Patents
Literature
22545results about How to "Low toxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and compositions useful for administration of chemotherapeutic agents
InactiveUS6096331AReduce morbidityLow toxicityPowder deliveryEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsActive agentIn vivo
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of a pharmaceutically active agent, wherein the agent is associated with a polymeric biocompatible material.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using a perfluoropolyether surfactant
The invention relates to an aqueous emulsion polymerization of fluorinated monomers using perfluoropolyethers of the following formula (I) or (II). In particular, the perfluoropolyether surfactants correspond to formula (I) or (II) CF3—(OCF2)m—O—CF2—X (I) wherein m has a value of 1 to 6 and X represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof, CF3—O—(CF2)3—(OCF(CF3)—CF2)z—O-L-Y (II) wherein z has a value of 0, 1, 2 or 3, L represents a divalent linking group selected from —CF(CF3)—, —CF2— and —CF2CF2— and Y represents a carboxylic acid group or salt thereof. The invention further relates to an aqueous dispersion of a fluoropolymer having the aforementioned perfluoropolyether surfactant(s).
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Drug/drug delivery systems for the prevention and treatment of vascular disease
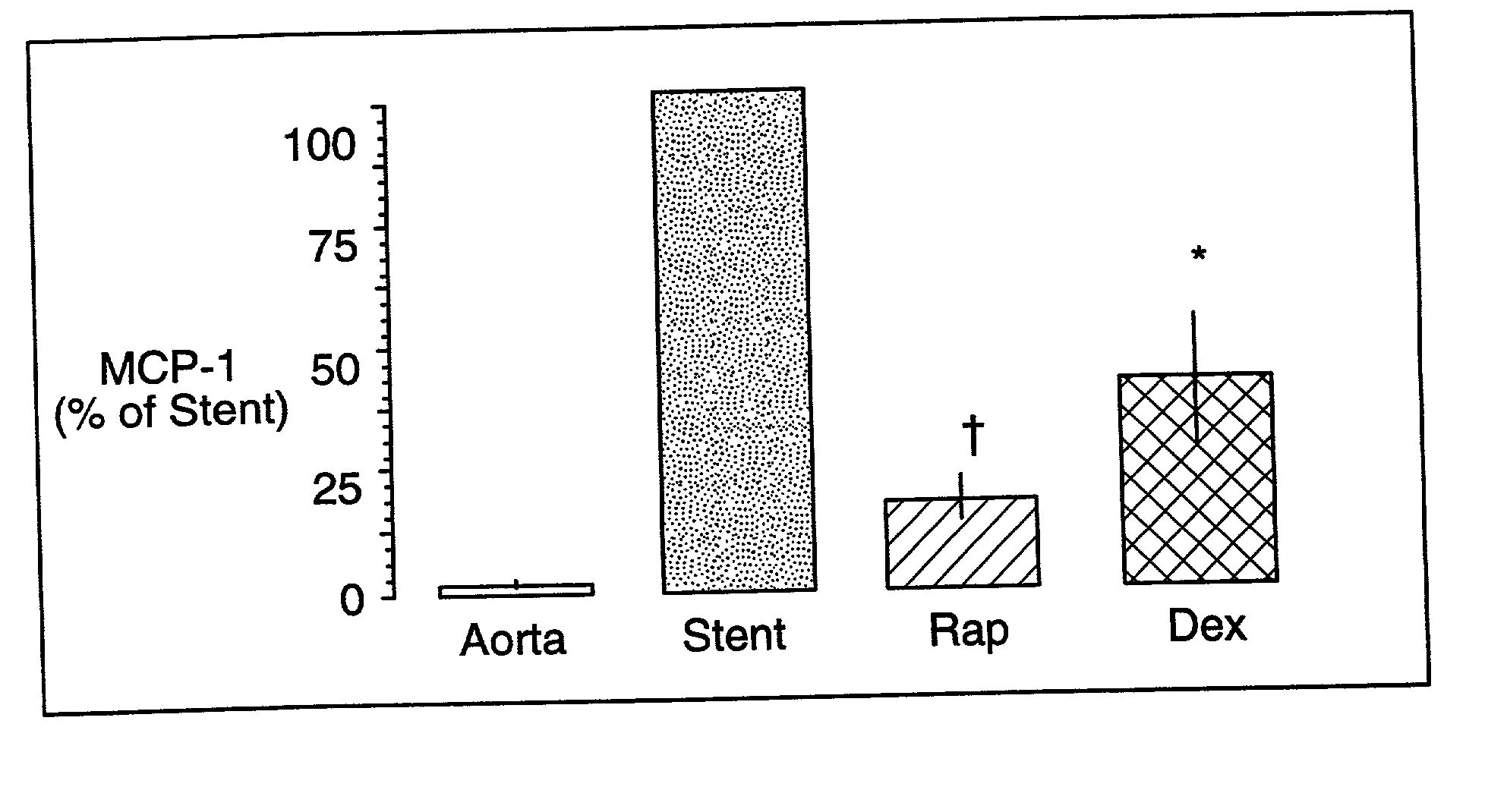
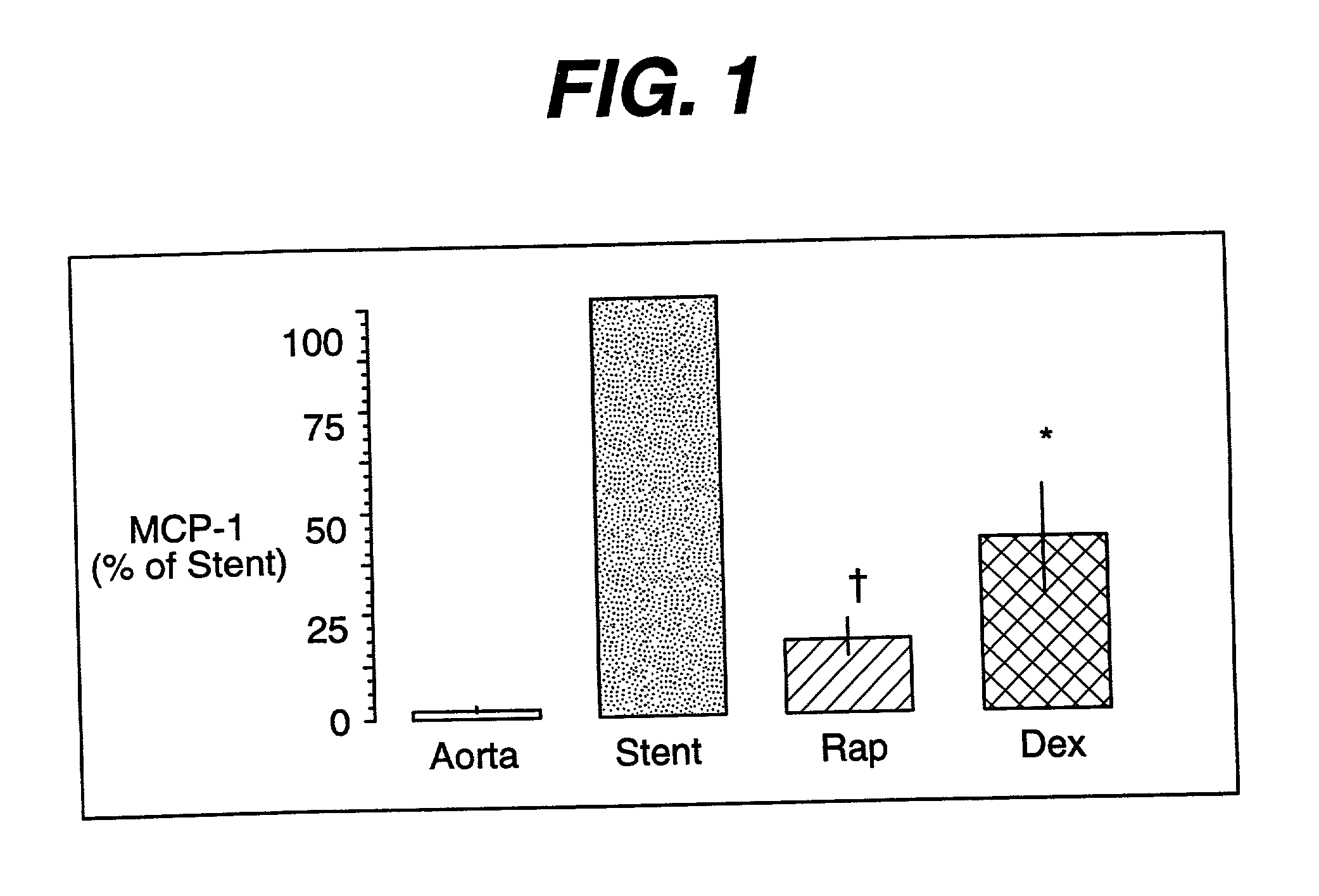
InactiveUS20020007215A1Prevent proliferationGood effectOrganic active ingredientsStentsVascular diseaseWhole body
A drug and drug delivery system may be utilized in the treatment of vascular disease. A local delivery system is coated with rapamycin or other suitable drug, agent or compound and delivered intraluminally for the treatment and prevention of neointimal hyperplasia following percutaneous transluminal coronary angiography. The local delivery of the drugs or agents provides for increased effectiveness and lower systemic toxicity.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Antireflective coatings comprising poly(oxyalkylene) colorants
InactiveUS6048662AReduce the amplitudeImprove anti-reflectionPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsCounterionThin layer
This invention relates to antireflective coatings comprising polymeric polyoxyalkylenated colorants. More particularly, the present invention relates to antireflective coatings for utilization in forming thin layers between reflective substrates and photoresist coatings. Such antireflective coatings are very useful and beneficial within the production and fabrication of semiconductors through photolithographic procedures due to the liquid, non-crystallizing nature of polyoxyalkylenated colorants, and the lack of potentially damaging counterions, metals, and / or electrolytes within the inventive antireflective colored coatings. The inventive coatings may also be applied on lenses, mirrors, and other optical components. Methods of forming such antireflective coatings are also contemplated within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Targeted pyrrolobenzodiazapine conjugates
ActiveUS20130028919A1Potent cytotoxic and cytostatic activityGood potencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemistry
Owner:SEAGEN INC +1
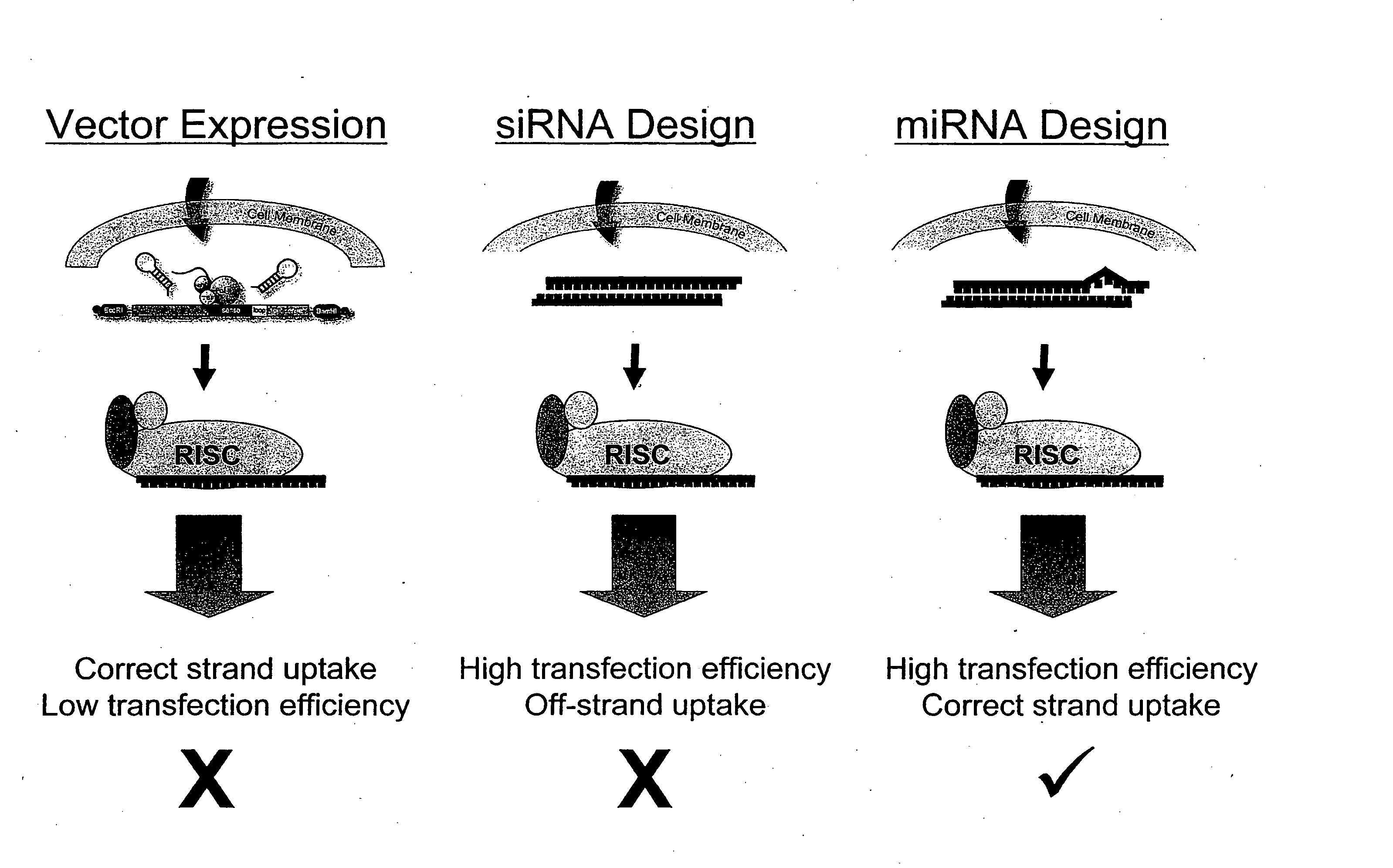
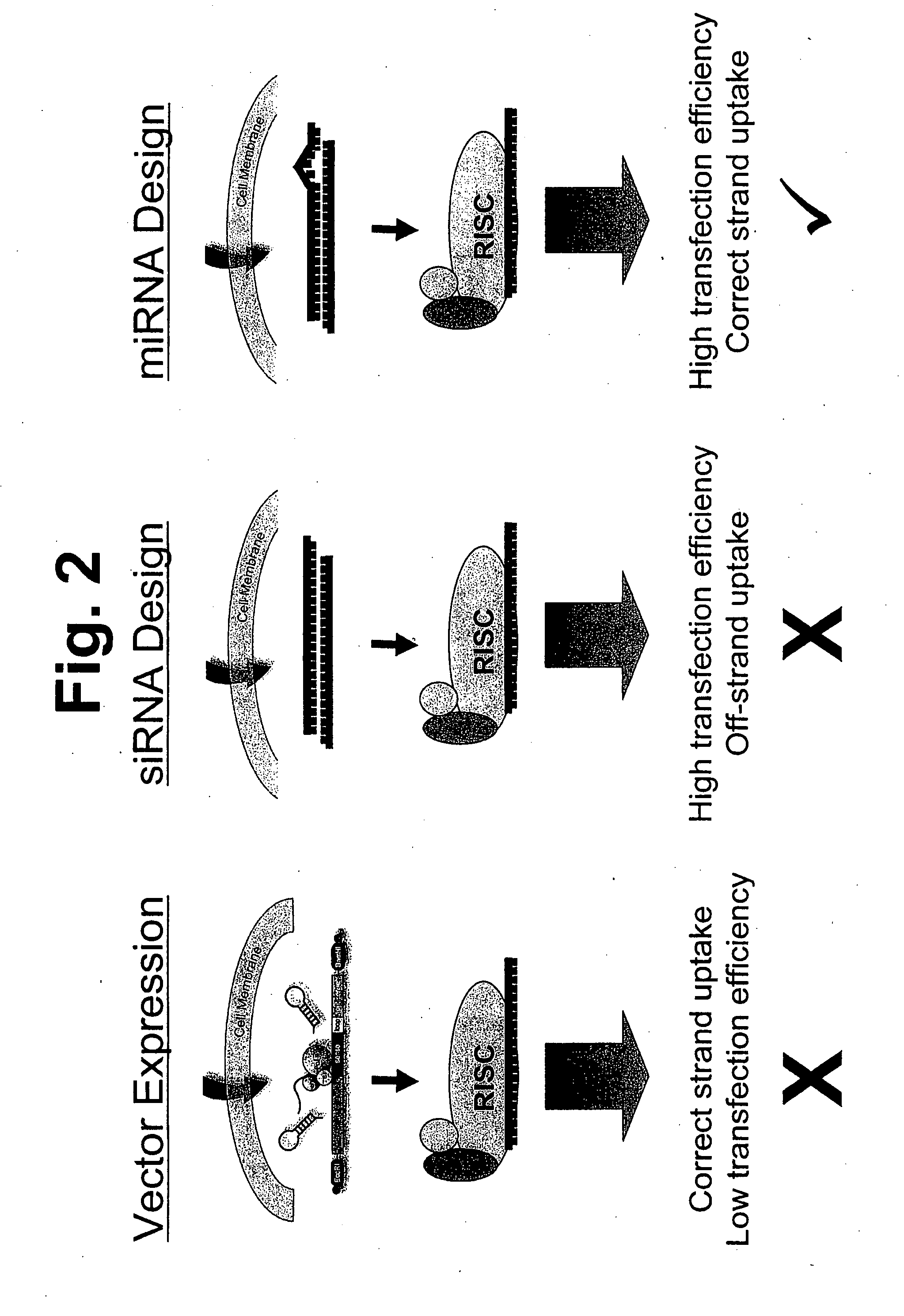
Methods and compositions involving mirna and mirna inhibitor molecules
InactiveUS20080050744A1Effective amountReduce percentageAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiologyCellular functions
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for introducing miRNA activity or function into cells using synthetic nucleic acid molecules. Moreover, the present invention concerns methods and compositions for identifying miRNAs with specific cellular functions that are relevant to therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic applications wherein synthetic miRNAs and / or miRNA inhibitors are used in library screening assays.
Owner:ASURAGEN
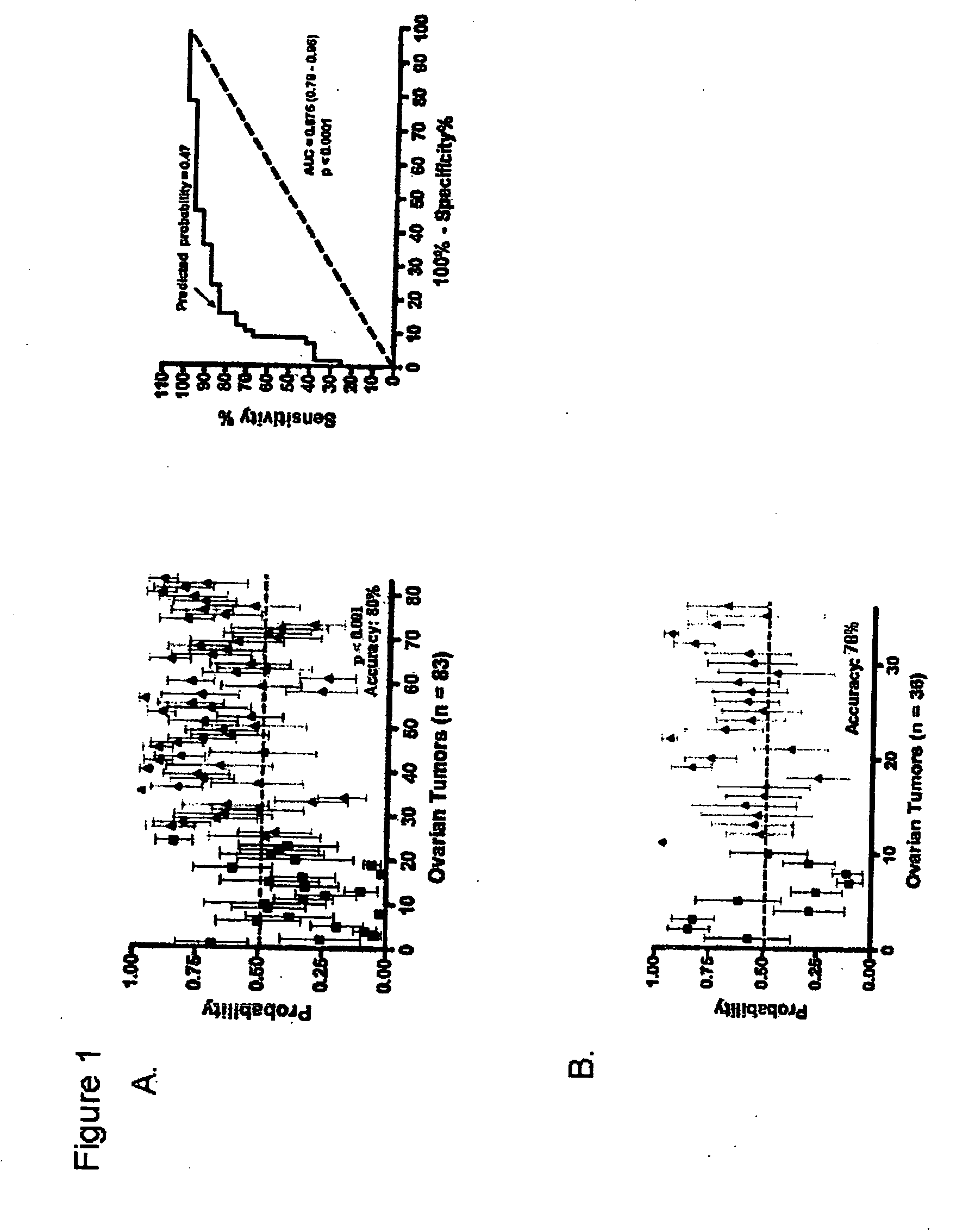
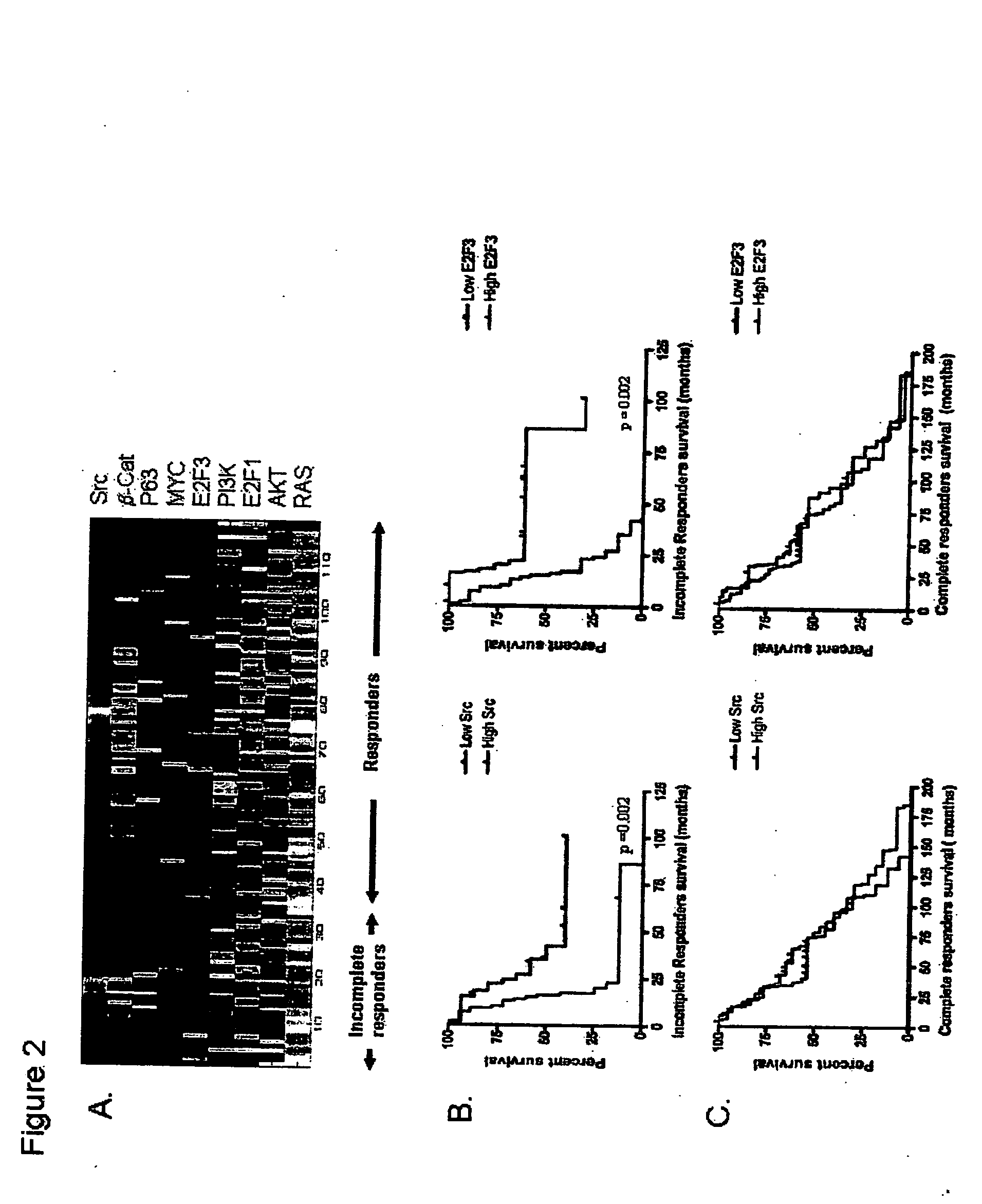
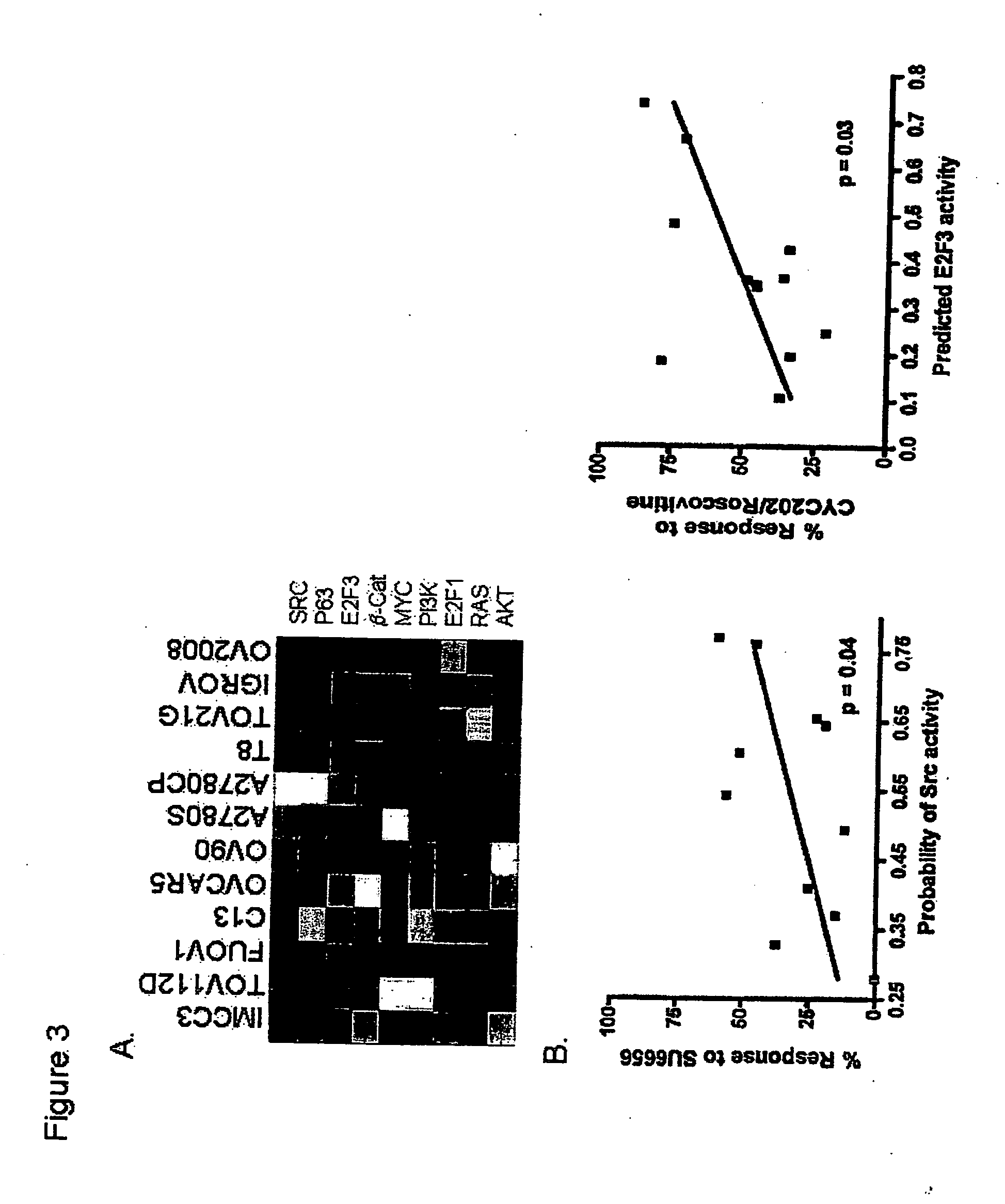
Individualized cancer treatments
InactiveUS20070172844A1Increase probabilityLow toxicityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA microarrayPlatinum
The invention provides for compositions and methods for predicting an individual's responsitivity to cancer treatments and methods of treating cancer. In certain embodiments, the invention provides compositions and methods for predicting an individual's responsitivity to chemotherapeutics, including platinum-based chemotherapeutics, to treat cancers such as ovarian cancer. Furthermore, the invention provides for compositions and methods for predicting an individual's responsivity to salvage therapeutic agents. By predicting if an individual will or will not respond to platinum-based chemotherapeutics, a physician can reduce side effects and toxicity by administering a particular additional salvage therapeutic agent. This type of personalized medical treatment for ovarian cancer allows for more efficient treatment of individuals suffering from ovarian cancer. The invention also provides reagents, such as DNA microarrays, software and computer systems useful for personalizing cancer treatments, and provides methods of conducting a diagnostic business for personalizing cancer treatments.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
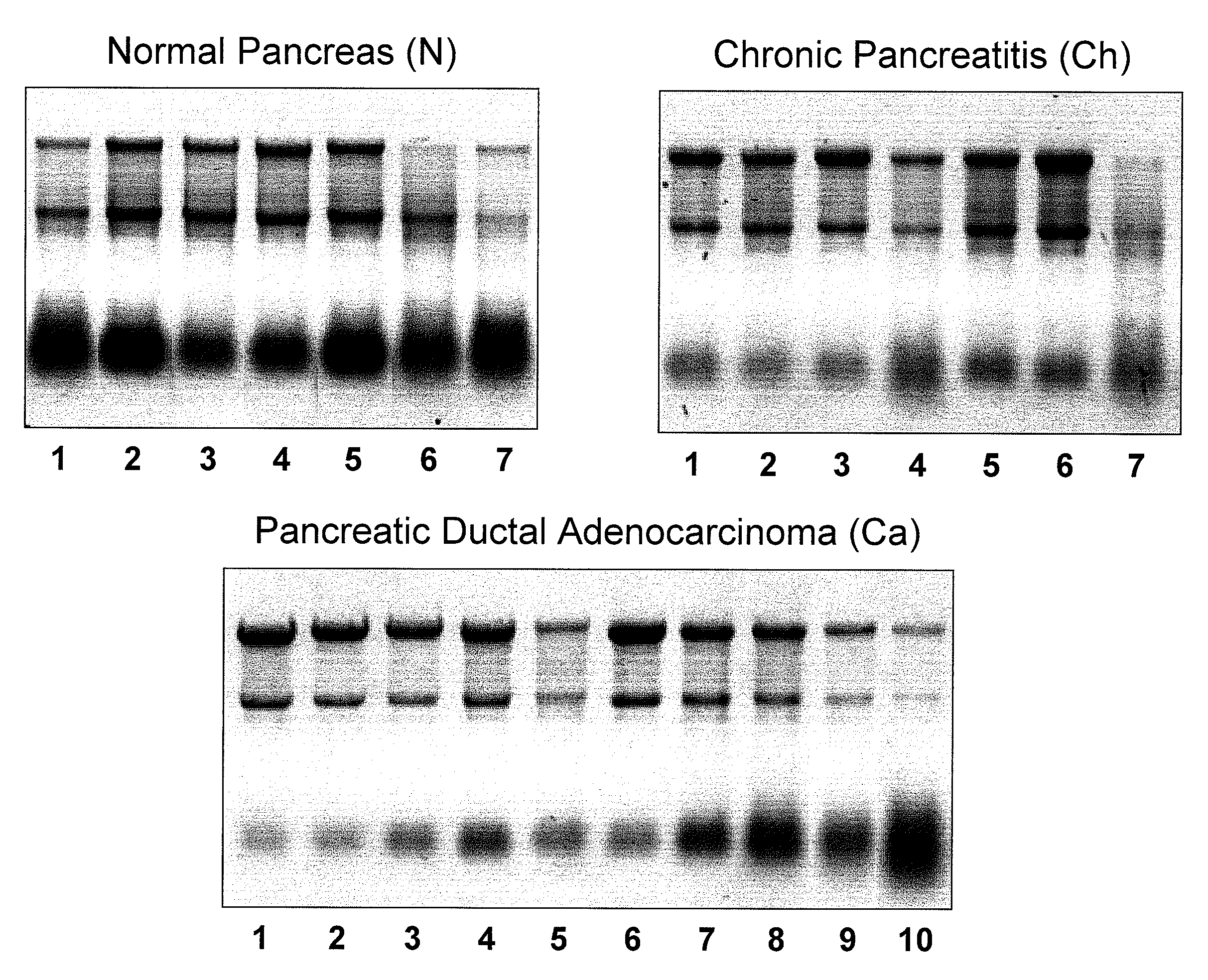
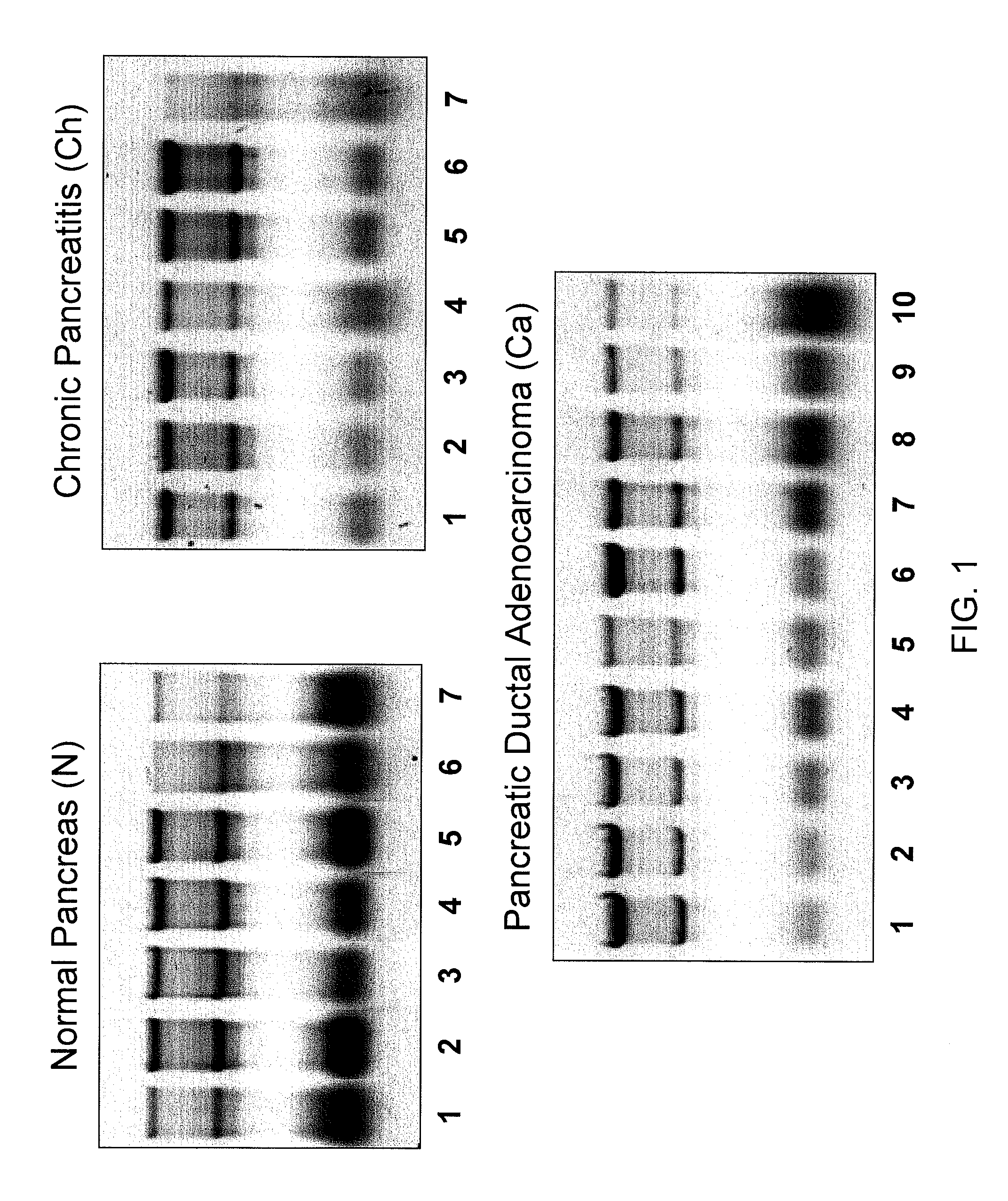
Micrornas differentially expressed in pancreatic diseases and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090131348A1Reduce cell proliferationIncrease and decreasing cell proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseasePancreatic disease
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for identifying a miRNA profile for a particular condition, such as pancreatic disease, and using the profile in assessing the condition of a patient.
Owner:INTERPACE DIAGNOSTICS LLC
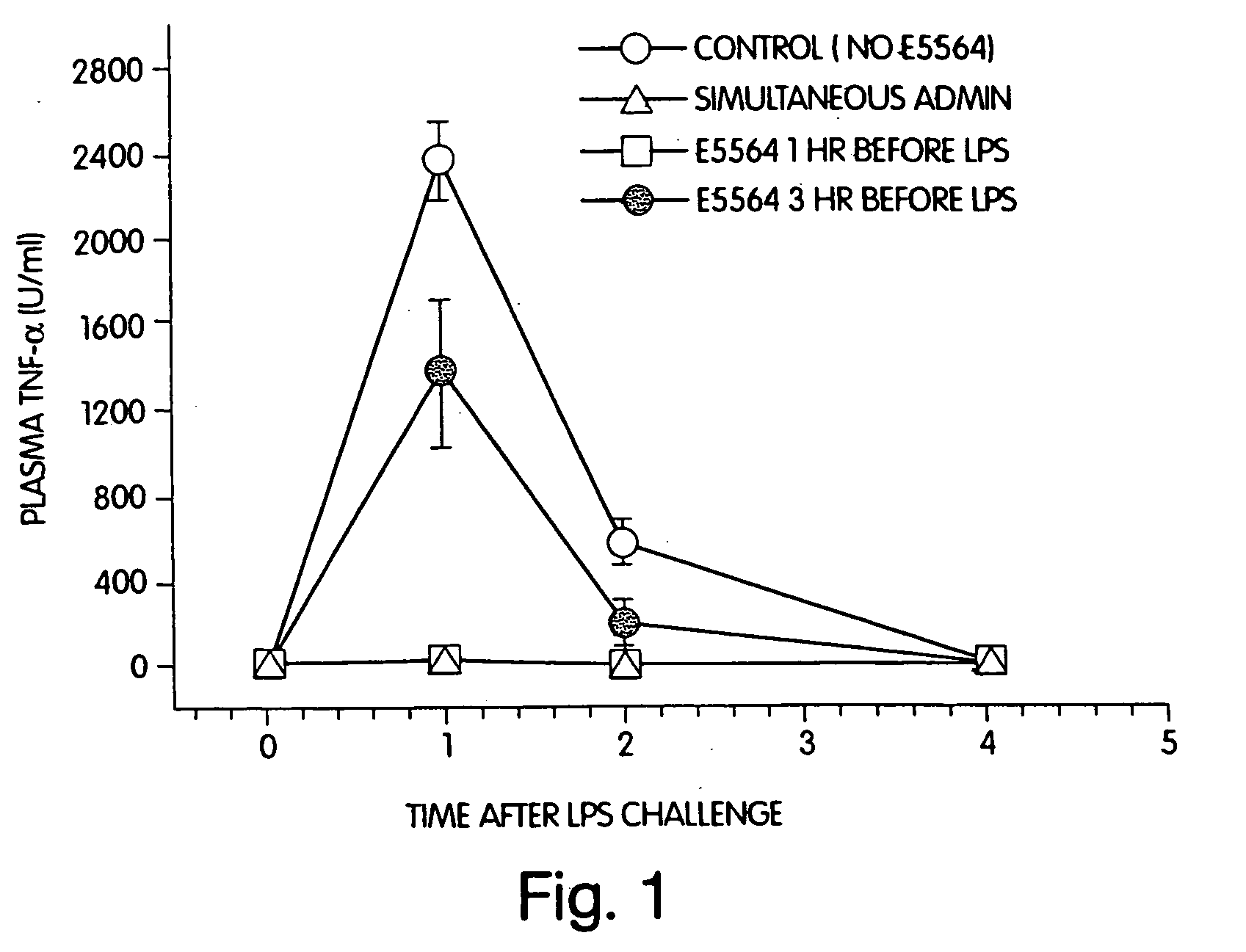
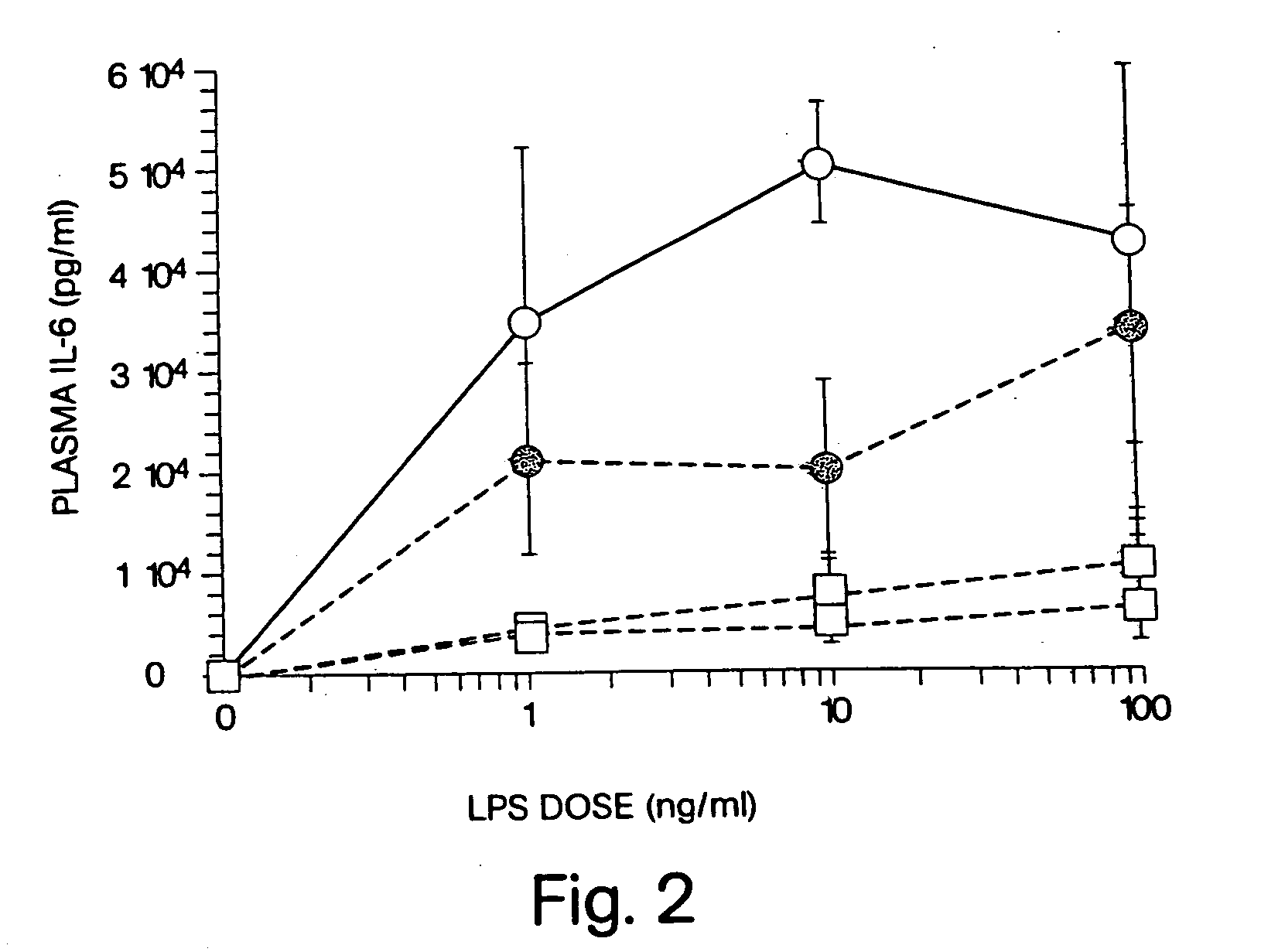
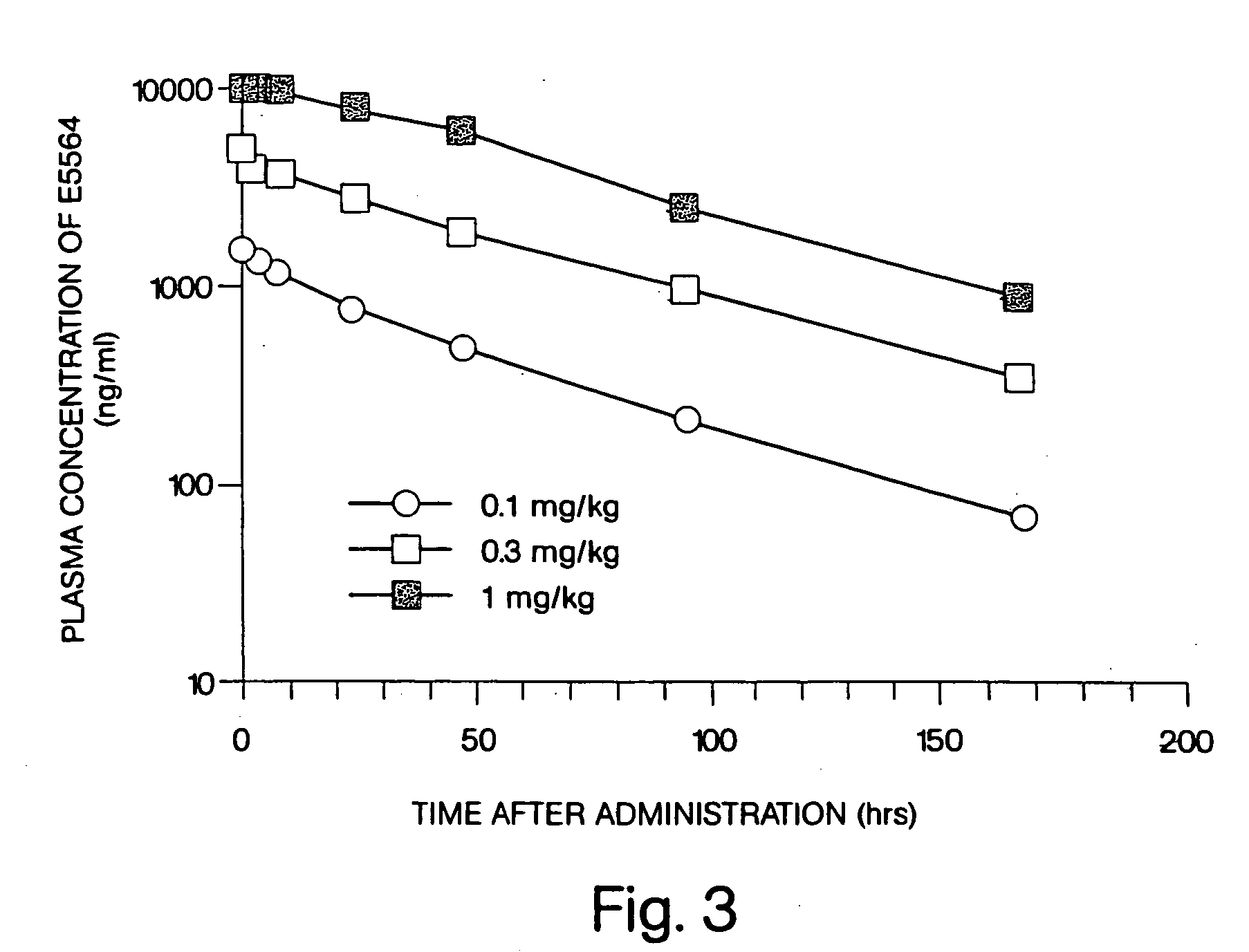
Use of an anti-endotoxin drug in the prevention and treatment of disease
InactiveUS20050215517A1Short pharmacodynamicShort pharmacodynamic half-lifeBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseasePharmacology
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
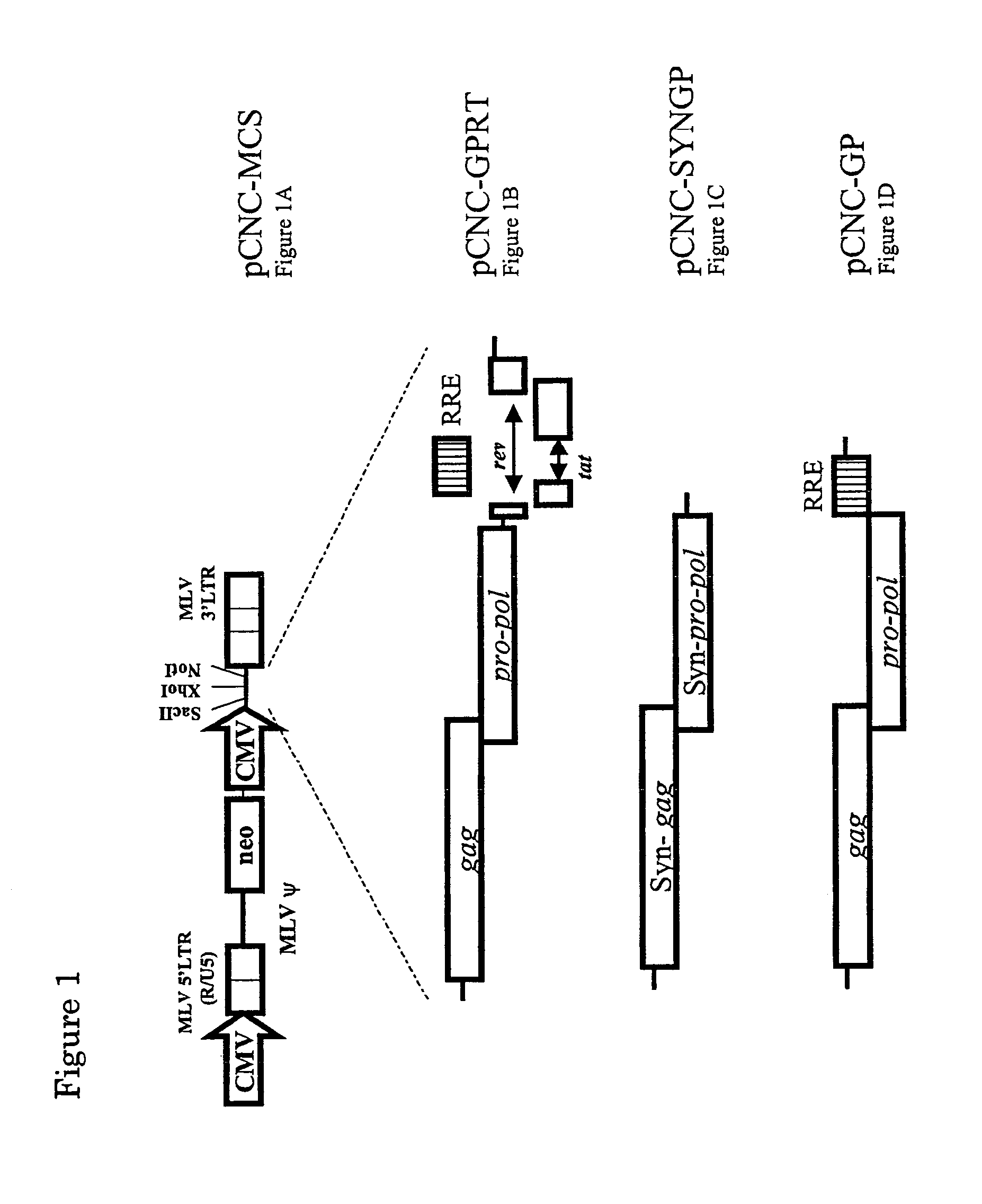
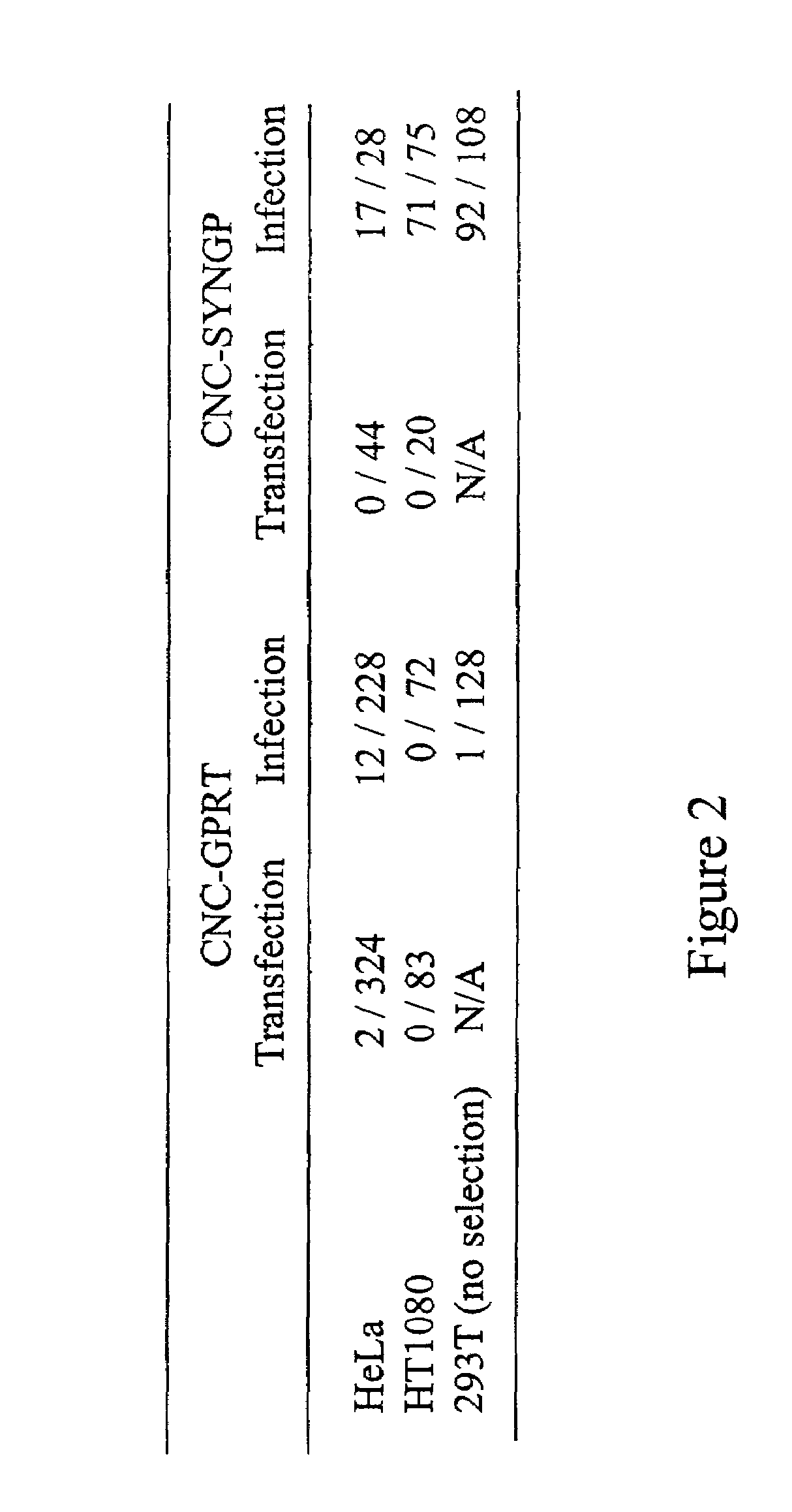
Retroviral vector
InactiveUS7351585B2High titerKeep for a long timeGenetic material ingredientsArtificial cell constructsNucleotideRetrovirus
Provided herein is a retroviral vector comprising, and capable of expressing, a nucleotide of interest (NOI), wherein the NOI encodes an RNA or protein which is harmful to a cell.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Compositions comprising tetrafluoeopropene & carbon dioxide
ActiveUS20060043331A1Maintain good propertiesReducing and eliminating deleterious ozone depletion potentialHeat-exchange elementsLiquid soapsHeat transfer fluidPhotochemistry
Disclosed are compositions useful in a wide variety of applications, including heat transfer fluids which possess a highly desirable and unexpectedly superior combination of properties, and heat transfer systems and methods based on these fluids. The preferred heat transfer fluid comprises from about 1 to about 40 percent, on a weight basis, of carbon dioxide (CO2) and from about 99 to about 60 percent, on a weight basis, of a compound having the Formula I XCFzR3-z (I), where X is a C2 or a C3 unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted, alkyl radical, each R is independently Cl, F, Br, I or H, and z is 1 to 3. A preferred compound of Formula I is tetrafluoropropene, particularly 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene and / or 1,1,1,3-tetrafluoropropene.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
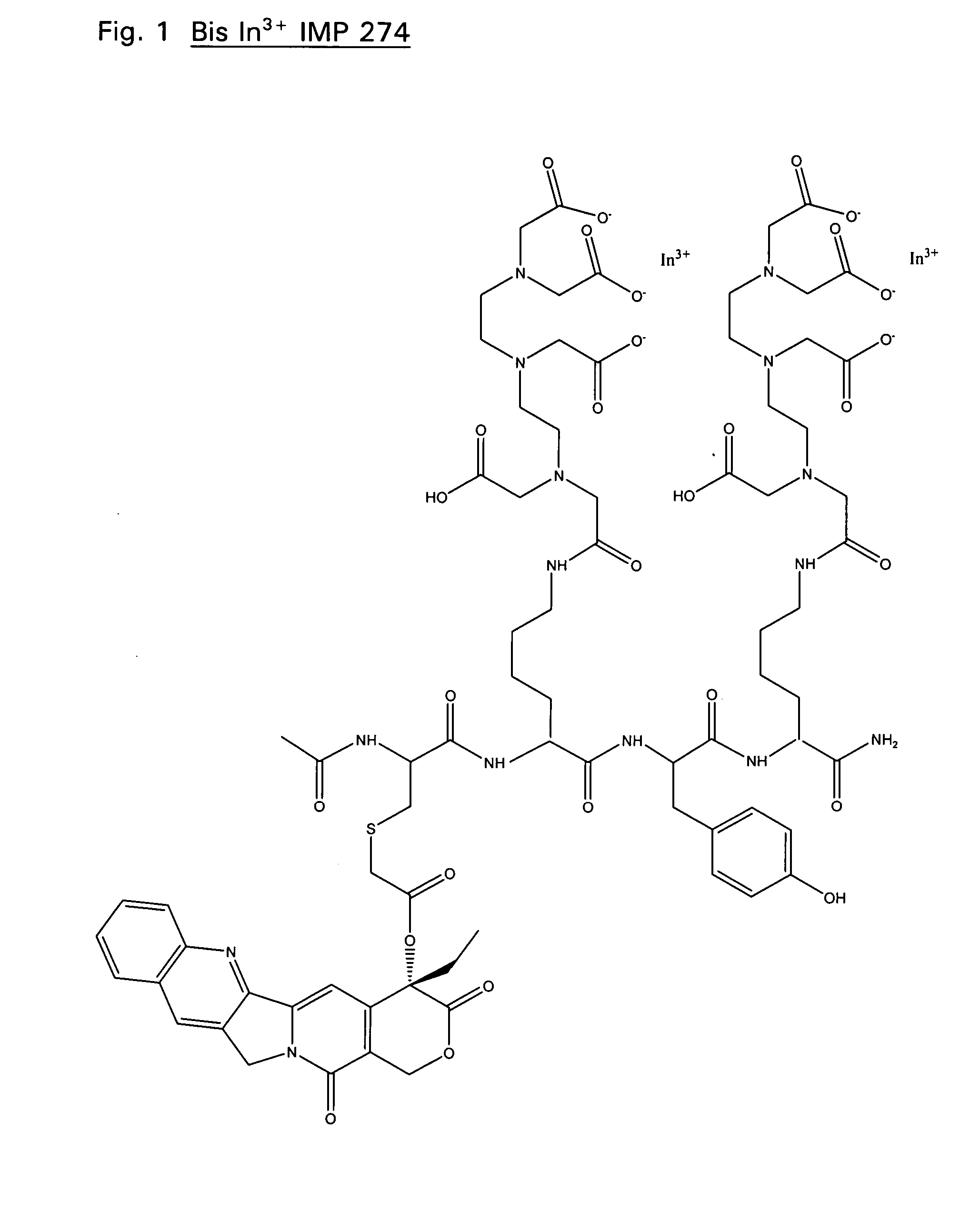
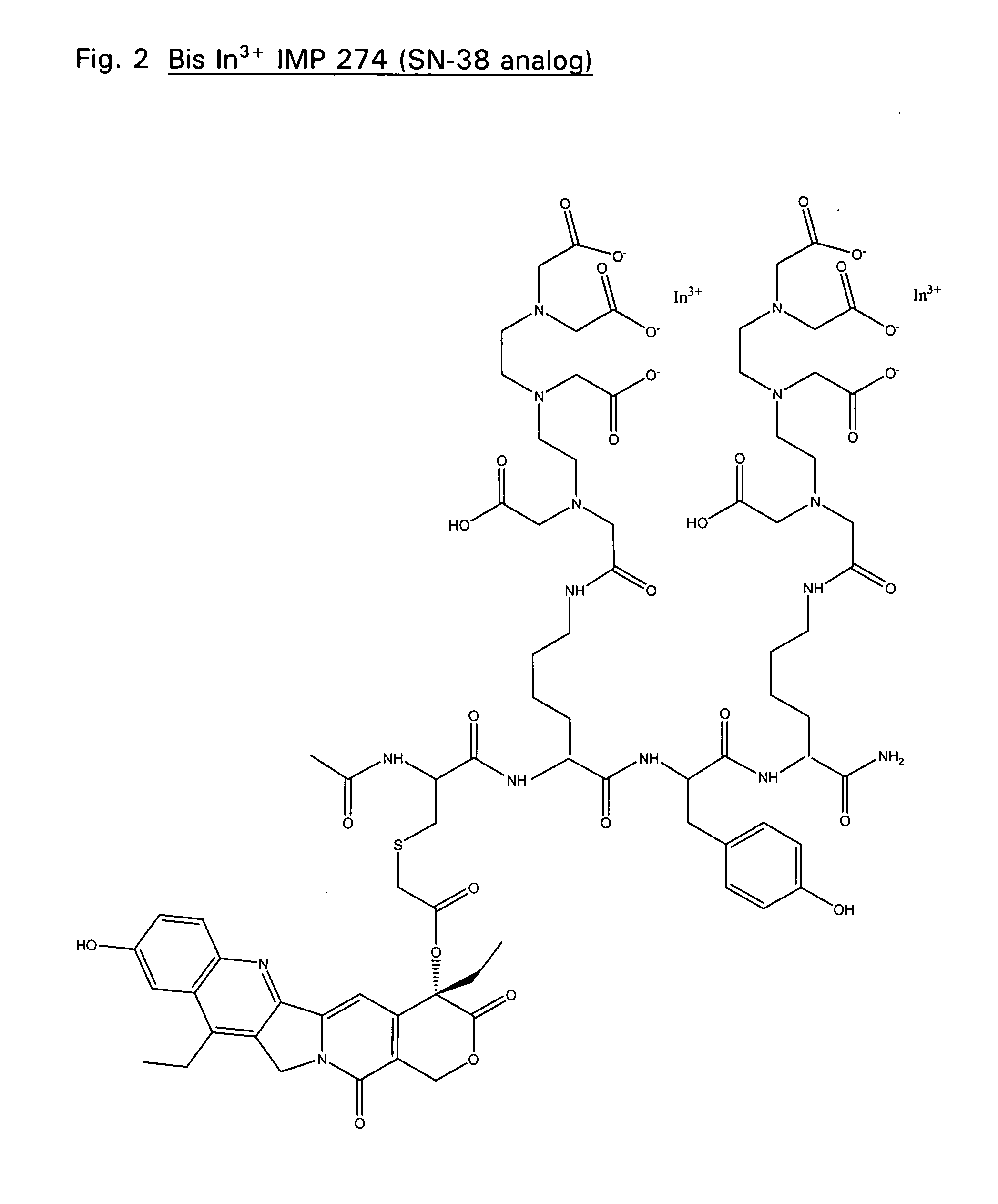
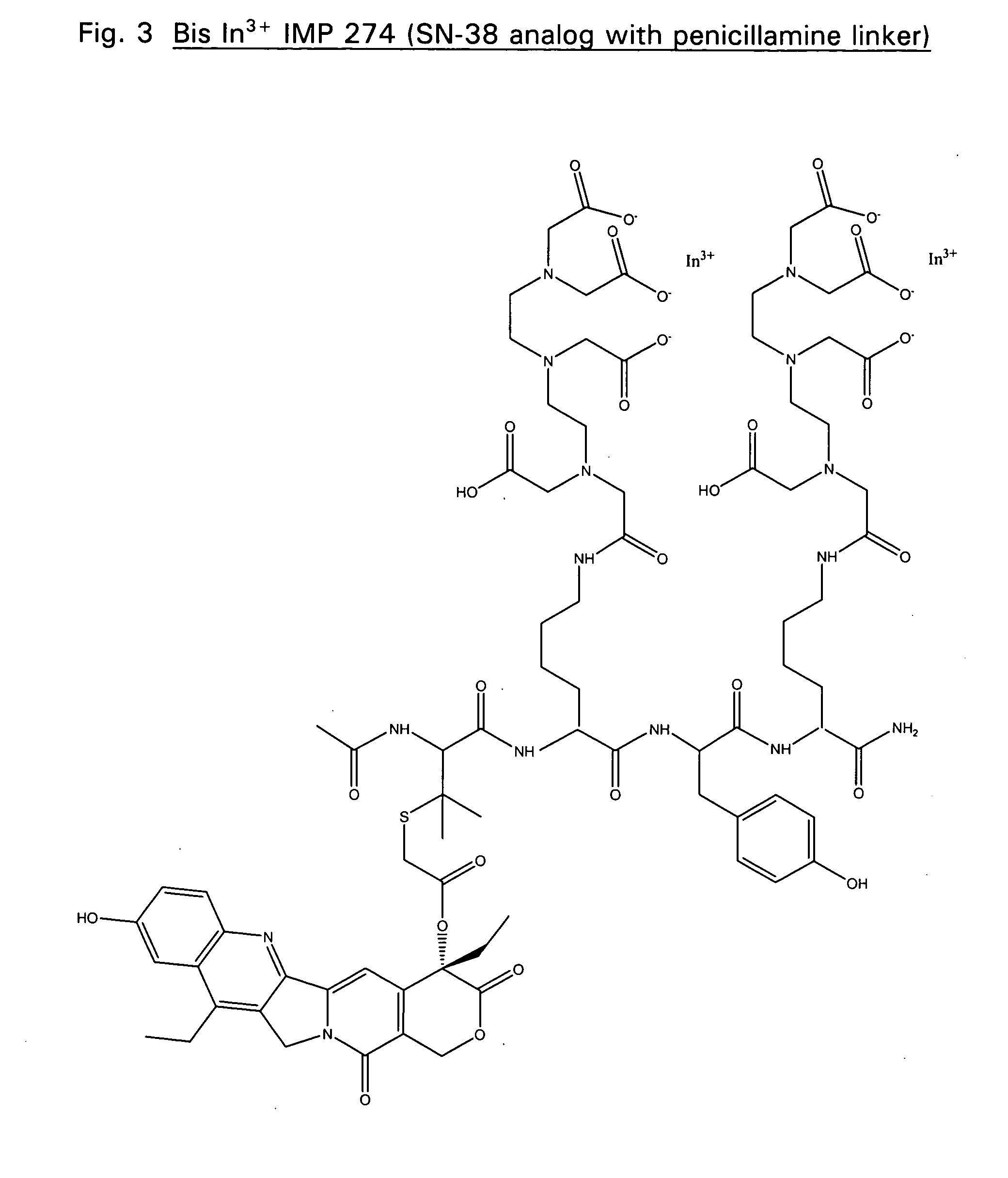
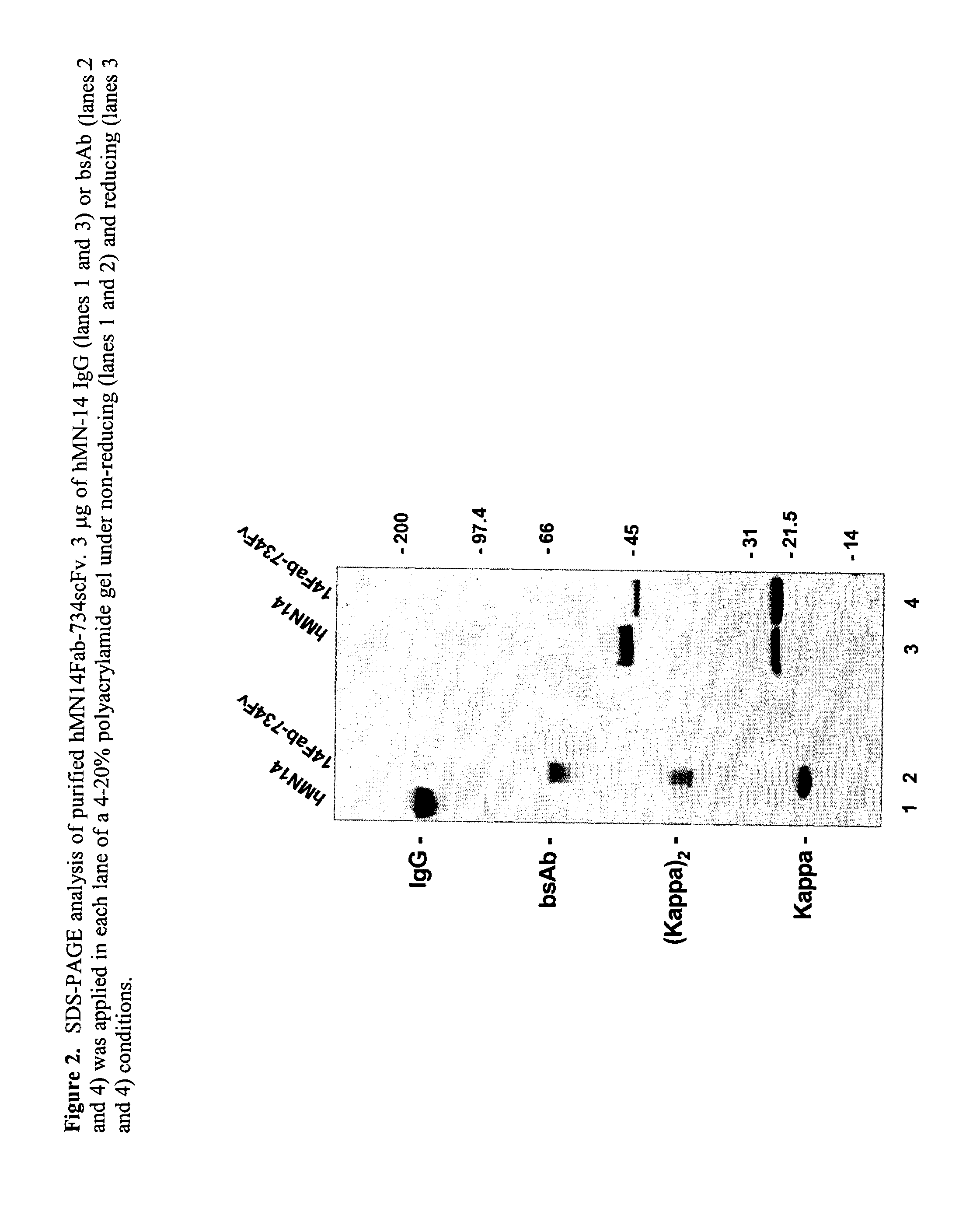
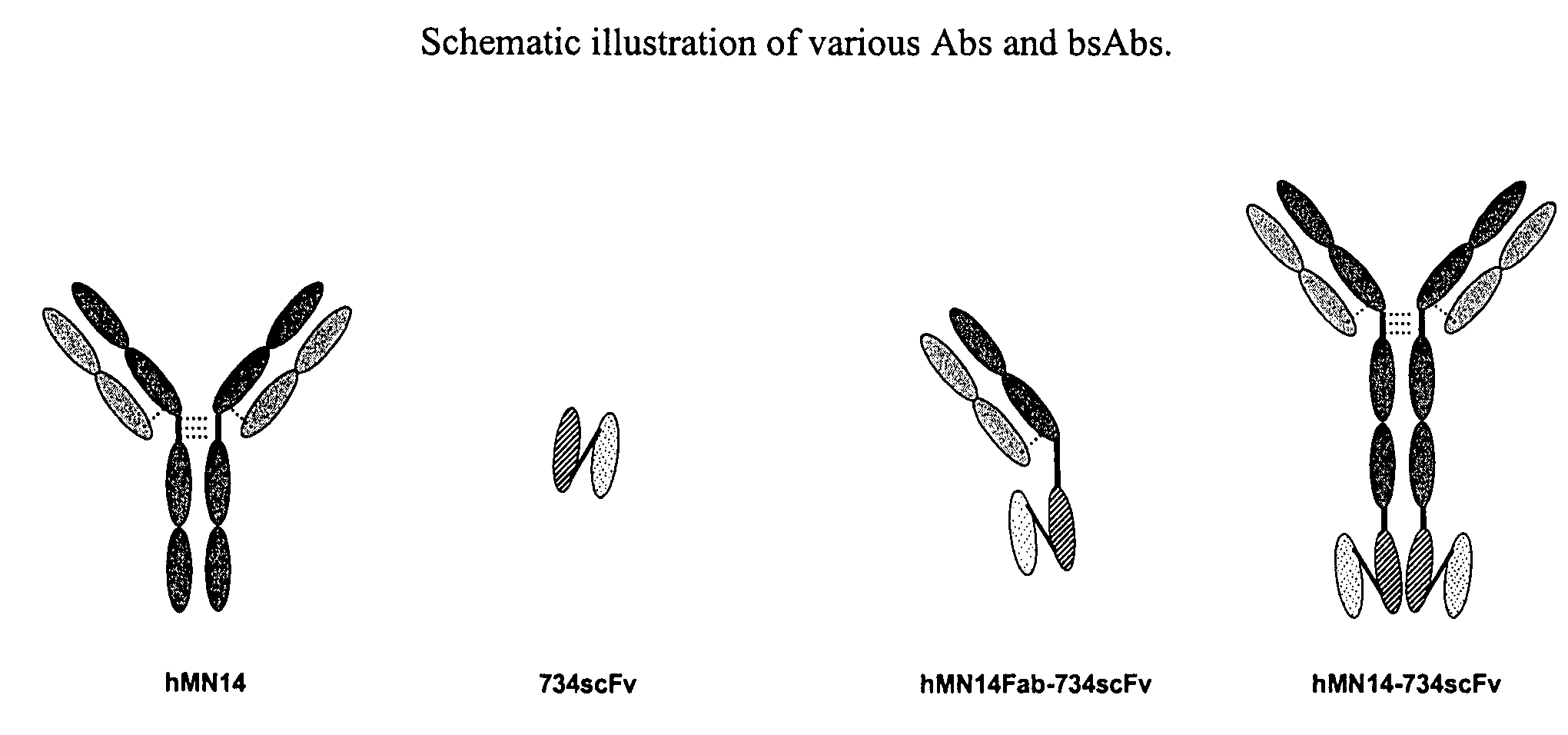
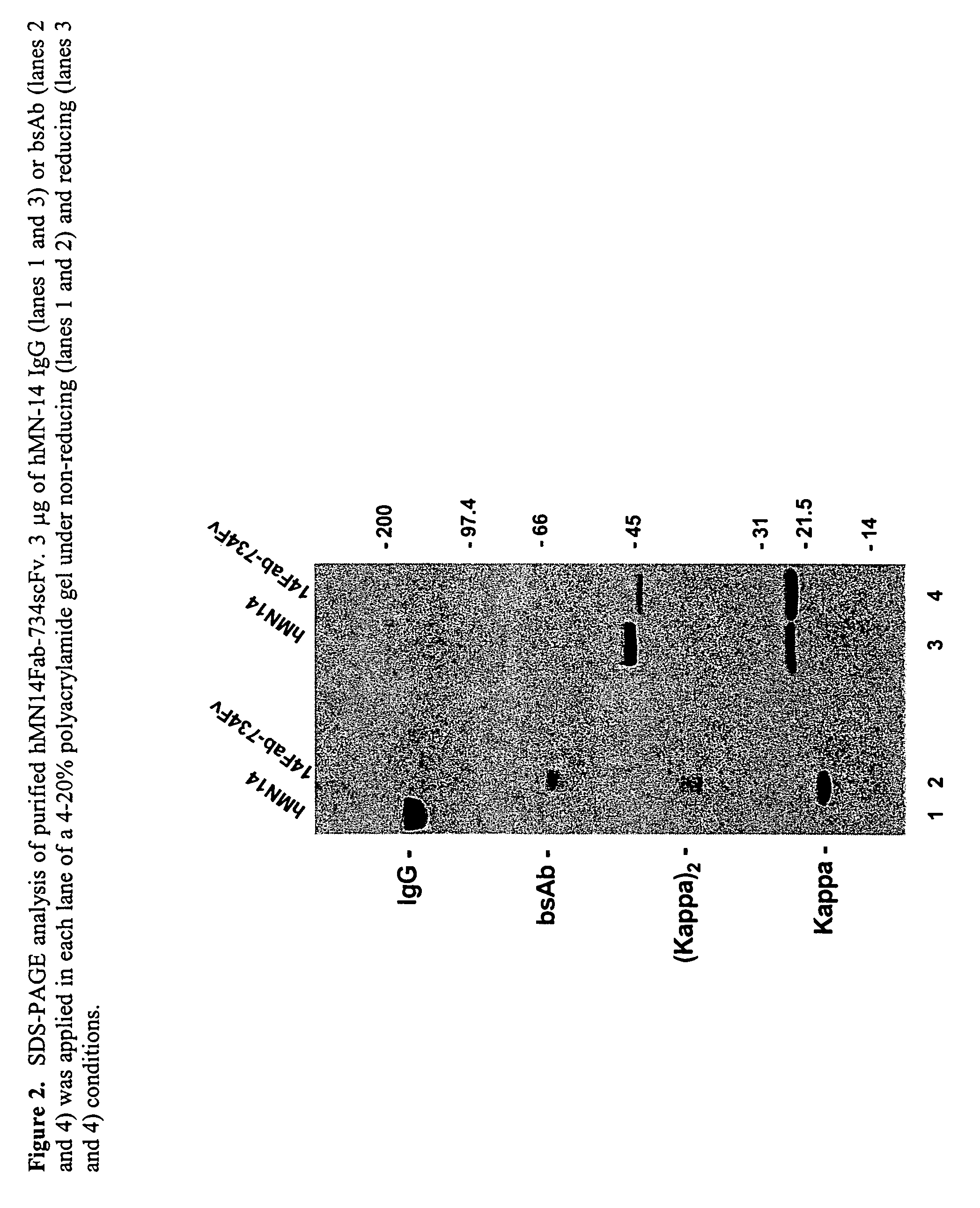
Therapeutic and diagnostic conjugates for use with multispecific antibodies
InactiveUS20050002945A1Low toxicityPromote localizationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsSemicarbazoneEther
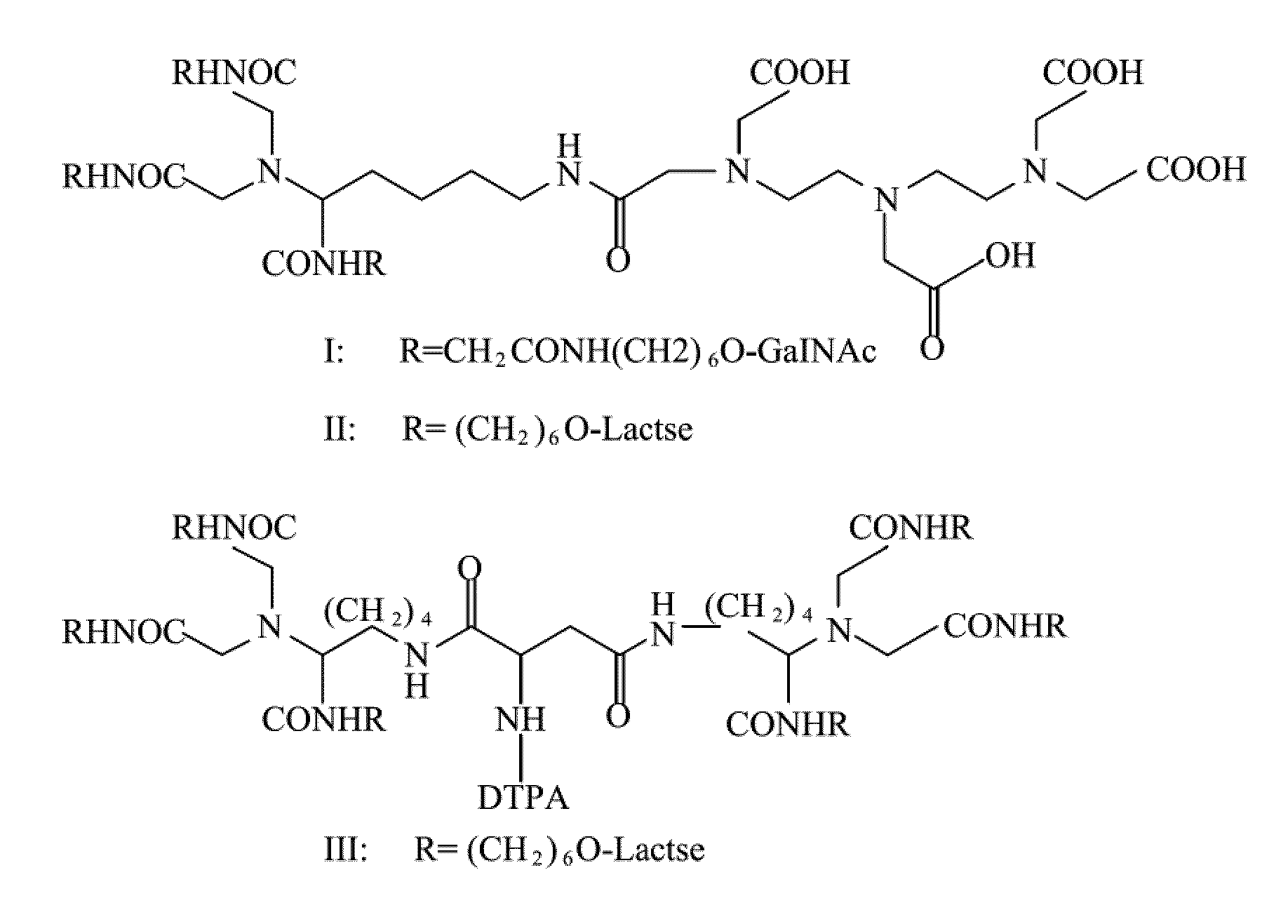
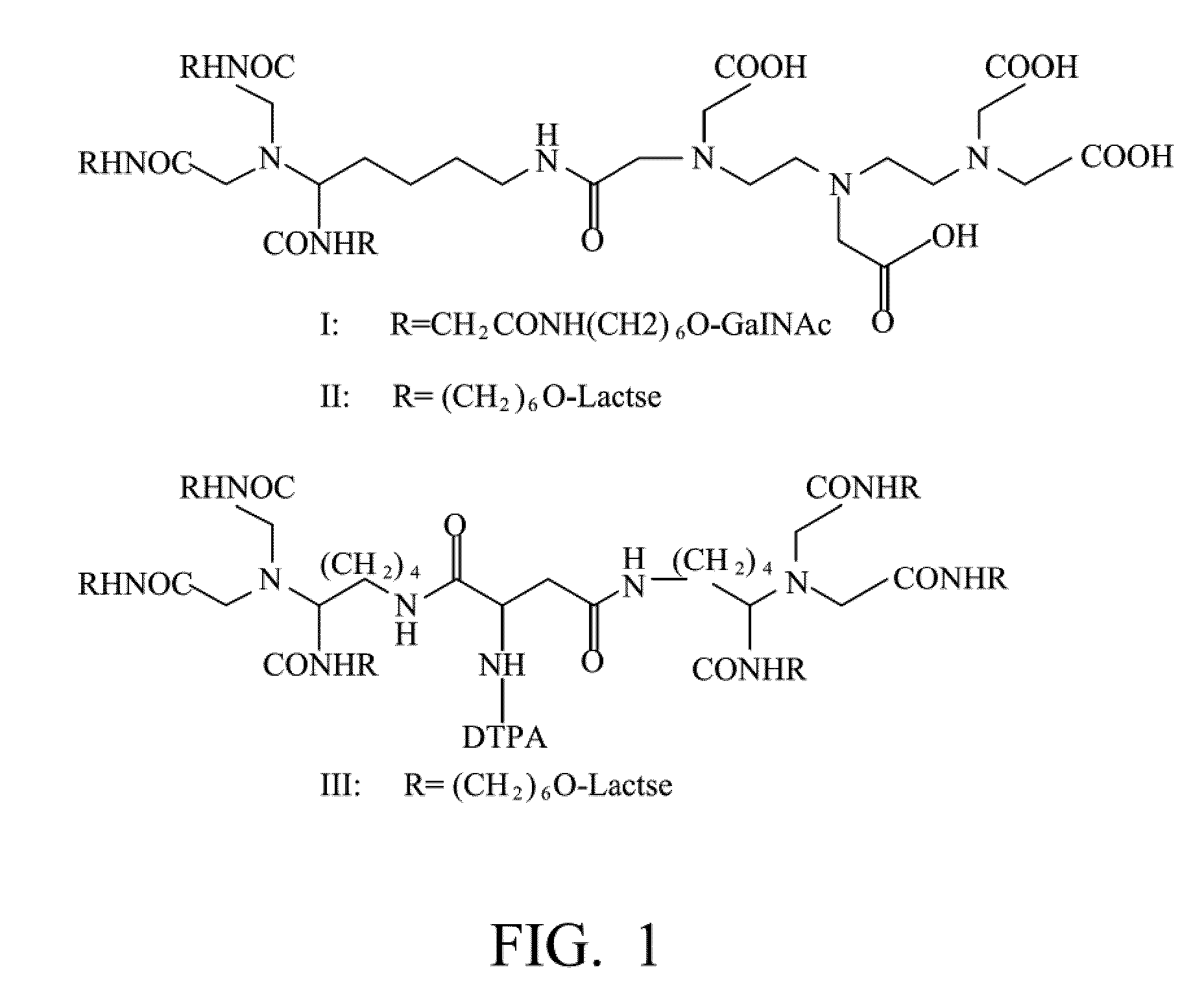
Disclosed are compounds that include two or more haptens conjugated by a spacer or a carrier. The haptens may include diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (DTPA), histimine-succinyl-glutamine (HSG), or combinations of DTPA and HSG. The compound also includes an effector molecule which may be conjugated to one or more of the haptens, the spacer / carrier, or both. The effector molecule may be conjugated by a number of linkages including an ester linkage, an imino linkage, an amino linkage, a sulfide linkage, a thiosemicarbazone linkage, a semicarbazone linkage, an oxime linkage, an ether linkage, or combinations of these linkages. Also disclosed are methods of synthesizing the compounds and / or precursors of the compounds.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
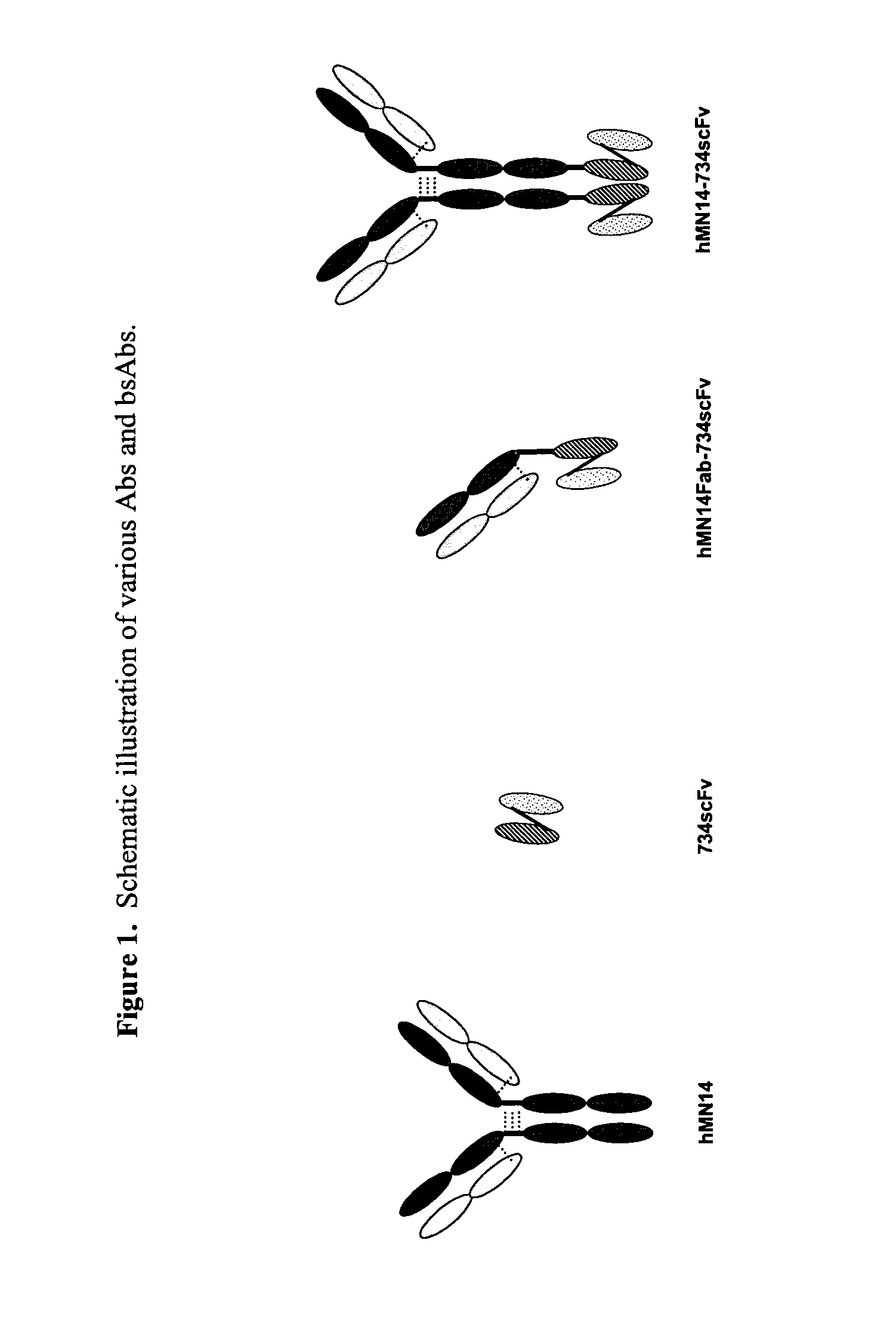
Use of bi-specific antibodies for pre-targeting diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS7074405B1Increased toxicityLow toxicityHybrid immunoglobulinsInorganic boron active ingredientsEpitopeDiagnostic agent
The present invention relates to a bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment having at least one arm that specifically binds a targeted tissue and at least one other arm that specifically binds a targetable conjugate. The targetable conjugate comprises a carrier portion which comprises or bears at least one epitope recognizable by at least one arm of said bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment. The targetable conjugate further comprises one or more therapeutic or diagnostic agents or enzymes. The invention provides constructs and methods for producing the bi-specific antibodies or antibody fragments, as well as methods for using them.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Abuse-resistant amphetamine compounds
InactiveUS7105486B2Reduced activityRelease is diminished and eliminatedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical MoietyDisease
The invention describes compounds, compositions and methods of using the same comprising a chemical moiety covalently attached to amphetamine. These compounds and compositions are useful for reducing or preventing abuse and overdose of amphetamine. These compounds and compositions find particular use in providing an abuse-resistant alternative treatment for certain disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), ADD, narcolepsy, and obesity. Oral bioavailability of amphetamine is maintained at therapeutically useful doses. At higher doses bioavailability is substantially reduced, thereby providing a method of reducing oral abuse liability. Further, compounds and compositions of the invention decrease the bioavailability of amphetamine by parenteral routes, such as intravenous or intranasal administration, further limiting their abuse liability.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Bi-specific antibodies for pre-targeting diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS7052872B1Increased toxicityLow toxicityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesEpitopeDiagnostic agent
The present invention relates to a bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment having at least one arm that specifically binds a targeted tissue and at least one other arm that specifically binds a targetable conjugate. The targetable conjugate comprises a carrier portion which comprises or bears at least one epitope recognizable by at least one arm of said bi-specific antibody or antibody fragment. The targetable conjugate further comprises one or more therapeutic or diagnostic agents or enzymes. The invention provides constructs and methods for producing the bi-specific antibodies or antibody fragments, as well as methods for using them.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
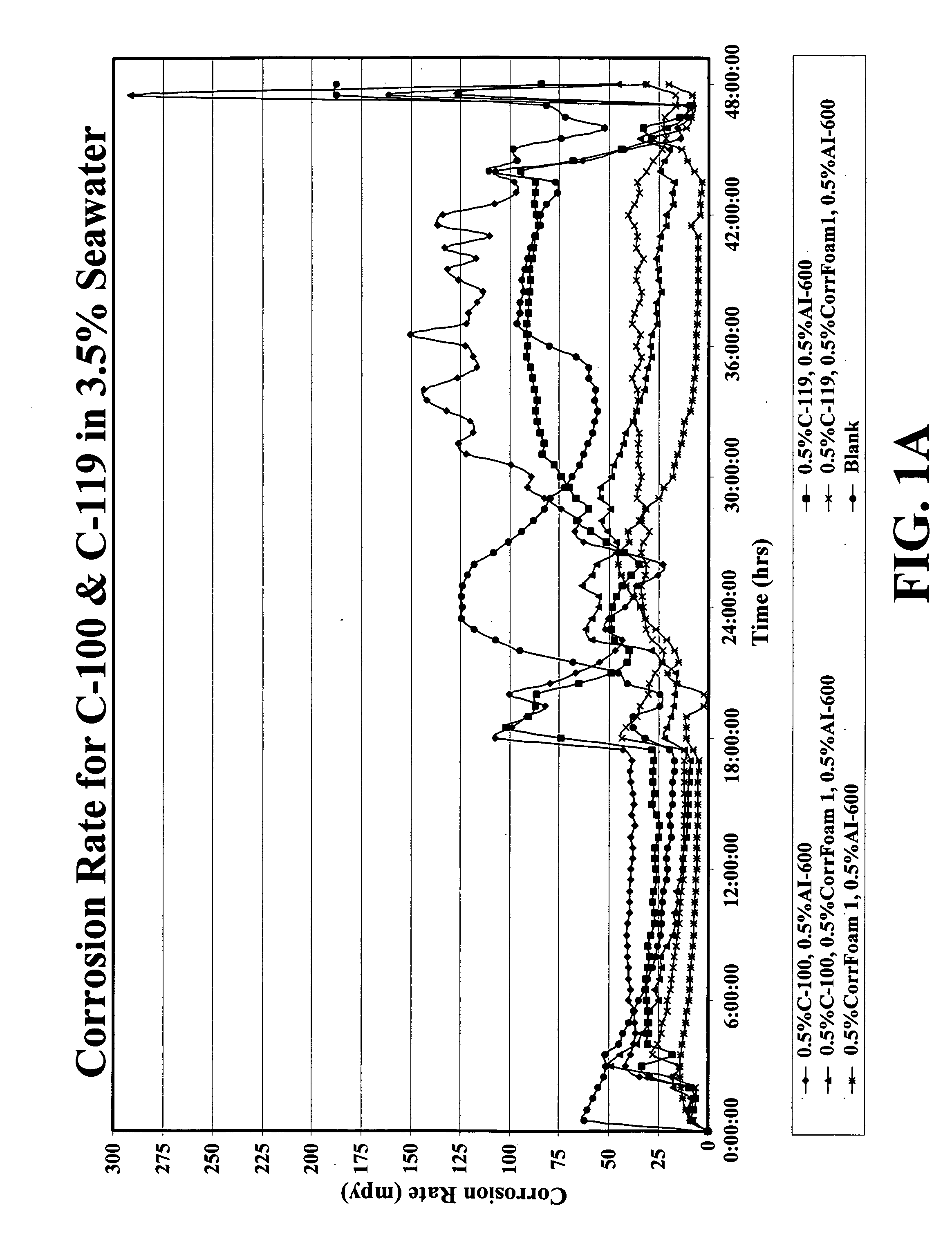
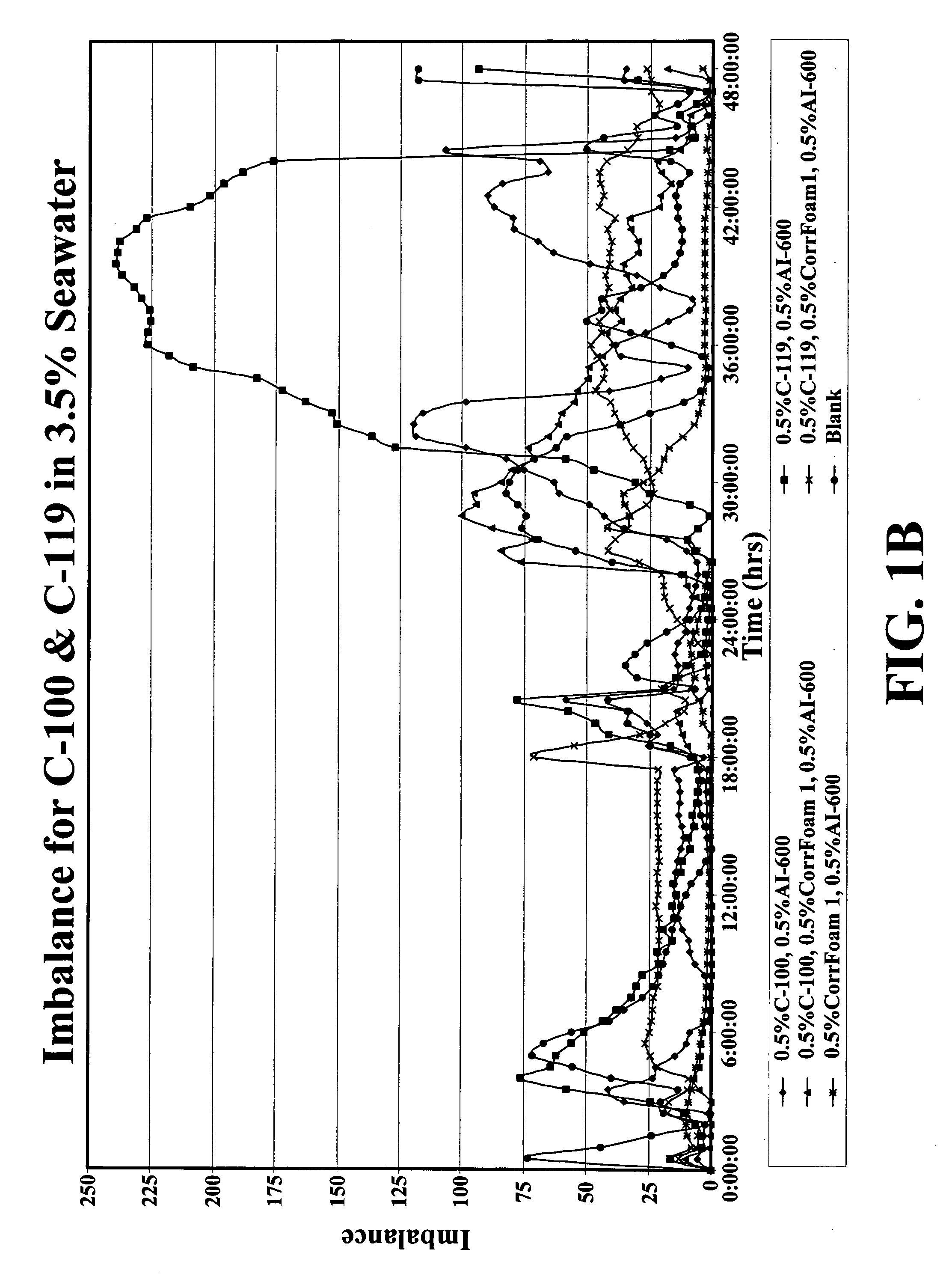
Corrosion inhibitor systems for low, moderate and high temperature fluids and methods for making and using same
A corrosion control system is disclosed including an anionic oxygen inhibitor, a cationic acid inhibitor or dispersant, and a noxious species inhibitor or scavenger for use in a fluid in contact with a metallic surface at low temperature, moderate temperature and especially at high temperature. A drilling fluid, a completion fluid, a production fluid and a geothermal fluid including an effective amount of the corrosion control system is also disclosed as well as methods for making and using same.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
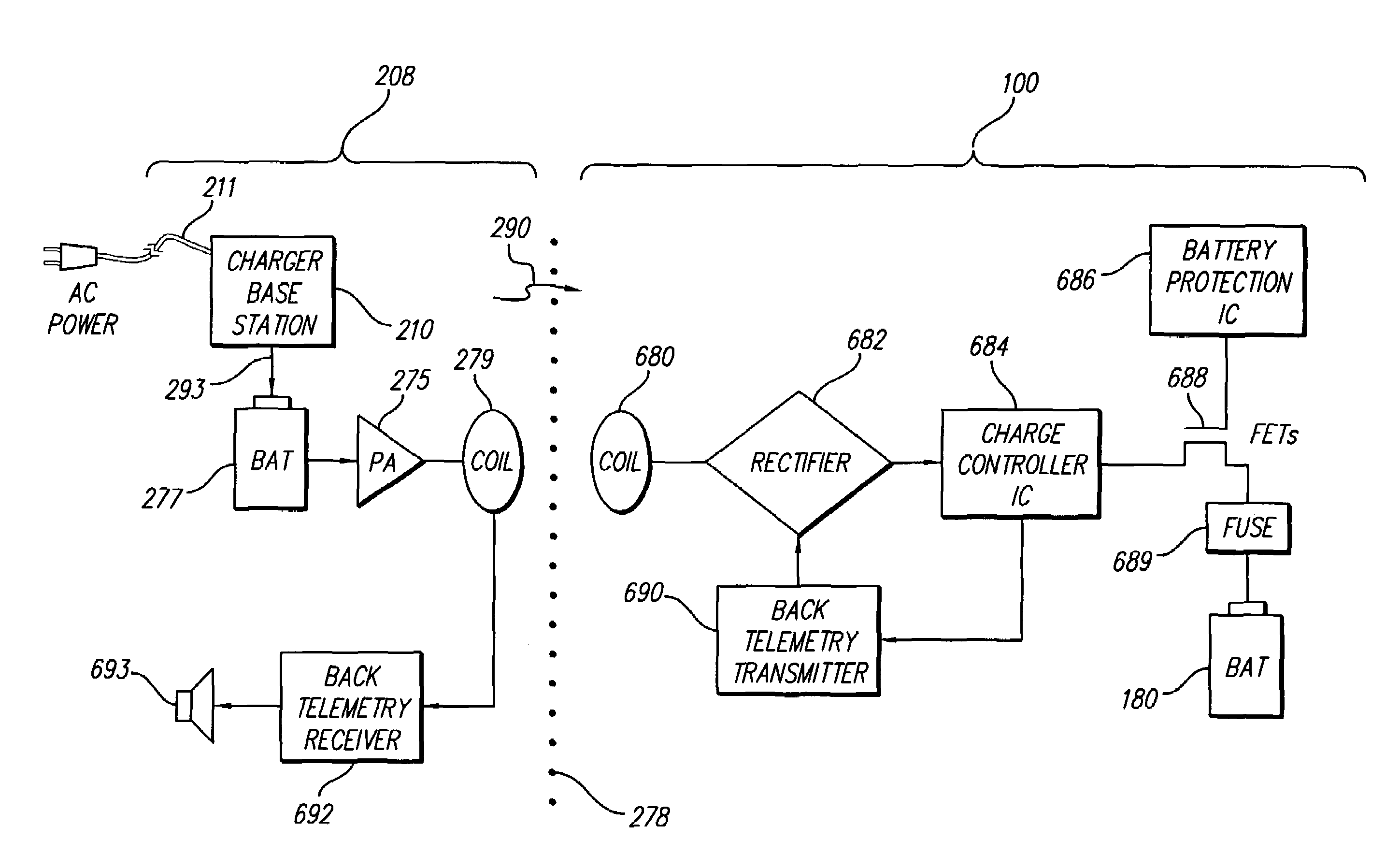
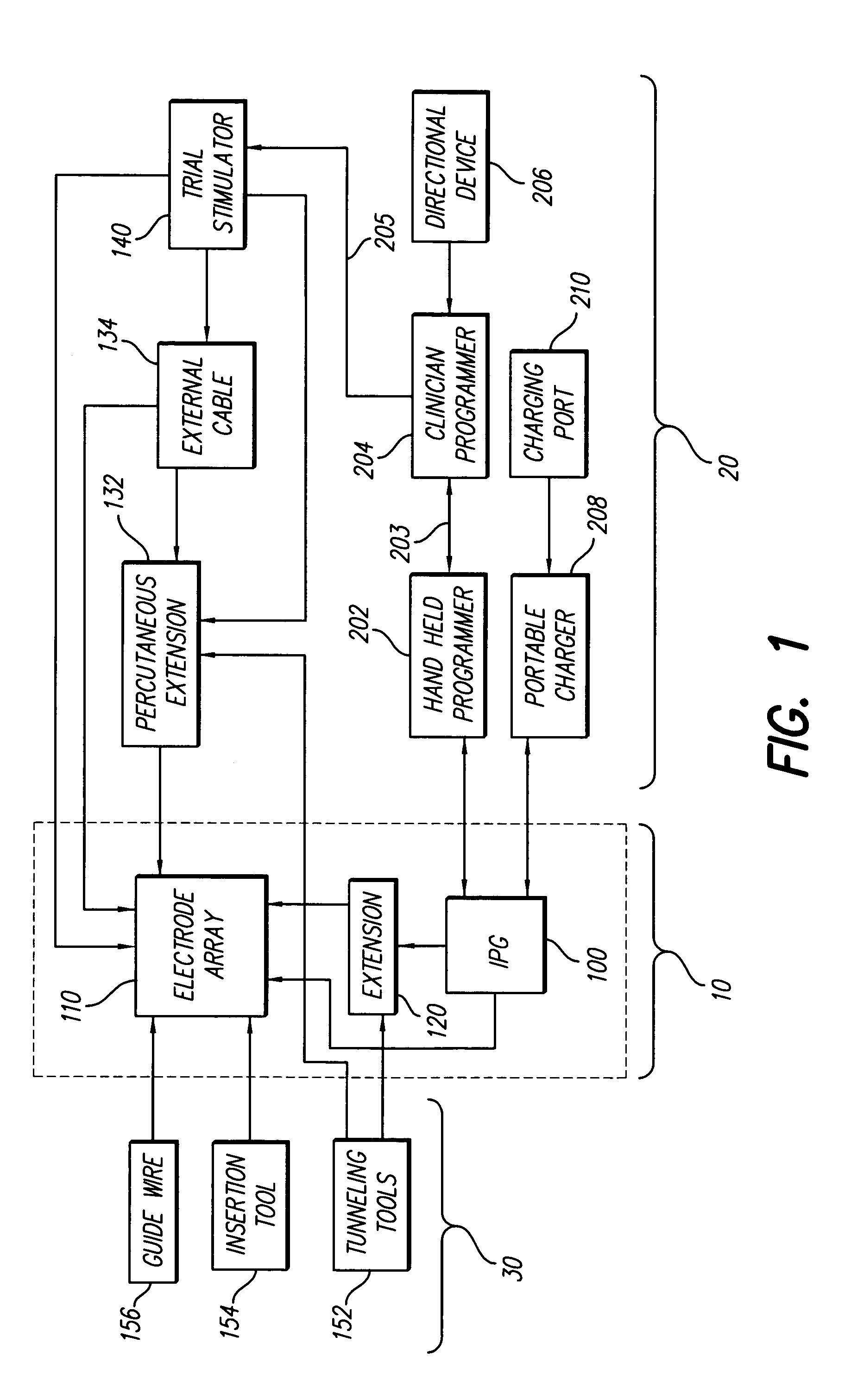
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
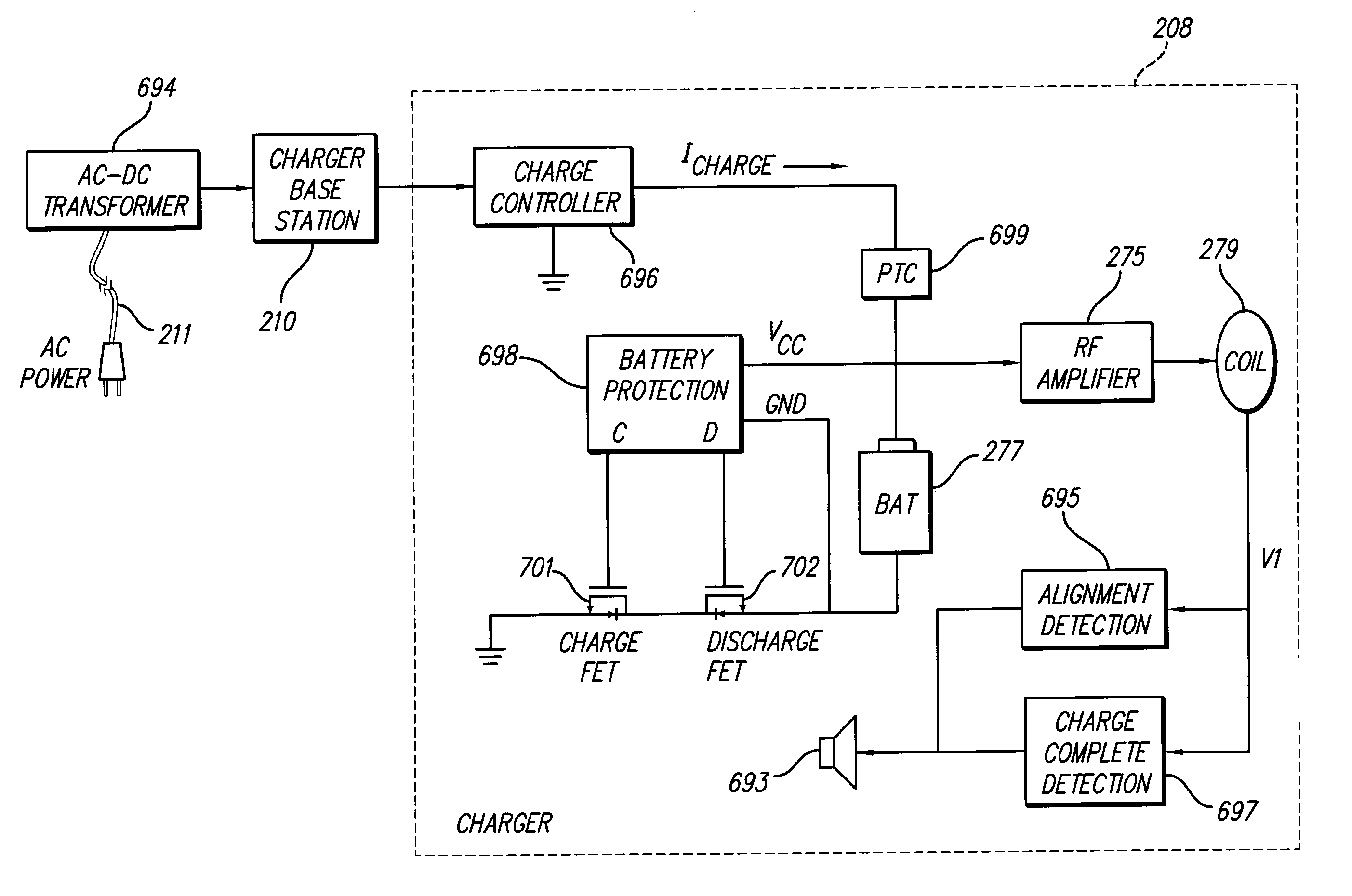
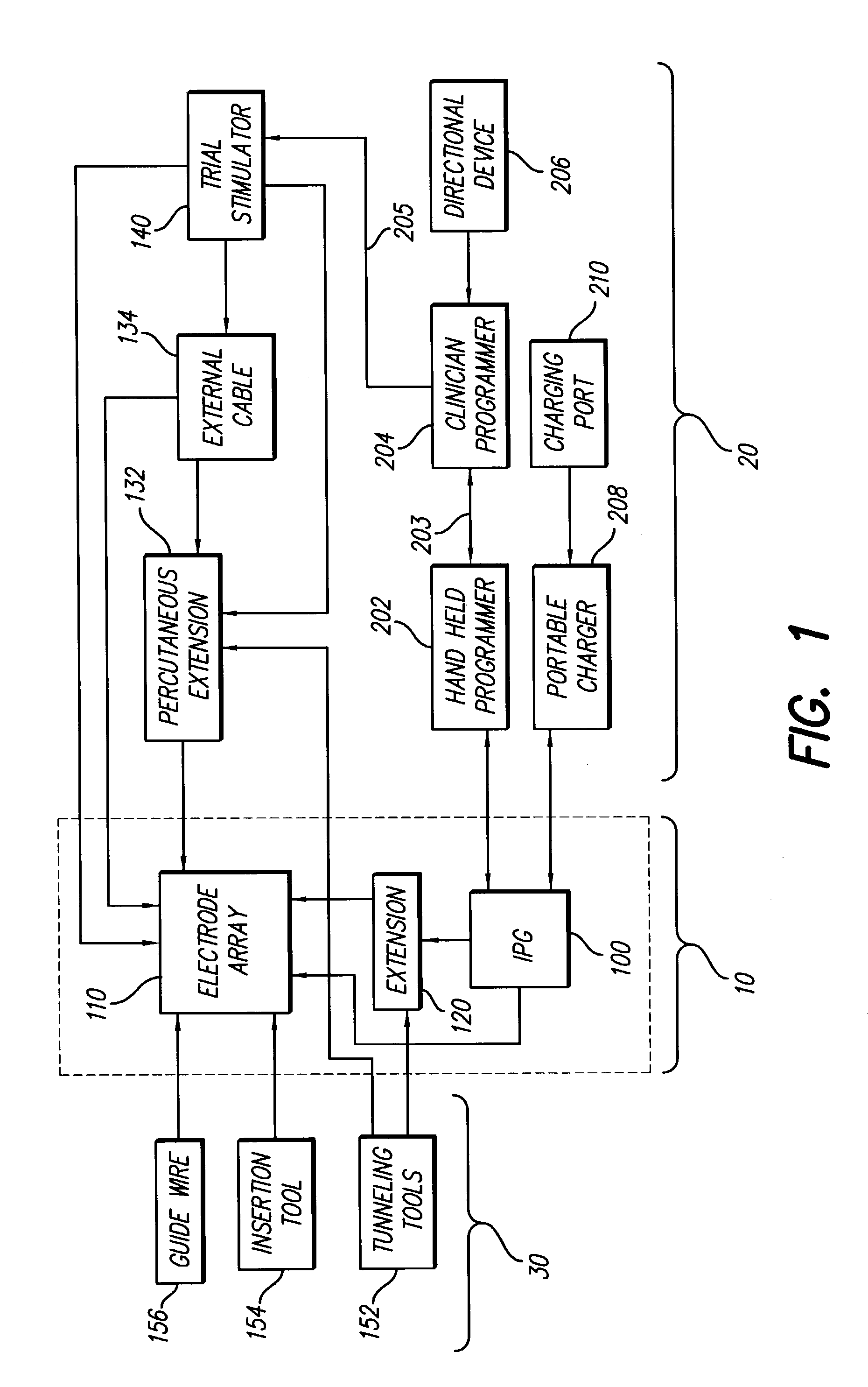
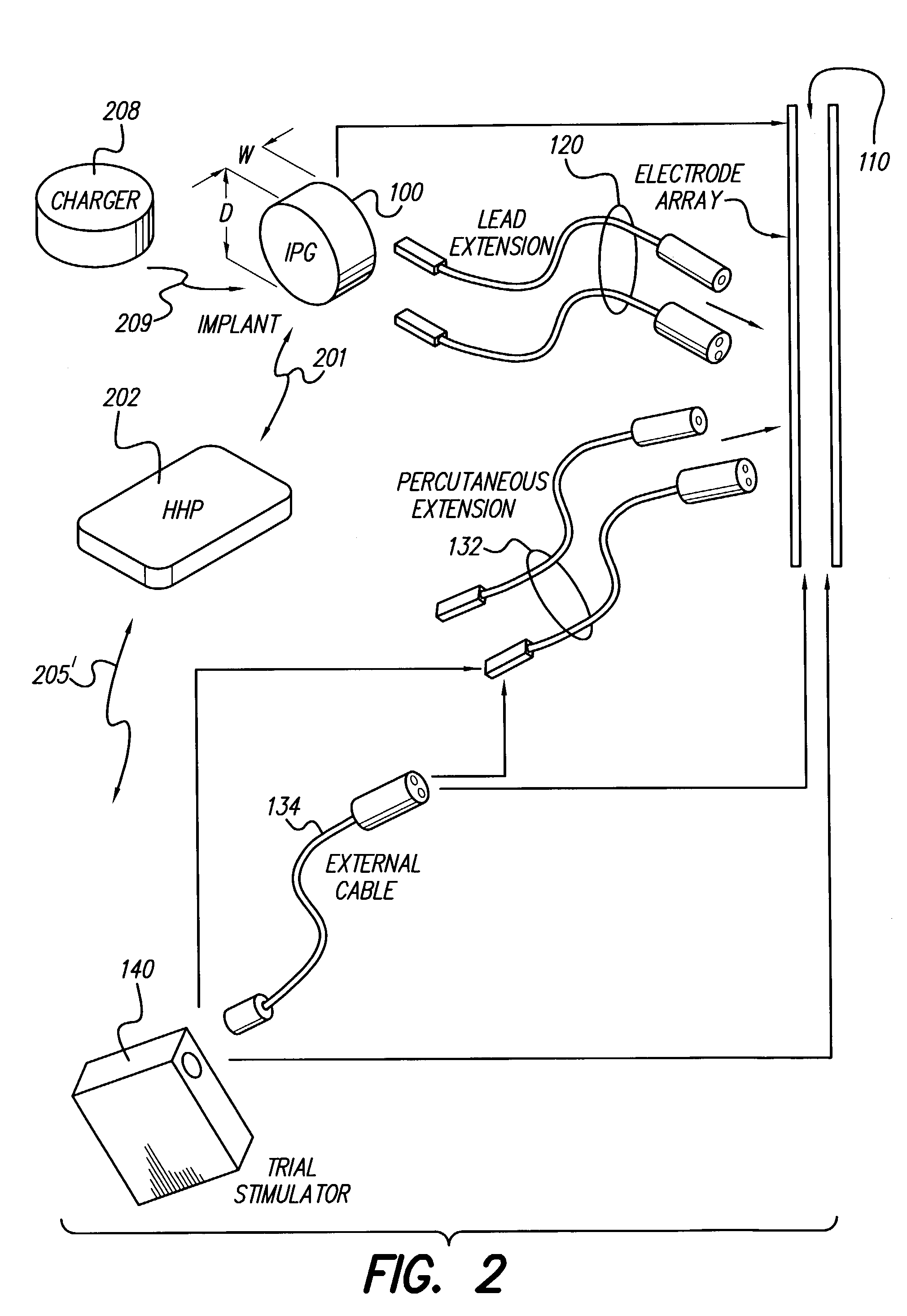
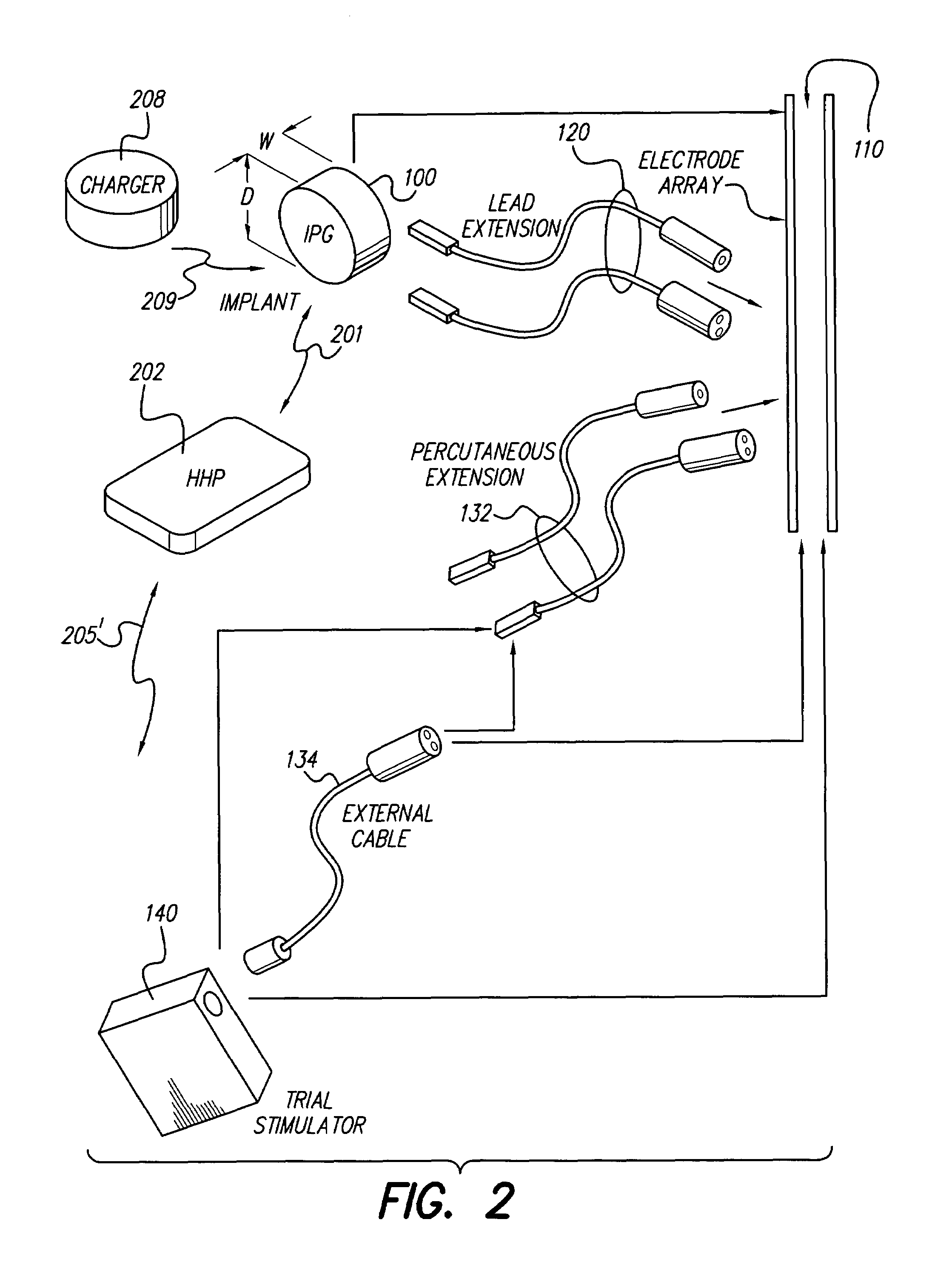
InactiveUS7184836B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedElectrotherapyLoad circuitLow voltage
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Fast charging occurs at safer lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage above about 2.5 V), and slower charging occurs when the battery nears full charge higher battery voltages (e.g., above about 4.0 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
Peptides and peptidomimetics with structural similarity to human P53 that activate P53 function
InactiveUS6245886B1Improve the immunityLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsP53 proteinWild typeP53 Mutation
The present invention provides peptides and peptidomimetics corresponding to part or to the entirety of the region encompassed by residues 360-386 of human p53, said peptides and peptidomimetics characterized by the ability to activate DNA binding of wild-type p53 and to select tumor-derived p53 mutants. Pharmaceutical compositions of the compounds of the invention and methods of using these compositions therapeutically are also provided.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
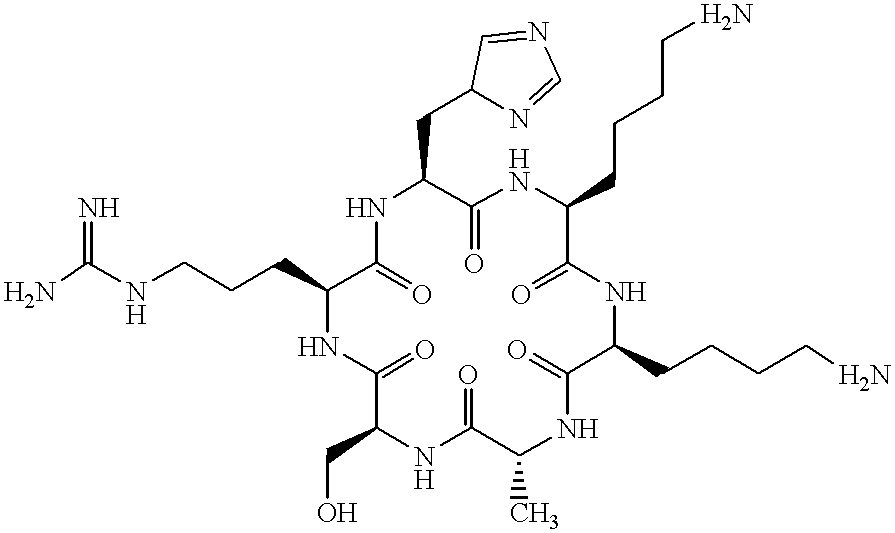
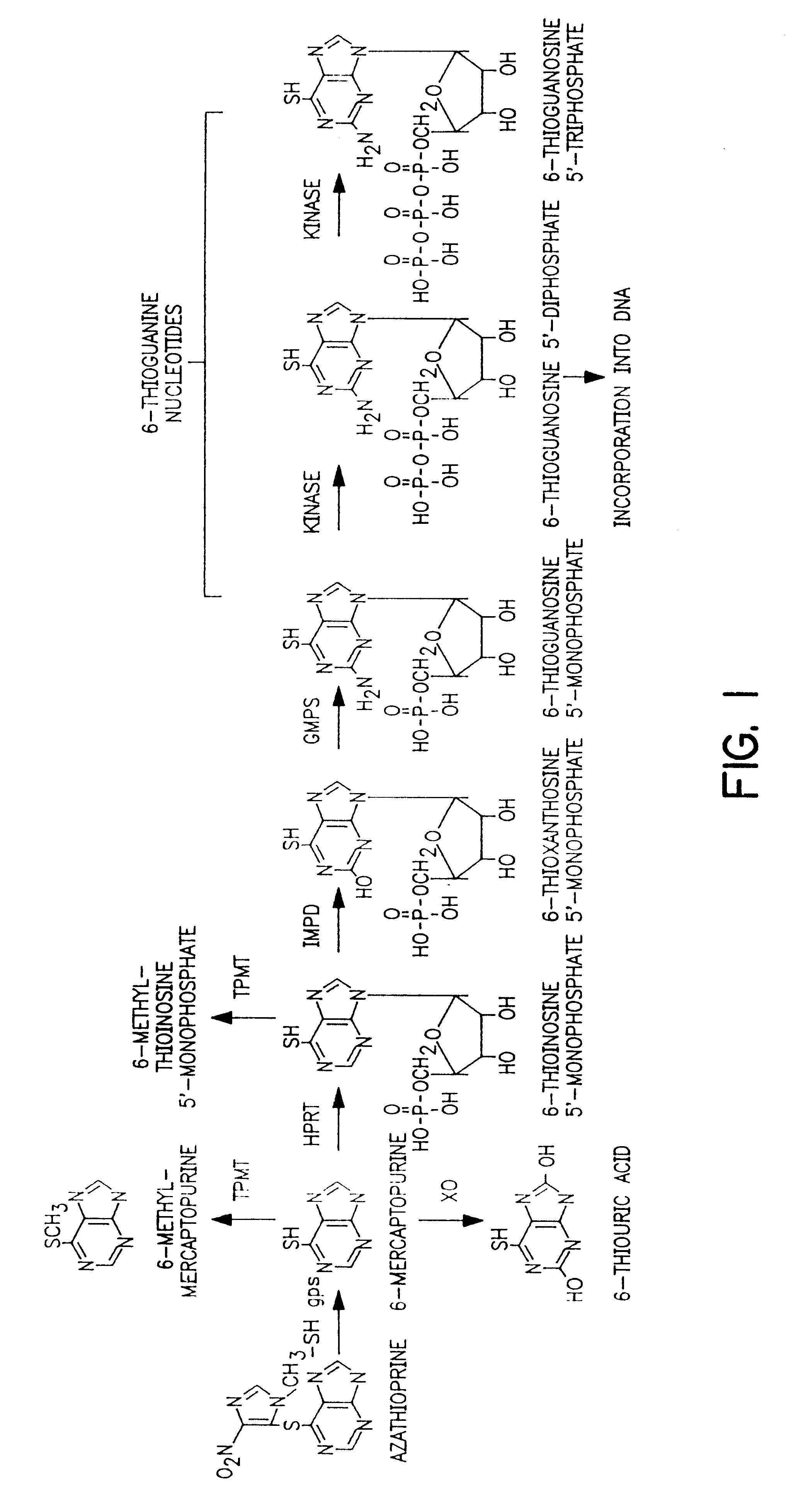
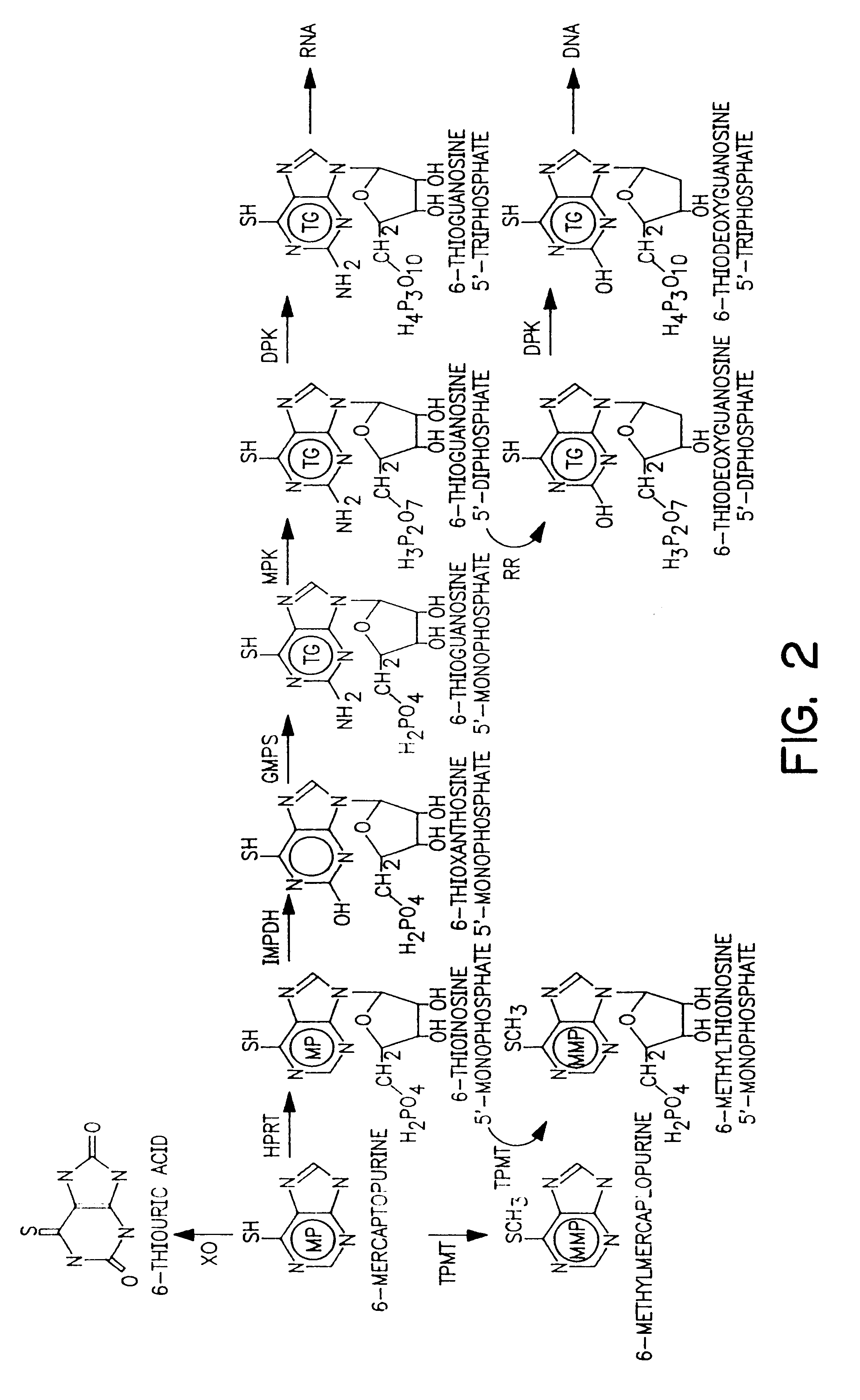
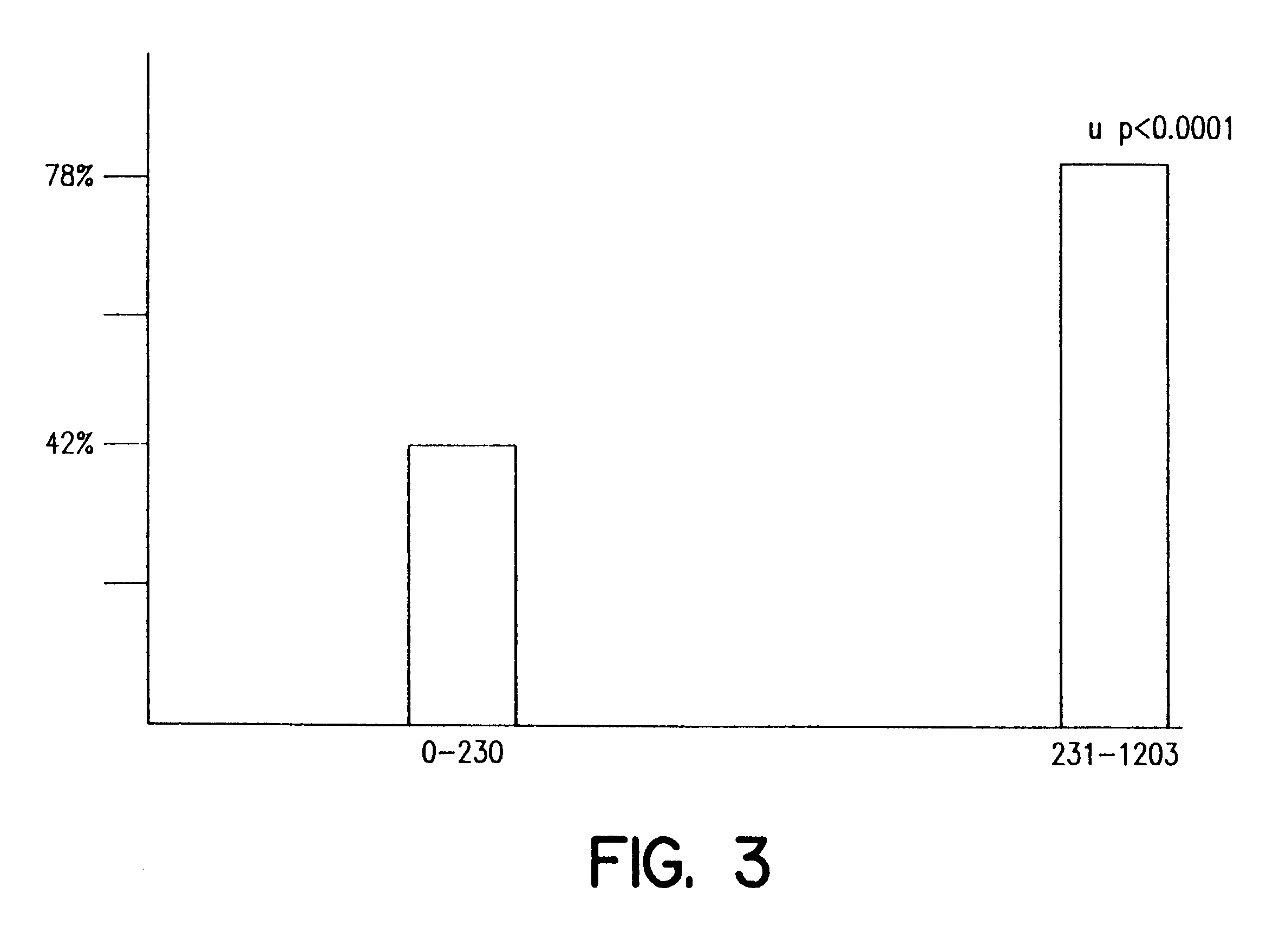
Method of treating IBD/Crohn's disease and related conditions wherein drug metabolite levels in host blood cells determine subsequent dosage
The present invention provides a method of optimizing therapeutic efficacy and reducing toxicity associated with 6-mercaptopurine drug treatment of an immune-mediated gastrointestinal disorder such as inflammatory bowel disease. The method of the invention includes the step of determining the level of one or more 6-mercaptopurine metabolites in the patient having an immune-mediated gastrointestinal disorder.
Owner:HOPITAL SAINTE JUSTINE
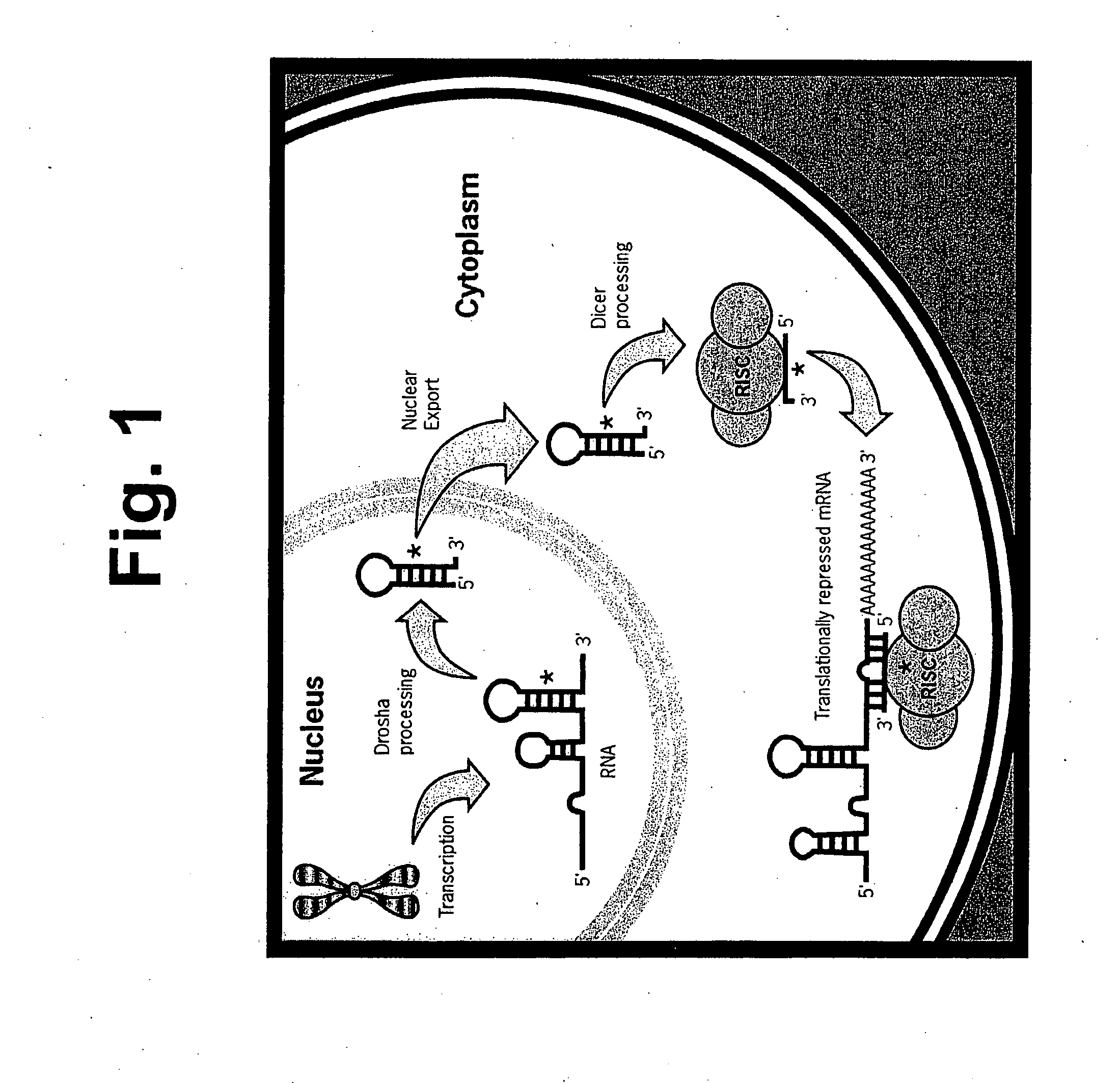
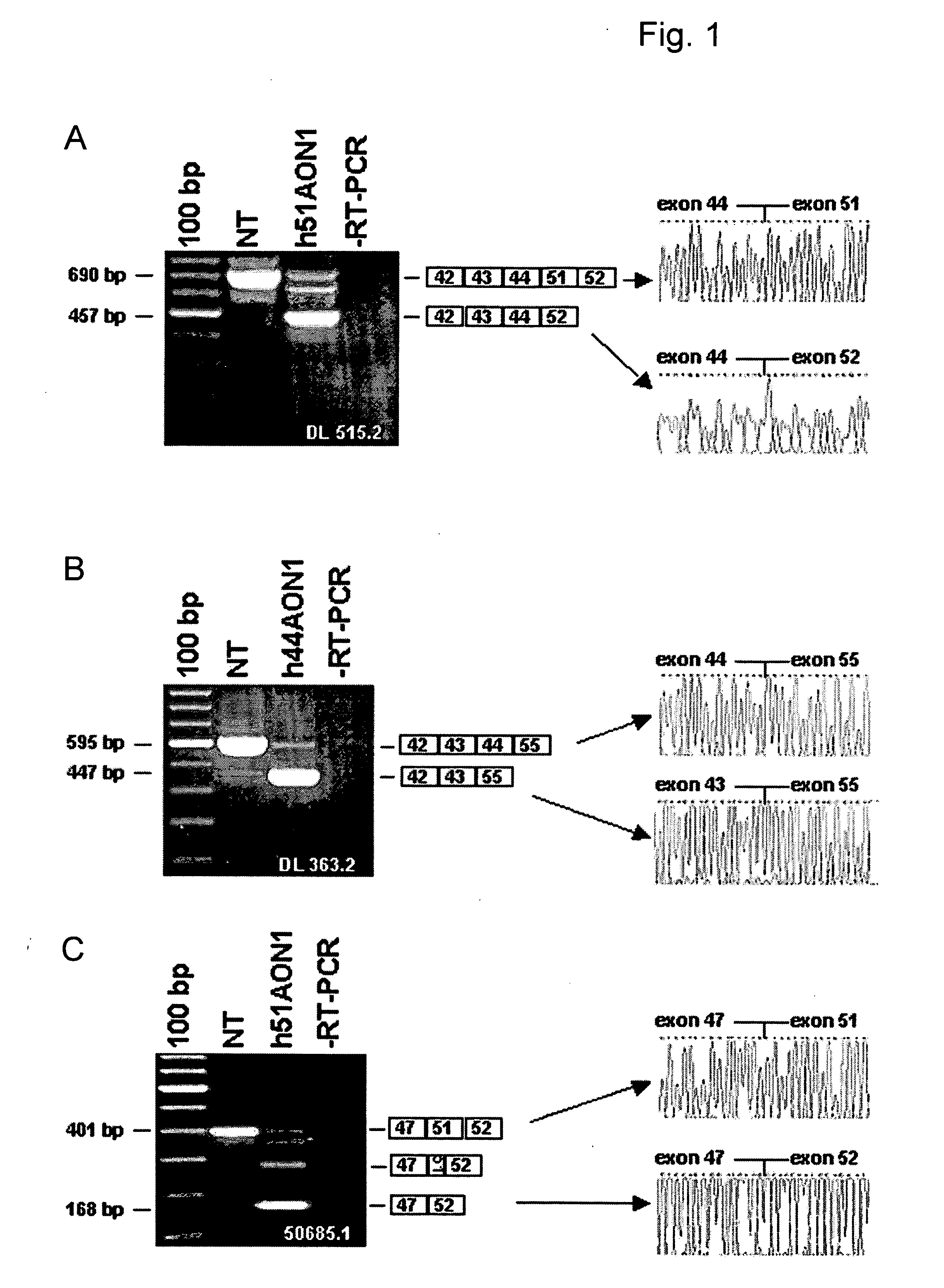
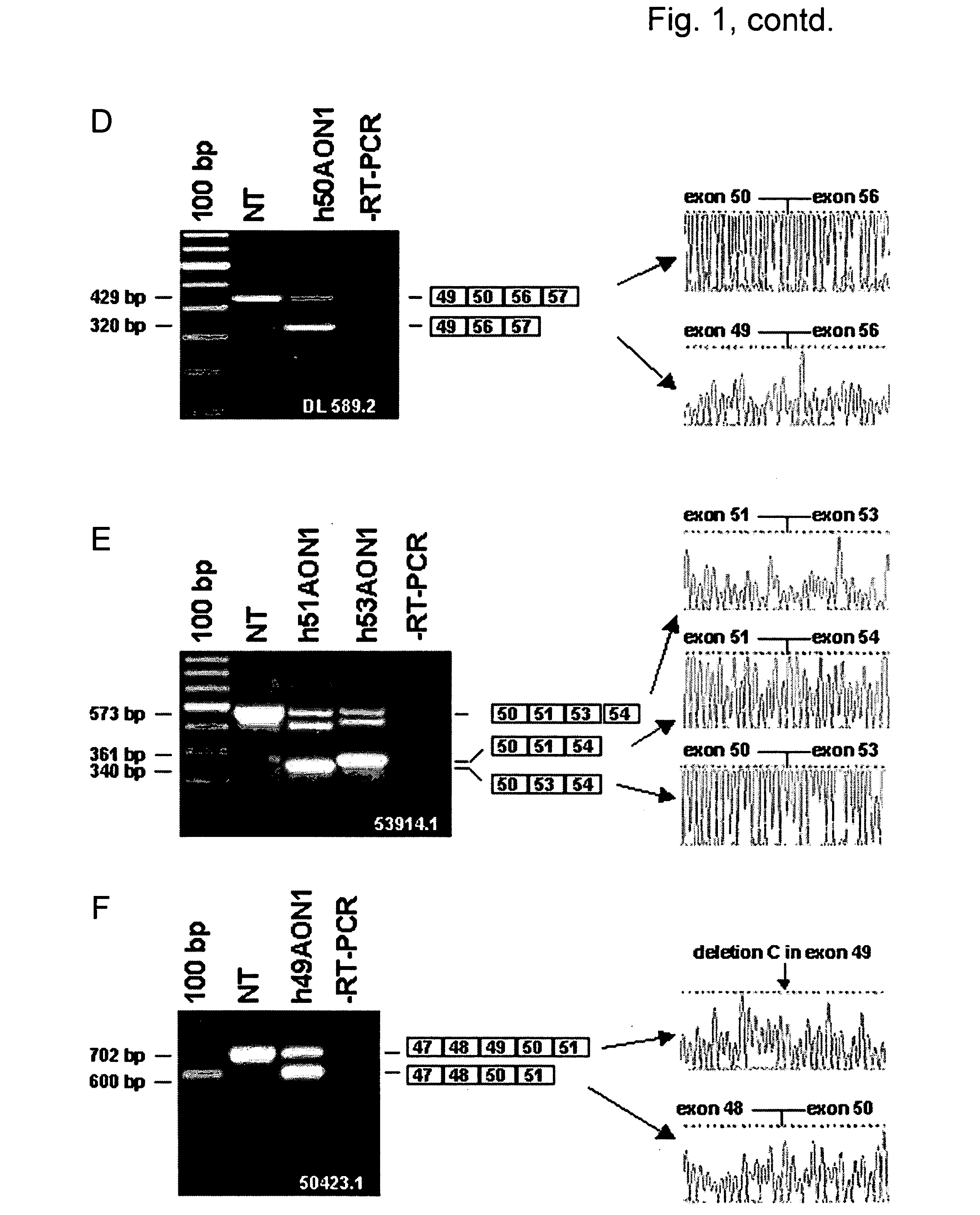
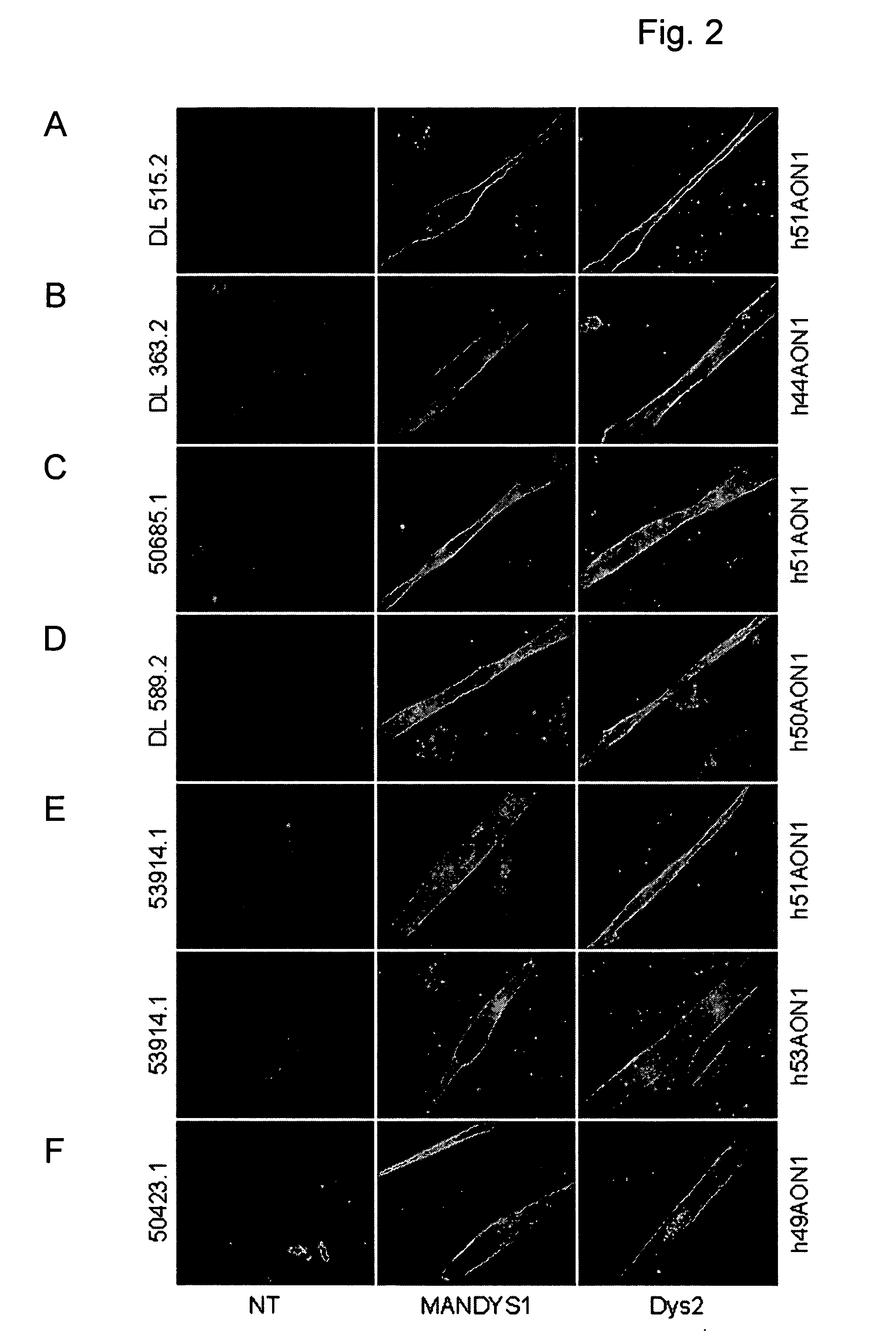
Modulation of exon recognition in pre-mRNA by interfering with the secondary RNA structure
InactiveUS20060099616A1Improves invasion efficiencyImprove efficiencySplicing alterationSugar derivativesPrecursor mRNAOligonucleotide
The invention provides a method for generating an oligonucleotide with which an exon may be skipped in a pre-mRNA and thus excluded from a produced mRNA thereof. Further provided are methods for altering the secondary structure of an mRNA to interfere with splicing processes and uses of the oligonucleotides and methods in the treatment of disease. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods and means for inducing skipping of several exons in a pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Probe arrays for detecting multiple strains of different species
InactiveUS20060160121A1Growth inhibitionReduced virulenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStreptococcus pyogenesTO-18
The present invention provides probe arrays and methods of using the same for concurrent and discriminable detection of multiple strains of different species. In one aspect, the probe arrays of the present invention are nucleic acid arrays comprising (1) a first group of probes, each of which is specific to a different respective strain of a first species; and (2) a second group of probes, each of which is specific to a different respective strain of a second species. In many embodiments, the nucleic acid arrays of the present invention further include a third group of probes, each of which is specific to a different strain of a third species. In one example, a nucleic acid array of the present invention includes probes for sequences selected from SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 18,598, and can discriminably detect different strains of Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Quantification method for remaining liver function and novel liver receptor imaging agent
ActiveUS20110097265A1High measurement accuracyImprove accuracySugar derivativesSaccharide peptide ingredientsDiseaseReceptor
A test indicator for quantifying remaining liver function is provided. A novel liver receptor imaging agent with liver targeting property is utilized to develop a method for quantifying remaining liver function to serve as test indicator for judging the liver failure outcome in clinic, particularly for judging the necessity of liver transplantation for patients with liver failure or liver disease. The radioactivity uptake of the test indicator was negatively correlated with the extent of liver reserve. The cutoff value of liver reserve for liver transplantation is also disclosed.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Radiolabeling method using multivalent glycoligands as hepatic receptor imaging agent
InactiveUS20110097264A1Low toxicityImprove securityRadioactive preparation carriersSaccharide peptide ingredientsImaging agentClinical trial
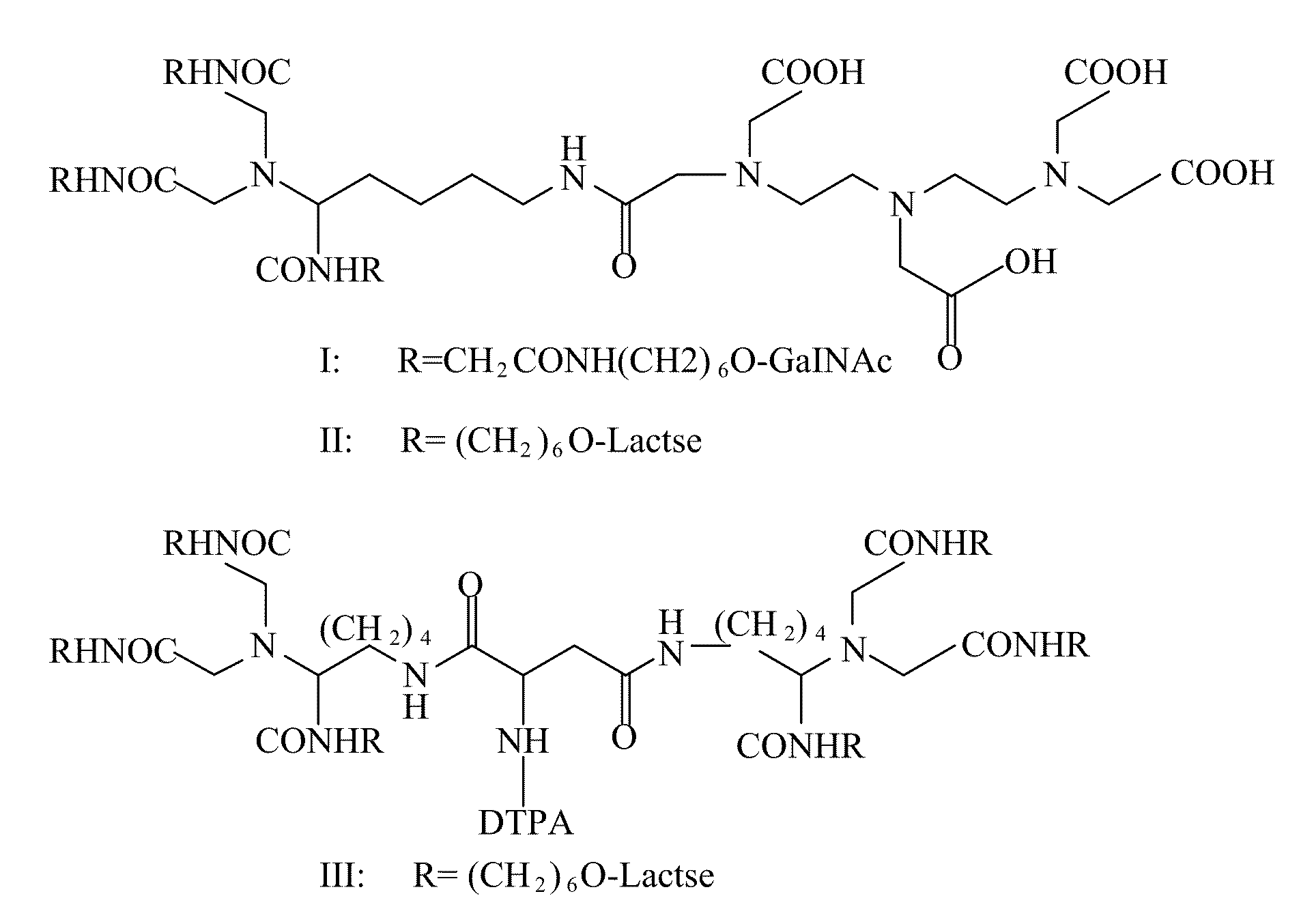
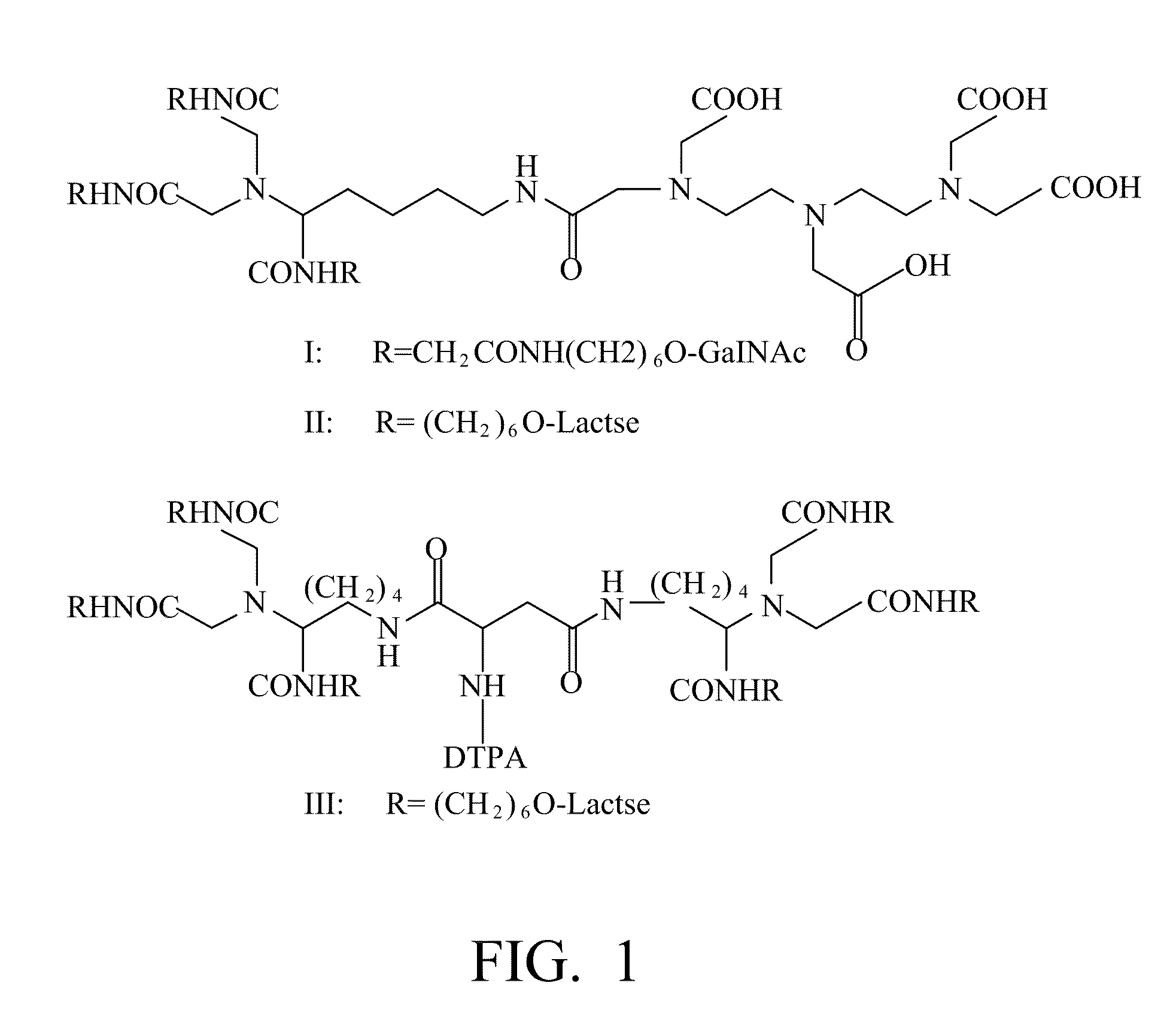
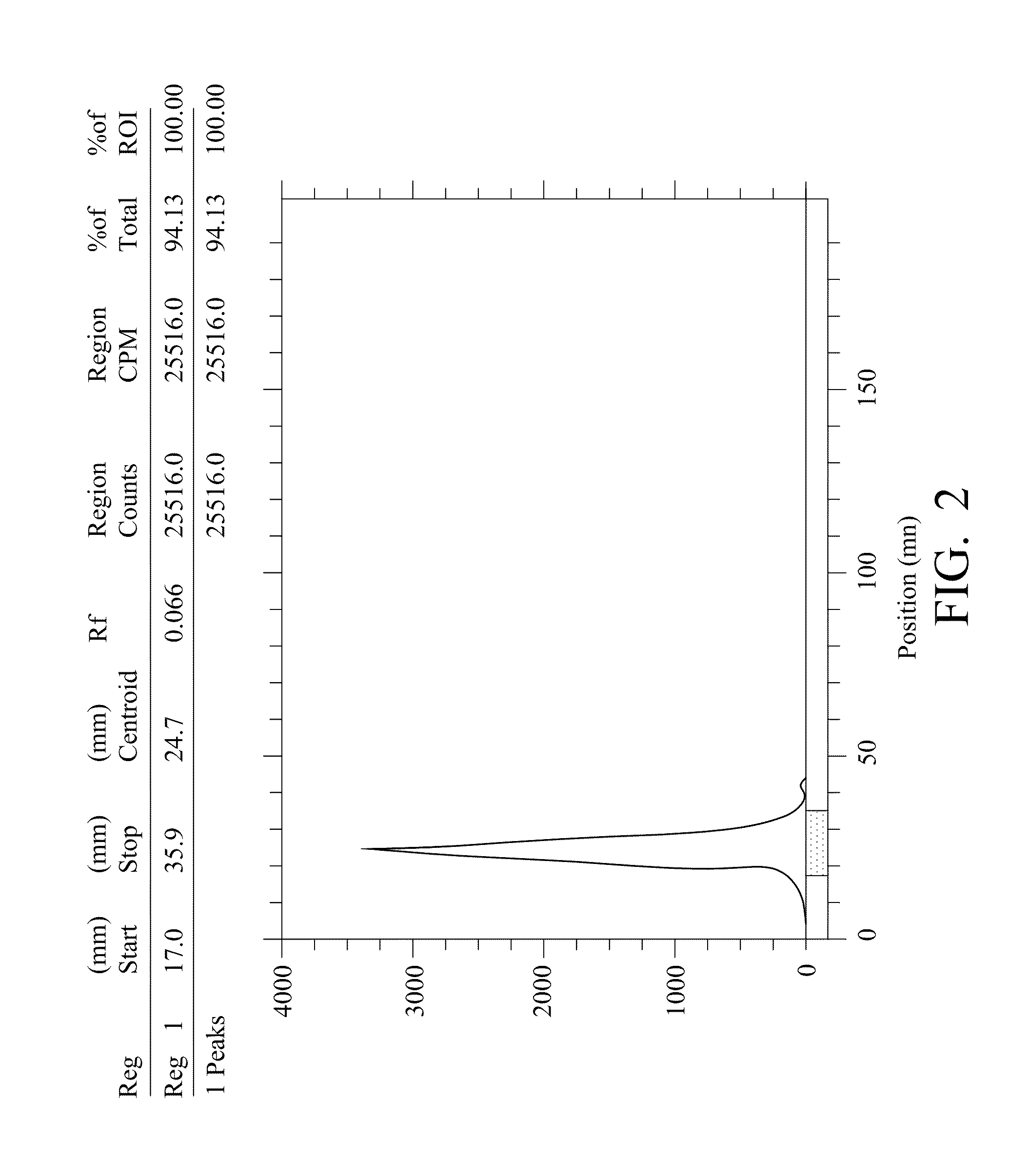
A radiolabeling method using a multivalent glycoligand as hepatic receptor imaging agent is provided. The multivalent glycoligand-DTPA derivatives (In-111-DTPA-hexa lactoside and In-111-DTPA-tri-galactosamine glycoside) labeled with In-111 are used as hepatic receptor imaging agent. The effects of imaging of a hepatic receptor in different species are evaluated, the lowest specific radioactivity values of hepatic receptor imaging required in different species are discovered. Since the specificity of the human ASGPR closely resembles that of the mouse. This kind of radiolabelling method, agent and related study about specific radioactivity could be used in clinical trial in the future.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Il-6 production inhibitors
InactiveUS20050119305A1Easy to prepareLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAutoimmune conditionHydroxamic acid
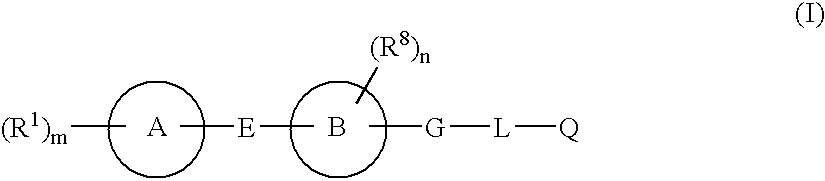
An IL-6 production inhibitor which comprises a hydroxamic acid derivative of formula (I) (wherein all the symbols have the same meanings as defined in the specification), an equivalent thereof, a non-toxic salt thereof or a prodrug thereof as an active ingredient. Because of having an IL-6 production inhibitory activity, the compound of formula (I) may be useful for the prevention and / or treatment of various inflammatory diseases, sepsis, multiple myeloma, plasma cell leukemia, osteoporosis, cachexia, psoriasis, nephritis, renal cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, rheumatoid arthritis, hypergammaglobulinemia (gammophathy), Castleman's disease, intra-atrial myxoma, diabetes, autoimmune disease, hepatitis, colitis, graft-versus-host disease, infectious diseases, endometriosis and solid cancer.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates
ActiveUS20120289457A1Easy to transportImprove propertiesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
Oligonucleotide analogues conjugated to carrier peptides are provided. The disclosed compounds are useful for the treatment of various diseases, for example diseases where inhibition of protein expression or correction of aberrant mRNA splice products produces beneficial therapeutic effects.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and products related to the intracellular delivery of polysaccharides
InactiveUS20060083711A1Inhibit cell proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAnticoagulant effectPolysaccharide
The invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for the intracellular delivery of polysaccharides. In particular, the methods and compositions relate to the intracellular delivery of glycosaminoglycans, such as heparin. The invention in other aspects relates to the use of glycosaminoglycans for the treatment of proliferative disorders, such as cancer. The invention is still other aspects relates to improving cell viability. The invention also relates to the delivery of polysaccharides while avoiding unwanted effects of the polysaccharides. For example, heparin can be delivered while avoiding its anticoagulant effects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Chimeric viruses presenting non-native surface proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120122185A1Readily immunizeEffective immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEctodomainVirosome
The present invention provides chimeric negative-stand RNA viruses that allow a subject, e.g., an avian, to be immunized against two infectious agents by using a single chimeric virus of the invention. In particular, the present invention provides chimeric influenza viruses engineered to express and incorporate into their virions a fusion protein comprising an ectodomain of a protein of an infectious agent and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of an influenza virus protein. Such chimeric viruses induce an immune response against influenza virus and the infectious agent. The present invention also provides chimeric Newcastle Disease viruses (NDV) engineered to express and incorporate into their virions a fusion protein comprising the ectodomain of a protein of an infectious agent and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of an NDV protein. Such chimeric viruses induce an immune response against NDV and the infectious agent.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
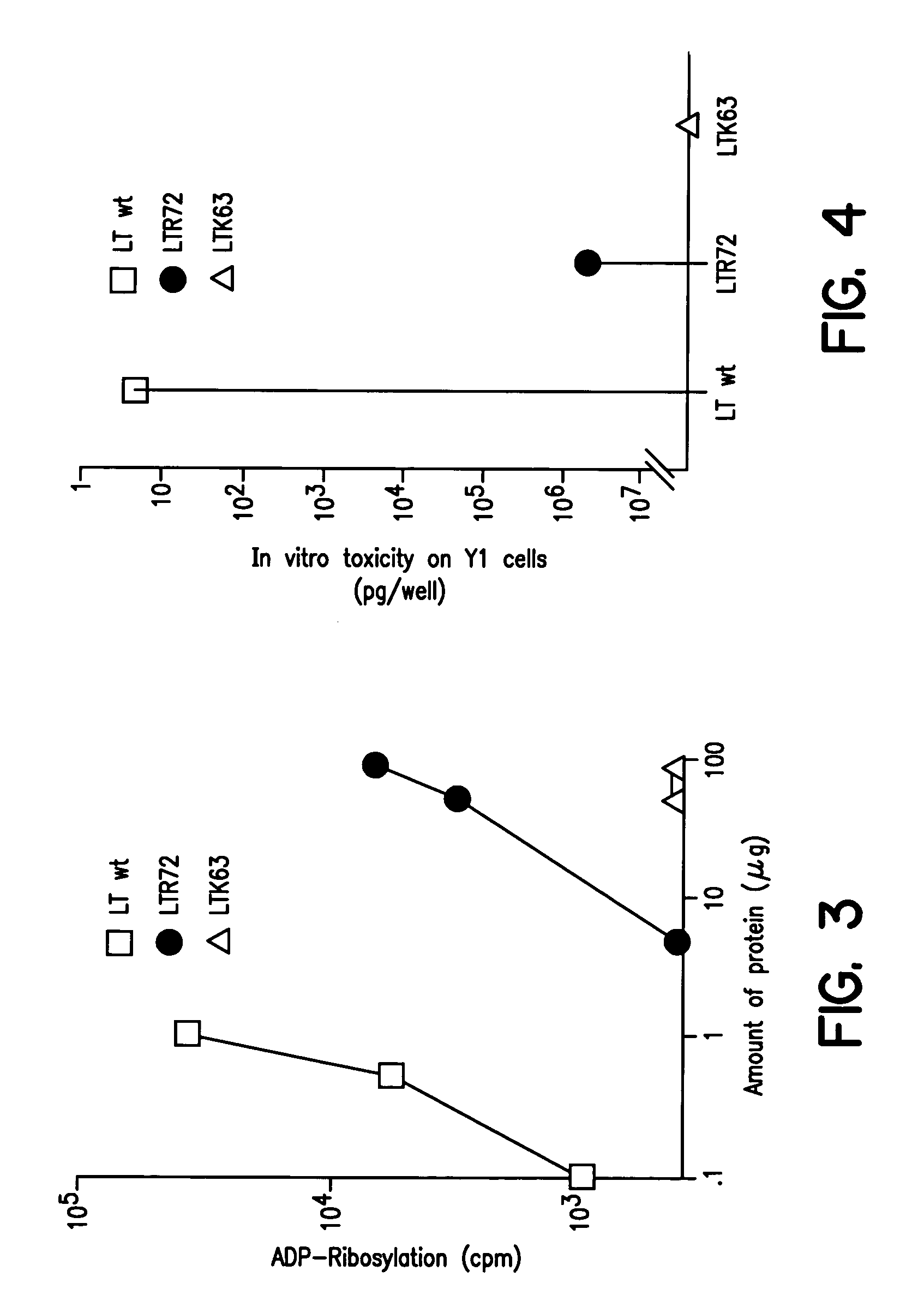
Immunogenic detoxified mutant E. coli LT-A-toxin
InactiveUS7115730B1Maximise adjuvanticityMaximise immunogenicityBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliAdjuvant
An immunogenic detoxified protein is provided which comprises the amino acid sequence of subunit A of an E. coli heat labile toxin (LT-A) or a fragment thereof in which at least amino acid Ala-72, numbered relative to SEQ ID NO:1, of the A subunits mutated, preferably by substitution with Arg. The toxoid is useful as vaccine against an enterotoxigenic strain of E. coli and is produced by recombinant DNA means by site-directed mutagenesis. It is also an effective adjuvant.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
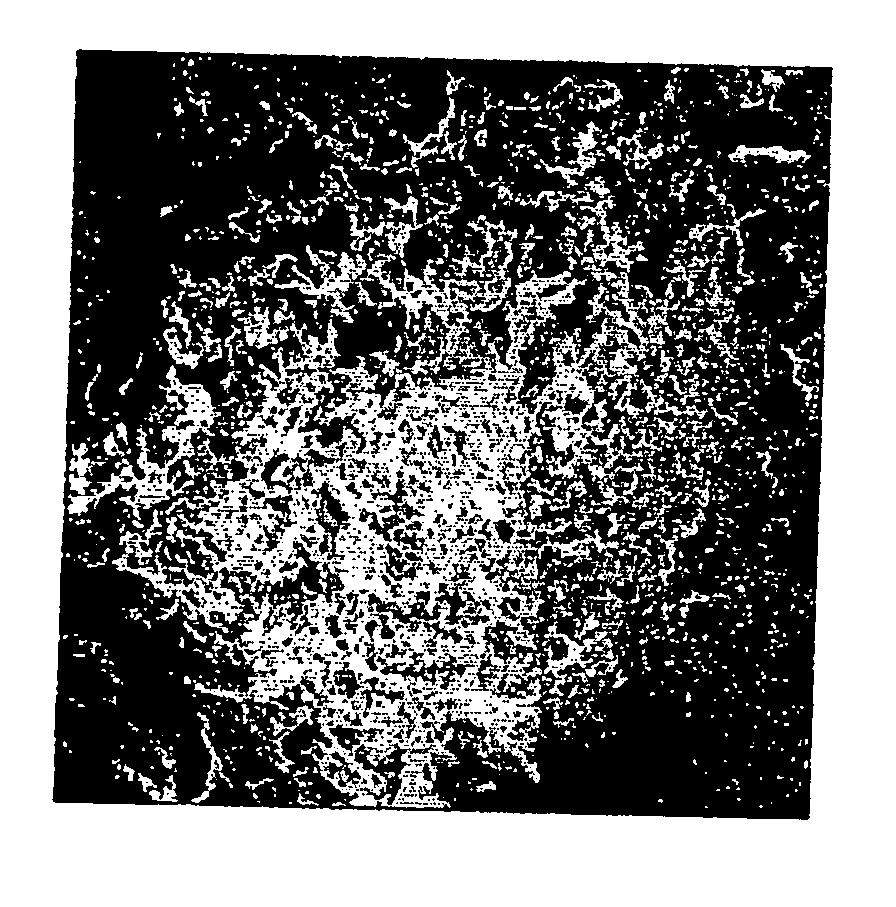
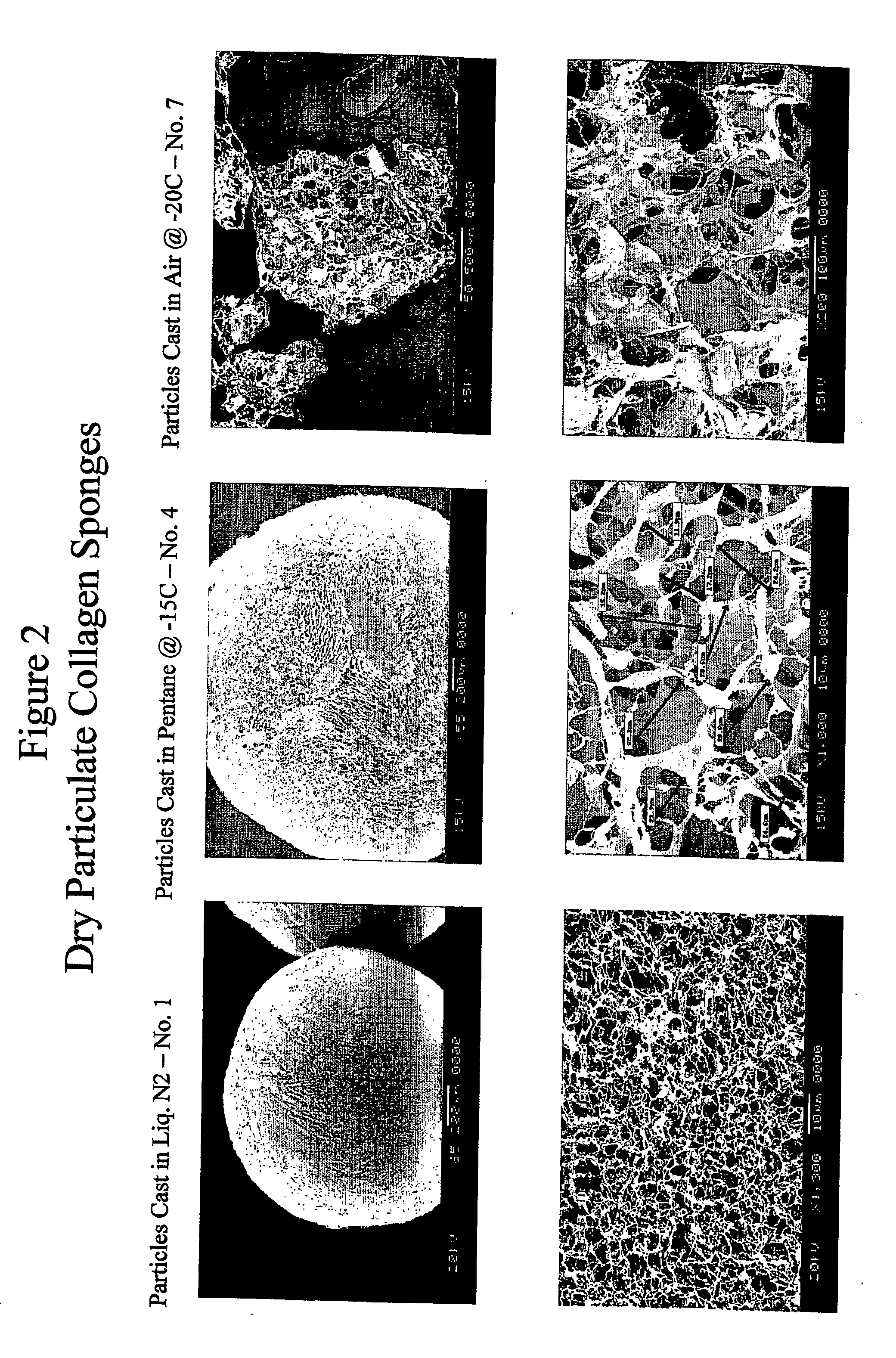
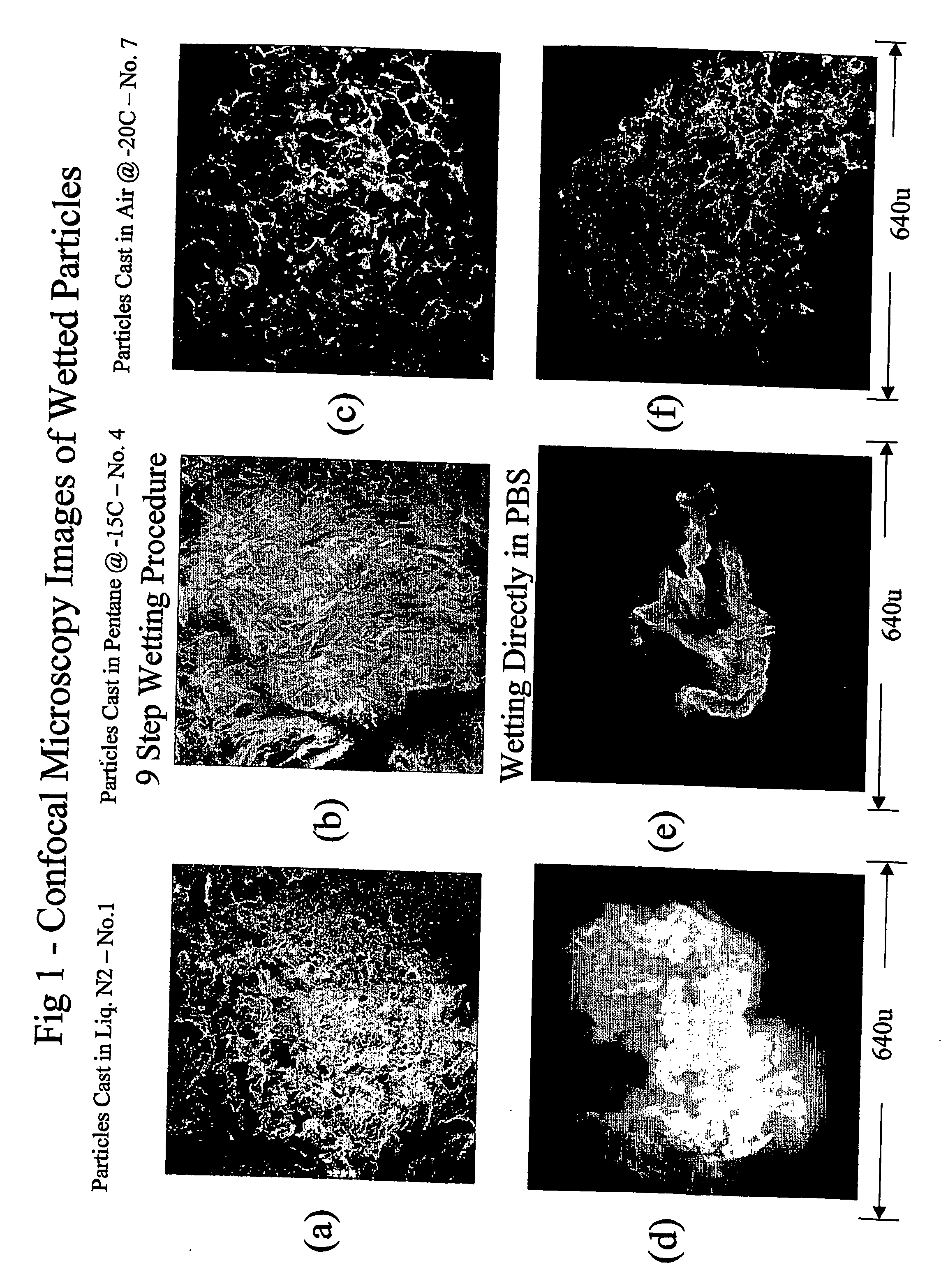
Porous particulate collagen sponges
InactiveUS20060135921A1Low toxicitySatisfactory porosityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsParticulatesCross-link
The present invention relates to the development of new porous particulate collagen sponges, combining the desirable features of low toxicity, resorbability, and satisfactory porosity, particularly when wetted in an aqueous medium. Accordingly, the present invention is directed to new porous, particulate, dehydrothermally cross-linked, wetted sponges, as well as a process for making them.
Owner:WIERCINSKI ROBERT A +2
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS7295878B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedImplantable neurostimulatorsLoad circuitLow voltage
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Slow charging occurs at lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage below about 2.5 V), and fast charging occurs when the battery voltage has reached a safe level (e.g., above about 2.5 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com