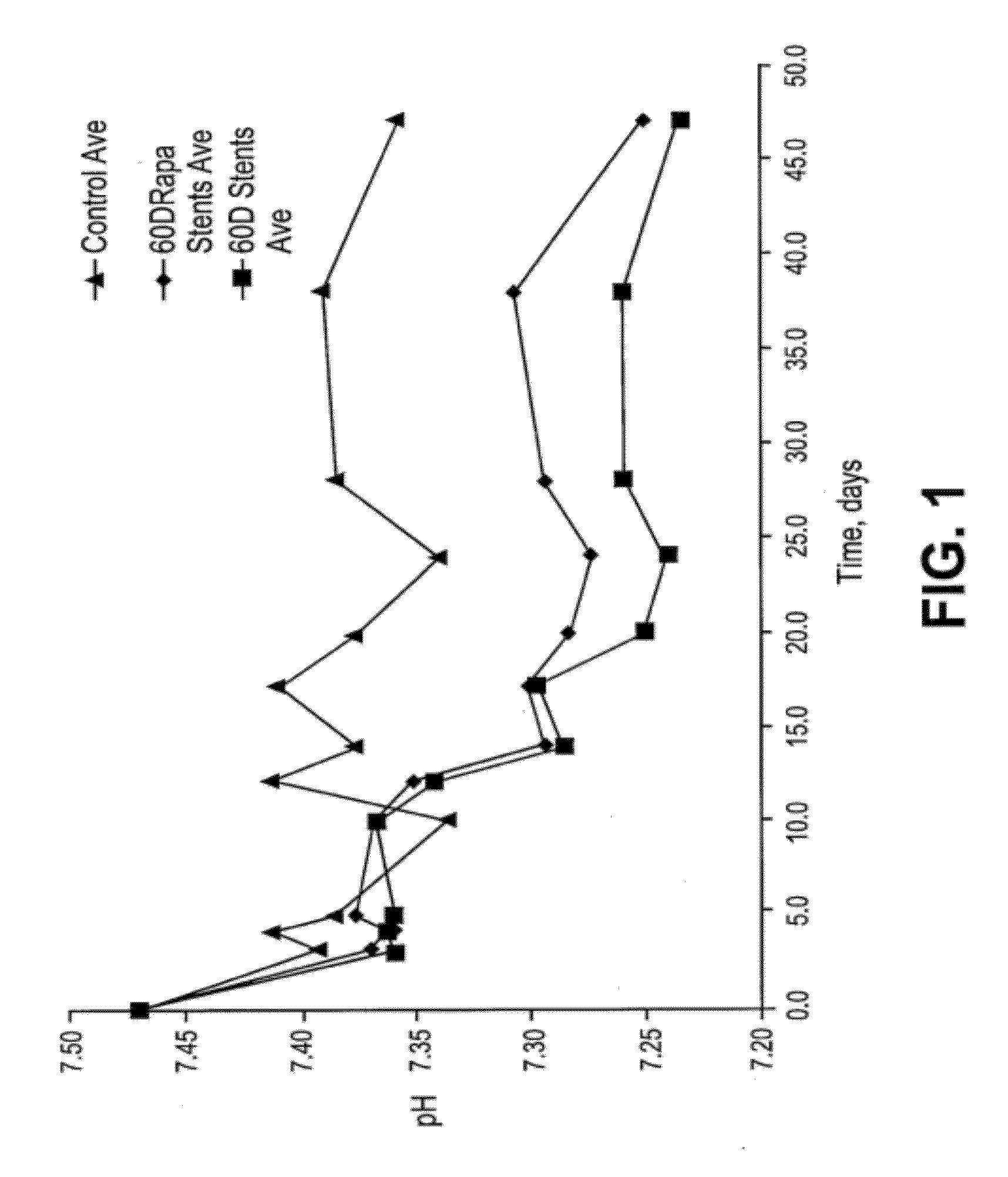
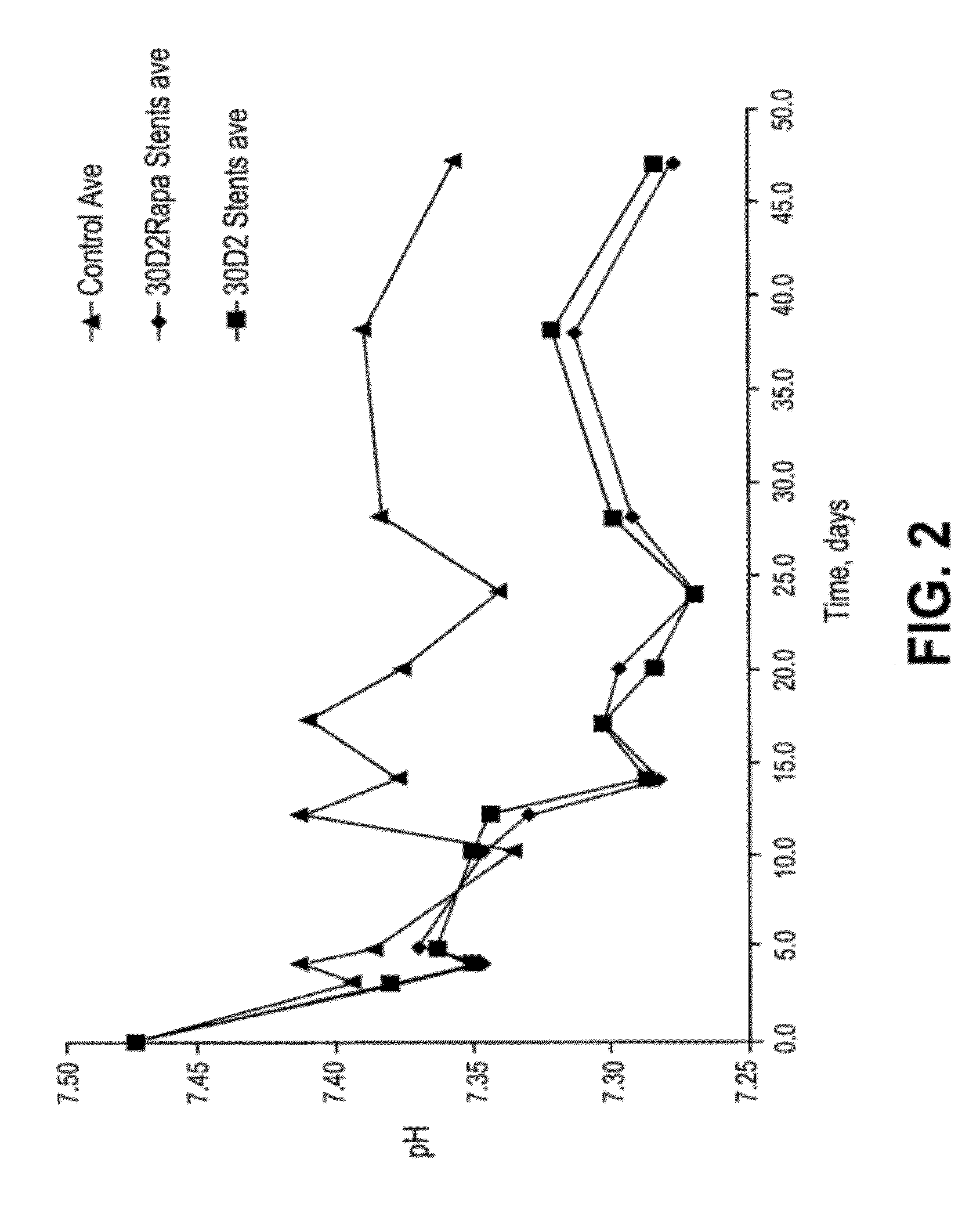
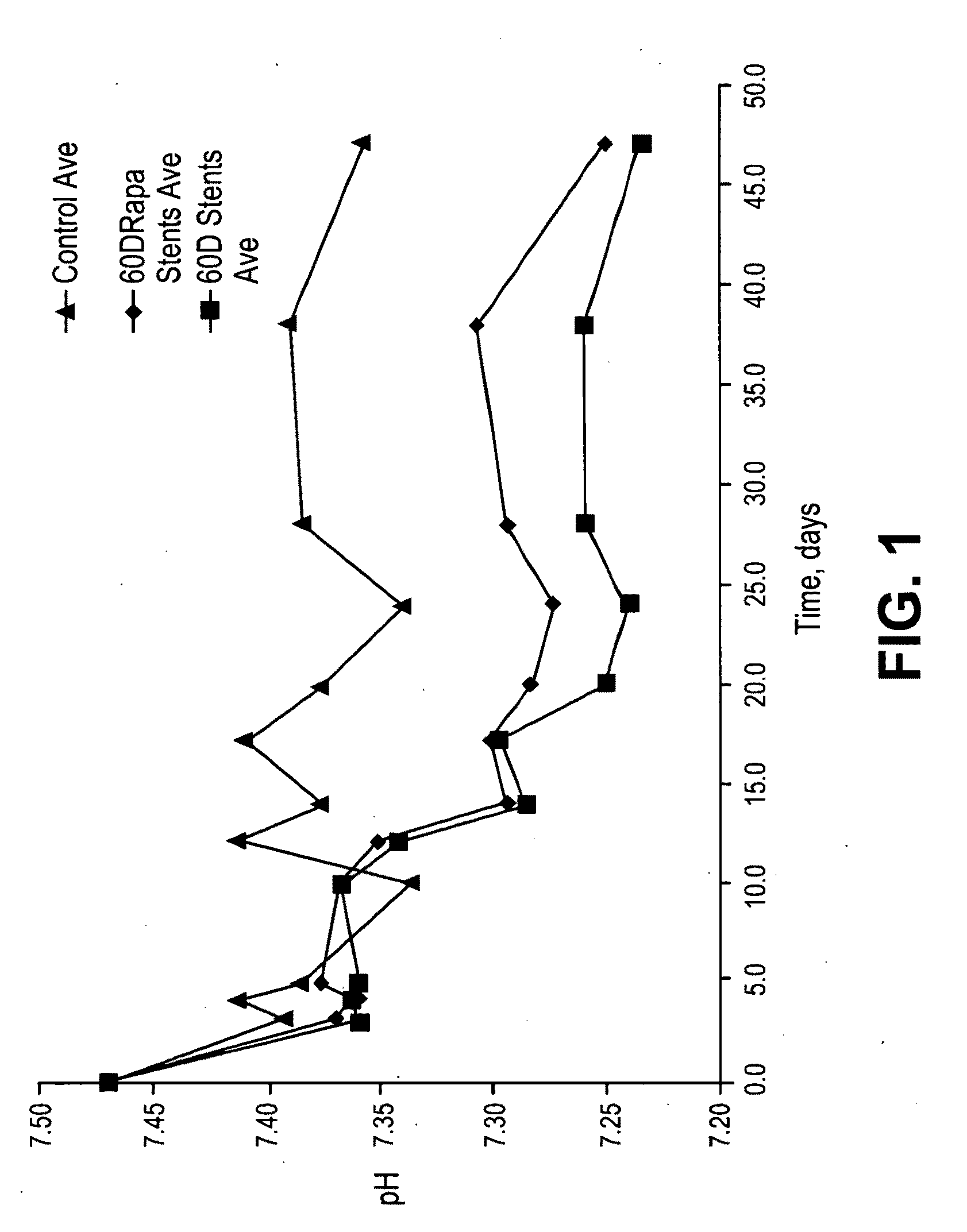
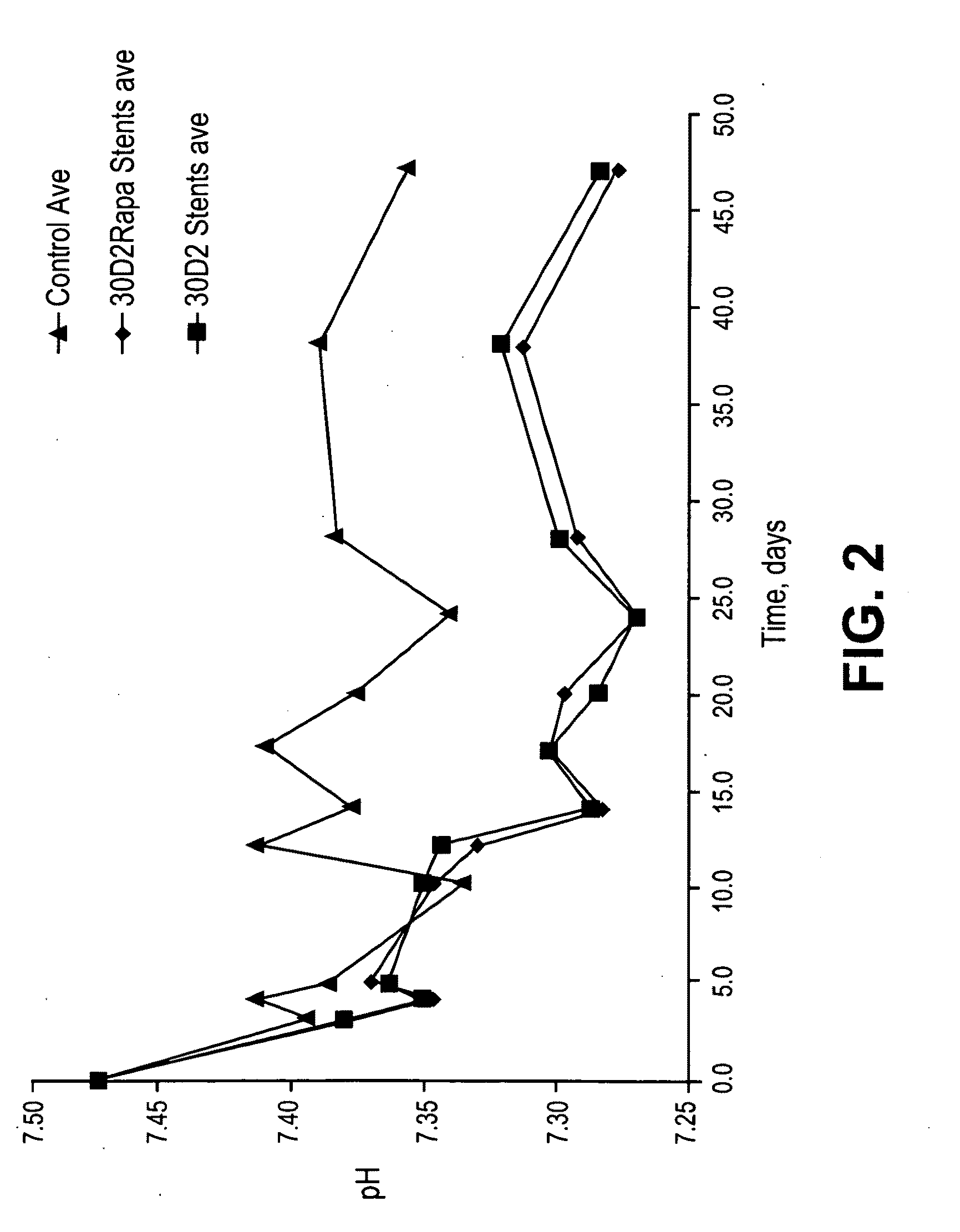
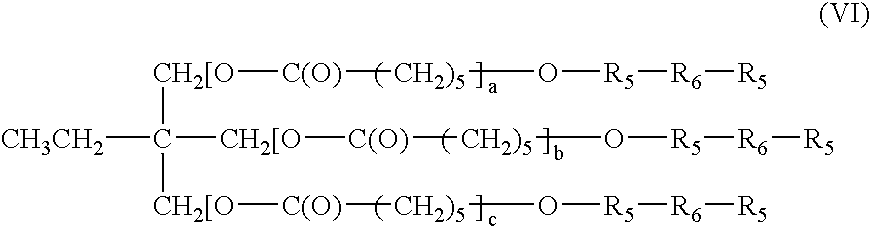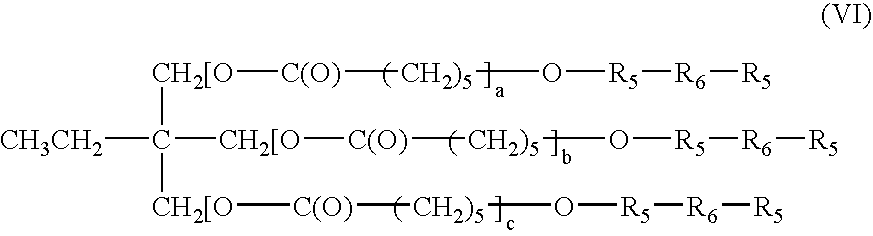Patents
Literature
180 results about "Bioabsorbable polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioabsorbable Polymer Definition. A bioabsorbable polymer is a chemical compound used in orthopedic implant devices that eventually dissolves and is absorbed by the body. Bioabosorbable polymers make suitable material for prosthetics because they can be engineered to dissolve at the same rate as new bone growth.
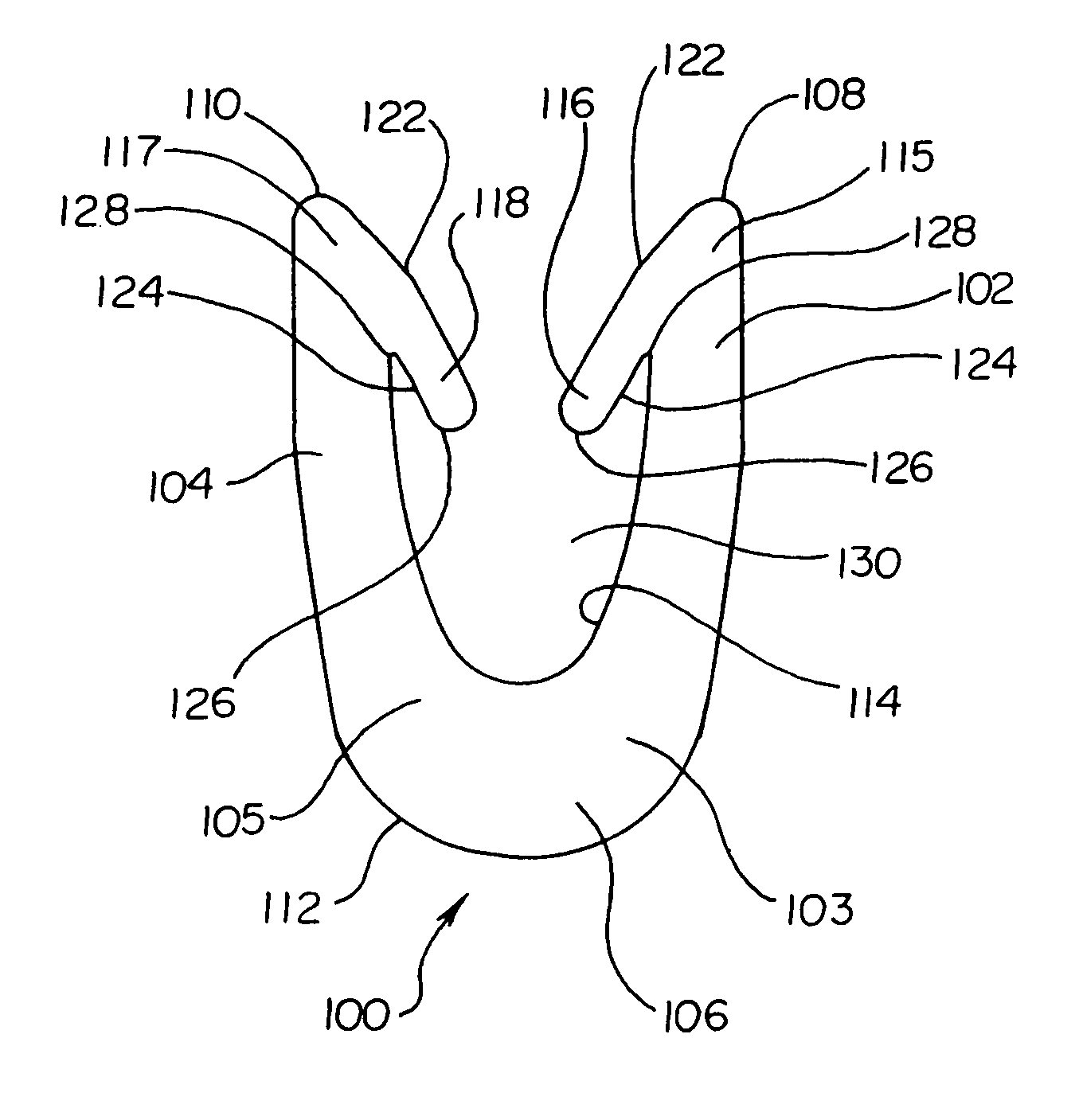
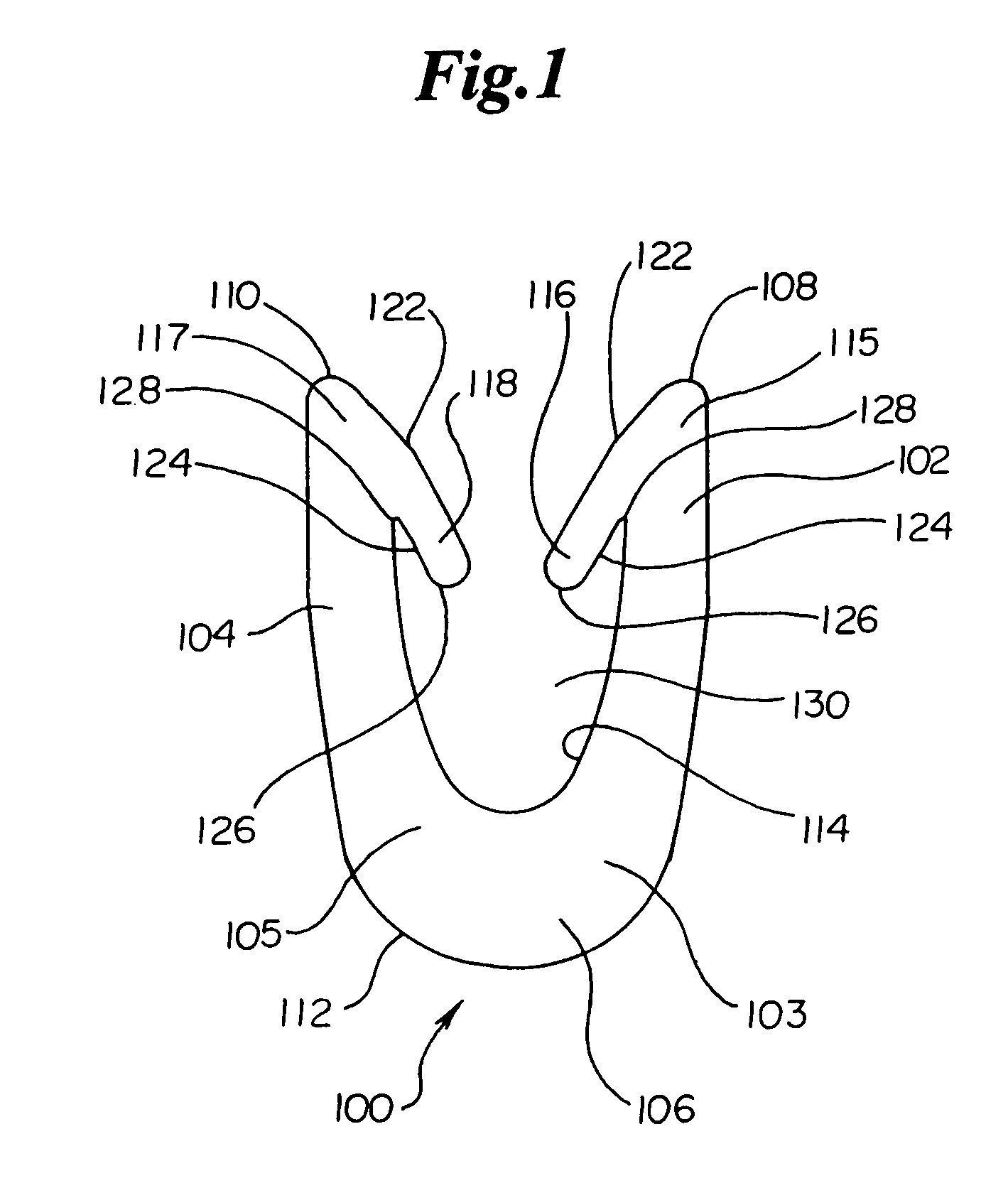
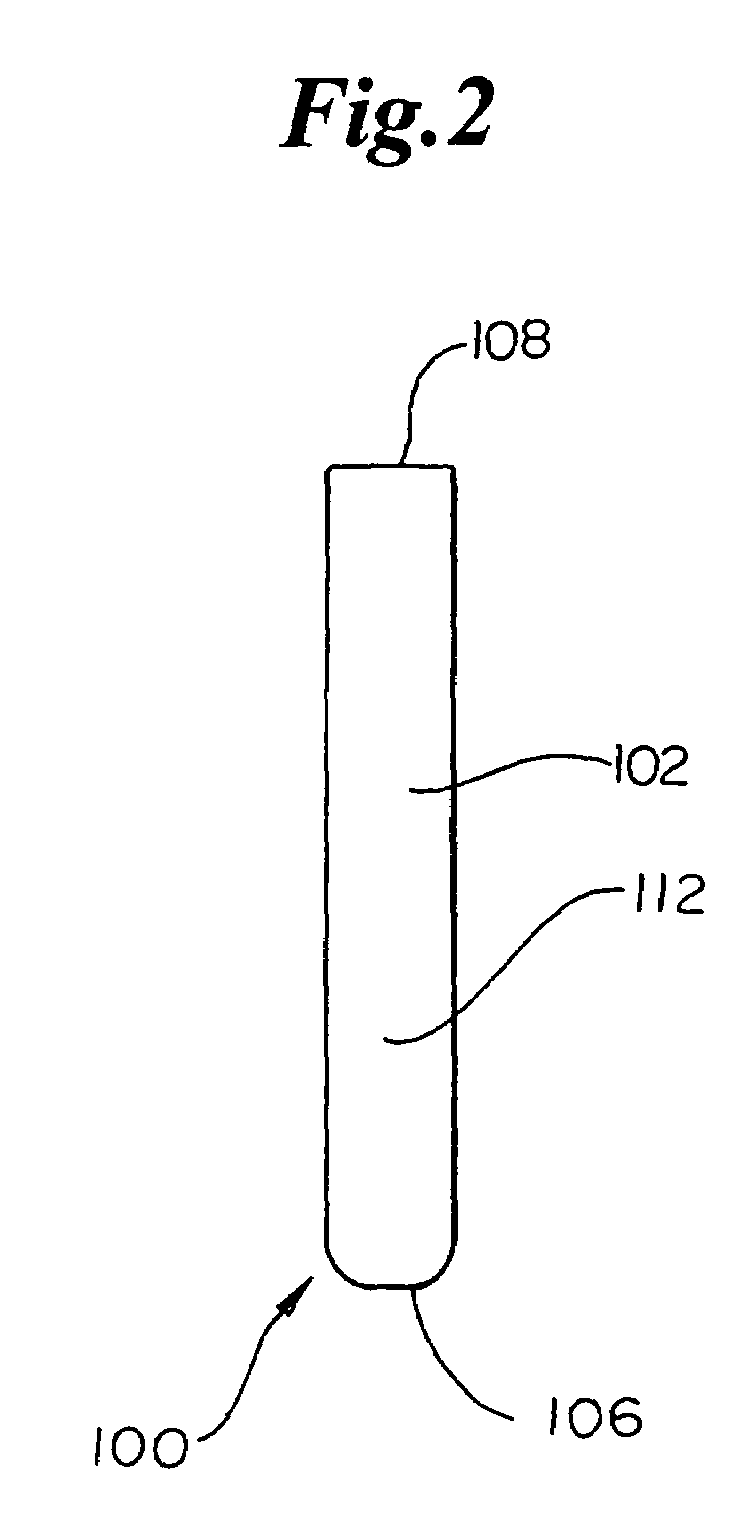
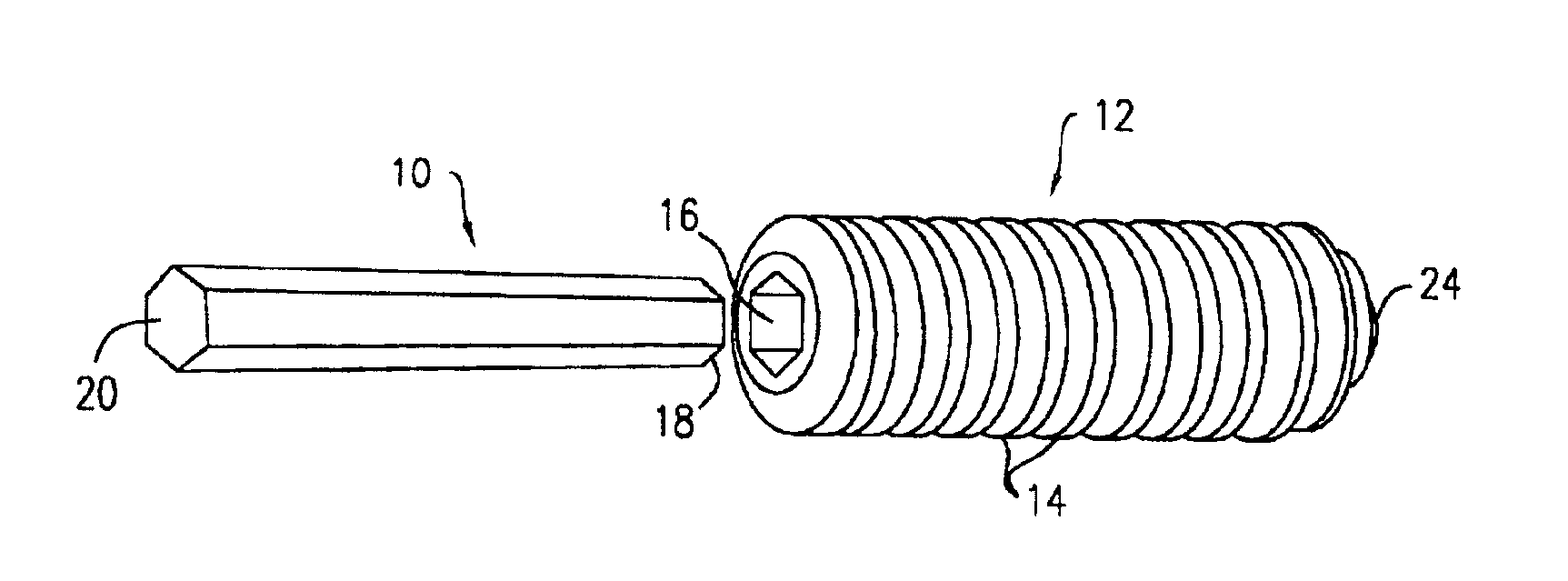
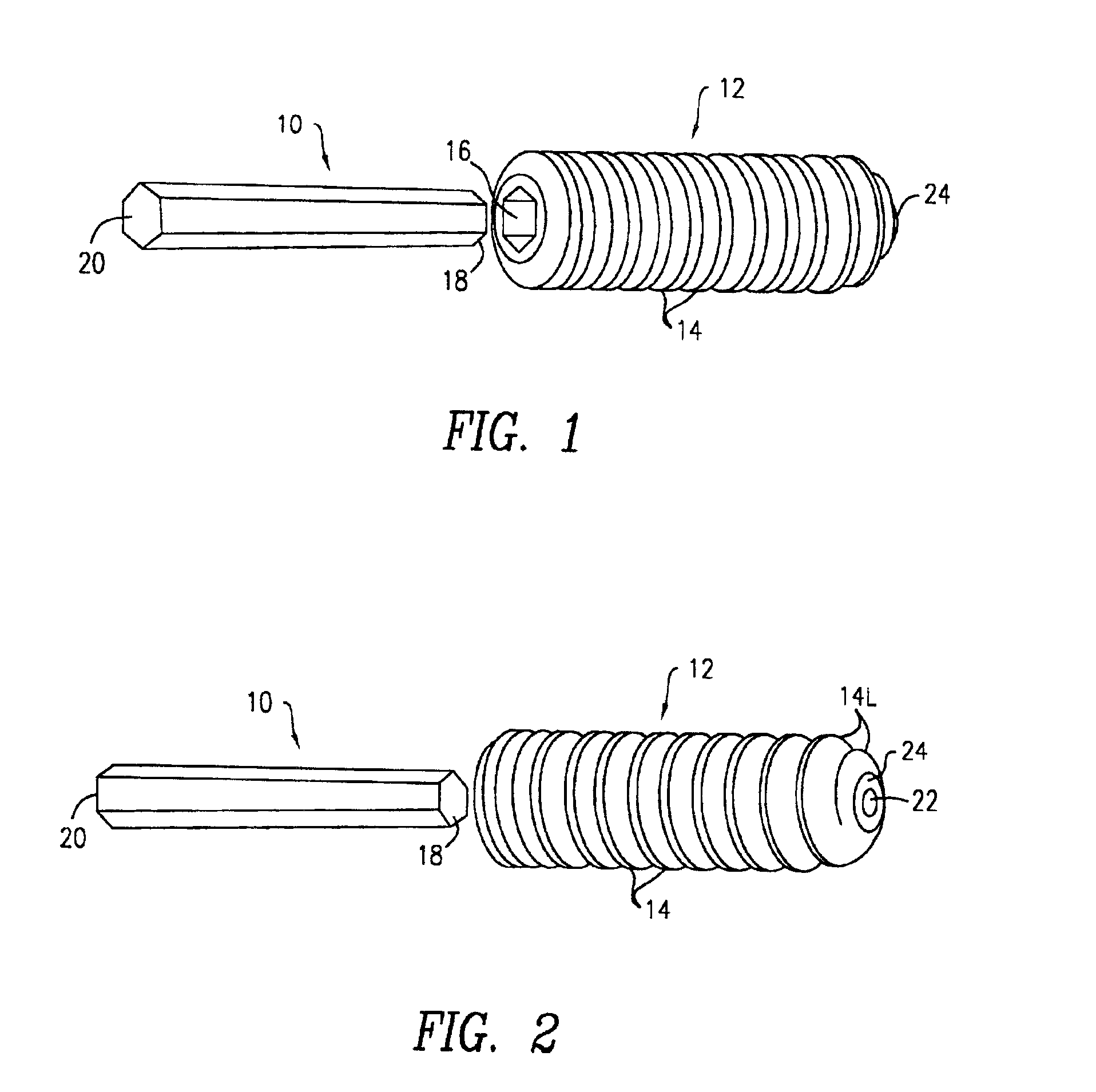
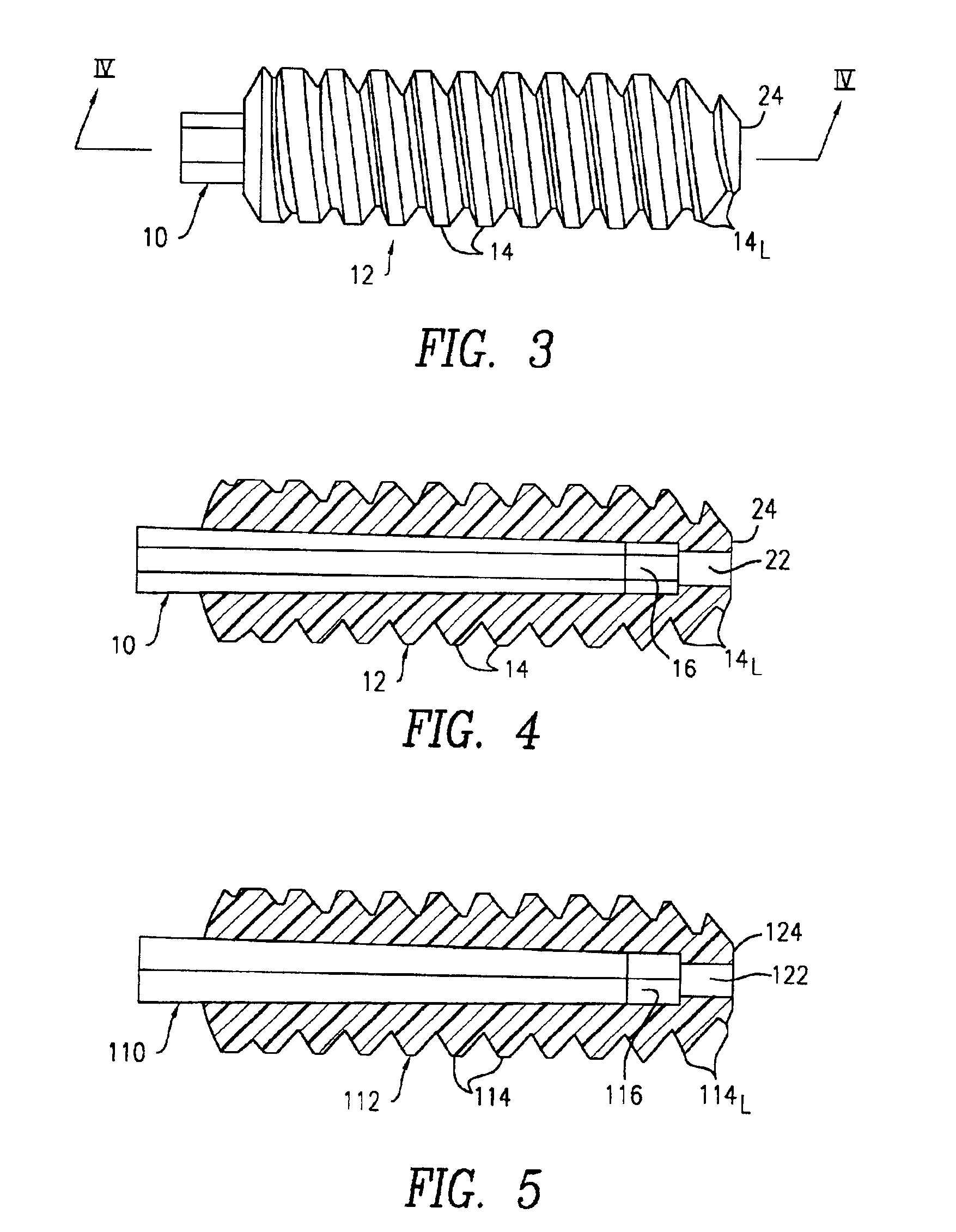
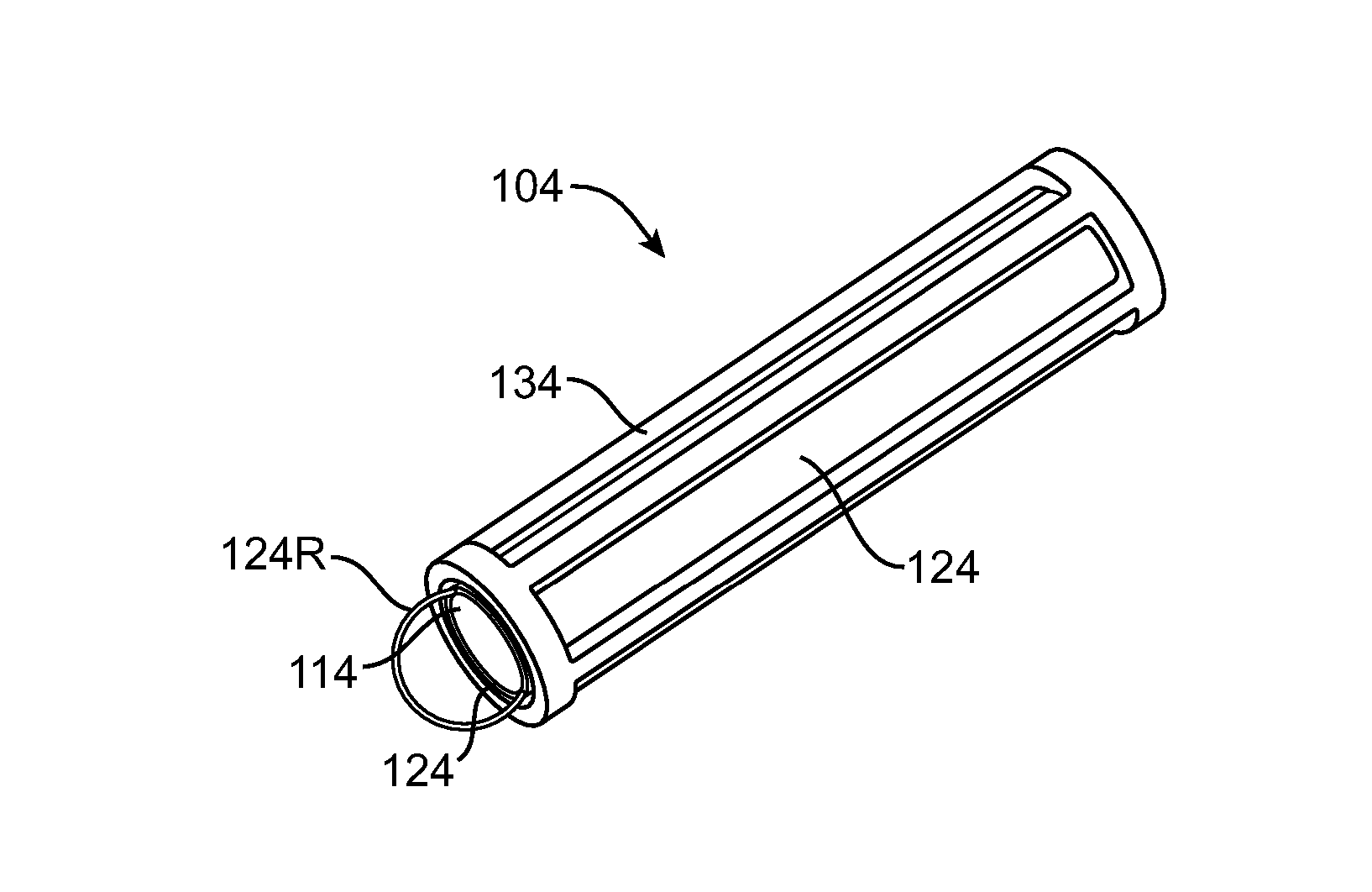
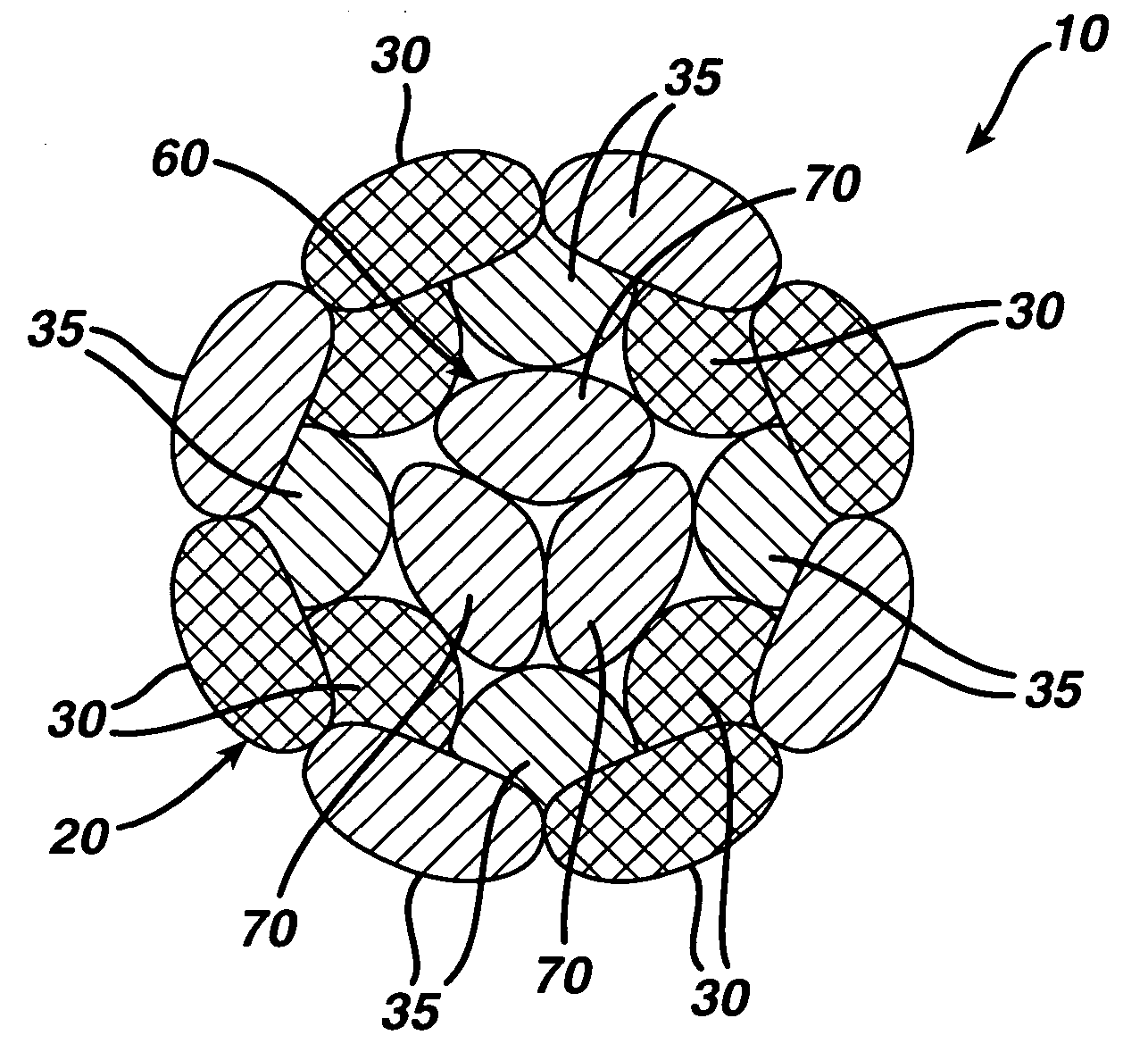
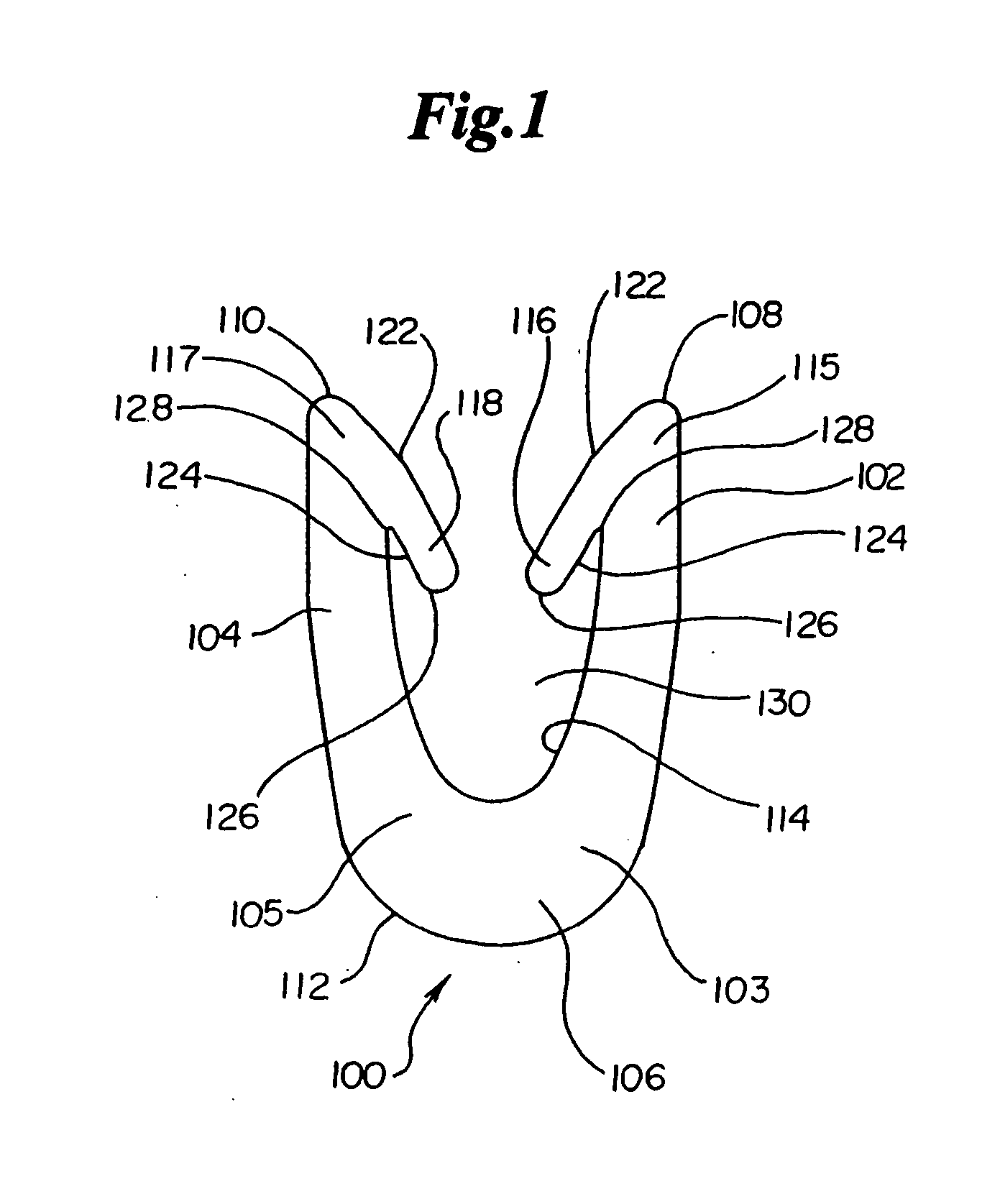
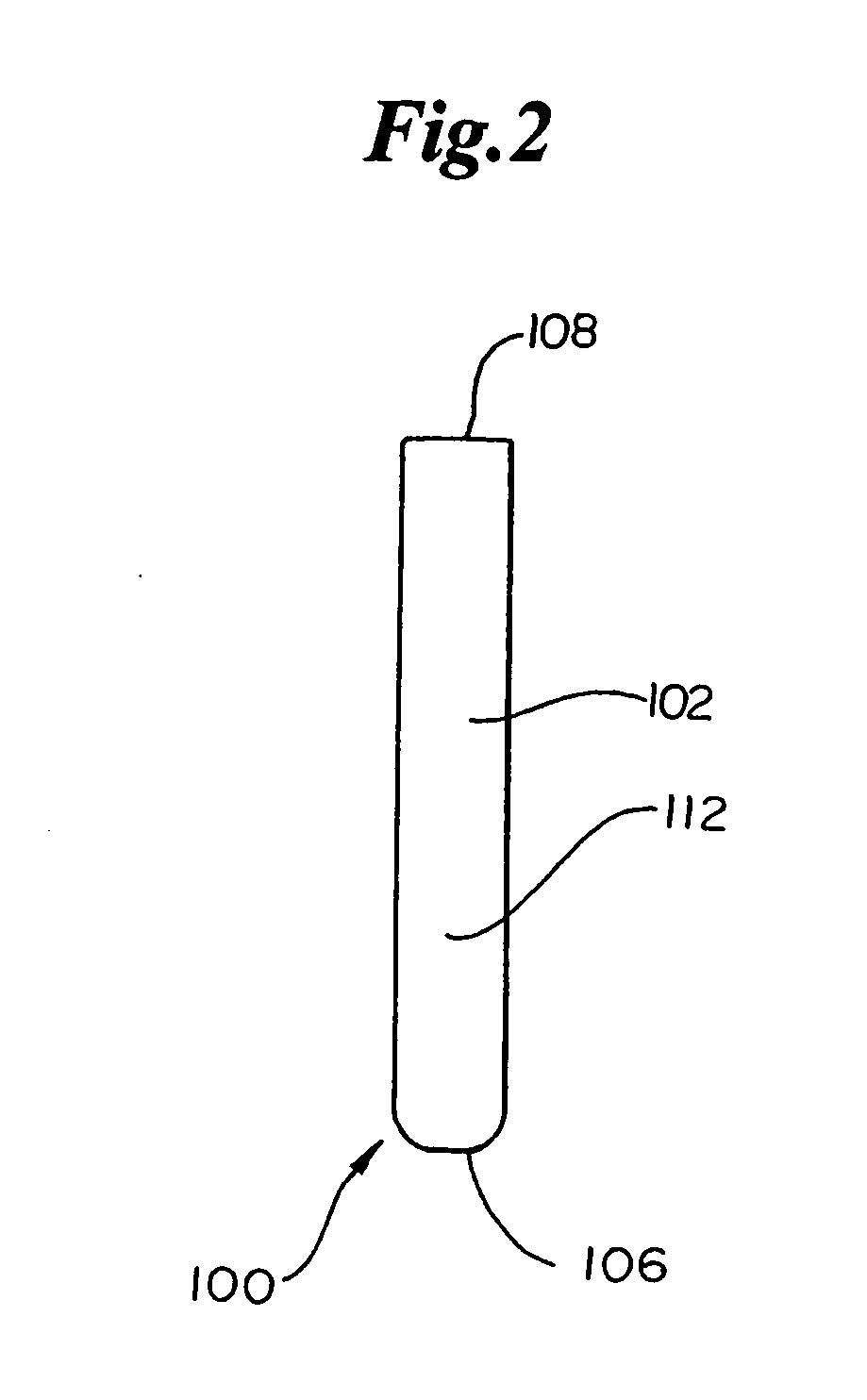
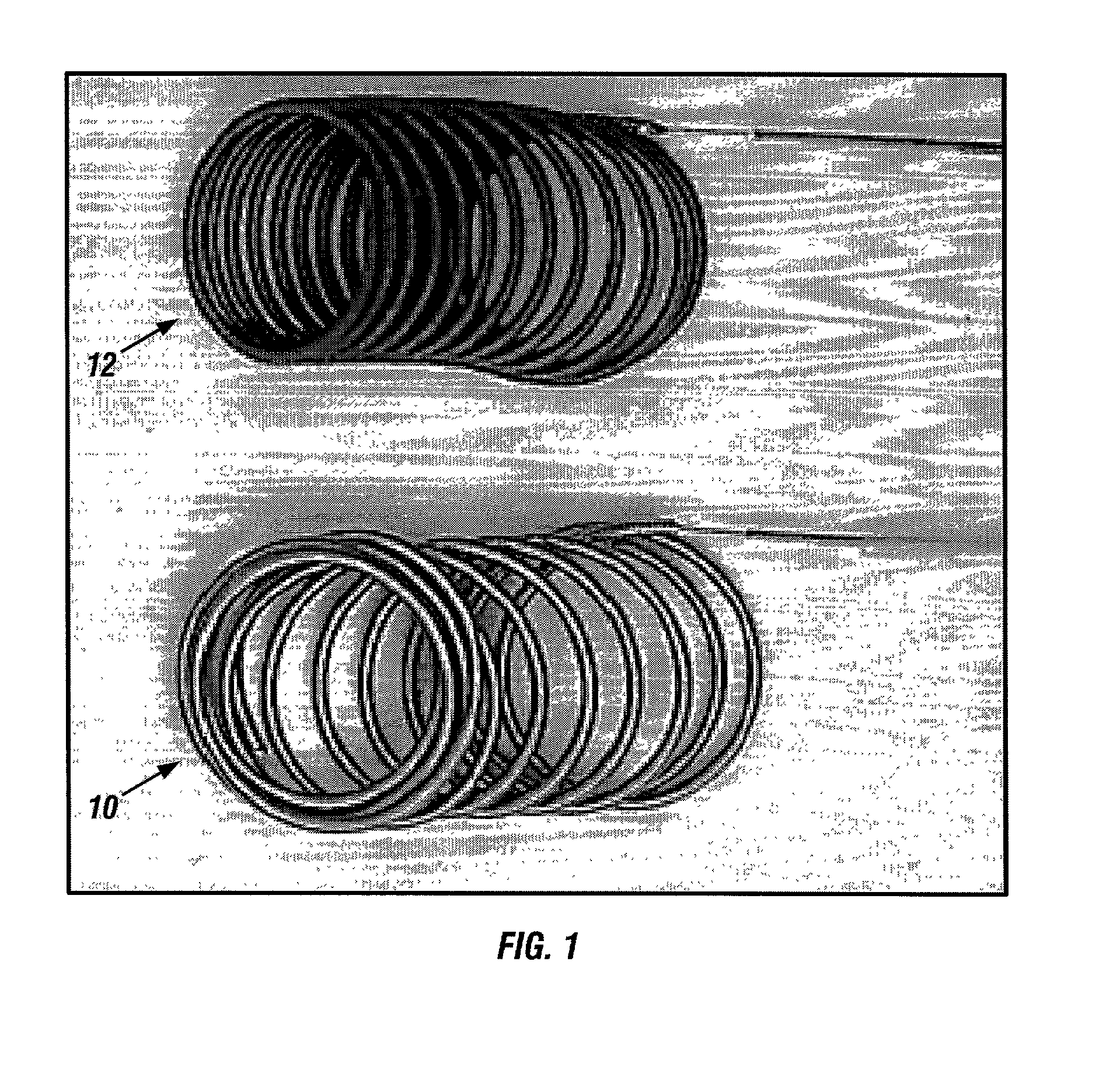
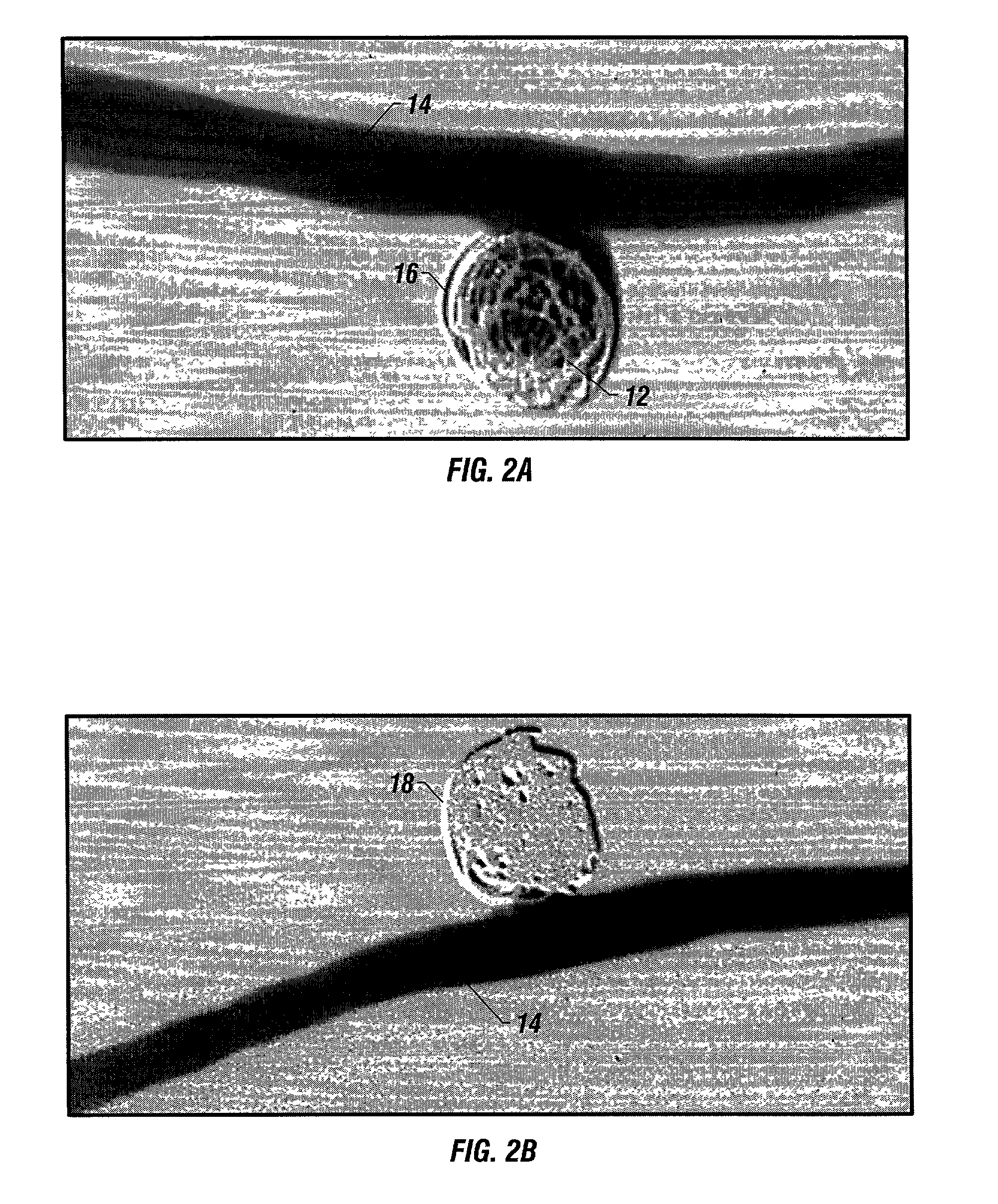
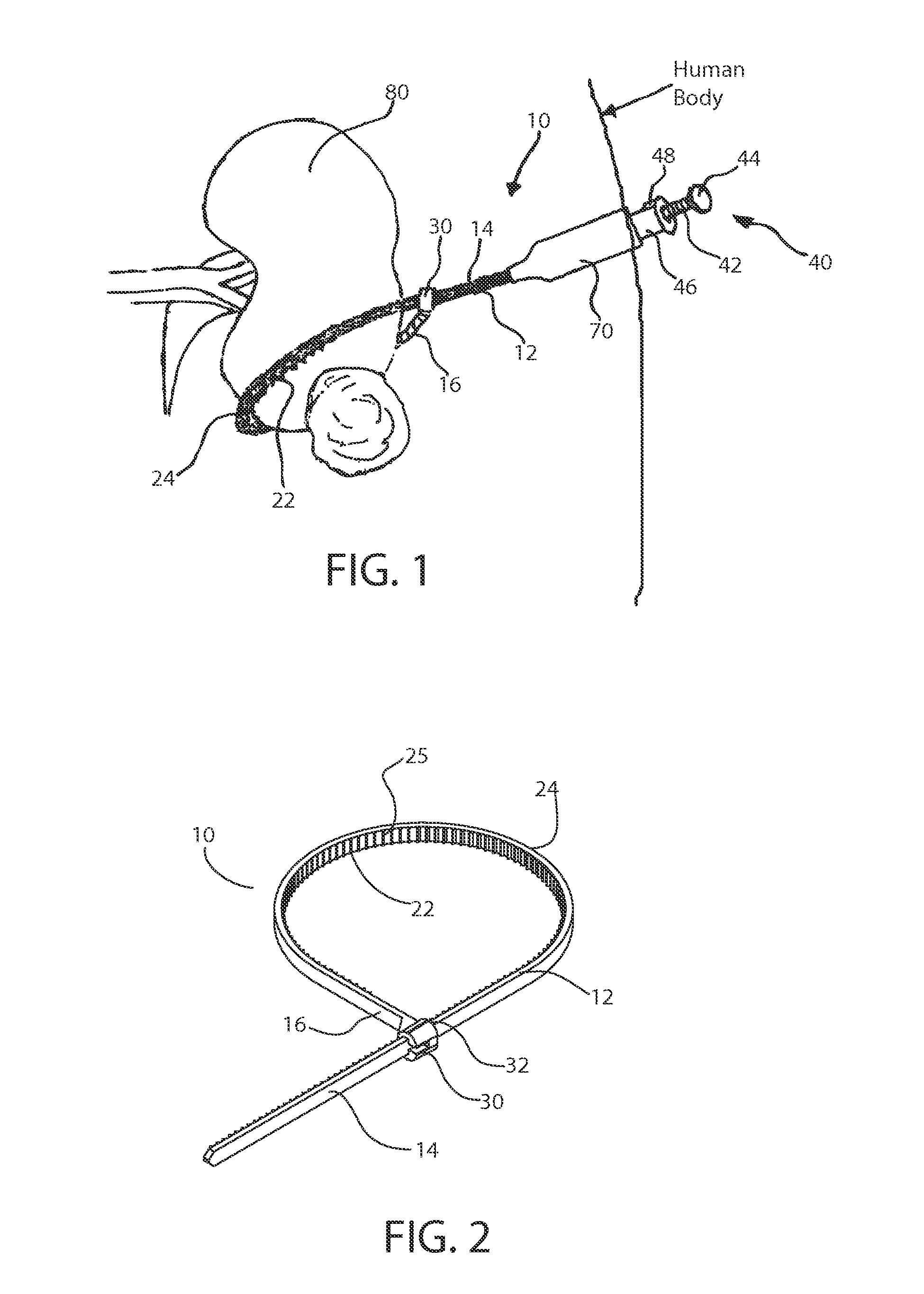
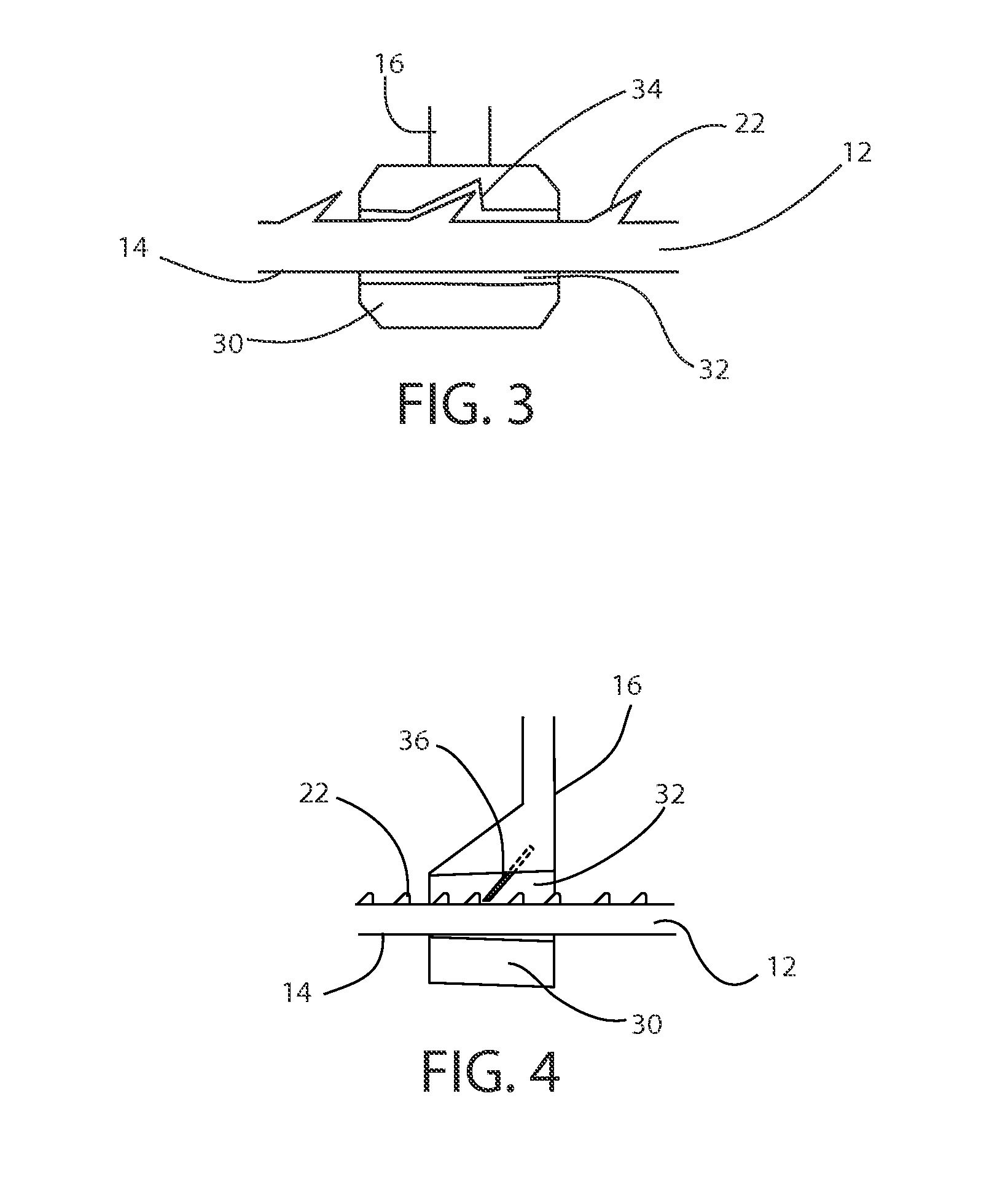
Dynamic bioabsorbable fastener for use in wound closure
InactiveUS7112214B2Prevent and reduce deformationAvoid deformationJoint implantsStaplesBiomedical engineeringBioabsorbable polymer
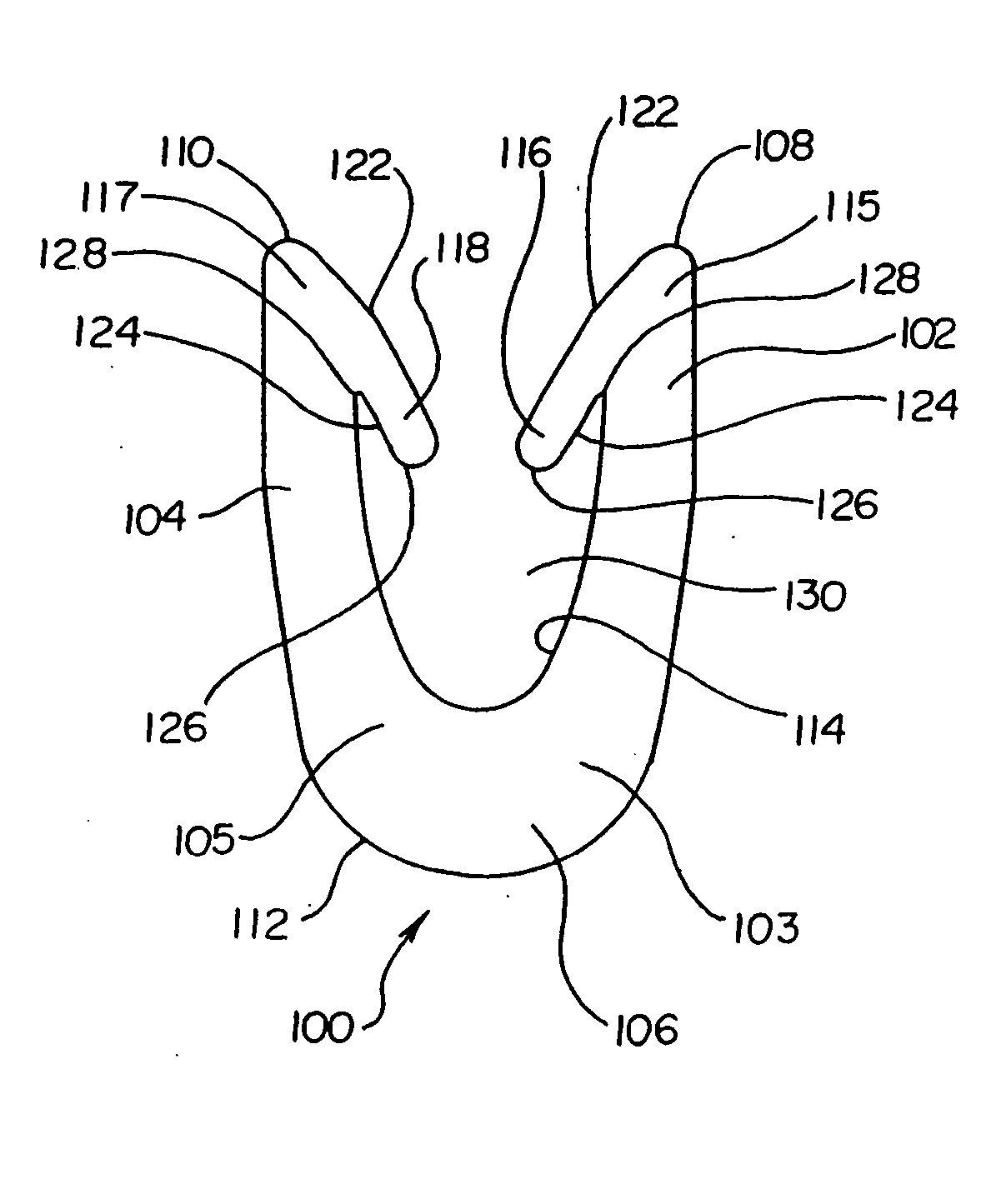
A fastener for insertion into pierced openings of a tissue wound has a body formed of a generally bioabsorbable polymer defining an initial capture area internal to the body. The body includes a pair of arms, each with an inwardly projecting cleat operably joined at an elbow portion defining an internal elbow angle. The arms are operably joined to a backspan at a shoulder portion defining an internal shoulder angle. A durable tissue retention zone is defined between the cleat and the arm. The elbow portion and the internal elbow angle define an insertion width greater than a width of the pierced openings resulting in the pierced openings stretching over the cleat and being elastically retained within the durable tissue retention zone. The fastener initially captures wound tissue in the initial capture area and then dynamically reforms in response to lateral stresses applied by the wound tissue without a fracture failure of the fastener until a minimum degradation period.
Owner:INCISIVE SURGICAL
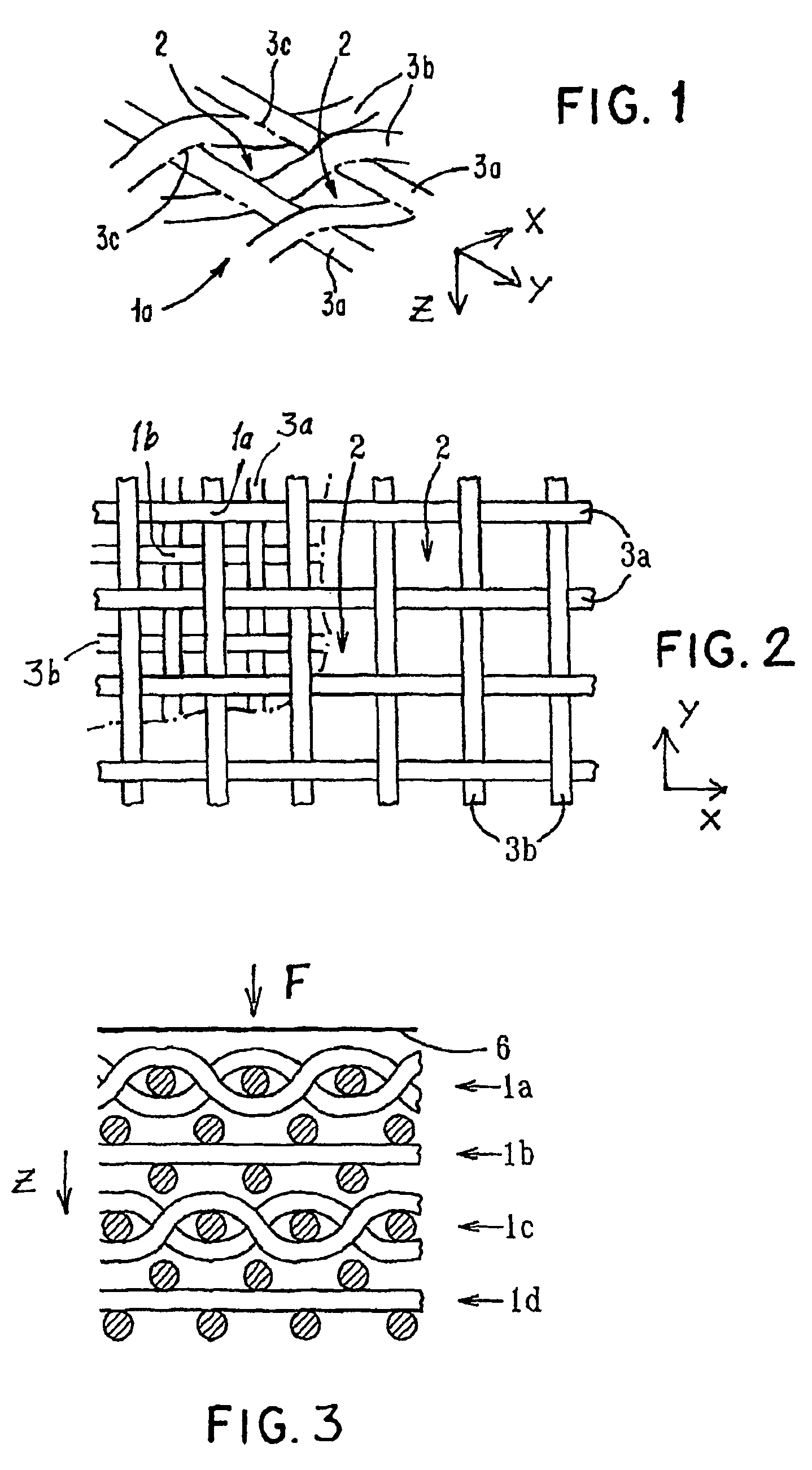
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
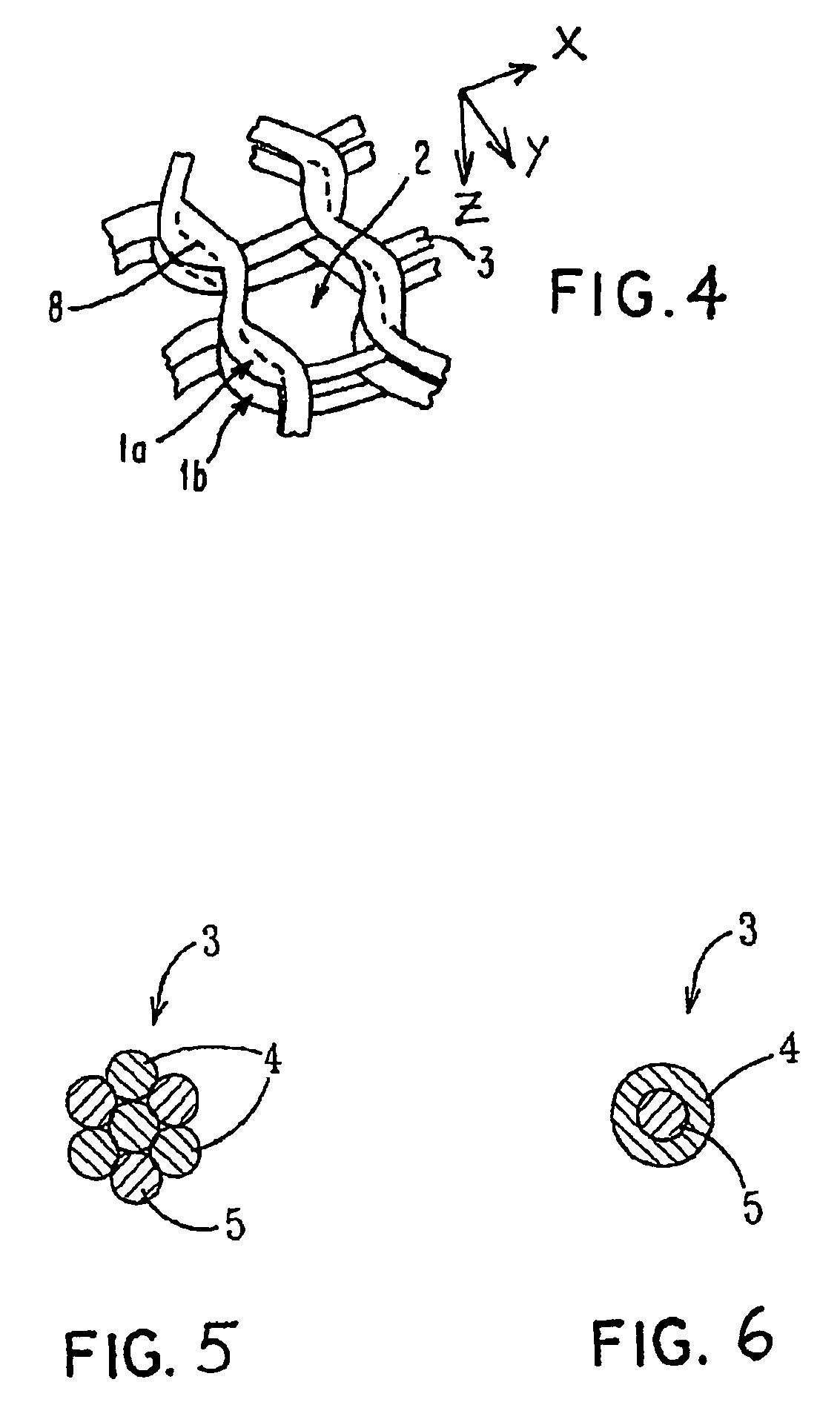
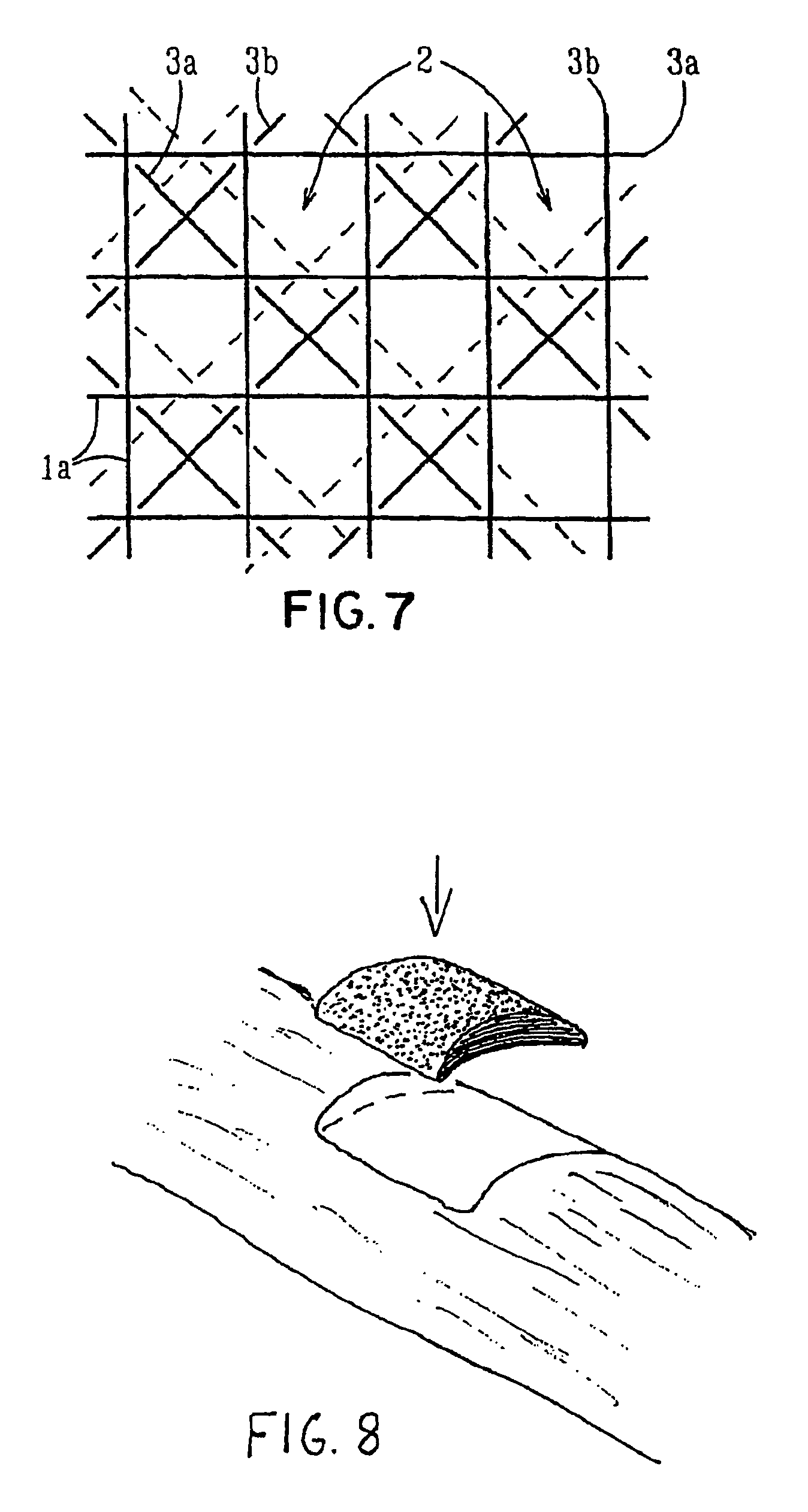
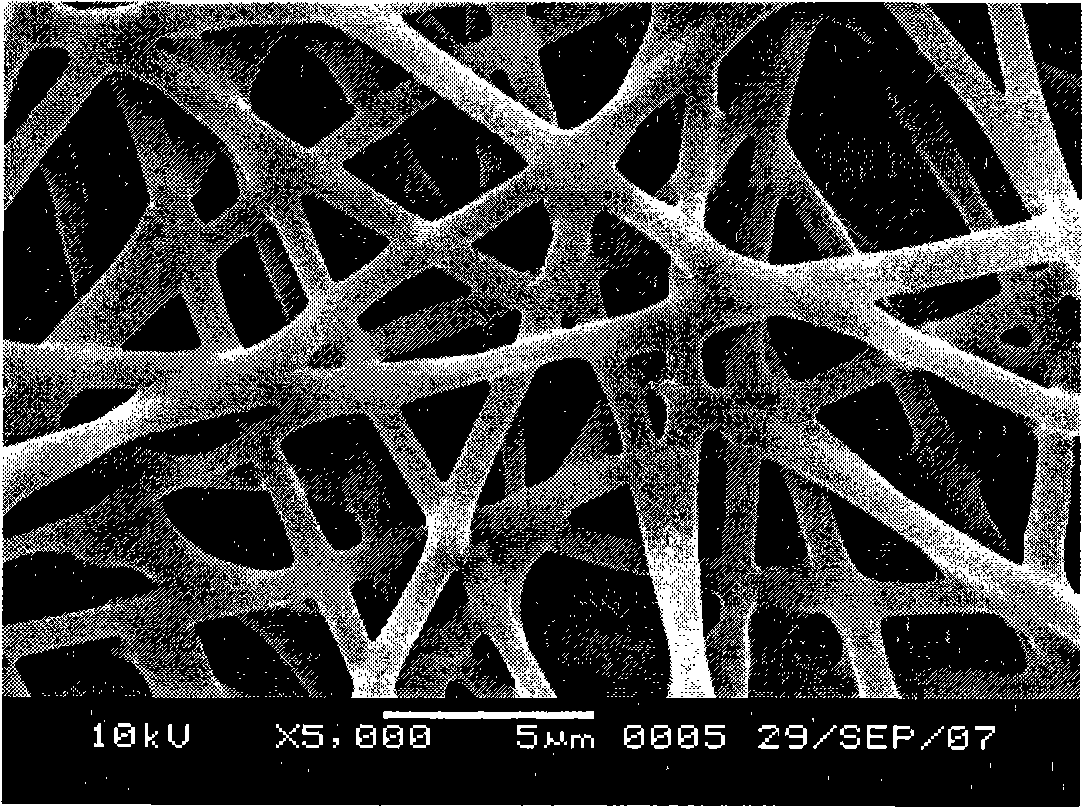
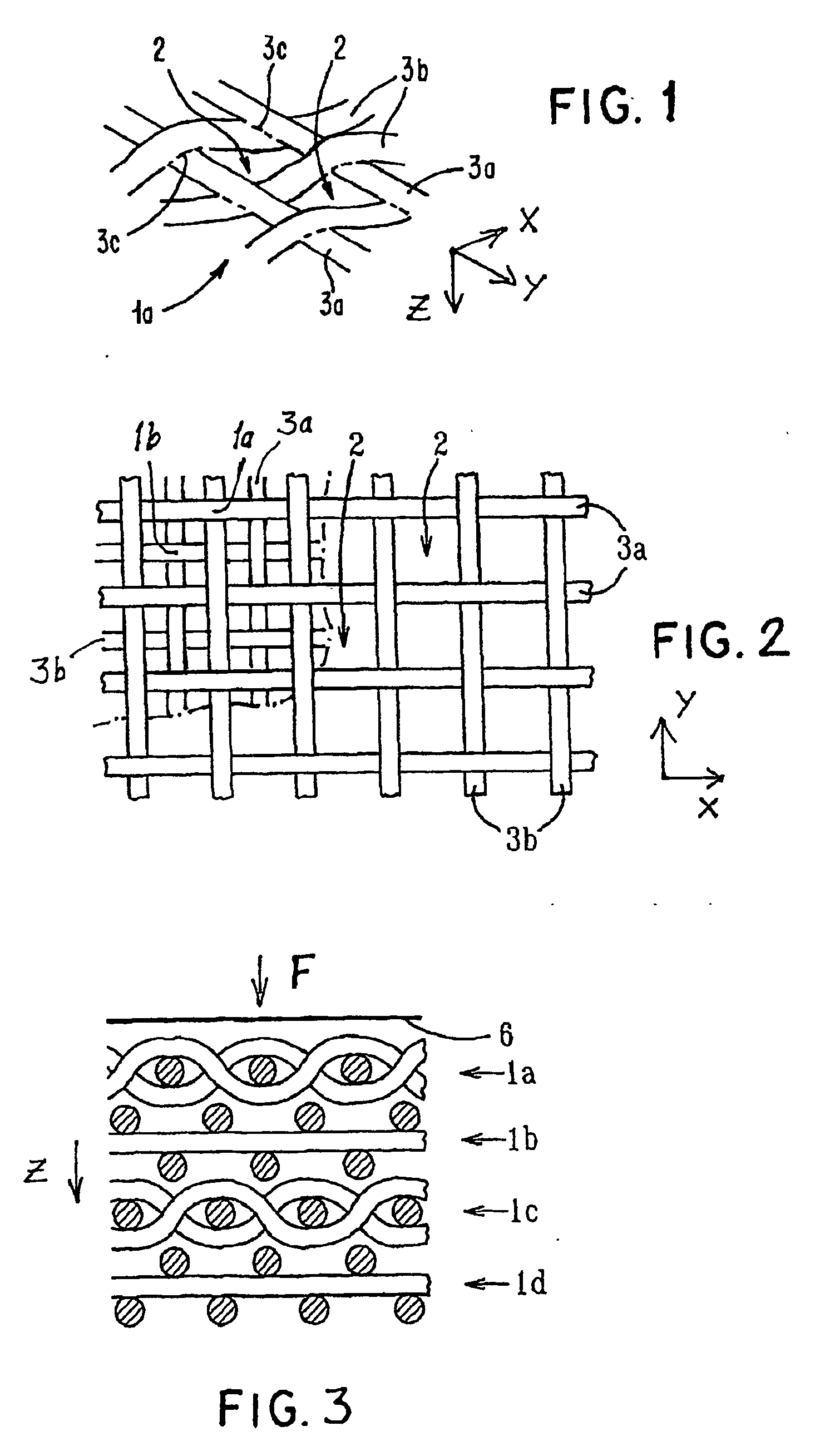
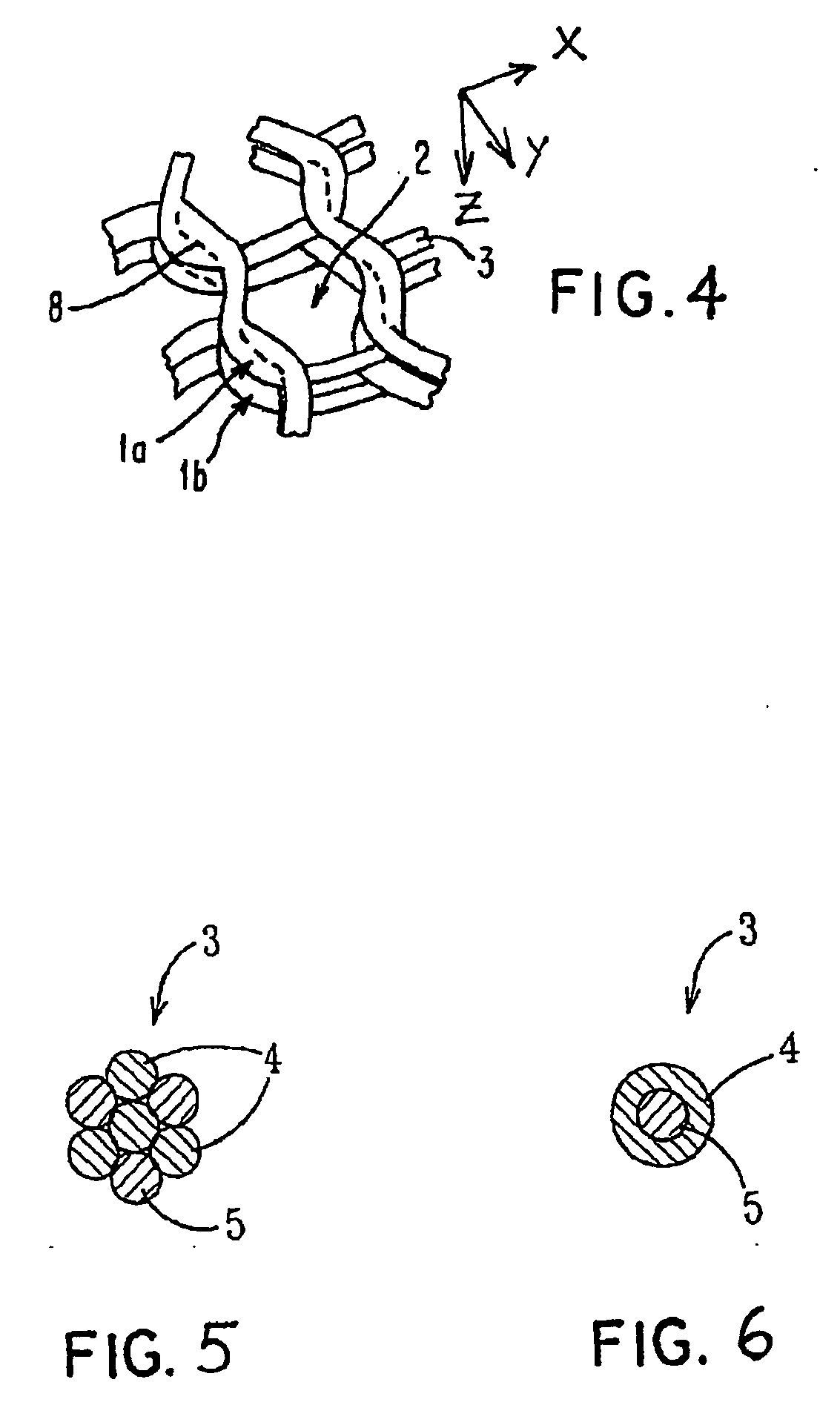
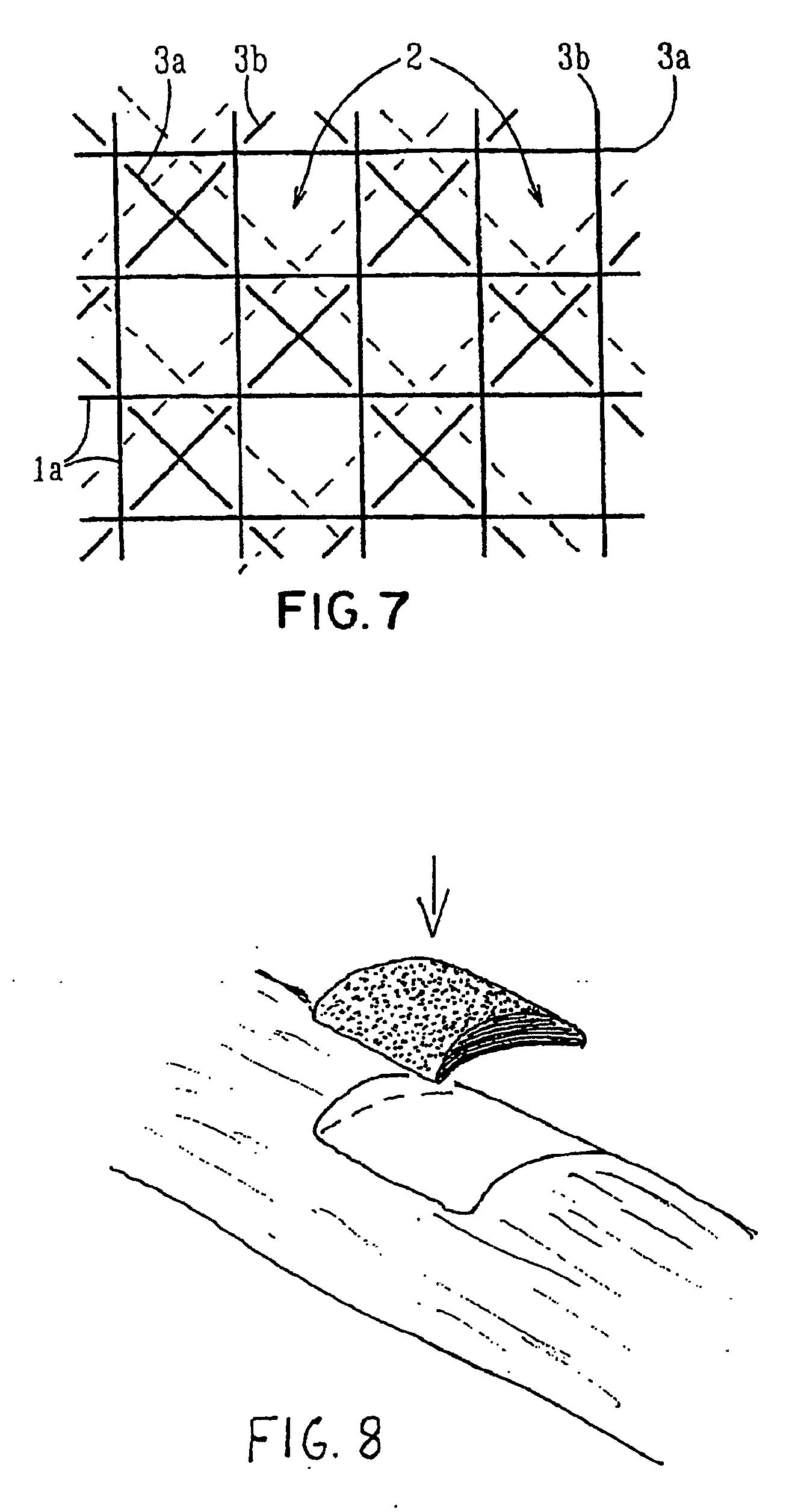
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Bioabsorbable Polymer, Bioabsorbable Composite Stents
InactiveUS20080249608A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureVarying of ductilityStentsSurgeryMetallic materialsMedical device
Biocompatible materials may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices including intraluminal stents. The biocompatible material may comprise metallic and non-metallic materials in hybrid structures. In one such structure, a device may be fabricated with one or more elements having an inner metallic core that is biodegradable with an outer shell formed from a polymeric material that is biodegradable. Additionally, therapeutic agents may be incorporated into the microstructure or the bulk material.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
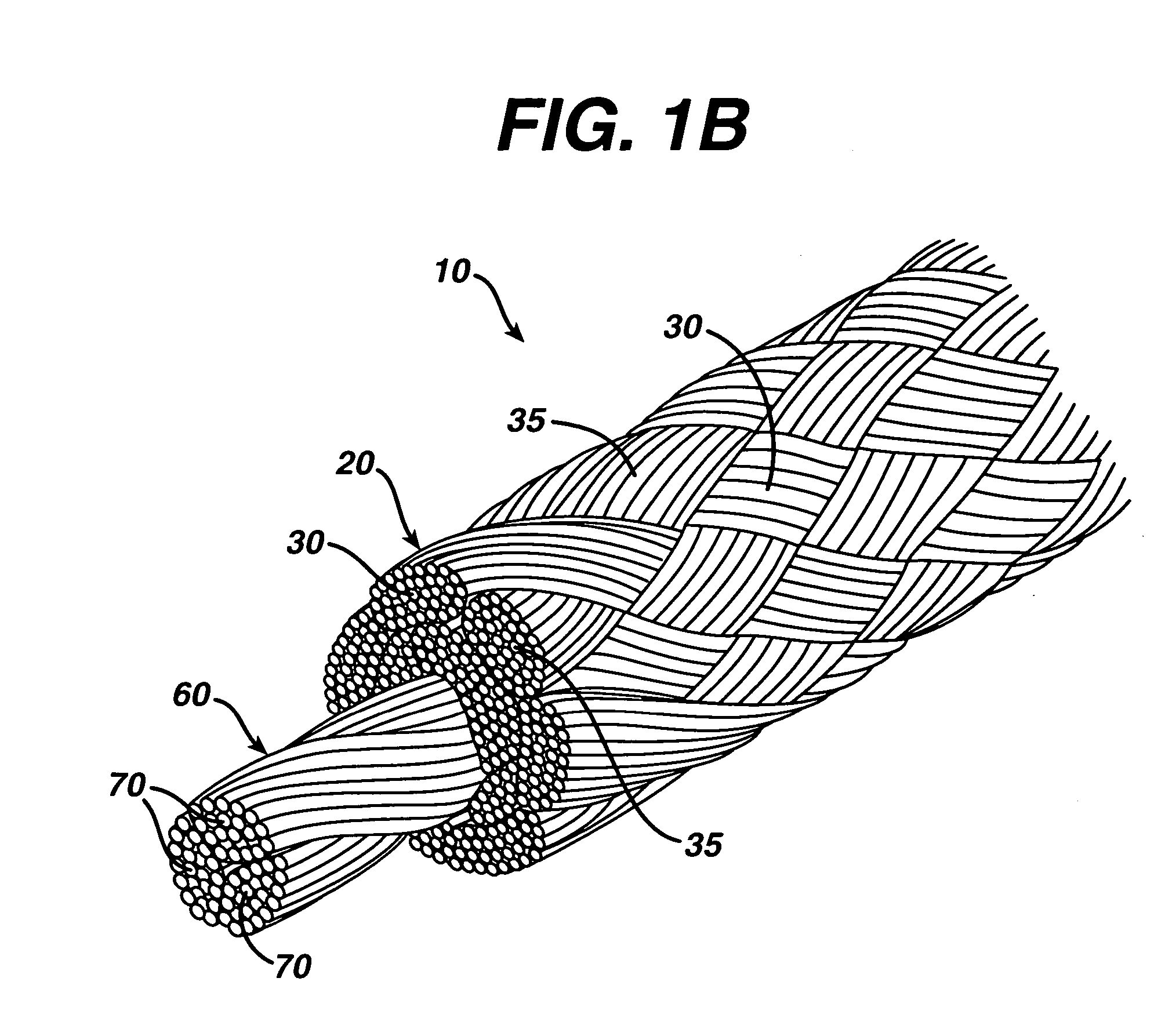
High strength suture with absorbable core and suture anchor combination
ActiveUS20050149118A1Improved absorption profileReducing knot profile of knotSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesYarnMedicine
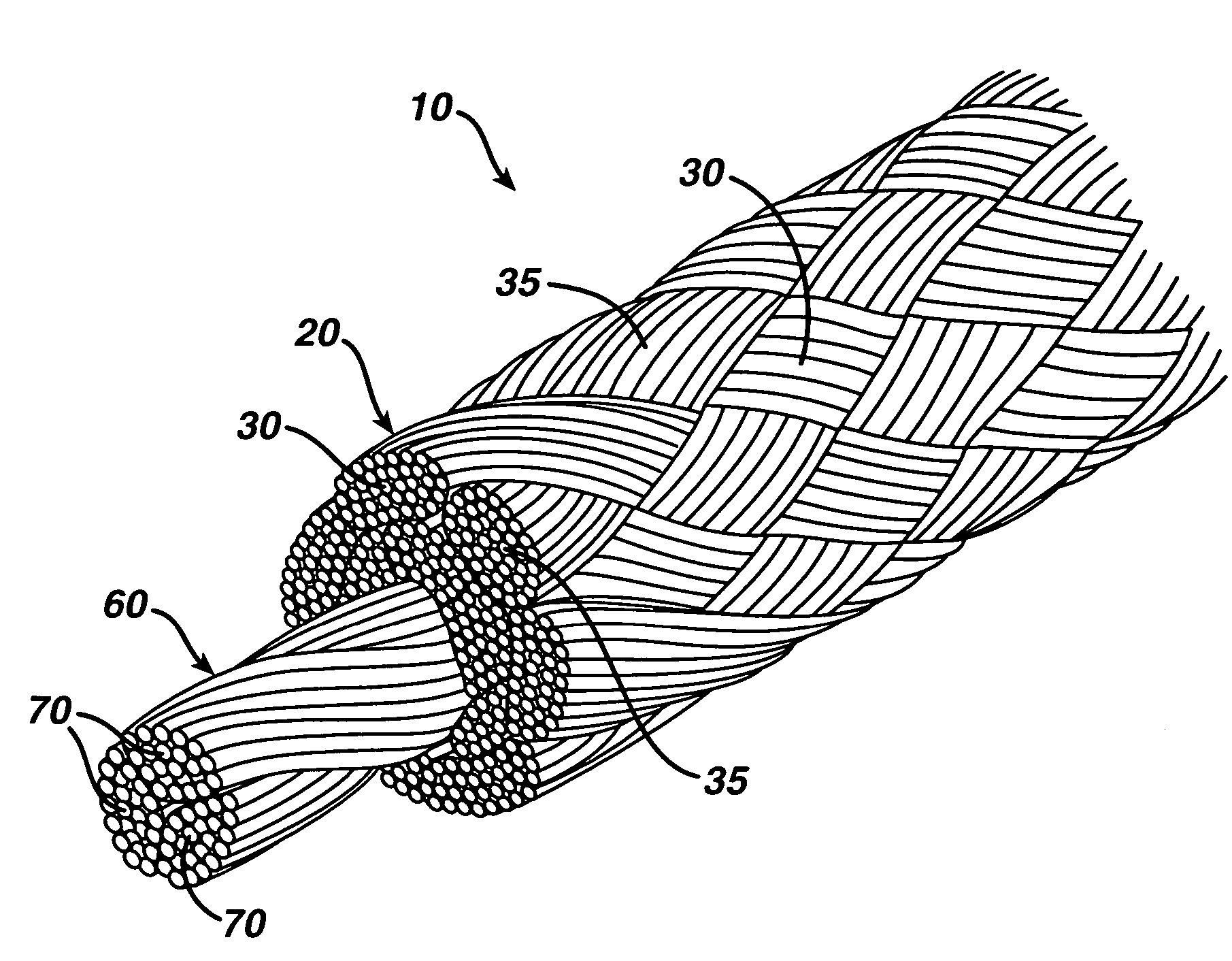
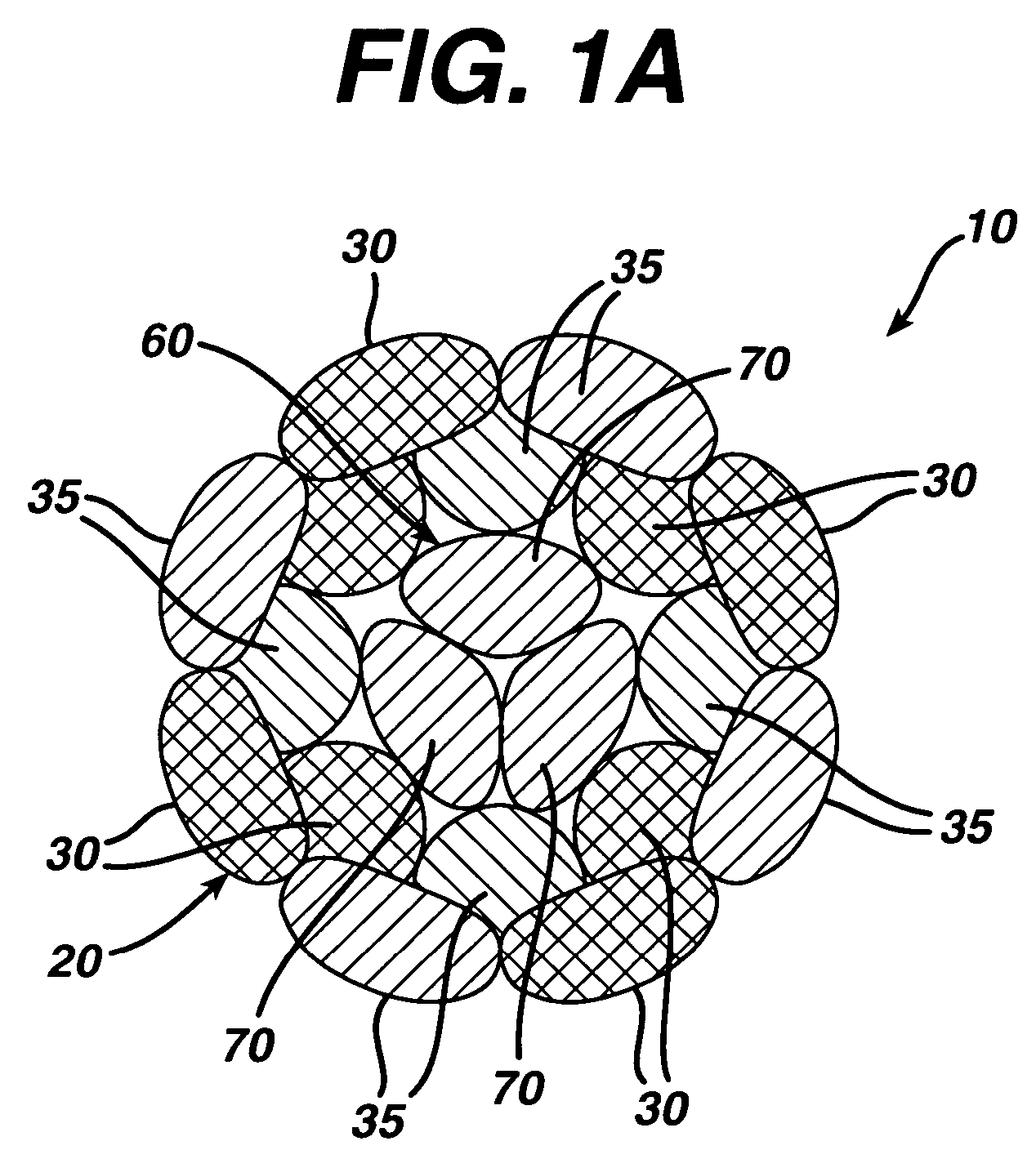
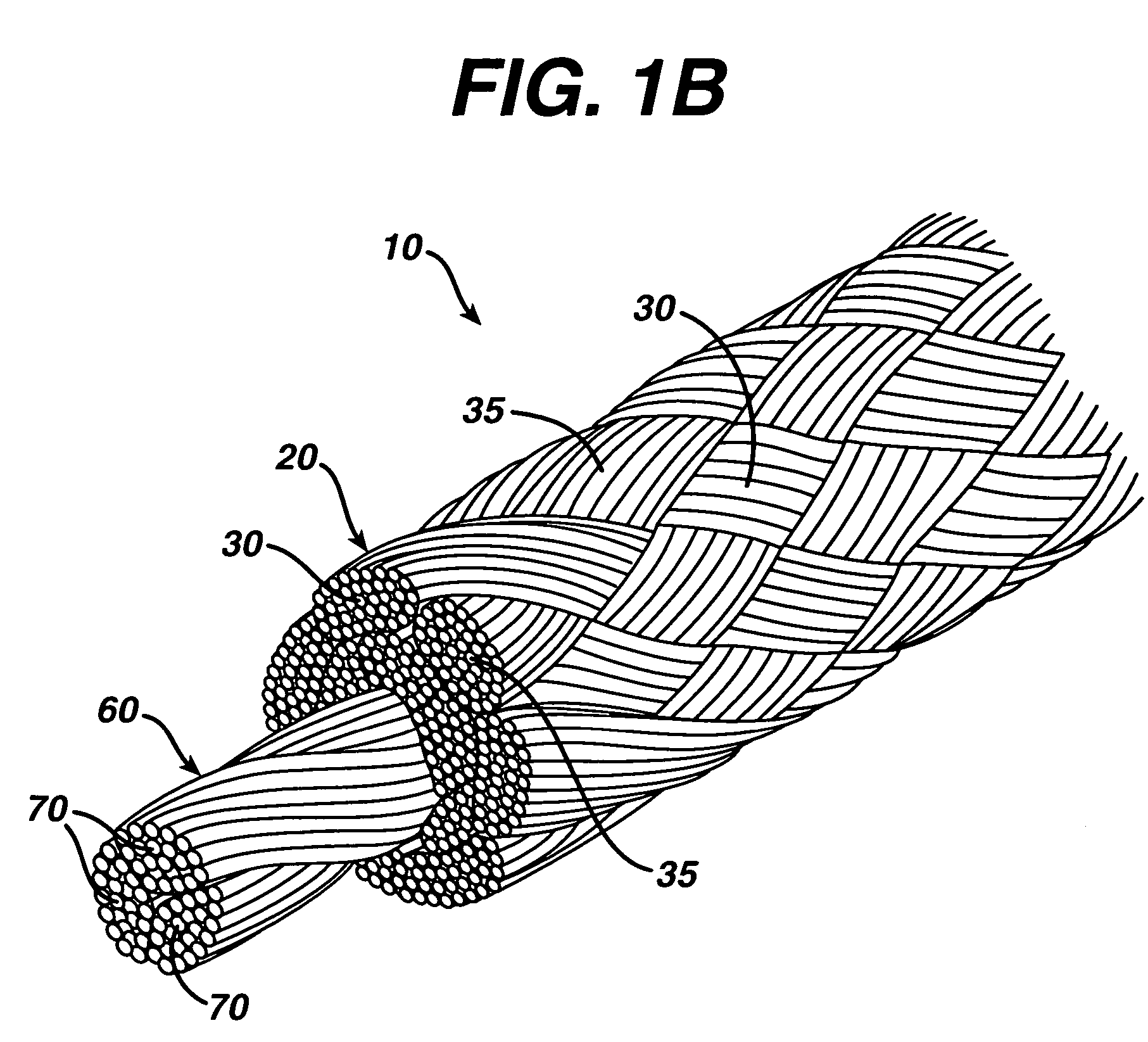
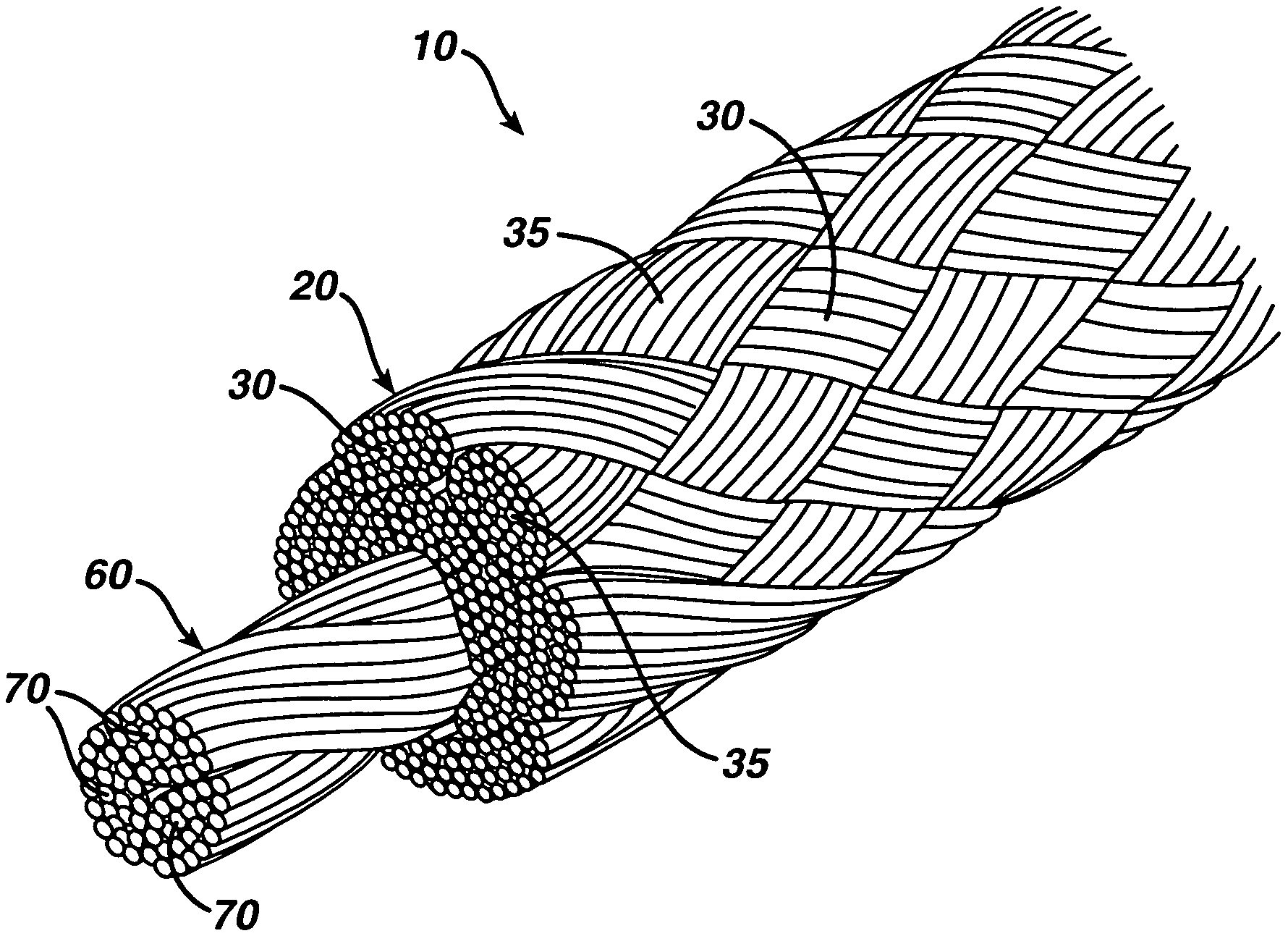
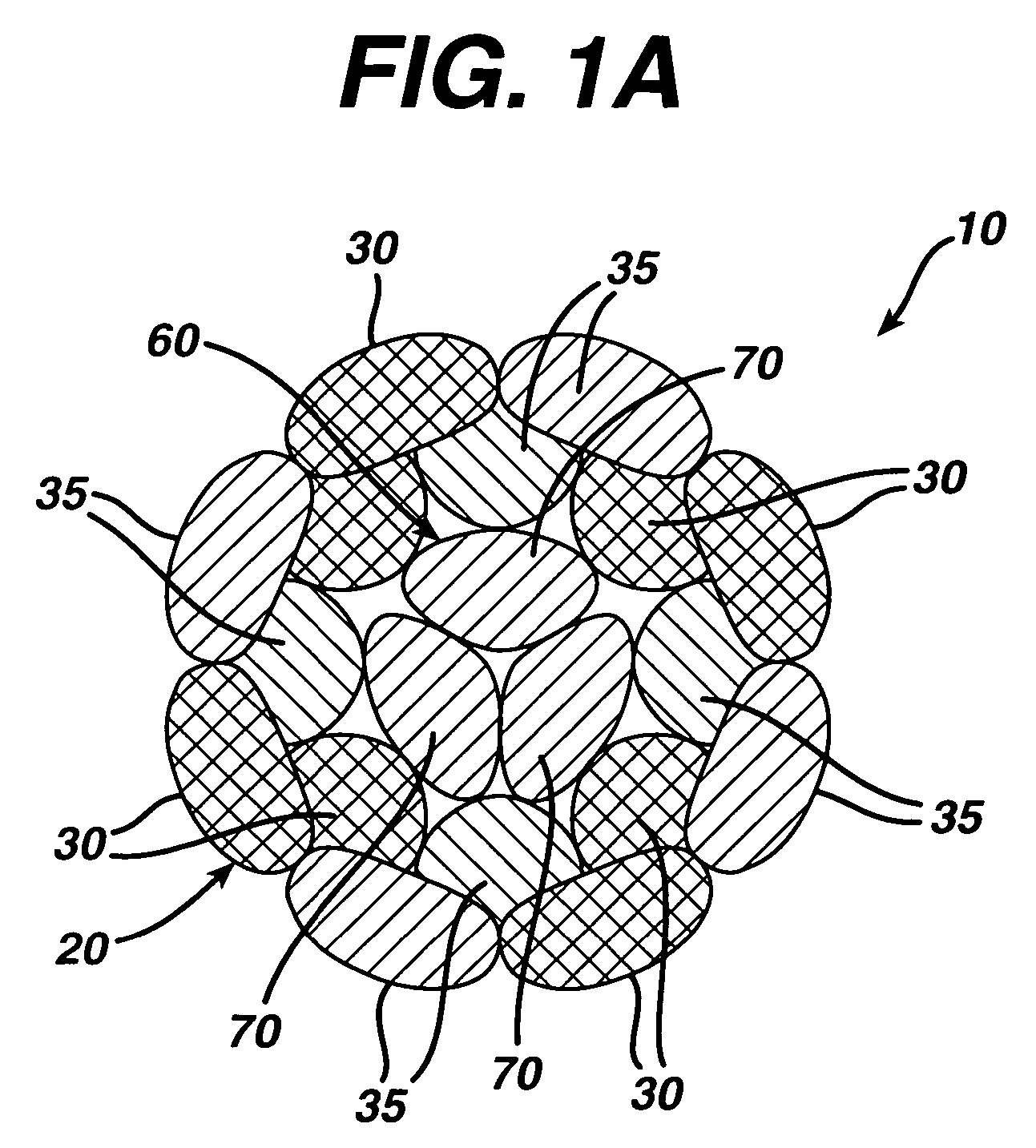
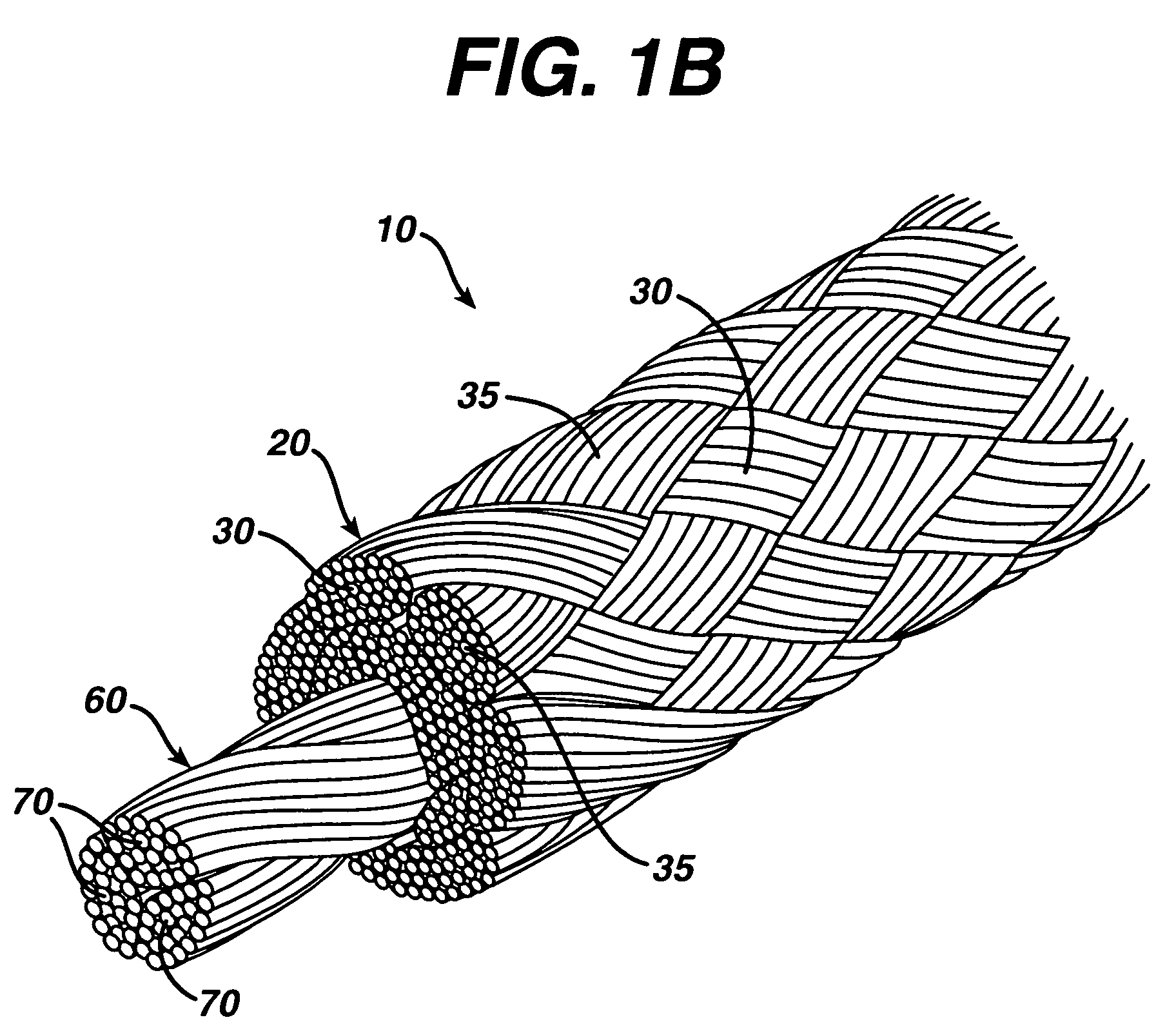
A novel high tensile strength semi-absorbable composite suture with minimized non-absorbable mass. The suture has a core made from a bioabsorbable polymer. The core is covered by a braided sheath. The braided sheath is made from an absorbable yarn and a bioabsorbable yarn. The bioabsorbable yarn is made from a least one filament of a bioabsorbable polymer. The nonabsorbable yarn is made from at least one filament of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Polymer-based orthopedic screw and driver system with increased insertion torque tolerance and associated method for making and using same
An orthopedic screw with an internal bore and mating driver has a bioabsorbable polymer component. To increase the torque tolerance of the screw and to minimize the likelihood of the driver stripping inside the bore of the screw, the screw and driver are heat treated together to shrink fit the screw onto the driver thereby increasing the driver-to-screw contact and distributing the loading force over a greater area to protect against material failure. The heat treatment involves heating the screw to an elevated temperature and holding that temperature for a period to promote stress relaxation and / or crystallization of the material.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
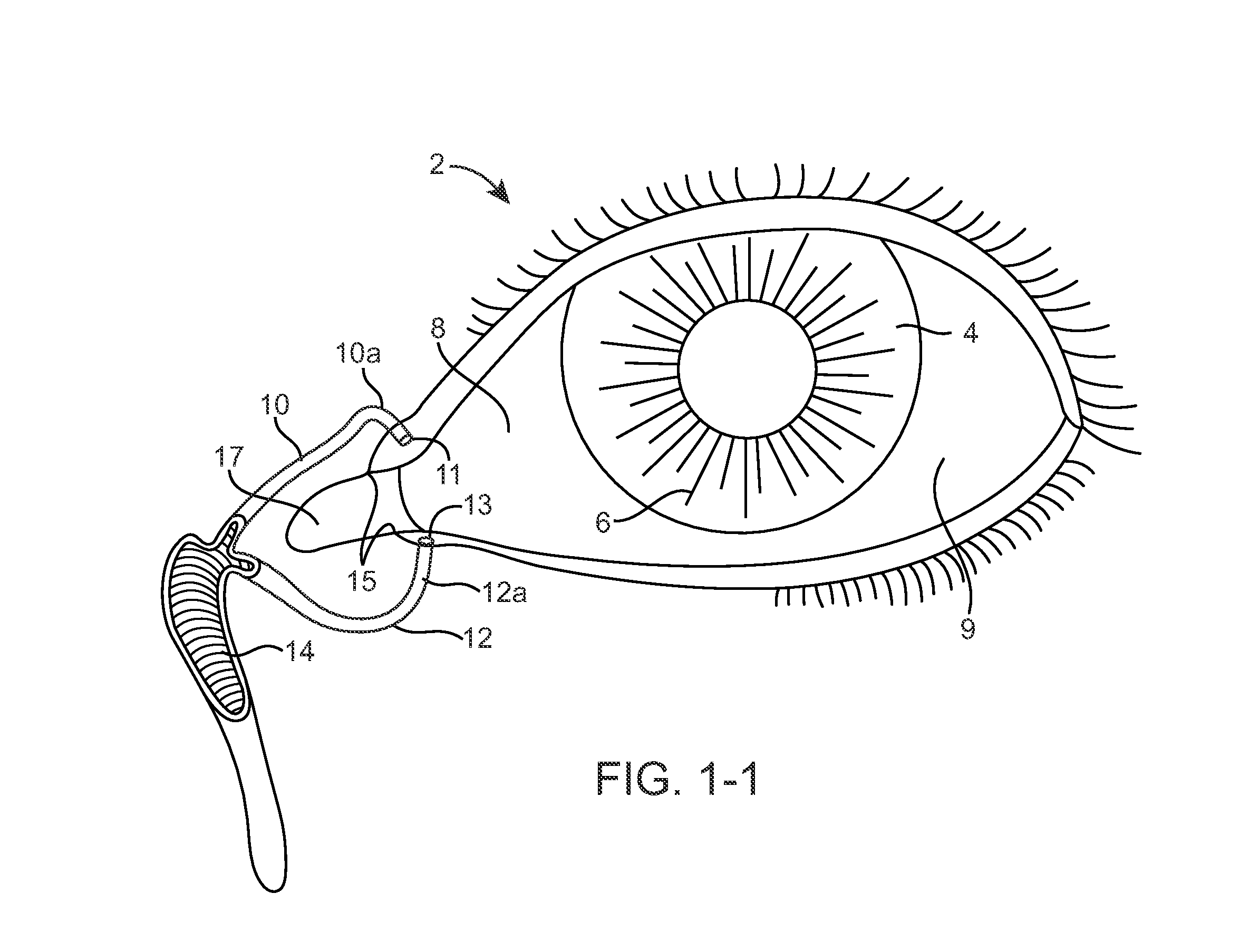
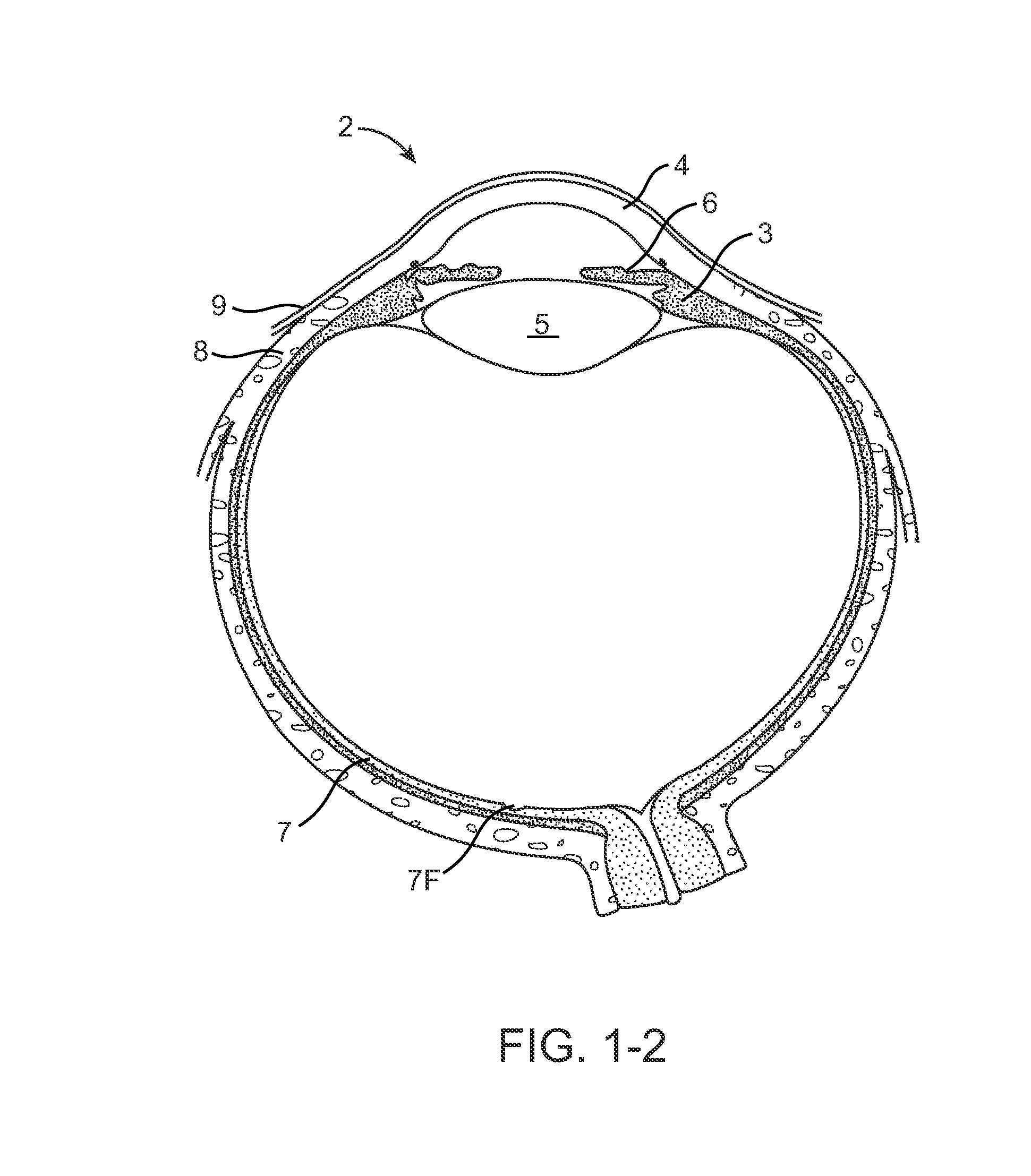
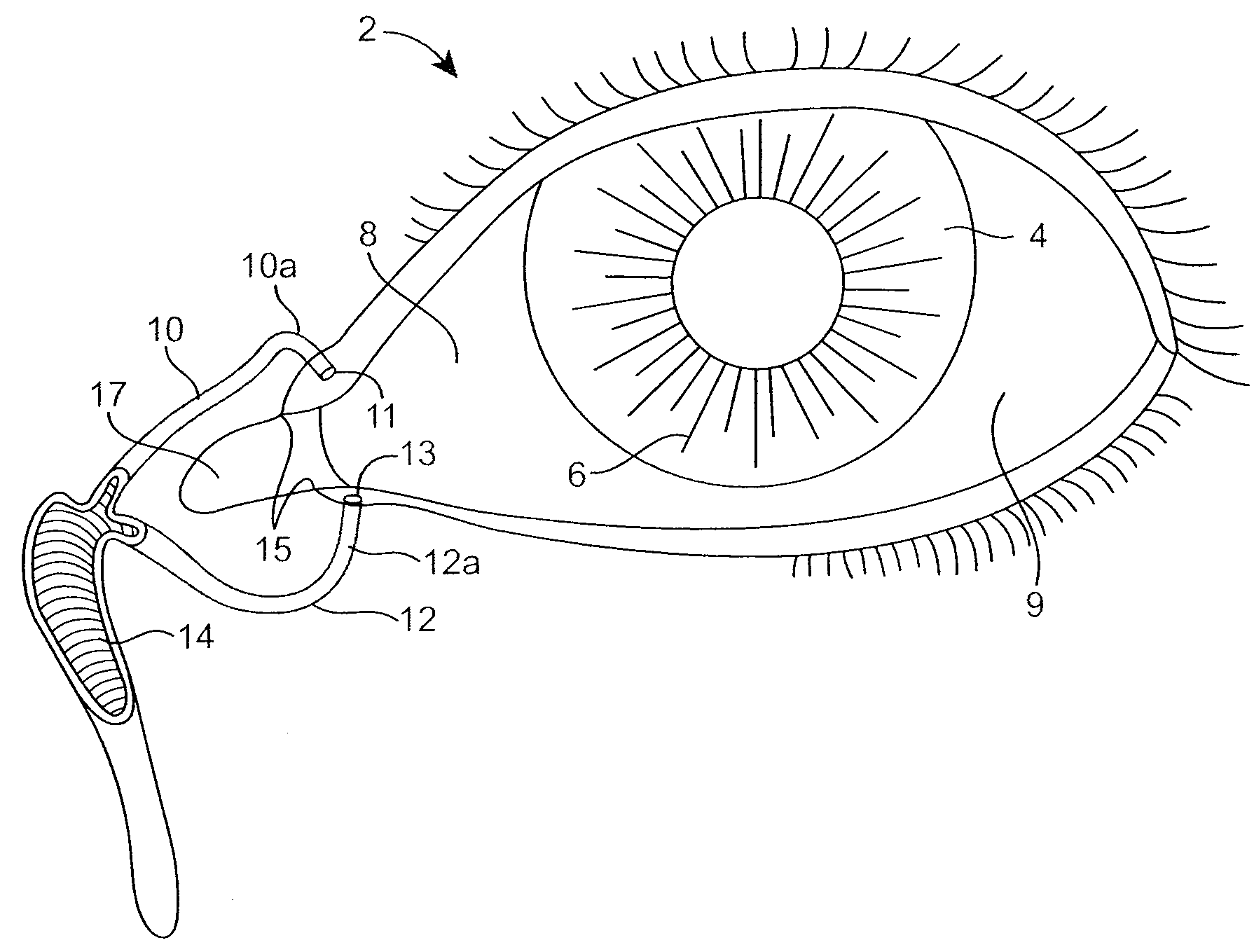
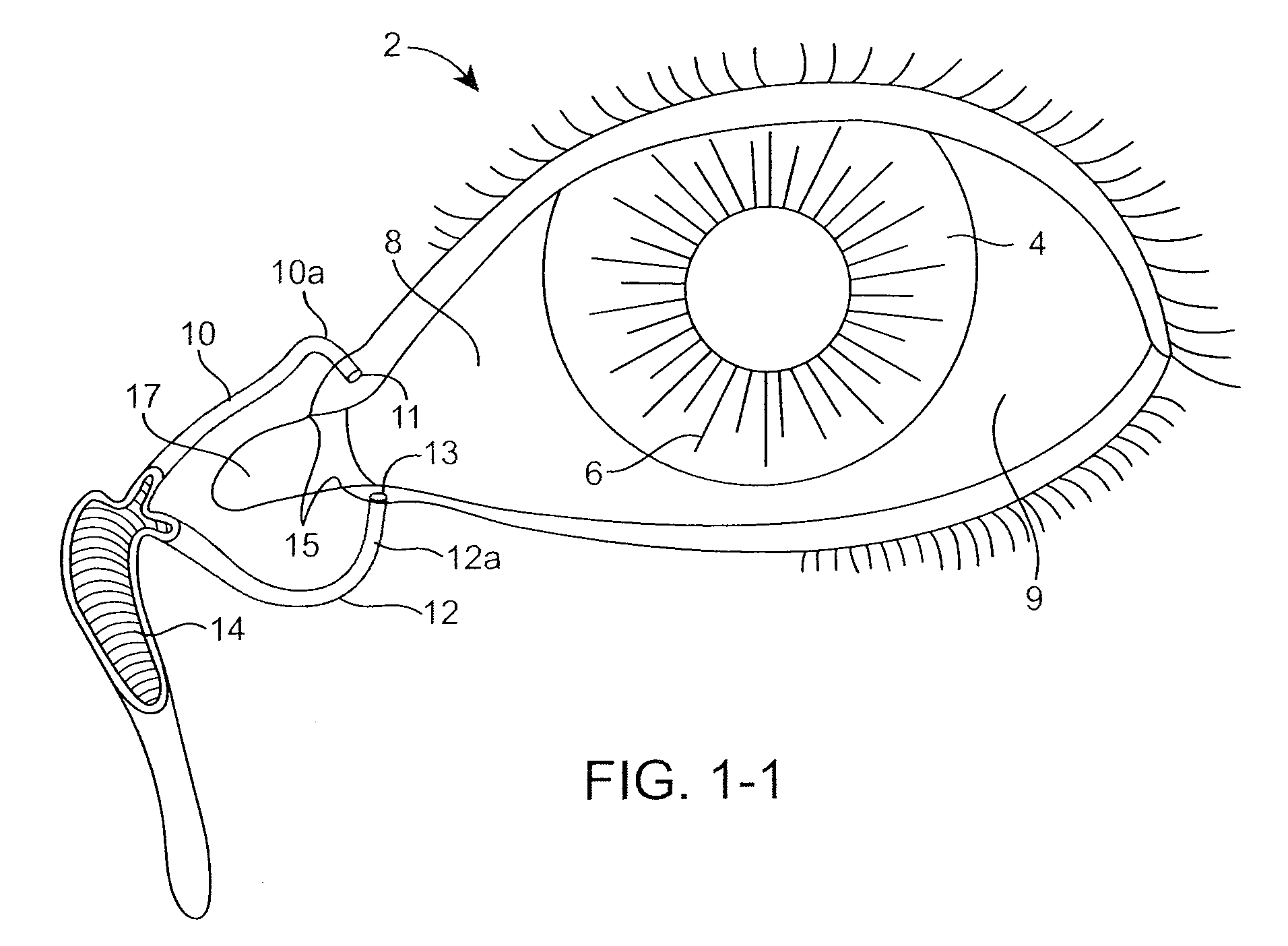
Drug Delivery Methods, Structures, and Compositions for Nasolacrimal System
ActiveUS20070269487A1Avoid expulsionInhibition releaseAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryEffective treatmentBiomedical engineering
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
Drug Delivery Methods, Structures, and Compositions for Nasolacrimal System
InactiveUS20090092654A1Avoid expulsionInhibition releaseAntibacterial agentsBiocideEffective treatmentBioabsorbable polymer
An implant for insertion into a punctum of a patient comprises a body. The body has a distal end, a proximal end, and an axis therebetween. The distal end of the body is insertable distally through the punctum into the canalicular lumen. The body comprises a therapeutic agent included within an agent matrix drug core. Exposure of the agent matrix to the tear fluid effects an effective therapeutic agent release into the tear fluid over a sustained period. The body has a sheath disposed over the agent matrix to inhibit release of the agent away from the proximal end. The body also has an outer surface configured to engage luminal wall tissues so as to inhibit expulsion when disposed therein. In specific embodiments, the agent matrix comprises a non-bioabsorbable polymer, for example silicone in a non-homogenous mixture with the agent.
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
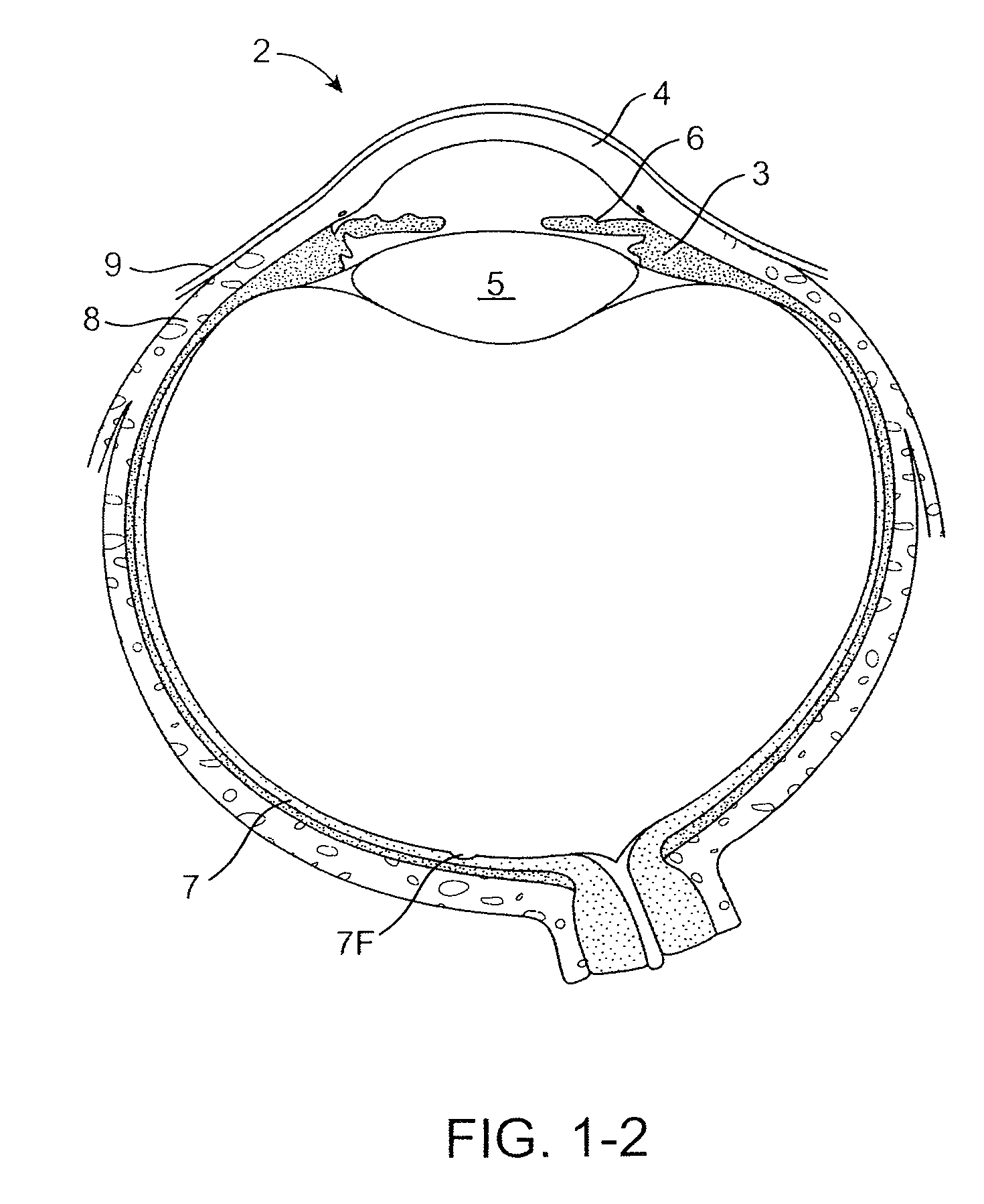
Mechanical heart valve and production method thereof
InactiveUS6875230B1Improve adhesionKeep pace with the infant's growthHeart valvesTissue regenerationBioabsorbable polymerBiomedical engineering
An artificial heart valve comprising a tubular base body having sinuse(s) of Valsalva and valve cusp(s) provided inside the base body, characterized in that the base body and the valve cusps comprise a bioabsorbable polymer material.
Owner:GUNZE LTD +1
Multifunctional biodegradable composite and surgical implant comprising said composite
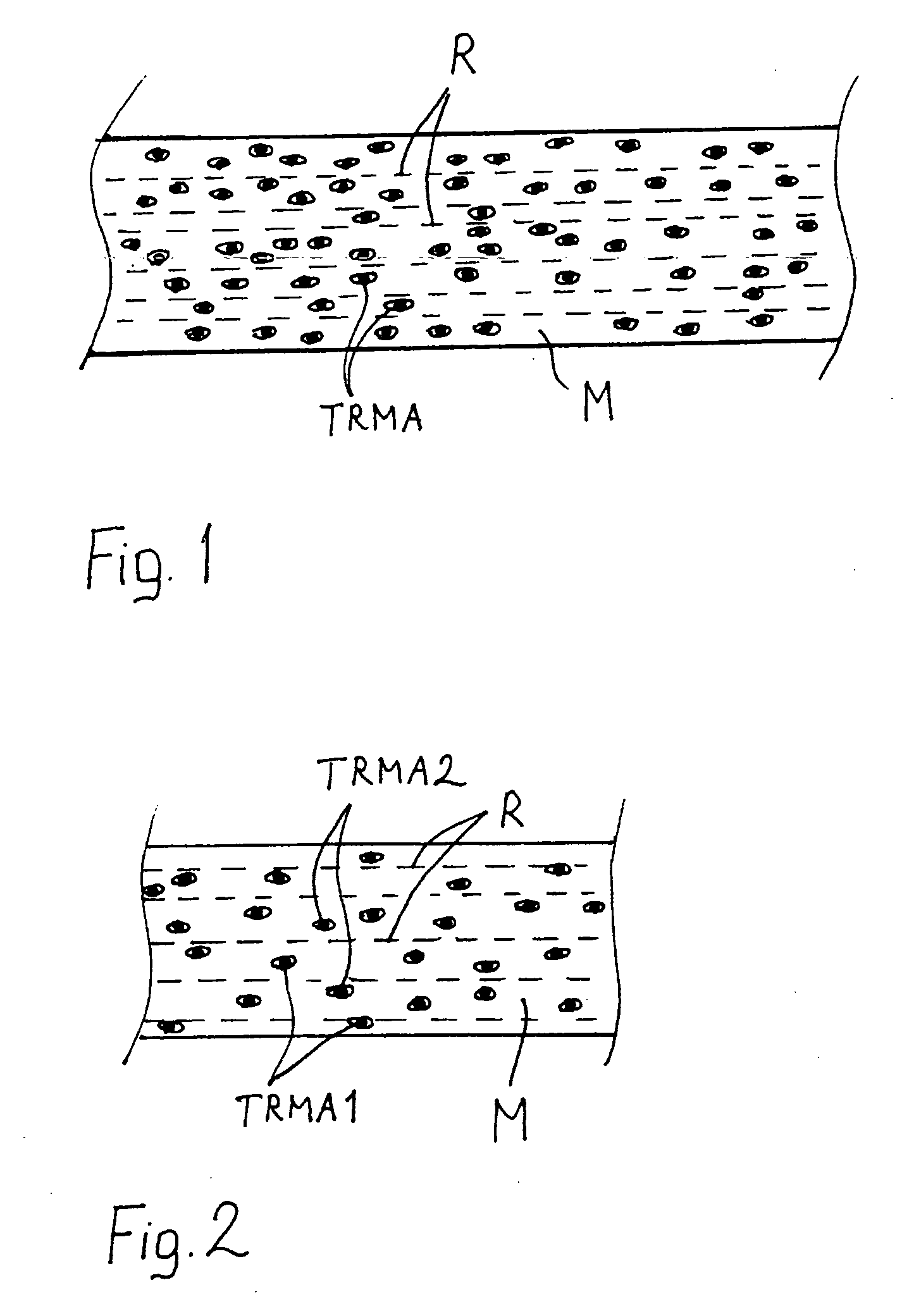
A multifunctional biodegradable composite has: a) bioabsorbable polymer matrix phase (M) b) bioabsorbable reinforcing element (R), and c) bioactive tissue / cell reaction modifying agent (TRMA) dispersed in said bioabsorbable matrix phase and selected from the group consisting of anti-inflammatory drugs and statins. Said biodegradable composite may be in a surgical implant capable of acting as a drug-delivery implant.
Owner:BIORETEC
Antibacterial nano fiber material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101358382ANo side effects on the human bodyContinuous and stable releaseFilament/thread formingMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFiberSide effect
The invention relates to an antibacterium nano fiber material and a preparation method thereof; the material comprises polymer superfine fiber and antibacterial agent, and the weight ratio is 60 to 98: 2 to 40; the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) the antibacterial agent is dissolved in distilled water to prepare solution; the polymer superfine fiber is dissolved in methylene dichloride or chloroform organic solvent, emulsifier is added to be mixed evenly, to obtain solution which is dispersed evenly; (2) the two types of solution are mixed to obtain even water-in-oil W / O latex, and then electrostatic spinning is conducted to the latex, to obtain the antibacterium nano fiber material. The nano fiber material has good ventilation property and filterability, still has bacteriostasis and sterilization functions for a long time after stably releasing the antibacterial agent, has simple preparation method, adopts the biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer as carrier materials, can be absorbed by the human body after fully releasing, is not left, does not need secondary operation and has no side effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Synthetic, bioabsorbable polymer materials and implants
Owner:BIORETEC
High strength suture with absorbable core
ActiveUS20050149119A1Improved absorption profileReducing knot profile of knotSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesYarnMedicine
A novel high tensile strength semi-absorbable composite suture with minimized non-absorbable mass. The suture has a core made from a bioabsorbable polymer. The core is covered by a braided sheath. The braided sheath is made from an absorbable yarn and a bioabsorbable yarn. The bioabsorbable yarn is made from a least one filament of a bioabsorbable polymer. The nonabsorbable yarn is made from at least one filament of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Drug delivery devices for delivery of therapeutic agents
Drug delivery devices comprising a non-bioabsorbable polymer structure and a composition comprising an active agent have been discovered. The drug delivery devices may be used to treat ocular conditions, among other diseases and conditions. In addition, a method of treating an ocular condition has been discovered comprising implanting a drug delivery device which releases the active agent at a rate ofQ=0.001×N×C wherein C is the topical effective concentration (in milligram / mL) of the active agent and N=0.01 to 0.5 for prostaglandins in their ester, amide, free acid or salt form, and N=0.5 to 5 for any active agent other than prostaglandins in their ester, amide, free acid or salt form.
Owner:NOVAER HLDG
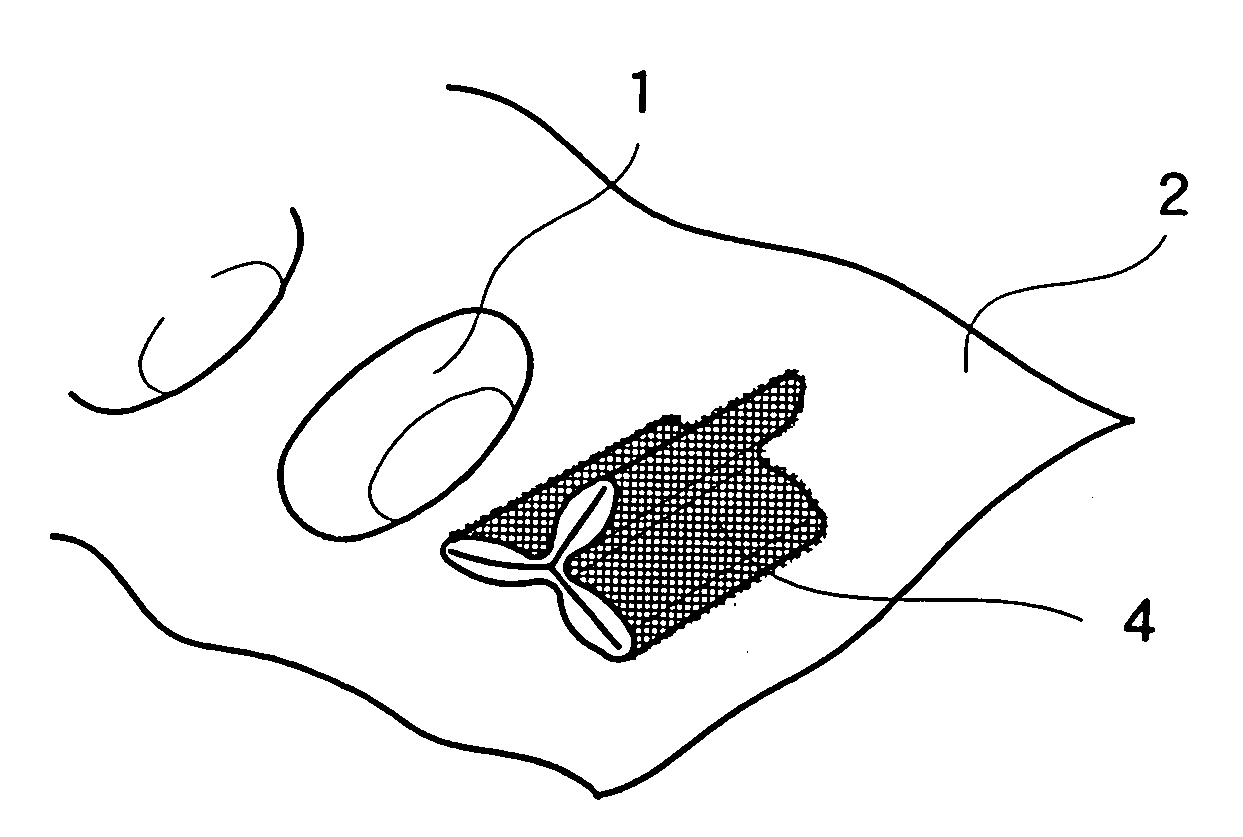
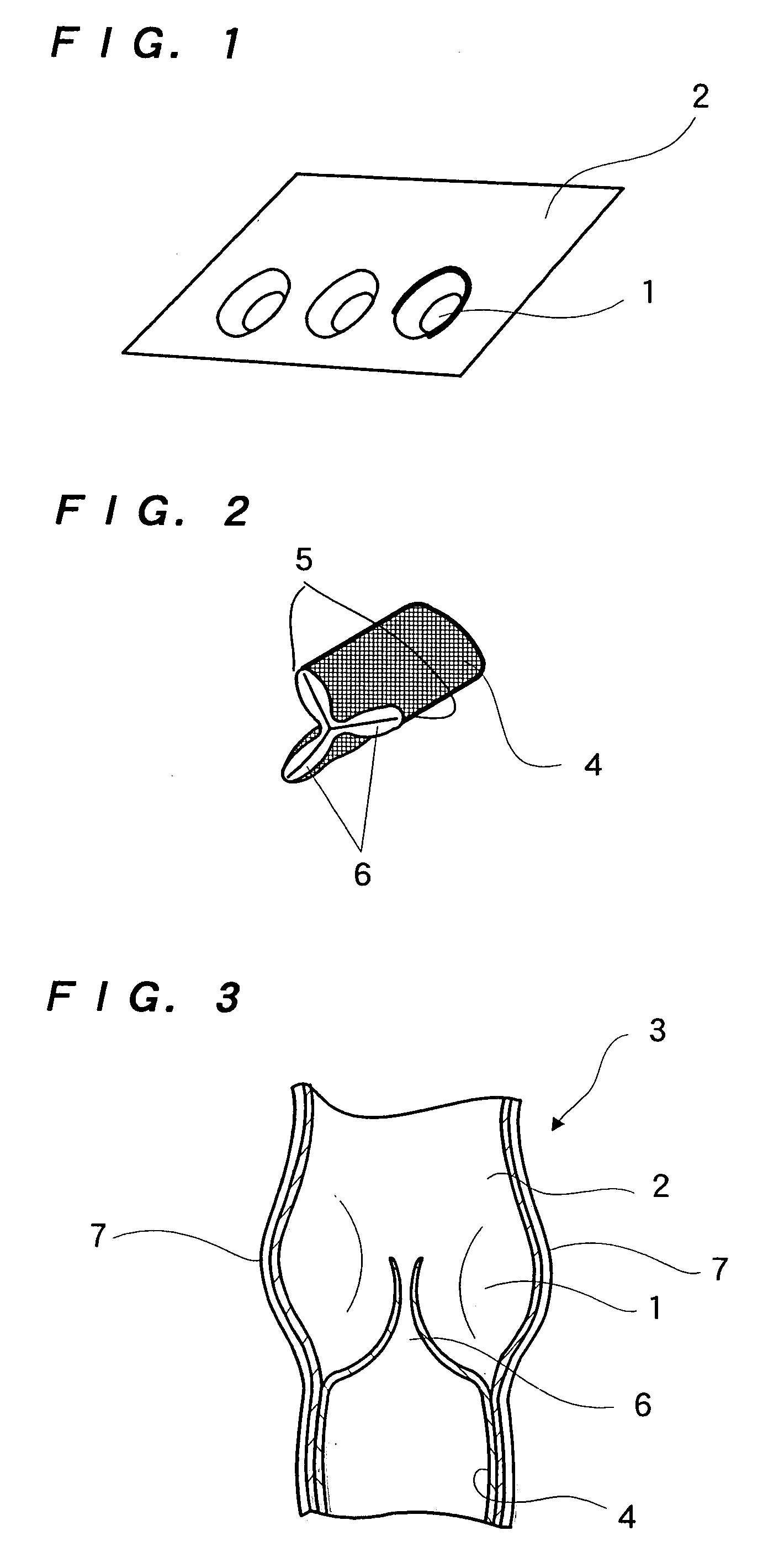
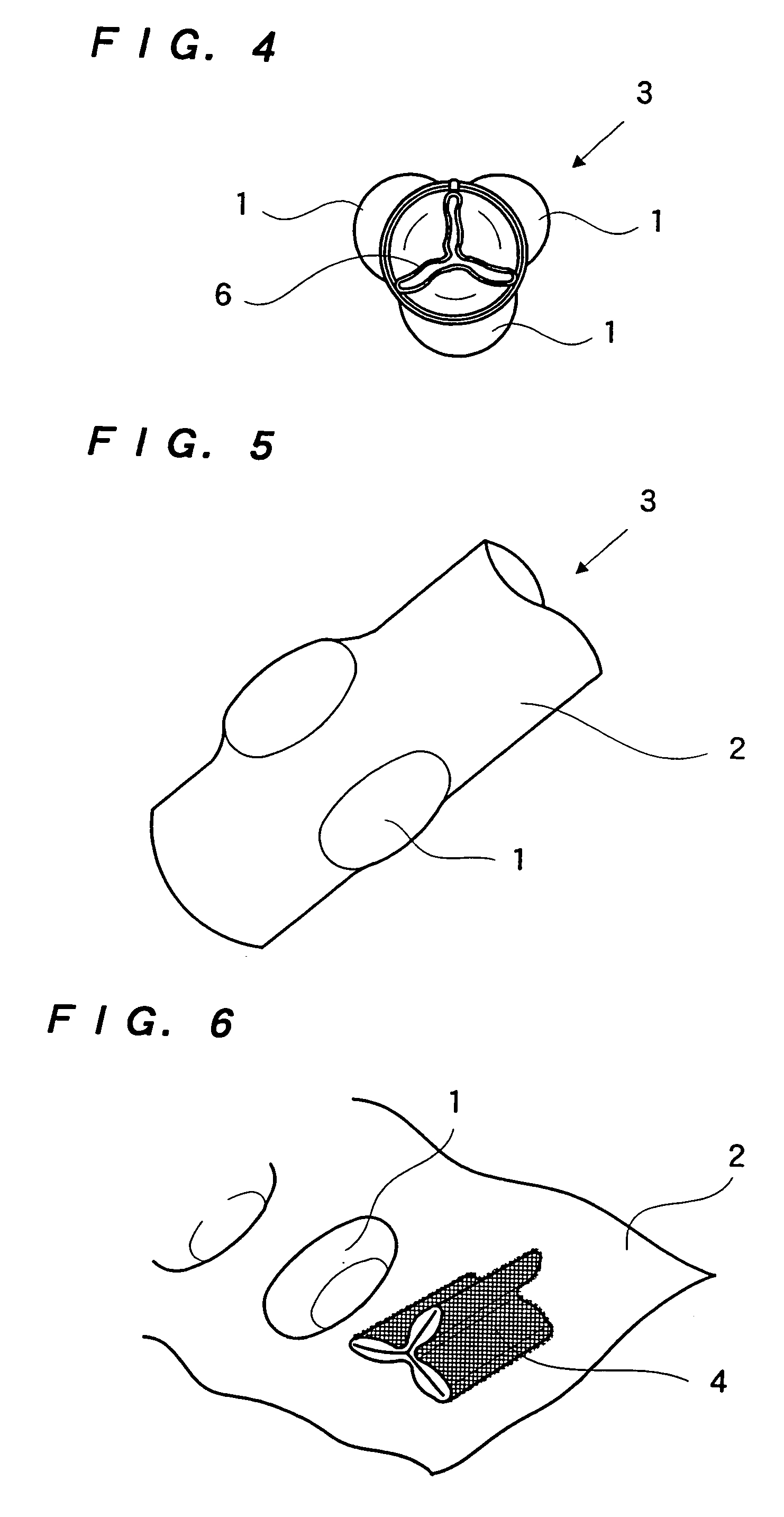
Method for modifying a medical implant surface for promoting tissue growth
InactiveUS20080091234A1Without excessive fibrosisIncreased riskCoatingsSurgical veterinaryBioabsorbable polymerPolyhydroxybutyrate
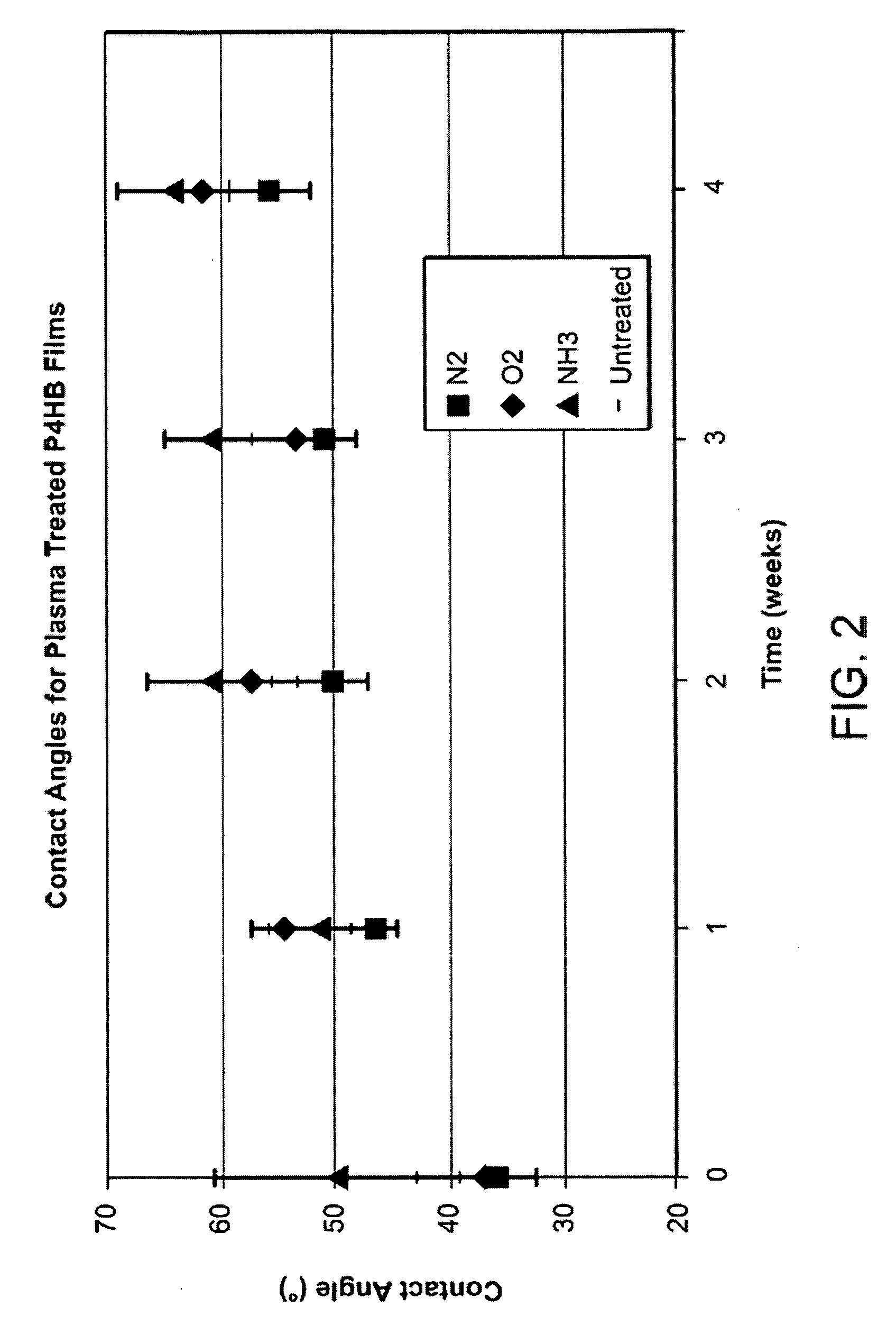
Disclosed is an occluder for closing an intracardiac defect, such as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), and a method for making the same. The occluder includes a frame and at least one scaffold which are formed from a bioabsorbable polymer, such as poly-4-hydroxybutyrate. The surface of the frame and scaffold are textured to promote cell attachment. Texturing of the surface can be achieved by any number of mechanical or chemical procedures. The device is coated with collagen and heparin which are covalently bound to the surface of the device. The occluder provides improved defect closure compared to other septal occluders known in the art. In particular, the occluder described is specifically designed to improve host cell attachment to and tissue ingrowth over the device when implanted in a patient as compared to the level of host cell attachment and tissue ingrowth achieved with other implantable devices made of bioabsorbable polymers.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
High strength suture with absorbable core
ActiveUS7329271B2Improved absorption profileReducing knot profile of knotSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesYarnMedicine
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS20070141111A1Uniform distribution of poresSuppress mutationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
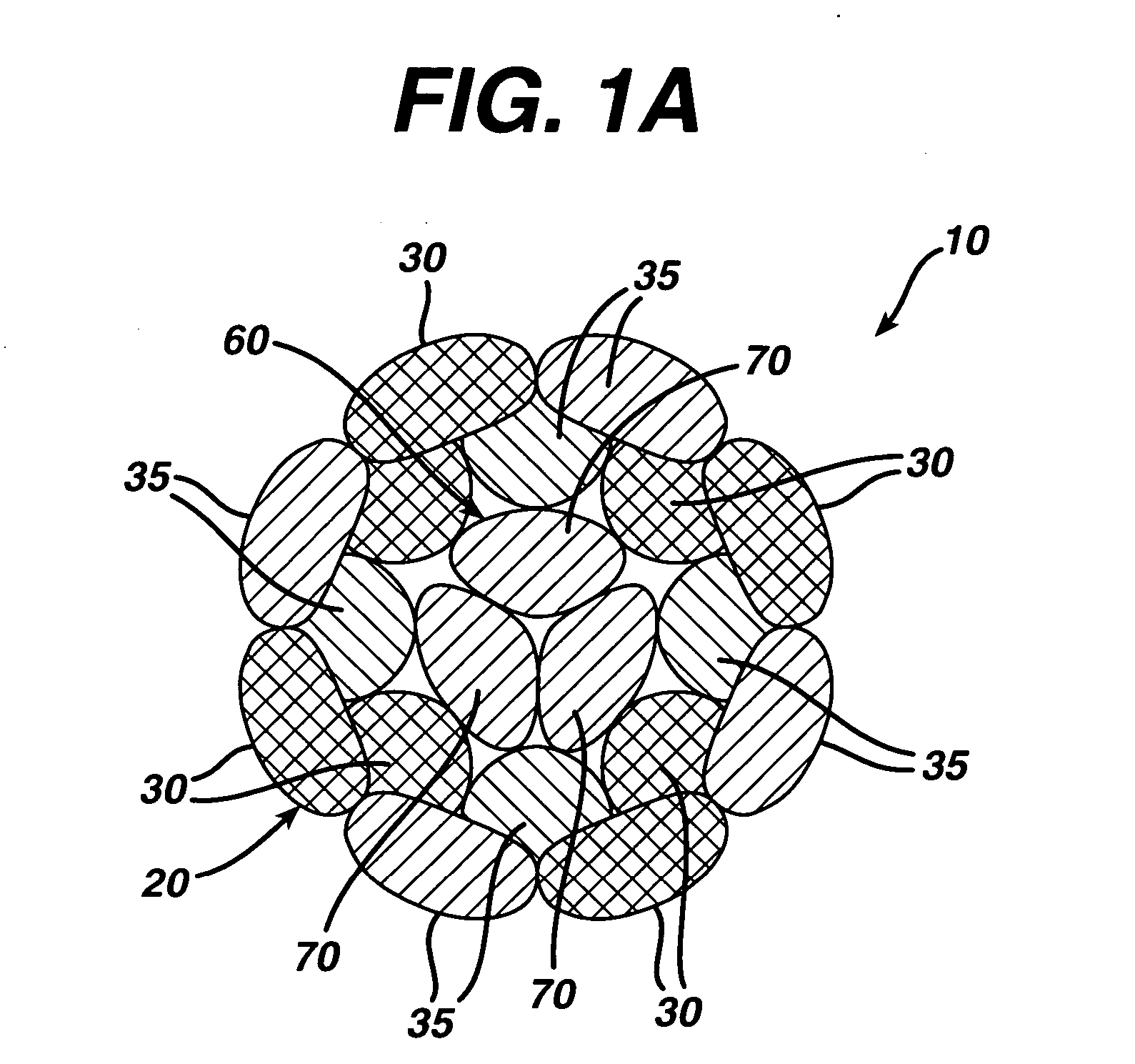
Dynamic bioabsorbable fastener for use in wound closure
InactiveUS20050182444A1Prevent and reduce deformationAvoid deformationStaplesJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringBioabsorbable polymer
A fastener for insertion into pierced openings of a tissue wound has a body formed of a generally bioabsorbable polymer defining an initial capture area. The body includes a pair of arms, each with an inwardly projecting cleat operably joined at an elbow portion defining an internal elbow angle. The arms are operably joined to a backspan at a shoulder portion defining an internal shoulder angle. A durable tissue retention zone is defined between the cleat and the arm. The elbow portion and the internal elbow angle define an insertion width greater than a width of the pierced openings resulting in the pierced openings stretching over the cleat and being elastically retained within the durable tissue retention zone. The fastener captures wound tissue in the initial capture area and then dynamically reforms in response to lateral stresses without a fracture failure of the fastener until a minimum degradation period.
Owner:INCISIVE SURGICAL
Coating Employing an Anti-Thrombotic Conjugate
InactiveUS20090018646A1Few stepsImprove versatilityStentsOrganic active ingredientsActive agentSide chain
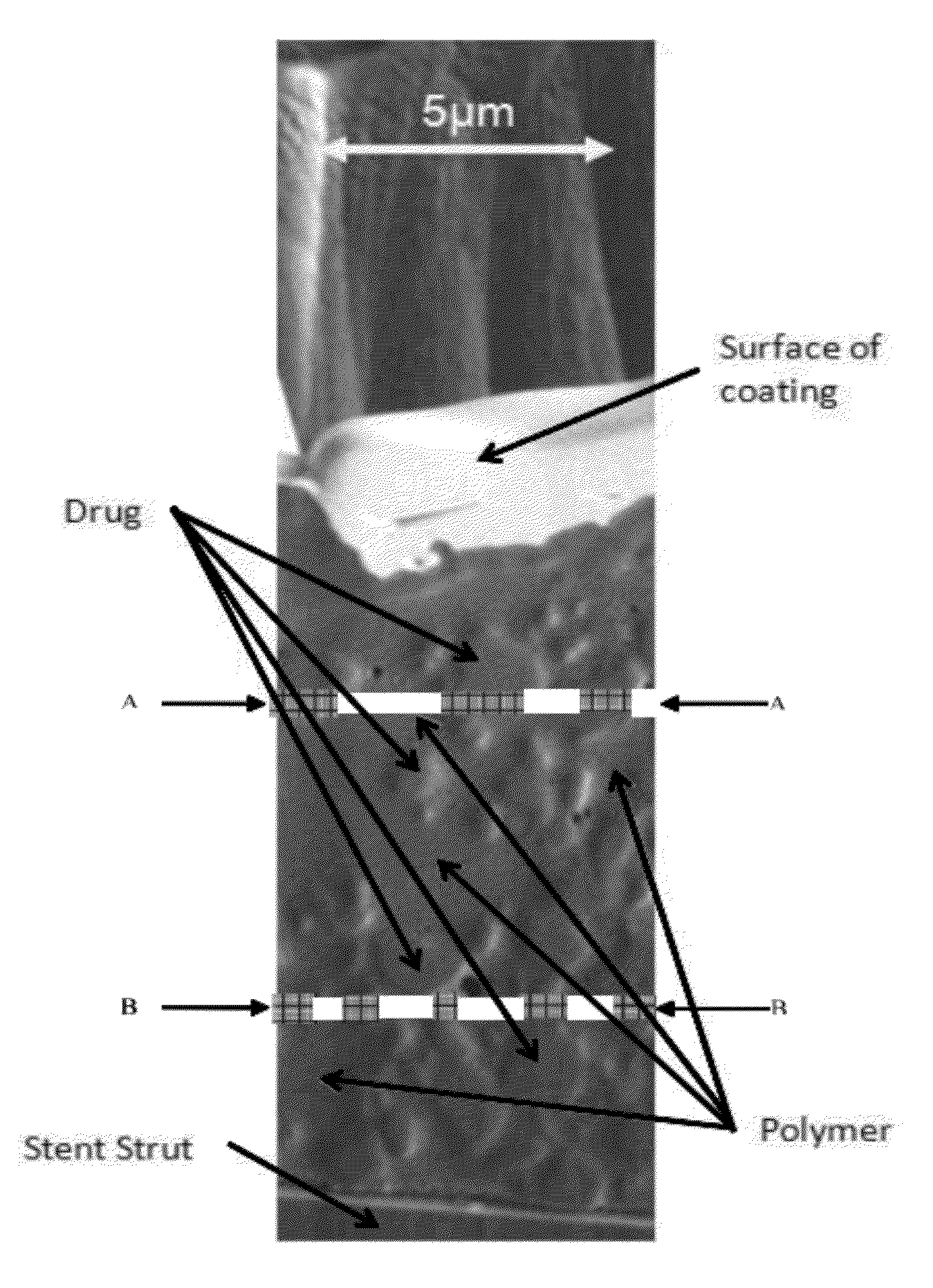
A biodegradable antithrombotic conjugate having heparin and other anti-thrombotic moieties are introduced as side chains to the polymer backbone modified by click chemistry. Various bioabsorbable monomers and dimers such as valerolactone may be used in the monomer derivation, homo- and co-polymerization, and the conjugation with a biologically active molecule by click chemistry. A coating comprising a biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer anti-thrombotic conjugate is applied to at least a portion of an implantable device to prevent or reduce the formation of thrombosis on the surface of the implantable device. A first or sub-layer of the coating is prepared by mixing a polymeric material and a biologically active agent with a solvent, thereby forming a homogeneous solution. A second or outer layer comprising the present anti-thrombotic conjugate may be applied over the inner drug-containing layers using, for example, a dip coating or spray coating process.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Stent Made From An Ultra High Molecular Weight Bioabsorbable Polymer With High Fatigue And Fracture Resistance
A stent made from an ultra high molecular weight bioabsorbable polymer is disclosed herein. The bioabsorbable polymer can have a Mw greater than 1 million g / mole or greater than 2 million g / mole. Methods of making the ultra high molecular weight polymer stent without degrading the molecular weight are further disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
High strength suture with absorbable core and suture anchor combination
ActiveUS7357810B2Improved absorption profileReducing knot profile of knotSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesYarnMedicine
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
InactiveUS20020040239A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical containersPoly-L-lactideVascular compartment
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bioabsorbable plugs containing drugs
InactiveUS6916483B2Easily affixedPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesCircular discAdhesive
Bioabsorbable modular drug delivery devices having shapes and sizes adapted to be inserted within a mating receptacle on the surface of an implantable prosthesis are disclosed. The devices may be attached to one another to create custom drug delivery devices having controllable drug release characteristics that depend on the composition of individual modules comprising the device. The modules may be cylinders, disks, tiles or tubes comprised of a bioabsorbable polymer and a therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent(s) may be homogeneously distributed throughout the polymeric body of the device or contained within a cavity within a module comprising the device, or both. The device(s) may be threaded or attached to a prosthesis by a biodegradable adhesive. The modular devices may also be formed into tapered plugs for insertion into a mating receptacle. In another embodiment, the drug delivery device may be inserted within a mesh bag that may be attached to a soft tissue as, for example, by sutures, for localized controlled dispensation of a therapeutic agent.
Owner:NEW AMSTERDAM LLC
Stents having controlled elution
Provided herein is a device comprising: a. stent; b. a plurality of layers on said stent framework to form said device; wherein at least one of said layers comprises a bioabsorbable polymer and at least one of said layers comprises one or more active agents; wherein at least part of the active agent is in crystalline form.
Owner:MICELL TECH INC
Implantable prosthetic devices containing timed release therapeutic agents
Owner:NEW AMSTERDAM LLC
Stents having controlled elution
InactiveUS20120323311A1Reduce hypersensitivityMitigates impaired healingStentsSurgeryActive agentElution
Provided herein is a device comprising: a. stent; b. a plurality of layers on said stent framework to form said device; wherein at least one of said layers comprises a bioabsorbable polymer and at least one of said layers comprises one or more active agents; wherein at least part of the active agent is in crystalline form.
Owner:MICELL TECH INC
Stents having bioabsorbable layers
Provided herein is a device comprising: a. stent; b. a plurality of layers on said stent framework to form said device; wherein at least one of said layers comprises a bioabsorbable polymer and at least one of said layers comprises one or more active agents; wherein at least part of the active agent is in crystalline form.
Owner:MT ACQUISITION HLDG LLC
Stents having controlled elution
Provided herein is a device comprising: a. stent; b. a plurality of layers on said stent framework to form said device; wherein at least one of said layers comprises a bioabsorbable polymer and at least one of said layers comprises one or more active agents; wherein at least part of the active agent is in crystalline form.
Owner:MT ACQUISITION HLDG LLC
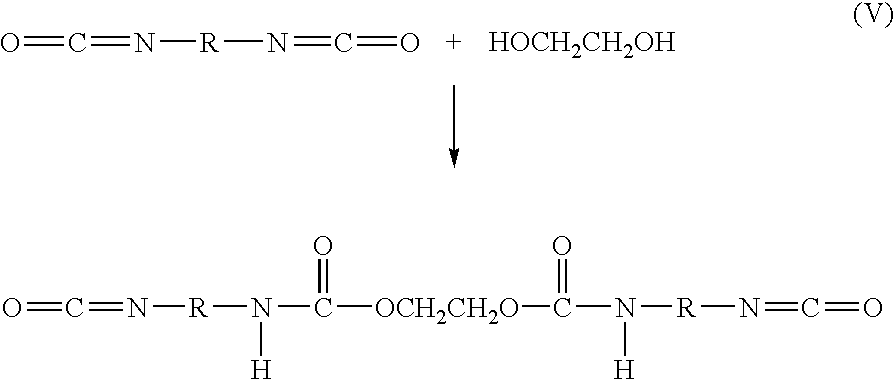
Bioabsorbable surgical composition
Bioabsorbable macromer compositions are provided including a diisocyanate-functional bioabsorbable polymer. In some embodiments, the diisocyanate-functional bioabsorbable polymer can be combined with a functionalized polyol. The resulting bioabsorbable macromer composition can be employed as an adhesive or sealant for medical / surgical uses.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
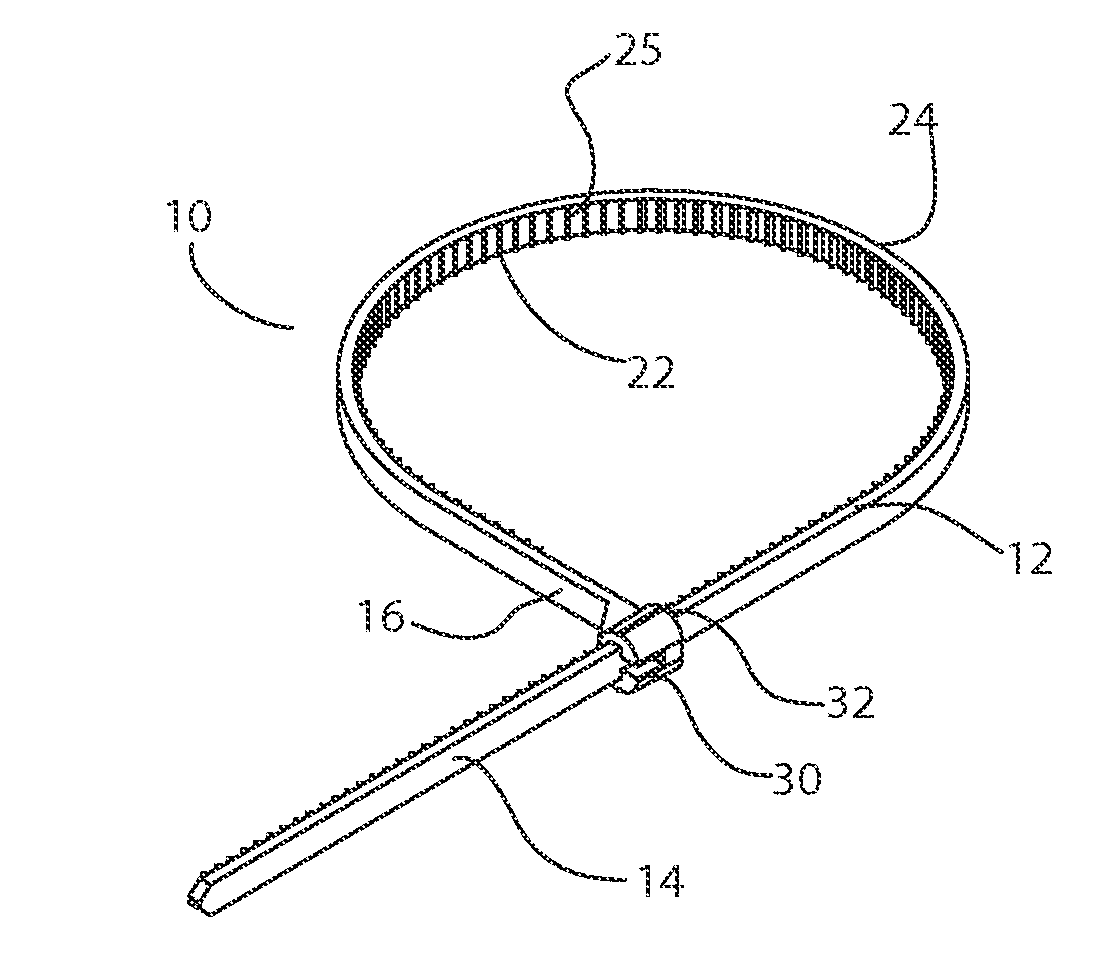
Surgical clamp and method of clamping an organ
A surgical clamp is provided that is applied through a laparoscopic port and is used for clamping off a portion of an organ. The surgical clamp comprises an elongated flexible bioabsorbable polymer band laced with a hemostatic agent. The band has a proximal end and a distal end. A bioabsorbable polymer tie secures in place the proximal end of the band to the distal end of the band. A conductive wire snare is provided to cut and cauterize a target.
Owner:PATEL MANOJ +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com