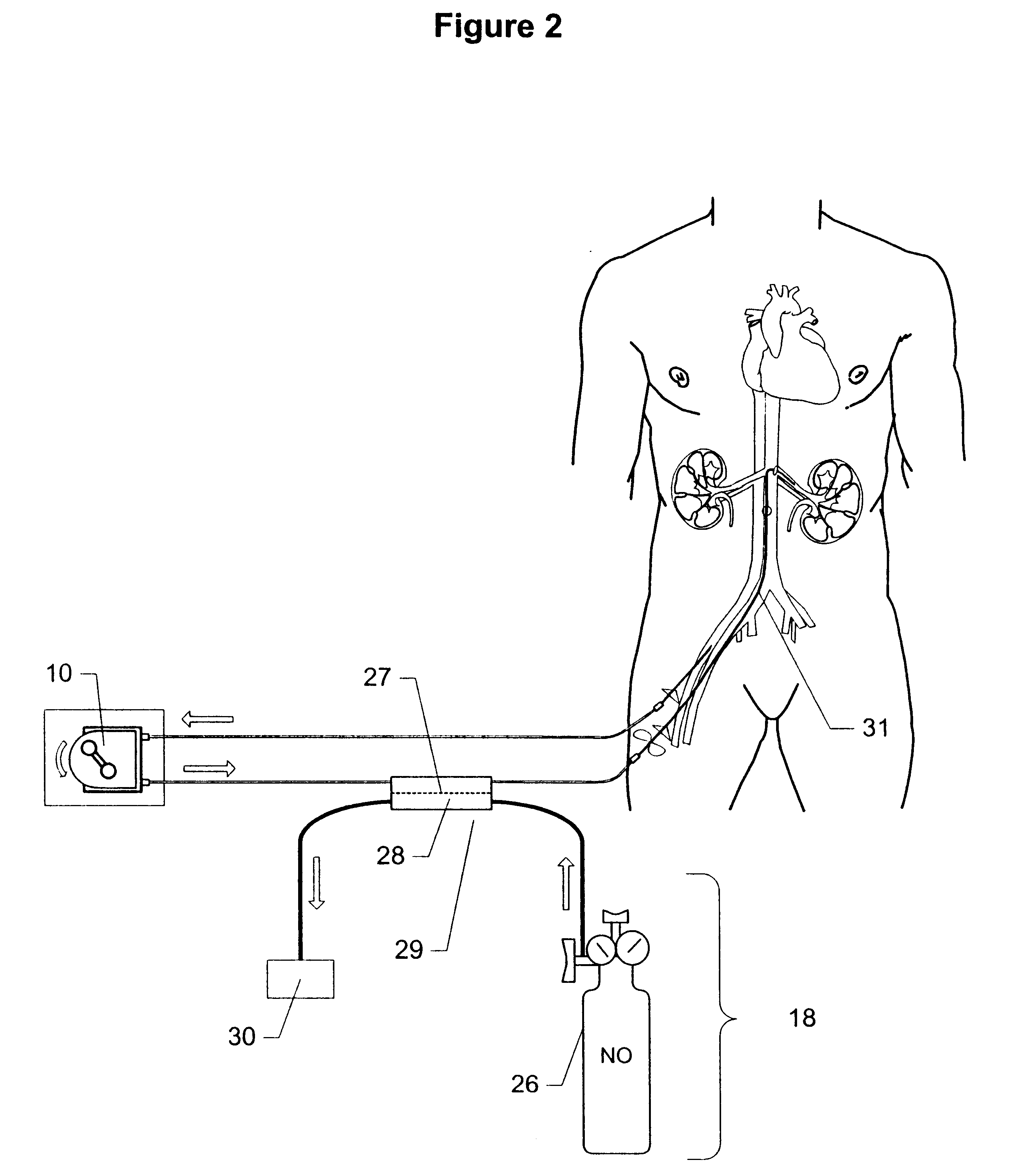
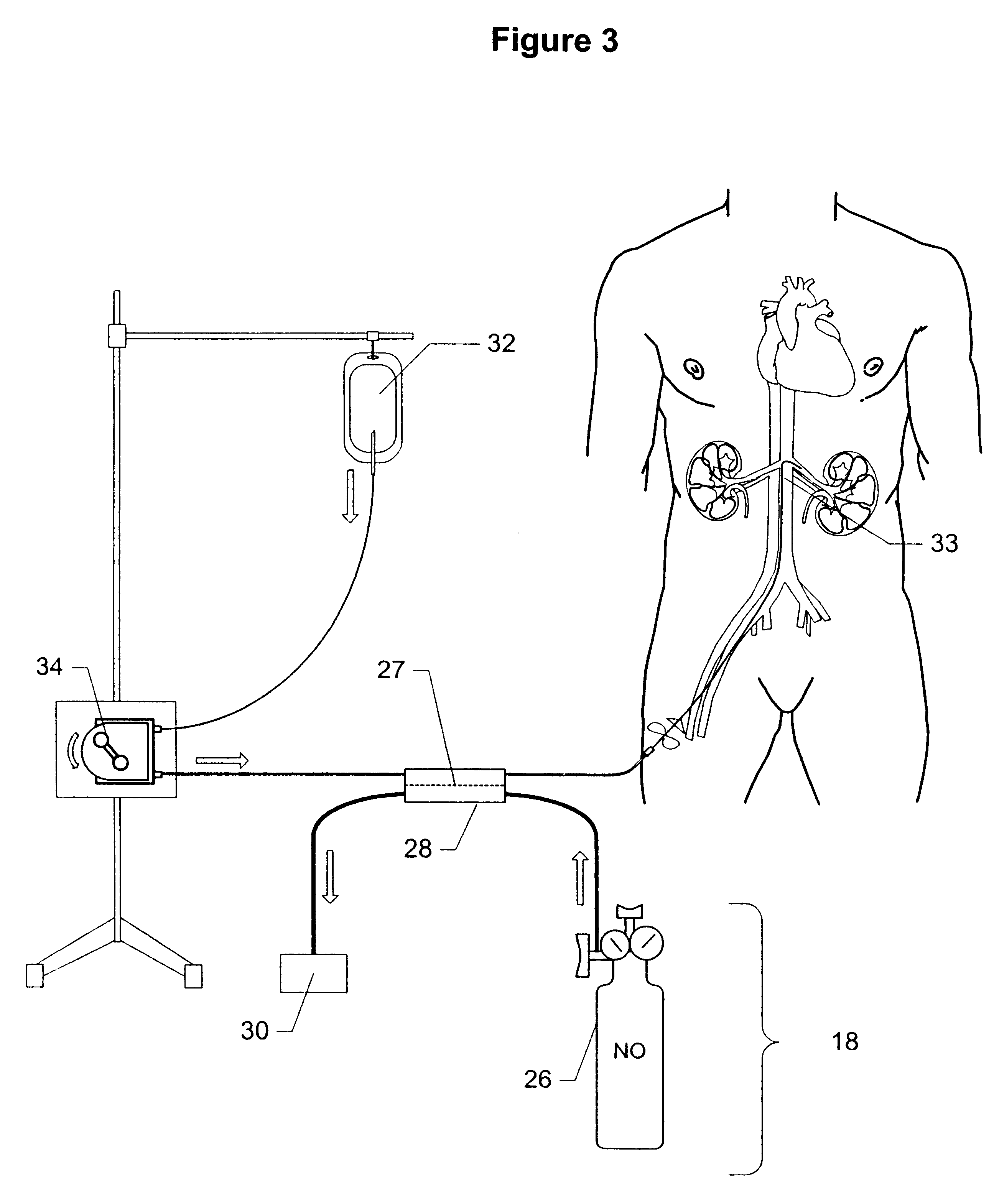
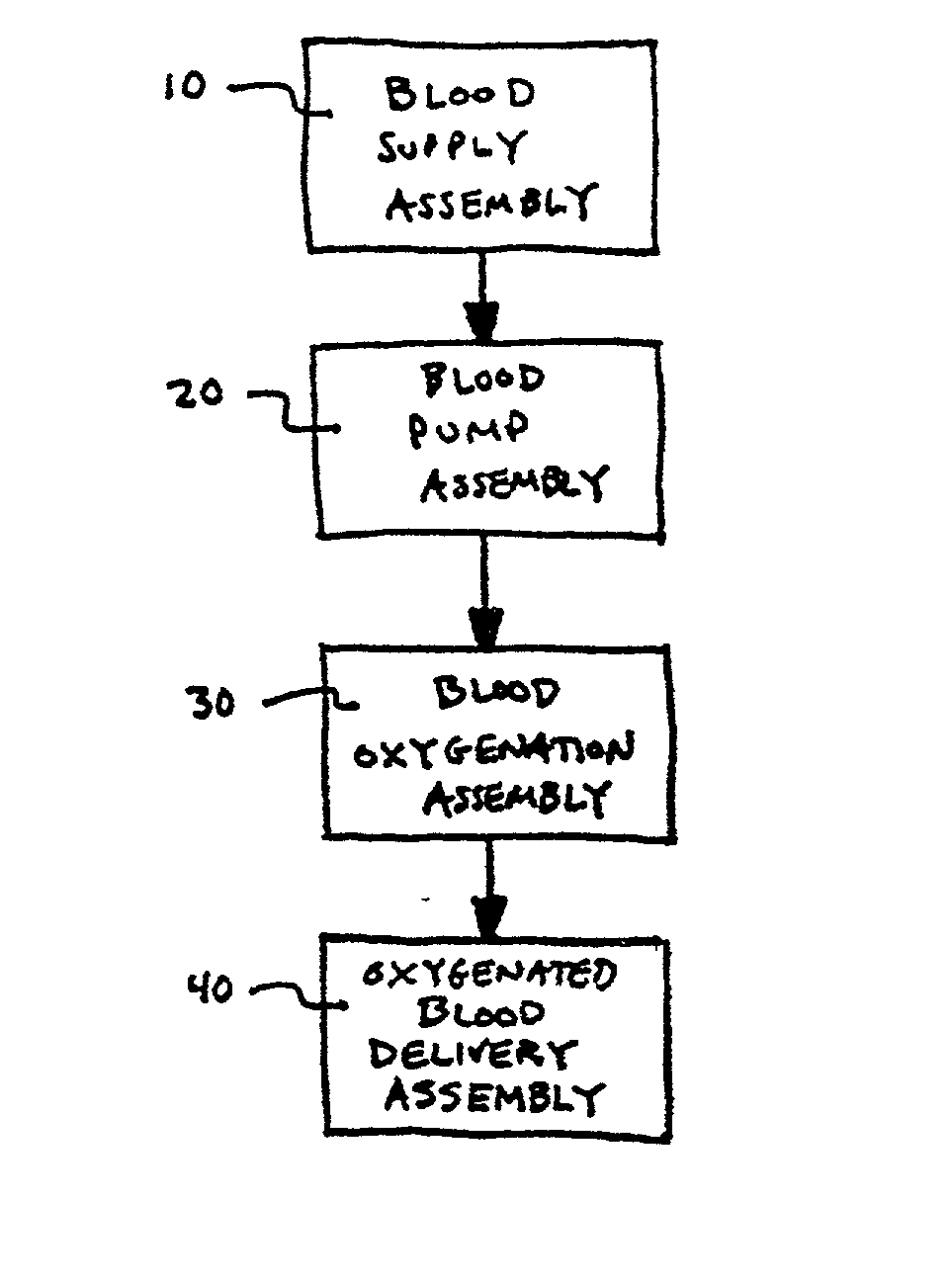
Method and apparatus for treatment of congestive heart failure by improving perfusion of the kidney by infusion of a vasodilator
InactiveUS6287608B1Improve the quality of lifeImprove survival rateBiocideInorganic active ingredientsRenin–angiotensin systemVascular dilatation
A method for treating congestive heart failure (CHF) has been developed that restores kidney renal functions by artificial vasodilation of at least one kidney. A vasodilator drug is locally delivered to the kidney via a kidney perfusion catheter. The drug can be mixed with the patient's blood, saline or other suitable solvent and the mixture directly applied to the kidney through the catheter. The restoration of kidney function assists the heart by removing excess fluid, urine and toxin from the patient, and by normalizing the patient's renin-angiotensin system and other neurohormonal substances. The method is applicable to treat chronic and acute CHF.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
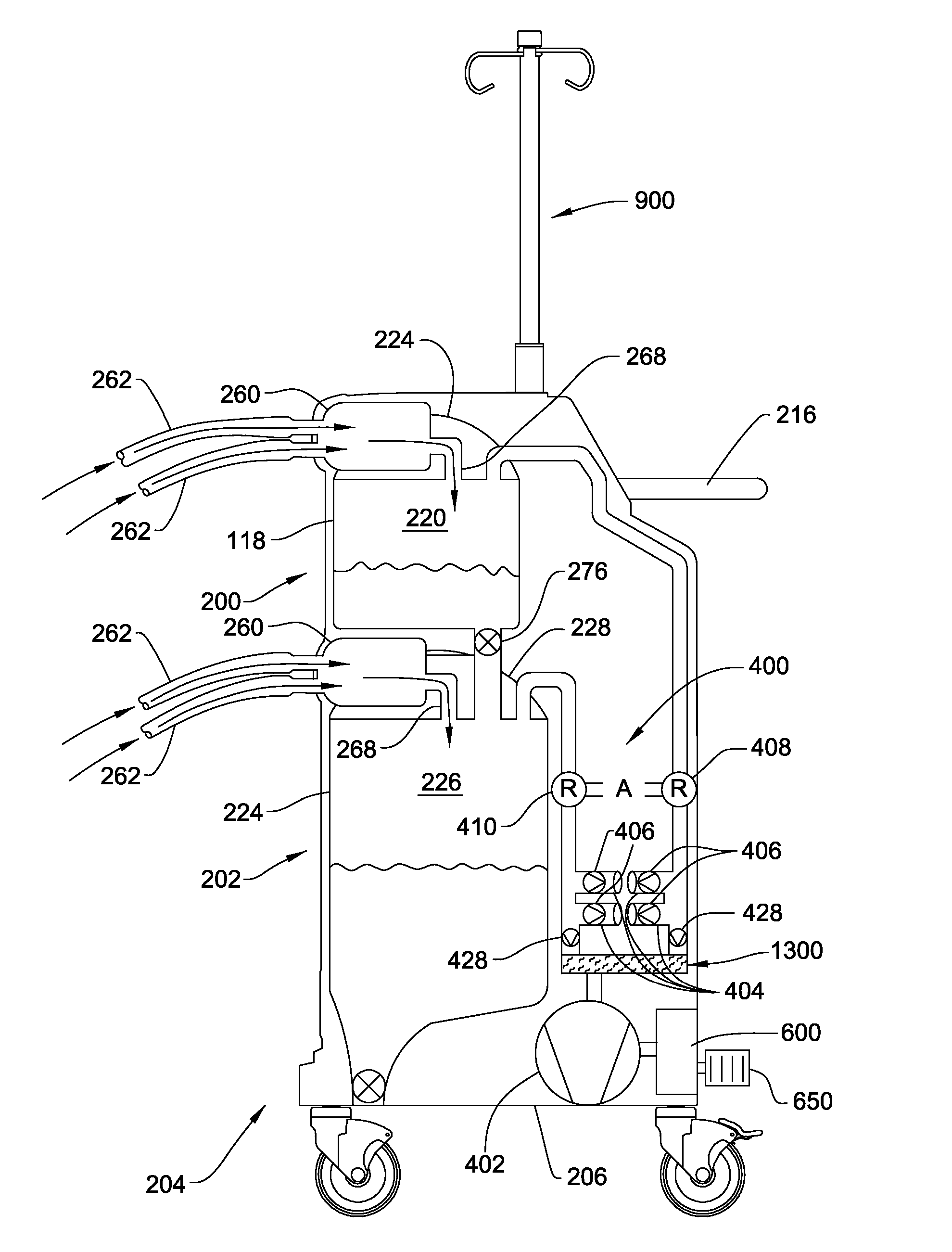
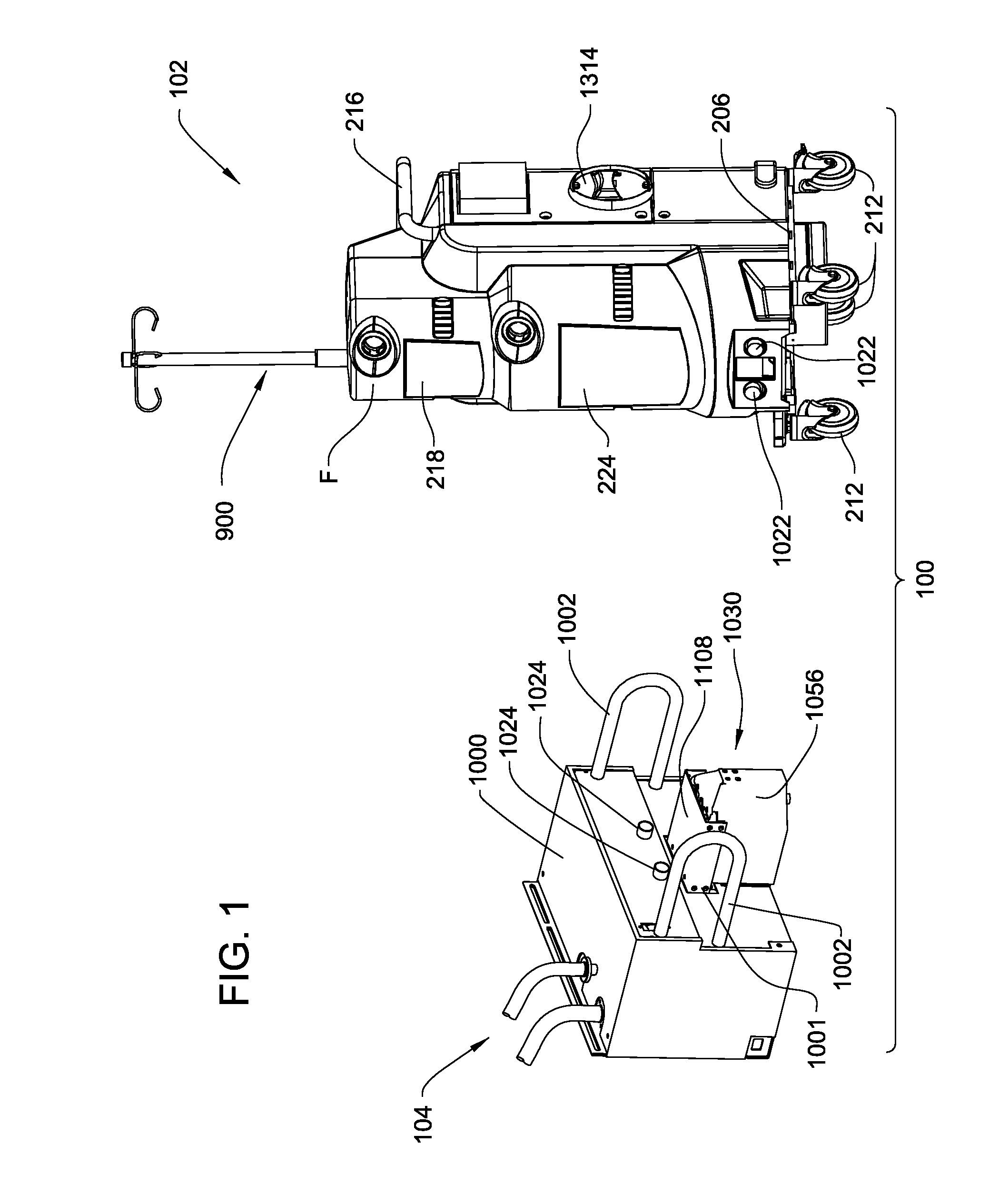
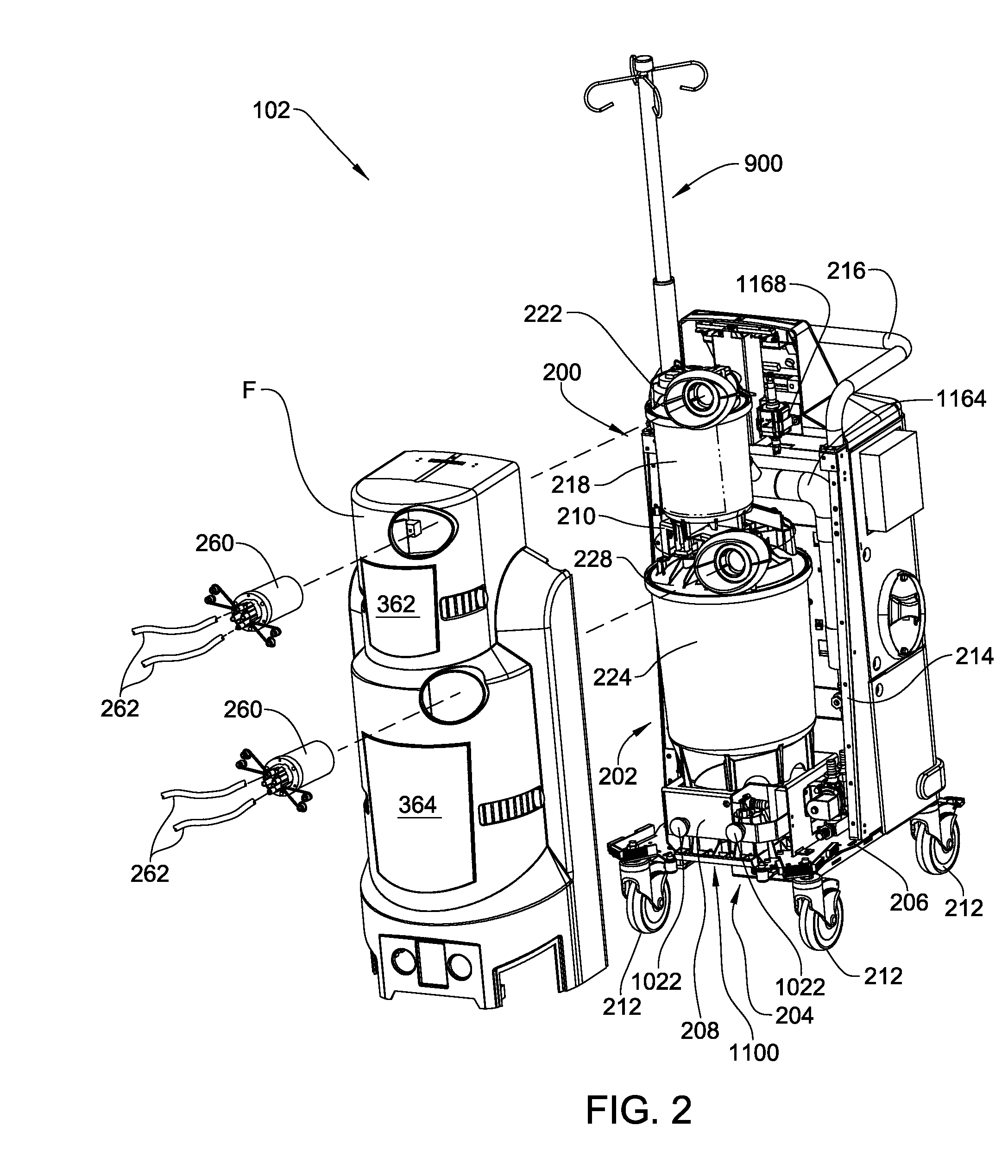
Medical/surgical waste collection and disposal system including waste containers of different storage volumes with inter-container transfer valve and independently controlled vacuum levels
ActiveUS20070135779A1Reduce the numberReduce tripsMechanical apparatusDispersed particle filtrationDocking stationWaste collection
A waste collection and disposal system for use in health care facilities is provided. The system includes a mobile waste collection unit for moving between use areas in the health care facility to collect waste material generated during medical procedures including body fluids, body tissues, saline, etc. The waste collection unit includes stacked upper and lower waste containers for receiving the waste material. During use, the upper waste container can be emptied into the lower waste container for temporary storage. In addition, different vacuum levels can be provided in the waste containers during complex procedures. Once a user desires to empty the waste collection unit, the waste collection unit is wheeled to a docking station. At the docking station, the waste material is off-loaded to a waste drain and the waste collection unit is cleaned and rinsed for further use.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Calcium based neutral and bioresorbable bone graft
InactiveUS20030055512A1Improve mechanical propertiesReduce decreaseSurgical adhesivesBone implantSulfateBone implant
An injectable and moldable putty comprising biodegradable calcium-based compounds including calcium sulfate, hydroxyapatite, and tricalcium phosphate is invented. The putty hardens into a solid body when mixed with water, saline, serum, or other neutral aqueous solutions. The hardening time of the putty can be tailored in order to meet the specific requirements of various dental or orthopedic applications. The pH of the putty is neutral during and after mixing. The invented putty may be used as bone graft, bone implant, or implantable drug delivery device.
Owner:BERKELEY ADVANCED BIOMATERIALS
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS20050143656A1Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
Apparatus for detecting the position of a percutaneously-inserted intravenous catheter
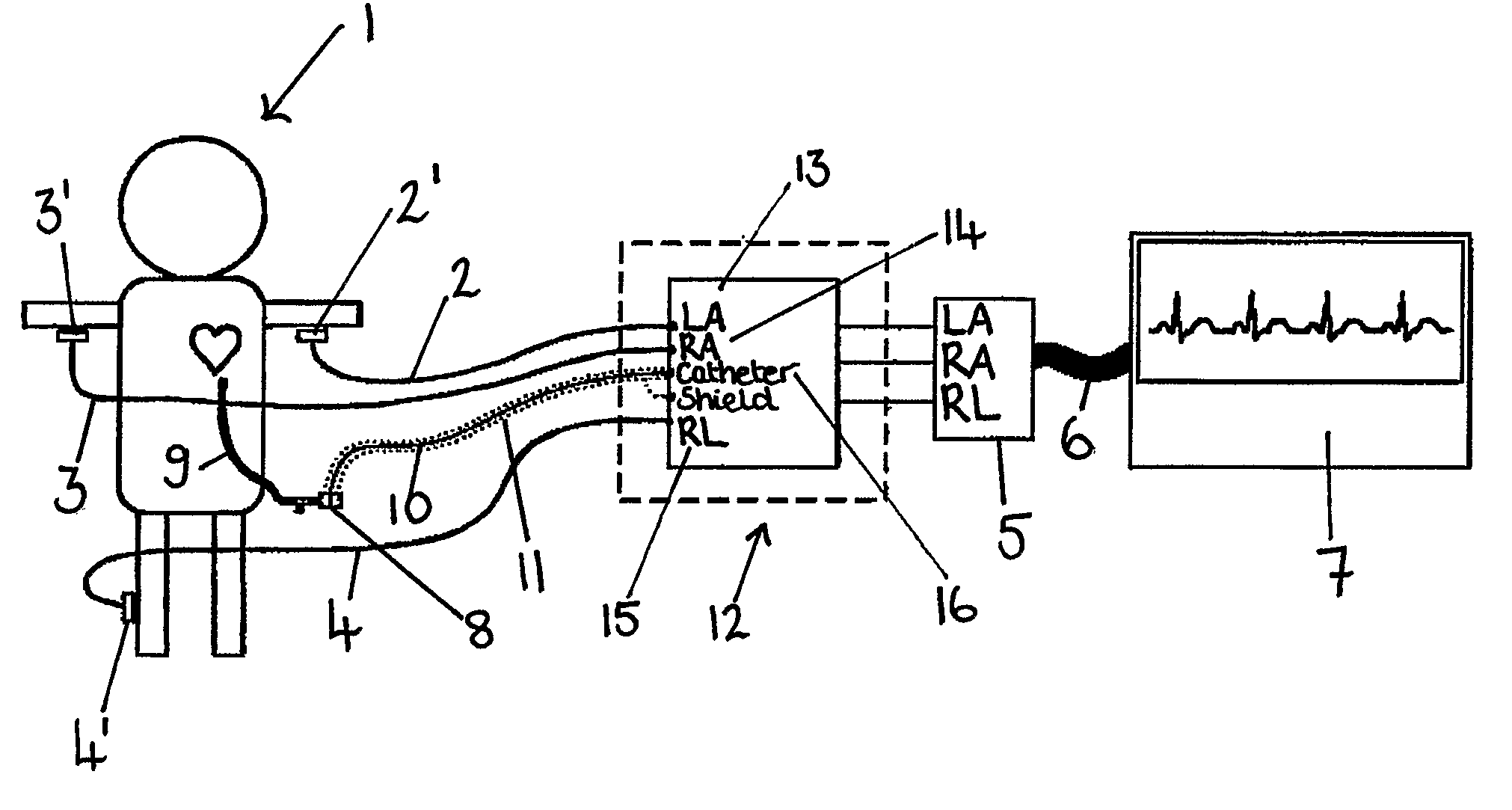
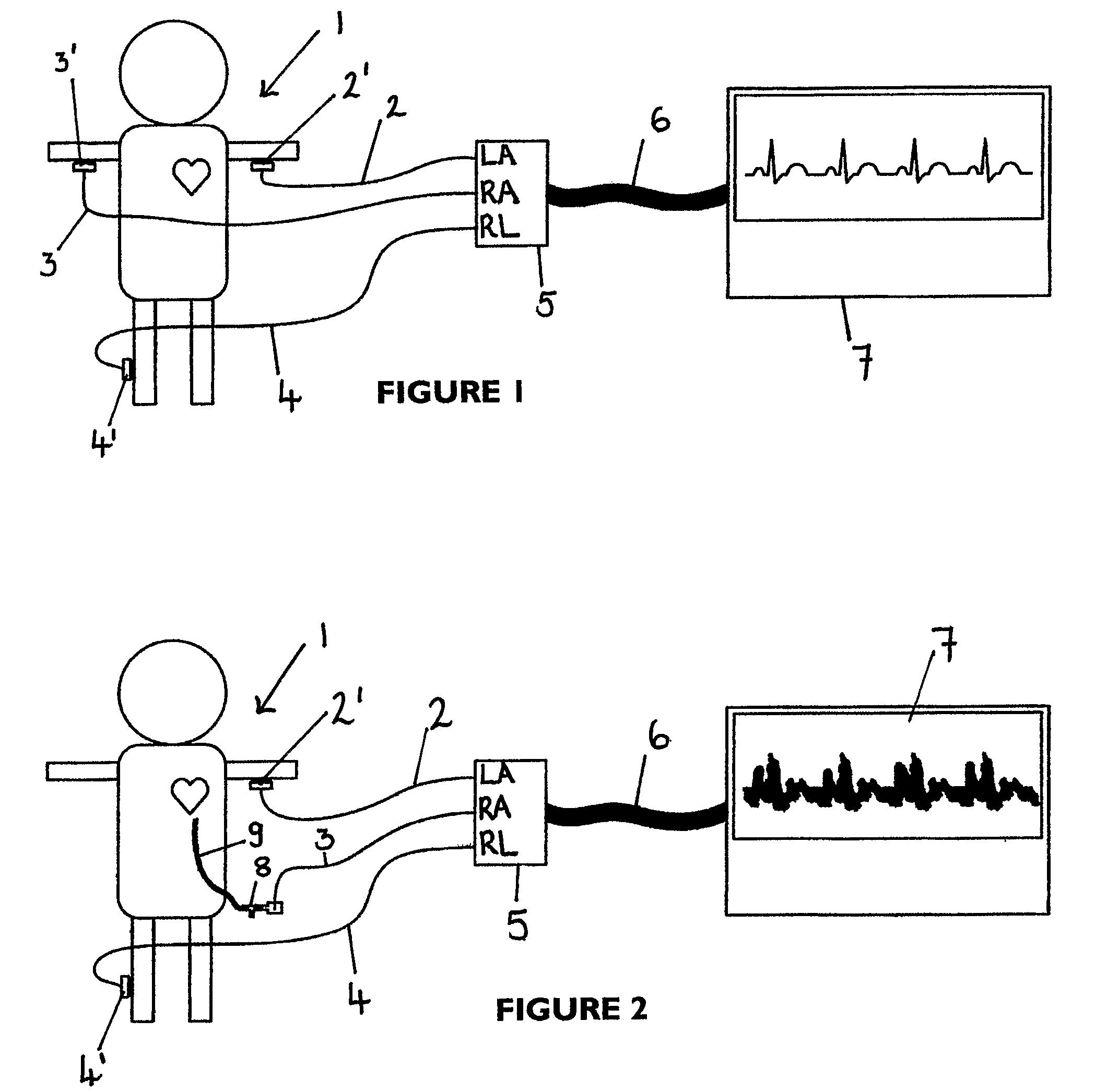
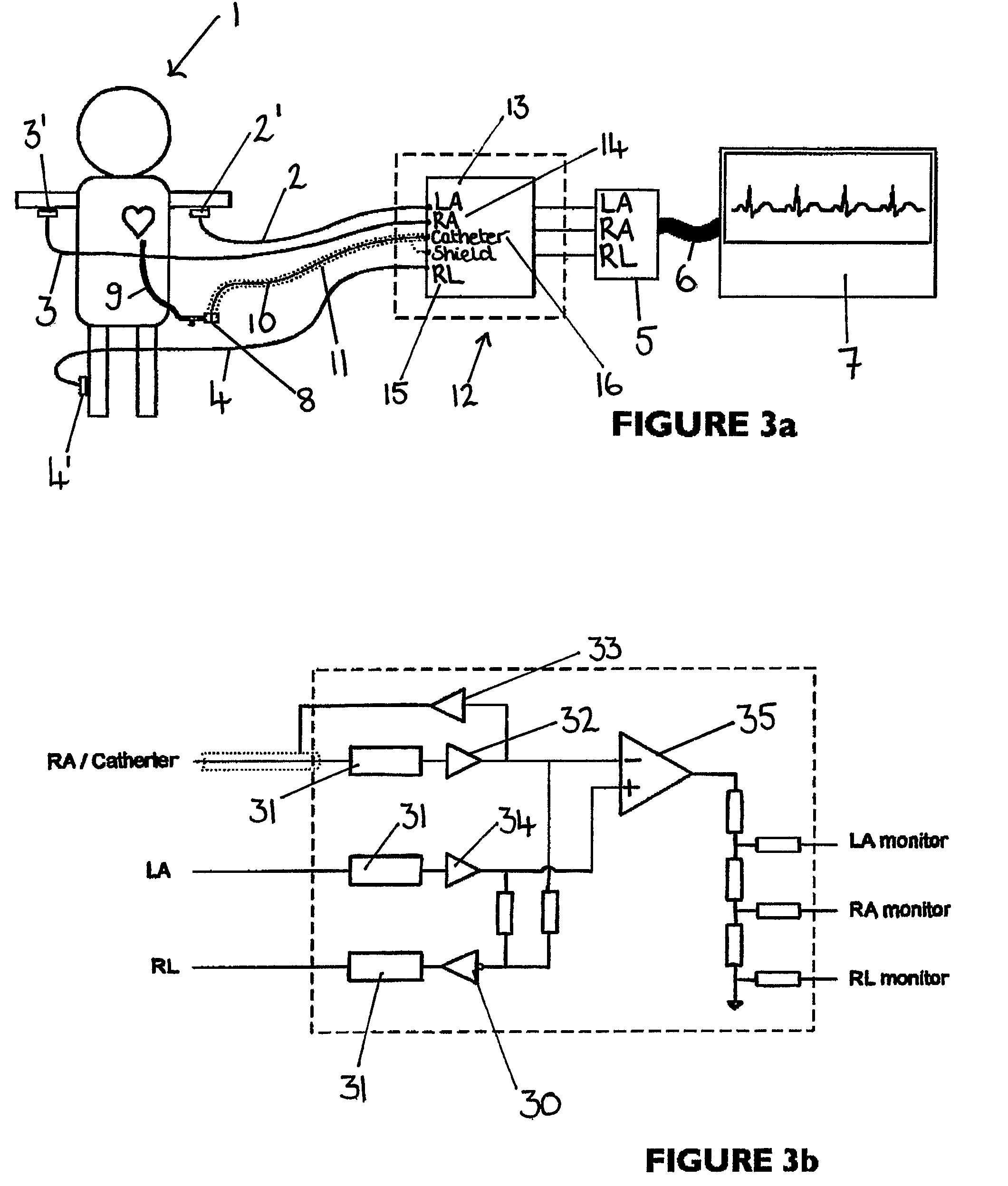
An apparatus that is able to detect the position of a catheter. The apparatus utilizes a catheter filled with electrically-conductive physiological saline and a connector for establishing an electrical connection between the saline of the catheter and an input of a controller. The controller includes at least one output connectable to a standard ECG lead connector, wherein the controller includes circuitry for generating a low impedance output signal. The controller provides an output which replicates the input a standard ECG patient lead connector is configured to receive. The apparatus provides a more convenient and cost effective solution for providing specialized ECG functions without having to replace a hospital's existing ECG beside monitoring equipment.
Owner:NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE HOSPITALS NAT HEALTH SERVICE TRUST
Modified starch absorbable hemostasia material and preparation method thereof
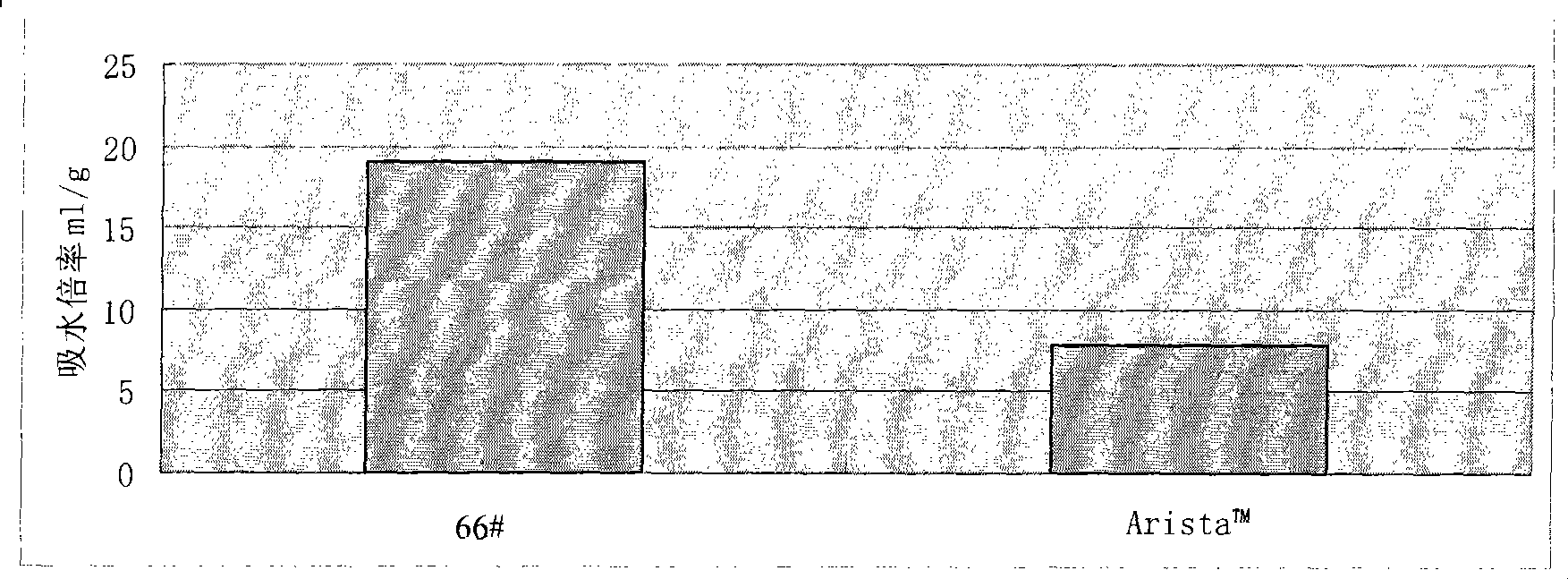
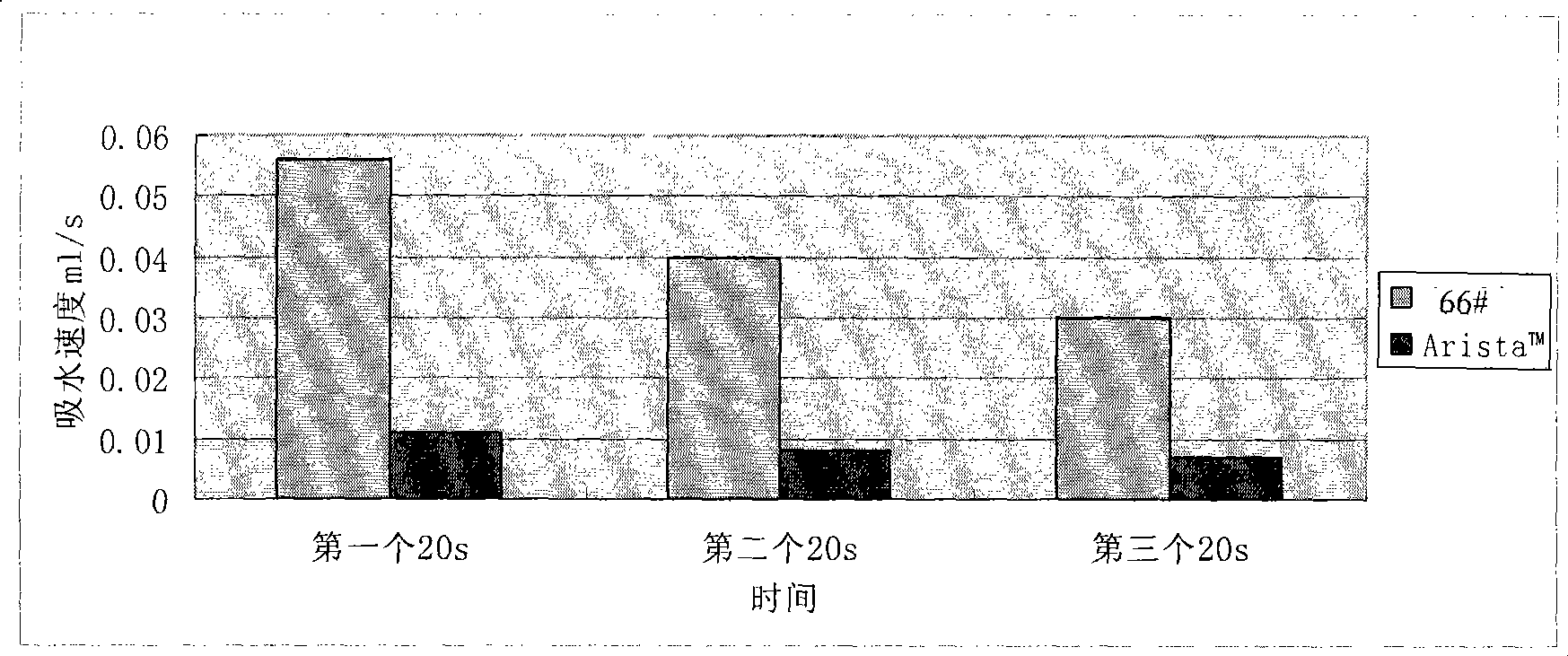
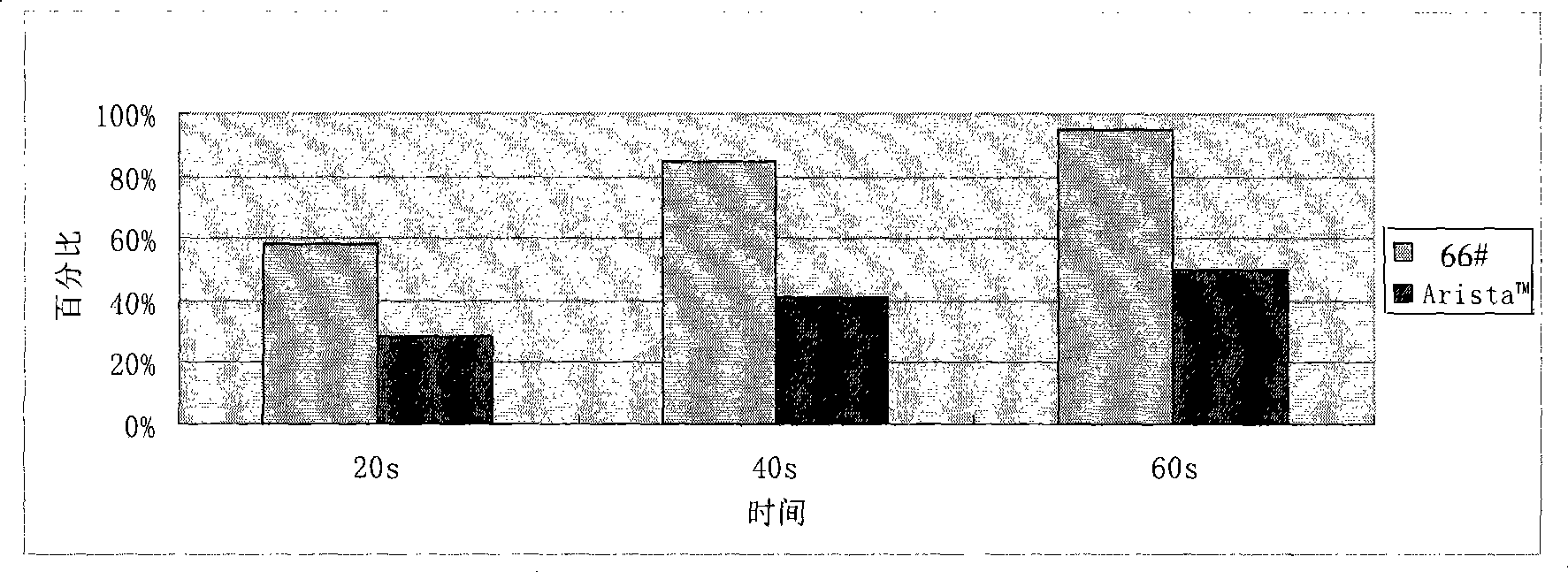
ActiveCN101361986AHigh viscosityImprove water absorption speedSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWound healingBiomedical engineering
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSAL LIKANG TECH CO LTD
Continuous whole blood glucose monitor
InactiveUS20110009720A1Improve fitOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationPeristaltic pumpPhotoconductive detector
A portable continuous whole blood glucose monitor comprising, a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser and driver in optical communication with a transmission cell and a photo-conductive detector and pre-amplifier. The monitor further comprises a peristaltic pump connected to a single lumen catheter peripherally inserted into a patient's vein. The single lumen catheter, in combination with the peristaltic pump, is operable to automatically withdraw a fixed and metered amount of whole blood from a patient, then a tube delivers a fixed and metered amount of the saline / surfactant supply to the whole blood. Methods of enhancing measurement sensitivity are also provided.
Owner:CASCADE METRIX LLC
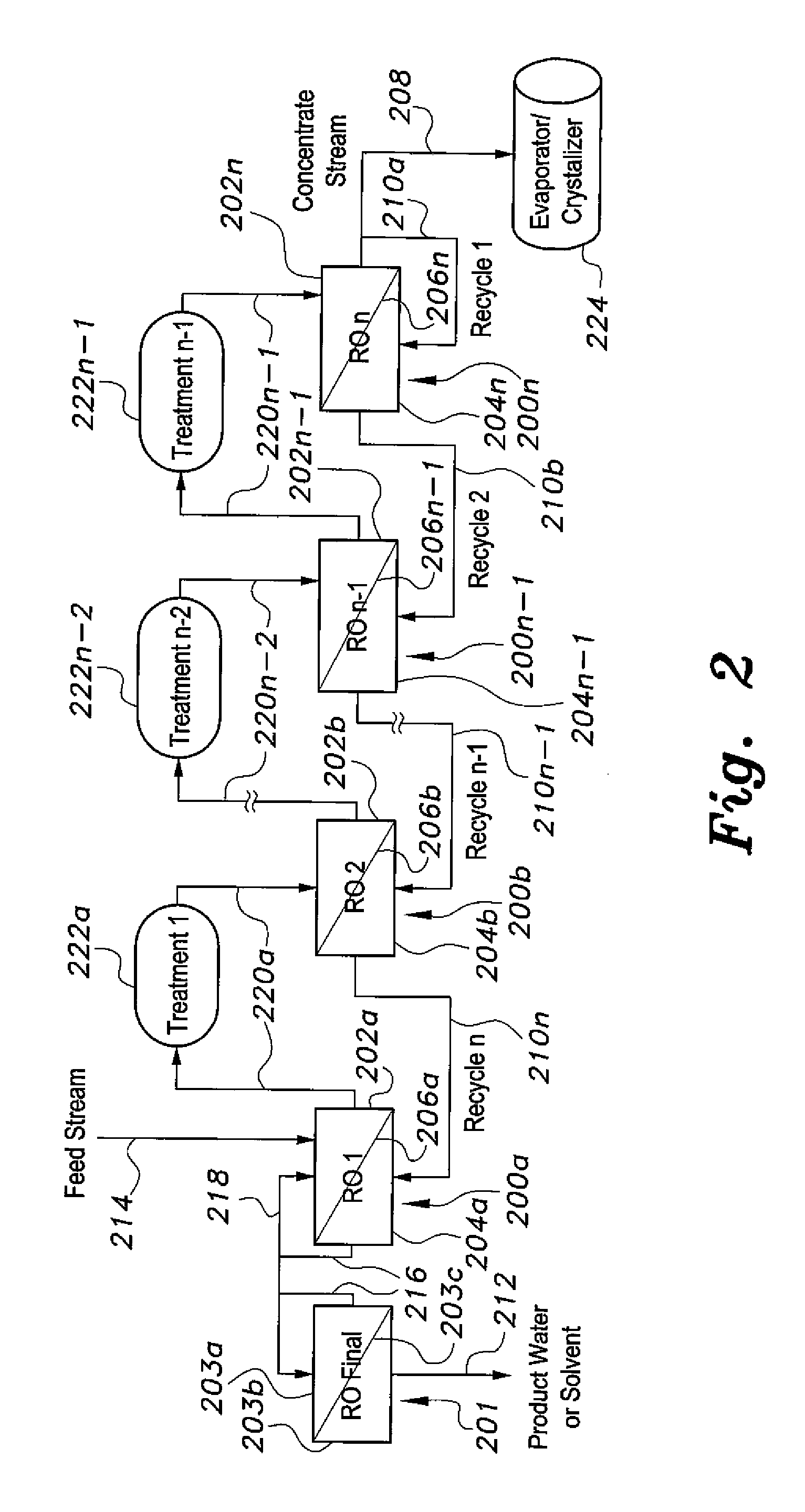
Method for purifying liquids
ActiveUS9206060B1Reduce gradientHigh rejectionMembranesGeneral water supply conservationSalt waterReverse osmosis
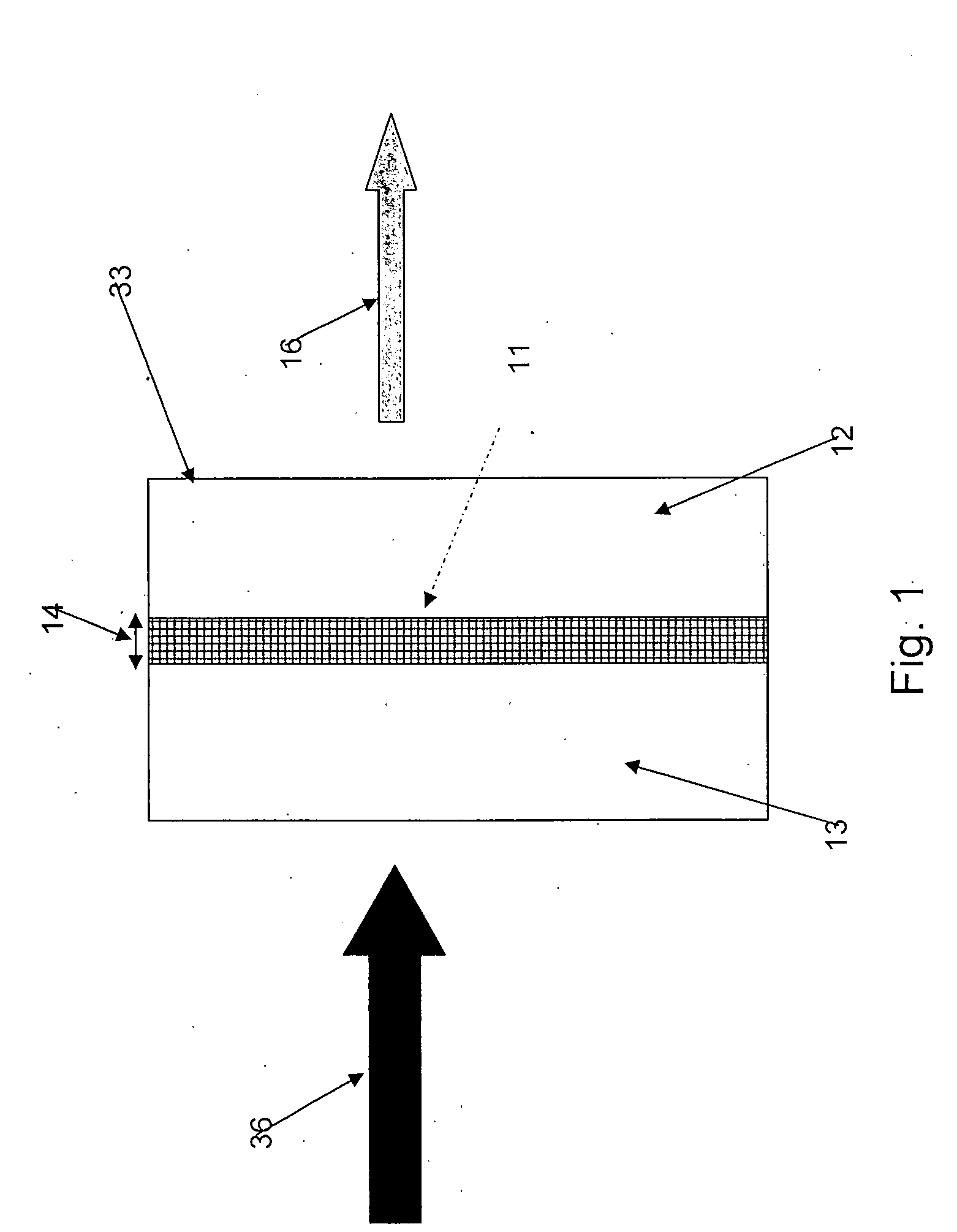
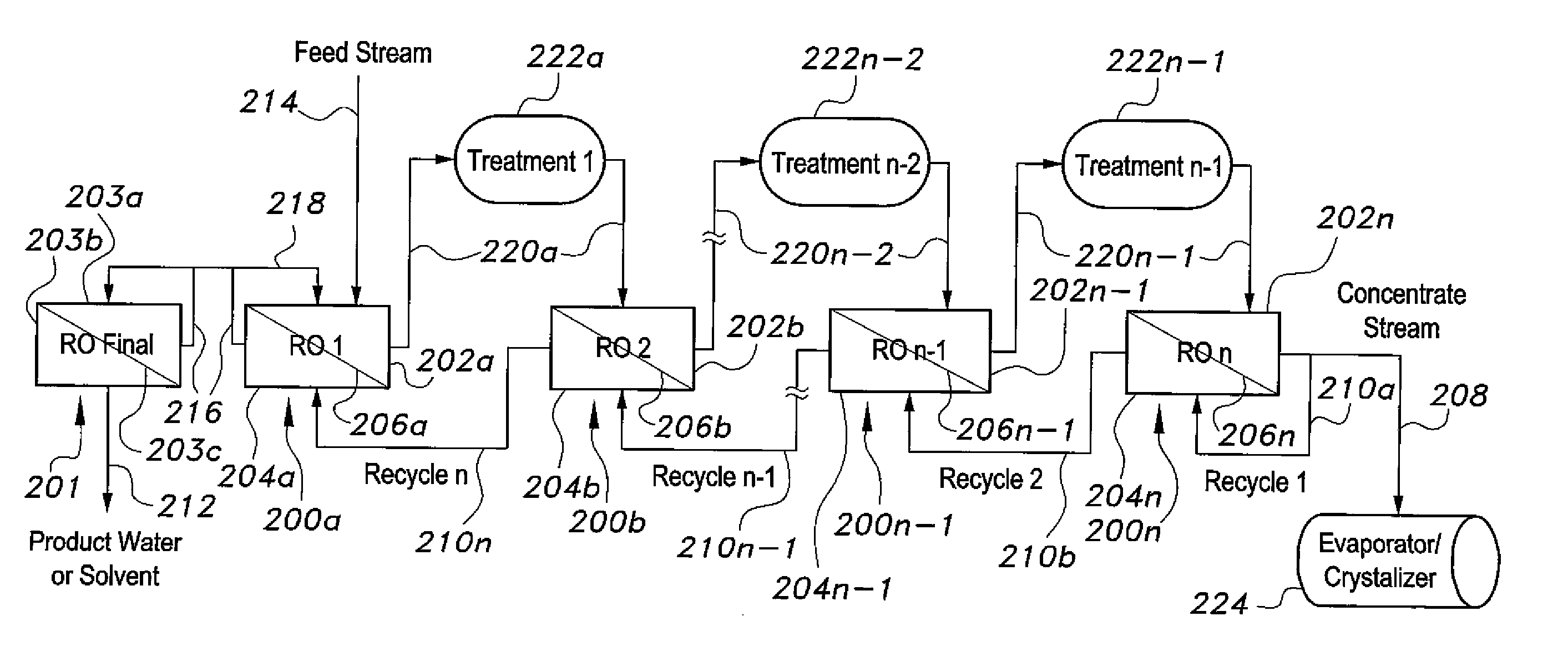
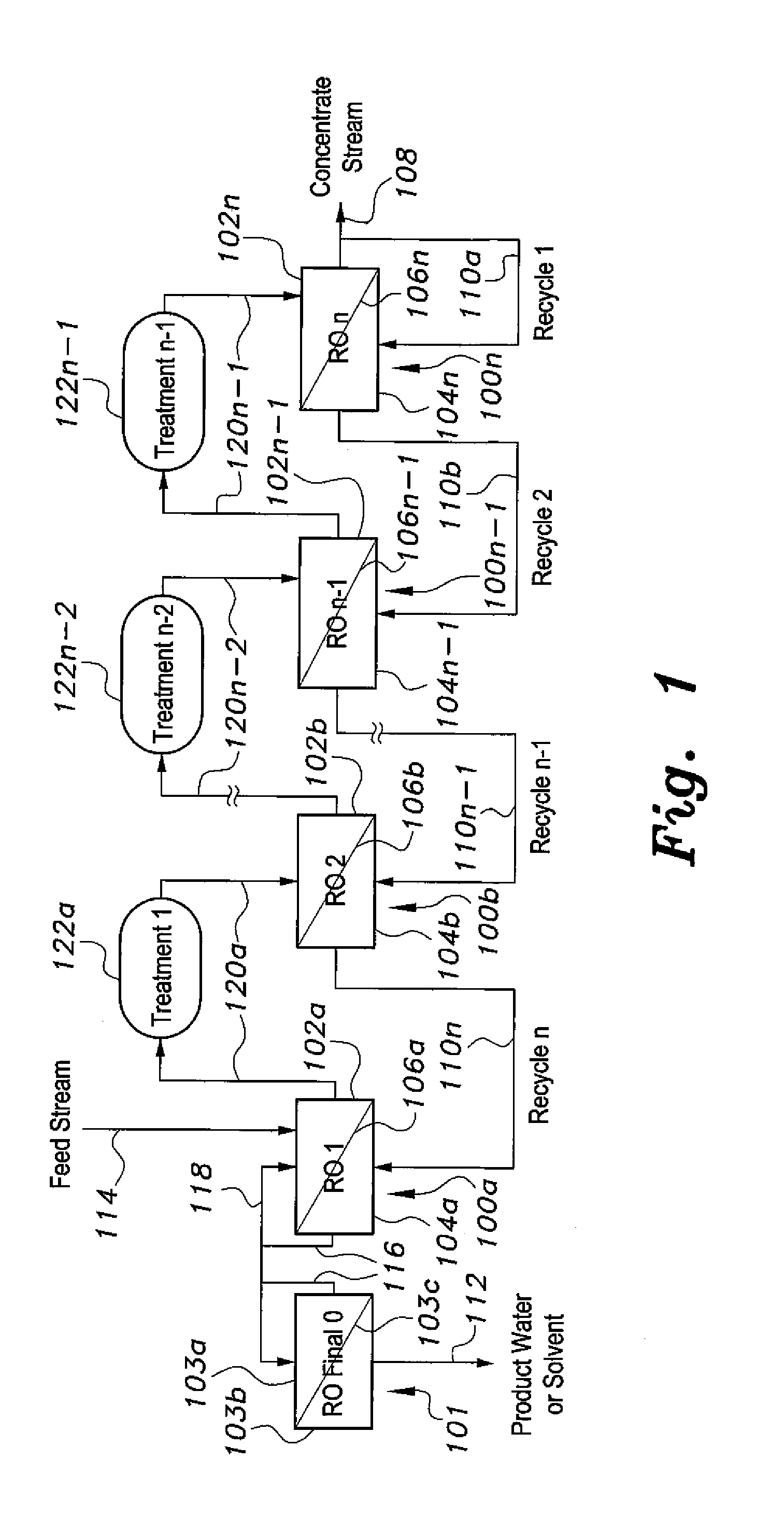
The method for purifying liquids purifies a saline liquid, e.g., salt water, using a plurality of first phase reverse osmosis (RO) units and at least one final phase reverse osmosis unit. The plurality of first phase reverse osmosis units are arranged in series. At least some of the concentrate in a last reverse osmosis unit of the series is recycled back to the permeate or output side of that unit to provide a mixed permeate. The mixed permeate is then passed successively to the permeate side of each preceding reverse osmosis unit in the series. This increases the salt content of the liquid in the permeate side of each phase, thus reducing the concentration differential across reverse osmosis membranes of the first phase reverse osmosis units.
Owner:AL BAKRI SAMI ABDULRAHMAN
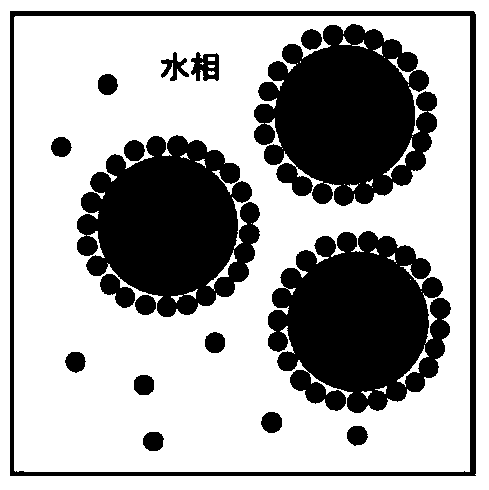
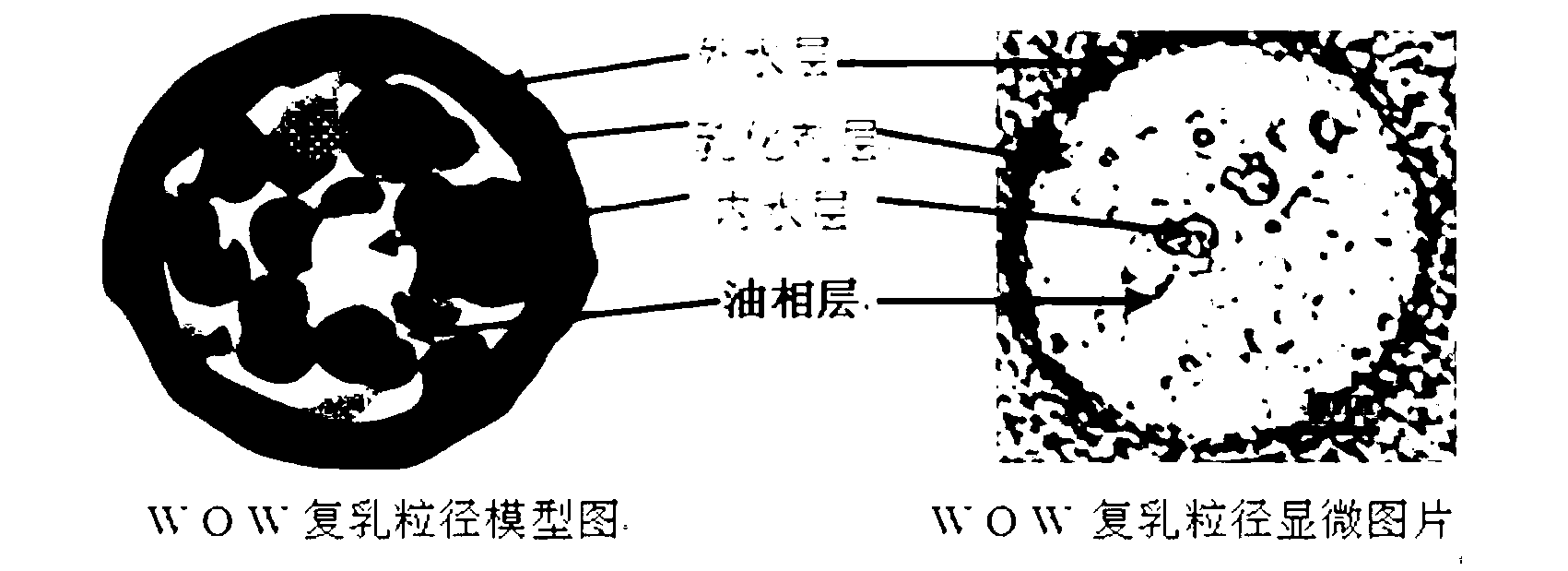
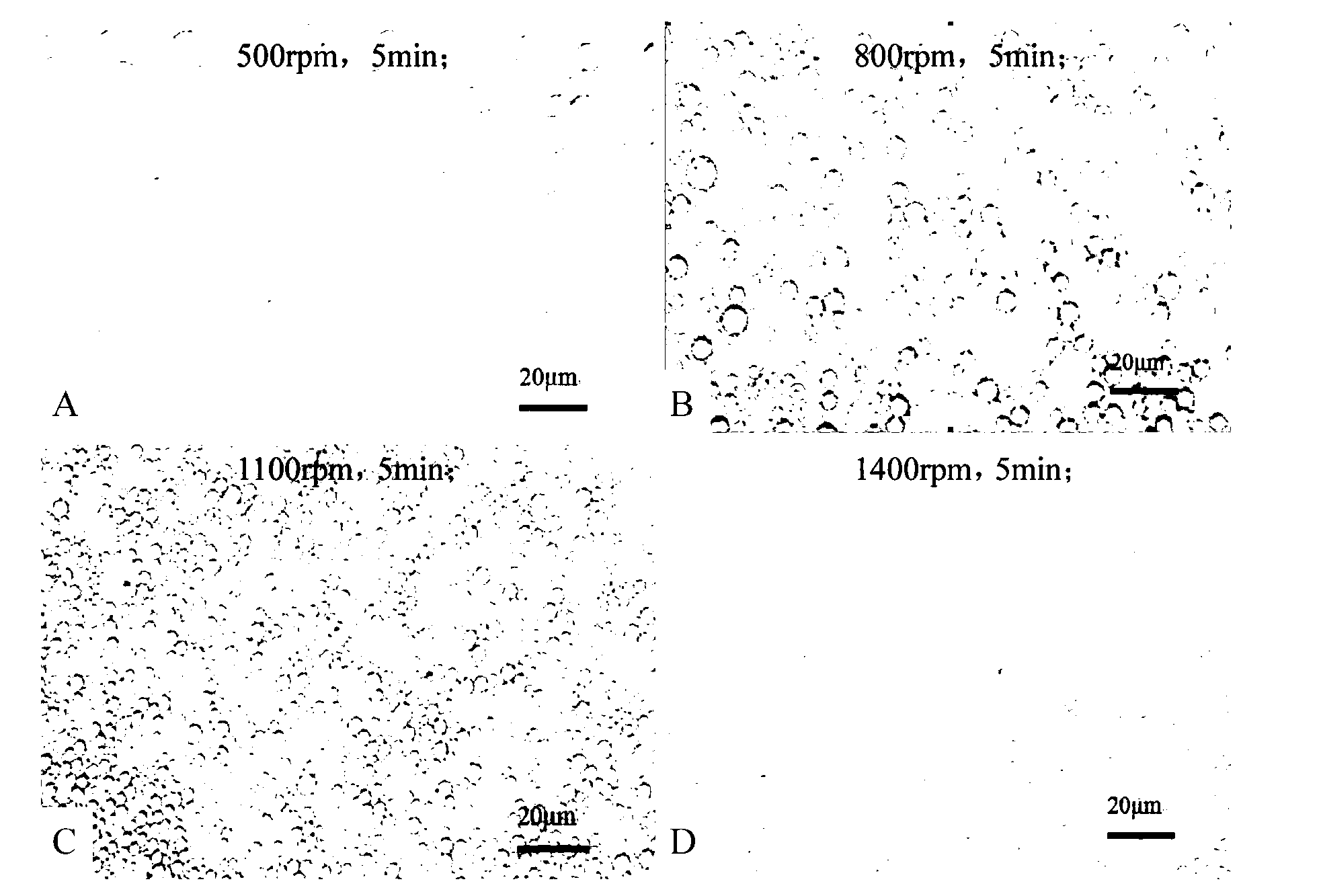
Oil-in-water emulsion free of surfactant and use thereof
ActiveCN104013955AThe nature is easy to controlGood biocompatibilitySsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryActive agentGlycerol
The invention discloses an oil-in-water emulsion free of surfactant. The emulsion comprises a metabolizable oil phase, a water phase and oil-water amphipathic solid particles dispersed in the water phase and having biocompatibility, wherein the oil phase comprises squalene or / and tocol; the water phase is any one or a combination of at least two of purified water, water for injection, aqueous liquid of glycerol, buffered saline liquid and clinically available infusion liquid; and the average grain diameter of the solid particles is at nanometer-to-micron grade. The emulsion can be used as a vaccine adjuvant or a medicine delivery or controlled release carrier; the properties of the emulsion can be controlled and regulated; the obtained emulsion is stable; the use of a surfactant is avoided; and harm to the human body and pollution on the environmental can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
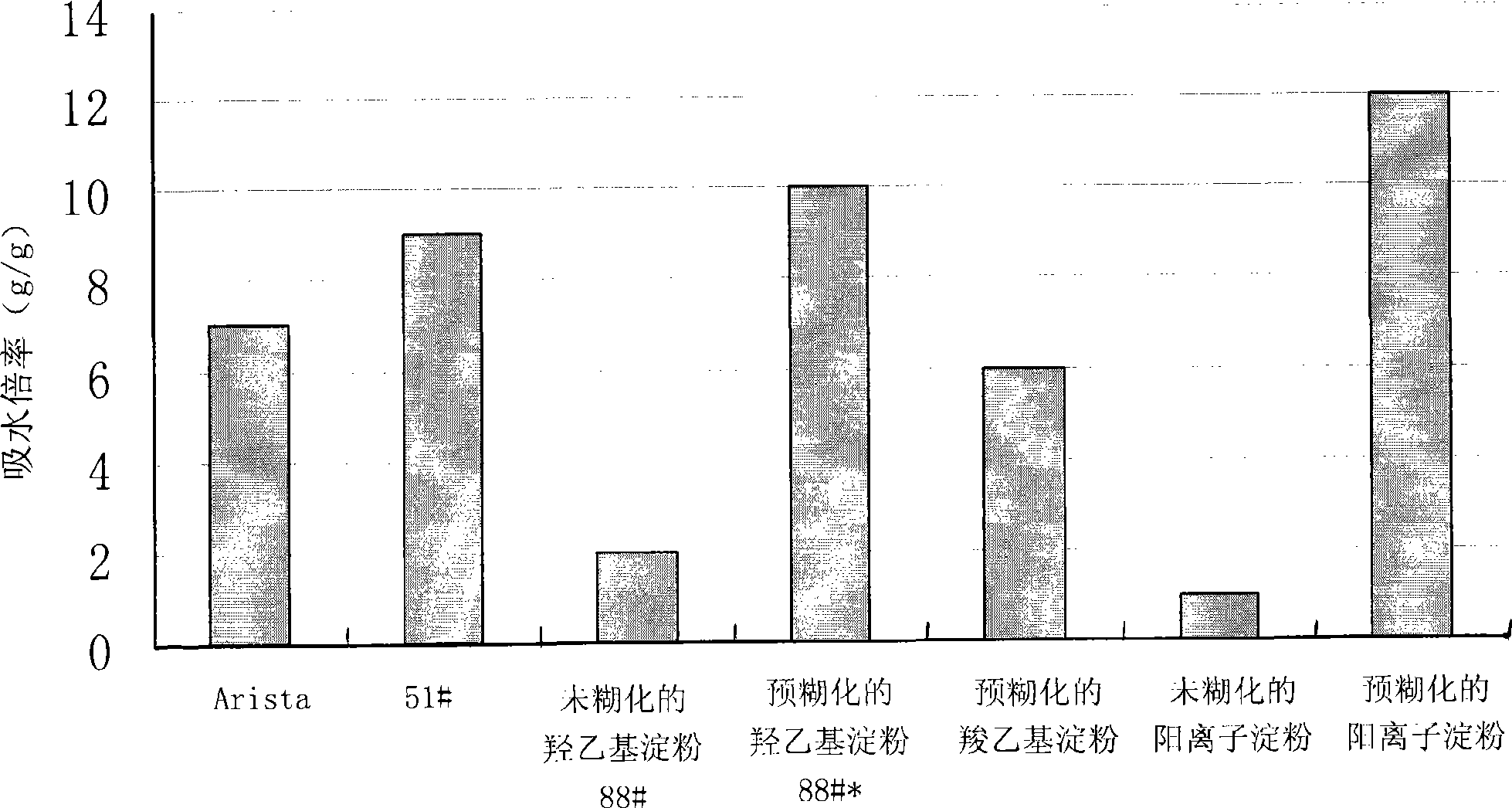
Biocompatibility pre-gelatinized modified starch and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101497670AAbsorbentSpeed up absorptionSurgical adhesivesFibre treatmentBiocompatibility TestingHigh pressure
The invention relates to a biocompatible pre-gelatinized modified starch. The water absorbency is not less than one time, and the biocompatible pre-gelatinized modified starch is taken as biocompatible hemostatic material, biocompatible anti-blocking material, biocompatible tissue-healing promoting material, biocompatible surgical sealant or biocompatible wound closure tissue glue. The invention has the advantages that the biocompatible pre-gelatinized modified starch is directly acted on the wounded area with blood for immediately stopping bleeding, has obviously increased water absorbency and speed of water absorption and greater viscosity and stickiness and further plays the role in preventing the tissue and the blood vessel from being damaged during the process of stopping bleeding; the modified starch is easy to swell or dissolve in water, and is washed by normal saline after the bleeding stopping so as to reduce the residual in the body, to be favorable for wound healing and to avoid the pain due to tearing the gauze and the bandage out; the pre-gelatinized modified starch has the actions of bacterial resistance and anti-inflammatory; and the pre-gelatinized modified starch is stable, not easy to decompose, long in guarantee period, convenient for storage, resistant at high pressure and low pressure, resistant at high temperature and low temperature and not easy to change the physicochemical characteristics.
Owner:纪欣
Hyperthermia, system, method and components
ActiveUS20090043256A1Effective and safe for patientInfusion devicesMedical devicesIntensive care medicineHigh body temperature
An IV pole mountable, therapeutic infusate processing device is incorporated into a hypothermia system to receive therapeutic fluid(s), such as normal saline, peritioneal dialysis solution, or other crystalloid solution, to heat such therapeutic fluid(s) a few degrees centigrade above normal body temperature and to direct the resulting heated infusate to and through a selected anatomical portion of a patients body to raise the temperature of that body portion so as to affect any cancerous or other tumors that may be located therein. The processing device is provided with touch screen controls and visual indicators to facilitate its proper use; while the system further includes temperature and pressure sensors to monitor the hyperthermia processing to insure patient safety.
Owner:BELMONT INSTR LLC
Composition for cleansing the sinuses
ActiveUS6899903B2Conveniently introduced through noseRelieve symptomsBiocideInorganic active ingredientsNostrilMedicine
A unique and synergistic composition is disclosed for cleansing the sinuses to reduce inflammation and improve breathing. The disclosure is also related to a composition for freshening and cleansing the sinus cavities and nostrils that includes a homeopathic ingredient and saline carrier solution. The disclosure is also related to the use of such composition to provide many anticipated and unexpected benefits that emanate from cleansing debris and microbes from the sinuses and nostrils.
Owner:QUILLIN PATRICK
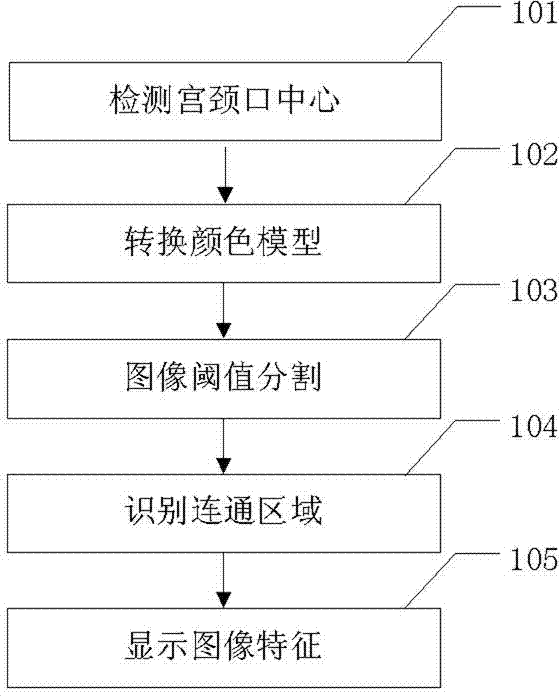
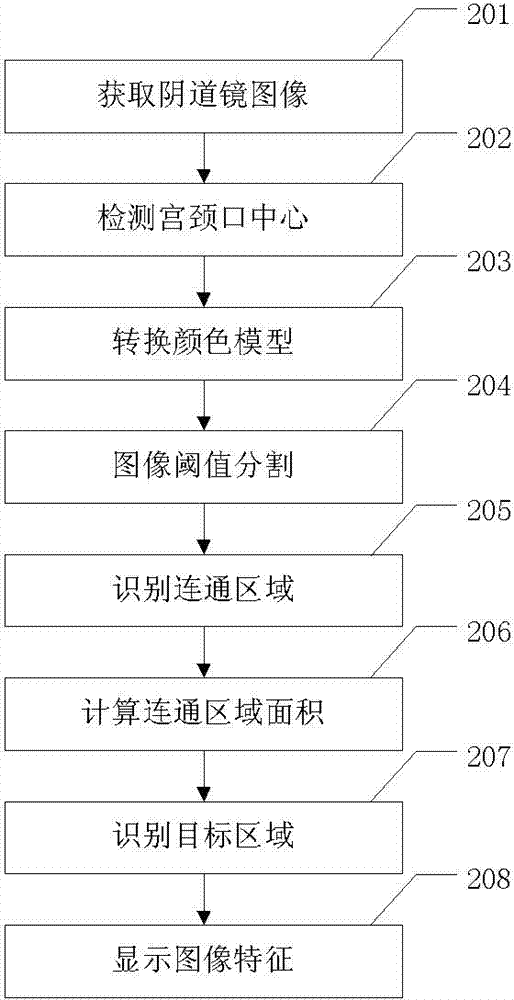
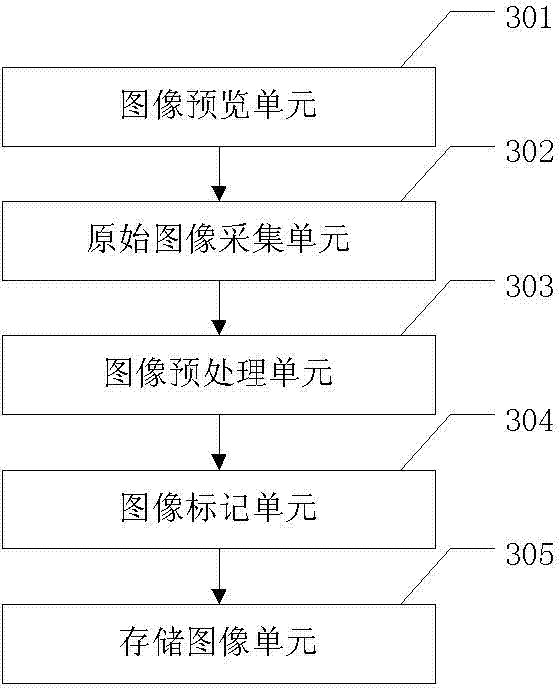
Method and device intelligently identifying characteristics of images collected by colposcope
ActiveCN103325128AImprove accuracyImprove consistencyImage analysisVaginoscopesEpitheliumColposcopes
The invention relates to a method and device intelligently identifying characteristics of images collected by a colposcope. Automatic extraction and identification are conducted on a normal saline test colposcope original image red characteristic, an original image green light image blood vessel distribution characteristic and an acetic acid test image white epithelium distribution characteristic; the central position of a cervical opening is positioned through an identifier shape easy to identify, the identifier shape and the position can be automatically identified, and therefore the characteristic images are distributed in four quadrants , the identifiability of the images is improved, the extracted characteristics are presented in a direct and visible mode on this basis. According to the method and device intelligently identifying characteristics of the images collected by the colposcope, a method of the combination of automatic image characteristic identification and automatic image characteristic display is adopted, the complexity of judging and reading of the images is simplified, the amount of information of judging and reading of the images is enriched, the image characteristics which are direct, visible and easy to identify are provided for a doctor, the precision, the uniformity and the repeatability of an image judgment, reading and assessing method are improved, and the dependence on subjective experience is reduced.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
Water-in-oil-in-water adjuvant vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103223164APromote absorptionGenerate fastAntiinfectivesAntibody medical ingredientsEngineeringImmunity response
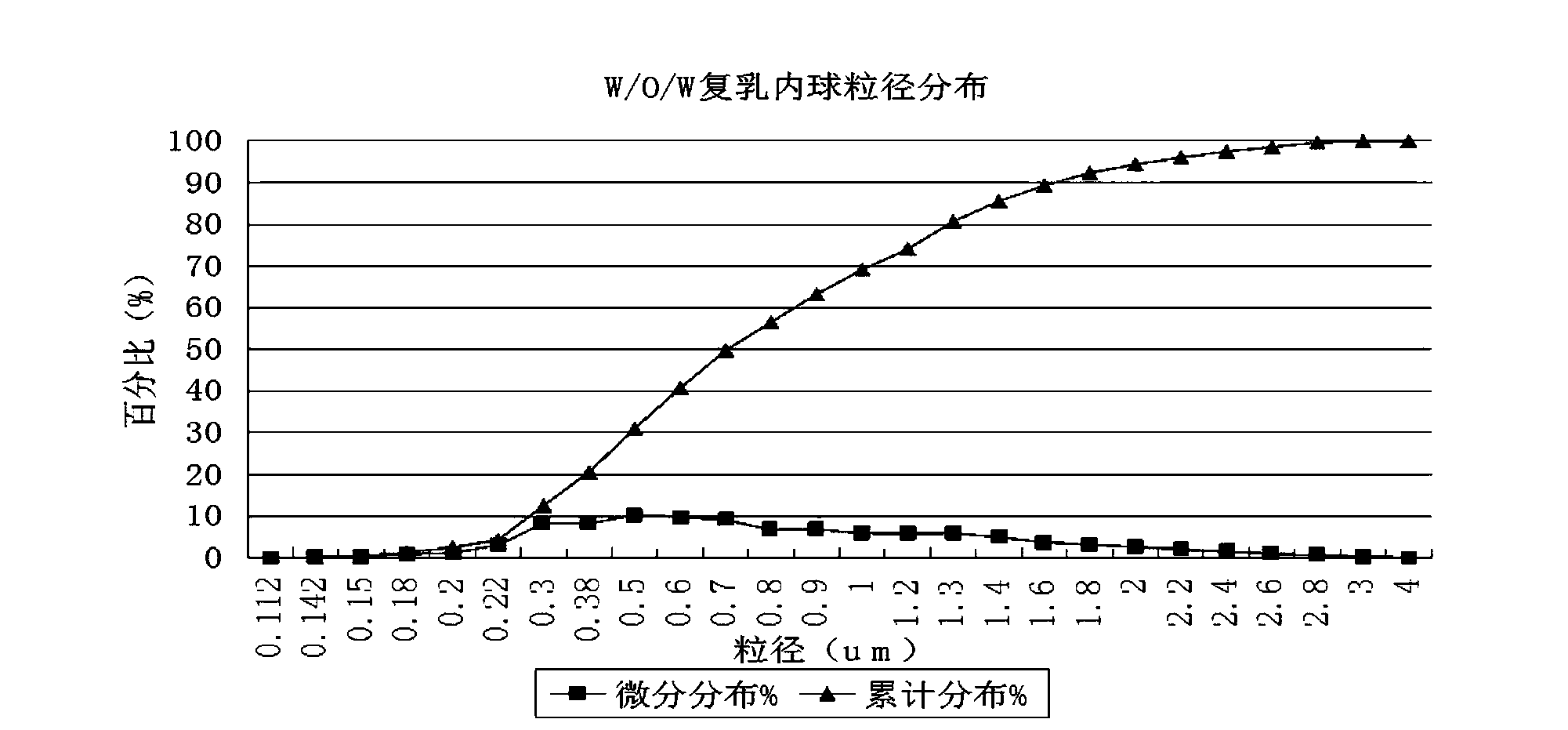
The invention discloses a water-in-oil-in-water adjuvant vaccine and a preparation method thereof. The adjuvant vaccine is composed of an internal water phase, a middle oil phase used for cladding the internal water phase, and an external water phase for cladding the middle oil phase. The external water phase comprises: a composite surfactant, a hydrophilic surfactant and mormal saline. The middle oil phase consists of: a lipophilic surfactant, a stabilizer and mineral oil. The internal water phase comprises: an immunopotentiator solution, the hydrophilic surfactant, and an inactivated antigen solution. The W / O / W (water-in-oil-in-water) type adjuvant vaccine provided in the invention can induce an immunoreaction earlier than traditional W / O (water-in-oil) type adjuvant vaccines, and can make experimental animals obtain earlier protective antibodies. The vaccine has good absorption, and causes a small inflammatory response at an inoculation site. The adjuvant vaccine disclosed in the invention has better stability than existing W / O / W type vaccines, and the antibody generation speed is fast.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
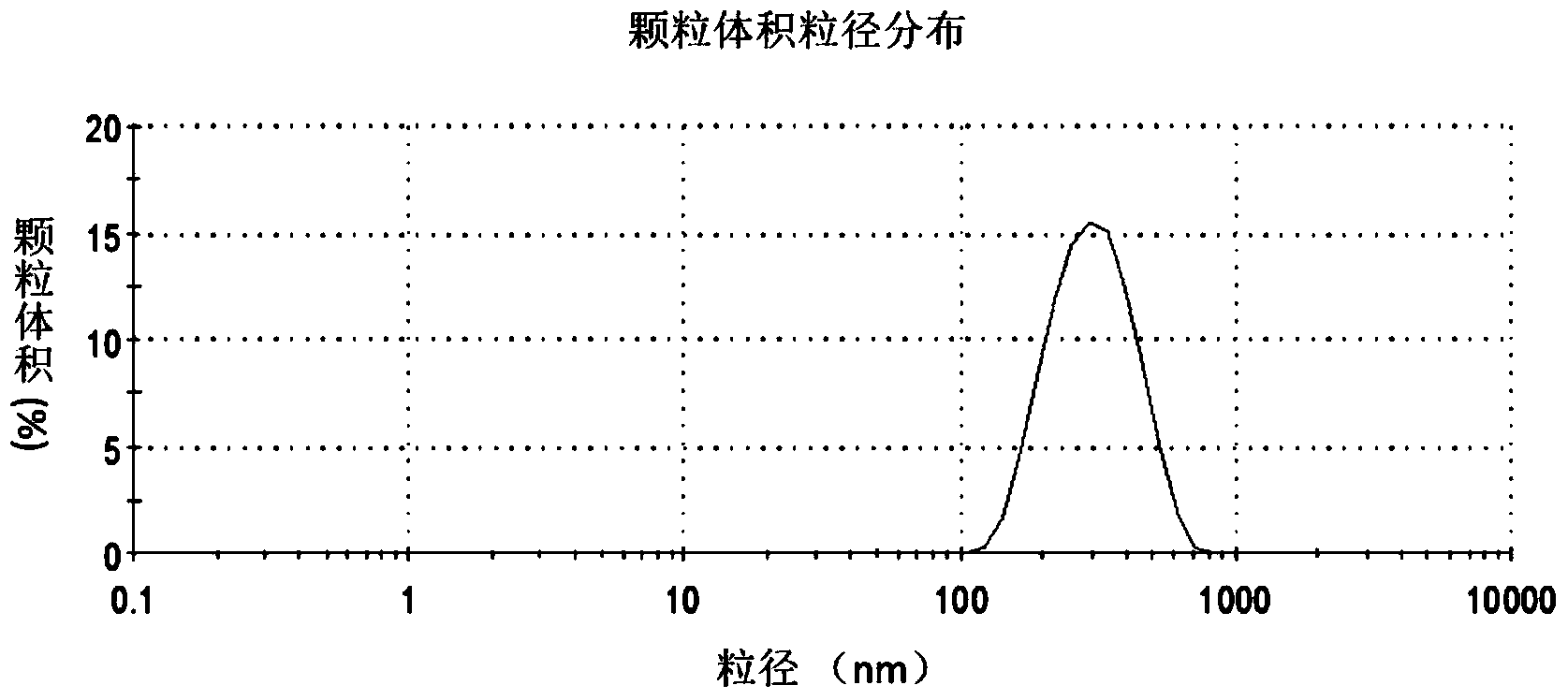
Folic acid receptor targeted liposome medicine carrier, its preparation and application
ActiveCN1621092AImprove convenienceImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsFreeze-dryingCholesterol
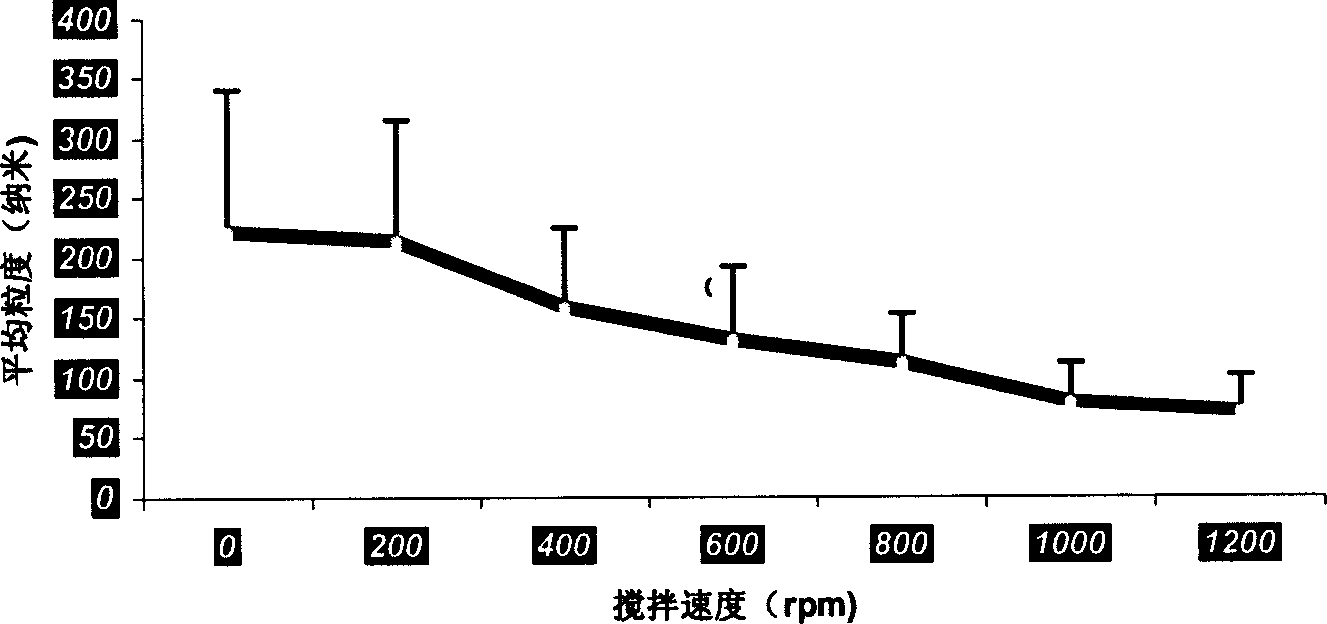
The present invention discloses one kind of folic acid acceptor targeting liposome as medicine carrier and its preparation process and application. The liposome has components including synthetic phospholipid, cholesterol, folic acid acceptor targeting anchor point and polyglycol hydrating anchor point. The present invention has relatively simple preparation process, and can prepare liposome of size smaller than 200 nm in large scale and prepare freeze dried powder of weak alkali medicine, including leurocristine, etc. carried on the liposome with greatly raised use convenience and stability. The medicine is re-constructed with bacteria-free water or brine before use, and the medicine leakage rate is lower than 10 %.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIANFENG HANSHENG BIOSCI +1
Method of blood oxygenation
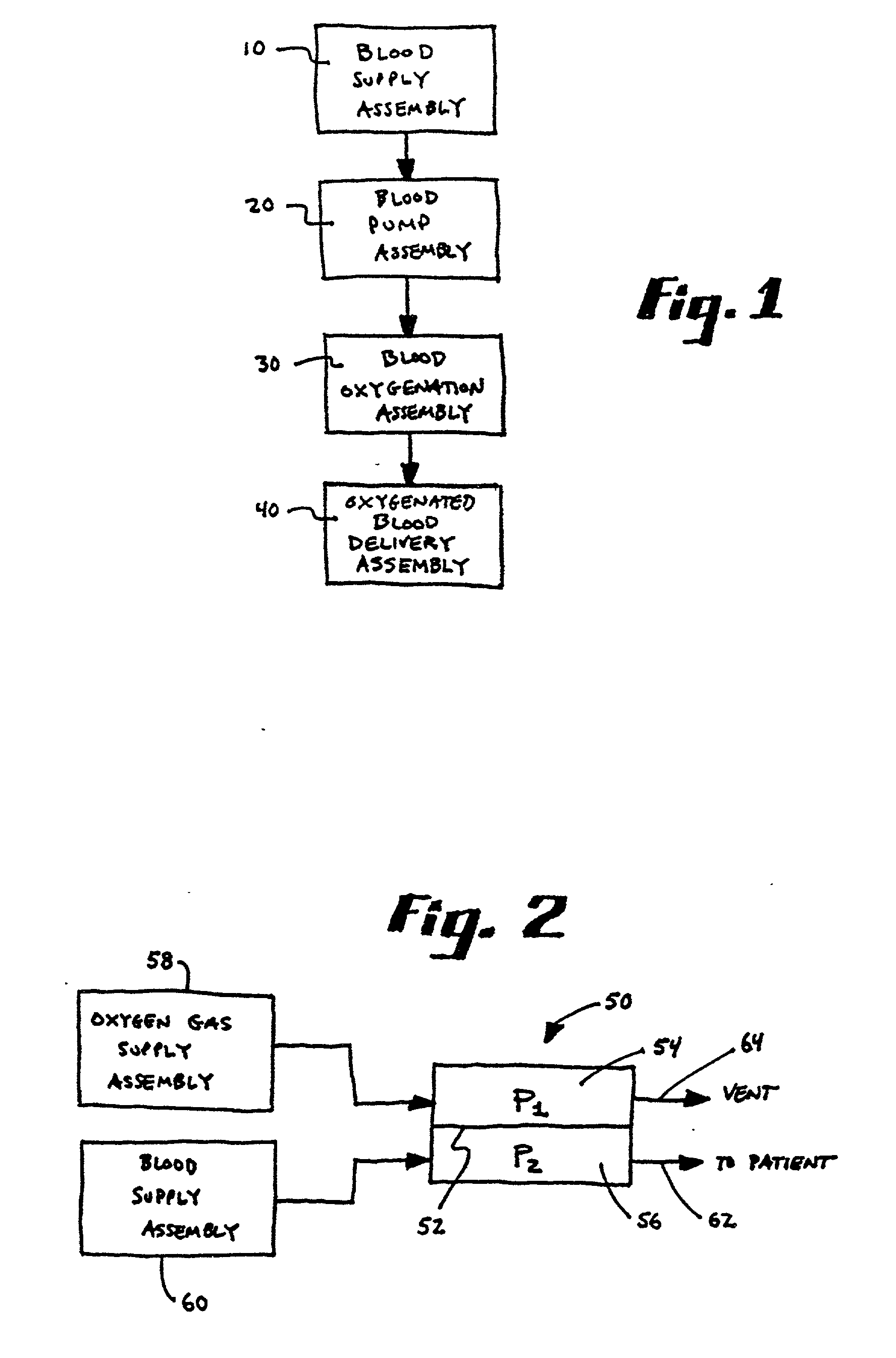
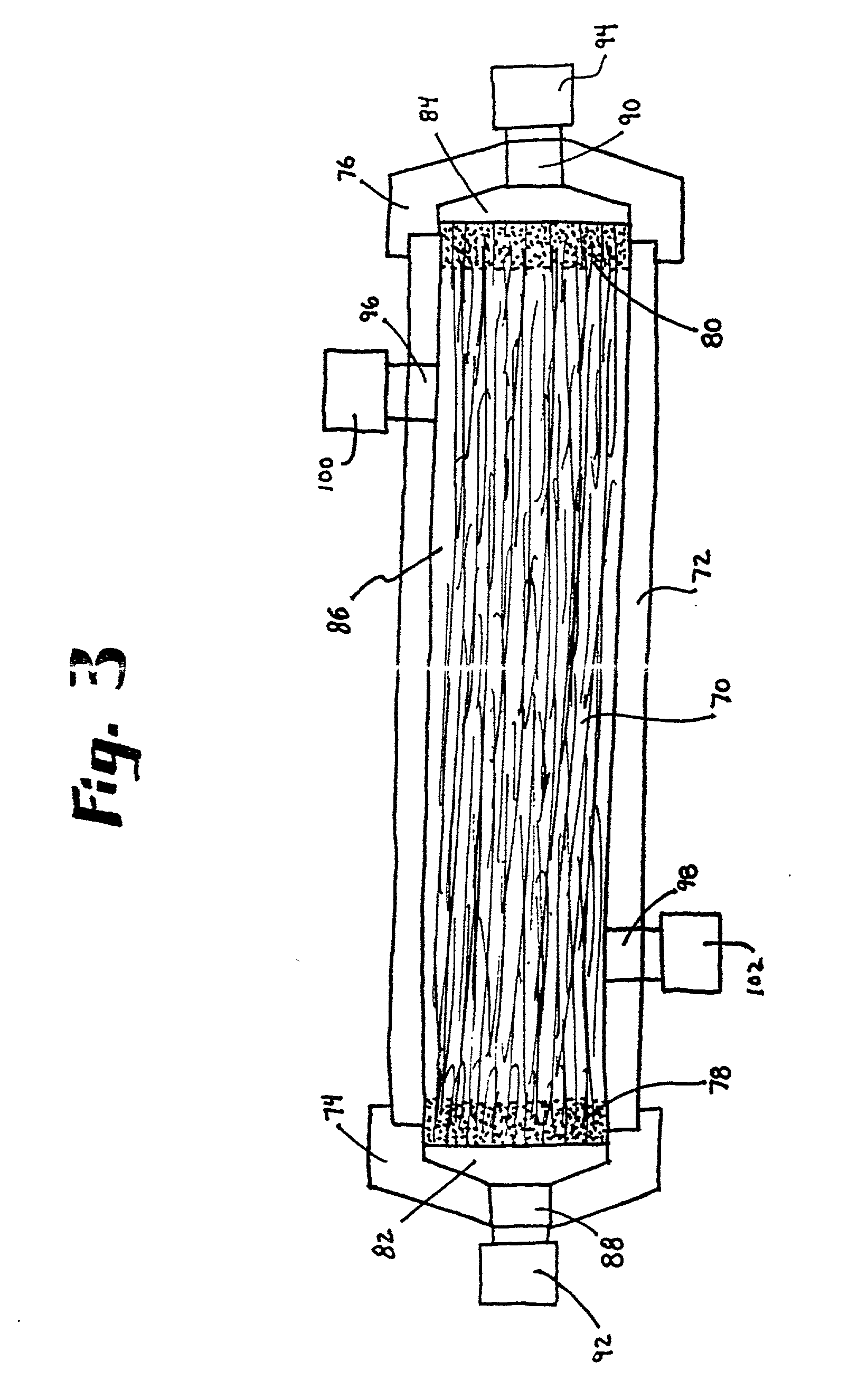
InactiveUS20030091470A1Inhibition formationPrevent escapeOther blood circulation devicesTransportation and packagingMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
An apparatus and method for blood oxygenation is provided, advantageously comprising an extracorporeal circuit for the preparation and delivery of hyperoxic or hyperbaric blood. In one embodiment, an apparatus for gas-supersaturating fluids, e.g., physiologic saline, includes a chamber having a first inlet to receive the fluid; a second inlet to receive a gas, e.g., oxygen, from a gas supply that maintains pressure within the chamber at a predetermined level, advantageously about 600 p.s.i.; and an outlet advantageously coupled to a capillary assembly. An atomizer nozzle coupled to the first inlet advantageously creates within the chamber fine droplets of fluid into which gas diffuses to create the gas-supersaturated fluid, which collects within the chamber below the atomizer nozzle for removal via the outlet. The removed gas-supersaturated fluid mixes with blood provided by a blood pump, the mixing occurring within a liquid-to-liquid oxygenation assembly including a pressurizable chamber having inlets for the gas-supersaturated fluid and blood, the inlets advantageously arranged to create a vortical or cyclonic fluid flow within the chamber to promote mixing. The mixed fluid exits the chamber via an outlet for delivery to a patient (e.g., sub-selective delivery) or other site via a catheter, infusion guidewire, or other interventional fluid delivery device, the mixed fluid advantageously comprising blood having increased oxygen levels, i.e., oxygenated blood. Alternately, the blood may be provided by the pump to a high pressure hollow fiber or other type membrane oxygenator within which oxygen, advantageously provided at a pressure greater than atmospheric, diffuses across the membrane(s) and into the blood to form oxygenated blood, again for delivery to a patient or other site. Advantageously, the oxygenated blood is delivered at a target pO2 greater than about 760 mm Hg and is delivered from the liquid-to-liquid oxygenation assembly or membrane oxygenator via a fluid conduit having an approximate pressure drop greater than the target pO2.
Owner:THEROX
Isolated nanocapsule populations and surfactant-stabilized microcapsules and nanocapsules for diagnostic imaging and drug delivery and methods for their production
InactiveUS20080279783A1Reduce deliveryUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsMicrobubblesPhosphate
A method for producing surfactant-stabilized microcapsules or nanocapsules including the steps of (a) preparing a suspension comprising a non-ionic sorbitan detergent and a salt in phosphate buffered saline; (b) adding to the suspension a nonionic polyoxyethylenesorbitan detergent to produce a solution; (c) heating while stirring the solution of step (b) to 55±5° C. and maintaining the temperature of the solution at 55±5° C. for several minutes; (d) allowing the solution to cool to room temperature; (e) autoclaving the solution; (f) creating surfactant-stabilized microbubbles and nanobubbles in the solution; and (g) collecting surfactant-stabilized nanocapsules and microcapsules formed from the microbubbles and nanobubbles.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Micronized wharton's jelly
The present invention provides compositions and formulations of micronized Wharton's jelly having a controlled viscosity such that when delivered to the injured region of a subject, it remains substantially localized with little or no migration out of the injured region for the repair and / or regeneration thereof. Micronized Wharton's Jelly can be suspended in a pharmaceutically acceptable aqueous carrier, such as saline, sterile water, or any suitable buffer, to form a suspension or a gelatinous gel composition, or it can be in the form of a paste, suitable for delivery into the space adjacent the articular surface cartilage injured region of a subject. The micronized Wharton's jelly when employed at sufficient concentrations can be hydrated into a gel or paste and administered topically, or it can be injected into the body through the use of a needle and syringe. Accordingly, micronized Wharton's Jelly, compositions, or formulations thereof, can be delivered in a manner that is more convenient than Wharton's jelly that has not been micronized in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:MIMEDX GROUP
Culture method, application and combined preparation of hypoxia mesenchymal stem cell
InactiveCN101792737AHigh activityImprove survival rateOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCell massTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a culture method, application and a combined preparation of a hypoxia mesenchymal stem cell. By adopting an umbilical or placenta mesenchymal stem cell and combining the means of transfusing compound amino acid injection and the like, the vitality, the implantation survival rate and the treating effect of the mesenchymal stem cell in vivo can be improved; and in order to avoid the possibility of conglutination, conglomerating and cell mass embolism of the mesenchymal stem cell in blood vessel, the matching of saline containing heparin during treatment can be carried out by a mode of intravenous injection or intravenous drip. With more than three times of treatment, physical conditions of curee can be remarkably improved and objective indicators such as immunity, blood fat, blood sugar and the like can be remarkably improved.
Owner:晏泽
Self-healing injectable supramolecular hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to self-healing injectable supramolecular hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The hydrogel is prepared by heating commercial guanosine and arylboronic acidcompound in brine or aqueous alkali and cooling. The preparation process is simple and green, is convenient to operate, requires no tedious synthesis or purification steps, has low production cost and is suitable for large-scale production. The prepared supramolecular hydrogel has good self-healing performance, viscoelasticity, injectability, ionic conductivity, mechanical property regulation anduse safety, and has a good application prospect in the field of ion skin and gel electrolytes.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Deer spleen extract preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102669669ASimple operation processSuitable for industrial productionUnknown materialsImmunological disordersBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention provides a deer spleen extract preparation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding water or normal saline or buffer solution into deer spleen, mashing with a colloid mill, performing enzymolysis, centrifuging, taking supernate, concentrating, and performing spray drying to obtain dry powder, wherein the dry powder can be mixed with other one or more Chinese medicaments to prepare a compound preparation, and the dry powder is prepared by the same method; and adding accessories acceptable in health-care food into the dry powder, and thus obtaining the oral preparation facilitating oral administration. The preparation has health-care functions of assisting in improving human immunity and the like; and the waste deer spleen is changed into valuable, so that the utilization rate of the deer spleen is improved.
Owner:融致丰生制药有限公司
Polyamide reverse osmose membrane and production thereof
InactiveCN1817423AExcellent and stable performanceWide variety of sourcesSemi-permeable membranesLiquid layerReverse osmosis
A reverse-osmosis polyamide member is prepared through providing the aqueous solution of lentine and piperazine, immersing the porous carrier in it to have a liquid layer on it, and single-surface contacting with the organic solution of symphenyl triformyl chloride for interface polymerizing reaction. Said reverse osmosis membrane can be used to treat the saline for removing either impurity (SO4 ions) or NaCl in different condition, having high selectivity.
Owner:凯膜过滤技术(上海)有限公司
Salt alkali resistance water preserving agent and its preparation method
InactiveCN1590504AImprove water absorptionHigh brine rateOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsSalt waterChemistry
A water-preserving agent resisting to saline and alkali is prepared from acrylic acid, acrylamide and attapulgite through graft copolymerizing under existance of trigger, cross-linking, washing, drying and pulverizing.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of injecting calcium based neutral and bioresorbable bone grafts
InactiveUS20090318982A1Reduce decreaseImprove mechanical propertiesSurgical adhesivesBone implantOrthopedic departmentTri calcium phosphate
Owner:BERKELEY ADVANCED BIOMATERIALS
Injectable mineralized collagen bone repair material and preparing method
InactiveCN105457097AAnti-collapseImprove microenvironmentTissue regenerationProsthesisFreeze-dryingBiocompatibility Testing
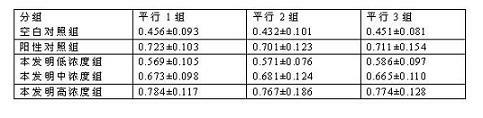
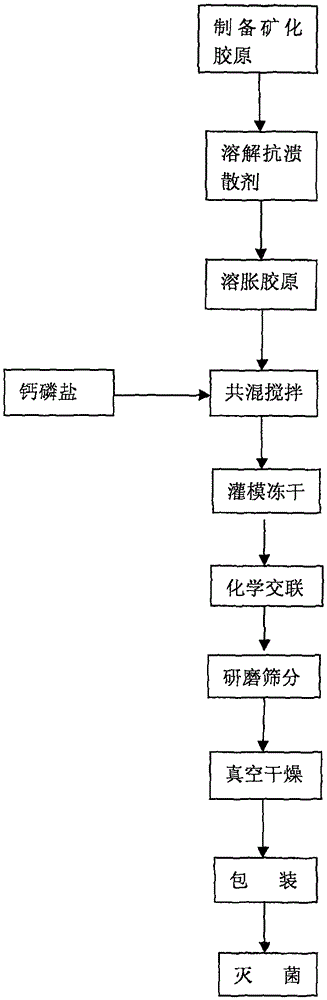
The invention provides an injectable mineralized collagen bone repair material and a preparing method. The bone repair material is prepared from mineralized collagen, collagen, calcium phosphate particles and an antiwashout agent. The preparing method for the material comprises the steps of preparing mineralized collagen powder; dissolving the antiwashout agent; swelling the collagen; carrying out blending; carrying out mould filling and freeze drying; carrying out cross-linking; carrying out grinding and screening. The bone material can be mixed with autoblood, marrow, normal saline and the like, has a good shape after being kneaded, is formed into dough, and has good cohesiveness, injectability and an antiwashout property. The material can be transplanted into a bone defect part in an injected or open operation mode, has good biocompatibility, promotes new bone generation, and can be used in the bone defect of a non-bearing part, path nailing, tooth fossa pulling, interbody fusion cage interior filling, autogenous bone fragment bonding and prefabricated and formed bone material gap supplementing materials. The bone material can carry antibiotic drugs and has a slow-release effect.
Owner:谢宝钢 +1
Adjuvant compositions and related methods
ActiveUS9636397B2Less DNAOvercome problemsSsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryAdjuvantCholesterol
The present disclosure provides for an adjuvant composition that is suited for injectable as well as transdermal administration. The adjuvant composition generally comprises a lipophile, a polymer of acrylic or methacrylic acid, saline, cholesterol, a saponin, and sodium hydroxide. A vaccine composition is also provided for that generally includes the vaccine composition of the present disclosure and a DNA component. A method for vaccinating animals and humans utilizing the adjuvant composition of the present disclosure is also provided.
Owner:HUVEPHARMA INC
Measurement of hematocrit and cardiac output from optical transmission and reflection changes
InactiveUS20100268090A1Easy to measureIncrease blood flowMaterial analysis by optical meansSensorsOptical reflectionHemodialysis
A system and method of non-invasive determination of hematocrit change from optical reflected light in combination with transmitted light or from reflected light measured from one or more locations on a blood carrying medium. Determining the cardiac output of a patient based on the amount of plasma or saline injected and the determined hematocrit change. The cardiac output may be determined on a patient undergoing hemodialysis. The hematocrit changes can be detected transcutaneously, transarterially, intraarterially, or across an extracorporeal arterial circulatory path.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Perfusion preservation fluid for isolated liver
ActiveCN104996396AReduce manufacturing costMeet the needs of transplantationDead animal preservationSodium bicarbonateAdenosine
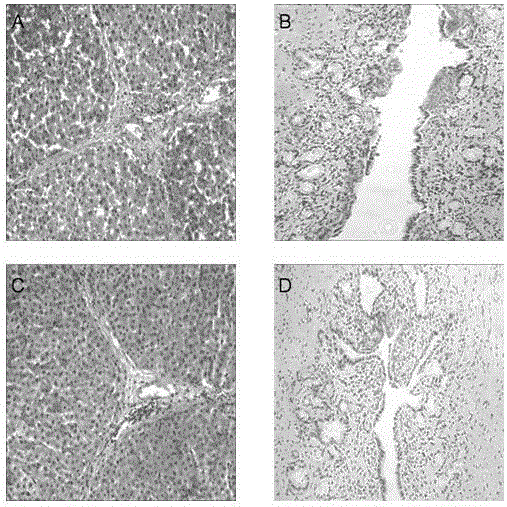
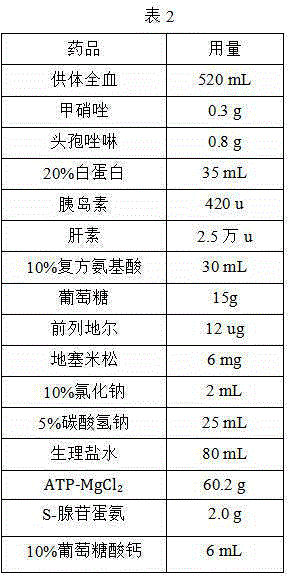
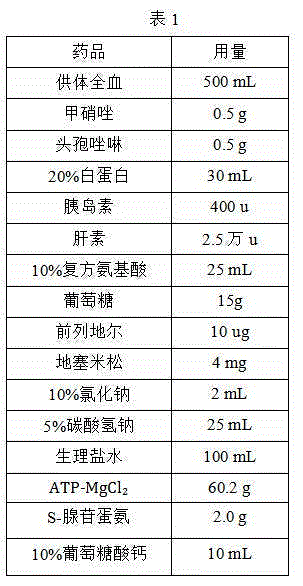
The invention relates to the technical field of organ transplantation, and particularly discloses perfusion preservation fluid for an isolated liver. The perfusion preservation fluid for the isolated liver comprises donor whole blood, albumin, antibiotics, insulin, heparin, compound amino acid, glucose, dexamethasone, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, normal saline, ATP-MgCl2 and S-adenosyl methionione which are mixed according to proportion. The isolated liver is preserved in the perfusion preservation fluid for 50 hours, the damage to liver cells is less, no complication occurs, the requirements of organ transplantation can be met, the survival time of a graft can be prolonged, and the survival rate of the graft in a host is improved; the perfusion preservation fluid is low in production cost and has the practical application value.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Targeted delivery of lidocaine and other local anesthetics and a method for treatment of cough and tussive attacks
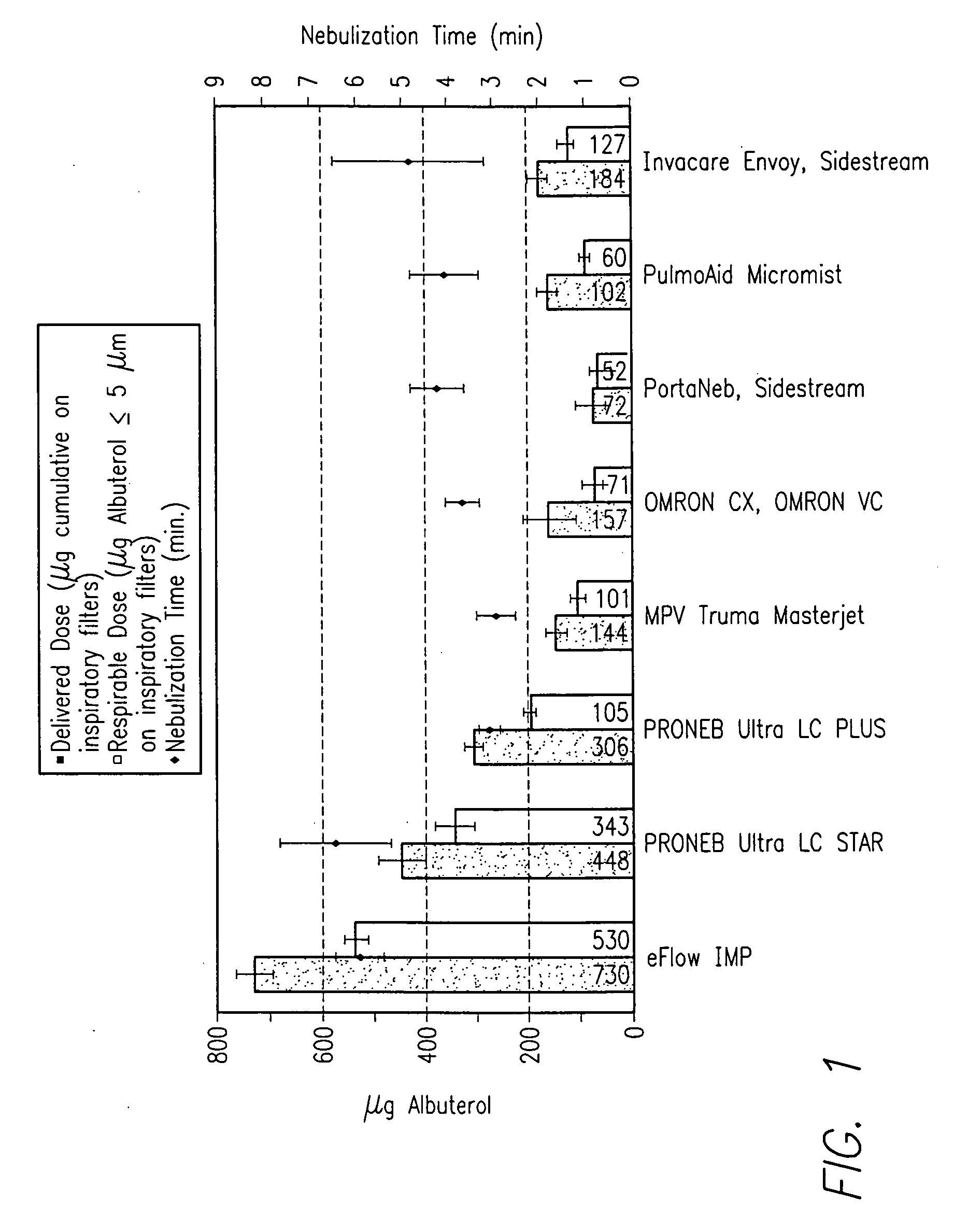
An anti-tussive nebulized solution for targeted delivery of lidocaine into conducting and central airways. A method for treatment of cough and tussive attacks or episodes using said lidocaine solution. A nebulized lidocaine solution administered in daily dose from about 10 mg to 80 mg of lidocaine dissolved in a saline and nebulized into an aerosol having a mass median aerodynamic diameter 3 μm to 10 μm and a geometric standard deviation less than 1.7 using an electronic nebulizer.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Modified starch material of biocompatible hemostasis
ActiveUS20130123213A1Promoting tissue healingGood effectPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsExtravasationBandage
A modified starch material for biocompatible hemostasis, biocompatible adhesion prevention, tissue healing promotion, absorbable surgical wound sealing and tissue bonding, when applied as a biocompatible modified starch to the tissue of animals. The modified starch material produces hemostasis, reduces bleeding of the wound, extravasation of blood and tissue exudation, preserves the wound surface or the wound in relative wetness or dryness, inhibits the growth of bacteria and inflammatory response, minimizes tissue inflammation, and relieves patient pain. Any excess modified starch not involved in hemostatic activity is readily dissolved and rinsed away through saline irrigation during operation. After treatment of surgical wounds, combat wounds, trauma and emergency wounds, the modified starch hemostatic material is rapidly absorbed by the body without the complications associated with gauze and bandage removal.
Owner:JI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com