Patents
Literature
1372 results about "Multiplex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the biological sciences, a multiplex assay is a type of immunoassay that uses magnetic beads to simultaneously measure multiple analytes in a single experiment. A multiplex assay is a derivative of an ELISA using beads for binding the capture antibody. Multiplex assays are much more common in research than in clinical settings.
Multiplex system for the detection of surgical implements within the wound cavity
InactiveUS20060241399A1Improve reliabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSurgical SpongesEngineering
The present invention provides a multiplex system for identifying the presence of surgical sponges, metal instruments, and other implements in a surgical wound by employing a plurality of discrete sensing systems. At least two modalities of operation are chosen from a plurality of detection modalities, which can include: 1) magnetomechanically resonant marker tags; 2) “smart markers” or RFID markers; and 3) a system designed to detect metallic objects solely based upon their metal content, without need for a separate, affixed marker. The selected modes of operation can operate sequentially or simultaneously. Consequently, the use of such a multiplex system eliminates the possibility that surgical implements, non-metallic or metallic, will be left behind within a surgical cavity.
Owner:FABIAN CARL E
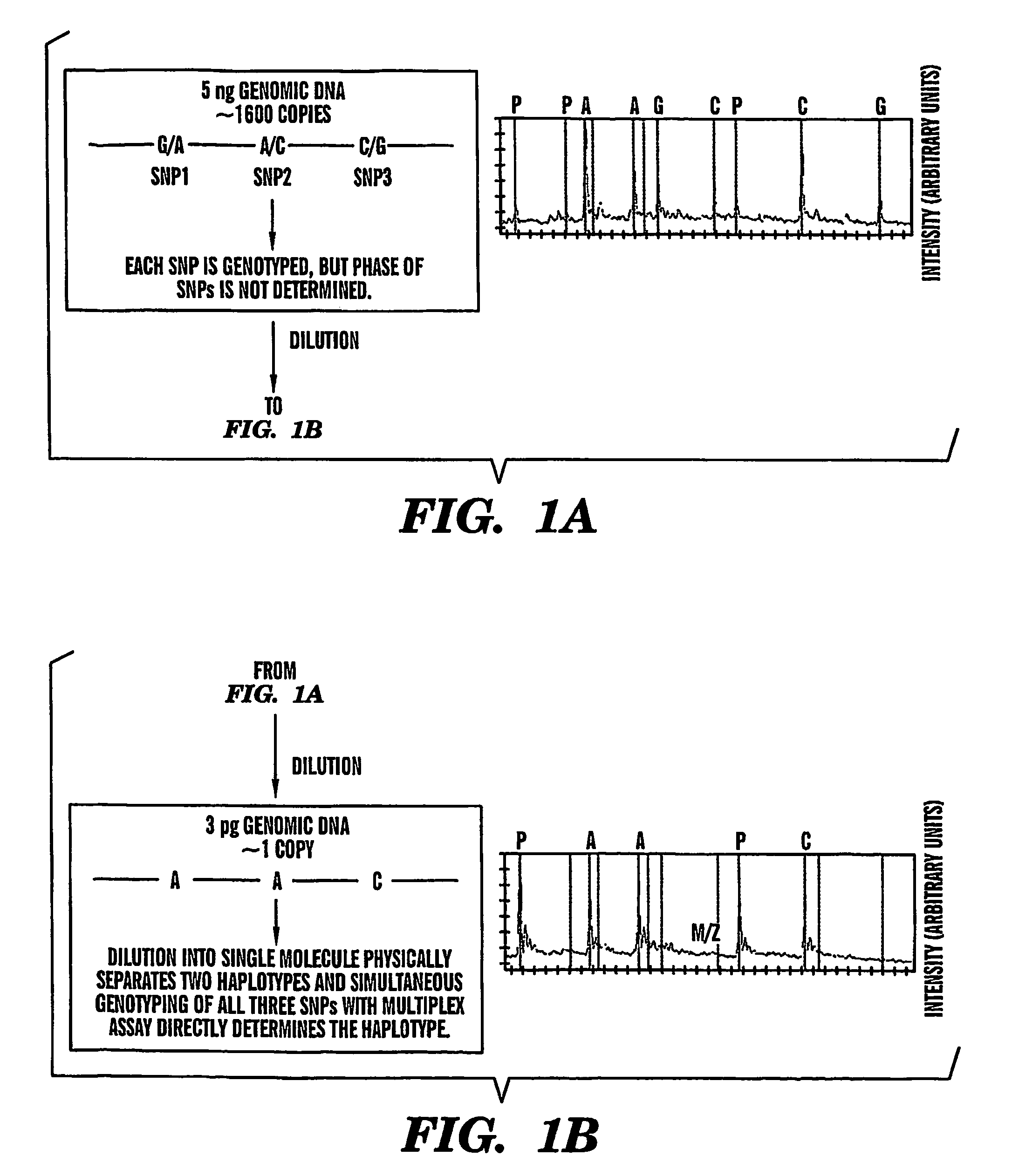
Haplotype analysis
InactiveUS7700325B2High analysisReliable determinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStatistical analysisHaplotype
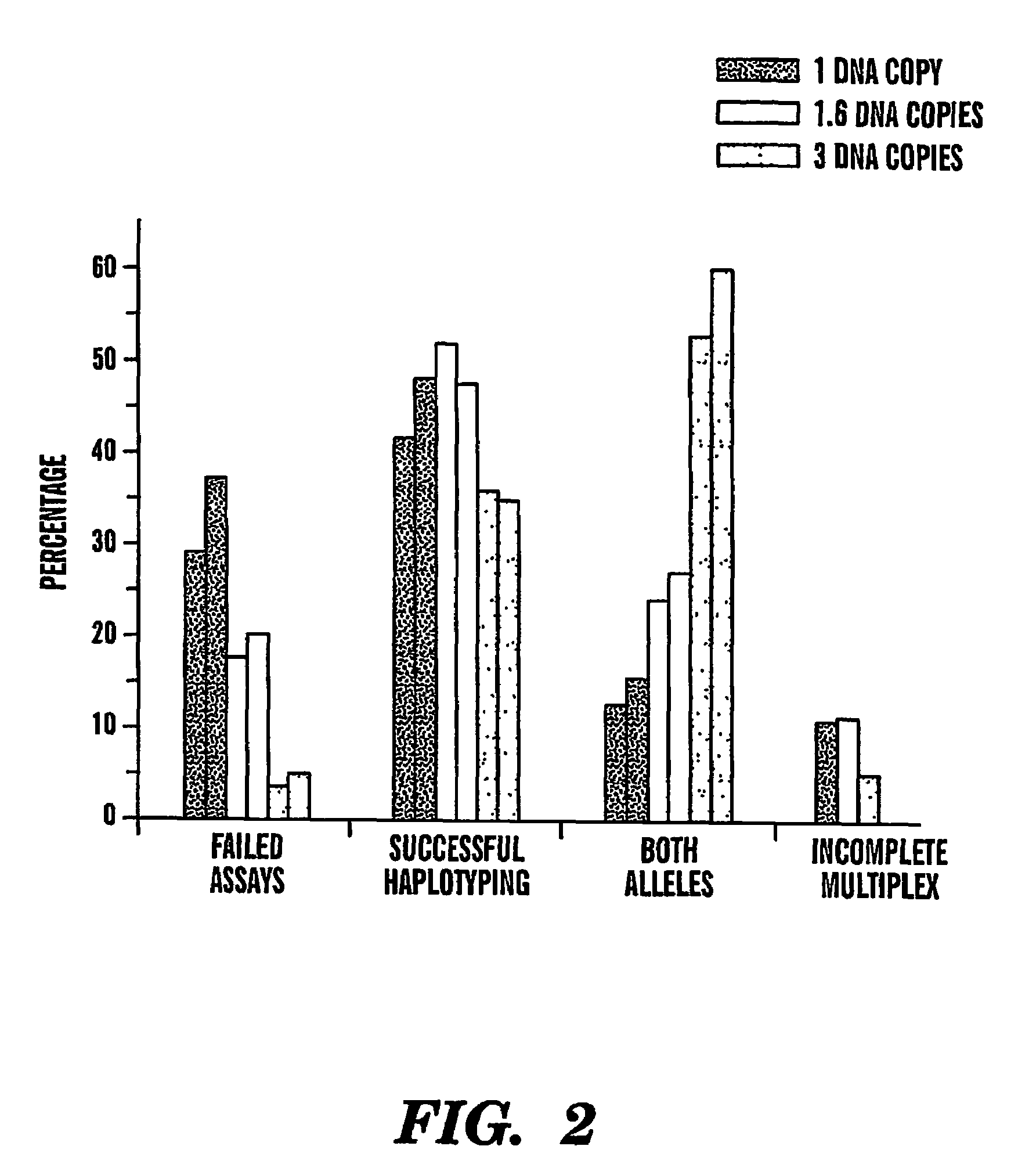
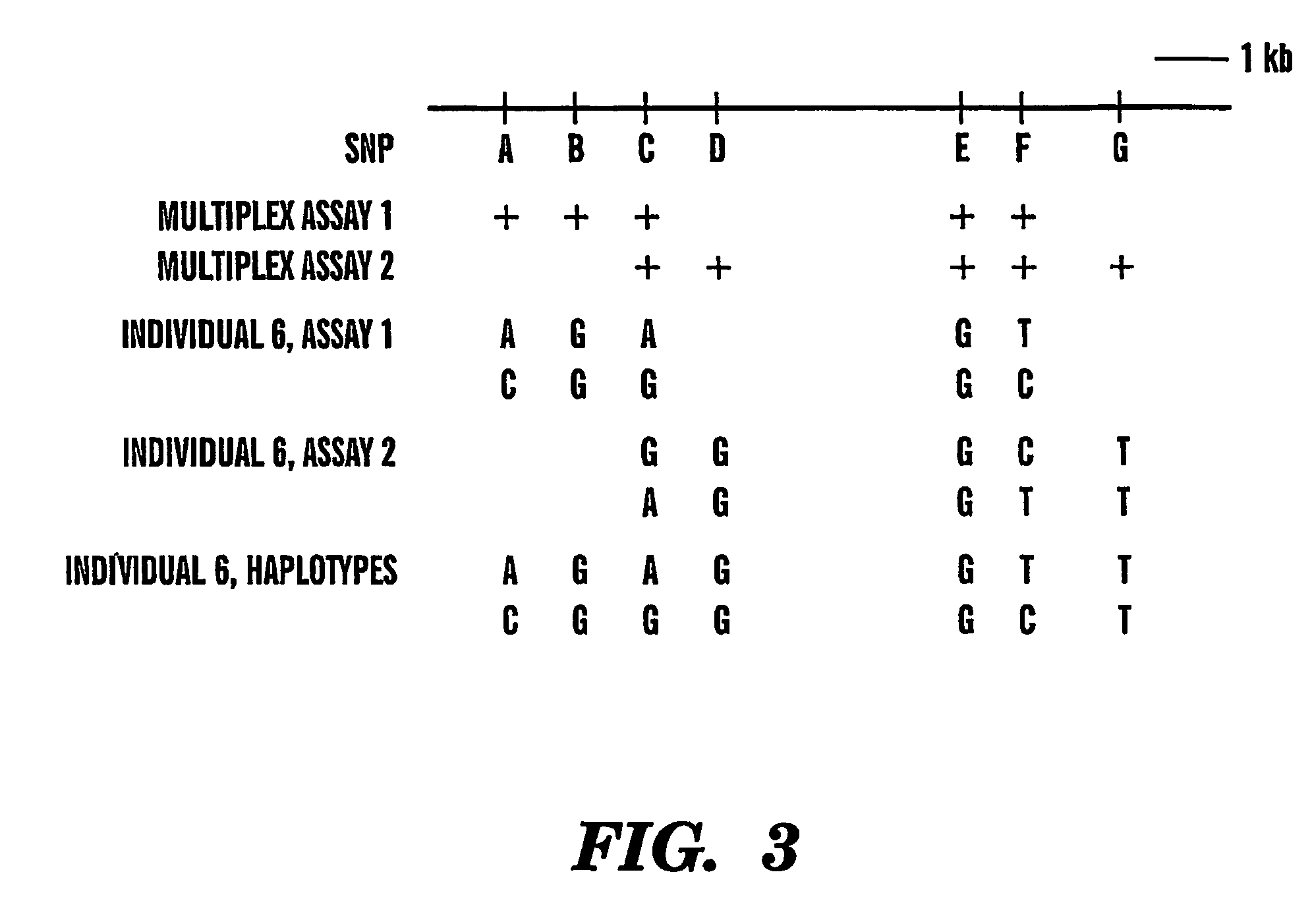
The present invention provides an efficient way for high throughput haplotype analysis. Several polymorphic nucleic acid markers, such as SNPs, can be simultaneously and reliably determined through multiplex PCR of single nucleic acid molecules in several parallel single molecule dilutions and the consequent statistical analysis of the results from these parallel single molecule multiplex PCR reactions results in reliable determination of haplotypes present in the subject. The nucleic acid markers can be of any distance to each other on the chromosome. In addition, an approach wherein overlapping DNA markers are analyzed can be used to link smaller haplotypes into larger haplotypes. Consequently, the invention provides a powerful new tool for diagnostic haplotyping and identifying novel haplotypes.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Highly Multiplex PCR Methods and Compositions
InactiveUS20130123120A1Increase opportunitiesHigh copy numberNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexDimer
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
Methods and compositions for assay readouts on multiple analytical platforms
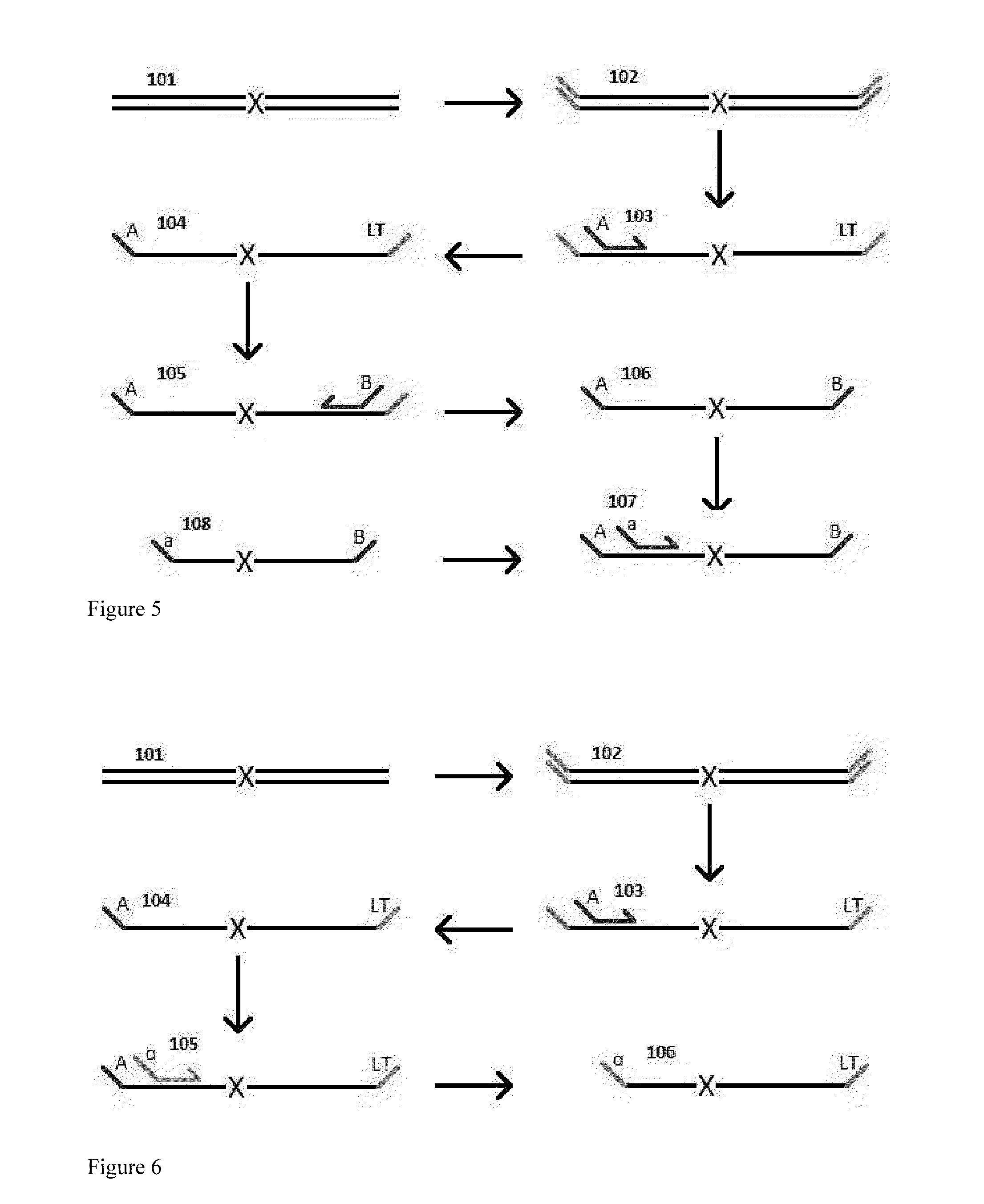
The invention provides methods and compositions for reading out the results of multiplex assays on various analytical platforms, such as microarrays, bead arrays, electrophoresis devices, and the like. An important feature of the invention includes methods for converting different sets of oligonucleotide tags used for labeling into oligonucleotide tags specific for a particular analytical platform. The invention further includes compositions comprising oligonucleotide tags having convenient properties for labeling and conversion, particularly ligation tags that employ ligation reaction specificity as well as sequence specificity in order to discriminate between tags.
Owner:POPULATION GENETICS TECH
Spatially distinguished, multiplex nucleic acid analysis of biological specimens
A method for spatially tagging nucleic acids of a biological specimen, including steps of (a) providing a solid support comprising different nucleic acid probes that are randomly located on the solid support, wherein the different nucleic acid probes each includes a barcode sequence that differs from the barcode sequence of other randomly located probes on the solid support; (b) performing a nucleic acid detection reaction on the solid support to locate the barcode sequences on the solid support; (c) contacting a biological specimen with the solid support that has the randomly located probes; (d) hybridizing the randomly located probes to target nucleic acids from portions of the biological specimen; and (e) modifying the randomly located probes that are hybridized to the target nucleic acids, thereby producing modified probes that include the barcode sequences and a target specific modification, thereby spatially tagging the nucleic acids of the biological specimen.
Owner:X GENOMICS SWEDEN AB +1
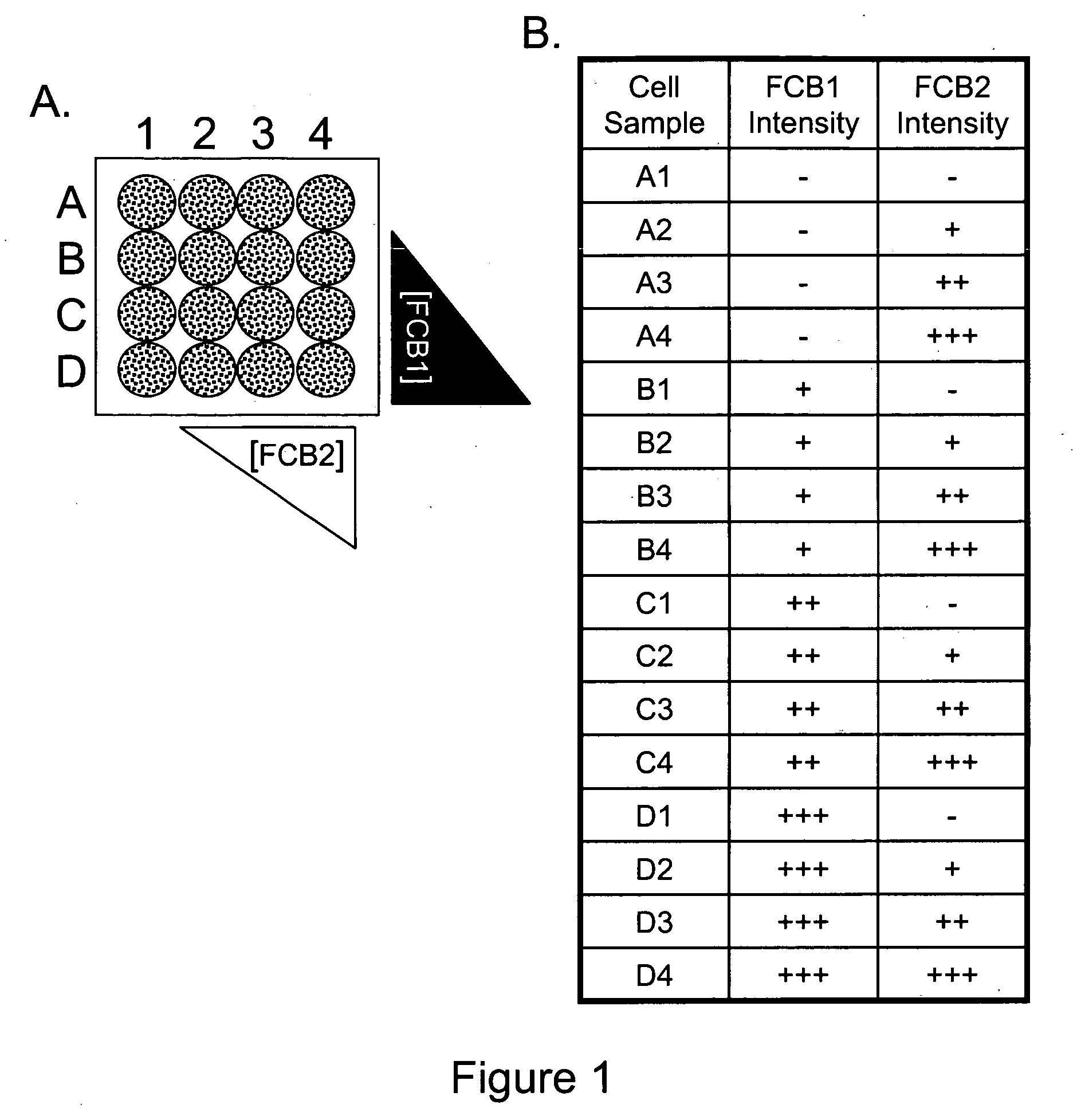
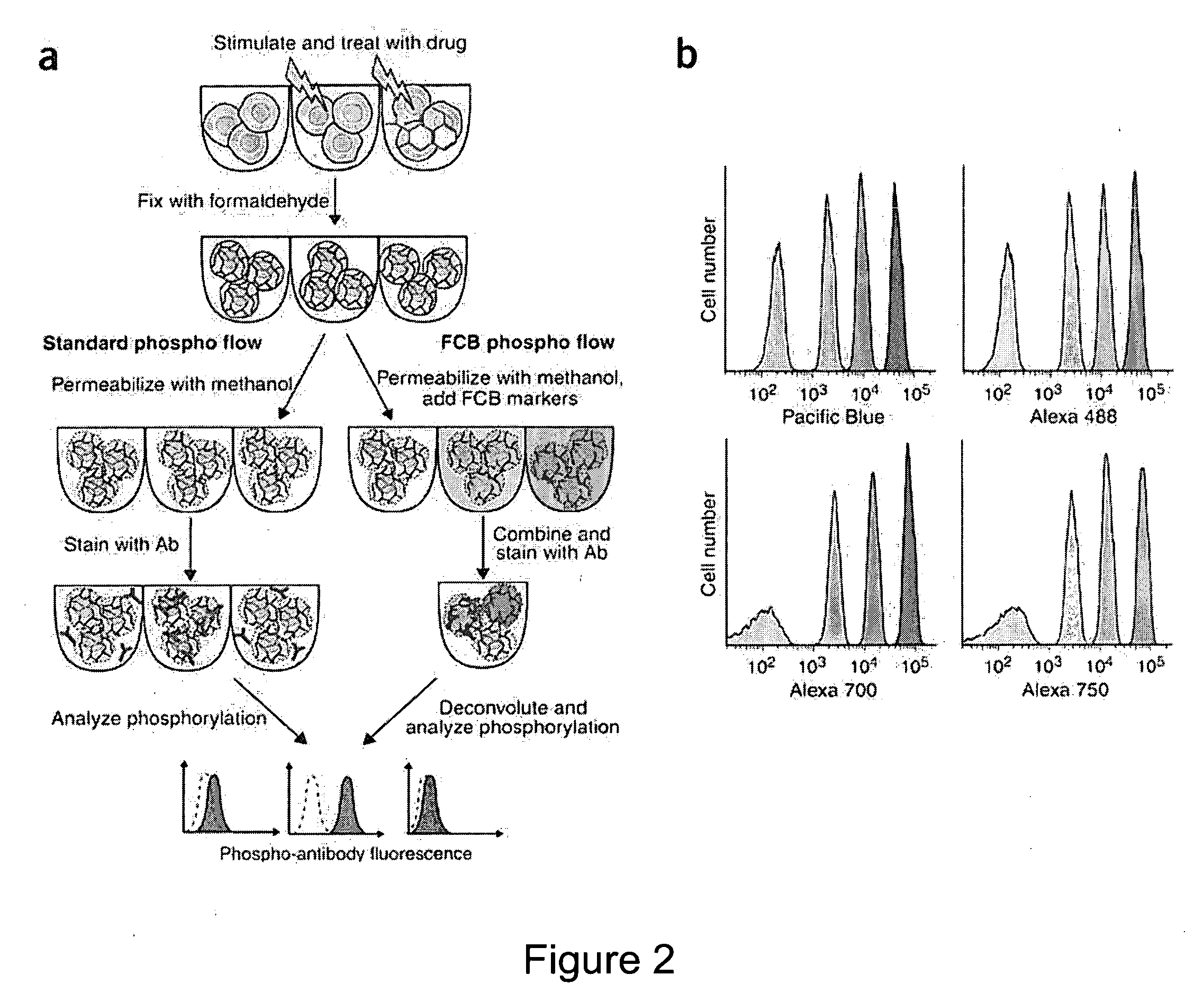
Multiplex cellular assays using detectable cell barcodes
ActiveUS20080241820A1Reduces regent consumptionImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMultiplexingAnalyte
We describe herein a cell-based multiplexing technique called detectable cell barcoding (DCB). In DCB, each individual sample is labeled with a different DCB signature that distinguishes each sample by one or both of detected intensity or type of detection characteristic. The samples are then combined and analyzed for a detectable characteristic of interest (e.g., presence of an analyte). By employing multiple distinct DCB labels at varying concentrations, one can perform multiplex analyses on up to hundreds or thousands (or more) of cell samples in a single reaction tube. DCB reduces reagent consumption by factors of 100-fold or more, significantly reduces data acquisition times and allows for stringent control sample analysis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and compositions for evaluating genetic markers
PendingUS20120165202A1Increase variabilityDisproportionate representationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationMultiplexNucleic acid sequencing
Aspects of the invention relates to methods and compositions that are useful to reduce bias and increase the reproducibility of multiplex analysis of genetic loci. In some configurations, predetermined preparative steps and / or nucleic acid sequence analysis techniques are used in multiplex analyses for a plurality of genetic loci in a plurality of samples.
Owner:MOLECULAR LOOP BIOSOLUTIONS LLC
Multiplex decoding of array sensors with microspheres
InactiveUS20060073513A1ConfidenceMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsMicrosphereBiology
The invention relates to compositions and methods for multiplex decoding of microsphere array sensors.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Multiplex amplification of polynucleotides
ActiveUS20040175733A1Improve efficiencyIncrease concentrationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideBiology
The present invention provides methods, reagents and kits for carrying out a variety of assays suitable for analyzing polynucleotides or samples that include an amplification step performed in a multiplex fashion. Also provided are methods for analyzing and improving the efficiency of amplification and for carrying out gene expression analysis.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
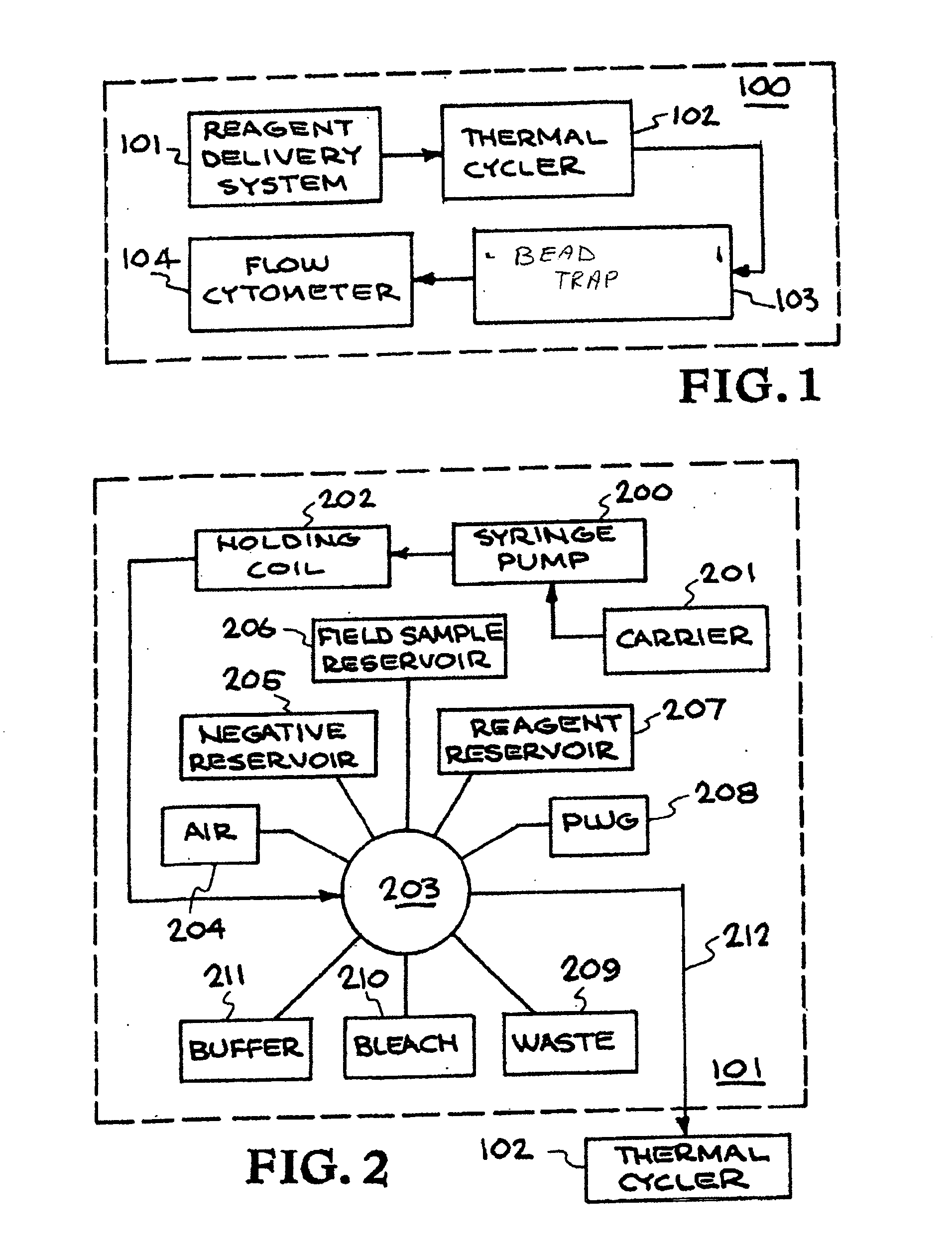
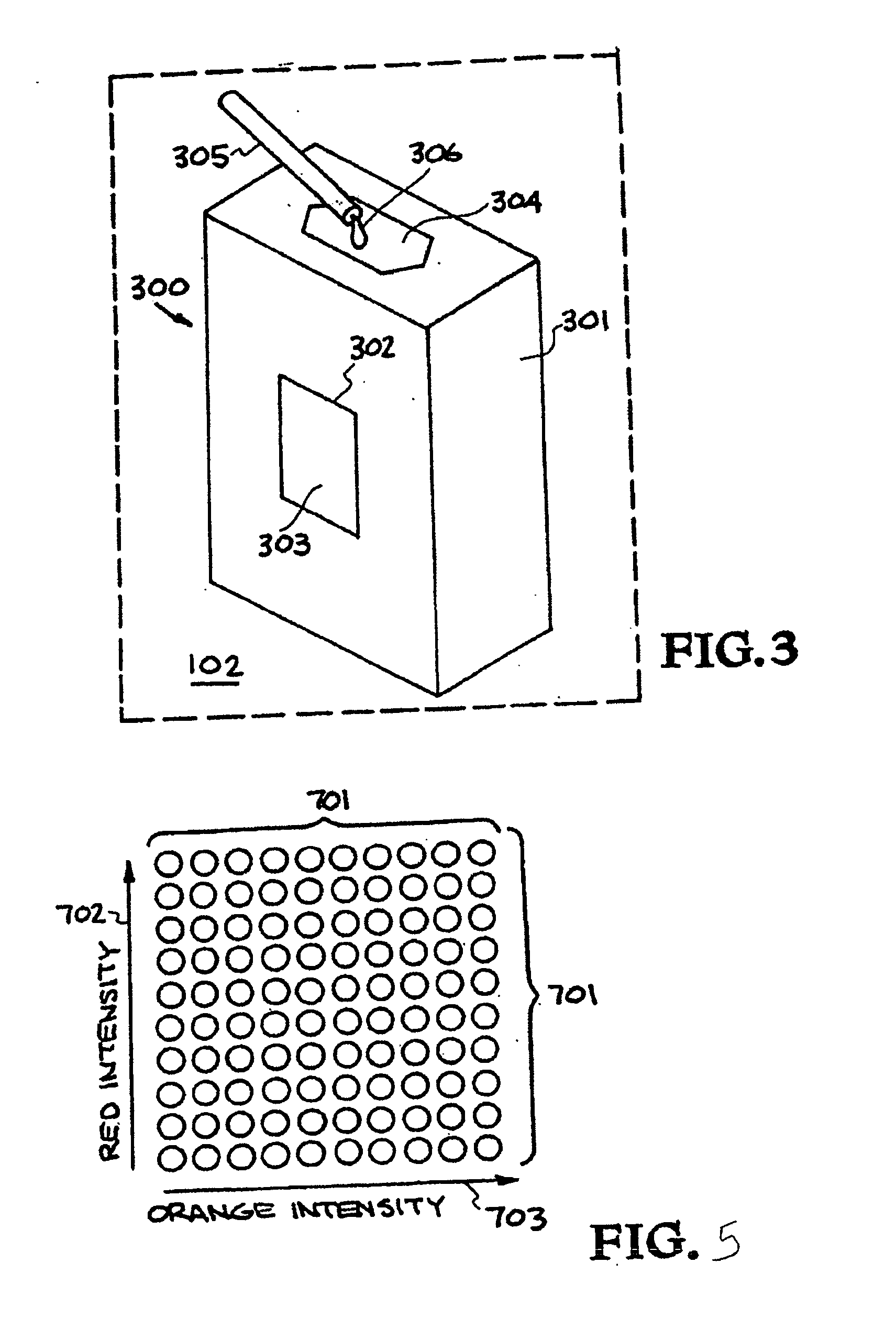
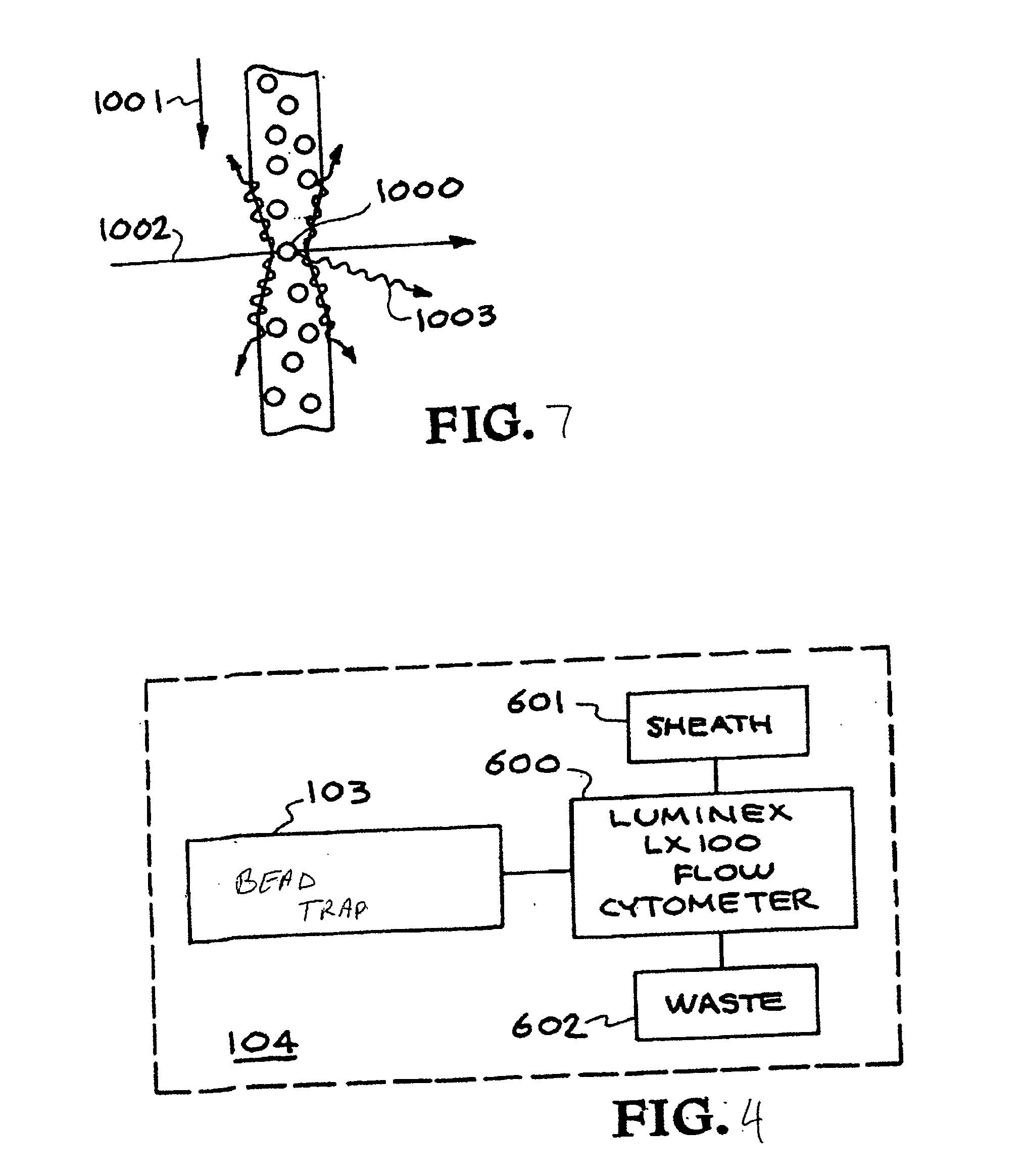
Multiplexed diagnostic platform for point-of care pathogen detection
InactiveUS20070166725A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusPoint of careMicrosphere
The invention provides a system for high-throughput multiplex analysis of target samples. A sample and reagent delivery unit is operatively connected to a thermal cycler for amplification of target nucleic acids. Microspheres are hybridized to the resulting amplicons in the thermal cycler. A flow cytometer is operatively connected to the thermal cycler or optionally a bead trap for washing the microspheres.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Methods and Compositions for Multiplex Sequencing
InactiveUS20110319290A1Accurate identificationSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesBarcodePolynucleotide
Adapters are joined to target polynucleotides to create adapter-tagged polynucleotides. Adapter-tagged polynucleotides are sequenced simultaneously and sample sources are identified on the basis of barcode sequences.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Highly multiplex PCR methods and compositions
InactiveUS20140094373A1High copy numberMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMultiplexDimer
The invention provides methods for simultaneously amplifying multiple nucleic acid regions of interest in one reaction volume as well as methods for selecting a library of primers for use in such amplification methods. The invention also provides library of primers with desirable characteristics, such as minimal formation of amplified primer dimers or other non-target amplicons.
Owner:NATERA
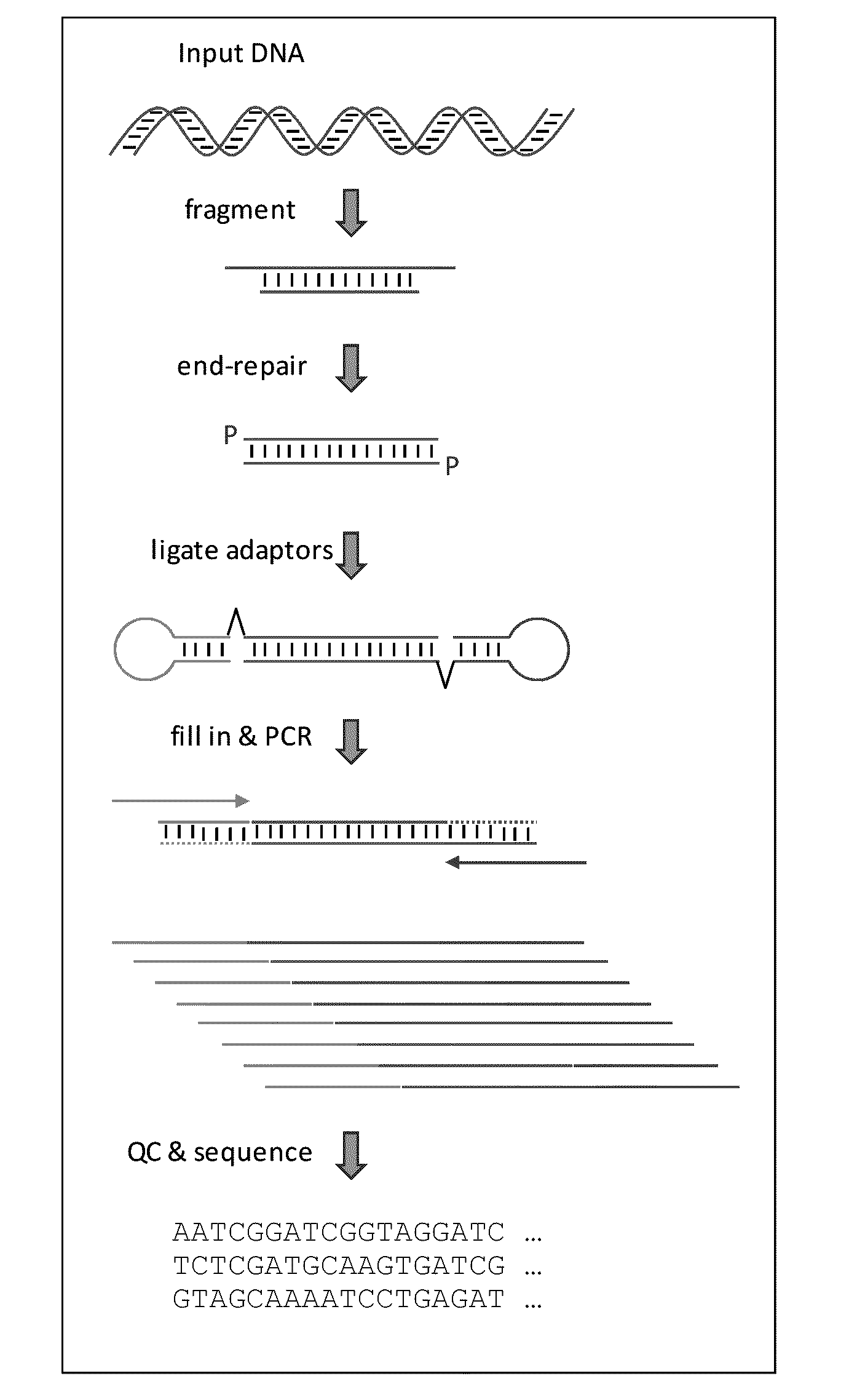
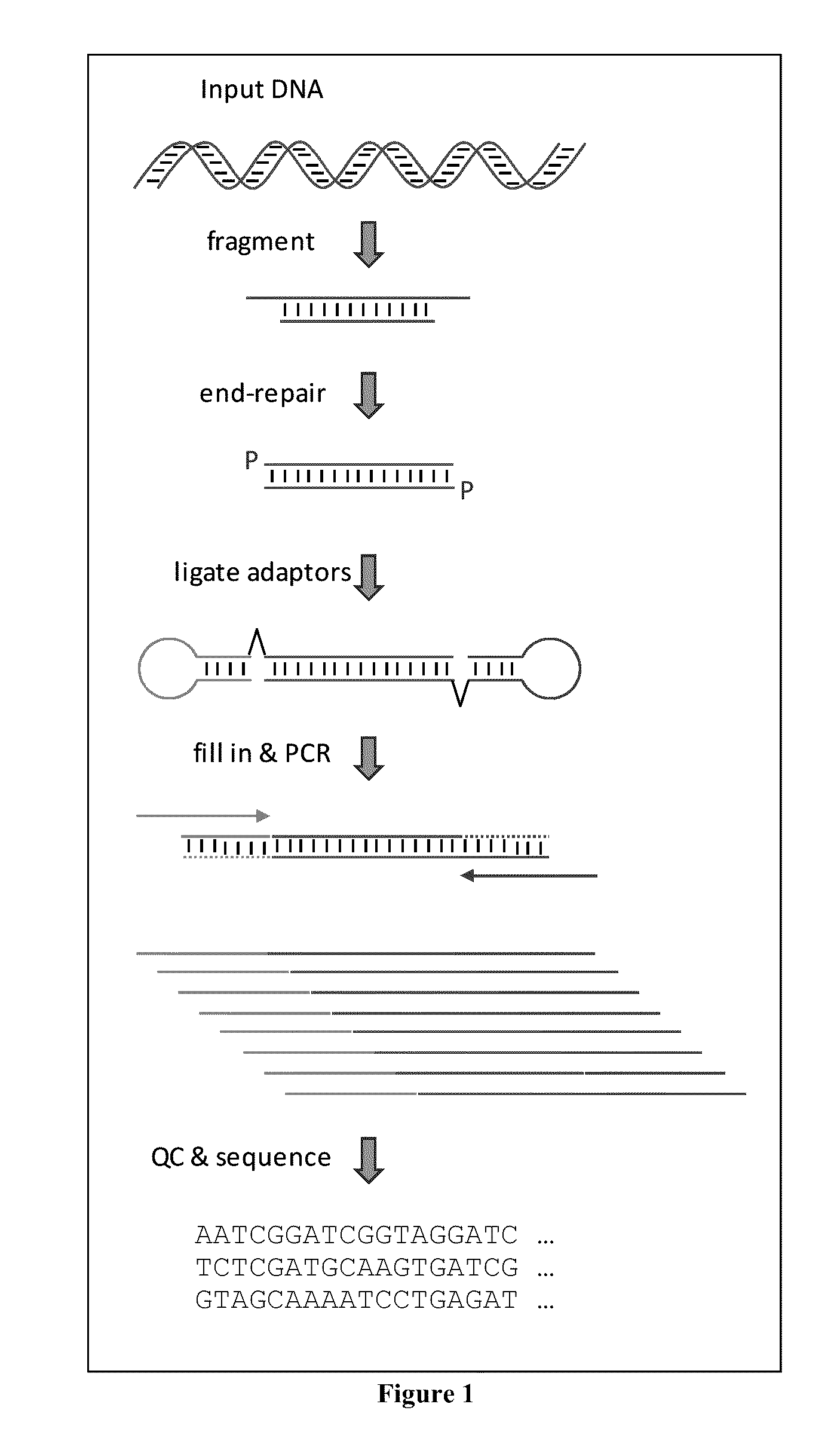
MULTIPLEX BARCODED PAIRED-END DITAG (mbPED) LIBRARY CONSTRUCTION FOR ULTRA HIGH THROUGHPUT SEQUENCING
Multiplex barcoded Paired-End Ditag (mbPED) library construction for ultra high throughput sequencing is disclosed. The mbPED library comprises multiple types of barcoded Paired-End Ditag (bPED) nucleic acid fragment constructs, each of which comprises a unique barcoded adaptor, a first tag, and a second tag linked to the first tag via the barcoded adaptor. The two tags are the 5′- and 3′-ends of a nucleic acid molecule from which they originate. The barcoded adaptor comprises a barcode, a first polynucleotide sequence comprising a first restriction enzyme (RE) recognition site, and a second polynucleotide sequence comprising a second RE recognition site and covalently linked to the first polynucleotide sequence via the barcode. The two REs lead to cleavage of a nucleic acid at a defined distance from their recognition sites. The length of the adaptor is set so that the bPED nucleic acid fragment fits one-step sequencing.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Dual phase multiplex polymerase chain reaction
ActiveUS7432055B2Further amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomic DNASingle pair
Highly specific and sensitive methods were developed for multiplex amplification of nucleic acids on supports such as microarrays. Based on a specific primer design, methods include five types of amplification that proceed in a reaction chamber simultaneously. These relate to four types of multiplex amplification of a target DNA on a solid support, directed by forward and reverse complex primers immobilized to the support and a fifth type—pseudo-monoplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of multiple targets in solution, directed by a single pair of unbound universal primers. The addition of the universal primers in the reaction mixture increases the yield over the traditional “bridge” amplification on a solid support by approximately ten times. Methods that provide multitarget amplification and detection of as little as 0.45-4.5×10−12 g (equivalent to 102-103 genomes) of a bacterial genomic DNA are disclosed.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Methods of detecting nucleic acid sequences with high specificity
InactiveUS20130023433A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
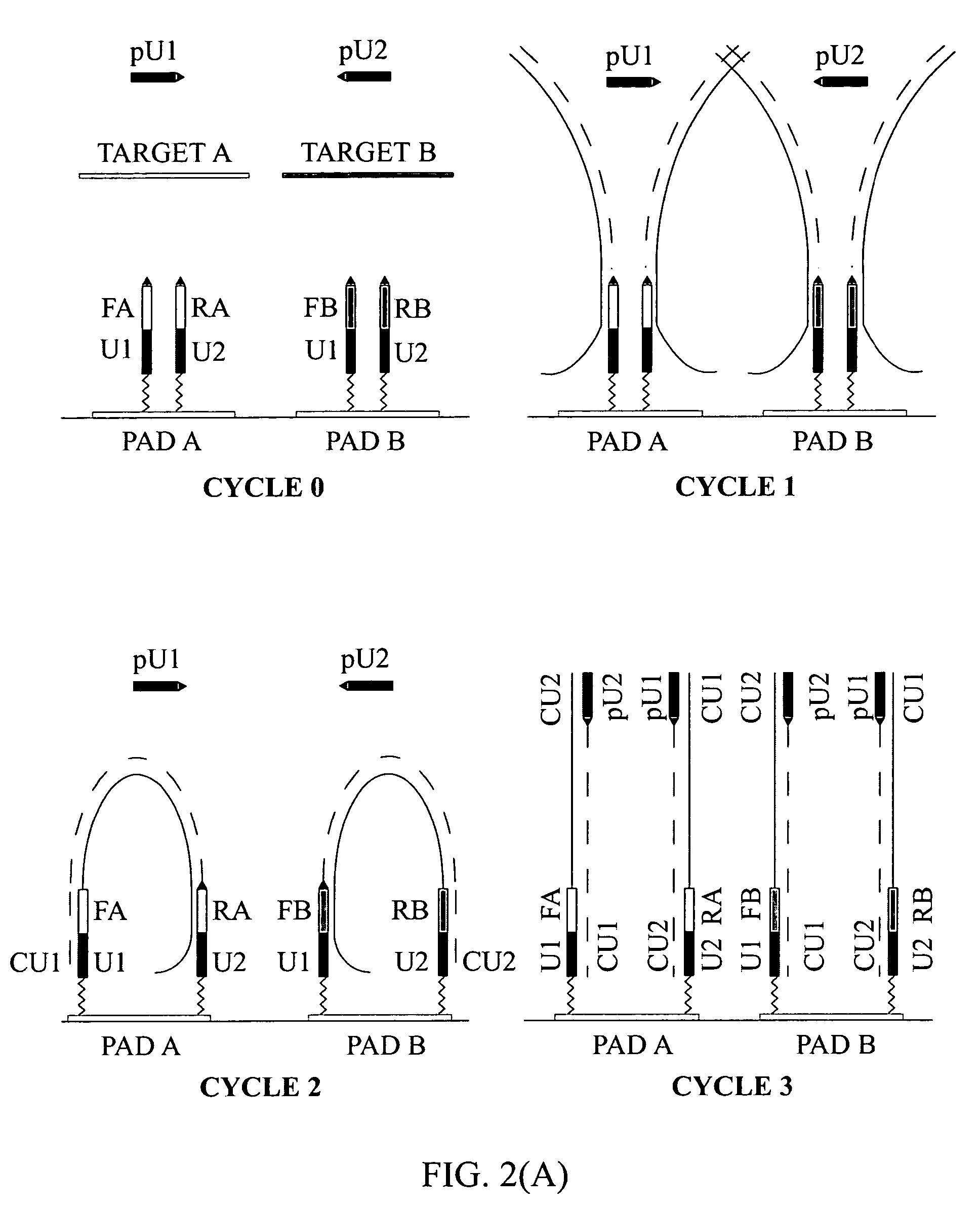
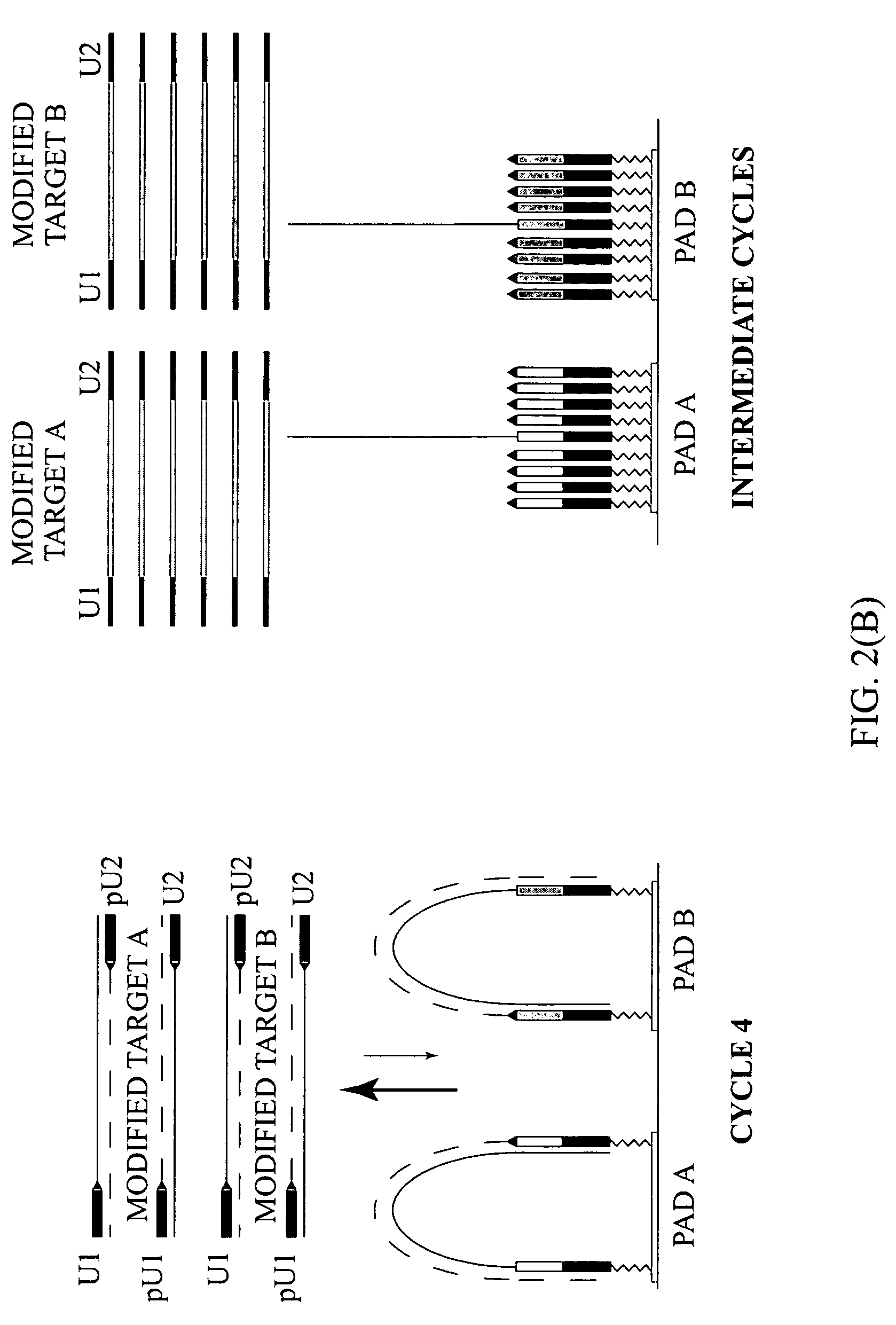
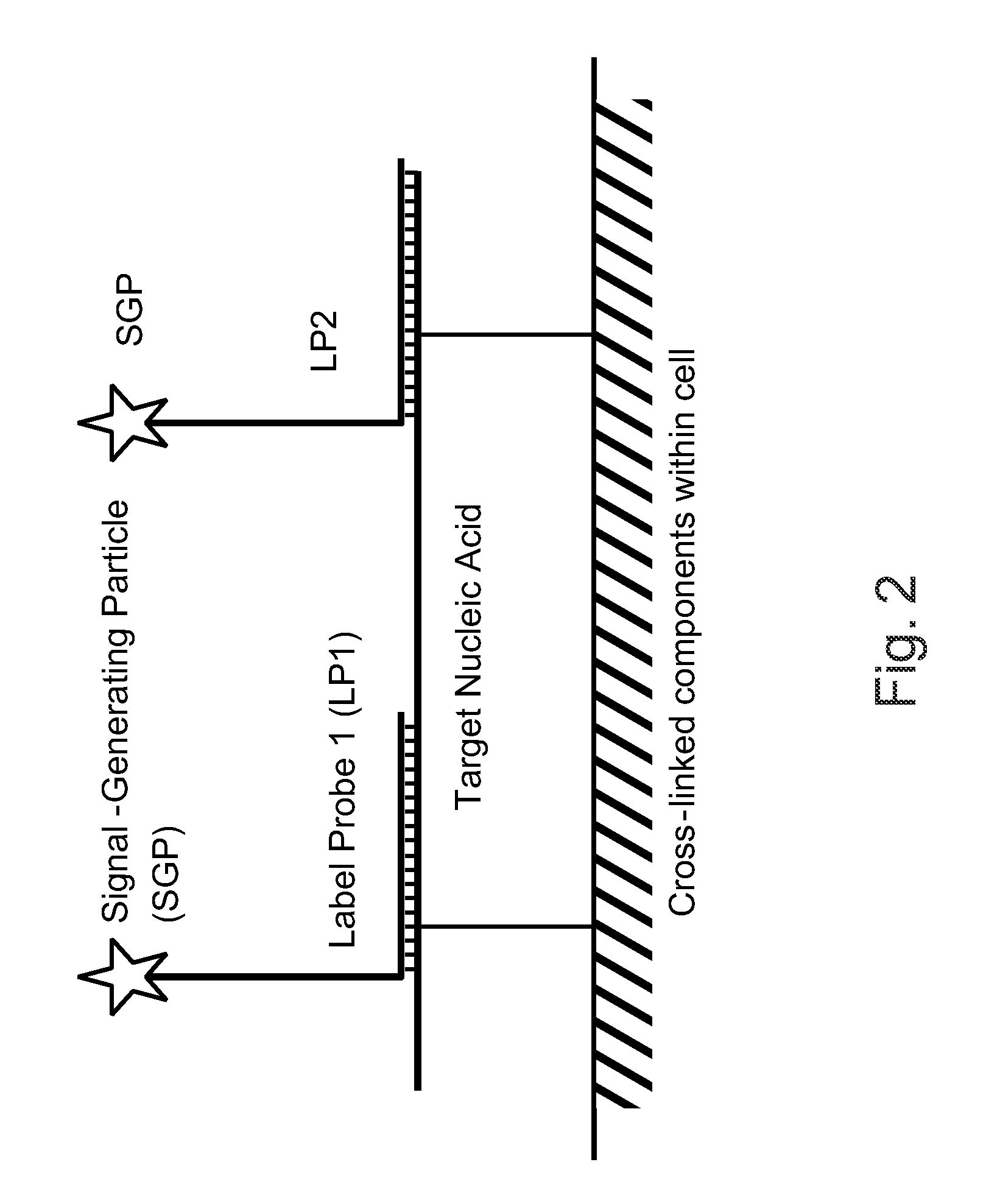
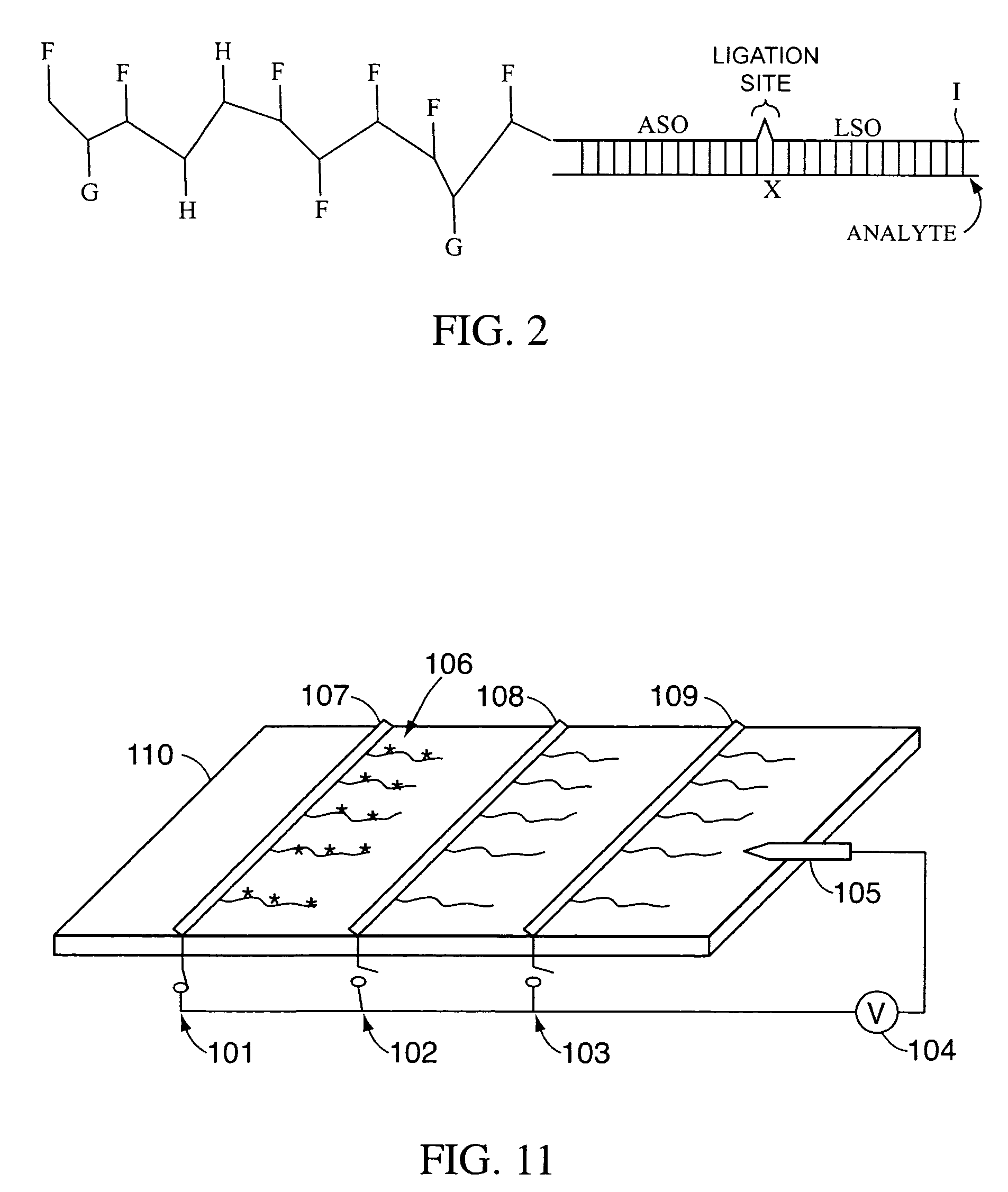
The invention relates to methods of detecting nucleic acids, including methods of detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences in multiplex branched-chain DNA assays, are provided. Nucleic acids captured on a solid support or suspending cells are detected, for example, through cooperative hybridization events that result in specific association of a label with the nucleic acids. The invention further relates to methods to improve probe hybridization specificity and their application in genotyping. The invention also relates to in situ detection of mis-joined nucleic acid sequences. The invention relates to reducing false positive signals and improve signal-to-background ratio in hybridization-based nucleic acid detection assay. The invention further relates to method to improve specificity in hybridization based nucleic acid using co-location probes. Compositions, tissue slides, sample of suspended cells, kits, and systems related to the methods are also described.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
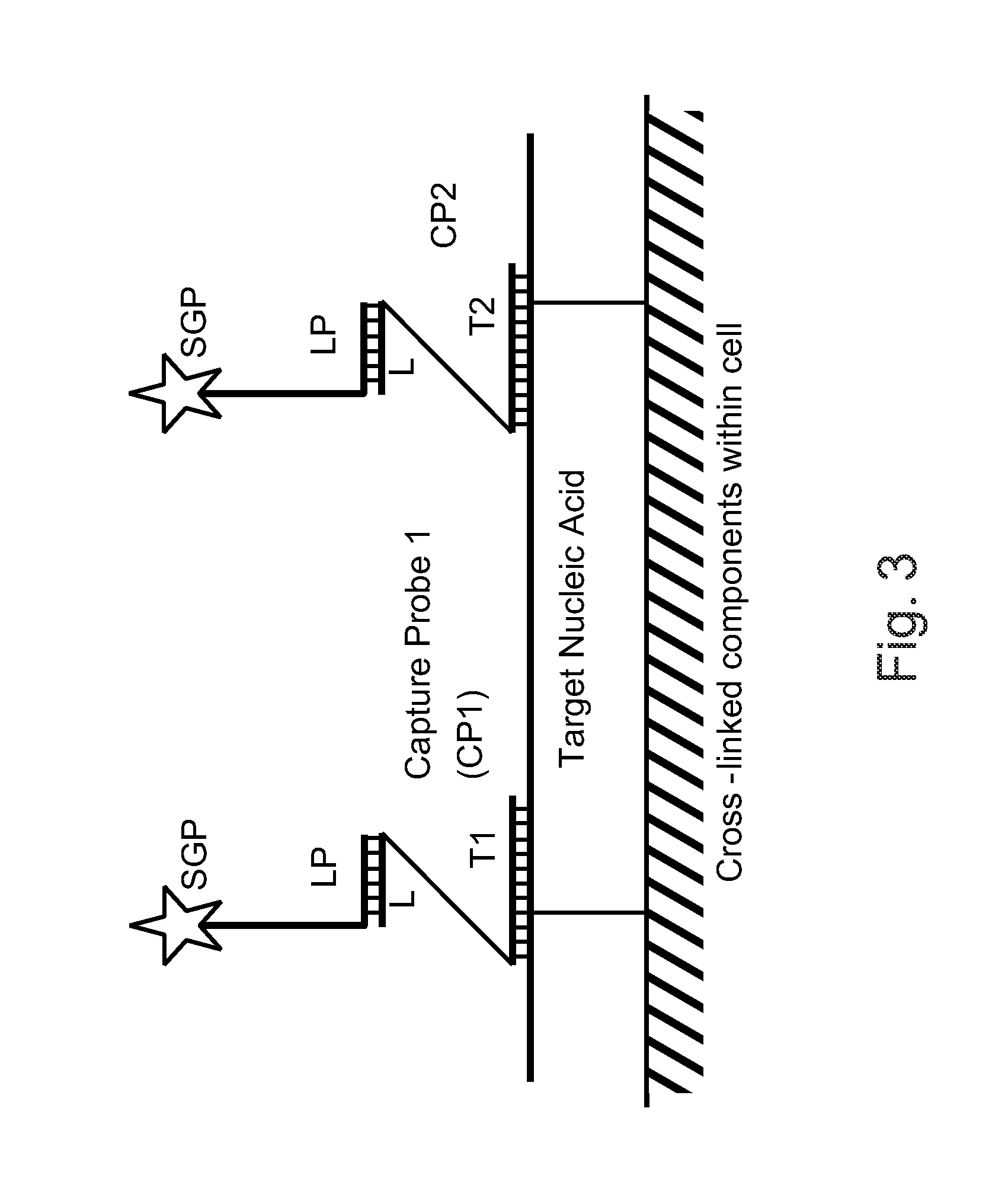
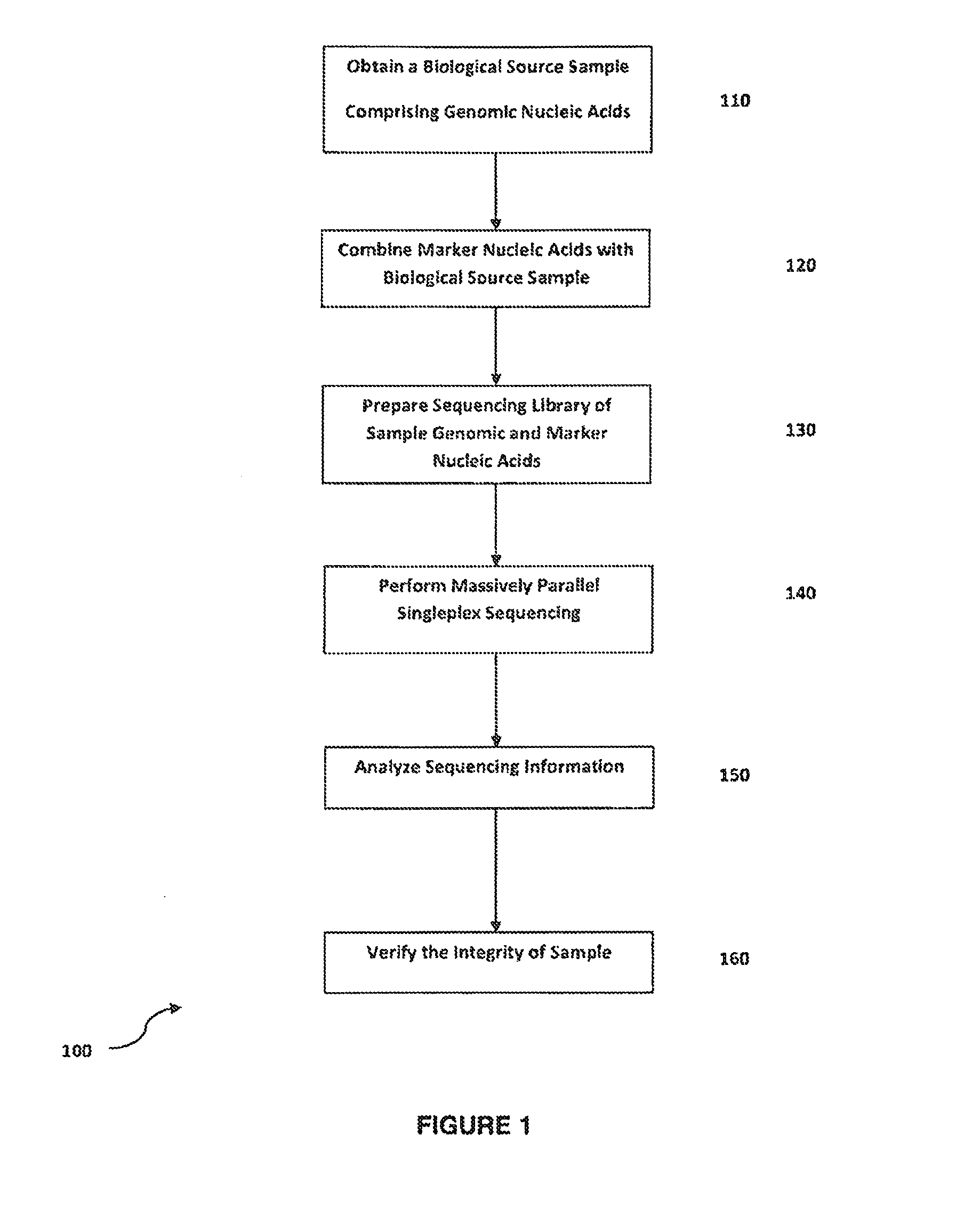
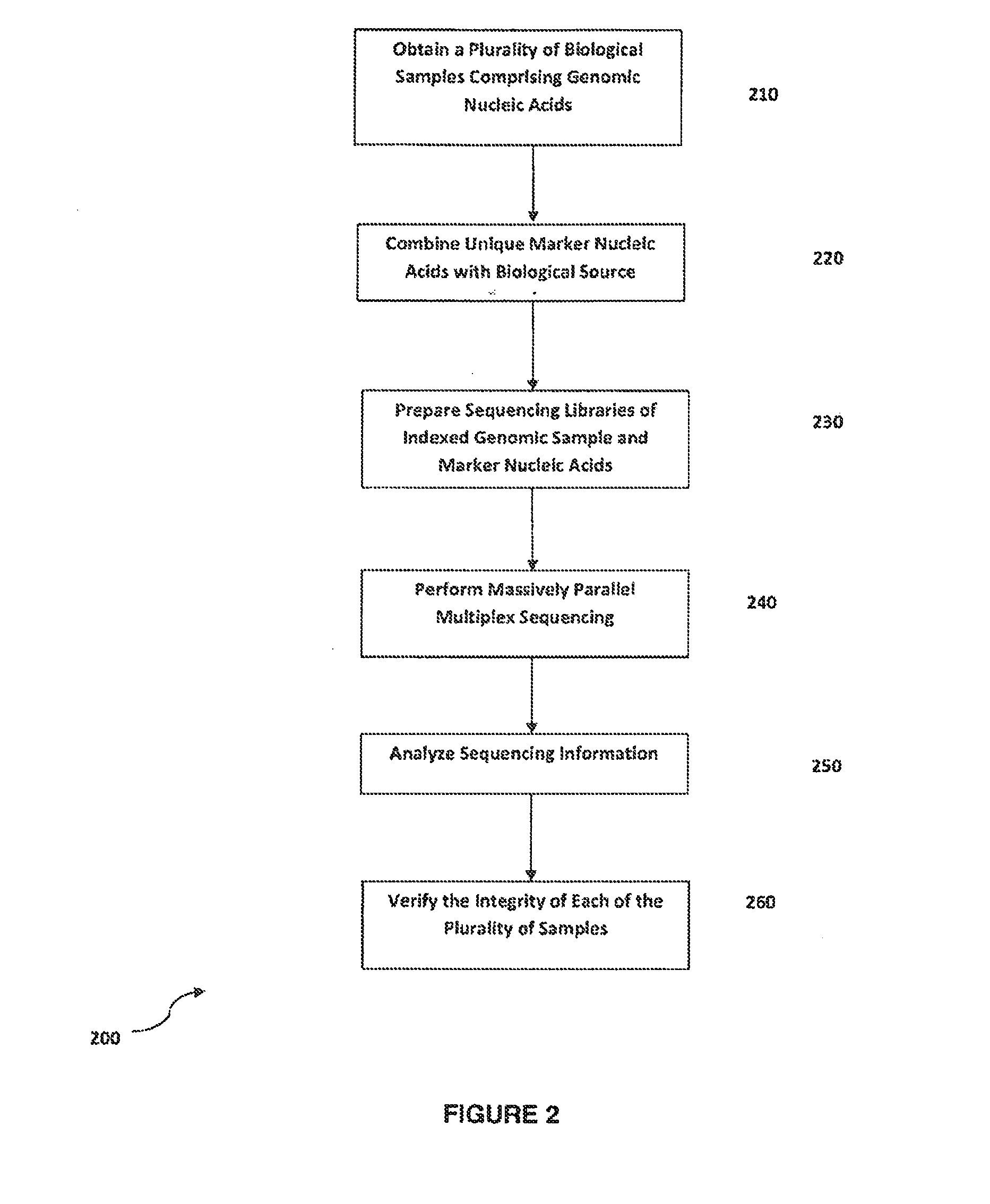
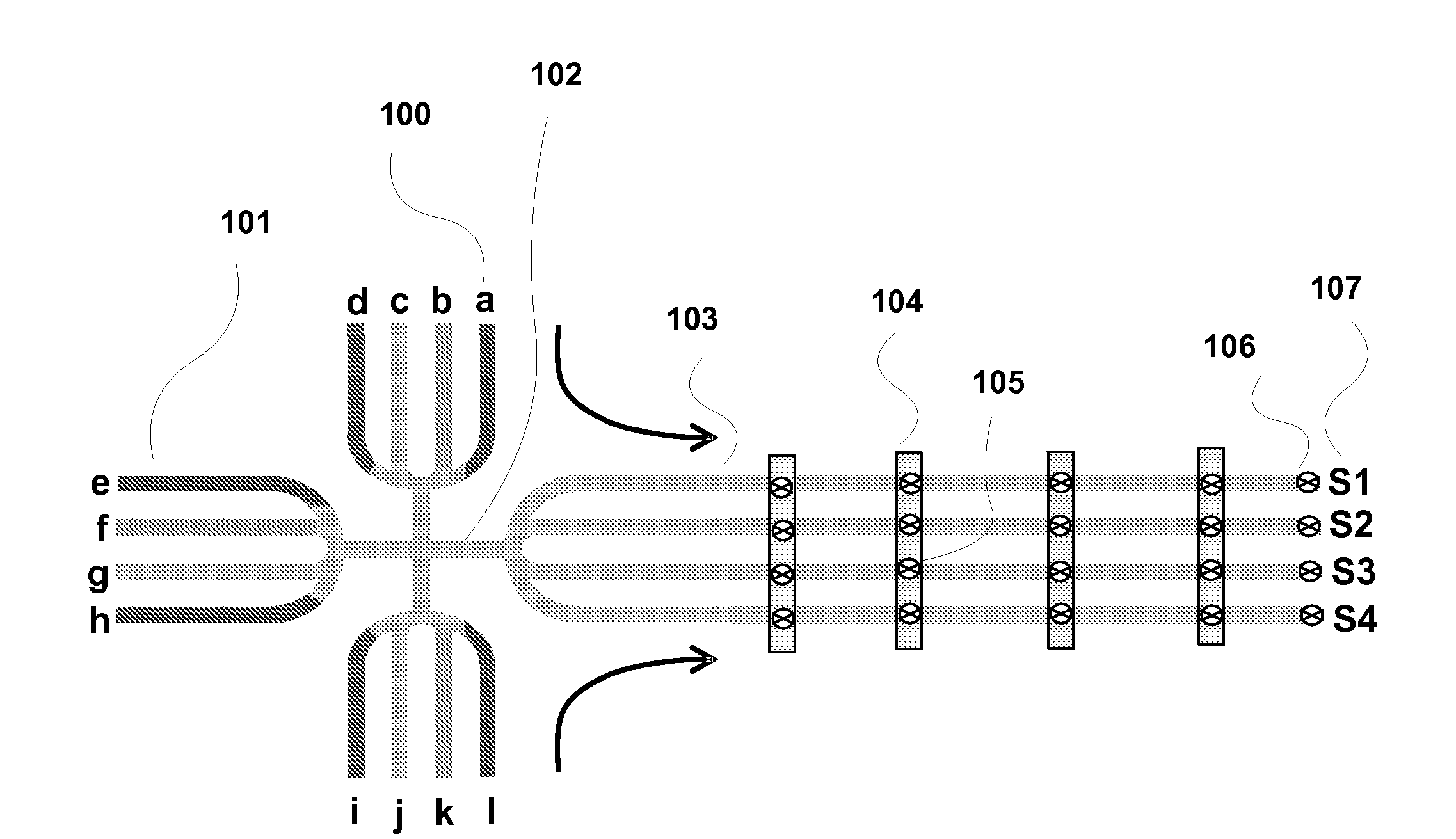
Method for verifying bioassay samples
The present invention relates to a method for verifying the integrity of biological source samples subjected to multistep bioassays that comprise massively parallel sequencing of the sample genomic nucleic acids. The integrity of the biological source samples is verified using unique marker nucleic acids that are combined with the biological source sample, and are sequenced concomitantly with the genomic nucleic acids of the biological source sample. The method provides verification of individual samples in single- and multiplex massively parallel sequencing assays.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
System and method for multiplex liquid handling
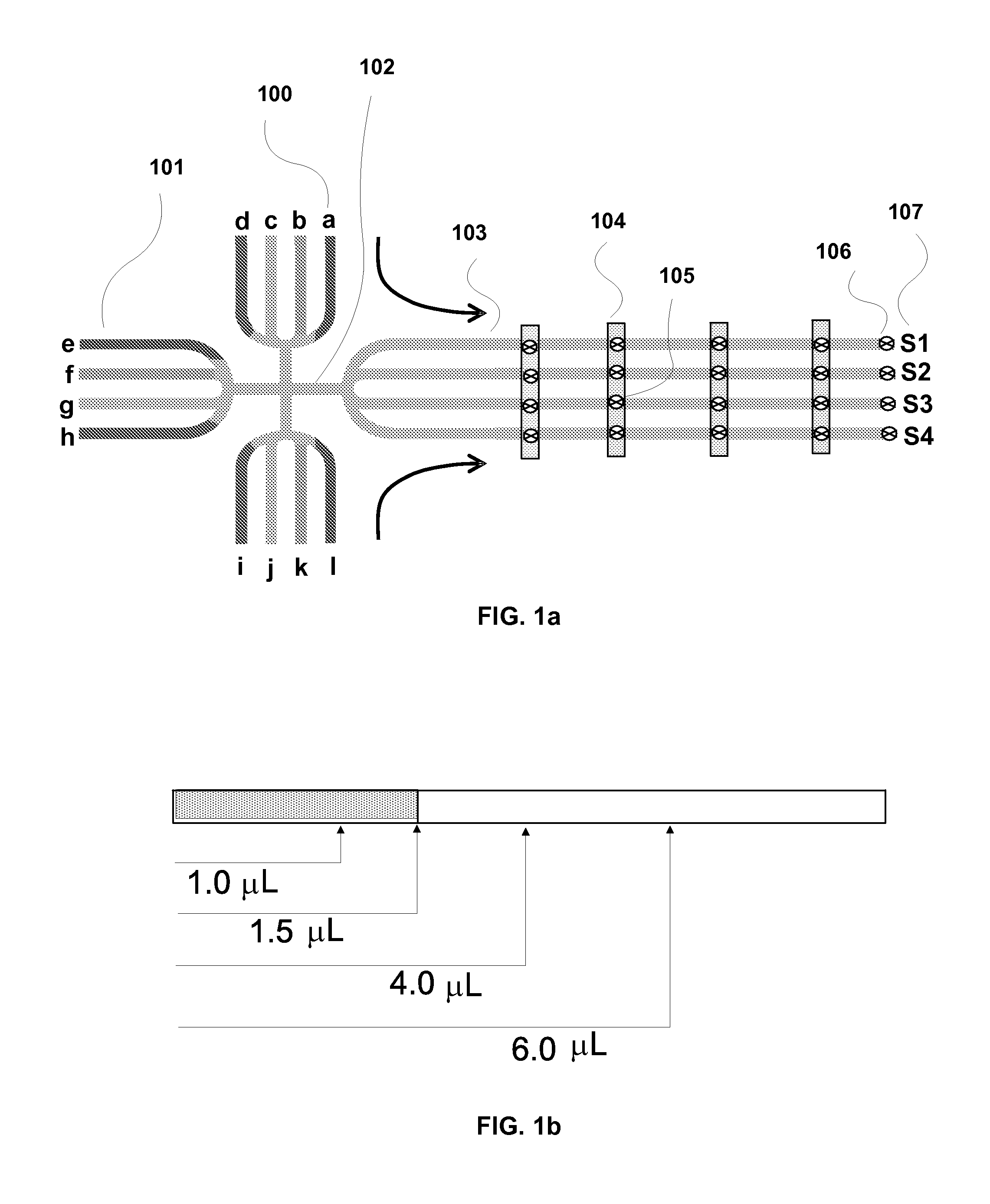
InactiveUS20080311585A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusChemical reactionEngineering
The present invention generally relates to microfabricated devices for carrying out and controlling chemical reactions and analysis. In particular, the present invention provides systems, methods, devices and computer software products related to multiplex liquid handling systems utilizing lab cards related to biological assays.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
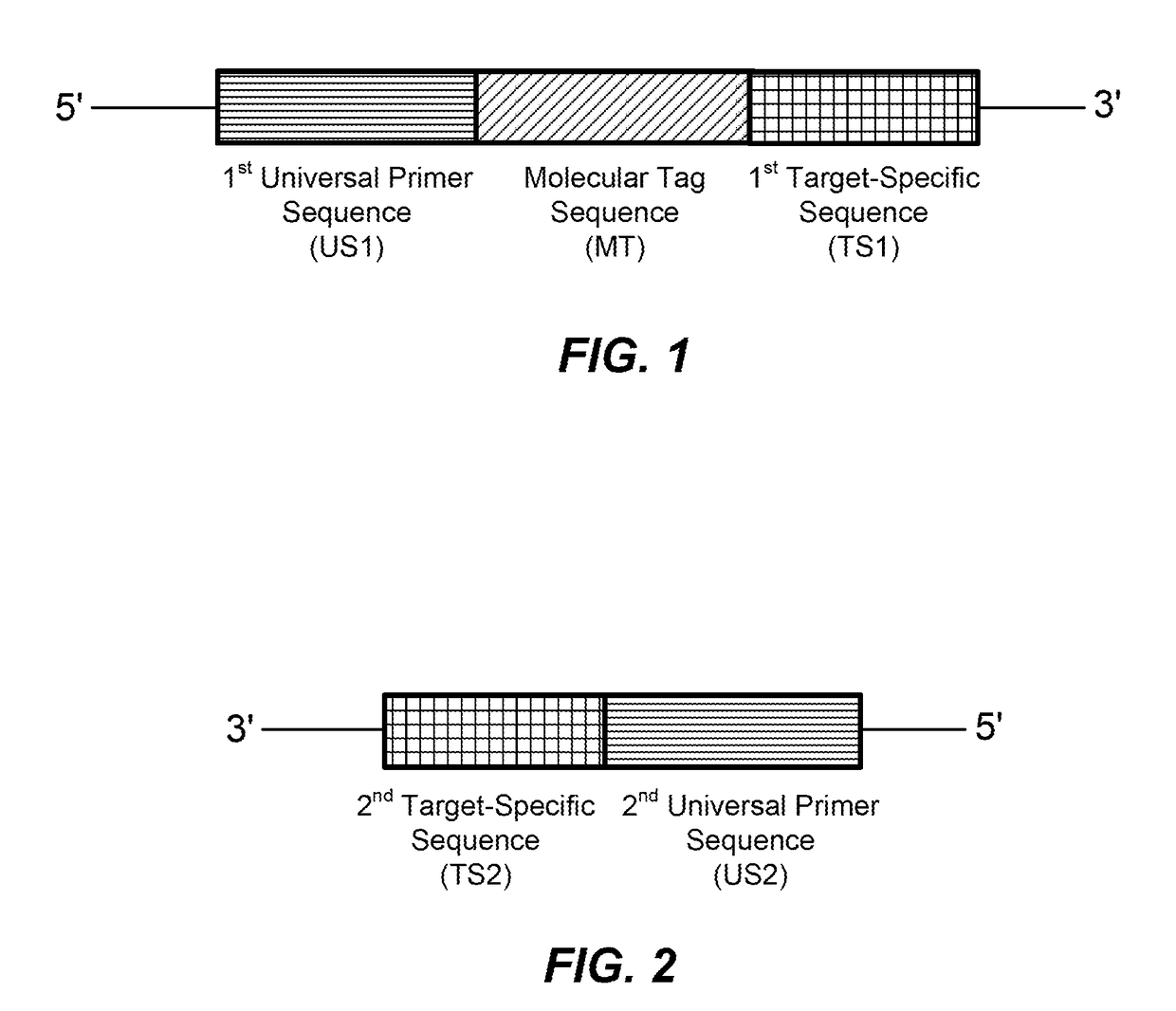
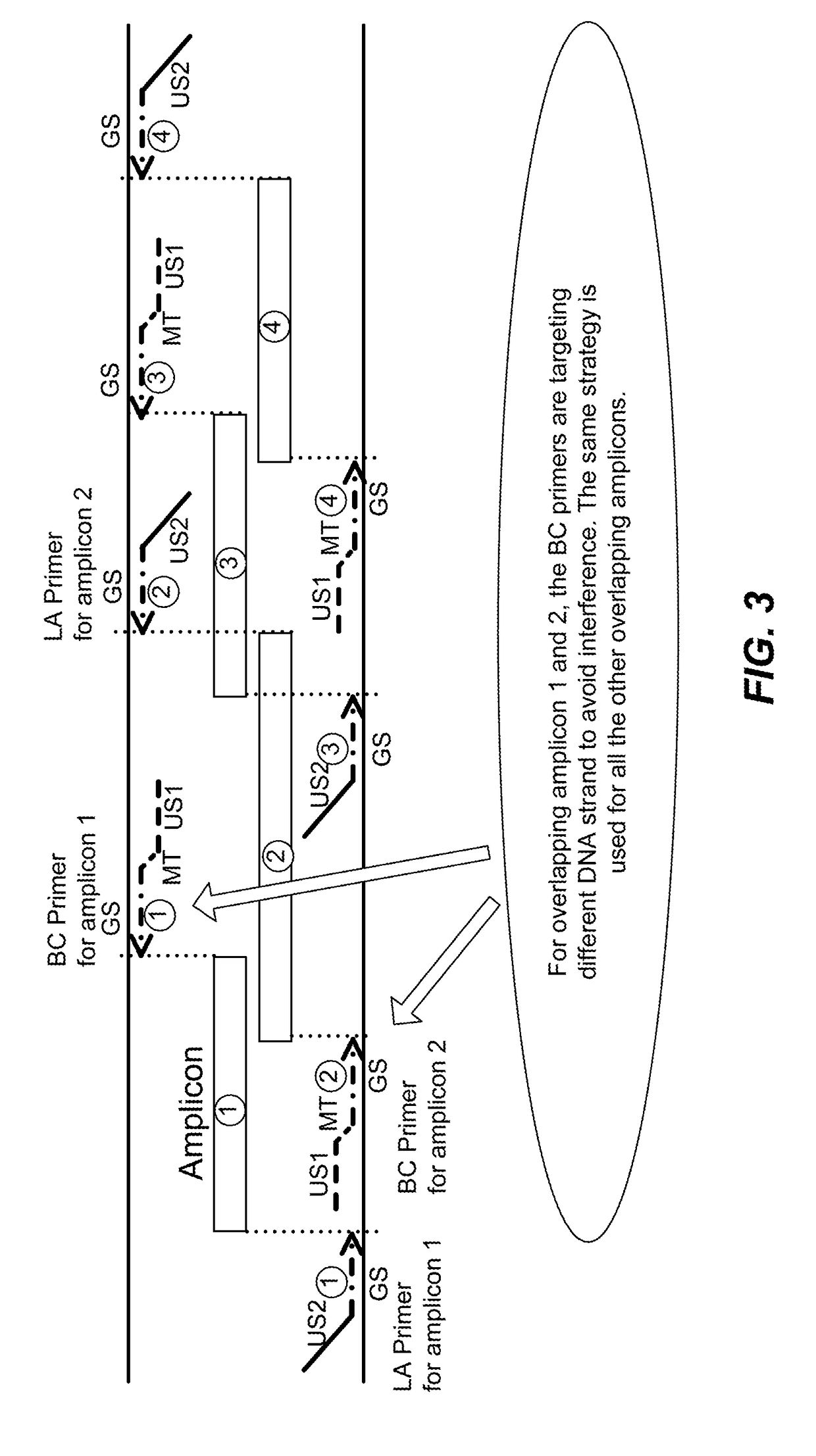
High multiplex PCR with molecular barcoding
The present disclosure provides methods and kits for performing high multiplex PCR using molecular barcodes. The methods disclosed herein separately extend a set of primers (BC primers) that each comprise a target-specific sequence, a molecular barcode and a universal sequence, and amplify the resulting extension products using another set of primers (LA primers) that each comprise another target-specific sequence and a universal sequence. The methods may further comprise amplification using universal primers (preferably comprising an adapter).
Owner:QIAGEN SCIENCES LLC
Cartridge for performing assays in a closed sample preparation and reaction system
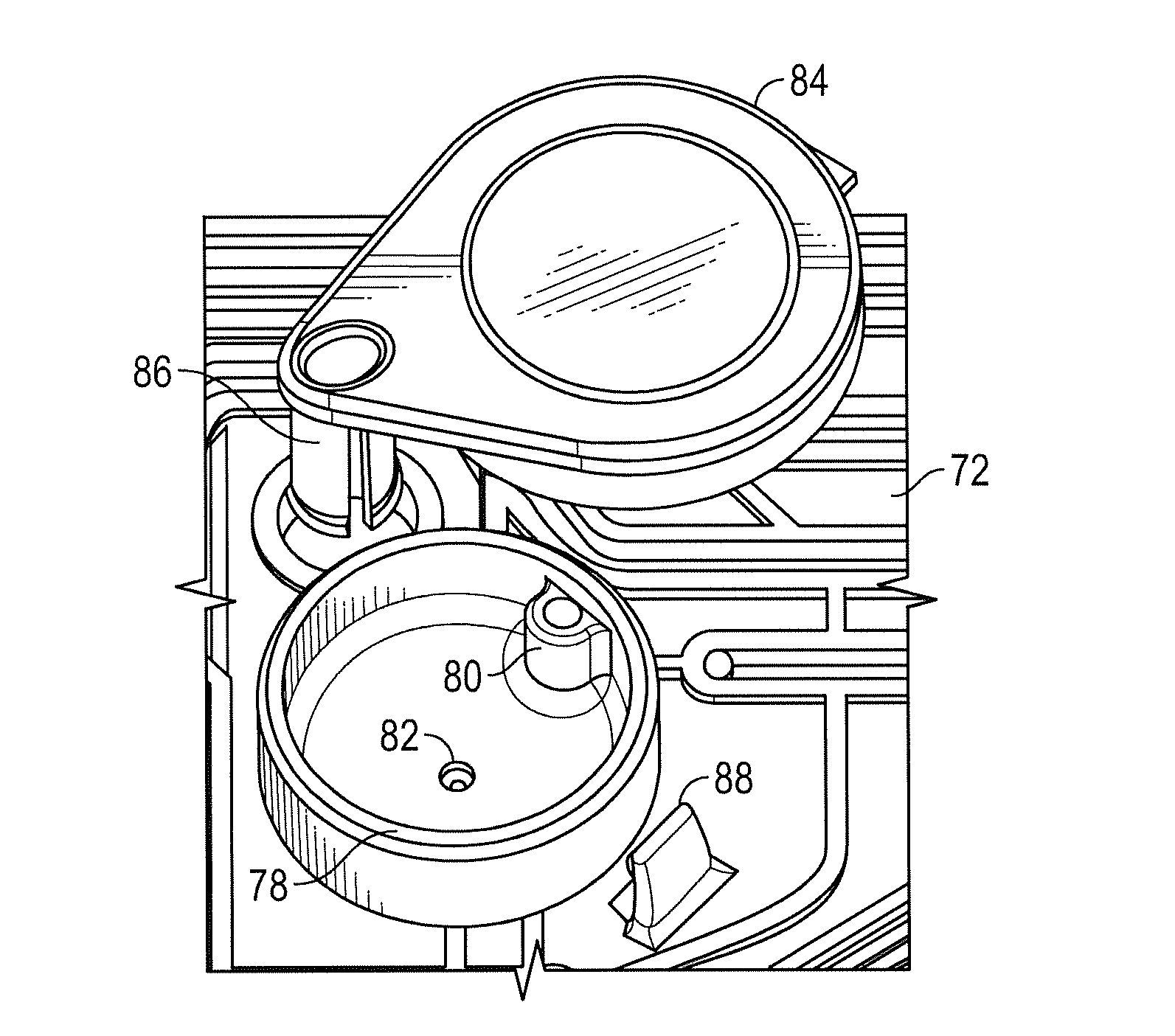
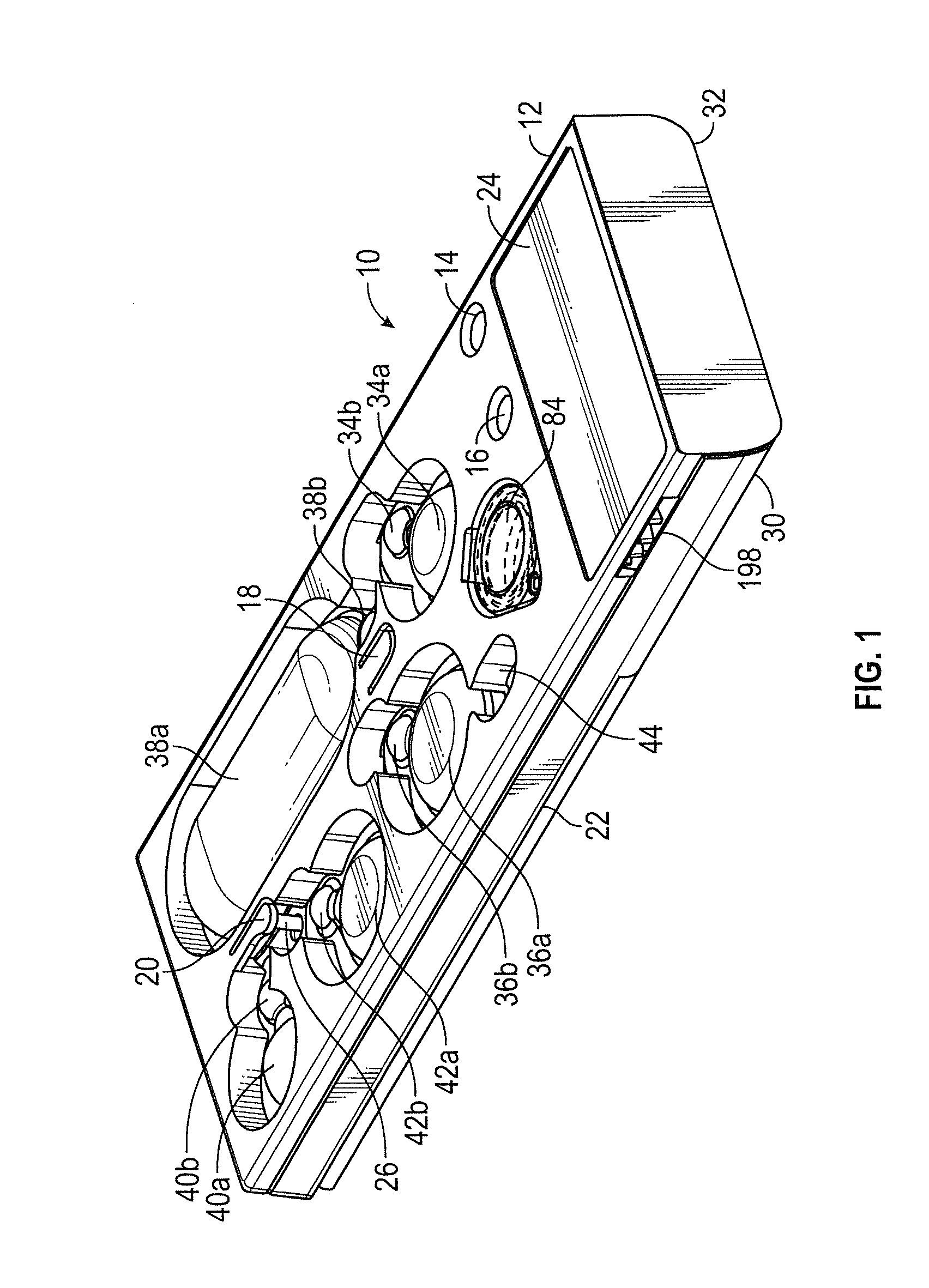
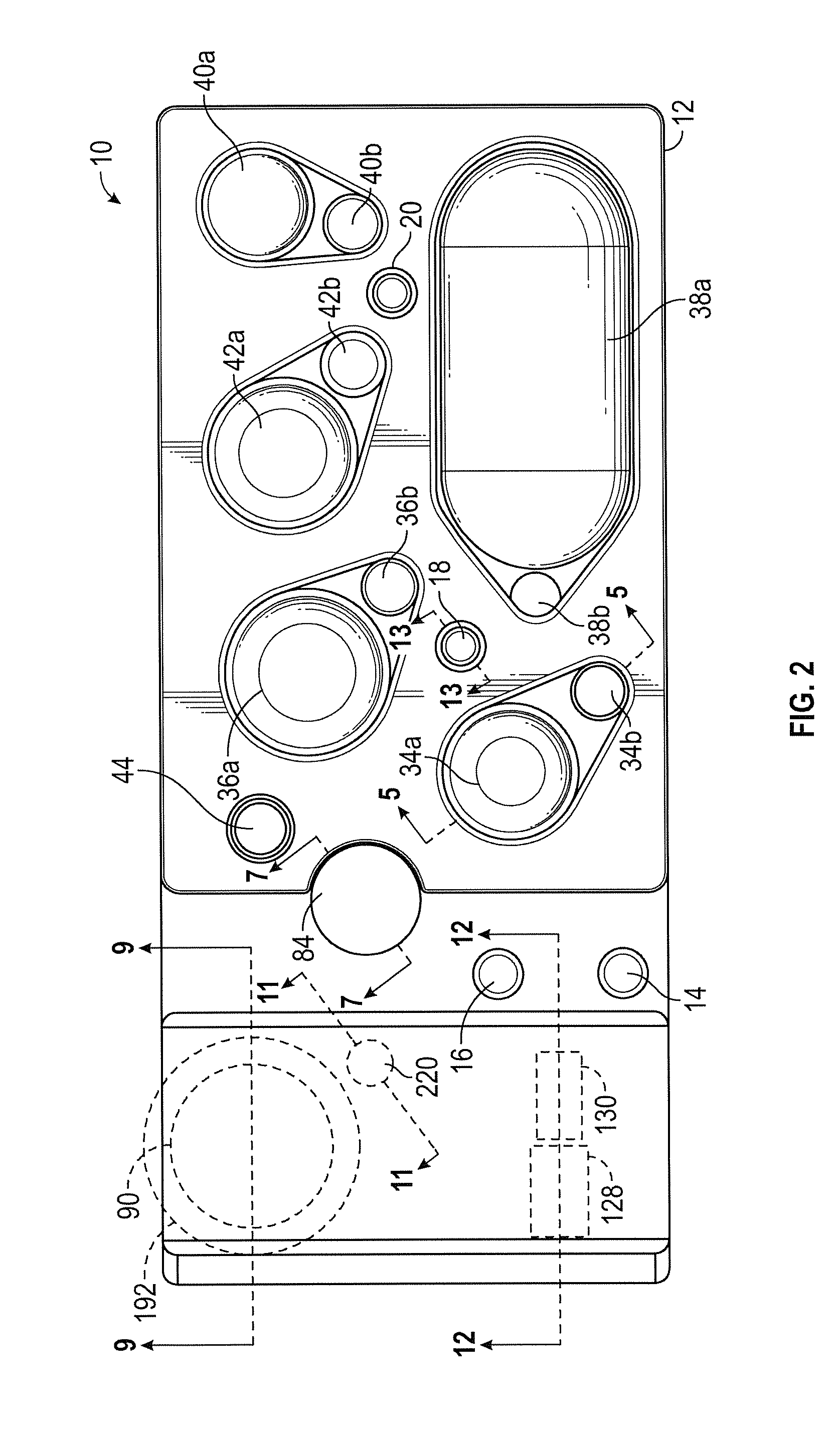
ActiveUS20160130640A1Ease and rapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusThermal energyLysis
In one embodiment, a multiplex fluid processing cartridge includes a sample well, a deformable fluid chamber, a mixing well with a mixer disposed therein, a lysis chamber including a lysis mixer, an electrowetting grid for microdroplet manipulation, and electrosensor arrays configured to detect analytes of interest. An instrument for processing the cartridge is configured to receive the cartridge and to selectively apply thermal energy, magnetic force, and electrical connections to one or more discrete locations on the cartridge and is further configured to compress the deformable chamber(s) in a specified sequence.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
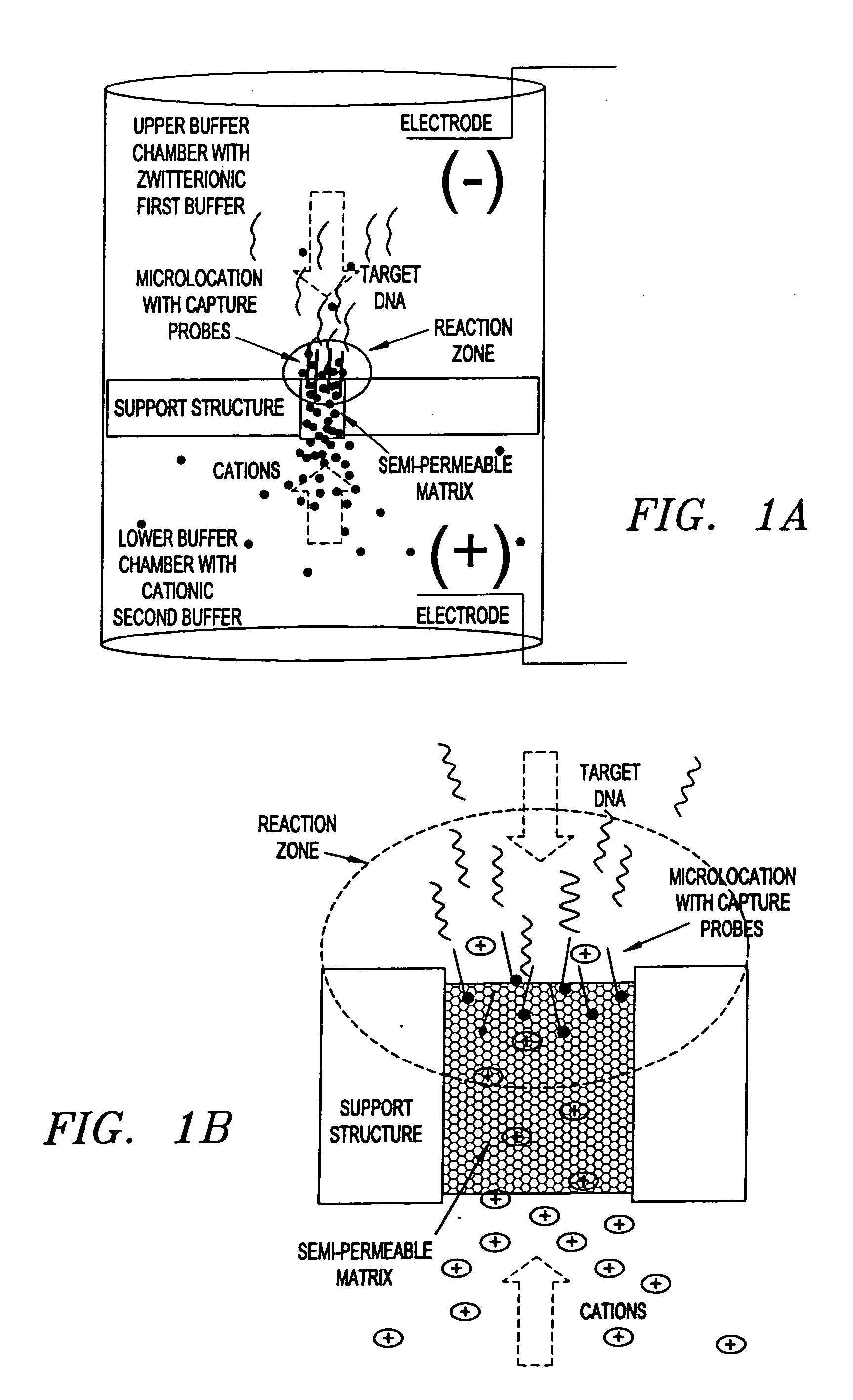
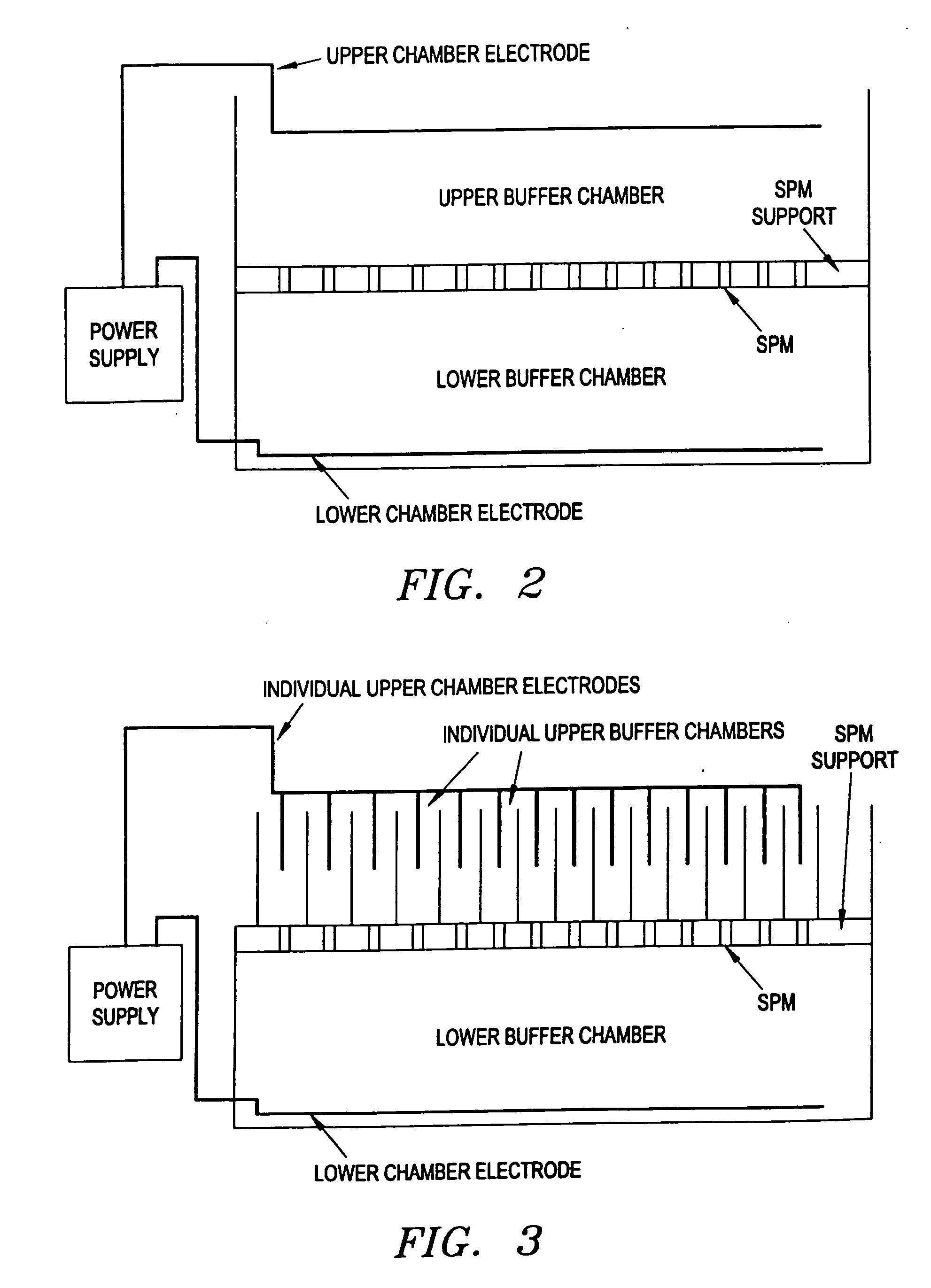
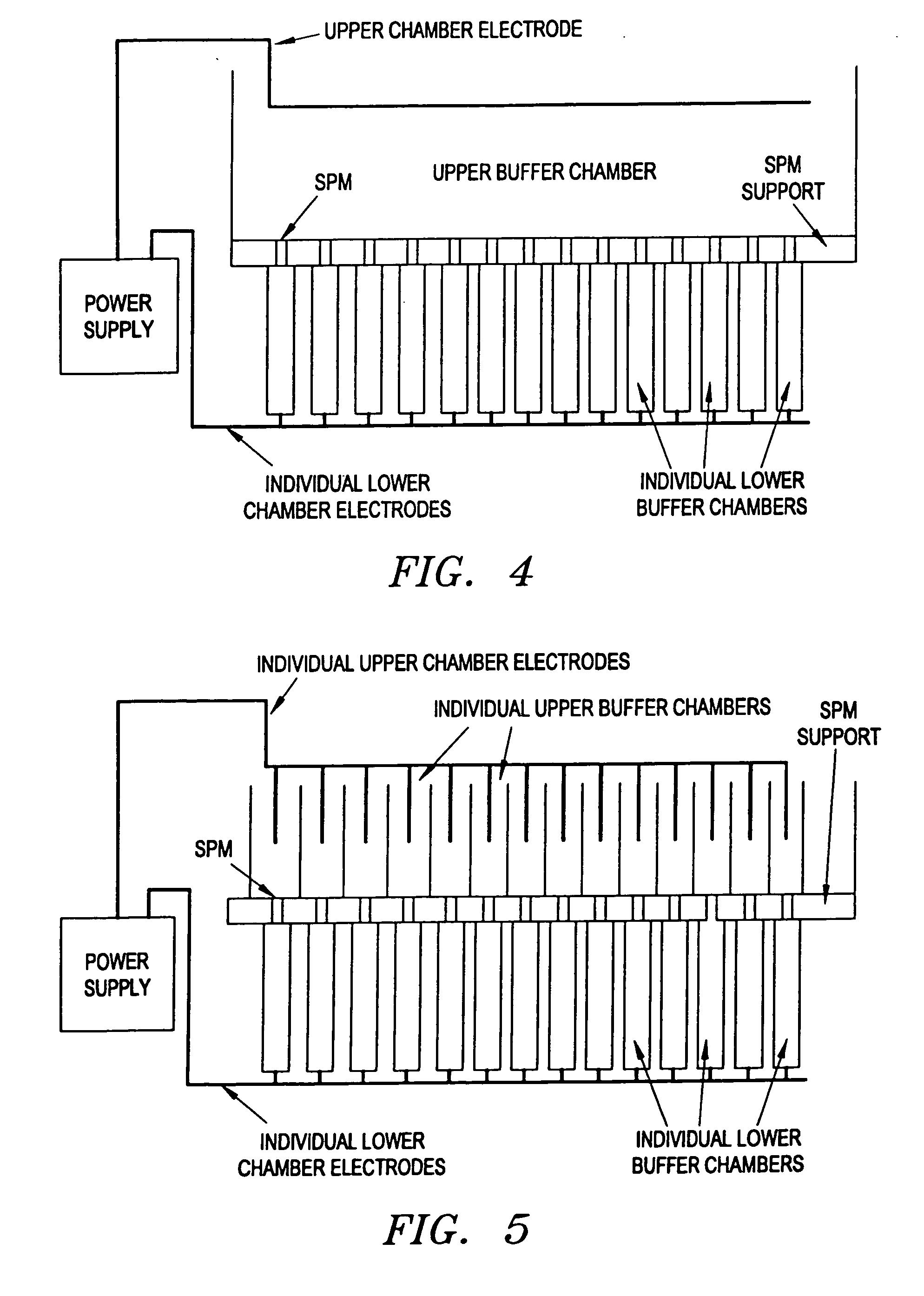
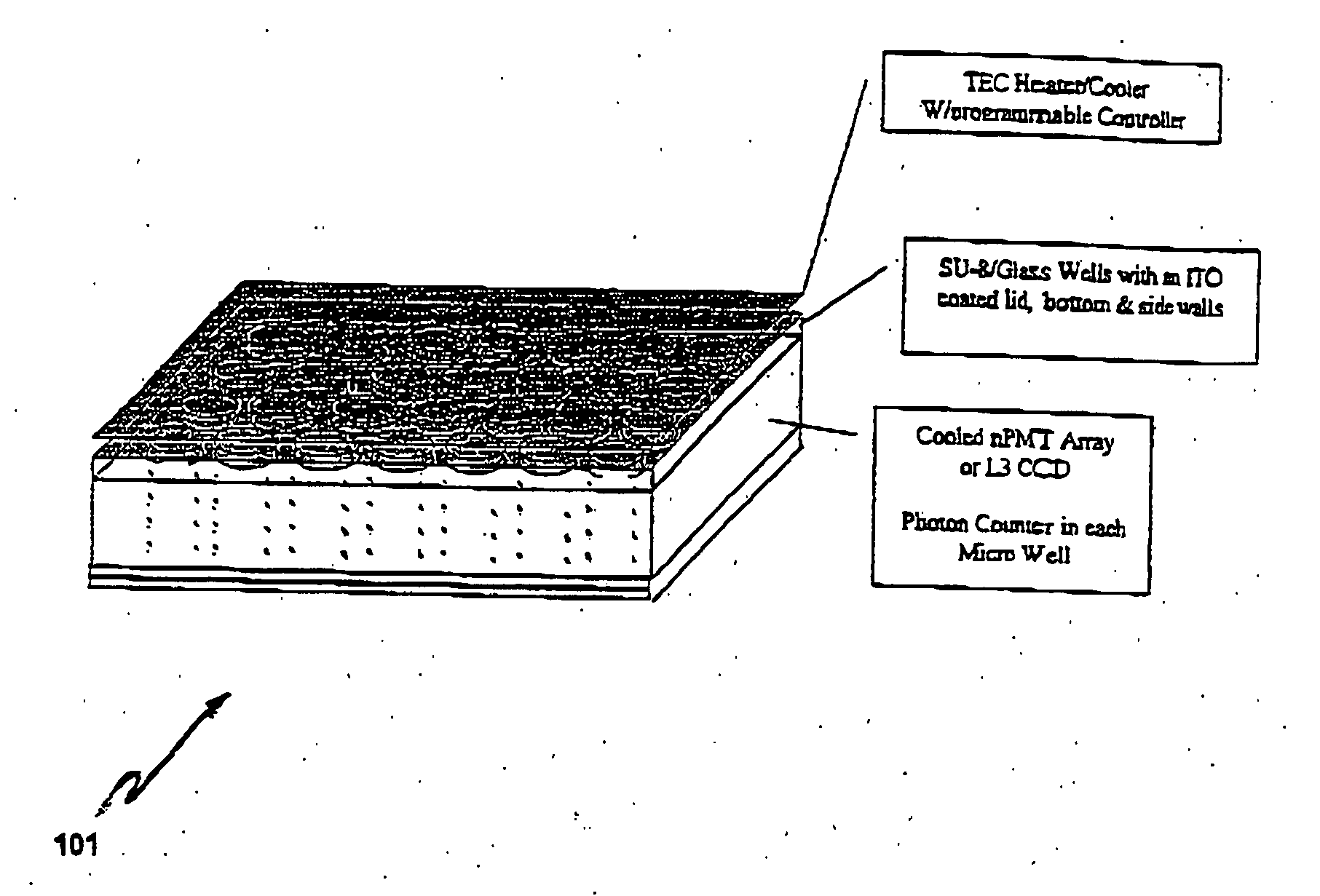
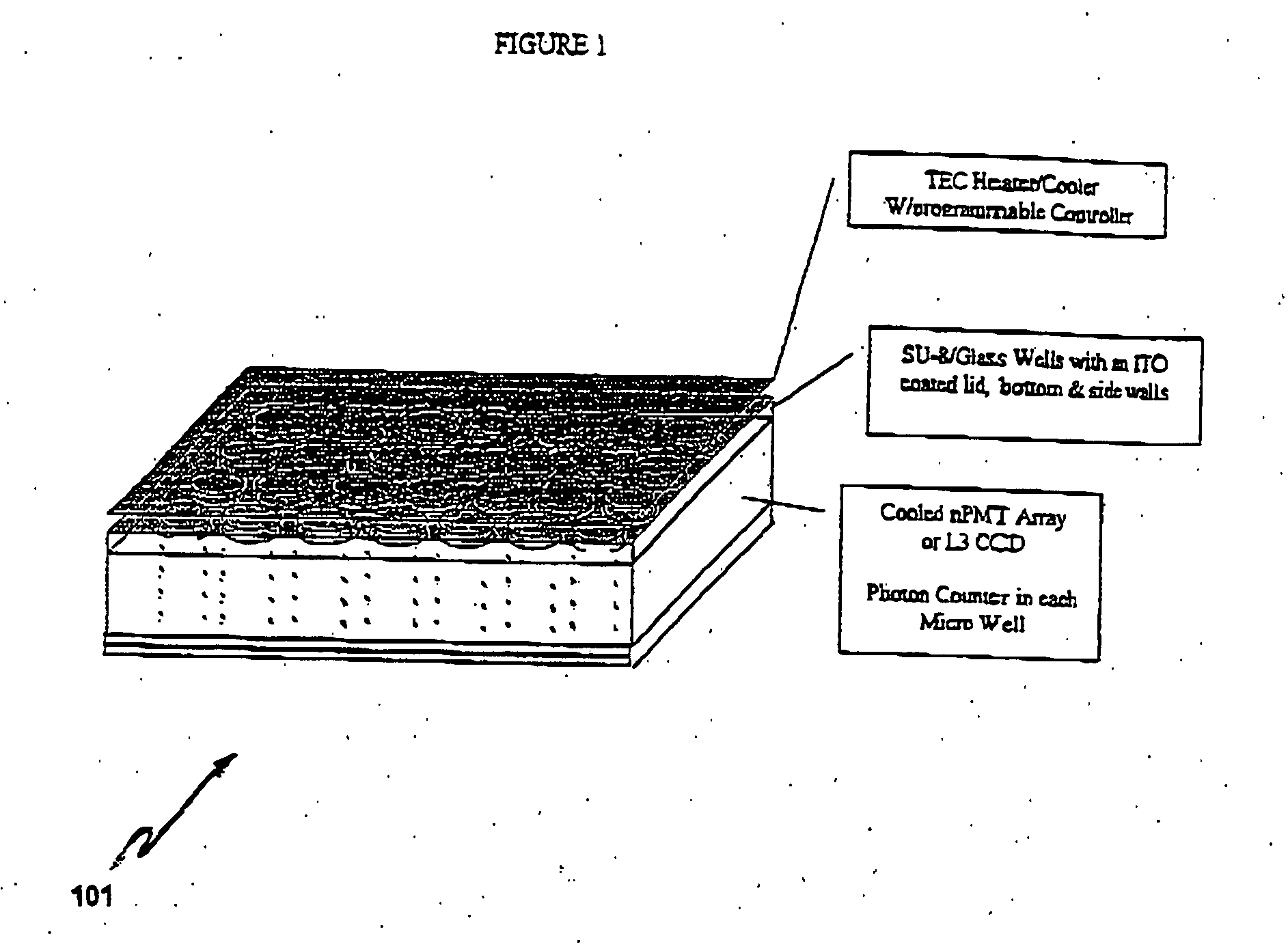
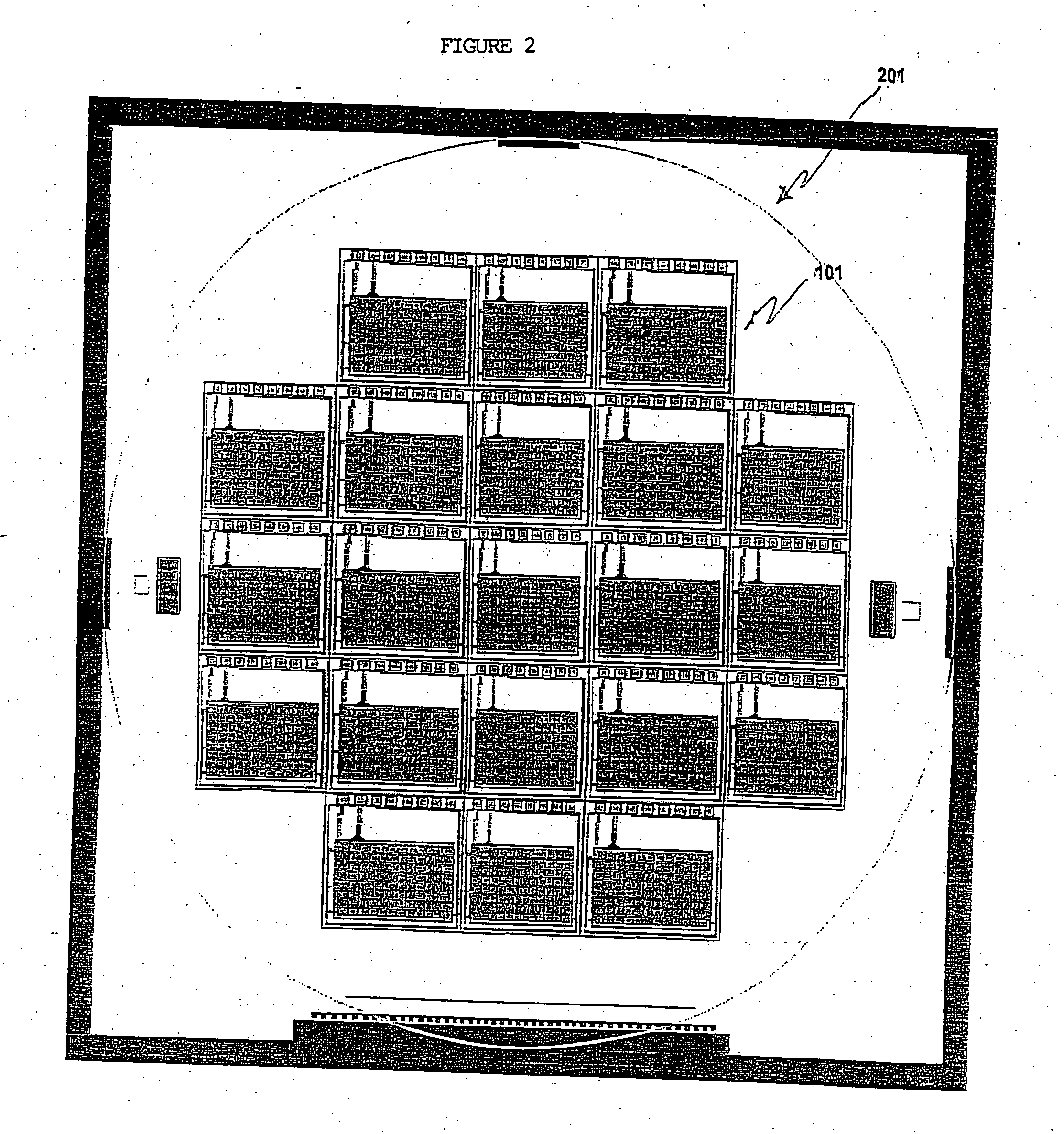
Electronic systems and component devices for macroscopic and microscopic molecular biological reaction, analyses, and diagnostics
InactiveUS20050026202A1Favorable zoneImprove responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyMultiplexBiopolymer
This invention pertains to the design, fabrication, and uses of an electronic system which can actively carry out and control multi-step and multiplex reactions in macroscopic or microscopic formats. In particular, these reactions include molecular biological reactions, such as nucleic acid hybridizations, nucleic acid amplification, sample preparation, antibody / antigen reactions, clinical diagnostics, combinatorial chemistry and selection, drug screening, oligonucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis, peptide synthesis, biopolymer synthesis, and catalytic reactions. A key feature of the present invention is the ability to control the localized concentration of two or more reaction-dependant molecules and their reaction environment in order to greatly enhance the rate and specificity of the molecular biological reaction
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL
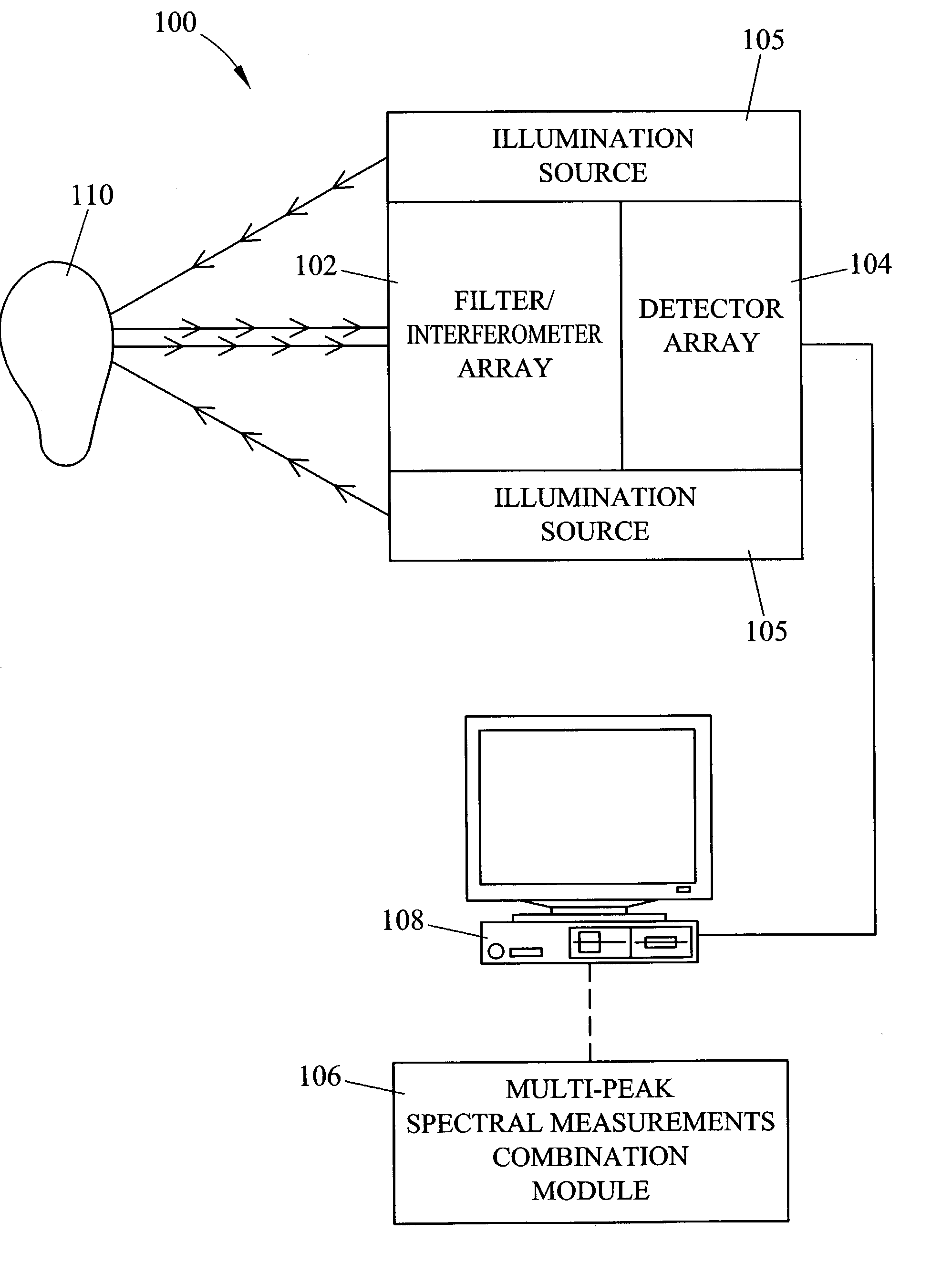
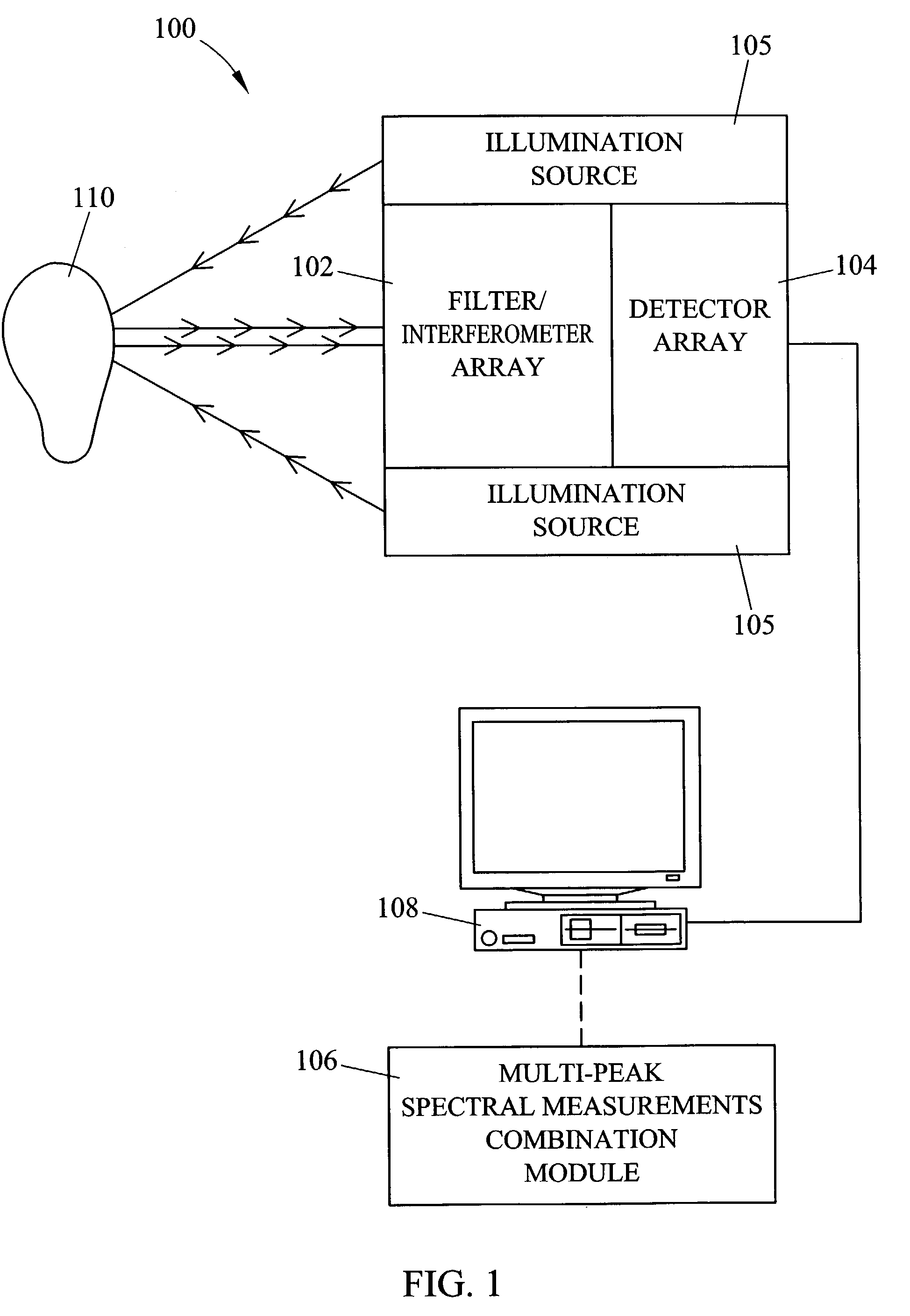
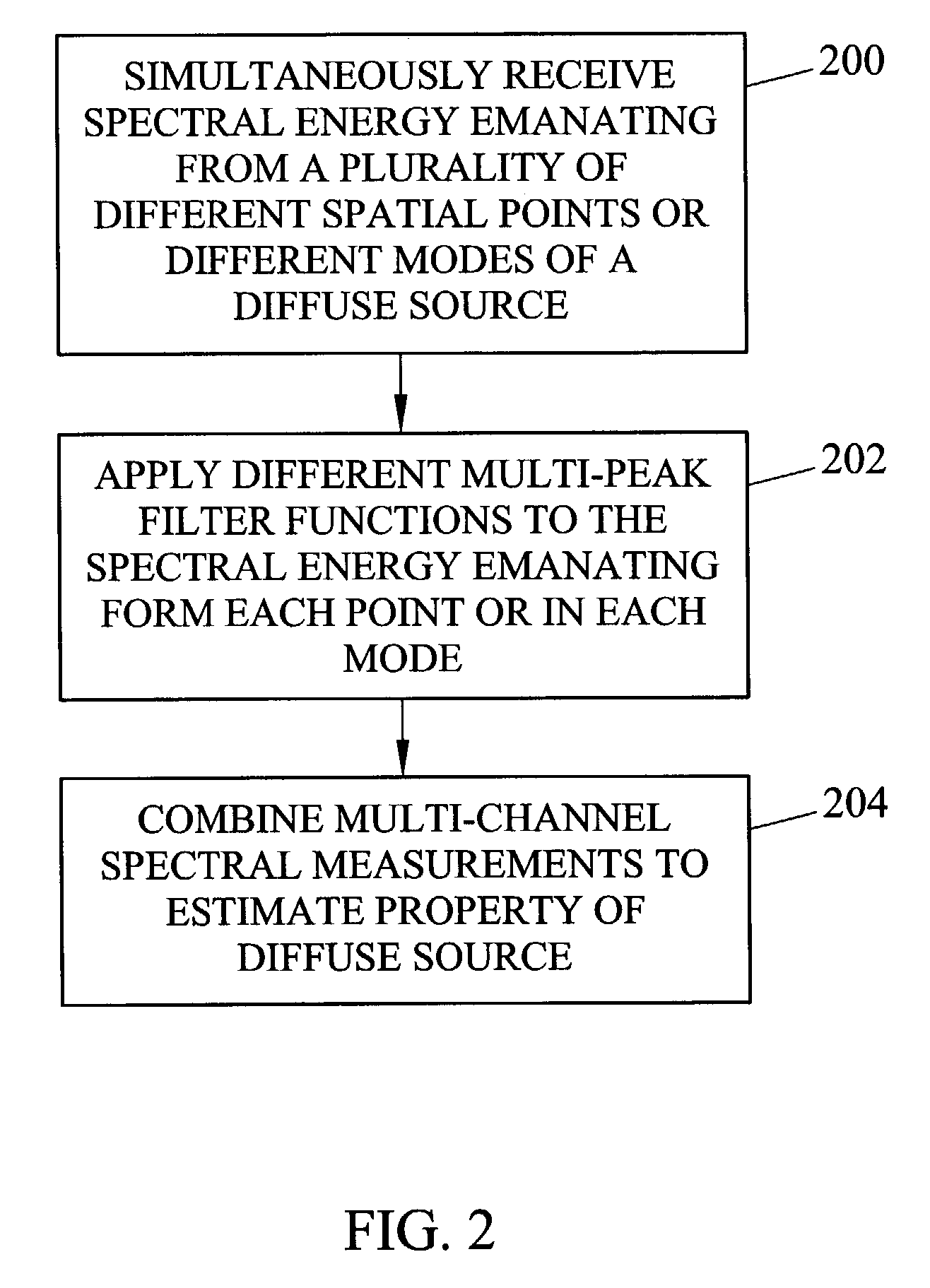
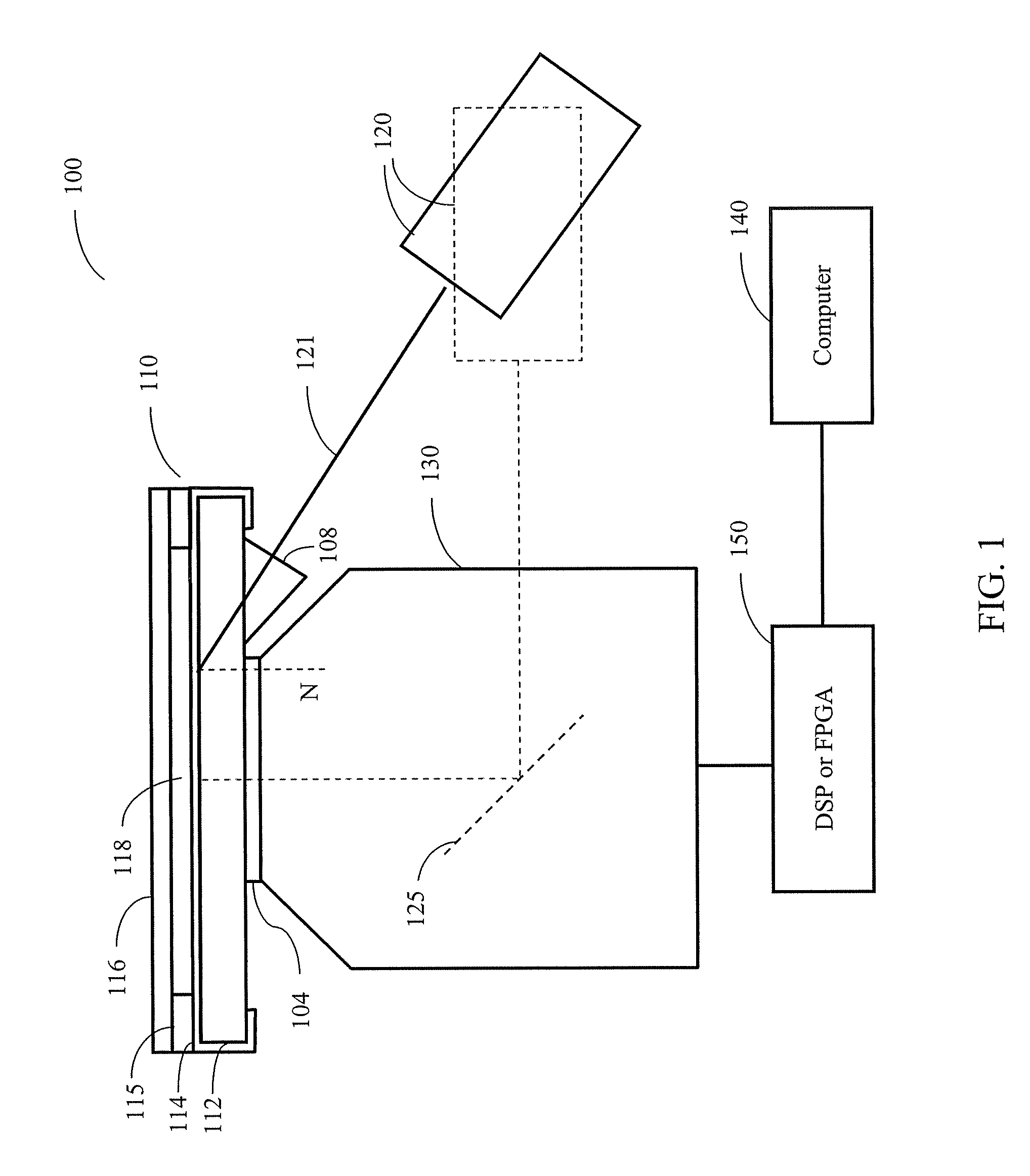
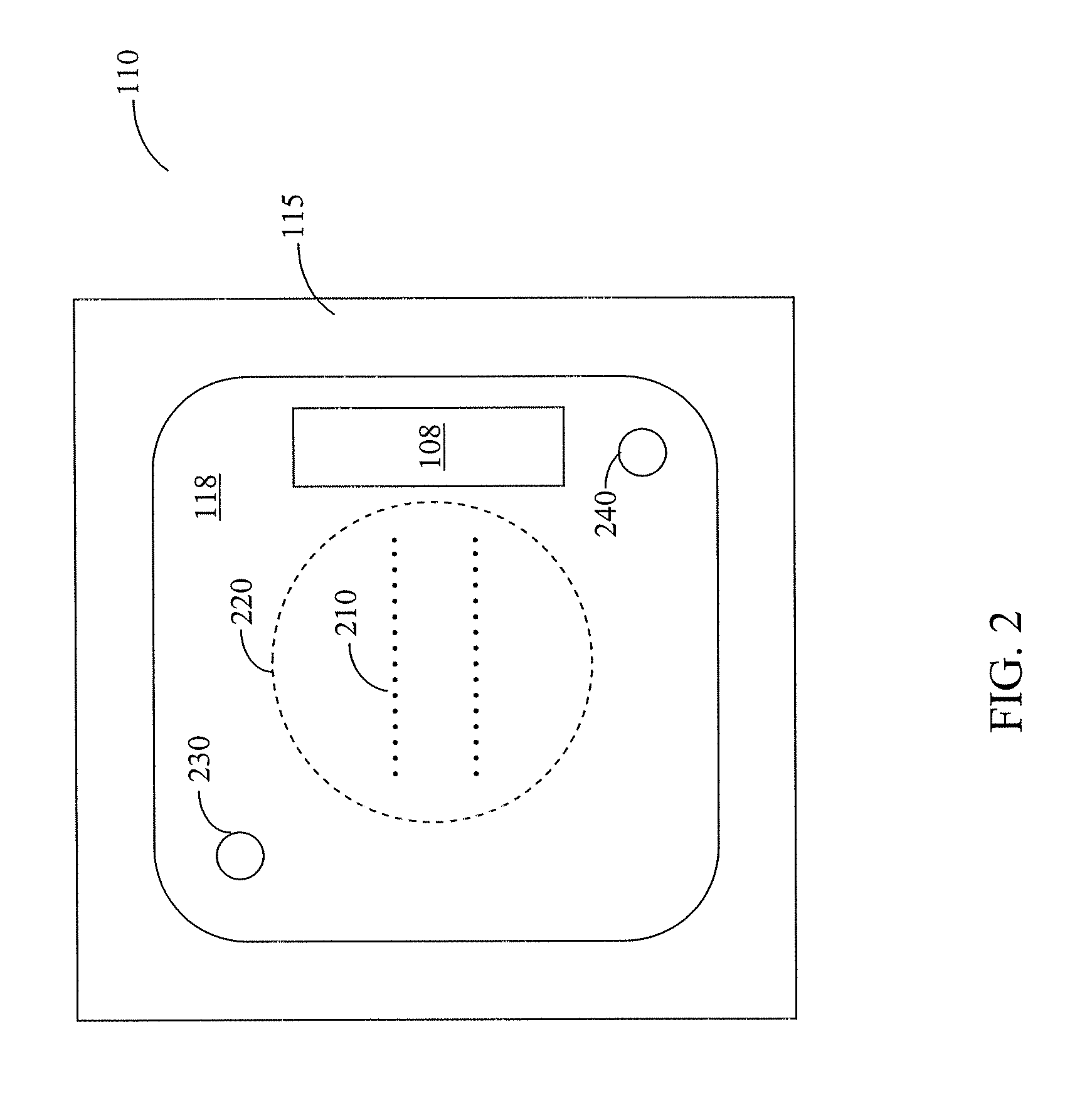
Methods and systems for static multimode multiplex spectroscopy
ActiveUS7092101B2Accurately and efficiently measuring spectral propertyIncrease speedRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectroscopy methodsStatics
Methods and systems for static multimode multiplex spectroscopy are disclosed. According to a method for static multimode multiplex spectroscopy, spectral energy emanating from different points of a diffuse source is simultaneously received. Different multi-peak filter functions are applied to the spectral energy emanating from the different points to produce a multi-channel spectral measurement for each point. The multi-channel spectral measurements are combined to estimate a property of the diffuse source.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Method and System for Multiplex Genetic Analysis
ActiveUS20100261158A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsAnalyteComputerized system
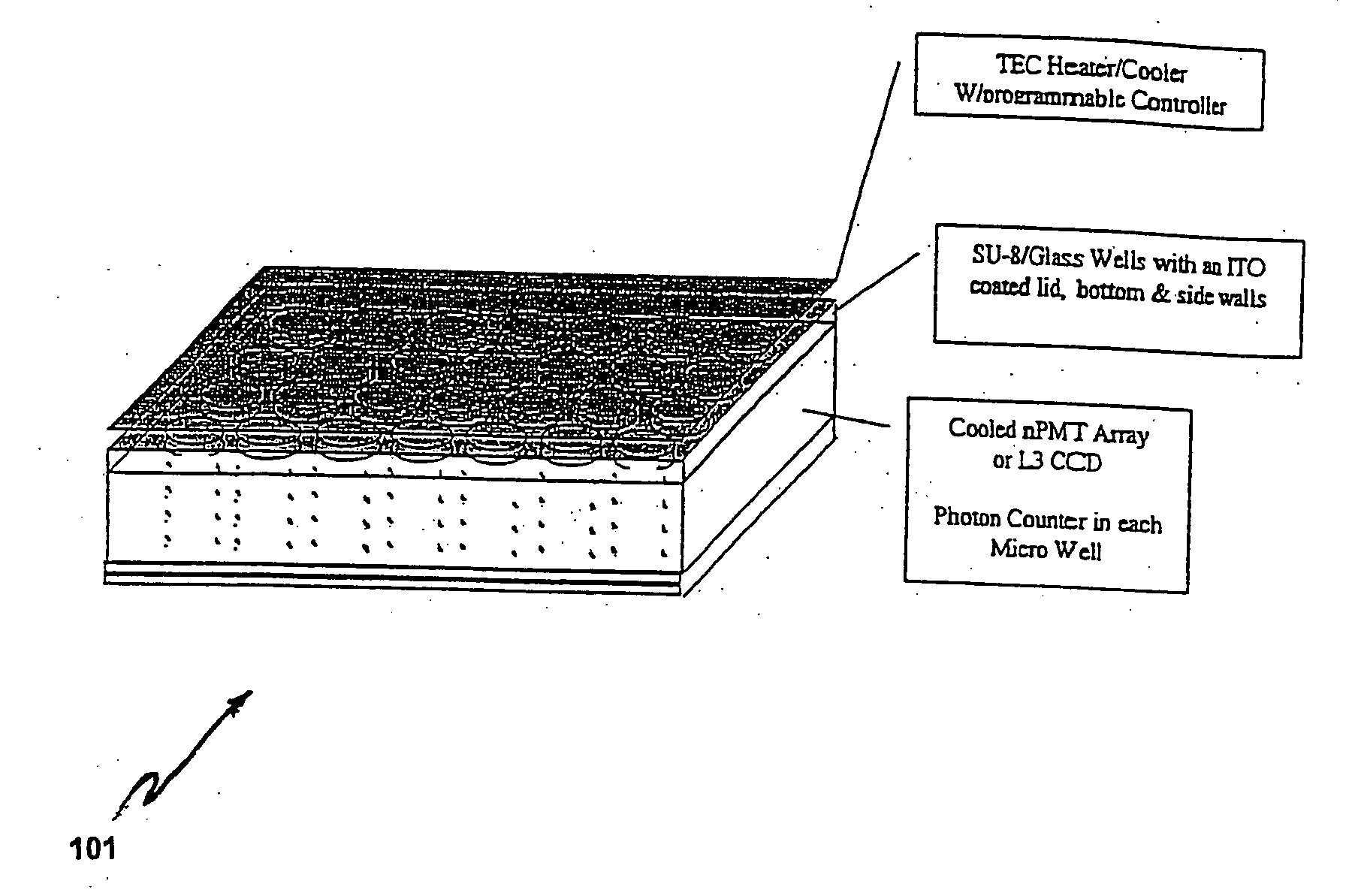
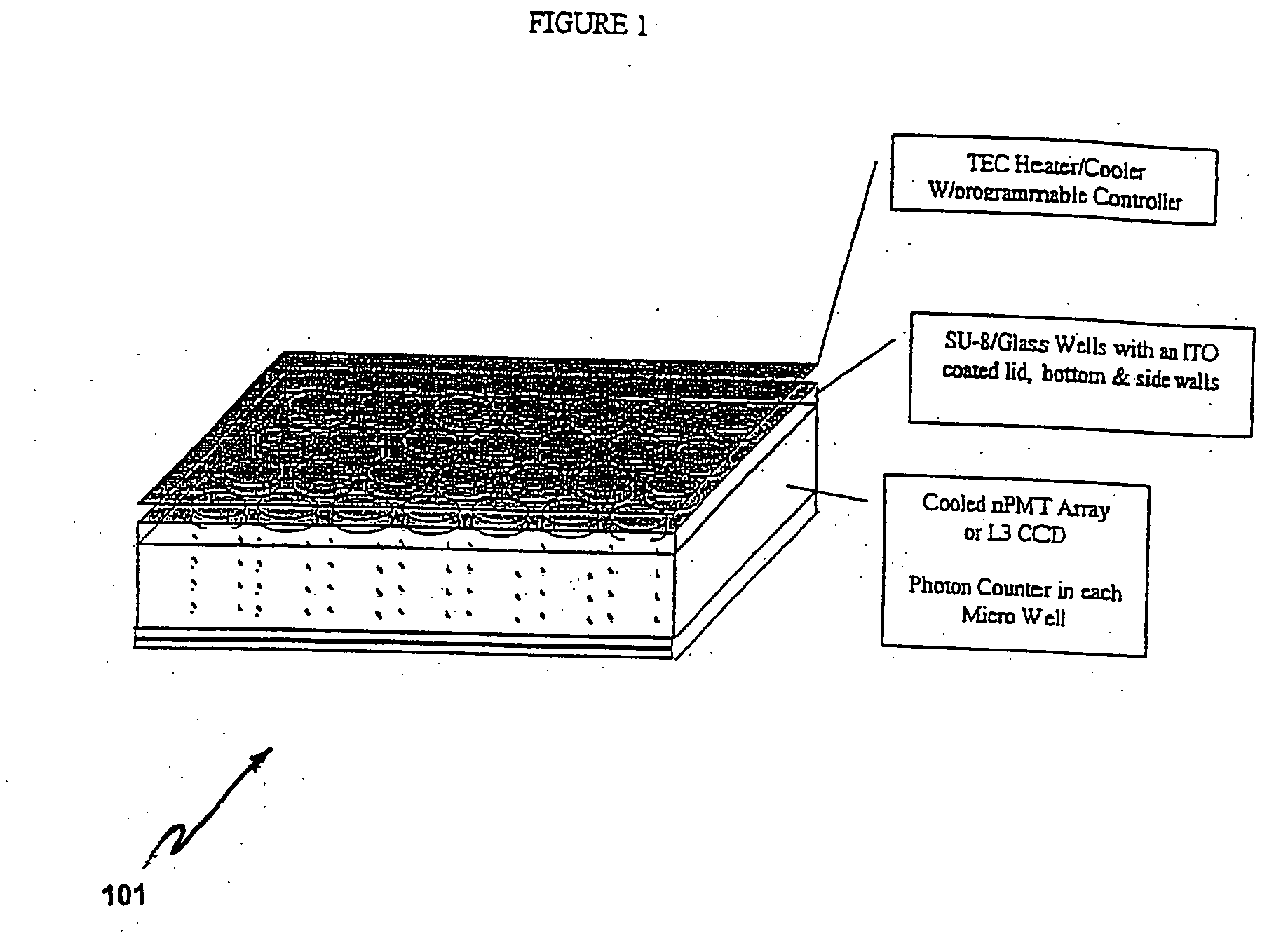
The present disclosure provides apparatus, systems and method for detecting separately and substantially simultaneously light emissions from a plurality of localized light-emitting analytes. A system according to exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure comprises a sample holder having structures formed thereon for spatially separating and constraining a plurality of light-emitting analytes each having a single nucleic acid molecule or a single nucleic acid polymerizing enzyme, a light source configured to illuminate the sample holder, an optical assembly configured to collect and detect separately and substantially simultaneously light emissions associated with the plurality of light emitting analytes. The system may further include a computer system configured to analyze the light emissions to determine the structures or properties of a target nucleic acid molecule associated with each analyte.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method of detecting tumour recurrence
PendingUS20200248266A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsMultiplexCell free
The invention relates to subject-specific methods for detecting recurrence of tumours based on an understanding of the clonal / subclonal mutation profile of the subject's tumour and detection of the mutations in their cell-free DNA (cfDNA), typically by multiplex PCR of tumour mutations such as single nucleotide variants (SNVs).
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Methods and mixtures pertaining to analyte determination using electrophilic labeling reagents
This invention pertains to methods, mixtures, kits and / or compositions for the determination of analytes by mass analysis using unique labeling reagents or sets of unique labeling reagents. The labeling reagents can be isomeric or isobaric and can be used to produce mixtures suitable for multiplex analysis of the labeled analytes.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Multiplex polynucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20060234264A1Solve low usageMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationChemical treatmentDna polymerasen
The invention provides a method of synthesizing complex mixtures of long polynucleotides by separately synthesizing and assembling shorter component oligonucleotides. In one aspect, pairs of oligonucleotides that form components of such polynucleotides are synthesized on one or more microarrays, or other large-scale parallel solid phase synthesis platforms, after which they are released. Members of each pair contain unique complementary barcode sequences that are used match-up pairs in a hybridization reaction to form duplexes. Such duplexes are then extended with a DNA polymerase and the resulting extension product is amplified to form an amplicon. The amplicon may be either used directly as the desired polynucleotide, or it may undergo further processing, such as capture on solid phase supports and / or additional enzymatic or chemical processing, to produce a desired polynucleotide product, such as a circularizing probe for multiplex analysis of genomic DNA, or the like.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
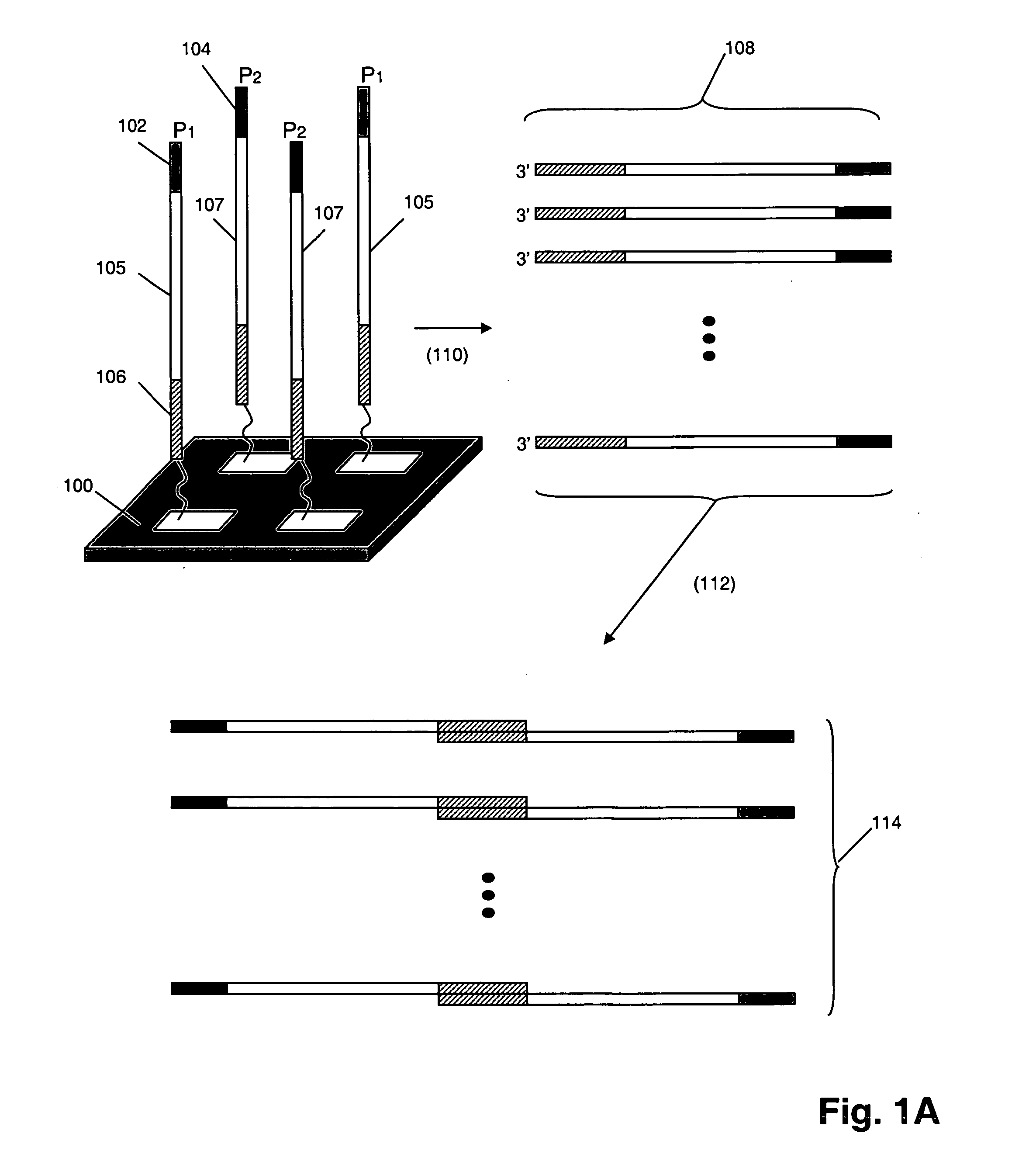
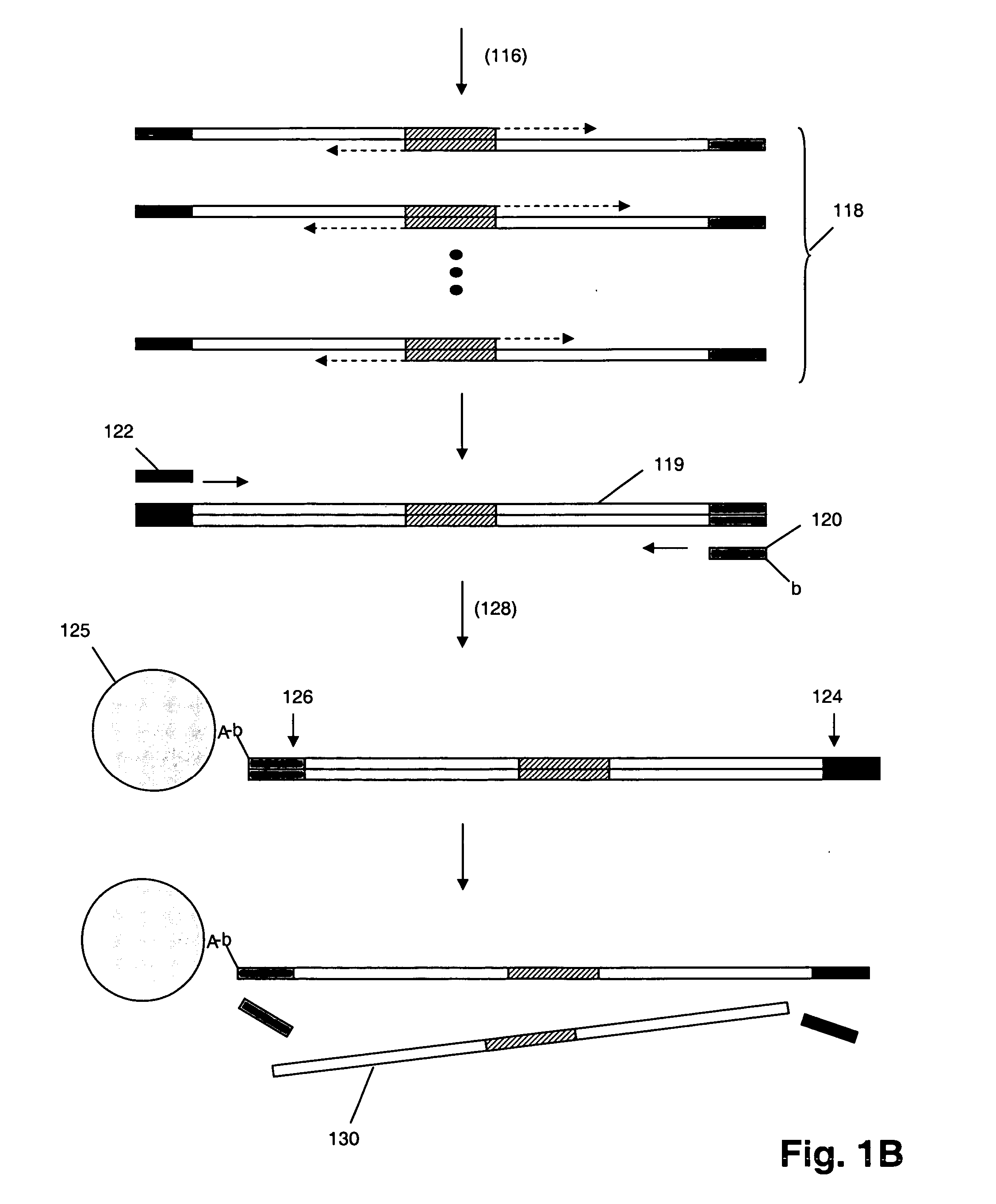
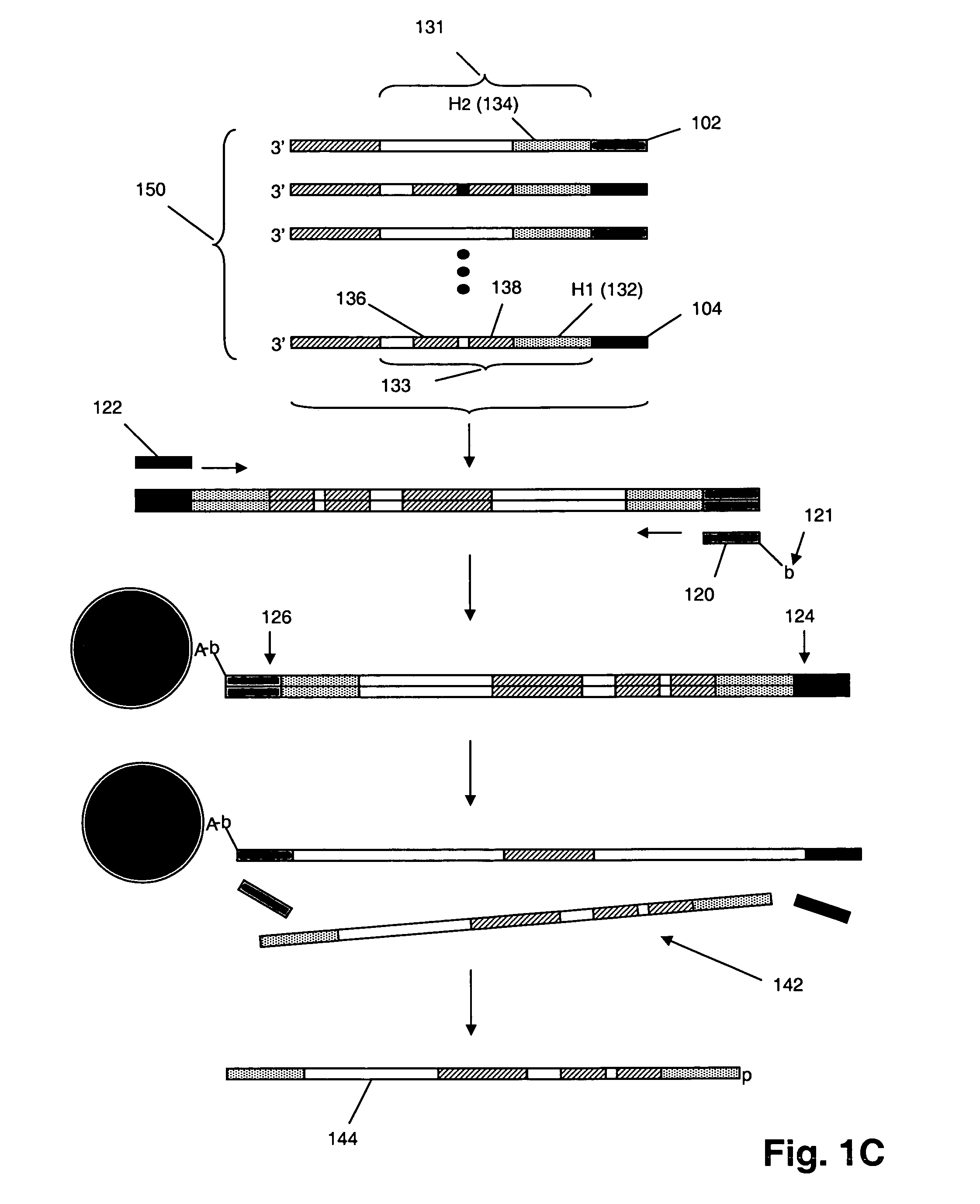
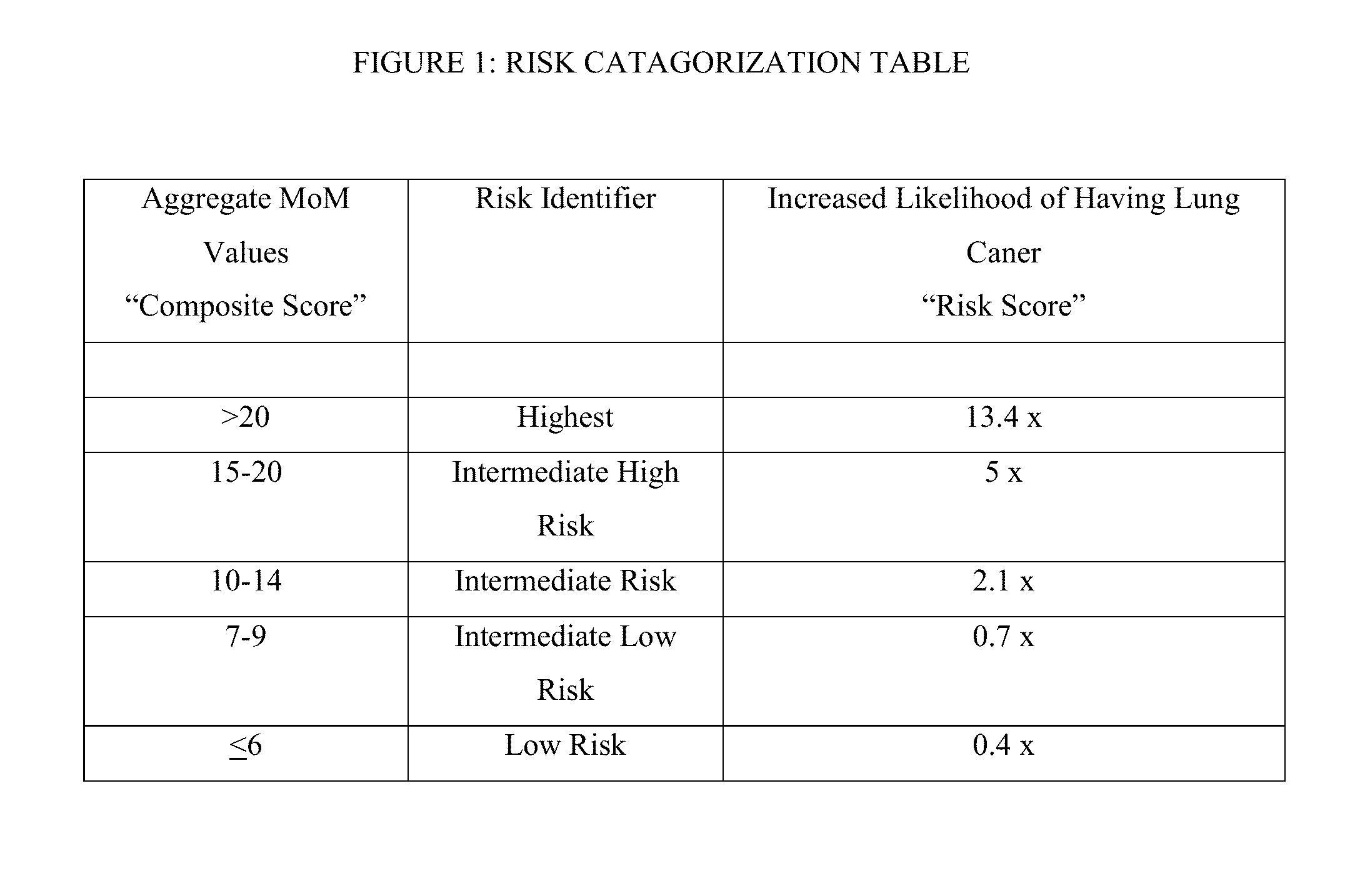
Methods and algorithms for aiding in the detection of cancer
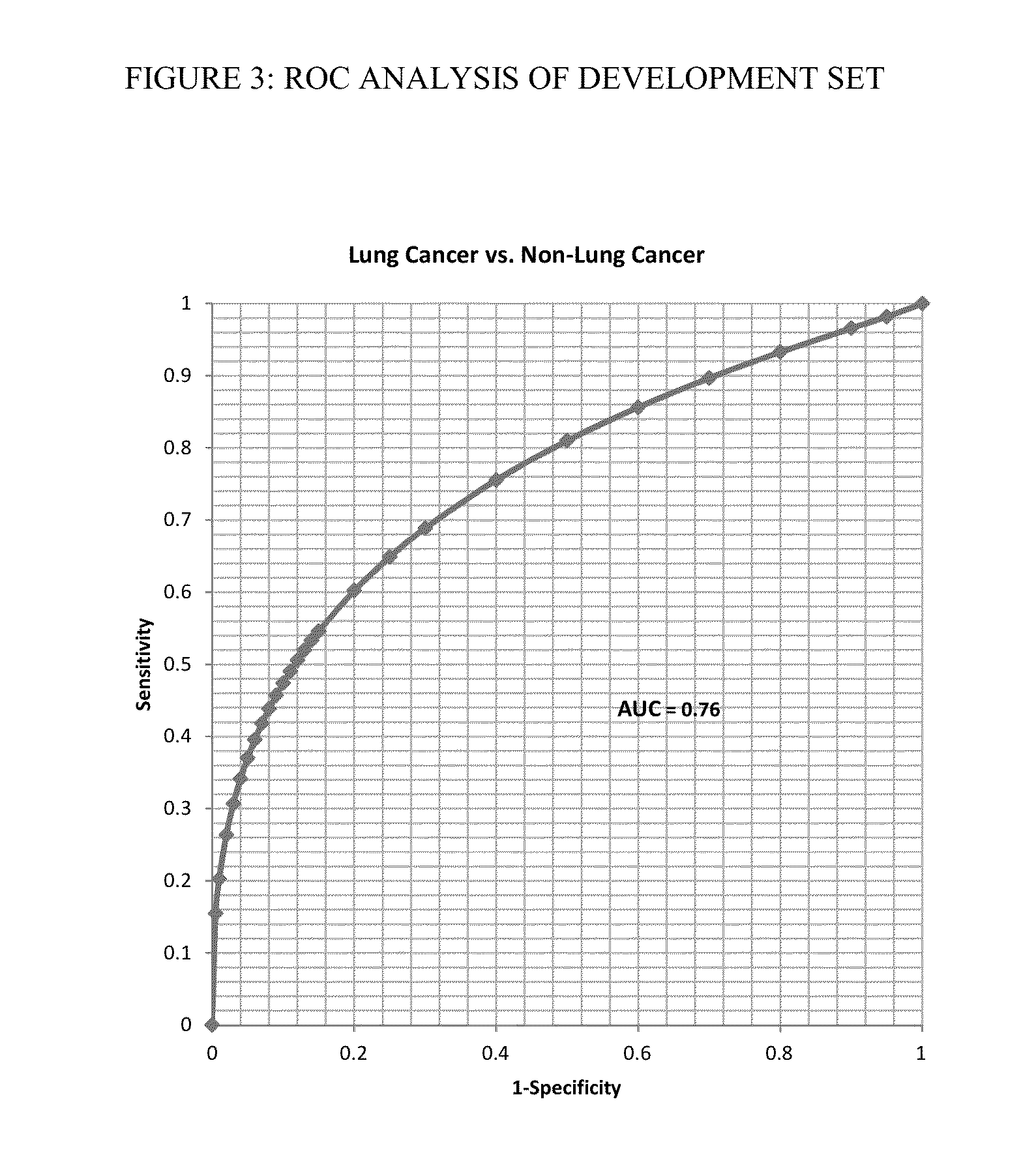
A method of data interpretation from a multiplex cancer assay is described. The aggregate normalized score from the assay is transformed to a quantitative risk score quantifying a human subject's increased risk for the presence of cancer as compared to the known prevalence of the cancer in the population before testing the subject.
Owner:20 20 GENESYSTEMS INC
Apparatus and method for multiplex analysis
ActiveUS20060073491A1Simplify laborious and expensive procedurePrevent evaporation and condensationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical reactionMonitoring temperature
The present invention provides miniaturized instruments for conducting chemical reactions where control of the reaction temperature is desired or required. Specifically, this invention provides chips and optical systems for performing and monitoring temperature-dependent chemical reactions. The apparatus and methods embodied in the present invention are particularly useful for high-throughput and low-cost amplification of nucleic acids.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Apparatus for Performing Amplicon Rescue Multiplex PCR
ActiveUS20100291668A1Efficient detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPipetteDna amplification
The present disclosure is a cassette for PCR amplification and detection of DNA amplicons, the cassette having a cassette pipette which may be moved vertically and horizontally within the cassette, at least one reagent chamber, and at least one detector, such as a microarray, for the detection of DNA amplified during the PCR amplification steps.
Owner:ICUBATE
Multiplex detection compositions, methods, and kits
ActiveUS7198900B2Minimise measureImprove method performanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexBio molecules
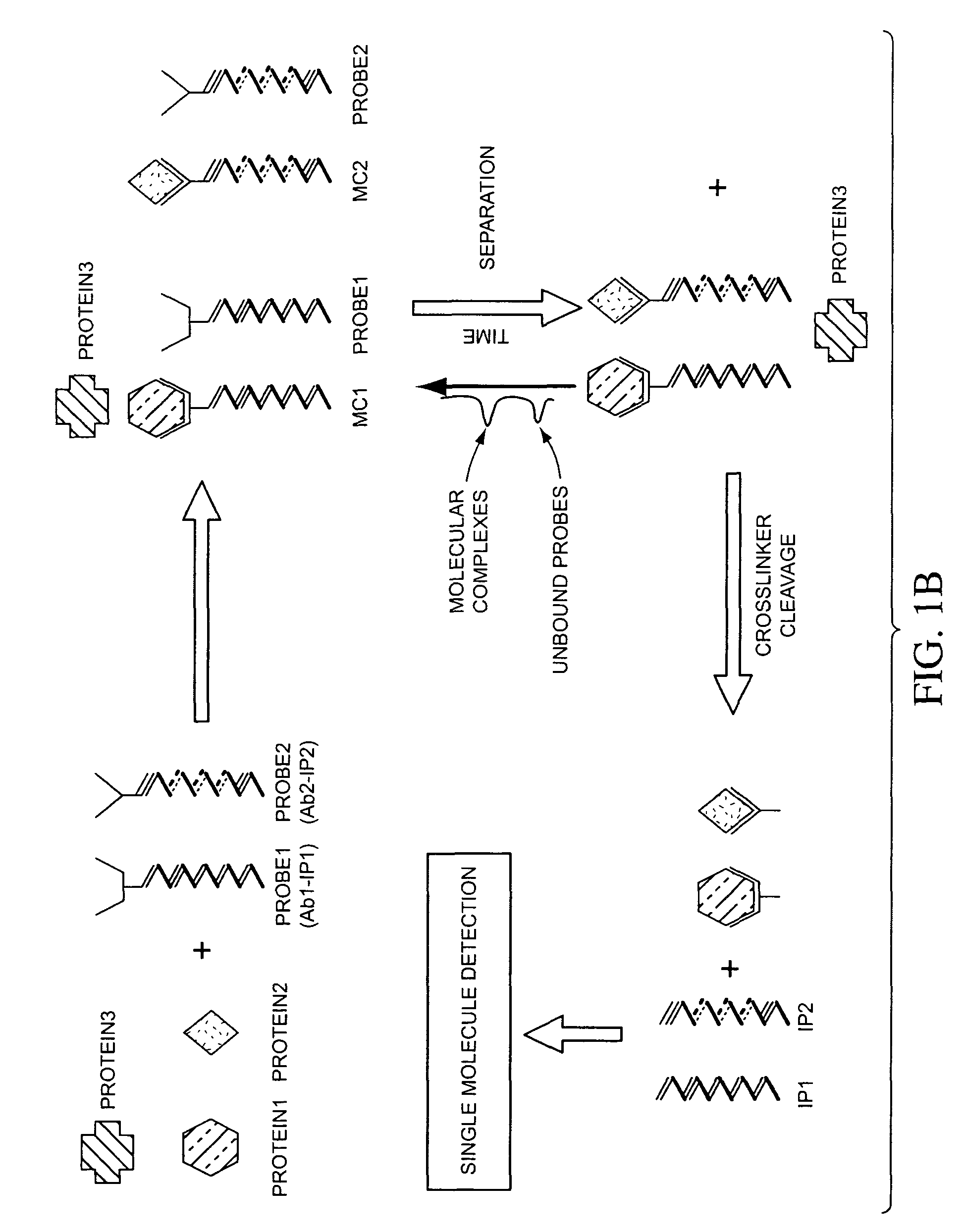
The present invention generally relates to the detection of analytes, particularly biomolecules in samples. The invention also relates to compositions, methods, and kits for detecting the presence of analytes, typically in multiplex detection formats. The invention also relates to methods for determining the presence of at least one analyte in a sample, the methods employing employ single molecule detection techniques to individually detect at least one molecular complex or at least part of a molecular complex.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Thermo-controllable high-density chips for multiplex analyses
InactiveUS20060030037A1Simplify laborSimplify expensive procedureMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMultiplexChemical reaction
The present invention provides miniaturized instruments for conducting chemical reactions where control of the reaction temperature is desired or required. Specifically, this invention provides chips and optical systems for performing and monitoring temperature-dependent chemical reactions. The apparatus and methods embodied in the present invention are particularly useful for high-throughput and low-cost amplification of nucleic acids.
Owner:WAFERGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com