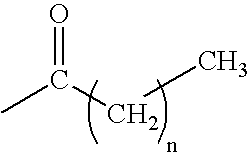
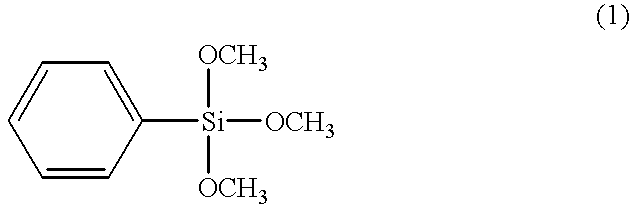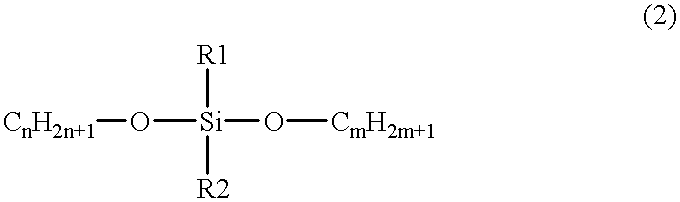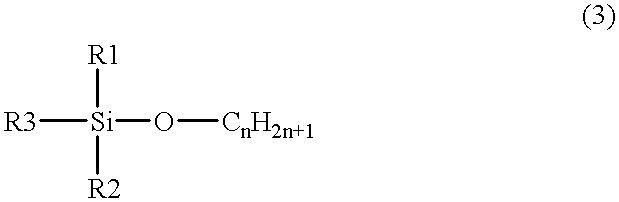Patents
Literature
104711 results about "Silicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard and brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre; and it is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, and lead are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C respectively are the second-highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being only surpassed by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is most widely distributed in dusts, sands, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates. More than 90% of the Earth's crust is composed of silicate minerals, making silicon the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust (about 28% by mass) after oxygen.
High-electron mobility transistor with zinc oxide
InactiveUS7105868B2Increase heightHigh electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierField-effect transistor
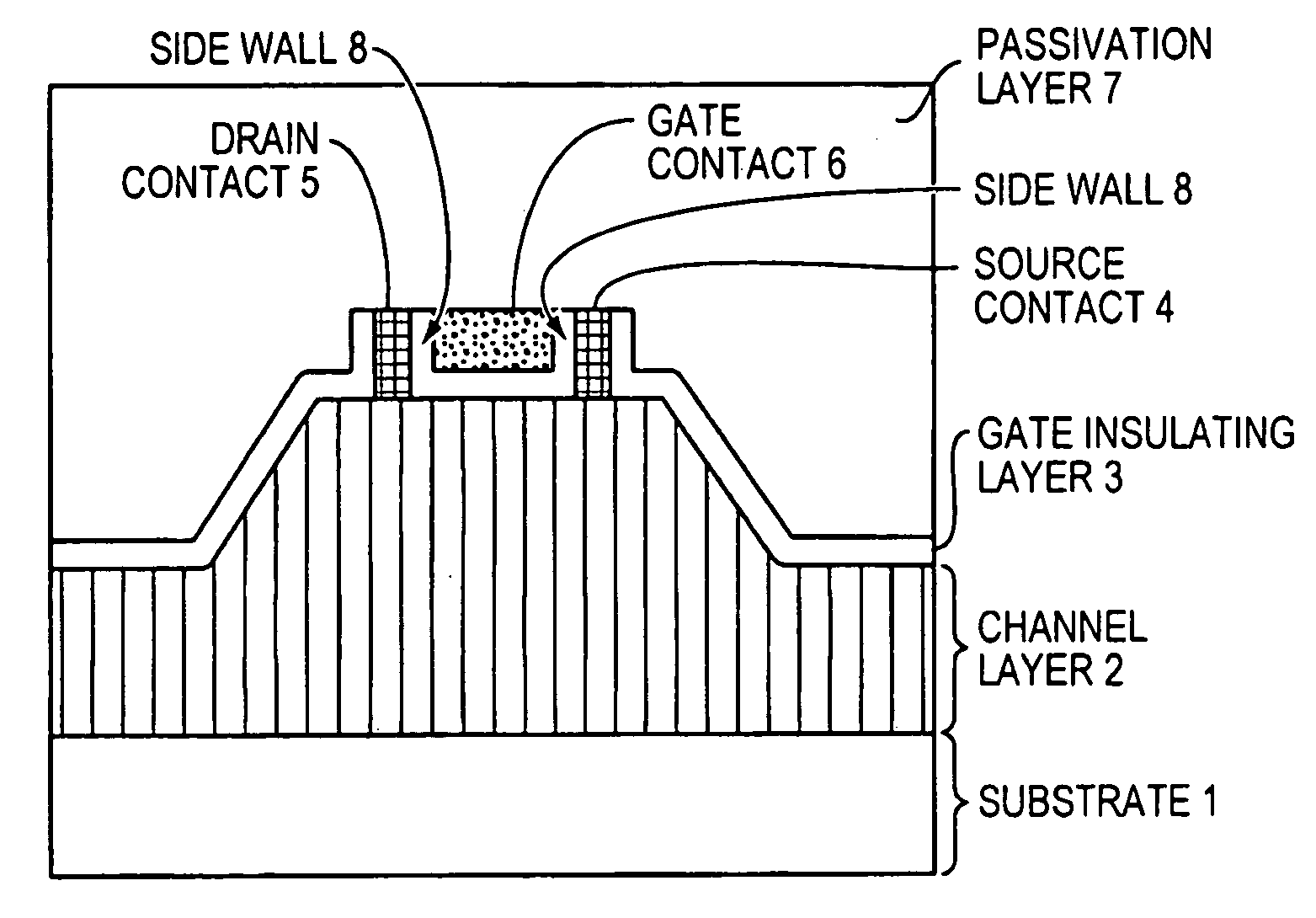
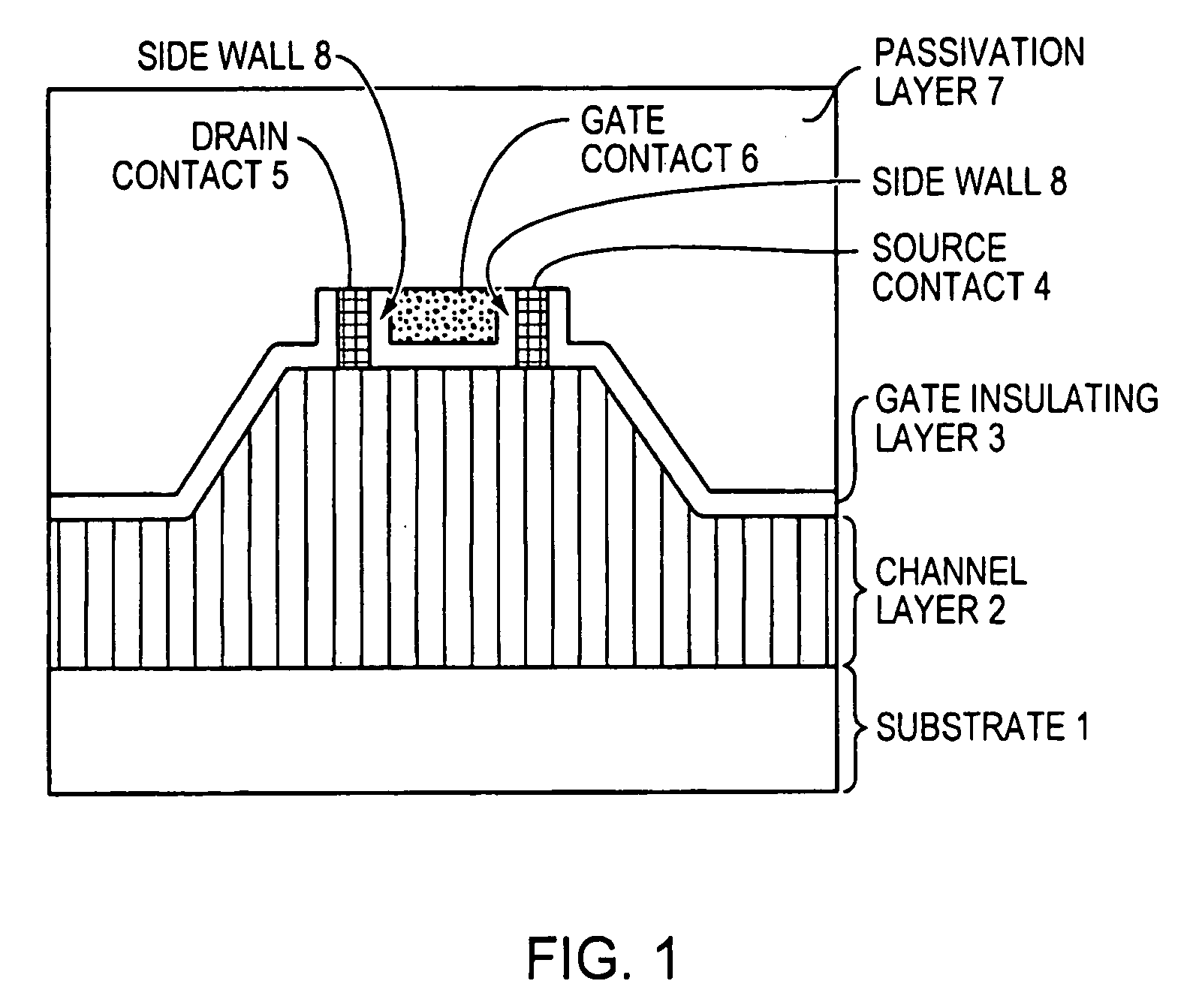
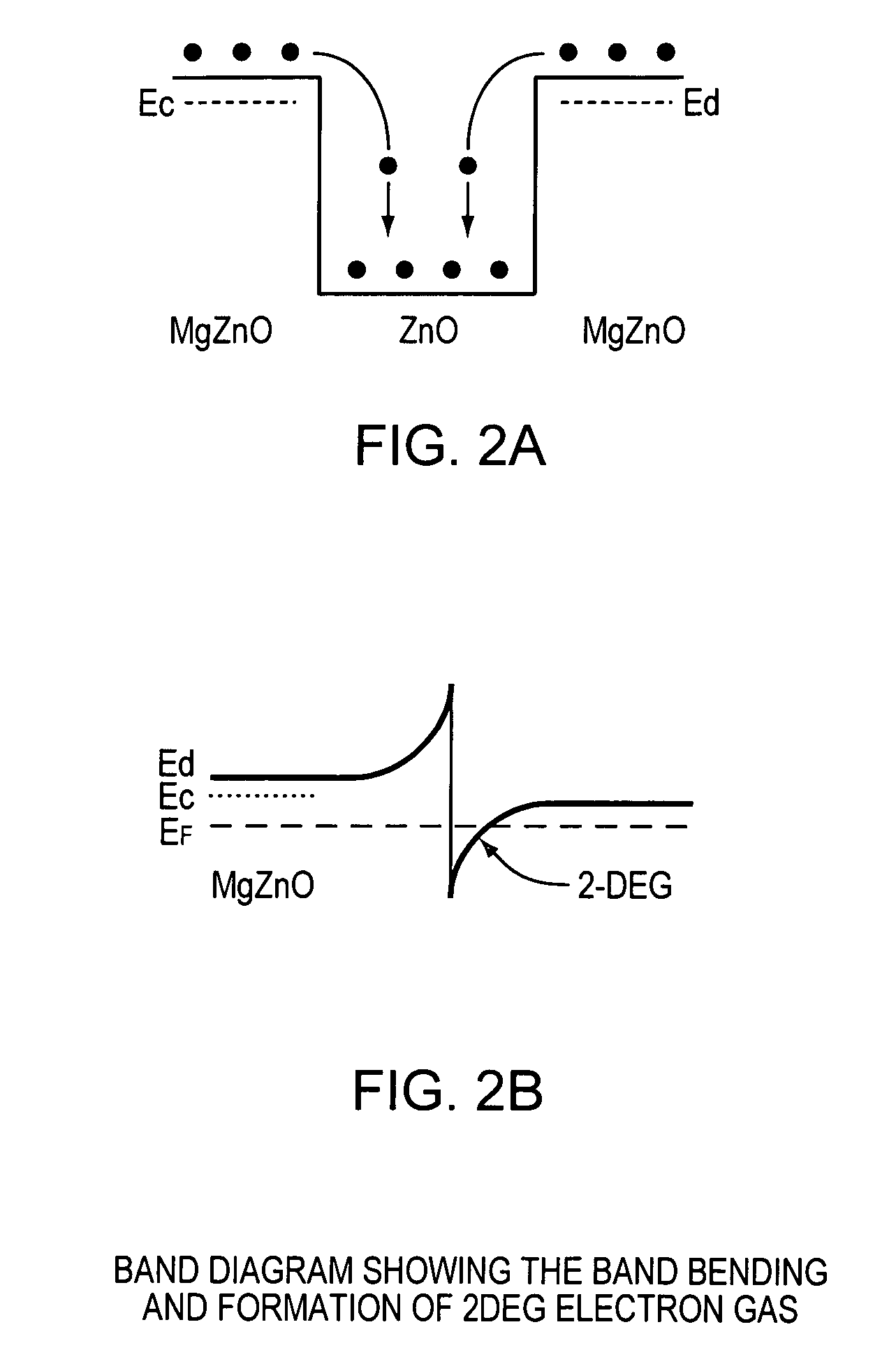
A zinc oxide (ZnO) field effect transistor exhibits large input amplitude by using a gate insulating layer. A channel layer and the gate insulating layer are sequentially laminated on a substrate. A gate electrode is formed on the gate insulating layer. A source contact and a drain contact are disposed at the both sides of the gate contact and are electrically connected to the channel layer via openings. The channel layer is formed from n-type ZnO. The gate insulating layer is made from aluminum nitride / aluminum gallium nitride (AlN / AlGaN) or magnesium zinc oxide (MgZnO), which exhibits excellent insulation characteristics, thus increasing the Schottky barrier and achieving large input amplitude. If the FET is operated in the enhancement mode, it is operable in a manner similar to a silicon metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (Si-MOS-type FET), resulting in the formation of an inversion layer.
Owner:NAUSE CATHERINE D
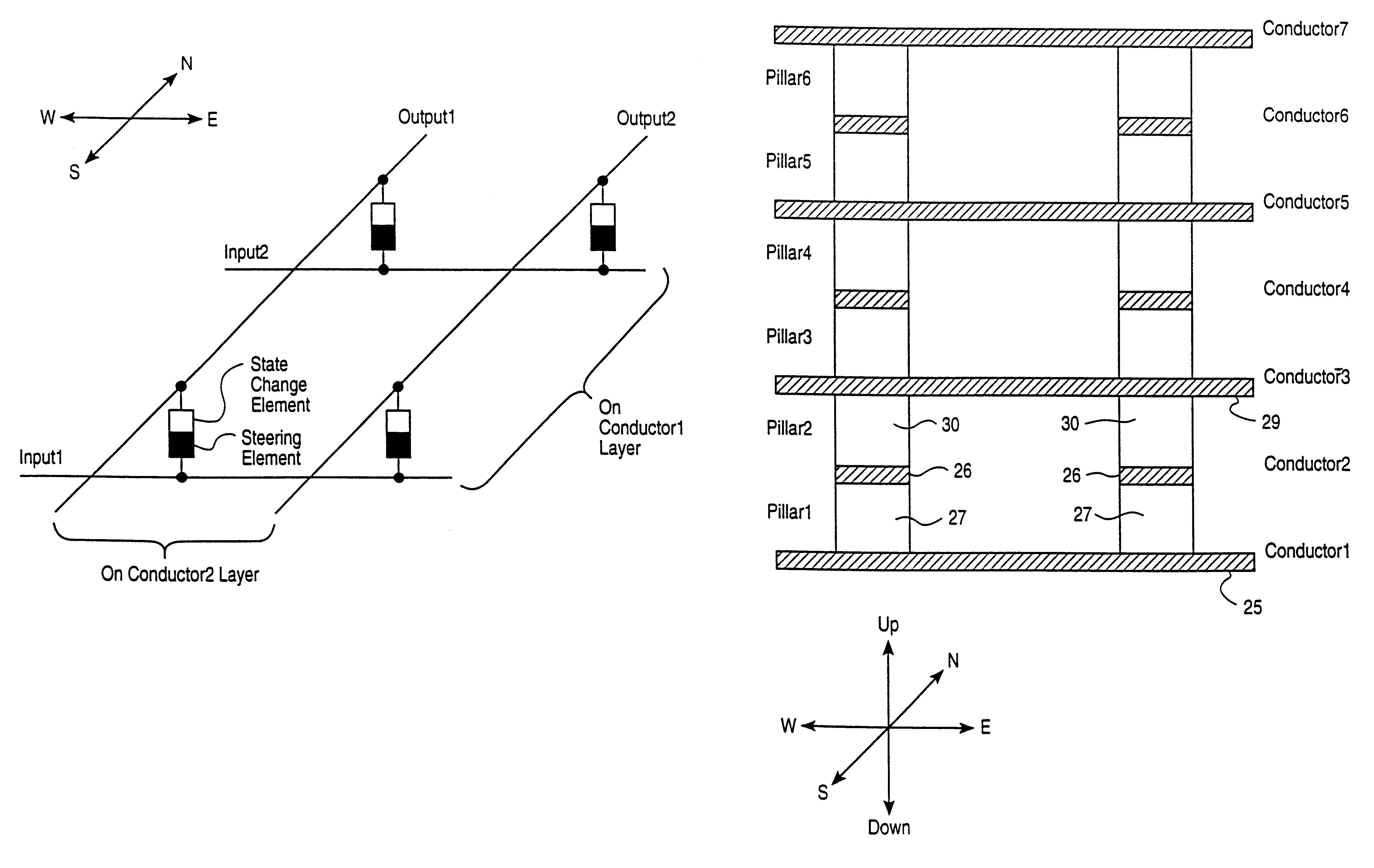
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
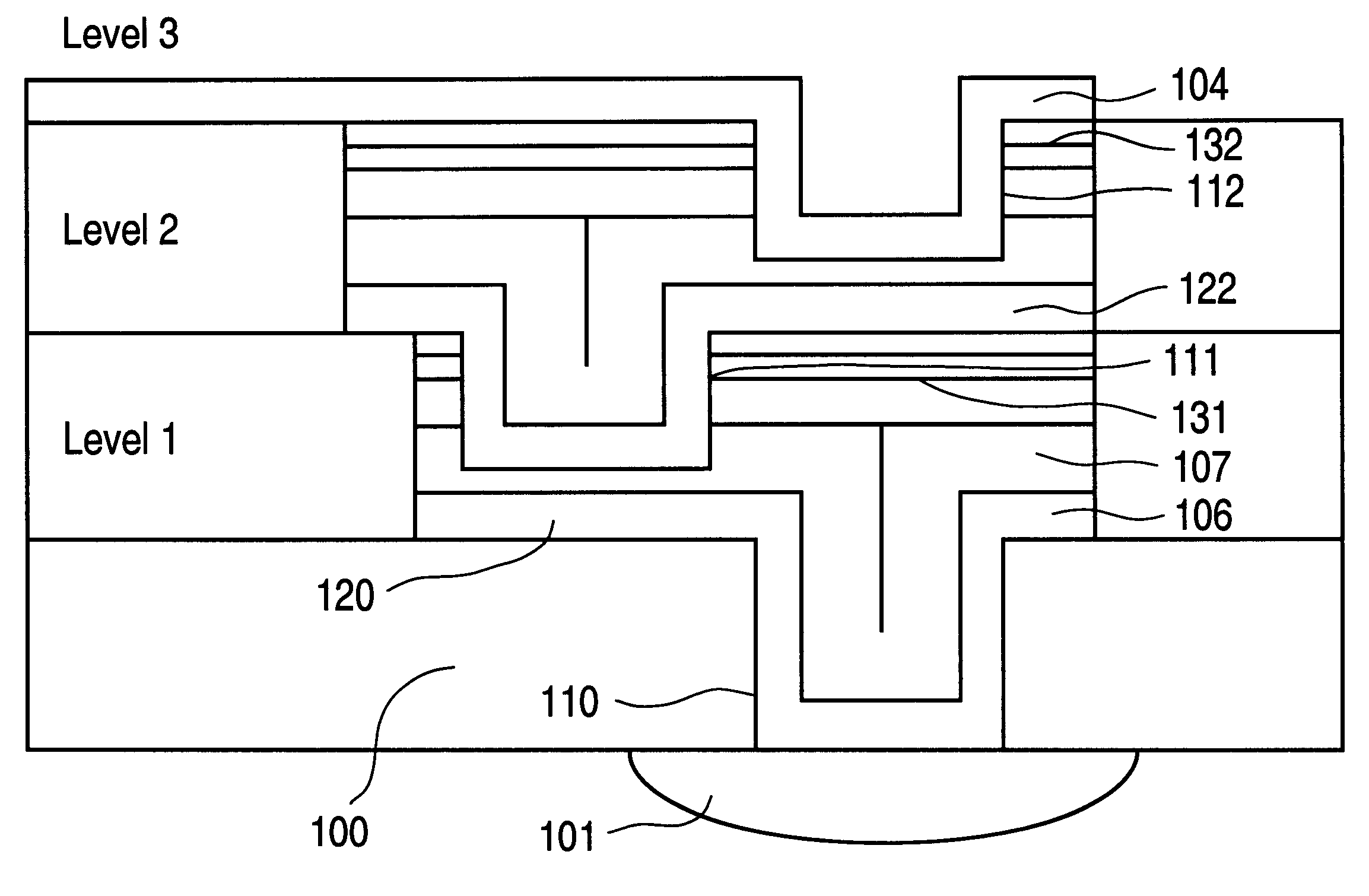
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:RHOMBUS
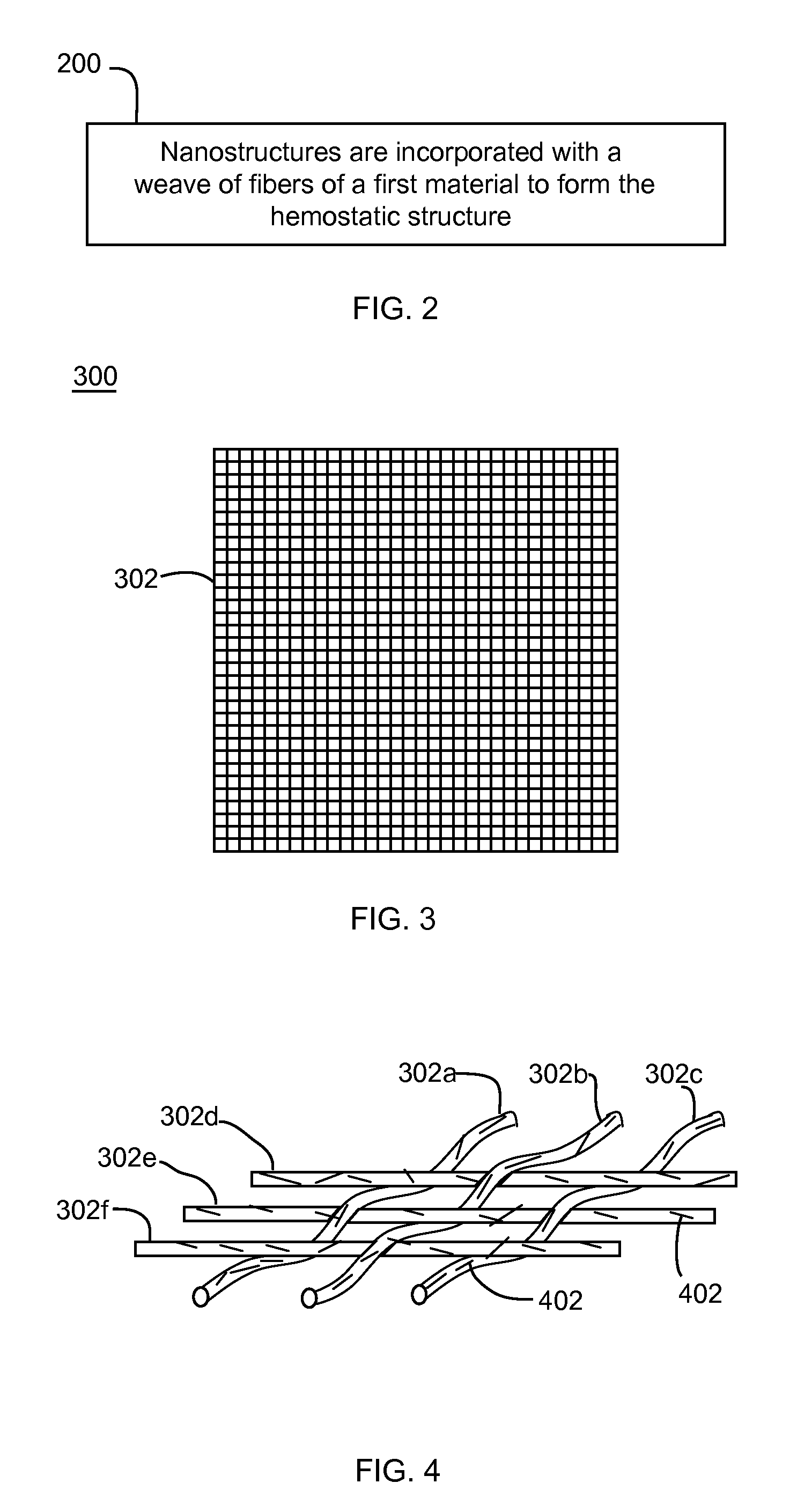
Nanostructure-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic structures
InactiveUS8319002B2Enhancing overall rate and strengthInduce platelet binding and efficient hemostasisBiocideSurgical adhesivesPlateletNanofiber
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for nanomaterial-enhanced platelet binding and hemostatic medical devices are provided. Hemostatic materials and structures are provided that induce platelet binding, including platelet binding and the coagulation of blood at a wound / opening caused by trauma, a surgical procedure, ulceration, or other cause. Example embodiments include platelet binding devices, hemostatic bandages, hemostatic plugs, and hemostatic formulations. The hemostatic materials and structures may incorporate nanostructures and / or further hemostatic elements such as polymers, silicon nanofibers, silicon dioxide nanofibers, and / or glass beads into a highly absorbent, gelling scaffold. The hemostatic materials and structures may be resorbable.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Method of forming metal layer using atomic layer deposition and semiconductor device having the metal layer as barrier metal layer or upper or lower electrode of capacitor
InactiveUS6287965B1High thermal resistantEasy to adjustSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsNiobiumDevice material
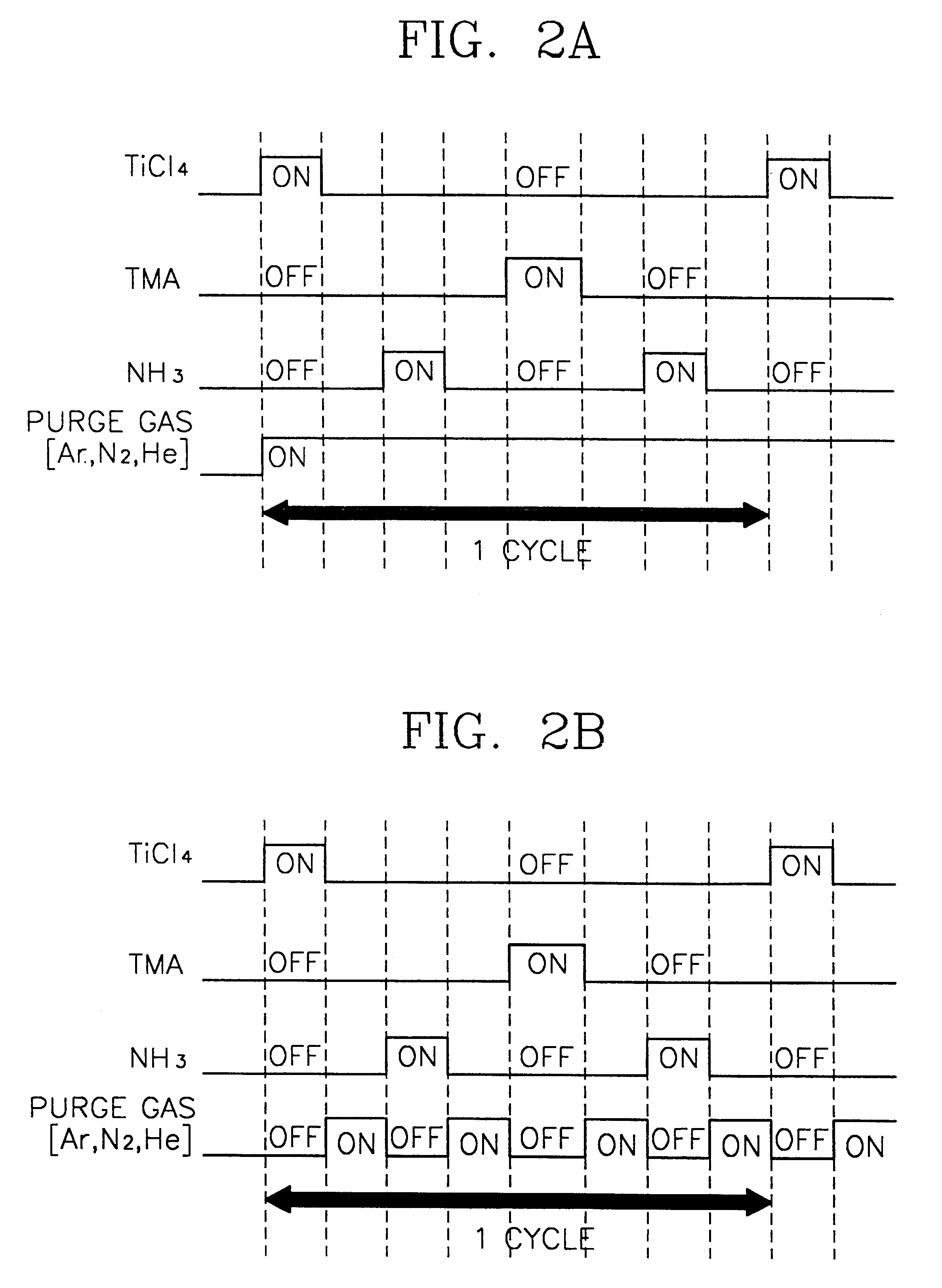
A method of forming a metal layer having excellent thermal and oxidation resistant characteristics using atomic layer deposition is provided. The metal layer includes a reactive metal (A), an element (B) for the amorphous combination between the reactive metal (A) and nitrogen (N), and nitrogen (N). The reactive metal (A) may be titanium (Ti), tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), zirconium (Zr), hafnium (Hf), molybdenum (Mo) or niobium (Nb). The amorphous combination element (B) may be aluminum (Al), silicon (Si) or boron (B). The metal layer is formed by alternately injecting pulsed source gases for the elements (A, B and N) into a chamber according to atomic layer deposition to thereby alternately stack atomic layers. Accordingly, the composition ratio of a nitrogen compound (A-B-N) of the metal layer can be desirably adjusted just by appropriately determining the number of injection pulses of each source gas. According to the composition ratio, a desirable electrical conductivity and resistance of the metal layer can be accurately obtained. The atomic layers are individually deposited, thereby realizing excellent step coverage even in a complex and compact region. A metal layer formed by atomic layer deposition can be employed as a barrier metal layer, a lower electrode or an upper electrode in a semiconductor device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
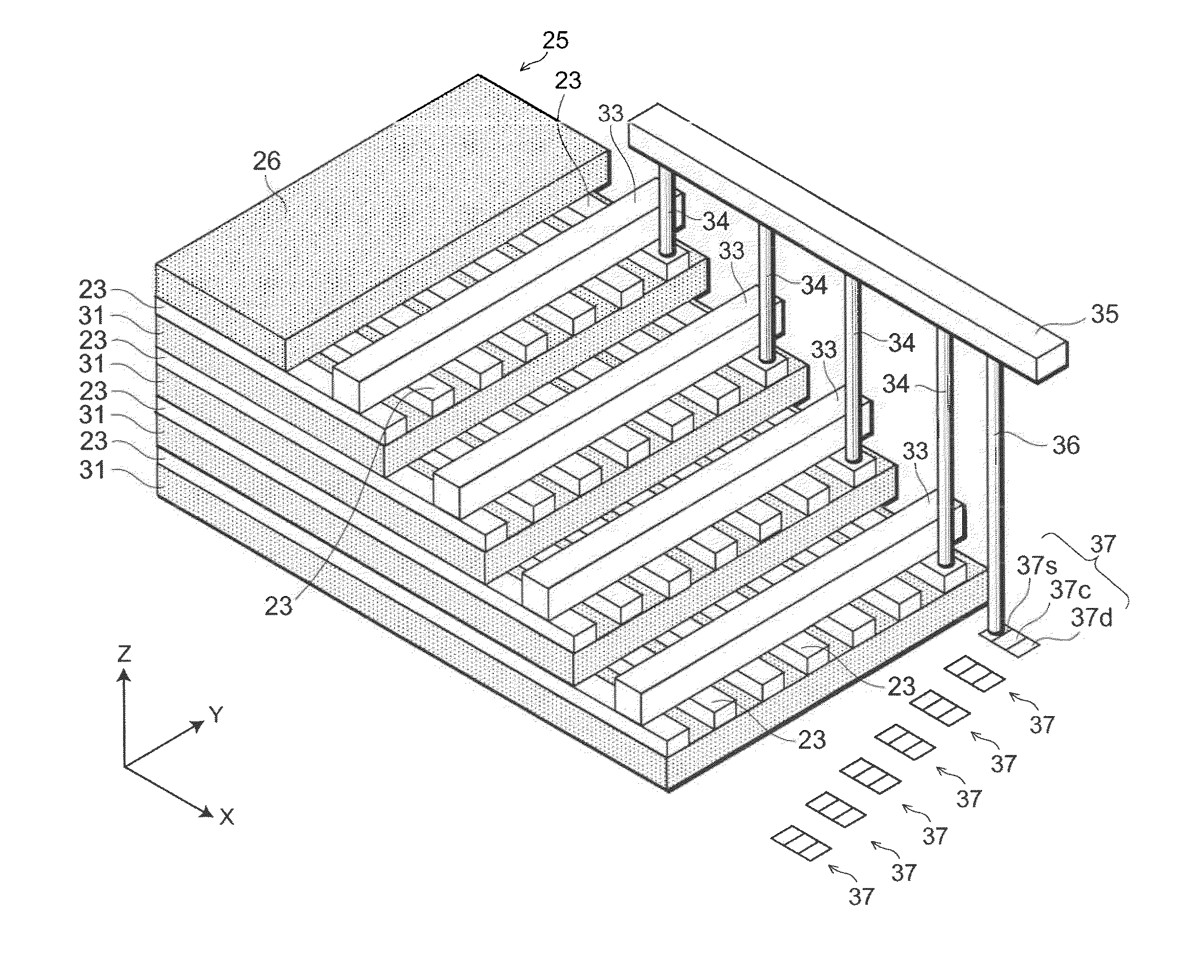
Semiconductor memory and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20110284946A1Increase bit densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSilicon
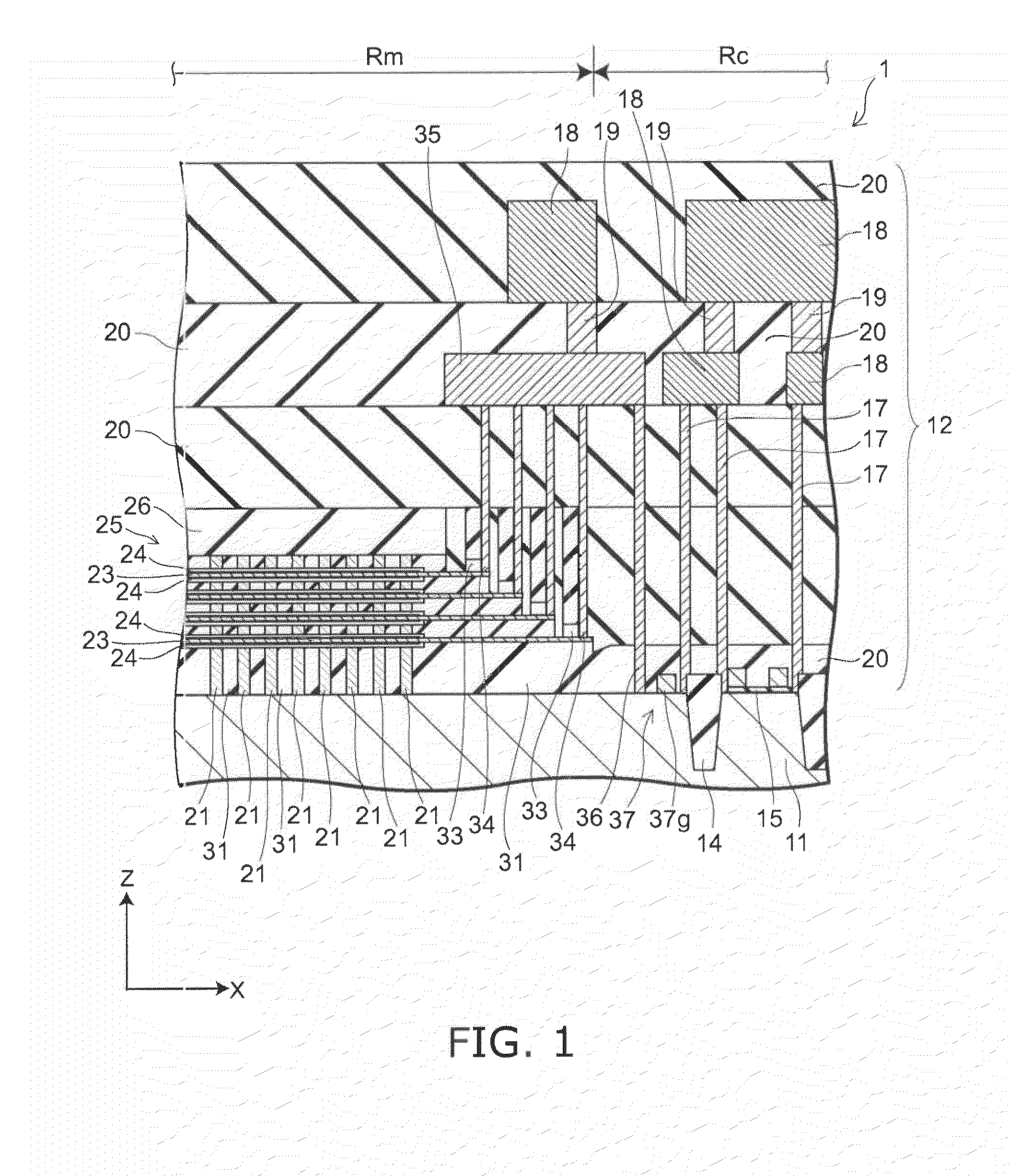
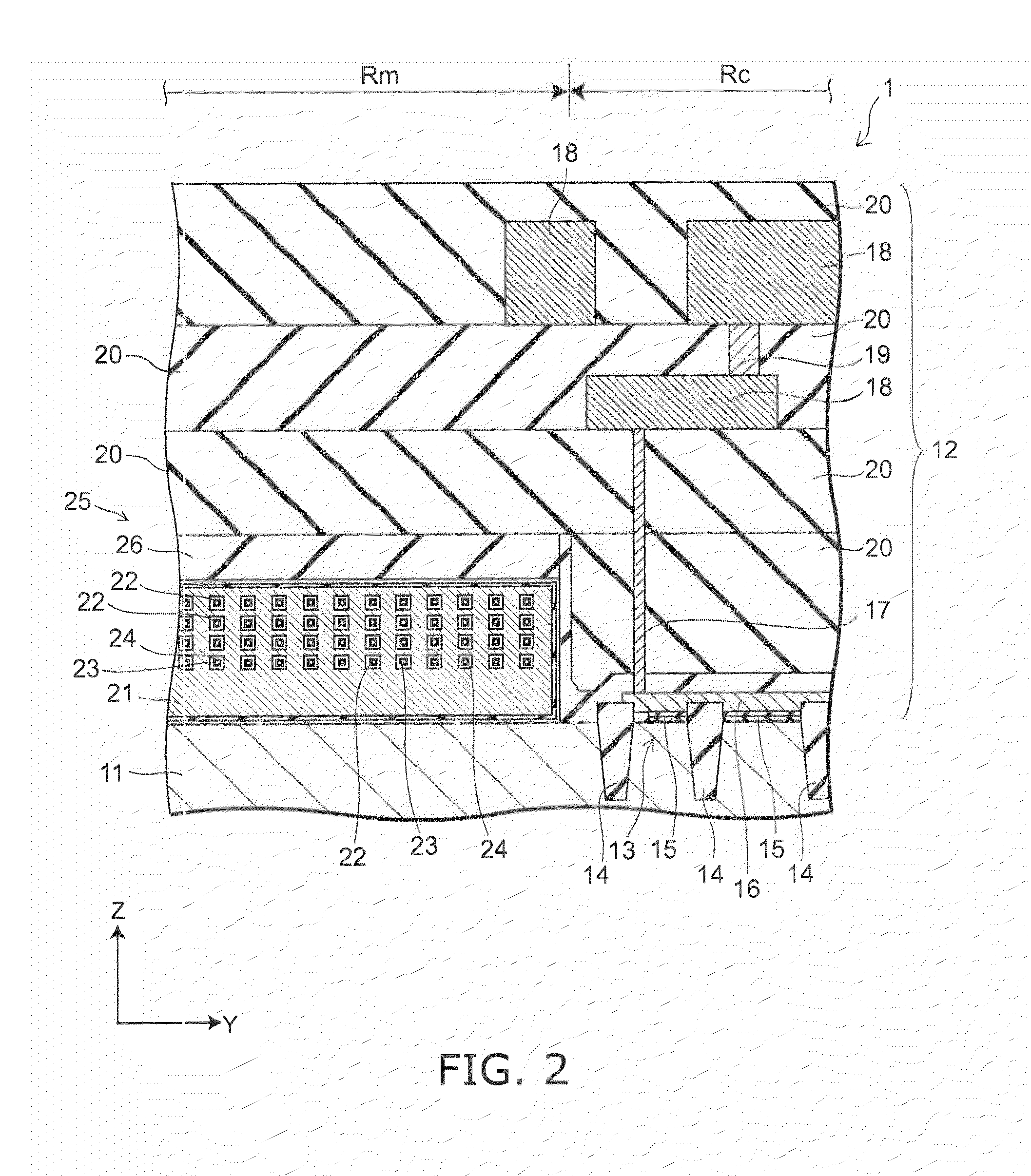
A semiconductor memory capable of increasing bit density by three-dimensional arrangement of cells and a method for manufacturing the same are provided.In a semiconductor memory 1, gate electrode films 21 are provided on a silicon substrate 11. The gate electrode films 21 are arranged in one direction parallel to the upper surface of the silicon substrate 11 (X direction). Each gate electrode film 21 has a lattice plate-like shape, having through holes 22 in a matrix form as viewed in the X direction. Silicon beams 23 are provided passing through the through holes 22 of the gate electrode films 21 and extending in the X direction. Further, an ONO film 24 including a charge storage layer is provided between the gate electrode film 21 and the silicon beam 23.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Silicone polymer insulation film on semiconductor substrate and method for forming the film
InactiveUS6352945B1Low dielectric constantImprove thermal stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolymer scienceHigh humidity
A method for forming a silicone polymer insulation film having a low relative dielectric constant, high thermal stability and high humidity-resistance on a semiconductor substrate is applied to a plasma CVD apparatus. The first step is introducing a silicon-containing hydrocarbon compound expressed by the general formula SialphaObetaCxHy (alpha, beta, x, and y are integers) to the reaction chamber of the plasma CVD apparatus. The silicon-containing hydrocarbon compound has at most two O-CnH2n+1 bonds and at least two hydrocarbon radicals bonded to the silicon. The residence time of the material gas is lengthened by, for example, reducing the total flow of the reaction gas, in such a way as to form a silicone polymer film having a micropore porous structure with a low relative dielectric constant.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
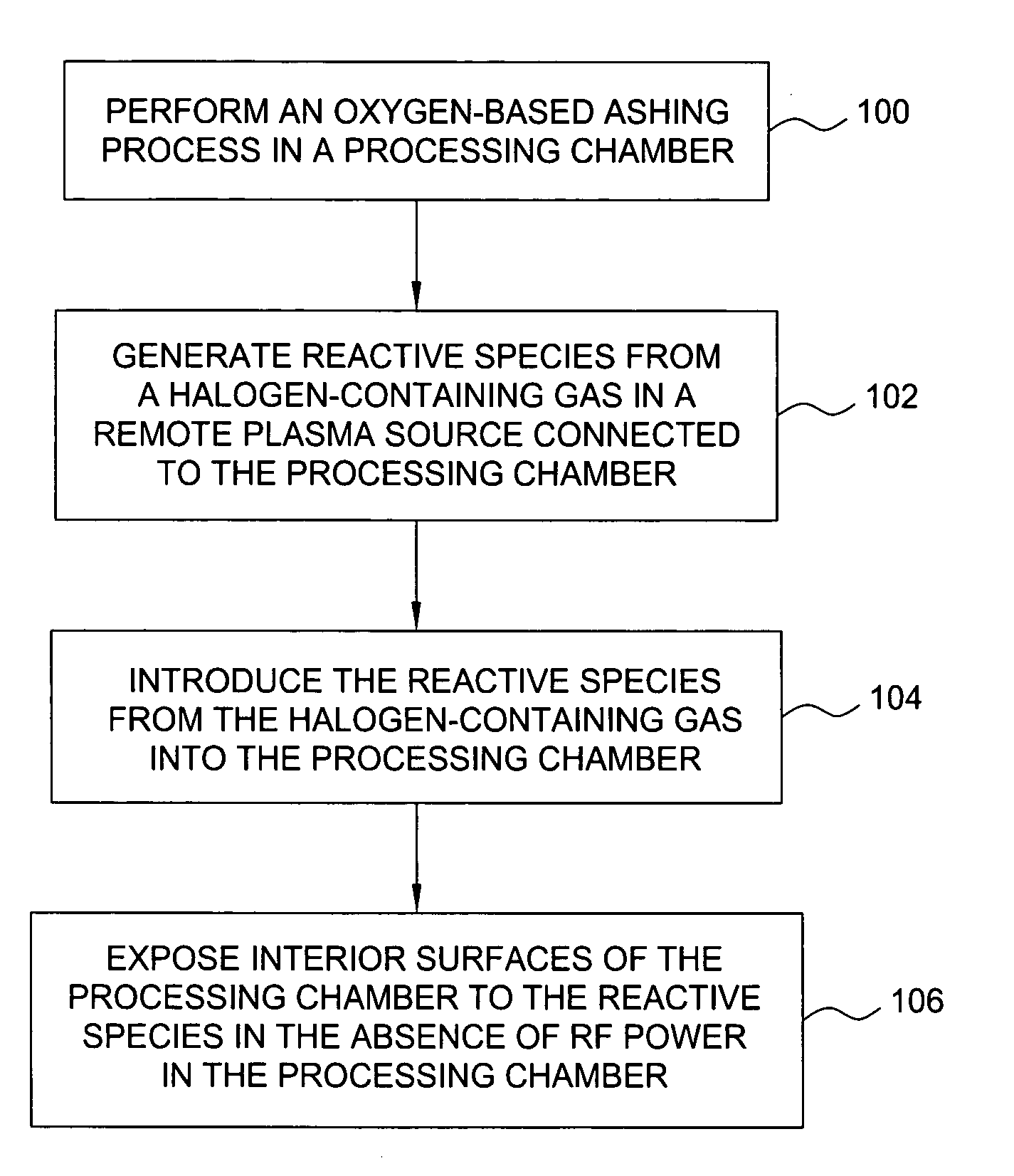
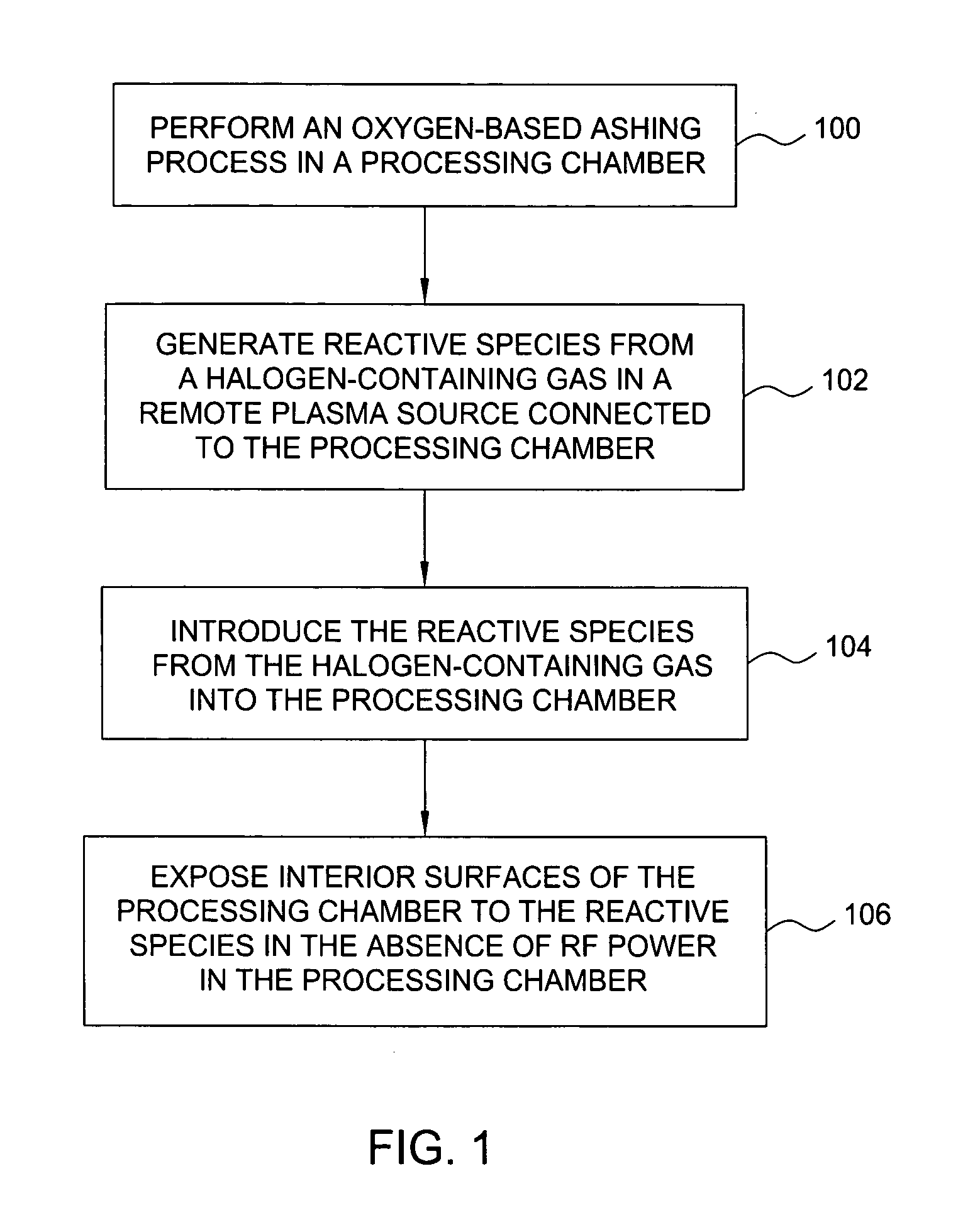
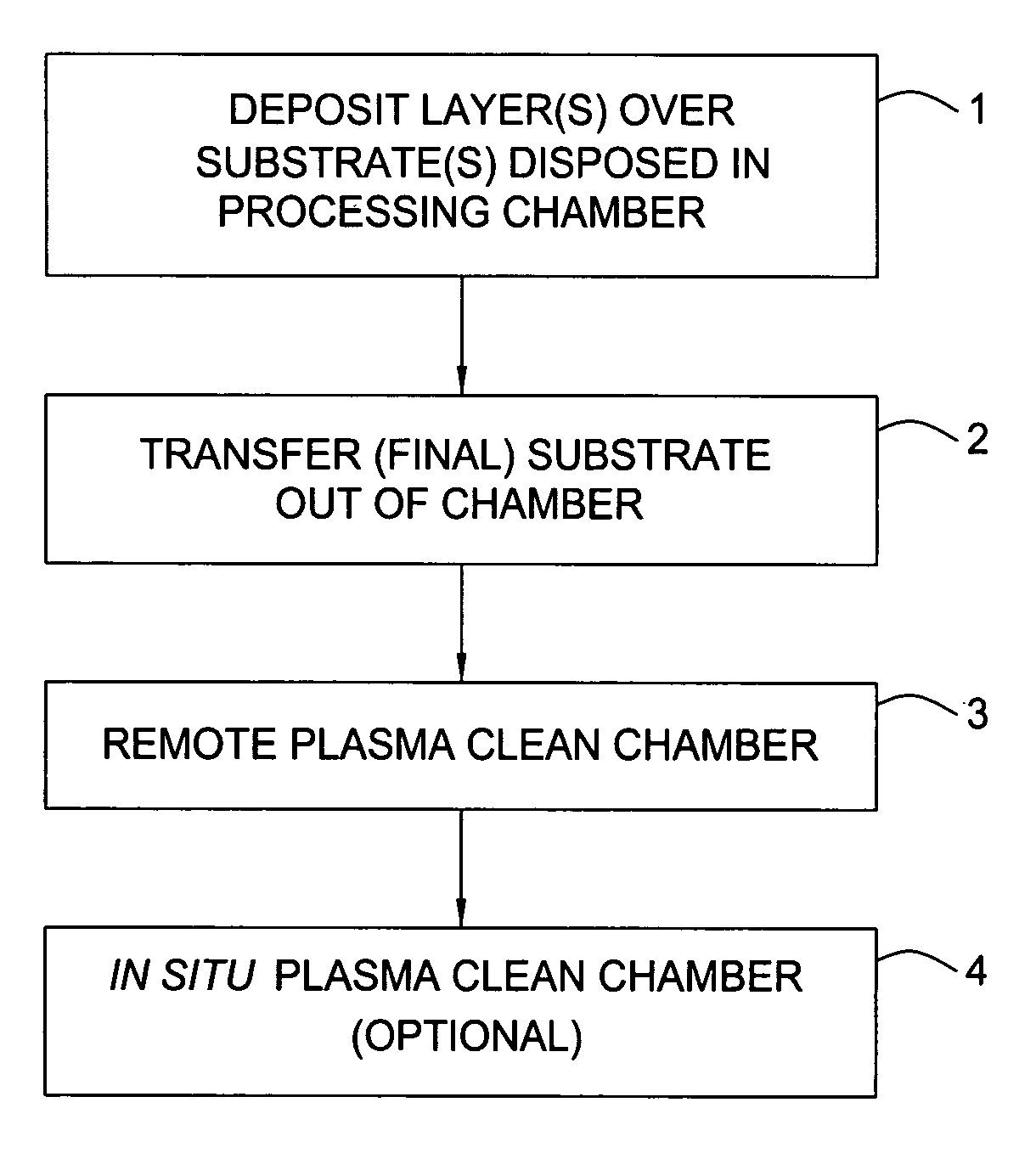
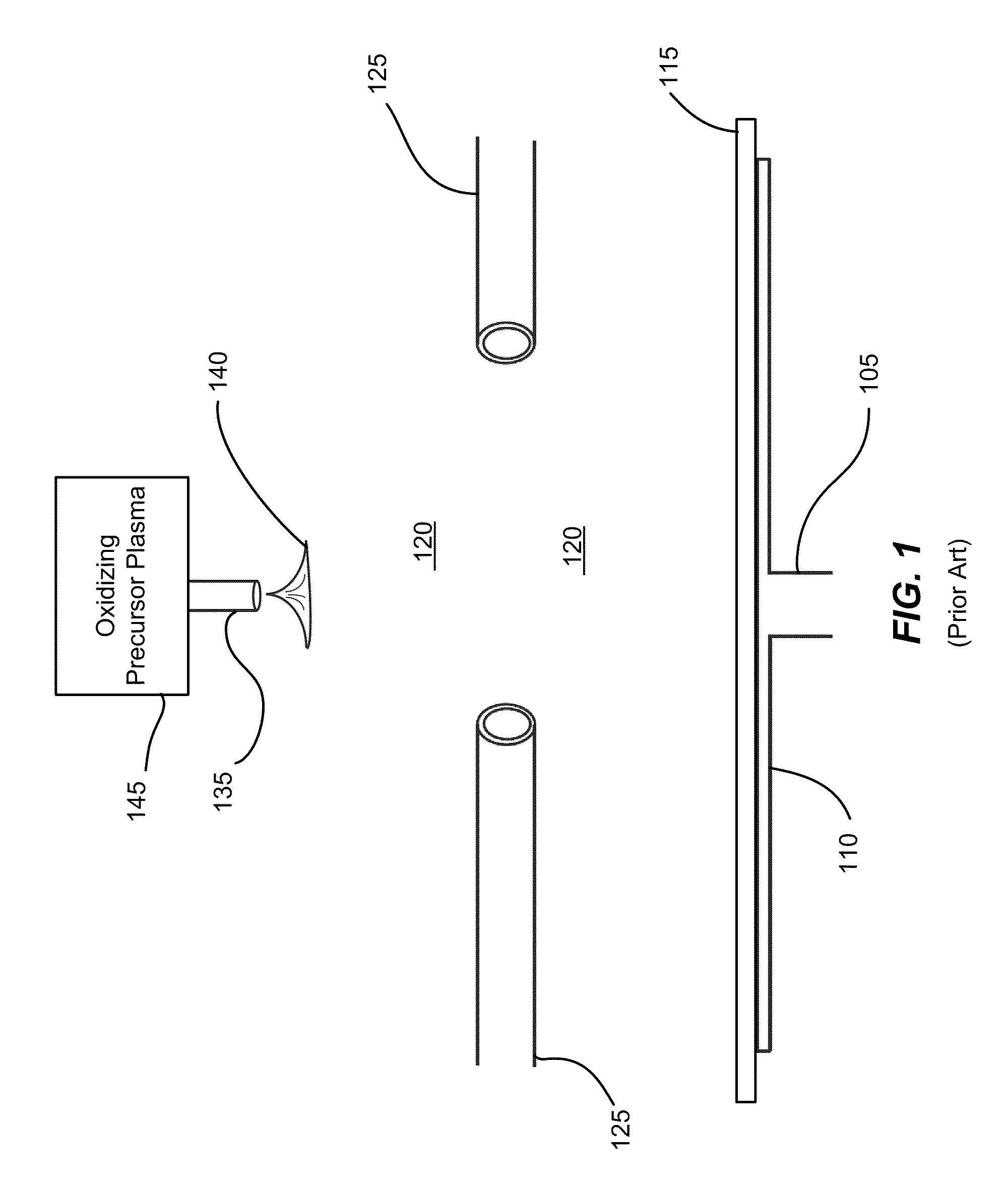
Enhancement of remote plasma source clean for dielectric films
Methods for cleaning semiconductor processing chambers used to process carbon-containing films, such as amorphous carbon films, barrier films comprising silicon and carbon, and low dielectric constant films including silicon, oxygen, and carbon are provided. The methods include using a remote plasma source to generate reactive species that clean interior surfaces of a processing chamber in the absence of RF power in the chamber. The reactive species are generated from an oxygen-containing gas, such as O2, and / or a halogen-containing gas, such as NF3. An oxygen-based ashing process may also be used to remove carbon deposits from the interior surfaces of the chamber before the chamber is exposed to the reactive species from the remote plasma source.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods, systems, and apparatus for atomic-layer deposition of aluminum oxides in integrated circuits
InactiveUS20030207032A1Small volumeConsumes less gasPretreated surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingProduct gasIntegrated circuit layout
Integrated circuits, the key components in thousands of electronic and computer products, are generally built layer by layer on a silicon substrate. One common layer-formation technique, known as chemical-vapor deposition (CVD), produces uneven layers and covers vertical surfaces poorly. An emergent technique, atomic-layer deposition, overcomes these shortcomings, but has others, such as slow deposition rates and longer than desirable cycle times, particularly as applied to deposition of aluminum oxide. Accordingly, the inventors devised unique atomic-layer deposition systems, methods, and apparatus suitable for aluminum-oxide deposition. One exemplary system includes an outer chamber, a substrate holder, and a gas-distribution fixture that engages or cooperates with the substrate holder to form an inner chamber within the outer chamber. The inner chamber has a smaller volume than the outer chamber, which ultimately requires less time to fill and purge and thus promises to reduce cycle times for deposition of materials, such as aluminum oxide.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
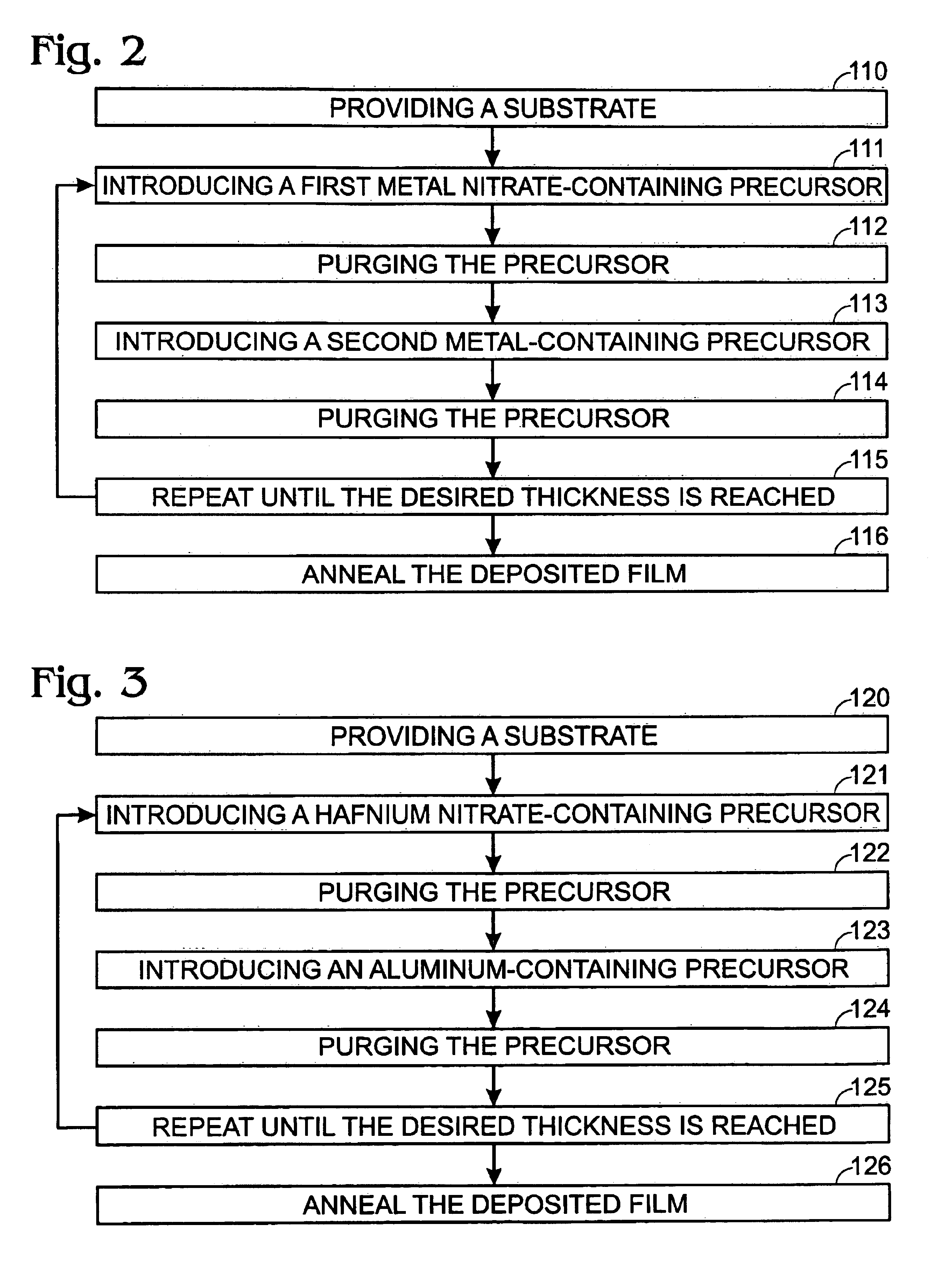
Method for depositing a nanolaminate film by atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS6930059B2Simple methodQuality improvementTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricHafnium
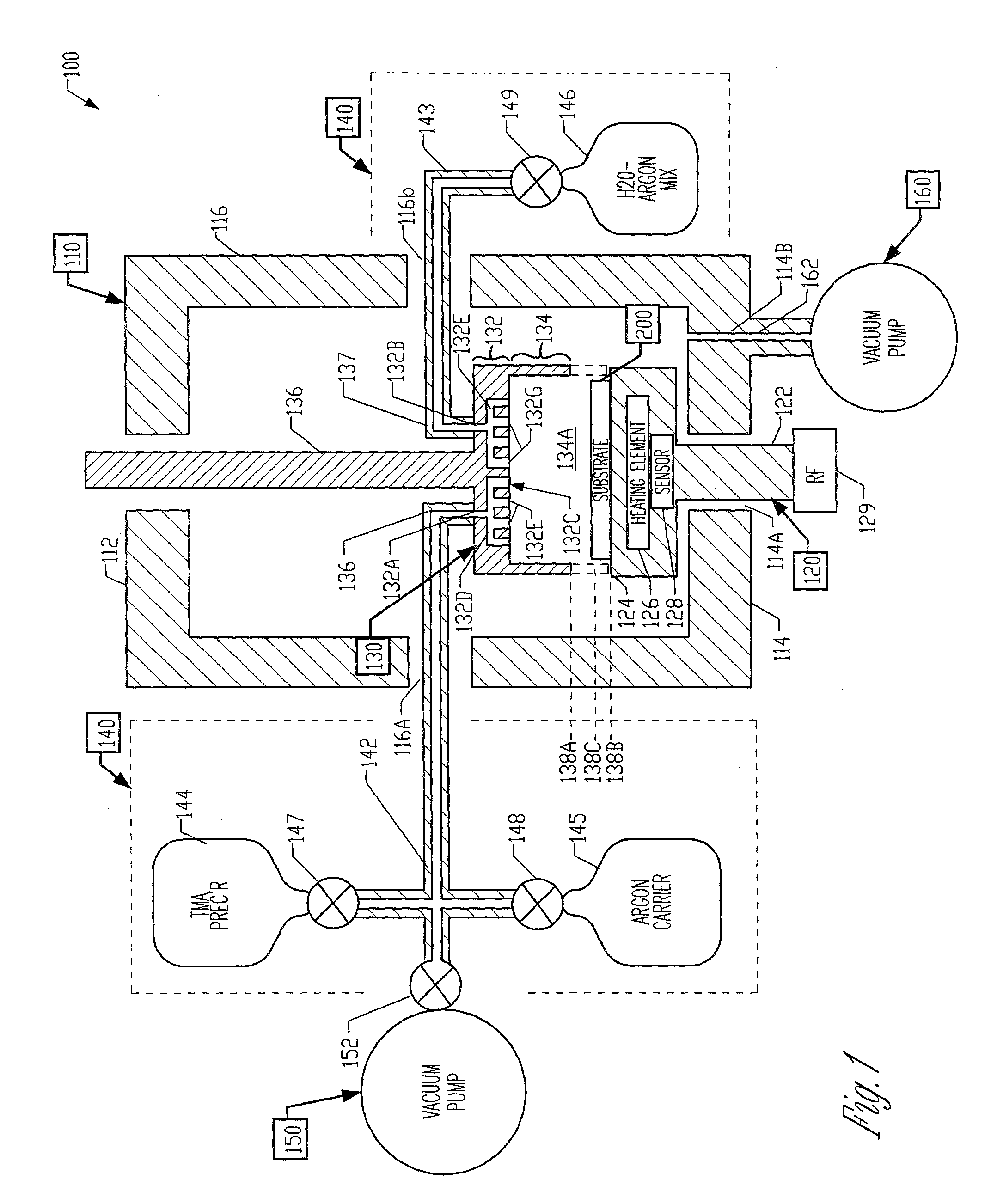
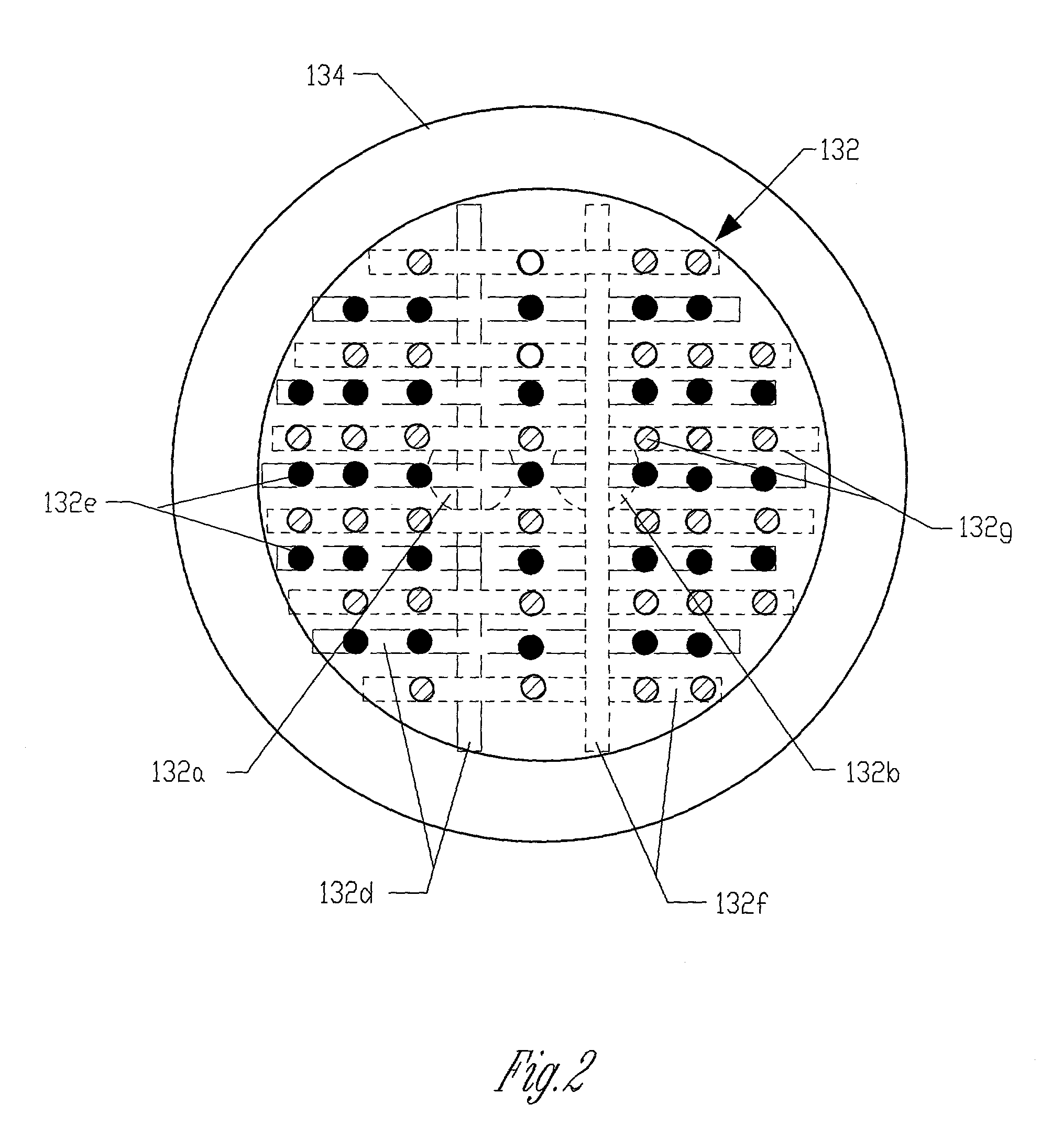
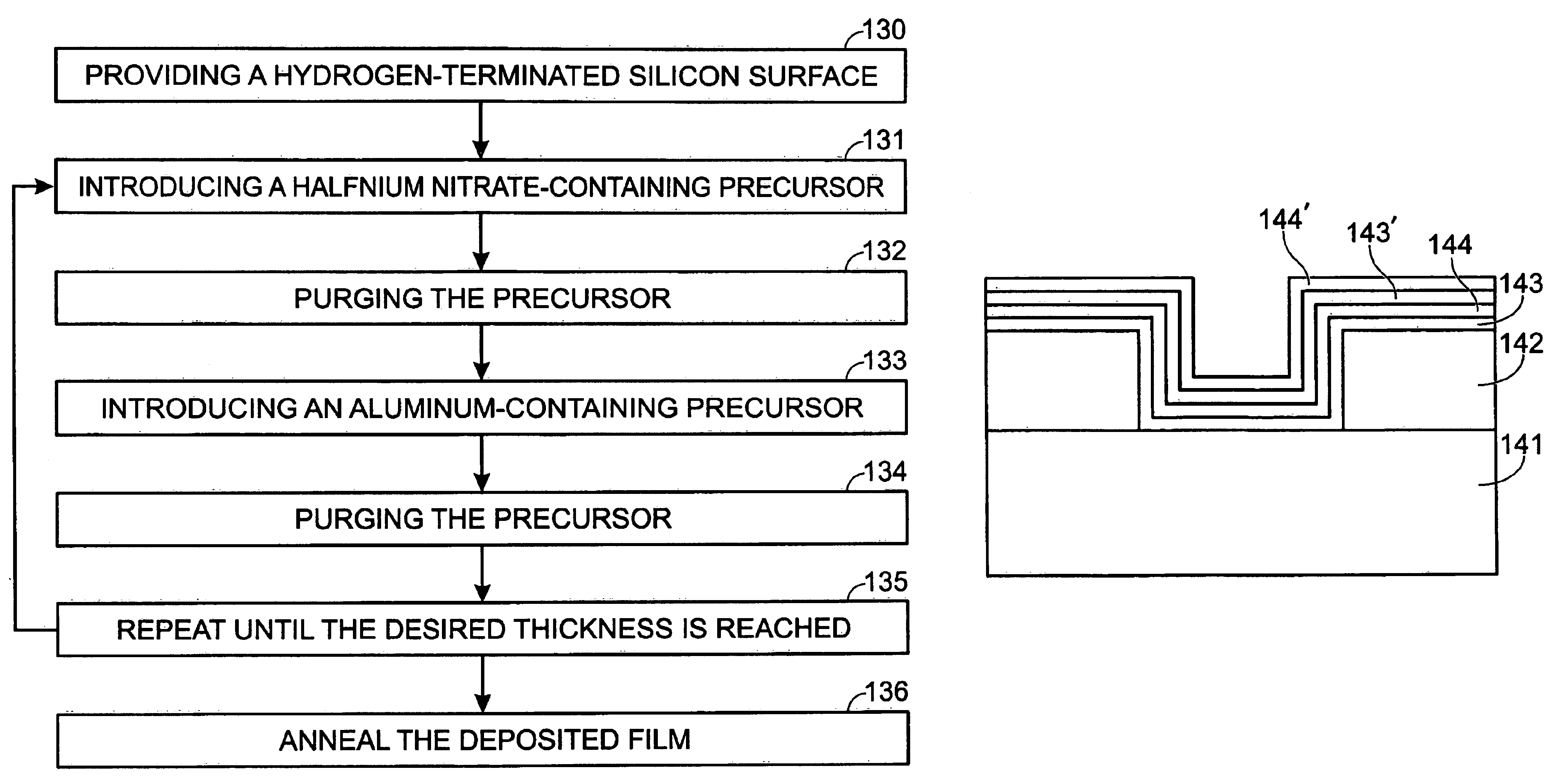
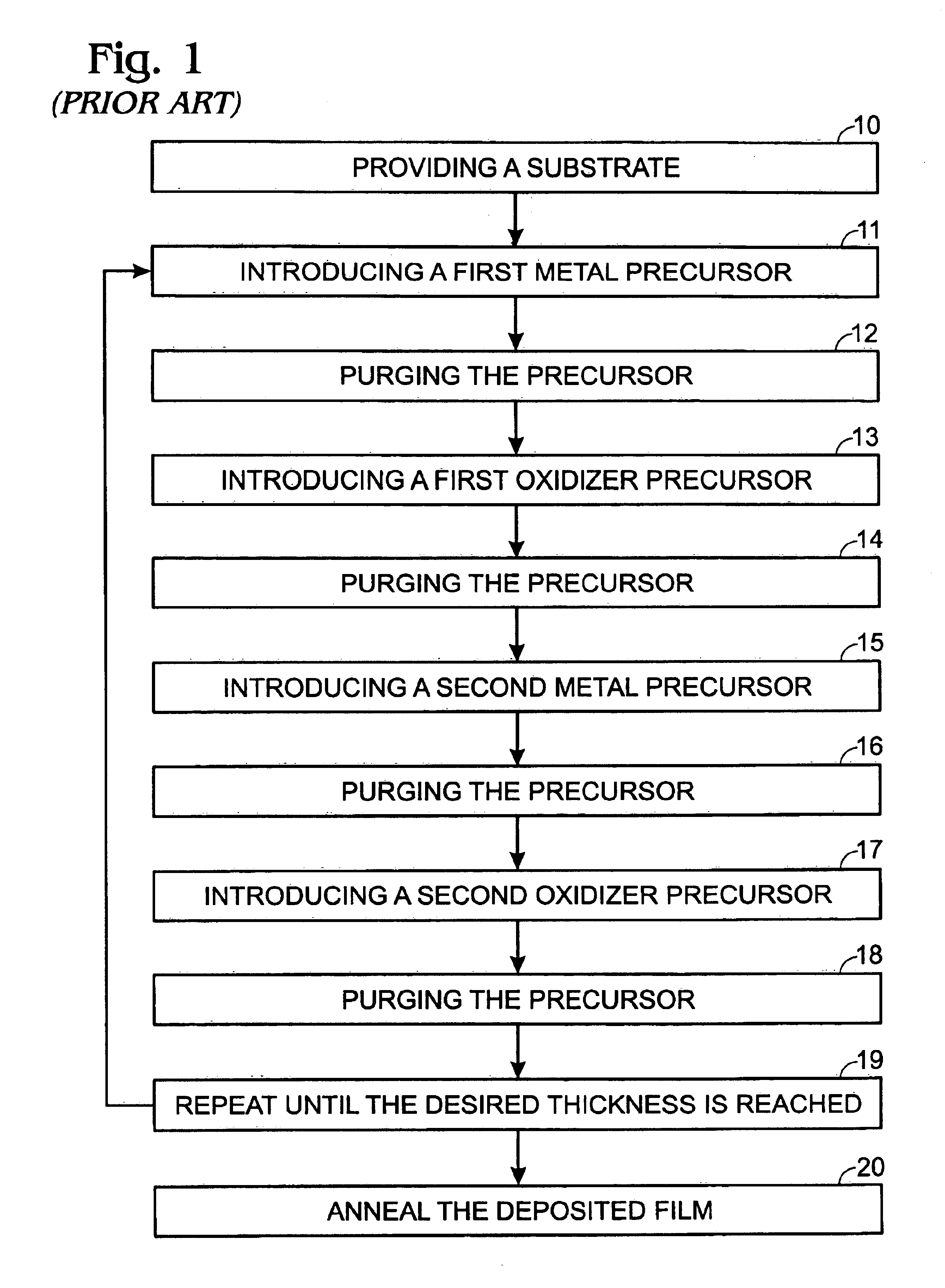
An atomic layer deposition method to deposit an oxide nanolaminate thin film is provided. The method employs a nitrate ligand in a first precursor as an oxidizer for a second precursor to form the oxide nanolaminates. Using a hafnium nitrate precursor and an aluminum precursor, the method is well suited for the deposition of a high k hafnium oxide / aluminum oxide nanolaminate dielectric for gate dielectric or capacitor dielectric applications on a hydrogen-terminated silicon surface.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
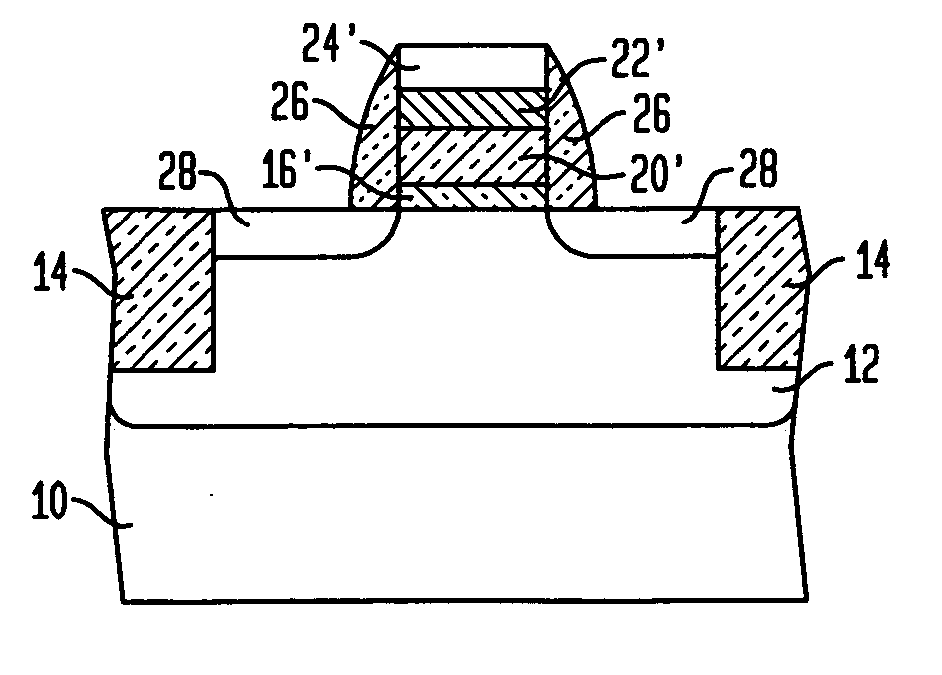
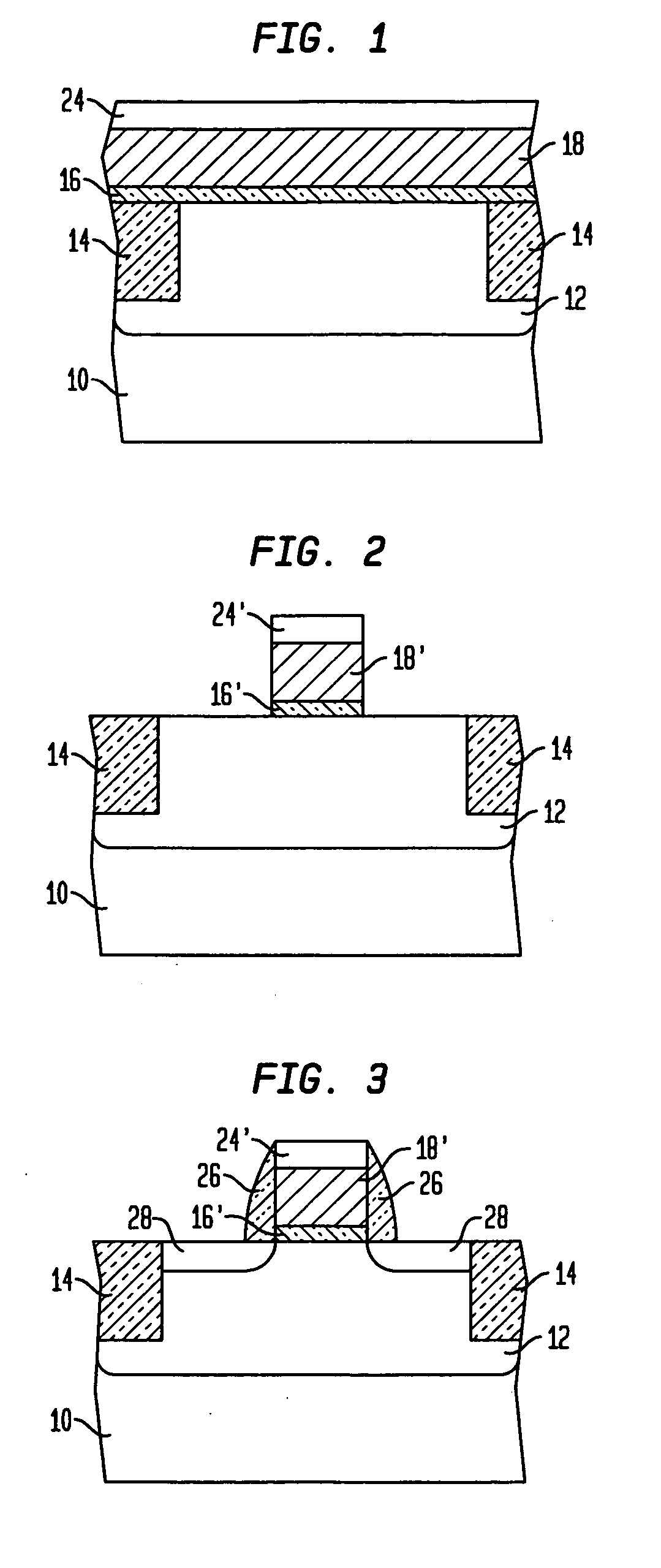
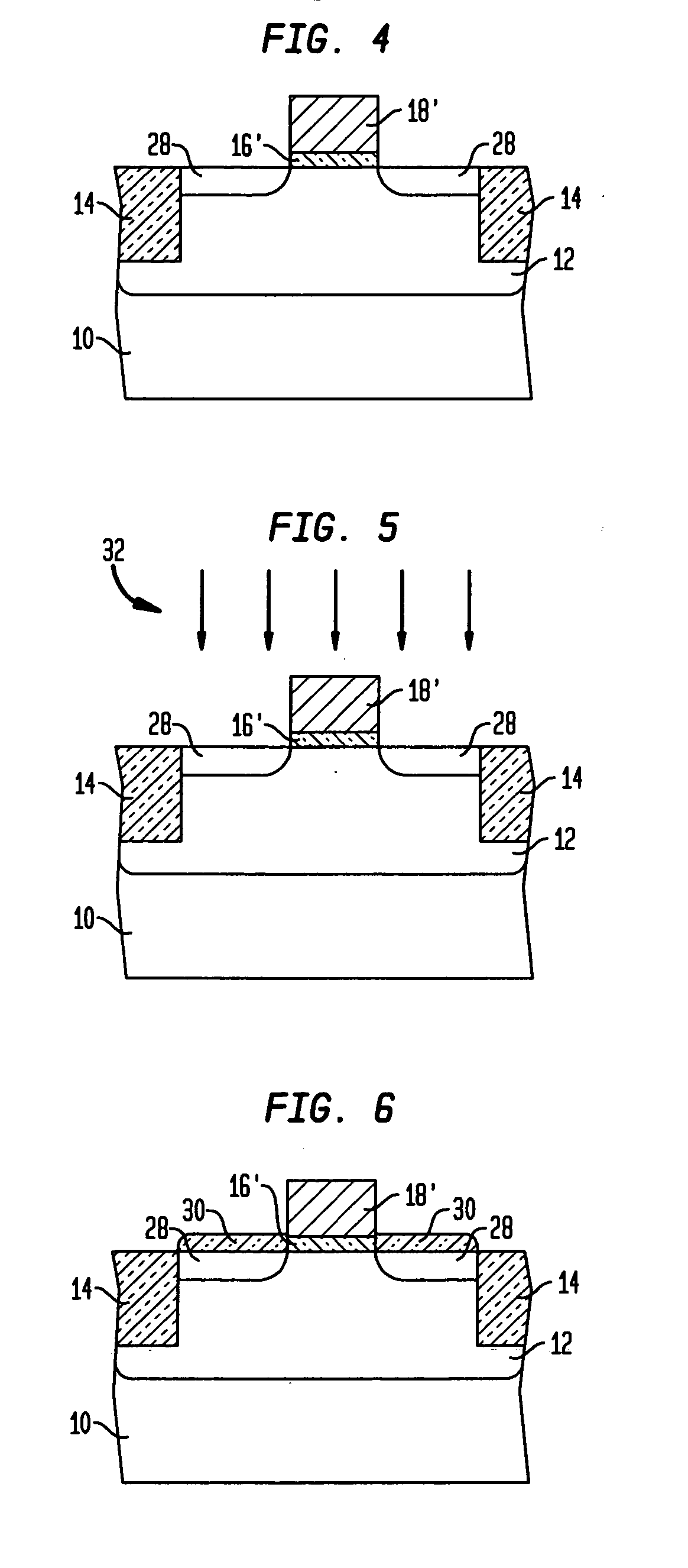
Opto-thermal annealing methods for forming metal gate and fully silicided gate field effect transistors
ActiveUS20070249131A1Avoid opto-thermal annealing damageAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideGate dielectric
An opto-thermal annealing method for forming a field effect transistor uses a reflective metal gate so that electrical properties of the metal gate and also interface between the metal gate and a gate dielectric are not compromised when opto-thermal annealing a source / drain region adjacent the metal gate. Another opto-thermal annealing method may be used for simultaneously opto-thermally annealing: (1) a silicon layer and a silicide forming metal layer to form a fully silicided gate; and (2) a source / drain region to form an annealed source / drain region. An additional opto-thermal annealing method may use a thermal insulator layer in conjunction with a thermal absorber layer to selectively opto-thermally anneal a silicon layer and a silicide forming metal layer to form a fully silicide gate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High-power dielectric seasoning for stable wafer-to-wafer thickness uniformity of dielectric CVD films
InactiveUS20060093756A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricCleaning methods
A method for seasoning a deposition chamber wherein the chamber components and walls are densely coated with a material that does not contain carbon prior to deposition of an organo-silicon material on a substrate. An optional carbon-containing layer may be deposited therebetween. A chamber cleaning method using low energy plasma and low pressure to remove residue from internal chamber surfaces is provided and may be combined with the seasoning process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Remote plasma source seasoning
ActiveUS7989365B2Increase deposition rateImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaDeposition process
Methods of seasoning a remote plasma system are described. The methods include the steps of flowing a silicon-containing precursor into a remote plasma region to deposit a silicon containing film on an interior surface of the remote plasma system. The methods reduce reactions with the seasoned walls during deposition processes, resulting in improved deposition rate, improved deposition uniformity and reduced defectivity during subsequent deposition.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
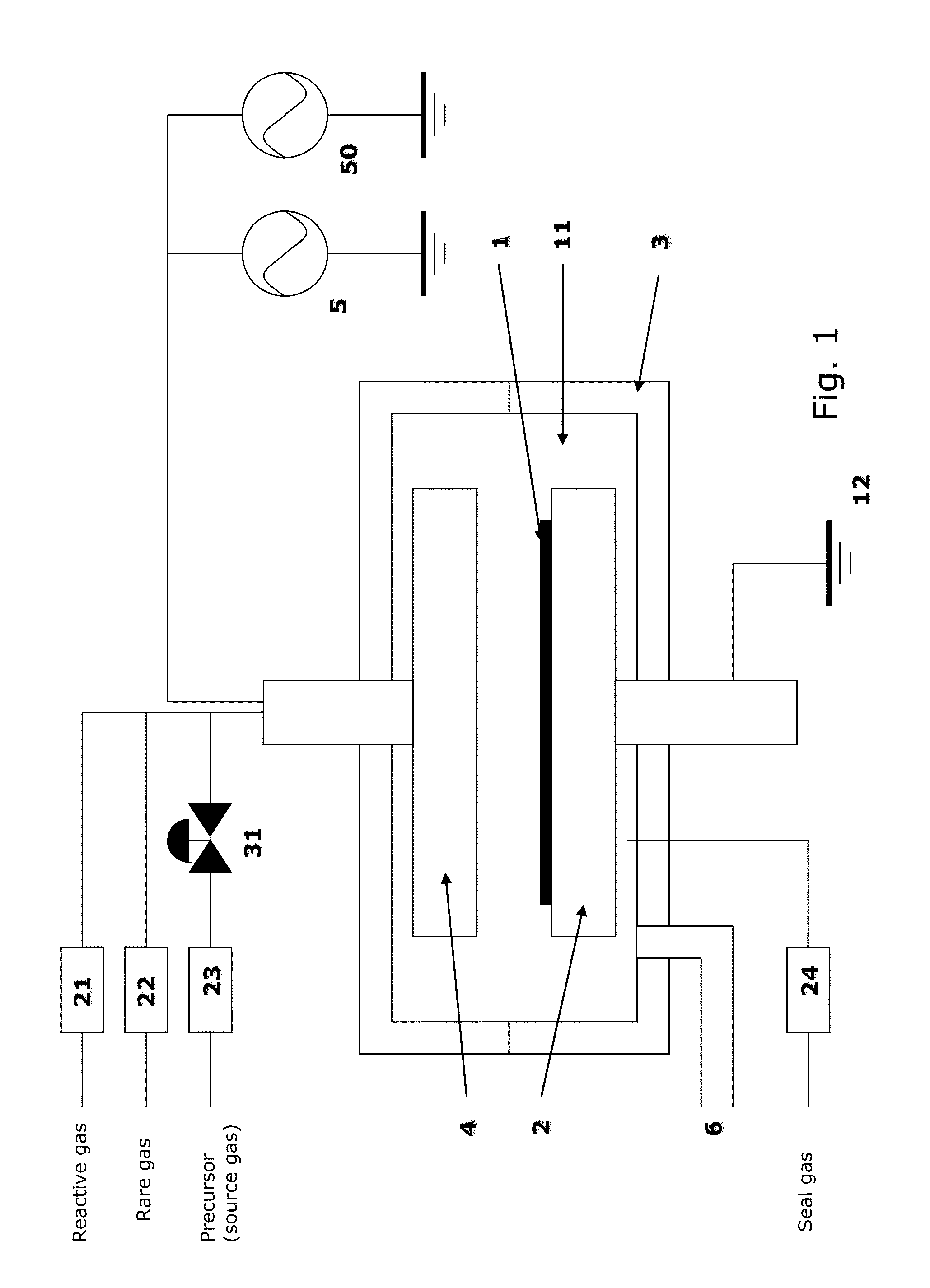
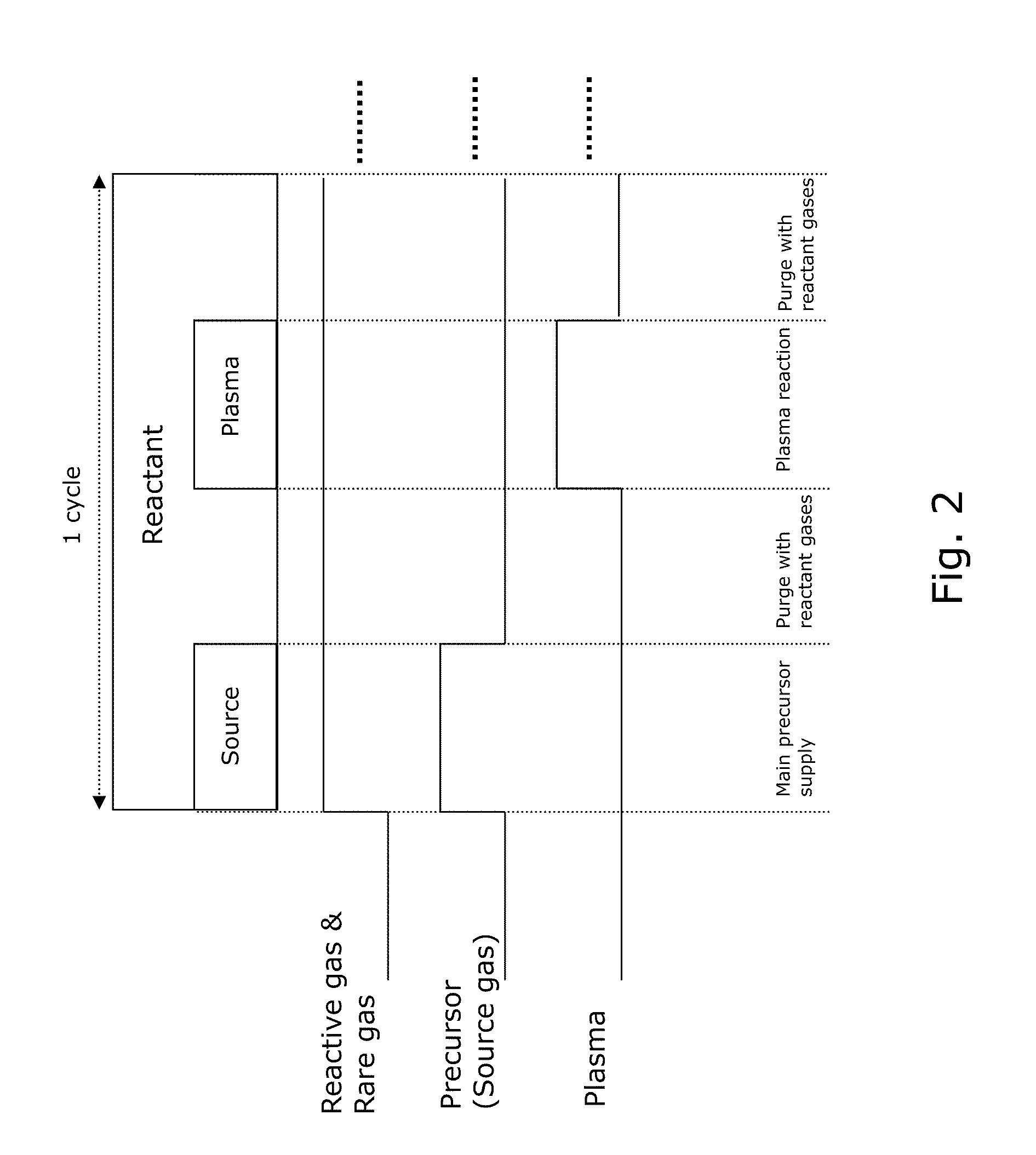
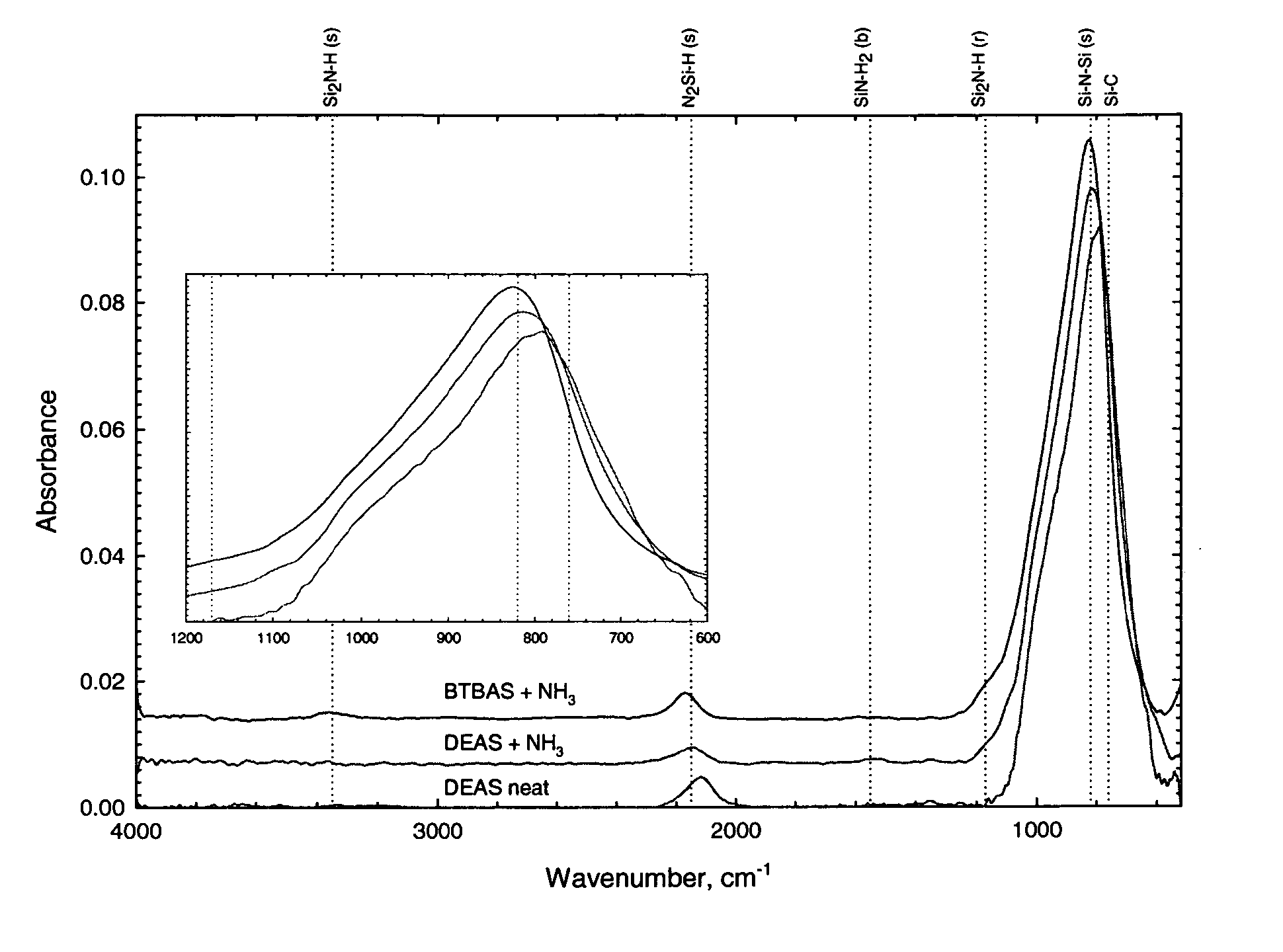
METHOD OF DEPOSITING DIELECTRIC FILM HAVING Si-N BONDS BY MODIFIED PEALD METHOD
ActiveUS20110086516A1High conformalityIncrease deposition rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricNoble gas
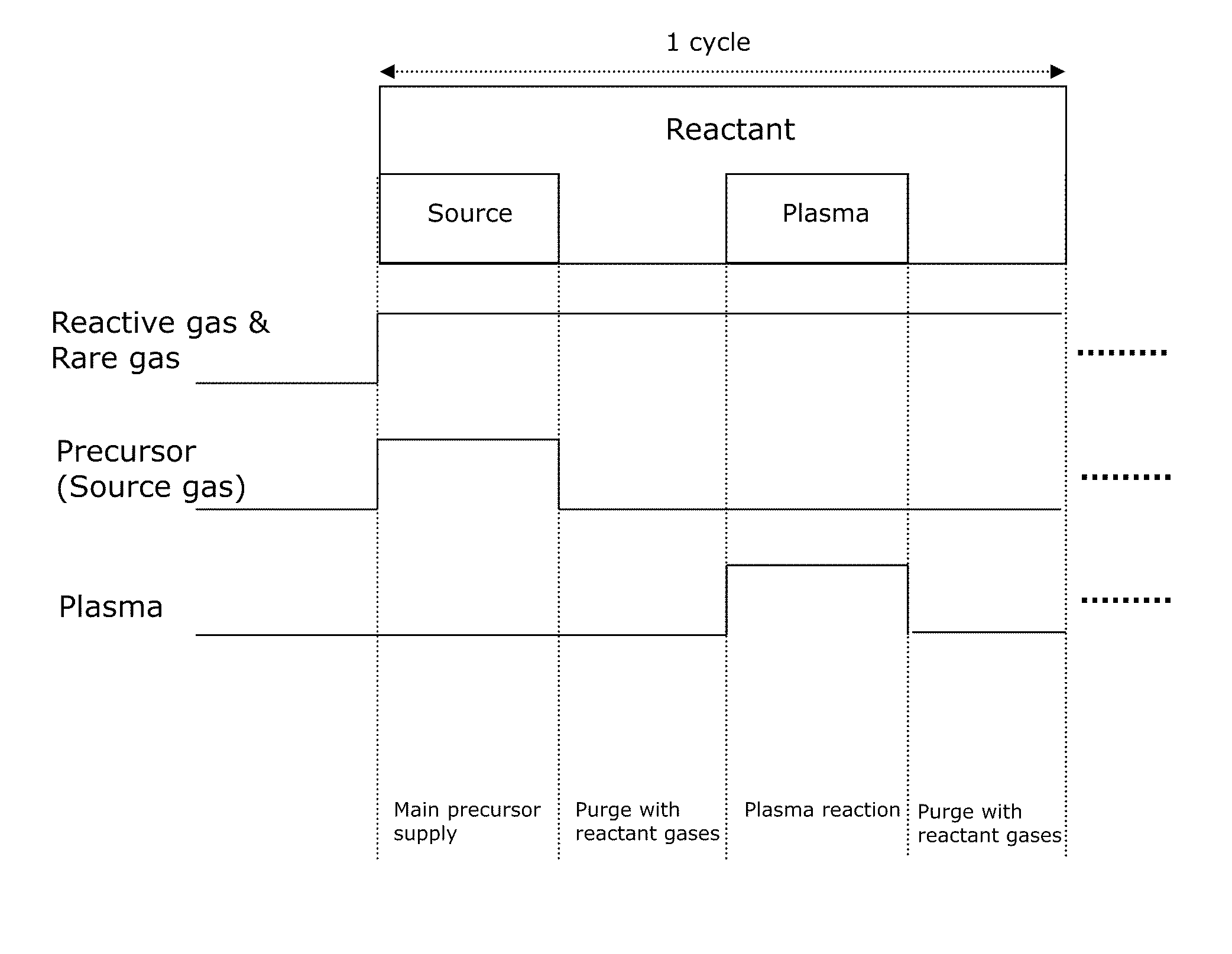
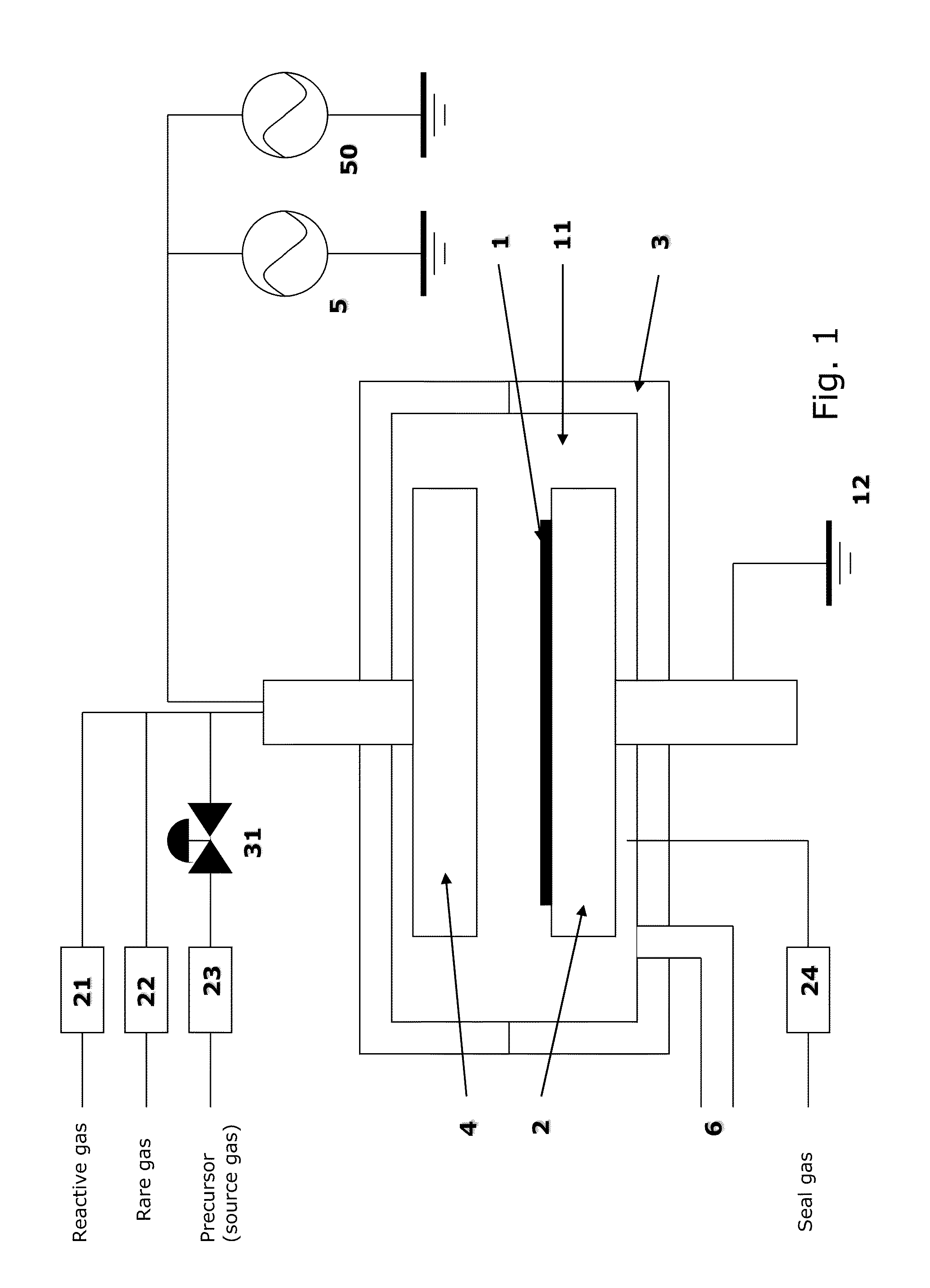
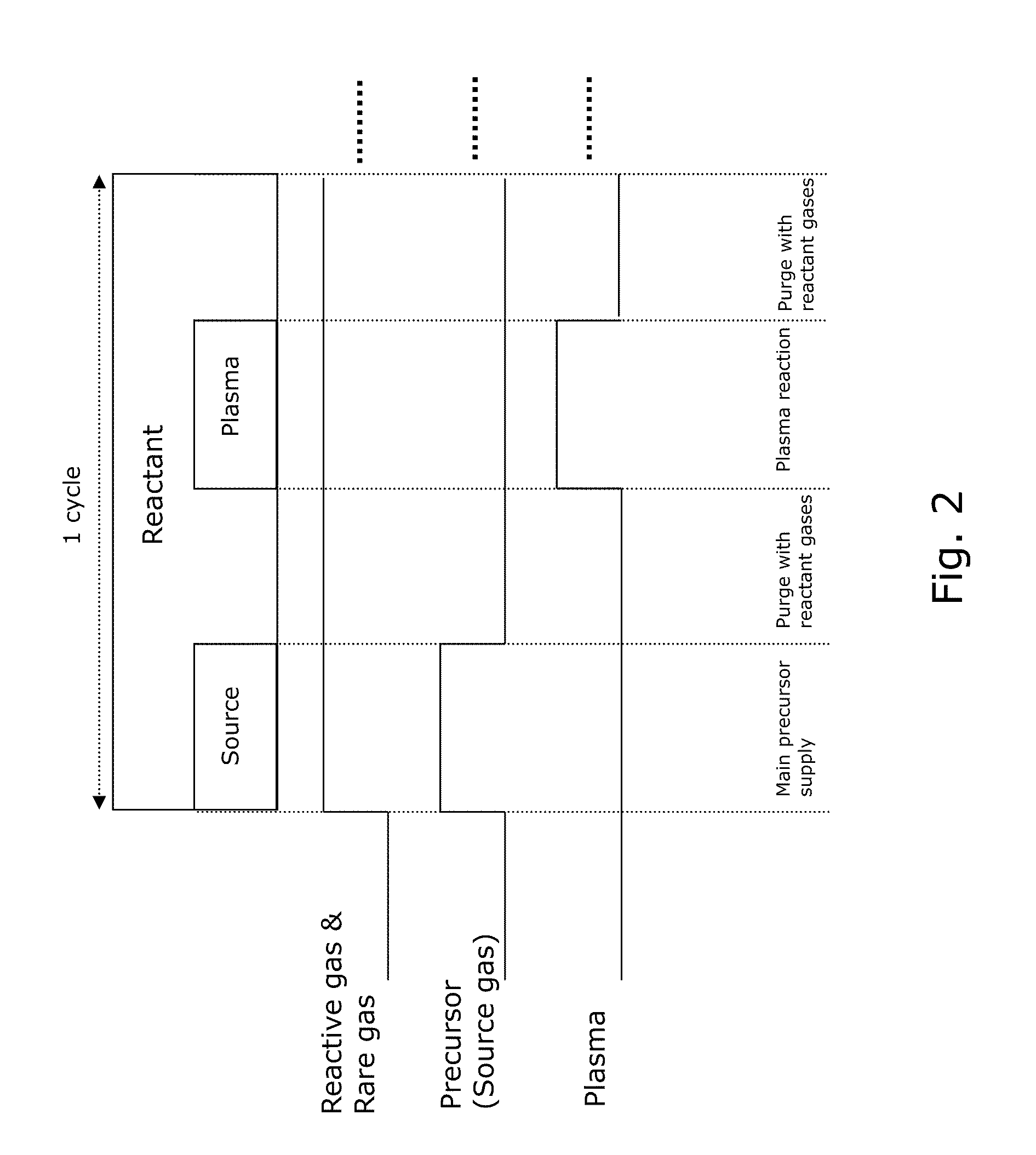
A method of forming dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and a rare gas into a reaction space inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration into the reaction space wherein the reactive gas and the rare gas are introduced; exiting a plasma in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration immediately after the silicon precursor is shut off; and maintaining the reactive gas and the rare gas as a purge of less than 2.0-second duration.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of depositing dielectric film having Si-N bonds by modified peald method
ActiveUS8173554B2Increase deposition rateHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricHydrogen
A method of forming dielectric film having Si—N bonds on a semiconductor substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing a nitrogen- and hydrogen-containing reactive gas and a rare gas into a reaction space inside which the semiconductor substrate is placed; introducing a hydrogen-containing silicon precursor in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration into the reaction space wherein the reactive gas and the rare gas are introduced; exiting a plasma in pulses of less than 1.0-second duration immediately after the silicon precursor is shut off; and maintaining the reactive gas and the rare gas as a purge of less than 2.0-second duration.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
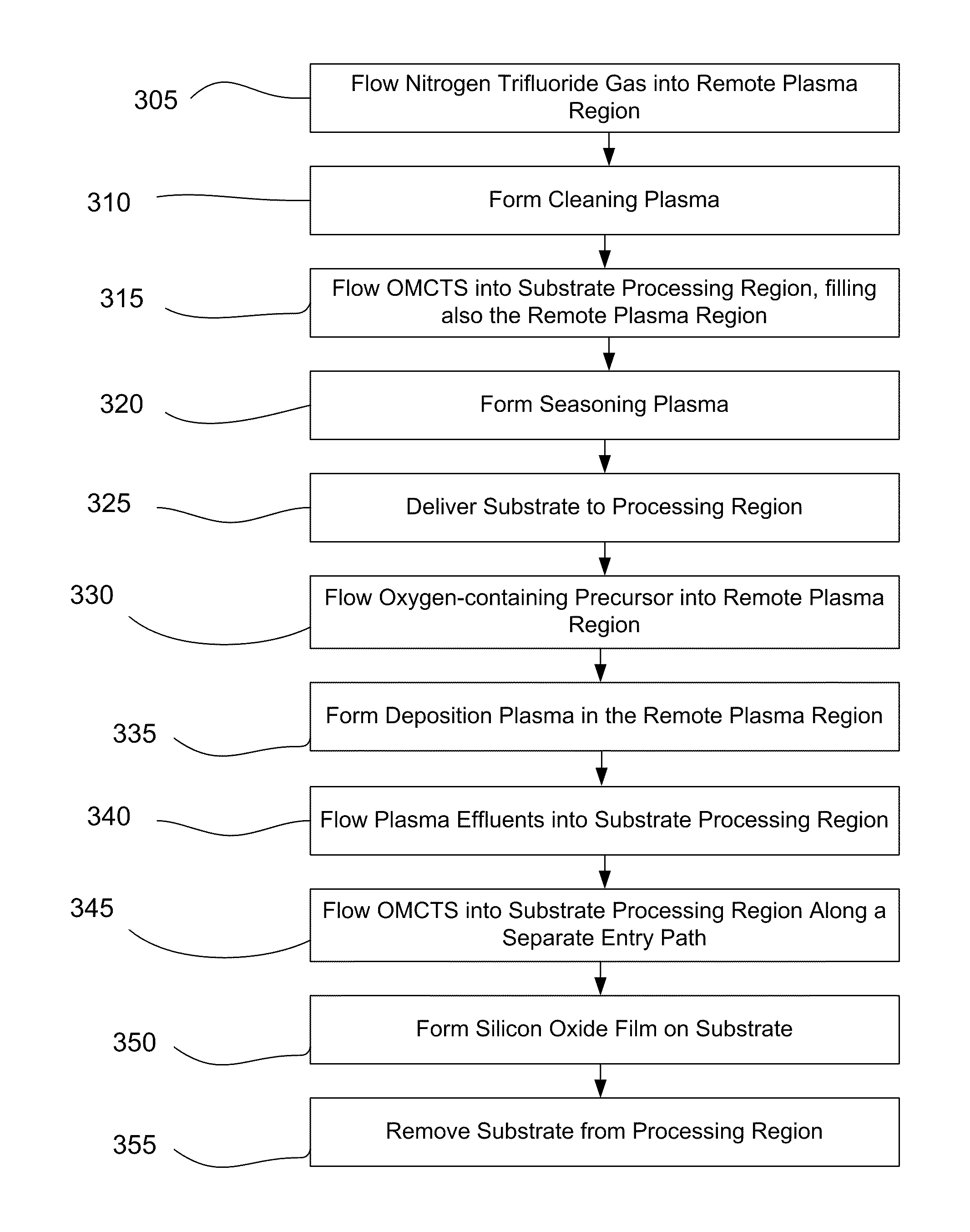
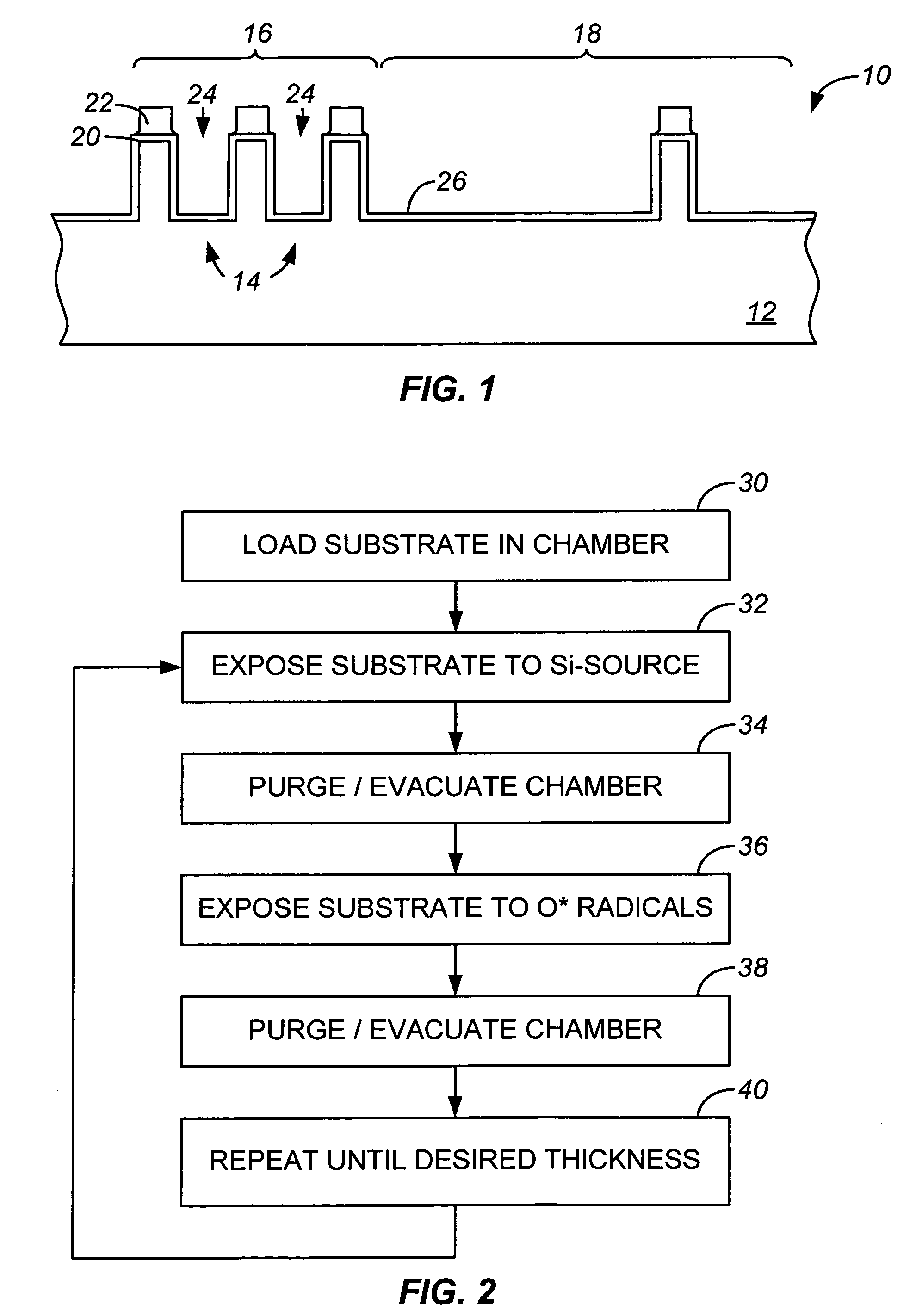
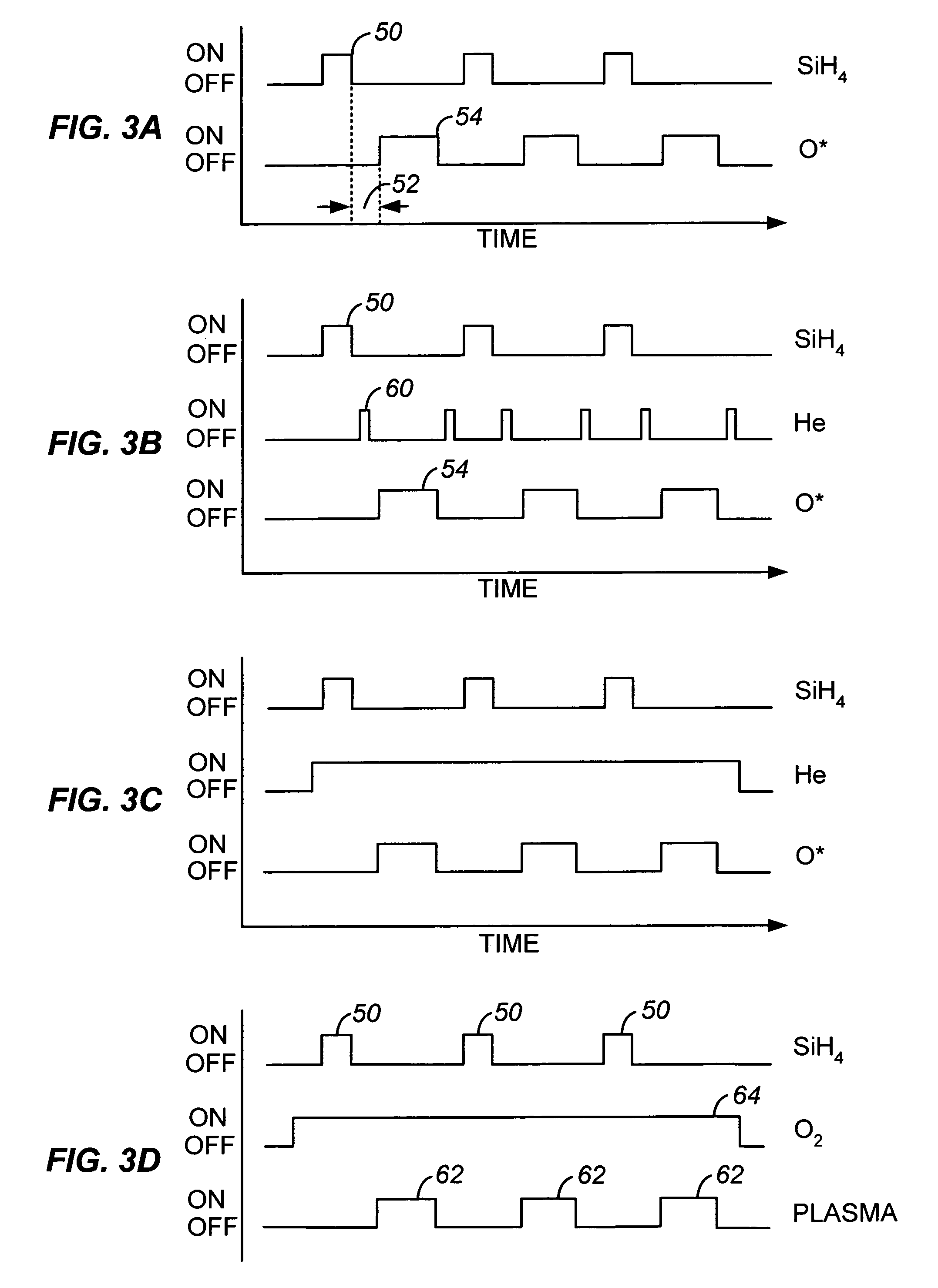
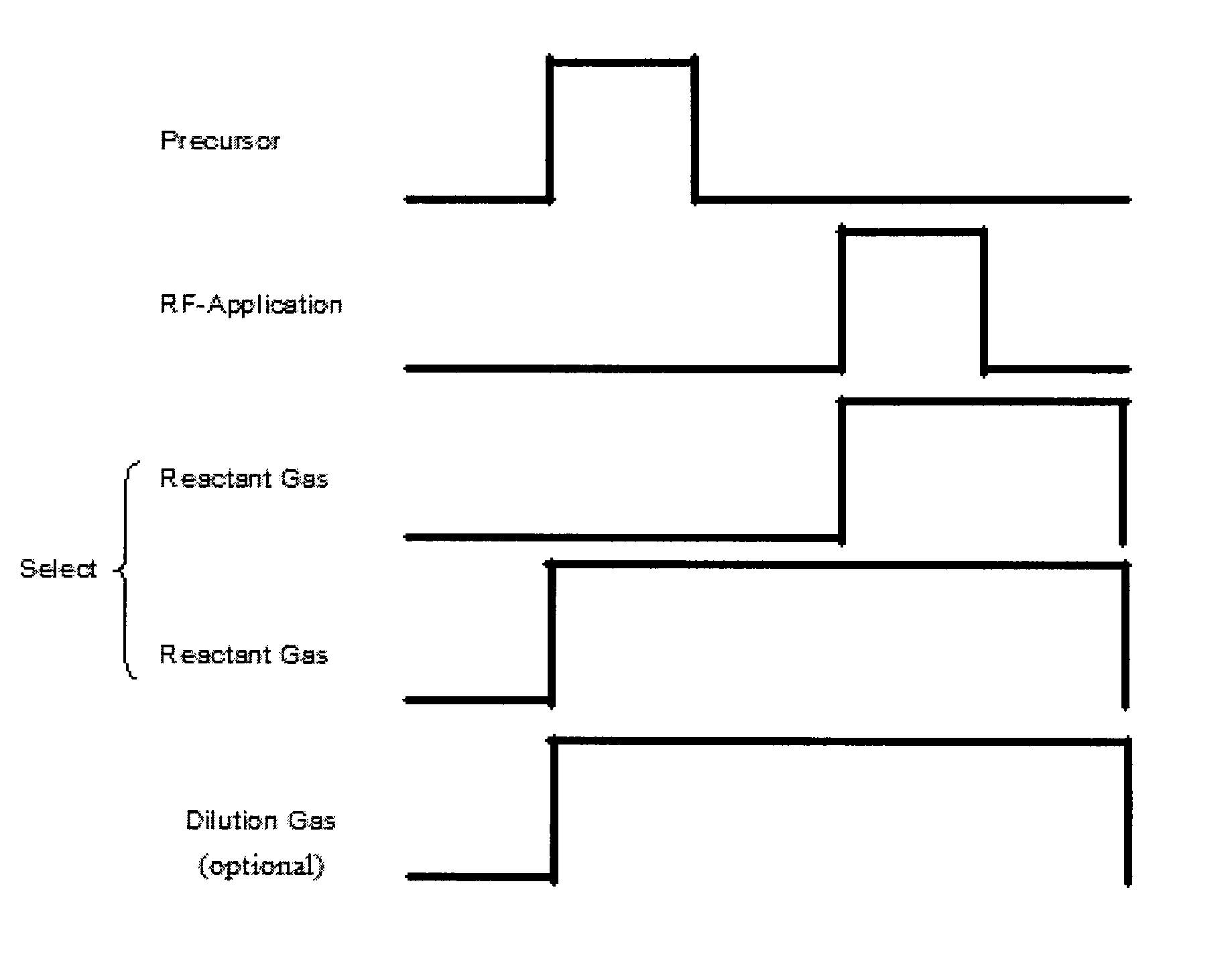
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
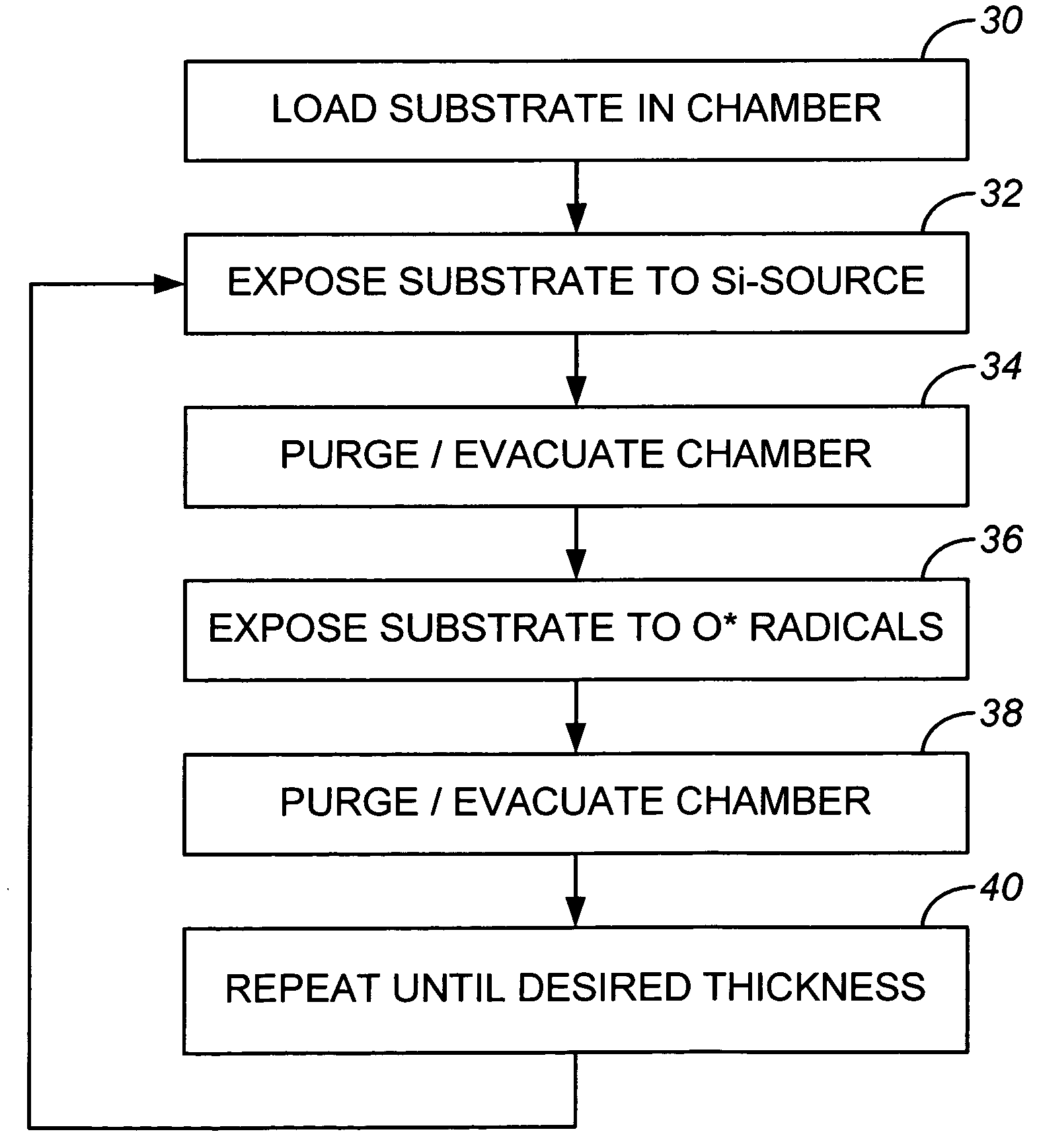
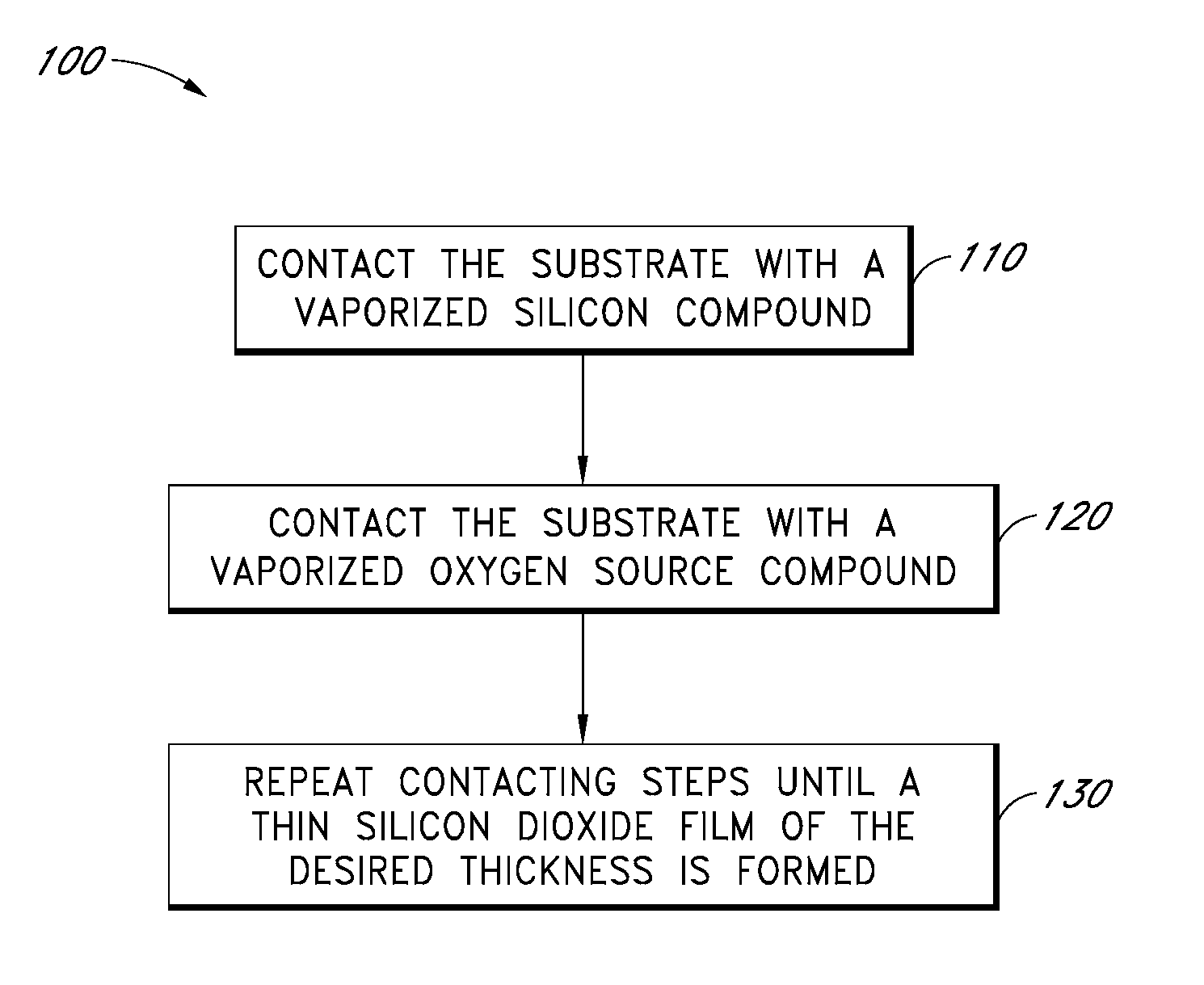
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Remote plasma source seasoning
ActiveUS20110045676A1Increase deposition rateReduce defectsElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaDeposition process
Methods of seasoning a remote plasma system are described. The methods include the steps of flowing a silicon-containing precursor into a remote plasma region to deposit a silicon containing film on an interior surface of the remote plasma system. The methods reduce reactions with the seasoned walls during deposition processes, resulting in improved deposition rate, improved deposition uniformity and reduced defectivity during subsequent deposition.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Silicon Dioxide Thin Films by ALD
ActiveUS20090209081A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon dioxideAtomic layer deposition
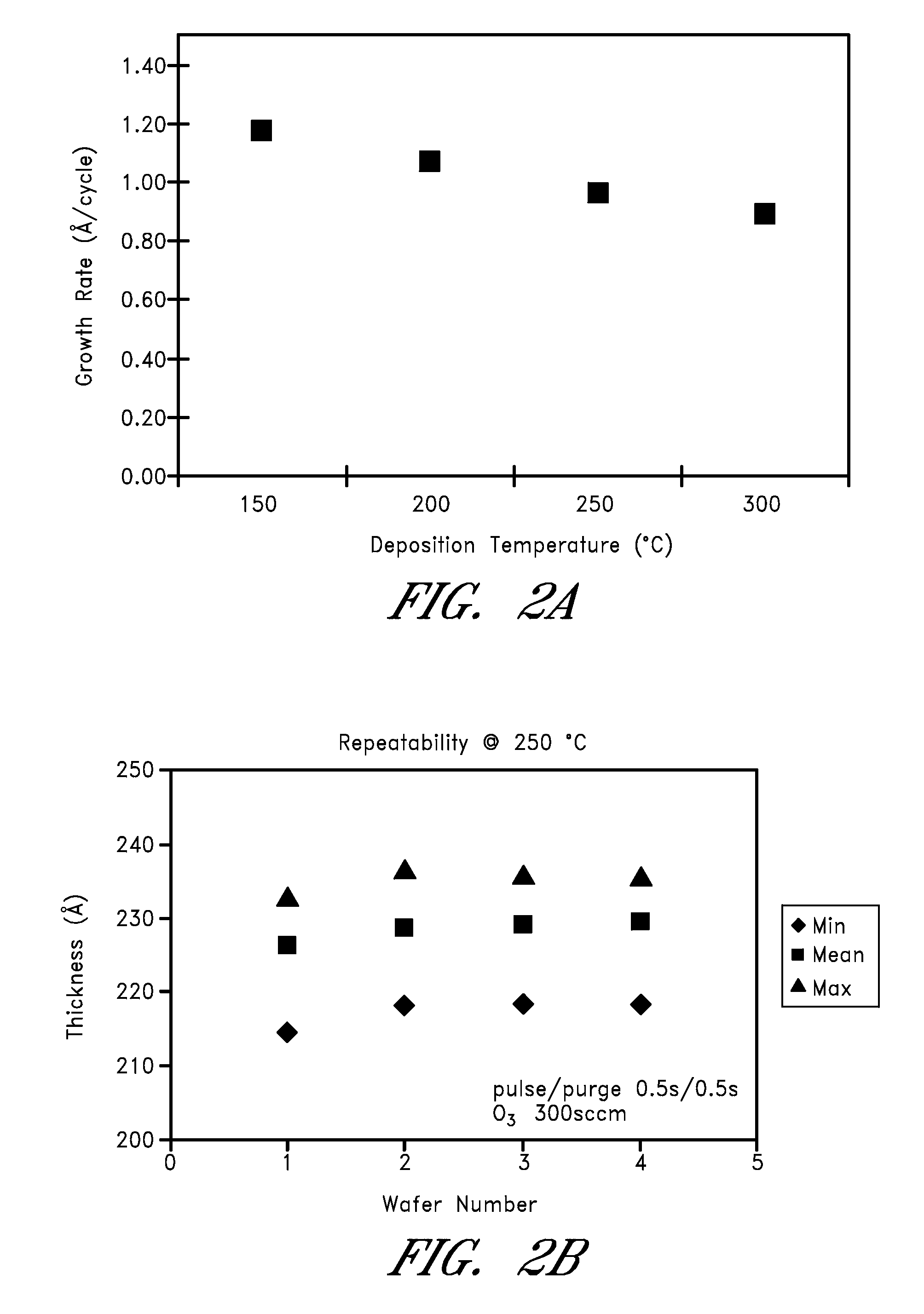
Methods are provided for depositing silicon dioxide containing thin films on a substrate by atomic layer deposition ALD. By using disilane compounds as the silicon source, good deposition rates and uniformity are obtained.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
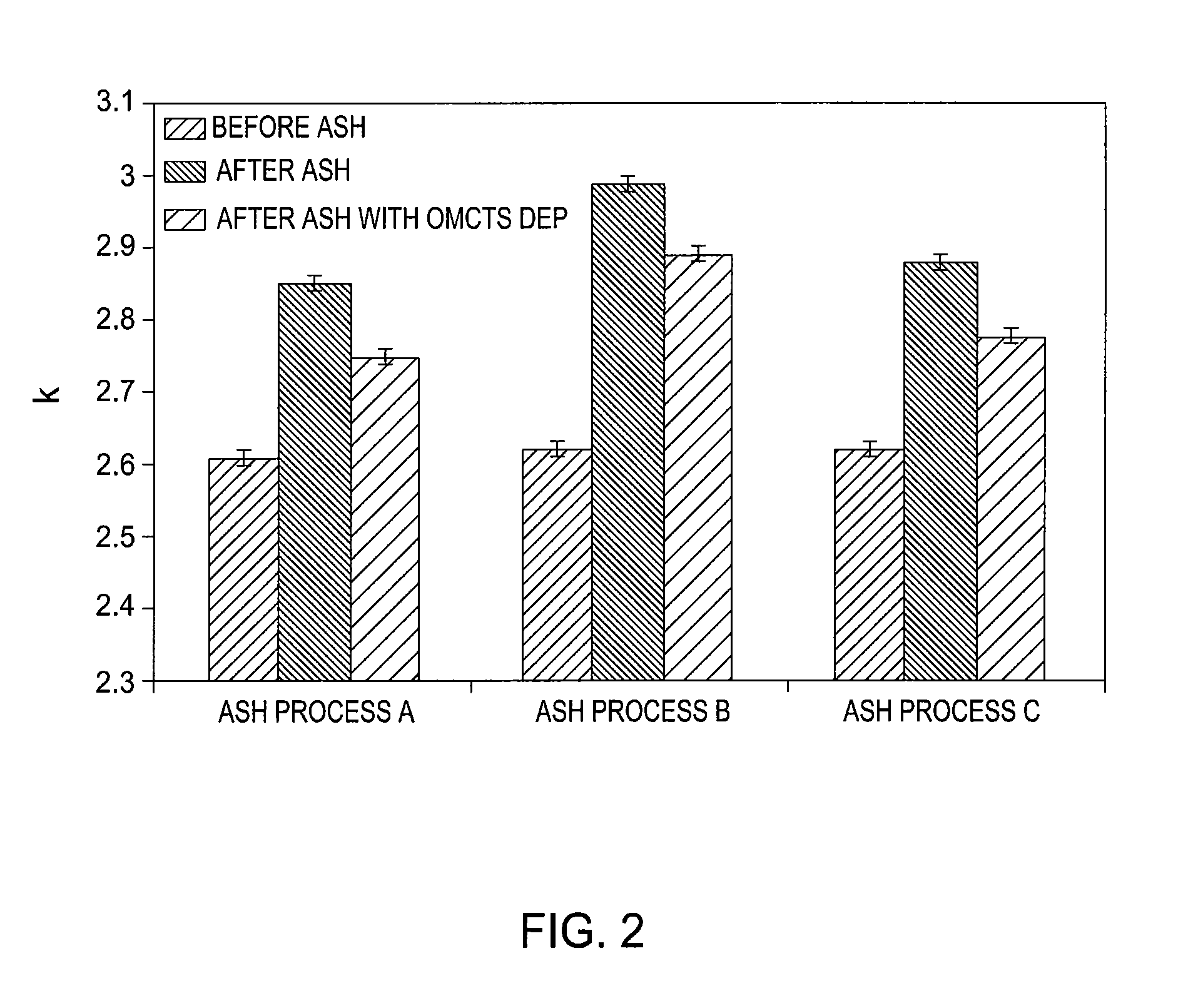
Activated Chemical Process for Enhancing Material Properties of Dielectric Films
ActiveUS20080199977A1High dielectric constantLow dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsDielectric layerElectron
A method for restoring a dielectric constant of a layer of a silicon-containing dielectric material having a first dielectric constant and at least one surface, wherein the first dielectric constant of the layer of silicon-containing dielectric material has increased to a second dielectric constant, the method comprising the steps of: contacting the at least one surface of the layer of silicon-containing dielectric material with a silicon-containing fluid; and exposing the at least one surface of the layer of silicon-containing dielectric material to an energy source selected from the group consisting of: UV radiation, heat, and an electron beam, wherein the layer of silicon-containing dielectric material has a third dielectric constant that is lower than the second dielectric constant after exposing the layer of silicon-containing dielectric material to the energy source.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
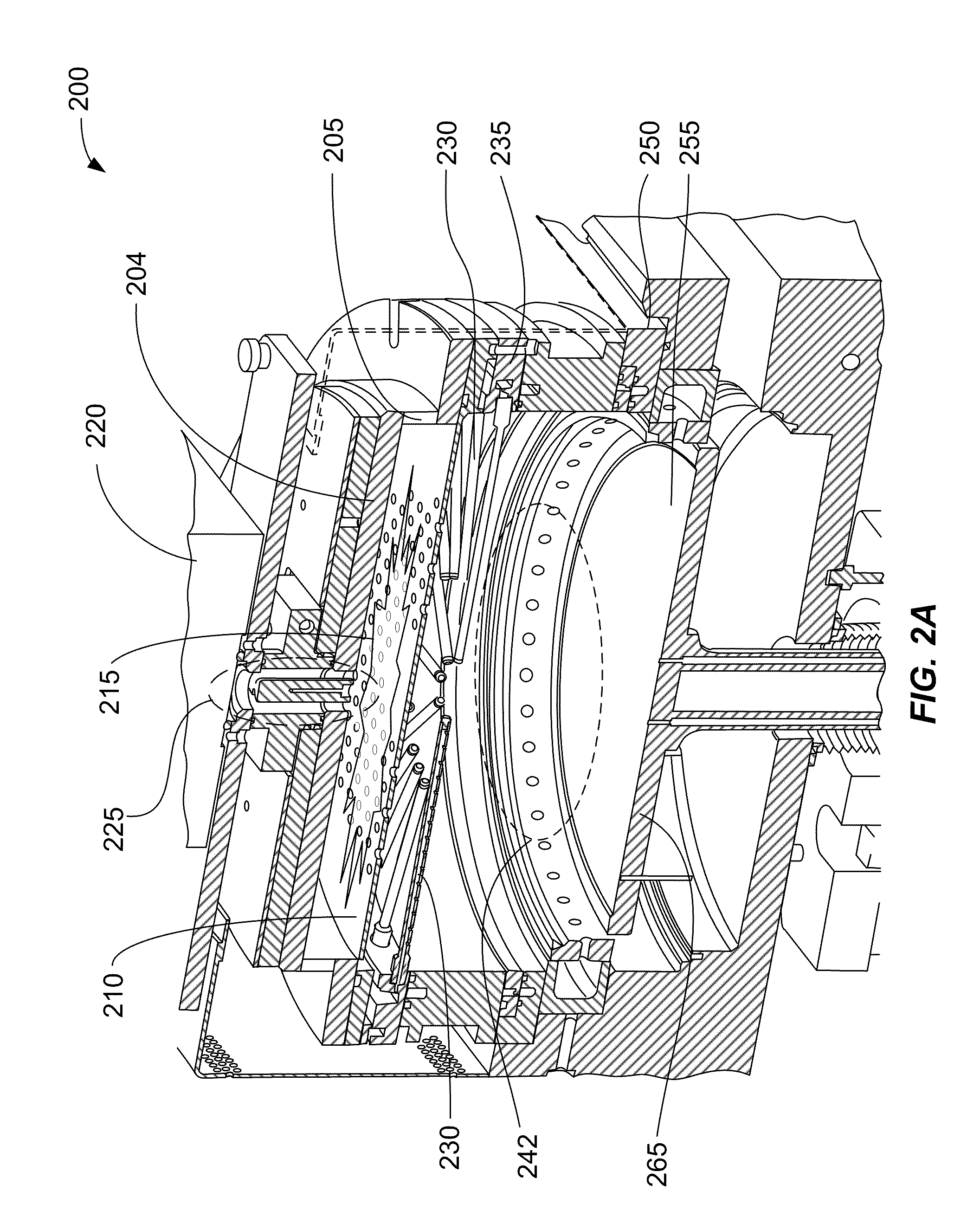
Substrate susceptors for receiving semiconductor substrates to be deposited upon and methods of depositing materials over semiconductor substrates
In one implementation, a substrate susceptor for receiving a semiconductor substrate for selective epitaxial silicon-comprising depositing thereon, where the depositing comprises measuring emissivity of the susceptor from at least one susceptor location in a non-contacting manner, includes a body having a front substrate receiving side, a back side, and a peripheral edge. At least one susceptor location from which emissivity is to be measured is received on at least one of the front substrate receiving side, the back side, and the edge. Such at least one susceptor location comprises an outermost surface comprising a material upon which selective epitaxial silicon will not deposit upon during selective epitaxial silicon depositing on a semiconductor substrate received by the susceptor for at least an initial thickness of epitaxial silicon depositing on said substrate. Other aspects and implementations are contemplated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor method and device with mixed orientation substrate
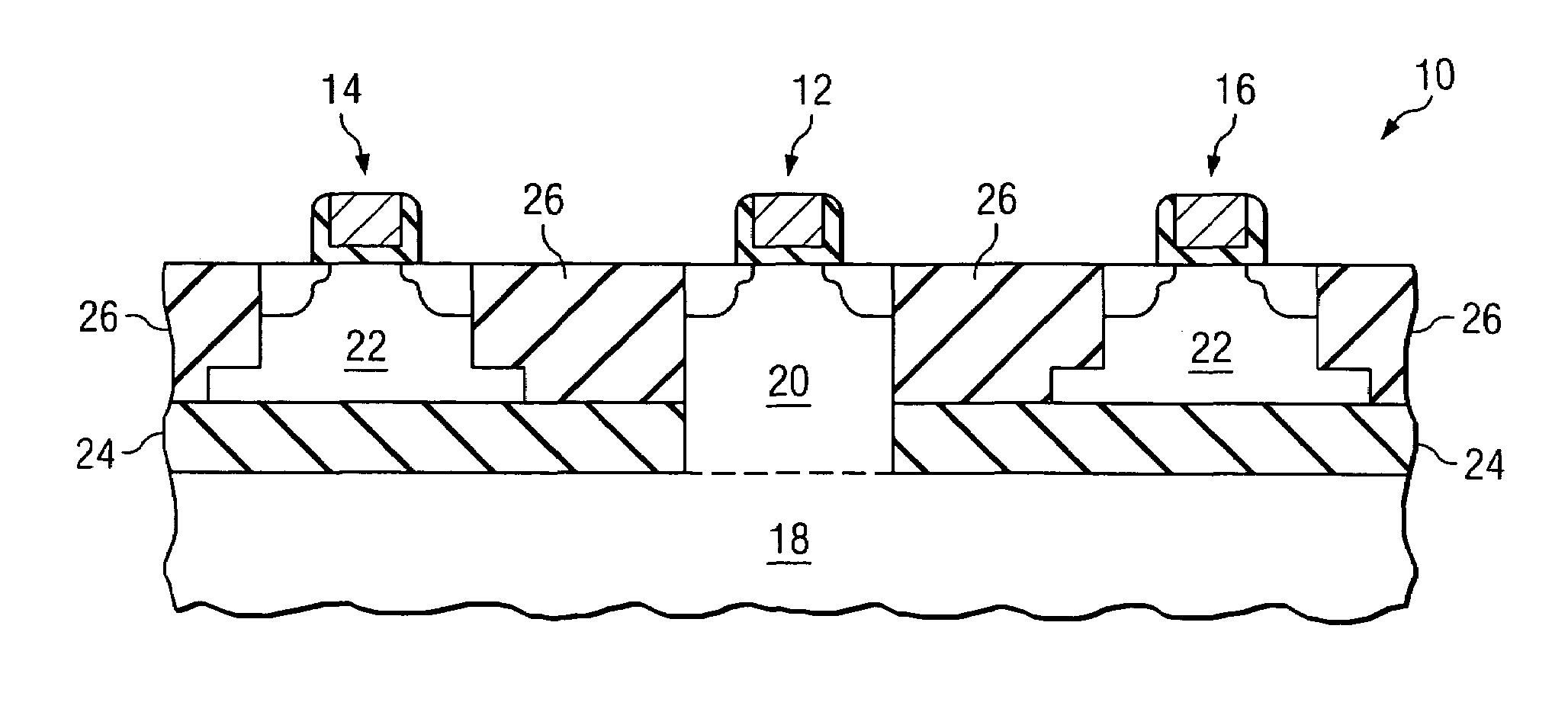
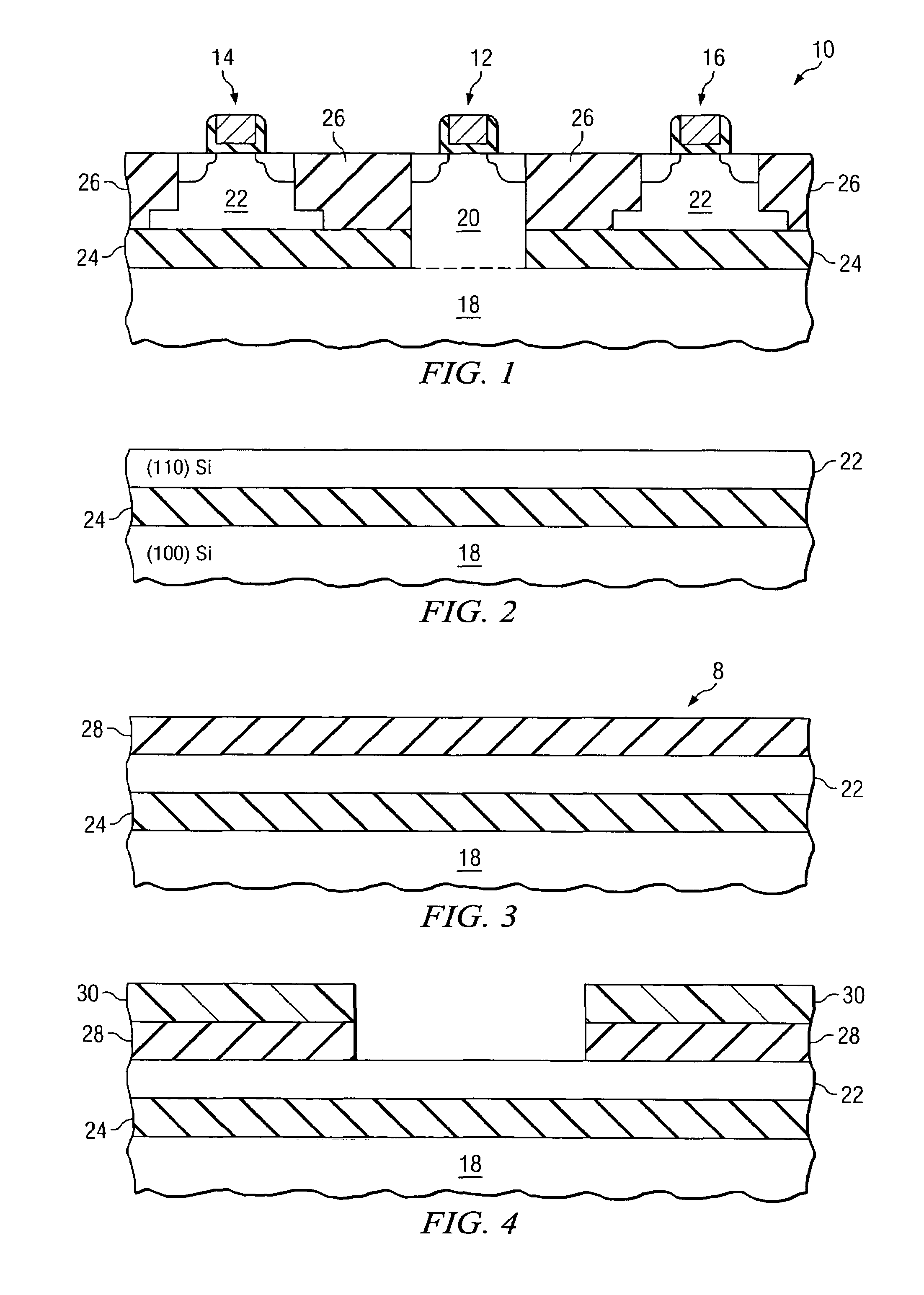
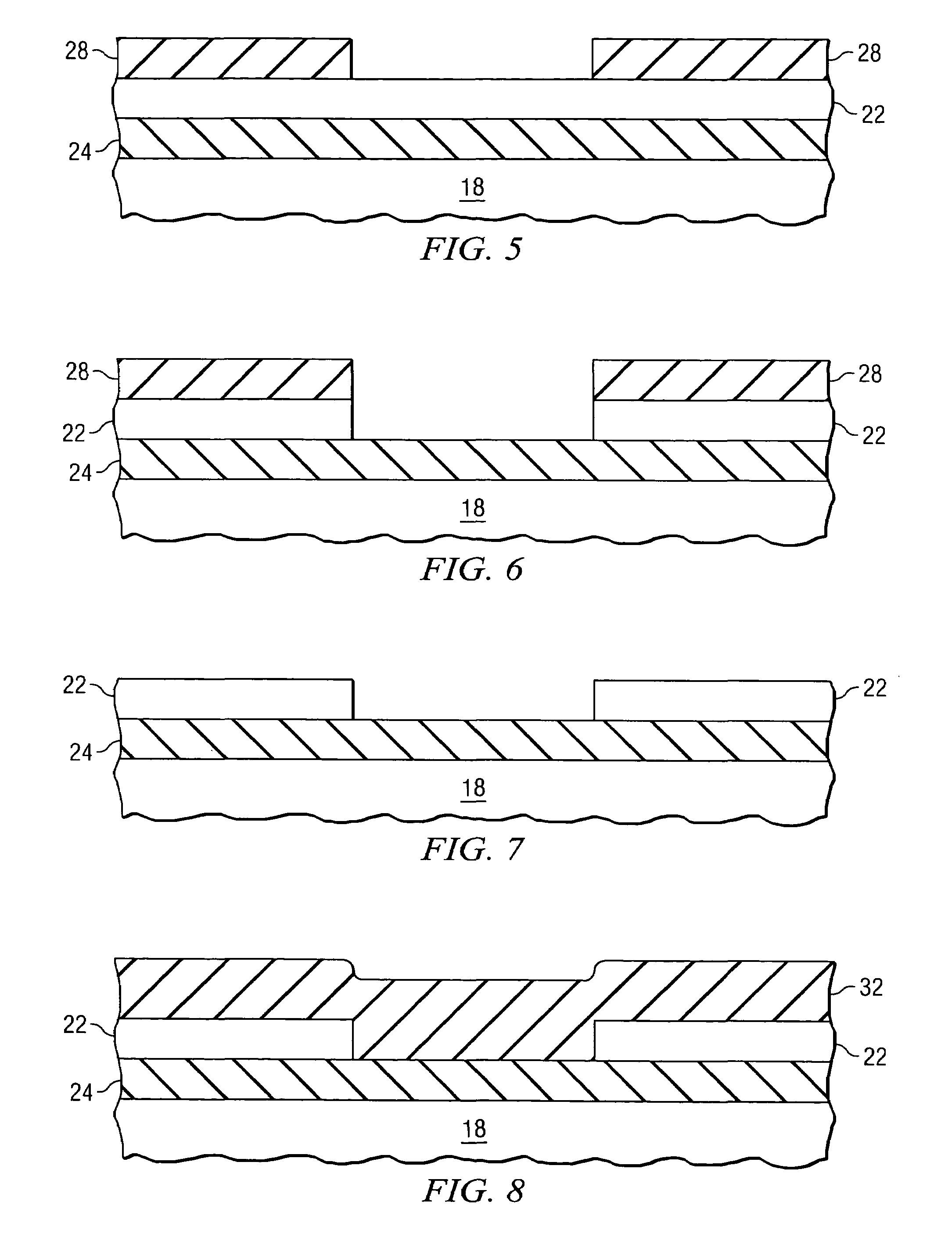
InactiveUS7298009B2Critical dimension of this mask is relaxedReduce processing stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsCrystal orientation
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
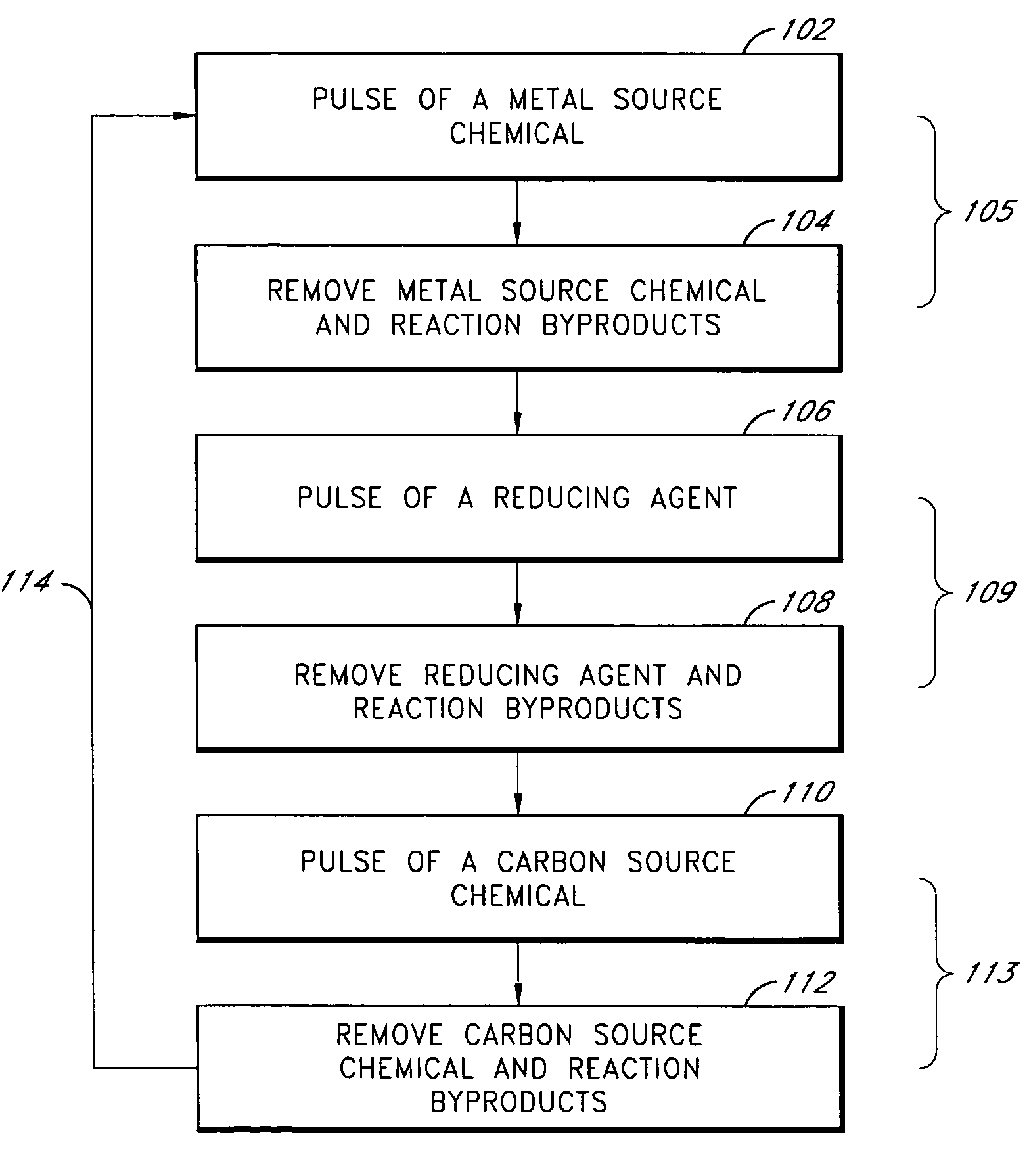
Vapor deposition of metal carbide films
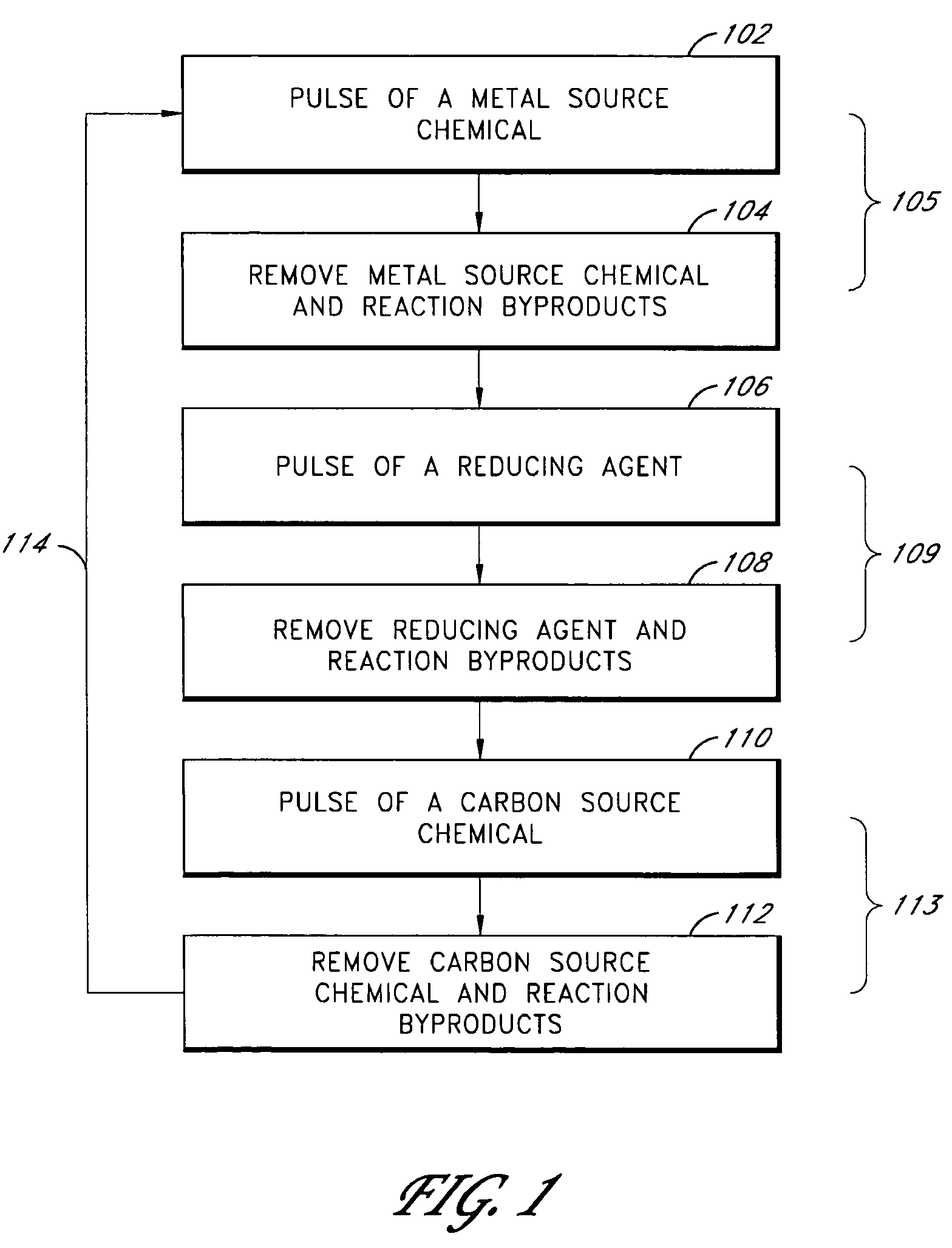
Methods of forming metal carbide thin films are provided. According to preferred embodiments, metal carbide thin films are formed in an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process by alternately and sequentially contacting a substrate in a reaction space with spatially and temporally separated vapor phase pulses of a metal source chemical, a reducing agent and a carbon source chemical. The reducing agent is preferably selected from the group consisting of excited species of hydrogen and silicon-containing compounds.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of forming conformal film having si-N bonds on high-aspect ratio pattern
ActiveUS8394466B2Increasing mobilityIncreasing diffusivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSiliconConformal map
Owner:ASM JAPAN
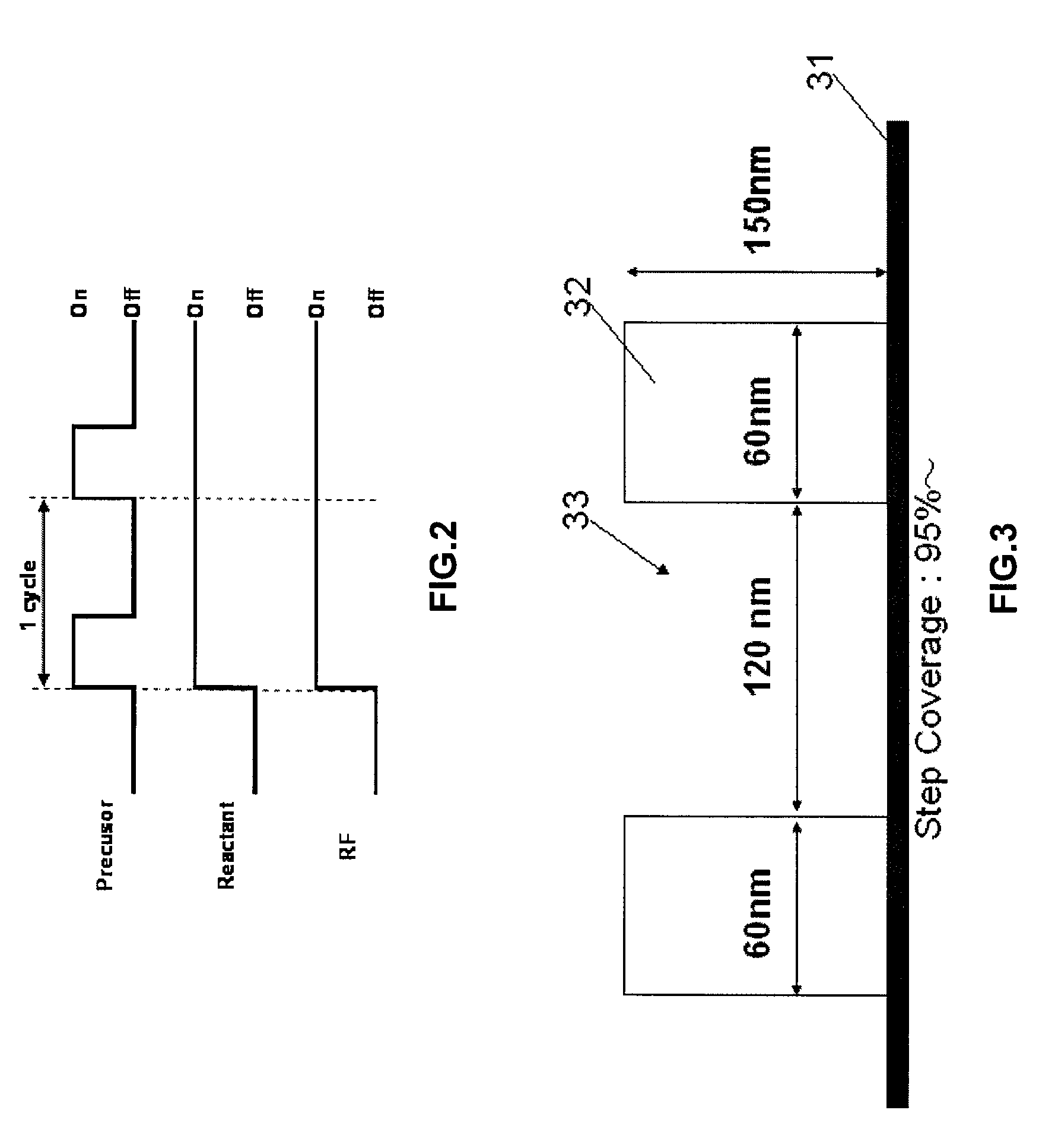
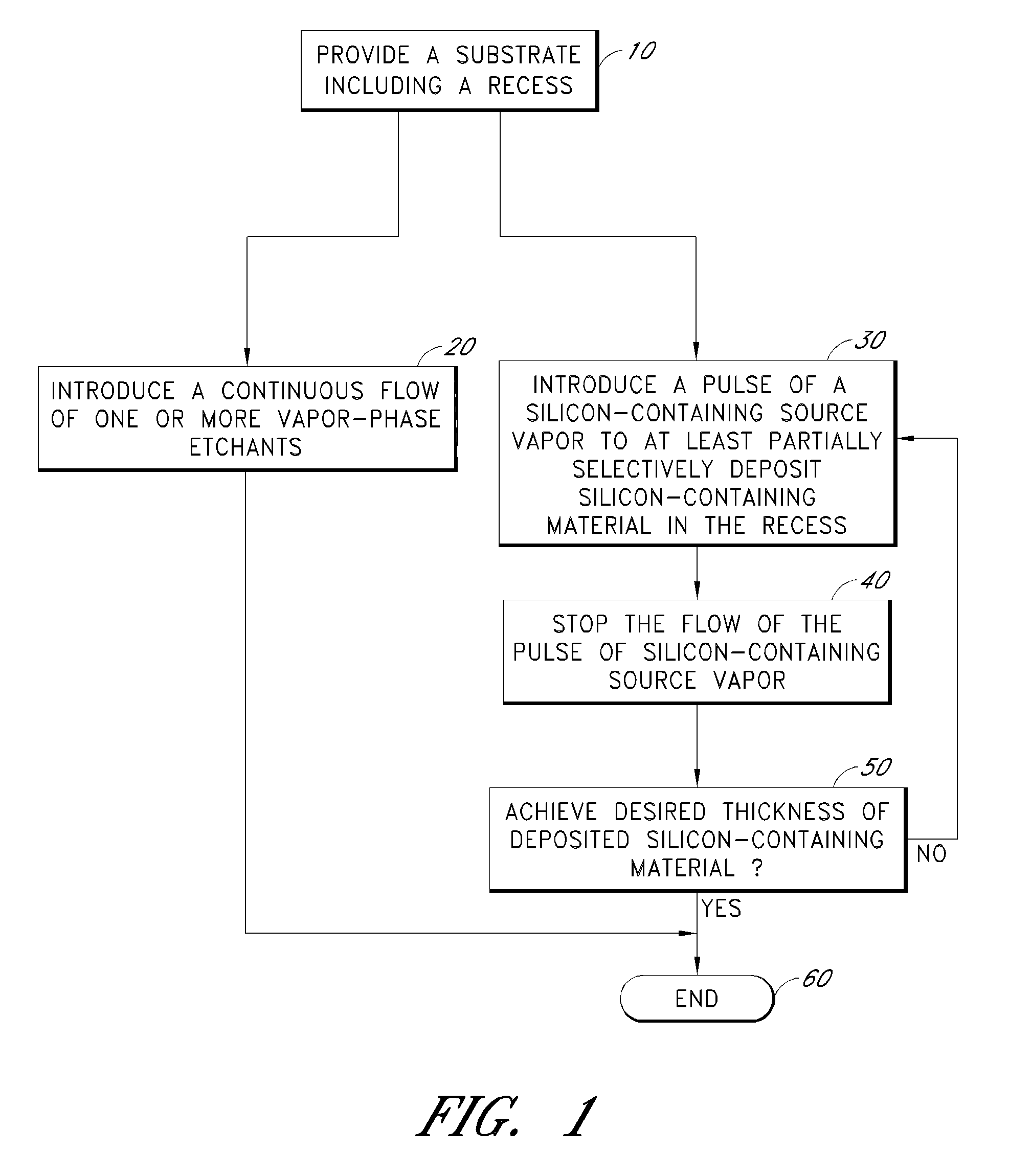
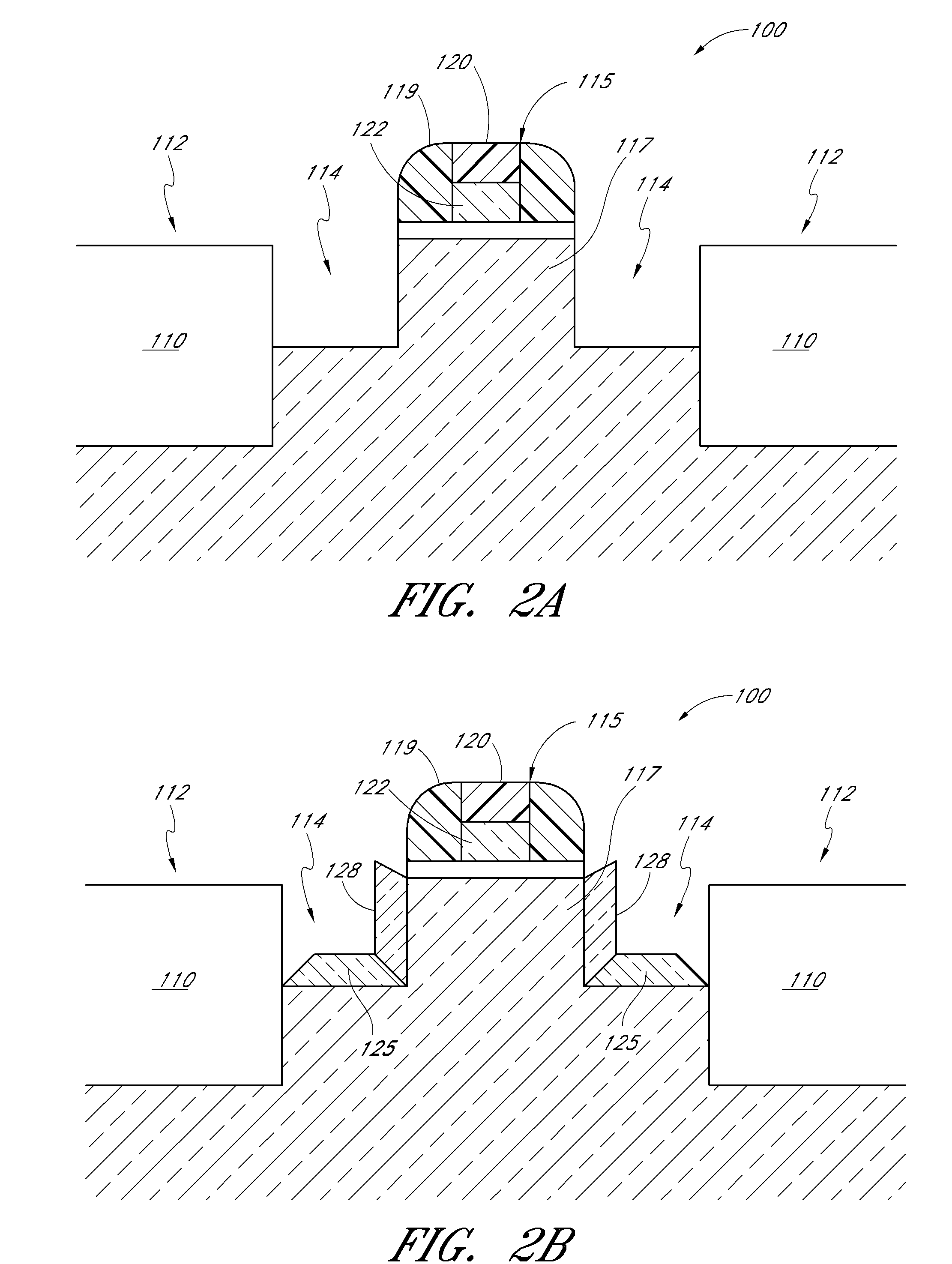
Cyclical epitaxial deposition and etch
ActiveUS8367528B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEpitaxial materialSemiconductor
Methods for selectively depositing high quality epitaxial material include introducing pulses of a silicon-source containing vapor while maintaining a continuous etchant flow. Epitaxial material is deposited on areas of a substrate, such as source and drain recesses. Between pulses, the etchant flow continues such that lower quality epitaxial material may be removed, as well as any non-epitaxial material that may have been deposited. The pulse of silicon-source containing vapor may be repeated until a desired thickness of epitaxial material is selectively achieved in semiconductor windows, such as recessed source / drain regions.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
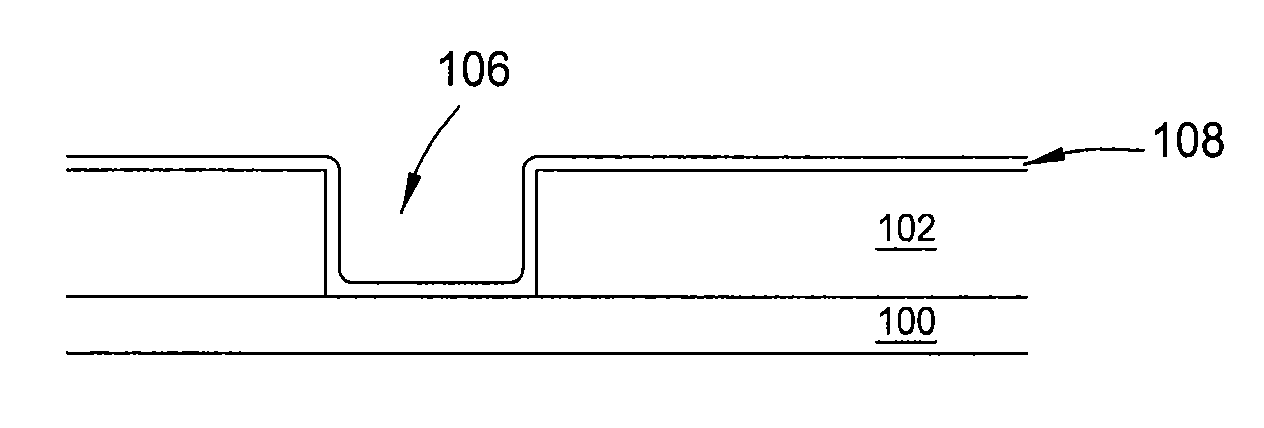
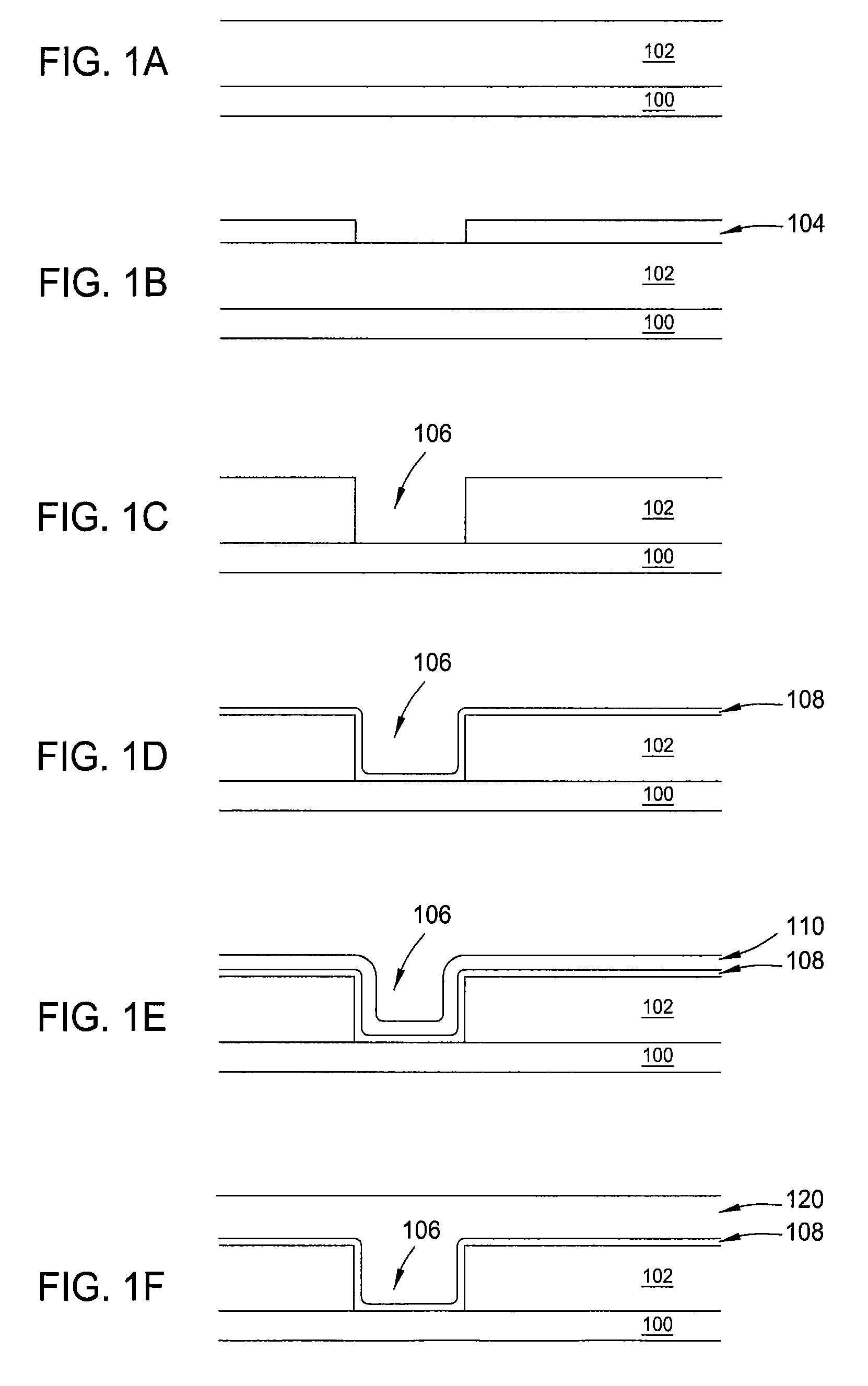
Method to minimize wet etch undercuts and provide pore sealing of extreme low k (k<2.5) dielectrics
ActiveUS8445075B2Constant ratePrevents undercuts and CD lossVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesNitrogenThin layer
Methods of processing films on substrates are provided. In one aspect, the methods comprise treating a patterned low dielectric constant film after a photoresist is removed from the film by depositing a thin layer comprising silicon, carbon, and optionally oxygen and / or nitrogen on the film. The thin layer provides a carbon-rich, hydrophobic surface for the patterned low dielectric constant film. The thin layer also protects the low dielectric constant film from subsequent wet cleaning processes and penetration by precursors for layers that are subsequently deposited on the low dielectric constant film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of depositing dielectric film by ALD using precursor containing silicon, hydrocarbon, and halogen
ActiveUS8329599B2Accelerates the carbonization processHigh conformalitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricHalogen
A method of forming a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on a semiconductor substrate by atomic layer deposition (ALD), includes: adsorbing a precursor on a surface of a substrate; supplying a reactant gas over the surface; reacting the precursor and the reactant gas on the surface; and repeating the above steps to form a dielectric film having at least Si—N, Si—C, or Si—B bonds on the substrate. The precursor has at least one Si—C or Si—N bond, at least one hydrocarbon, and at least one halogen attached to silicon in its molecule.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Atomic layer deposition of high k metal silicates
InactiveUS20060228888A1Reduce carbon pollutionReduce stepsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHafniumAtomic layer deposition
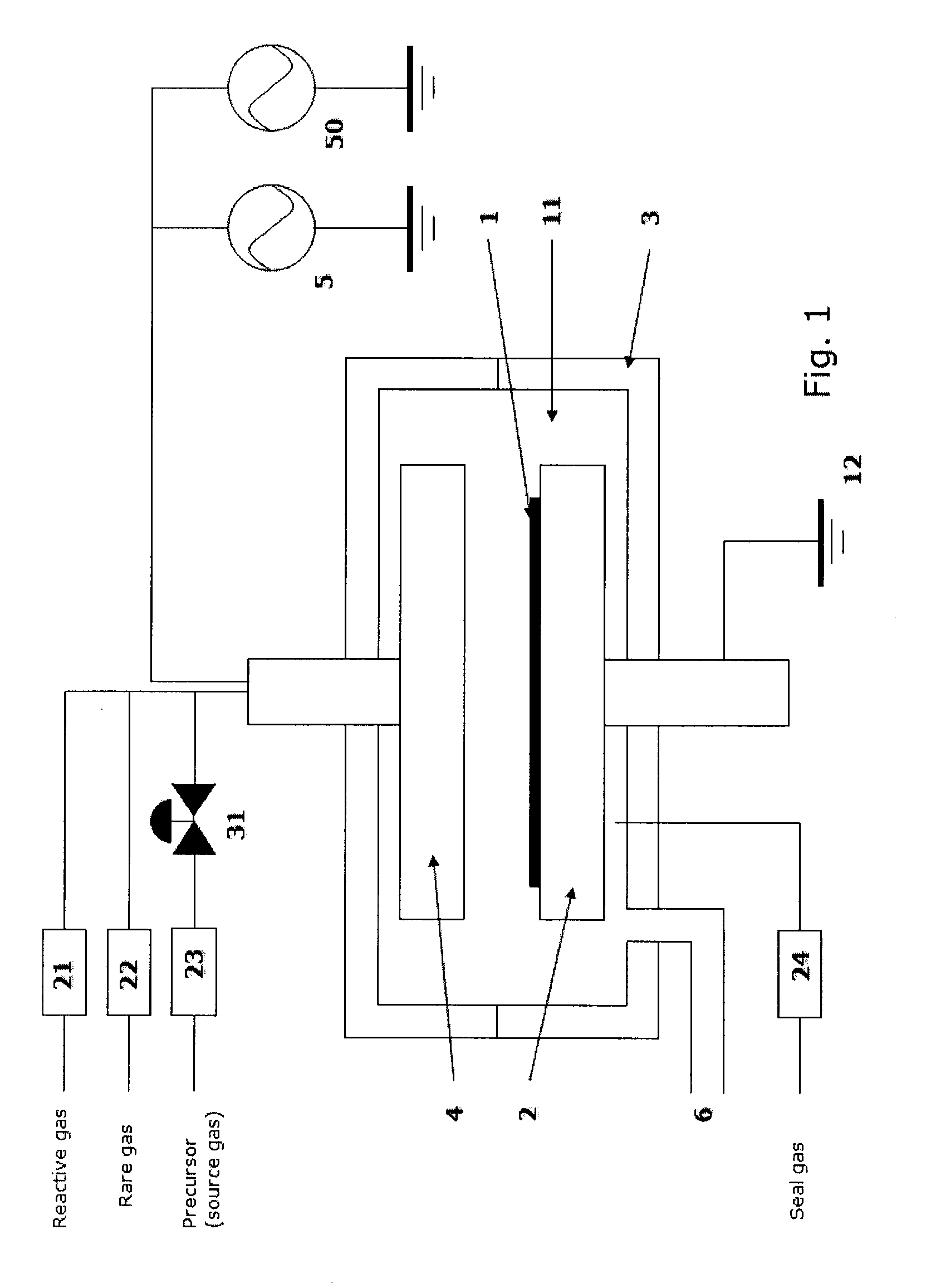
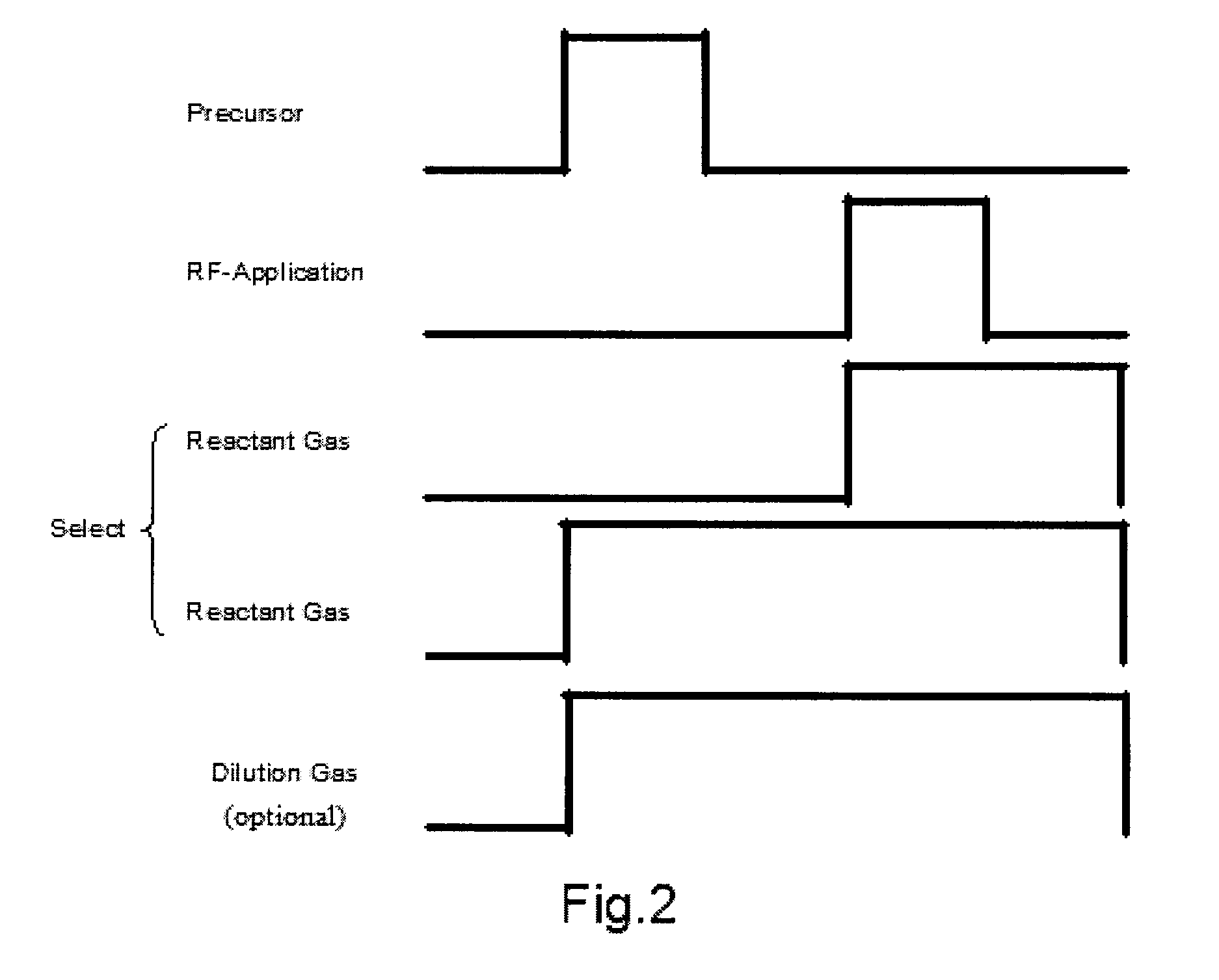
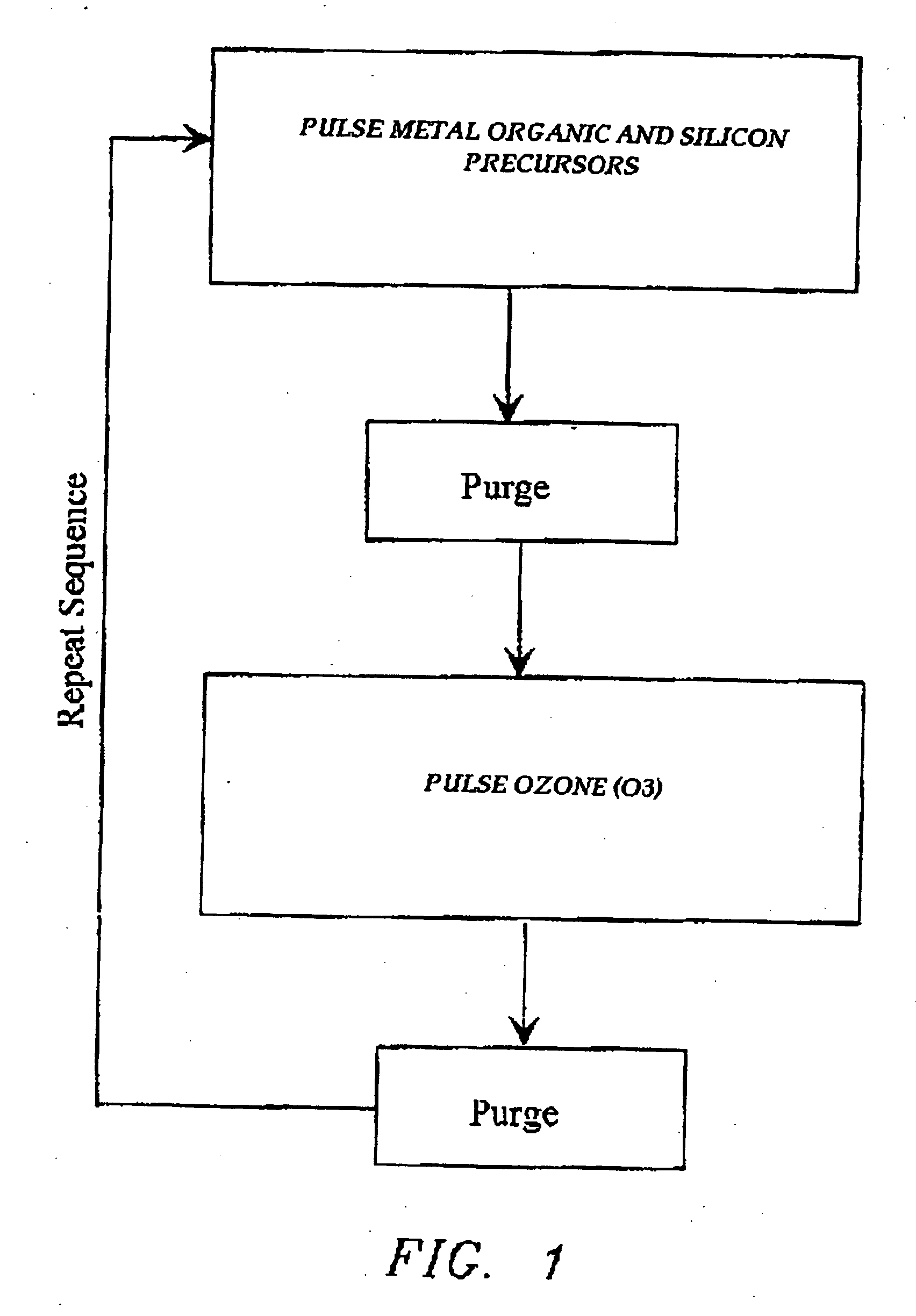
The present invention relates to the atomic layer deposition (“ALD”) of high k dielectric layers of metal silicates, including hafnium silicate. More particularly, the present invention relates to the ALD formation of metal silicates using metal organic precursors, silicon organic precursors and ozone. Preferably, the metal organic precursor is a metal alkyl amide and the silicon organic precursor is a silicon alkyl amide.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC +1
Heat treatment jig for semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS7329947B2Reduce stressSlips can be suppressed from occurringSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCharge supportsSemiconductorSilicon
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
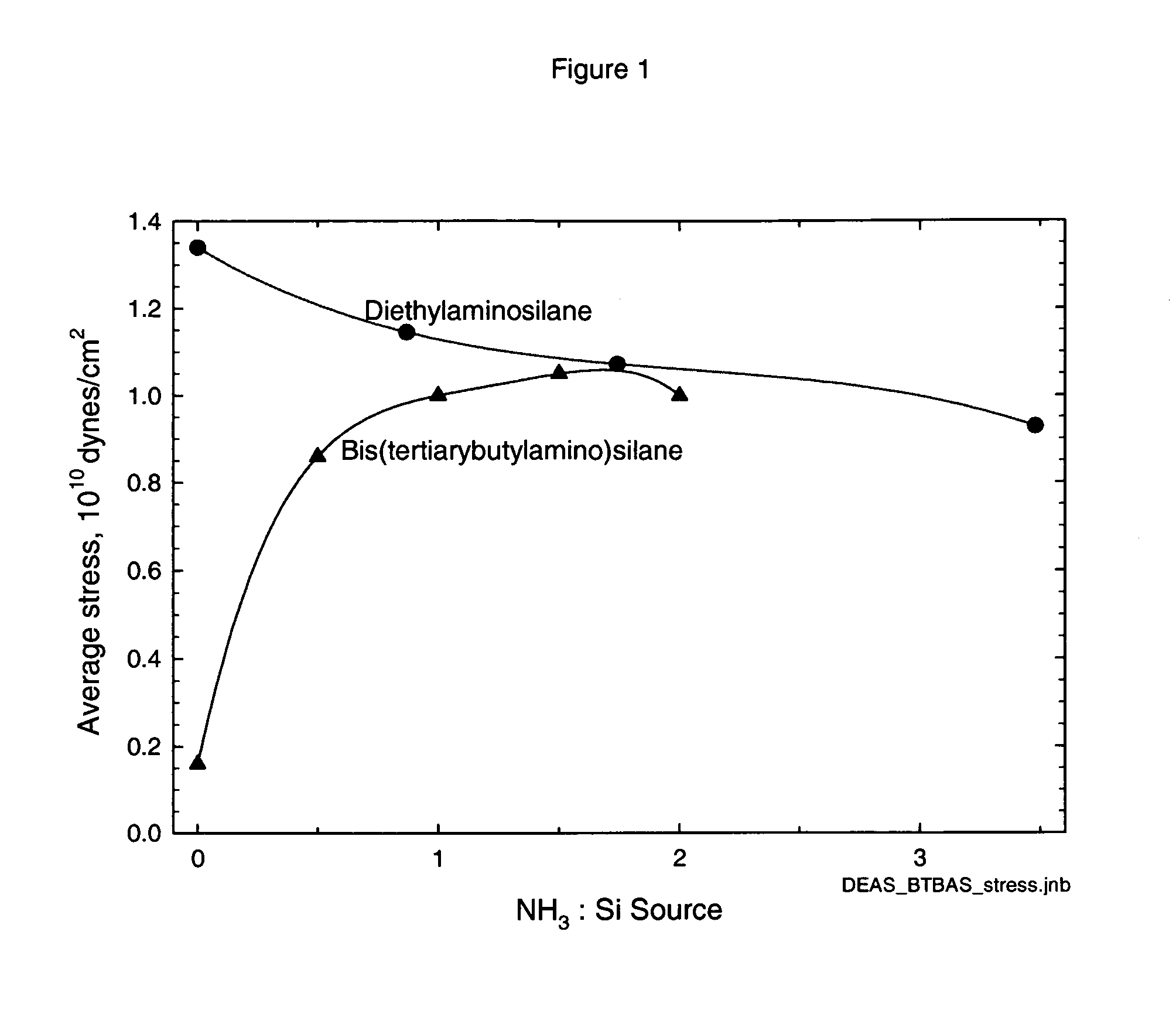
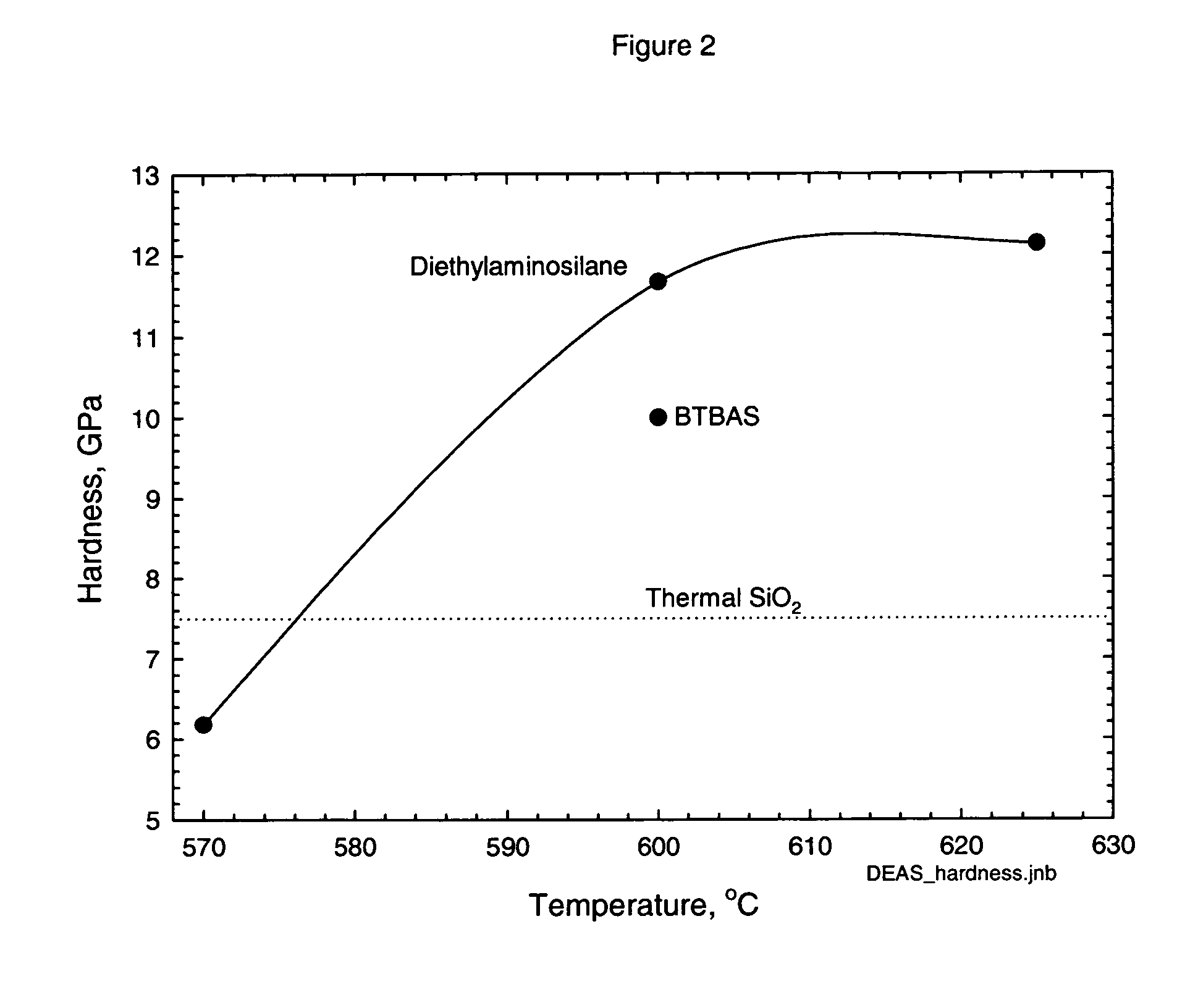
Precursors for CVD silicon carbo-nitride films
ActiveUS20060258173A1Easy to movePromote formationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesRoom temperature
Classes of liquid aminosilanes have been found which allow for the production of silicon carbo-nitride films of the general formula SixCyNz. These aminosilanes, in contrast, to some of the precursors employed heretofore, are liquid at room temperature and pressure allowing for convenient handling. In addition, the invention relates to a process for producing such films. The classes of compounds are generally represented by the formulas: and mixtures thereof, wherein R and R1 in the formulas represent aliphatic groups typically having from 2 to about 10 carbon atoms, e.g., alkyl, cycloalkyl with R and R1 in formula A also being combinable into a cyclic group, and R2 representing a single bond, (CH2)n, a ring, or SiH2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com