Patents
Literature
2879 results about "Library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
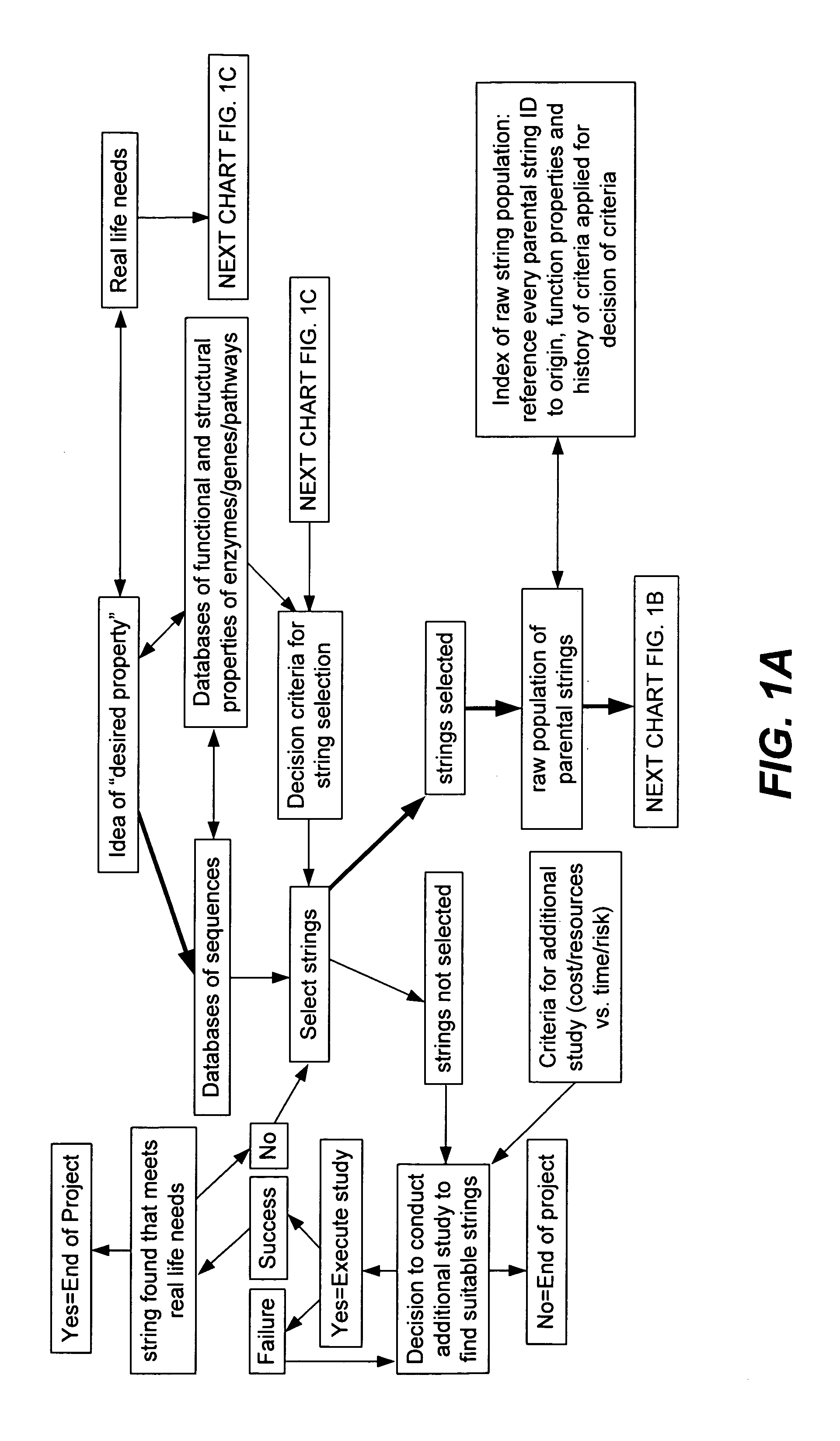
In molecular biology, a library is a collection of DNA fragments that is stored and propagated in a population of micro-organisms through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including cDNA libraries (formed from reverse-transcribed RNA), genomic libraries (formed from genomic DNA) and randomized mutant libraries (formed by de novo gene synthesis where alternative nucleotides or codons are incorporated). DNA library technology is a mainstay of current molecular biology, and the applications of these libraries depends on the source of the original DNA fragments. There are differences in the cloning vectors and techniques used in library preparation, but in general each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria (a Bacterial Artificial Chromosome or BAC library) or yeast such that each organism contains on average one construct (vector + insert). As the population of organisms is grown in culture, the DNA molecules contained within them are copied and propagated (thus, "cloned").
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
InactiveUS20050079574A1High-quality target binding characteristicGenerate efficientlyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousIntravenous gammaglobulin
The invention provides immunoglobulin polypeptides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. In one embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant CDRH3 region. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Humanization of antibodies
InactiveUS20050042664A1Limited diversityFast and less labor intensive productionHybrid immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingHumanized antibody
The present invention provides methods of re-engineering or re-shaping an antibody from a first species, wherein the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody does not elicit undesired immune response in a second species, and the re-engineered or re-shaped antibody retains substantially the same antigen binding-ability of the antibody from the first species. In accordance with the present invention, a combinatorial library comprising the CDRs of the antibody from the first species fused in frame with framework regions derived from a second species can be constructed and screened for the desired modified antibody. In particular, the present invention provides methods utilizing low homology acceptor antibody frameworks for efficiently humanizing an antibody or a fragment thereof. The present invention also provides antibodies produced by the methods of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Methods for detecting and identifying single molecules
InactiveUS6287765B1Highly specific controlImprove securityNanotechSugar derivativesSynthetic nucleotideMolecular adsorption
Multimolecular devices and drug delivery systems prepared from synthetic heteropolymers, heteropolymeric discrete structures, multivalent heteropolymeric hybrid structures, aptameric multimolecular devices, multivalent imprints, tethered specific recognition devices, paired specific recognition devices, nonaptameric multimolecular devices and immobilized multimolecular structures are provided, including molecular adsorbents and multimolecular adherents, adhesives, transducers, switches, sensors and delivery systems. Methods for selecting single synthetic nucleotides, shape-specific probes and specifically attractive surfaces for use in these multimolecular devices are also provided. In addition, paired nucleotide-nonnucleotide mapping libraries for transposition of selected populations of selected nonoligonucleotide molecules into selected populations of replicatable nucleotide sequences are described.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
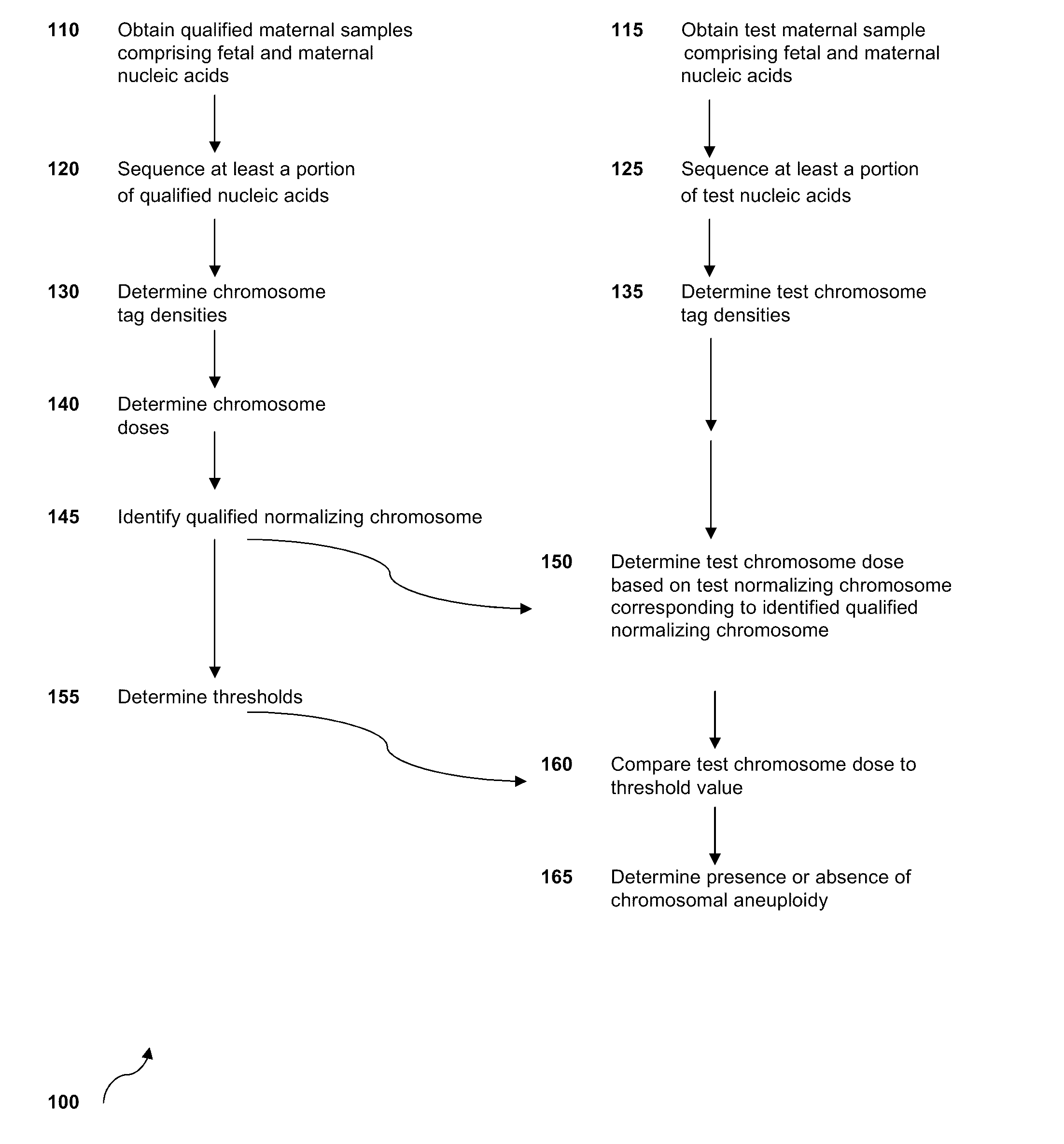
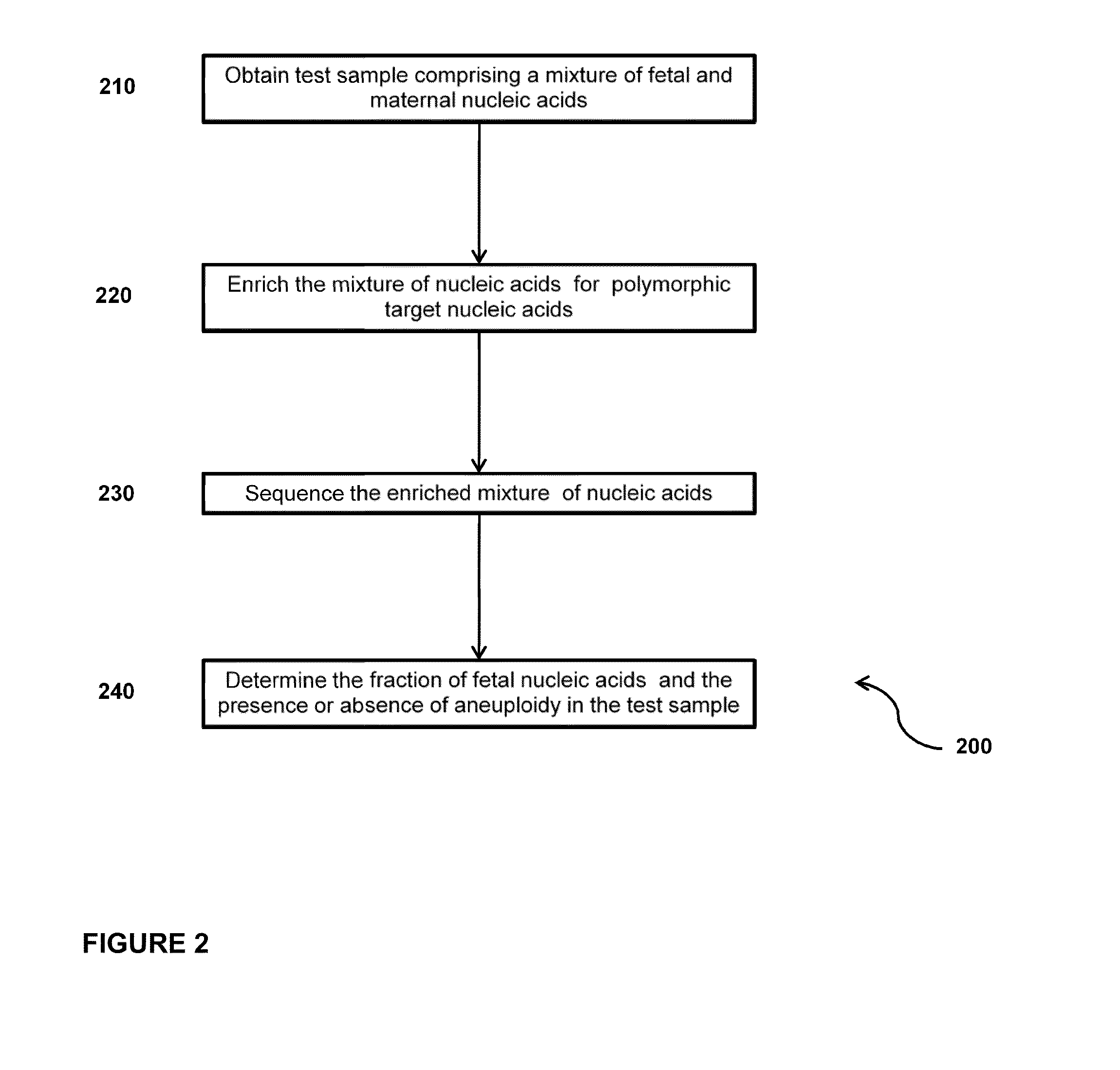
Sequencing methods and compositions for prenatal diagnoses
ActiveUS20110201507A1Quality improvementEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPrenatal diagnosisGenetics
The invention provides methods for determining aneuploidy and / or fetal fraction in maternal samples comprising fetal and maternal cfDNA by massively parallel sequencing. The method comprises a novel protocol for preparing sequencing libraries that unexpectedly improves the quality of library DNA while expediting the process of analysis of samples for prenatal diagnoses.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
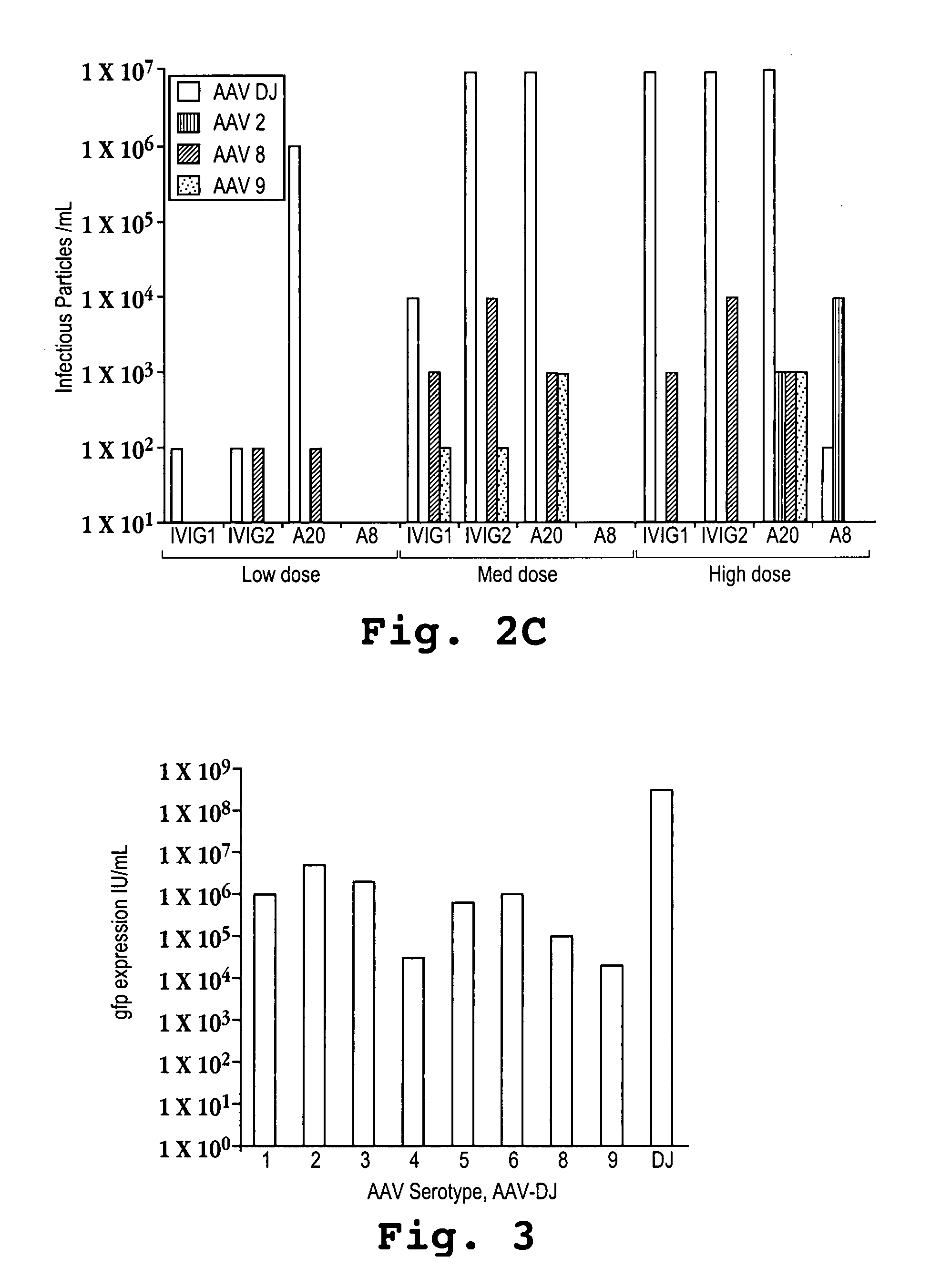
AAV capsid library and AAV capsid proteins
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
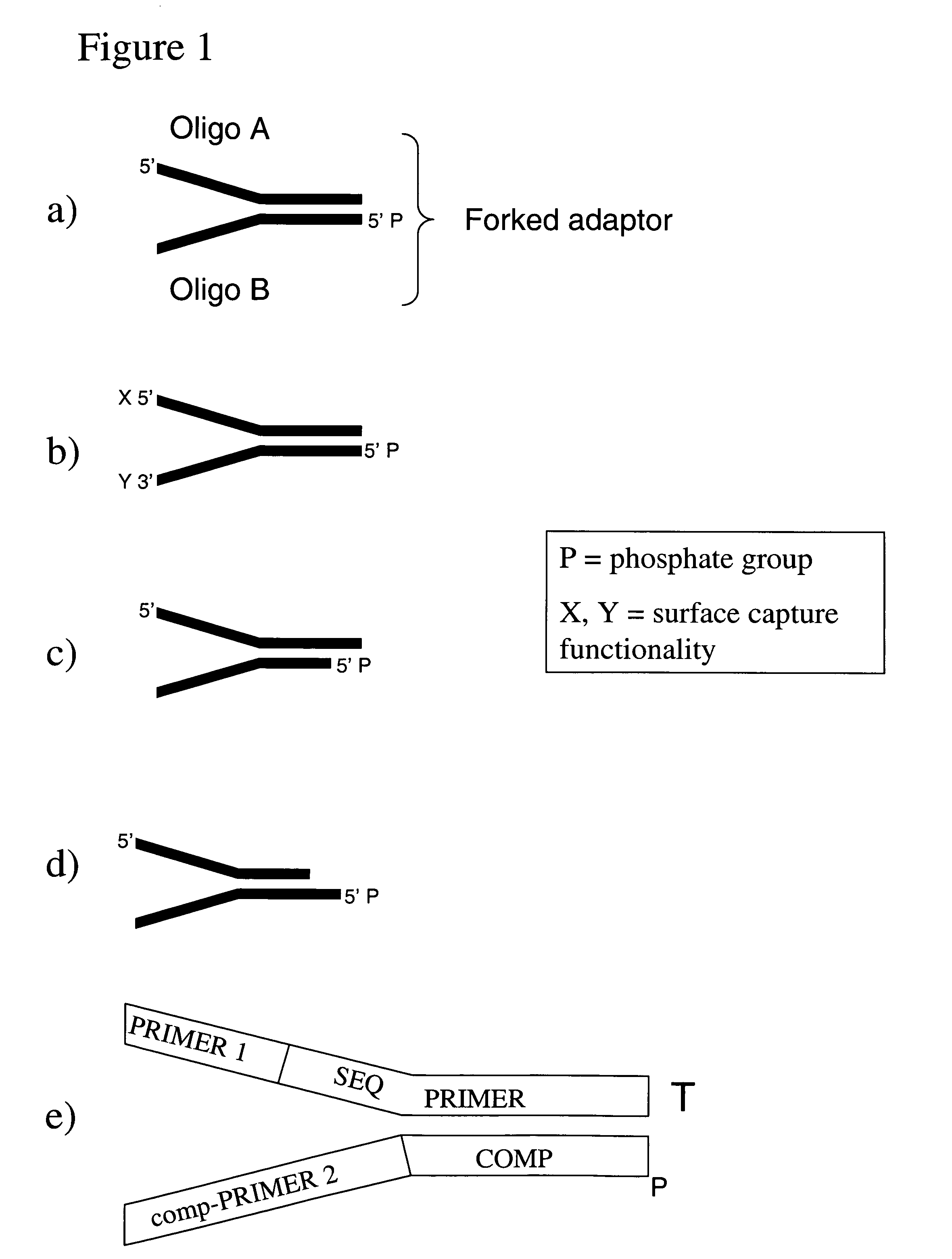
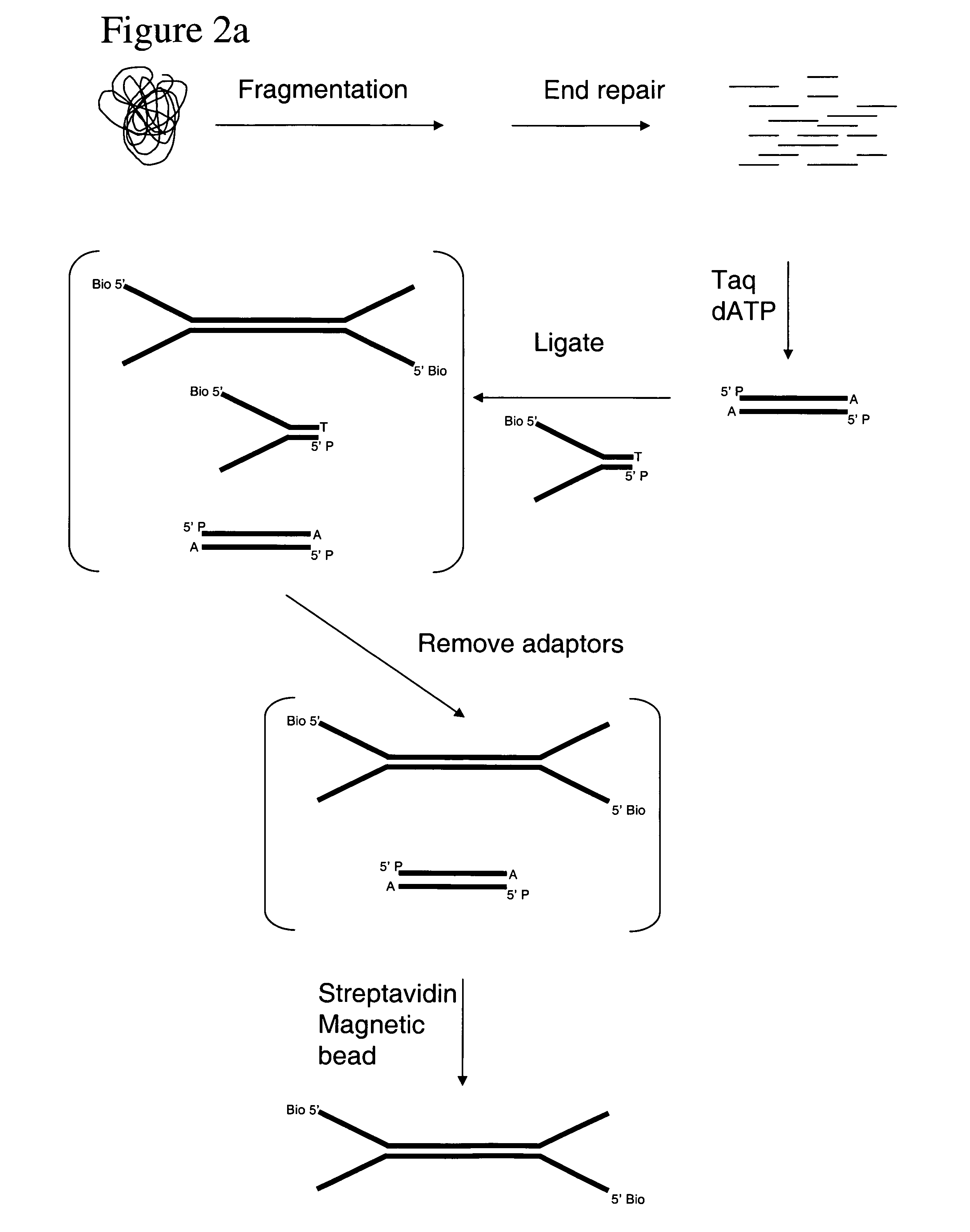
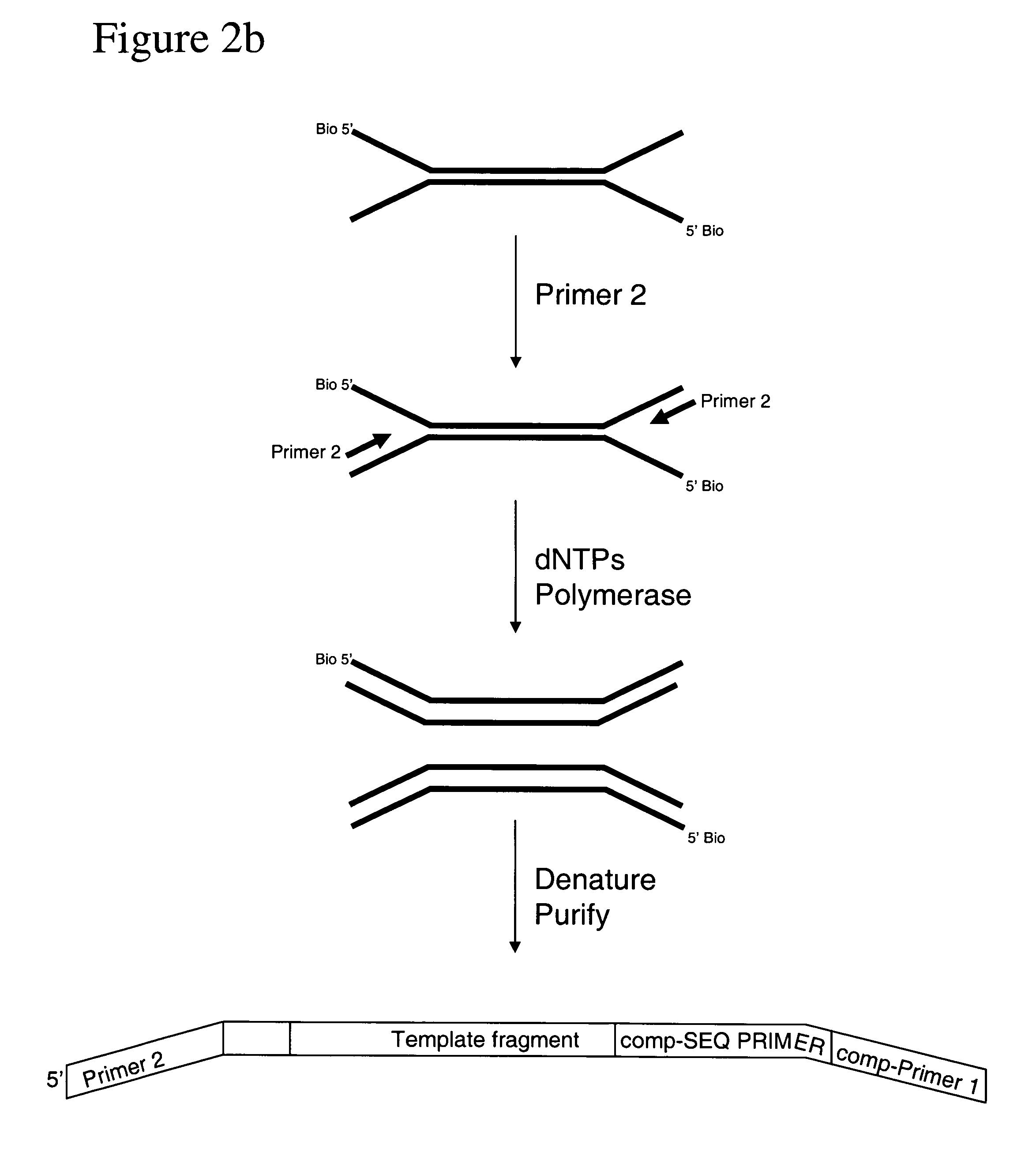
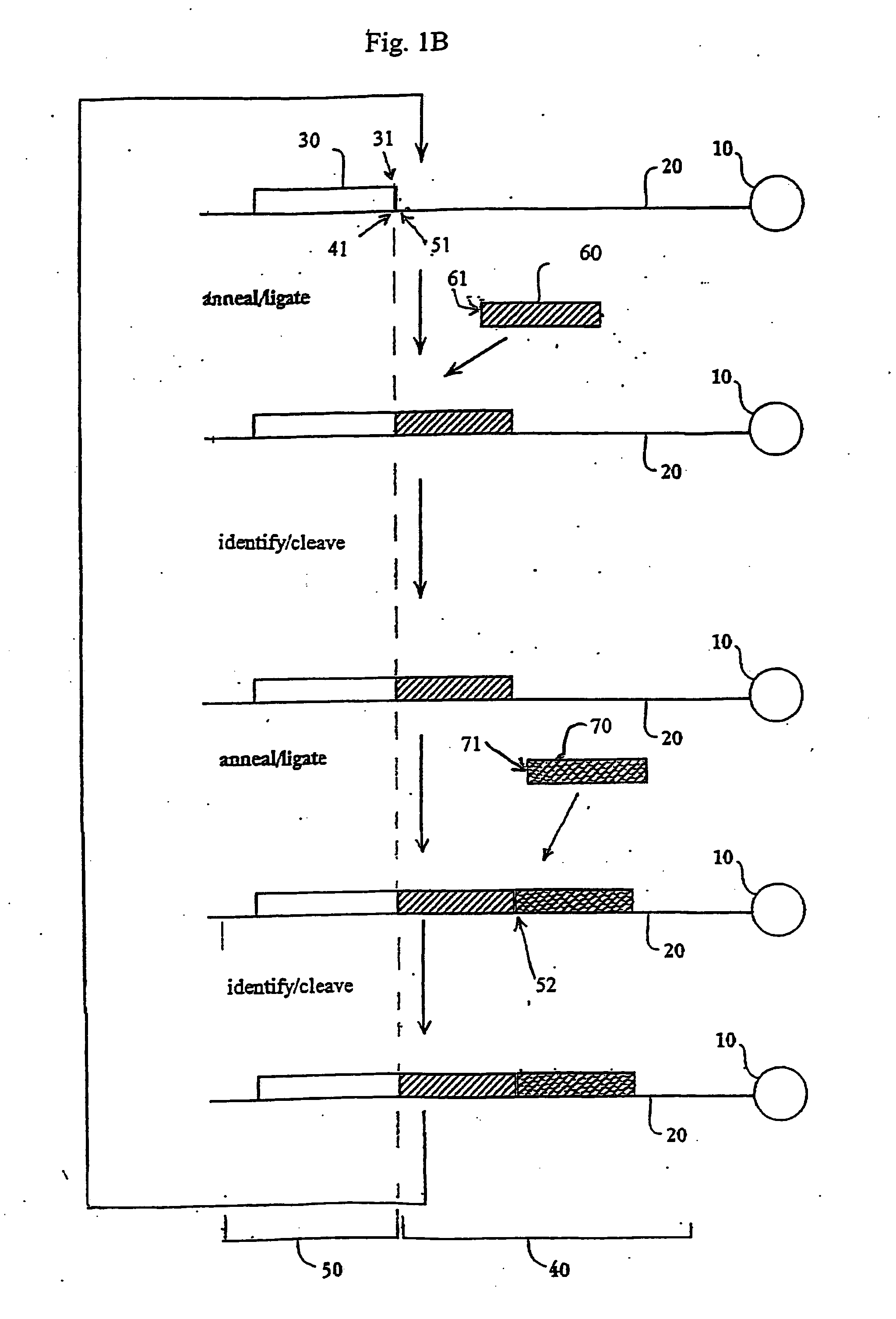
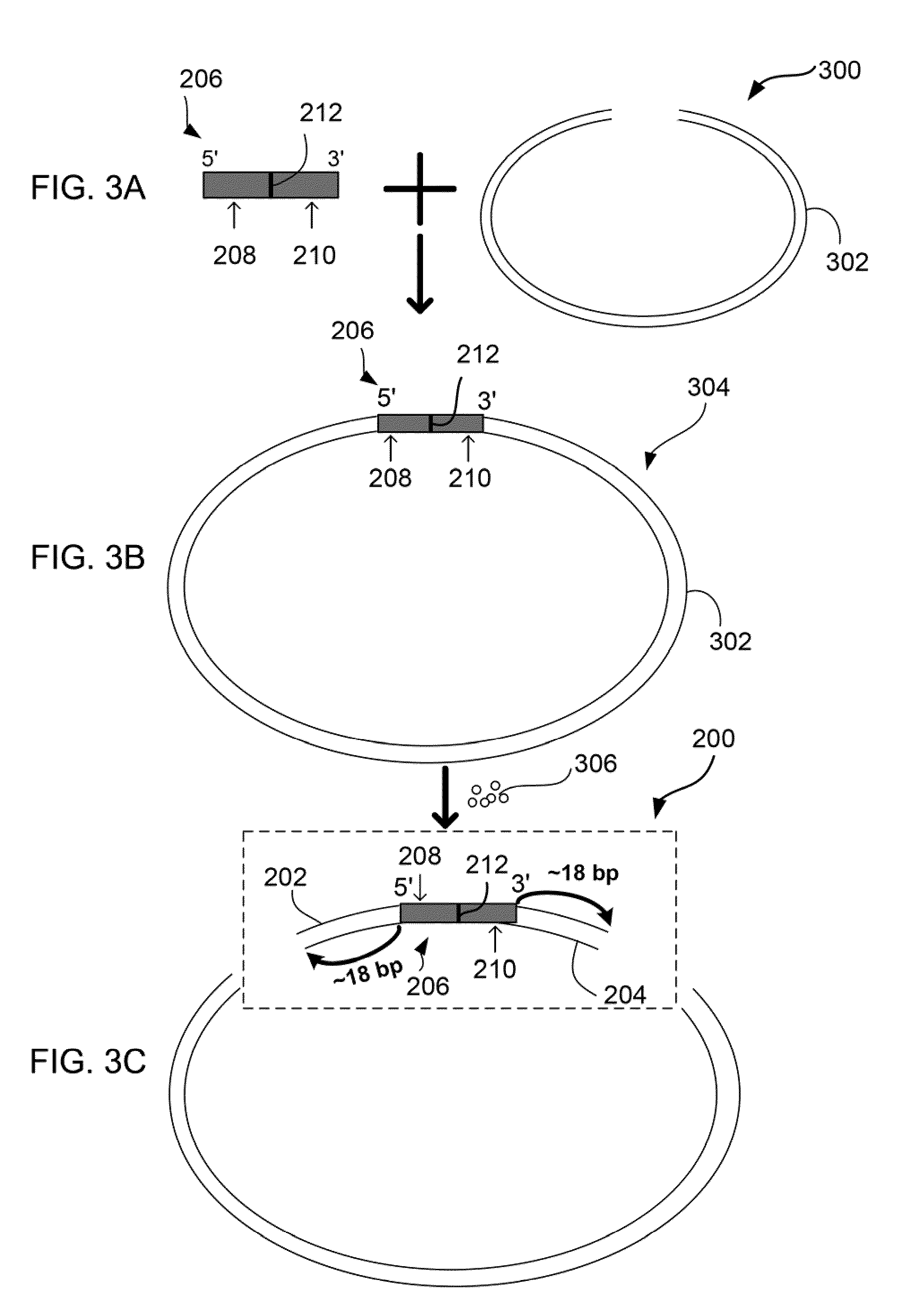
Method of preparing libraries of template polynucleotides
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a library of template polynucleotides and use thereof in methods of solid-phase nucleic acid amplification. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for preparing a library of template polynucleotides that have common sequences at their 5′ ends and at their 3′ ends.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
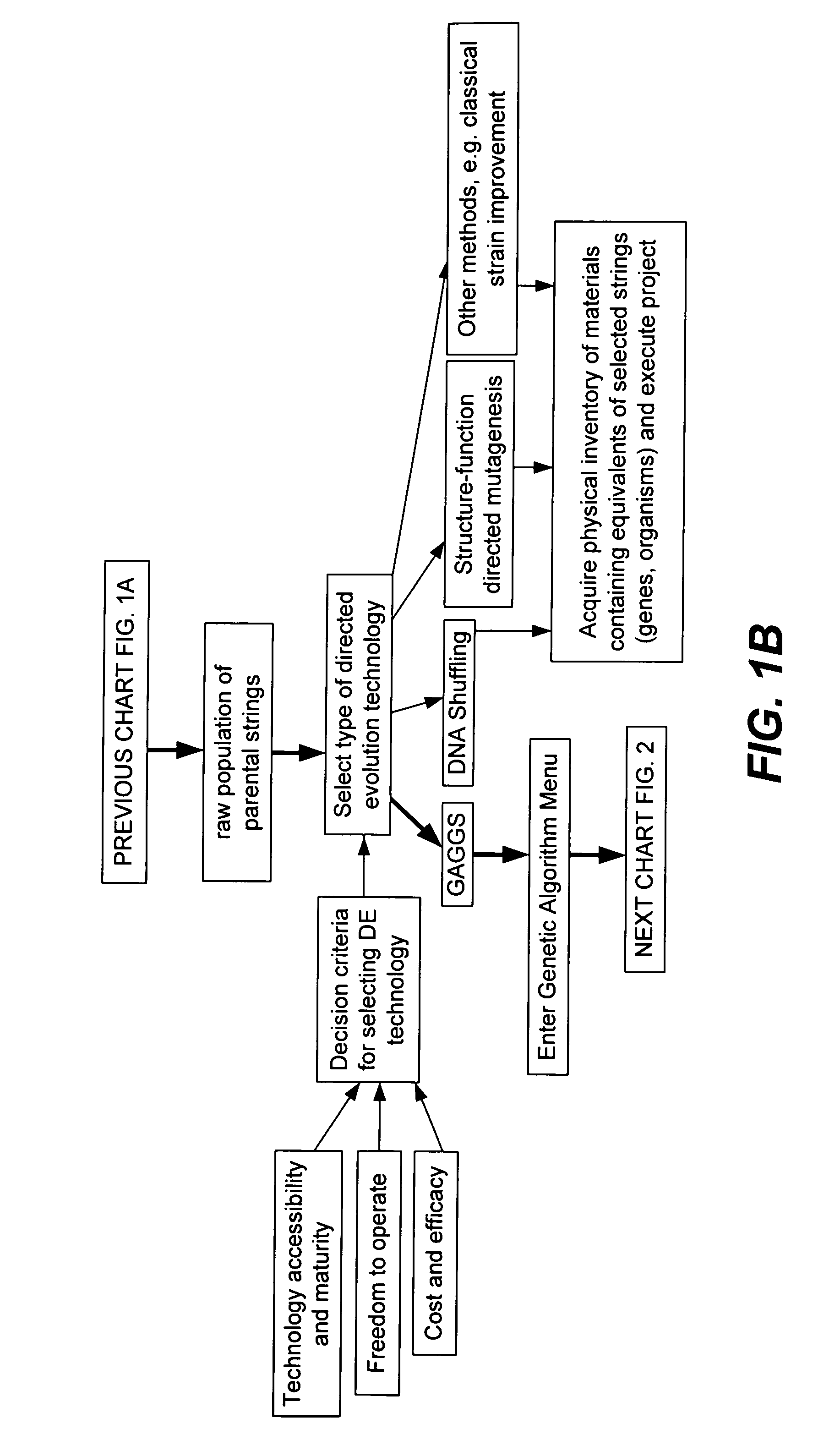
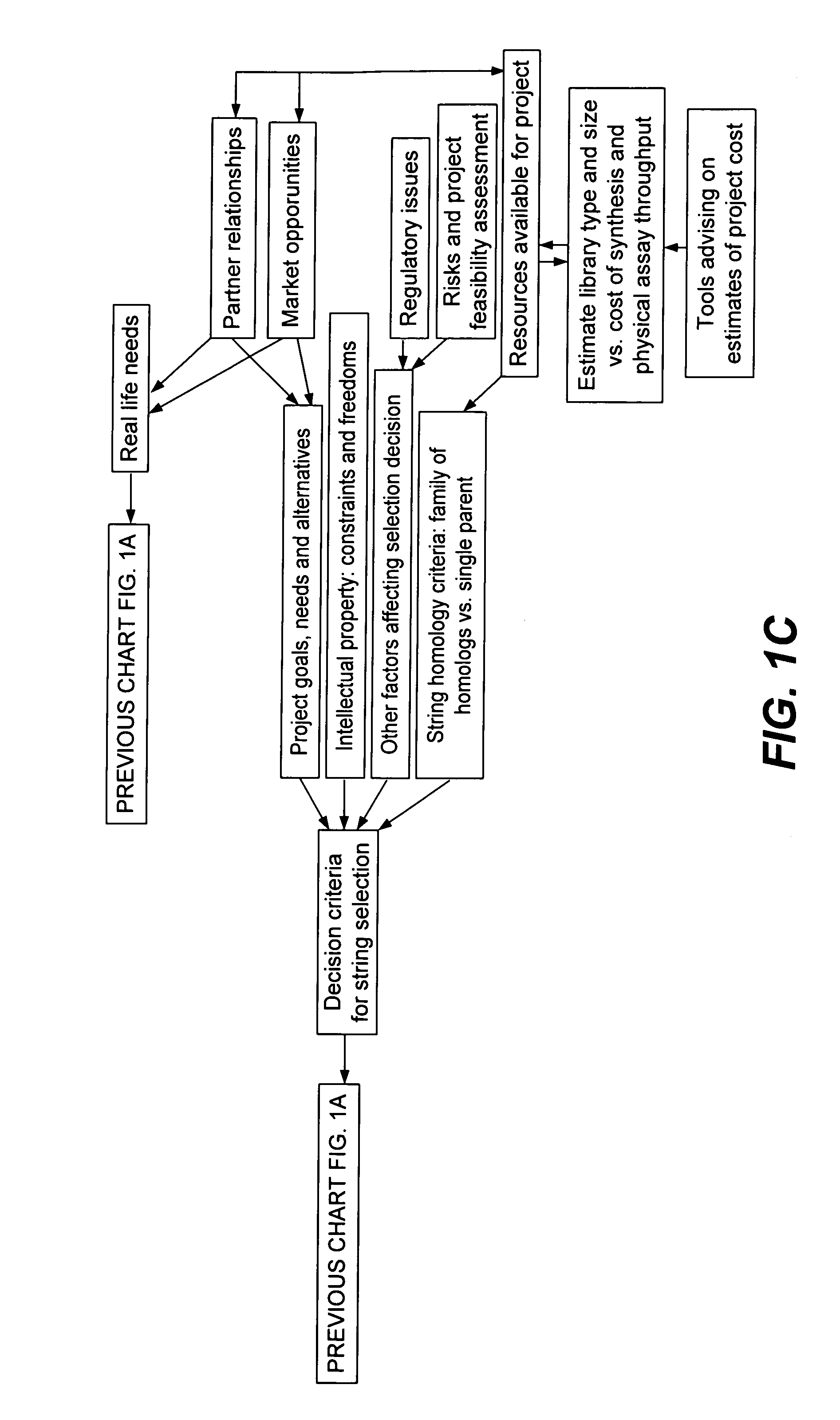
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
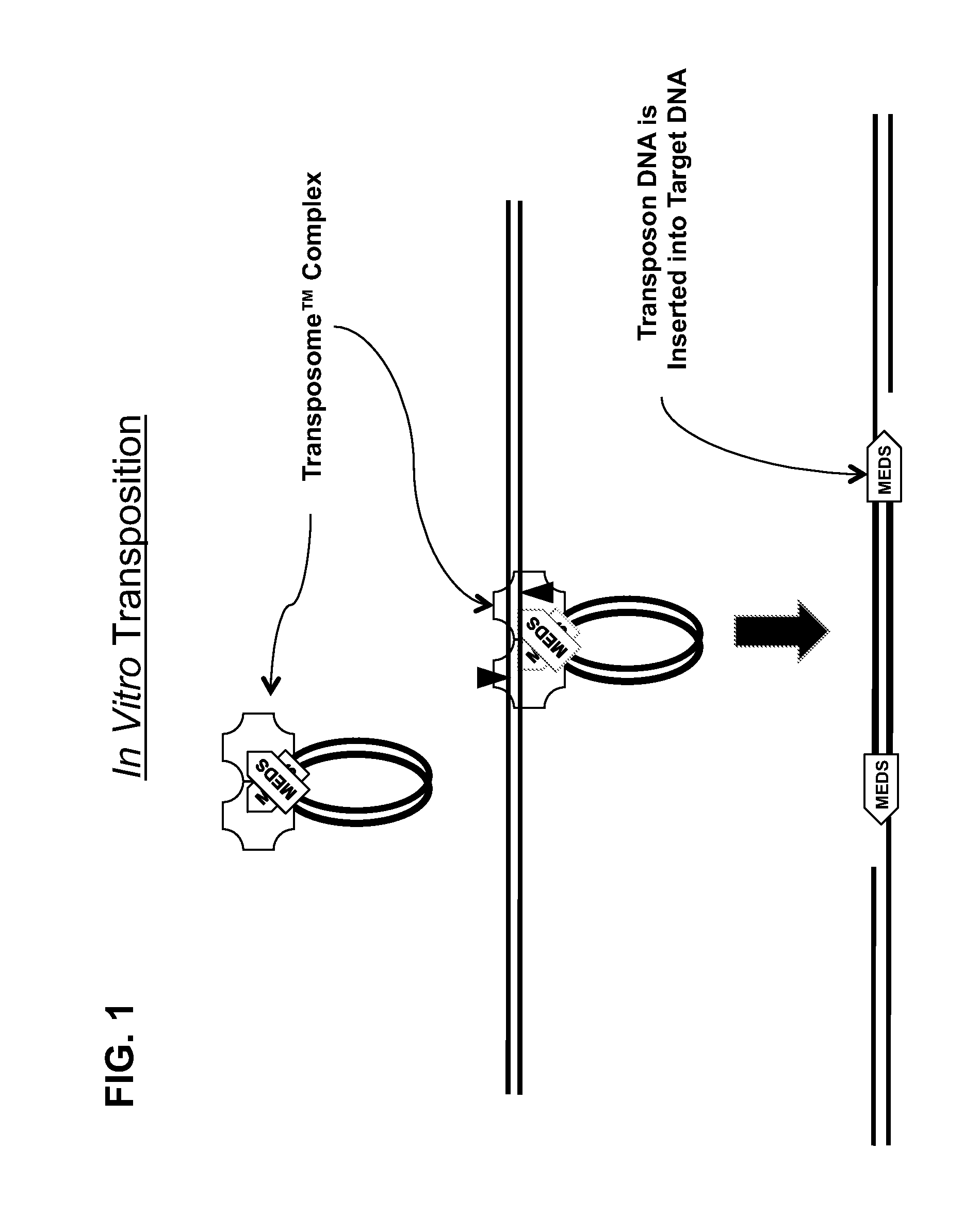
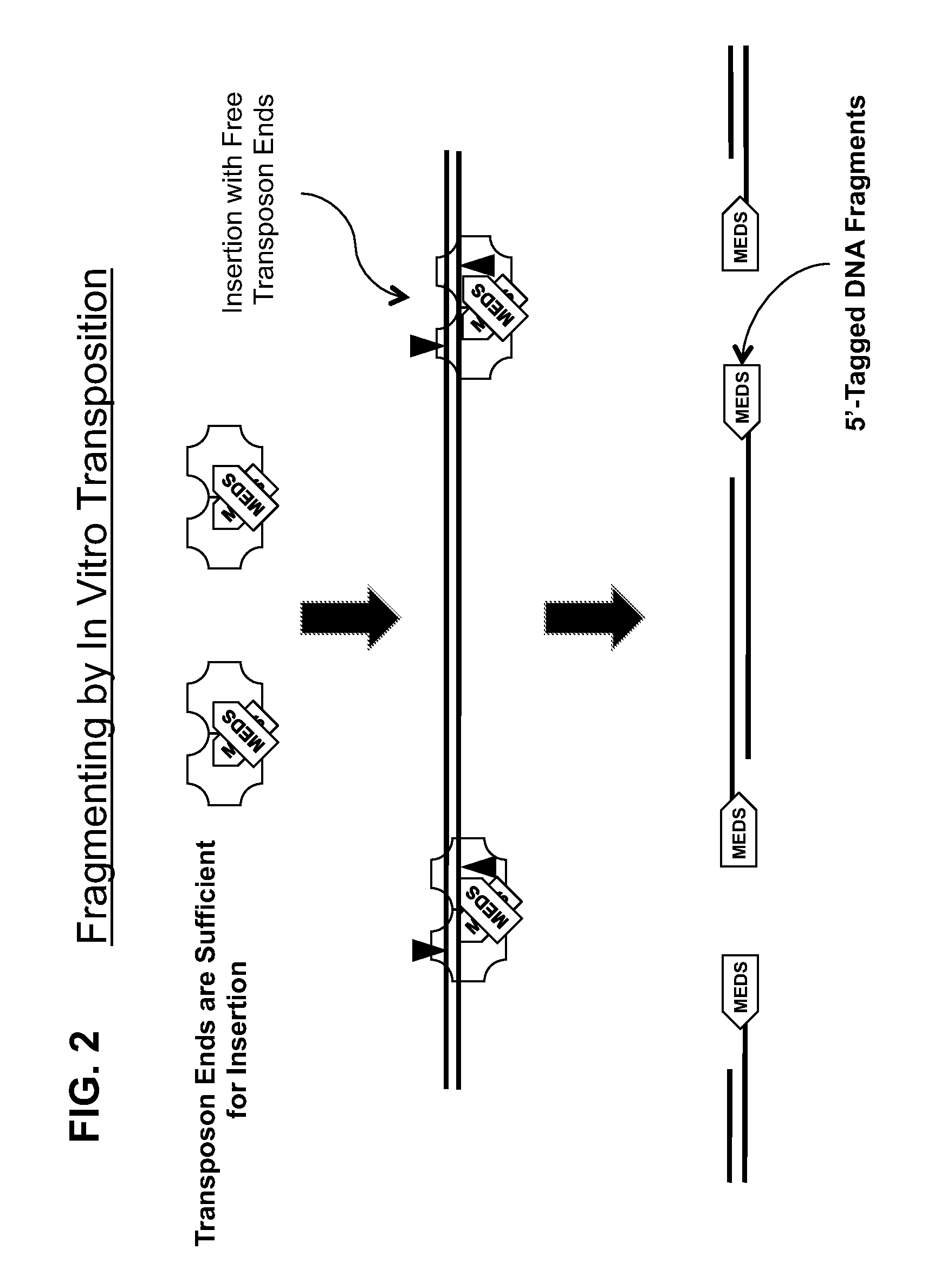
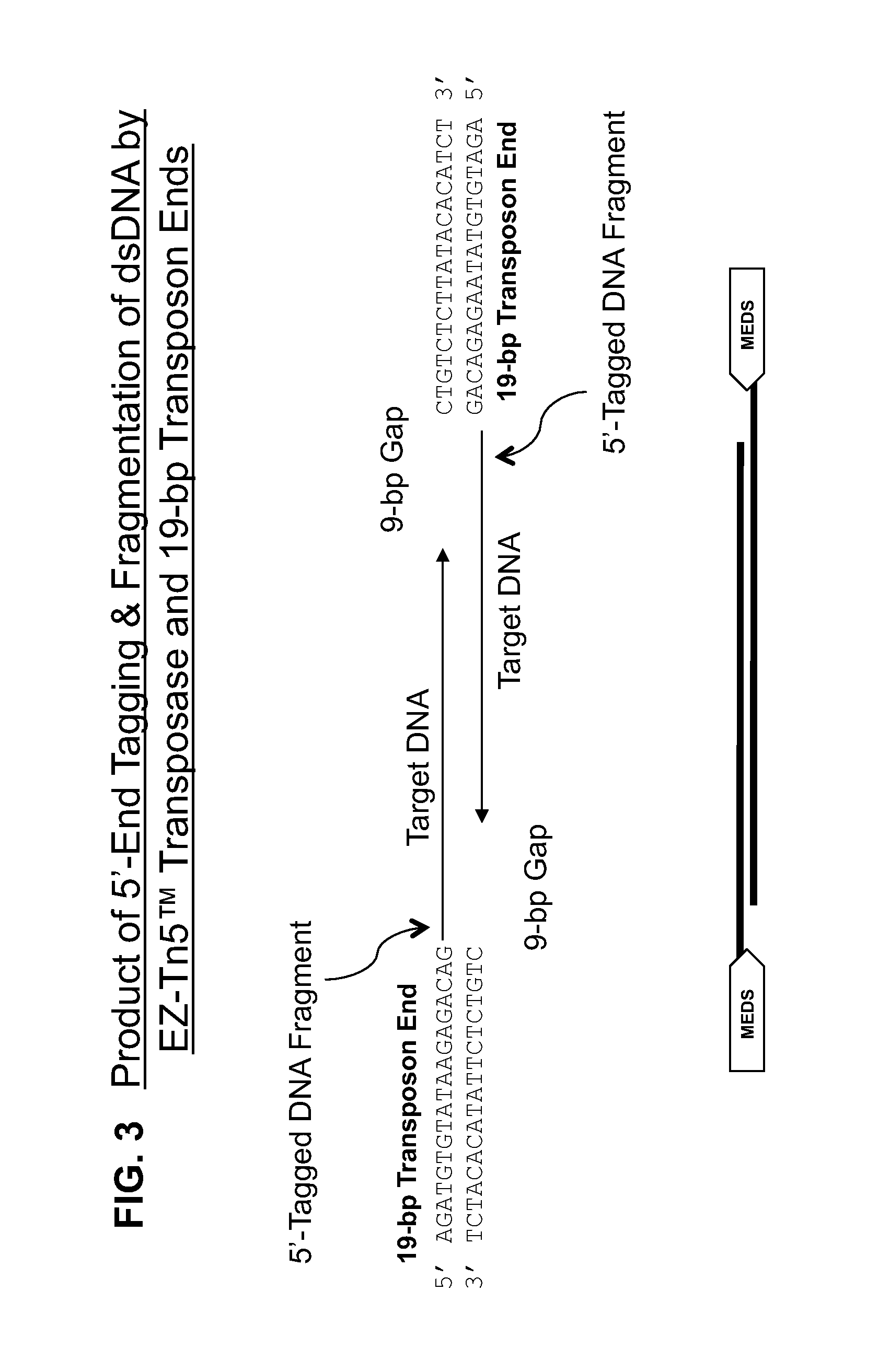
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
Compositions of transposome complexes for generating DNA fragments with specific 5′- and 3′-tags. Kits for generating libraries for sequencing, with transposome complexes, enzymes, oligonucleotides or other components.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
InactiveUS20080003571A1Efficient methodEfficient implementationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
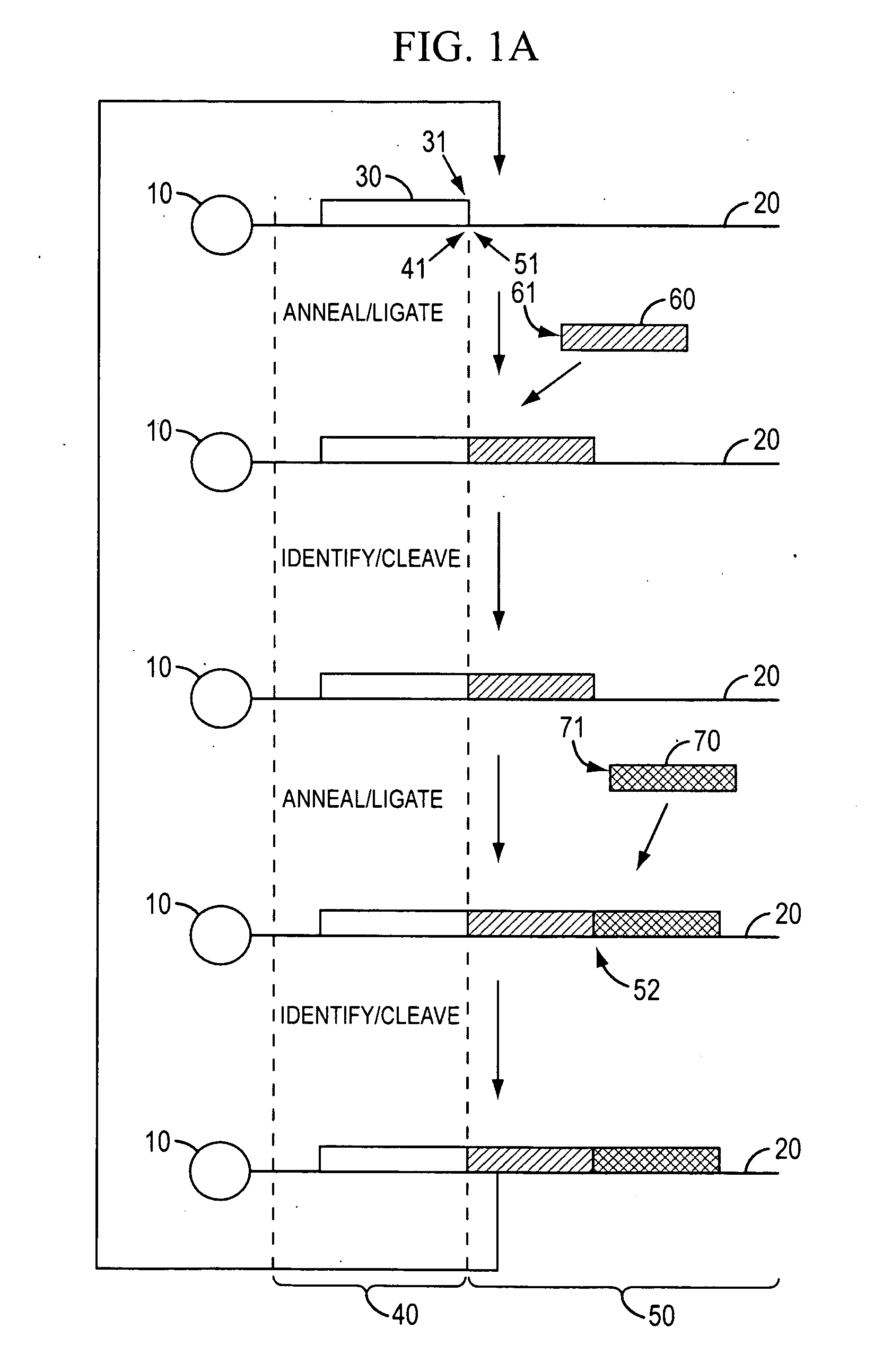
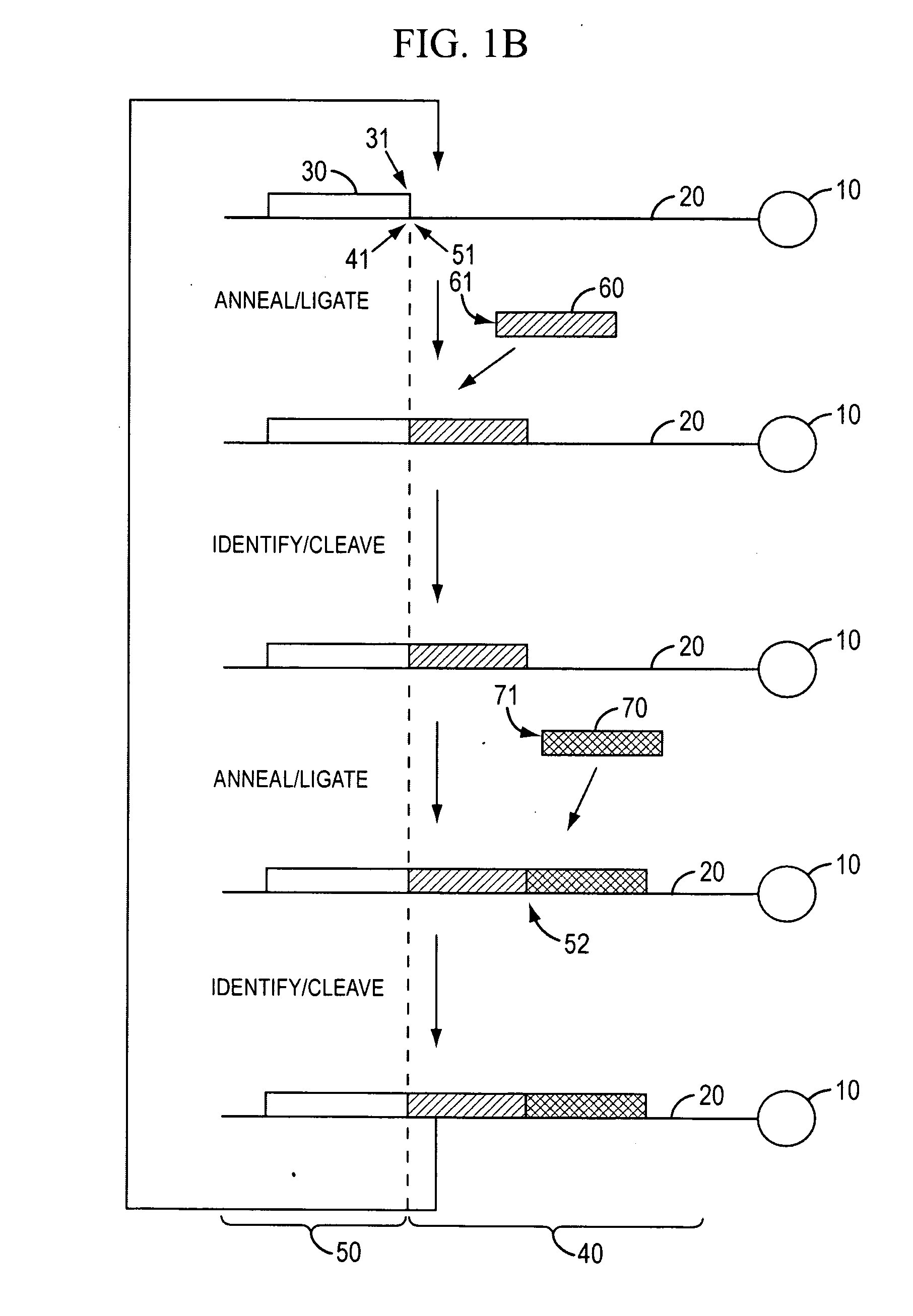
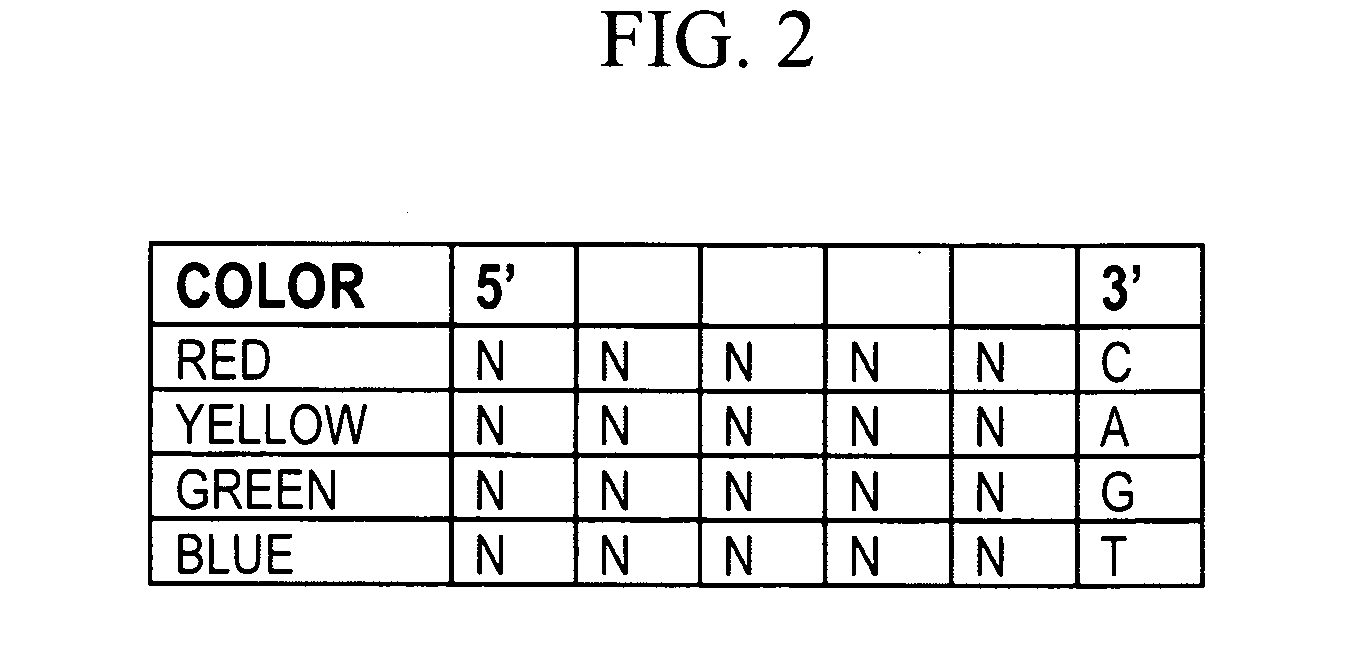
The present invention provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles comprise steps of extension, ligation, and, preferably, cleavage. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and employ agents appropriate to cleave such linkages. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing an abasic residue or a damaged base and employ agents appropriate to cleave linkages between a nucleoside and an abasic residue and / or agents appropriate to remove a damaged base from a nucleic acid. The invention provides methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families. In certain embodiments the methods acquire less than 2 bits of information from each of a plurality of nucleotides in the template in each cycle. In certain embodiments the sequencing reactions are performed on templates attached to beads, which are immobilized in or on a semi-solid support. The invention further provides sets of labeled extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages or trigger residues that are suitable for use in the method. In addition, the invention includes performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template by removing initializing oligonucleotides and extended strands and performing subsequent reactions using different initializing oligonucleotides. The invention further provides efficient methods for preparing templates, particularly for performing sequencing multiple different templates in parallel. The invention also provides methods for performing ligation and cleavage. The invention also provides new libraries of nucleic acid fragments containing paired tags, and methods of preparing microparticles having multiple different templates (e.g., containing paired tags) attached thereto and of sequencing the templates individually. The invention also provides automated sequencing systems, flow cells, image processing methods, and computer-readable media that store computer-executable instructions (e.g., to perform the image-processing methods) and / or sequence information. In certain embodiments the sequence information is stored in a database.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method for generating a library of oligonucleotides comprising a controlled distribution of mutations
InactiveUS6582914B1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsOligonucleotideComputational biology
Methods are disclosed for producing libraries of nucleic acid molecules which libraries are derived from a nucleic acid template. The libraries comprise variant nucleic acids which are produced from a mutagenesis strategy using, e.g., a plurality of defined mutagenic and / or non-mutagenic primers and specific reaction conditions which favor the production of varied combinatorial mutants.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
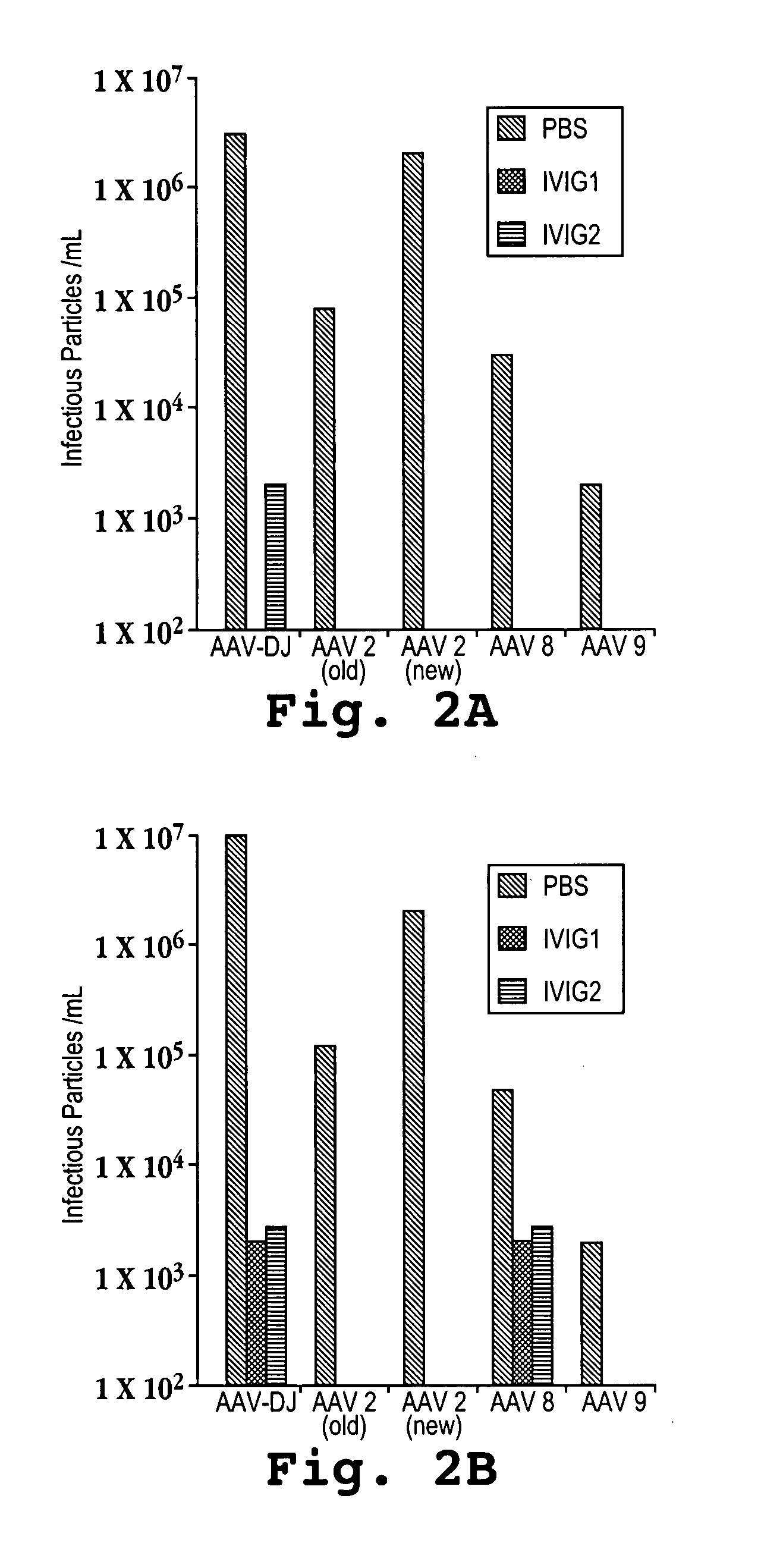
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
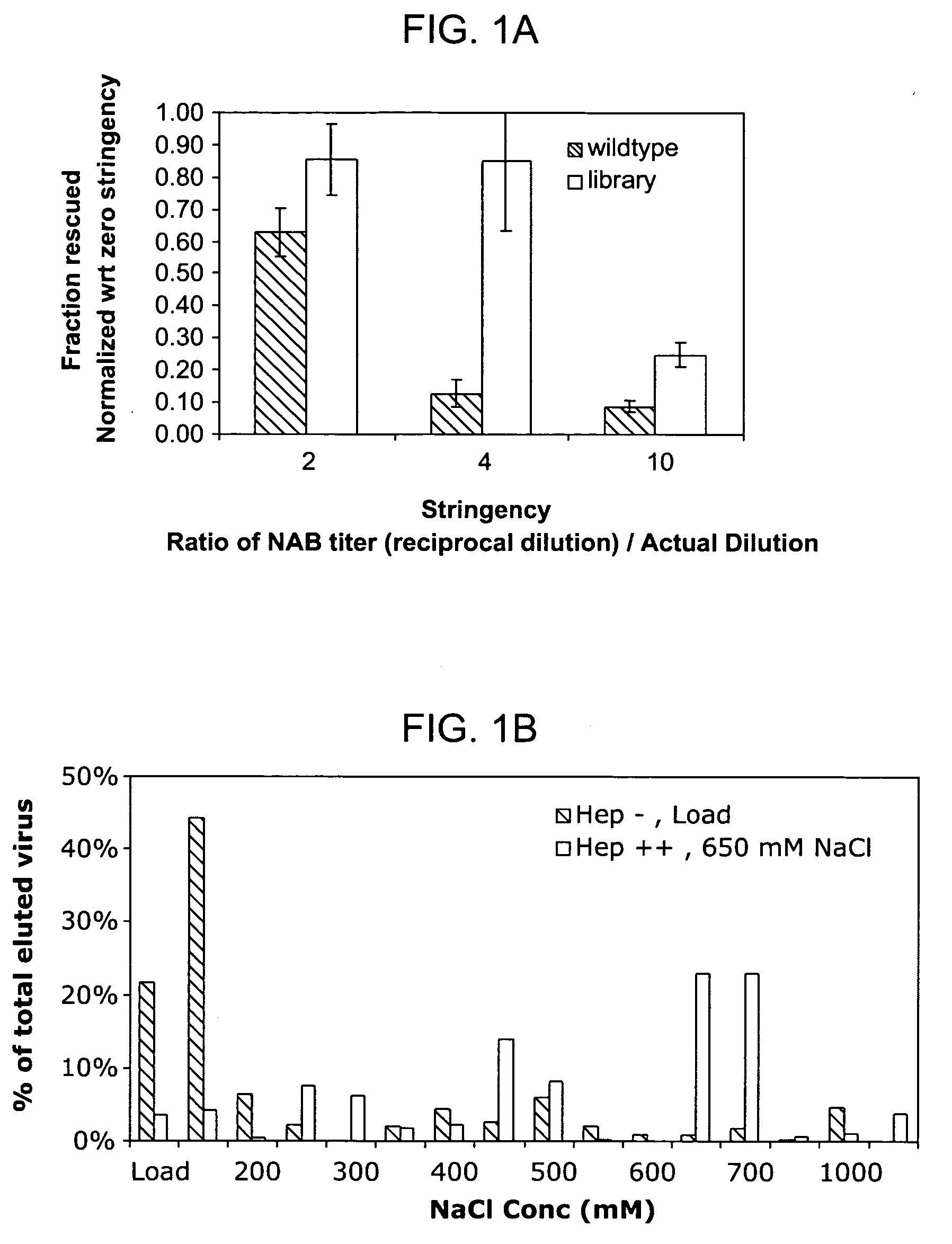
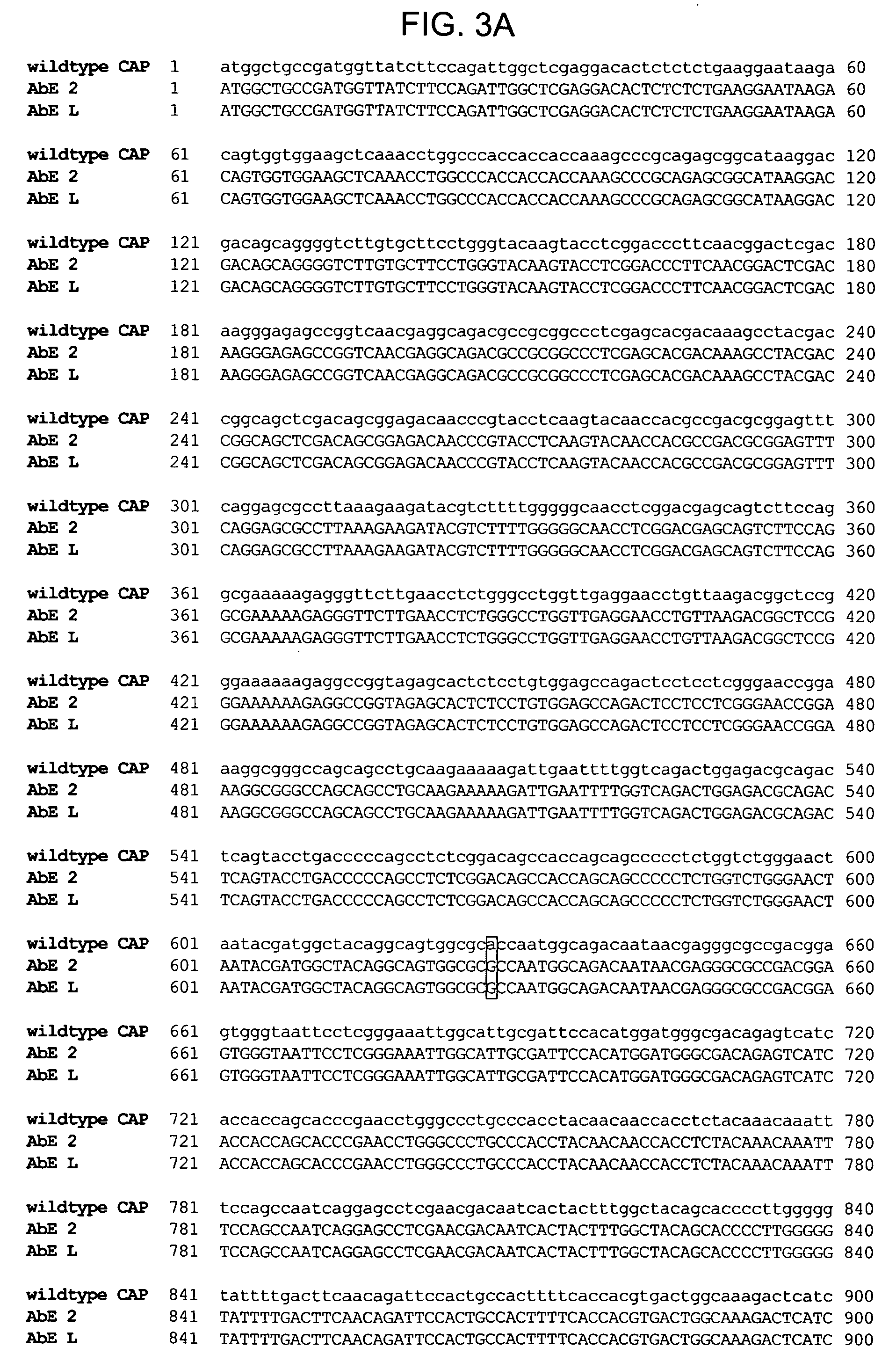
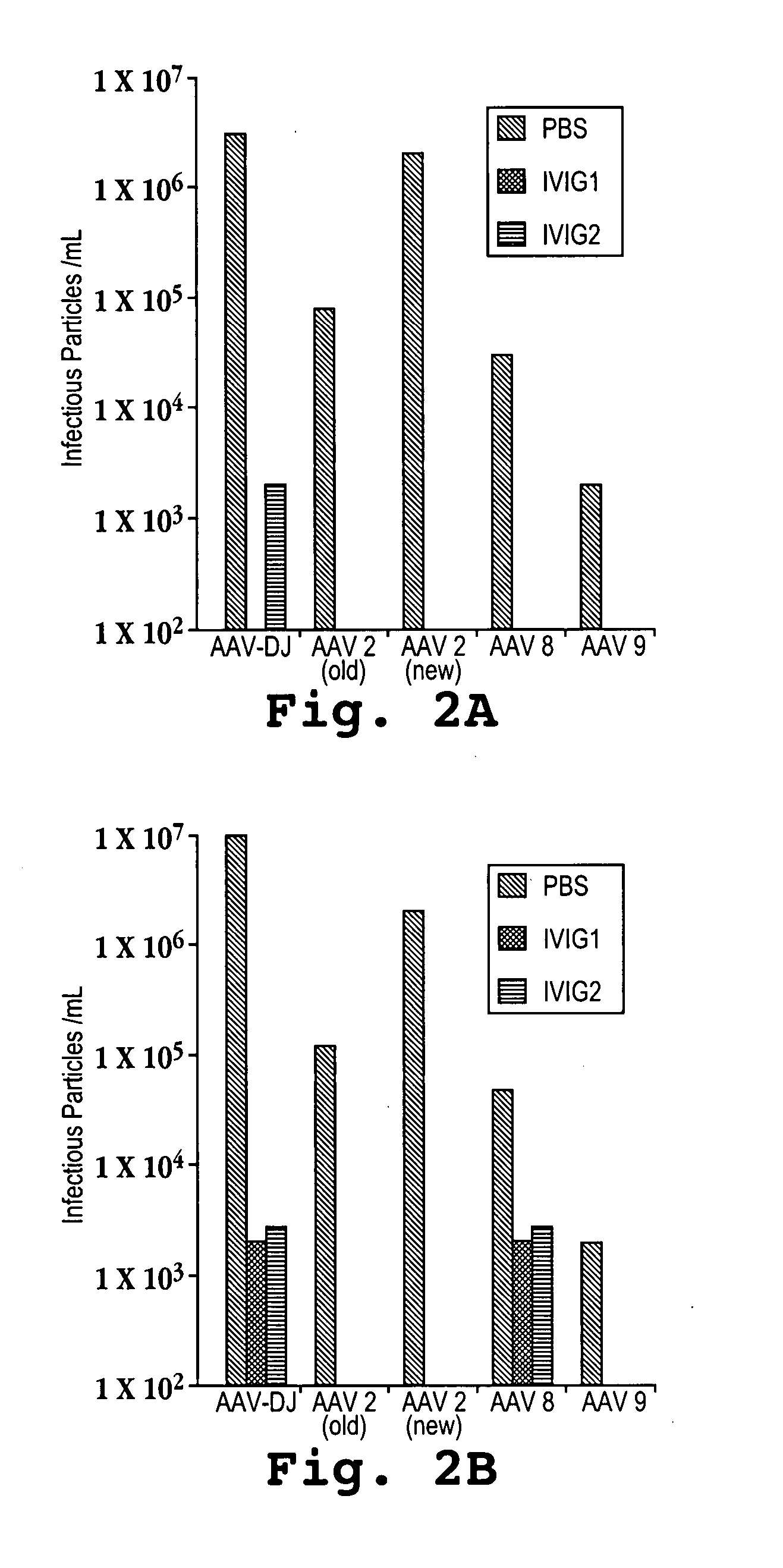
ActiveUS20050053922A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityAntibacterial agentsVirusesReassortant VirusesNeutralizing antibody
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE GENE THERAPEUTICS +1
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
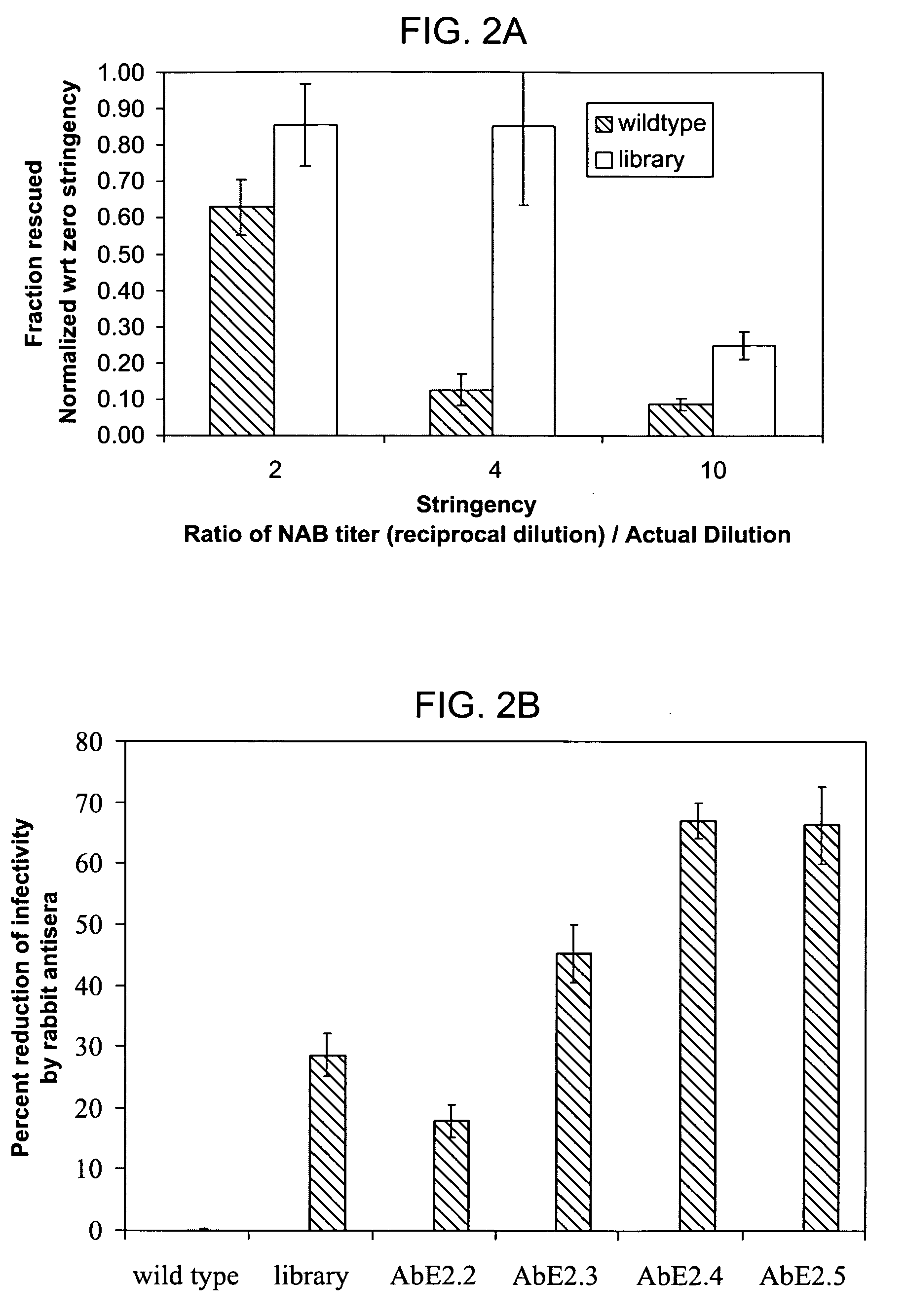
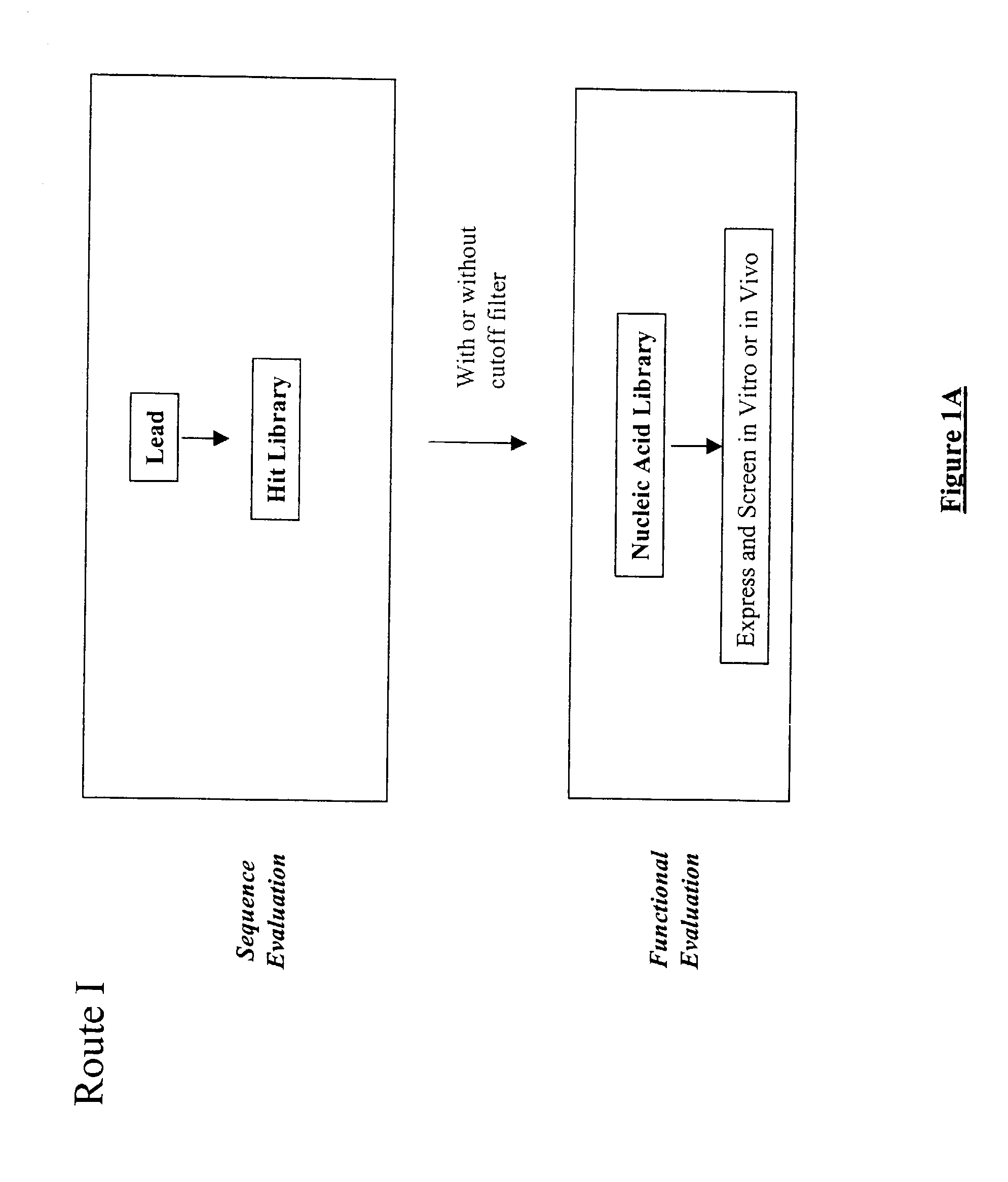
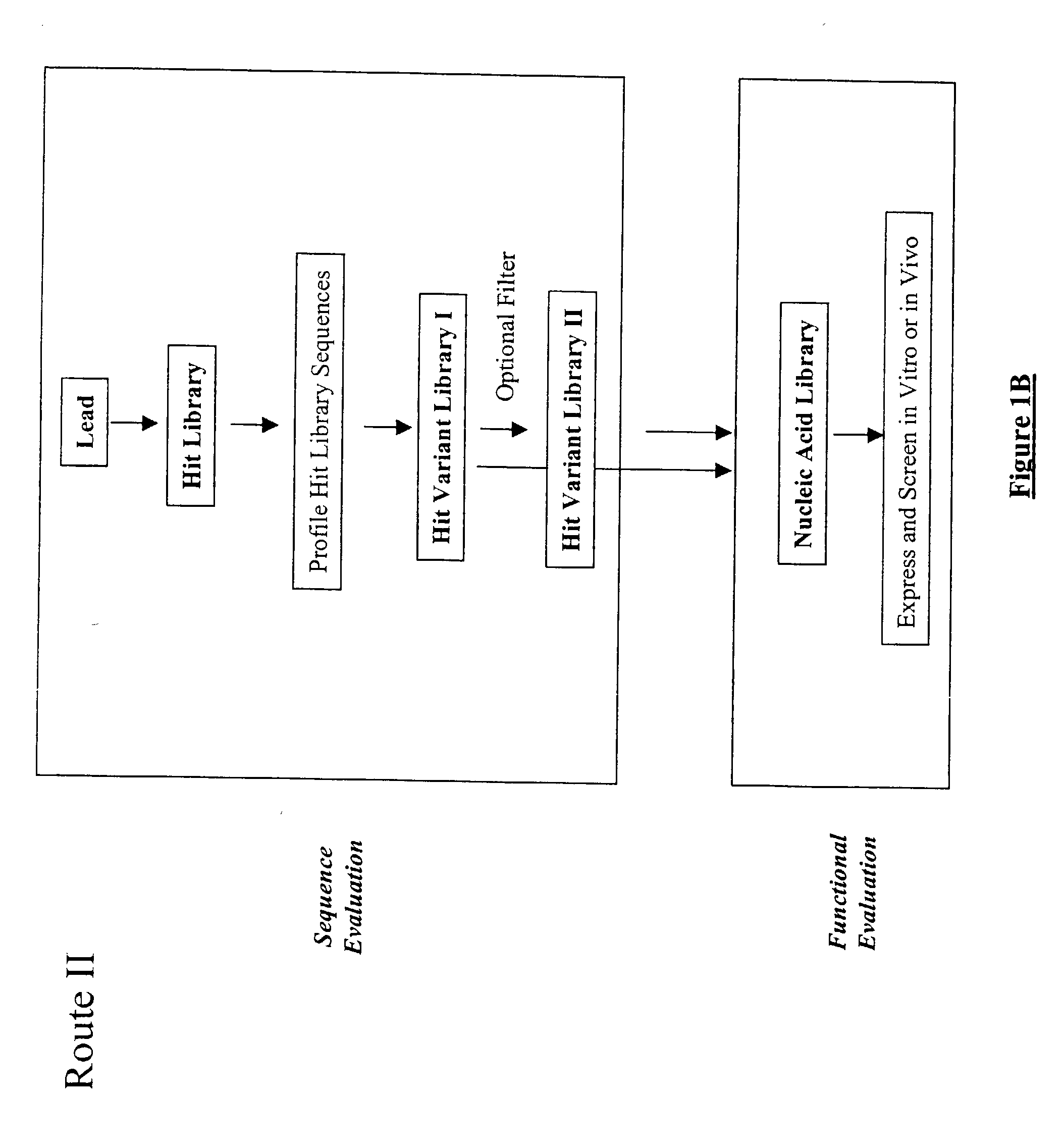
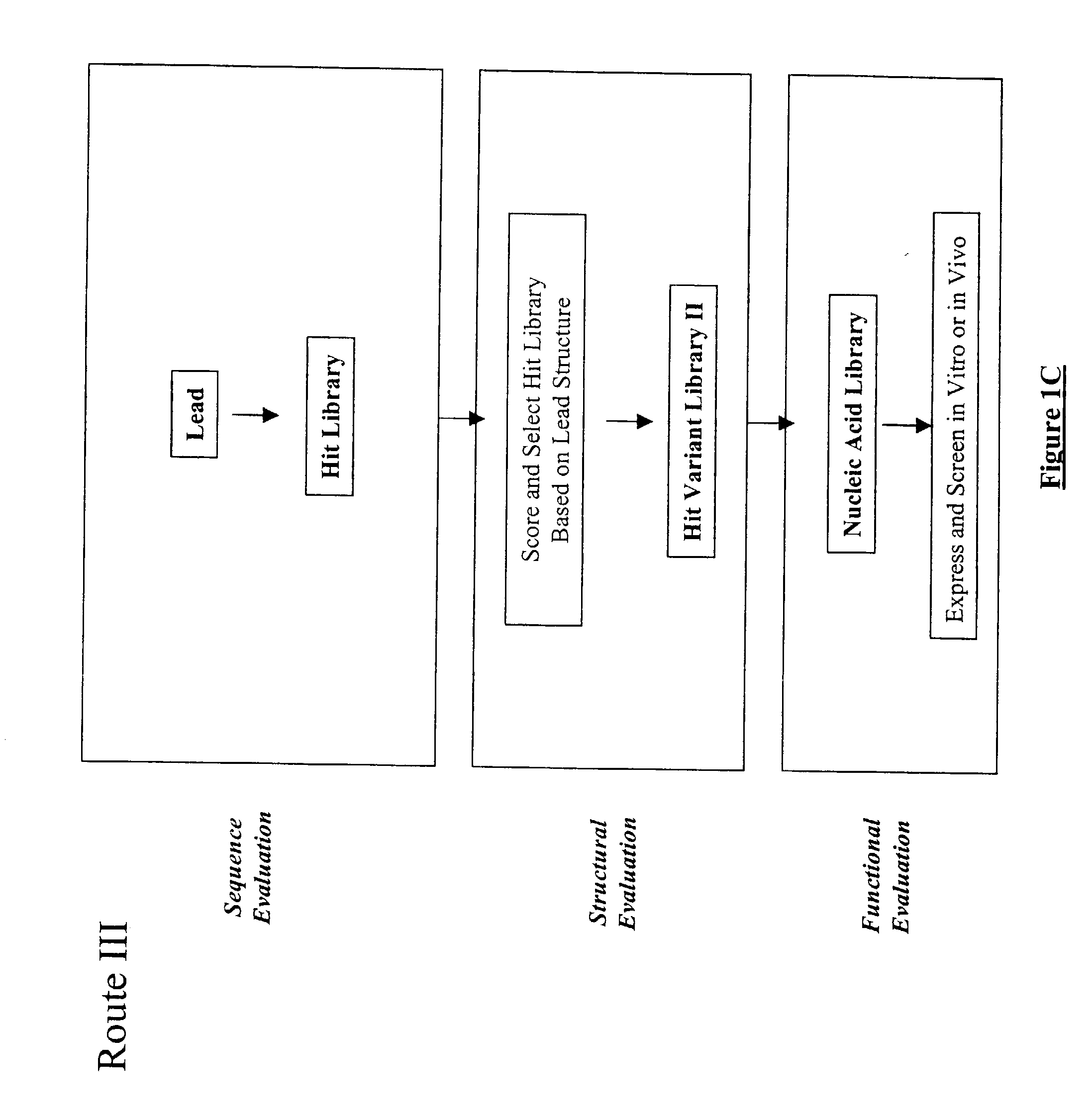
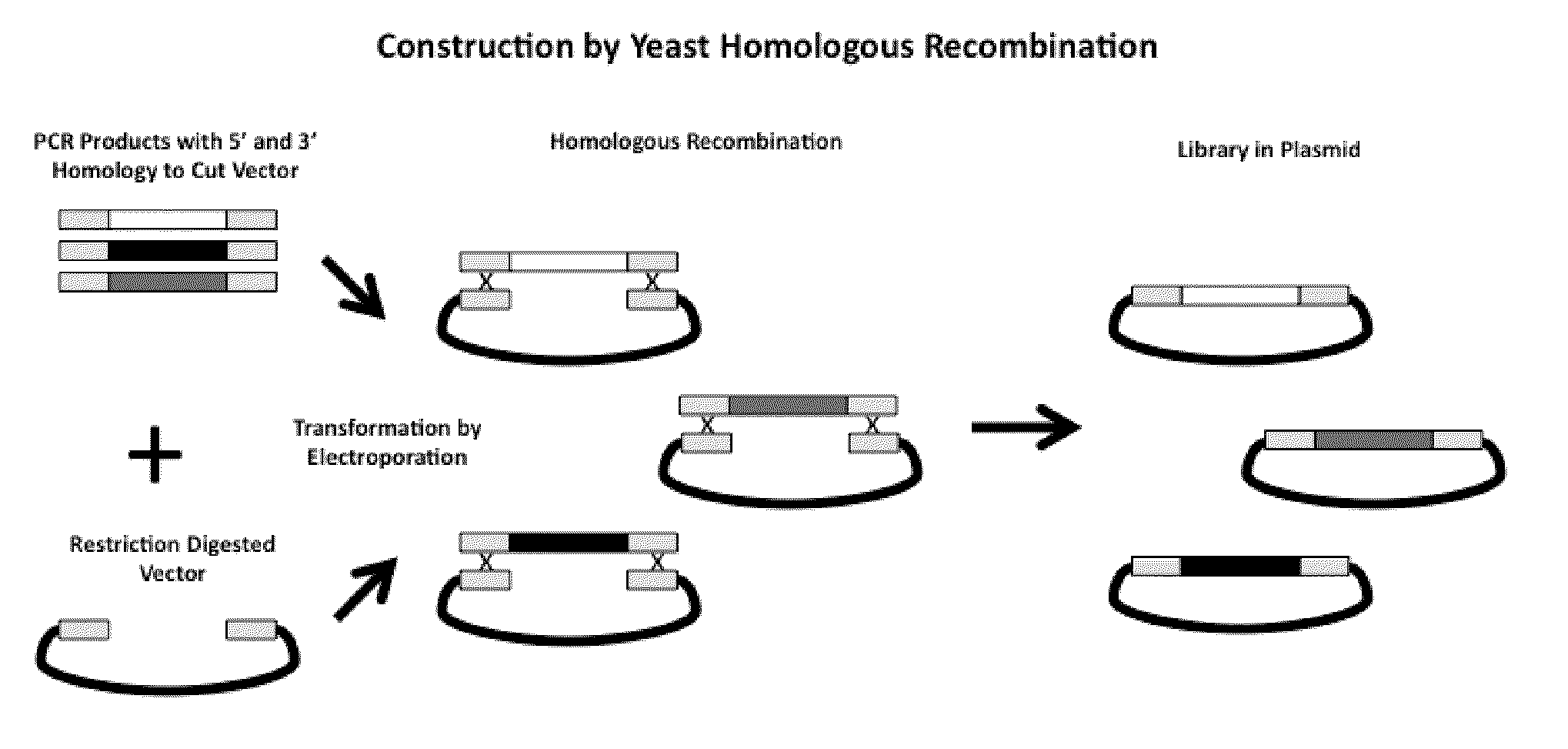
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Rationally Designed, Synthetic Antibody Libraries and Uses Therefor
ActiveUS20090181855A1Peptide librariesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPolynucleotideSynthetic antibody
The present invention overcomes the inadequacies inherent in the known methods for generating libraries of antibody-encoding polynucleotides by specifically designing the libraries with directed sequence and length diversity. The libraries are designed to reflect the preimmune repertoire naturally created by the human immune system and are based on rational design informed by examination of publicly available databases of human antibody sequences.
Owner:ADIMAB LLC
Identification and comparison of protein-protein interactions that occur in populations and identification of inhibitors of these interactors
InactiveUS6057101AEfficient screeningLess experimentally significant and specific indicationMaterial nanotechnologyFungiDiseaseBinding site
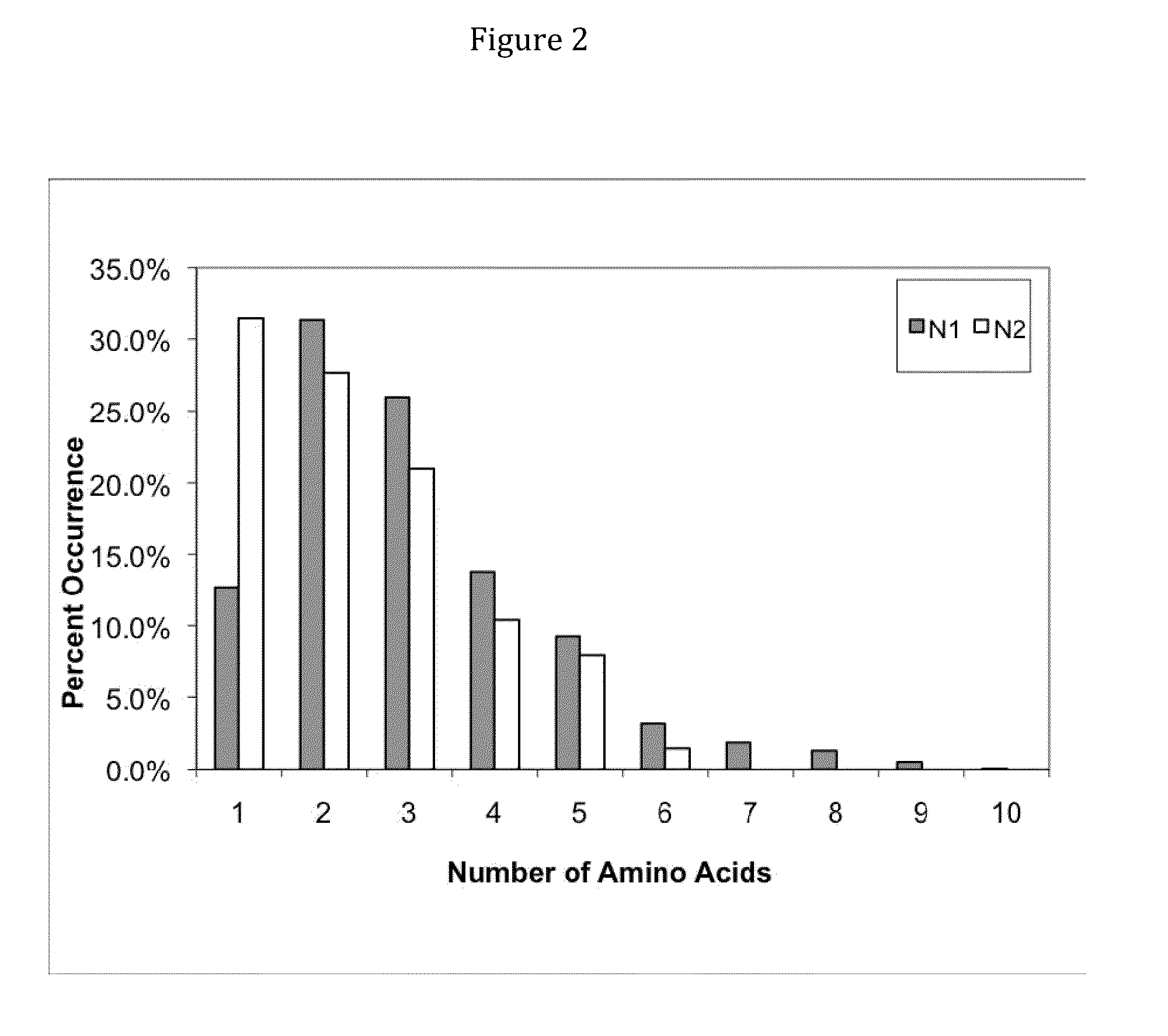
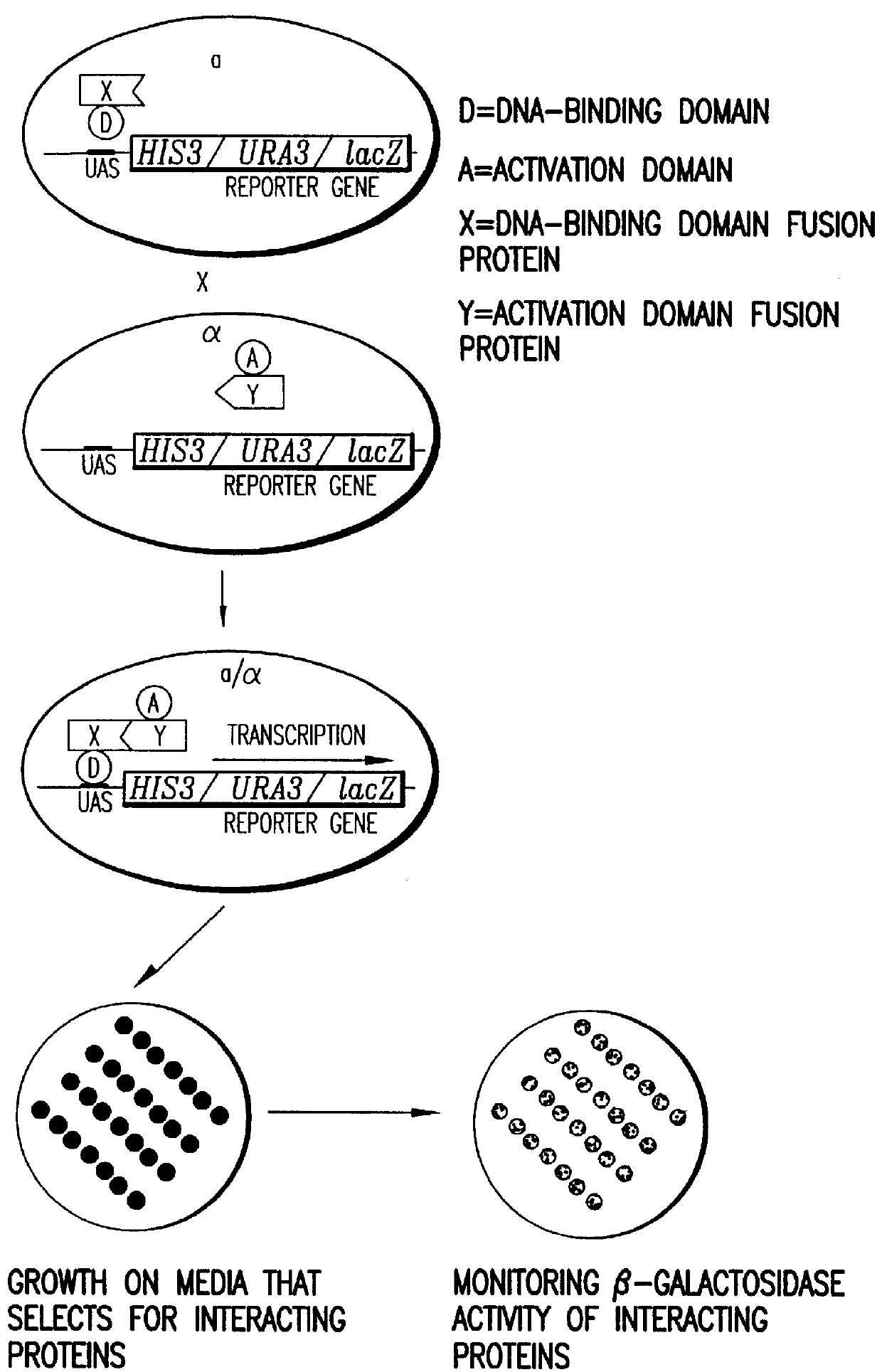
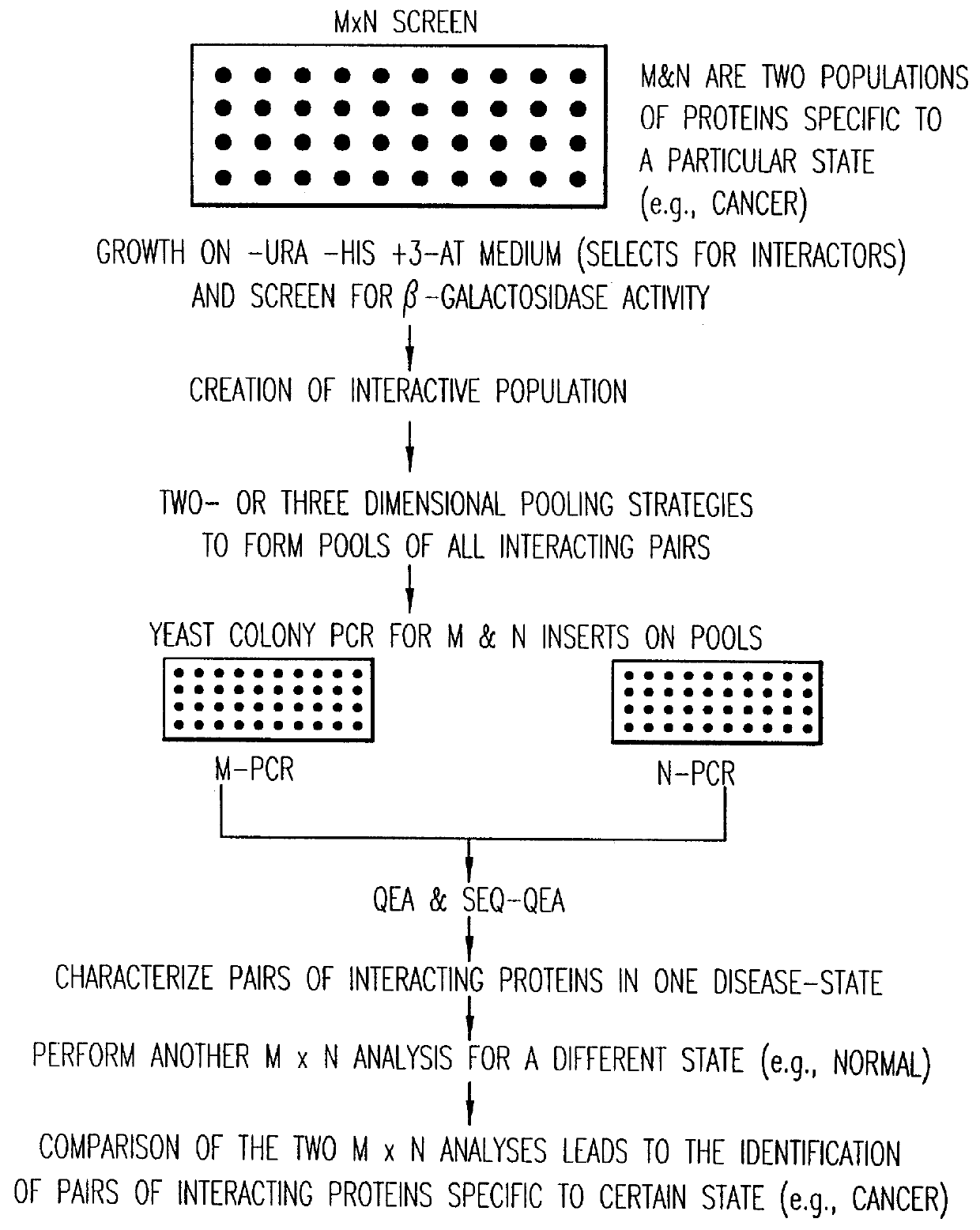
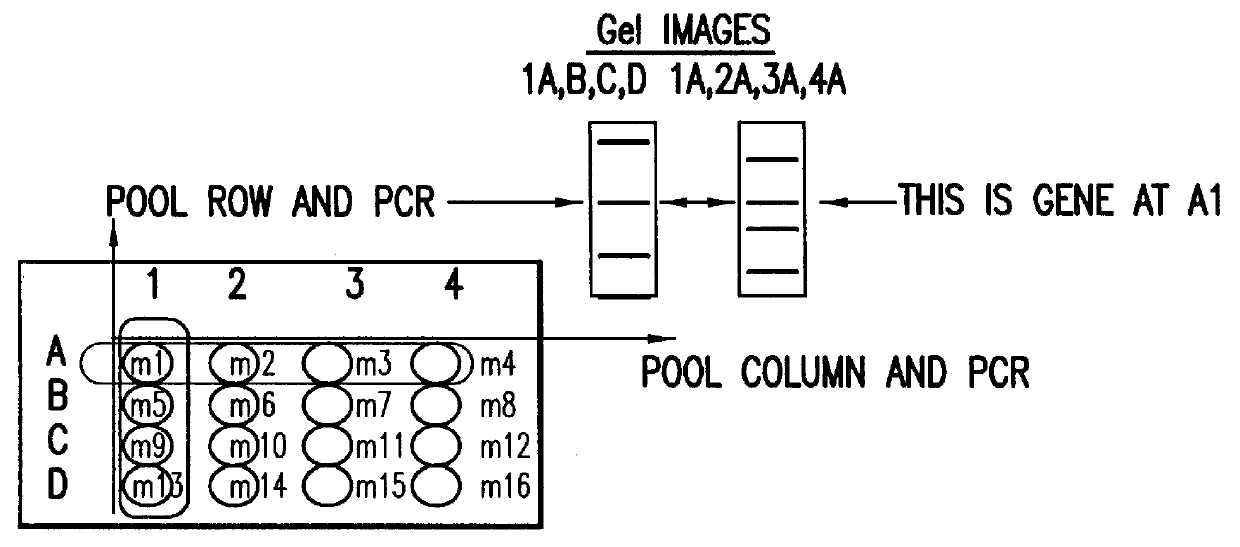
Methods are described for detecting protein-protein interactions, among two populations of proteins, each having a complexity of at least 1,000. For example, proteins are fused either to the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional activator or to the activation domain of a transcriptional activator. Two yeast strains, of the opposite mating type and carrying one type each of the fusion proteins are mated together. Productive interactions between the two halves due to protein-protein interactions lead to the reconstitution of the transcriptional activator, which in turn leads to the activation of a reporter gene containing a binding site for the DNA-binding domain. This analysis can be carried out for two or more populations of proteins. The differences in the genes encoding the proteins involved in the protein-protein interactions are characterized, thus leading to the identification of specific protein-protein interactions, and the genes encoding the interacting proteins, relevant to a particular tissue, stage or disease. Furthermore, inhibitors that interfere with these protein-protein interactions are identified by their ability to inactivate a reporter gene. The screening for such inhibitors can be in a multiplexed format where a set of inhibitors will be screened against a library of interactors. Further, information-processing methods and systems are described. These methods and systems provide for identification of the genes coding for detected interacting proteins, for assembling a unified database of protein-protein interaction data, and for processing this unified database to obtain protein interaction domain and protein pathway information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
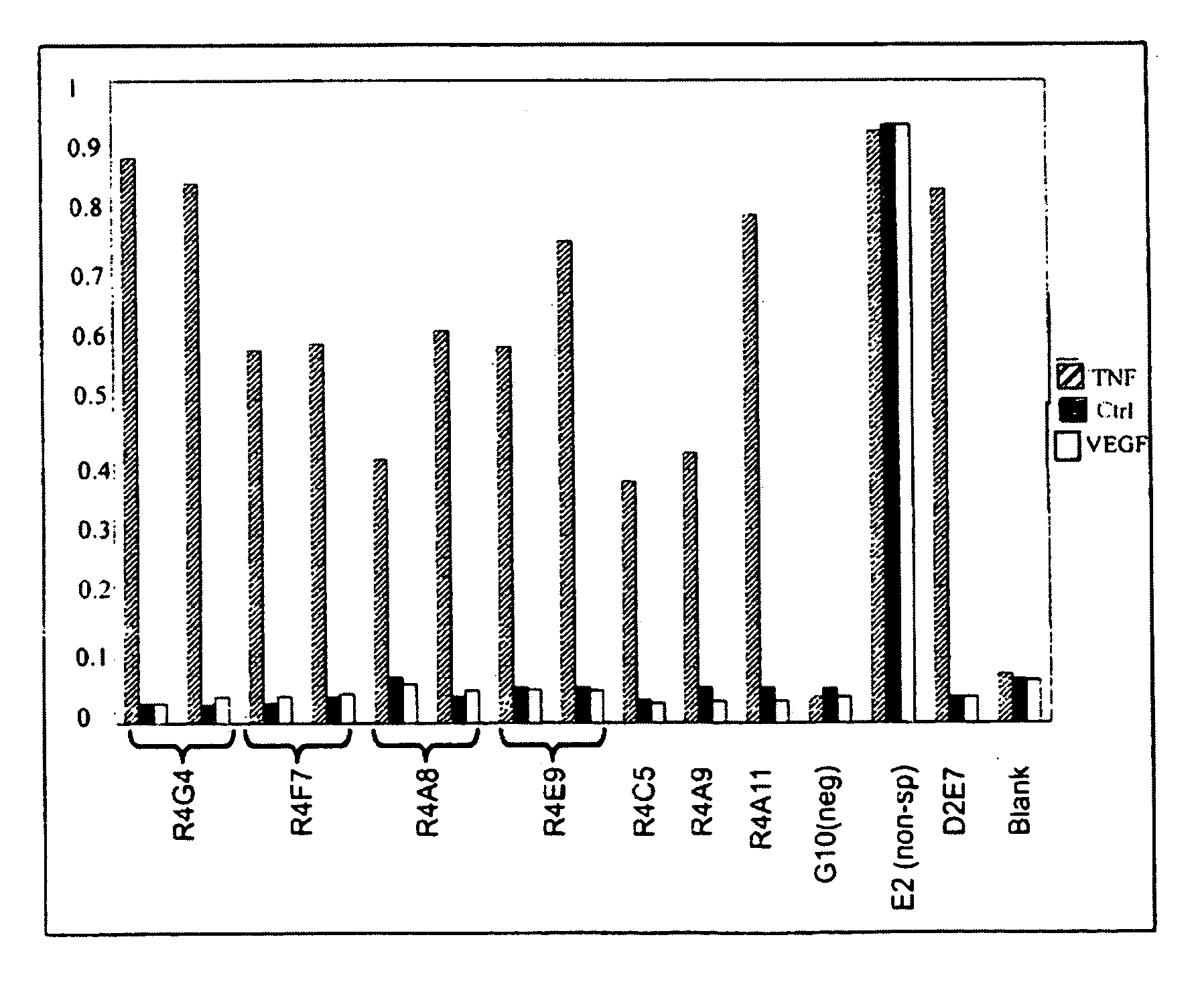
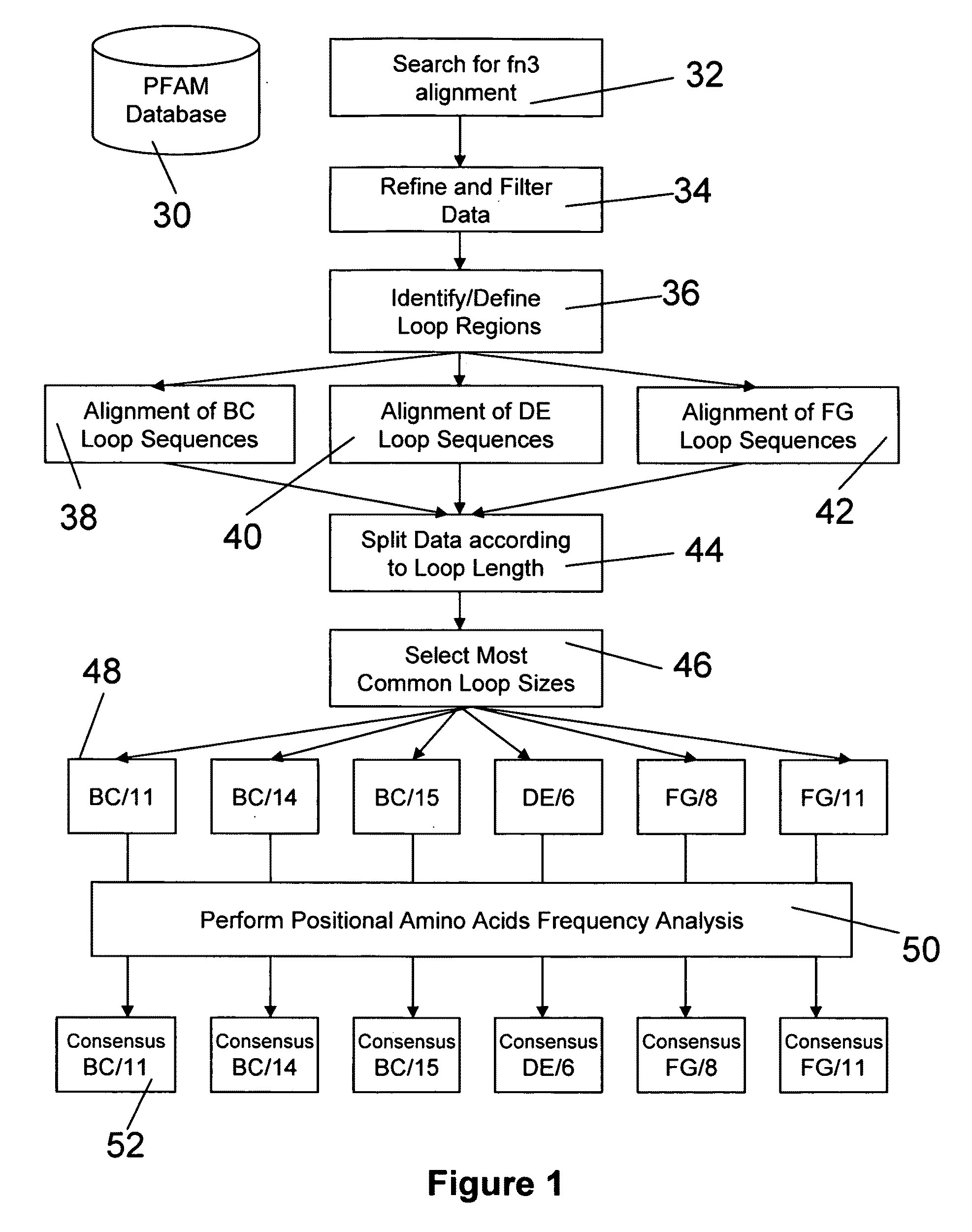
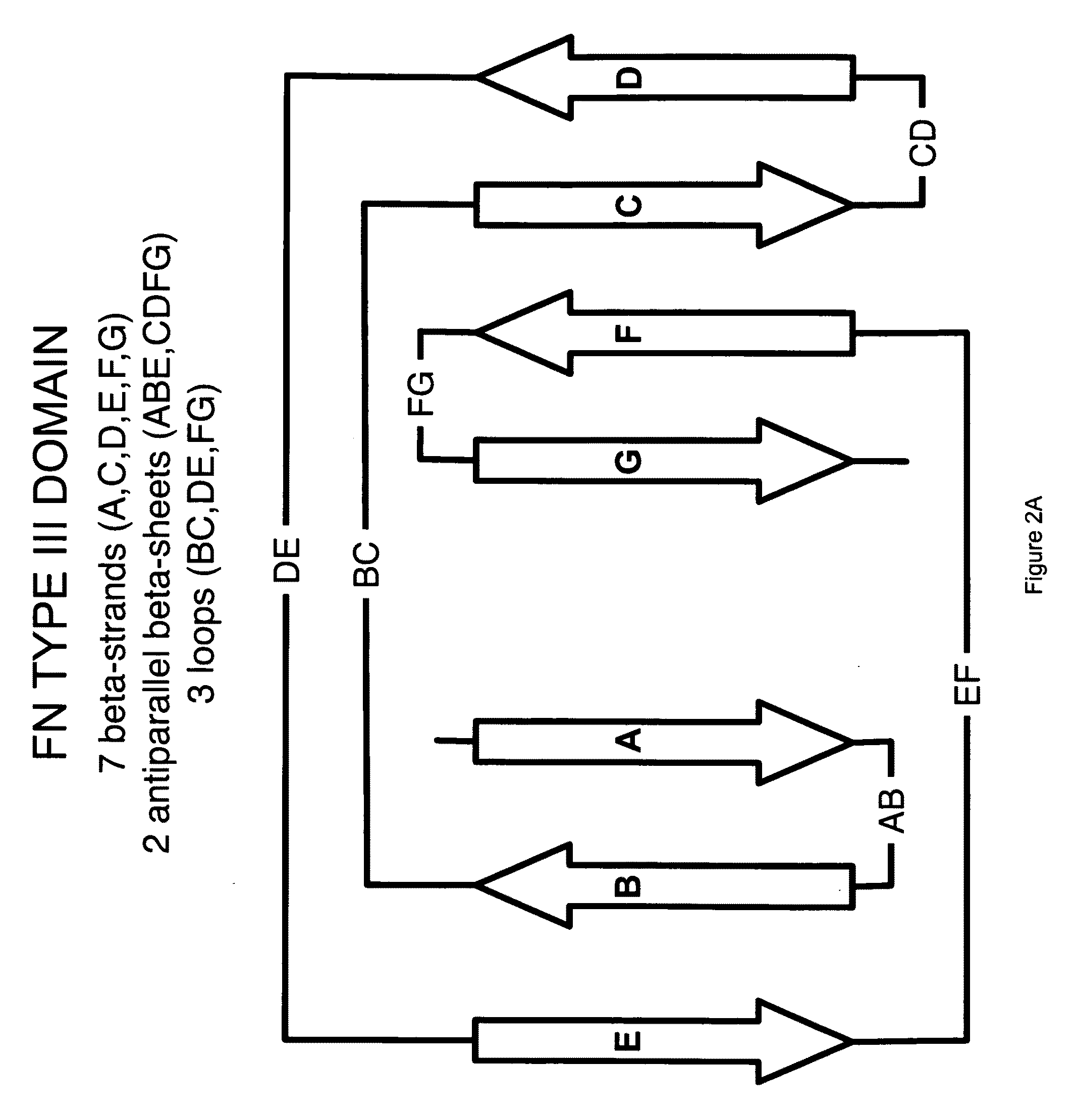
Universal fibronectin type III binding-domain libraries
Walk-through mutagenesis and natural-variant combinatorial fibronectin Type III (FN3) polypeptide libraries are described, along with their method of construction and use. Also disclosed are a number of high binding affinity polypeptides selected by screening the libraries against a variety of selected antigens.
Owner:PROTELIX
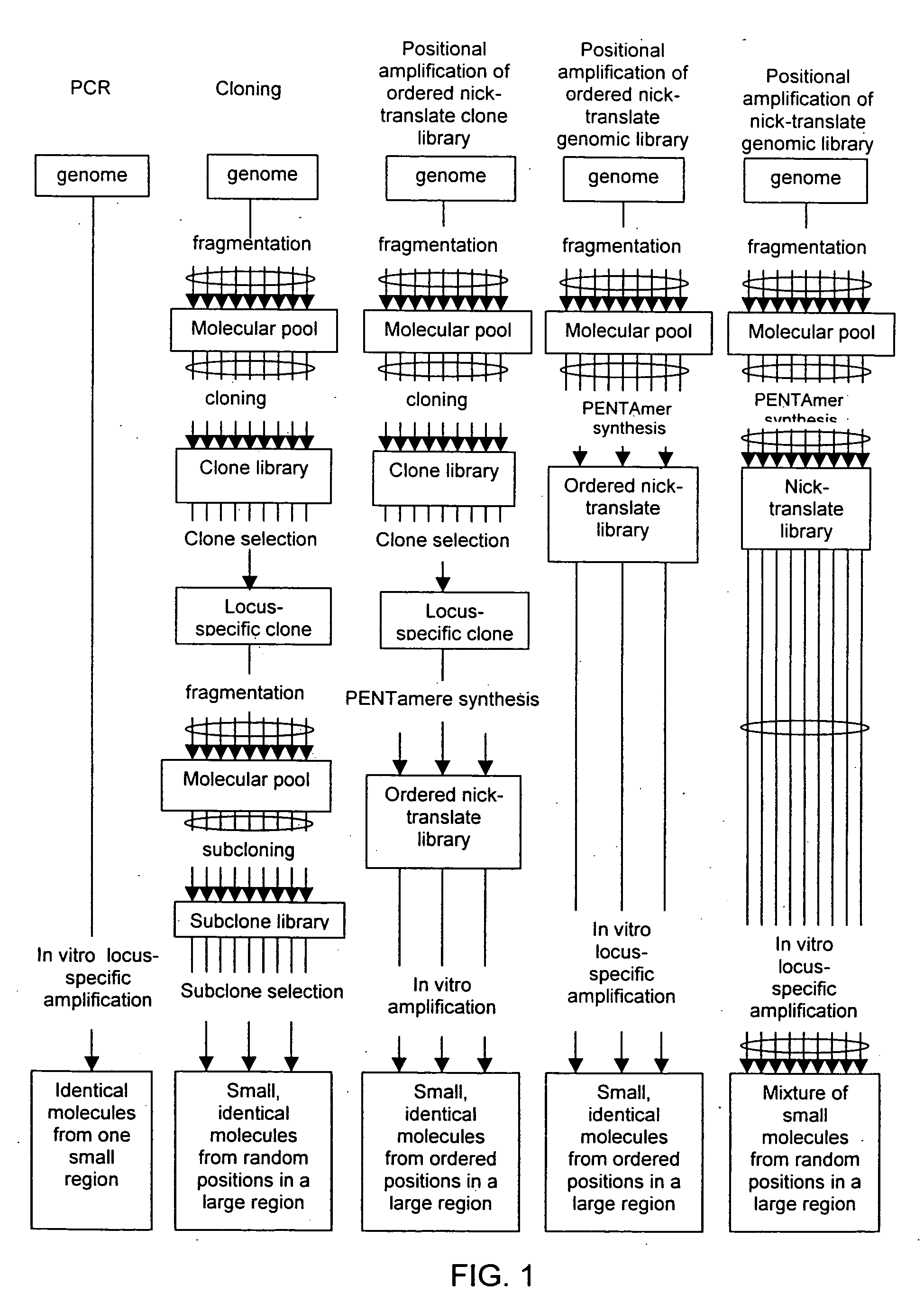
Method of producing a DNA library using positional amplification
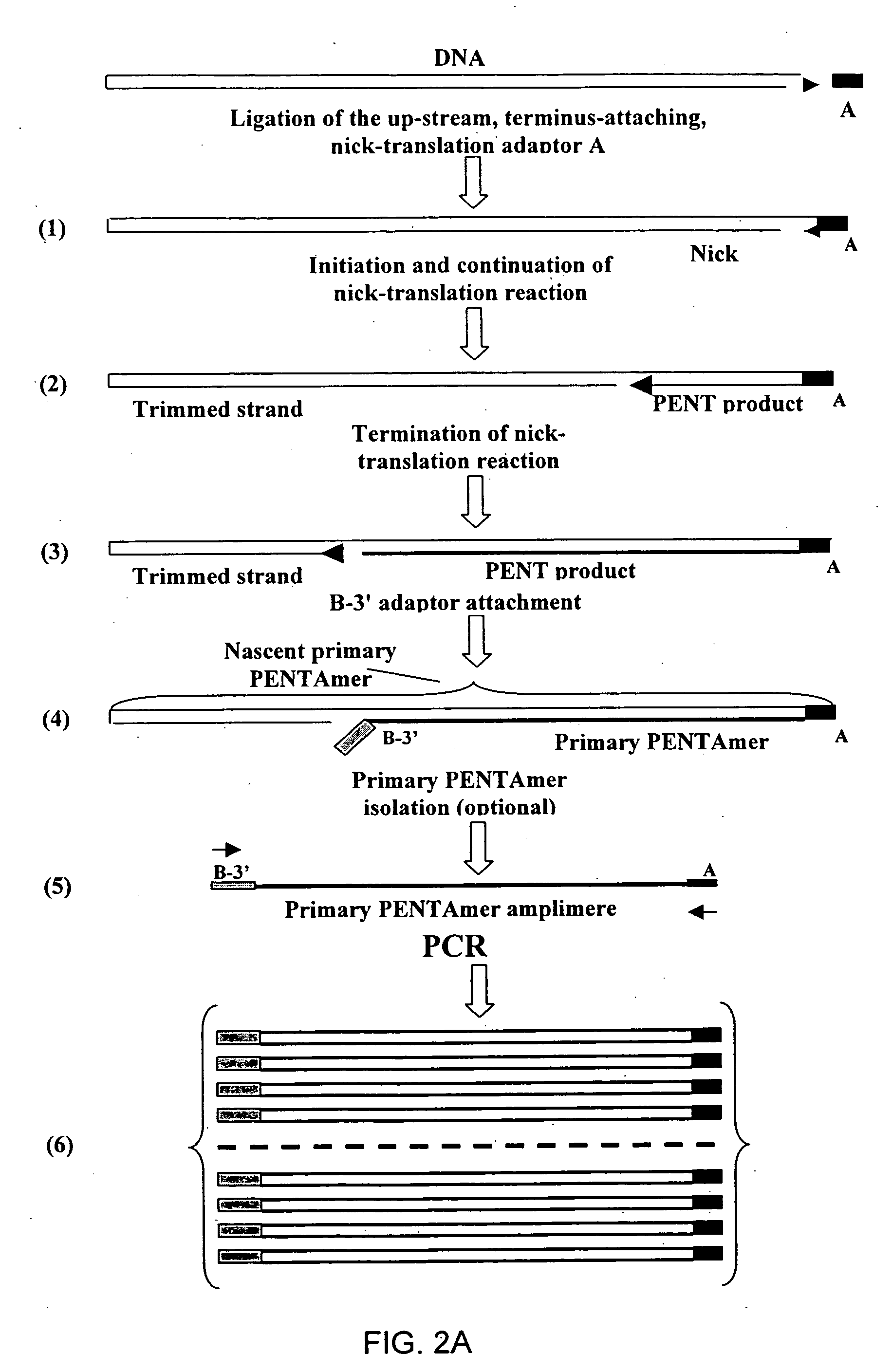
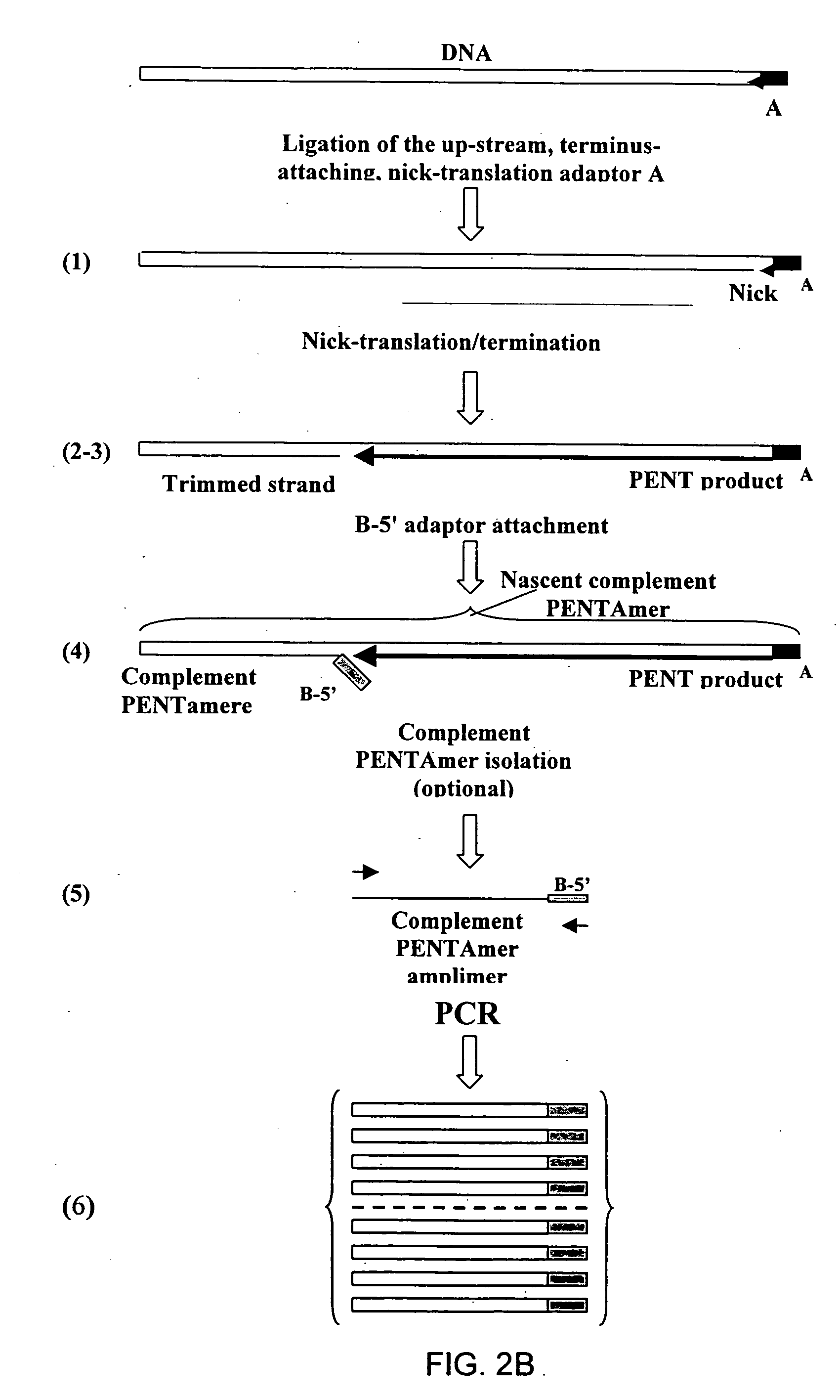
InactiveUS20060068394A1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsCDNA libraryPentamer
The disclosed invention relates to general and specific methods to use the Primer Extension / Nick Translation (PENT) reaction to create an amplifiable DNA strand, called a PENTAmer. A PENTAmers can be made for the purpose of amplifying a controlled length of DNA located at a controlled position within a DNA molecule, a process referred to as Positional Amplification by Nick Translation (PANT). In contrast to PCR, which amplifies DNA between two specific sequences, PANT can amplify DNA between two specific positions. PENTAmers can be created to amplify-very large regions of DNA (up to 500,000 bp) as random mixtures (unordered positional libraries), or as molecules sorted according to position (ordered positional libraries). PANT is fast and economical, because PENTAmer preparation can be multiplexed. A single PENTAmer preparation can include very complex mixtures of DNA such as hundreds of large-insert clones, complete genomes, or cDNA libraries. Subsequent PCR amplification of the preparation using a single specific primer can positionally amplify contiguous regions along a specific clone, along a specific genomic region, or along a specific expressed sequence.
Owner:LANGMORE JOHN +1
Methods for producing members of specific binding pairs
InactiveUS7063943B1Simple procedureSpeedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFree formGenetic diversity
A member of a specific binding pair (sbp) is identified by expressing DNA encoding a genetically diverse population of such sbp members in recombinant host cells in which the sbp members are displayed in functional form at the surface of a secreted recombinant genetic display package (rgdp) containing DNA encoding the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof, by virtue of the sbp member or a polypeptide component thereof being expressed as a fusion with a capsid component of the rgdp. The displayed sbps may be selected by affinity with a complementary sbp member, and the DNA recovered from selected rgdps for expression of the selected sbp members. Antibody sbp members may be thus obtained, with the different chains thereof expressed, one fused to the capsid component and the other in free form for association with the fusion partner polypeptide. A phagemid may be used as an expression vector, with said capsid fusion helping to package the phagemid DNA. Using this method libraries of DNA encoding respective chains of such multimeric sbp members may be combined, thereby obtaining a much greater genetic diversity in the sbp members than could easily be obtained by conventional methods.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
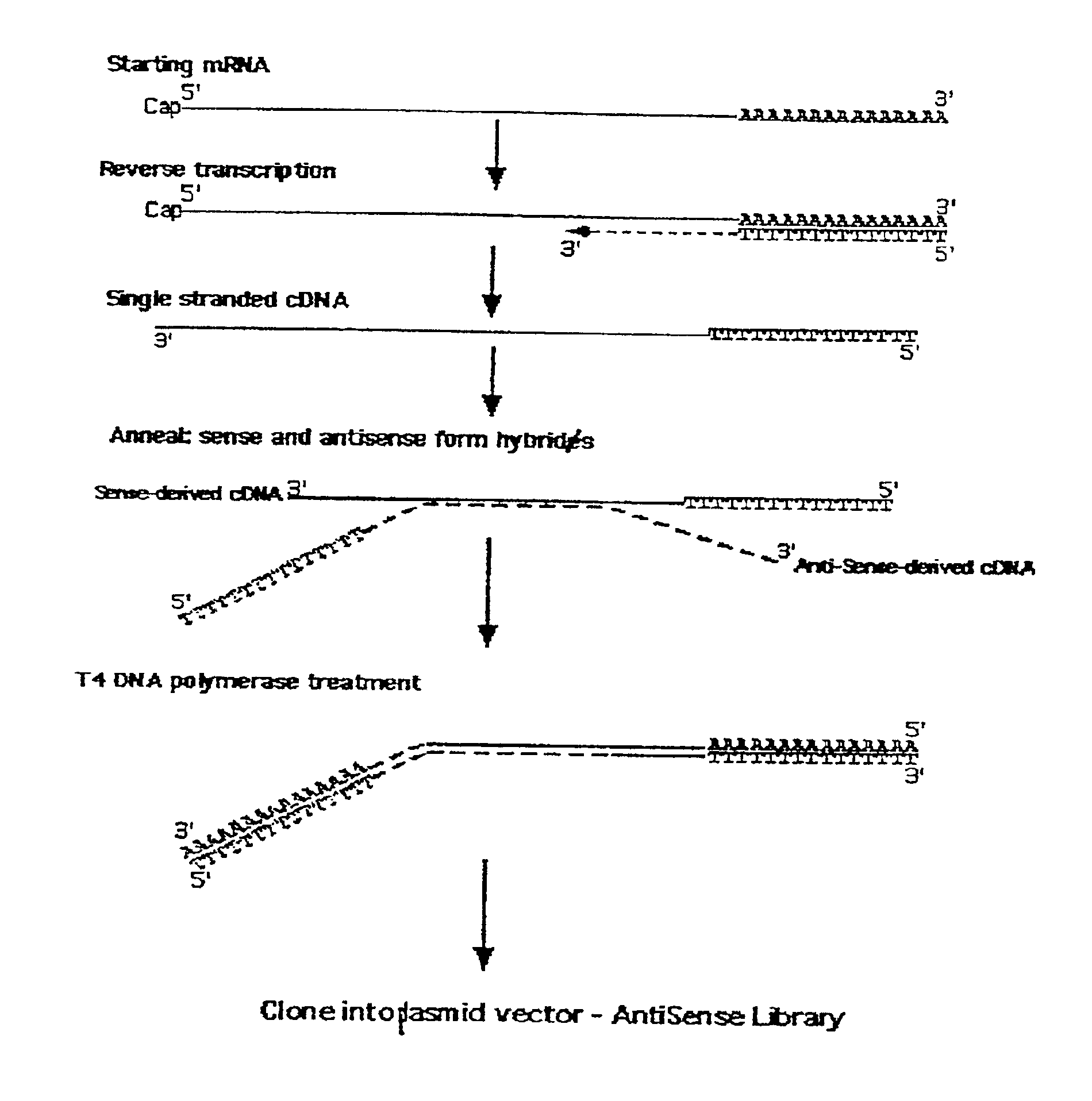
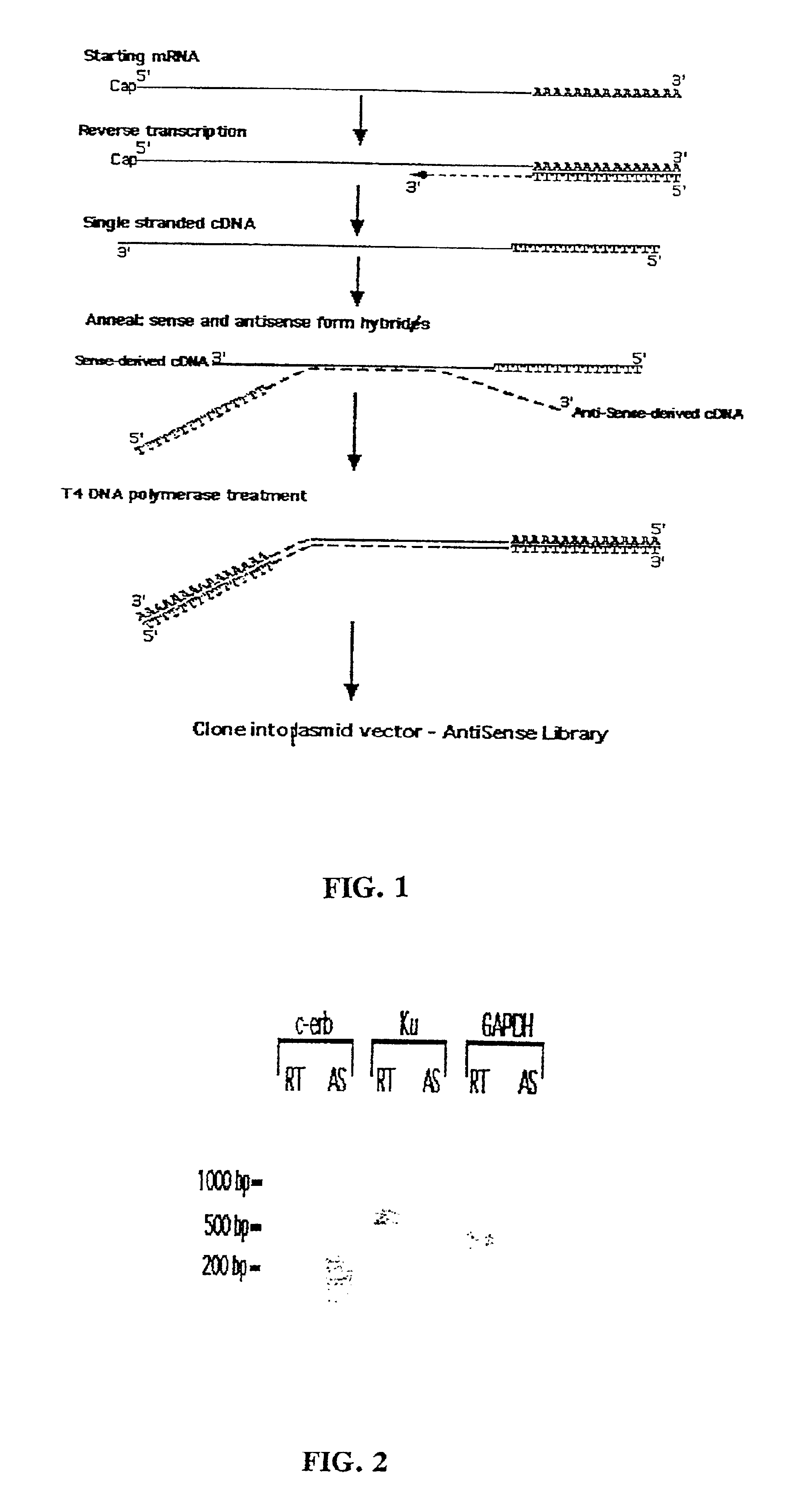
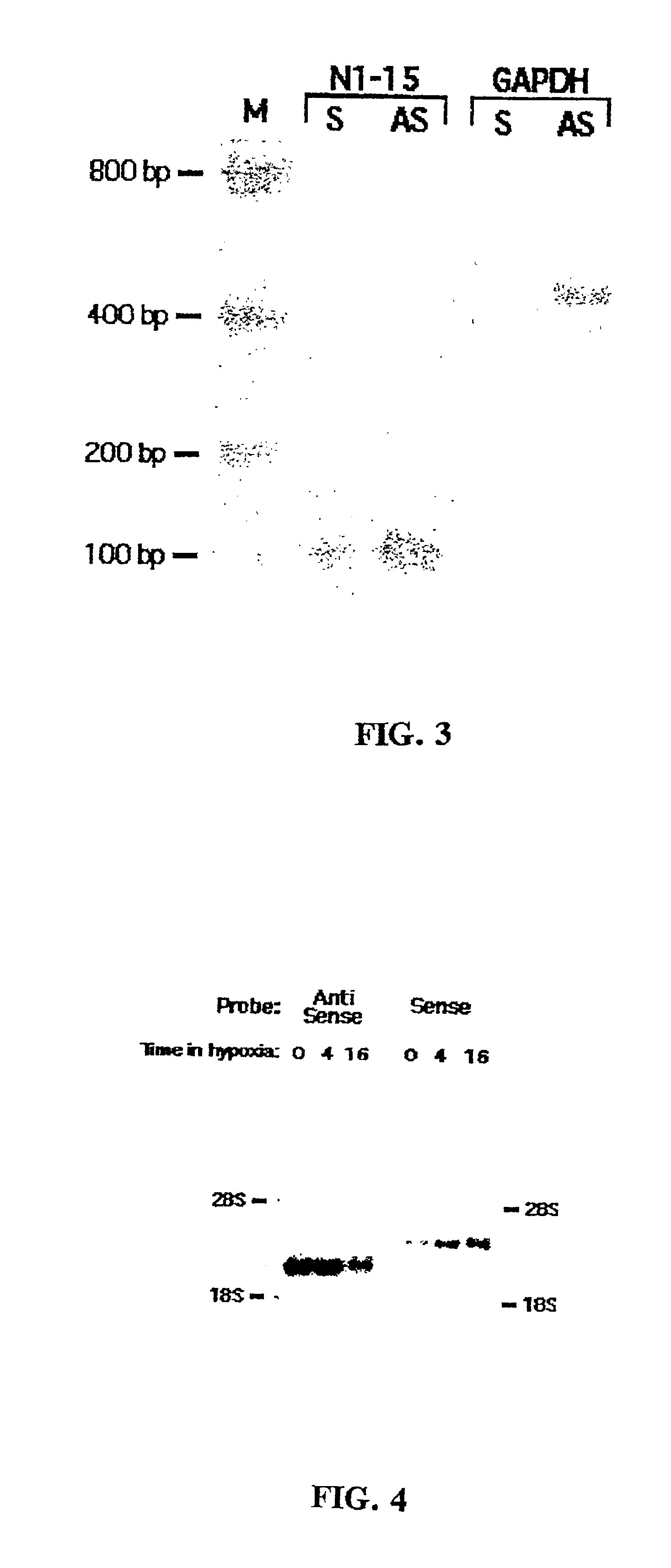
Method for enrichment of natural antisense messenger RNA
A method for enrichment of natural antisense mRNA which involves hybridization of cDNA obtained from sense RNA with cDNA obtained from antisense RNA, followed by DNA polymerase treatment of the sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecule. A natural antisense library can be generated by cloning of sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecules in a vector.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
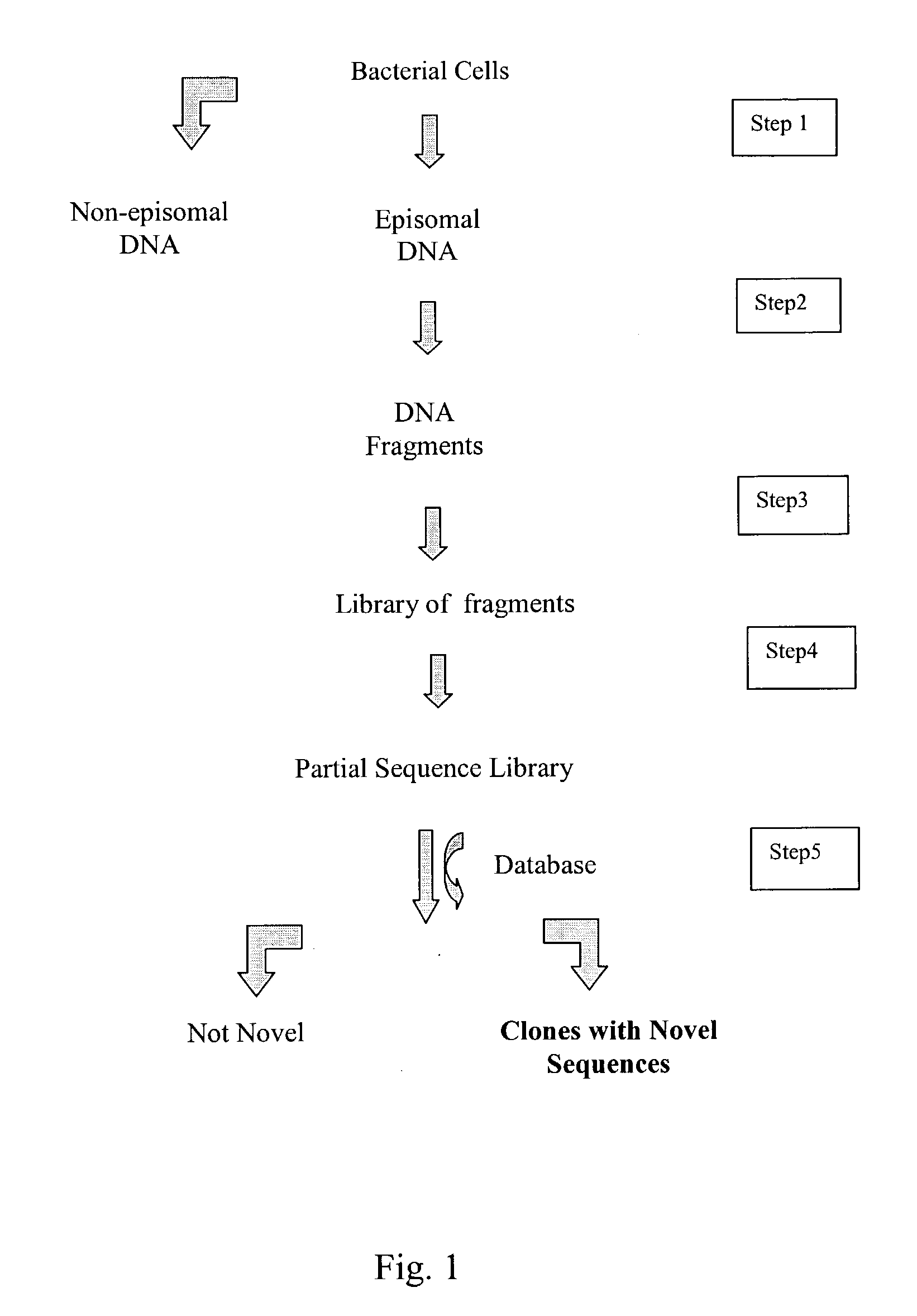
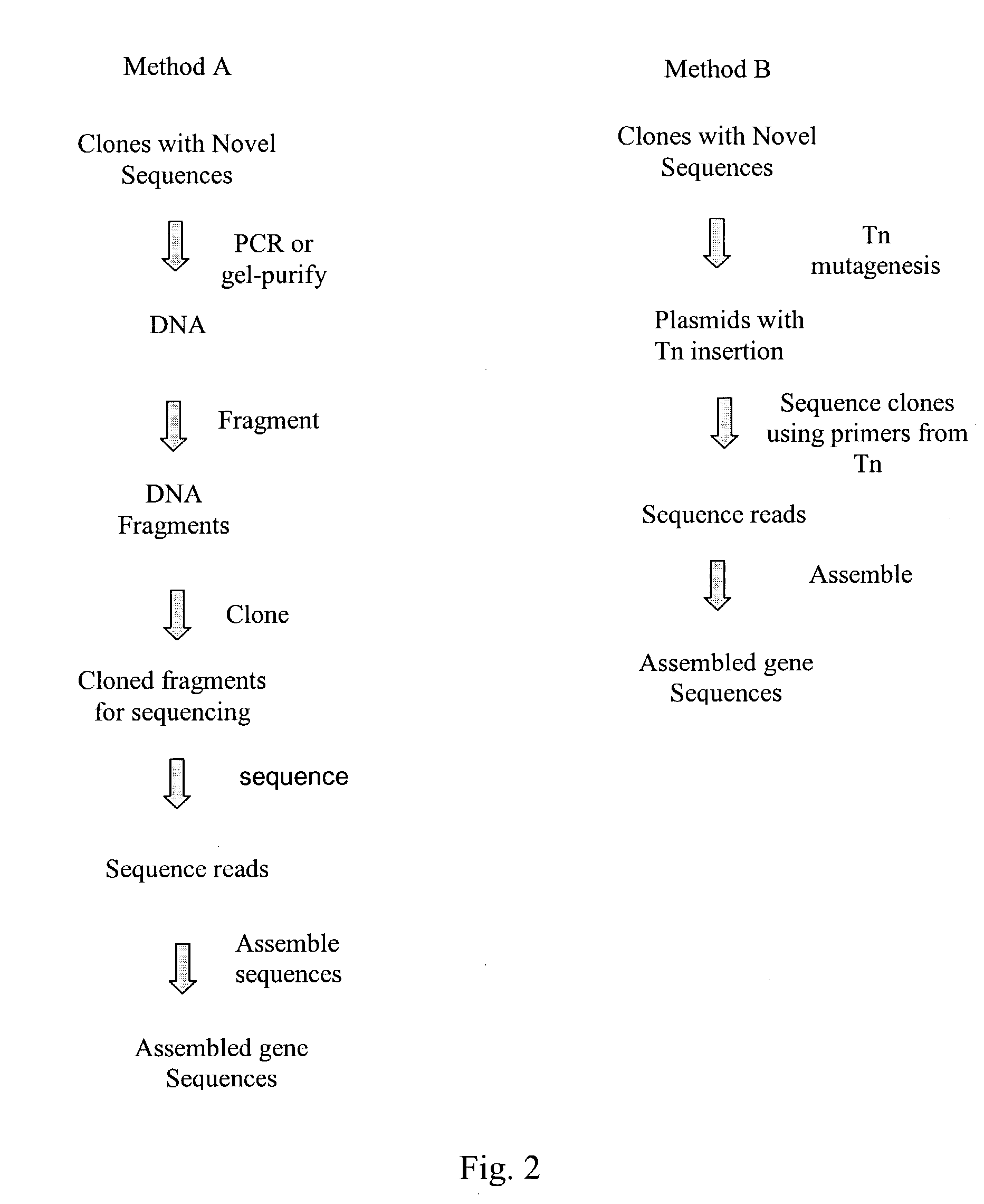
Integrated system for high throughput capture of genetic diversity
InactiveUS20040014091A1Rapid and highly efficient characterizationFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenetic diversitySequence database
Compositions and methods for rapid and highly efficient characterization of genetic diversity in organisms are provided. The methods involve rapid sequencing and characterization of extrachromosomal DNA, particularly plasmids, to identify and isolate useful nucleotide sequences. The method targets plasmid DNA and avoids repeated cloning and sequencing of the host chromosome, thus allowing one to focus on the genetic, elements carrying maximum genetic diversity. The method involves generating a library of extrachromosomal DNA clones, sequencing a portion of the clones, comparing the sequences against a database of existing DNA sequences, using an algorithm to select said novel nucleotide sequence based on the presence or absence of said portion in a database, and identification of at least one novel nucleotide sequence. The DNA sequence can also be translated in all six frames and the resulting amino acid sequences can be compared against a database of protein sequences. The integrated approach provides a rapid and efficient method to identify and isolate useful genes. Organisms of particular interest include, but are not limited to bacteria, fungi, algae, and the like. Compositions comprise a mini-cosmid vector comprising a stuffer fragment and at least one cos site.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
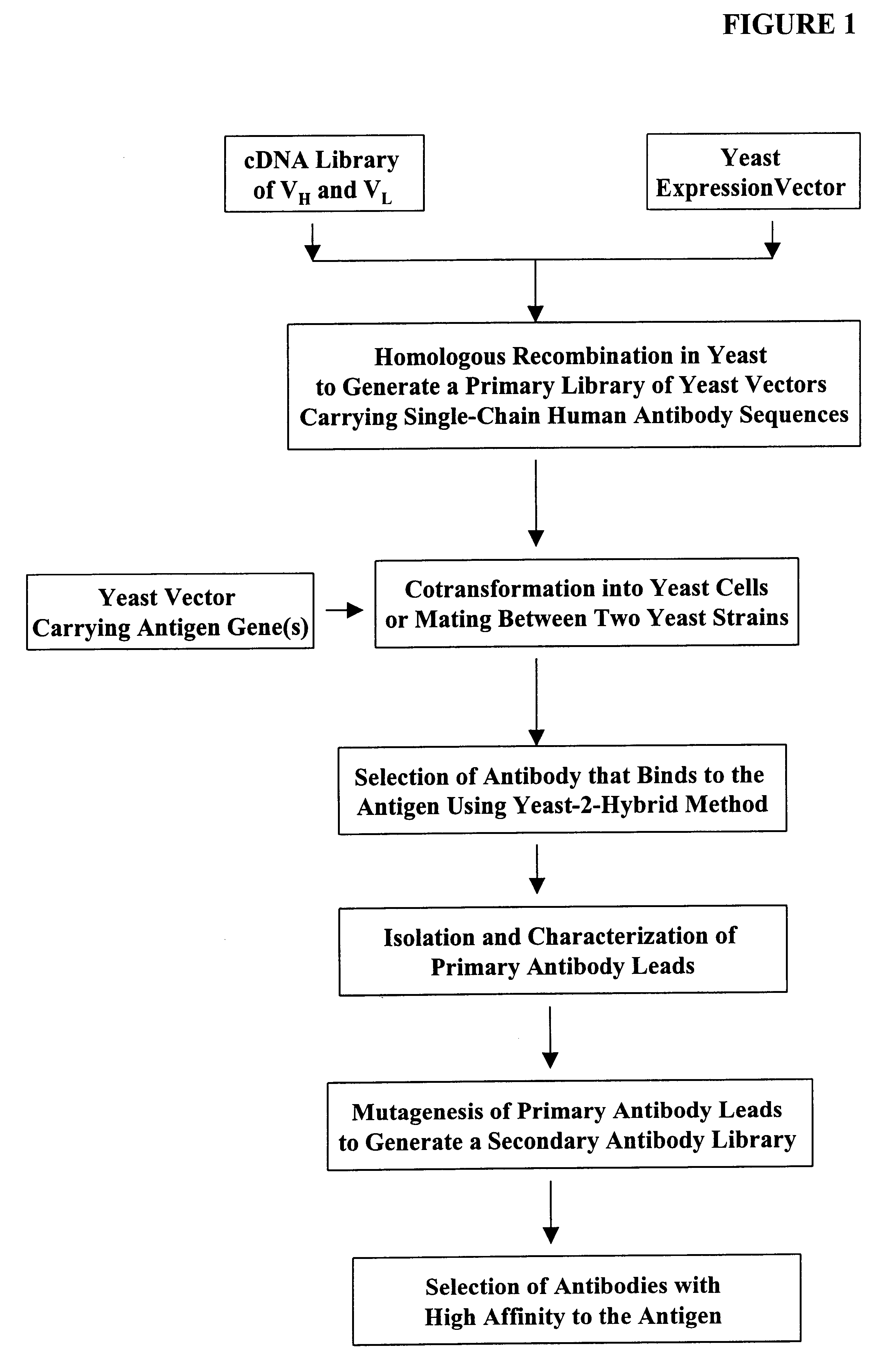
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
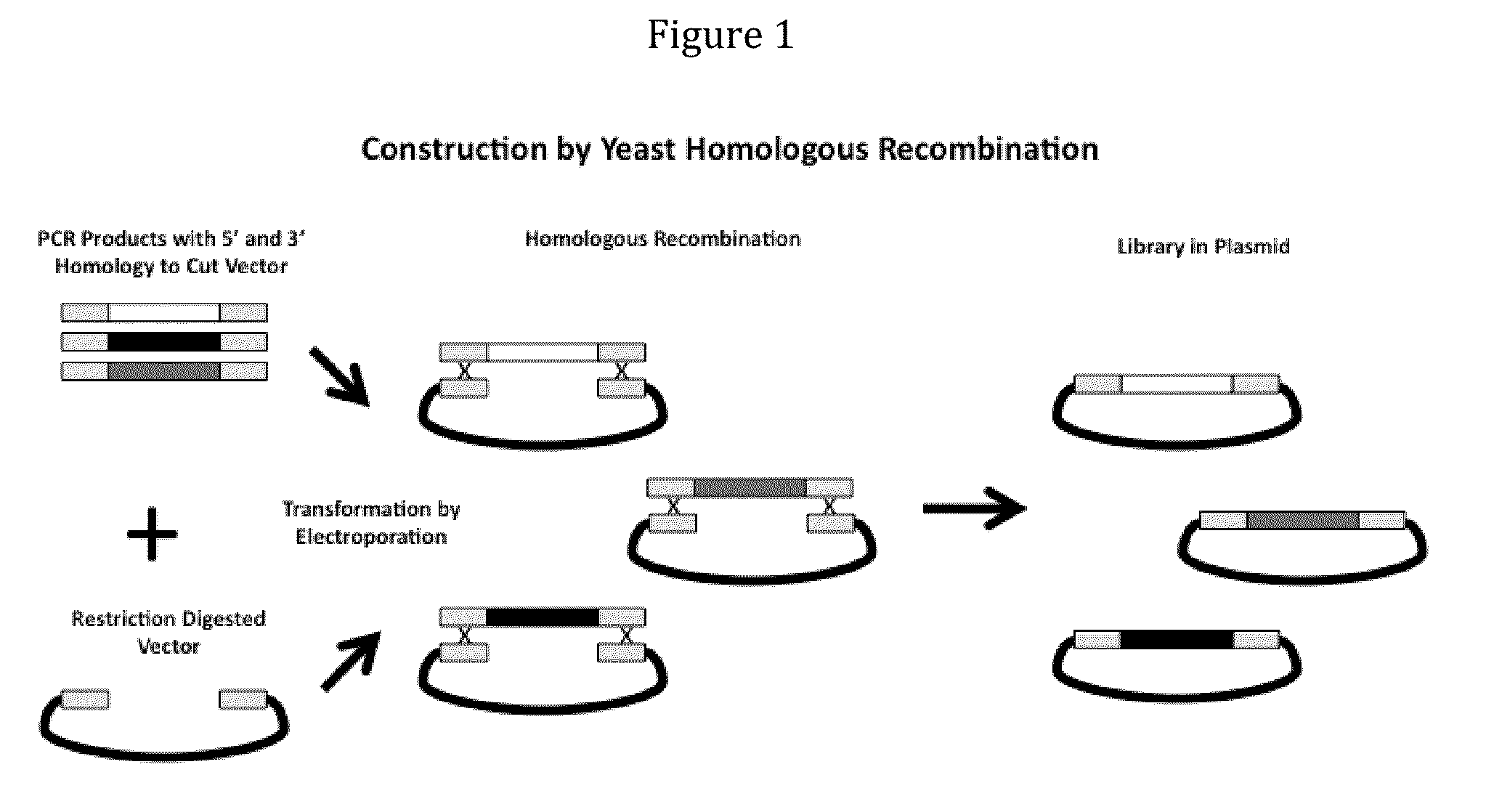
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
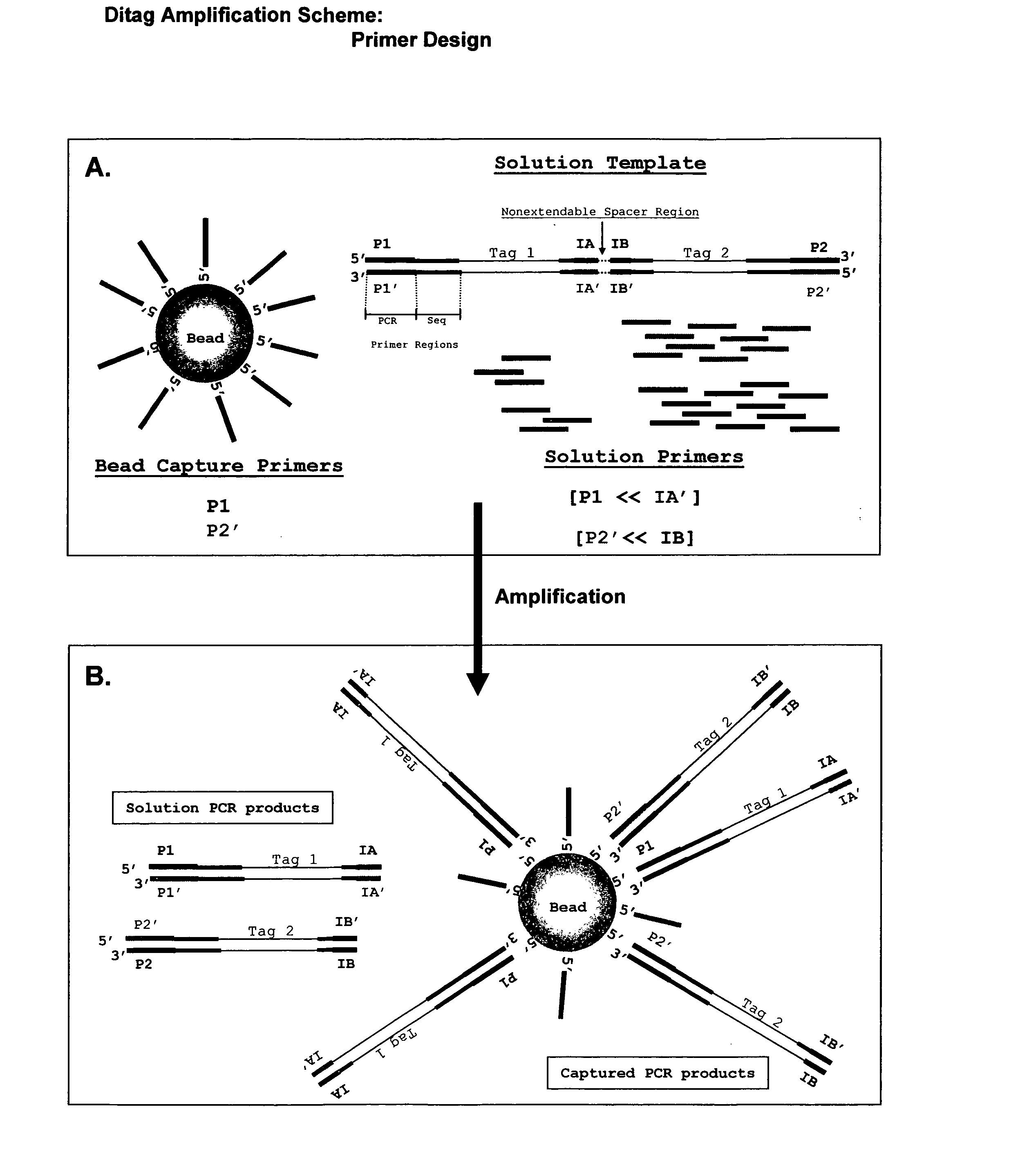
MULTIPLEX BARCODED PAIRED-END DITAG (mbPED) LIBRARY CONSTRUCTION FOR ULTRA HIGH THROUGHPUT SEQUENCING
Multiplex barcoded Paired-End Ditag (mbPED) library construction for ultra high throughput sequencing is disclosed. The mbPED library comprises multiple types of barcoded Paired-End Ditag (bPED) nucleic acid fragment constructs, each of which comprises a unique barcoded adaptor, a first tag, and a second tag linked to the first tag via the barcoded adaptor. The two tags are the 5′- and 3′-ends of a nucleic acid molecule from which they originate. The barcoded adaptor comprises a barcode, a first polynucleotide sequence comprising a first restriction enzyme (RE) recognition site, and a second polynucleotide sequence comprising a second RE recognition site and covalently linked to the first polynucleotide sequence via the barcode. The two REs lead to cleavage of a nucleic acid at a defined distance from their recognition sites. The length of the adaptor is set so that the bPED nucleic acid fragment fits one-step sequencing.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
InactiveUS20090181385A1Efficient implementationQuick sortingMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
The present invention provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles comprise steps of extension, ligation, and, preferably, cleavage. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and employ agents appropriate to cleave such linkages. The invention provides methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families. In certain embodiments the methods acquire less than 2 bits of information from each of a plurality of nucleotides in the template in each cycle. In certain embodiments the sequencing reactions are performed on templates attached to immobilized beads. The invention further provides sets of labeled probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages. In addition, the invention includes performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template by removing initializing oligonucleotides and extended strands and performing subsequent reactions using different initializing oligonucleotides.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods of RNA amplification in the presence of DNA
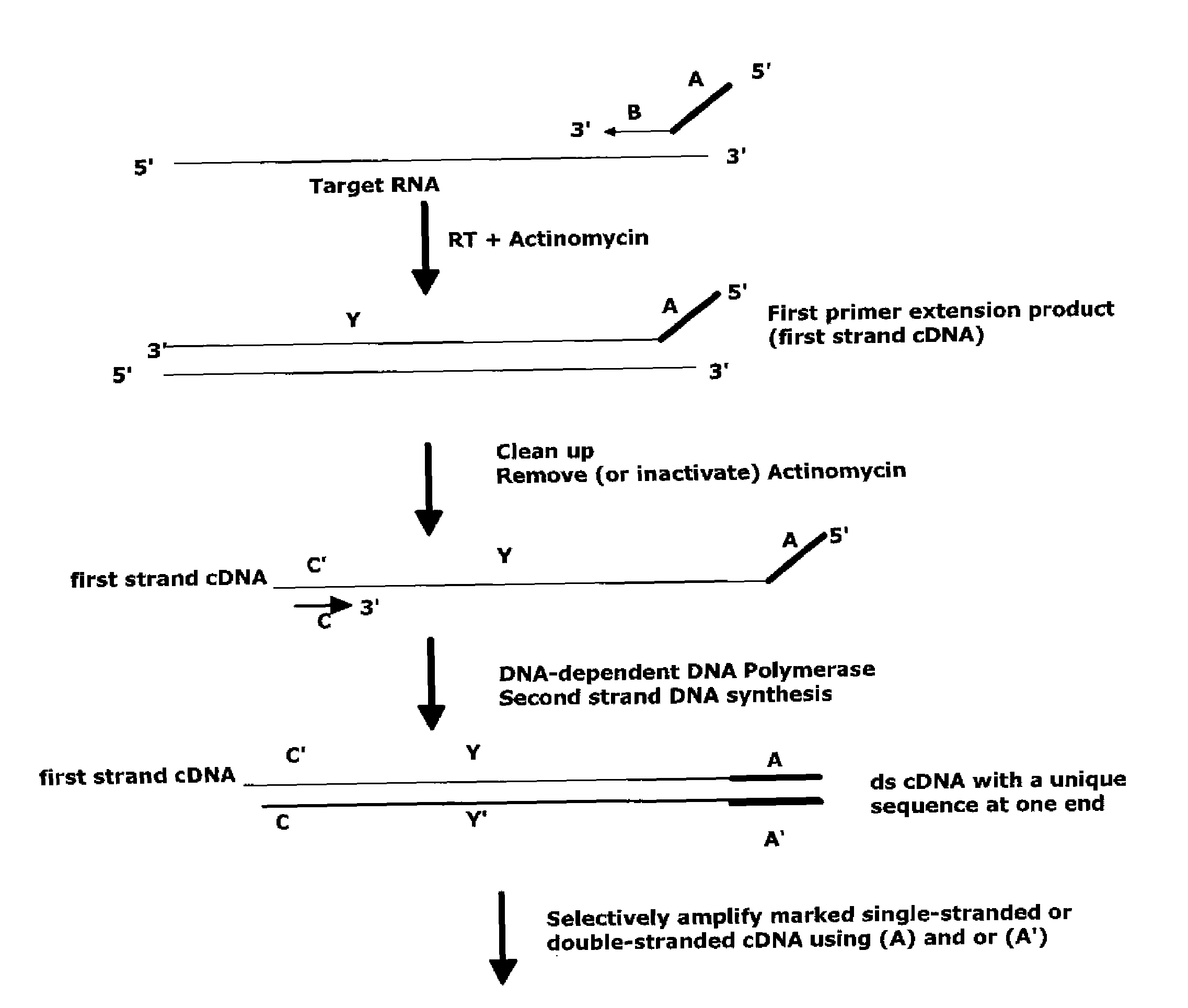
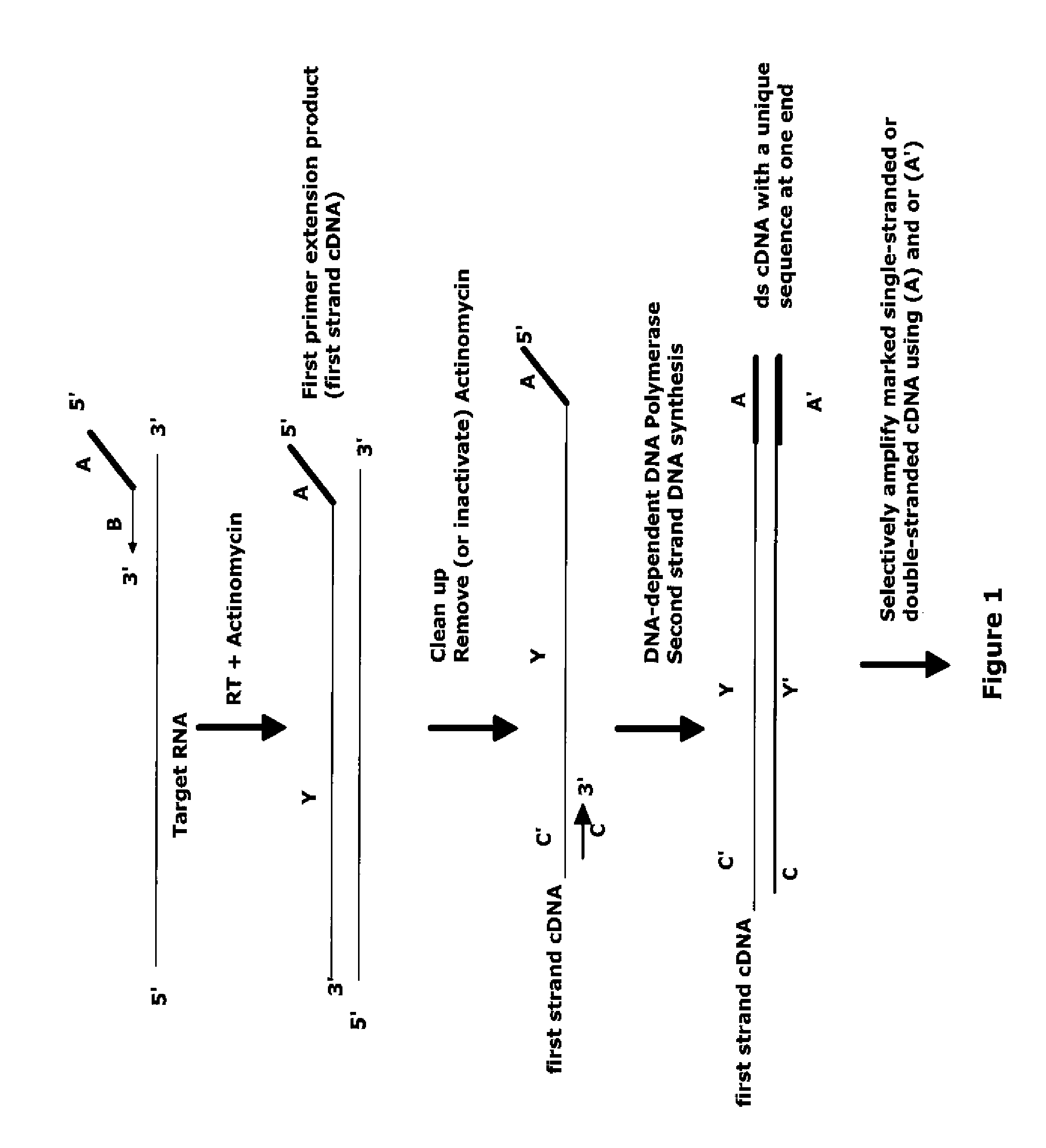
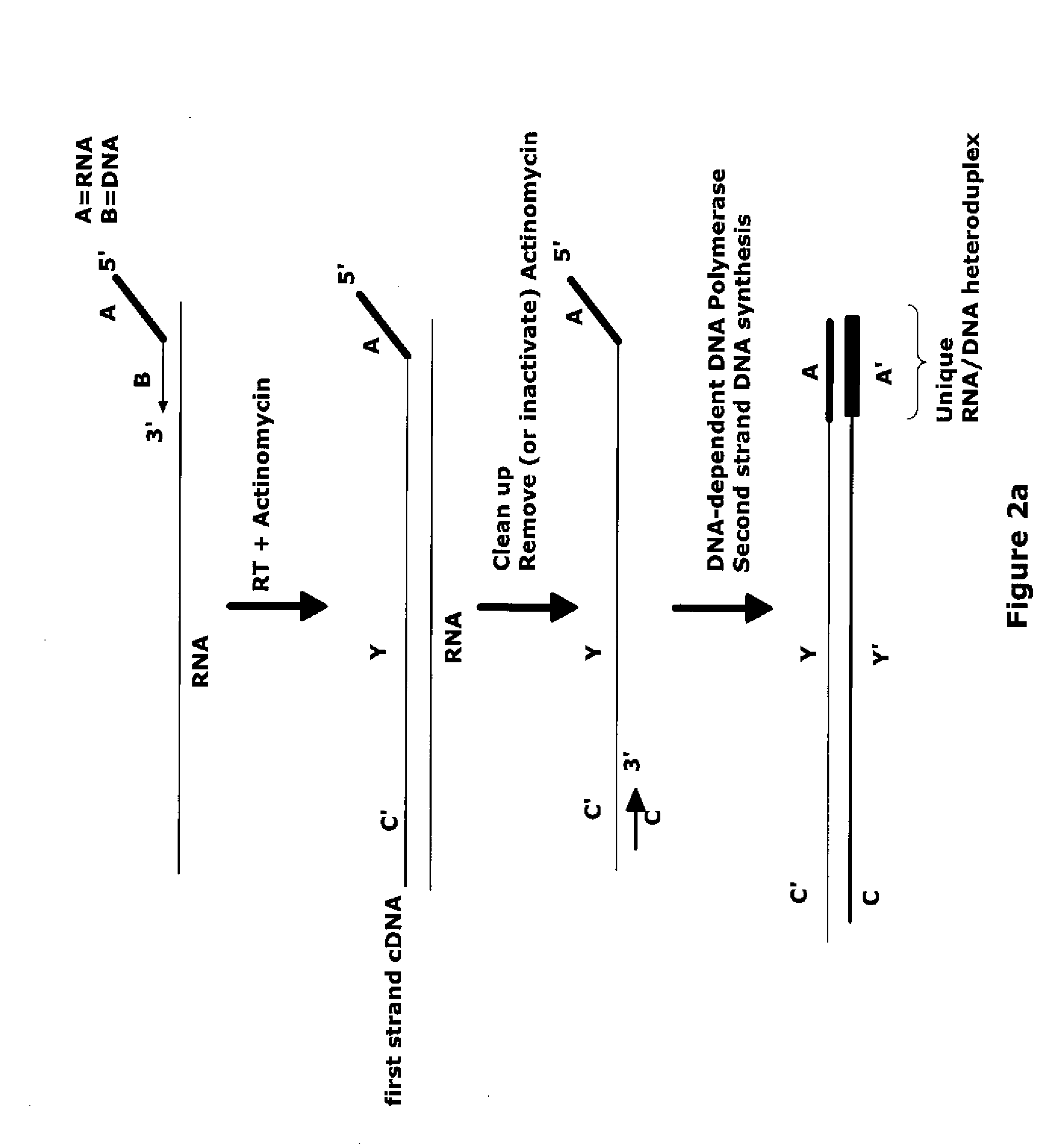
The invention provides methods for amplification of RNA. The methods are particularly suitable for specifically amplifying RNA in the presence of DNA. The methods involve producing a marked first primer extension product from a target RNA in the presence of a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase inhibitor, which prevents replication of DNA by the reverse transcriptase enzyme. The marked nucleic acid products are subsequently selectively amplified in the presence on non-marked nucleic acids. The methods are useful for production and analysis of polynucleotide sequences complementary to an RNA sequence. The methods are useful for preparation of nucleic acid libraries and substrates for analysis of gene expression of cells in biological samples. The invention also provides compositions and kits for practicing the amplification methods, as well as methods which use the amplification products.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
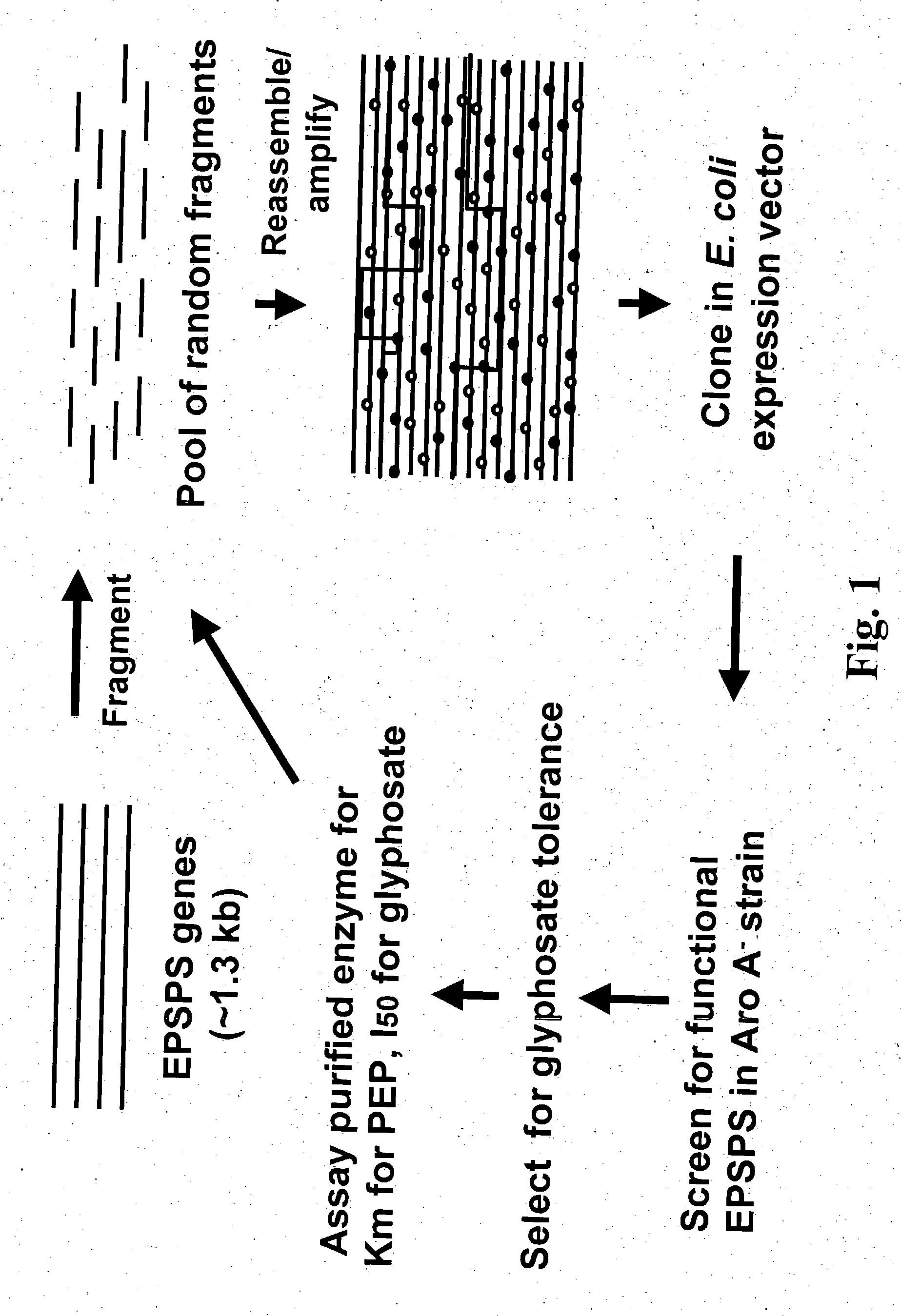
DNA shuffling to produce herbicide selective crops
InactiveUS20050060767A1Improve abilitiesReduce sensitivityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGMO PlantsDNA shuffling
Owner:SUBRAMANIAN VENKITESWARAN +4
In vitro peptide expression library
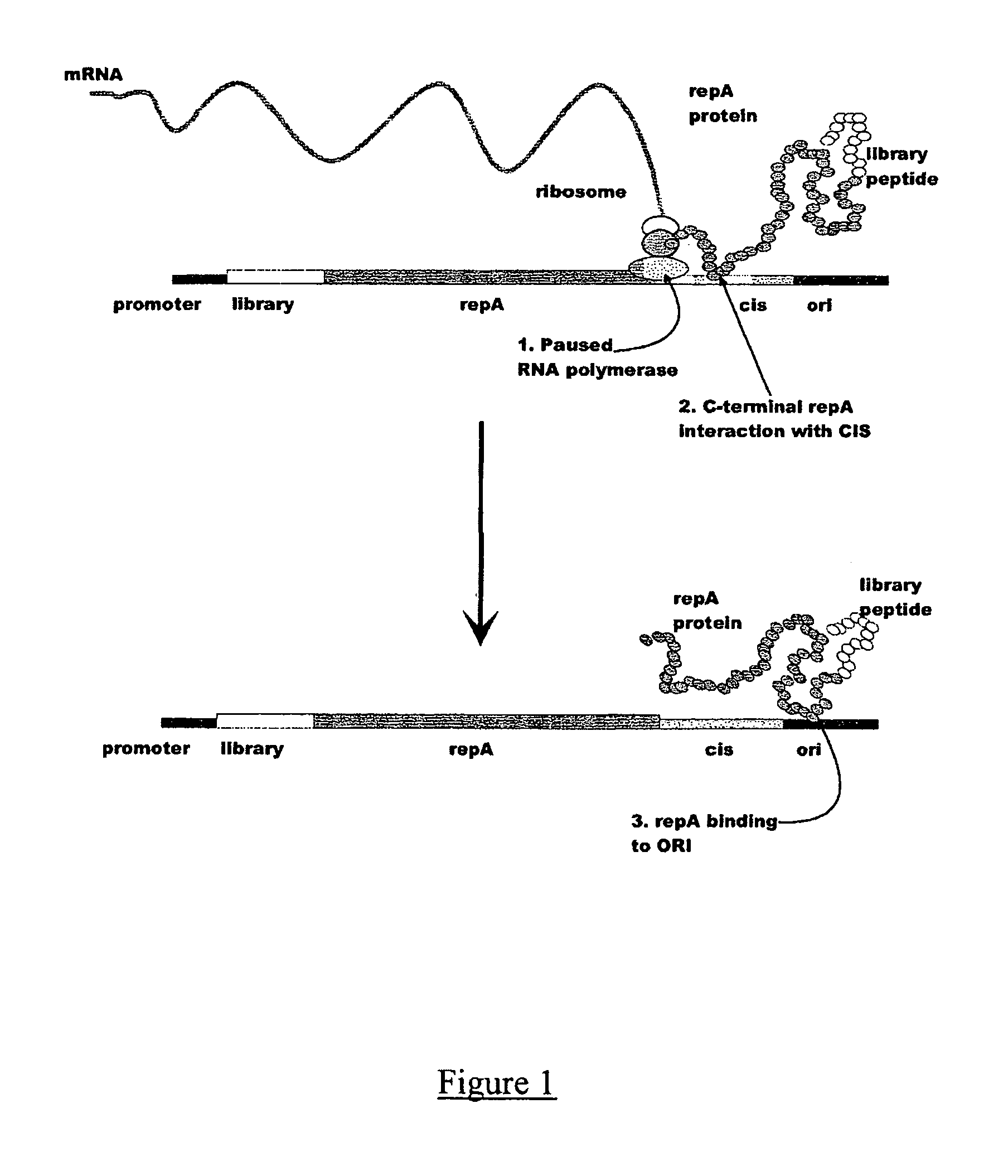
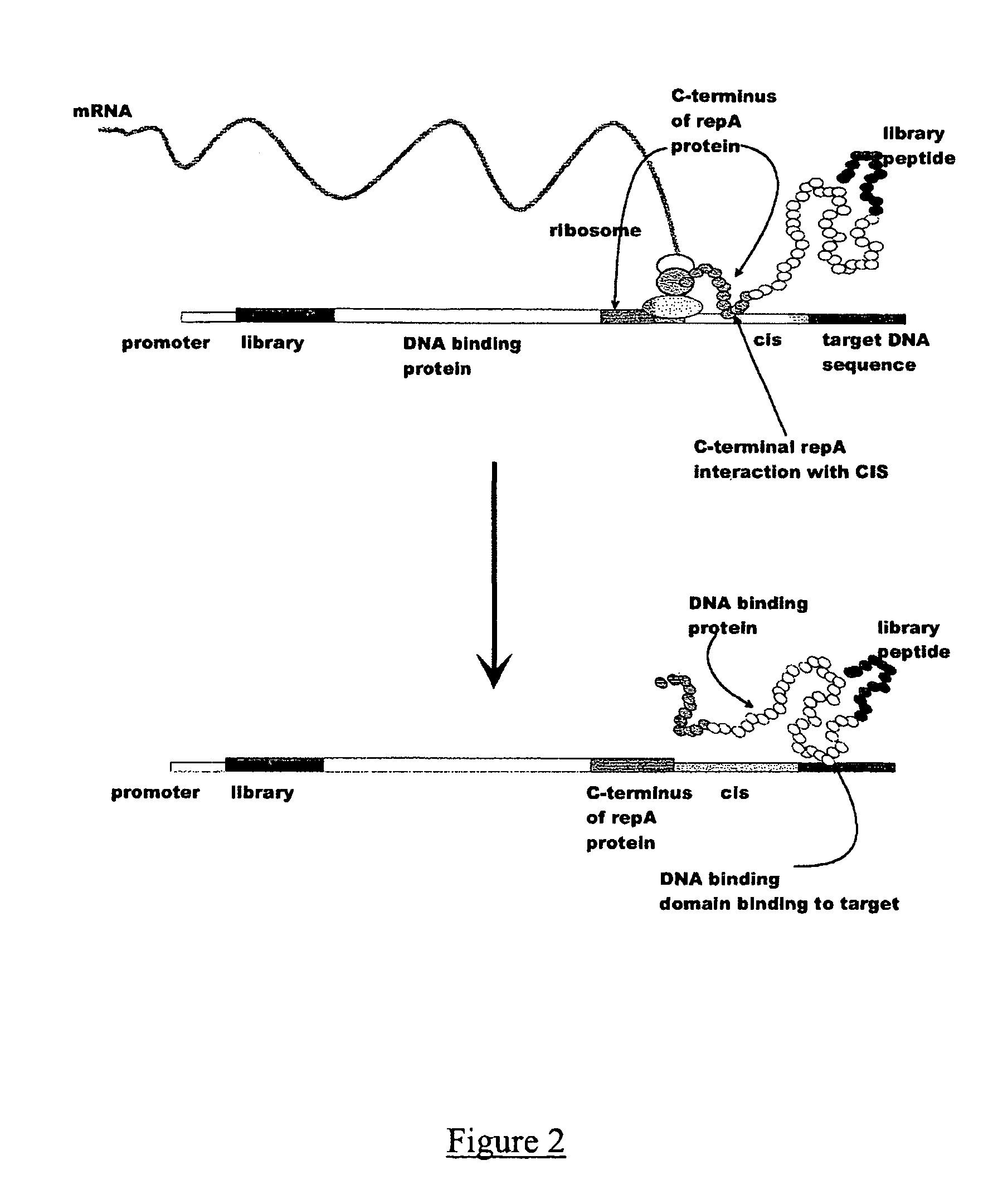
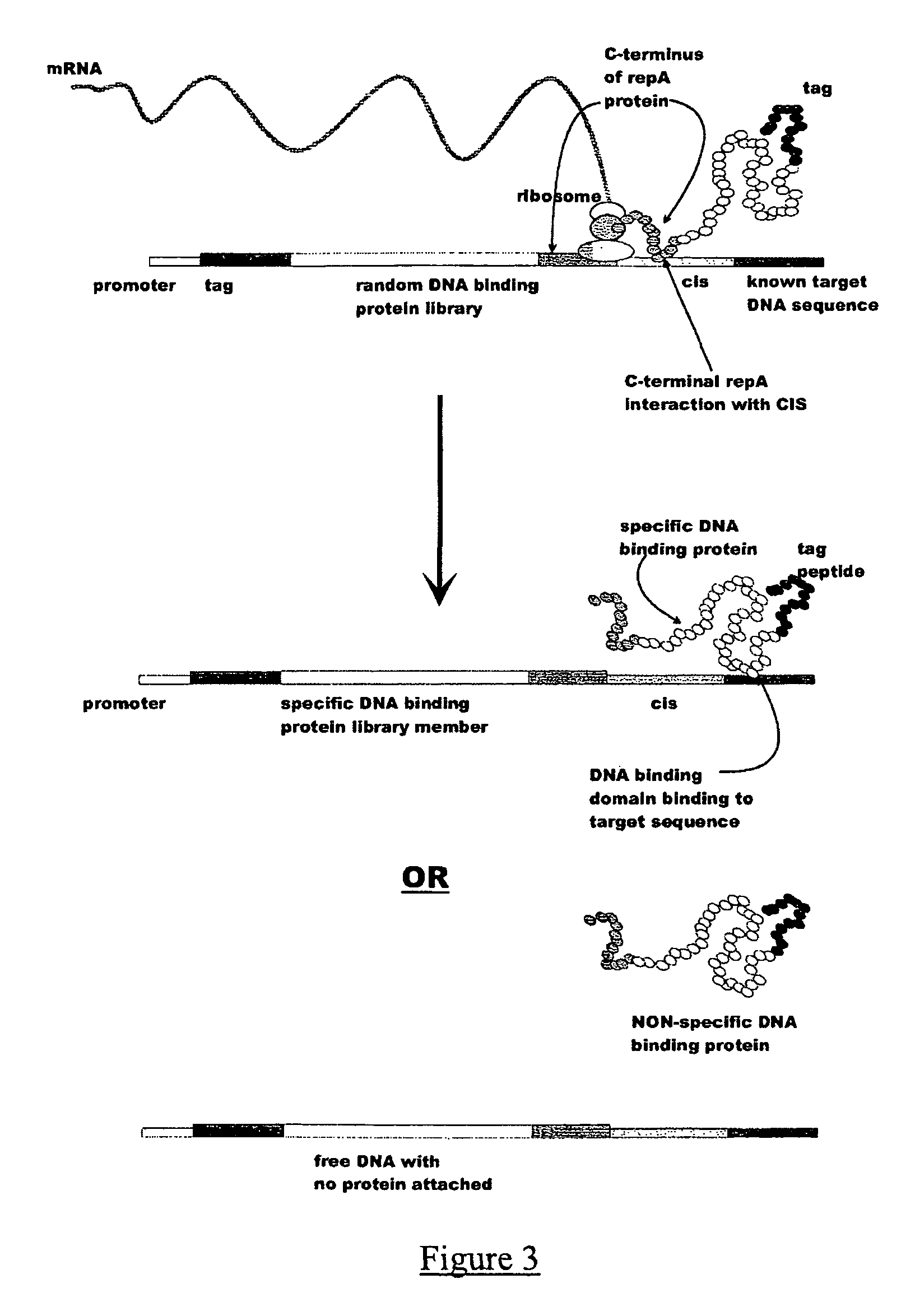
ActiveUS7842476B2Fusion with DNA-binding domainMicrobiological testing/measurementExpression LibraryNucleotide
The invention provides a method for making in vitro peptide expression libraries, and for the isolation of nucleotide sequences encoding peptides of interest, wherein the peptides or proteins are specifically associated with the DNA encoding them through non-covalent protein:DNA binding. The method describes ways of making the library itself, DNA molecules encoding the library and uses of the expression library.
Owner:ISOGENICA LTD
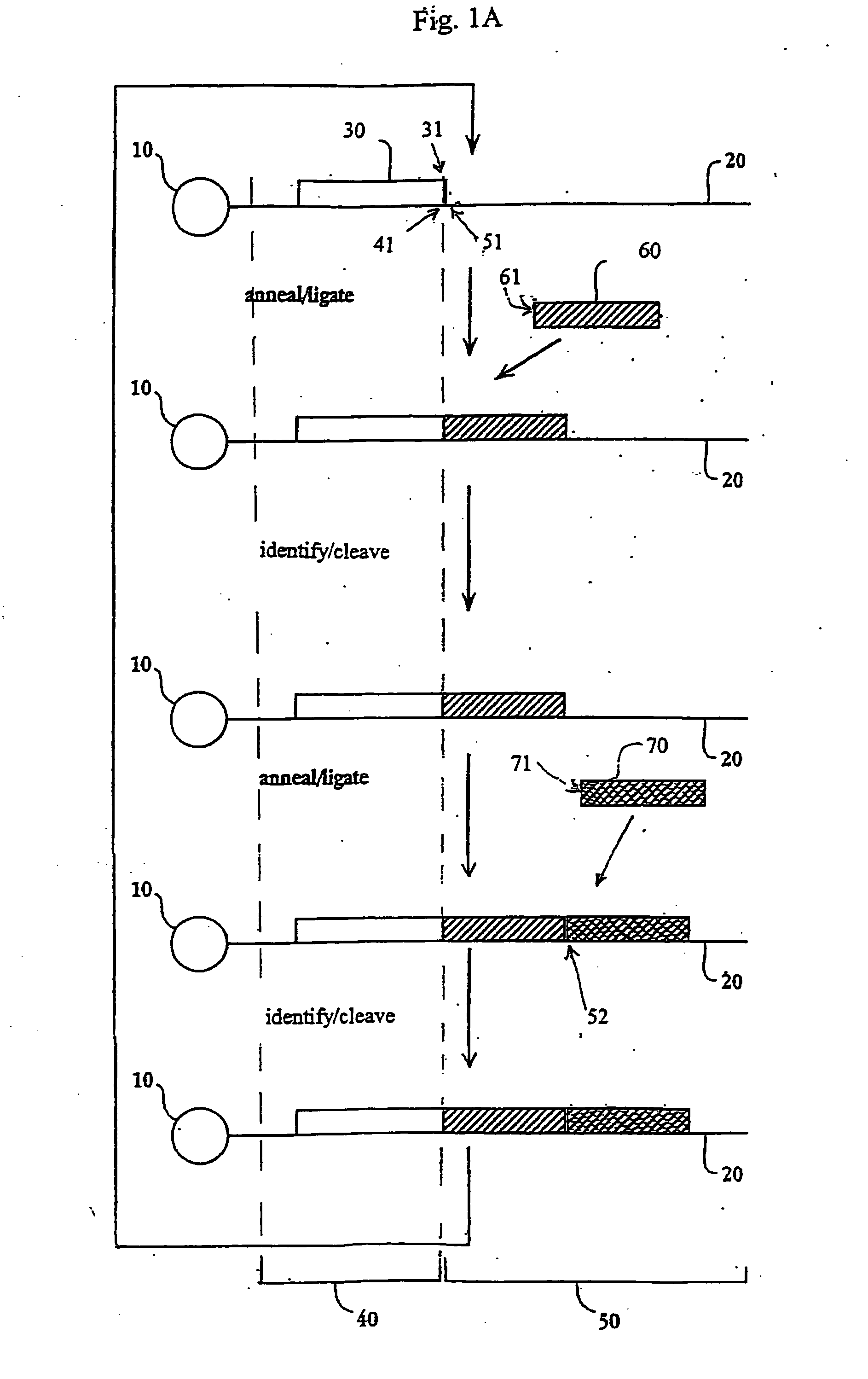
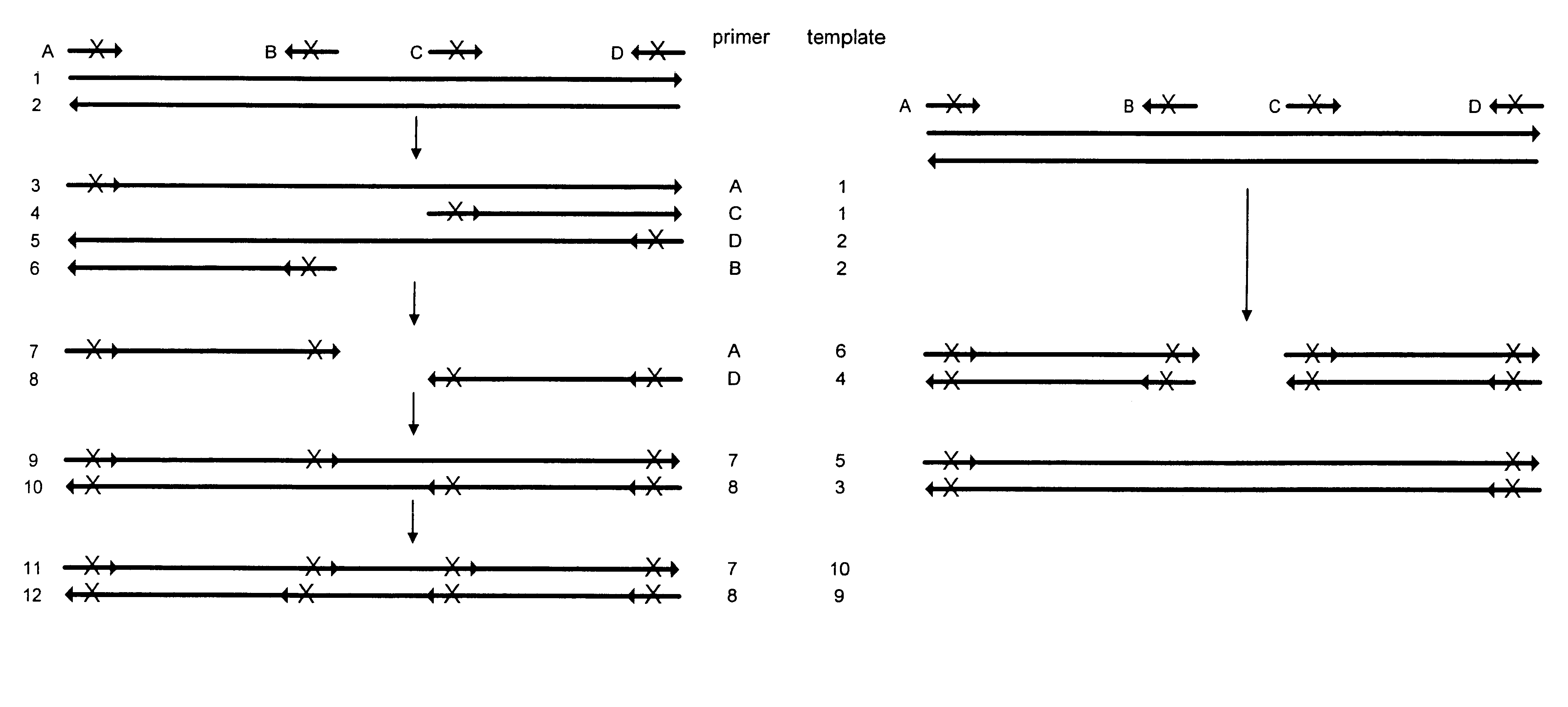
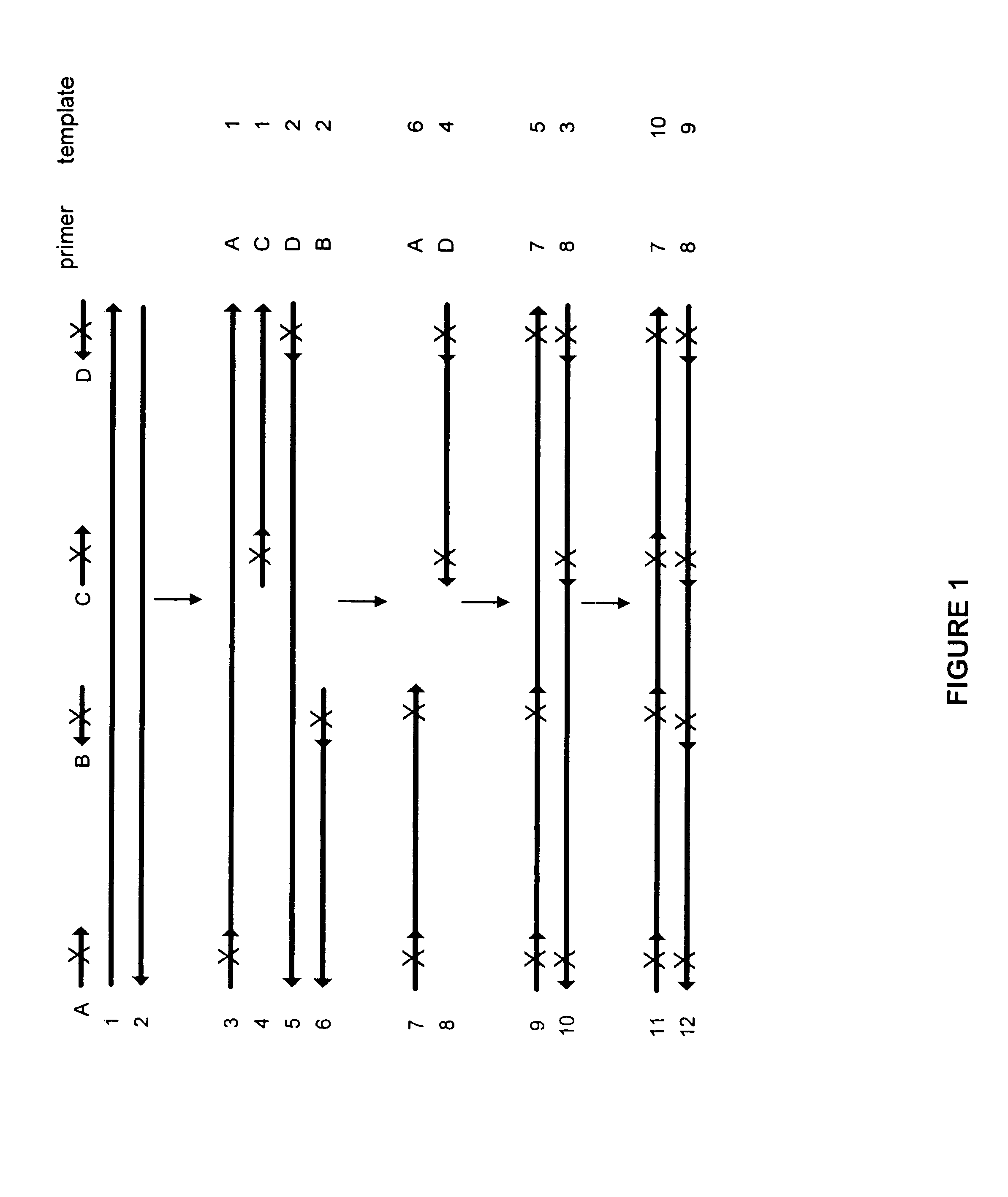
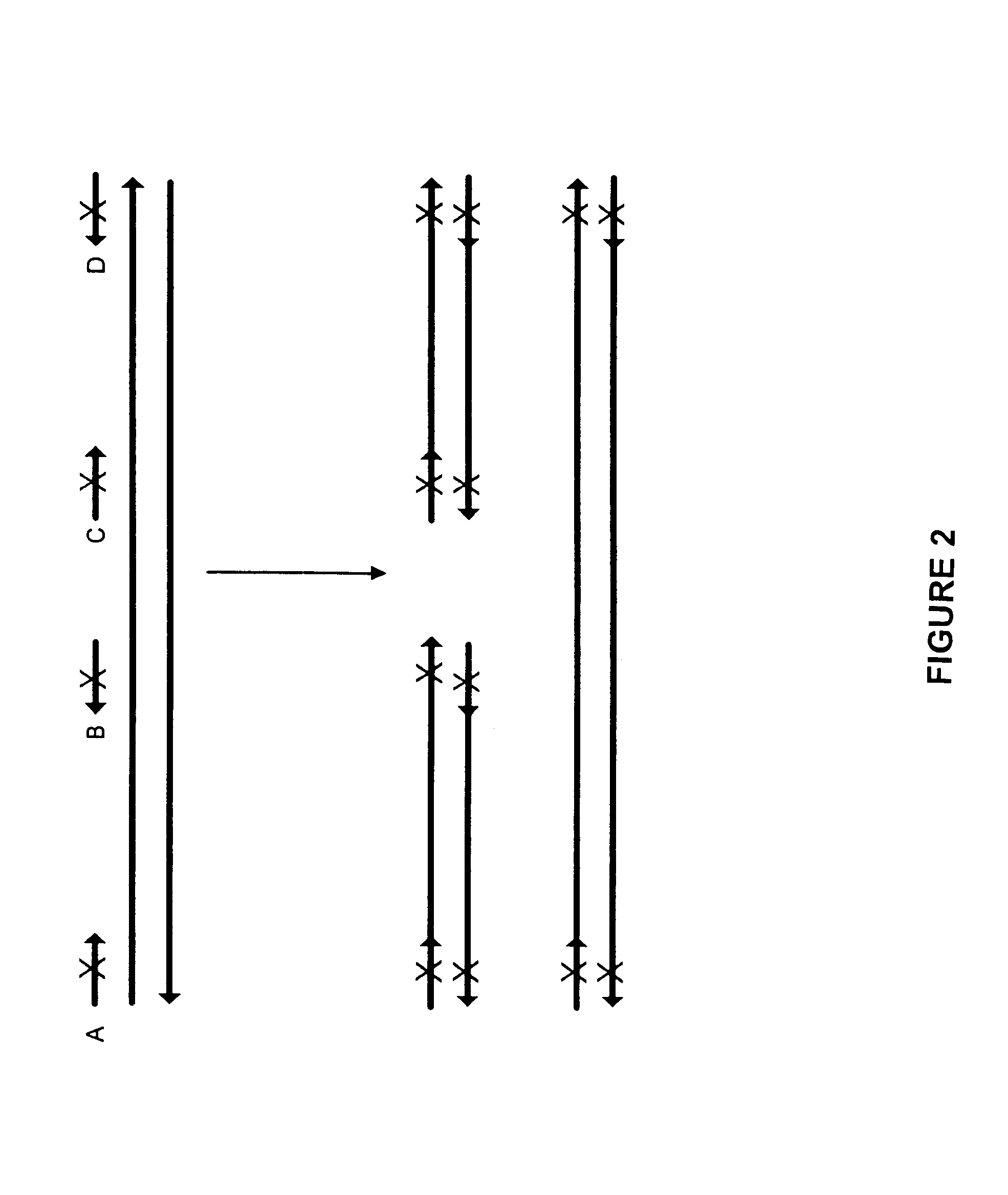
Methods for in vitro joining and combinatorial assembly of nucleic acid molecules
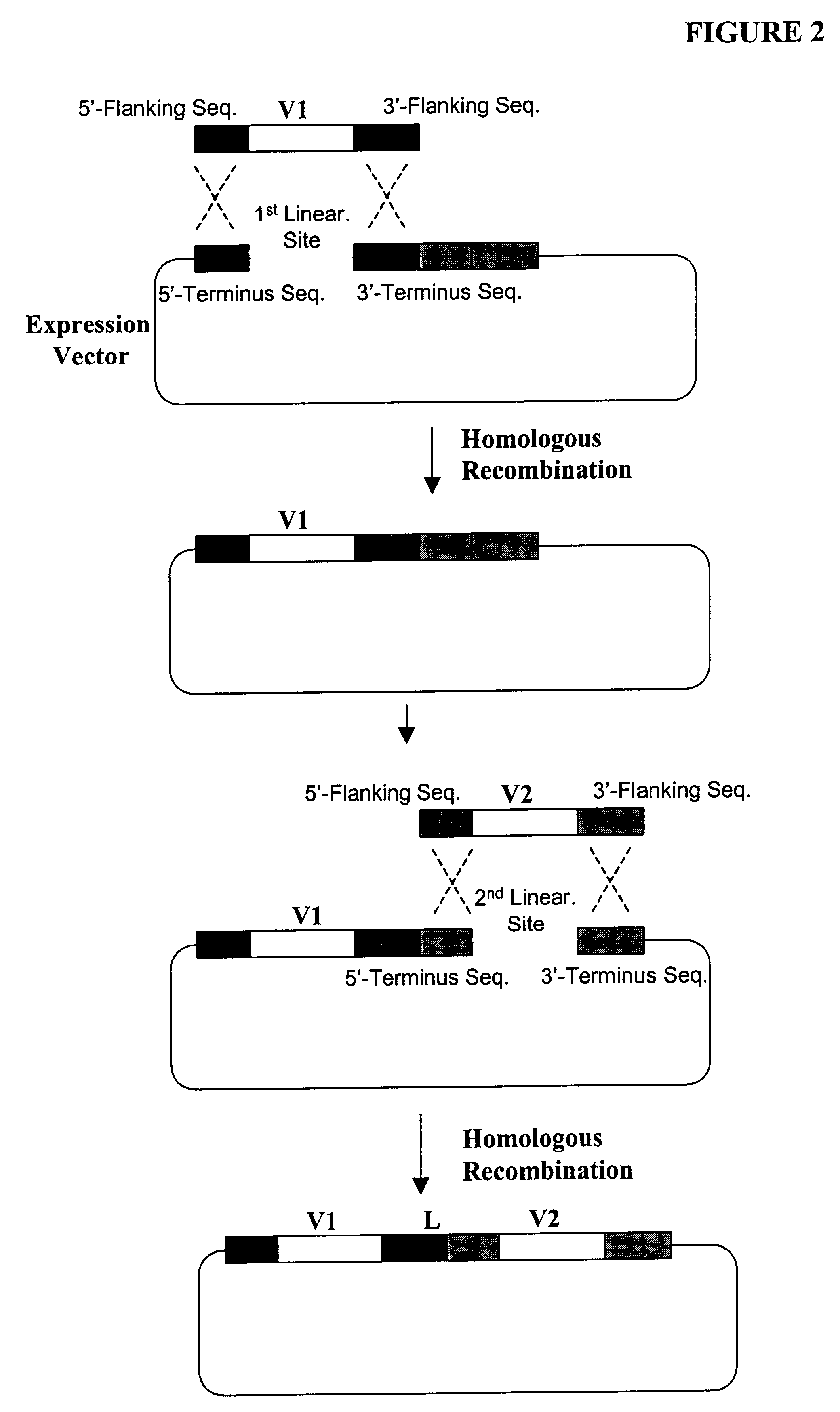
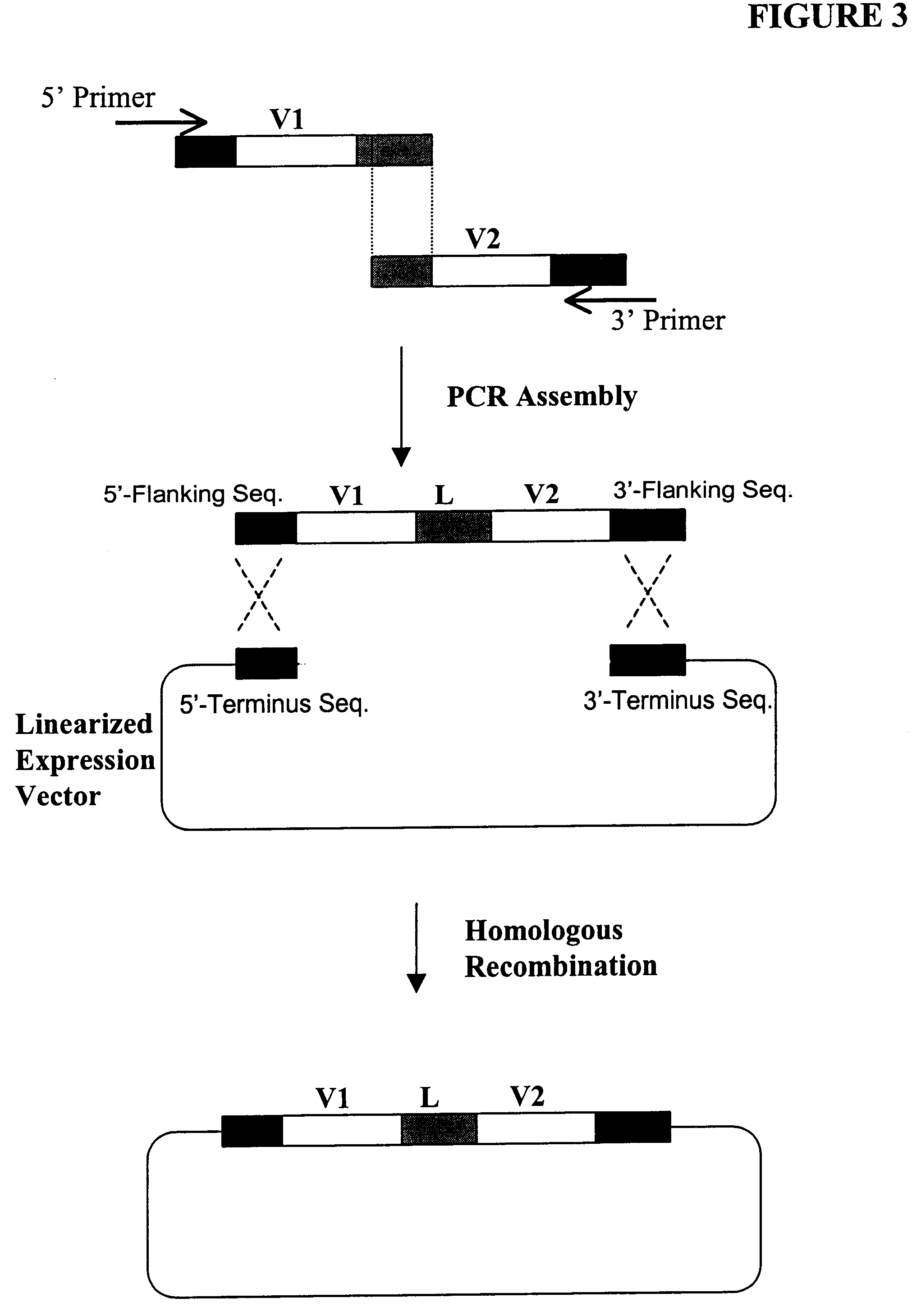
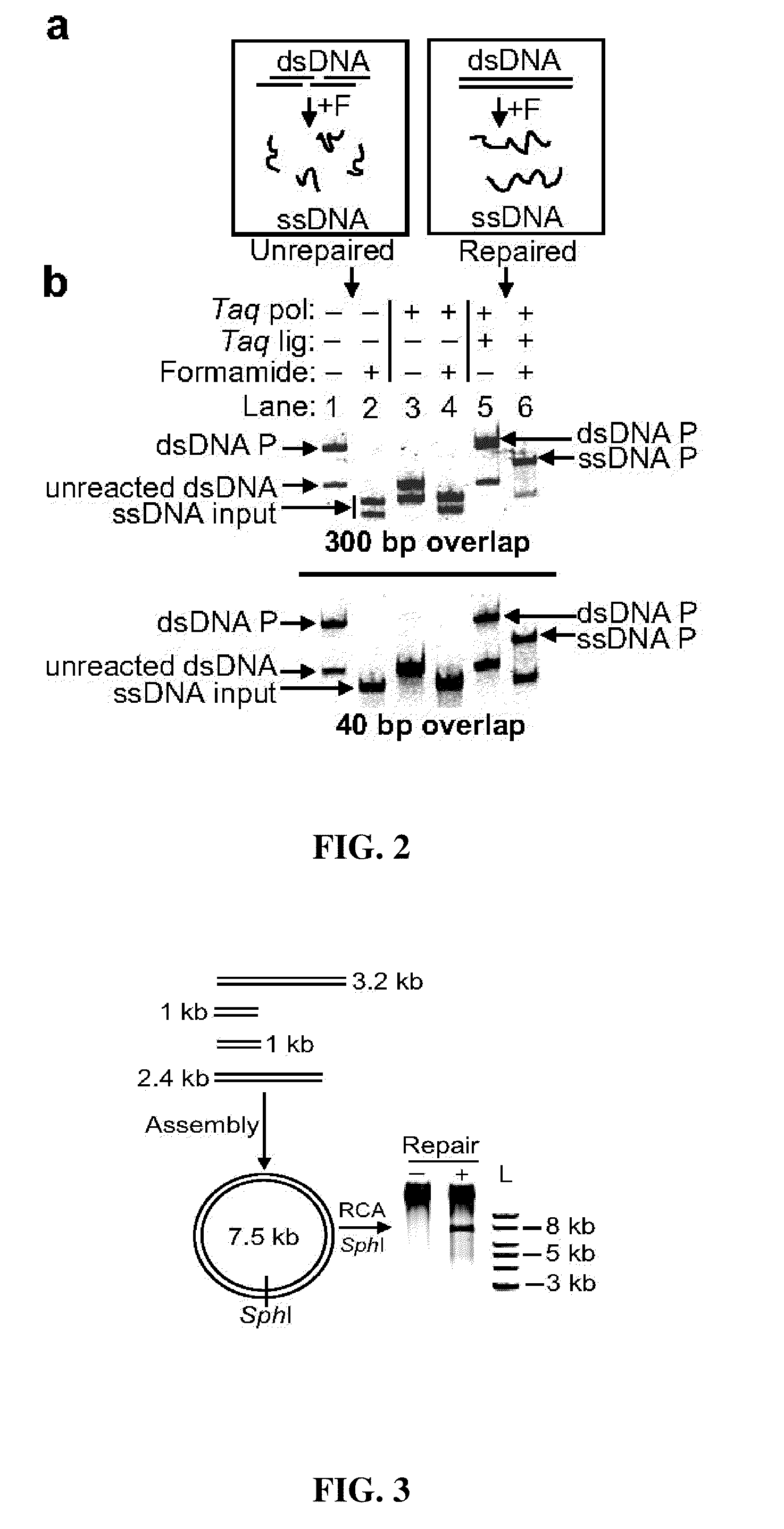
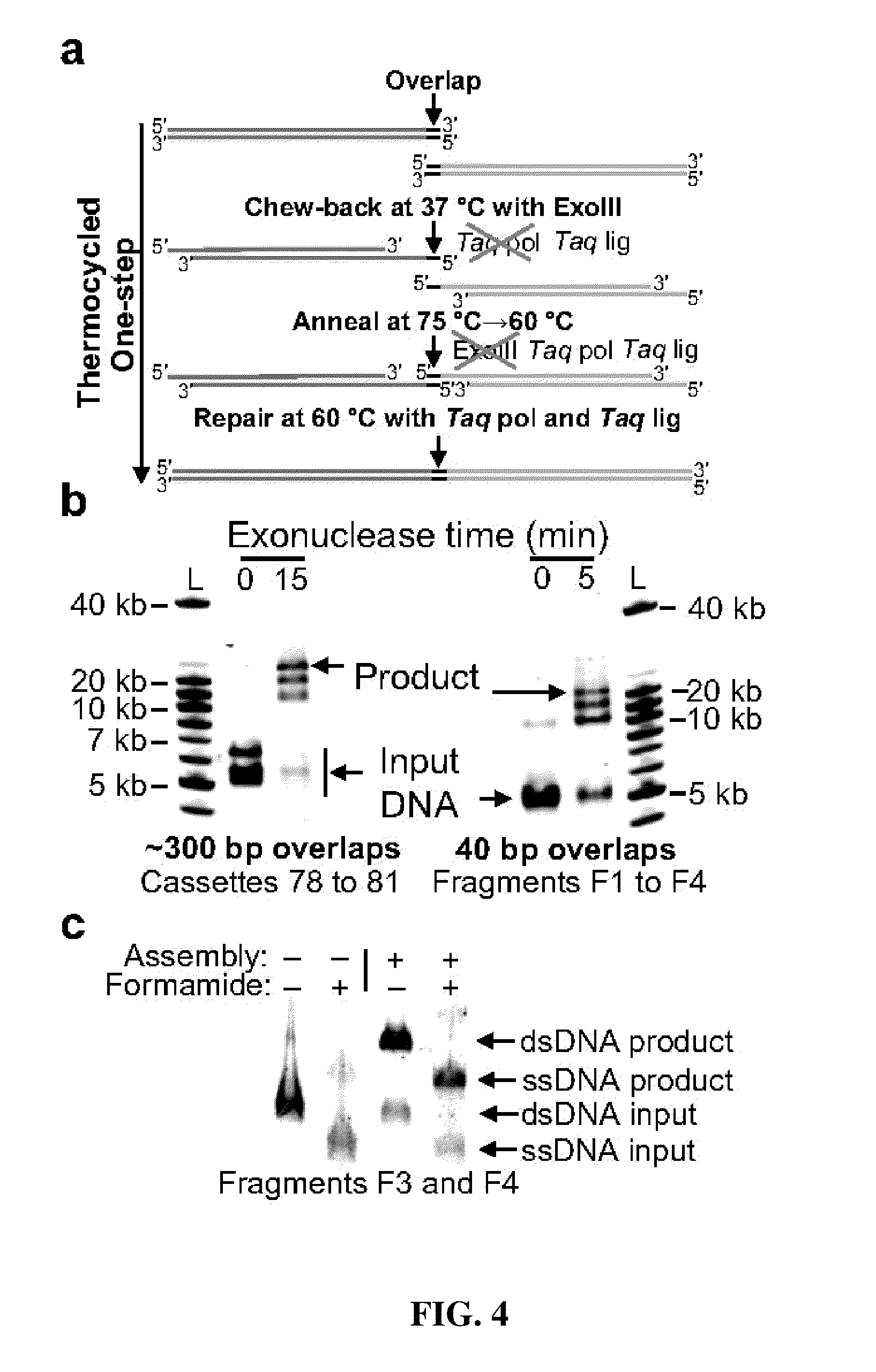
The present invention relates to methods of joining two or more double-stranded (ds) or single-stranded (ss) DNA molecules of interest in vitro, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule of each pair share a region of sequence identity. The method allows the joining of a large number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes. It can be used, e.g., to join synthetically produced sub-fragments of a gene or genome of interest. Kits for performing the method are also disclosed. The methods of joining DNA molecules may be used to generate combinatorial libraries useful to generate, for example, optimal protein expression through codon optimization, gene optimization, and pathway optimization.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS6762025B2Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideOligonucleotide
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
cDNA library preparation
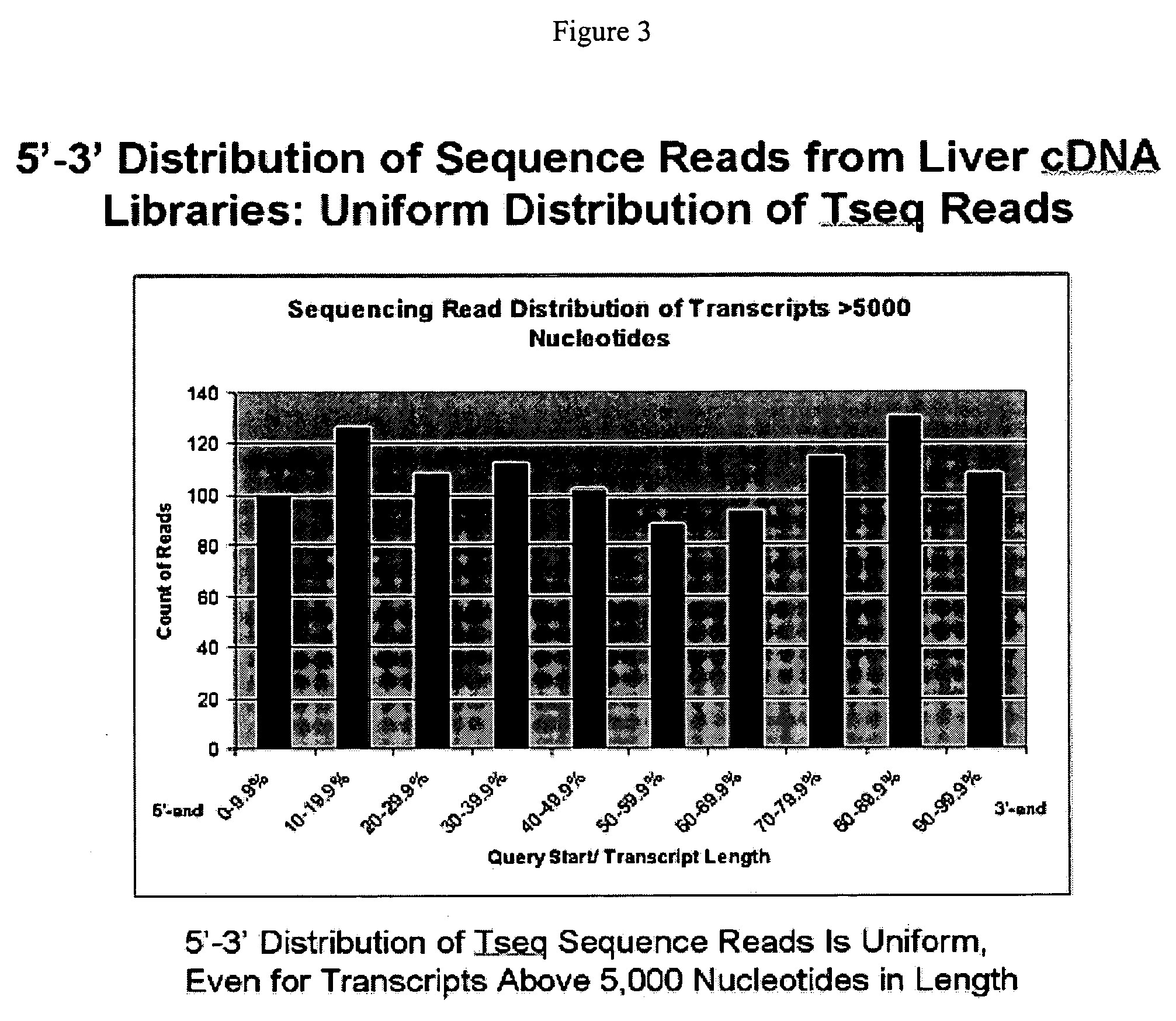
InactiveUS20070117121A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCDNA libraryAutomated sequencing
New biochemical protocols for high throughput processing of mRNA samples into cDNA libraries with adaptor sequences compatible with automated sequencing systems are provided. The provided methods produces cDNA libraries which do not have 3′ bias associated with current cDNA library production methods. New methods for the production of DNA libraries from DNA are also provided.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Amplification and analysis of whole genome and whole transcriptome libraries generated by a DNA polymerization process
ActiveUS8206913B1Increase success rateEnhance single-copy sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LA-DNA
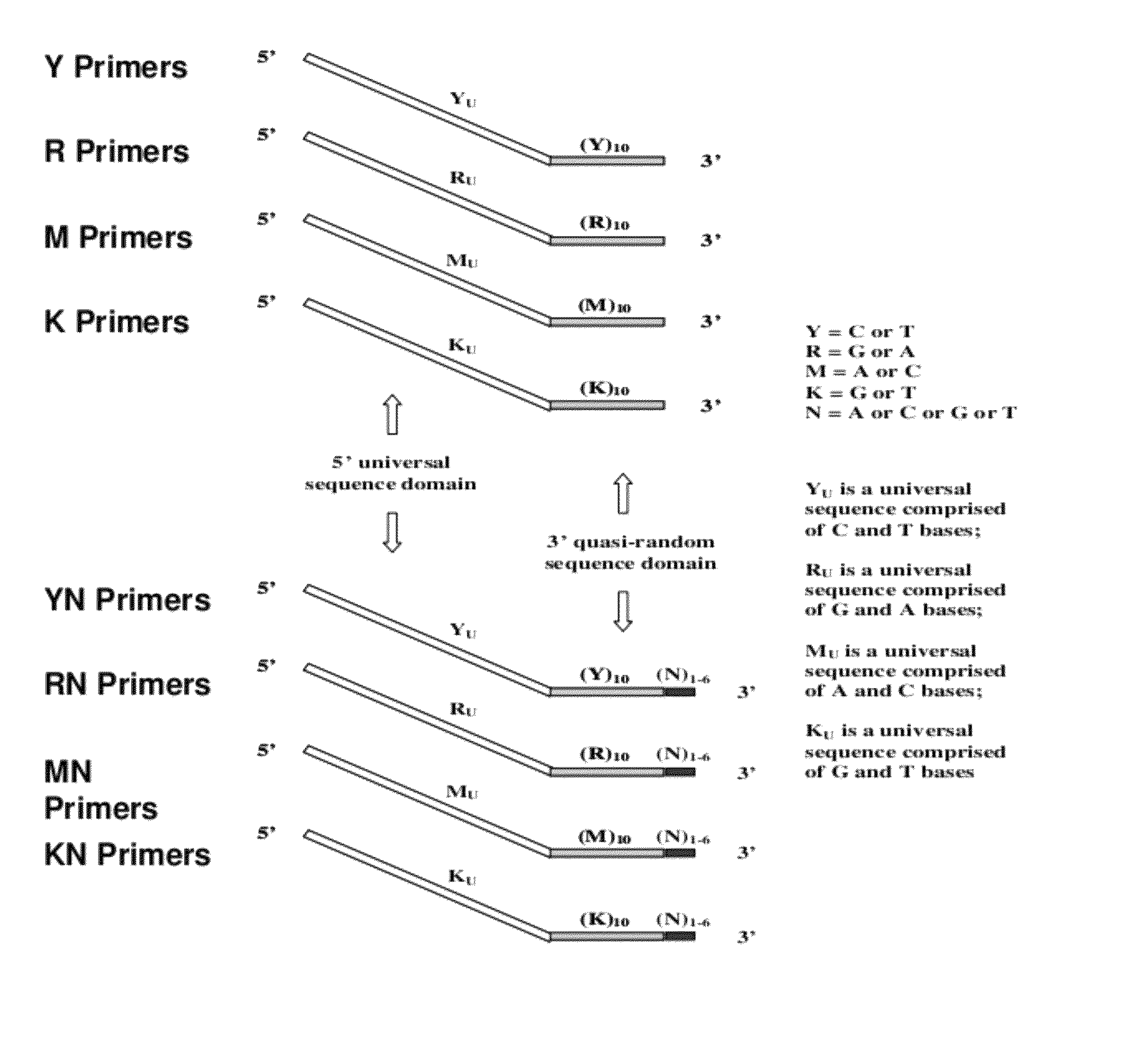
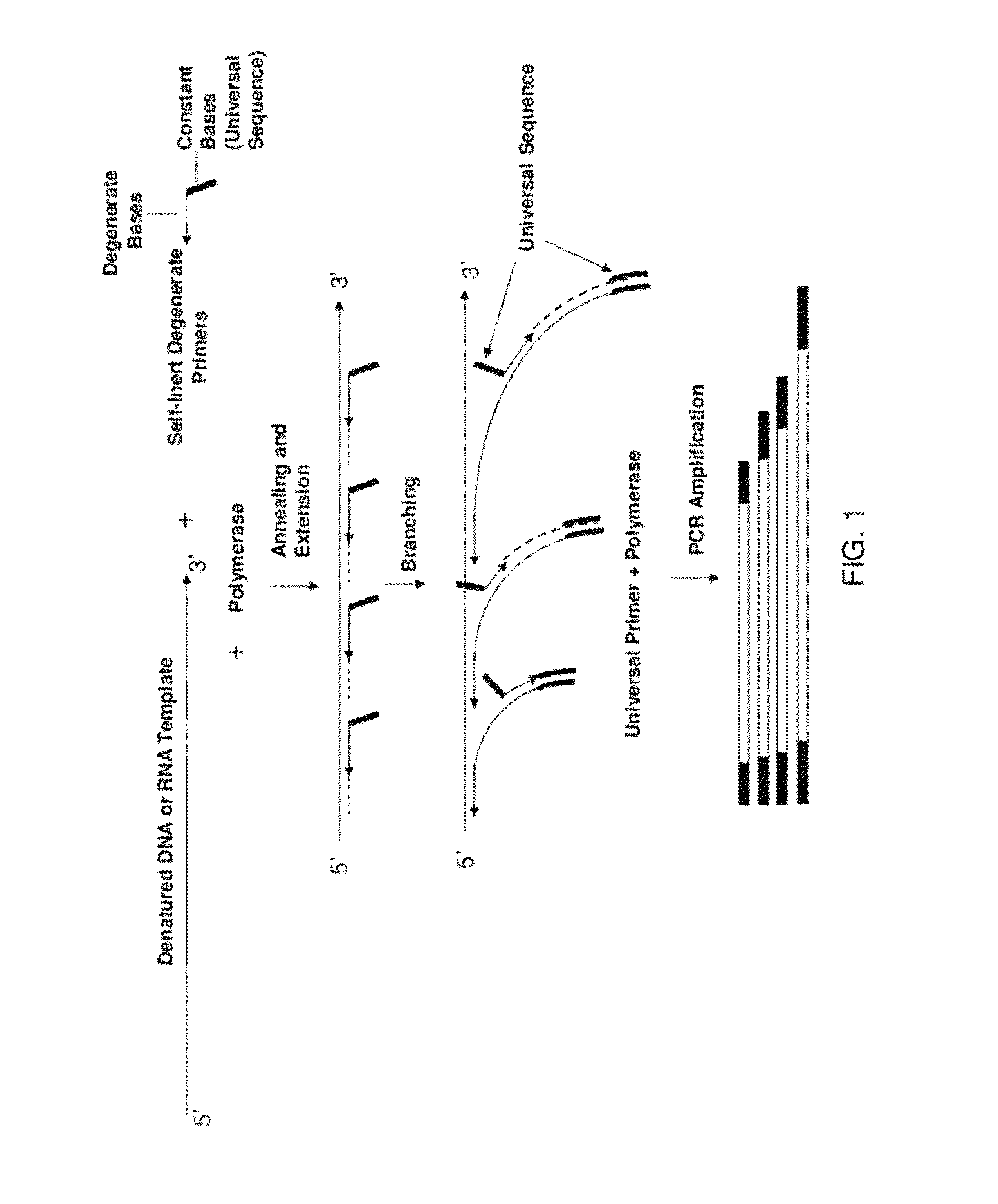
The present invention regards a variety of methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and whole transcriptome amplification. In a particular aspect of the present invention, there is a method of amplifying a genome comprising a library generation step followed by a library amplification step. In specific embodiments, the library generating step utilizes specific primer mixtures and a DNA polymerase, wherein the specific primer mixtures are designed to eliminate ability to self-hybridize and / or hybridize to other primers within a mixture but efficiently and frequently prime nucleic acid templates.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
AAV capsid library and AAV capsid proteins
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com