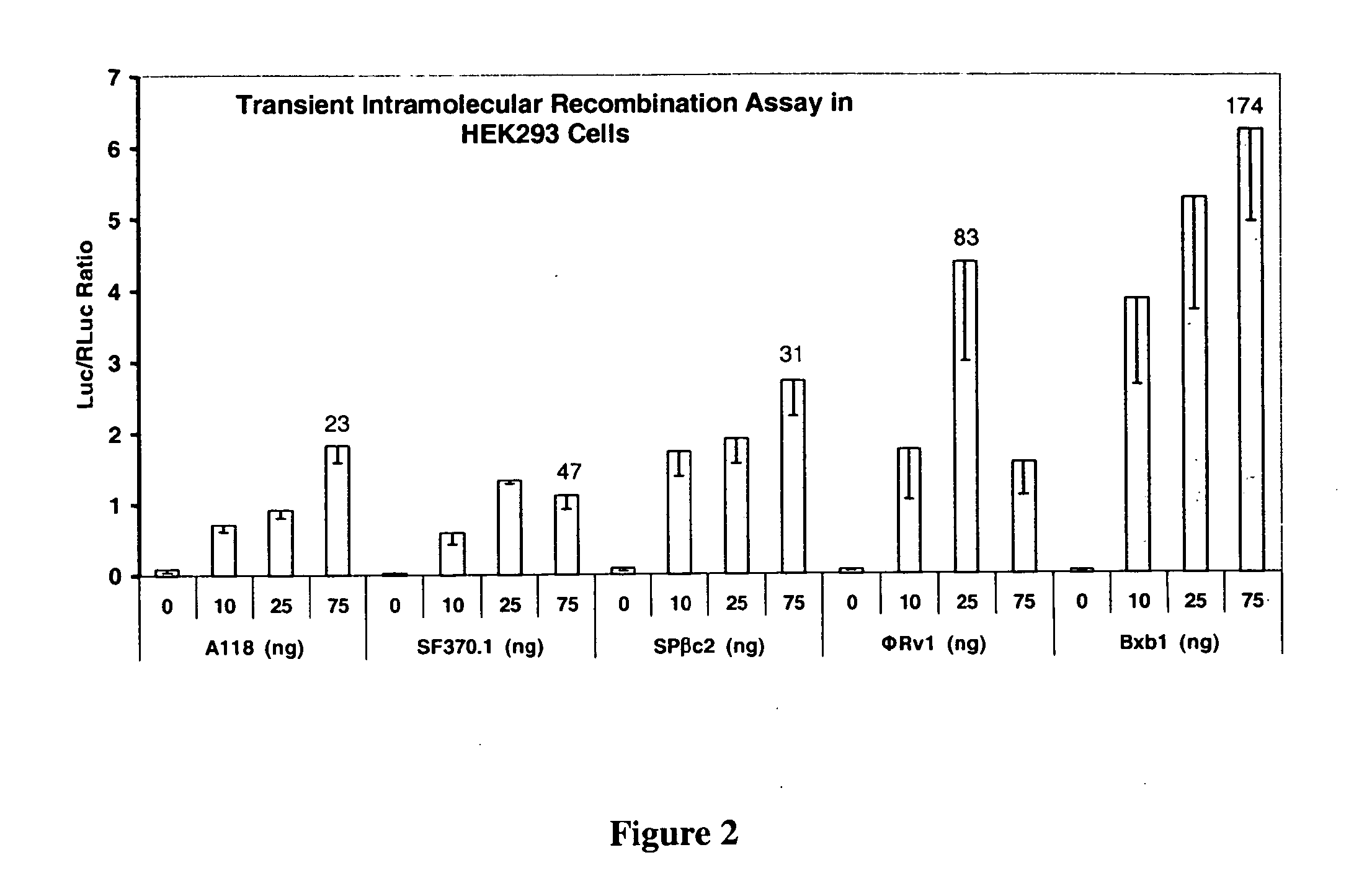
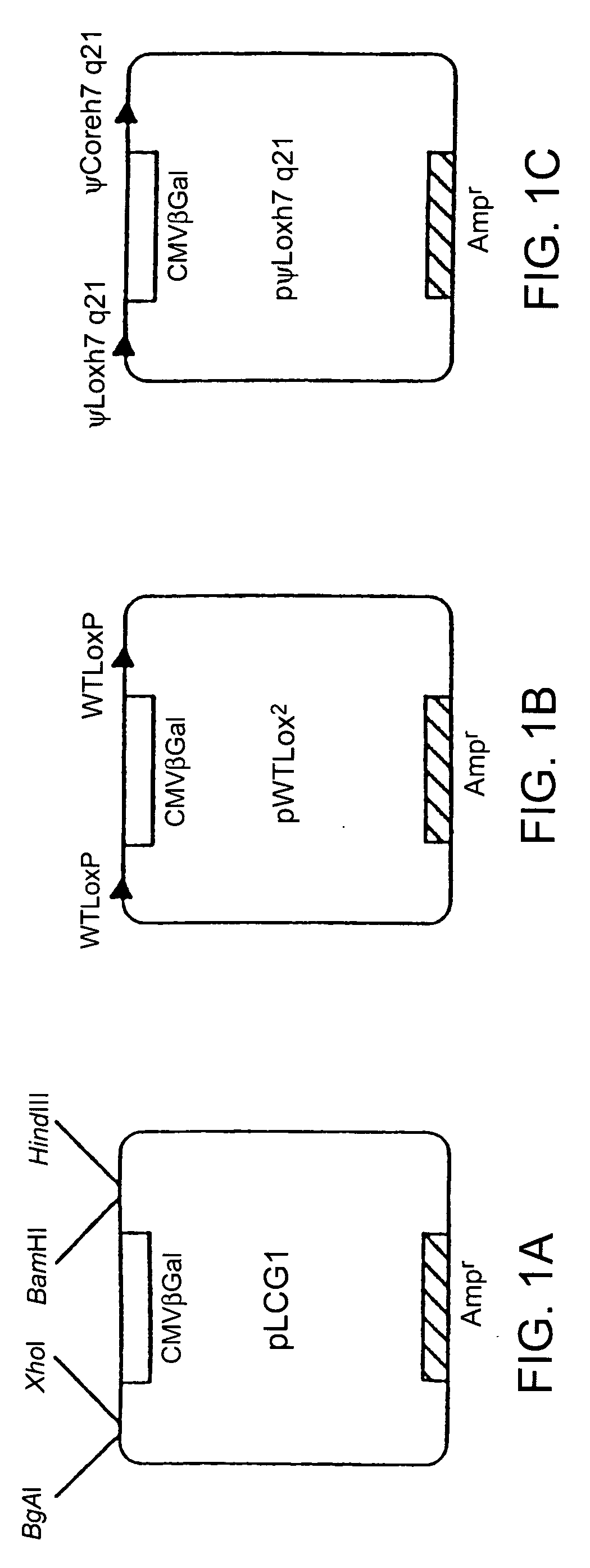
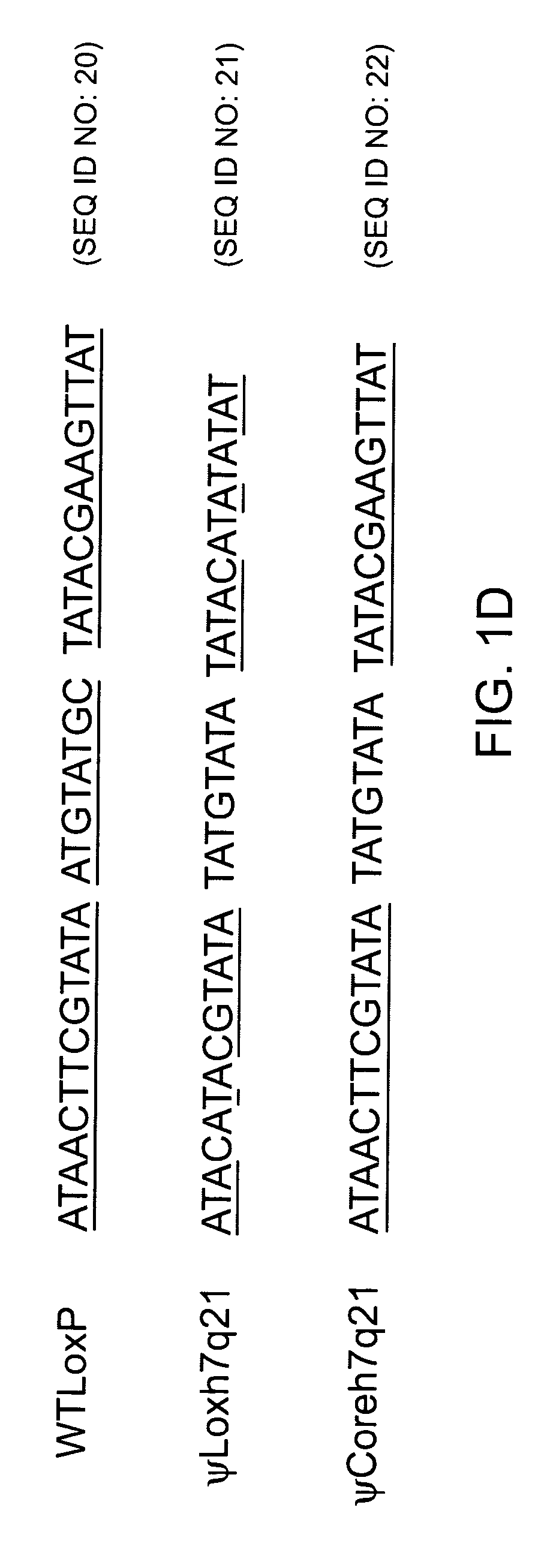
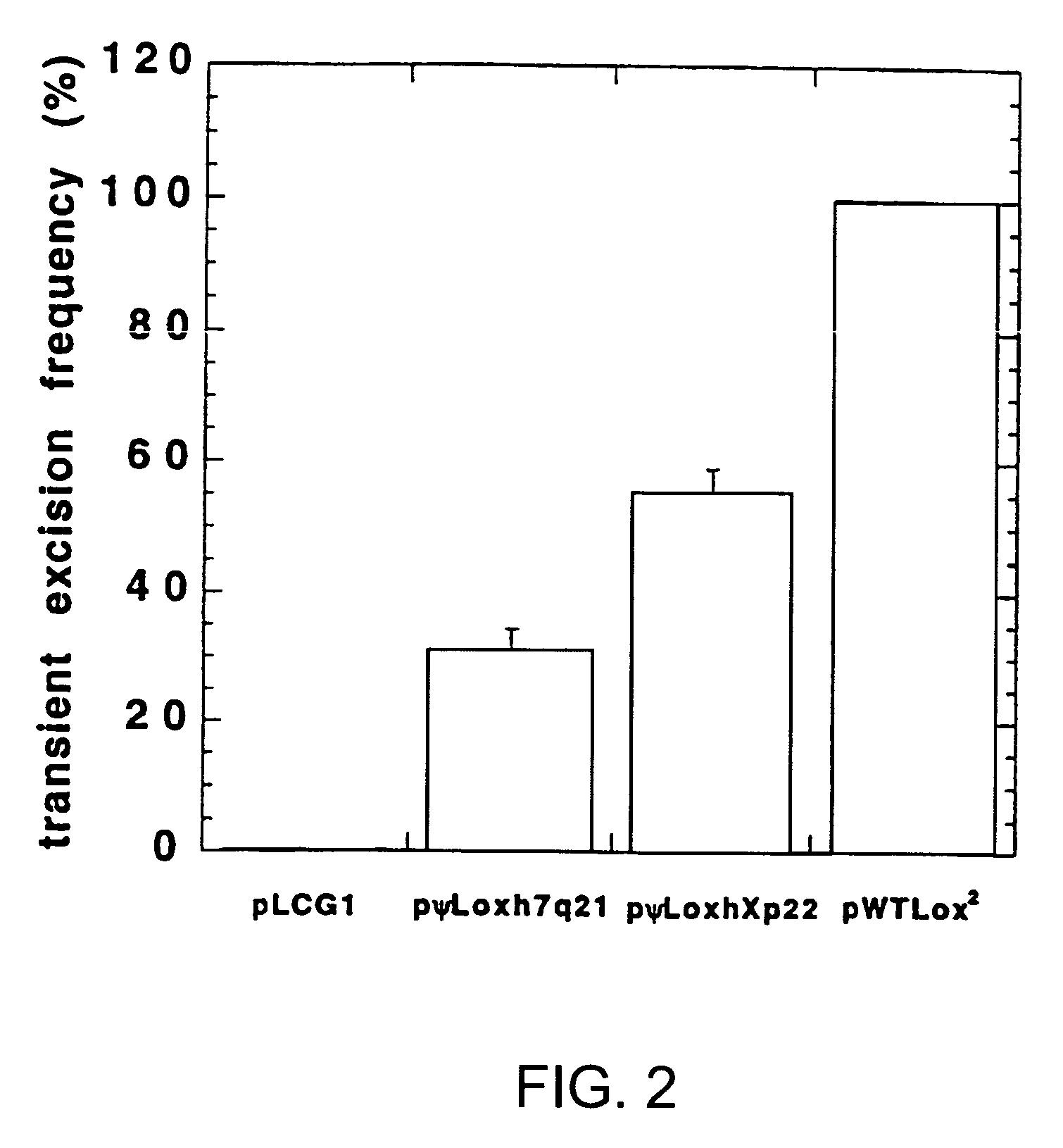
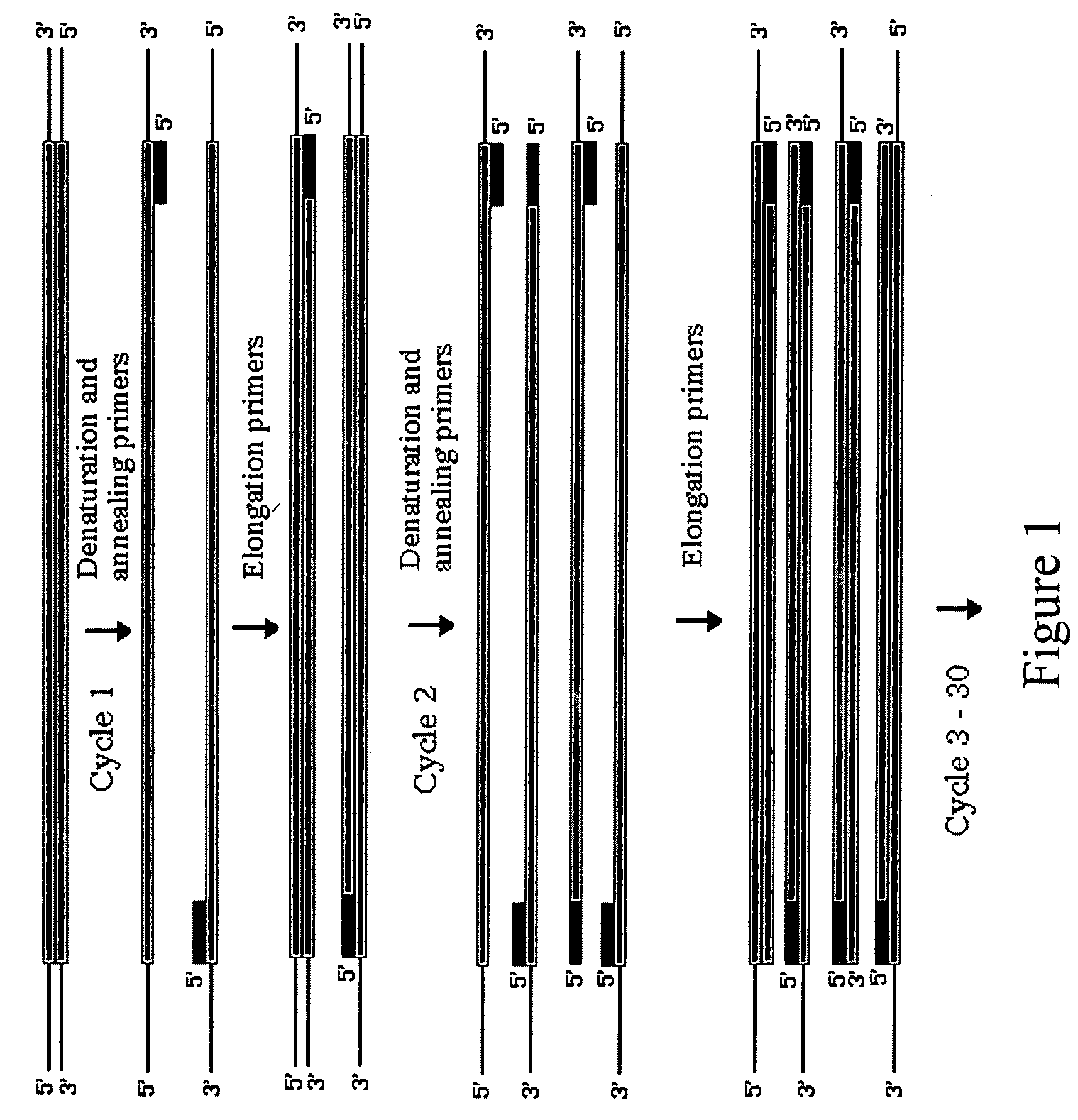
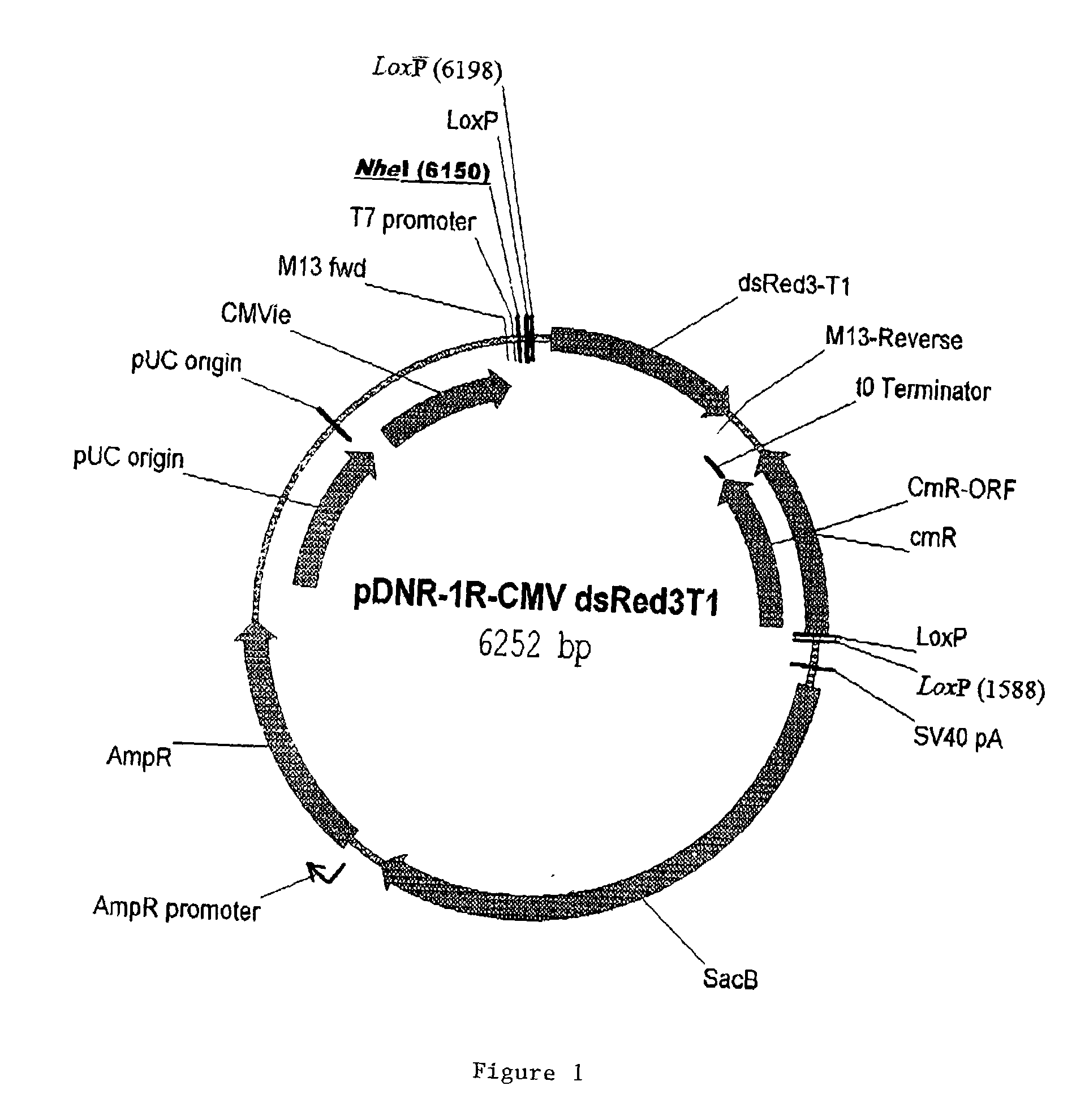
Patents
Literature
208 results about "Site-specific recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
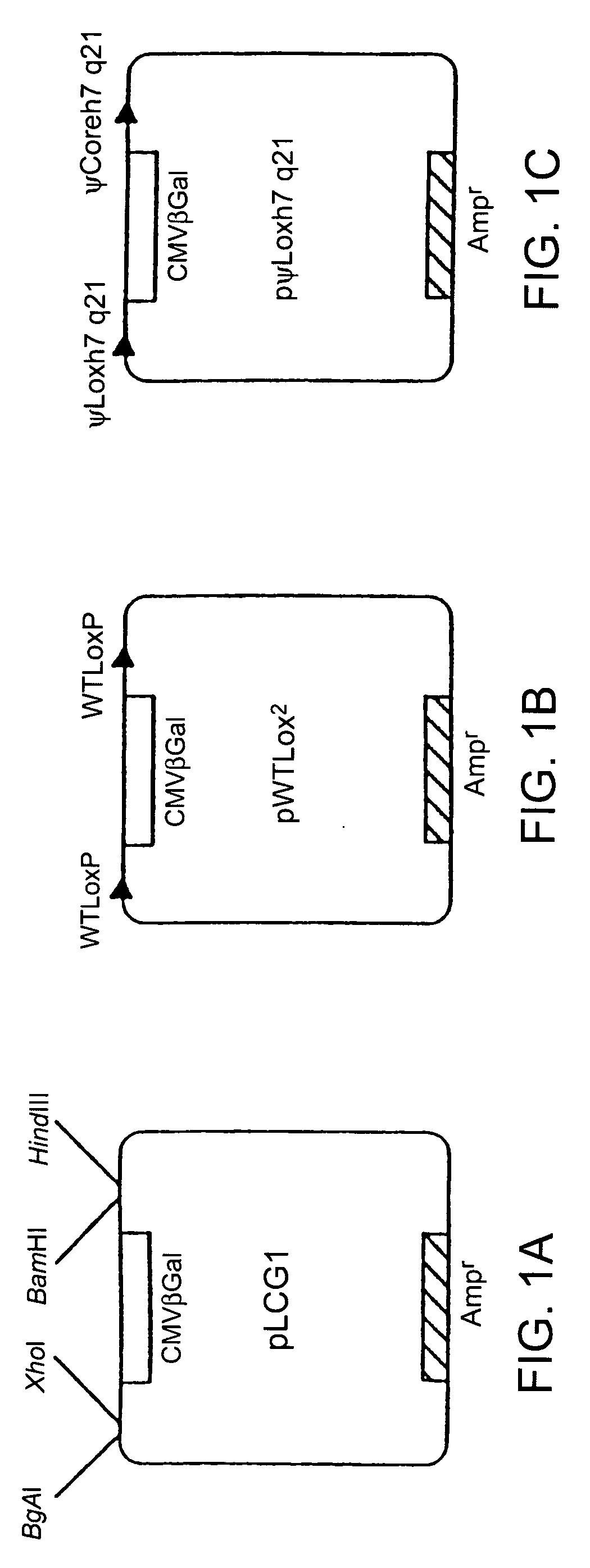
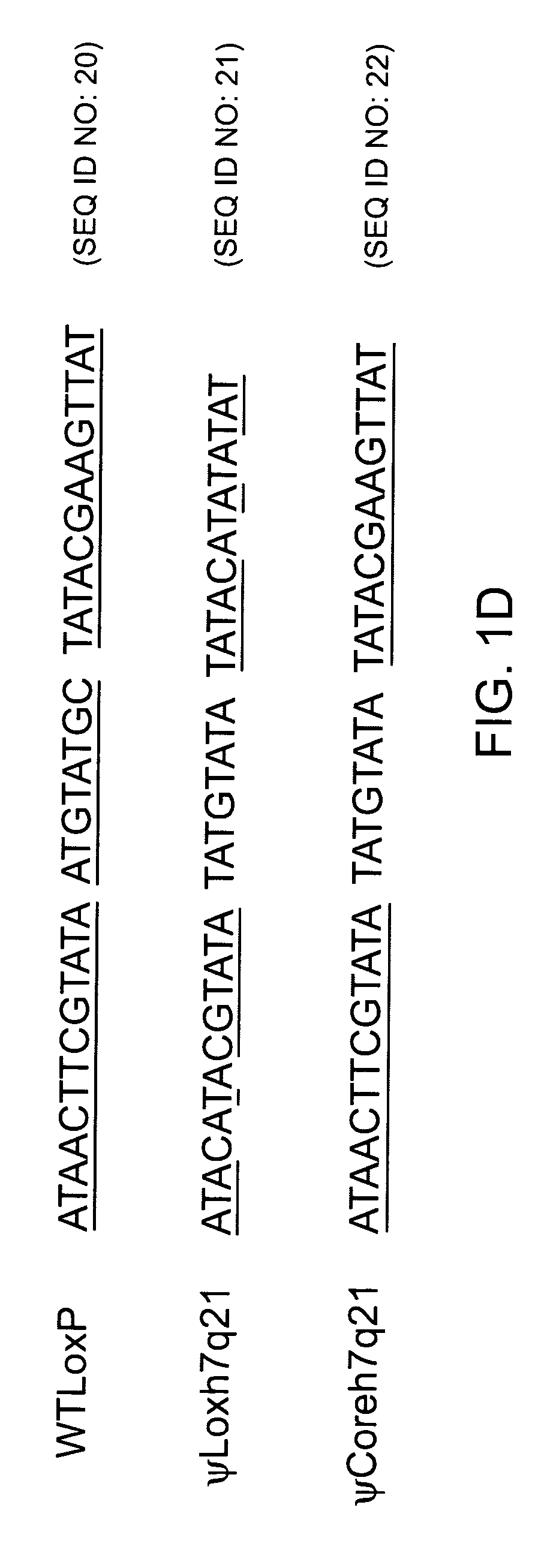
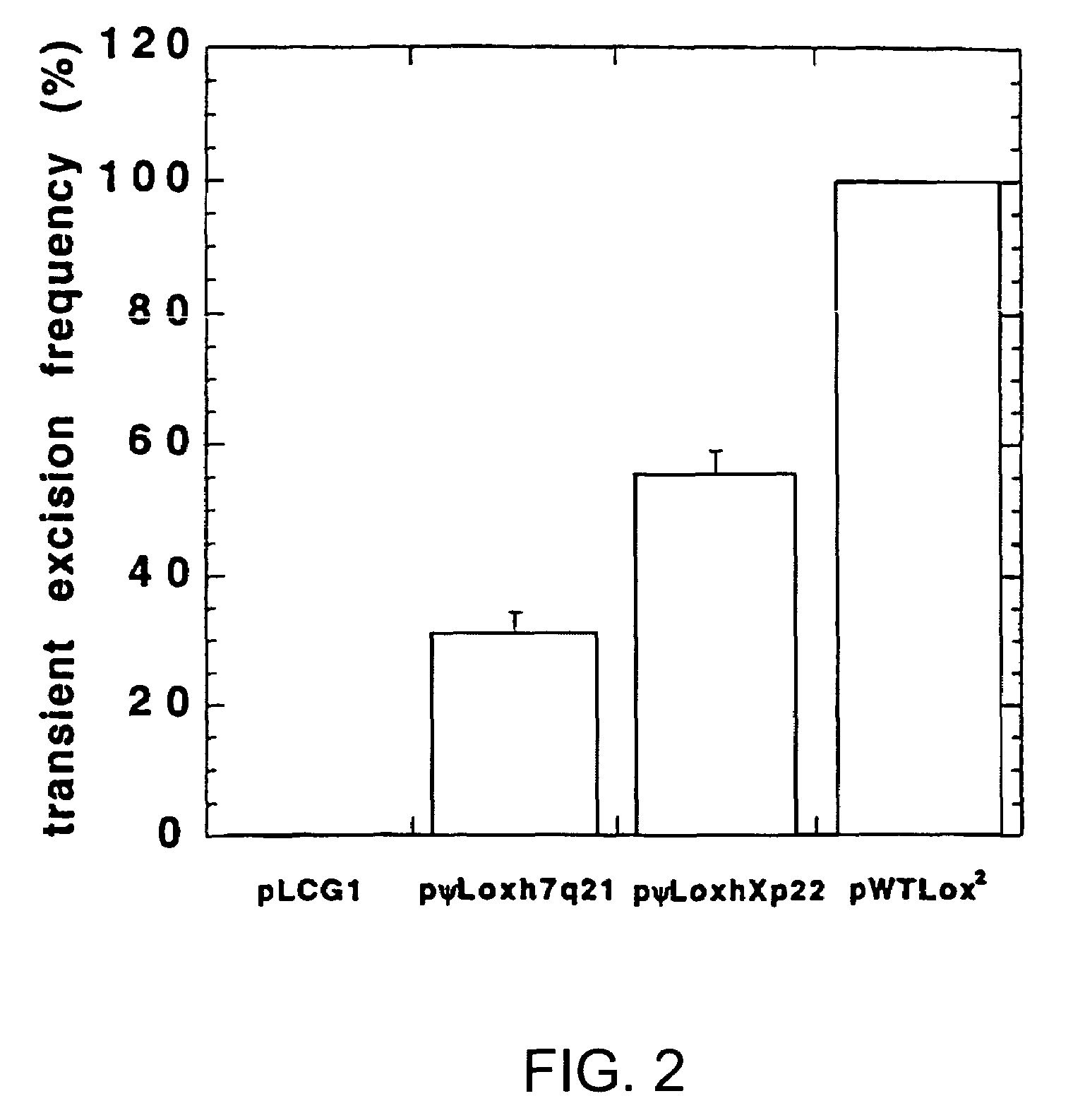
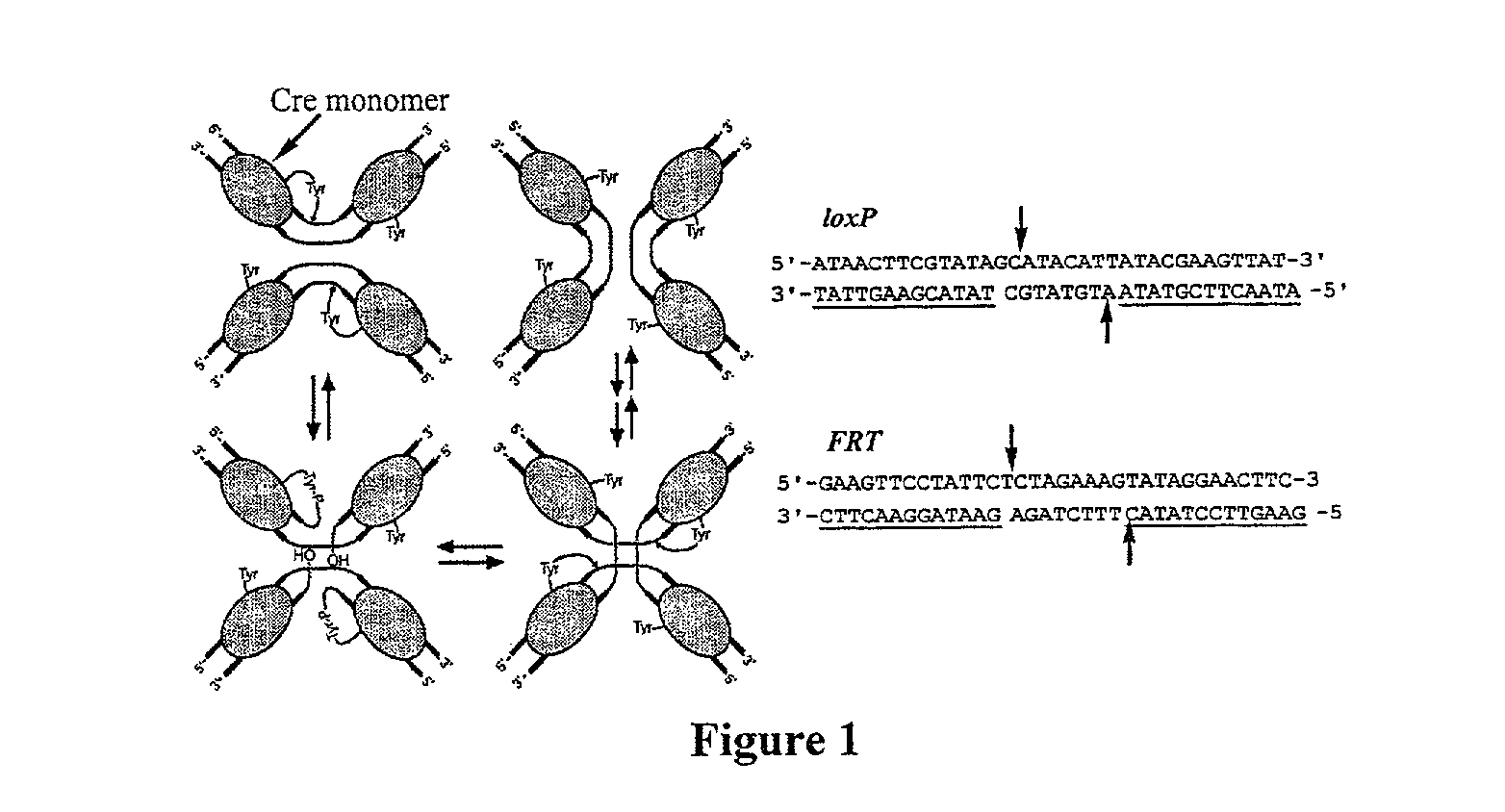
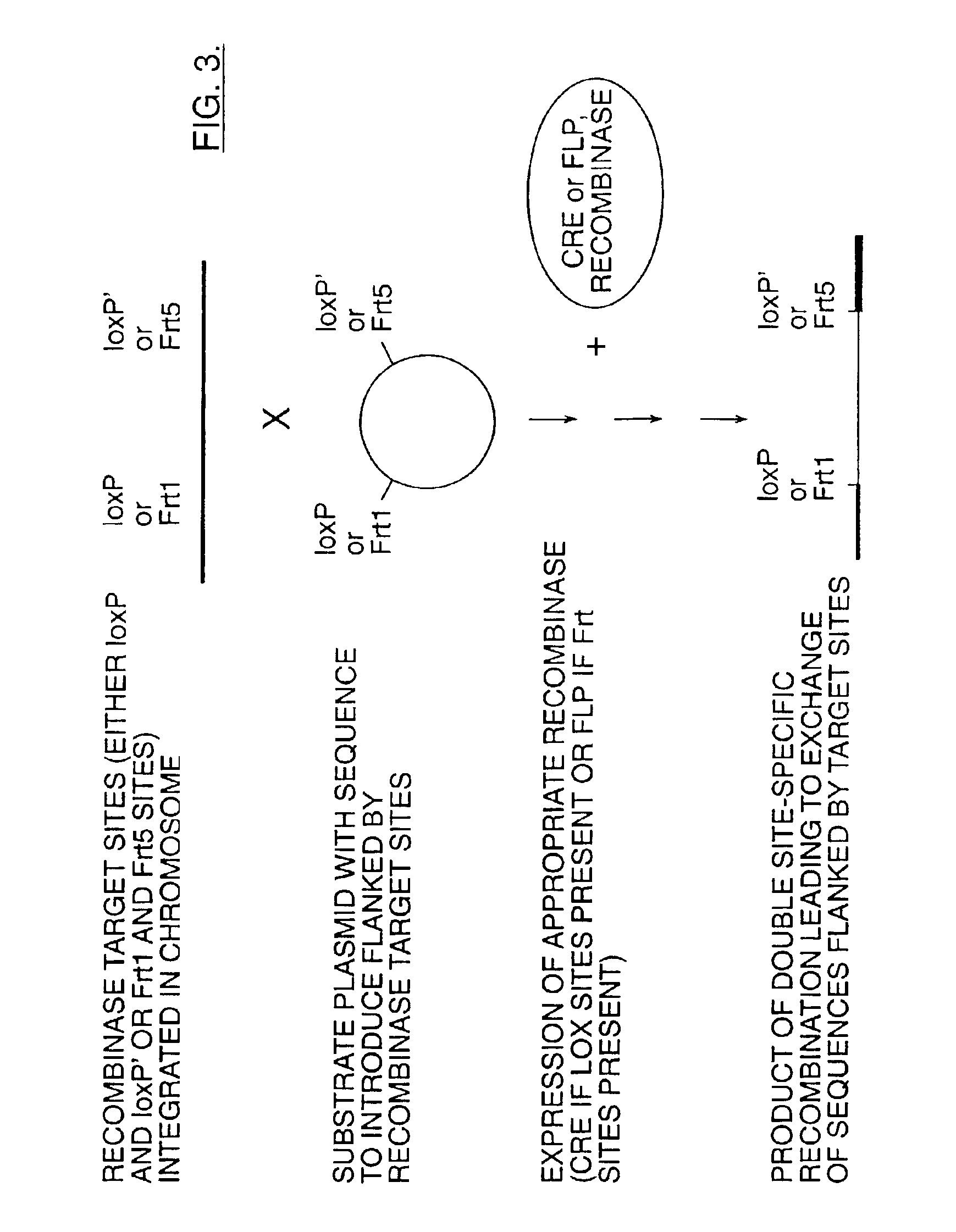
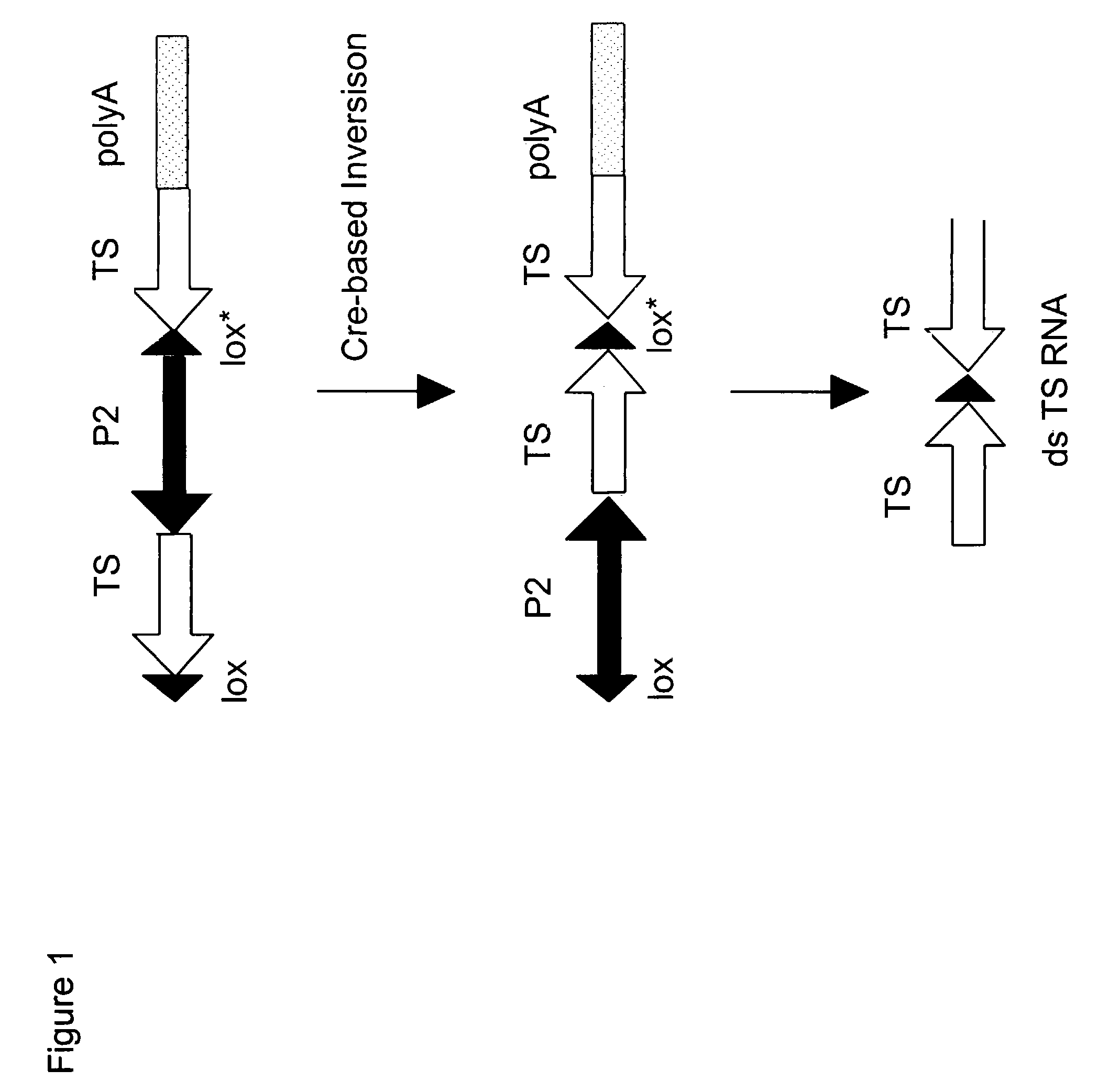
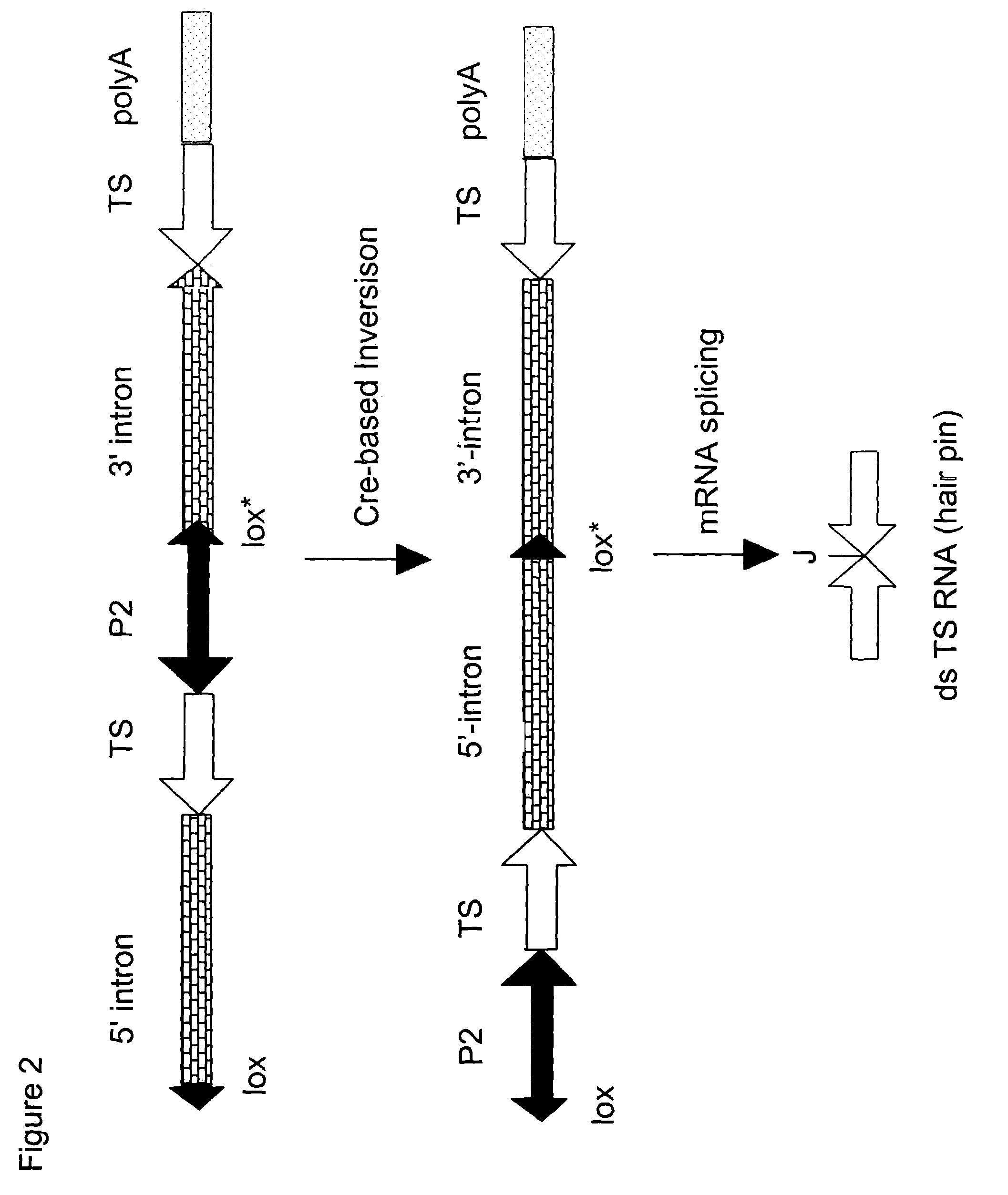
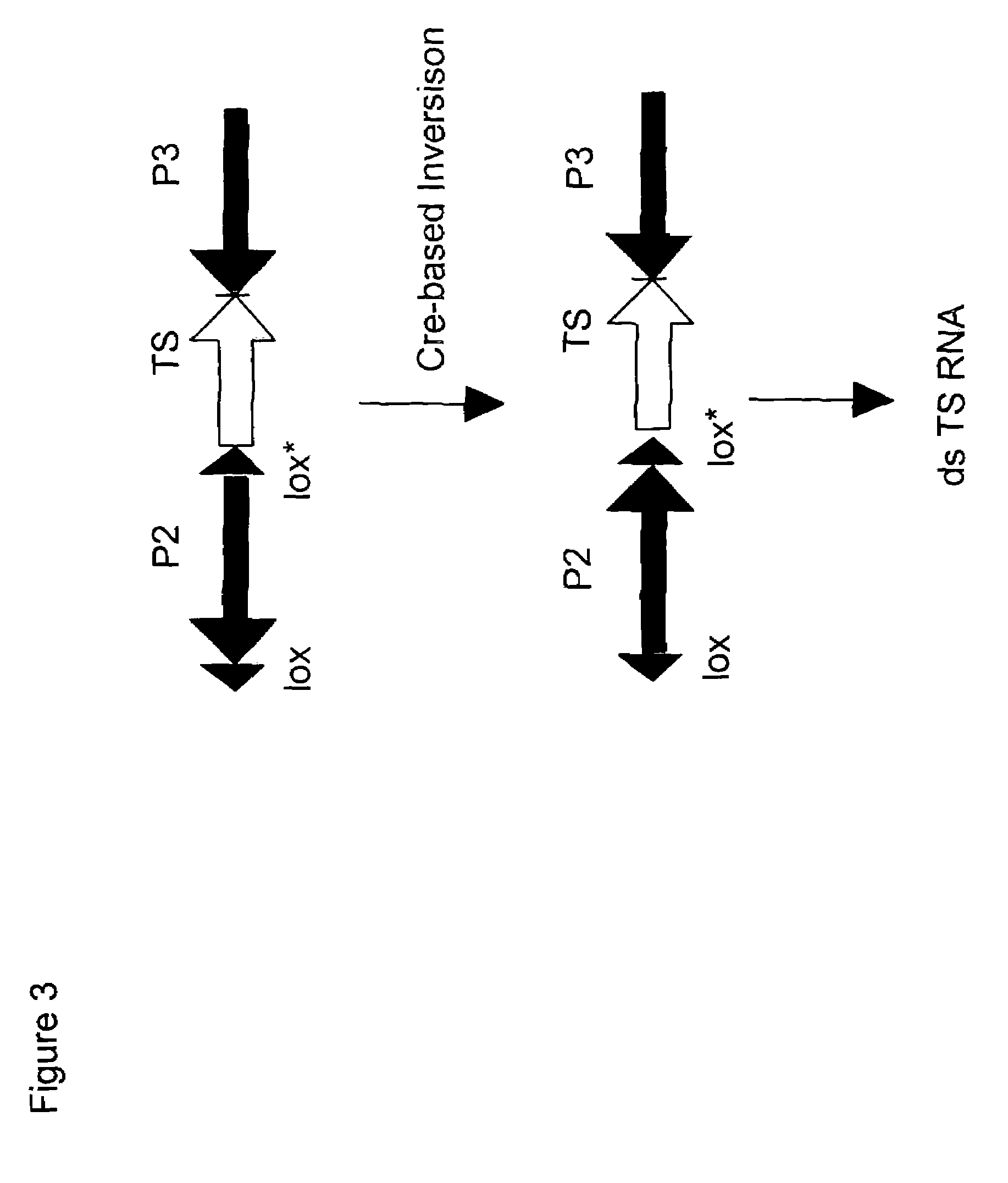
Site-specific recombination, also known as conservative site-specific recombination, is a type of genetic recombination in which DNA strand exchange takes place between segments possessing at least a certain degree of sequence homology. Site-specific recombinases (SSRs) perform rearrangements of DNA segments by recognizing and binding to short DNA sequences (sites), at which they cleave the DNA backbone, exchange the two DNA helices involved and rejoin the DNA strands. While in some site-specific recombination systems just a recombinase enzyme and the recombination sites is enough to perform all these reactions, in other systems a number of accessory proteins and/or accessory sites are also needed. Multiple genome modification strategies, among these recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE), an advanced approach for the targeted introduction of transcription units into predetermined genomic loci, rely on the capacities of SSRs.
Recombinant binding proteins and peptides
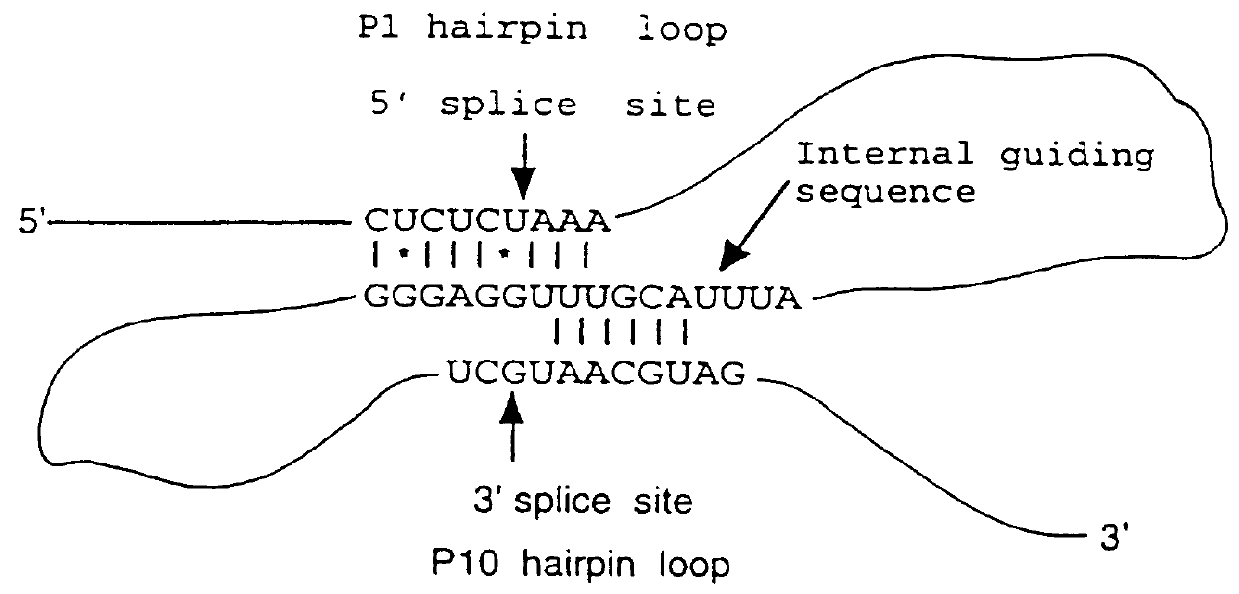
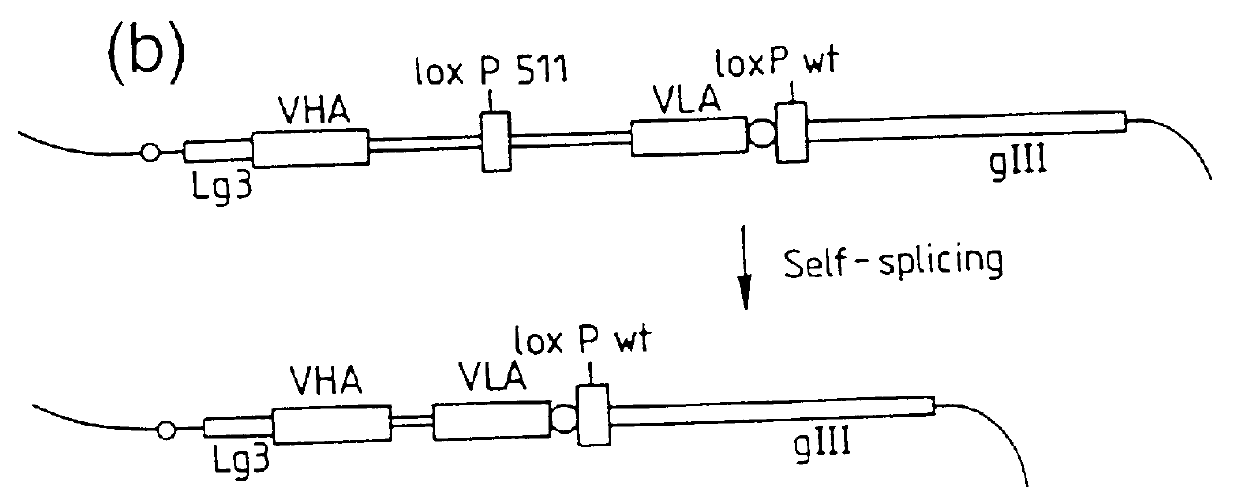
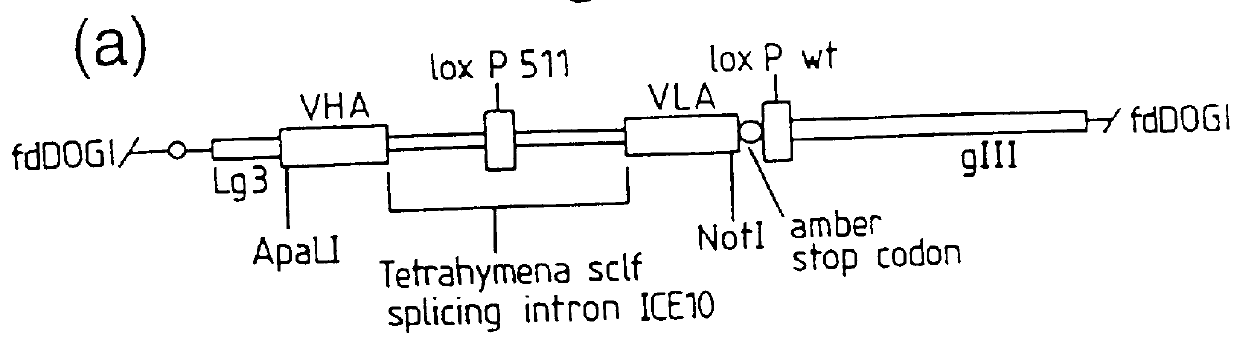
DNA constructs comprise a first exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a first peptide or polypeptide, a second exon sequence of nucleotides encoding a second peptide or polypeptide and a third sequence of nucleotides between the first and second sequences encoding a heterologous intron, for example that of Tetrahymena thermophila nuclear pre-rRNA, between RNA splice sites and a site-specific recombination sequence, such as loxP, within the intron, the exons together encoding a product peptide or polypeptide. Such constructs are of use in methods of production of peptides or polypeptides, transcription leading to splicing out of the intron enabling translation of a single chain product peptide or polypeptide. Isolated nucleic acid constructs consisting essentially of a sequence of nucleotides encoding a self-splicing intron with a site-specific recombination sequence within the intron, for use in creation of constructs for expression of peptides or polypeptides, are also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150071898A1Strong specificityReduce the possibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaSite-specific recombinationResearch setting
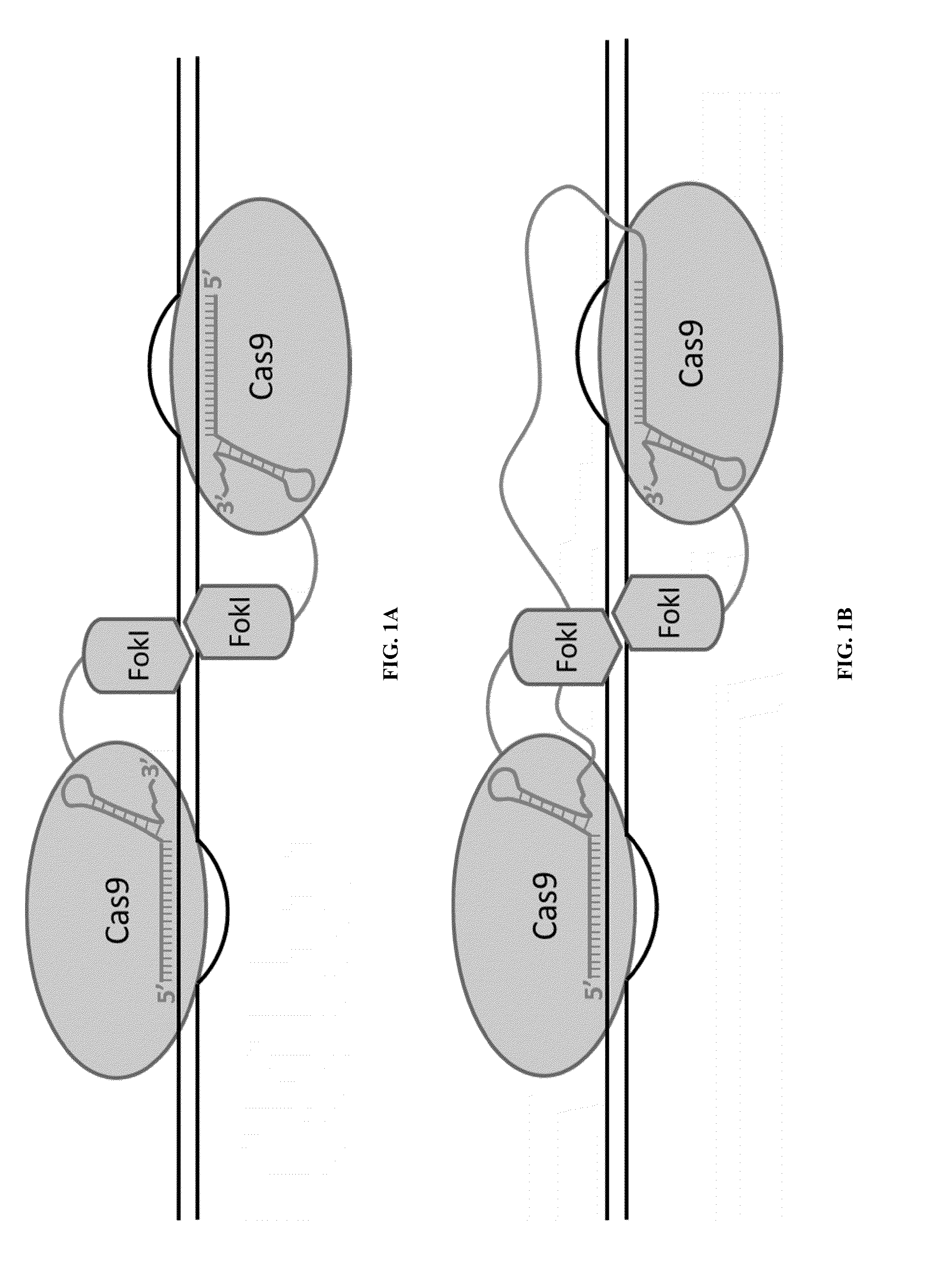
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, and kits for improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. Also provided are variants of Cas9, e.g., Cas9 dimers and fusion proteins, engineered to have improved specificity for cleaving nucleic acid targets. Also provided are compositions, methods, and kits for site-specific recombination, using Cas9 fusion proteins (e.g., nuclease-inactivated Cas9 fused to a recombinase catalytic domain). Such Cas9 variants are useful in clinical and research settings involving site-specific modification of DNA, for example, genomic modifications.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
InactiveUS20080020465A1Antibacterial agentsHydrolasesStreptococcus pyogenesSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PADIDAM MALLA
Methods and compositions for genomic modification
InactiveUS20040203152A1Genetic material ingredientsStable introduction of DNAEucaryotic cellSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides methods of site-specifically integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest in a genome of a eucaryotic cell, as well as, enzymes, polypeptides, and a variety of vector constructs useful therefore. In the method, a targeting construct comprises, for example, (i) a first recombination site and a polynucleotide sequence of interest, and (ii) a site-specific recombinase, which are introduced into the cell. The genome of the cell comprises a second recombination site. Recombination between the first and second recombination sites is facilitated by the site-specific recombinase. The invention describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors, and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
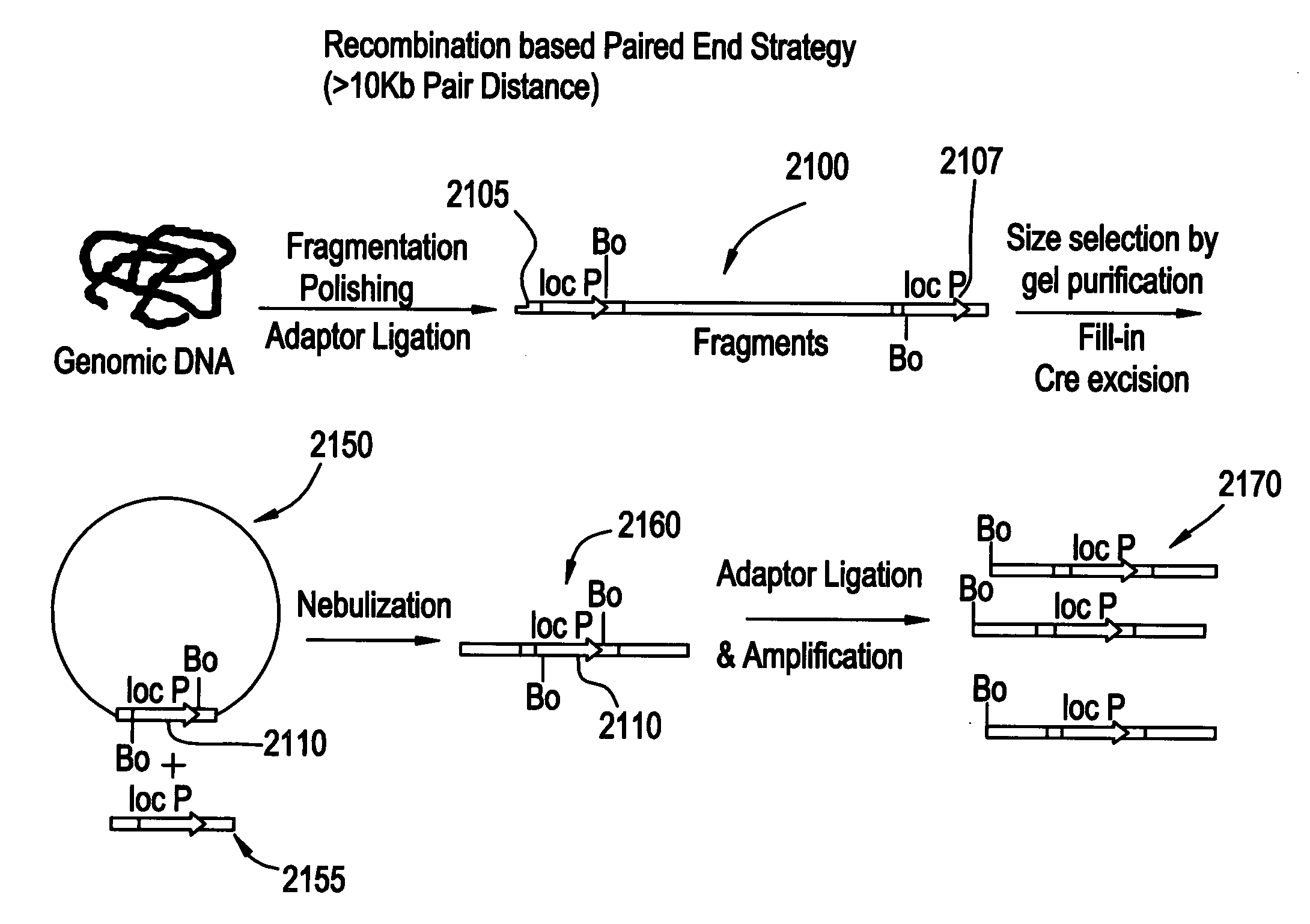
Paired end sequencing
An embodiment of a method for obtaining a DNA construct comprising two end regions of a target nucleic acid in an in vitro reaction is described that comprises the steps of: fragmenting a large nucleic acid molecule to produce a target nucleic acid molecule; ligating a recombination adaptor element to each end of the target nucleic acid molecule to produce an adapted target nucleic acid molecule; exposing the adapted target nucleic acid to a site specific recombinase to produce a circular nucleic acid product and a linear nucleic acid product from the adapted target nucleic acid, wherein the circular nucleic acid product comprises the target nucleic acid molecule; and fragmenting the circular nucleic acid product to produce a template nucleic acid molecule comprising a sequence region from each end of the target nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
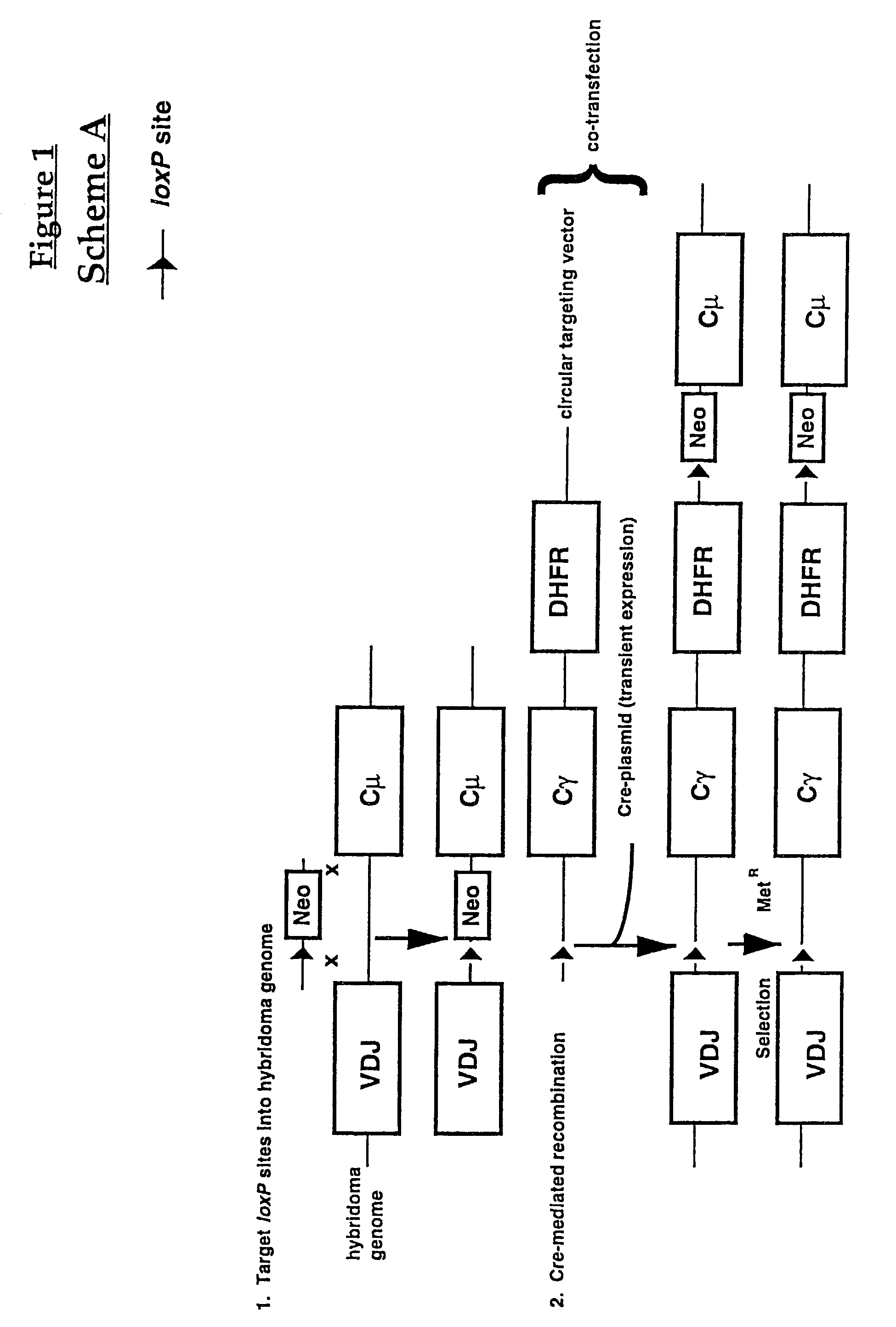
Production of antibodies using cre-mediated site-specific recombination
InactiveUS7145056B2Improve recombination efficiencyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationAntibody-Producing Cells
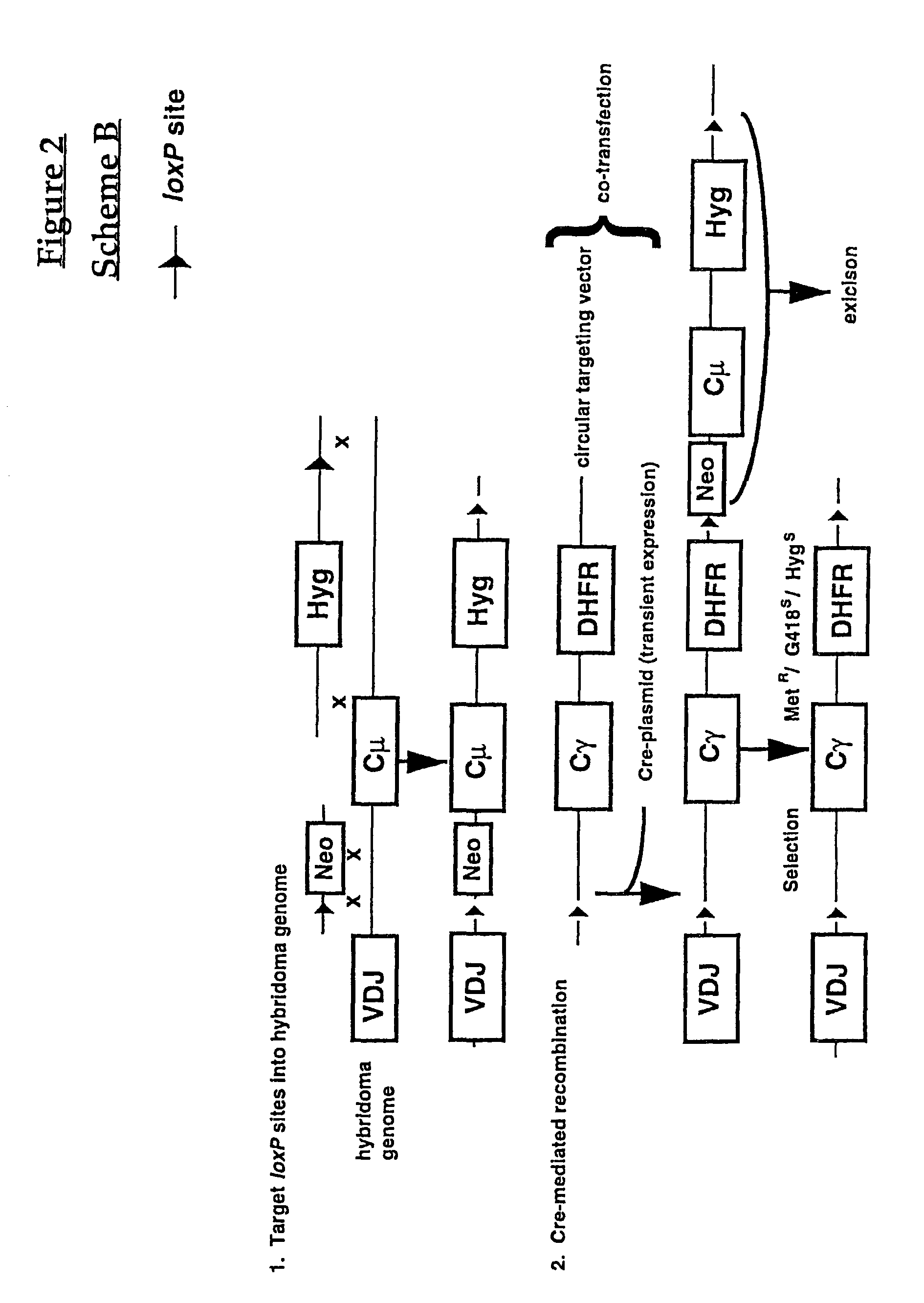
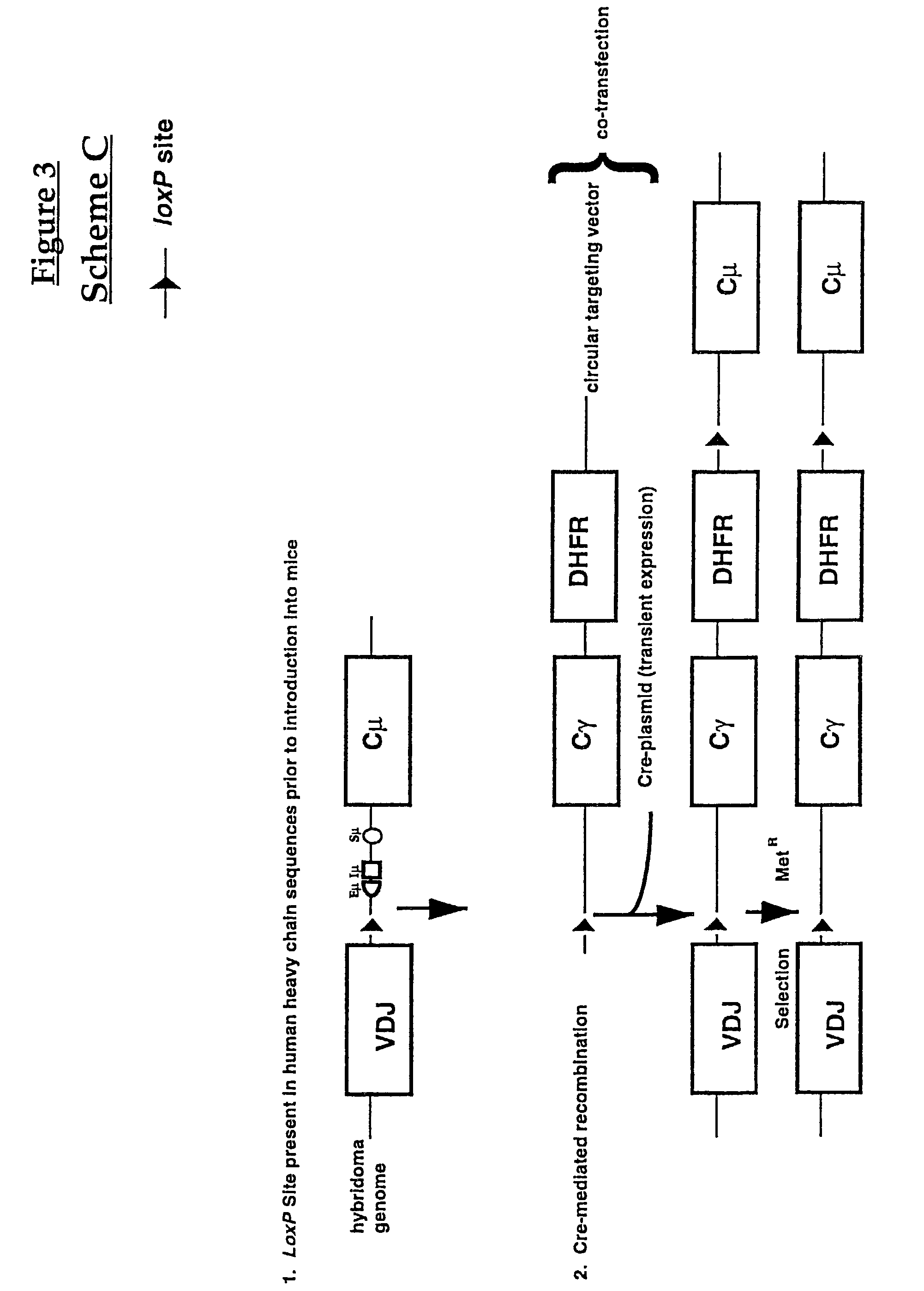
A method to produce a cell expressing an antibody from a genomic sequence of the cell comprising a modified immunoglobulin locus using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination is disclosed. The method involves first transfecting an antibody-producing cell with a homology-targeting vector comprising a lox site and a targeting sequence homologous to a first DNA sequence adjacent to the region of the immunoglobulin loci of the genomic sequence which is to be converted to a modified region, so the first lox site is inserted into the genomic sequence via site-specific homologous recombination. Then the cell is transfected with a lox-targeting vector comprising a second lox site suitable for Cre-mediated recombination with the integrated lox site and a modifying sequence to convert the region of the immunoglobulin loci to the modified region. This conversion is performed by interacting the lox sites with Cre in vivo, so that the modifying sequence inserts into the genomic sequence via Cre-mediated site-specific recombination of the lox sites. Also disclosed are a form of the method used to produce a cell expressing a modified antibody molecule using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination, and antibody-producing cells obtainable by the disclosed methods. Class-switching modifications of human antibodies produced in murine hybridoma cells are exemplified.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC +1
Engineered Listeria and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070207170A1Improve survivalIncreasing expression and secretionBiocideBacteriaHeterologous AntigensSite-specific recombination
The invention provides a bacterium containing a polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous antigen, as well as fusion protein partners. Also provided are vectors for mediating site-specific recombination and vectors comprising removable antibiotic resistance genes.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
System for the rapid manipulation of nuculeic acid sequences
InactiveUS20070128724A1Eliminate needFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCell freeSite-specific recombination
Owner:INVITROGEN
Universal stem cells
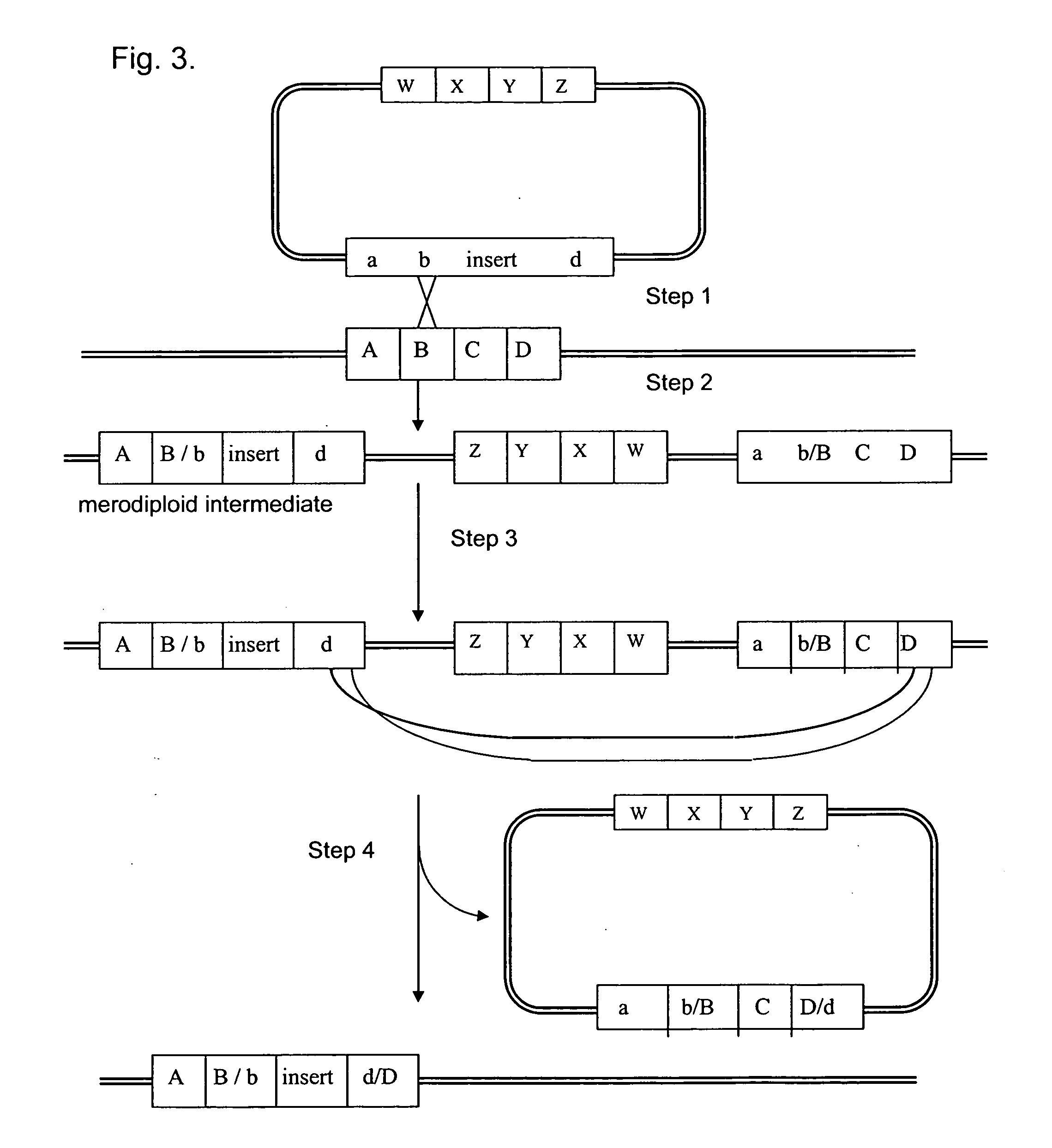
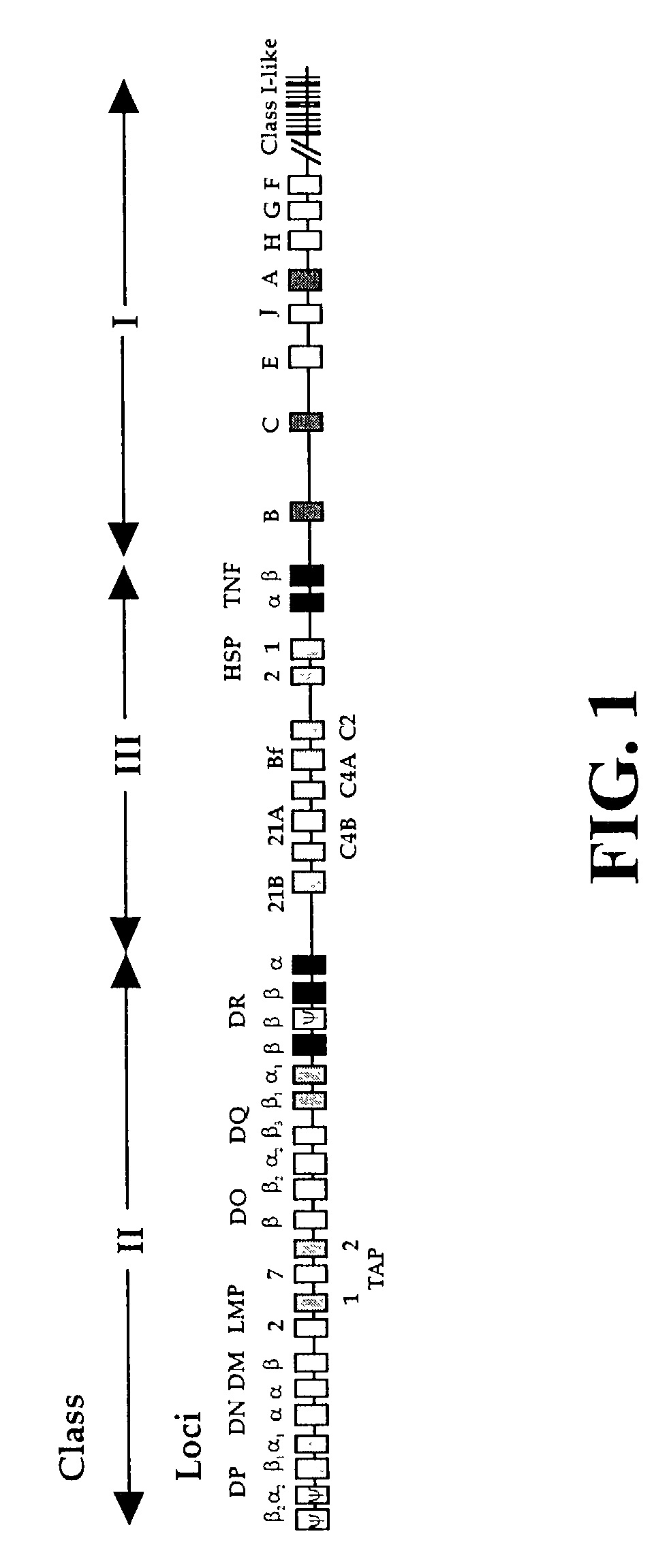
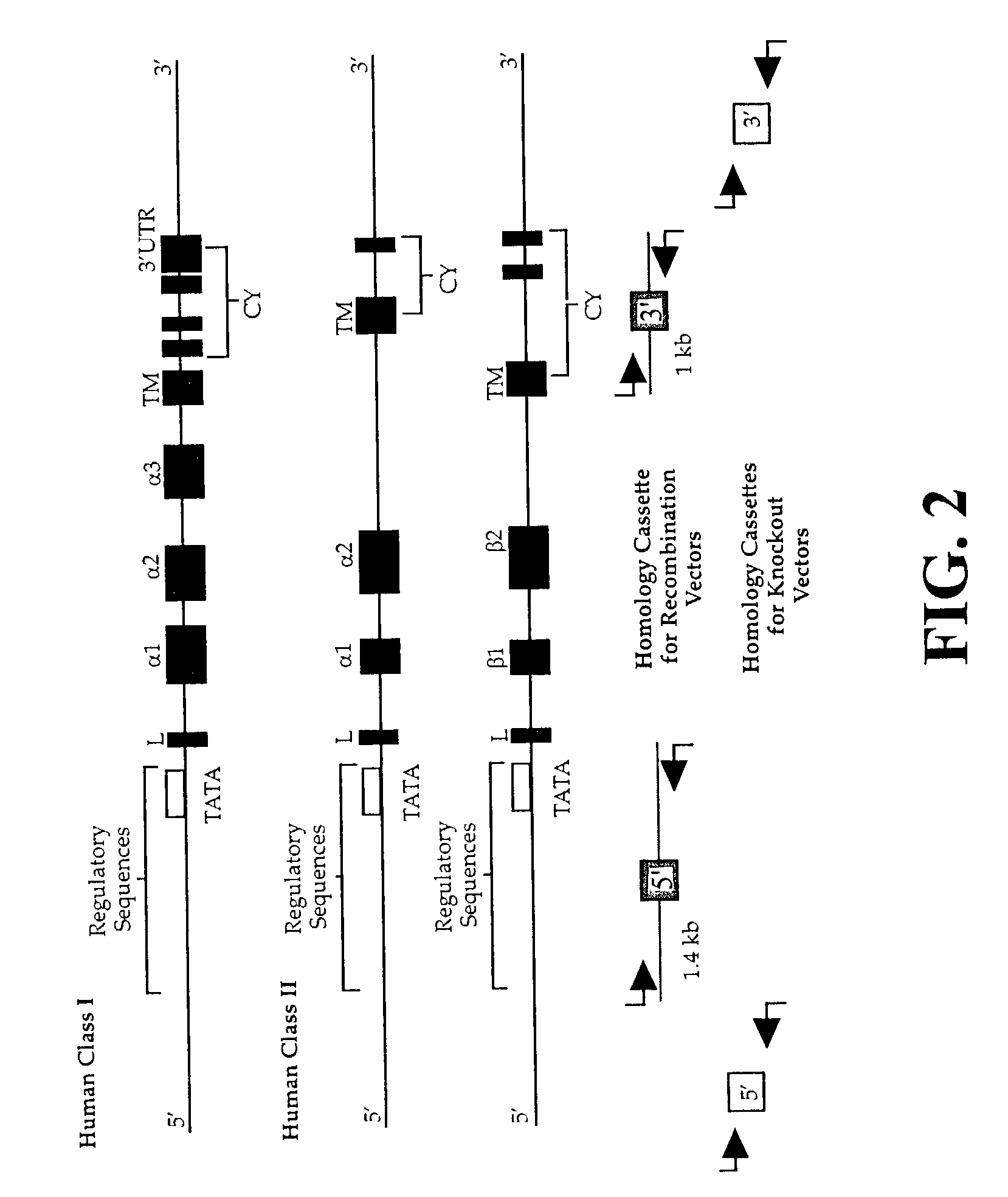
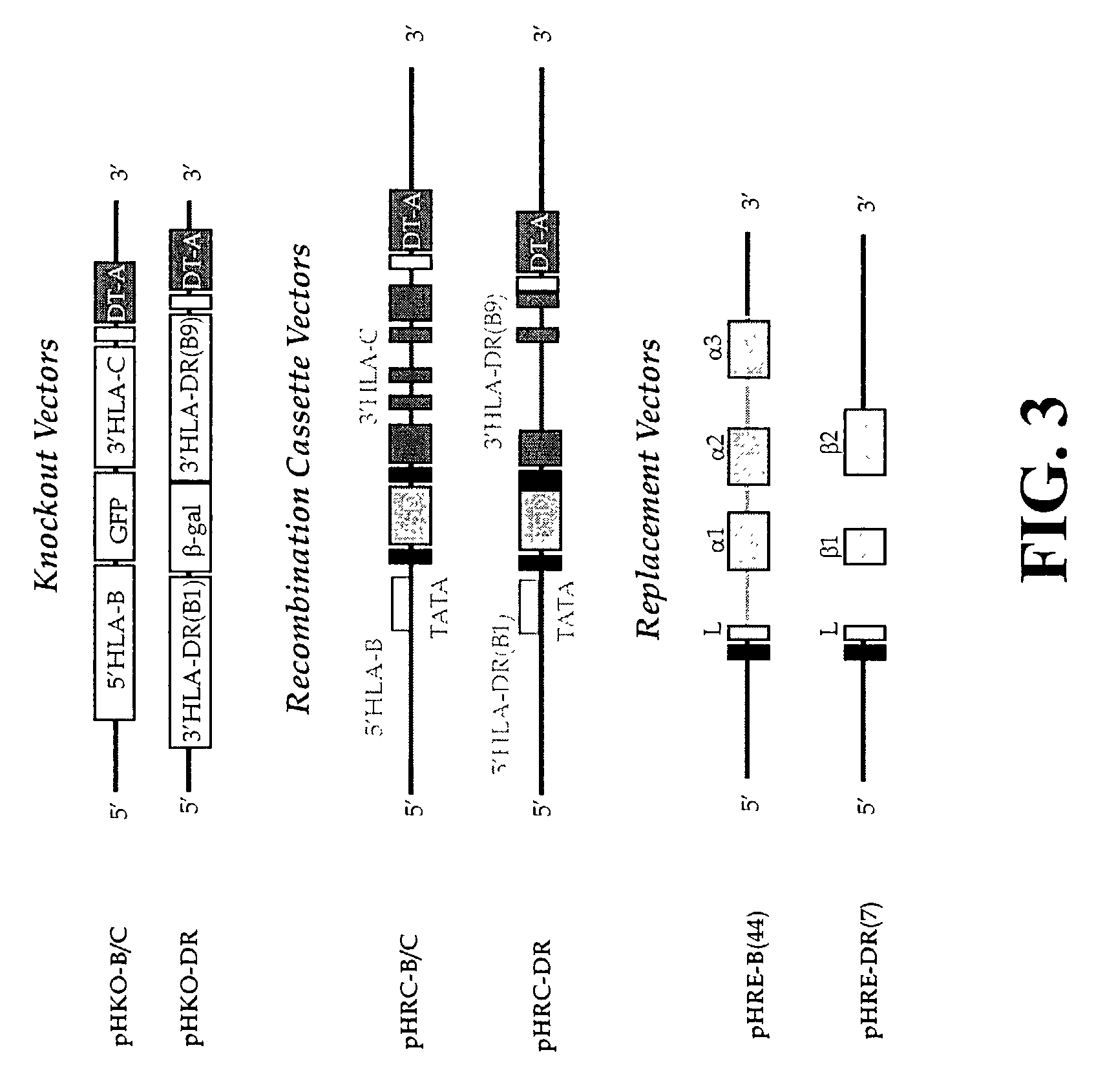
The subject invention pertains to materials and methods for preparing multi-potential stem cells having a pre-selected expression of MHC antigens. Stem cells of the subject invention can be used to generate histocompatible tissues / organs for transplantation. The process of the subject invention comprises the use of targeting vectors capable of gene knockout, insertion of site-specific recombination cassettes, and the replacement of histocompatibility alleles in the stem cell. Novel knockout vectors are used to delete designated regions of one chromosome. Recombination cassette vectors are then used to delete the same region on the second chromosome and deposit a site-specific recombination cassette which can be utilized by replacement vectors for inserting the new MHC genes on the chromosome of the engineered cell. The subject invention also pertains to cells, tissues, and transgenic mammal prepared using the methods and materials of the invention.
Owner:MORPHOGENESIS
Method for assembling PCR fragments of DNA
InactiveUS7629120B2Simple stepsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrigin of replicationSite-specific recombination
A process for assembling a series of DNA fragments generated by PCR into an ordered circular arrangement for replication and genetic work in cells. The PCR fragments are made with a modified nucleotide in the primers that can be removed with a DNA excision repair enzyme to generate a 3′ overhang. The 3′ overhangs are designed to allow directional annealing and thus sequential PCR fragments can be assembled by annealing the overhangs and subsequent ligation. Sequential addition of PCR fragments is facilitated by growing the chain on a solid support, and the assembled chain can be removed with a site specific recombinase if the first and last primers contain the recombinase site. The circularized assembled fragment can be directly used for cell transformation if the appropriate sequences are included, such as an origin of replication and a selectable marker.
Owner:RICE UNIV
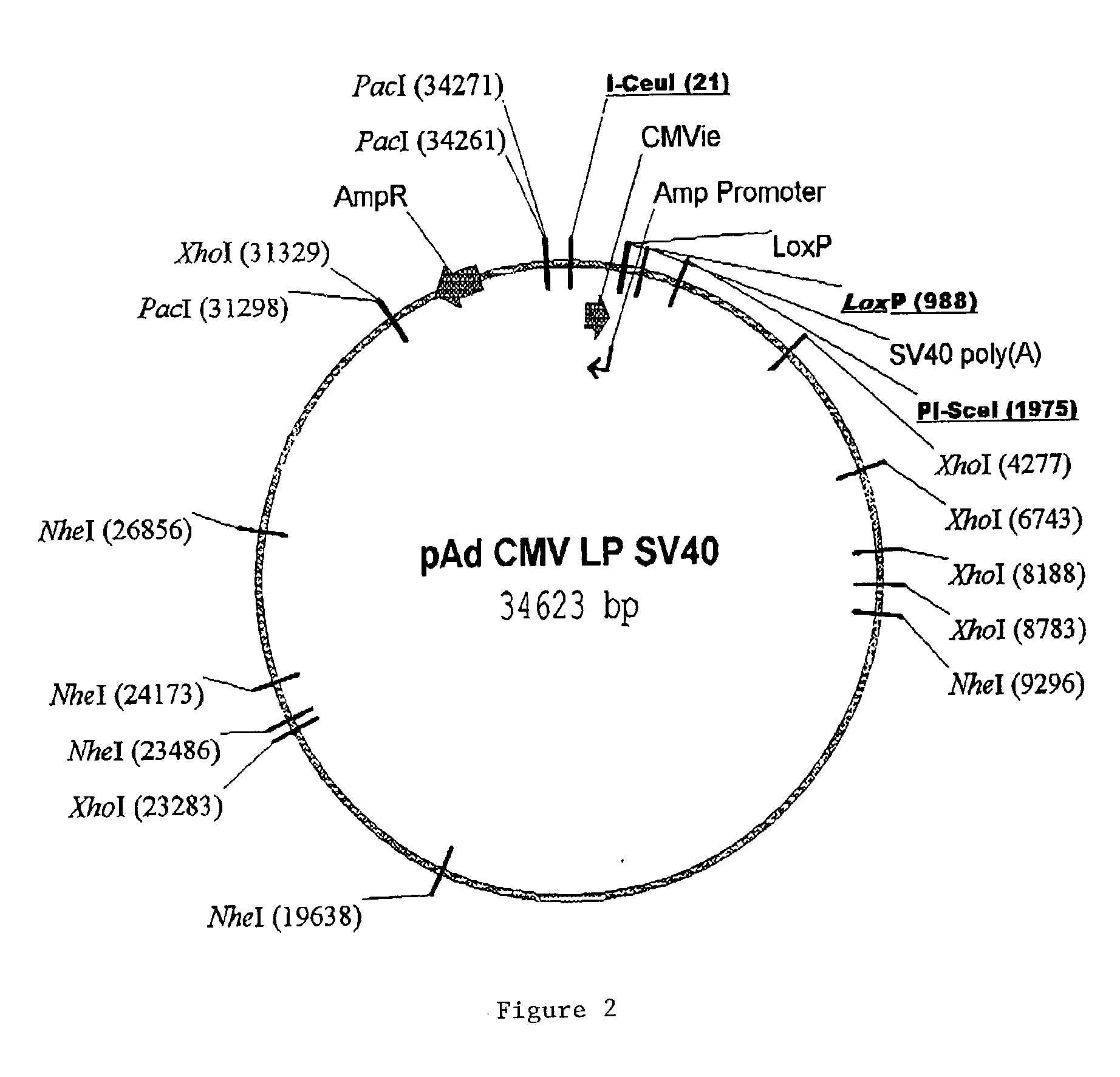
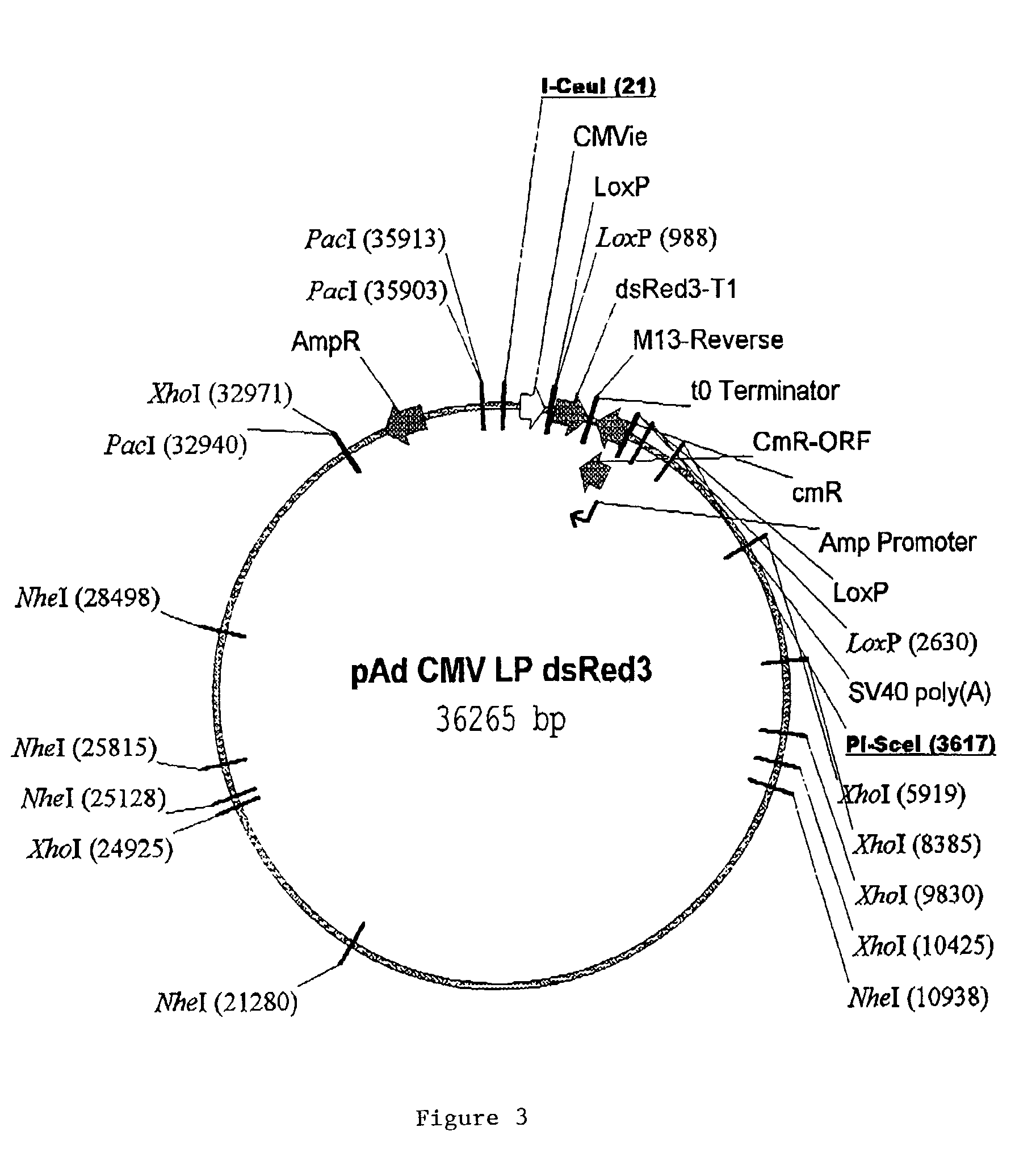
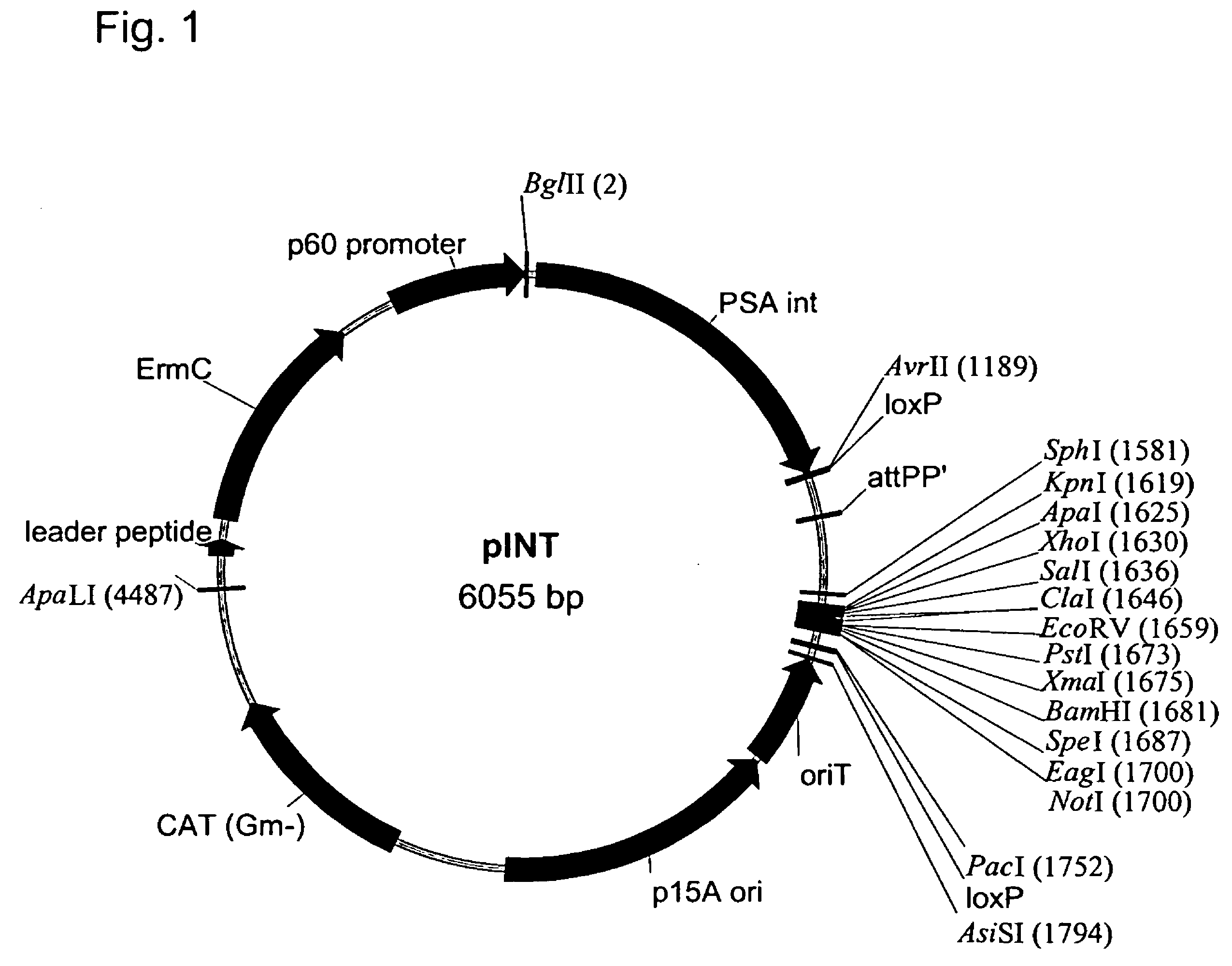
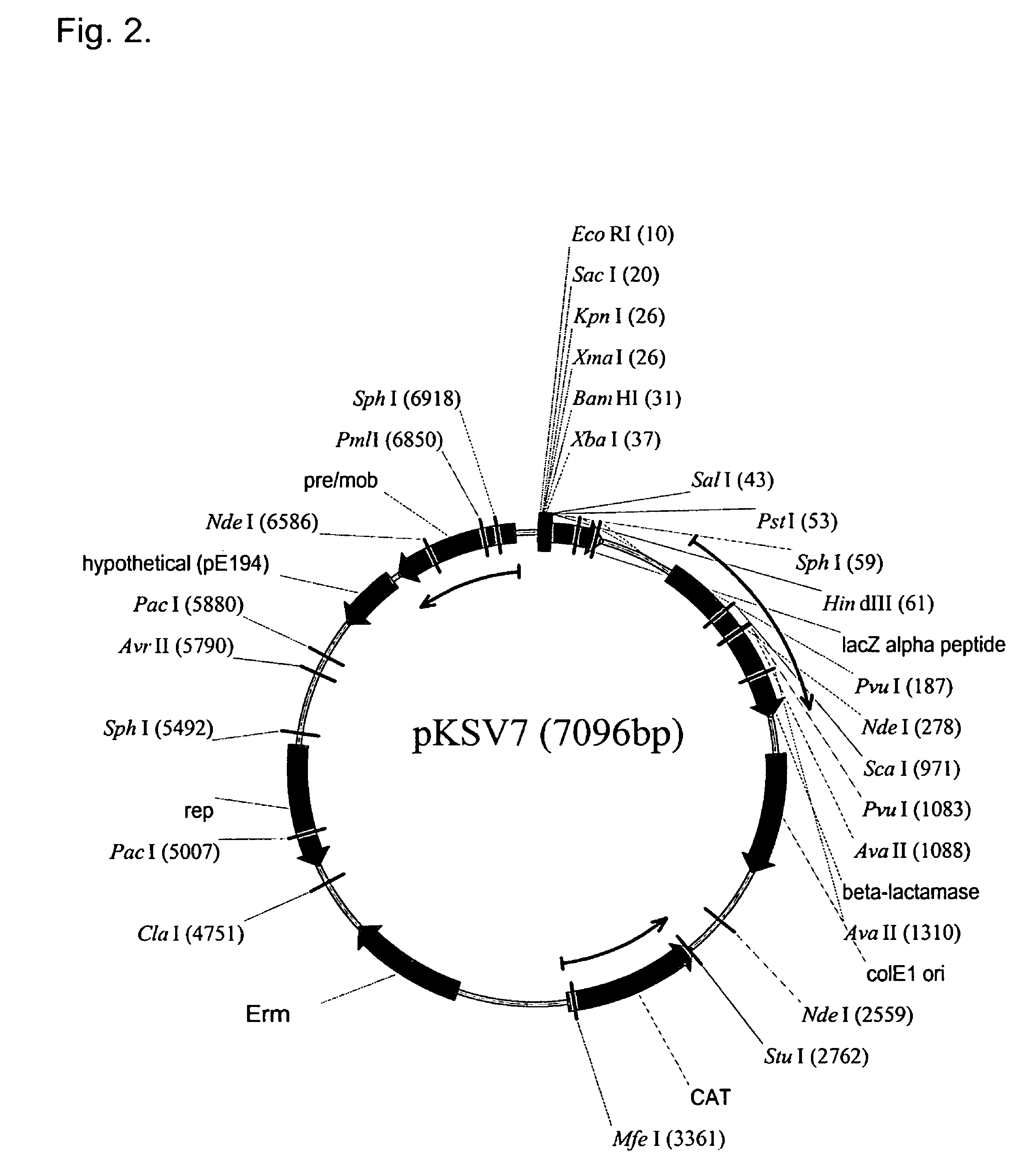
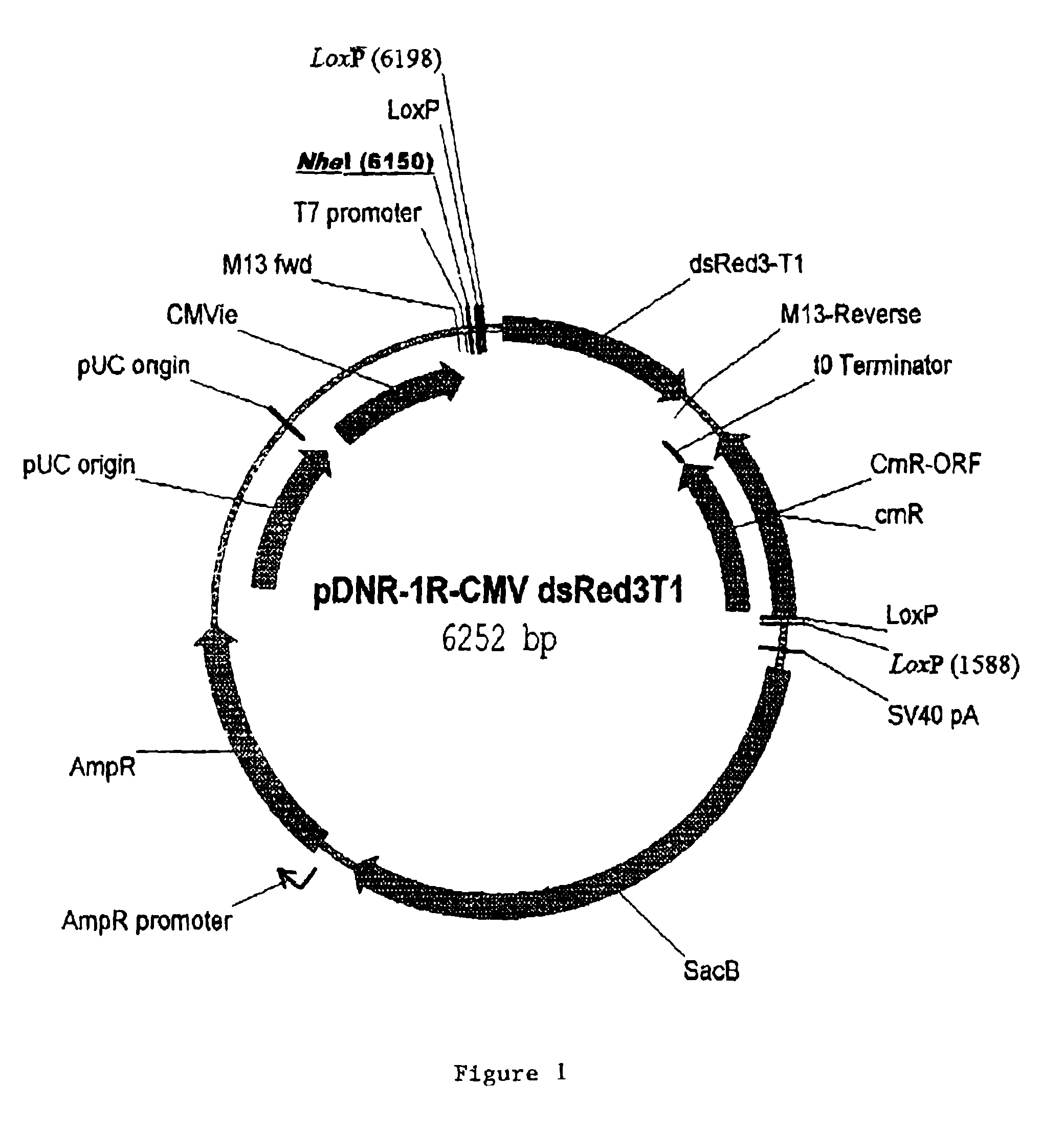
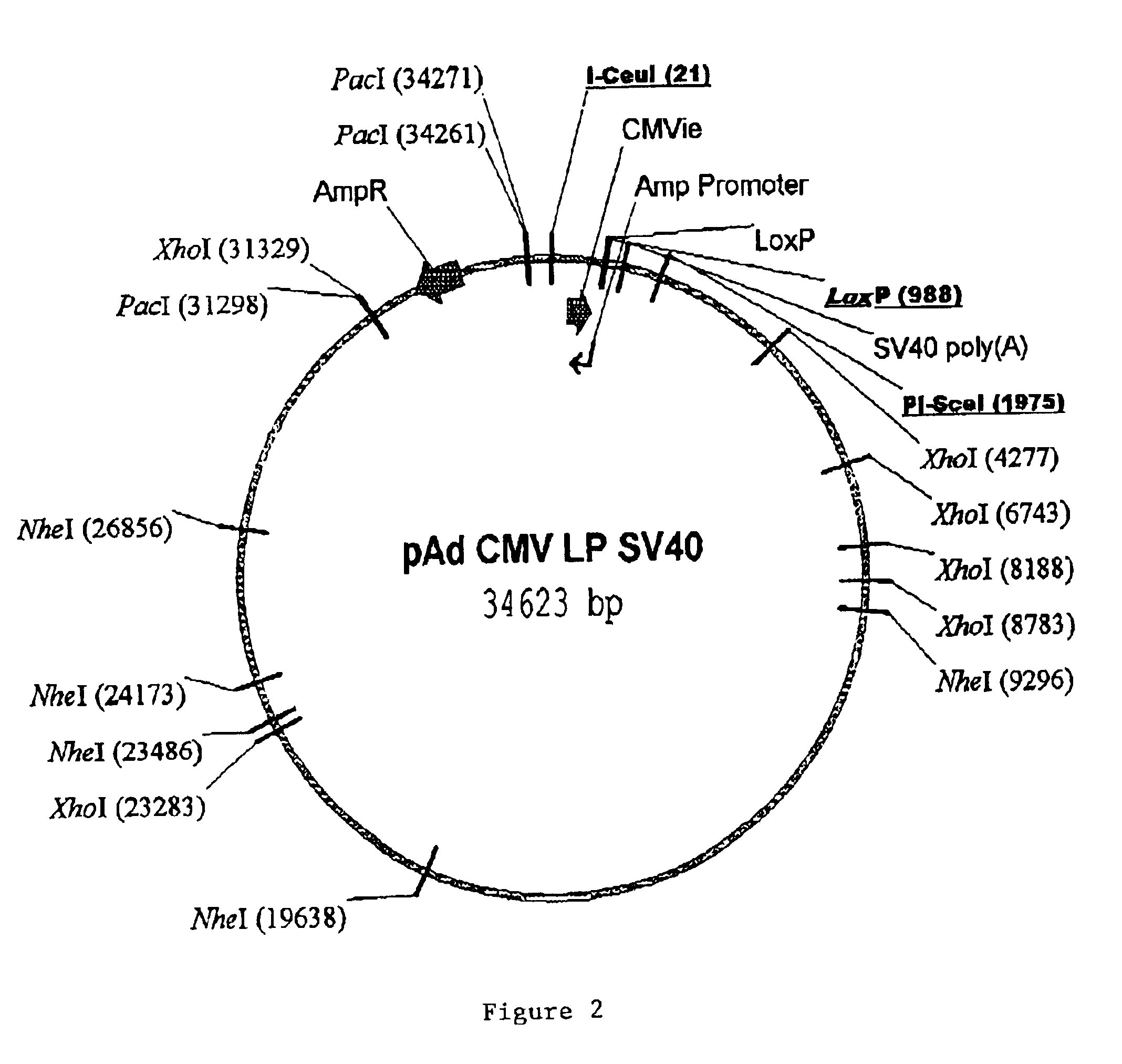
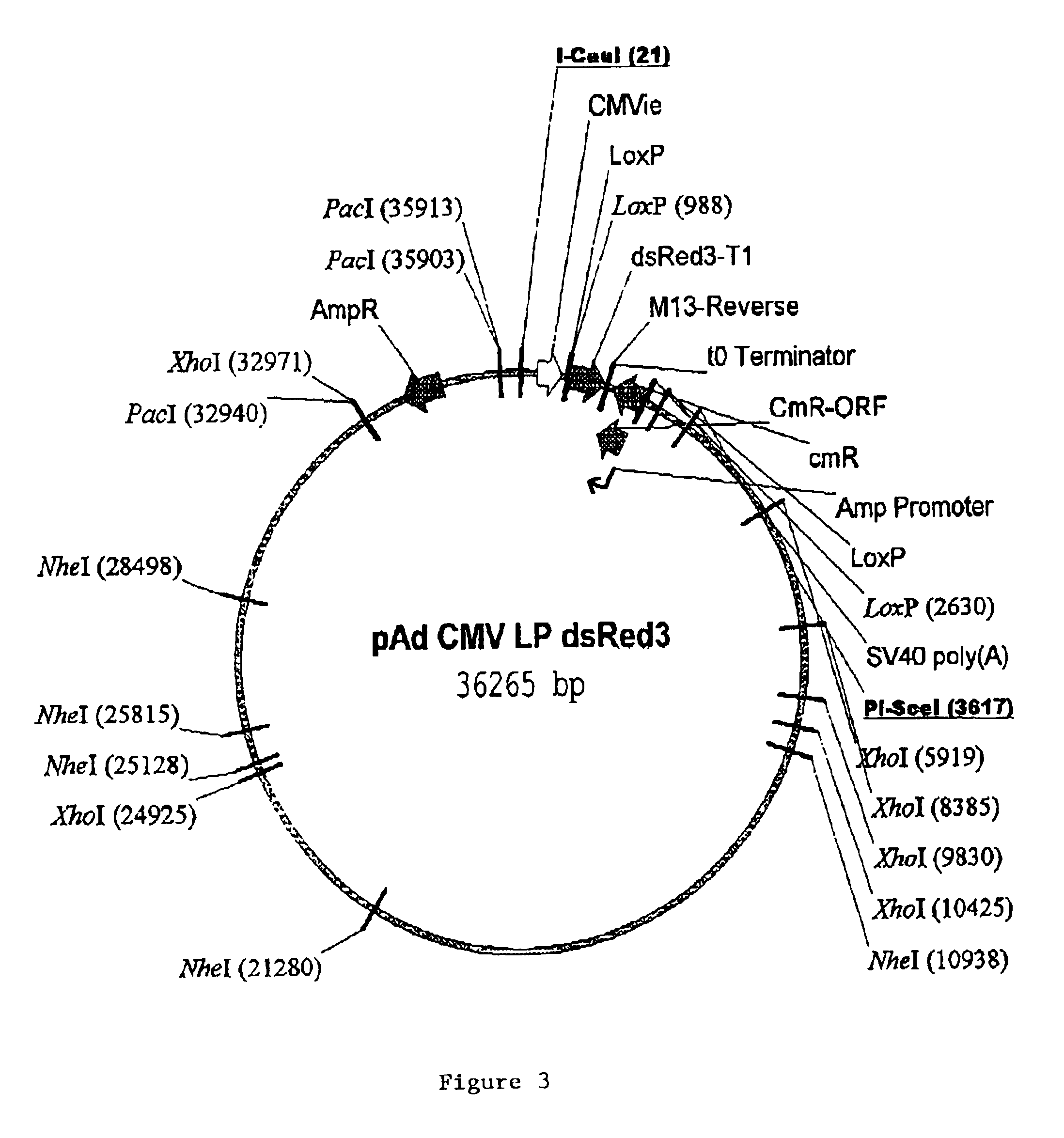
Site specific recombinase based method for producing adenoviral vectors
Site-specific recombinase based methods for making a recombinant adenoviral genome, as well as kits for practicing the same and the recombinant adenovirus vectors produced thereby, are provided. In the subject methods, the subject genomes are prepared from donor and acceptor vectors that each include at least one site recombinase recognition site, where in certain preferred embodiments, one of the donor and acceptor vectors includes a single recombinase recognition site while the other includes two recombinase recognition sites. The acceptor vector includes an adenoviral genome having an E region deletion. The donor vector includes an insertion nucleic acid. In the subject methods, the donor and acceptor vectors are combined in the presence of a recombinase to produce an adenoviral genome that includes the insertion nucleic acid. The subject adenoviral genomes find use in a variety of applications, including as vectors for use in a variety of applications.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods of unidirectional, site-specific integration into a genome, compositions and kits for practicing the same
InactiveUS20060128020A1Facilitate site-specific recombinationReducing and avoiding secondary recombination eventSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNAIntegrasesSite-specific recombination
The subject invention provides a unidirectional site-specific integration system for integrating a nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell. The provided system includes a site-specific integrating expression cassette (INTEC) vector, consisting of (a) a polynucleotide of interest operably linked to a promoter, (b) a single recombination site, and (c) a hybrid recombination site. In using the subject systems for site-specific integration, the INTEC vector and integrase are introduced into the target cell and the cell is maintained under conditions sufficient to provide for site-specific integration of the nucleic acid into the target cell genome via a recombination event mediated by the site-specific recombinase. Also provided are kits that include the subject systems. The subjects systems, methods and kits find use in a variety of different applications, several representative ones of which are described in detail as well.
Owner:POETIC GENETICS +1
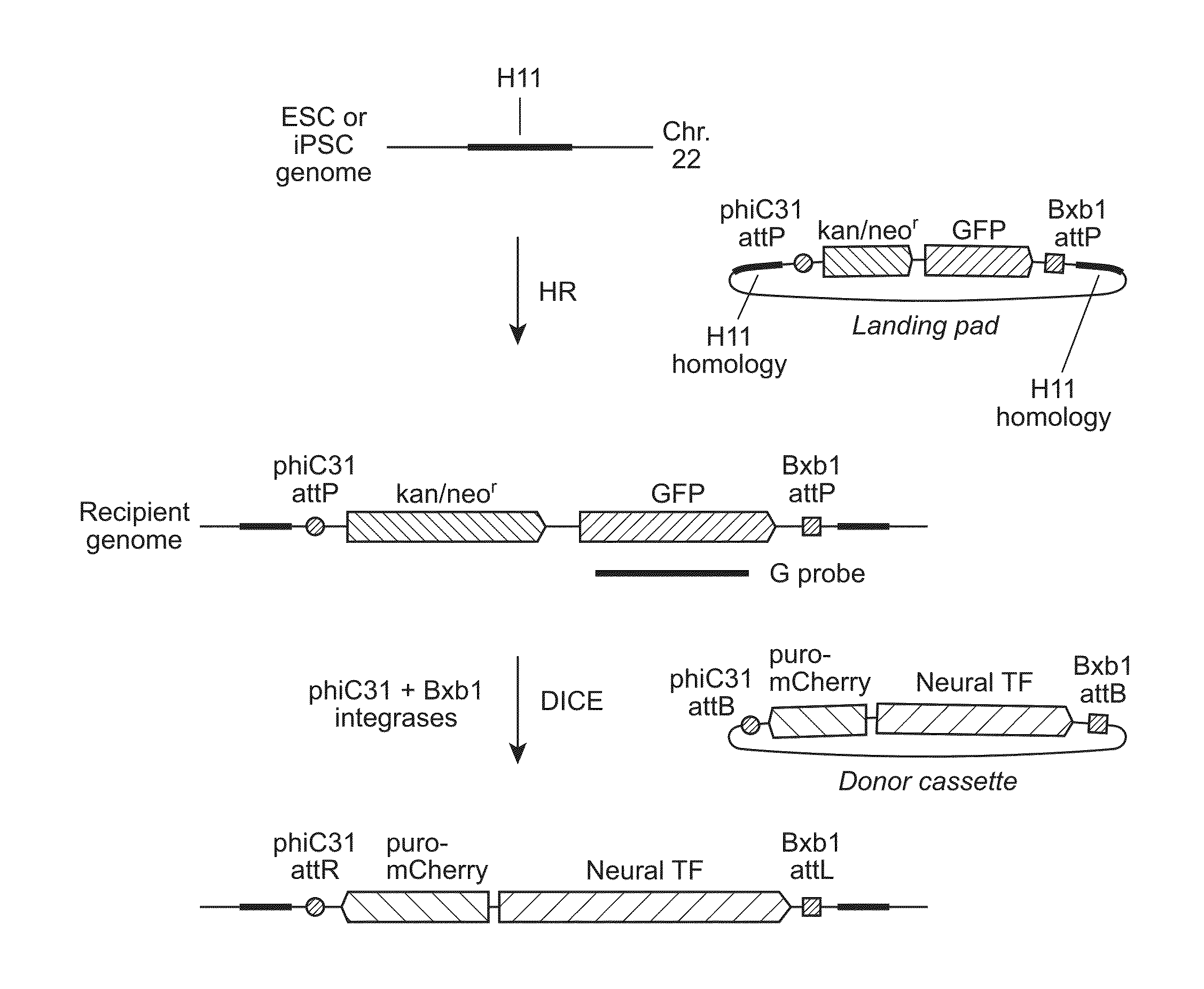
Site-Specific Integration of Transgenes into Human Cells
ActiveUS20150140665A1Easy to optimizeEasy to reorganizeStable introduction of DNAFermentationPresent methodNucleotide
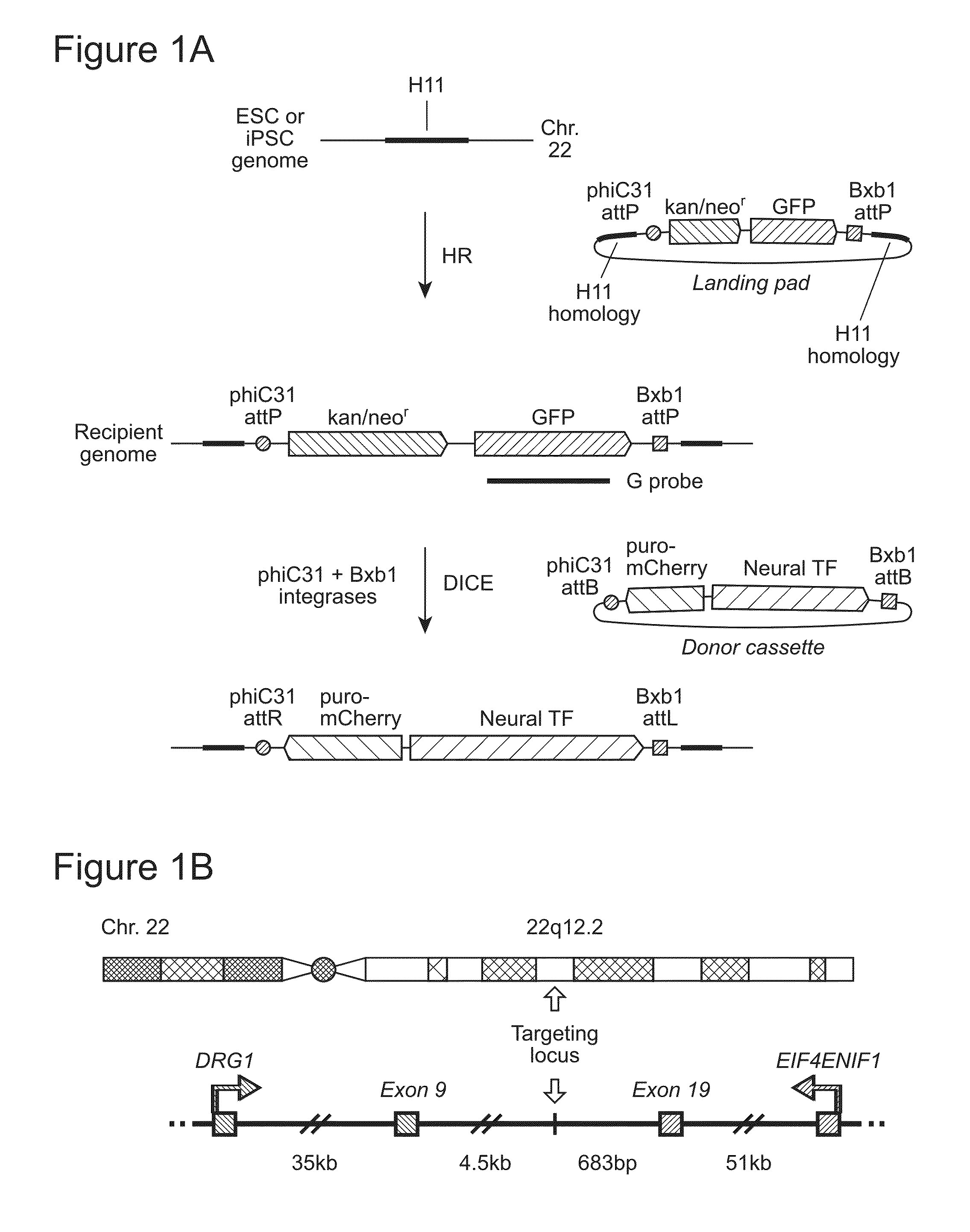
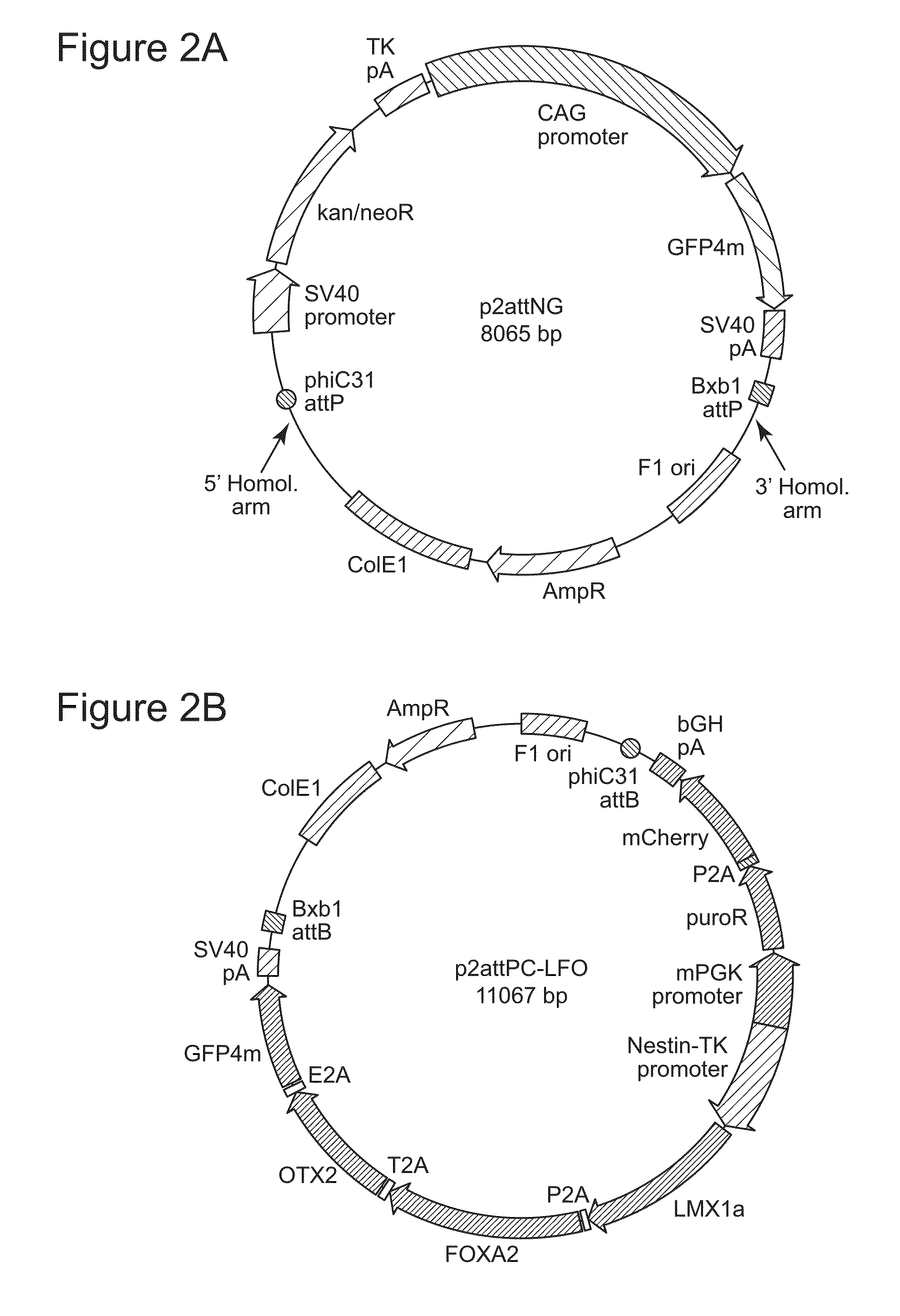
Methods for inserting a polynucleotide sequence into the genome of a human cell are provided. The present methods result in insertion of a polynucleotide sequence of interest into the H11 locus in the genome of a human cell. Also provided are nucleic acids that include sequences for integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest into the H11 locus in the genome of a human cell. A transgenic human cell including site specific recombination sites at the H11 locus is also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Site-specific recombination in eukaryotes and constructs useful therefor
InactiveUS7135608B1Effective recombinationEfficient productionEnzymesFermentationMammalSite-specific recombination
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Engineered Listeria and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7935804B2Improve survivalIncreasing expression and secretionBiocideBacteriaHeterologousHeterologous Antigens
The invention provides a bacterium containing a polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous antigen, as well as fusion protein partners. Also provided are vectors for mediating site-specific recombination and vectors comprising removable antibiotic resistance genes.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
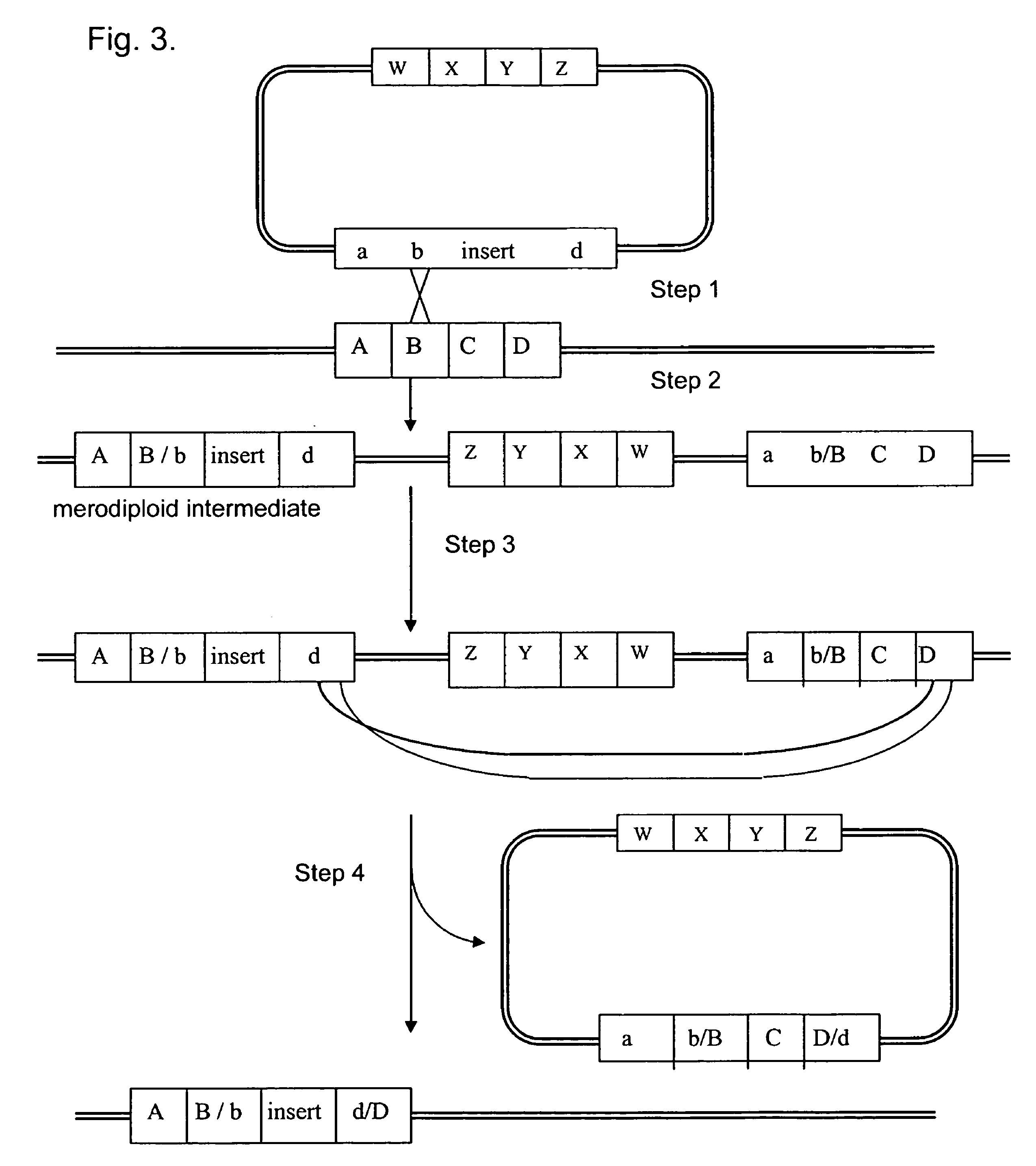
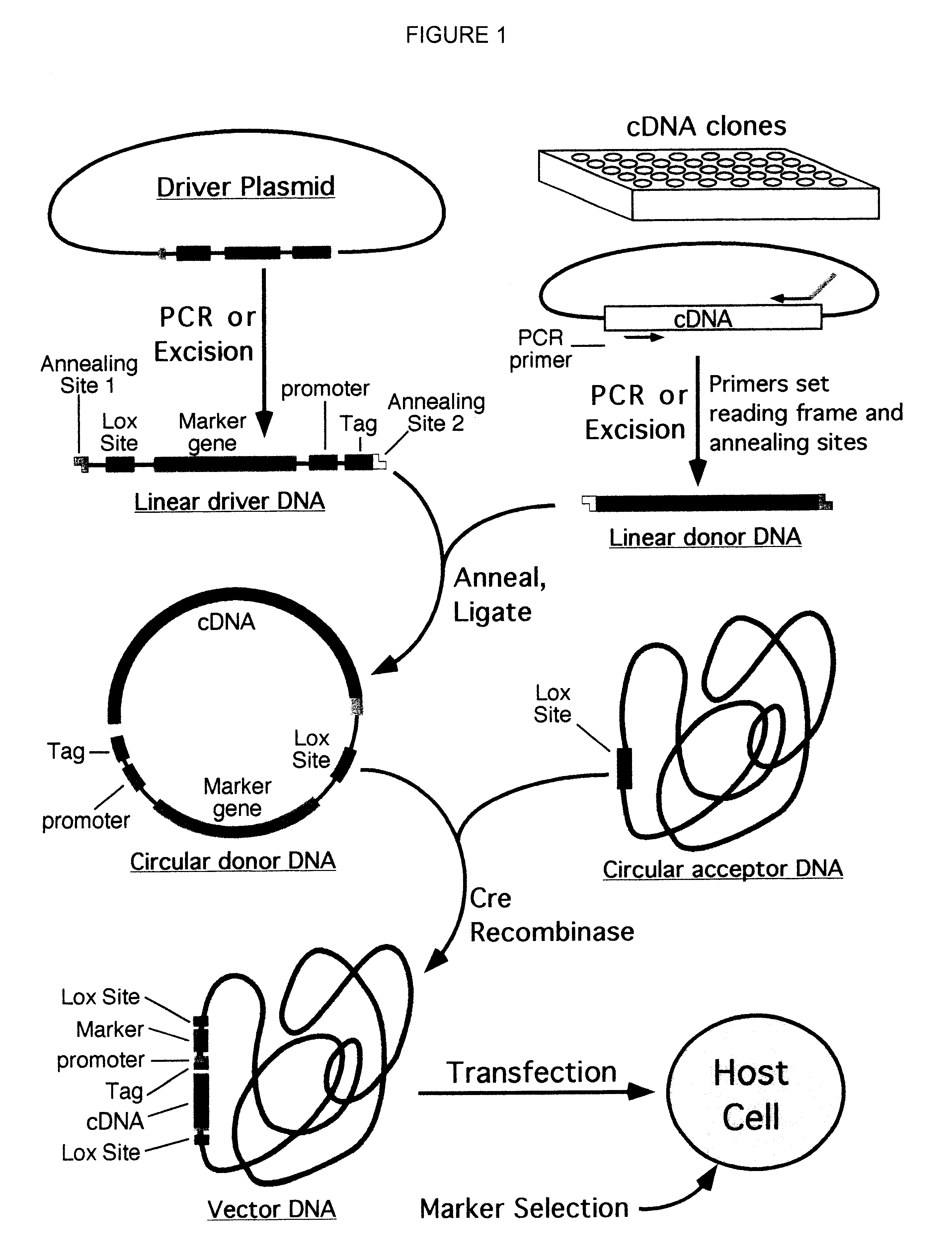
Compositions and methods for generating expression vectors through site-specific recombination
InactiveUS6551828B1Rapid and efficient generationImprove throughputOther foreign material introduction processesBiological testingOrigin of replicationSite-specific recombination
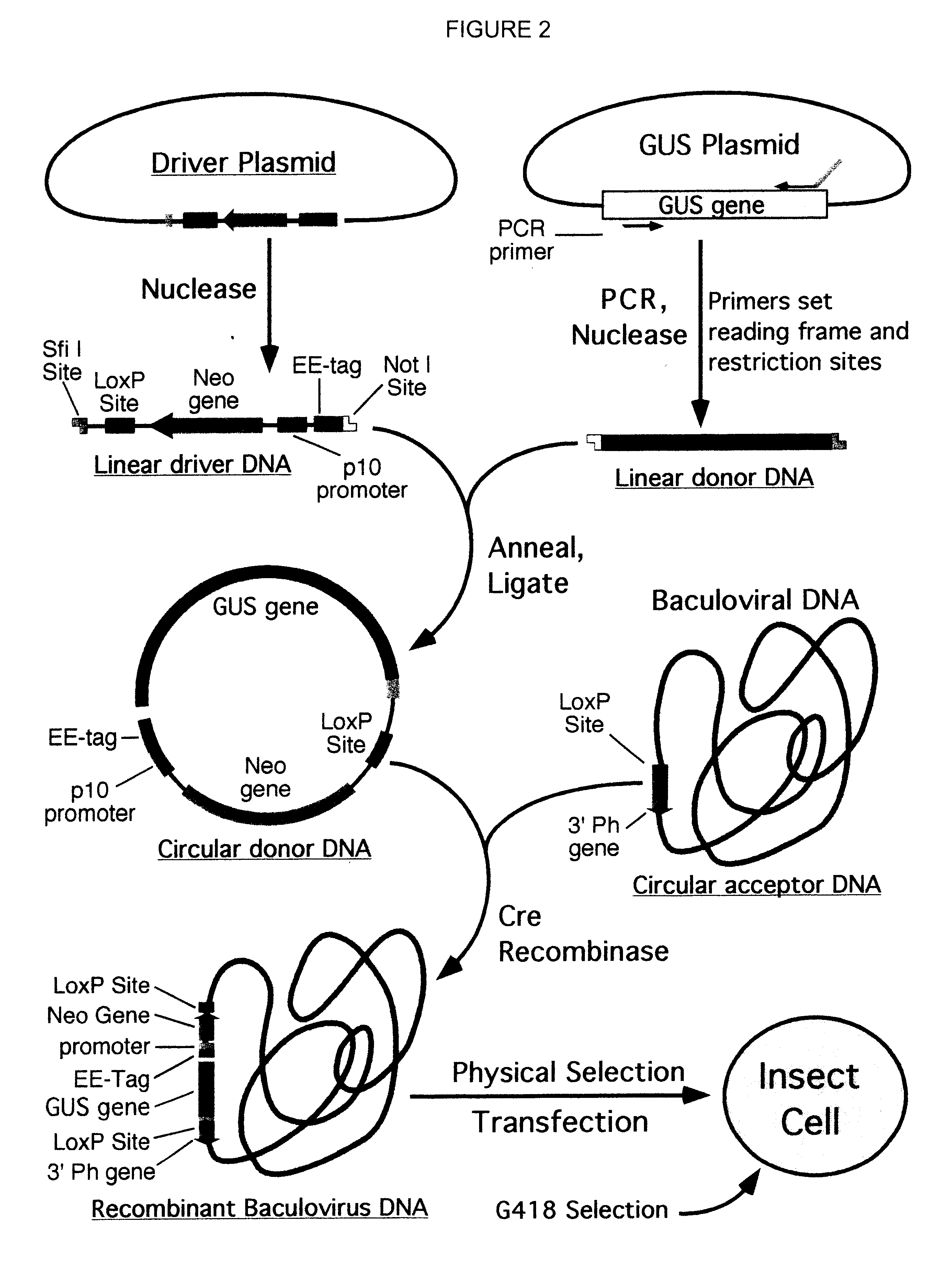
Compositions, kits, and methods are provided for use in a recombinational cloning or subcloning methods for constructing expression vectors which comprise: ligating a library of double-stranded linear donor DNAs, where each member of the library includes a donor DNA sequence, with a double-stranded linear driver DNA which includes a promoter sequence and a donor recombination site to form a single circular donor DNA, the single circular donor DNA not including an origin of replication, where the donor DNA sequence is under the transcriptional control of the promoter; and contacting the circular donor DNA and a circular acceptor acceptor vector in the presence of a recombinase to form a single fused circular vector, the circular acceptor vector comprising an origin of replication and an acceptor recombination site capable of recombining with the circular donor DNA.
Owner:PROTEMATION
System for the rapid manipulation of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20030153055A1Eliminate needLow backgroundFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCell freeSite-specific recombination
The present invention is a cell-free subcloning system utilizing three elements: (1) a donor vector that contains a nucleic acid sequence to be transferred to another vector flanked by a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, (2) an acceptor vector that contains a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, and (3) a site-specific recombinase that recognizes the site-specific recombination sequences in the donor and acceptor vectors so as to transfer the transfer sequence from the donor to the acceptor vector upon contact of the three elements of the system. Also disclosed are rapid subcloning methods employing the vectors and enzymes disclosed herein and kits for use in such methods.
Owner:INVITROGEN
Methods and compositions for genomic modification
InactiveUS7361641B2Genetic material ingredientsStable introduction of DNAEucaryotic cellSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides methods of site-specifically integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest in a genome of a eucaryotic cell, as well as, enzymes, polypeptides, and a variety of vector constructs useful therefore. In the method, a targeting construct comprises, for example, (i) a first recombination site and a polynucleotide sequence of interest, and (ii) a site-specific recombinase, which are introduced into the cell. The genome of the cell comprises a second recombination site. Recombination between the first and second recombination sites is facilitated by the site-specific recombinase. The invention describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors, and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
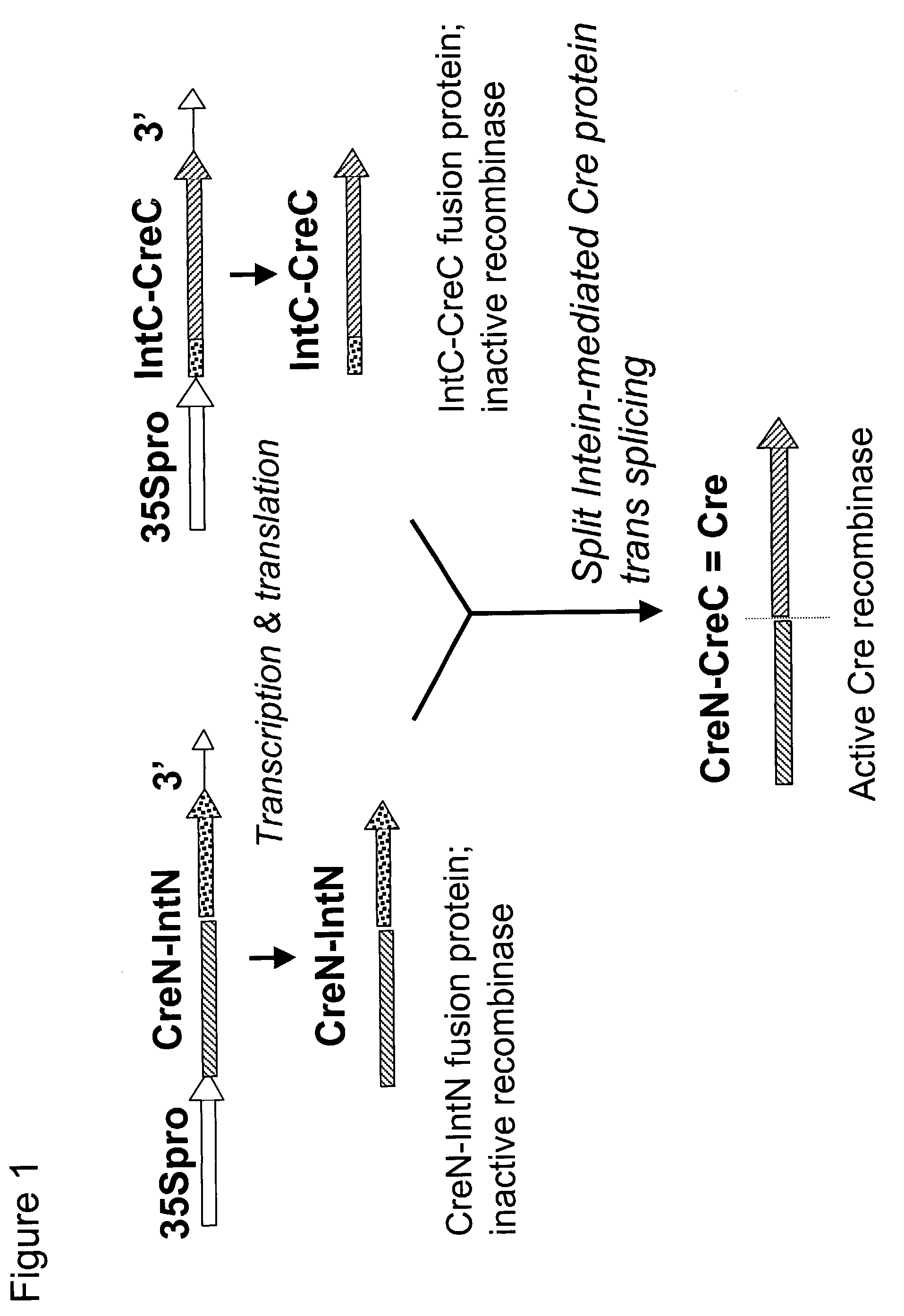
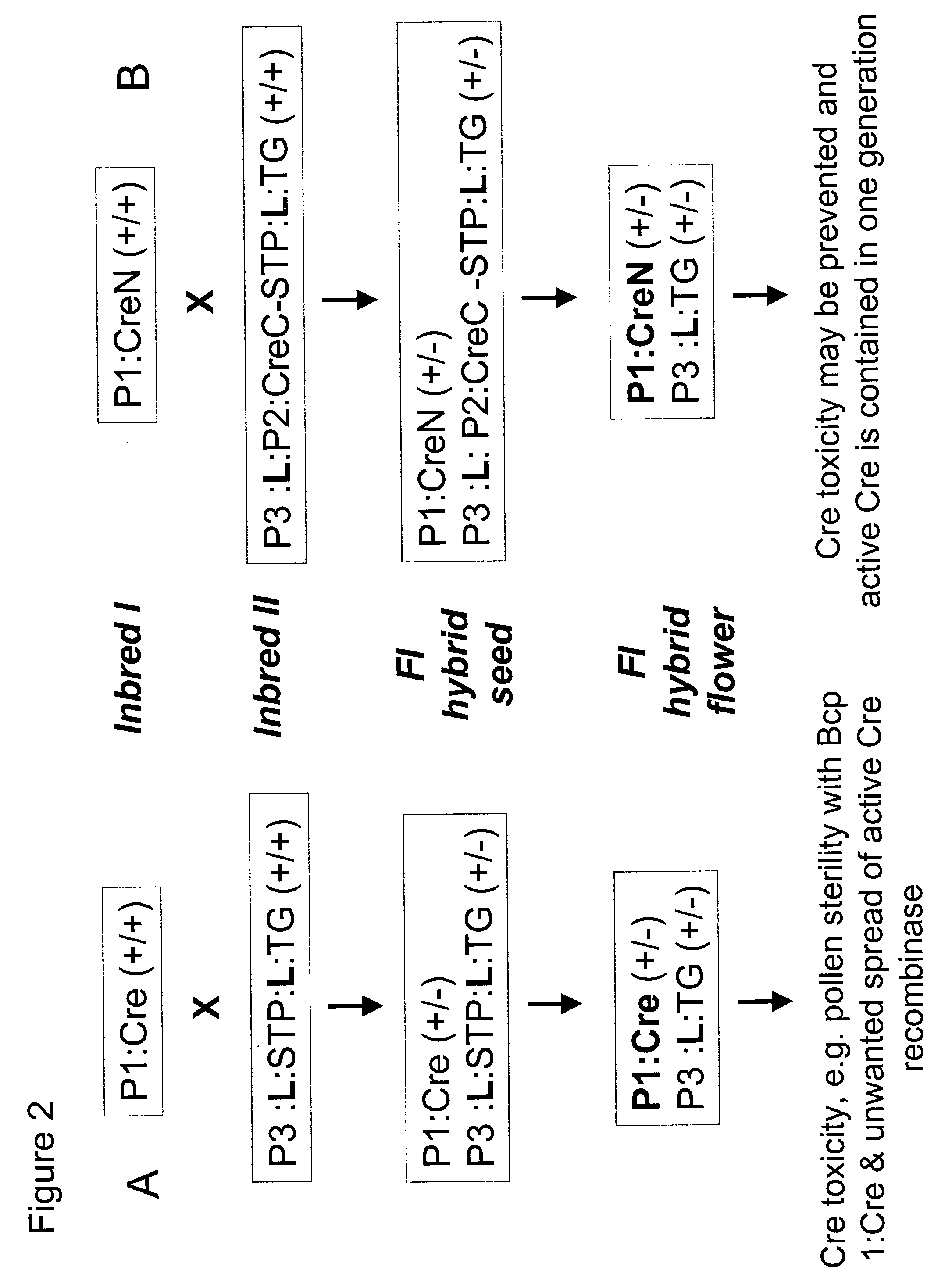
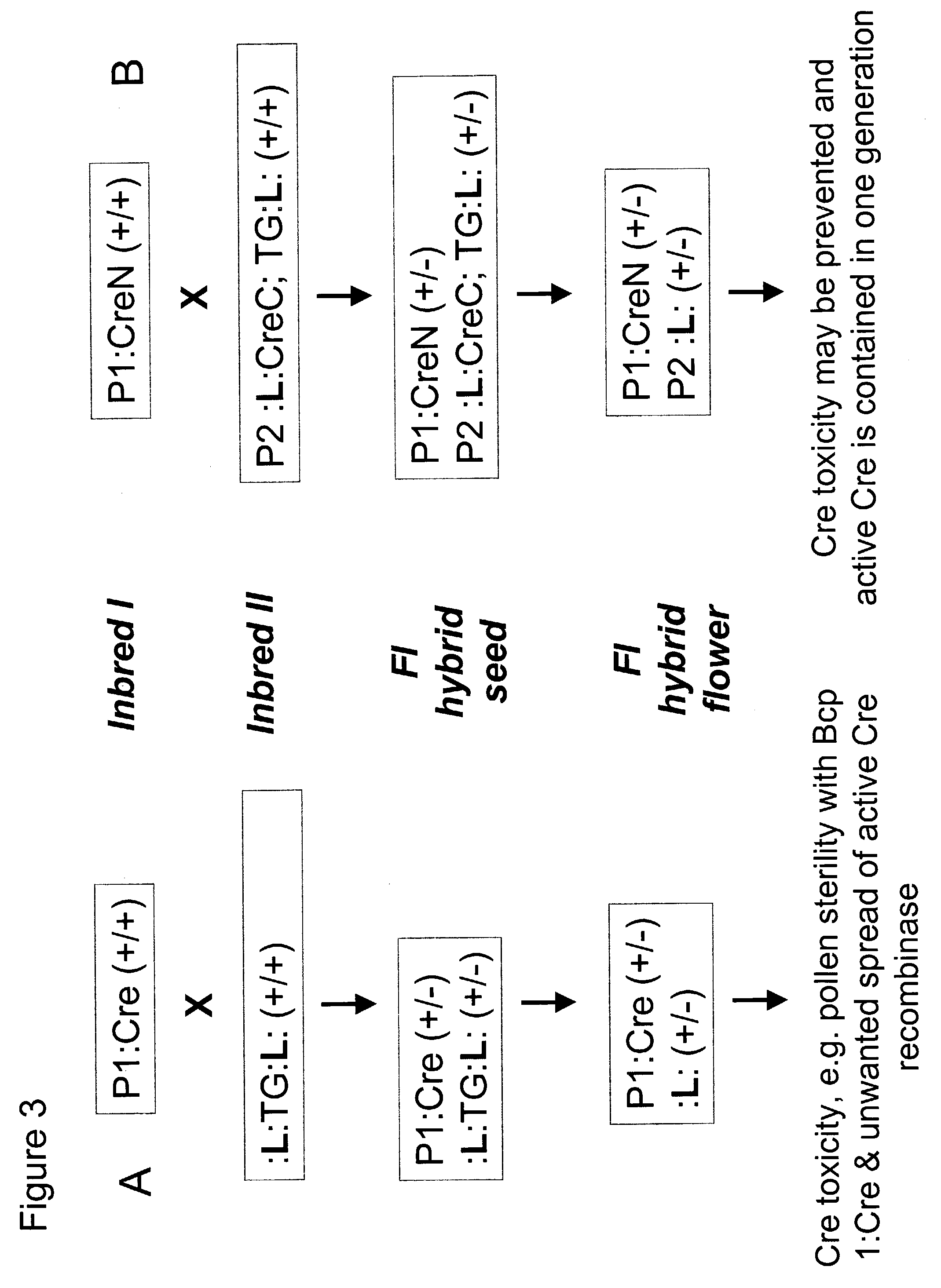
Method of controlling site-specific recombination
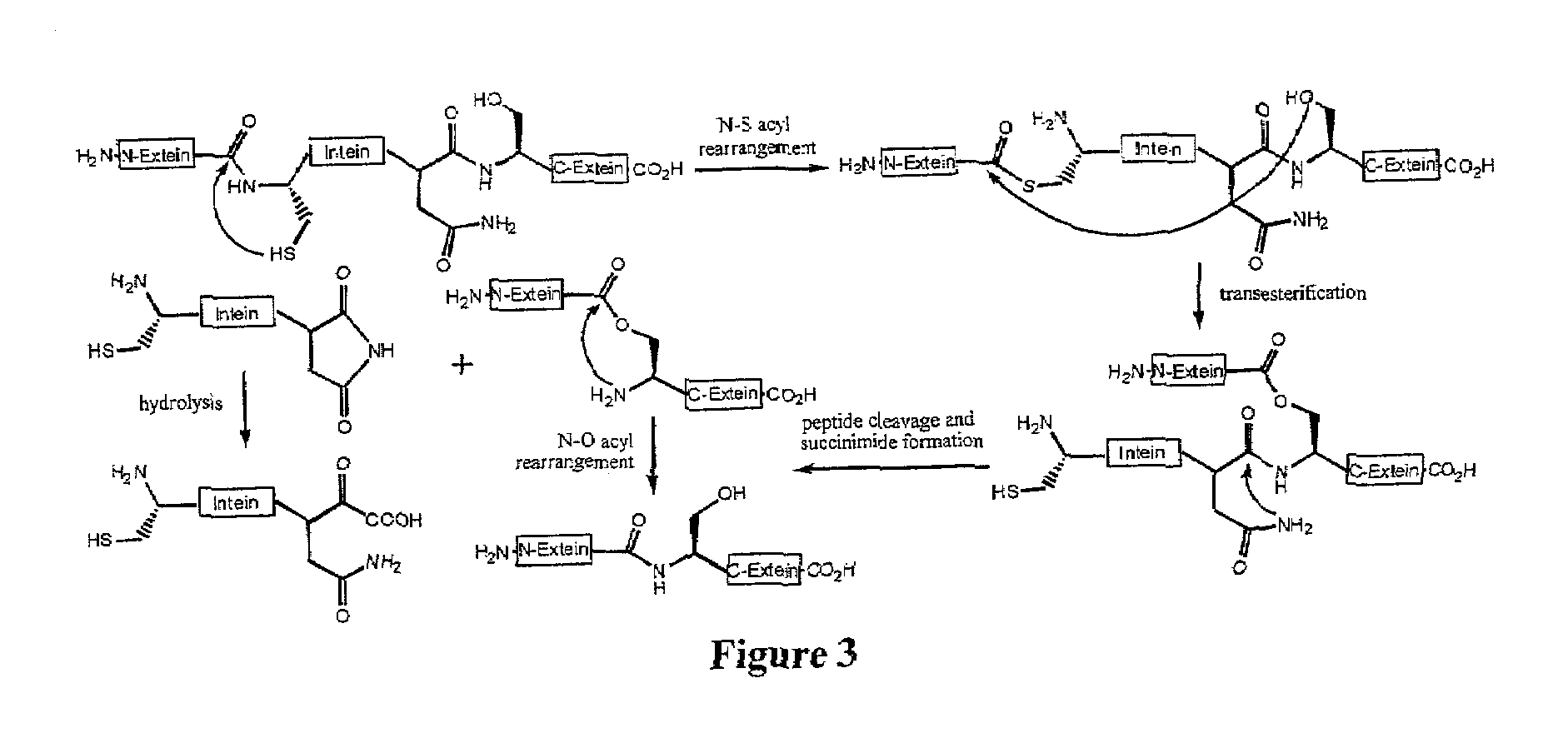
InactiveUS7238854B2High expressionAvoid Potential ToxicitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSite-specific recombinationIntein
The present invention provides methods for the conditional or regulated expression of a site-specific recombinase using split intein-mediated protein splicing. This enhances the temporal and tissue-specificity of trait gene expression and allows for fine tuning of expression specificity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
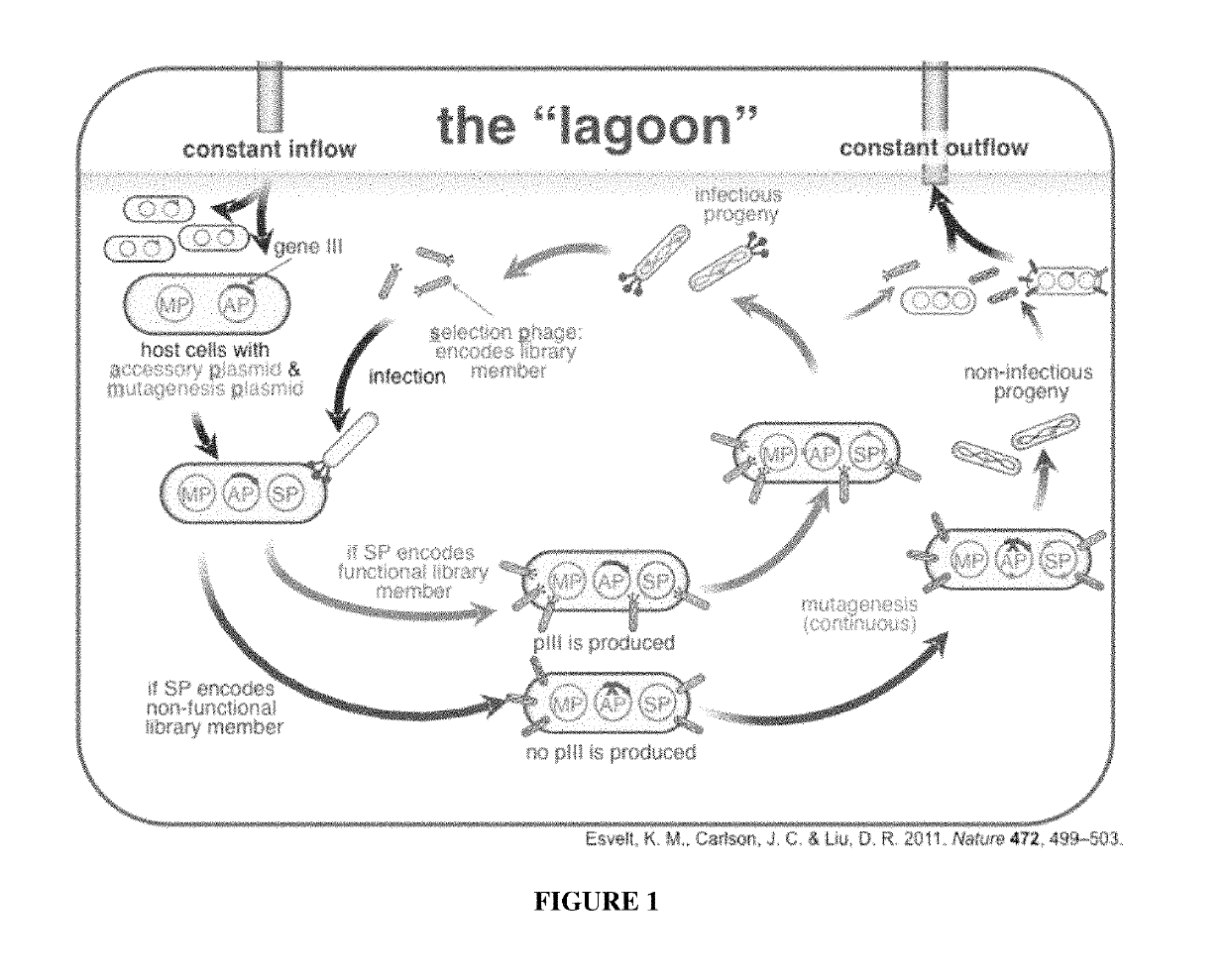
Evolution of site-specific recombinases
ActiveUS10392674B2Improve efficiencyStrong specificityPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSite-specific recombinationScreening method
Some aspects of the present disclosure provide methods for evolving recombinases to recognize target sequences that differ from the canonical recognition sequences. Some aspects of this disclosure provide evolved recombinases, e.g., recombinases that bind and recombine naturally-occurring target sequences, such as, e.g., target sequences within the human Rosa26 locus. Methods for using such recombinases for genetically engineering nucleic acid molecules in vitro and in vivo are also provided. Some aspects of this disclosure also provide libraries and screening methods for assessing the target site preferences of recombinases, as well as methods for selecting recombinases that bind and recombine a non-canonical target sequence with high specificity.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Transgenic chickens with an inactivated endogenous gene locus
InactiveUS20100138946A1Convenient treatmentGood curative effectVirusesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFowlIntegrases
The present invention is transgenic chickens obtained from long-term cultures of avian PGCs and techniques to produce and transgenic birds derived from prolonged PGC cultures. In some embodiments, these PGCs can be transfected with genetic constructs to modify the DNA of the PGC, specifically to introduce a transgene encoding an exogenous protein. When combined with a host avian embryo by known procedures, those modified PGCs are transmitted through the germline to yield transgenic offspring. This invention includes compositions comprising long-term cultures of PGCs and offspring derived from them that are genetically modified. The genetic modifications introduced into PGCs to achieve the gene inactivation may also include, but are not restricted to, random integrations of transgenes into the genome, transgenes inserted into the promoter region of genes, transgenes inserted into repetitive elements in the genome, site specific changes to the genome that are introduced using integrase, site specific changes to the genome introduced by homologous recombination, and conditional mutations introduced into the genome by excising DNA that is flanked by lox sites or other sequences that are substrates for site specific recombination.
Owner:ORIGEN THERAPEUTICS +1
In vivo selection system for enzyme activity
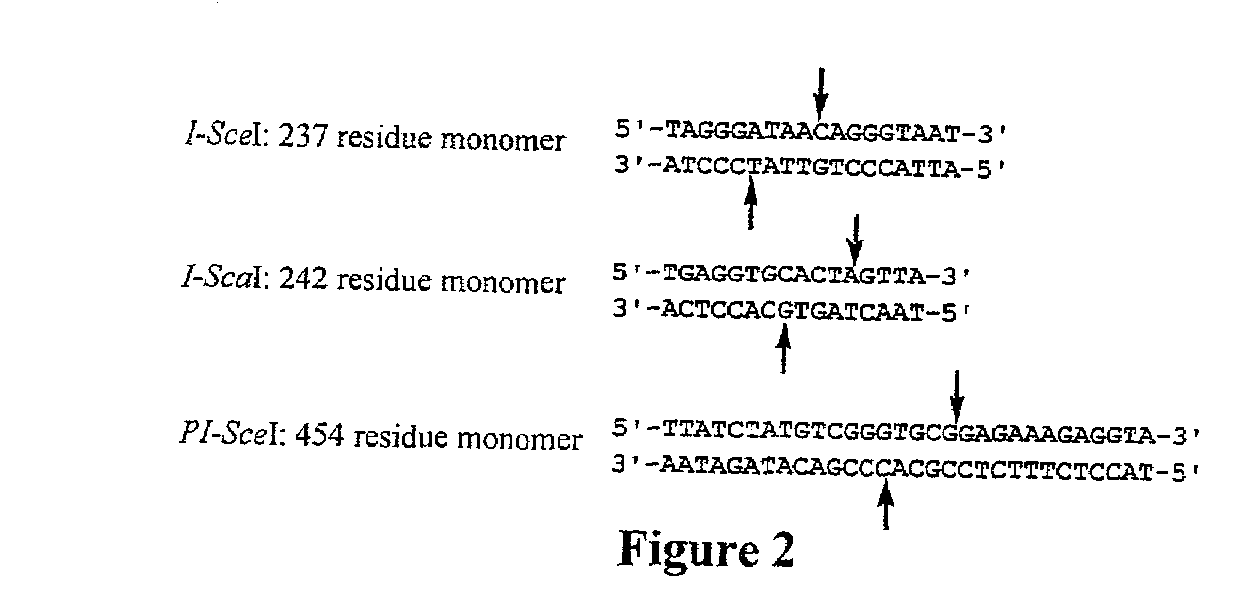
The present invention provides in vivo systems in which activity of a biological cleavage enzyme, such as a site-specific recombinase, a homing endonuclease, or an intein, is linked to cell viability and therefore can be selected. The invention further provides methods of making cells in which the activity of a biological cleavage enzyme is linked to viability, as well as methods of identifying new biological cleavage enzymes, including enzymes having altered site specificity, using such cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
System for the rapid manipulation of nucleic acid sequenaces
InactiveUS20050181417A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell freeSite-specific recombination
The present invention is a cell-free subcloning system utilizing three elements: (1) a donor vector that contains a nucleic acid sequence to be transferred to another vector flanked by a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, (2) an acceptor vector that contains a site-specific recombination sequence and one or more optional additional nucleic acid sequences, and (3) a site-specific recombinase that recognizes the site-specific recombination sequences in the donor and acceptor vectors so as to transfer the transfer sequence from the donor to the acceptor vector upon contact of the three elements of the system. Also disclosed are rapid subcloning methods employing the vectors and enzymes disclosed herein and kits for use in such methods.
Owner:INVITROGEN
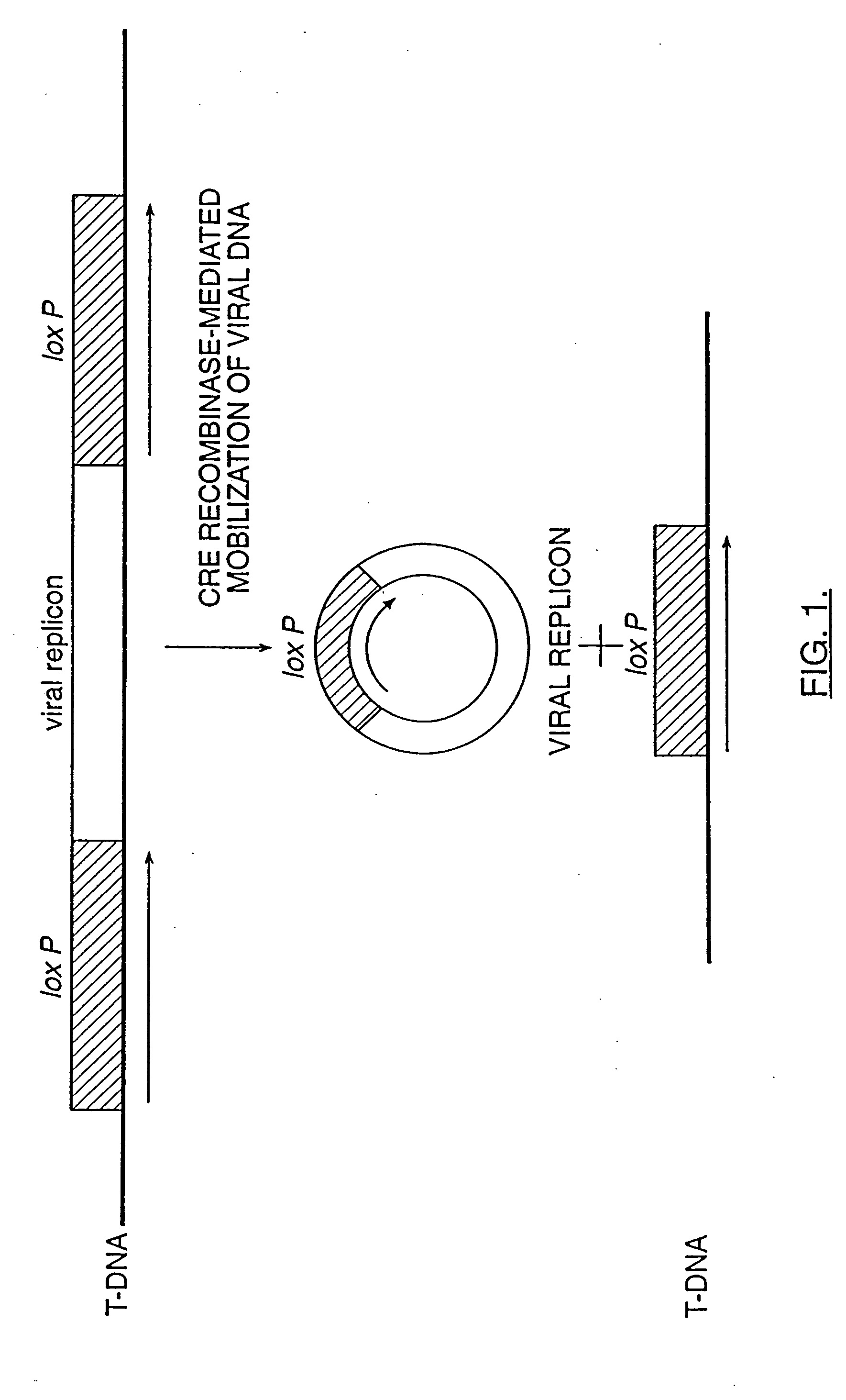
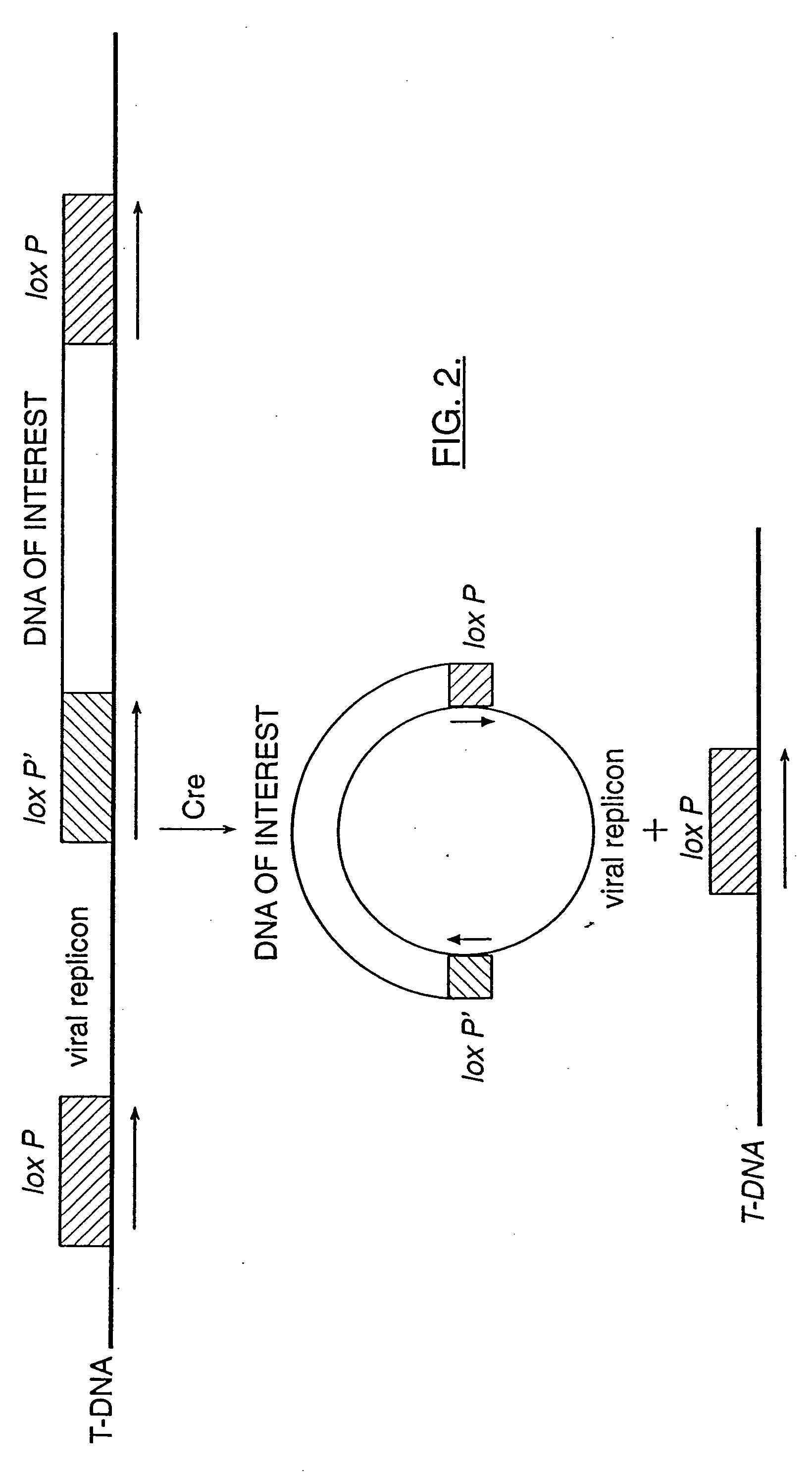
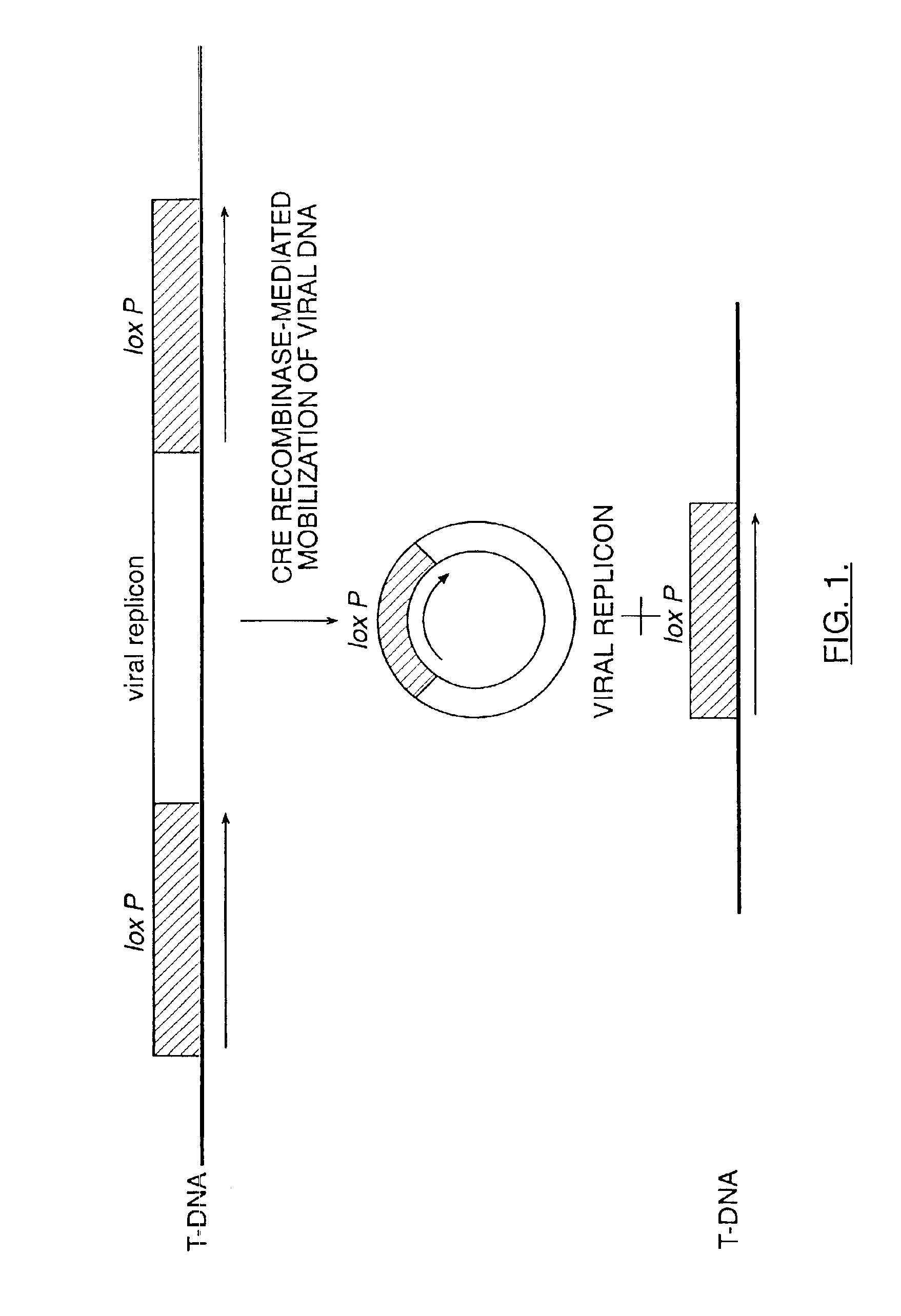
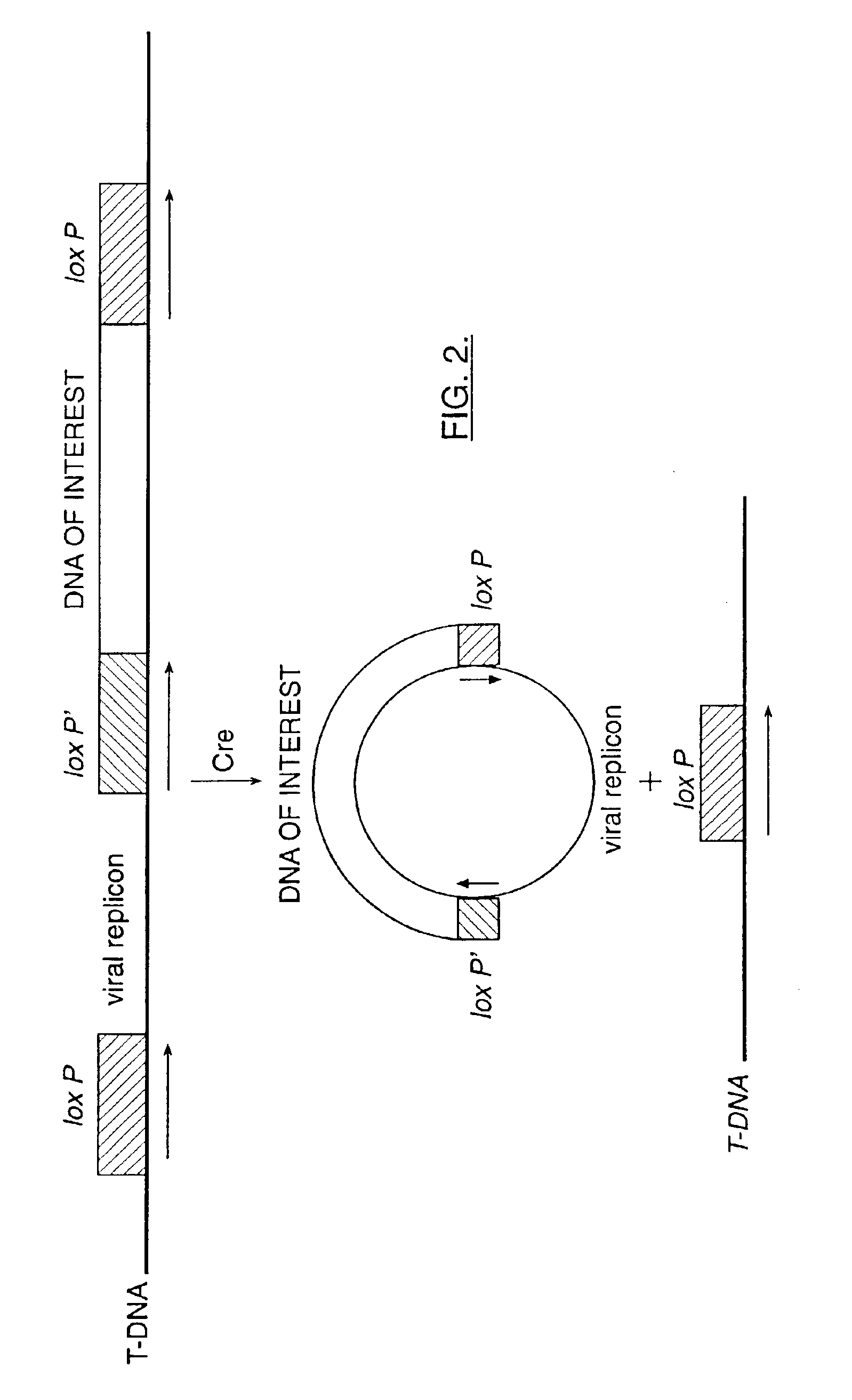
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS20060253939A1Easy constructionSimplifying stable maintenanceBacteriaSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7179599B2Simplifying construction and stable maintenanceImprove efficiencyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method of controlling gene silencing using site specific recombination
InactiveUS7267979B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationDevelopmental stageIntein
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Site specific recombinase based method for producing adenoviral vectors
Site-specific recombinase based methods for making a recombinant adenoviral genome, as well as kits for practicing the same and the recombinant adenovirus vectors produced thereby, are provided. In the subject methods, the subject genomes are prepared from donor and acceptor vectors that each include at least one site recombinase recognition site, where in certain preferred embodiments, one of the donor and acceptor vectors includes a single recombinase recognition site while the other includes two recombinase recognition sites. The acceptor vector includes an adenoviral genome having an E region deletion. The donor vector includes an insertion nucleic acid. In the subject methods, the donor and acceptor vectors are combined in the presence of a recombinase to produce an adenoviral genome that includes the insertion nucleic acid. The subject adenoviral genomes find use in a variety of applications, including as vectors for use in a variety of applications.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
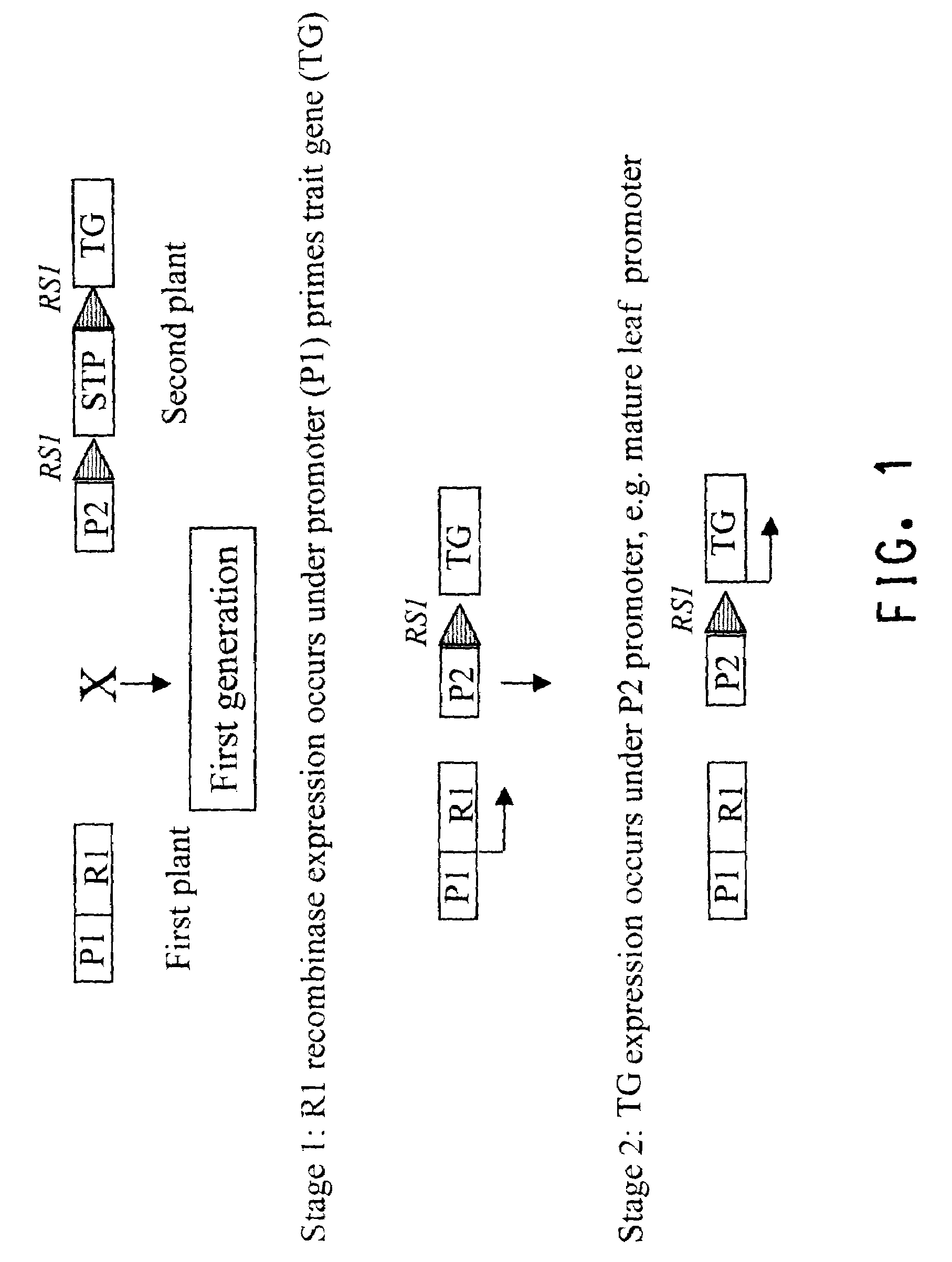
Methods for regulated expression of triats in plants using multiple site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7115798B1Promote reproductionProcess safety and environmental protectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesDevelopmental stagePlant tissue
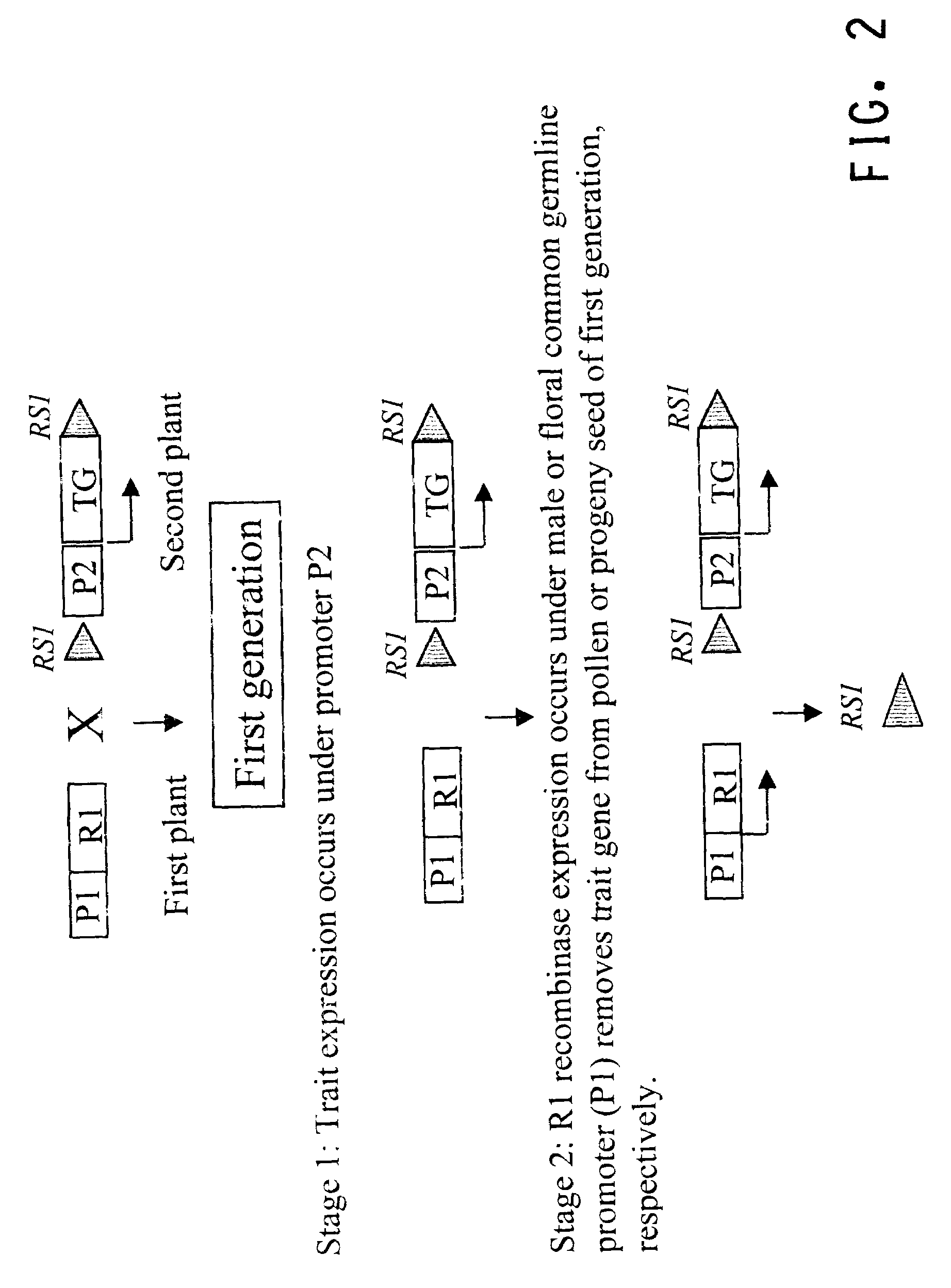
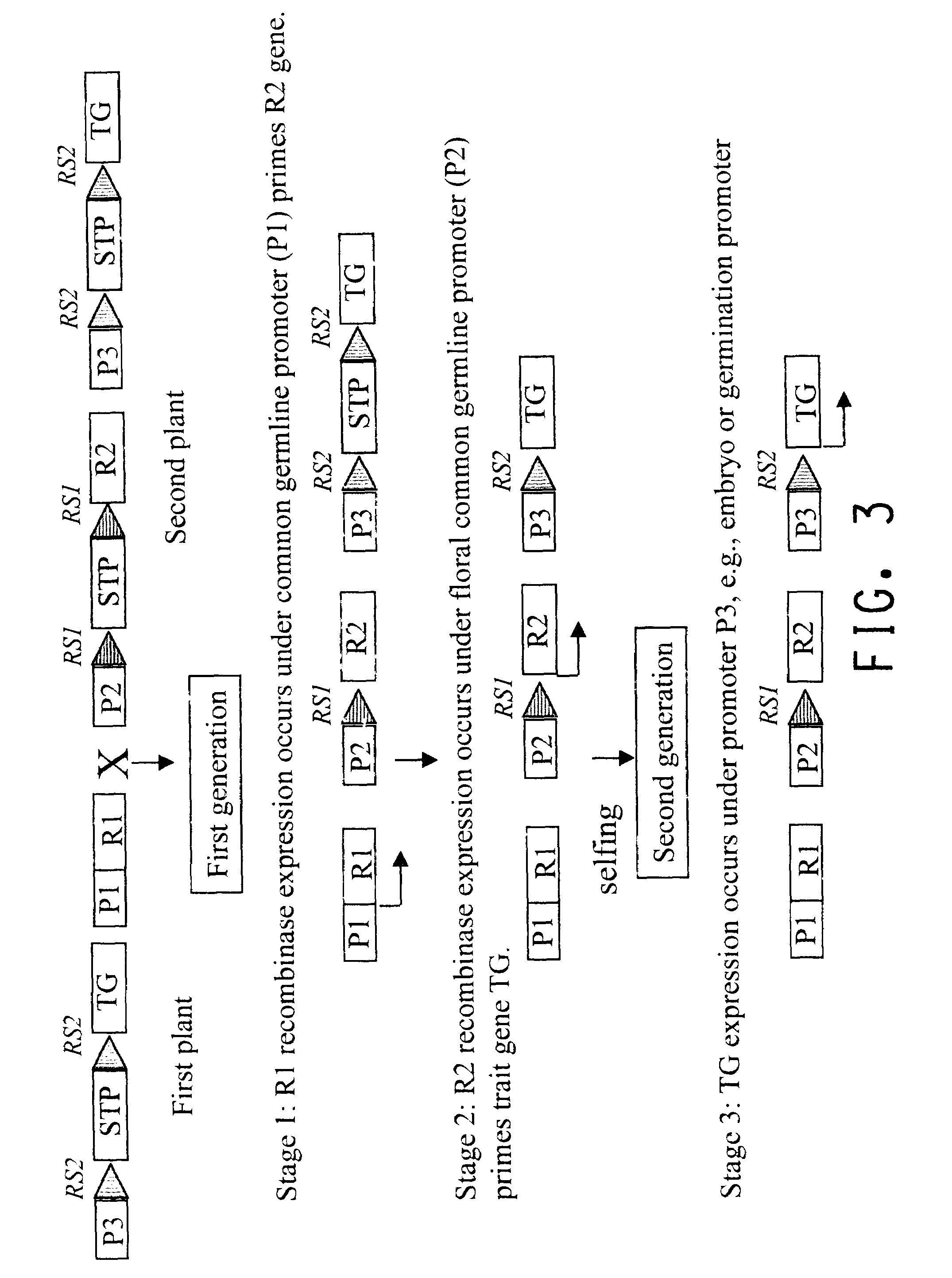
This invention relates to constructs for the conditional or regulated expression of transgenes in plants using site-specific recombinase systems. The constructs comprise a variety of constitutive, inducible, tissue specific or developmental stage-specific promoters operably linked to either a transgene or the elements of one or more site-specific recombinase system. By matching promoters, responsive to various inducers, plant tissues or plant developmental states with the recombinase systems, stop fragments and transgenes, virtually any trait may be expressed at any plant development stage or in any plant generation.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Engineered listeria and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20120121643A1Improve survivalIncreasing expression and secretionBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologous AntigensNucleotide
The invention provides a bacterium containing a polynucleotide comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous antigen, as well as fusion protein partners. Also provided are vectors for mediating site-specific recombination and vectors comprising removable antibiotic resistance genes.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for constructing recombinant expression vector simultaneously expressing a plurality of genes
InactiveCN101979596ATime-saving multigene assembly methodLow costFungiBacteriaBiotechnologySite-specific recombination
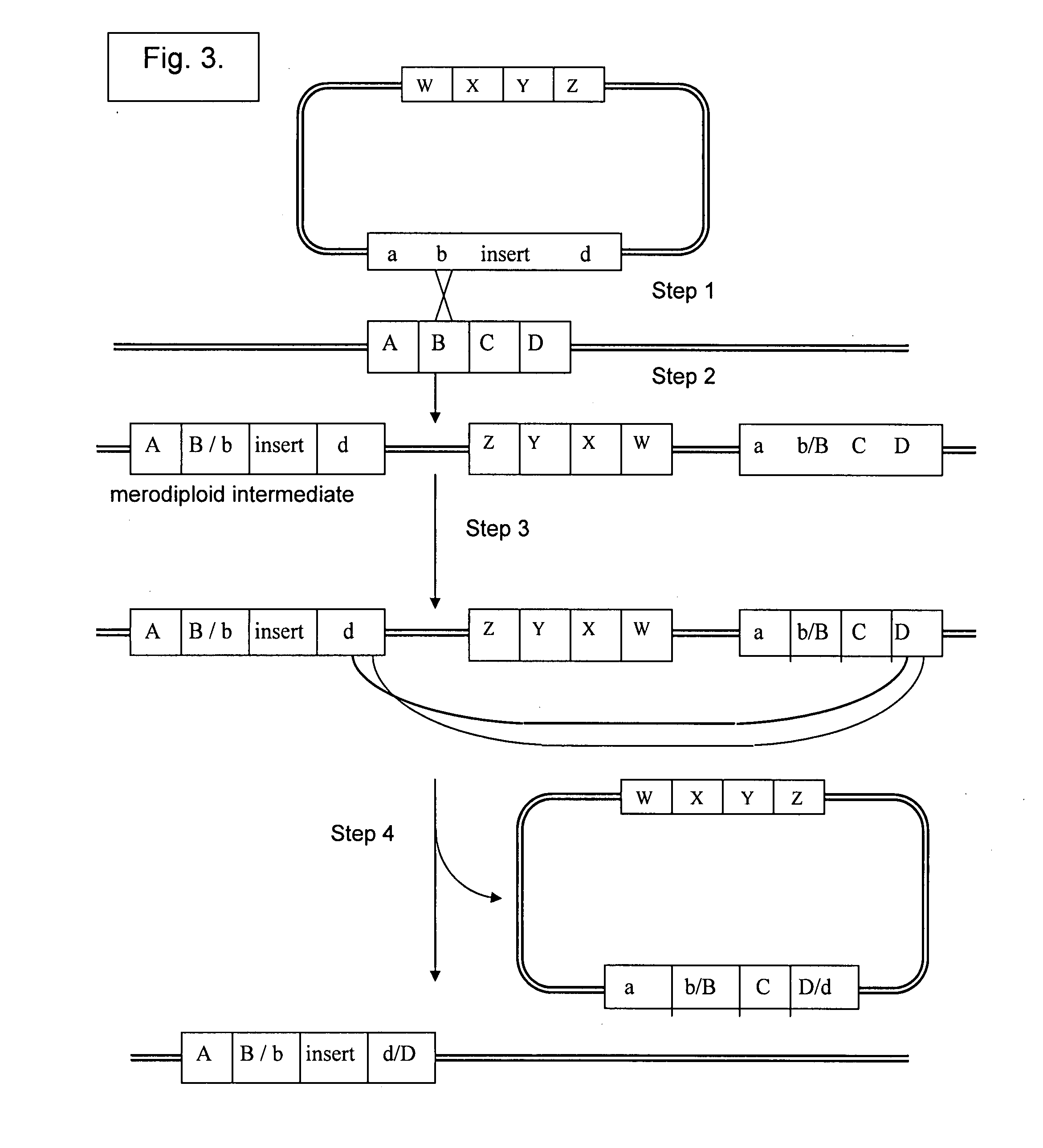
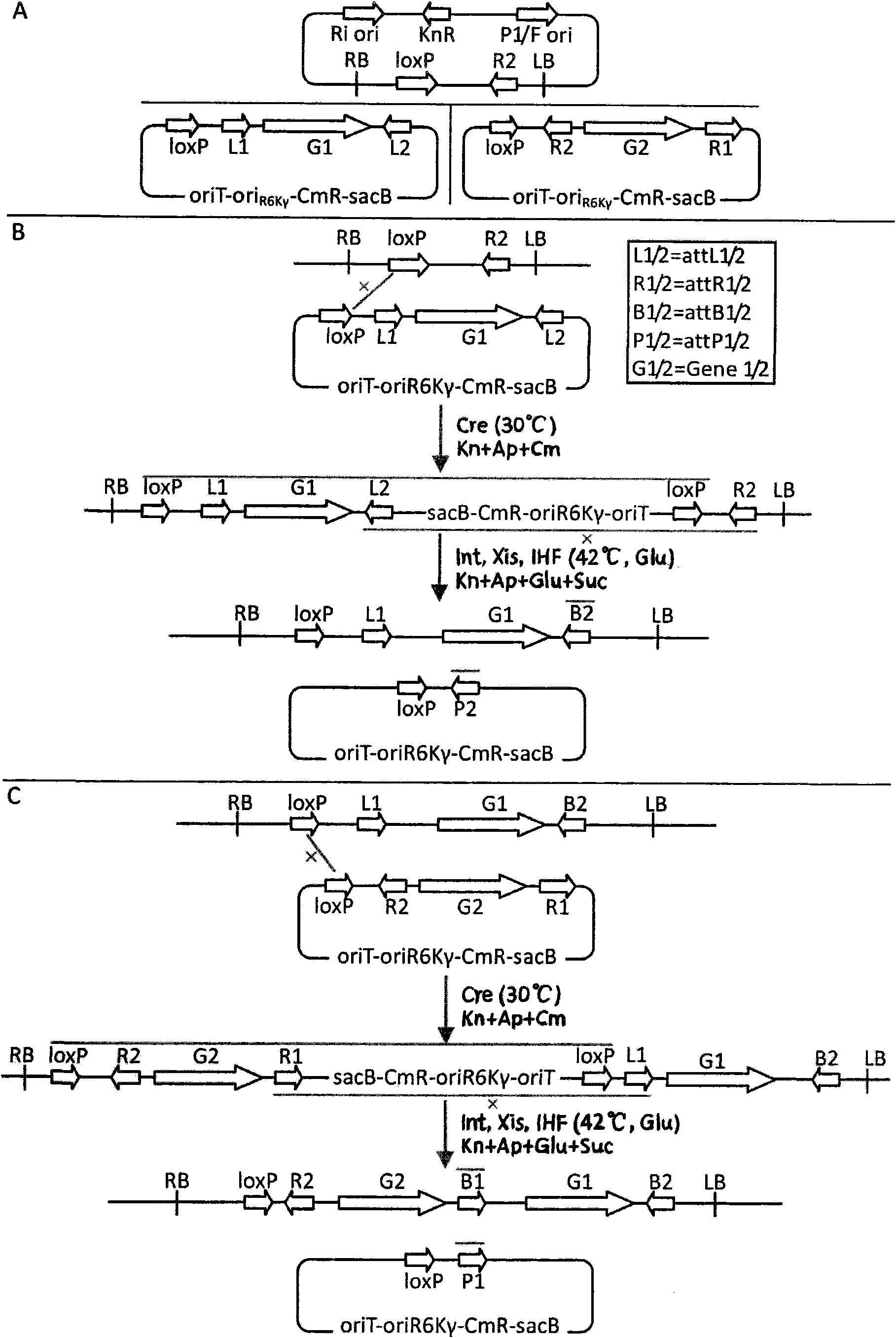
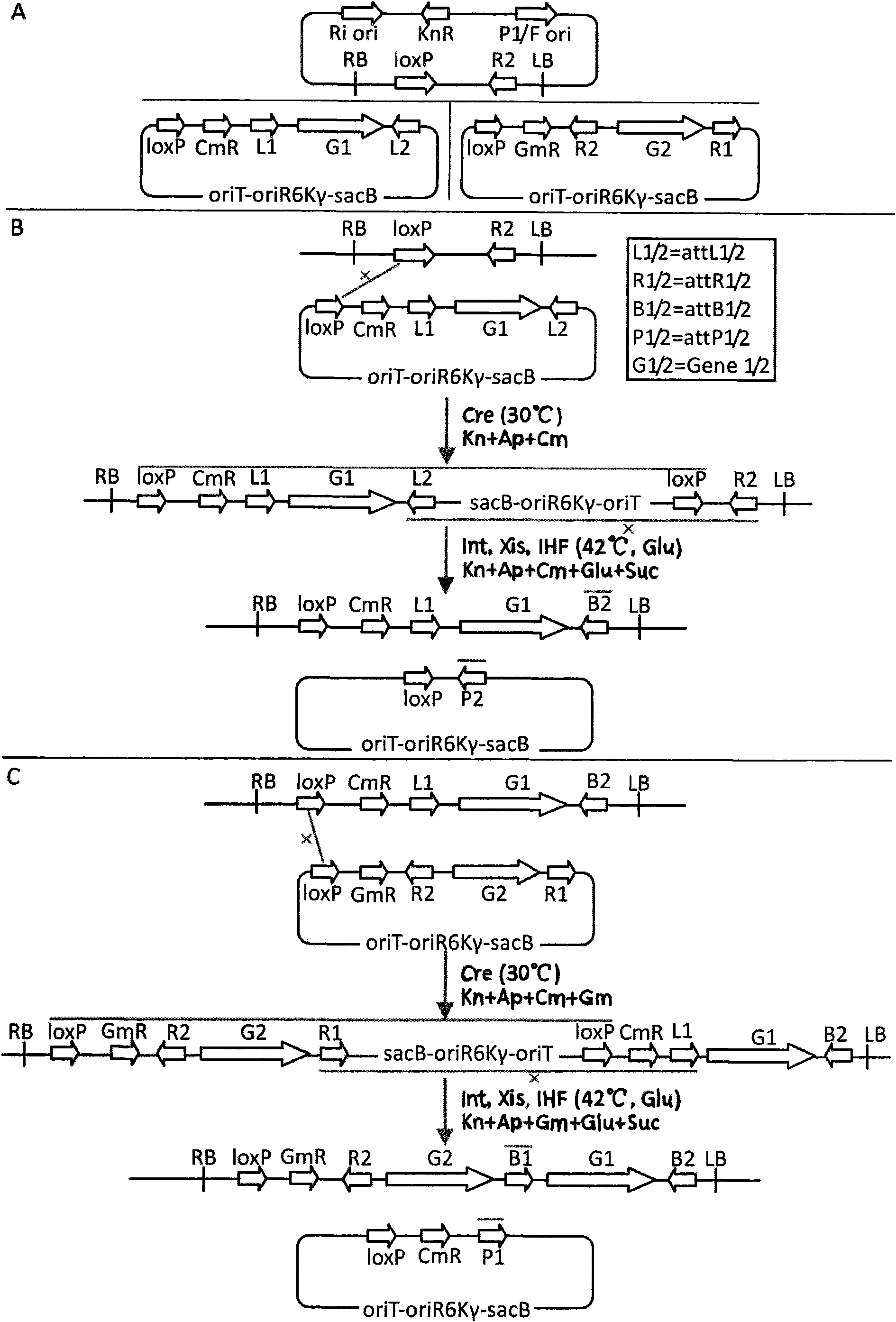
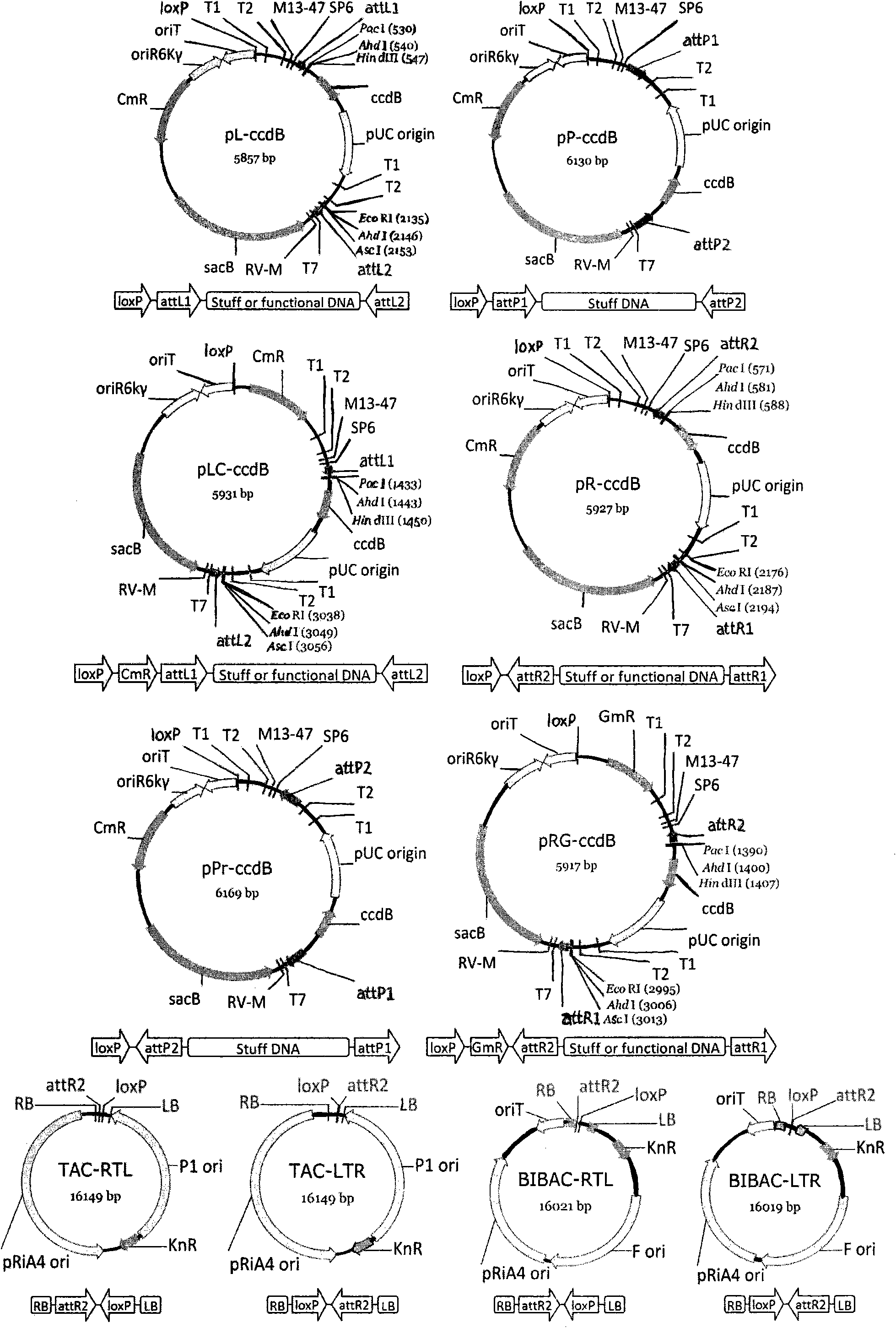
The invention discloses a method for constructing a recombinant expression vector simultaneously expressing a plurality of genes. An MISSA system consists of a strain and a vector, wherein the strain comprises a donor strain and an acceptor strain; the vector comprises a donor vector and an acceptor vector; replication initiation protein carried by a chromosome of the donor strain is responsible for replicating and amplifying a suicidal donor vector, and the carried conjugal transfer protein Tra is responsible for conjugal transfer of the donor vector; the acceptor strain can induce and express two sets of locus specific recombinant proteins, namely Cre recombinant enzyme and lambda phage locus specific recombinant proteins; when the donor strain is mixed with the acceptor strain, the donor strain and the acceptor strain are conjugated, and the donor strain is transferred into the acceptor vector because the donor vector in the donor strain carries an oric element; and the donor vector and the acceptor vector undergo recombination reaction in the acceptor strain under the action of the two sets of locus specific recombinant proteins, so that a target gene carried by the donor vector is assembled onto the acceptor vector. The process is repeated, so a plurality of target genes can be assembled onto the acceptor vector according to the preset direction and order.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com