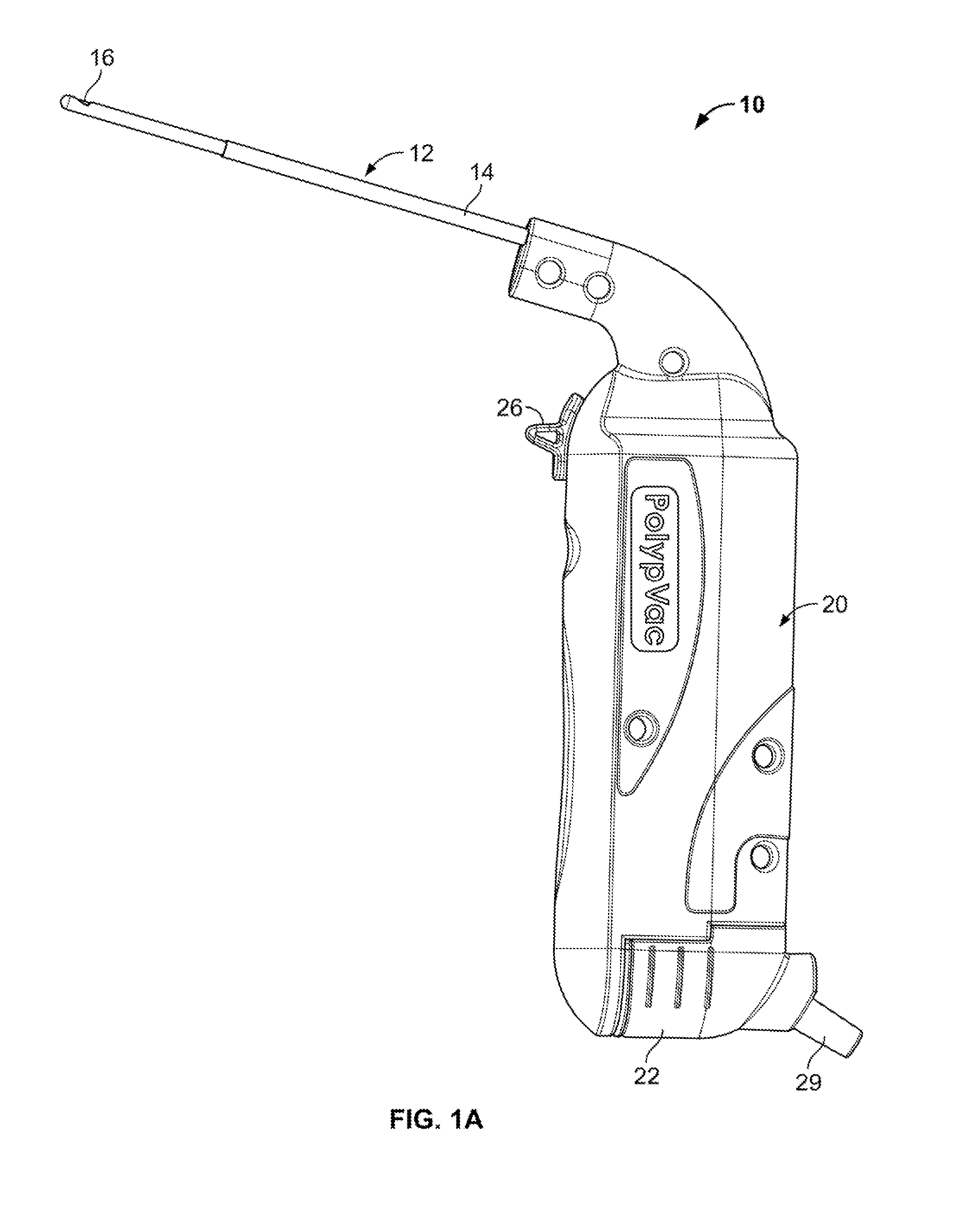
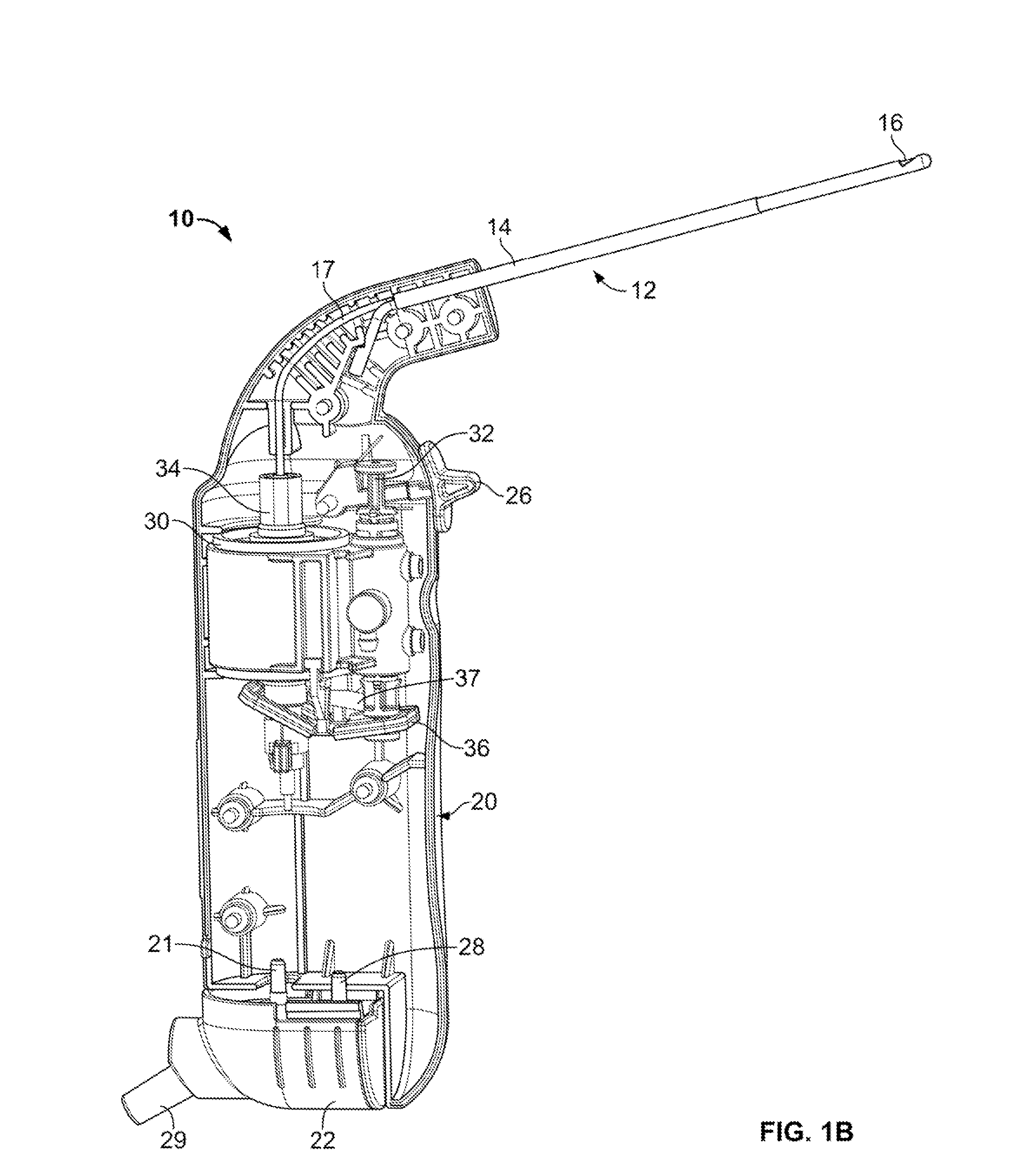
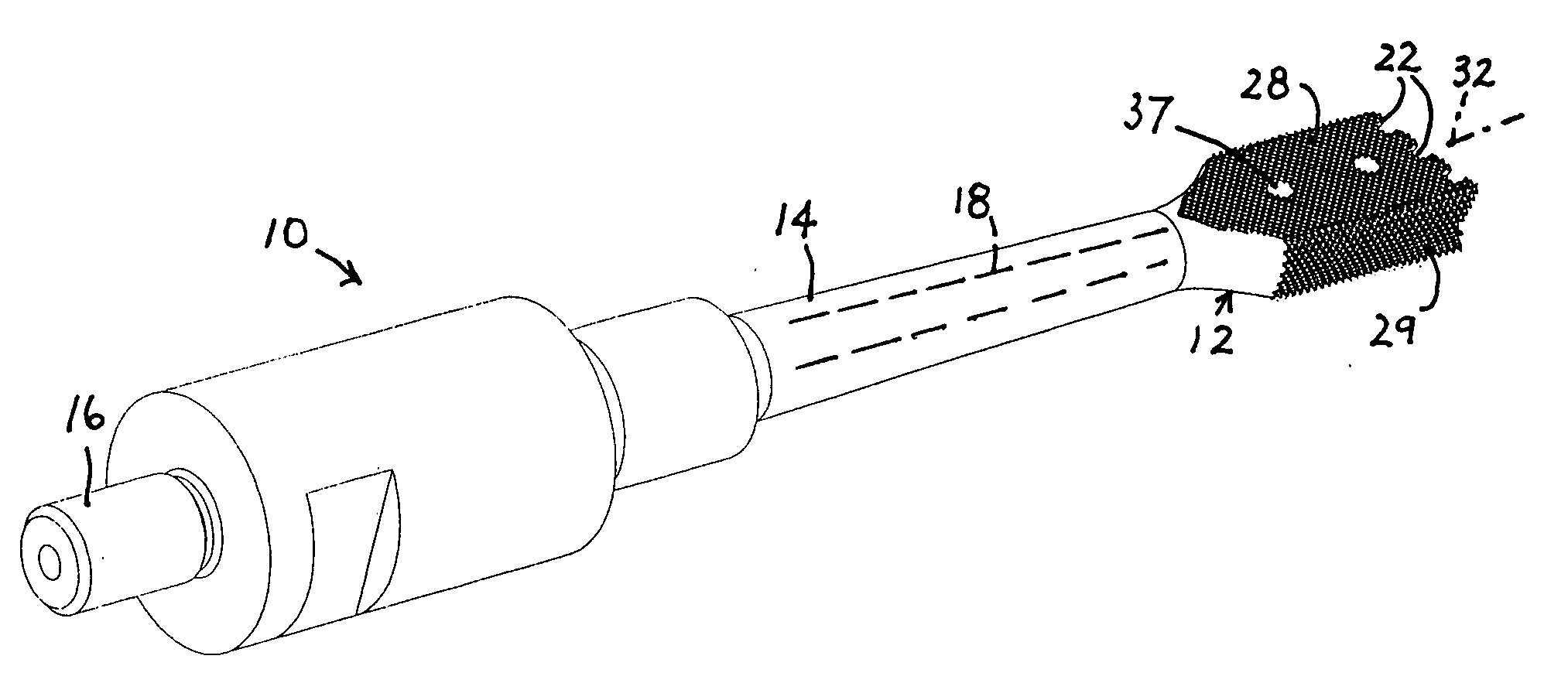
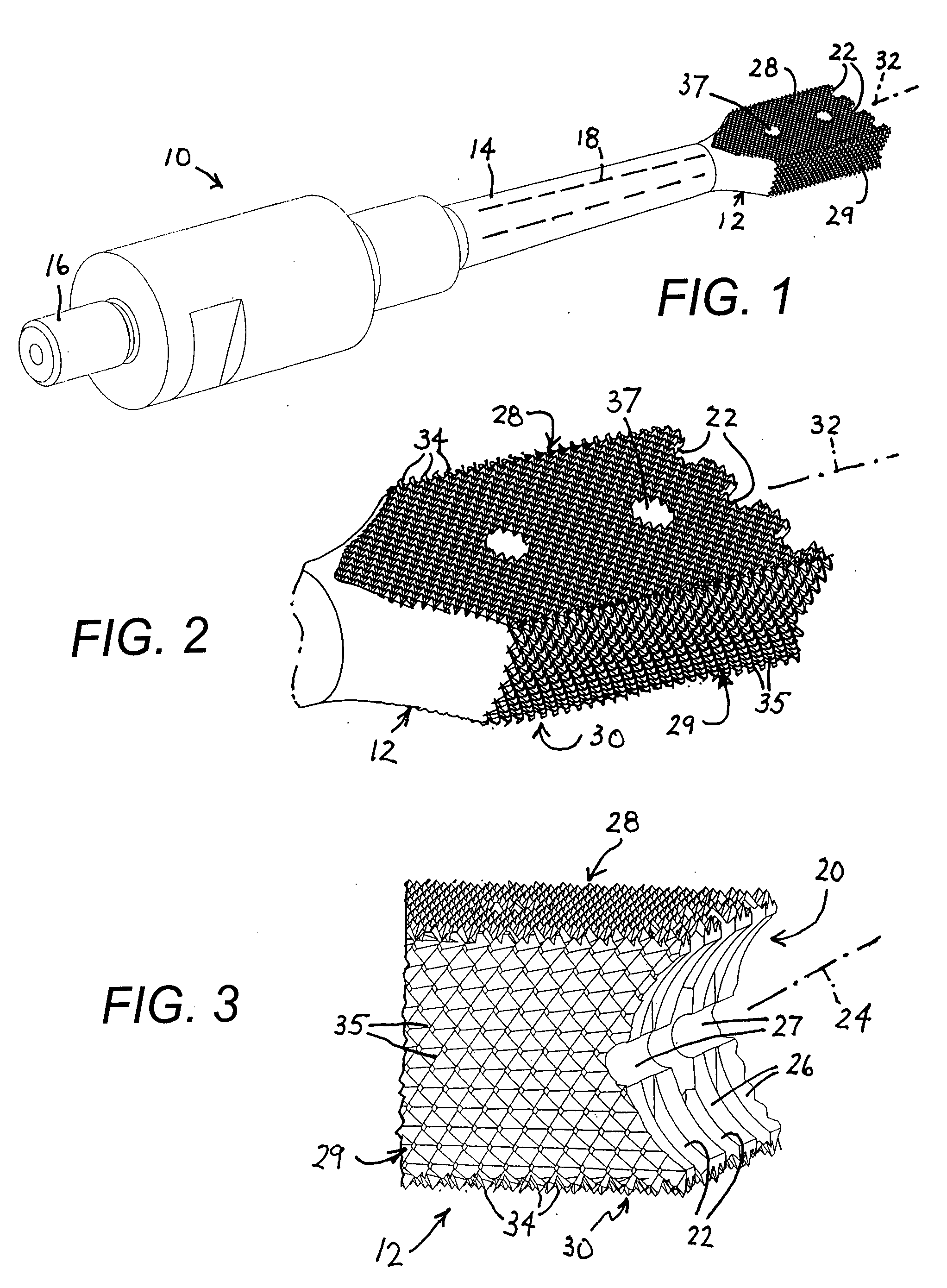
Patents
Literature
101 results about "Discectomy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
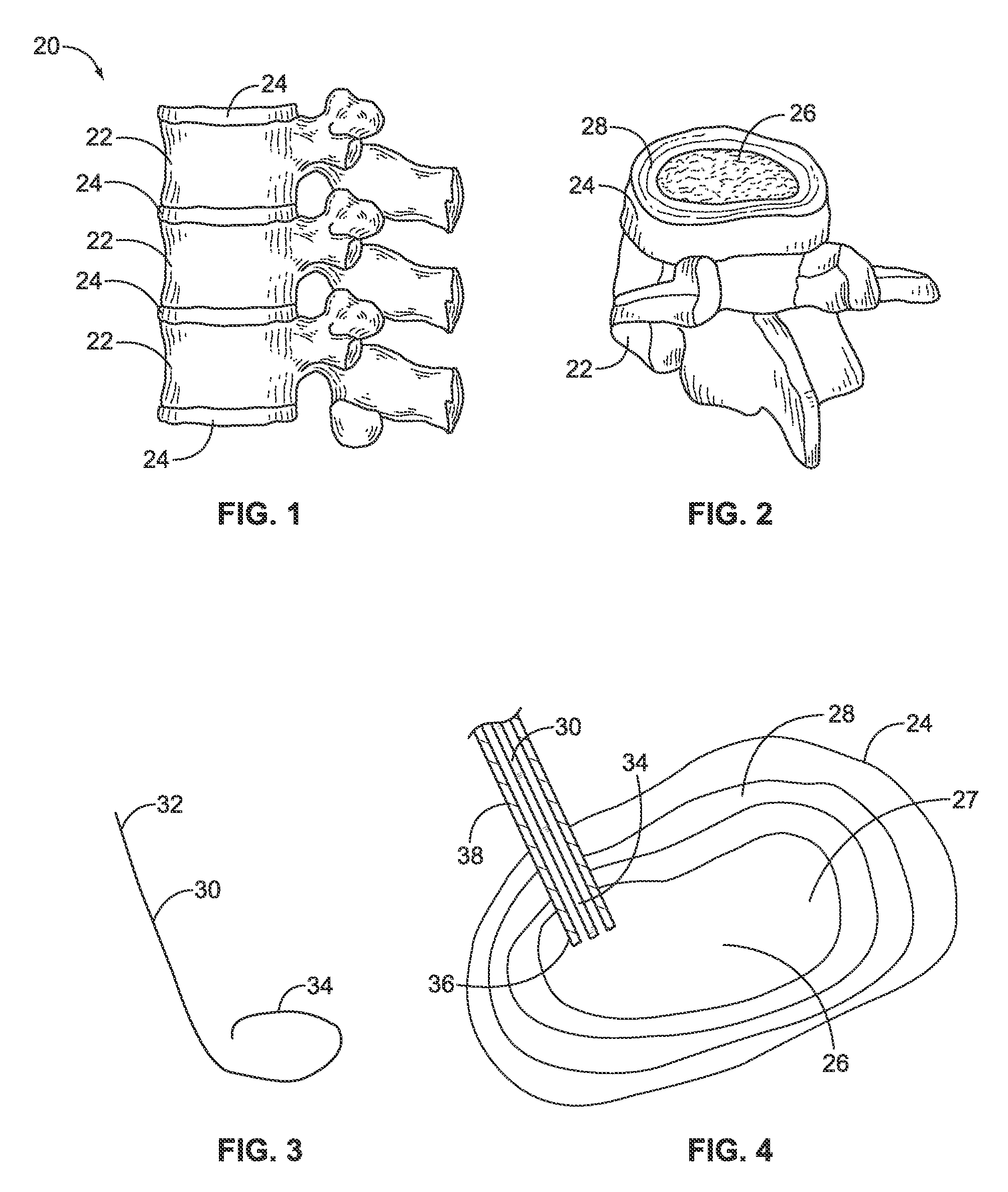
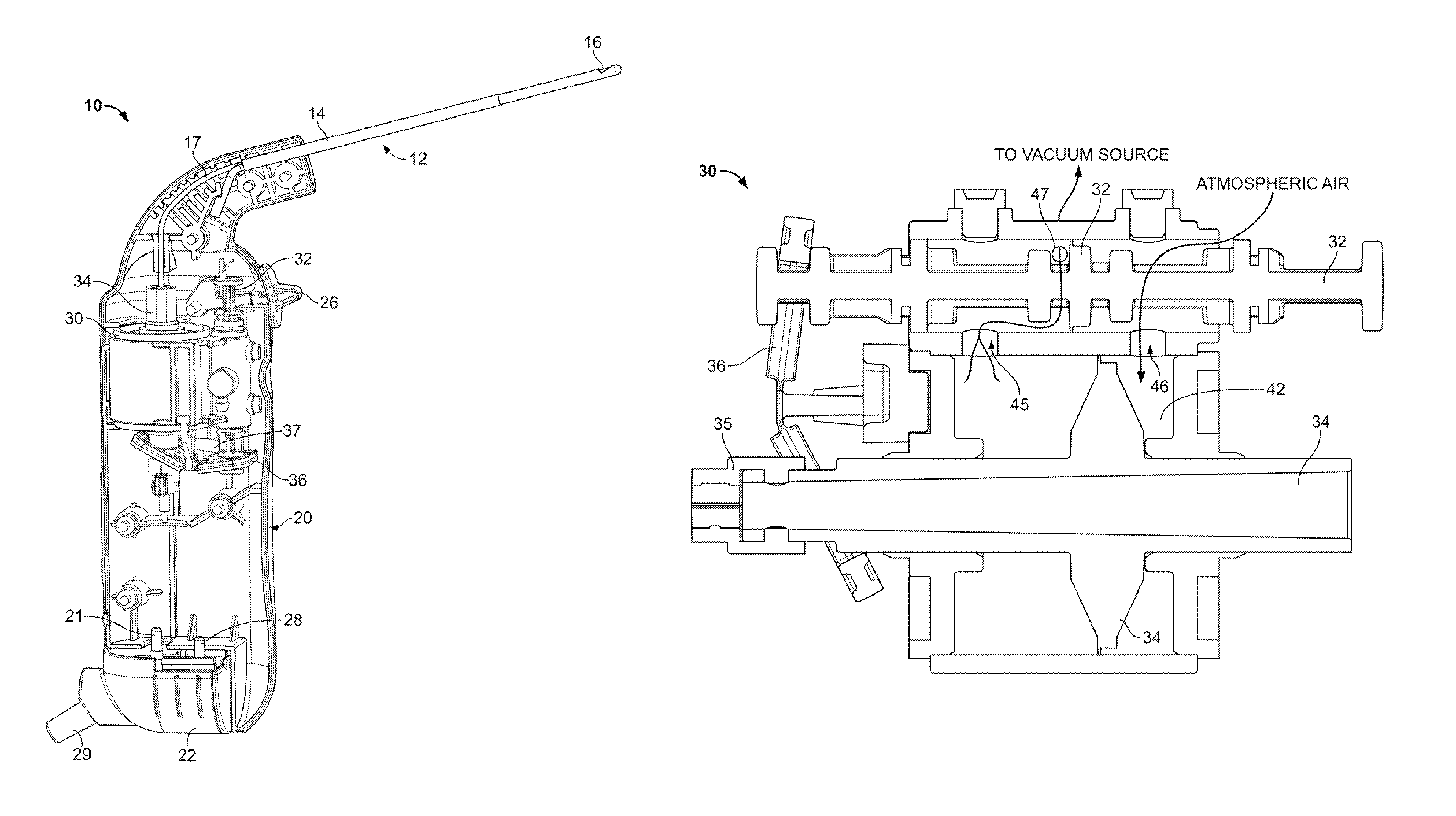
A discectomy (also called open discectomy, if done through a 1/2 inch or larger skin opening) is the surgical removal of abnormal disc material that presses on a nerve root or the spinal cord. The procedure involves removing a portion of an intervertebral disc, which causes pain, weakness or numbness by stressing the spinal cord or radiating nerves. The traditional open discectomy, or Love's technique, was published by Ross and Love in 1971. Advances have produced visualization improvements to traditional discectomy procedures (e.g. microdiscectomy, an open discectomy using an external microscope typically done through a 1 inch or larger skin opening), or endoscopic discectomy (the scope passes internally and typically done through a 2 mm skin opening or larger, up to 12 mm). In conjunction with the traditional discectomy or microdiscectomy, a laminotomy is often involved to permit access to the intervertebral disc. Laminotomy means a significant amount of typically normal bone (the lamina) is removed from the vertebra, allowing the surgeon to better see and access the area of disc herniation.
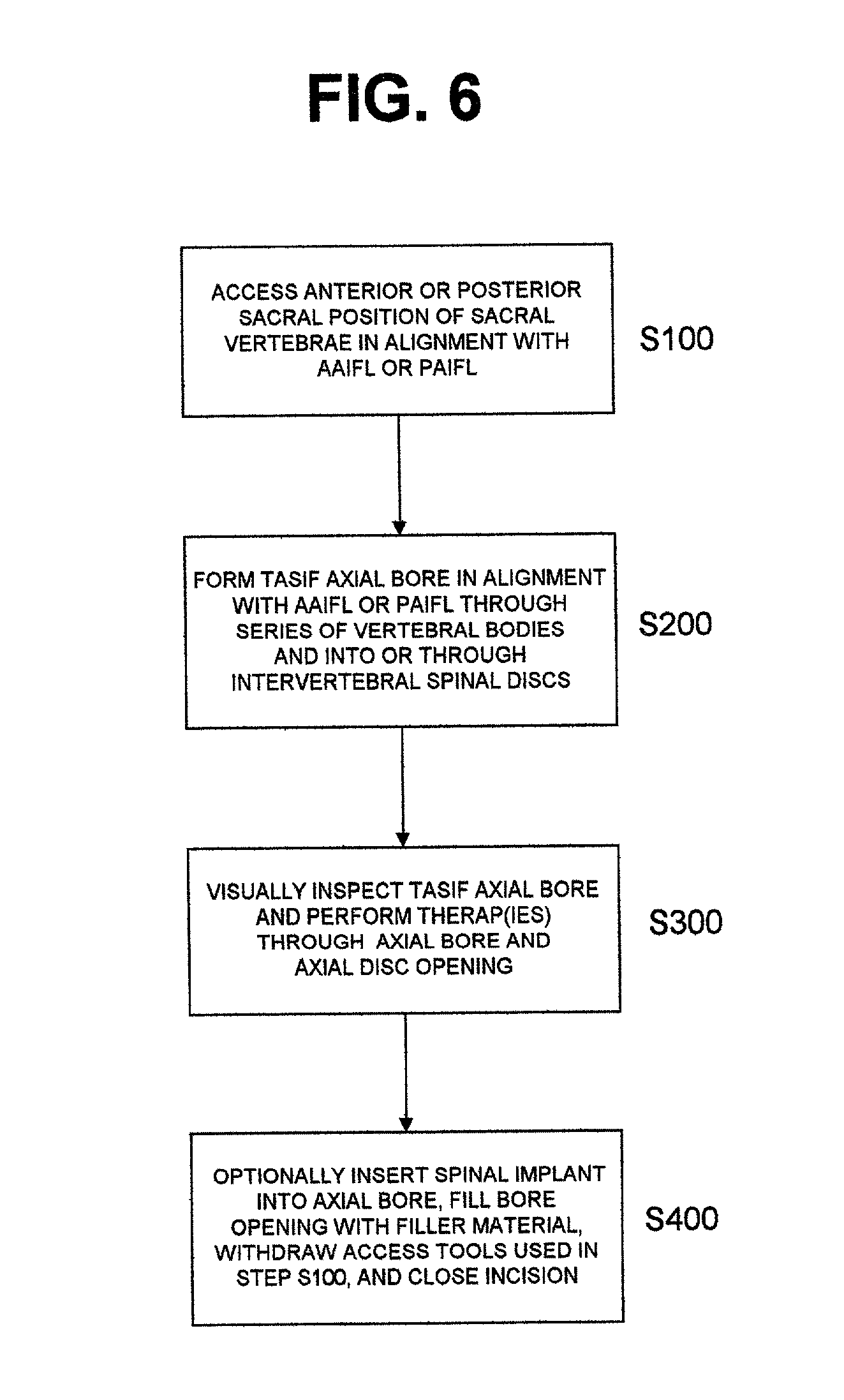
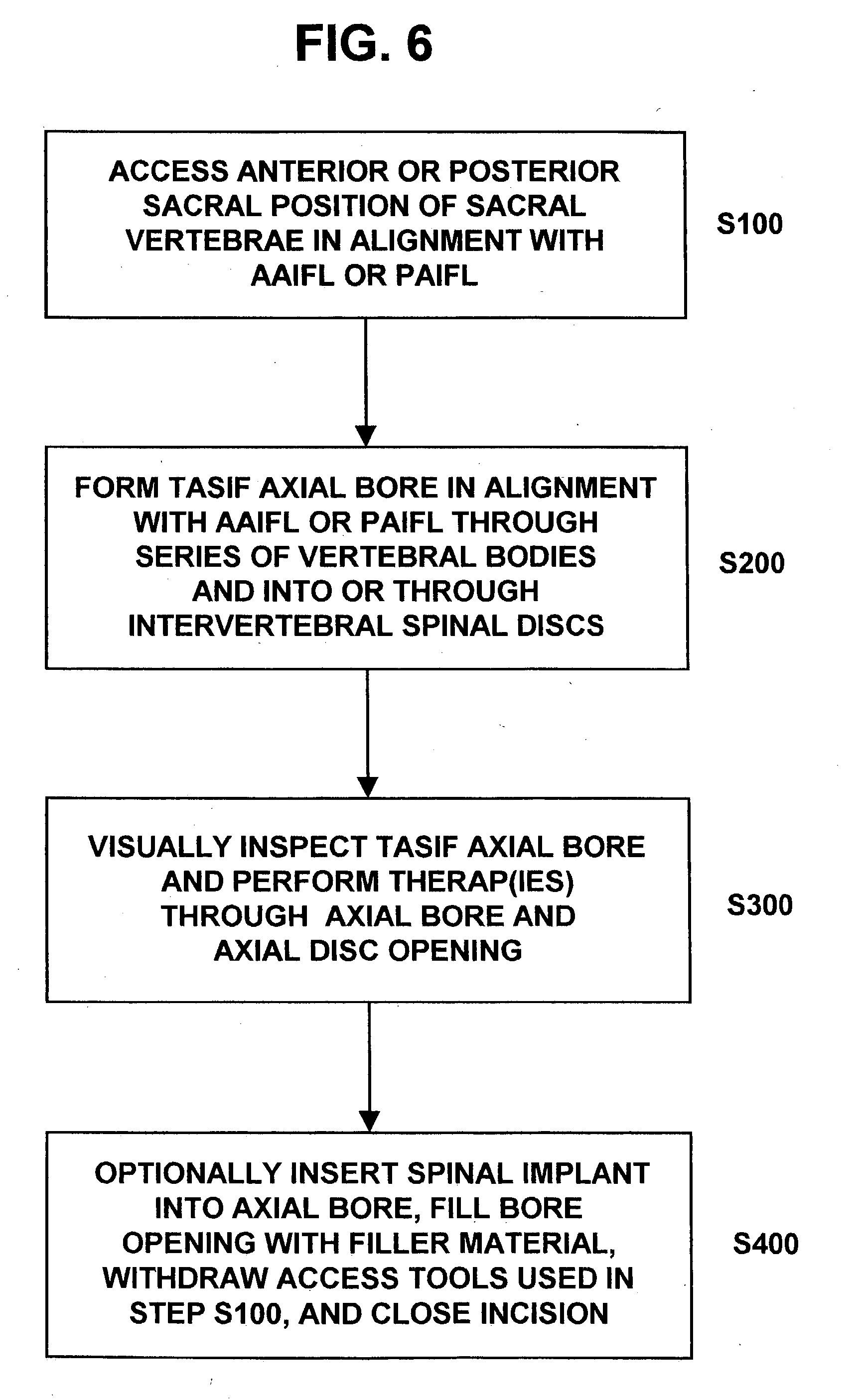
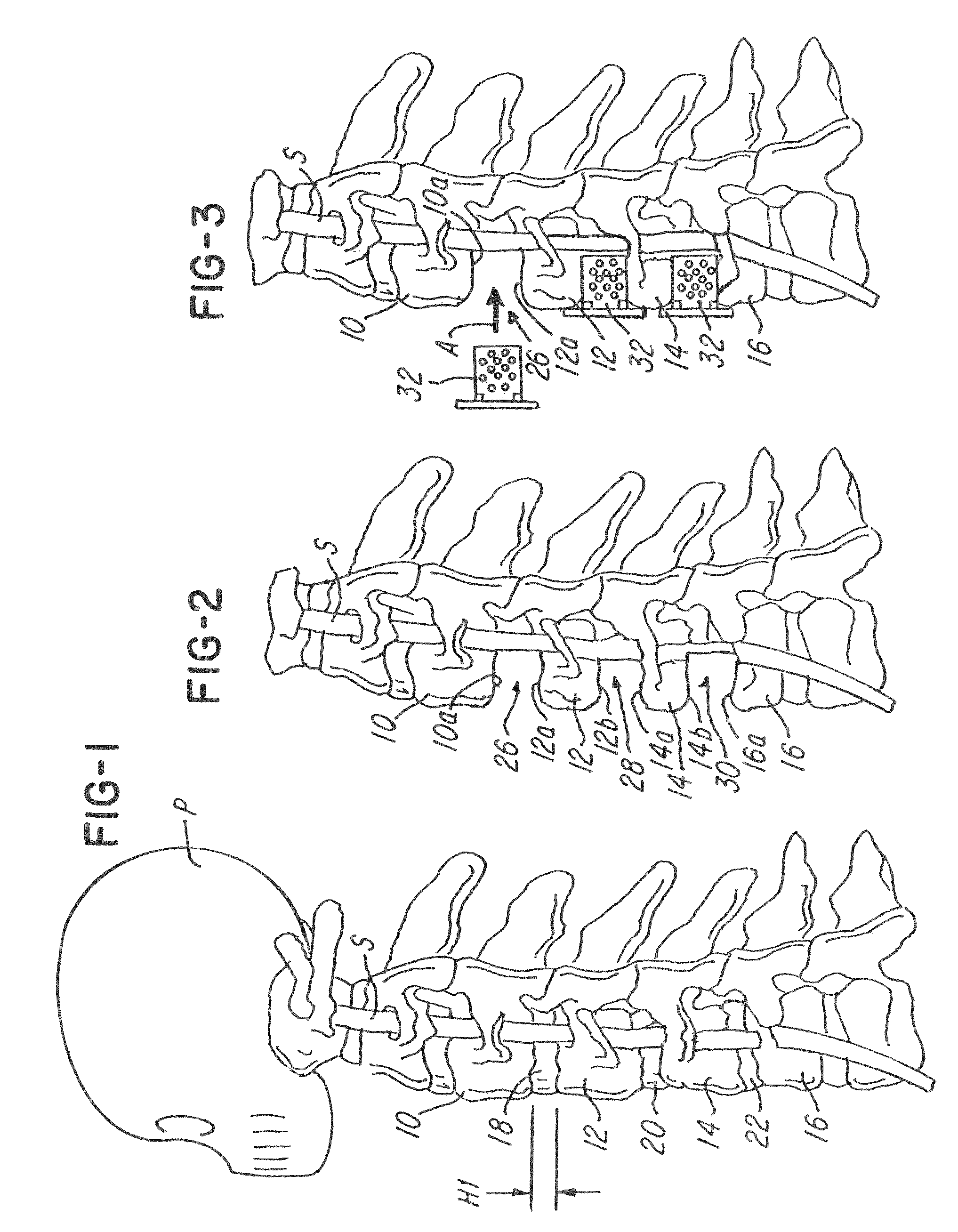
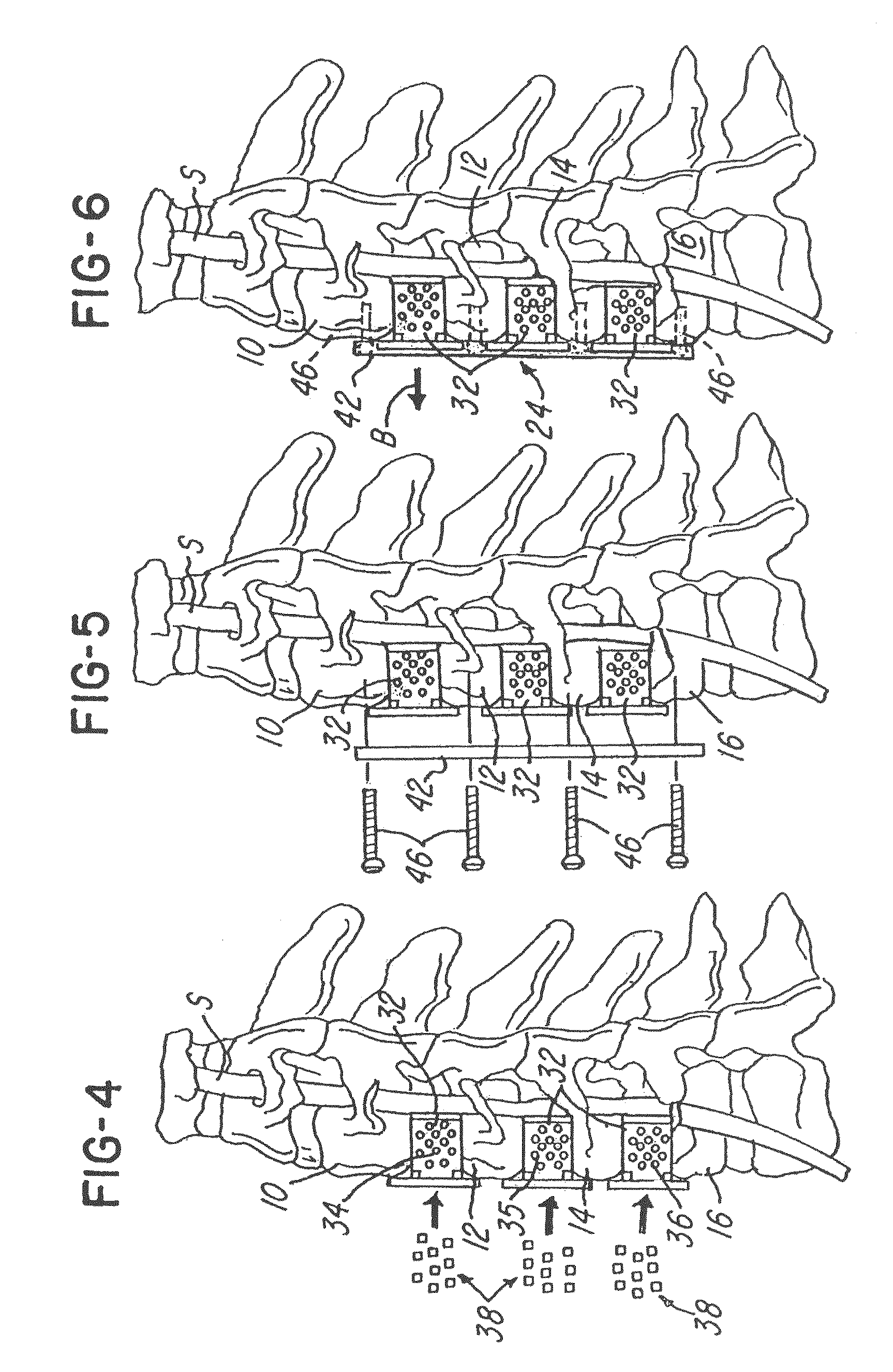
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
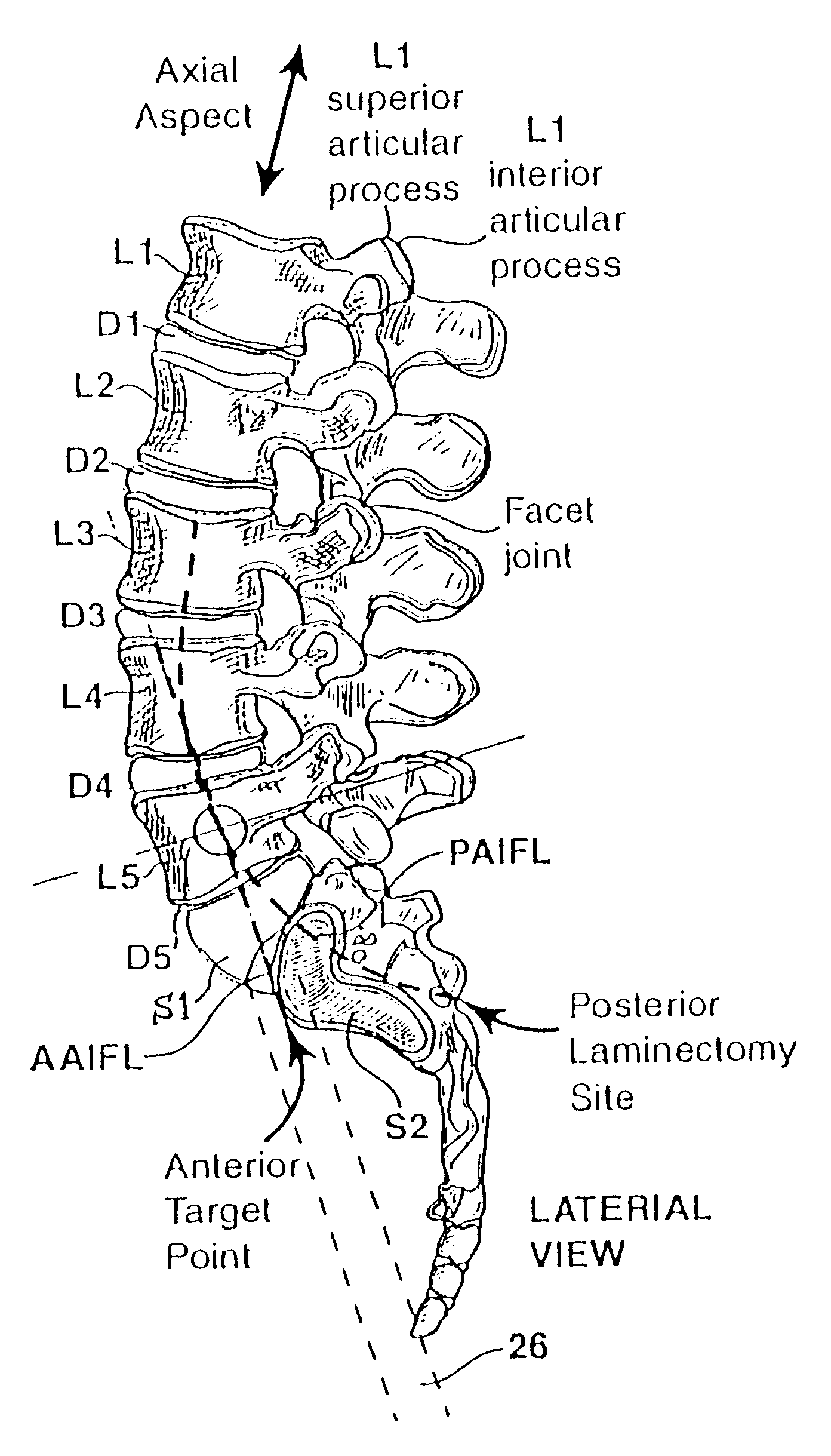
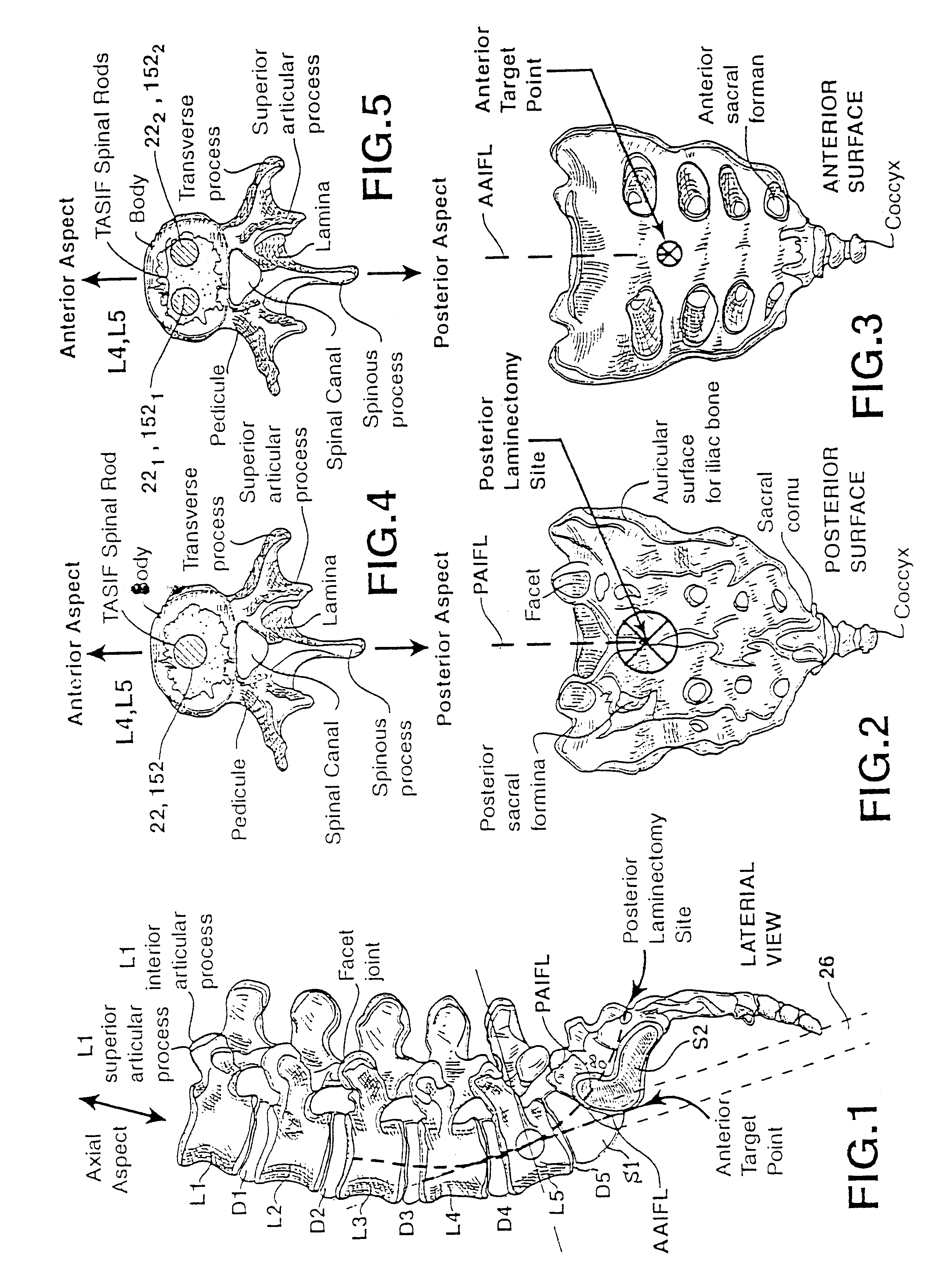
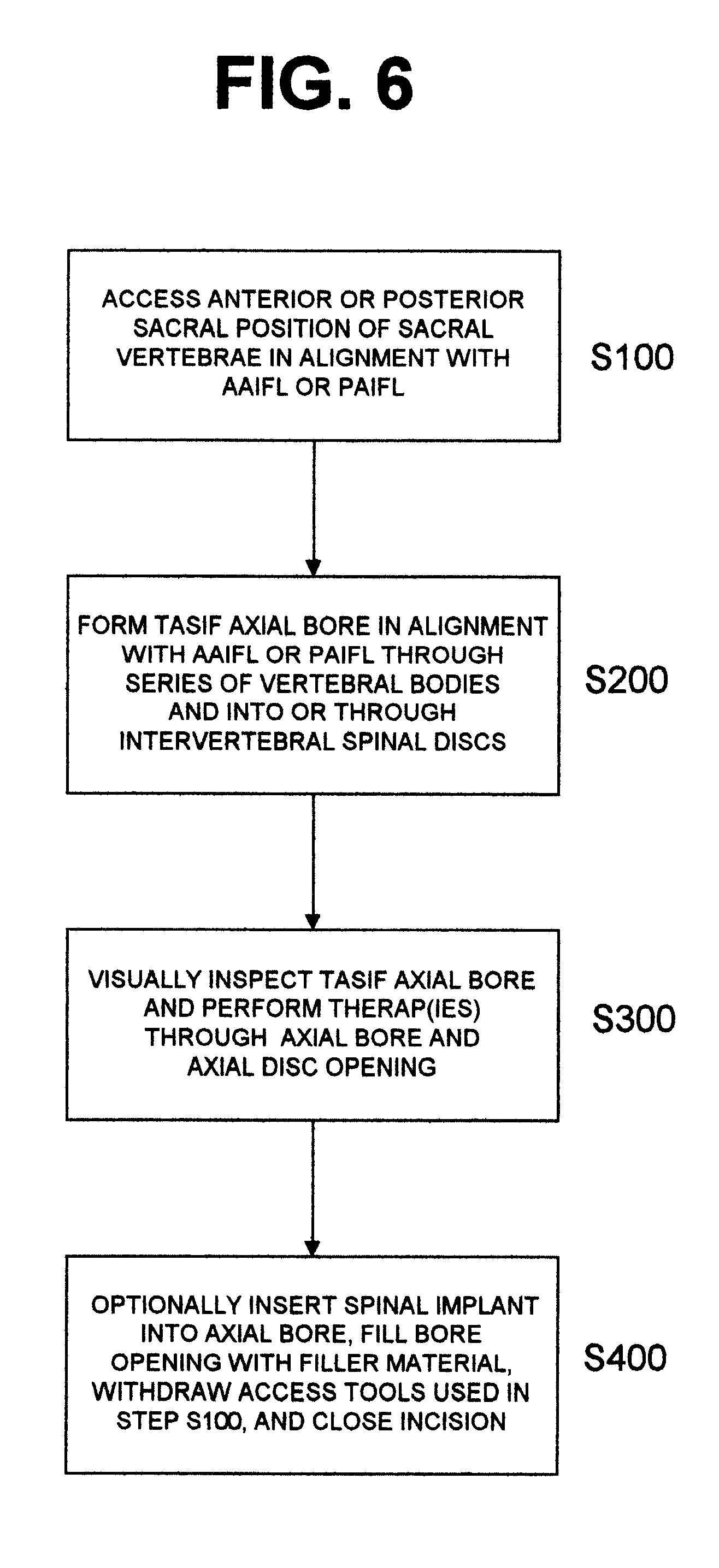
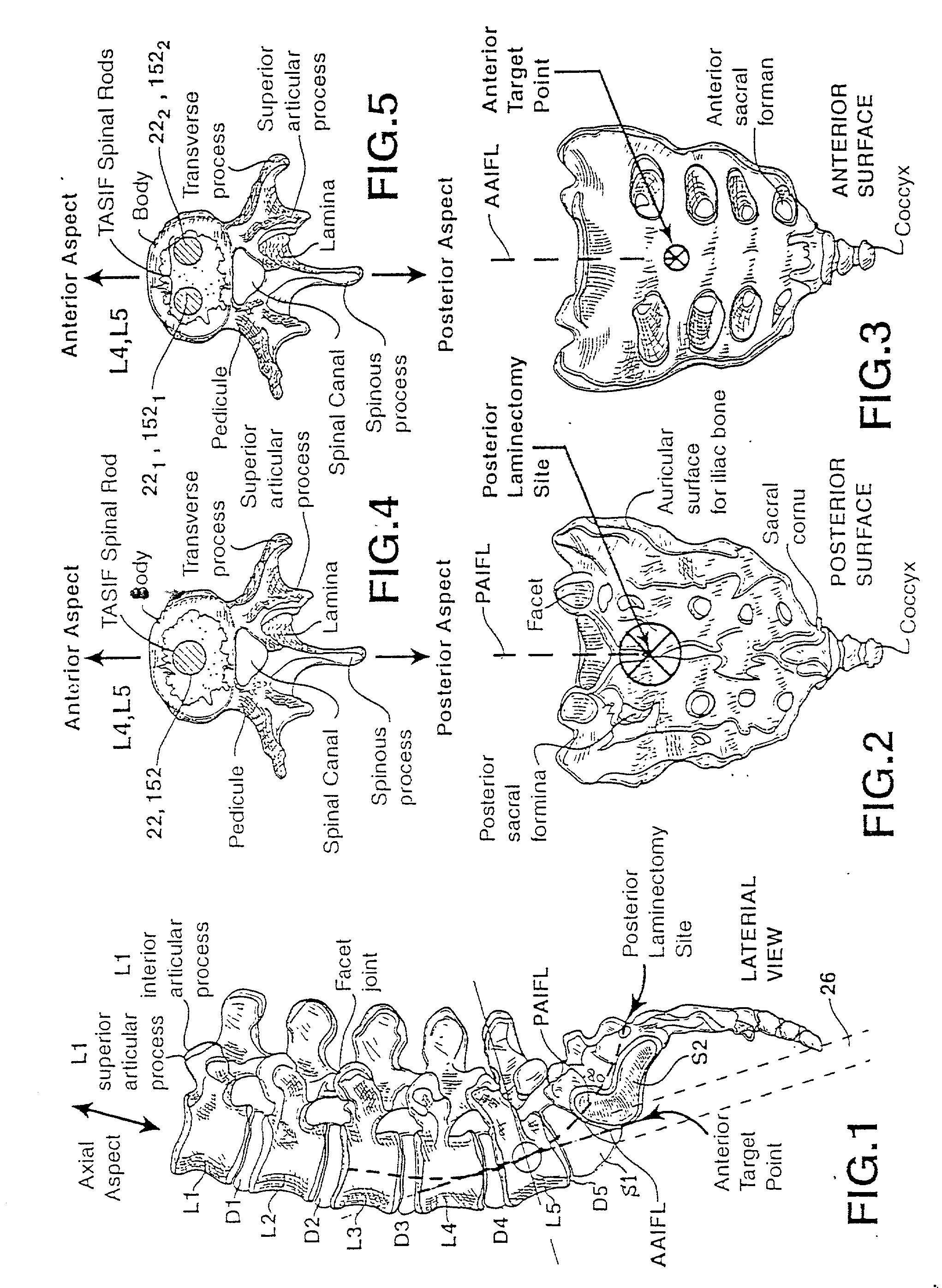
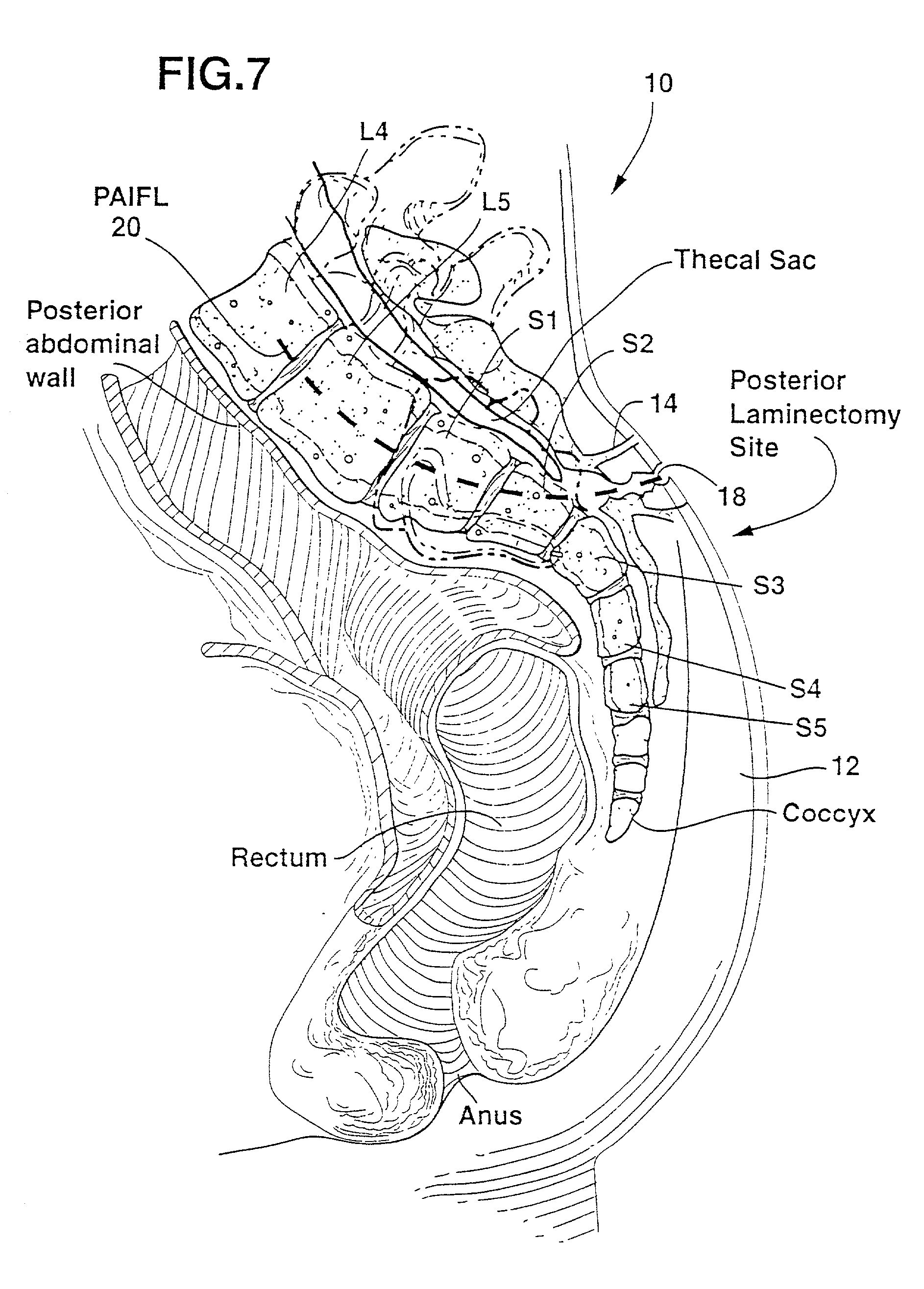
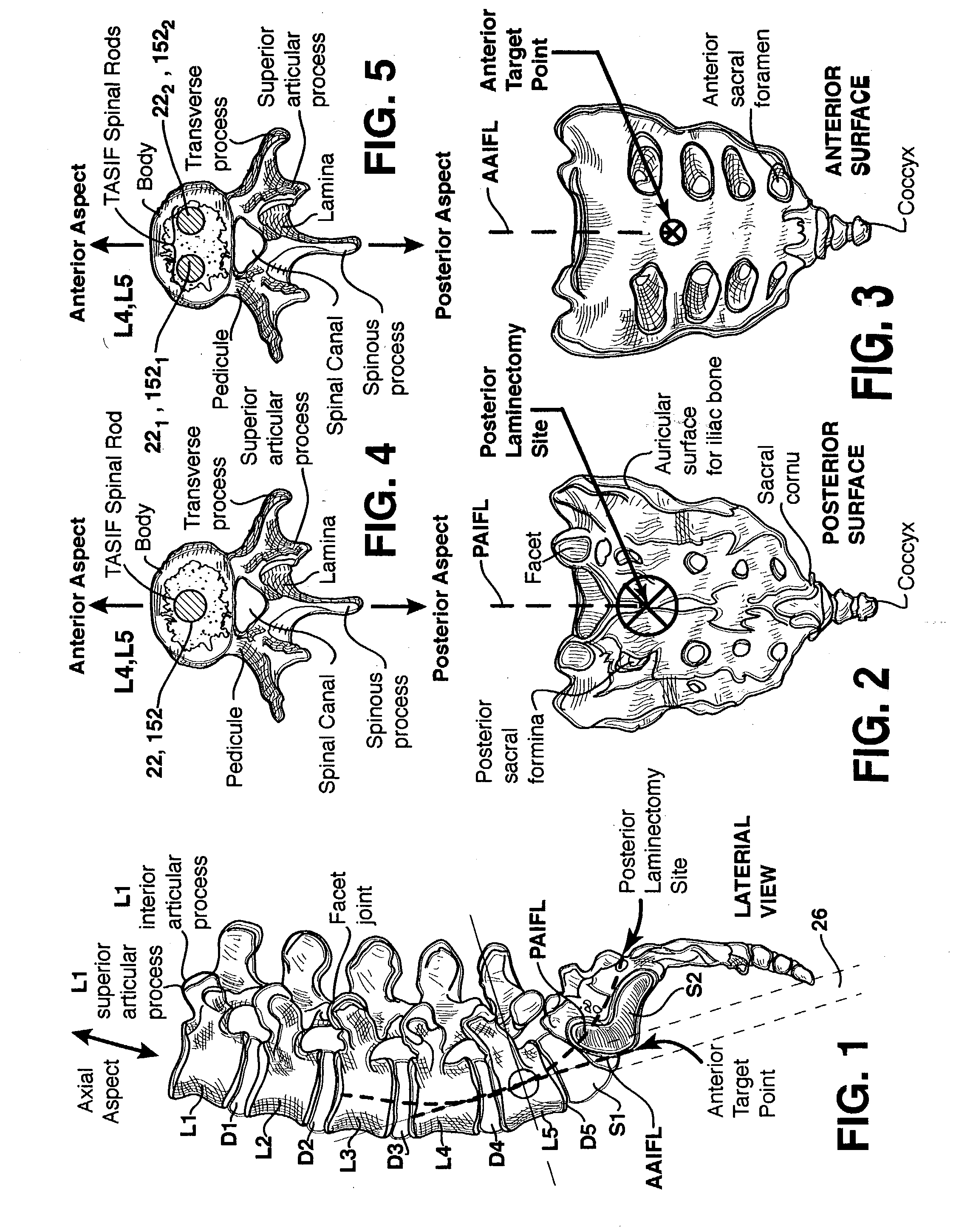
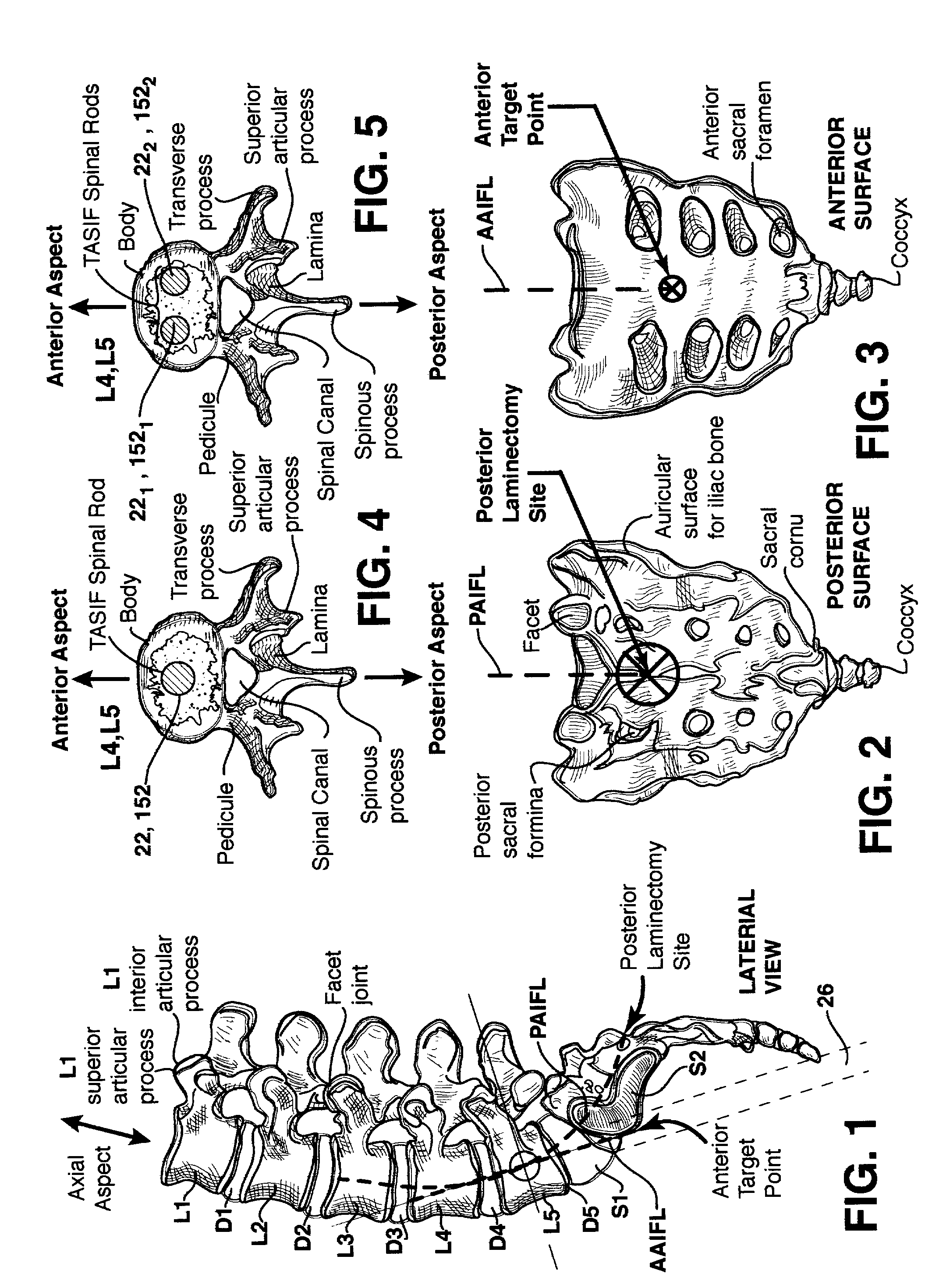
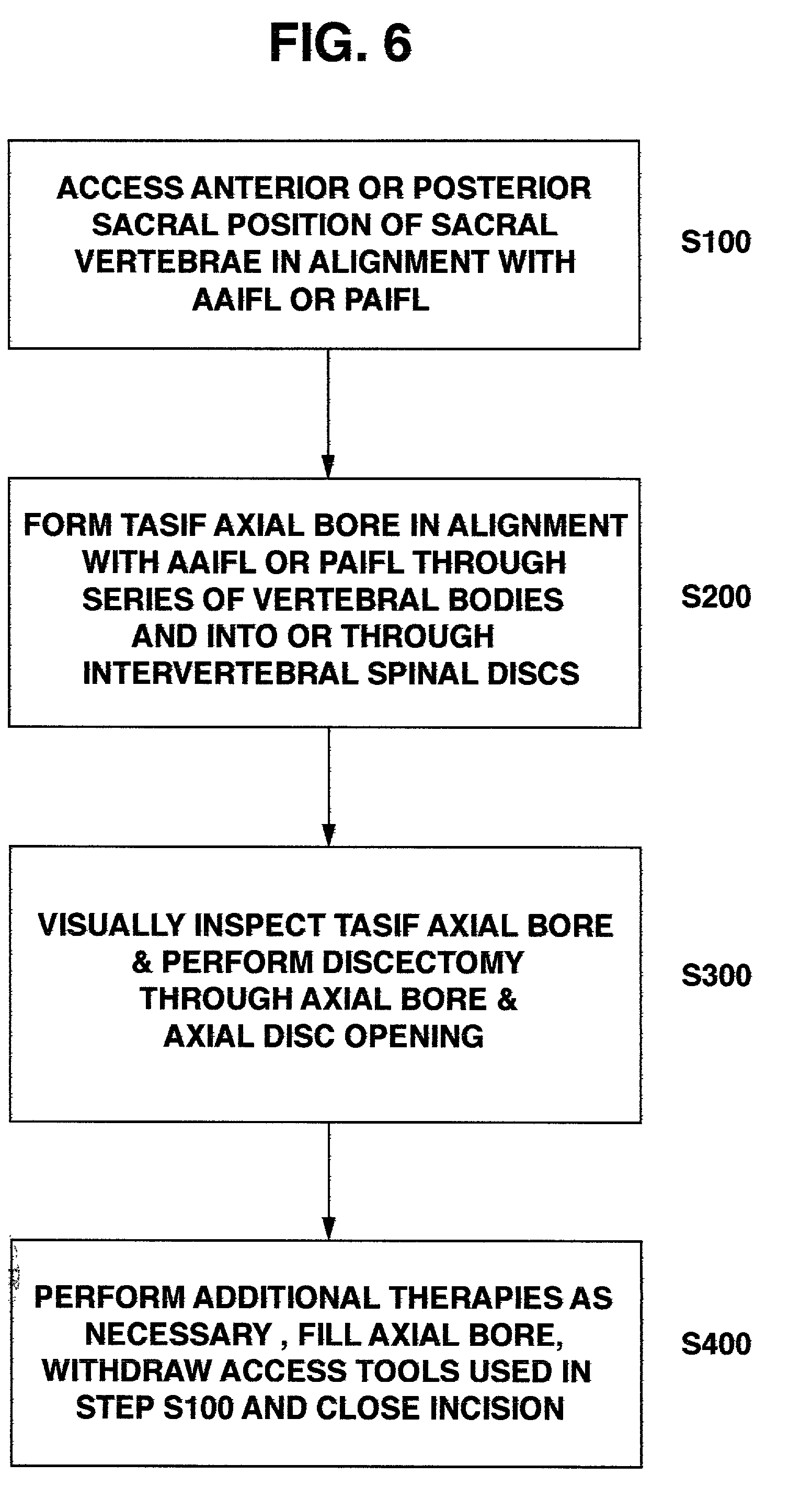
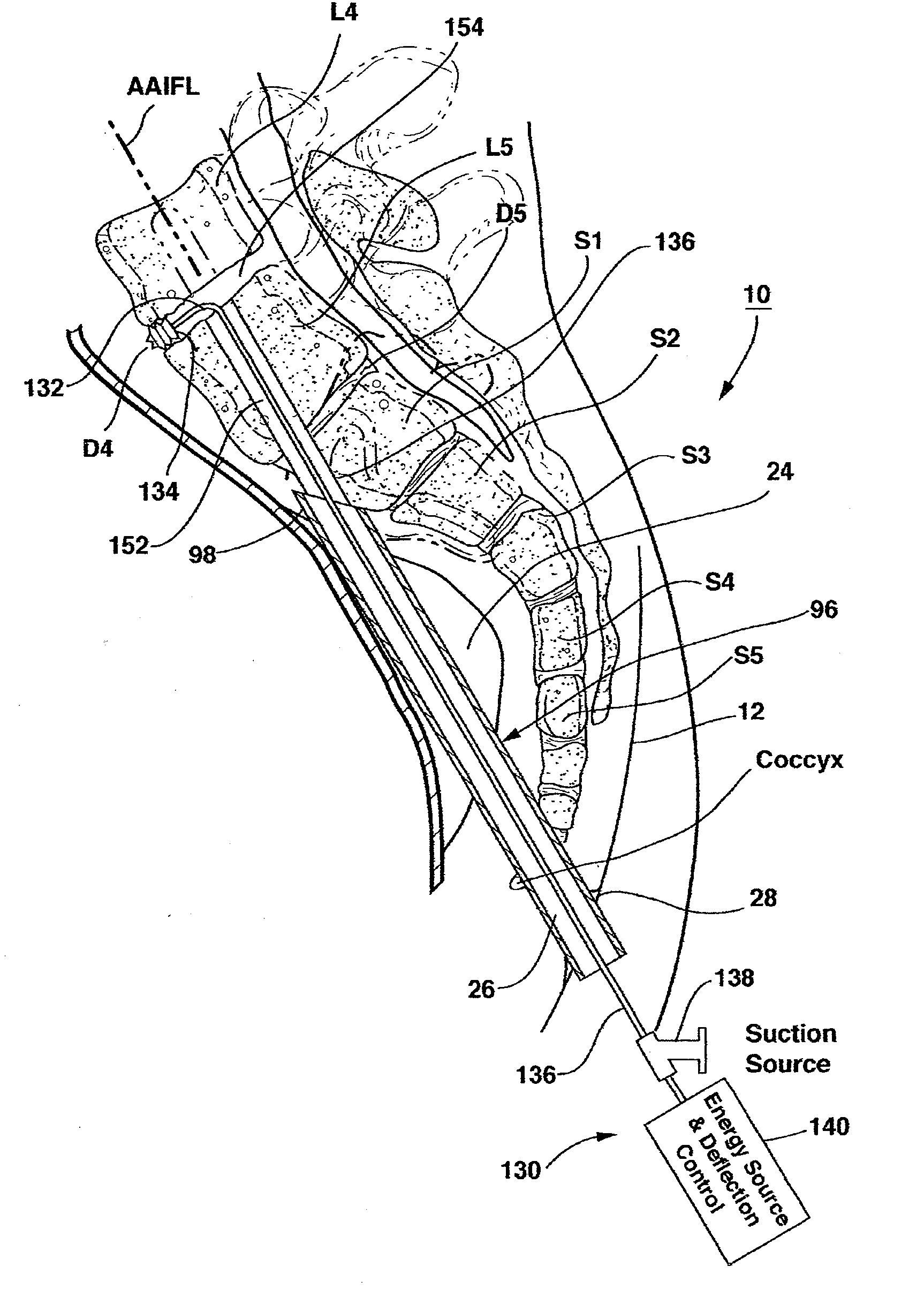
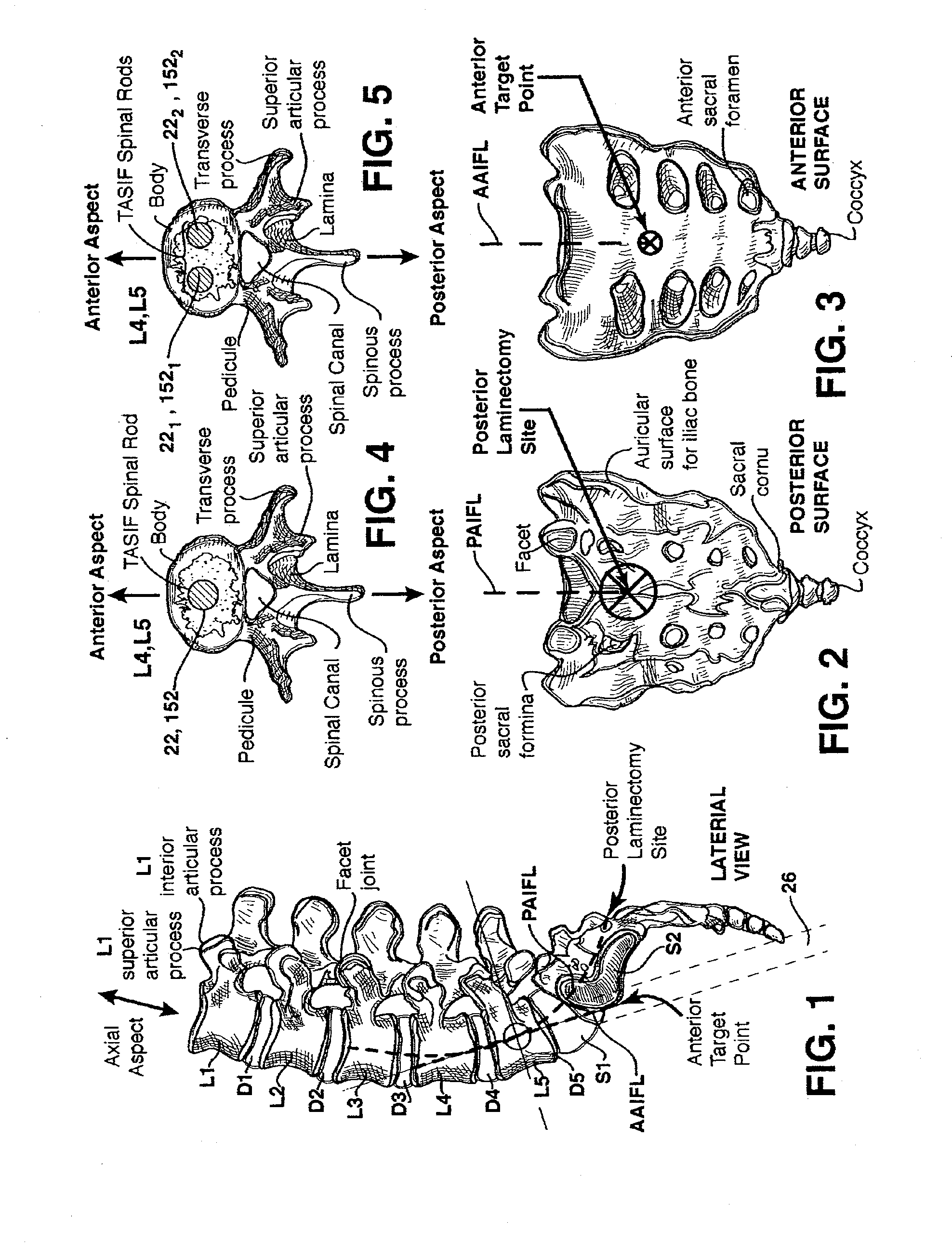
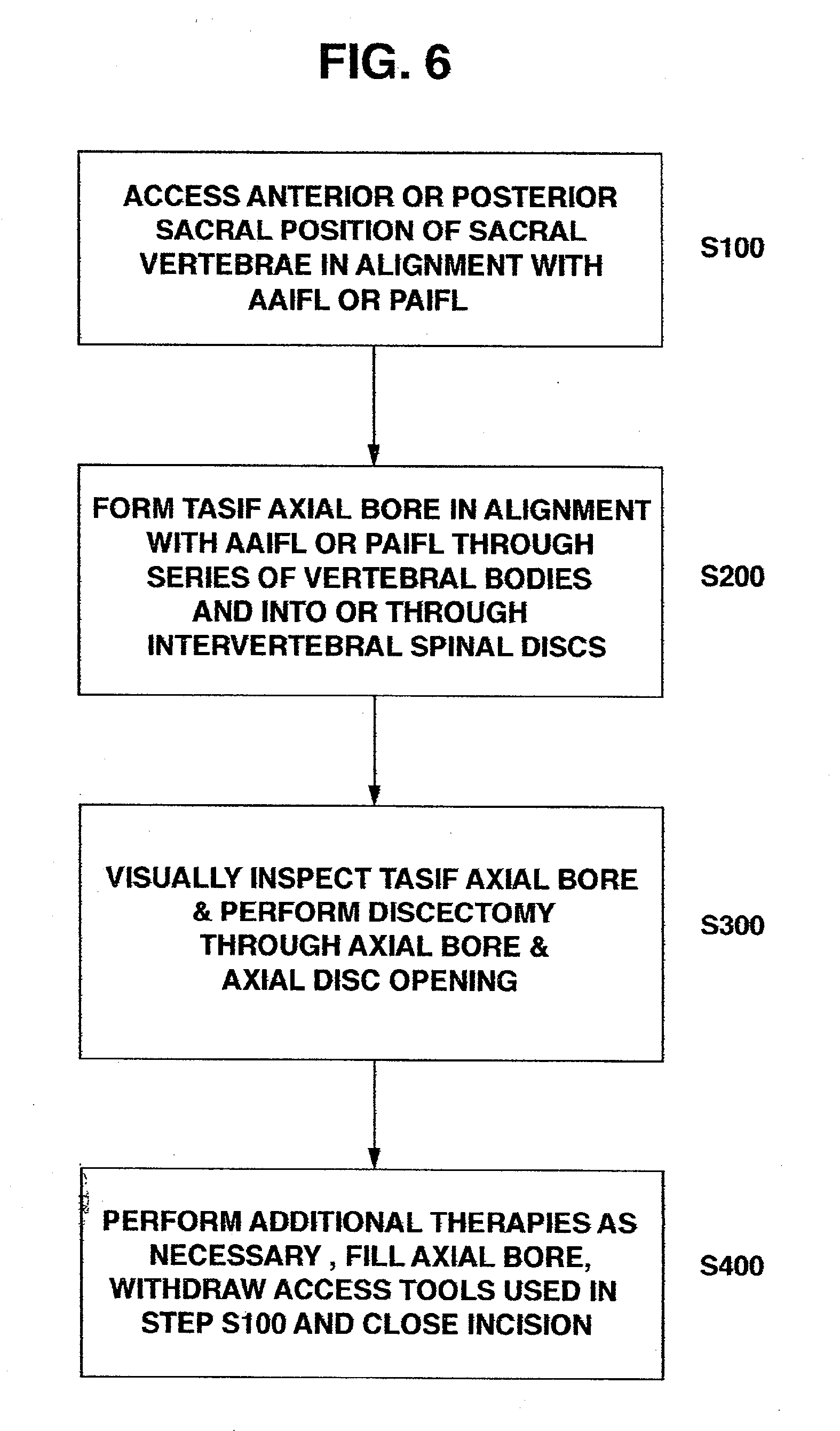
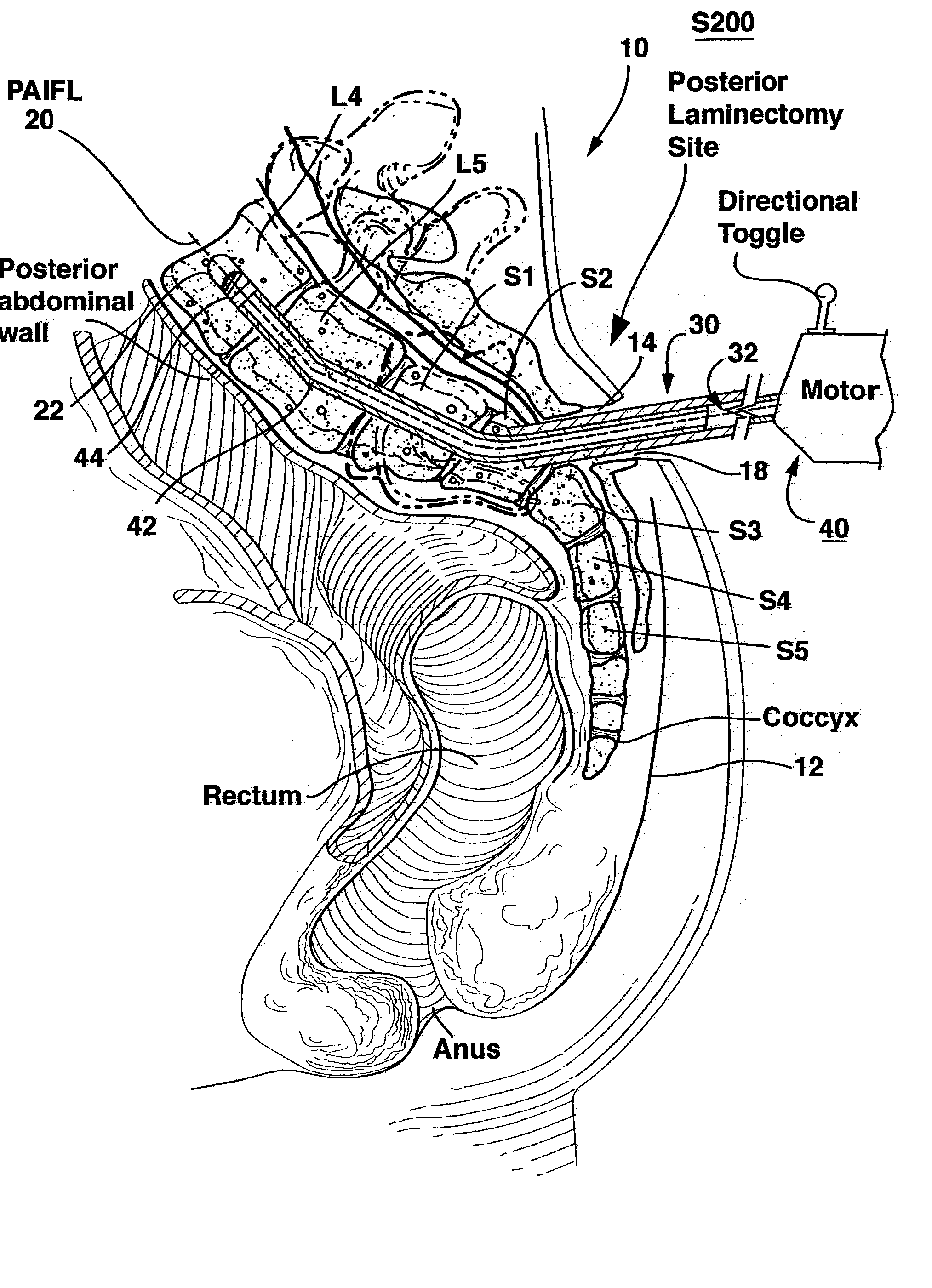
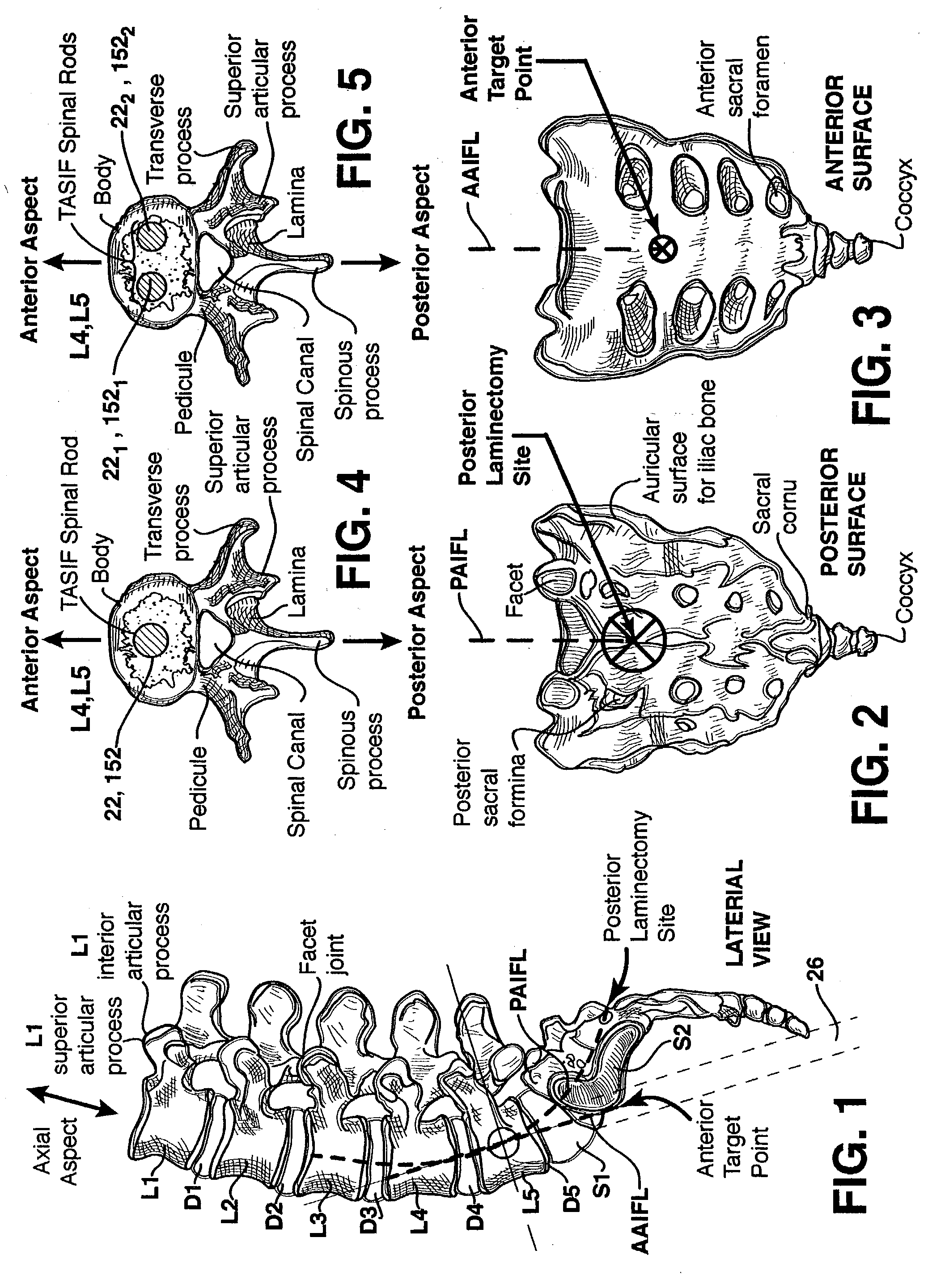
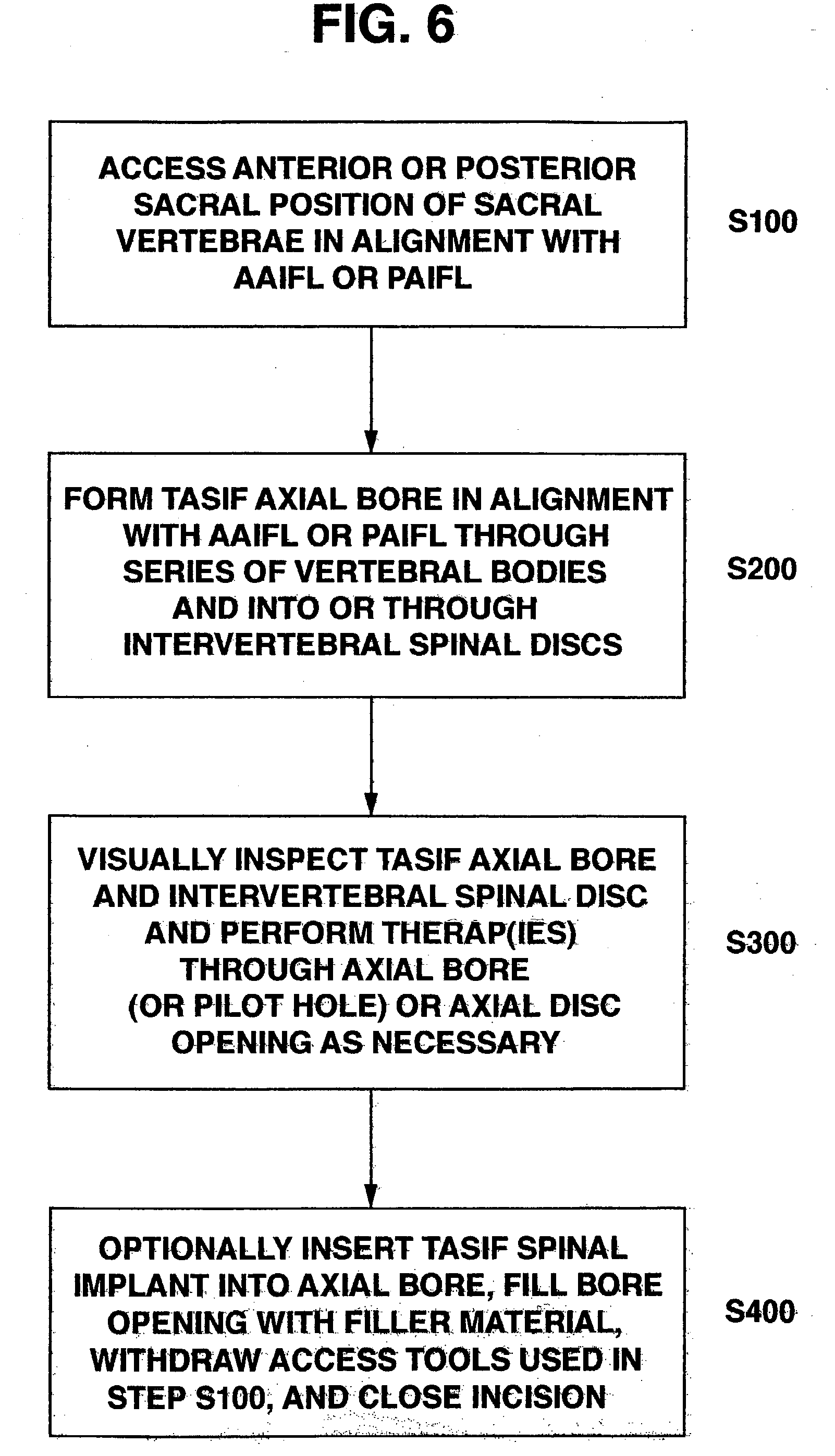
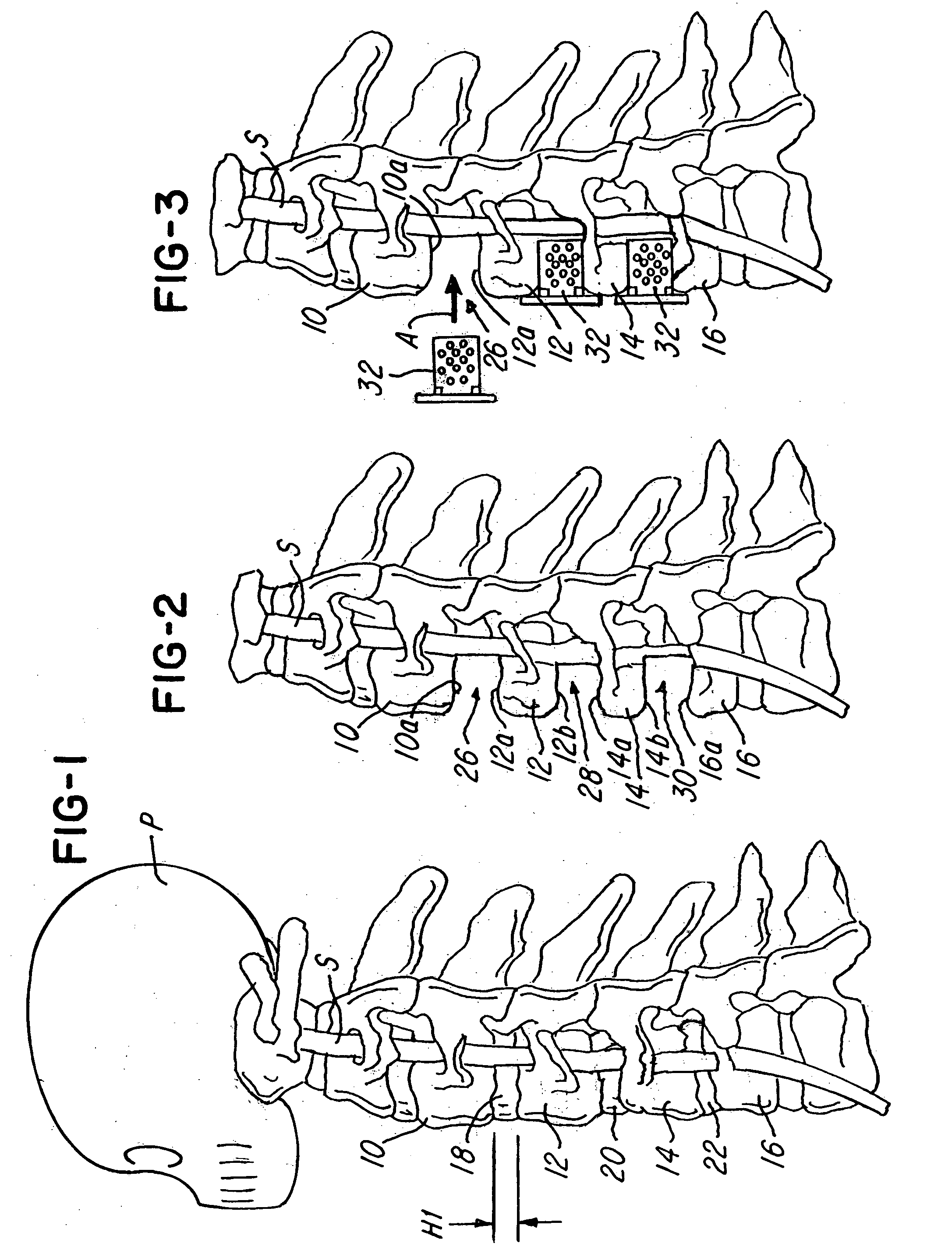
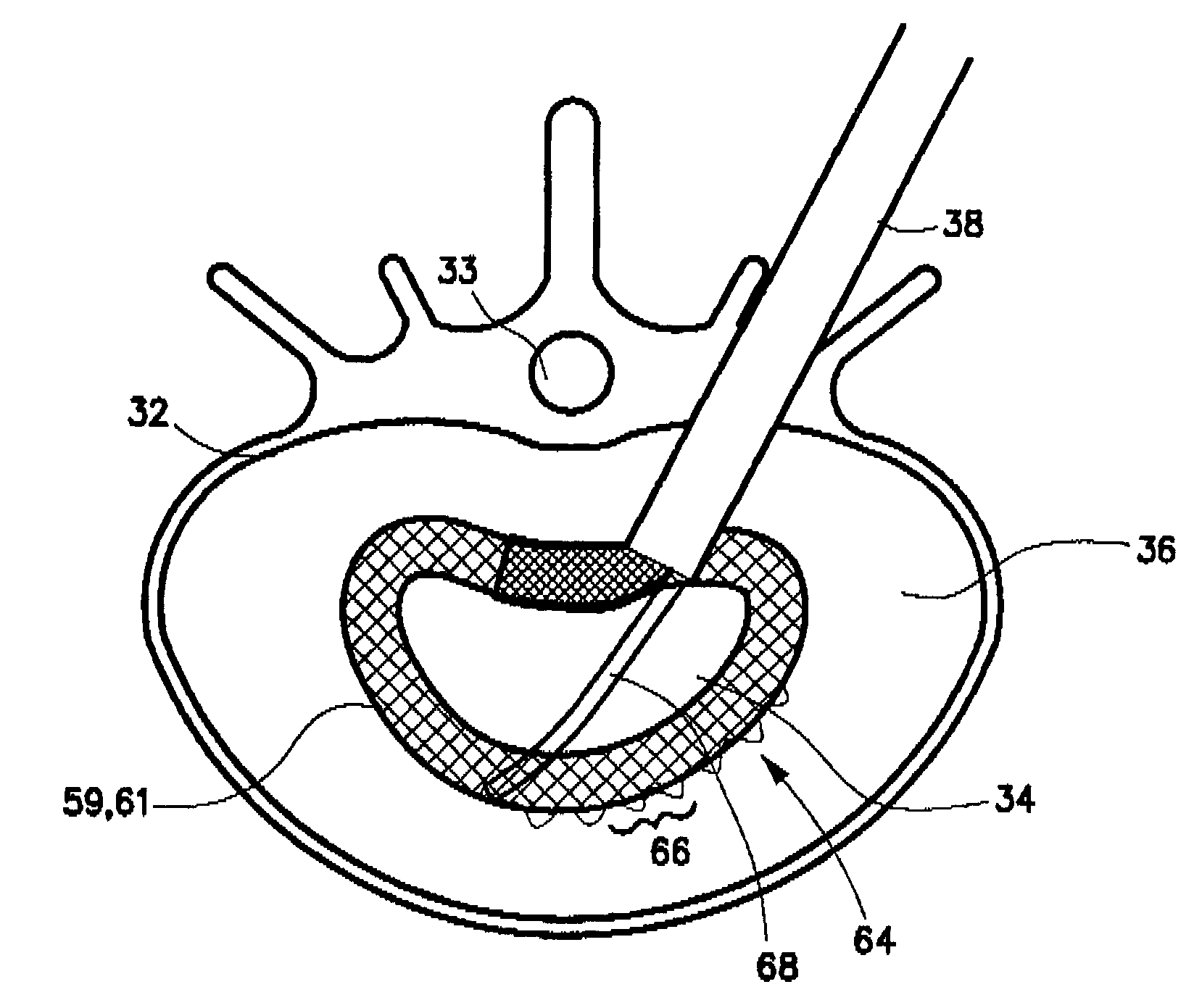
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
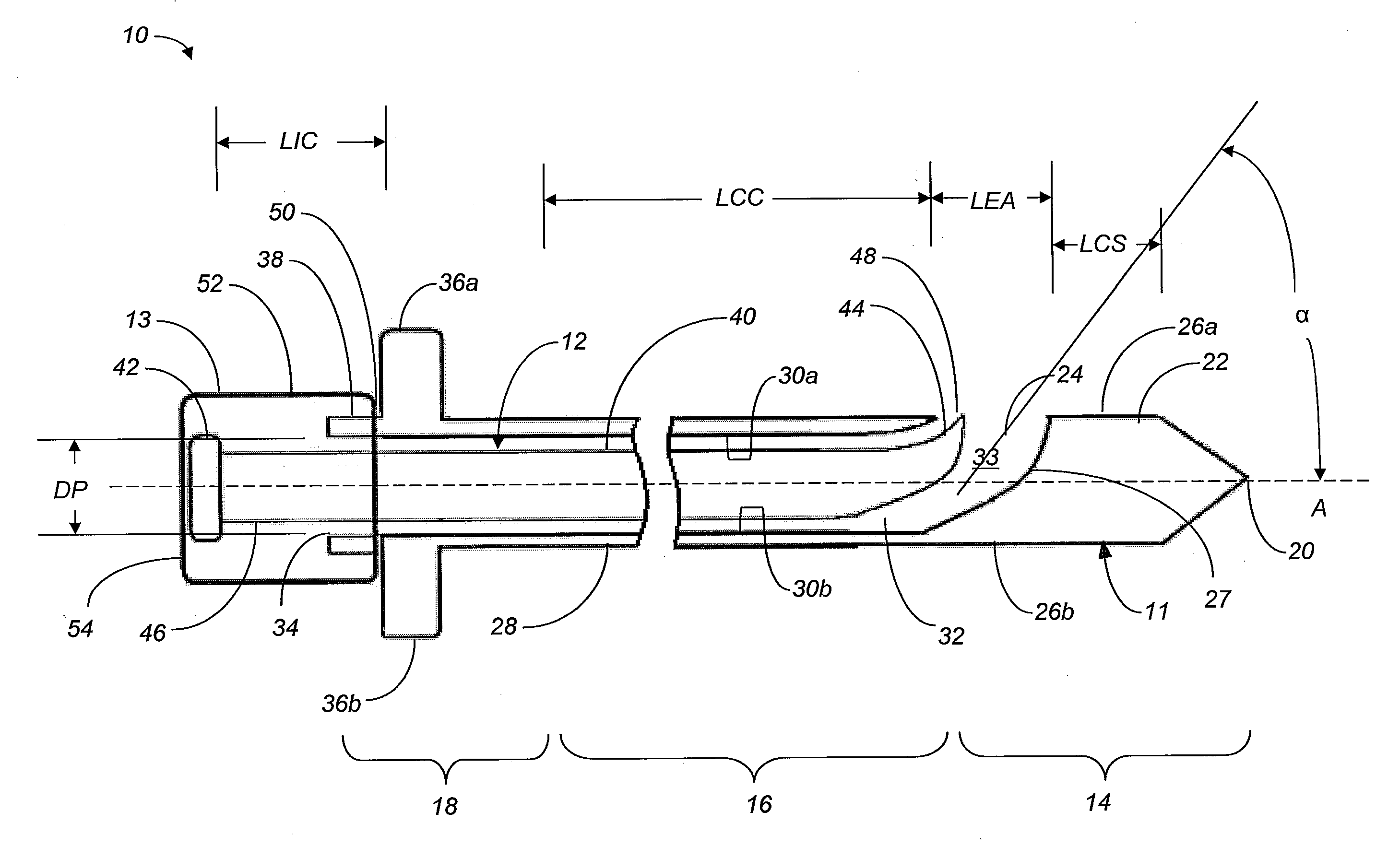
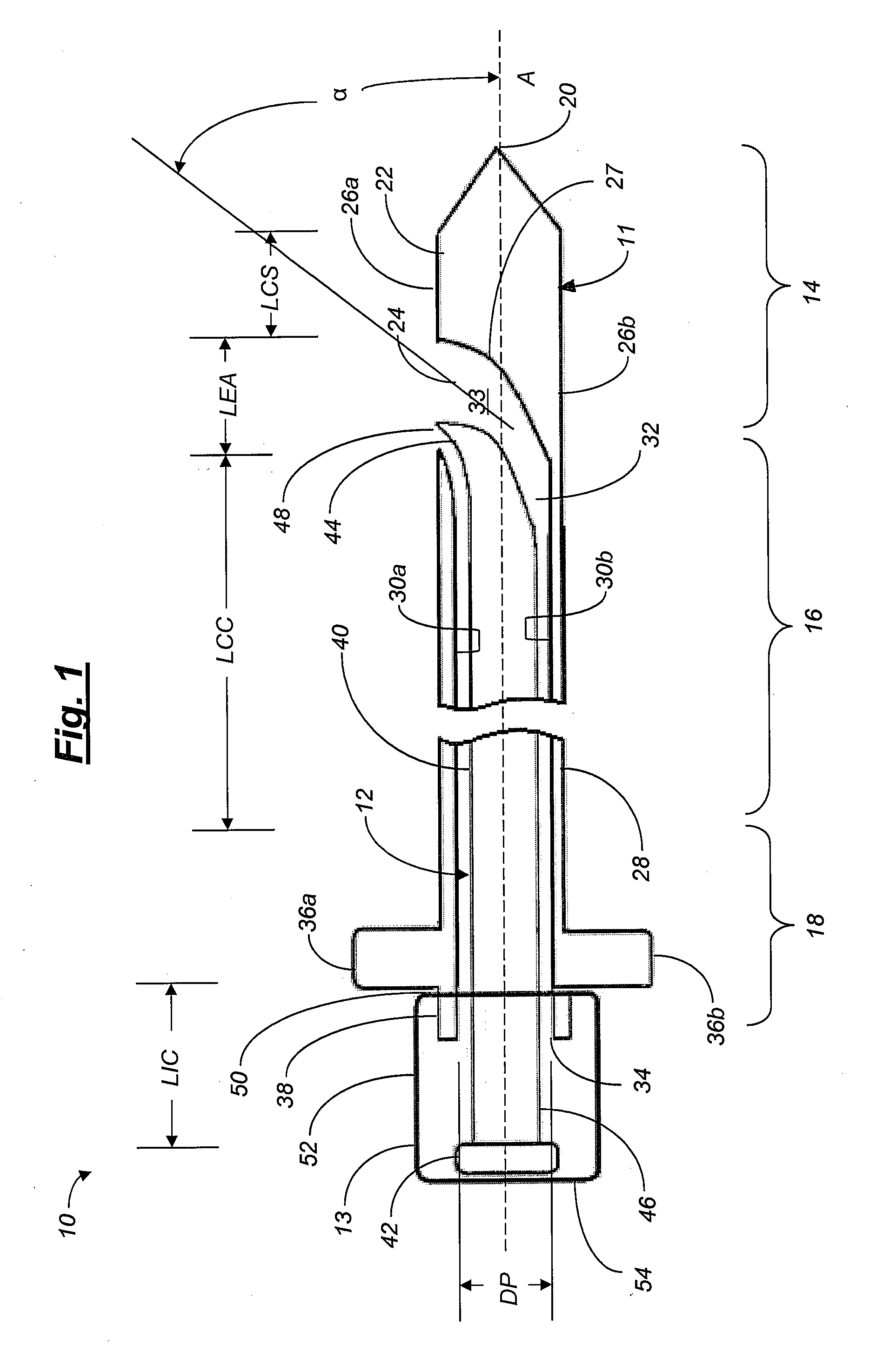
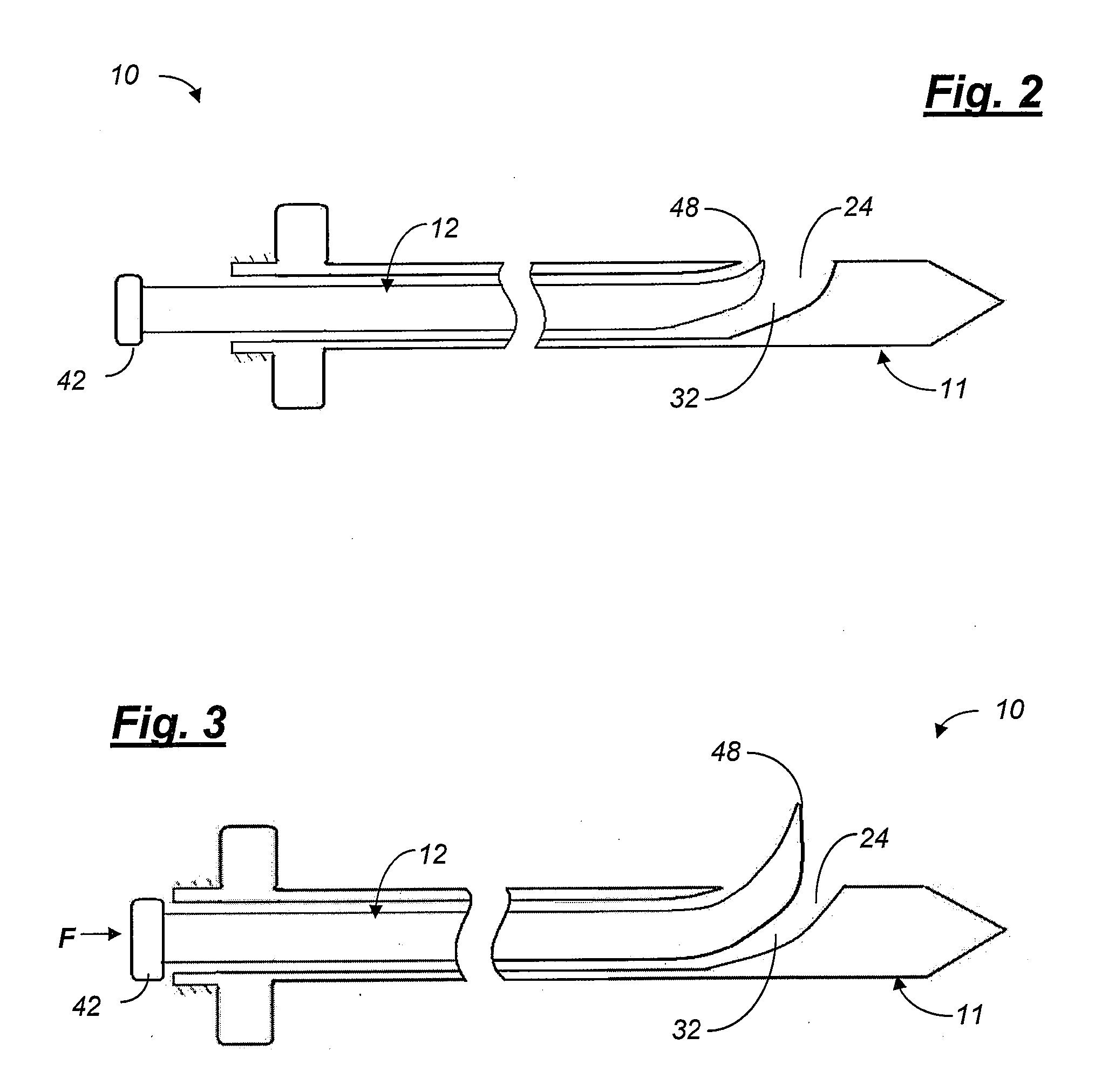
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
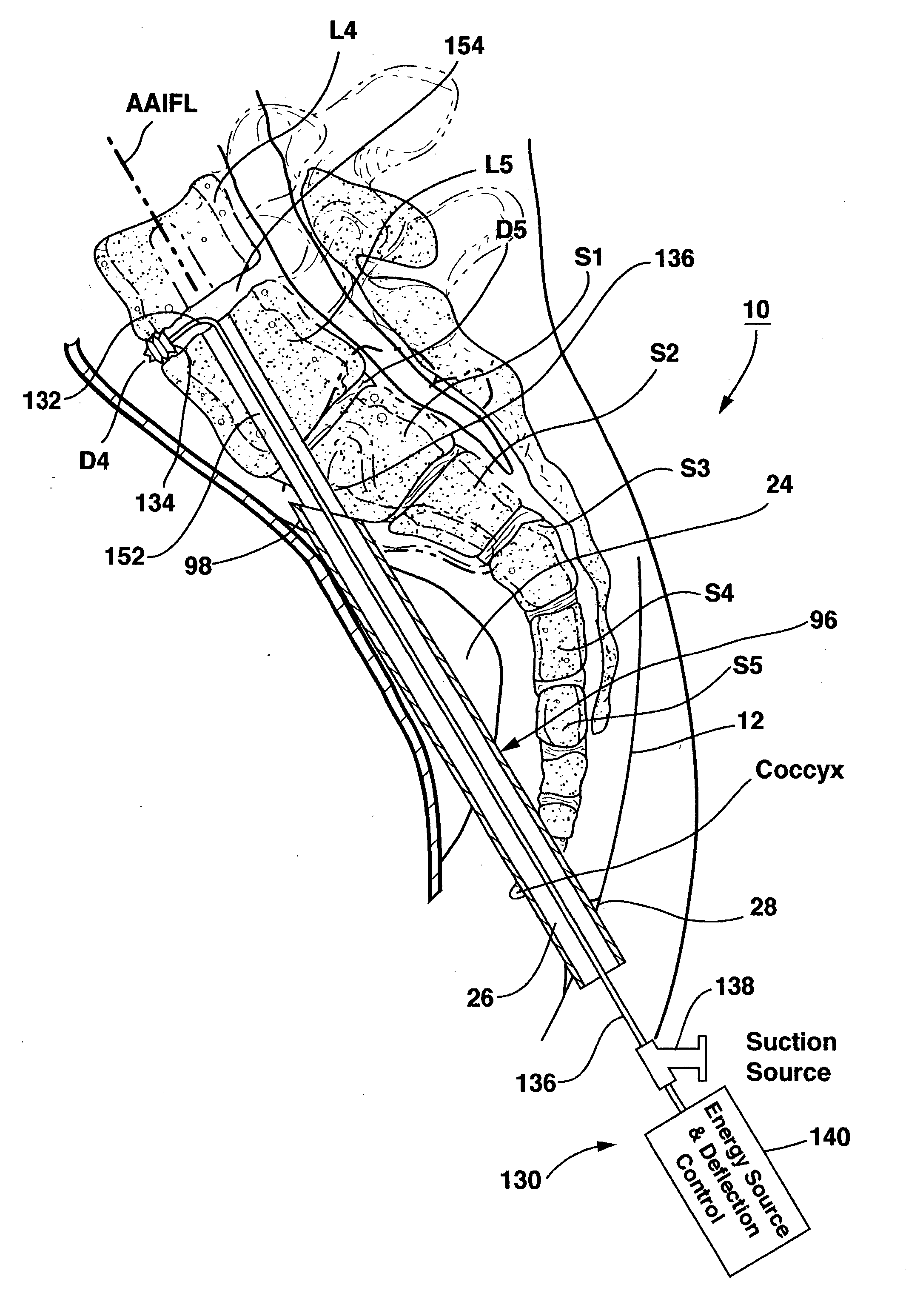
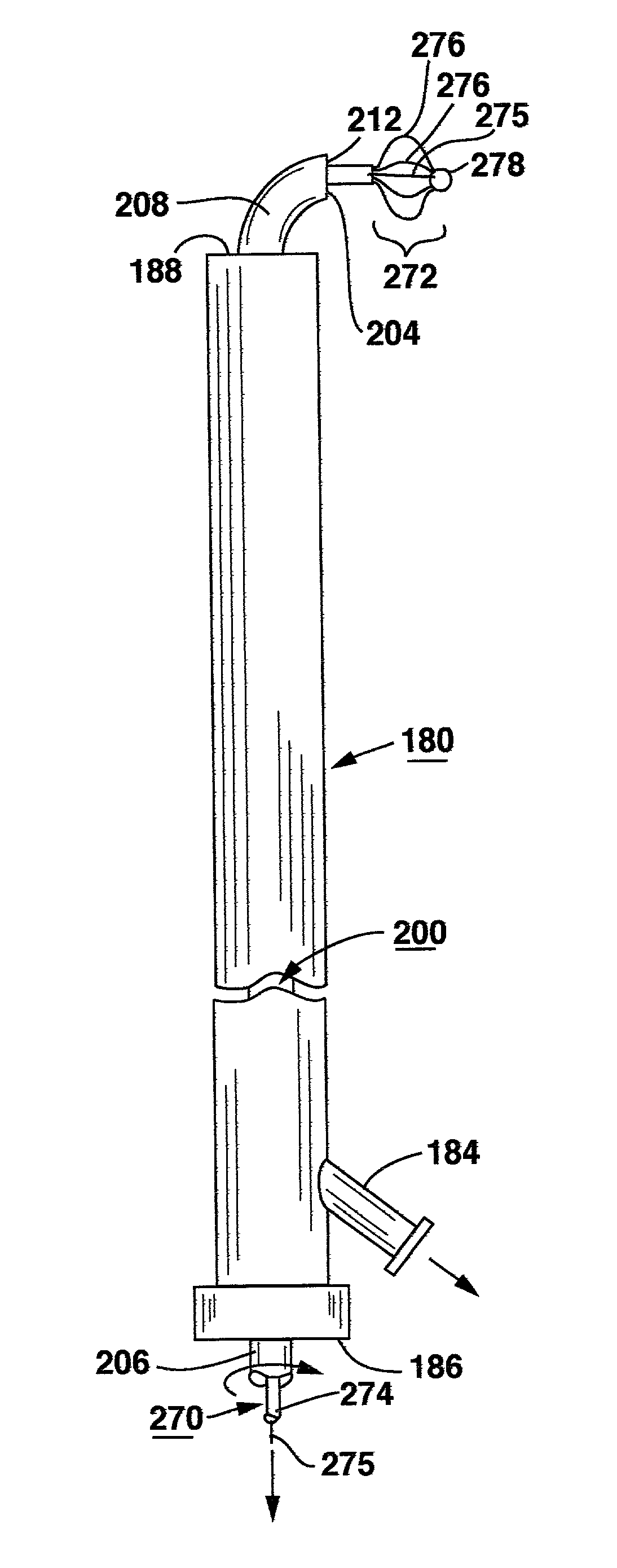
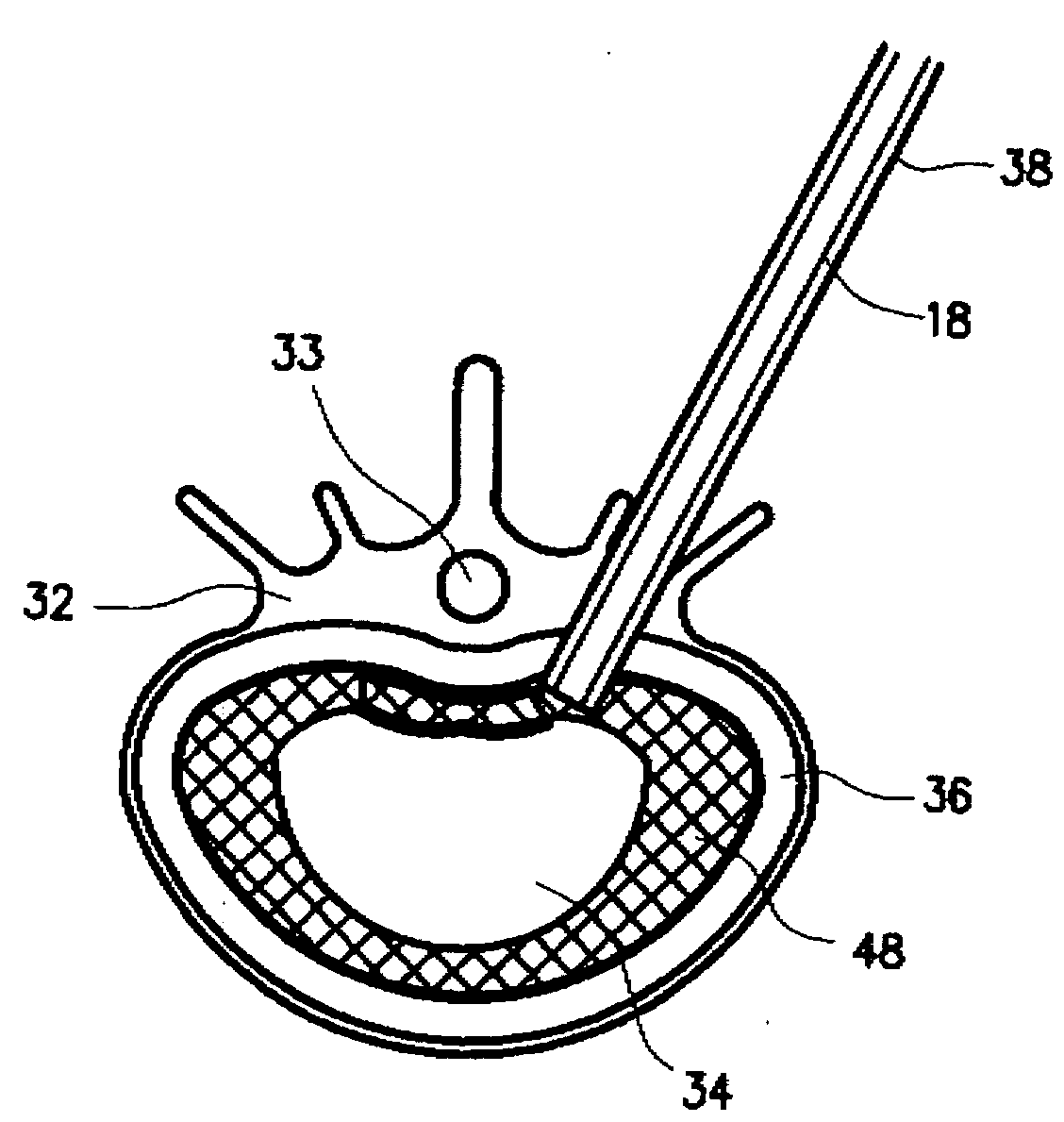
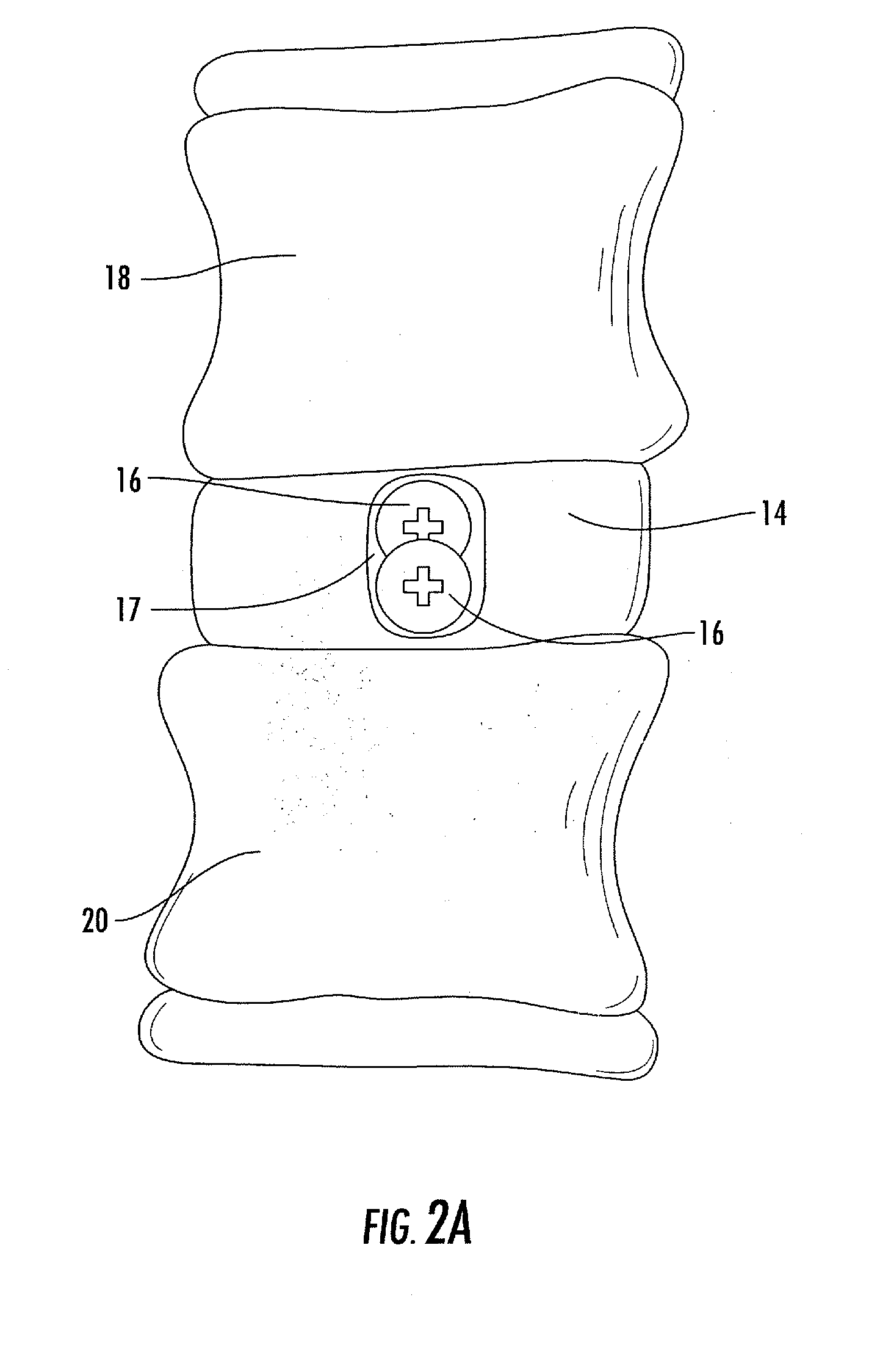
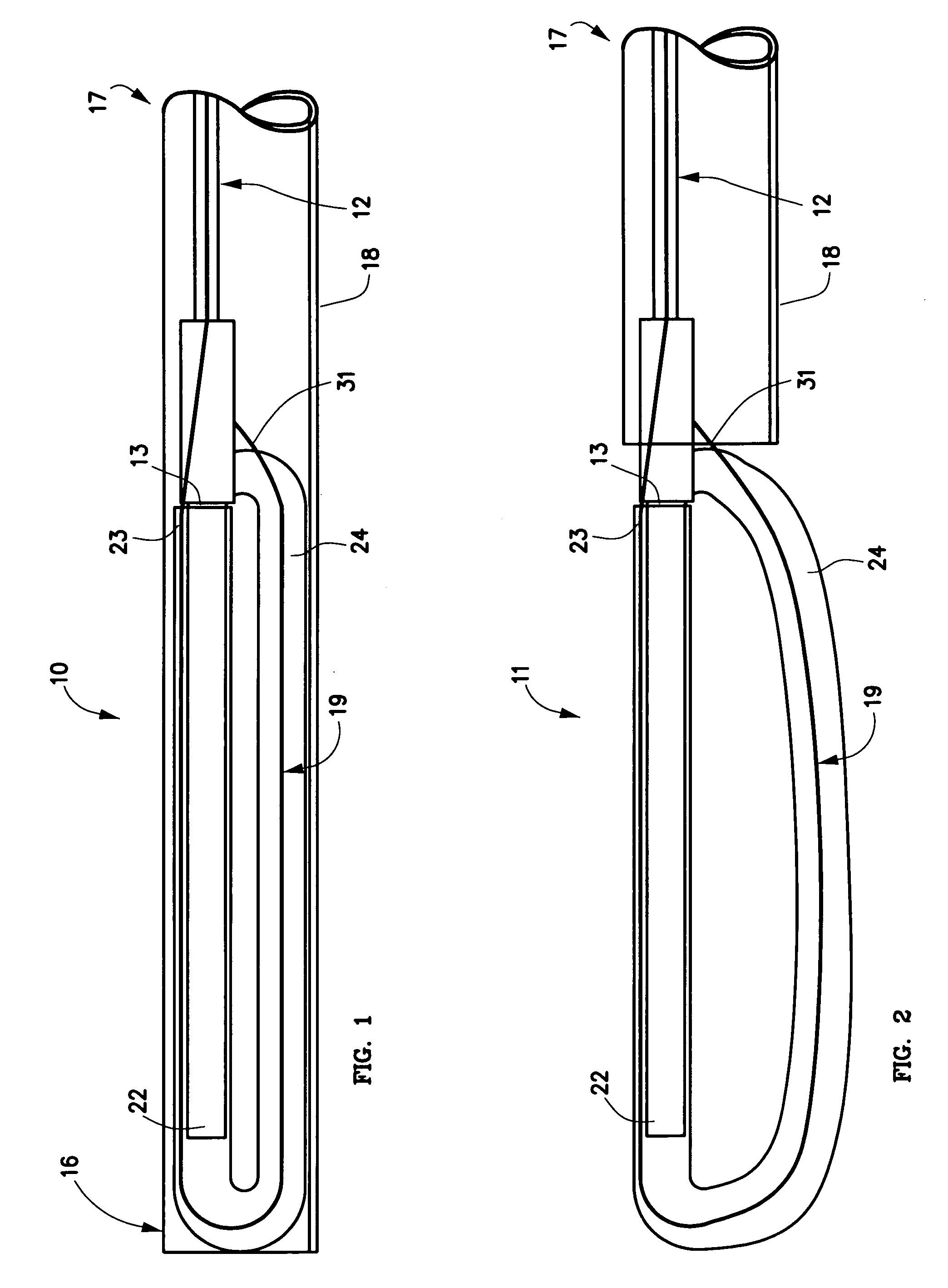
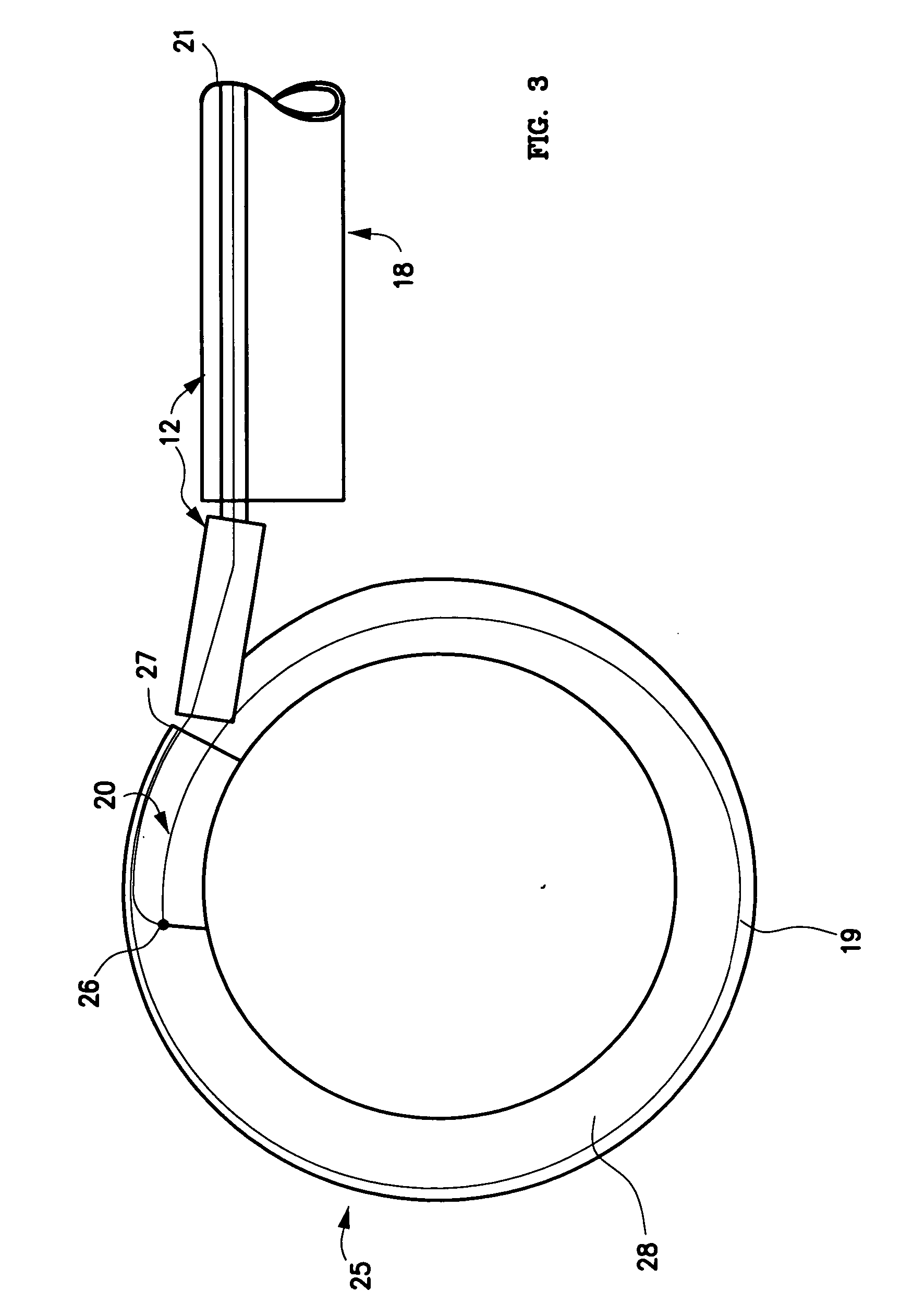
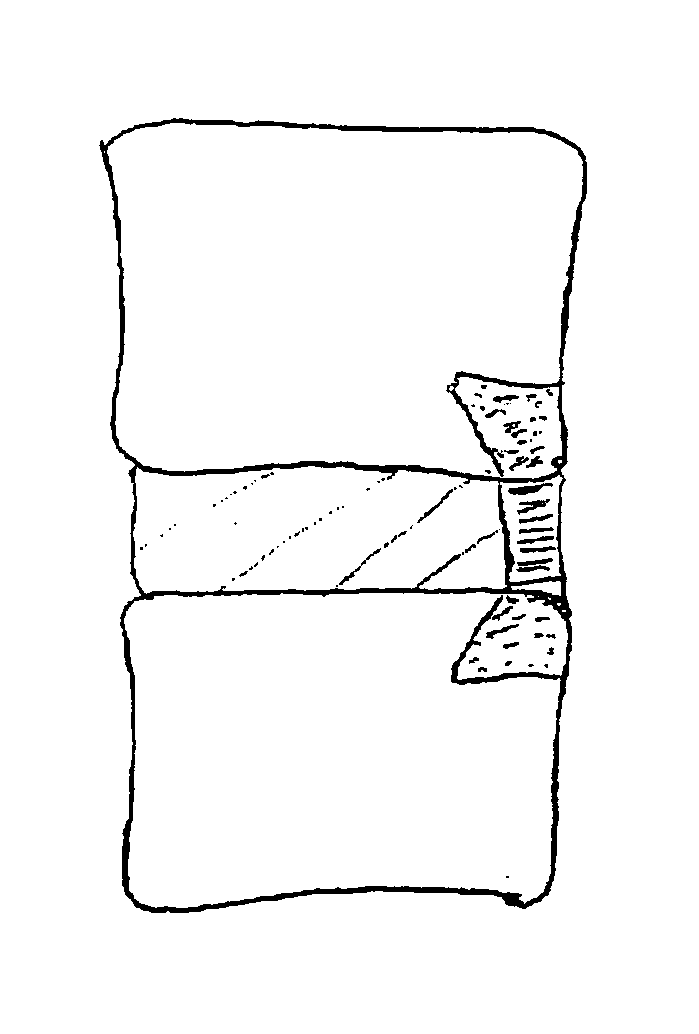
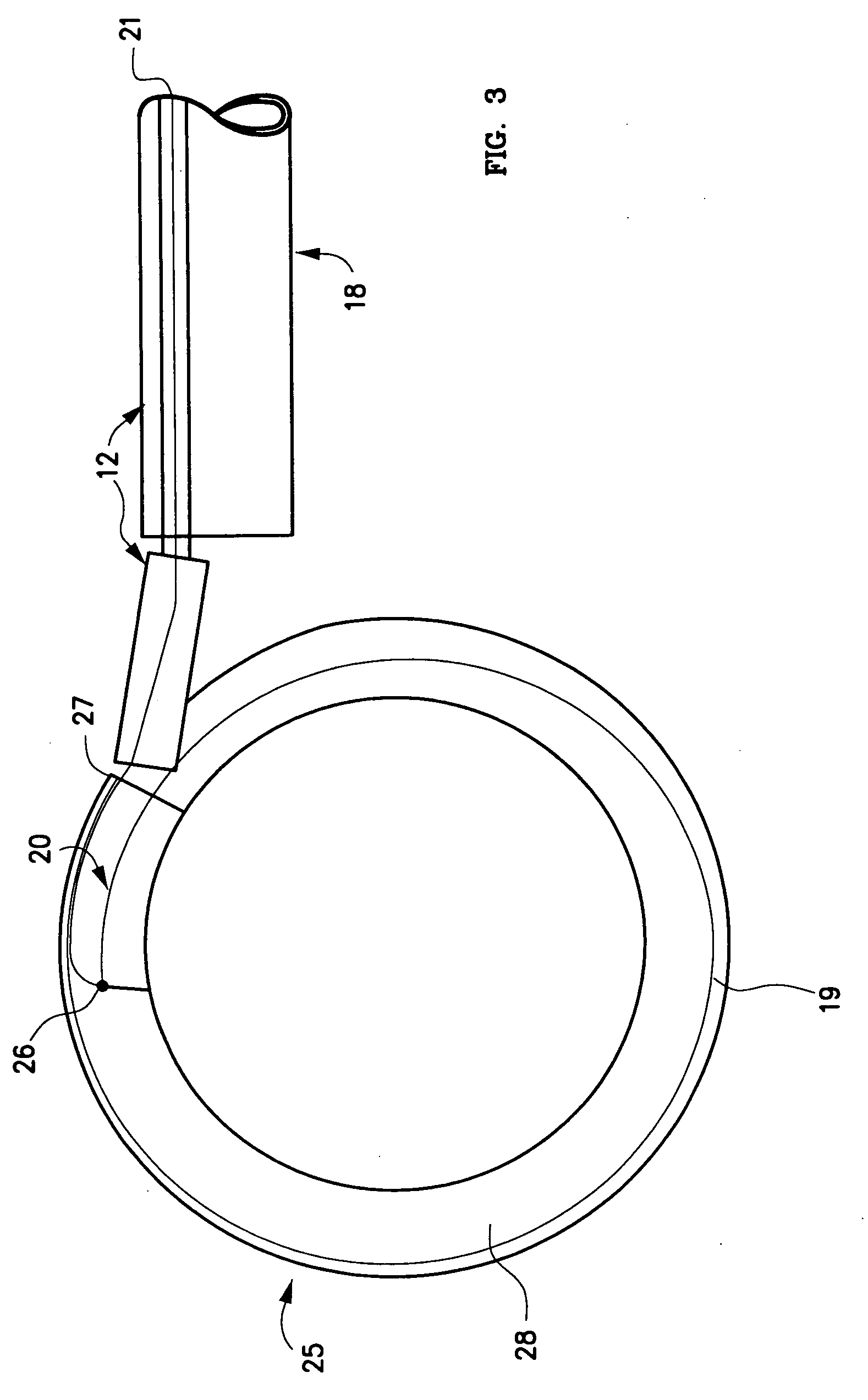
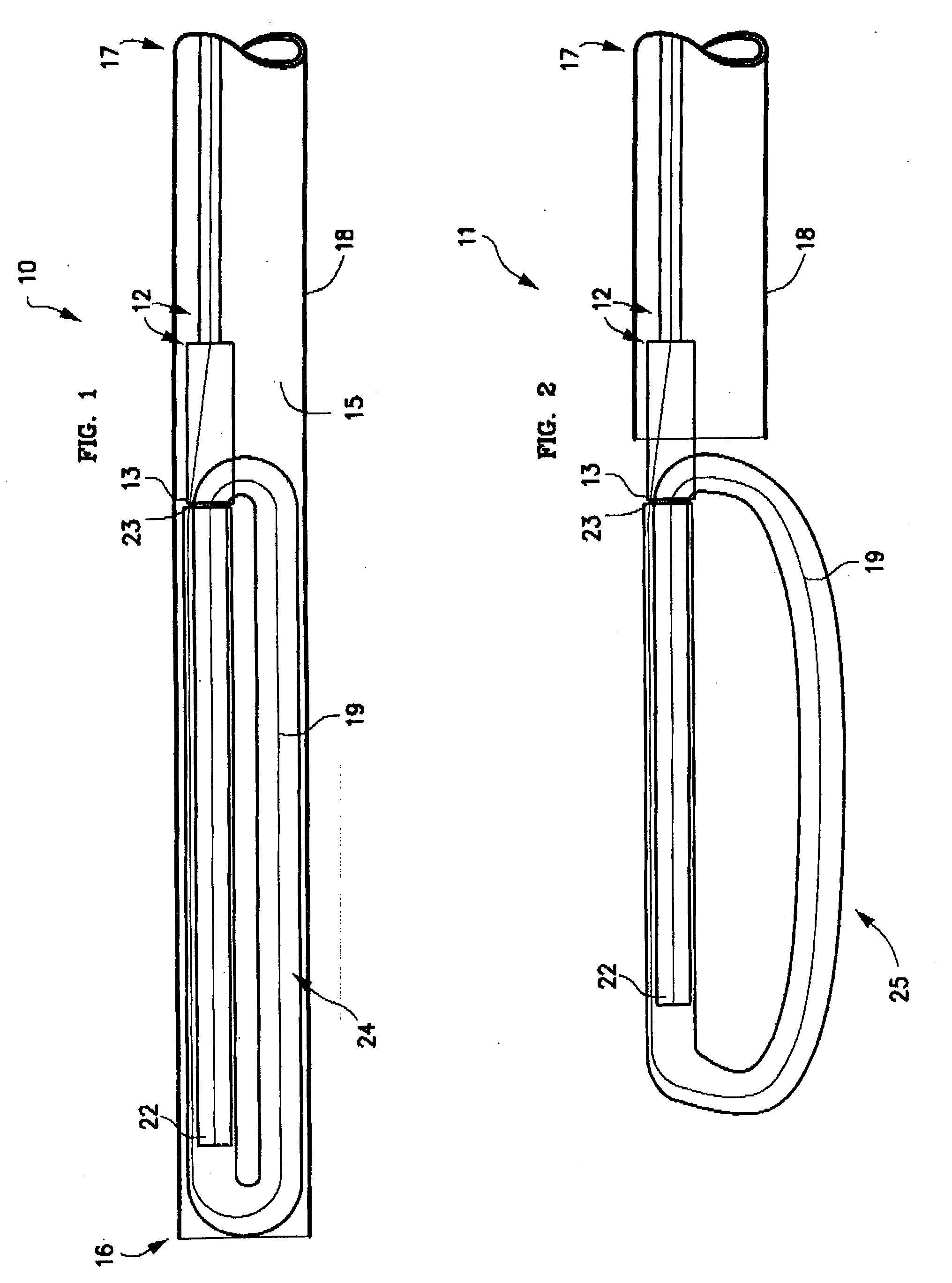
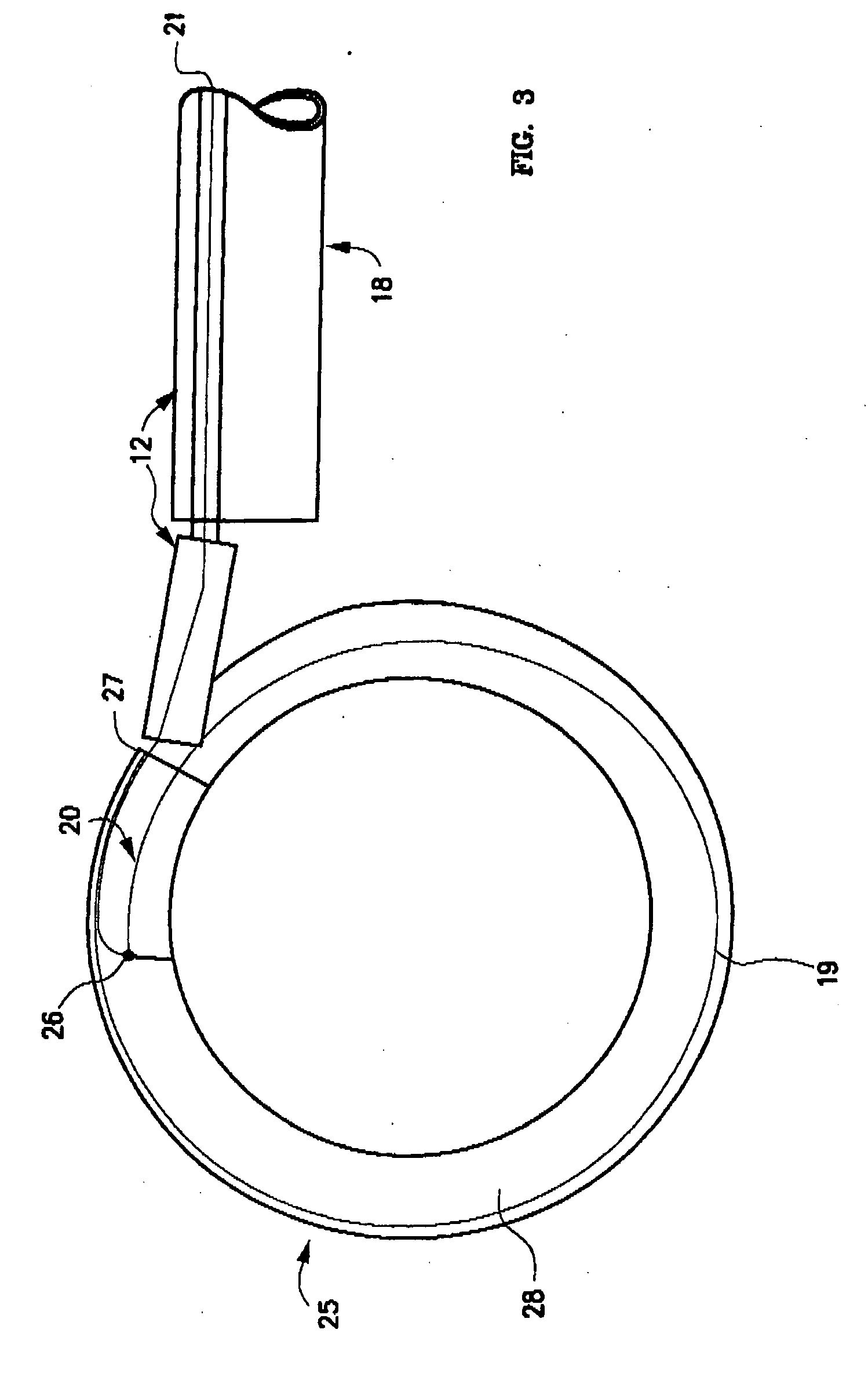
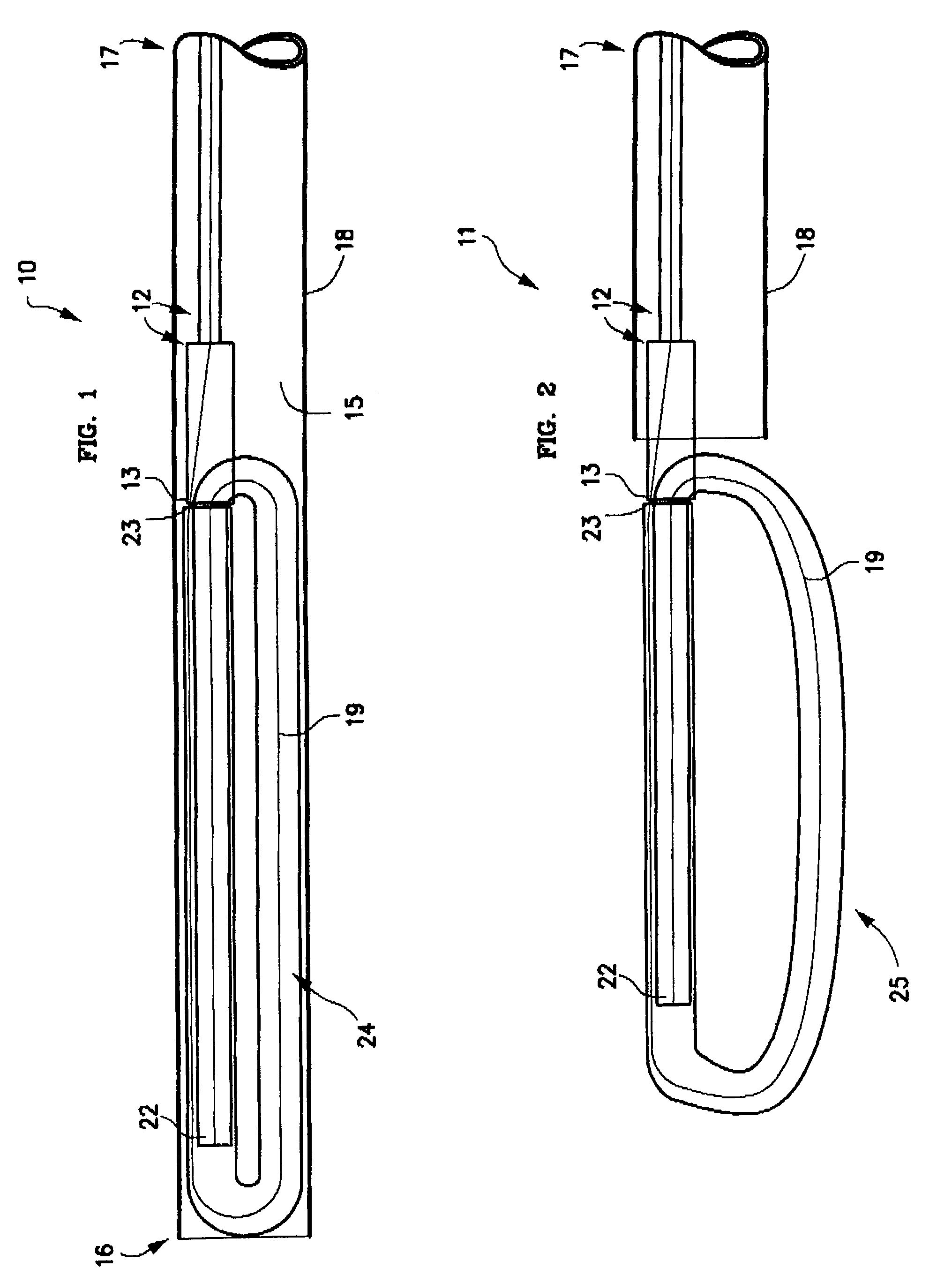
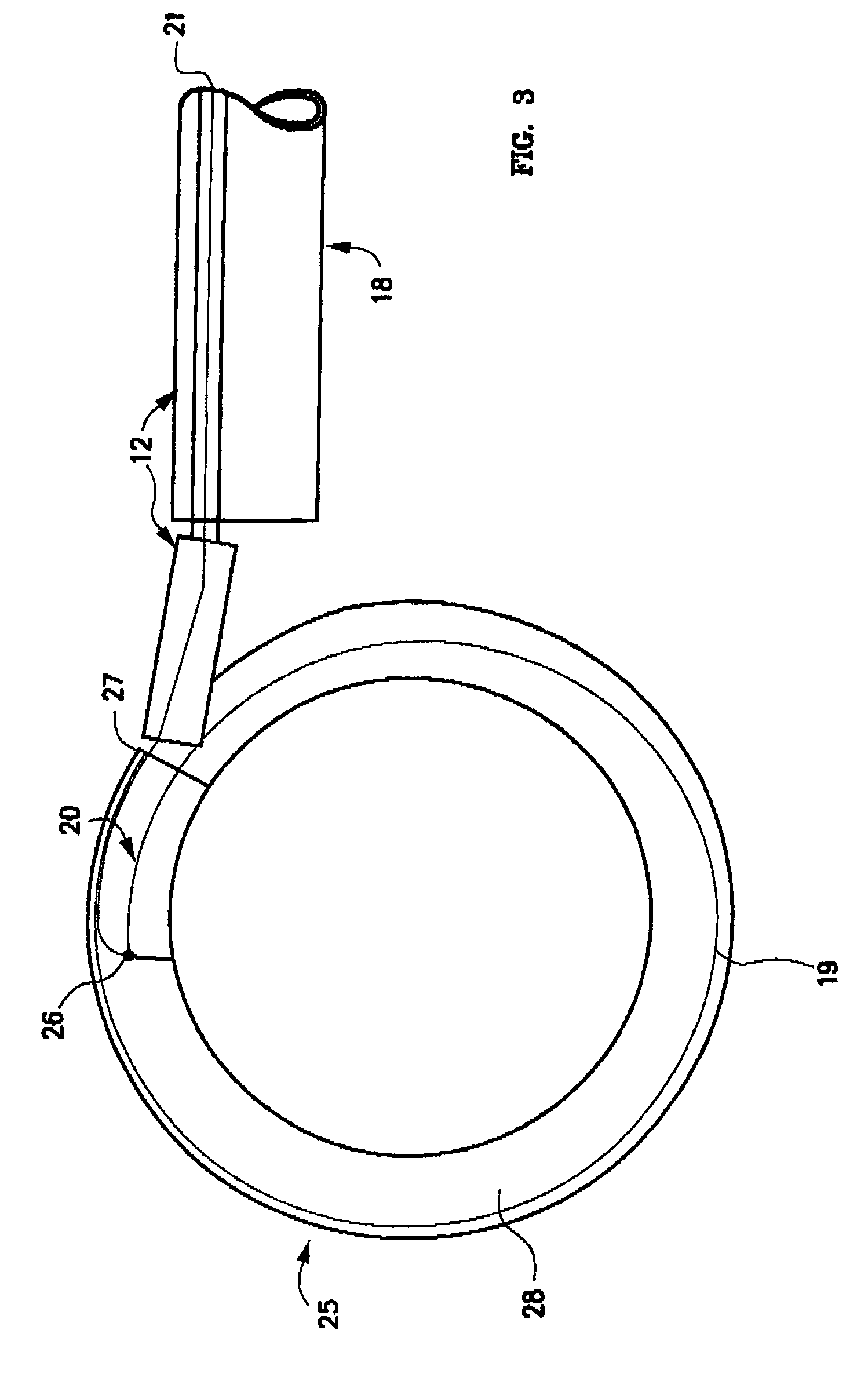
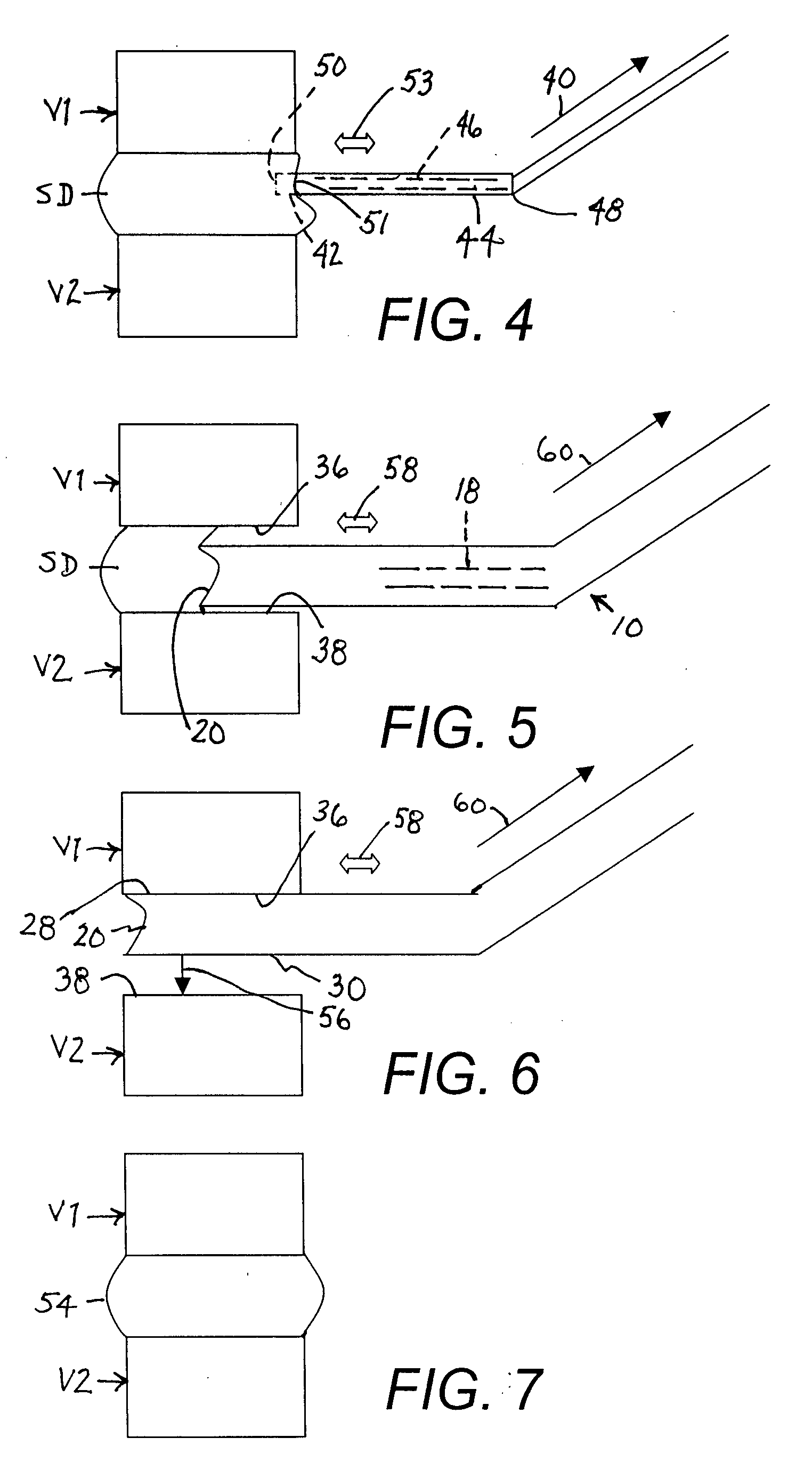
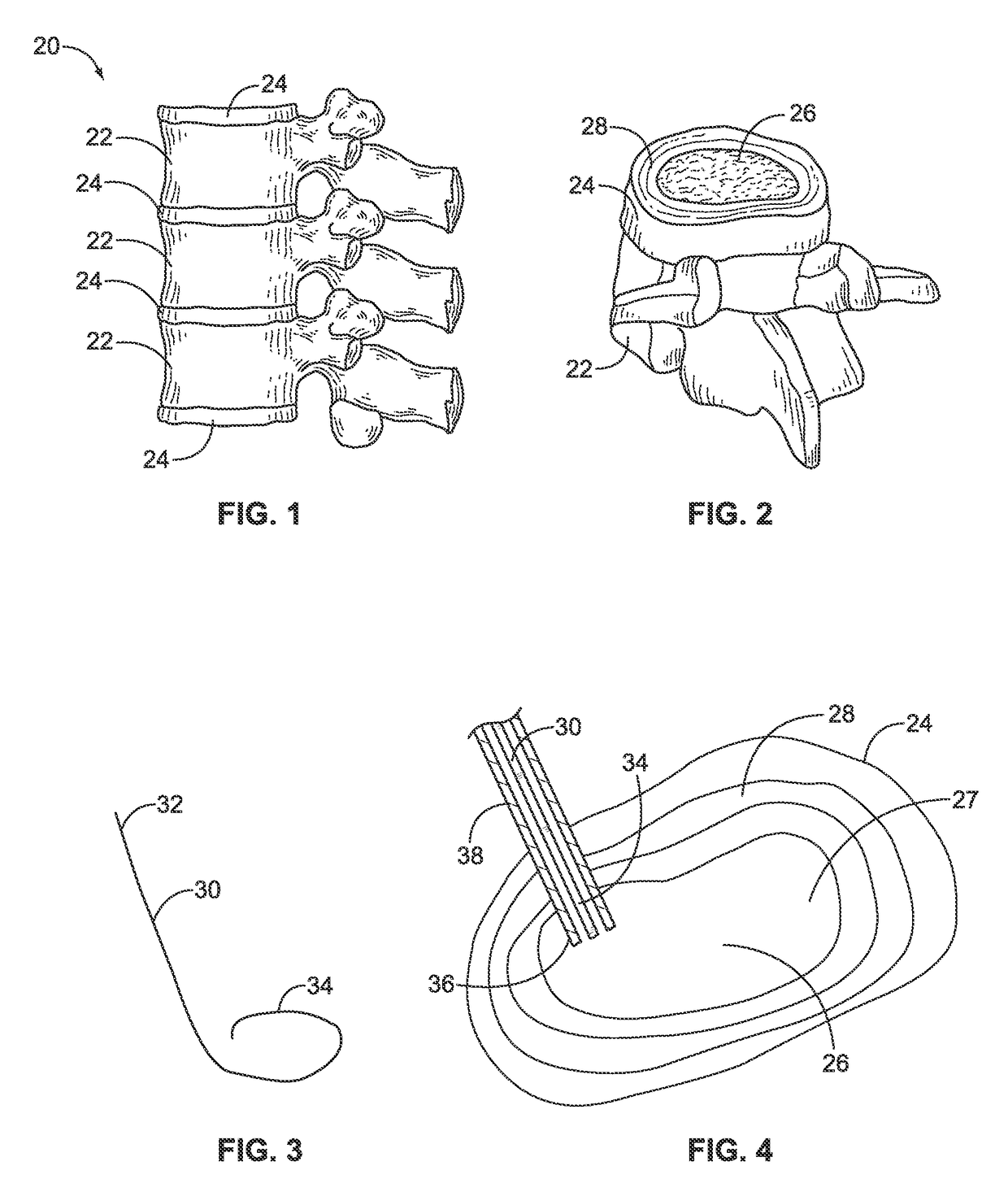
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:TRANSI
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287726A1Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPolyesterClosed loop
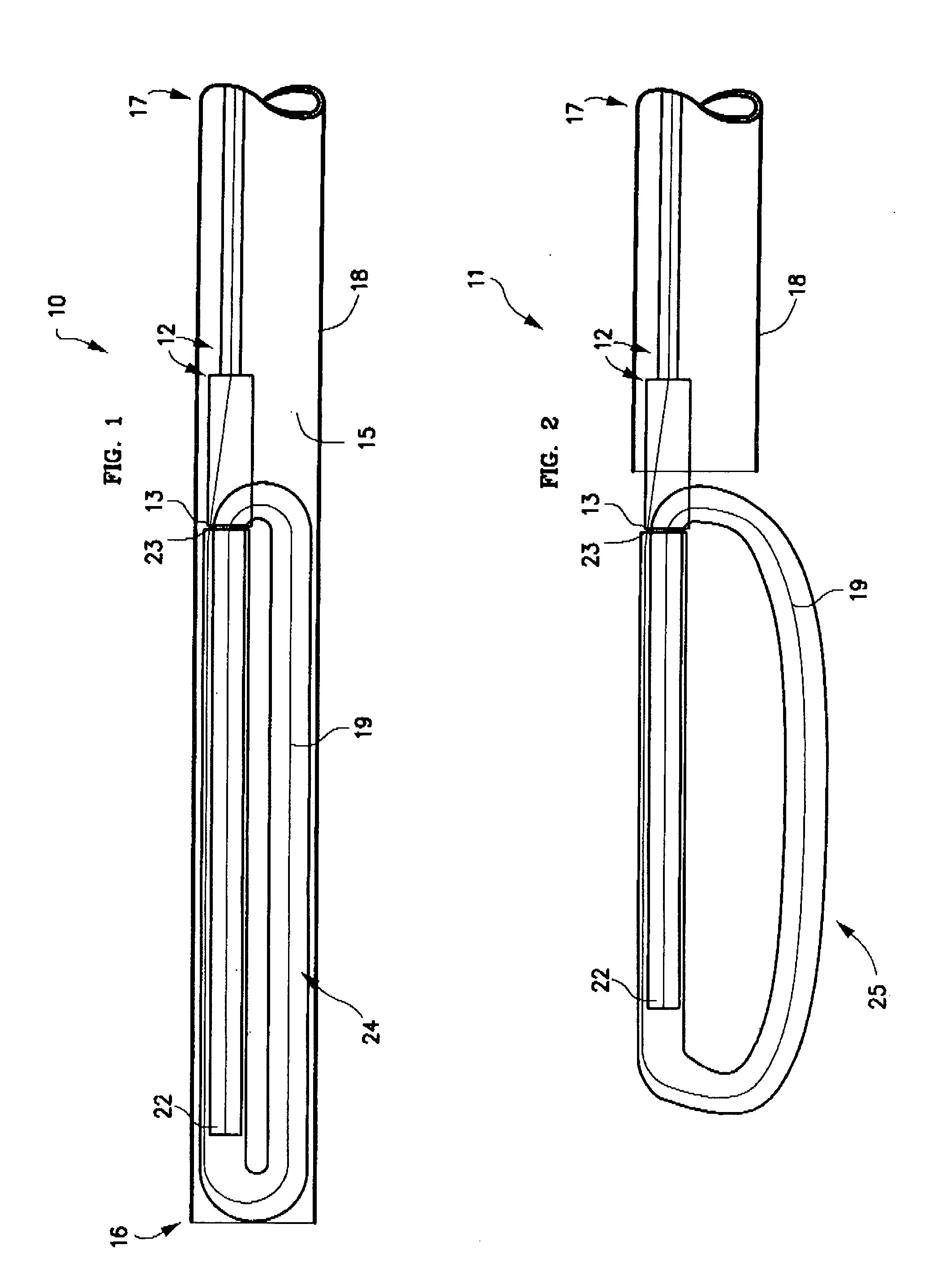
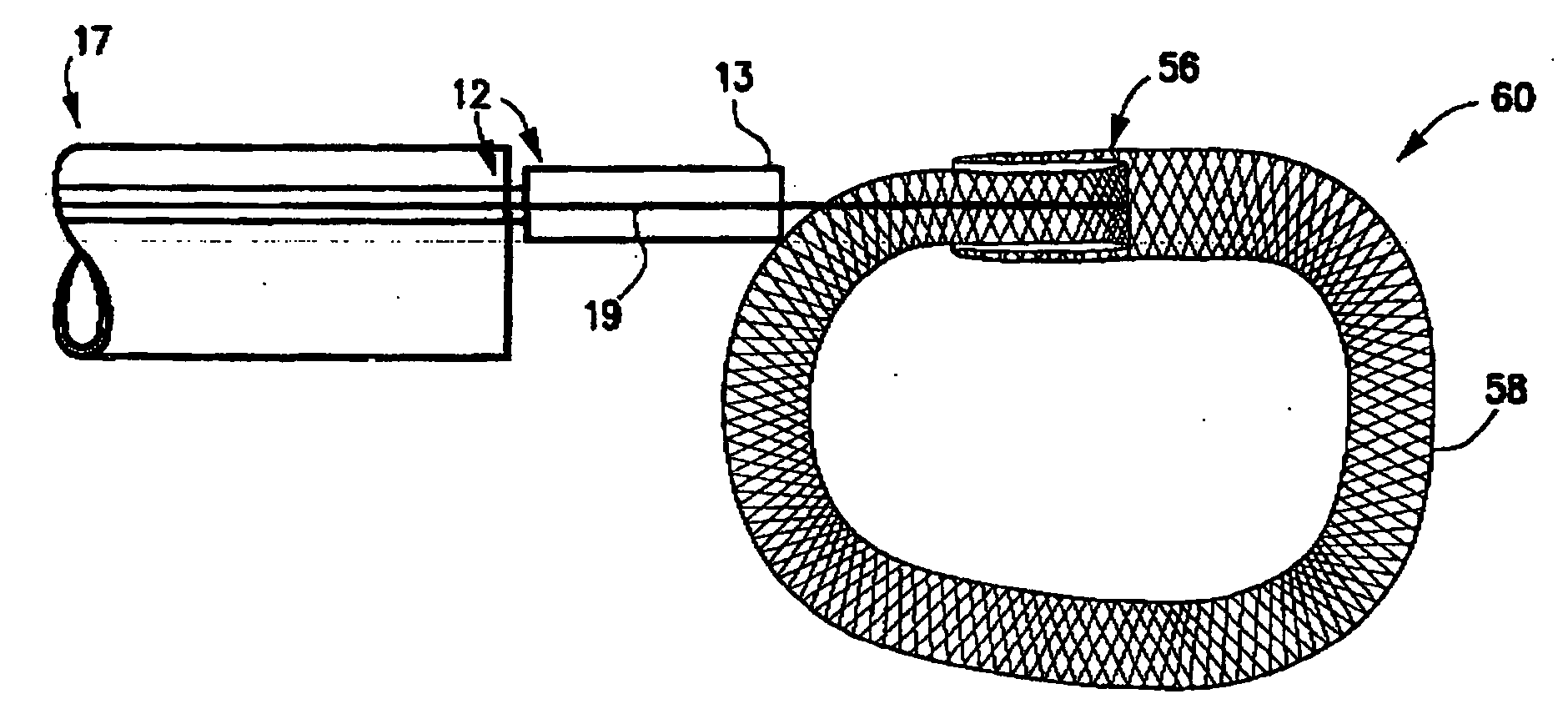
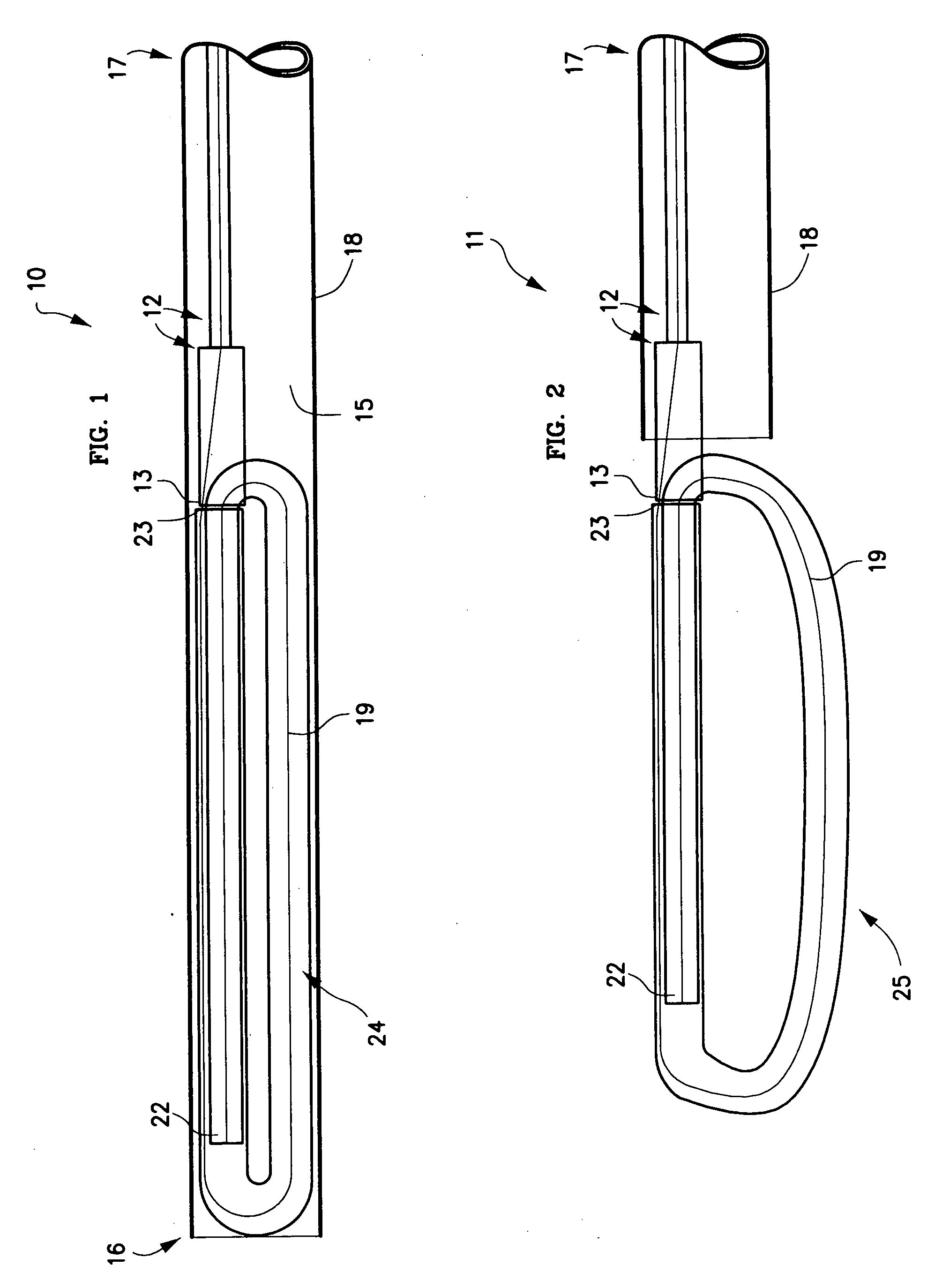
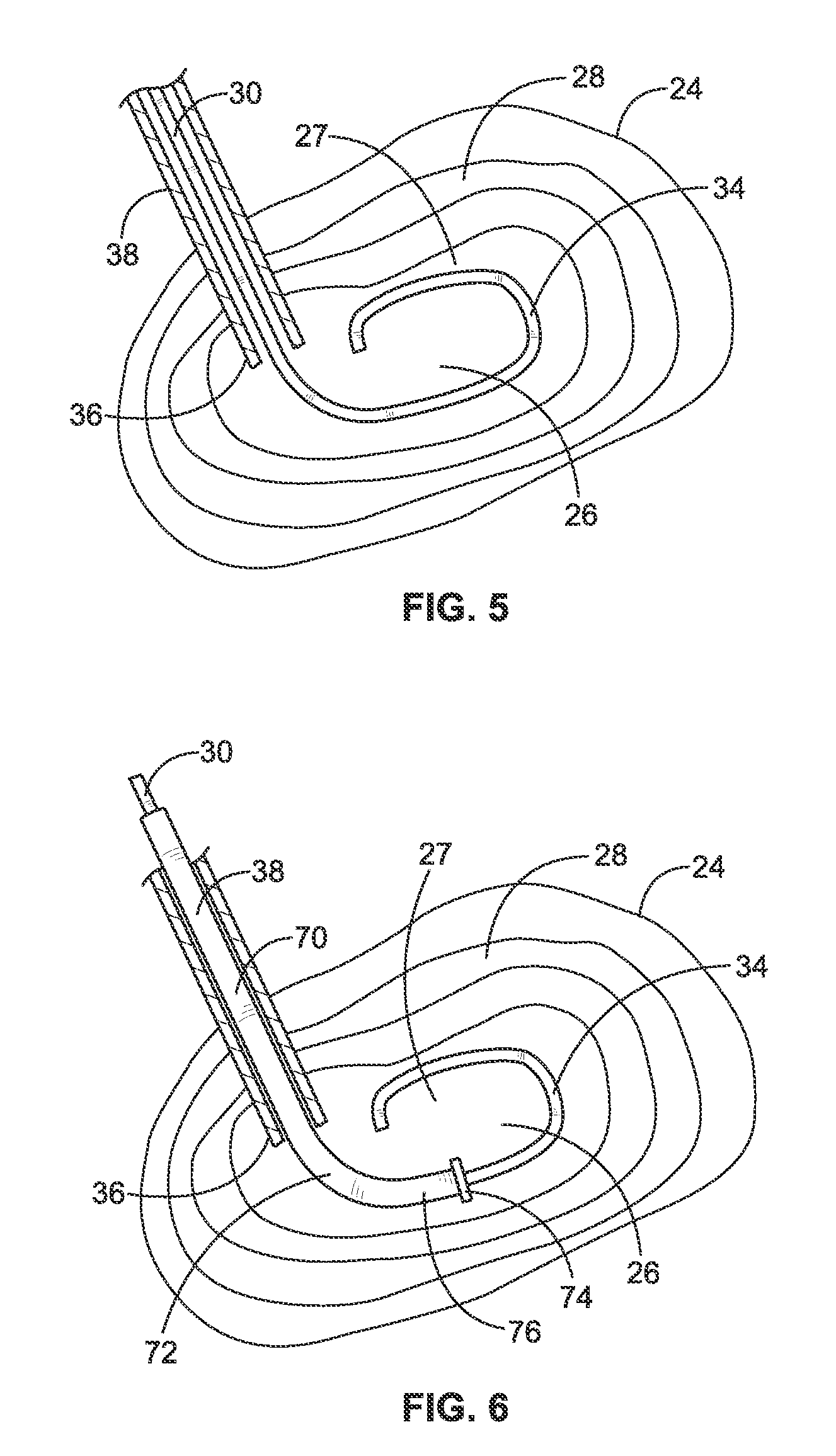
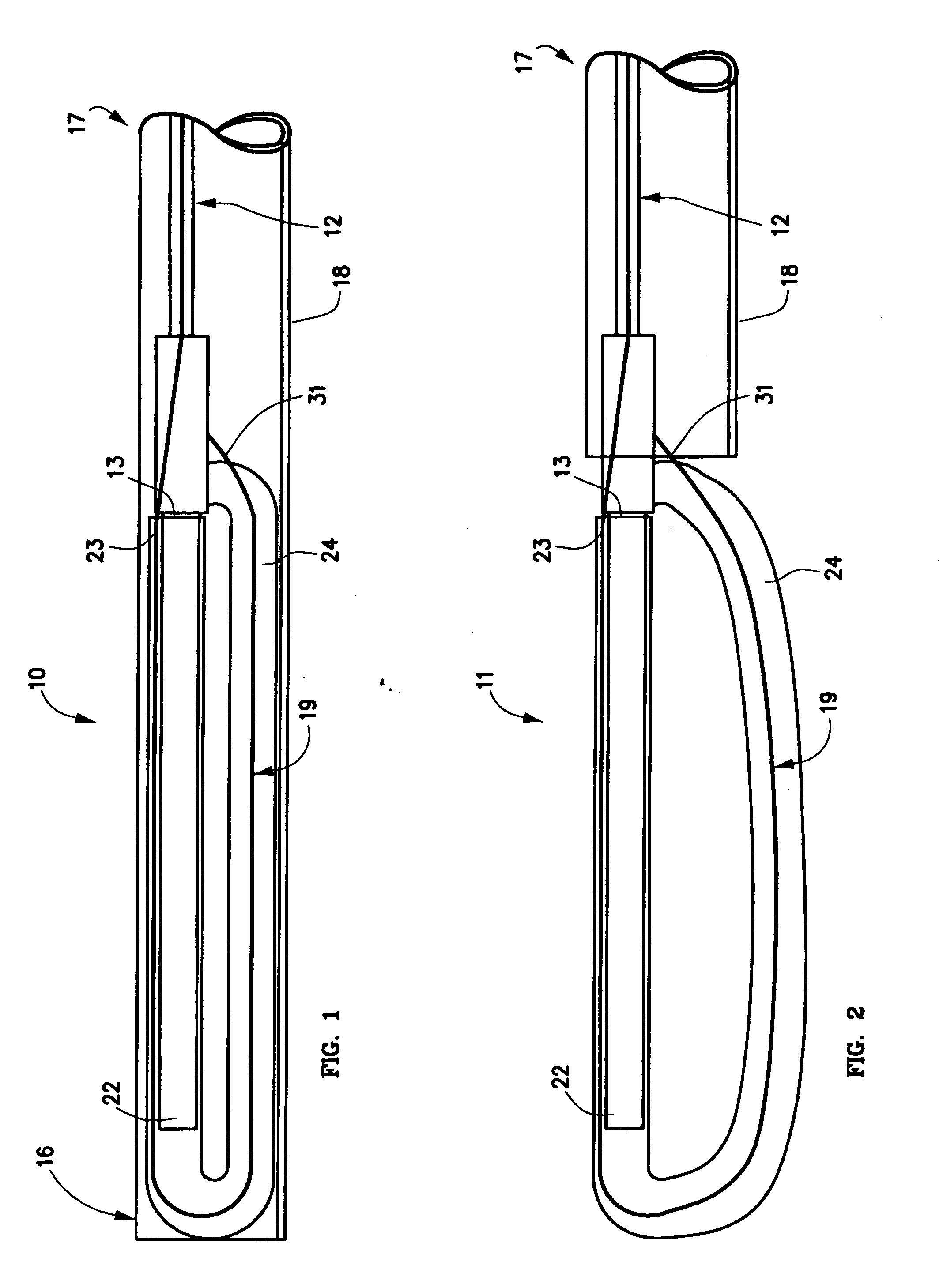
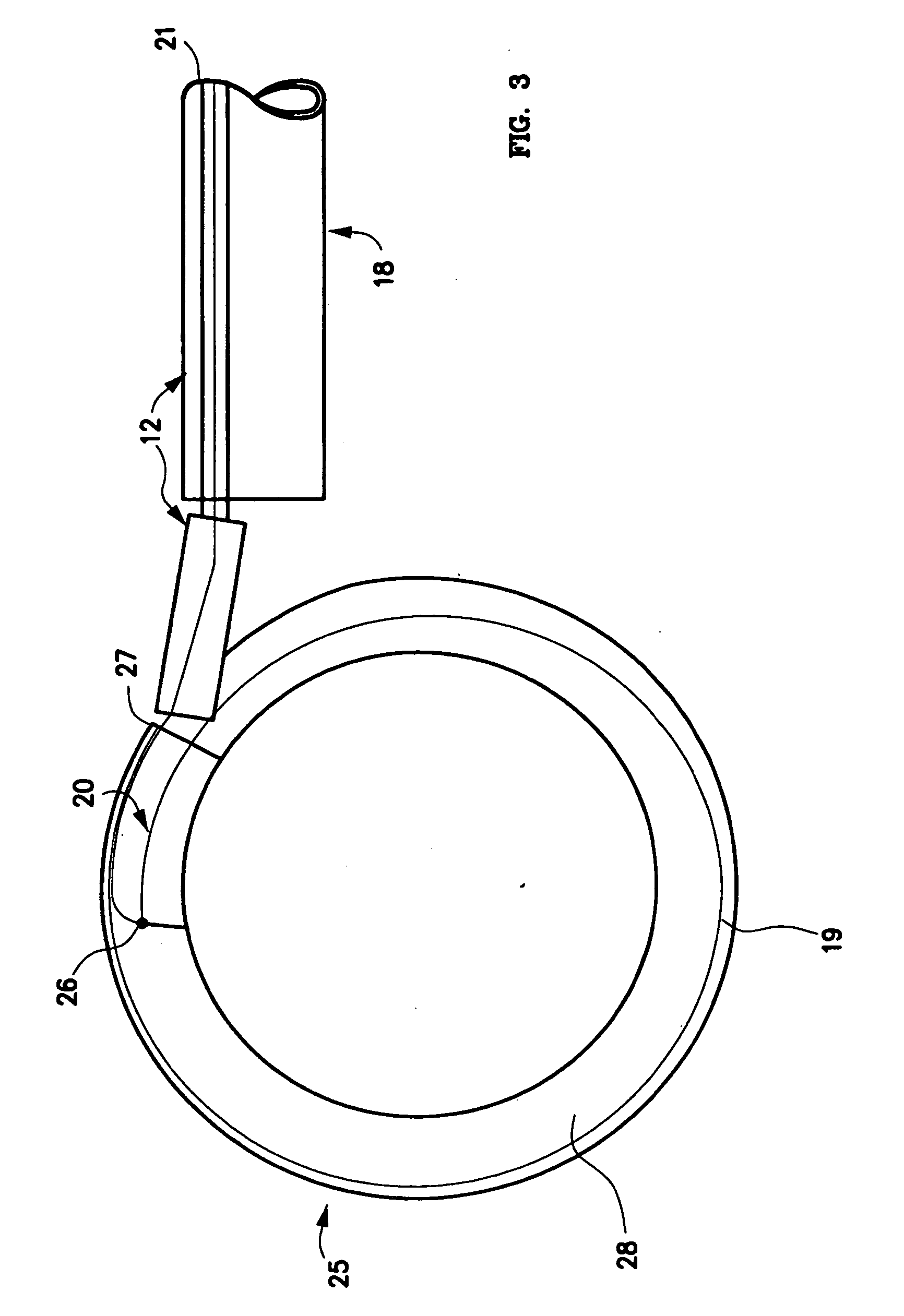
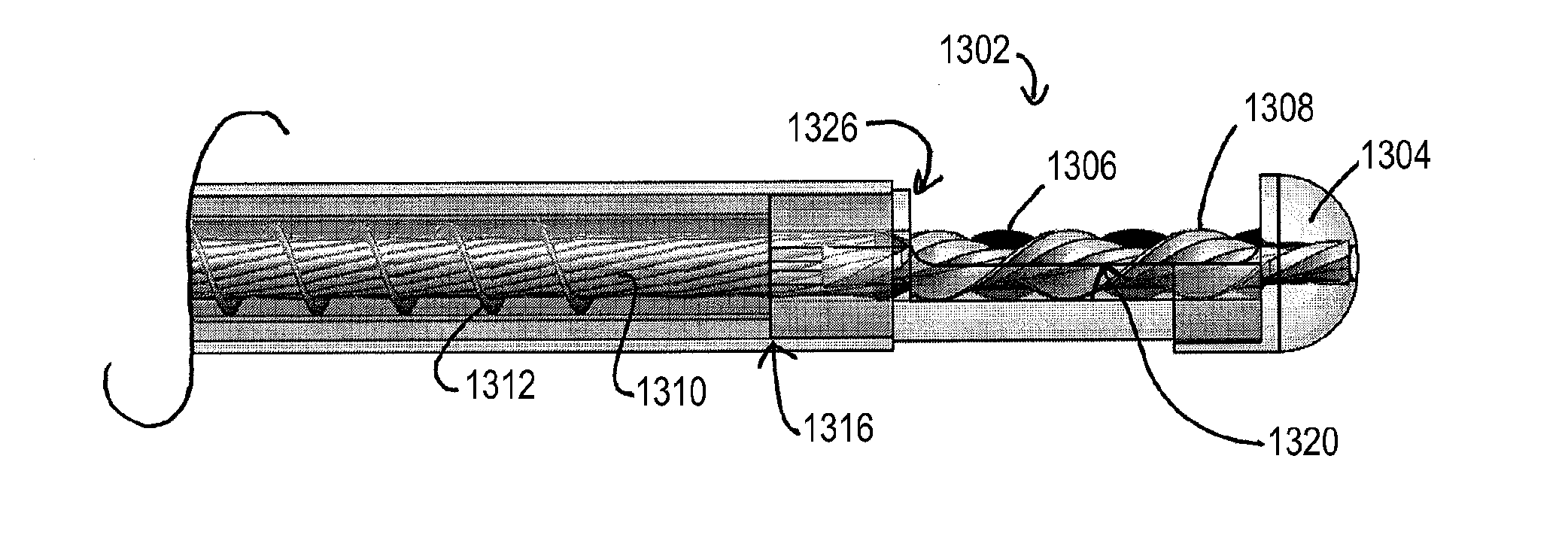
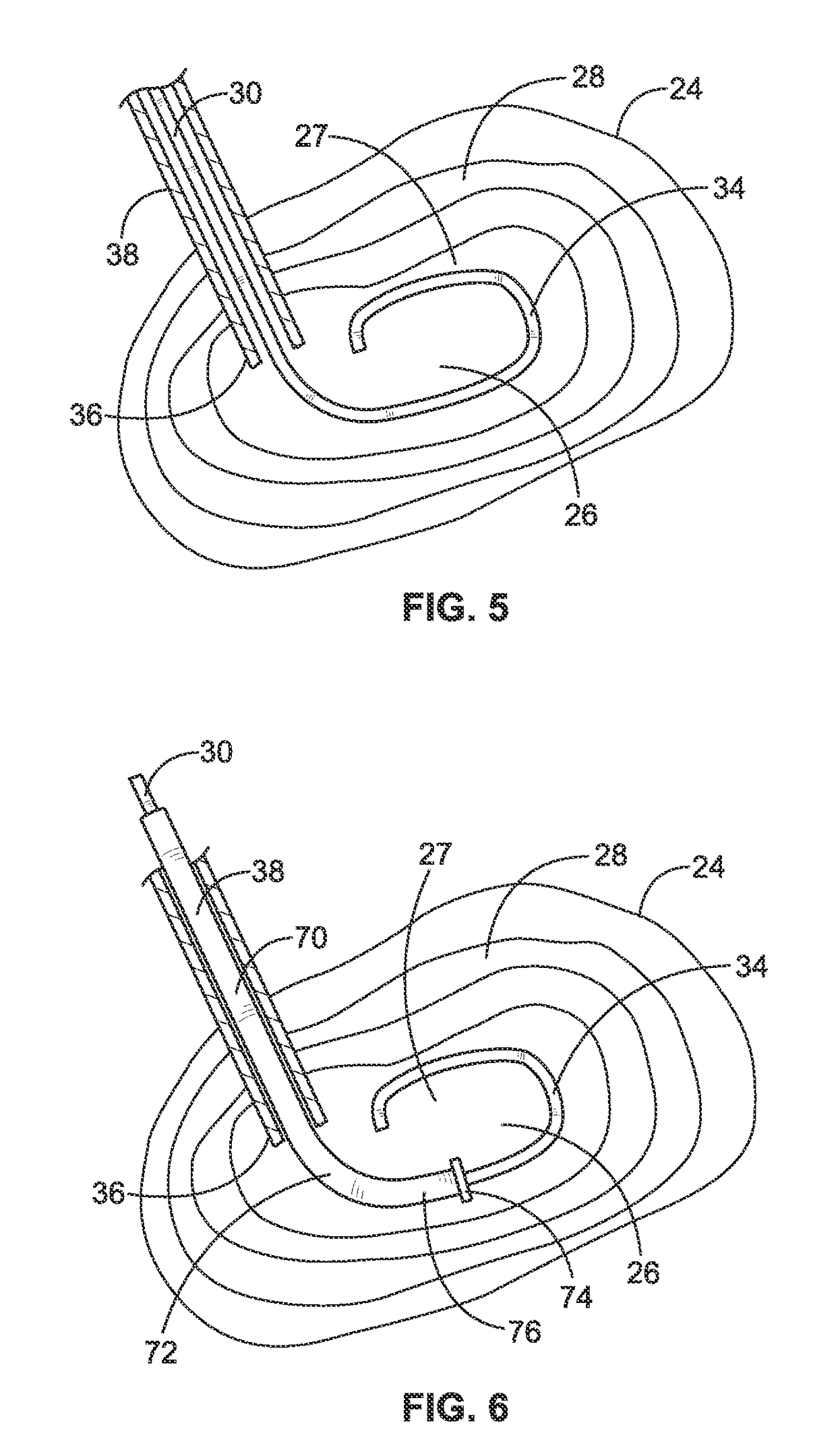
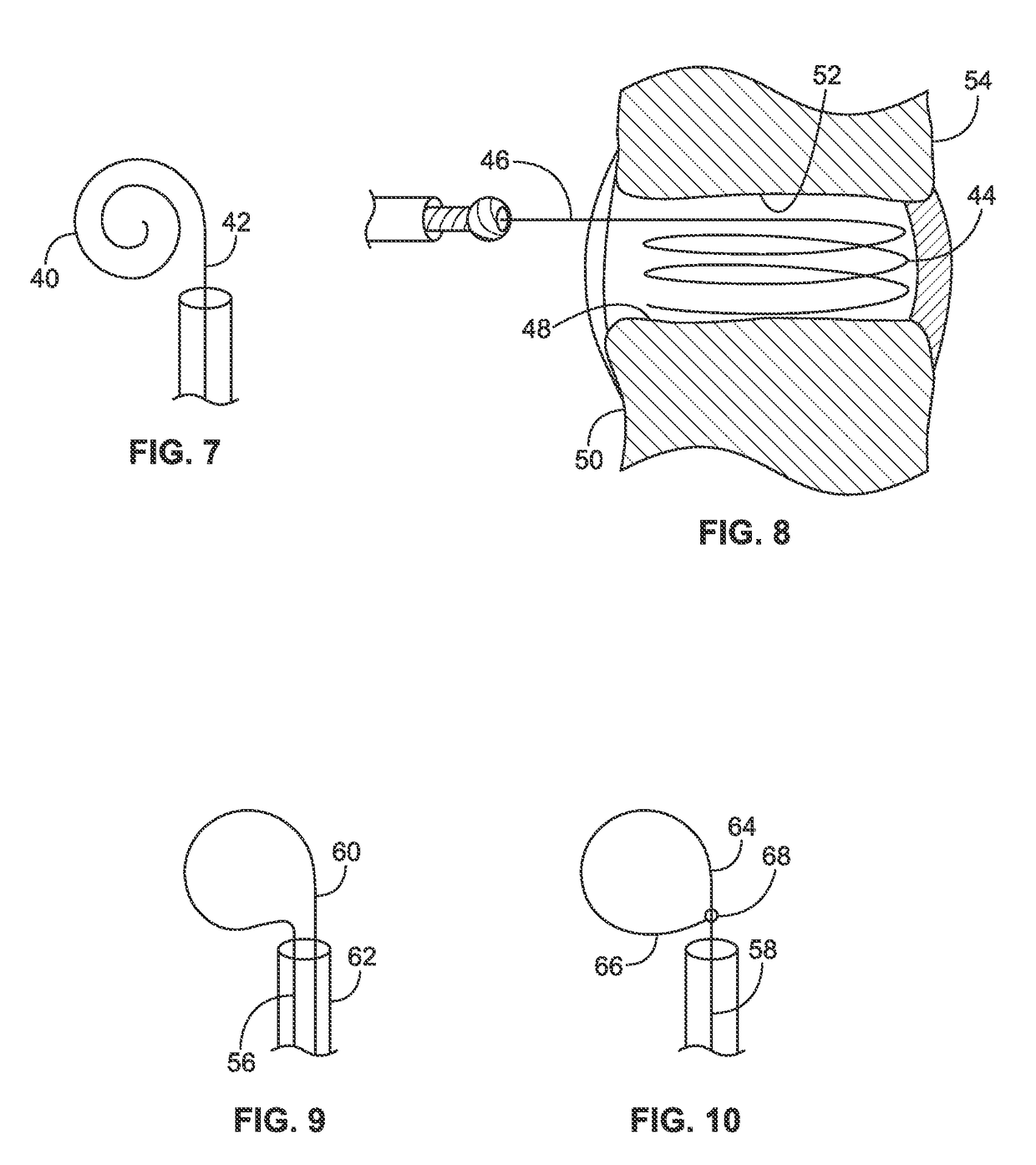
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed of a woven or braided material and may be made of a polymer such as nylon, polyurethane, polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene or any of the well known and biocompatible polymers. Alternatively the expansile portion of the catheter may be formed from a metallic braid of stainless steel, elgiloy, Nitinol, or other biocompatible metals. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Interbody fusion system with intervertebral implant retention assembly
ActiveUS20100217393A1Eliminating exacerbation of instabilityImprove stabilitySpinal implantsFastenersPosterior instrumentationCorpectomy
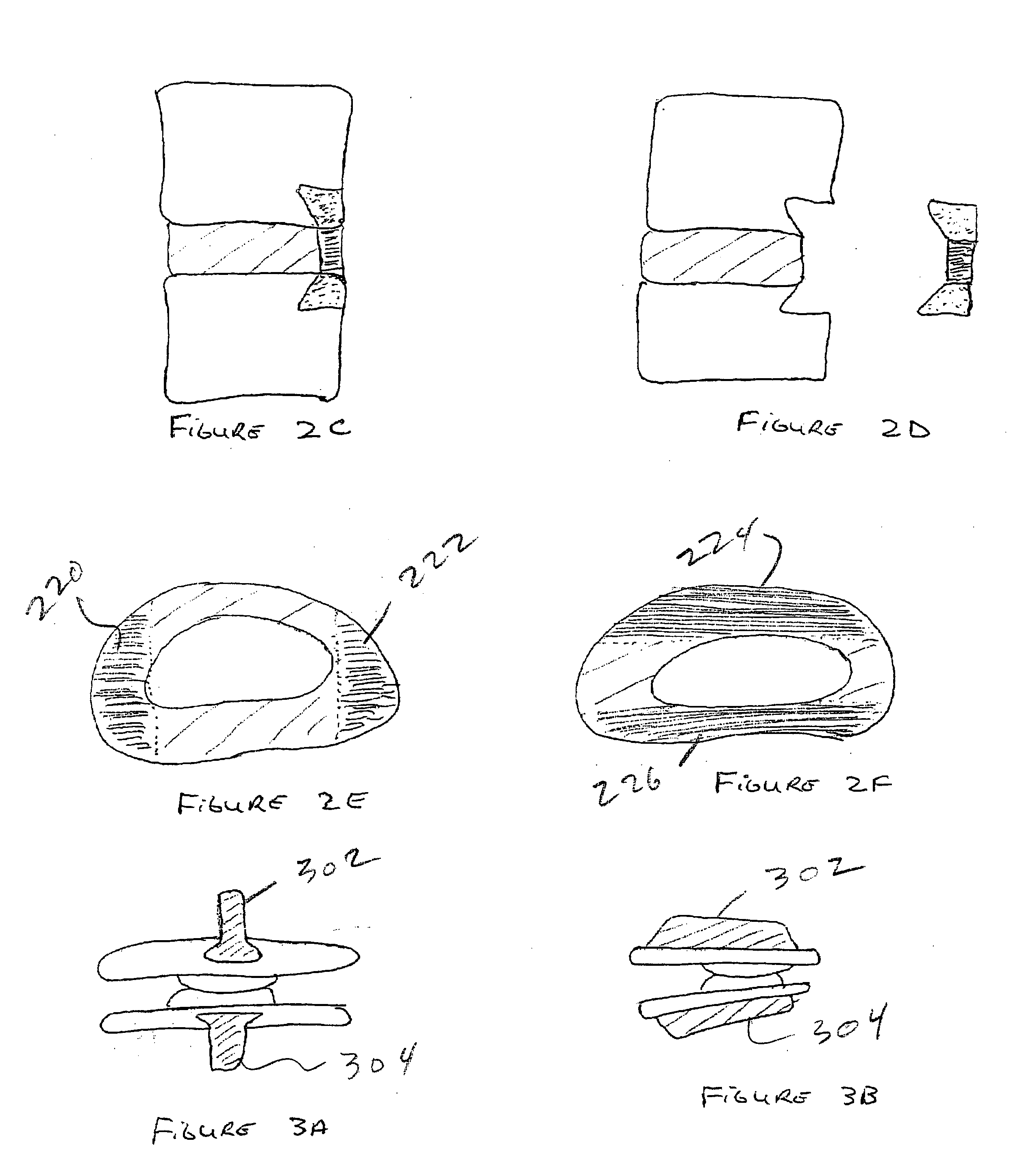
The present disclosure is directed towards a biomechanical implant and anterior, lateral or posterior instrumentation construct. The construct may be of unitary or modular construction, whereby a single molded construction can form the entire assembly, in which case the through holes may be adapted to receive a metallic insert for screw fixation; or alternatively be of a modular construction wherein the anterior / lateral instrumentation and intervertebral spacer are designed for removable locking engagement, one with the other, for insertion by the surgeon as a unitary construct. A unique feature of the construct resides within the instrumentation construction, whereby a single opening formed therein permits two bone screws, or the like fastener device, to be positioned within both the superior and inferior vertebral bodies surrounding the spacer implant, or, for example in the case of a corpectomy or diskectomy with cage insertion, wherein two screws can be fixed within a single vertebral body through a single through hole, and wherein the bone screws are constructed and arranged to cooperate with the retention plate so as to provide locking engagement, one to the other, with the retention plate, upon final fixation thereof. Screw retention elements of alternative shape, based upon the choice of vertical or horizontal orientation, based upon an opened figure eight design, are provided for insertion in a groove formed in the borehole of the instrumentation plate which allows insertion of each fixation element but will prevent a loosened fixation element from falling out of the plate.
Owner:SPARTAN CAGE HLDG
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:BAXANO SURGICAL
Spinal fusion system and method for fusing spinal bones
ActiveUS7182782B2Material is facilitatedFacilitates fixing a relative relationInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnSurgical operation
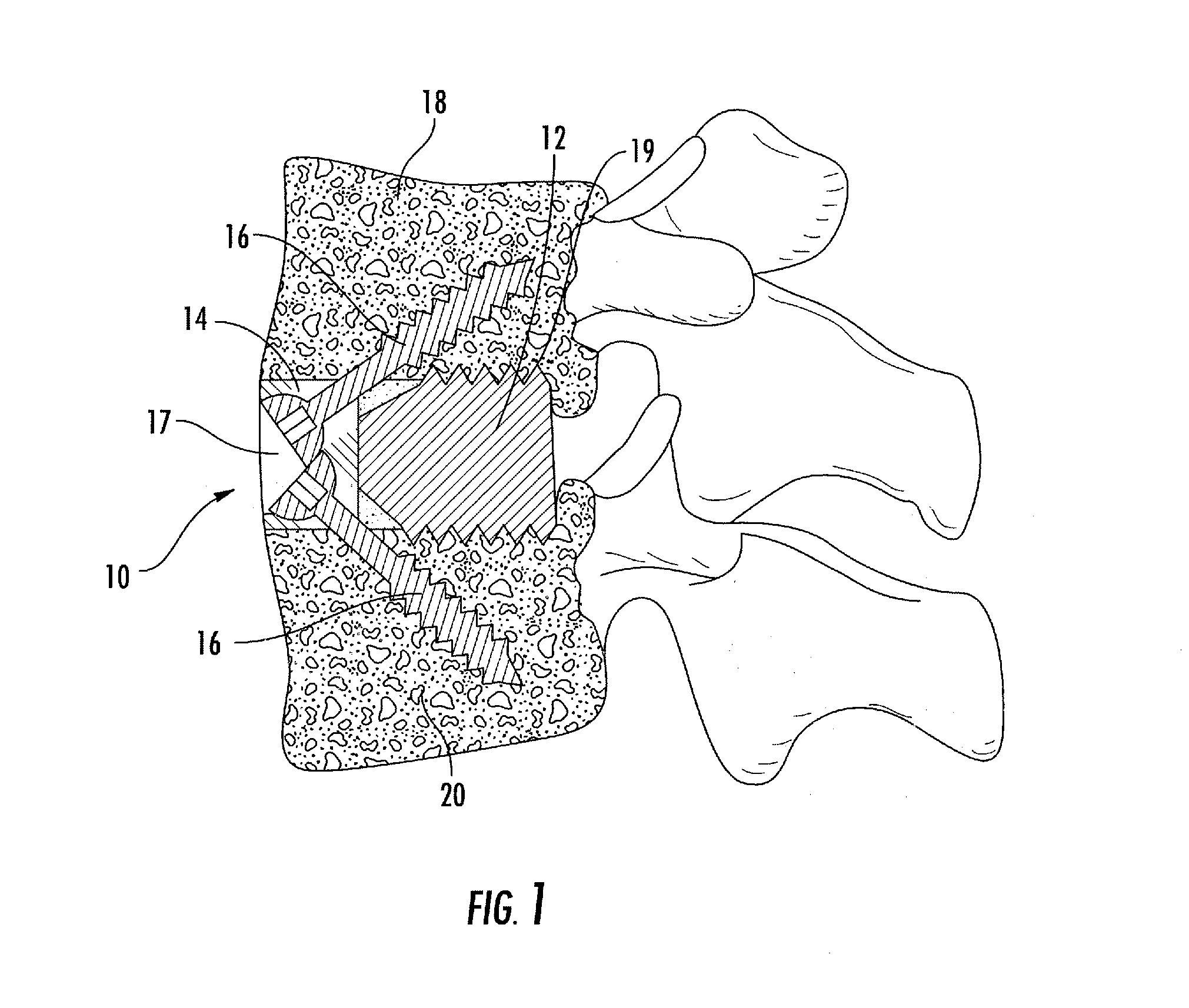
This invention relates to a spinal fusion system and method for use as a prosthetic implant. The system and method includes a housing dimensioned to be situated between adjacent spinal bones, such as adjacent vertebrae. The housing cooperates with the spinal bones to define a graft area for receiving graft material, which may be inserted anteriorly into the housing during a surgical operation such as a vertebrectomy or discectomy. A housing may have various features such as migration preventers to prevent the housing from migrating posteriorly towards a spinal column during or after insertion of the housing; a plurality of projections or crossbars may be removably inserted into the housing and can be used with a cover that permits the housing to “float” relative thereto.
Owner:X SPINE SYST
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287730A1Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLamina terminalisClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop can use an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
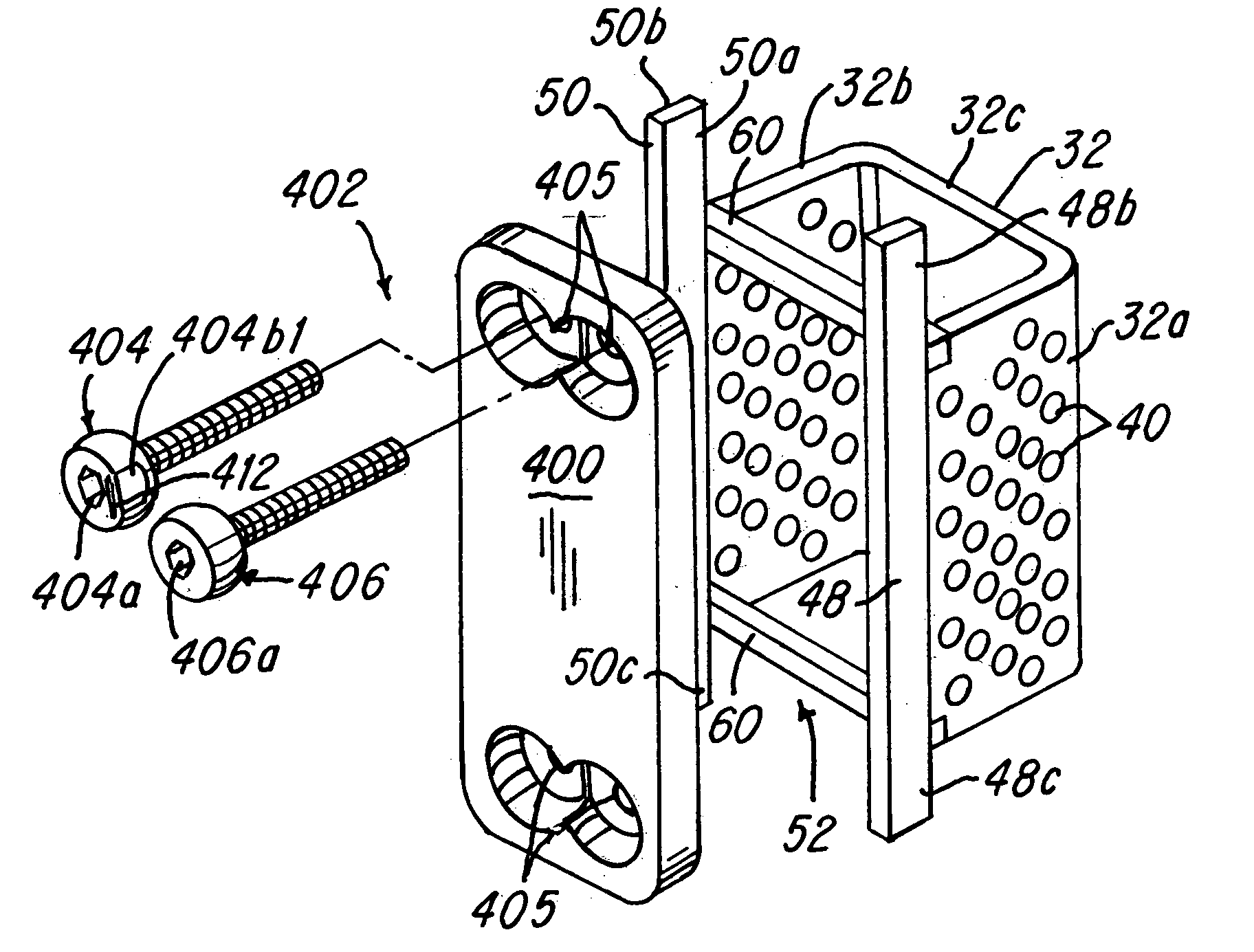
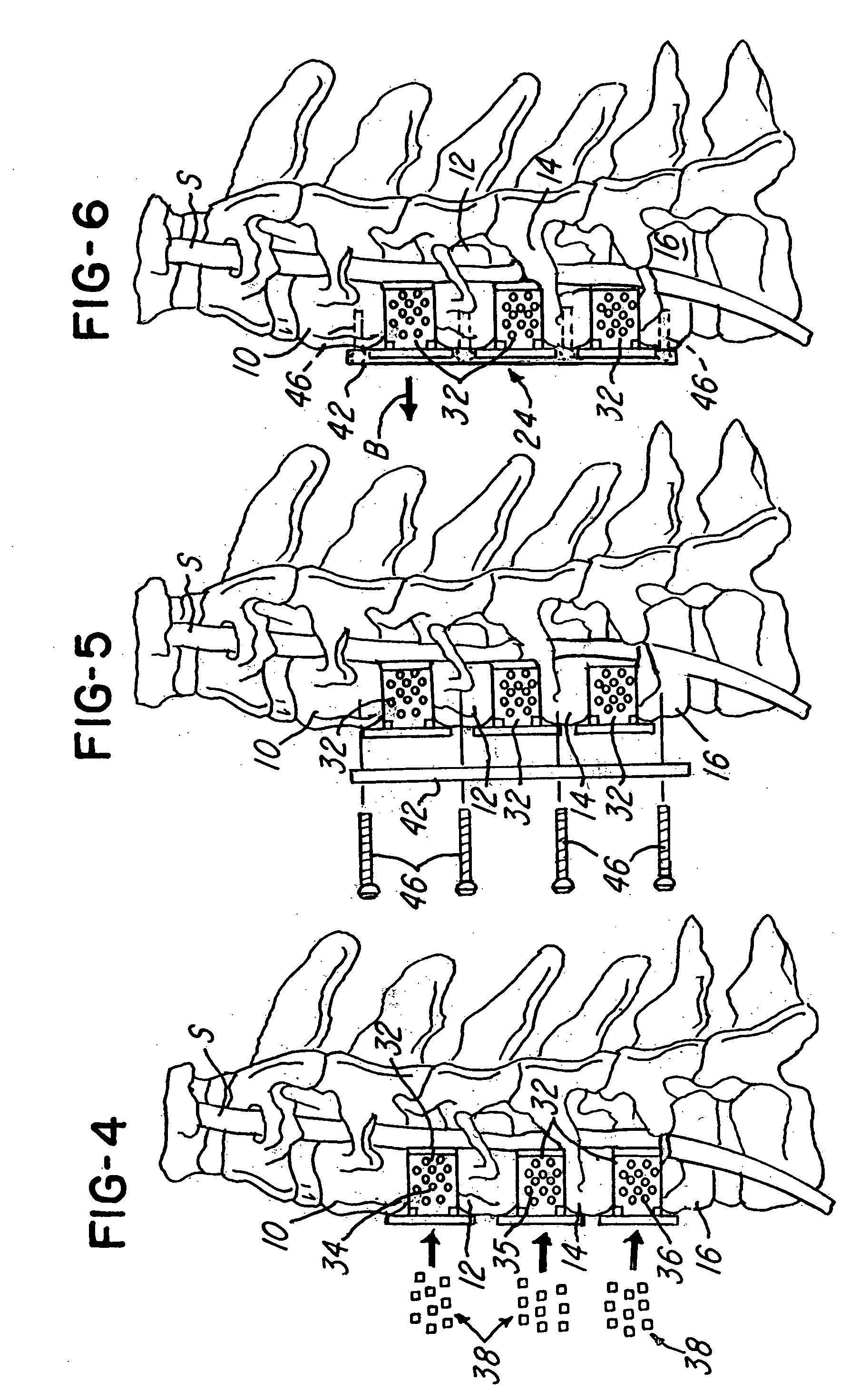
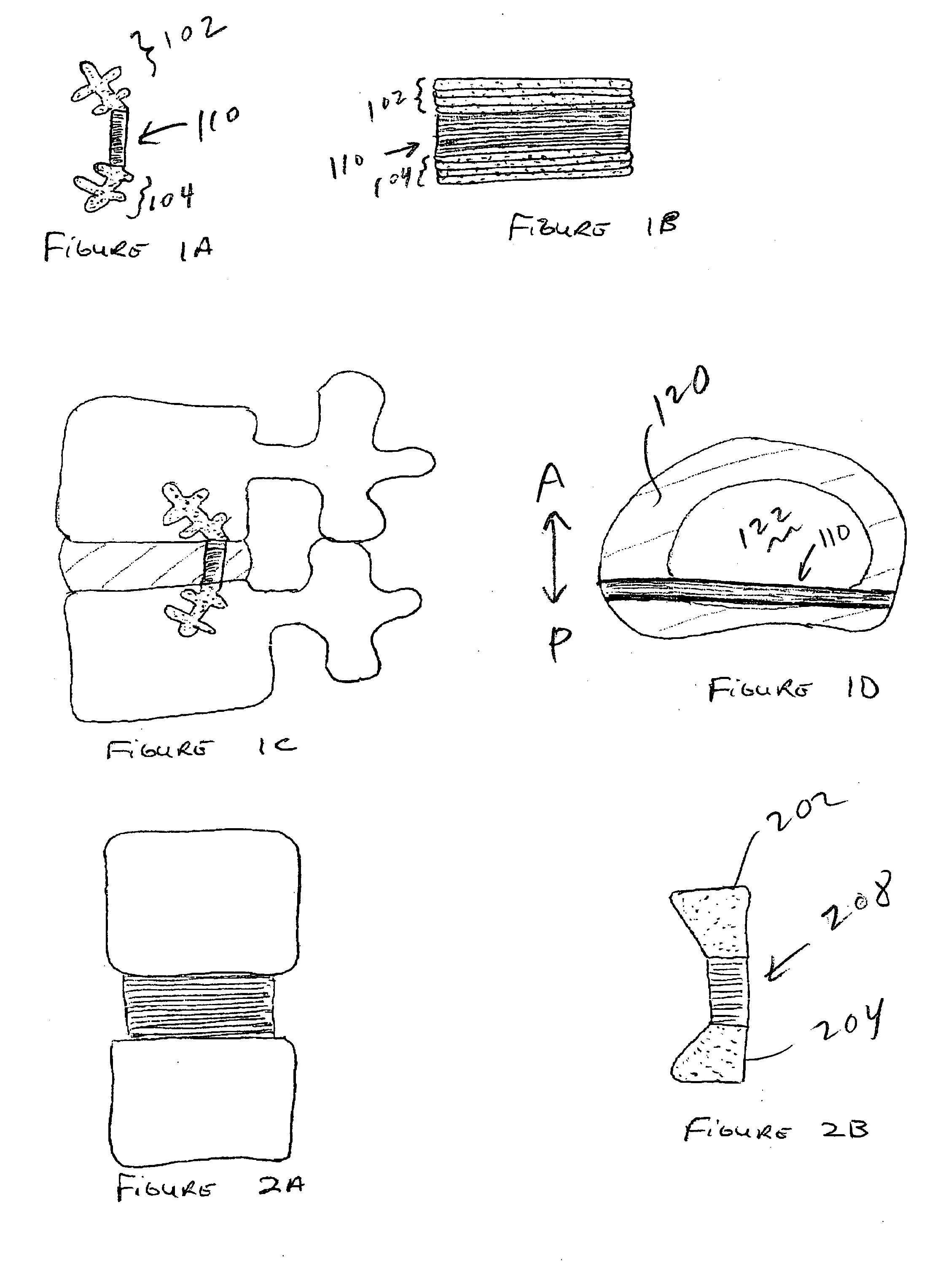
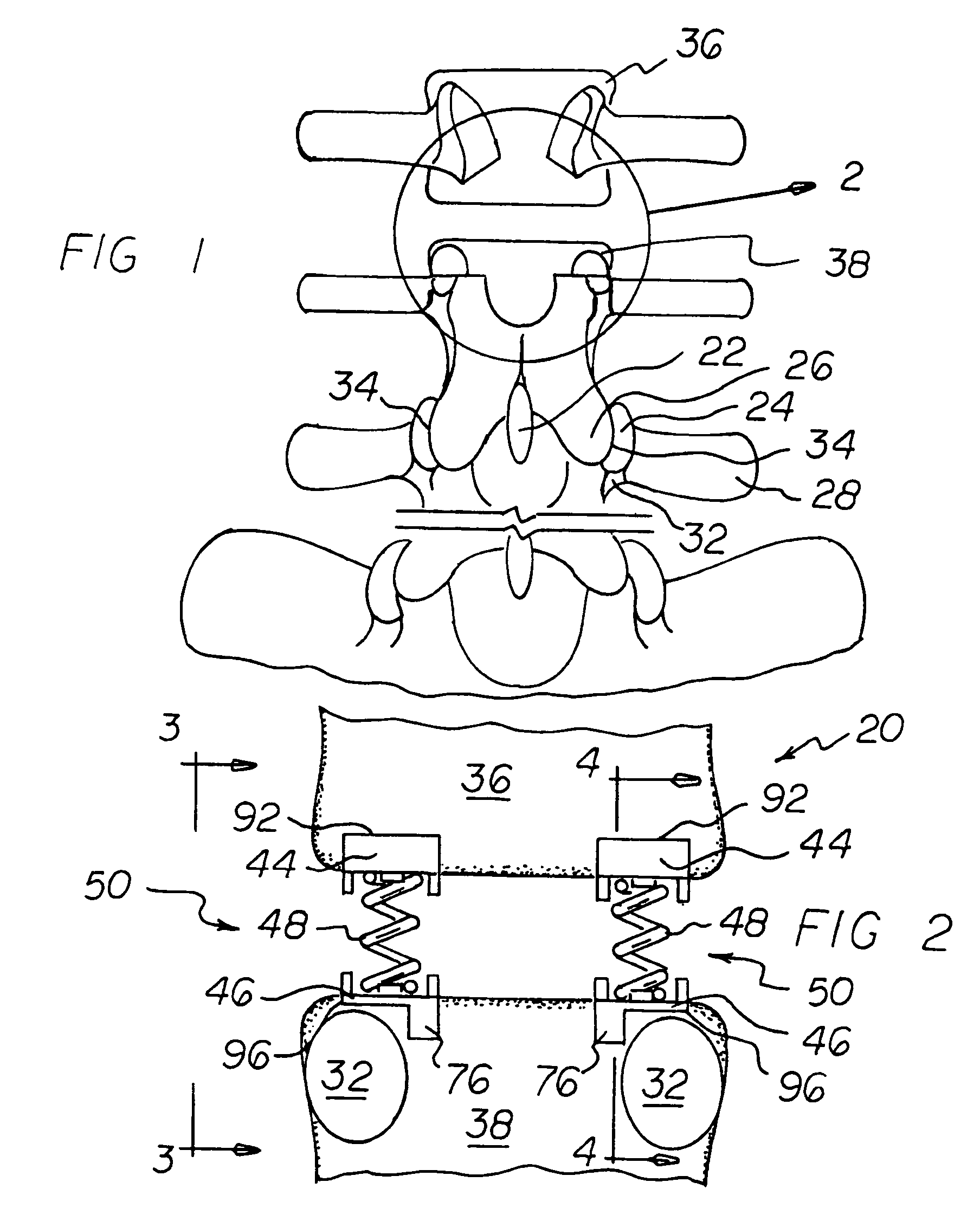
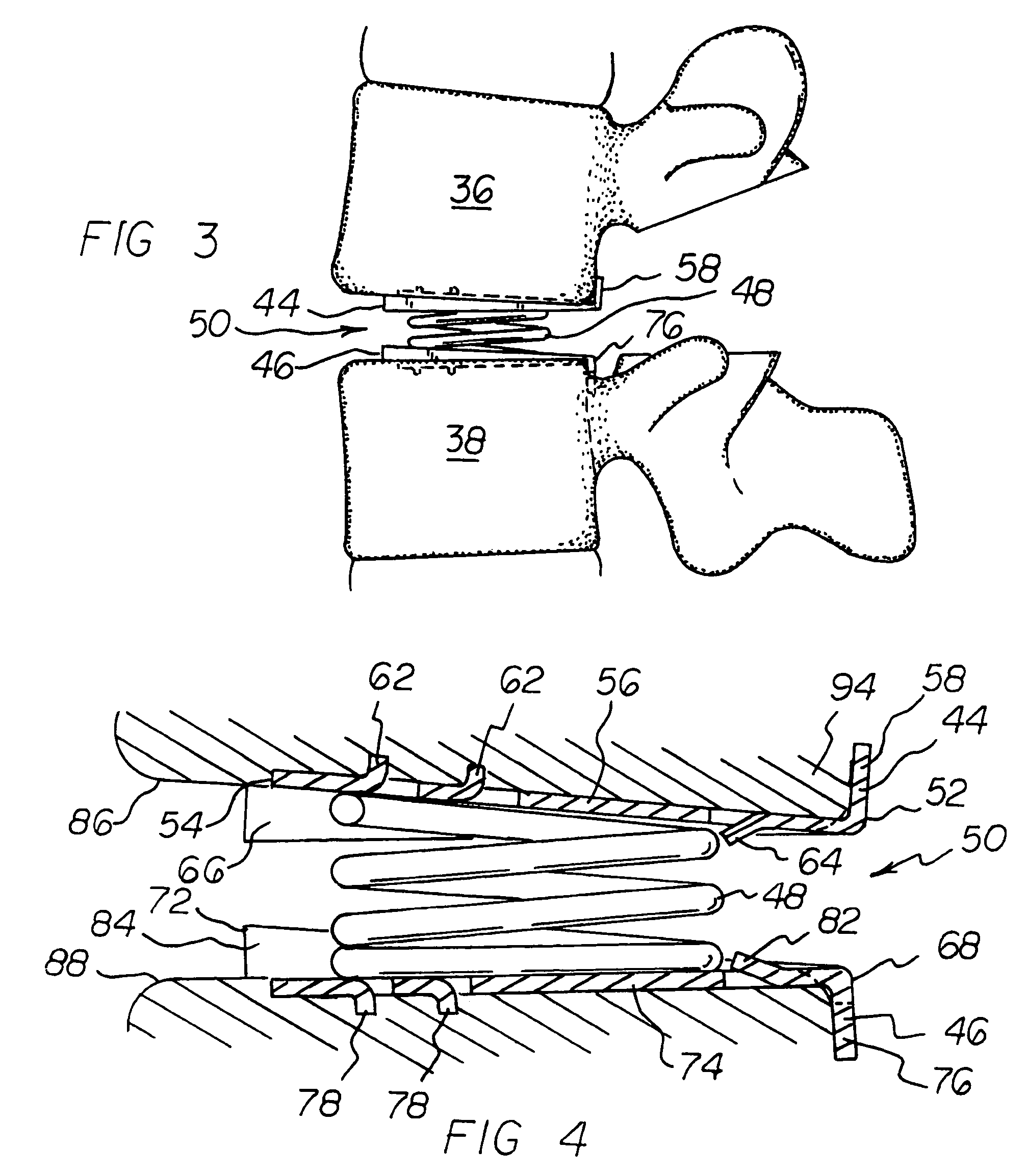
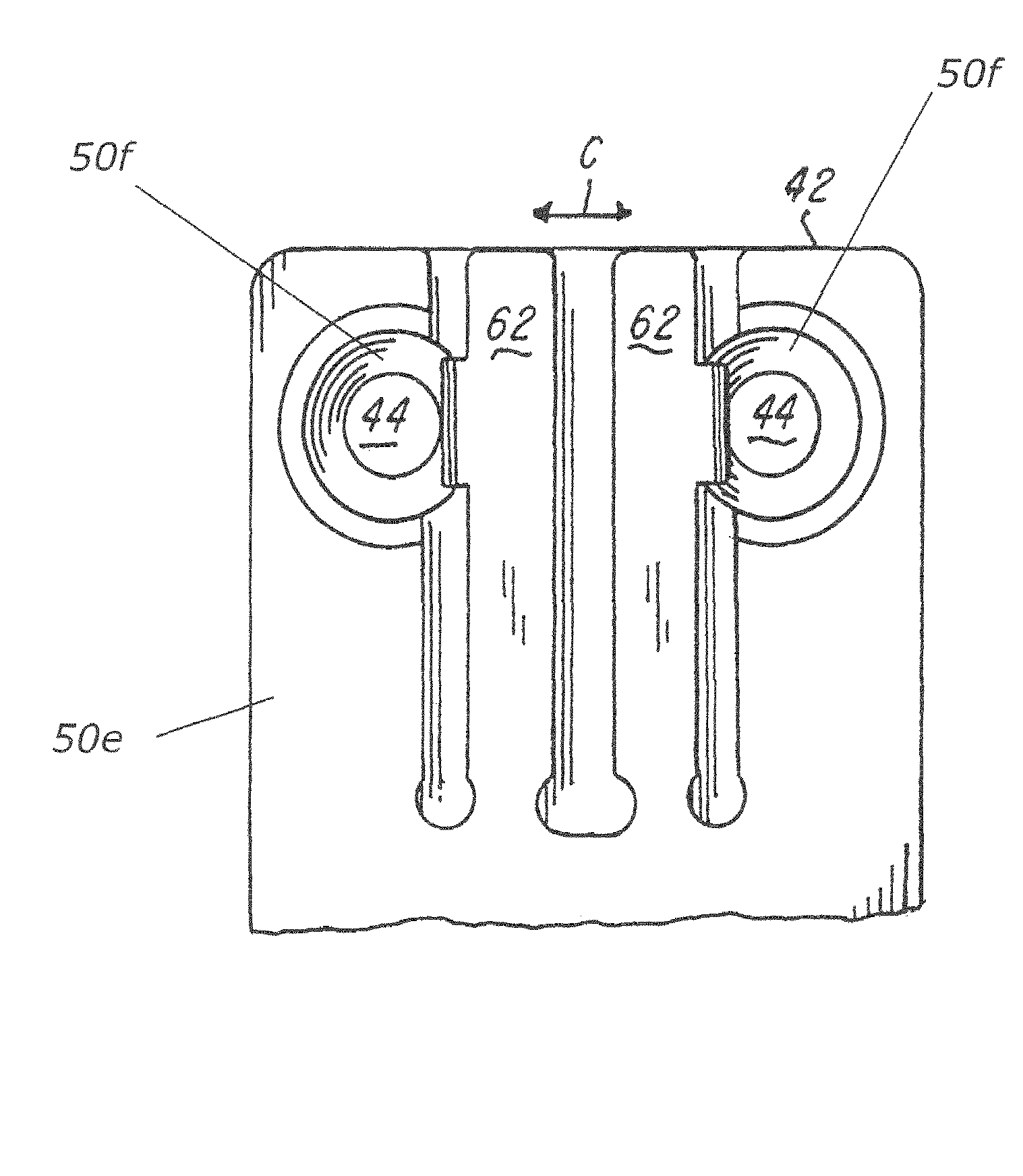
Axial spinal implant and method and apparatus for implanting an axial spinal implant within the vertebrae of the spine
Spinal implants for fusing and / or stabilizing spinal vertebrae and methods and apparatus for implanting one or more of such spinal implants axially within one or more axial bore within vertebral bodies in alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner are disclosed. Attachment mechanisms are provided that attach or affix or force the preformed spinal implants or rods to or against the vertebral bone along the full length of a TASIF axial bore or bores or pilot holes or at the cephalad end and / or caudal end of the TASIF axial bore or bores or pilot holes. The engagement of the vertebral body is either an active engagement upon implantation of the spinal implant into the TASIF axial bore or a passive engagement of the external surface configuration with the vertebral bone caused by bone growth about the external surface configuration. A plurality of such spinal implants can be inserted axially in the same TASIF axial bore or pilot hole or separately in a plurality of TASIF axial bores or pilot holes that extend axially and in a side-by-side relation through the vertebrae and discs, if present, between the vertebrae. Discectomies and / or vertebroblasty can be performed through the TASIF axial bore or bores or pilot holes prior to insertion of the spinal implants. Vertebroblasty is a procedure for augmentation of collapsed vertebral bodies by pumped-in materials, e.g., bone cement or bone growth materials. Materials or devices can also be delivered into the disc space to separate the adjoining vertebrae and / or into damaged vertebral bodies or to strengthen them.
Owner:TRANSI
Spinal fusion system and method for fusing spinal bones
ActiveUS20050071008A1Material is facilitatedFacilitates fixing a relative relationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnSurgical operation
This invention relates to a spinal fusion system and method for use as a prosthetic implant. The system and method includes a housing dimensioned to be situated between adjacent spinal bones, such as adjacent vertebrae. The housing cooperates with the spinal bones to define a graft area for receiving graft material, which may be inserted anteriorly into the housing during a surgical operation such as a vertebrectomy or discectomy. A housing may have various features such as migration preventers to prevent the housing from migrating posteriorly towards a spinal column and can be used with a cover that permits the housing to “float” relative thereto. Screws are provided in one embodiment and are dimensioned or configured to lock against each other to retain the screws and, consequently, the cover in place.
Owner:X SPINE SYST
Spinal implants, including devices that reduce pressure on the annulus fibrosis
InactiveUS20050256582A1Promote reconstructionPrevents herniationInternal osteosythesisBone implantFibrosisDiscectomy
The invention broadly facilitates reconstruction of the Annulus Fibrosus (AF) or the AF and the Nucleus Pulposus (NP). Such Reconstruction prevents recurrent herniation following Microlumbar Discectomy (MLD) other procedures. The invention may also be used in the treatment of herniated discs, annular tears of the disc, or disc degeneration, while enabling surgeons to preserve the contained NP. The methods and apparatus may be used to treat discs throughout the spine including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines of humans and animals. In the preferred embodiment, a spinal repair system according to the invention comprises a first end portion adapted for placement within an intervertebral body, a second end portion adapted for placement within an adjacent intervertebral body, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second end portions, the bridge portion being adapted to span a portion of an intervertebral disc space and prevent excessive outward bulging.
Owner:ANOVA
Vertebral implants adapted for posterior insertion
InactiveUS7485134B2Improve wear lifeHigh strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnFibrocartilage
Disclosed is an endoprosthetic implant for a human spinal disc. The structure of the implant allows it to be inserted posteriorly. This insertion is accomplished by performing a partial discectomy in the affected region. An intervertebral space is then created by removing the fibrocartilage between the facing surfaces of adjacent vertebrae. The implant is then inserted into the intervertebral space. The implant is thus adapted to replace damaged or worn intervertebral discs. Furthermore, the structure of the implant, and its posterior insertion, alleviate most spinal pathologies.
Owner:SIMONSON CYNTHIA JEANNE
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287727A1Increase the diameterEasy to integrateSuture equipmentsBone implantPolyesterClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed of a woven or braided material and may be made of a polymer such as nylon, polyurethane, polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene or any of the well known and biocompatible polymers. Alternatively the expansile portion of the catheter may be formed from a metallic braid of stainless steel, elgiloy, Nitinol, or other biocompatible metals. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
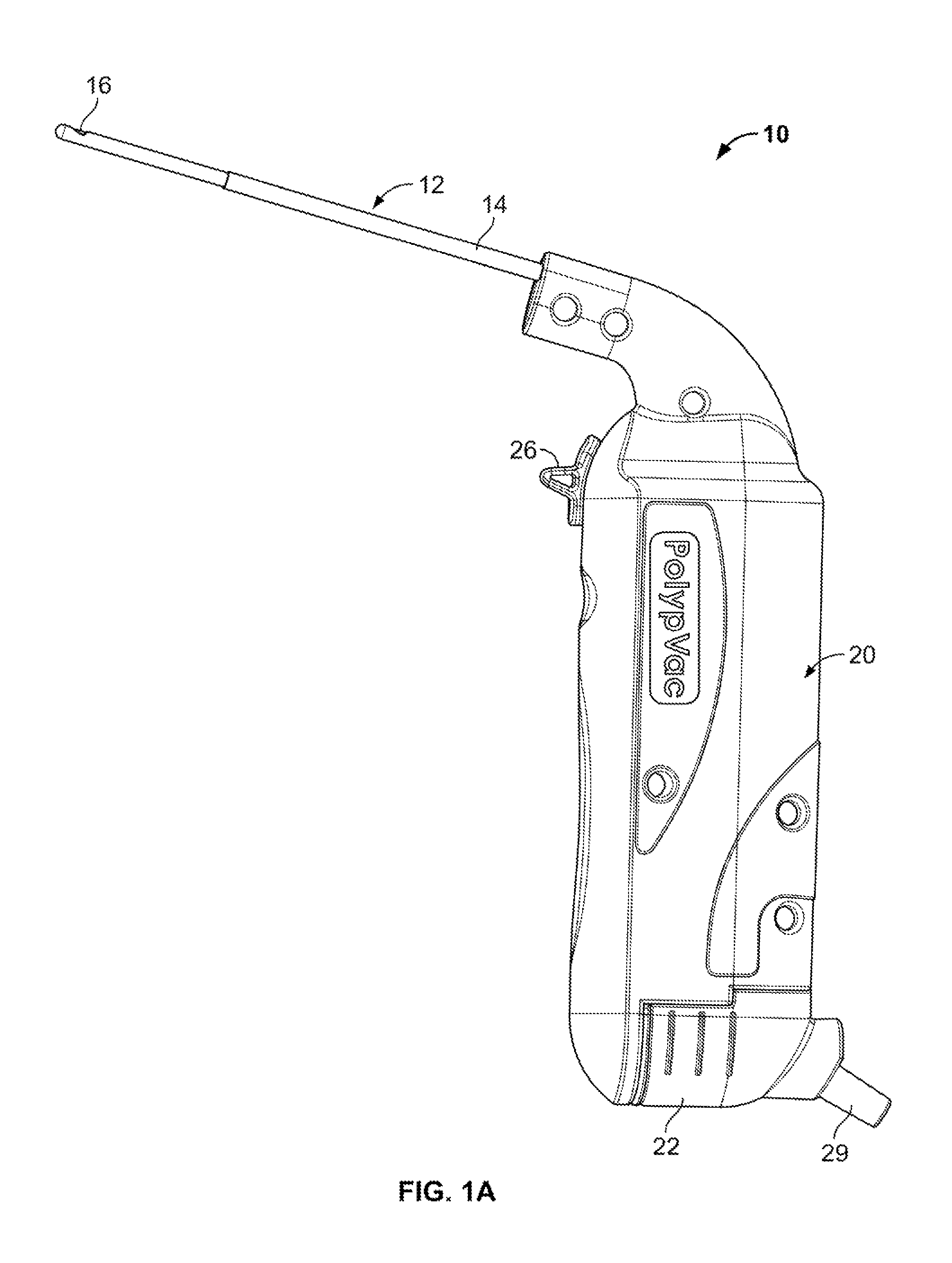
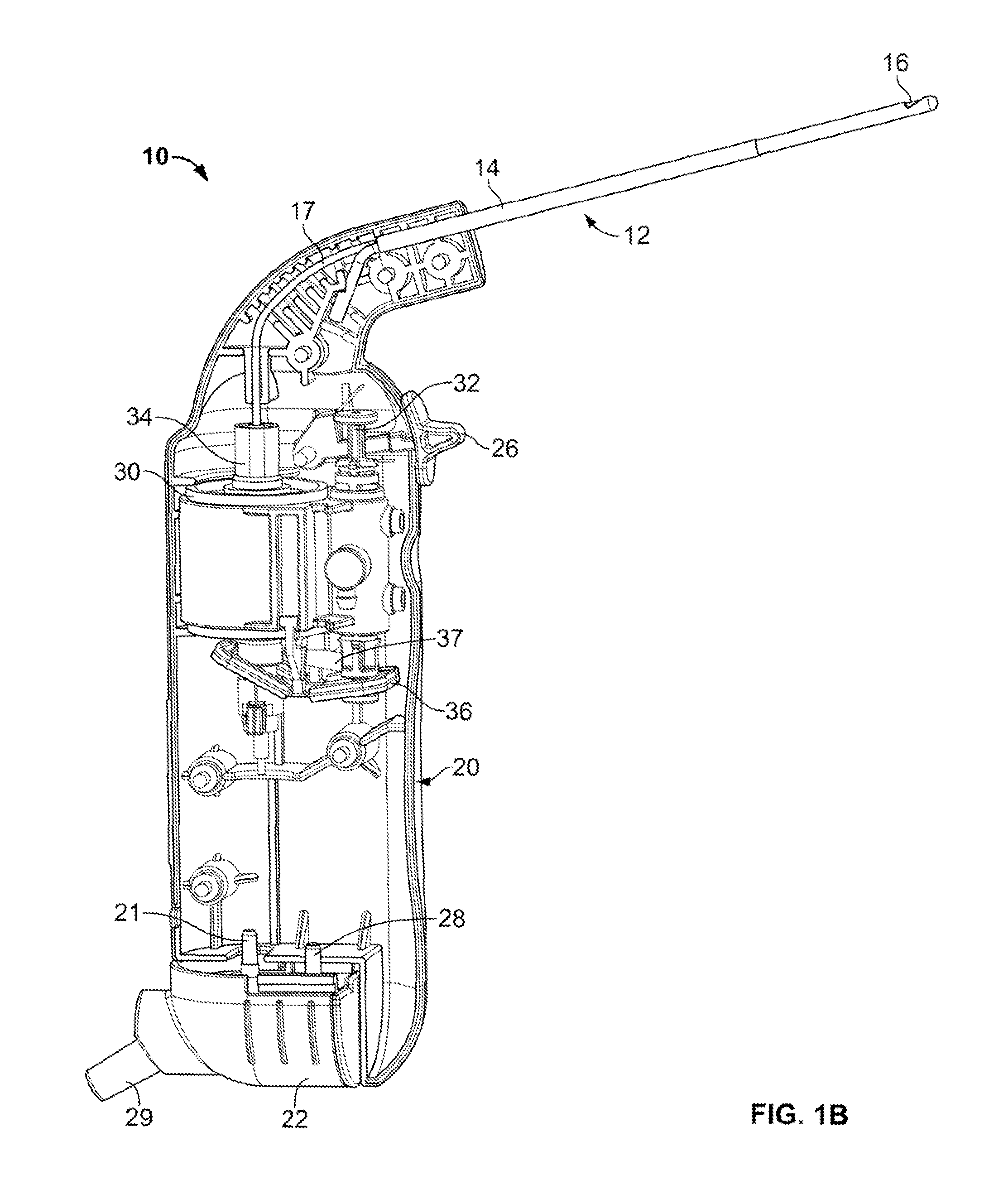
Tissue Removal Tools And Methods Of Use
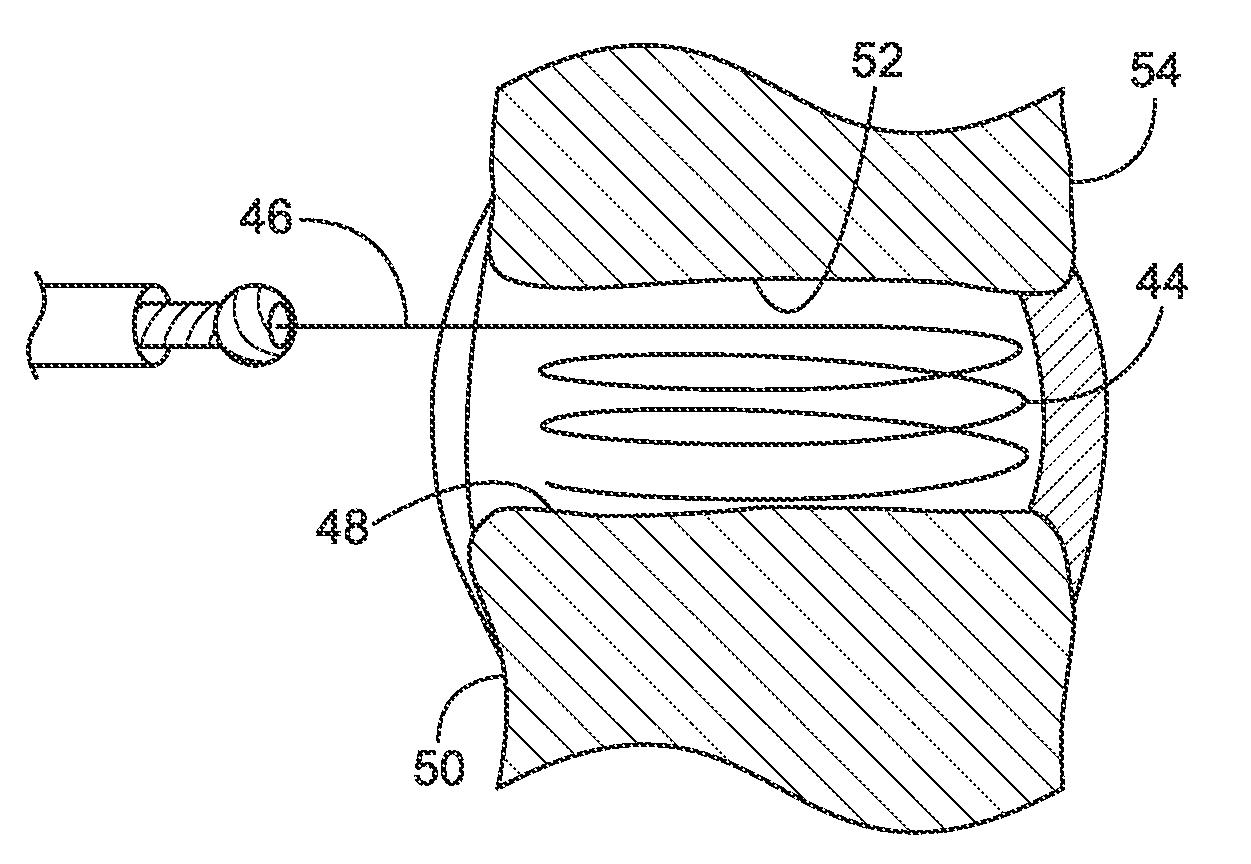
Discectomy or disc preparation system that includes a guide member that is changeable from a deployment configuration for insertion into an intervertebral disc space to a deployed configuration upon being deployed into the intervertebral disc. The system also includes at least one tissue manipulator, such as cutting, scraping and extraction elements, that can be moved or tracked longitudinally along the guide member into and through the intervertebral disc space.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Vertebral implant with dampening matrix adapted for posterior insertion
InactiveUS7052515B2Prolong lifeHigh strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral disc
Disclosed is an endoprosthetic implant for a human spinal disc. The structure of the implant allows it to be inserted posteriorly. This insertion is accomplished by performing a partial discectomy in the affected region. An intervertebral space is then created by removing the fibrocartilage between the facing surfaces of adjacent vertebrae. The implant is then inserted into the intervertebral space. The implant is thus adapted to replace damaged or worn intervertebral discs. Furthermore, the structure of the implant, and its posterior insertion, alleviate most spinal pathologies.
Owner:SIMONSON CYNTHIA JEANNE
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20070162135A1Increase the diameterEasy to integrateSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLamina terminalisClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop can use an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Discectomy devices and related methods
Tissue removal devices are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, a tissue removal device may comprise a handheld housing, a motor, and a tissue removal mechanism coupled to the handheld housing. The tissue removal mechanism may comprise a tubular member, a rotatable elongated member disposed within a lumen of the tubular member, a first impeller distal to the rotatable elongated member, and a second impeller adjacent the first impeller.
Owner:EXPANDING INNOVATIONS INC
Spinal fusion system and method for fusing spinal bones
ActiveUS20050071006A1Material is facilitatedFacilitates fixing a relative relationInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnSurgical operation
This invention relates to a spinal fusion system and method for use as a prosthetic implant. The system and method includes a housing dimensioned to be situated between adjacent spinal bones, such as adjacent vertebrae. The housing cooperates with the spinal bones to define a graft area for receiving graft material, which may be inserted anteriorly into the housing during a surgical operation such as a vertebrectomy or discectomy. A housing may have various features such as migration preventers to prevent the housing from migrating posteriorly towards a spinal column during or after insertion of the housing; a plurality of projections or crossbars may be removably inserted into the housing and can be used with a cover that permits the housing to “float” relative thereto.
Owner:X SPINE SYST
Transpedicular access to the intervertebral disc space for discectomy, end plate preparation, and interbody fusion
An insertion device is configured to access a disc positioned between adjacent vertebrae. The insertion device includes a cannula having a passage formed therein. The cannula has an exit aperture. An obturator is substantially positioned within the passage formed in the cannula. One end of the obturator has a probe and the other end of the obturator has a head. An impaction cap is in contact with the cannula and is positioned to cover the head of the obturator. The impaction cap is configured to allow at least a portion of the cannula to be inserted through a portion of one vertebra without deployment of the probe of the obturator through the exit aperture of the cannula.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287729A1Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsBone implantClosed loopDiscectomy
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop then uses an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS7601172B2Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsBone implantLamina terminalisClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The expansile loop then uses an attachment means to secure it to substantially healthy tissues of the annulus, nucleus, or endplates. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Discectomy devices and methods
InactiveUS20140180321A1Assist dilatingExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsImpellerDiscectomy
A tissue removal device may comprise a handle portion and a tissue removal mechanism coupled to the handle portion. The tissue removal mechanism may include a tubular member having a lumen therethrough and an elongate member rotatably and slidably disposed within the lumen of the tubular member. A proximal end of the elongate member may be coupled to a drive source to impart rotational movement thereof. A distal end of the elongate member may include an impeller for cutting tissue. The elongate member may be configured to exit the distal end of the lumen of the first tubular member, such that the distal end of the second tubular member is distal to the distal end of the first tubular member. The impeller may include a blunt distal end to minimize undesirable tissue damage when the distal end of the elongate member is distal to the distal end of the tubular member.
Owner:EXPANDING INNOVATIONS INC
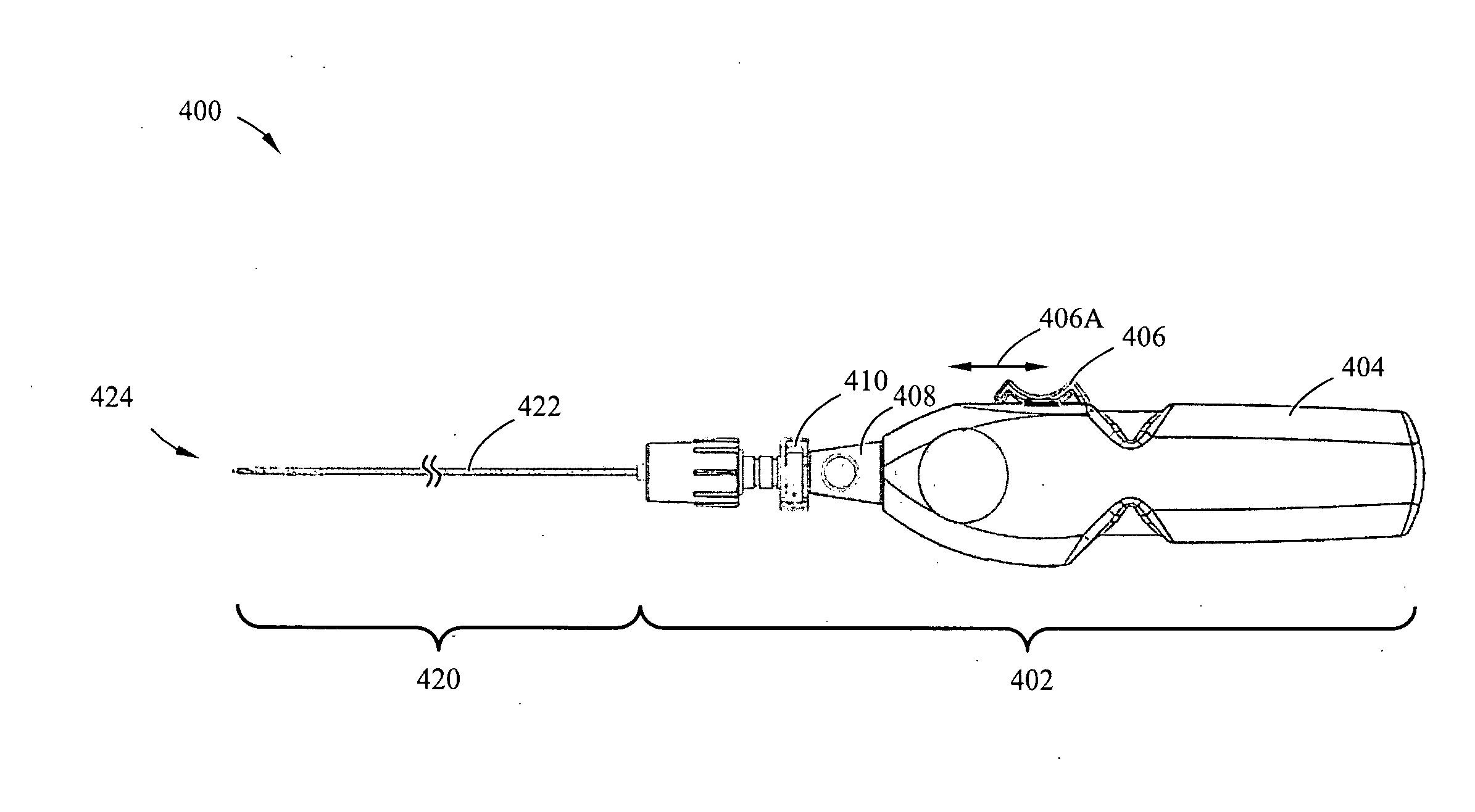
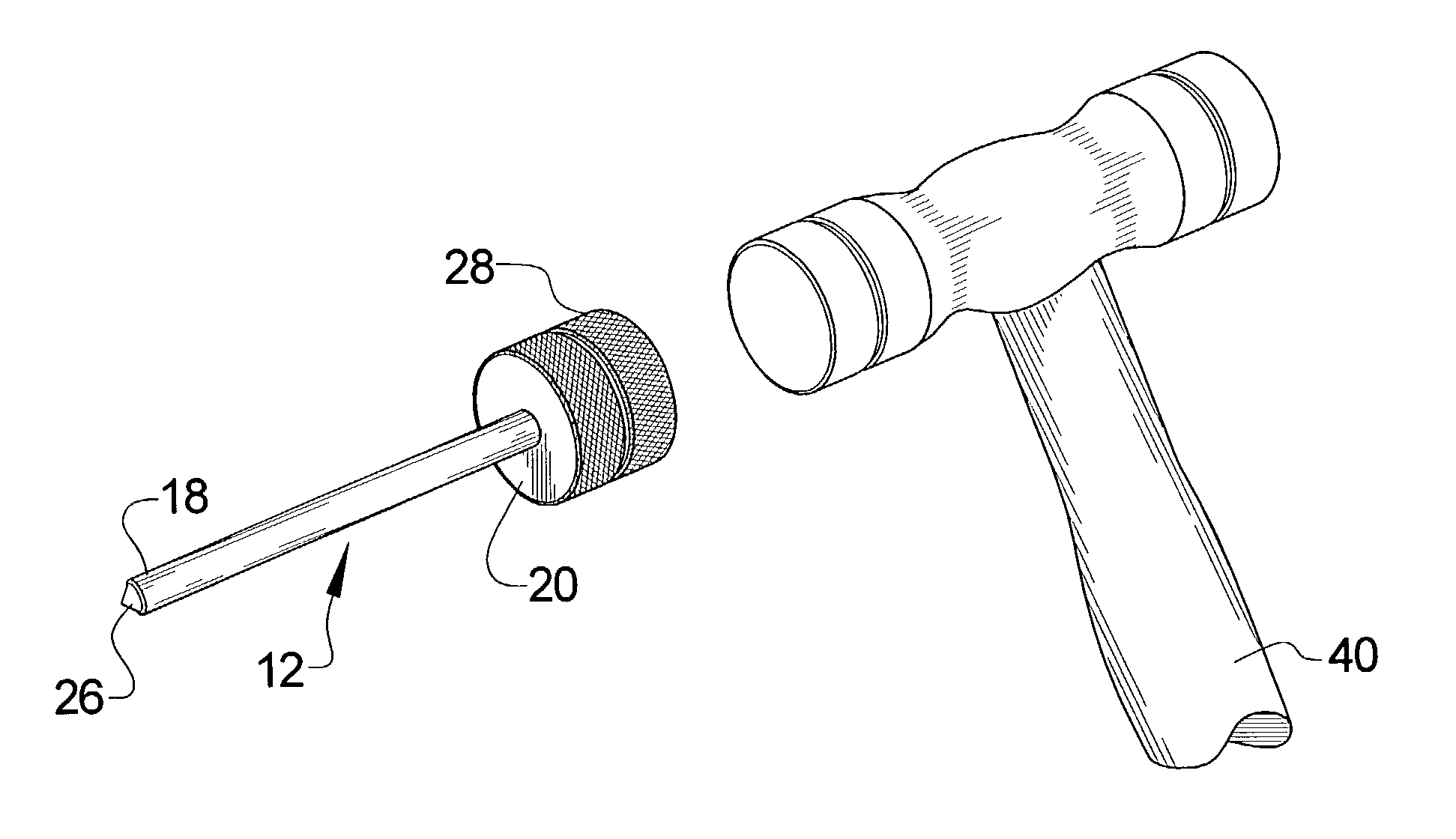
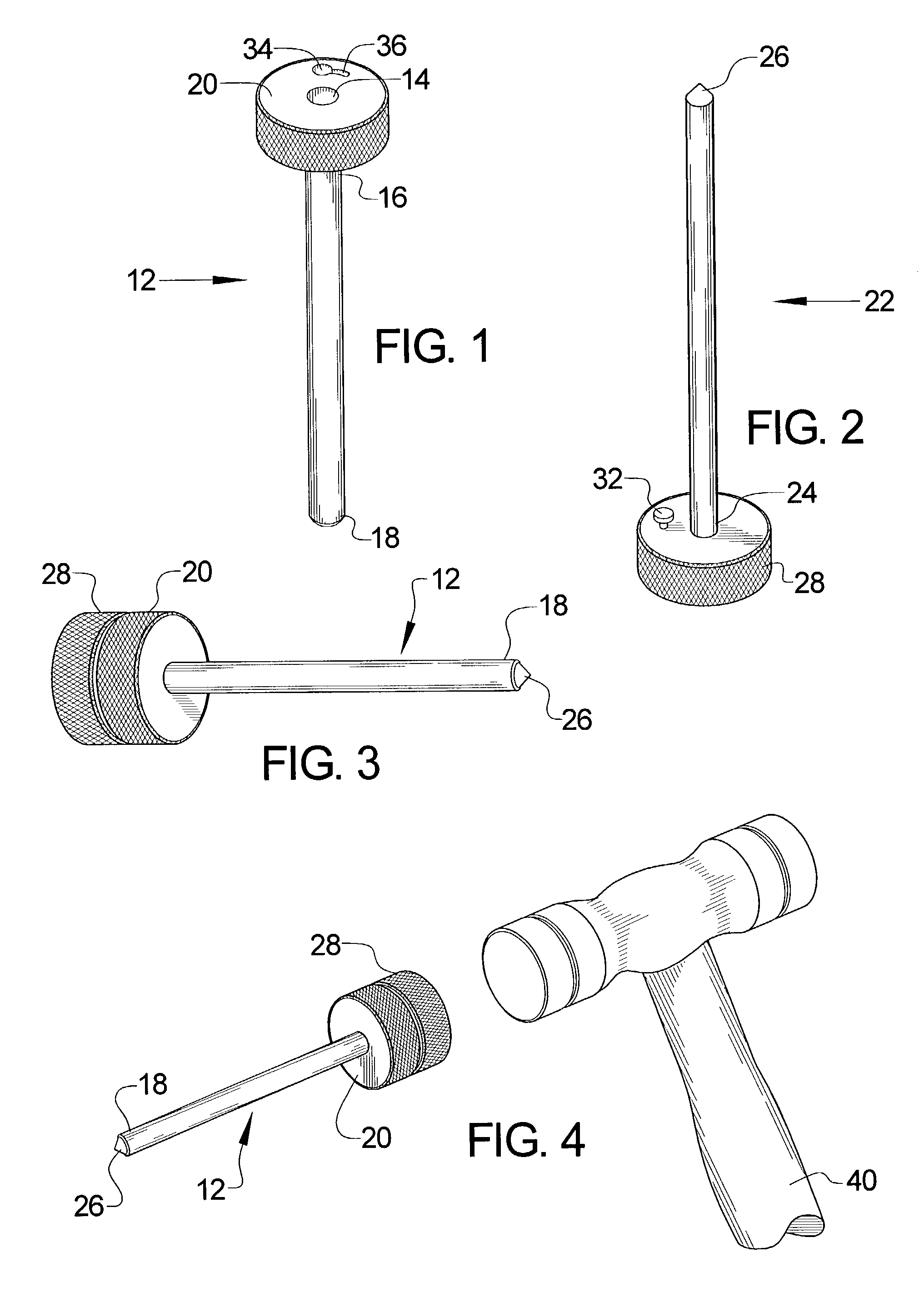
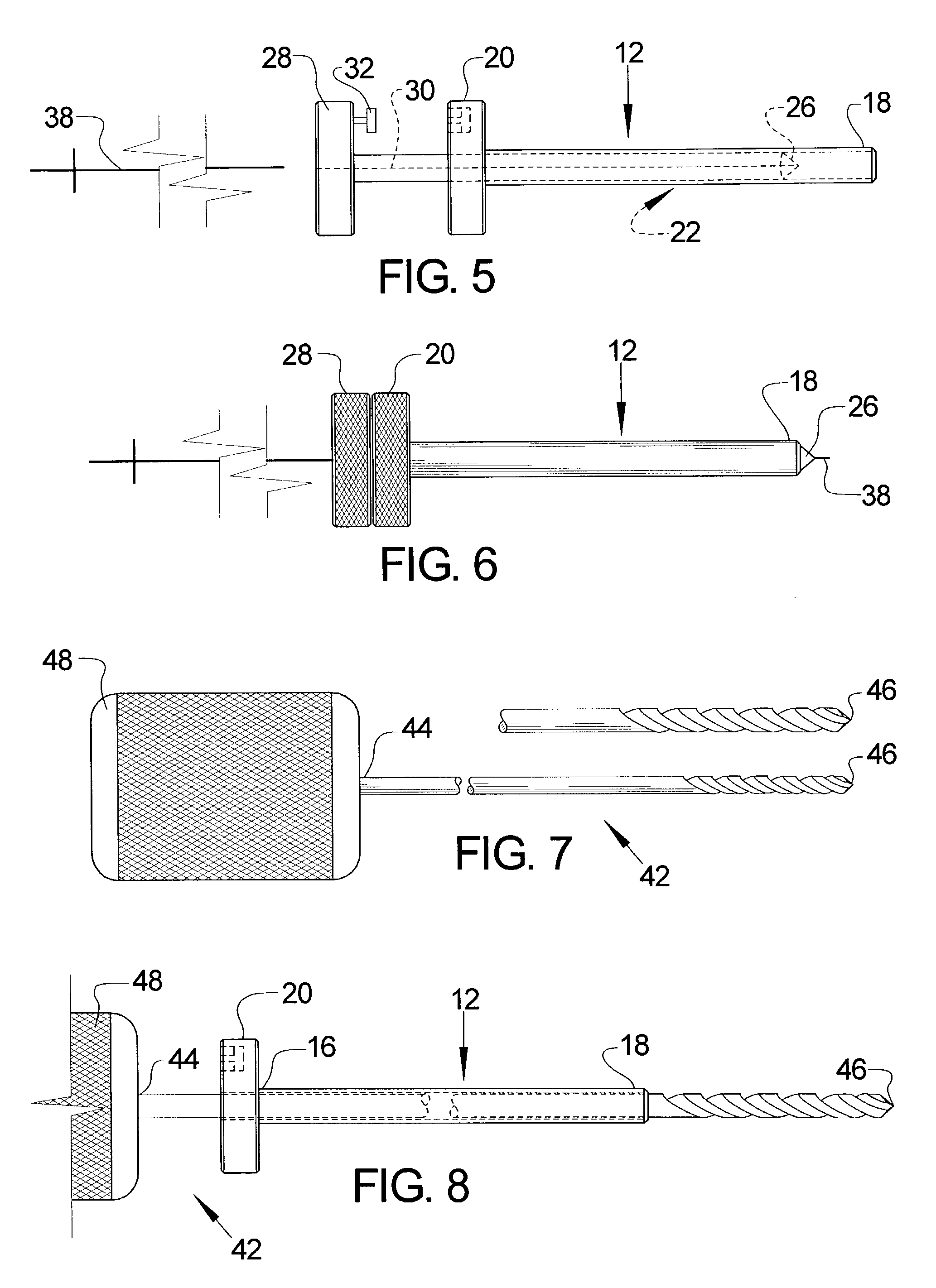
Anterior cervical facet discectomy surgery kit and method for its use
A surgical kit is used for performing an anterior cervical disectomy, the surgical kit having a sheath that is inserted into a mammal by using a bullet coupled to the sheath and impacting on the bullet. Various cutters, including a cervical cutter having a drill tip end, a serrated cutter having an enclave for receiving cutting spoils therein, and a deburrment cutter having a burr end, are insertable through the sheath for cutting bone and disc matter. An impactor can be used to move the sheath within the mammal during use of the serrated cutter and deburrment cutter without the need to remove either tool. A pituitaries is used to remove loose bone and disc material.
Owner:SPINE DESIGN
Devices and methods for cutting and evacuating tissue
Various medical devices and methods for cutting and / or evacuating tissue are provided. The devices and methods may utilize a reciprocating mechanism or motor powered by suction from a vacuum source. The medical devices and methods may be used on tissue in various regions of a patient's body and for treating various conditions, e.g., for performing a polypectomy or discectomy.
Owner:MYROMED LLC
Ultrasonic spinal surgery method
ActiveUS20080300591A1Improve approachQuicker and easy to carry-outElectrotherapySurgical needlesSpinal columnDiscectomy
In a discectomy method one removes at least a substantial portion of a spinal disc. Thereafter one operates an ultrasonic instrument to level opposing faces of vertebrae on opposite sides of the removed spinal disc. Graft or synthetic disc material is inserted between the vertebrae so that the graft or synthetic disc material is in contact with the leveled opposing faces. In an associated nucleotomy, a cannulated probe is inserted into a spinal disc and used to remove the nucleus pulposus. A synthetic or substitute nucleus material may then be inserted into the evacuated annulus.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Spinal fusion system and method for fusing spinal bones
ActiveUS7641701B2Material is facilitatedFacilitates fixing a relative relationInternal osteosythesisBone implantSurgical operationSpinal column
This invention relates to a spinal fusion system and method for use as a prosthetic implant. The system and method includes a housing dimensioned to be situated between adjacent spinal bones, such as adjacent vertebrae. The housing cooperates with the spinal bones to define a graft area for receiving graft material, which may be inserted anteriorly into the housing during a surgical operation such as a vertebrectomy or discectomy. A housing may have various features such as migration preventers to prevent the housing from migrating posteriorly towards a spinal column and can be used with a cover that permits the housing to “float” relative thereto. Screws are provided in one embodiment and are dimensioned or configured to lock against each other to retain the screws and, consequently, the cover in place.
Owner:X SPINE SYST
Devices and methods for cutting tissue
InactiveUS8292909B1Prevents unstable flutterPreventing unstable flutterEndoscopic cutting instrumentsAbrasive surgical cuttersDiscectomyMedical device
Various medical devices and methods for cutting and / or evacuating tissue are provided. The devices and methods may utilize a reciprocating mechanism or motor powered by suction from a vacuum source. The medical devices and methods may be used on tissue in various regions of a patient's body and for treating various conditions, e.g., for performing a polypectomy or discectomy.
Owner:MYROMED LLC
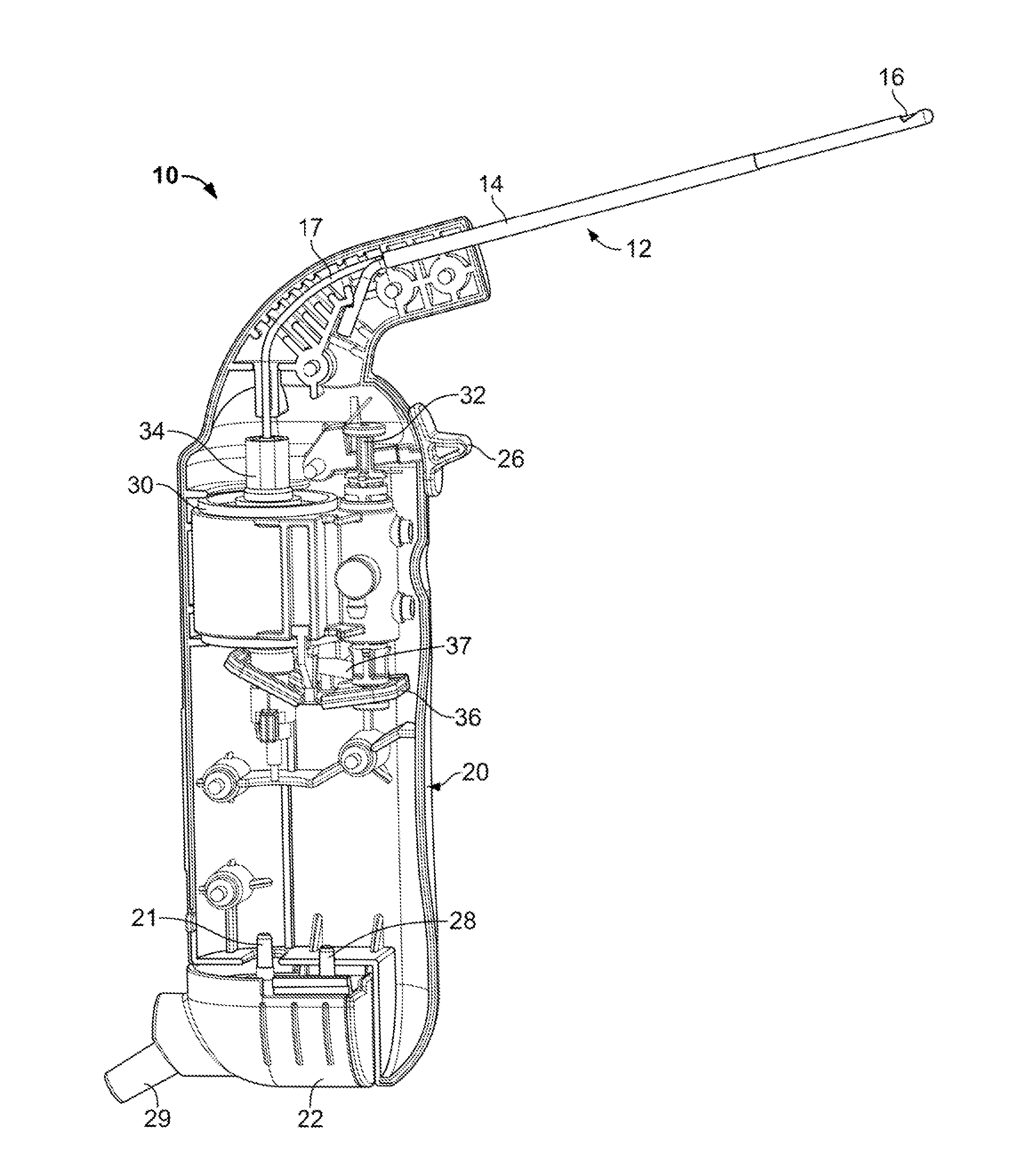
Percutaneous Disc Clearing Device
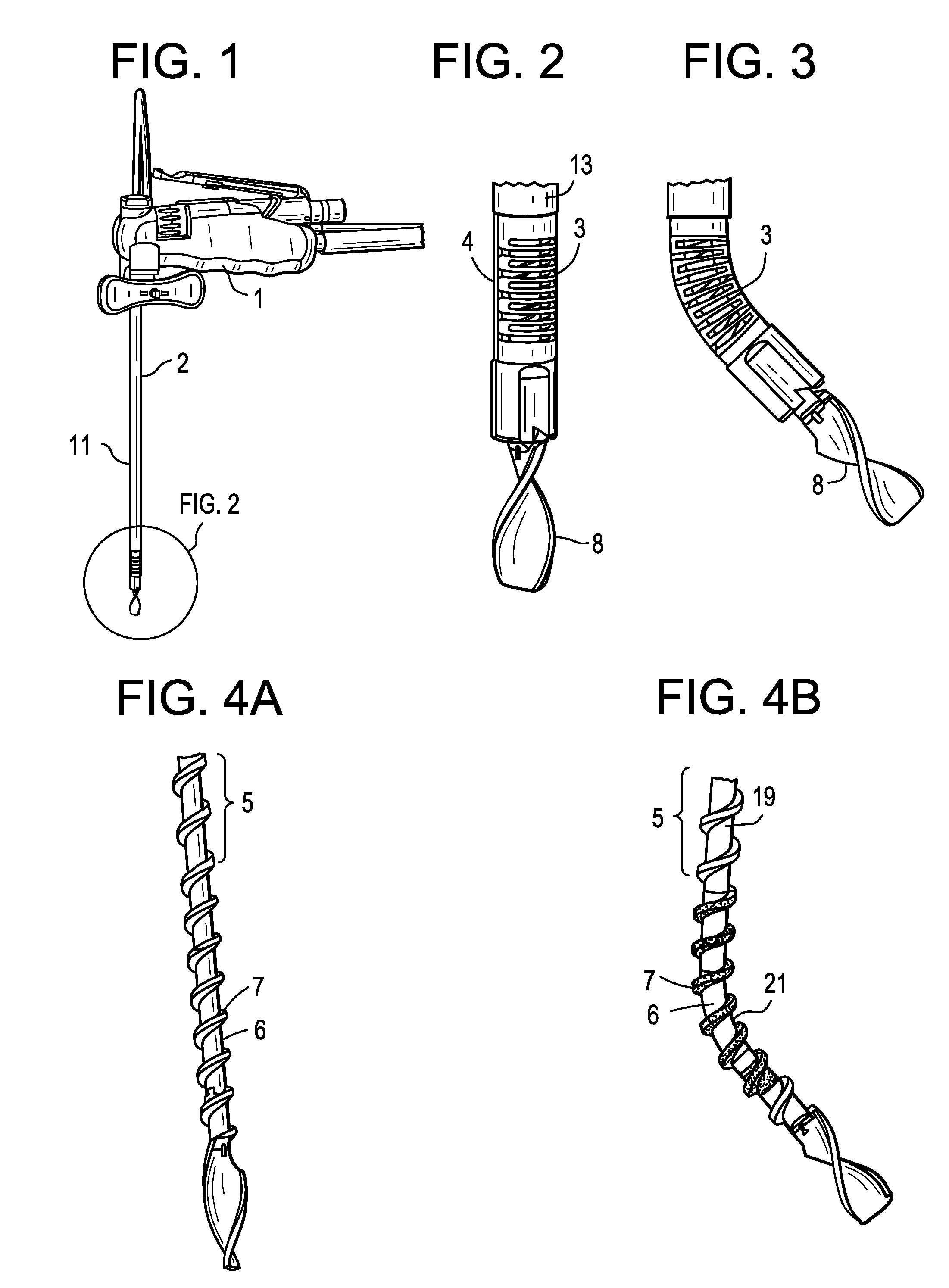
ActiveUS20160287264A1Prevent tissue-clottingImprove discectomy aspectEndoscopic cutting instrumentsDrive shaftDiscectomy
A discectomy tool comprising:a) a cannula having an outer surface having a longitudinal bore therein, a proximal end and a distal end;b) a steering wire disposed in the longitudinal bore;c) a flexible, hollow transmission shaft disposed in the cannula, the shaft having a throughbore, a proximal end portion, a distal end portion and an outer surface having a thread extending therefrom;d) an irrigation source fluidly connected to the throughbore;e) a cutting tip attached to the distal end portion of the transmission shaft.
Owner:MEDOS INT SARL
Tissue removal tools and methods of use
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com