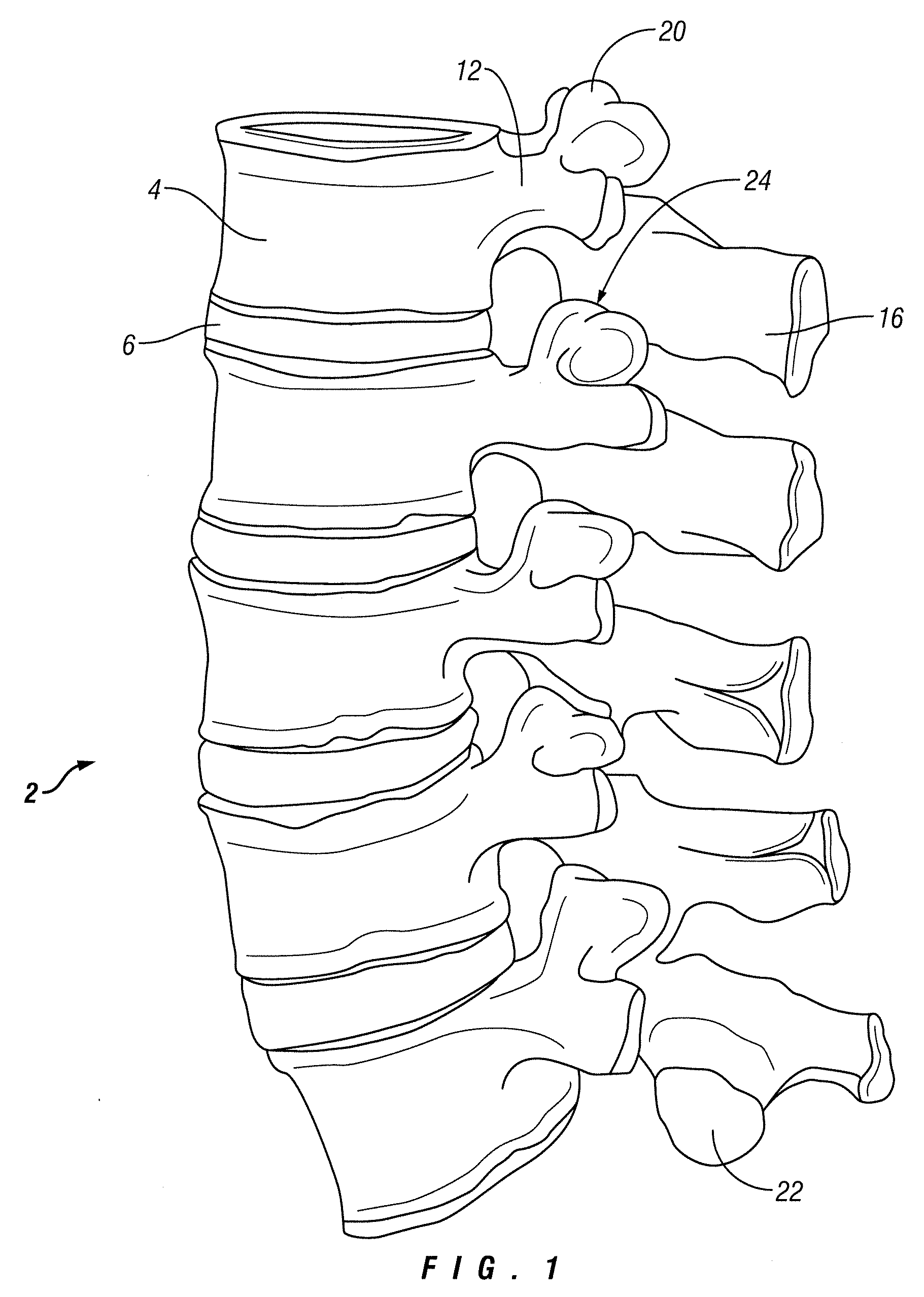Patents
Literature
2559 results about "Cartilage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
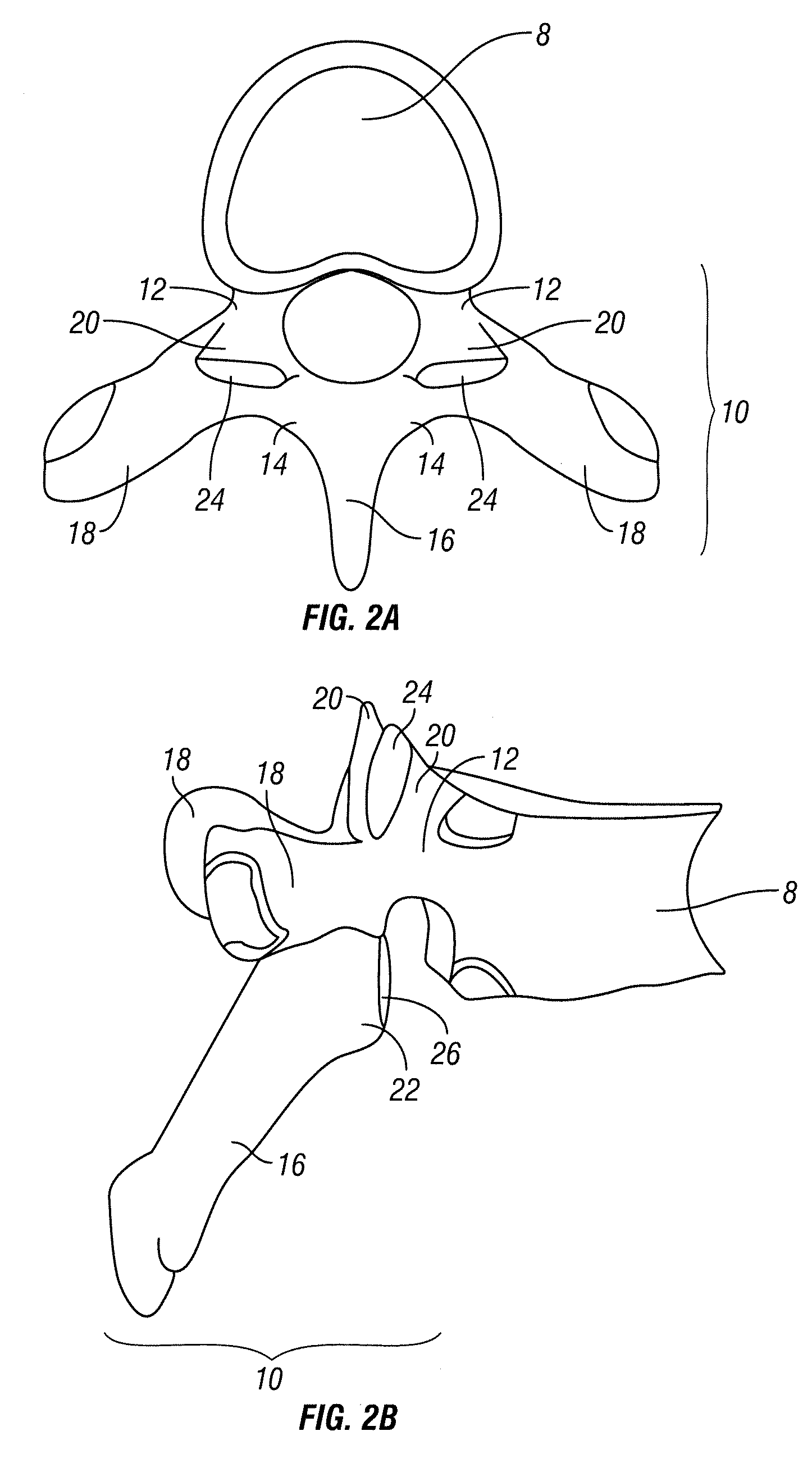
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth elastic tissue, a rubber-like padding that covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints, and is a structural component of the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the bronchial tubes, the intervertebral discs, and many other body components. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin.
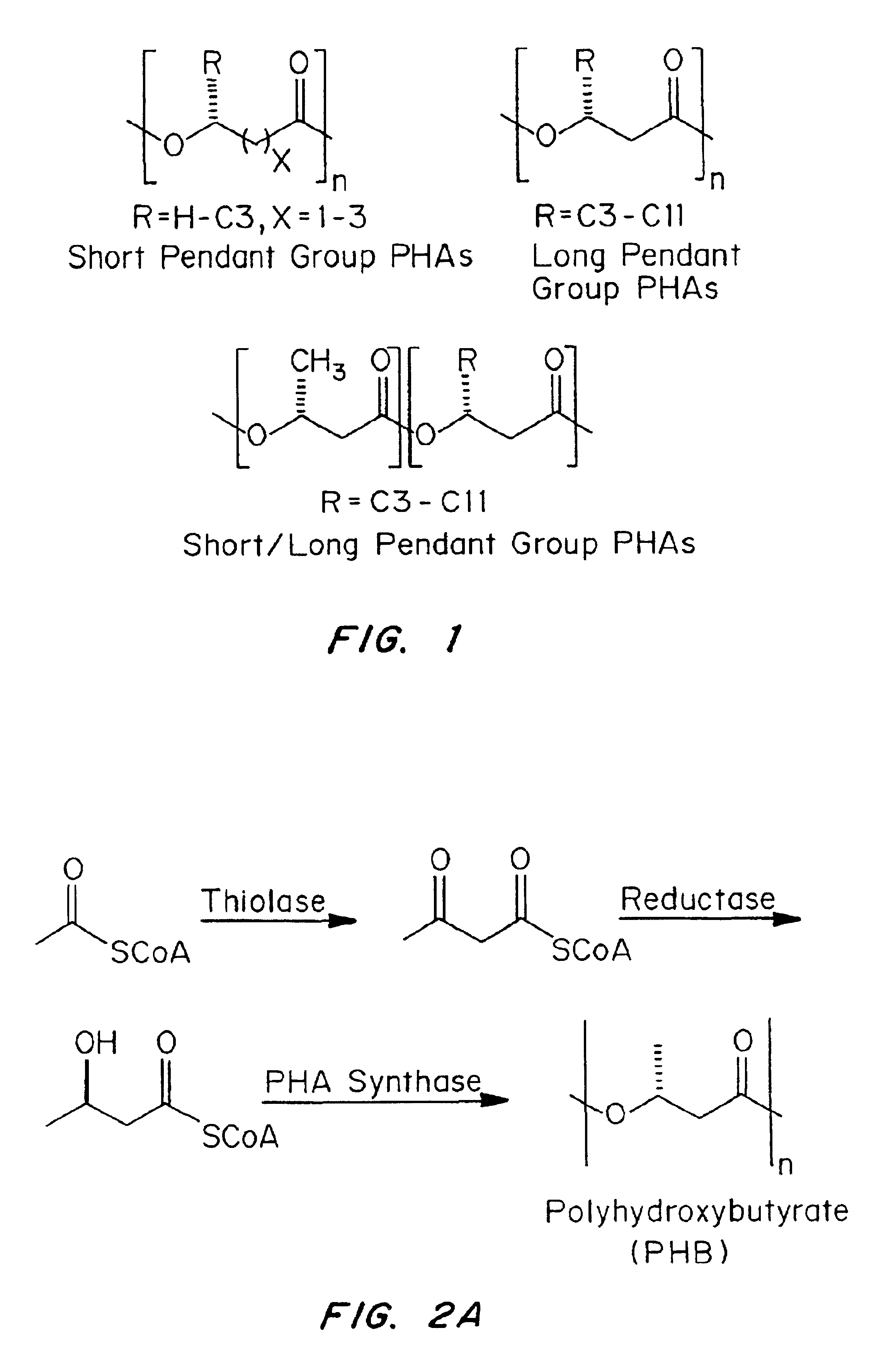
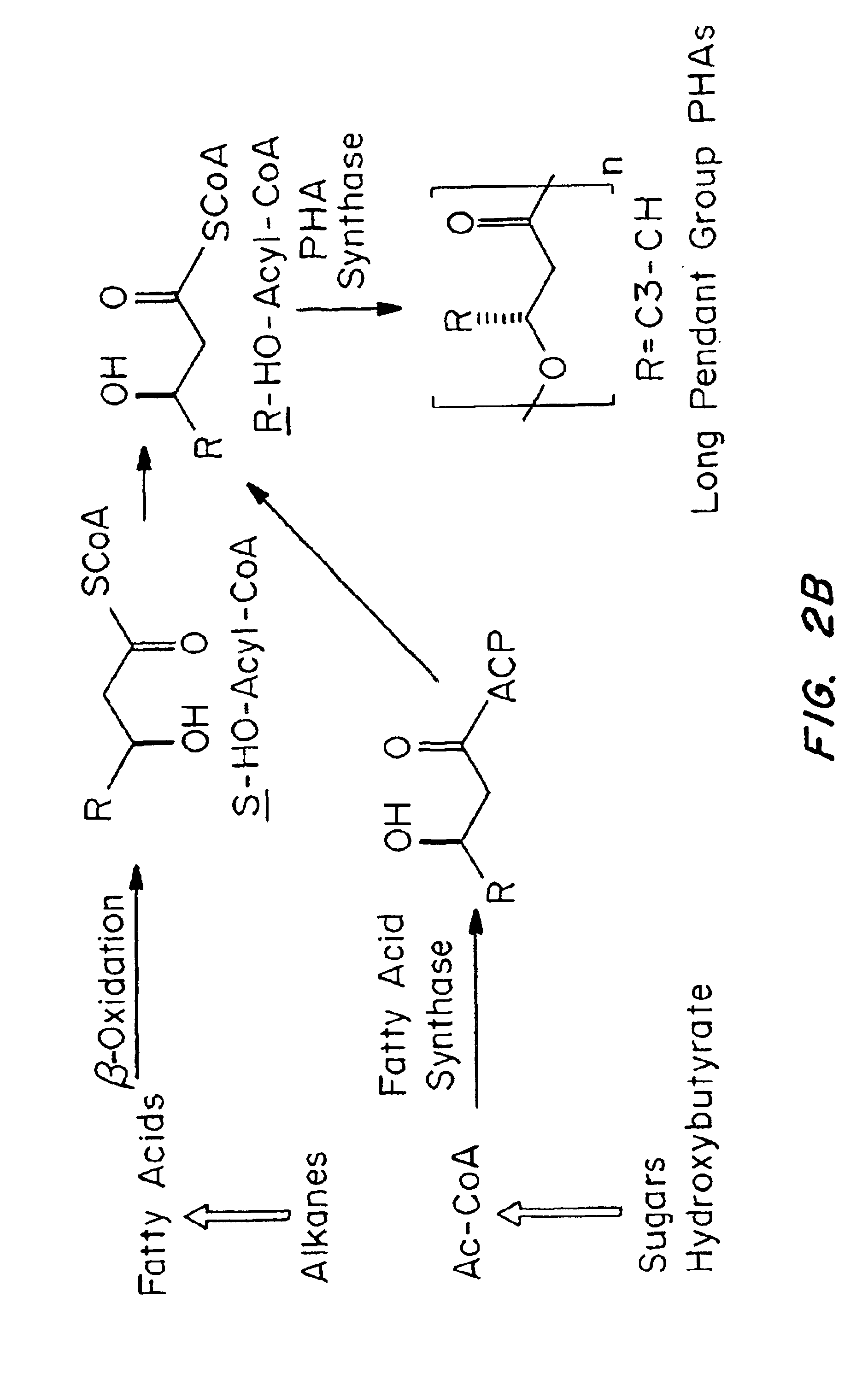
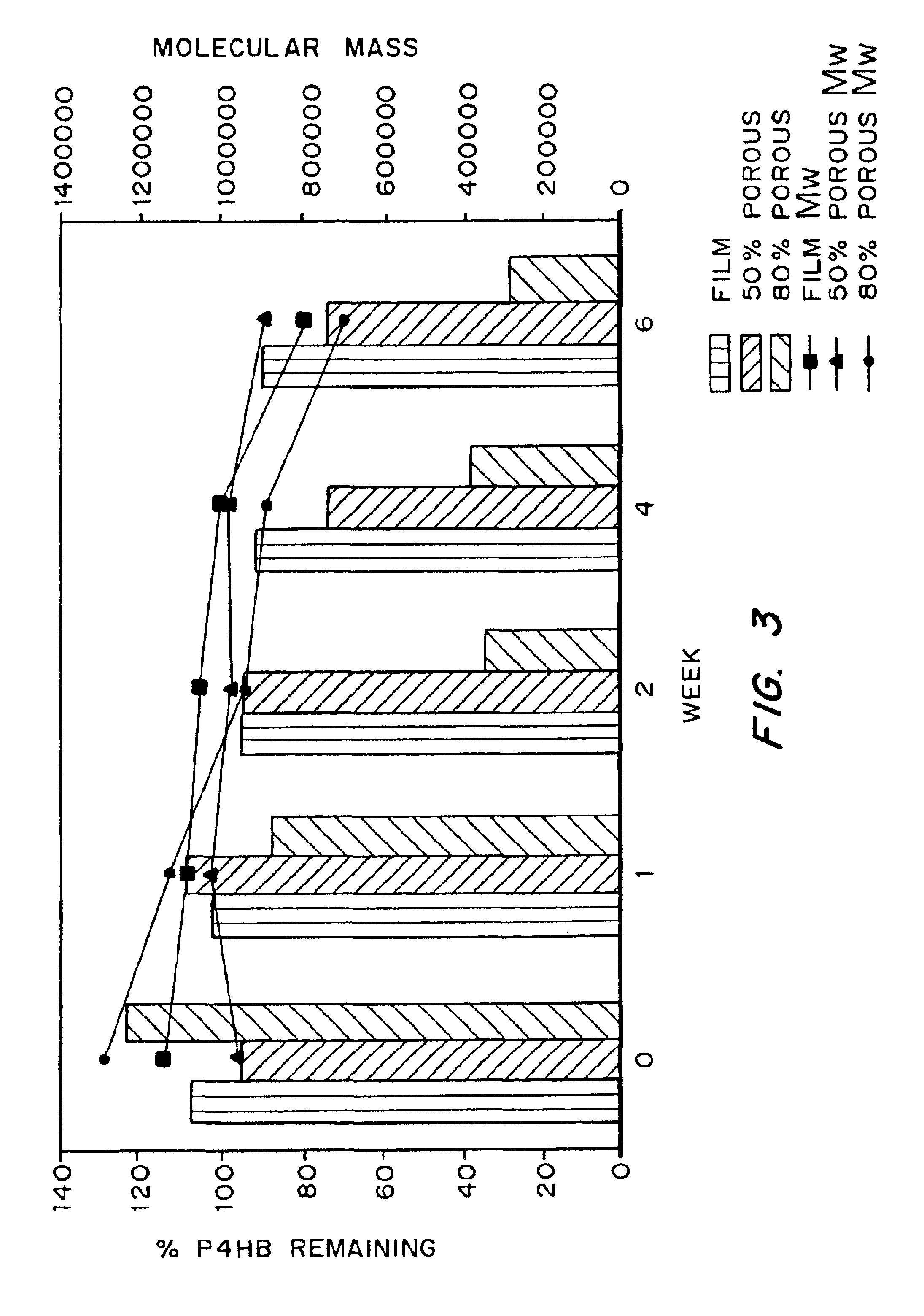
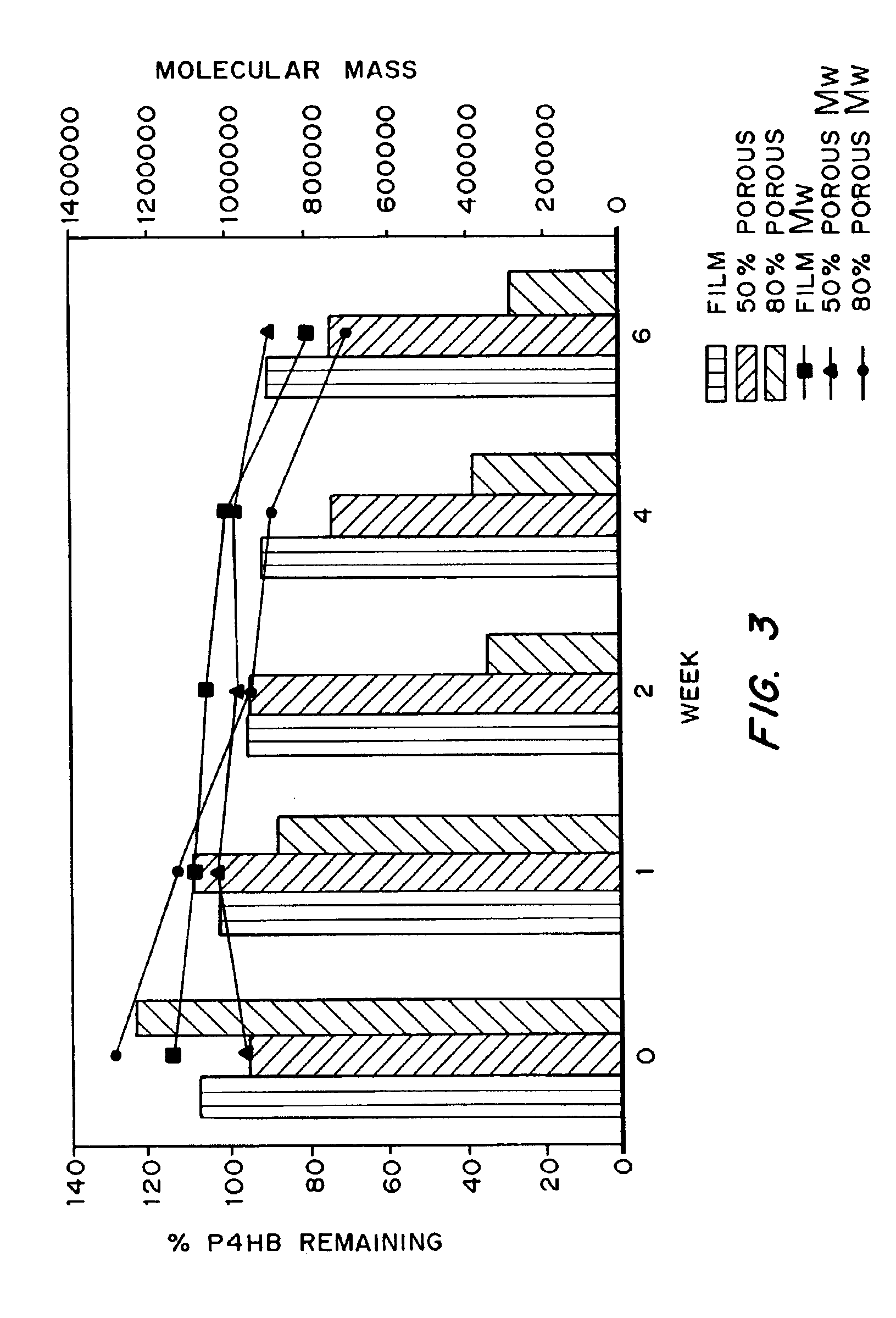
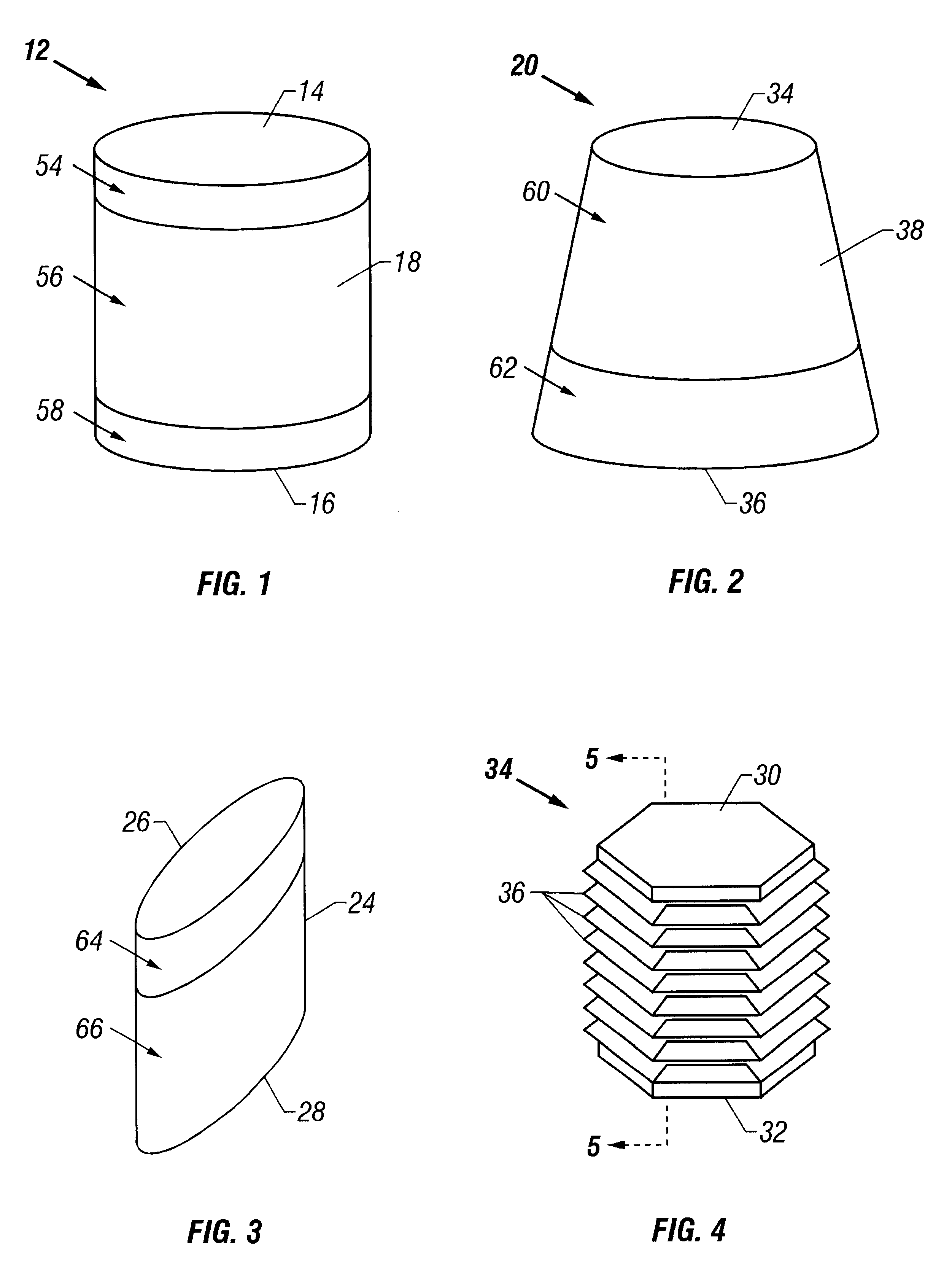
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
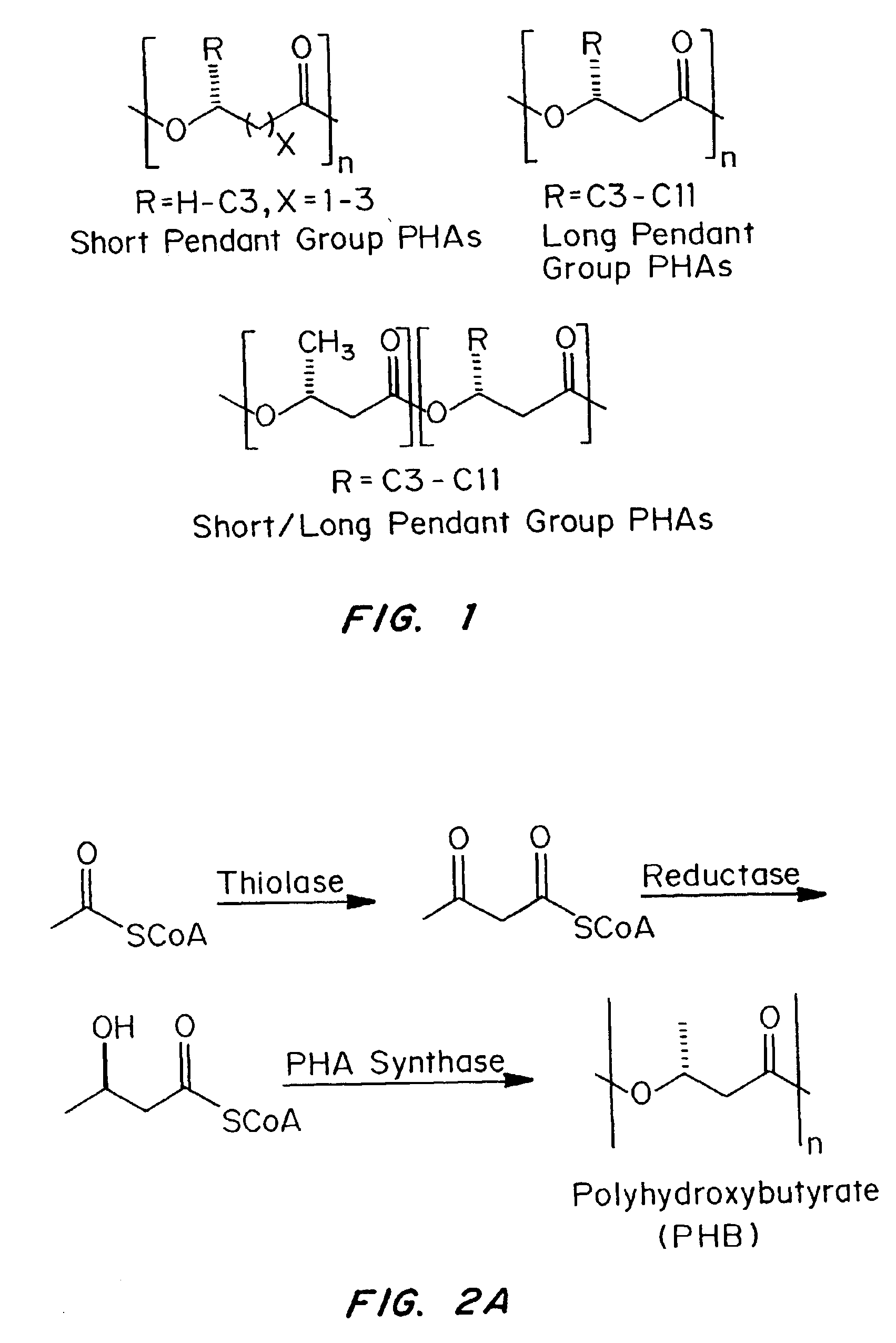
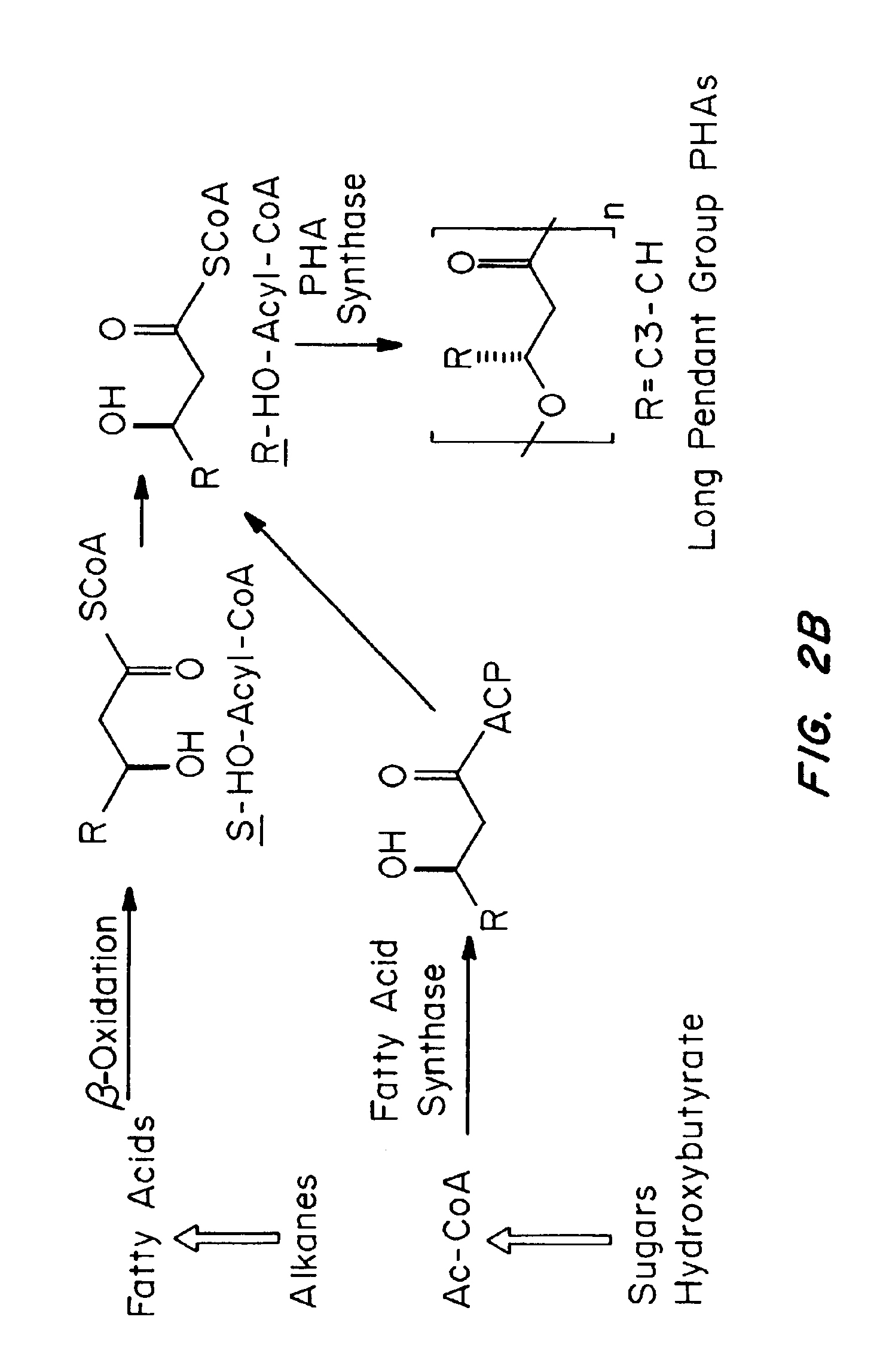
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
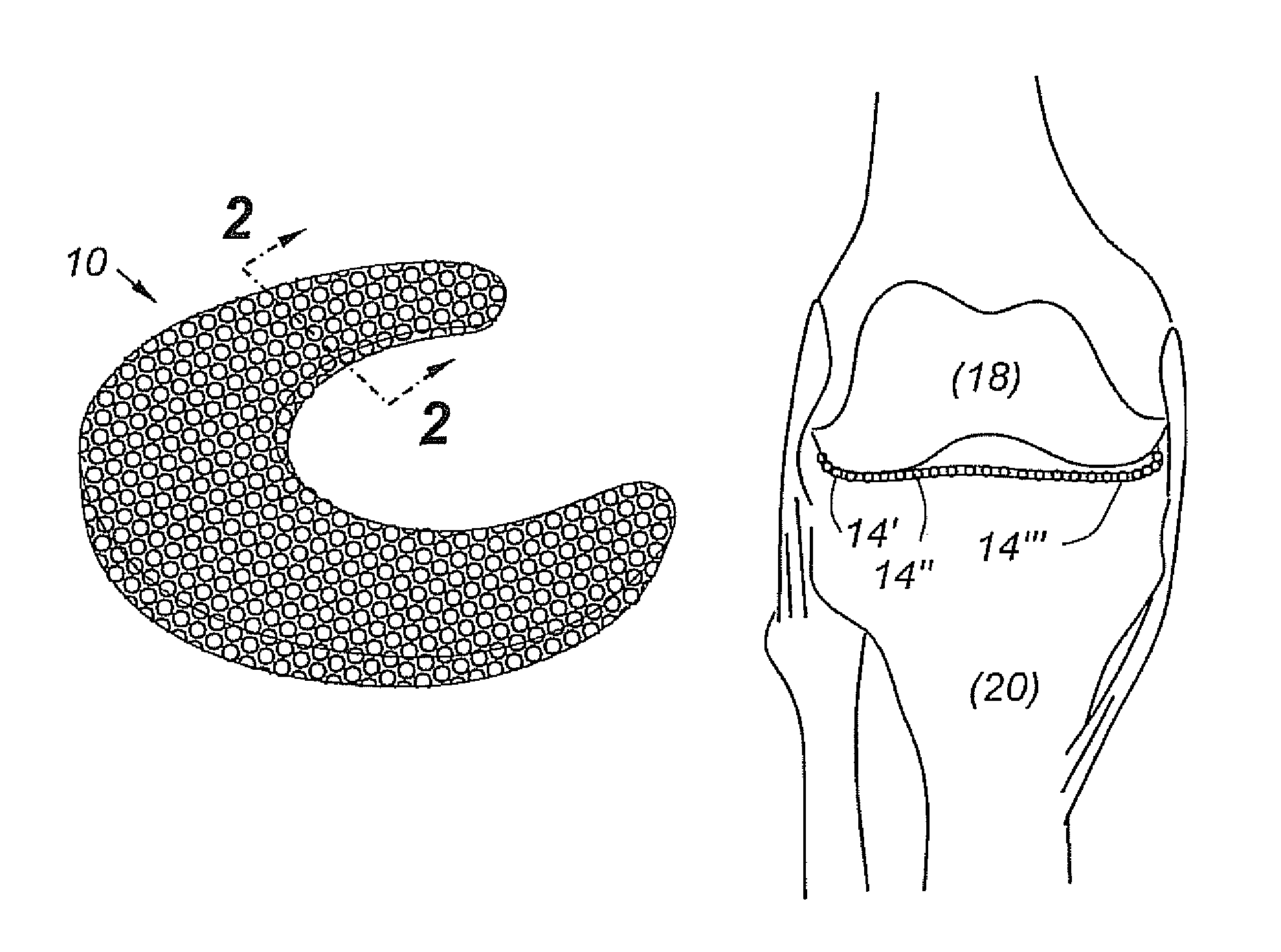
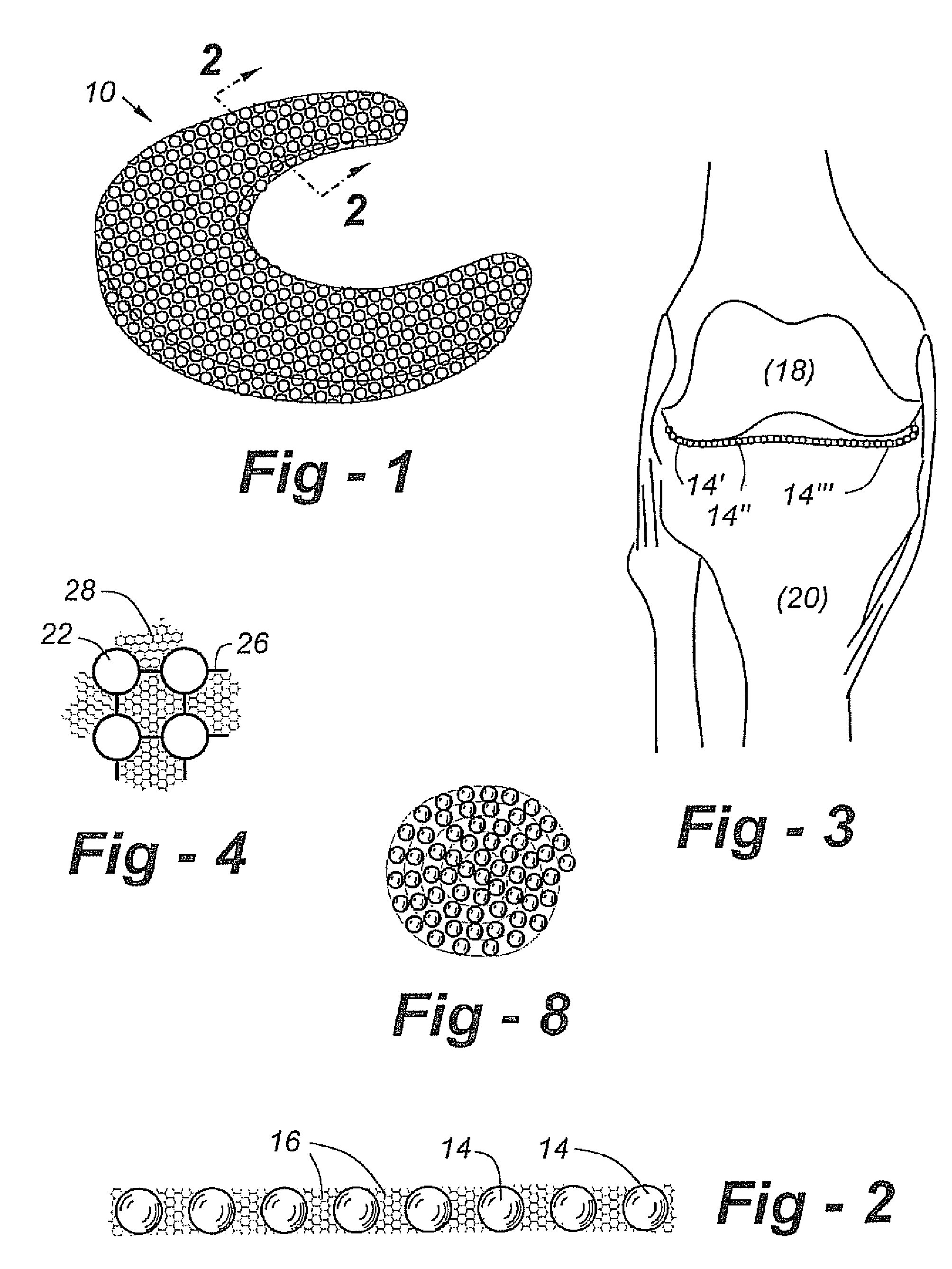
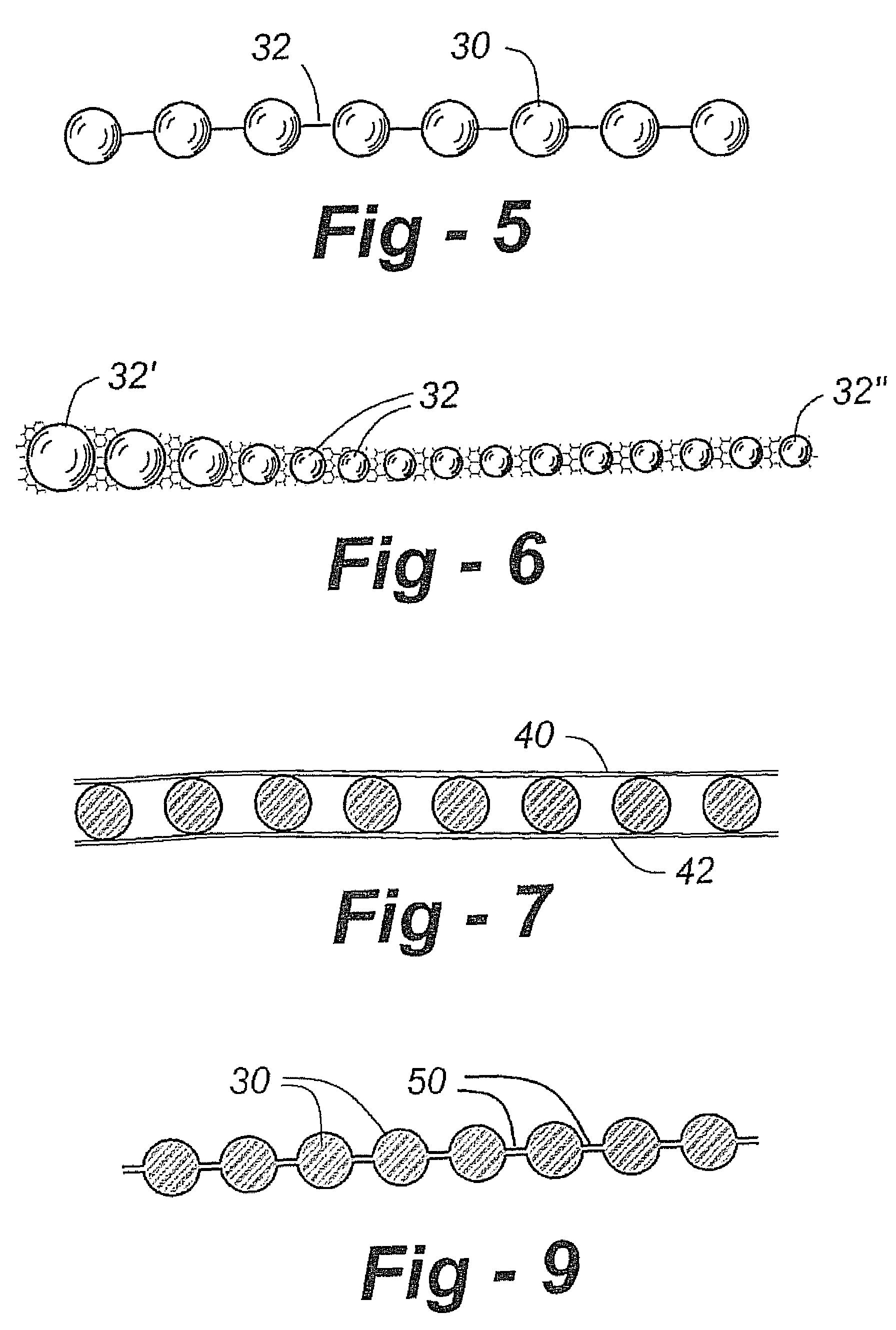
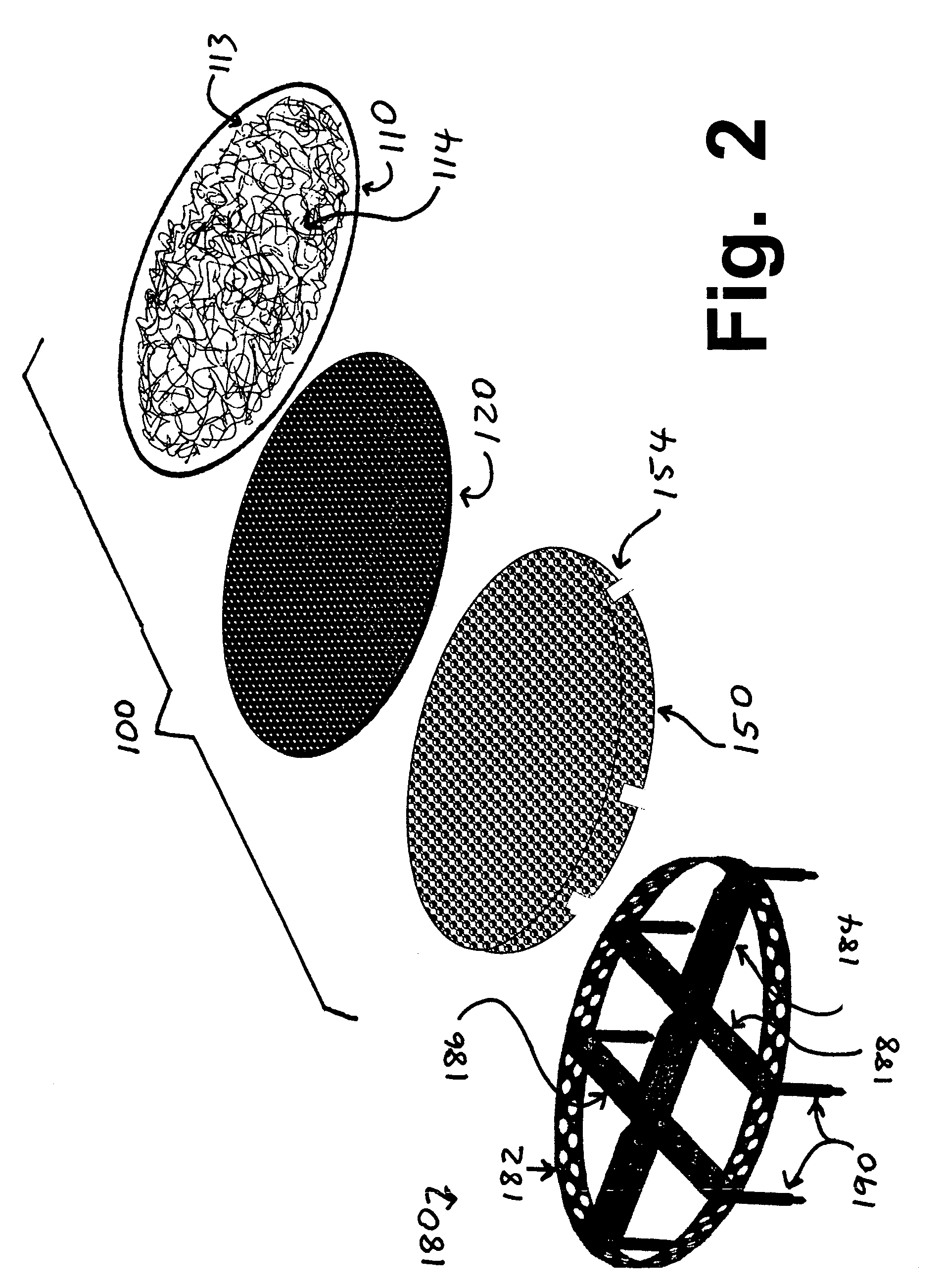
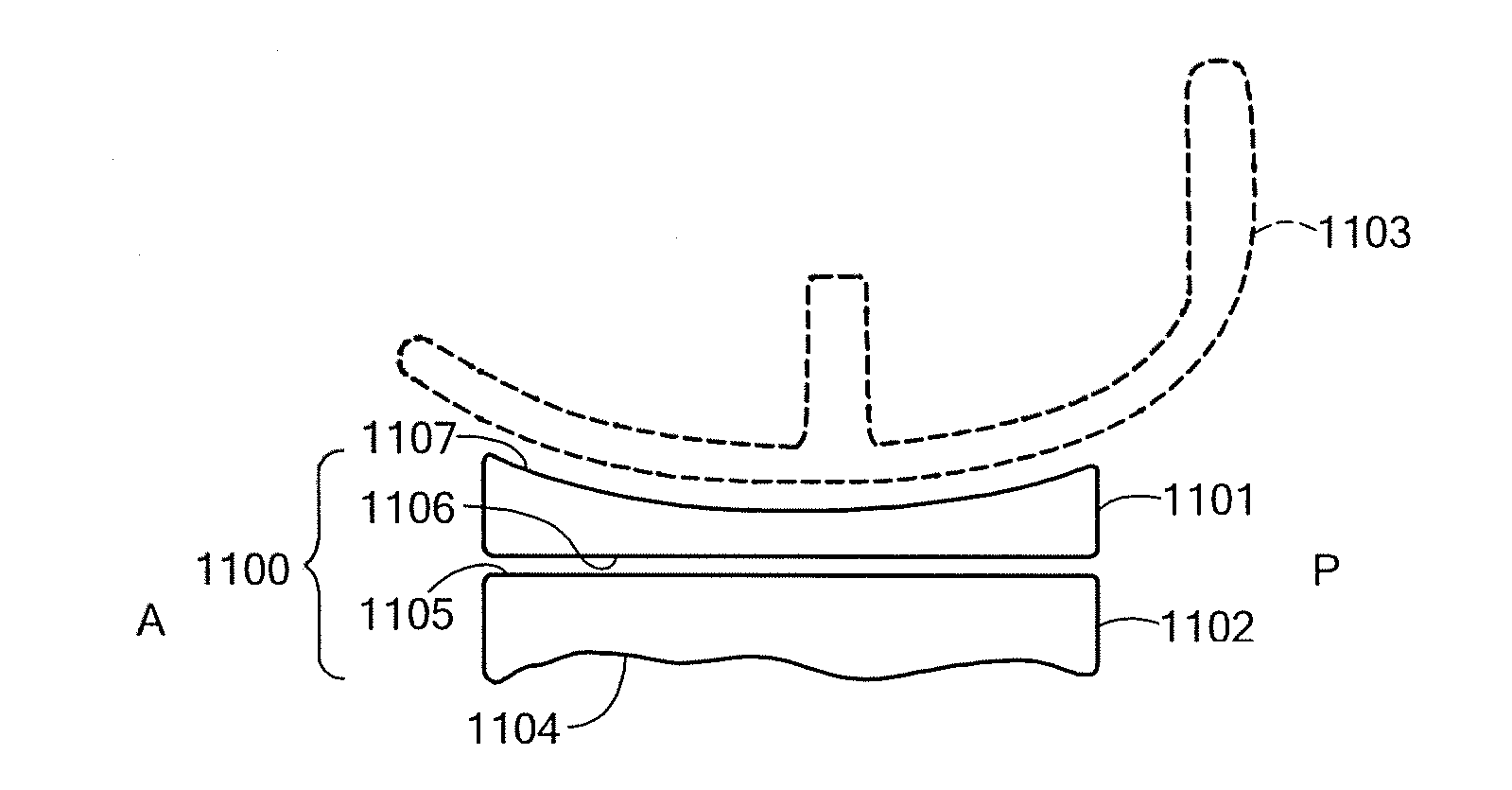
Prosthesis for replacement of cartilage
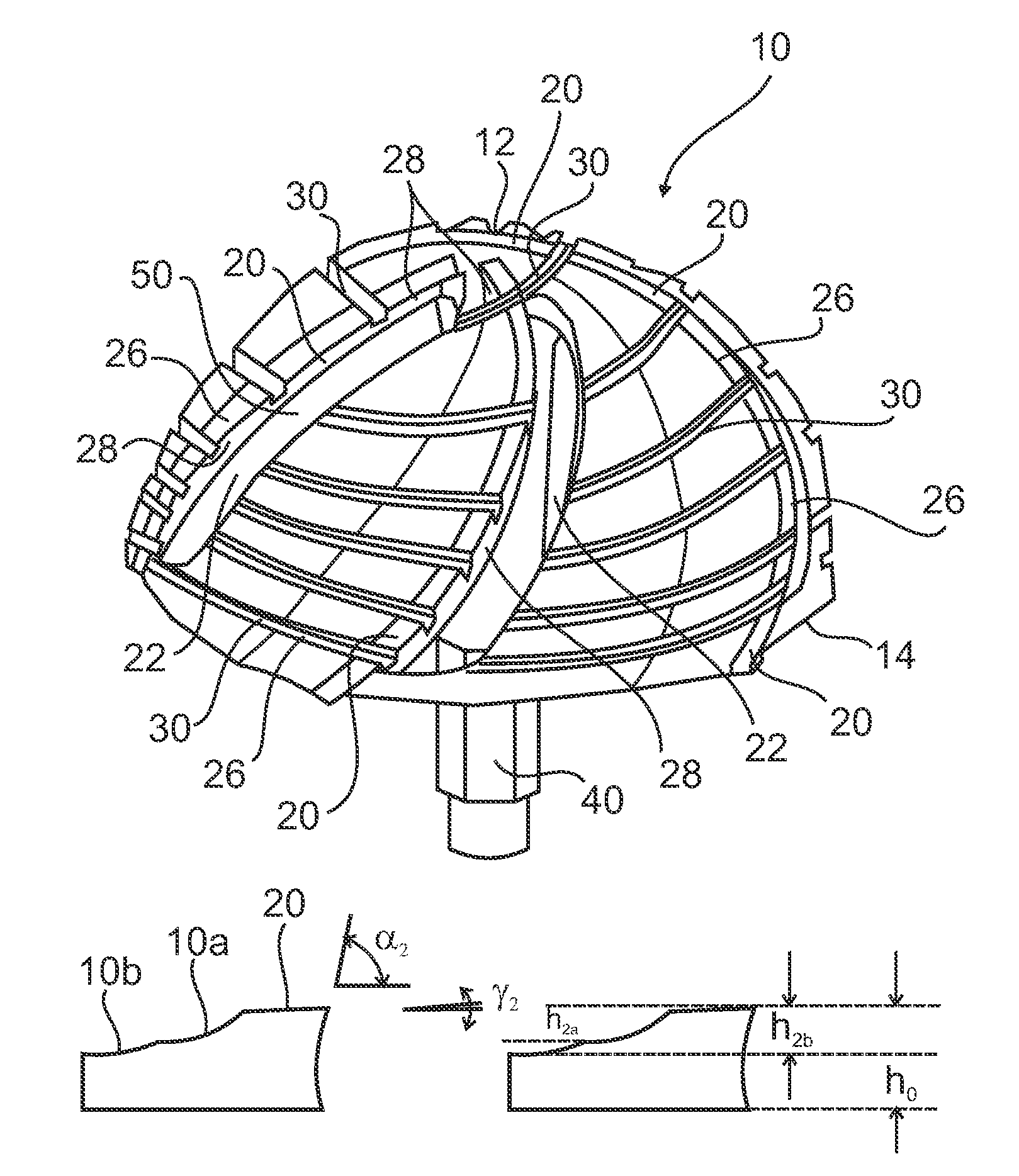
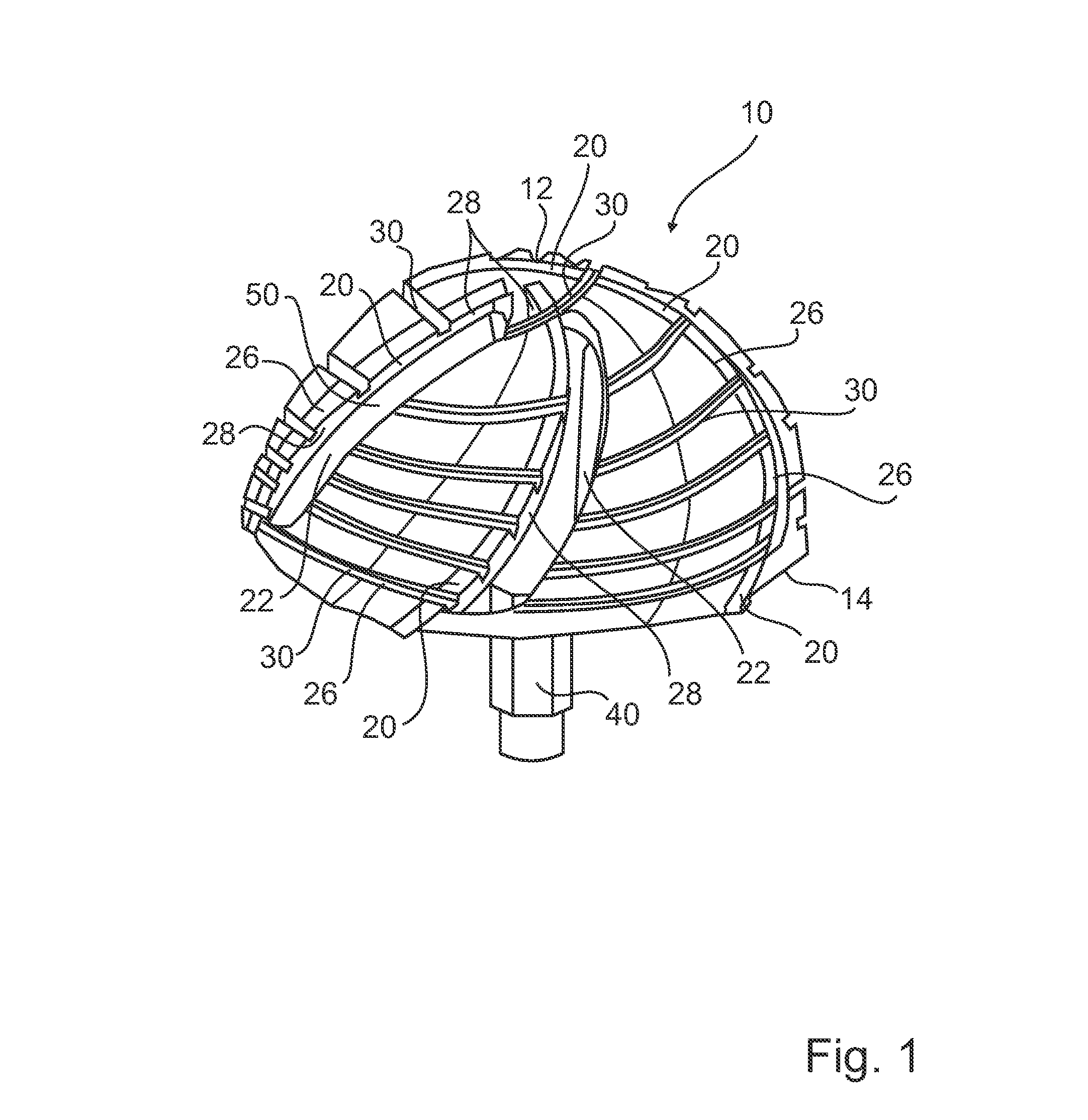
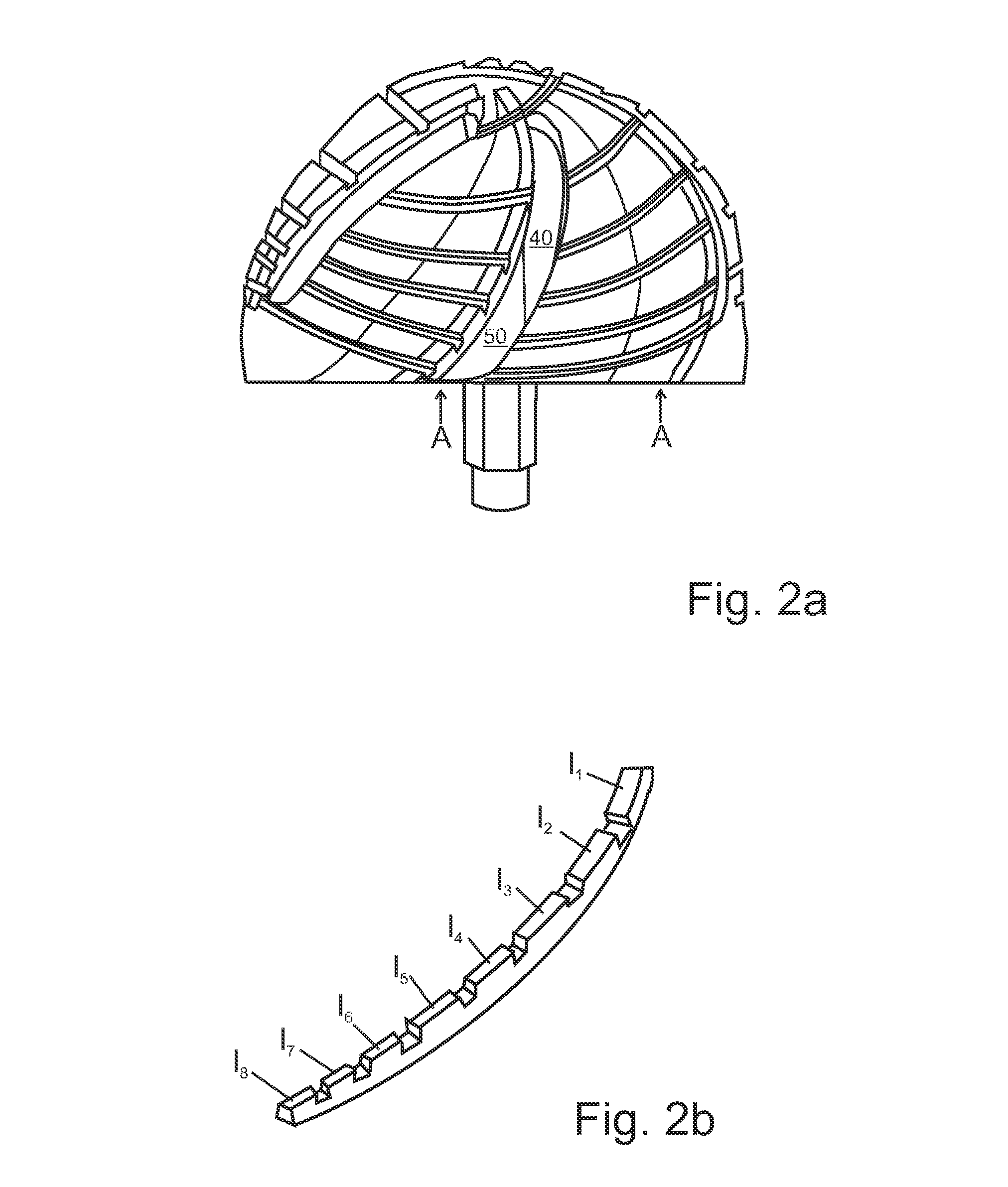
A cartilage replacement or repair prosthesis comprises a layer of streamlined elastomer elements, preferably in the form of spheres, supported in a matrix material so that the radially opposed surfaces of the spheres are positioned on opposite surfaces of the layer and make contact with the opposed surfaces of the femur and tibia and the forces exerted between these bones extend through the streamlined elements. The matrix material has a substantially lower resistance to deformation than the spheres to control the position of the spheres relative to one another without significantly restraining their load-responsive deformation under forces exerted between the femur and tibia. The layer, with its elastomeric inserts, is sufficiently thin and flexible to allow it to be rolled for arthroscopic insertion into a knee joint.
Owner:SUCCESSOR TRUSTEE OF THE EUGENE RIVIN LIVING TRUST +2
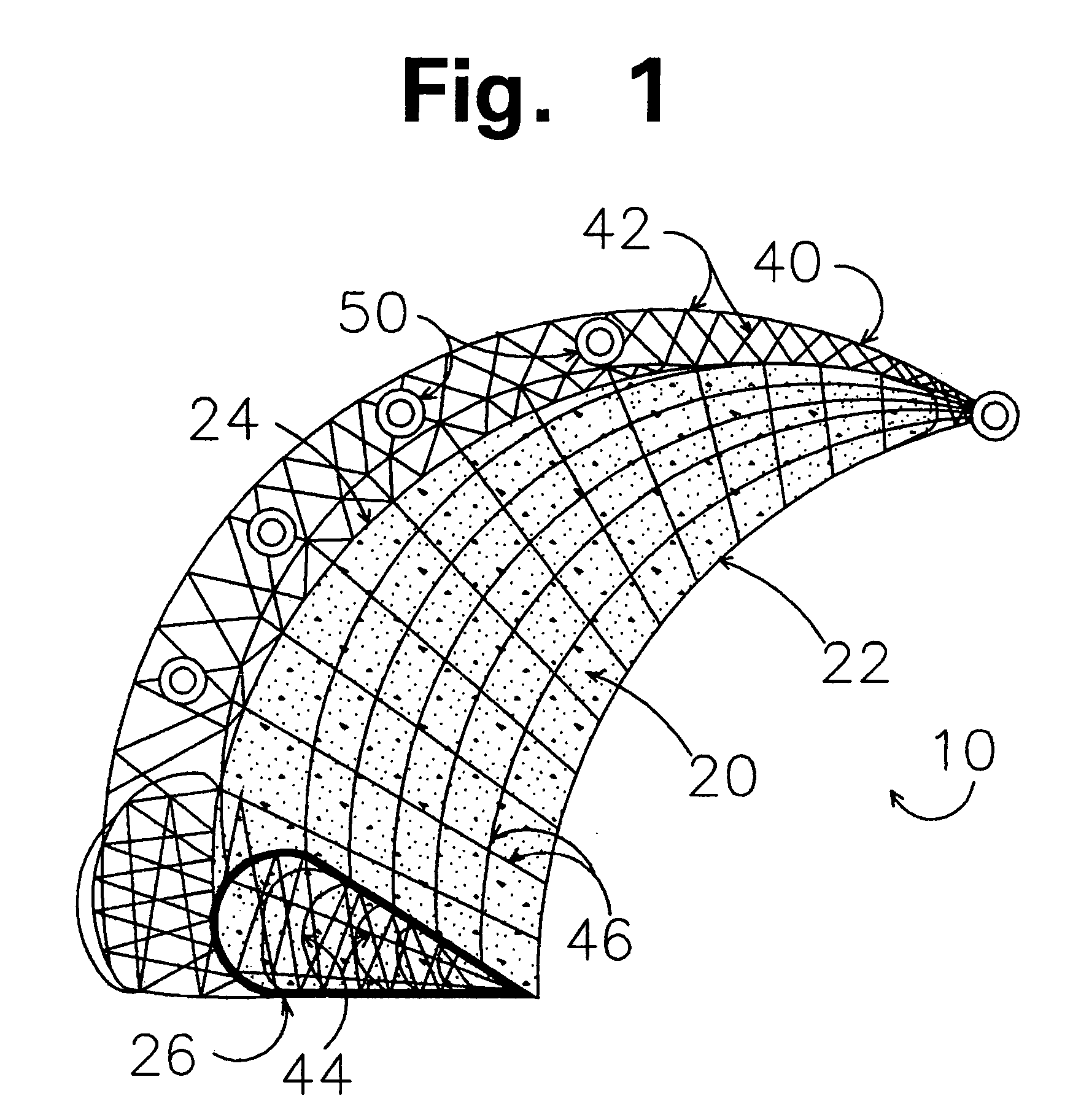
Implants for replacing cartilage, with negatively-charged hydrogel surfaces and flexible matrix reinforcement
ActiveUS9314339B2Strong and durableStrong and secure anchoringFinger jointsWrist jointsFiberChemical agent
A permanent non-resorbable implant allows surgical replacement of cartilage in articulating joints, using a hydrogel material (such as a synthetic polyacrylonitrile polymer) reinforced by a flexible fibrous matrix. Articulating hydrogel surface(s) are chemically treated to provide a negative electrical charge that emulates the negative charge of natural cartilage, and also can be treated with halogenating, cross-linking, or other chemical agents for greater strength. For meniscal-type implants, the reinforcing matrix can extend out from the peripheral rim of the hydrogel, to allow secure anchoring to soft tissue such as a joint capsule. For bone-anchored implants, a porous anchoring layer enables tissue ingrowth, and a non-planer perforated layer can provide a supportive interface between the hard anchoring material and the softer hydrogel material.
Owner:FORMAE
System and method for spinal fusion
The current invention is directed to a system and method for fusing two adjacent vertebrae. In one embodiment, the vertebrae are fused by inserting a self-broaching interbody apparatus into a disc space without the need for separately drilling and broaching. The self-broaching interbody apparatus may include cutting flutes or other broaching means capable of cutting through the cartilaginous endplates of the vertebrae. In another embodiment, an interbody apparatus with an expanding means capable of distracting the disc space between the adjacent vertebrae is inserted into the disc space. Another embodiment includes a sleeve that fits around an interbody apparatus that has at least one opening in its outer surface leading to a cavity filled with bone and / or ortho-biological materials.
Owner:AEOLIN
Joint Arthroplasty Devices
A mobile bearing implant includes a first component. The first component includes a bone facing surface for engaging one of a substantially uncut articular cartilage surface and a substantially uncut subchondral bone surface. The bone facing surface substantially matches the one of the articular cartilage surface and the subchondral bone surface. The mobile bearing implant further includes an external surface. A bearing component has a first surface for slidingly engaging the external surface of the first component, and a second surface for engaging at least one of a second component, bone, and cartilage.
Owner:CONFORMIS
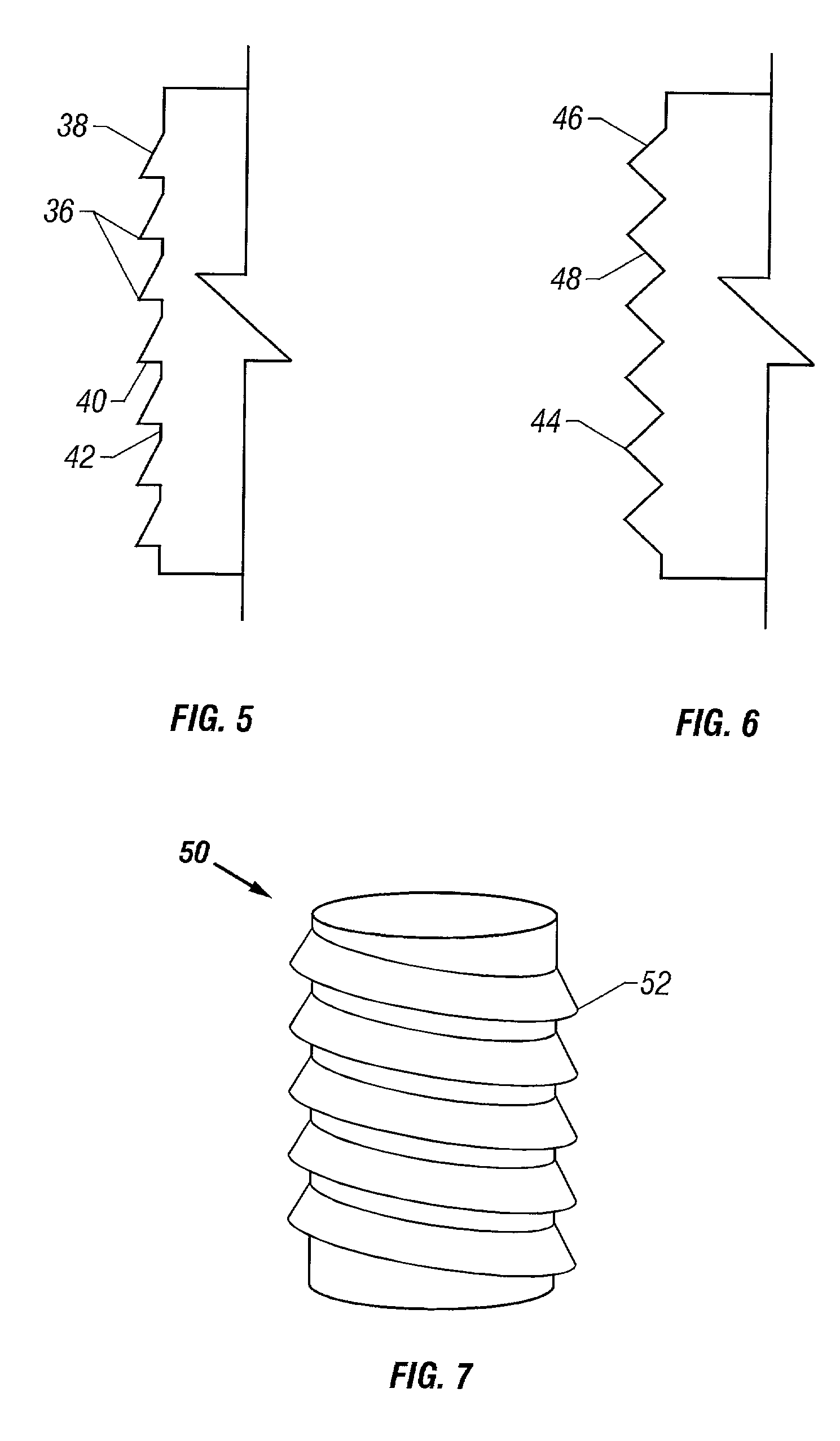
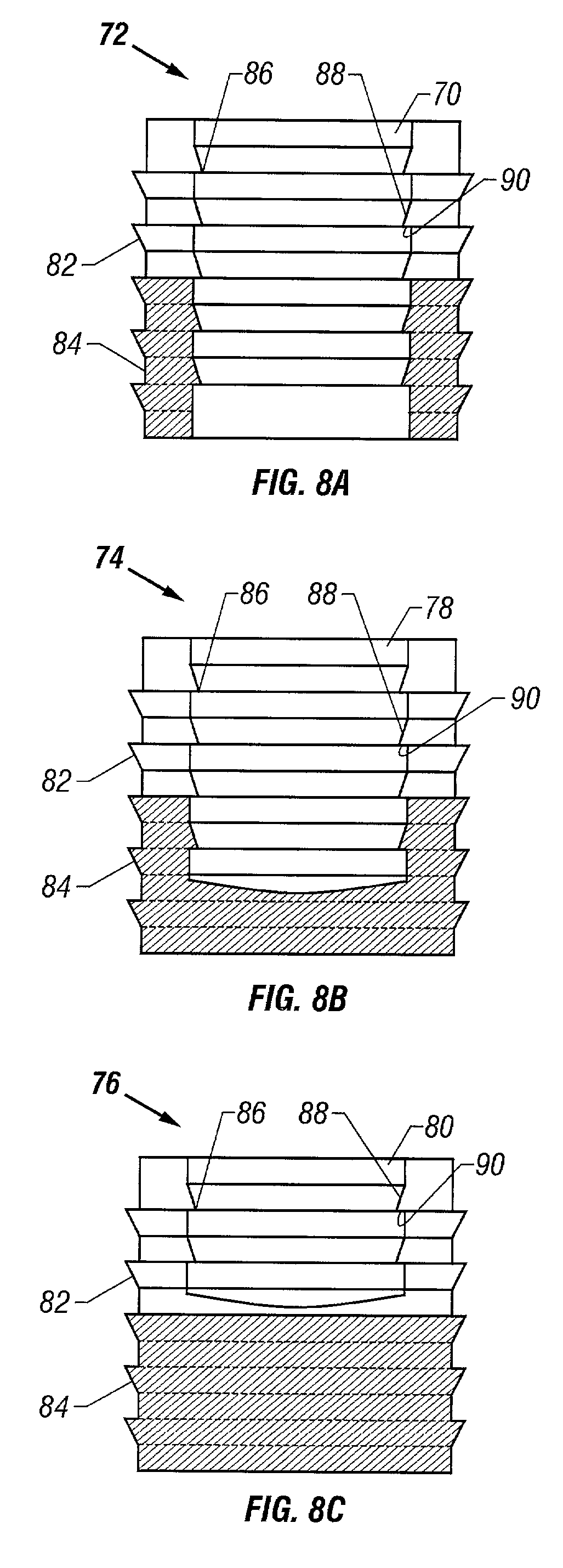
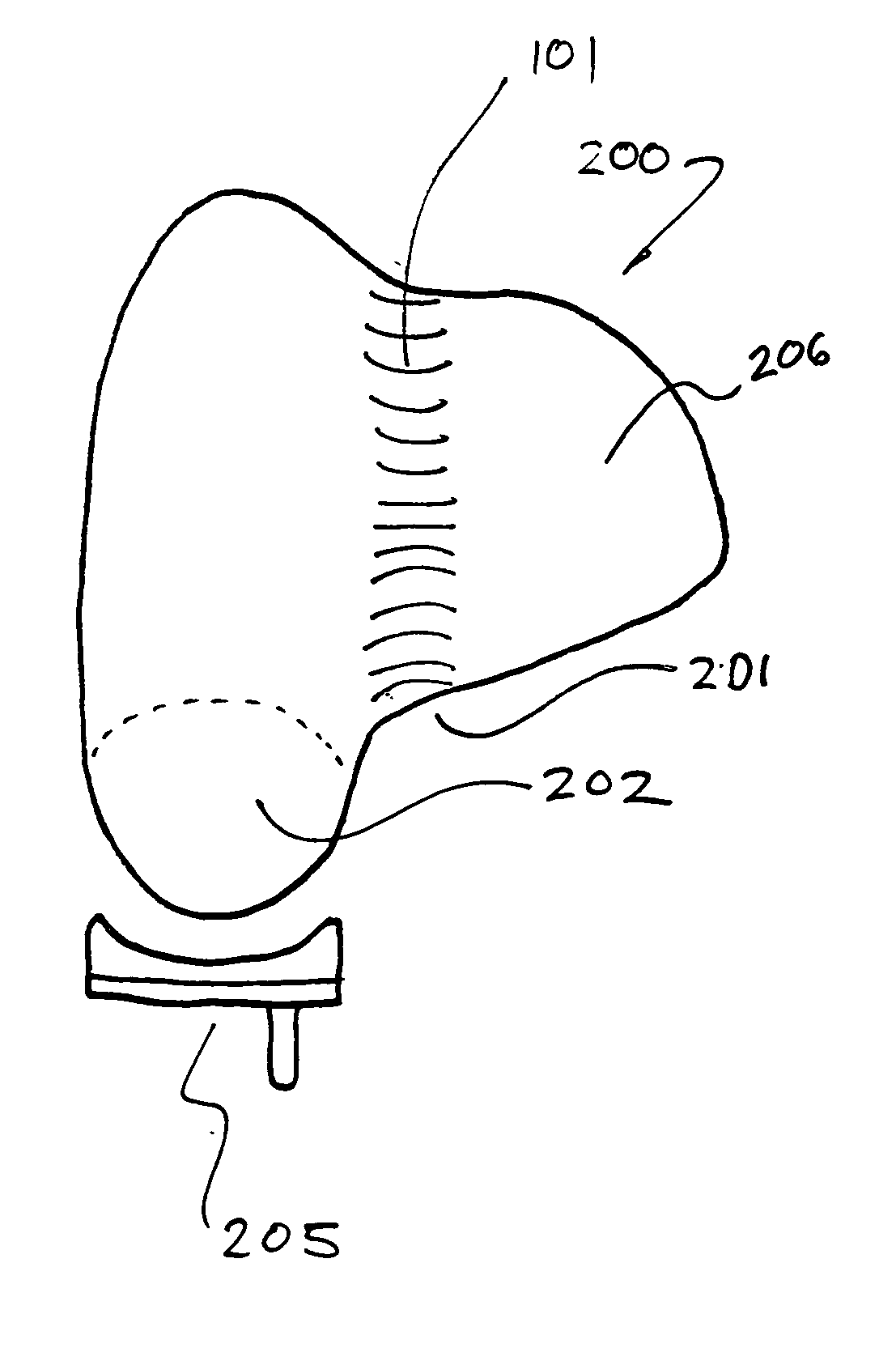
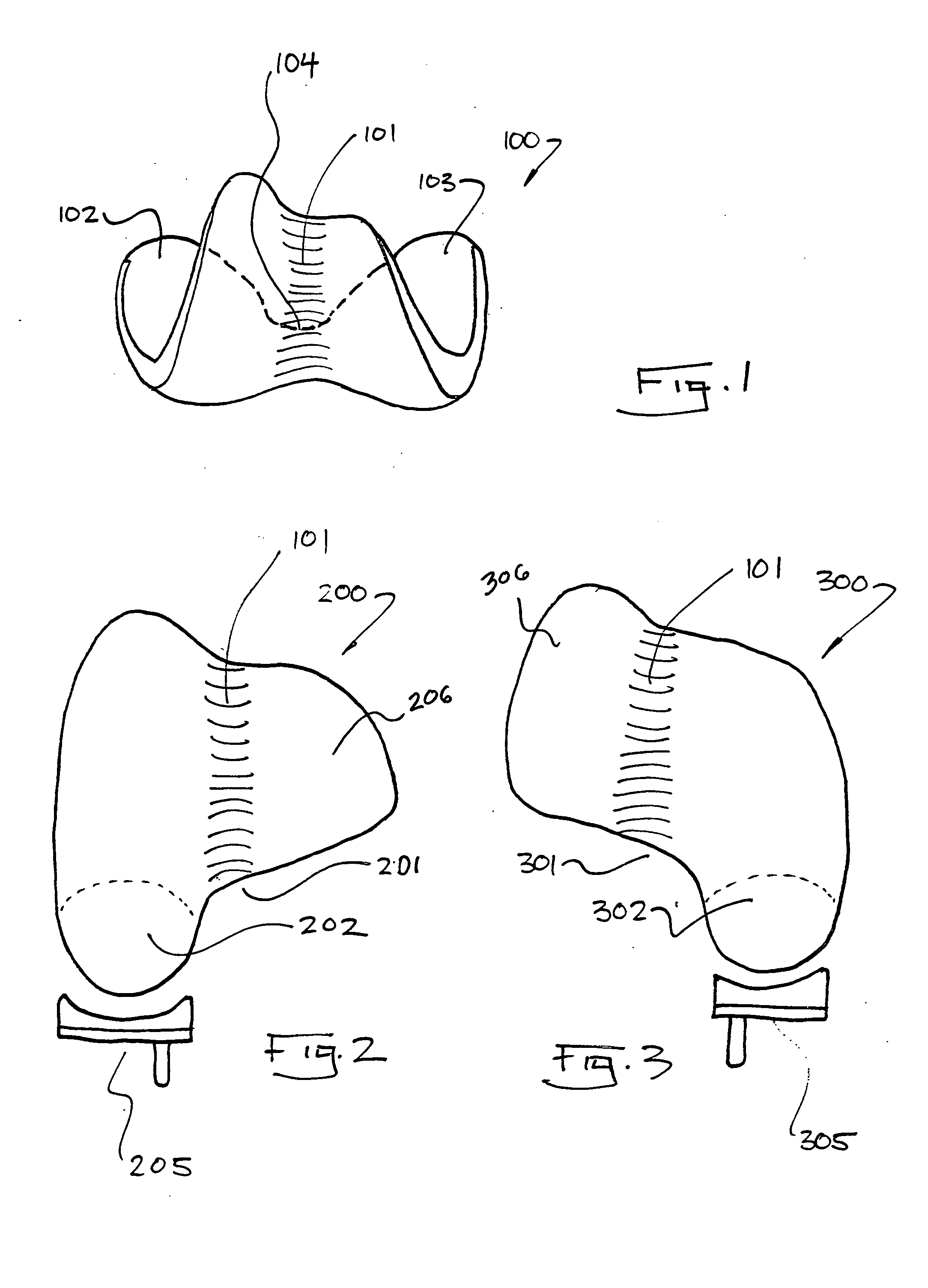
Cartilage repair plug
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prefabricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. A plurality of anchoring elements may share a single upper layer.
Owner:ABS
Apparatus and method for the treatment of tissue with ultrasound energy by direct contact
Apparatus and method for the treatment of tissue, such as hard and soft tissues, wounds, tumors, muscles, and cartilage, through the direct contact of ultrasound energy is disclosed. Ultrasound energy is delivered to a target area through direct contact with an ultrasound tip. Ultrasound energy is also delivered through direct contact with a coupling medium. The ultrasound tip is specially designed to comprise of a cavity area for controlled fragmentation and the simultaneous sonication of a target area. The specially designed ultrasound tip allows for ultrasound energy to focus on a target area. The ultrasound apparatus may be moved in a variety of different directions during the treatment of tissue.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
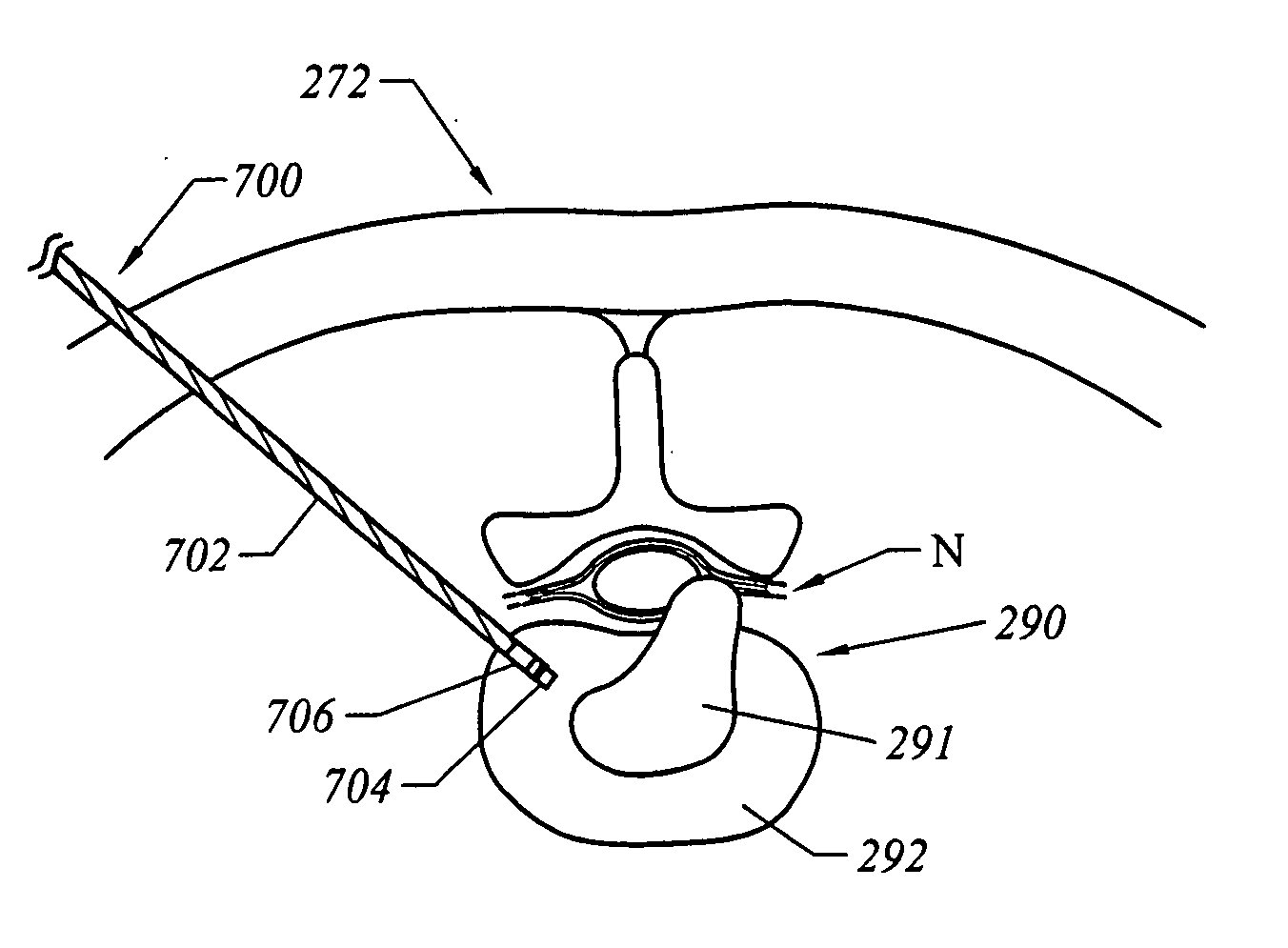
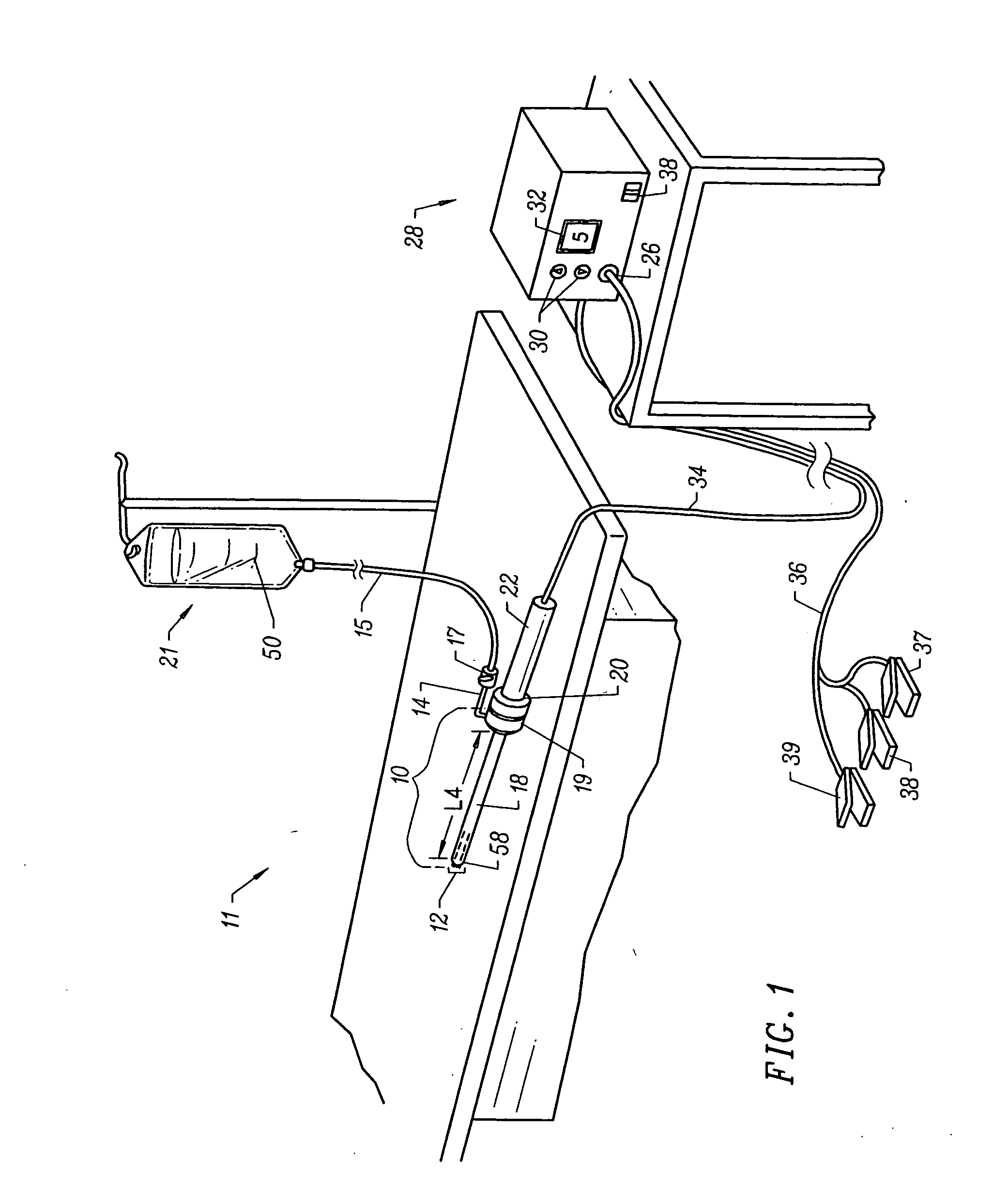
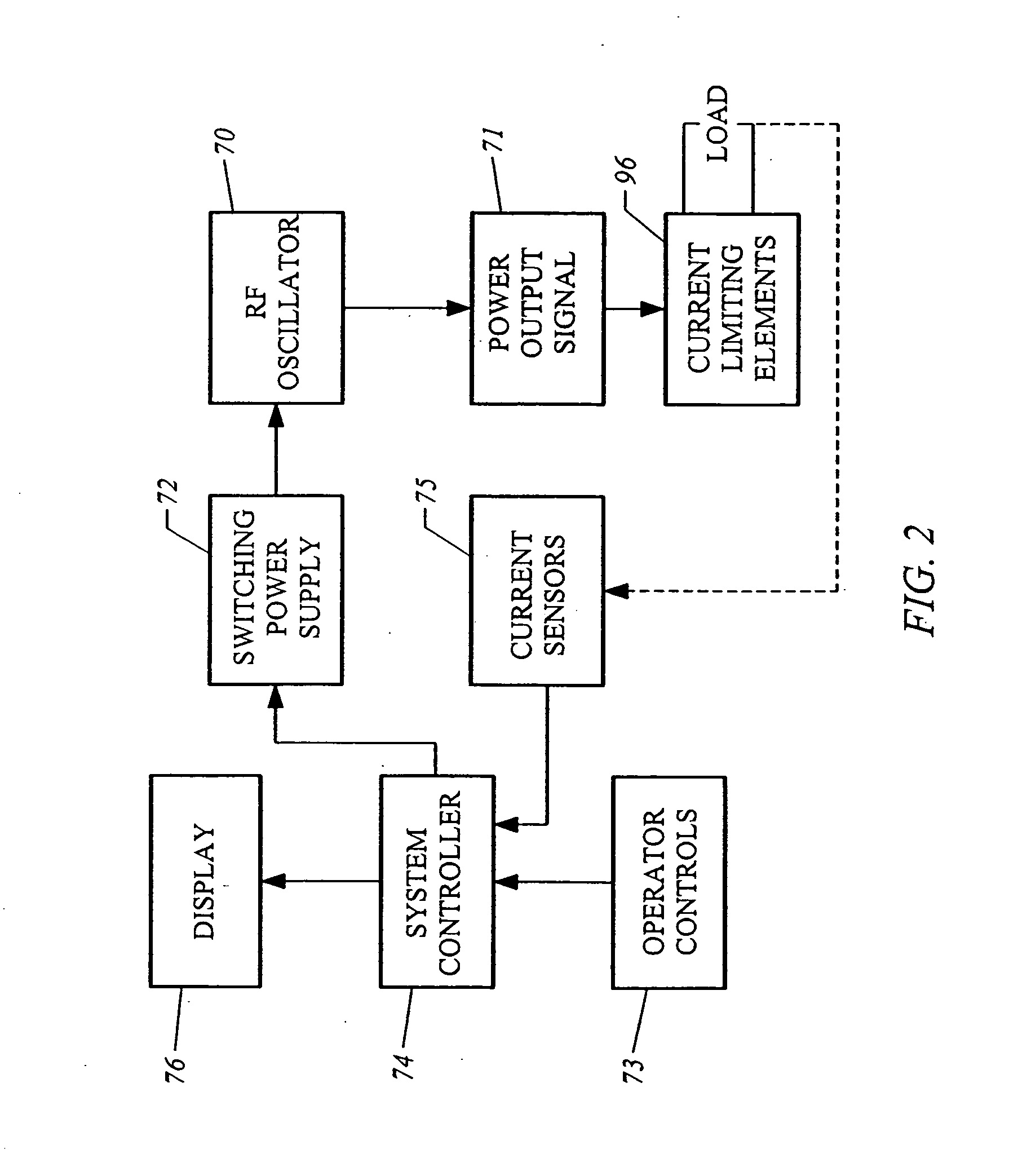
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20050004634A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesThermal energySpinal ligaments
Systems, apparatus, and methods for treating spinal tissue and other body structures in open and endoscopic spine surgery to relieve symptoms, such as neck or back pain. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the controlled heating of various tissues in or around the vertebral column, including various interspinous tissues, such that spinal ligaments and cartilage surrounding the vertebrae and the facet joints are shrunk or tightened to stabilize the vertebral column of a patient. Thermal energy is applied to the target tissue in a subablation mode of an electrosurgical system to cause shrinkage of the tissue, thereby stiffening the interspinous tissue and stabilizing the vertebral column. In an exemplary embodiment, a high frequency RF voltage can be applied between one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to heat a target interspinous tissue to within a temperature range at which irreversible shrinkage of the tissue occurs.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
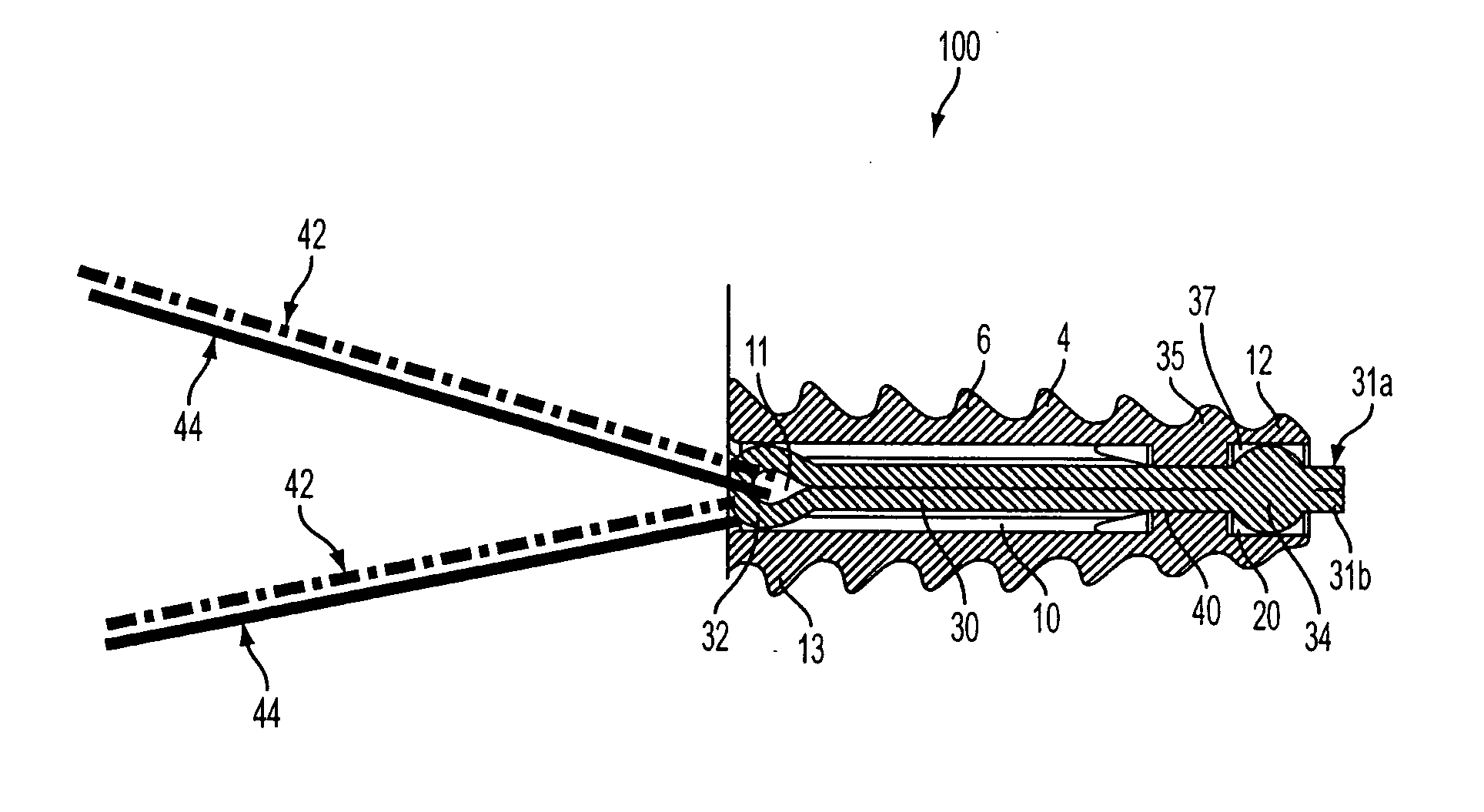
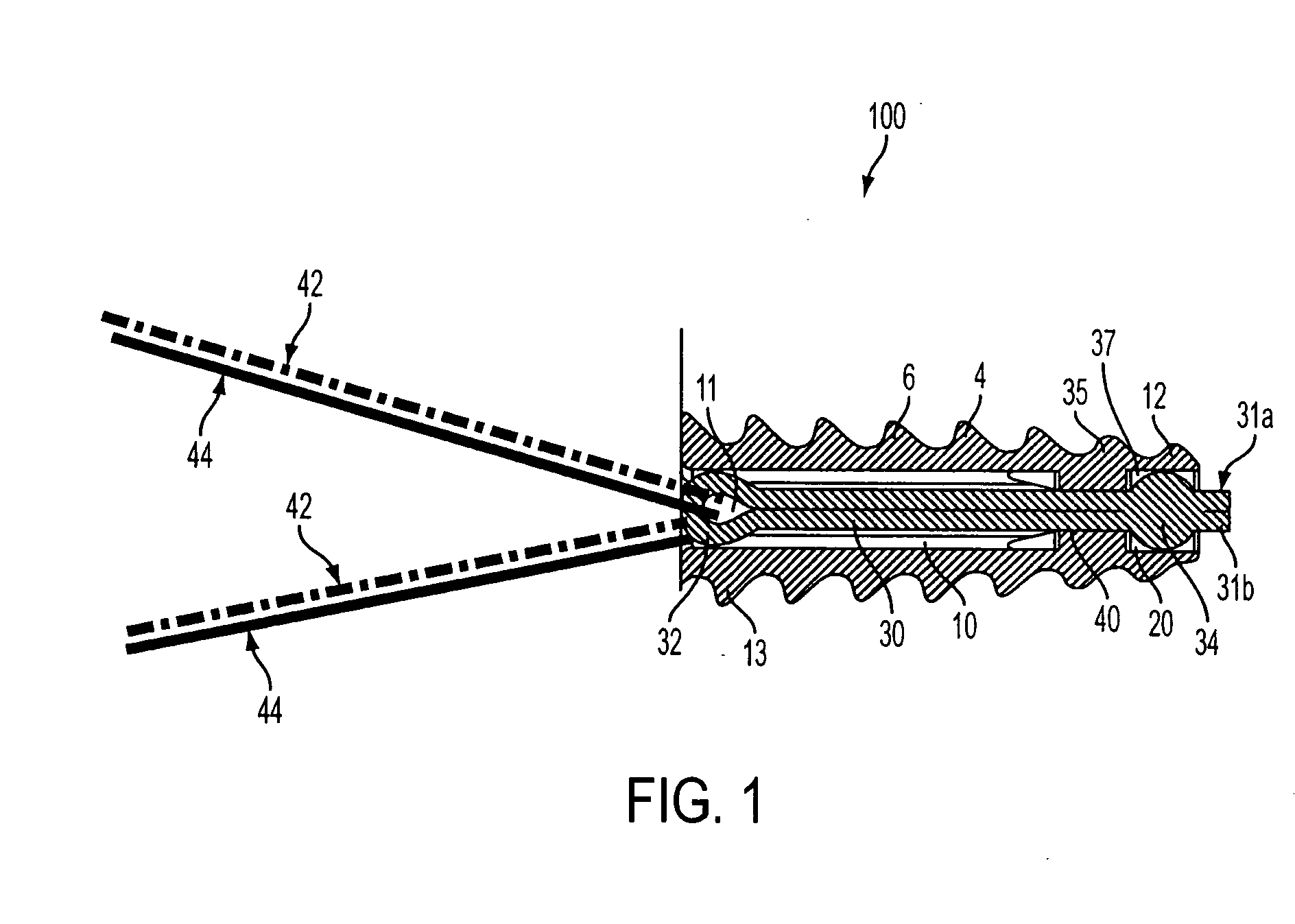
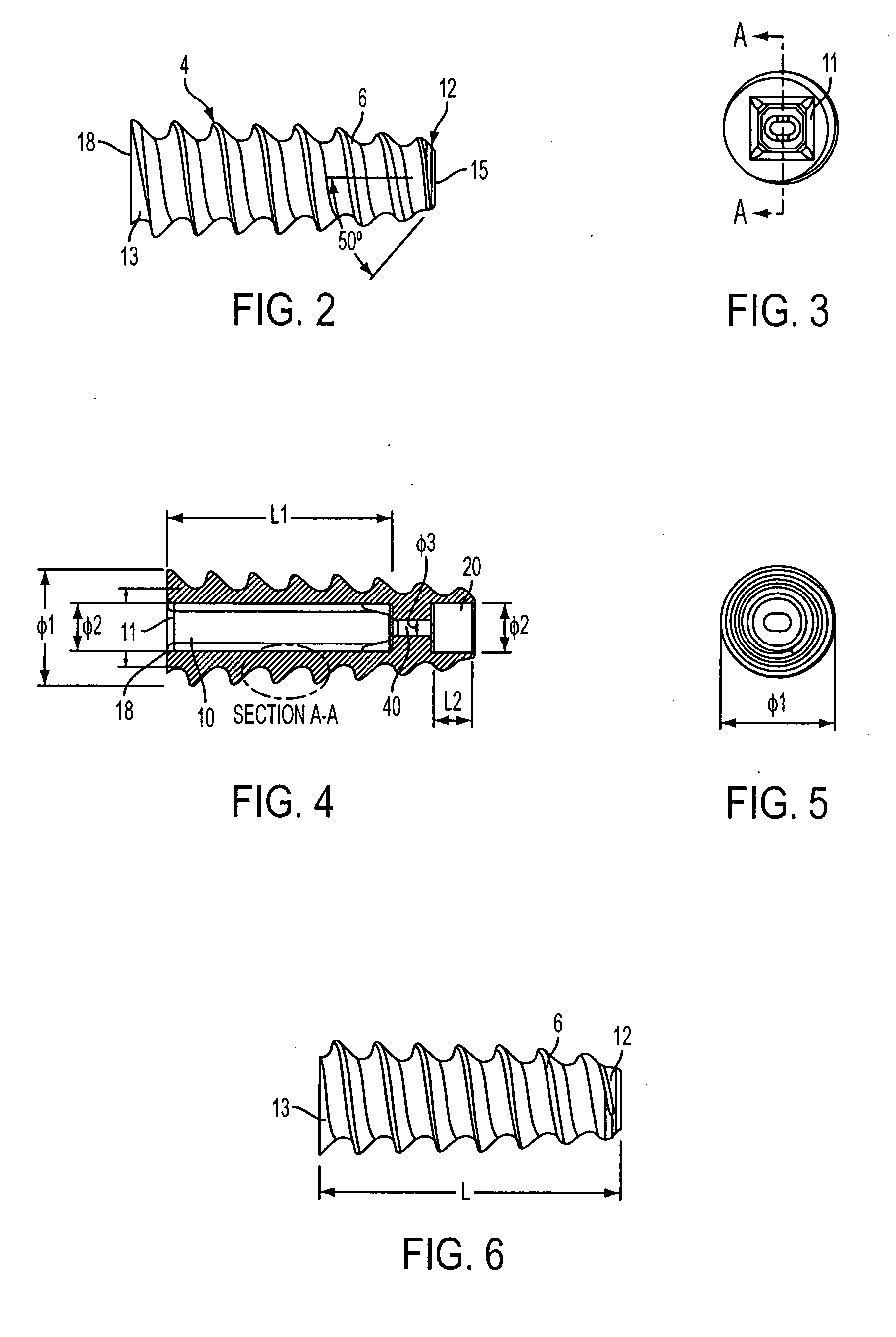
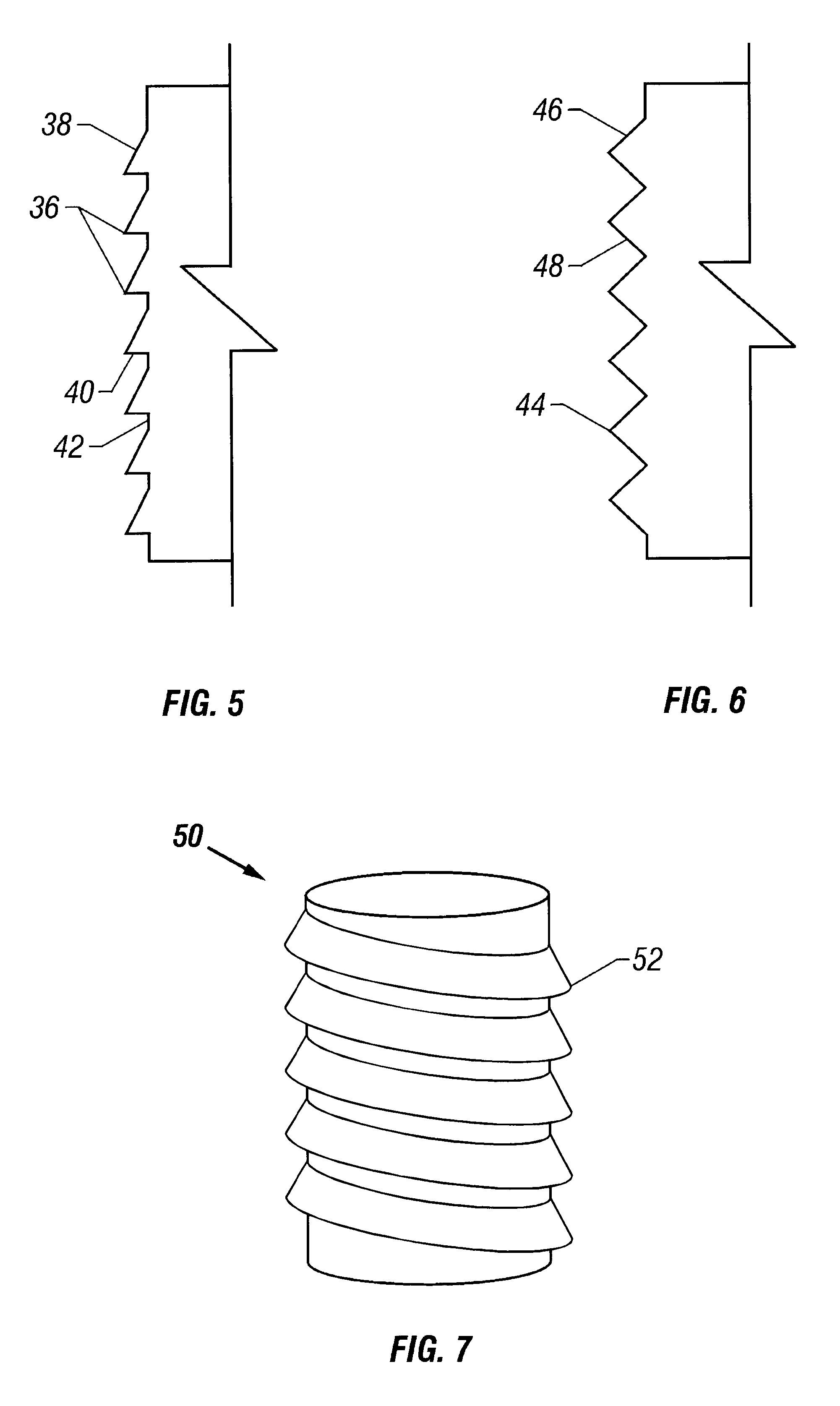
Fully-threaded bioabsorbable suture anchor
ActiveUS20070060922A1Minimal frictionIncreased pull-out strengthSuture equipmentsLigamentsPullout strengthUltimate tensile strength
A suture anchor includes a threaded anchor body having a first central bore in communication with a second central bore. The suture anchor includes an internal eyelet formed of a loop disposed at least partially inside the first central bore. The ends extending from the loop are tied together to form at least one knot which is housed in the second central bore provided at the distal end of the anchor body. The knot increases the pullout strength of the suture even in soft bone, provides increased suture fixation, and eliminates the anchor “pull back.”
Owner:ARTHREX
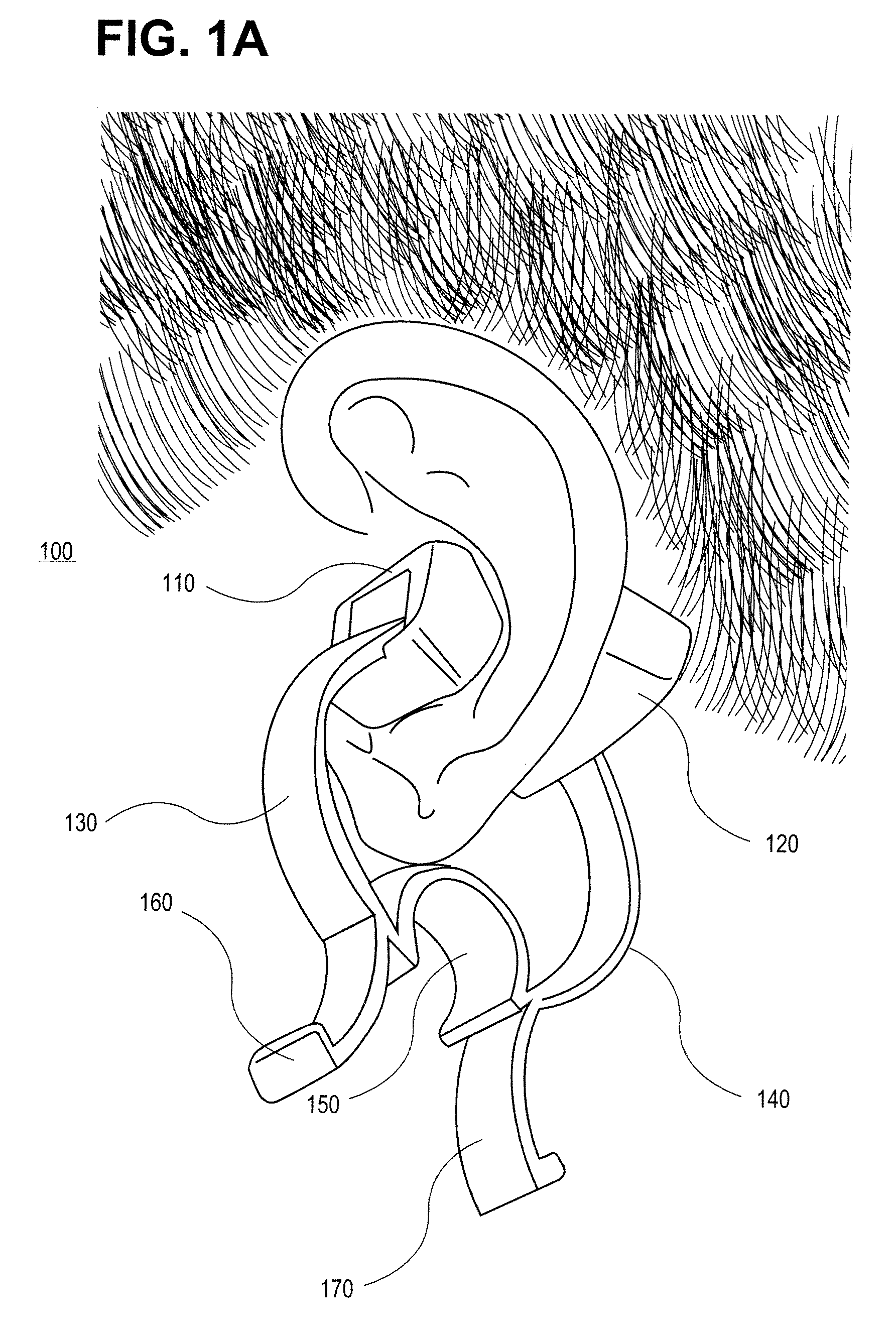
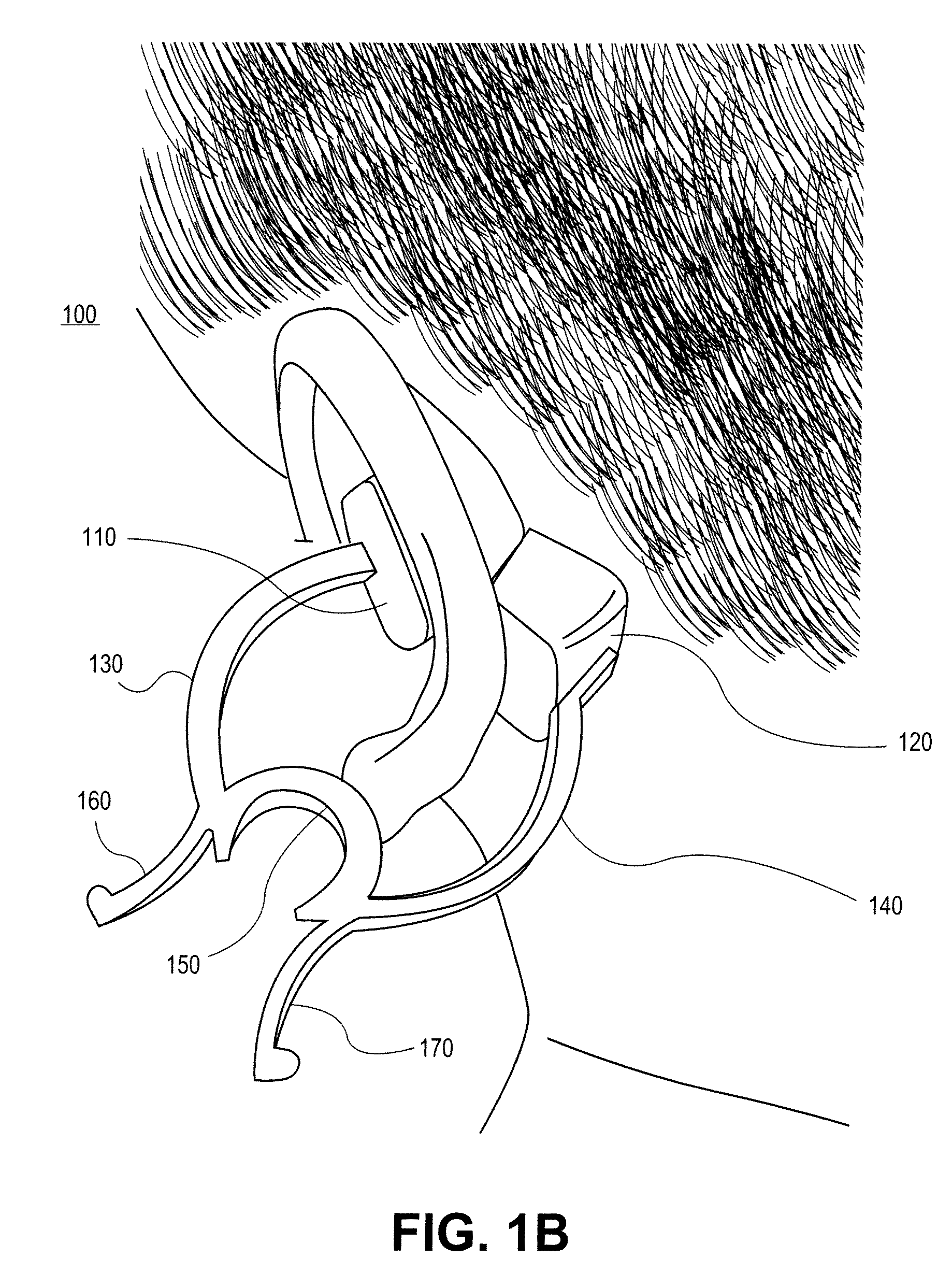
External ear-placed non-invasive physiological sensor
ActiveUS20090275813A1Lower latencyFast trackDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsExternal earsMedicine
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
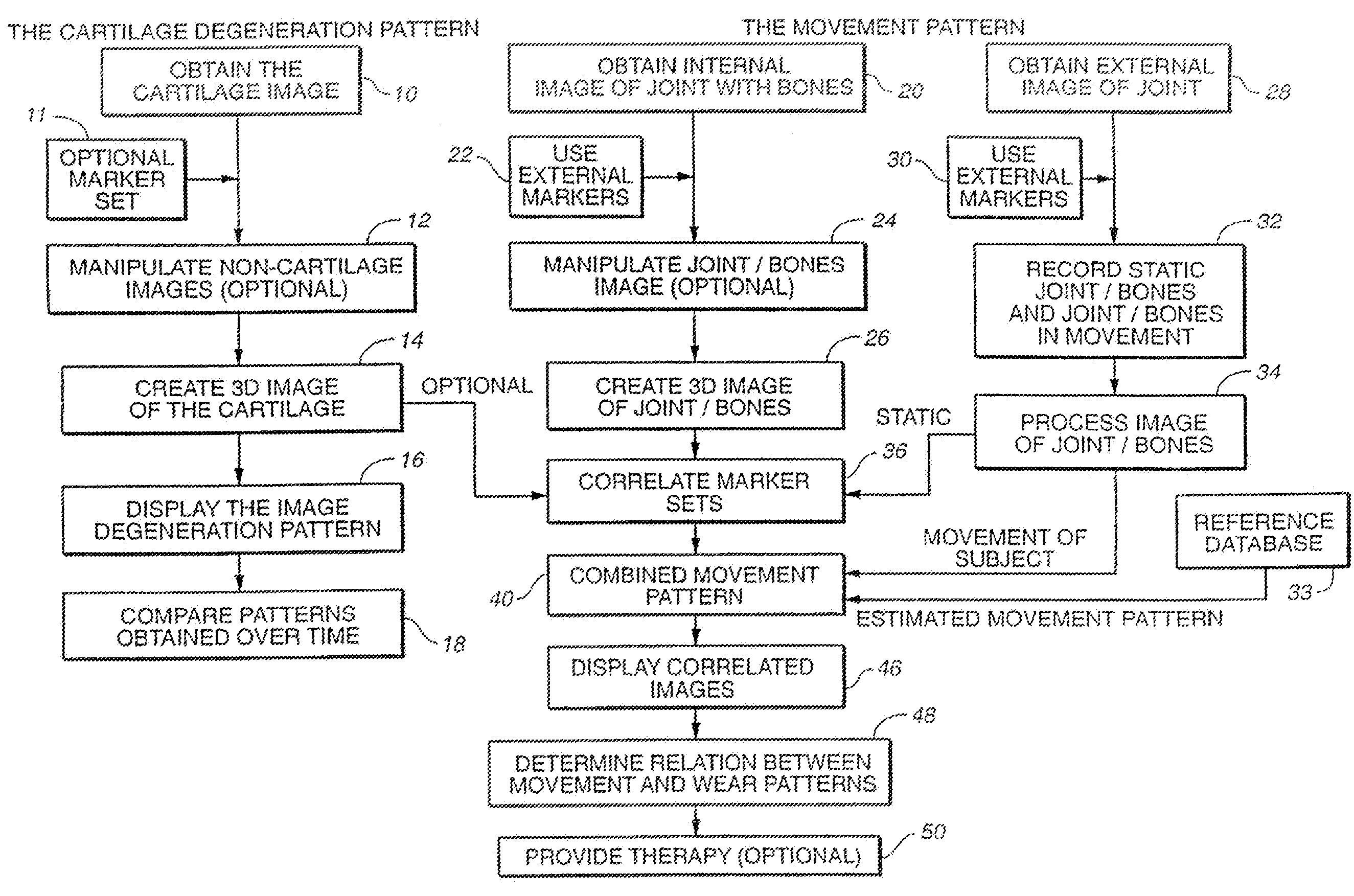
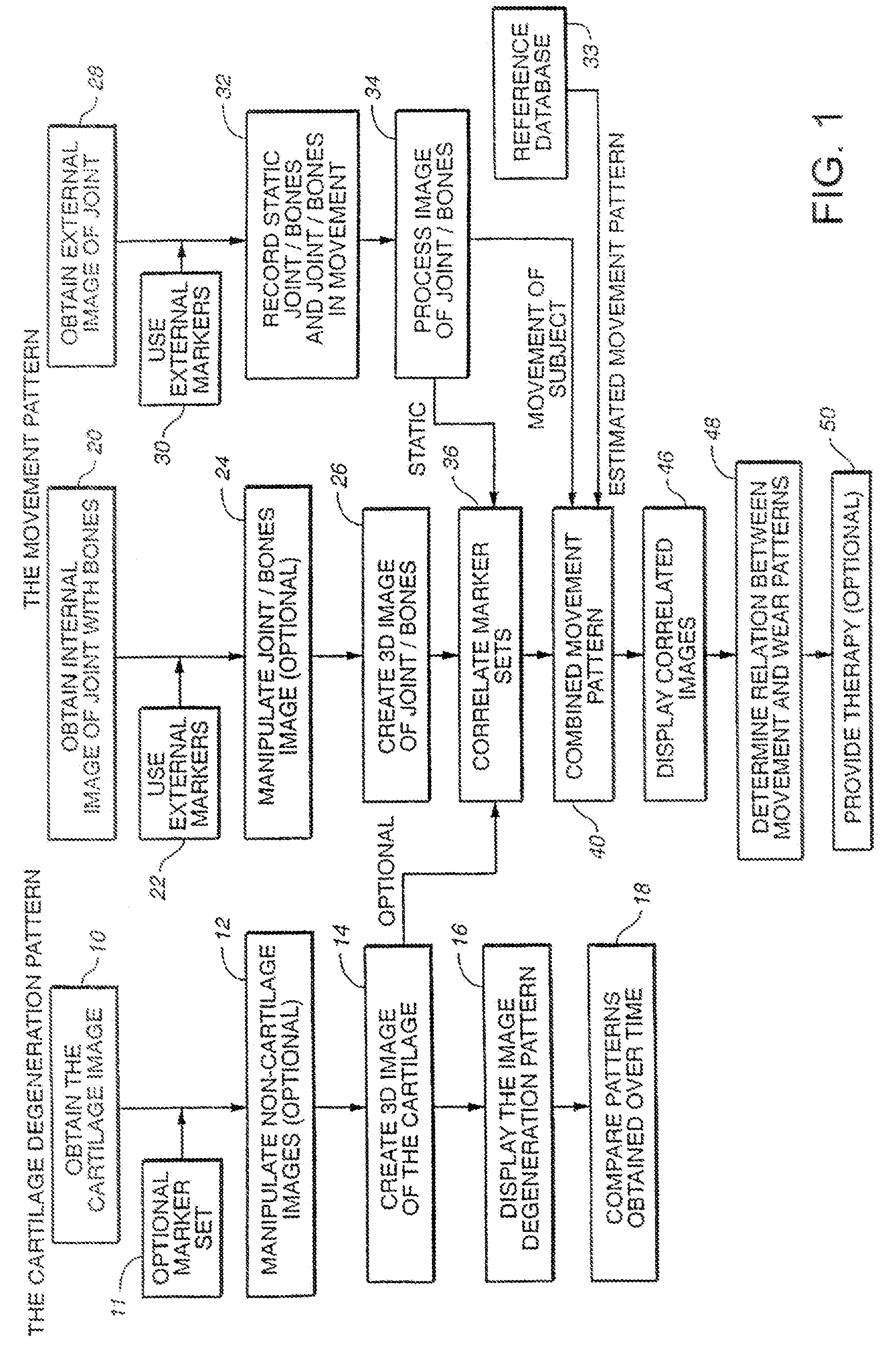
Joint and Cartilage Diagnosis, Assessment and Modeling
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
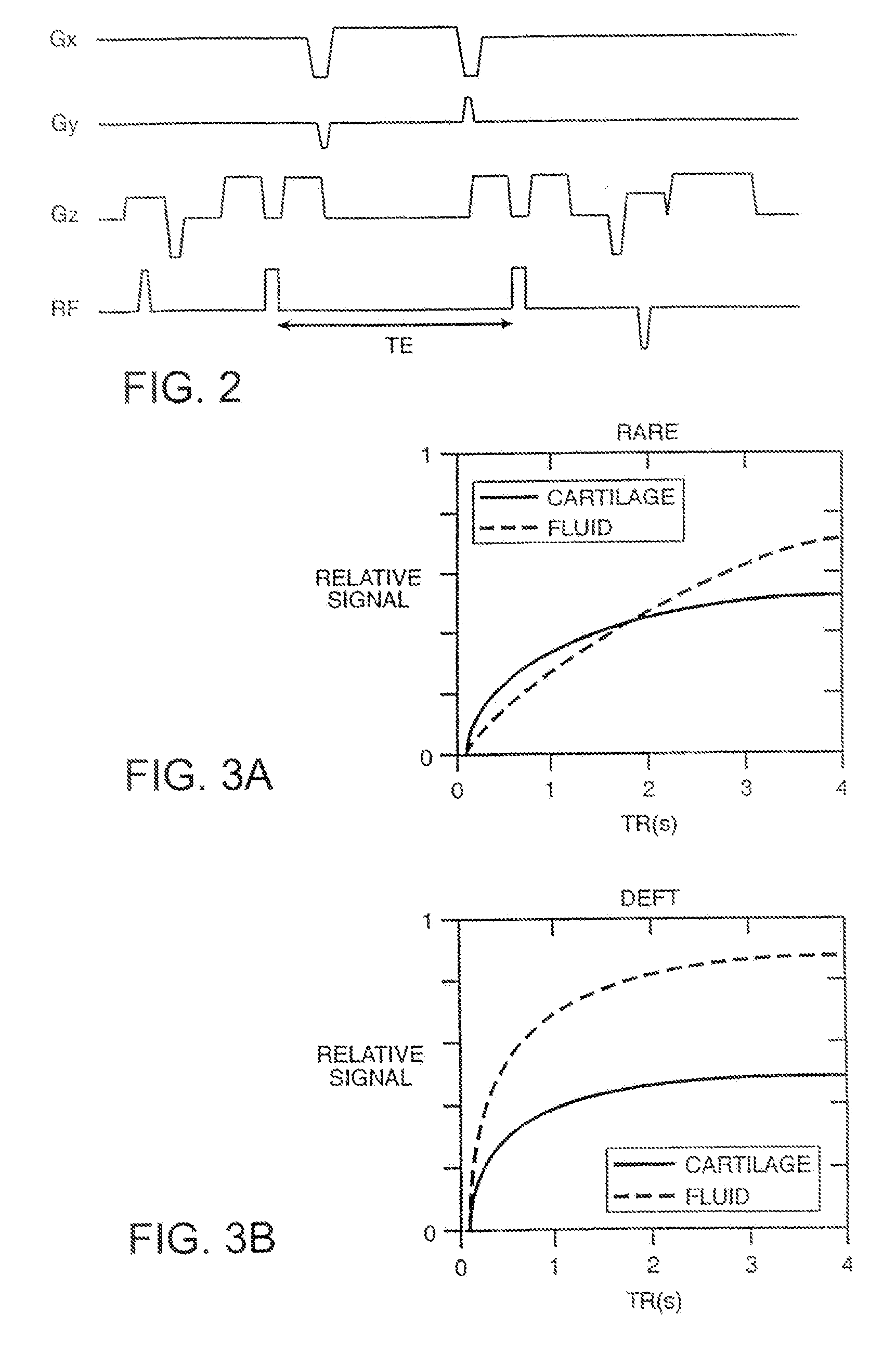
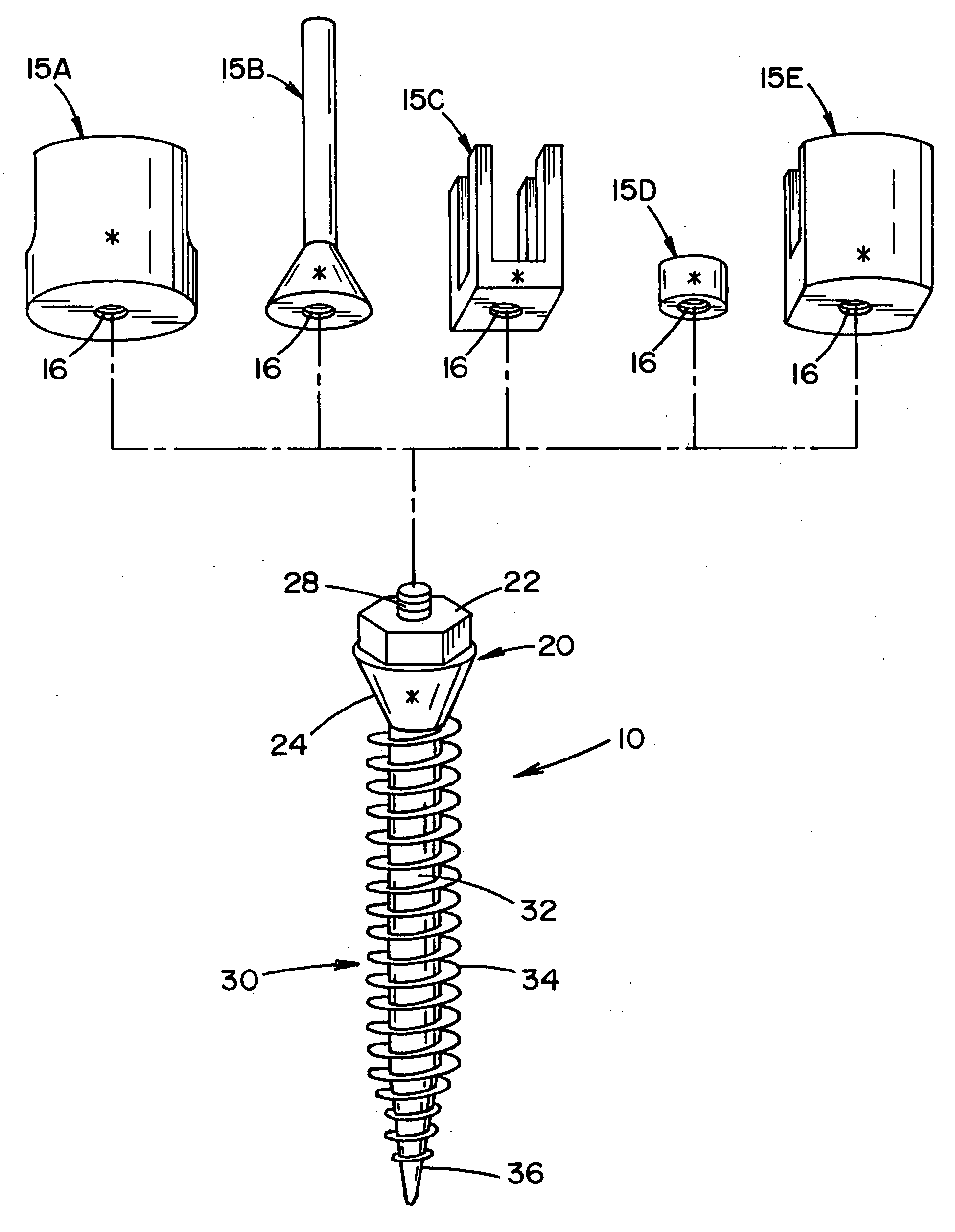
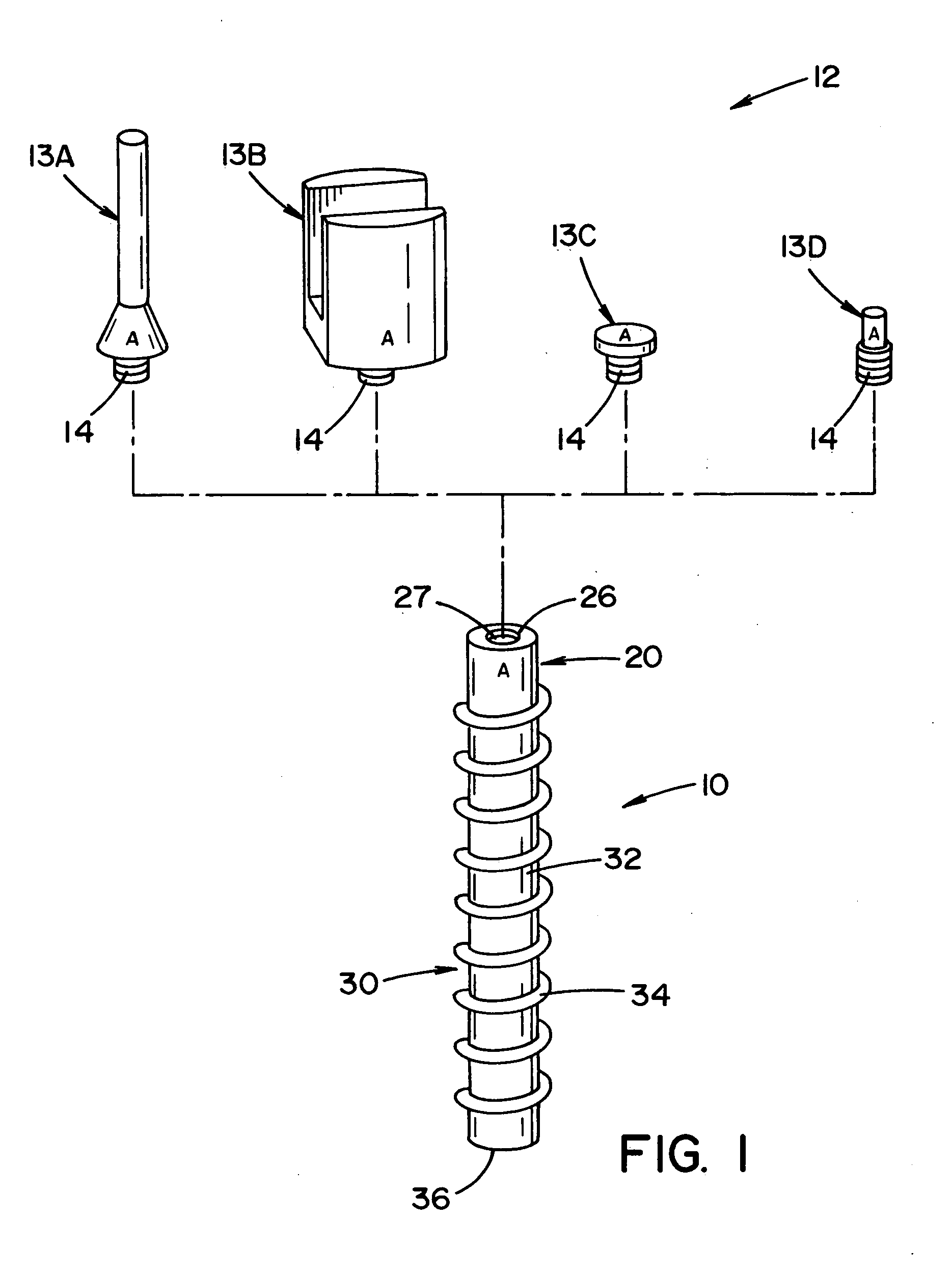
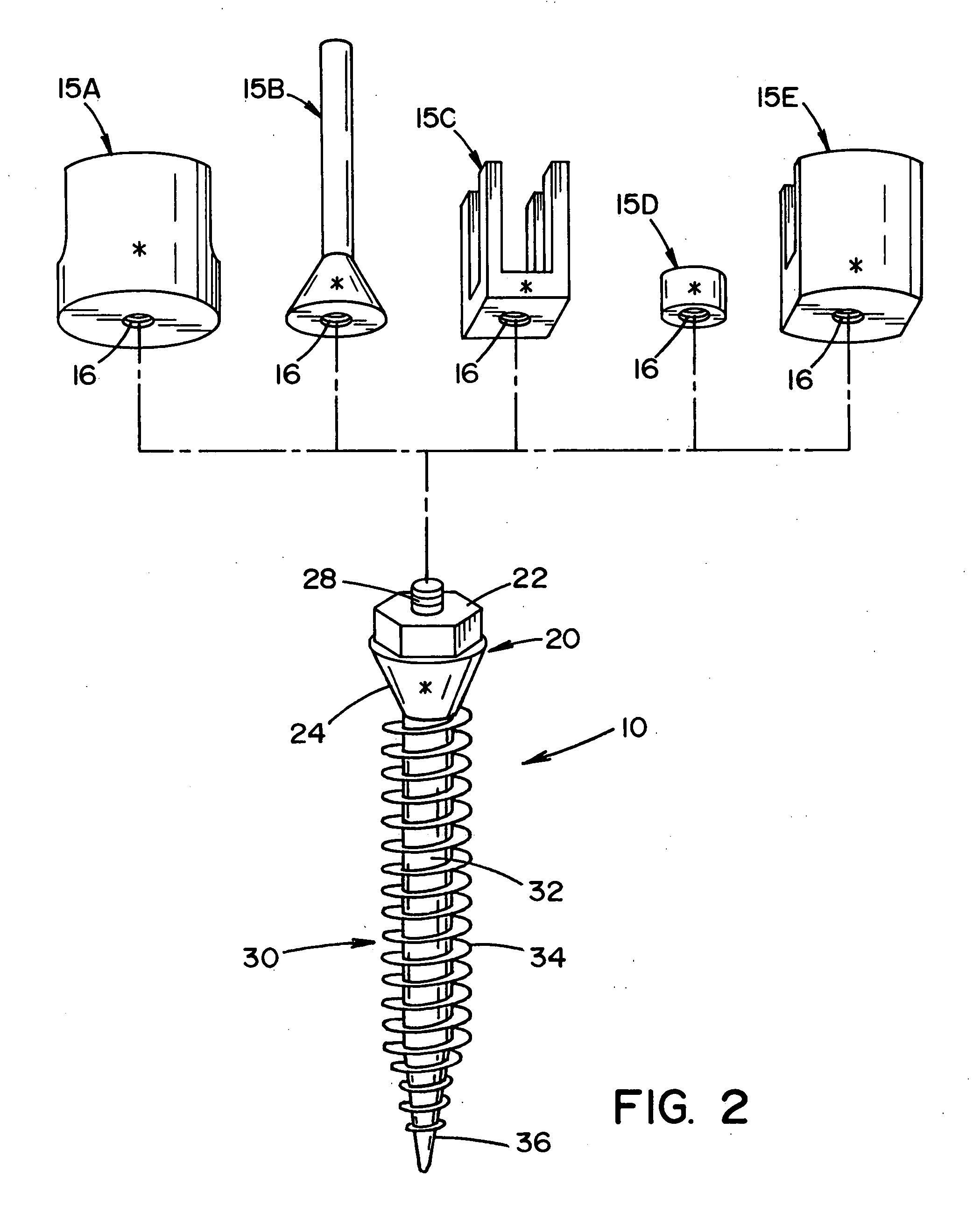
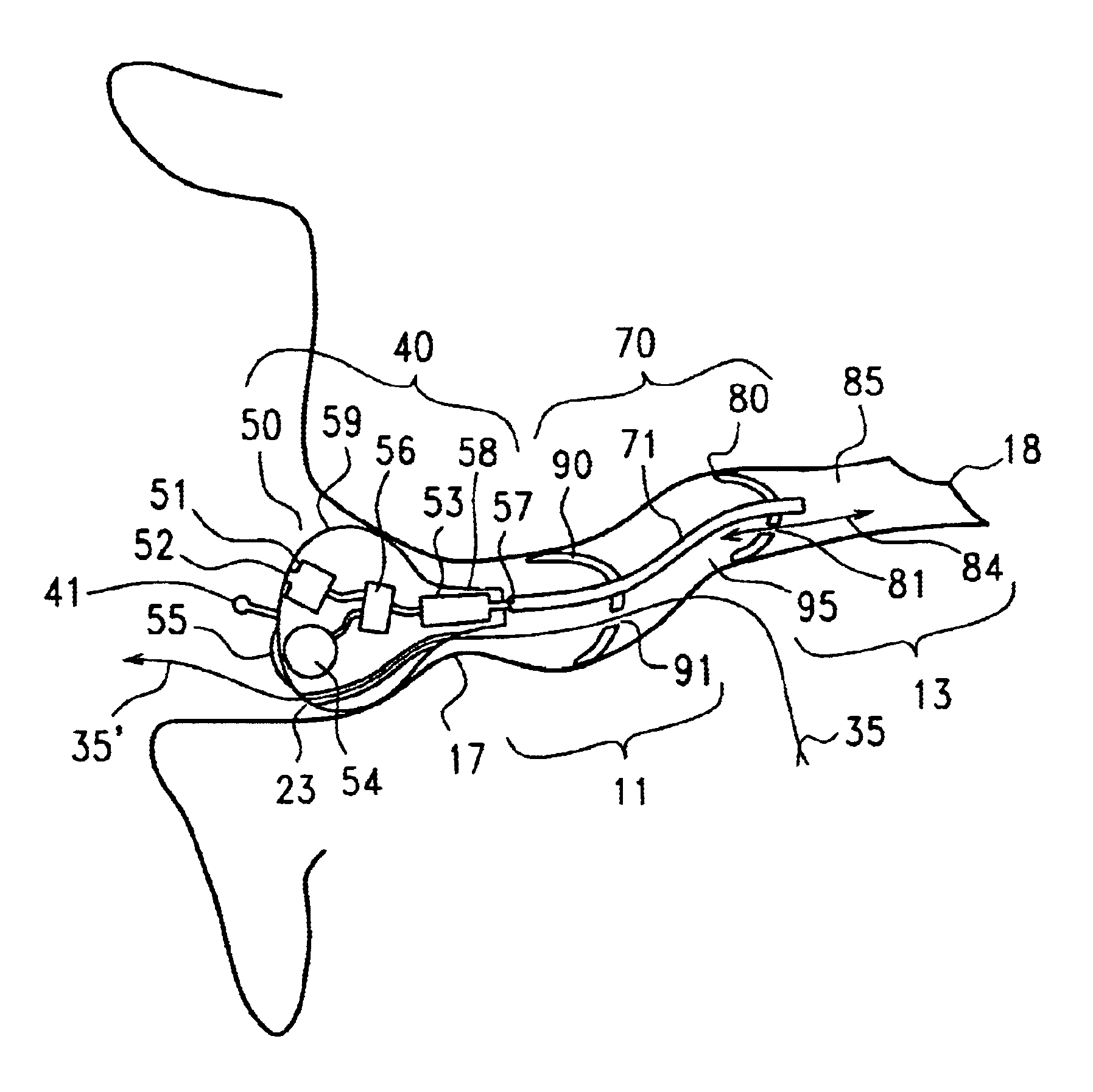
Bone anchor prosthesis and system
InactiveUS20050059972A1Easy to removeEasy to insertSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyMedicineProsthesis
A prosthetic screw system that includes a prosthetic screw for at least partial insertion into a bone and / or cartilage. The prosthetic screw includes a head and a lower portion connected to the head. The prosthetic screw system also includes a set of head-pieces that can be connected to the head of the prosthetic screw. The head-pieces have differing configurations that are designed to be connected to different types of components of a prosthetic system. The universal connection arrangement between the prosthetic screw and the set of head-pieces enables the prosthetic screw to be customized for connection with a variety of components of a prosthetic system. The head-pieces can alternatively or additionally include a mechanical and / or electrical mechanism that provides one or more substances (e.g., medicine and / or other biological agent, etc.) and / or electrostimulation to a surgical site.
Owner:SPINECO
Surgical cutting tool
Surgical cutting tool for manufacturing of a recess in a firm body tissue, in particular in a bone and / or in a cartilage, with a milling range rotatable around a central axis of rotation, with an outside lateral surface and an internal area substantially defined by the lateral surface and turned away from the worked on body tissue. The lateral surface is formed with at least two machining cutting edges, which proceed at the lateral surface from a machining center to a machining edge of the milling range and which are in particular spiral curved. Apertures are arranged adjacent to the cutting edges for the transport of the cutting splinters into the internal area, whereby the cutting edges are interrupted by means of recesses in such a way that the cutting edges are formed by individually cutting elements.
Owner:MULLER ERICH JOHANN
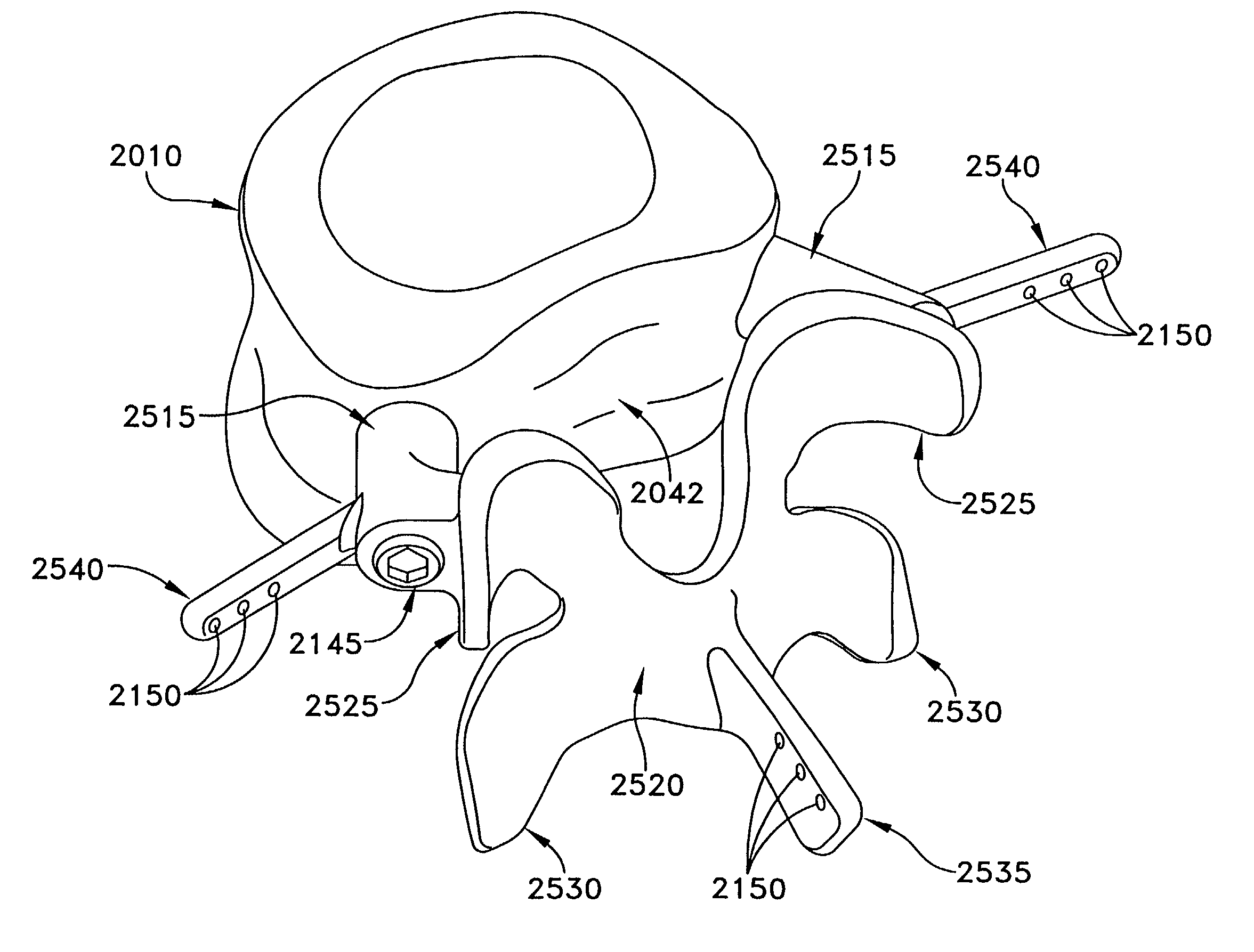
Method and apparatus for spine joint replacement
InactiveUS7090698B2Reduce frictionEliminate growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFacet joint prosthesisIntervertebral disc
A prosthesis for the replacement of the cartilaginous structures of a spine motion segment is described. The prosthesis comprises an intervertebral disc prosthesis in combination with a facet joint prosthesis.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC +1
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Method and instrumentation for osteochondral repair using preformed implants
Osteochondral repair of damaged articular joint surfaces is achieved using implants in the form of cylindrical osteochondral plugs. The plugs have an articular surface formed on at least one end. If articular surfaces are provided on both ends of the implant, the articular surfaces have differently curved surfaces. The defective cartilage is removed to create a recipient socket for the implant. An implant sized to fit the recipient socket is chosen from a plurality of implants provided to the surgeon. The implants are preferably formed of a hydrogel material such as Salubria™, although metal or allograft implants can also be used.
Owner:ARTHREX
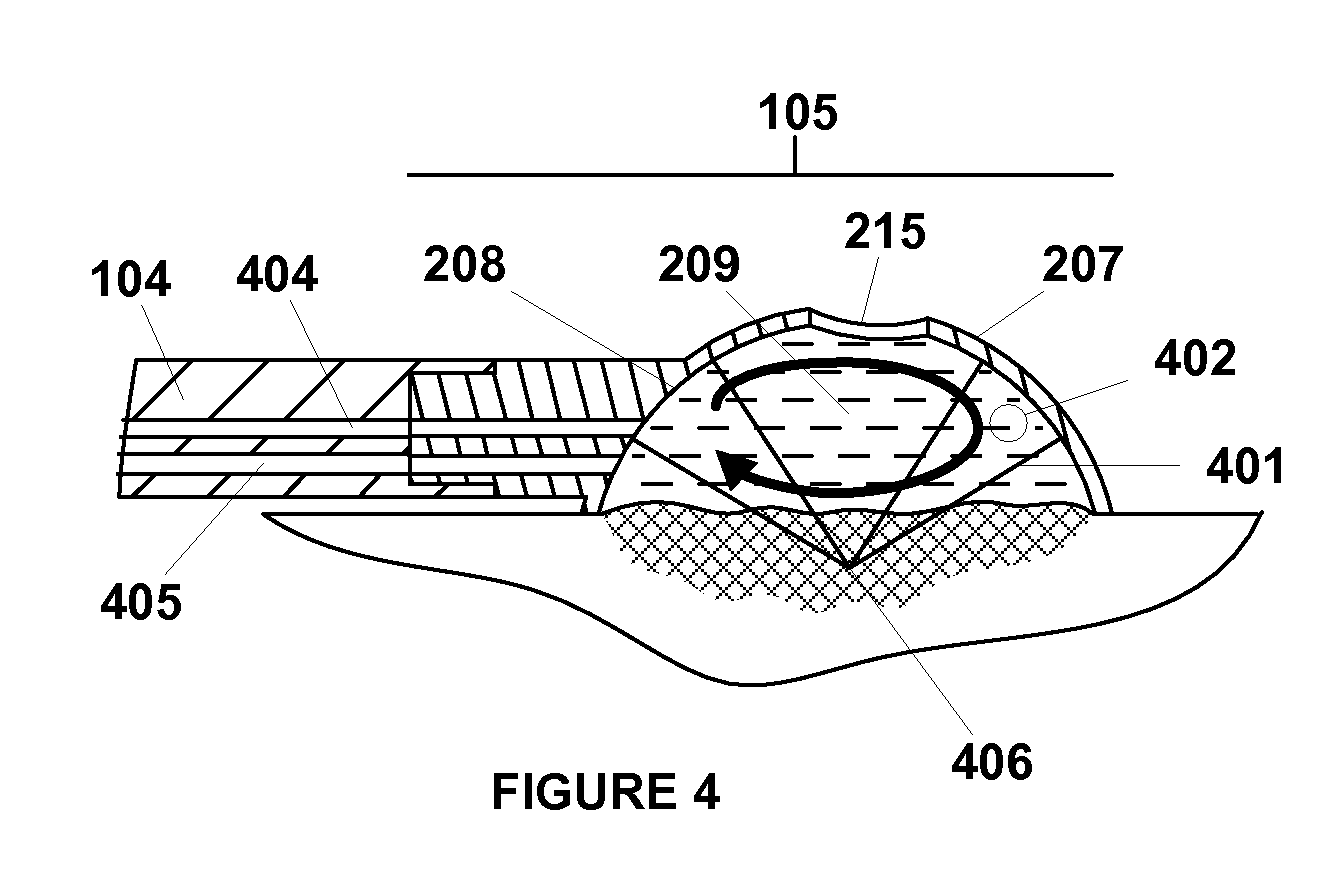
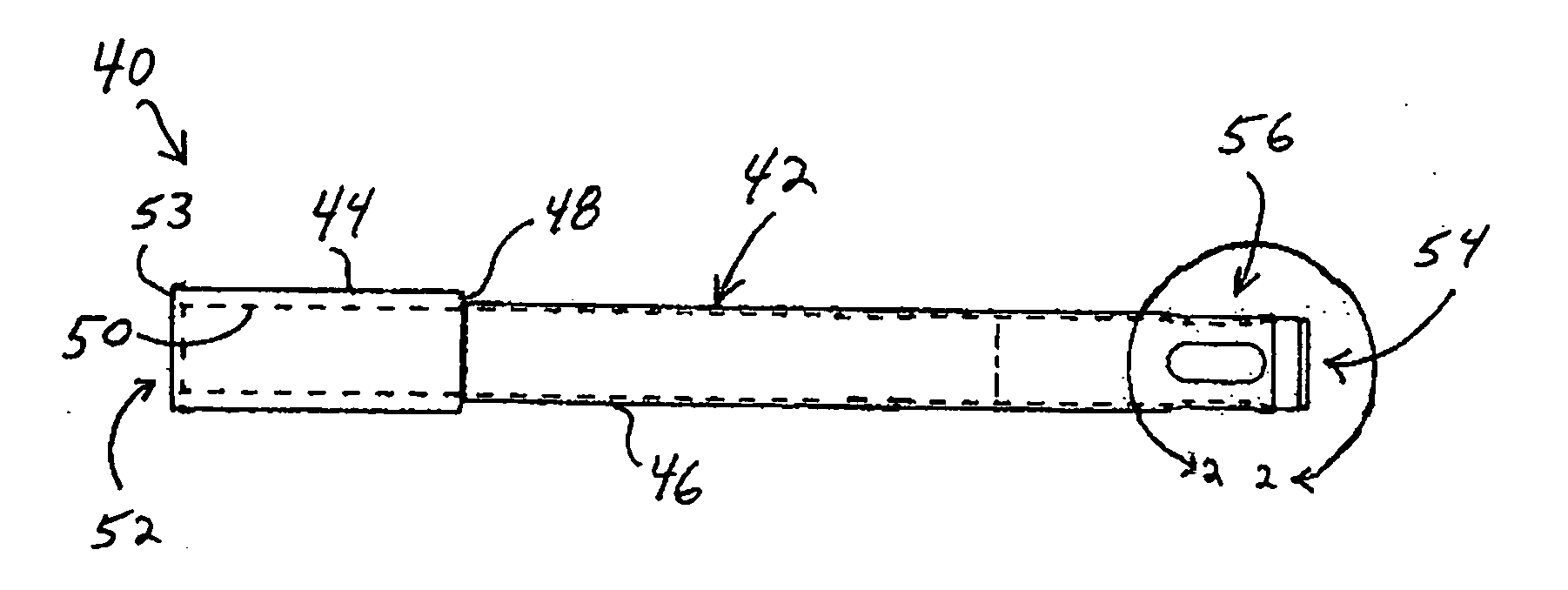
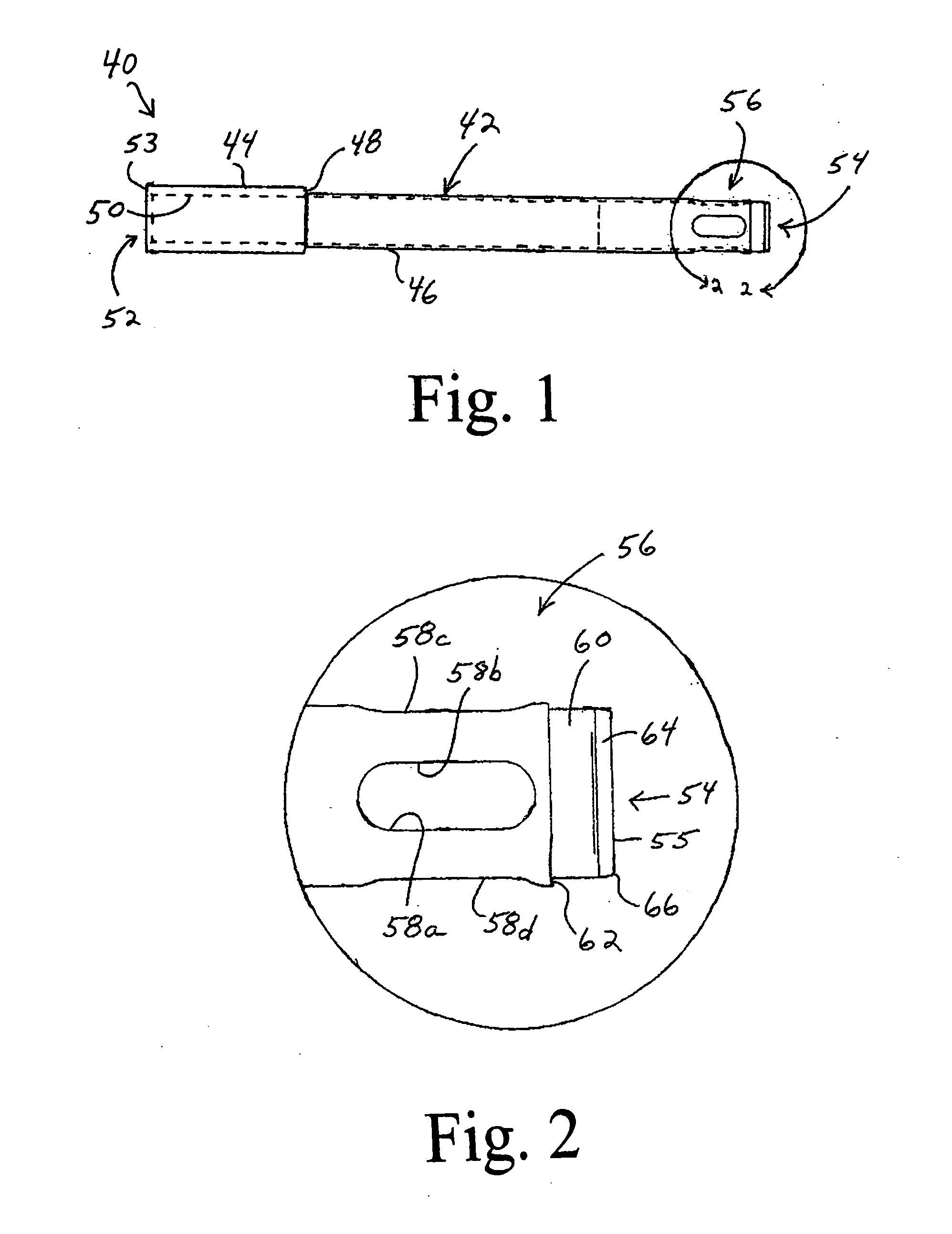
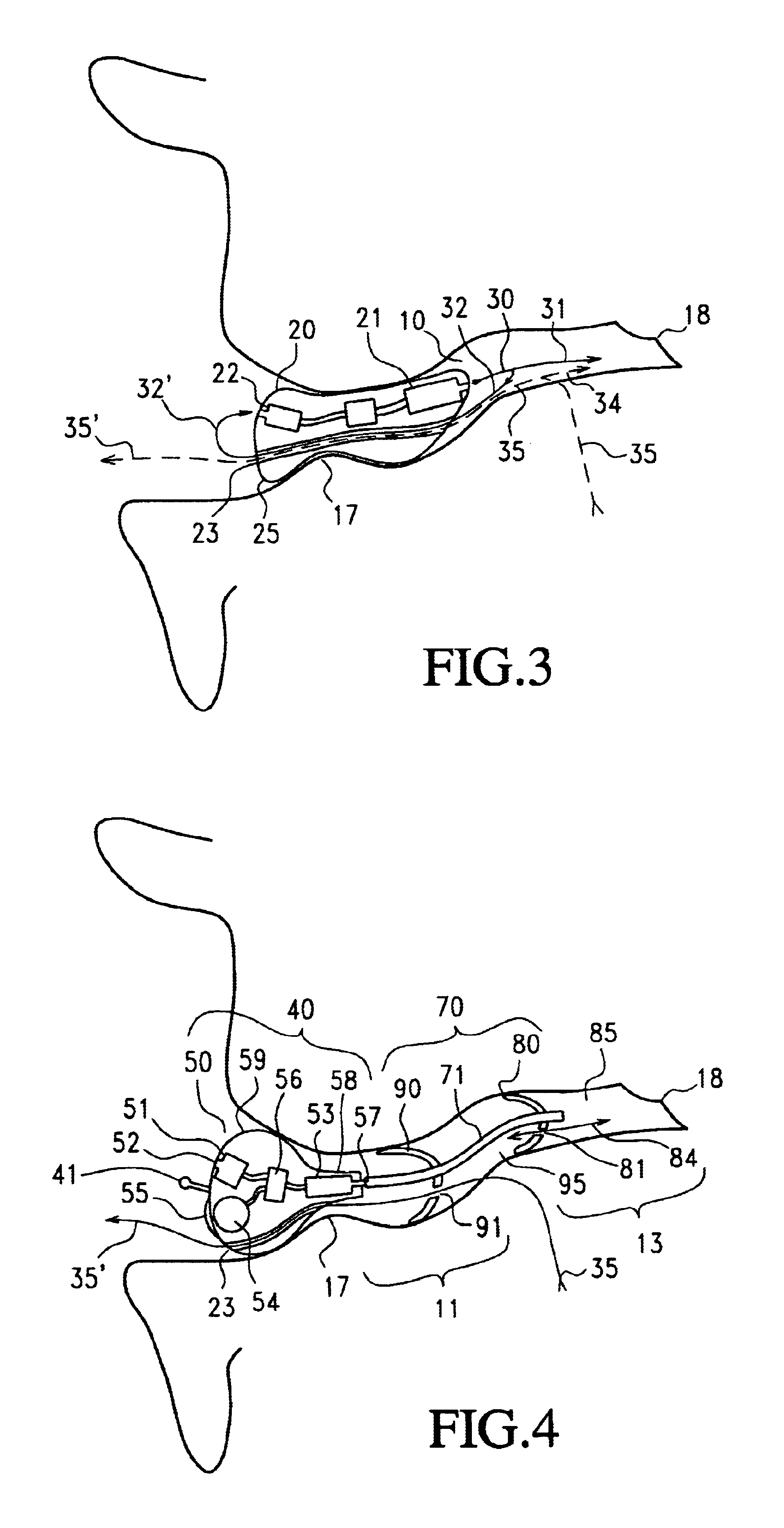
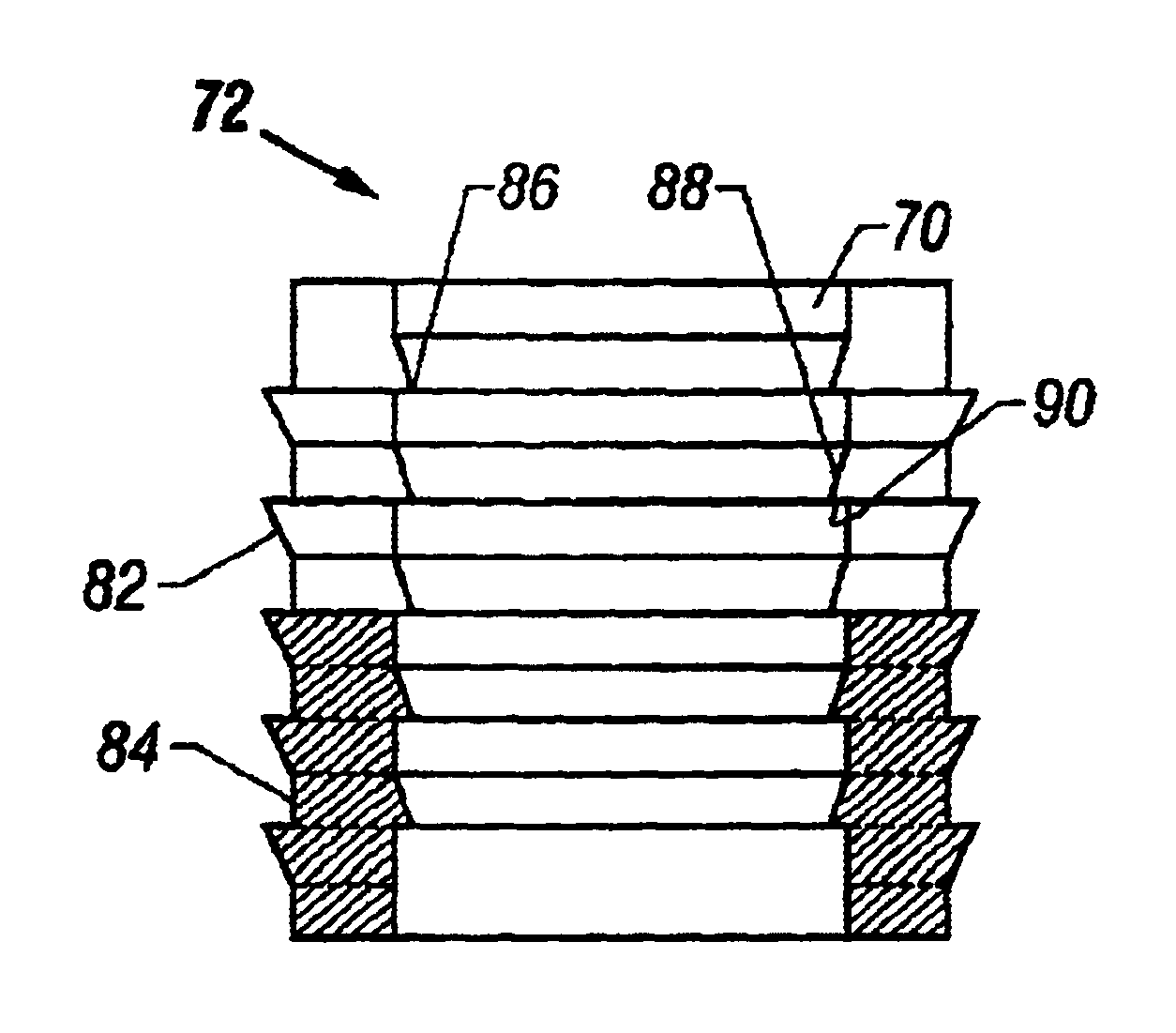
Articular cartilage repair implant delivery device and method of use
A technique for the arthroscopic delivery and fixation of an articular cartilage repair device or implant is provided. The technique includes the use of a cannula tube that functions as both a cartilage cutter and a guide to pass instruments into the body arthroscopically. One such instrument is an end-cutting reamer that both prepares the subchondral bone by re-surfacing it down to a specified depth and also simultaneously drills a pilot hole in the subchondral bone to accept the cartilage repair device. A delivery device is utilized to hold and deliver the cartilage repair device to the delivery site.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Cartilage repair plug
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prefabricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. A plurality of anchoring elements may share a single upper layer.
Owner:ABS
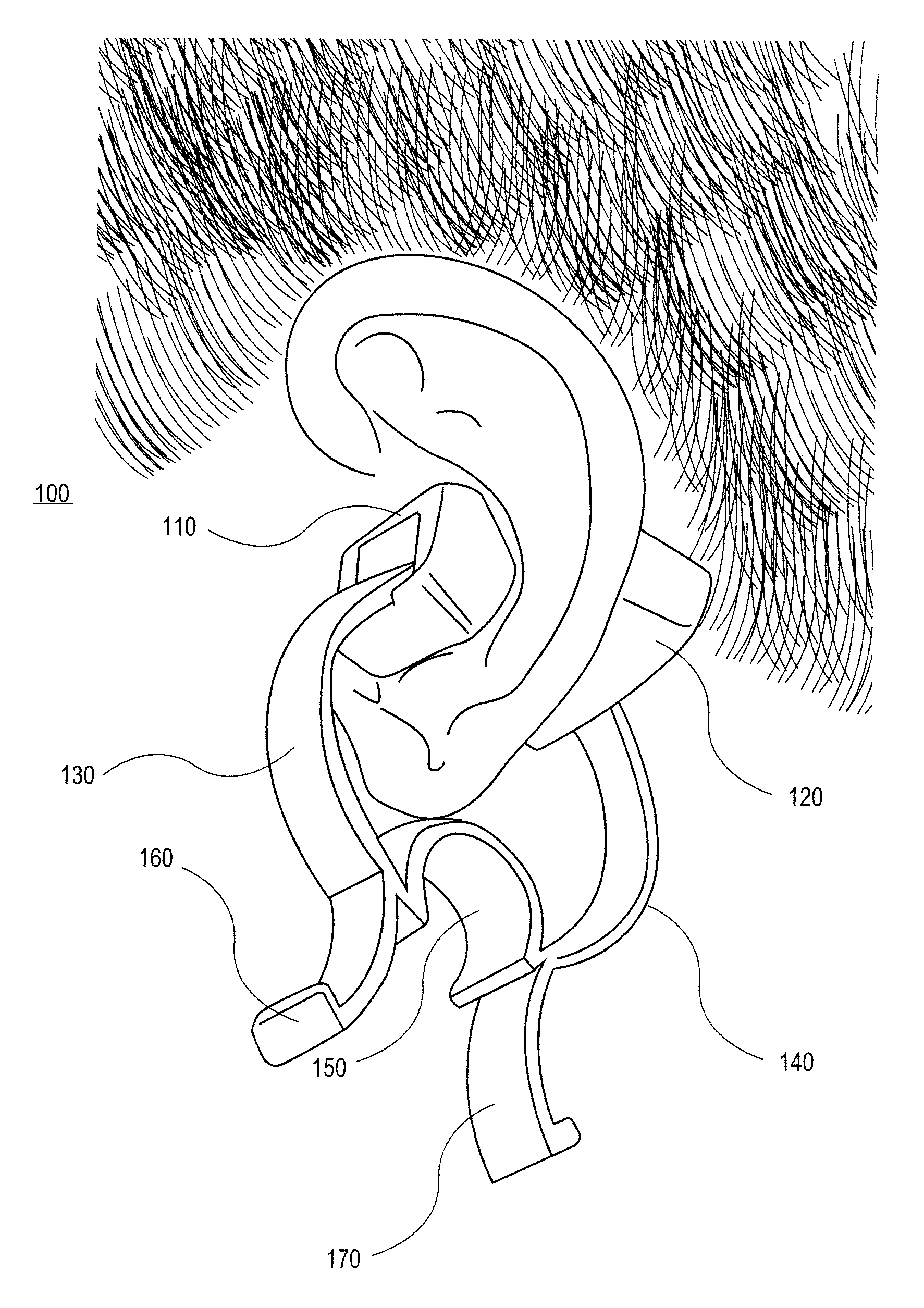
Canal hearing device with tubular insert
InactiveUS6724902B1Alleviate the social stigmaImprove high frequency responseElectrotherapyHearing aid ventsOcclusion effectCatheter
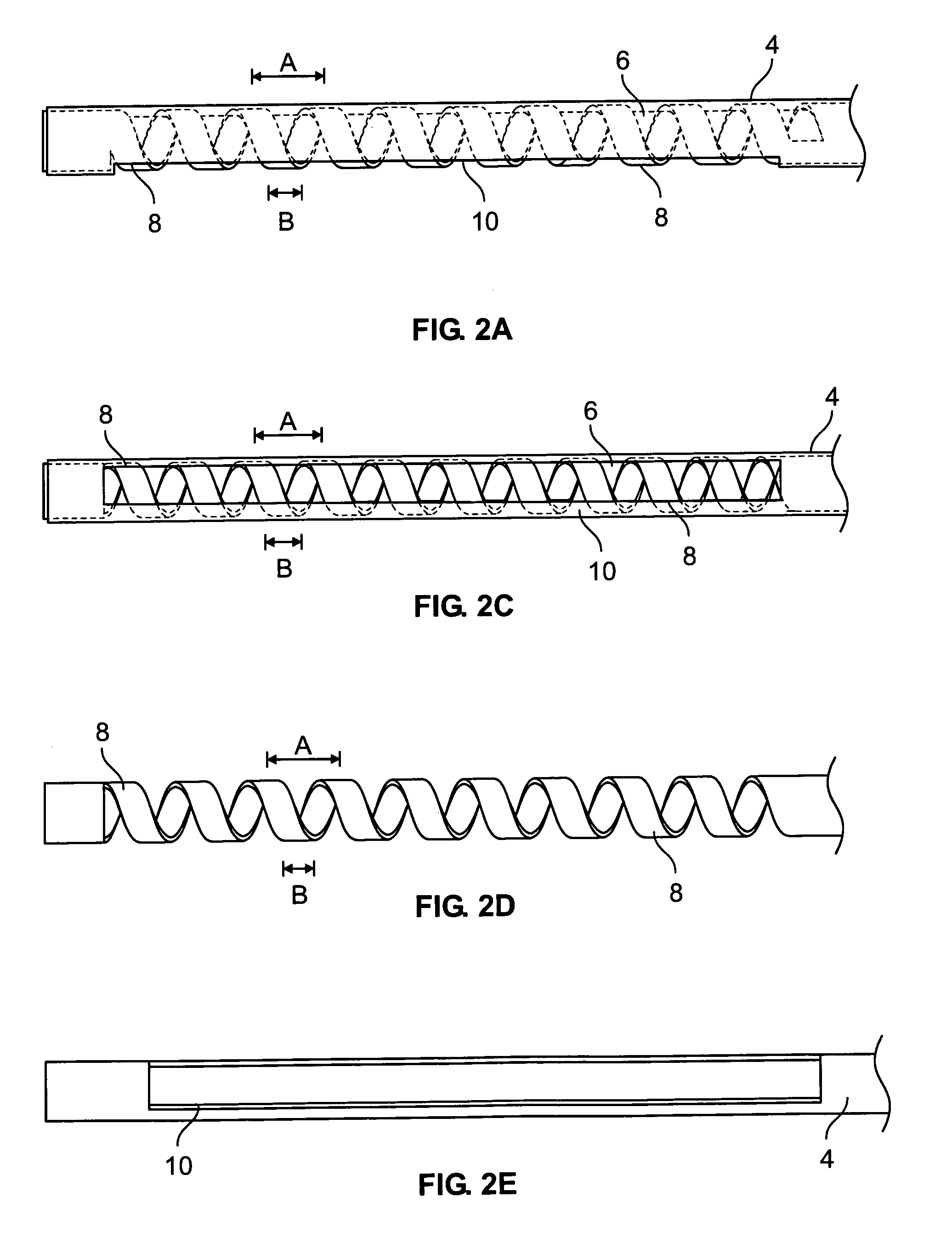
A canal hearing device with a dual acoustic seal system for preventing feedback while minimizing occlusion effects. The two-part device comprises a main module and an elongated tubular insert for conducting sound to the tympanic membrane and sealing within the bony region of the ear canal. The main module is positioned in the cartilaginous portion of the ear canal. The tubular insert comprises a sound conduction tube and a cylindrically hollow primary seal medially positioned in the bony region. The device also comprises a secondary seal laterally positioned in the cartilaginous region. The secondary seal, although providing additional acoustic sealing for the prevention of feedback, is sufficiently vented to provide a path of least acoustic resistance for occlusion sounds within the ear canal. In a preferred embodiment, the tubular insert comprises a coiled skeletal frame to provide high radial flexibility while maintaining sufficient axial rigidity for comfortable, kink-resistant, and consistent placement within the ear canal.
Owner:INSOUND MEDICAL INC
Two-thirds prosthetic arthroplasty
A two-thirds prosthetic arthroplasty having a trochlear groove, a patello-femoral component, and either a lateral condyle or a medial condyle. The arthroplasty may be configured to be a prosthetic for either a right or left knee. The condyle and patello-femoral component are separated by a modified intercondylar notch that is blended to avoid protrusions or sharp angles. The prosthetic arthroplasty is inserted after preoperative MRI mapping of articular cartilage damage. The prosthetic arthroplasty may be cemented during surgery and the two-thirds design of the present invention obviates the problem of cement retrieval from remote parts of the prosthesis.
Owner:WOOD DAVID JOHN
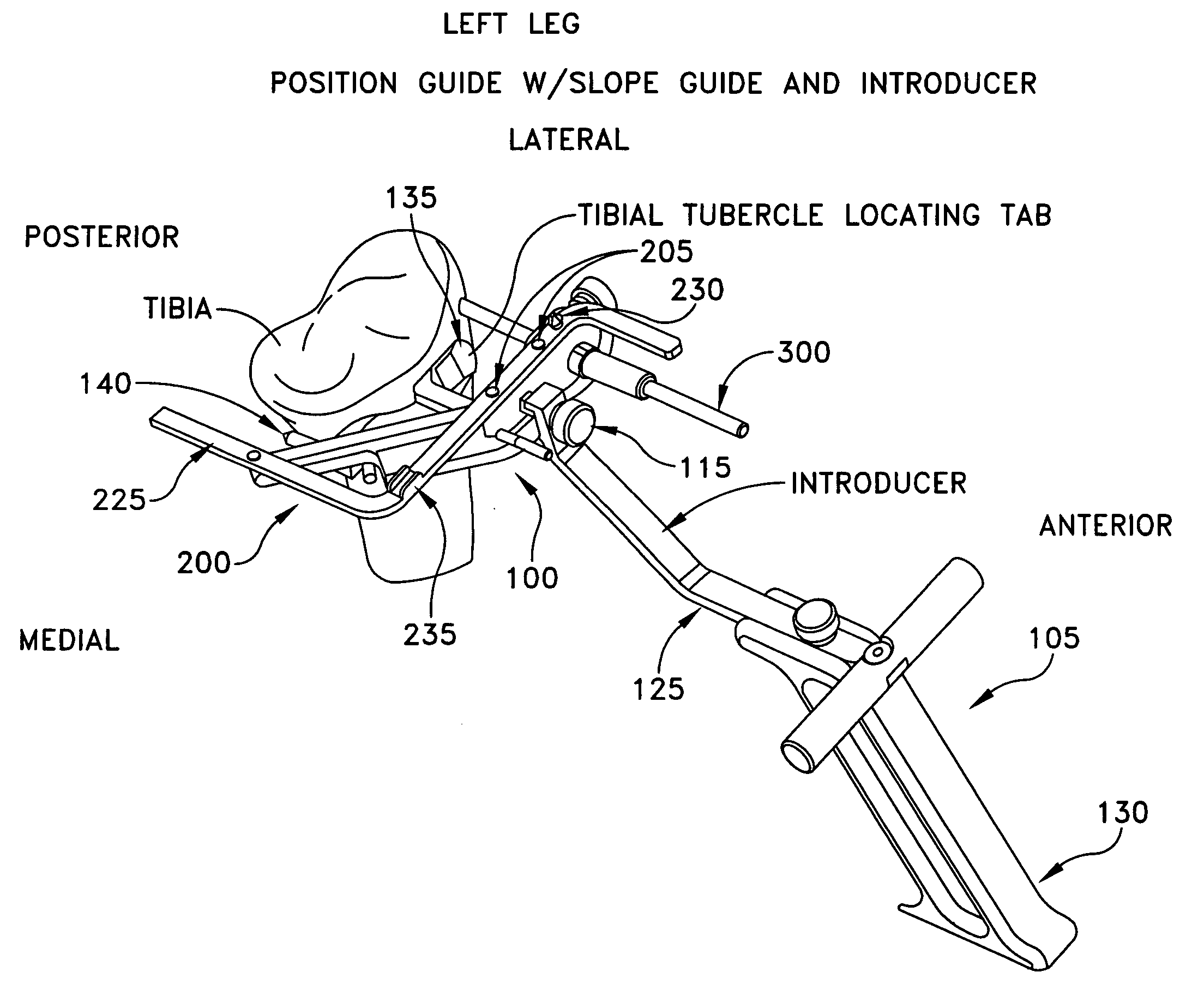
Method and apparatus for reconstructing a ligament and/or repairing cartilage, and for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
A method for reconstructing a knee ligament and for performing a tibial osteotomy on the knee in a single procedure, the method comprising:forming a bone tunnel through the tibia at a location appropriate for the ligament reconstruction, disposing a graft ligament in the bone tunnel, and securing the graft ligament in the bone tunnel, and forming a wedge-like opening in the bone at a location appropriate for the tibial osteotomy, positioning an osteotomy implant in the wedge-like opening in the bone, and securing the osteotomy implant in the wedge-like opening in the bone;wherein the osteotomy implant is secured in the wedge-like opening in the bone with a fastener which extends through the implant and into the bone tunnel.
Owner:ARTHREX
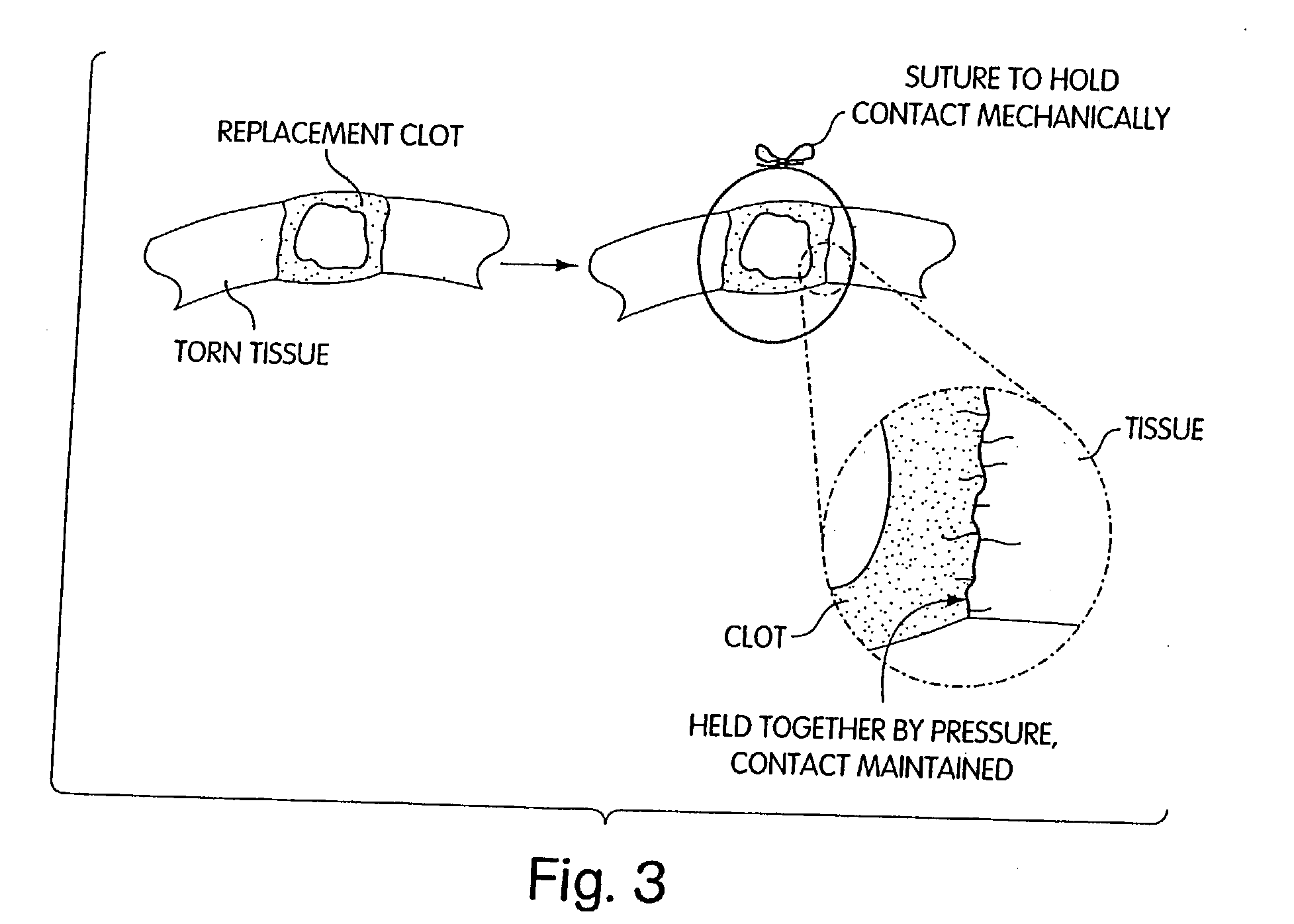
Biologic replacement for fibrin clot
InactiveUS20040059416A1Promote regenerationWound closure is subsequentlySuture equipmentsVirusesLigament structureBiomedical engineering
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
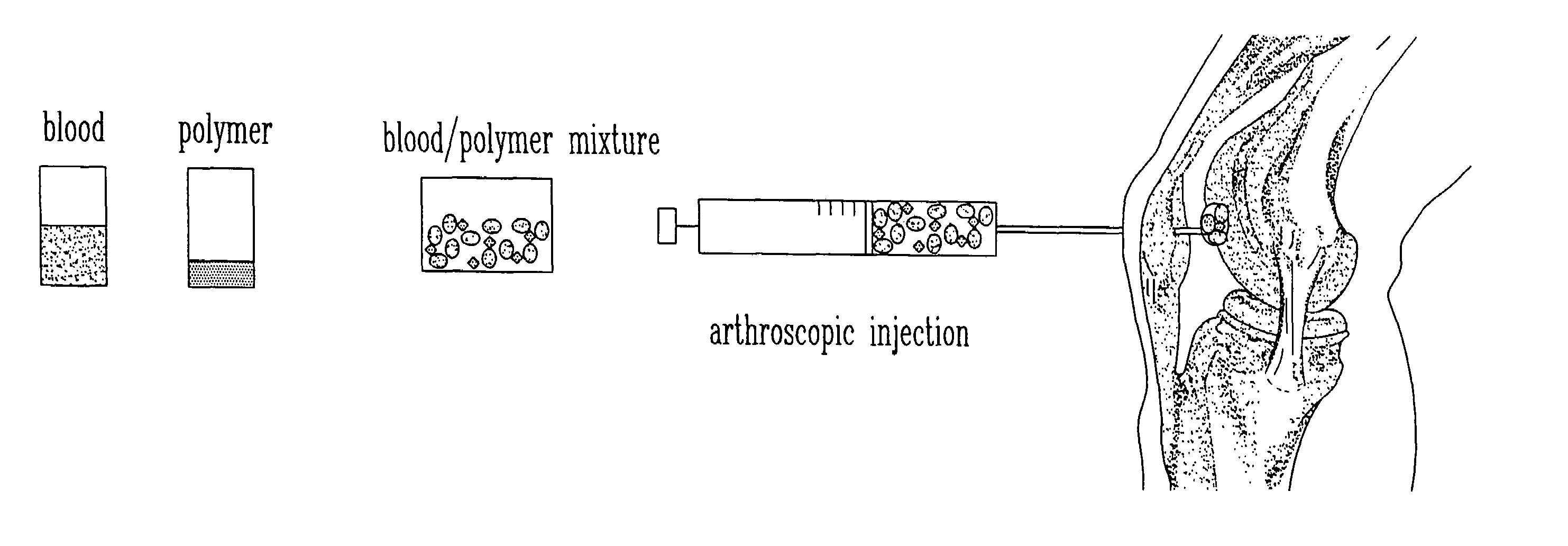
Composition and method for the repair and regeneration of cartilage and other tissues
InactiveUS7148209B2Add supportImprove coagulation/solidificationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthRepair tissue
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Cartilage repair plug
InactiveUS6632246B1Facilitate cell ingrowthMechanically fixedBone implantDiagnosticsCartilage repairSurgical department
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease is disclosed. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prebricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. Additionally, ridges may be formed about the periphery of each plug to facilitate its anchoring to surrounding cartilage, bone and / or adjacent plugs. A procedure for resecting damaged or diseased cartilage and for implanting a replacement plug or plugs according to this invention, as well as a set of instruments for effecting the procedure, and a self-contained system for orthopedic surgeons, which includes a variety of differently sized and shaped plugs, as well as a set of instruments for the procedure are also disclosed.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ABS
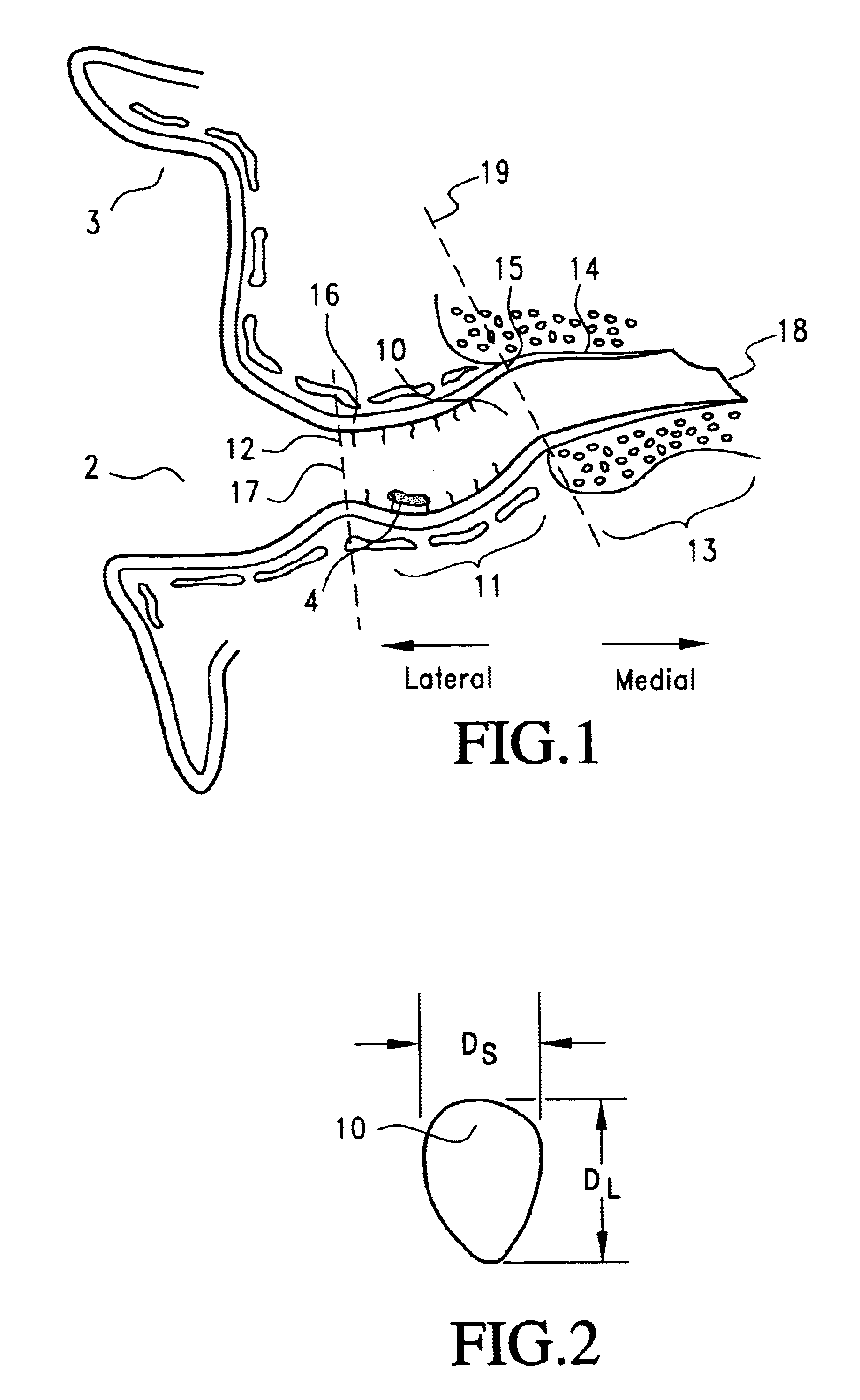
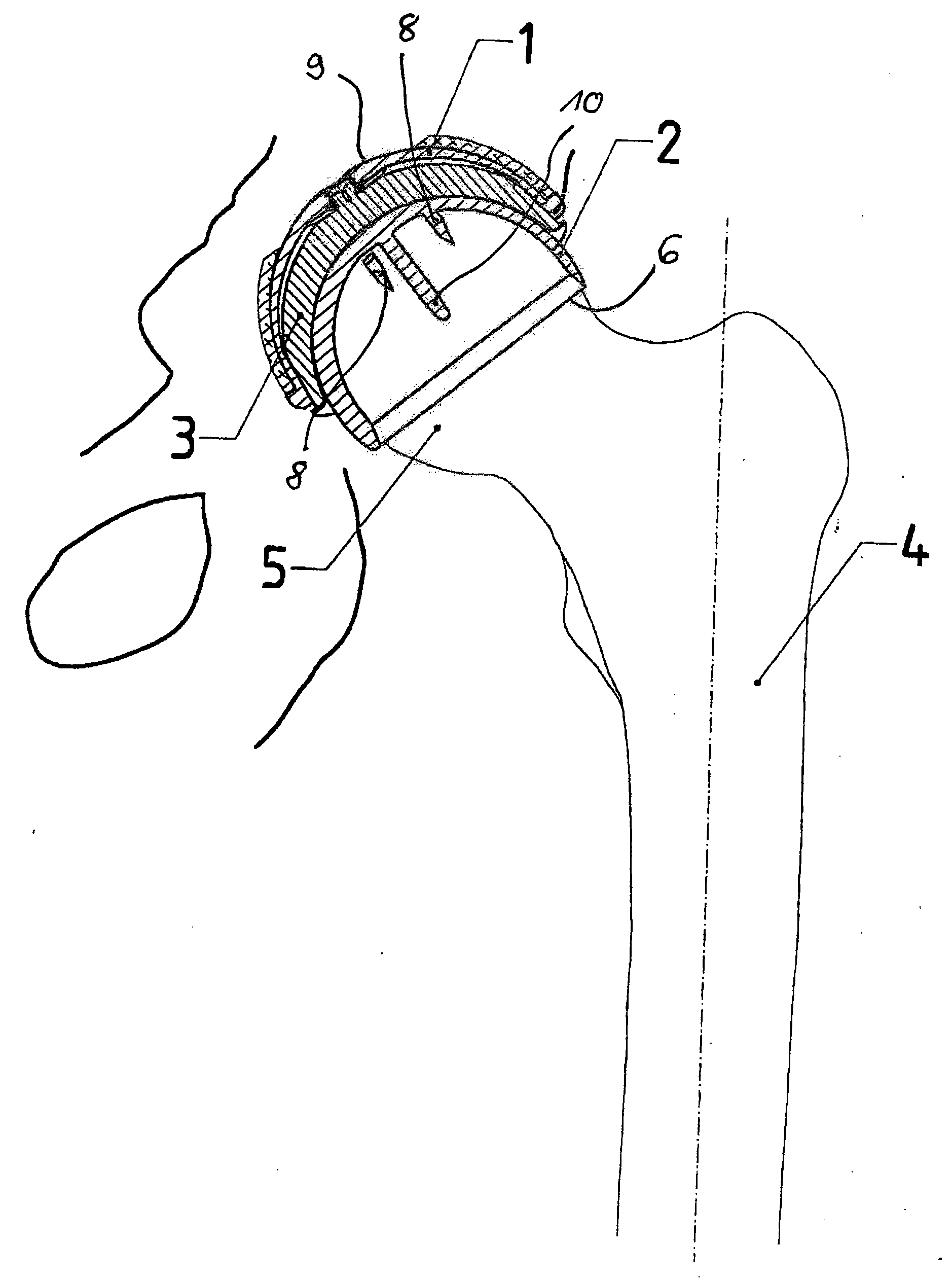
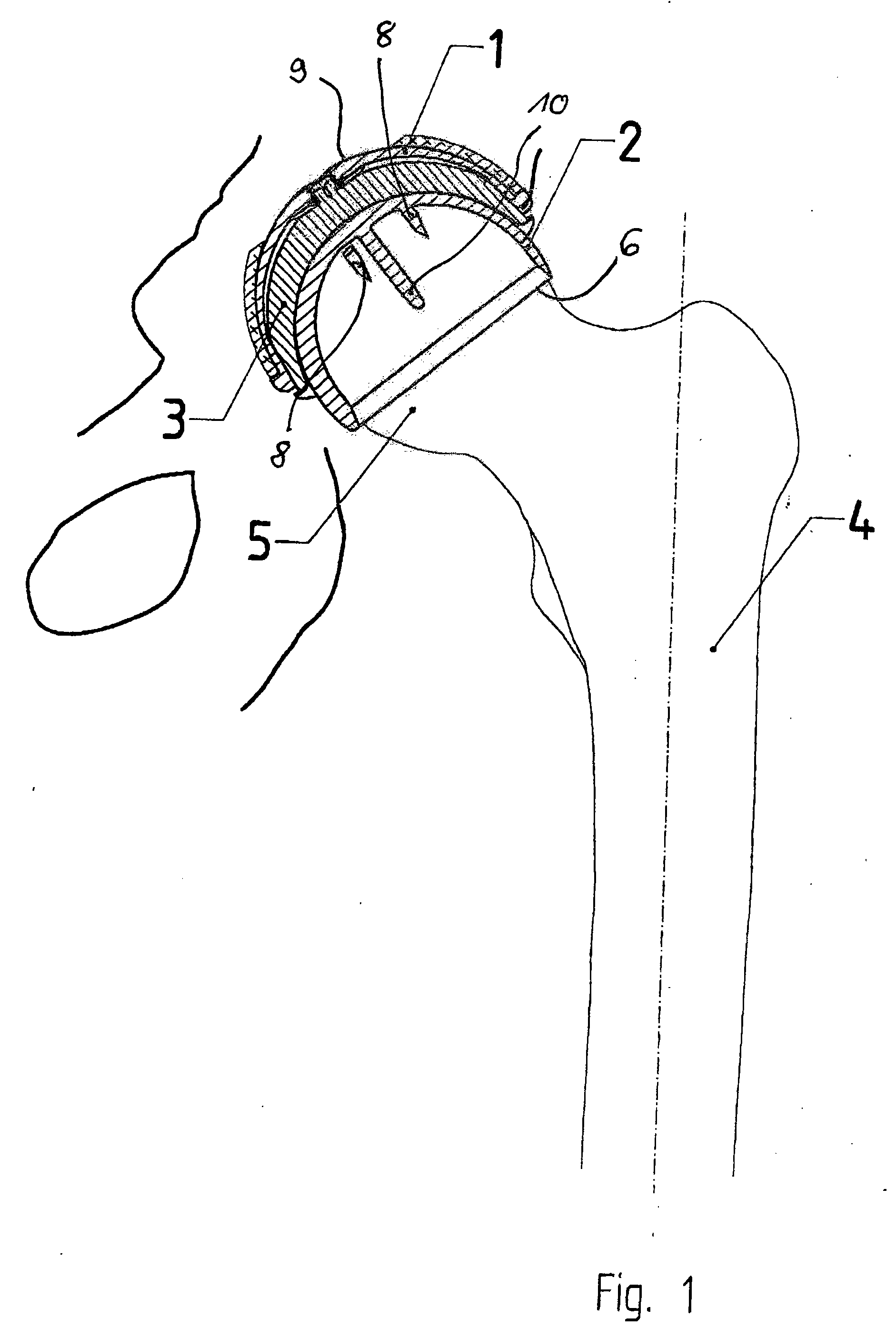
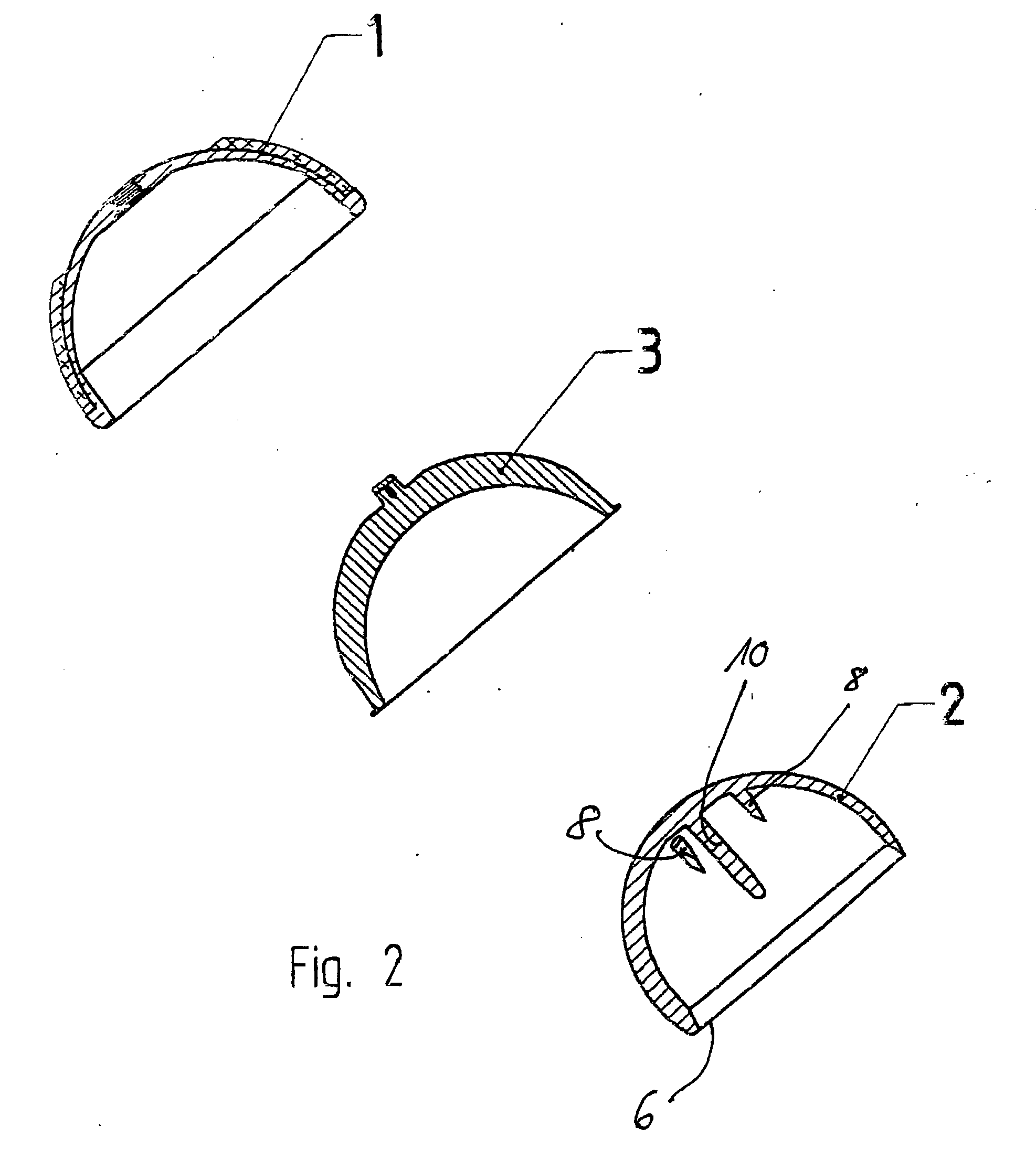
Set For Creating An Offset-Resurfacing Hip-Joint Implant
A set is provided for creating an offset-resurfacing hip-joint implant. The set includes a 1 to 1.5 mm thick metallic acetabulum shell (1) for insertion into the natural acetabulum, from which only cartilage has been removed, a metallic head cap (2) for placement on the natural hip-joint head, from which only cartilage has been removed, and an inlay (3) for insertion into the acetabulum shell (1) as a sliding partner for the head cap (2). The inlay has a material thickness of 2 to 5 mm. The head cap (2) has a wall thickness which increases constantly from a thickness of 2 mm to 6 mm viewed in cross section in the region of the base edge (6) of the head cap, so that an eccentricity is produced in its outer shape
Owner:ORTHODYNAMICS GMBH
Vacuum coagulation probes
InactiveUS7063698B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesRadio frequencyArticular cartilage
An embodiment of the invention includes a surgical device for coagulating soft tissue such as atrial tissue in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrial tachycardia; tendon or ligament shrinkage; or articular cartilage removal. The surgical device integrates a suction mechanism with the coagulation mechanism improving the lesion creation capabilities of the device. The surgical device comprises an elongate member having an insulative covering attached about conductive elements capable of coagulating soft tissue when radiofrequency or direct current energy is transmitted to the conductive elements. Openings through the insulative covering expose regions of the conductive elements and are coupled to lumens in the elongate member which are routed to a vacuum source. Suction causes the soft tissue to actively engage the opening thus the integrated, exposed conductive elements to facilitate the coagulation process and ensure the lesions created are consistent, continuous, and transmural. The embodiments of the invention can also incorporate cooling mechanisms associated with the conductive elements and coupled to a fluid source to passively transport fluid along the contacted soft tissue surface to cool thus pushing the maximum temperature deeper into tissue.
Owner:ATRICURE
Method for supplementing the diet
InactiveUS6579544B1Increased susceptibilityPrevent diseaseHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDietary supplementAlpha-Lipoic Acid
A dietary supplement blend composition is disclosed, the basic formulation of the composition containing vitamins, minerals, and carotenoids. The composition can also contain bioflavonoids, cartilage protectors such as glucosamine or chondroitin, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, and a source of omega-3 fatty acids such as flax seed oil. The composition is beneficial for improving health and preventing disease, particularly for degenerative conditions. A method for supplementing the diet is also disclosed, wherein the quantity of daily rations of the dietary supplement blend composition is determined based on the person's age, body weight, and quality of diet.
Owner:NUTRIEX
Open helical organic tissue anchor having recessible head and method of making the organic tissue anchor
InactiveUS7189251B2Easy to anchorStrengthens helixSuture equipmentsPinsSelf reinforcedLigament structure
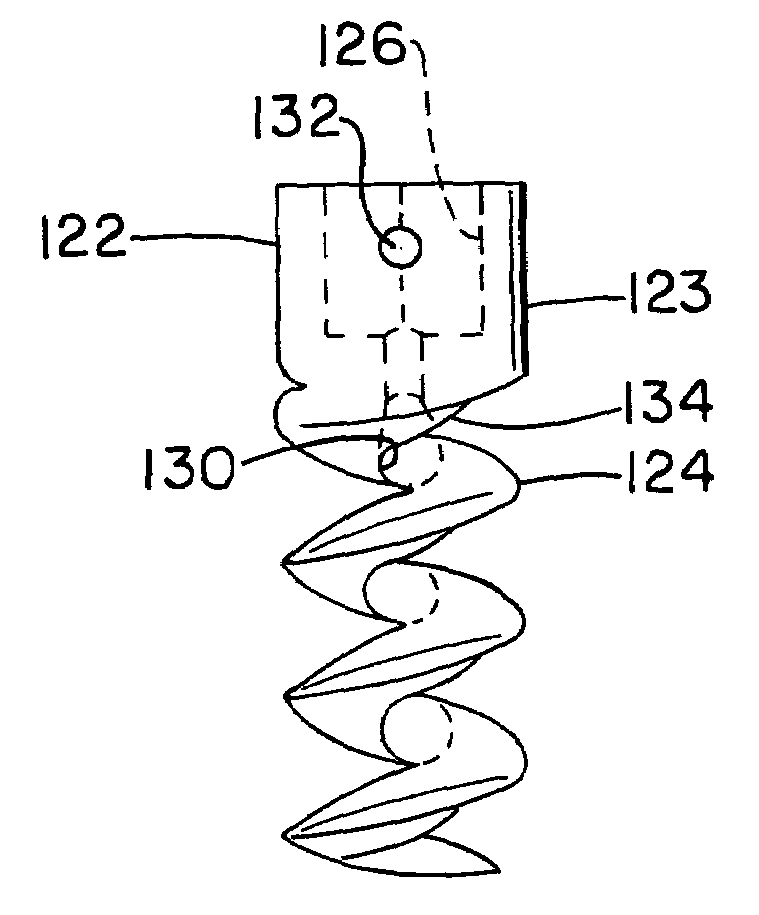
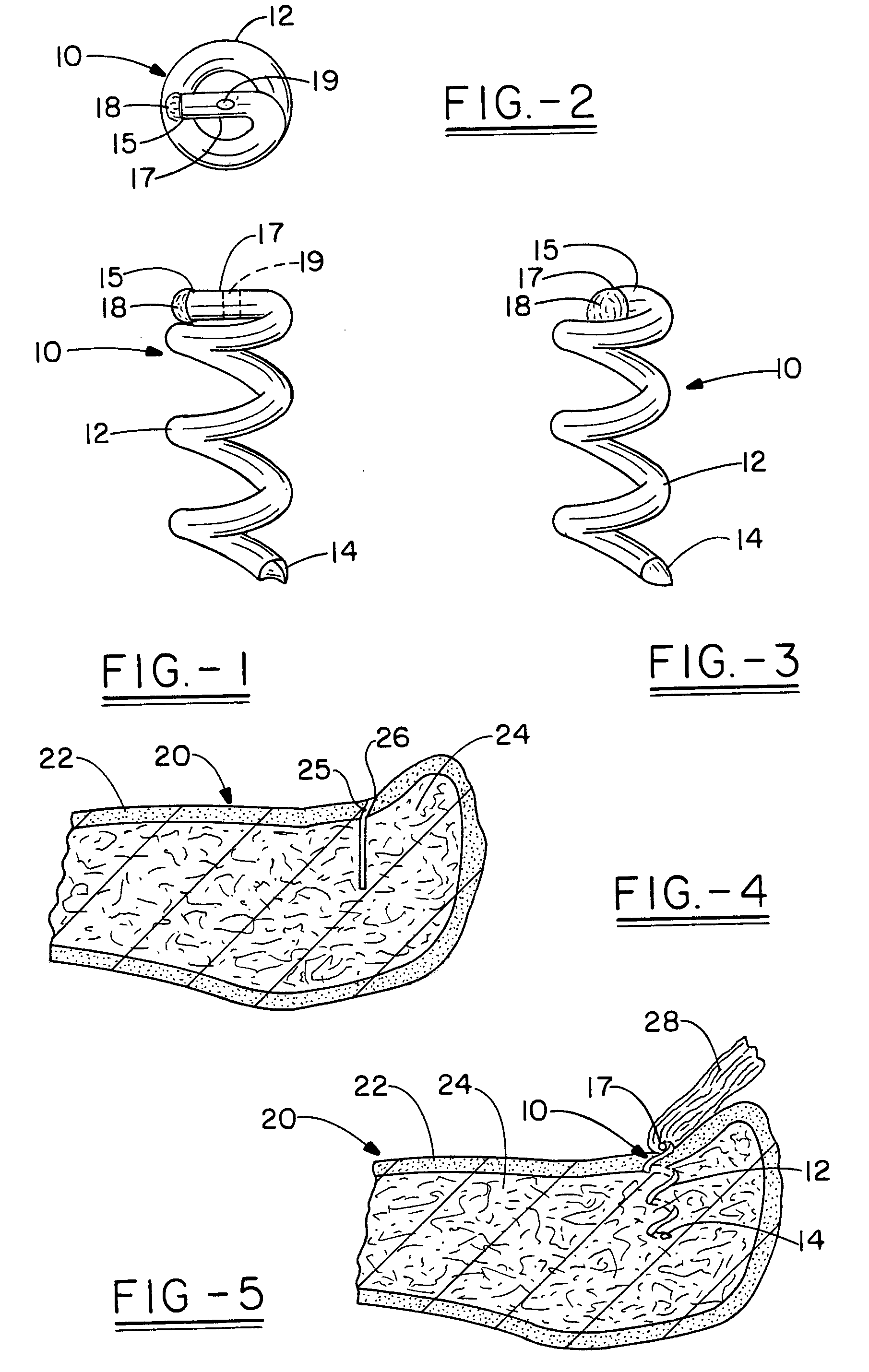
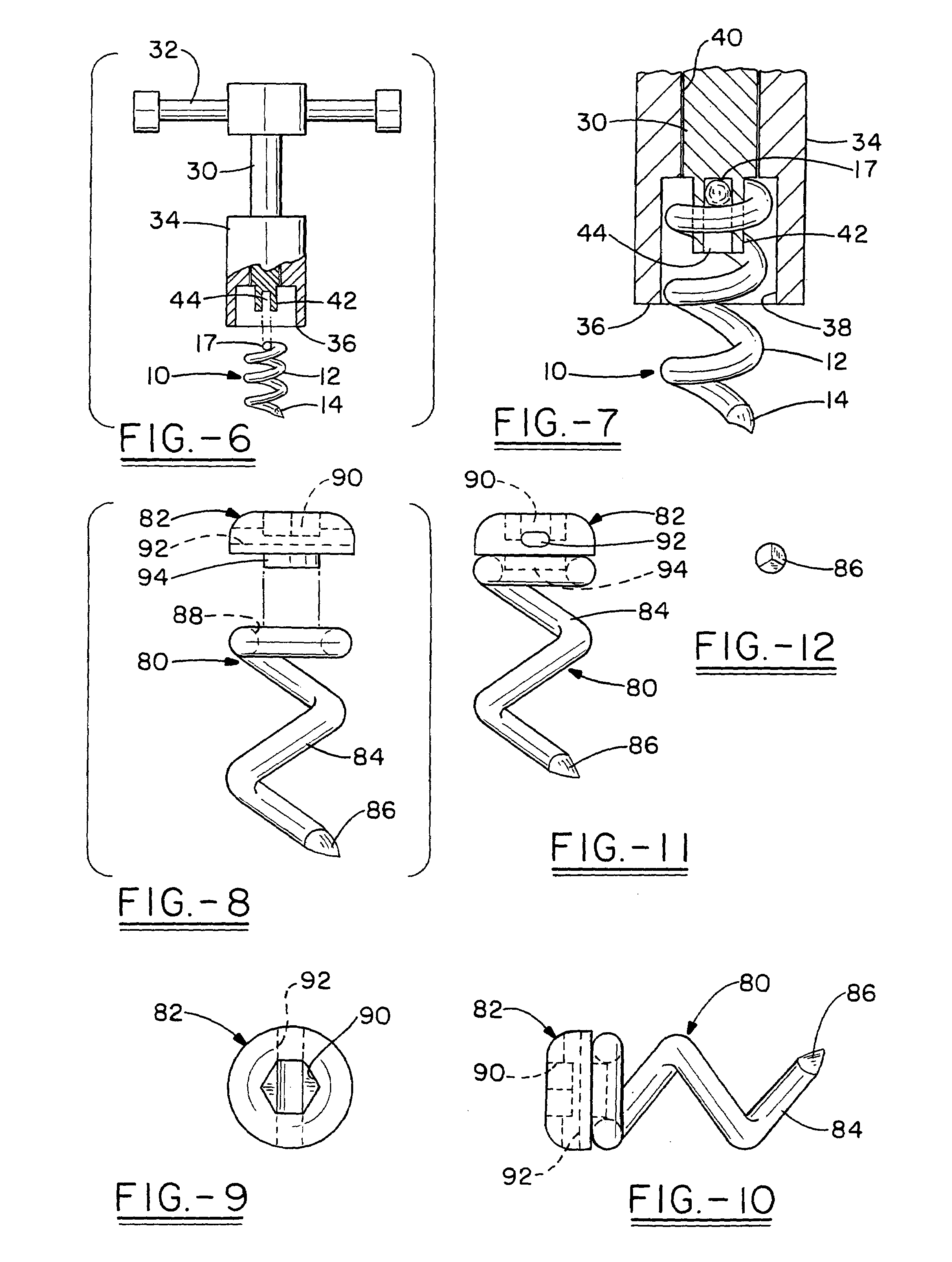
The invention relates to a tissue anchor which is an open helix of biocompatible material having a slope of from 0.5 to 10 turns per centimeter, a length from 3 to 75 millimeters, a diameter of from 1.5 to 11 millimeters, and an aspect ratio of from about 3 to about 5 to 1. The anchor can have a head which is capable of securing or clamping tissue together, such as holding a suture to secure a ligament or tendon to bone. The anchor can also have a head which causes an inward, compressive loading for use in fastening bone to bone, orthopedic plates to bone, or cartilage to bone. The head may be an integral member and may include a self-reinforcing wedge which joins the helix to the head. Further, the elongate member, or filament that forms the helix may have a tapering diameter along its length.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
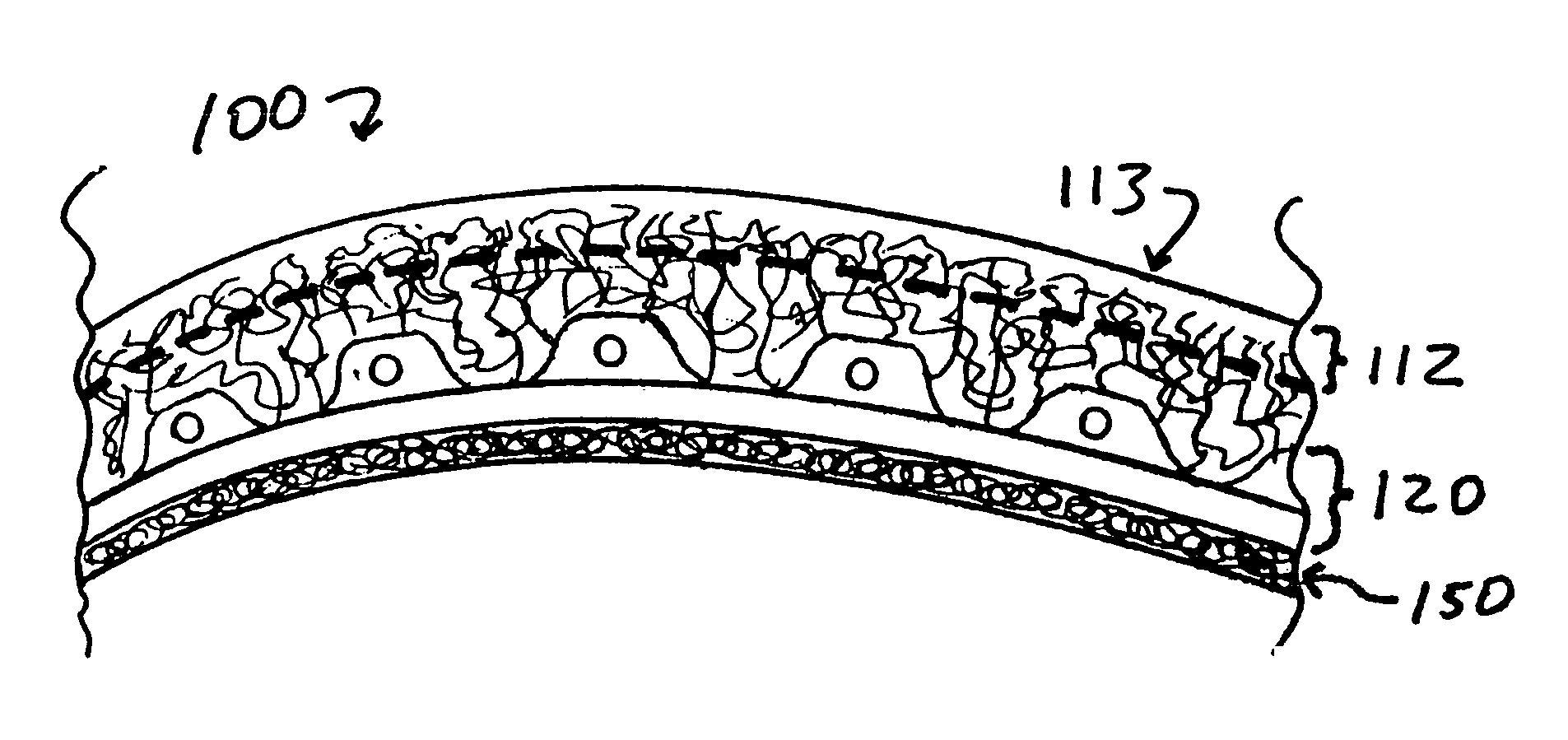
Implant device for cartilage regeneration in load bearing articulation regions
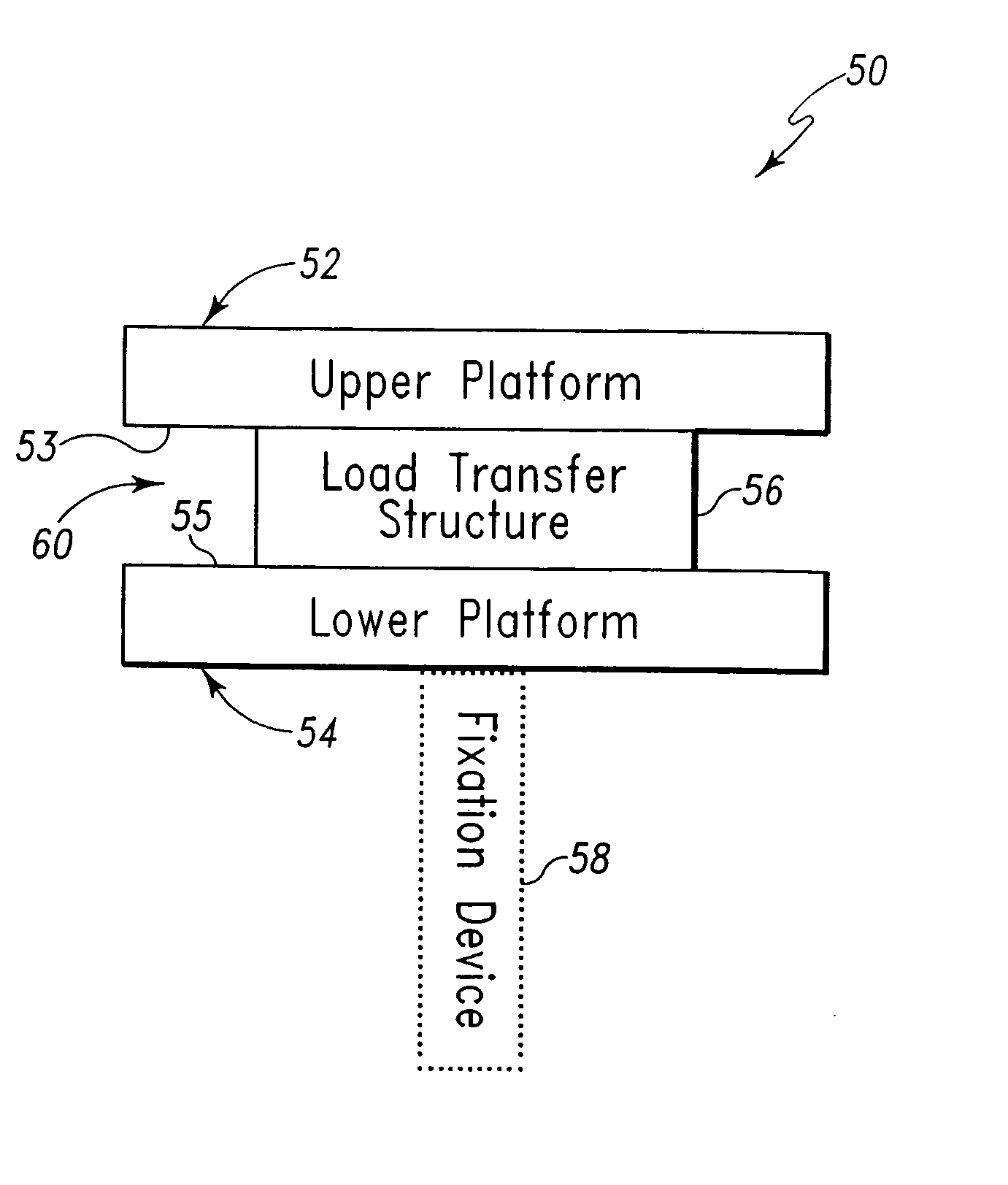
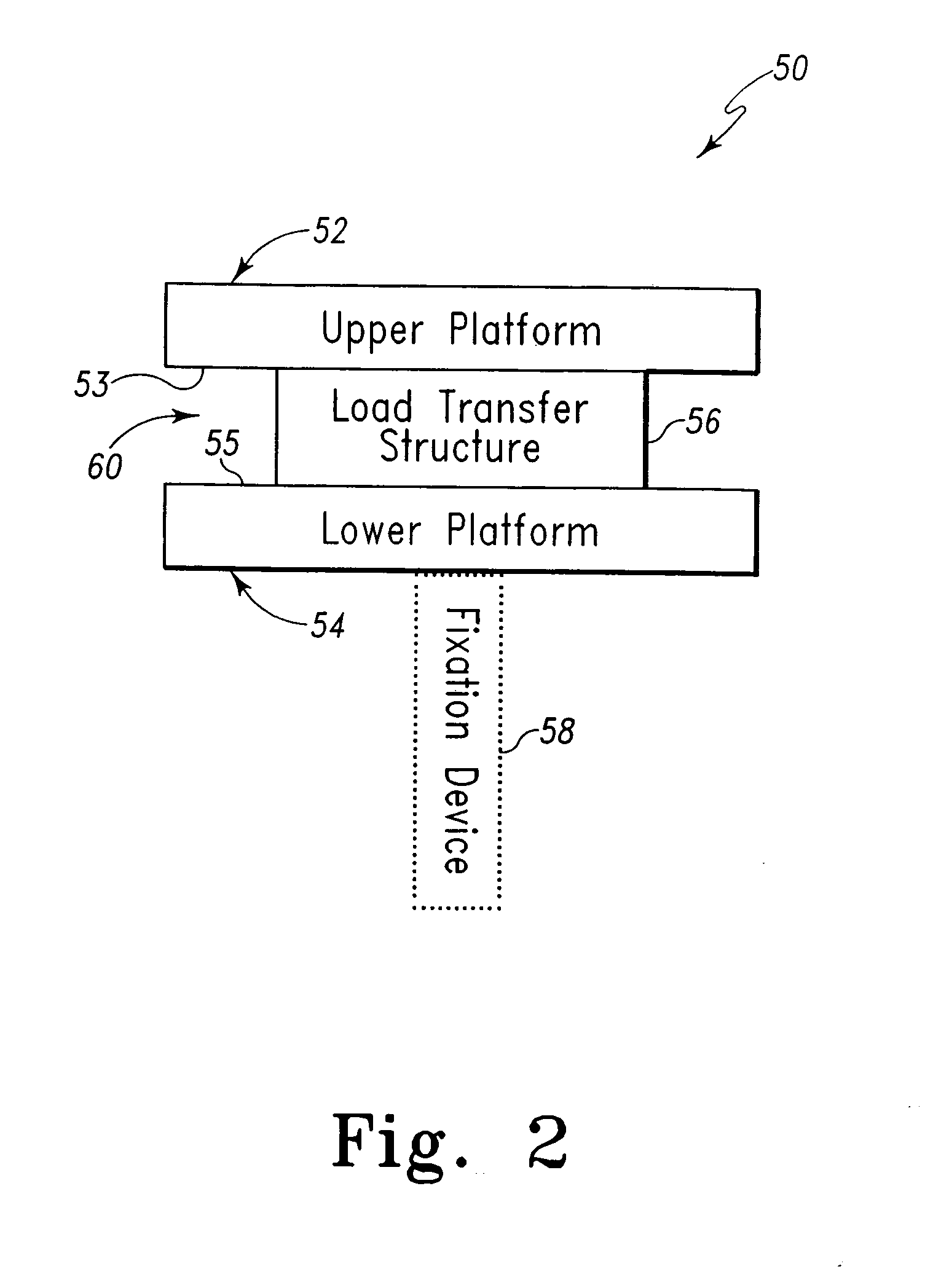
An implant device for cartilage regeneration in loading-bearing regions uses the osteochondral defect model. The implant is formed of resorbable polymeric materials. The implant is designed such that load is transmitted from the articulating surface of the bone platform through the implant to the entire area of subchondral bone of the bone platform. Application of load in this manner results in reduced subchondral bone resorption, leading to joint stabilization and maintenance of normal joint biomechanics. The implant allows for the incorporation therein of a resorbable scaffold or matrix material. The present implant solves the current inability to regenerate cartilage in load-bearing articulating surfaces using engineered scaffold devices.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Implant and method for facet immobilization
ActiveUS20090264928A1Reduce relative motionRestores motionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAdhesiveSacroiliac joint
Devices and methods are provided for immobilizing facet joints of the vertebral column. Embodiments of the invention provide an implant that is inserted in a facet joint from which cartilage has been removed, and which retains the approximate original spacing of the facets in the joint. A retaining arrangement, such as an adhesive, a threaded fastener, or a screw is then used to secure the implant in the joint.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com