Patents
Literature
1062 results about "Spinal implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
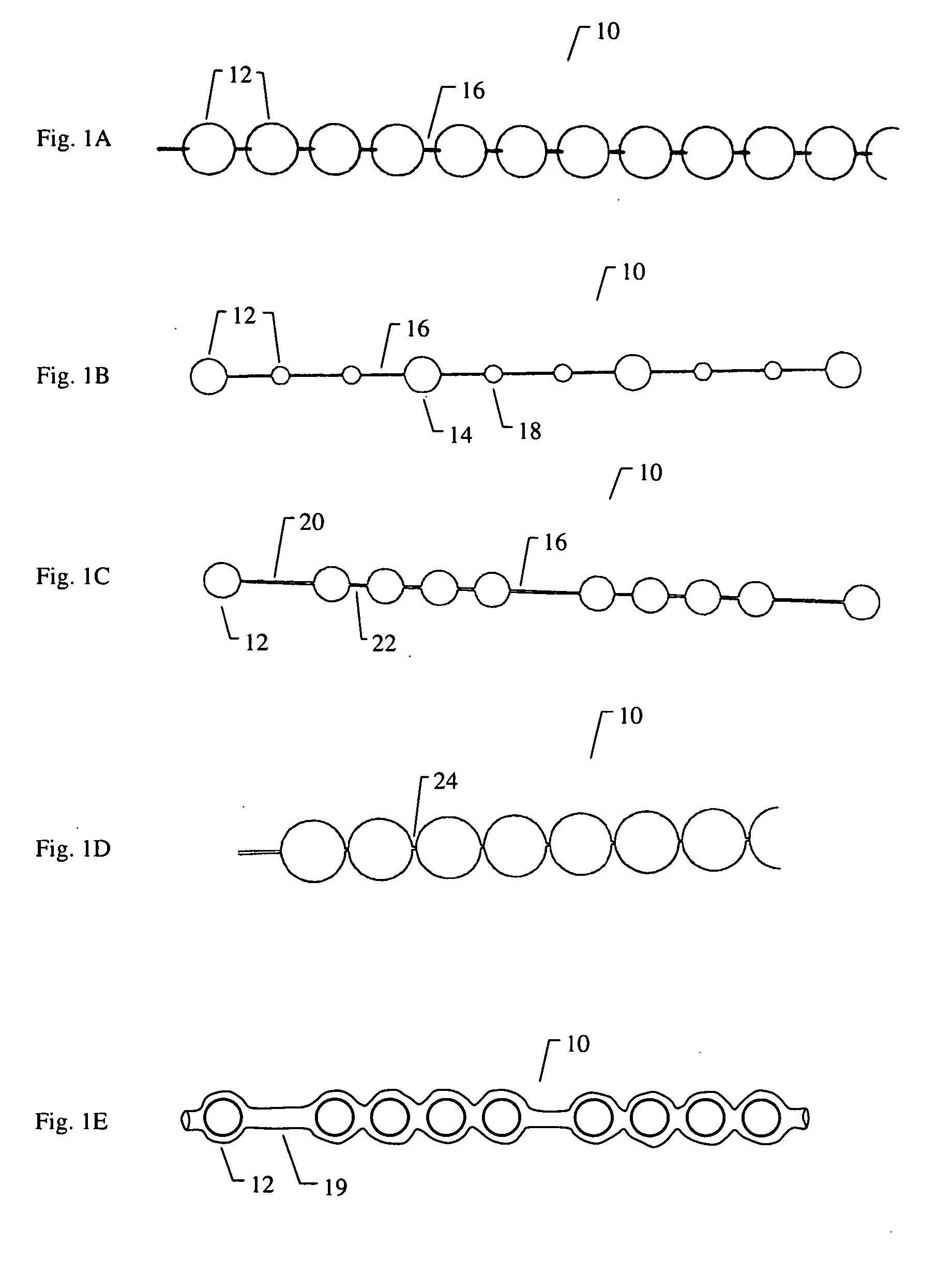
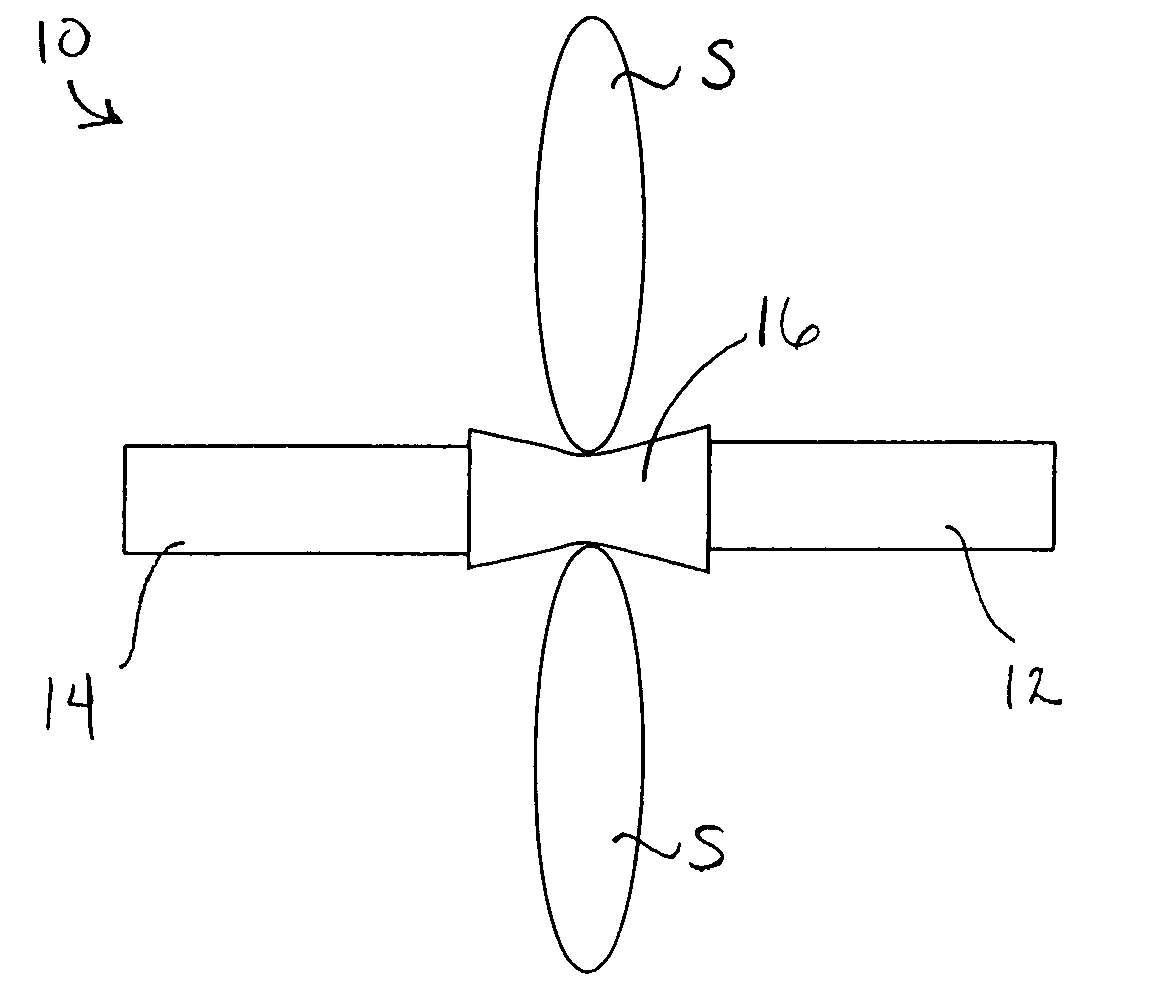
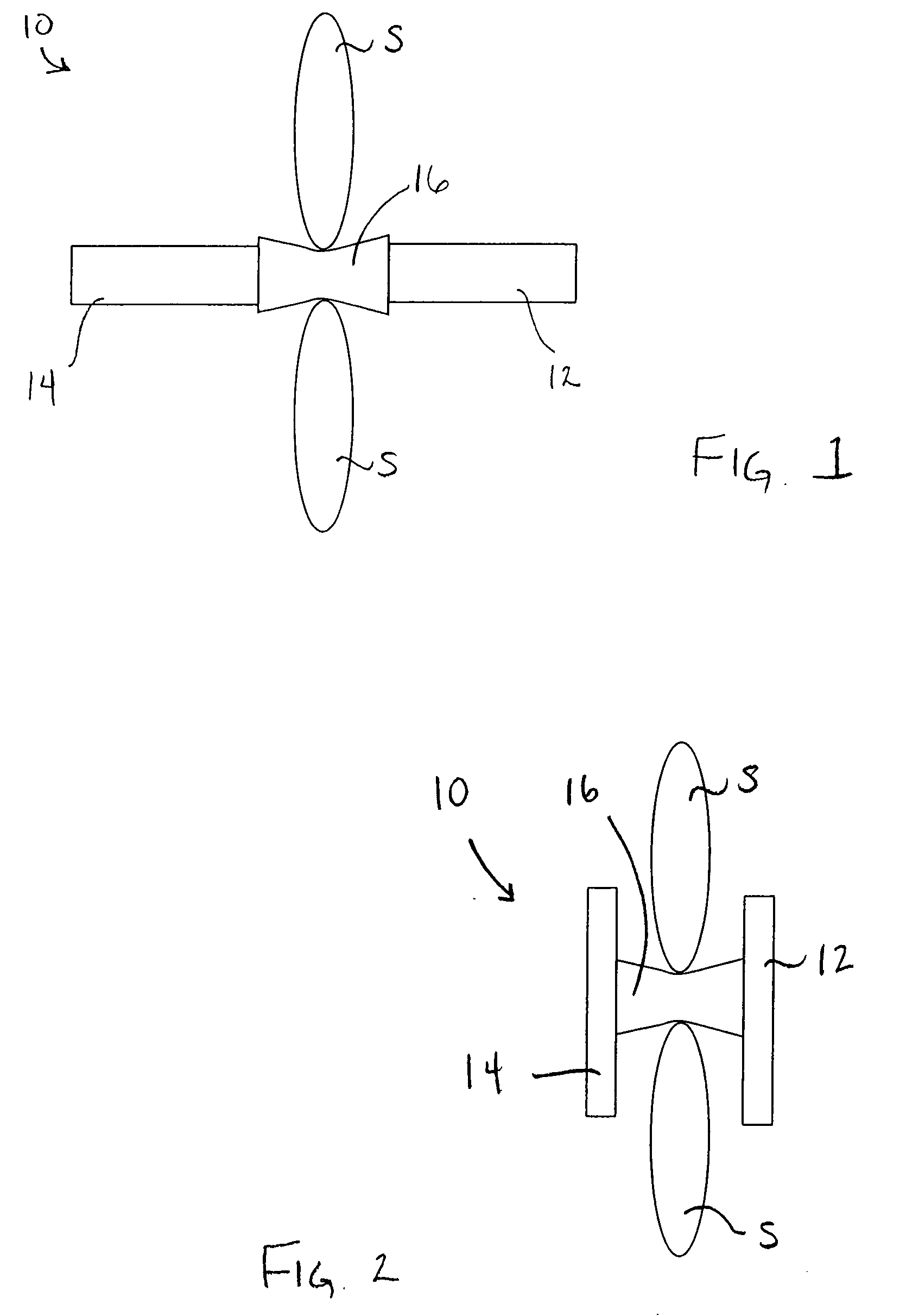
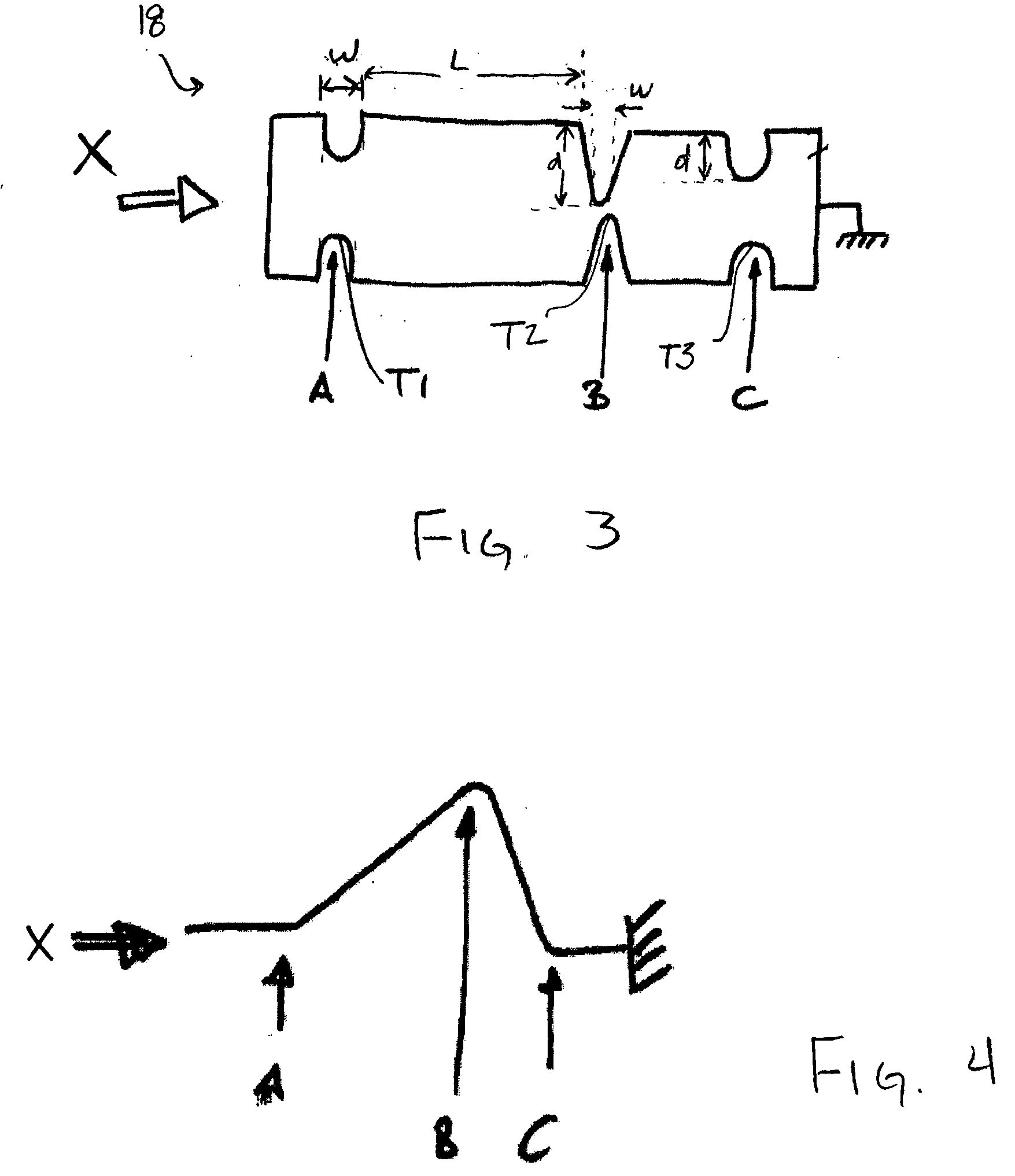
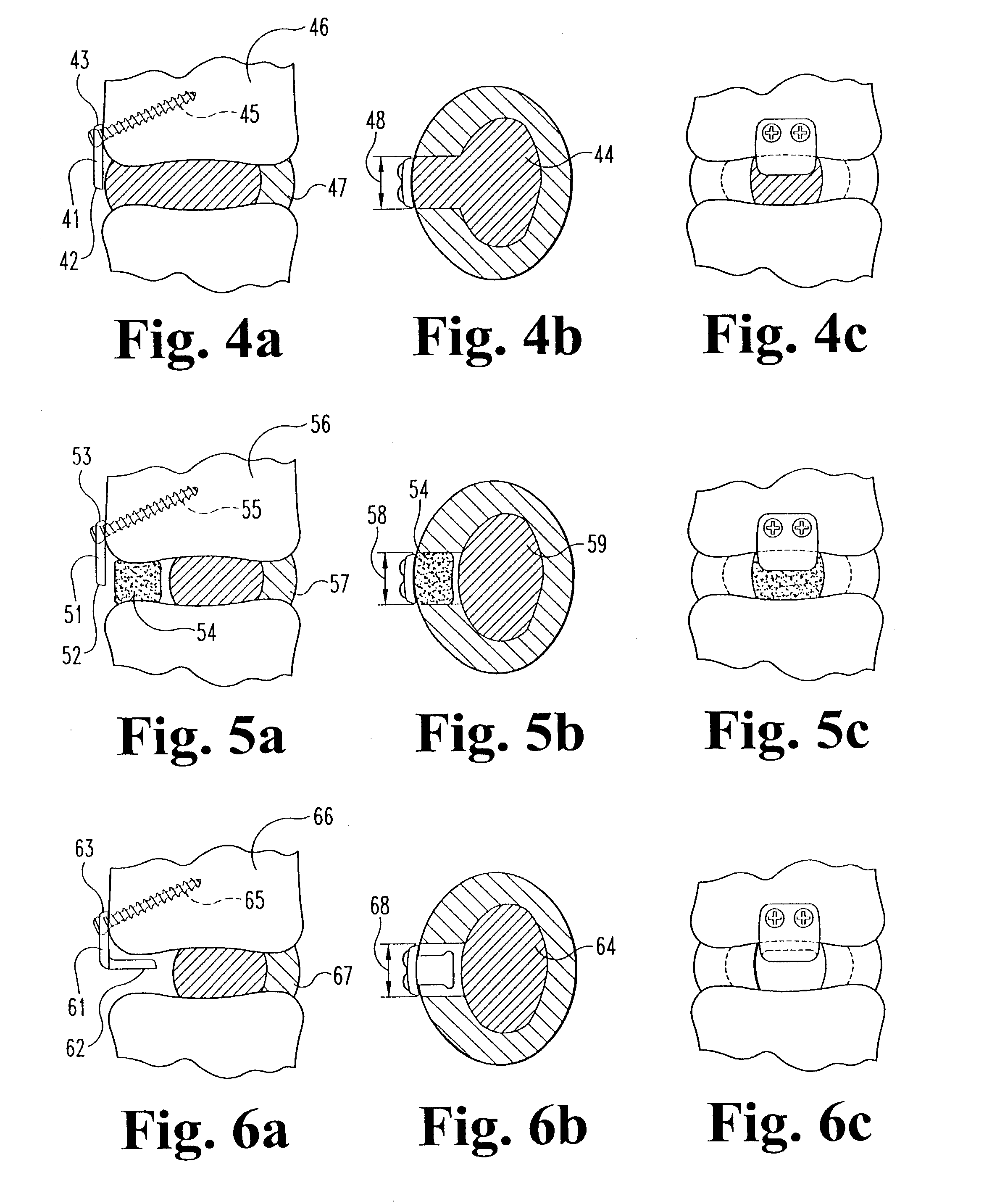
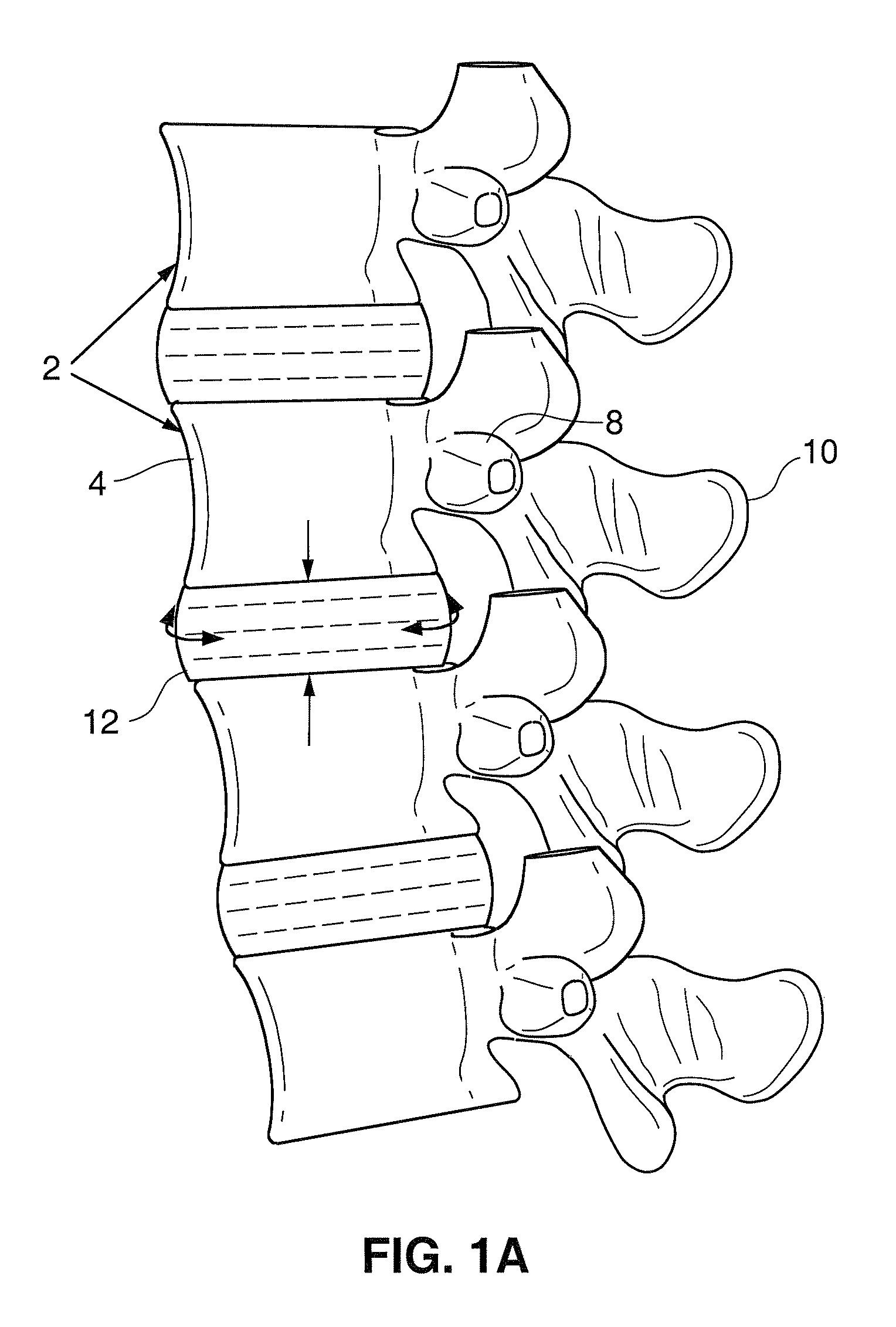
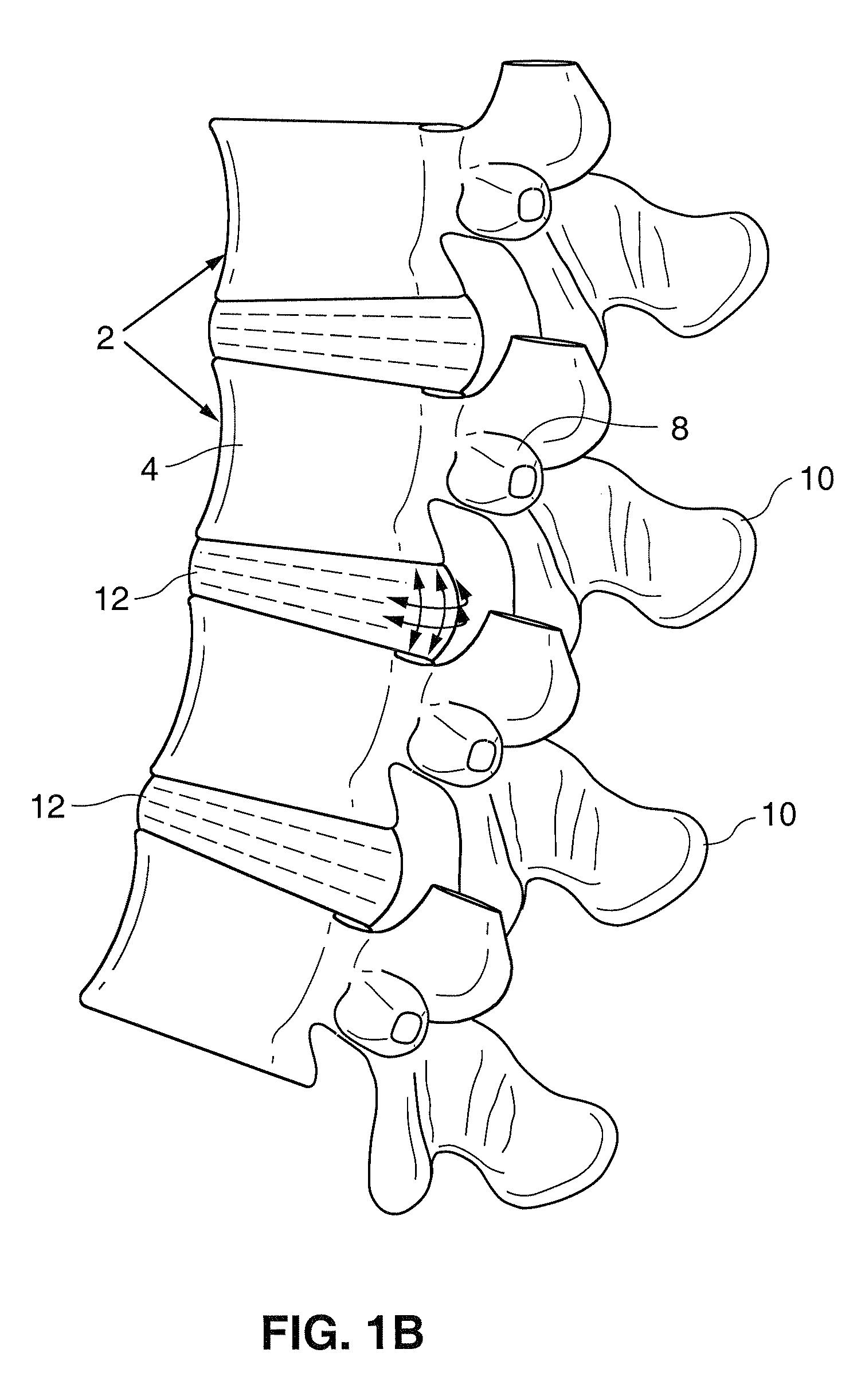
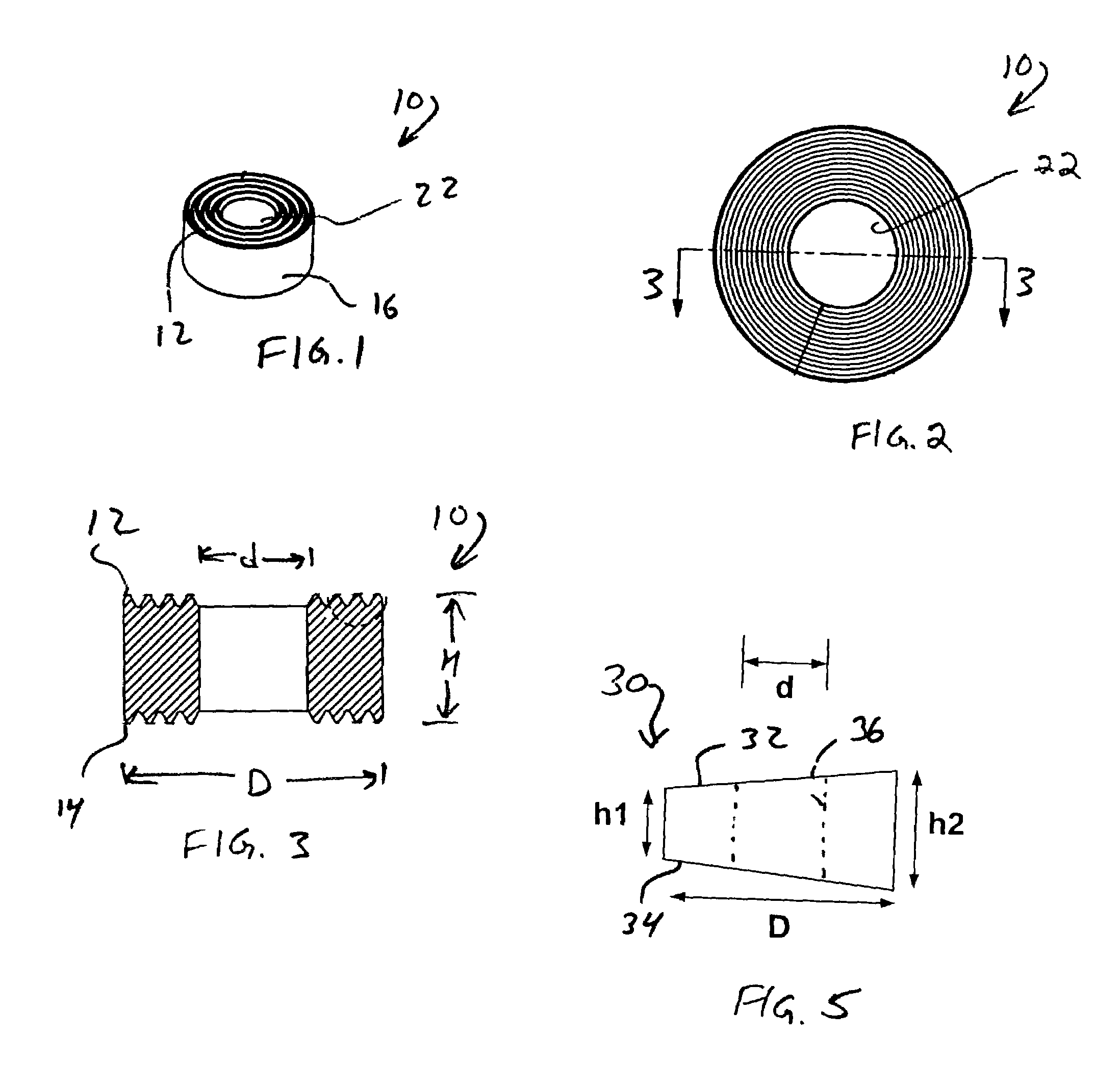
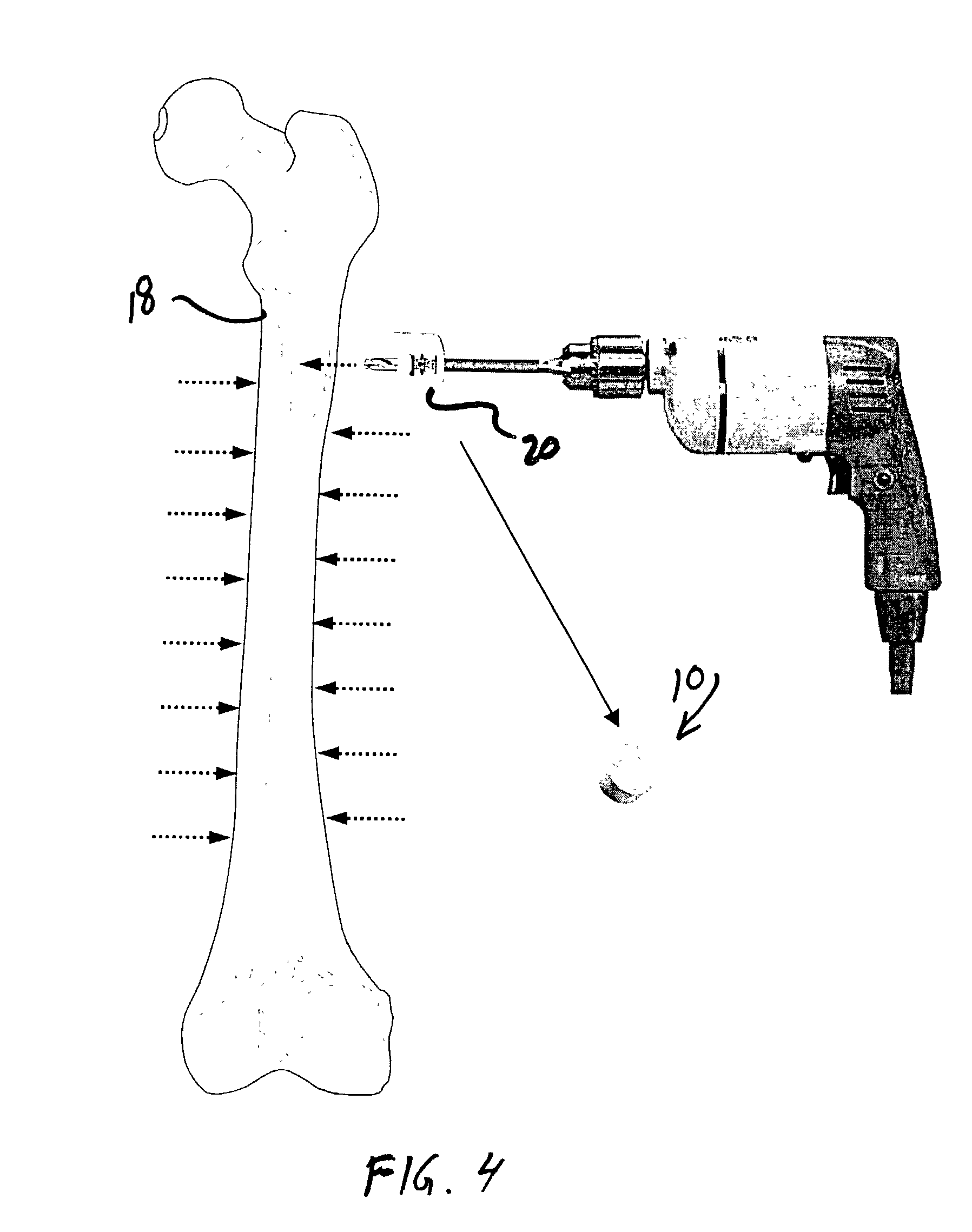
Spinal implants are devices surgeons use during surgery to treat deformity, stabilize and strengthen the spine, and facilitate fusion. Disorders treated using spinal implants include degenerative disc disease, scoliosis, kyphosis, spondylolisthesis, and fracture.
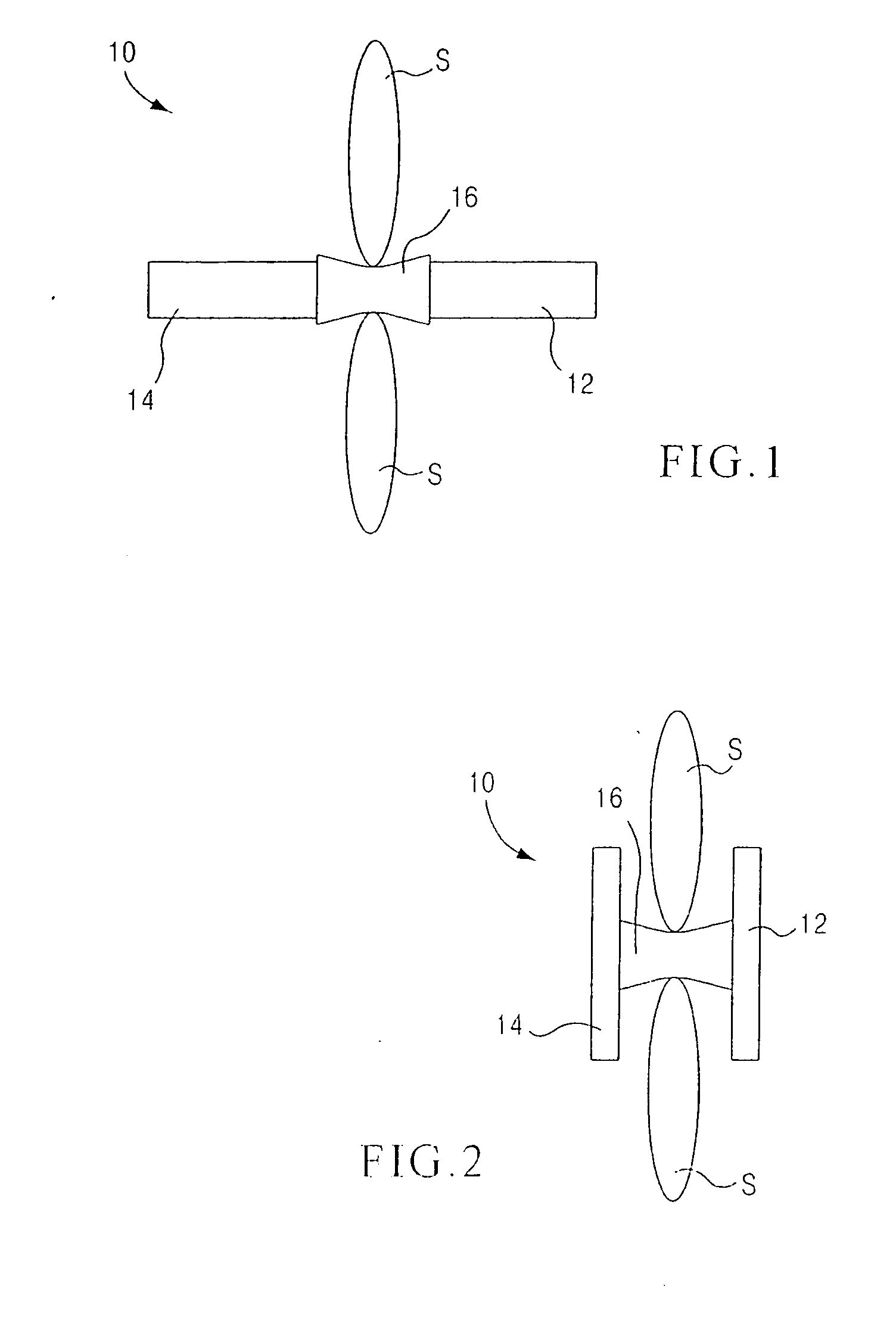
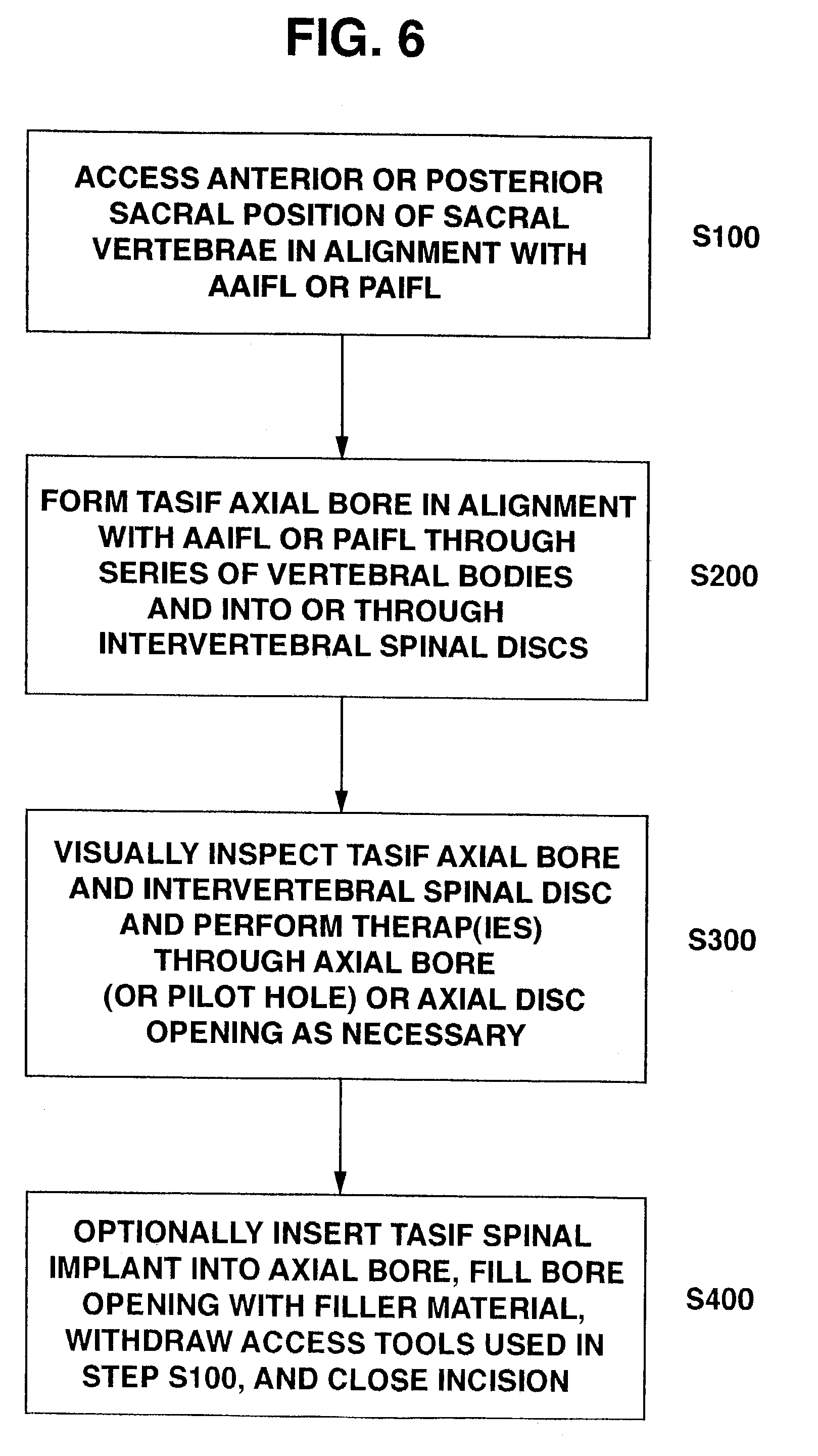
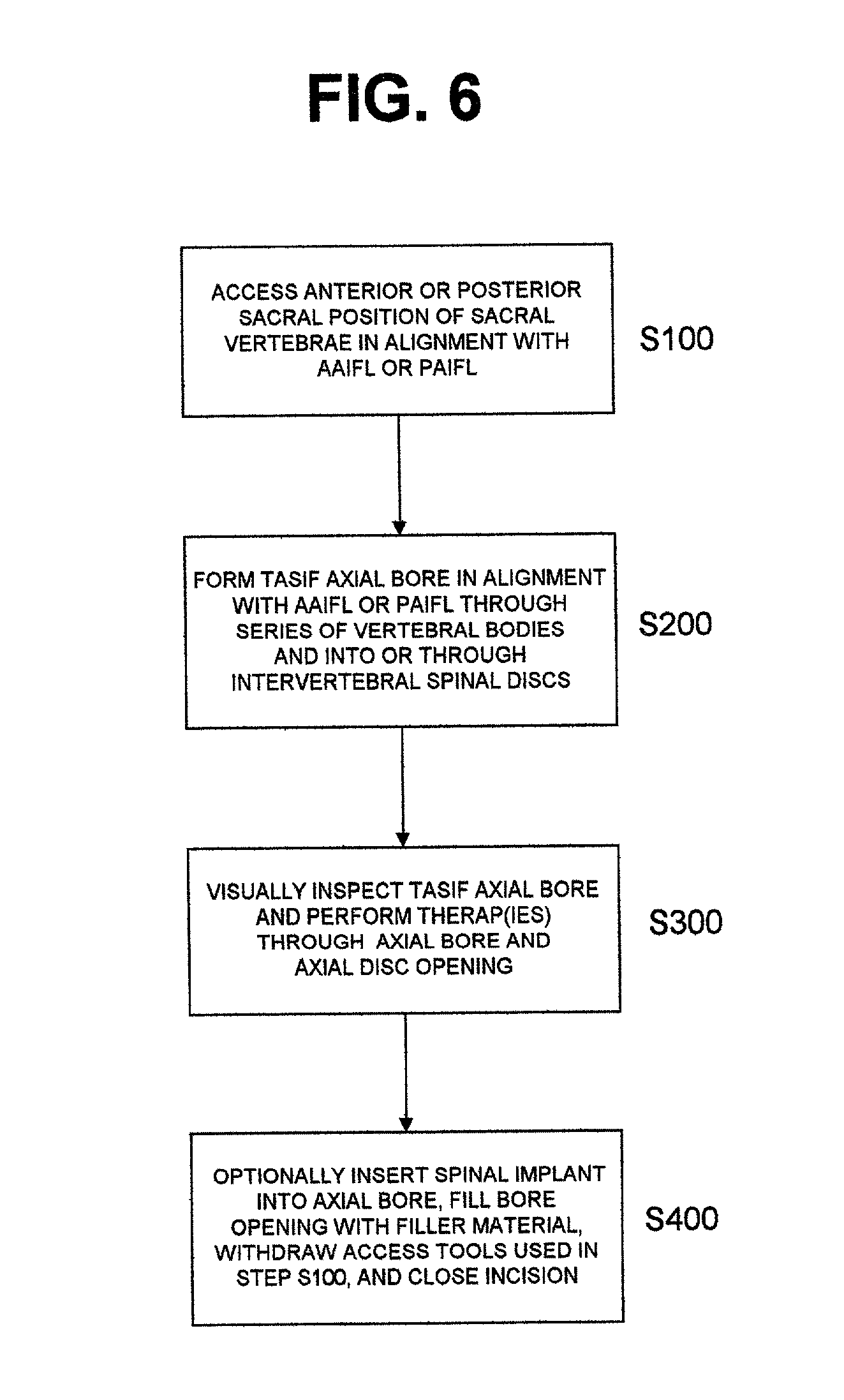
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
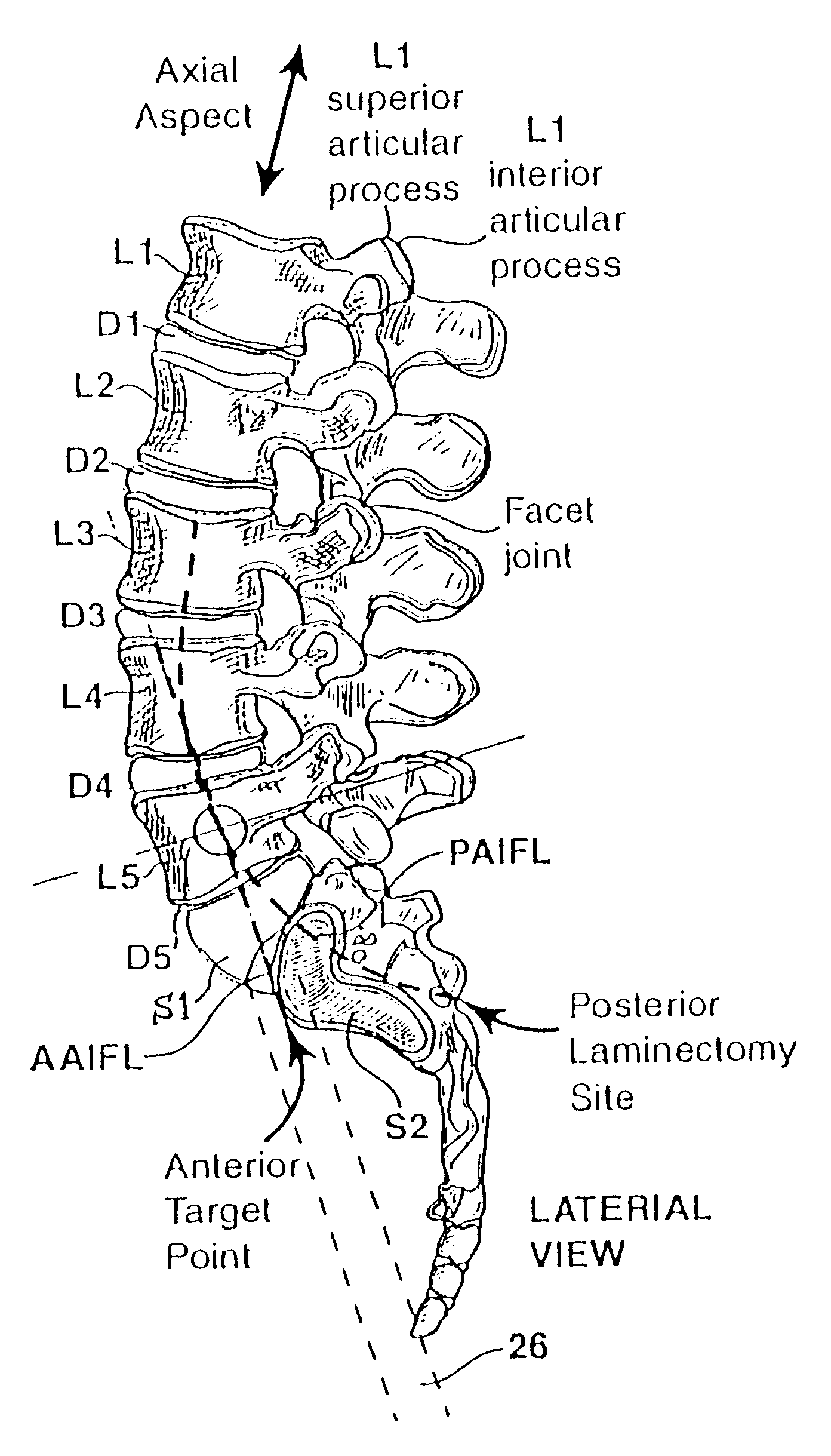
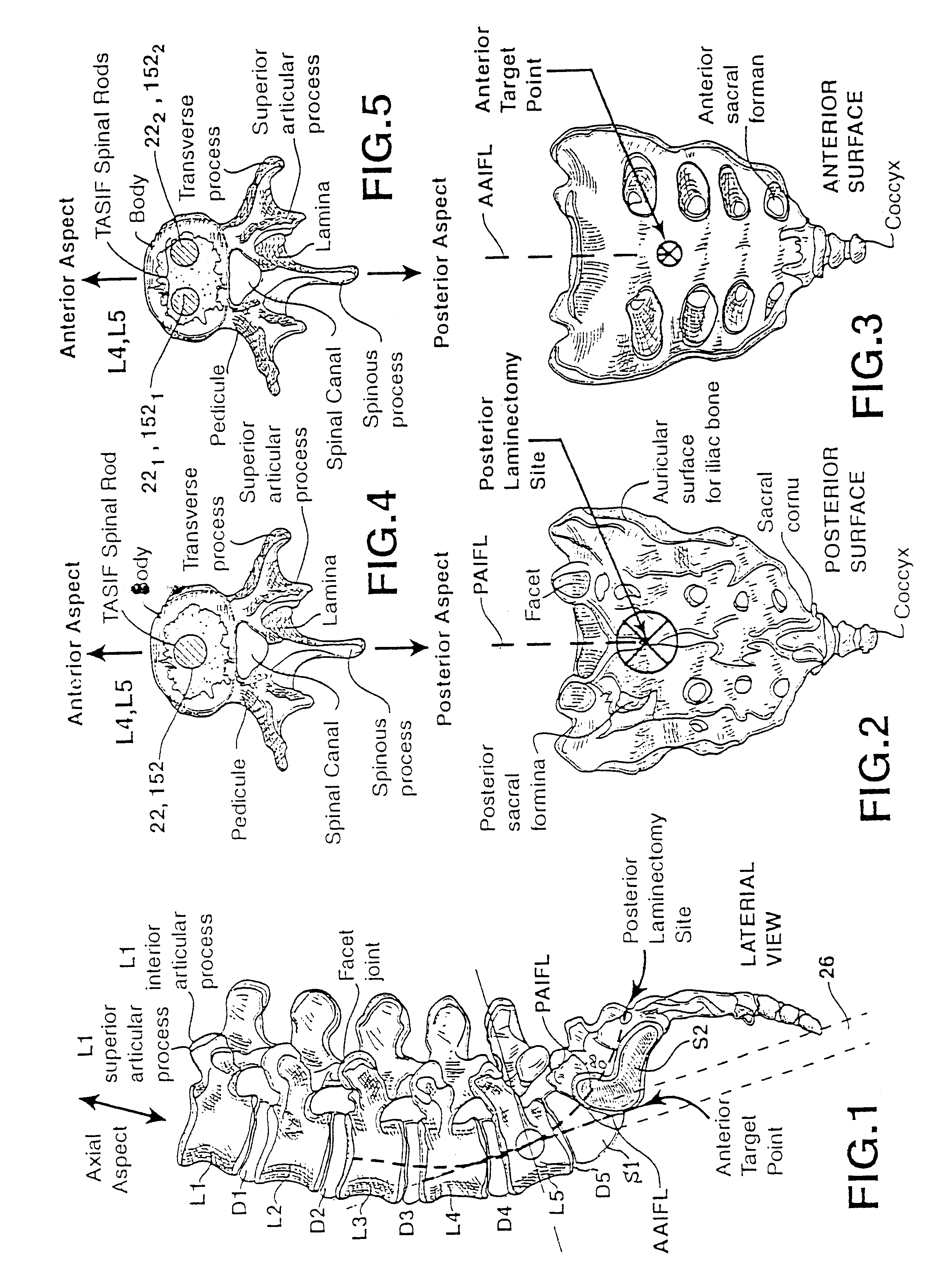
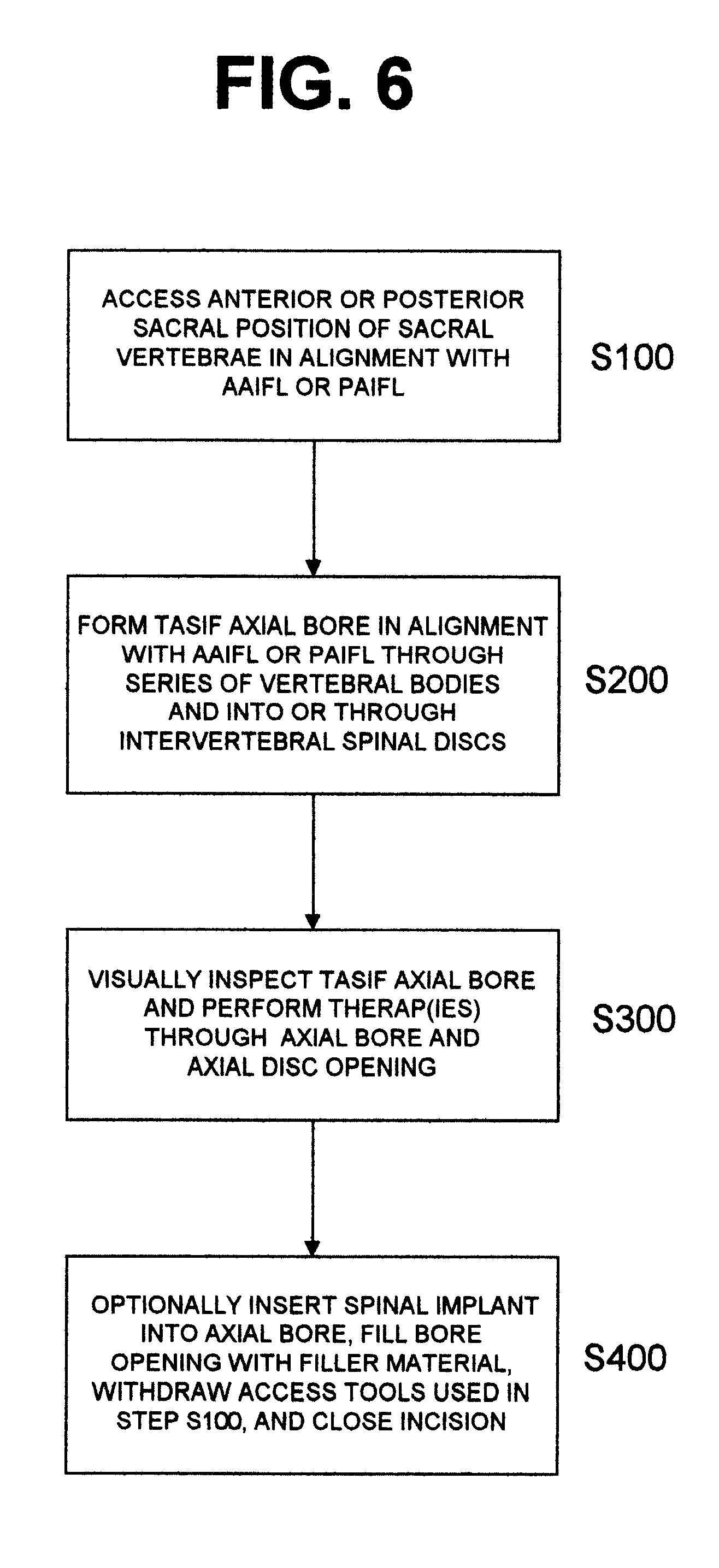
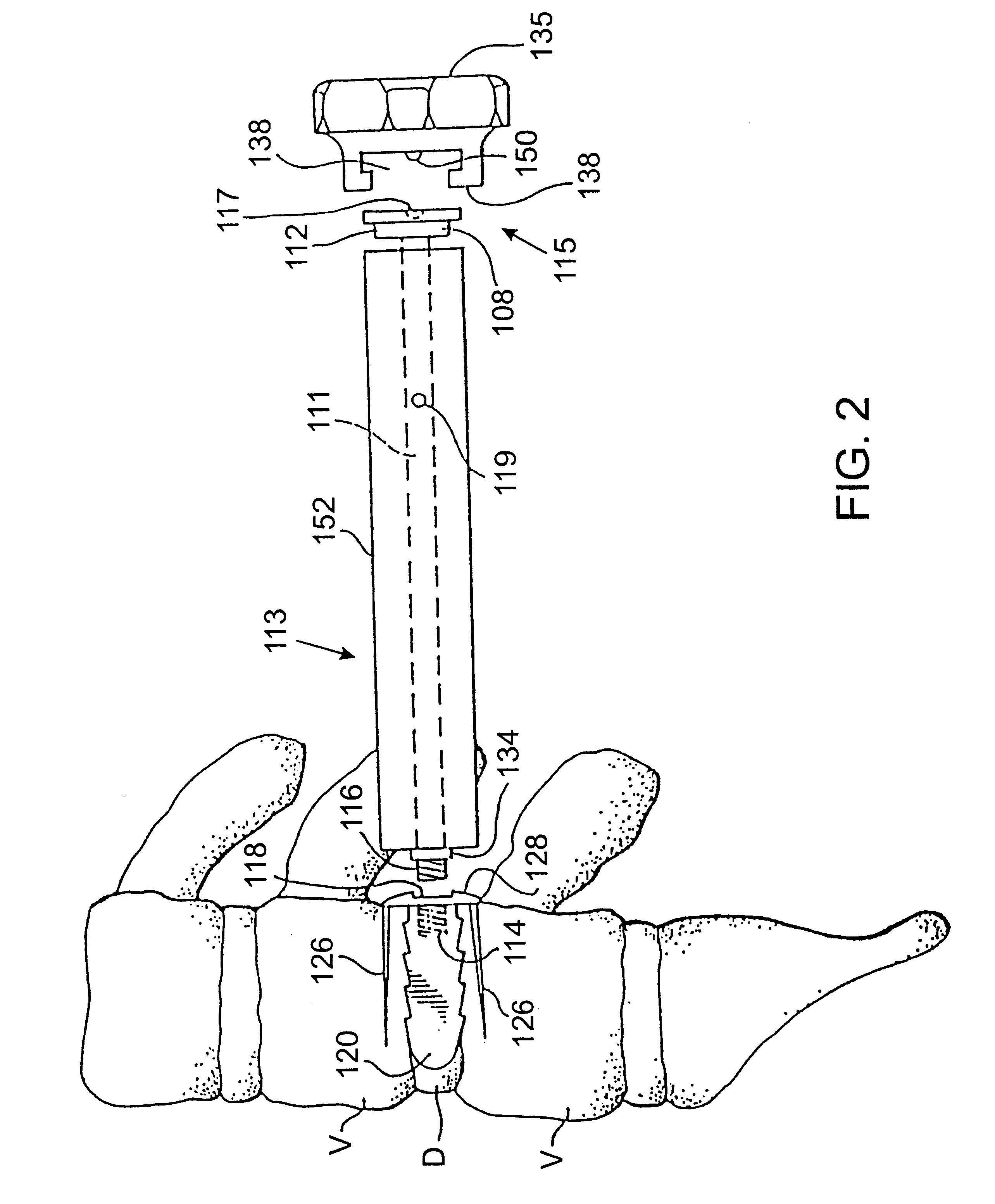
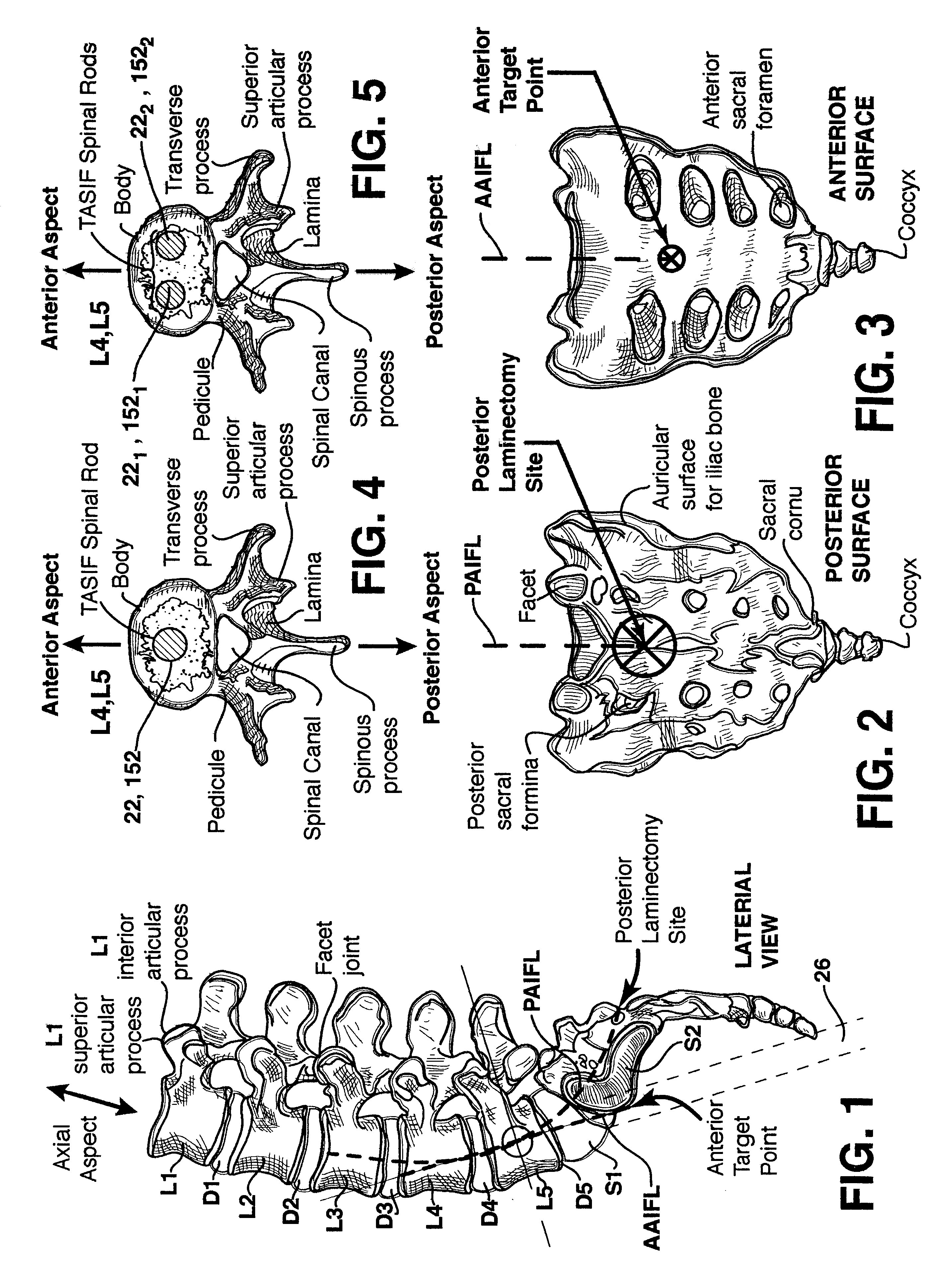
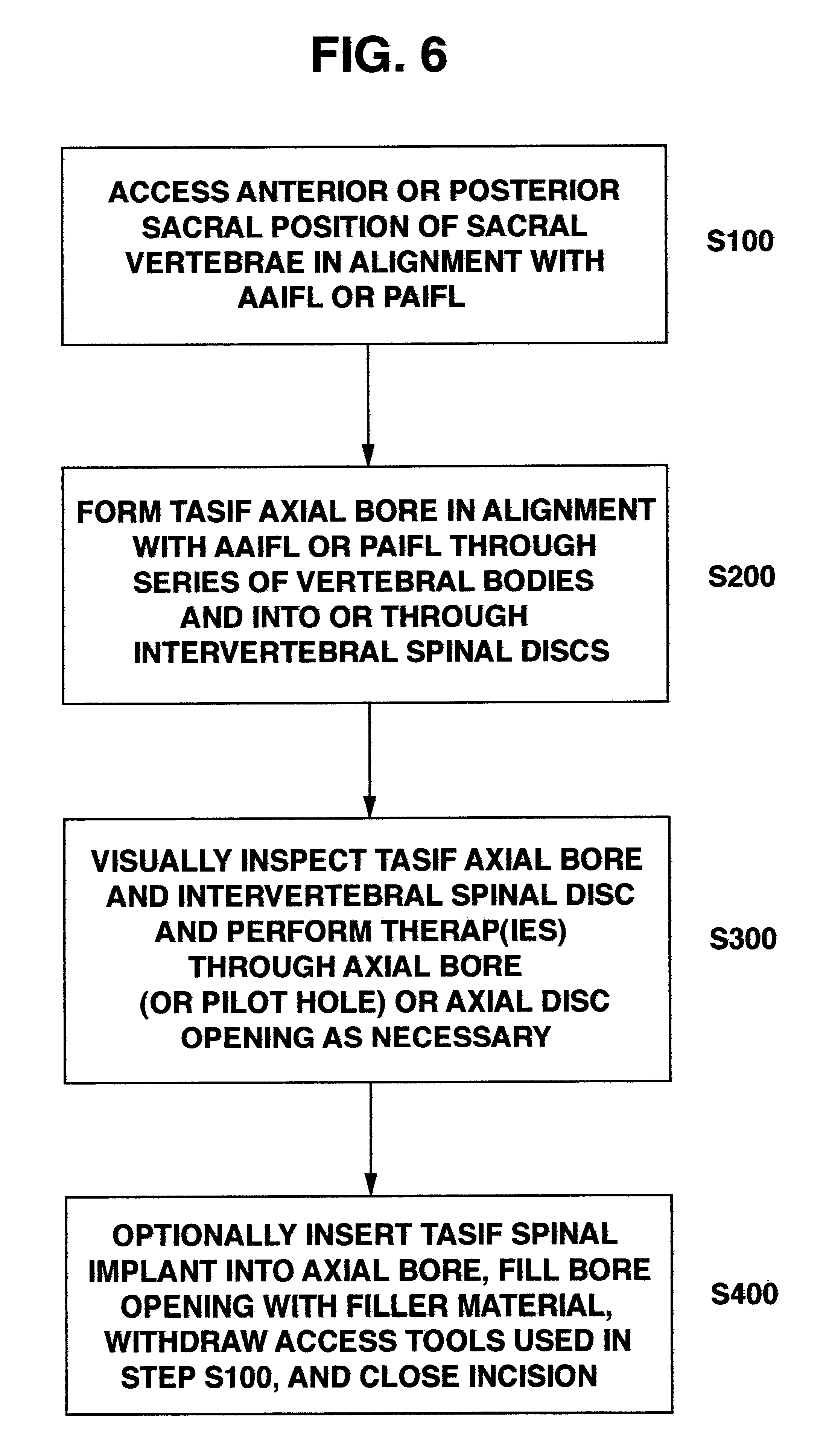
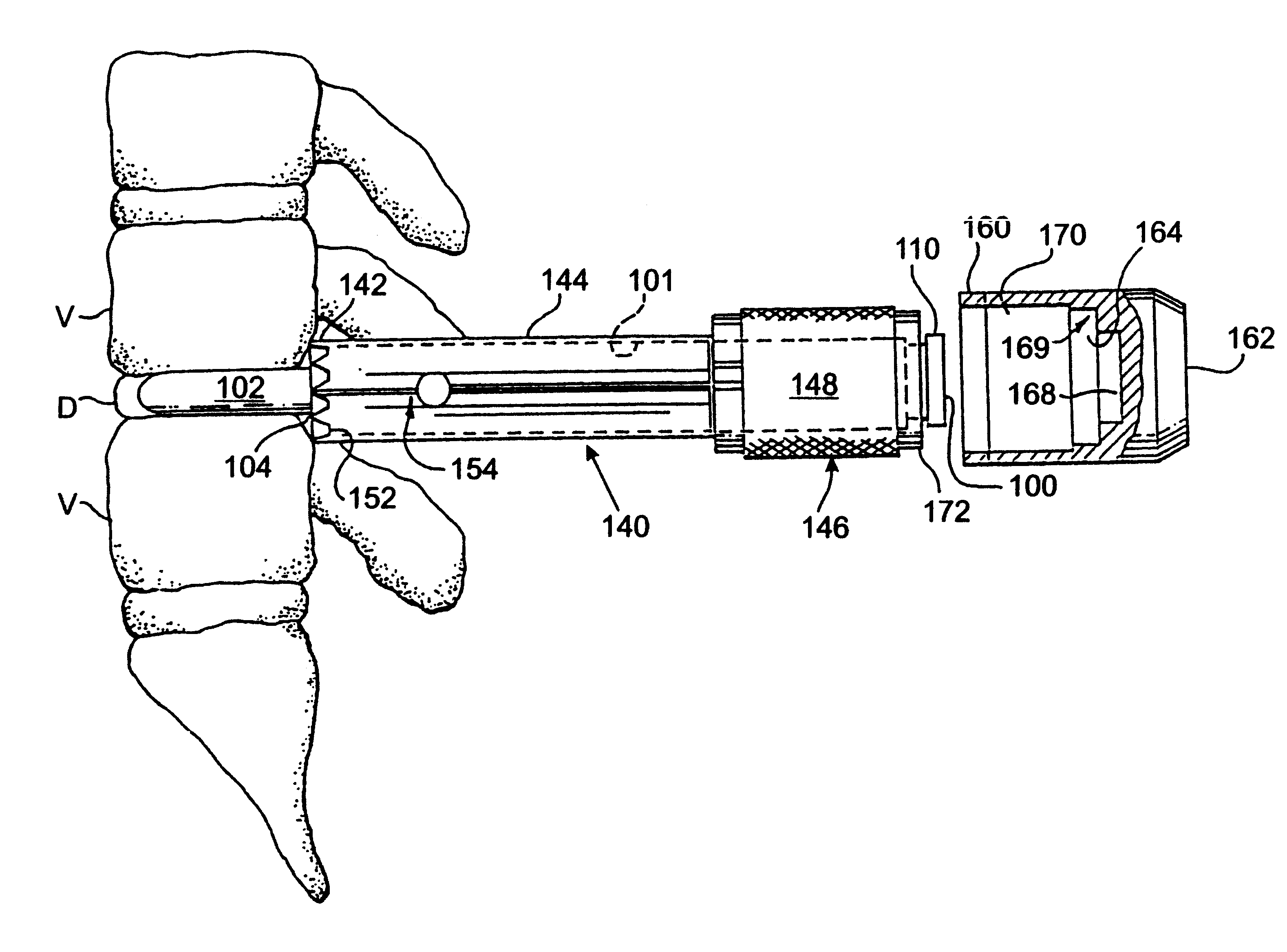
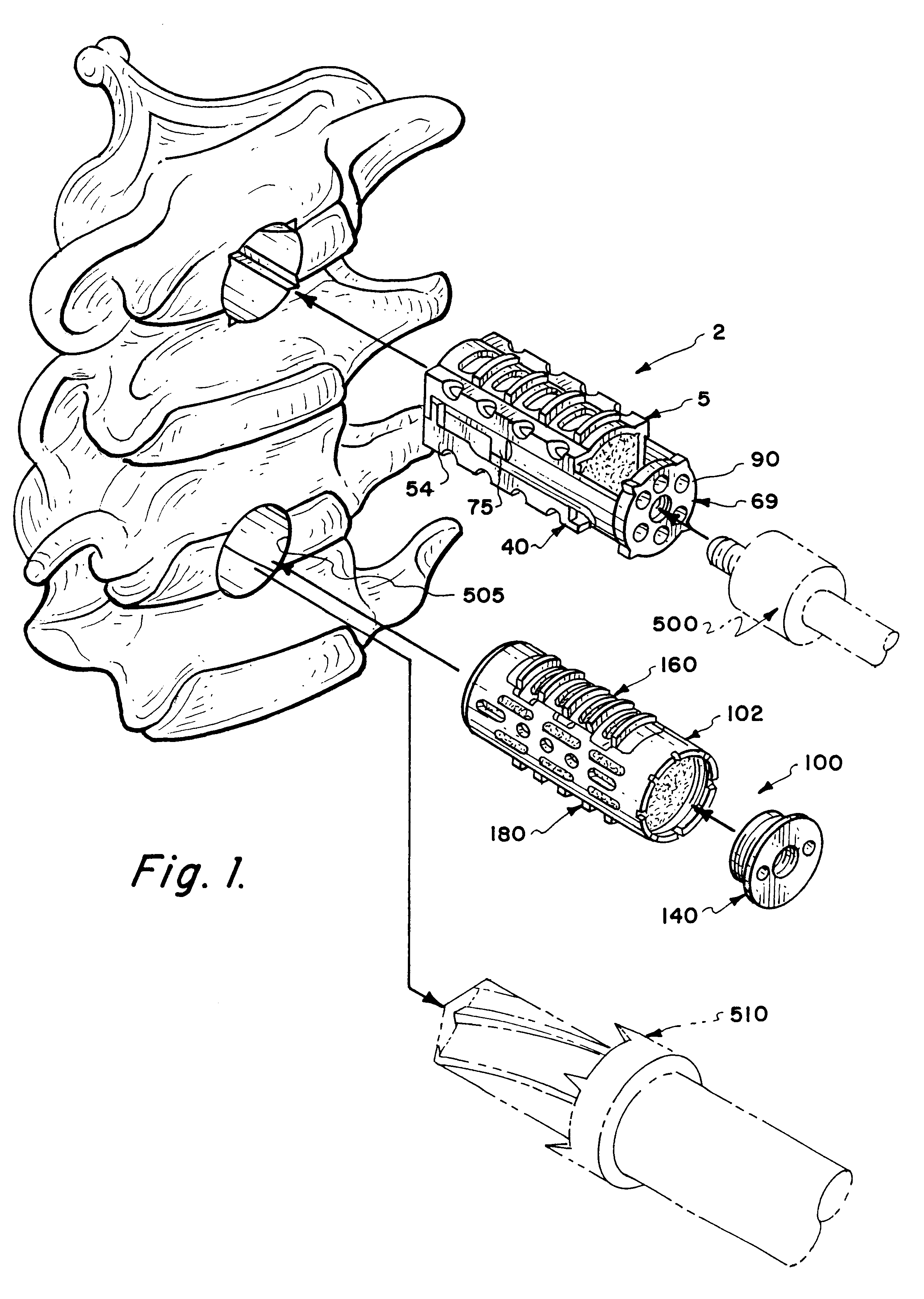
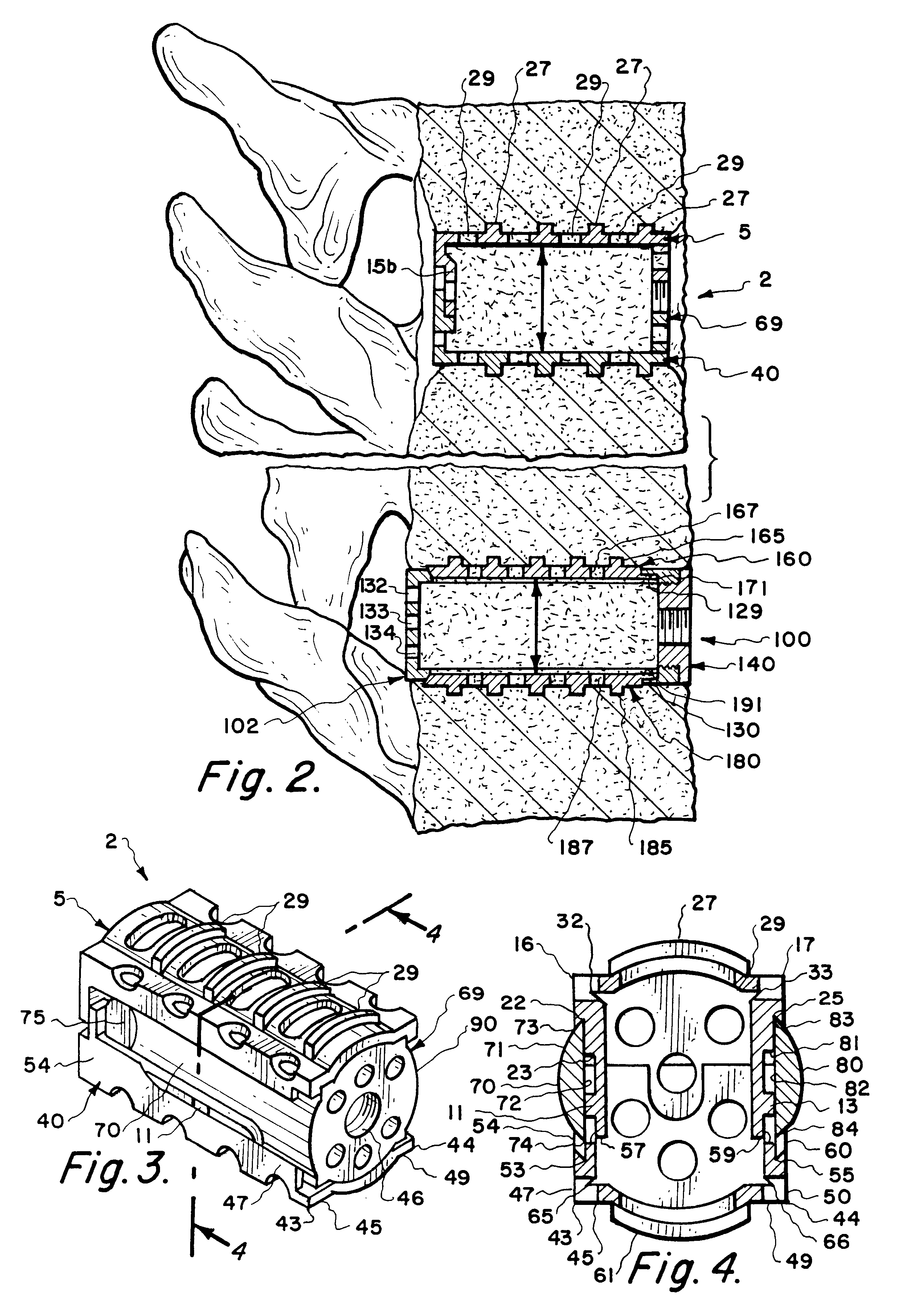
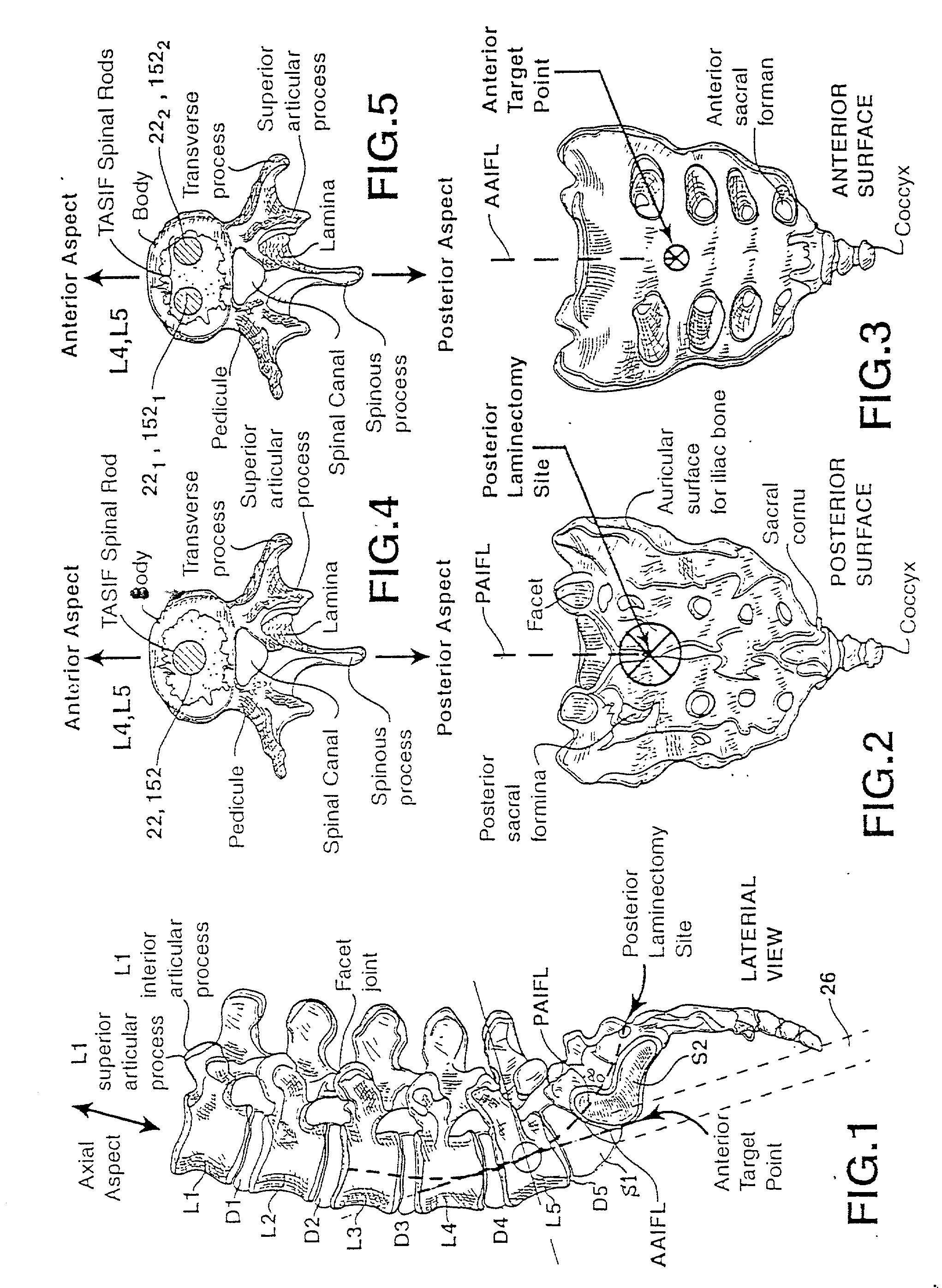
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
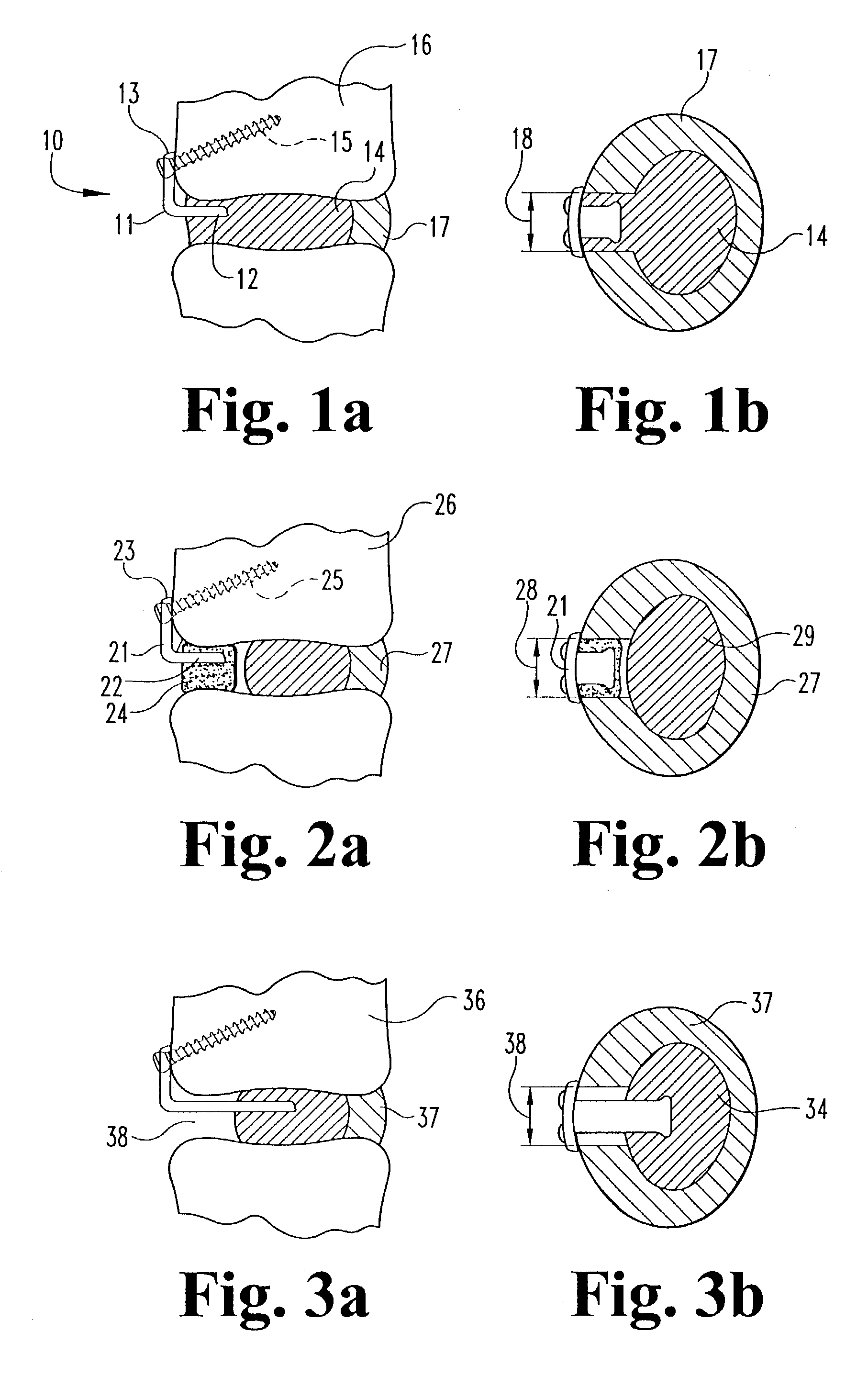
Method of inserting and preloading spinal implants
InactiveUS6080155ARestoring and maintaining normal angular relationshipFaster and safe and more efficaciousInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6096038AEliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Articulating spinal implant
A spinal implant for intervertebral disc replacement. The implant is formed from two hemicylindrical elements, each engaging one of an adjacent pair of vertebrae. An articulating ball-and-socket joint between the two elements resists compression and lateral movement between the vertebra, but allows pivotal movement, thereby preserving mobility. Fusion chambers are provided for allowing bone ingrowth to fuse the elements to the vertebrae. Biocompatible, bioreabsorbable struts, shims, fillers and / or end caps are provided for temporary stabilization of the first and second hemicylindrical elements. Bone chips removed from the vertebrae during implantation or bone growth stimulators can be inserted into the fusion chamber or otherwise applied to the implant to enhance bone ingrowth.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
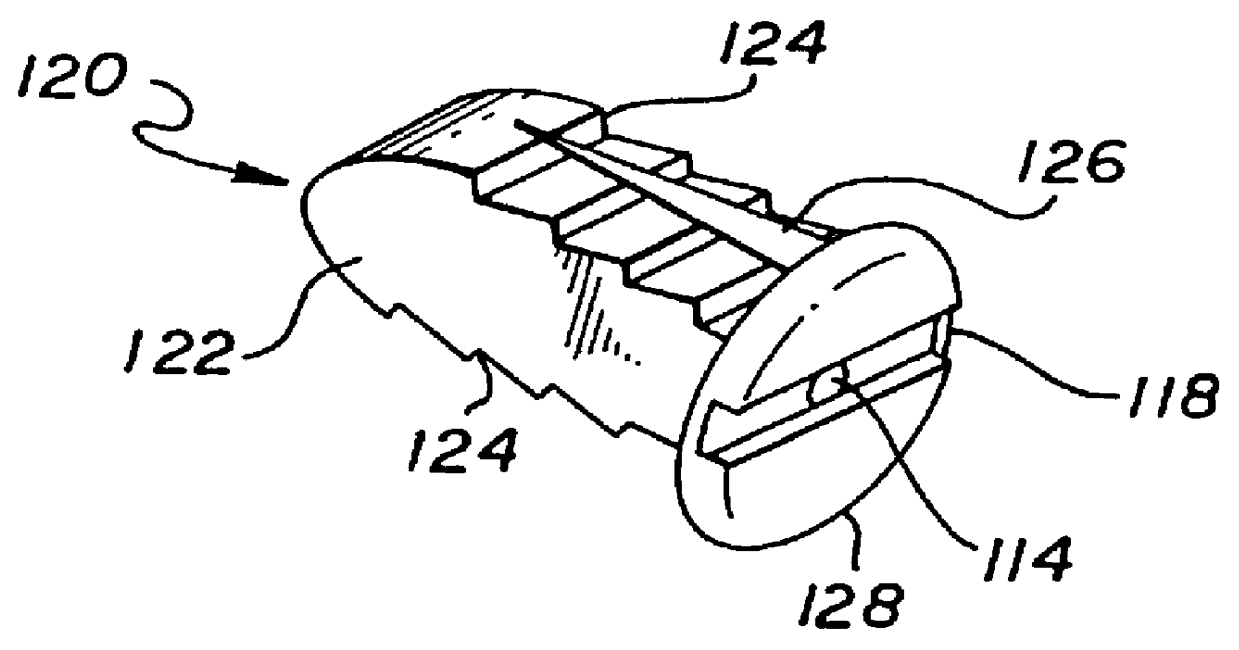
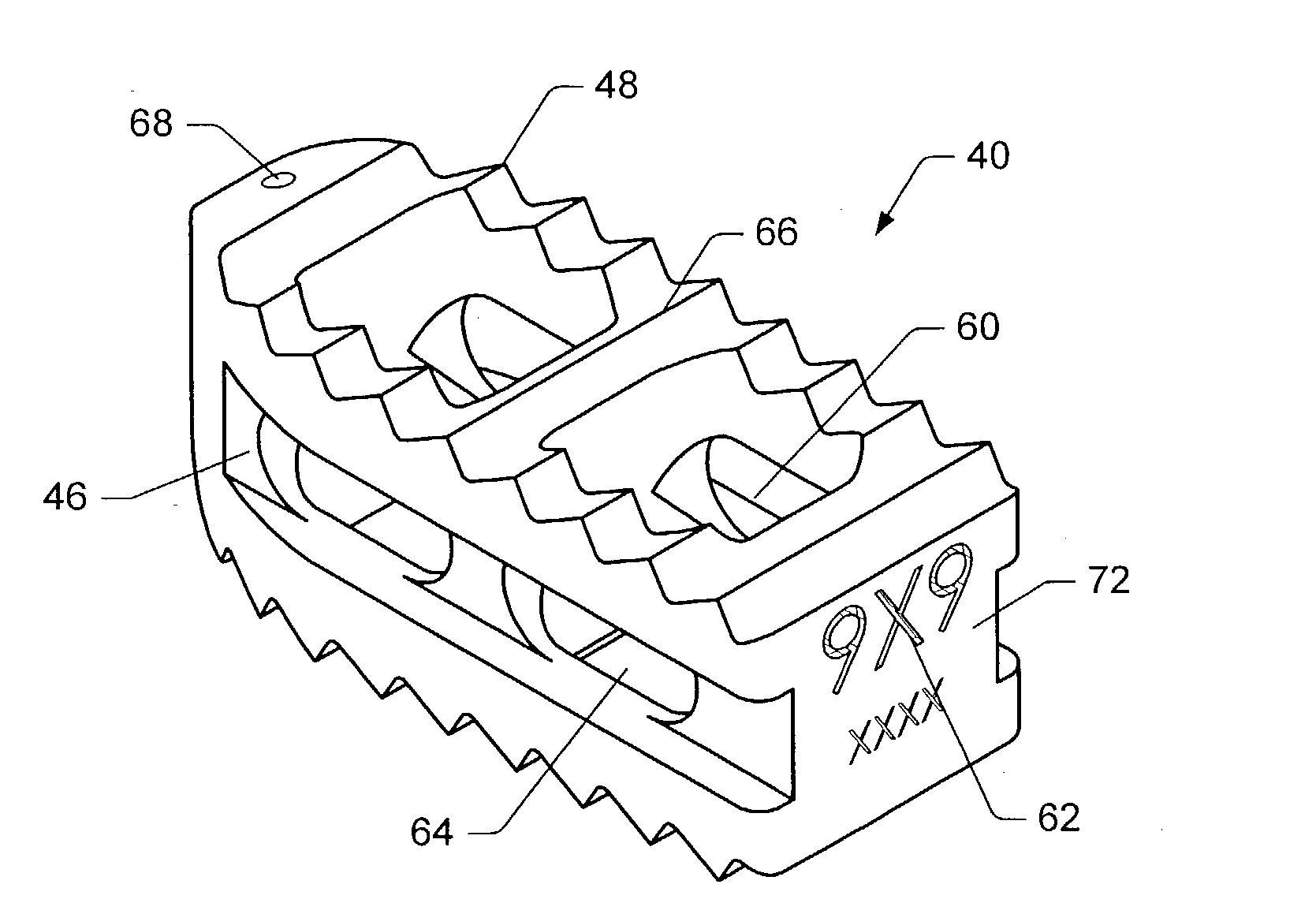
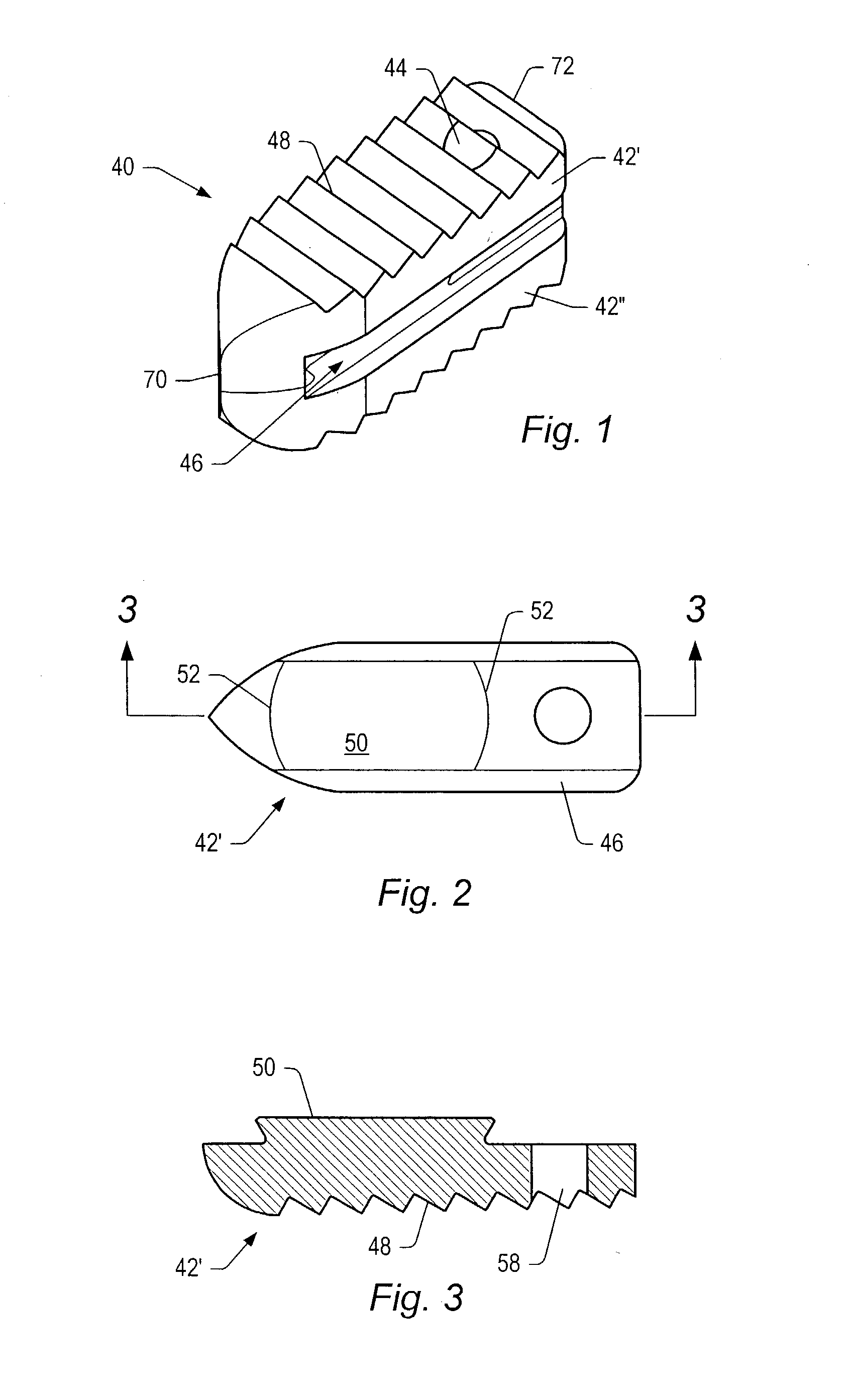
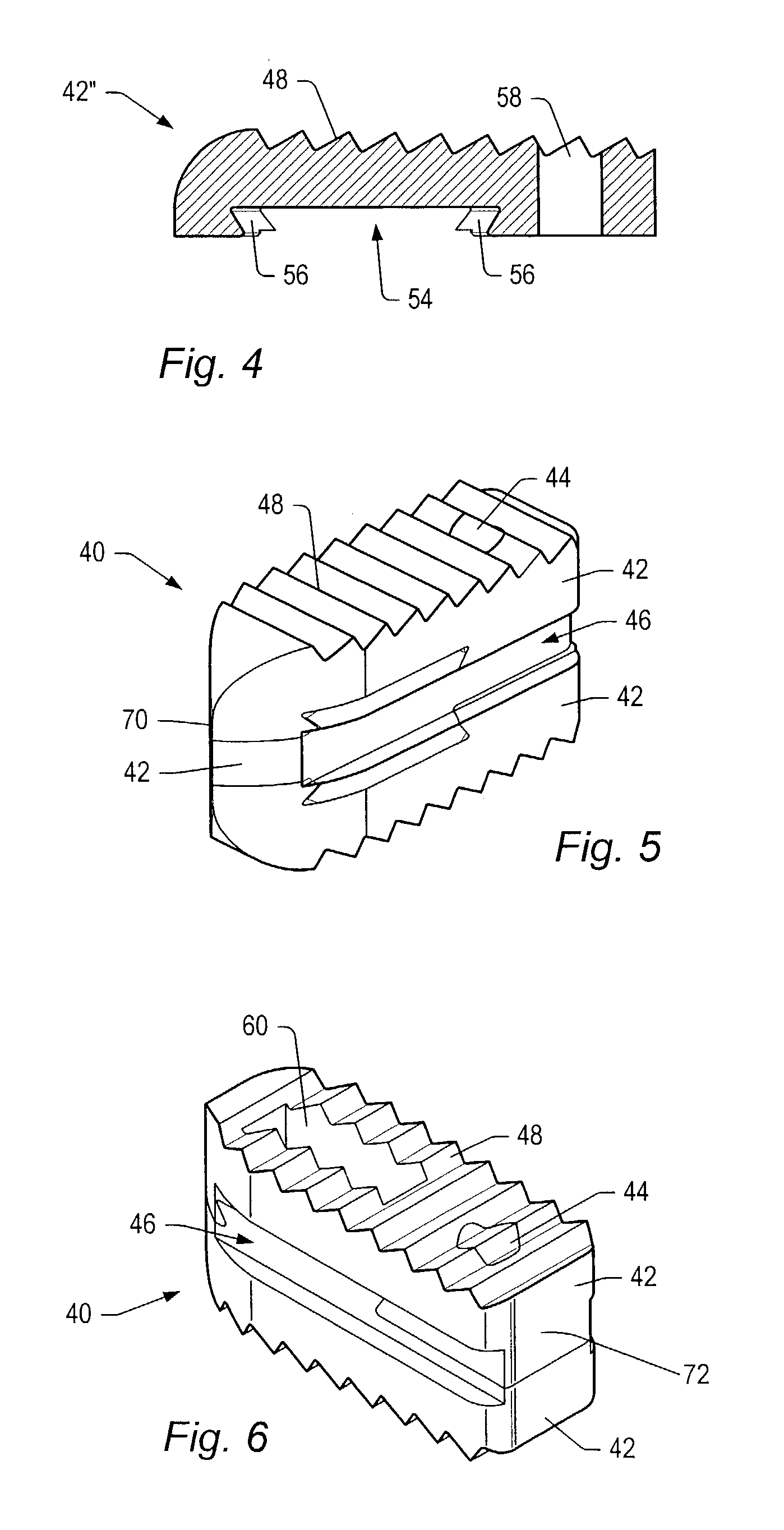
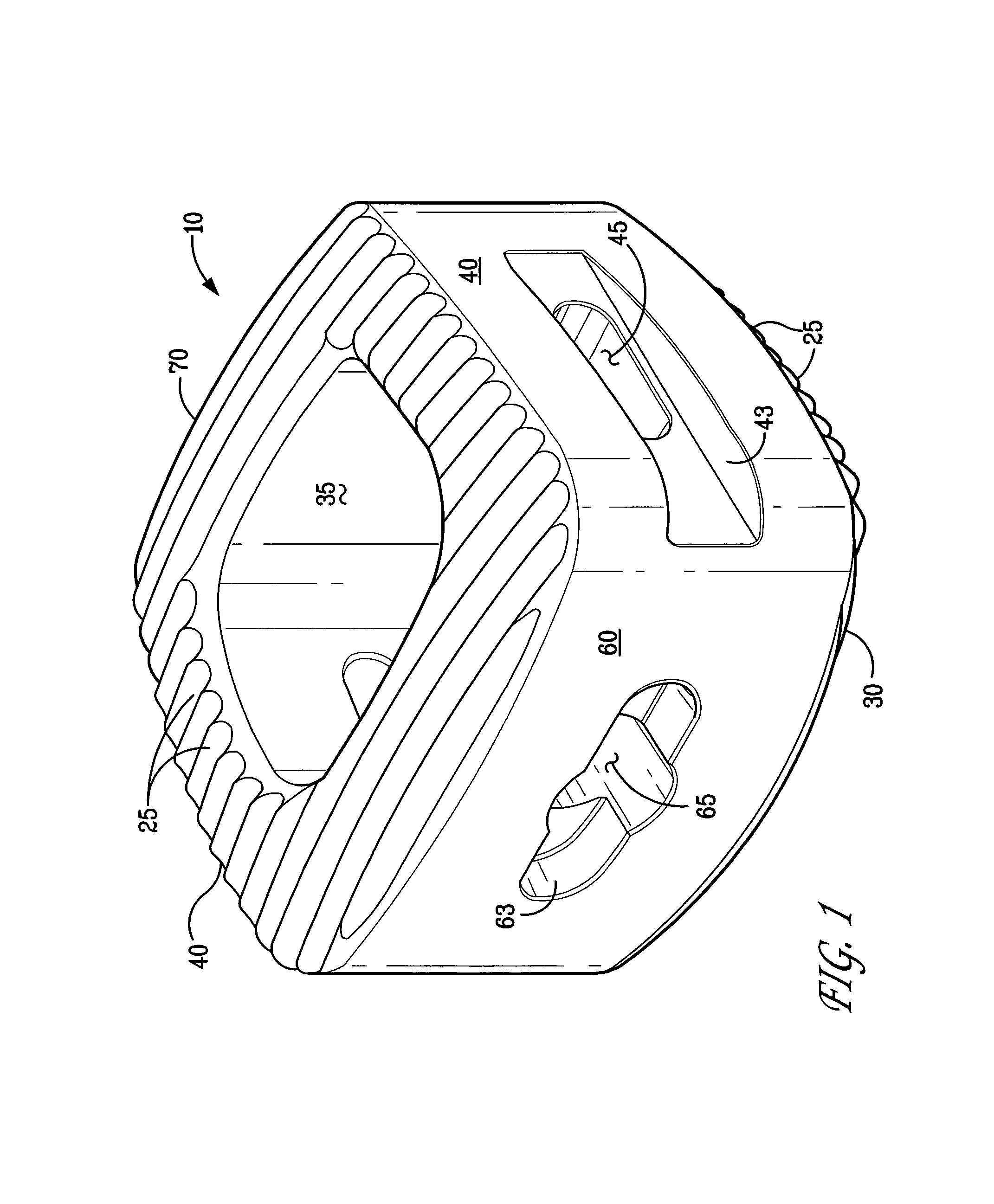
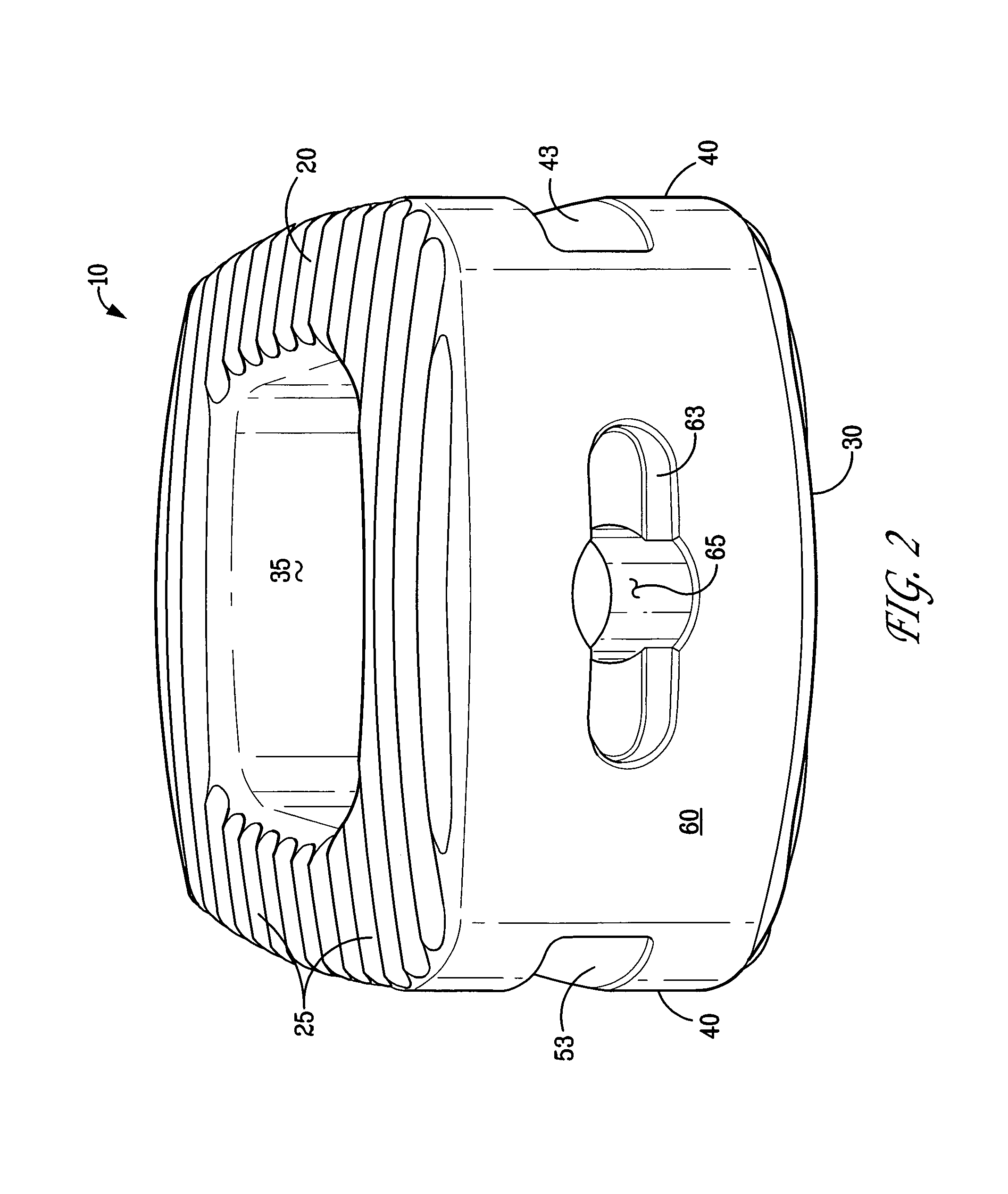
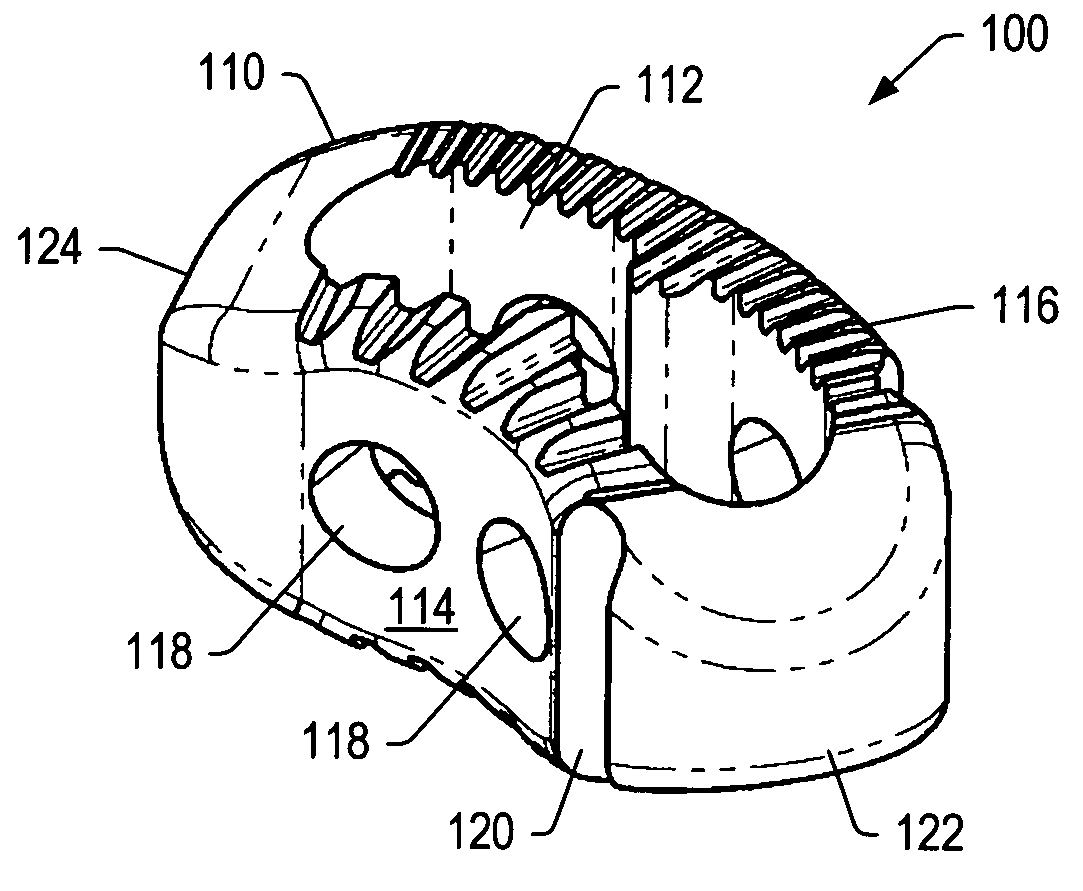
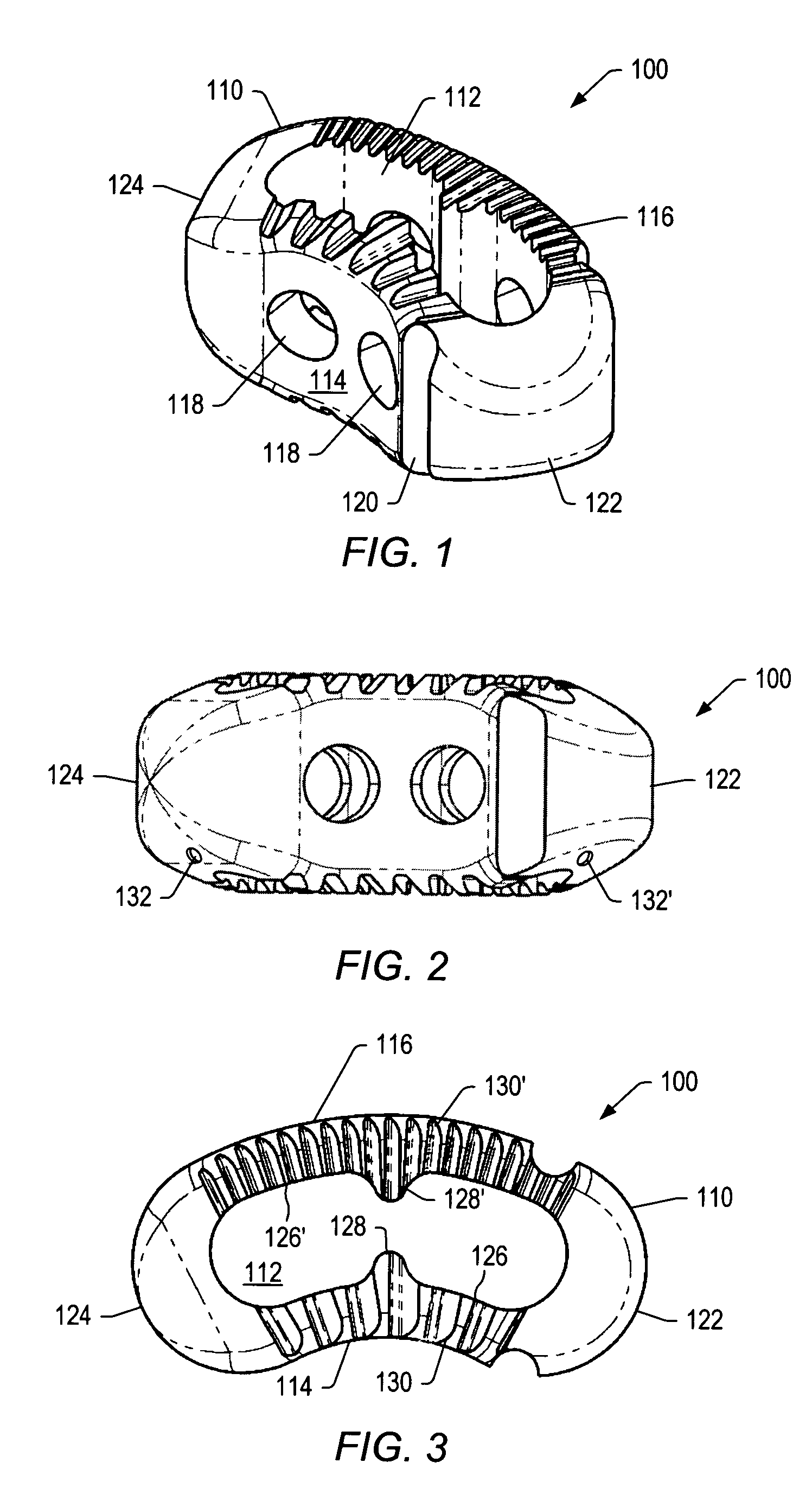
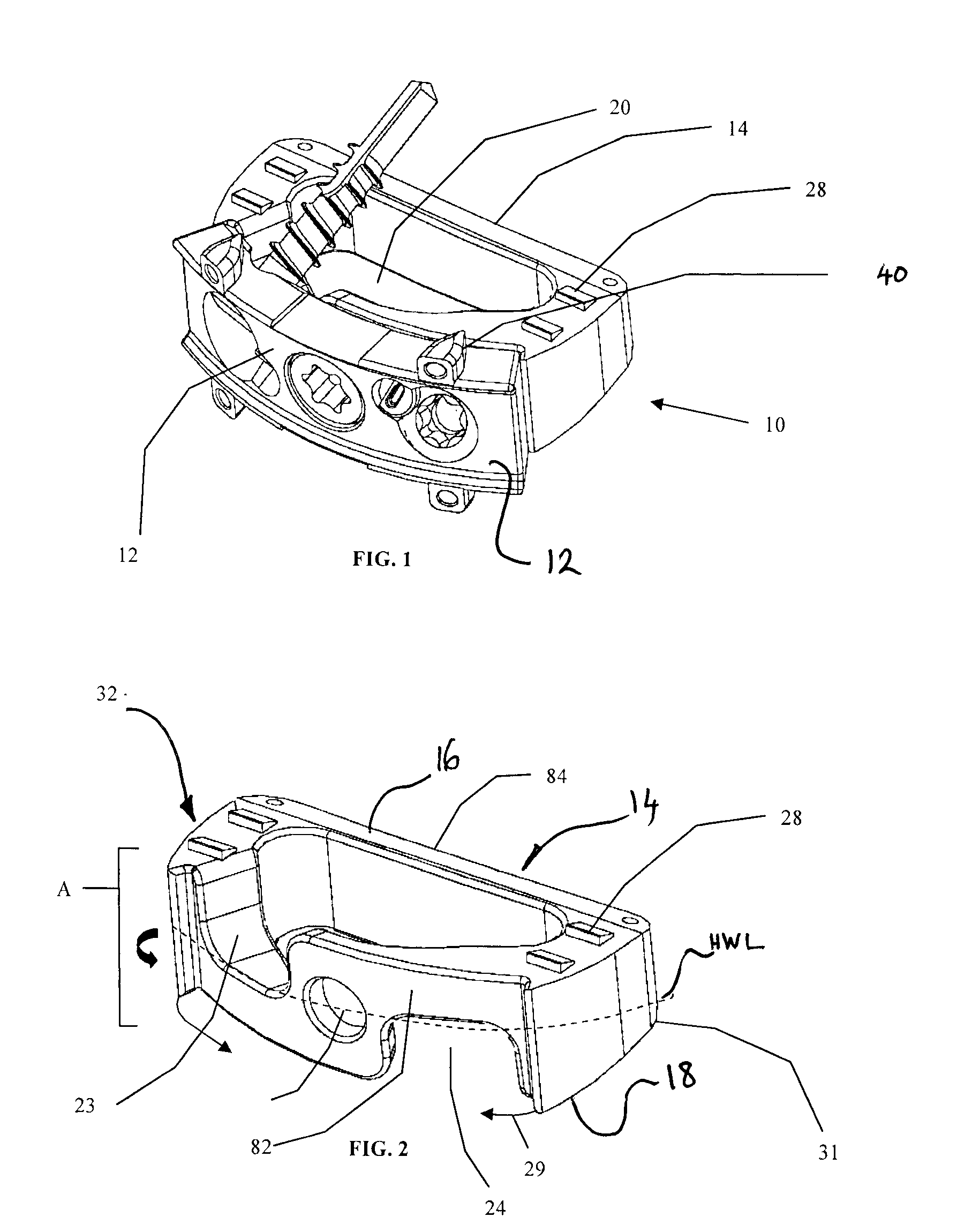
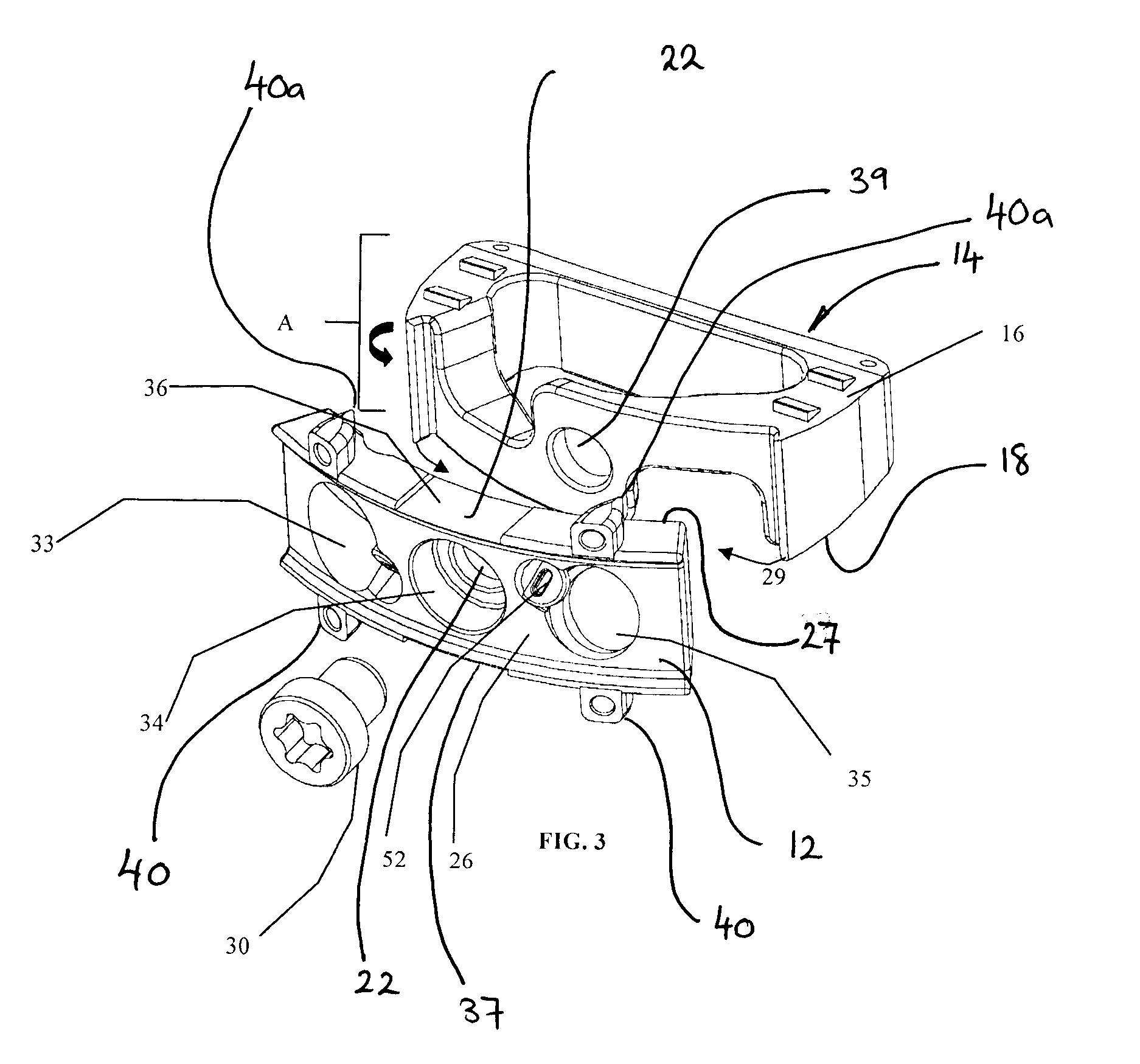
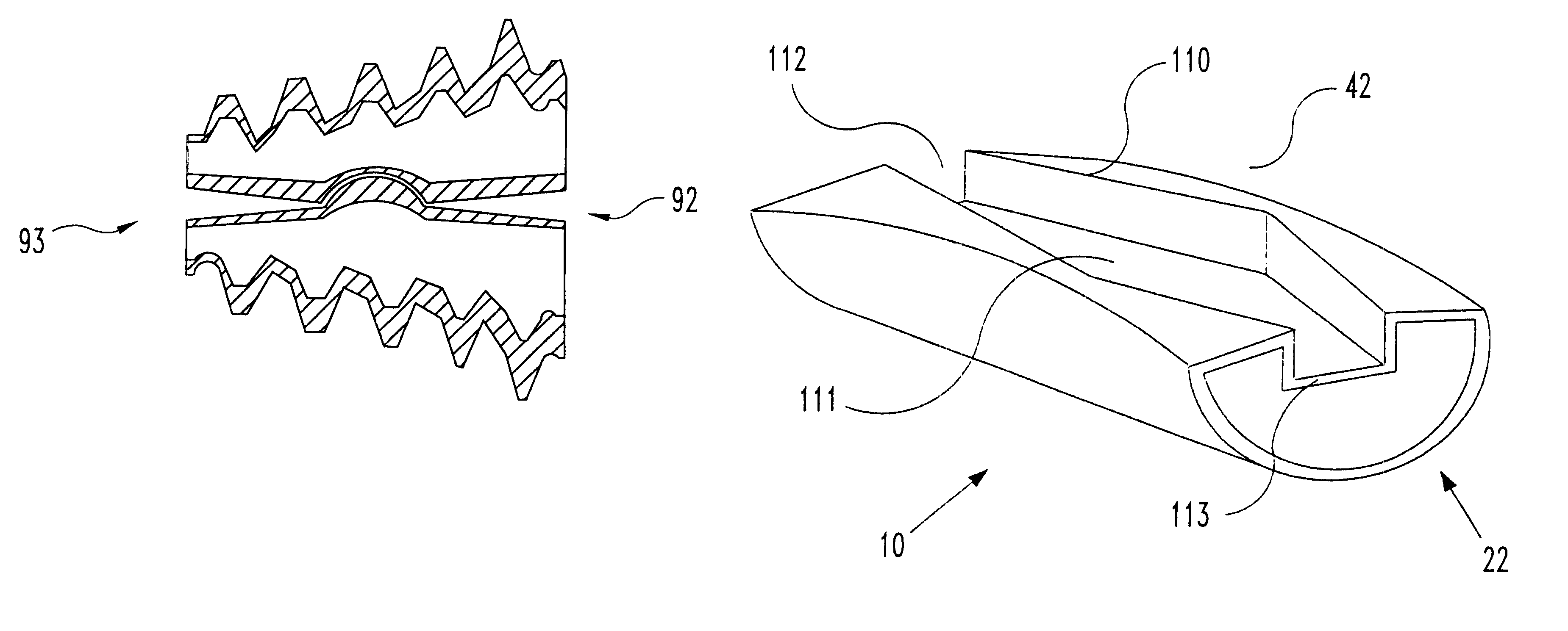
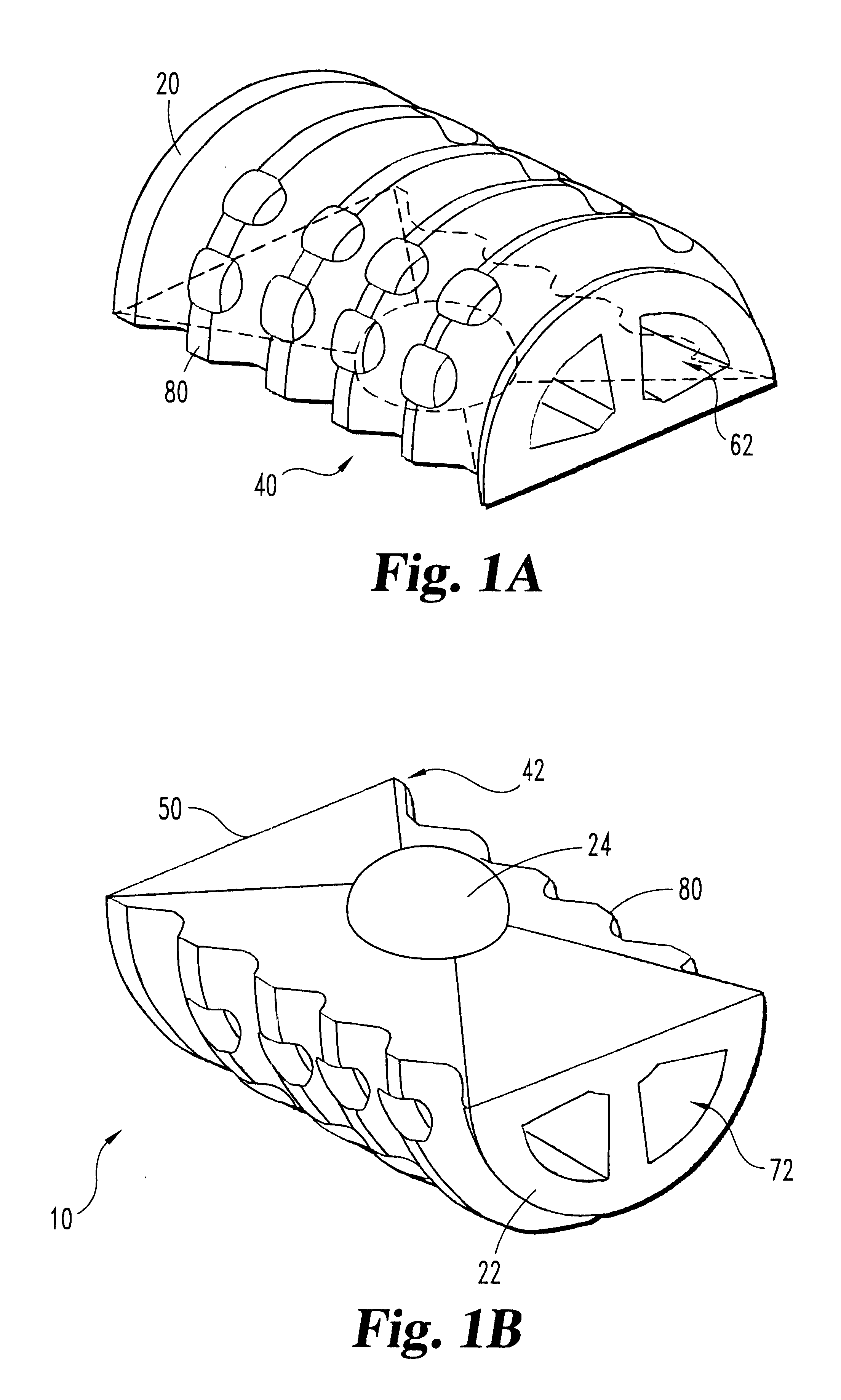
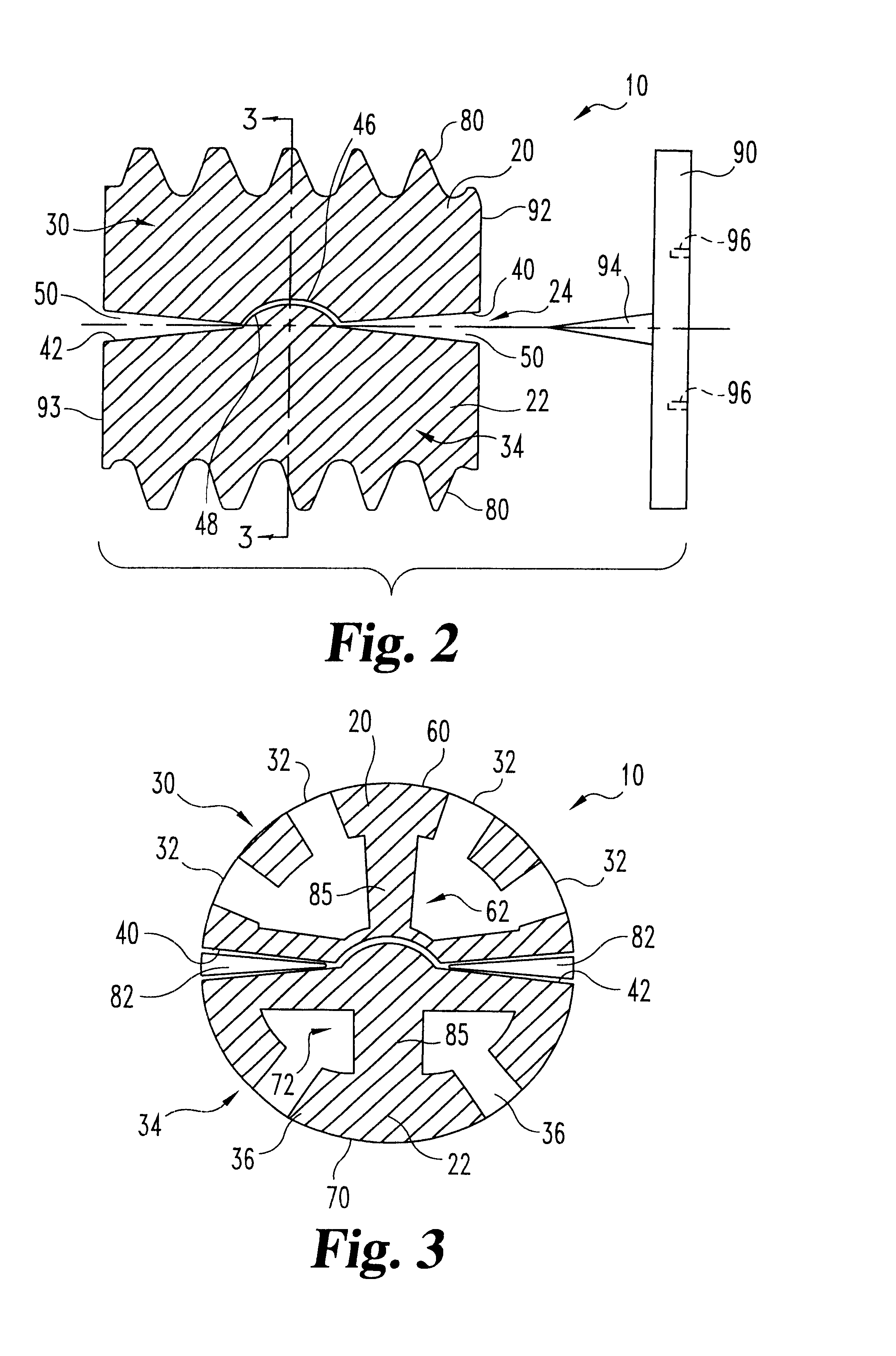
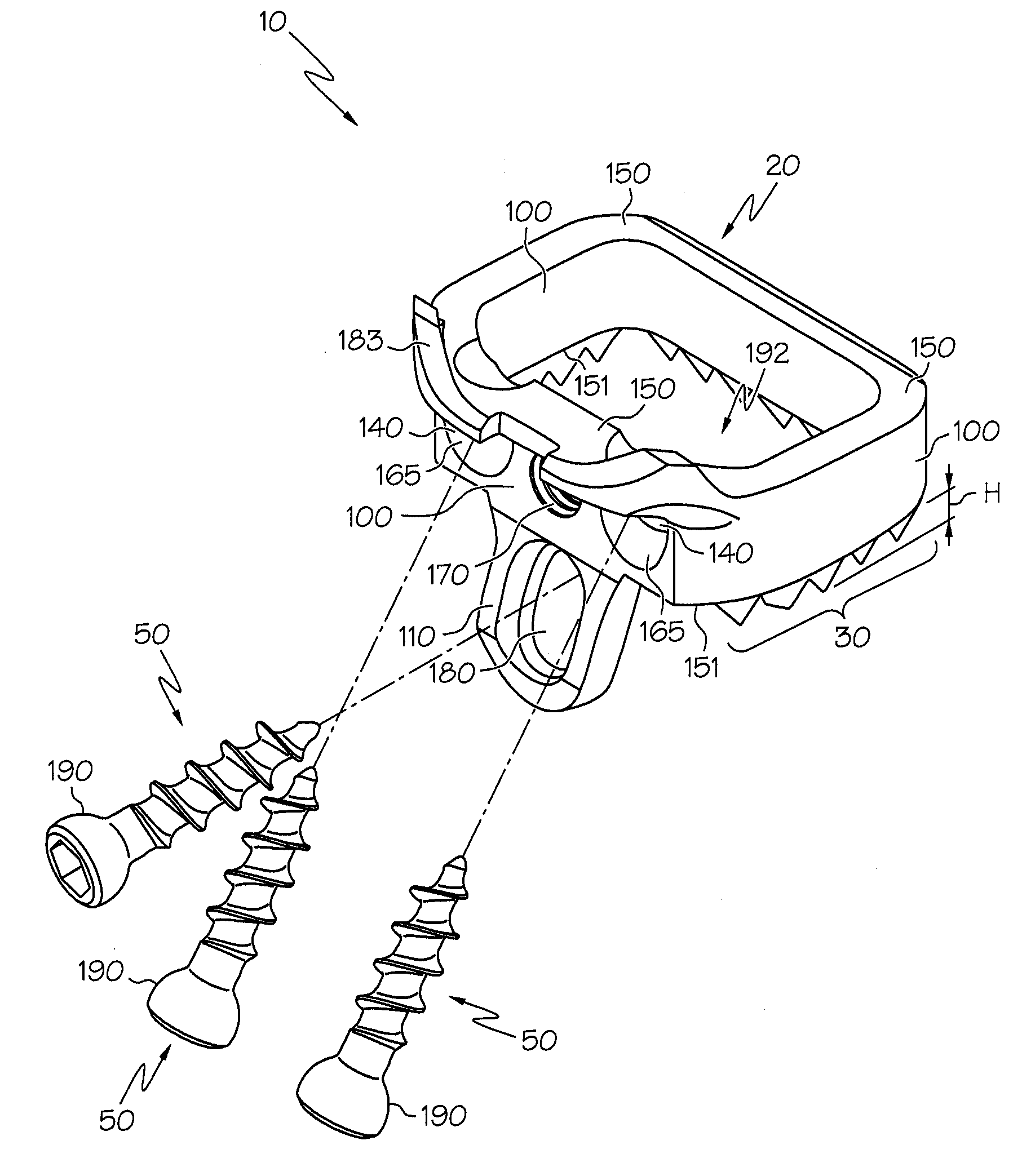
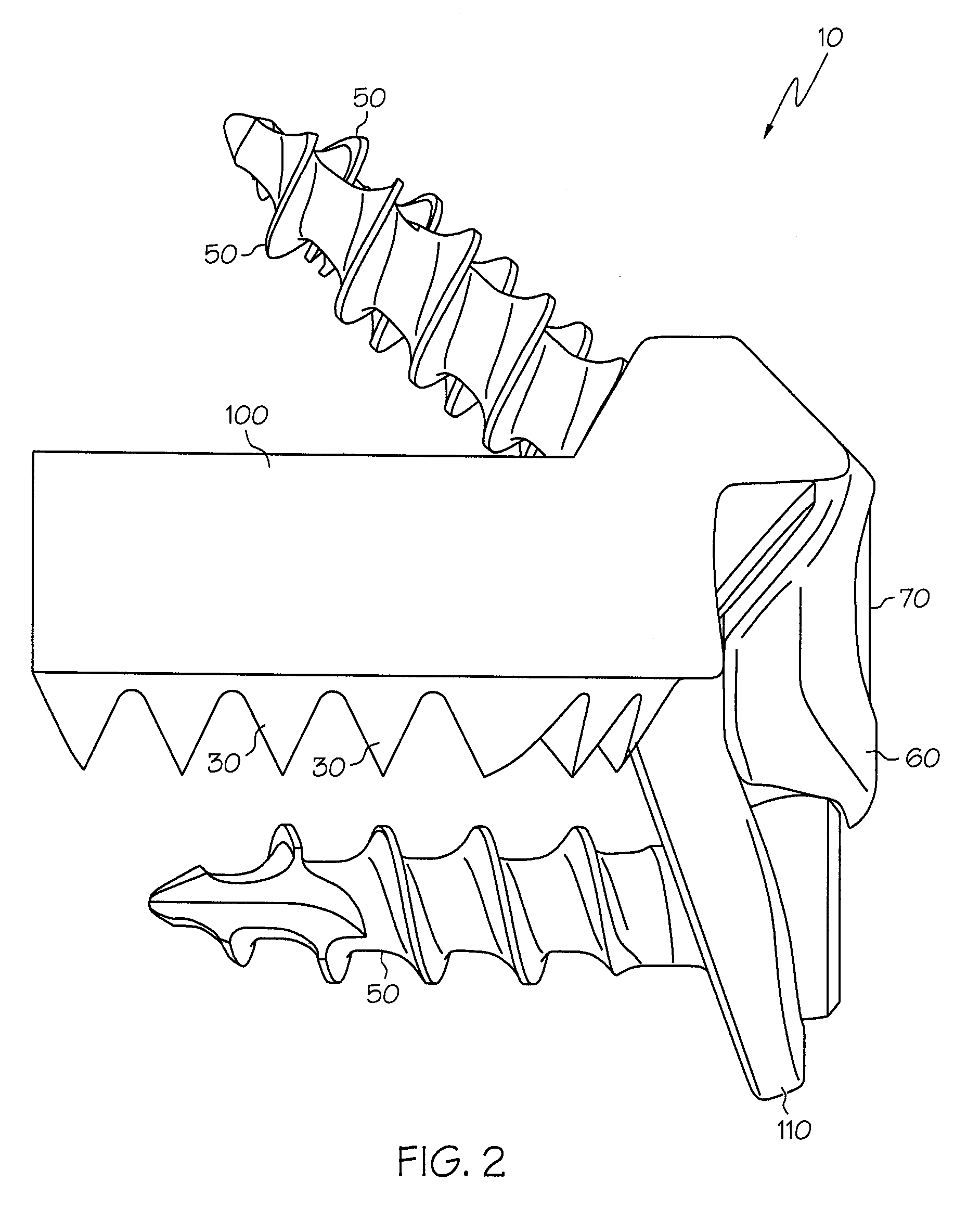
Spinal implant
A spinal implant may be made of two or more implant members. In an embodiment, implant members may be joined together by a rotational connection that inhibits separation of the members as well as axial movement of the members relative to each other. Implant members may be coupled together by a pin or pins, adhesive, or other fasteners to inhibit separation and / or rotation of the members relative to each other.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Bioactive spinal implants and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS7238203B2Facilitating radiographic assessmentEnhance bone contact and stability and fusionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLumbar vertebraeCervical fusions
A bioactive spinal implant used in cervical fusion, Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF), Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF), and Transforaminal Interbody Fusion (TLIF), having properties and geometries that enhance bone contact, stability, and fusion between adjacent vertebral bodies.
Owner:VIA SPECIAL PURPOSE CORP +1
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6270498B1Eliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
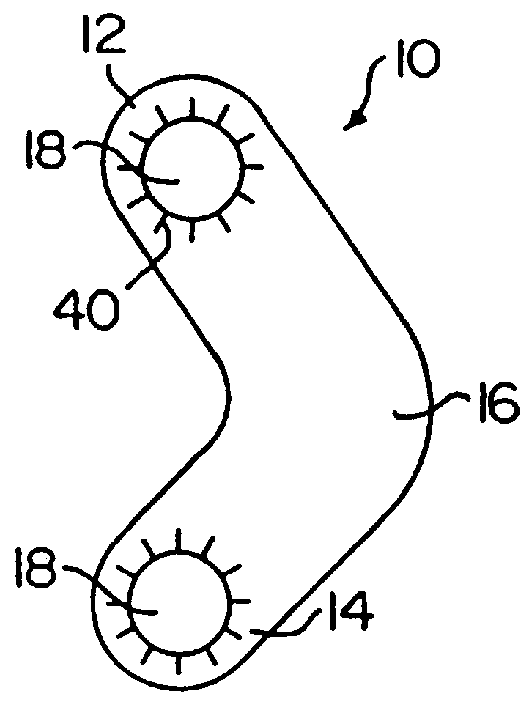
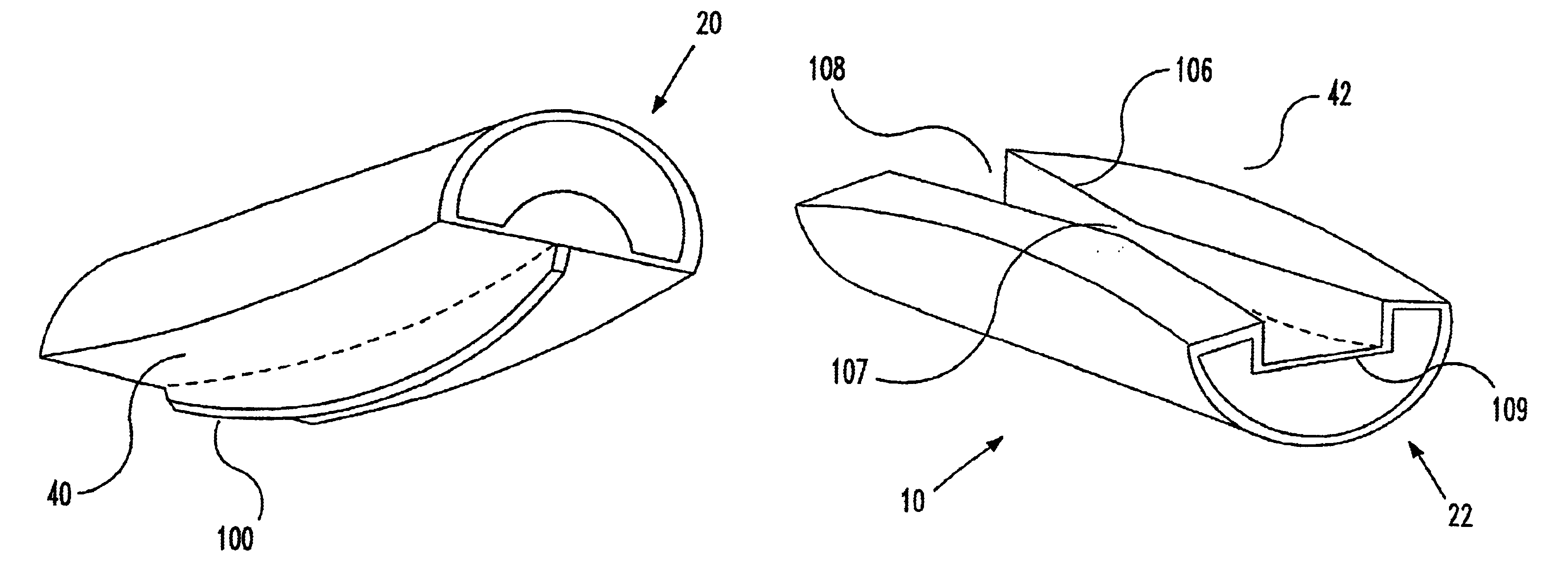
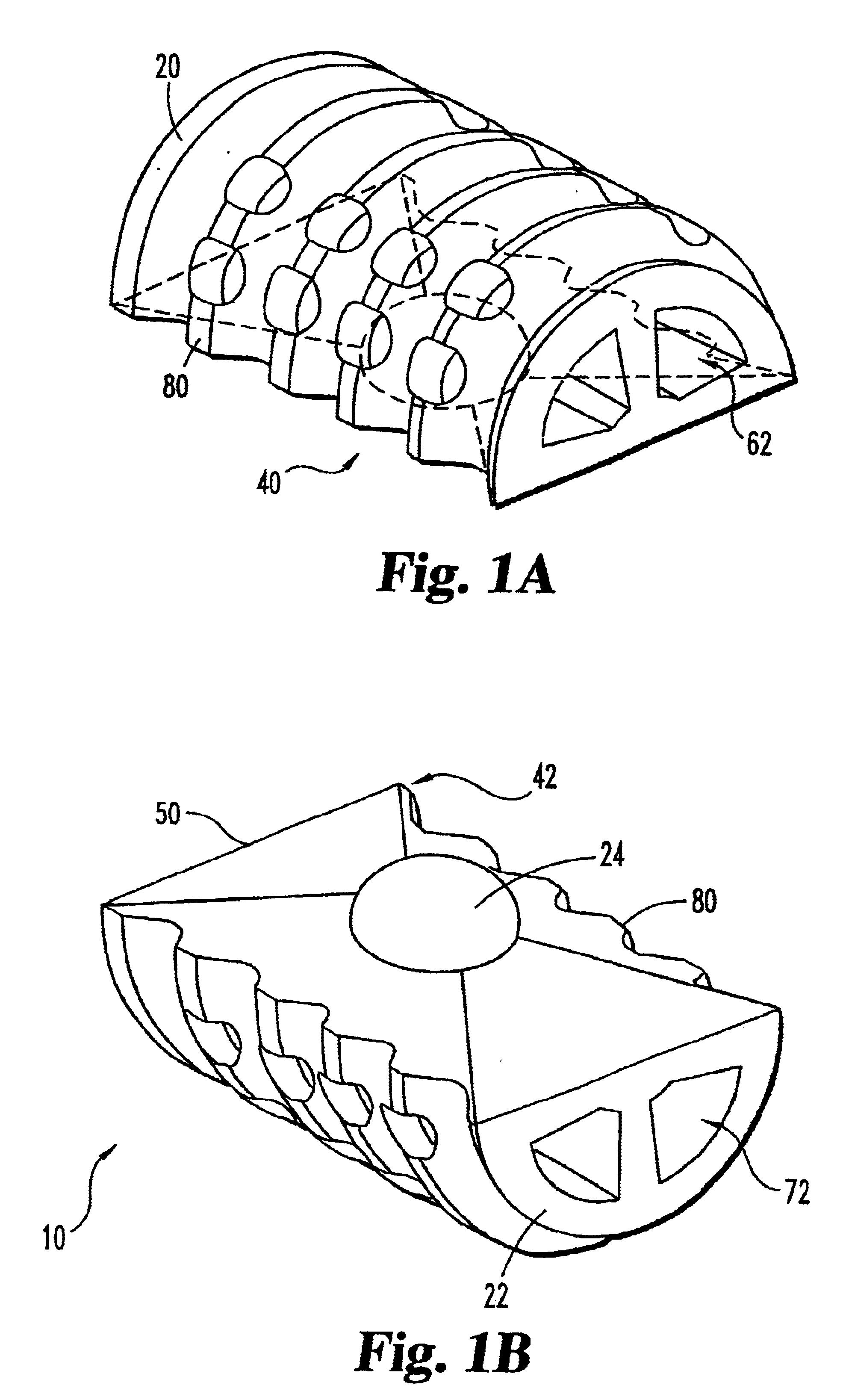
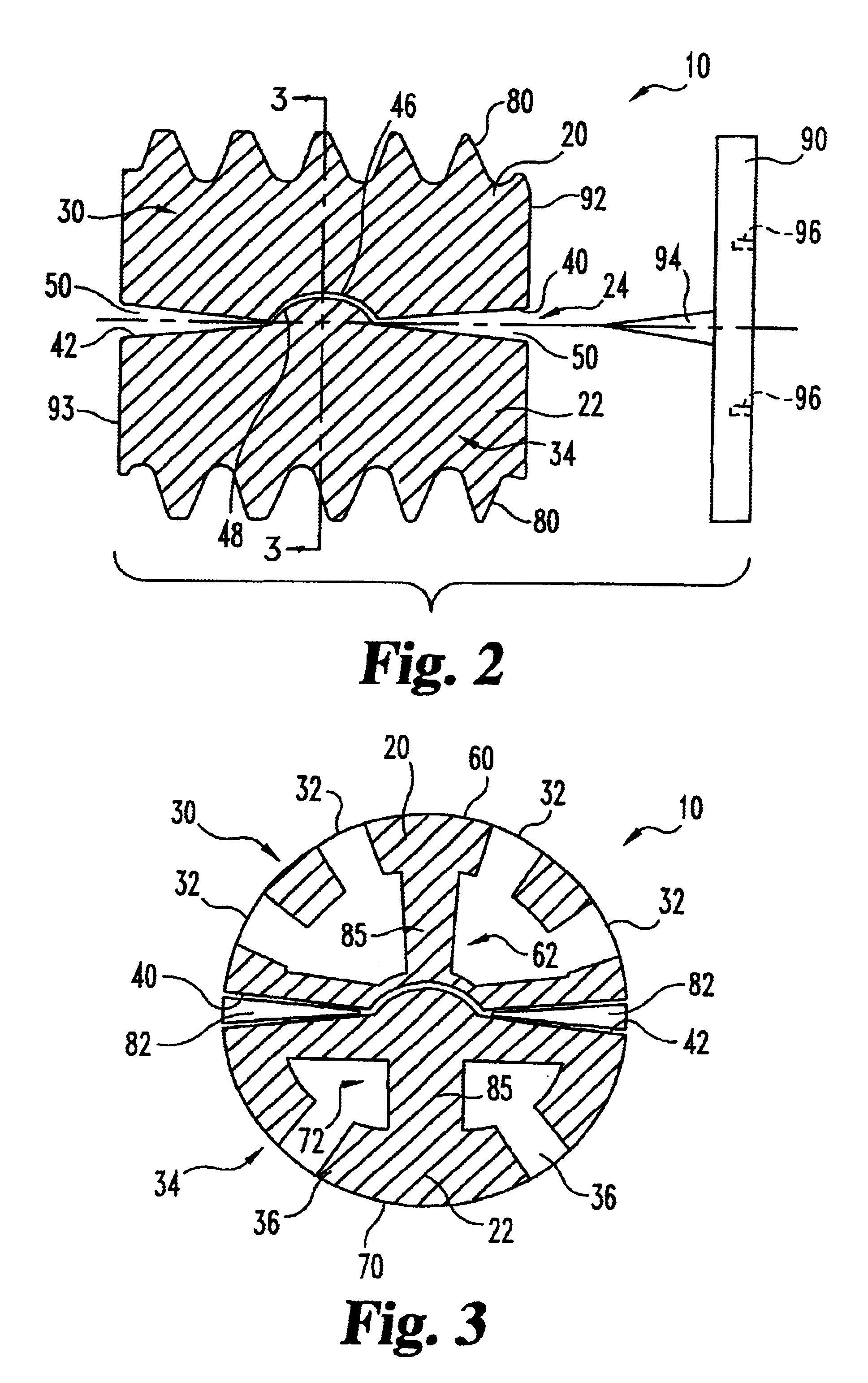
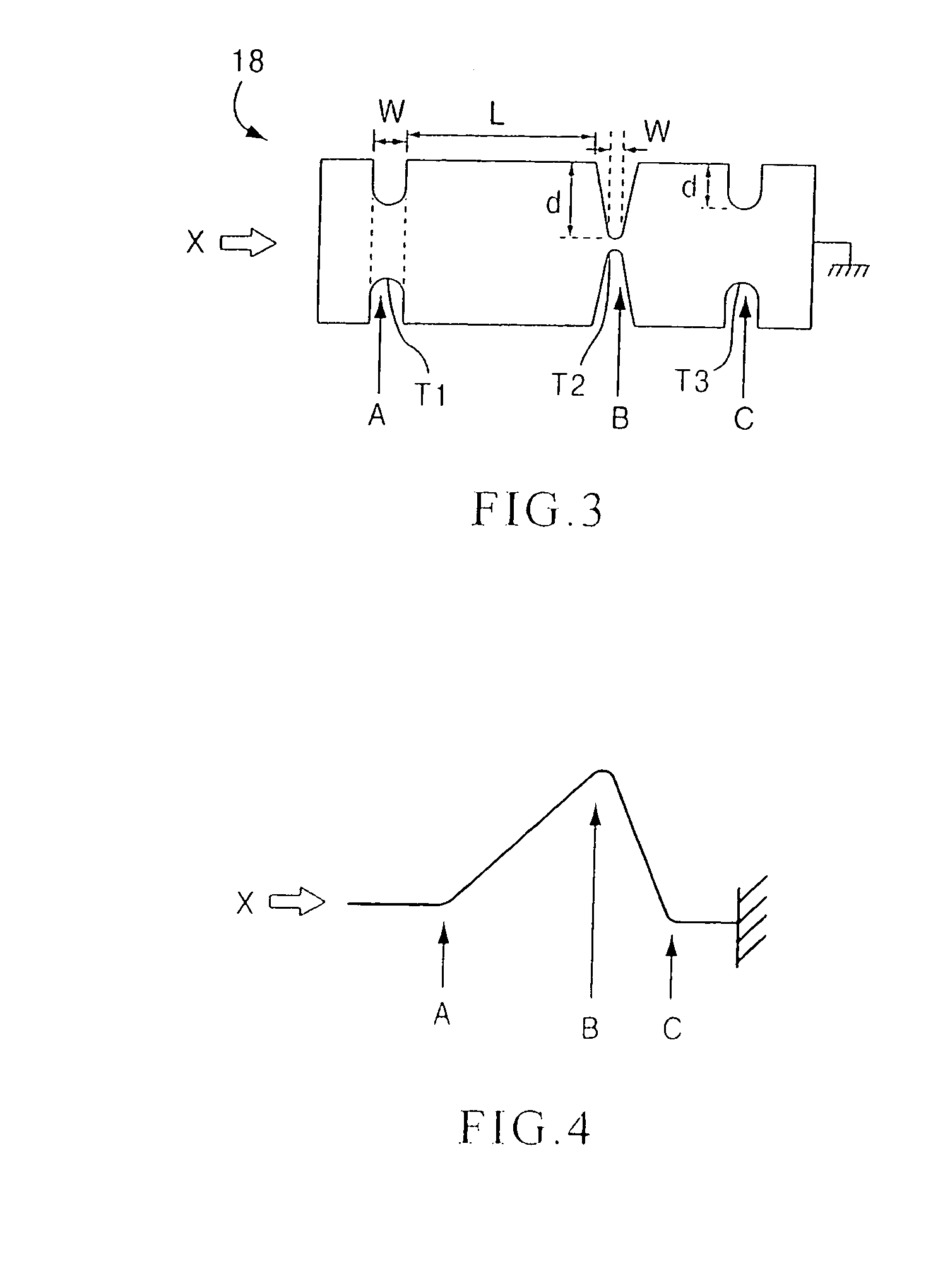
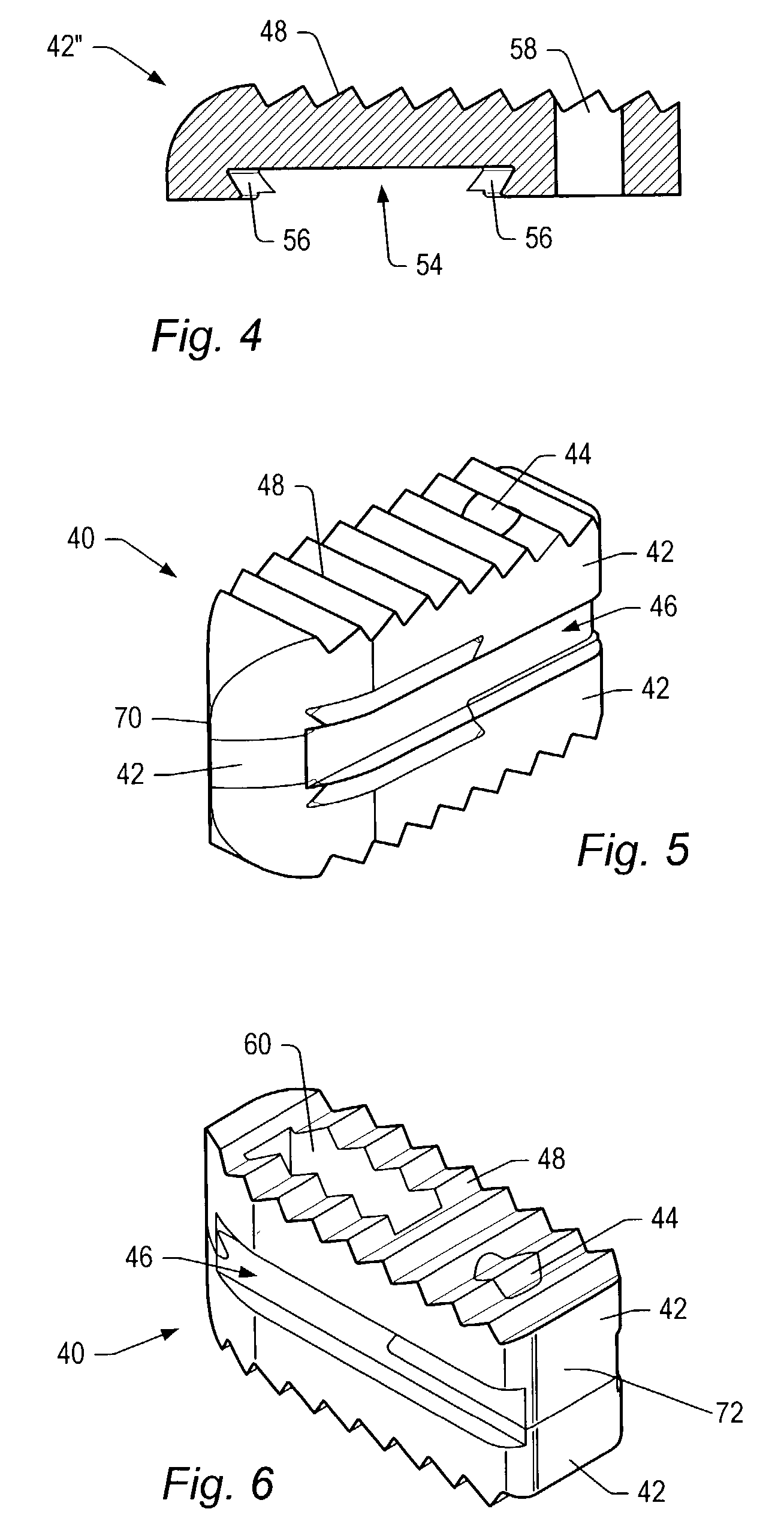
Methods and apparatus for forming shaped axial bores through spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS6740090B1Easy to understandInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal CurvaturesSpinal implant
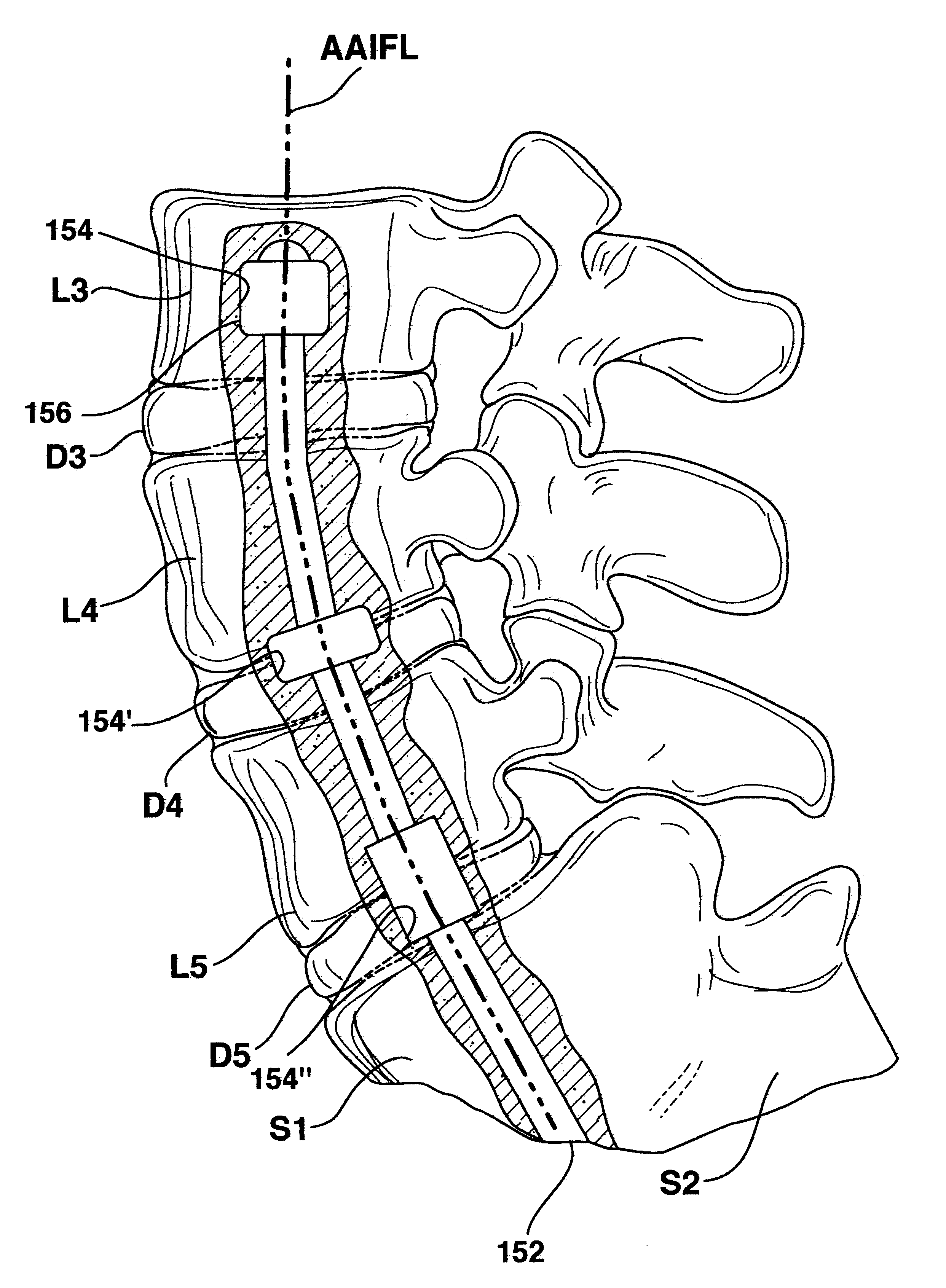
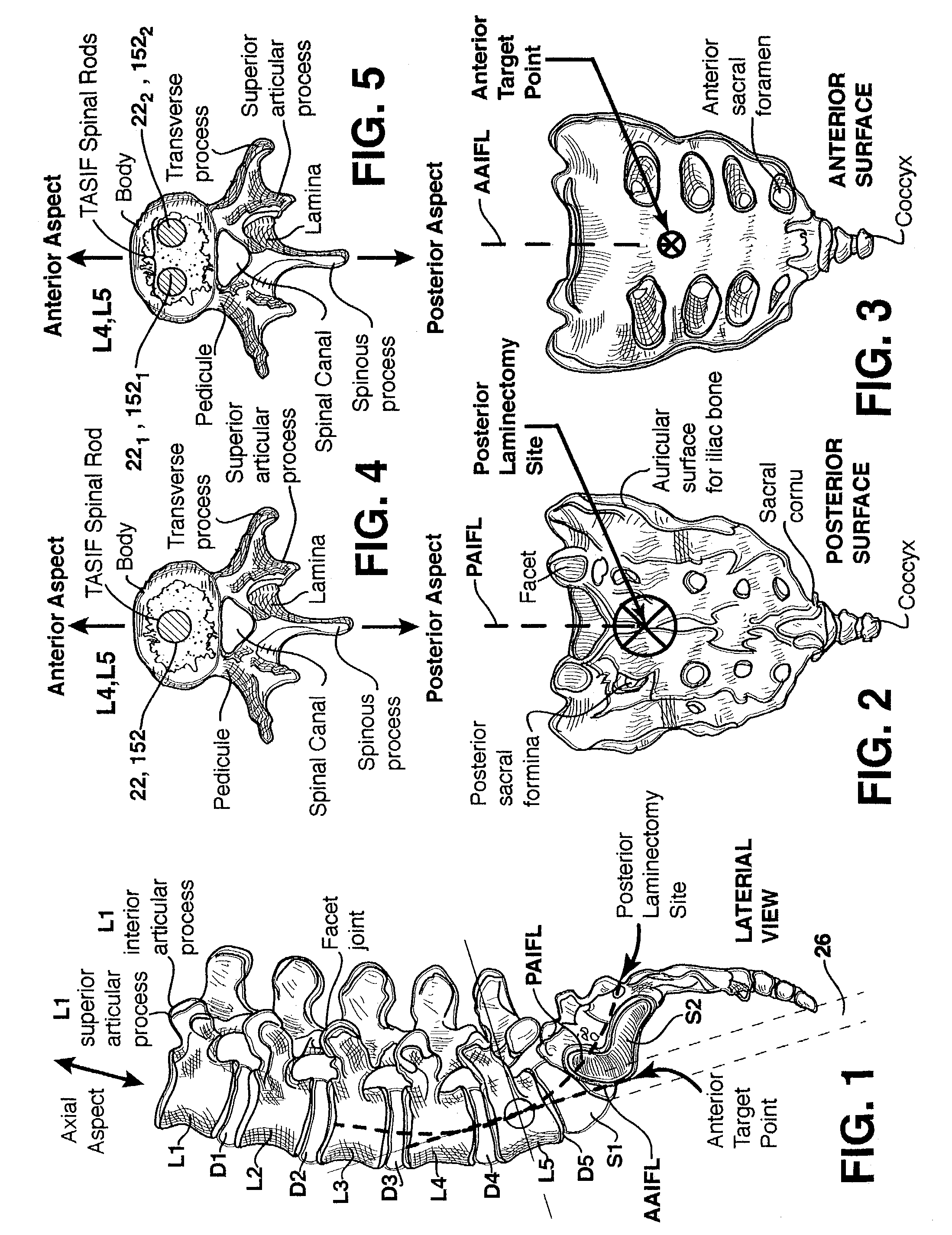
One or more shaped axial bore extending from an accessed posterior or anterior target point are formed in the cephalad direction through vertebral bodies and intervening discs, if present, in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner. An anterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL) or a posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (PAIFL) that extends from the anterior or posterior target point, respectively, in the cephalad direction following the spinal curvature through one or more vertebral body is visualized by radiographic or fluoroscopic equipment. Preferably, curved anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores are formed in axial or parallel or diverging alignment with the visualized AAIFL or PAIFL, respectively, employing bore forming tools that can be manipulated from proximal portions thereof that are located outside the patient's body to adjust the curvature of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bores as they are formed in the cephalad direction. Further bore enlarging tools are employed to enlarge one or more selected section of the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bore(s), e.g., the cephalad bore end or a disc space, so as to provide a recess therein that can be employed for various purposes, e.g., to provide anchoring surfaces for spinal implants inserted into the anterior or posterior TASIF axial bore(s).
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
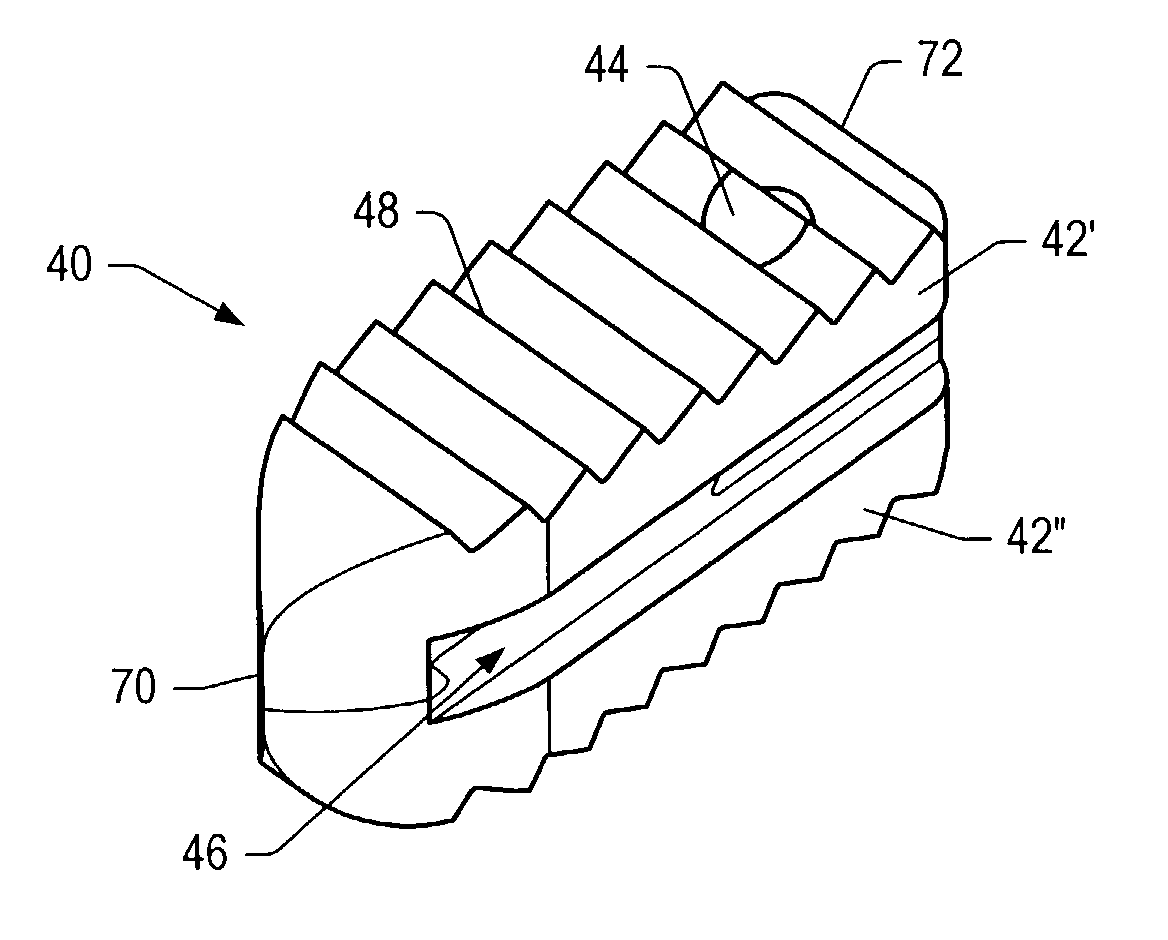
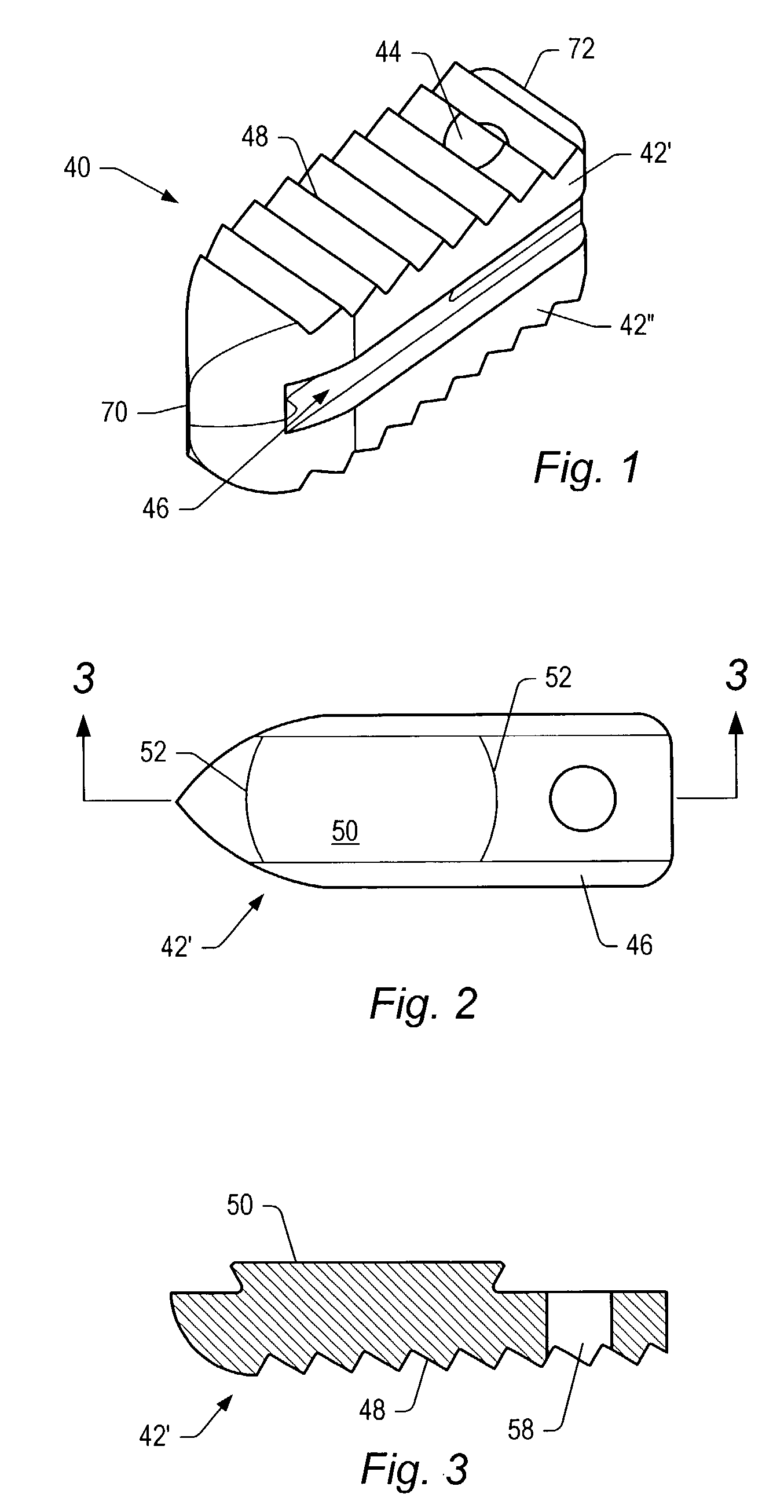
Spinal repair
InactiveUS20060265077A1Great strength and stabilityInternal osteosythesisBone implantPosterior regionSpinal implant
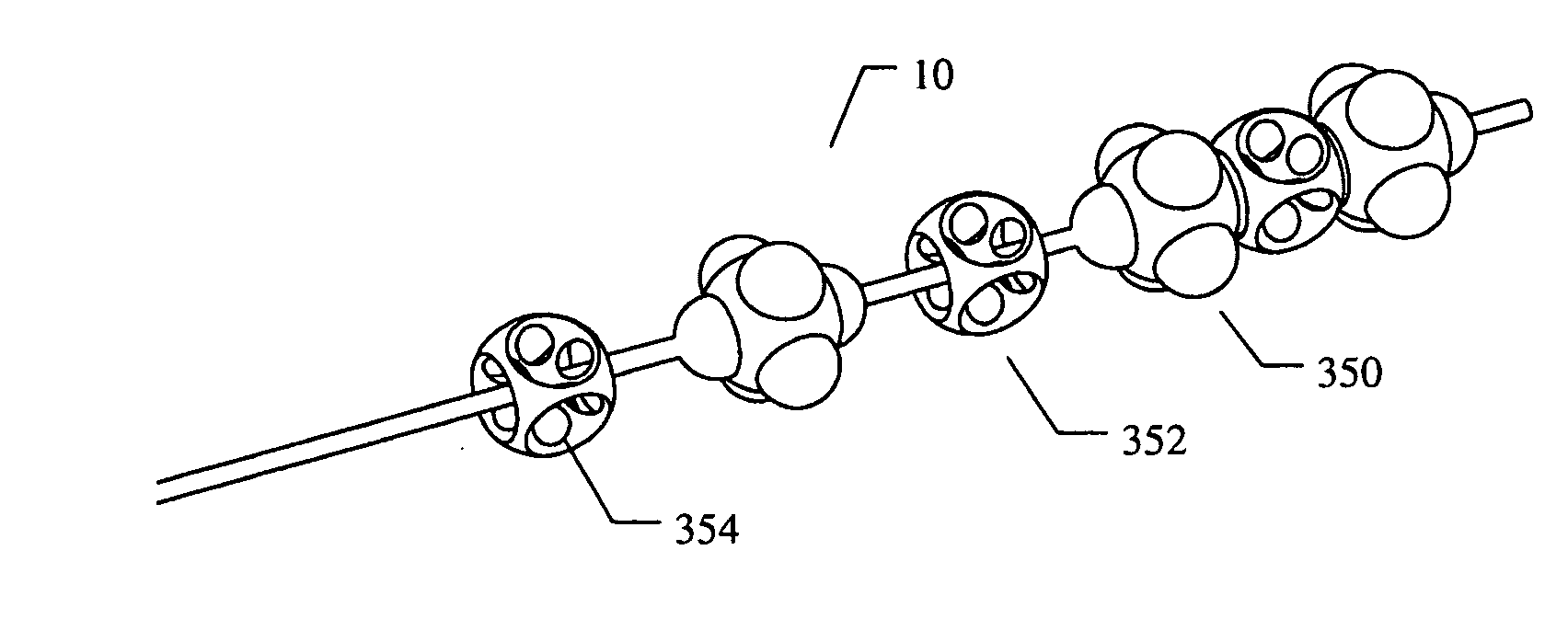
A spinal implant for repairing a region of a subject's spine may have a plurality of interlockable segments that can be deployed from a delivery configuration (e.g., a linear array) into a deployed configuration. When the implant is in the delivery configuration, the implant comprises a linear array of the segments that are flexibly connected, and when the implant is in the deployed configuration, the segments are interlocked into a stable structure so that each segment is adjacent to and interlocked with at least two other segments. in the deployed configuration, the implants may have a greater strength (e.g., crush strength) and may help maintain the stability of the body region. The implant may be inserted into the spinal region by an applicator from the posterior region of the subject in the delivery configuration and assembled within the body to form the deployed configuration.
Owner:SPINAL VENTURES
Apparatus for use in inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6770074B2Eliminate separationEfficient removalBone implantDiagnosticsMedicineIntervertebral space
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
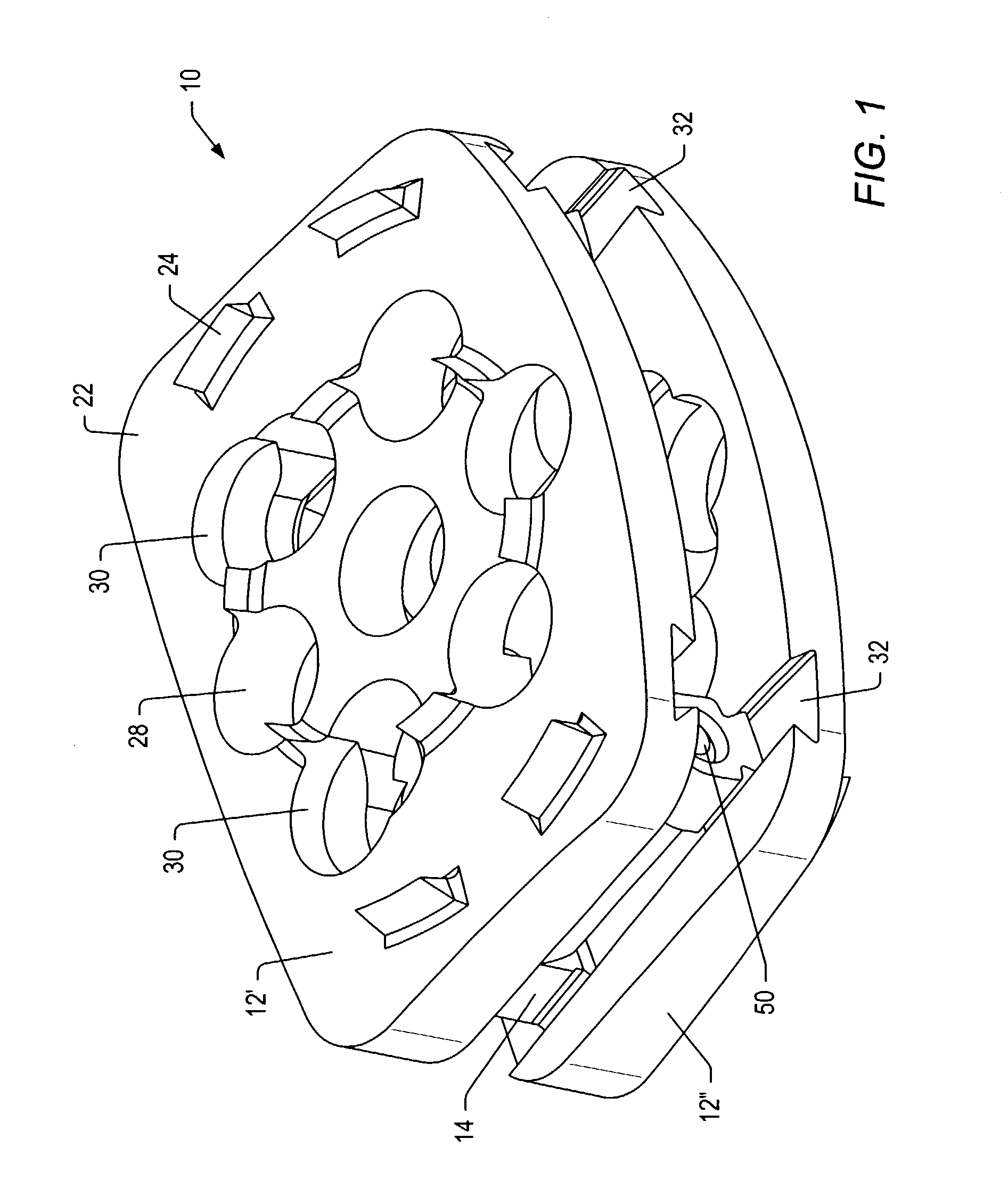
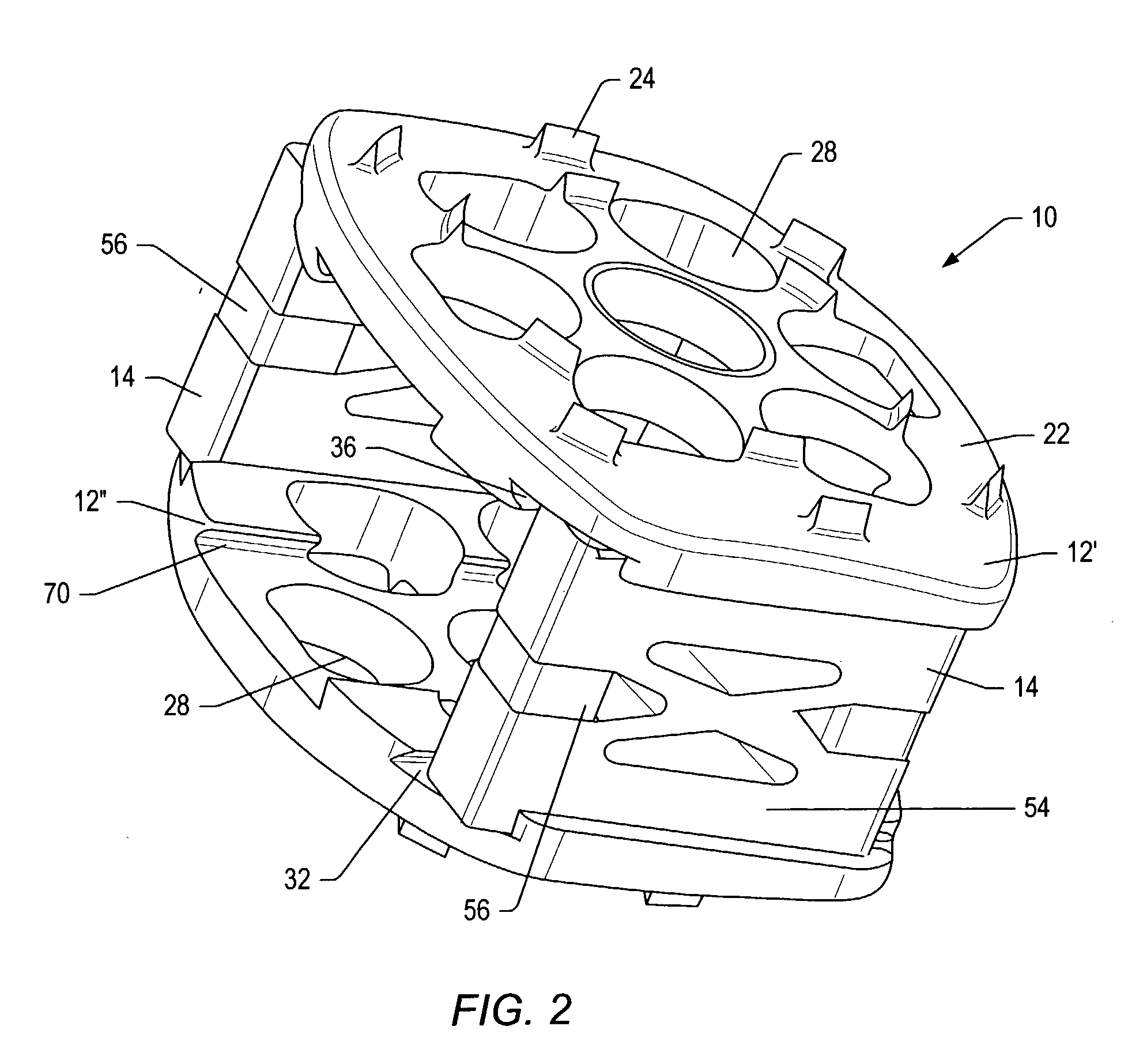
Multi-Directional fasteners or attachment devices for spinal implant elements
InactiveUS6019759AIncreased bone volumeAvoid damageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMultiple pointSpinal implant
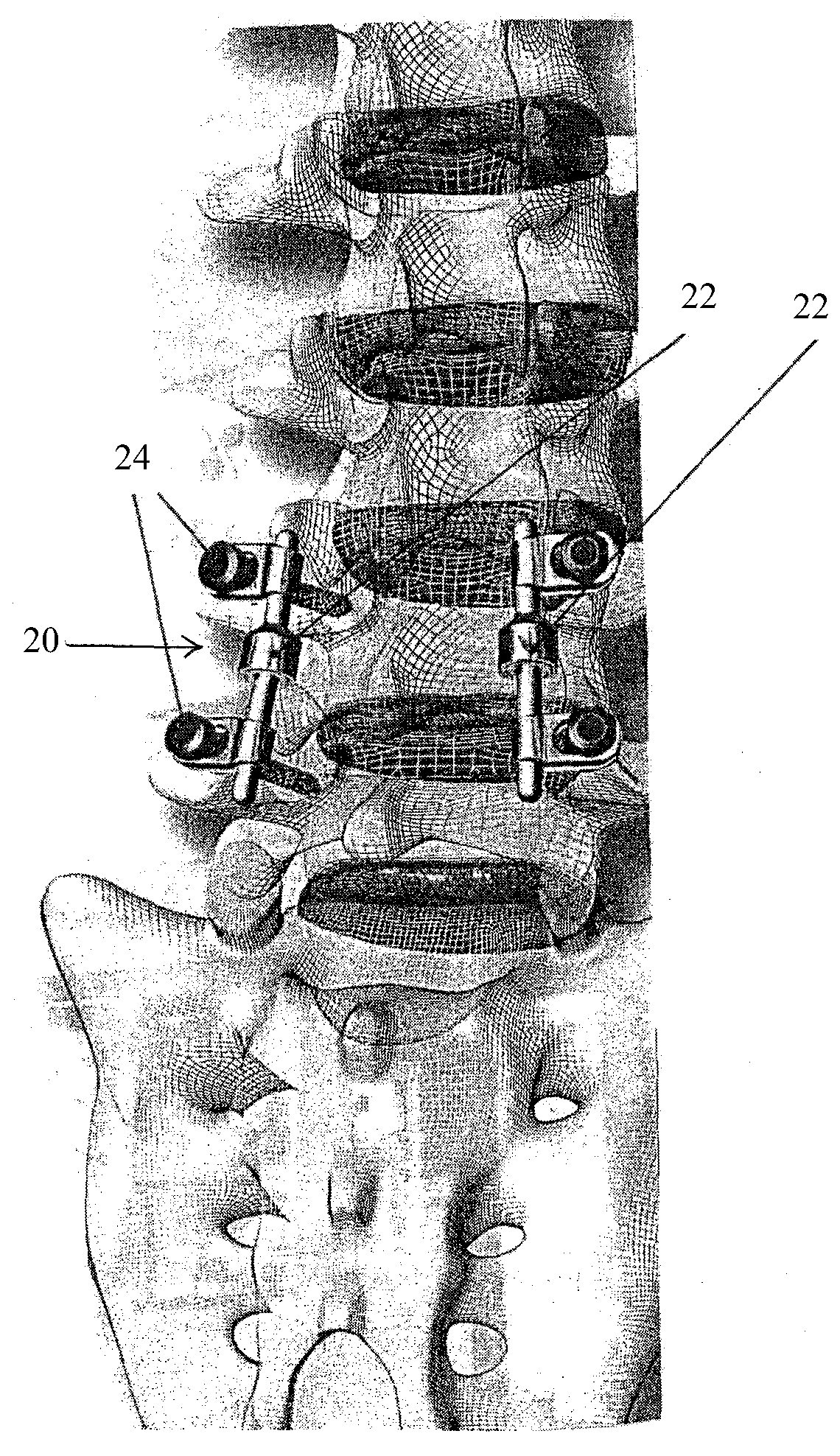
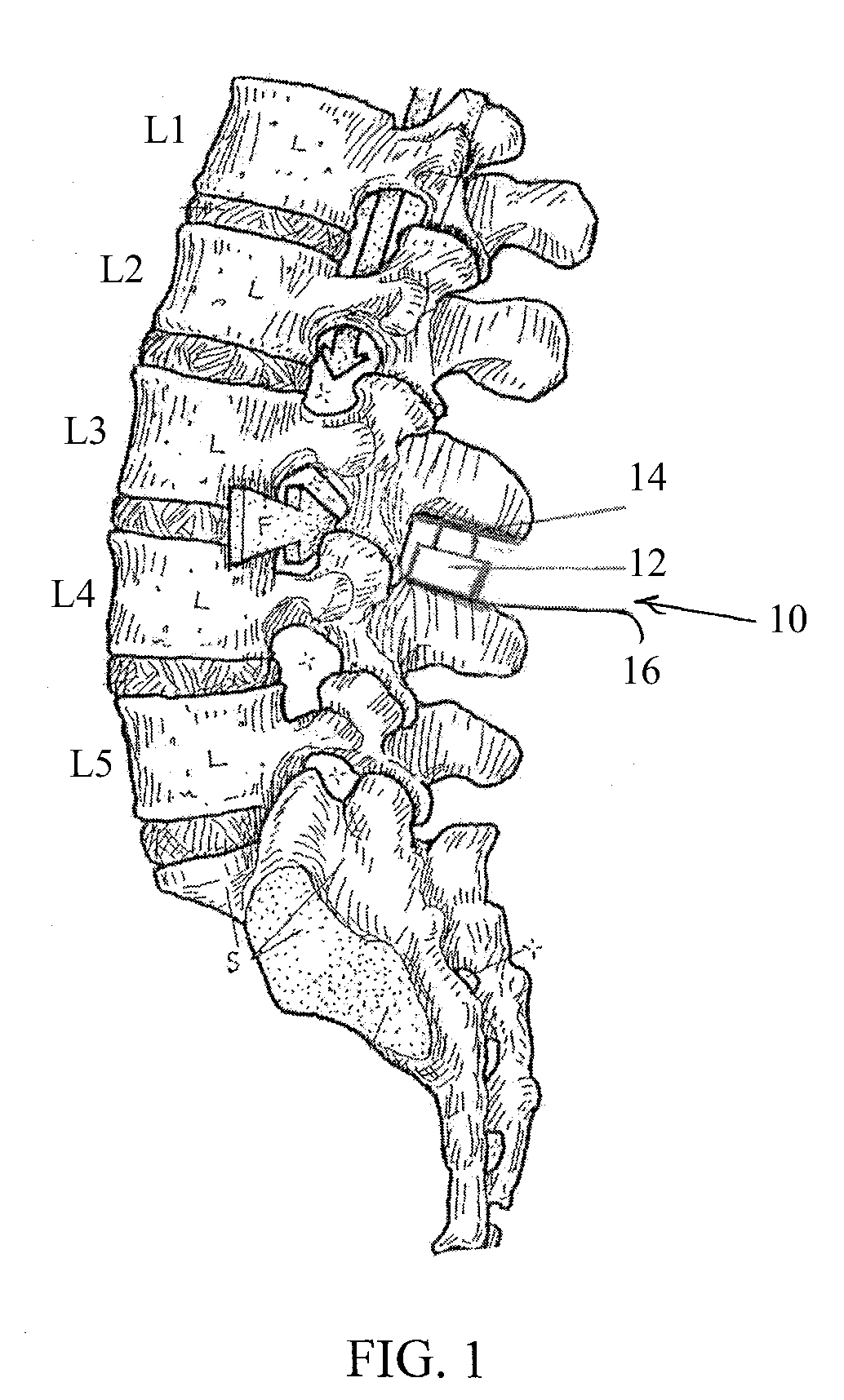
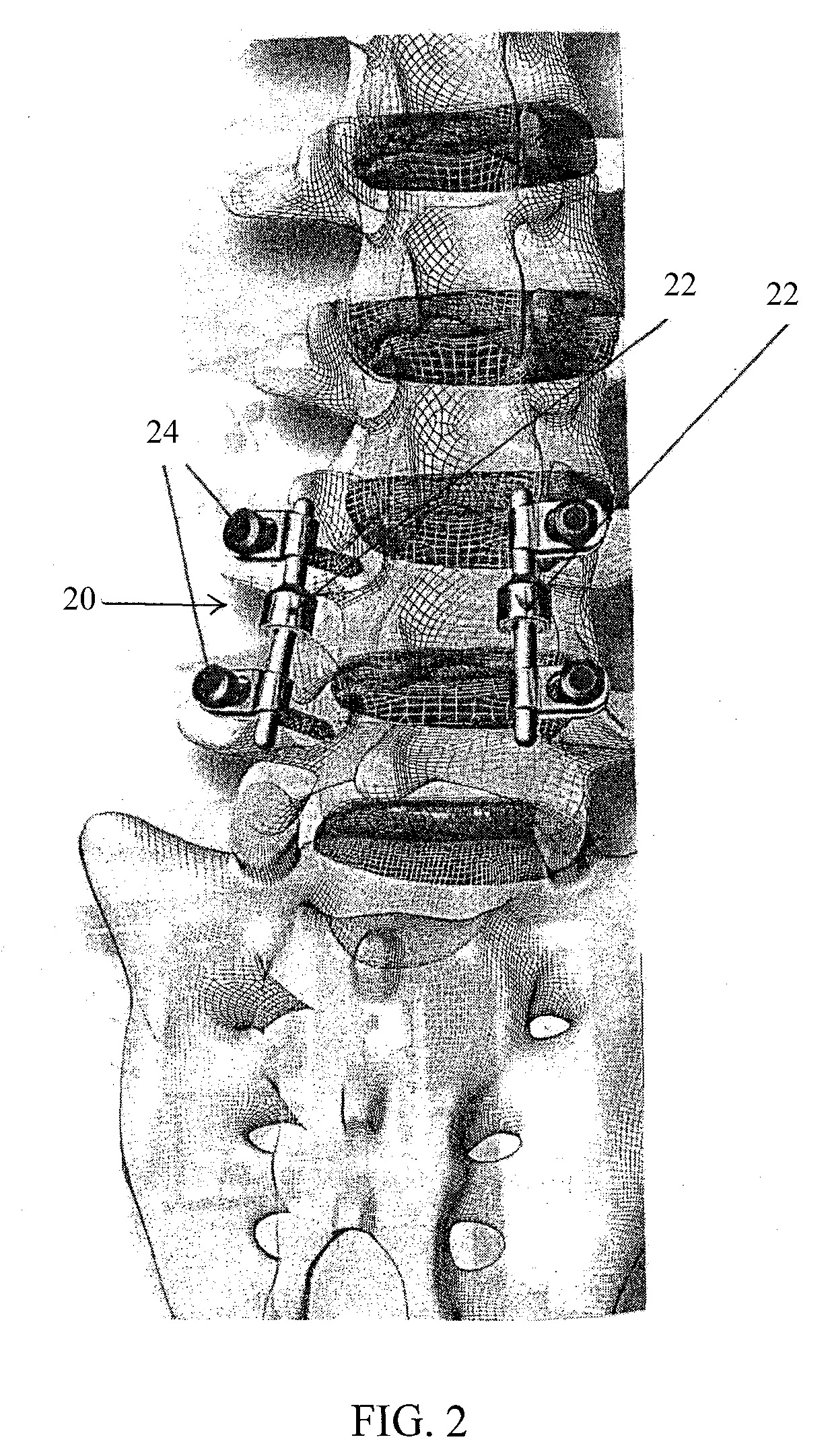
An apparatus, method and system for treating spinal conditions by moving or spatially fixing at least one vertebra relative to another vertebra. The invention includes a link member the ends of which are configured to be secured to adjacent vertebrae and which are offset from a central portion of the link member. The link members can be in the form of a C-shaped or V-shaped rod or plate to form the offset. The offset provides increased bone volume that can be used for grafts or fusion. Attachment structure in the form of bone screws, bolts, or hook members are provided to secure the link members to respective vertebrae or other bones. A plurality of link members can be connected in chain-like fashion to connect multiple points on a plurality of vertebrae or other bones even though those points are nonlinear. In another aspect of the invention, a multi-directional attachment member is provided and may be used with the link members to form a spinal implant or external bone fixation system.
Owner:ROGOZINSKI CHAIM
Articulating spinal implant
An articulating spinal implant for intervertebral disc replacement. The articulating spinal implant is formed from two elements, each engaging one of an adjacent pair of vertebra. Articulation features between the two elements resist compression and lateral movement between the vertebra, but allow the adjacent vertebra to articulate about an instantaneous axis of rotation.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
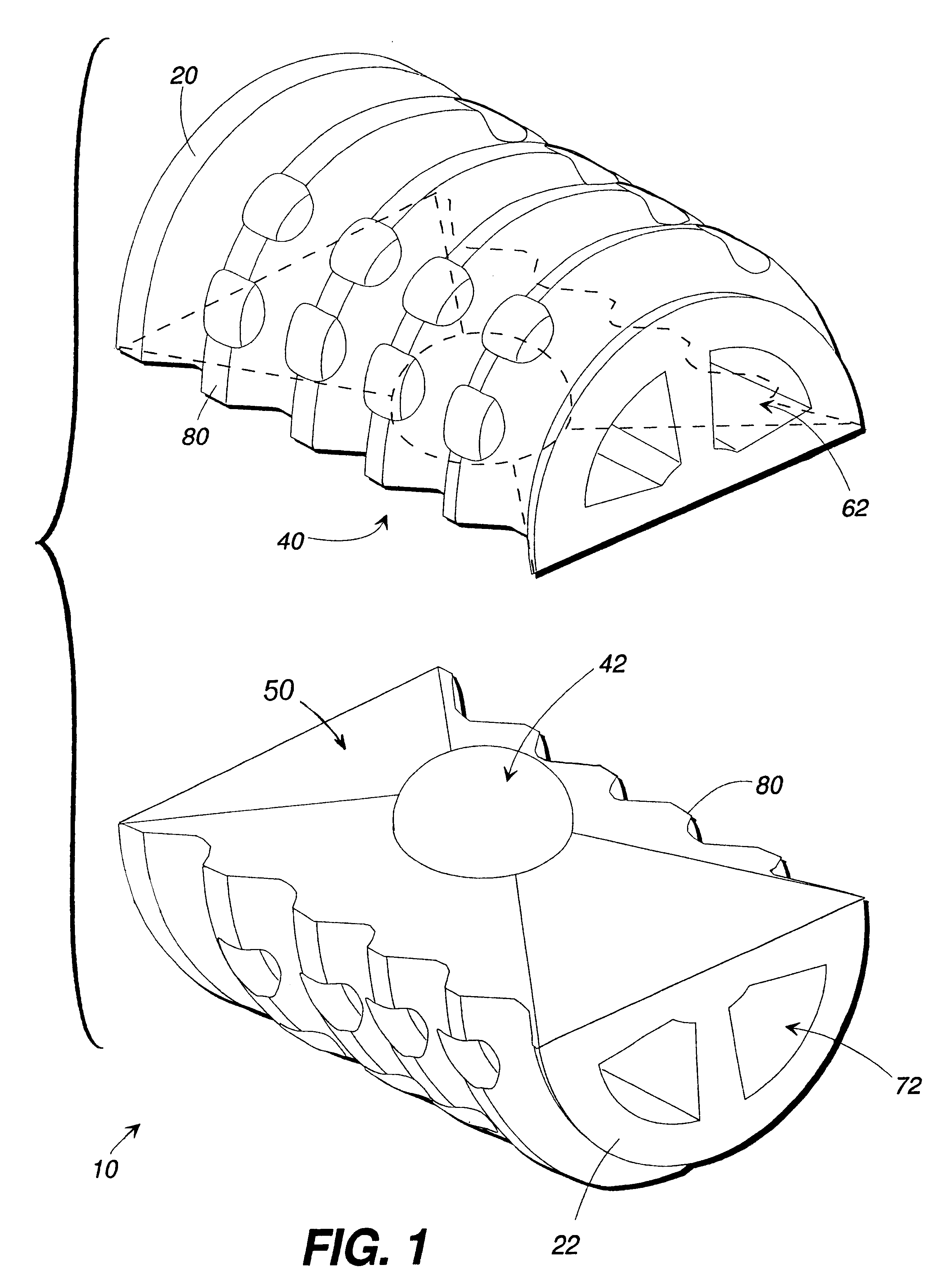
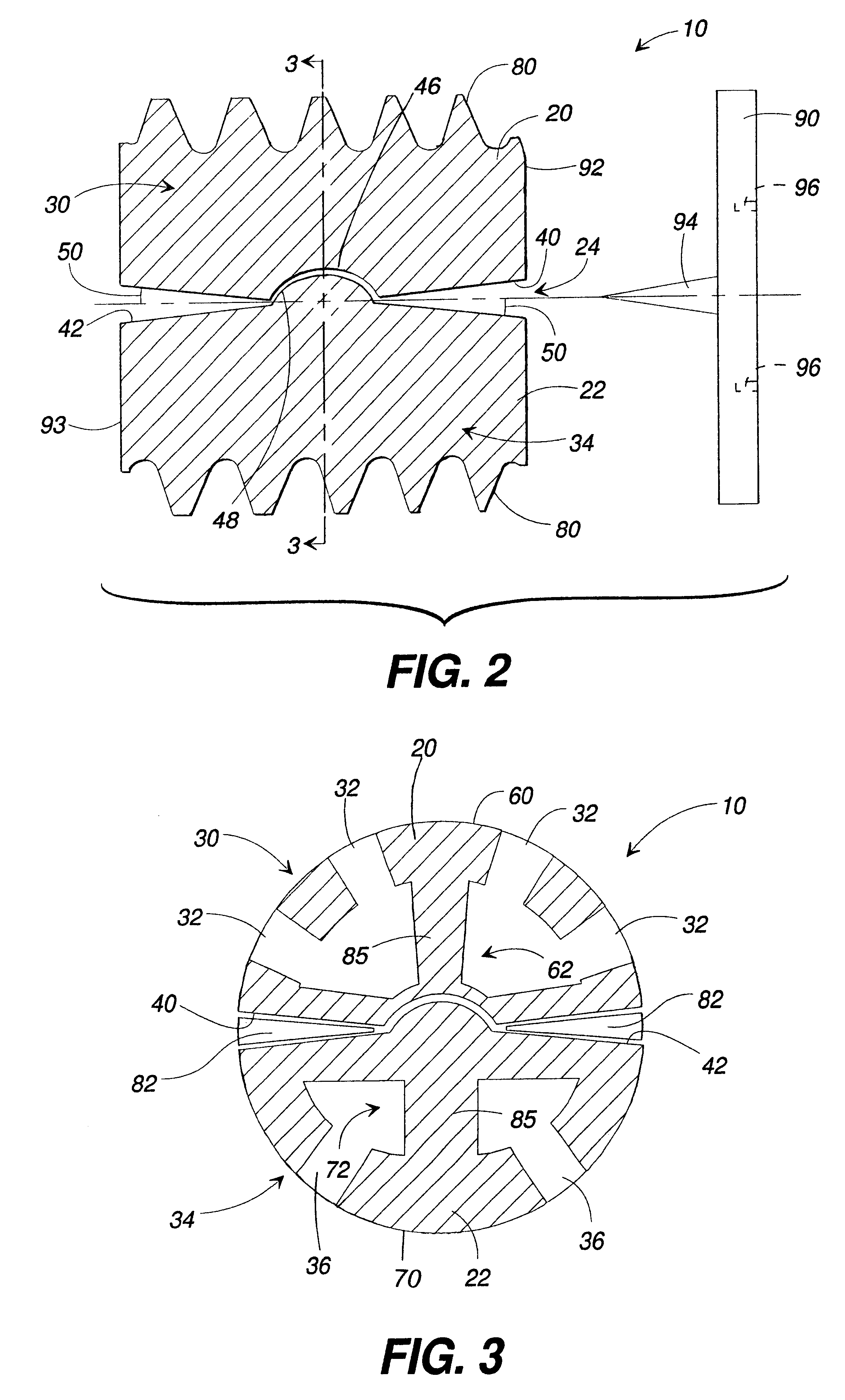
Spinal implant
ActiveUS20050027360A1Easy to integratePromote bone growthDiagnosticsBone implantRaspIntervertebral disk
A spinal implant may be used to stabilize a portion of a spine. The implant may promote bone growth between adjacent vertebrae that fuses the vertebrae together. An implant may include an opening through a height of a body of the implant. The body of the implant may include curved sides. A top and / or a bottom of the implant may include protrusions that contact and / or engage vertebral surfaces to prevent backout of the implant from the disc space. A variety of instruments may be used to prepare a disc space and insert an implant. The instruments may include, but are not limited to, a distractor, a rasp, and one or more guides. The implant and instruments may be supplied in an instrument kit.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Percutaneous spinal implants and methods
Owner:MEDTRONIC EURO SARL
Instruments and methods for inserting a spinal implant
Instruments of an instrumentation set may be used to prepare a disc space and to insert an implant into the prepared disc space. The instruments may include fixed tip distractors and / or modular tip distractors. The instruments may include a chisel. The chisel may allow simultaneous removal of a desired amount of bone from each of a pair of vertebrae. The instruments may include an implant inserter. The implant inserter may grip sides of an implant. A portion of the implant inserter may fit within grooves of the implant to minimize or eliminate portions of the implant that extend beyond side surfaces of the implant.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Devices and methods for explantation of intervertebral disc implants
Methods and devices are provided for the explantation of spinal implants. A cutting tool may be extended into the spinal implant. The spinal implant may be cut into pieces and the pieces removed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
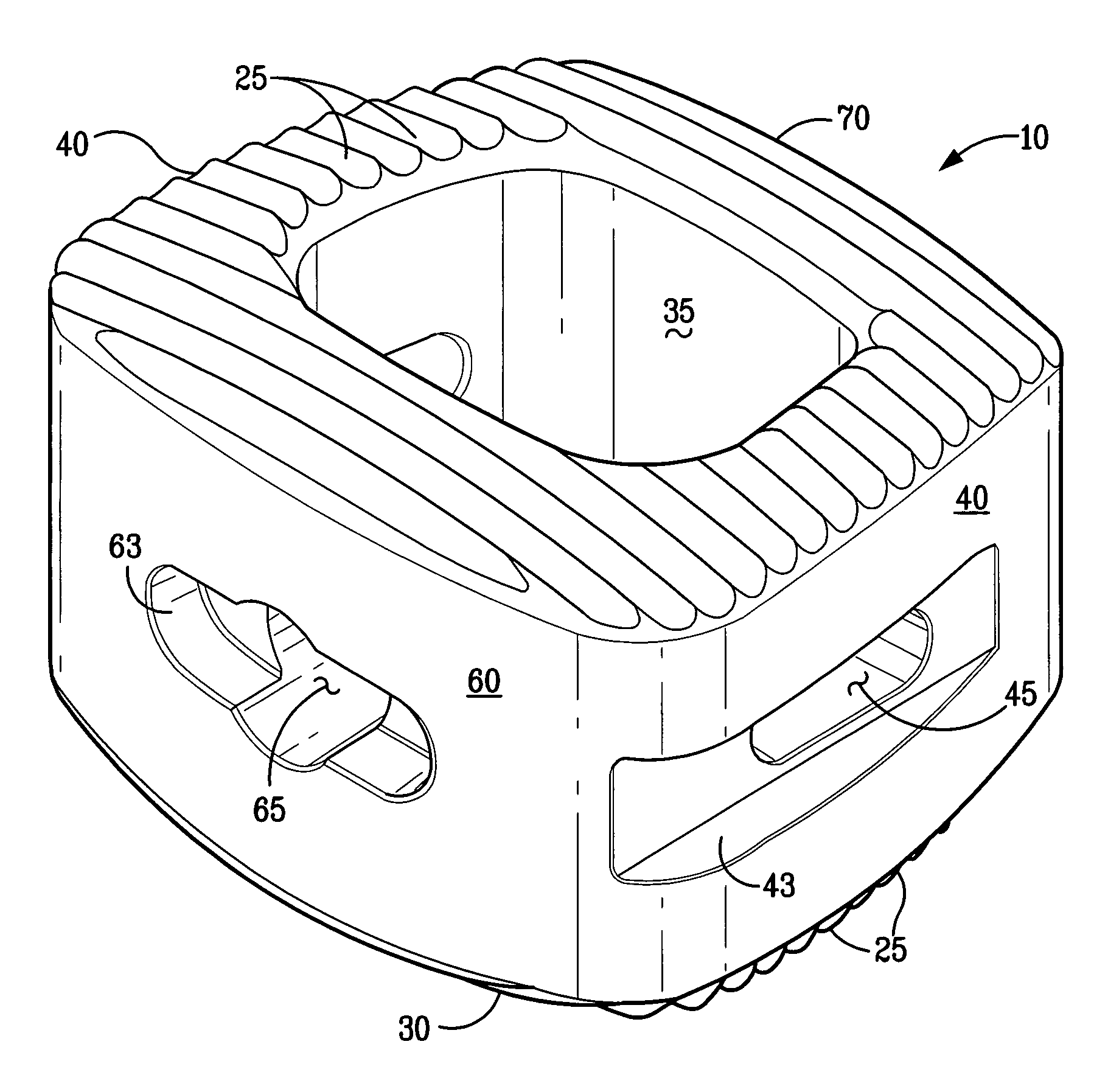
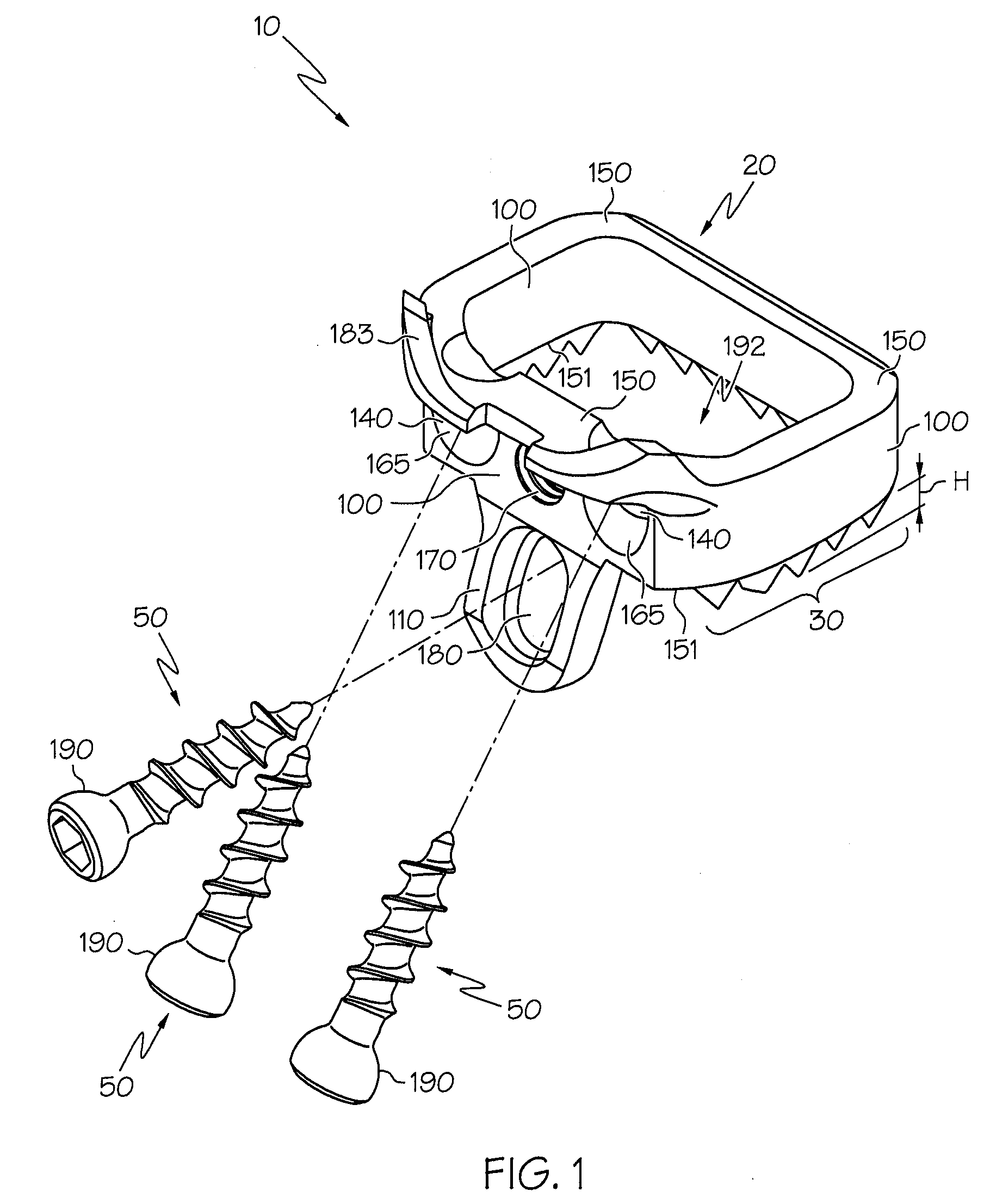
Orthopaedic Implants and Prostheses
InactiveUS20090210062A1Small sizeAdjustable sizeSuture equipmentsBone implantSurgical siteSurgical department
Disclosed herein are spinal implants particularly useful in interbody fusion surgery. One embodiment pertains to a plate configured to establish desired lordosis and / or disc height that may be implanted and secured to a superior and inferior vertebral body. The plate may be interlocked with a spacer component to form a single implant. Also disclosed is an anti-backout mechanism that helps prevent fixators from backing out upon securement of the plate in the spine. Kits comprising different sizes and inclination angles of components are disclosed, which can assist the surgeon in preoperatively assembling an implant to best fit in the surgical site of the patient.
Owner:THALGOTT JOHN +1
Articulating spinal implant
A spinal implant for intervertebral disc replacement. The implant is formed from two hemicylindrical elements, each engaging one of an adjacent pair of vertebrae. An articulating ball-and-socket joint and / or rocker and channel between the two elements resists compression and lateral movement between the vertebra, but allows pivotal movement, thereby preserving mobility. Fusion chambers are provided for allowing bone ingrowth to fuse the elements to the vertebrae. Biocompatible, bioreabsorbable struts, shims, fillers and / or end caps are provided for temporary stabilization of the first and second hemicylindrical elements. Bone chips removed from the vertebrae during implantation or bone growth stimulators can be inserted into the fusion chamber or otherwise applied to the implant to enhance bone ingrowth.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Spine implants
InactiveUS20070250167A1Restrict movementBone implantSpinal implantsSpinal implantBiomedical engineering
Owner:RSB SPINE
Spinal implant having a post-operative adjustable dimension
ActiveUS20090125062A1Change distanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantBiomedical engineering
A spinal implant including first spinal attachment member for attaching to a first spinal portion, second spinal attachment member for attaching to a second spinal portion, and a post-implantation variable dimension device disposed between the first and second spinal attachment members, which is operable after completing surgery in which said spinal implant was installed into a patient, to cause relative movement between the first and second spinal attachment members.
Owner:SPINE21 LTD
Percutaneous spinal implants and methods
An apparatus includes a guide shaft, an expansion member coupled to the guide shaft, and an actuator. The expansion member is configured to impart a force from within an interior of an implant to deform the implant. The actuator is coupled to the expansion member, the actuator is configured to move the expansion member from a first position to a second position.
Owner:KYPHON
Instrumentation and procedure for implanting spinal implant devices
An instrumentation set may include insertion instruments for forming an implant between bone structures. The insertion instruments may include a spreader and a separator. The bone structures may be vertebrae. Implant members may be attached to the spreader and positioned between the bone structures. The separator may be inserted into the spreader to establish a desired separation distance between the implant members. Connectors may be inserted into the implant members to join the implant members together and form the implant. The insertion instruments may be removed. A seater may be used to set the position of the connectors relative to the implant members to inhibit disassembly of the implant.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
System and method for blocking and/or retaining a prosthetic spinal implant
Devices for anchoring and / or blocking spinal implants in an intervertebral disc space are disclosed. In one aspect of the invention the device includes a rigid blocking member having one end unconnected and free to block a spinal implant, and another end attached to a securing member to secure the blocking member to the spine. Methods for using the inventive anchoring / blocking implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Orthopaedic Implants and Prostheses
Disclosed herein are modular spinal implants having components which are interlocked together to form a single implant. Specifically exemplified herein are implants that are sectioned along a longitudinal plane. Implants are disclosed which include channels for inter-fragmentary association with an elongate bone screw and which allow for angular variability of the screw relative to the channel. Also disclosed is an anti-backout mechanism that helps prevent fixators from backing out upon securement of the implant in the spine. Kits comprising different sizes and inclination angles of components are disclosed, which can assist the surgeon in preoperatively assembling an implant to best fit in the surgical site of the patient.
Owner:SURGICRAFT LTD
Self-Distracting Cage
ActiveUS20080288073A1Stabilizing spineEfficient communicationSpinal implantsSpinal implantBiomedical engineering
Various spinal implants and methods for stabilizing the spine are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, a spinal implant is provided having an expandable container with an interior volume that is selectively expandable between a compressed condition and an expanded condition. The expandable container is coupled to a superior endplate member having a bone-contacting surface and an engagement surface effective to mate with a superior surface of the expandable container, and an inferior endplate member having a bone-contacting surface and an engagement surface effective to mate with an inferior surface of the expandable container. In addition, at least one inlet port is formed in the expandable container and is effective to communicate a fluid to at least one cavity disposed within the interior volume of the expandable container.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
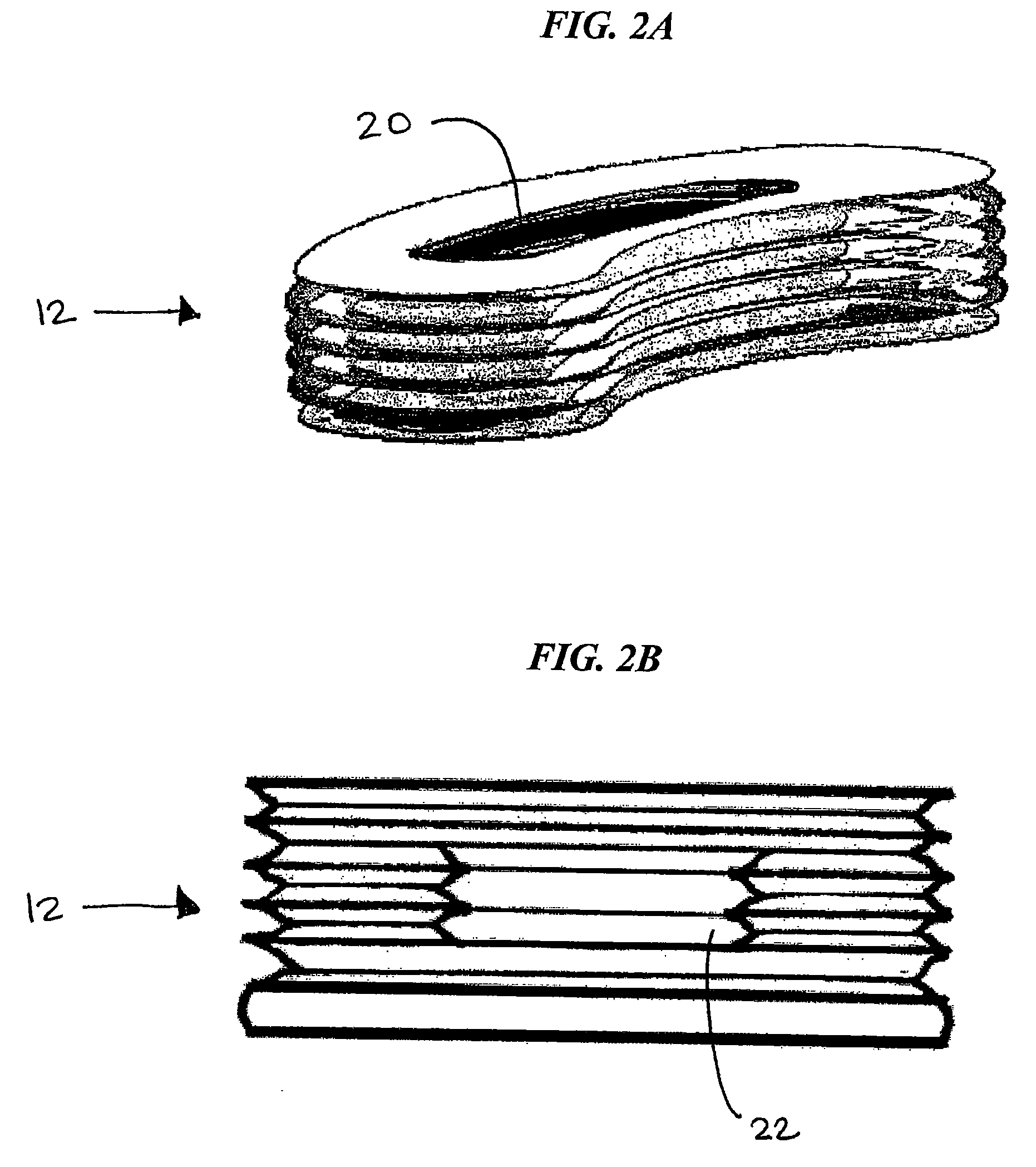
Expandable spinal implants
A cylinder-shaped expandable spinal implant is disclosed. The implant is a hollow housing having a cylinder-shaped wall, with a circular sealed distal end, and an opposite proximal circular open end. The open end of the housing has internal threads for securing a cap to it. A removable cap is threaded on the open end of the housing. The housing has two opposite large rectangular openings located longitudinally in the wall of the housing for receiving two arcuate sections. Each arcuate section is positioned in the rectangular opening in the wall of the implant. A locking means for locking the arcuate section in the rectangular opening in the wall is provided. A plurality of small ports are drilled in the wall for allowing bone growth after implantation of said implant in a patient. The arcuate sections have transverse ribs for locking the implant in position are implantation. Openings between the ribs are provided for allowing bone growth.
Owner:KOROS TIBOR
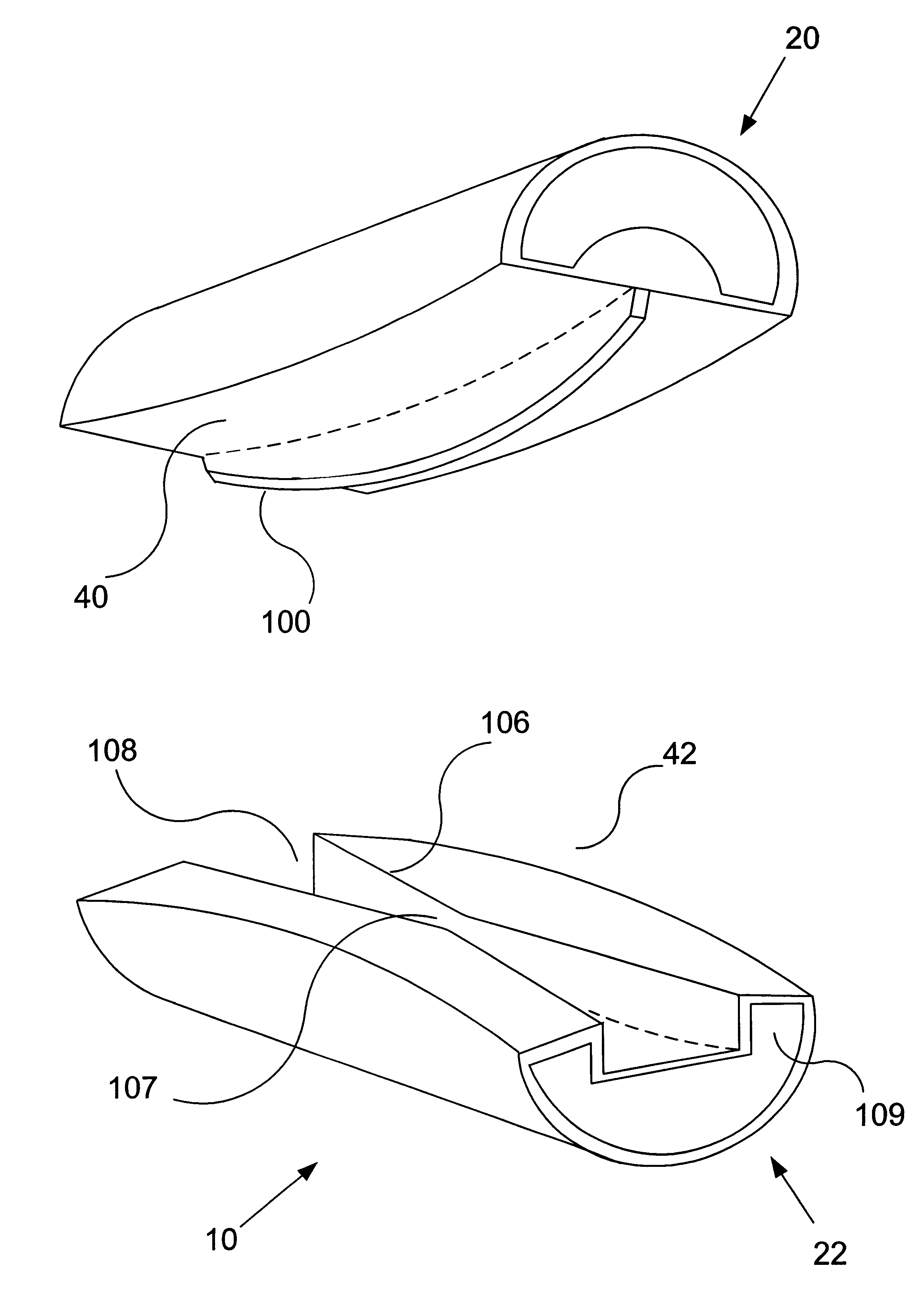
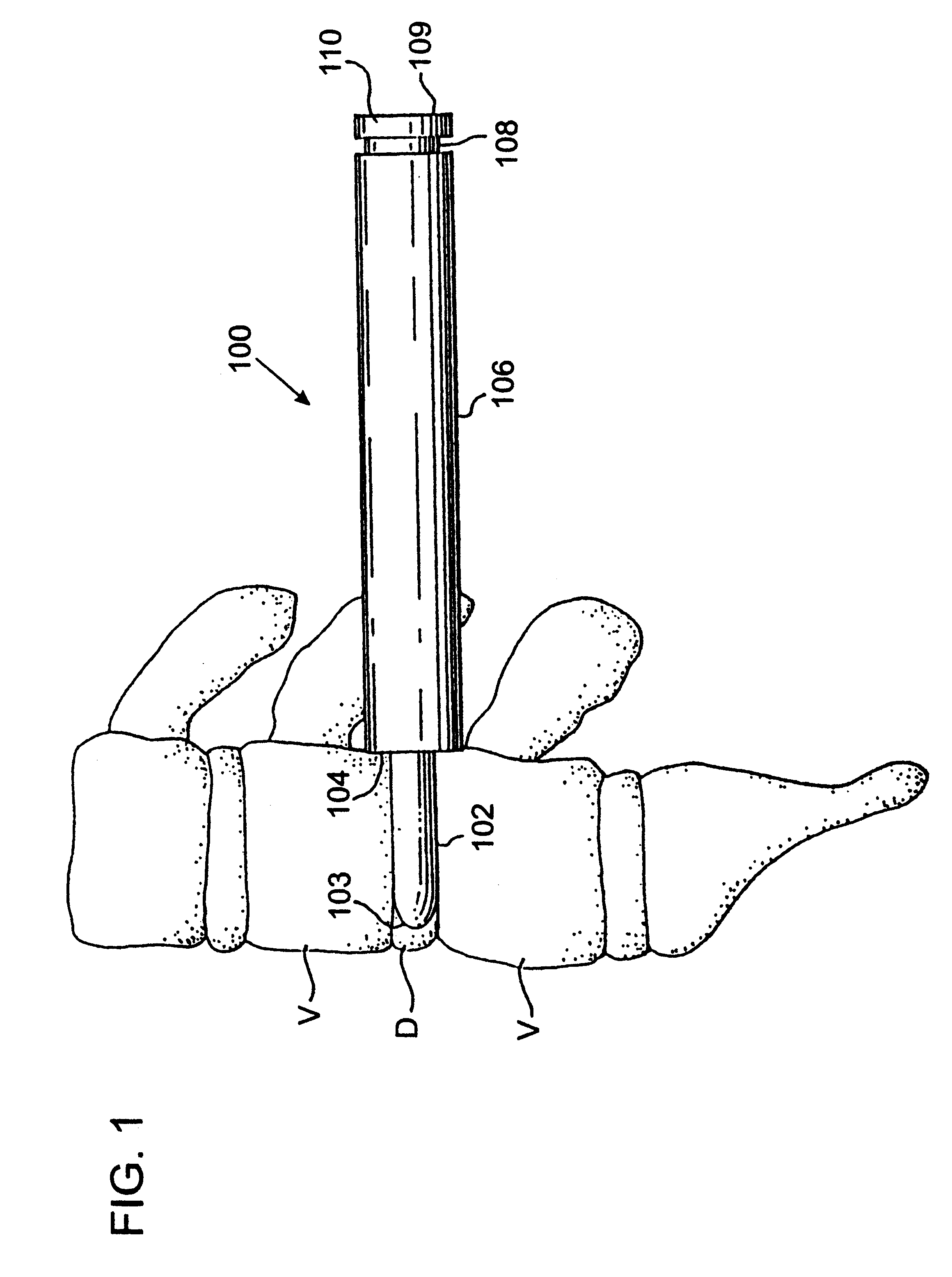
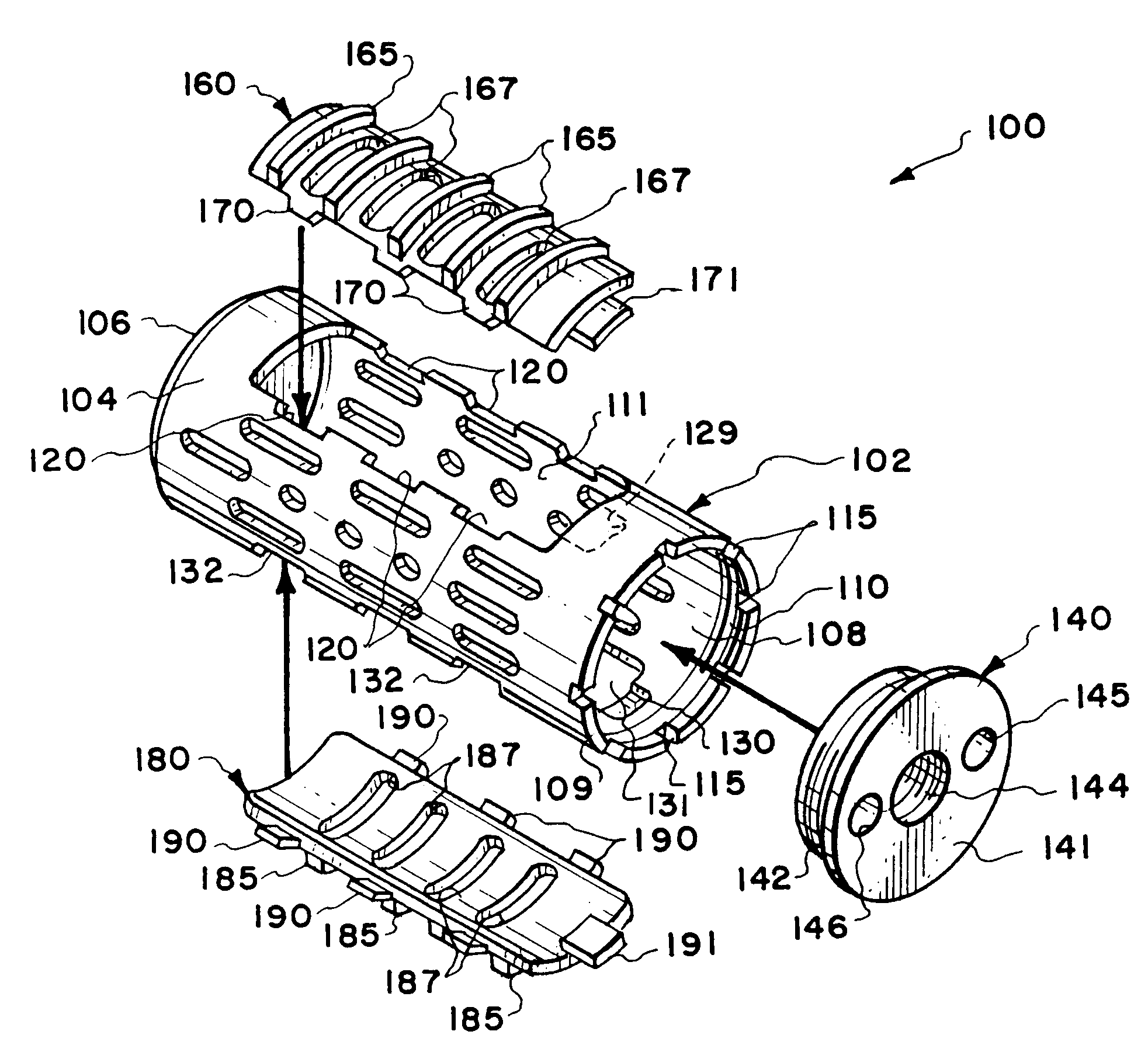
Method and apparatus for providing posterior or anterior trans-sacral access to spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS7087058B2Less discomfortMinimally invasiveInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinal columnSacrum
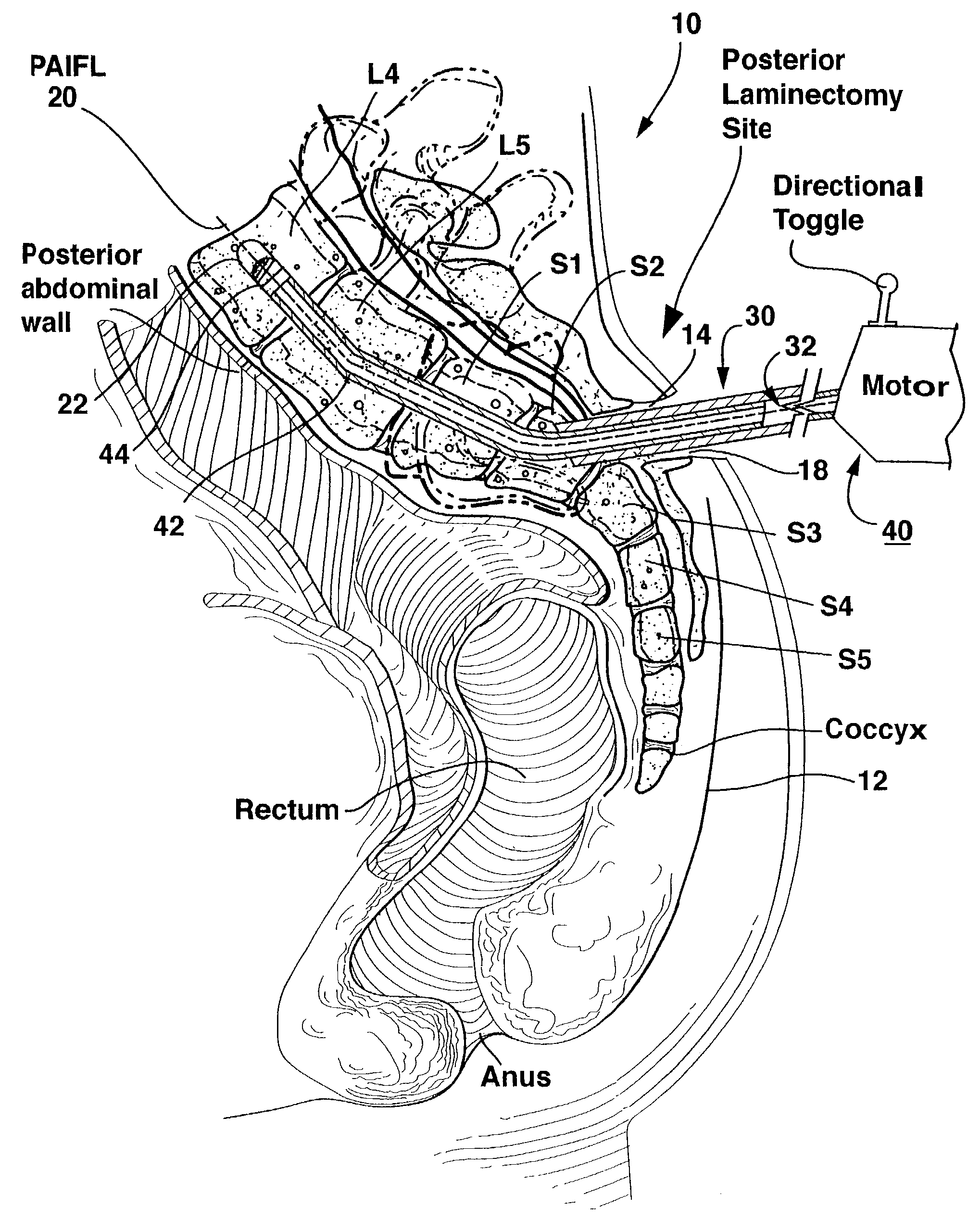
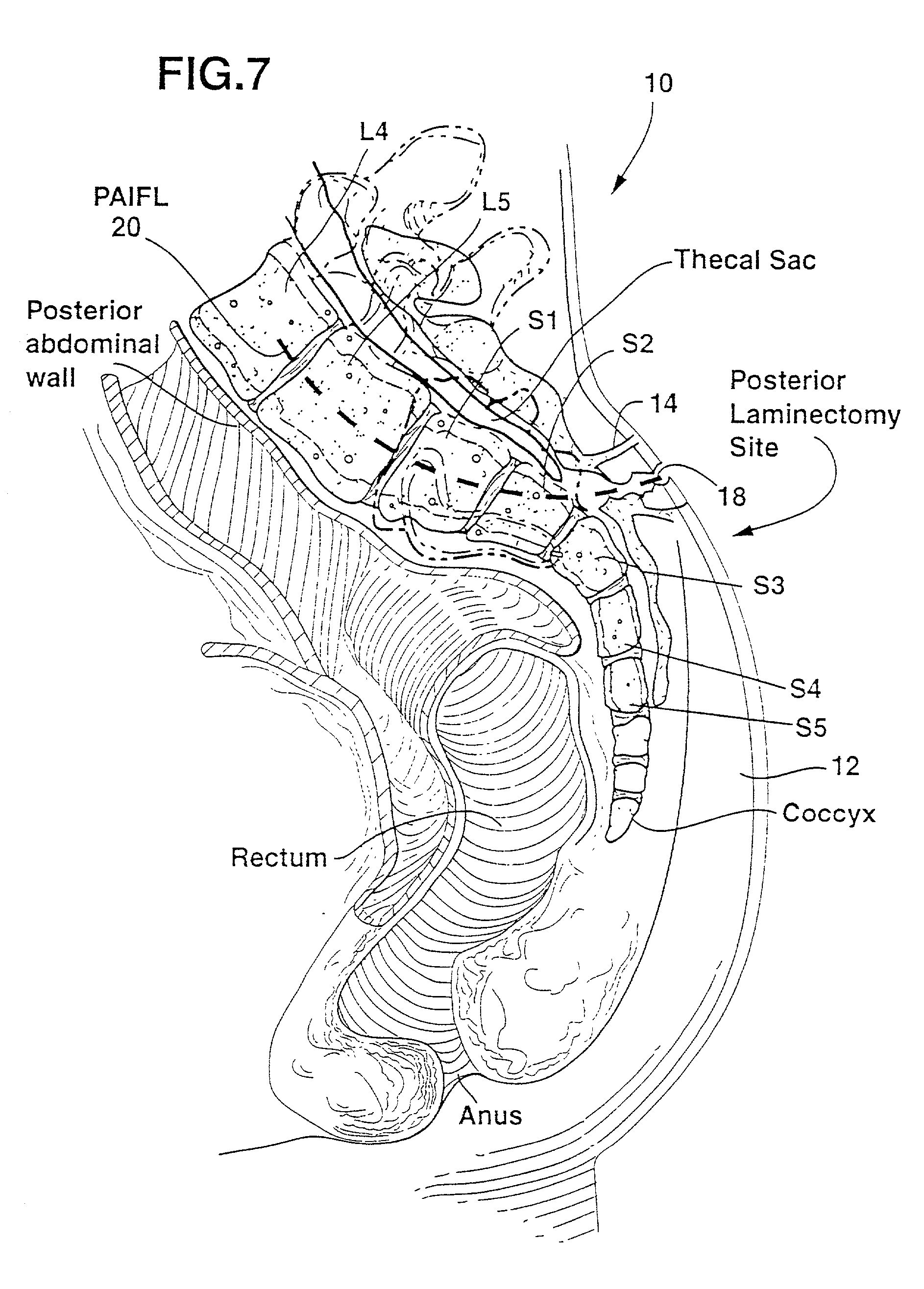
Methods and apparatus for providing percutaneous access to vertebrae in alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner are disclosed. A number of related TASIF methods and surgical tool sets are provided by the present invention that are employed to form a percutaneous pathway from an anterior or posterior skin incision to a respective anterior or posterior target point of a sacral surface. The percutaneous pathway is generally axially aligned with an anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line extending from the respective anterior or posterior target point through at least one sacral vertebral body and one or more lumbar vertebral bodies in the cephalad direction. The provision of the percutaneous pathway described herein allows for the formation of the anterior or posterior TASIF bore(s) and / or the introduction of spinal implants and instruments.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
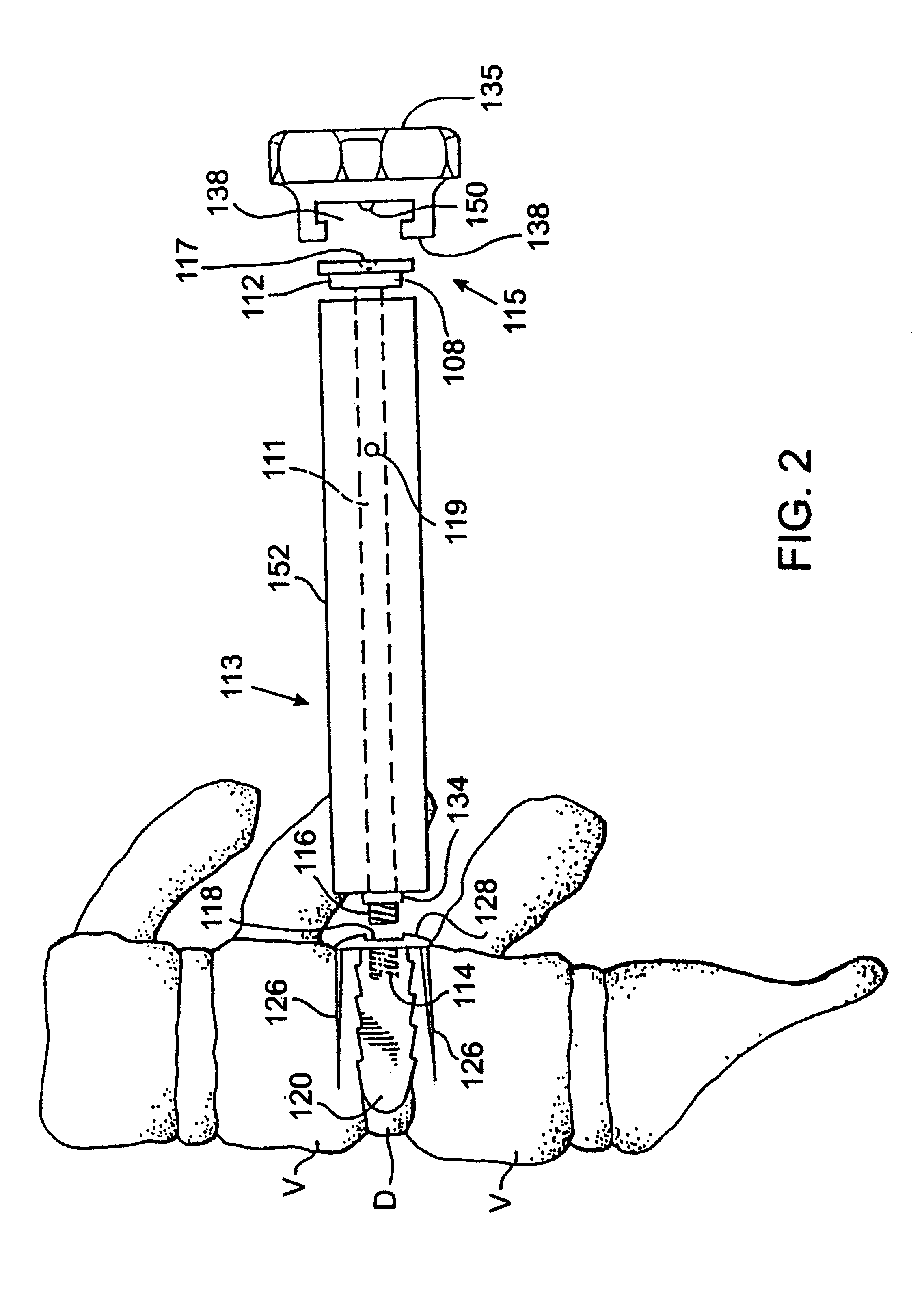
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
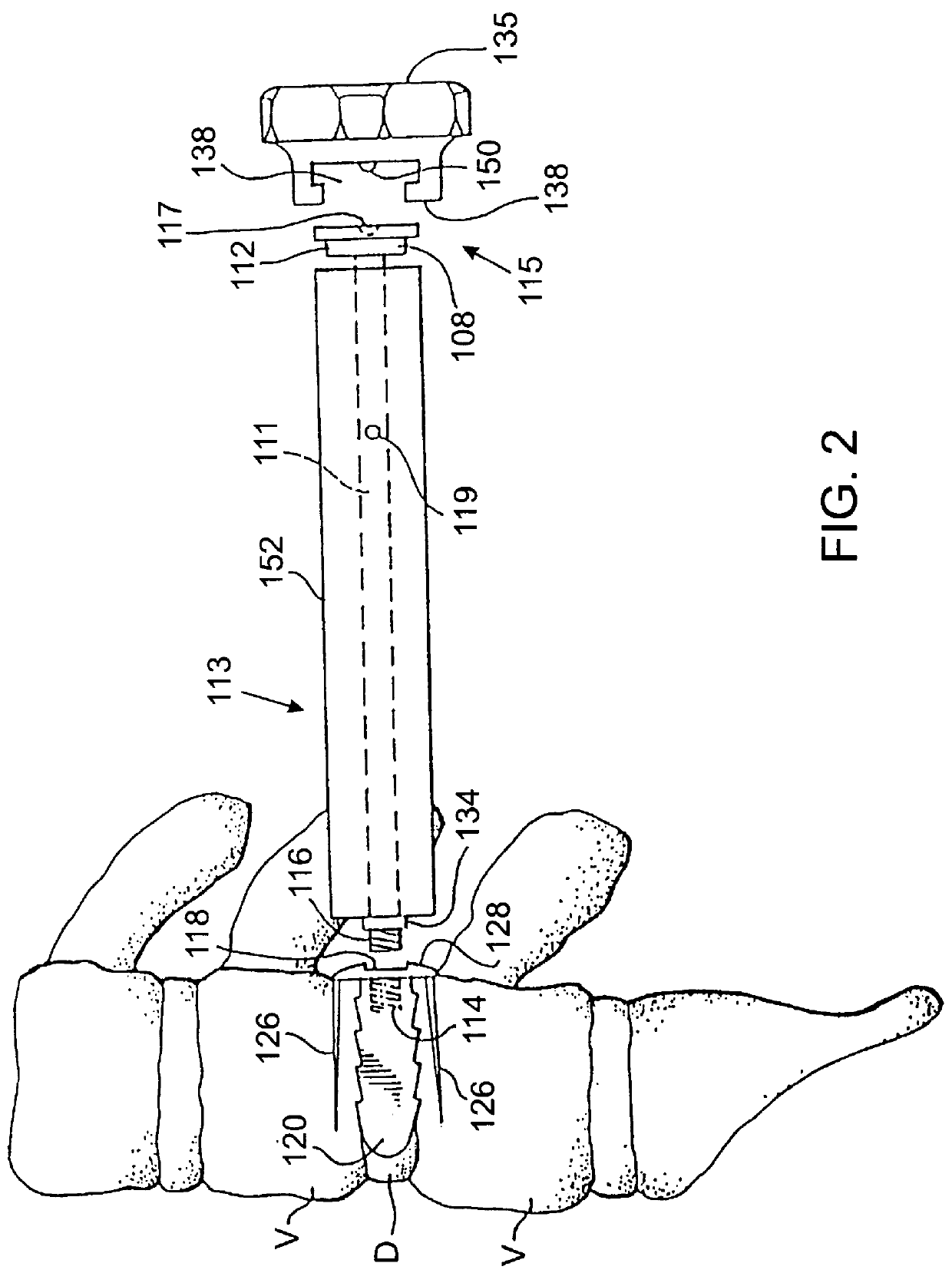
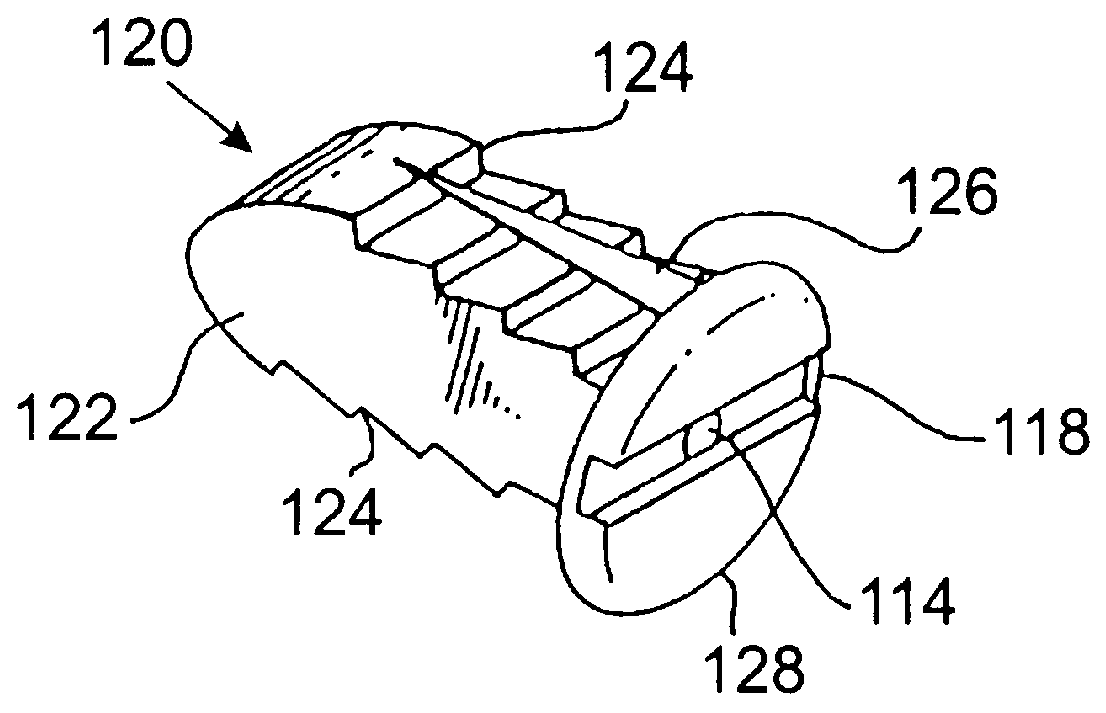
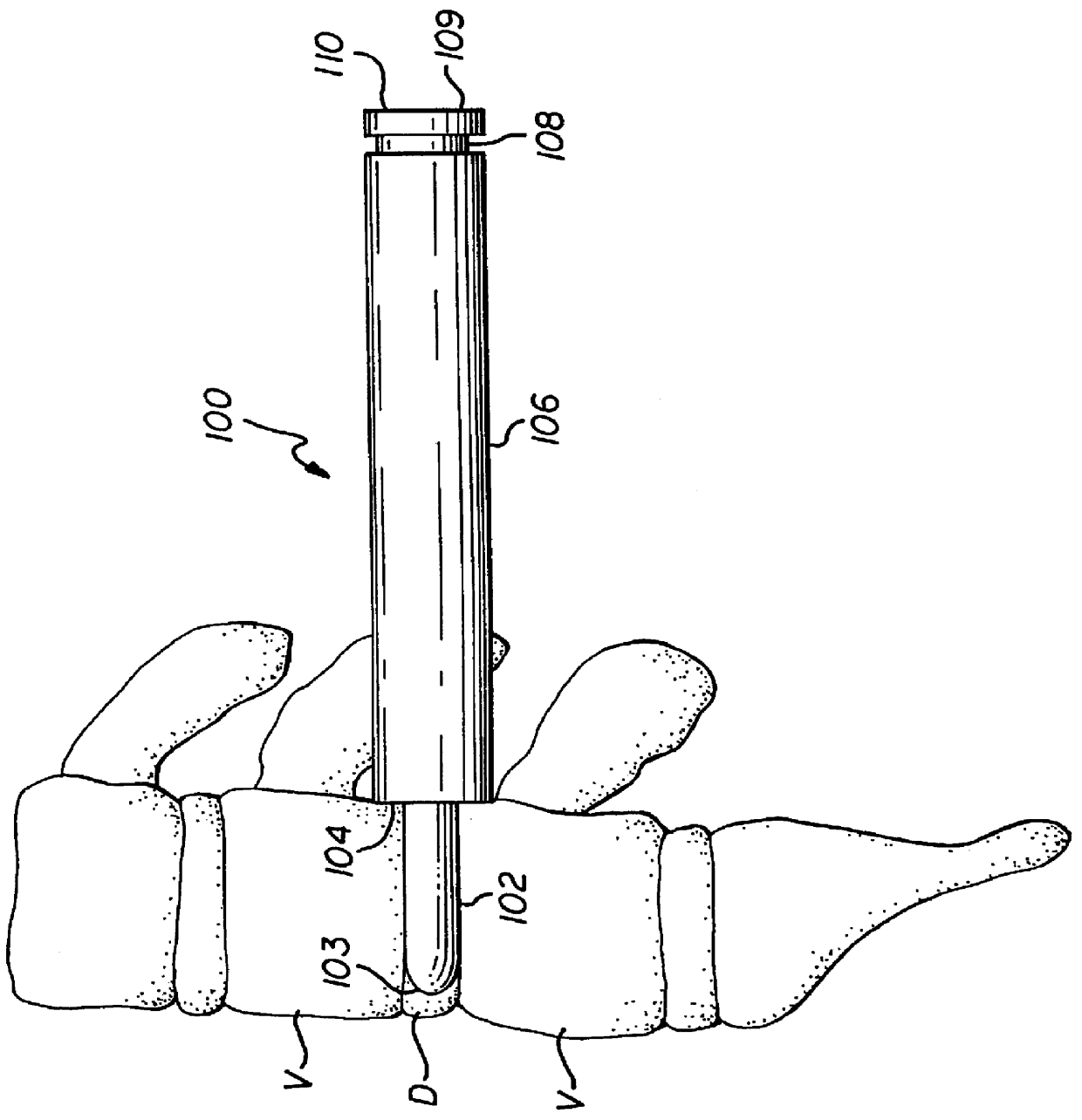
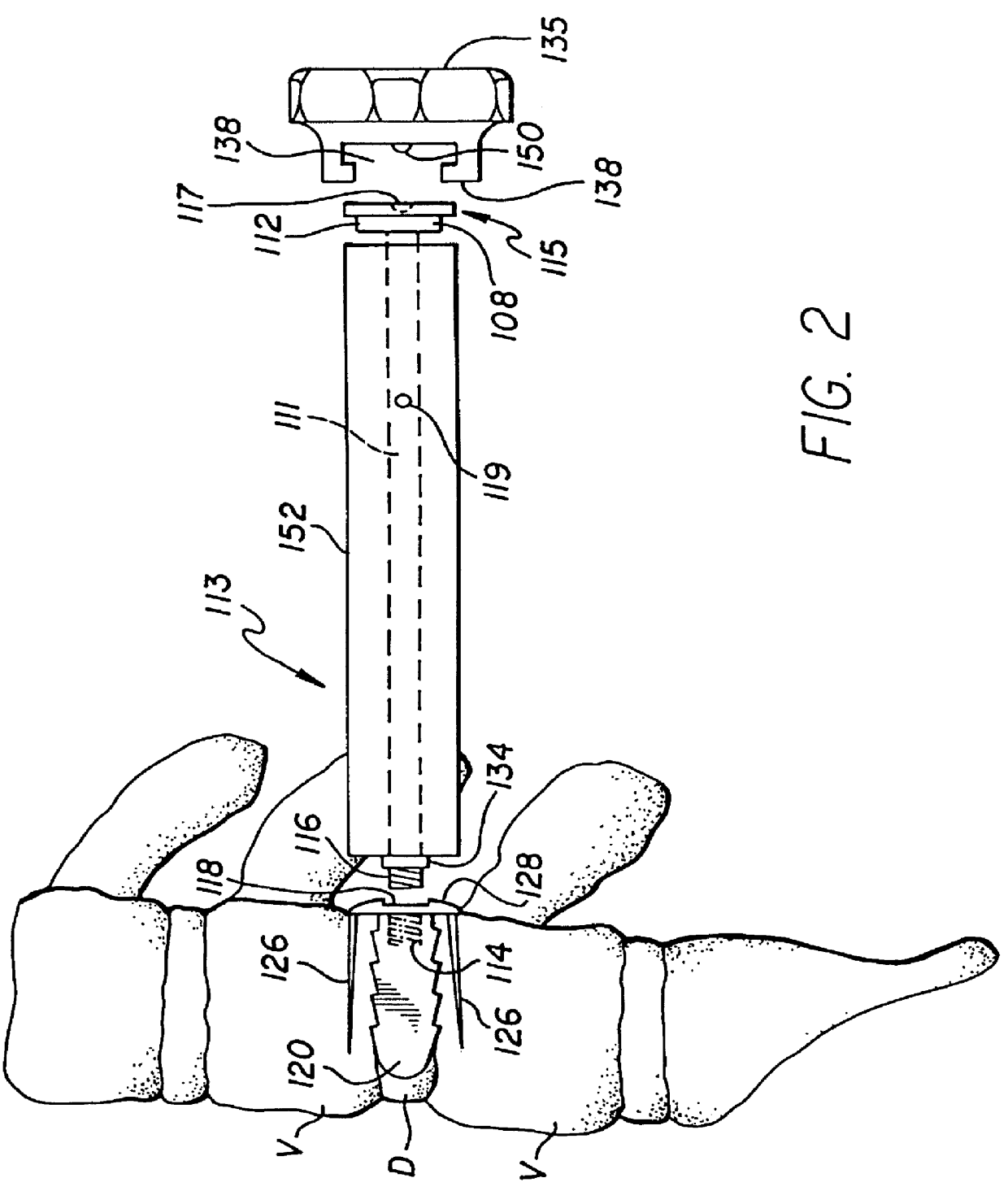
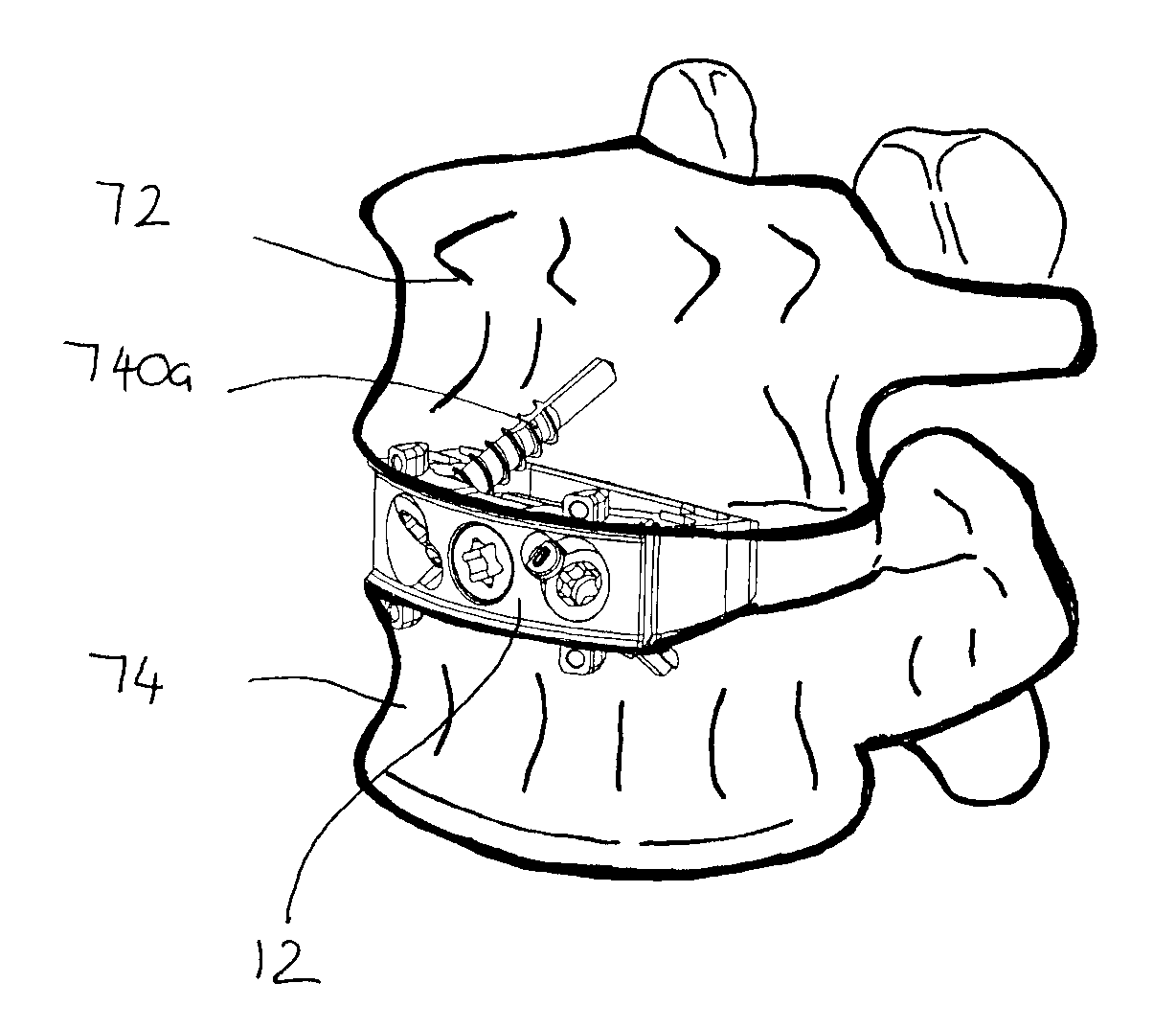
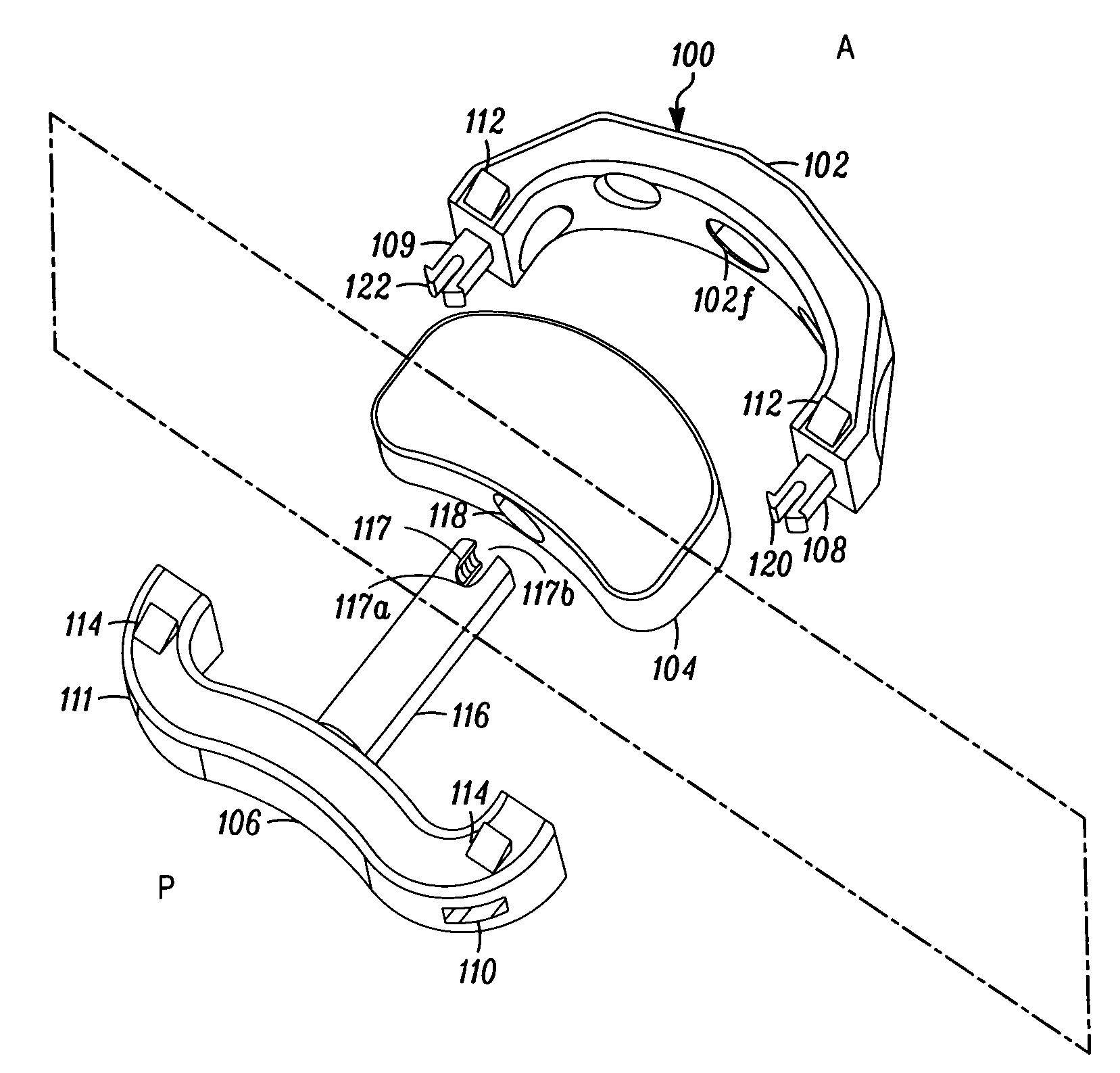
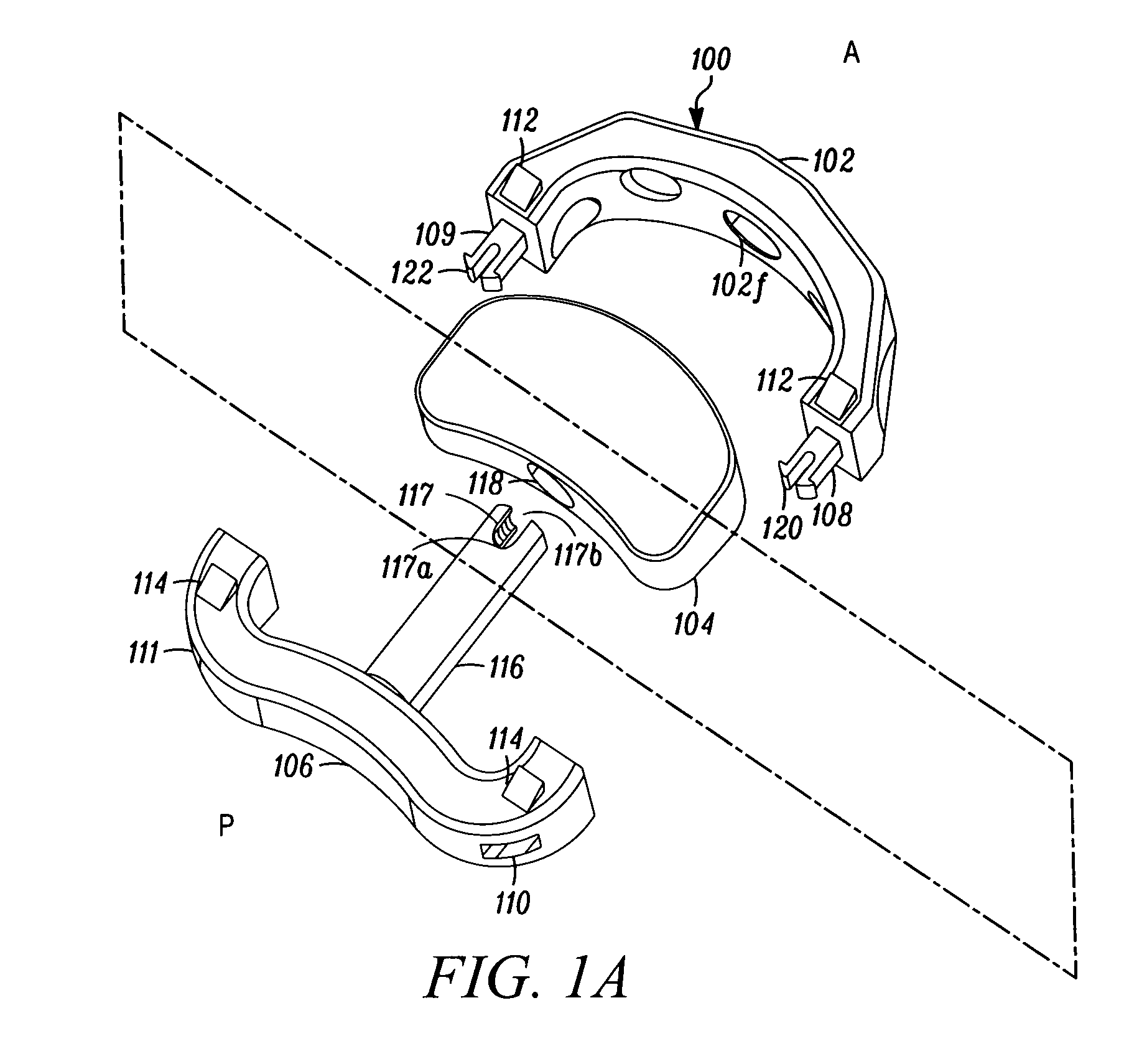
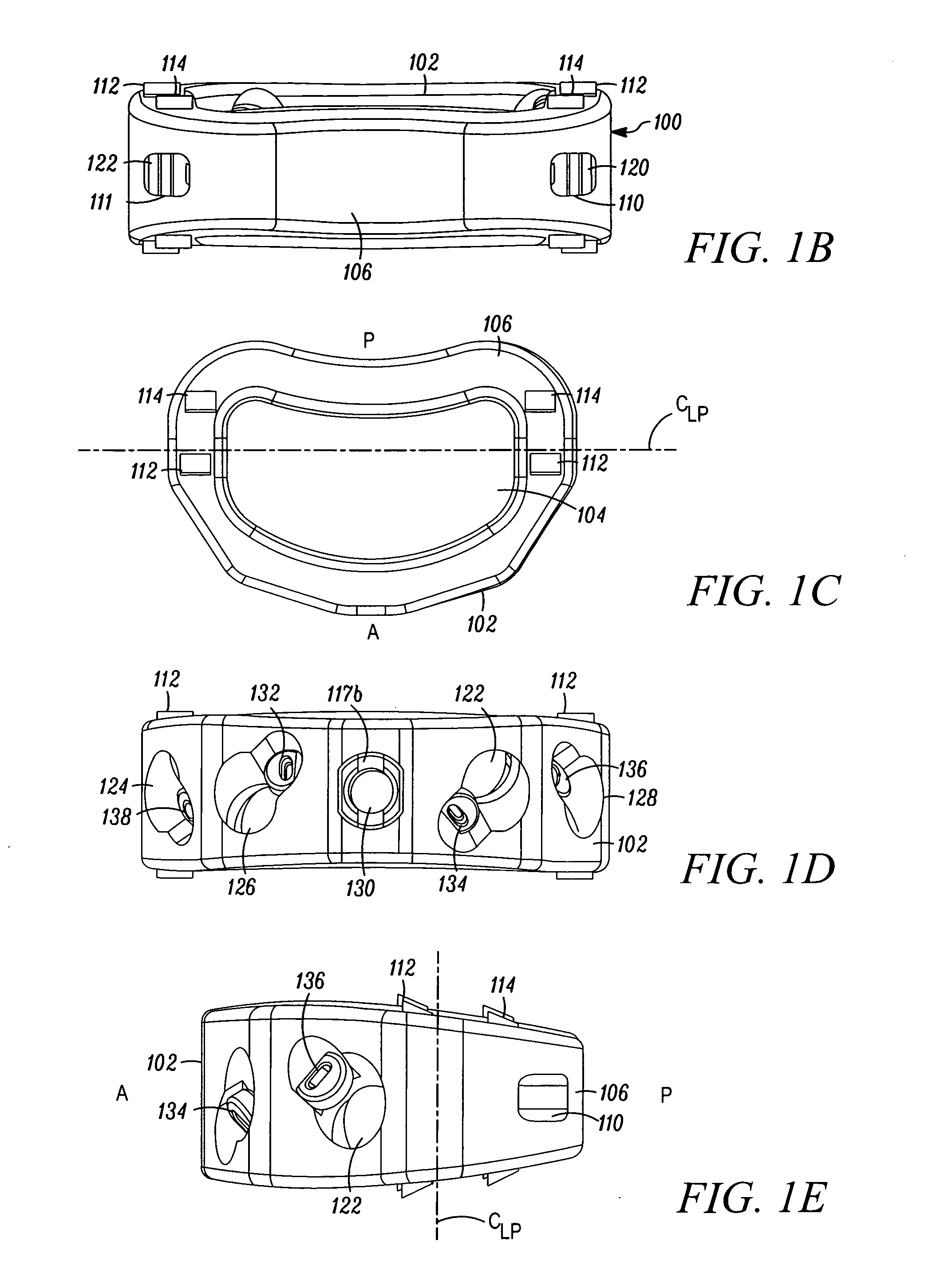
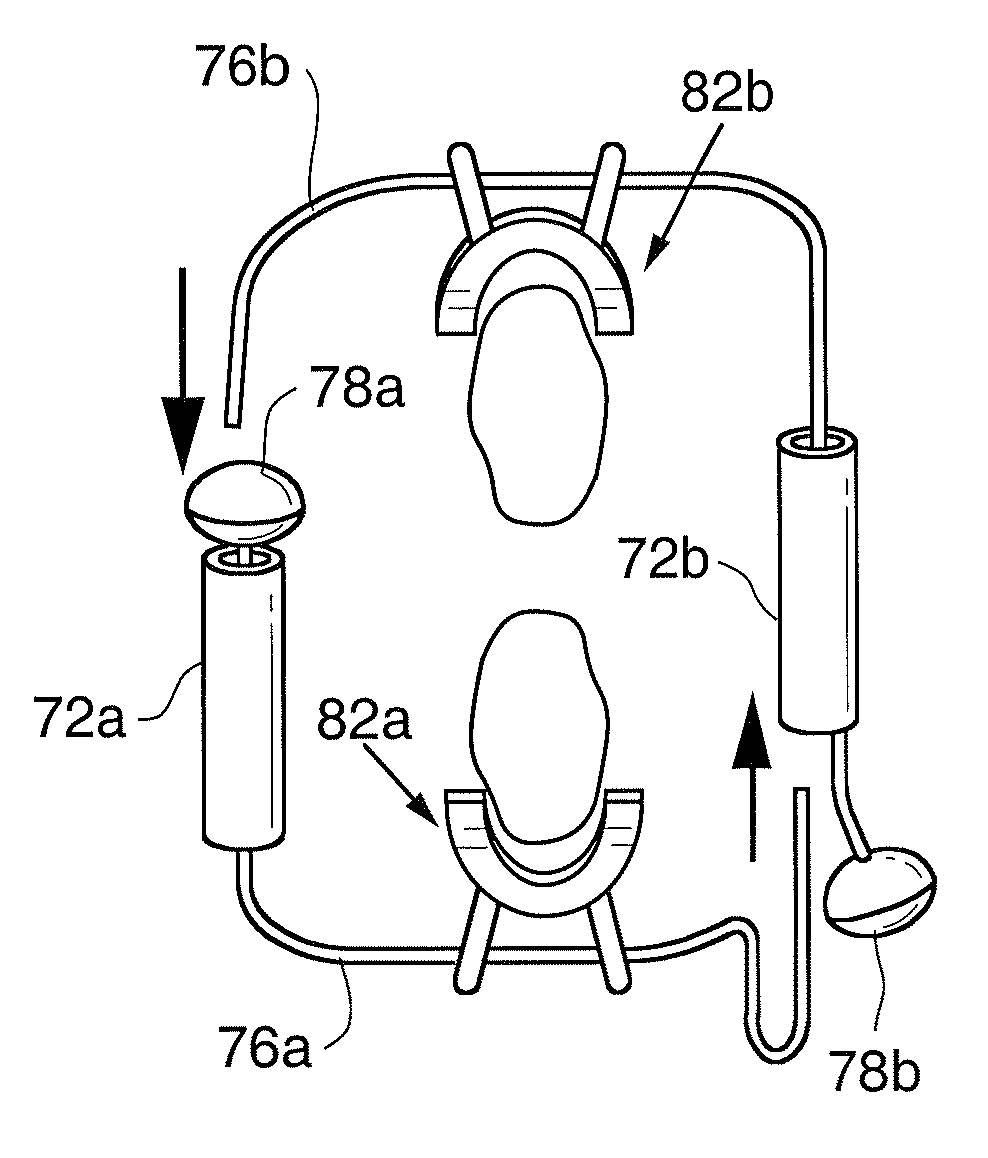
Spinal implant and method for restricting spinal flexion
A spinal implant system for restricting flexion of a spine includes an elongate band proportioned to engage at least two spinous processes. During use, the band is positioned engaging the spinous processes at a spinal segment of interest, where it restricts flexion at the segment. The length and tension of the band may be adjustable following to implantation using percutaneous or transcutaneous means.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
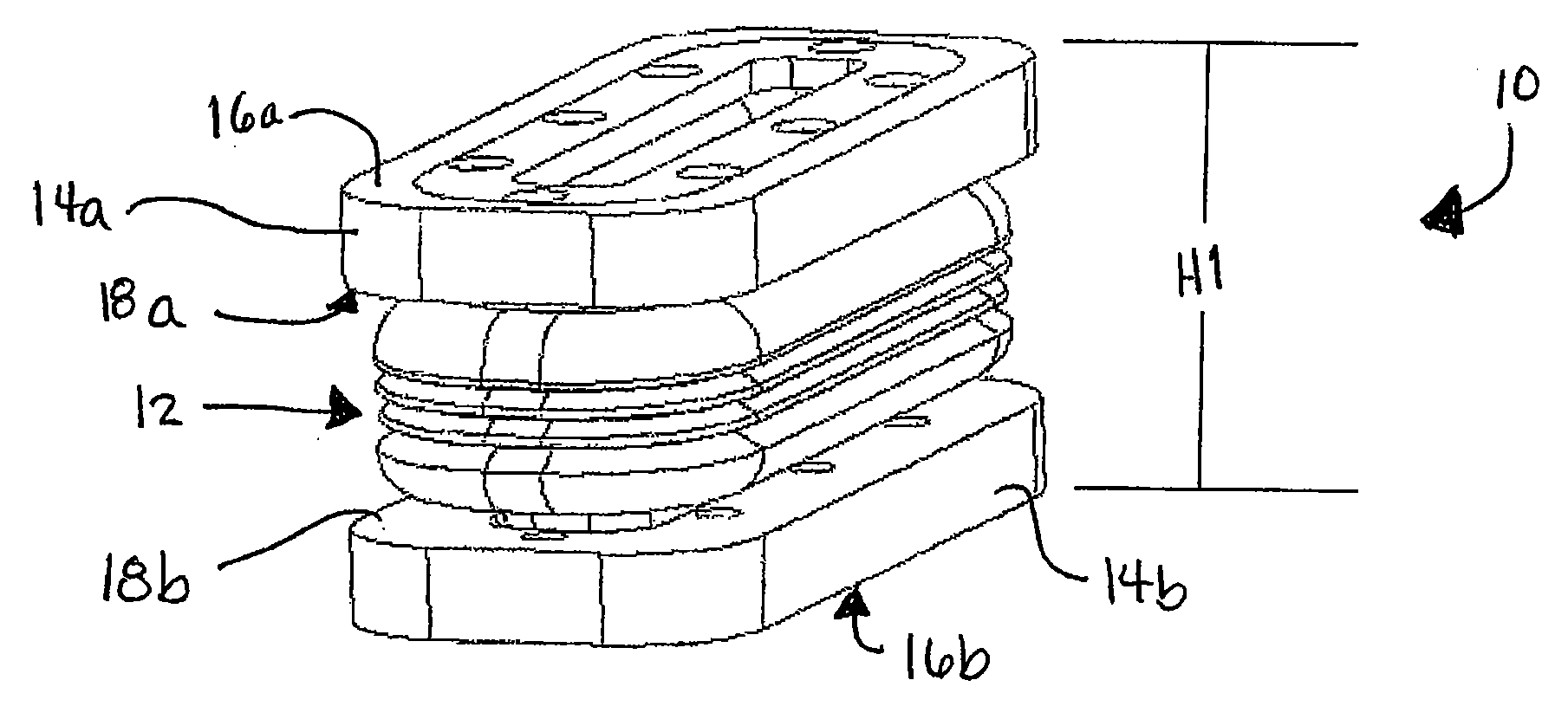
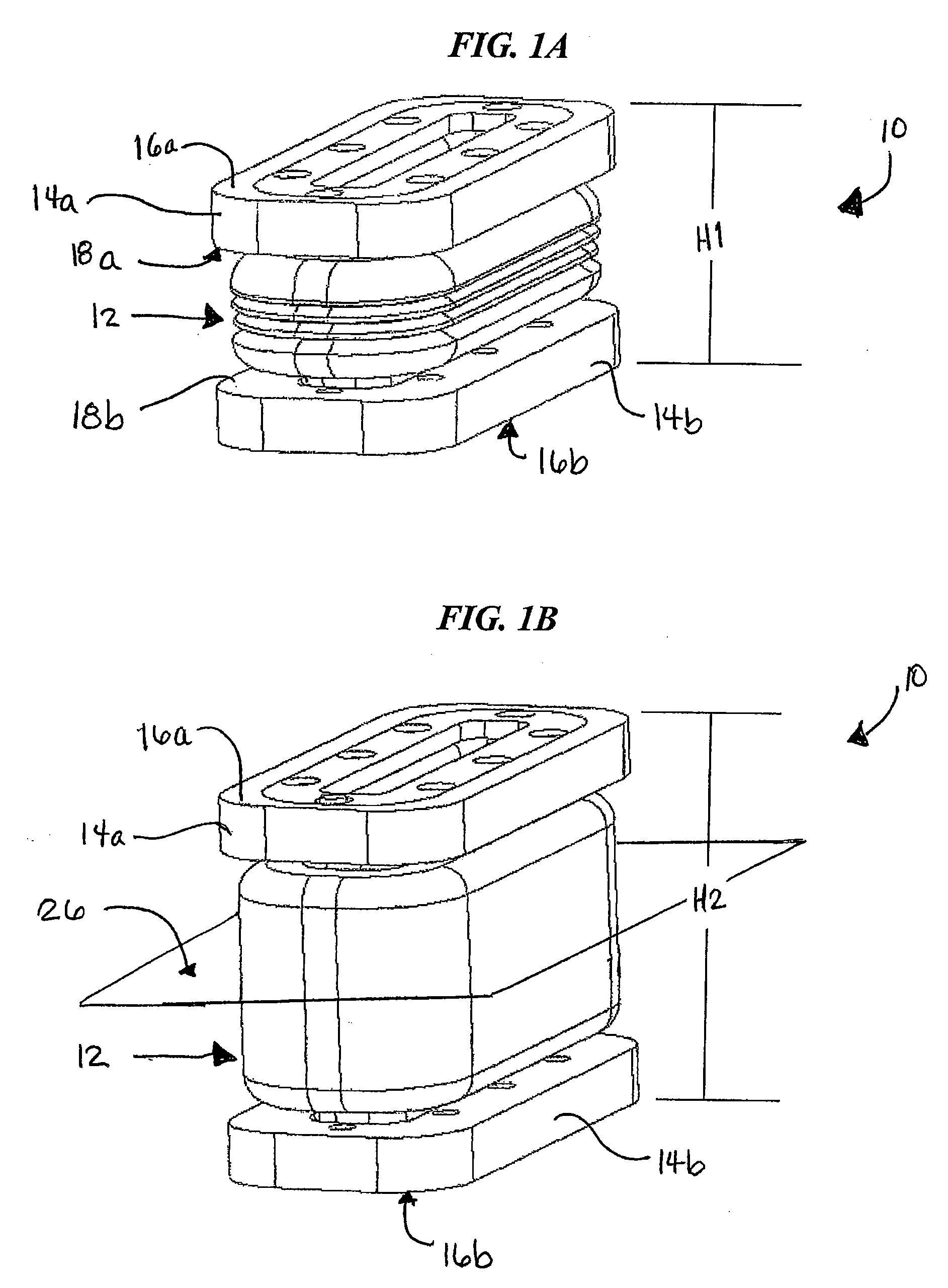
Allograft spinal implant
InactiveUS7018412B2Enhancing fusion of boneImprove fusionInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal implantBiomedical engineering
An allograft spinal implant includes a generally planar superior end face, a generally planar inferior end face and a generally cylindrical sidewall. The generally cylindrical sidewall extends between the superior end face and the inferior end face. At least one of the superior end face and the inferior end face includes a plurality of concentric circular ridges.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com