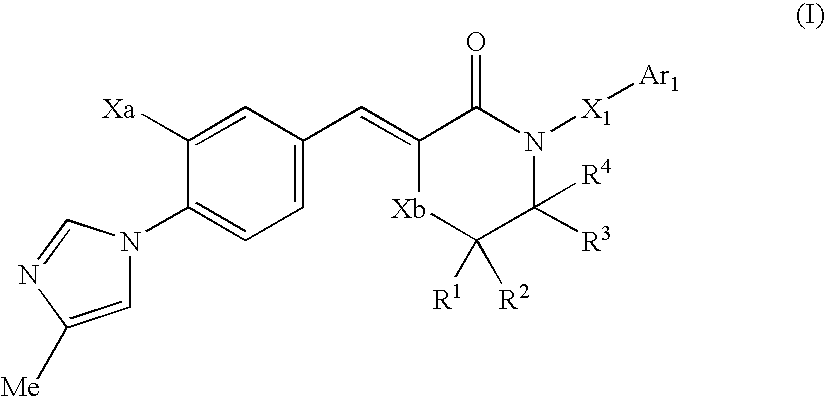
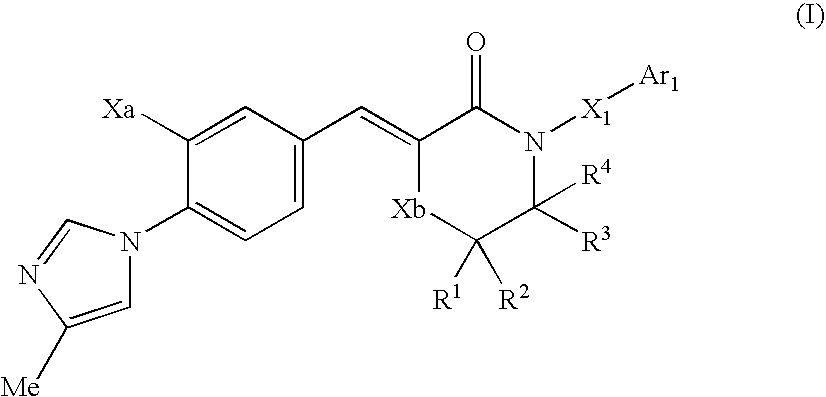
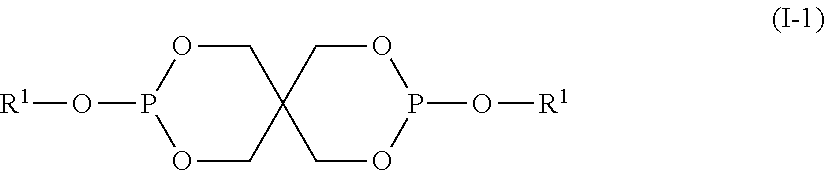
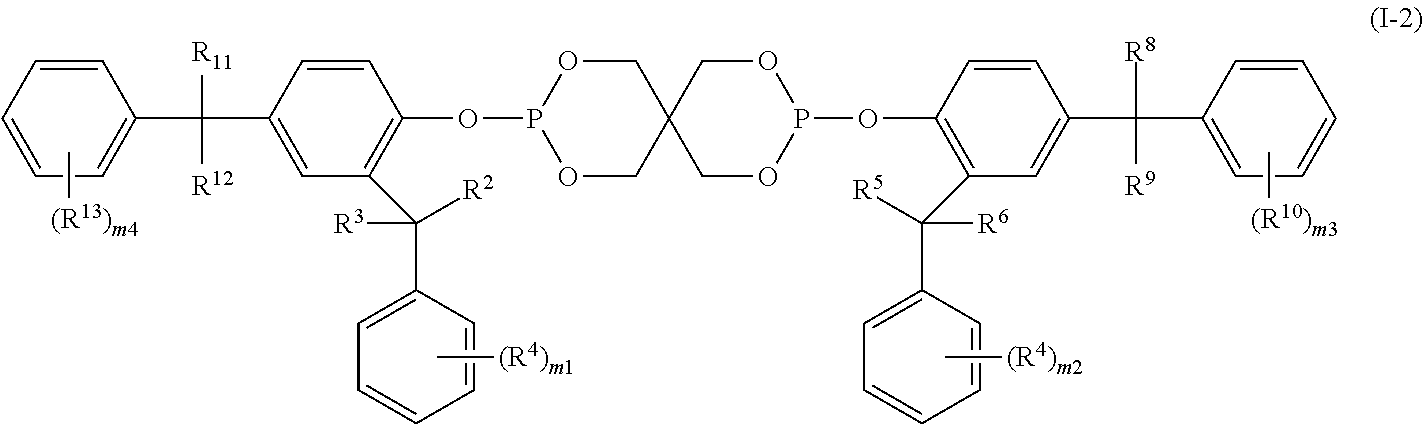
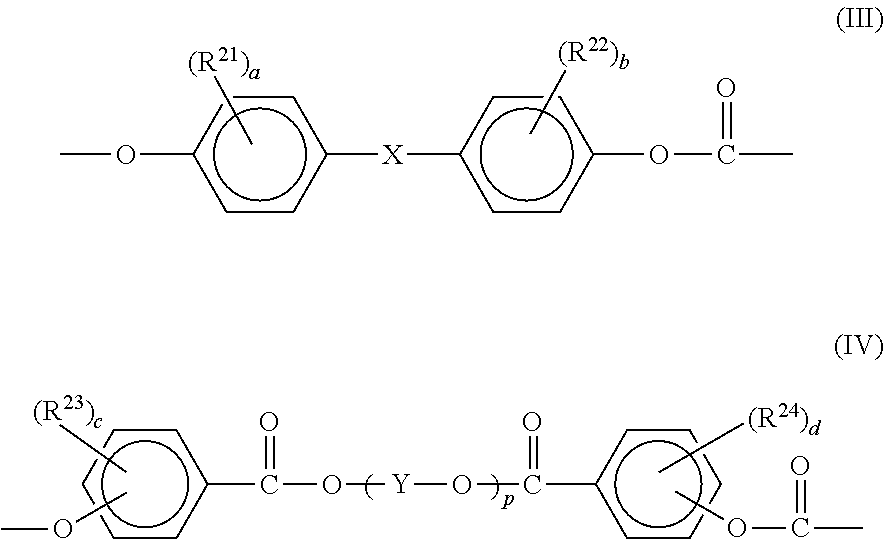
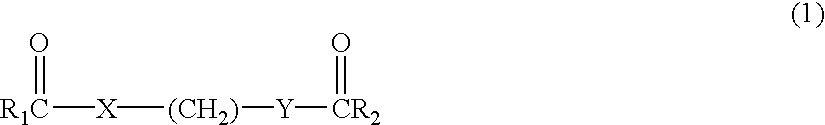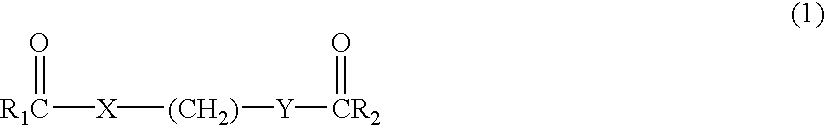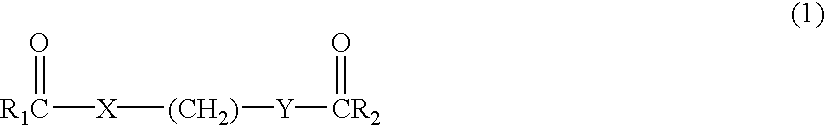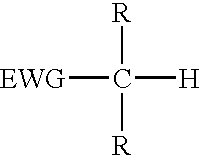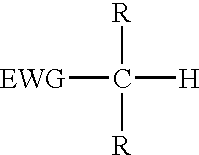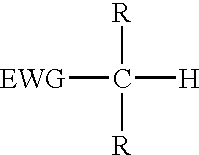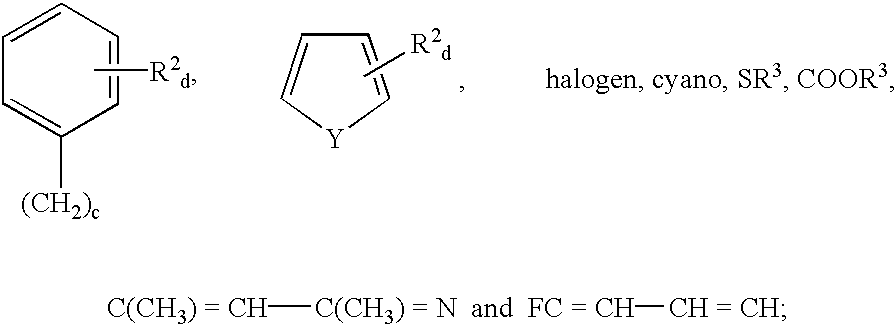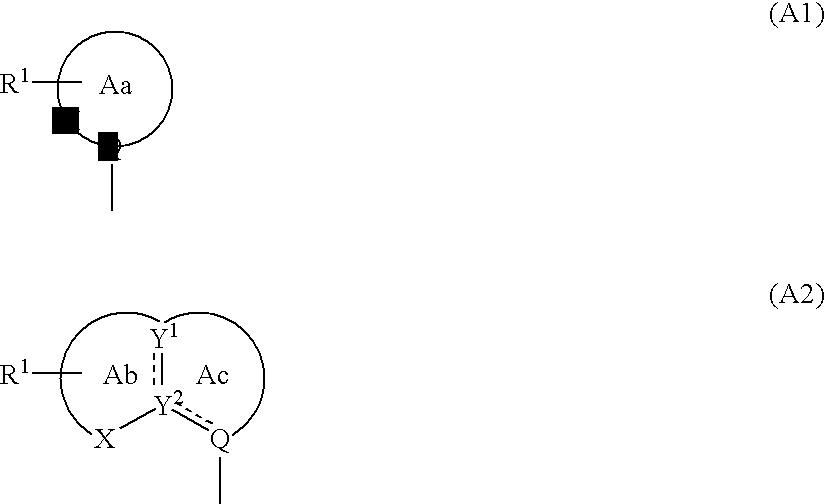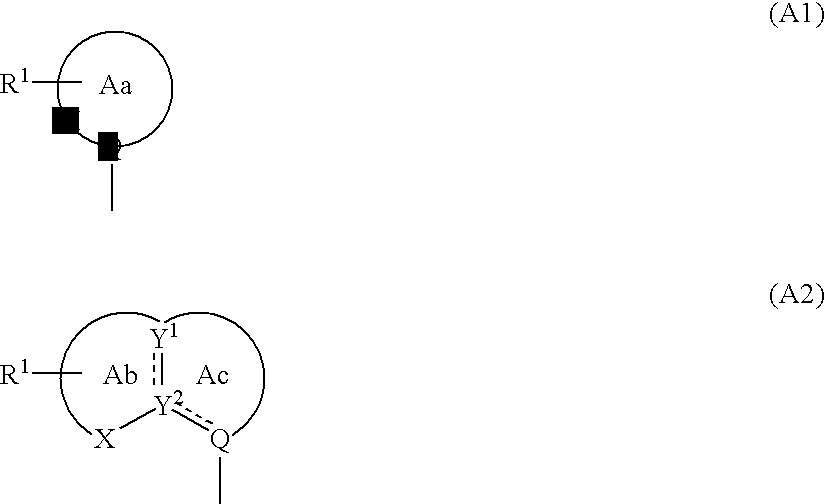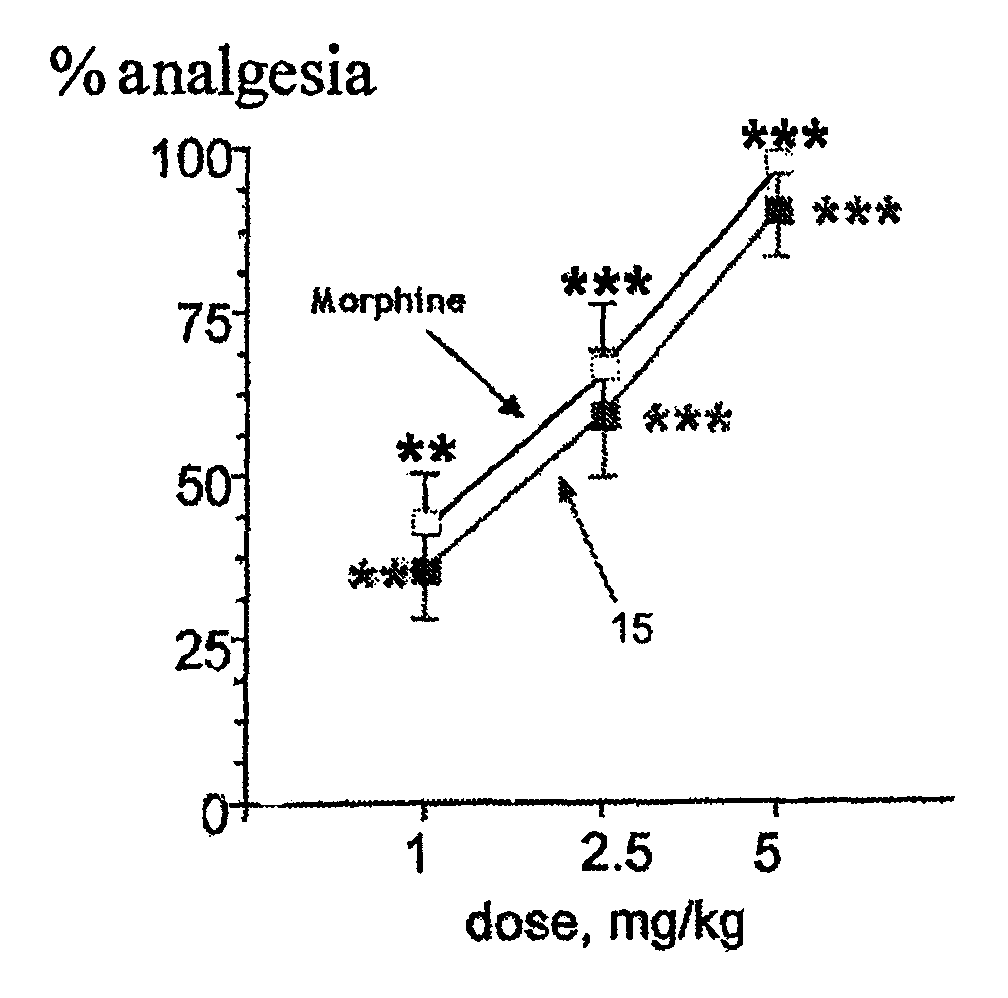Patents
Literature
2263 results about "Methylene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methylene (systematically named methylidene and dihydridocarbon; also called carbene) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH₂ (also written [CH₂]). It is a colourless gas that fluoresces in the mid-infrared range, and only persists in dilution, or as an adduct.
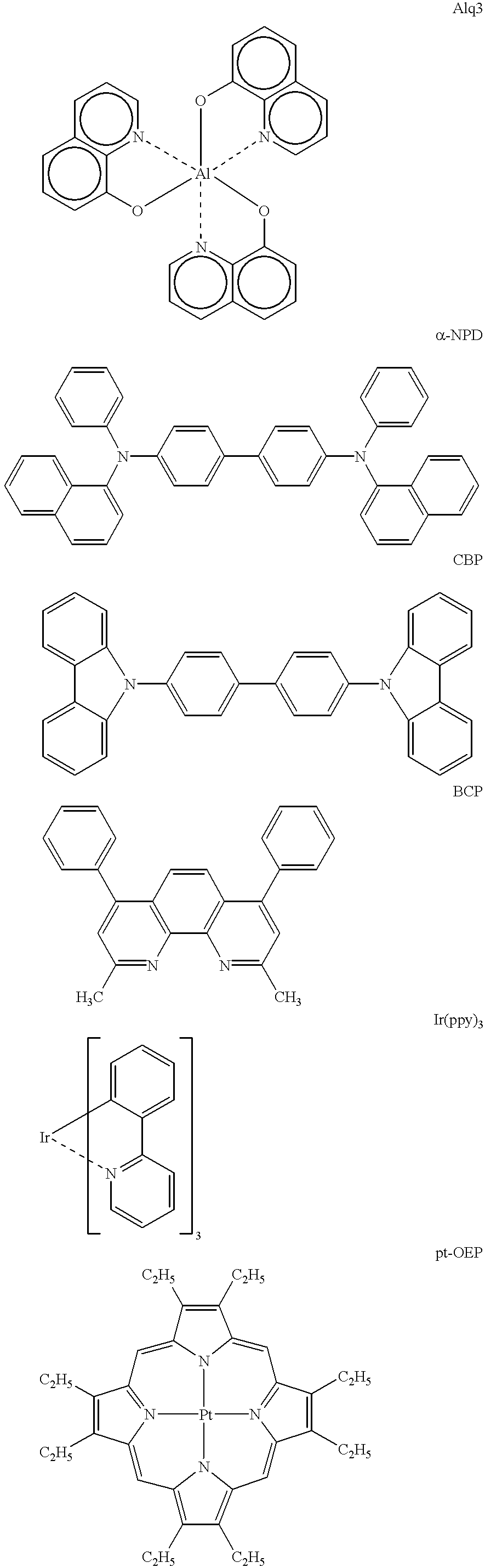
Limuninescence device, display apparatus and metal coordination compound
InactiveUS20020063516A1Indium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic compoundLuminescence
A luminescence device is principally constituted by a pair of electrodes and an organic compound layer disposed therebetween. The layer contains a metal coordination compound represented by the following formula (1): wherein M denotes Ir, Rh or Pd; n is 2 or 3; CyN denotes a substituted or unsubstituted cyclic group containing a nitrogen atom connected to M and capable of containing another nitrogen atom and / or a sulfur atom; and CyC denotes a substituted or unsubstituted cyclic group containing a carbon atom connected to M and capable of containing a nitrogen atom and / or a sulfur atom, CyN and CyC being connected to each other via a covalent bond, and each of substituents for CyN and CyC being selected from the group consisting of a halogen atom; nitro group; a trialkylsilyl group containing three linear or branched alkyl groups each independently having 1-8 carbon atoms; and a linear or branched alkyl group having 1-20 carbon atoms capable of including one or at least two non-neighboring methylene groups which can be replaced with -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CO-O-, -O-CO-, -CH=CH- or -C=C- and capable of including a hydrogen atom which can be replaced with a fluorine atom; with the proviso that a sum of nitrogen atom and sulfur atom present in ring structures of CyN and CyC is at least 2.
Owner:CANON KK
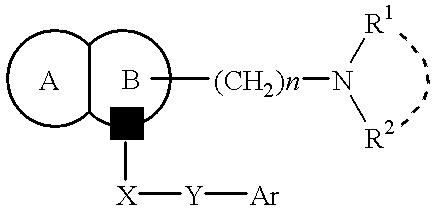
Amine compounds, their production and use
InactiveUS6329389B1Enhance and inhibit production and secretionLow toxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryArylNitrogen
The present invention provides a compound of the formula:wherein Ar represents an aromatic group which may be substituted;X represents methylene, S, SO, SO2 or CO;Y represents a spacer having a main chain of 2 to 5 atoms;n represents an integer of 1 to 5;i) R1 and R2 each represents a hydrogen atom or a lower alkyl which may be substituted,ii) R1 and R2 form, taken together with the adjacent nitrogen atom, a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring which may be substituted, oriii) R1 or R2 together with -(CH2)n-N= form, bonded to a component atom of Ring B, a spiro-ring which may be substituted;Ring A represents an aromatic ring which may be substituted;Ring B represents a 4- to 7-membered nitrogen-containing non-aromatic ring which may be further substituted by alkyl or acyl,with a proviso that X represents S, SO, SO2 or CO when Ring A has as a substituent a group represented by the formula:where R11 represents alkyl, alkoxyalkyl, alkylthioalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl or a group represented by the formula:where R12 represents alkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, aryl or arylalkyl, or a salt thereof; which has an excellent somatostatin receptor binding inhibition action.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Highly available particulate controlled release nitrogen fertilizer
InactiveUS6048378ASpeed up the conversion processImprove efficiencyBiocideGranulation in rotating dishes/pansParticulatesWater insoluble
A method preparing controlled release nitrogen in particulate fertilizers which exhibit single growing season availabilities to plants of about 80 percent or higher. The method utilizes relatively low urea and ammonia to formaldehyde mol ratios of about 1.7 urea to 0.1 ammonia to 1 formaldehyde to assure high conversions to controlled release nitrogen with low free ureas, and carefully controlled elevated temperatures, acid dehydration condensation catalyst concentrations and short dehydration reaction times of about 2-4 minutes to provide effective conversion of hydroxymethyl nitrogen compounds by dehydration condensation reaction to controlled release methylene nitrogen compounds. Quick neutralization of the dehydration catalyst in a turbulent mixing reactor minimizes the formation of undesirable methylene nitrogen polymers which are hot water insoluble and unavailable to plants in a single growing season.
Owner:AGRINUTRIENTS TECH GRP INC
Delta dicarbonyl compounds and methods for using the same
Owner:ERRANT GENE THERAPEUTICS
Saturated and unsaturated N-alkamides exhibiting taste and flavor enhancement effect in flavor compositions
ActiveUS20060057268A1Fatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCyclopenteneEthyl group
Saturated and unsaturated compounds having sweet, salt or umami taste enhancement qualities. The compounds have the structure: where R1═H or methyl; R2 is selected from the group consisting of H, C1-C4 alkyl, alkenyl and methylene; R3 is selected from the group consisting of H, C1-C8 straight or branched chain alkyl, alkenyl, dienalkyl or phenyl; or if R1═H, R2 and R3 taken together can represent cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclopentenyl, cyclohexyl, or cyclohexenyl; R4 is selected from the group consisting of H, methyl and ethyl; R5 is selected from the group consisting of H, methyl and ethyl; R6 is selected from the group consisting of H, C1-C9 straight or branched chain alkyl, alkenyl, alkyldienyl, acyclic or containing no more than one ring; with the proviso that in structure 1 when R4 is H or Me; and R5═H or methyl, R6 may be selected from the group described above or phenyl.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Medicament for treating composite water in hot water boiler as well as preparation method and use method thereof
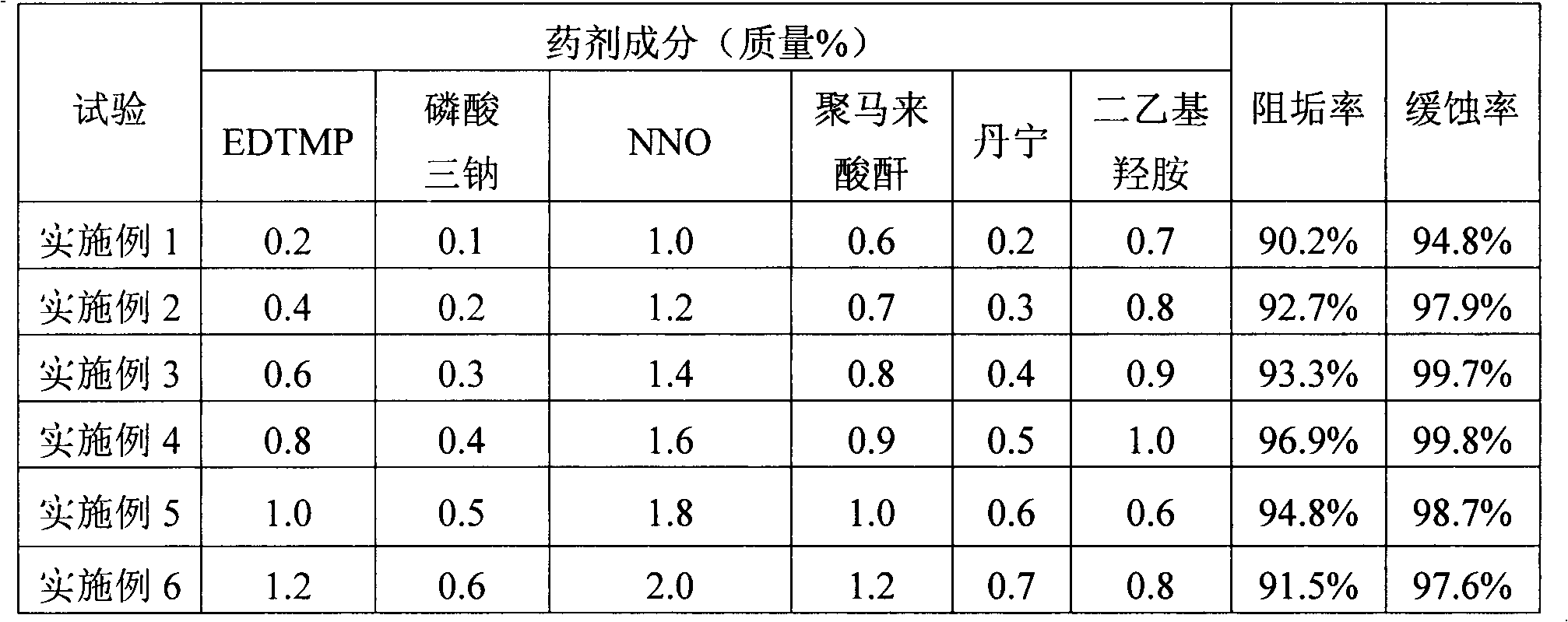
ActiveCN103183417ADoes not reduce corrosion inhibitionWill not reduce the effect of anti-scalingScale removal and water softeningInorganic phosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a medicament for treating composite water in a hot water boiler. The medicament comprises the following components by mass percent: 0.1-3% of inorganic phosphate, 0.1-2% of organic phosphoric acid and / or organic phosphate, 0.1-4% of component A, 0.1-3% of component B, 0.6-1.0% of organic amine deoxidizer, 0.1-2% of tannin and / or chitosan and the balance of water, wherein the mass percent of the components is 100%, the component A is one or more of an organic antisludging agent, an organic dispersant and an organic dispersible antisludging agent, and the component B is one or more of an organic carboxylic acid corrosion inhibitor, an organic carboxylate corrosion inhibitor and sodium methylene dinaphthalenesulfonate. The invention further discloses a preparation method and a use method of the medicament, the preparation process is clean, and the medicament is low in toxicity for body health and environment in the using process. The medicament is excellent in corrosion resistance and scale inhibition effects and simple and convenient to store and transport, and the corrosion and scale inhibition effects cannot be reduced after the medicament is stored and transported for a long term.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPEROR OF CLEANING HI TECH
Reagents for oligonucleotide cleavage and deprotection
InactiveUS6664388B2Convenient and ready-to-use formatContaminate the synthesized oligonucleotides can be minimizedSugar derivativesRecombinant DNA-technologyChemical synthesisAryl
The present invention provides a process for the removal of protecting groups, i.e. deprotection, from chemically synthesized oligonucleotides. In one embodiment, the invention provides reagents suitable for use in such a process, and kits incorporating such reagents in a convenient, ready-to-use format. By use of the process and reagents of the invention, side-reactions leading to certain impurities that contaminate the synthesized oligonucleotides can be minimized.Methods and reagents are provided for deprotection of an oligonucleotide by reacting a protected oligonucleotide with a deprotection reagent wherein the deprotection reagent comprises an active methylene compound and an amine reagent. The active methylene compound has the structure:where substituent EWG is an electron-withdrawing group and R is hydrogen, C1-C12 alkyl, C6-C20 aryl, heterocycle or an electron-withdrawing group.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
High-strength temporary blocking agent and preparation method thereof
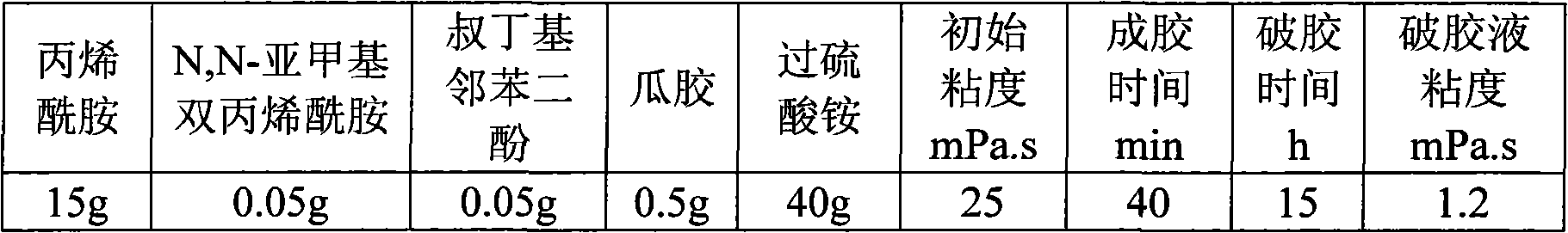
ActiveCN101906292AGood sealingMeet the needs of on-site constructionDrilling compositionHigh intensityMethylene bisacrylamide
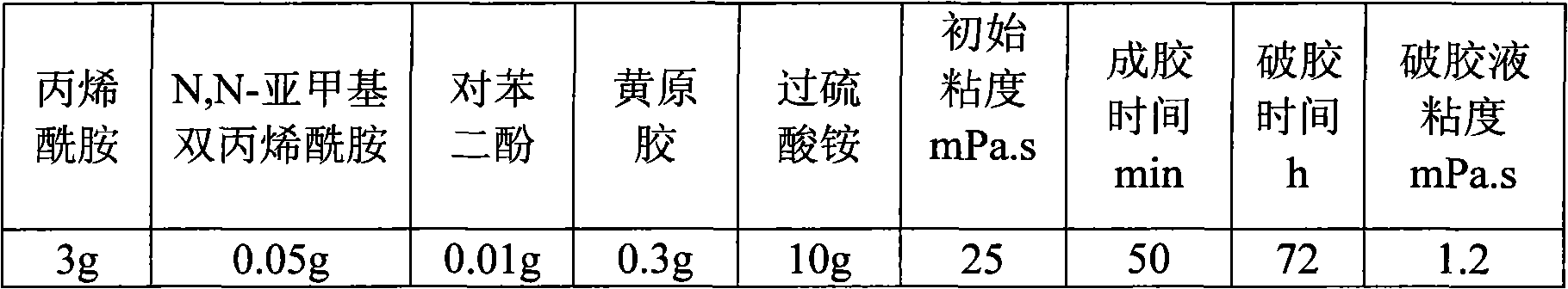
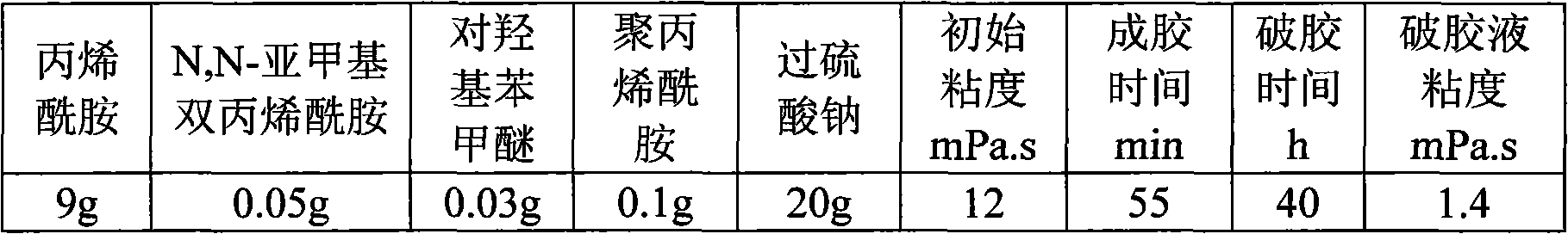
The invention relates to a high-strength temporary blocking agent and a preparation method thereof. The temporary blocking agent consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 2 to 20 percent of acrylamide, 0.02 to 0.1 percent of N,N-methylene-bisacrylamide, 0.001 to 0.1 percent of polymerization inhibitor, 0 to 1.0 percent of thickening agent, 2 to 50 percent of initiation gel breaker and the balance of water. The high-strength temporary blocking agent can form high-strength gel under intermediate / low-temperature reservoir conditions, can realize gel-formation and complete gel breaking in a given time, has no damage to the reservoir after the gel breaking and can be adapted to the temporary blocking operation of intermediate / low temperature oil-gas reservoirs.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
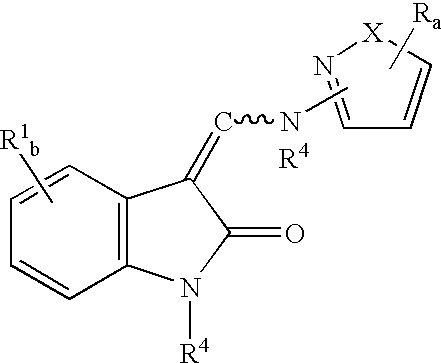
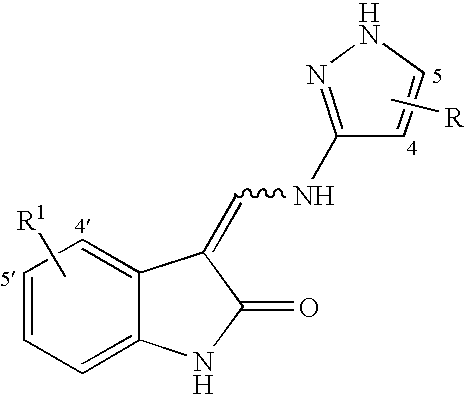
3-(heteroarylamino)methylene-1, 3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-ones as kinase inhibitors
The present invention relates to organic molecules capable of modulating tyrosine kinase signal transduction in order to regulate, modulate and / or inhibit abnormal cell proliferation.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
2,3-difluorophenyl derivative having negative dielectric anisotropy, liquid crystal composition, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6548126B1Good compatibilityIncrease resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryLiquid crystallineCrystallography
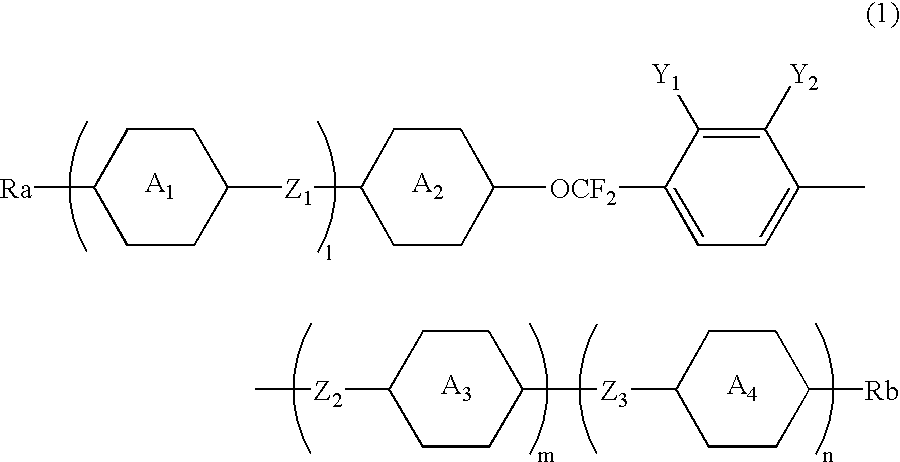
The invention is to provide liquid crystalline compounds having a negative and extremely large dielectric anisotropy value and a small optical anisotropy value at the same time; liquid crystal compositions comprising the compound; and liquid crystal display devices fabricated by using the liquid crystal composition; the liquid crystalline compounds have 2,3-dihalogenophenylene moiety and are expressed by formula (1)wherein Ra and Rb each independently represents a linear or branched alkyl having 1 to 10 carbon, any methylene in the alkyl may be replaced by -O-, -S-, -CH=CH-, or -C=C-, but -O- is not successive, and any hydrogen in the alkyl may be replaced by halogen; rings A1 to A4 each independently represents trans-1,4-cyclohexylene, cyclohexene-1,4-diyl, pyridine-1,4-diyl, pyrimidine-2,5-diyl, or 1,4-phenylene, wherein at least one hydrogen in these rings may be replaced by halogen, and any nonadjacent methylene in cyclohexane ring may be replaced by -O-; Y1 and Y2 each independently represents F or Cl; Z1, Z2 and Z3 each independently represents a single bond, -CH2CH2-, -(CH2)4-, -COO-, -OCO-, -CH2O-, -OCH2-, -CF2O-, or -OCF2-; and l, m and n each independently is 0, 1 or 2, and the sum of l+m+n is 3 and less.
Owner:CHISSO CORP
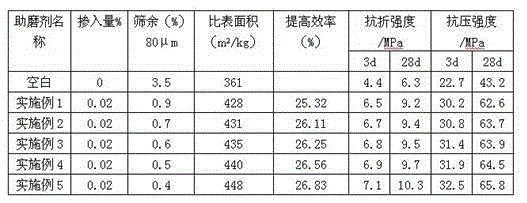
Silicate cement grinding aid and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a silicate cement grinding aid and a preparation method thereof. The silicate cement grinding aid is prepared from the following main raw materials by weight: 3-6 parts of sodium hexametaphosphate, 2-5 parts of aluminum sulfate, 5-8 parts of tetra sodium salt of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP.Na4), 4-6 parts of ethylene diamine tetra (methylene phosphonic acid) sodium, 38-45 parts of polymeric alkylol amine, 34-42 parts of triisopropanolamine, 8-12 parts of waste engine oil, 2-5 parts of sodium alpha-olefin sulfonate, 10-16 parts of sorbitol, 15-20 parts of diethylene glycol, 8-13 parts of polypropylene wax, 6-10 parts of oxidized polyethlene wax, 4-8 parts of lignite wax, 20-30 parts of odium thiosulfate, 12-18 parts of sodium thiosulfate and 15-20 parts of quicklime powder. The prepared silicate cement grinding aid has the advantages that the quality is stable, the effect is remarkable, the adding amount is small, the use is simple, and the adding is more convenient and reliable to control.
Owner:王金奎
Modified lignin and urea-formaldehyde resin synthesized from same and preparation methods of modified lignin and urea-formaldehyde resin
InactiveCN102241826AHigh bonding strengthReduce formaldehyde emissionAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesSynthesis methodsEther
The invention discloses a modified lignin and a urea-formaldehyde resin synthesized from same and preparation methods of the modified lignin and the urea-formaldehyde resin, belonging to the field of bonding agents used in wood processing. A technological synthetic route with weak base-weak acid-weak base is adopted, the molar ratio of formaldehyde to urea is controlled during an addition stage to generate a reasonable structure, the modified lignin as well as residual hydroxymethyl and free formaldehyde are added at the later stage of reaction in order to accomplish reaction, thus the content of methylene ether link (-CH2-O-CH2-) and the content of hydroxymethyl in the resin are reduced to a certain extent, the formaldehyde emission of the resin is lowered, and simultaneously, higher bonding strength and water resistance are ensured. The urea-formaldehyde resin in the invention is simple and brief in process and low in cost, the formaldehyde emission of the plate prepared by adoptingthe bonding agent reaches the E0-level standard and the plate can maintain high bonding strength after being cooked in hot water. The modified lignin is simple in synthesis method and low in cost andis especially suitable for the modification of the urea-formaldehyde resin with low molar ratio.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
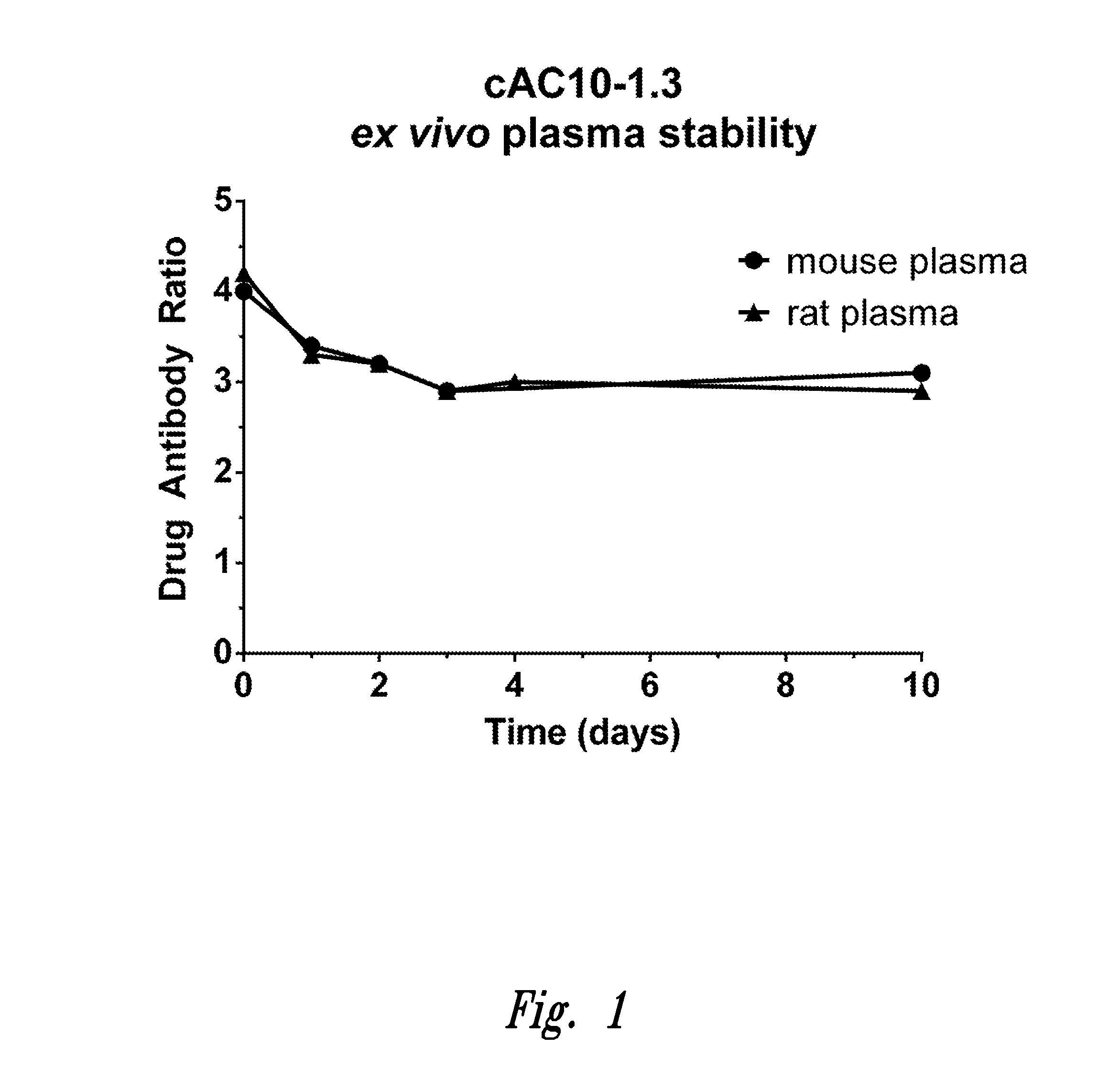
Methylene carbamate linkers for use with targeted-drug conjugates
ActiveUS20160303254A1Pharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImmunological disordersCarbamateTargeting ligands
The present invention provides Lig-and-Drug Conjugates and Drug-Linker Compounds comprising a methylene carbamate unit. The invention provides inter alia, Ligand-Drug Conjugates, wherein the Ligand-Drug Conjugate is comprised of a Self-immolative Assembly Unit having a methylene carbamate unit for conjugation of a drug to a targeting ligand, methods of preparing and using them, and intermediates thereof. The Ligand-Drug Conjugates of the present invention are stable in circulation, yet capable of inflicting cell death once free drug is released from a Conjugate in the vicinity or within tumor cells.
Owner:SEAGEN INC
Rubber composition for a colored tire
InactiveUS6344506B2Assess the hardness of the compositionsReduce clearanceOrganic chemistrySpecial tyresElastomerPolymer science
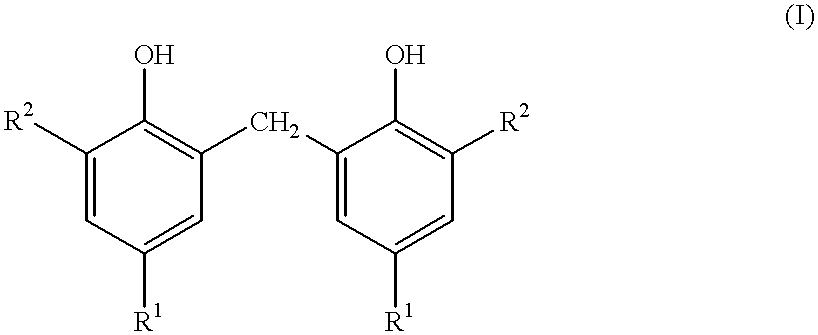
The invention concerns a white, light-colored tire rubber composition, devoid of carbon black, comprising at least a diene elastomer, a reinforcing white or colored filler, and an anti-photo-oxidizing system, wherein said protective system comprises (A) a 2,2'-methylene-bis-[4-alkyl (C1-C10)-6-alkyl(C1-C12)phenol]; (B) a dialkylthiodipropionate, the alkyl radicals thereof, which may be identical or different, are (C1-C20), radicals; (C) a 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl) benzotriazole; and (D) a "HALS" amine derived from 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Cyclic compounds
There is provided a CRF receptor antagonist comprising a compound of the formula (I):A-W—Ar (I)wherein, A is a group represented by the formula (A1) or (A2): (wherein, ring Aa is a 5- or 6-membered ring which may be further substituted; ring Ab is a 5- or 6-membered ring which may be further substituted; ring Ac is a 5- or 6-membered ring which may be substituted; R1 is optionally substituted alkyl, substituted amino, substituted hydroxy, etc.; X is carbonyl, —O—, —S—, etc.; Y1, Y2 and Q are independently optionally substituted carbon or nitrogen; is a single or double bond); W is a bond, optionally substituted methylene, optionally substituted imino, —O—, —S—, etc.; Ar is optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl; or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
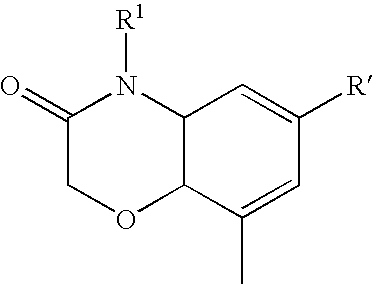
Morpholine type cinnamide compound
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
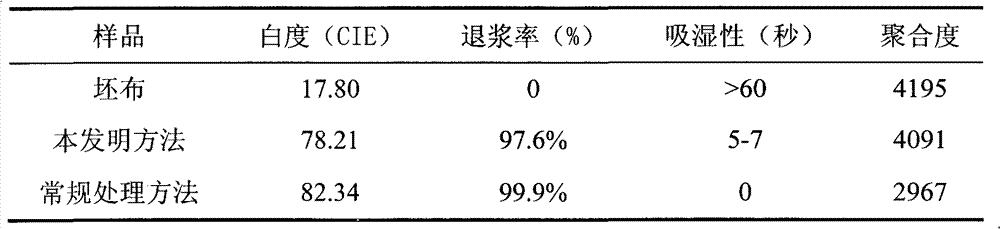
Method for pretreating cotton fabric at low temperature by using biological enzymes and hydrogen peroxide through one bath process
ActiveCN103046383AReduce consumptionSave energyBiochemical fibre treatmentBleaching apparatusFiberMoisture absorption
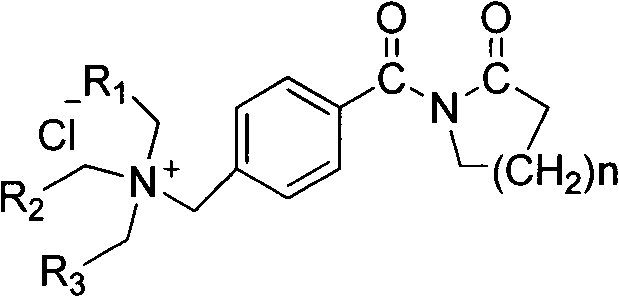
The invention relates to a method for pretreating a cotton fabric at low temperature by using biological enzymes and hydrogen peroxide through one bath process. The method adopts N-[4-(trialkyl ammonium methylene)benzoyl] lactam chloride activator, hydrogen peroxide, a desizing enzyme, a scouring enzyme and supporting aids and has the characteristics of low temperature of 25-60 DEG C in the whole course, nearly neutral reaction condition (with pH value being 6.5-7.5) and low fiber damage. The cotton fabric treated by the adopting the method has no residual sizing agent and cottonseed hull, is equivalent to the cotton fabric treated by adopting the conventional method in whiteness and moisture absorption and is superior to the cotton fabric treated by adopting the conventional method in strength and handfeel. The process of the method is shortened greatly, the energy is saved, and the sewage treatment burden is lightened.
Owner:QINGDAO FRONTIERCHEM
Phenanthrene and imidazole-coumarin double-fluorescent group ratio fluorescent molecular probe for iron ion detection and synthesis and use methods thereof
InactiveCN105255481AHigh fluorescence intensityExcellent fluorescence performanceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceKetonePhenyl group
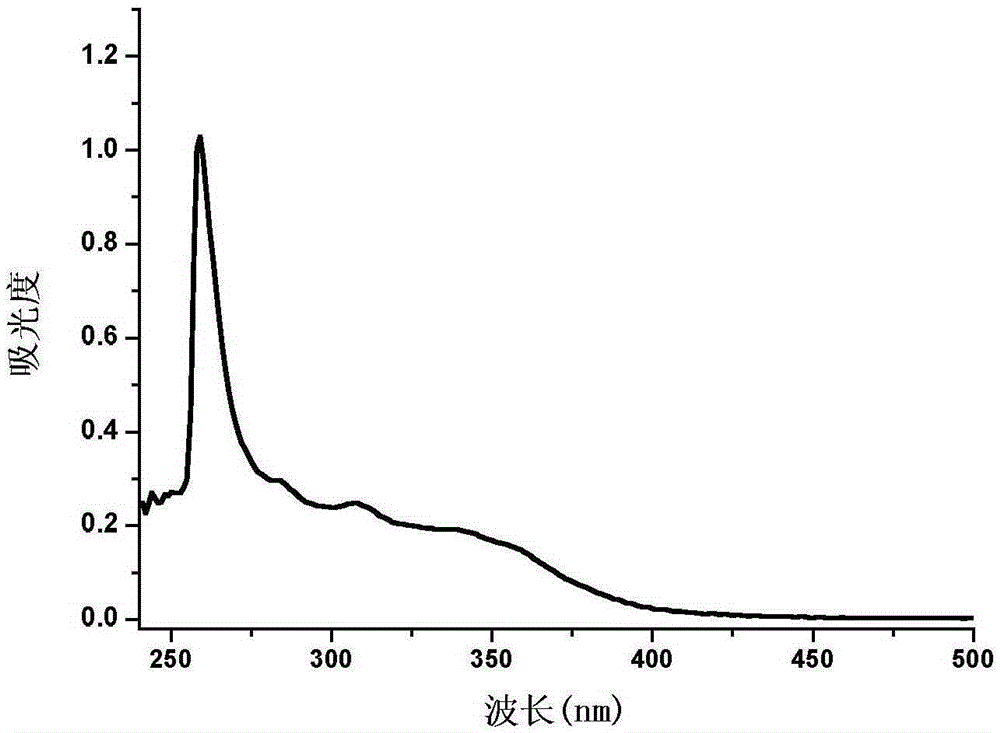
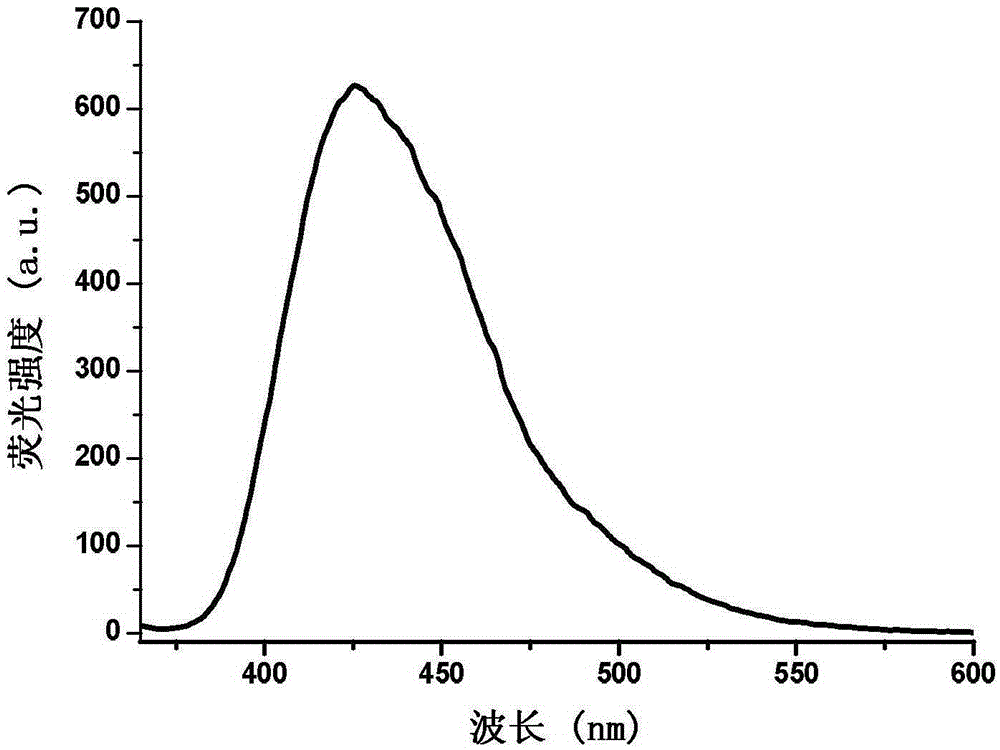
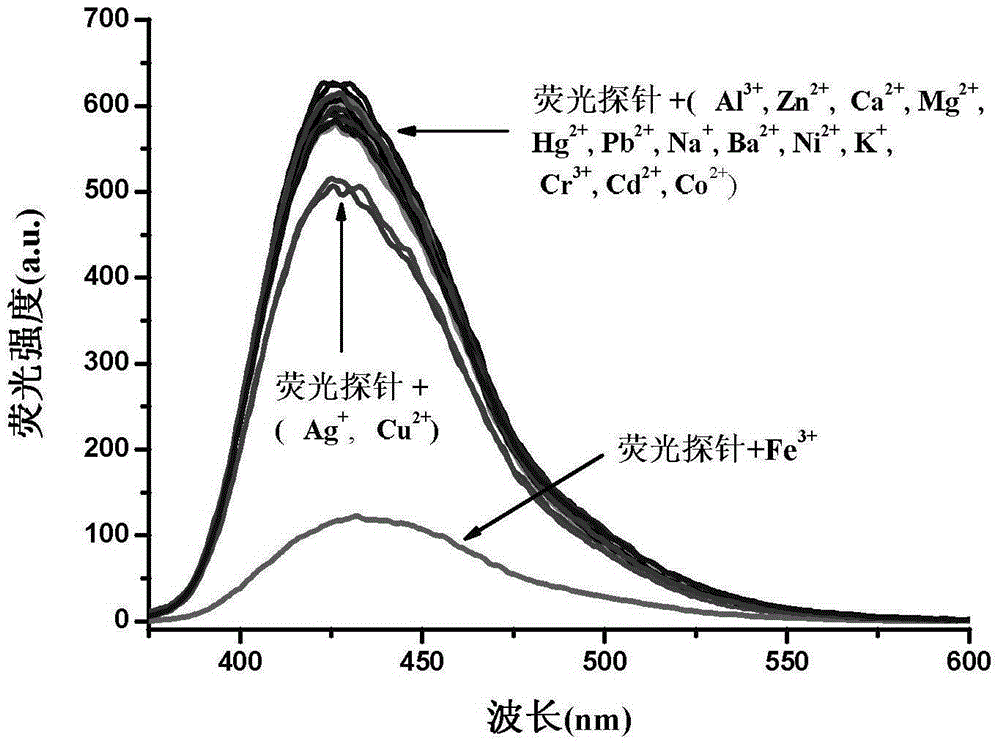
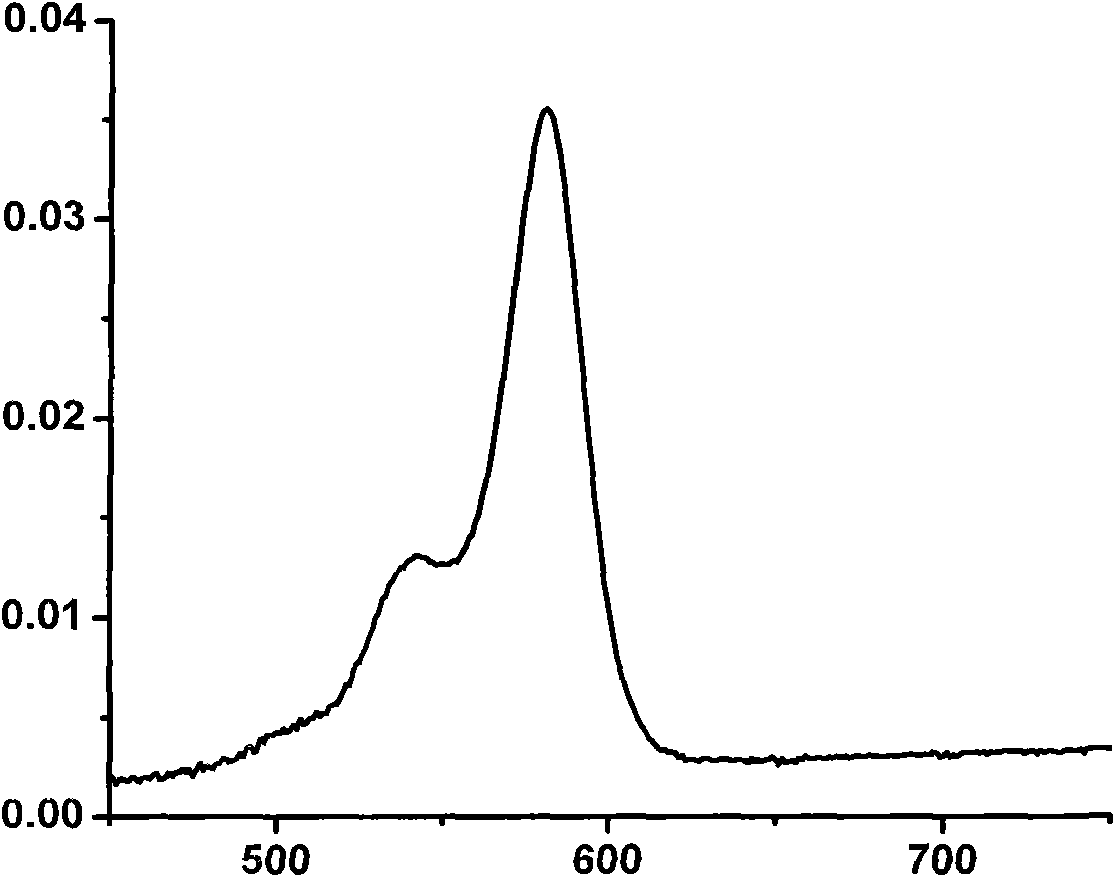
The invention provides a phenanthrene and imidazole-coumarin double-fluorescent group ratio fluorescent molecular probe for iron ion detection and synthesis and use methods thereof, relates to fluorescent molecular probes and synthesis and application thereof and aims to solve the problem that an existing Fe<3+> fluorescent probe is prone to being interfered by pH, concentration and other metal ions. The fluorescent molecular probe is 4-methyl-7-hydroxide radical-8-[2-(1- phenyl group-1H-phenanthrene and [9, 10-d] imidazole-2-)benzene ammonia methylene]-2H-pyran-2-ketone. The phenanthrene and imidazole-coumarin double-fluorescent group ratio fluorescent molecular probe is formed by conducting condensation on 1-N-phenyl group-2-(2-aminophenyl)-1H-phenanthrene and [9, 10-d] imidazole and 4-methyl-7-hydroxide radical-8- formyl group coumarin, and the yield is 75-85%. The fluorescent molecular probe is dissolved in mixed liquid of N, N- dimethylformamide and an HEPES buffering solution, existence of iron ions is judged through the absorbance value or fluorescence intensity change before and after adding of test samples, and the fluorescent molecular probe can be used for detection of Fe<3+> pollution in water.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Strong-fluorescence boron dipyrromethene dye containing carbazole structure
InactiveCN101565554AChange light propertiesHigh fluorescence quantum yieldAzo dyesLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldNitrogen gas
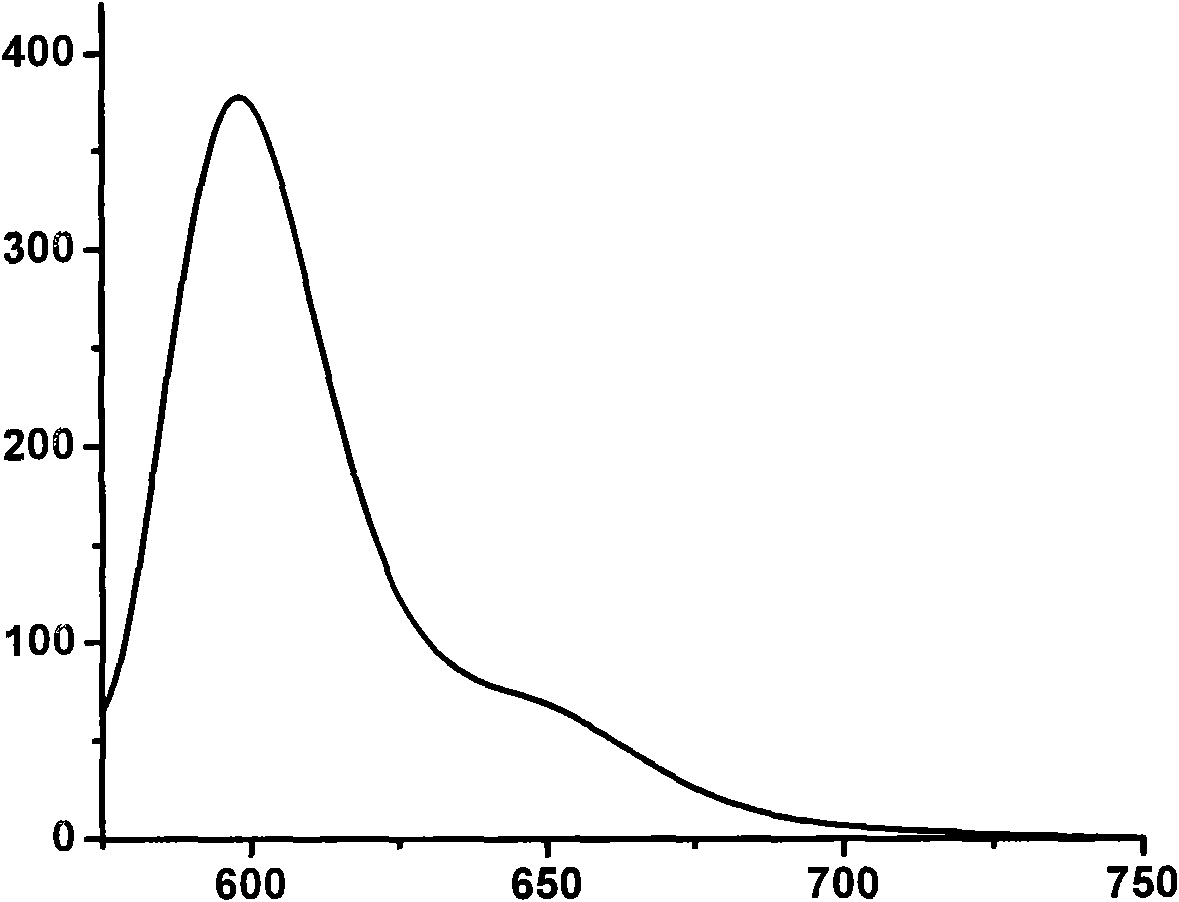
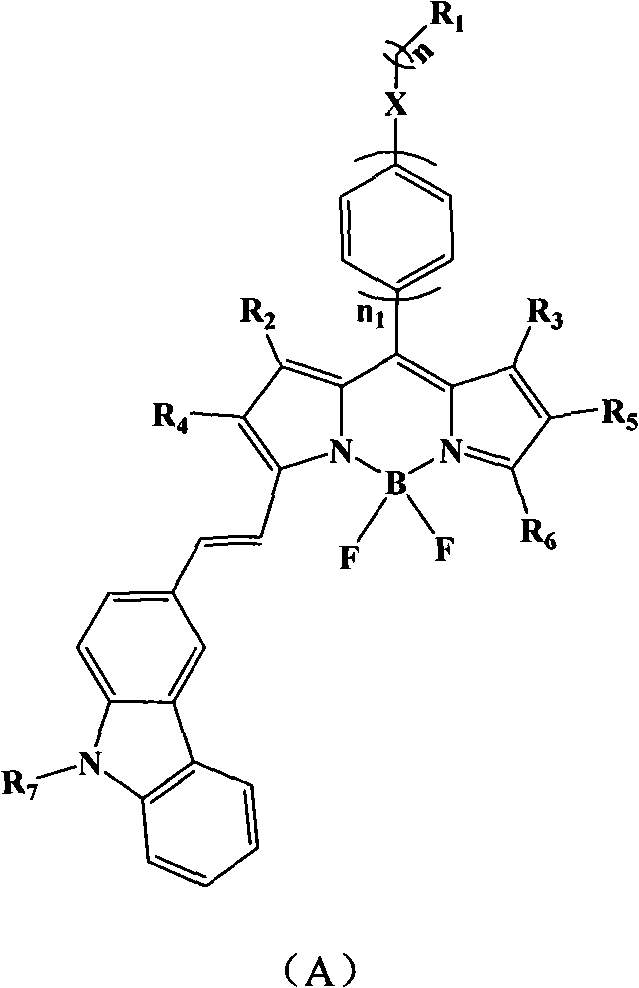
The invention belongs to strong-fluorescence boron dipyrromethene dyes containing a carbazole structure in the technical field of organic chemical industry and fine chemical industry. Because a method for preparing the strong-fluorescence boron dipyrromethene dye containing the carbazole structure and derivatives thereof adopts boron dipyrromethene and carbazole aldehyde with substituent as raw materials, the molar ratio of the boron dipyrromethene to the carbazole aldehyde is 1:2-5, piperidine is a catalyst, a 4-angstrom molecular sieve is a dehydrating agent, and the molar ratio of the borondipyrromethene to the catalyst is 1:0.01-0.20; in an organic solvent, at the temperature of between 100 and 150 DEG C and under the protection of argon or nitrogen, the mixture reacts for 8 to 50 hours by stirring, the carbazole aldehyde and the active methylene of the boron dipyrromethene are dehydrated to generate the boron dipyrromethene derivatives; and after the carbazole structure with different substituents is introduced into the boron dipyrromethene, the optical property of the boron dipyrromethene compound is changed, the red shift of the absorption spectrum thereof is 80 nanometers, the red shift of the emission spectrum is 90 nanometers, higher fluorescence quantum yield is kept at 0.67, the laser efficiency reaches more than 30 percent, and the strong-fluorescence boron dipyrromethene derivatives containing the carbazole structure are obtained.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Heterocyclic compounds having tachykinin receptor antagonist activity their preparation and their use
Compounds of the formula and quaternary ammonium ions thereof, wherein R1 and R2 are the same or different and are carbocyclic aryl or aromatic heterocyclic; A is methylene, carbonyl or sulfonyl; B is a single bond, C1-C4 alkylene or C2-C4, alkenylene; D is oxygen; E is C2 alkylene; G is C1-C4 alkylene or C2-C4 alkenylene; and L is -C(R4)(R5), wherein R4 and R5 together with the carbon atom to which they are attached represent a C5-C10 cycloalkyl or a C5-C10 heterocyclic. Especially preferred are compounds wherein L represents wherein J is a C1-C6 alkylene; Ar is a ring carbocyclic or aromatic heterocyclic and S*->O is a sulfoxide in which the sulfur atom is in the 5-configuration. The compounds have tachykinin receptor antagonist activity and exhibit an activity against both the NK1 and NK2 receptors.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
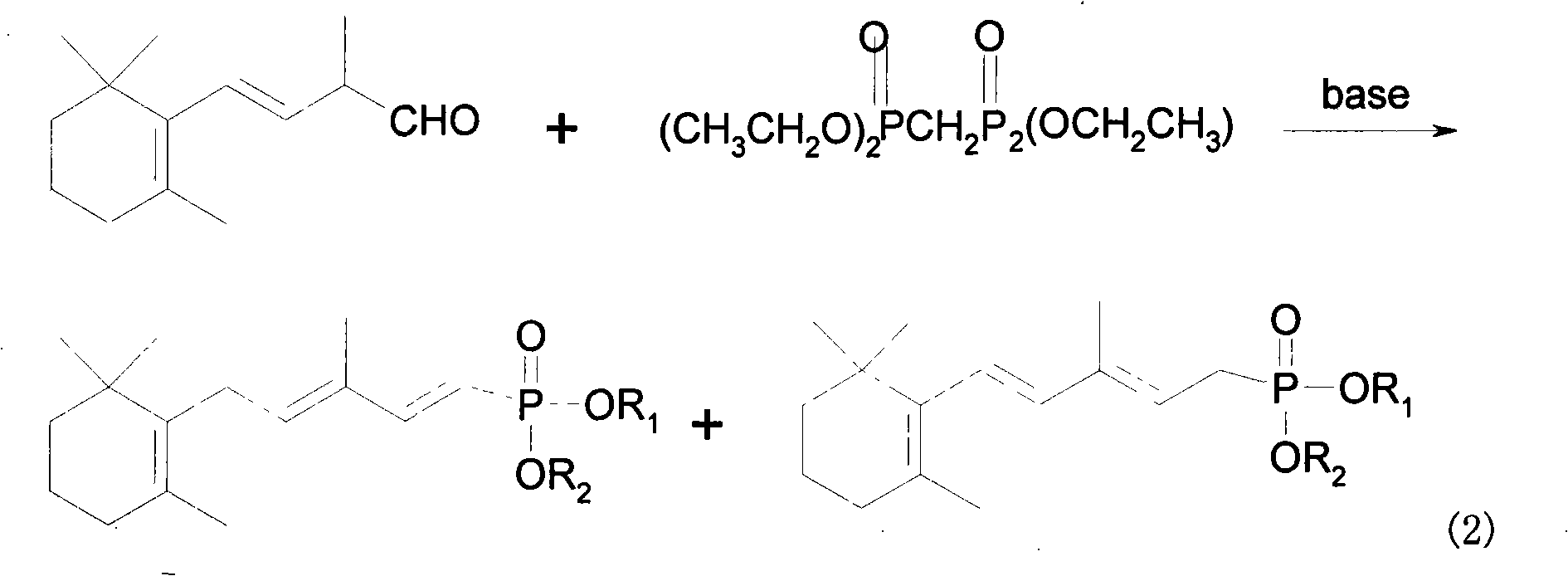
Method for preparing 3-methyl-5-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-base)-2, 4-pentadiene-dialkyl phosphoric ester
InactiveCN101318975AReduce energy consumption and difficulty of production operationsConducive to industrial productionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsTolueneCyclohexenes
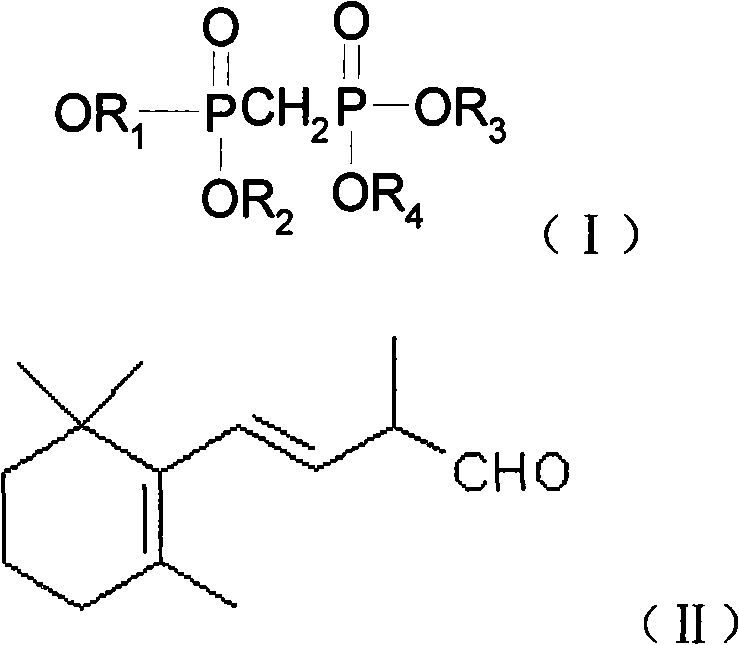
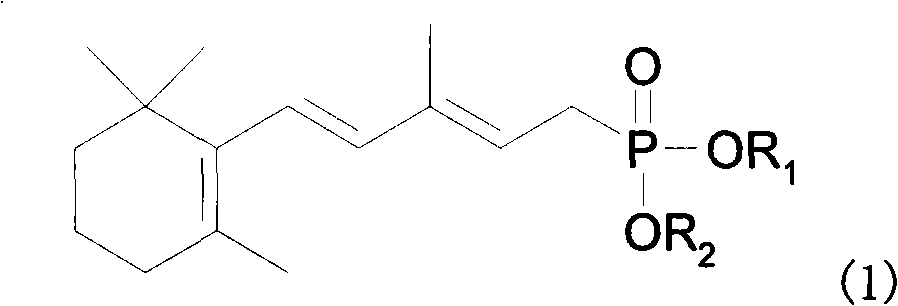
The invention provides a method for preparing 1, 3-methyl-5-(2, 6, 6-trimethyl-1- cyclohexene-1-yl)-2, 4-pentadiene methyl phosphonate. In the method, a benzophenone compound preventing transposition is added in the process of generating the 1, 3-methyl-5-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-yl)-2,4-pentadiene methyl phosphonate by the reaction of methylene diphosphate four alkyl and C14 aldehyde in a mixed solvent of methylbenzene and tetrahydrofuran, thereby inhibiting the generation of a target product isomer in order that the content of the target product in a final product reaches up to 97 percent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WISDOM BIO TECH
Rubber composition and tire with component of diene-based elastomer composition with corncob granule dispersion
InactiveUS20060021688A1Format be limitIncrease effective frictional surfaceWood treatment detailsSpecial tyresThin membraneCarbon black
This invention relates to a rubber composition and tire having at least one component of a rubber composition comprised of at least one diene-based elastomer, to the exclusion of butyl type elastomers, which contains an internal dispersion of corncob granules. Such tire component may be, for example, a tire tread and / or cord reinforced rubber ply and / or belt. A tire tread intended for winter driving, although not necessarily limited to winter driving, is provided of a rubber composition containing at least one diene-based sulfur vulcanizable elastomer having a Tg below −30° C. and an internal dispersion therein of corncob granules. The running surface of the tire tread is configured with a combination of micro-protrusions of corncob granules from said corncob granule internal dispersion and micro-cavities therein created by a release of a portion of the protruded corncob granules during the abrading, or wearing, of the tire tread running surface as the tire is being run. At least a portion of said corncob granular micro-protrusions may be covered by a relatively thin membrane of tread rubber. The corncob granules may be colored with a suitable colorant of a non-black color to contrast with the tire tread color to better visualize their presence on the tread running surface. The tire tread rubber composition may optionally also contain a starch / plasticizer composite, sorbitan ester, methylene donor compound, methylene acceptor compound or combination of methylene donor and acceptor compounds, and may be reinforced with carbon black, synthetic amorphous silica aggregates or their combination.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Fuel compositions
Middle distillate fuel composition is provided containing (a) a middle distillate base fuel, in particular a diesel base fuel, and (b) a Fischer-Tropsch derived paraffinic base oil component with a viscosity of at least 8 mm2 / s at 100° C. In component (b), the ratio of the percentage of epsilon methylene carbon atoms to the percentage of isopropyl carbon atoms is suitably 8.2 or below. Its pour point may be −30° C. or lower. Also disclosed is the use of a Fischer-Tropsch derived paraffinic heavy base oil in a middle distillate fuel composition, for the purpose of improving the cold flow properties of the composition and / or for reducing the concentration of a cold flow or flow improver additive in the composition.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Aminoacid derivatives containing a disulfanyl group in the form of mixed disulfanyl and aminopeptidase N inhibitors
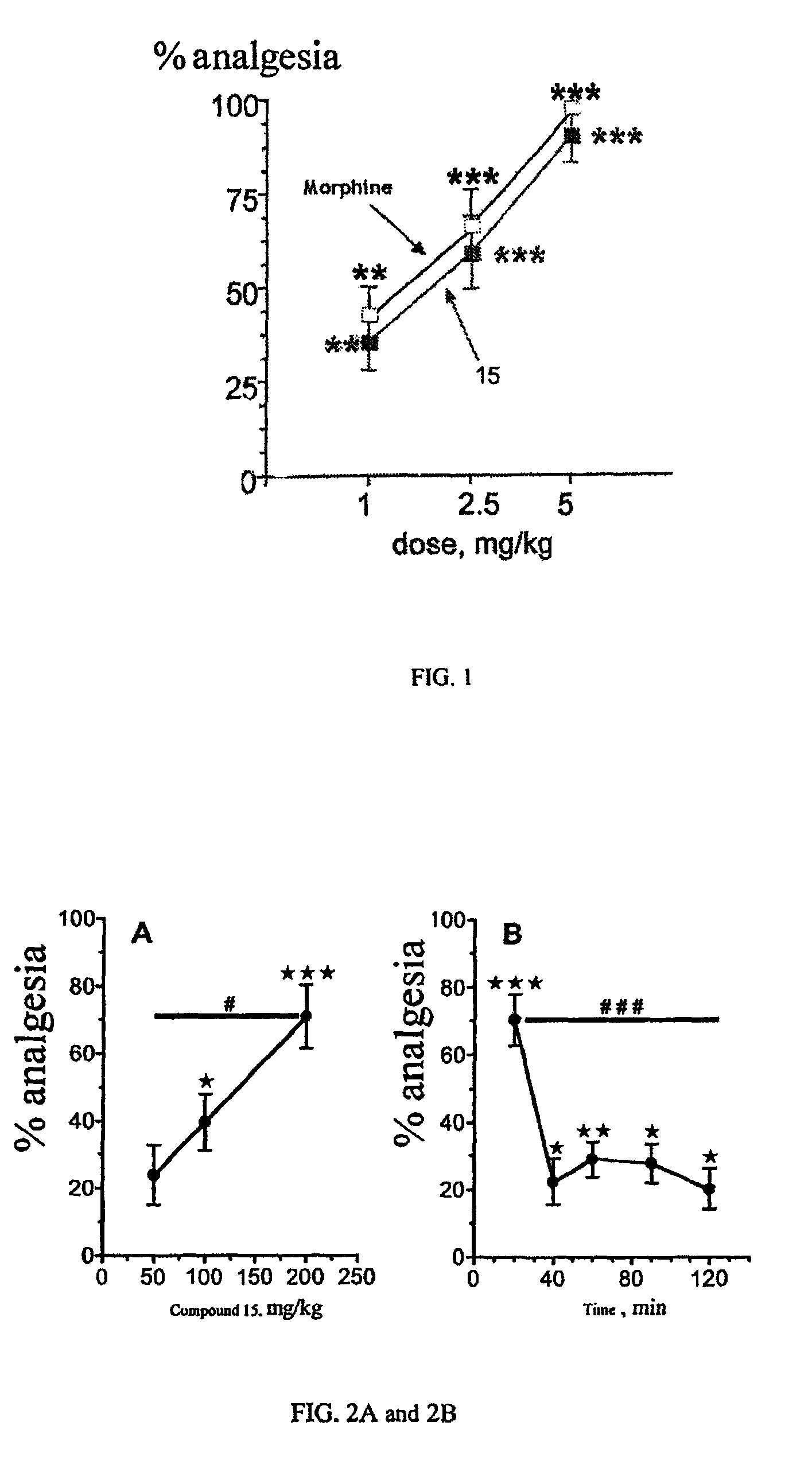
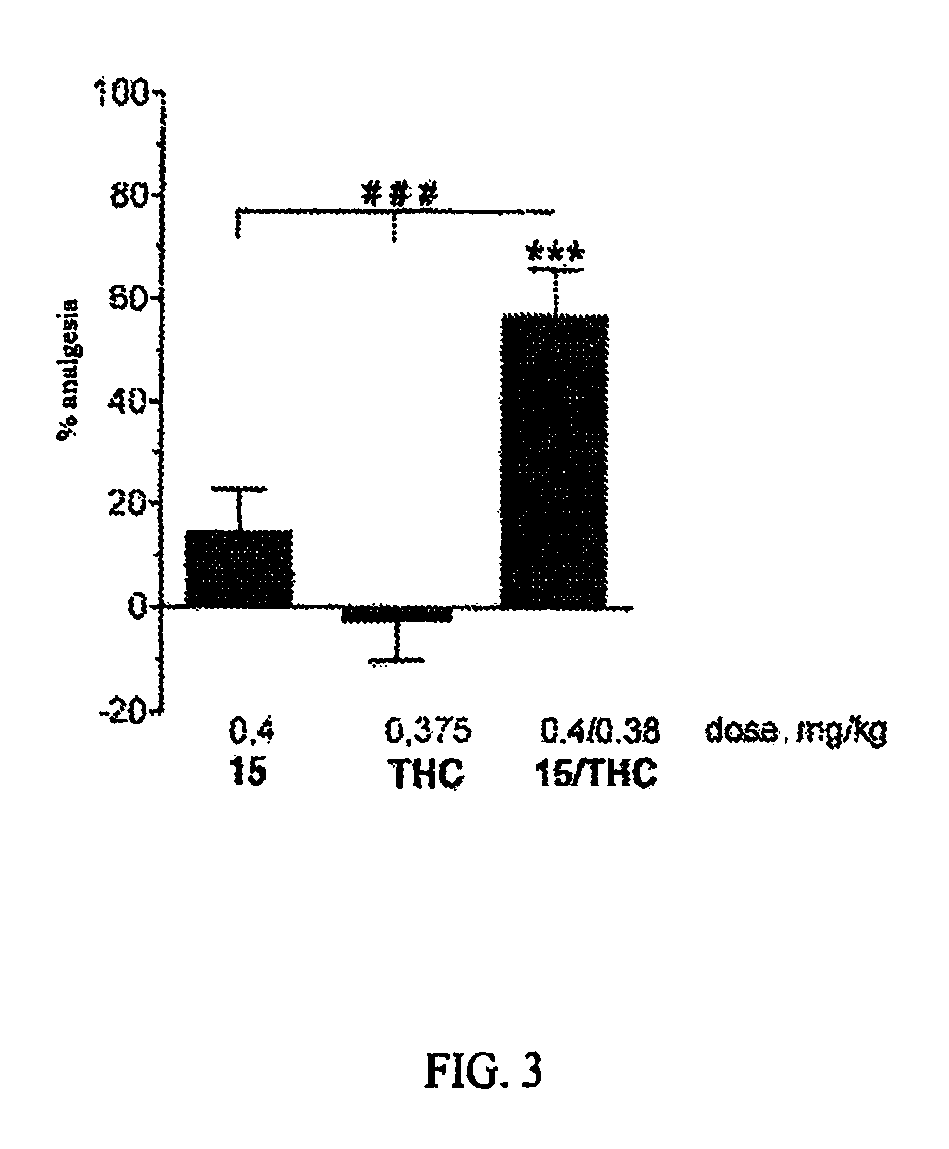
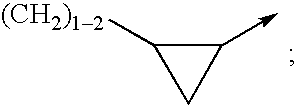
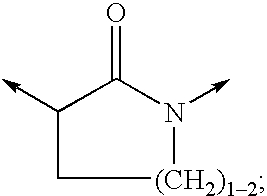
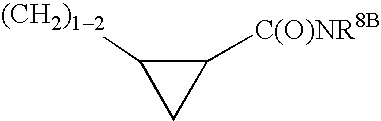
The invention relates to novel compounds of formula (I): H2N—CH(R1)—CH2—S—S—CH2—CH(R2)—CONH—R5, wherein R1 is a hydrocarbon chain, phenyl or benzyl radical, methylene radical substituted by a 5 or 6 atom heterocycle; R2 is a phenyl or benzyl radical, a 5 or 6 atom aromatic heterocycle, methylene group substituted by a 5 or 6 atom heterocycle; R5 is a CH(R3)—COOR4 radical, wherein R3 is hydrogen, an OH or OR group, a saturated hydrocarbon group, a phenyl or benzyl radical and OR4 is hydrophile ester, or 5 or 6 membered heterocycle comprising several heteroatoms selected from a group consisting of nitrogen, sulphur and oxygen, with at least two nitrogene atoms, wherein said heterocycle is substitutable by an alkyl C1-C6, phenyl or benzyl radical. The use of the inventive compounds in the form of drugs, a pharmaceutical composition comprising said compounds, a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, the use in conjunction of at least one type of cannabinoid derivative for potentiating the analgesic and antidepressant effect of the novel compounds of formula (I) and / or morphine or the derivatives thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:KOS THERAPEUTICS INC
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Disclosed herein are compounds of formula Ar1—X—W—Ar2 wherein Ar1 and Ar2 represent aryl groups characterized generally as aromatic heterocycles (e.g. imidazolyl or tetrazolyl) or carbocycles (e.g. phenyl or naphthalenyl); the aryl groups are optionally substituted or fused with other heterocycles or carbocycles; the aryl groups can bear substituents such as alkyl, halo or O-alkyl. X is a heteroatom, a valence bond or an optionally substituted divalent methylene, and W represents a spacer; typical spacers include divalent alkylene or alkylene-amido, -amido or -oxy radicals, which may optionally be substituted (e.g. hydroxyl or oxo). A typical compound is a derivative of 2-(N-napthalenyltetrazolylthio)-N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide. The compounds have inhibitory activity against Wild Type and single or double mutant strains of HIV.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Polycarbonate resin composition pellets and process for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20140364546A1Reduced in yellow tingeHigh light transmittanceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElectric lightingMethylene DichlorideOptical transmittance
Provided is a polycarbonate resin composition pellet, which has a light transmittance at a wavelength of 380 nm of 97.0% or more when the light transmittance is measured by using a methylene chloride solution having a concentration of 12 g / dL, the solution being charged into a quartz glass cell having an optical path length of 5 cm, and which has a viscosity-average molecular weight (Mv) of from 11,000 to 22,000.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
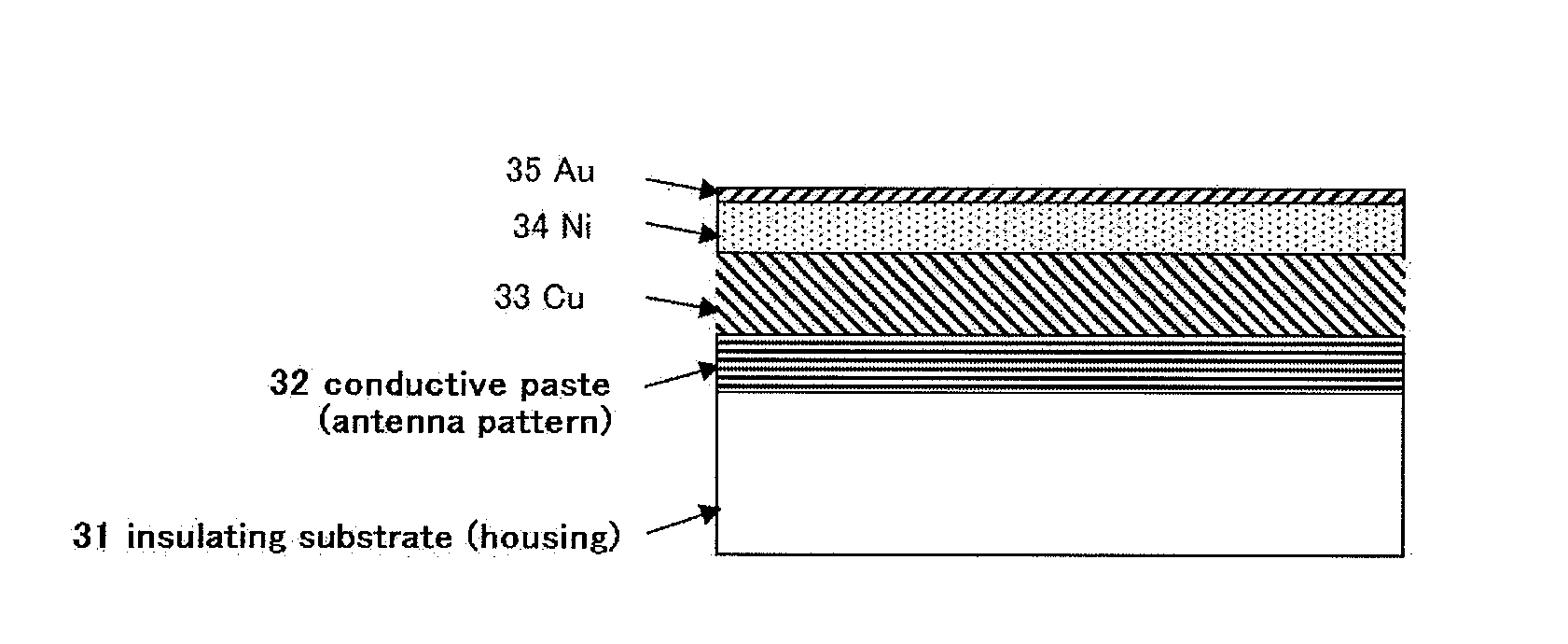
Low-temperature curable conductive paste for plating and electric wiring using the same
InactiveUS20100101842A1Improve conductivityLow heat resistanceConductive materialRadiating elements structural formsConductive pasteVitrification
A conductive paste containing a conductive powder (A), a vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate resin (B), a polyester resin and / or polyurethane resin (C), a blocked isocyanate (D) blocked with an active methylene compound, and an organic solvent (E), wherein the resin (C) has a glass transition temperature of −50° C. to 20° C., a sum of amounts of the resin (C) is 50 to 400 parts by weight relative to 100 parts by weight of the resin (B), and a sum of amounts of the resin (B), the resin (C) component, and the blocked isocyanate (D) is 10 to 60 parts by weight relative to 100 parts by weight of the conductive powder (A). An electric wiring in which this conductive paste is formed on an insulating substrate.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD +1
Volume hologram recording photosensitive composition and its use
InactiveUS20050185232A1Excellent interference fringeLight weightRecord information storageRecord carrier materialsCarbanionCompound (substance)
Disclosed is a photosensitive composition for volume hologram recording which shows excellent interference fringe record and a volume hologram recording medium having lighter weight and excellent storage stability. The invention is directed to a volume hologram recording photosensitive composition comprising: (a) a compound having at least one active methylene group in one molecule or a compound having at least two active methine groups in one molecule; (b) a compound containing in one molecule two or more groups which are nucleophilicly added by a carbanion generating from an active methylene group or an active methine group; (c) a Michael-reaction catalyst; (d) a photopolymerizable compound; and (e) a photopolymerization initiator composition.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT CO LTD
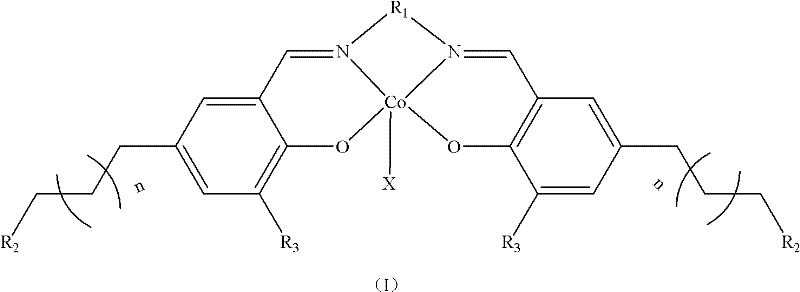
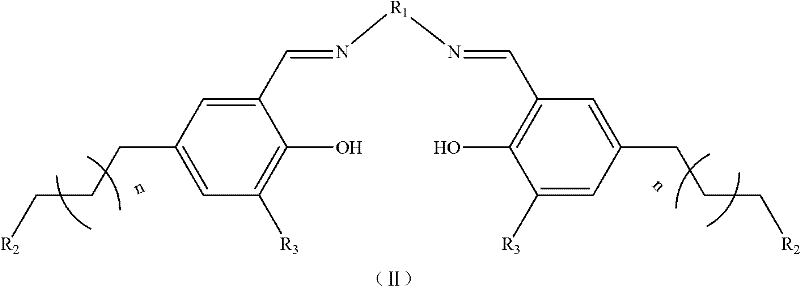
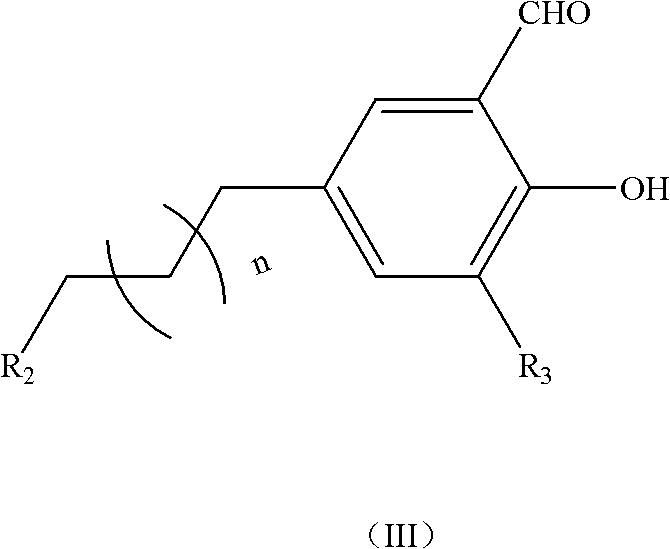
Method for preparing Salen-metal complex
InactiveCN102212085ALow costHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCobalt organic compoundsSodium methoxideFiltration
The invention provides a method for preparing a Salen-metal complex. The method comprises the following steps of: under the argon atmosphere, adding ligands(II), sodium methoxide, absolute methanol soluble ligands(II) and sodium methoxide into a reactor in sequence; stirring the mixture for 2 minutes, and adding 1mol / L cobalt acetate anhydrous / methanol solution dropwise, wherein the molar ratio of the ligands(II) to sodium methoxide to cobalt acetate is 1:1:1; and making the mixture reacted at the room temperature for 24 hours, adding anionic salt which has the same molar weight as the cobalt acetate, stirring the mixture for three days in the air, stopping the reaction, concentrating the mixture, performing dissolution and filtration by adding methylene chloride, drying the filtrate by anhydrous sodium sulfate overnight, filtering the mixture, concentrating under reduced pressure, and drying the mixture under the vacuum condition to obtain the Salen-metal complex. The Salen-metal complex prepared by the method has the advantages of simple method, low cost and high catalytic efficiency.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
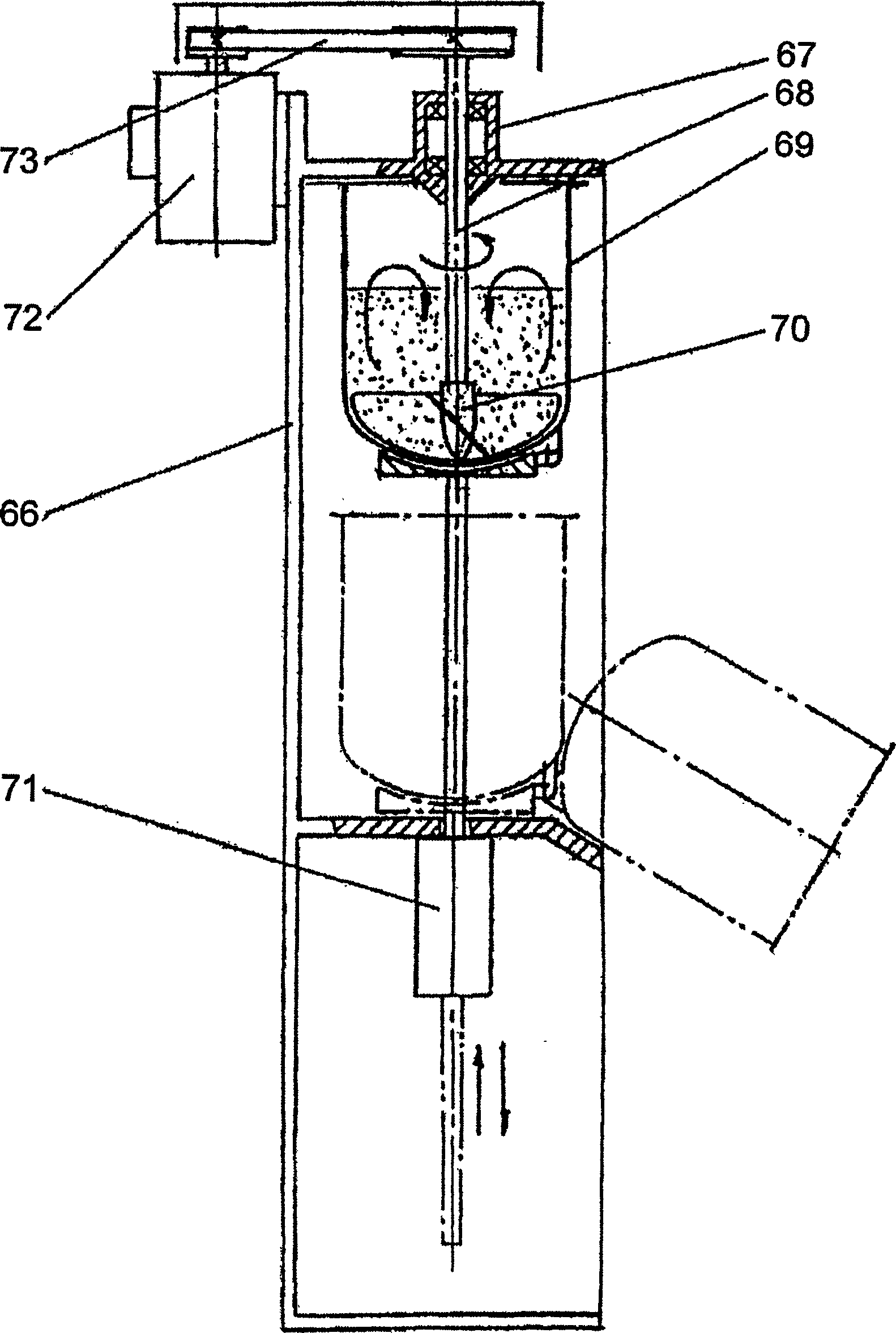
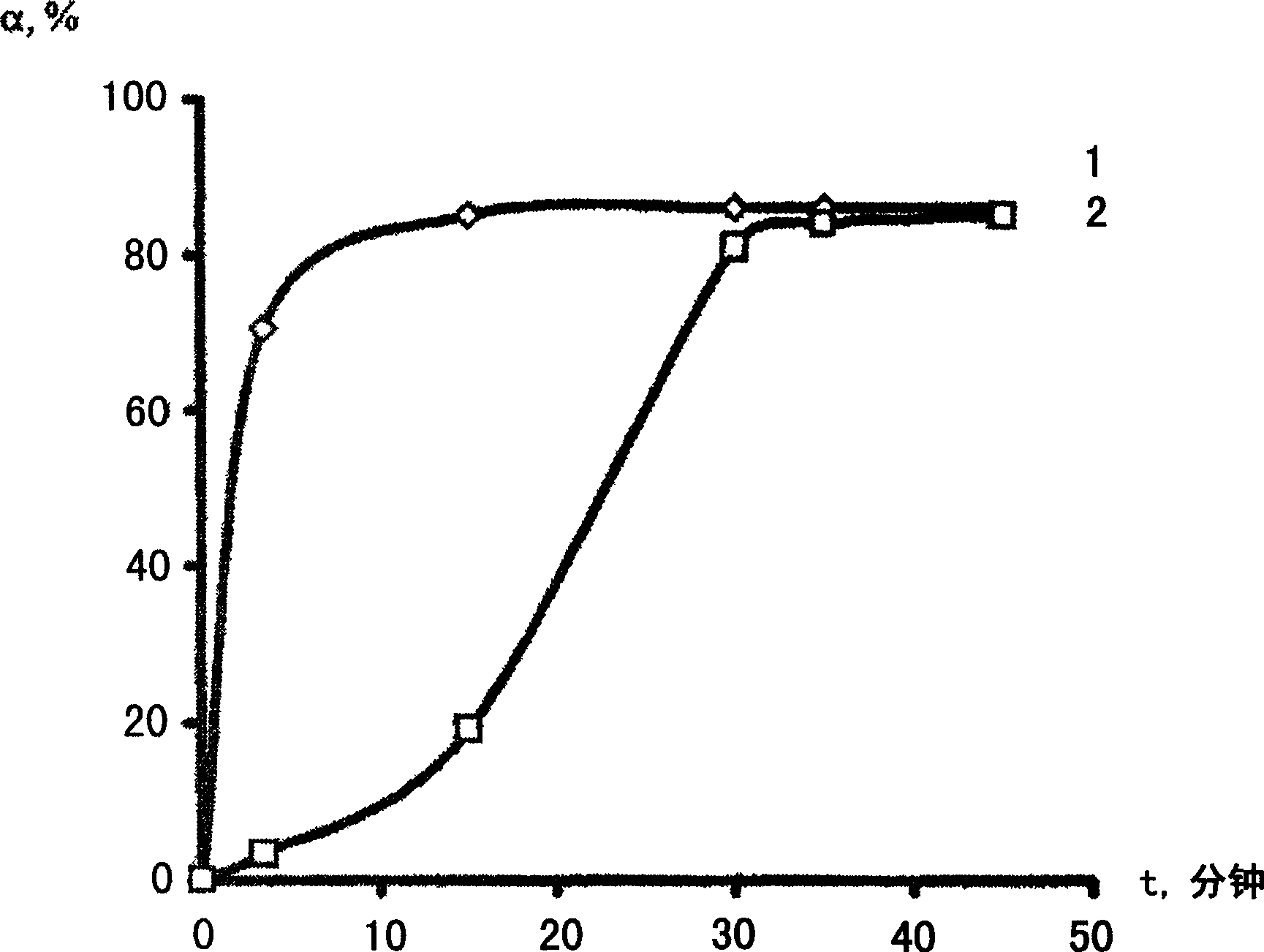
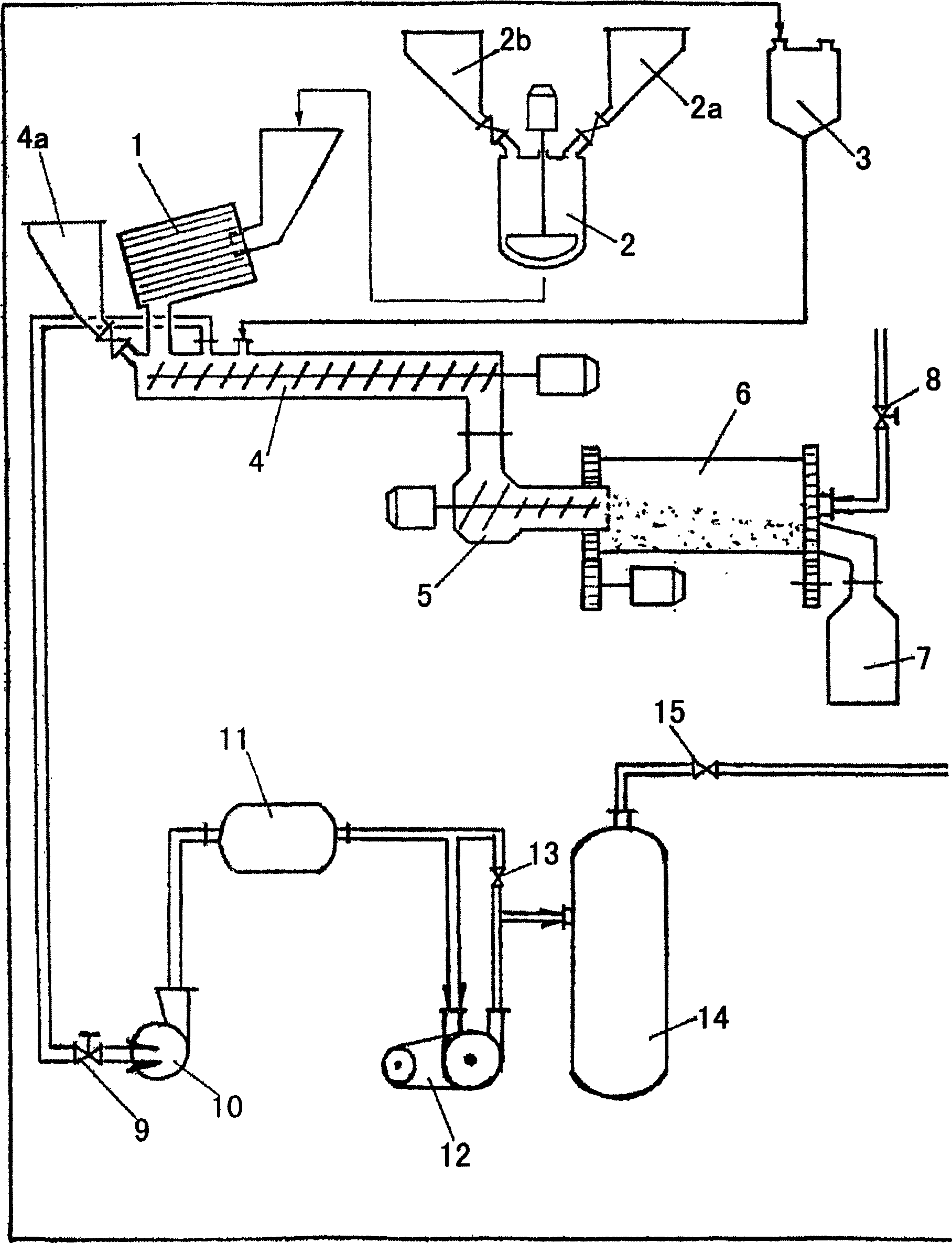
Method for producing granulated sorbents and installation for carrying out the method
The invention relates to a method for producing granulated sorbents, and to an installation for carrying out the method. The aim of the invention is to obtain the chloride form of the double hydroxide of aluminium and lithium as LiCL2AI / OH)3 nH2O (DHAL-CL) in a waste-free solid phase of aluminium hydroxide and lithium salts in a mixer, with subsequent continuous activation of crystalline DHAL-CI in a centrifugal mill activator in order to obtain a defectuous material structure. The product obtained is mixed with chlorinated polyvinyl chloride as a binding agent and with liquid methylene chloride. The granulation is carried out by extruding the paste produced and refining the same in the granulator. The methylene chloride produced is collected by an organic liquid absorbent having a high boiling point. The methylene chloride steam is guided out of the material flow in the carrier gas flow in the manner of an ideal displacement in the counter-current of the contact phases. The methylene chloride recuperation is carried out in two steps according to the thermal method, during the heating of the absorbent used. The inventive method is characterised by essentially reduced environmental impact in relation to prior art, due to the closed material circuits used. The granulated sorbent is especially suitable for the selective extraction of lithium from chloride salt lye of any mineralization, with an extraction degree of 95 %.
Owner:青海盐湖蓝科锂业股份有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com