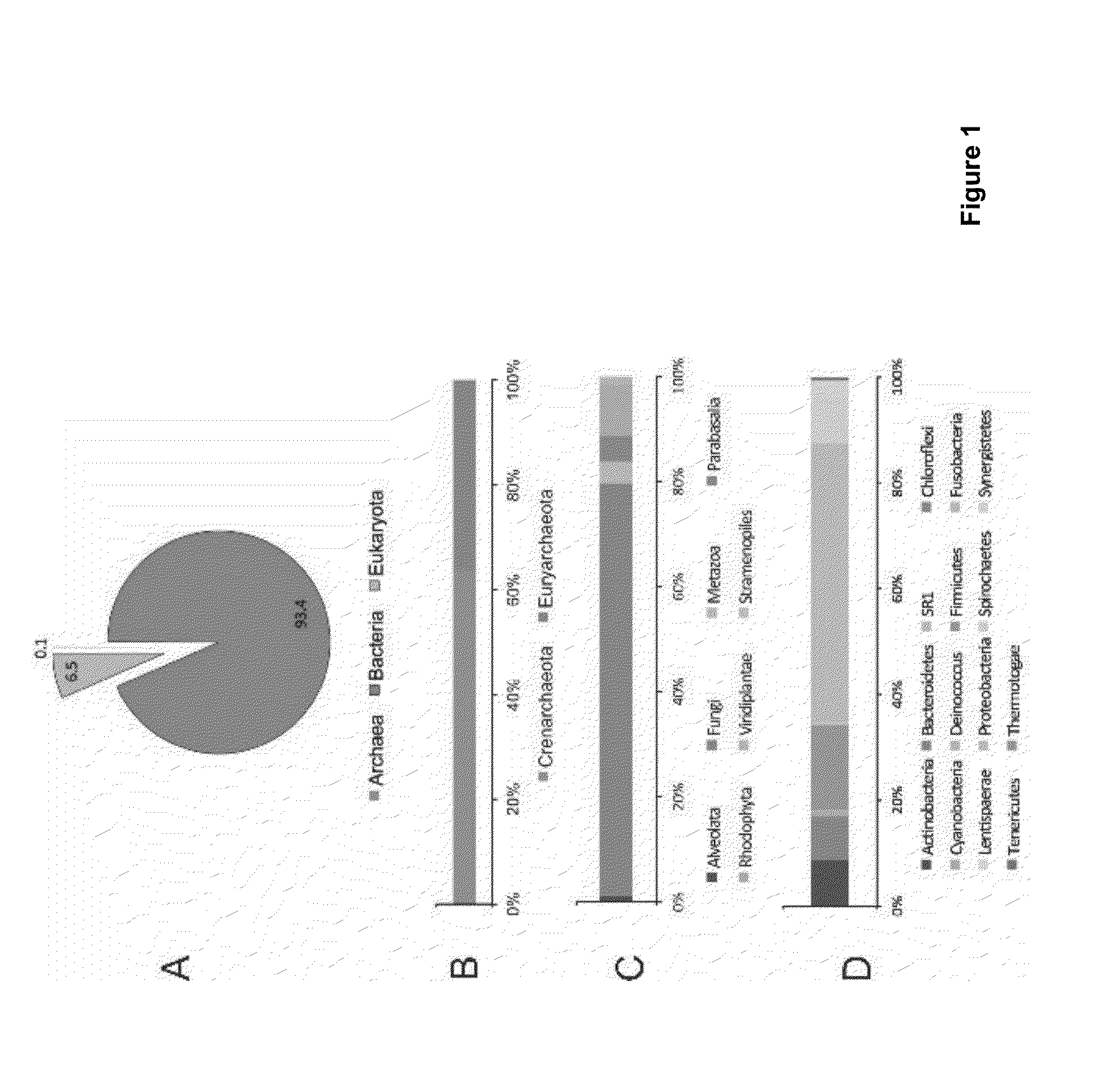
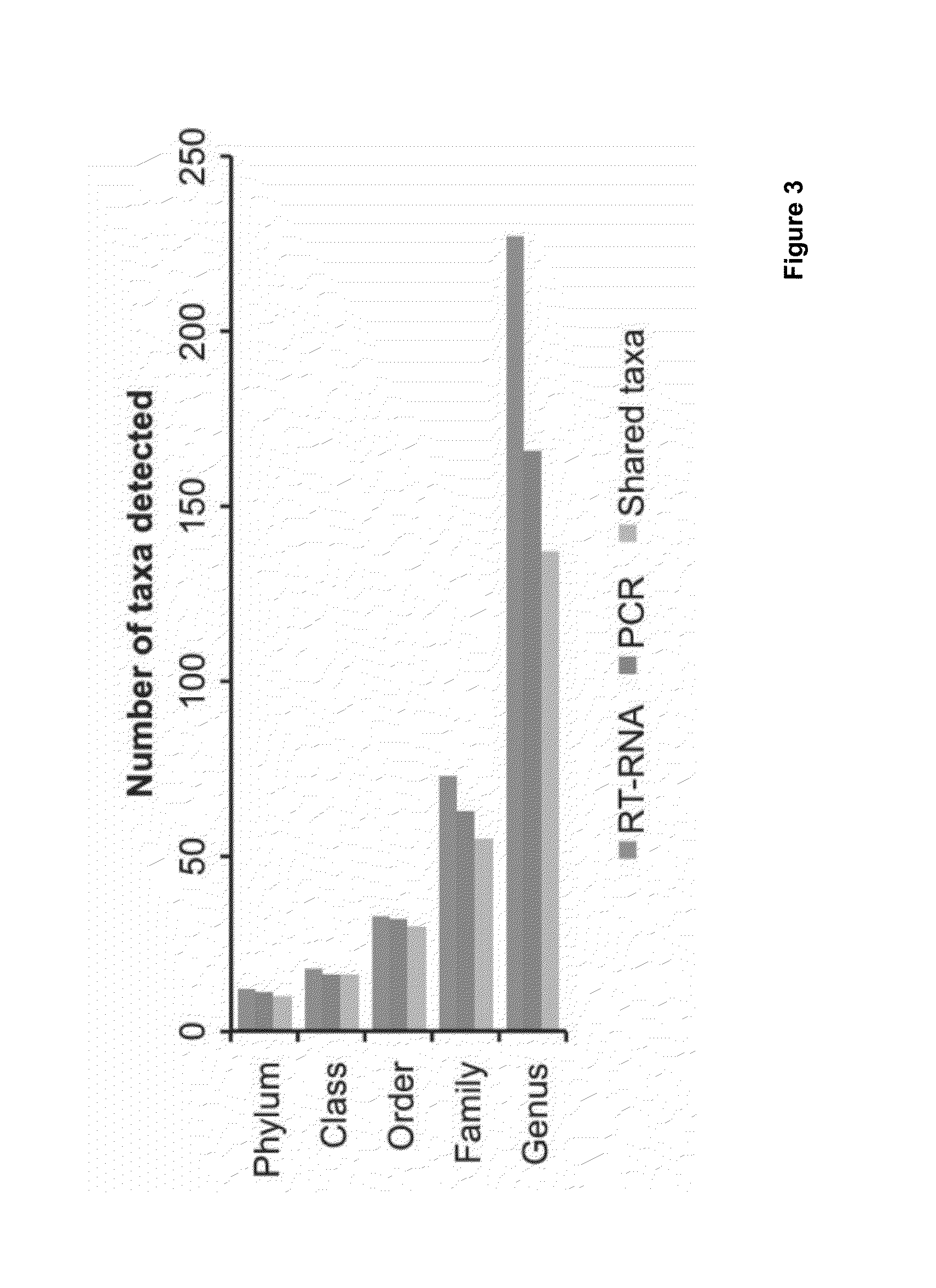
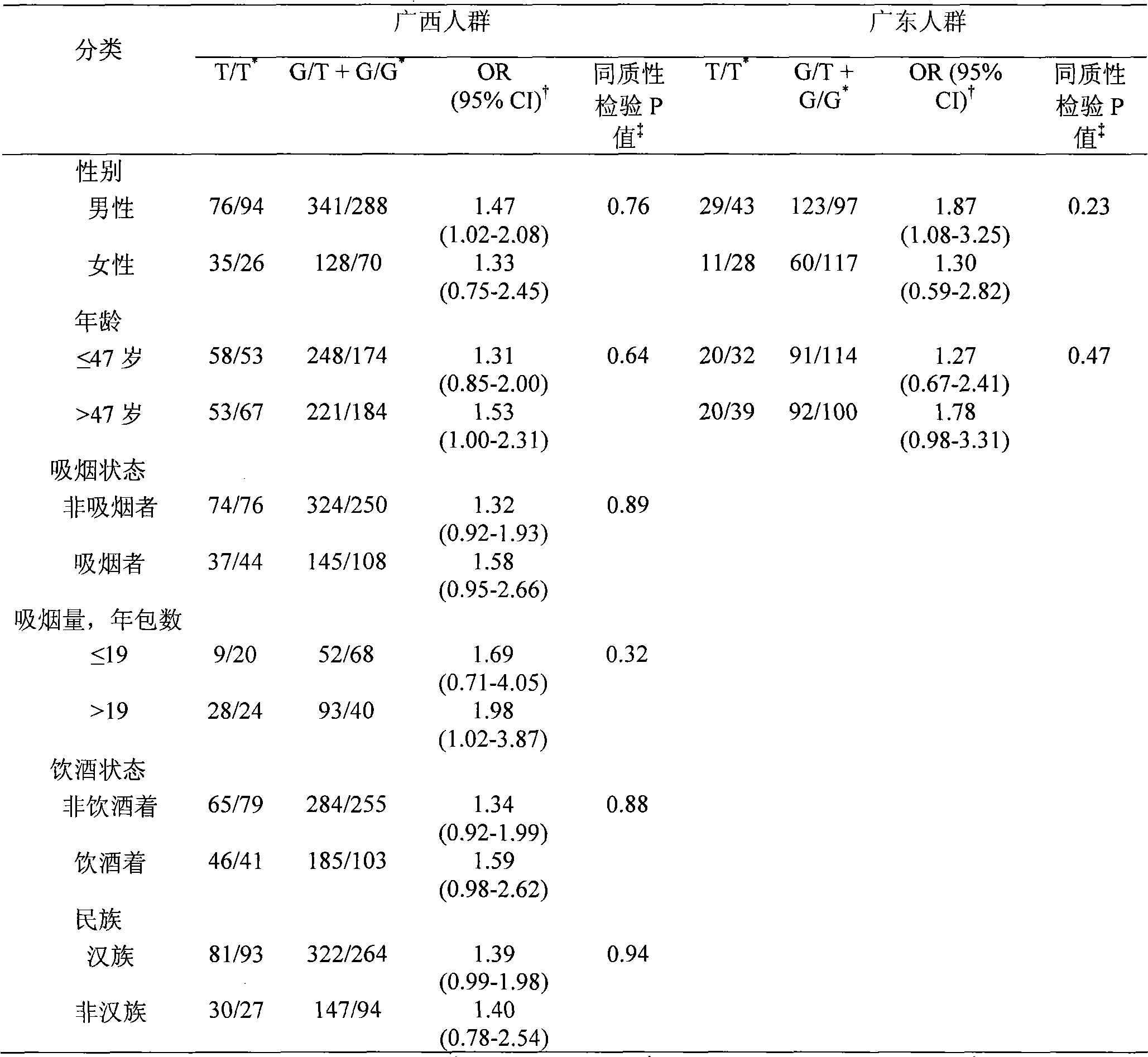
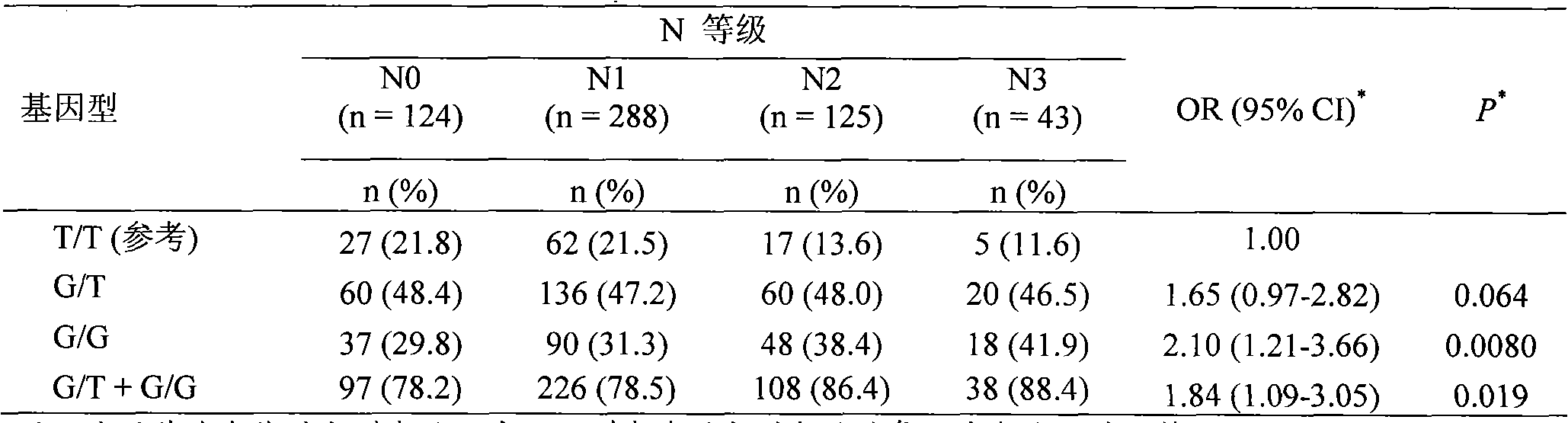
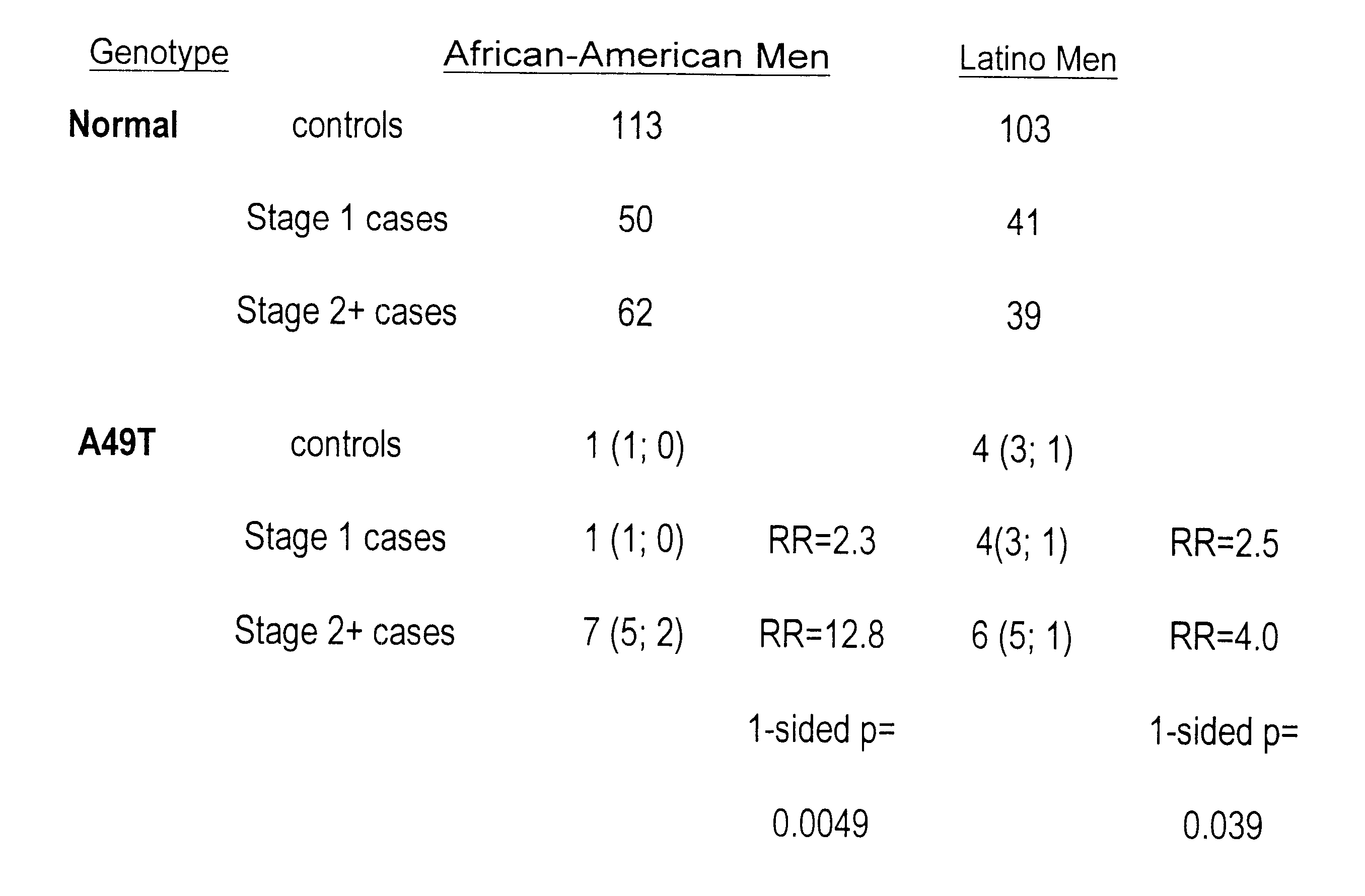
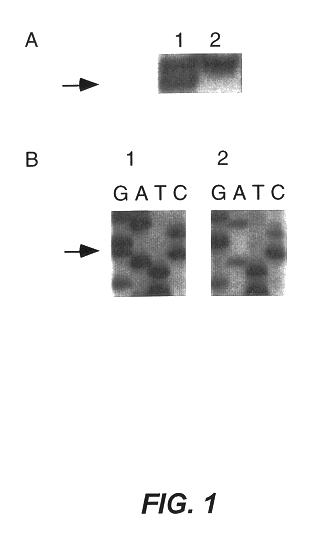
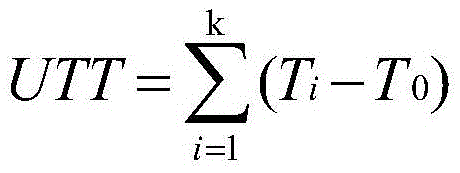Patents
Literature
164 results about "Direct sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
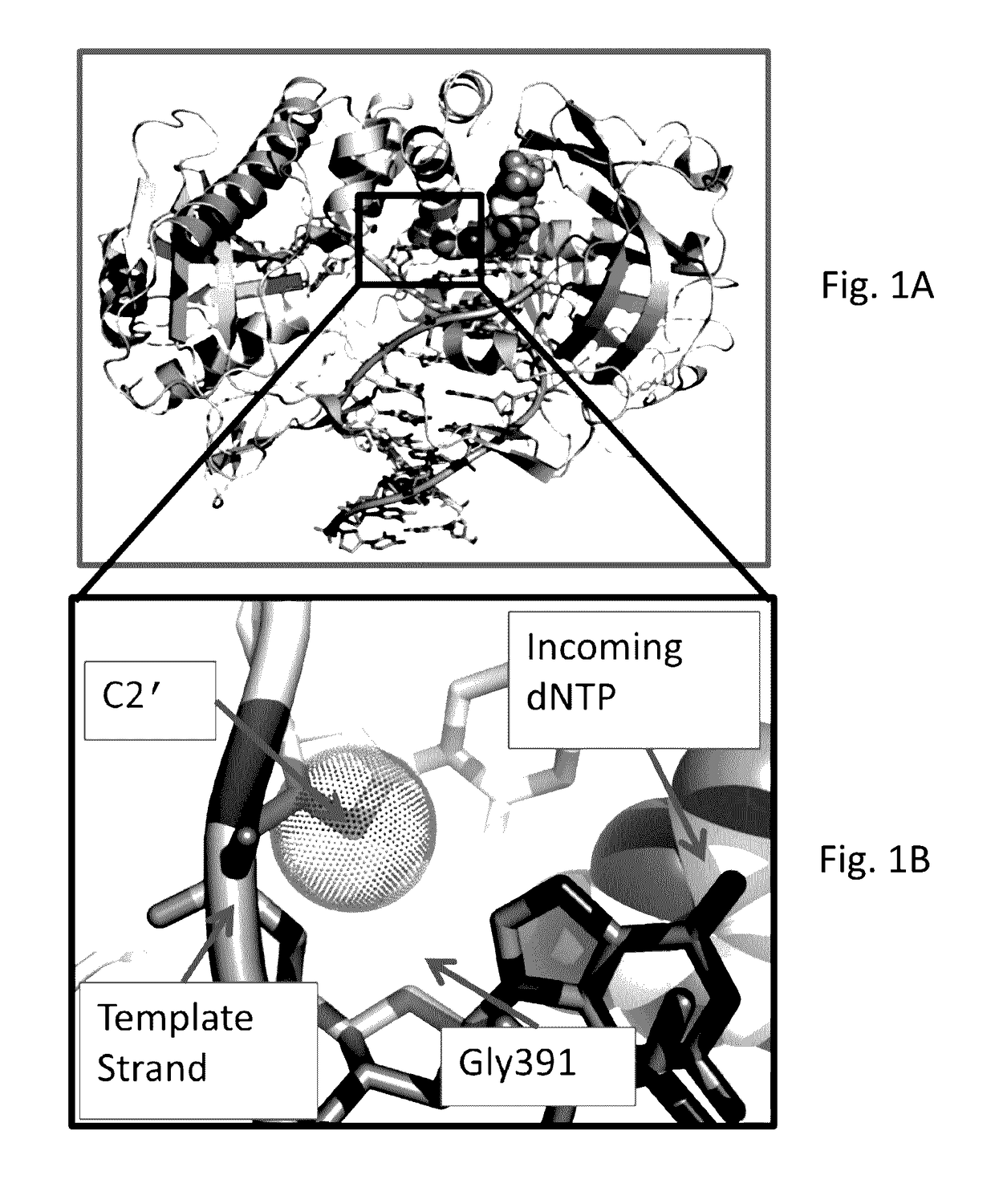
Direct sequencing means that the letters of the genetic code are read directly, as if with a magnifying glass. A DNA or RNA strand has a diameter of only two nanometers, so the magnification must be correspondingly powerful.
Methods for determining sequence variants using ultra-deep sequencing
InactiveUS20060228721A1Reduce effortShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationUltra deep sequencingDirect sequencing
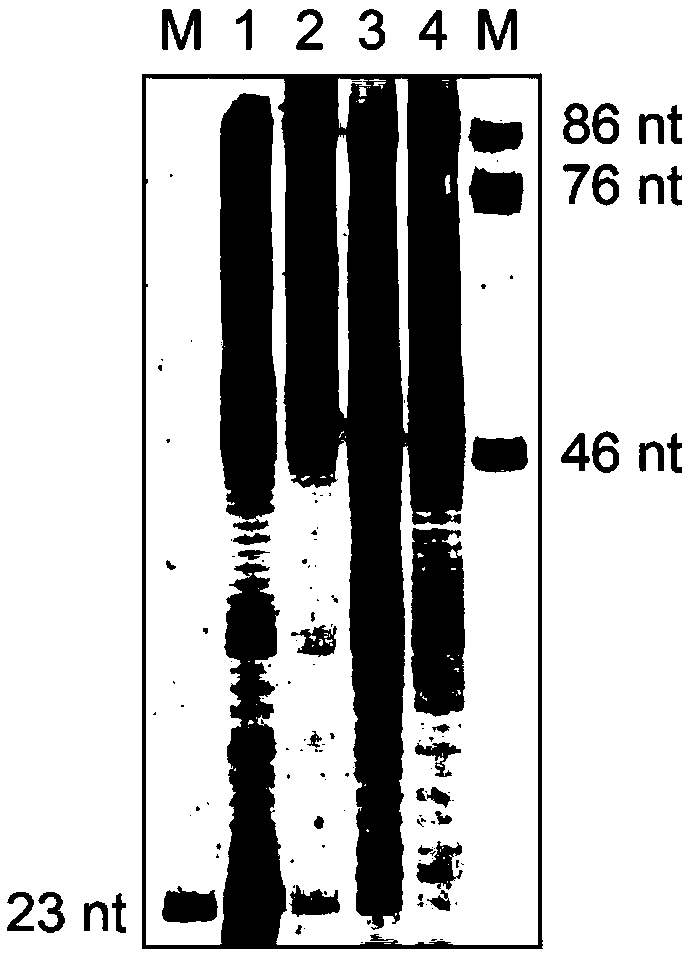
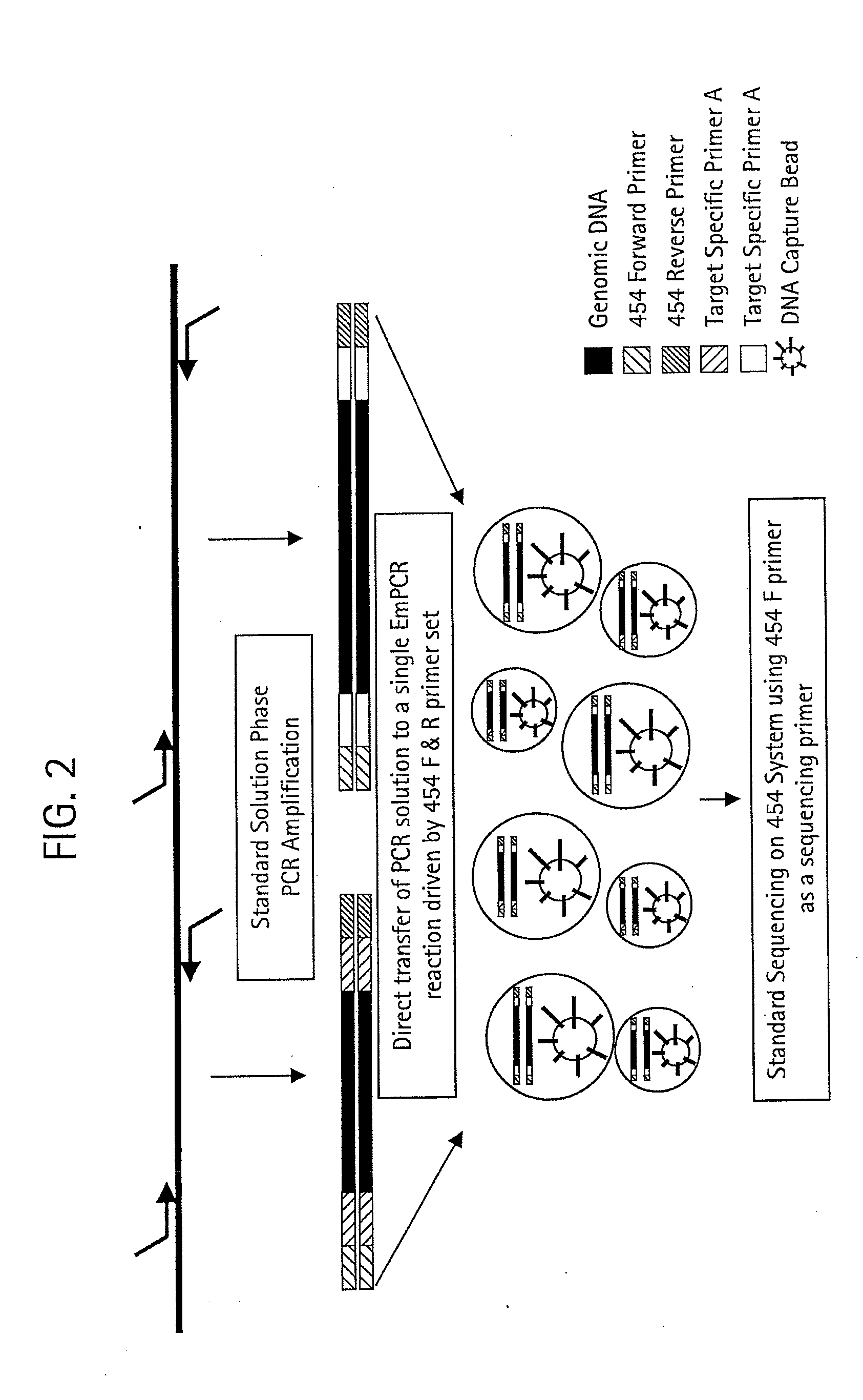
The claimed invention provides for new sample preparation methods enabling direct sequencing of PCR products using pyrophosphate sequencing techniques. The PCR products may be specific regions of a genome. The techniques provided in this disclosure allows for SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) detection, classification, and assessment of individual allelic polymorphisms in one individual or a population of individuals. The results may be used for diagnostic and treatment of patients as well as assessment of viral and bacterial population identification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Method for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules and its application
InactiveUS6605428B2Improved and rapid and reliable methodReduction of initial amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
A method is described for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing ("DEXAS") of a DNA molecule from a complex mixture of nucleic acids, wherein truncated DNA molecules as well as DNA molecules of full length are synthesized simultaneously and exponentially between two positions on the said DNA molecule, which initially contains a DNA molecule in a thermocycling reaction, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a thermostable DNA polymerase, a thermostable pyrophosphatase (optionally), deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed using one polymerase having a Tabor-Richardson mutation, or a functional derivative thereof, and reverse transcriptase activity. In a more preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed in one step, in one vessel.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
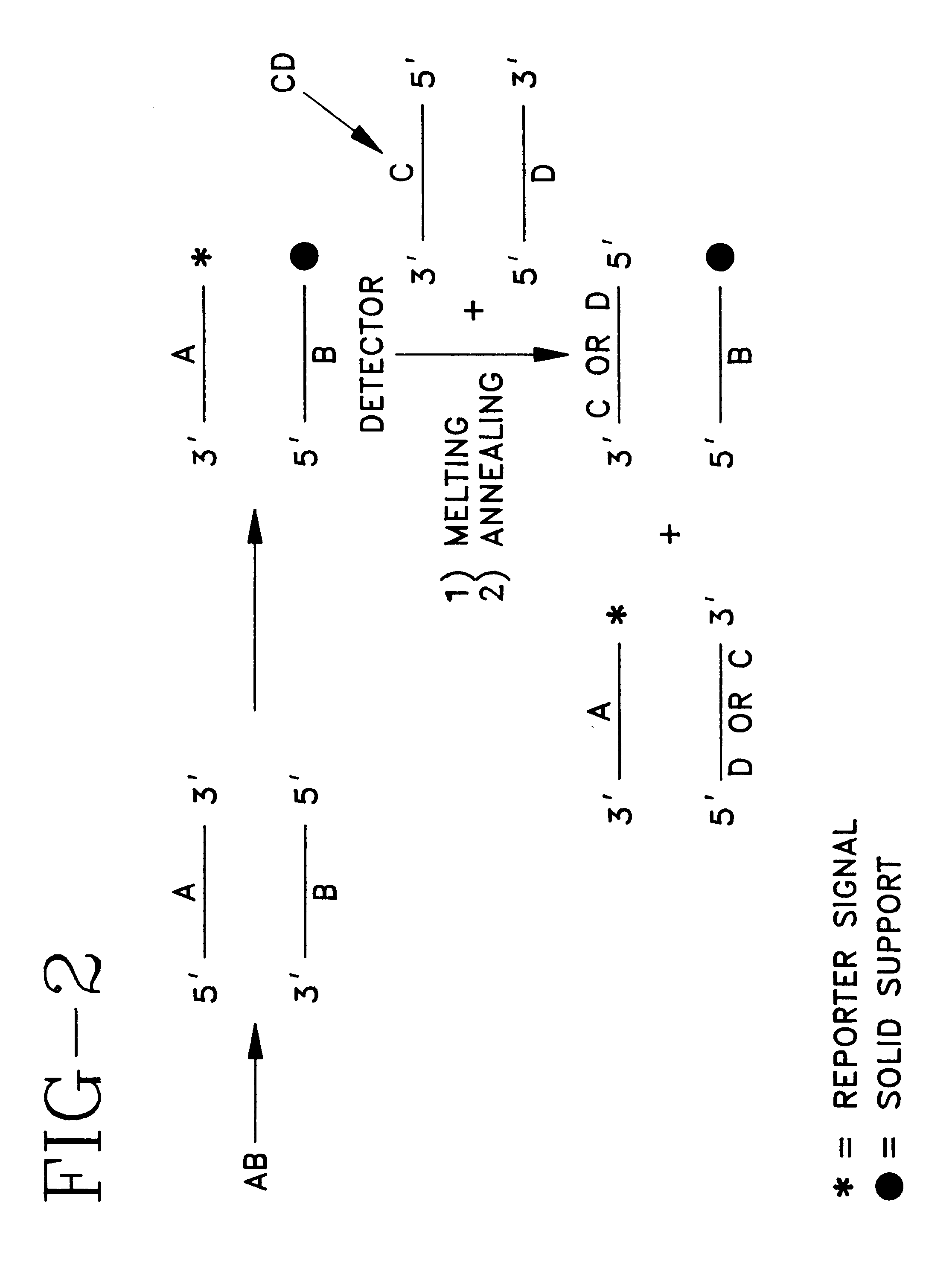
Detector for nucleic acid typing and methods of using the same
InactiveUS6238866B1Easy constructionSimple designSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteTyping
The present invention provides devices and methods for detecting or characterizing a nucleic acid analyte without requiring electrophoresis or the direct sequencing of analyte samples or analyte fragments. The device includes a panel or array of double stranded oligonucleotide probes immobilized on a solid support. each probe comprising a nucleotide sequence having a hypervariable number of tandem repeat sequences. Desirably, the specificity of the probes is varied with the location on the panel or array. One strand of each probe is preferably anchored at one terminus to a solid support and the opposite terminus of a second strand is not so anchored. The probes and / or the analyte are labeled by one or more reporter moieties, designed, for example, to allow for visual or instrument based detection of hybridization events.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Direct identification and measurement of relative populations of microorganisms with direct DNA sequencing and probabilistic methods
ActiveUS8478544B2Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic SegmentProbabilistic method
Owner:COSMOSID INC
ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and detection method
InactiveCN102367478AIncreased sensitivityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementViral OncogenePositive control
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and aims to provide an ARMS-qPCR (Allele Refractory Mutation System-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for KRAS (Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog) gene mutation subtype and a detection method. The kit comprises a qPCR hybrid reaction solution, a locked nucleic acid retardant probe, a reference primer, an ARMS primer and a positive control sample, wherein the qPCR hybrid reaction solution comprises a PCR buffer solution, dNTPs (Deoxynucleotide Triphosphates), MgCl2, GoldStarbest Taq enzyme, a universal PCR reverse primer and a universal TaqMan probe. The kit provided by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting specific locus mutation of KRAS genes in various cancer tissues with high sensitivity, has high sensitivity, and can be used for detecting genome DNA with various tissue origins, specially free DNA segments adopting cell-free systems, such as blood serum and blood plasma, orother body fluid origins, wherein the genome DNA is derived from cell systems. Compared with direct sequencing and other mutation detection technologies, the kit and the detection method thereof havethe advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high throughput, safety, definiteness and objectivity in result identification and the like for detecting the KRAS gene mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods, systems, and reagents for direct RNA sequencing
ActiveUS20170159033A1Improve polymerase performanceDesirable propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAmino acid substitutionPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising recombinant polymerases that include amino acid substitutions, insertions, deletions, and / or exogenous features that confer modified properties upon the polymerase for sequencing RNA or RNA / DNA templates. Polymerases that topologically encircle the template nucleic acid are provided. Also provided are methods of using such polymerases to make a DNA or to sequence a template comprising RNA.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods for Determining Sequence Variants Using Ultra-Deep Sequencing
InactiveUS20120264632A1Reduce and effort and lossReduce and and product lossMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningUltra deep sequencingDirect sequencing
The claimed invention provides for new sample preparation methods enabling direct sequencing of PCR products using pyrophosphate sequencing techniques. The PCR products may be specific regions of a genome. The techniques provided in this disclosure allows for SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) detection, classification, and assessment of individual allelic polymorphisms in one individual or a population of individuals. The results may be used for diagnostic and treatment of patients as well as assessment of viral and bacterial population identification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
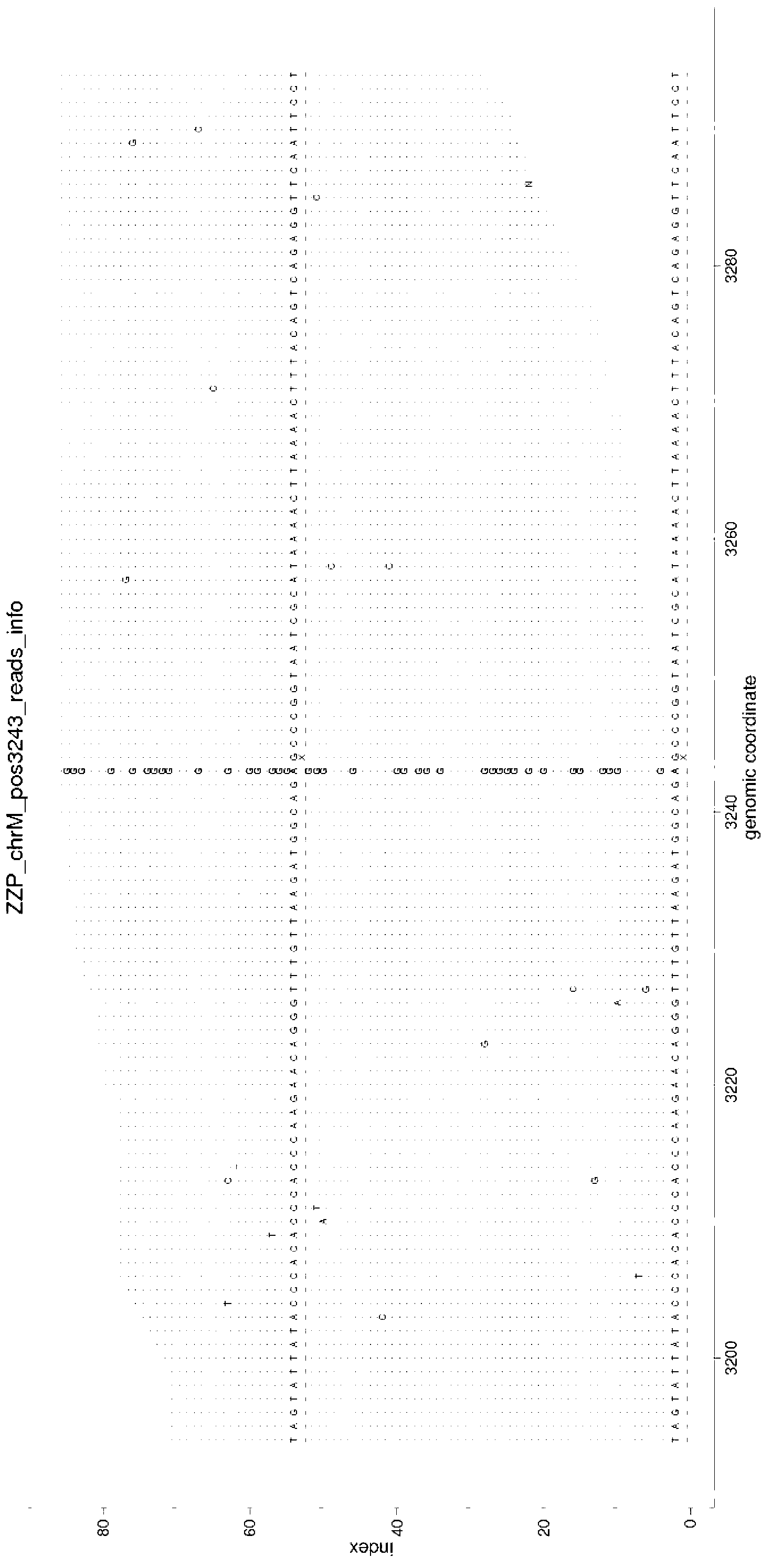
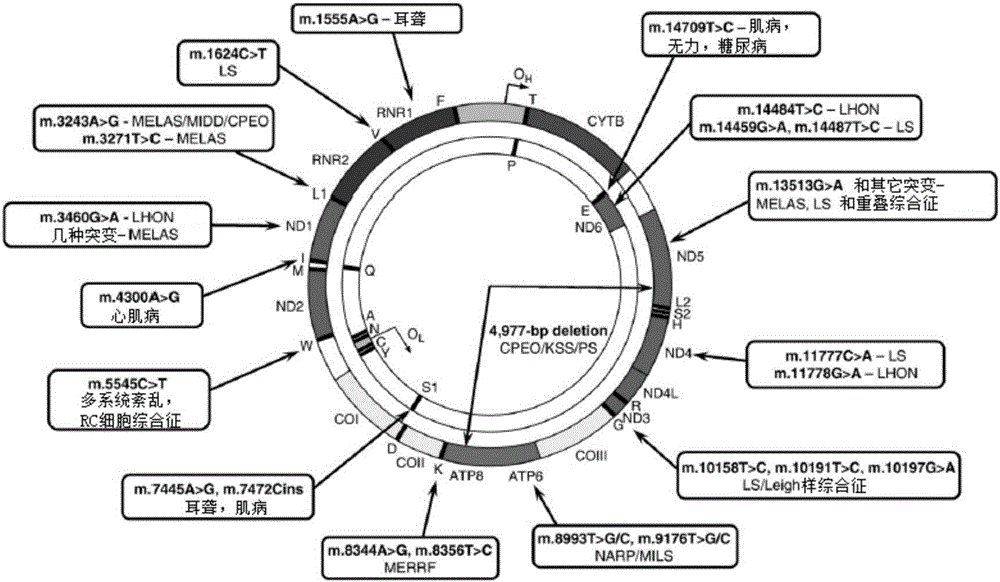
Amplification method, primer, sequencing method and mutation detection method of mitochondria whole genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
InactiveCN103173441ALow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseMutation detection
The invention discloses a primer pair and a kit for amplification of a mitochondria whole genome. The invention further discloses an amplification method, a sequencing method and a mutation detection method of the mitochondria whole genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). According to the invention, the direct amplification of the given primer is combined with the direct sequencing method, so that a mitochondria whole genome sequence can be obtained; all mutations of the mitochondria genes can be detected by one step for being used for detecting the diseases caused by most of the mitochondria gene mutations.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Method for detecting gene mutation genotyping based on Taqman-ARMS (Amplification Refractory Mutation System) technology and kit
ActiveCN102776291AStrong specificityEnrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionHigh flux
The invention discloses a method for detecting gene mutation genotyping based on a Taqman-ARMS (Amplification Refractory Mutation System) technology, relating to the field of molecular biology. According to the method, an ARMS mutation enrichment technology and a Taqman-MGB (Minor Groove Binder) specificity fluorescence detection technology are combined, a mutation target sequence is subjected to specificity PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using an ARMS primer, a Taqman-MGB probe is used for carrying out specificity locus detection on an amplification product, and specific mutation is identified on the basis of Real-time PCR. Compared with mutation detection technologies such as direct sequencing, chip detection and the like, the method has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity and rapidness in operation, high flux and the like when used for detecting gene mutation.
Owner:JIANGSU MICRODIAG BIOMEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Method for building high-flux single-cell full-length transcriptome sequencing library and application of method
ActiveCN109811045AGuaranteed accuracyIntegrity guaranteedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationTn5 transposaseLysis
The application discloses a method for building a high-flux single-cell full-length transcriptome sequencing library and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: recognizing single cells by adopting a customized micro-hole chip and an ICELL8 platform, and performing cell lysis, mRNA reverse transcription, cDNA pre-amplification and Tn5 transposase library building on the single cells, wherein a product can be directly applied to sequencing; in a process of mRNA reverse transcription or Tn5 transposase library building, introducing a dual-terminal Barcode sequence with a 5' terminal and a 3' terminal in order to obtain a single cell full-length transcriptome. By adopting the method, the single cell recognition flux is high, and the product can be directly appliedto sequencing. When the method is applied to single-cell sequencing, only two days are required for efficiently obtaining thousands of single-cell full-length transcriptome libraries at one time, sothat the labor cost and time cost are lowered greatly; moreover, the reagent cost is lowered greatly through a trace reaction system, and a basis is laid for large-scale single-cell full-length transcript sequencing.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Method for identifying variations in polynucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6048689AHigh speedSimple technologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThree stageDirect sequencing
A step-wise integrated process for identifying sequence variations in polynucleotide sequences is disclosed. The identification process is composed of three stages, including allele specific hybridization assays of known sequence variations (Stage I), sequence variation locating assays (Stage II), and direct sequencing (Stage III). The methods can be used for efficient and accurate detection of mutations in any test gene sample.
Owner:GENE LOGIC
Methods and systems for direct sequencing of single DNA molecules
InactiveUS20110294116A1Rapid DNA sequencingAccurate measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDirect sequencingPersonalized medicine
The invention provides improved methods for sequencing nucleic acids, e.g., for medical applications and biomedical research. The disclosed methods can be applied to rapid personalized medicine, genetic diagnosis, pathogen identification, and sequencing species genomes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Molecular and bioinformatics methods for direct sequencing
InactiveUS20160180018A1Fast and accurate methodMinimize degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisBiotechnologyRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The present invention relates to methods for preparing an isolated biological sample containing at least one of DNA and RNA, such that the DNA and / or RNA is preserved in the sample at ambient temperatures for at least thirty days, the method comprising: contacting the isolated biological sample with a composition comprising a chaotropic agent, and subjecting the contacted sample to microbial cell lysis; and optionally, contacting the lysed biological sample with a slurry of size-selected silicon dioxide to form at least one of DNA-silicon dioxide complexes or RNA-silicon dioxide complexes in the sample; isolating at least one of DNA-silicon dioxide complexes or RNA-silicon dioxide complexes from the sample; and, separating at least one of DNA and RNA from the silicon dioxide and collecting at least one of the DNA and RNA.The present invention further relates to methods for preparing an isolated biological sample, the method comprising, separating the components in an isolated biological sample according to their size, wherein the components are at least one of DNA and RNA; purifying and isolating SSU rRNA from the biological sample using a composition comprising a ribonuclease inhibitor and a deoxyribonuclease to remove DNA from the sample, reverse transcribing the SSU rRNA into ds cDNA using random primers for SSU rRNA.The present invention also relates to computer implemented methods comprising, receiving an isolated sample prepared according to the methods of the invention, sequencing the sample, and providing the sequence with a sequence identifier (ID), the sequence comprising a plurality of groups of k-mers, each group of k-mers defining a node in a multi-level hierarchy which defines the relationship between the groups of k-mers; providing each group of k-mers with a respective group identifier (ID), determining the frequency of the k-mers in each group; generating a group signature array for each group of k-mers, each group signature array comprising the k-mers in each group that have the most increased frequency compared with the sibling k-mers; generating a signature map comprising each group signature array and at least one of the identifiers, the identifier of at least one parent group and the identifier of at least one child group; and outputting the signature map to be used to classify the sequence.
Owner:16S TECH INC
Molecular marker related to yellow chicken feather and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN103898102AImprove consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMedicineGenetics
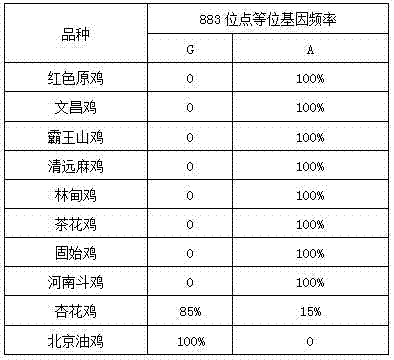
The invention discloses a molecular marker related to yellow chicken feather and an application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is obtained by A / G base mutation at the 883rd site in a sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. The molecular marker is amplified by using primers SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3, and the obtained amplification product is directly sequenced. The method is simple and convenient in operation and reliable in result. A genotype of the yellow feather trait of a target chicken flock can be determined by detecting the A / G mutation site, and whether the feather color of a certain individual is homozygous yellow feather or heterozygous yellow feather can also be judged through the genotype, so that a basis is provided for purposefully selecting the feather trait of the chicken flock, and the uniformity of the yellow offspring chicken feather is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Super-Resolution Sequencing
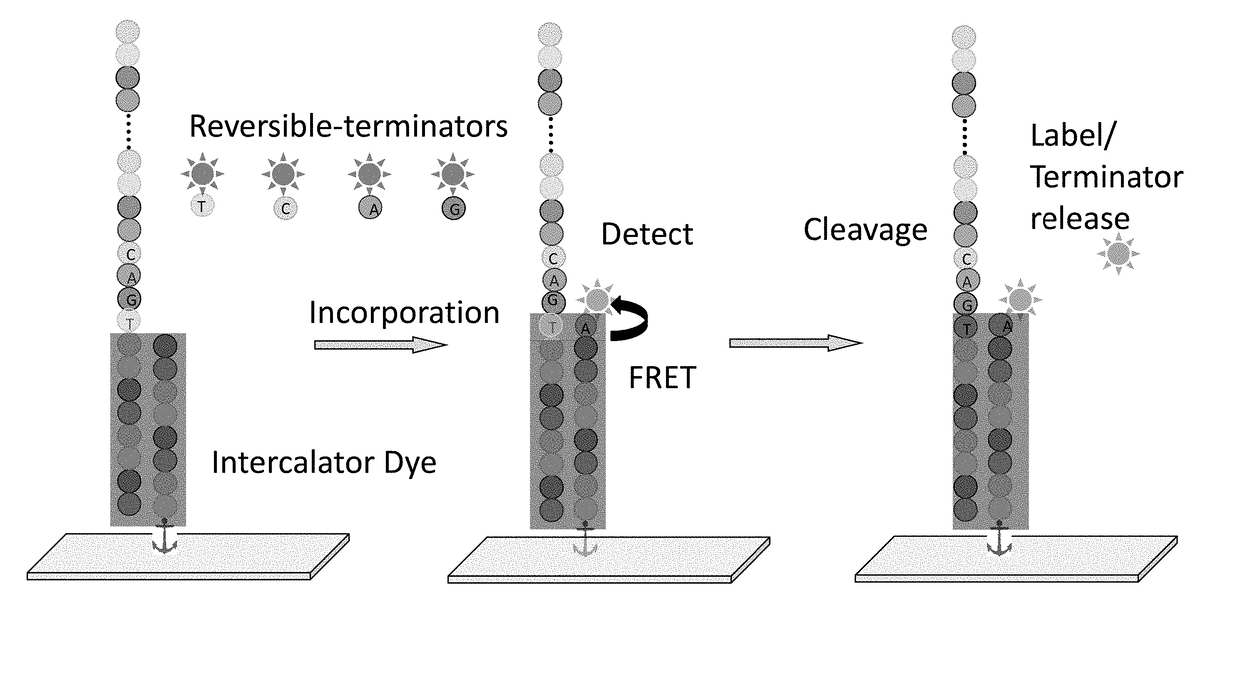
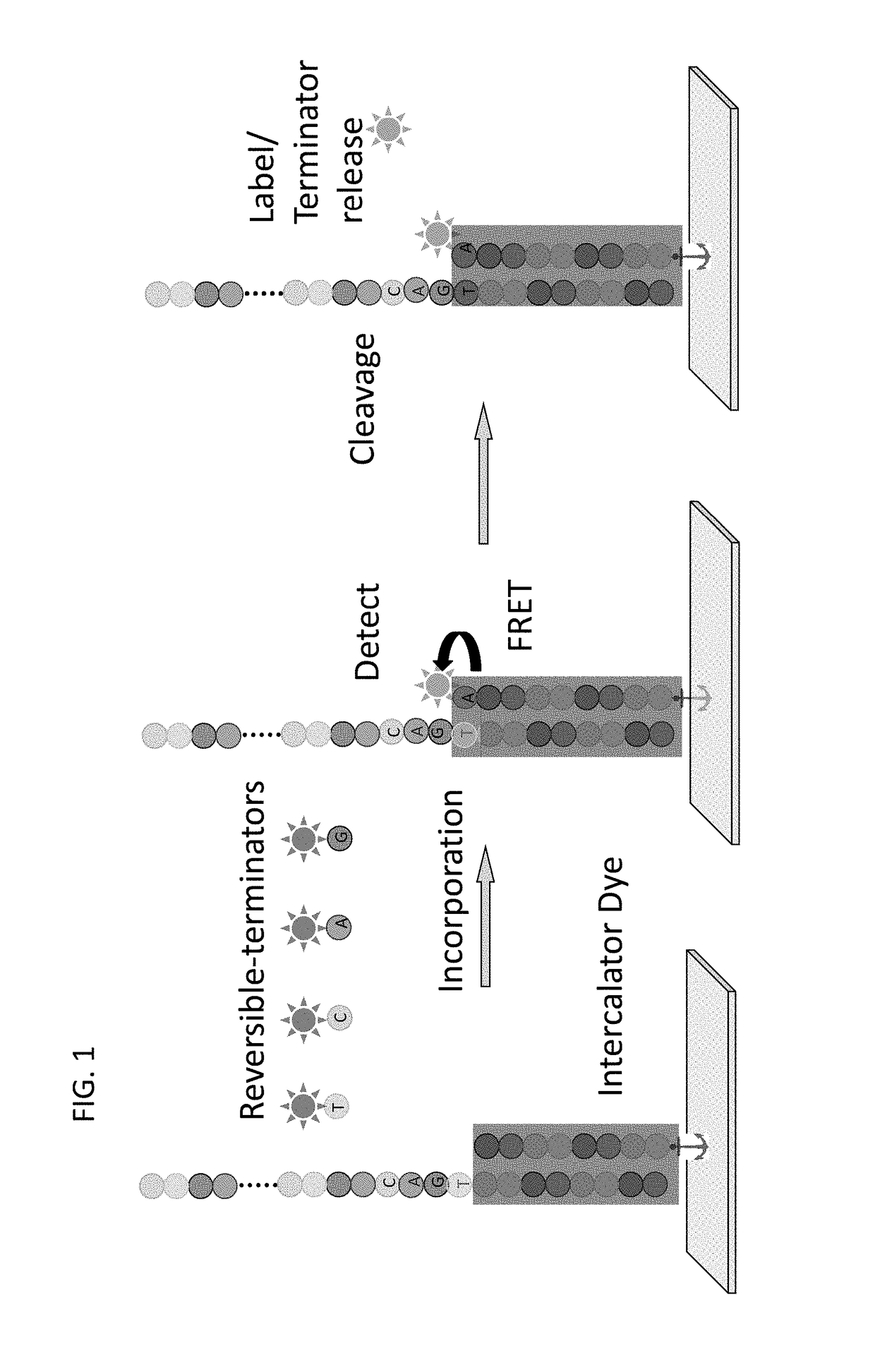
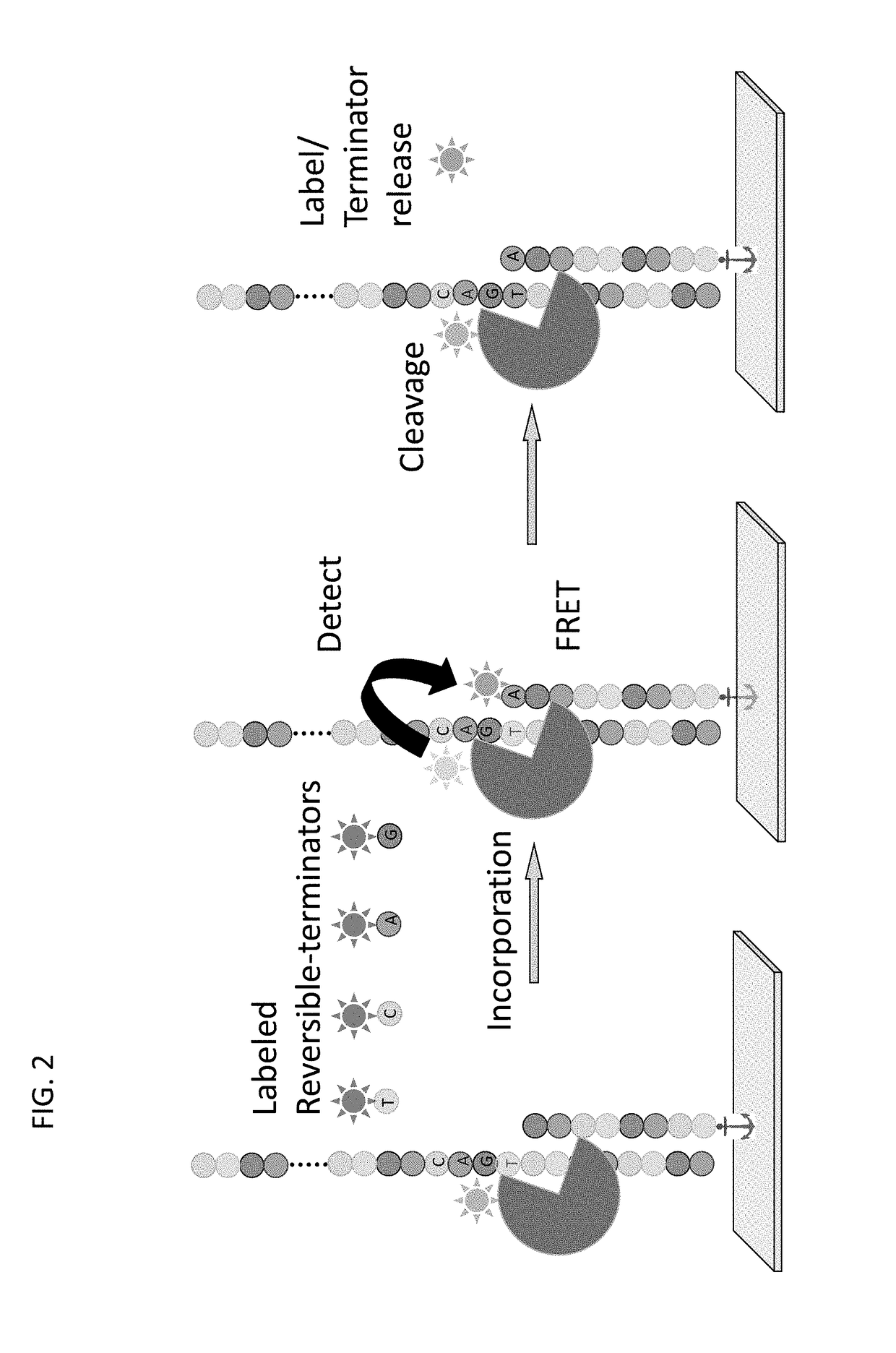
ActiveUS20180327829A1Overcomes shortcomingMass numberMicrobiological testing/measurementDirect sequencingPolynucleotide
A method for template-directed sequencing-by-synthesis of an array of target polynucleotide can include:(a) providing an array of target polynucleotides in a fluidic vessel;(b) contacting the array of polynucleotides with a solution comprising (i) polymerization complex and (ii) reversibly terminating and differently labeled A,C,G, and T / U nucleotides;(c) incorporating one of the differently labeled nucleotides, using the polymerization complex, into a chain complementary to at least one of the array of polynucleotides;(d) binding imaging tags to the differently labeled nucleotides of step (c);(e) imaging and storing the identity and position of the imaging tags of step (d);(f) reversing termination (b)-(e);(g) repeating steps (b)-(e) and assembling a sequence for each of the array of target polynucleotides from the stored identity and position of the imaging tags, optionally as a homogeneous or one pot reaction. Additional methods of sequencing target polynucleotides are described herein.
Owner:MIR KALIM U
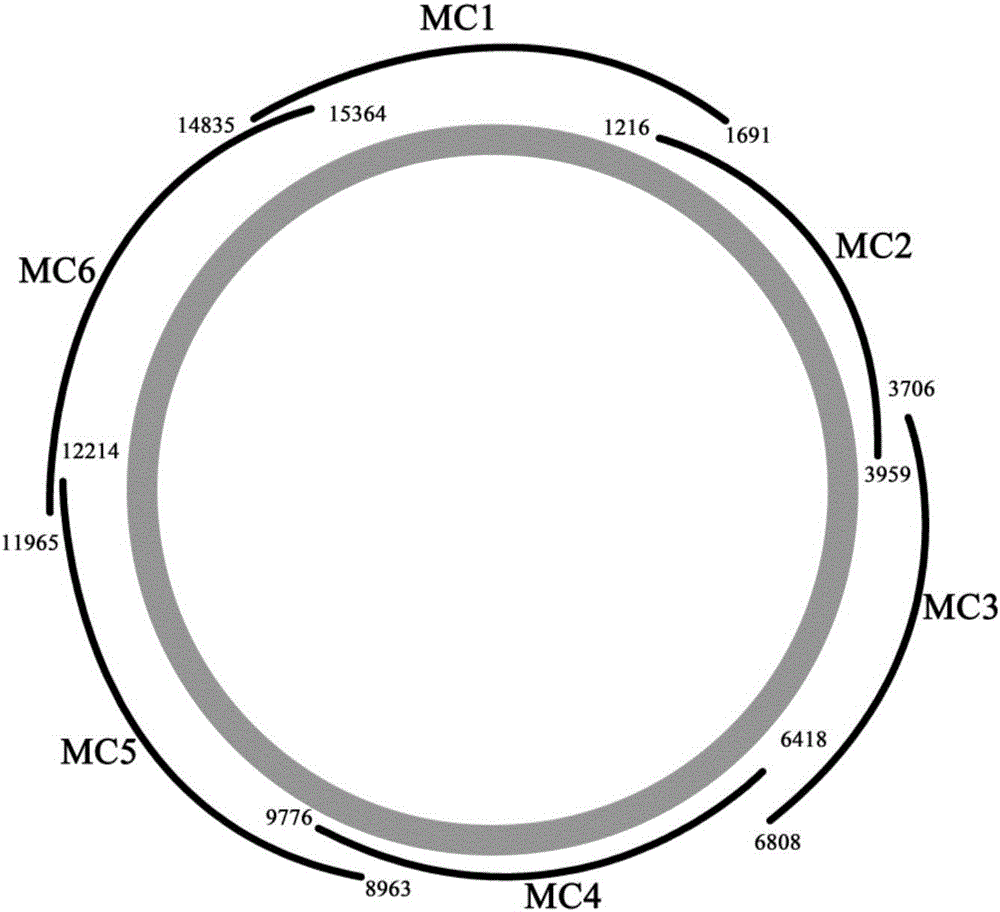
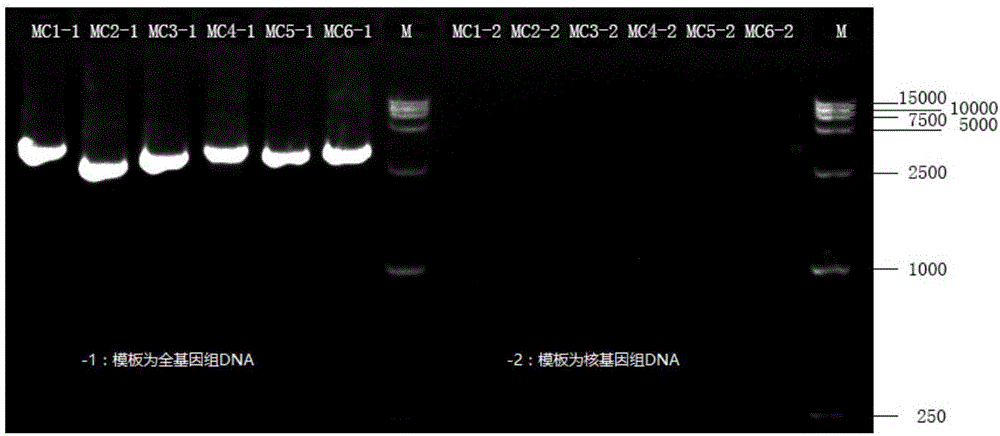
Primer combination and reagent kit for complete mitochondrial genome detection
ActiveCN106755456ASimple and fast operationShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDirect sequencingMitochondrial disease
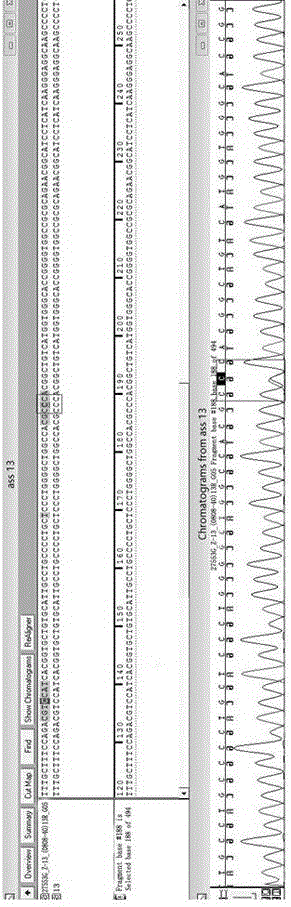
The invention relates to a primer combination and a reagent kit for complete mitochondrial genome detection. A PCR and Sanger sequencing technology is used for detecting a complete mitochondrial genome for auxiliary diagnosis of a mitochondrial disease caused by mtDNA (mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid) mutation. Six specific primer pairs are used for amplification of the whole mitochondrial genome first; each amplification product is 2700-3500bp in size; 200bp or more parts of adjacent amplification segments are overlapped; then, 21 sequencine primers are used for direct sequencing of the amplification products; the sequencing range covers the whole mitochondrial genome. With the adoption of the primer combination, the whole mitochondrial genome can be detected by 6 amplification reactions and 21 sequencing reactions; the detection workload is greatly reduced; moreover, the detection cost is also greatly lowered.
Owner:北京圣谷智汇医学检验所有限公司
Method of direct DNA sequencing for screening hepatolenticular degeneration disease gene mutation site through PCR amplification
InactiveCN104830966AThe method is simple and fastIdentify mutation sitesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenatal diagnosisAtp7b gene
A method of direct DNA sequencing for screening a hepatolenticular degeneration disease gene mutation site through PCR amplification. The invention relates to a method of direct DNA sequencing after the PCR amplification for screening a disease mutation site of ATP7B gene, thereby providing the basis for accurately diagnosis and prenatal diagnosis of the hepatolenticular degeneration disease. The method includes the processes of primer design, genome DNA extraction, PCR amplification, PCR product purification, PCR product sequencing and sequence comparative analysis and the like, wherein the key to decide effectiveness of the method is specificity and sensitivity of the primer. The primer in the invention is strong in specificity and high in sensitivity and is wide in coverage. The method can detect the all 21 exon regions, promoter regions and partial intron regions of the ATP7B gene, and can provide firm foundation of clinical diagnosis application of the hepatolenticular degeneration through genetic detection.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU
Primer pair capable of detecting specificity of human mitochondrial genome
InactiveCN104480207AAccurately obtainedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseDirect sequencing
The invention discloses a primer pair capable of detecting specificity of a human mitochondrial genome. The primer pair capable of detecting the specificity of the human mitochondrial genome comprises primer sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.32. Sixteen pairs of primers are designed, then direct sequencing is carried out on a PCR product, and finally a splicing method is carried out; compared with the long-fragment sequencing in the prior art, the PCR product of the designed primers covers the whole genome sequence of the whole mitochondrion, length of the PCR product of each pair of primers is 1200-1300bp, and a sequence obtained by two adjacent pairs of primers is overlapped for 100-300bp, and thus information of the mitochondrial genome can be accurately obtained at one time, all the mutation on the mitochondrial genome can be detected, and diagnosis of mitochondrion-related diseases can be assisted.
Owner:HANGZHOU JILUO BIOLOGICAL PHARMA CO LTD
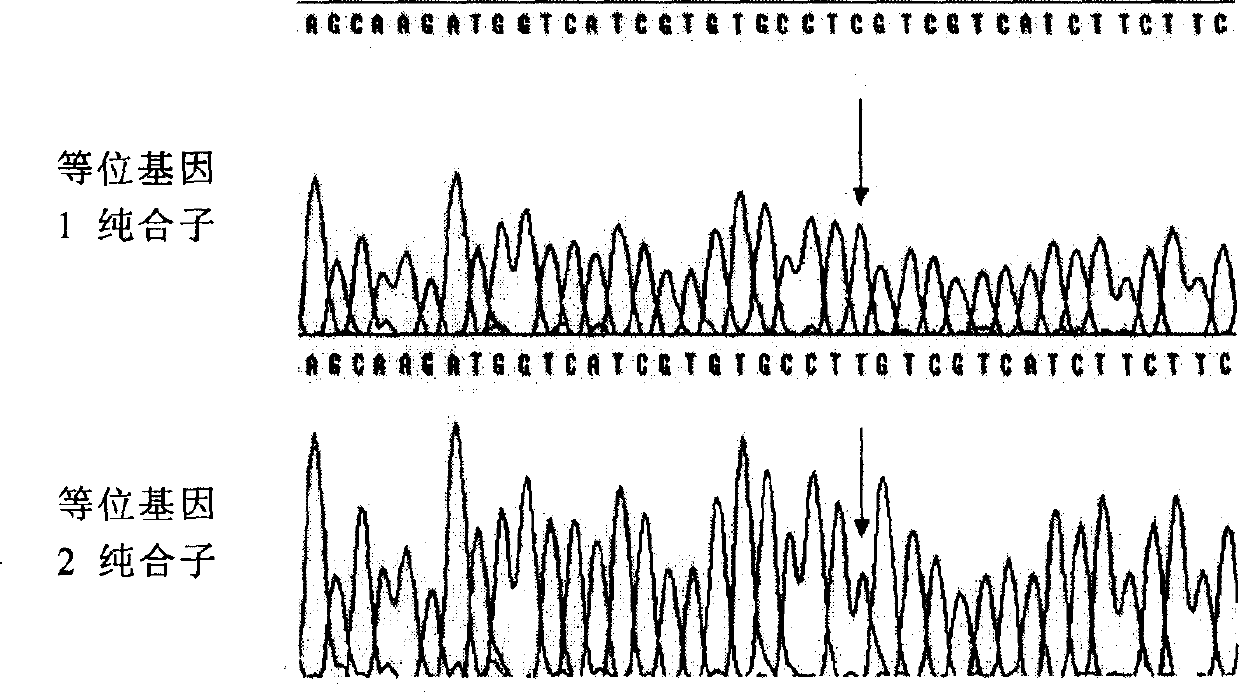
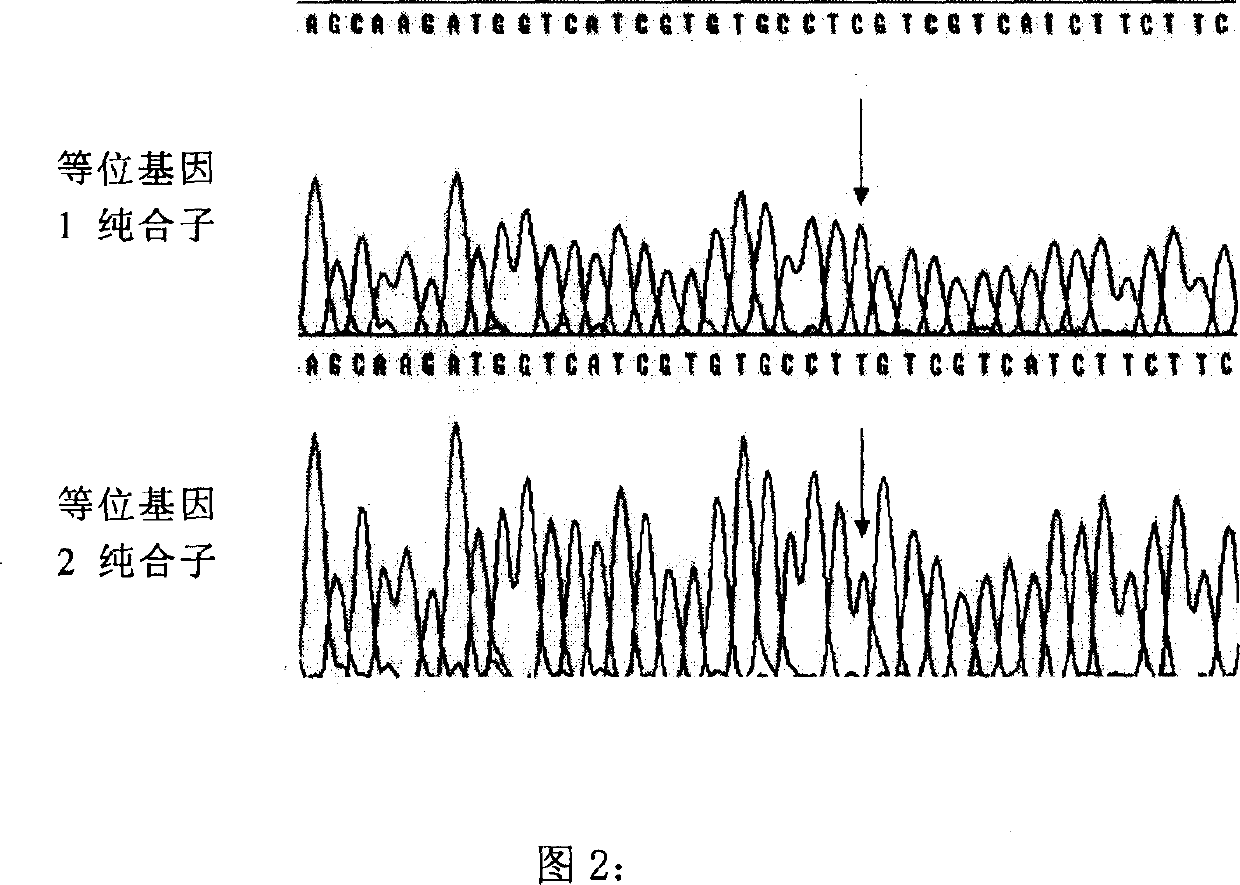
Method for detecting PCR-RFLP of pig bone morphogenetic protein 15 gene polymorphism
InactiveCN1537942AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringDirect sequencingDNA extraction
A bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP 15) gene and the PCR-RFLP method for detecting its single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) are disclosed. Its steps include extracting hog blood genom DNA, designing primer PCR amplifying, direct sequencing to amplified product, comparing and analyzing the sequence, and detecting SNP. It provides new marker for the marker aided breeding of pig.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
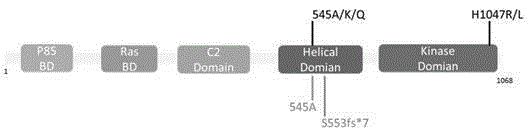
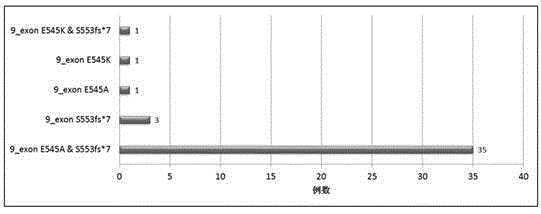
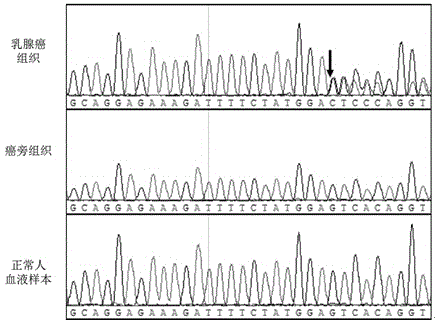
Breast cancer PIK3CA mutant gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a breast cancer PIK3CA mutant gene and an application thereof. The breast cancer PIK3CA mutant gene has the c.1658_1659GT>C mutation site, and the nucleotide sequence of the breast cancer PIK3CA mutant gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. According to the invention, through a direct sequencing method, PIK3CA gene mutation in 88 breast cancer tissues, 19 breast cancer para-carcinoma tissues and 22 normal human blood samples is detected, and for the first time, it is found that the PIK3CA gene S553fs*7 mutation is as high as 44.3% in the breast cancer tissues, while no mutation occurs in the breast cancer para-carcinoma tissues and the normal human blood samples; it prompts that the mutation can be used for assisting the early diagnosis of breast cancer; and therefore, the breast cancer PIK3CA mutant gene has great significances for preventing and treating occurrence and development of breast cancer in clinic.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Primer, kit and detection method for detecting chicken green shin character linkage SNP locus genotype
ActiveCN104293905ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionEnzyme digestion
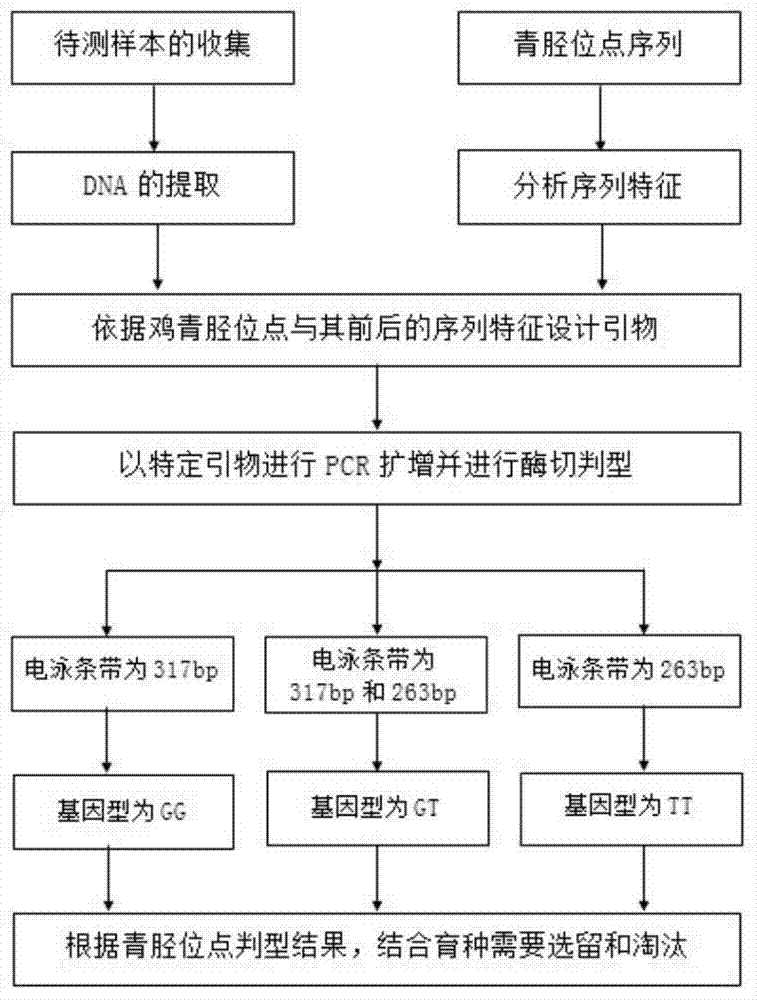
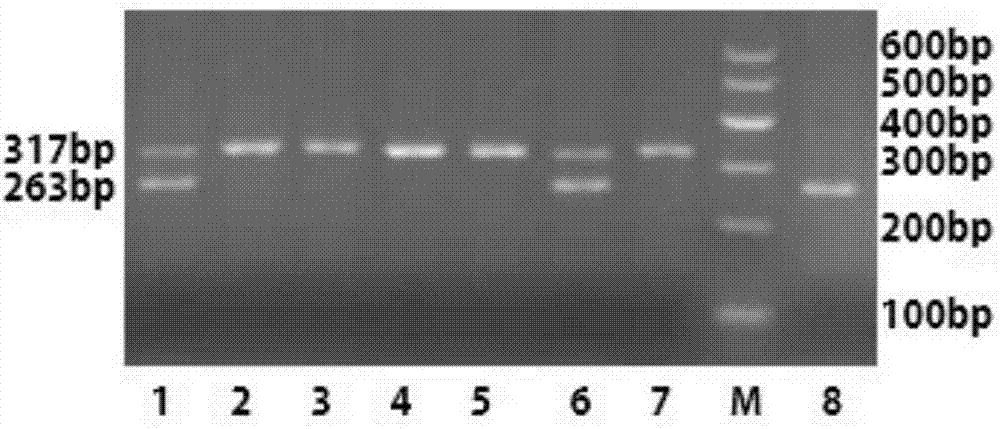
The invention discloses a primer, a kit and a detection method for detecting chicken green shin character linkage SNP locus genotype, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. Aiming at an SNP locus specific for the chicken green shin character, a primer pair (P) is designed at DNA segment near the SNP locus; and BamHI enzyme digestion is performed on an amplified product after PCR amplification. If the mutation site is G and a BamHI enzyme digestion sequence GGATCC presents, the segment of the PCR product after enzyme digestion is 263bp; and if the mutation site is T and no BamHI enzyme digestion sequence GGATCC presents, the segment of the PCR product after enzyme digestion is 317 bp. Compared with SSCP and a direct sequencing method, the detection method is simple to operate, low in cost and short in cycle, can greatly increase accuracy for determining the SNP locus genotype, is in no need of special instruments, and can be popularized easily. Experiments demonstrate that the method can effectively determine the genotype of the chicken green shin character SNP locus, can be used for marker-assisted selection of the chicken green shin characters, and provide effective molecular marker for establishing green shin chickens.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
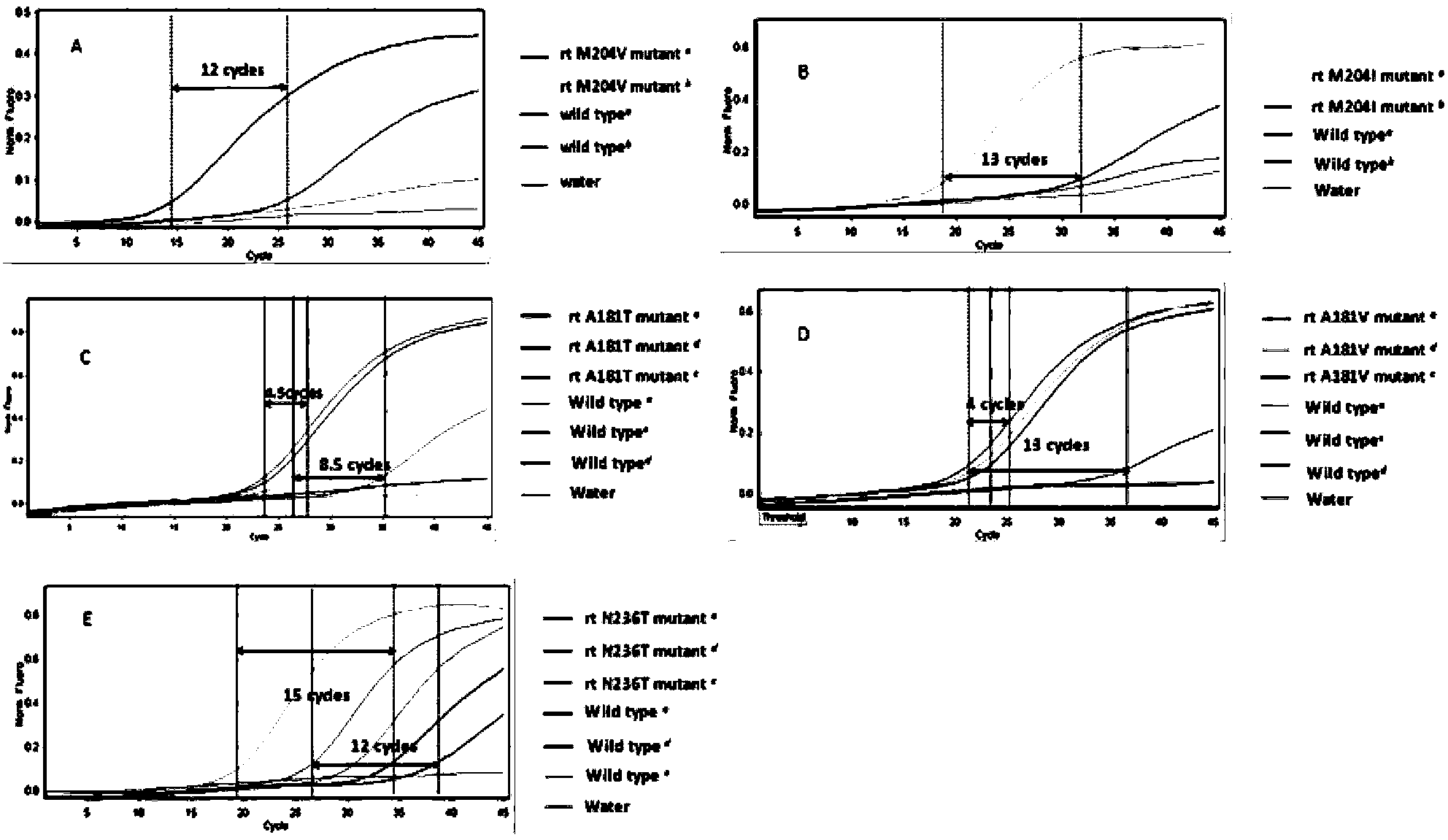
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for detecting drug resistance of HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) lamivudine and/or adefovir
InactiveCN103409551AEfficient detectionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplificationFluorescence
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field and particularly relates to a multiplex ligation-dependent probe real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology for detecting the drug resistance of chronic hepatitis B. A multiplex ligation-dependent probe real-time fluorescence PCR kit comprises an MLPA (Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification) probe set, a filling sequence and a universal primer, wherein probes are respectively designed according to mutation sites rtM204V, rtM204I, rtA181T, rtA181V and rtN236T of a P gene reverse transcription region of HBV (Hepatitis B Virus); the sequences of the probes are represented by SEQ ID NO: 1-10. The invention further relates to a method for detecting the drug resistance of the HBV lamivudine and adefovir by virtue of the kit. The method combines the high throughput of an MPLA technology, and the rapidness, sensitivity and real-time detection of real-time fluorescence PCR, and has a high coincidence rate compared with a direct sequencing method, and can be used for detecting samples which cannot be detected by the sequencing method due to insufficient sensitivity; a whole detection process takes 4-5 hours; the clinic hepatitis B drug resistance detection method provided by the invention is low in cost and quick in detection.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Nanopore based dislocation sequencing method for direct sequencing of non-natural nucleic acid
The invention discloses a nanopore based dislocation sequencing method for direct sequencing of non-natural nucleic acid. The method includes the steps of: (1) conducting solid-phase synthesis of a non-natural nucleic acid to-be-sequenced chain, connecting the non-natural nucleic acid to-be-sequenced chain with a DNA-guided sequencing chain by enzymatic ligation to serve as a complete to-be-sequenced chain; (2) preparing a nano-sensing pore channel with single-molecule resolution ability; and (3) mixing the to-be-sequenced chain with a DNA primer, conducting denaturing annealing to construct asequencing library, and then adding the library and nucleic acid polymerase into a cis chamber of the nanopore together, under the action of an electric field force, passing the nucleic acid chain through the nanopore, reading the electrical signal generated when the nucleic acid chain passes through the pore, and analyzing the signal to obtain the sequence. Compared with the prior art, the invention utilizes a low-cost and high efficiency nanopore sequencing method to realize direct sequencing of the continuous unnatural nucleic acid chain for the first time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
ESR1 gene polymorphism related to liver cancer and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN101078027AIncreased susceptibilityReduce the risk of liver cancerMicrobiological testing/measurementDirect sequencingHaplotype
This invention proposes a detection method of haplotype comprised of polymophic loci (rs3138774) in (TA)n, rs2077647 in T29C, rs2234693 in Pvu II and (TA)n, T29C, Pvu II and Xba I in susceptibility gene ESR1 relates to liver cancer risk. The methods are PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism), fragment analysis and direct sequencing PCR products. The haplotype is constructed by PHASE program. The invention also relates to the kits detecting susceptibility polymophic locis and using methods. In addition, site(TA)n (rs3138774), T29C(rs2077647) , Pvu II(rs2234693) and the haplotype comprising of (TA)n, T29C, Pvu II and Xba I were related to liver cancer risk. ESR1 is determined as a new susceptibility gene of liver cancer, which provides new genetic consultation content for the liver cancer prevention and control.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
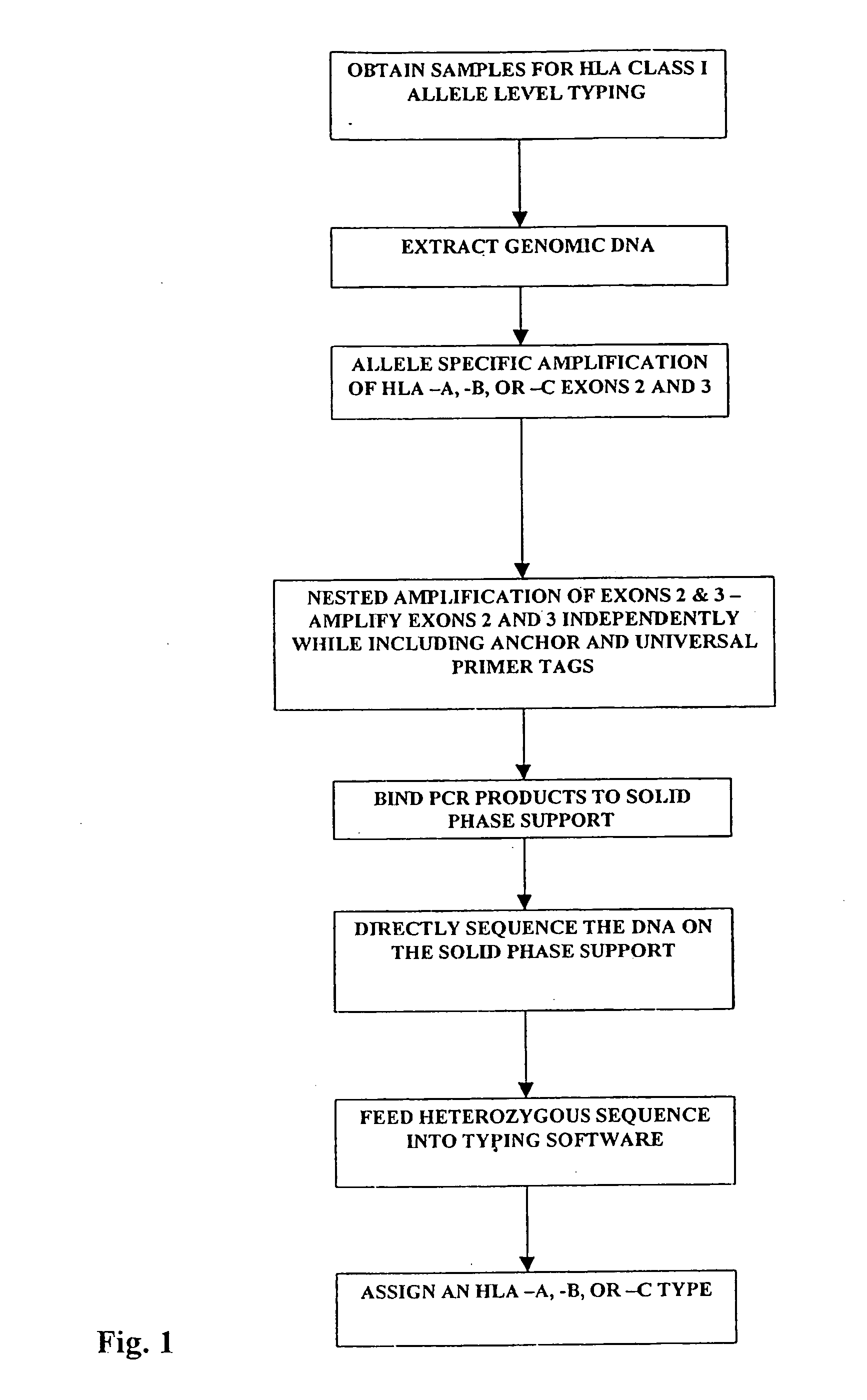
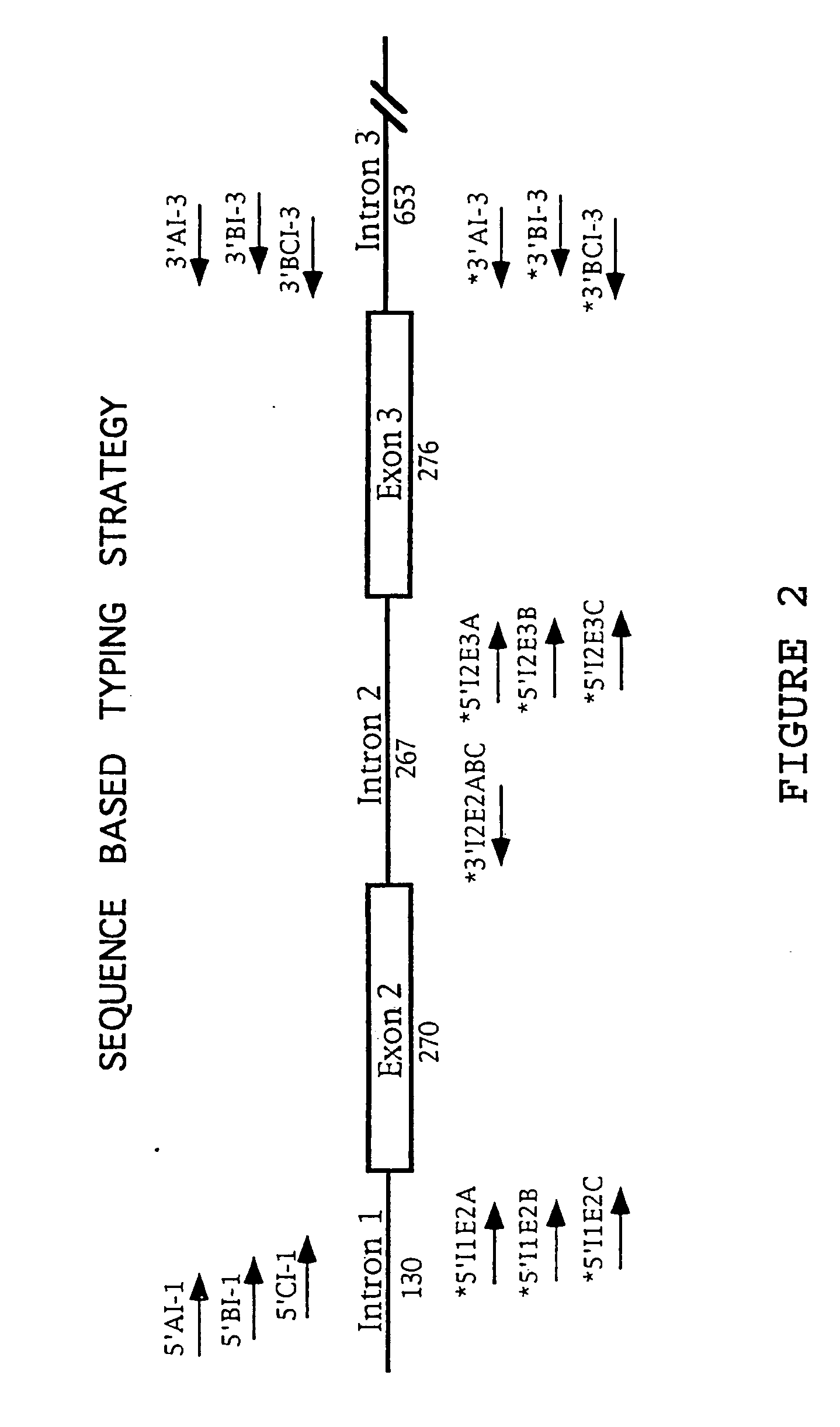
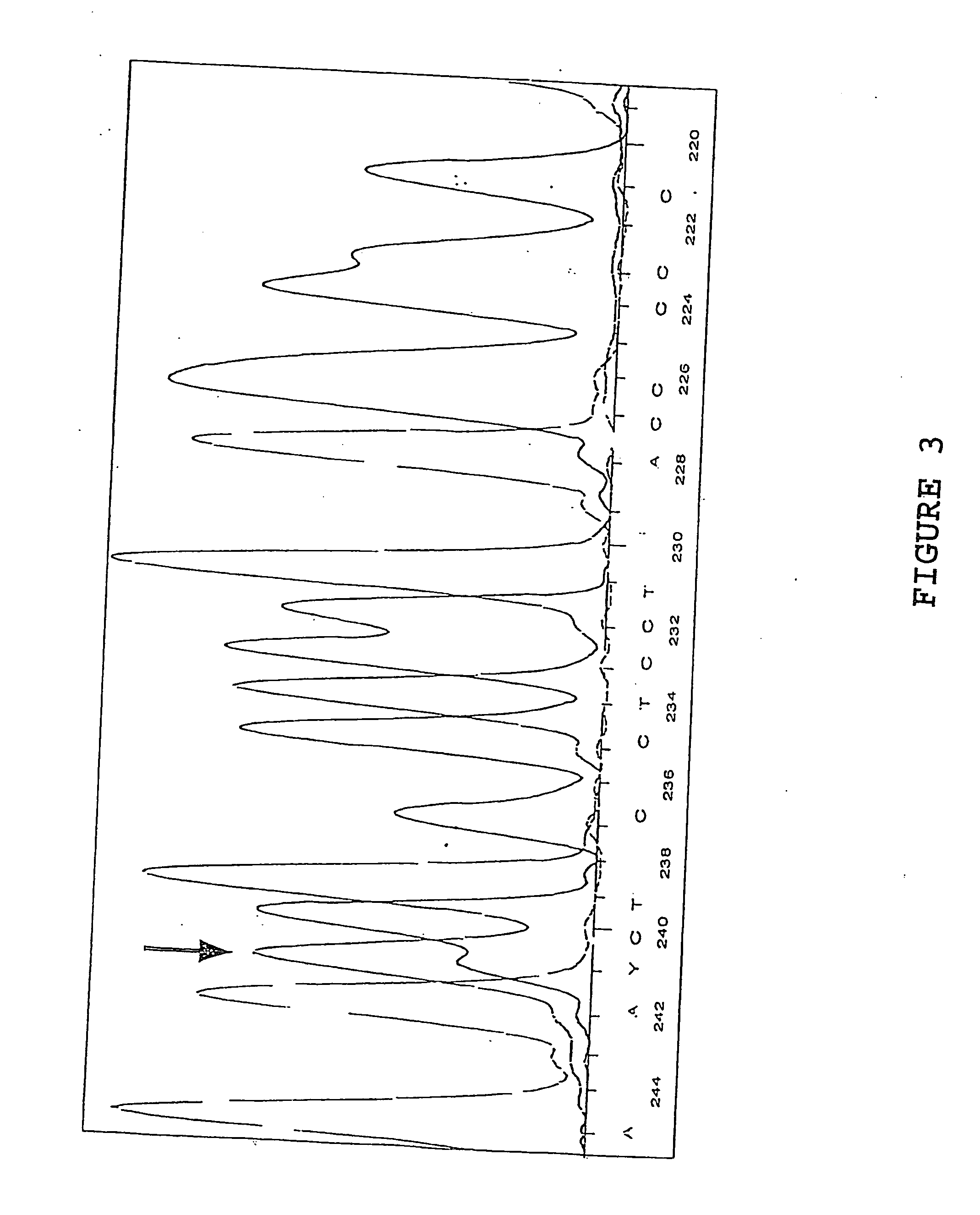
Class I sequence based typing of HLA-A, -B, and -C alleles by direct DNA sequencing
InactiveUS20070128629A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationTissue sampleDirect sequencing
There is provided a method for directly typing or sequencing HLA-A, -B, or -C alleles from a tissue sample wherein exons 2 and 3 of the HLA-A, -B, or -C alleles from the sample are amplified together in a locus specific manner and then separated out and individually amplified in a locus specific manner. After the two amplifications, the amplified exons are directly sequenced, the sequences are recombined, and a comparison is made between the derived HLA allele sequence and an HLA allele database, thereby giving an exact HLA-A, -B, or -C type for the sample being tested.
Owner:HILDEBRAND WILLIAM H +3
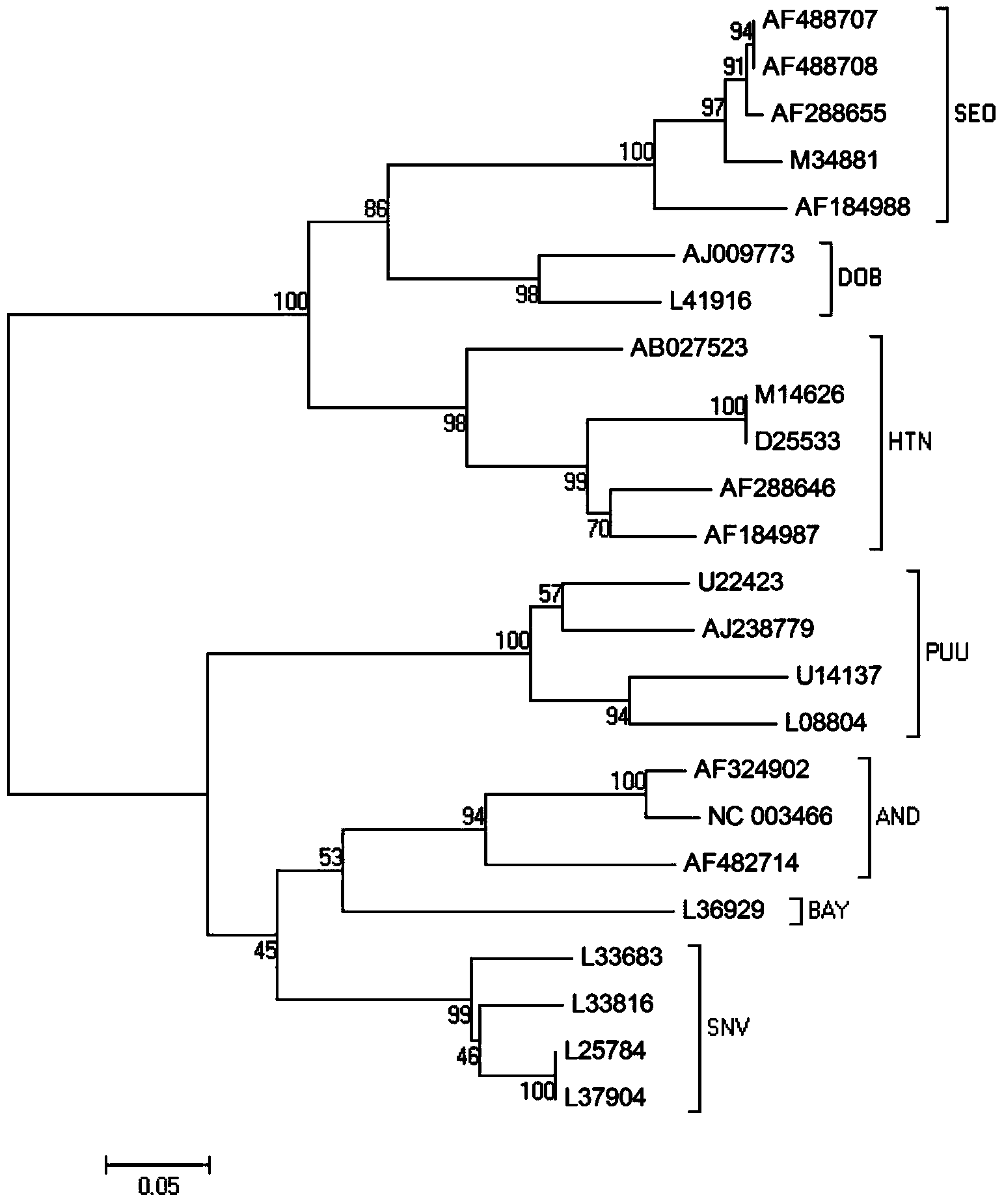
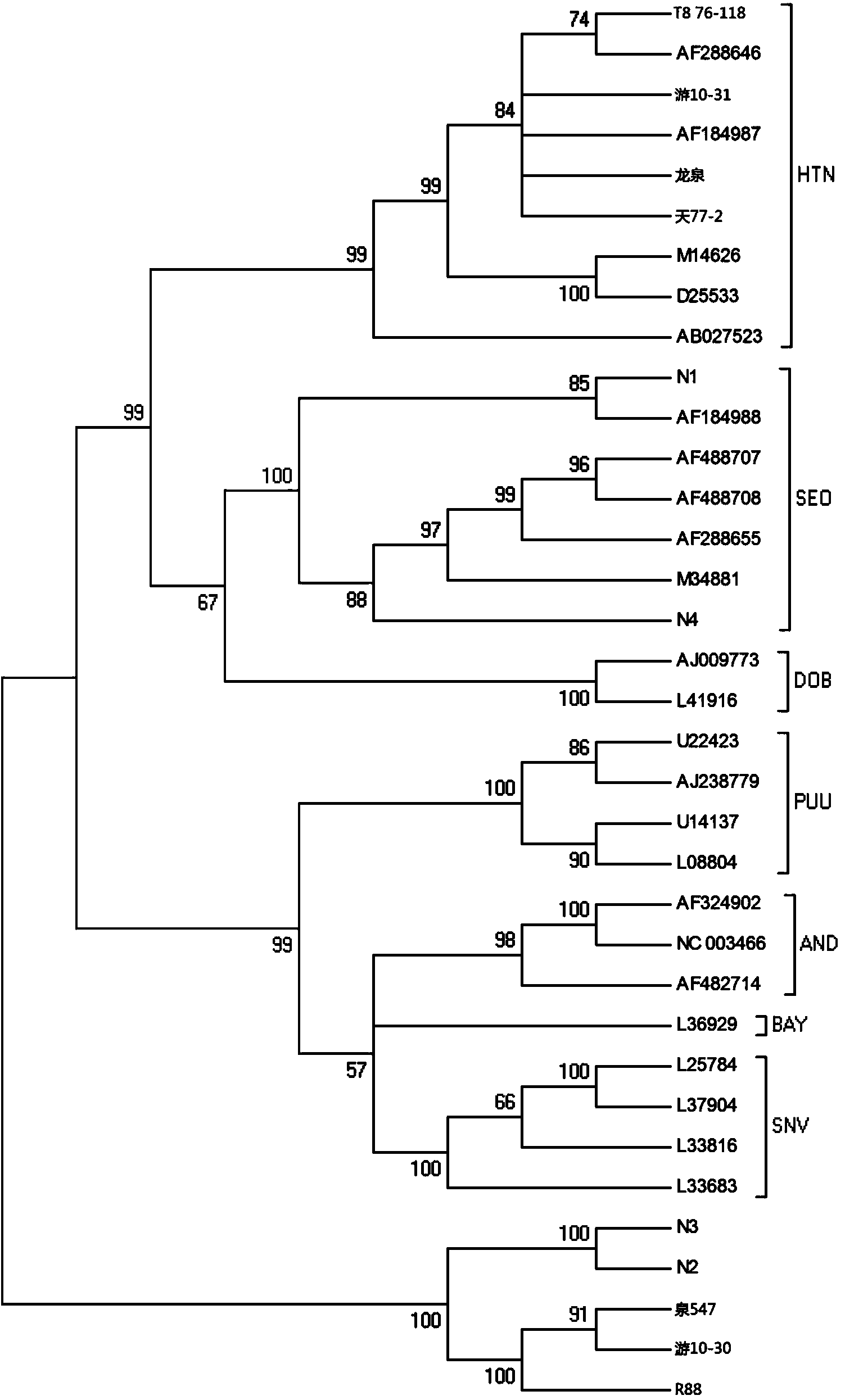
Primer, kit and method for conducting genetic typing on hantavirus by means of PCR direct sequencing method
ActiveCN103484566AEasy and fast genotypingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTotal rnaDirect sequencing
The invention discloses a primer, kit and method for conducting genetic typing on the hantavirus by means of a PCR direct sequencing method. The primer comprises an upstream primer: ATTAGCCCWGTCATGAGTGT, and a downstream primer: CTTTGACTCYTTTGKYTCCA, wherein the Y is a C or a T, the W is an A or a T, and the K is a G or a T. The method comprises the steps of extracting a total RNA of a virus sample to be tested, conducting reverse transcription to obtain a cDNA, using the cDNA as a template, utilizing the primer for conducting PCR amplification, conducting sequencing on an amplified target fragment, constructing a phylogenetic tree by using corresponding fragments of known genotype representative strains as a reference on the basis of sequence information of the target fragment, and conducting the genetic typing on the virus sample to be tested according to the phylogenetic tree. When the primer is used, a specificity sequence of an S gene of the hantavirus can be obtained by only conducting one-time PCR amplification, and the genetic typing can be easily, conveniently and rapidly carried out on the hantavirus by utilizing the specificity sequence.
Owner:嘉兴实践医学科技有限公司
Gene of cortexin-3 receptor of pig melanin and method for detecting polymorphism of mononucleotide
InactiveCN1480532AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMelanocortin 3 receptorDirect sequencing
A process for detecting pig melanocortin-3 receptor (MC3R) gene and its single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) includes extracting DNA from pig blood genom, designing primer based on human and mouse MC3R gene conservative region, PCR amplification, directly sequencing the PCR product, comparing sequence, analyzing and detecting SNP.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
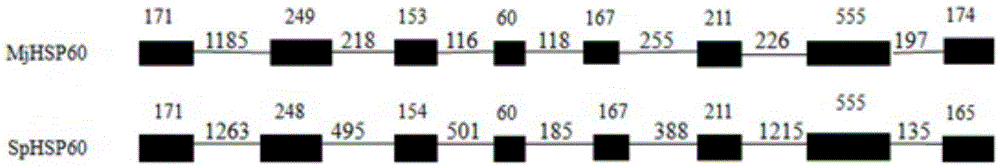
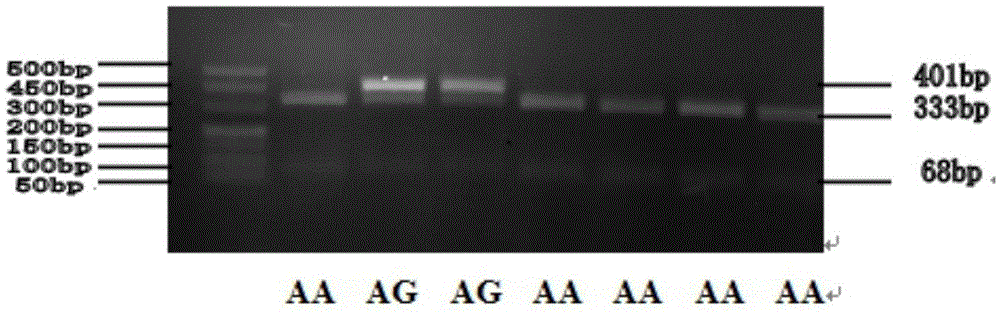
SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat resistance and detection method thereof
InactiveCN105567865AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringCorrelation analysisBiology
The invention provides an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat resistance and a detection method thereof, relating to detection of shrimp heat-resistant populations in aquiculture. The invention firstly provides an SNP marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat tolerance by using a direct sequencing process. The SNP marker related to Marsupenaeus japonicus heat tolerance is the 3289th site of the HSP60 gene of which the nucleic acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.1, and the base is A or G. The detection method comprises the following steps: carrying out a Marsupenaeus japonicus heat resistance experiment; calculating the heat resistance value; carrying out genotyping by using a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) technique; and analyzing the heat tolerance of the Marsupenaeus japonicus individuals with different genotypes. The direct sequencing process and the PCR-RFLP process are utilized to give out the polymorphism of the MjHSP60 gene, and the correlation analysis is carried out on the SNP polymorphism and Marsupenaeus japonicus heat tolerance, thereby providing theoretical references for screening high-temperature-resistant SNP molecular markers and developing molecular breeding of Marsupenaeus japonicus heat-resistant lines.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Polymorphism of MDM2 gene related to occurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and lymphatic metastasis and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101298628AReduce disease riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDirect sequencingMdm2 Protein
The invention discloses an MDM2 gene which is a novel predisposing gene of nasopharyngeal darcinoma by relating the SNP 309 polymorphic loci of the MDM2 gene with the risk of the nasopharyngeal darcinoma and the more serious lymph node metastasis, thereby providing new genetic counseling contents and the molecule criterion for people to prevent and control the nasopharyngeal darcinoma. In addition, the invention also relates to a method for detecting the SNP309 polymorphic loci and the corresponding detecting kit, wherein, the detecting method is the PCR product direct sequencing method that is the polymerase chain reaction-sequencing method.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Androgen-metabolic gene mutations and prostate cancer risk
This present invention identifies mutations in several androgen-metabolic genes (SRD5A2, CYP17, HSD3B2, and HSD17B3) and methods of using such mutations in the diagnosis and treatment of inheritable prostate cancer susceptibility. Isolation of genomic DNA of various racial / ethnic populations followed by SSCP scanning and direct PCR sequencing of the aberrant SSCP (single-strand conformation dependent DNA polymorphism) patterns allows for identification of the disclosed polymorphisms. Screening for the disclosed mutations establishes a differential distribution among various racial / ethnic groups as well as altered in vivo enzyme activity that parallels prostate cancer risk.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com