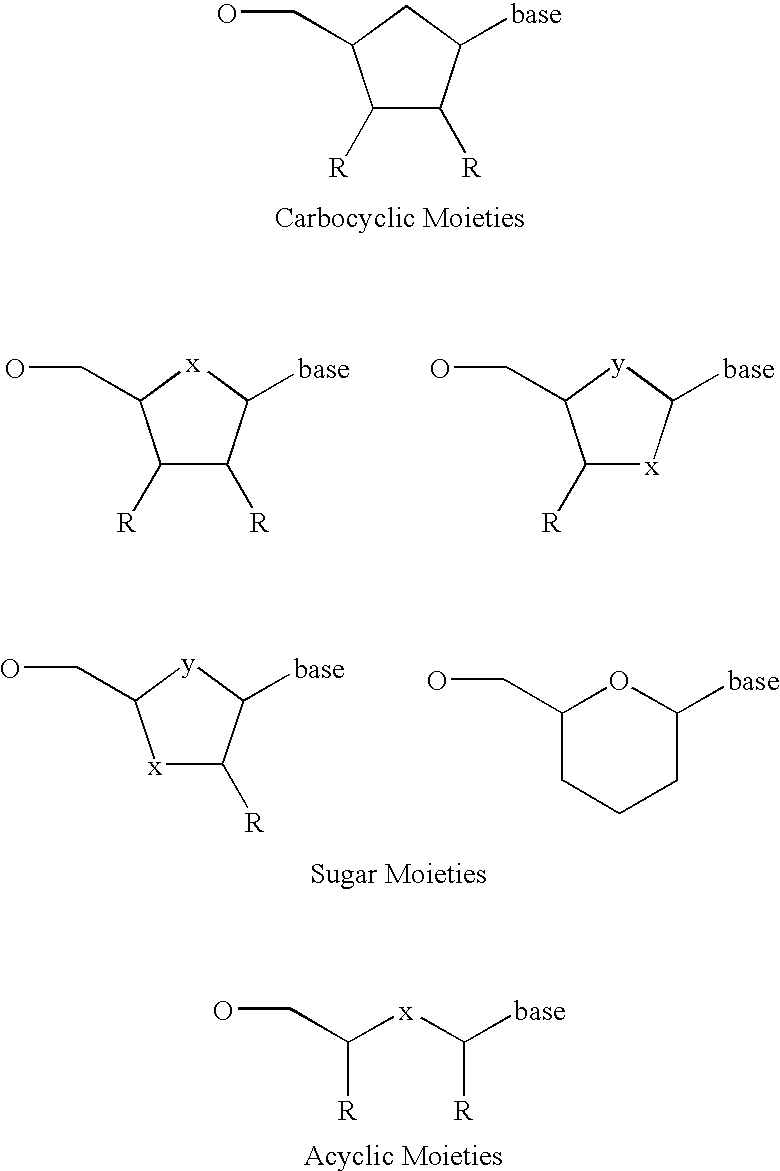
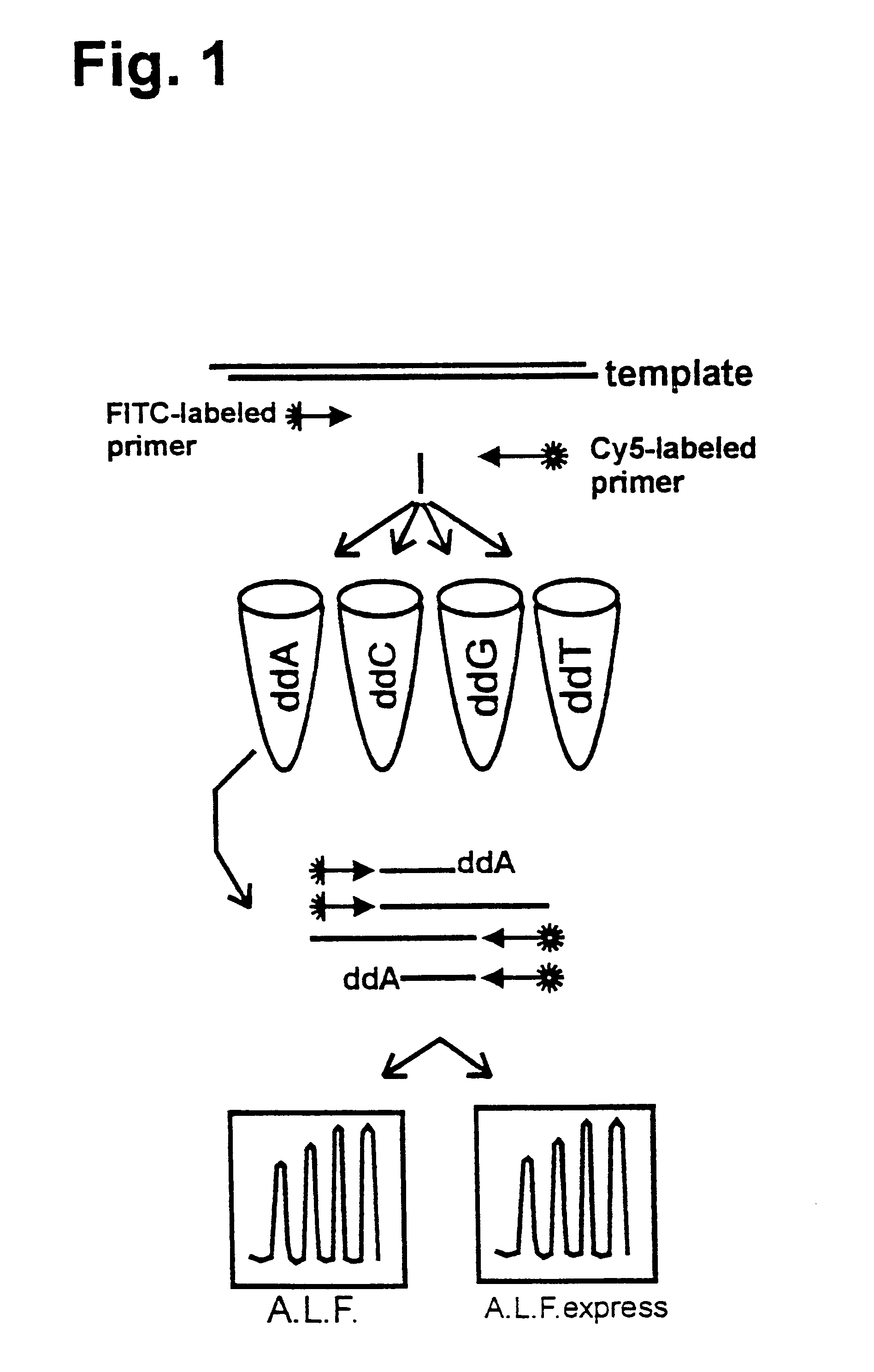
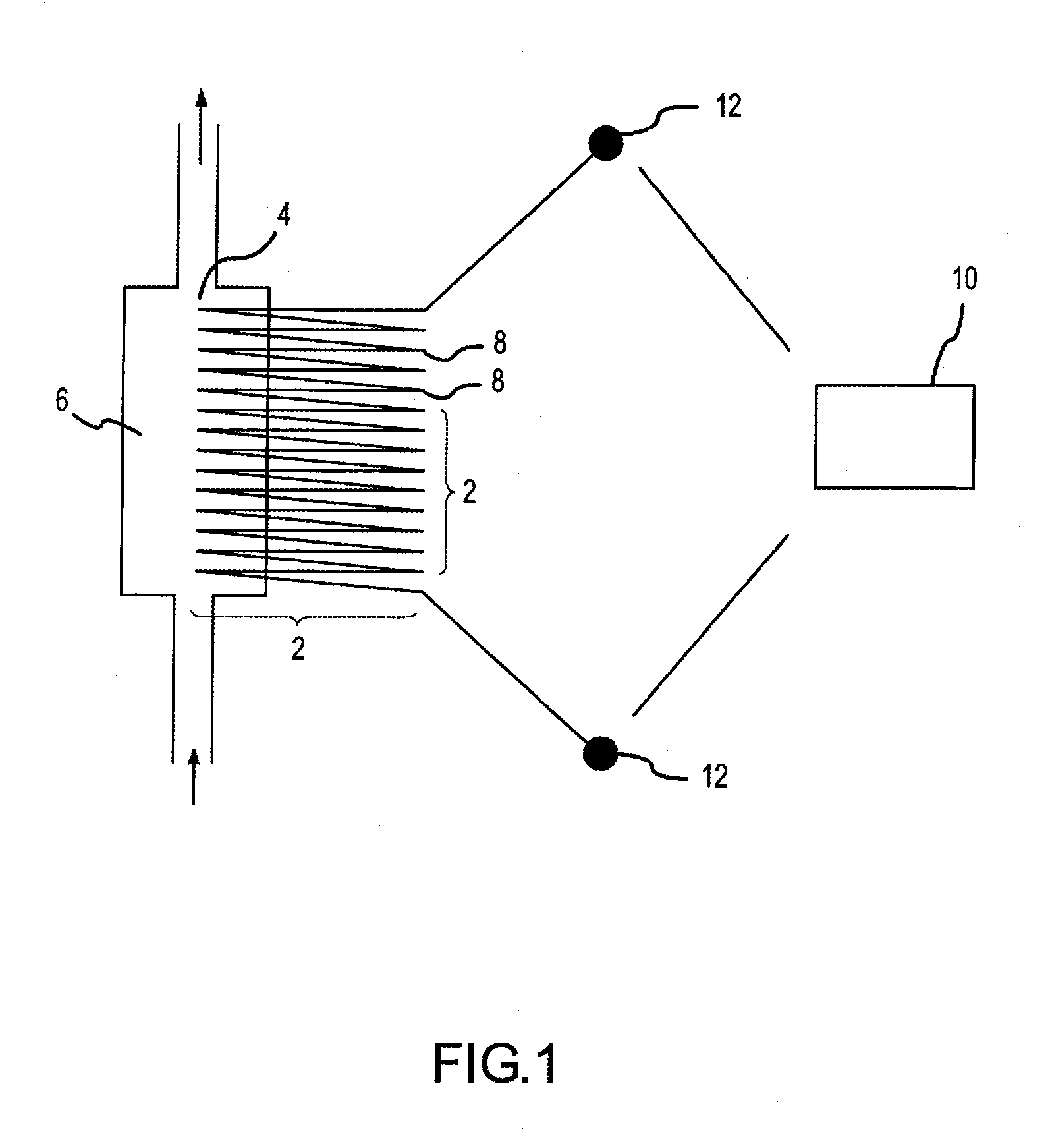
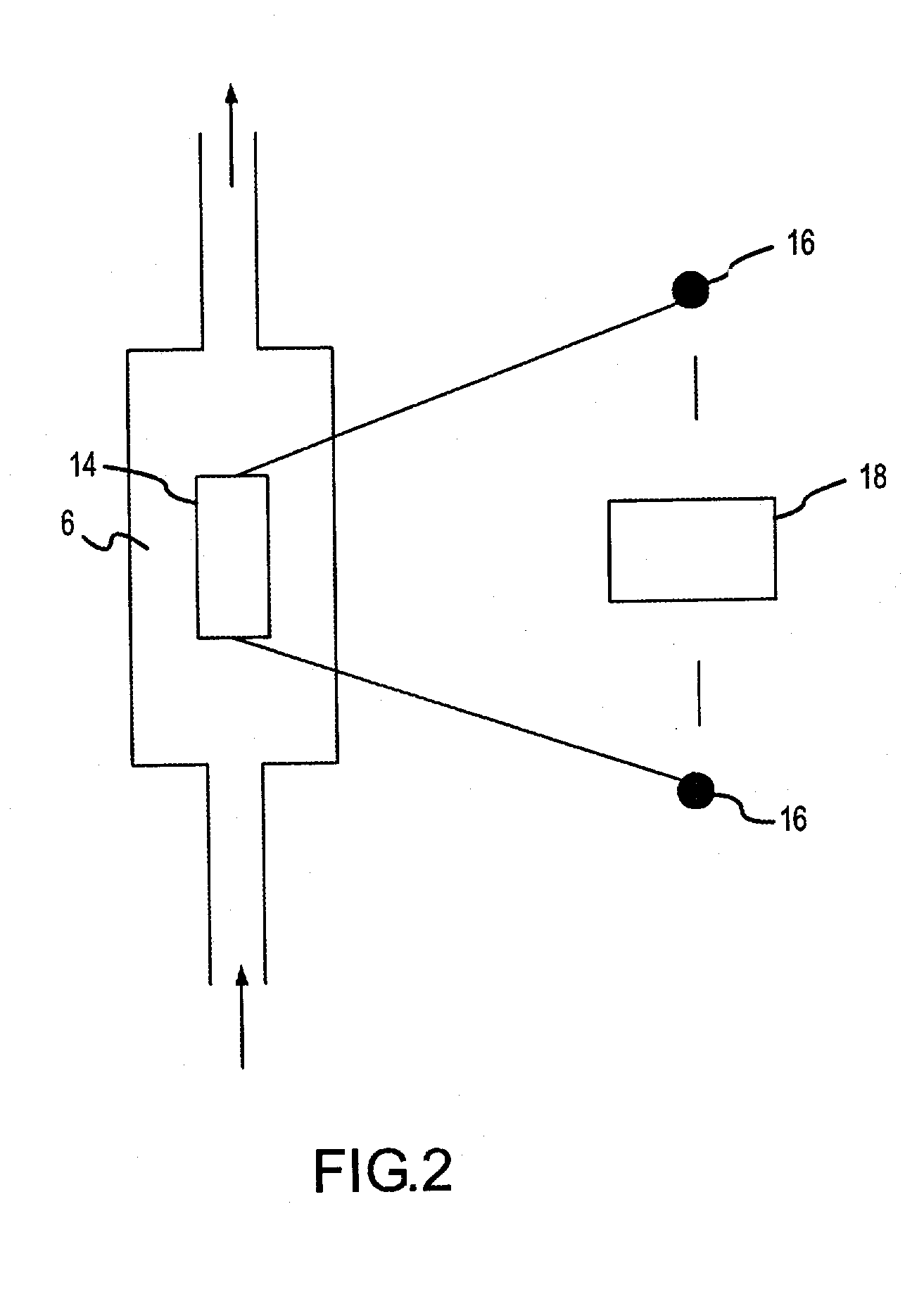
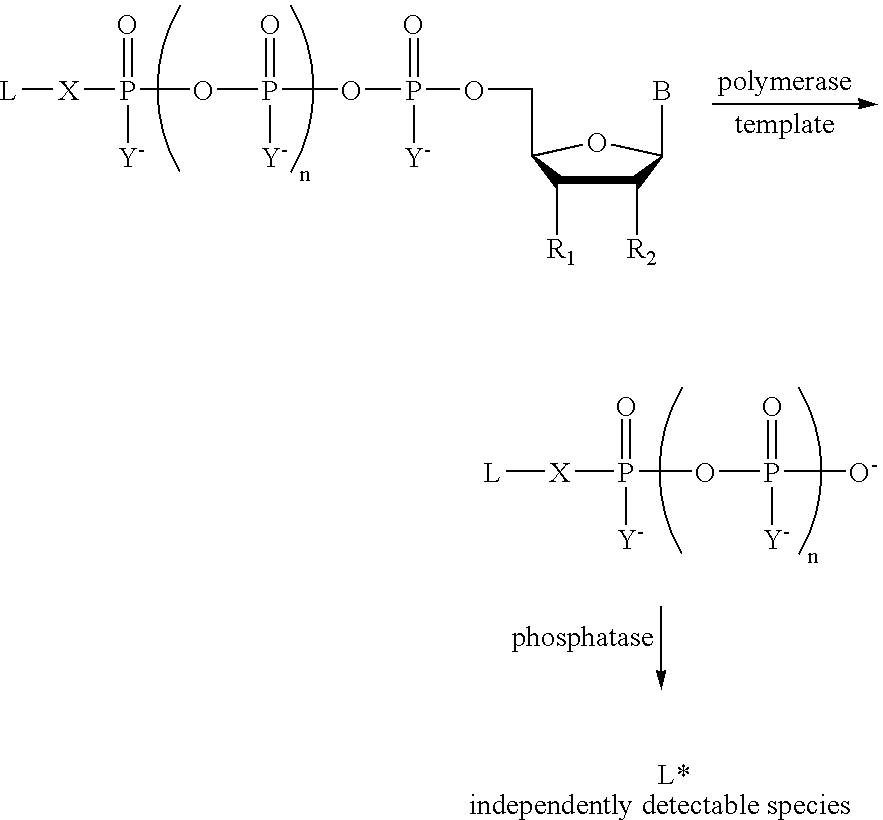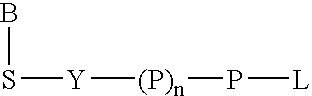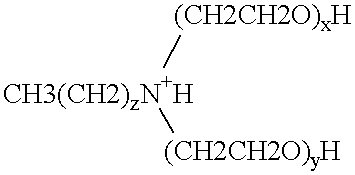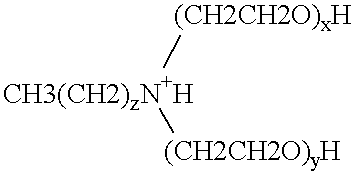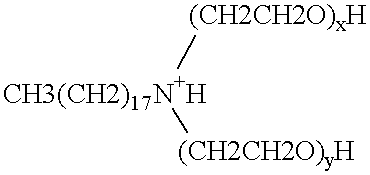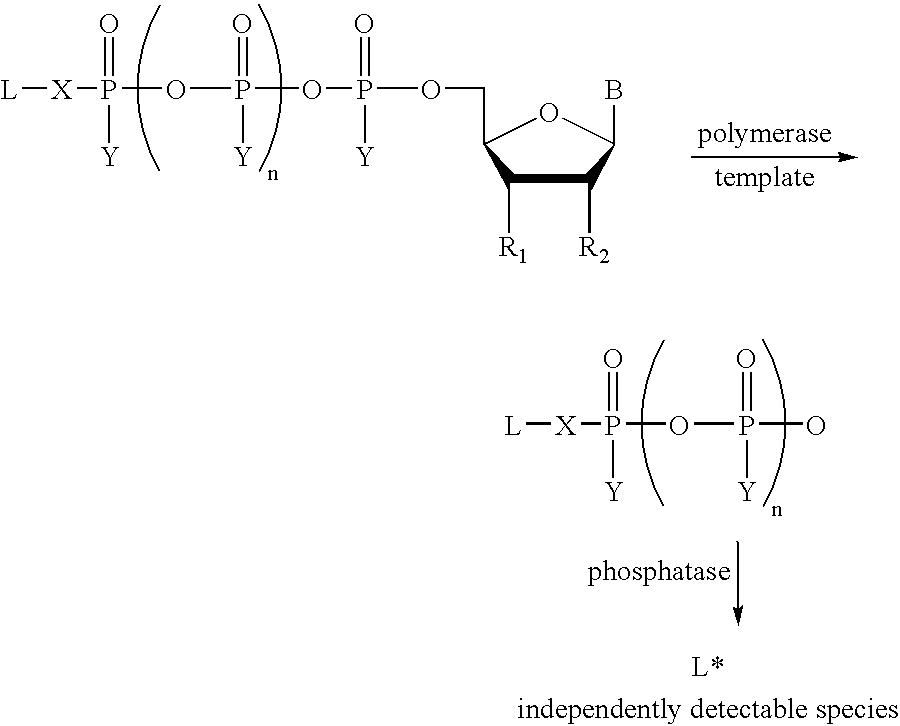Patents
Literature
2232 results about "DNA polymerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes DNA molecules from deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.
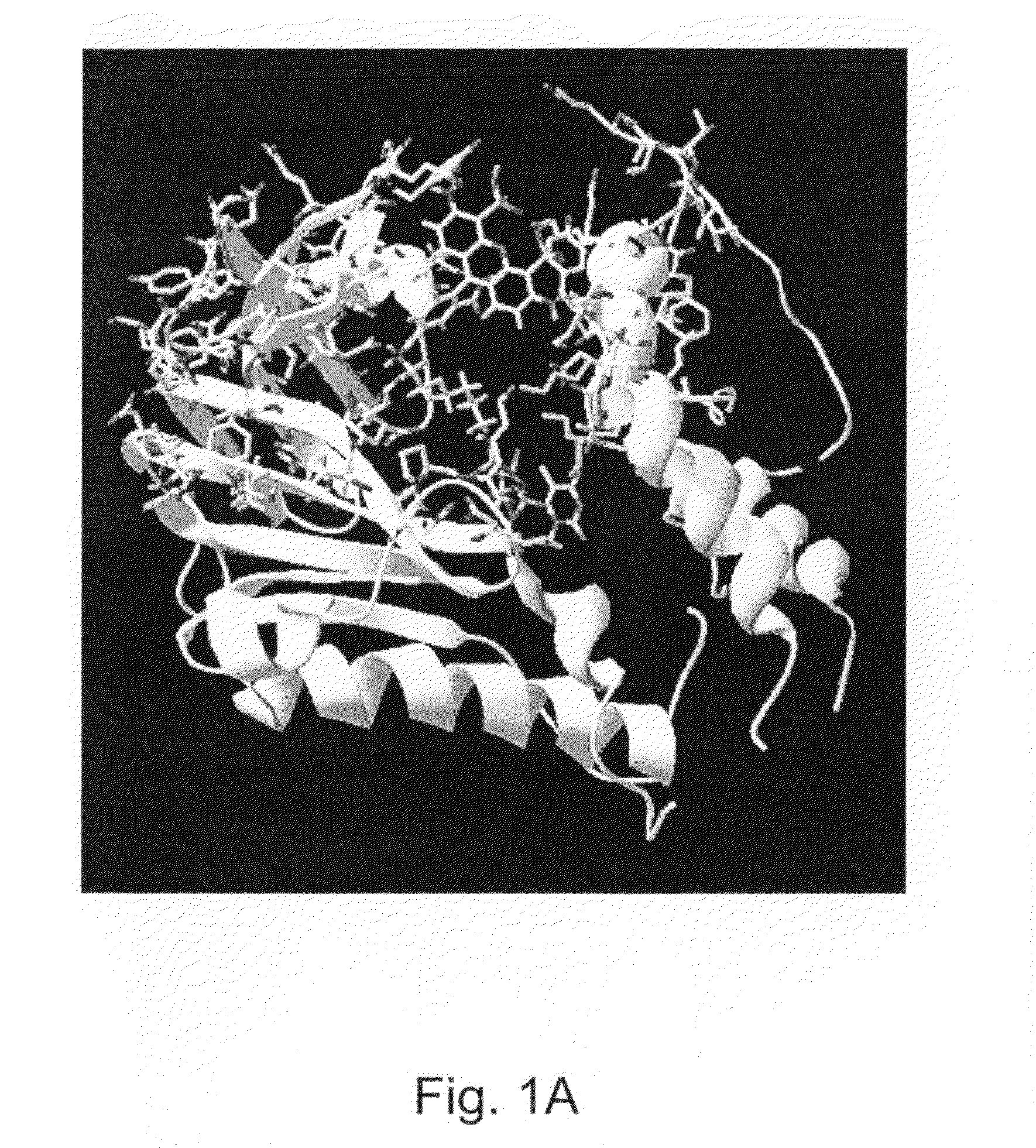
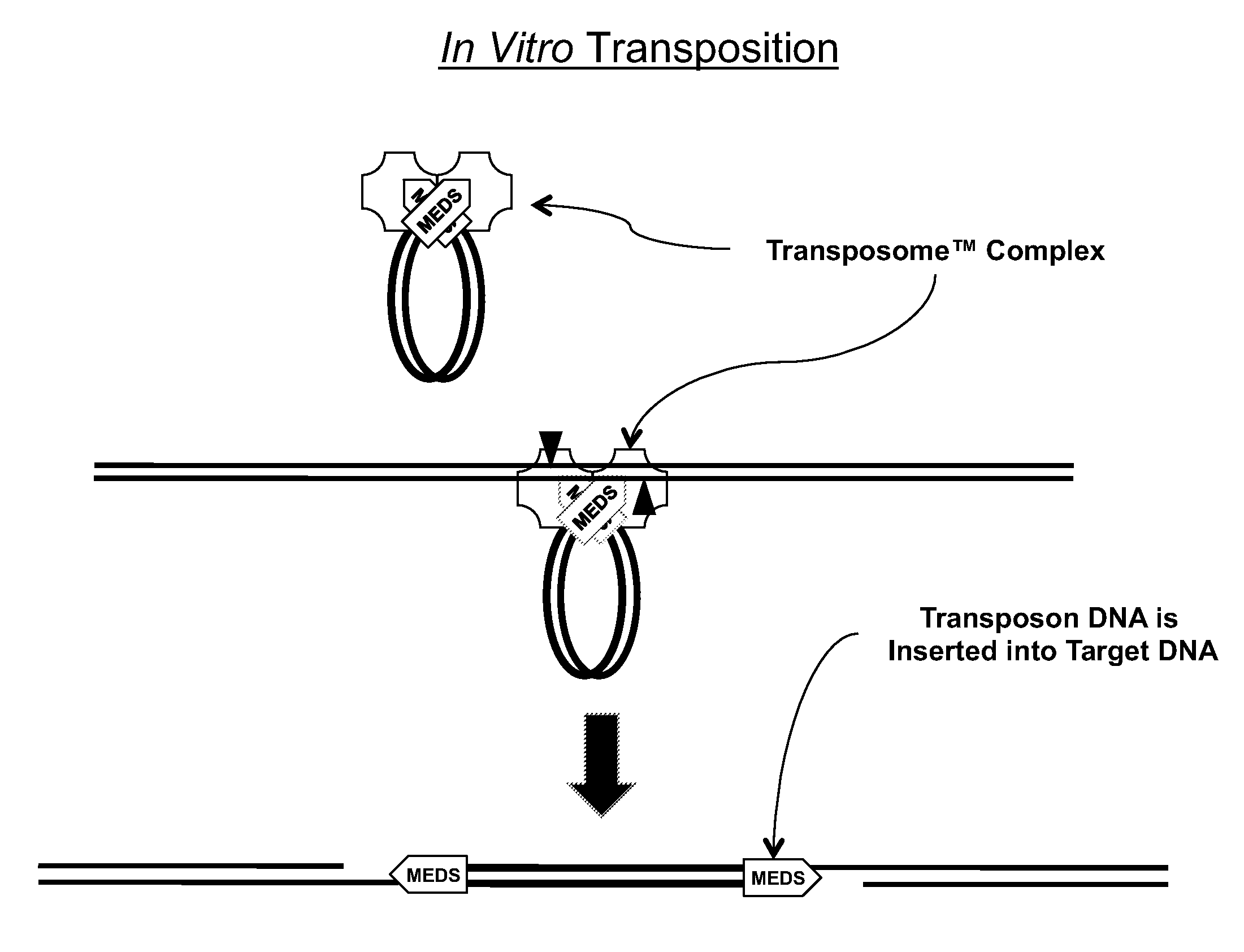
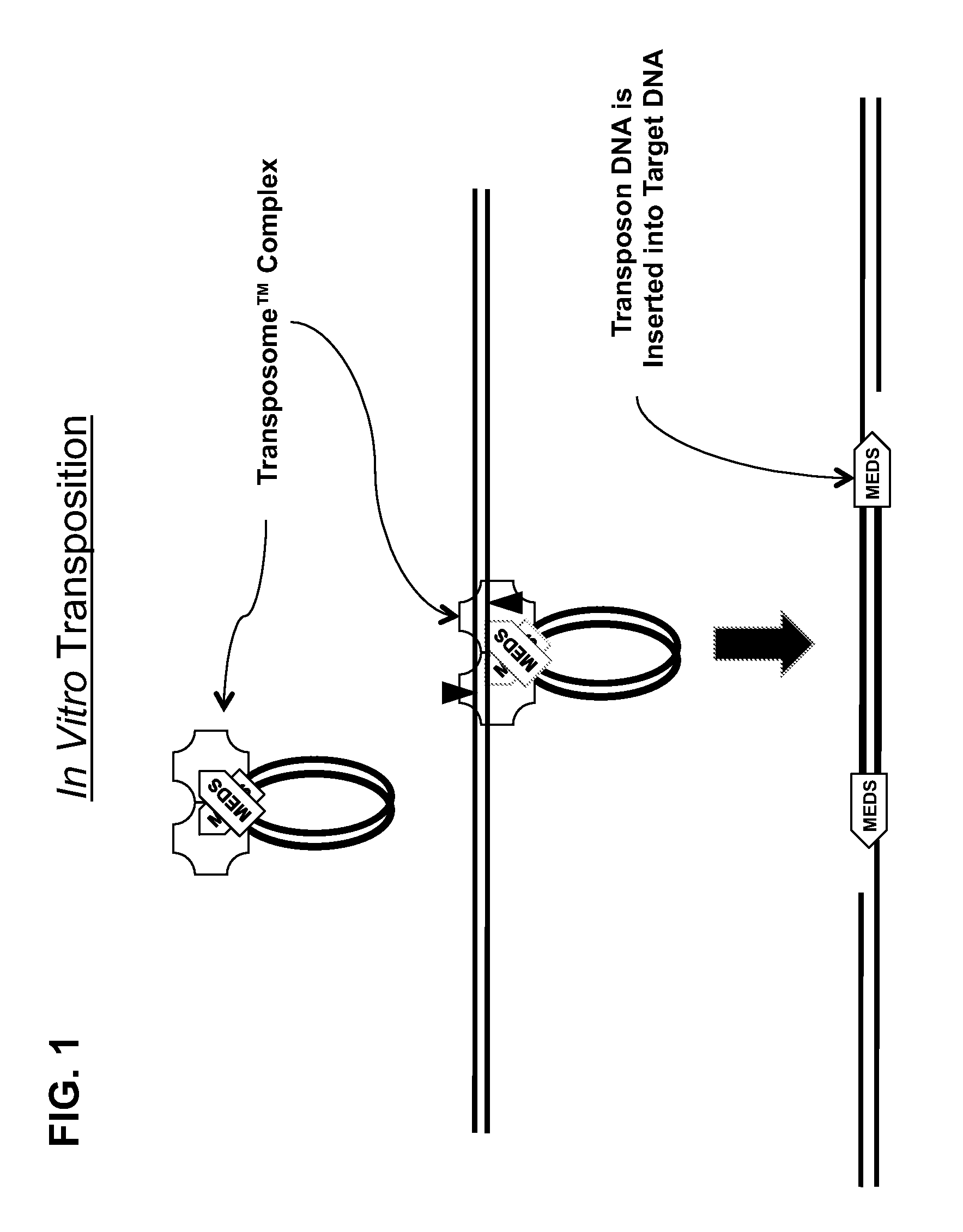
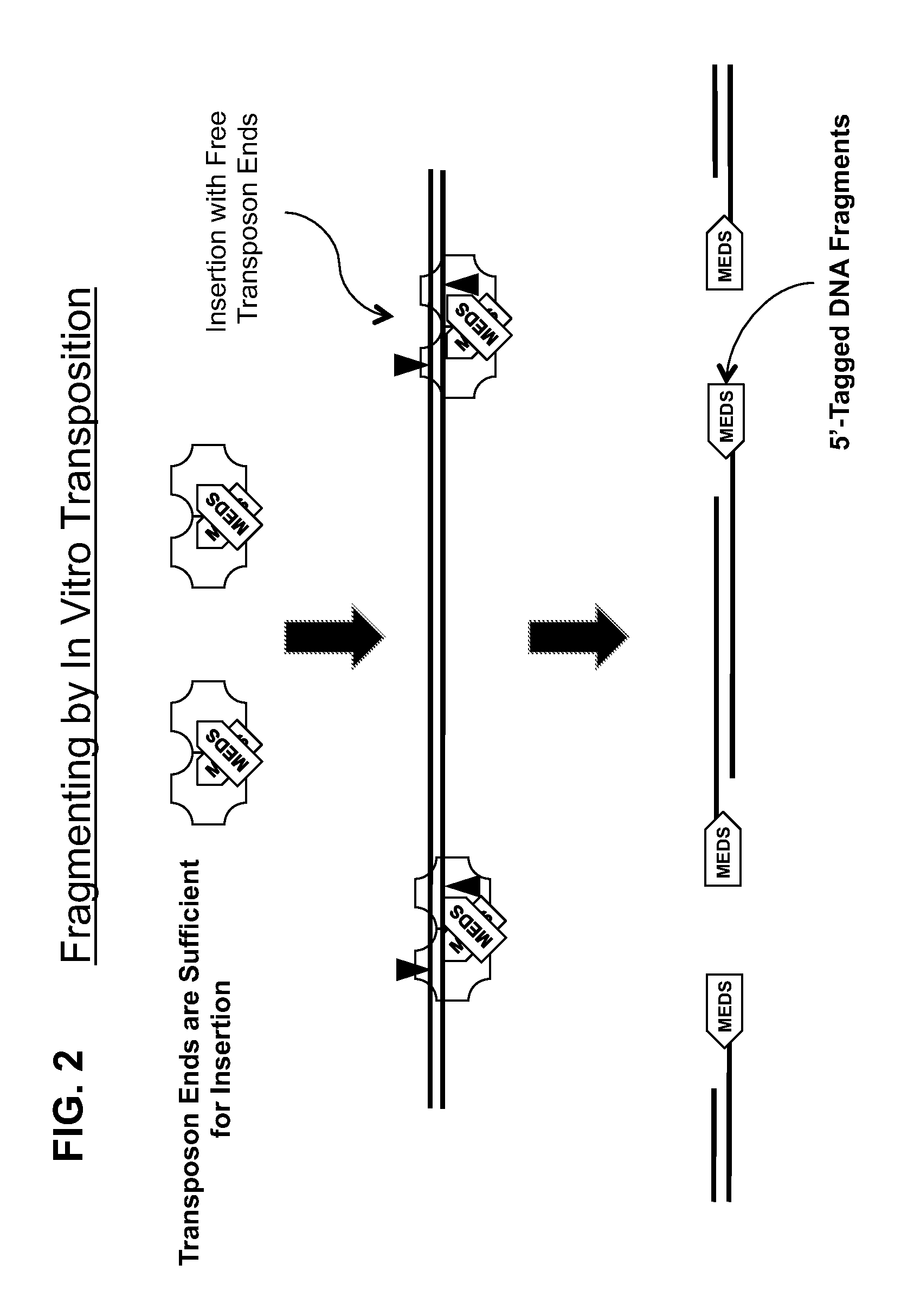
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS7037687B2Eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligonucleotide primersThermopile
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:ALBERTA UNIV OF +1
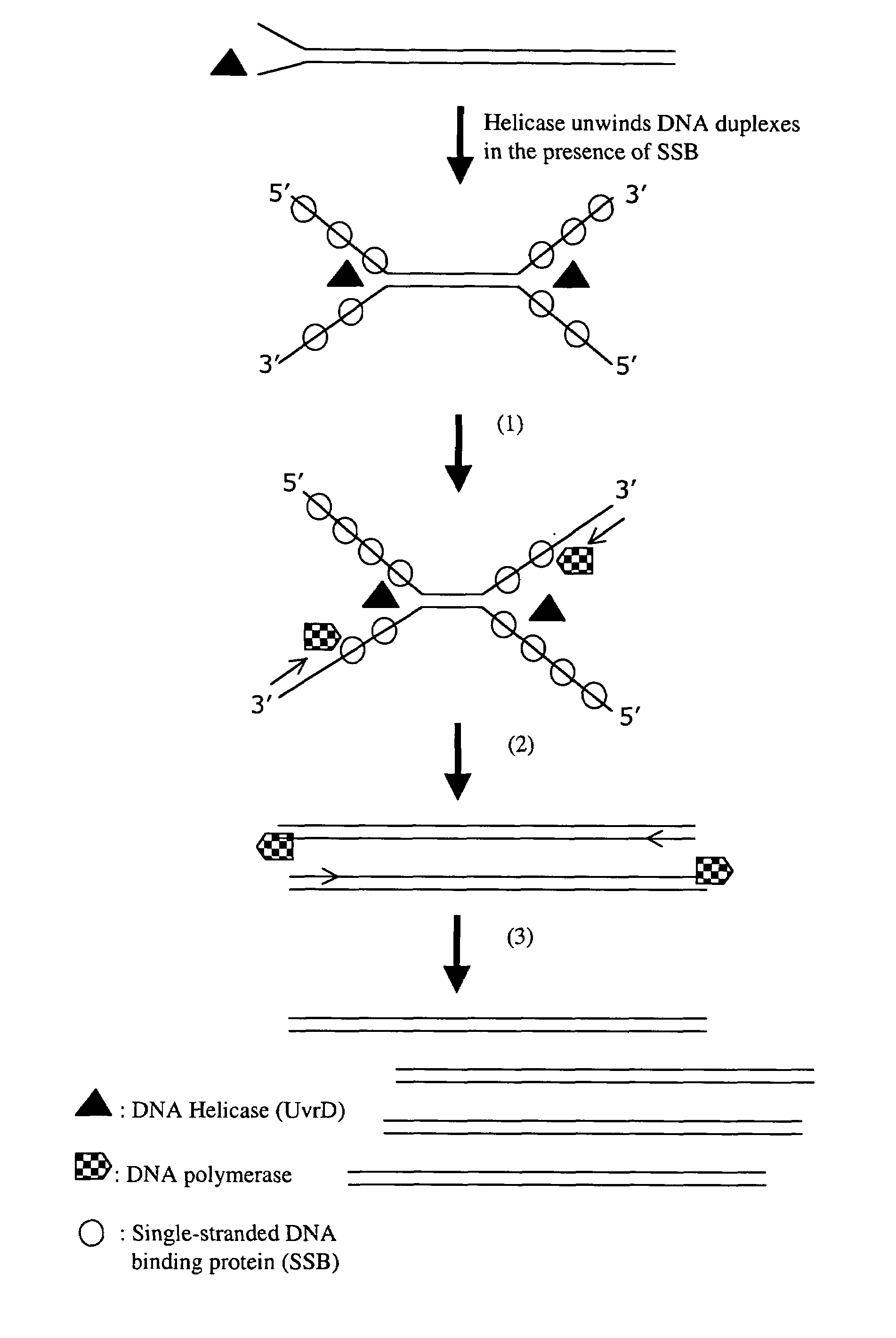
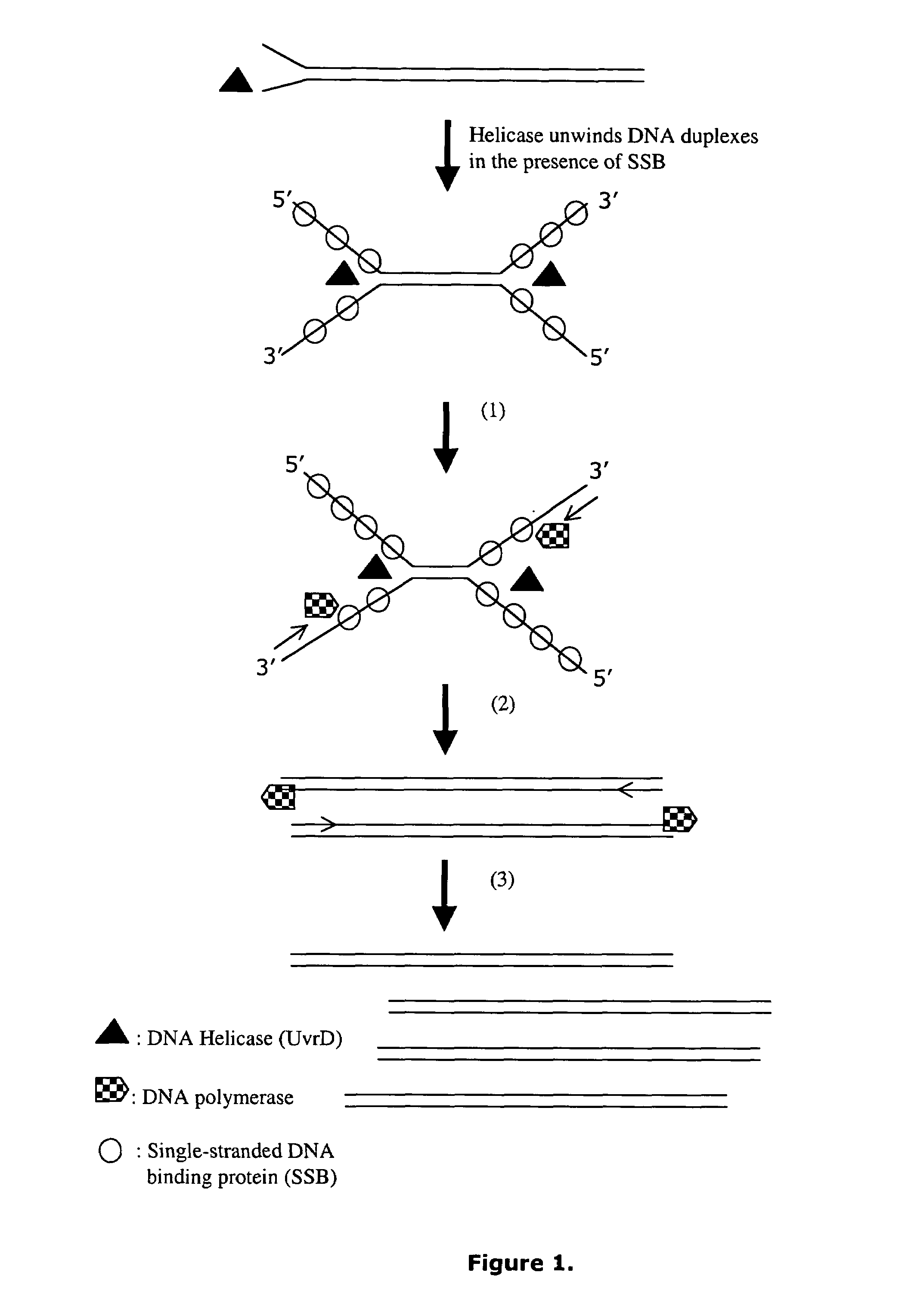
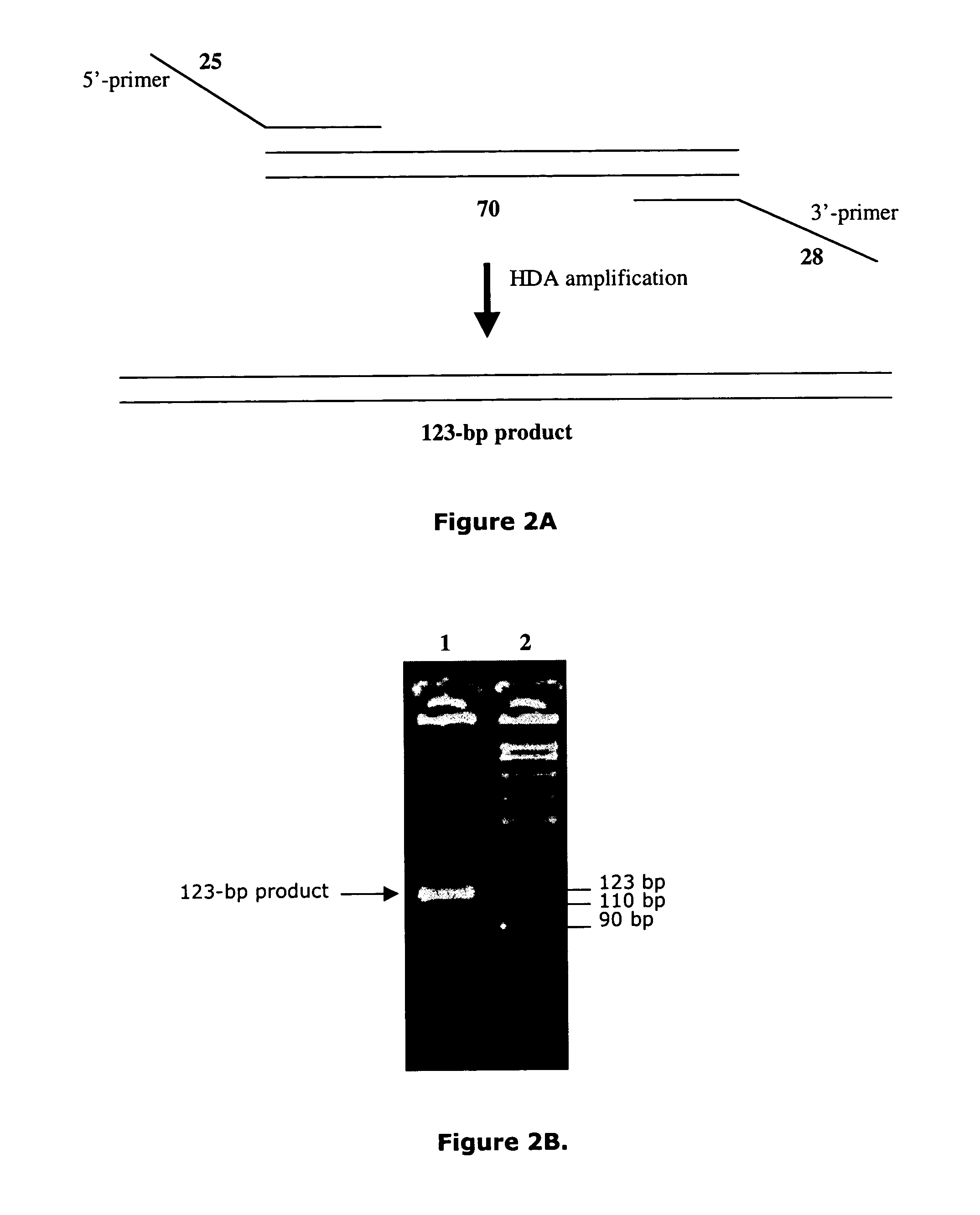
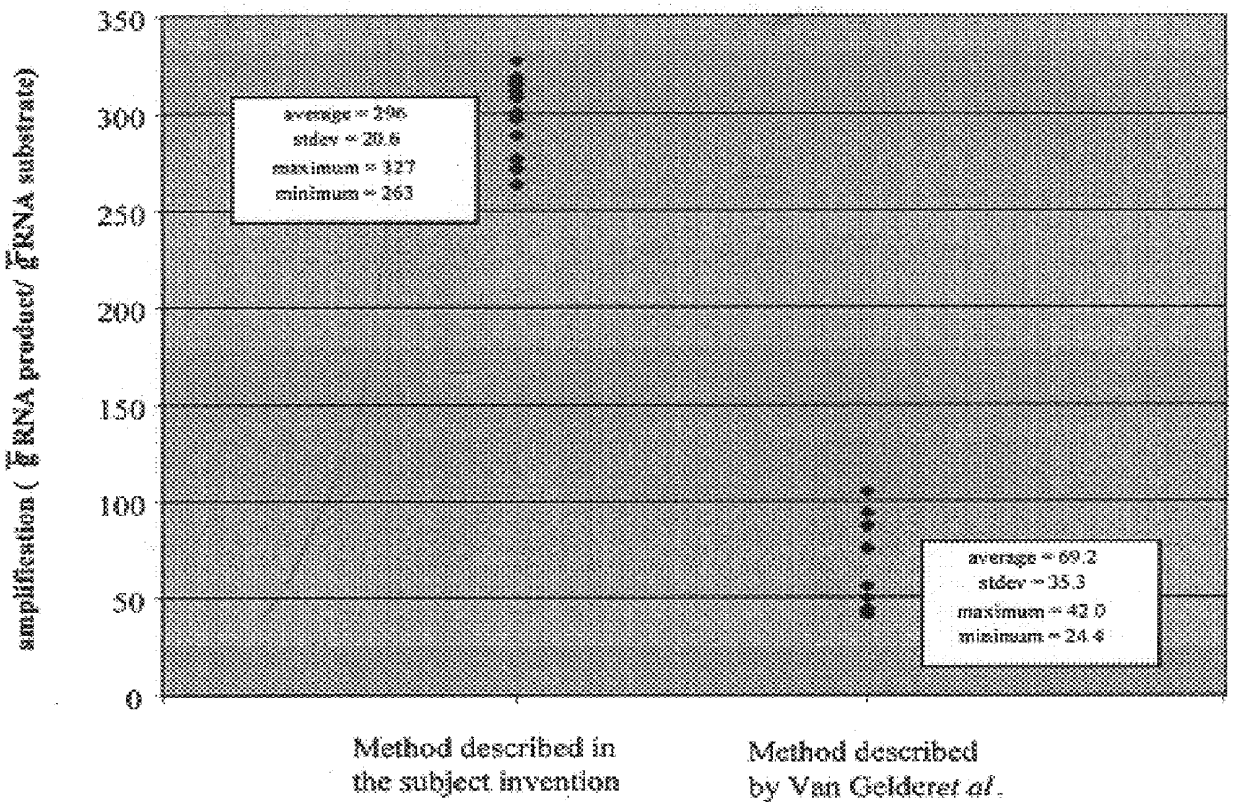
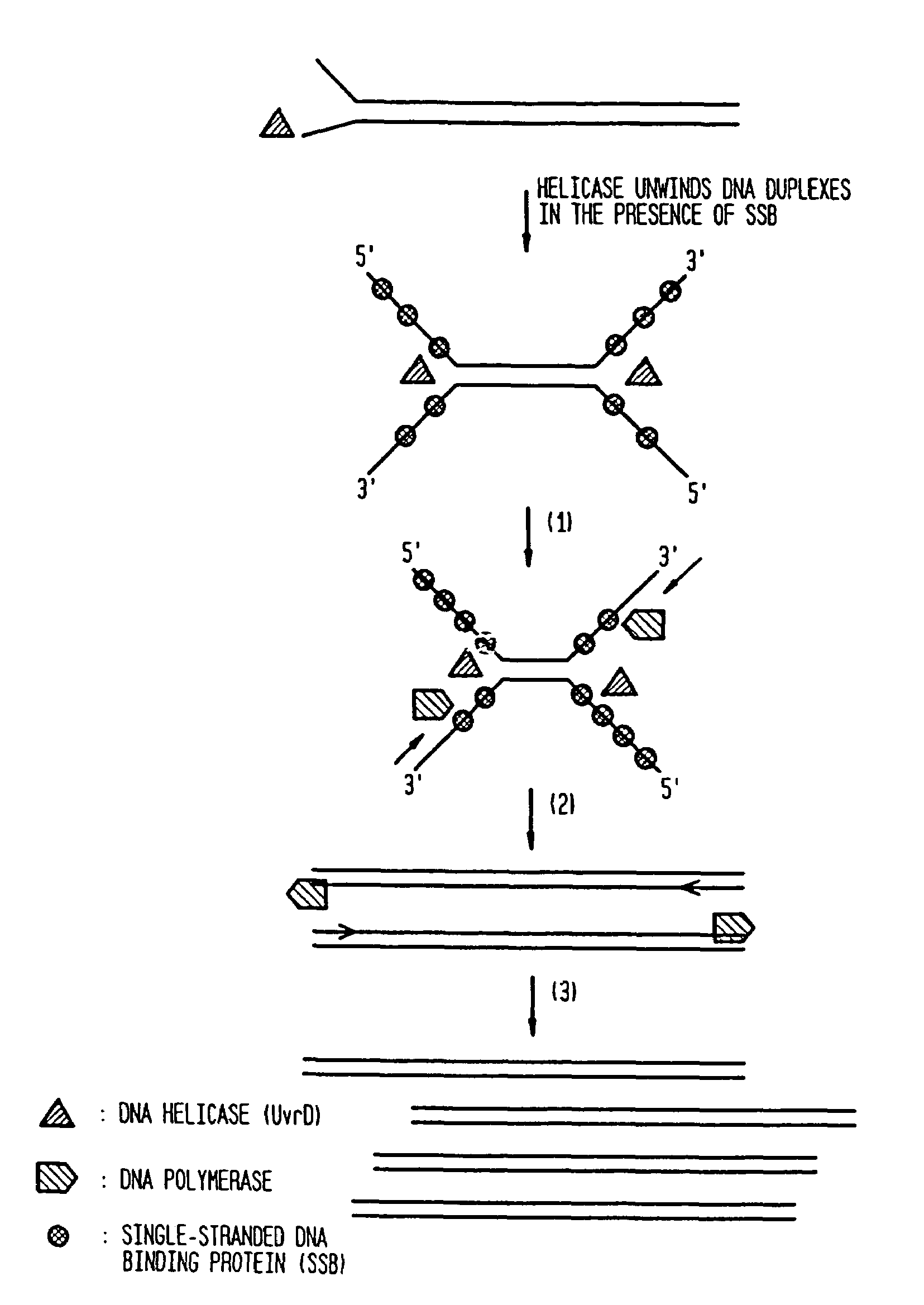
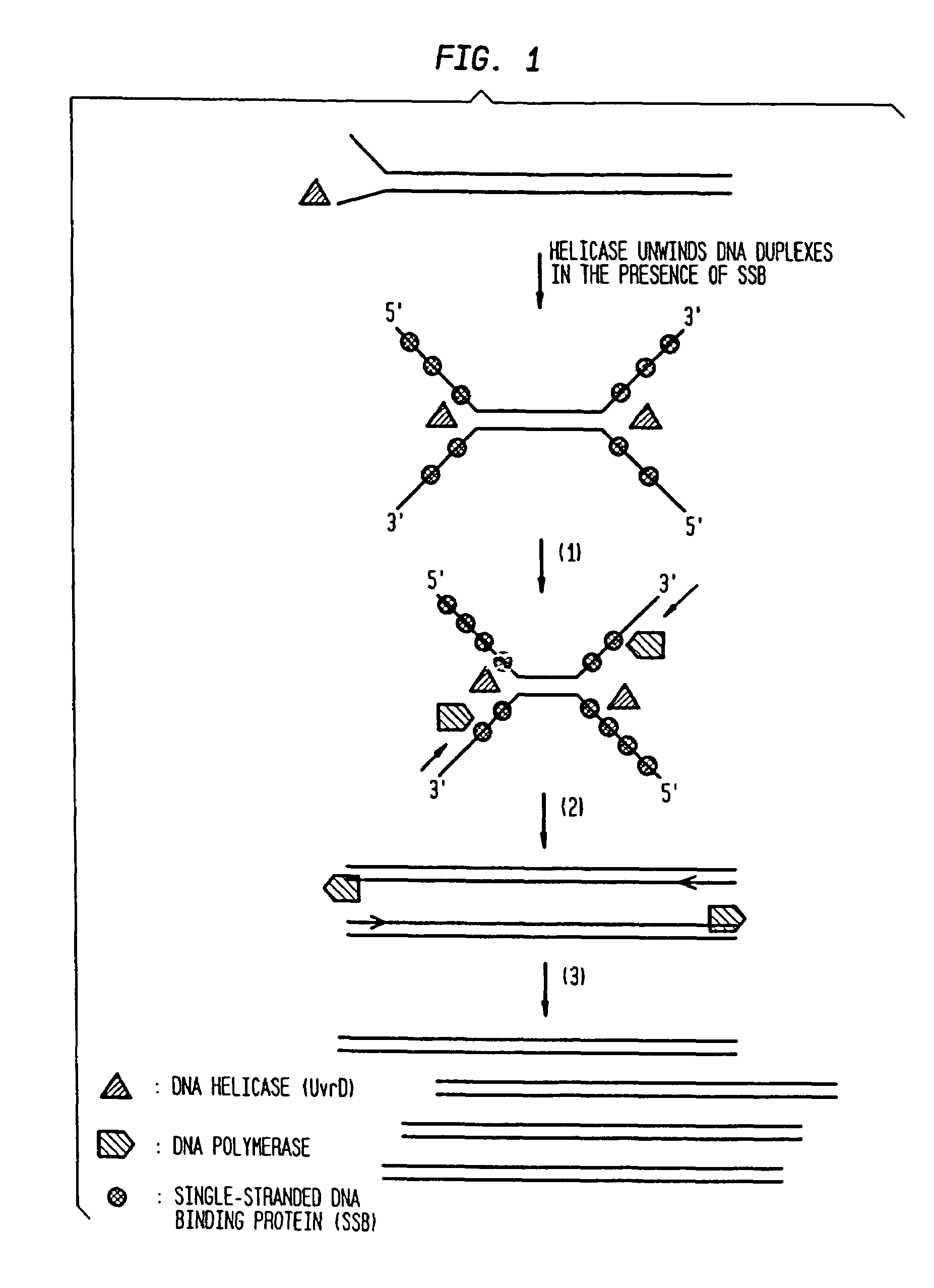
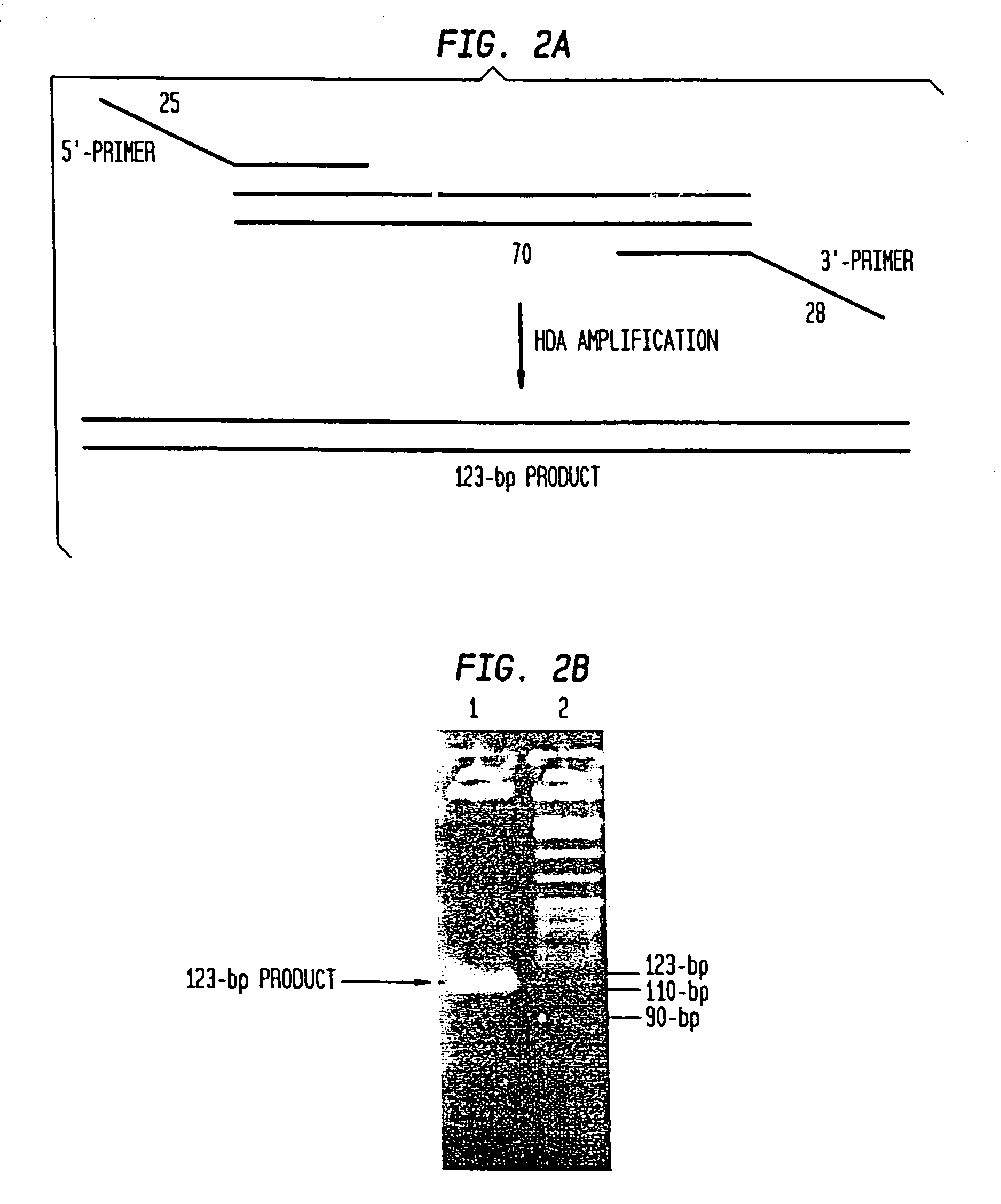
Helicase dependent amplification of nucleic acids
ActiveUS7282328B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA unwinding enzyme
Methods and a kit are provided for selectively and exponentially amplifying nucleic acids and include the use of a helicase preparation and a DNA polymerase such that the amplification can be performed isothermally.
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6132997ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
Methods for linearly amplifying mRNA to produce antisense RNA are provided. In the subject methods, mRNA is converted to double-stranded cDNA using a promoter-primer having a poly-dT primer site linked to a promoter sequence so that the resulting double-stranded cDNA is recognized by an RNA polymerase. The resultant double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into antisense RNA in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods find use a variety of different applications in which the preparation of linearly amplified amounts of antisense RNA is desired. Also provided are kits for practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS6780591B2Eliminate needHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyFluorescenceOligonucleotide primers
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Single nucleotide amplification and detection by polymerase
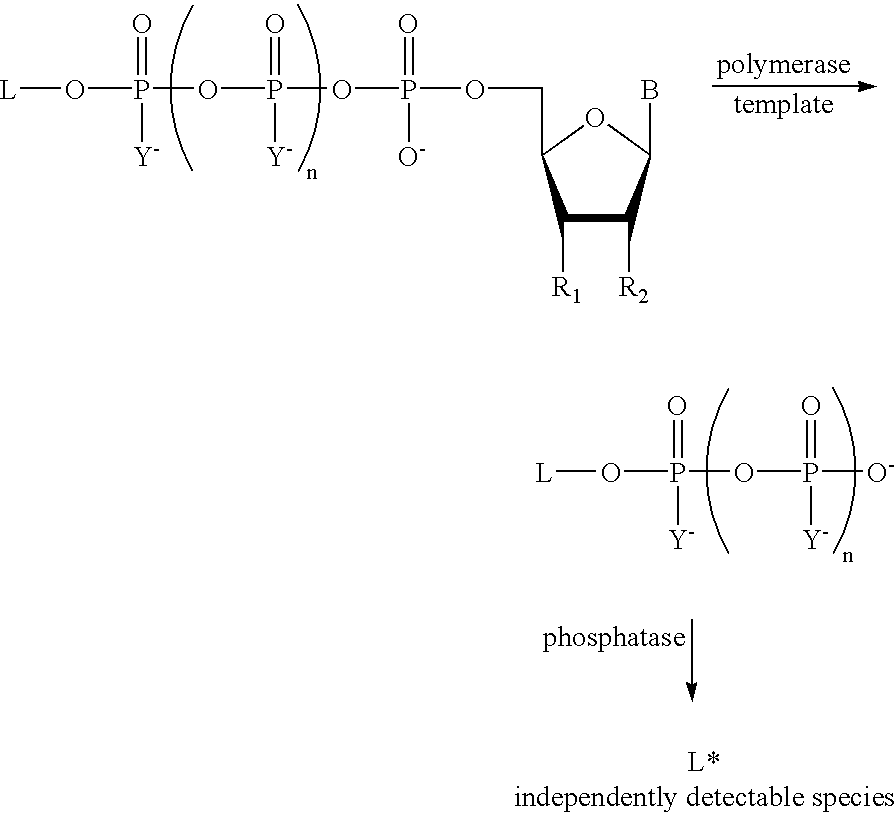
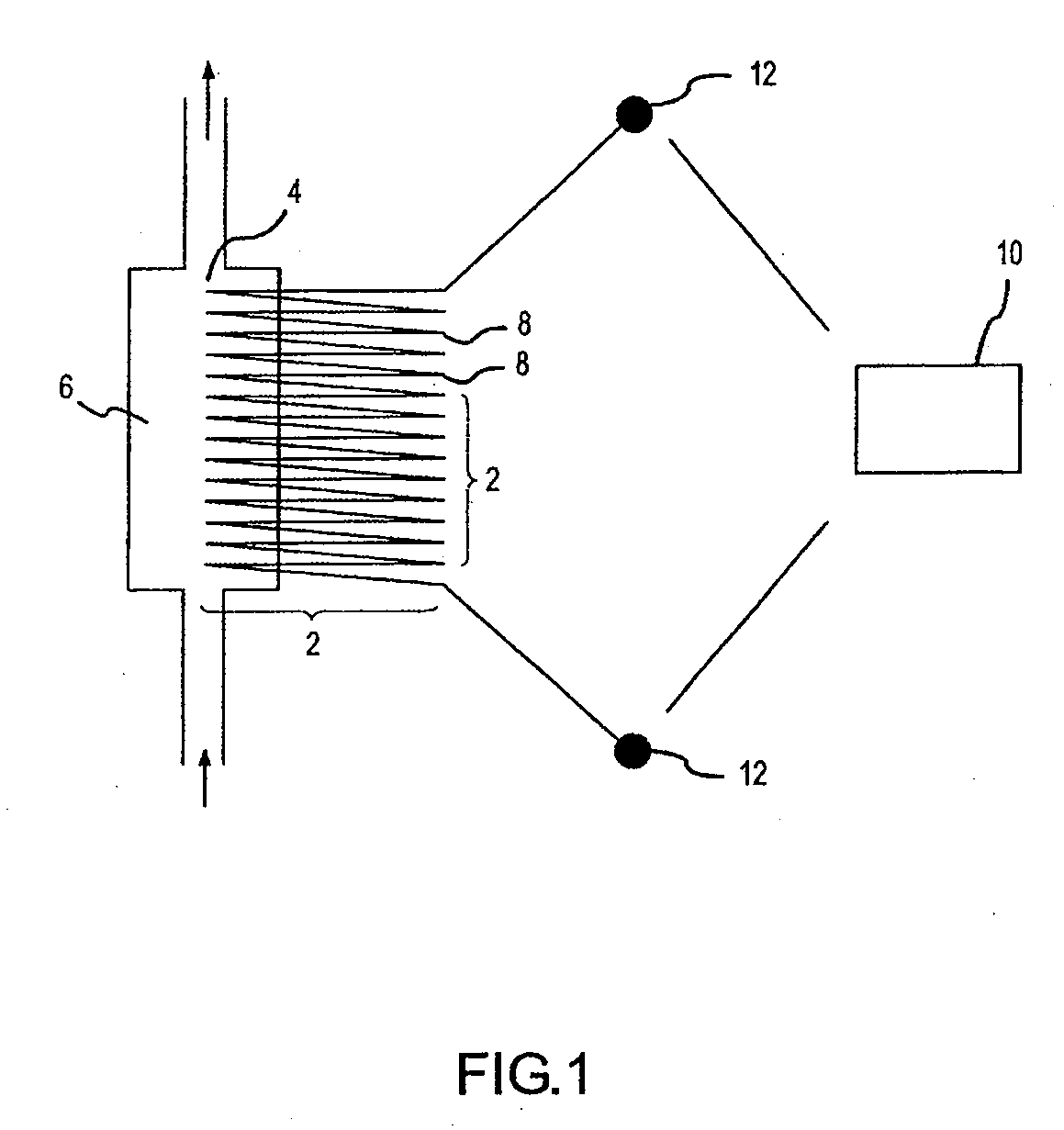
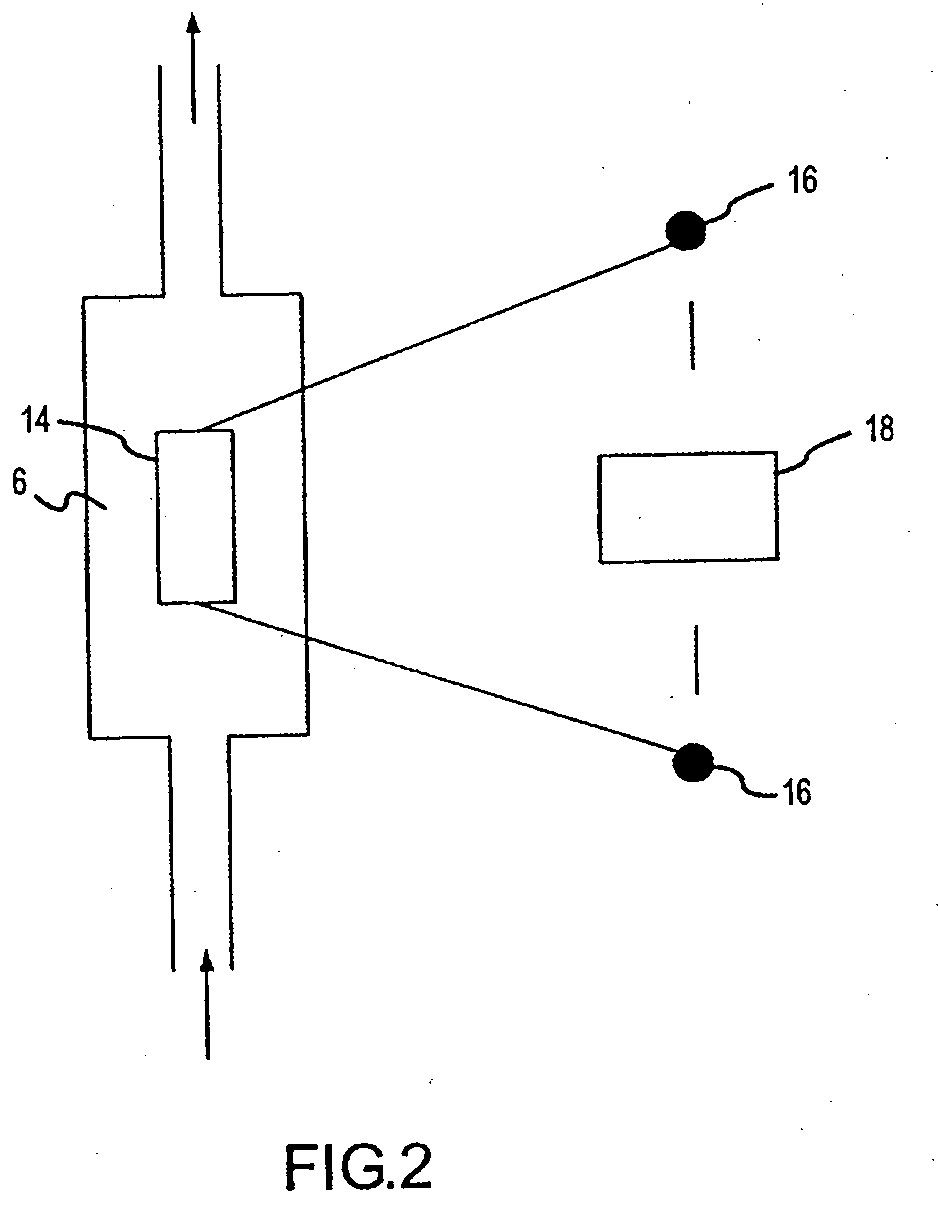
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
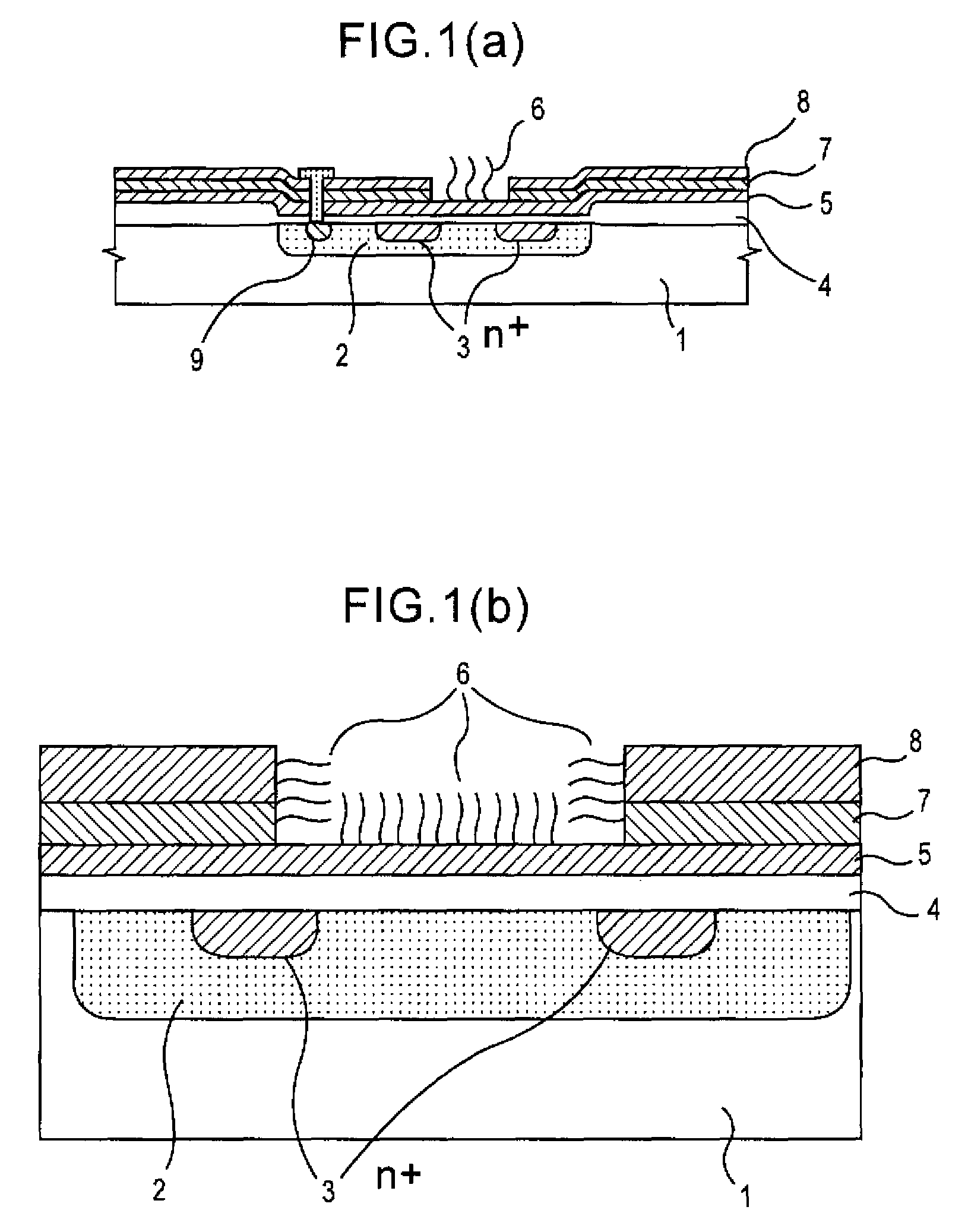
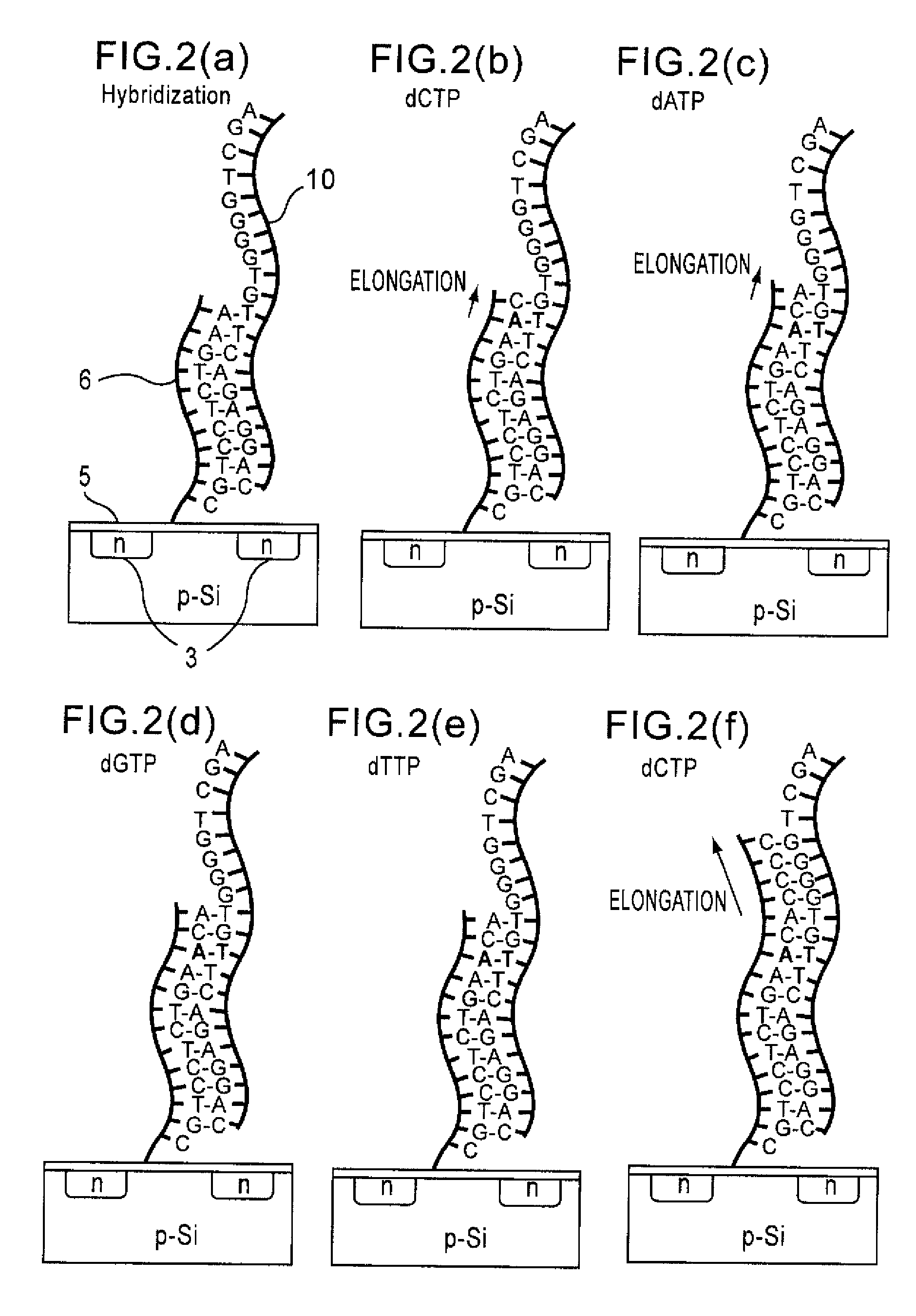
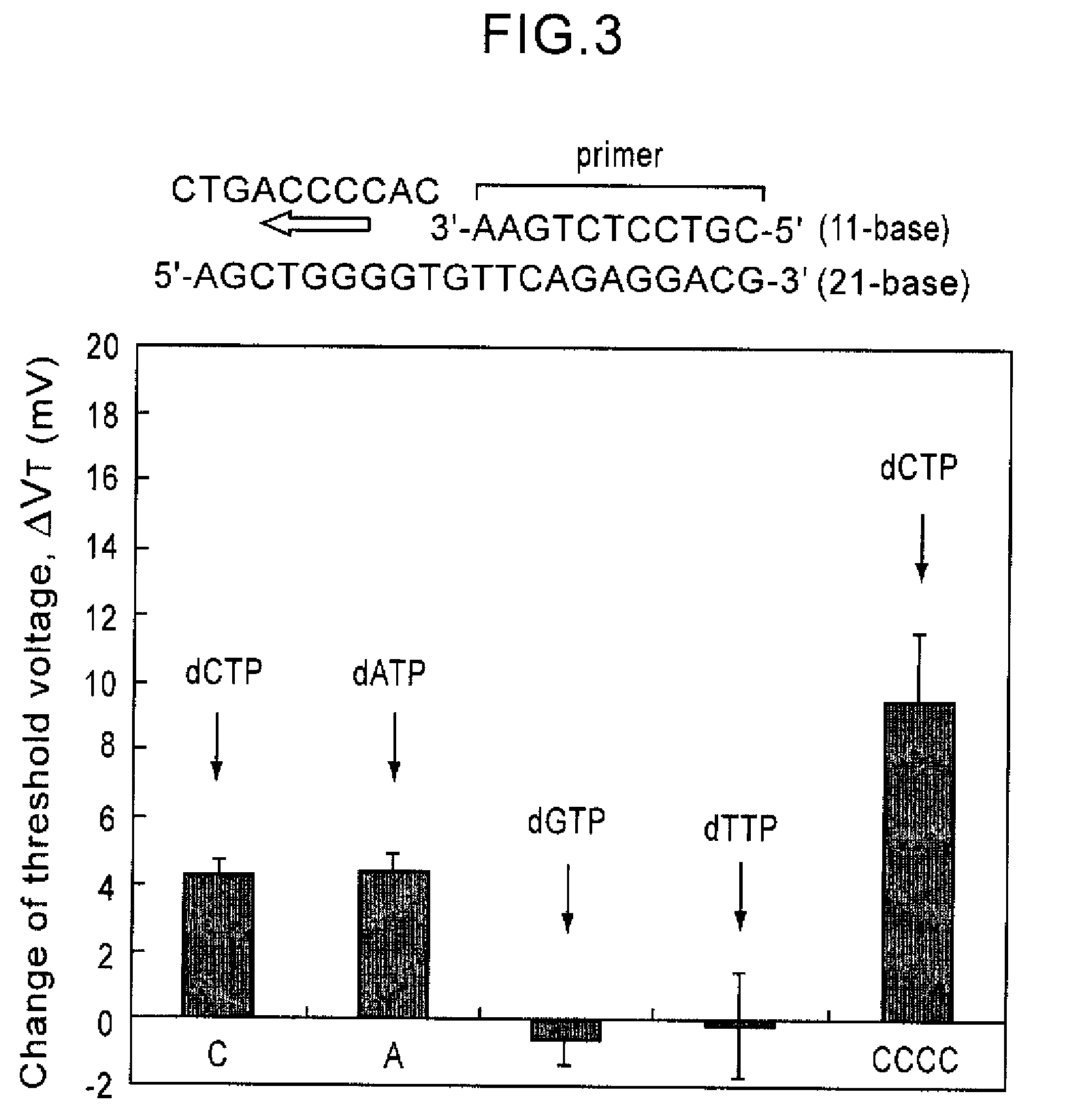
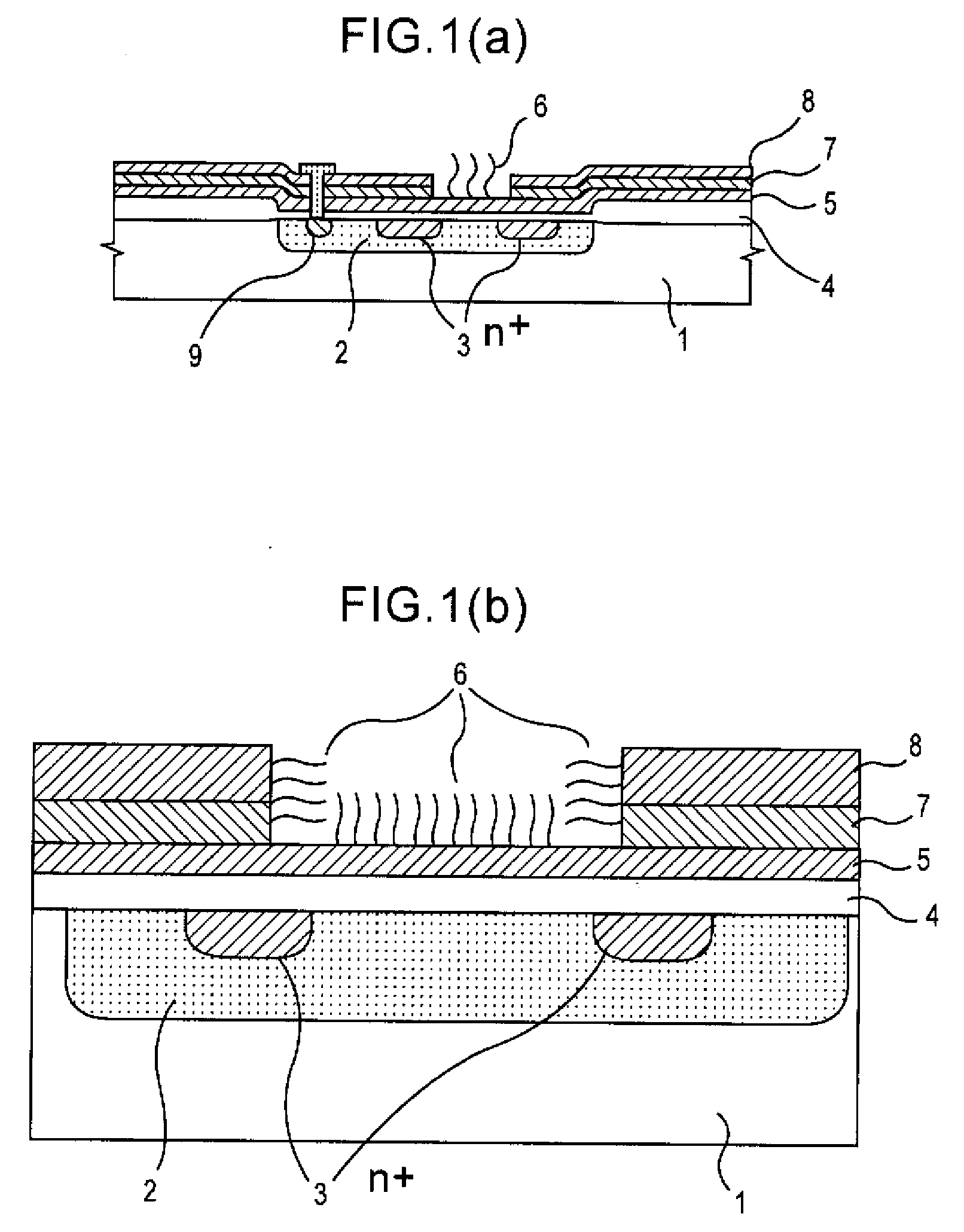
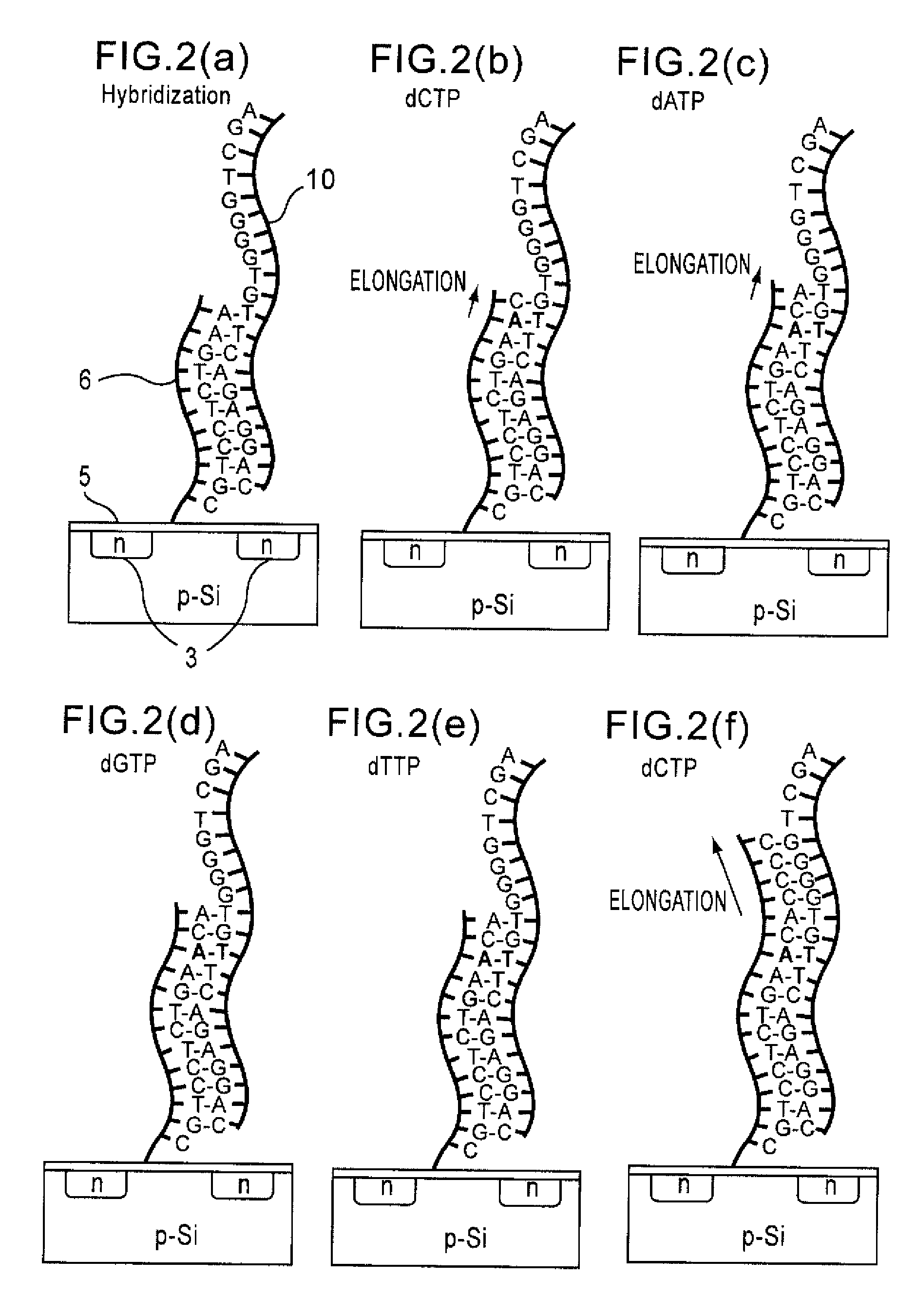
Method of analyzing DNA sequence using field-effect device, and base sequence analyzer
ActiveUS7888013B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
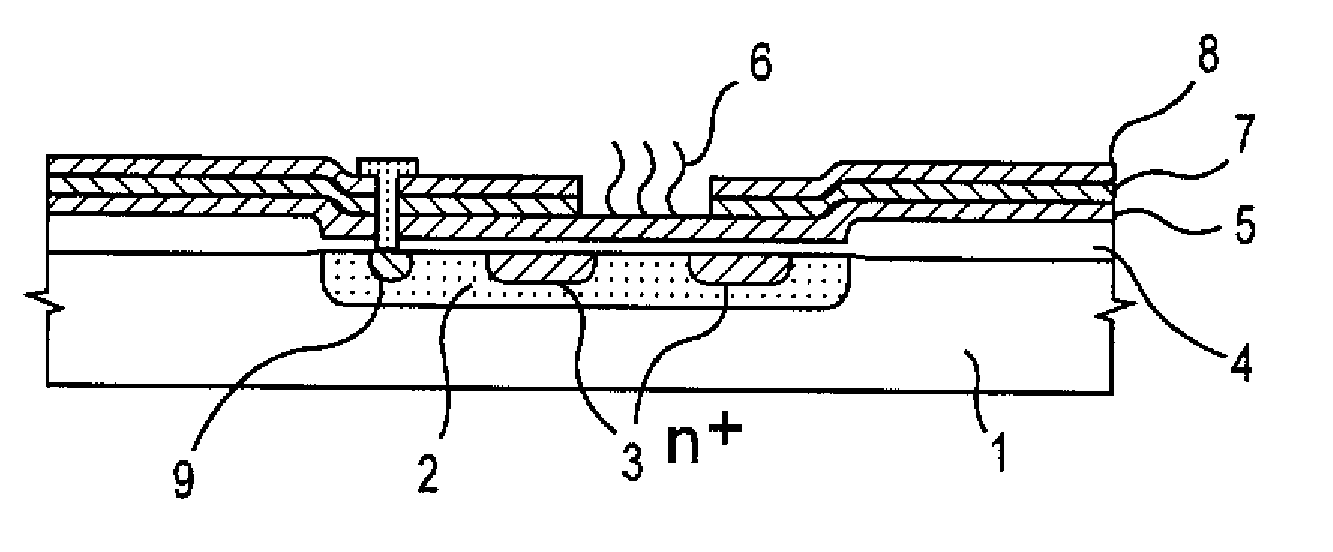
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
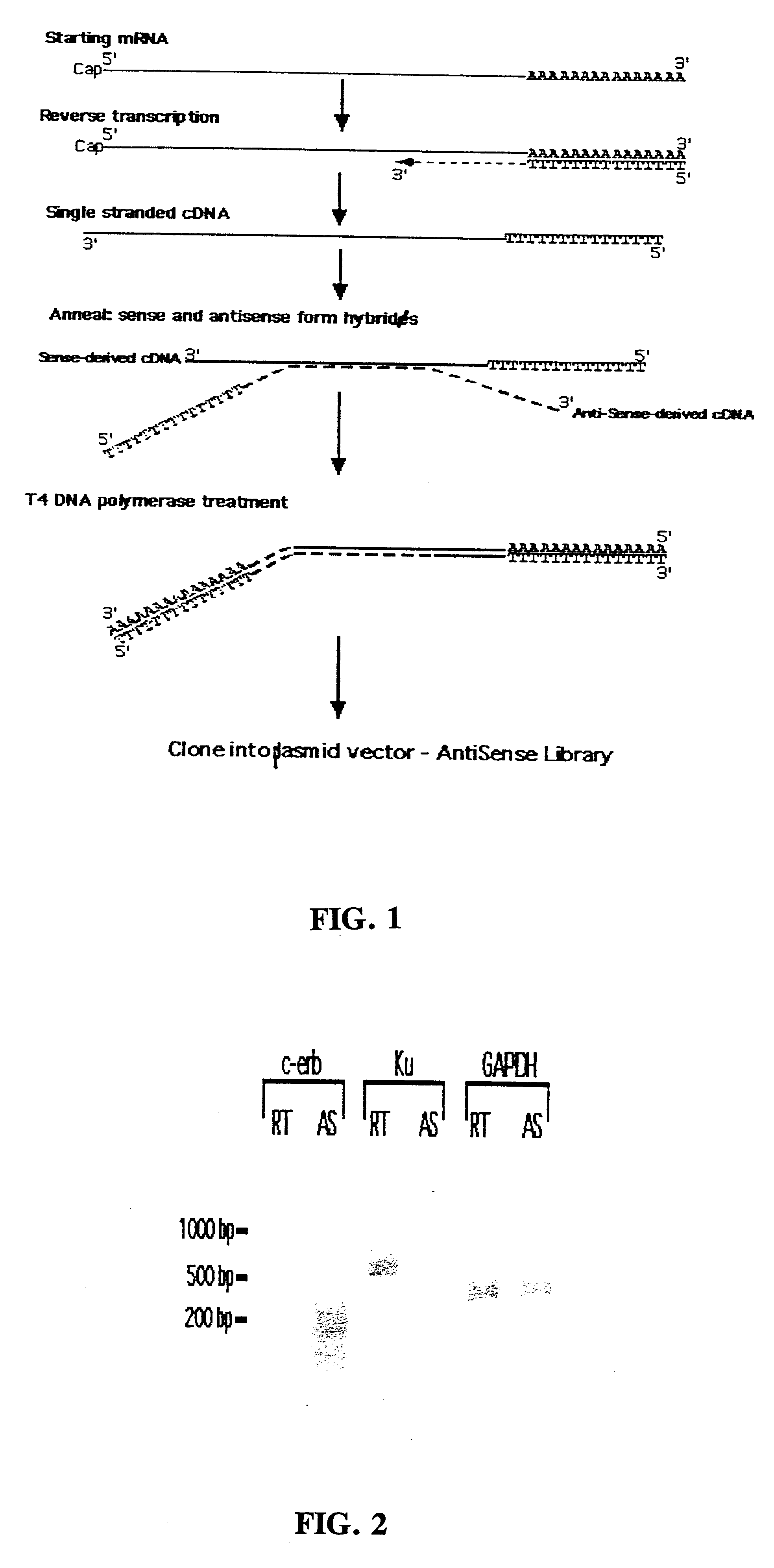
Method for enrichment of natural antisense messenger RNA
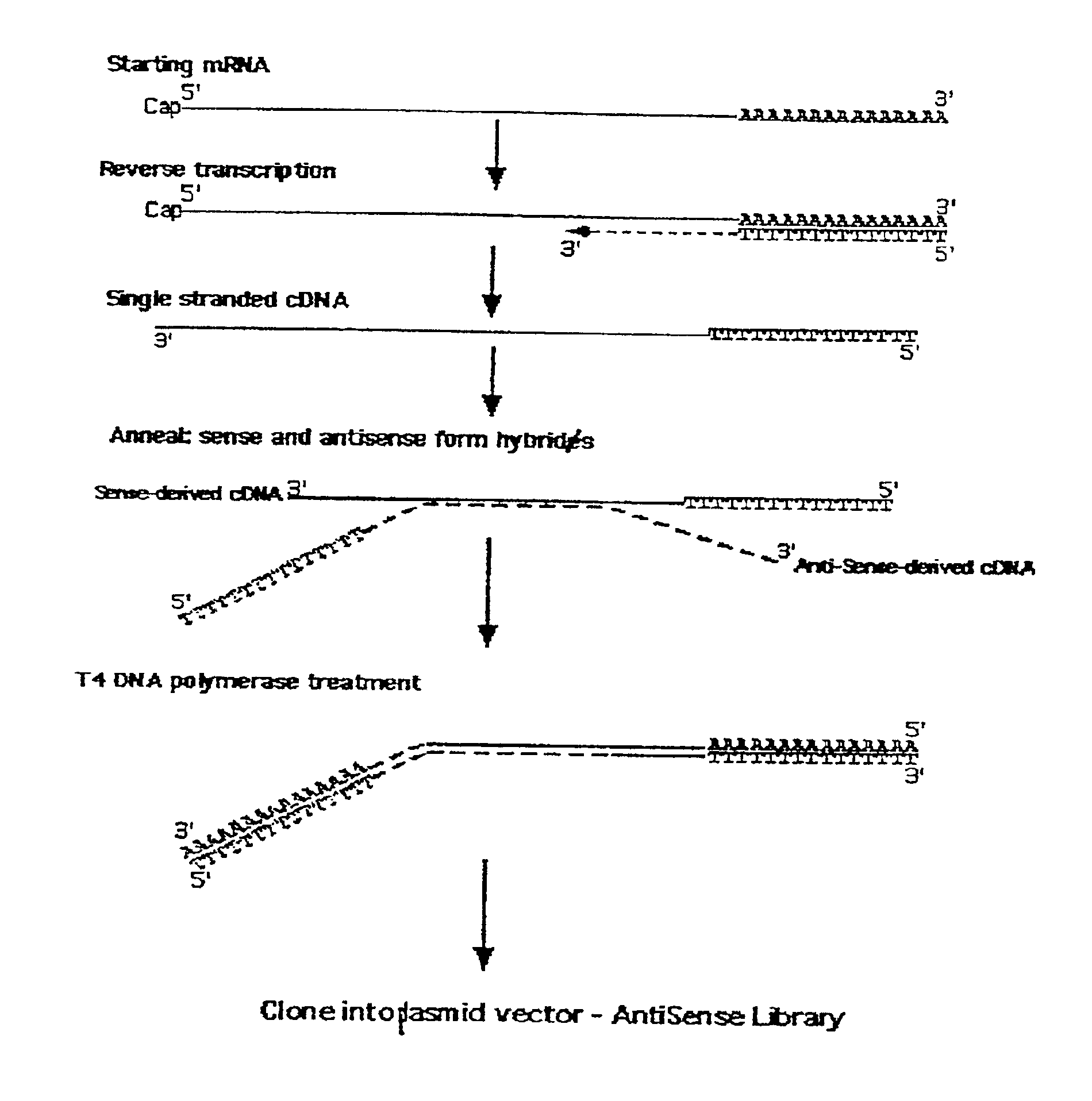
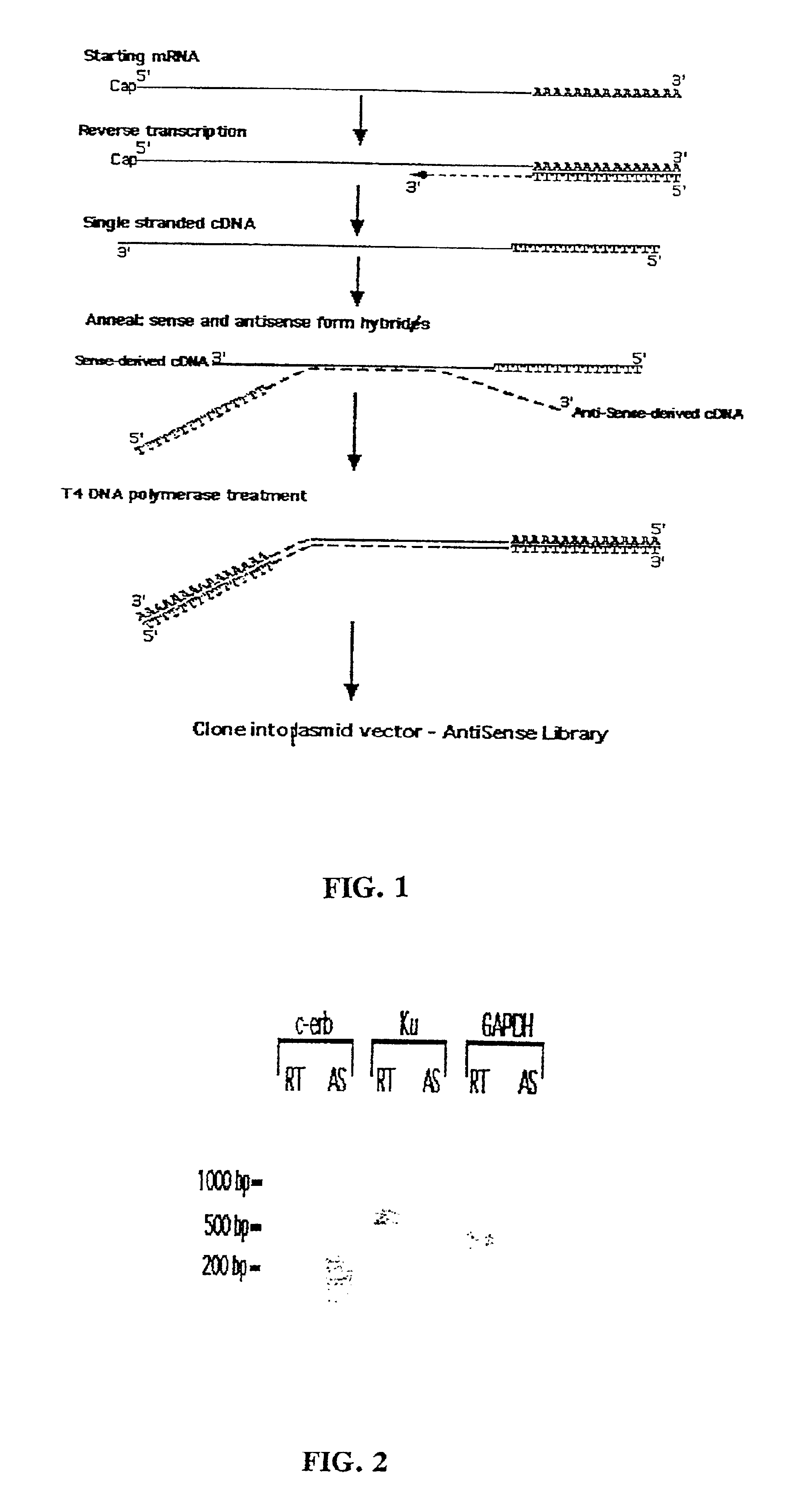
A method for enrichment of natural antisense mRNA which involves hybridization of cDNA obtained from sense RNA with cDNA obtained from antisense RNA, followed by DNA polymerase treatment of the sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecule. A natural antisense library can be generated by cloning of sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecules in a vector.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
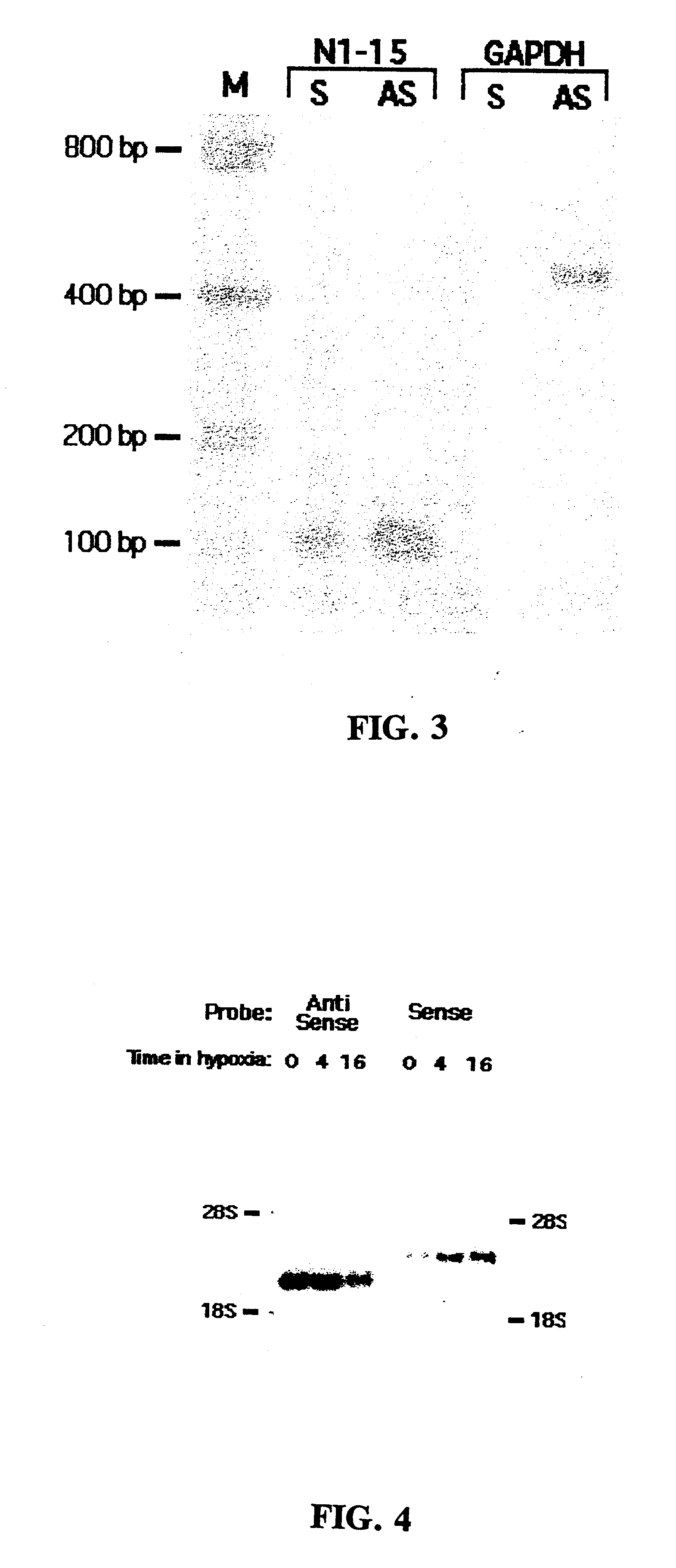
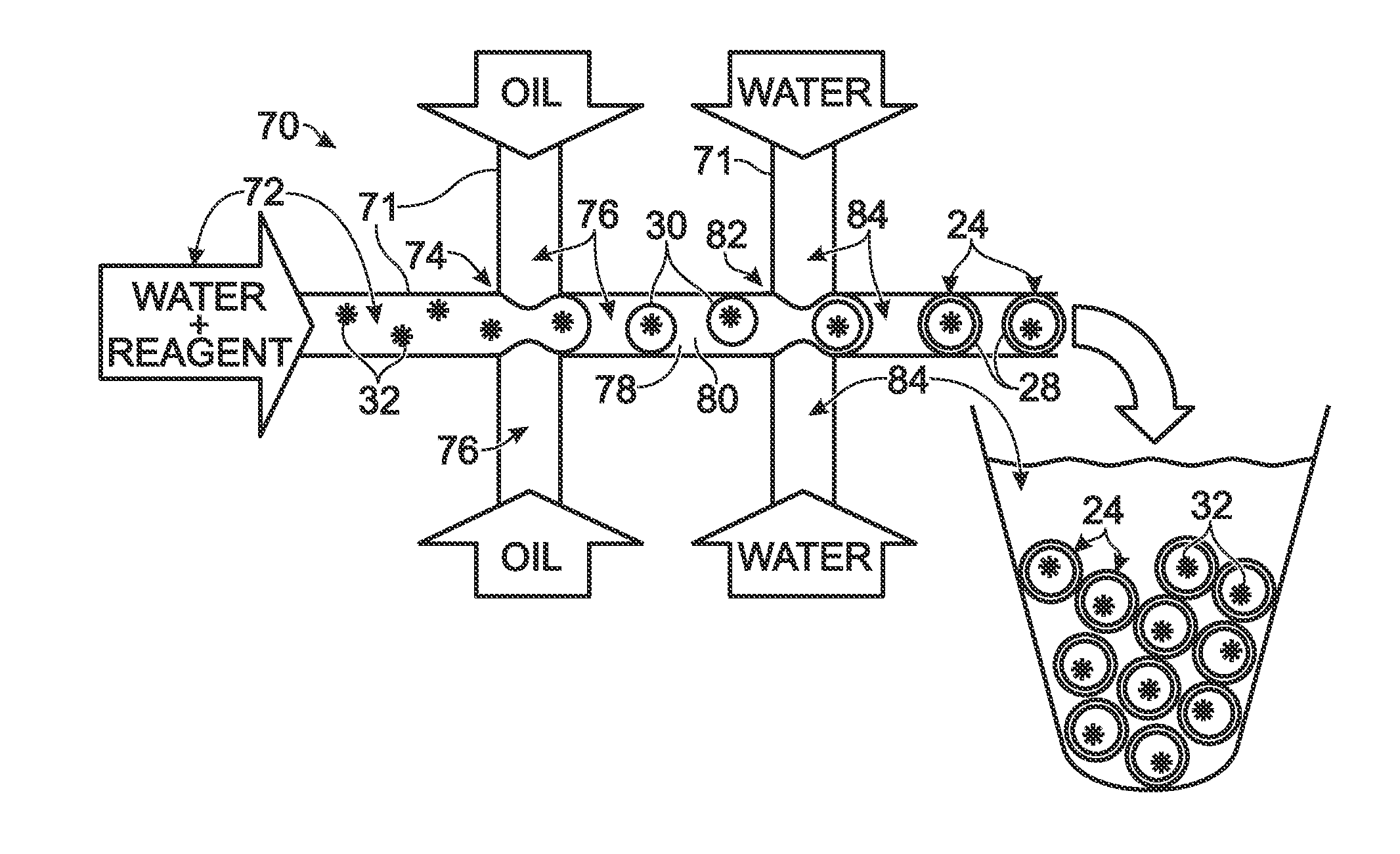
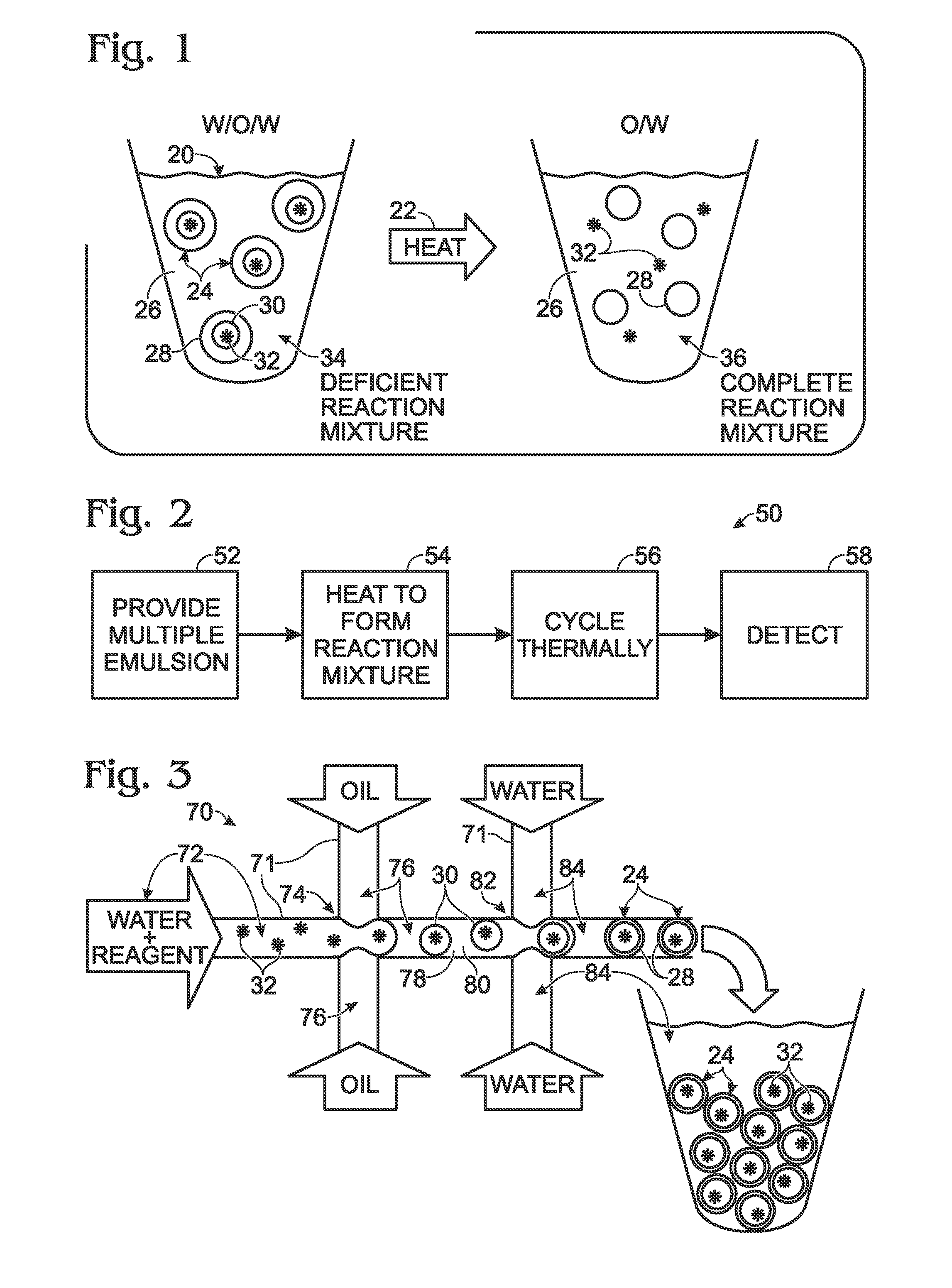
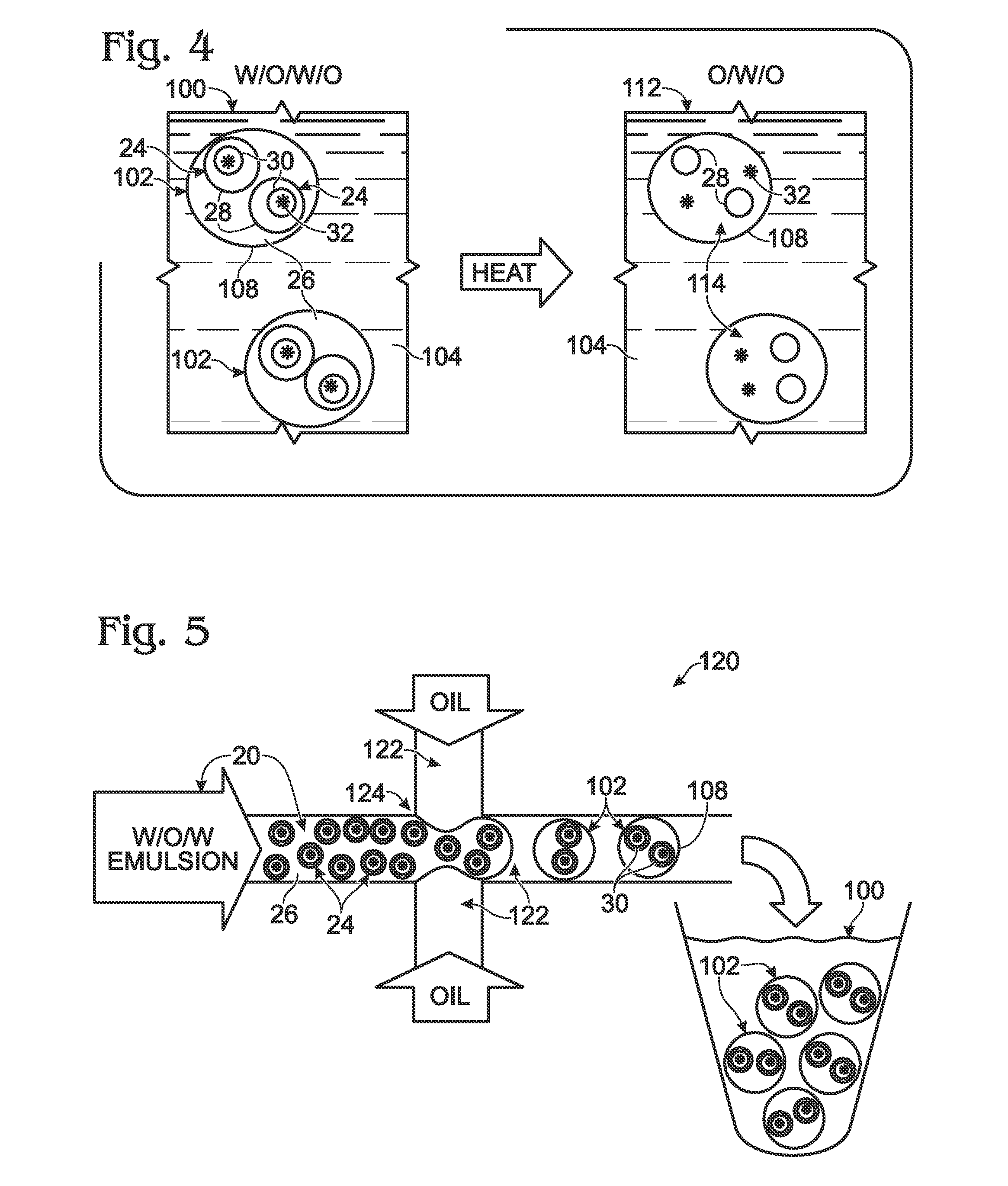
System for hot-start amplification via a multiple emulsion
System, including methods, apparatus, compositions, and kits, for making and using compound droplets of a multiple emulsion to supply an amplification reagent, such as a heat-stable DNA polymerase or DNA ligase, to an aqueous phase in which the compound droplets are disposed. The compound droplets may be induced to supply the amplification reagent by heating the multiple emulsion, to achieve hot-start amplification.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Helicase-dependent amplification of RNA
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Method of Determining The Nucleotide Sequence of Oligonucleotides and DNA Molecules
InactiveUS20080213770A1Eliminate needHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceOligonucleotide primers
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Analyte detection
A method of characterizing an analyte sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) anchoring the analyte to a nucleic acid template of known sequence; (b) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (c) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (d) detecting the detectable species. The method may include the step of characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection. Also provided are methods of analyzing multiple analytes in a sample, and kits for characterizing analyte samples.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Method for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules and its application
InactiveUS6605428B2Improved and rapid and reliable methodReduction of initial amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
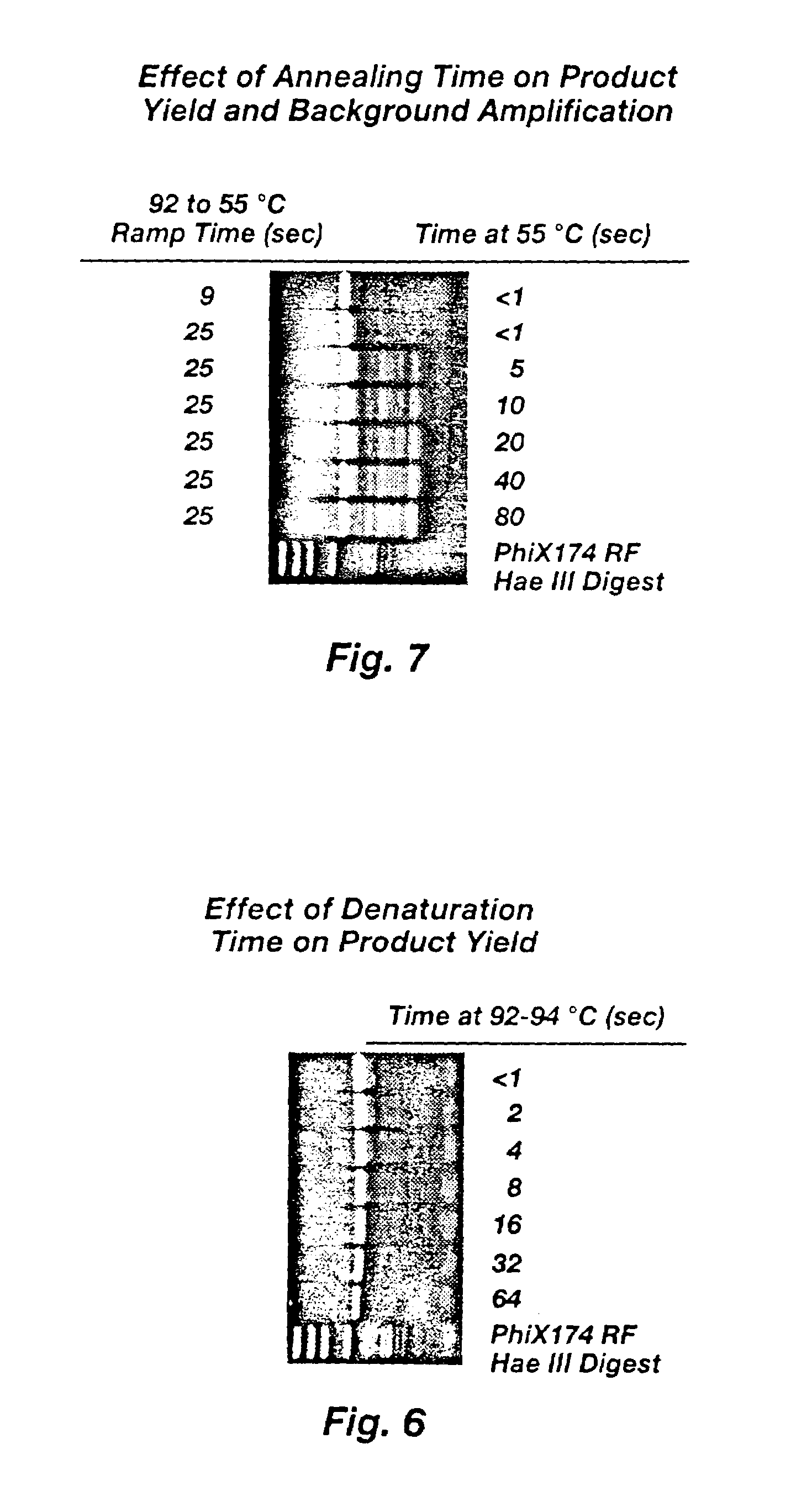
A method is described for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing ("DEXAS") of a DNA molecule from a complex mixture of nucleic acids, wherein truncated DNA molecules as well as DNA molecules of full length are synthesized simultaneously and exponentially between two positions on the said DNA molecule, which initially contains a DNA molecule in a thermocycling reaction, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a thermostable DNA polymerase, a thermostable pyrophosphatase (optionally), deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed using one polymerase having a Tabor-Richardson mutation, or a functional derivative thereof, and reverse transcriptase activity. In a more preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed in one step, in one vessel.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS7875440B2Eliminate needHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide primersFluorescence
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS20050032076A1Eliminate needHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThermopileOligonucleotide primers
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA poly-merase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Stabilized compositions of thermostable DNA polymerase and anionic or zwitterionic detergent
ActiveUS20080145910A1Avoid inactivationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAnionic detergentOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for protecting thermostable DNA polymerase during amplification reactions conducted at a temperature ranging from about 40° C. to greater than 100° C. The composition comprises a thermostable DNA polymerase and an anionic detergent or zwitterionic detergent.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
System and method for fluorescence monitoring
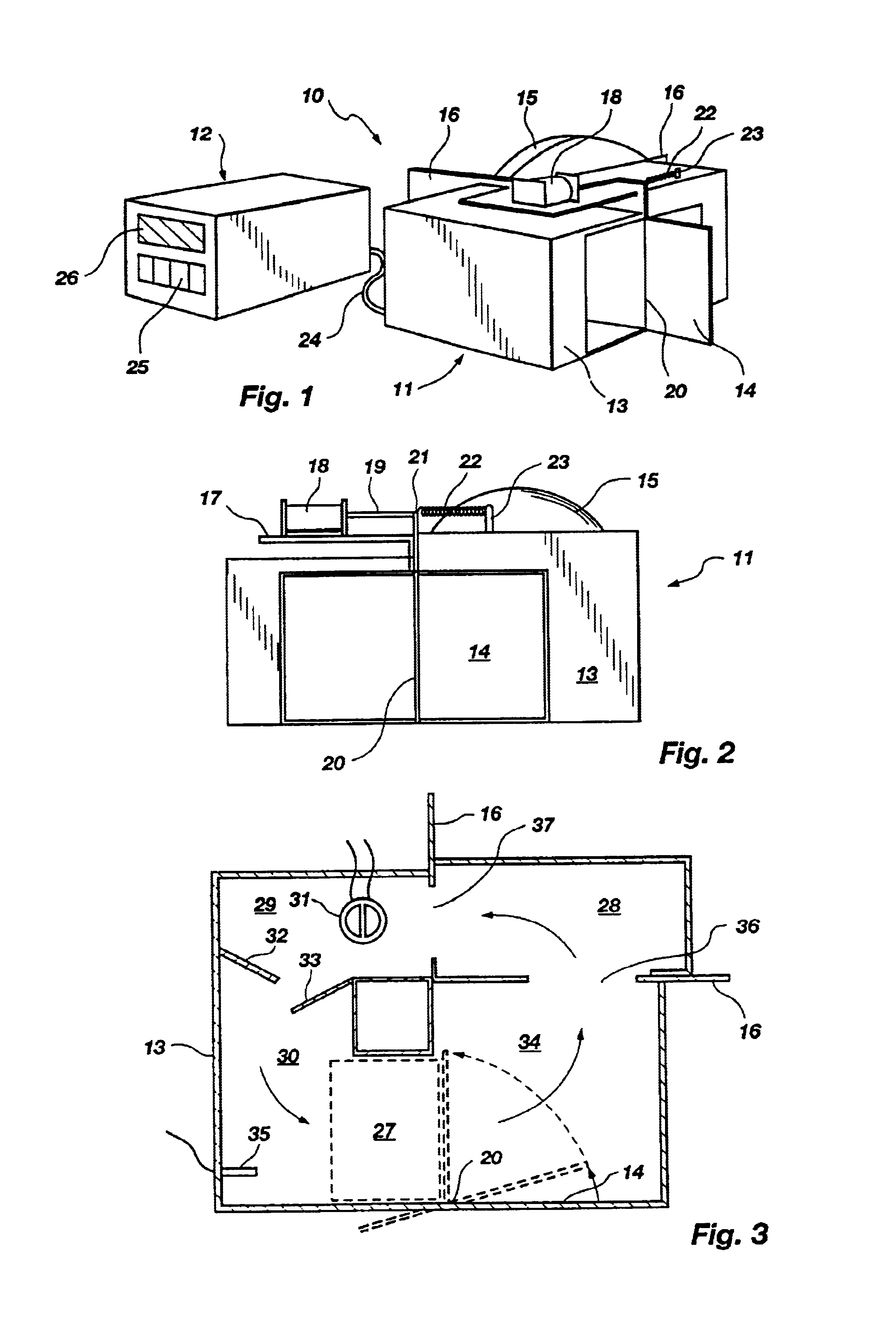
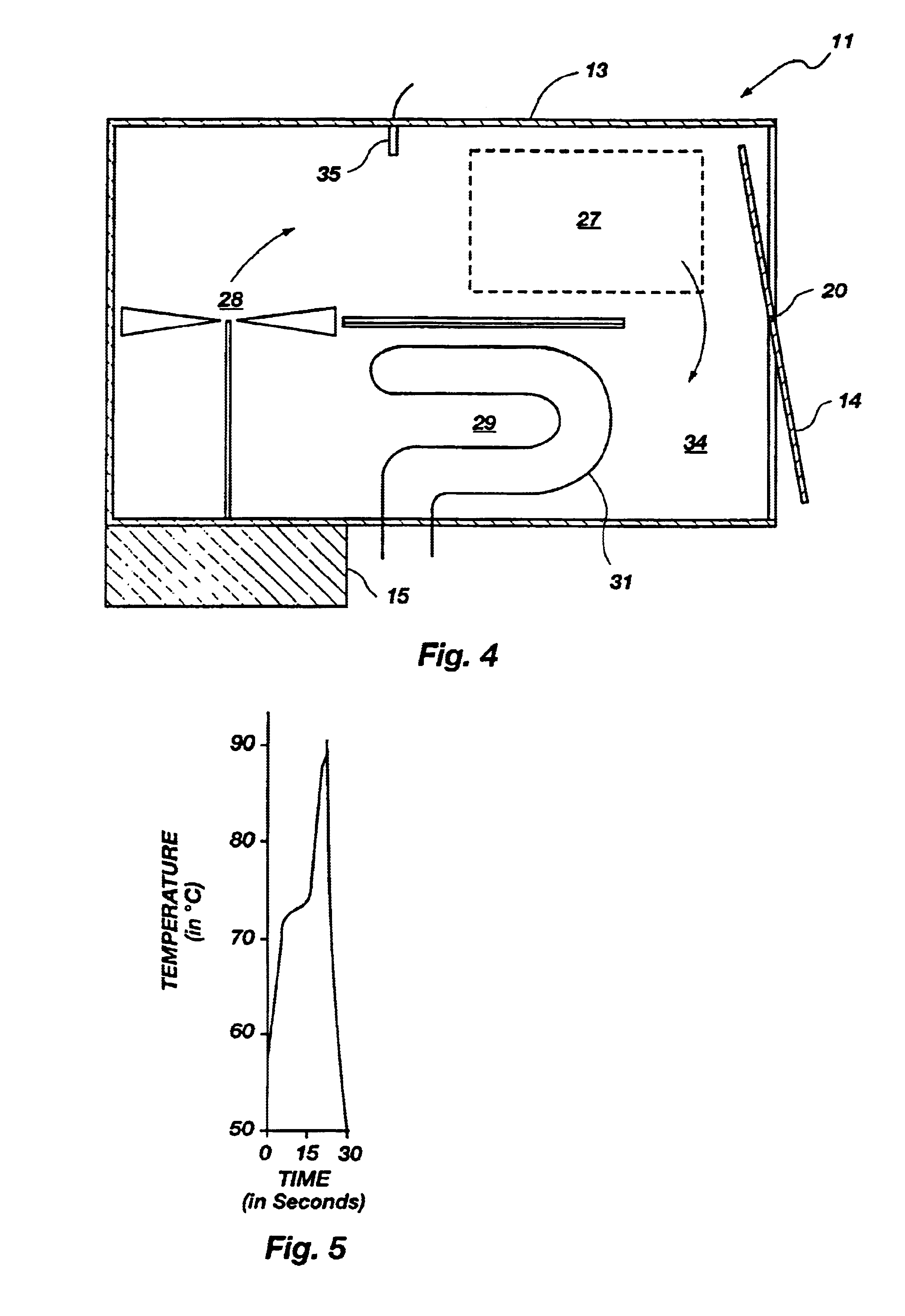
InactiveUS7081226B1Easy to controlHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceDna amplification
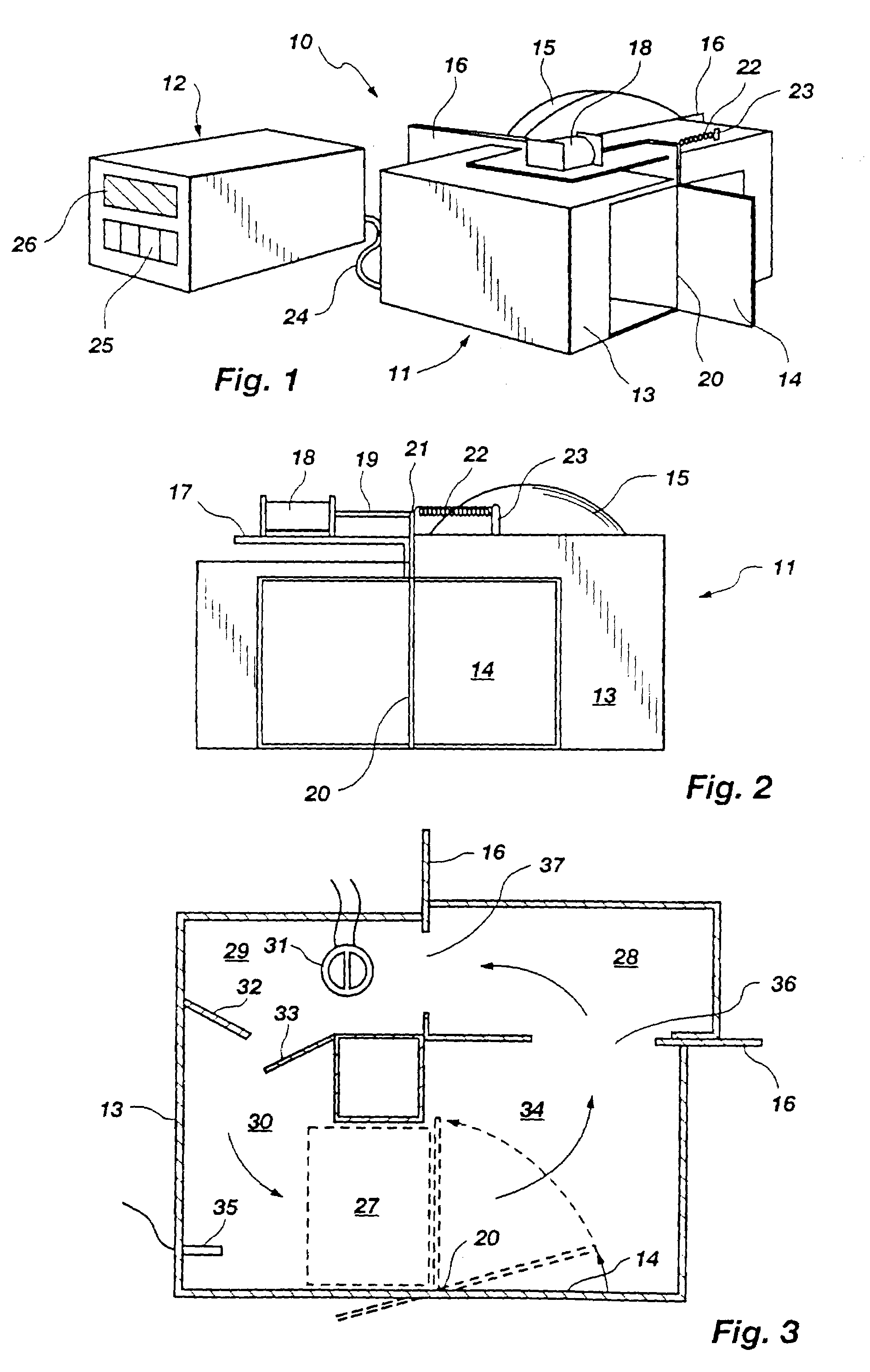
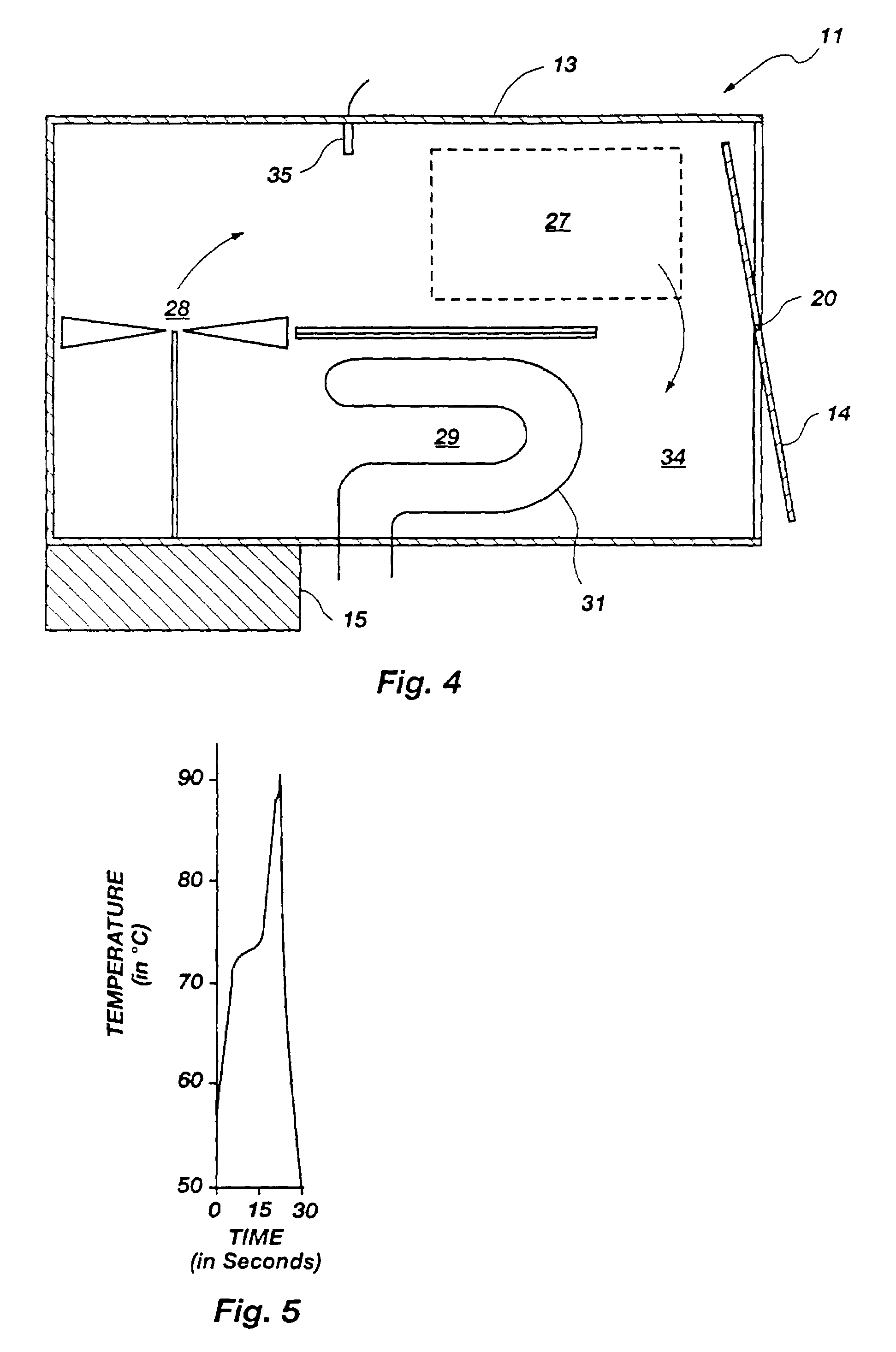
A thermal cycling method and device is disclosed. The device comprises a sample chamber whose temperature can be rapidly and accurately modulated over a range of temperatures needed to carry out a number of biological procedures, such as the DNA polymerase chain reaction. Biological samples are placed in glass micro capillary tubes and then located inside the sample chamber. A programmable controller regulates the temperature of the sample inside the sample chamber. Monitoring of the DNA amplification is monitored by fluorescence once per cycle or many times per cycle. The present invention provides that fluorescence monitoring of PCR is a powerful tool for DNA quantification.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method of Analyzing Dna Sequence Using Field-Effect Device, and Base Sequence Analyzer
ActiveUS20080286767A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Enzymes resistant to photodamage
ActiveUS20100093555A1Reduce oxidationImprove the immunitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising modified DNA polymerases that exhibit improved photostability compared to the parental polymerases from which they were derived. Provided are methods for generating enzymes, such as DNA polymerases, with the aforementioned phenotype. Provided are methods of using polymerases with increased resistance to photodamage to make a DNA or to sequence a DNA template.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Reagents for reversibly terminating primer extension
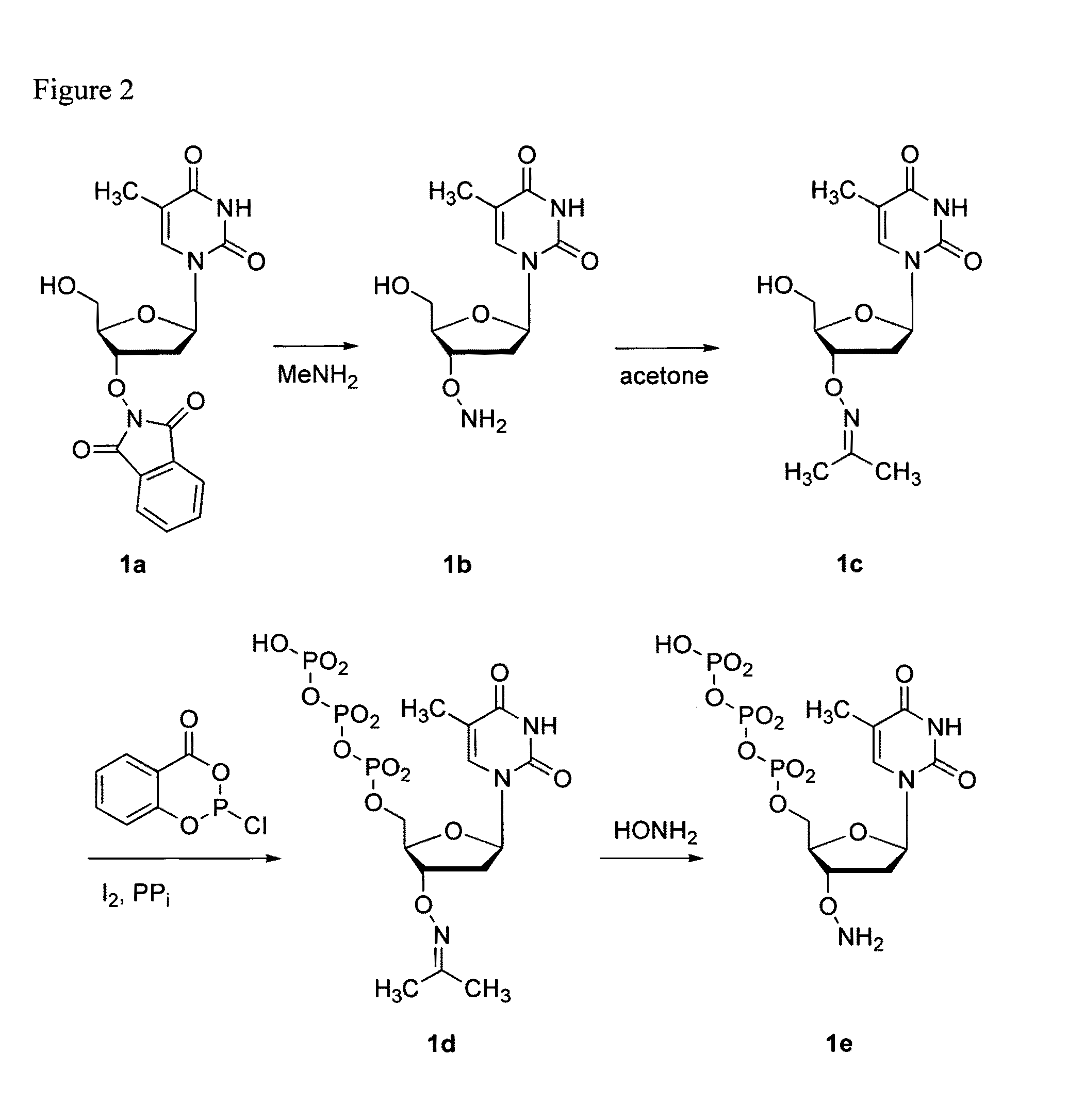
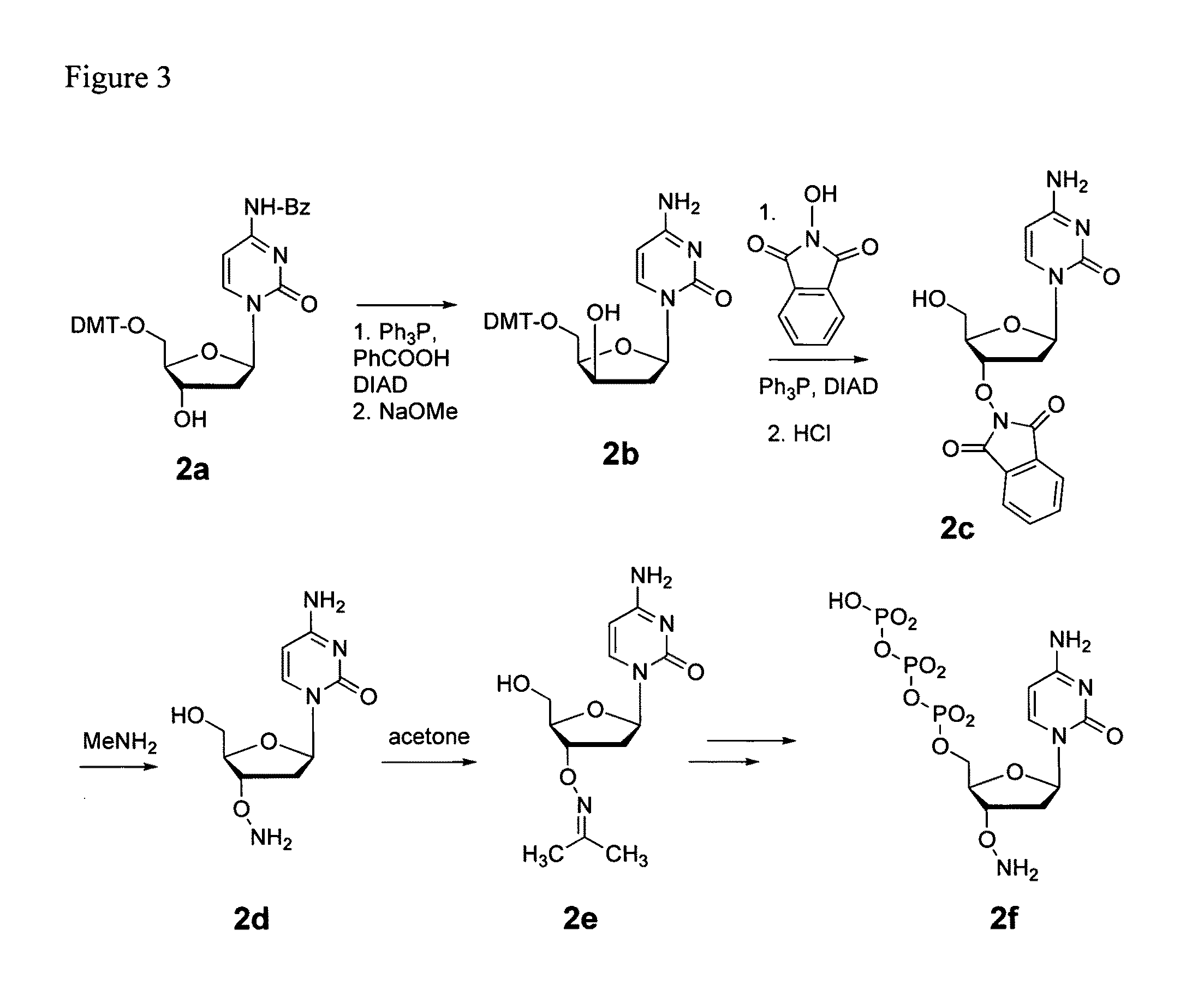
Processes are disclosed that use 3′-reversibly terminated nucleoside triphosphates to analyze DNA for purposes other than sequencing using cyclic reversible termination. These processes are based on the unexpected ability of terminal transferase to accept these triphosphates as substrates, the unexpected ability of polymerases to add reversibly and irreversibly terminated triphosphates in competition with each other, the development of cleavage conditions to remove the terminating group rapidly, in high yield, and without substantial damage to the terminated oligonucleotide product, and the ability of reversibly terminated primer extension products to capture groups. The presently preferred embodiments of the disclosed processes use a triphosphate having its 3′-OH group blocked as a 3′-ONH2 group, which can be removed in buffered NaNO2 and use variants of Taq DNA polymerase, including one that has a replacement (L616A).
Owner:BENNER STEVEN ALBERT +3
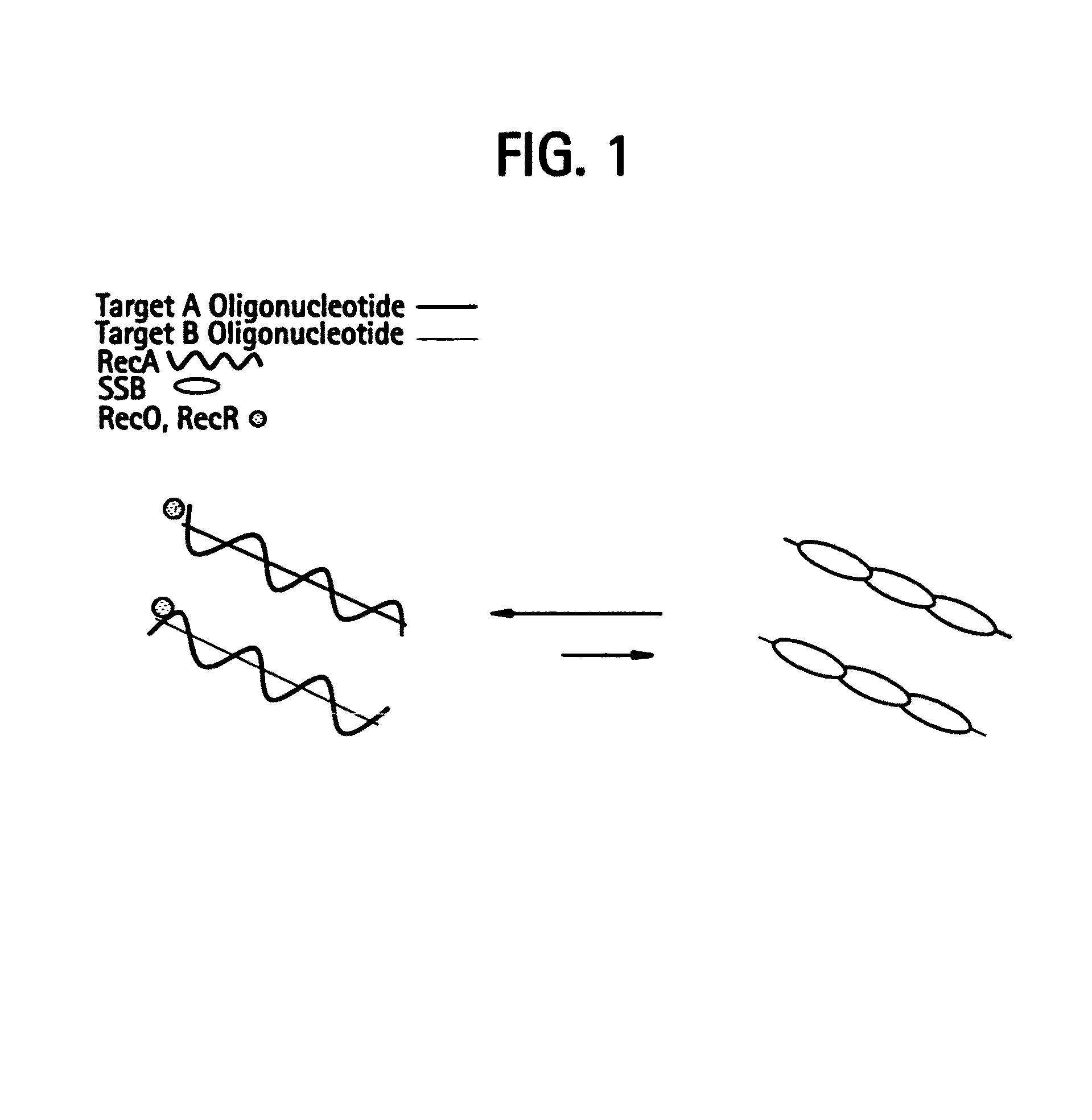
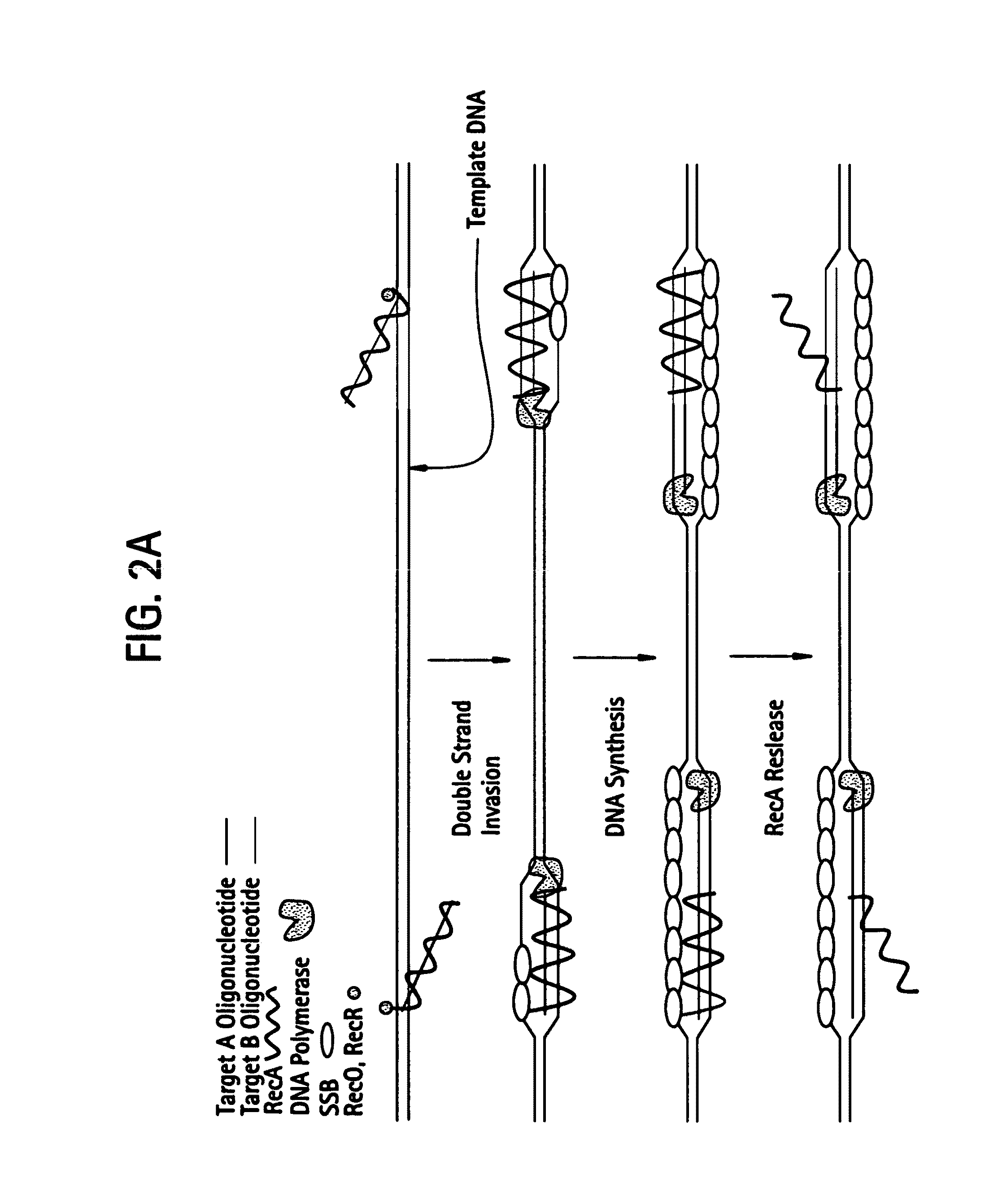
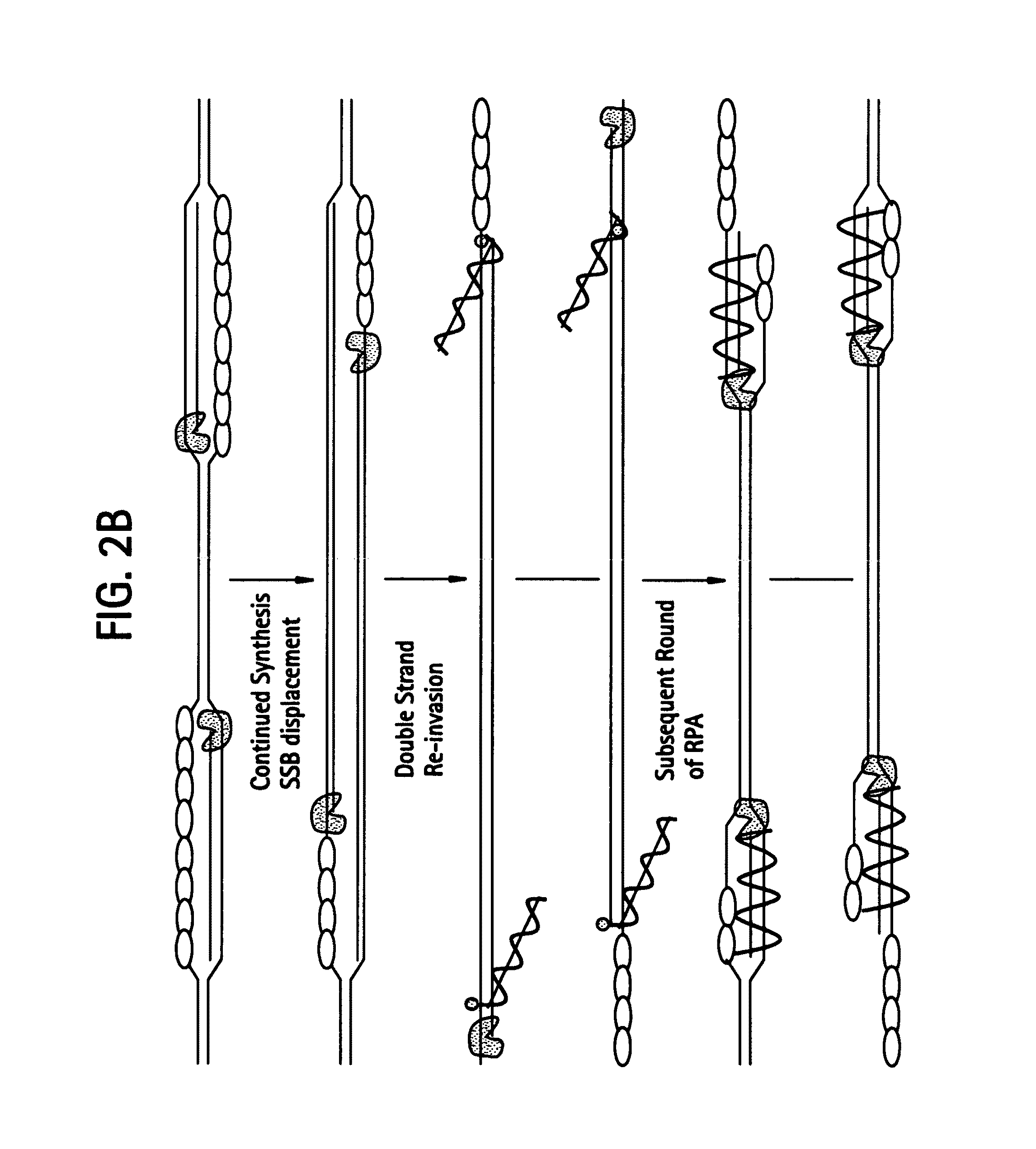
Recombinase polymerase amplification
This disclosure describes related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of recombinase and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods have the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes, thus offering easy and affordable implementation and portability relative to other amplification methods. Further RPA reactions using light and otherwise, methods to determine the nature of amplified species without a need for gel electrophoresis, methods to improve and optimize signal to noise ratios in RPA reactions, methods to optimize oligonucleotide primer function, methods to control carry-over contamination, and methods to employ sequence-specific third ‘specificity’ probes. Further described are novel properties and approaches for use of probes monitored by light in dynamic recombination environments.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
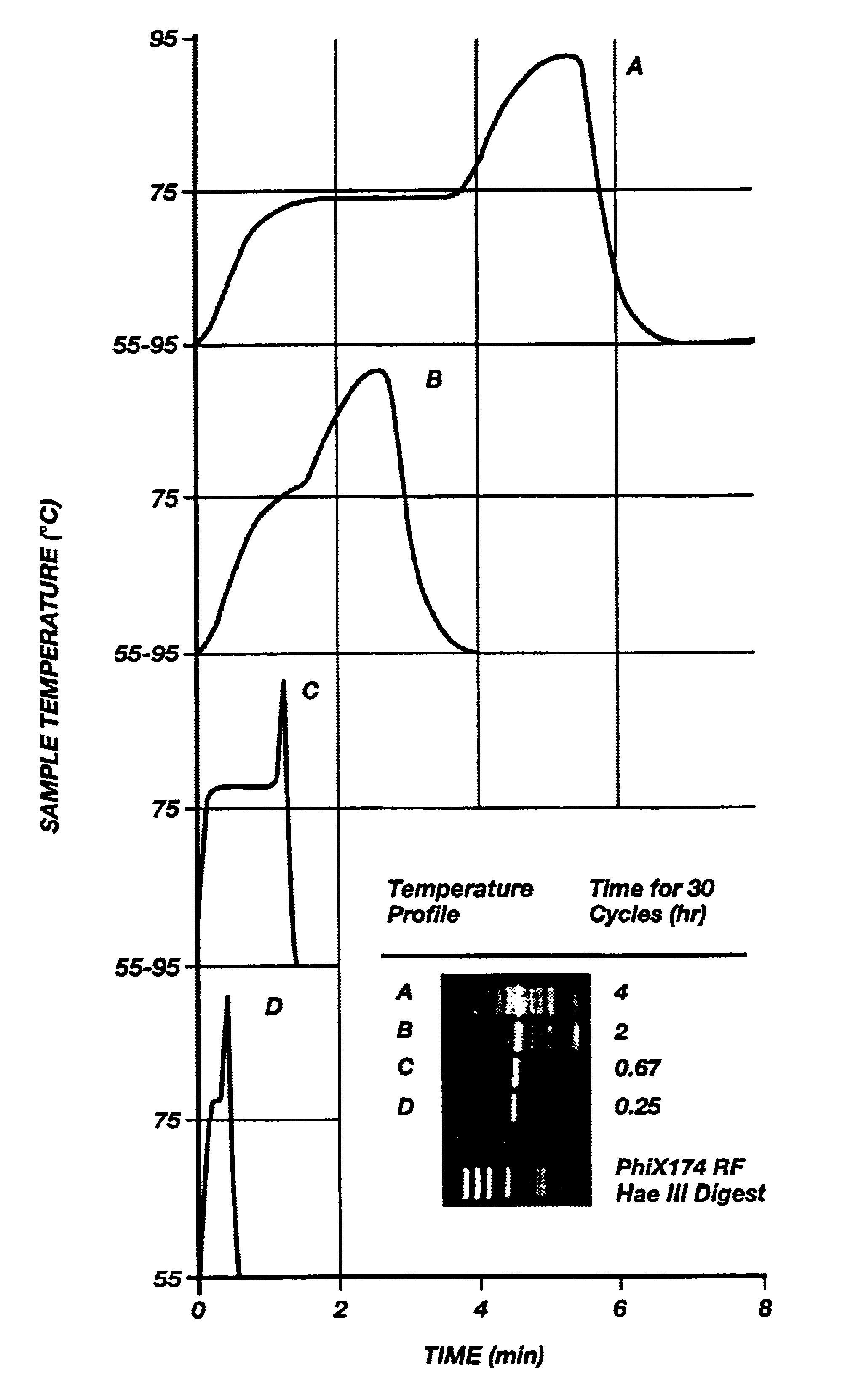
Method for rapid thermal cycling of biological samples
InactiveUS6787338B2Thermal massHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTime profileAmplification dna
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
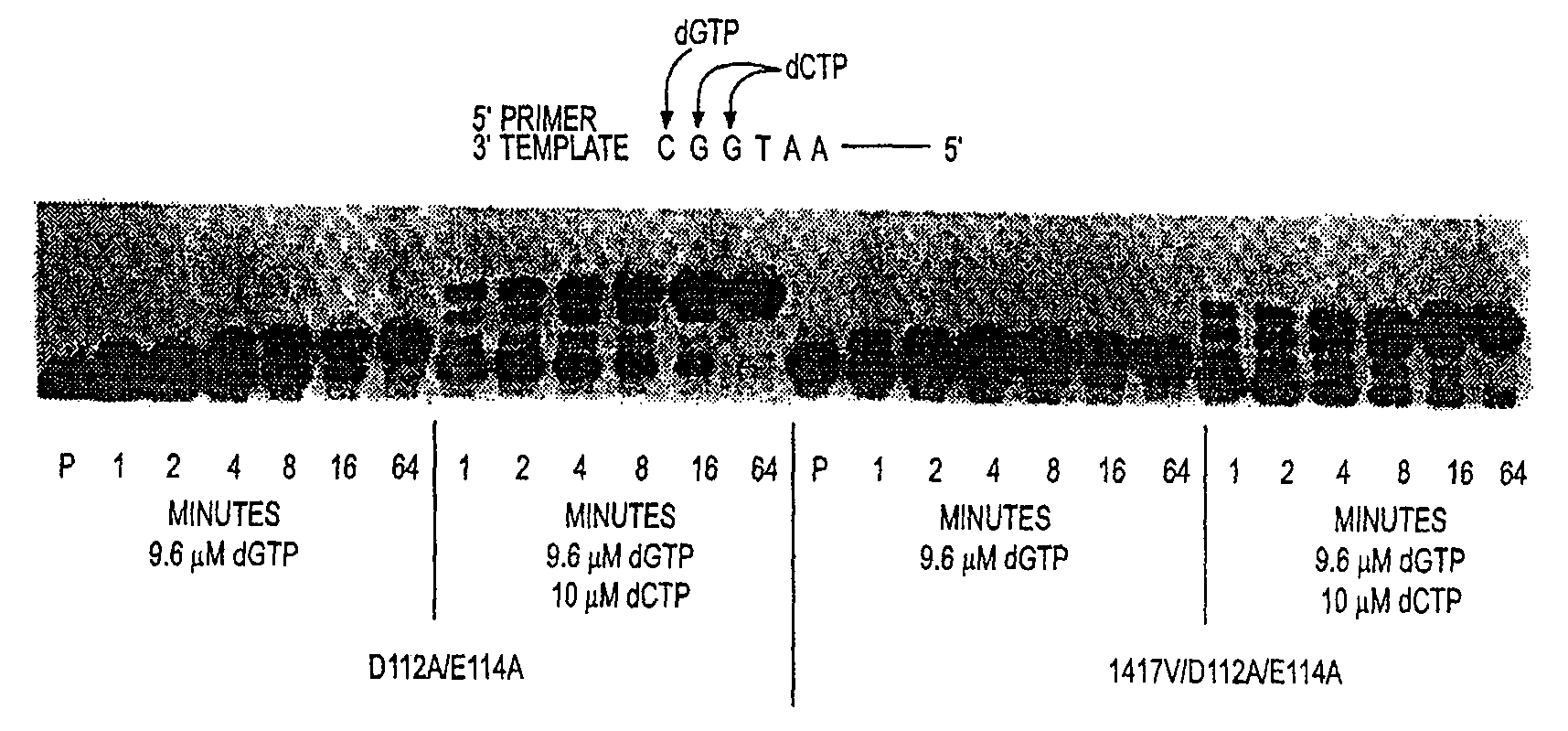
DNA polymerases and related methods
ActiveUS20090148891A1Improved nucleic acid extension rateIncrease chanceBacteriaSugar derivativesPolymerase LDNA polymerase
Disclosed are mutant DNA polymerases having improved extension rates relative to a corresponding, unmodified polymerase. The mutant polymerases are useful in a variety of disclosed primer extension methods. Also disclosed are related compositions, including recombinant nucleic acids, vectors, and host cells, which are useful, e.g., for production of the mutant DNA polymerases.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry
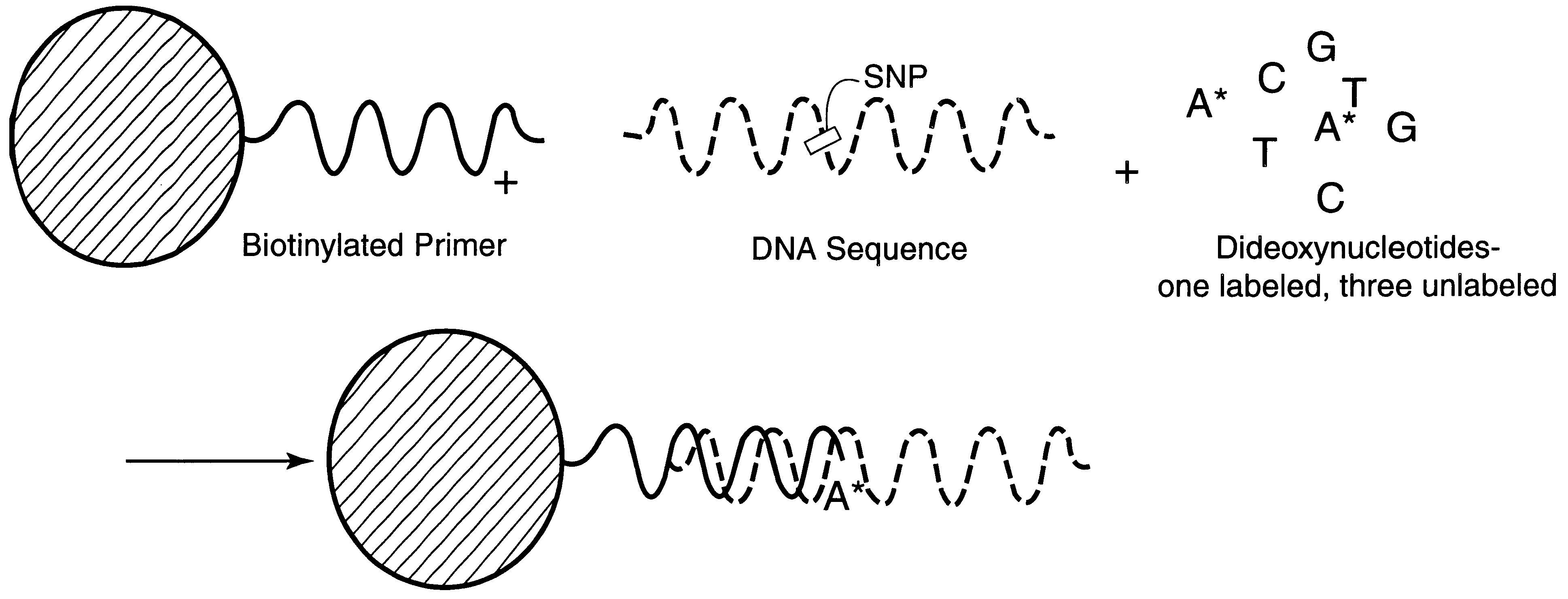
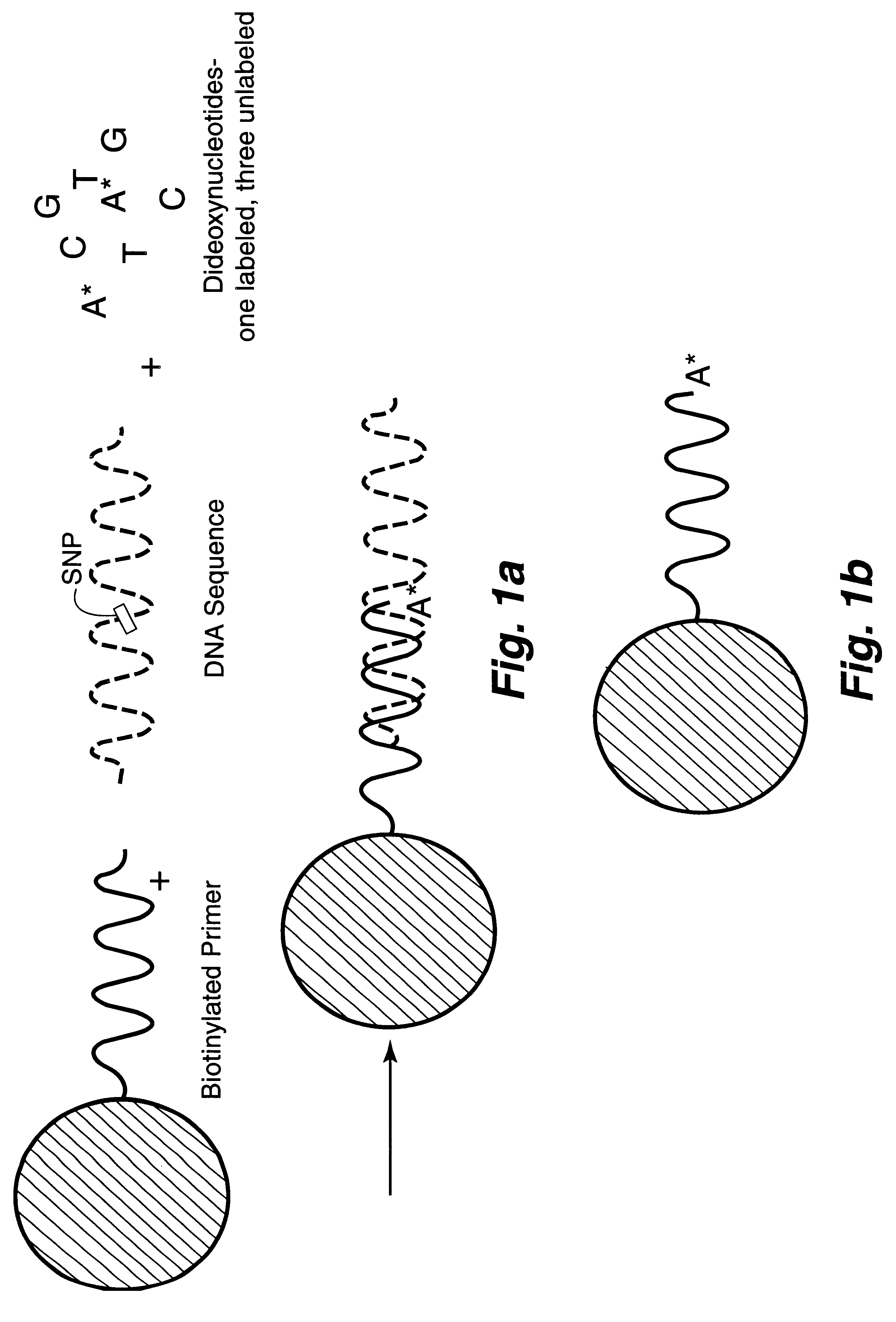
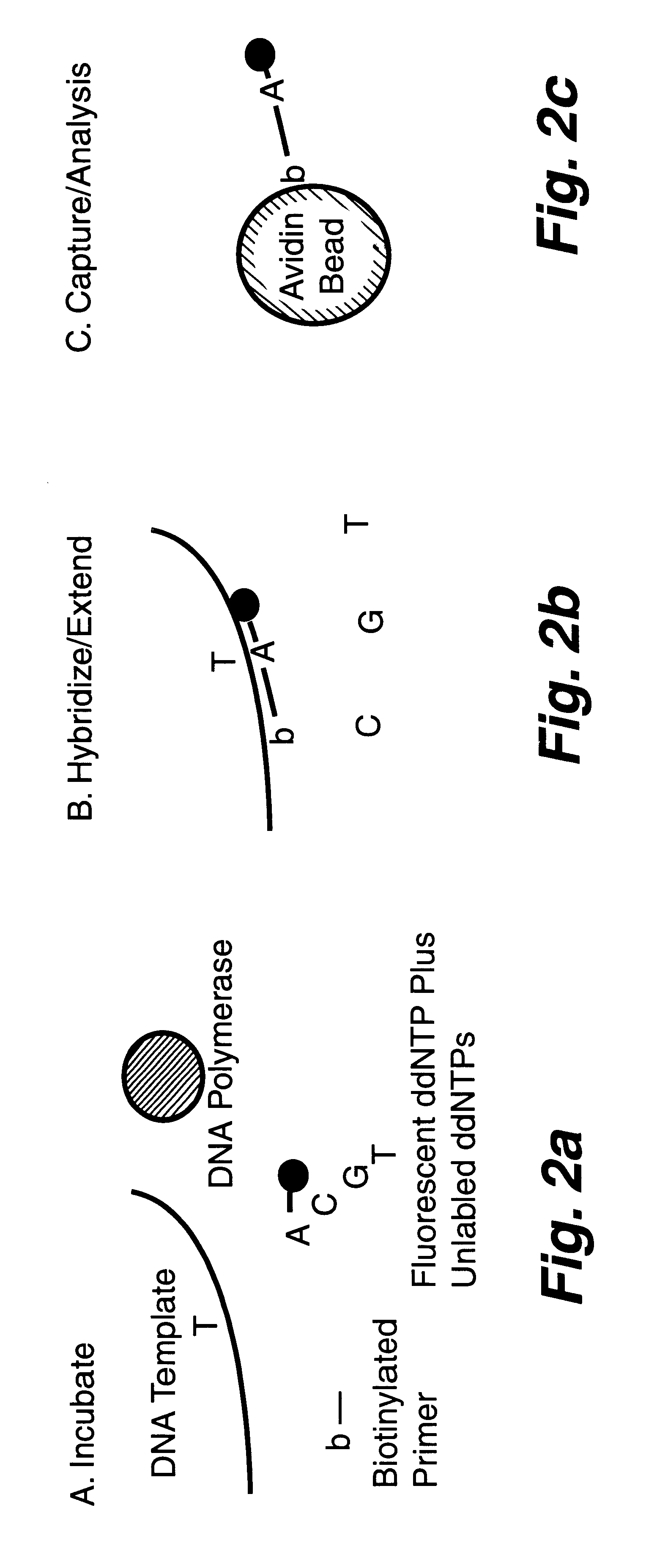
InactiveUS6287766B1Sensitive, homogenous, and flexibleSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry. Primers designed to be immobilized on microspheres are allowed to anneal to the DNA strand under investigation, and are extended by either DNA polymerase using fluorescent dideoxynucleotides or ligated by DNA ligase to fluorescent reporter oligonucleotides. The fluorescence of either the dideoxynucleotide or the reporter oligonucleotide attached to the immobilized primer is measured by flow cytometry, thereby identifying the nucleotide polymorphism on the DNA strand.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for enrichment of natural antisense messenger RNA
A method for enrichment of natural antisense mRNA which involves hybridization of cDNA obtained from sense RNA with cDNA obtained from antisense RNA, followed by DNA polymerase treatment of the sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecule. A natural antisense library can be generated by cloning of sense-antisense hybrid DNA molecules in a vector.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Method of determining the nucleotide sequence of oligonucleotides and DNA molecules
InactiveUS20020137062A1Eliminate needHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyFluorescenceOligonucleotide primers
The present invention relates to a novel method for analyzing nucleic acid sequences based on real-time detection of DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of each of the four nucleotide bases, supplied individually and serially in a microfluidic system, to a reaction cell containing a template system comprising a DNA fragment of unknown sequence and an oligonucleotide primer. Incorporation of a nucleotide base into the template system can be detected by any of a variety of methods including but not limited to fluorescence and chemiluminescence detection. Alternatively, microcalorimetic detection of the heat generated by the incorporation of a nucleotide into the extending template system using thermopile, thermistor and refractive index measurements can be used to detect extension reactions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Polymerase stabilization by polyethoxylated amine surfactants
The present invention provides methods and compositions for protein stabilization, particularly the stabilization of polymerases in aqueous solutions with cationic surfactants. The present invention further provides cationic surfactants, including polyethoxylated amines, that stabilize thermostable and thermolabile enzymes in solution. These surfactants stabilize the activity of various enzymes, including thermostable DNA polymerases, thermolabile DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases.
Owner:PROMEGA
Allele specific primer extension
InactiveUS20040048301A1Rapid rise in fluorescenceEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, an allele specific primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and optionally an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity when the primer is non-hydrolyzable, which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on such detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
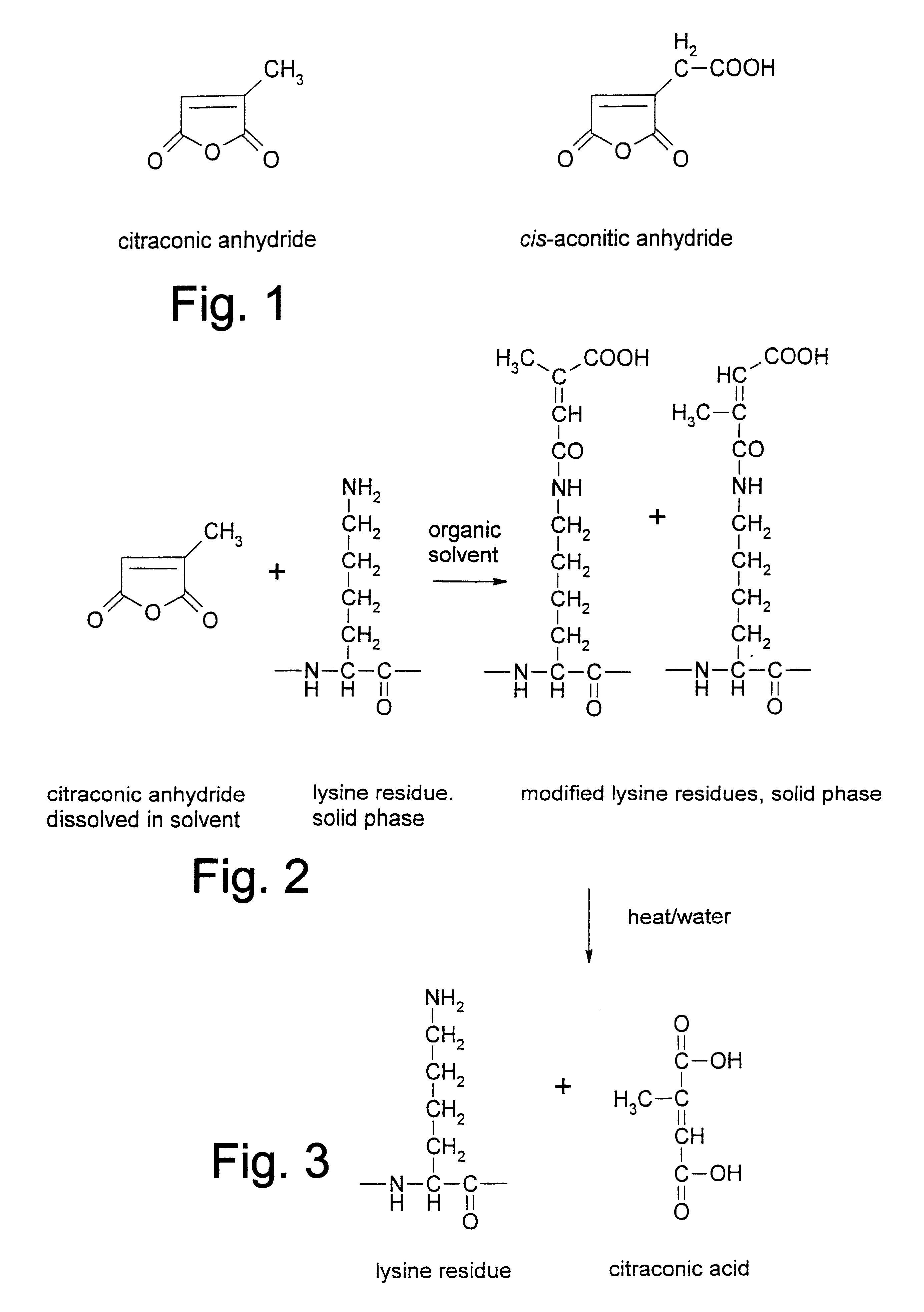
Reversible inactivation enzymes
InactiveUS6479264B1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsOrganic solventDicarboxylic acid
A method for reversibly inactivating thermostable DNA polymerase or ligase, which method comprises reacting a mixture of the thermostable DNA polymerase or ligase with a dicarboxylic acid anhydride, wherein the reaction is carried out using a dried DNA polymerase or ligase in an anhydrous aprotic organic solvent, the dicarboxylic acid anhydride being also substantially anhydrous, whereby the reaction results in essentially complete inactivation of enzyme activity.
Owner:ADVANCED BIOTECHNOLOGIES LTD
Composition and method for hot start nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS20030119150A1Good choiceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyPolymerase L
The present invention is directed to a new composition for performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction comprising (i) a thermostable DNA-Polymerase, (ii) a thermostable 3'-5' Exonuclease, and (iii) at least one primer for nucleic acid amplification with a modified 3' terminal residue which is not elongated by said thermostable DNA-Polymerase as well as methods for performing a PCR reaction using this composition. Furthermore, the method is directed to kits comprising such a composition.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com