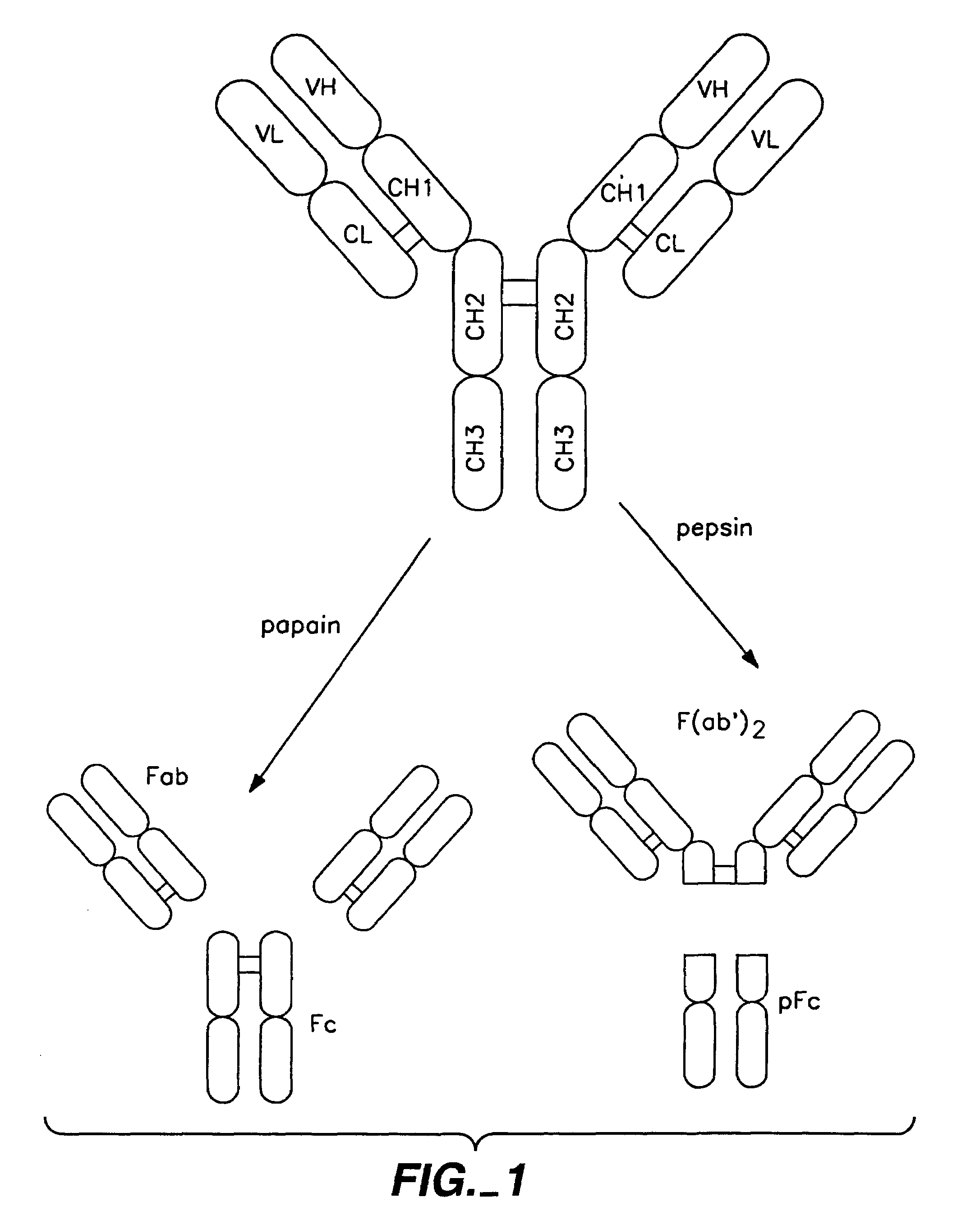
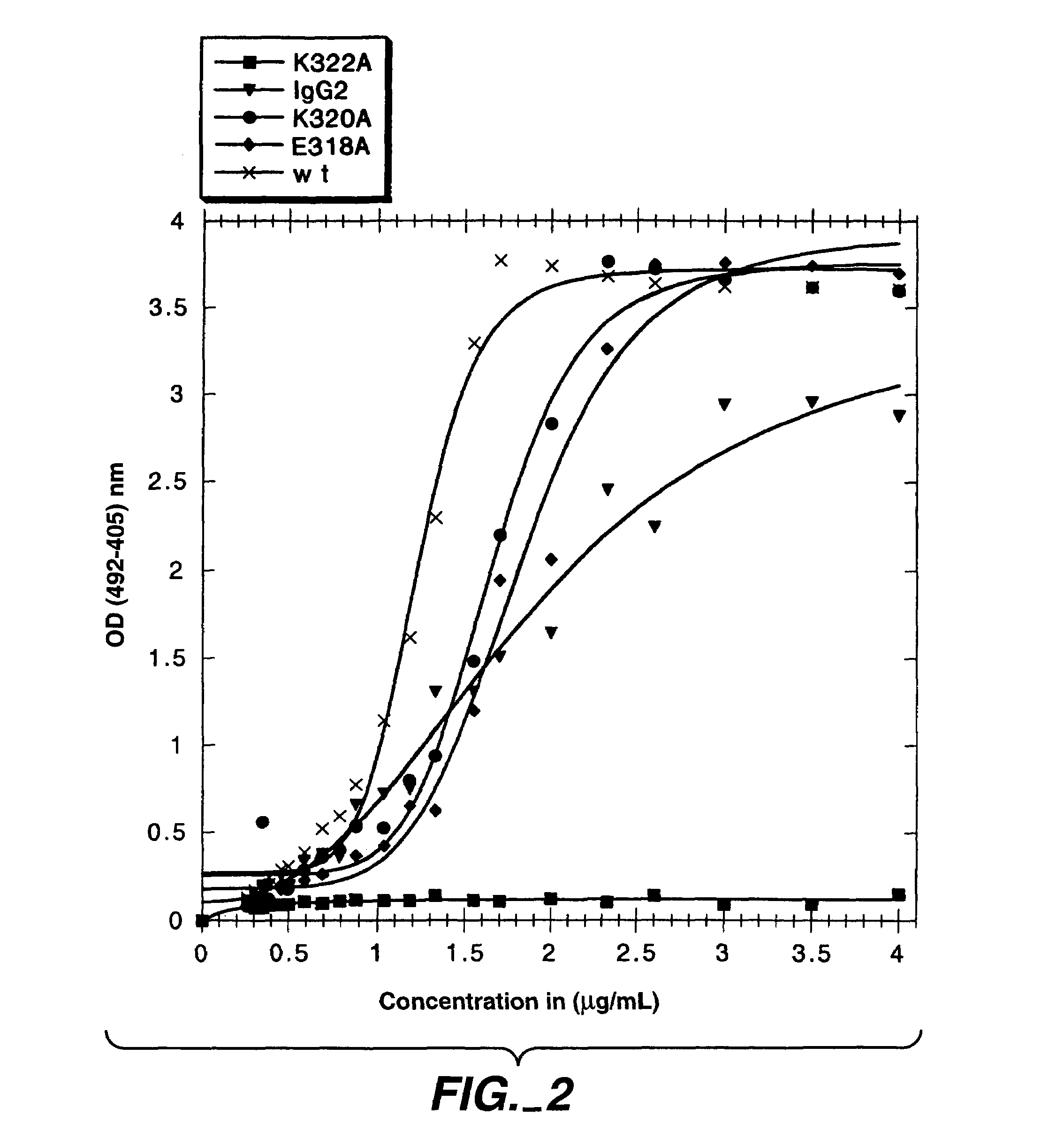
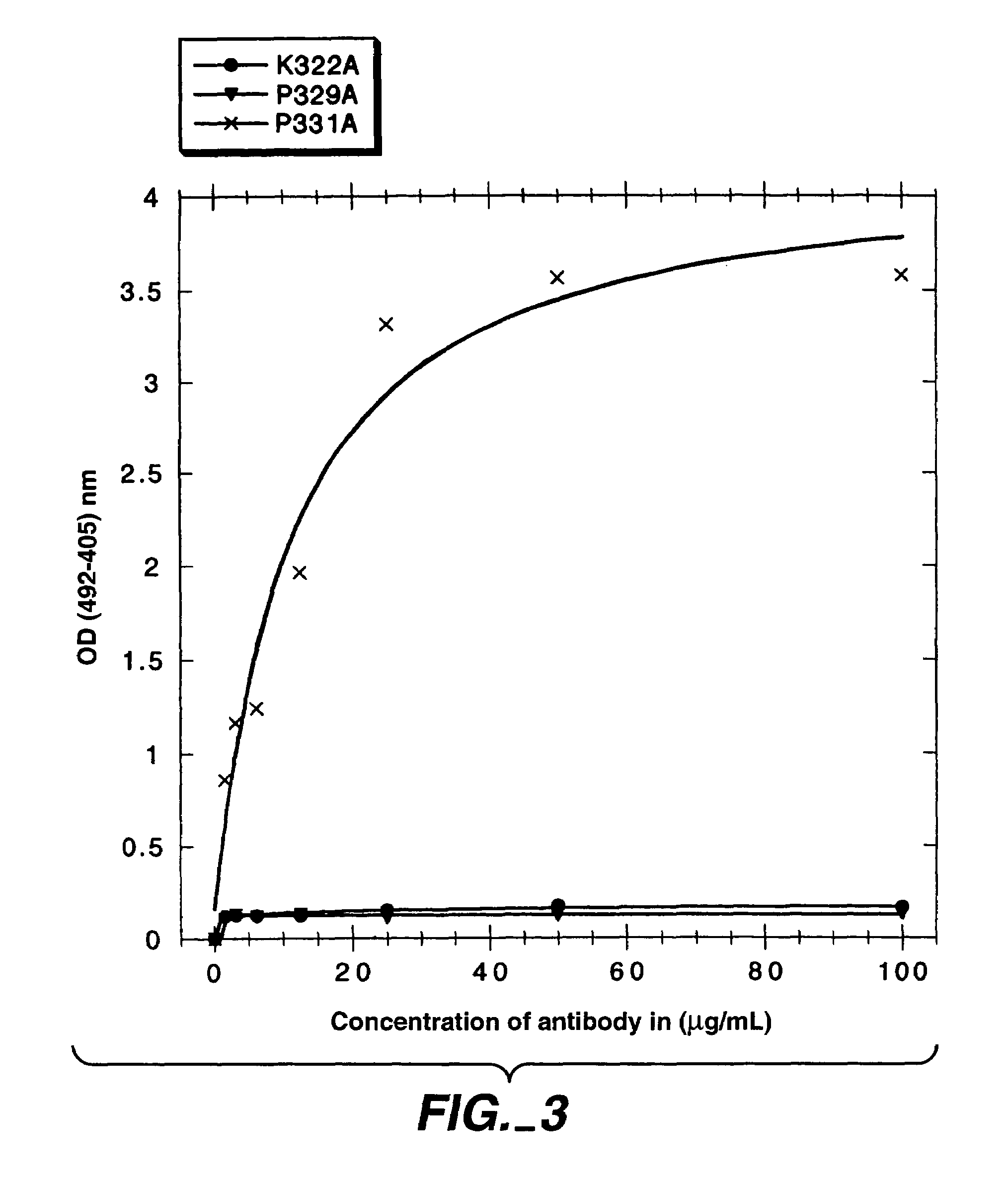
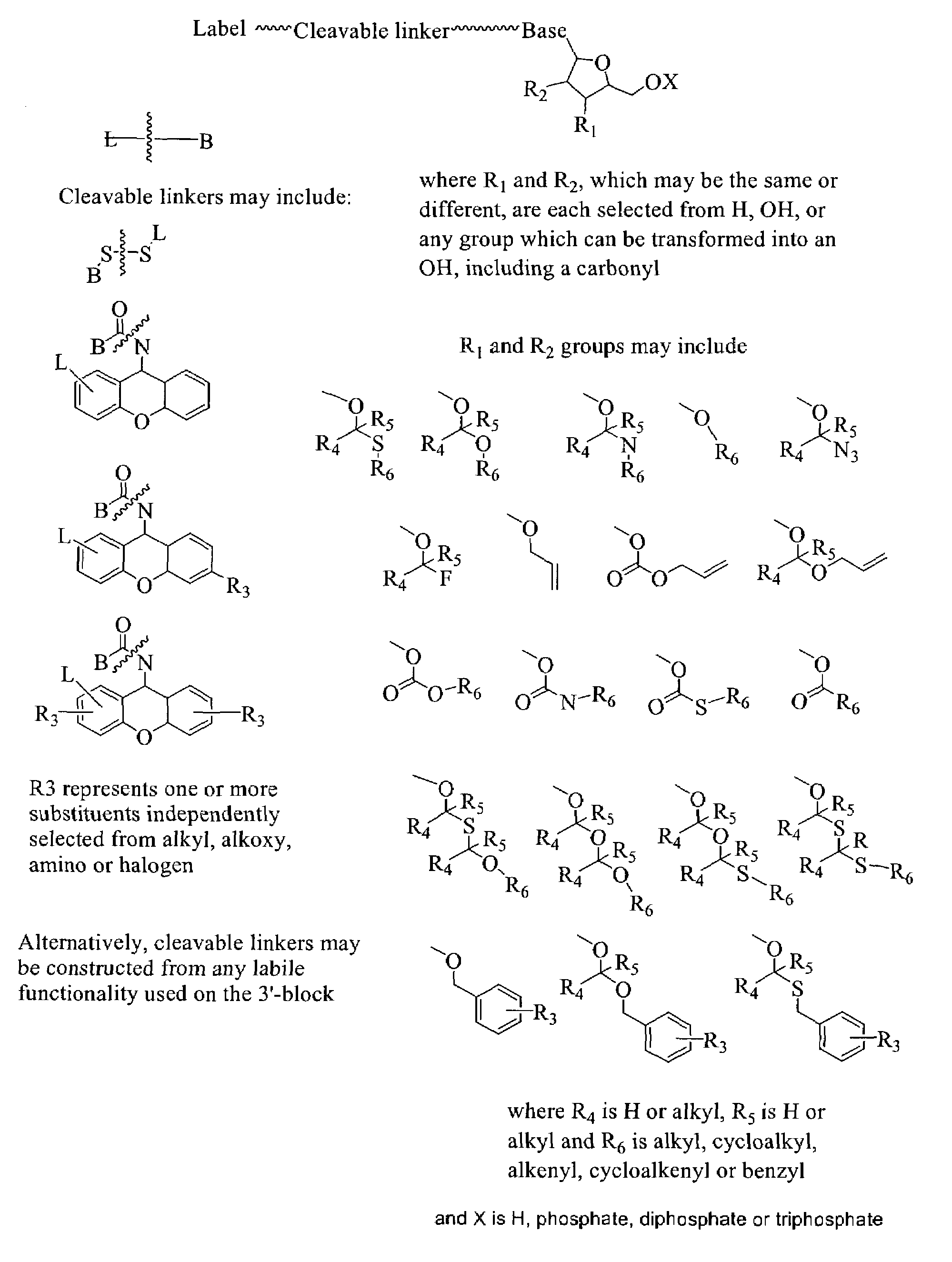
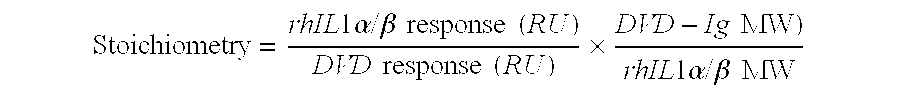Patents
Literature
64242results about "Sugar derivatives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
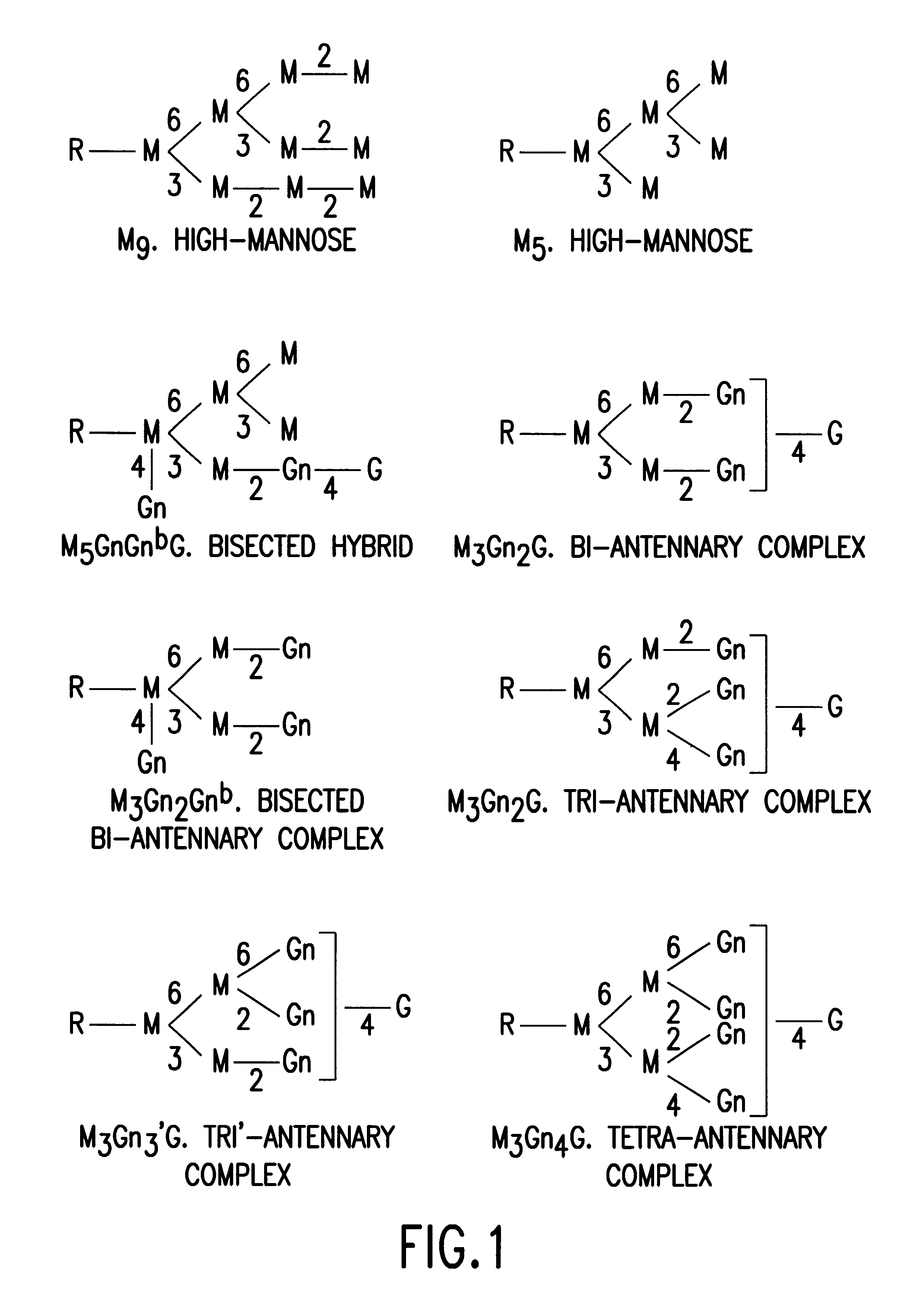
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS6602684B1Increase healing valueEnhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicityNanotechFungiAntibody fragmentsADAMTS Proteins
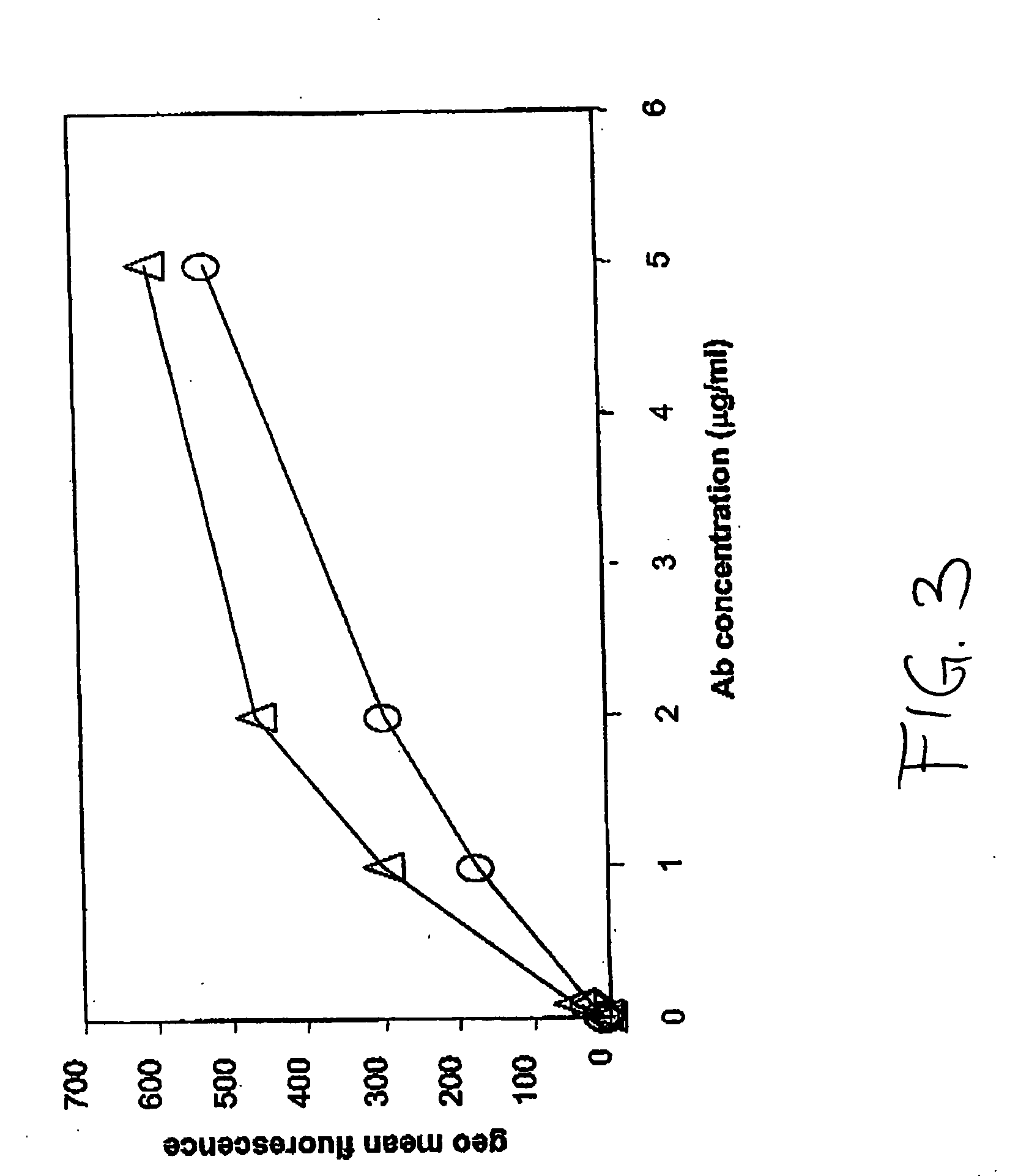
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
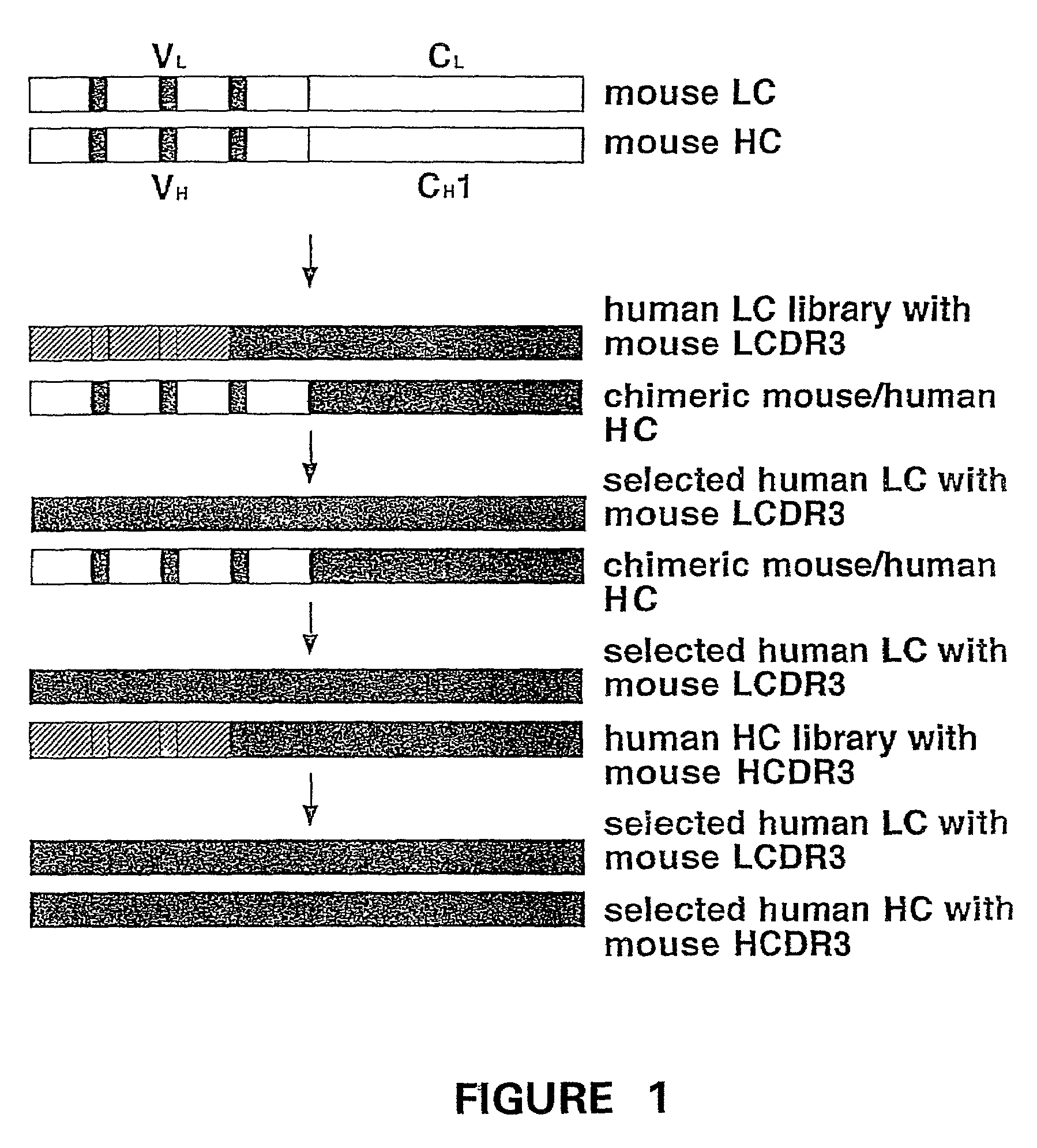
Humanization of murine antibody
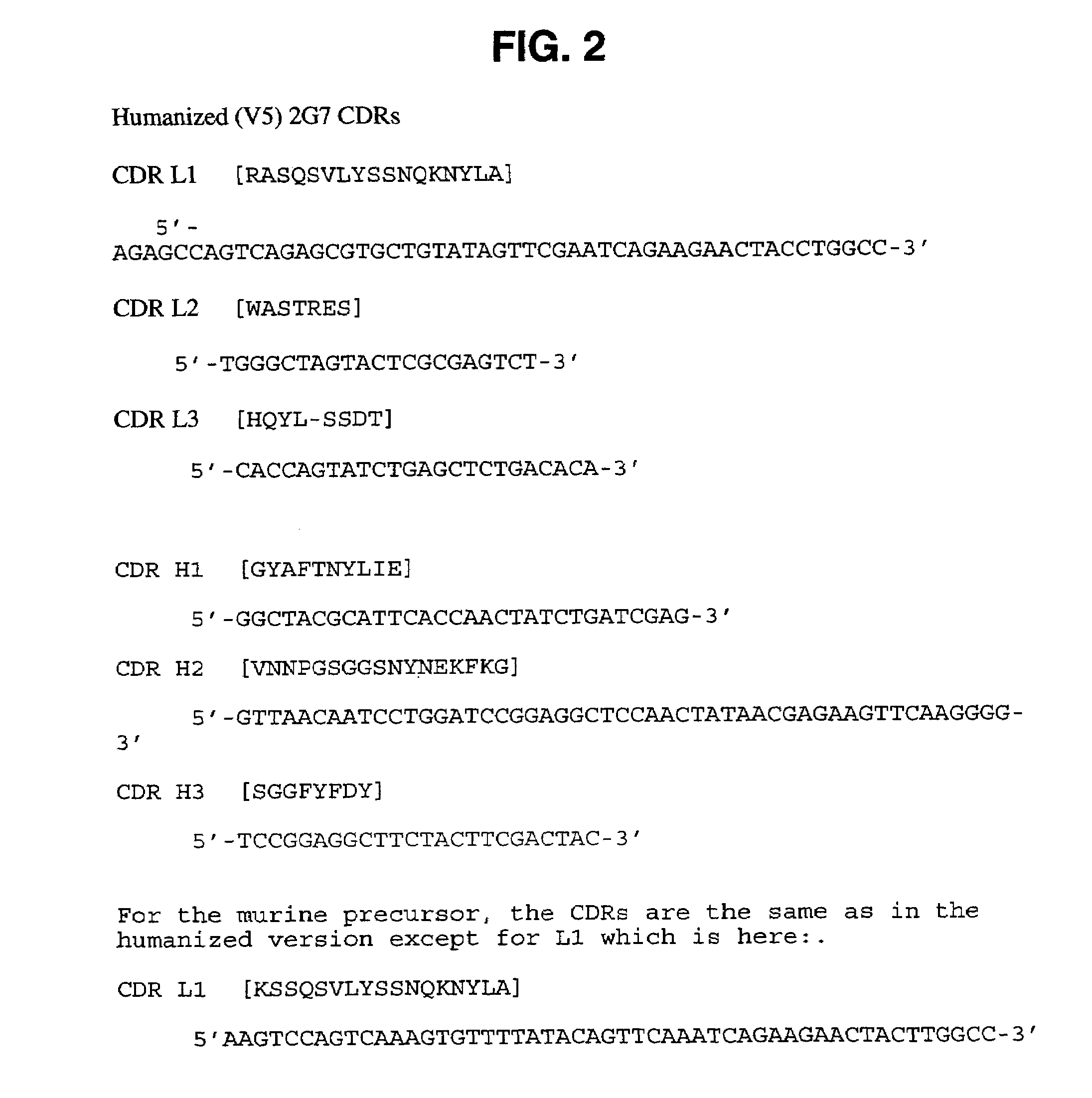
InactiveUS7087409B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesComplementarity determining regionHeavy chain
A humanized murine antibody is provided. The amino acid sequences of a light chain complementarity determining region from a mouse antibody are grafted onto a human light chain, and a heavy chain complementarity determining region from a mouse antibody are grafted onto a human antibody heavy chain to produce libraries from which a humanized murine antibody having the desired specificity is selected.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Antigen binding molecules with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human CD20. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
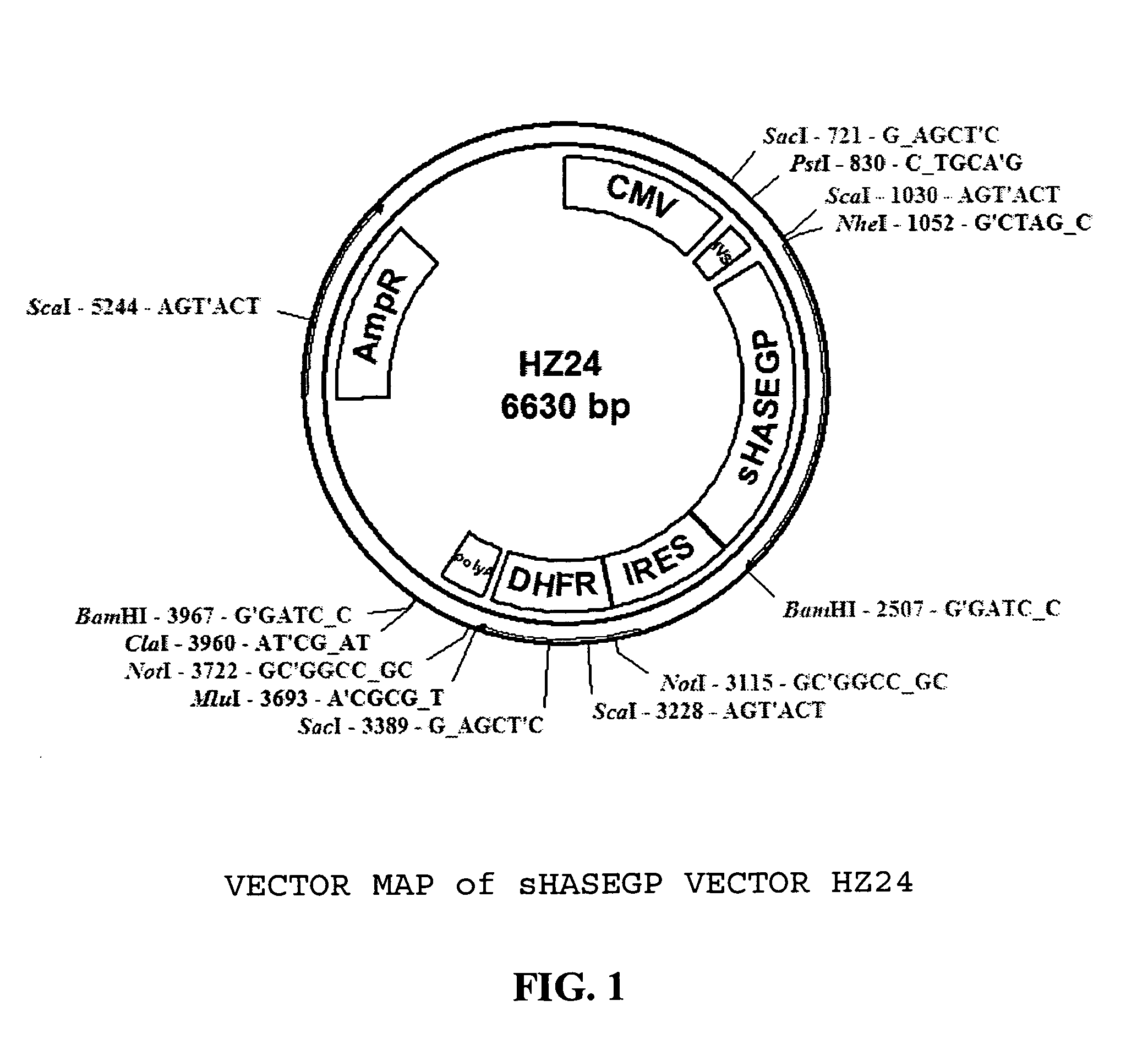
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
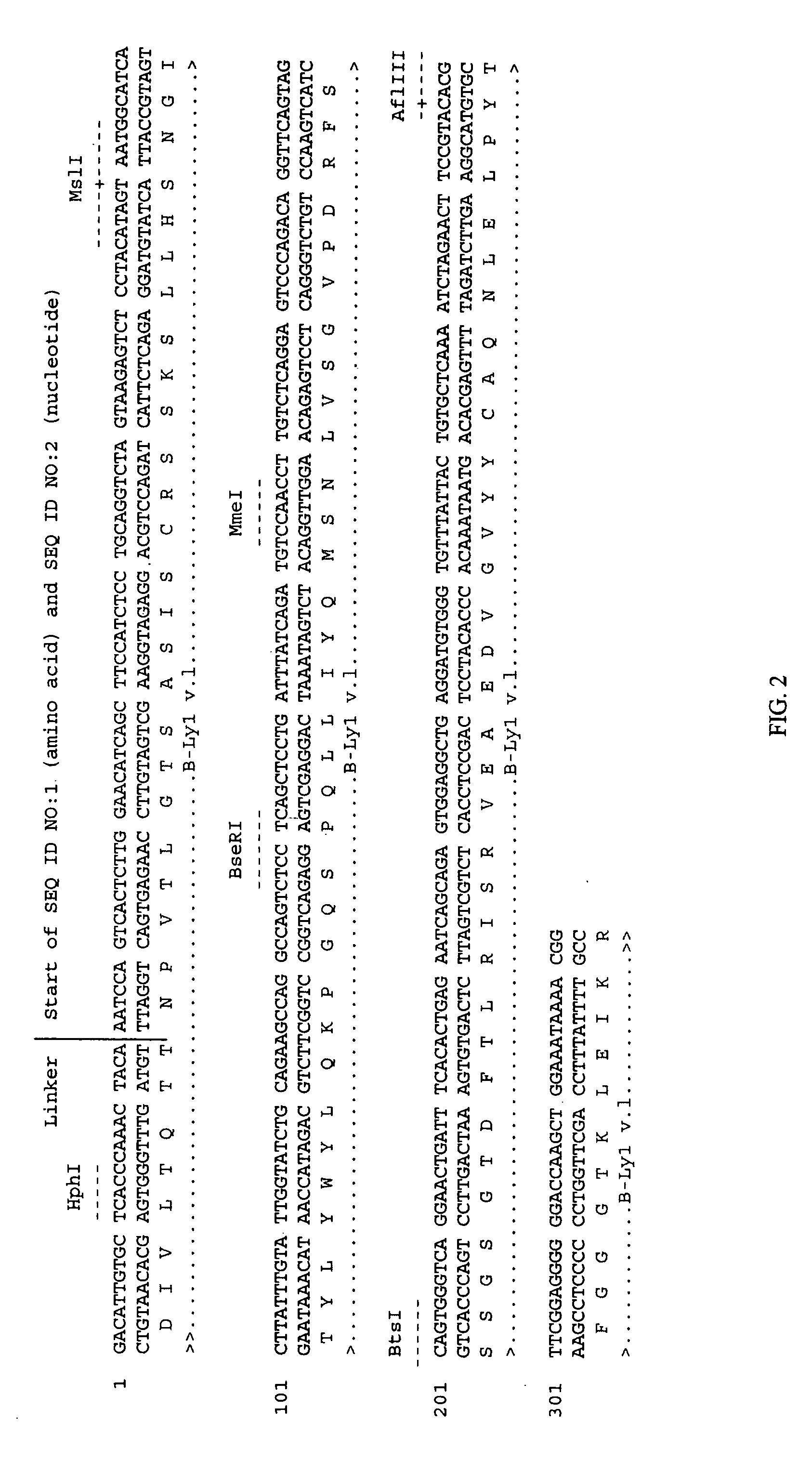
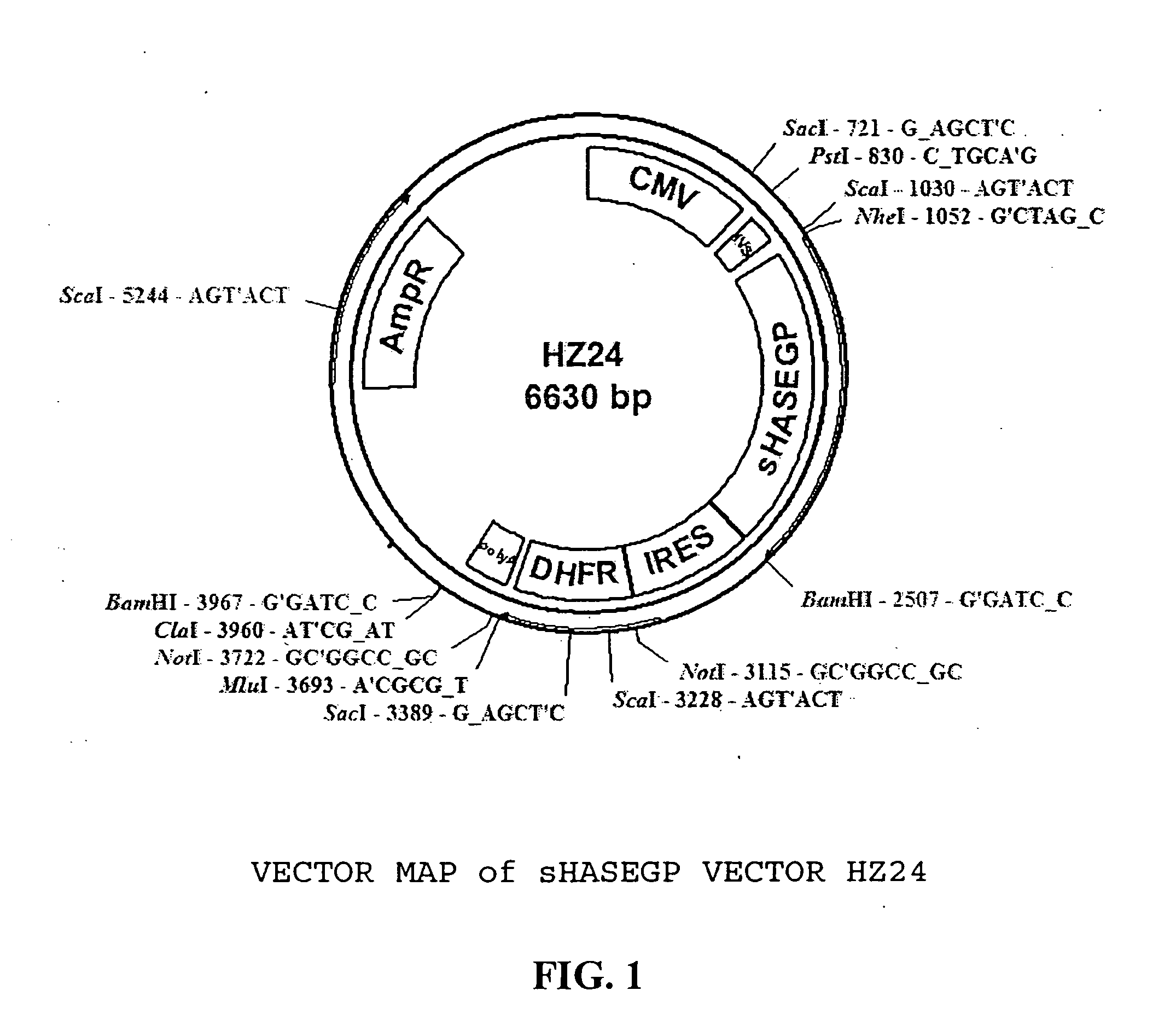
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Polypeptide variants with altered effector function
The present invention concerns polypeptides comprising a variant Fc region. More particularly, the present invention concerns Fc region-containing polypeptides that have altered effector function as a consequence of one or more amino acid modifications in the Fc region thereof.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
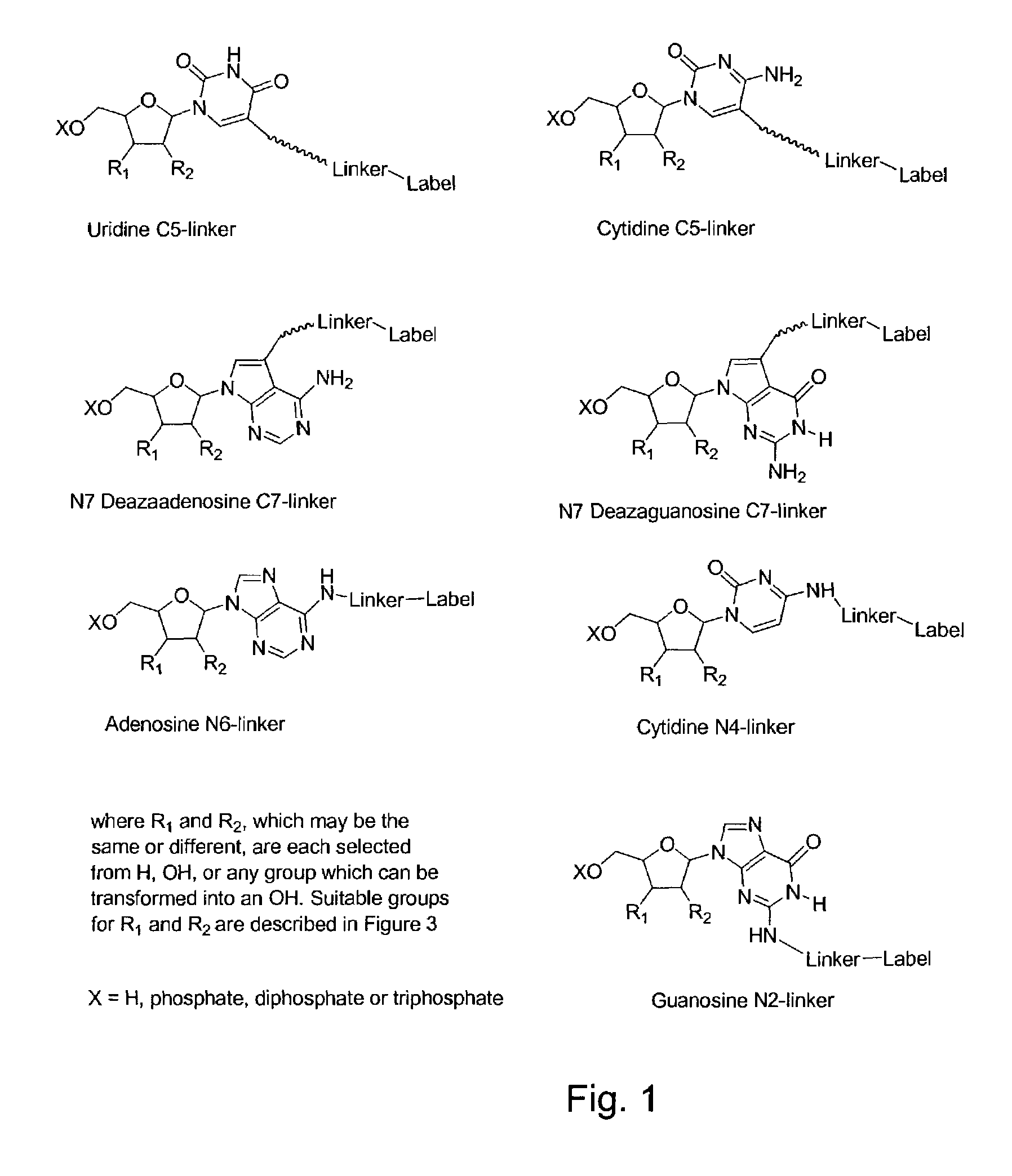
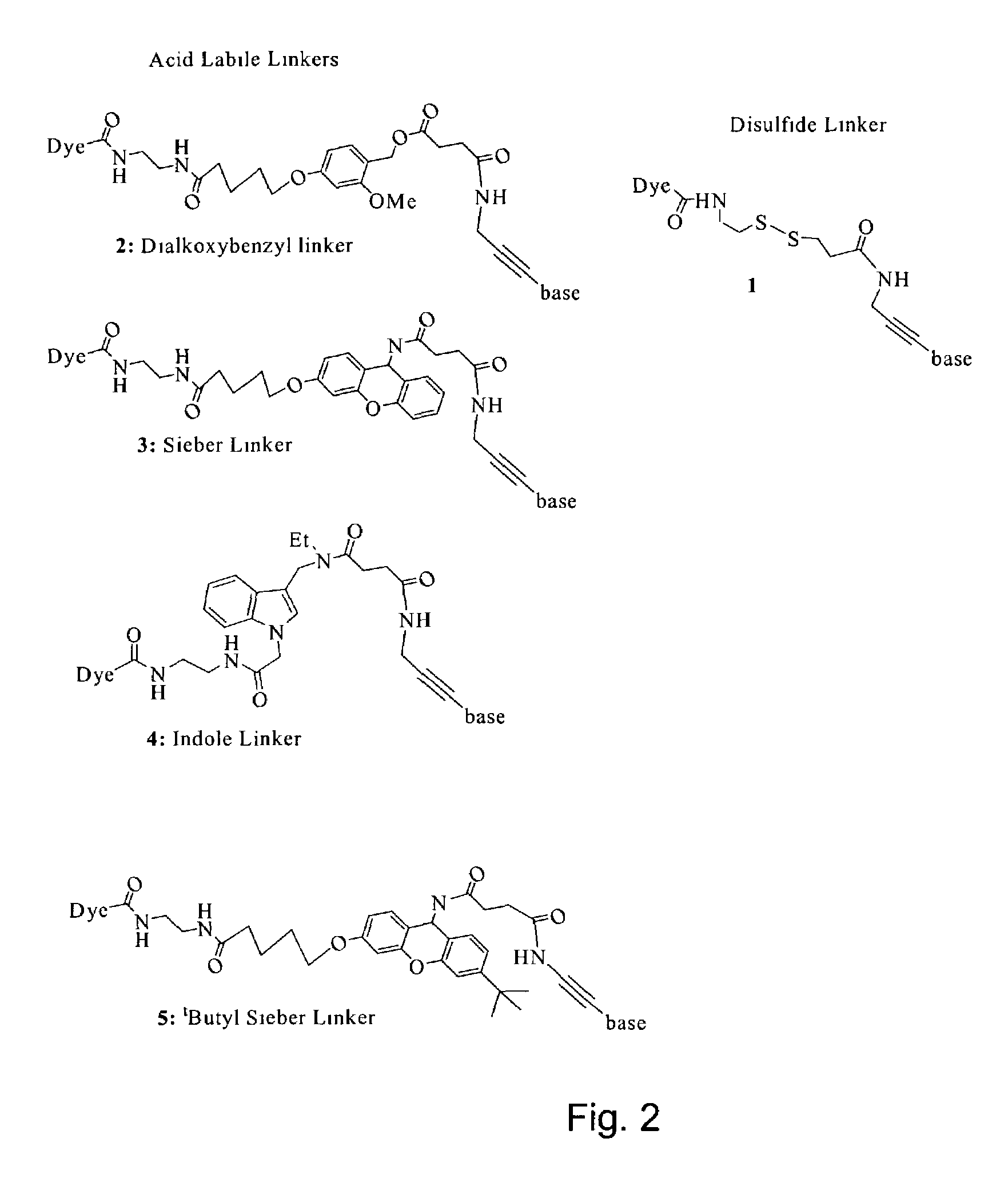
Labelled nucleotides
InactiveUS7057026B2Use of techniqueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic chemistryNucleoside
Nucleosides and nucleotides are disclosed that are linked to detectable labels via a cleavable linker group.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
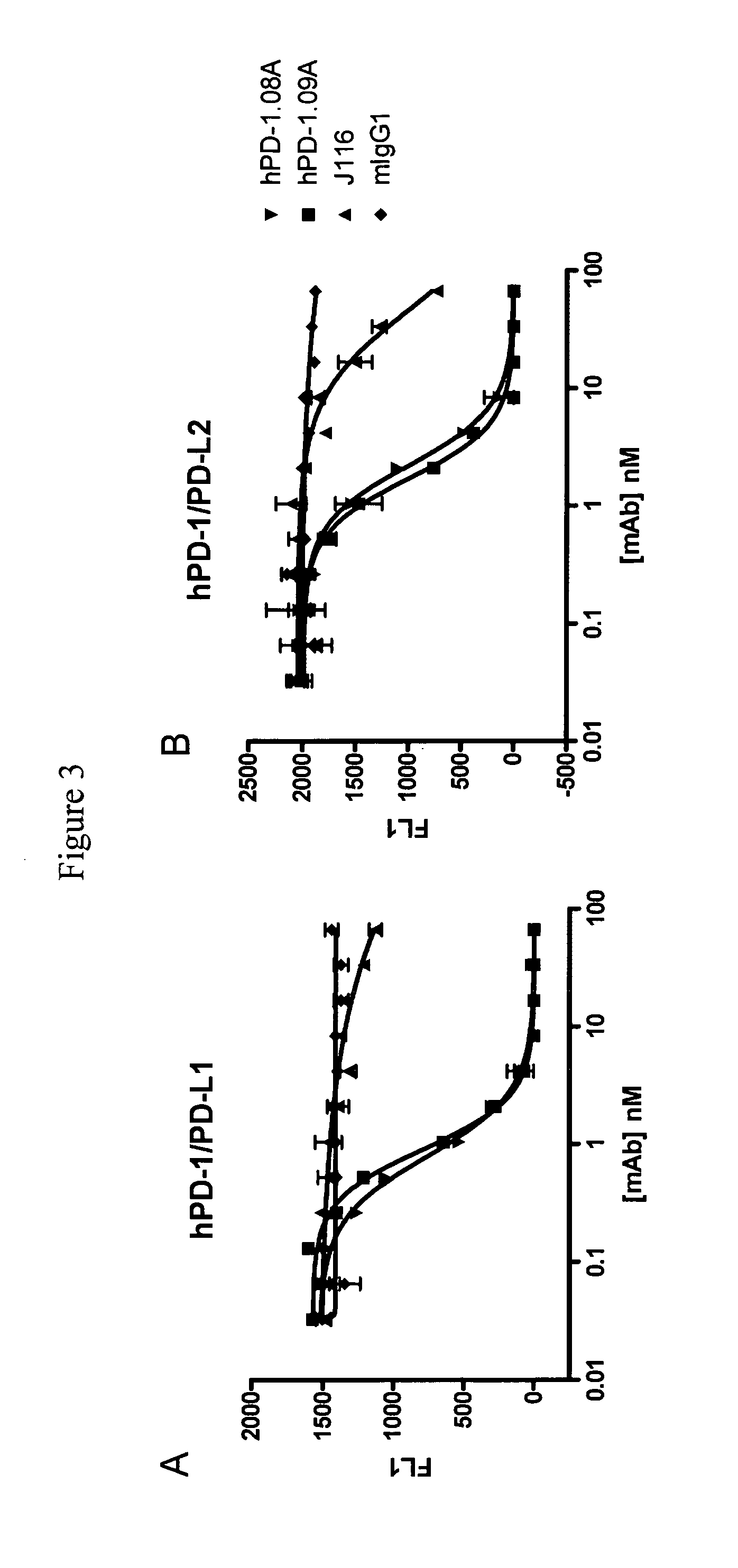
Antibodies to human programmed death receptor PD-1
ActiveUS8354509B2Increased activationIncreased proliferationSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsProgrammed deathReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Antibodies which block the binding of human Programmed Death Receptor 1 (hPD-1) to its ligands (hPD-L1 or hPD-L2) and their variable region sequences are disclosed. A method of increasing the activity (or reducing downmodulation) of an immune response through the PD-I pathway is also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME BV
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Promoter for regulating expression of foreign genes
InactiveUS7125978B1Regulate expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesOrganismFhit gene
The present invention relates to a promoter for regulating expression of foreign genes in transgenic organisms, which comprises a promoter having the identifying characteristics of a promoter having a sequence selected from the group consisting of sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOS:1 to 3 and functional fragments or derivatives thereof, wherein said promoter is adapted to be operationally located with respect to said foreign gene for expression of said gene.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
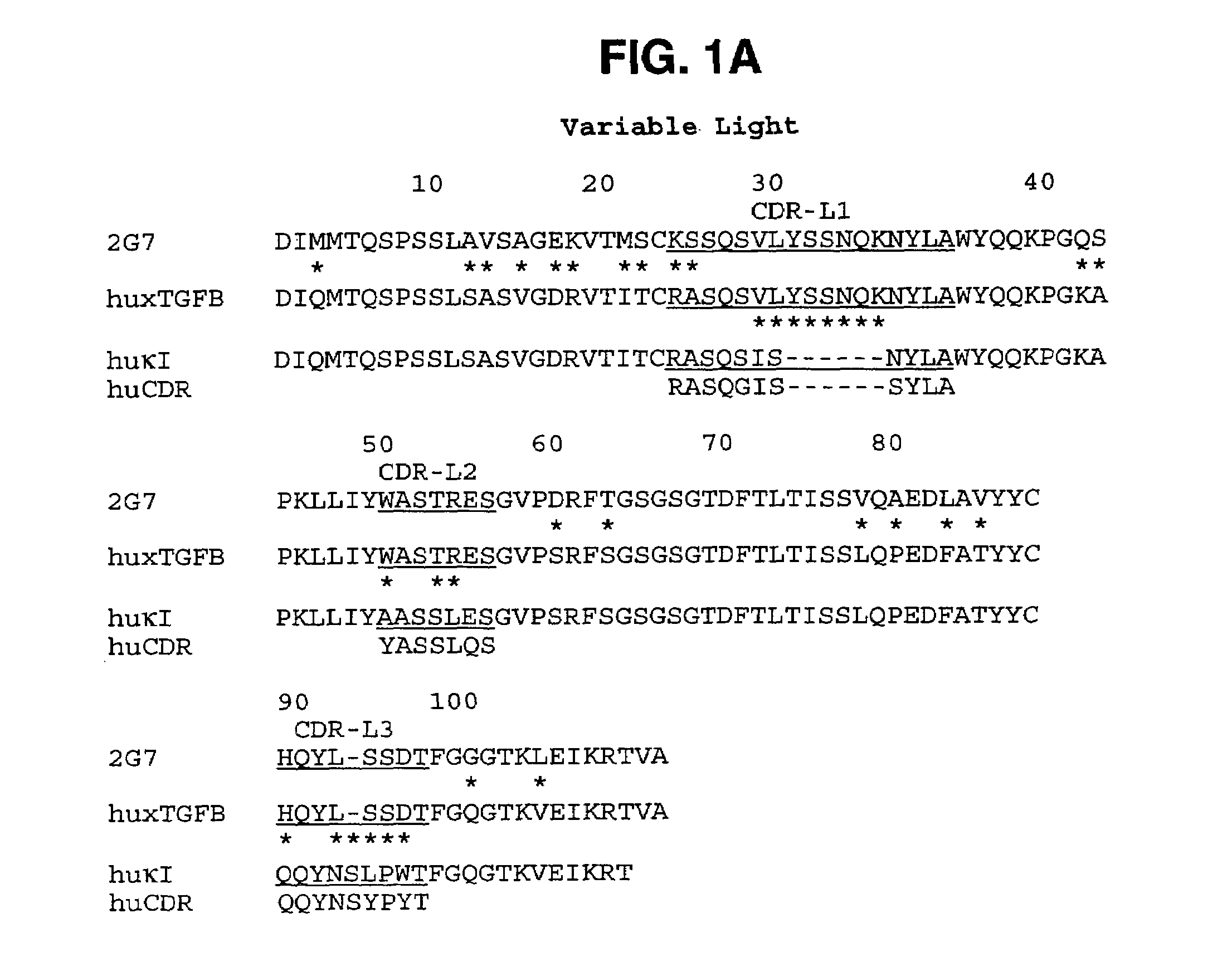
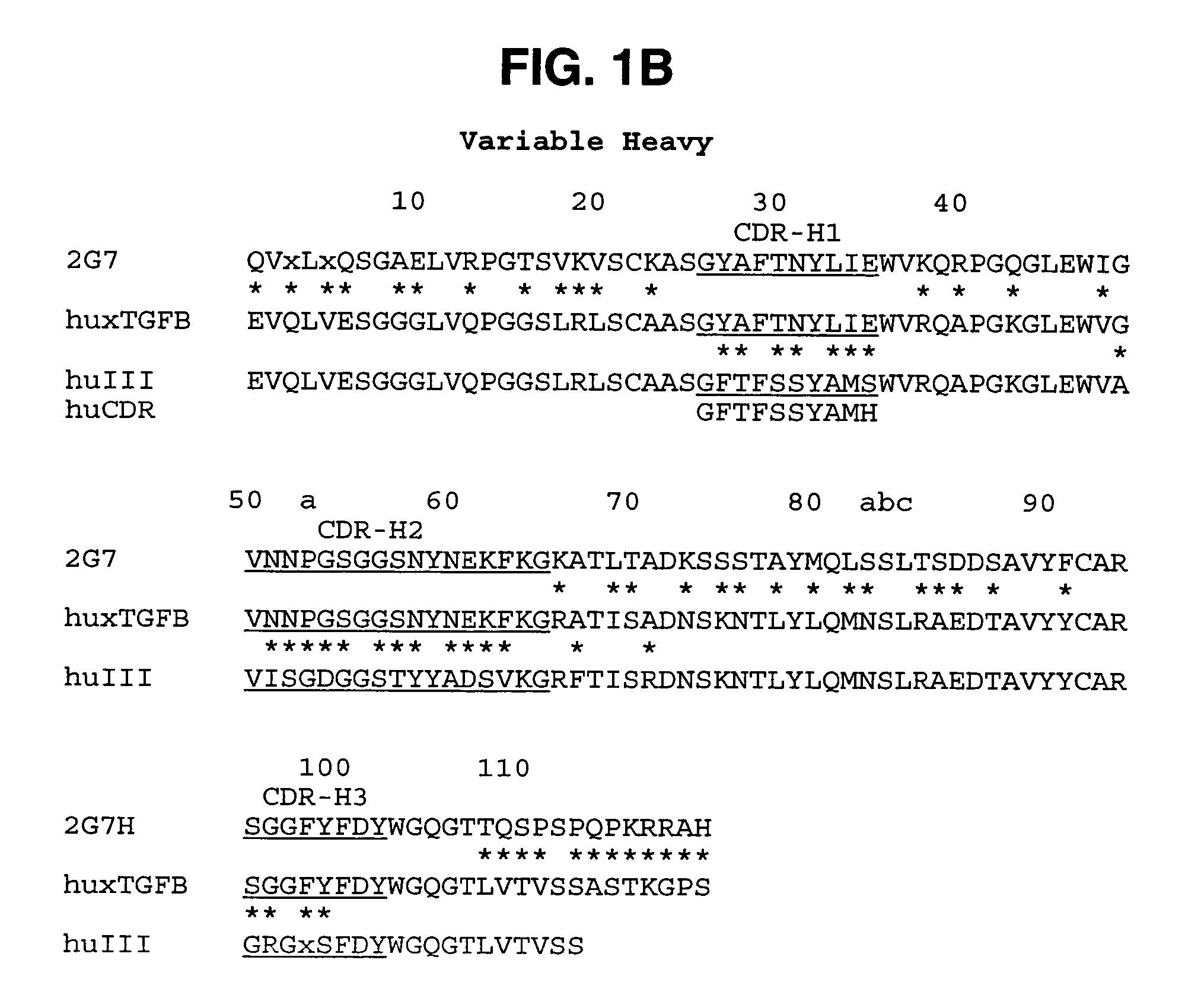
Humanized anti-TGF-beta antibodies
Humanized anti-TGF-beta antibodies are provided, as well as methods for their preparation and use, including methods for treating TGF-beta disorders, for example, cancer. Also provided are articles of manufacture designed for various uses that contain the humanized antibodies.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
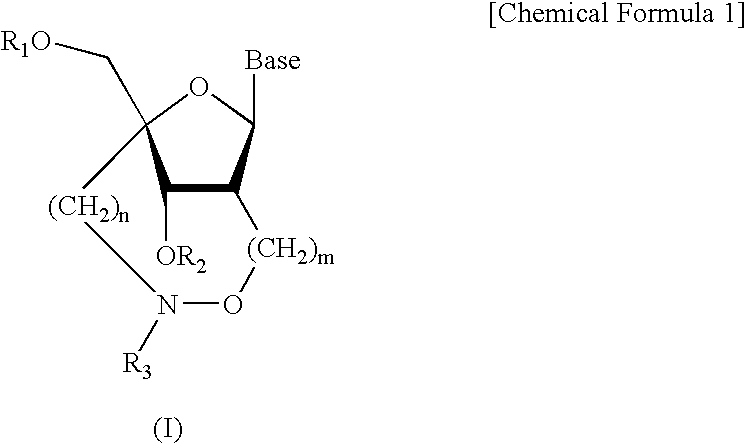
L-ribo-LNA analogues
Provided are L-ribo bicyclic nucleotide compounds as well as syntheses of such compounds. The nucleoside compounds of the invention are useful in forming oligonucleotides that can produce nucleobase specific duplexes with complementary single stranded and double stranded nucleic acids.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
6-modified bicyclic nucleic acid analogs
The present invention provides 6-modified bicyclic nucleoside analogs and oligomeric compounds comprising these nucleoside analogs. In preferred embodiments the nucleoside analogs have either (R) or (S)-chirality at the 6-position. These bicyclicnucleoside analogs are useful for enhancing properties of oligomeric compounds including nuclease resistance.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligonucleotide analogues
Novel oligomers, and synthesis thereof, comprising one or more bi-, tri, or polycyclic nucleoside analogues are disclosed herein. The nucleoside analogues have a “locked” structure, termed Locked Nucleoside Analogues (LNA). LNA's exhibit highly desirable and useful properties. LNA's are capable of forming nucleobase specific duplexes and triplexes with single and double stranded nucleic acids. These complexes exhibit higher thermostability than the corresponding complexes formed with normal nucleic acids. The properties of LNA's allow for a wide range of uses such as diagnostic agents and therapeutic agents in a mammal suffering from or susceptible to, various diseases.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
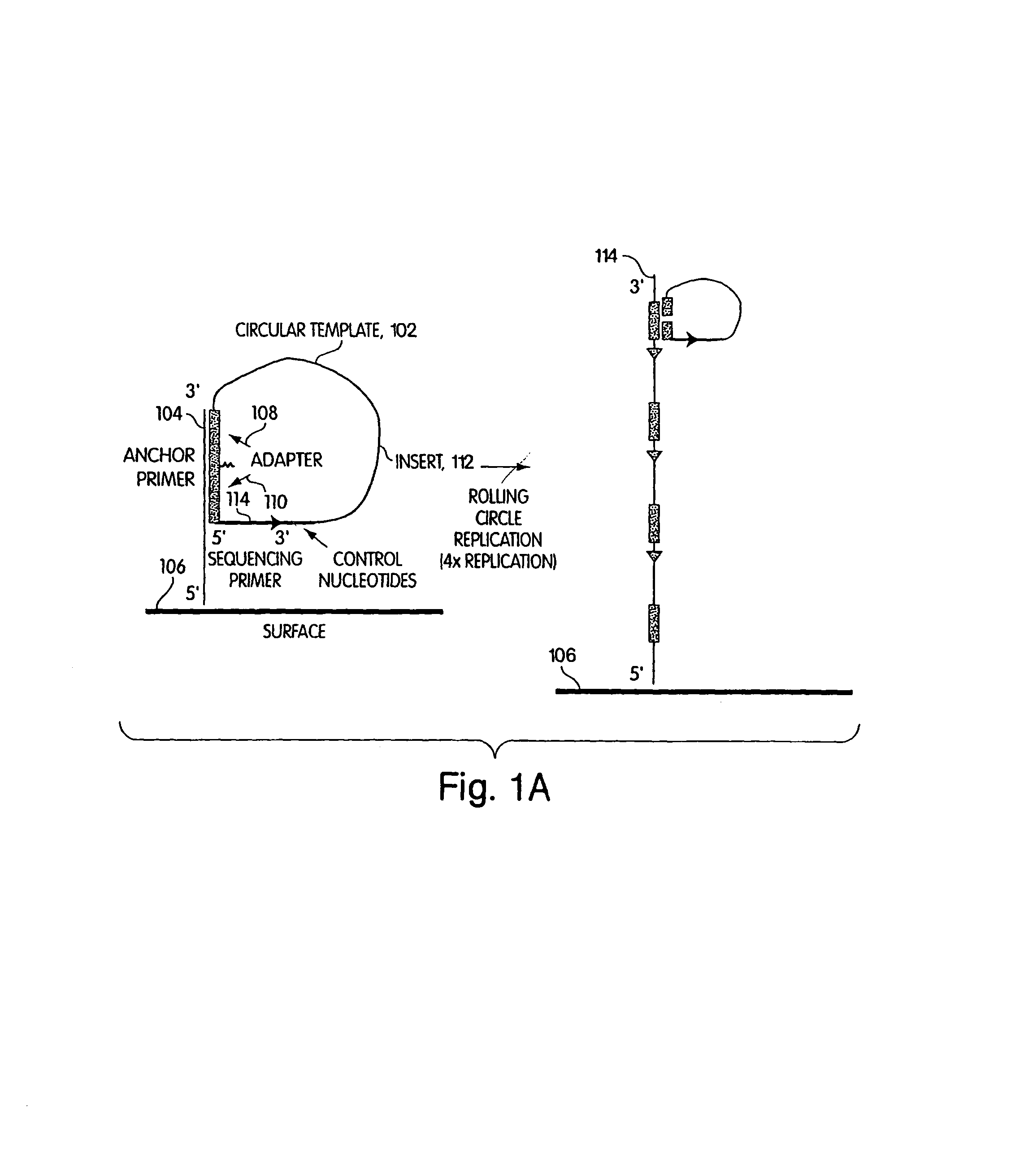
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Soybean cultivar SN79525
InactiveUS6967263B2Improve nutritional qualitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCultivar
A novel soybean cultivar, designated SN79525, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar SN79525, to the plants of soybean SN79525 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar SN79525 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar SN79525 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Soybean cultivar 0037357
A soybean cultivar, designated 0037357, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar 0037357, to the plants of soybean 0037357 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar 0037357 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar 0037357 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Soybean variety SE90346
InactiveUS6958436B2Improve nutritional qualitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCultivar
A soybean cultivar, designated SE90346, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of soybean cultivar SE90346, to the plants of soybean SE90346 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing the cultivar SE90346 with itself or another soybean variety. The invention further relates to hybrid soybean seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar SE90346 with another soybean cultivar.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Genetic constructs for delaying or repressing the expression of a target gene
The present invention relates generally to synthetic genes for modifying endogenous gene expression in a cell, tissue or organ of a transgenic organism, in particular a transgenic animal or plant. More particularly, the present invention provides novel synthetic genes and genetic constructs which are capable of repressing delaying or otherwise reducing the expression of an endogenous gene or a target gene in an organism when introduced thereto.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Artificial nucleic acids of n-o bond crosslinkage type
ActiveUS7427672B2High sensitivity analysisConfirmed its usefulnessBiocideSugar derivativesSingle strandDouble strand
Owner:RIKEN GENESIS
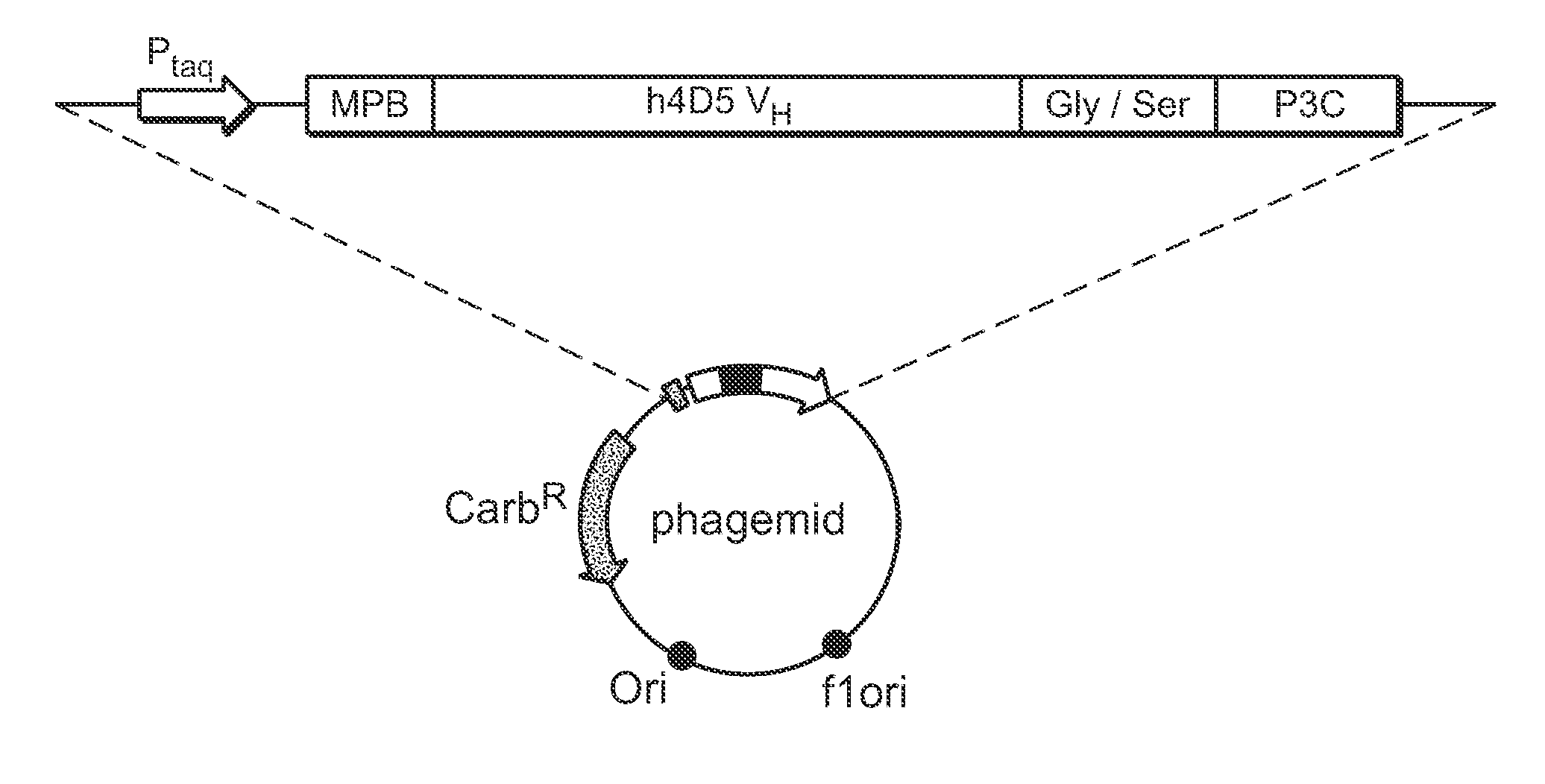
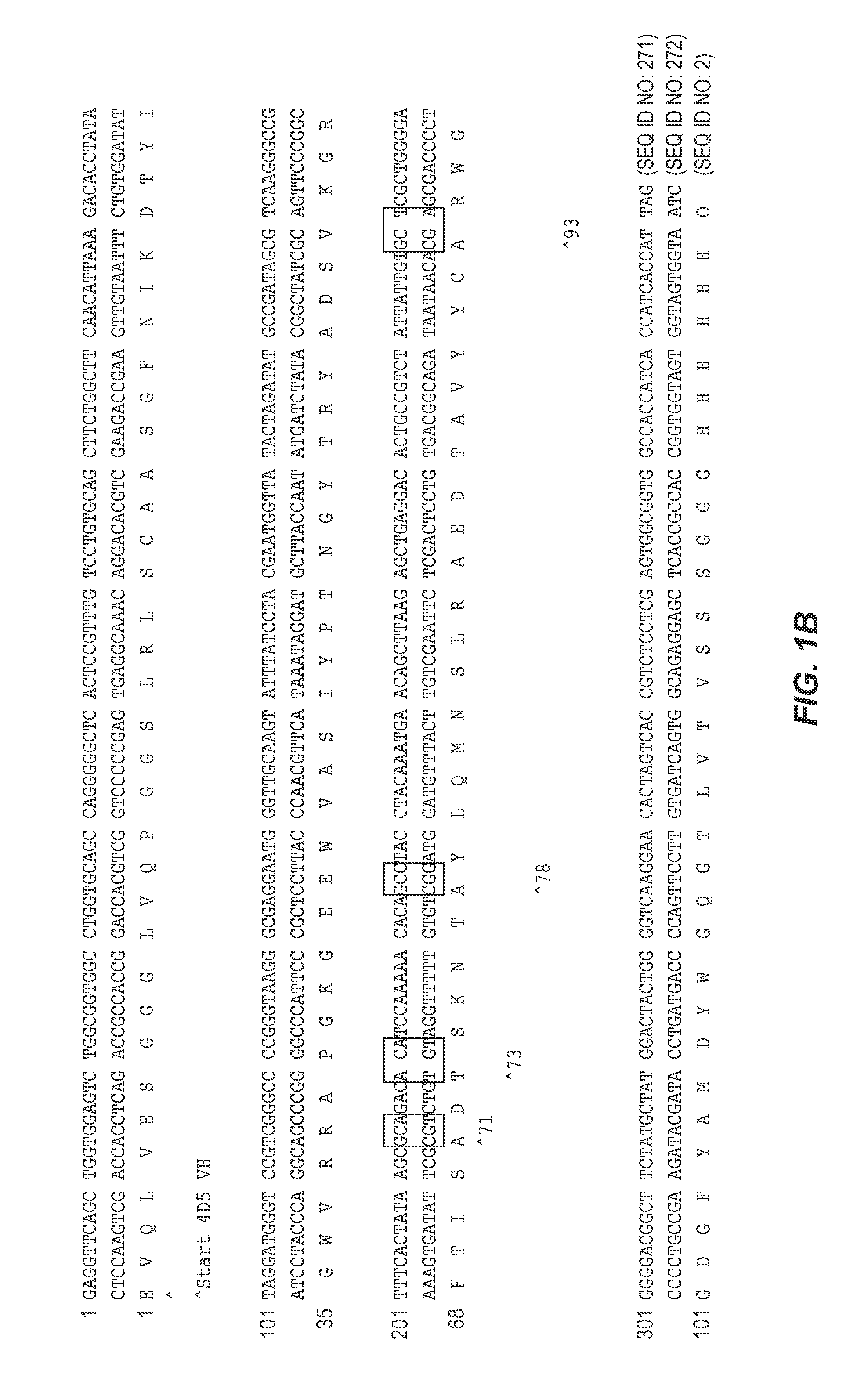
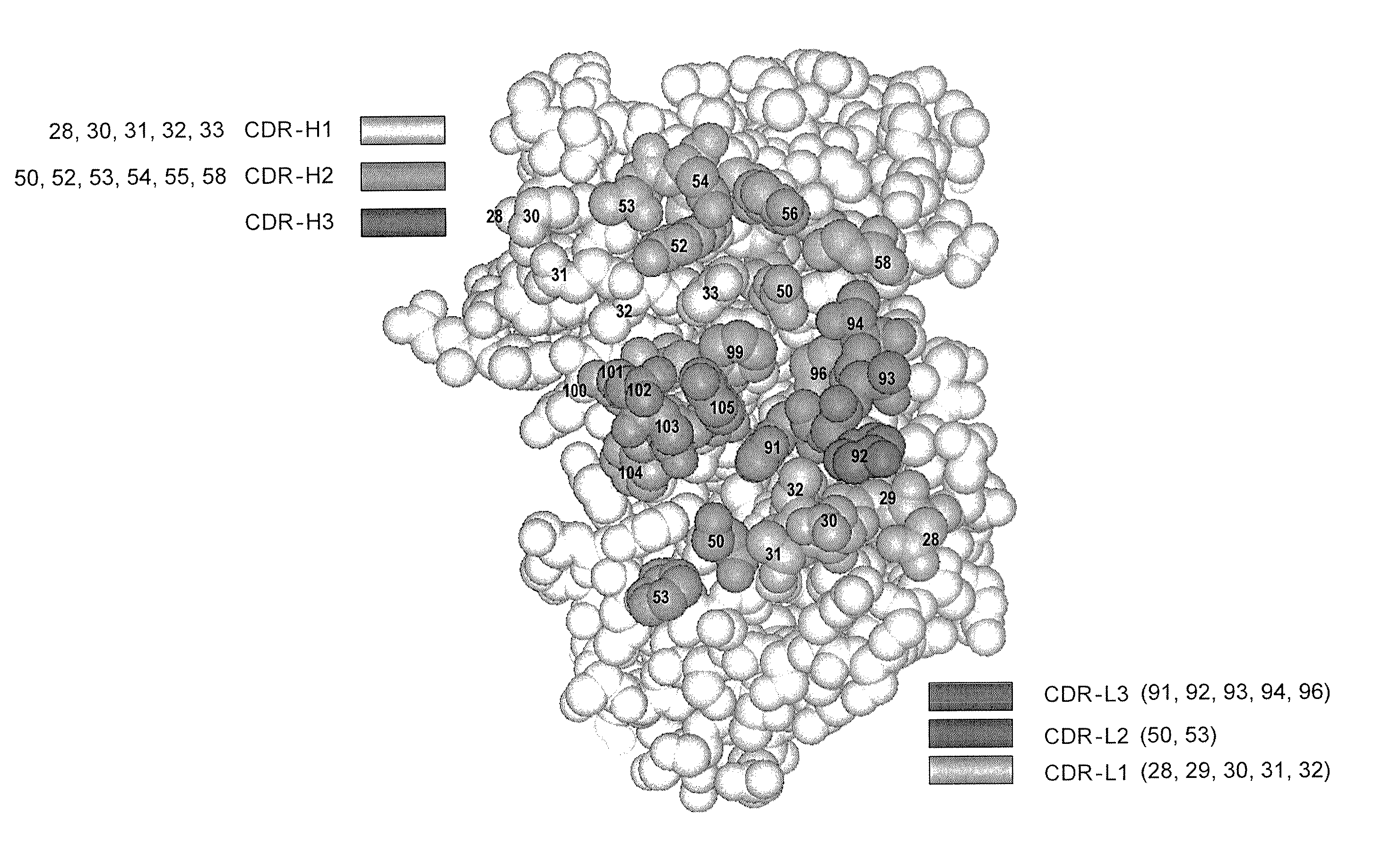
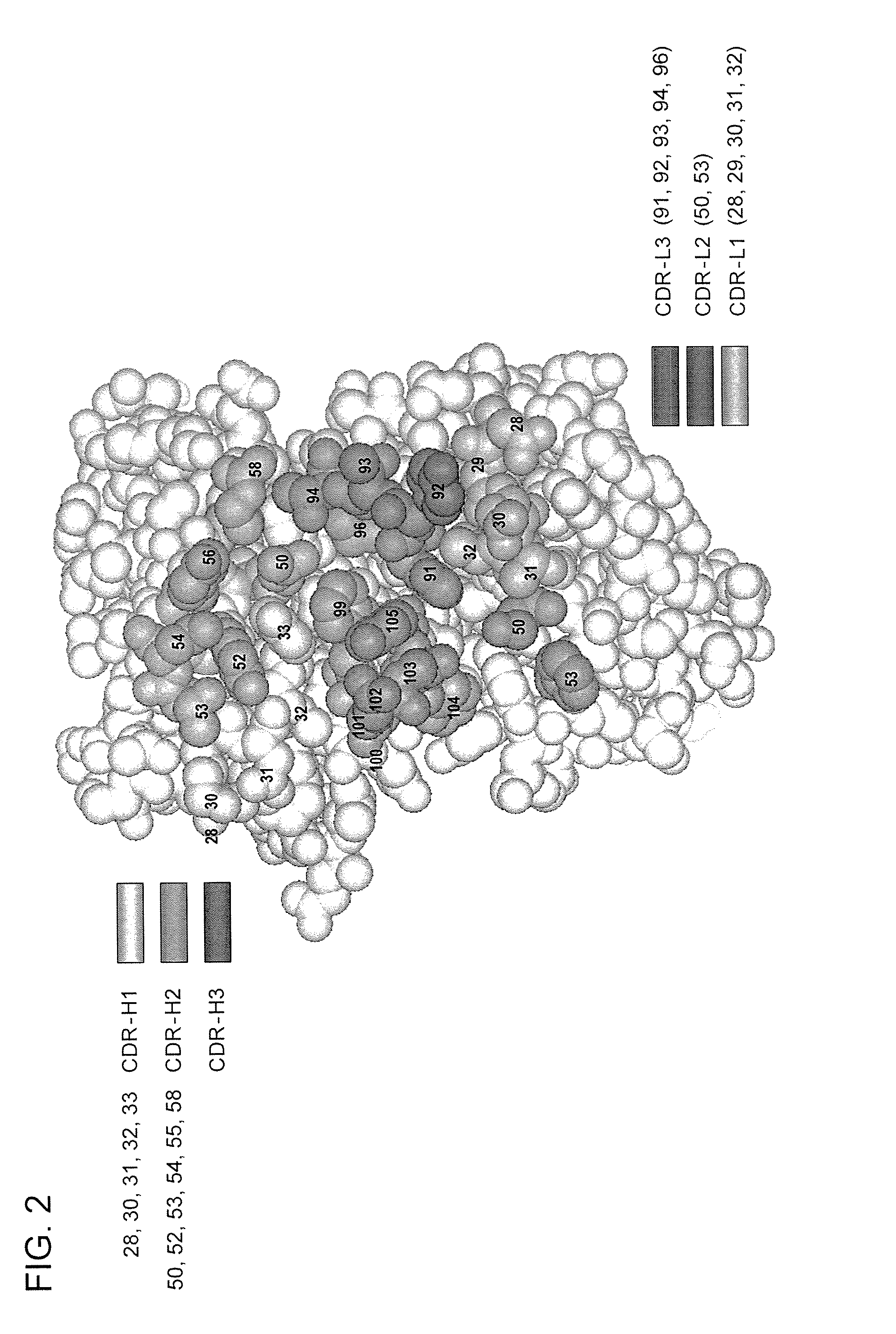
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
InactiveUS20050079574A1High-quality target binding characteristicGenerate efficientlyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousIntravenous gammaglobulin
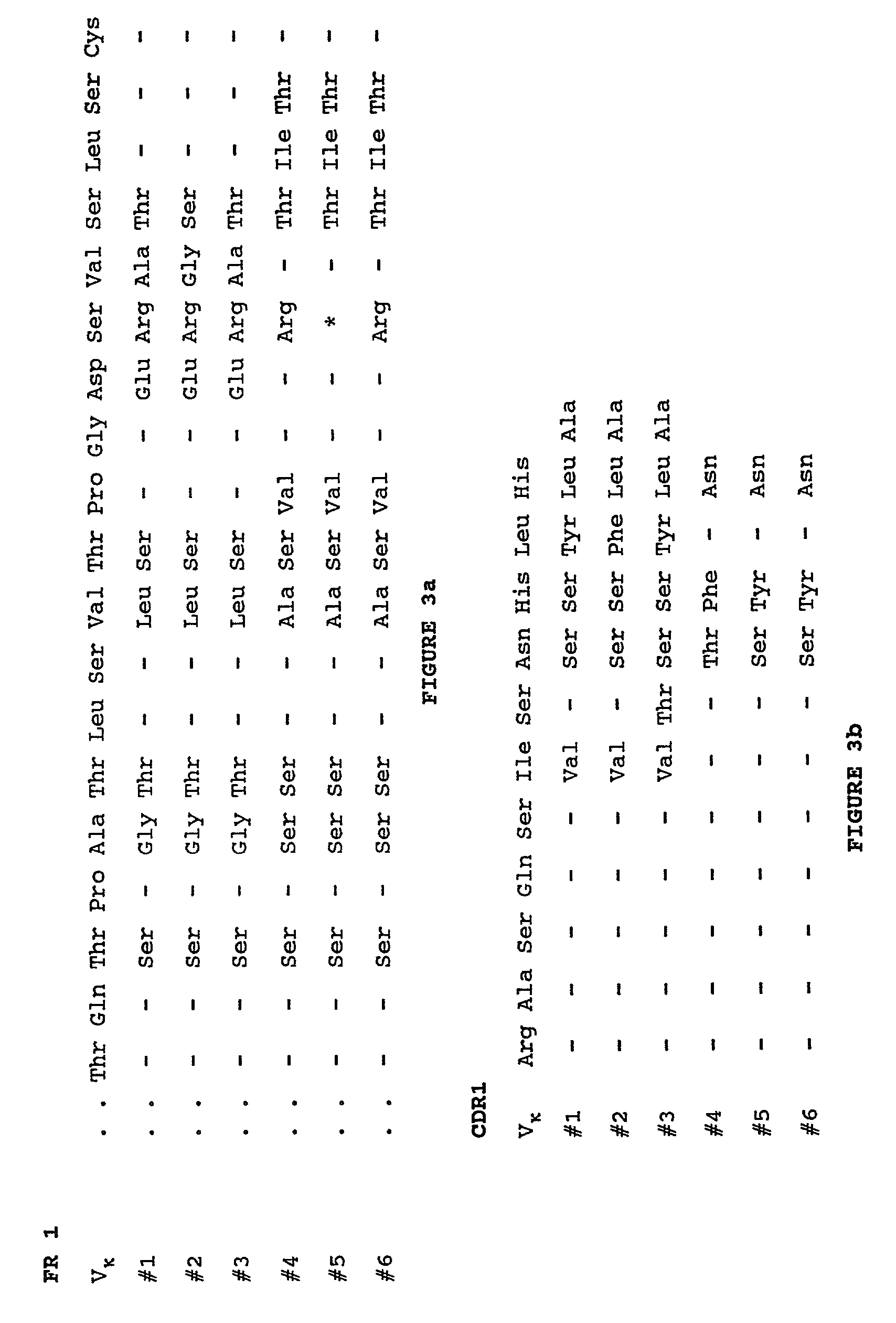
The invention provides immunoglobulin polypeptides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. In one embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant CDRH3 region. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Binding polypeptides with optimized scaffolds
InactiveUS20070292936A1Improve folding stabilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsVariable domainChemistry
The invention provides variant heavy chain variable domains (VH) with increased folding stability. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, compositions and methods of generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
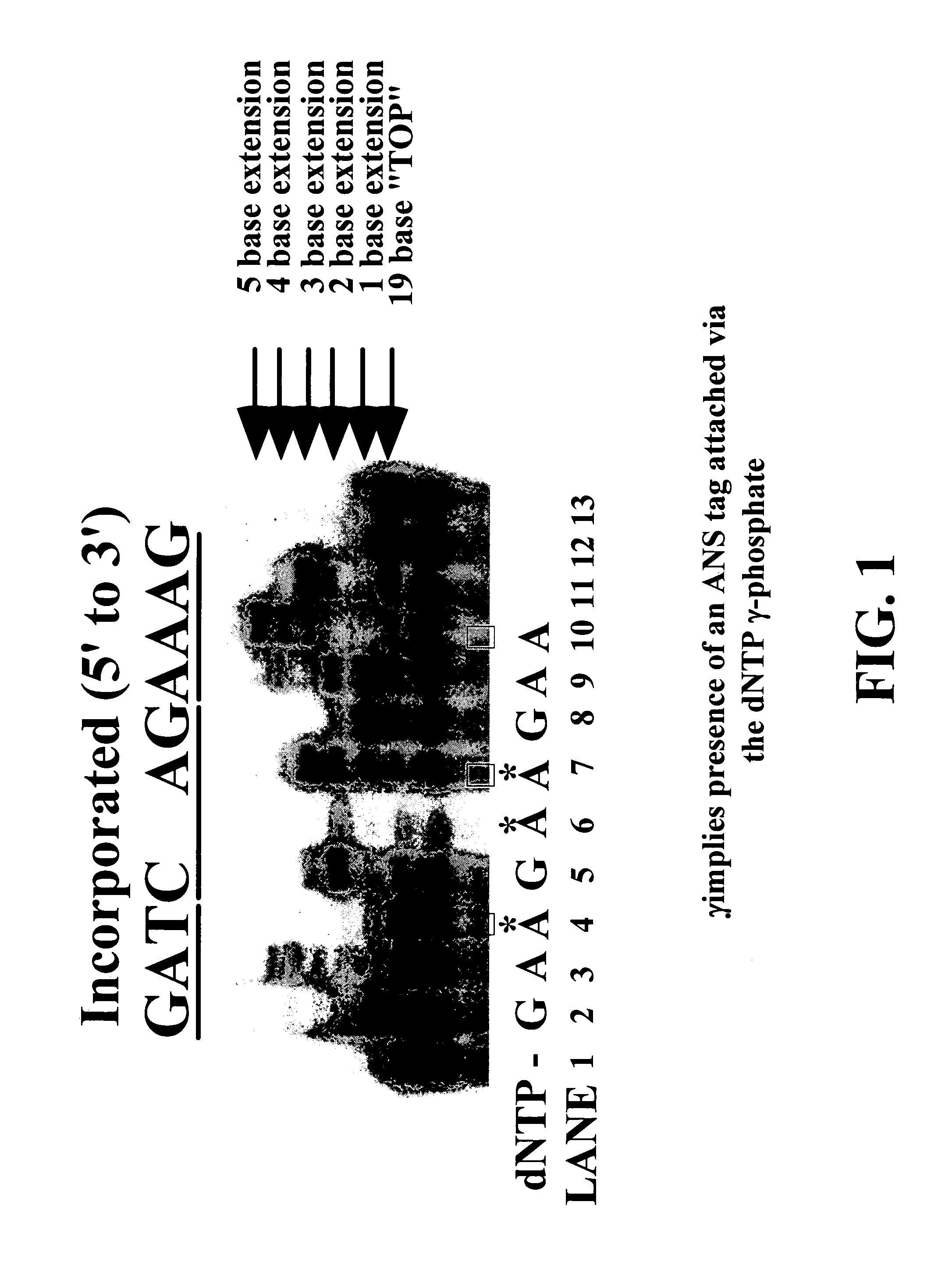
Enzymatic nucleic acid synthesis: compositions and methods for altering monomer incorporation fidelity
InactiveUS7211414B2Extent of pyrophosphorolysis of a primer extension product is reducedImprove fidelityBiocideSugar derivativesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
Nucleotide triphosphate probes containing a molecular and / or atomic tag on a a γ and / or β phosphate group and / or a base moiety having a detectable property are disclosed, and kits and method for using the tagged nucleotides in sequencing reactions and various assay. Also, phosphate and polyphosphate molecular fidelity altering agents are disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
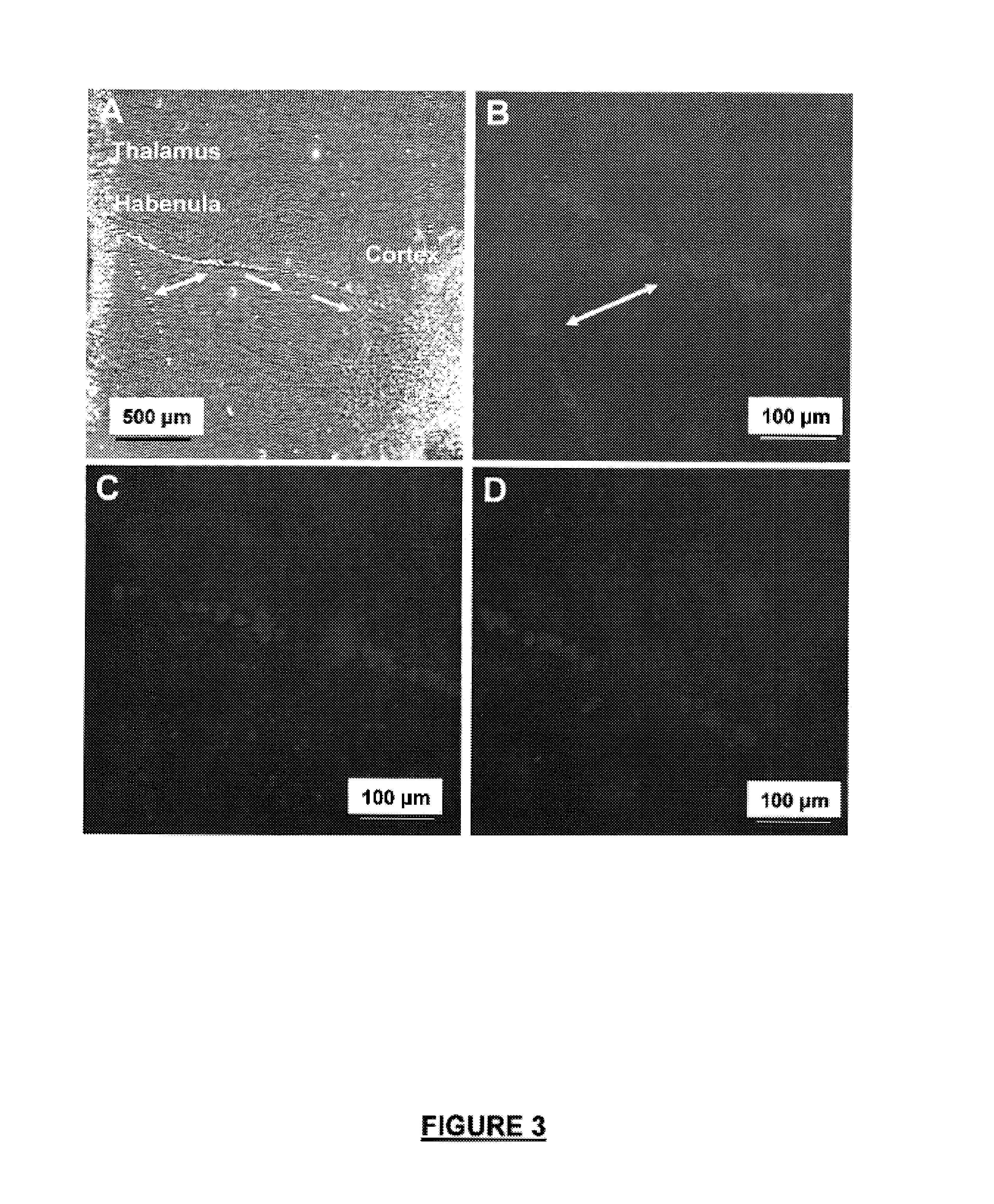
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
InactiveUS7563862B2High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
InactiveUS20070237764A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousAntigen binding
The invention provides variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. These polypeptides provide a flexible and simple source of sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Binding polypeptides with diversified and consensus vh/vl hypervariable sequences
ActiveUS20070160598A1Raise the possibilitySmall sizeAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntibody hypervariable regionBioinformatics
The invention provides variant hypervariable regions comprising selected amino acid sequence diversity. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
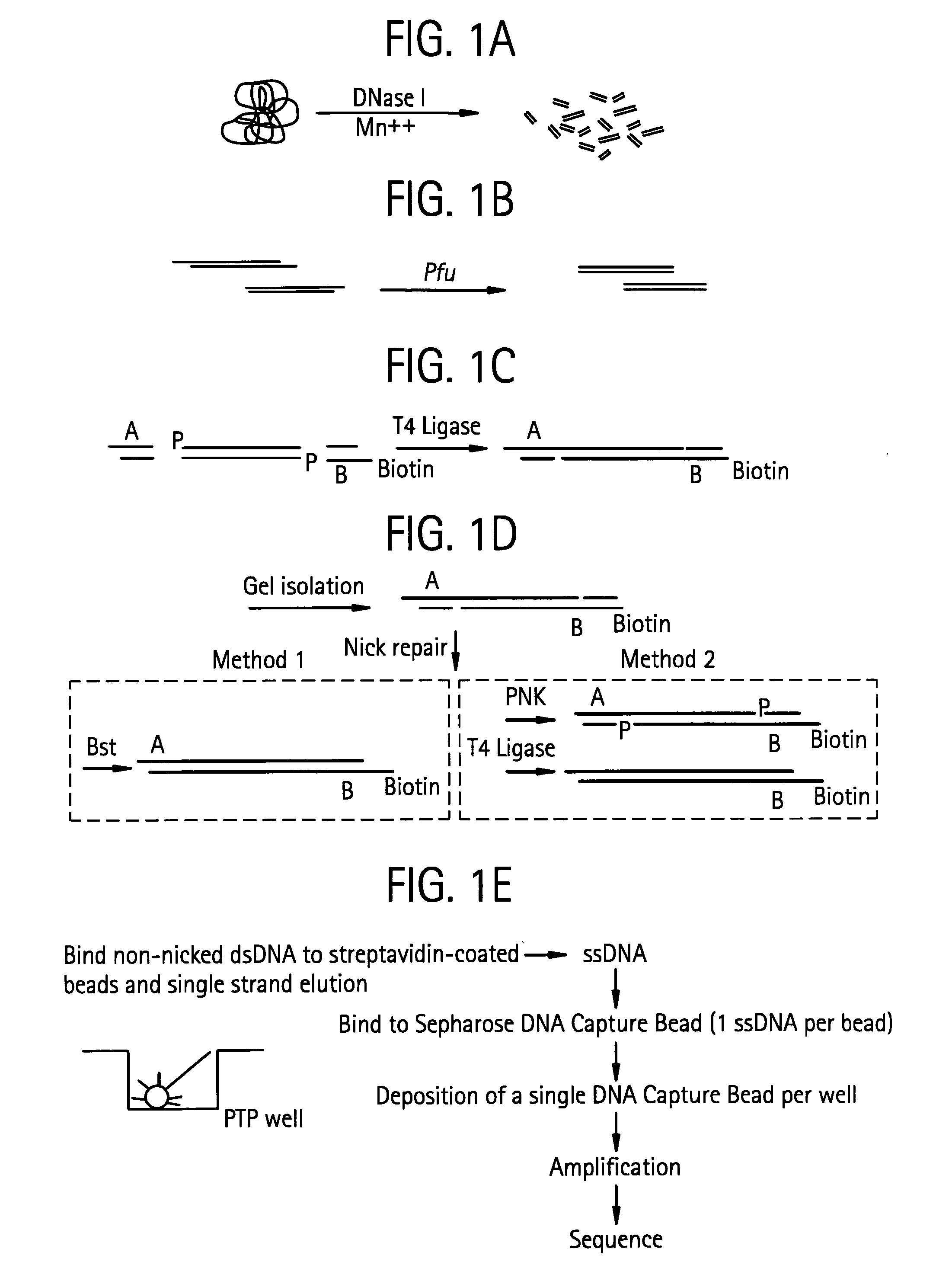
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
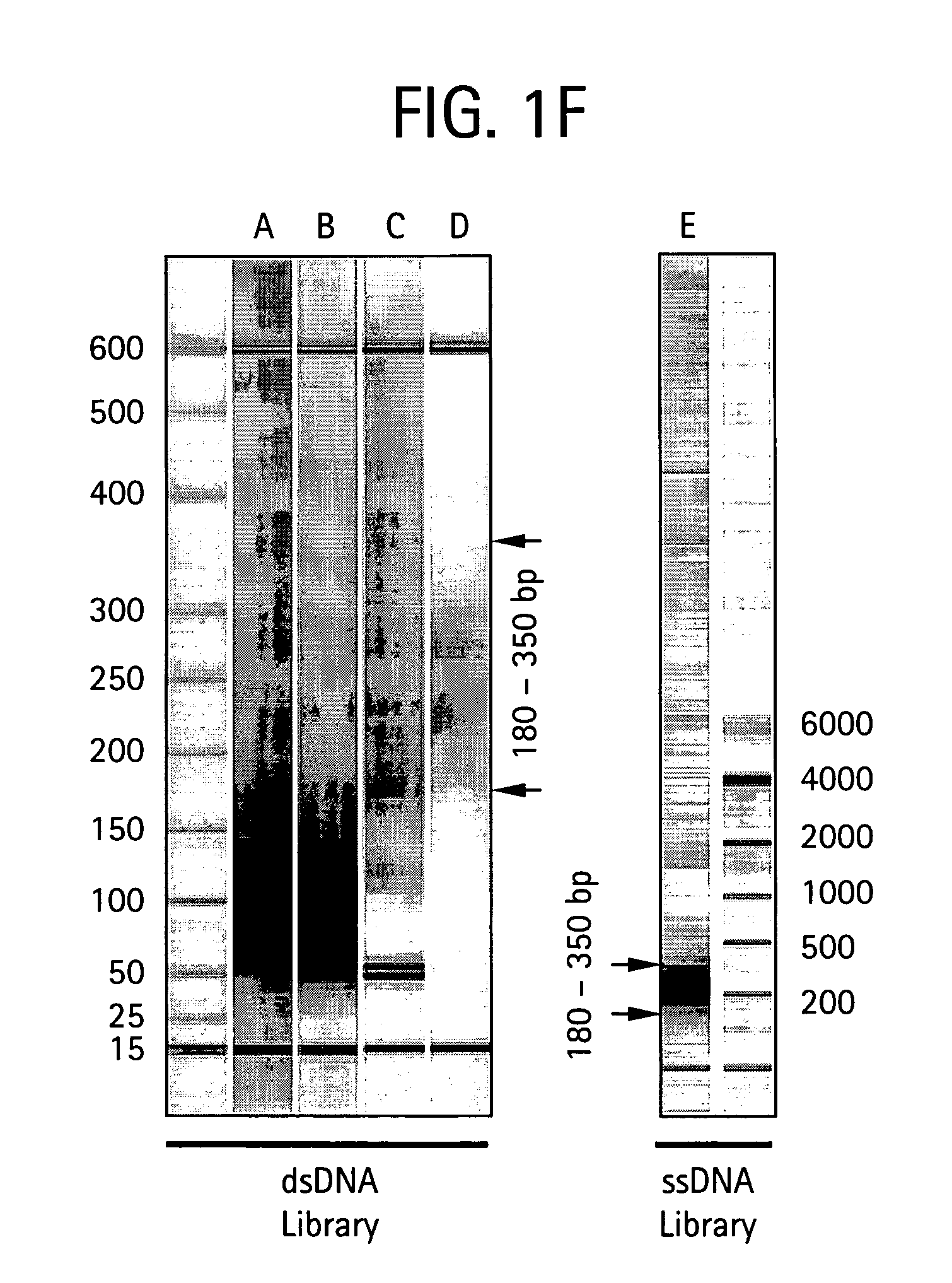
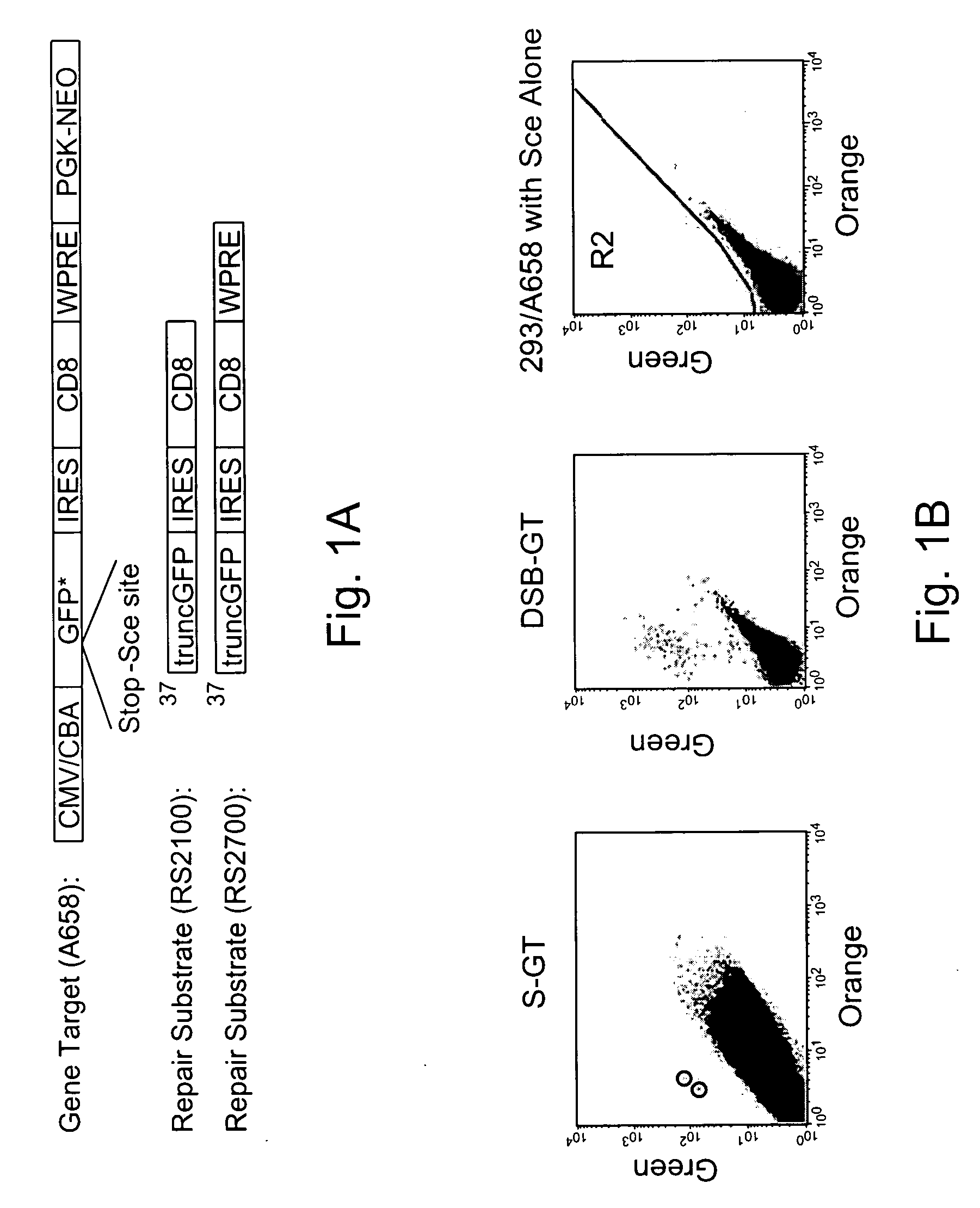
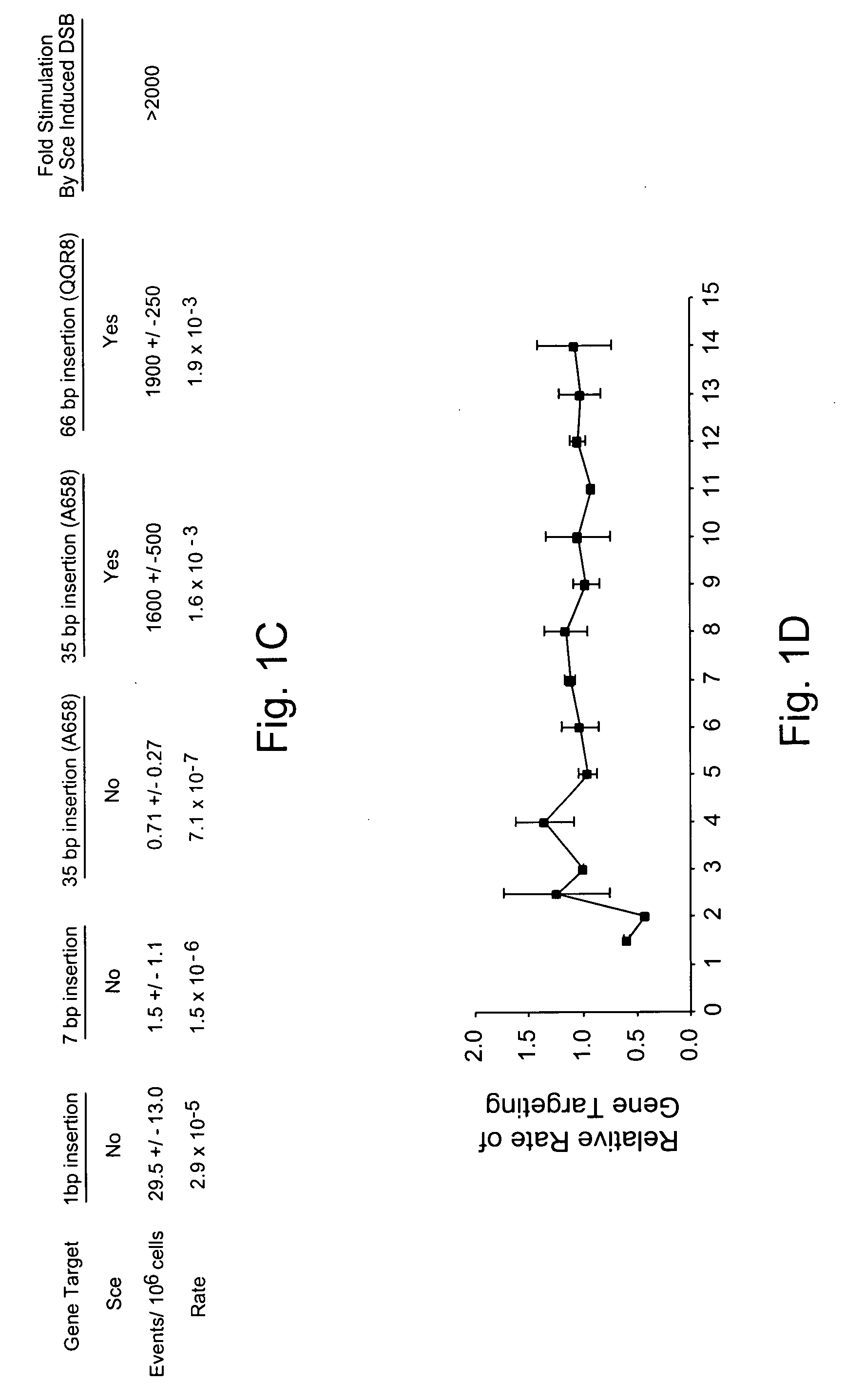
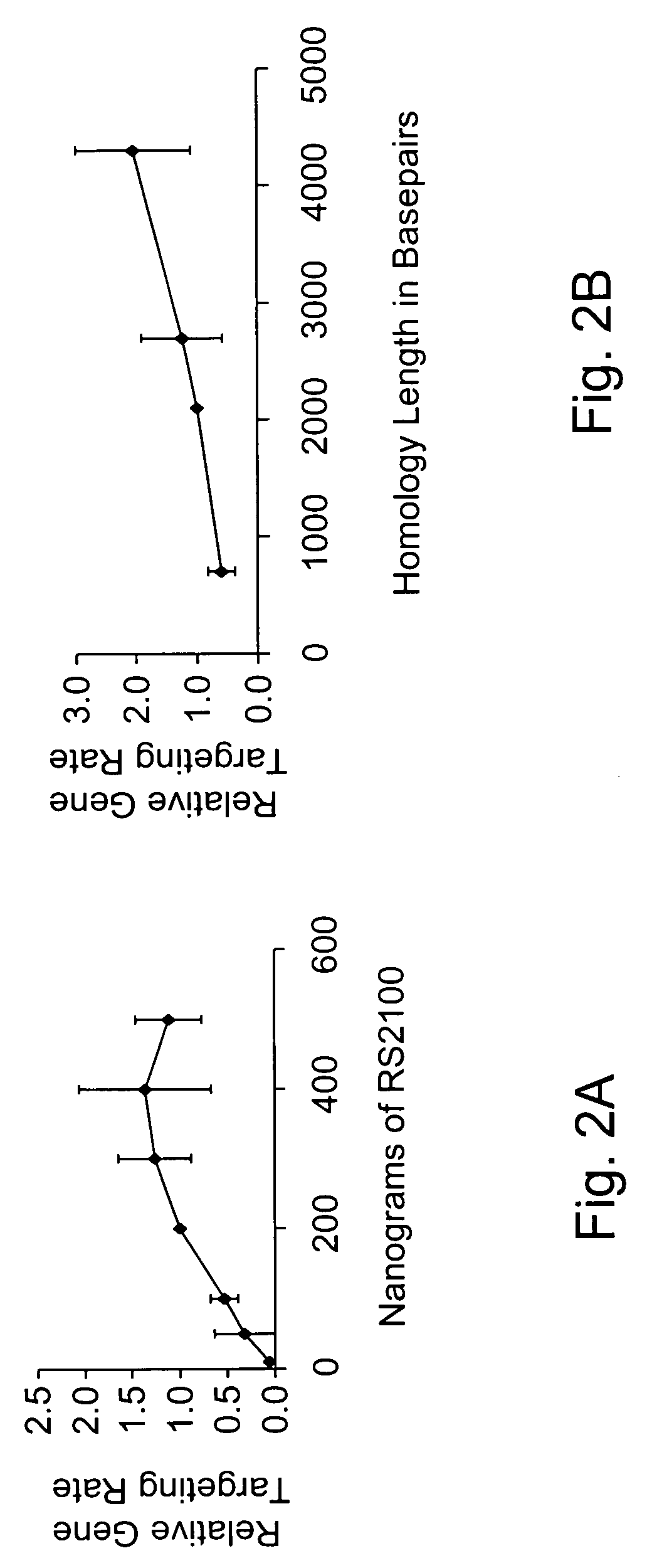
Use of chimeric nucleases to stimulate gene targeting
ActiveUS20050026157A1Ameliorate genetic disorderIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsFusion with DNA-binding domainGene targetsGenetic Change
Gene targeting is a technique to introduce genetic change into one or more specific locations in the genome of a cell. For example, gene targeting can introduce genetic change by modifying, repairing, attenuating or inactivating a target gene or other chromosomal DNA. In one aspect, this disclosure relates to methods and compositions for gene targeting with high efficiency in a cell. This disclosure also relates to methods of treating or preventing a genetic disease in an individual in need thereof. Further disclosed are chimeric nucleases and vectors encoding chimeric nucleases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
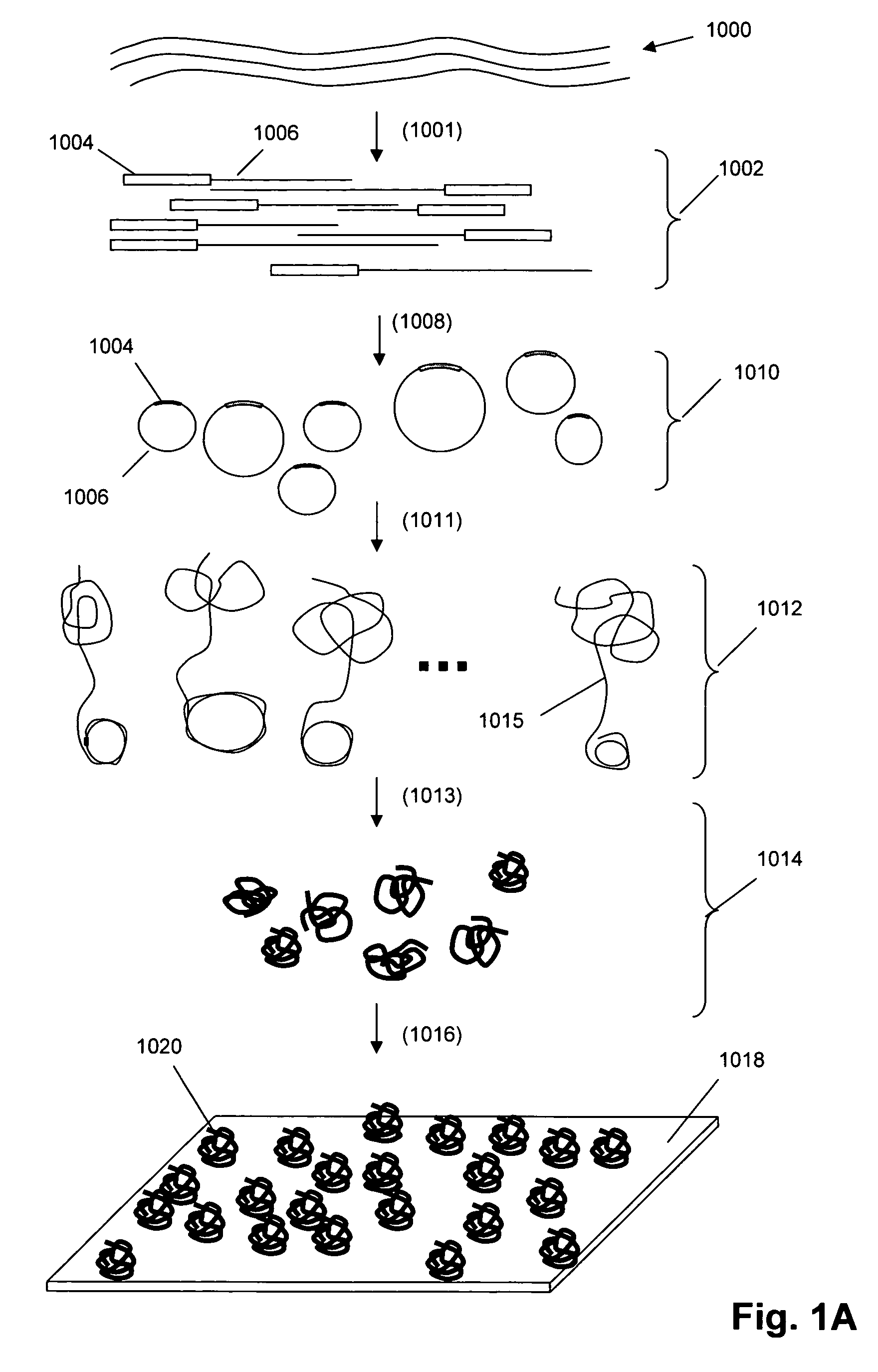
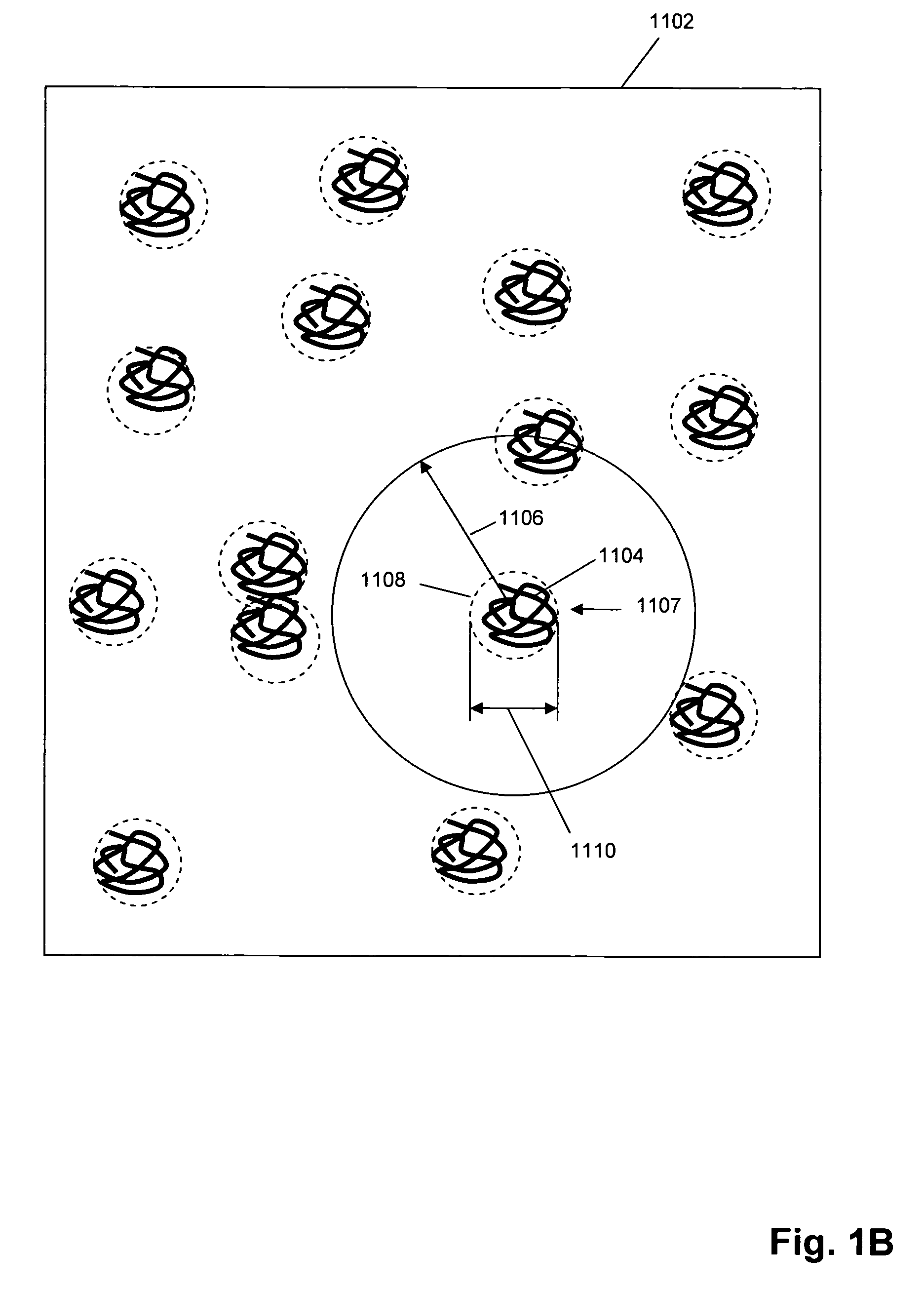
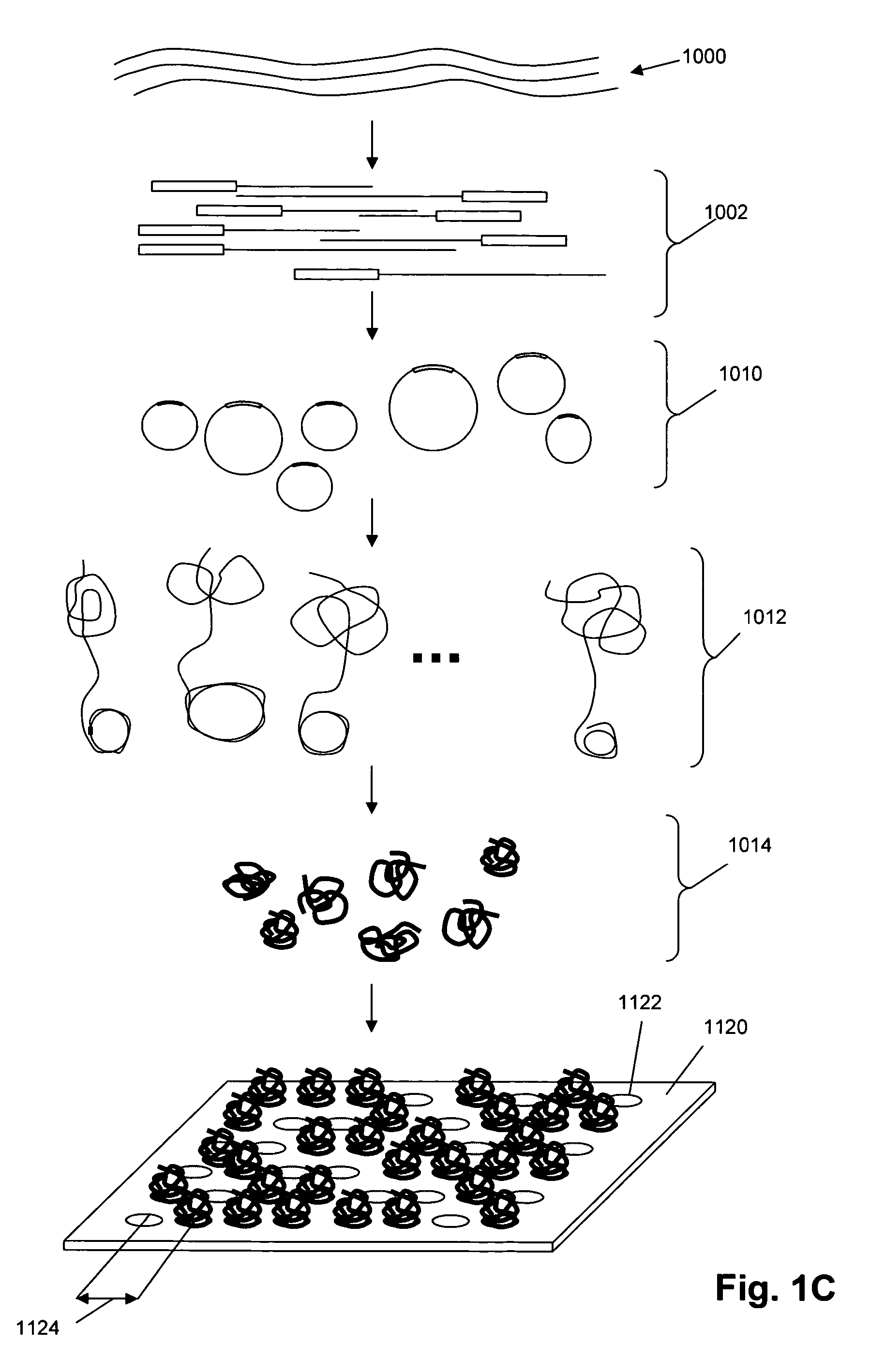
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Method of sequencing a nucleic acid
InactiveUS7244559B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyNucleic acid detectionOligonucleotide
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
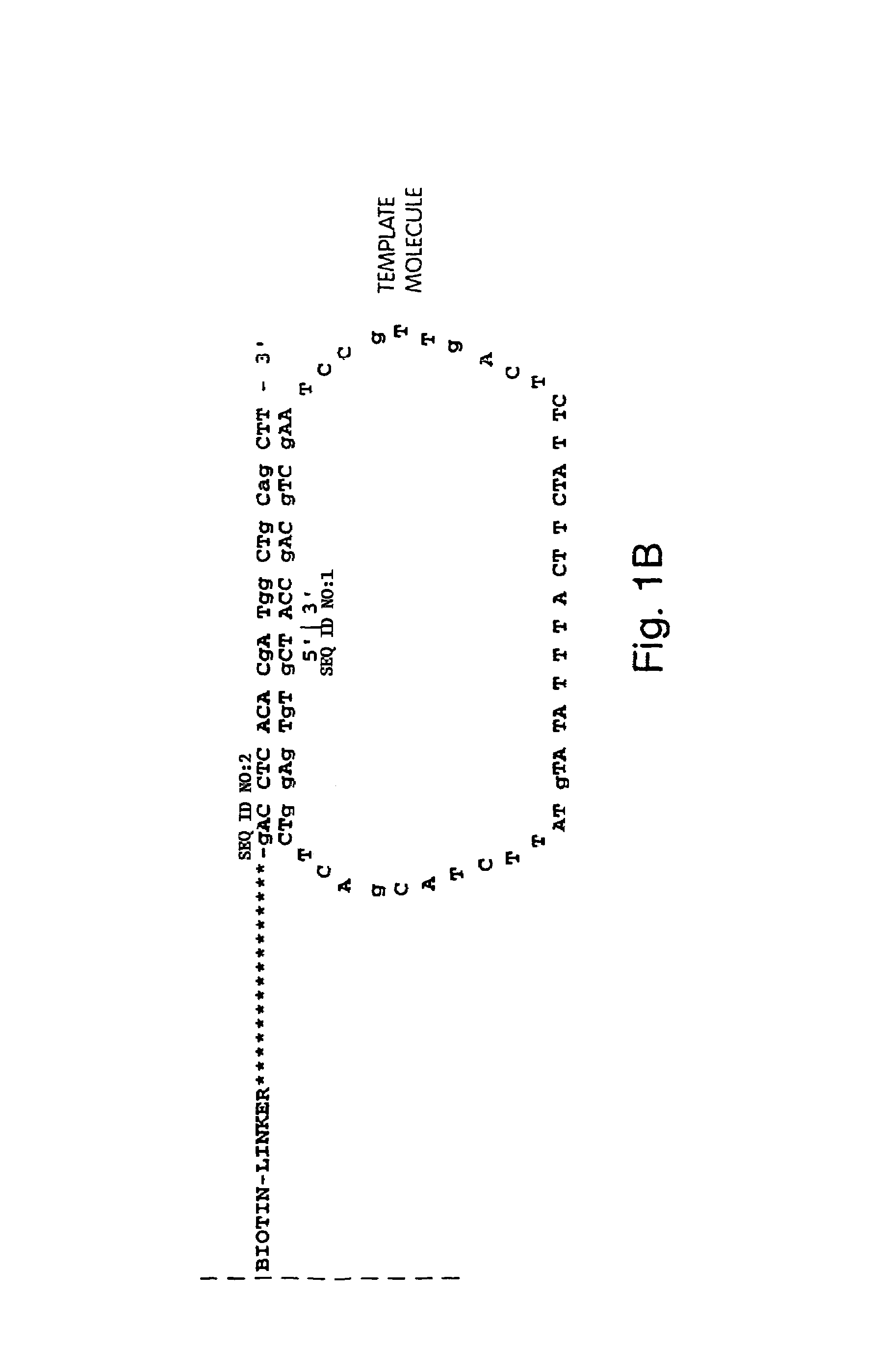
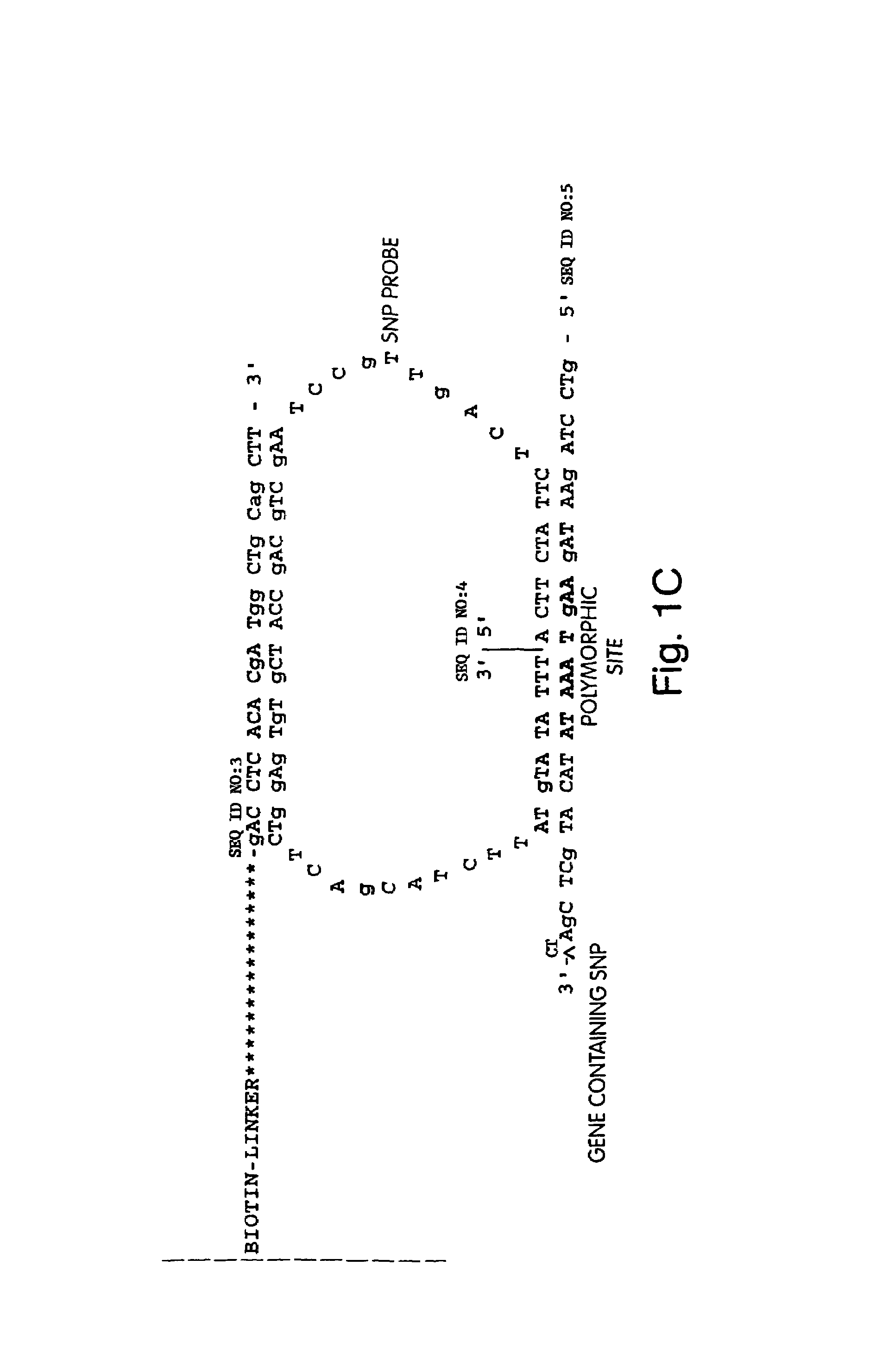
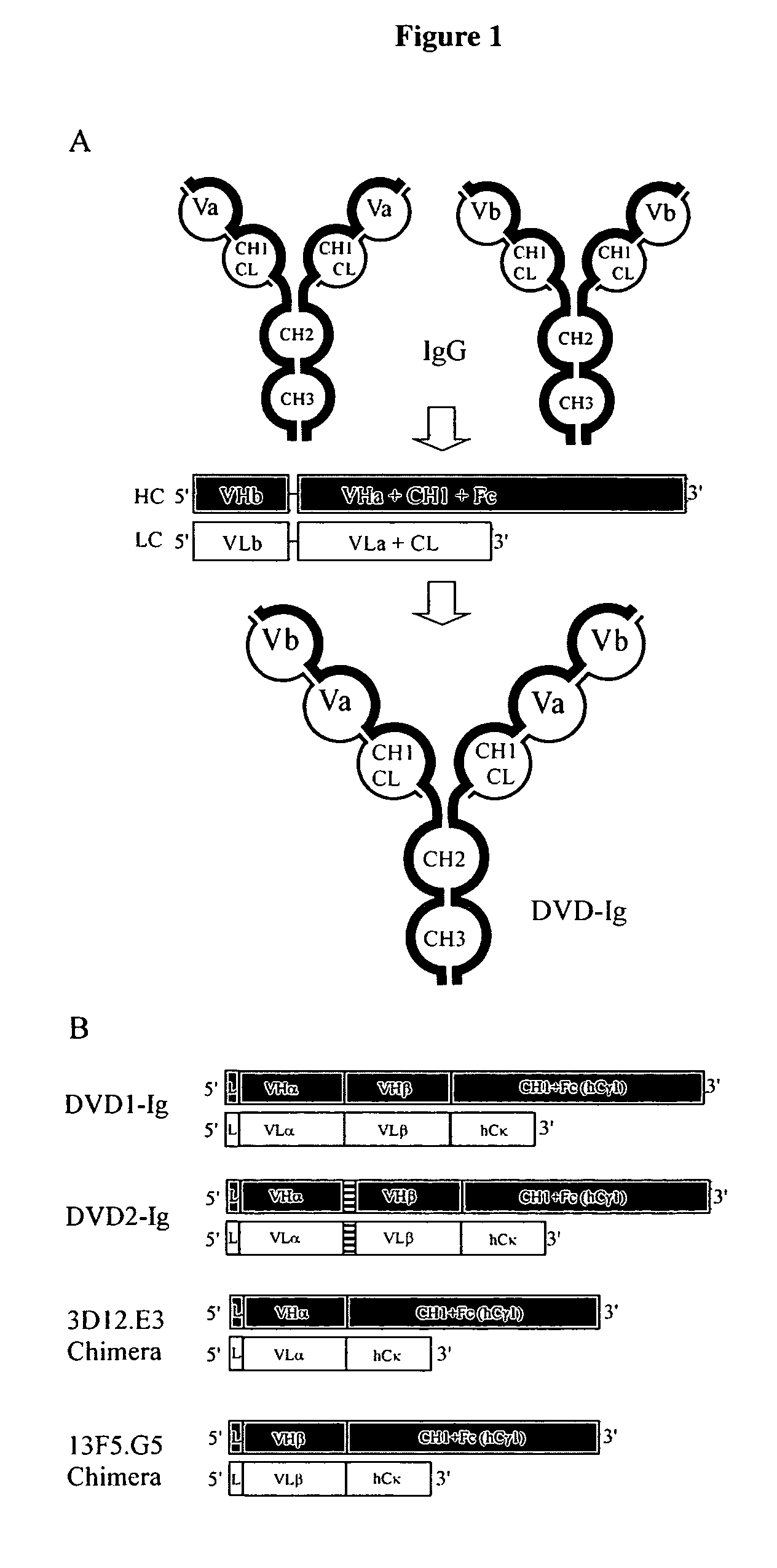
Dual variable domain immunoglobulin and uses thereof
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com