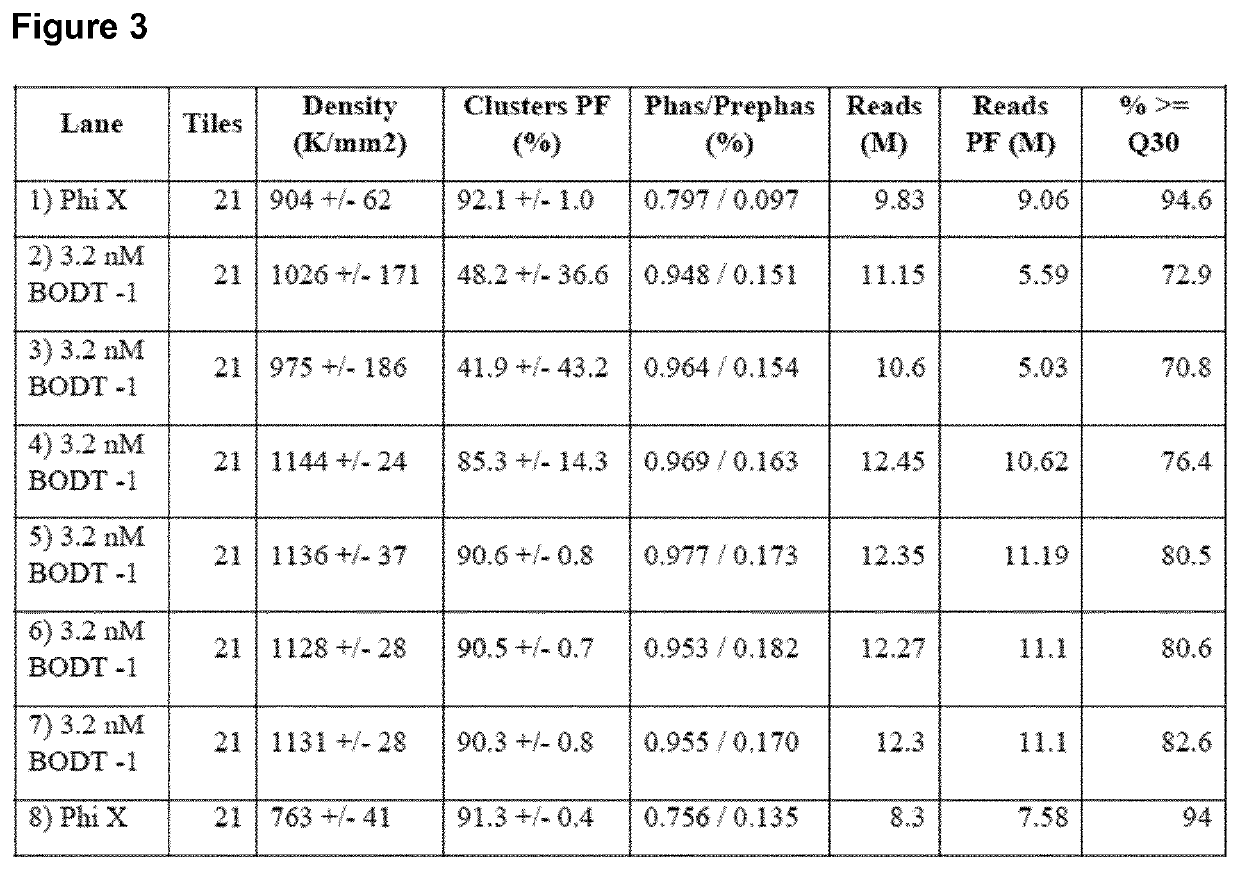
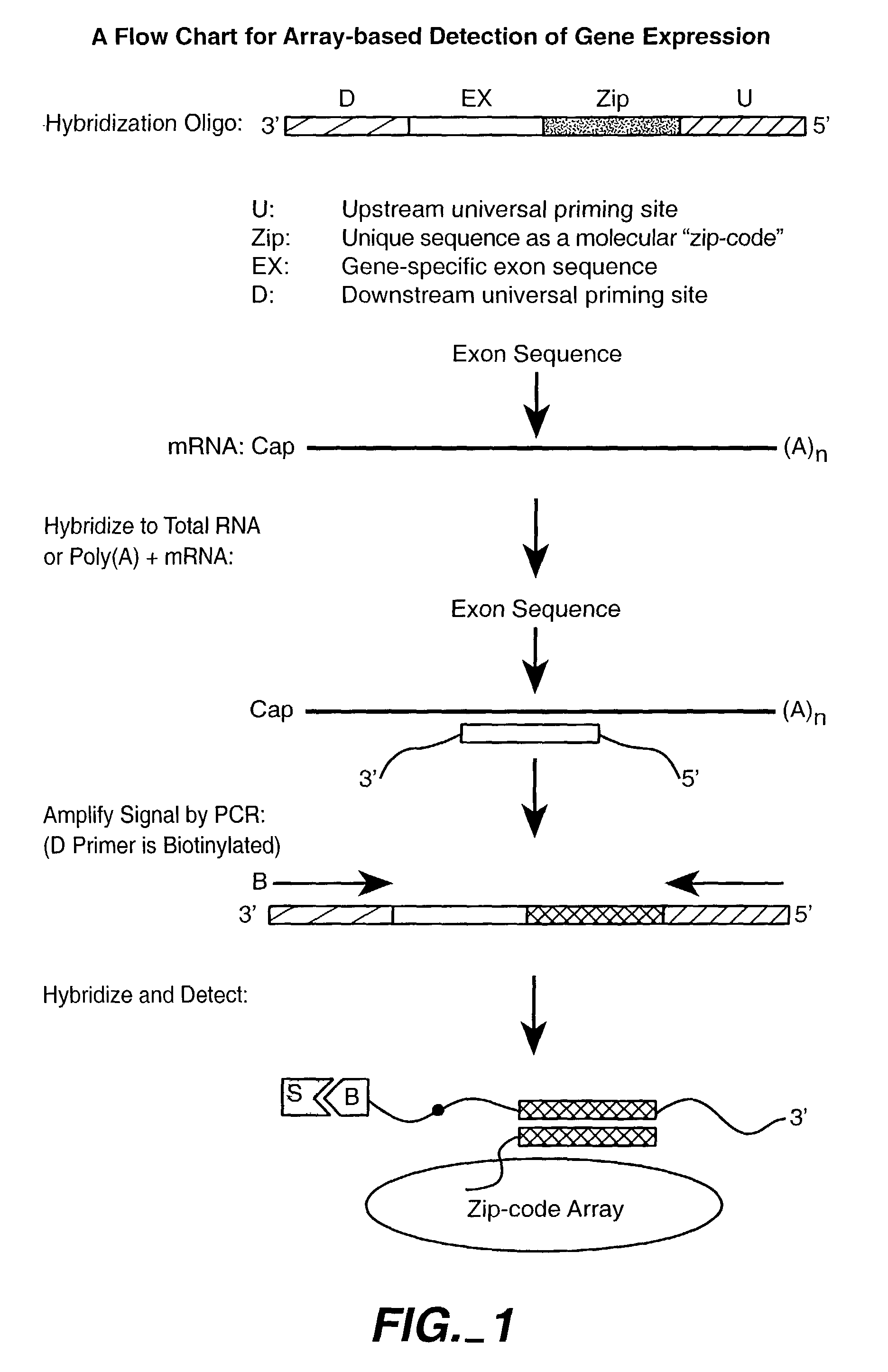
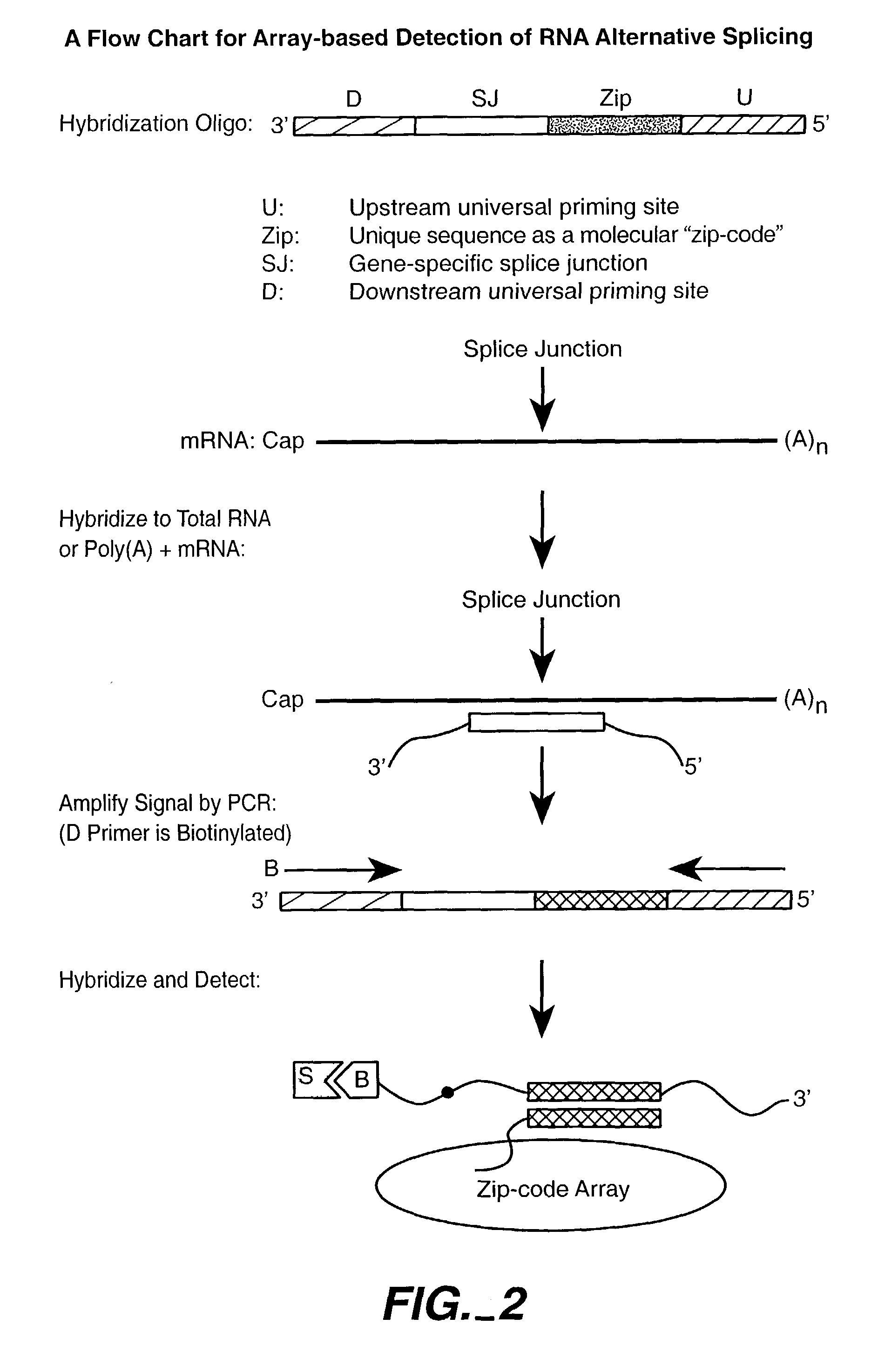
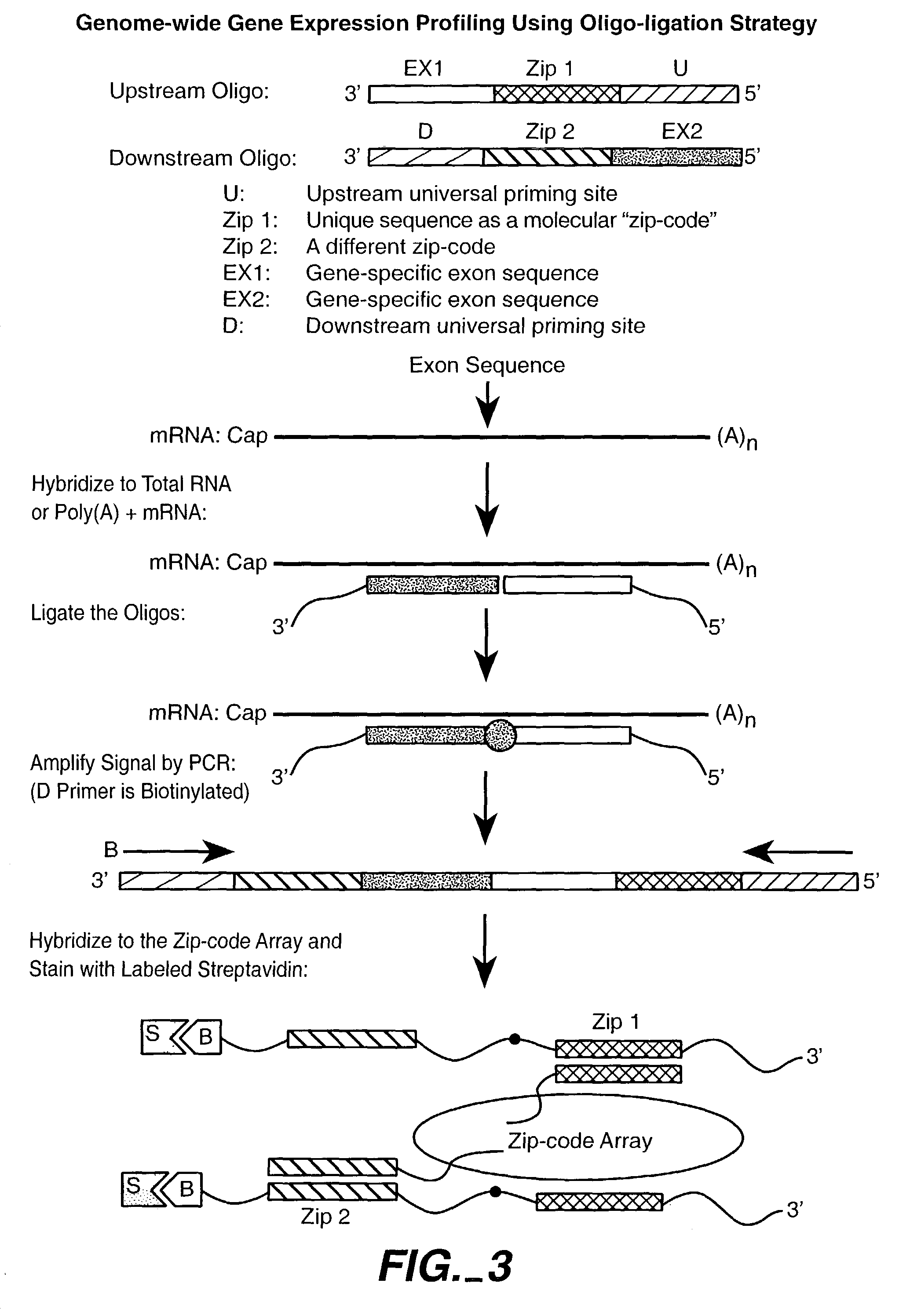
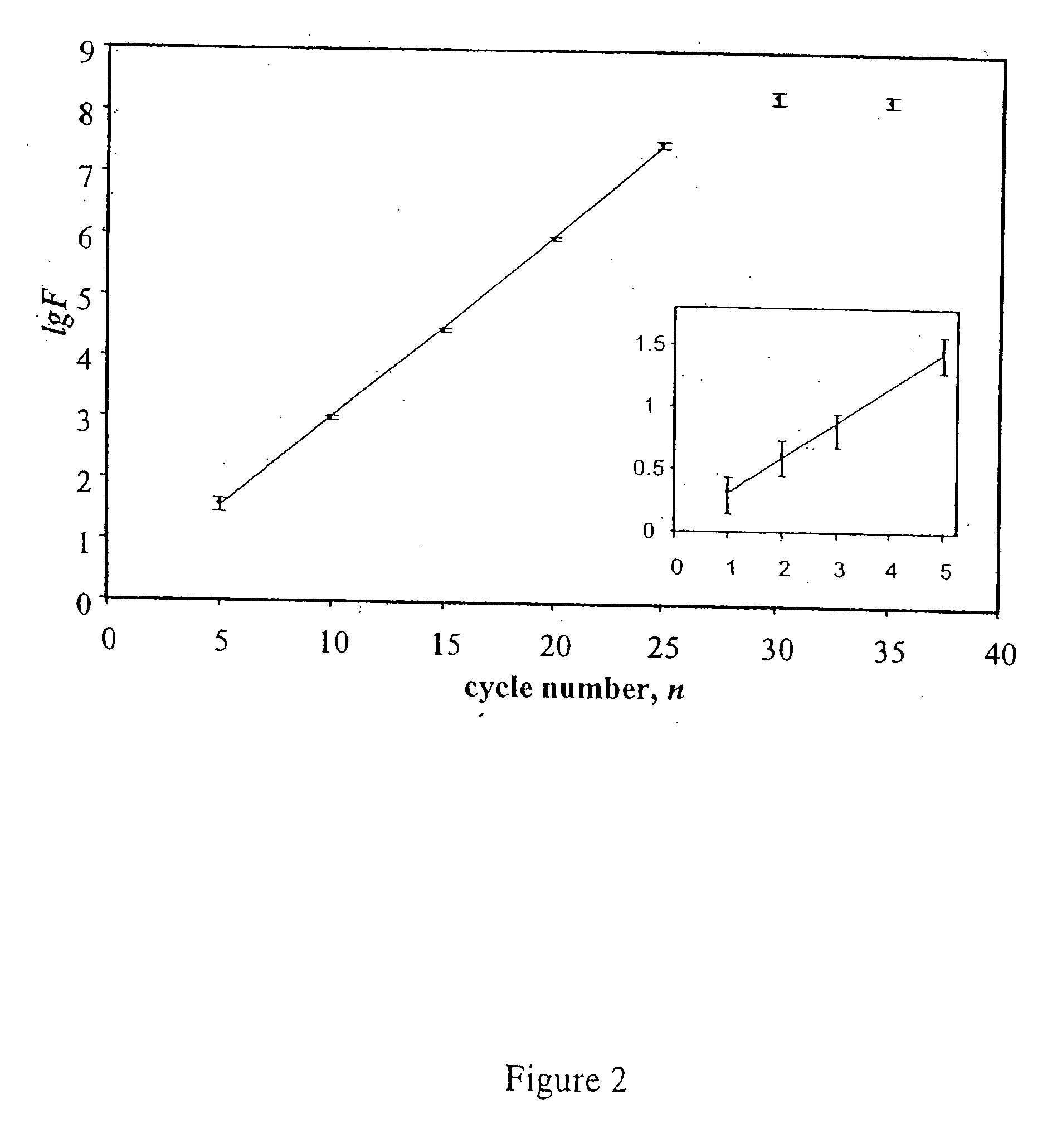
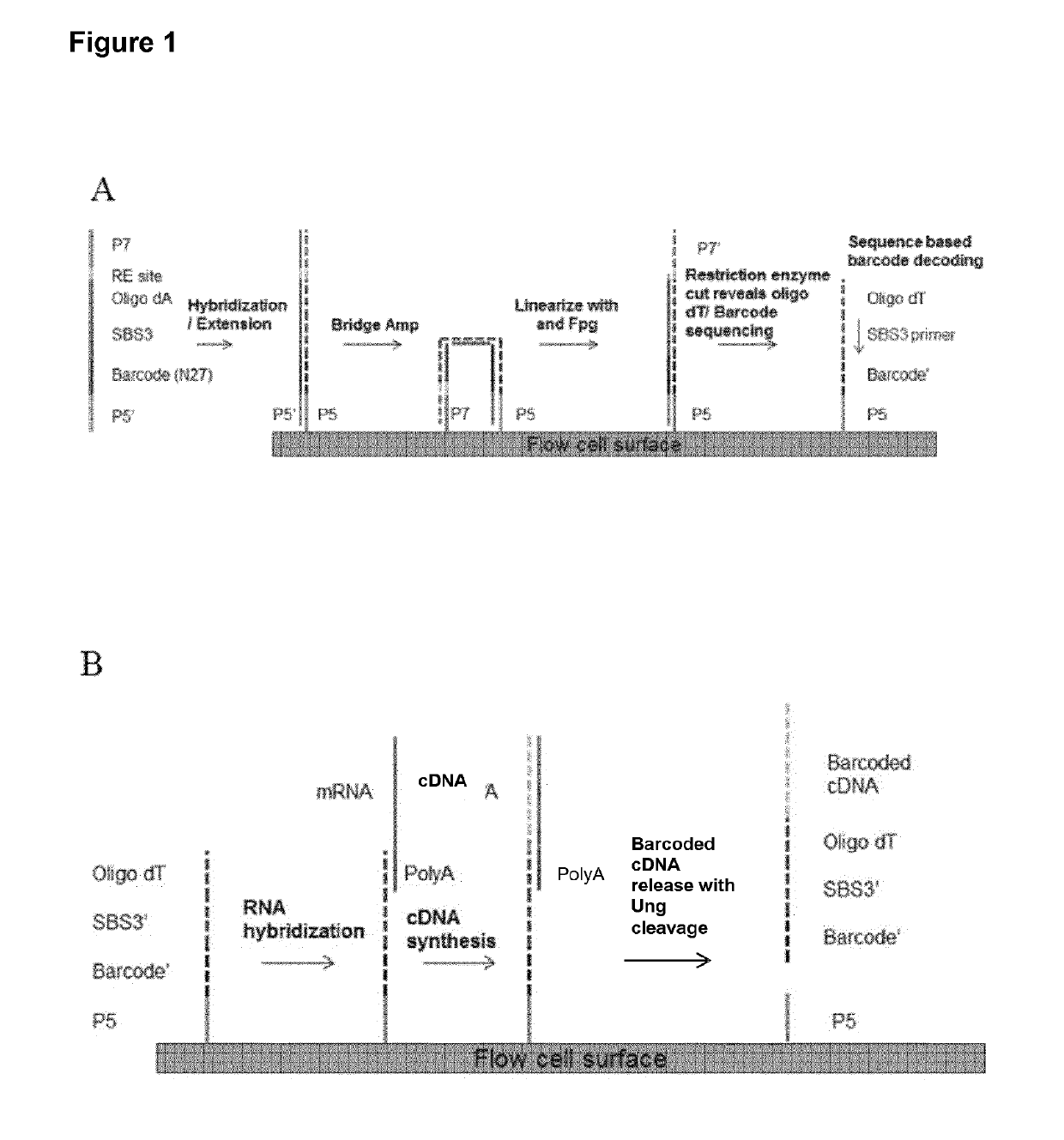
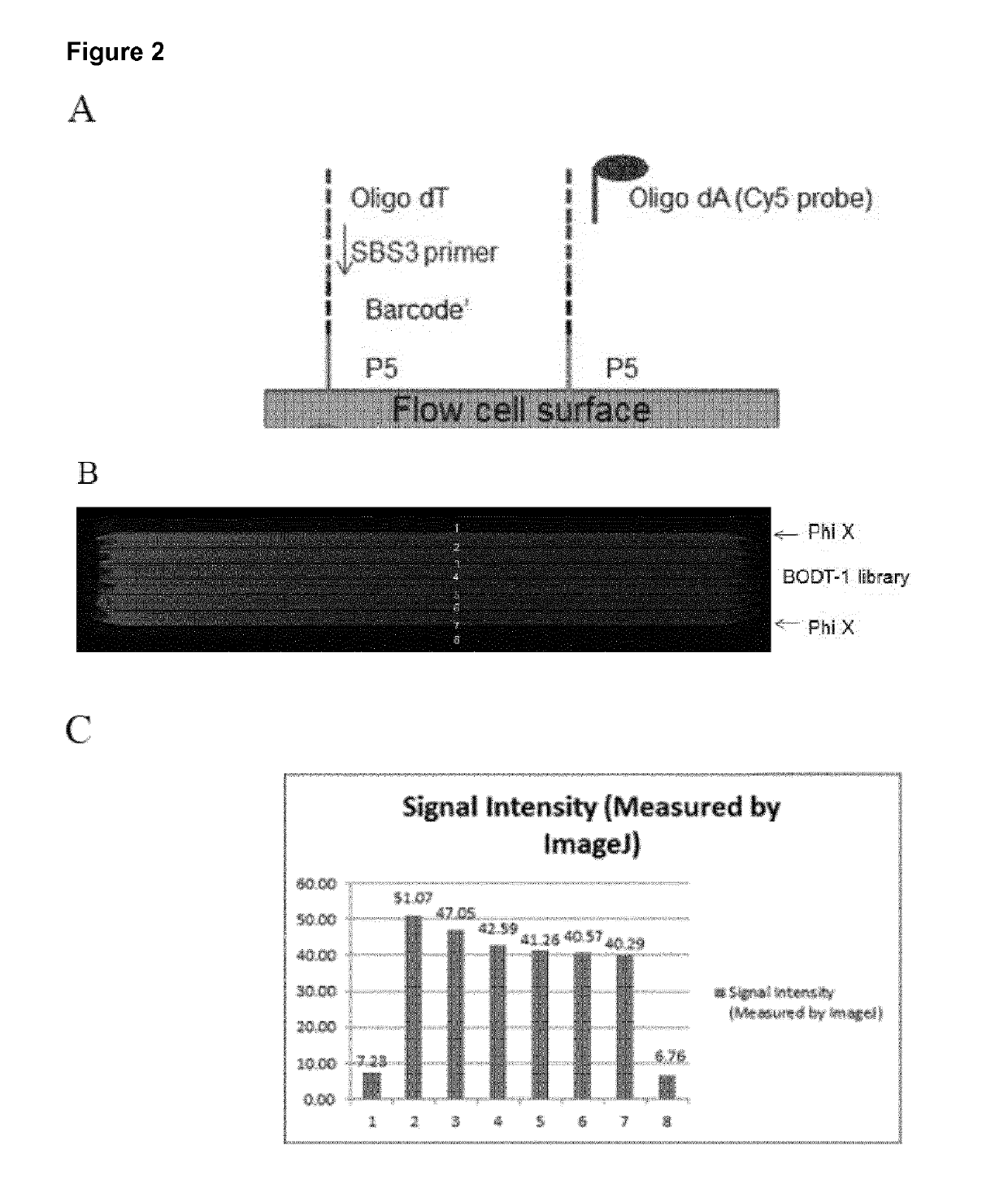
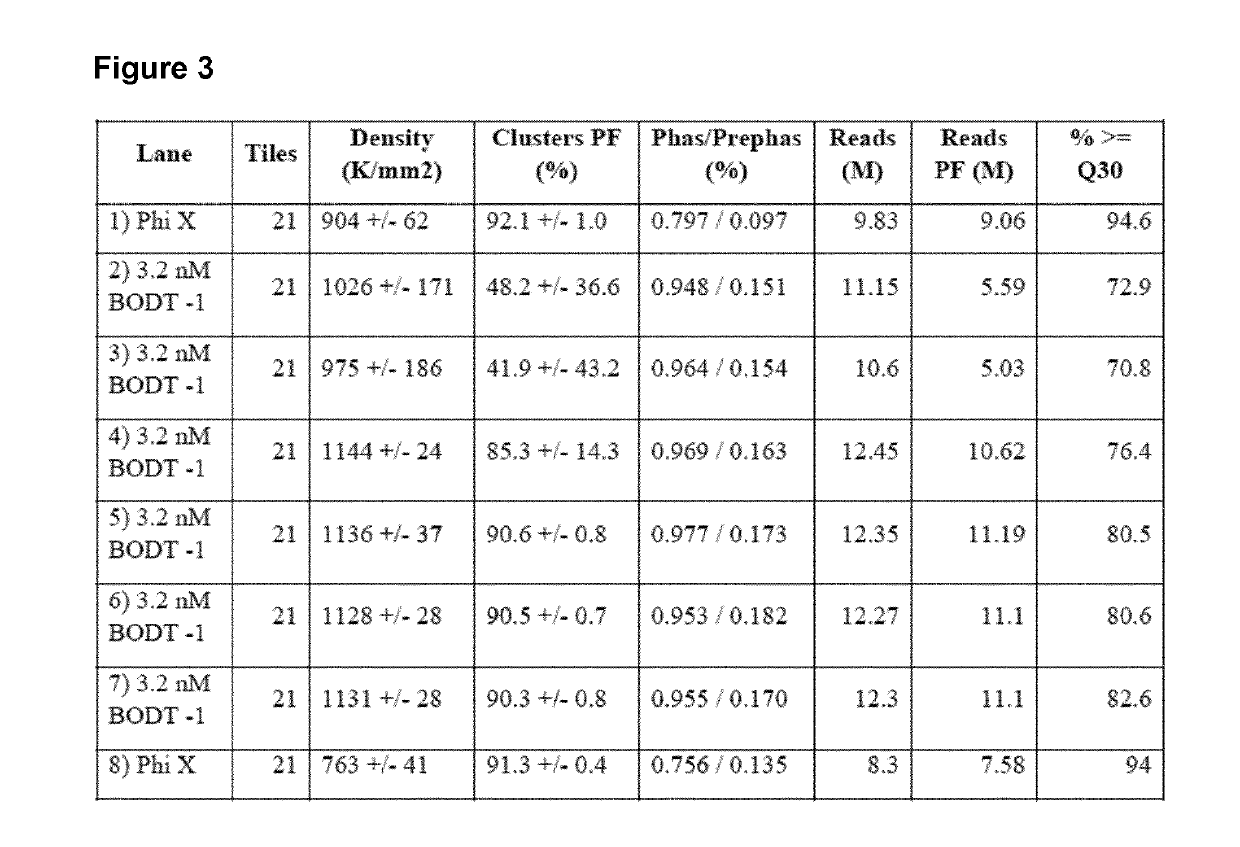
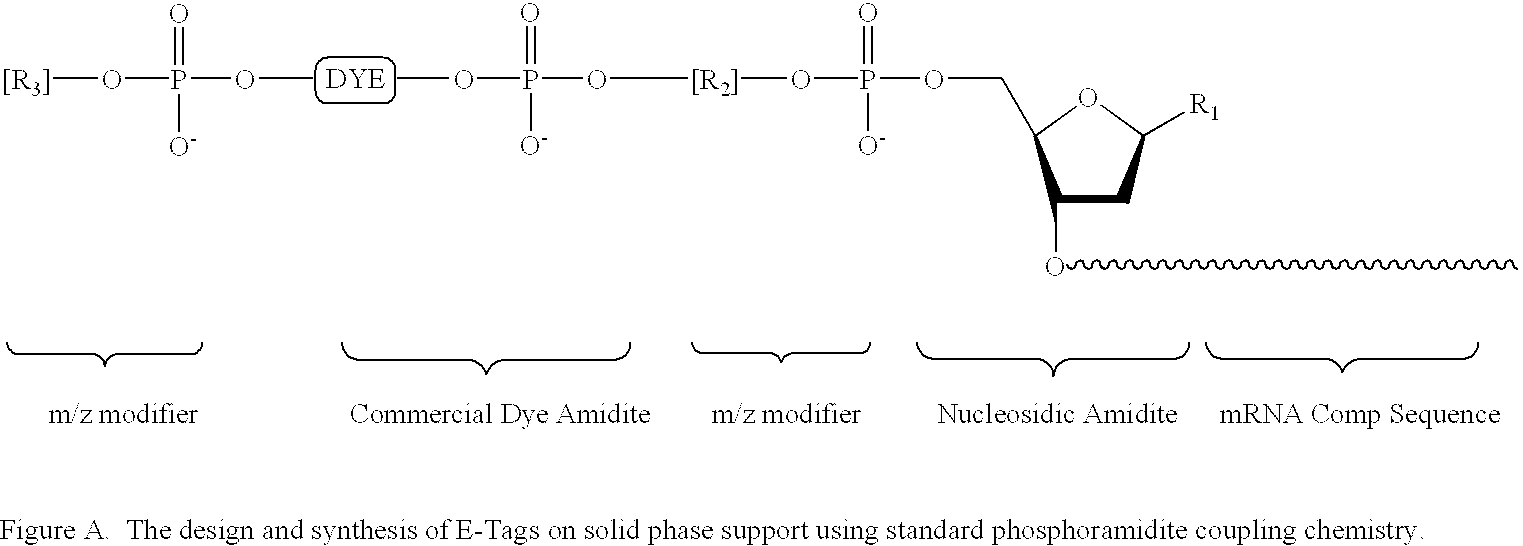
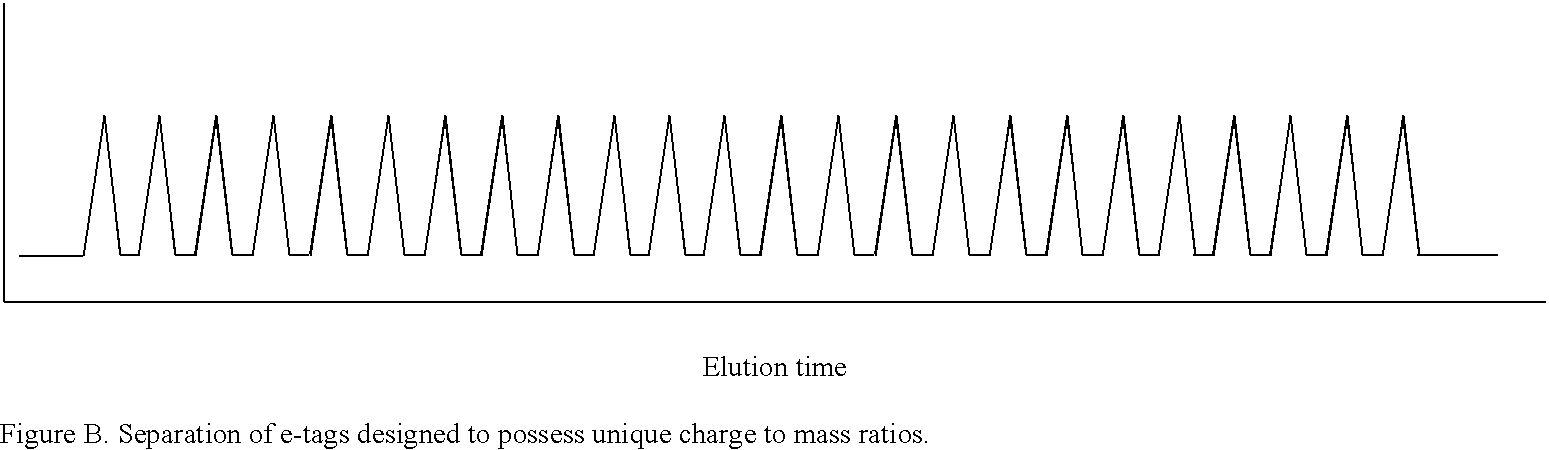
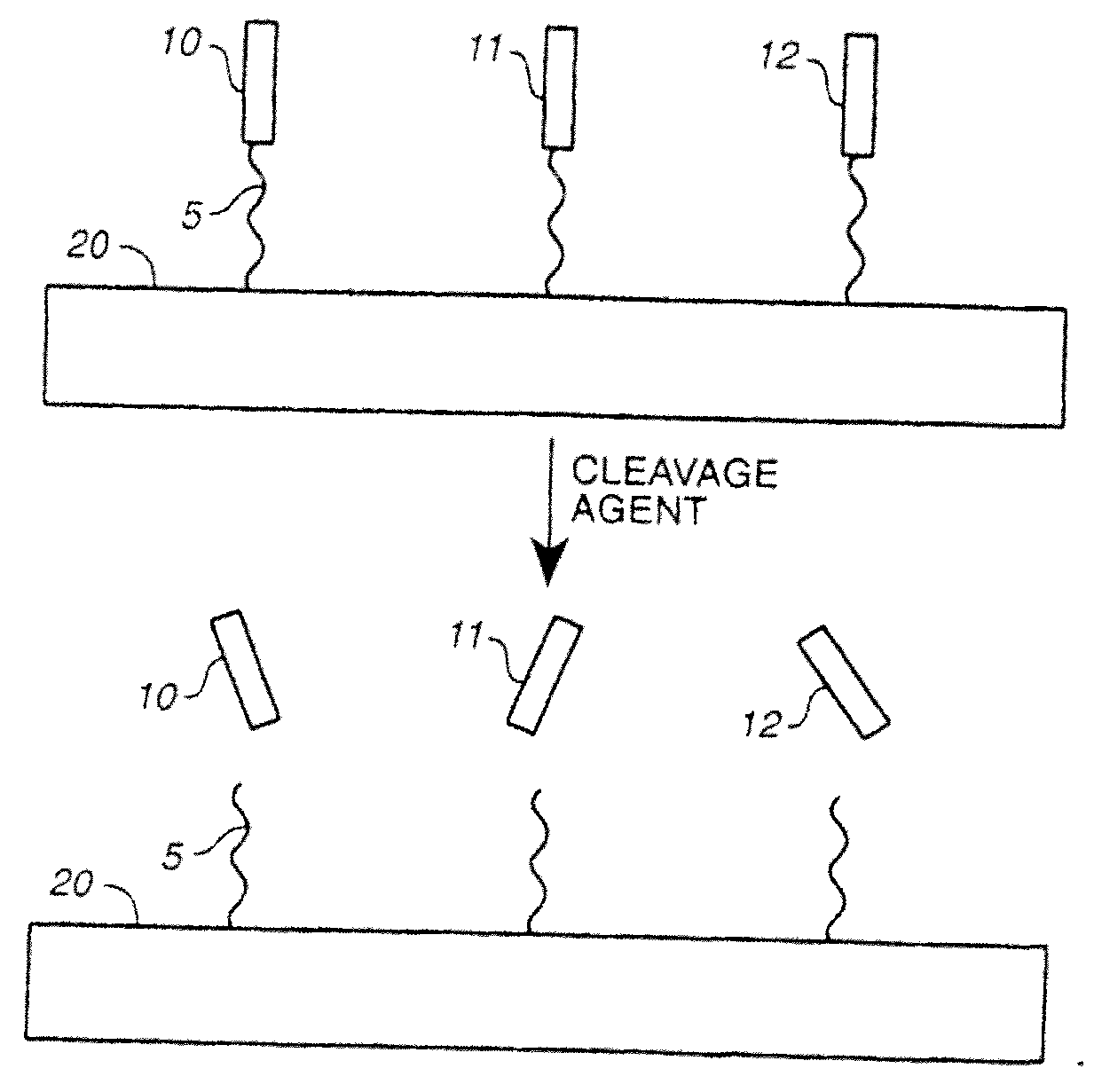
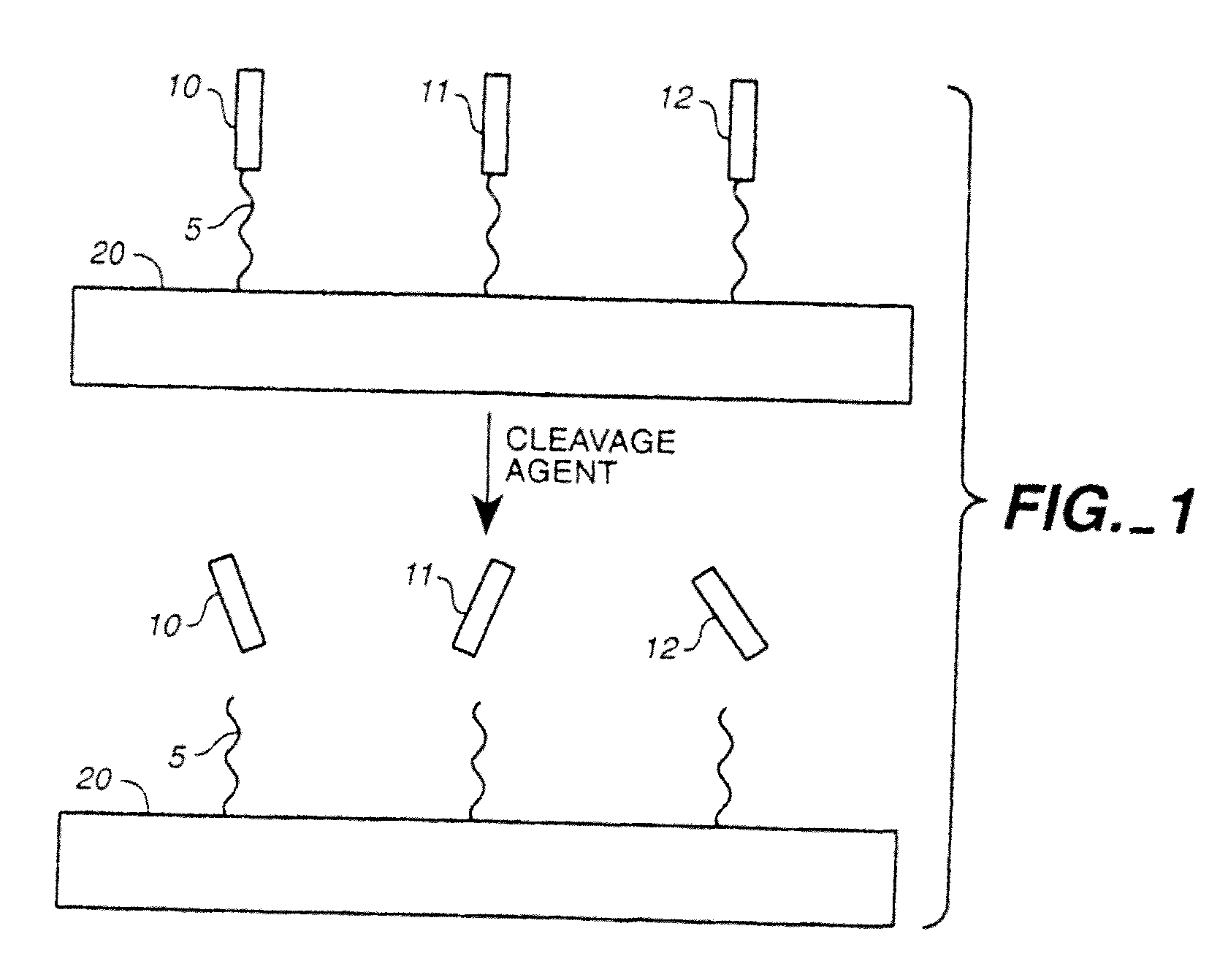
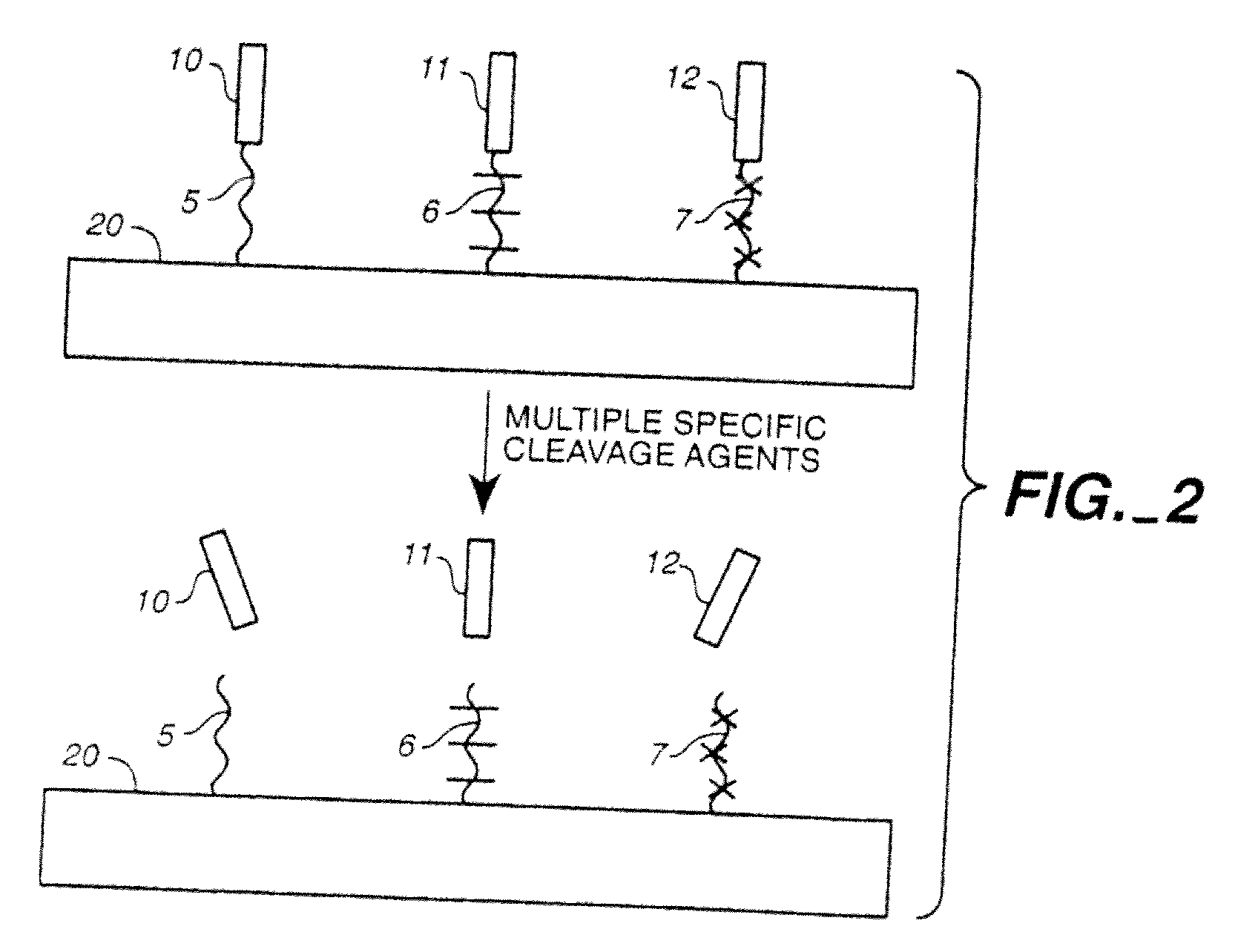
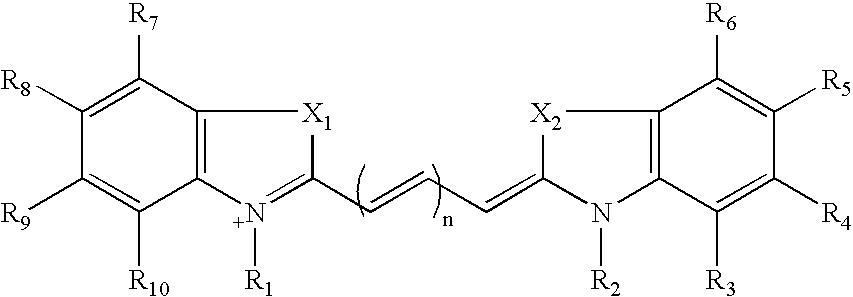
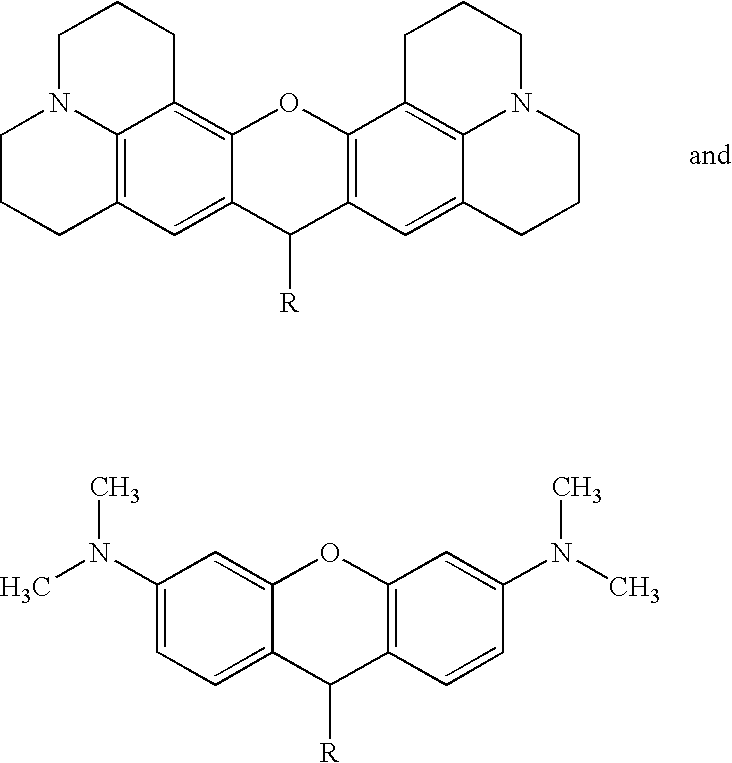
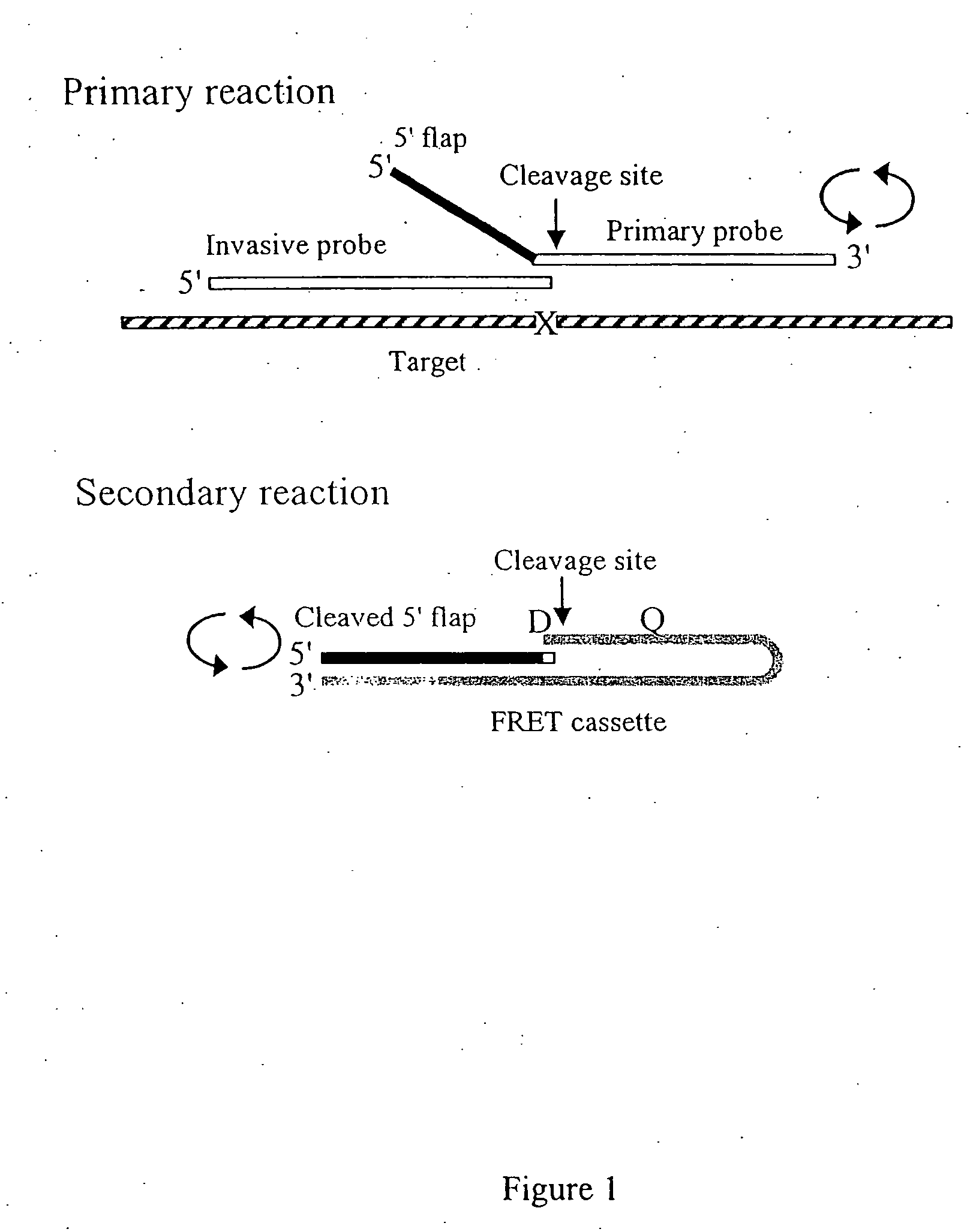
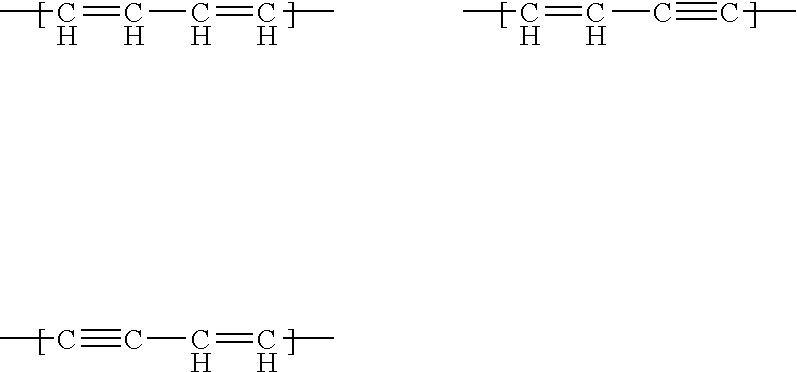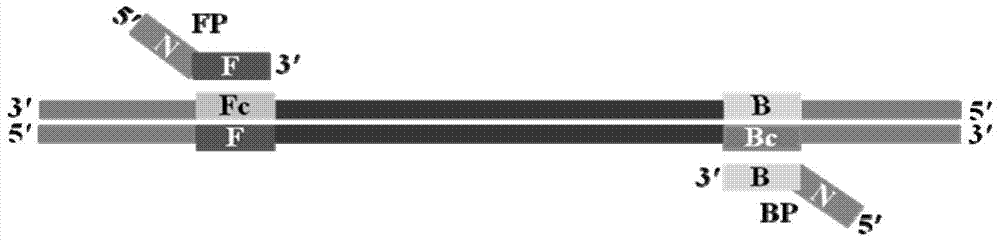Patents
Literature
2350 results about "Nucleic acid detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
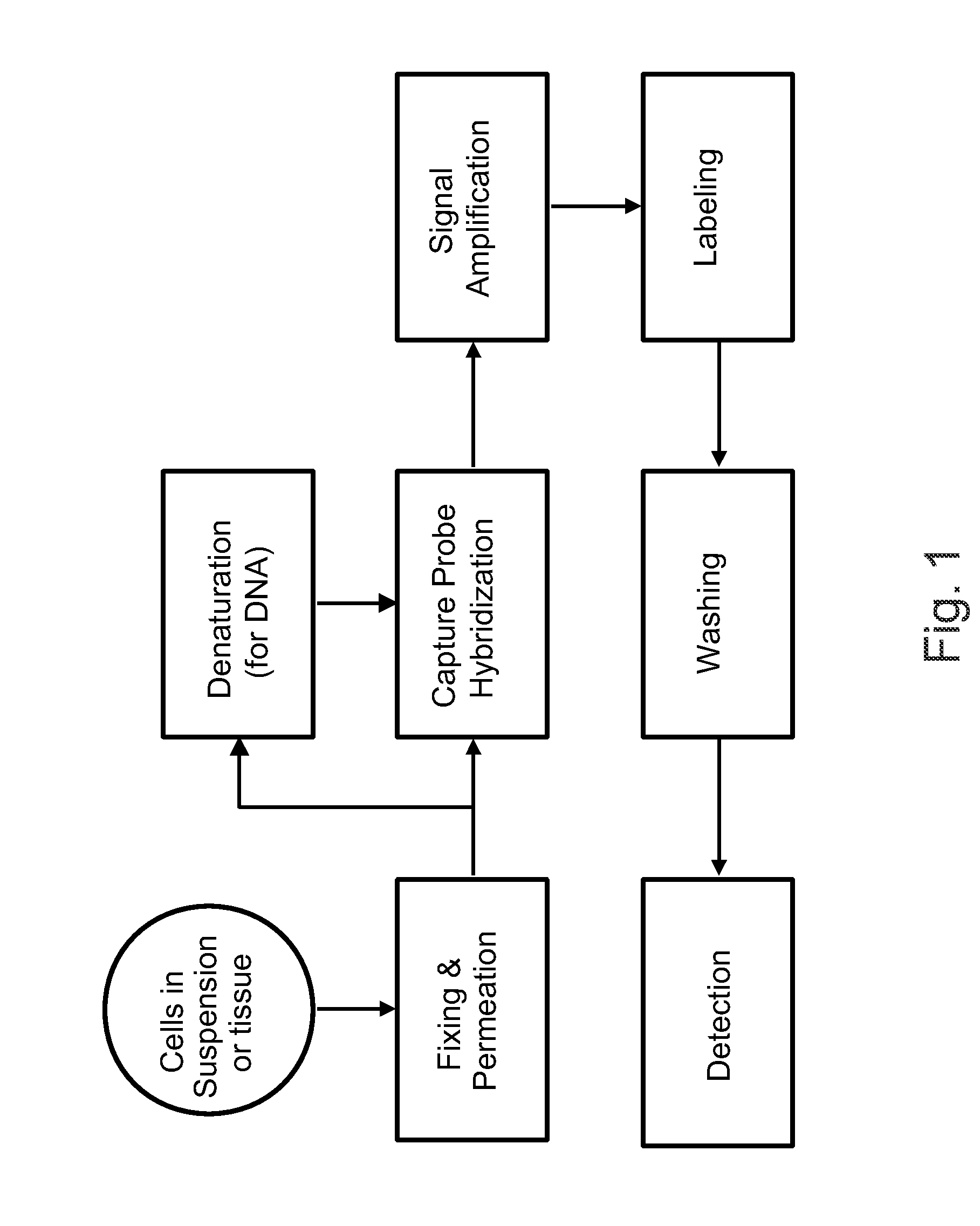
A nucleic acid test (NAT) or nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) is a technique utilized to detect a particular nucleic acid, virus, or bacteria which acts as a pathogen in blood, tissue, urine, etc. The NAT system differs from other tests in that it detects genetic materials rather than antigens or antibodies.
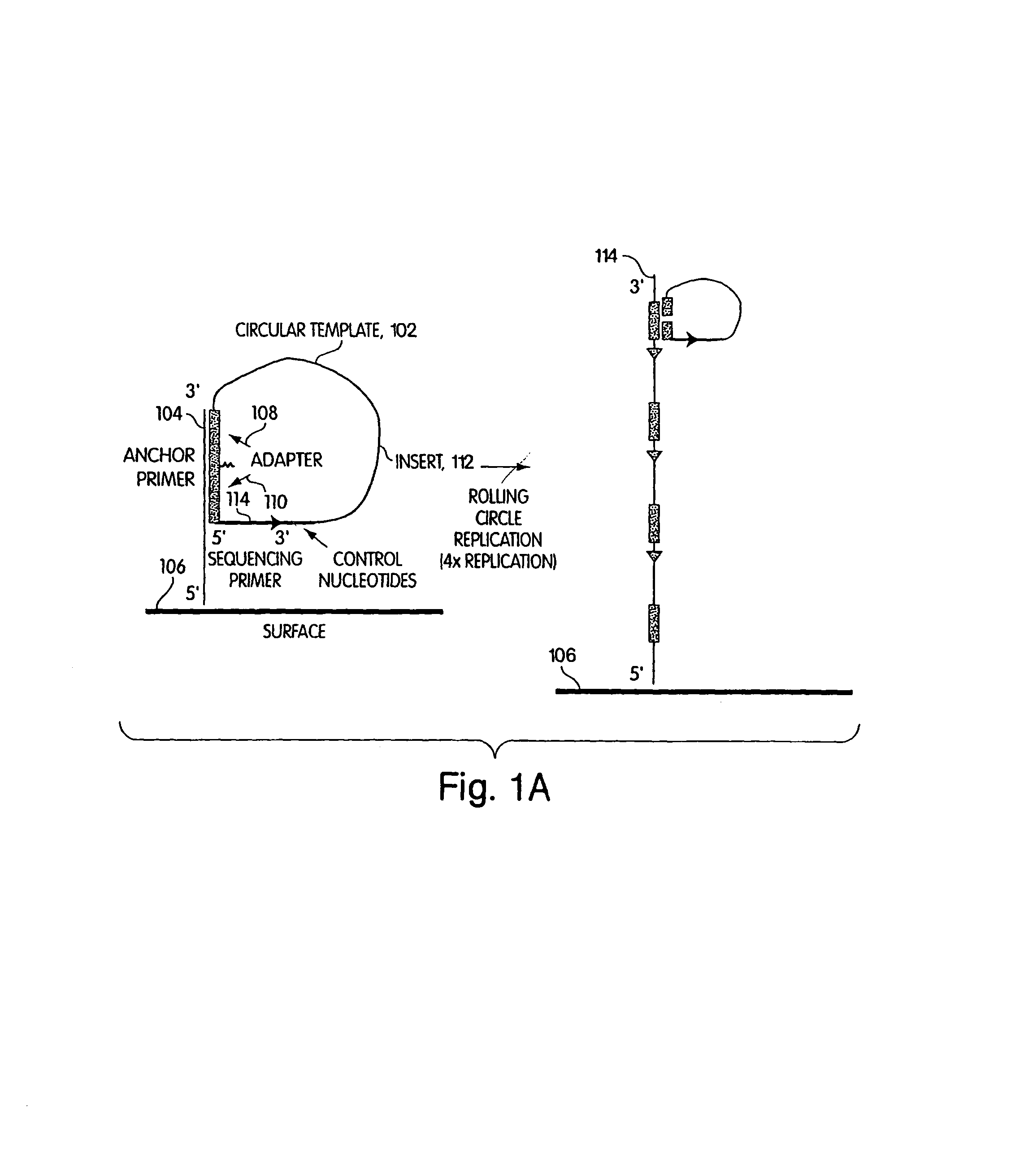
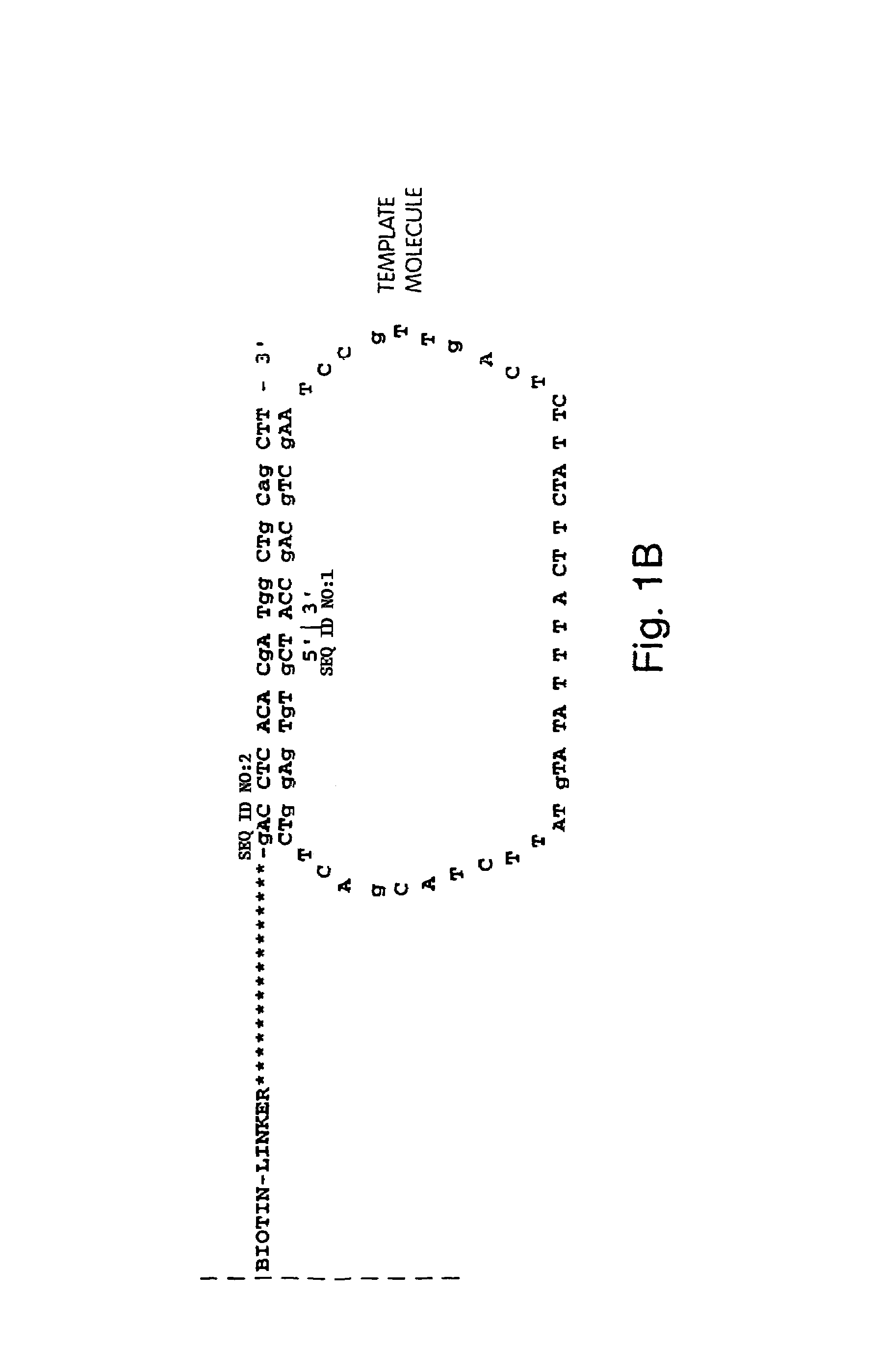
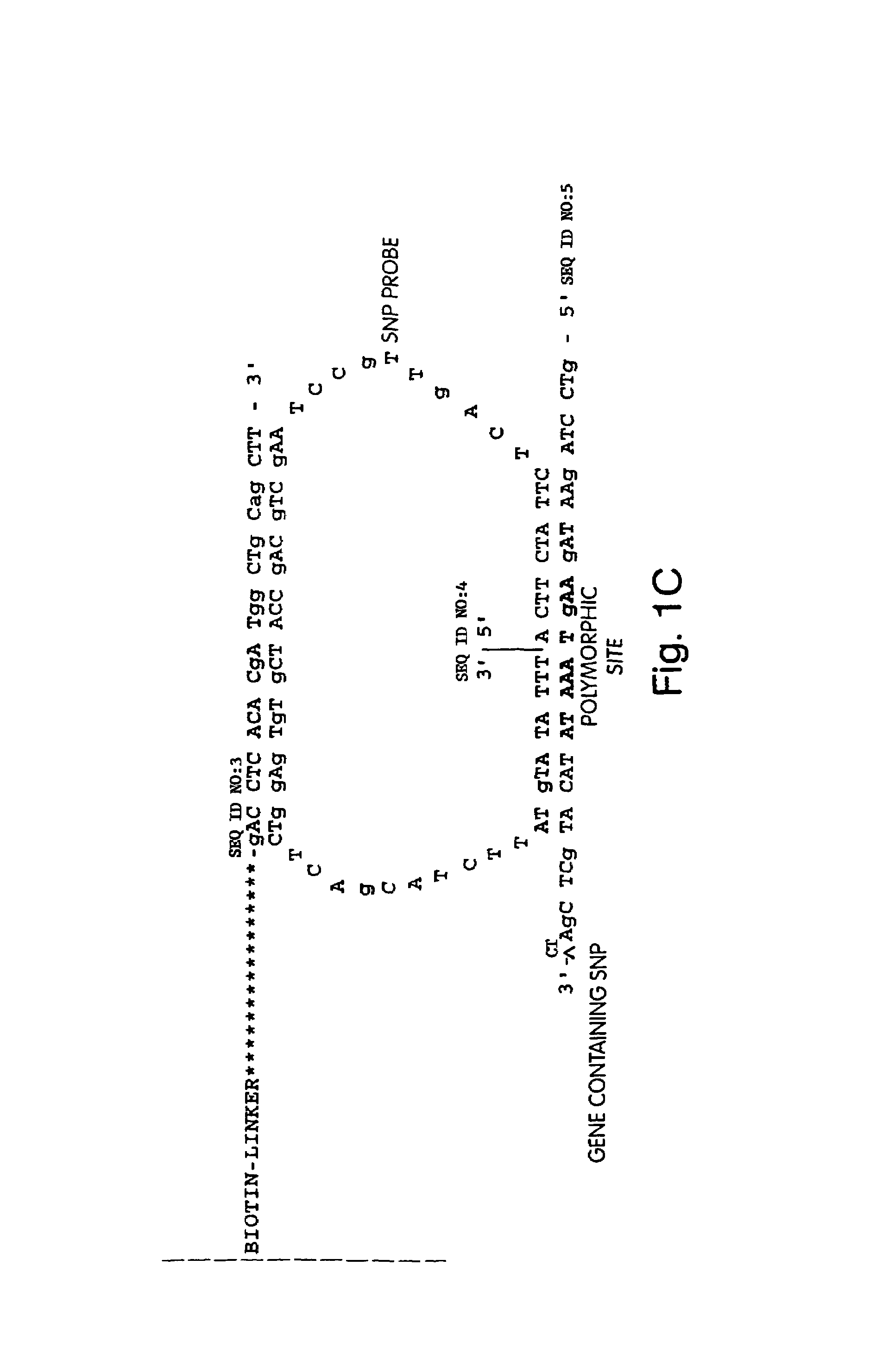
Method of sequencing a nucleic acid
InactiveUS7244559B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyNucleic acid detectionOligonucleotide
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
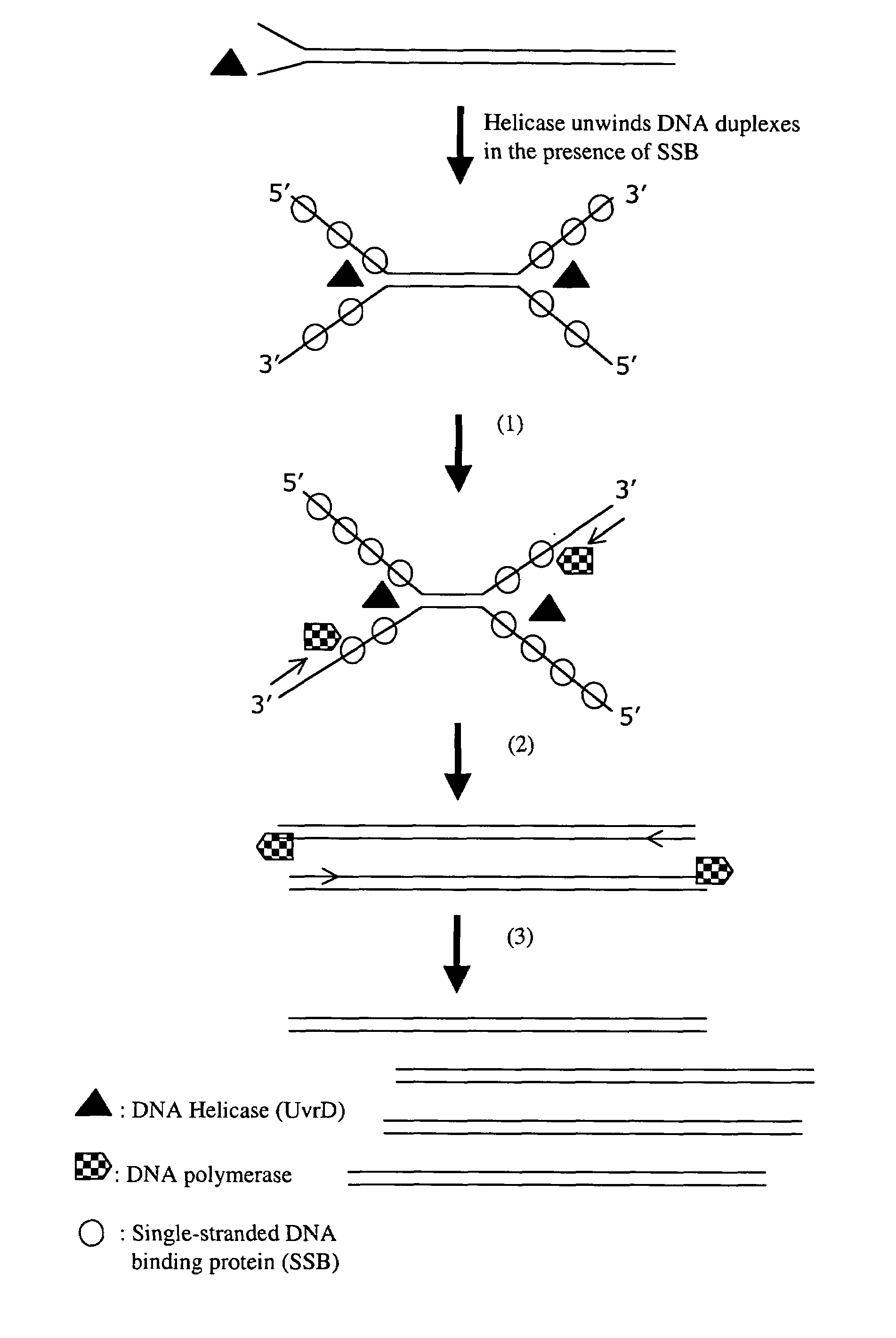
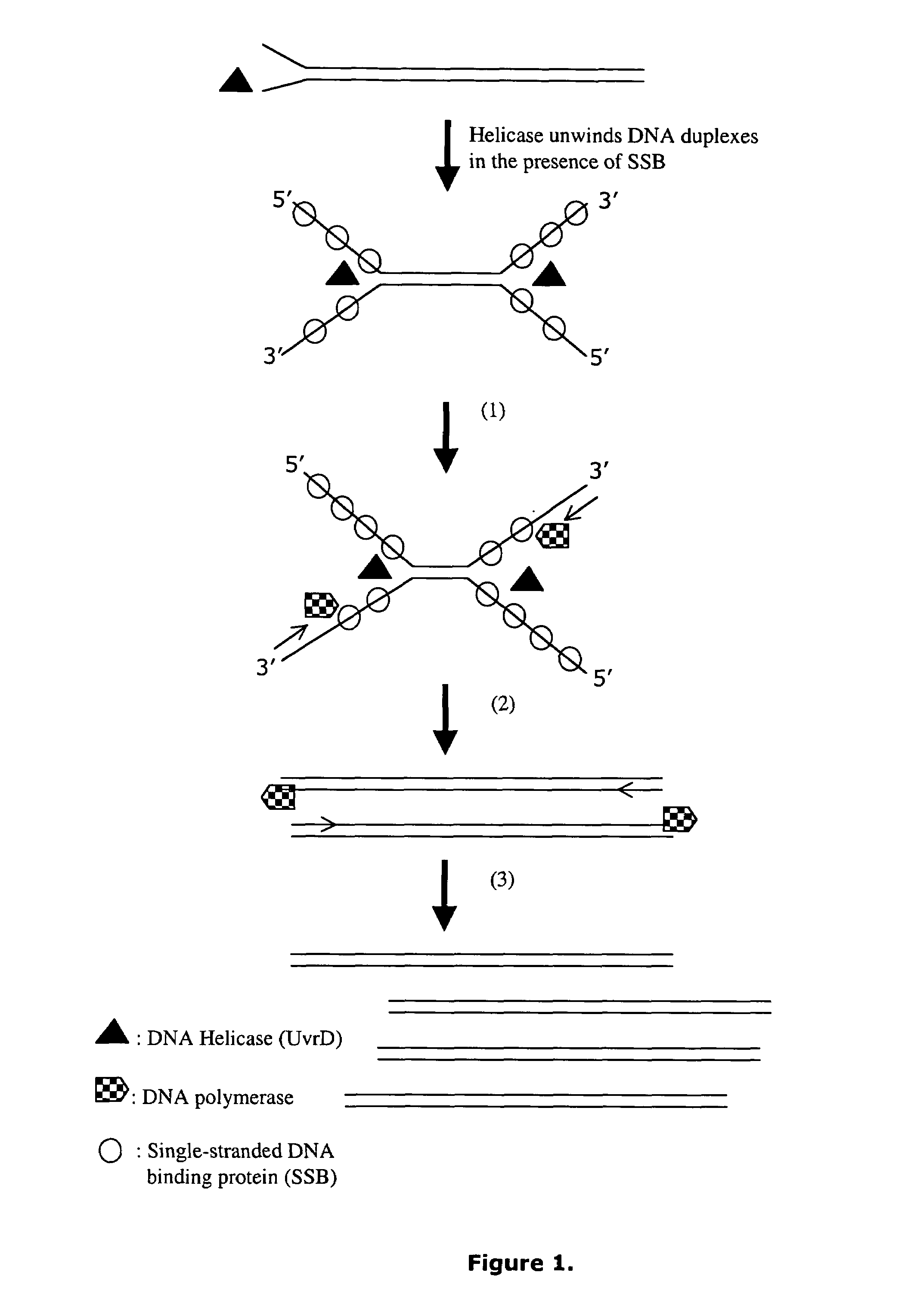
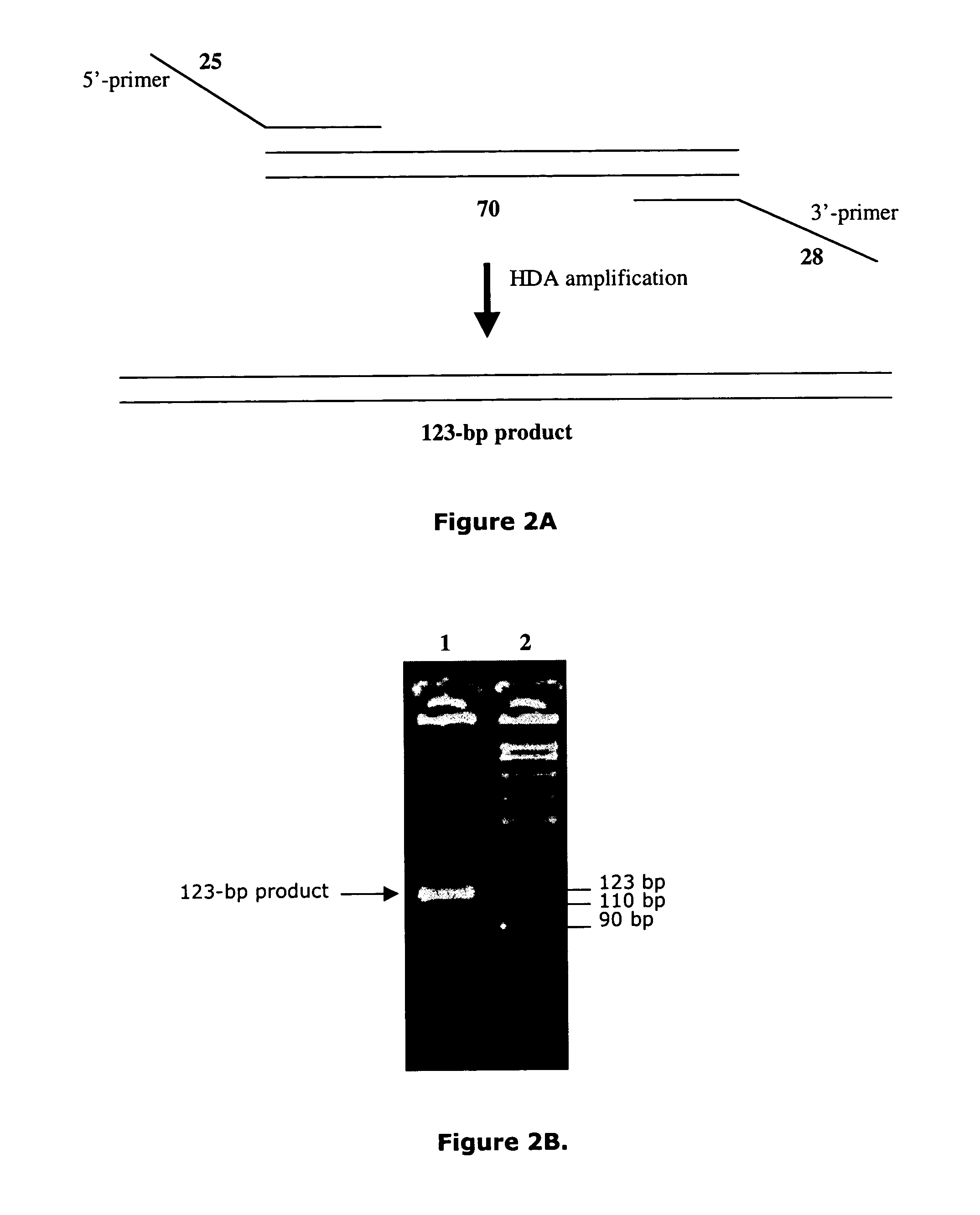
Helicase dependent amplification of nucleic acids
ActiveUS7282328B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA unwinding enzyme
Methods and a kit are provided for selectively and exponentially amplifying nucleic acids and include the use of a helicase preparation and a DNA polymerase such that the amplification can be performed isothermally.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS7041812B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, characterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have colorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Removal of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphate or polyphosphate transferring enzyme leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
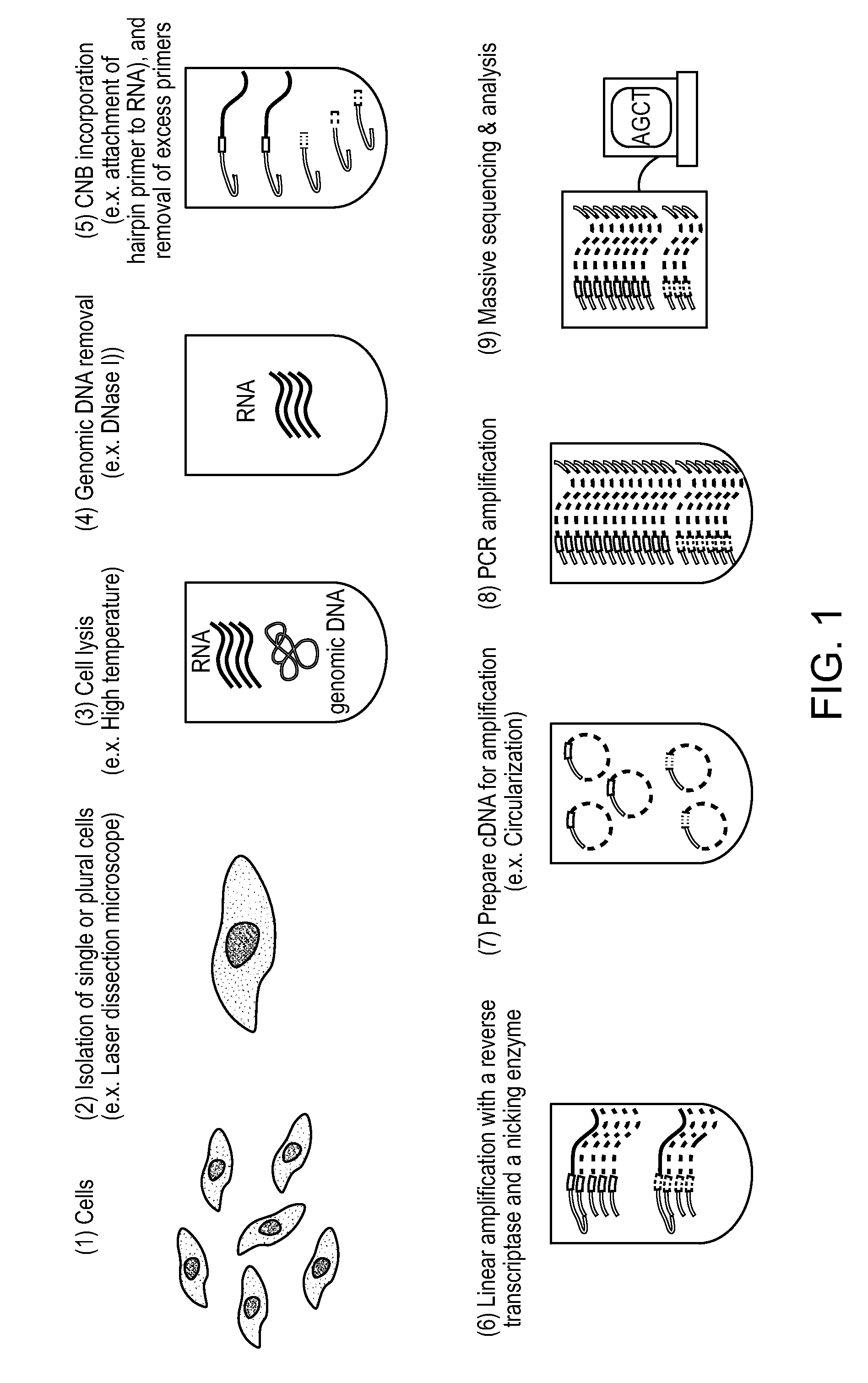
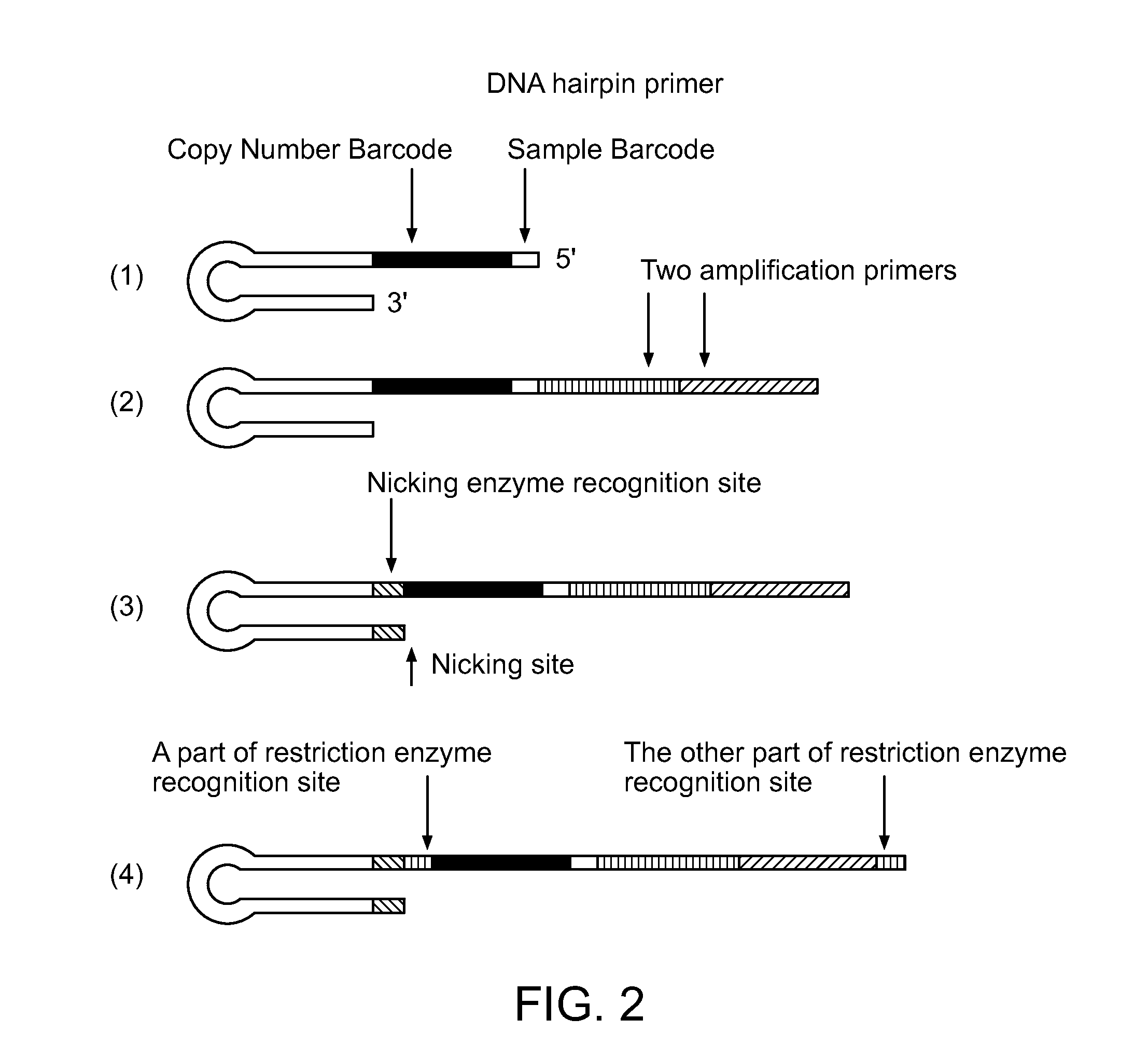
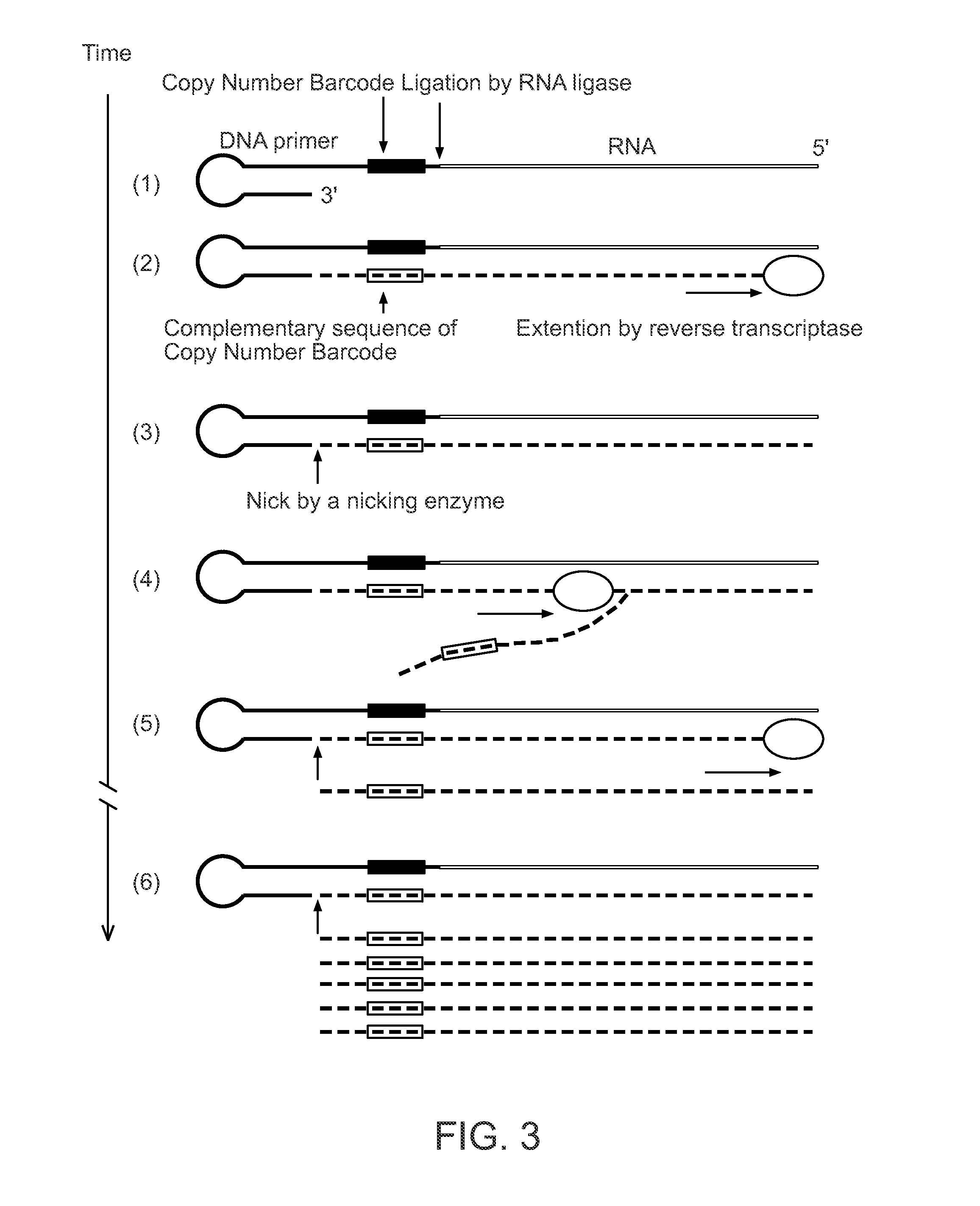
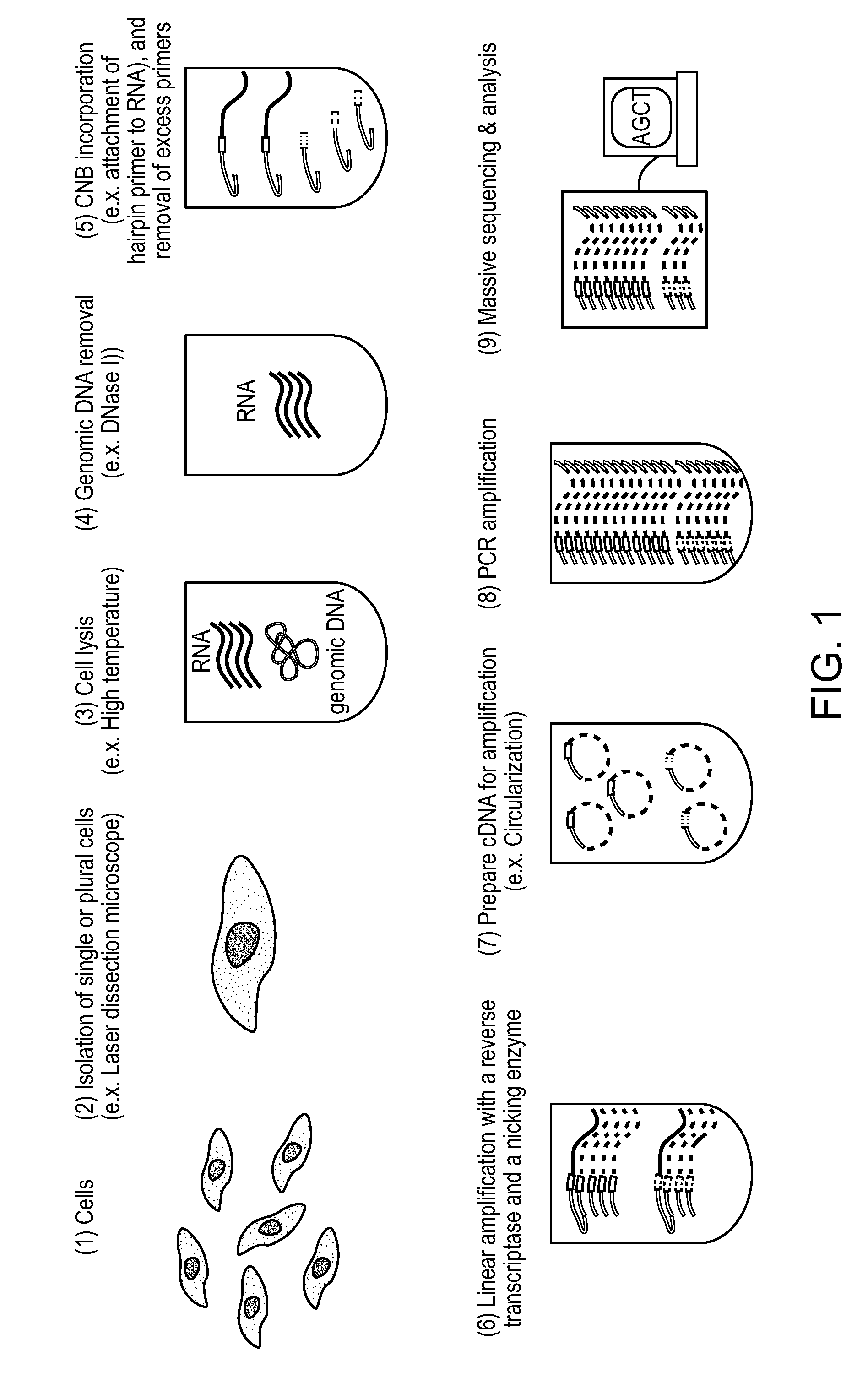
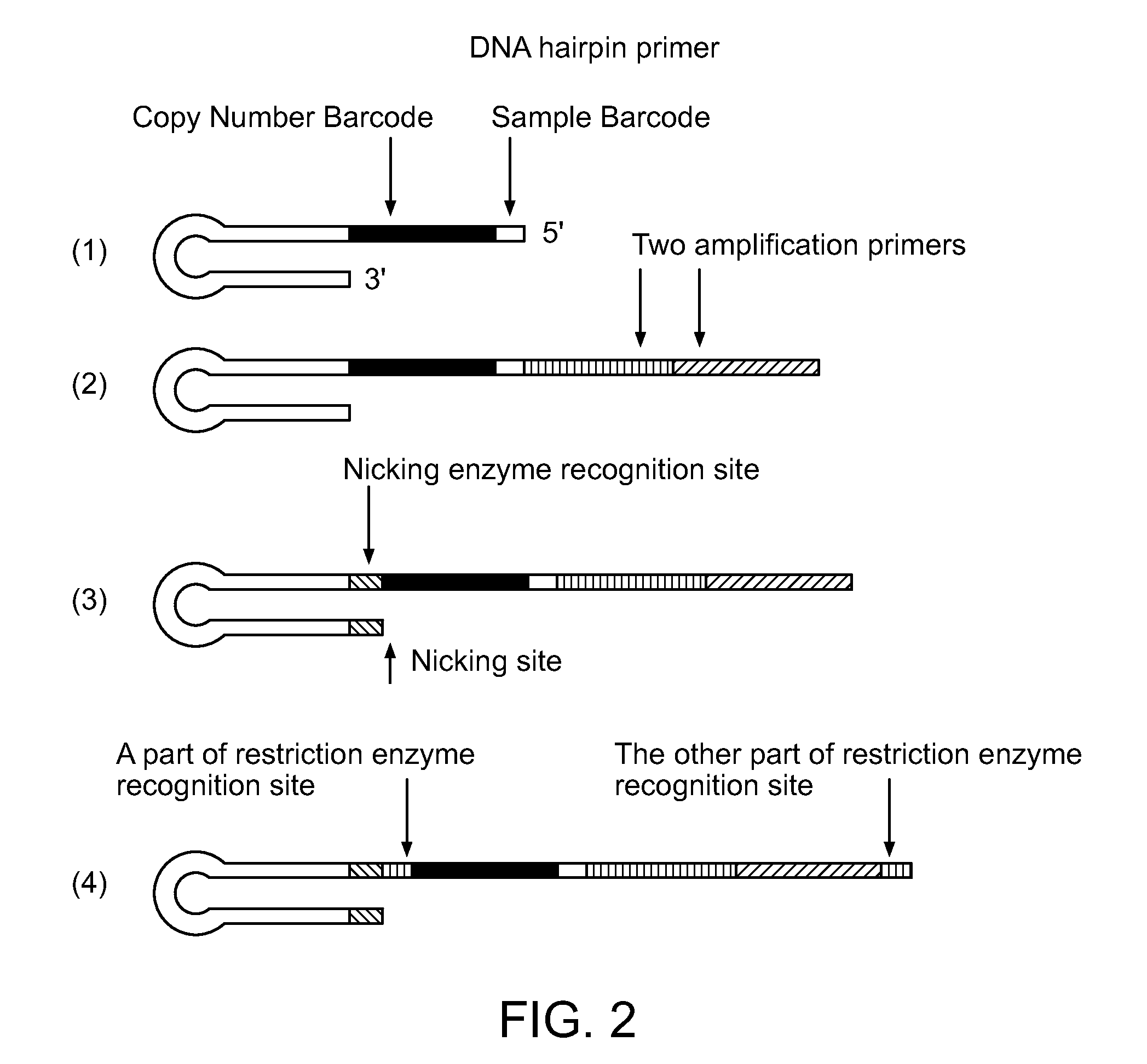
Single Cell Nucleic Acid Detection and Analysis
ActiveUS20140155274A1High amplification efficiencyEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
Methods and compositions for digital profiling of nucleic acid sequences present in a sample are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6391558B1Quick checkComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
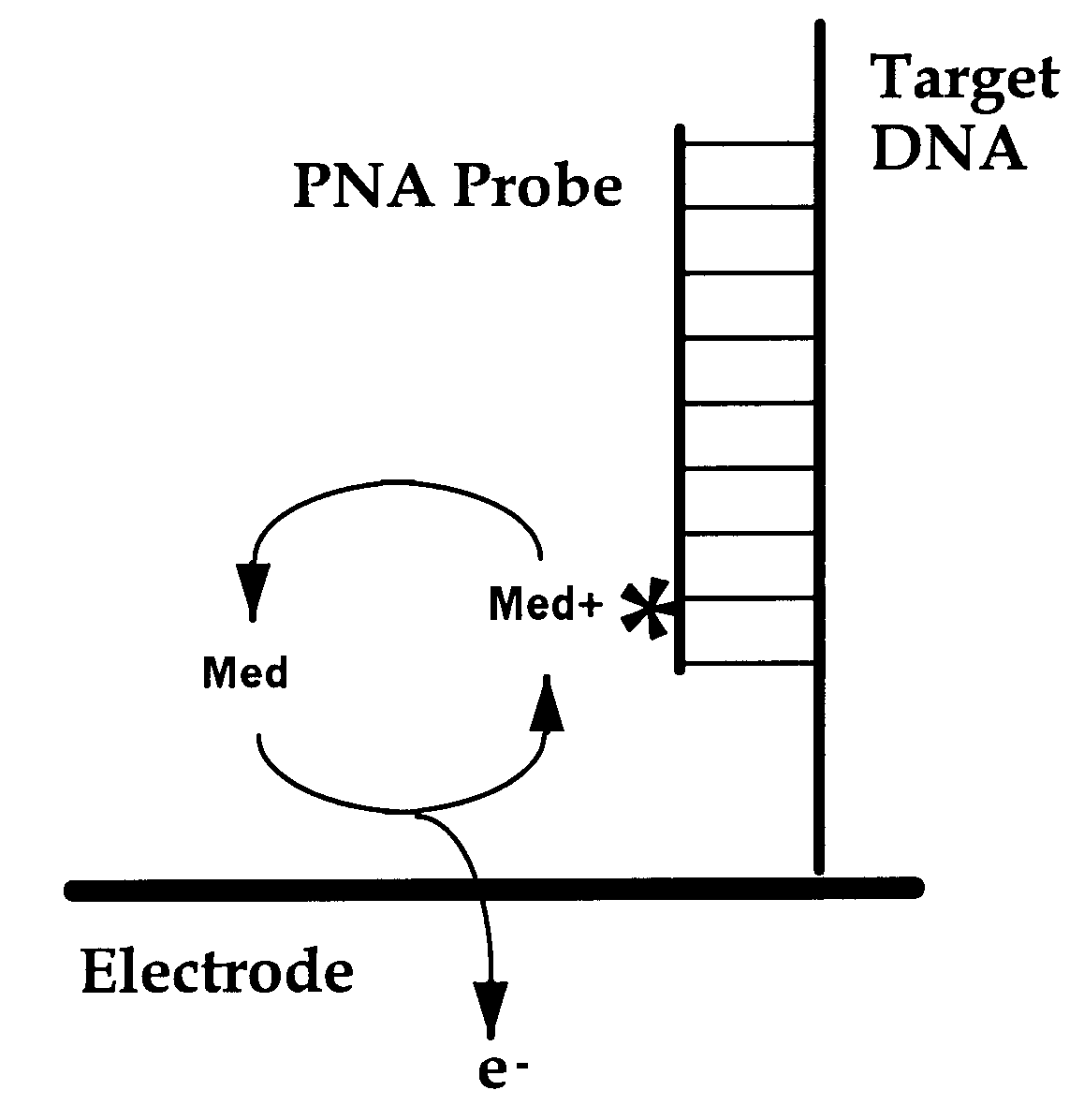
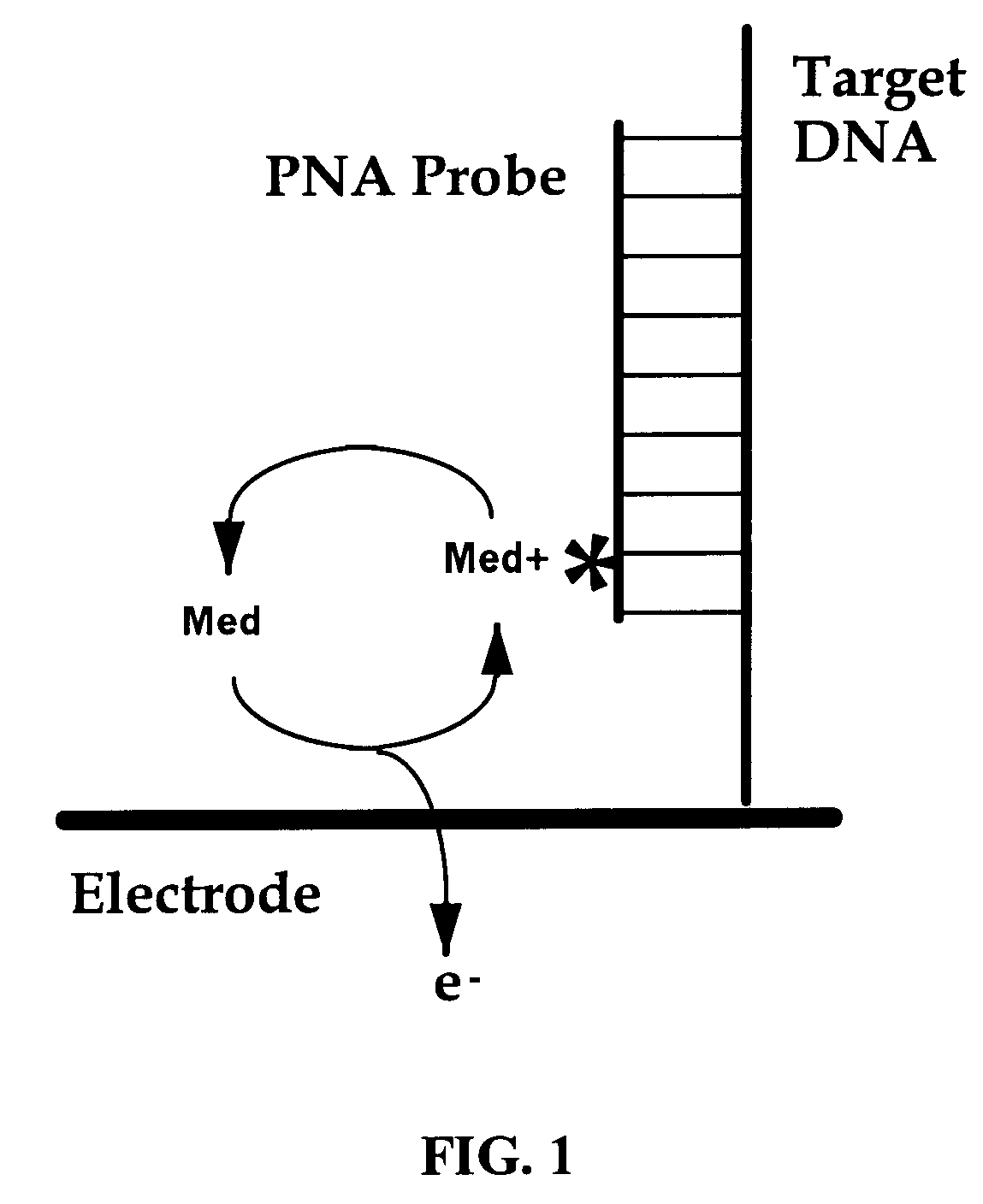
An electrochemical detection system which specifically detects selected nucleic acid segments is described. The system utilizes biological probes such as nucleic acid or peptide nucleic acid probes which are complementary to and specifically hybridize with selected nucleic acid segments in order to generate a measurable current when an amperometric potential is applied. The electrochemical signal can be quantified.
Owner:MAGELLAN DIAGNOSTICS
Single cell nucleic acid detection and analysis
ActiveUS9260753B2Improve dynamic rangeReduce or eliminate the amplification biasMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
Methods and compositions for digital profiling of nucleic acid sequences present in a sample are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
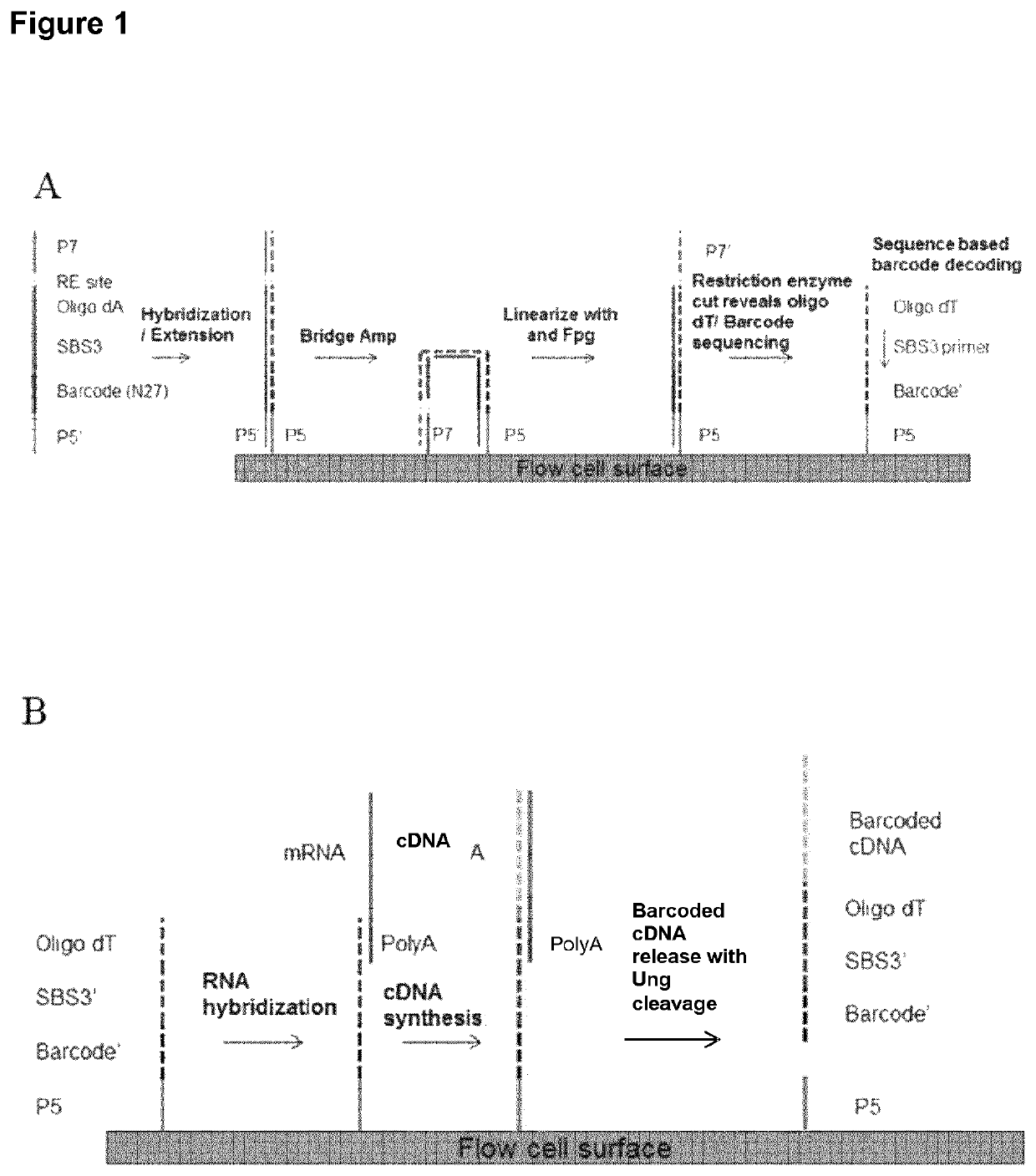
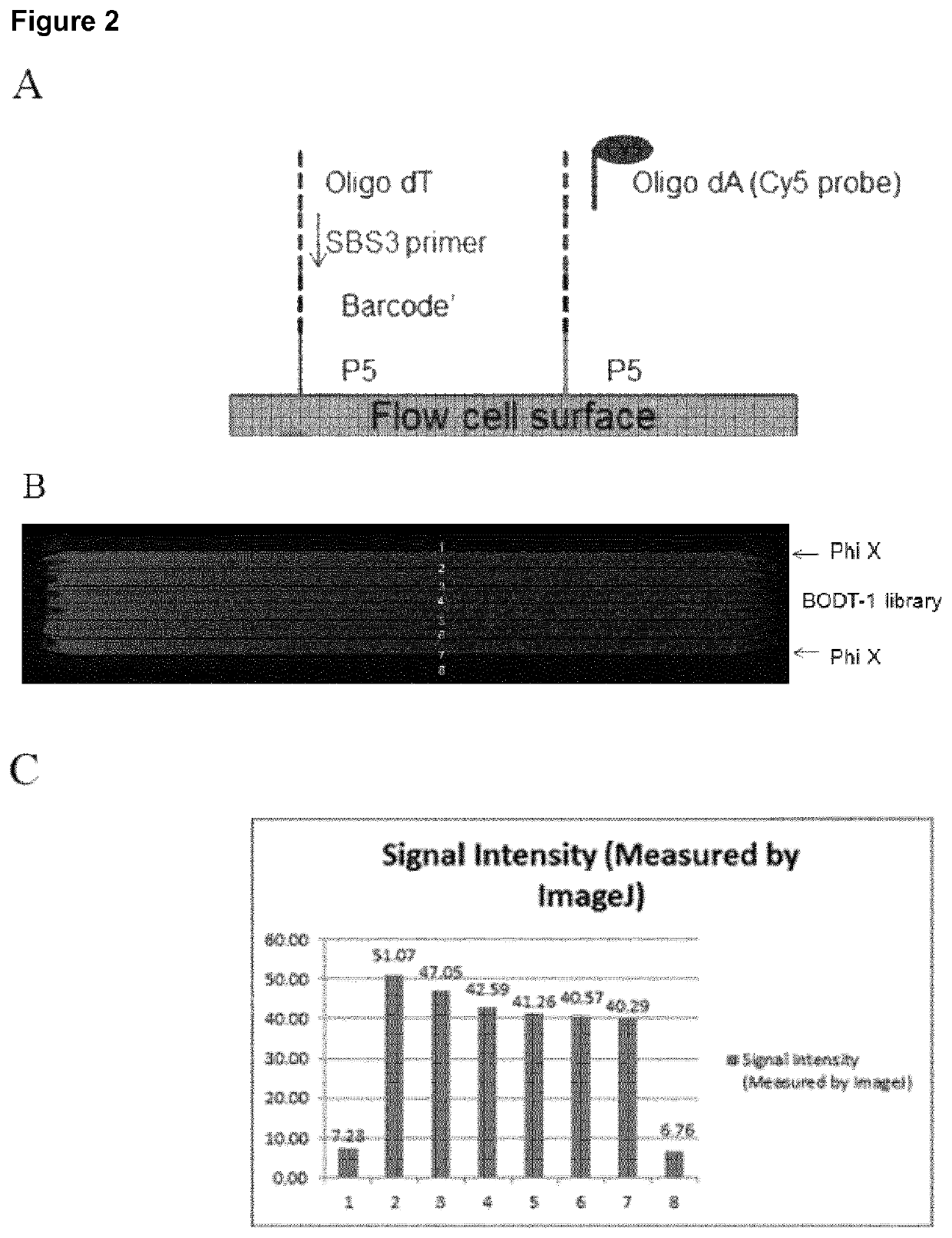
Spatially distinguished, multiplex nucleic acid analysis of biological specimens
A method for spatially tagging nucleic acids of a biological specimen, including steps of (a) providing a solid support comprising different nucleic acid probes that are randomly located on the solid support, wherein the different nucleic acid probes each includes a barcode sequence that differs from the barcode sequence of other randomly located probes on the solid support; (b) performing a nucleic acid detection reaction on the solid support to locate the barcode sequences on the solid support; (c) contacting a biological specimen with the solid support that has the randomly located probes; (d) hybridizing the randomly located probes to target nucleic acids from portions of the biological specimen; and (e) modifying the randomly located probes that are hybridized to the target nucleic acids, thereby producing modified probes that include the barcode sequences and a target specific modification, thereby spatially tagging the nucleic acids of the biological specimen.
Owner:X GENOMICS SWEDEN AB +1
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS20030124576A1Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, charcterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have calorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Pyrophosphorolysis and incorporation of nucleotide method for nucleic acid detection
InactiveUS7090975B2Useful in detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDepolymerizationNucleic acid detection
Processes are disclosed using the depolymerization of a nucleic acid hybrid and incorporation of a suitable nucleotide to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze for the presence of predetermined nucleic acid target sequences. Applications of those processes include the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms, identification of single base changes, genotyping, medical marker diagnostics, mirosequencing, and.
Owner:PROMEGA
Nucleic acid sequence analysis
ActiveUS20120115736A1Improve accuracyImprove processivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesNucleic acid detectionPolymerase L
Provided are methods for sequencing a nucleic acid with a sequencing enzyme, e.g., a polymerase or exonuclease. The sequencing enzyme can optionally be exchanged with a second sequencing enzyme, which continues the sequencing of the nucleic acid. In certain embodiments, a template is fixed to a surface through a template localizing moiety. The template localizing moiety can optionally anneal with the nucleic acid and / or associate with the sequencing enzyme. Also provided are compositions comprising a nucleic acid and a first sequencing enzyme, which can sequence the nucleic acid and optionally exchange with a second sequencing enzyme present in the composition. Compositions in which a template localizing moiety is immobilized on a surface are provided. Also provided are methods for using data from analytical reactions wherein two different enzymes are employed, e.g., at a same or different reaction regions.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
ActiveUS7601498B2Low toxicityIncrease signal strengthMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesNucleic acid detectionStaining
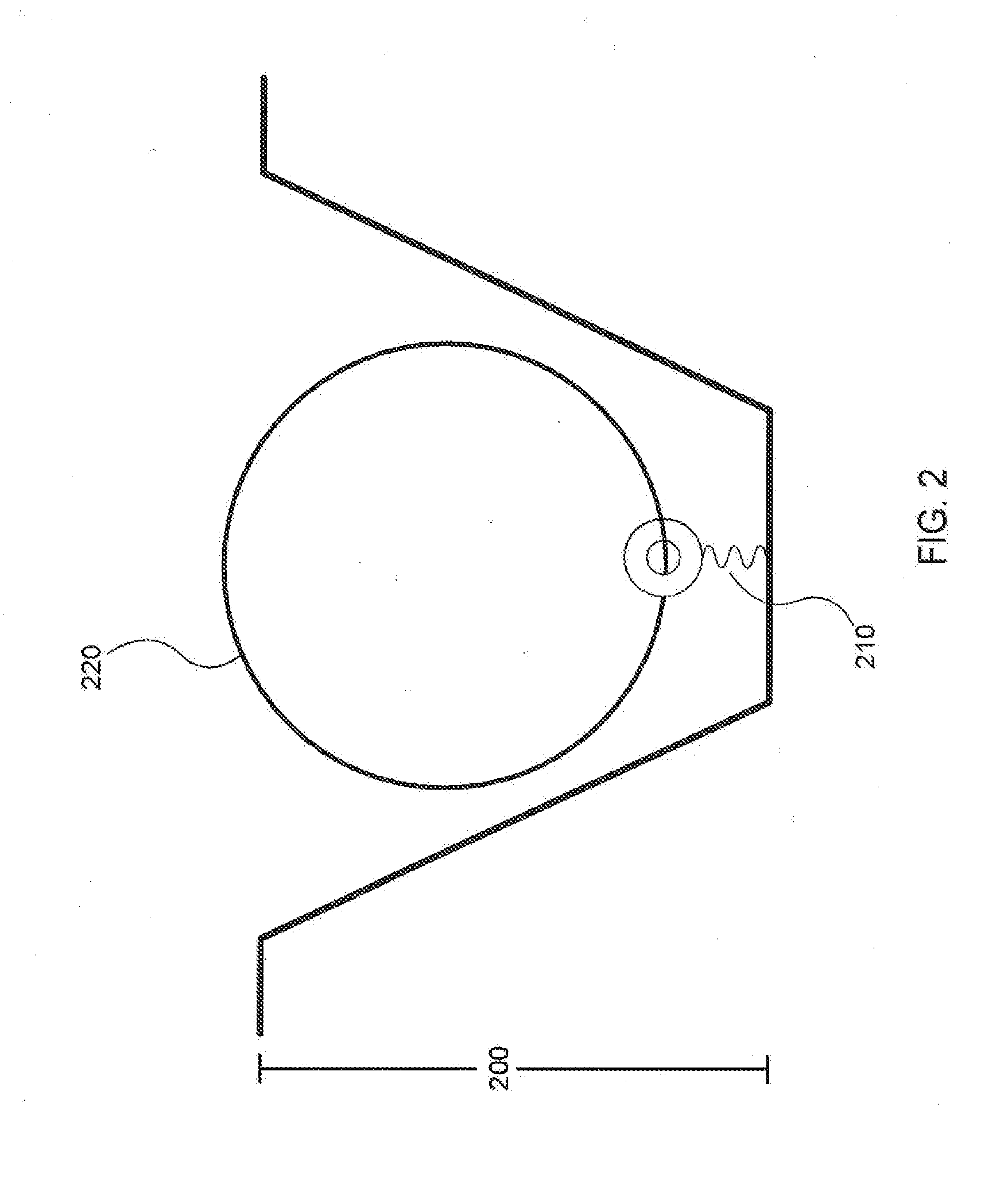
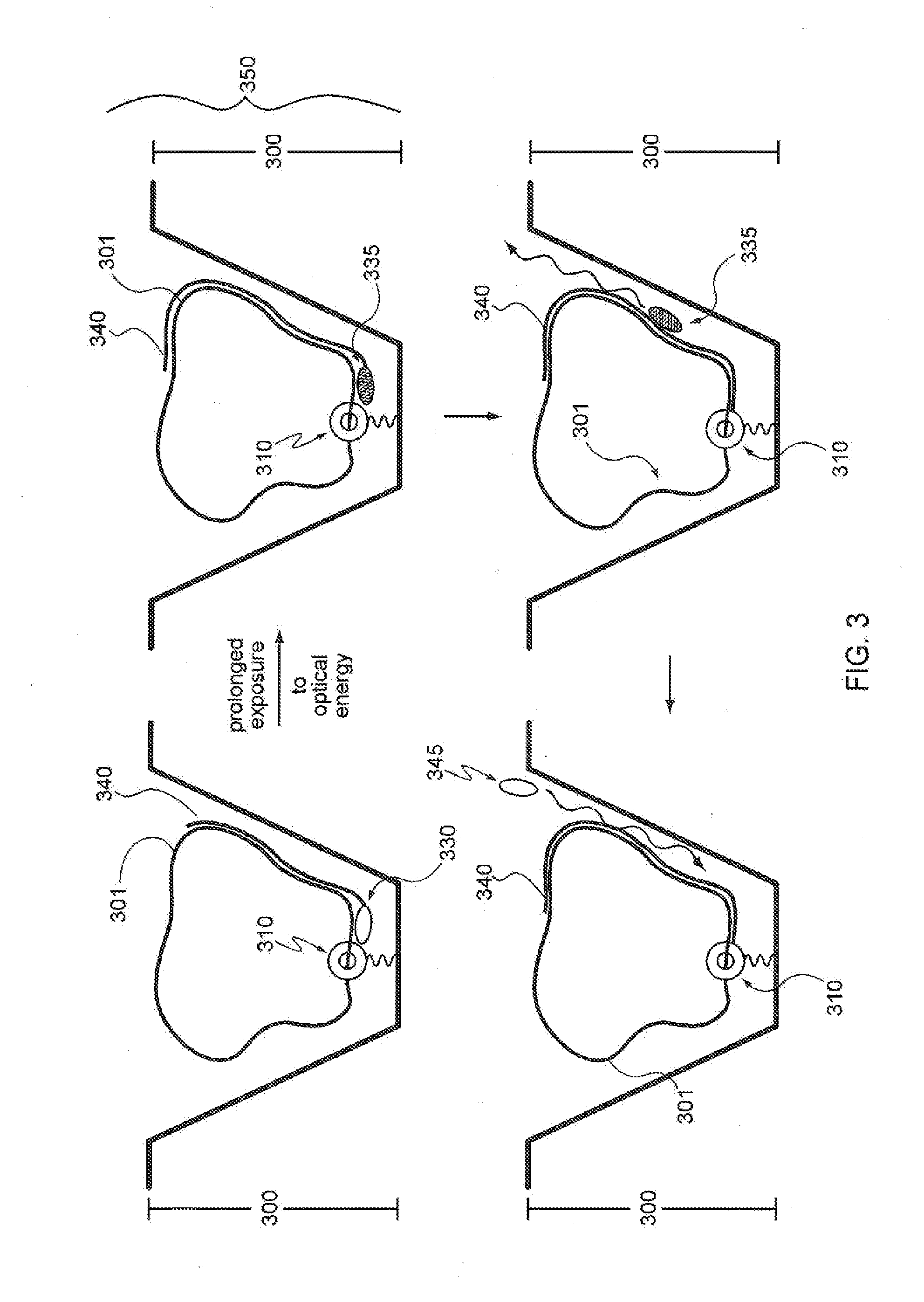
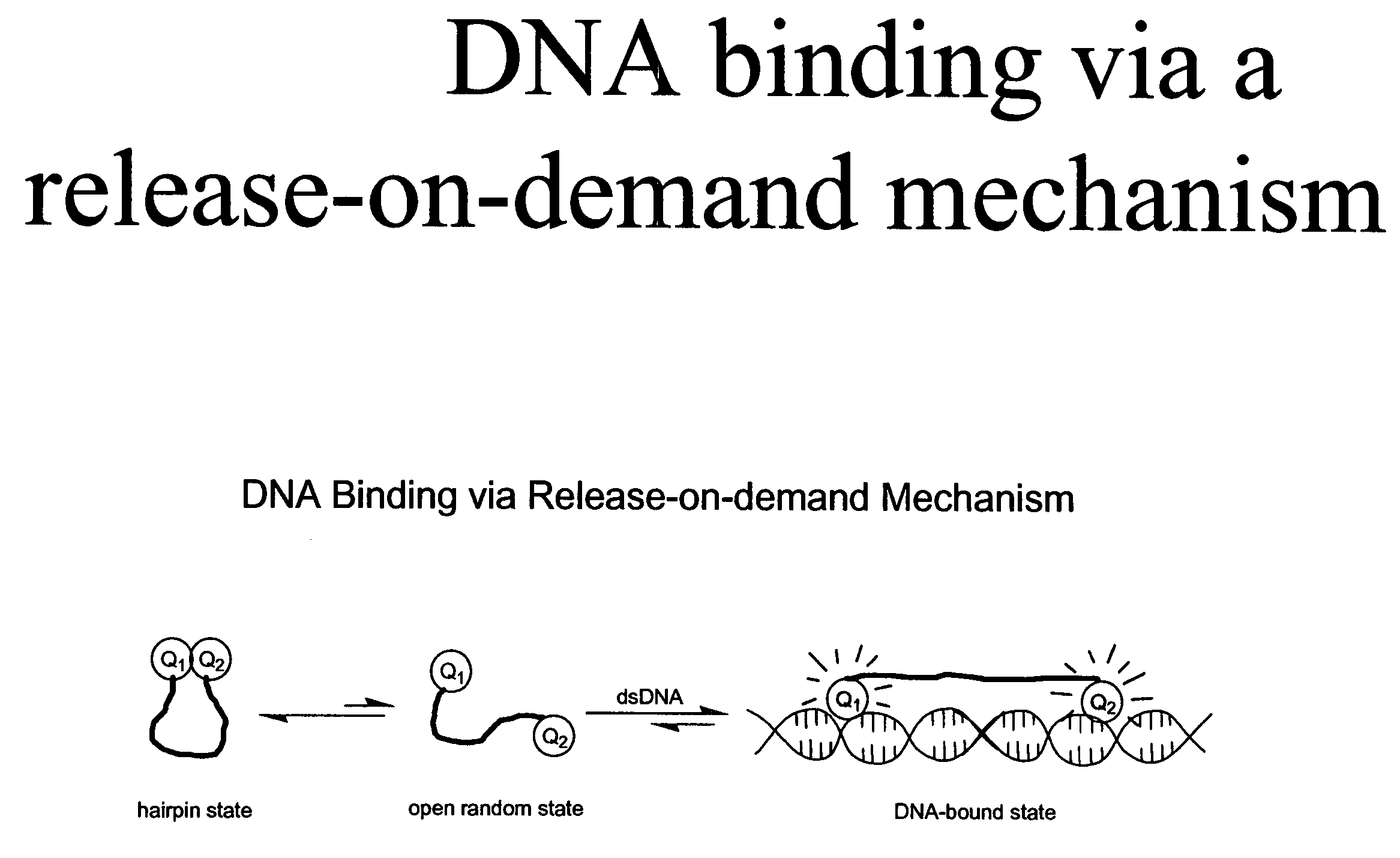
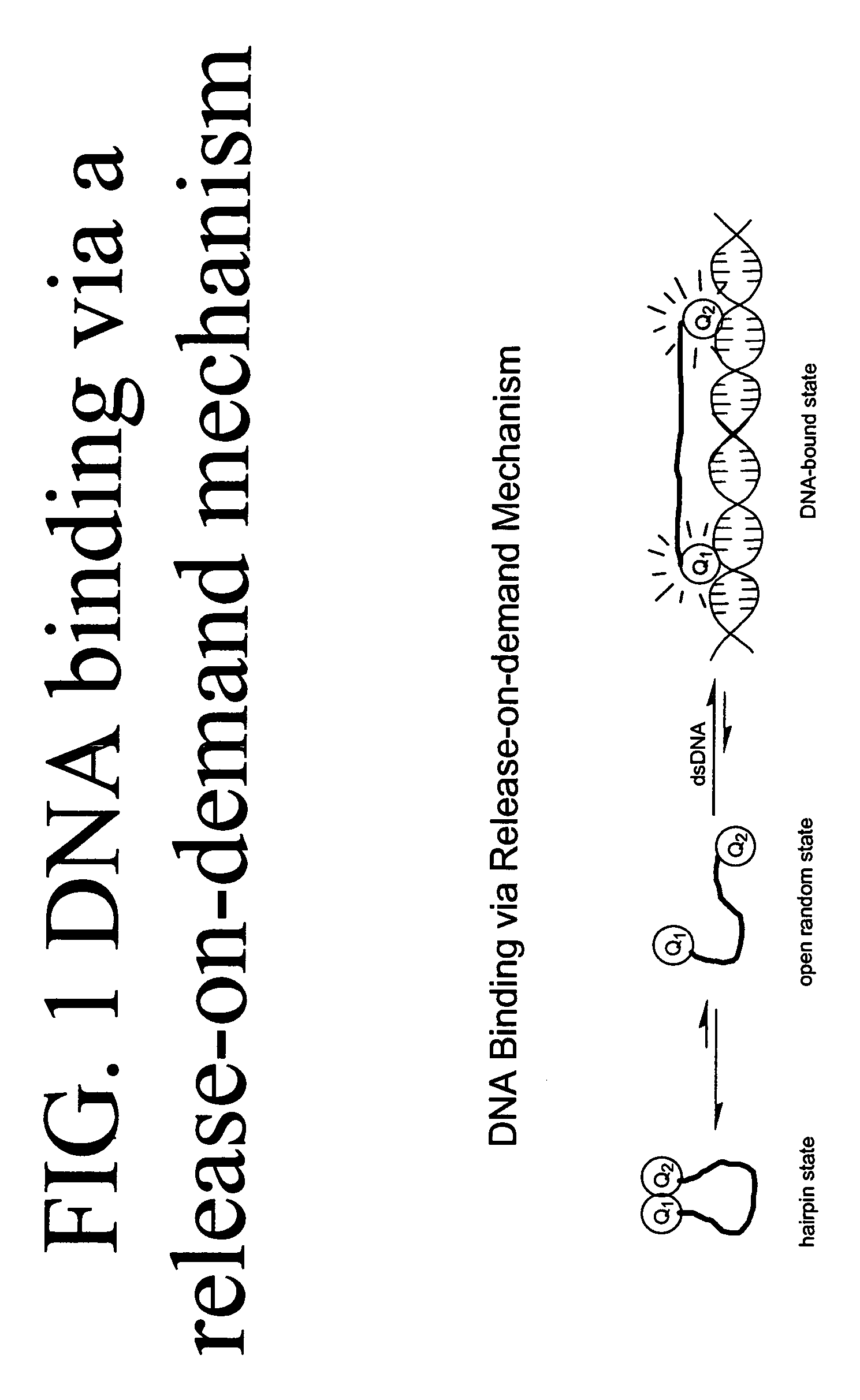
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
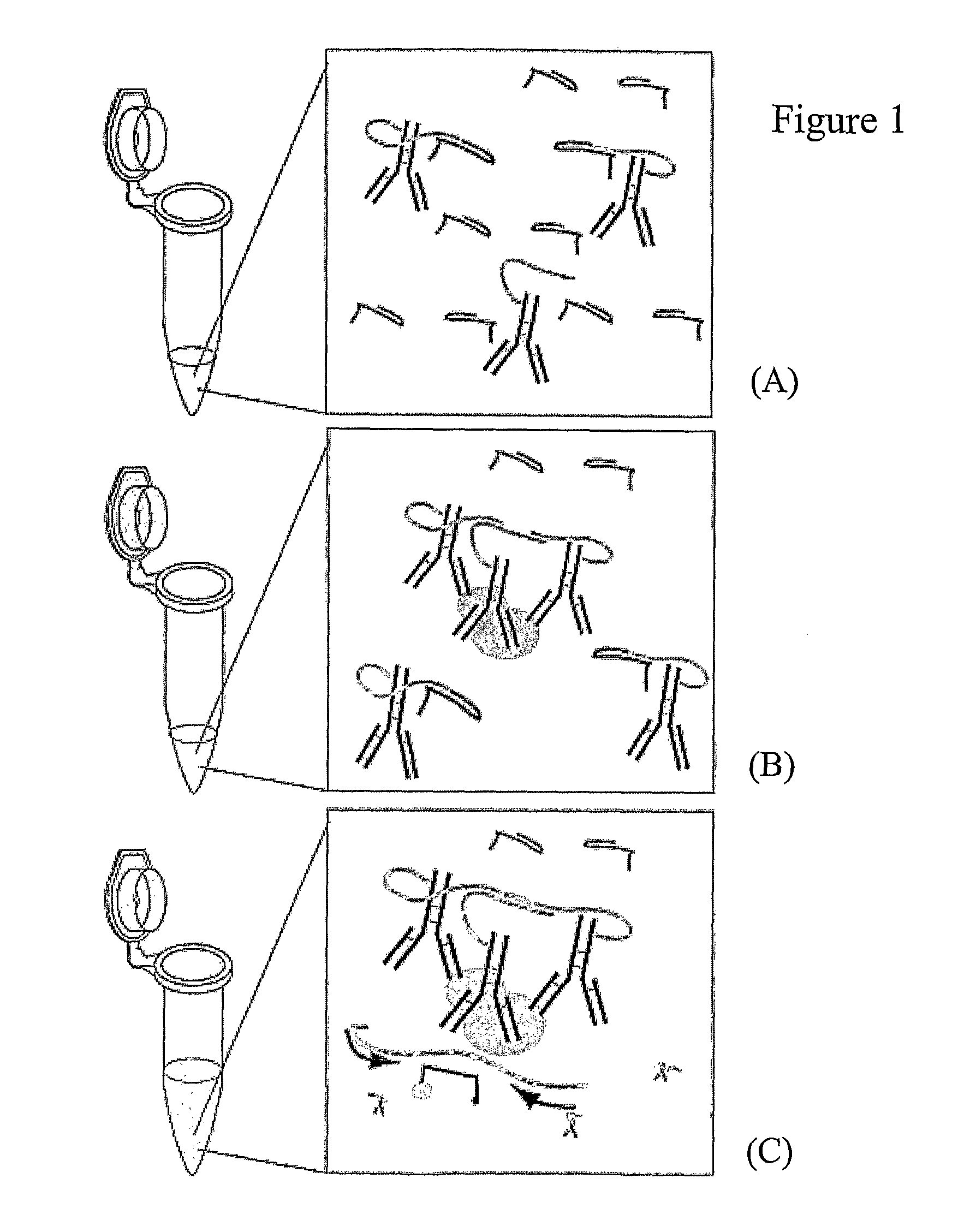
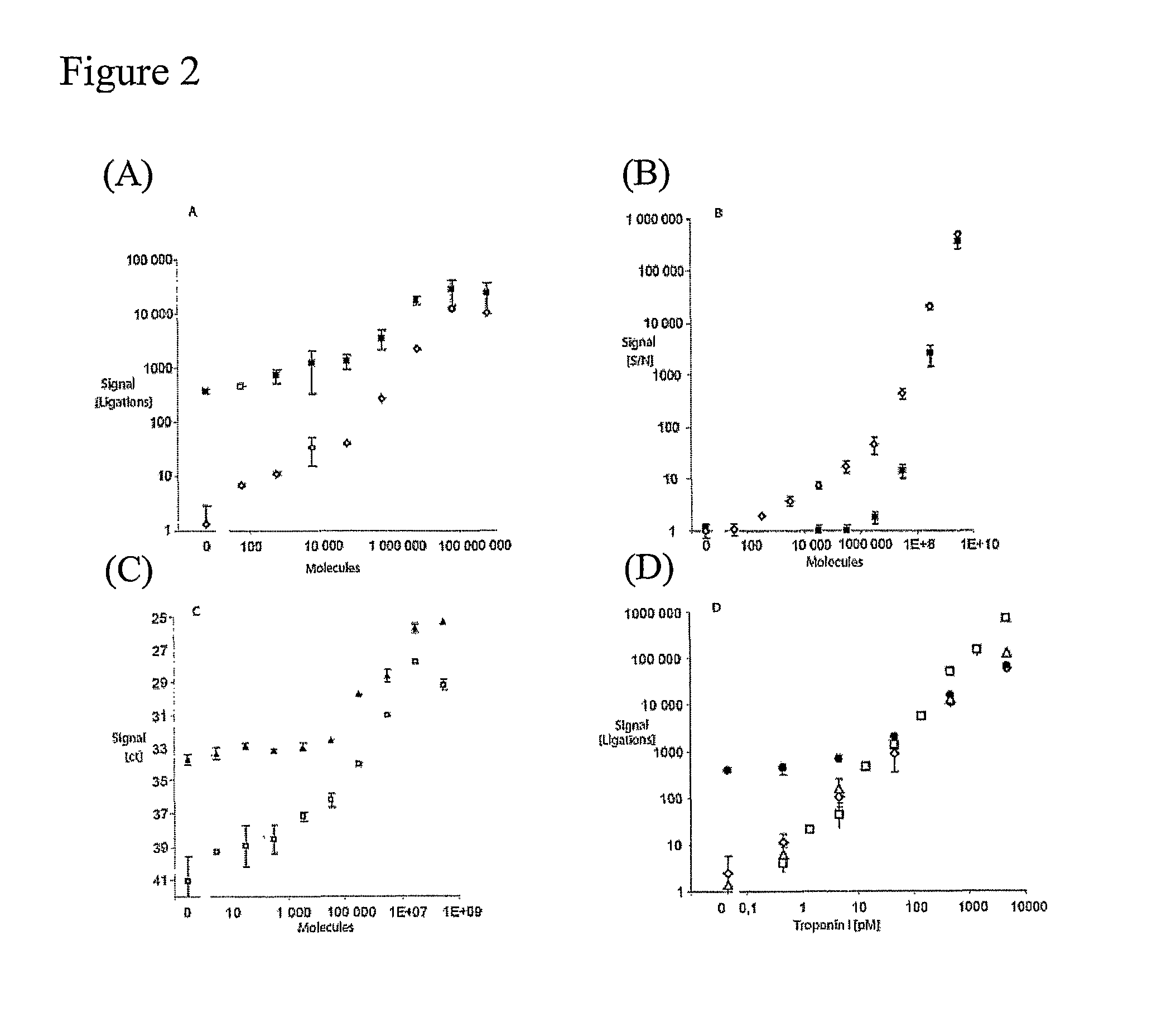
Method for analyte detection using proximity probes
A method for detecting an analyte in a sample, comprising (a) contacting the sample with at least one set of at least first, second and third proximity probes, which probes each include an analyte-binding domain and a nucleic acid domain and can simultaneously bind to the analyte, the nucleic acid domain of the third proximity probe being a splint which is capable of hybridizing at least to the nucleic acid domains of the first and second proximity probes, wherein when all of the at least three proximity probes bind to the analyte, the nucleic acid domains of the first and second proximity probes are conjugatable by means of an interaction mediated by the hybridized splint of the third proximity probe; (b) conjugating the nucleic acids, of the first and second proximity probes; and (c) detecting the conjugation. Also provided is a kit for use in such a method.
Owner:OLINK PROTEOMICS AB
Method for nucleotide detection
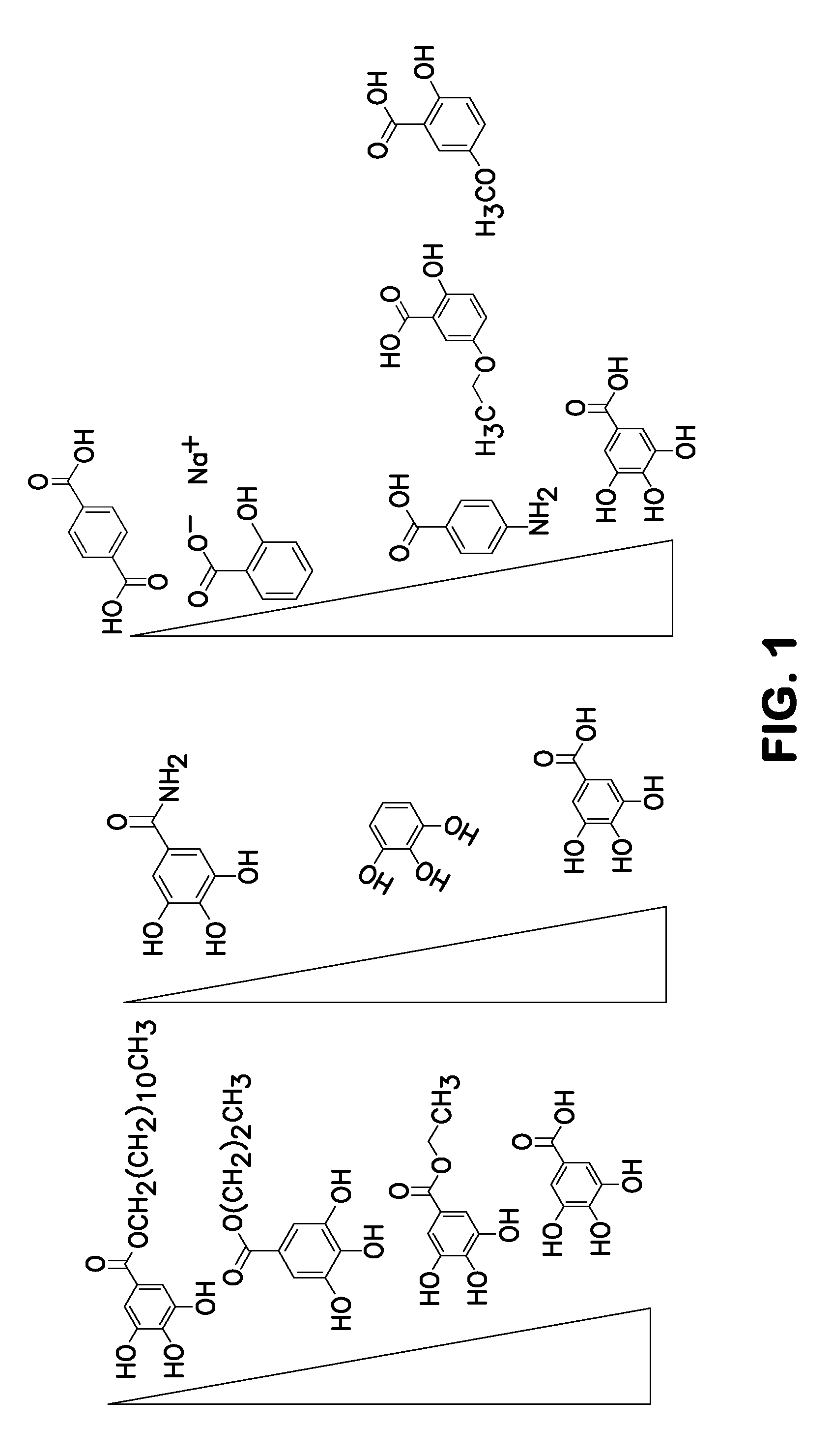
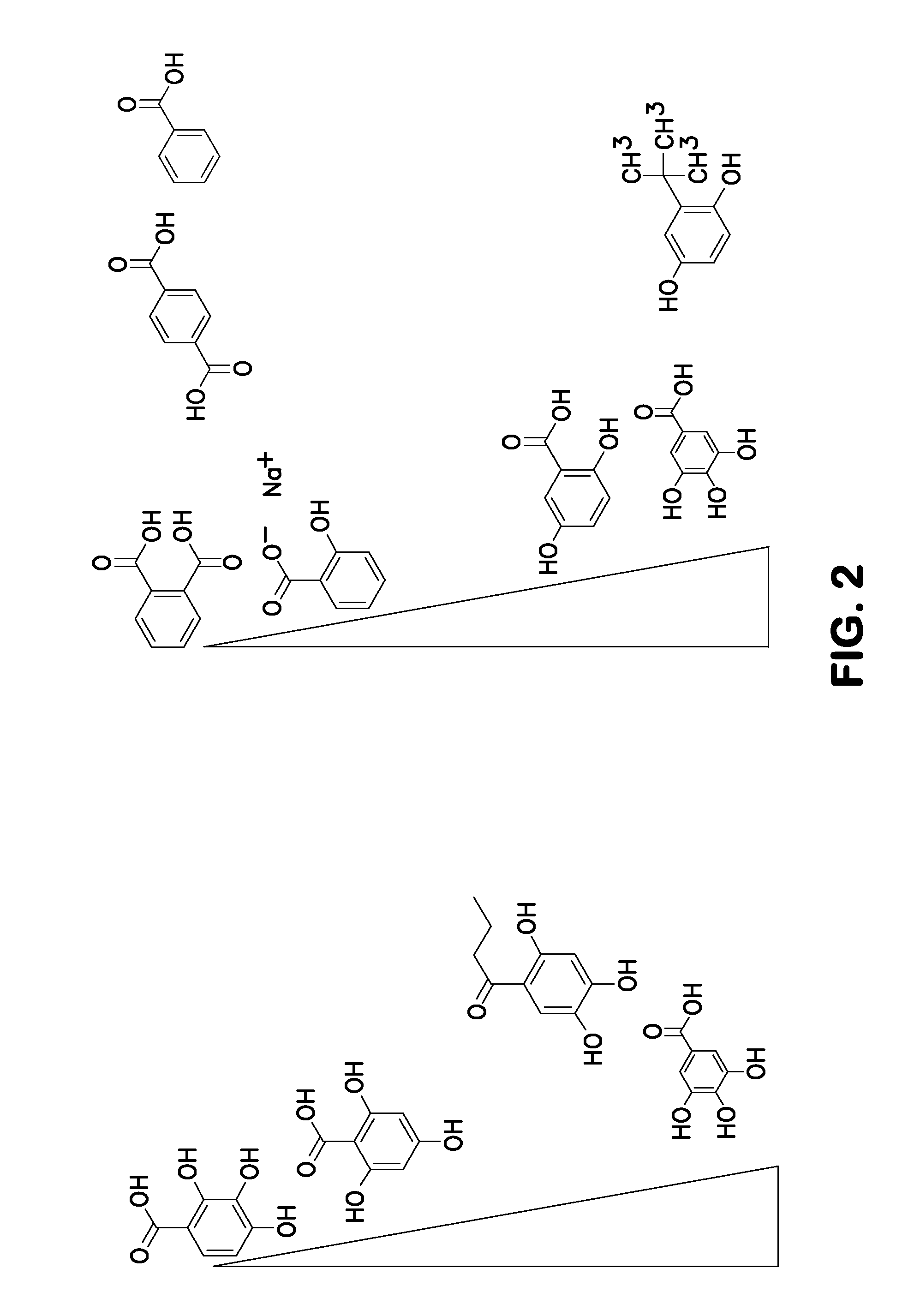
ActiveUS20120196758A1Prevent degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGallic acid esterNucleic acid detection
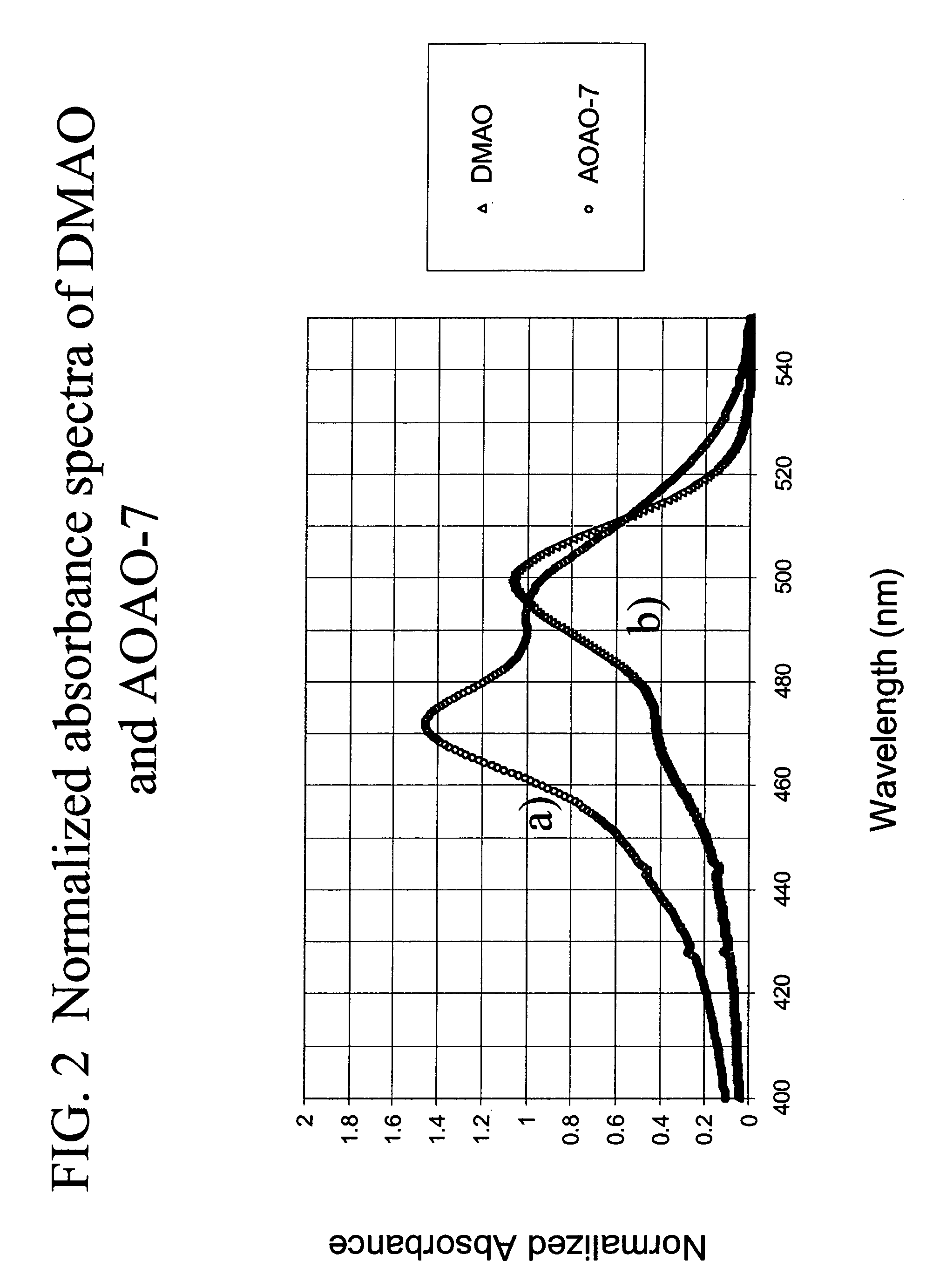
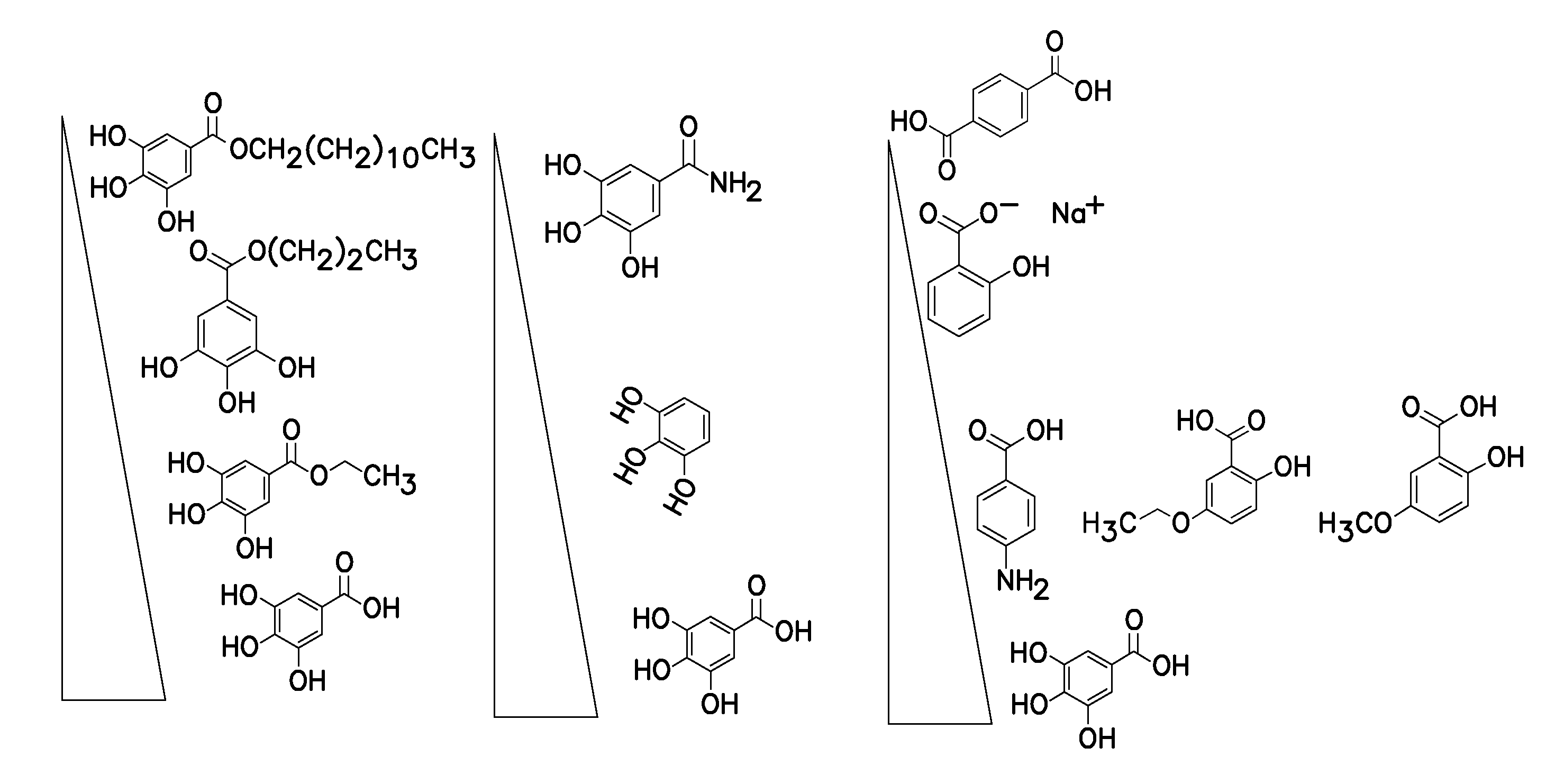
A method of inhibiting light-induced degradation of nucleic acids includes irradiating a portion of the nucleic acids in the presence of a detection solution comprising a polyphenolic compound. A method of detecting a nucleic acid having a fluorescent tag includes irradiating at least a portion of the nucleic acid with light of a suitable wavelength to induce a fluorescence emission and detecting the fluorescence emission. Optionally, the polyphenolic compound is gallic acid, a lower alkyl ester thereof, or mixtures thereof. A kit includes one or more nucleotides, an enzyme capable of catalyzing incorporation of the nucleotides into a nucleic acid strand and a polyphenolic compound suitable for preparing a detection solution.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
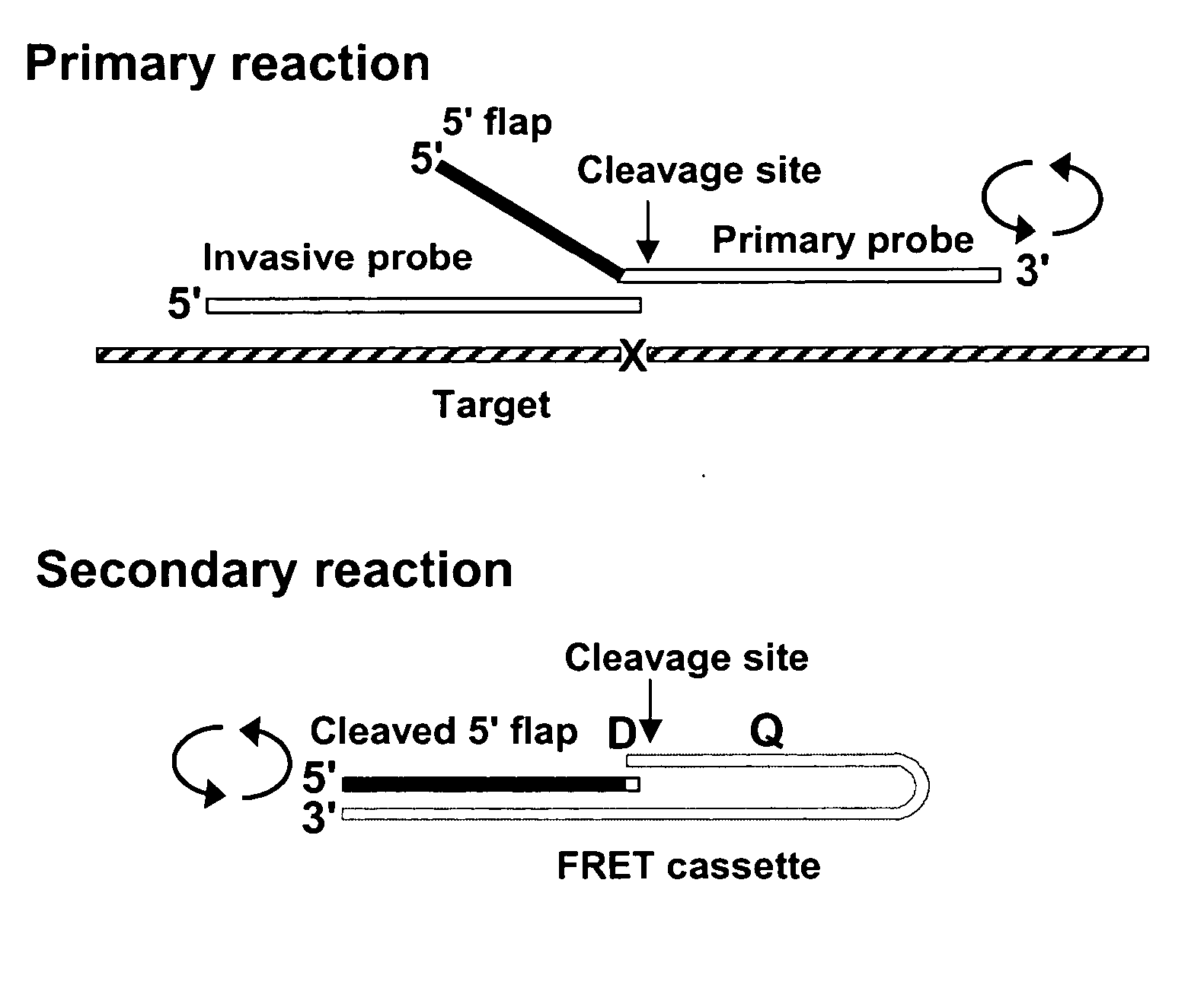
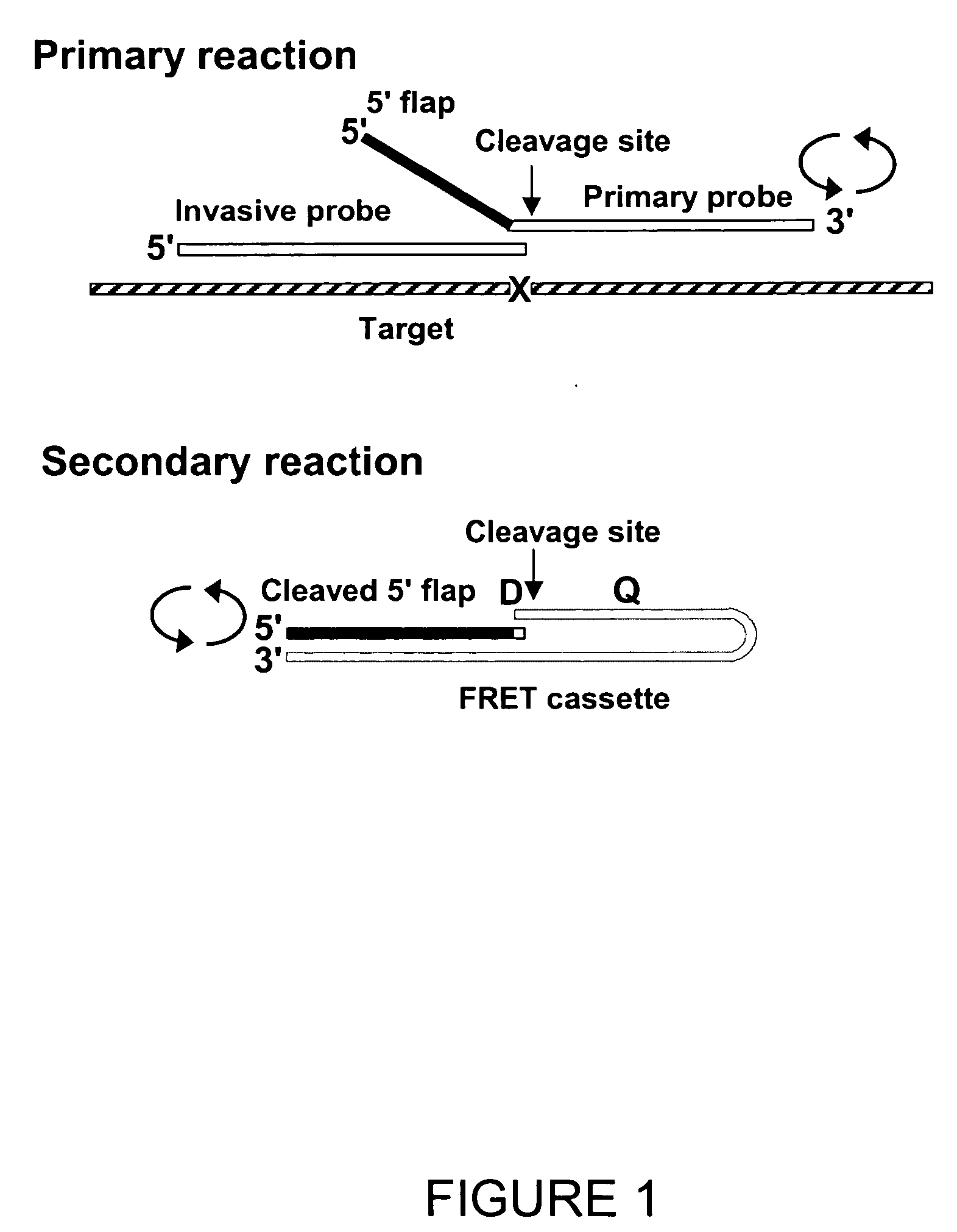
Single step detection assay
InactiveUS20060147955A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid detectionBasic research
The present invention provides methods and routines for developing and optimizing nucleic acid detection assays for use in basic research, clinical research, and for the development of clinical detection assays. In particular, the present invention provides methods for designing oligonucleotide primers to be used in multiplex amplification reactions. The present invention also provides methods to optimize multiplex amplification reactions. The present invention also provides methods for combined target and signal generation assays.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Detection of nucleic acids by target-specific hybrid capture method
InactiveUS20060051809A1Rapid and sensitive and accurateFunction increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA
Target-specific hybrid capture (TSHC) provides a nucleic acid detection method that is not only rapid and sensitive, but is also highly specific and capable of discriminating highly homologous nucleic acid target sequences. The method produces DNA:RNA hybrids which can be detected by a variety of methods.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
Spatially distinguished, multiplex nucleic acid analysis of biological specimens
ActiveUS20190203275A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNucleic acid detectionNucleic Acid Probes
A method for spatially tagging nucleic acids of a biological specimen, including steps of (a) providing a solid support comprising different nucleic acid probes that are randomly located on the solid support, wherein the different nucleic acid probes each includes a barcode sequence that differs from the barcode sequence of other randomly located probes on the solid support; (b) performing a nucleic acid detection reaction on the solid support to locate the barcode sequences on the solid support; (c) contacting a biological specimen with the solid support that has the randomly located probes; (d) hybridizing the randomly located probes to target nucleic acids from portions of the biological specimen; and (e) modifying the randomly located probes that are hybridized to the target nucleic acids, thereby producing modified probes that include the barcode sequences and a target specific modification, thereby spatially tagging the nucleic acids of the biological specimen.
Owner:SPATIAL TRANSCRIPTOMICS +1
Nucleic acid detection using degradation of a tagged sequence
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting target molecules, e.g. DNA sequences, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms, using a pair of nucleotide sequences, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence binds downstream from the primer to the target DNA in the direction of primer extension, or ligands and receptors. The methods employ e-tags comprising a mobility-identifying region joined to a detectable label and a target-binding region. The result of the binding of the target-binding region to the target is to have a bond cleaved in the starting material with the production of a detectable product with a different mobility from the starting material, where the different e-tags can be separated and detected.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
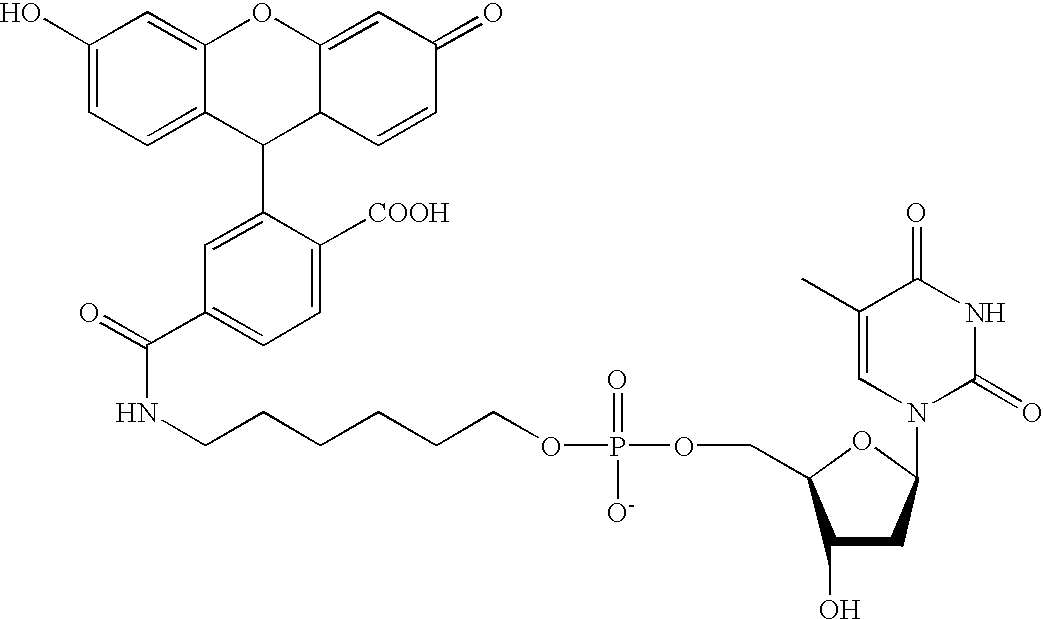
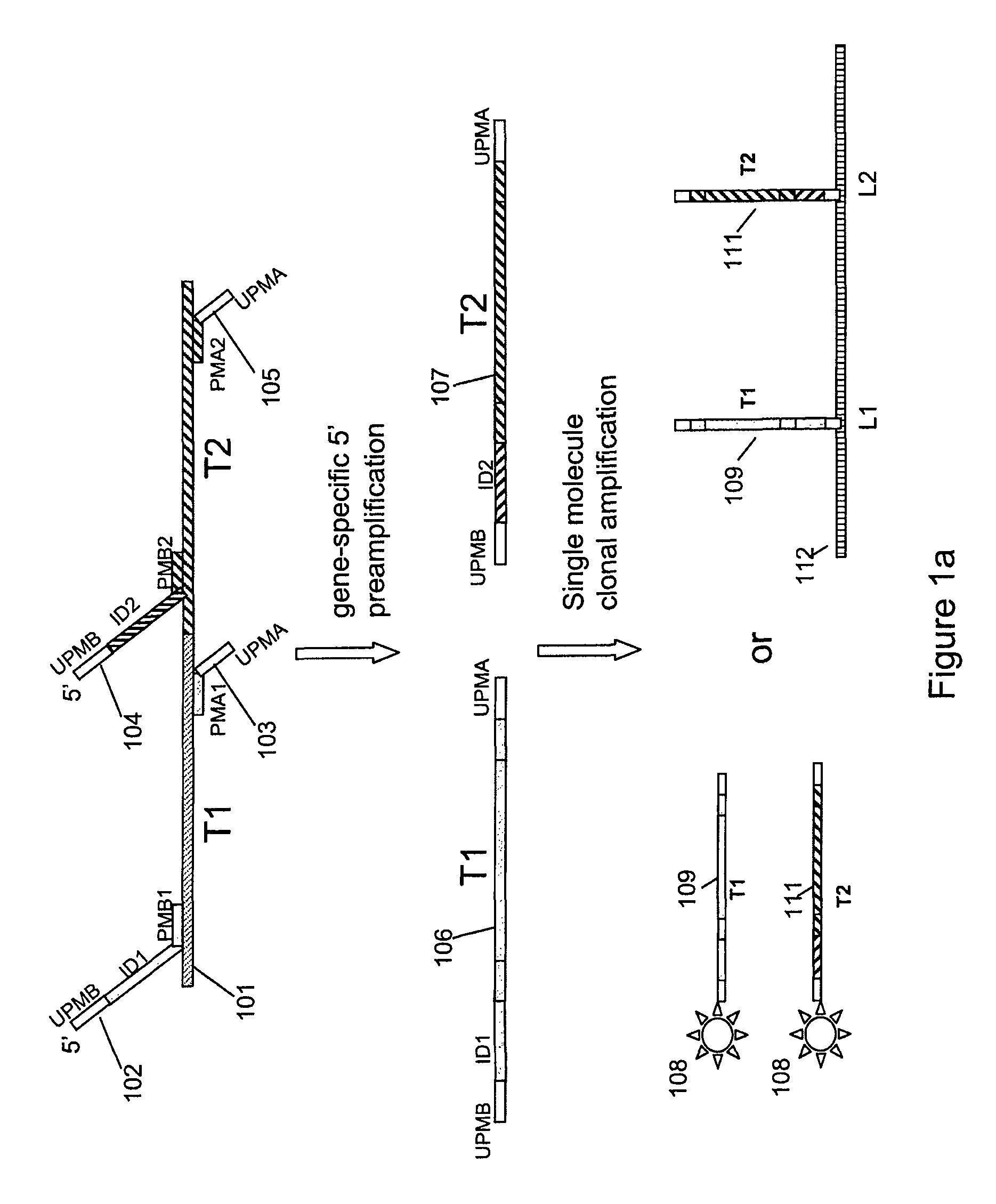
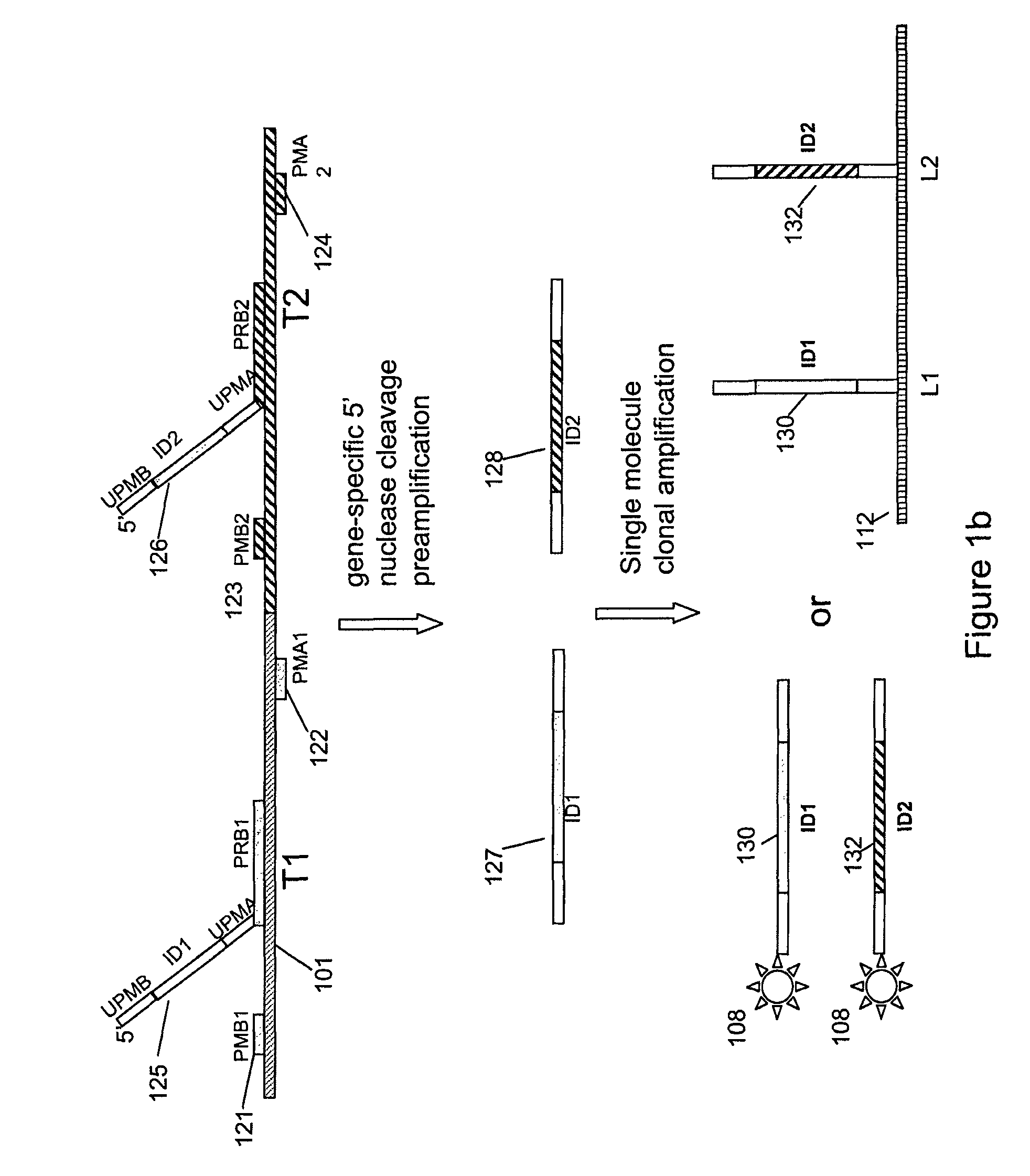
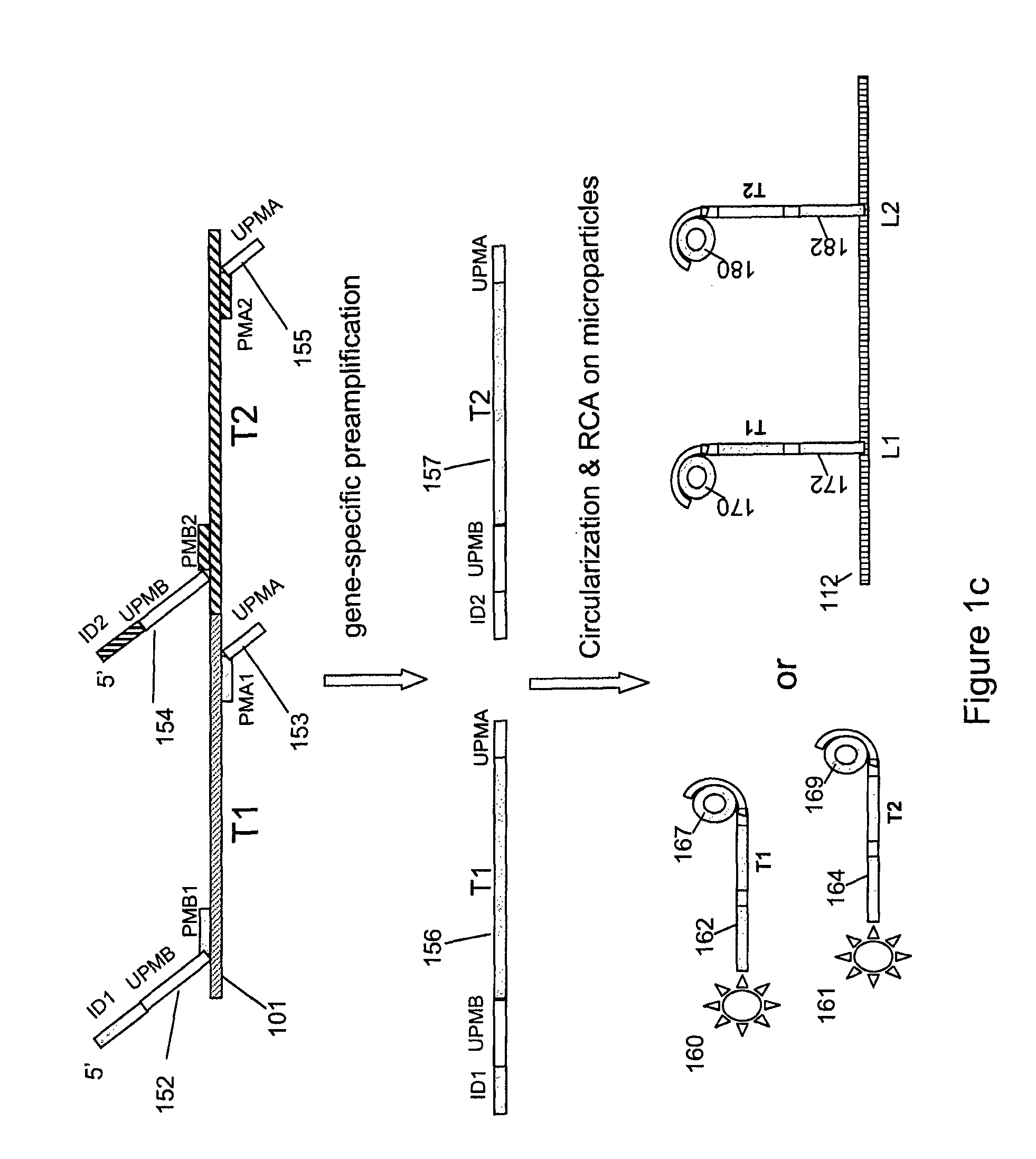
Multiplex nucleic acid detection methods and systems
ActiveUS8603743B2Prevent evaporationSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesDiseaseNucleic acid detection
The present invention relates to methods and systems for single molecule based clonal amplification and subsequent detection of nucleic acid molecules, and particularly to the determination of SNPs, mutations, and to the diagnosis of diseases associated with the changes of these nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:LIFEOS GENOMICS
System for charge-based detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20070178470A1Preventing non-specific bindingGood adhesionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMacromoleculeBioinformatics
This present invention relates methods for detecting the presence of nucleic acids in a sample. In these methods, neutral capture probes are exposed to a sample possibly containing complementary nucleic acid targets. The foregoing mixture is submitted to conditions that provide for the nucleic acid targets to bind with the neutral probes thereby generating hybrids. These hybrids are submitted to positively charged reporters such as atoms, molecules or macromolecules, which electrostatically bind to the hybrids. The complexes formed between reporters and hybrids are detected by a variety of detection methods. Kits for detecting the presence of nucleic acids in a sample are also disclosed herein.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Methods of detecting nucleic acid sequences with high specificity
InactiveUS20130023433A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
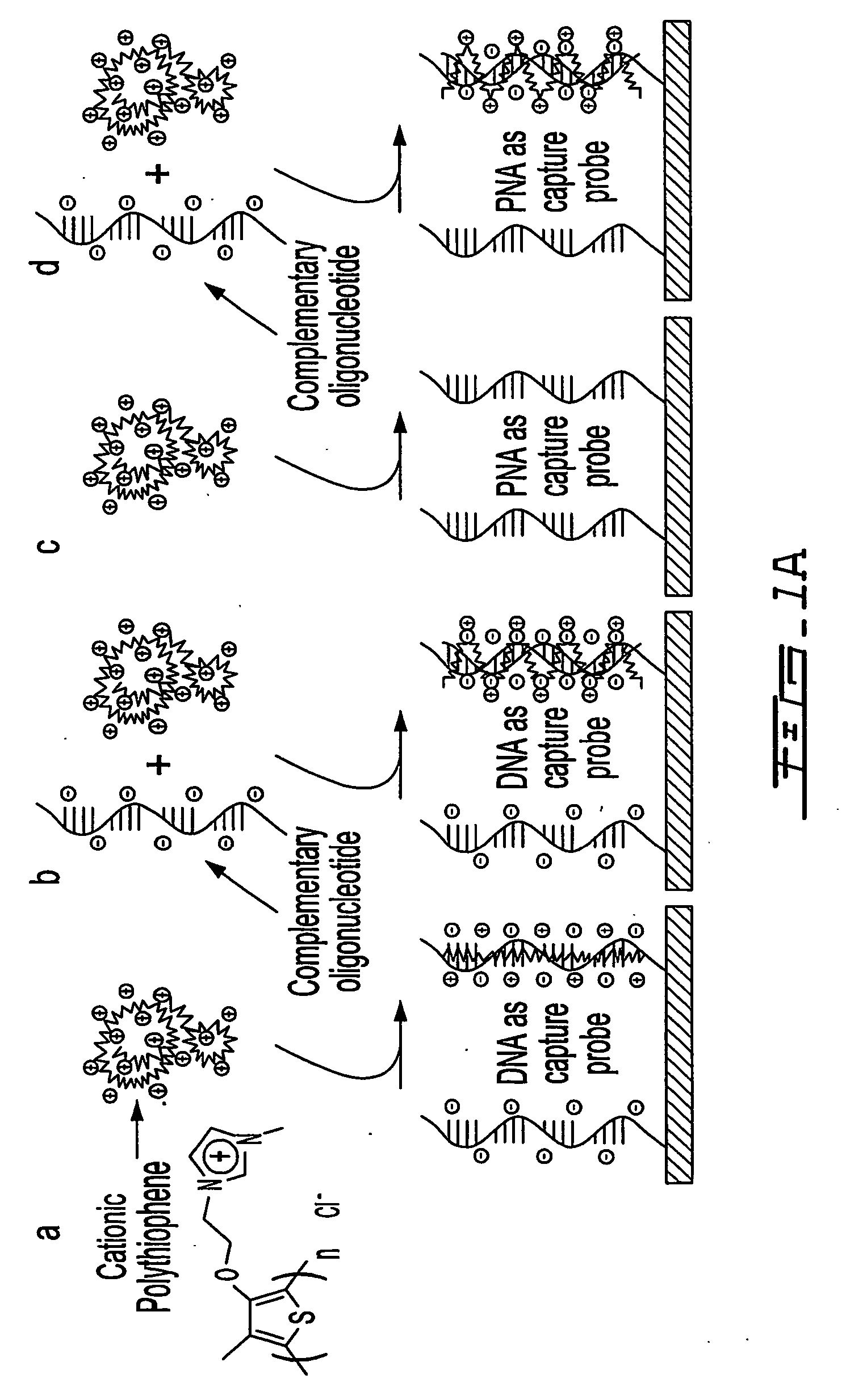
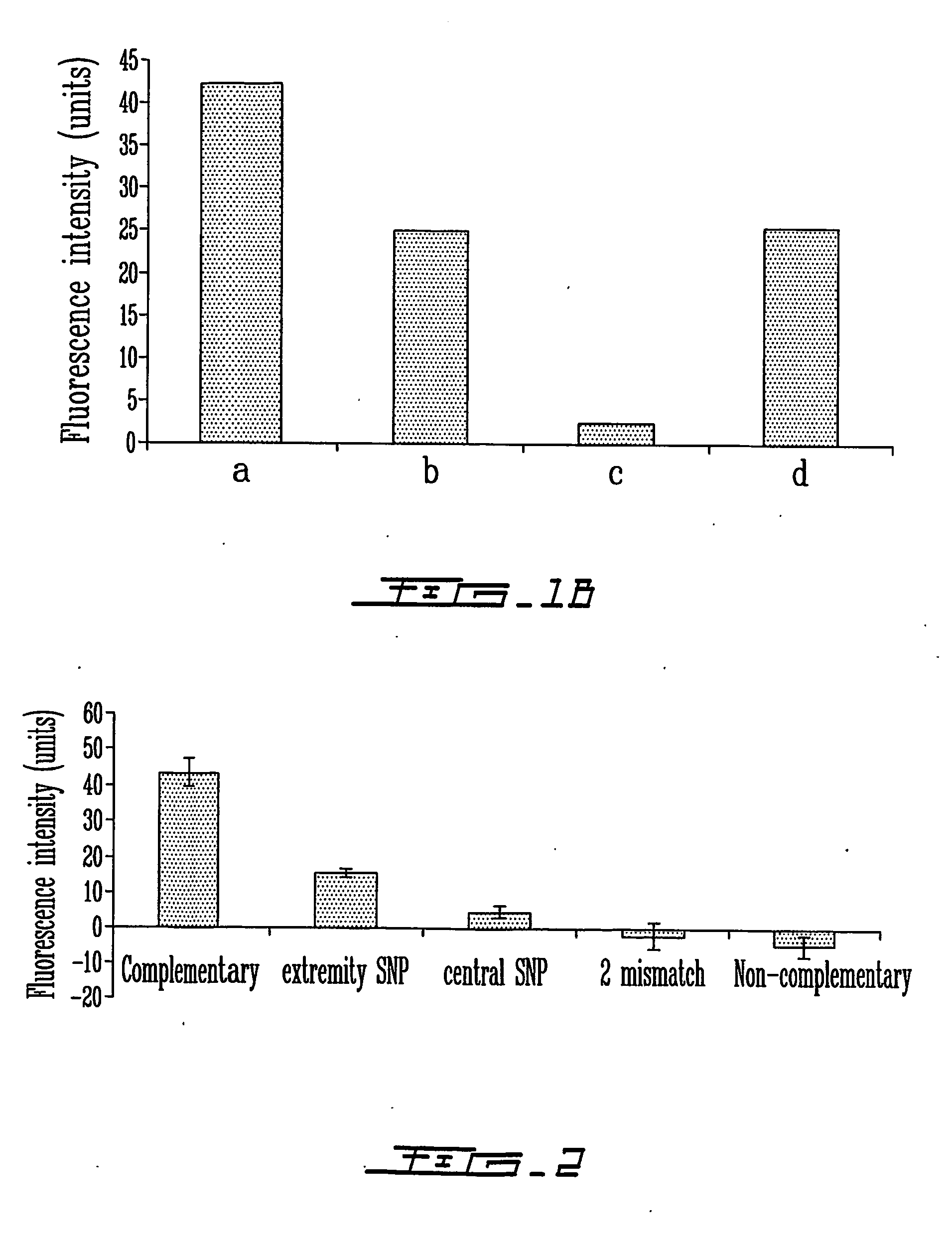
The invention relates to methods of detecting nucleic acids, including methods of detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences in multiplex branched-chain DNA assays, are provided. Nucleic acids captured on a solid support or suspending cells are detected, for example, through cooperative hybridization events that result in specific association of a label with the nucleic acids. The invention further relates to methods to improve probe hybridization specificity and their application in genotyping. The invention also relates to in situ detection of mis-joined nucleic acid sequences. The invention relates to reducing false positive signals and improve signal-to-background ratio in hybridization-based nucleic acid detection assay. The invention further relates to method to improve specificity in hybridization based nucleic acid using co-location probes. Compositions, tissue slides, sample of suspended cells, kits, and systems related to the methods are also described.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
AC methods for the detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7056669B2Simple compositionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligomerBiological materials
The invention relates to nucleic acids covalently coupled to electrodes via conductive oligomers. More particularly, the invention is directed to the site-selective modification of nucleic acids with electron transfer moieties and electrodes to produce a new class of biomaterials, and to methods of making and using them.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC +1
Nucleic acid detection method
InactiveUS7282355B2Rapid and reliable and cost-effectiveDetect presenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleotide sequencing
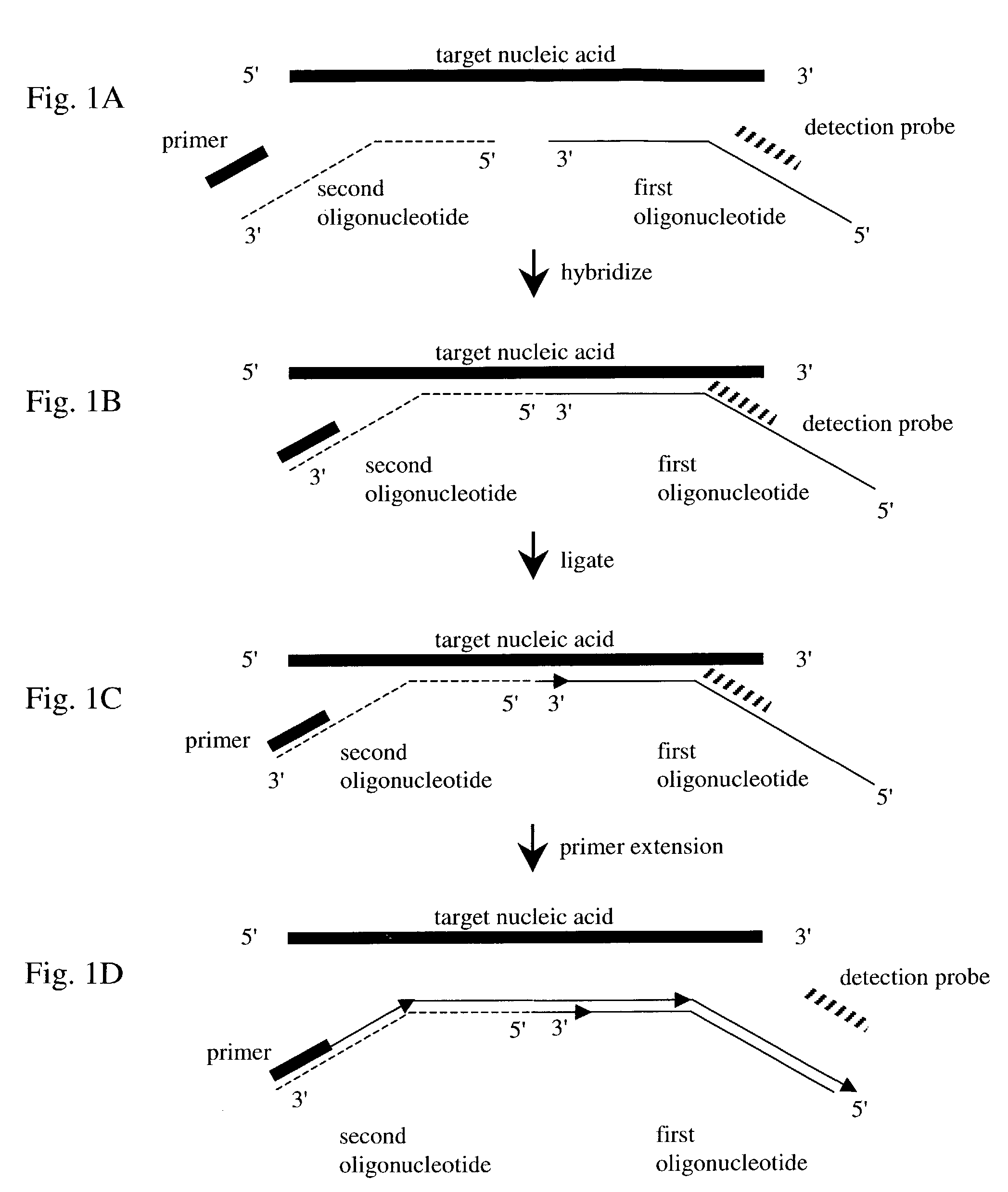
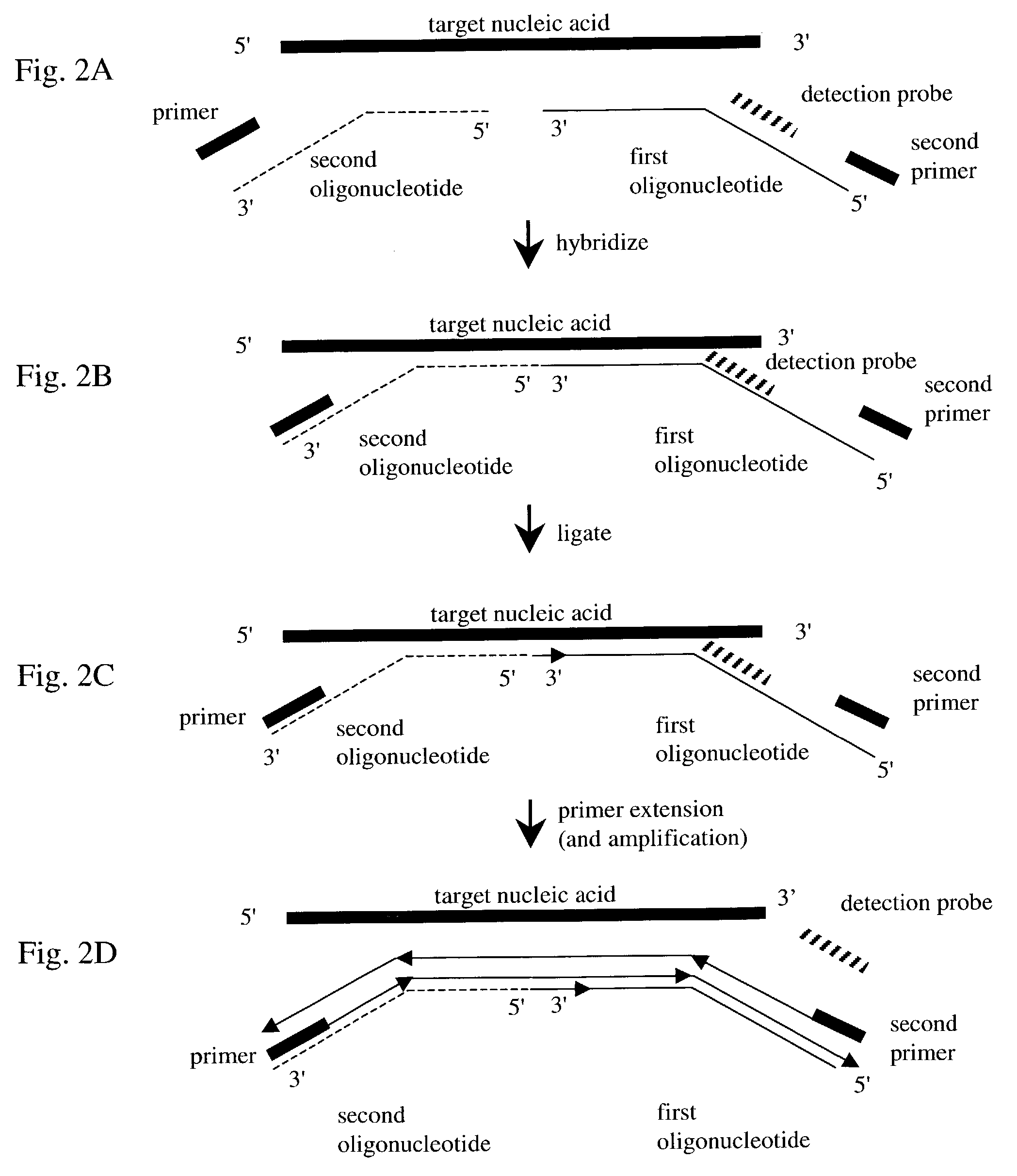
Disclosed are methods for detecting a target nucleic acid molecule having a known sequence among a plurality of nucleic acid molecules. The method includes hybridizing two oligonucleotides to adjacent nucleotide sequences on the target nucleic acid molecule, ligating the two oligonucleotides together, and extending a primer that hybrizes to the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide that hybrized to the 5′ nucleotide sequence on the target nucleic acid molecule. If the target nucleic acid molecule is present (and thereby allowing ligation of the two oligonucleotides), extension of the primer dislodges a detection probe hybridized to the 5′ end of the oligonucleotide that hybridized to the 3′ nucleotide sequence on the target nucleic acid molecule.Also disclosed are kits for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
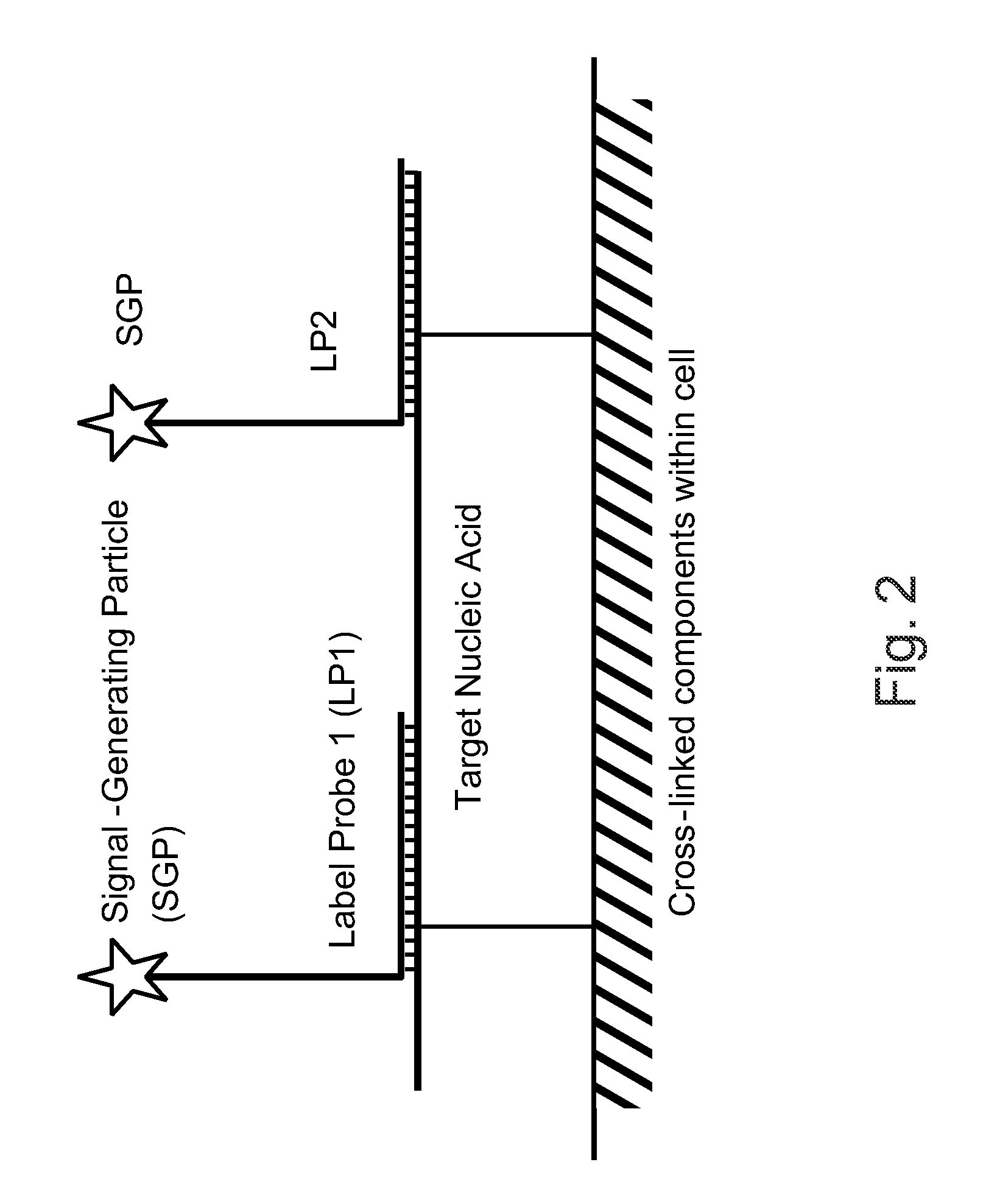
Detection of target molecules with labeled nucleic acid detection molecules
InactiveUS20070048759A1Easy to detectImprove utilizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionChemistry
The invention is directed to a detection molecule for detection of a target molecule. The detection molecule includes a probe specific to the target molecule. One or more multimer nucleic acid molecules are connected to the probe, whereby the multimer is also coupled to at least one detectable label. The detection molecules are utilized in a method to detect the presence of one or more target molecules in a sample.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Compositions and methods for preparing oligonucleotide solutions
InactiveUS20100151464A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechNucleic acid detectionOligonucleotide
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for generating a pool of oligonucleotides. The invention finds use in preparing a population or subpopulations of oligonucleotides in solution. The pool of oligonucleotides finds use in a variety of nucleic acid detection and / or amplification assays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Real-time nucleic acid detection processes and compositions
InactiveUS20050137388A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid detectionAnalyte
This invention provides for compositions for use in real time nucleic acid detection processes. Such real time nucleic acid detection processes are carried out with energy transfer elements attached to nucleic acid primers, nucleotides, nucleic acid probes or nucleic acid binding agents. Real time nucleic acid detection allows for the qualitative or quantitative detection or determination of single-stranded or double-stranded nucleic acids of interest in a sample. Other processes are provided by this invention including processes for removing a portion of a homopolymeric sequence, e.g., poly A sequence or tail, from an analyte or library of analytes. Compositions useful in carrying out such removal processes are also described and provided.
Owner:ENZO LIFE SCI INC
Direct nucleic acid detection in bodily fluids
The present invention provides methods and routines for developing and optimizing nucleic acid detection assays for use in basic research, clinical research, and for the development of clinical detection assays. In particular, the present invention provides methods for designing oligonucleotide primers to be used in multiplex amplification reactions. The present invention also provides methods to optimize multiplex amplification reactions. The present invention also provides methods for combined target and signal generation assays.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Crude biological derivatives competent for nucleic acid detection
InactiveUS20050277121A1Increase concentrationLow number of cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNucleic acid detectionBiological unit
The invention relates generally to the fields of making biological unit lysates or admixtures of body fluids and of RNA analysis. More specifically, it relates to direct methods for the detection of a specific sequence of RNA in a biological unit, for example a virus, cell or tissue sample, or a body fluid, for example saliva, sputum, blood plasma, etc. More generally, the invention may be used to enzymatically manipulate and protect the RNA in lysate or bodily fluids for a number of applications.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
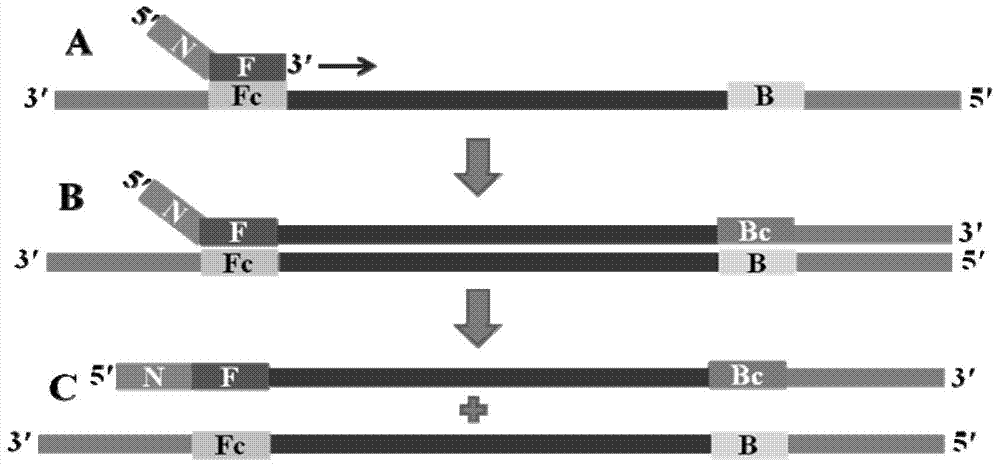
Nucleic acid isothermal amplification method and application thereof by polymerase spiral reaction
ActiveCN104232622AMeet the experimental requirementsSimple designMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSocial benefitsNucleic acid detection
The invention discloses a nucleic acid isothermal amplification method by polymerase spiral reaction (PSR). A pair of oligonucleotide primers is used, mutually reverse nucleotide fragments are added to 5' ends of the primers, a target gene is subjected to PSR under the action of the primers and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase and under the isothermal condition, self-spiral extending of the target gene can be achieved, and thereby, nucleic acid amplification can be finished. According to the nucleic acid isothermal amplification method by PSR, a novel technology platform is provided for nucleic acid detection, amplification of a product is simple, an amplification product is applicable to the field of detection and can be slightly processed to be subjected to clone recycling and sequencing, the method can be applied to all fields which require nucleic acid amplification, the market prospect is wide, the economic and social benefits are large, and the method is suitable for large-range popularization and application.
Owner:中国人民解放军疾病预防控制中心
Single molecule detection and sequencing using fluorescence lifetime imaging
InactiveUS20110236983A1Avoid detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by electrical excitationEnergy transferNucleic acid detection
A nucleic acid detection system and method are provided, in which excitation energy is transmitted from a pulsed excitation source to a reaction site including a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based dye system to generate a fluorescent signal at the reaction site, the fluorescent signal is detected by a detector from the reaction site, and detection of the fluorescent signal is respectively blocked and permitted at the detector by a detector gate this is timed based on an emission start time of the transmitted excitation energy.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com