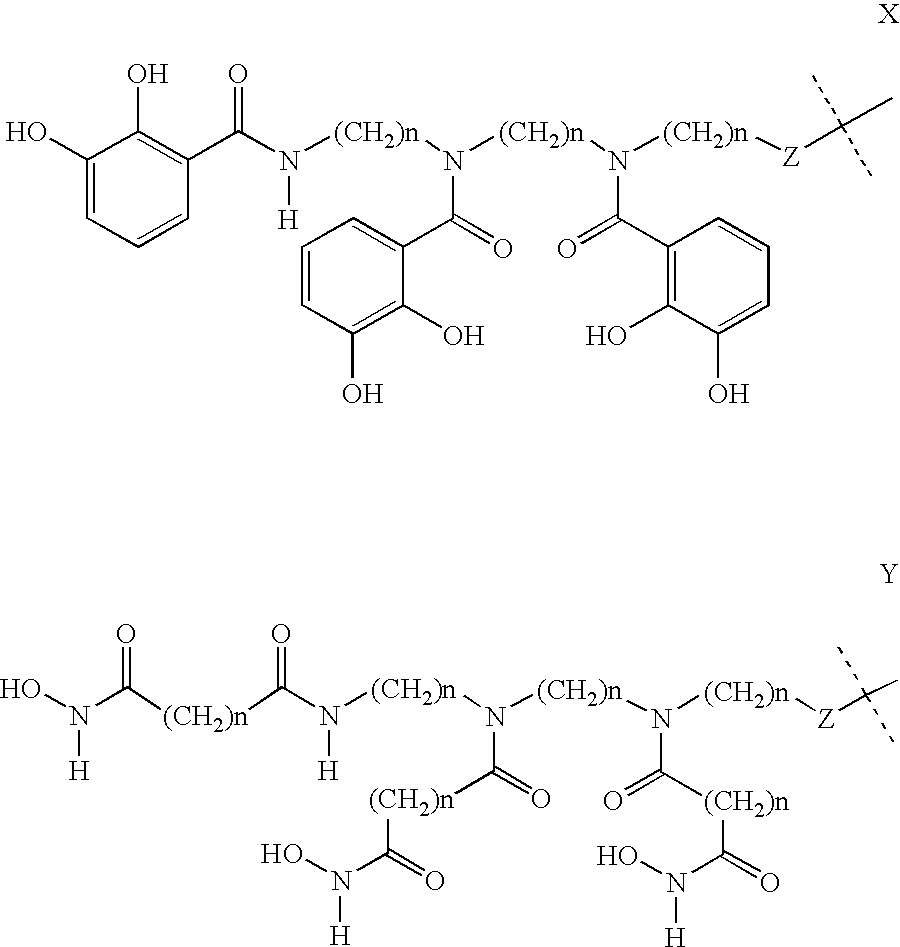
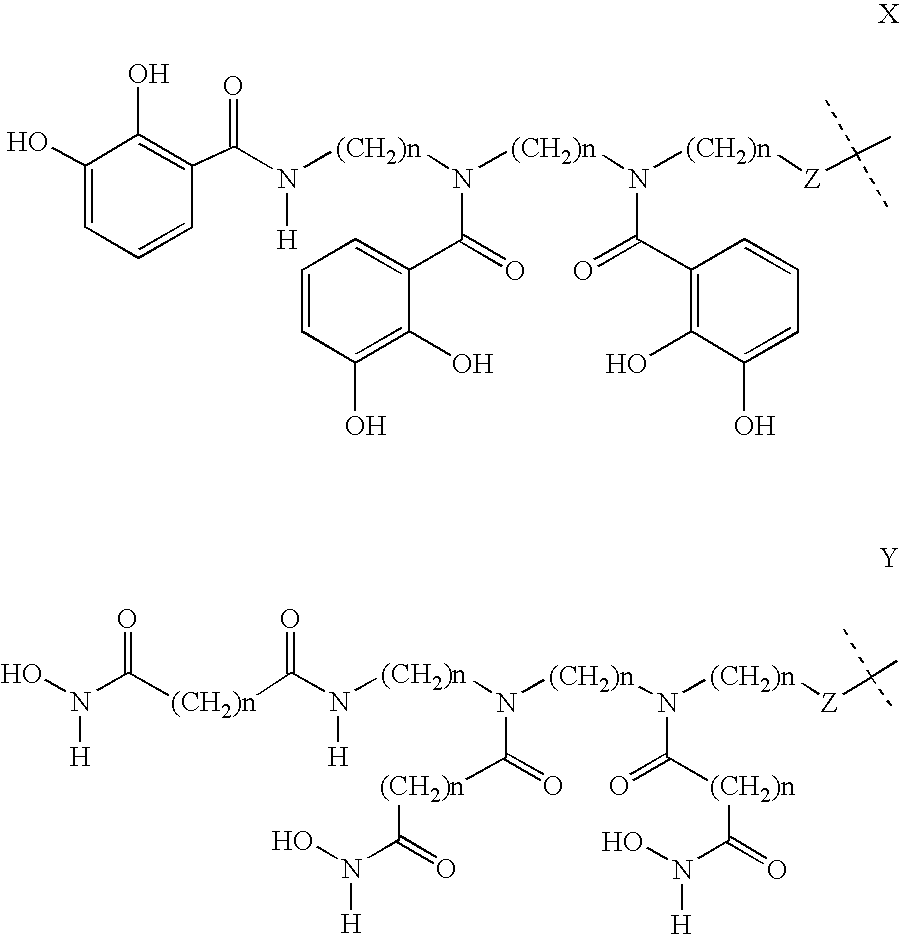
Patents
Literature
165 results about "Streptococcus pyogenes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streptococcus pyogenes is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacterium in the genus Streptococcus. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci. It is clinically important for humans. It is an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota. It is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A Streptococcus (GAS). However, both Streptococcus dysgalactiae and the Streptococcus anginosus group can possess group A antigen. Group A streptococci when grown on blood agar typically produces small zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. (A zone size of 2–3 mm is typical.) It is thus also called group A (beta-hemolytic) Streptococcus (GABHS), and it can make colonies greater than 5 mm in size.
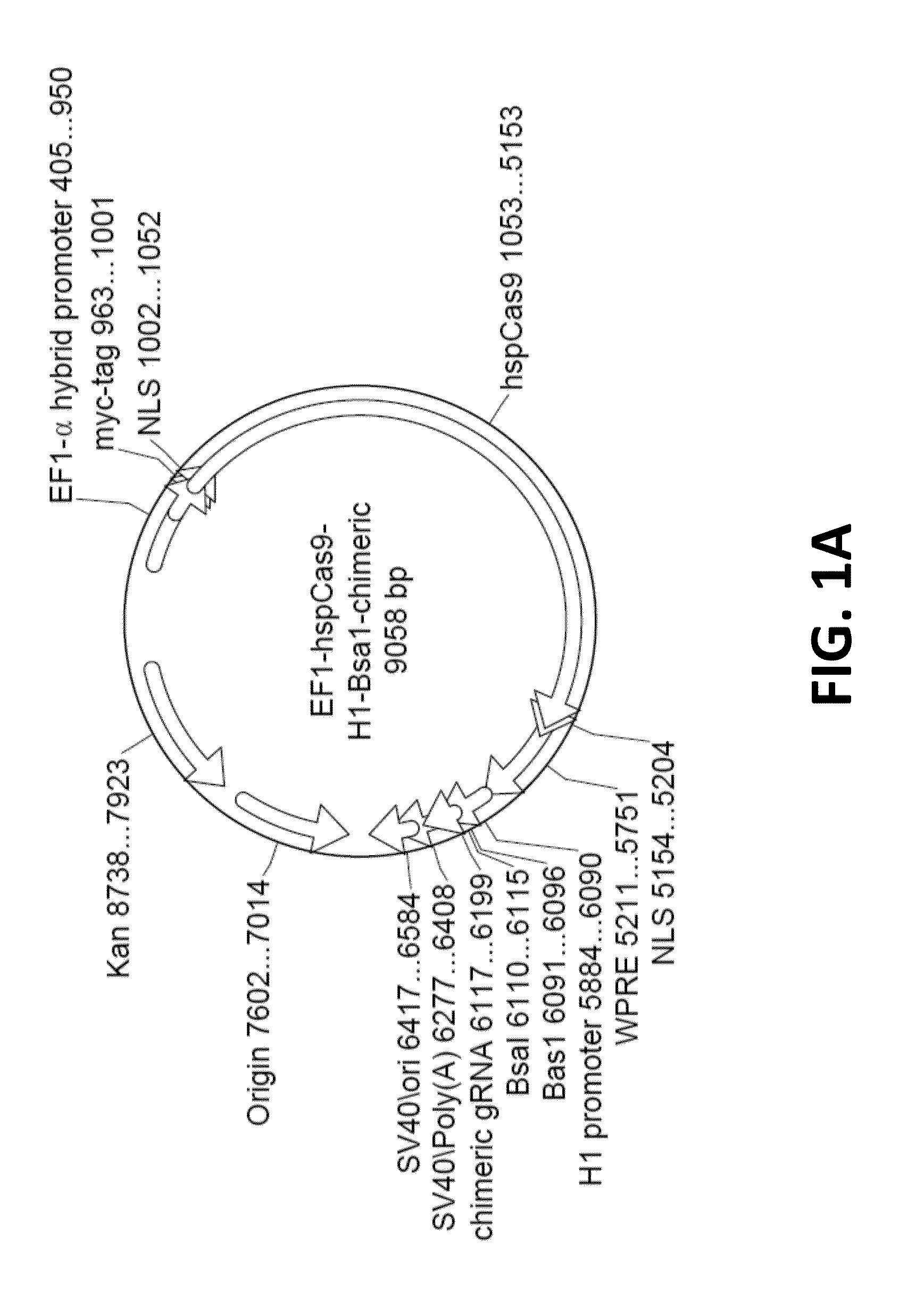
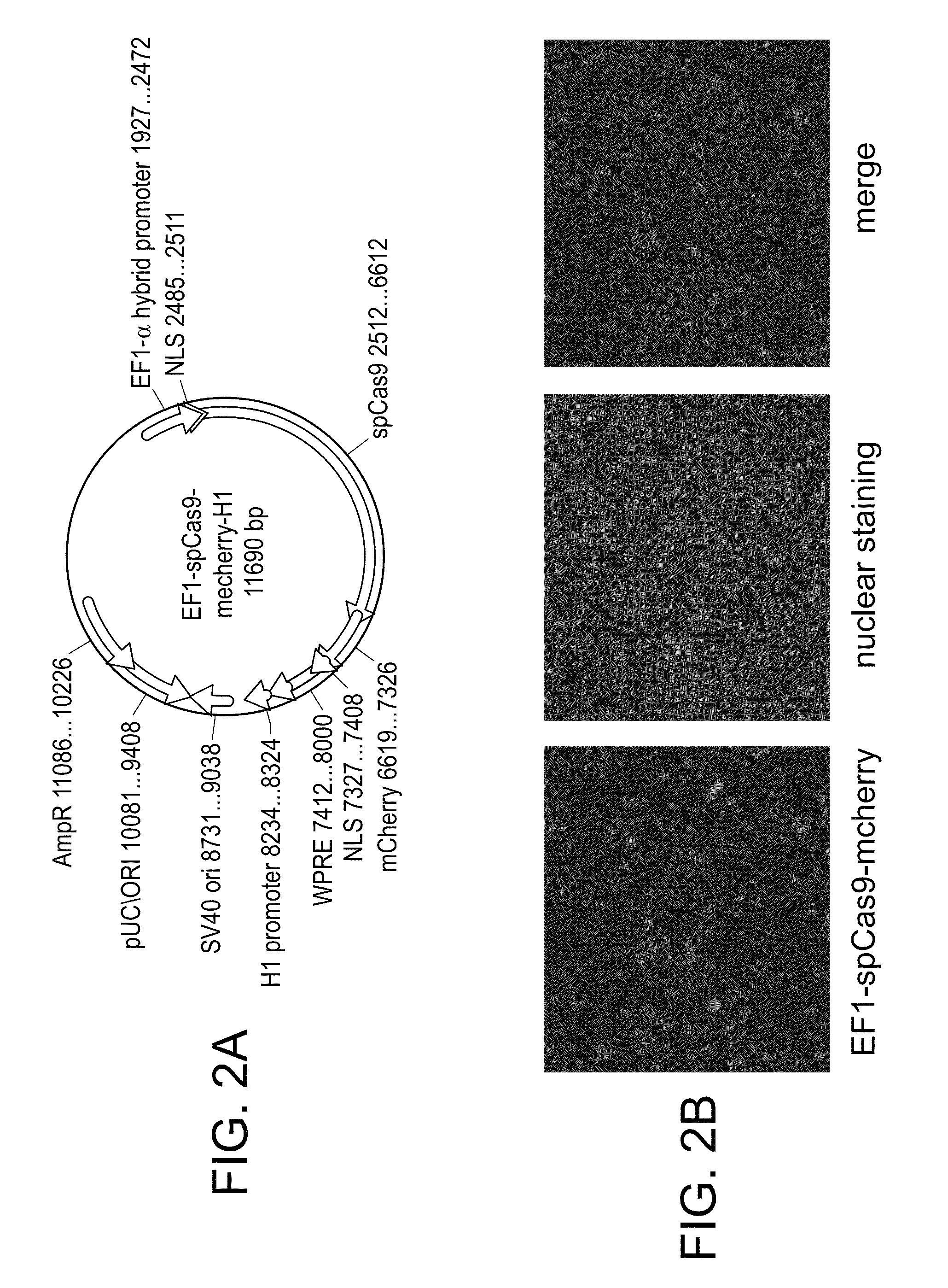
Crispr/cas systems for genomic modification and gene modulation
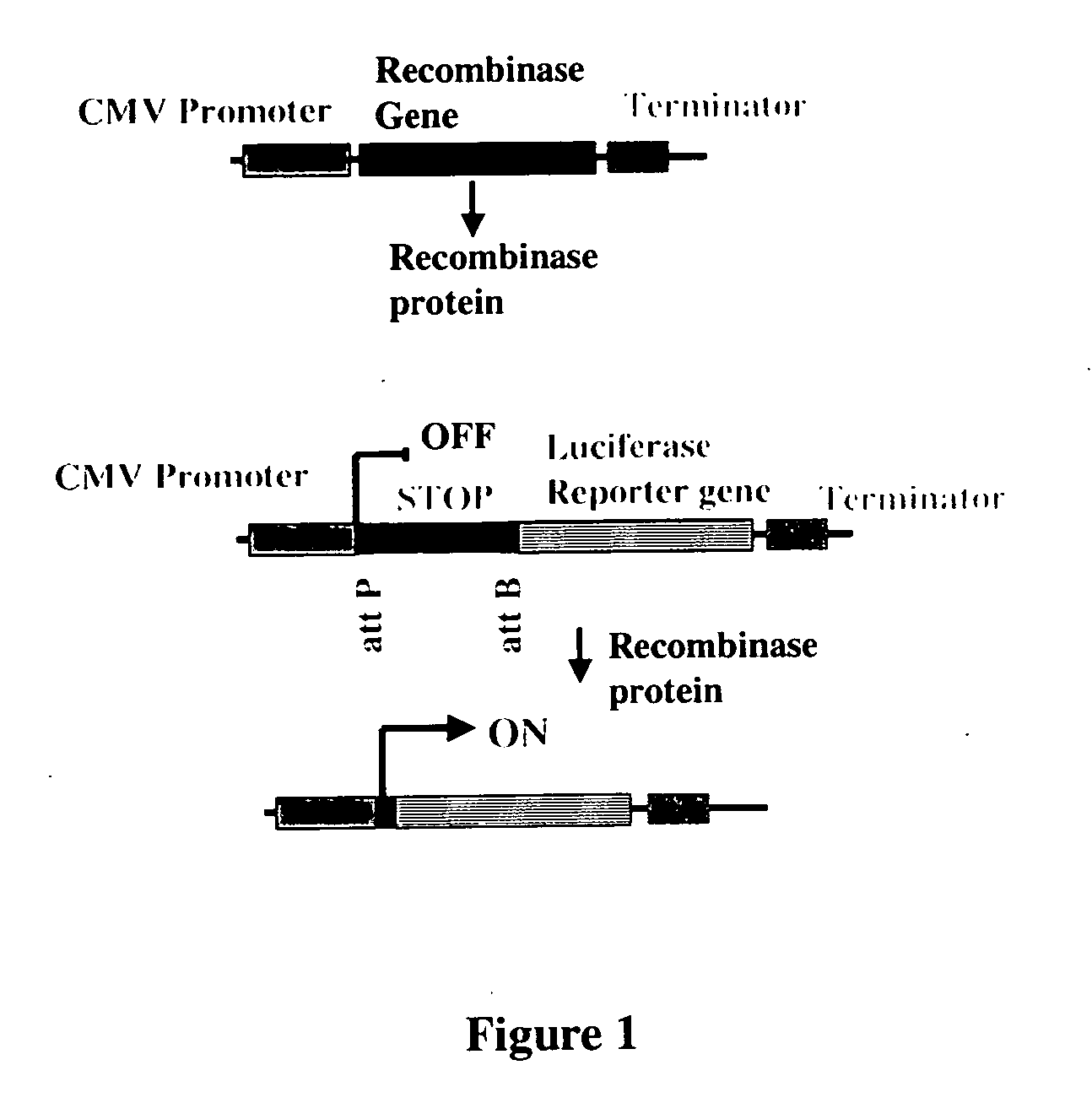
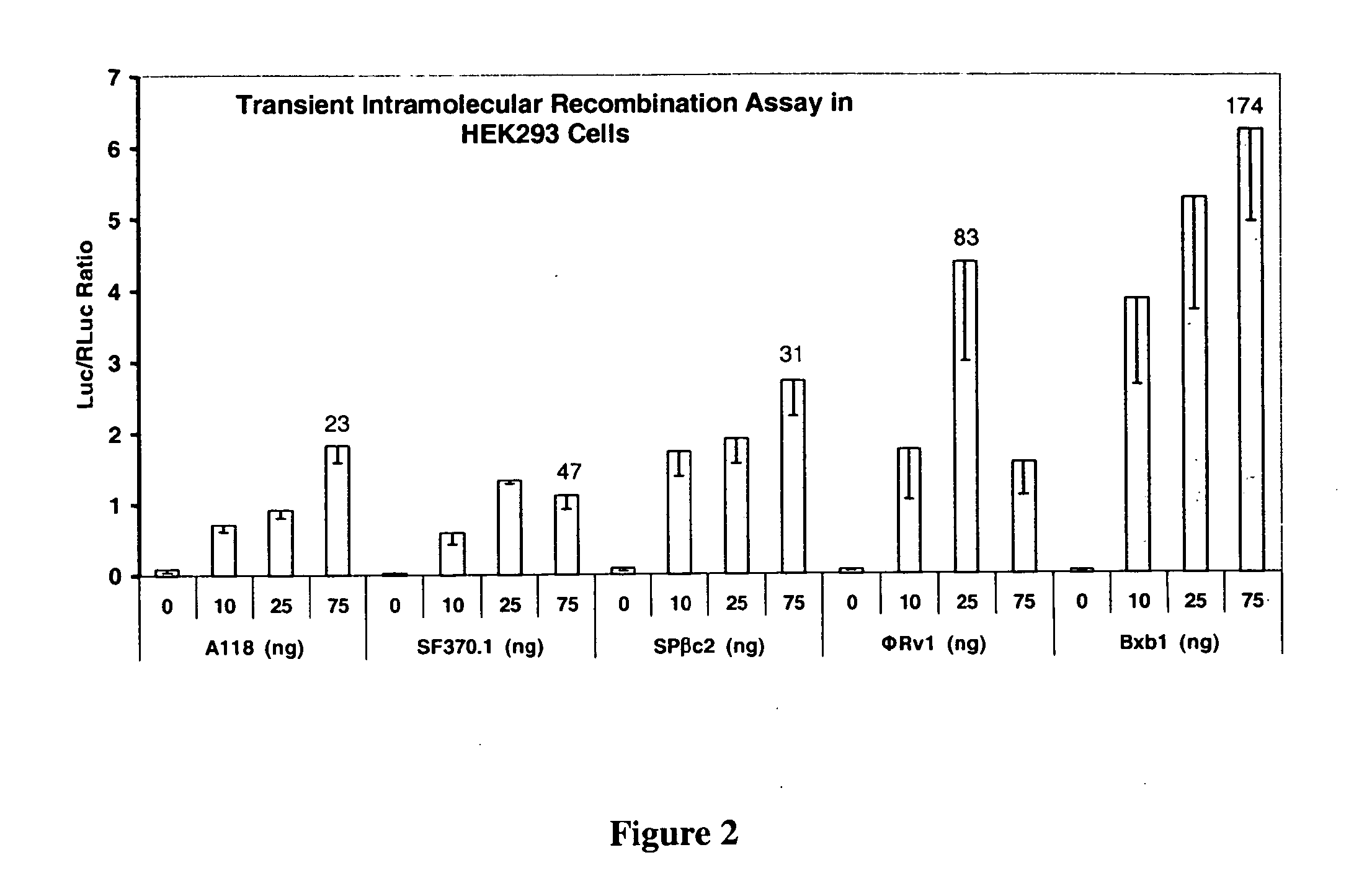
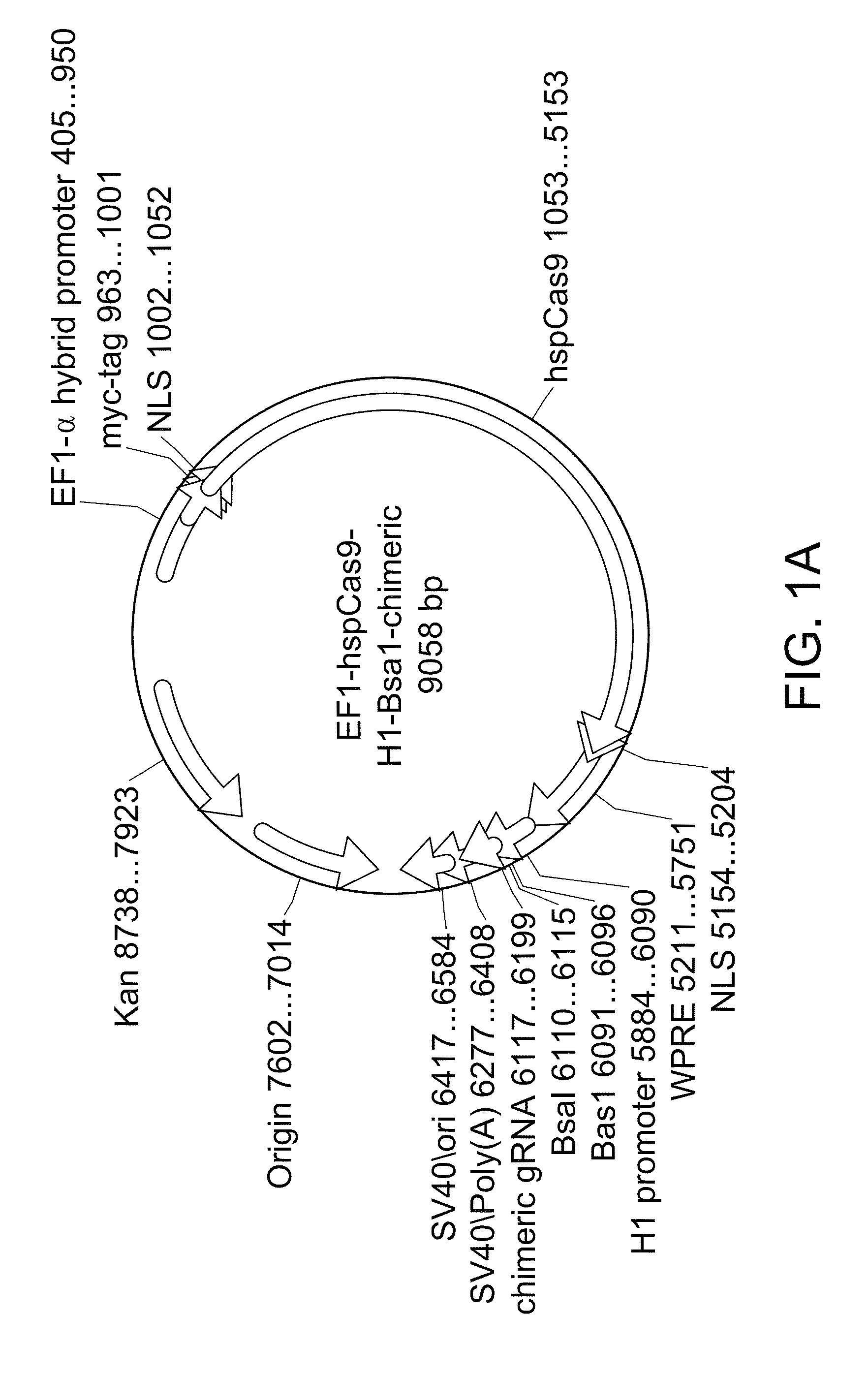
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification and regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells. The specification describes the design and validation of polynucleotides encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 gene and protein and variants of that protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells, and also modified by fused sequences that enhance various aspects of the CRISPR / Cas system. The specification also describes systems for RNA-guided genome engineering and gene regulation in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
Probe arrays for detecting multiple strains of different species
InactiveUS20060160121A1Growth inhibitionReduced virulenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStreptococcus pyogenesTO-18
The present invention provides probe arrays and methods of using the same for concurrent and discriminable detection of multiple strains of different species. In one aspect, the probe arrays of the present invention are nucleic acid arrays comprising (1) a first group of probes, each of which is specific to a different respective strain of a first species; and (2) a second group of probes, each of which is specific to a different respective strain of a second species. In many embodiments, the nucleic acid arrays of the present invention further include a third group of probes, each of which is specific to a different strain of a third species. In one example, a nucleic acid array of the present invention includes probes for sequences selected from SEQ ID NOs: 1 to 18,598, and can discriminably detect different strains of Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Owner:WYETH LLC
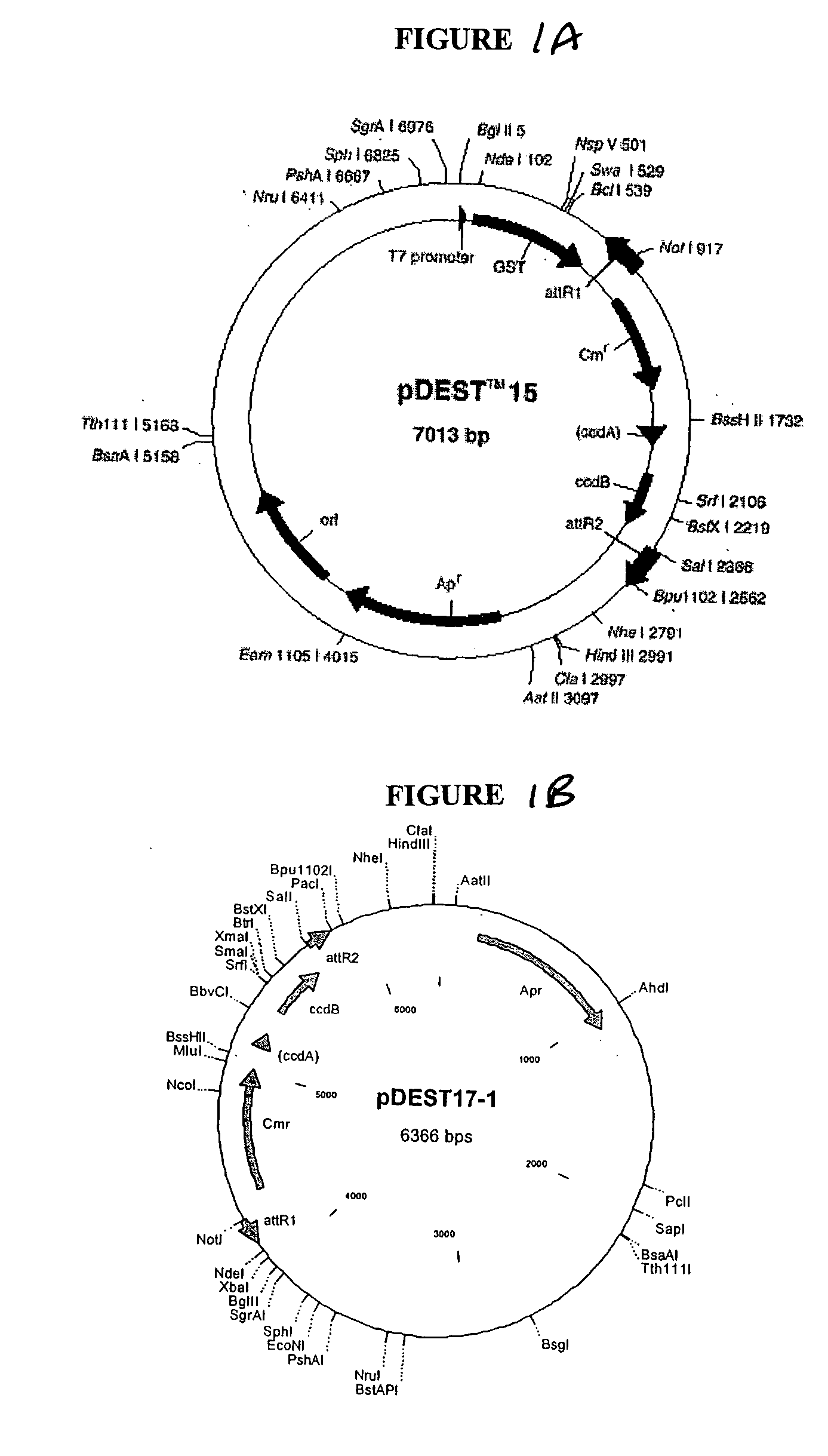
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
InactiveUS20080020465A1Antibacterial agentsHydrolasesStreptococcus pyogenesSite-specific recombination
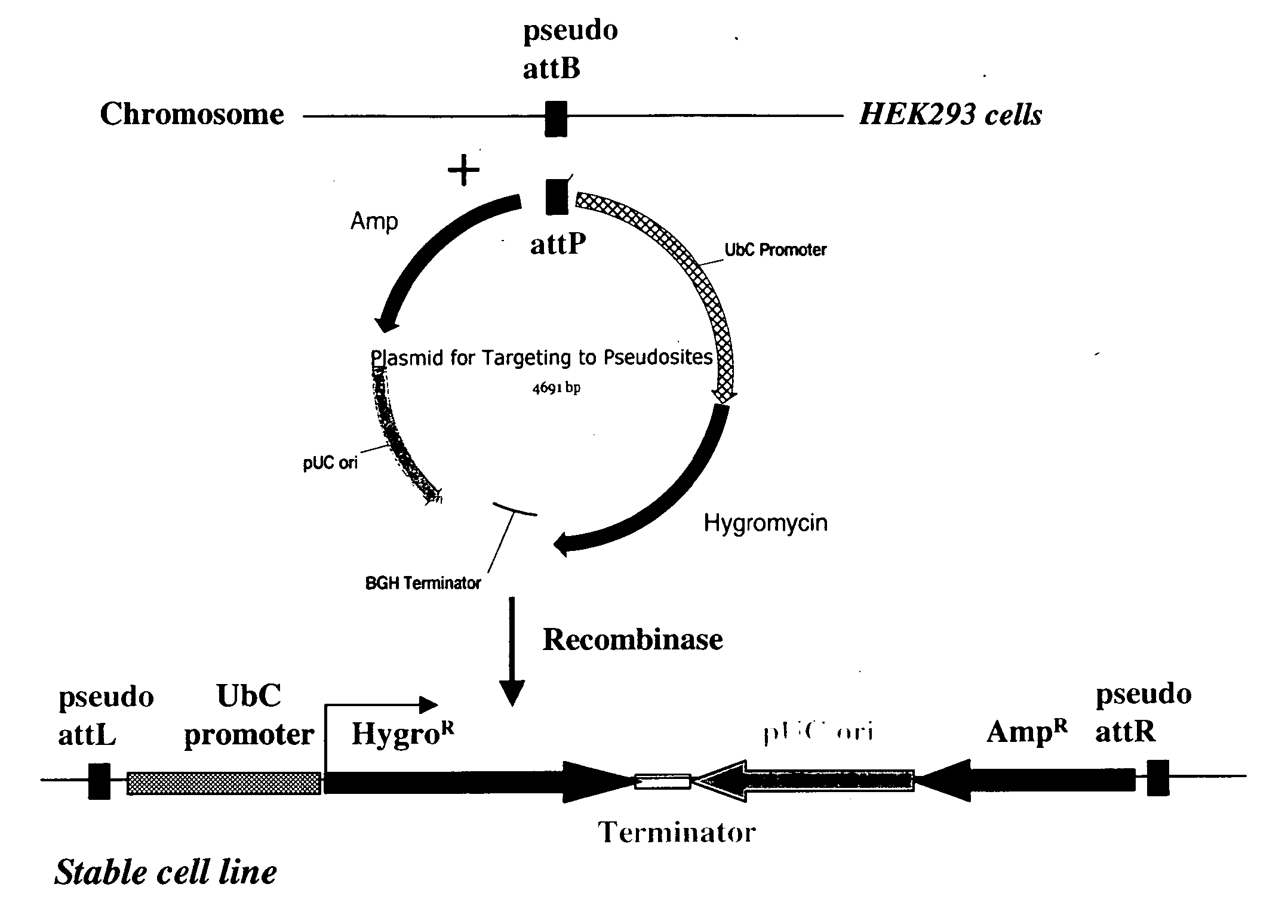
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PADIDAM MALLA
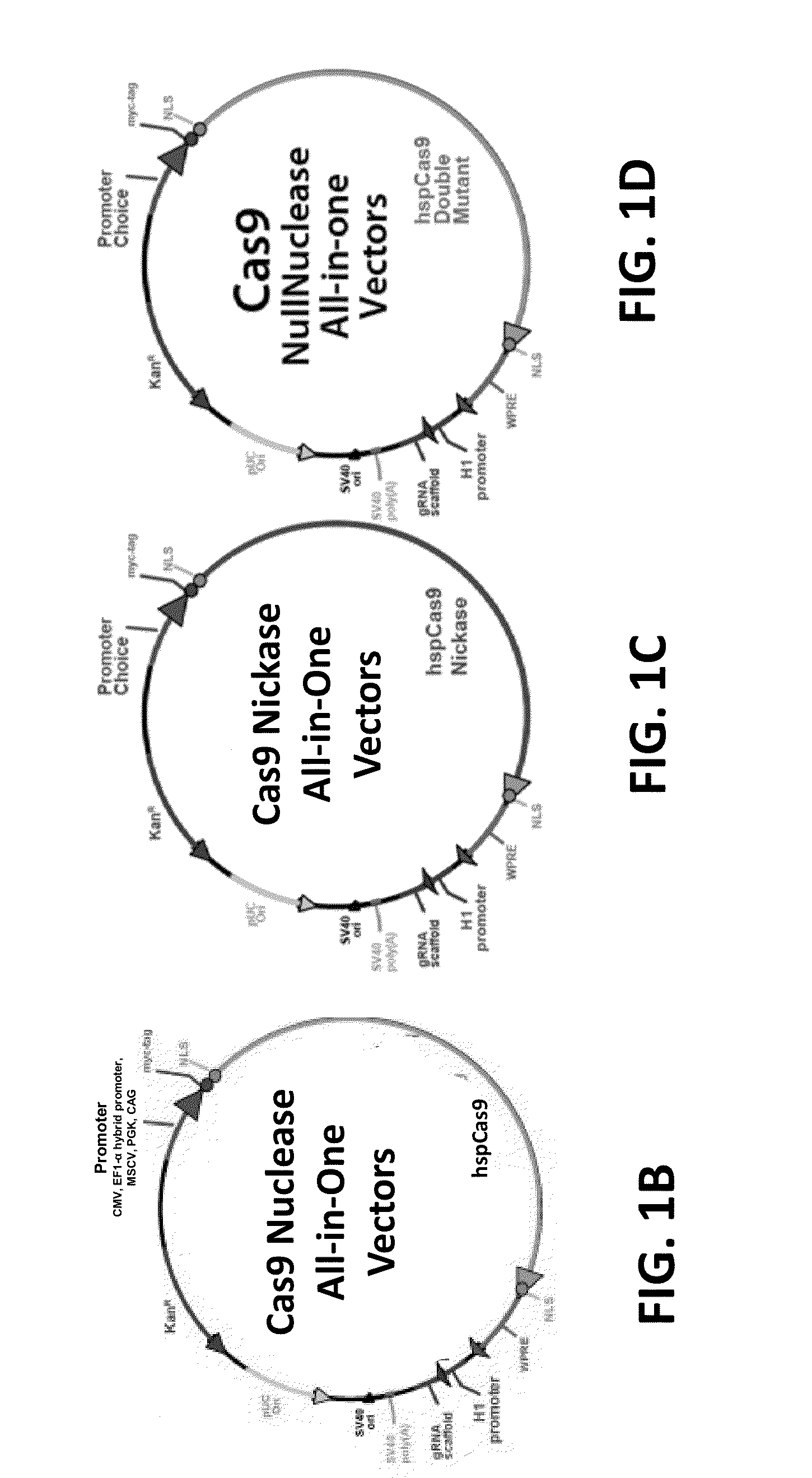
Compositions and methods directed to CRISPR/Cas genomic engineering systems
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification in mammalian cells. The present specification describes the design and testing of a polynucleotide encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells. The specification also describes all-in-one systems for RNA-guided genome engineering in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
Nucleic acids and proteins from streptococcus groups A & B
InactiveUS20060210580A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderStreptococcus pyogenesStreptococcus agalactiae
The invention provides proteins from group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) and group A streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes), including amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences. Data are given to show that the proteins are useful antigens for vaccines, immunogenic compositions, and / or diagnostics. The proteins are also targets for antibiotics.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
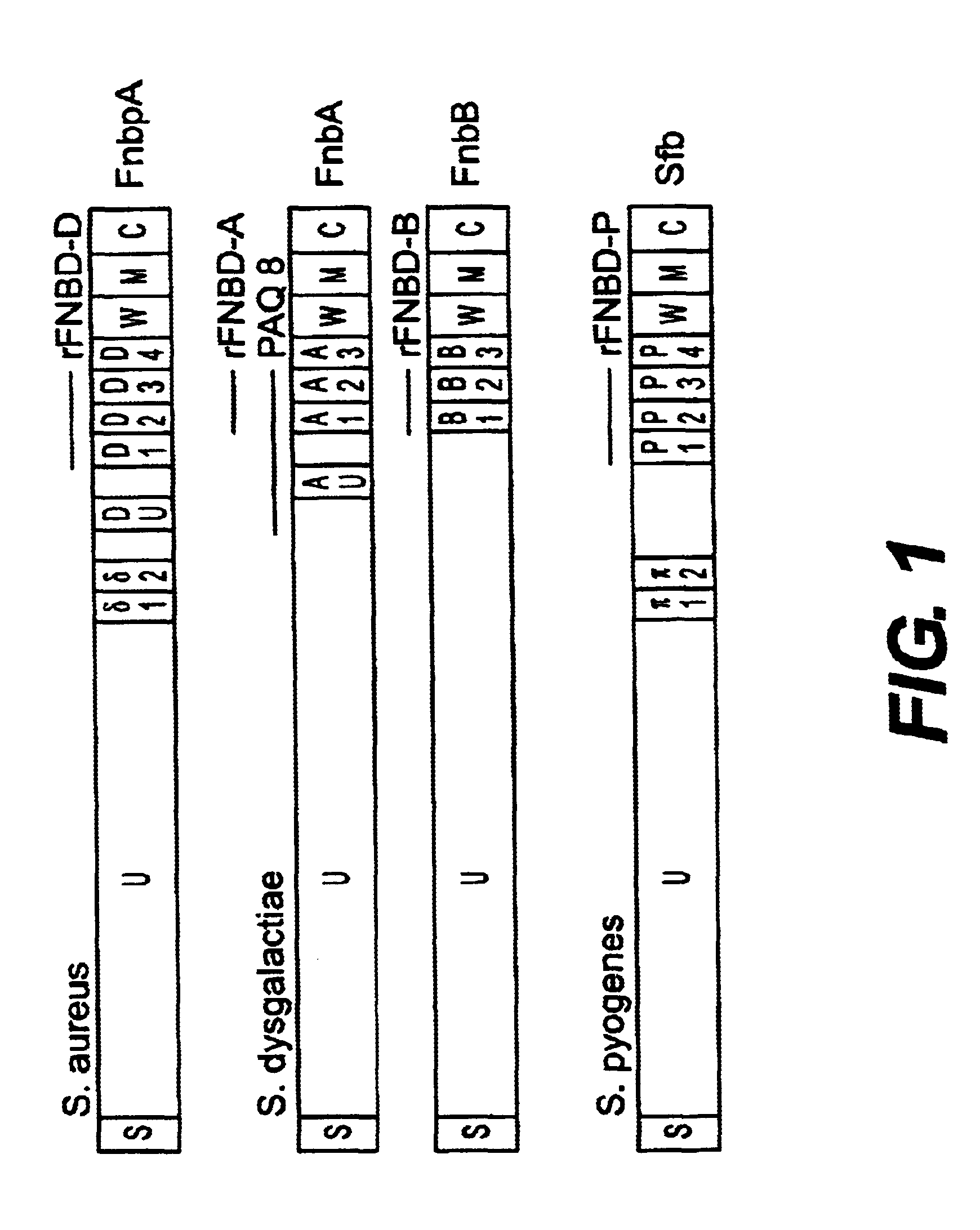
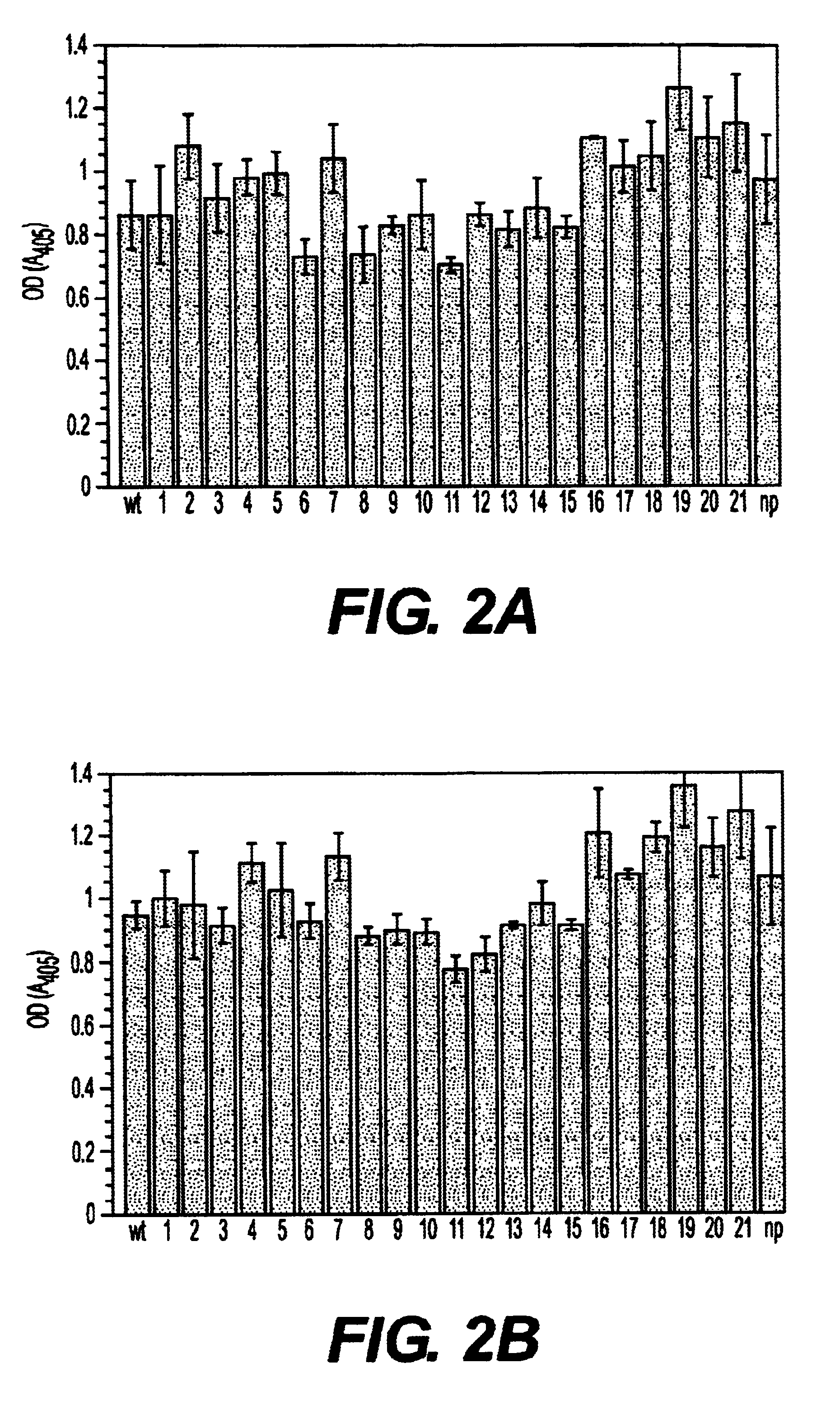
Fibronectin binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6685943B1Avoid problemsOvercomes drawbackPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPassive ImmunizationsStreptococcus pyogenes
Disclosed are antibodies that block the binding of fibronectin protein to fibronectin. Also disclosed are site specifically-mutated and truncated peptide epitopes derived from the fnbA and fnbB genes of Staphylococcus aureus, the fnba and fnbB genes of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, and the sfb gene of Streptococcus pyogenes, and nucleic acid segments encoding these peptides and epitopes. The anti-(fibronectin binding site) antibodies, peptides and epitopes that give rise to antibodies that block the binding of fibronectin binding proteins to fibronectin, and DNA segments encoding these proteins and are of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of streptococcal and staphylococcal colonization in animals or humans. These. DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are proposed to be of use directly in the preparation of vaccines and also for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA +2
Novel lactic acid bacteria and compositions containing them against bacterial colds
ActiveUS20140065218A1Low viscosityImprove distributionAntibacterial agentsBiocideStreptococcus pyogenesMicroorganism
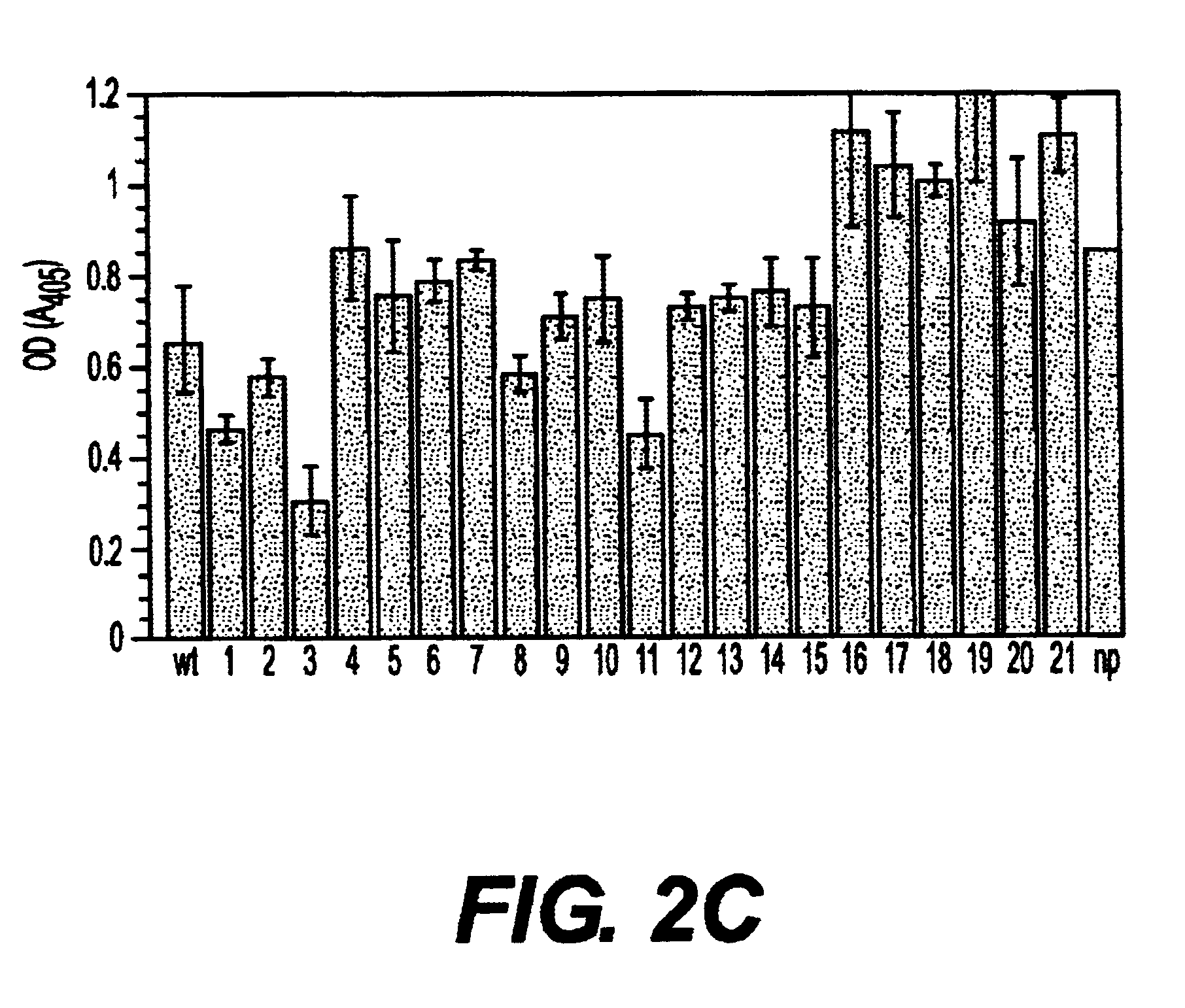
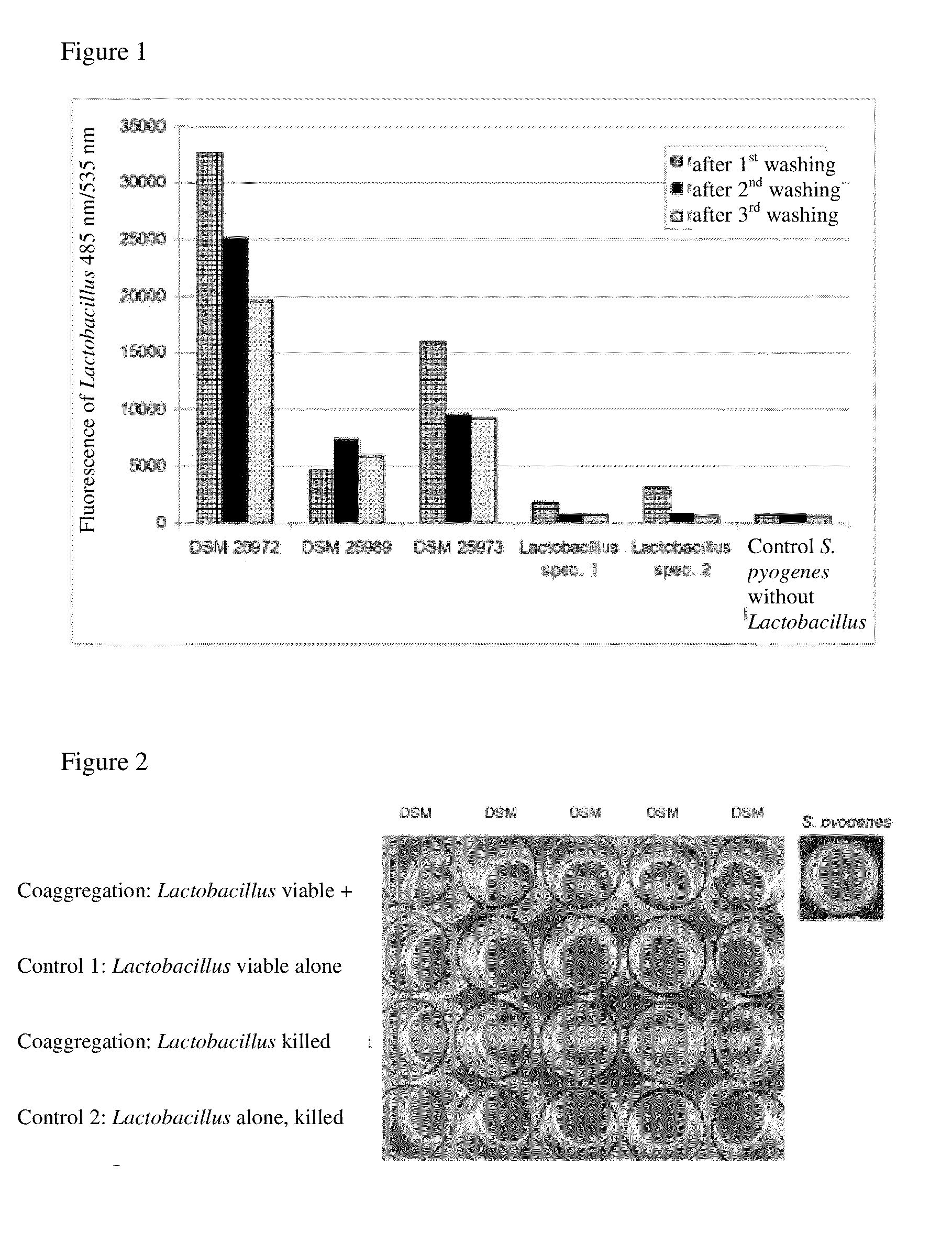
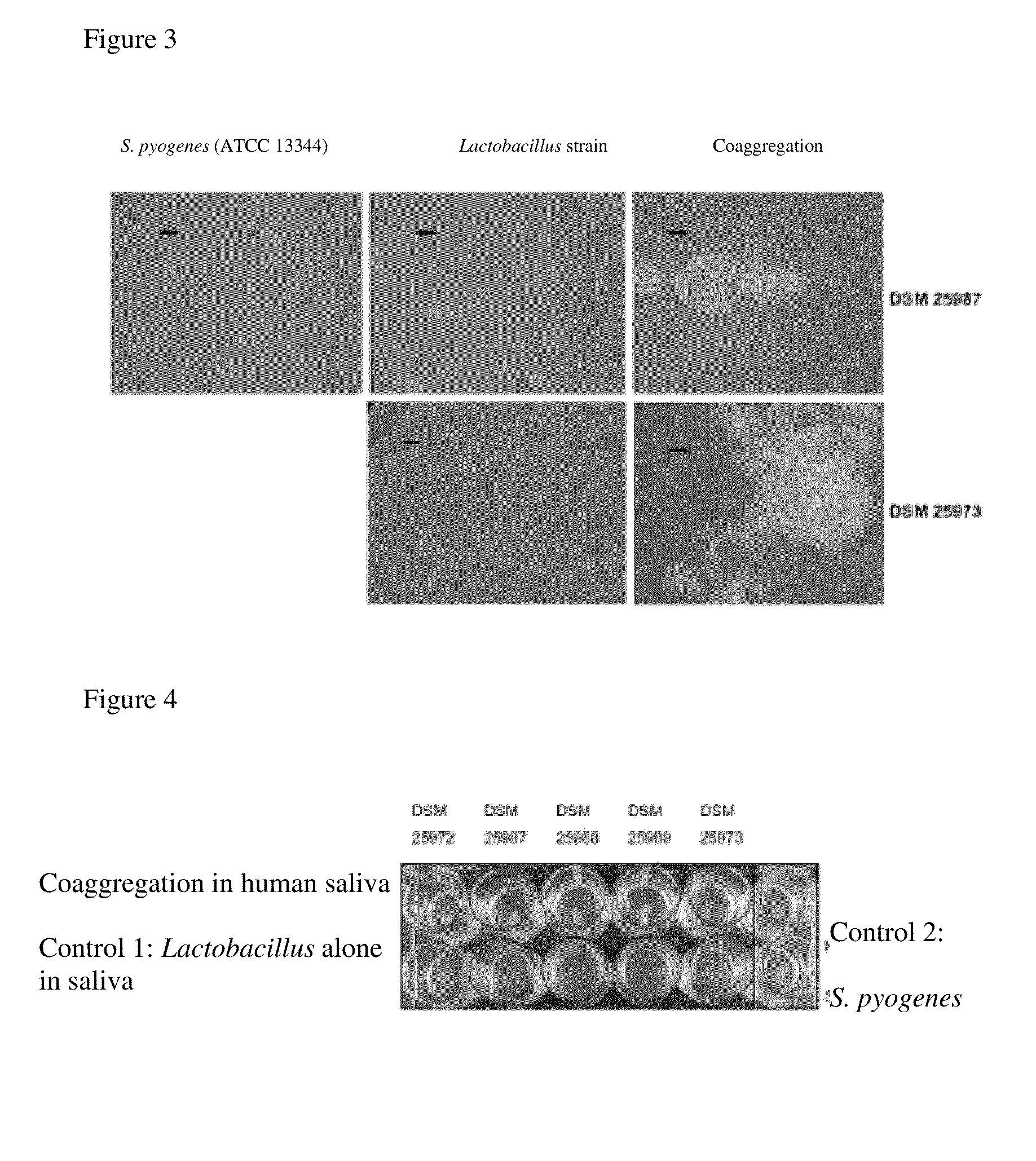
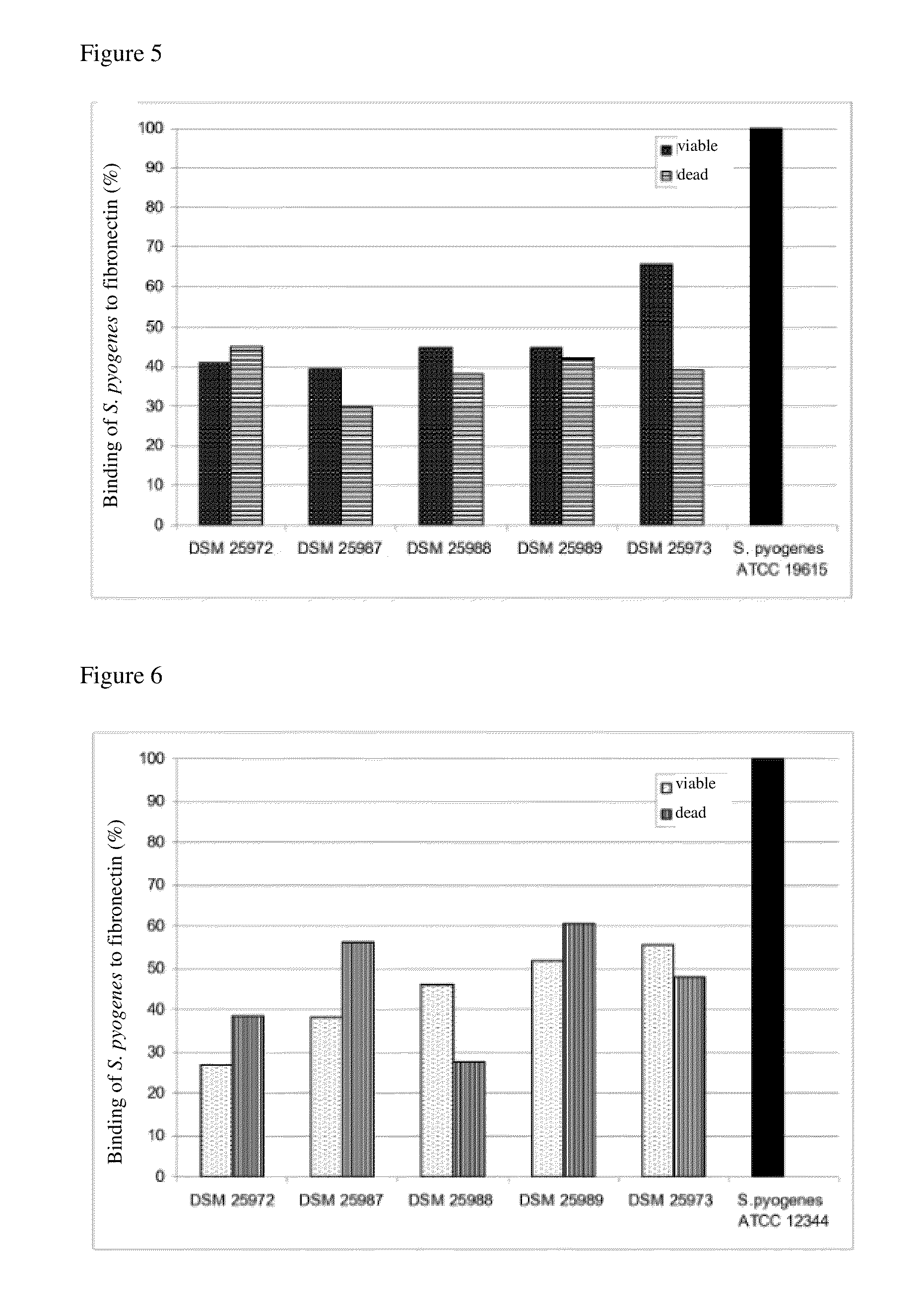
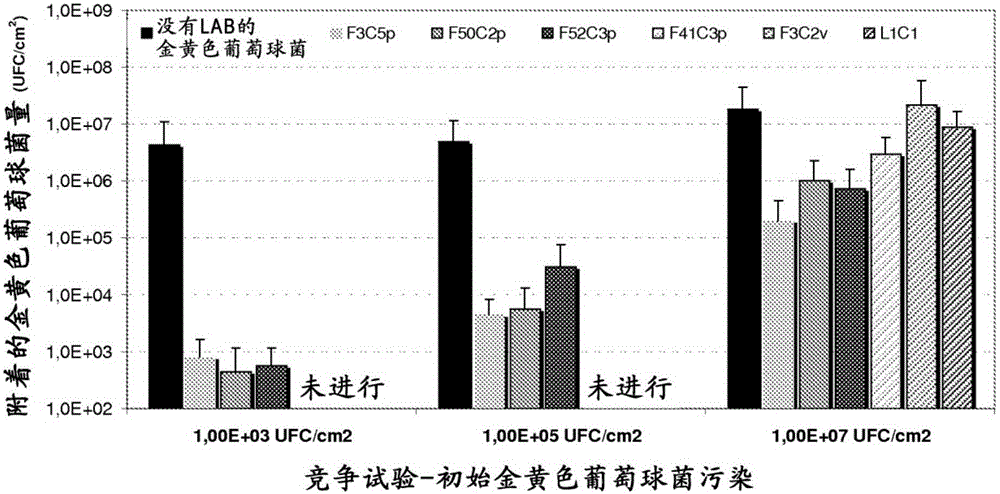
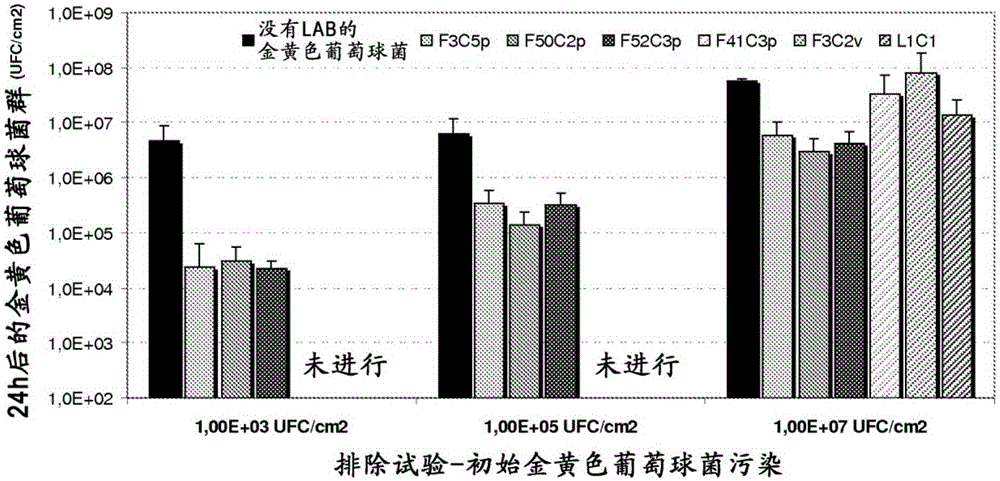
The invention describes a microorganism of the order of lactic acid bacteria or an analogue, fragment, derivative, mutant or combination thereof, wherein the microorganism, or analogue, fragment, derivative, mutant or combination thereof can coaggregate with Streptococcus pyogenes.
Owner:ORGANOBALANCE MEDICAL AG
Nucleic acids and proteins from streptococcus groups A & B
InactiveUS20060210579A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderStreptococcus pyogenesStreptococcus agalactiae
The invention provides proteins from group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) and group A streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes), including amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences. Data are given to show that the proteins are useful antigens for vaccines, immunogenic compositions, and / or diagnostics. The proteins are also targets for antibiotics.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Collagen-binding proteins from Streptococcus pyogenes
InactiveUS7169902B2Avoid infectionInhibit bindingBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaStreptococcus pyogenesOrganism
Isolated proteins, designated Cpa1 and Cpa49, and their corresponding amino acid and nucleic acid sequences are provided which are useful in the prevention and treatment of infection caused by group A streptococcal bacteria such as Streptococcus pyogenes. These proteins have been observed to bind to collagen, and thus methods are provided, such as by administration of the proteins or antibodies generated thereto, whereby streptococcal binding of collagen can be inhibited, and streptococcal infection can be greatly reduced. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the collagen-binding proteins of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the proteins are advantageous because they may be used as vaccine components or antibodies thereof, and they may be administered to wounds or used to coat biomaterials in order to act as collagen blocking agents and reduce or prevent severe infection by group A streptococcal bacteria.
Owner:PODBIELSKI ANDREAS
Nucleic acids and proteins from streptococcus groups a & b
InactiveUS20060275315A1Easy to insertEfficient HarvestingAntibacterial agentsBacteriaStreptococcus pyogenesStreptococcus agalactiae
The invention provides proteins from group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) and group A streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes), including amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences.
Owner:CHIRON CORP +1
Nucleic acids and proteins from streptococcus groups A & B
InactiveUS20060210582A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderStreptococcus pyogenesStreptococcus agalactiae
The invention provides proteins from group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) and group A streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes), including amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences. Data are given to show that the proteins are useful antigens for vaccines, immunogenic compositions, and / or diagnostics. The proteins are also targets for antibiotics.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
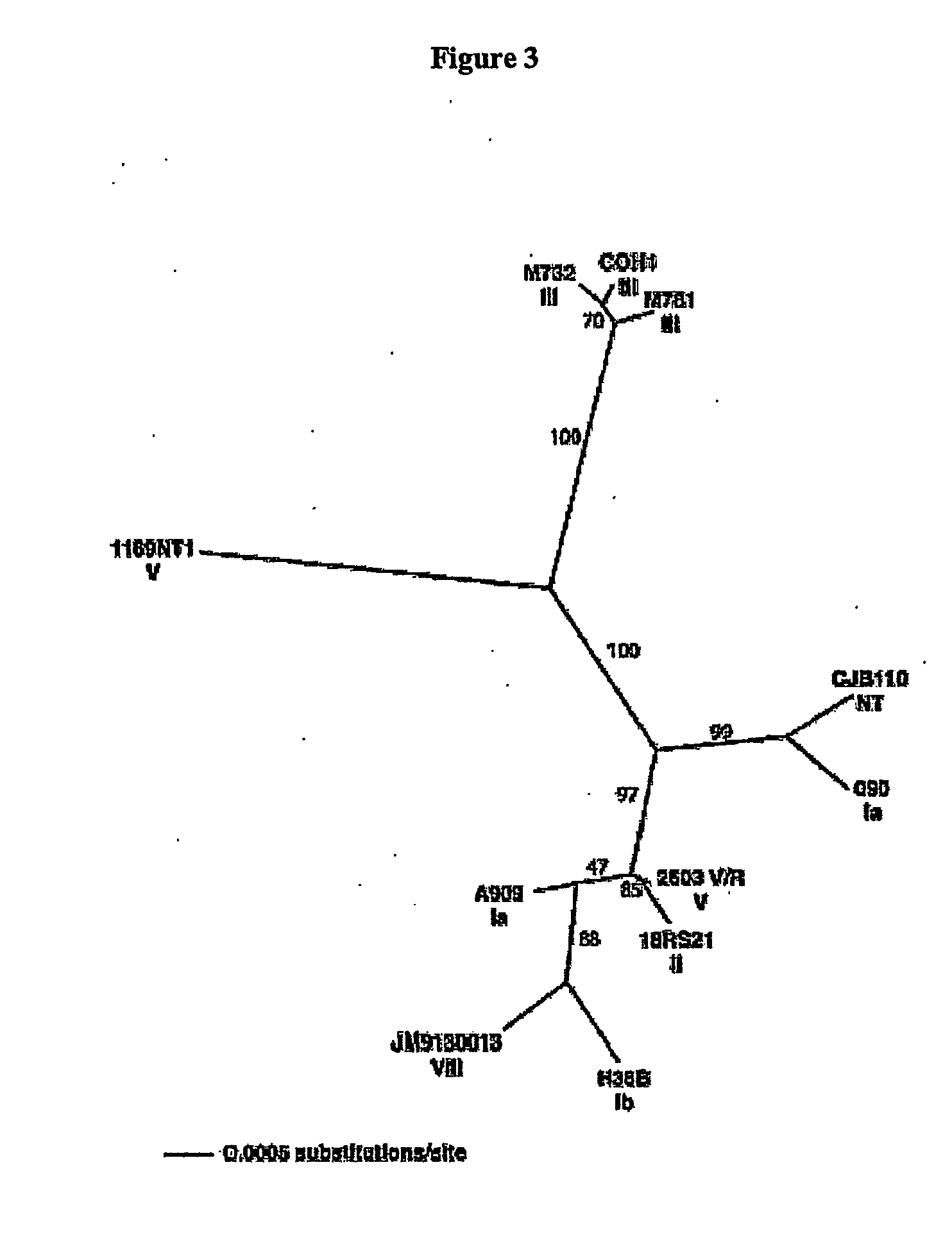
Conserved and specific streptococcal genomes
InactiveUS20070053924A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus pyogenesCoccidia
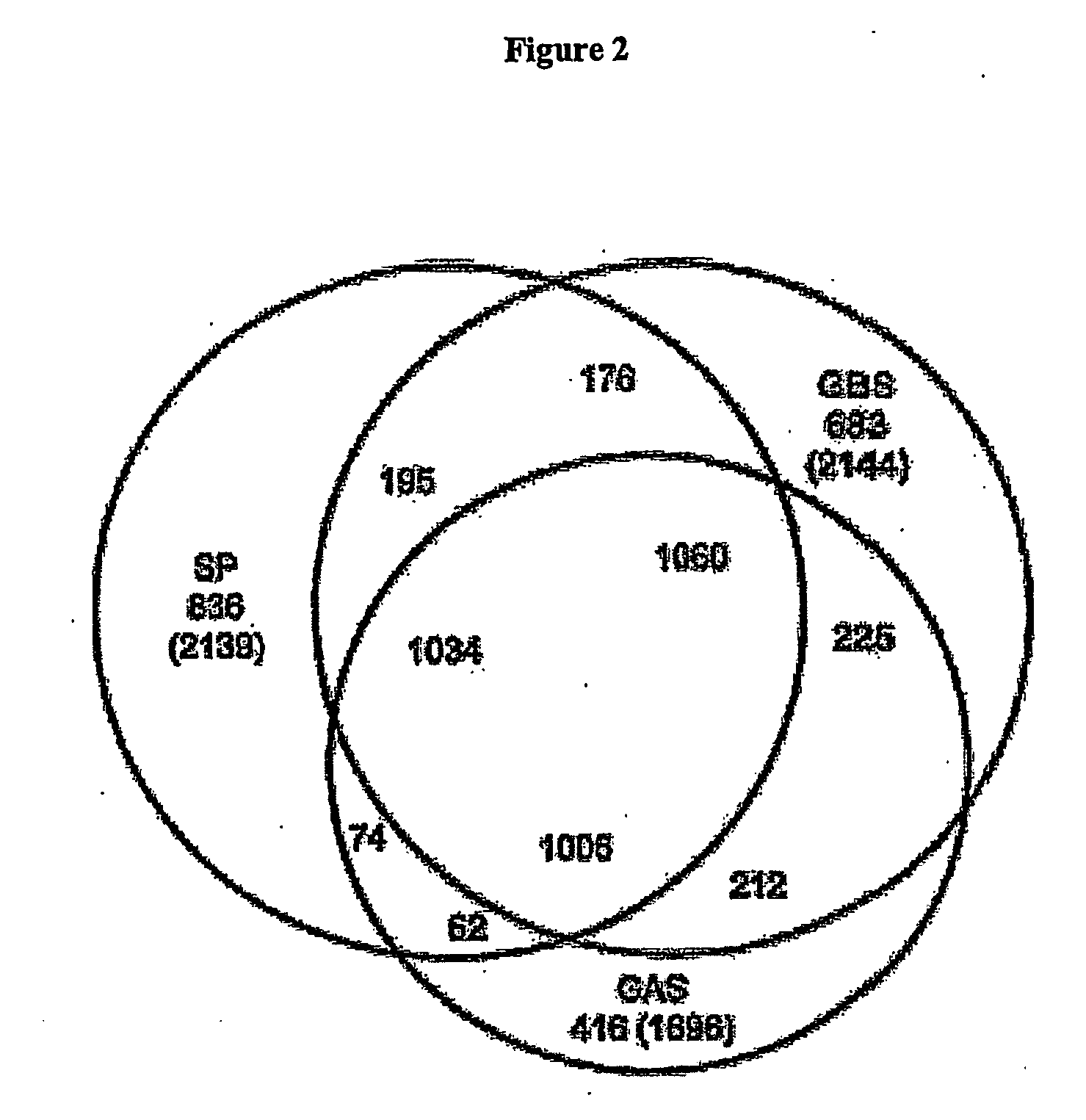
The invention relates to polynucleotides which are conserved or specific to one or more species of Streptococcus, Streptococcus species serotypes, and / or serotype isolates. In particular, the invention relates to polynucleotides from Streptococcus which are conserved or specific to one or more of the species of S. pneumoniae (“pneumococcus” or “S. pn.”), S. pyogenes (“group A streptococcus” or “GAS”), and S. agalactiae (“group B streptococcus” or “GBS”). The invention further relates to polynucleotides which are conserved or specific to one or more Streptococcal species serotypes, such as GBS serotypes Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, and VIII. The invention still further relates to polynucleotides which are conserved or specific to one or more clinical isolates of a Streptococcus species.
Owner:TETTELIN HERVE +1
Nucleic acids and proteins from streptococcus groups A & B
The invention provides proteins from group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) and group A streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes), including amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences. Data are given to show that the proteins are useful antigens for vaccines, immunogenic compositions, and / or diagnostics. The proteins are also targets for antibiotics.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Streptococcus pyogenes antigens
The present invention relates to antigens, more particularly an antigen of Streptococcus pygenes (also called group A Streptococcus (GAS)) bacterial pathogen which is useful as vaccine component for therapy and / or prophylaxis.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL +1
Streptococcal heat shock proteins of the Hsp60 family
Methods and compositions comprising isolated nucleic acid molecules specific to Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes, as well as vector constructs and isolated polypeptides specific to Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes are provided. Such compositions and methods are useful for the diagnosis of Streptococcal infection and for generating an immune response to Streptococcal bacteria.
Owner:NVENTA BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CORP
Nucleic acids and proteins from streptococcus groups A & B
InactiveUS20060210581A1Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderStreptococcus pyogenesStreptococcus agalactiae
The invention provides proteins from group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae) and group A streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes), including amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences. Data are given to show that the proteins are useful antigens for vaccines, immunogenic compositions, and / or diagnostics. The proteins are also targets for antibiotics.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Collagen-binding proteins from Streptococcus pyogenes
InactiveUS20050019345A1Avoid infectionInhibit bindingBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesStreptococcus pyogenesNucleic acid sequencing
Isolated proteins, designated Cpa1 and Cpa49, and their corresponding amino acid and nucleic acid sequences are provided which are useful in the prevention and treatment of infection caused by group A streptococcal bacteria such as Streptococcus pyogenes. These proteins have been observed to bind to collagen, and thus methods are provided, such as by administration of the proteins or antibodies generated thereto, whereby streptococcal binding of collagen can be inhibited, and streptococcal infection can be greatly reduced. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the collagen-binding proteins of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the proteins are advantageous because they may be used as vaccine components or antibodies thereof, and they may be administered to wounds or used to coat biomaterials in order to act as collagen blocking agents and reduce or prevent severe infection by group A streptococcal bacteria.
Owner:PODBIELSKI ANDREAS
Streptococcus Pyogenes Antigens
The present invention relates to antigens, more particularly an antigen of Streptococcus pyogenes (also called group A Streptococcus (GAS)) bacterial pathogen which is useful as vaccine component for therapy and / or prophylaxis.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL
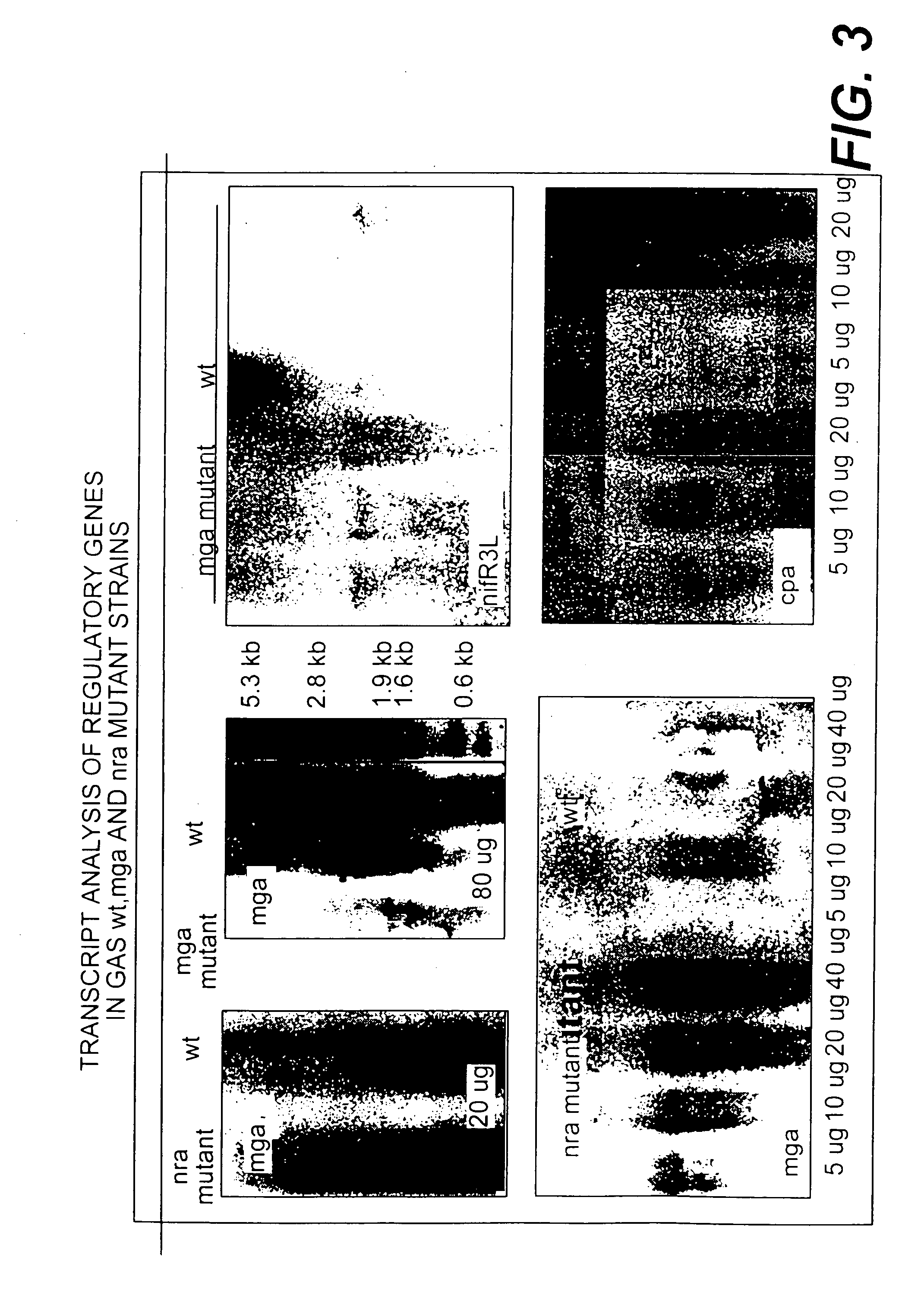
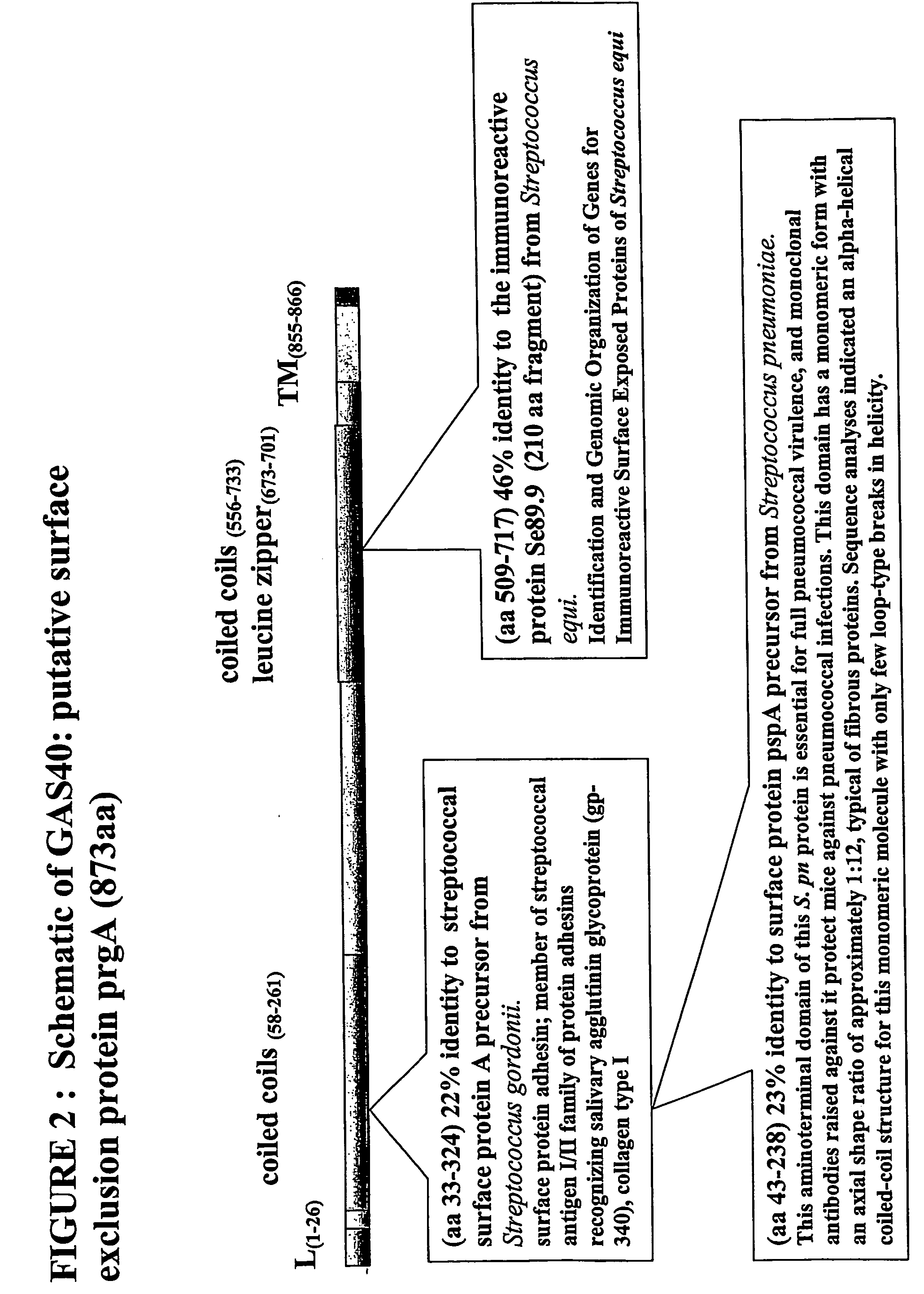
Immunogenic compositions for streptococcus pyogenes
The invention includes a GAS antigen, GAS 40, which is particularly suitable for use either alone or in combinations with additional GAS antigens, such as GAS 117, GAS 130, GAS 277, GAS 236, GAS 40, GAS 389, GAS 504, GAS 509, GAS 366, GAS 159, GAS 217, GAS 309, GAS 372, GAS 039, GAS 042, GAS 058, GAS 290, GAS 511, GAS 533, GAS 527, GAS 294, GAS 253, GAS 529, GAS 045, GAS 095, GAS 193, GAS 137, GAS 084, GAS 384, GAS 202, and GAS 057.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Artificial carrier system with site-specific mutagenesiss and site-specific mutagenesis method
ActiveCN107177625AImprove editing efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsStreptococcus pyogenesNucleotide
The application relates to a set of artificial systm applied for site-specific alternation of rice genome basic group and a site-specific mutagenesis method. The artificial system comprises a I adjusting element and a II adjusting element; the I adjusting element comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of encoding an amino acid sequence I; the amino acid sequence I is selected from one of SEQ ID Nos. 1-6; the II adjusting element comprises a II-1 nucleotide sequence and a II-2 nucleotide sequence from 5' terminal to 3' terminal; the II-1 nucleotide sequence comprises a target nucleotide sequence; the II-2 nucleotide sequence comprises sgRNA nucleotide sequence originated from Streptococcus pyogenes; the II nucleotide sequence is transcribed and fused with the II-2 nucleotide sequence, and its product can guide the protein encoded by the I adjusting element to a target site to be mutated in the target biological genome, and induce and mutate C at the target site to be one of T, A and G, or G is mutated to be one of A, T and C.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preventing and/or treating infections, colonisations, or illnesses related to staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococcus pyogenes, enterococcus faecium, enterobacter cloacae, proteus mirabilis, bacteroides fragilis, staphylococcus epidermidis, propionibacterium acnes, candida albicans and/or malassezia furfur
The subject matter of the present invention is a bacteria or mix of bacteria having an antagonistic activity with respect to stains of S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecium, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides fragilis Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium acnes, Candida albicans and / or Malassezia furfur as well as the use thereof in the treatment and / or prevention of infections or colonisations related to those pathogens. The invention pertains to care products containing one or more non-pathogenic antagonistic strains intended to prevent and / or treat infections or colonisations on skin, wounds, mucous membranes and appendages.
Owner:URGO RECH INNOVATION & DEVEMENT
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20070009947A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090053702A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStreptococcus pyogenes
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogen in dairy products
ActiveCN101240335AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsKlebsiella oxytocaStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention provides a gene chip for detecting common pathogen in dairy, which comprises a solid-phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase vector, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes DNA fragment or its complementary DNA or RNA sequence selected from E. sakazakii, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Listeria monocytogenes, salmonella and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region of Bacillus cereus, as well as ipaH gene of Shigella or gyrB gene of citrobacter freundii. The invention further provides a reagent box which uses the gene chip to detect pathogen in dairy. The gene chip and the reagent box of the invention for detecting pathogen in dairy are easy to operate, highly precise and greatly repeatable.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD +1
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090047671A1Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
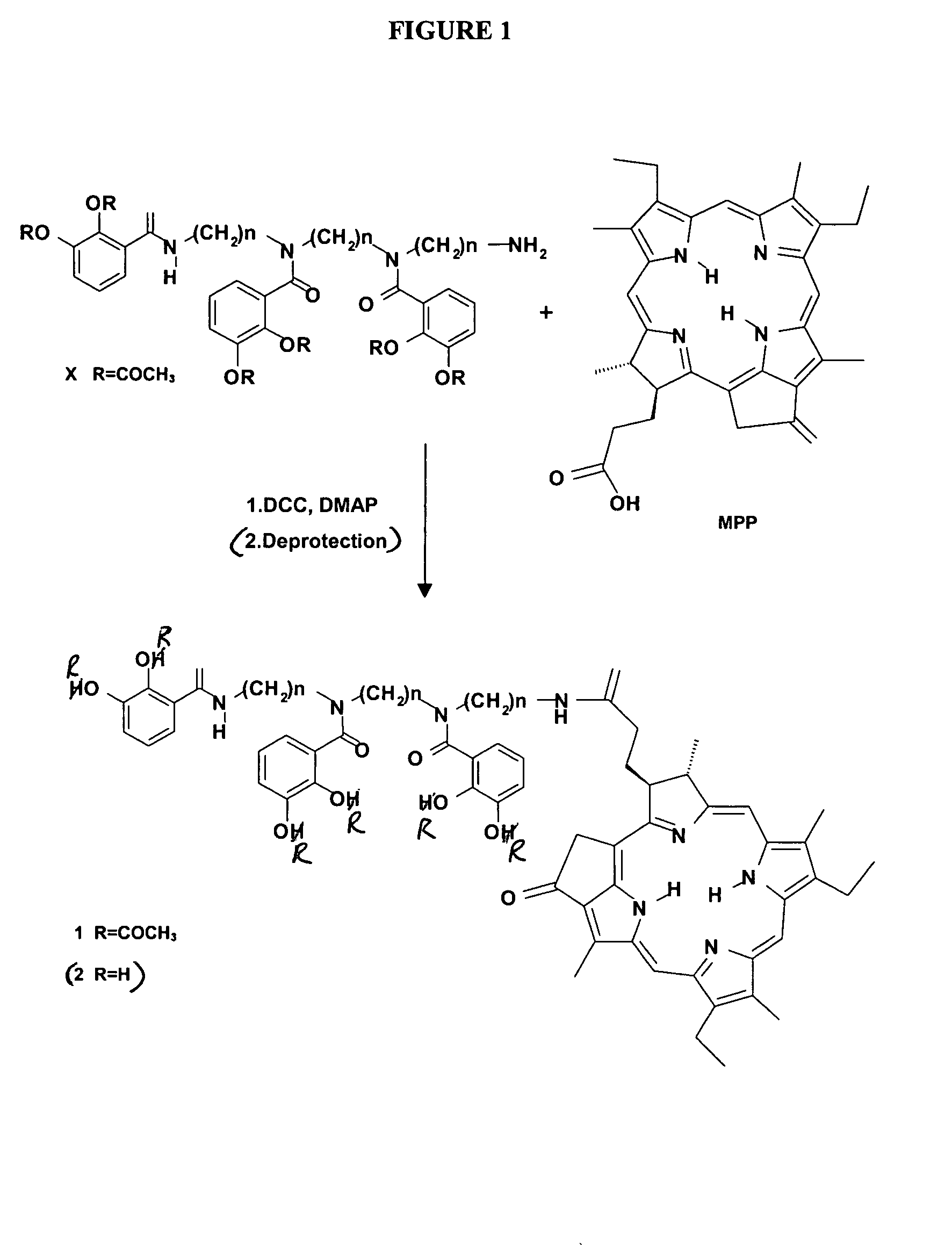
Siderophore conjugates of photoactive dyes for photodynamic therapy
InactiveUS20040186087A1High selectivityImprovement of photodynamic antimicrobial therapyAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesEscherichia coli
Siderophore-photosensitizer conjugates, their synthesis and use in photodynamic antimicrobial therapy (PACT) is disclosed. The advantage of this method is improvement of photodynamic antimicrobial therapy against, for example, pathogenic micro-organisms such as bacteria and fungi. Naturally occurring and synthetically available siderophore structures are conjugated chemically with photoactive compounds such as Chlorin e6 to improve their penetration into bacterial cells and to increase antibacterial efficacy of photosensitizers via microbial proteins that recognize and transport iron-loaded siderophores. In this way, photosensitizers can be transported inside bacteria that otherwise could not cross the cell wall and membranes. Photodynamic activation of photosensitizers inside the cells of pathogenic microbes enables a more effective inhibition of cellular functions than application at the outer side of the cells. The siderophore-transporting systems of microbes are known to be specific for bacteria and fungi. Consequently, siderophore conjugates with photosensitizers are not taken up by mammalian cells and photodynamic effects can thus be exerted specifically on pathogenic microbes. Applications of these conjugates include highly efficient treatment of pathogenic gram-negative and -positive bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, treatment of microbial infections that often occur in chronic wounds as well as therapy of other antibiotic resistant microbial infections.
Owner:BIOLITEC PHARMA MARKETING
Primer probe combination and kit for combined inspection of 15 kinds of respiratory tract infection pathogens
ActiveCN107937578ARapid combined detectionGuaranteed matchMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStreptococcus pyogenesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a pathogen inspection reagent, and concretely discloses a primer probe combination and a kit for combined inspection of 15 kinds of respiratory tract infection pathogens. By aiming at specific target sequences of the gene sequence conserved region of klebsiella pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, chlamydia pneumoniae, mycobacterium tuberculosis, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, baumanii, mycoplasma pneumoniae, enterococcus faecalis, ligionella pneumohpillia, streptococcus pneumoniae, bacillus pyocyaneus and mycobacterium abscessus, primers and probes which do not have mutual crossed reaction are designed, so that the problem that detection probes of different pathogens can easily generate mutual influenceor interference is solved; the combination and matching of different primers and probes are ensured; the goal of simultaneously performing efficient specific inspection at the same temperature can also be achieved.
Owner:西安九安生物技术有限公司
LAMP primer combination for detecting 6 infectious pathogens of dairy cow mastitis and application thereof
ActiveCN107541509AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStreptococcus pyogenesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses an LAMP primer combination for detecting 6 infectious pathogens of dairy cow mastitis and application thereof. The invention first provides a primer combination consisting of 36 DNA molecules shown in sequence 1 to sequence 36. The primer combination can be used for detecting whether a to-be-detected bacterium is Mycoplasma bovis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Corynebacterium bovis or Staphylococcus epidermidis, and can be used for detecting whether a to-be-detected sample contains Mycoplasma bovis and / or Staphylococcus aureusand / or Streptococcus agalactiae and / or Streptococcus pyogenes and / or Corynebacterium bovis and / or Staphylococcus epidermidis. The primer combination provided by the invention is used for identifying and detecting the 6 infectious pathogens of dairy cow mastitis, has high specificity and high sensitivity, and can realize simple, rapid and accurate detection, thus having great popularization value.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP
Antimicrobial denture cleansing compositions
InactiveUS6309622B1Efficient killingSafe and effective compositionCosmetic preparationsLiquid degasificationBacteroidesStreptococcus pyogenes
A denture cleansing composition includes a monoperoxysulfate compound, an effective amount a sequestering agent, such as a citrate compound, for removal of calculus and to provide a pH to the composition in solution (water) of about 3 to 5, and an effective amount of an antimicrobial agent, such as a benzoate compound, to provide antimicrobial activity to the composition to effectively kill bacteria, or other microorganisms found on the dentures. Tests conducted show that the composition is particularly effective in killing microbial strains of Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus pyogenes, Candida albicans and Actinomyces viscosus within 20 minutes of contact.
Owner:PROTECH PROFESSIONAL PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com