Patents
Literature
6217results about "Bone implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
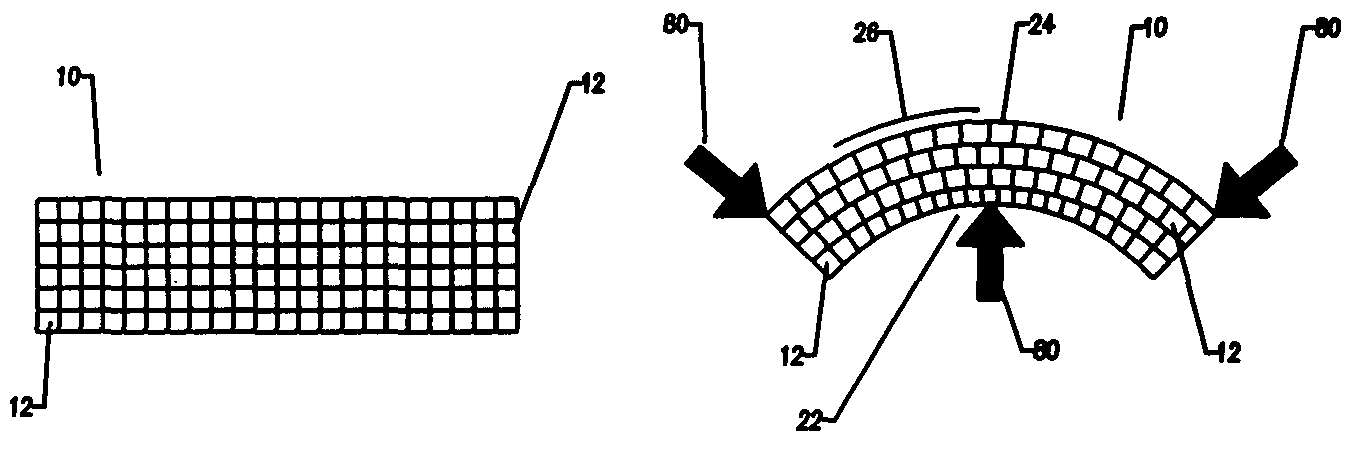
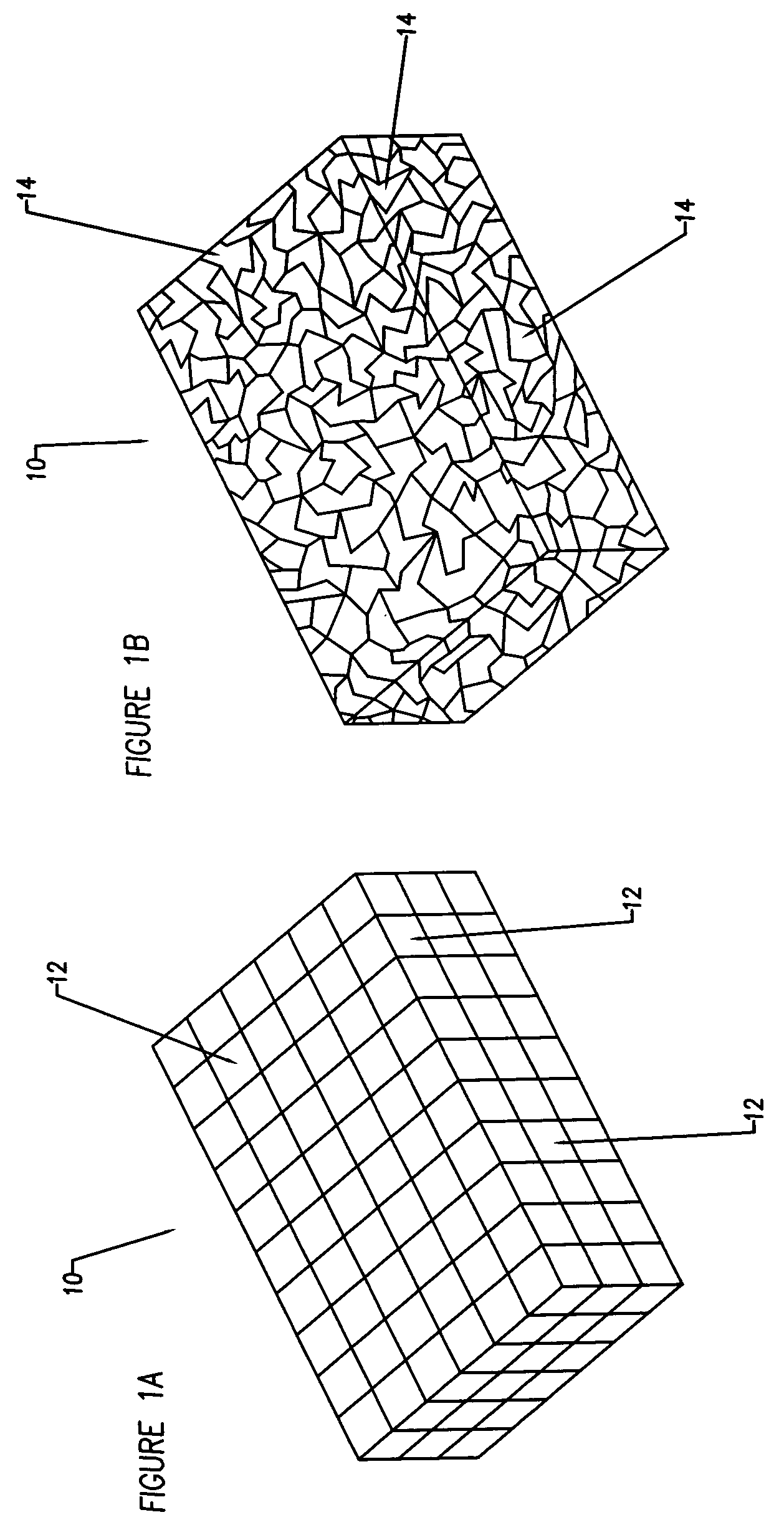
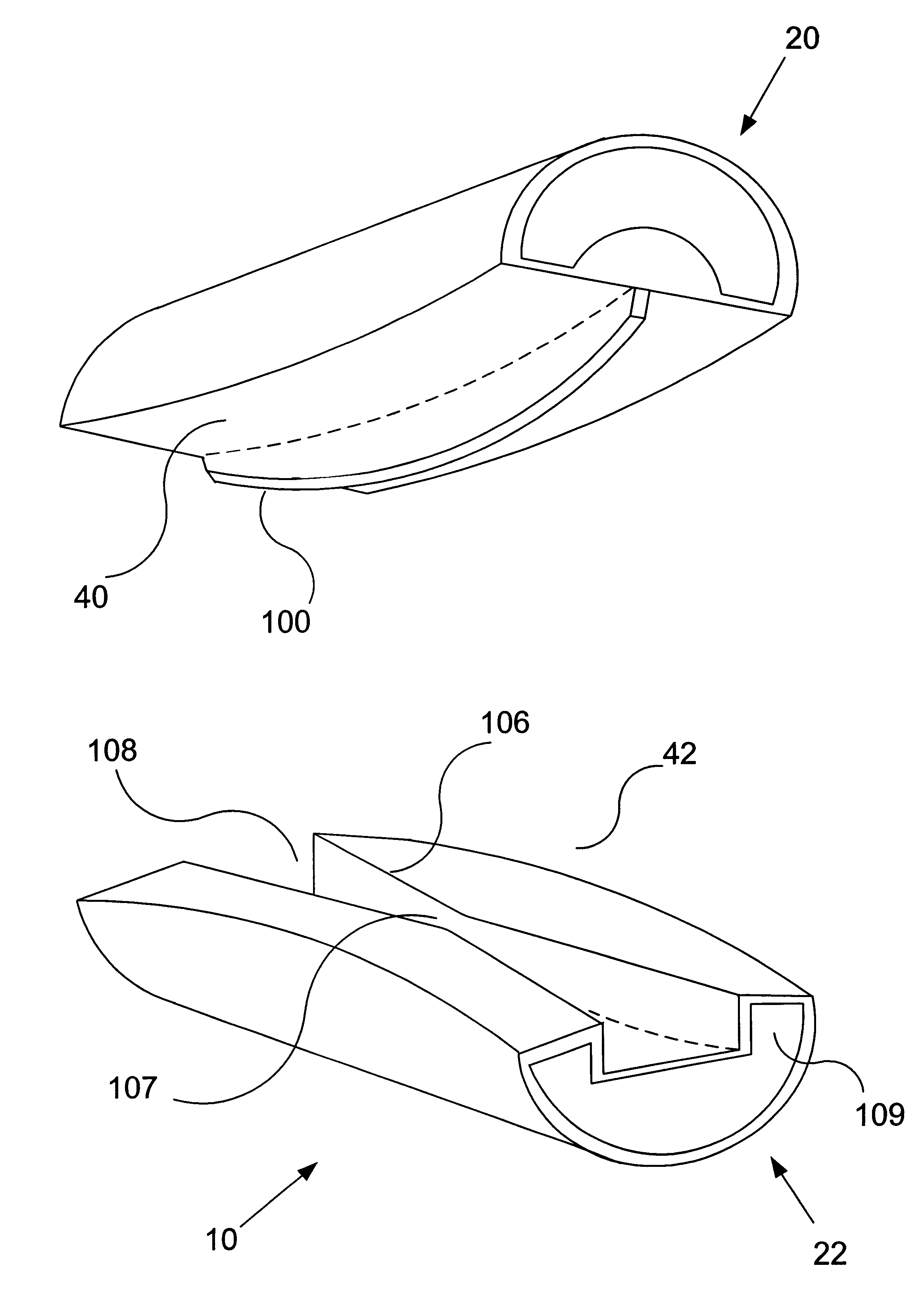
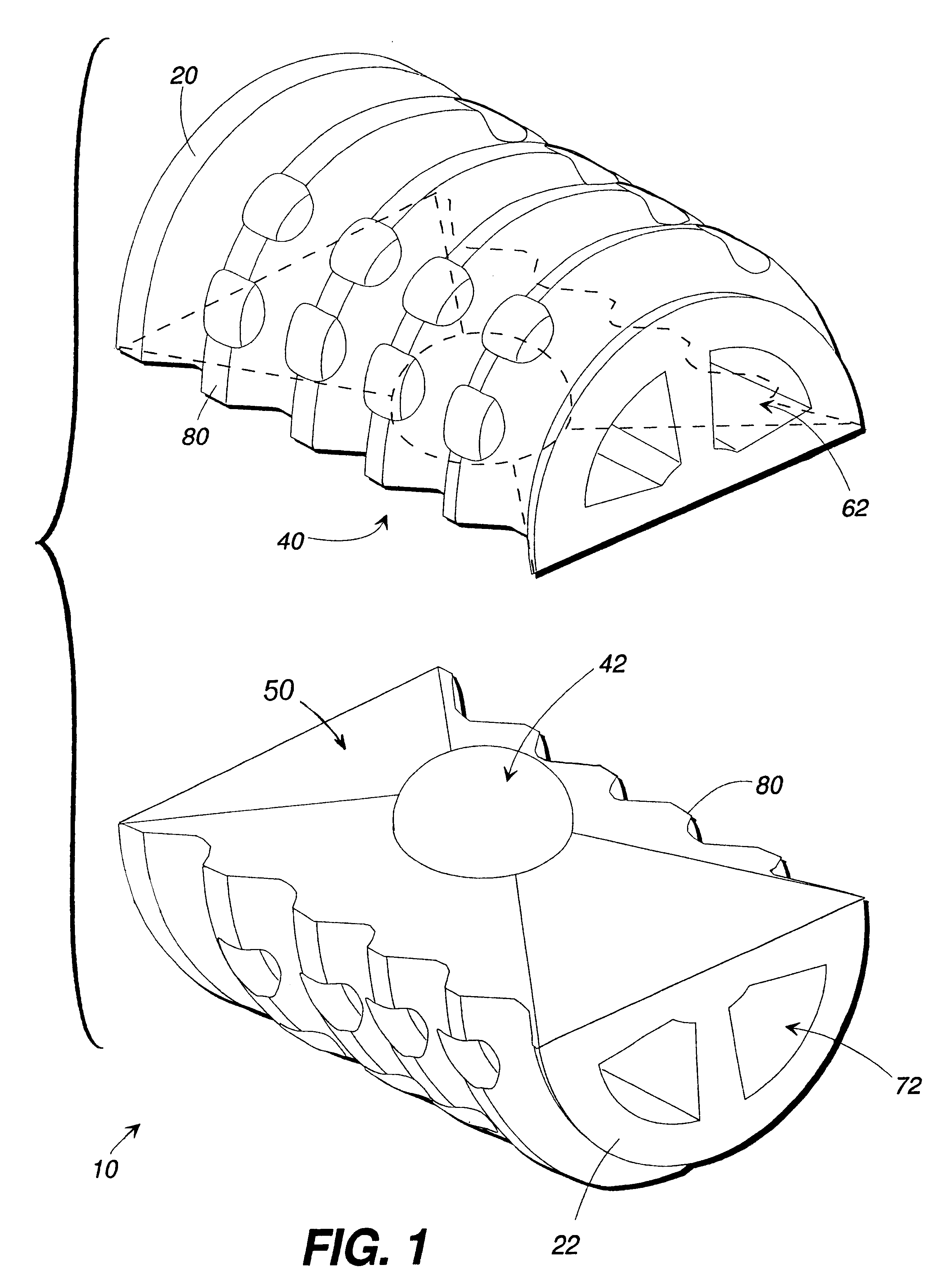
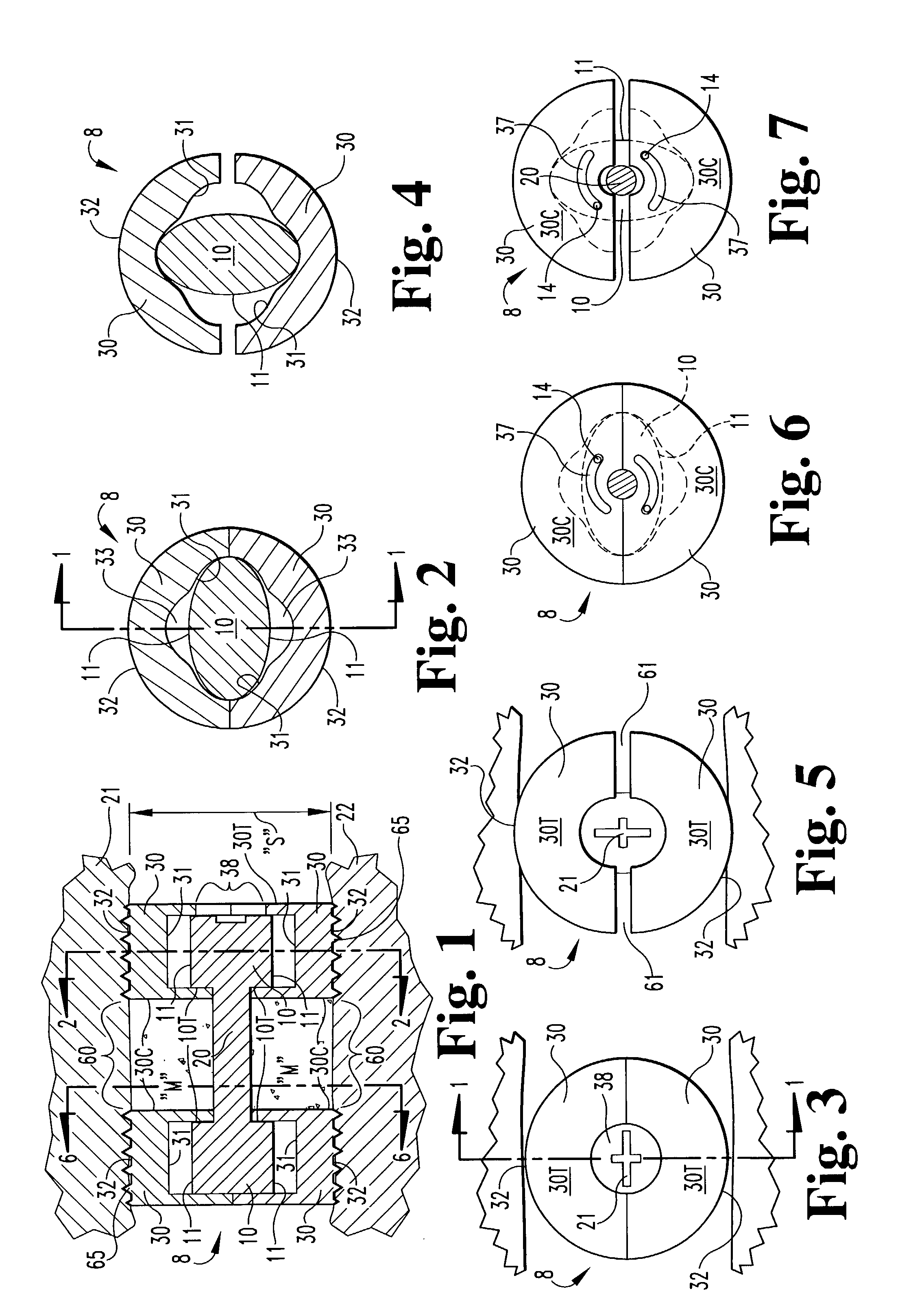
Porous tissue scaffoldings for the repair of regeneration of tissue
InactiveUS6333029B1Promote growthPromote regenerationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticRepair tissueOpen cell
The present patent describes a three-dimensional inter-connected open cell porous foams that have a gradient in composition and / or microstructure through one or more directions. These foams can be made from a blend of absorbable and biocompatible polymers that are formed into foams having a compositional gradient transitioning from predominately one polymeric material to predominately a second polymeric material. These gradient foams are particularly well suited to tissue engineering applications and can be designed to mimic tissue transition or interface zones.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
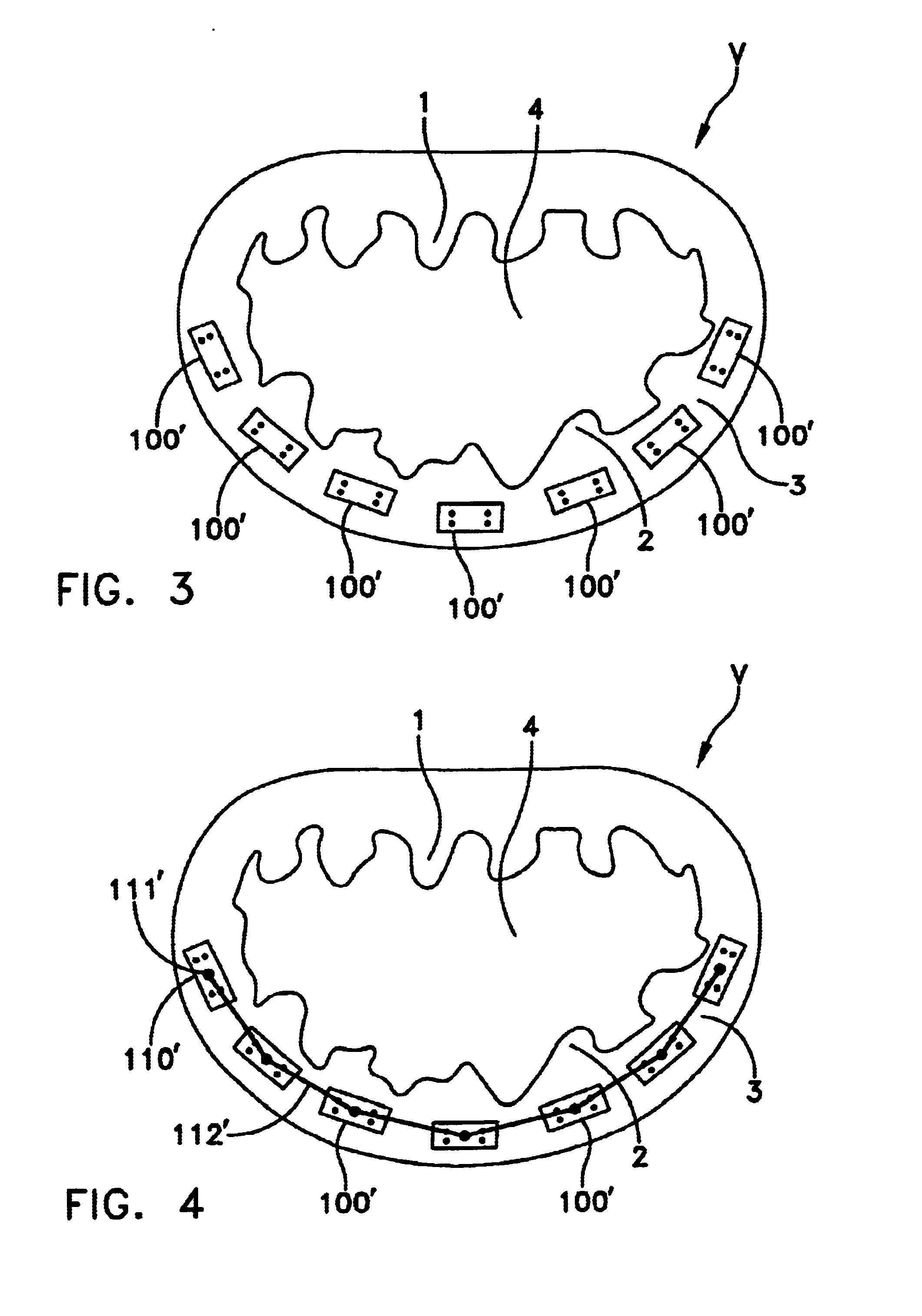
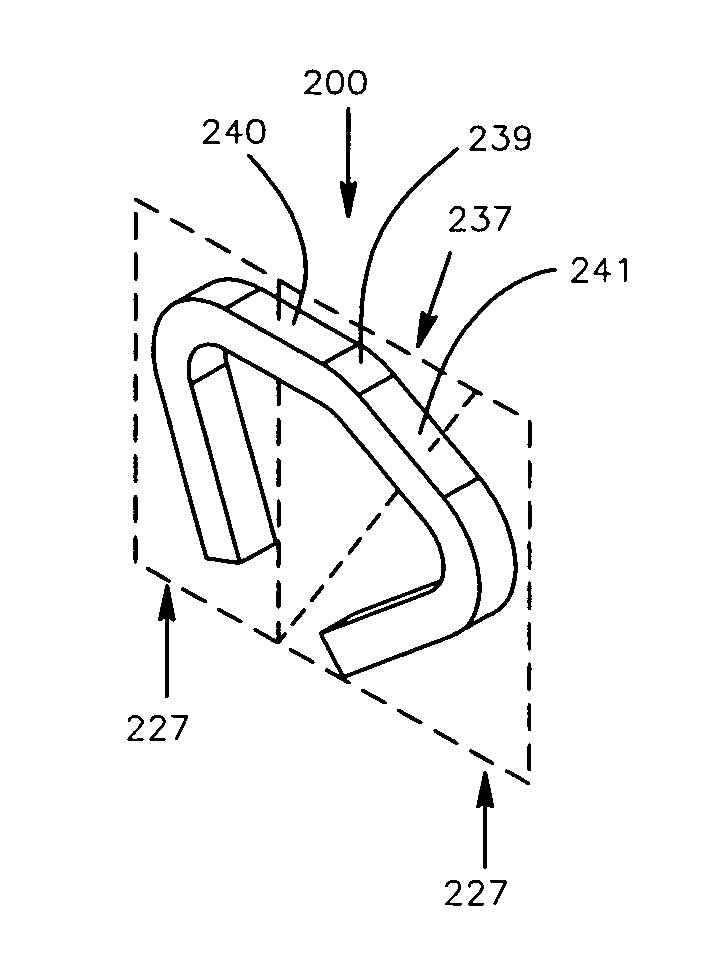
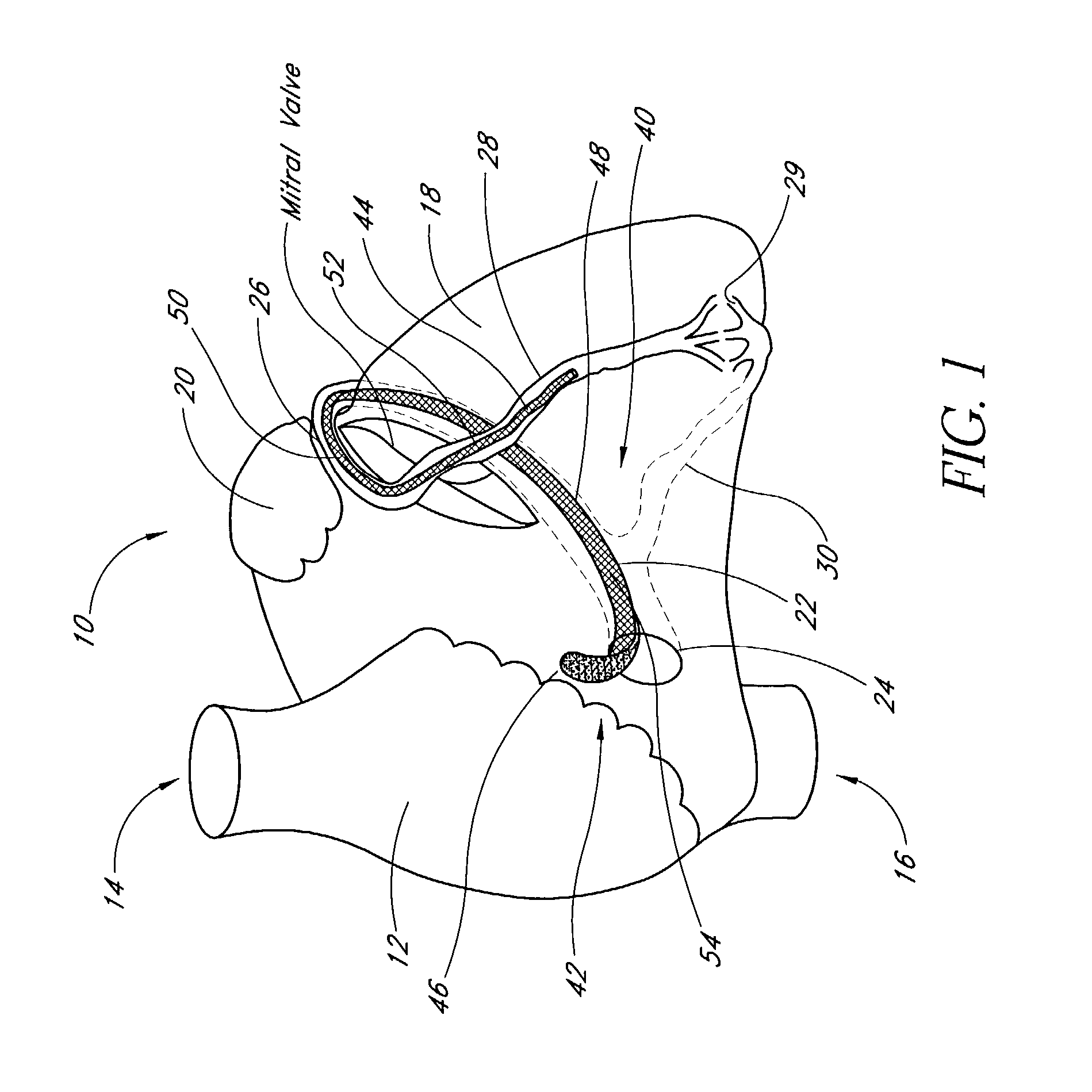
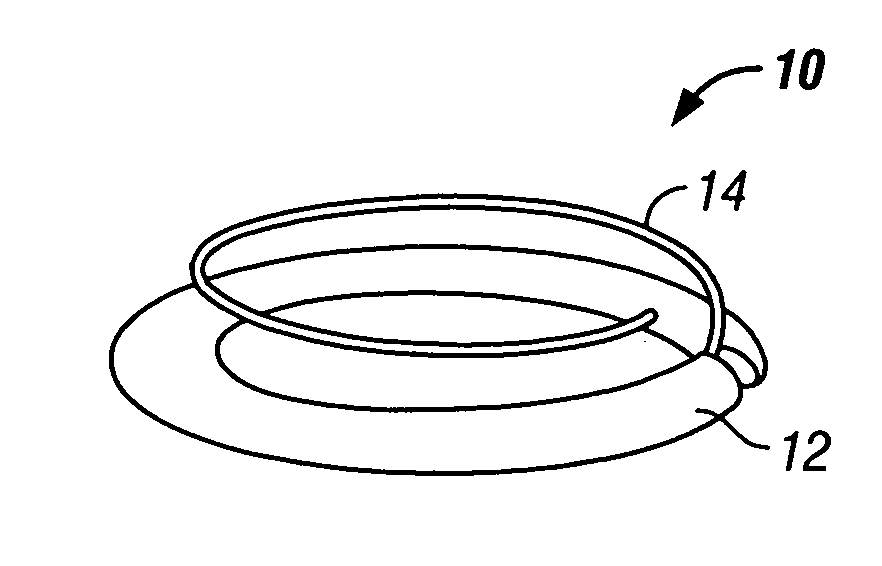
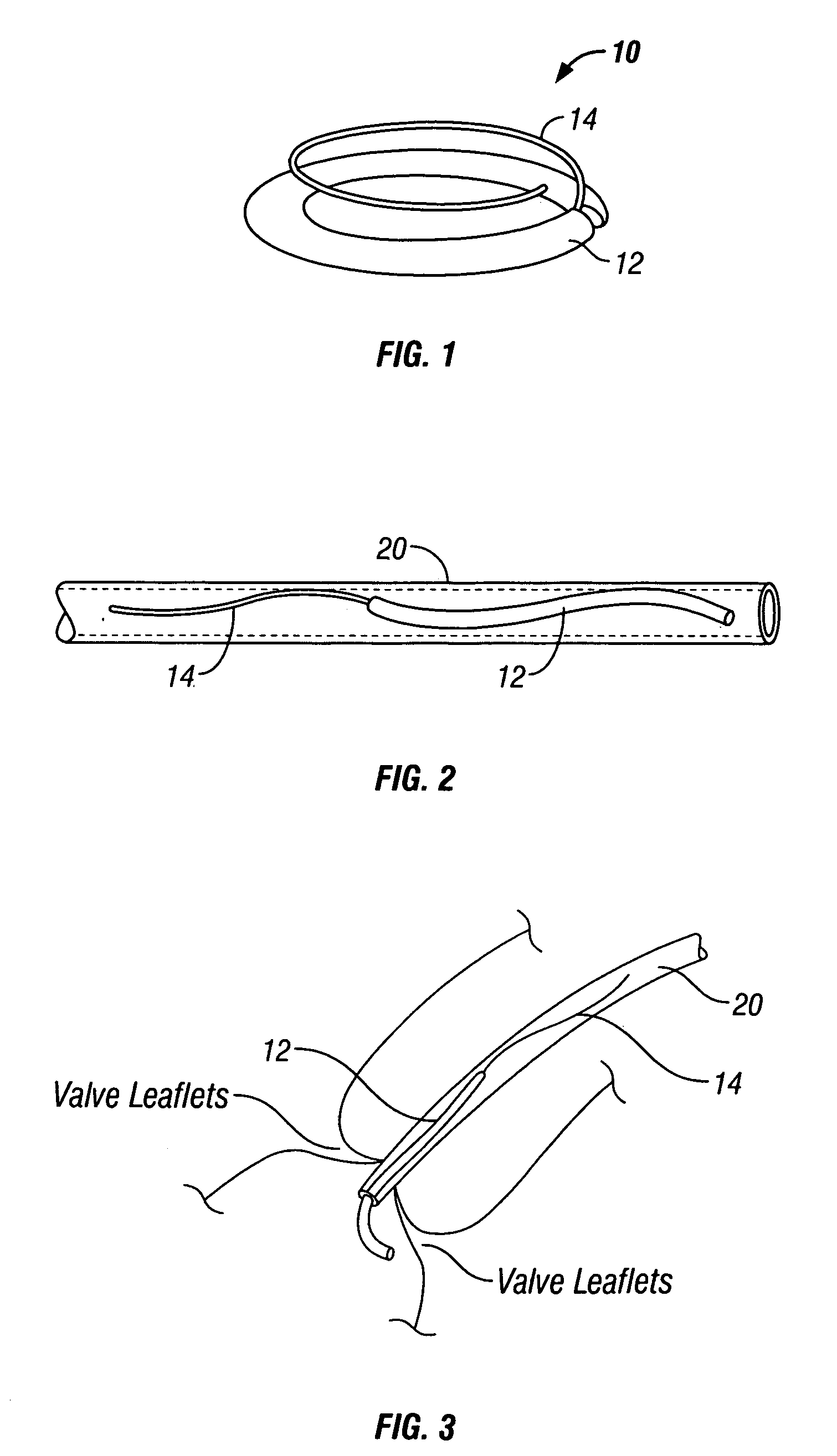
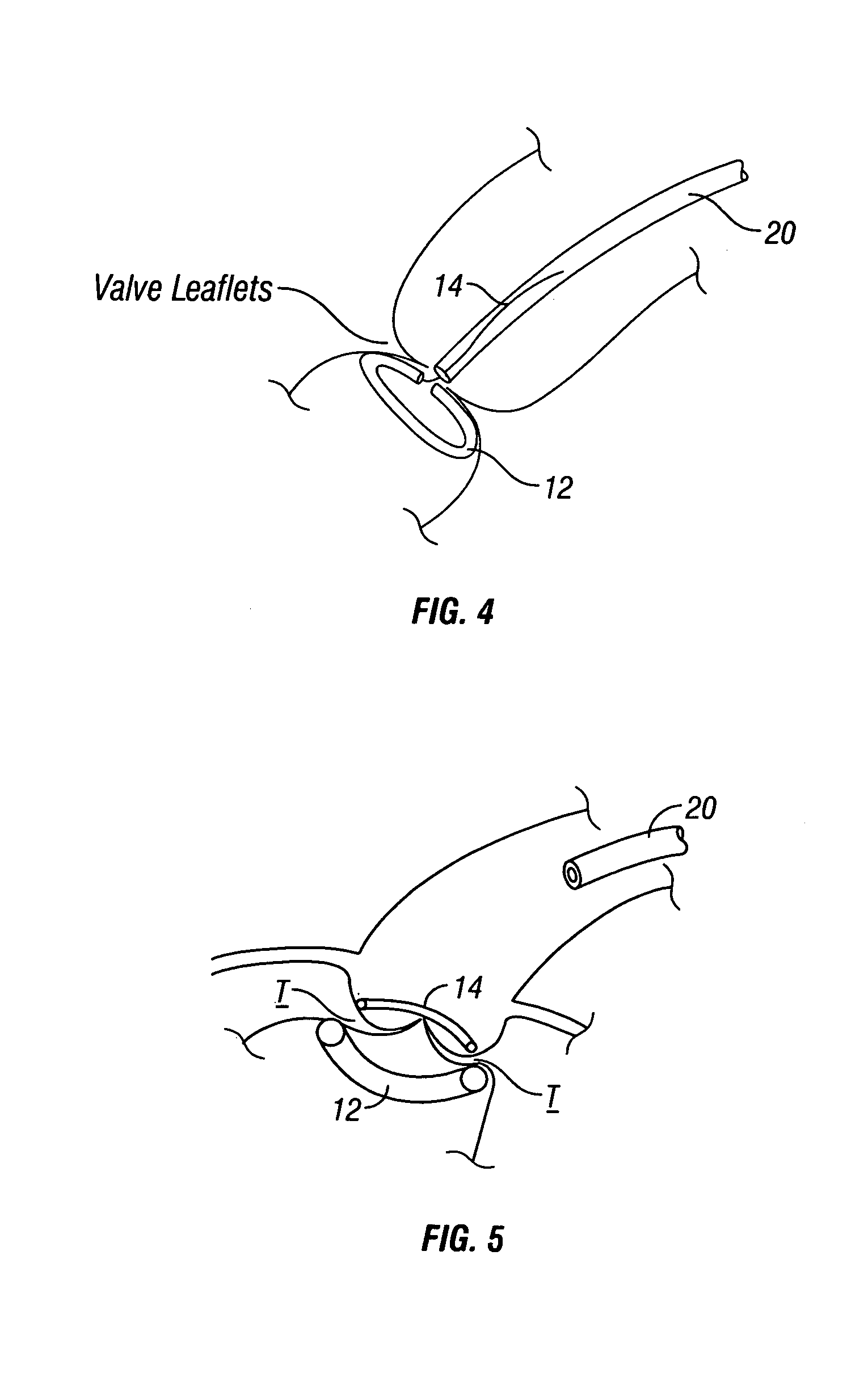
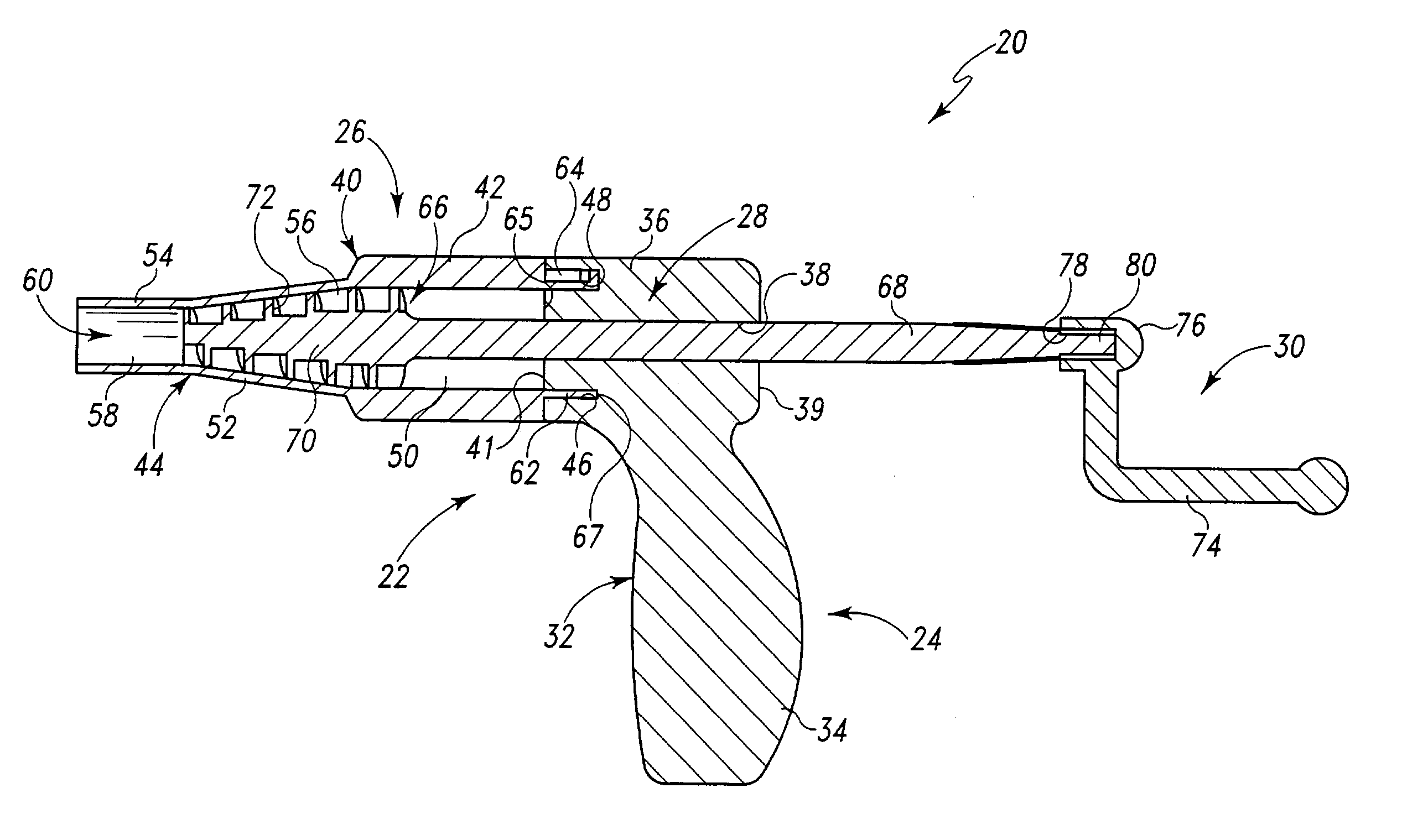
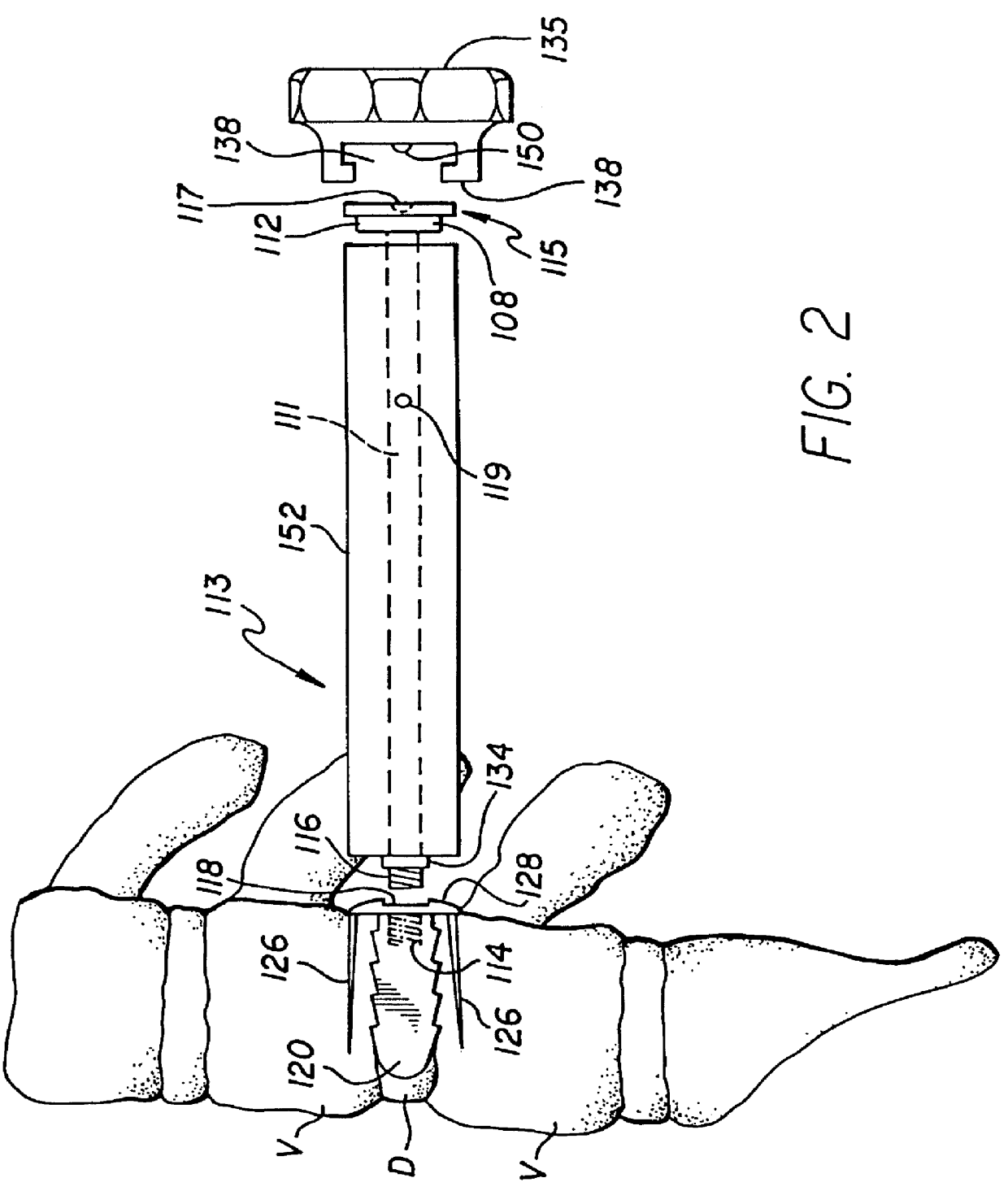
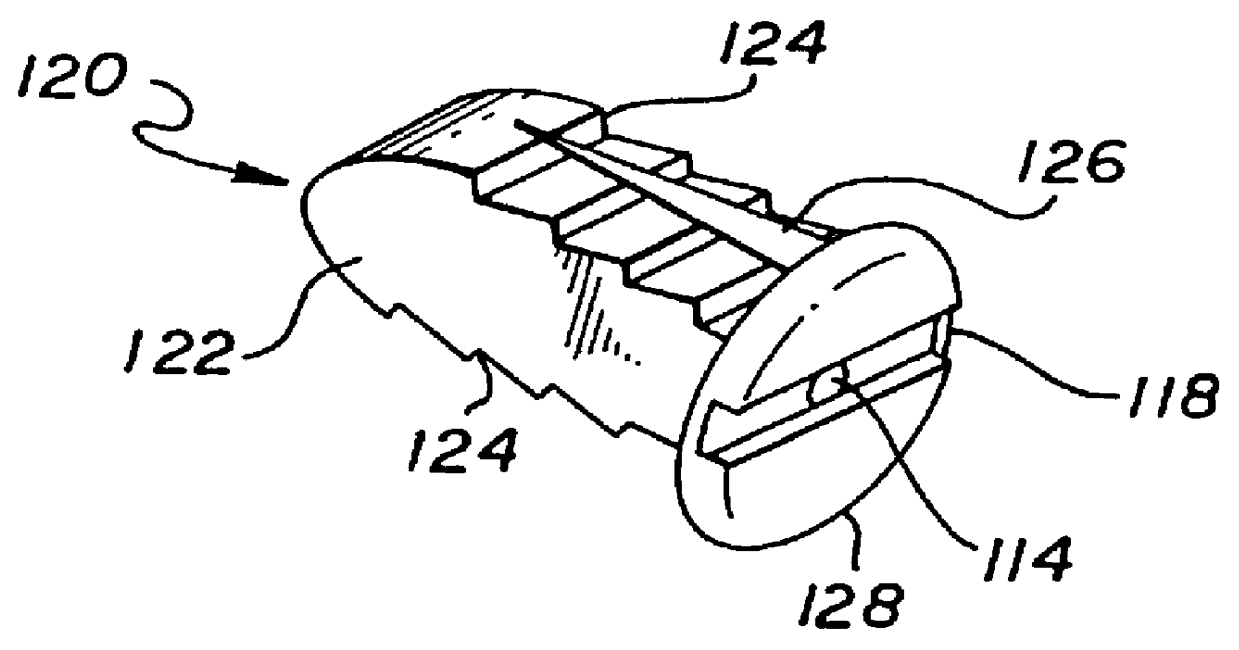
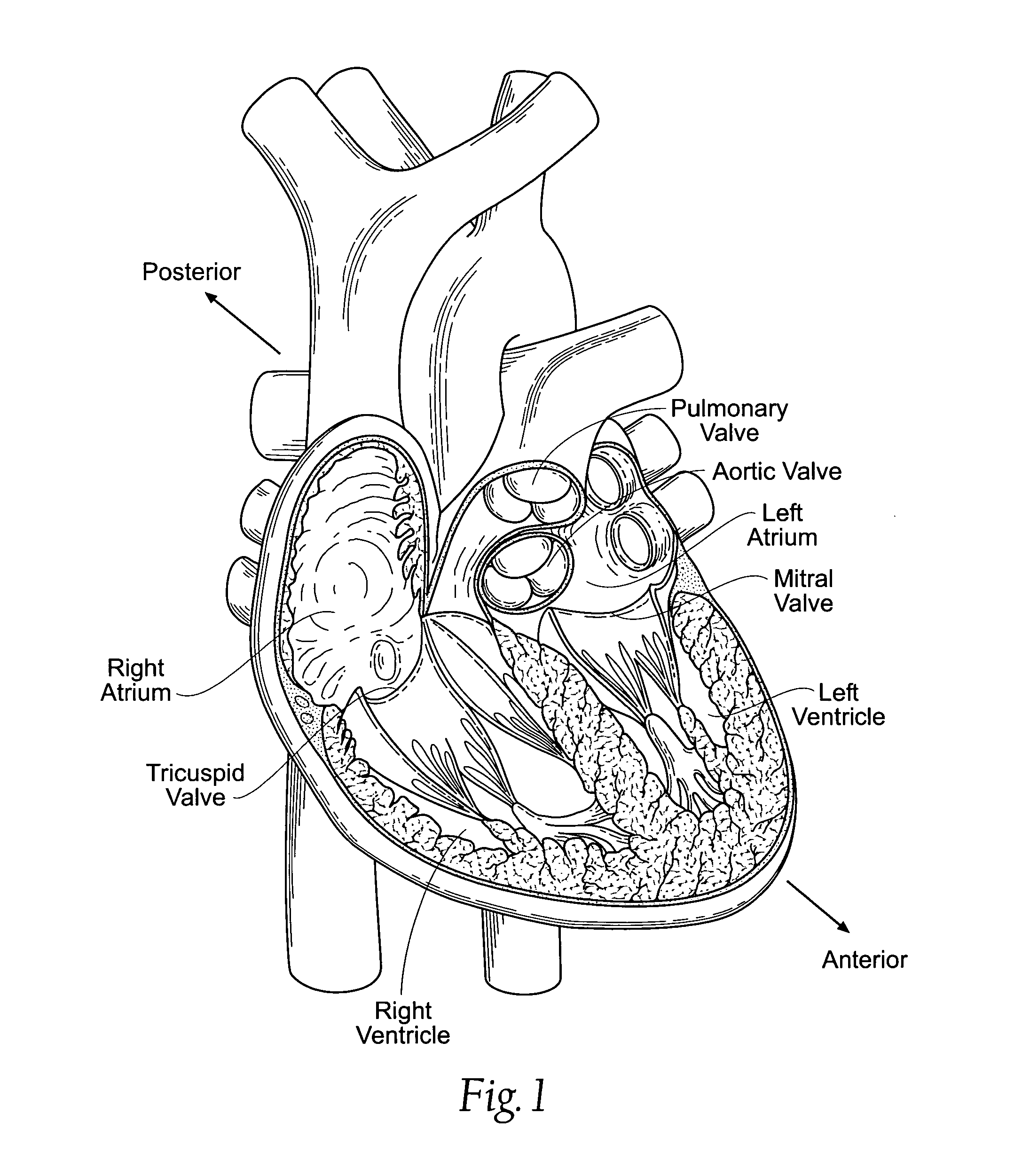
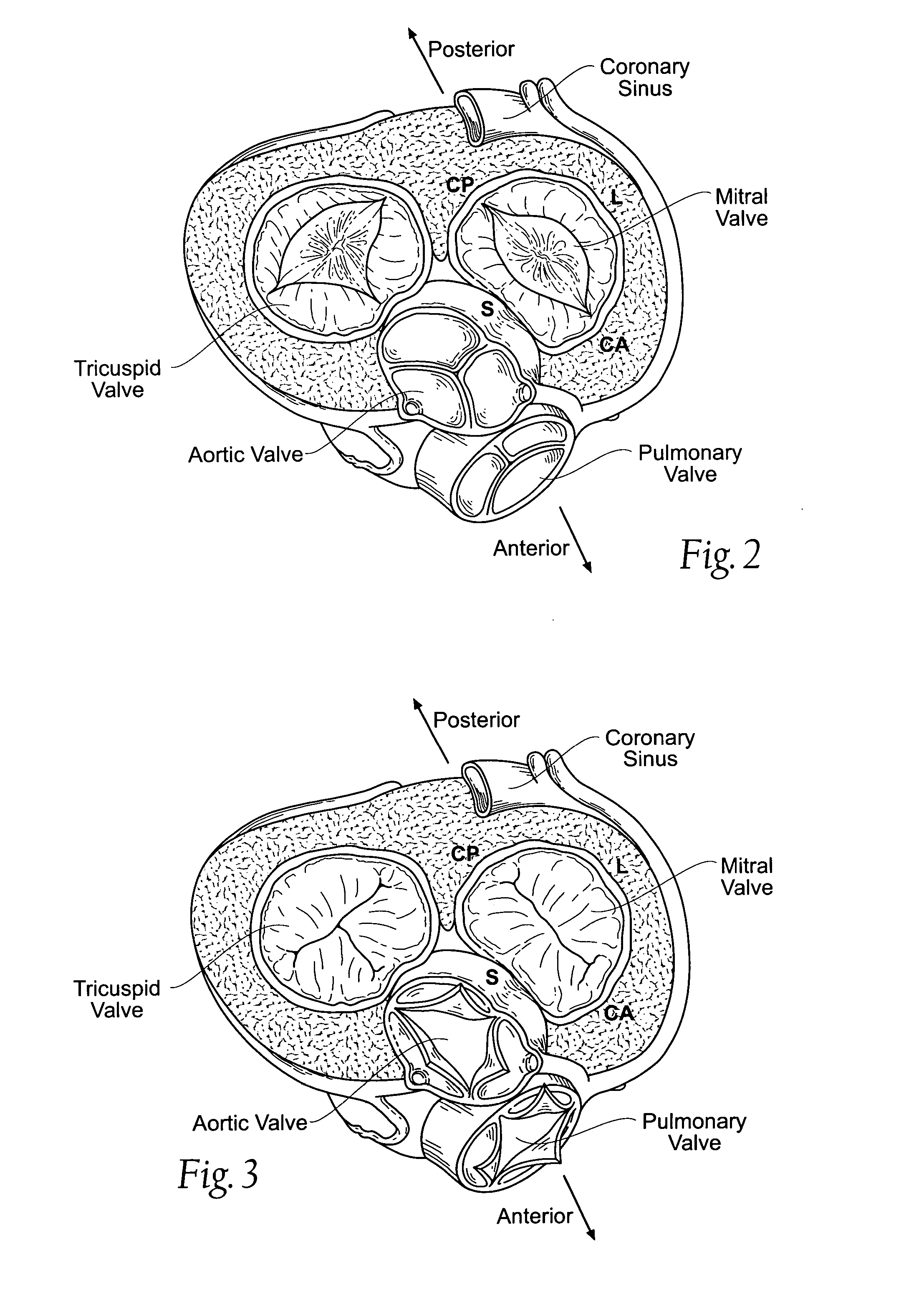
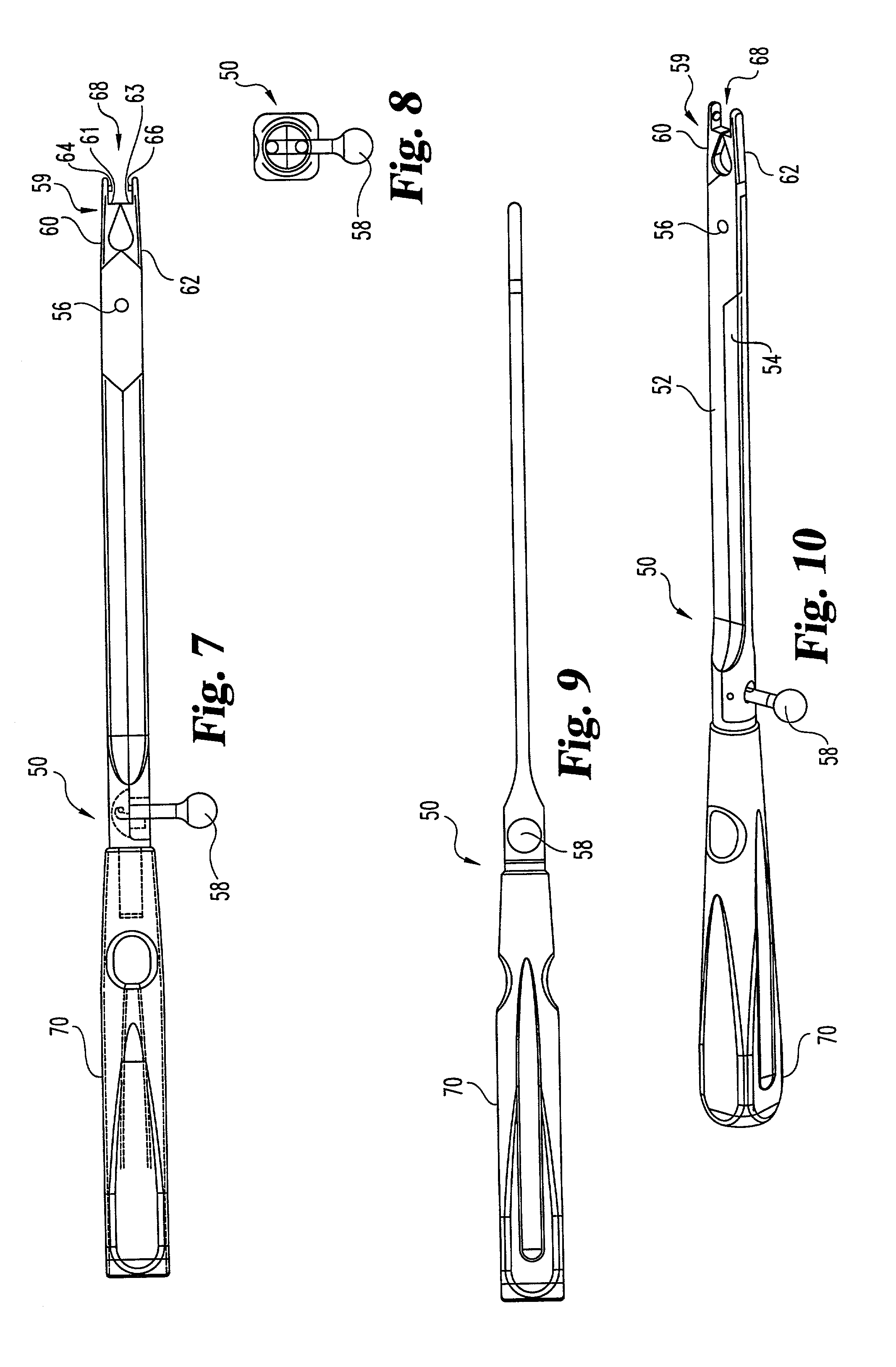
Automated annular plication for mitral valve repair
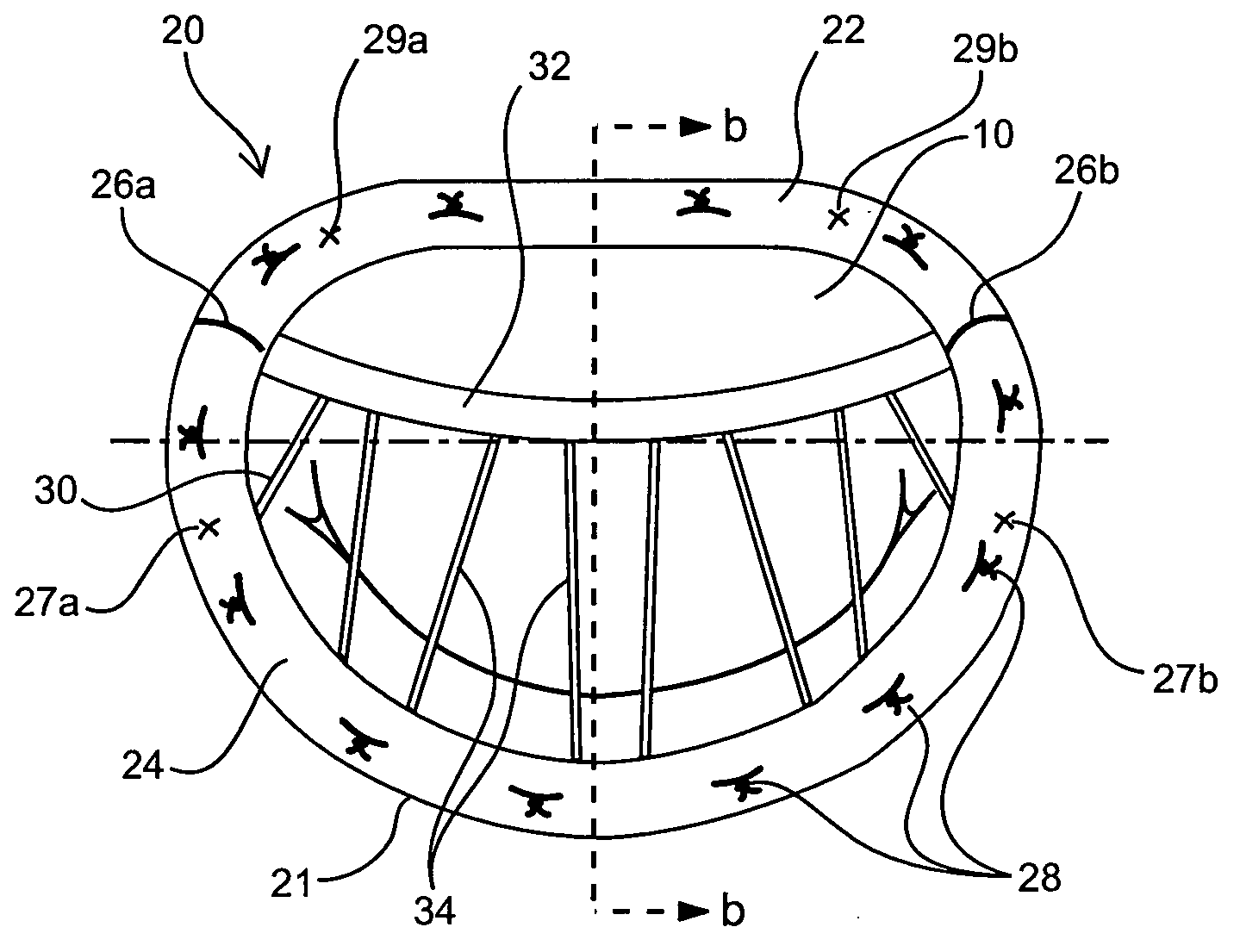
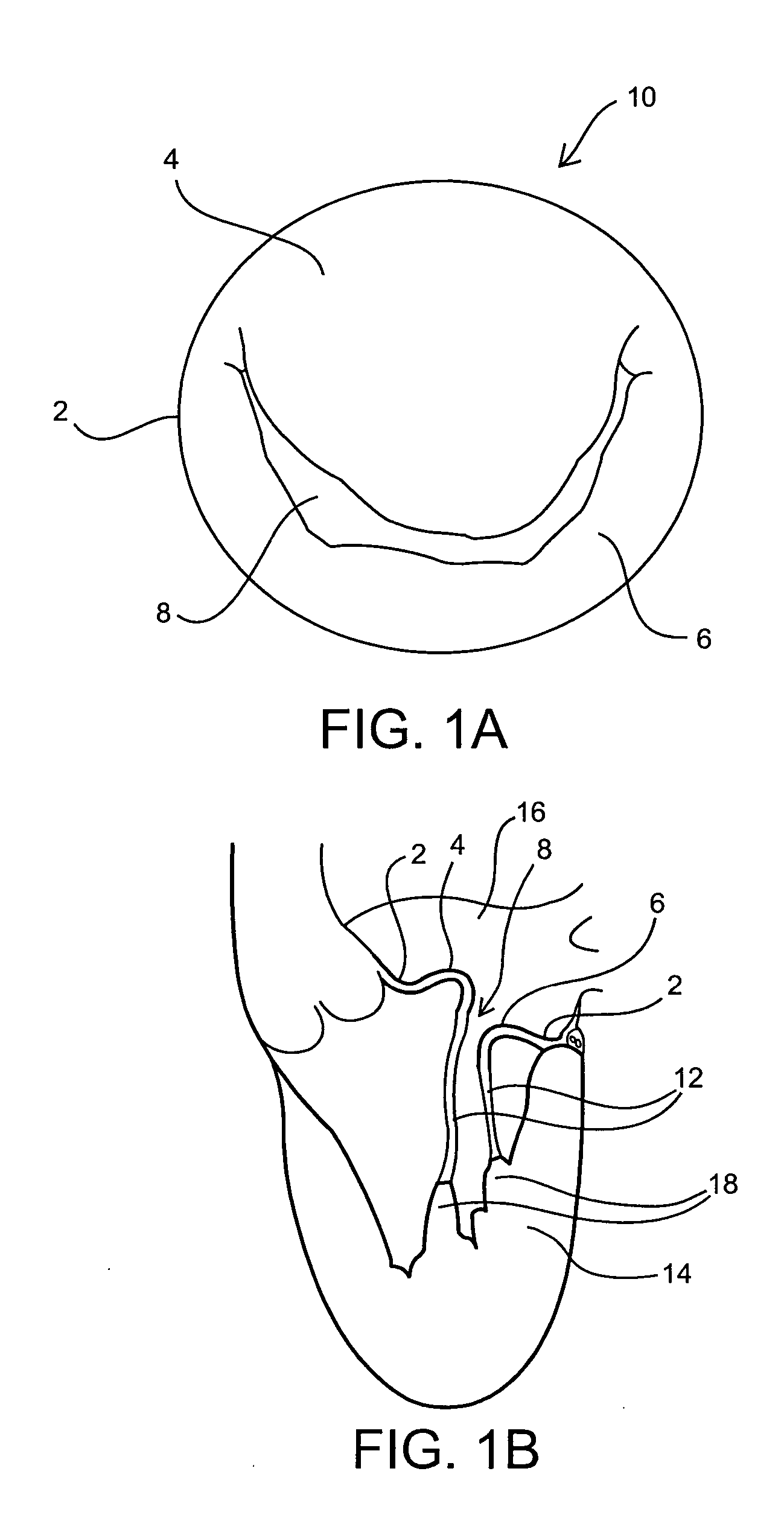
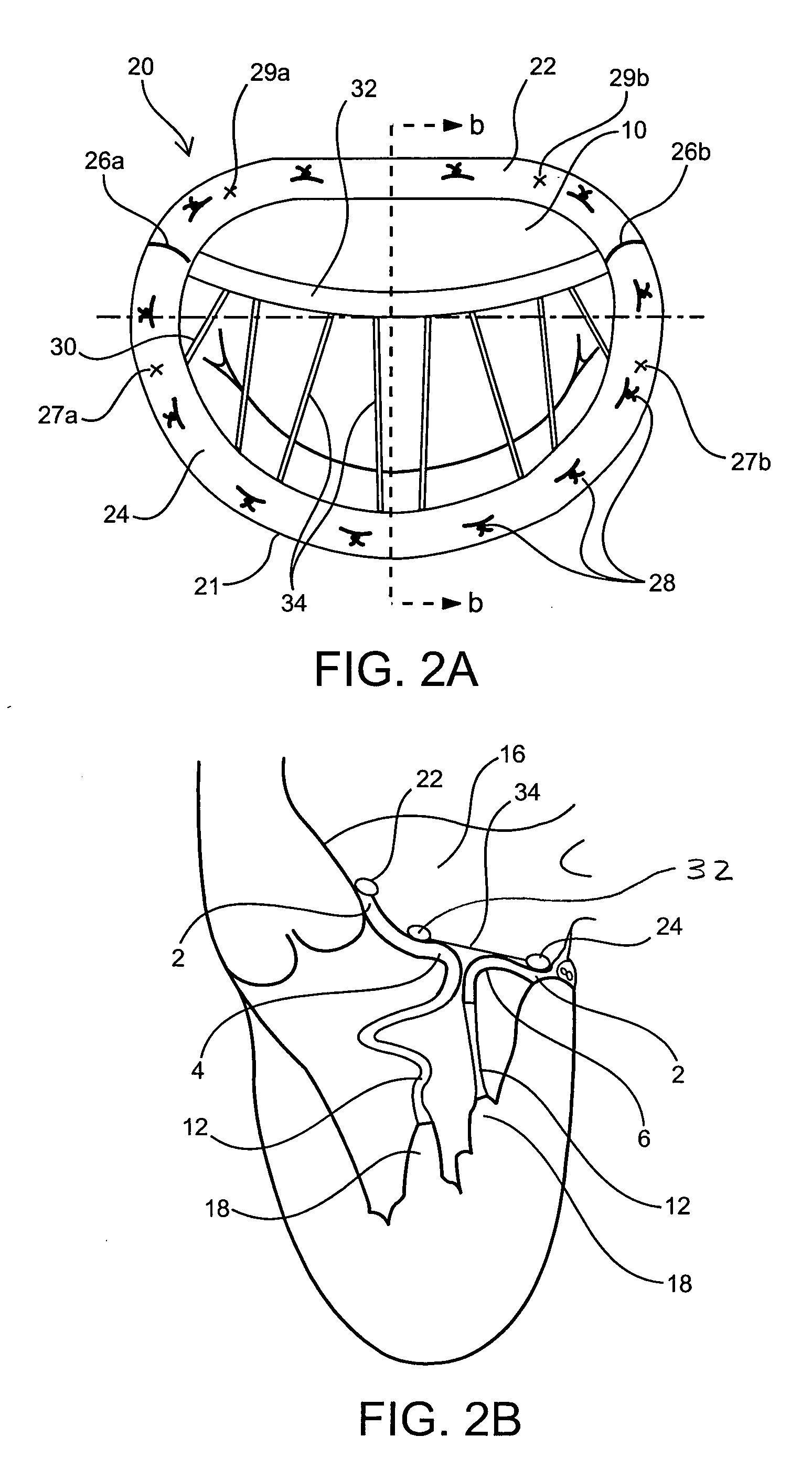
InactiveUS6913608B2Stabilize and improve left ventricular functionAvoid developmentSuture equipmentsBone implantMitral valve leafletMitral valve operation
A novel system for performing a heart valve annuloplasty. The system involves the use of a plication band. In one embodiment, the annulus of the valve is reduced by constriction of the plication band itself. More particularly, each plication band enters the tissue at two or more points which are spaced from one other by a distance which is dictated by the geometry of the plication band. Subsequent constriction of the plication band causes these points to move toward each other, thereby constricting the tissue trapped between these points and thus reducing the overall circumference of the valve annulus. In a second embodiment, the annulus of the valve is reduced by linking multiple plication bands to one other, using a linkage construct, and then using a shortening of the length of the linkage construct between each plication band so as to gather the tissue between each plication band, whereby to reduce the overall circumference of the valve annulus.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Medical device, kit and method for constricting tissue or a bodily orifice, for example, a mitral valve
InactiveUS20110082538A1Prevent retreatSuture equipmentsBone implantPosterior leafletAnnuloplasty rings
A device, kit and method may include or employ an implantable device (e.g., annuloplasty implant) and a tool operable to implant such. The implantable device is positionable in a cavity of a bodily organ (e.g., a heart) and operable to constrict a bodily orifice (e.g., a mitral valve). The tissue anchors may be guided into precise position by an intravascularly or percutaneously deployed anchor guide frame of the tool and embedded in an annulus of the orifice. Constriction of the orifice may be accomplished via a variety of structures, for example by cinching a flexible cable or via a anchored annuloplasty ring, the cable or ring attached to the tissue anchors. The annuloplasty ring may be delivered in an unanchored, generally elongated configuration, and implanted in an anchored generally arch, arcuate or annular configuration. Such may approximate the septal and lateral (clinically referred to as anterior and posterior) annulus of the mitral valve, to move the posterior leaflet anteriorly and the anterior leaflet posteriorly, thereby improving leaflet coaptation to eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
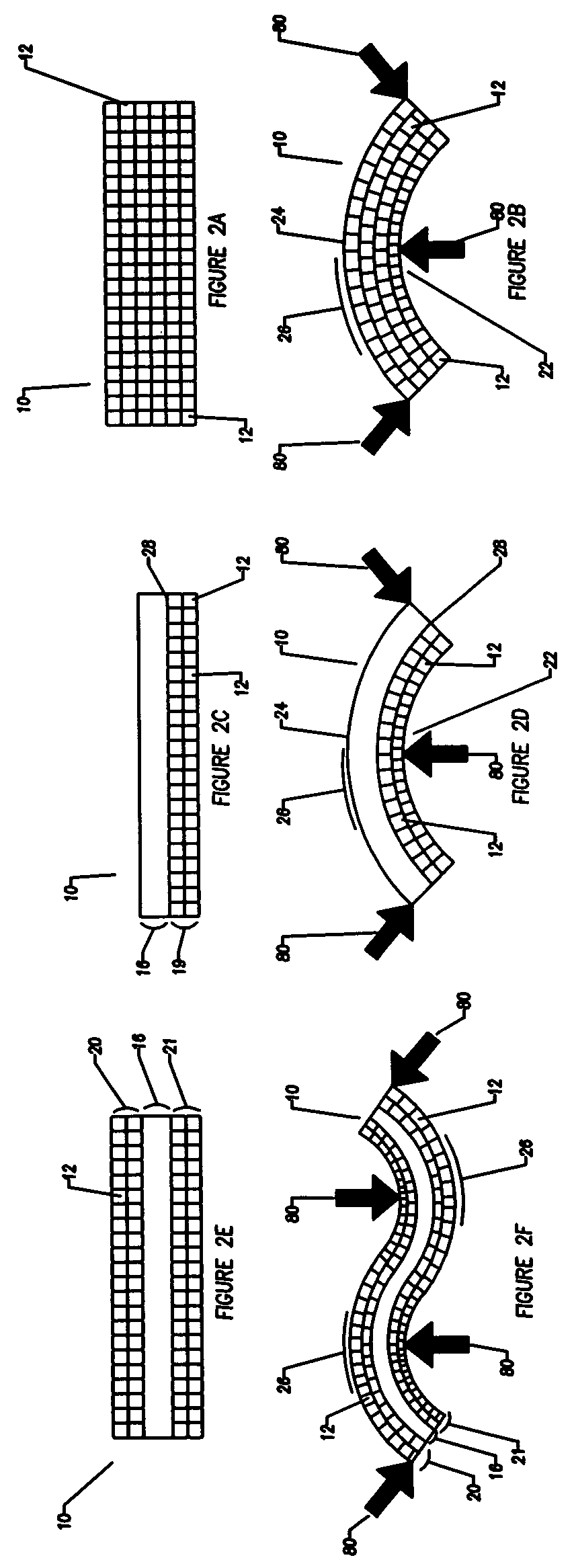
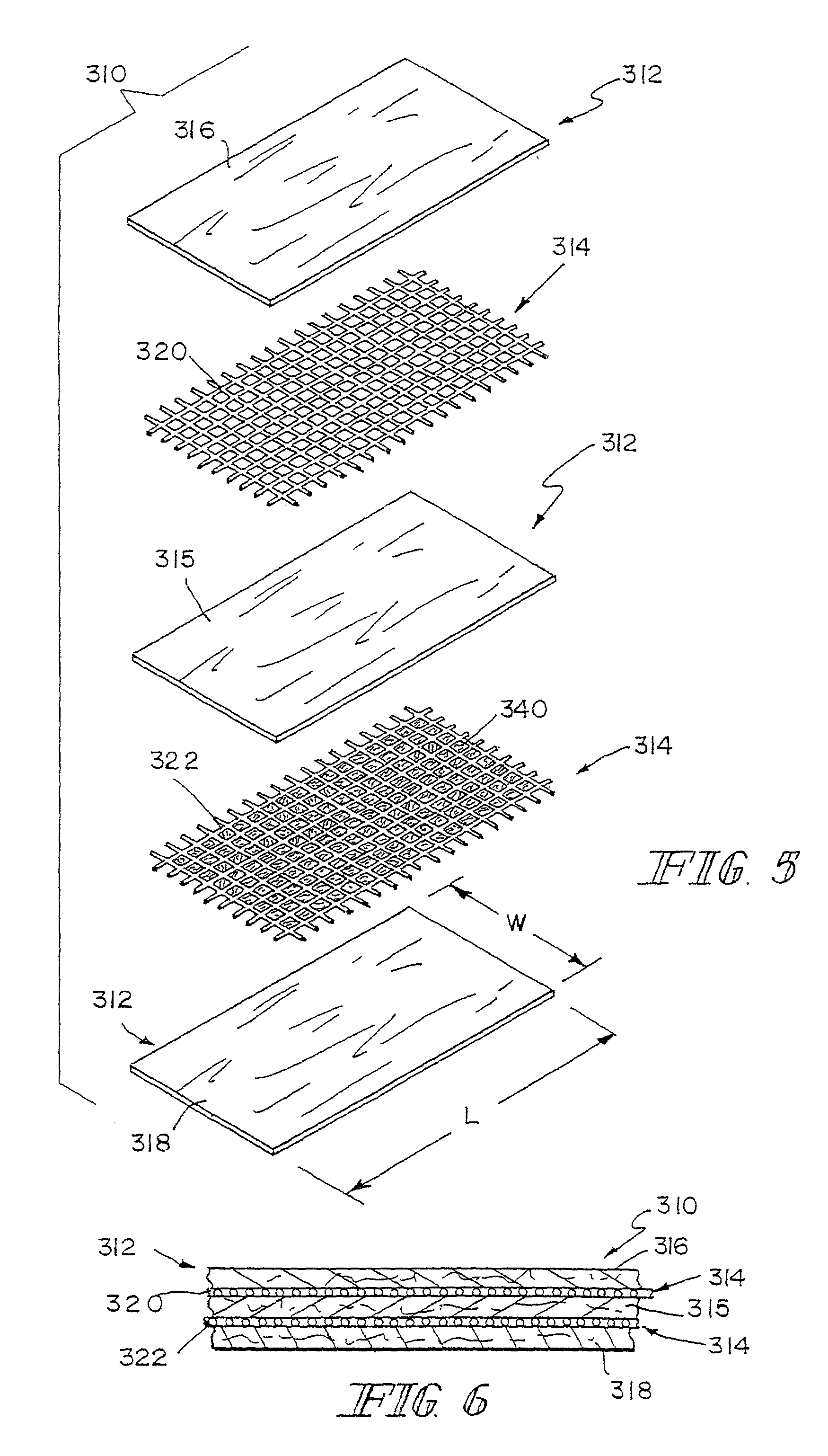
Compliant osteosynthesis fixation plate
ActiveUS7931695B2Maintaining structural rigidityBending stabilityBone implantBone platesMedicineLiving body
A bendable polymer tissue fixation device suitable to be implanted into a living body, comprising a highly porous body, the porous body comprising a polymer, the porous body comprising a plurality of pores, the porous body being capable of being smoothly bent, wherein the bending collapses a portion of the pores to form a radius curve, the polymer fixation device being rigid enough to protect a tissue from shifting. In a preferred embodiment the polymer fixation device may be capable of being gradually resorbed by said living body. In one embodiment, the polymer fixation device comprises a plurality of layers distinguishable by various characteristics, such as structural or chemical properties. In another embodiment, the polymer fixation device may comprise additional materials; the additional materials serving to reinforce or otherwise alter the structure or physical characteristics of the device, or alternatively as a method of delivering therapy or other agents to the system of a living being.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
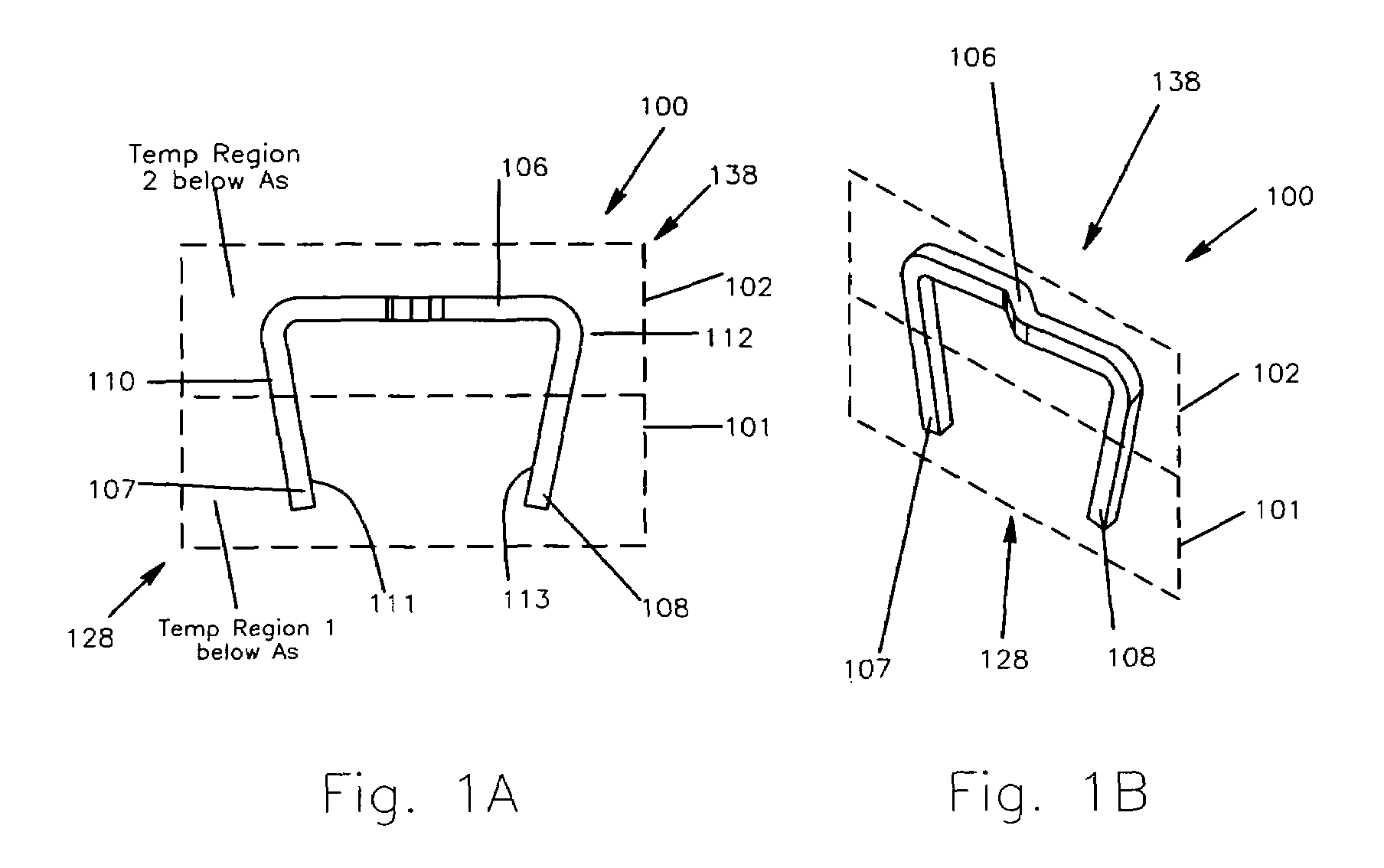
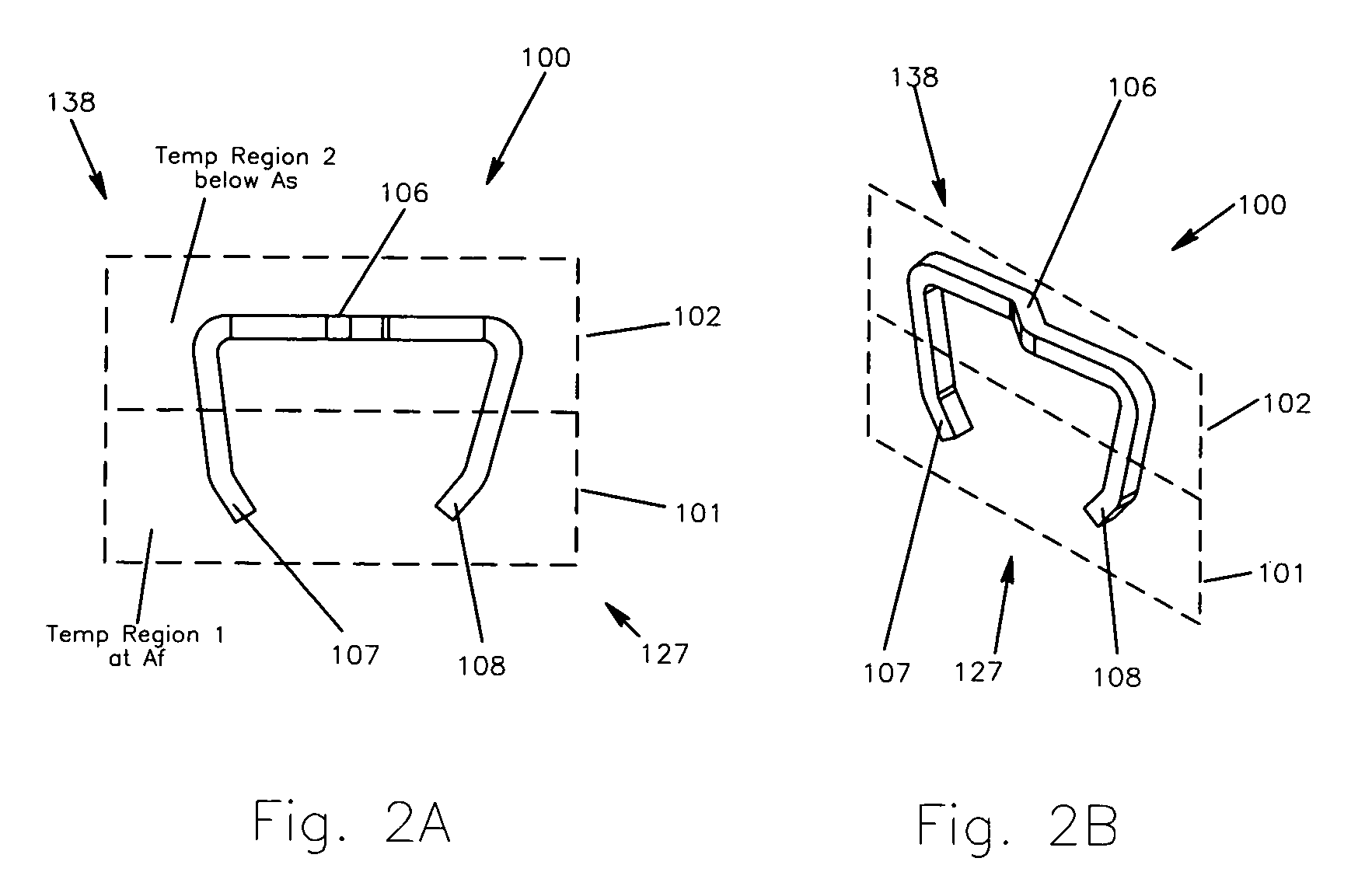
Method and apparatus for a multiple transition temperature implant
A shape-memory device manufactured from shape memory material includes multiple activation temperatures. The multiple activation temperatures arise from either the heat treatment of the device during manufacturing, or by combining different elements with different activation temperatures. To manufacture a shape-memory device with multiple activation temperatures, it is formed into a first shape. A first portion of the shape-memory device is heated to a first temperature, and a second portion of the shape-memory device is heated to a second temperature. The shape-memory device is then worked into a second shape. Accordingly, the first portion has a first transition temperature, and the second portion has a second transition temperature. In use, the shape-memory device is placed into a desired position. Energy is applied such that the first portion, second portion, or both portions are transformed.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
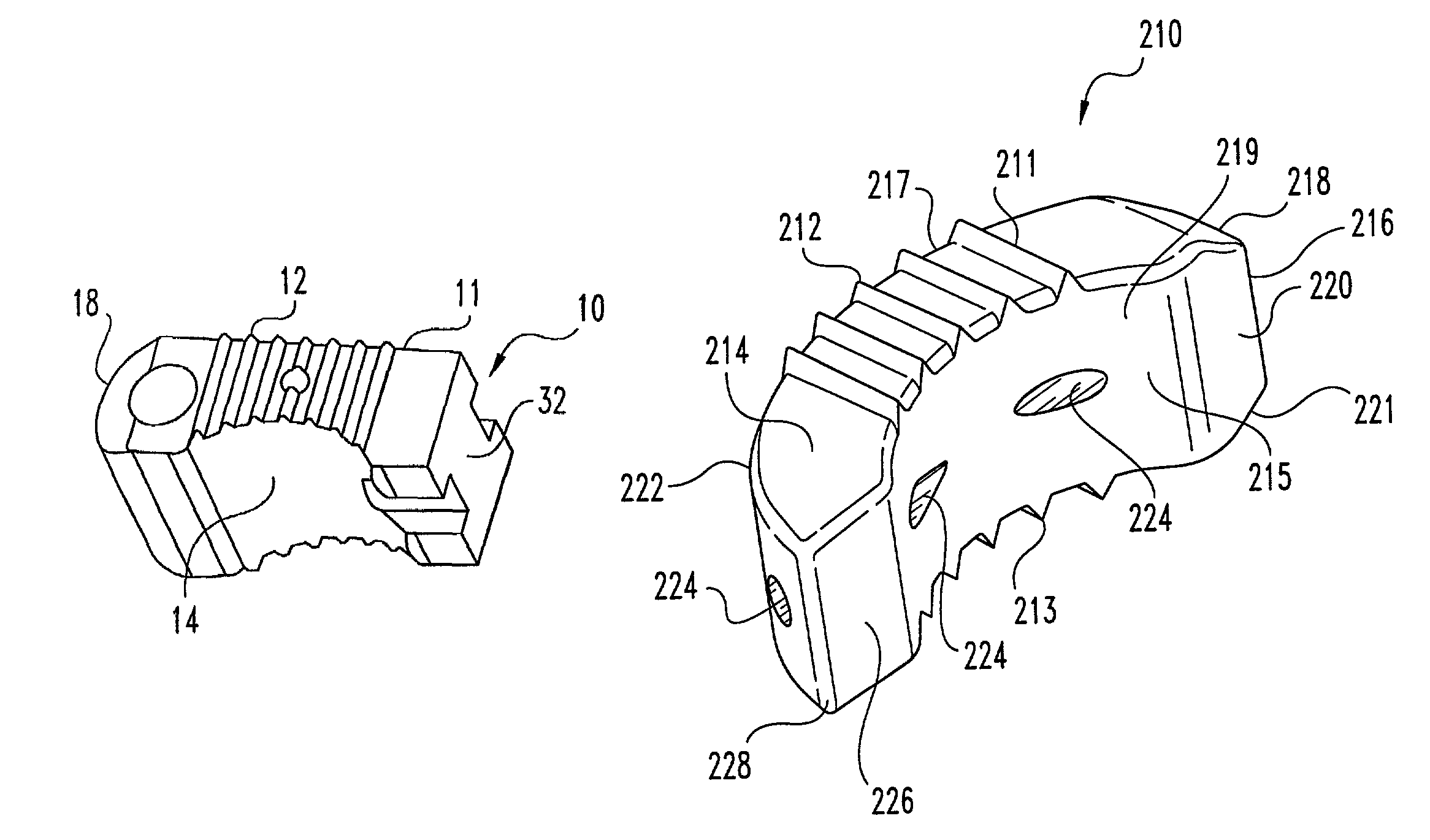
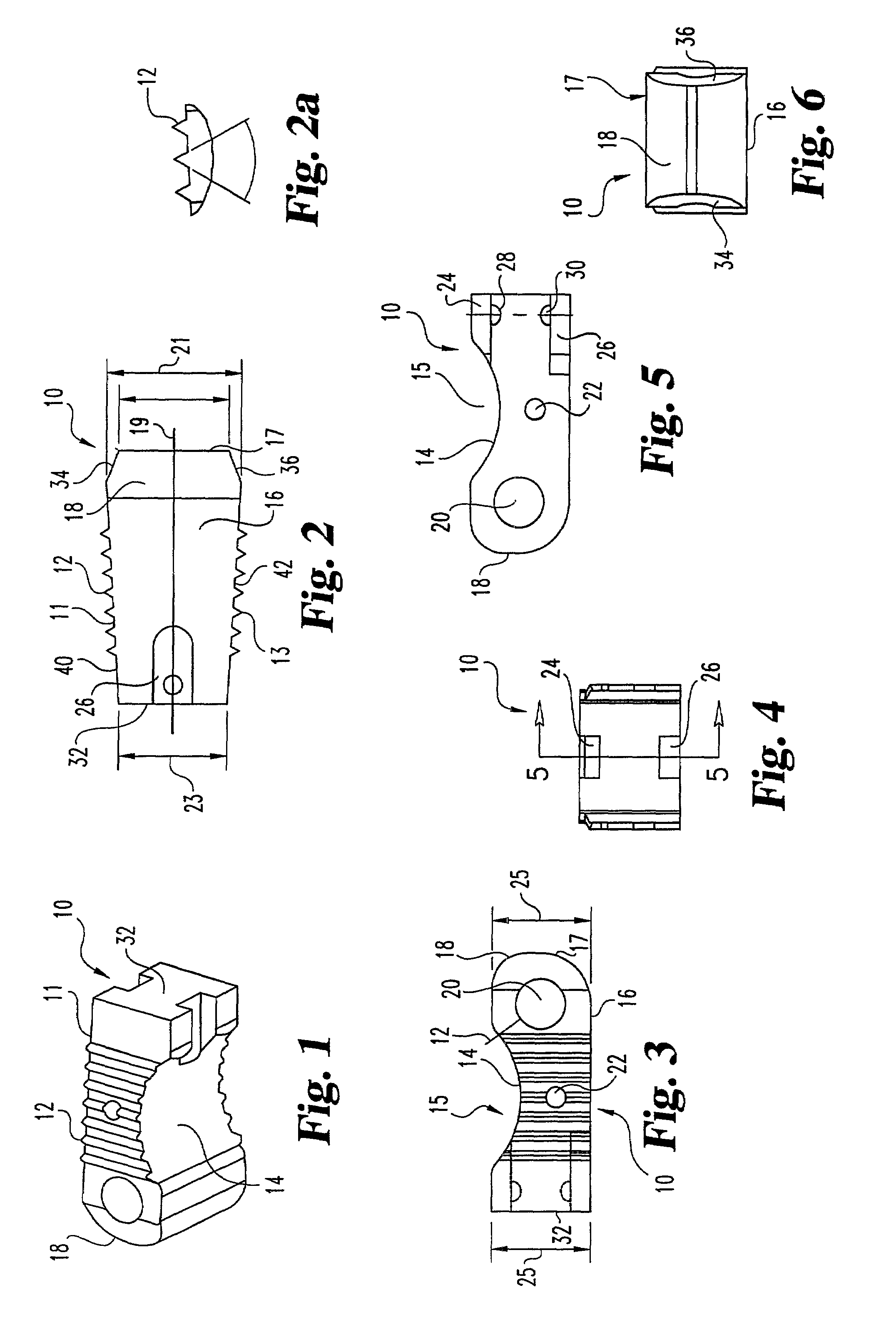
Unitary surgical device and method
Unitary surgical devices (10) are disclosed. One group of the illustrated devices has a pair of biocompatible, bioresorbable anchors (16,18) connected to fixed lengths suture. The anchors (16,18) and fixed length of suture are connected to each other prior to surgery. Another group of unitary surgical devices has a pair of fixating mechanisms (15,17) connected to a base (21) prior to surgery. The second group of illustrated devices generally includes extracellular matrix material either as part of the base (21) or supported on the base (21). The extracellular matrix material serves as tissue regenerating material. In the second group of unitary surgical devices, the fixating mechanisms illustrated generally comprise suture, anchors or pre-formed holes in the base. All of the illustrated unitary surgical devices are useful in repairing a damaged meniscus. The first group of unitary surgical devices can be used to approximate inner surfaces of a tear in the meniscus. The second group of devices can be used either as an insert to be placed between and approximated to the inner surfaces of the tear or as an insert to replace a void in the meniscus left after a meniscectomy.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Attachment of absorbable tissue scaffolds to fixation devices
The present invention relates to tissue scaffold implant devices useful in the repair and / or regeneration of diseased and / or damaged musculoskeletal tissue and that include a tissue scaffold component fixedly attached to a scaffold fixation component via at least one of sutures, fabrics, fibers, threads, elastomeric bands, reinforcing elements and interlocking protrusions for engaging and maintaining the scaffold component fixedly attached to the fixation component.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Tissue-derived mesh for orthopedic regeneration
An implant including a substantially cohesive aggregate comprising bone-derived particles. Cohesiveness is maintained by a member of mechanical interlocking, engagement of adjacent bone-derived particles with one another through engagement with a binding agent, thermal bonding, chemical bonding, or a matrix material in which the bone-derived particles are retained. The aggregate is shaped as a one-dimensional or two-dimensional body.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
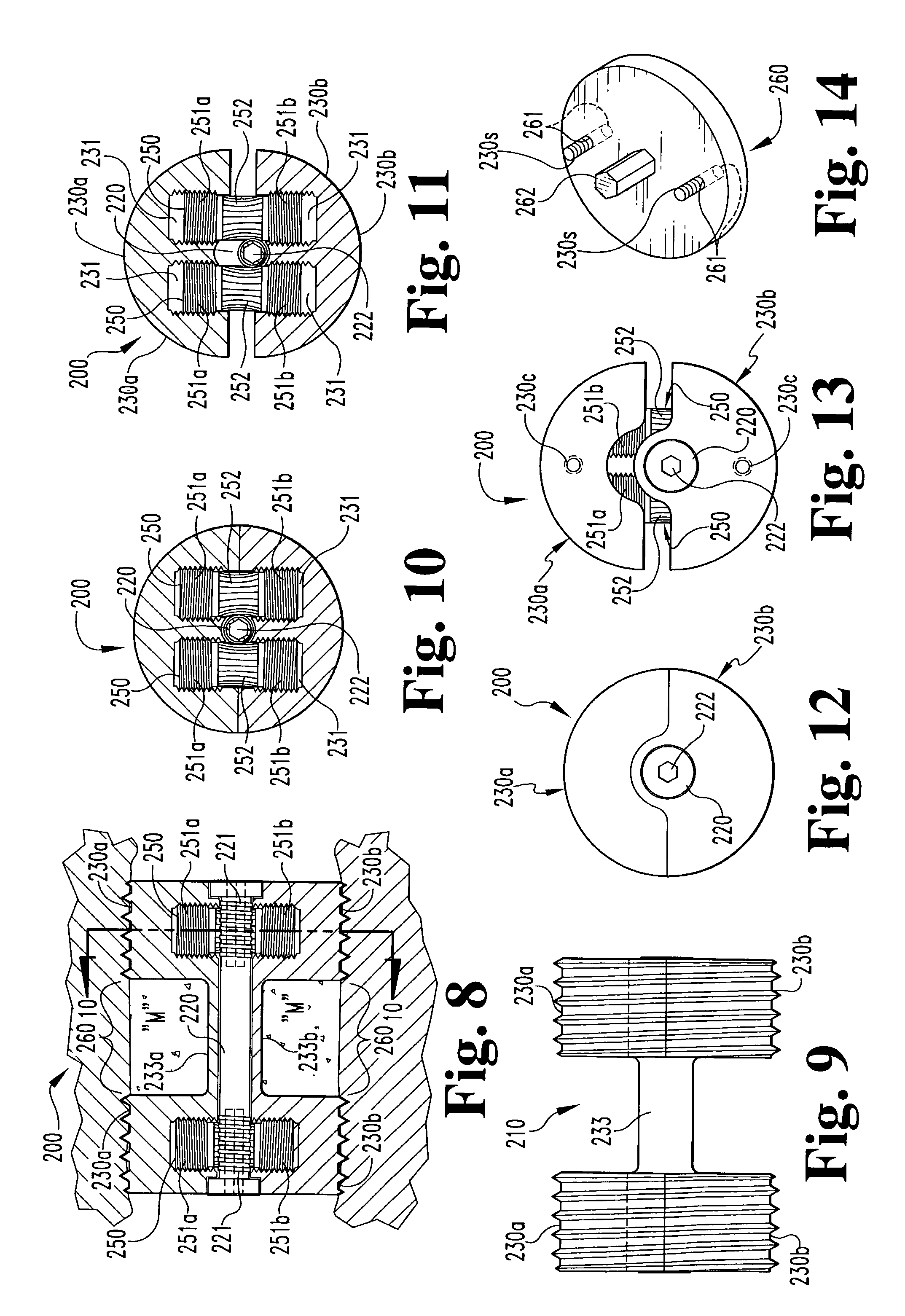
Hybrid biologic-synthetic bioabsorbable scaffolds
ActiveUS8366787B2Increase surface areaGood mechanical integritySuture equipmentsBone implantBioabsorbable scaffoldCell-Extracellular Matrix
A bioprosthetic device is provided for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, and or reconstruction. The device comprises a naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion and a three-dimensional synthetic portion. In illustrated embodiments, the naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion comprises layers of small intestine submucosa, and the three-dimensional synthetic portion comprises a foam or a three-dimensional mesh, textile, or felt.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
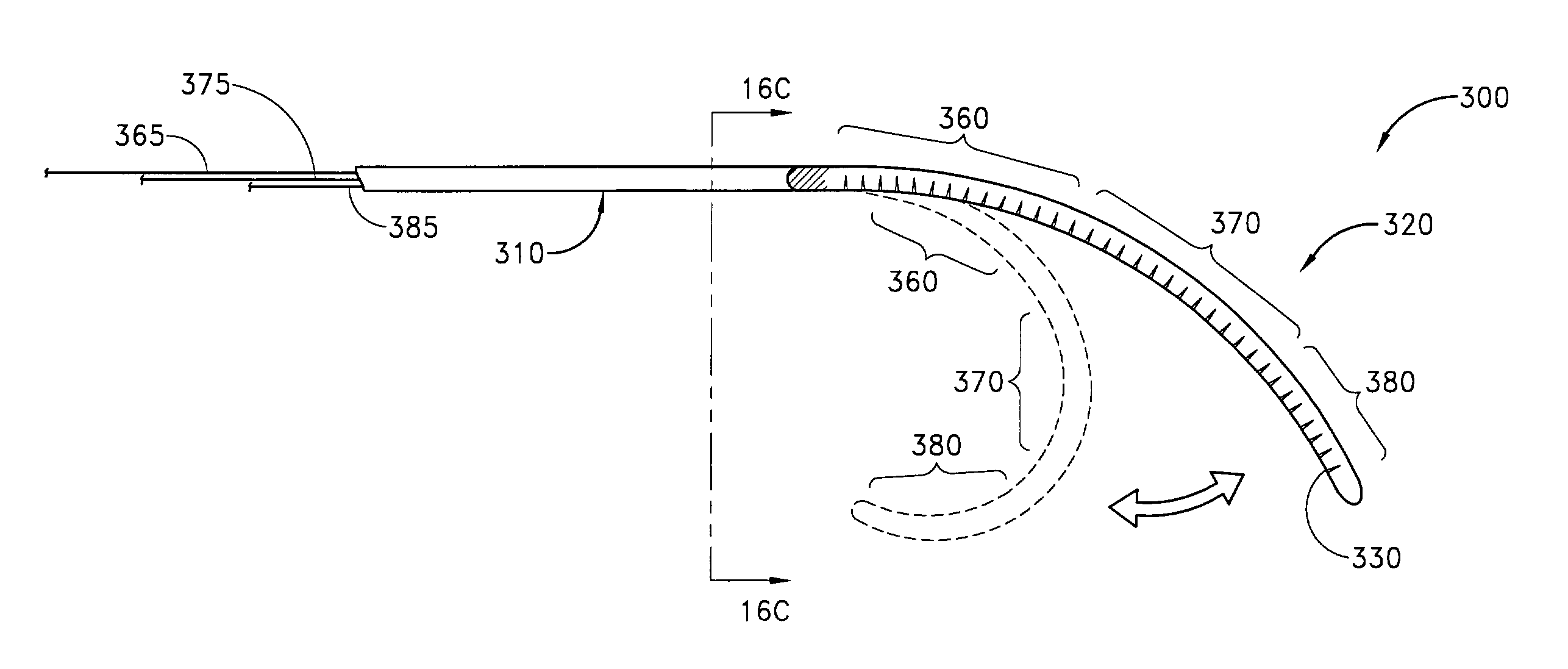
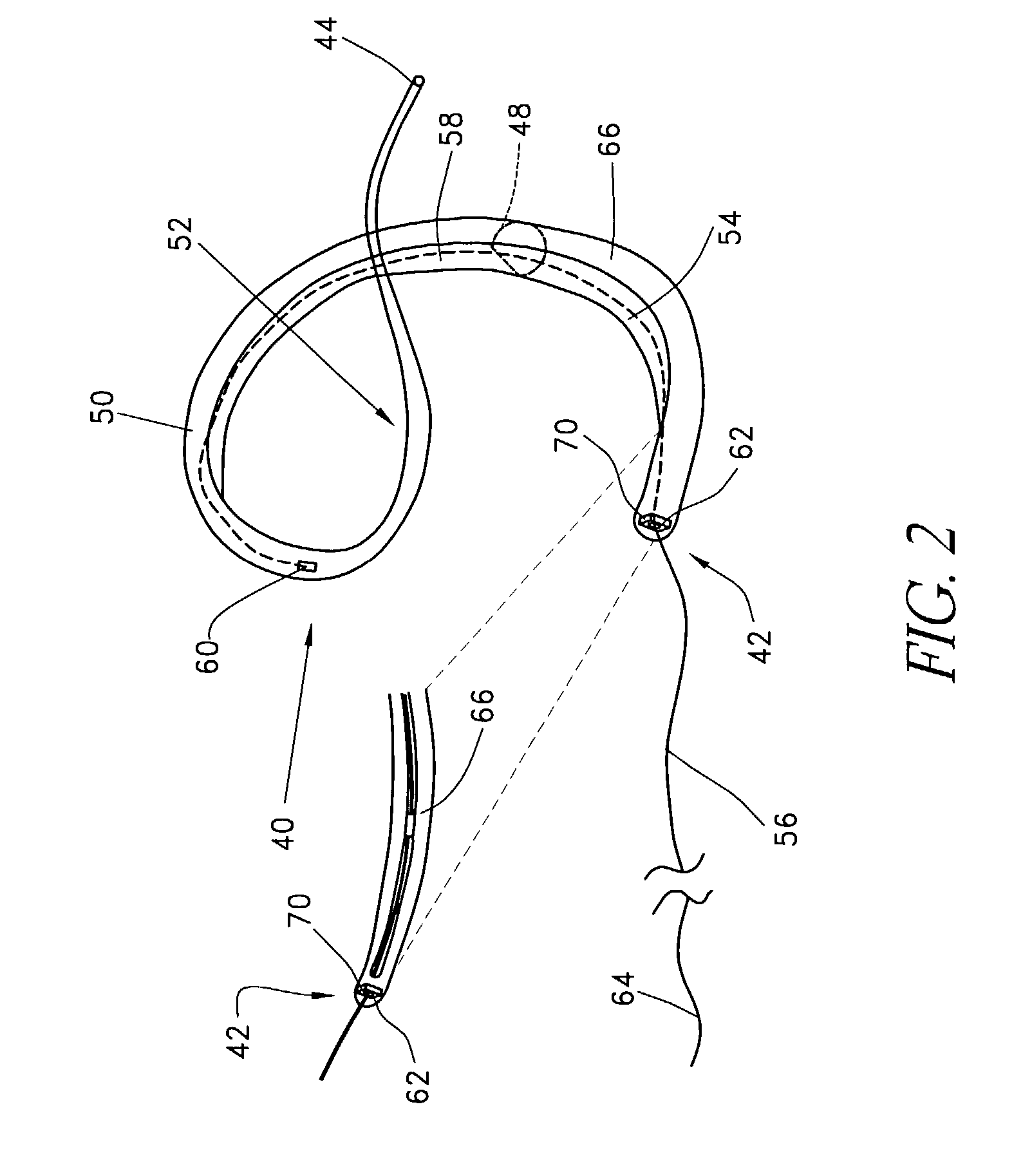
Medical system and method for remodeling an extravascular tissue structure
A medical apparatus and method suitable for remodeling a mitral valve annulus adjacent to the coronary sinus. The apparatus comprises an elongate body having a proximal region and a distal region. Each of the proximal and distal regions is dimensioned to reside completely within the vascular system. The elongate body may be moved from a first configuration for transluminal delivery to at least a portion of the coronary sinus to a second configuration for remodeling the mitral valve annulus proximate the coronary sinus. A forming element may be attached to the elongate body for manipulating the elongate body from the first transluminal configuration to the second remodeling configuration. Further, the elongate body may comprise a tube having a plurality of transverse slots therein.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
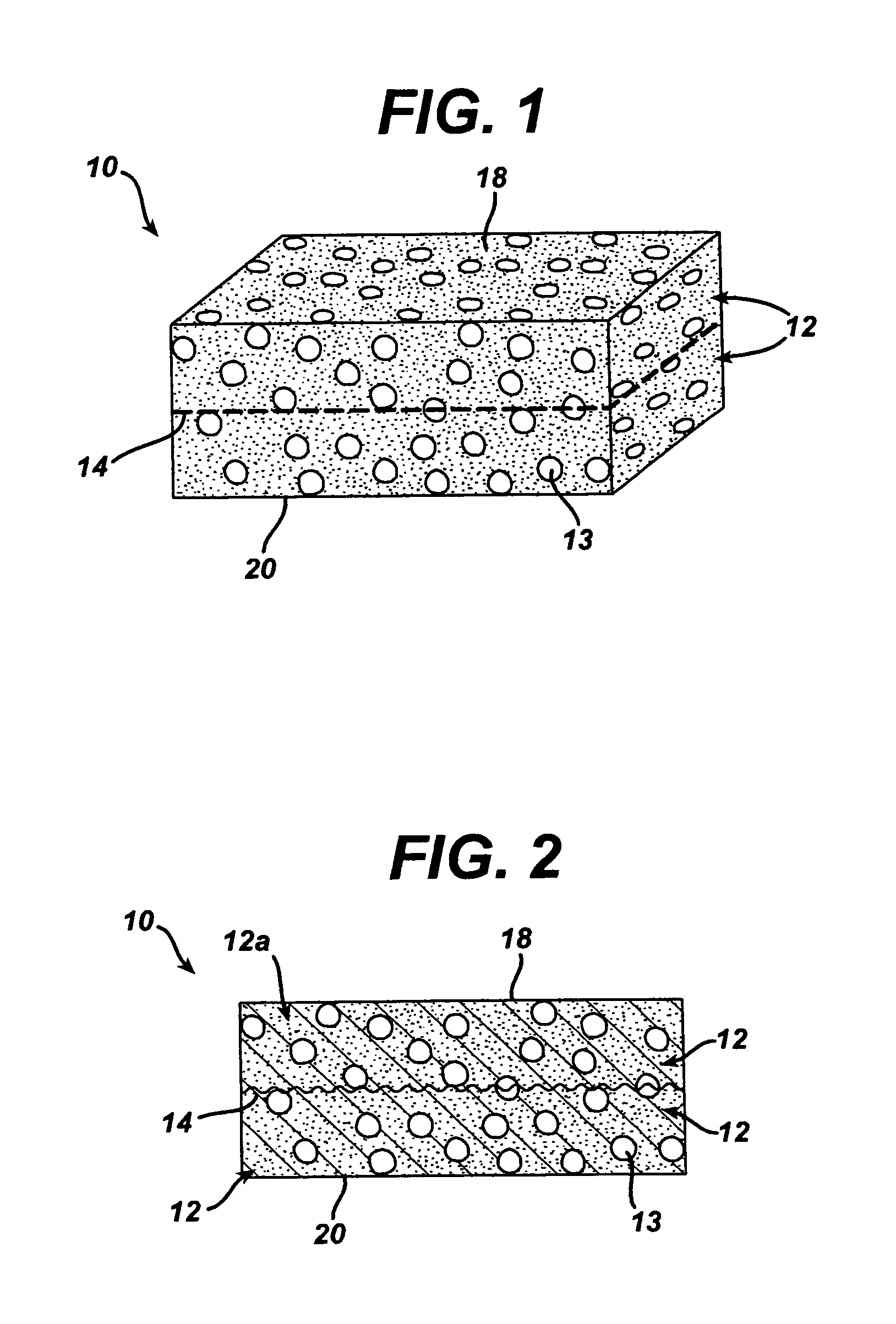
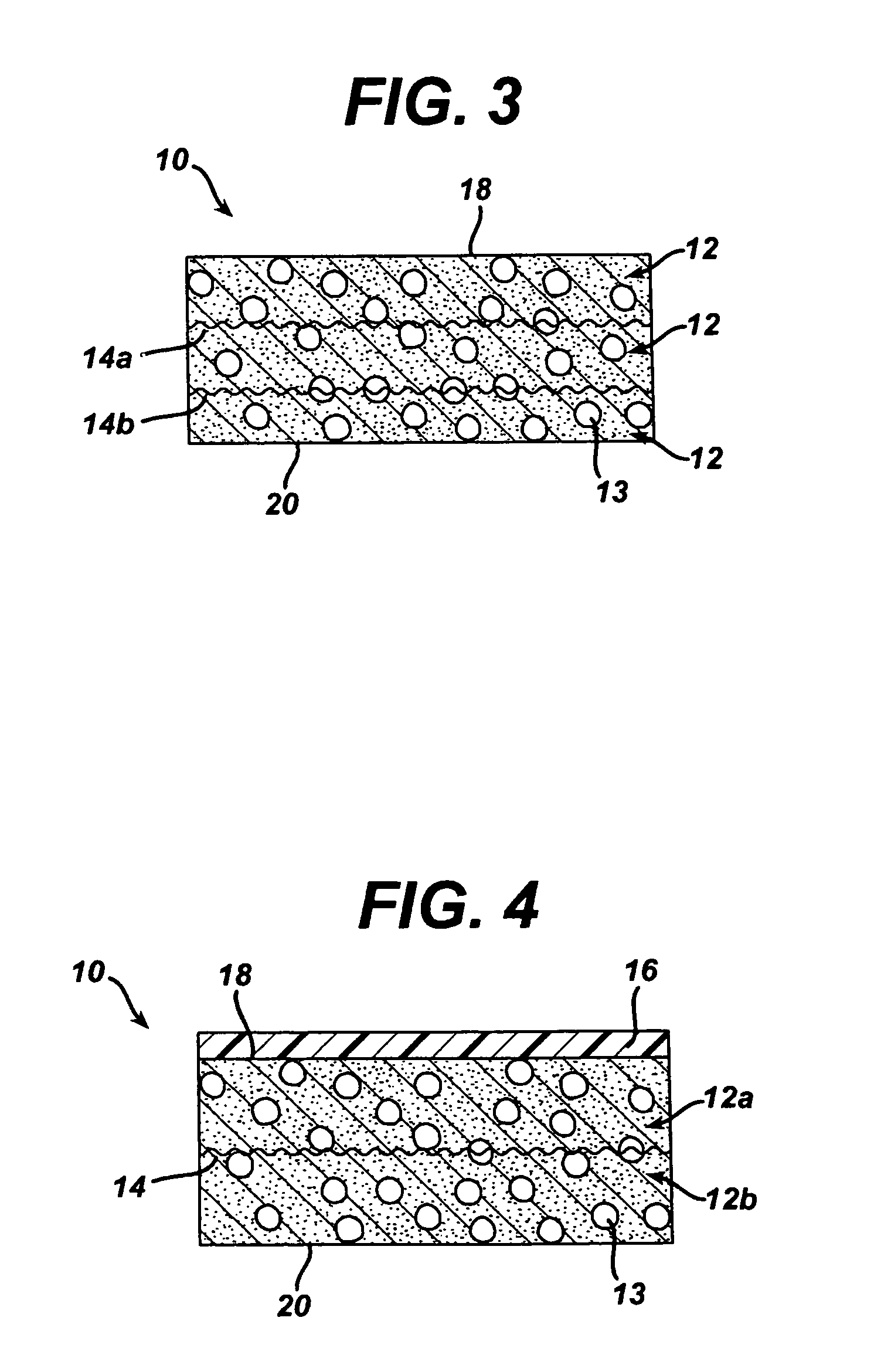
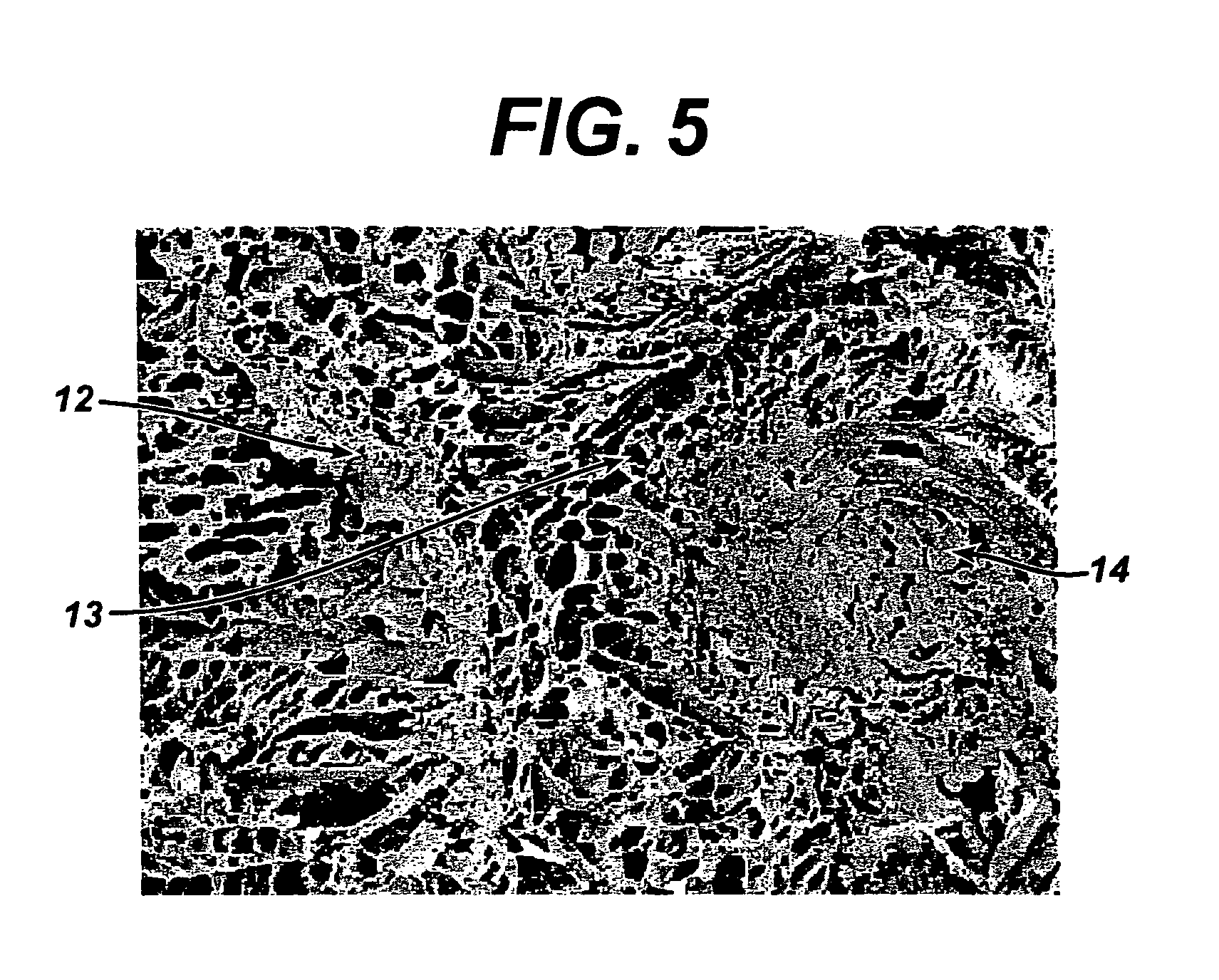
Method of preparation of bioabsorbable porous reinforced tissue implants and implants thereof
A biocompatible tissue implant. The tissue implant may be bioabsorbable, consists of a biocompatible polymeric foam. The tissue implant also includes a biocompatible reinforcement member. The polymeric foam and the reinforcement member are soluble in a lyophilizing solvent. The reinforcement may be annealed and / or coated.
Owner:DEPUY MITEK INC
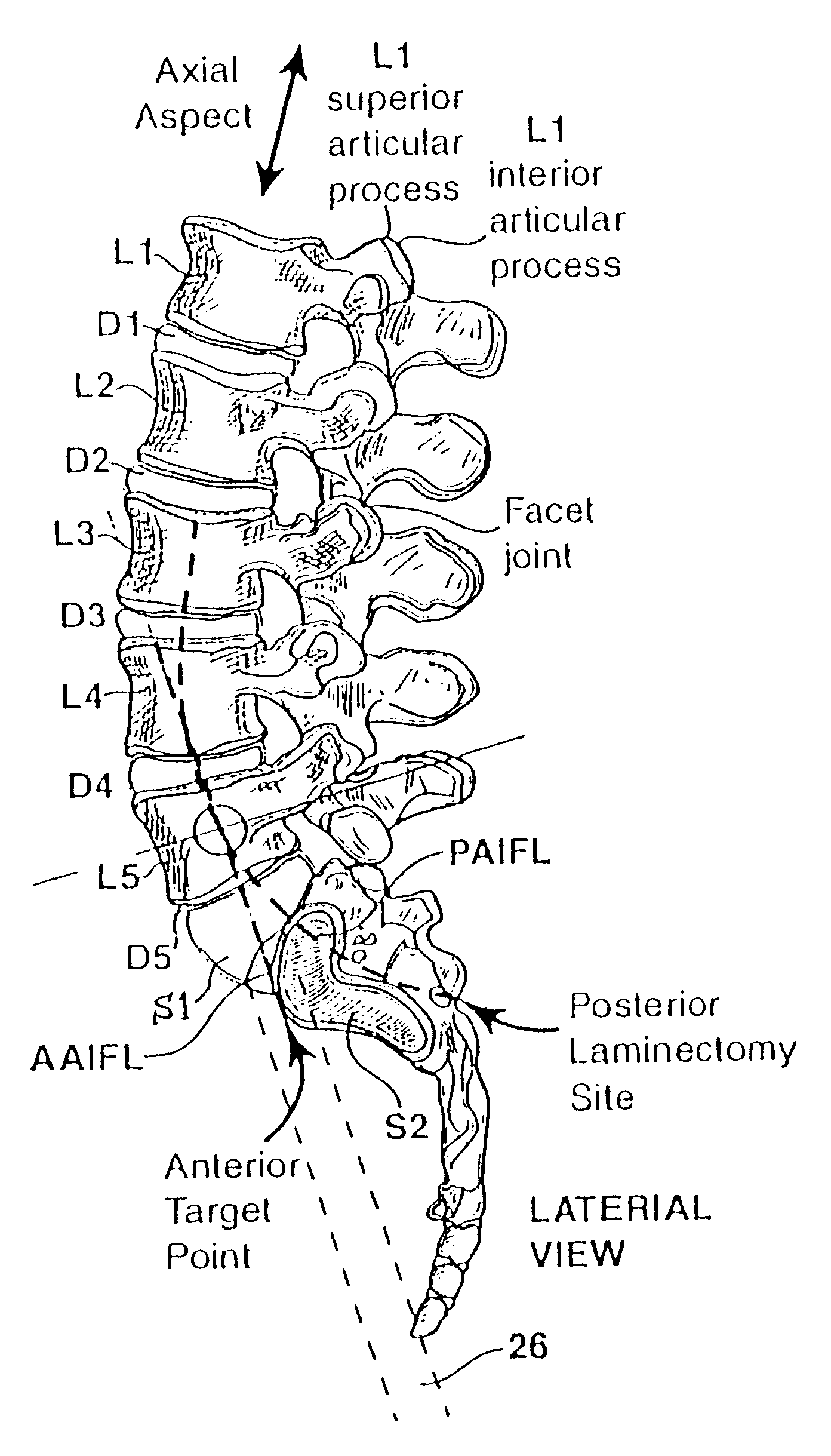
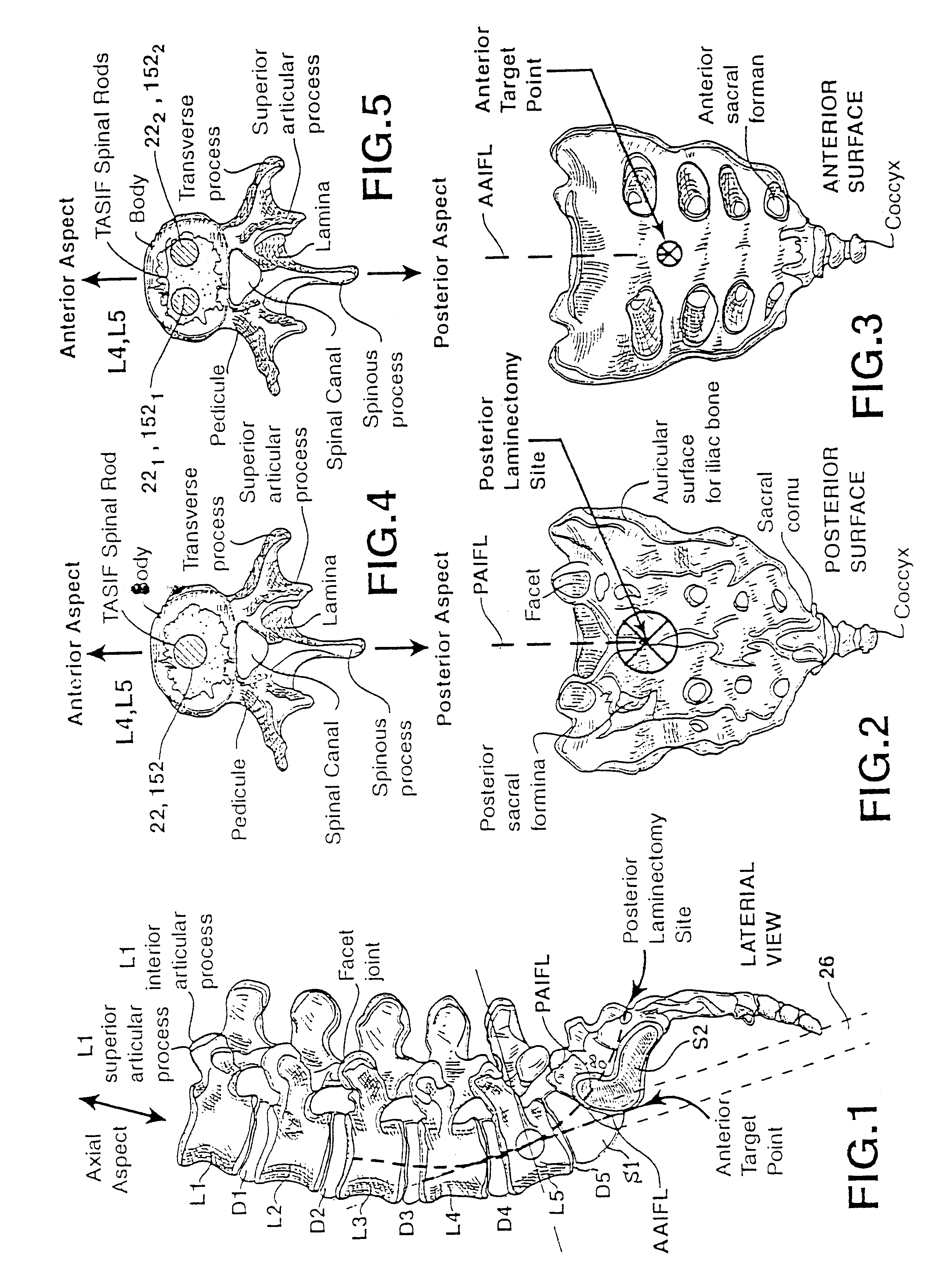
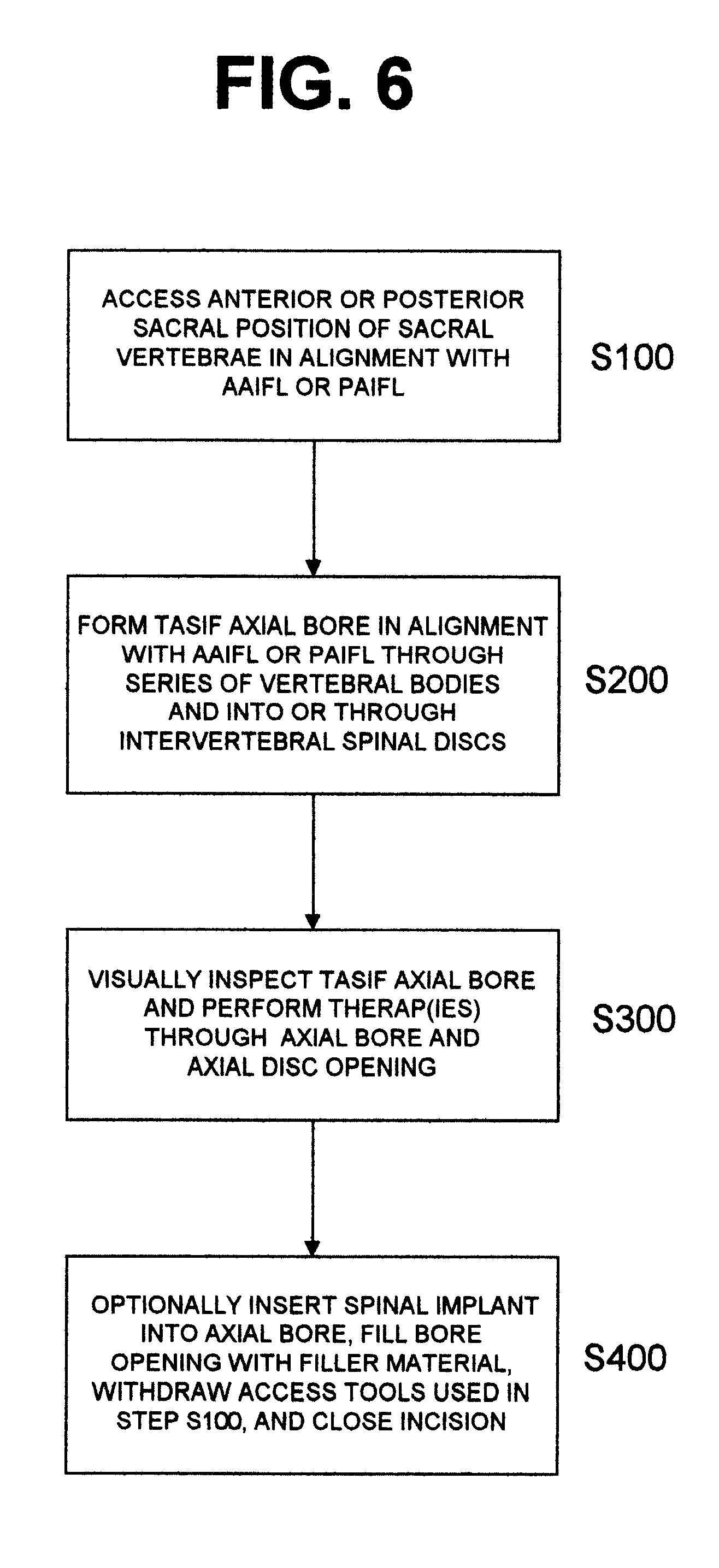
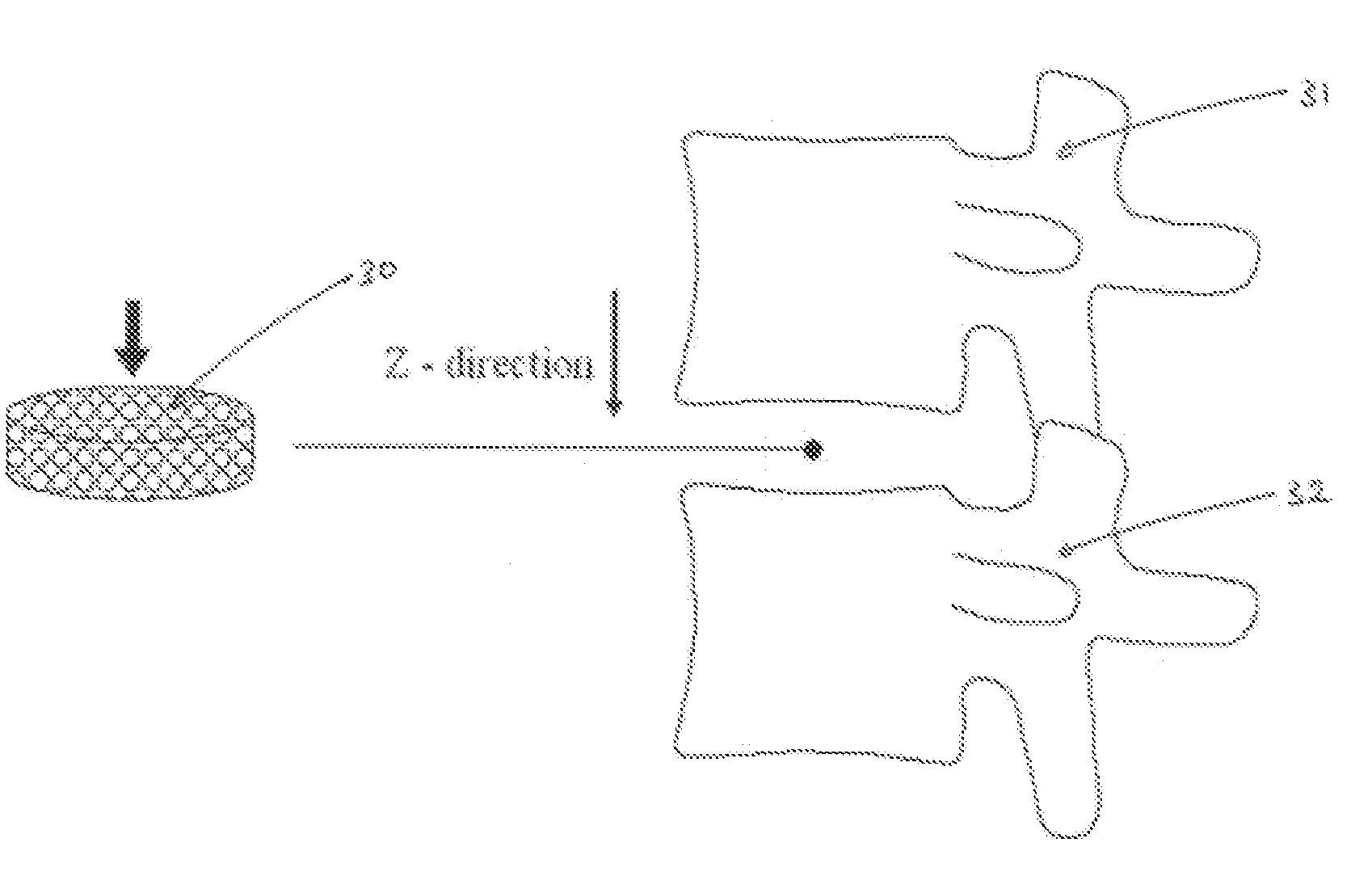
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
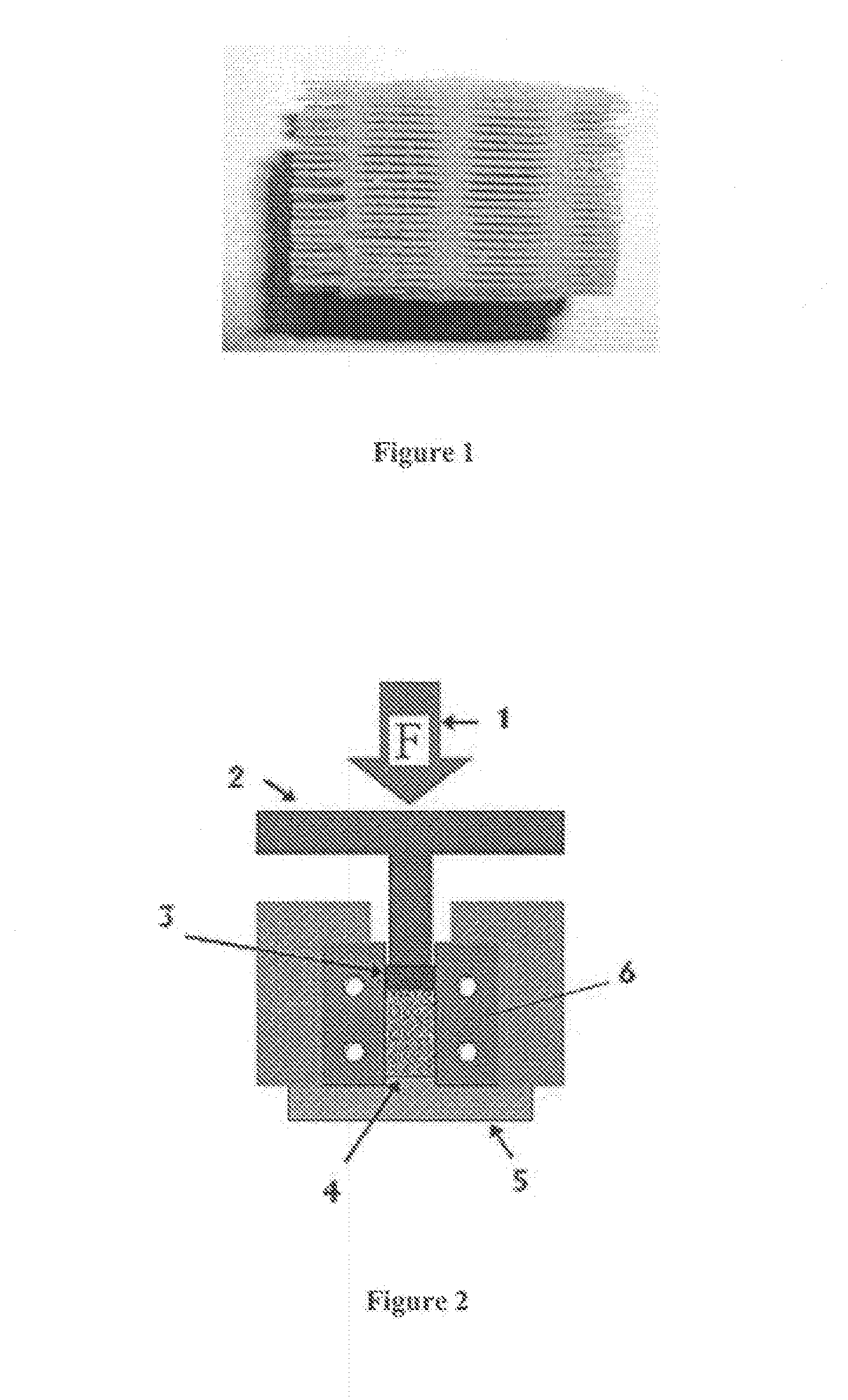
Bi-phasic compressed porous reinforcement materials suitable for implant
ActiveUS8389588B2Efficient use ofHigh and low porosity zoneBone implantSkeletal disorderFluid migrationUltimate tensile strength
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
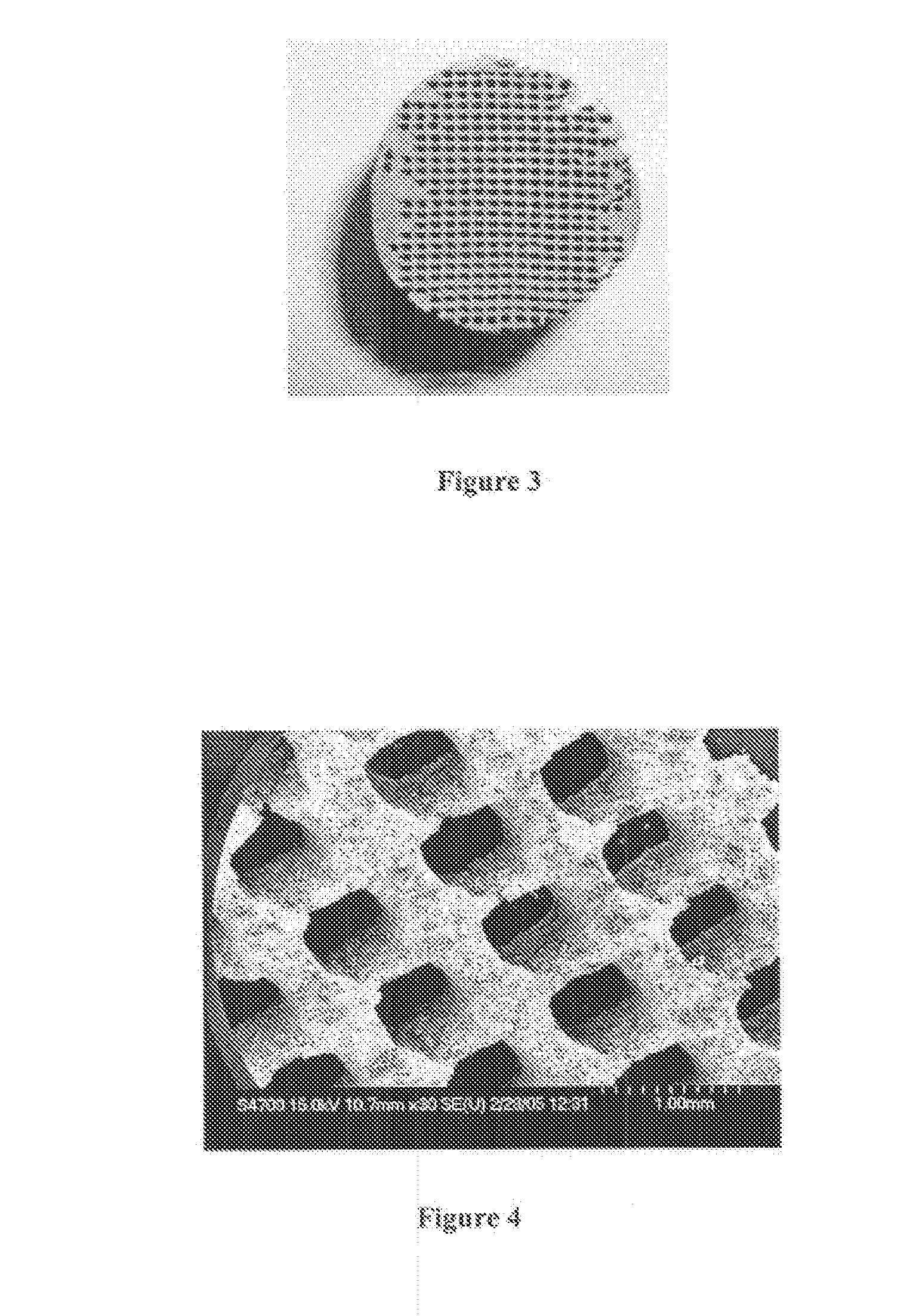
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
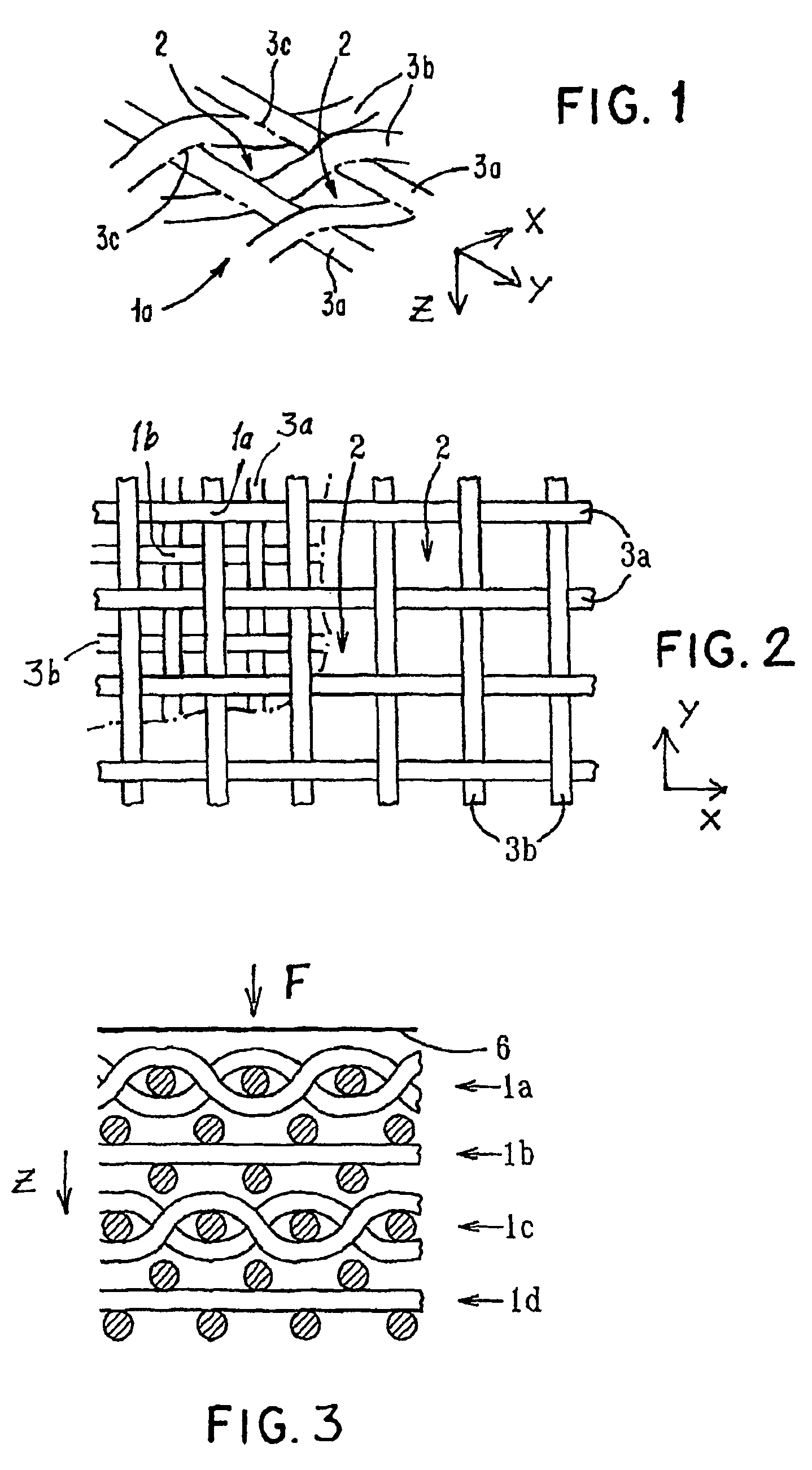
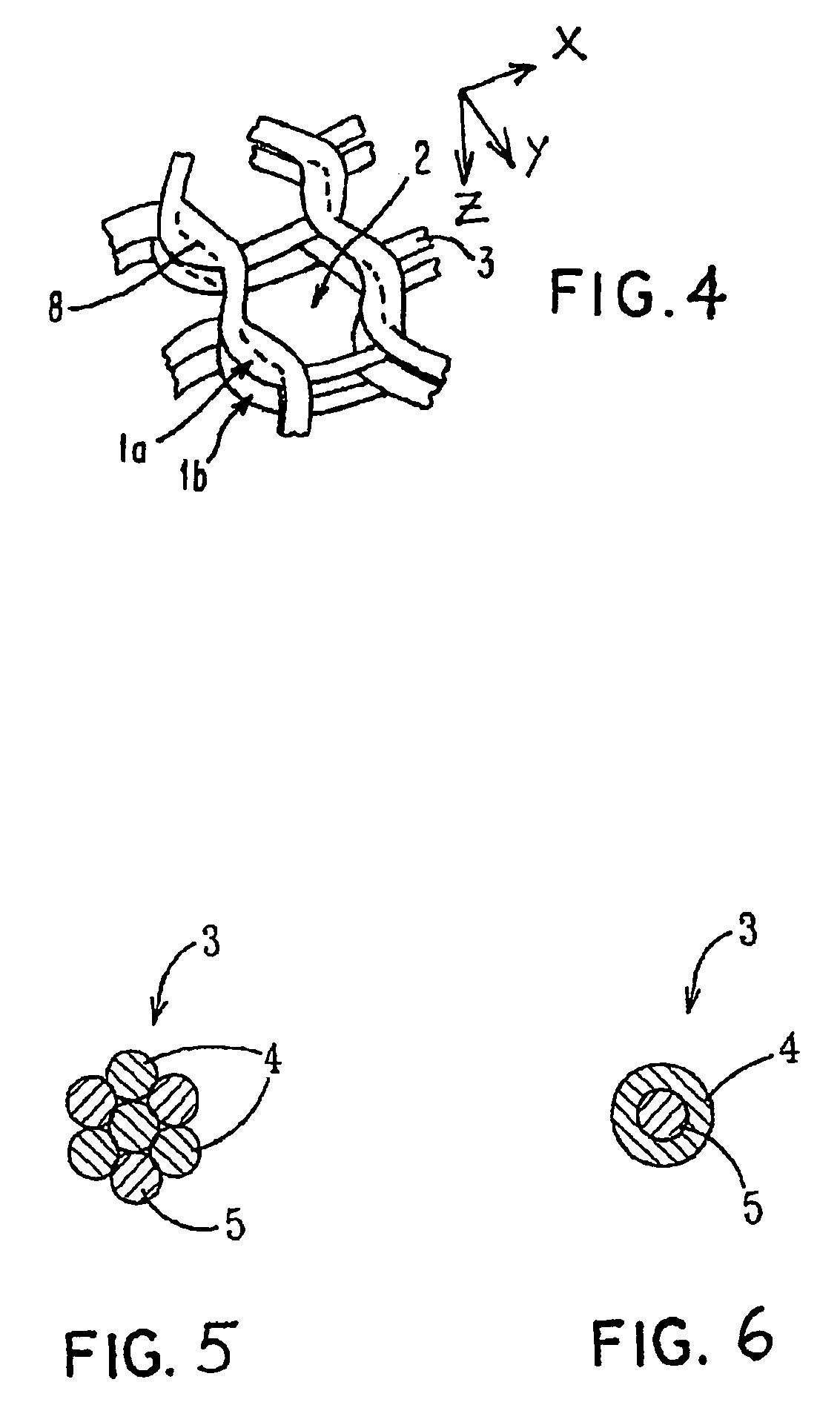
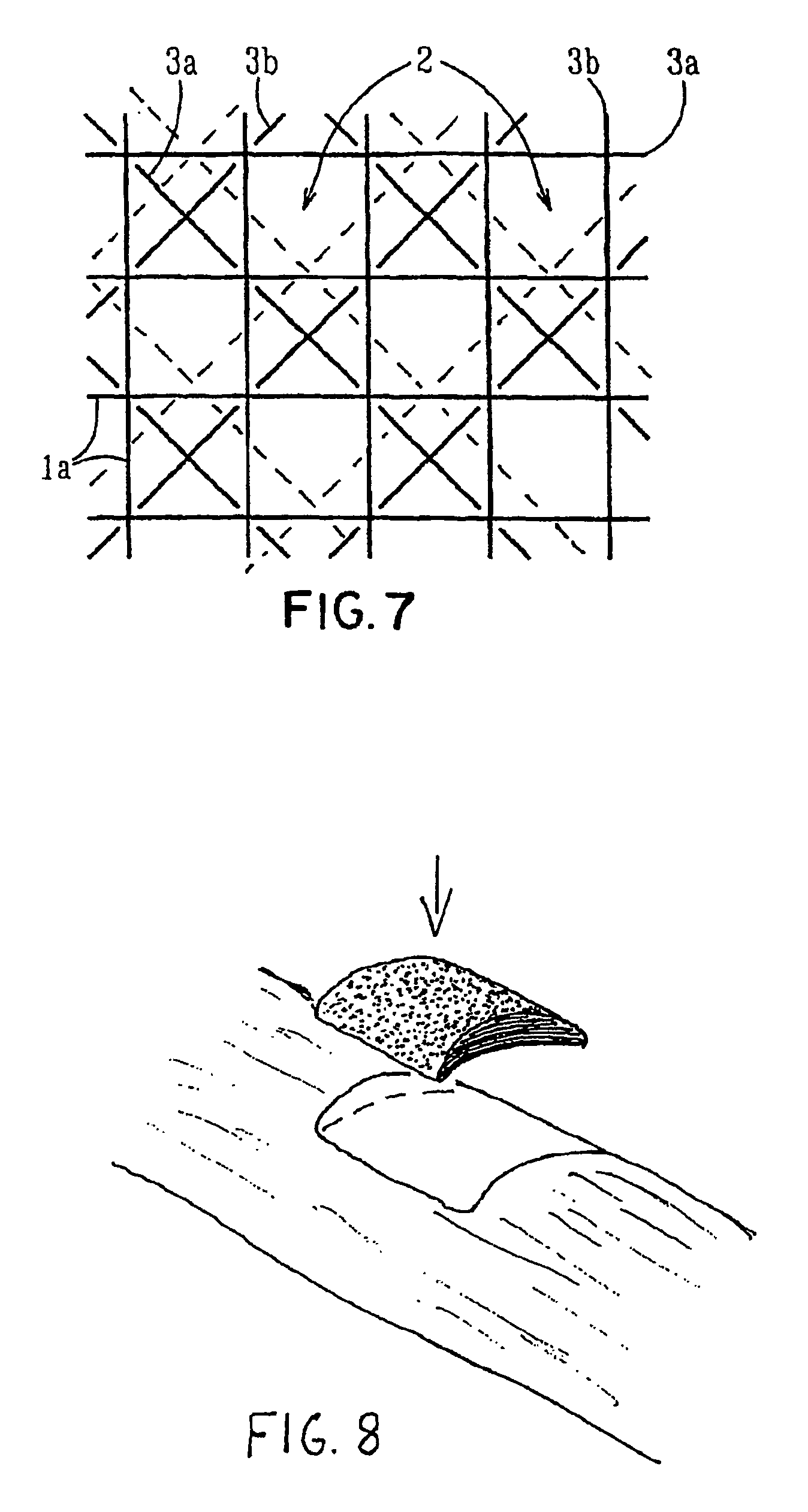
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
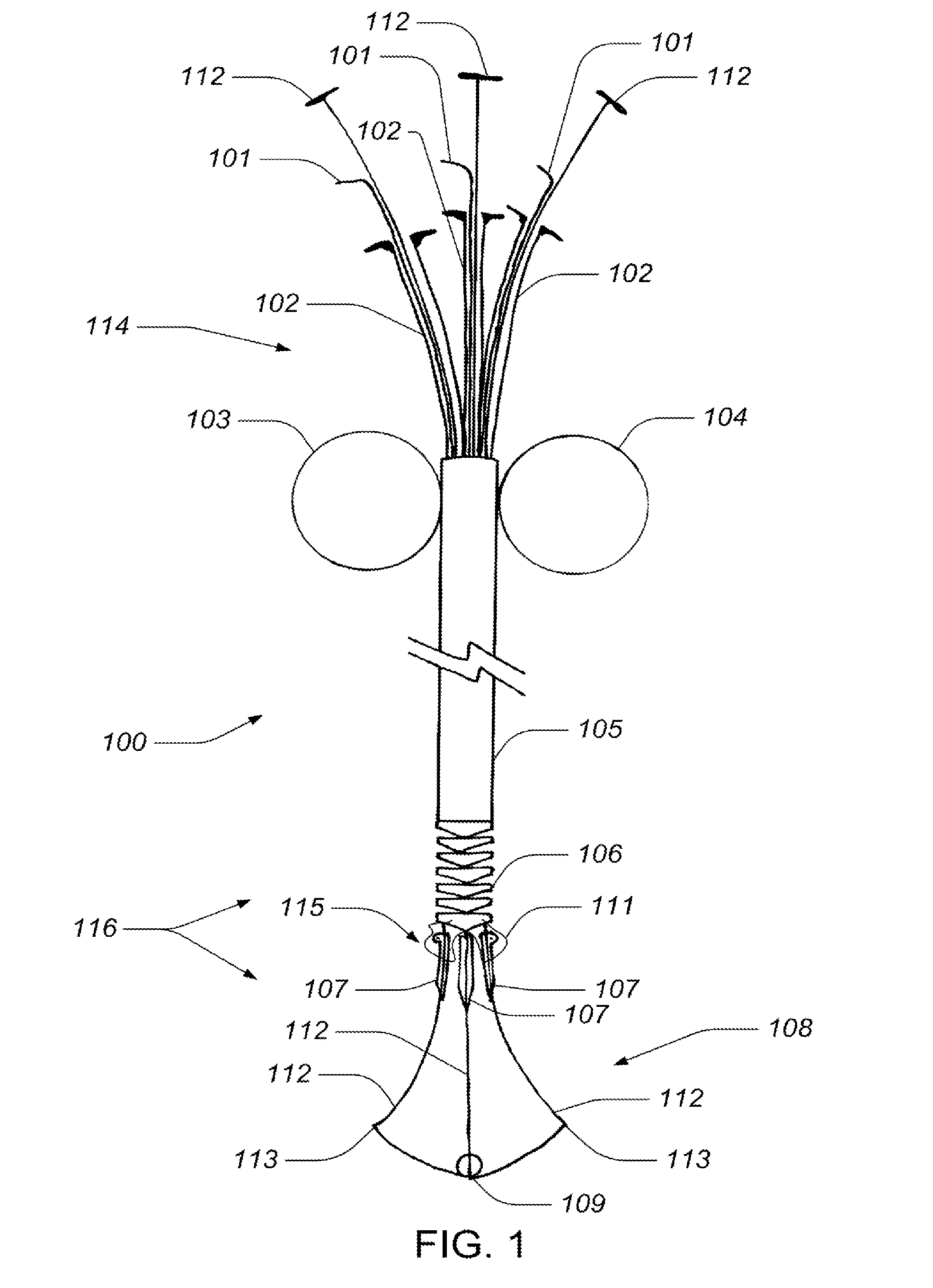
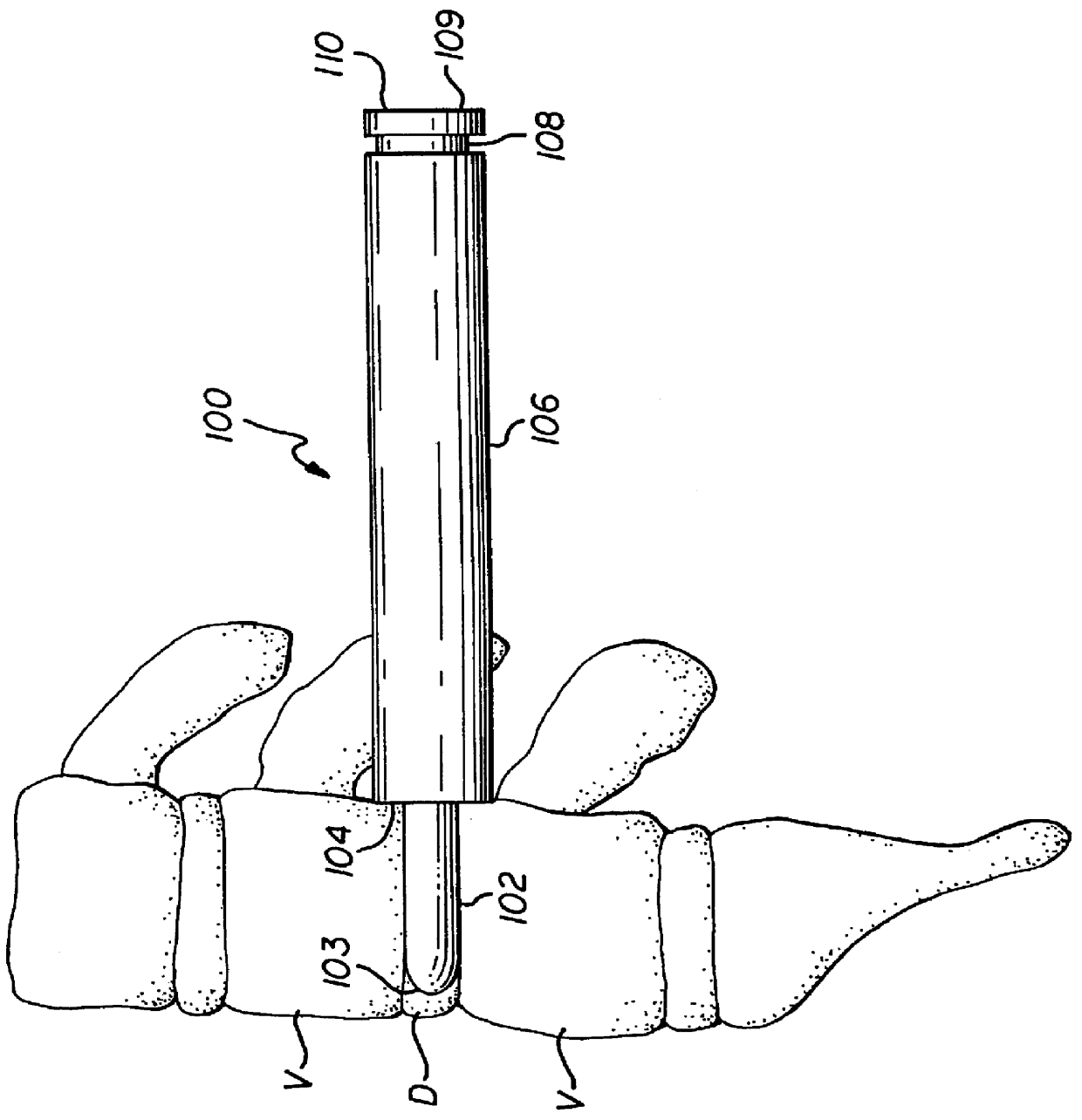
Method and apparatus for tissue connection
InactiveUS7101395B2Minimize traumaFunction increaseSuture equipmentsEar treatmentBiomedical engineering
A tissue connecting device is provided. The device comprise an elongate delivery device having a lumen, a proximal end, and a distal end. The distal end is configured to engage tissue and advance said device into tissue. At least one anchor deliverable through a lumen of the elongate delivery device. The distal end of the device may be designed to engage tissue upon rotation of the device about its longitudinal axis.
Owner:MITRAL INTERVENTIONS INC
Bone graft delivery device and method of use
InactiveUS7014640B2Easy to cleanEasy to disassembleBone implantJoint implantsParticulatesSubject matter
A dispensing device for granule bone graft of varying and / or irregular shape is characterized by a body defining a handle / hopper portion, a dispensing portion, and a feed system. The subject device permits reloading or refilling of bone graft at the time of use of the device. The bone graft dispensing device also accepts vials of bone graft. The vials are loaded onto and releasably retained by the dispensing device. In both forms, the feed system allows a controlled and / or variable rate of flow of bone graft during dispensing. The subject device may be made disposable as well as re-usable. The subject device is also modular in design allowing easy assembly / disassembly. The is subject bone graft dispenser is particularly suited for the dispensing of dry, particulate and / or granule bone graft. Particularly, the bone graft dispensing device is especially suited for the dispensing of particulate or granule bone graft having particulates or granules of various and / or irregular size, shape and combinations thereof.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Method of inserting and preloading spinal implants
InactiveUS6080155ARestoring and maintaining normal angular relationshipFaster and safe and more efficaciousInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve. Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted to restore the normal angular relationship of the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. An extended outer sleeve having extended portions capable of maintaining the vertebrae distracted in their normal angular relationship is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method of preparation of bioabsorbable porous reinforced tissue implants and implants thereof
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
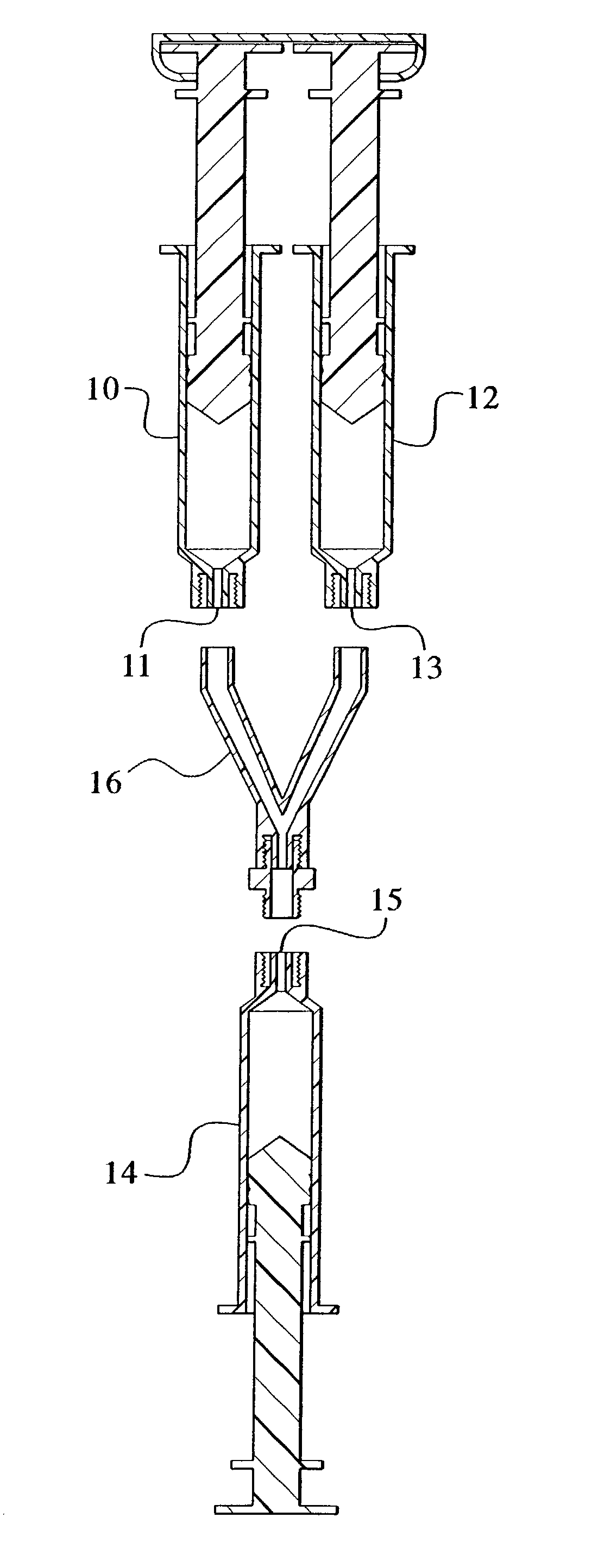
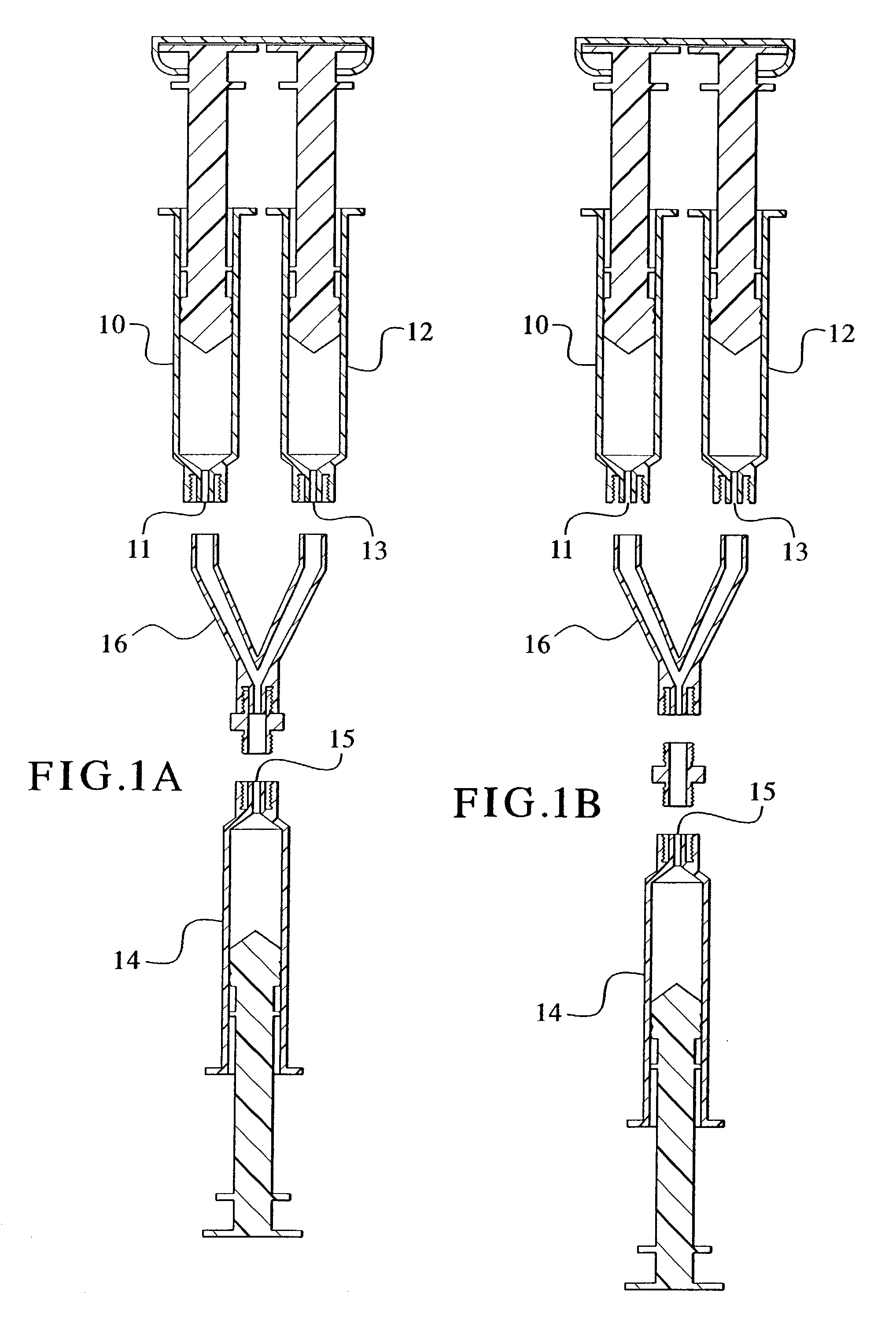
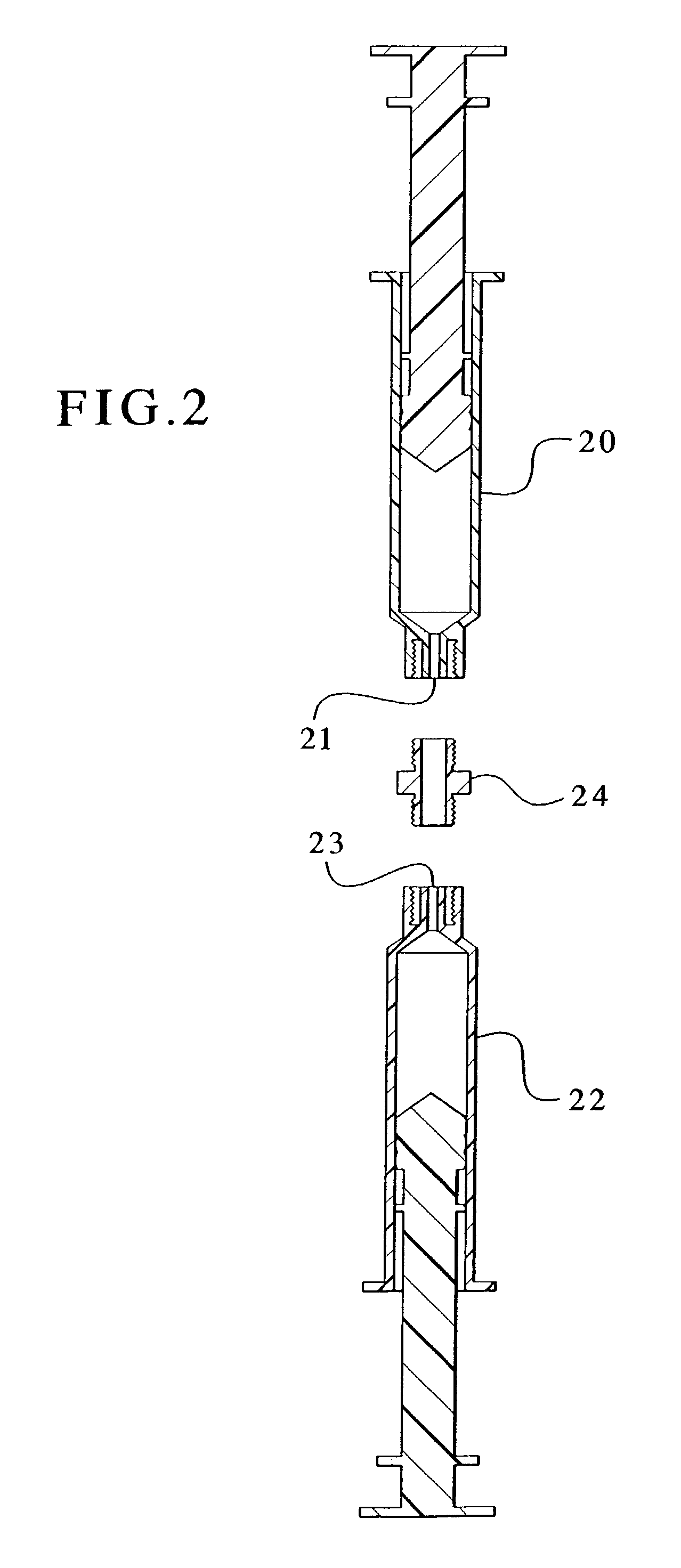
Devices and methods for mixing and extruding medically useful compositions
This invention provides devices and methods for mixing and extruding compositions which are medically and non-medically useful. The devices are particularly useful for mixing substances which are relatively inert when alone but become reactive when mixed. A common feature of all of the devices is that they allow the user to mix and ultimately extrude a composition from a single device which includes a single container or multiple interconnected containers.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Apparatus for inserting spinal implants
InactiveUS6096038AEliminate separationEfficient removalInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceIntervertebral disk
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Articulating spinal implant
A spinal implant for intervertebral disc replacement. The implant is formed from two hemicylindrical elements, each engaging one of an adjacent pair of vertebrae. An articulating ball-and-socket joint between the two elements resists compression and lateral movement between the vertebra, but allows pivotal movement, thereby preserving mobility. Fusion chambers are provided for allowing bone ingrowth to fuse the elements to the vertebrae. Biocompatible, bioreabsorbable struts, shims, fillers and / or end caps are provided for temporary stabilization of the first and second hemicylindrical elements. Bone chips removed from the vertebrae during implantation or bone growth stimulators can be inserted into the fusion chamber or otherwise applied to the implant to enhance bone ingrowth.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Expandable intervertebral spacer method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060129244A1Restore disc heightBone implantSurgeryBiological activationIntervertebral disk
An expandable interbody spacer (IBS) device designed to restore the disc height between vertebral bodies. The expandable interbody spacer device has an integral, moveable expansion member or spreader, provided between two plates. The plates are connected by one or more connecting members that retain the plates in a position proximate to one another while allowing the plates to move from a first unexpanded position to a second expanded position upon activation of the expansion member. According to aspects of the invention, the interbody spacer device can be implanted in an unexpanded or collapsed configuration, and then expanded to full height by engaging the expansion member. In other embodiments, the interbody spacer device may take various forms, for example, it may be cashew, rectangular or annular.
Owner:ALPINESPINE
Porous Substrates for Implantation
InactiveUS20100137990A1Easy to integrateGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsDental implantsPorous substrateAnimal body
A porous substrate or implant for implantation into a human or animal body constructed from a structural material and having one or more regions which when implanted are subjected to a relatively lower mechanical loading. The region(s) are constructed with lesser mechanical strength by having a lesser amount of structural material in said region(s) relative to other regions. This is achieved by controlling pore volume fraction in the regions. A spacer is adapted to define an open-cell pore network by taking a model of the required porous structure, and creating the spacer to represent the required porous structure using three-dimensional modelling. Material to form the substrate about the spacer in infiltrated the scaffold structure formed.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
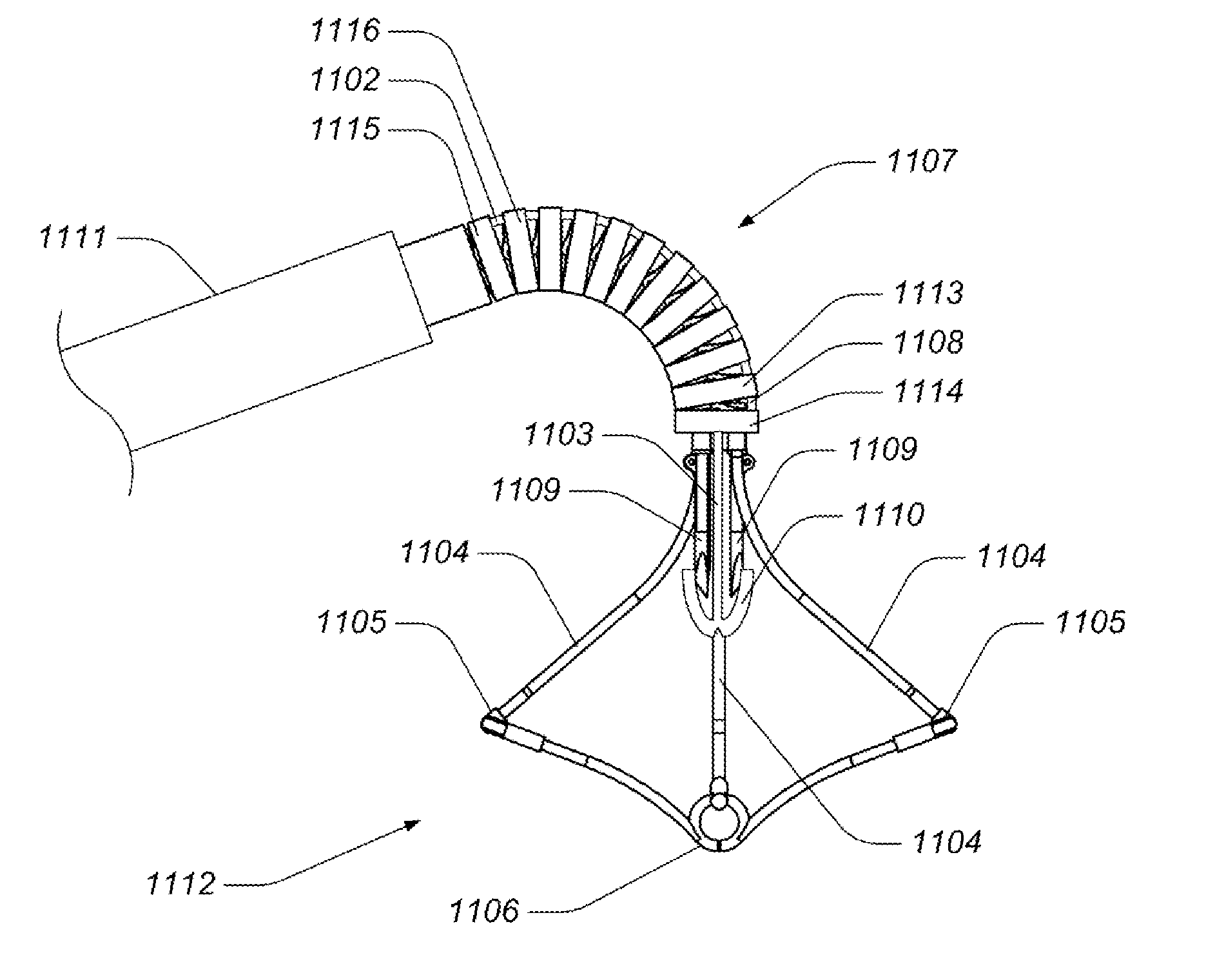
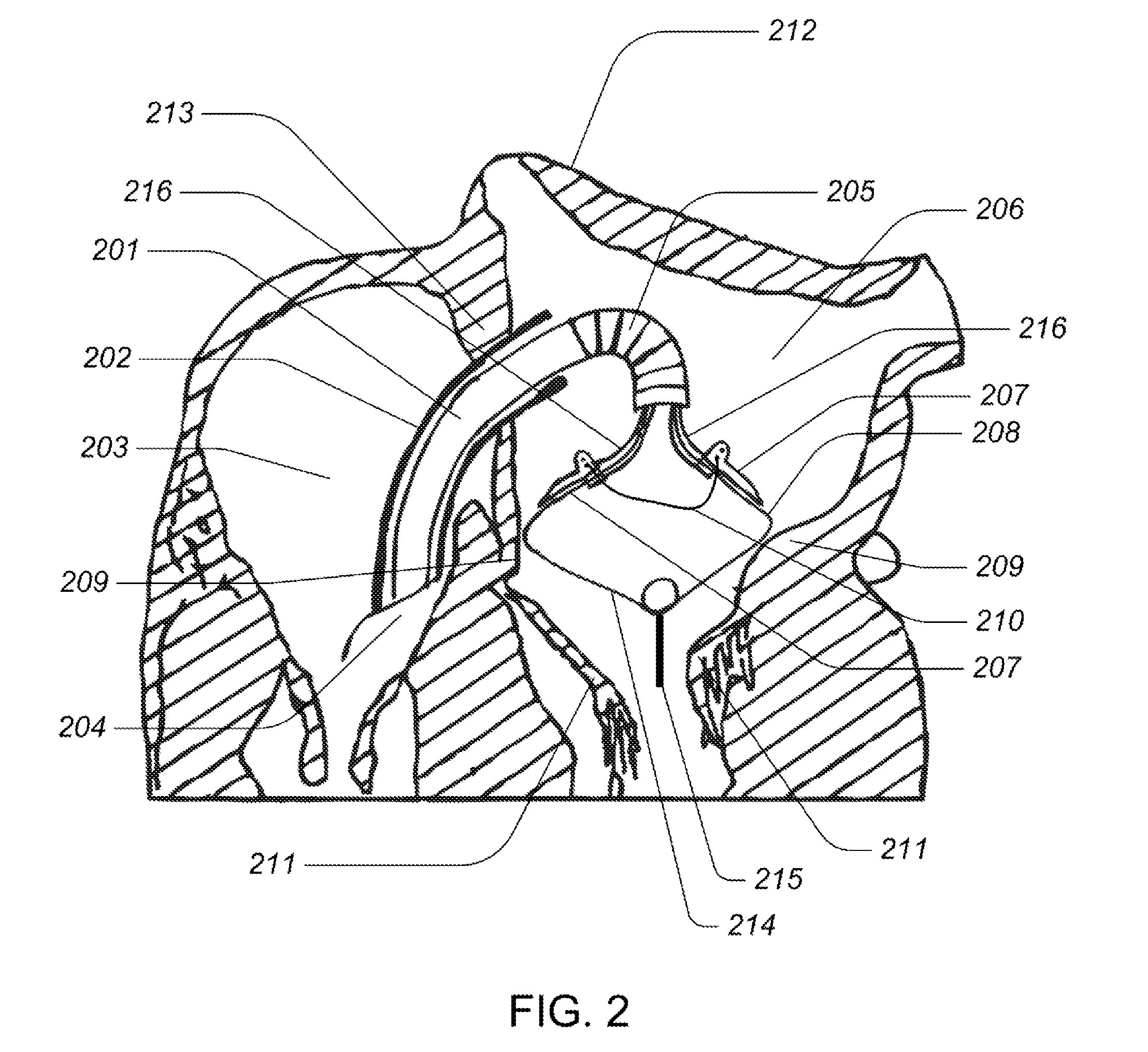
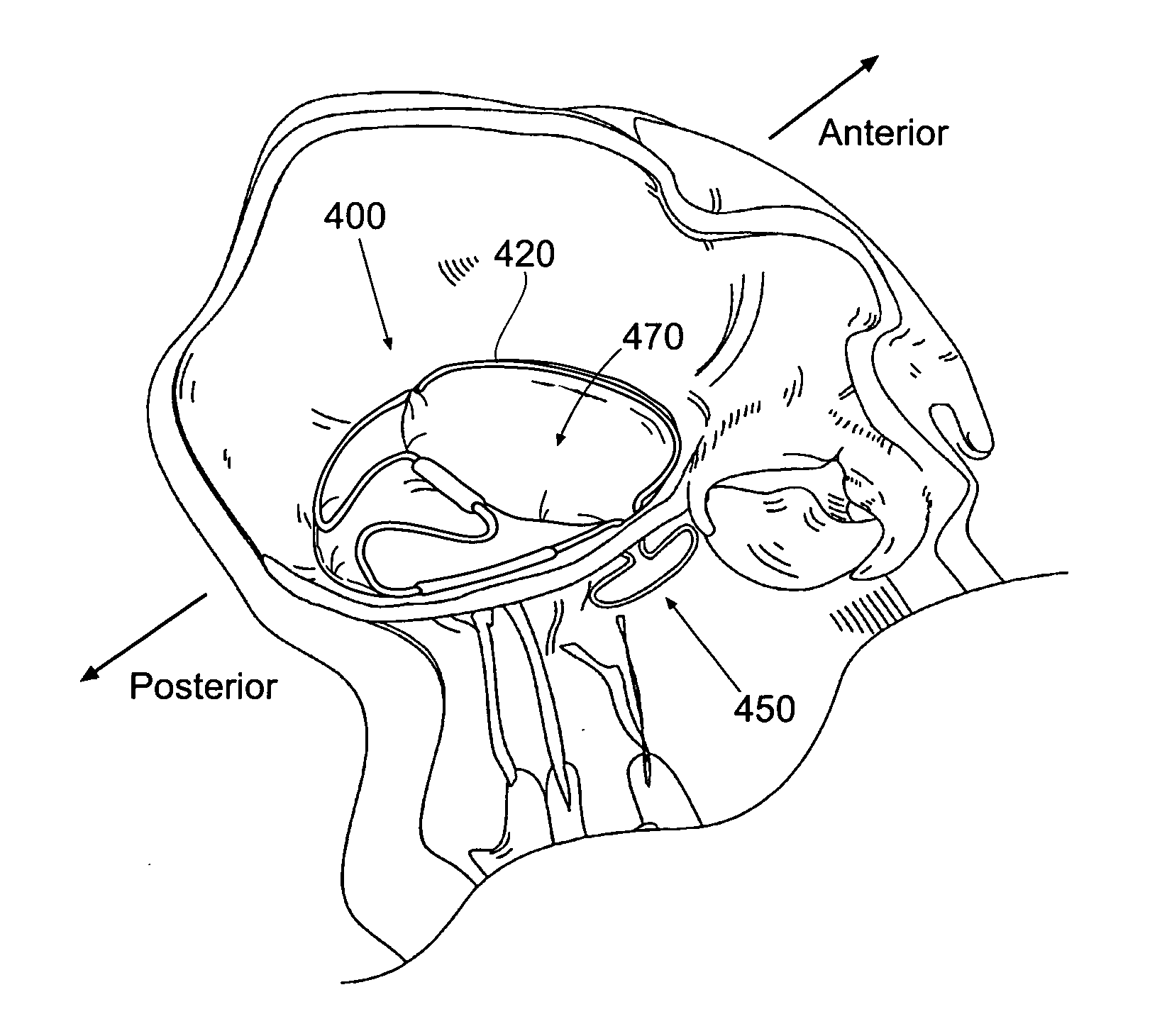
Devices, systems, and methods for supplementing, repairing, or replacing a native heart valve leaflet
Devices, systems and methods supplement, repair, or replace a native heart valve. The devices, systems, and methods employ an implant that, in use, extends adjacent a valve annulus. The implant includes a mobile neoleaflet element that occupies the space of at least a portion of one native valve leaflet. The implant mimics the one-way valve function of a native leaflet, to resist or prevent retrograde flow. The implant restores normal coaptation of the leaflets to resist retrograde flow, thereby resisting eversion and / or prolapse, which, in turn, reduces regurgitation.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Intersomatic setting and fusion system
A system for intersomatic fusion and setting of vertebrae. The system includes at least one open internal cage arranged for receiving spongy bone or bone substitute and is designed to be interposed between two vertebrae during diskectomy. The cage (1) includes on its anterior face (5) an external element forming a plate (12) extending in a plane substantially perpendicular to the insertion plane of the cage (1), and has at each of its ends an anchor device (13,14) adapted for anchoring to at least two adjacent vertebrae to be secured to each other by the cage (1). The system can be separated into two parts, the cage and the plate.
Owner:SCIENTX
Expandable osteosynthesis cage
InactiveUS6129763AGood jamLarge inside volumeBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
PCT No. PCT / FR97 / 01617 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 28, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 12, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 10722 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 19, 1998An expandable osteosynthesis implant has branches (5) each connected at one end to a seat (7) which is pierced by an orifice (8), suitable for being slid from a posterior direction between the facing faces of two consecutive vertebrae in order to hold them a given distance apart and restore stability of the spinal column. According to the invention, the branches (5) and the seat (7) define a hollow cage (1) which, in a "rest" position, has an outside general shape that is a cylinder of circular section, and a portion at least of the inside volume (9) of the cage (1) towards the distal ends of the branches (5) is in the form of a circular truncated cone whose large base is towards the seat (7), which implant has at least three branches (5) and, inside the inside volume (9) at least one spacer (2) suitable for passing through the orifice (8) and the large base of the truncated cone.
Owner:OSTEOIMPLANT TECH
Annuloplasty rings and methods for repairing cardiac valves
InactiveUS20050004668A1Facilitate customized remodelingAccurate shapeBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsStructure functionImplanted device
Owner:FLEXCOR
Expandable spinal fusion device and methods of promoting spinal fusion
InactiveUS7018415B1Promoting osteogenic fusionMinimal exposureBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBone growth
An intervertebral disc space implant includes spaced-apart bone engagement portions that define an intermediate chamber that holds bone growth inducing material into contact with adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant is expandable to establish and maintain desired intervertebral spacing during fusion. The implant includes a first member and a second member arranged to move relative to each other by action of an expansion member, the first member being engageable with the vertebral body below the disc space.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
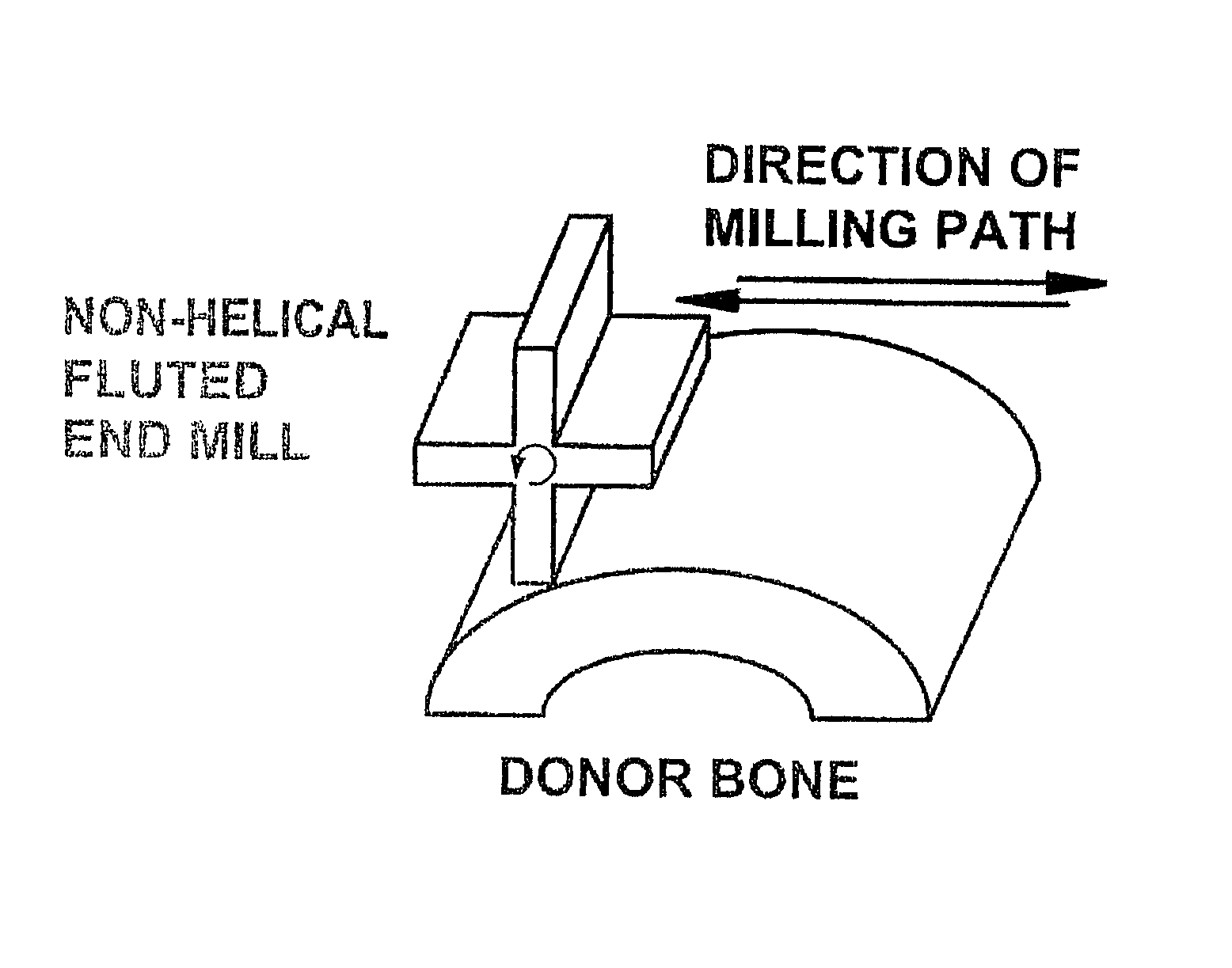
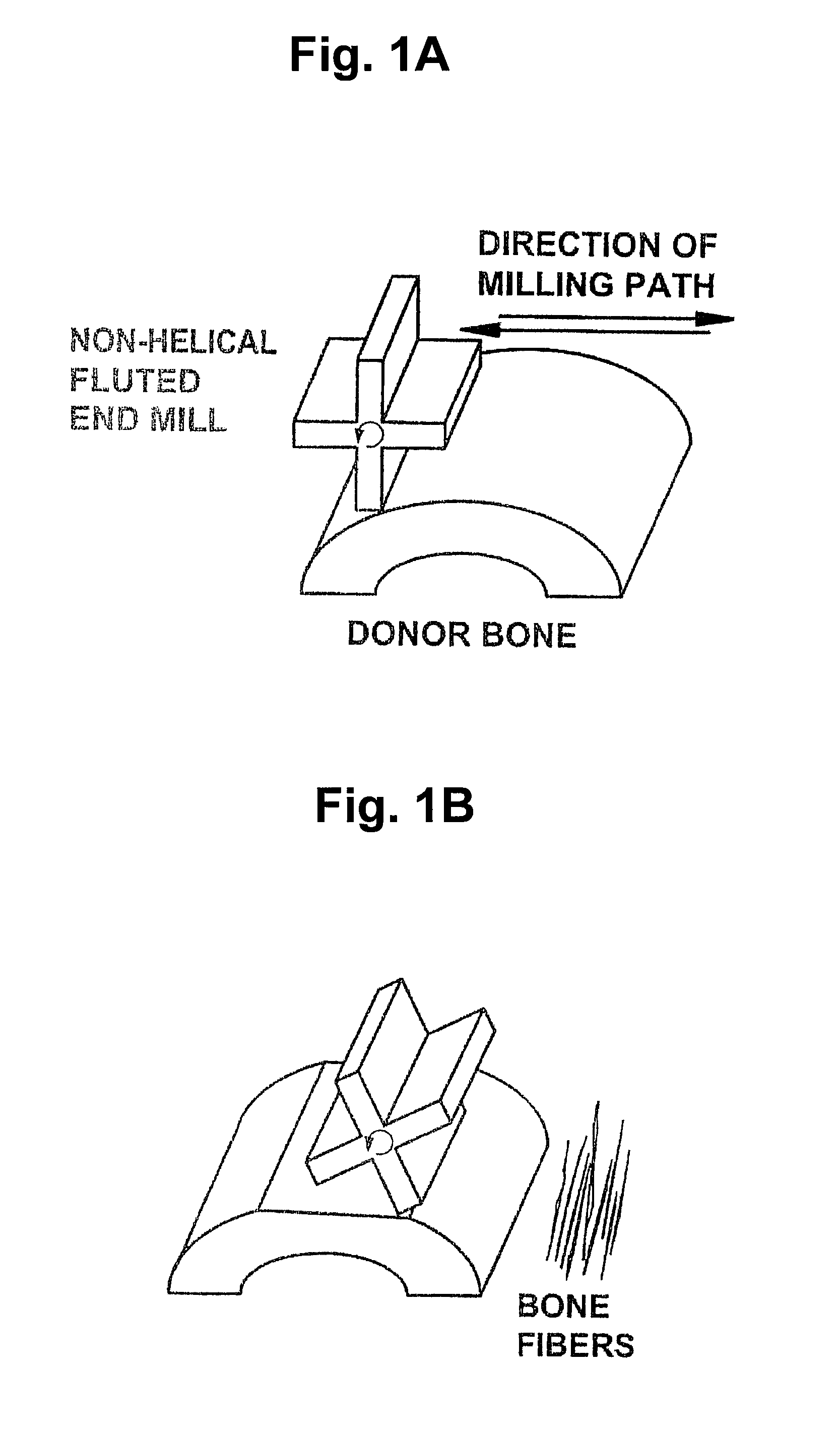
InactiveUS7479160B2Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantMedicineDonor bone
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concaved surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
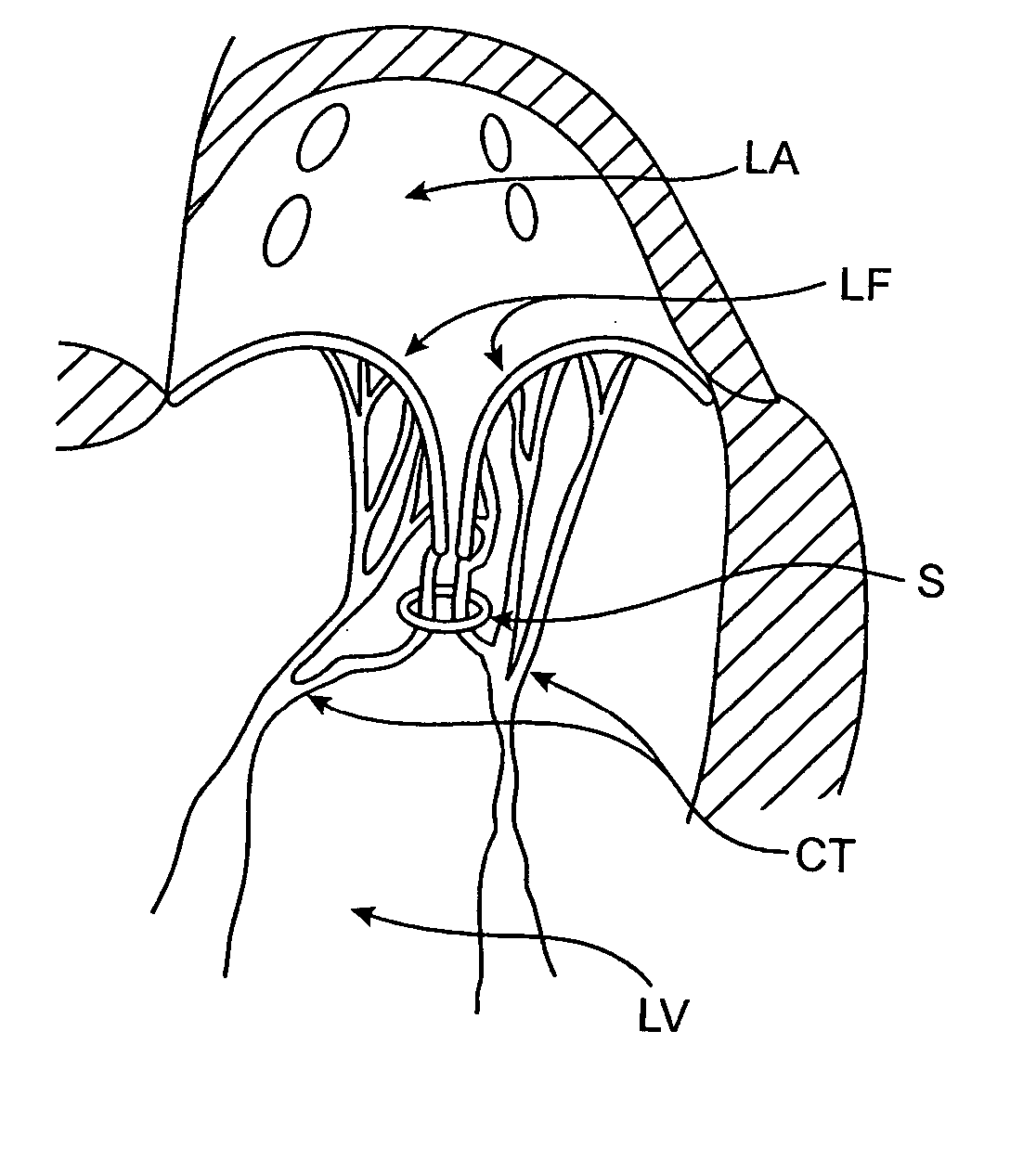
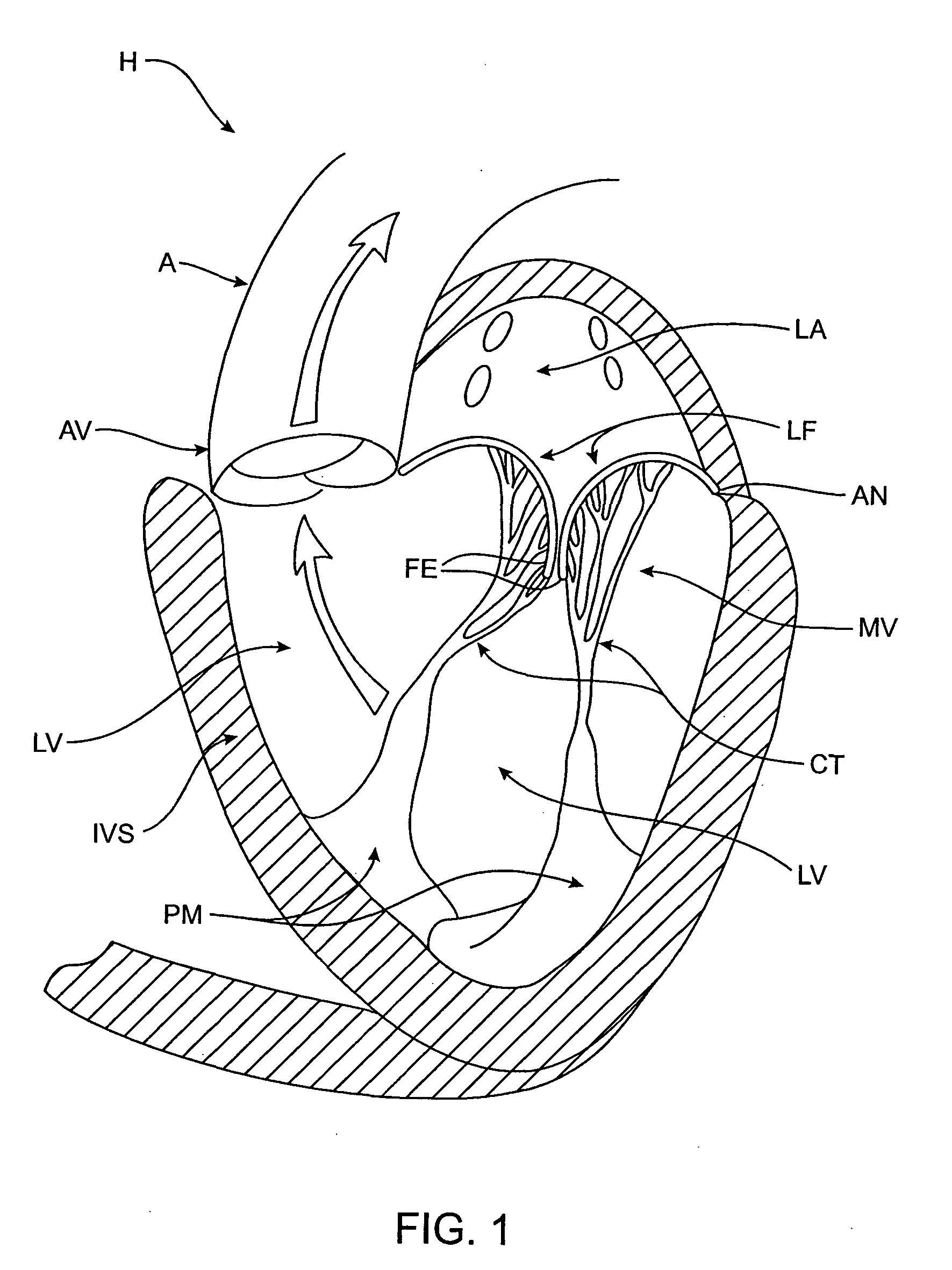
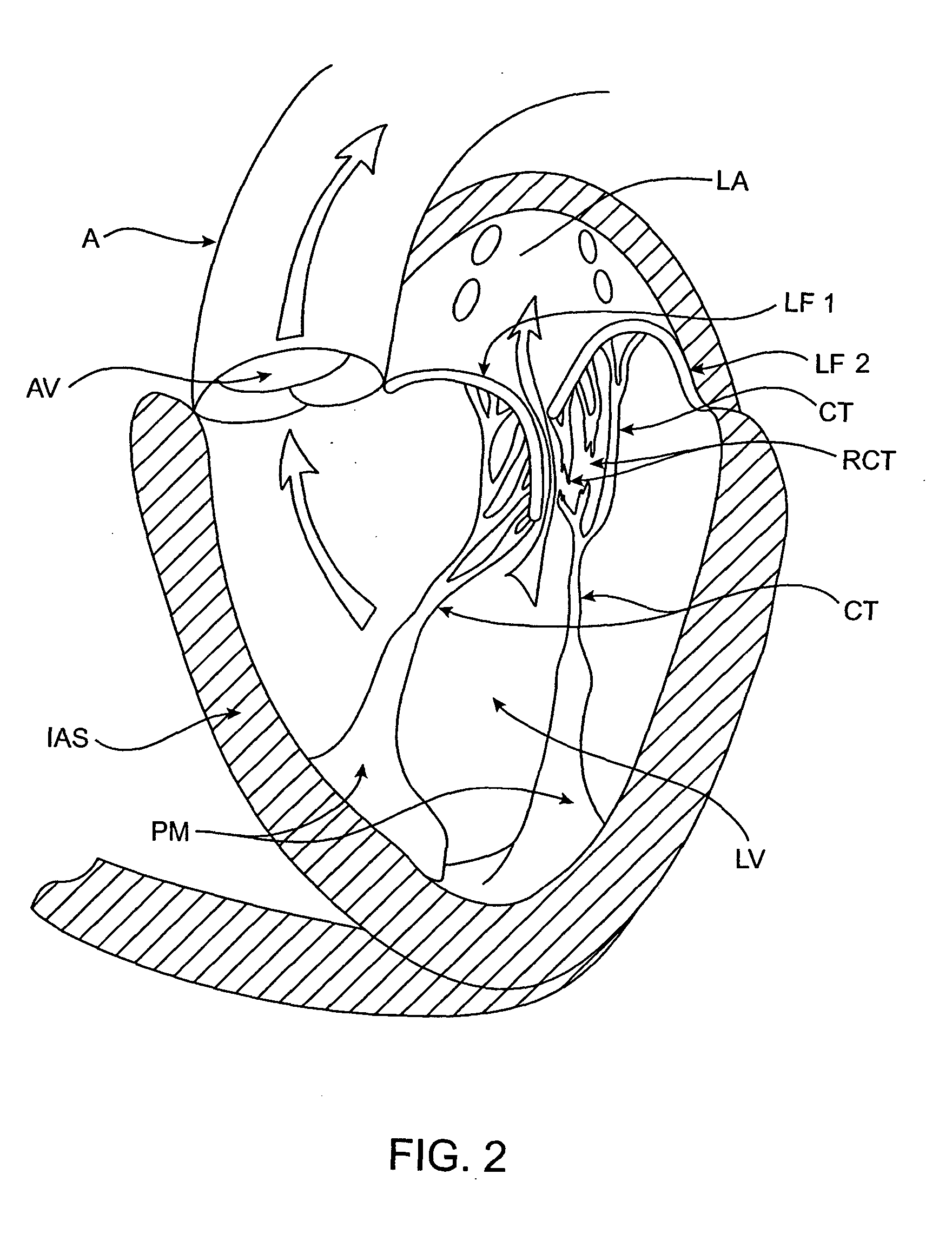
Methods and apparatus for cardiac valve repair
ActiveUS20040030382A1Reduce leakageReduce regurgitationSuture equipmentsBone implantHeart chamberPapillary muscle
The methods, devices, and systems are provided for performing endovascular repair of atrioventricular and other cardiac valves in the heart. Regurgitation of an atrioventricular valve, particularly a mitral valve, can be repaired by modifying a tissue structure selected from the valve leaflets, the valve annulus, the valve chordae, and the papillary muscles. These structures may be modified by suturing, stapling, snaring, or shortening, using interventional tools which are introduced to a heart chamber. Preferably, the tissue structures will be temporarily modified prior to permanent modification. For example, opposed valve leaflets may be temporarily grasped and held into position prior to permanent attachment.
Owner:EVALVE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com