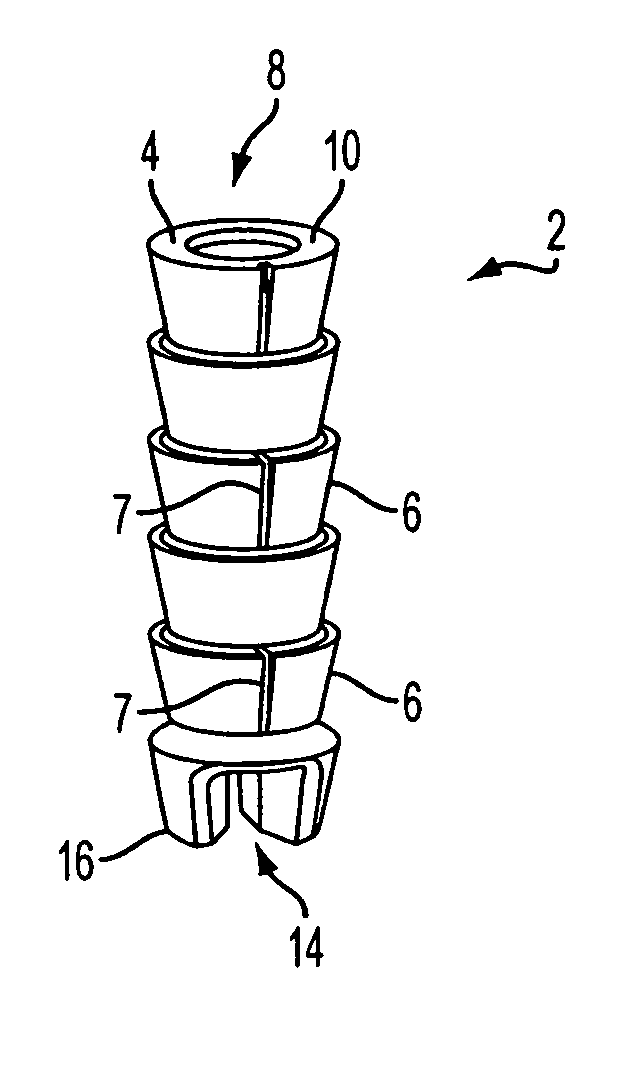
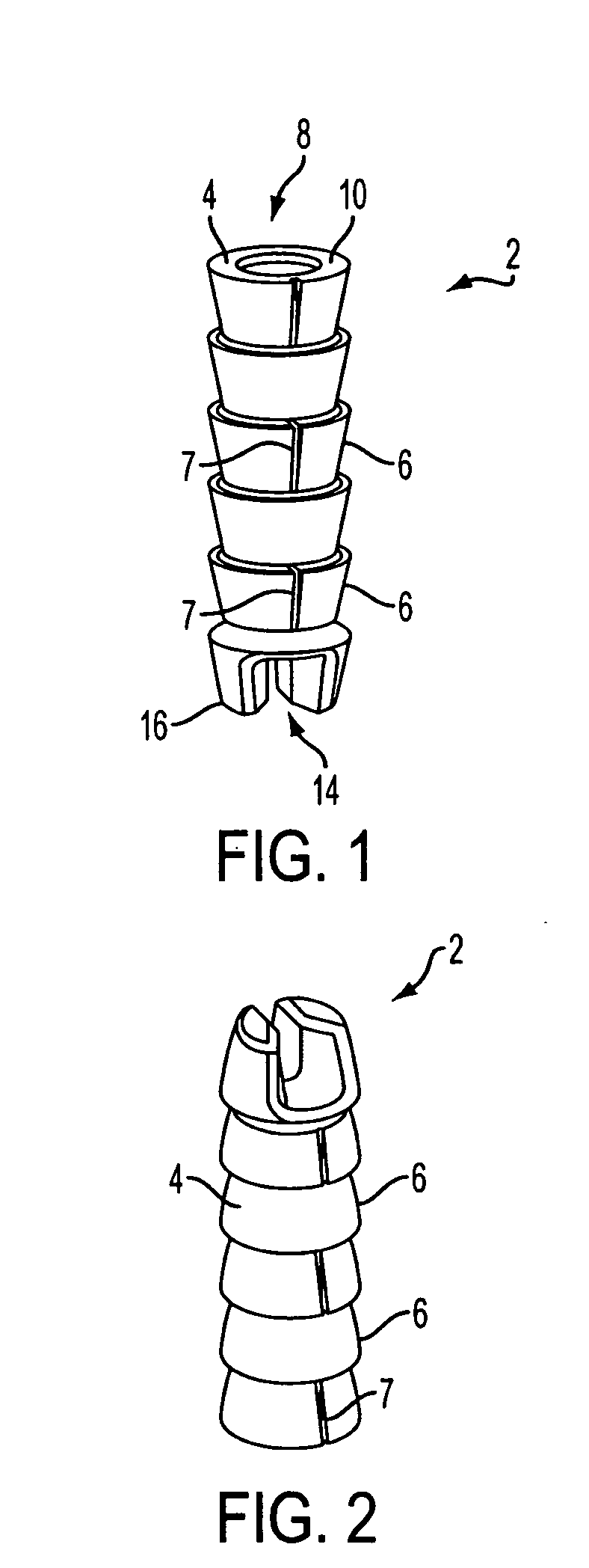
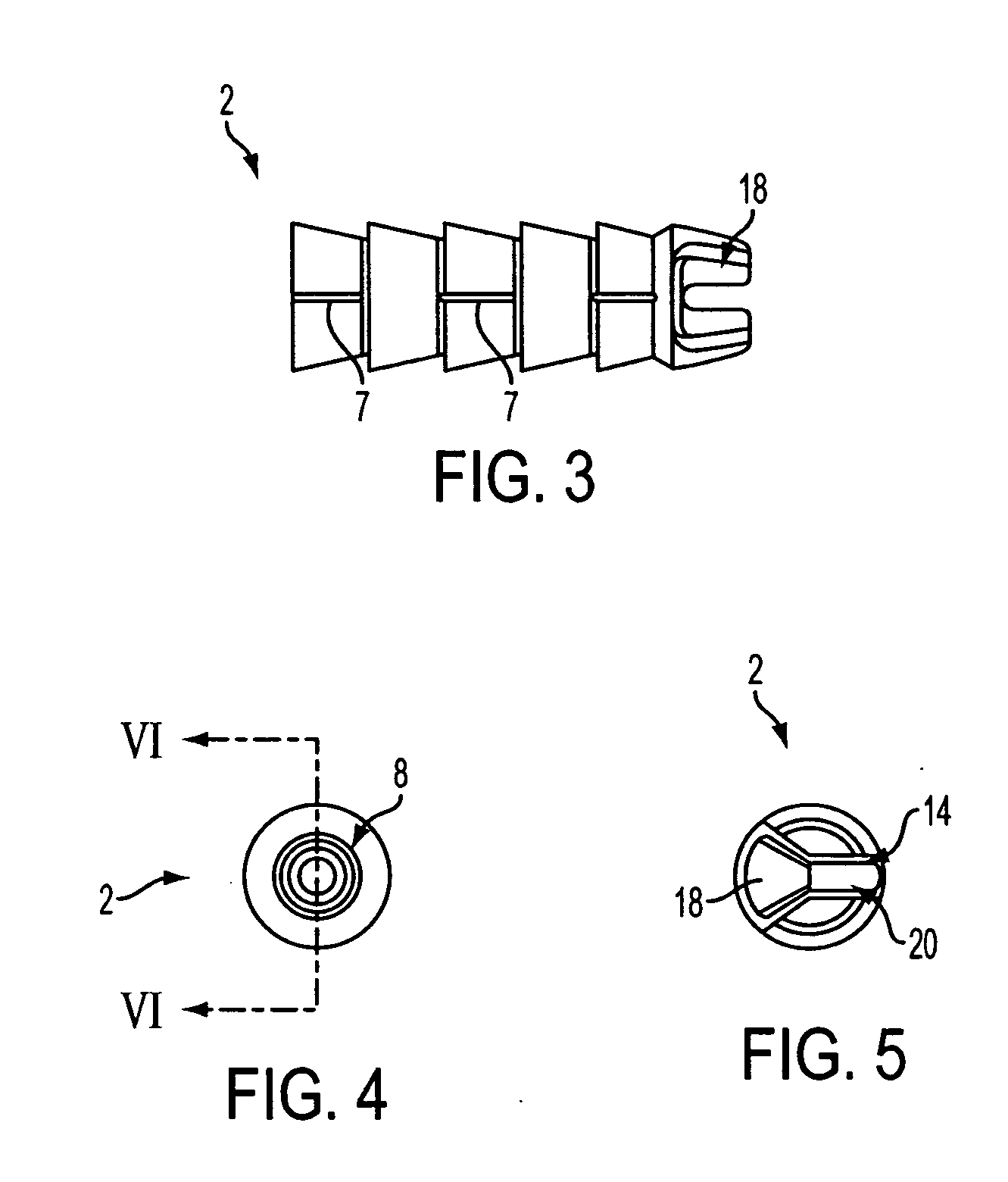
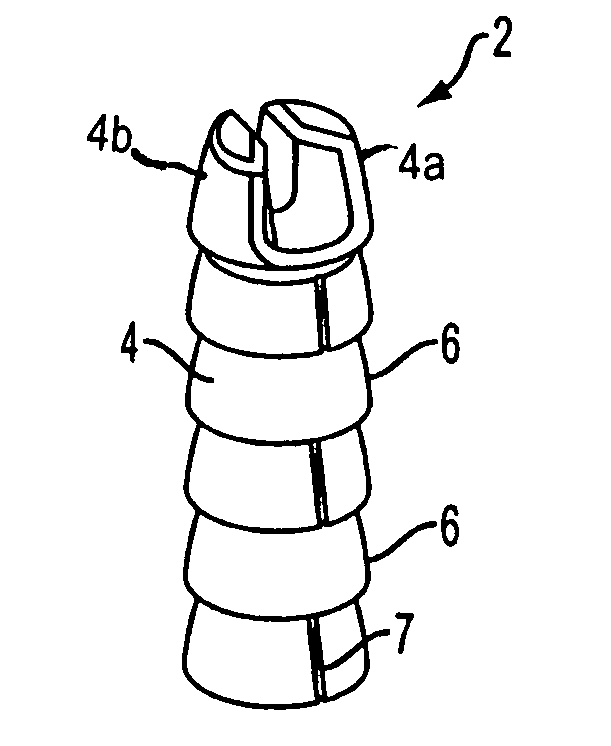
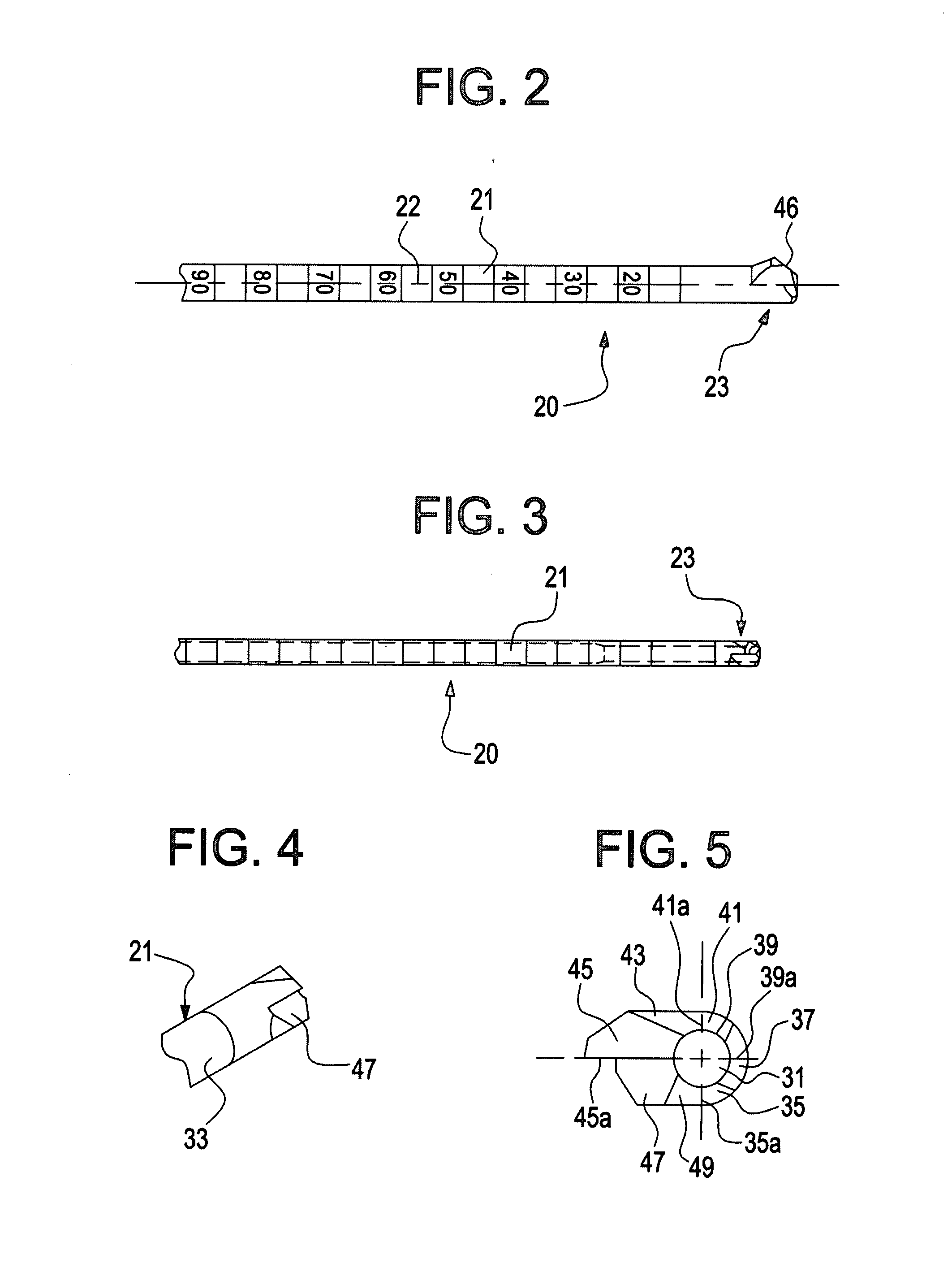
Patents
Literature
1567 results about "Pilot hole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
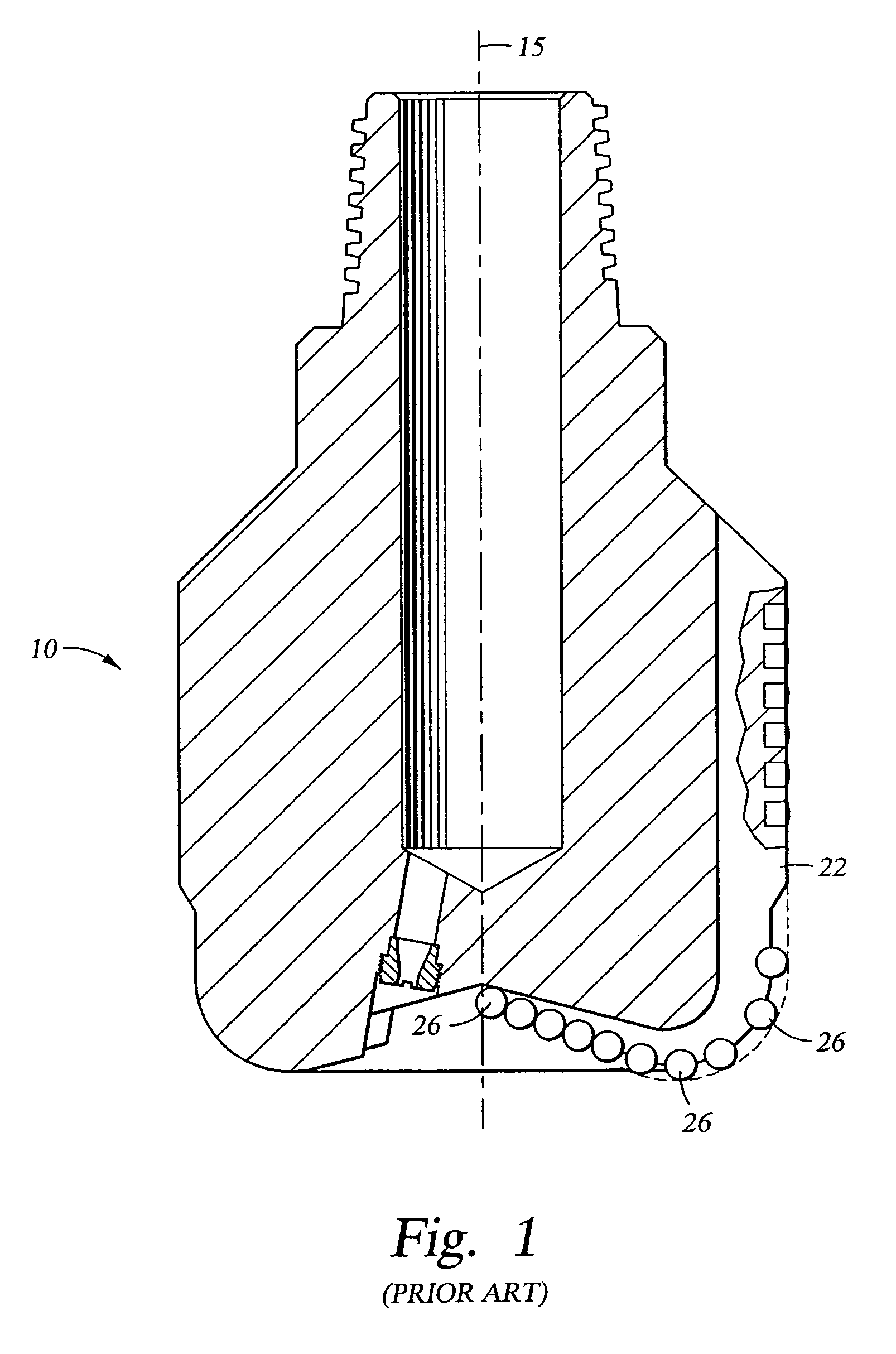
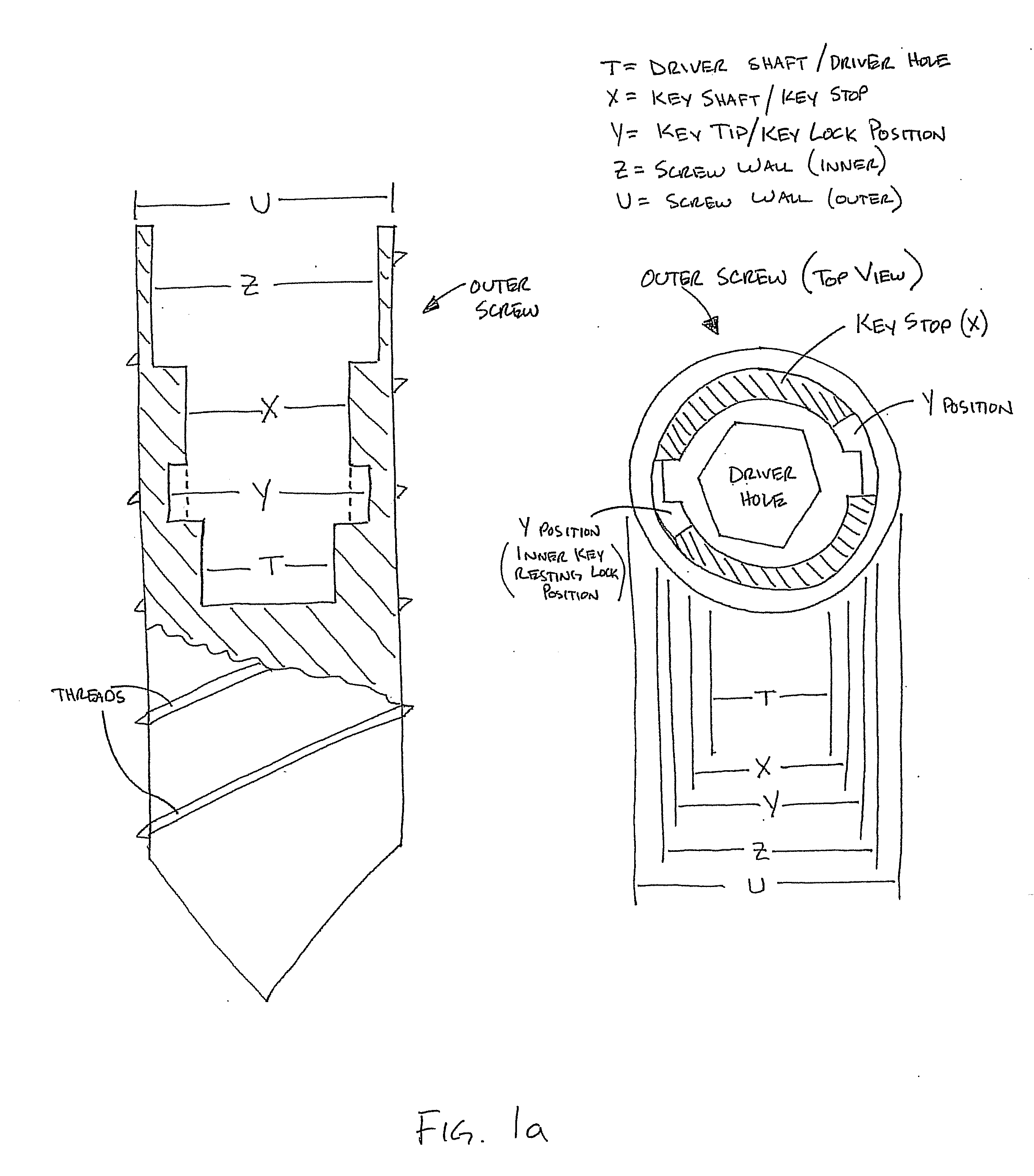
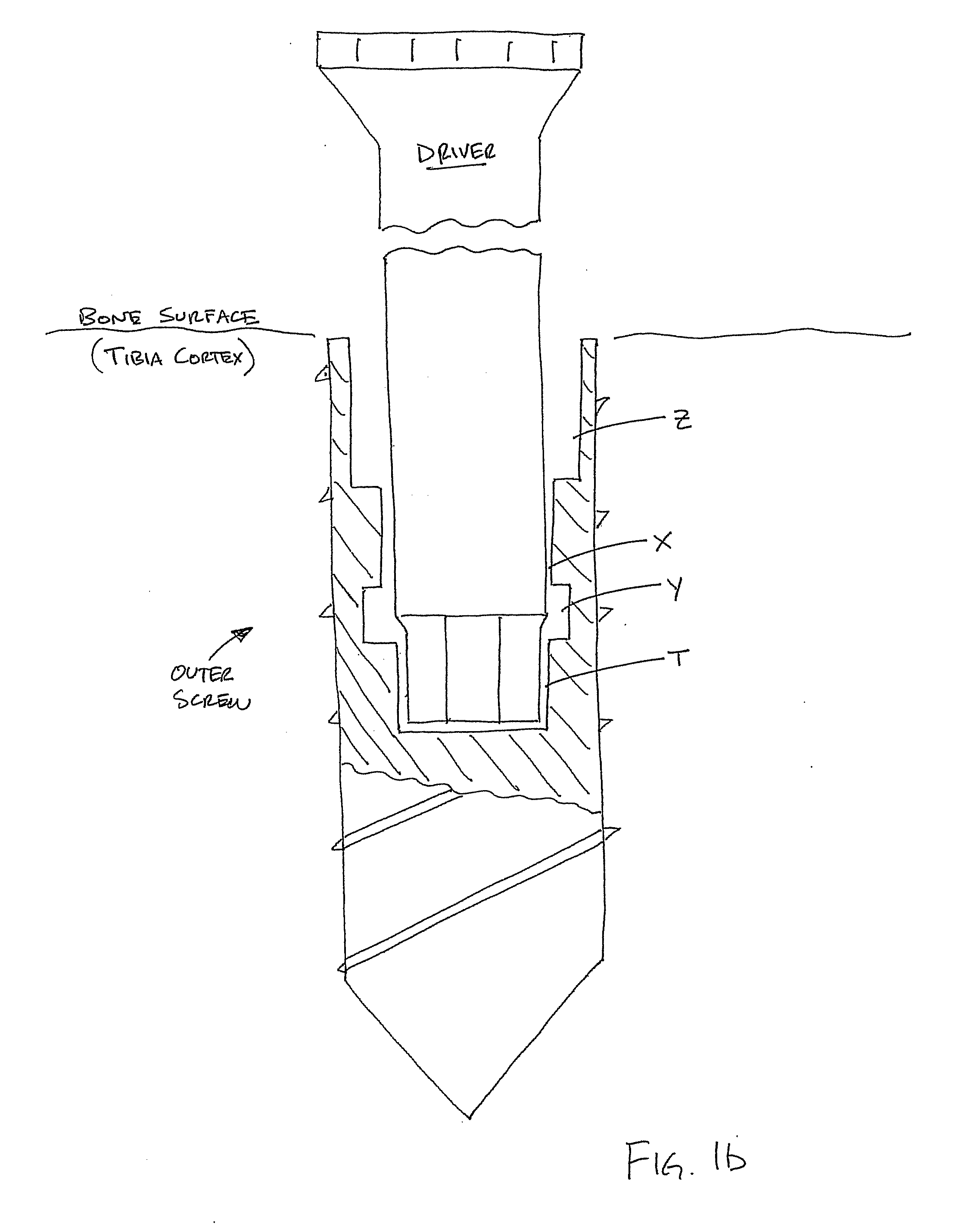
A pilot hole is a small hole drilled into a piece of construction material. Its purpose is a) to guide a larger drill to the appropriate location and ease the job of the larger drill, b) to allow for the insertion of another hole-making tool, such as a knockout punch, that will produce the final-sized hole, or c) to locate, guide, and provide clearance for a self-threading screw in wood or plastic to prevent damaging the material or breaking the screw.
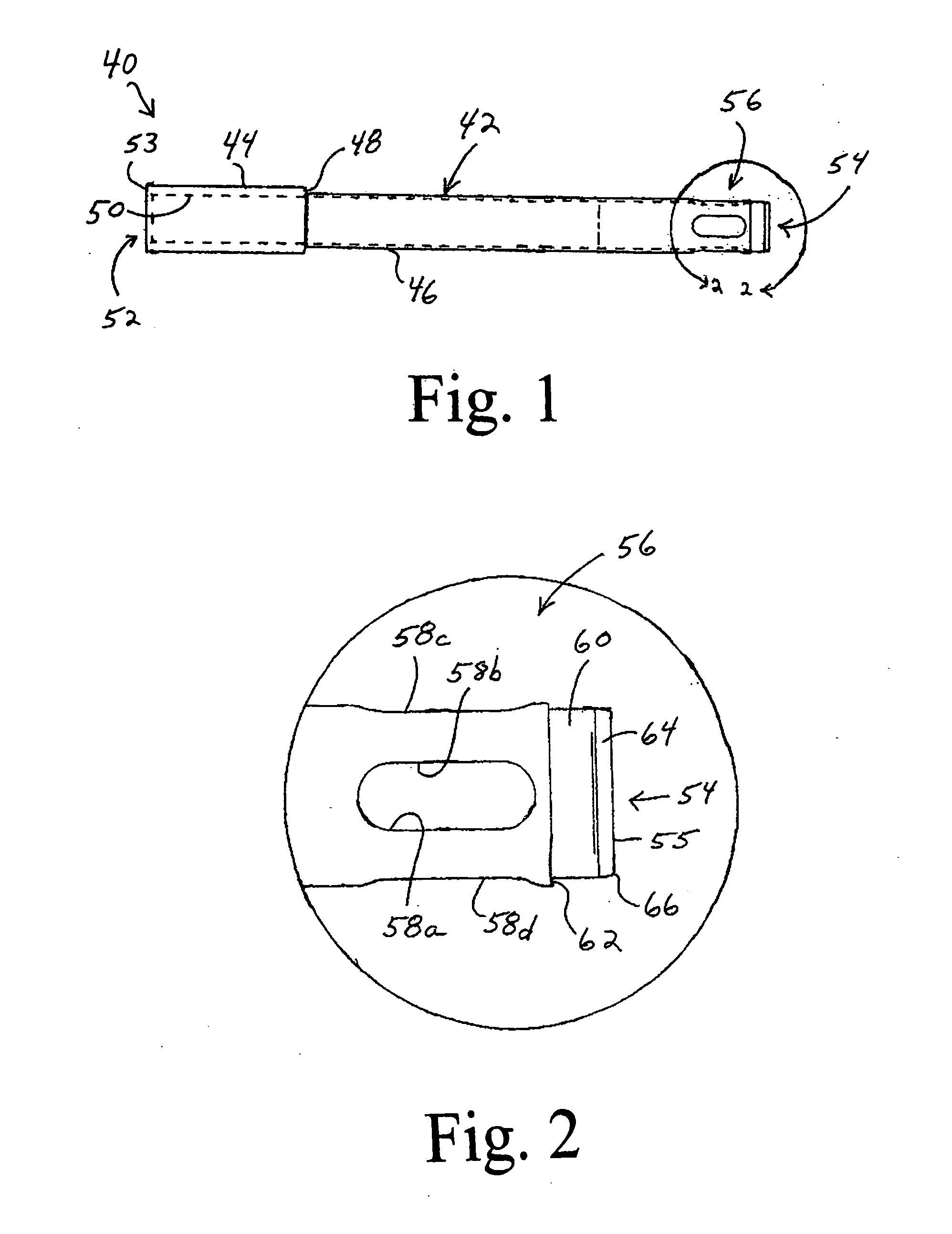
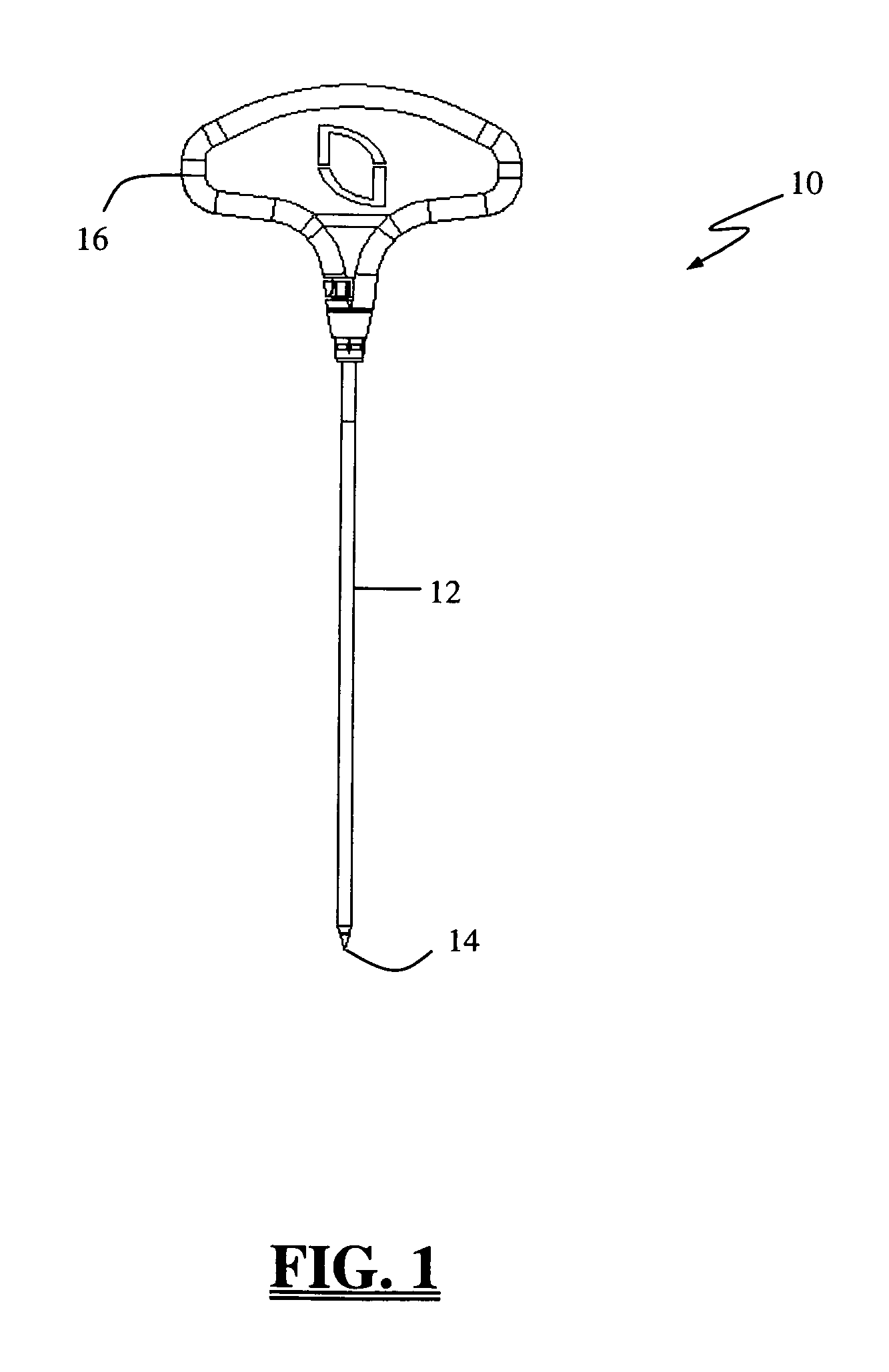
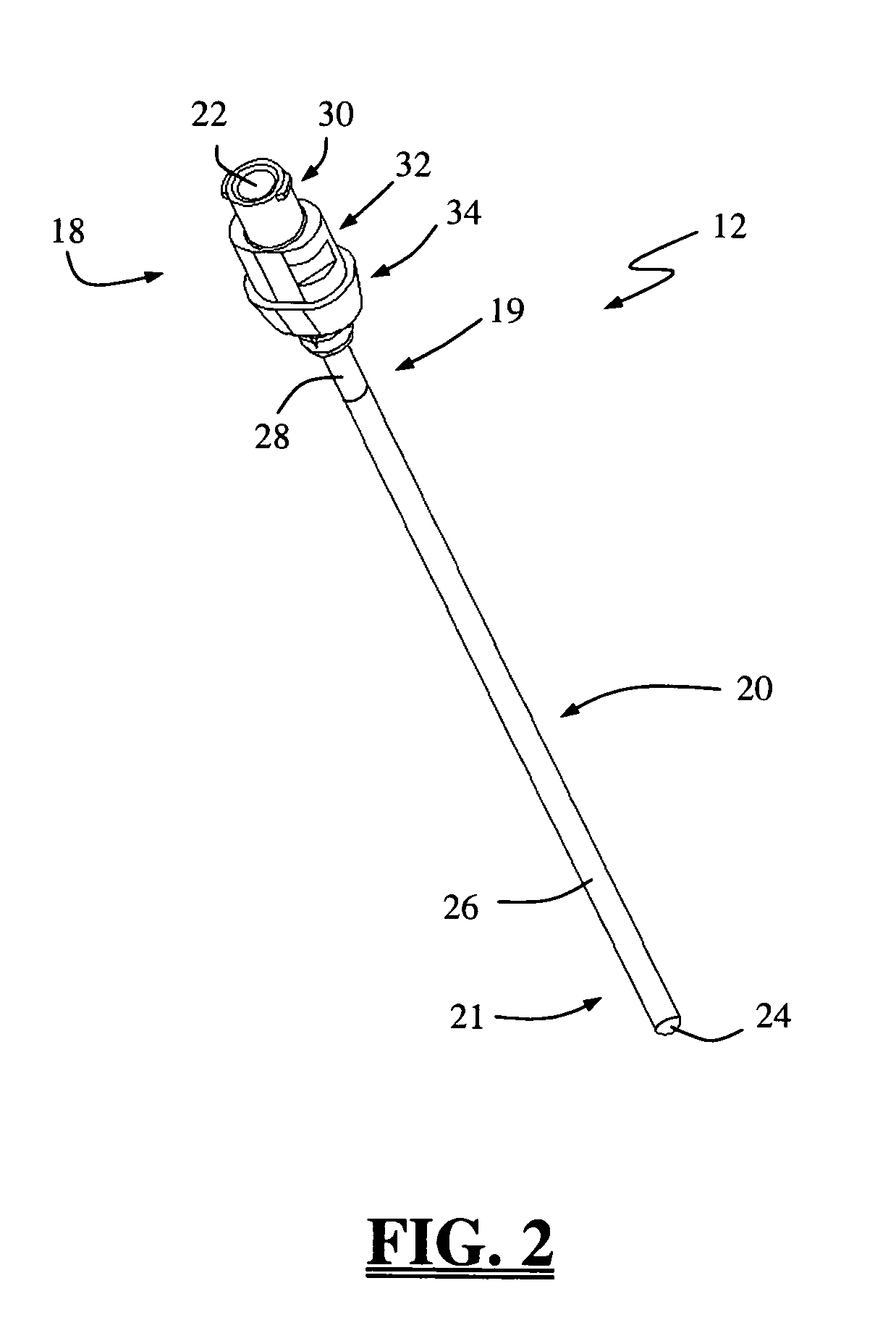
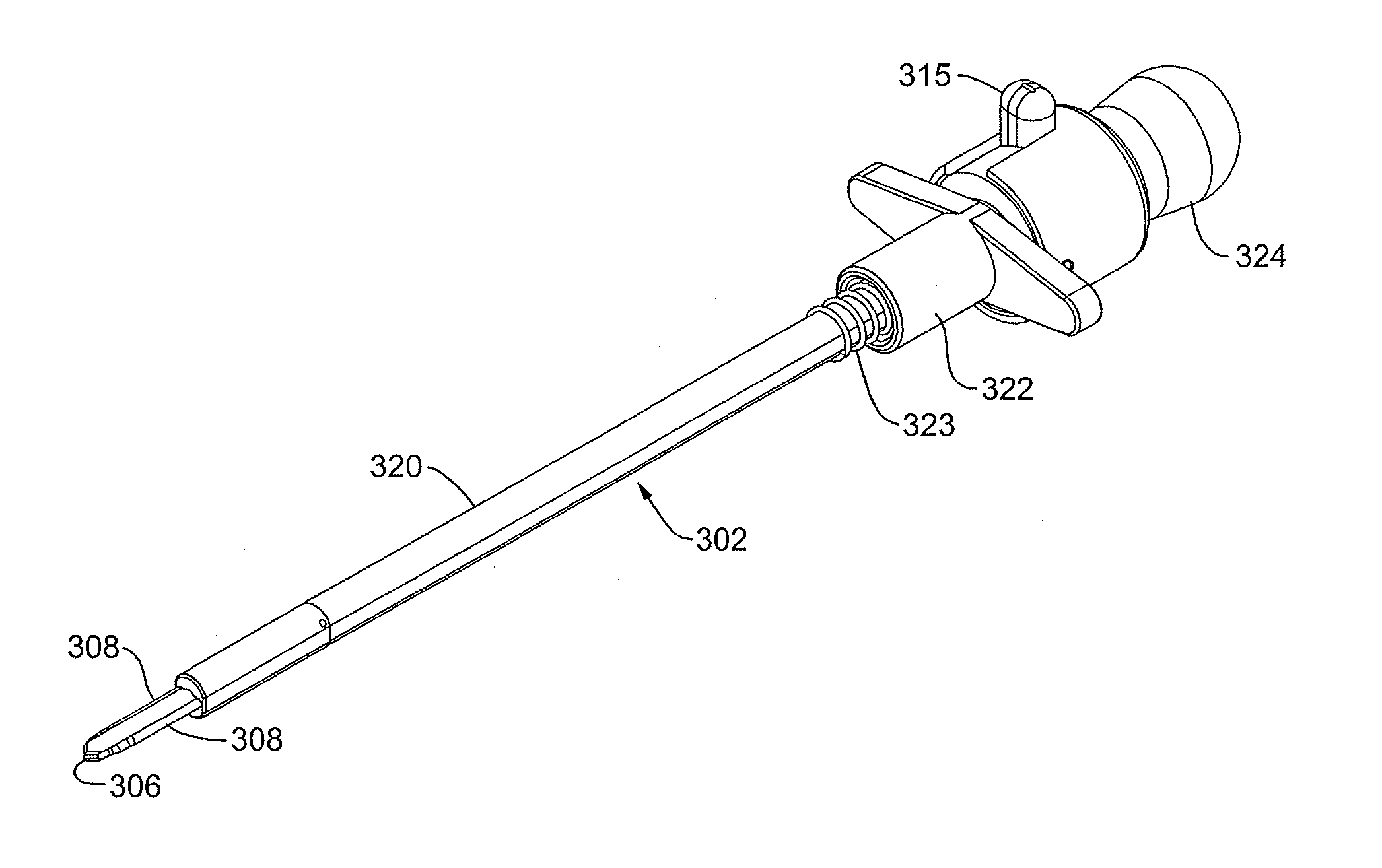
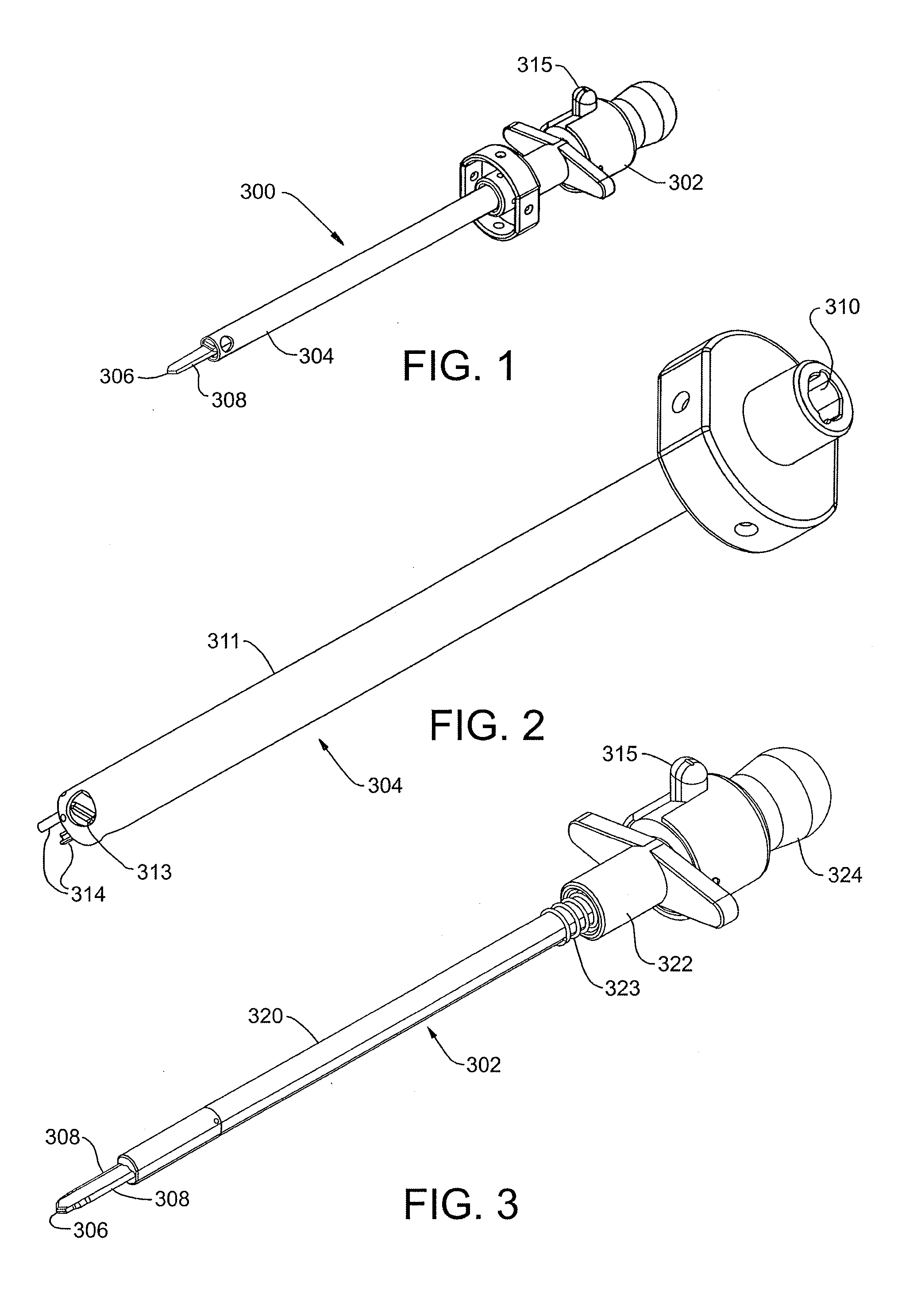
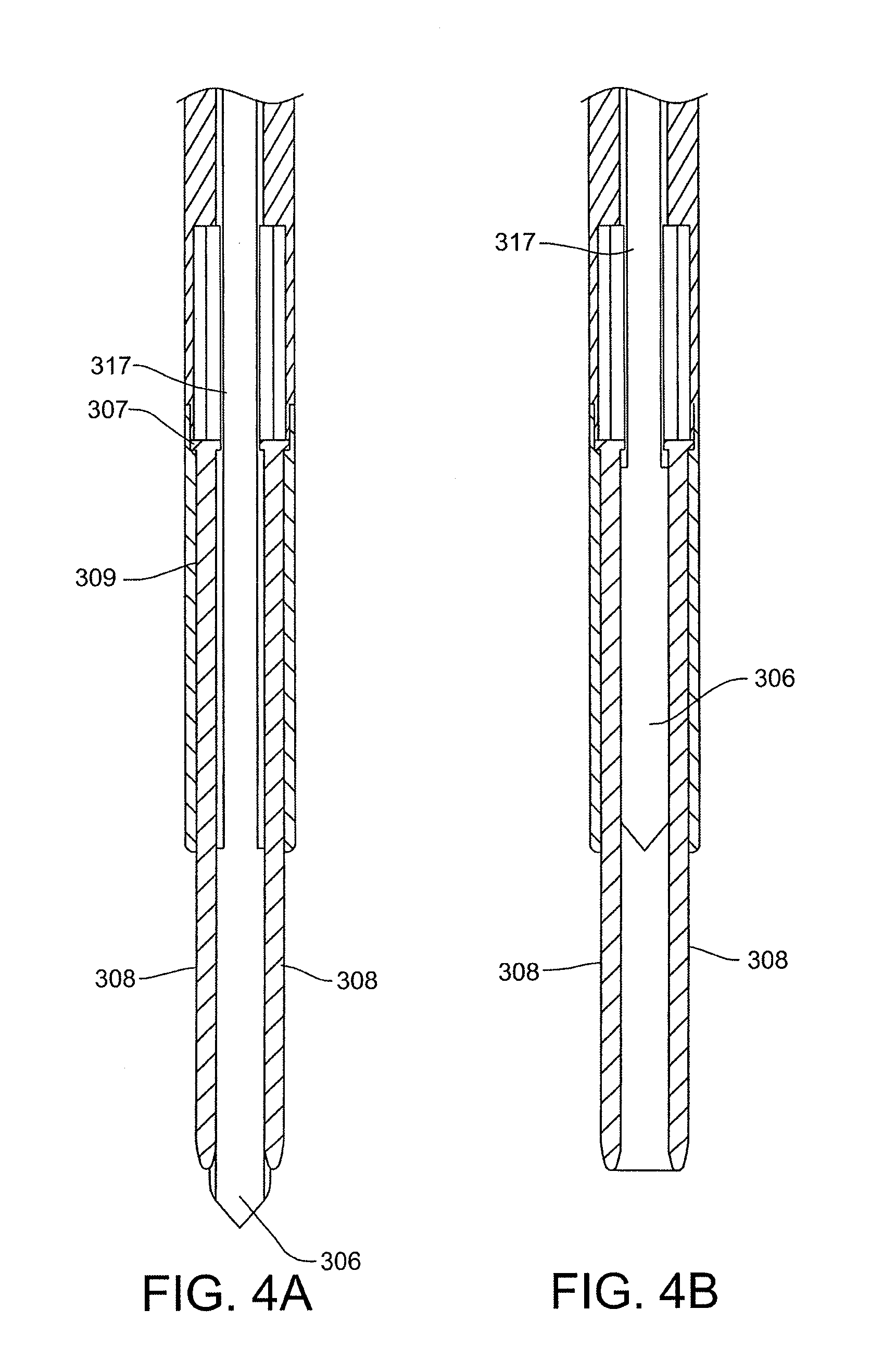
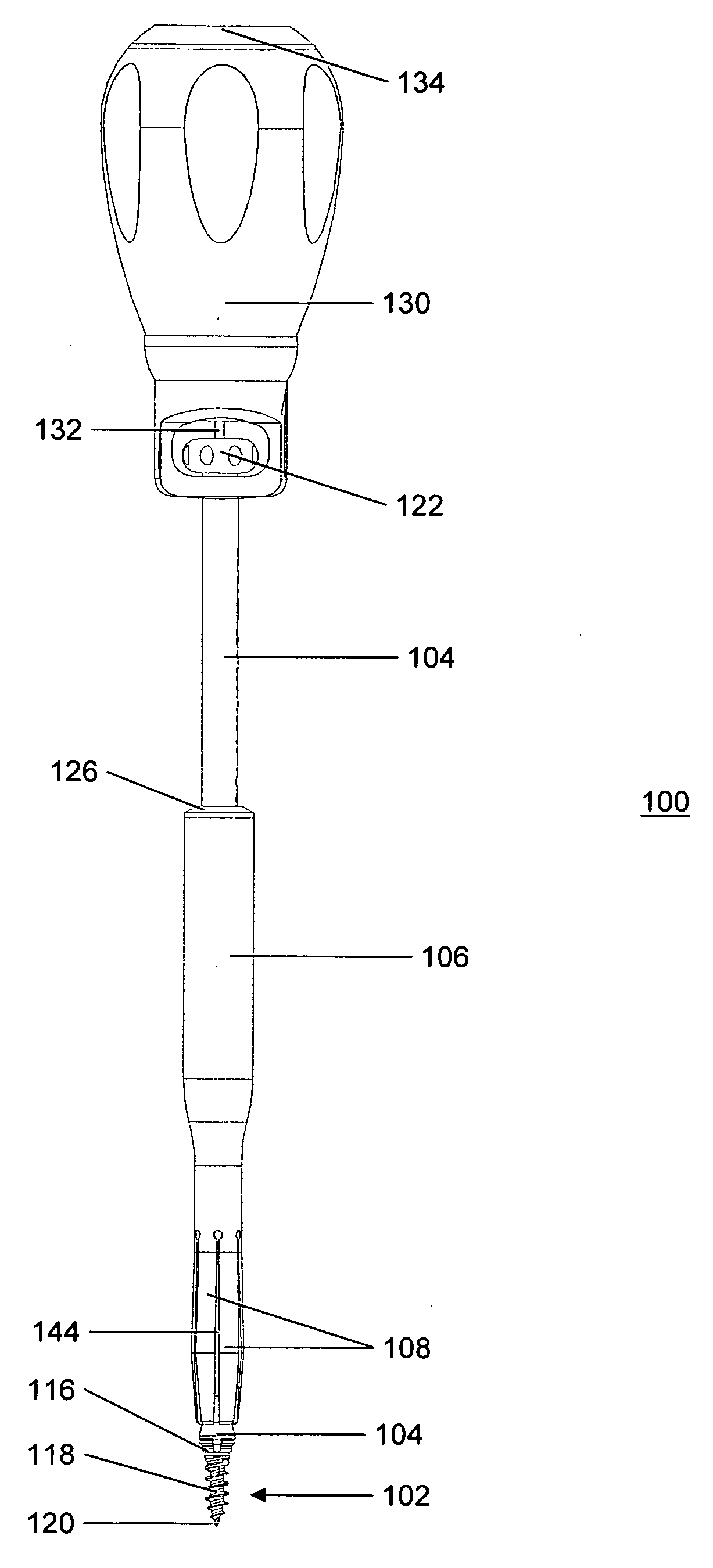
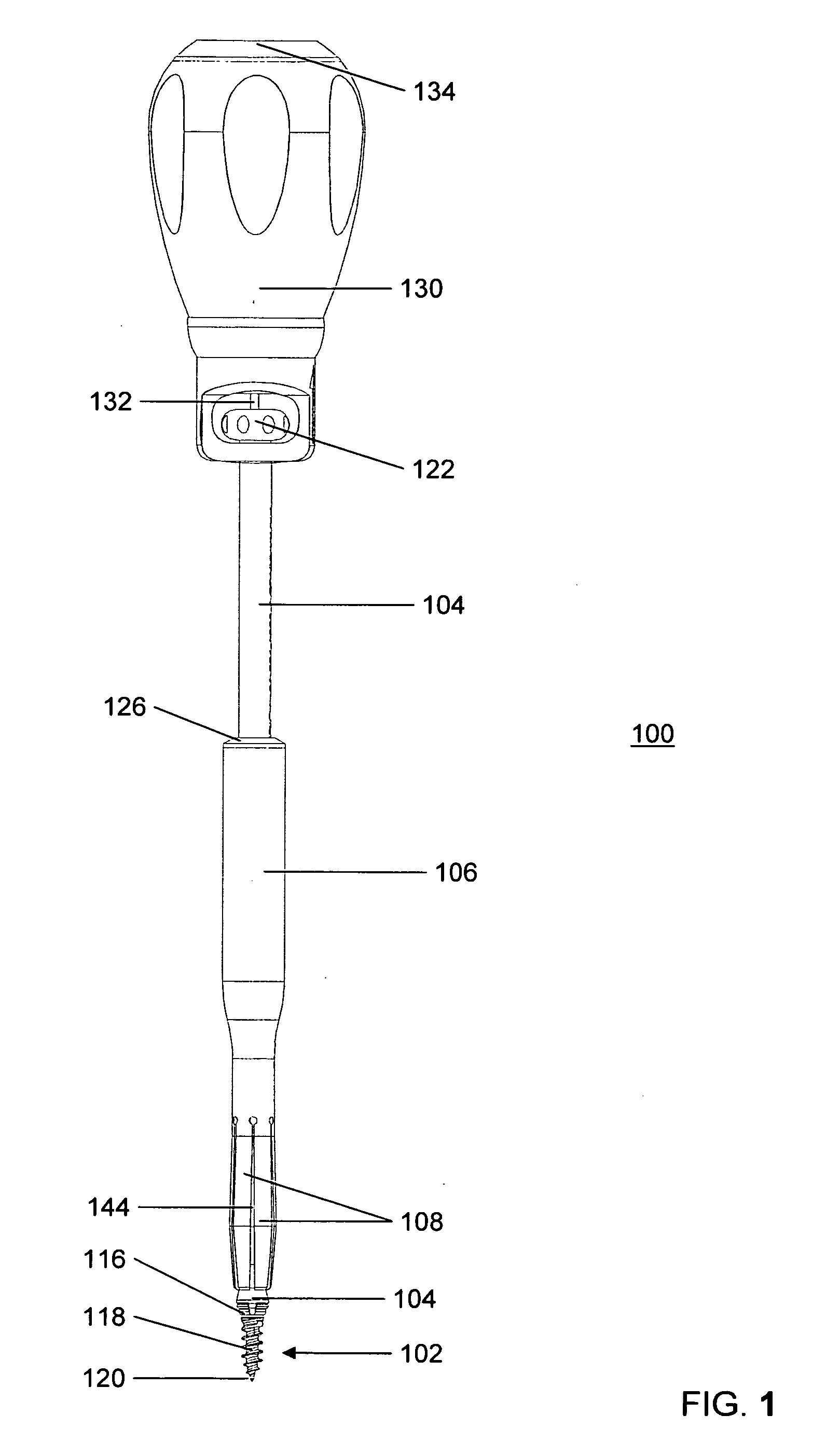
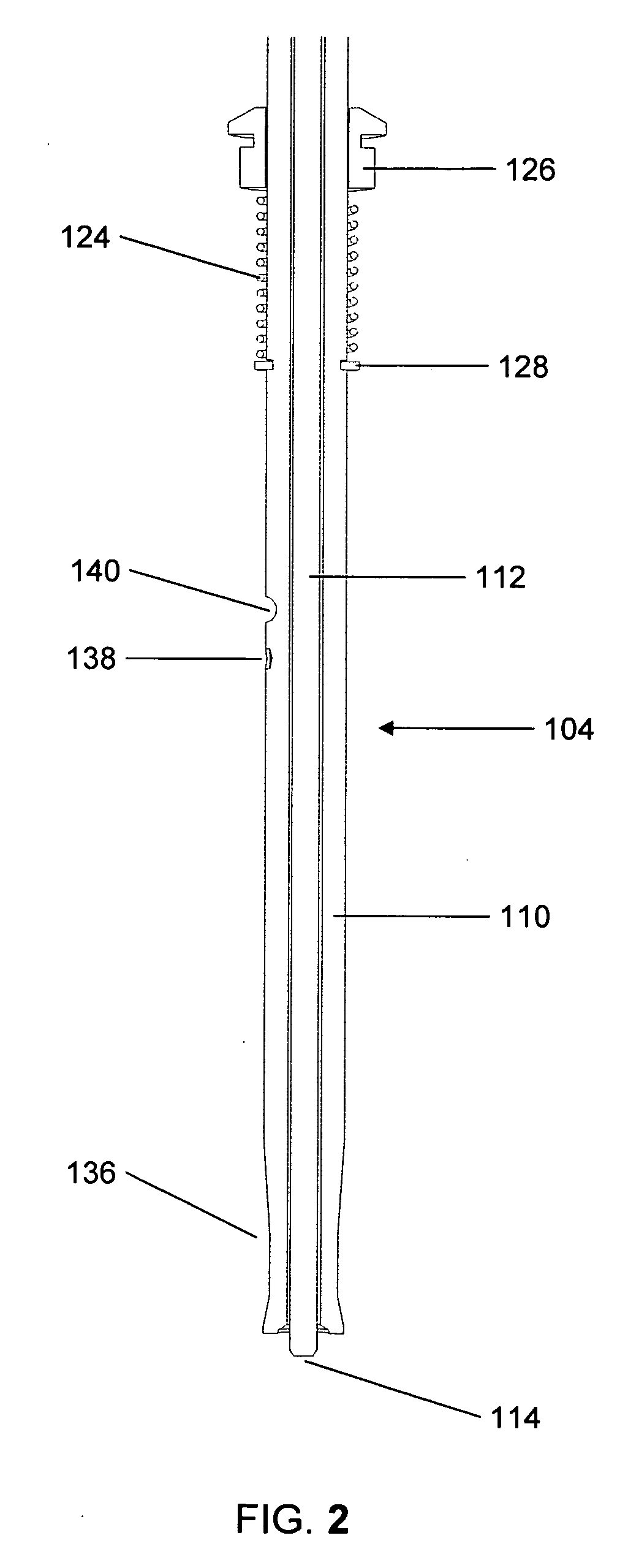
Graft fixation using a plug against suture
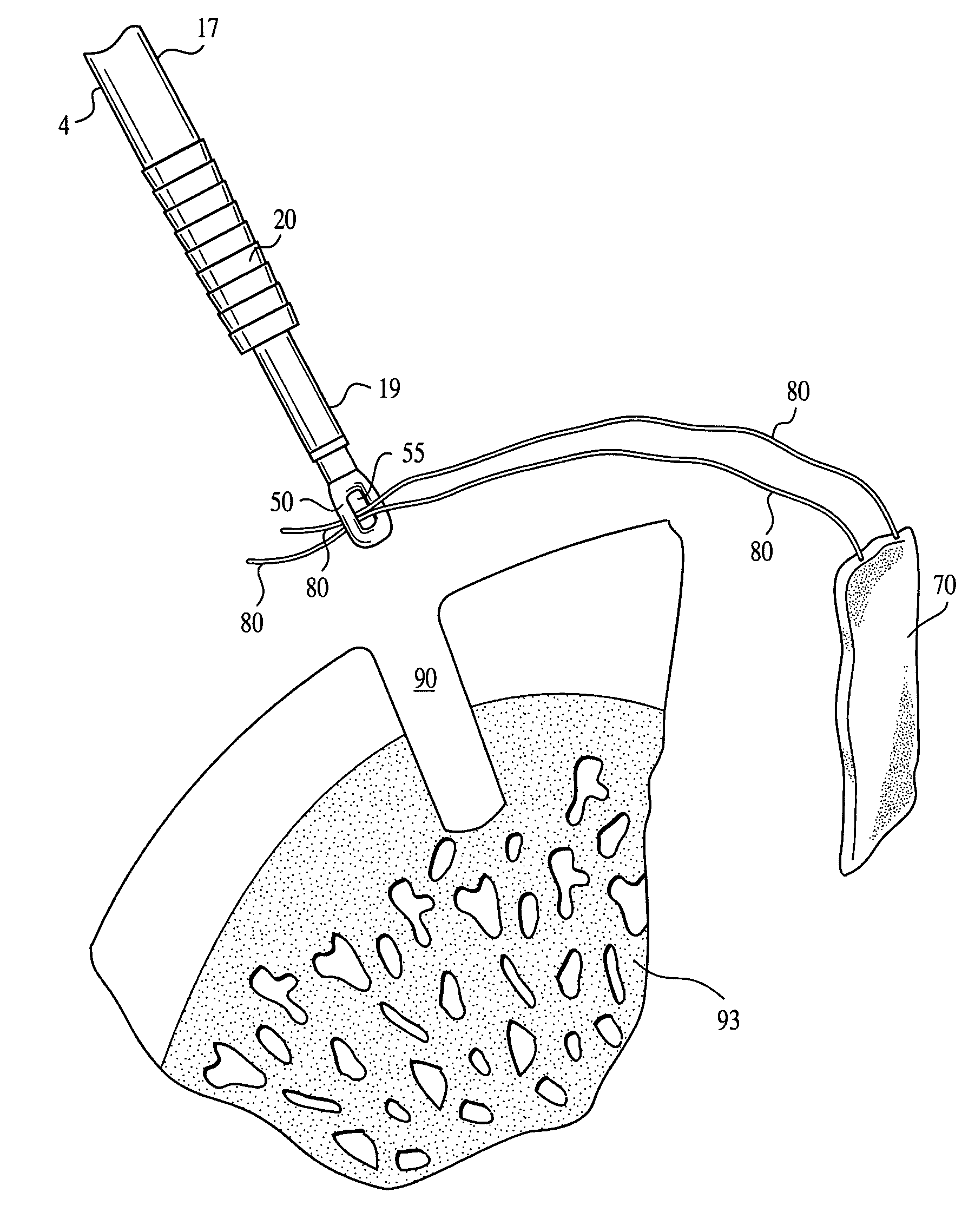
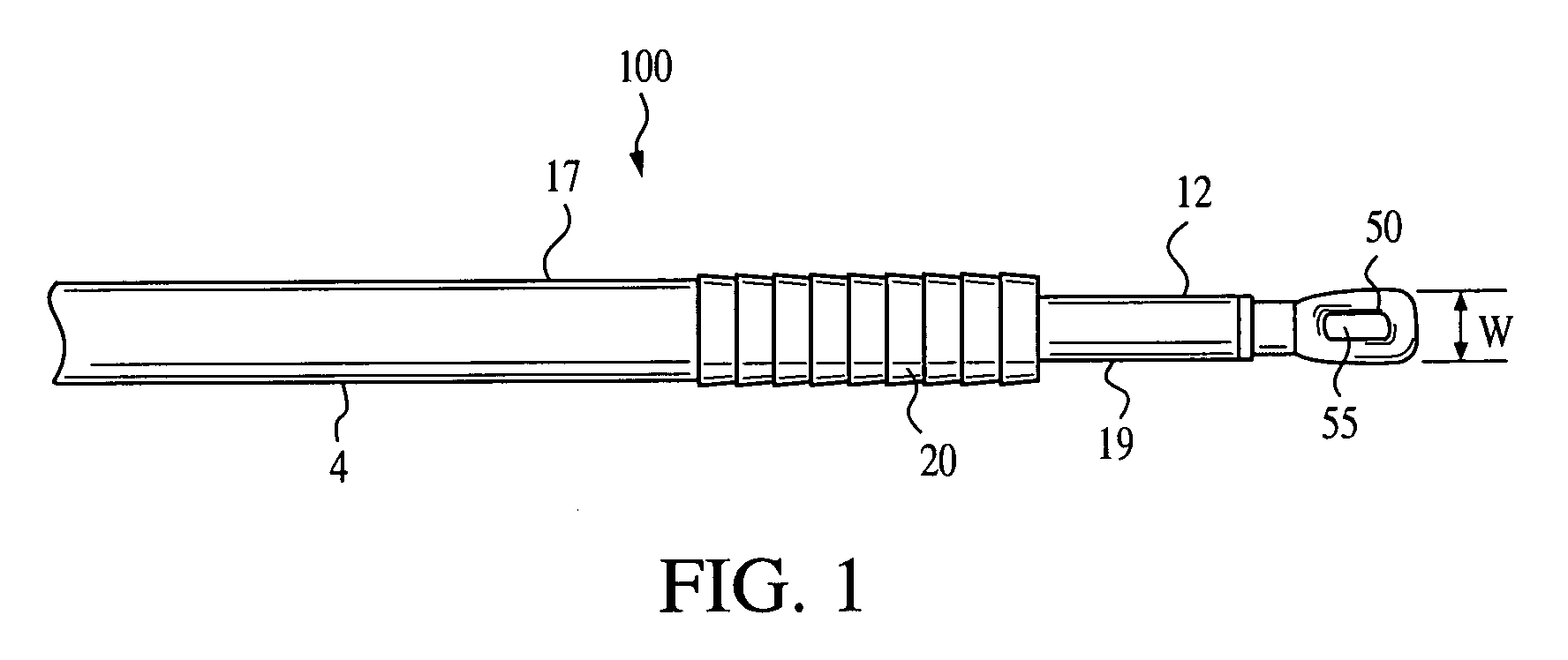
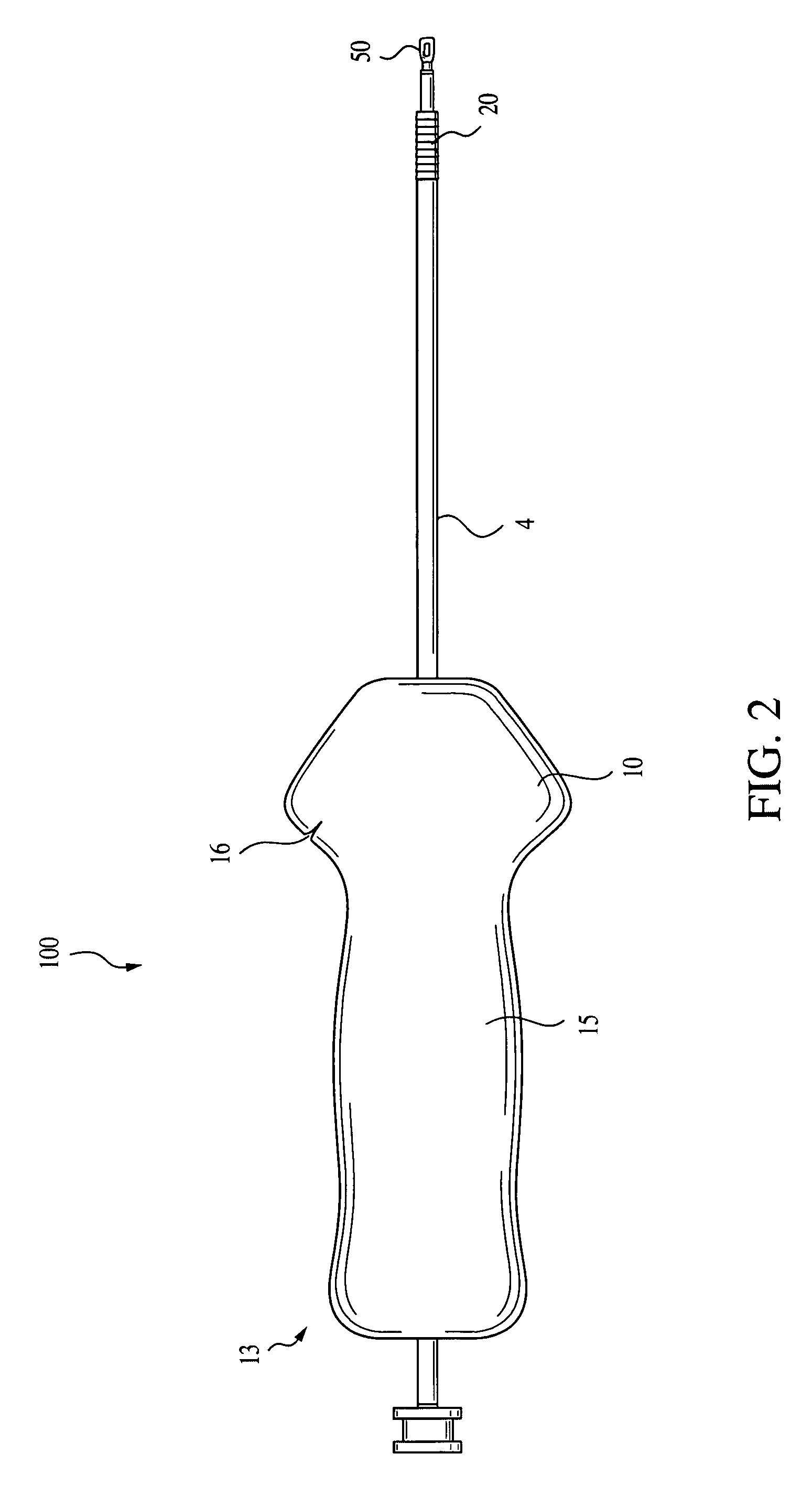
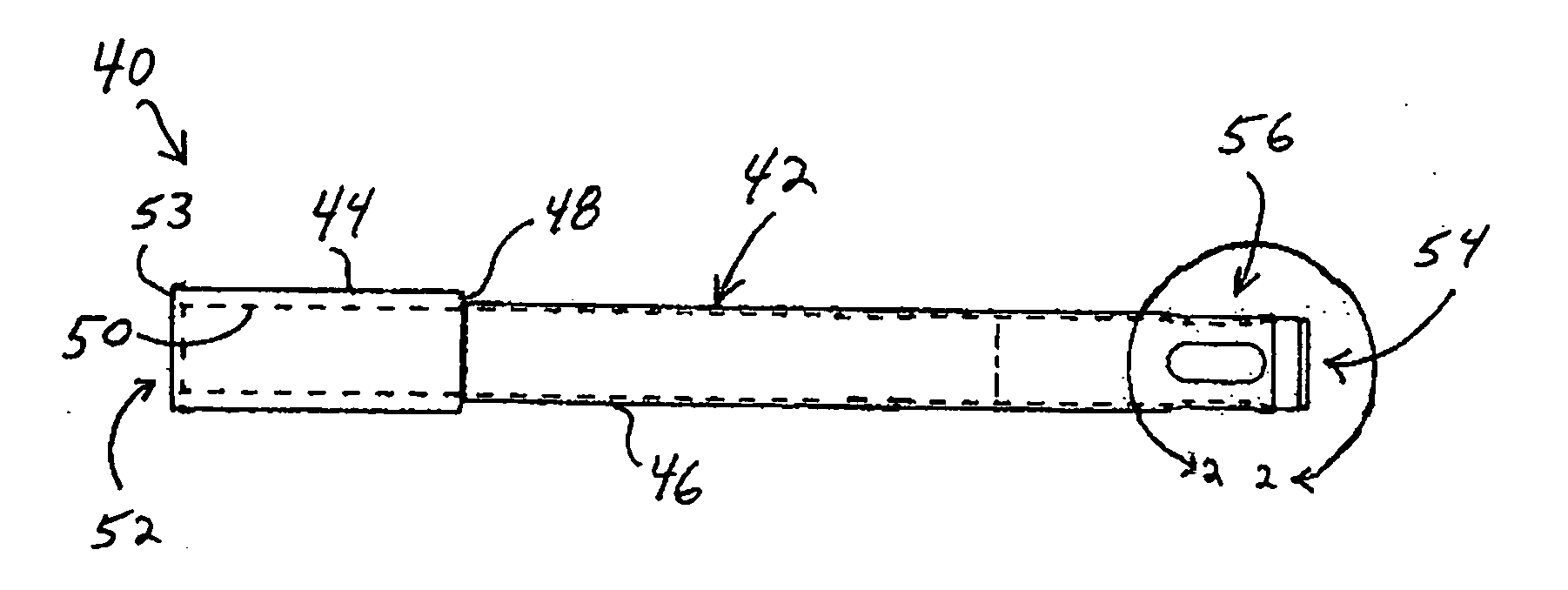
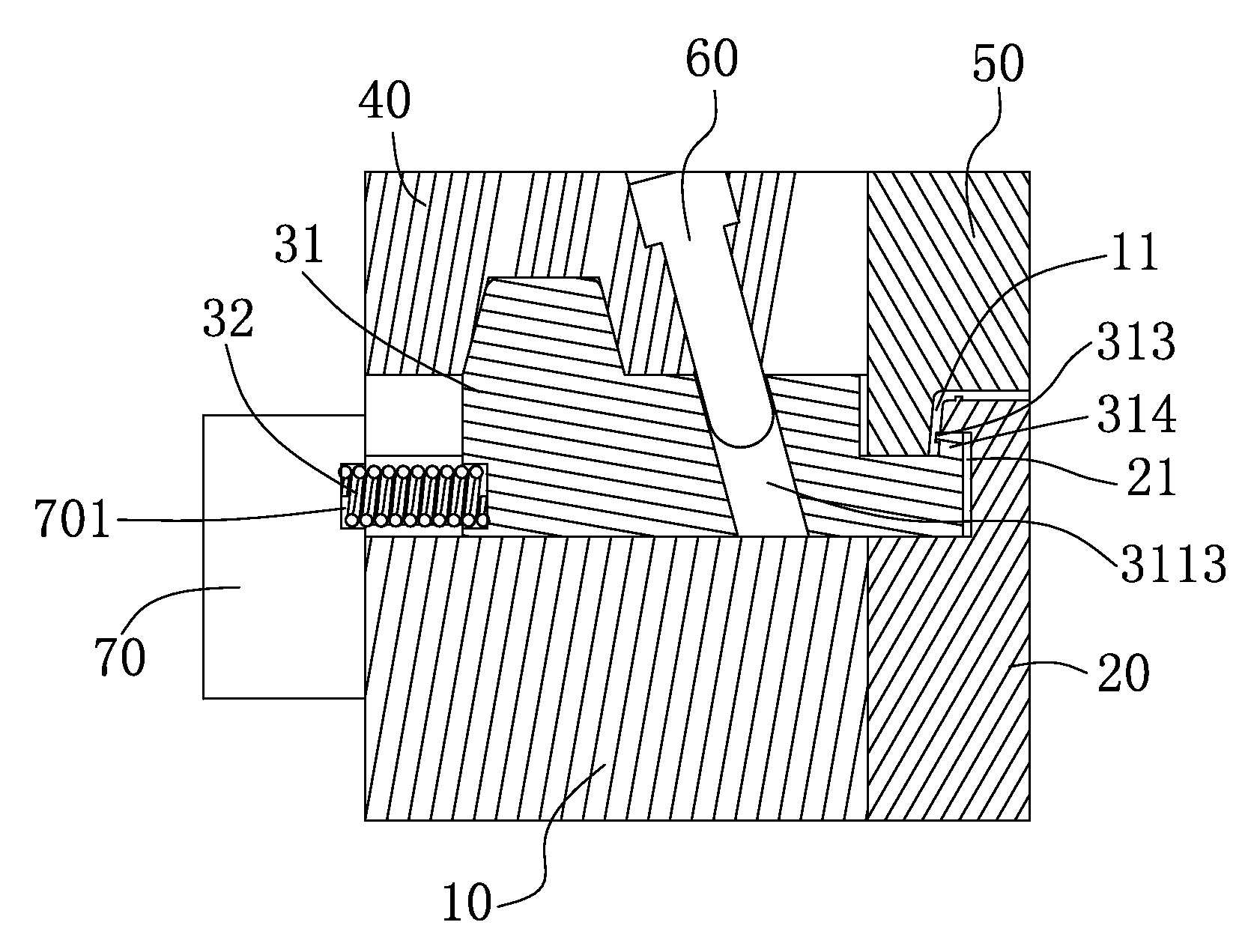
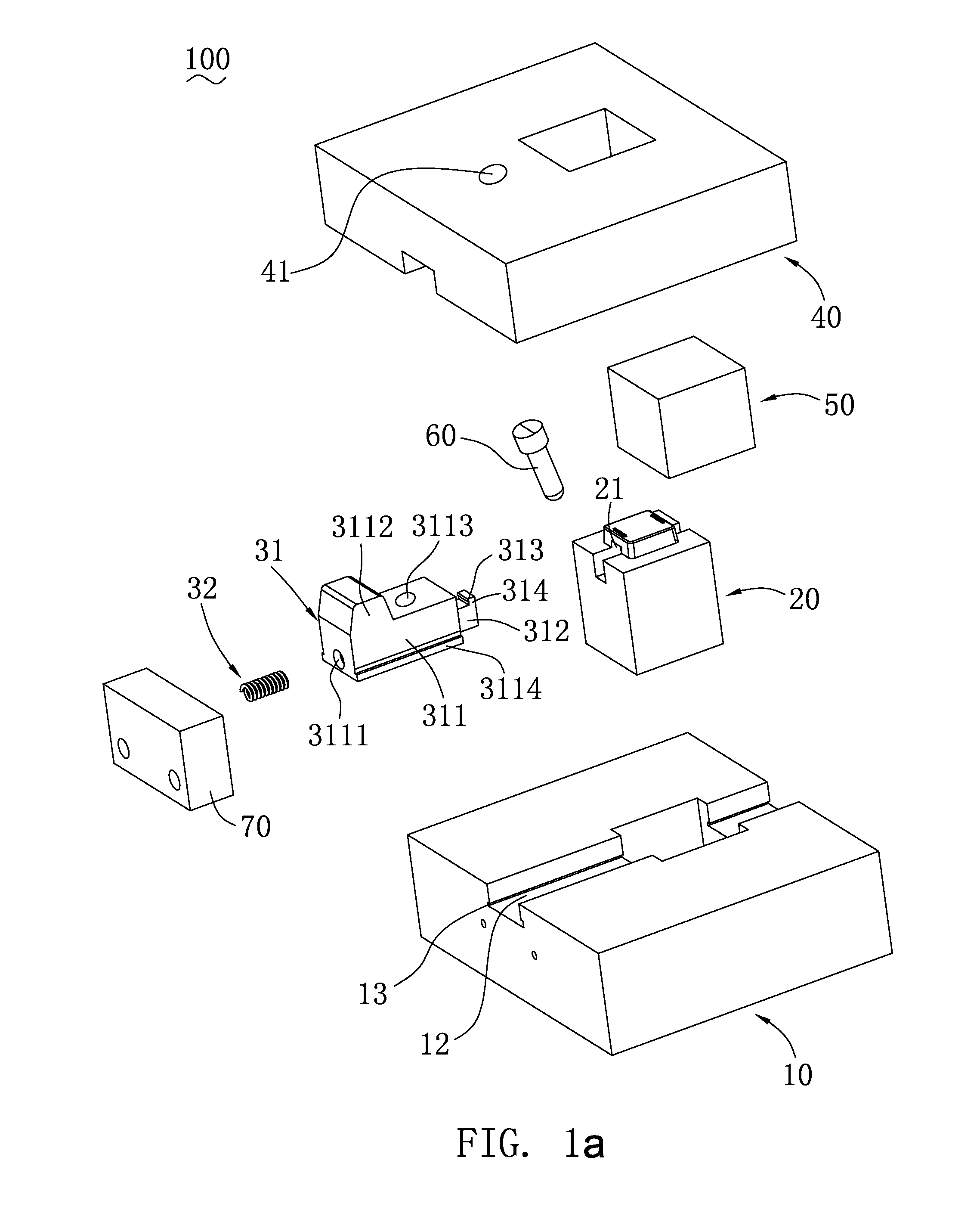
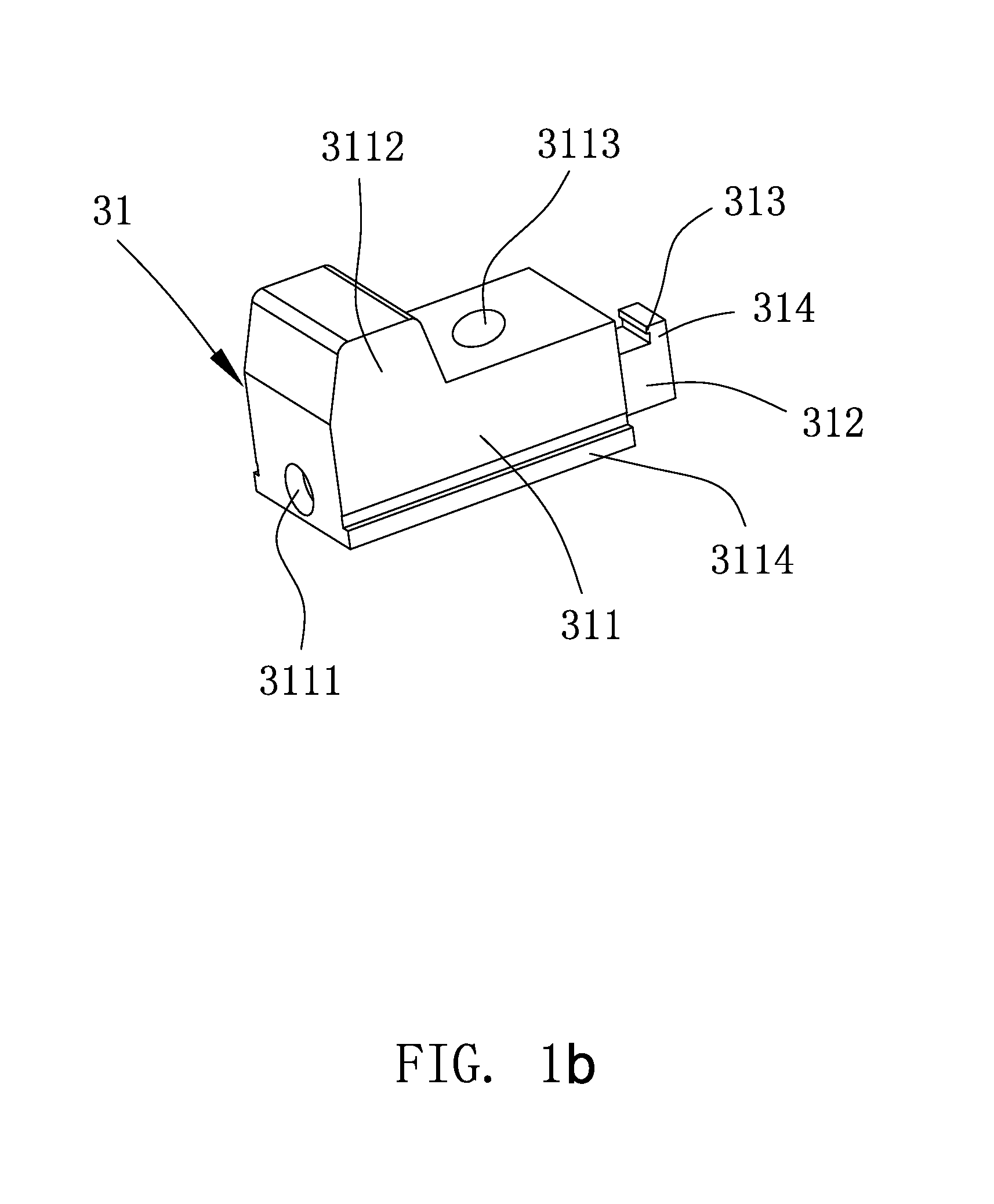
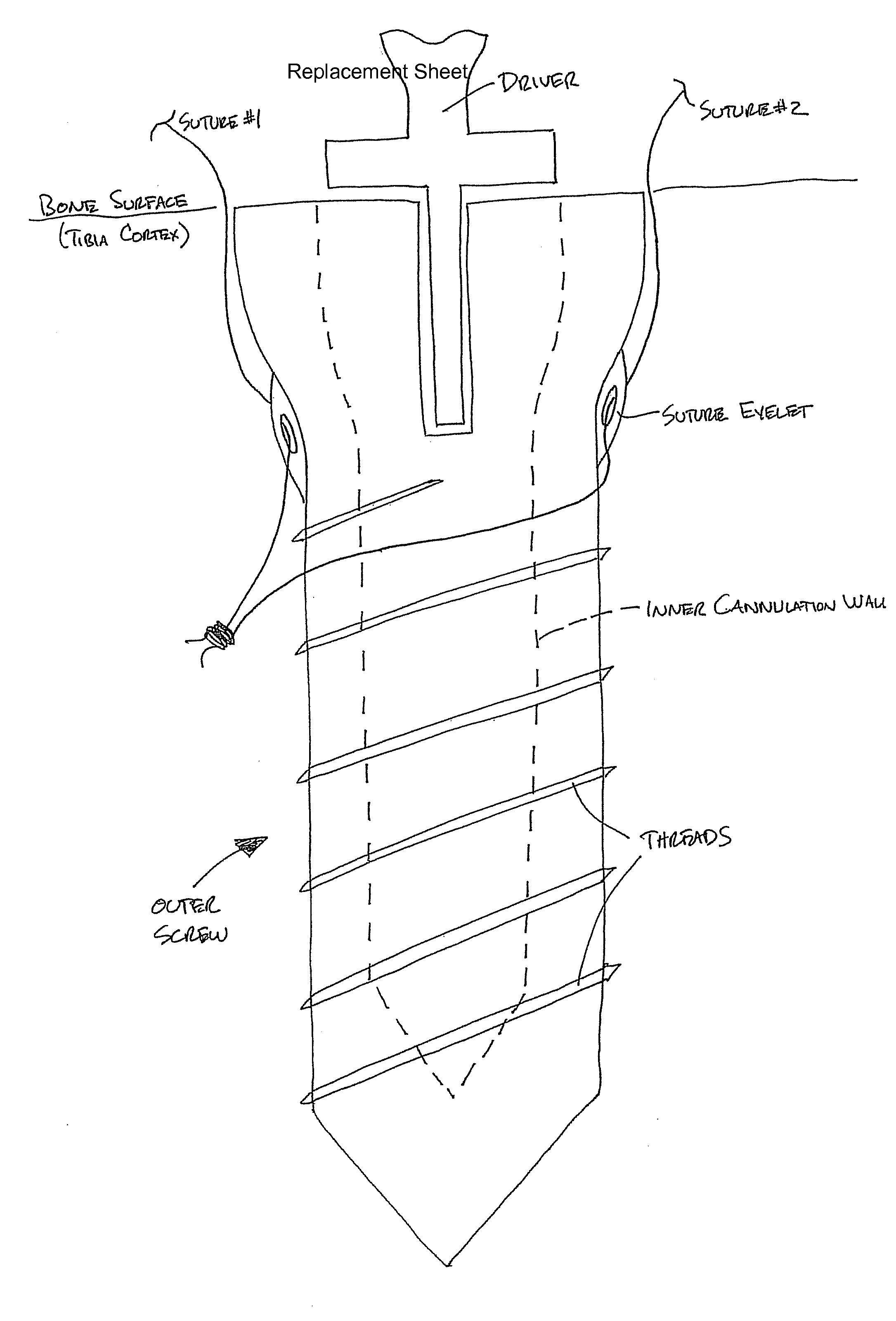
A method for securing soft tissue to bone which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. A pilot hole or socket is created in the bone at the location that the graft is to be secured. Suture is passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated plug or screw is pre-loaded onto the distal end of a driver provided with an eyelet implant at its distal end. Suture attached to the graft is passed through the eyelet of the implant located at the distal end of the driver. The distal end of the driver together with the eyelet implant is inserted into the bottom of the hole, with the screw or plug disposed just outside the hole. Tension is applied to the suture to position the graft at the desired location relative to the bone hole. The screw or plug is then frilly advanced into the pilot hole by turning the interference screw or tapping the plug until the cannulated screw or plug securely engages and locks in the eyelet implant, so that the cannulated plug or screw with the engaged eyelet implant is flush with the bone. Once the screw or plug is fully inserted and the suture is impacted into the pilot hole, the driver is removed and any loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site are then clipped short.
Owner:ARTHREX
Articular cartilage repair implant delivery device and method of use
A technique for the arthroscopic delivery and fixation of an articular cartilage repair device or implant is provided. The technique includes the use of a cannula tube that functions as both a cartilage cutter and a guide to pass instruments into the body arthroscopically. One such instrument is an end-cutting reamer that both prepares the subchondral bone by re-surfacing it down to a specified depth and also simultaneously drills a pilot hole in the subchondral bone to accept the cartilage repair device. A delivery device is utilized to hold and deliver the cartilage repair device to the delivery site.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Graft fixation using a plug against suture
A method for securing soft tissue to bone which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. Suture is passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated plug or screw is pre-loaded onto the distal end of a driver provided with an eyelet implant at its distal end. Suture attached to the graft is passed through the eyelet of the implant located at the distal end of the driver. The distal end of the driver together with the eyelet implant is inserted into the bone. Tension is applied to the suture to position the graft at the desired location relative to the bone. The screw or plug is advanced into the pilot hole by turning the interference screw or tapping the plug until the cannulated screw or plug securely engages and locks in the eyelet implant, so that the cannulated plug or screw with the engaged eyelet implant is flush with the bone. Once the screw or plug is fully inserted and the suture is impacted into the bone, the driver is removed and any loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site are then clipped short.
Owner:ARTHREX
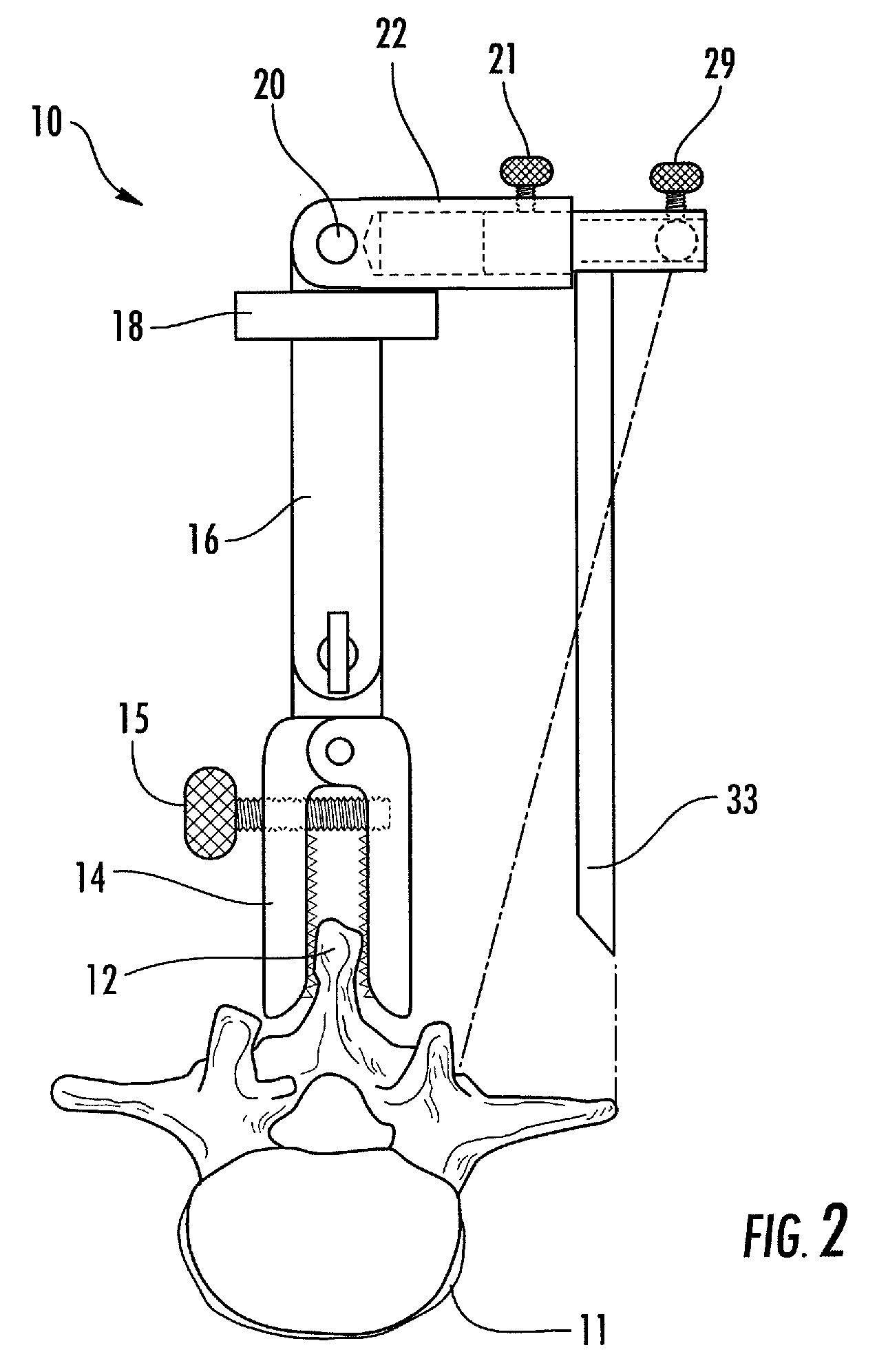
Axial spinal implant and method and apparatus for implanting an axial spinal implant within the vertebrae of the spine
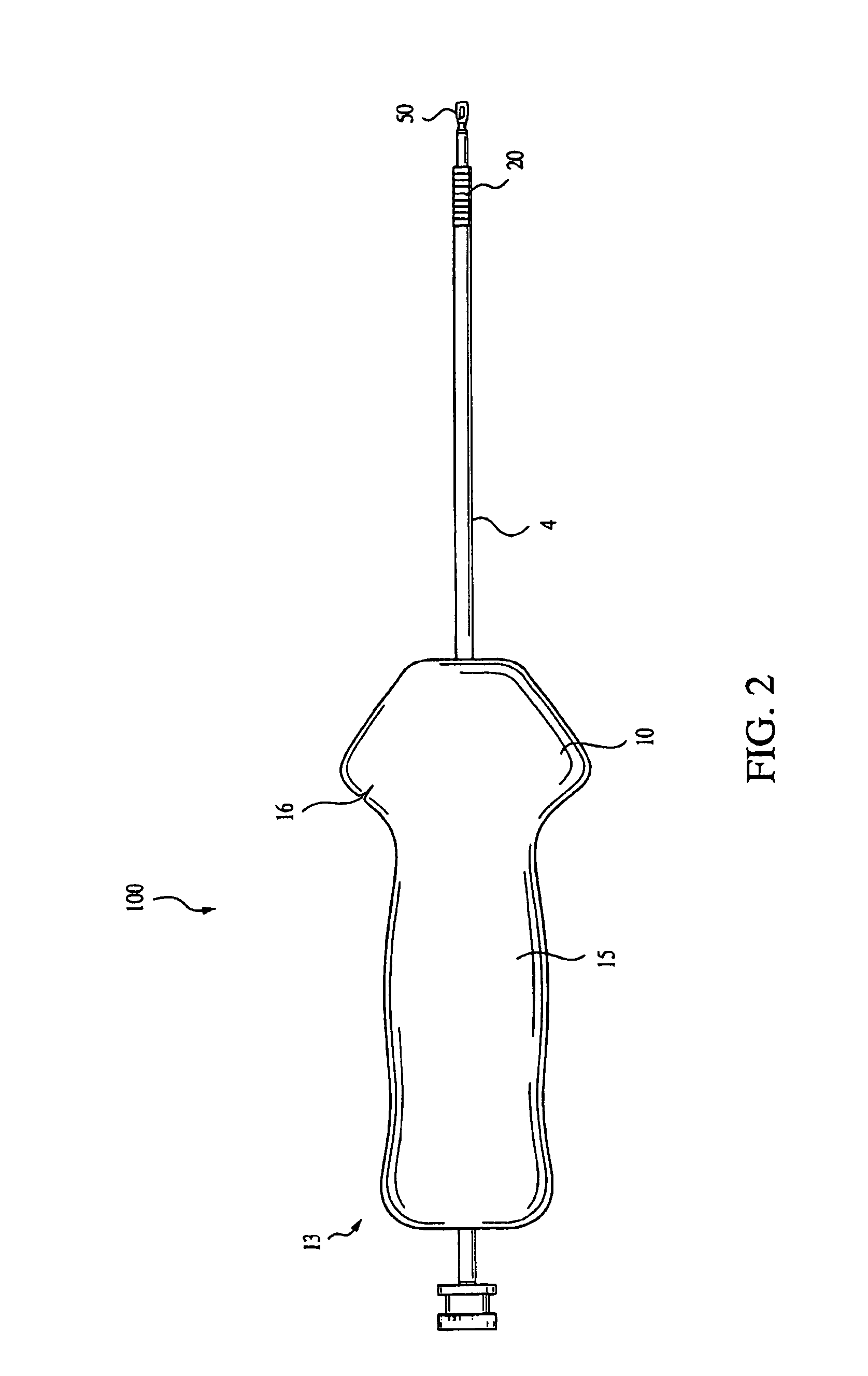
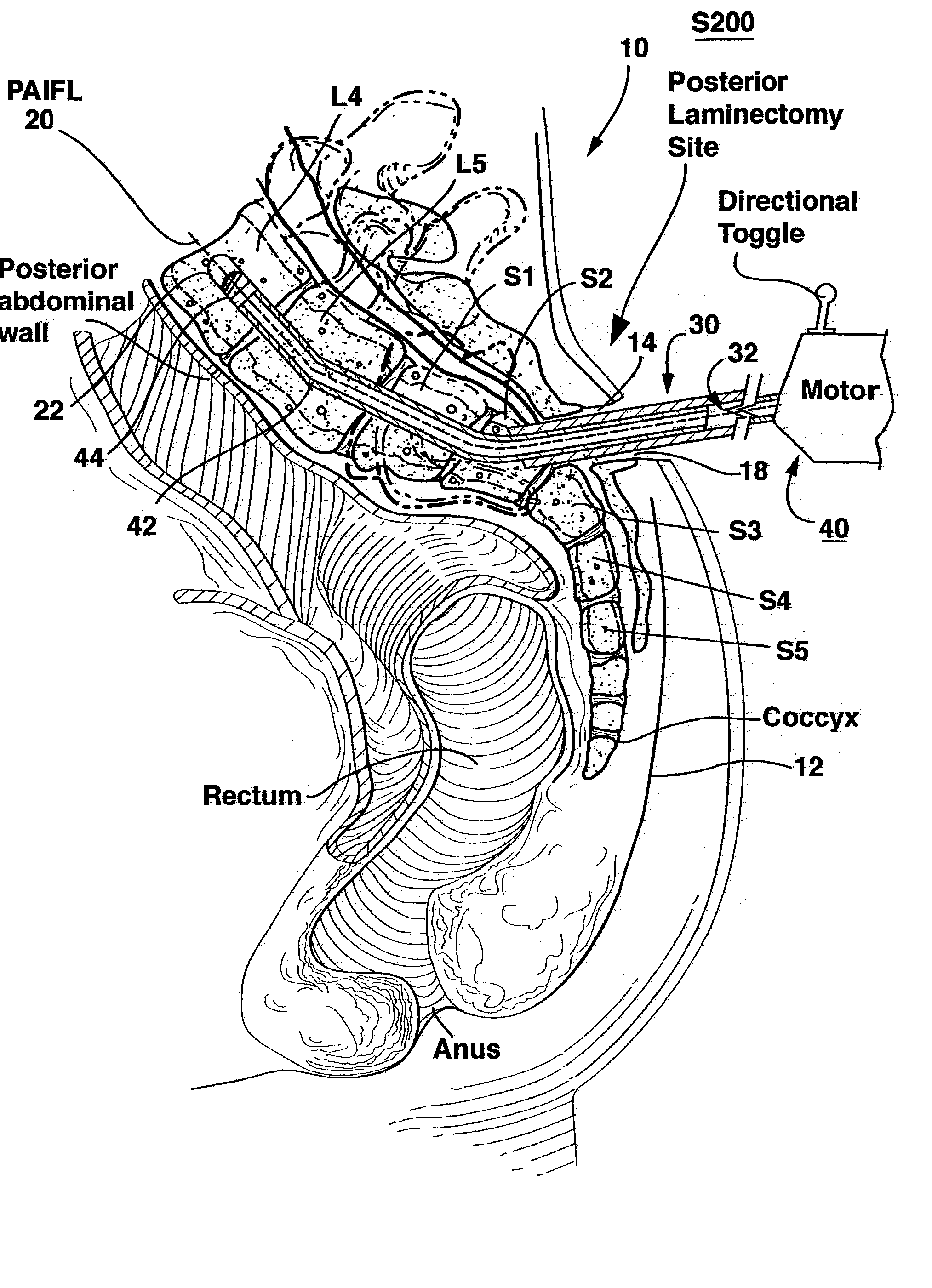
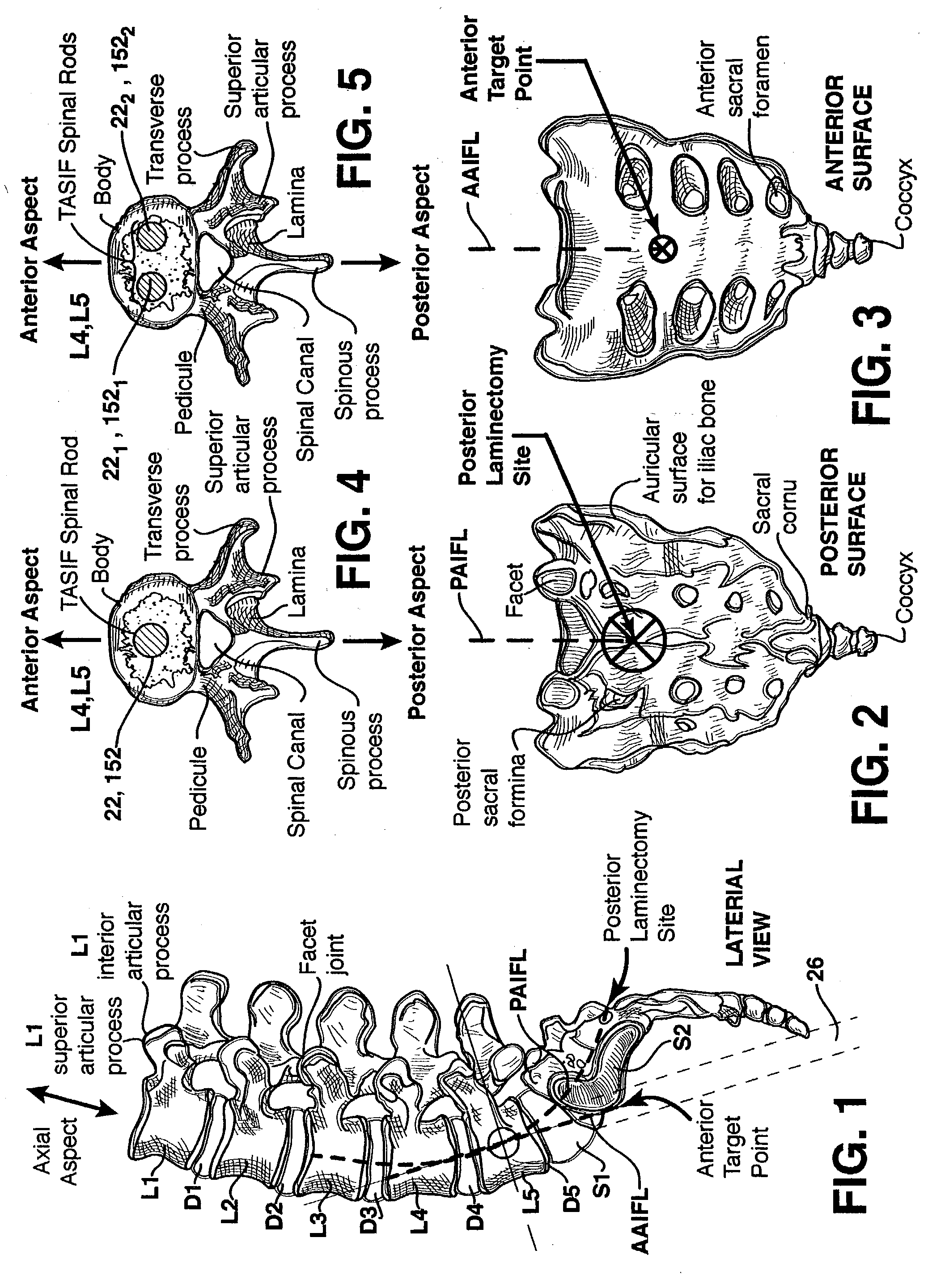
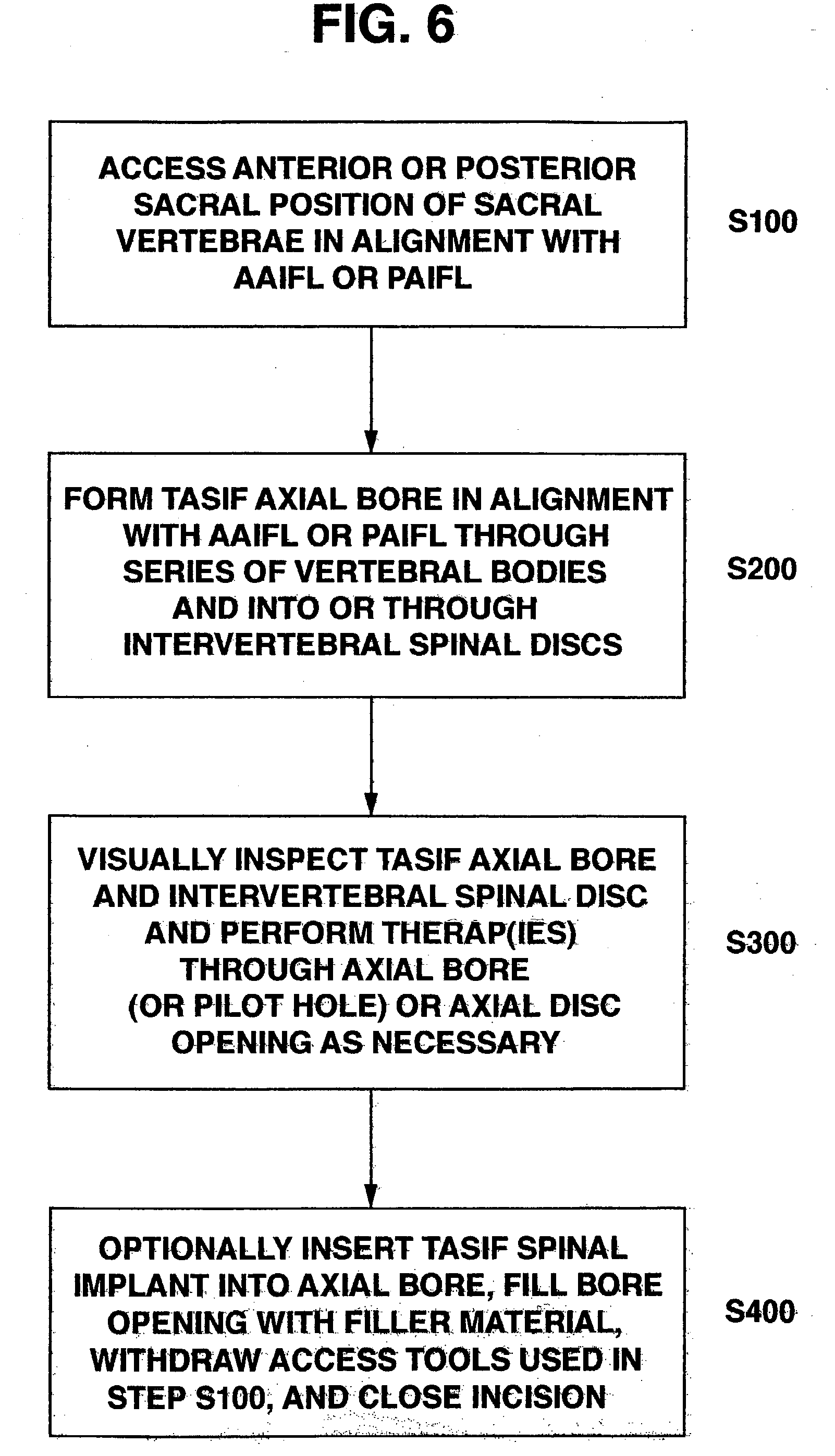
Spinal implants for fusing and / or stabilizing spinal vertebrae and methods and apparatus for implanting one or more of such spinal implants axially within one or more axial bore within vertebral bodies in alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner are disclosed. Attachment mechanisms are provided that attach or affix or force the preformed spinal implants or rods to or against the vertebral bone along the full length of a TASIF axial bore or bores or pilot holes or at the cephalad end and / or caudal end of the TASIF axial bore or bores or pilot holes. The engagement of the vertebral body is either an active engagement upon implantation of the spinal implant into the TASIF axial bore or a passive engagement of the external surface configuration with the vertebral bone caused by bone growth about the external surface configuration. A plurality of such spinal implants can be inserted axially in the same TASIF axial bore or pilot hole or separately in a plurality of TASIF axial bores or pilot holes that extend axially and in a side-by-side relation through the vertebrae and discs, if present, between the vertebrae. Discectomies and / or vertebroblasty can be performed through the TASIF axial bore or bores or pilot holes prior to insertion of the spinal implants. Vertebroblasty is a procedure for augmentation of collapsed vertebral bodies by pumped-in materials, e.g., bone cement or bone growth materials. Materials or devices can also be delivered into the disc space to separate the adjoining vertebrae and / or into damaged vertebral bodies or to strengthen them.
Owner:TRANSI
Knotless anchor for tissue repair
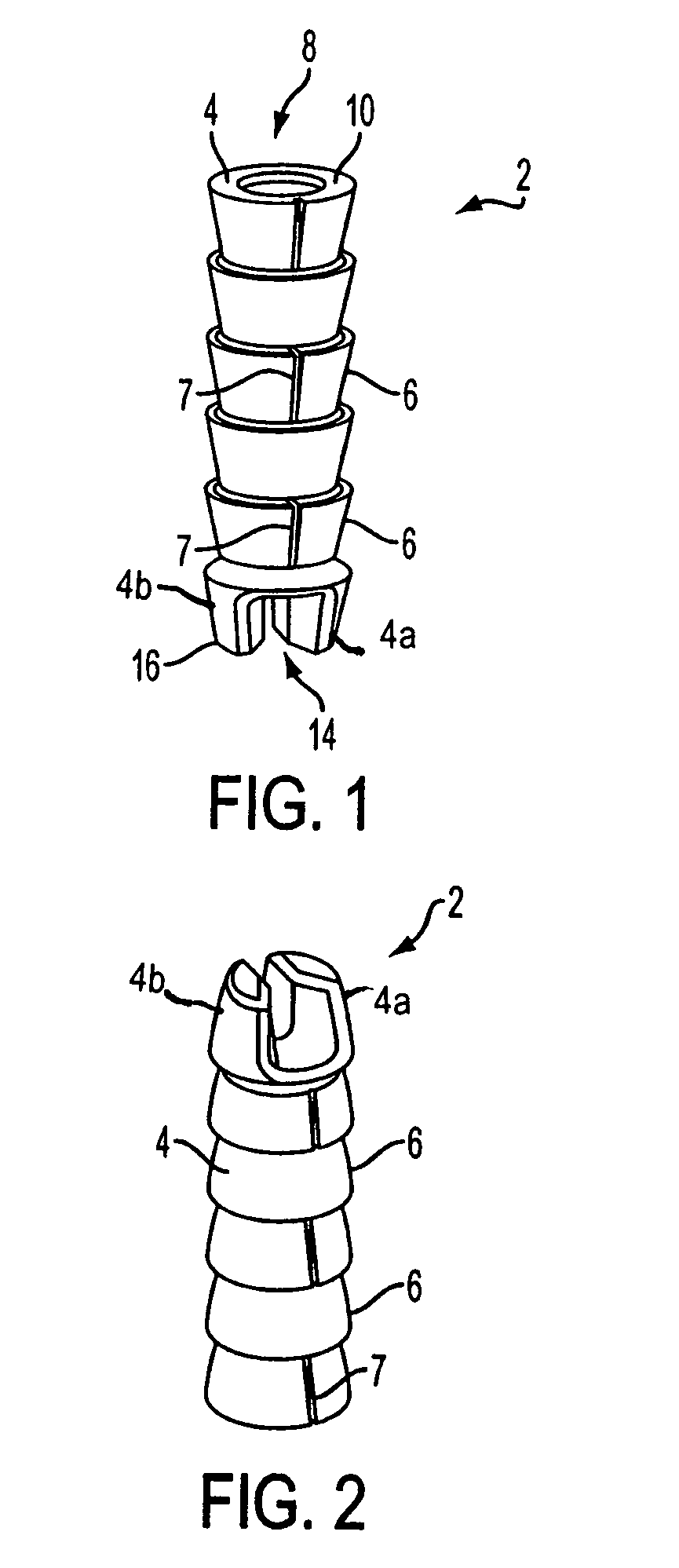
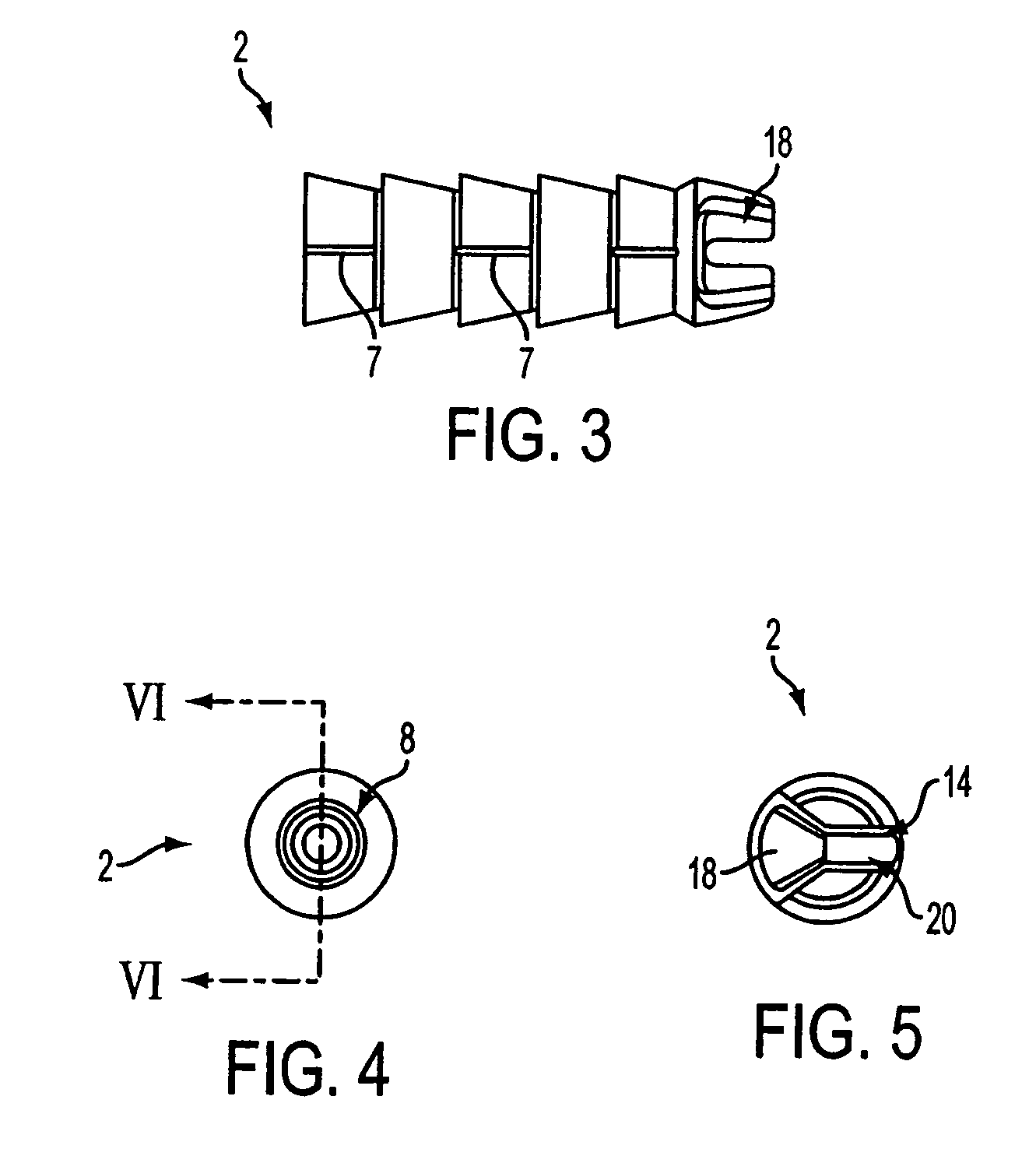
A knotless suture anchor for reattachment of tissue to bone features a barbed body having a Y-shaped slot formed distally for capturing a length of suture. The suture is passed through the tissue to be reattached, and a simple knot formed in the suture is captured in the slot on the suture anchor. The anchor is installed with the captured suture into a pre-formed pilot hole to draw the tissue to the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
Knotless anchor for tissue repair
A knotless suture anchor for reattachment of tissue to bone features a barbed body having a Y-shaped slot formed distally for capturing a length of suture. The suture is passed through the tissue to be reattached, and a simple knot formed in the suture is captured in the slot on the suture anchor. The anchor is installed with the captured suture into a pre-formed pilot hole to draw the tissue to the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method for replacing a ligament in a knee
A method of providing a replacement anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) provides a tibial tunnel and at least one femoral tunnel for receiving the replacement ligament, the femoral and tibial tunnels not being colinear but rather in an orientation that more closely mimics the natural ACL. The femoral tunnel is formed through the anterior medial portal. A cross pinning guide having a femoral rod for insertion into the femoral tunnel, a spaced apart arc shaped track and a guide block having one or more bores aligned with the femoral rod whereby an instrument inserted through one of the bores creates a pilot hole for the cross pin which intersects the femoral tunnel and an appropriate angle thereof which avoids ligaments and other sensitive tissue can be selected by adjusting the guide block along the track.
Owner:TROGER MARCUS +1
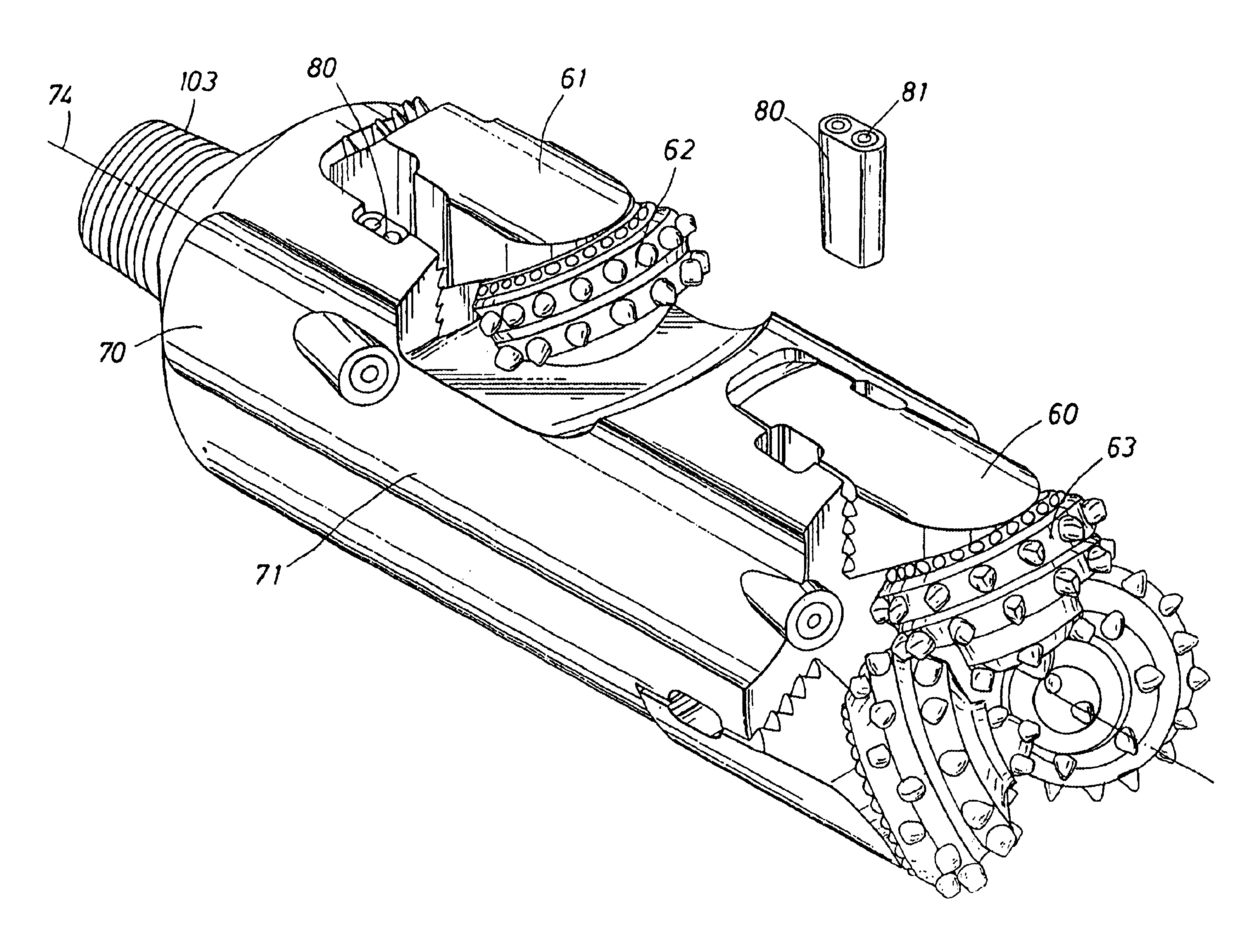
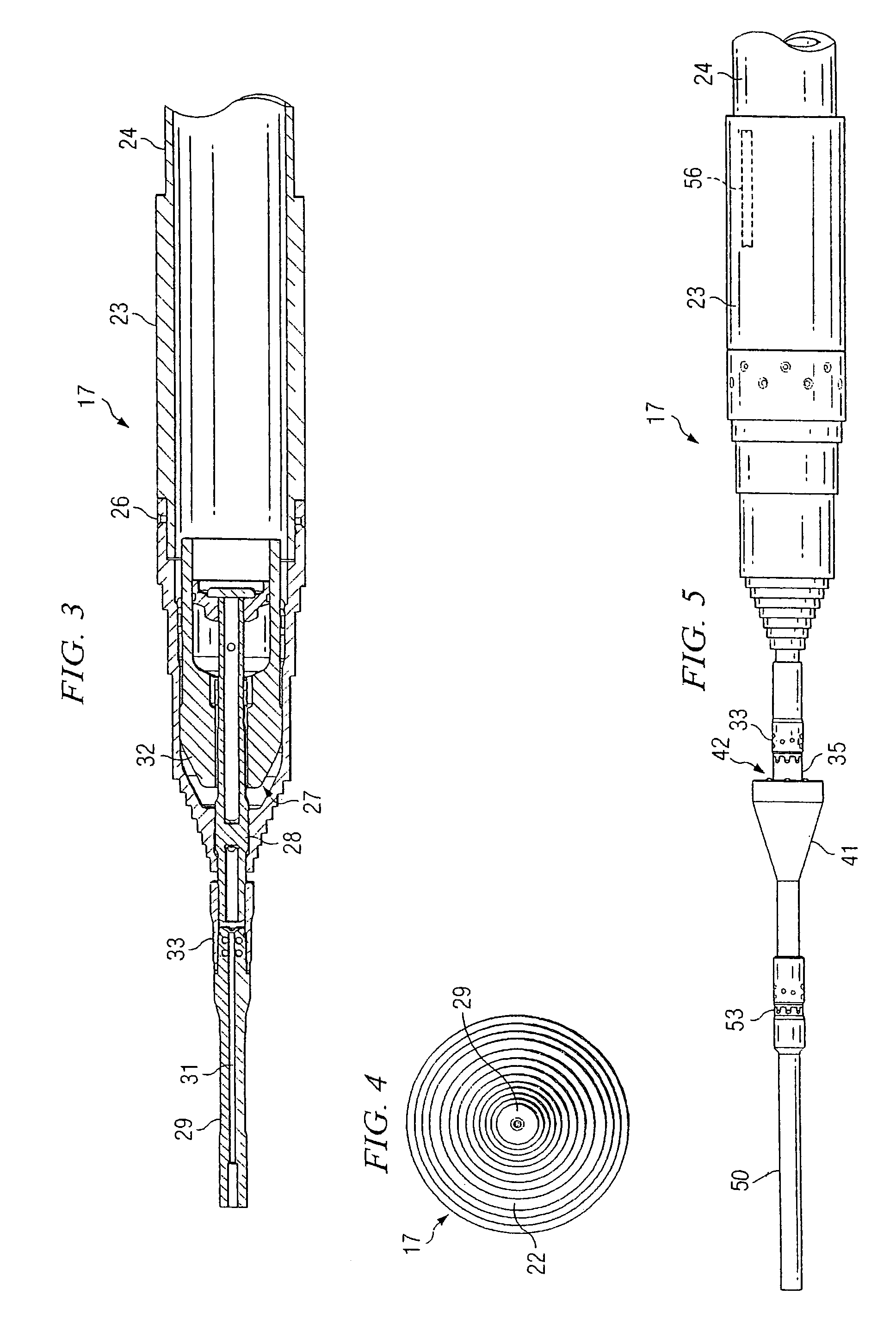
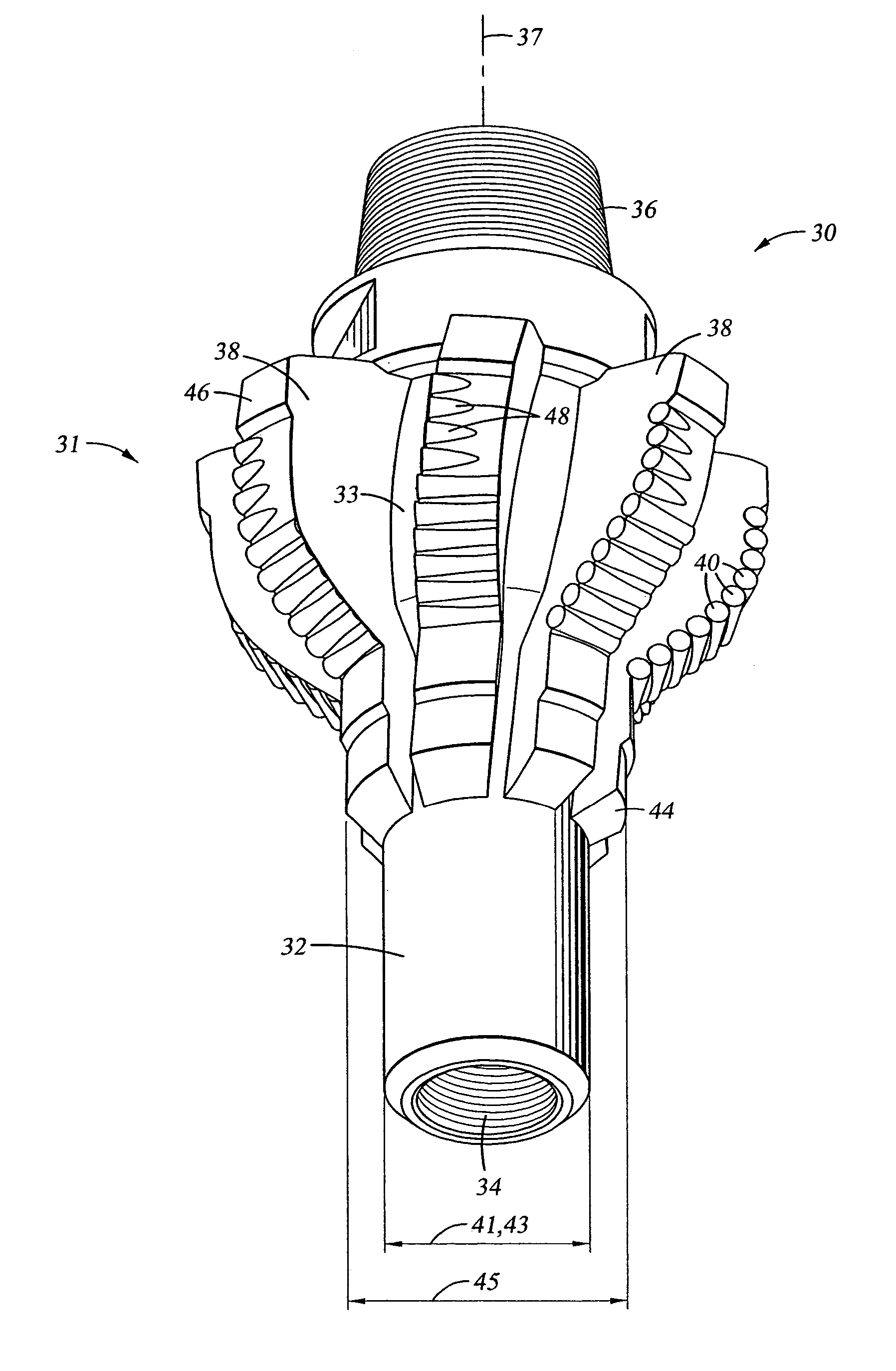
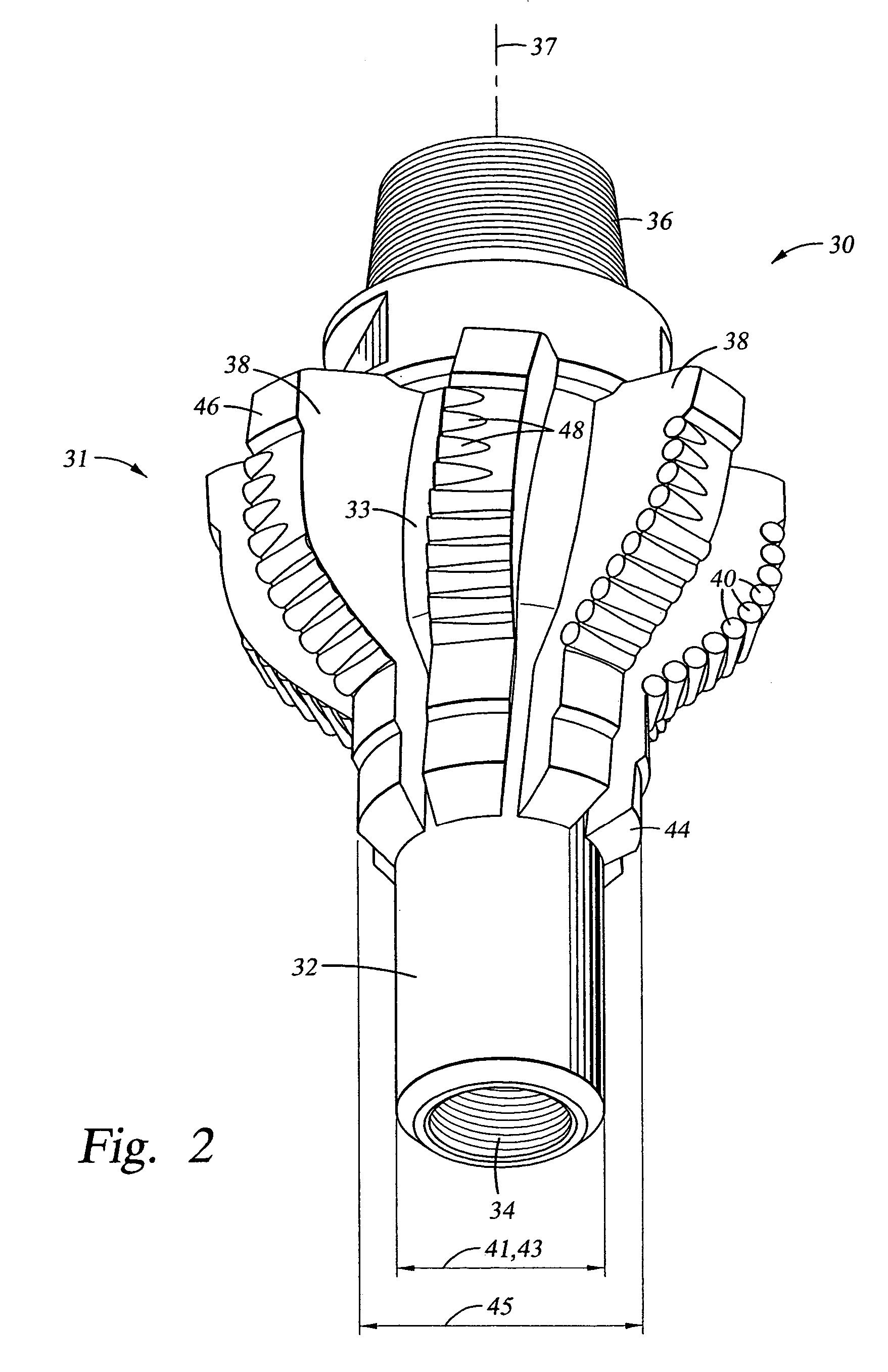
Roller cone bi-center bit
InactiveUS6902014B1Enhance drilling outEasy to disassemble and replaceDrill bitsCutting machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A roller cone bi-center bit for economically drilling an enlarged borehole below casing in earth formation is provided. The bi-center bit includes a rolling cone cutter or other appropriate cutter to enlarge a pilot bore also made by rolling cone or other type of cutters. The bit comprises a single-diameter body with a recess to accommodate the trailing cutter which enlarges the pilot bore. The bi-center bit may also provide the ability to change out the cutters efficiently in the field. The cutters are oriented to enhance drilling out the cement plug at the bottom of the casing. The cone cutter may be also be mounted on segments which are designed to be easily removed for replacement or adjustment in position in the field.
Owner:ROCK BIT INT +2
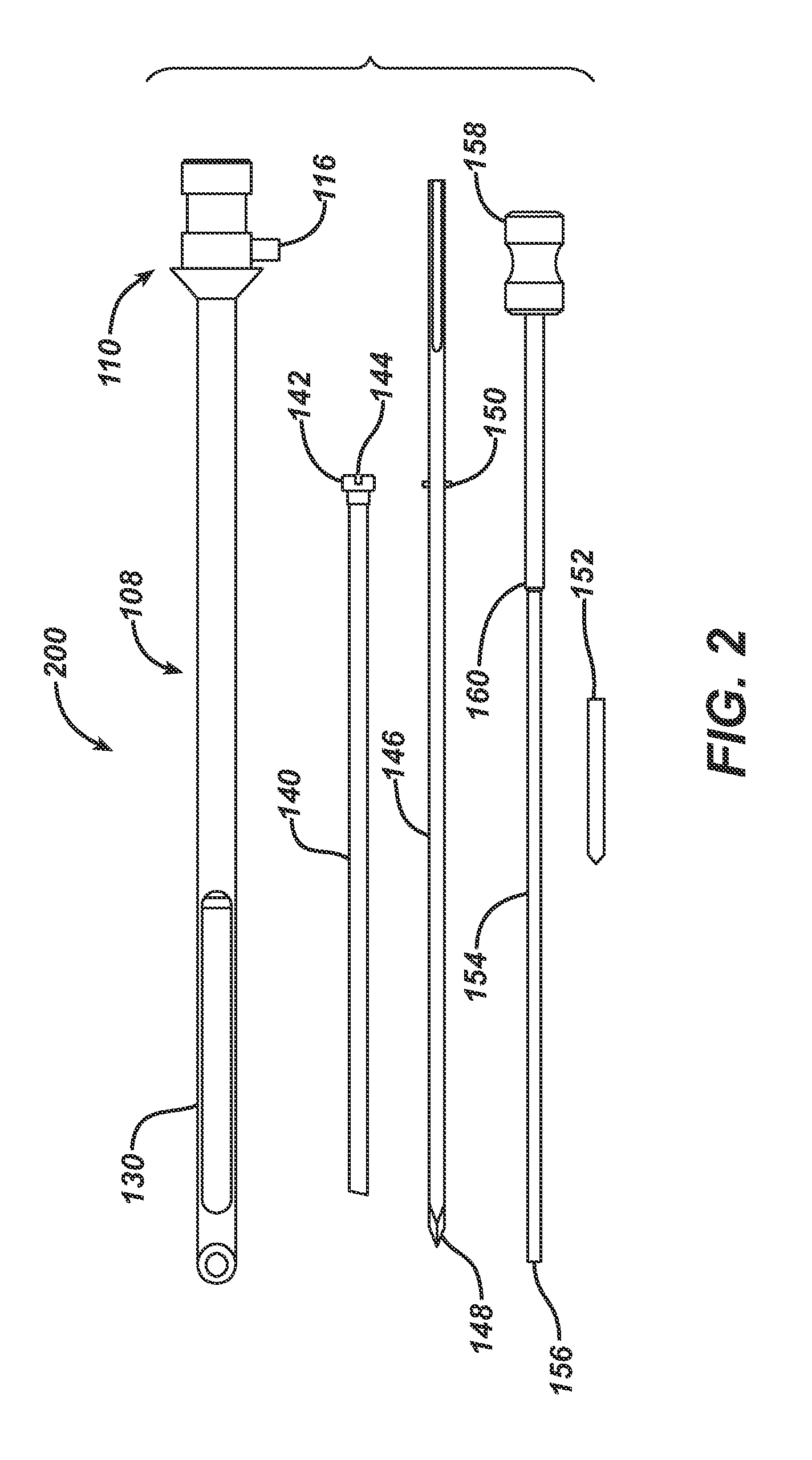
Methods and apparatus for delivering staples to a target tissue
ActiveUS20100312250A1Easy to bendAvoid insufficient lengthSuture equipmentsLigamentsPilot holeTarget tissue
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
Insulated pedicle access system and related methods
ActiveUS7942826B1Easy to operateFacilitate easy movement and positioningSpinal electrodesElectromyographyIntegrity assessmentPilot hole
A pedicle access system including a cannula, a stylet, and a removable T-handle. The pedicle access system may be used to percutaneously approach the pedicle, initiate pilot hole formation, and conduct a stimulation signal to the target site for the purposes of performing a pedicle integrity assessment during the pilot hole formation. To do this, the cannula and stylet are locked in combination and inserted through an operating corridor to the pedicle target site, using the T-handle to facilitate easy movement and positioning of the cannula / stylet combination. A stimulation signal may be applied during pilot hole formation to conduct the pedicle integrity assessment. In a significant aspect, the T-handle may be detached from the cannula / stylet combination to facilitate the use of various surgical tools as necessary.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Method and apparatus for performing dental implantation
InactiveUS20070065777A1Reduce irregularitiesProcedure is difficultDental implantsDental toolsPilot holeEngineering
In a dental implantation, after exposure of the alveolar crest and drilling a pilot hole into the crest, a novel mill having an axial guide pin which extends into the pilot hole is used to form clearance for a cover screw or temporary healing abutment. The pilot hole is then enlarged to form clearance for the implant and the screw or abutment is attached.
Owner:BECKER ROBERT
Dental implantation system and method
Drilling of an implant shaft is carried out with a handpiece tool whose location and angular orientation with respect to a radiographic working guide is updated in real time with respect to the radiographic working guide and anatomical structures of the patient, free of viewing obstructions. Prior to the drilling, the radiographic working guide is fitted to a particular patient. Real-time imaging support is provided on a display of a computer, wherein the radiographic workpiece guide includes a plurality of fiducial markers that define a substantially planar reference surface of the radiographic workpiece guide. The radiographic workpiece guide also includes an alignment structure located a predetermined distance from a pilot hole proximate the work site. The image is updated based on an initial radiographic scan and updated position information from the handpiece tool as to location and angular orientation of the handpiece tool relative to the workpiece guide.
Owner:PRECISION THROUGH IMAGING
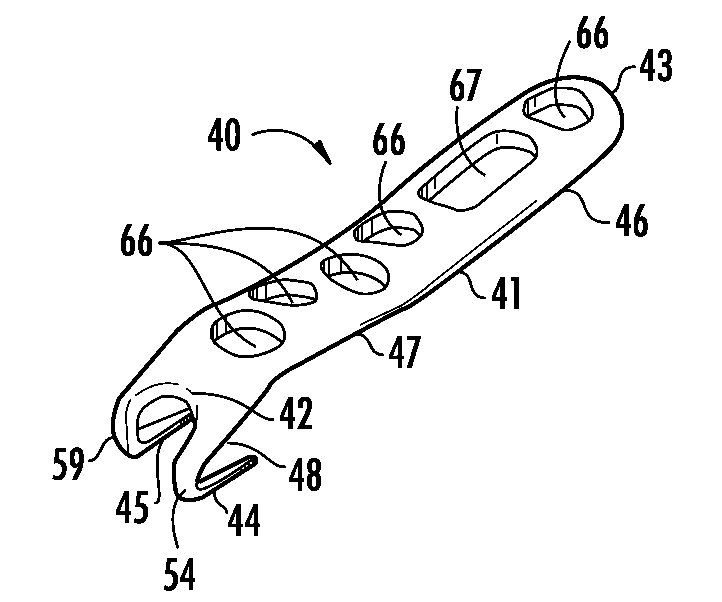
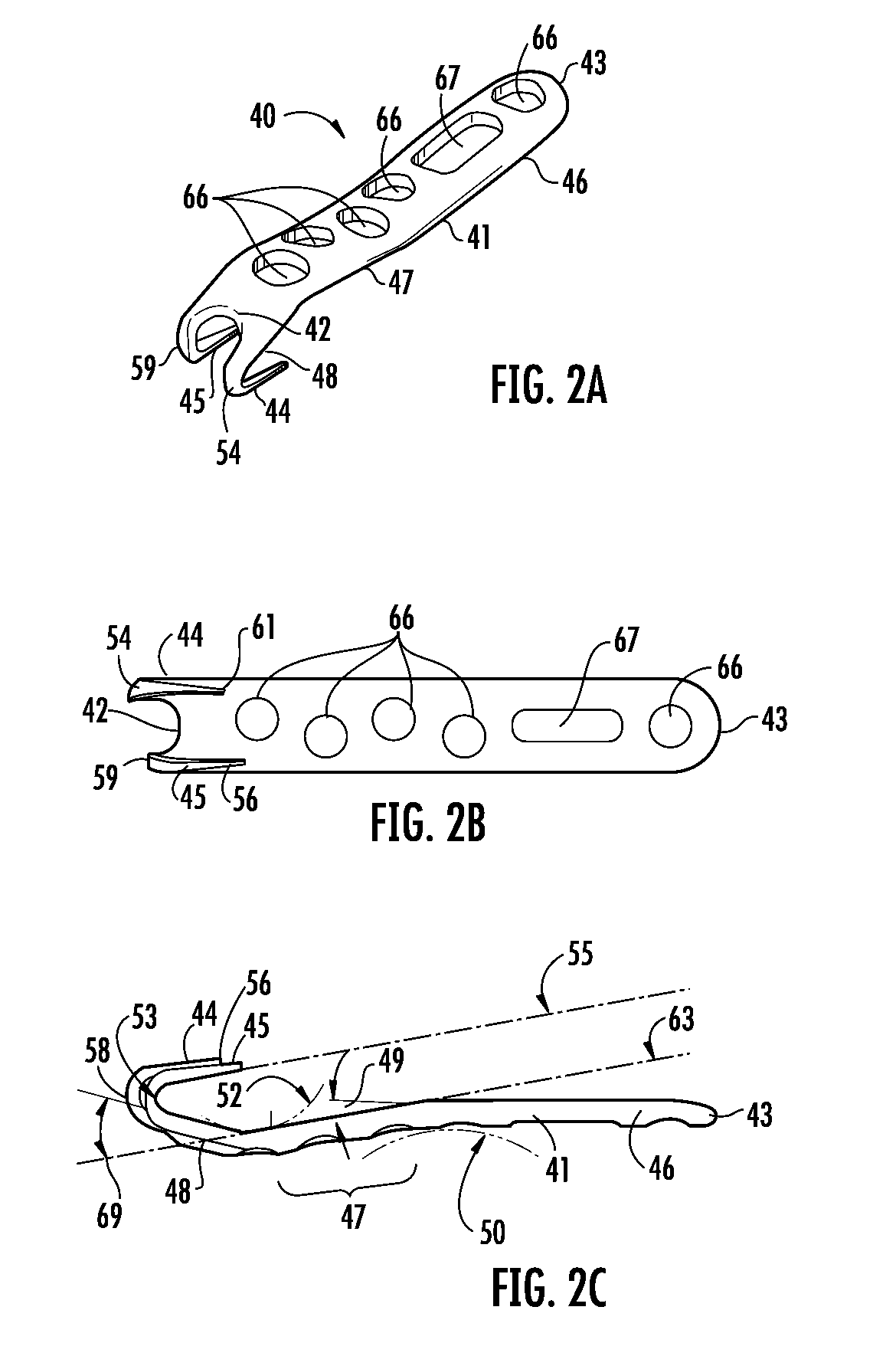
Contoured bone plate for fracture fixation having hook members and drill guide for same
A bone fixation plate for fixation of fractures having a small terminal bone fragment, such as fractures of the lateral malleolus. The bone fixation plate includes an elongated body, and two hook members extending from a first end of the elongated body. Each hook member curves back upon a bottom surface of the elongated body, back towards a second end of the elongated body, and terminating in a pointed prong region. The elongated body includes a first region, a second region, and an angled region disposed between the first and second region. The prong region has a longitudinal axis that is substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the angled region of the elongated body of the bone plate. A double barreled drill guide and associated interchangeable cooperating inner drill guides and gauges are provided to facilitate the drilling of pilot holes in a terminal bone fragment for axial insertion of the pointed prong regions of the hook members.
Owner:TRIMED
Graft fixation using a plug against suture
A method for securing soft tissue to bone which does not require the surgeon to tie suture knots to secure the tissue to the bone. Suture is passed through the graft at desired points. A cannulated plug or screw is pre-loaded onto the distal end of a driver provided with an eyelet implant at its distal end. Suture attached to the graft is passed through the eyelet of the implant located at the distal end of the driver. The distal end of the driver together with the eyelet implant is inserted into the bone. Tension is applied to the suture to position the graft at the desired location relative to the bone. The screw or plug is advanced into the pilot hole by turning the interference screw or tapping the plug until the cannulated screw or plug securely engages and locks in the eyelet implant, so that the cannulated plug or screw with the engaged eyelet implant is flush with the bone. Once the screw or plug is fully inserted and the suture is impacted into the bone, the driver is removed and any loose ends of the sutures protruding from the anchor site are then clipped short.
Owner:ARTHREX
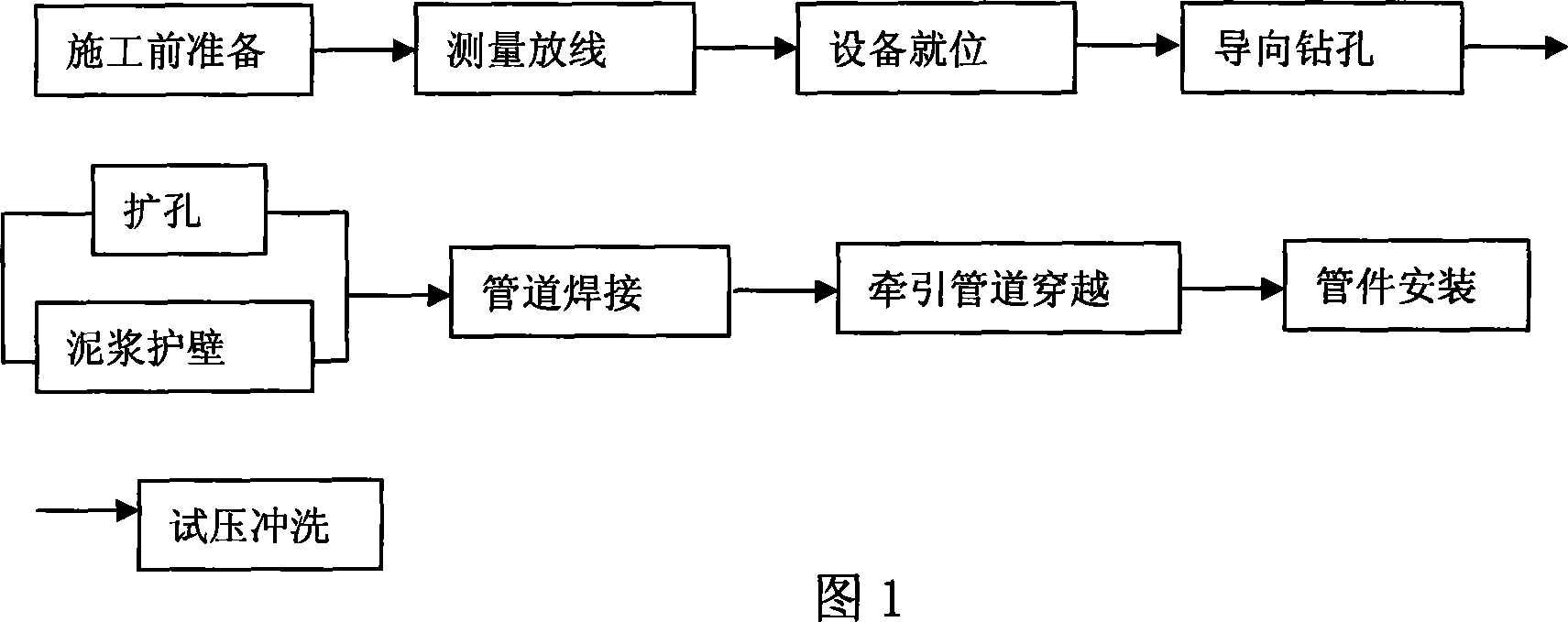
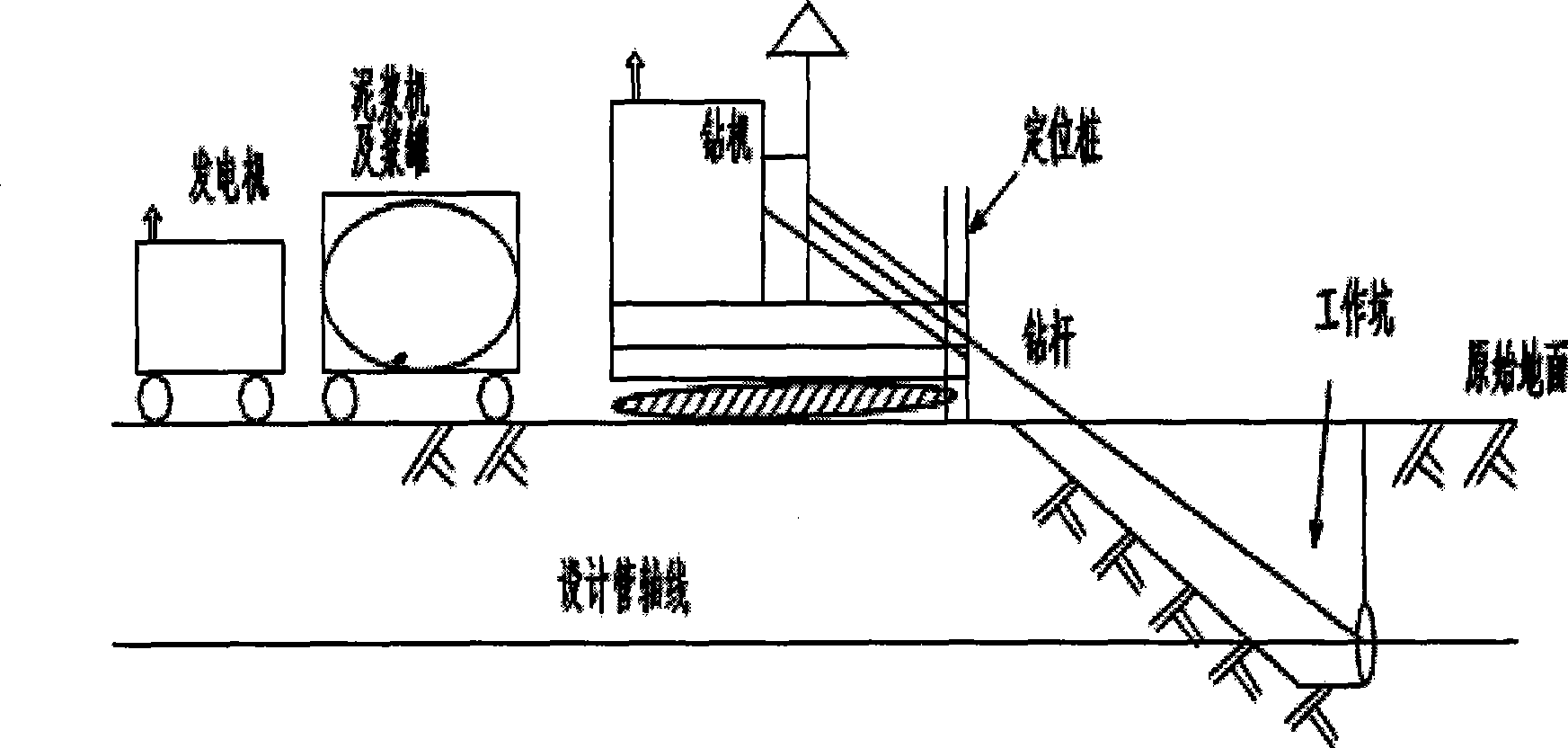
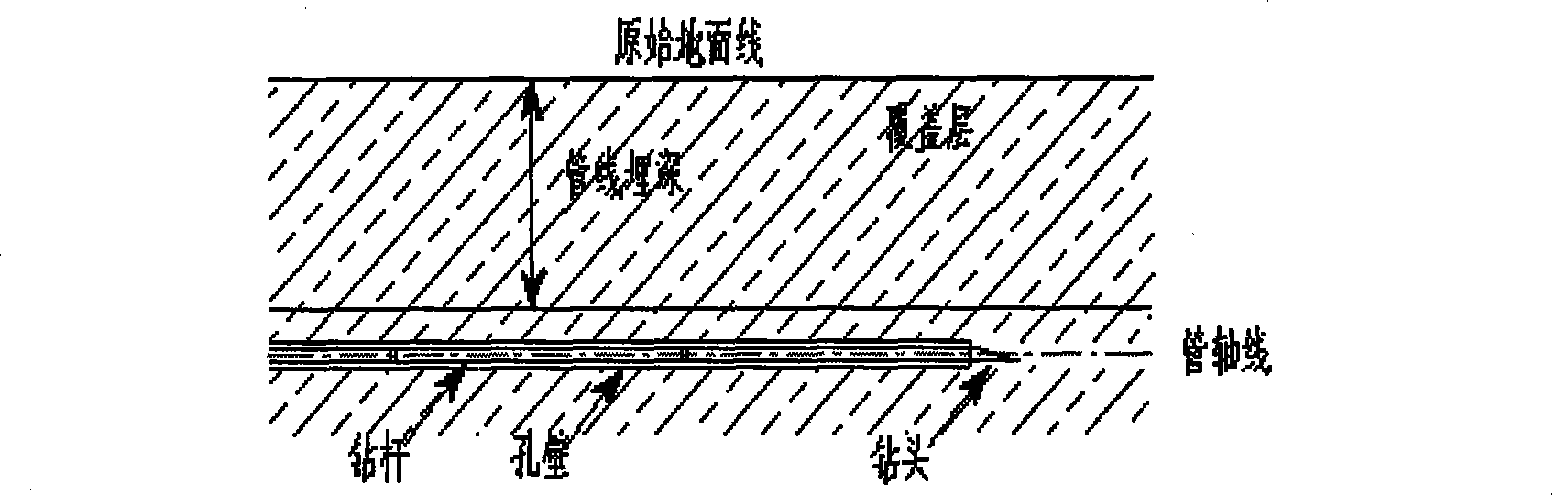
Non-digging tube-pulling construction method
InactiveCN101457853AReduce excavationReduce backfill workloadPipe laying and repairSocial benefitsGeomorphology
The invention relates to a non-excavation tube pulling construction method which comprises the following steps: (1) preparation work: understanding stratum and underground condition, calculating the number of chambering and the size of a return compandor, and formulating the control data of a pipeline midline and elevation and correction measures; (2) measuring plane surface, controlling payingoff, and measuring the elevation of each pile; (3) setting an active well, and receiving and setting a drilling machine; (4) preparing drilling fluid; (5) drilling pilot holes,; (6) adopting the compandor to chambering, cleaning the hole at the same time, and protecting walls with slurry; (7) welding the pipeline; (8) pulling the tube, and simultaneously pulling a steel tube with the same length as that of the tube; (9) casting slip and fixing; (10) mounting tubes; (11) testing pressure and flushing. The invention can effectively increases economical benefit and social benefit, and has the advantages of environmental protection and energy saving.
Owner:江苏广宇建设集团有限公司
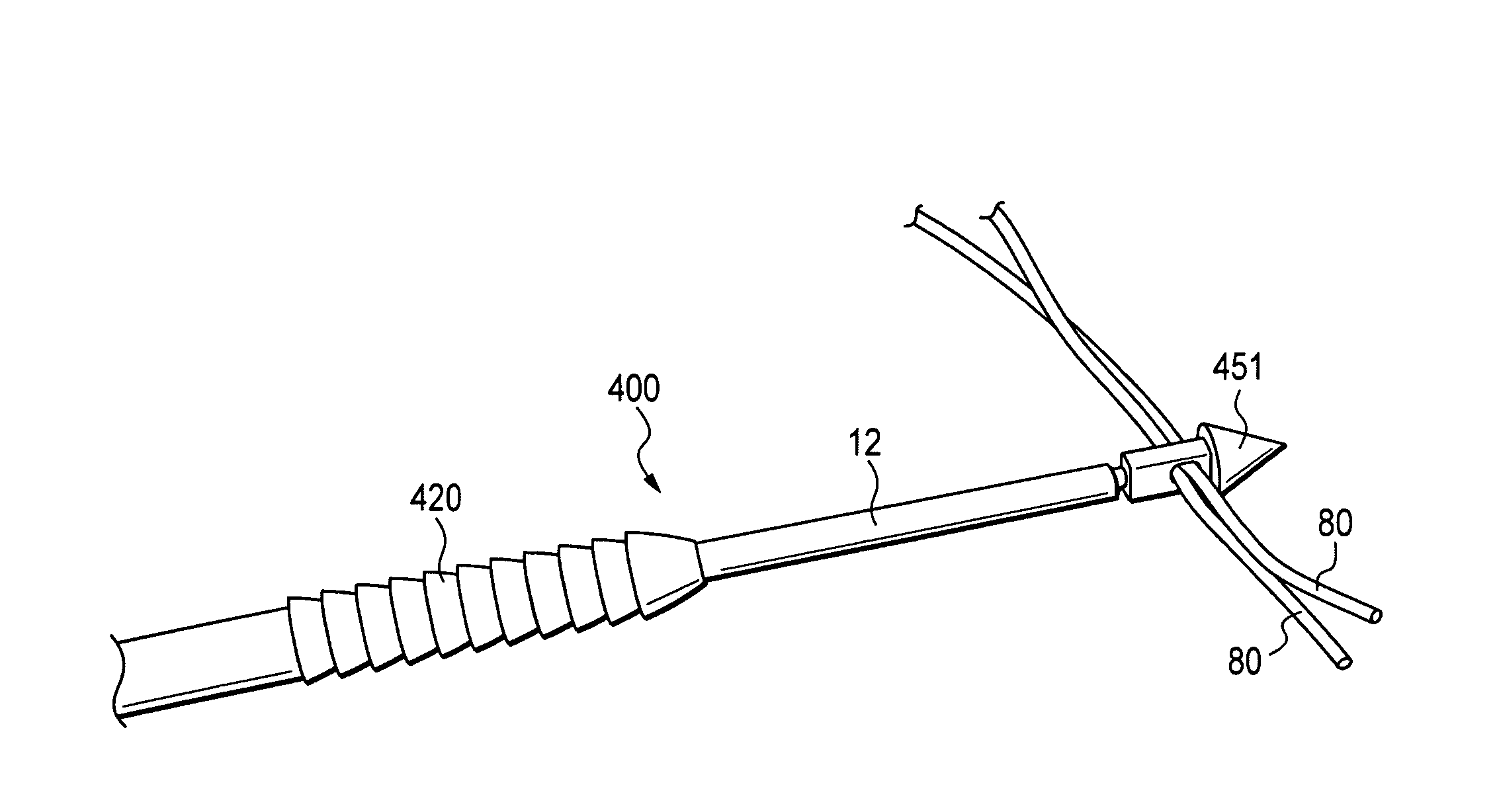
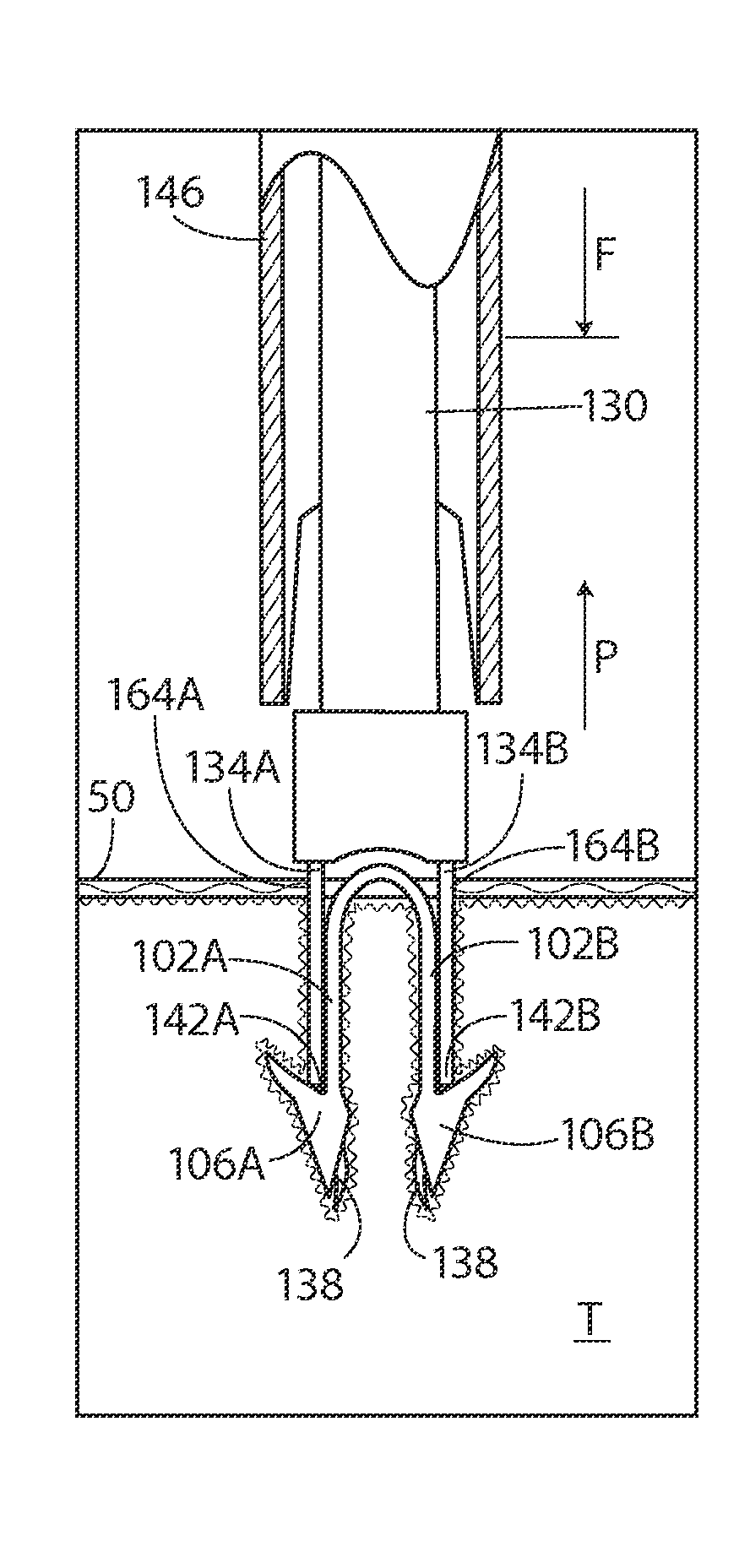
Apparatus and method for forming pilot holes in bone and delivering fasteners therein for retaining an implant
Apparatus and methods for forming pilot holes in bone and deploying a staple therein for fixing a sheet-like implant to the bone. A pilot hole forming trocar assembly including a trocar and a position retention sleeve can be included. The trocar can be releasably coupled to the position retention sleeve and slide in keyed arrangement within the sleeve when uncoupled. The trocar can include a distal portion having a retractable blade and a pair of pilot hole forming spikes extending distally from the trocar shaft. Once the pilot holes are formed, the position retention sleeve maintains the position relative to the pilot holes while the trocar is removed and a staple delivery device can be inserted in the lumen of the position retention sleeve to deploy a staple in the pilot holes.
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for forming pilot holes in bone and delivering fasteners therein for retaining an implant
Apparatus and methods for forming pilot holes in bone and deploying a staple therein for fixing a sheet-like implant to the bone. A pilot hole forming trocar assembly including a trocar and a position retention sleeve can be included. The trocar can be releasably coupled to the position retention sleeve and slide in keyed arrangement within the sleeve when uncoupled. The trocar can include a distal portion having a retractable blade and a pair of pilot hole forming spikes extending distally from the trocar shaft. Once the pilot holes are formed, the position retention sleeve maintains the position relative to the pilot holes while the trocar is removed and a staple delivery device can be inserted in the lumen of the position retention sleeve to deploy a staple in the pilot holes.
Owner:ROTATION MEDICAL
Stabilizing system and methods for a drill bit
InactiveUS6971459B2Promote lowerIncrease contact pressureEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsPilot holeEngineering
A drill bit stabilizing system comprising a body member having an axis and at least one recess formed in the body member housing at least one stabilizing member when in a first retracted position. The stabilizing member is positionable along a diagonal angle with the axis to a second extended operating position which extends downward and outward relative to the main body to selectively engage the surface of a pilot bore hole wall during a drilling operation so as to stabilize an under gauge drill bit used in association with the stabilizing system. The body member further comprises at least one fixed stabilizing surface positioned in an axially spaced relationship to the at least one movable stabilizing member. The body member further comprises a gauge cutter positioned above the moveable stabilizing member and below the fixed stabilizing surface to expand the pilot hole to the final gauge.
Owner:RANEY RICHARD C
Spinous process fixated bilateral drilling guide
InactiveUS20100023018A1Precise positioningAccurate and repeatable drilling and screw placementProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAnatomical landmarkCoronal plane
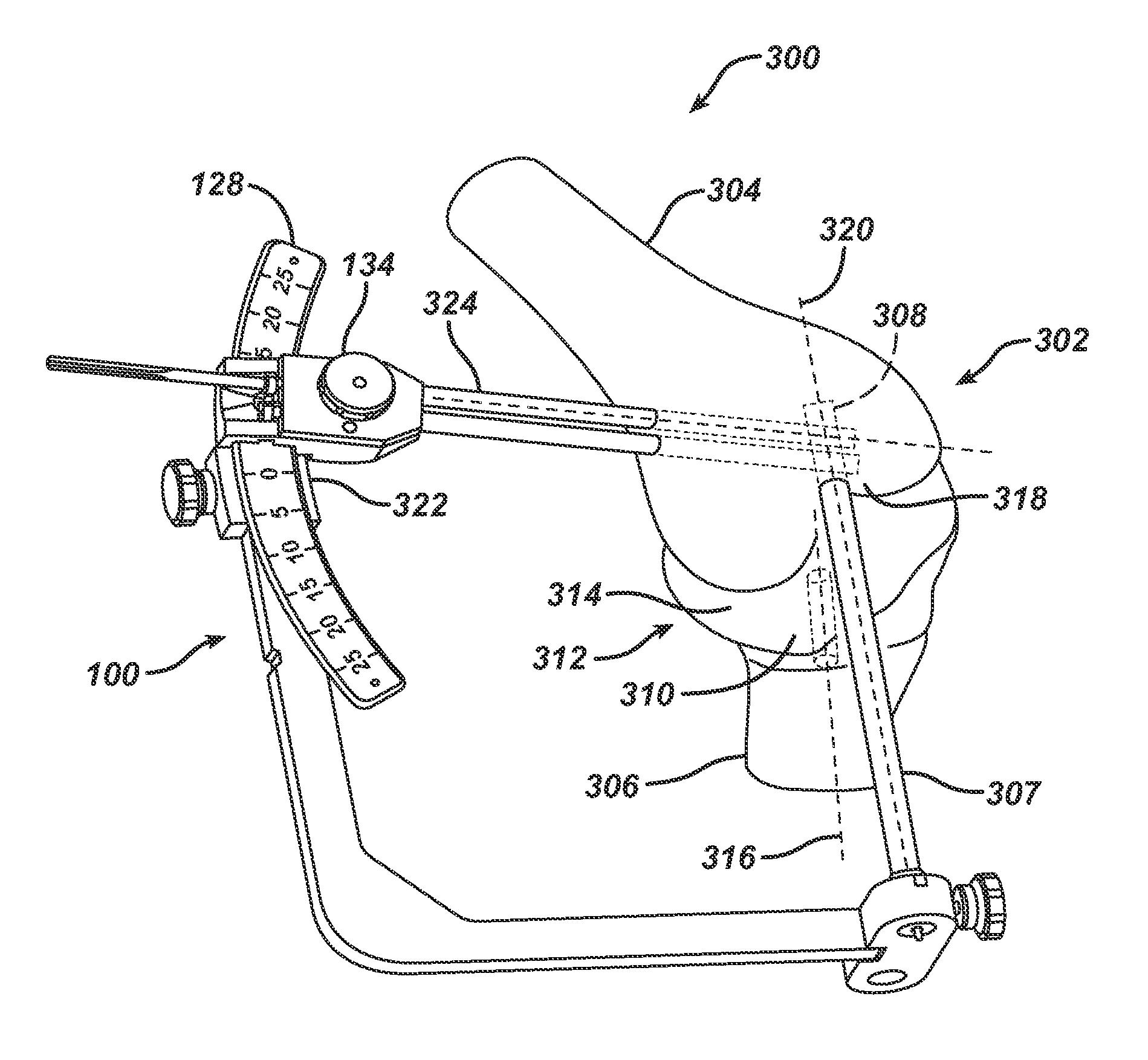
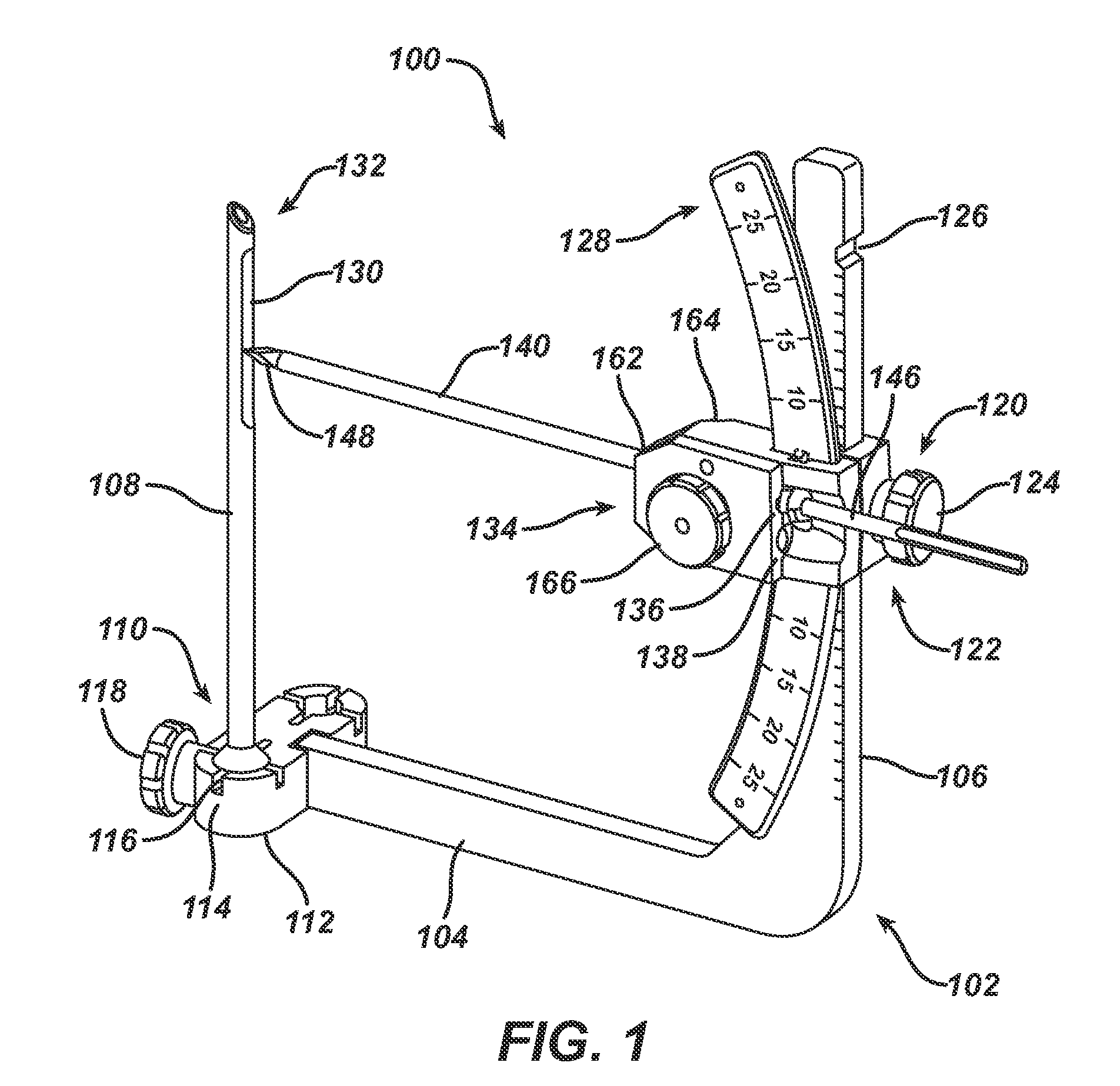
The application describes a bilateral drilling and screw placement guide adapted for fixation to the spinous process of a vertebral body. The positioning and surgical guiding instrument is adapted for use during a spinal surgical procedure in conjunction with a drilling tool, fastening device, e.g. a pedicle screw, K-wire or the like. The guide includes an engagement device for attachment to a region of the spinous process, to which an adjustably attached support member is affixed. This allows for immobilizing the guide upon the spinous process anatomical landmark, in a specific orientation with respect thereto. The guide includes a bilaterally adjustable drill guide assembly for precise anatomical positioning of the drill and screw placement guides bilaterally about the sagittal, axial and coronal planes so as to enable the defining of a plurality of drilling axes extending toward the vertebral body. The device further provides for adjustment to account for anatomical variations in width along the axial plane, and includes pointing and angular positioning functionality to insure repeatable and reliable pilot hole and screw placement along a plurality of angles.
Owner:ALPHA GUIDE HLDG LLC
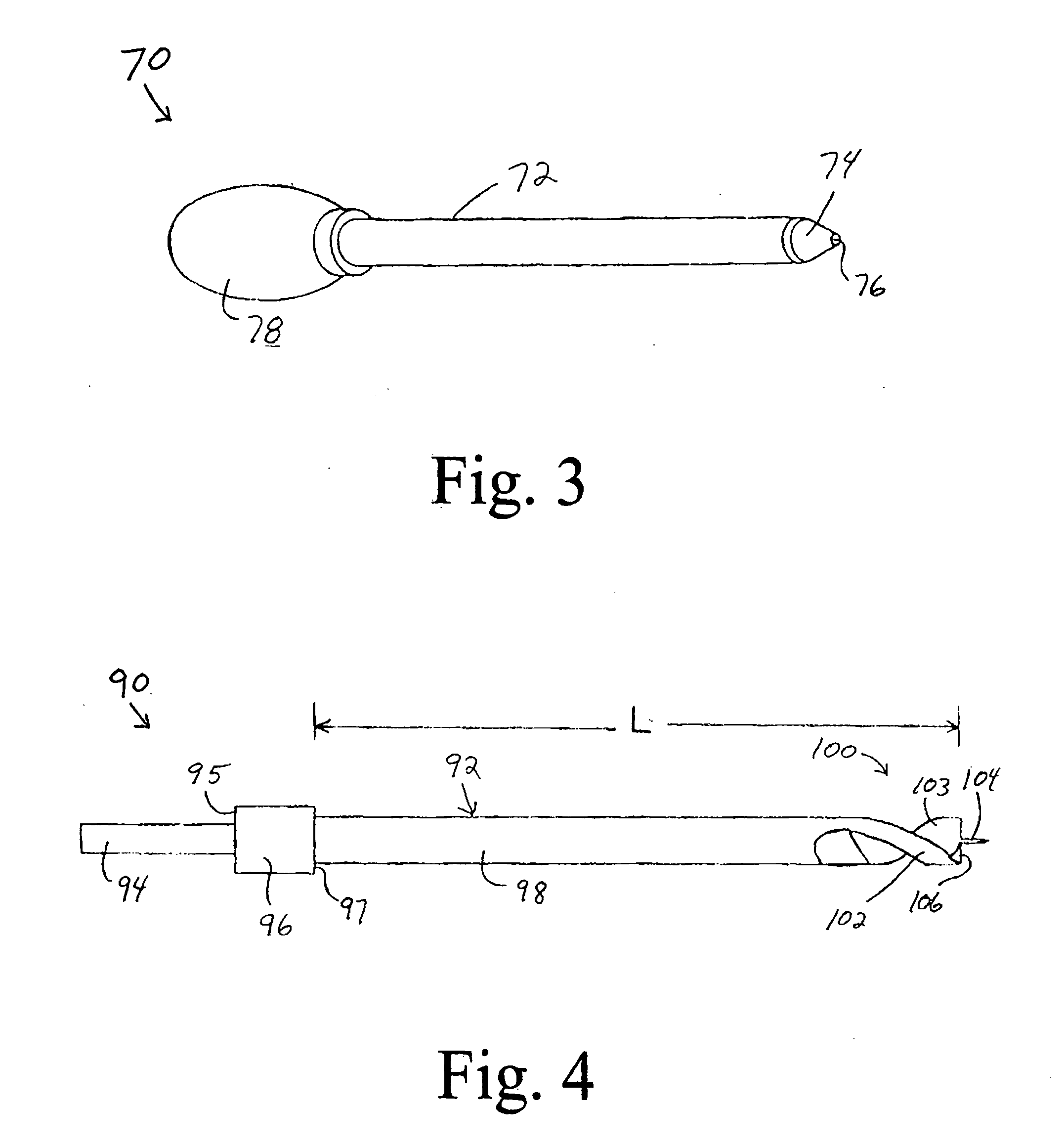
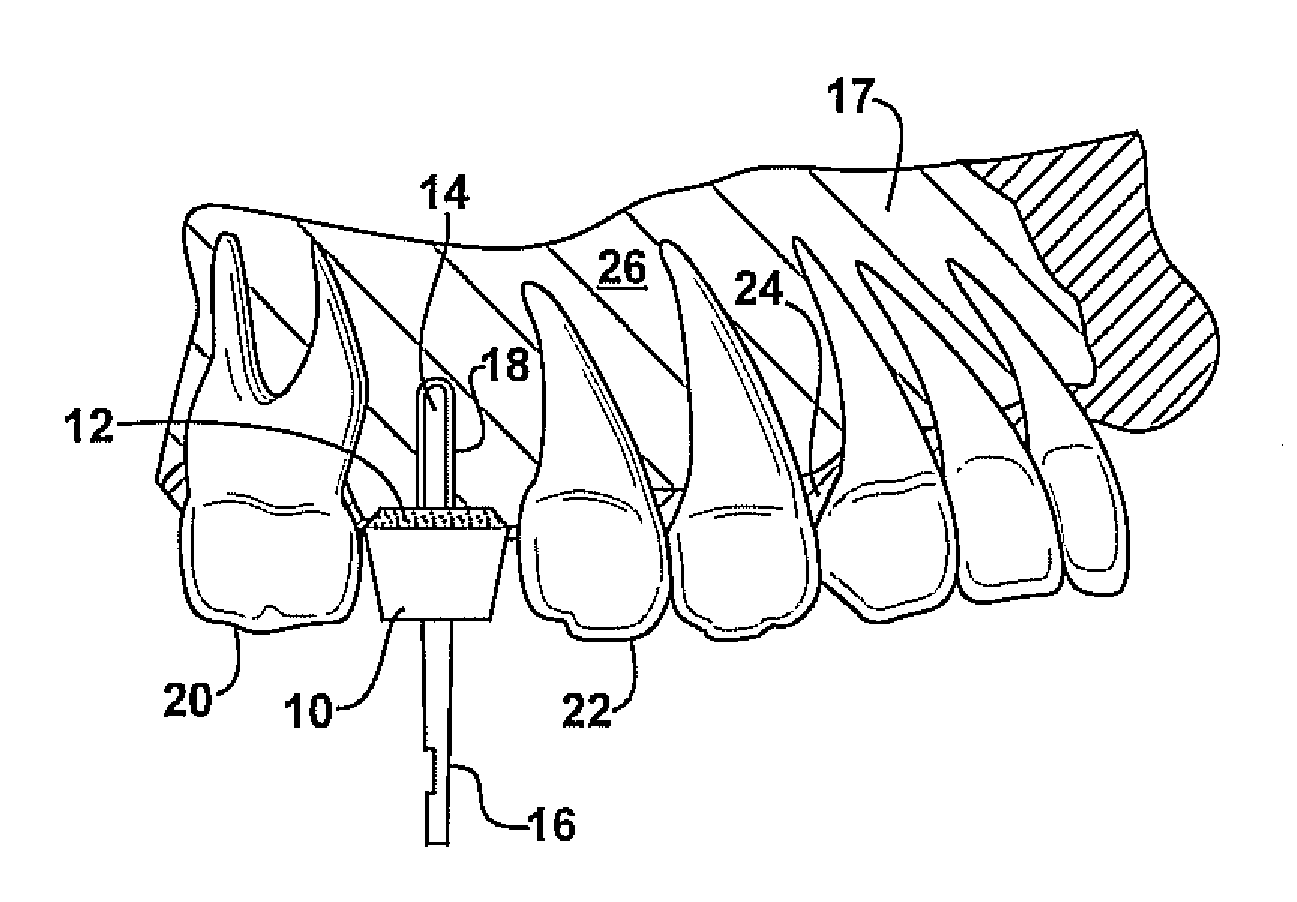
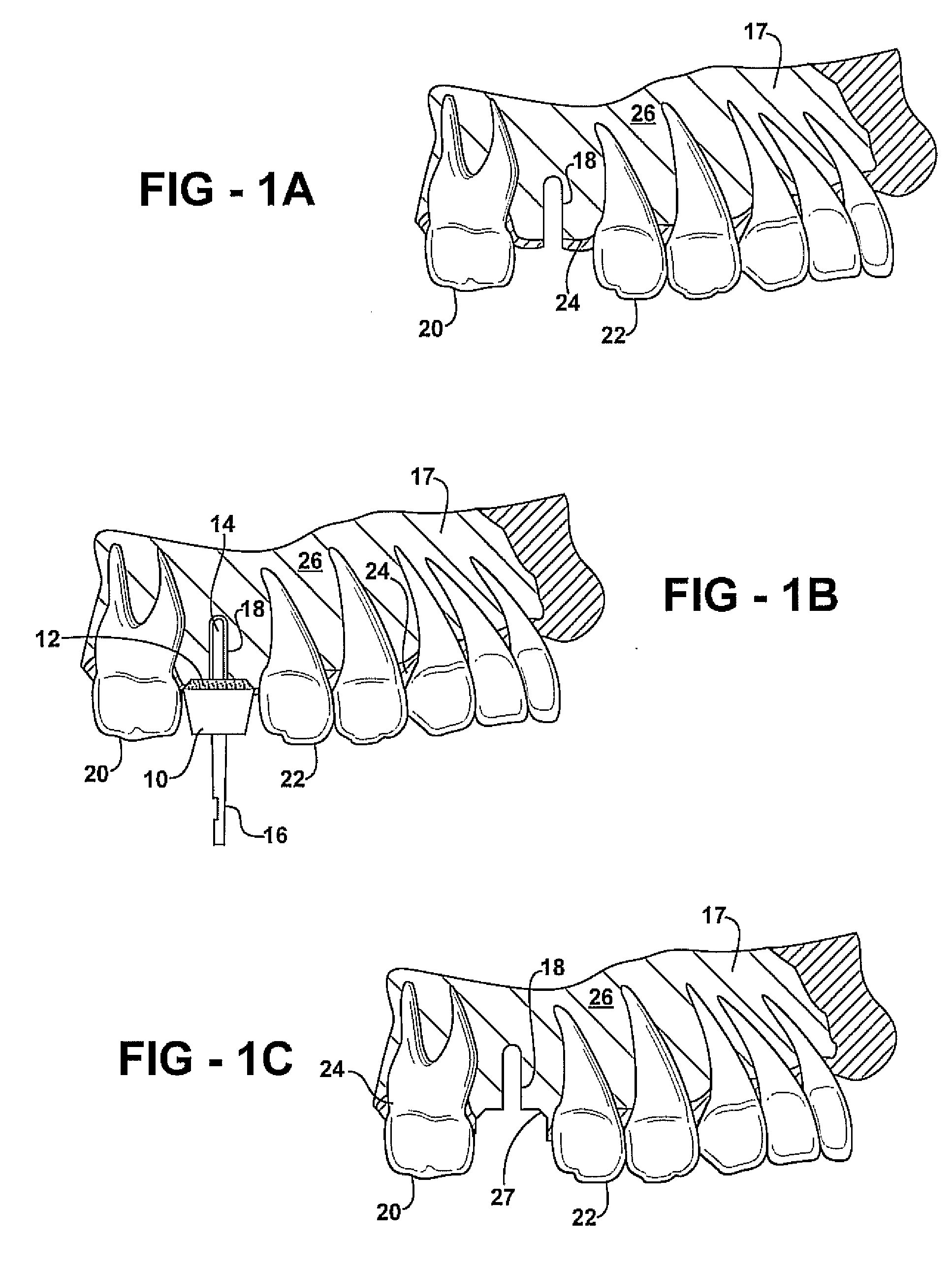
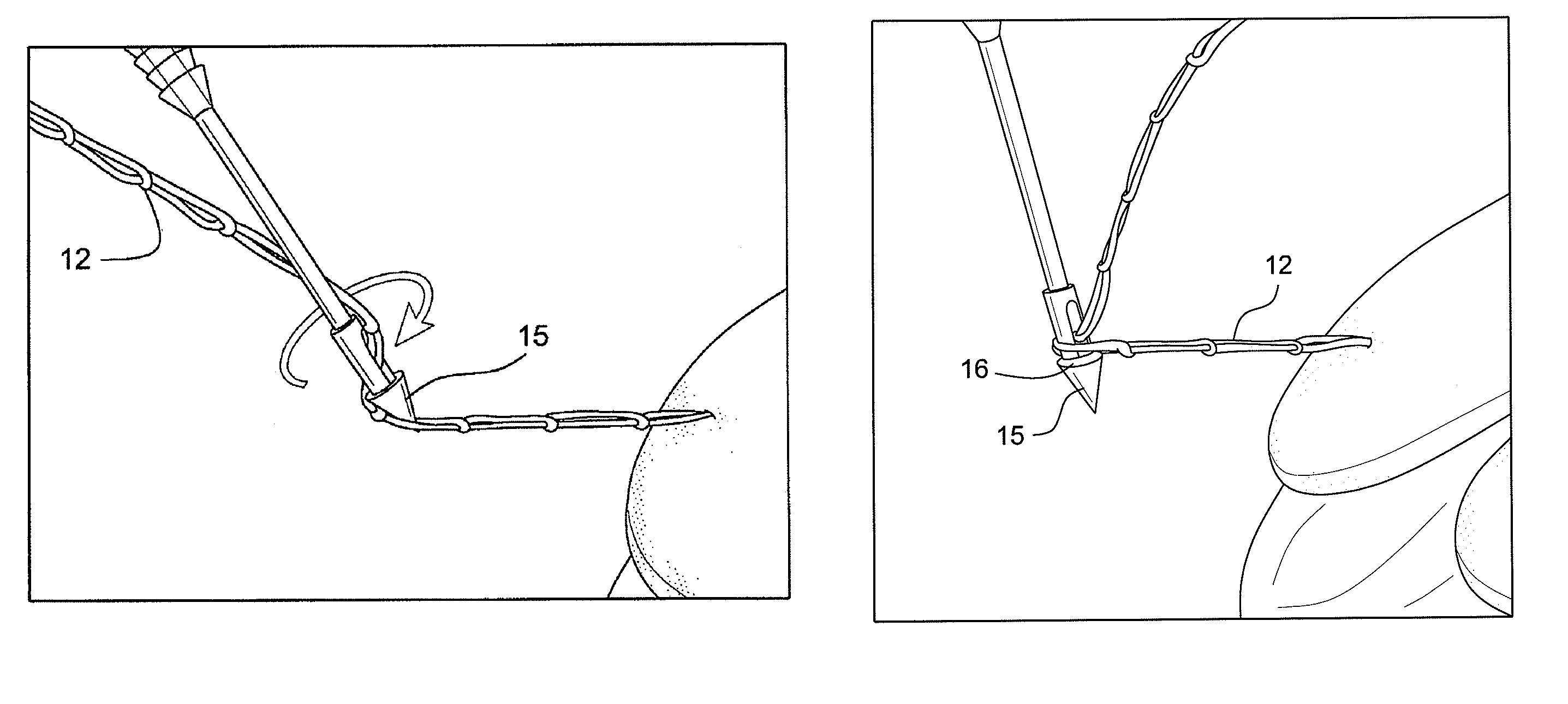
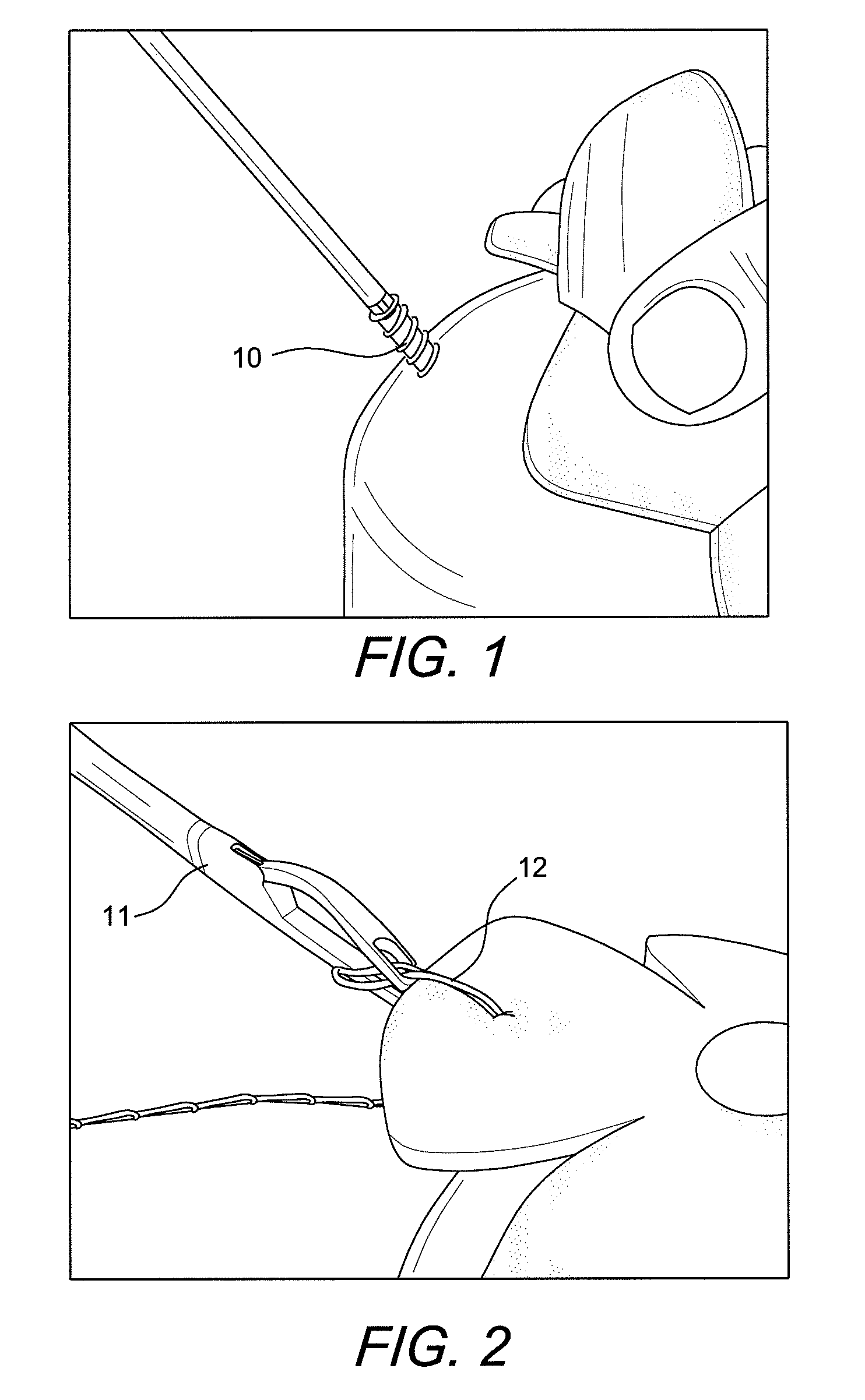
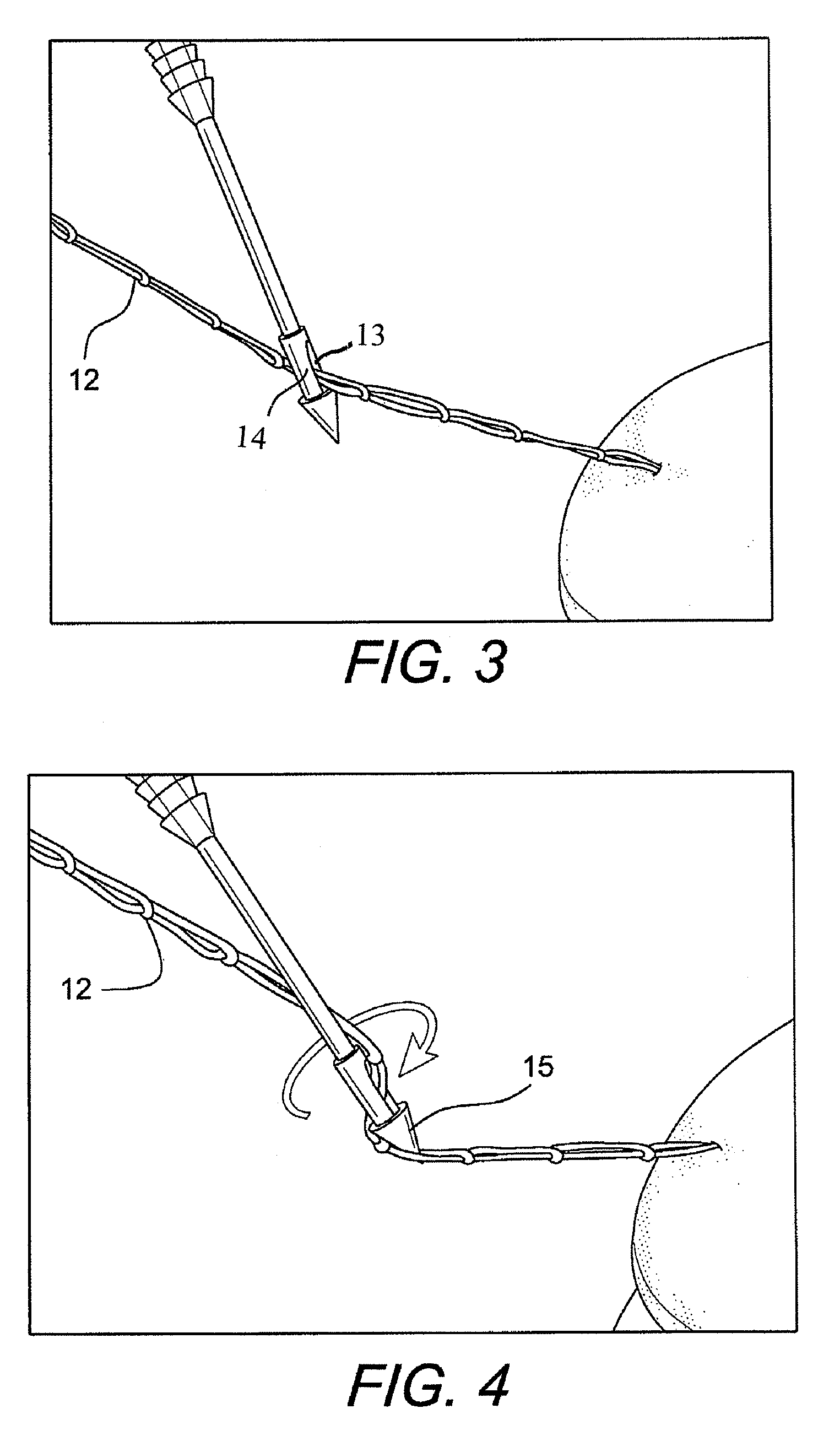
Technique for tissue fixation by capturing and anchoring a link of suture chain attached to tissue
A method and device for knotless fixation of tissue. The method utilizes a push-in type anchor (for example, a self-punching anchor) and a suture chain that includes a plurality of loops. A first portion of the suture chain is secured to the tissue to be fixated. The suture chain is next secured to the push-in type anchor (for example, by passing the suture chain through an eyelet of the anchor). The anchor is then advanced along the suture chain to bring a tip of the anchor above a chosen loop or link of the suture chain. The tip of the anchor is pushed through the chosen loop so that the tip locks the chosen loop in place (for example, by capturing both sides of the link above a shoulder of the anchor). With the captured link, the anchor is advanced into a pilot hole or socket formed in the bone to fixate the tissue. The captured link provides a hard stop that does not slip, in addition to frictional interference between the anchor and the bone socket.
Owner:ARTHREX
Systems and methods for inserting a bone anchor without a pilot hole
Bone anchor insertion assemblies and methods are provided for inserting a bone anchor (e.g., bone screw) into bone without having to create a pilot hole. In some embodiments, the assembly includes a bone anchor, a housing member, and a rod. The housing member, which is coupled to the rod, is movable between proximally and distally advanced positions relative to the rod. In the proximal position, the bone anchor can be coupled to the rod. In the distal position, a tip of the bone anchor is generally aligned with a distal end of the housing member. The bone anchor is advanced into the bone under guidance of the housing member, where the tip of the bone anchor serves as a bone awl. Once the bone anchor is seated within the bone, the housing member can be returned to the proximal position to improve visibility of the surgical procedure.
Owner:AMEDICA A DELAWARE
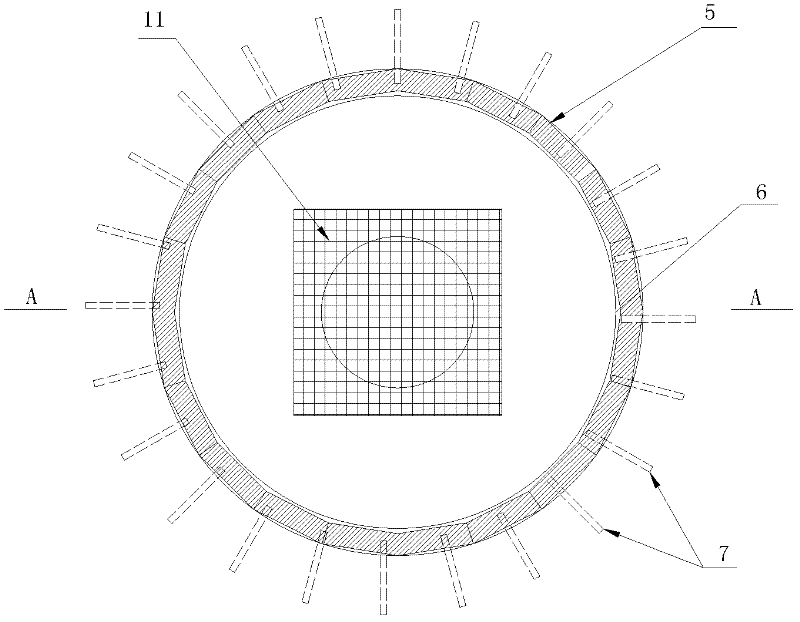
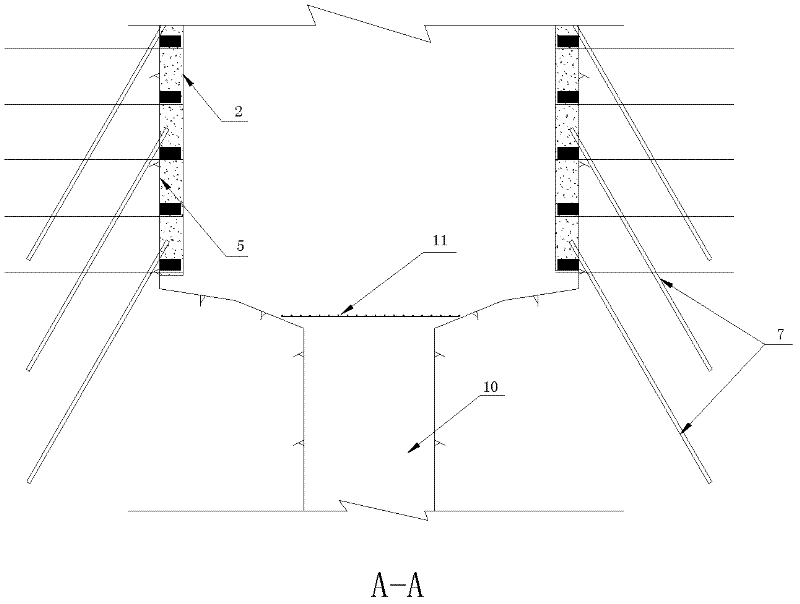
Vertical shaft construction method under unfavorable geological condition
The invention discloses a vertical shaft construction method under a unfavorable geological condition, comprising the following construction steps of: 1, pouring cover-weight concrete at a position wherein a well head of a vertical shaft is; 2, arranging two circles of advance consolidation grouting holes in the cover-weight concrete and arranging anchor bar bundles in the grouting holes, wherein the depths of the grouting holes are the same as the depth of the vertical shaft and the depths of the anchor bar bundles are the same as the depths of the grouting holes; 3, drilling pilot holes from top to bottom of the vertical shaft by utilizing a raise-boring machine; 4, drilling pilot shafts from bottom to top of the vertical shaft by utilizing the raise-boring machine; 5, carrying out advance support before expanding excavation; 6, carrying out hole drilling , blasting and the expanding excavation from top to bottom on the vertical shaft; and 7, carrying out reinforced support after the expanding excavation. By means of the vertical shaft construction method disclosed by the invention, the problems of the excavation of the light-section deep vertical shaft under the unfavorable geological condition are solved; and through the advance consolidation before the pilot hole construction, the advance support of small pipes before the expanding excavation and the steel support and bolt-spray support after the excavation, the influences of hole collapsing during the pilot shaft excavating and collapse after the expanding excavation on the construction are effectively eliminated.
Owner:SINOHYDRO BUREAU 5
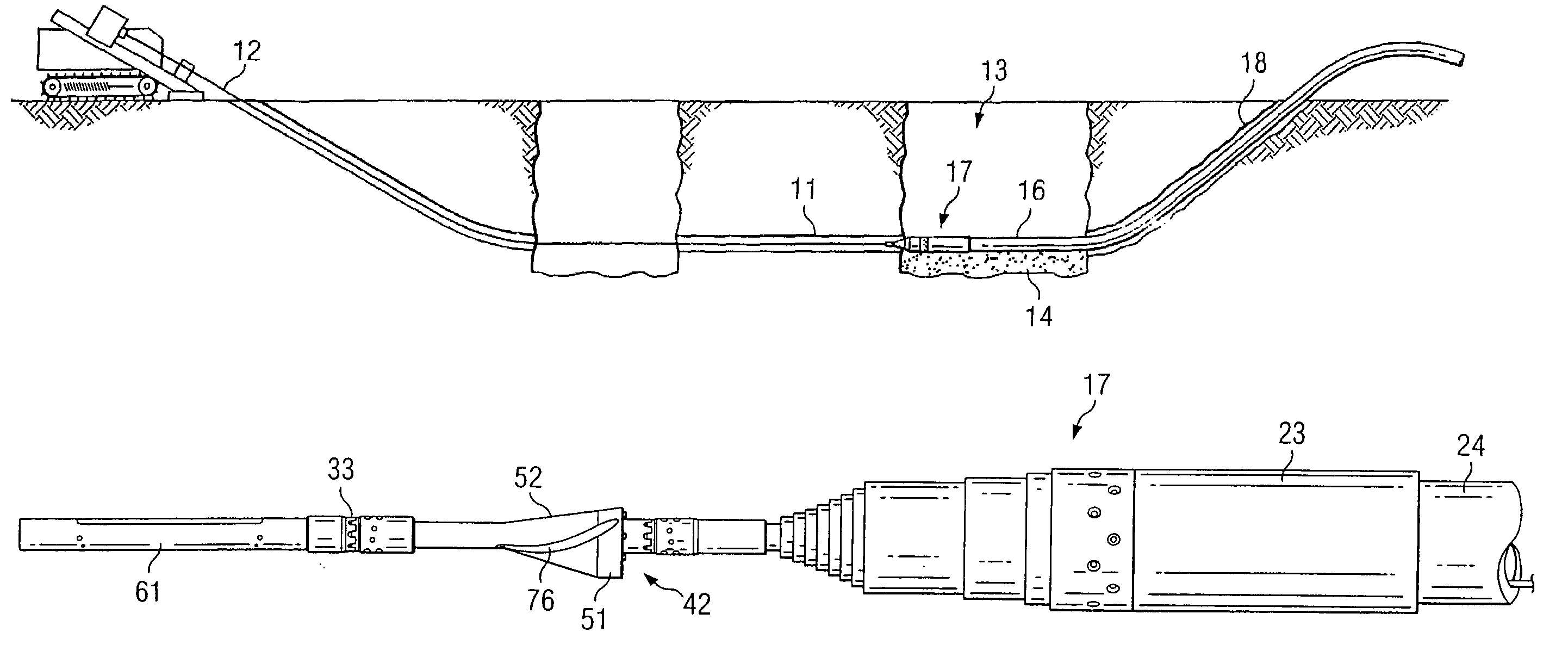
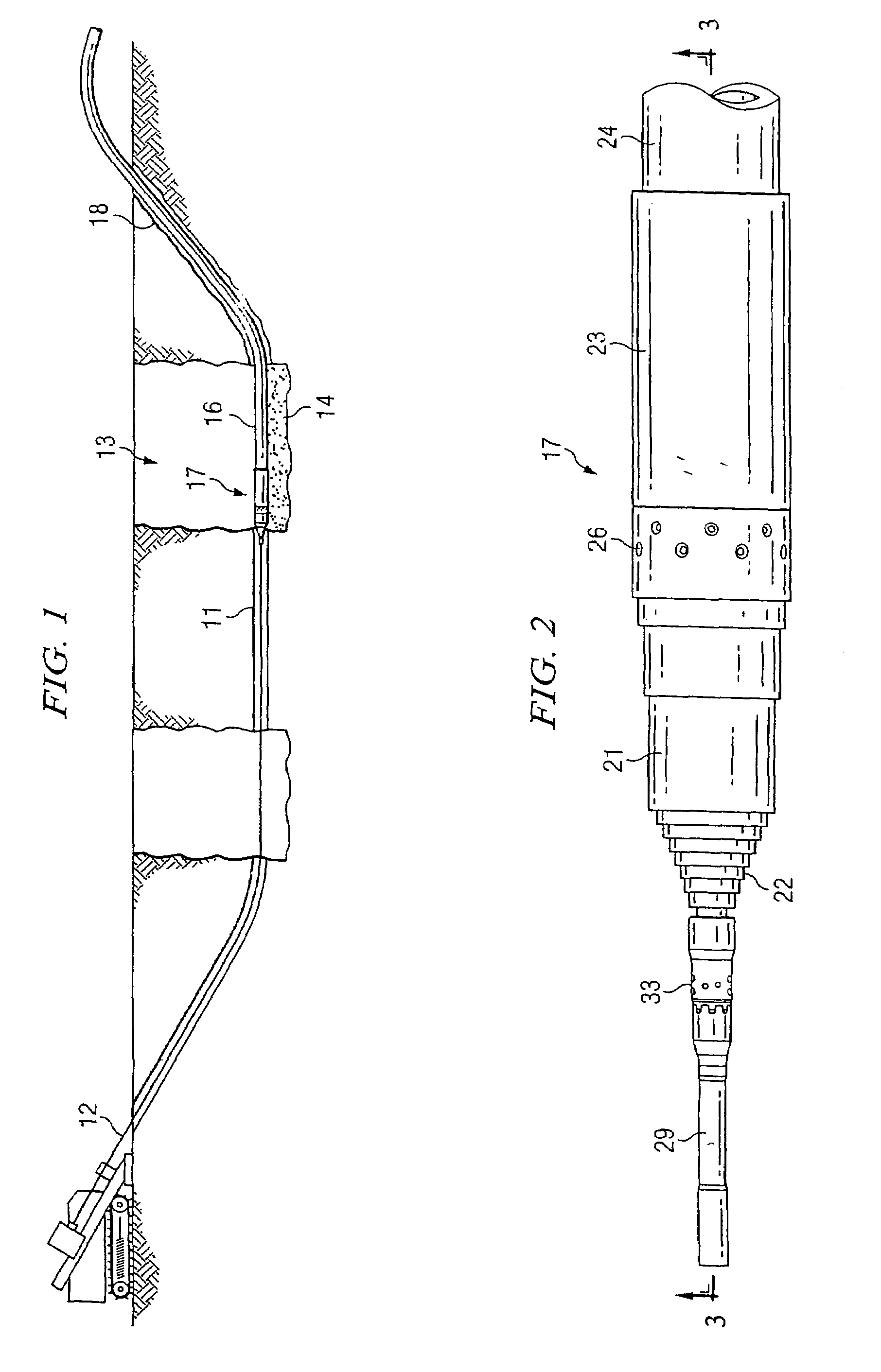
Method and apparatus for on-grade boring
A method for installation of an underground pipe includes an initial step of boring a pilot hole through the ground at a predetermined grade angle by extending a drill string having a steerable boring bit mounted thereon through the ground. Upon reaching an end location for the pilot hole, the bit is removed from the drill string, and an expander having a diameter greater than the pilot hole is attached to the drill string, which expander is backed by an impact device such as a pneumatic impactor including a striker that delivers repeated impacts to a rearwardly facing surface of the expander, and by a pipe drawn along behind the expander. The expander is pulled back through the pilot hole at the grade angle while the impactor is operated to aid progress of the expander through the ground and pull the pipe into place behind the expander. Typically in this method the replacement pipe is coupled to a rear end of the expander and the boring bit has a sonde housing containing a sonde attached thereto to indicate to an operator the orientation of a steering face on the boring bit.
Owner:EARTH TOOL L L C
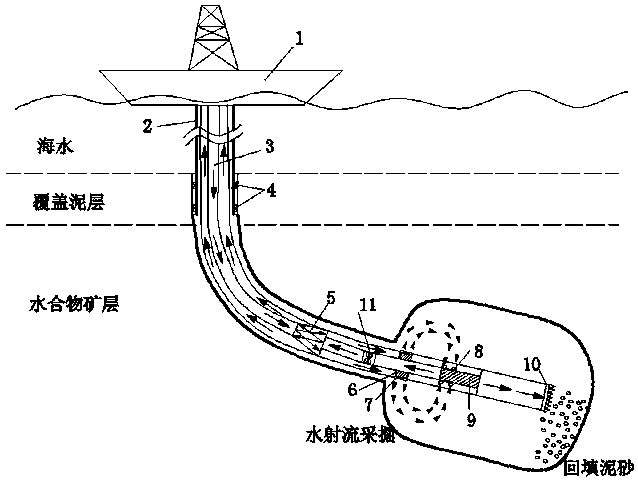
Submarine shallow layer non-stratified natural gas hydrate pilot hole pull-back jet break-up exploitation method and exploitation device
The invention discloses a submarine shallow layer natural gas hydrate pilot hole pull-back jet break-up exploitation method and exploitation device, and belongs to the technical field of submarine hydrate exploitation. The exploitation method mainly comprises the following steps that a water insulation pipe is lowered to the position adjacent to a hydrate deposit, turn drilling is conducted in thehydrate deposit by means of mechanical or jet-flow drilling, and a pilot hole with a certain inclined angle is formed; after drilling reaches a preset position, a continuous pipe and an exploitationcrushing system are pulled back, meanwhile the surrounding hydrate ore body is crushed by means of a spray head jet flow, hydrate particles formed are collected into a closed pipeline with seawater, silt in the crushed particles is separated out by means of an in-pipe downhole separator, curing agent is added, then the particles are backfilled to a gob in situ, and the hydrate particles after separation are pumped to the sea surface for treatment together with the seawater. By means of the exploitation method and the exploitation device, efficient, safe and sustainable exploitation of the submarine shallow layer natural gas hydrate is achieved, the exploitation efficiency is ensured, and meanwhile a potential safety problem is effectively avoided.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +2
Fixed blade fixed cutter hole opener
A hole opener including a tool body having upper and lower ends. The upper and lower ends may be coupled to adjacent drilling tools. At least two blades are formed on the tool body and are arranged so that the hole opener is positioned concentric with a wellbore, and cutting elements are located on the blades. The at least two blades and the cutting elements are arranged to increase a diameter of a previously drilled wellbore.A hole opener including a tool body having upper and lower ends. The upper and lower ends may be coupled to adjacent drilling tools. At least two blades are formed on the tool body and are arranged so that the hole opener is positioned concentric with a wellbore, and cutting elements are located on the blades. The hole opener includes a pilot hole conditioning section. The pilot hole conditioning section includes at least two pilot blades formed on the tool body in a position axially ahead of the blades. The pilot blades include a taper at a downhole end and gage pads positioned at selected diameters. At least one cutting element is disposed on the pilot blades.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
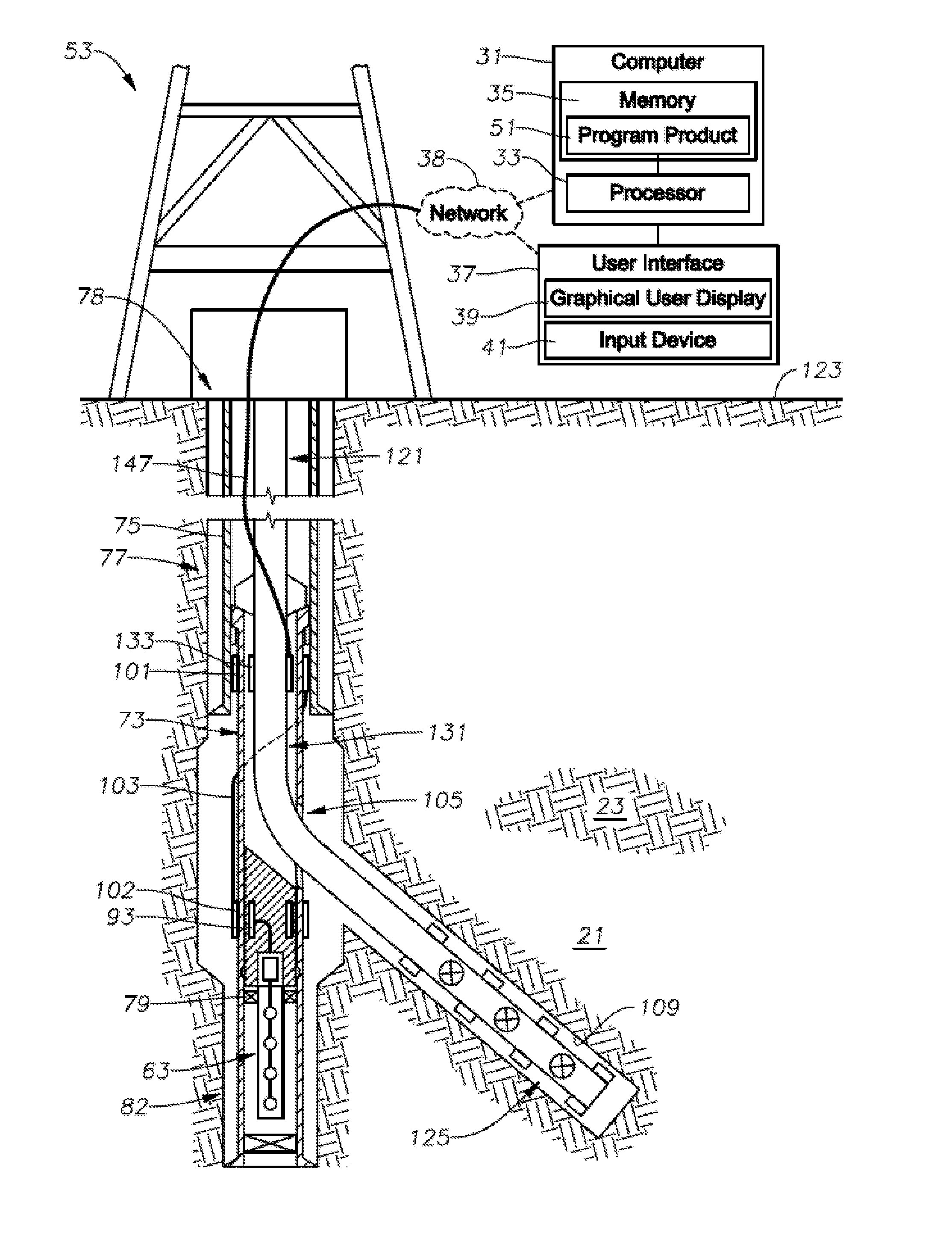
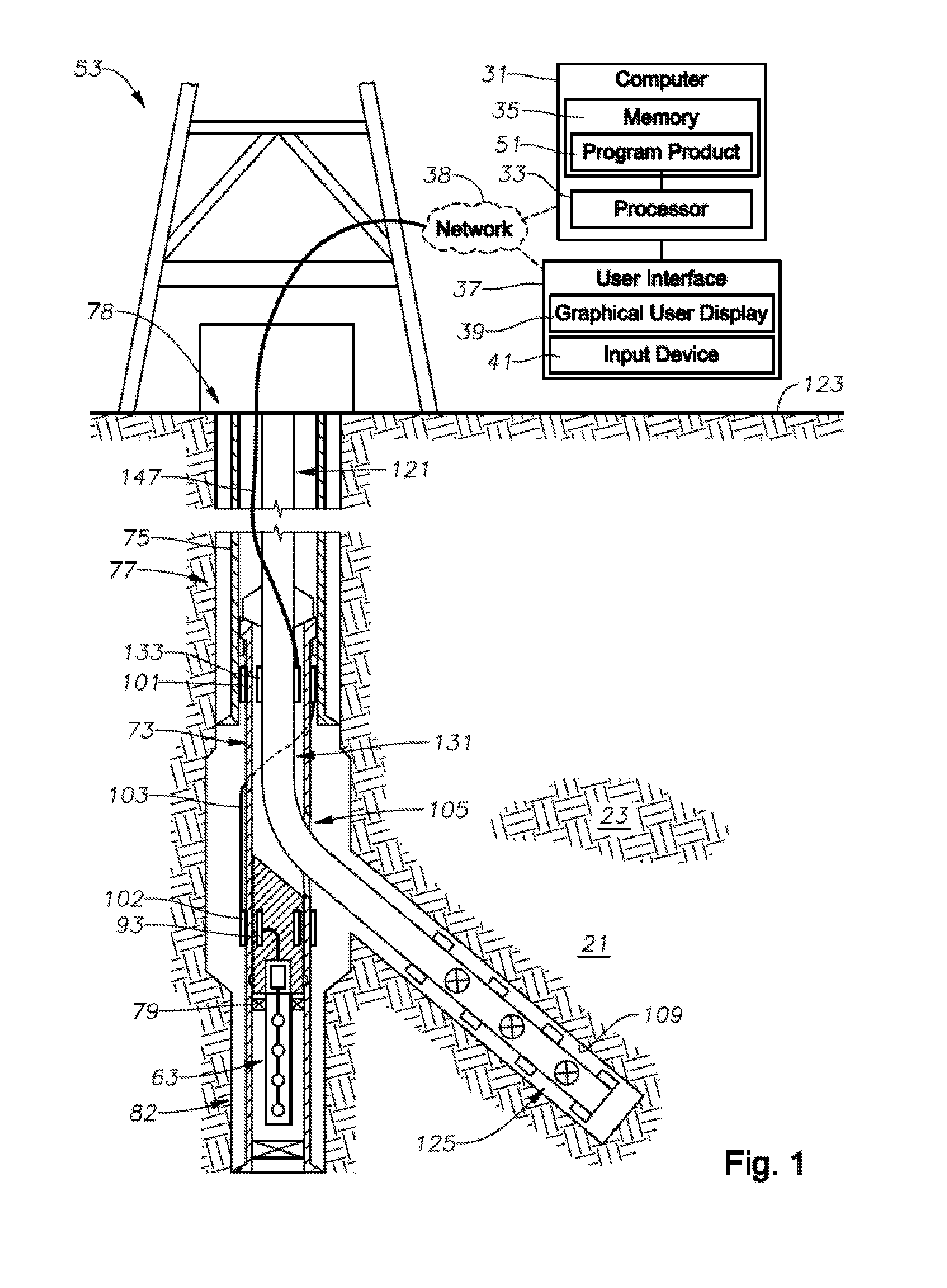
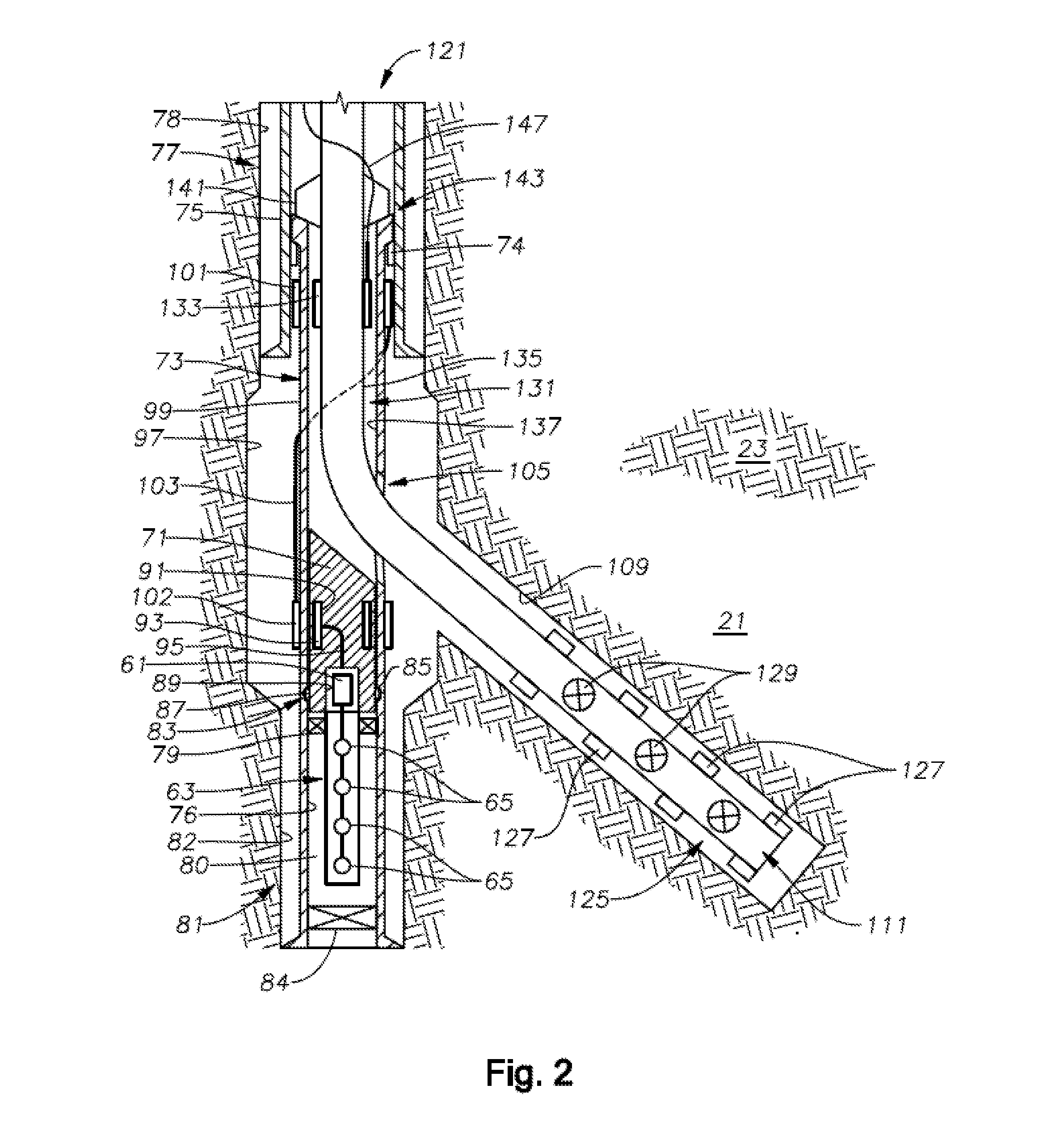
Method For Real-Time Monitoring and Transmitting Hydraulic Fracture Seismic Events to Surface Using the Pilot Hole of the Treatment Well as the Monitoring Well
Methods for determining hydraulic fracture geometry and / or areal extent of an area of interest in a reservoir, are provided. An exemplary method includes isolating downhole acoustic receiver equipment in a lower portion of a first wellbore from fracturing operations located in a second wellbore connected to the first wellbore. Communications between surface equipment in the downhole acoustic receiver equipment is provided through a communications conduit bypass that permits well operations in the second wellbore without interfering with communications between the surface equipment and the downhole acoustic receiver equipment.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Mould having core-pulling mechanism
A mould having core-pulling mechanism includes a core plate, a core insert, a cavity plate, a cavity insert, a guide dowel and a slide block. The cavity insert and the core insert define a mould cavity. A sliding groove of the core plate and a recess of the core insert are communicated with the mould cavity. The guide dowel is received in a dowel-receiving hole of the cavity plate and tiltedly extending out of the cavity plate. The slide block has an inserting block and a forming block. A lower portion of the slide block is slideably located in the sliding groove. The guide dowel can be inserted into an angle guiding hole of the slide block. The inserting block can be inserted into the recess. The forming block may enter into the mould cavity. The mould produces plastic products on the inner surface of which the groove is formed.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
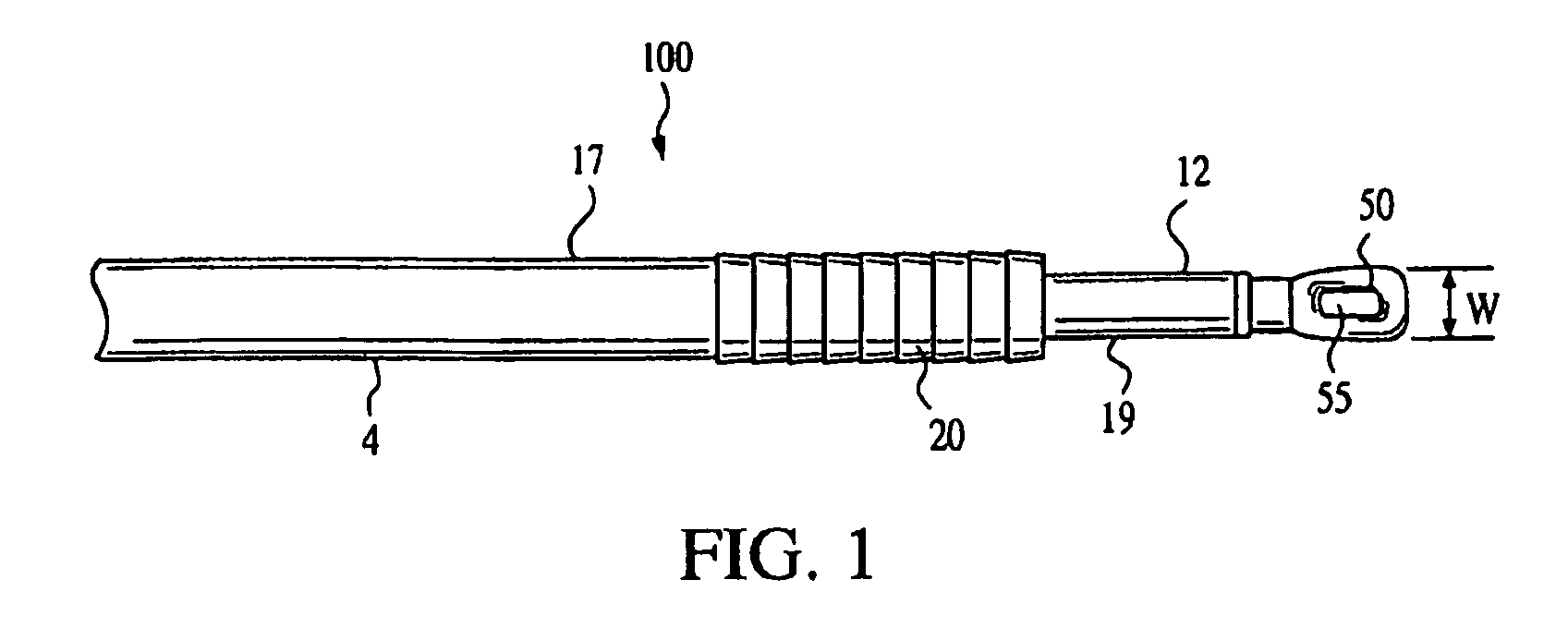
Variable tension post fixation
A variable tension post fixation device includes an outer body including a shaft, a tip, and a central core, and an inner body including a suture hole and configured to be advanceable within the central core, wherein the outer body is configured for allowing insertion of the outer body into a pilot hole in a bone, and wherein the outer body and inner body cooperate to secure sutures in the bone.
Owner:ROCKFORD ORTHOPAEDIC SPORTS MEDICINE SERVICES
Cannulated drill bit with radially offset cutting edge
A drill bit has a cylindrical proximal end coupled to a driving device with a central axis of rotation about which the proximal end rotates. A distal portion of the drill bit is a cutting device attached to the proximal end in such a way that it extends outside the periphery of the proximal end for a distance less than the entirety of the circumference of the proximal end. A guide wire extends through a passageway in the bit and is provided to create a pilot hole before the distal portion enlarges that hole. With this configuration of the cutting device, it is possible to position the cutting device in the distal portion in a direction facing away from the medial femoral condyle so that the proximal end of the drill bit can slide past the medial femoral condyle, with its axis of rotation much closer to that condyle than would be the case in prior art drill bits.
Owner:LINVATEC
Pedicle punch with cannula
InactiveUS20080071302A1Facilitating its cannulationReduce exposureInfusion syringesDiagnostic markersPilot holeBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to pedicle implements, in particular pedicle implants that involve screws. The present invention includes a handle, a pointy tip, a shaft, a cannula located therethrough and mini protrusions used to prevent toggling. The crux of the present invention is the ability of the user to create an accurate pilot hole via the pointy tip. In addition, the present invention allows the user the ability to insert a pedicle probe through the cannula out through the pointy tip. This allows the user to perform the cannulation portion of the procedure without the use of any thrombatic agents.
Owner:ORTHO IMPACT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com