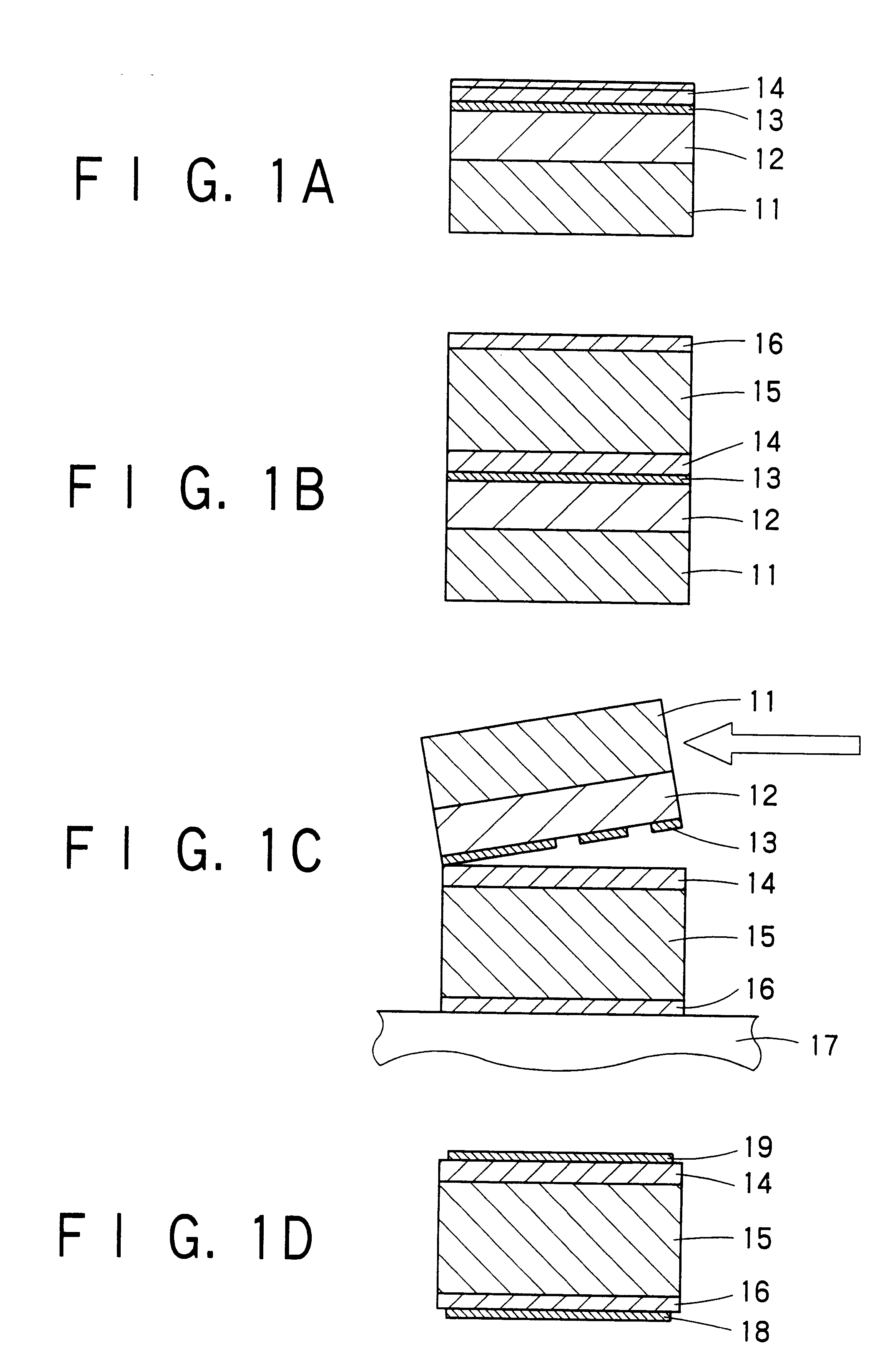
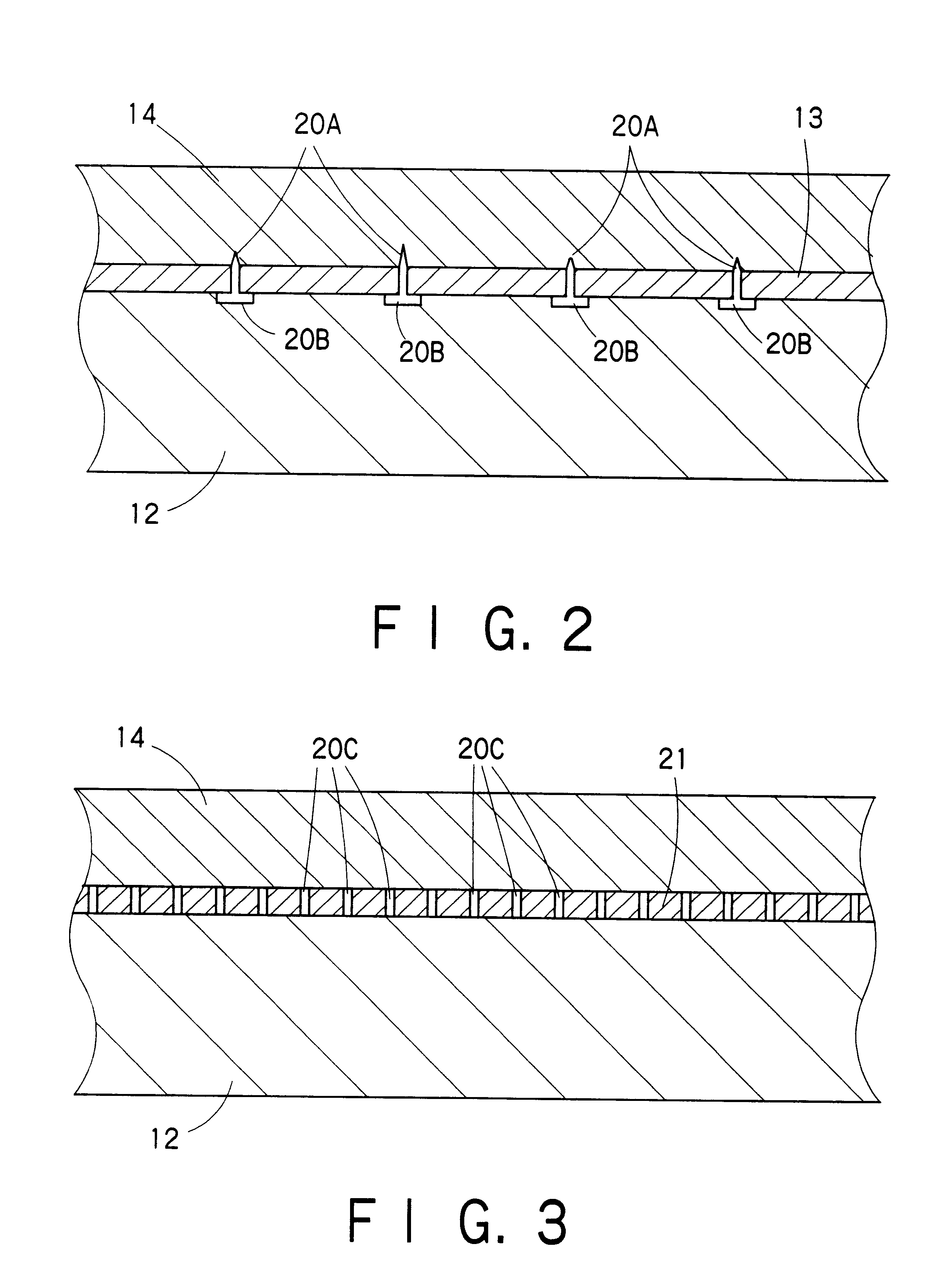
Patents
Literature
18001 results about "Nitride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a nitride is a compound of nitrogen where nitrogen has a formal oxidation state of −3. Nitrides are a large class of compounds with a wide range of properties and applications. The nitride ion, N³⁻, is never encountered in protic solution because it is so basic that it would be protonated immediately. Its ionic radius is estimated to be 140 pm.
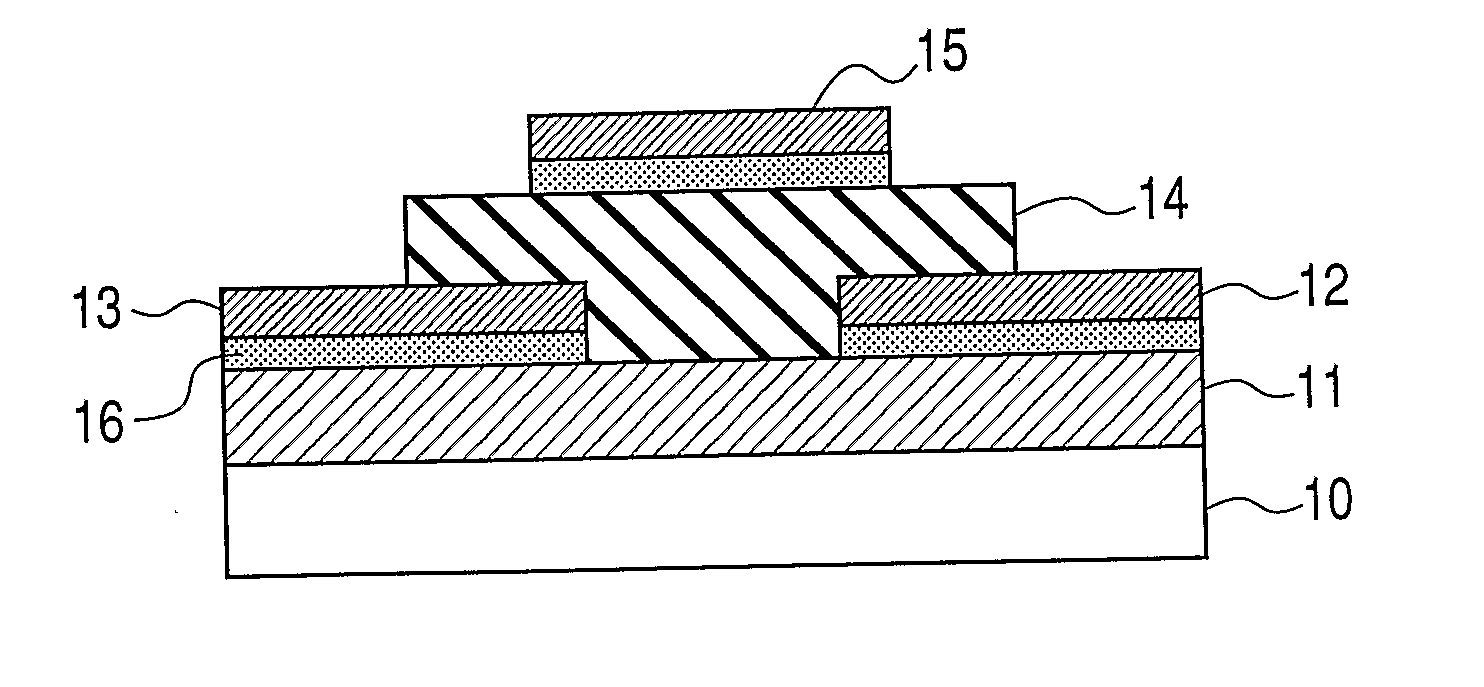
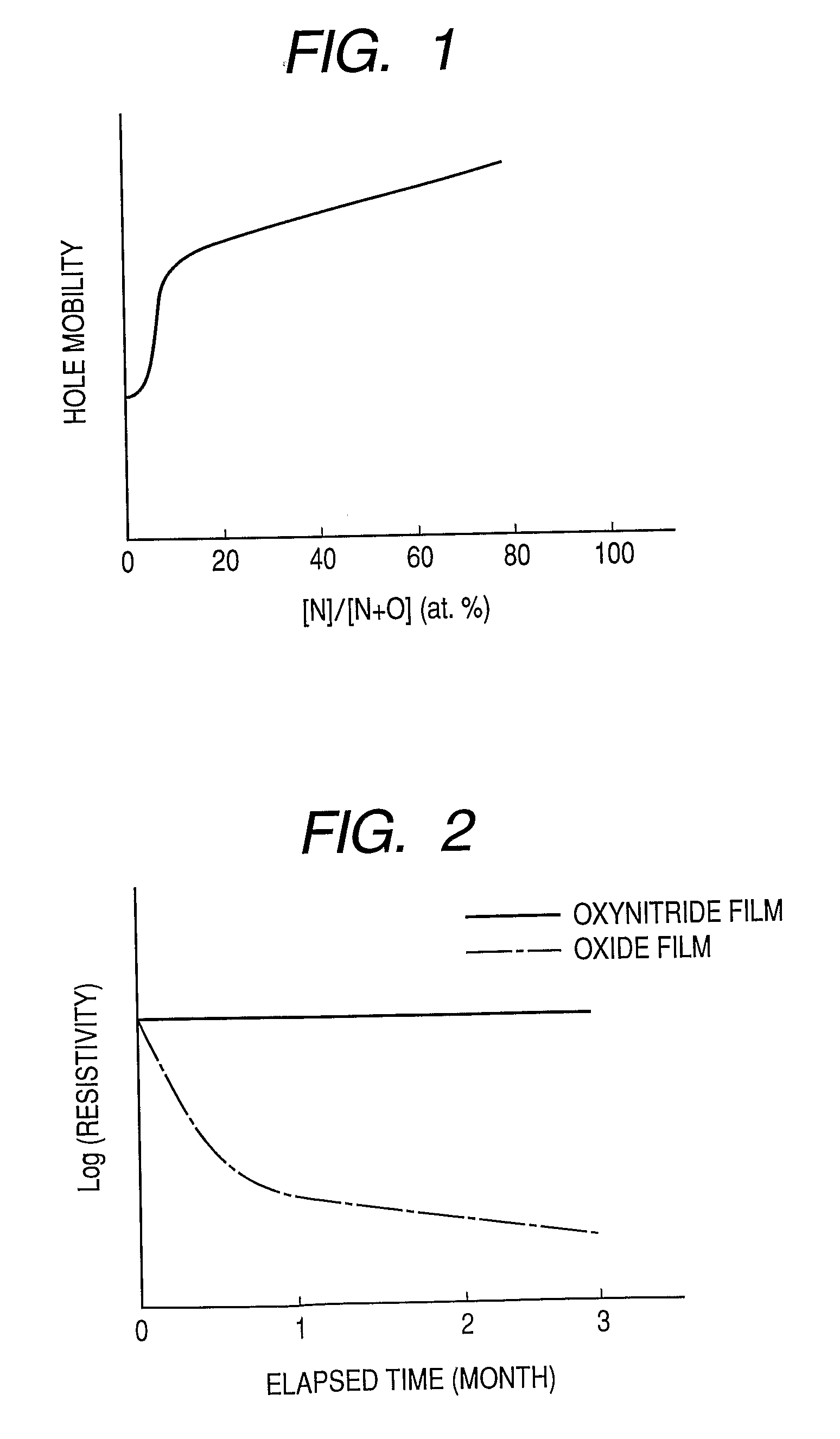
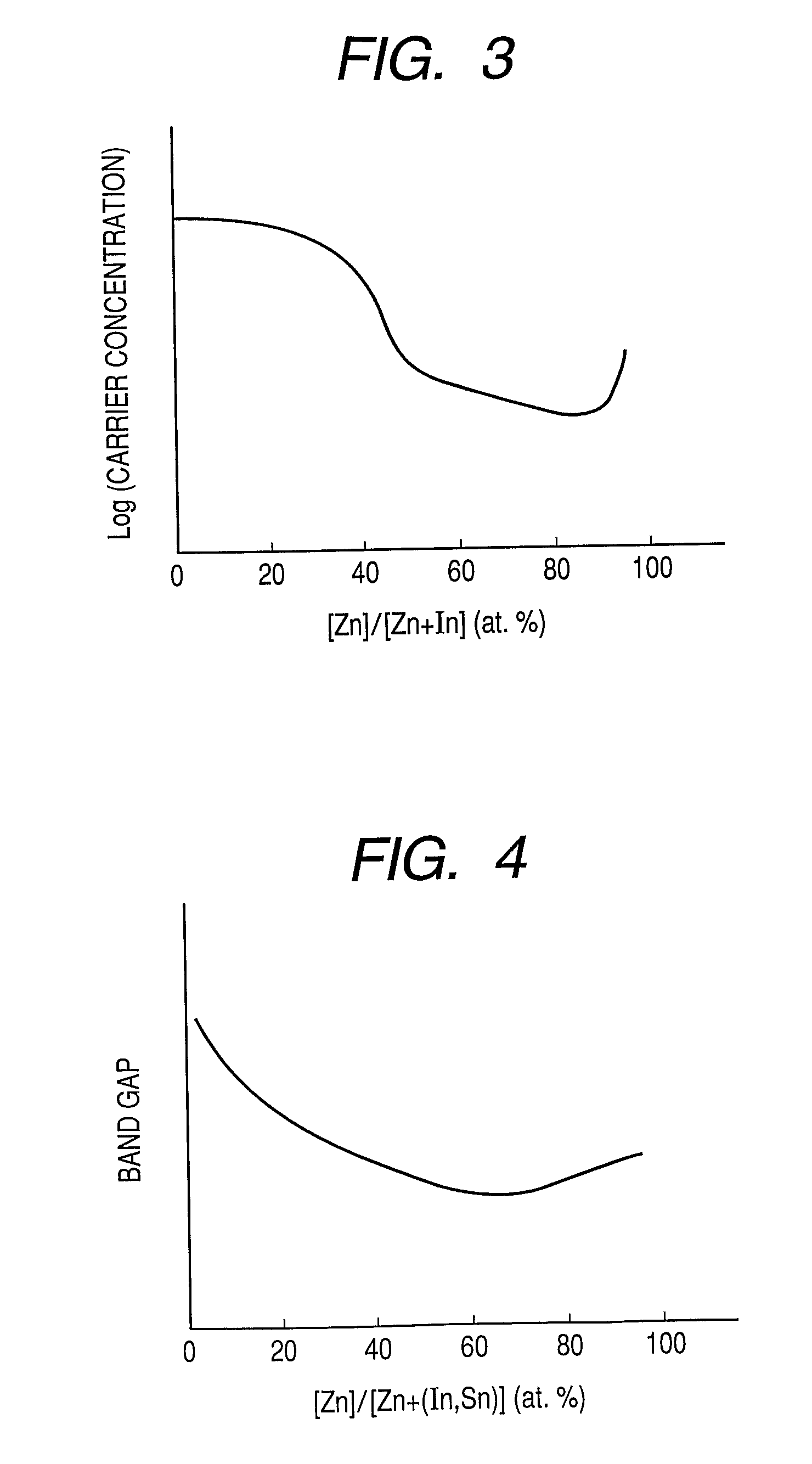
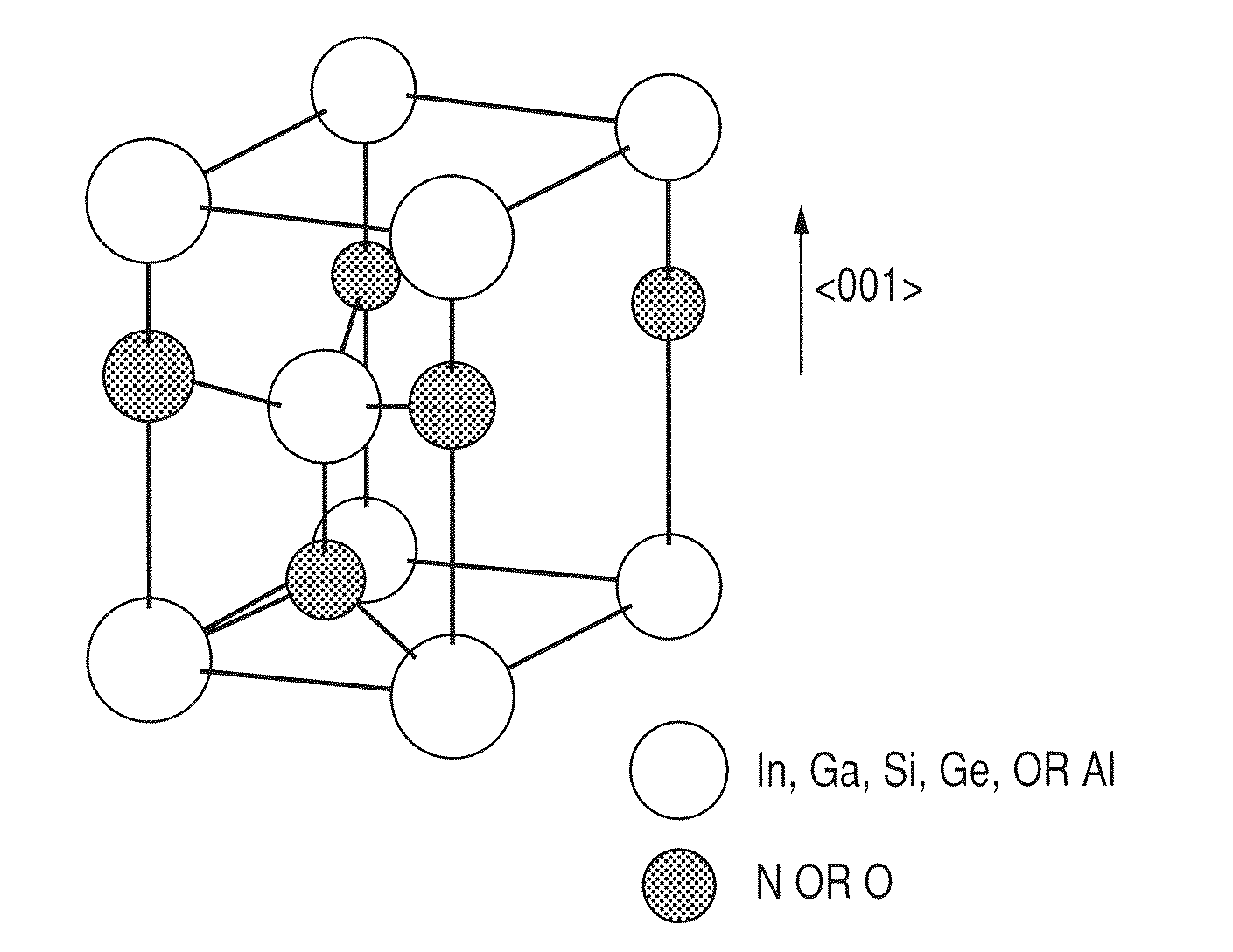
Oxynitride semiconductor
ActiveUS20100109002A1High mobility and environmental stabilityImprove mobilitySemiconductor devicesNitrogen oxideOxygen
Provided is an oxynitride semiconductor comprising a metal oxynitride. The metal oxynitride contains Zn and at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Sn, Mg, Si, Ge, Y, Ti, Mo, W, and Al. The metal oxynitride has an atomic composition ratio of N, N / (N+O), of 7 atomic percent or more to 80 atomic percent or less.
Owner:CANON KK
Substrate for growing wurtzite type crystal and method for manufacturing the same and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100092800A1Low costHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingNitrideSemiconductor
A laminated structure comprises a first layer comprising a crystal with six-fold symmetry, and a second layer comprising a metal oxynitride crystal formed on the first layer, wherein the second layer comprises at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Si, Ge and Al, N, O and Zn, as main elements, and wherein the second layer has in-plane orientation.
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20030040158A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETElectron mobility
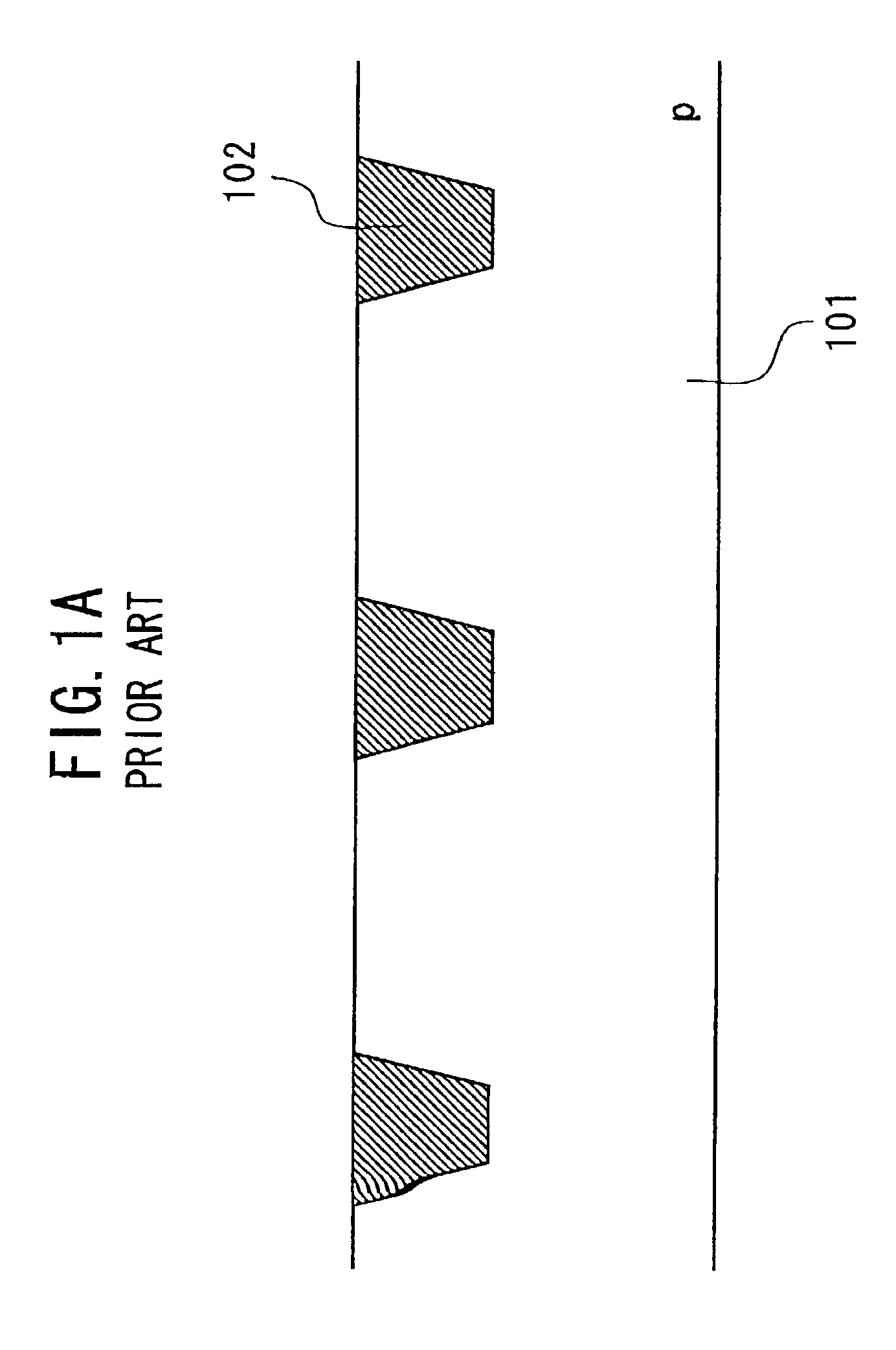
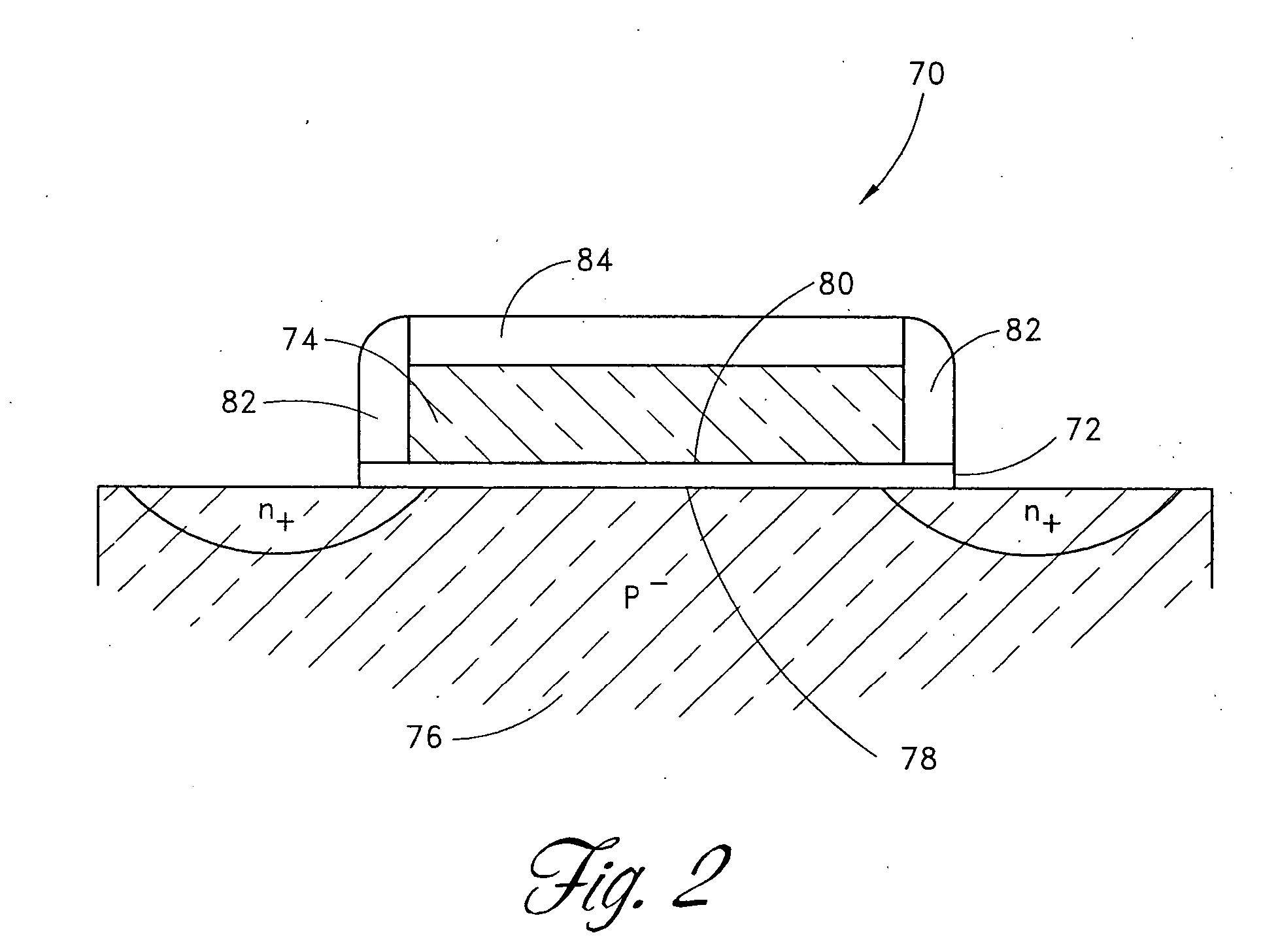
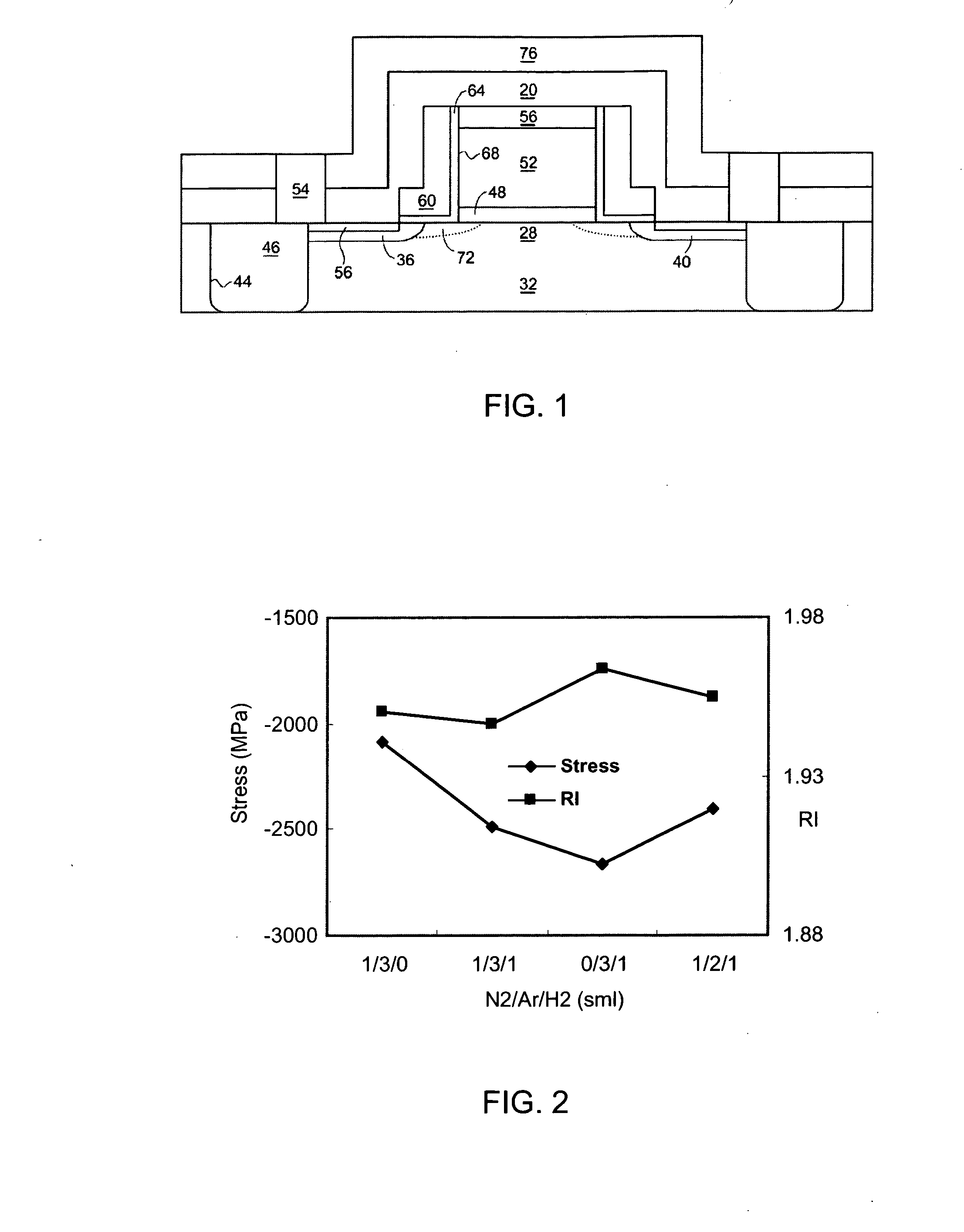
A semiconductor device improves the electron mobility in the n-channel MOSFET and reduces the bend or warp of the semiconductor substrate or wafer. The fist nitride layer having a tensile stress is formed on the substrate to cover the n-channel MOSFET. The tensile stress of the first nitride layer serves to relax a compressive stress existing in the channel region. The second nitride layer having an actual compressive stress is formed on the substrate to cover the p-channel MOSFET. The first and second nitride layers serve to decrease bend or warp of the substrate. Preferably, the first nitride layer is a nitride layer of Si formed by a LPCVD process, and the second nitride layer is a nitride layer of Si formed by a PECVD process.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Group III nitride photonic devices on silicon carbide substrates with conductive buffer interlay structure
InactiveUS6201262B1Avoid crackingEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedStress relieving
An optoelectronic device with a Group III Nitride active layer is disclosed that comprises a silicon carbide substrate; an optoelectronic diode with a Group III nitride active layer; a buffer structure selected from the group consisting of gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride between the silicon carbide substrate and the optoelectronic diode; and a stress-absorbing structure comprising a plurality of predetermined stress-relieving areas within the crystal structure of the buffer structure, so that stress-induced cracking that occurs in the buffer structure occurs at predetermined areas rather than elsewhere in the buffer structure.
Owner:CREE INC
Group III nitride photonic devices on silicon carbide substrates with conductive buffer interlayer structure
InactiveUS6187606B1Avoid crackingMinimize and eliminate heterobarrierSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedStress relieving
An optoelectronic device with a Group III Nitride active layer is disclosed that comprises a silicon carbide substrate; an optoelectronic diode with a Group III nitride active layer; a buffer structure selected from the group consisting of gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride between the silicon carbide substrate and the optoelectronic diode; and a stress-absorbing structure comprising a plurality of predetermined stress-relieving areas within the crystal structure of the buffer structure, so that stress-induced cracking that occurs in the buffer structure occurs at predetermined areas rather than elsewhere in the buffer structure.
Owner:CREE INC
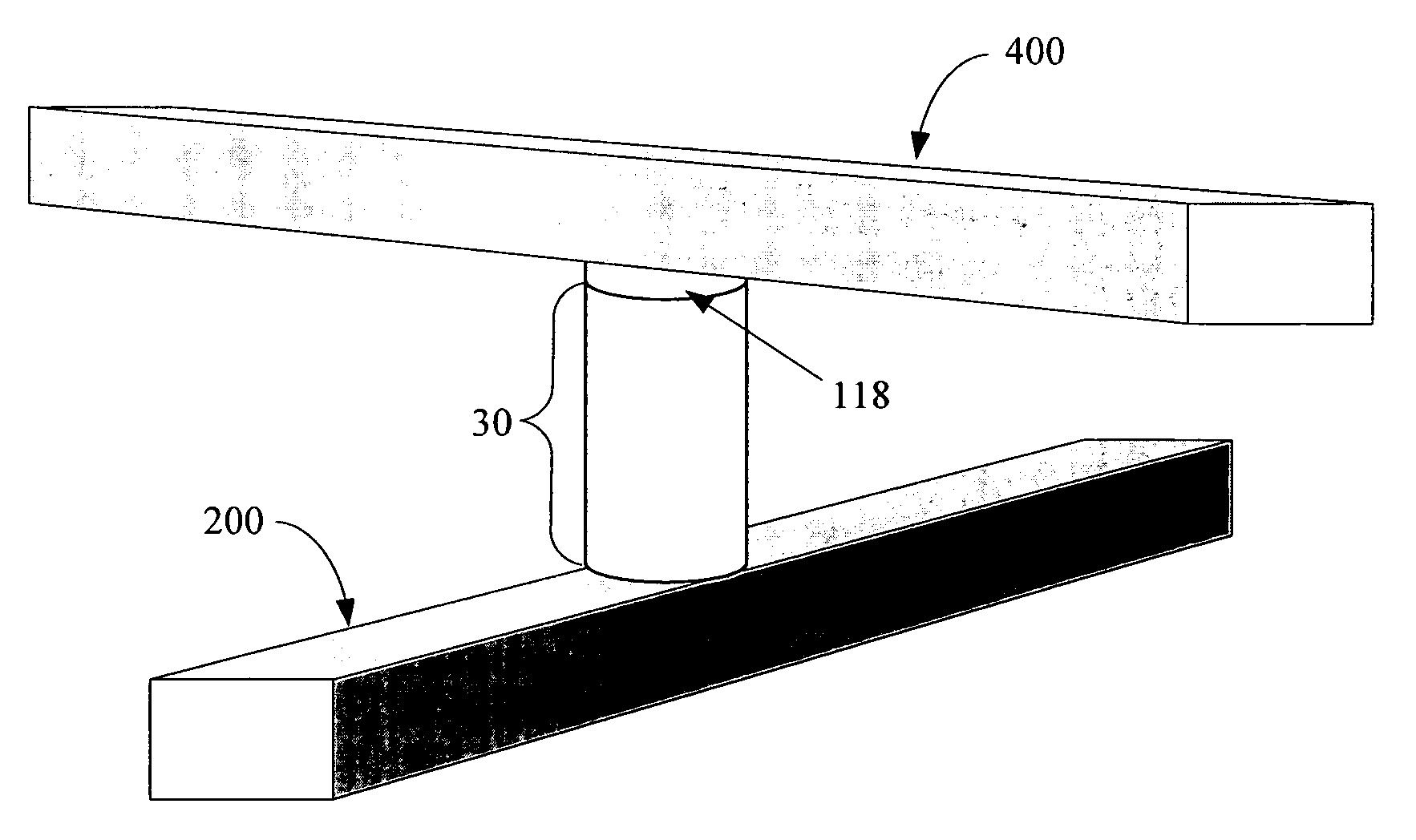
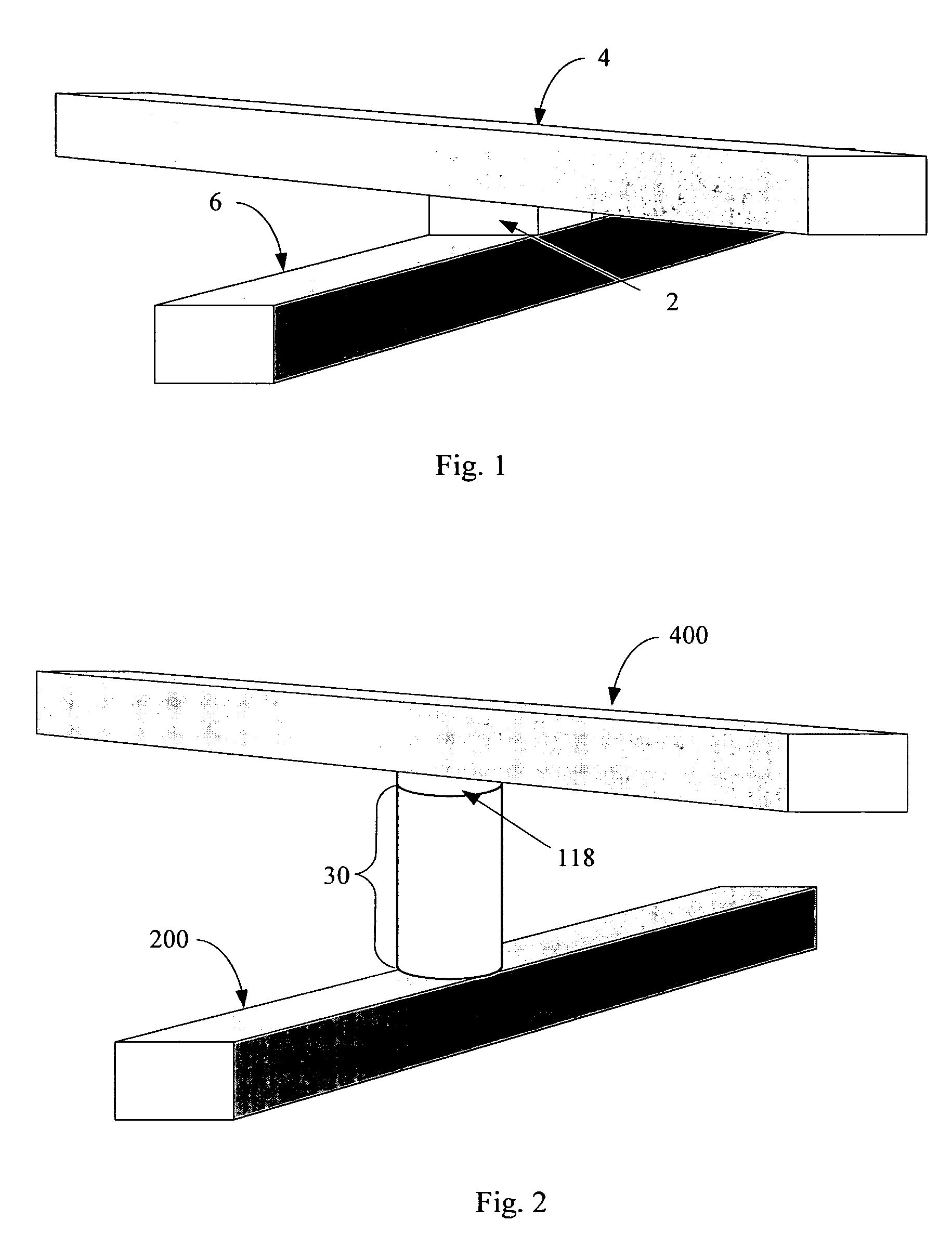
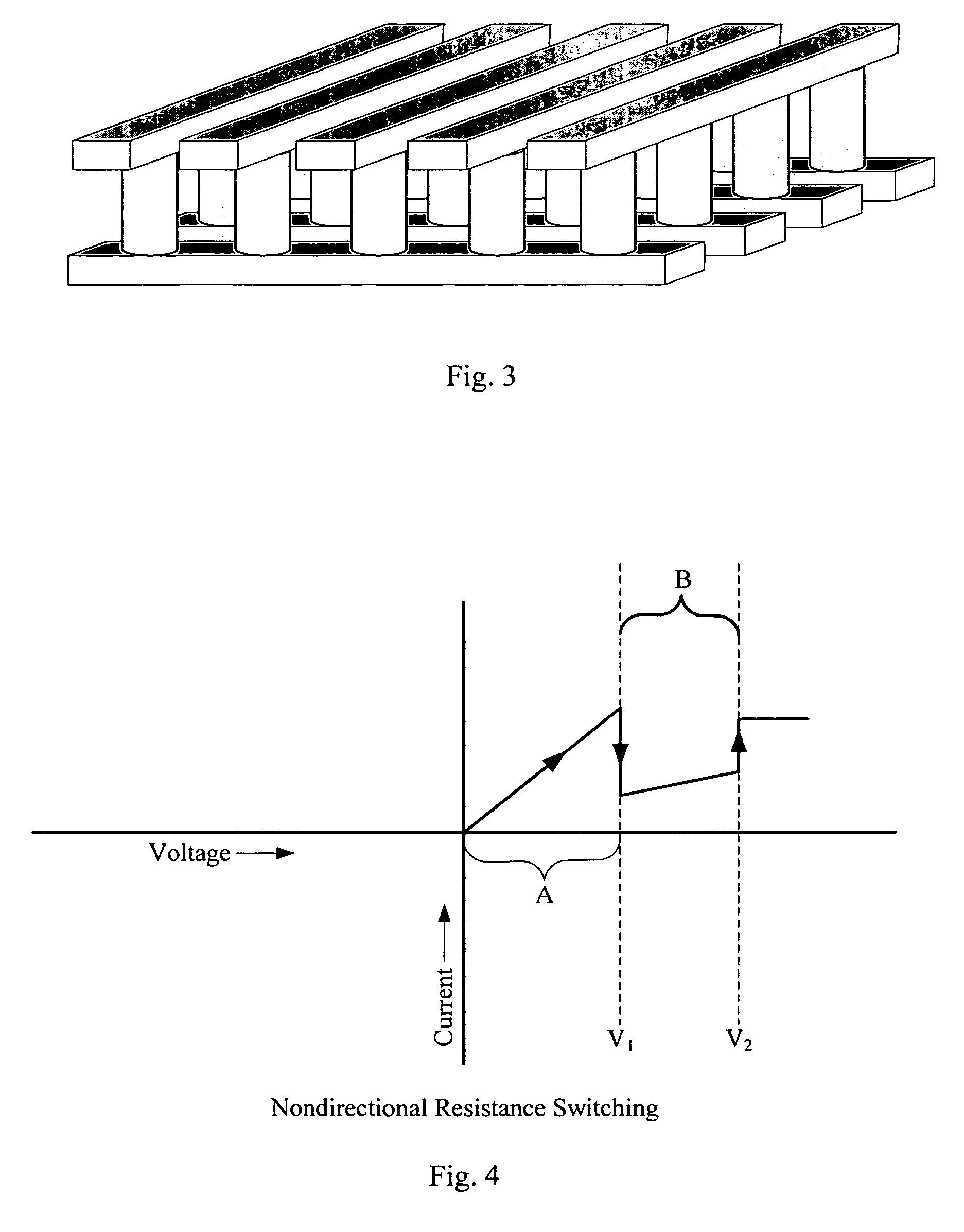
Rewriteable memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
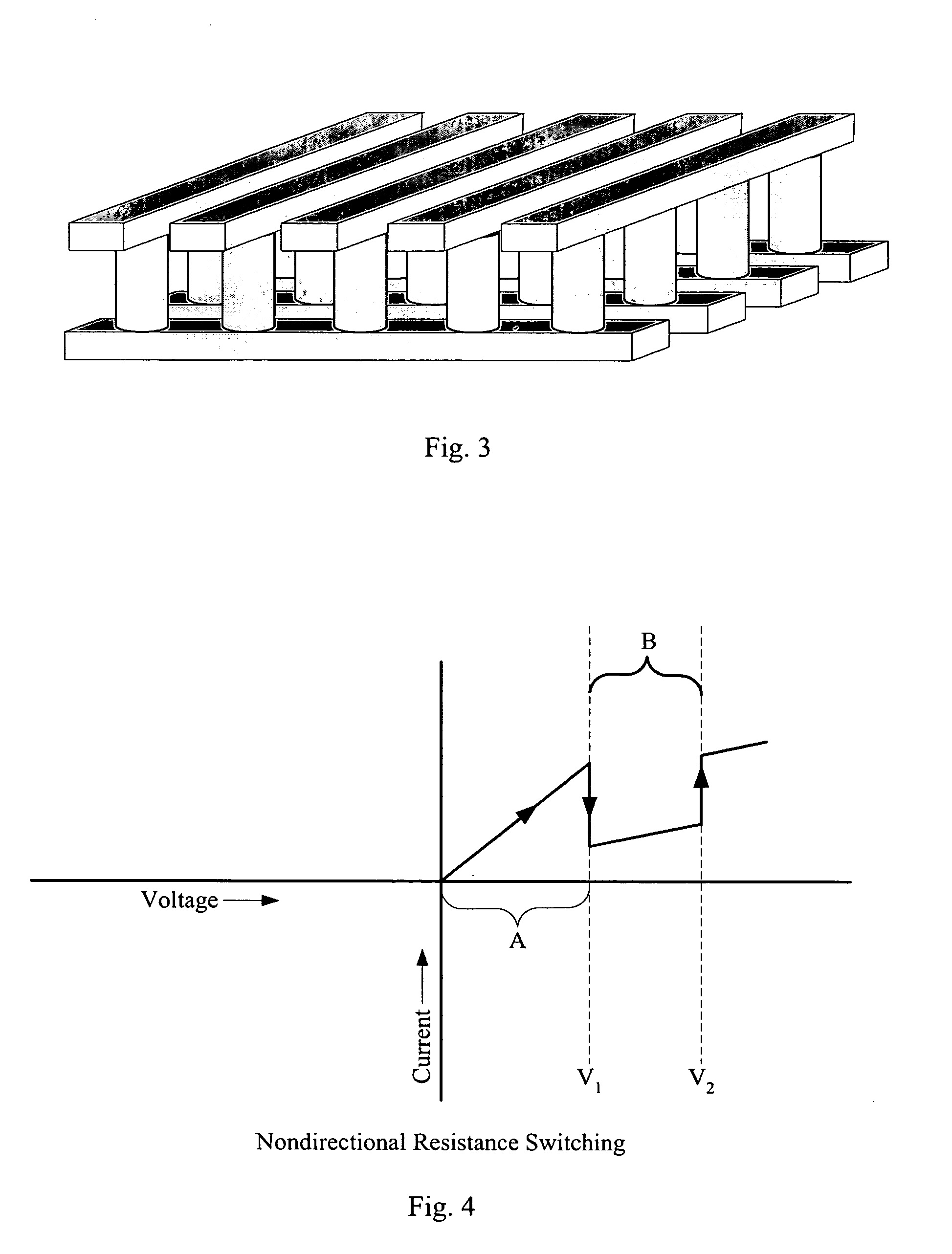
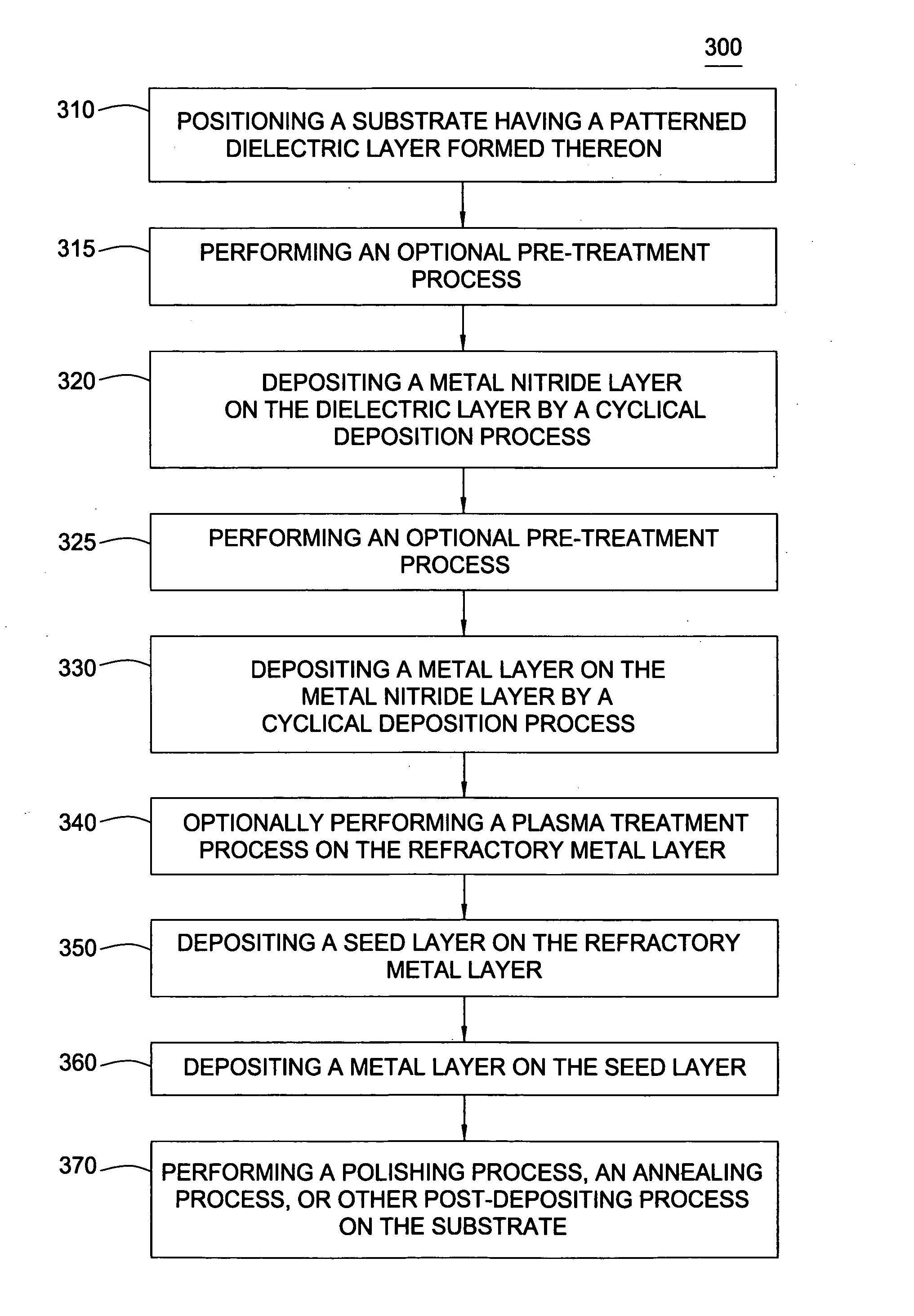
In a novel rewriteable nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NiO, Nb2O5, TiO2, HfO2, Al2O3, MgOx, CrO2, VO, BN, and AlN. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Atomic layer deposition of barrier materials
InactiveUS20050009325A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenNitride
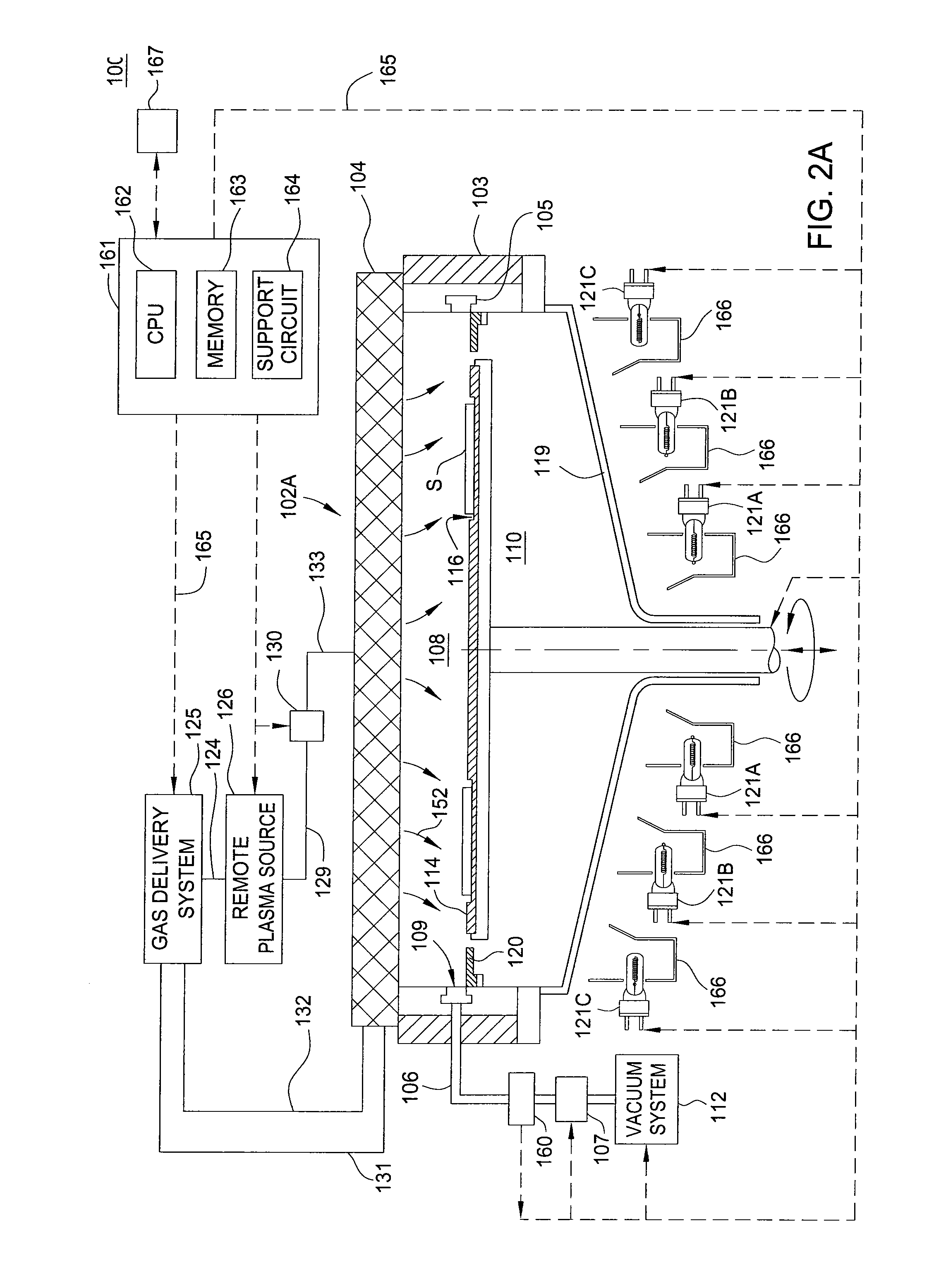
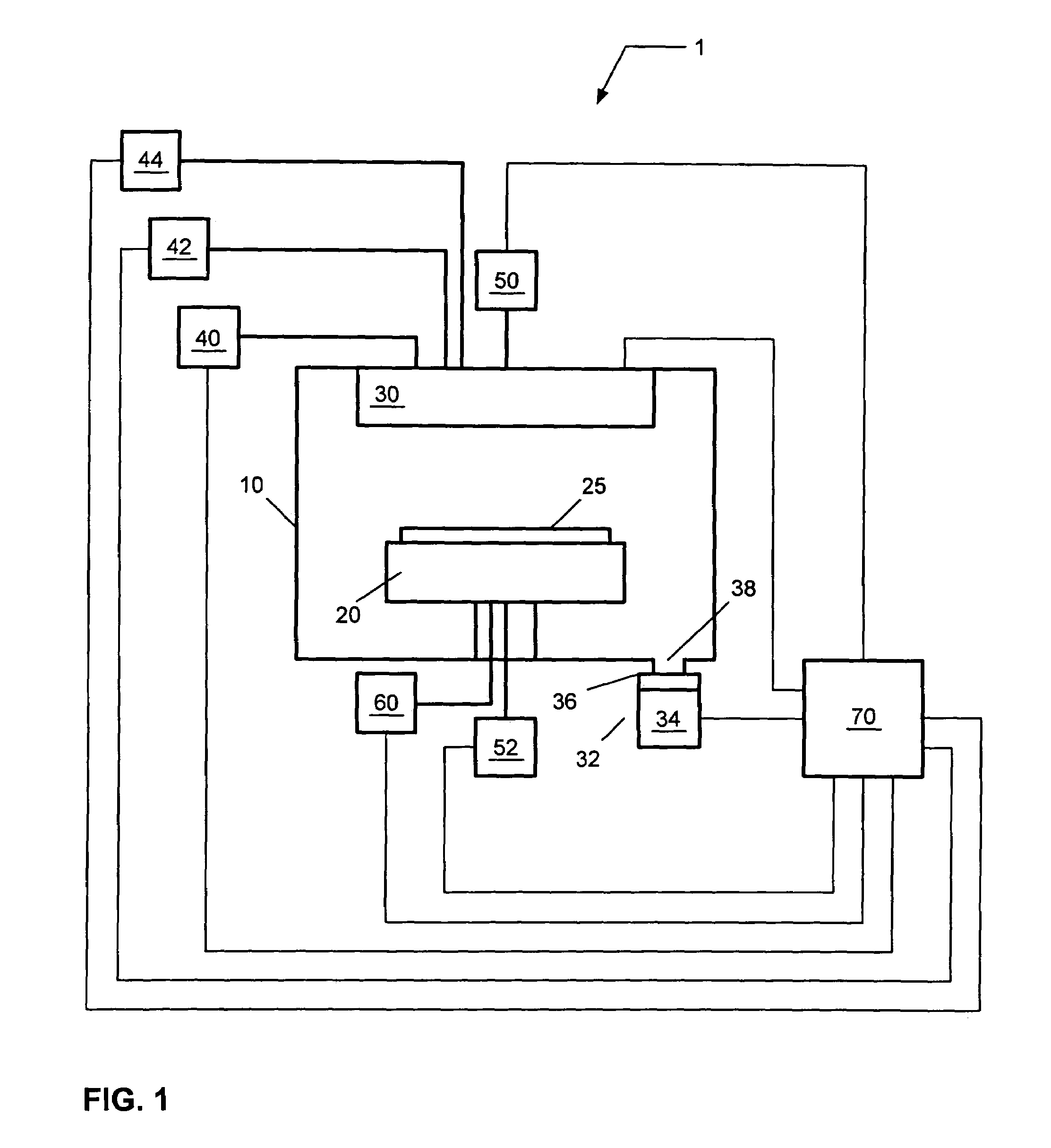
Methods for processing substrate to deposit barrier layers of one or more material layers by atomic layer deposition are provided. In one aspect, a method is provided for processing a substrate including depositing a metal nitride barrier layer on at least a portion of a substrate surface by alternately introducing one or more pulses of a metal containing compound and one or more pulses of a nitrogen containing compound and depositing a metal barrier layer on at least a portion of the metal nitride barrier layer by alternately introducing one or more pulses of a metal containing compound and one or more pulses of a reductant. A soak process may be performed on the substrate surface before deposition of the metal nitride barrier layer and / or metal barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Barrier material and process for Cu interconnect
InactiveUS20060113675A1Improved electromigration performanceImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDiffusion barrier
A semiconductor diffusion barrier layer and its method of manufacture is described. The barrier layer includes of at least one layer of TaN, TiN, WN, TbN, VN, ZrN, CrN, WC, WN, WCN, NbN, AlN, and combinations thereof. The barrier layer may further include a metal rich surface. Embodiments preferably include a glue layer about 10 to 500 Angstroms thick, the glue layer consisting of Ru, Ta, Ti, W, Co, Ni, Al, Nb, AlCu, and a metal-rich nitride, and combinations thereof. The ratio of the glue layer thickness to the barrier layer thickness is preferably about 1 to 50. Other alternative preferred embodiments further include a conductor annealing step. The various layers may be deposited using PVD, CVD, PECVD, PEALD and / or ALD methods including nitridation and silicidation methods.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
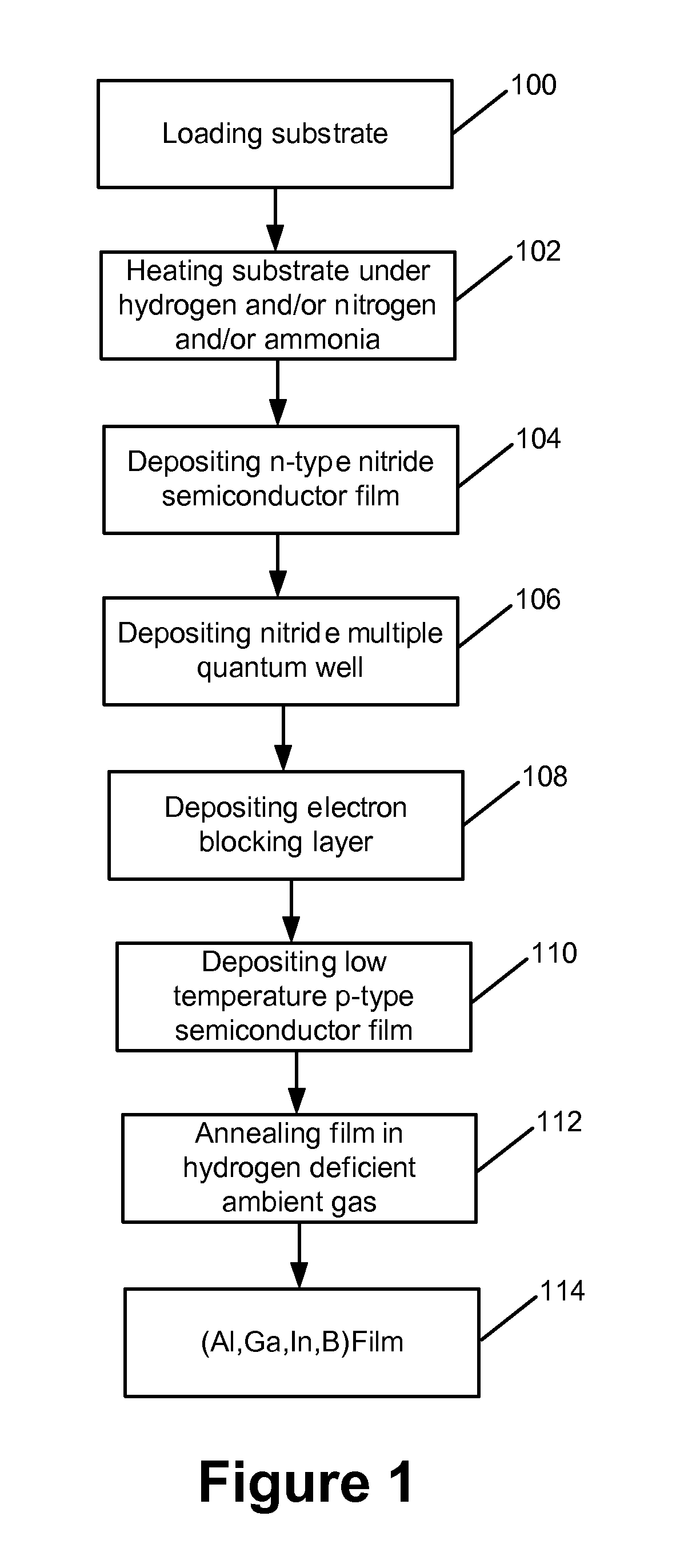
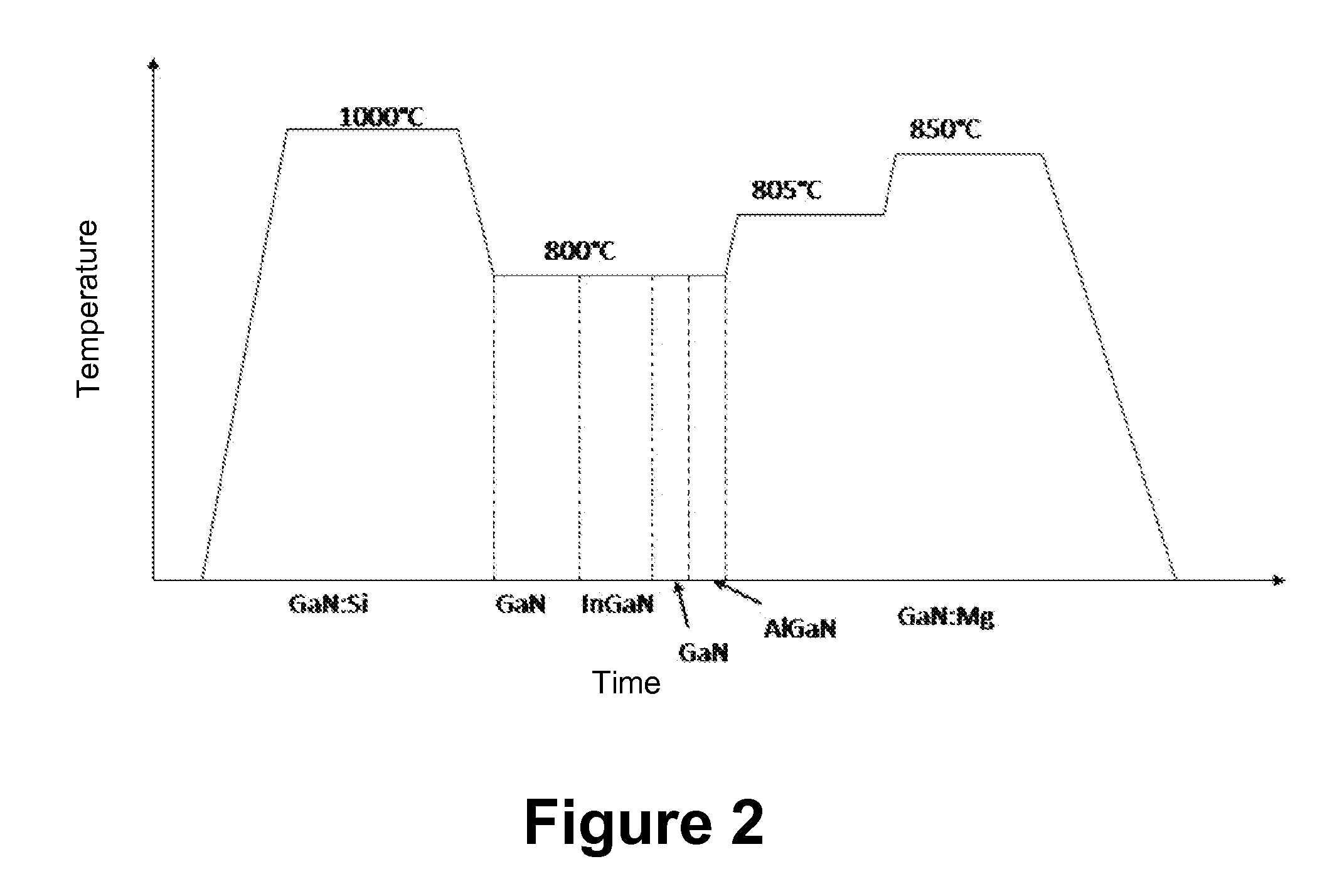
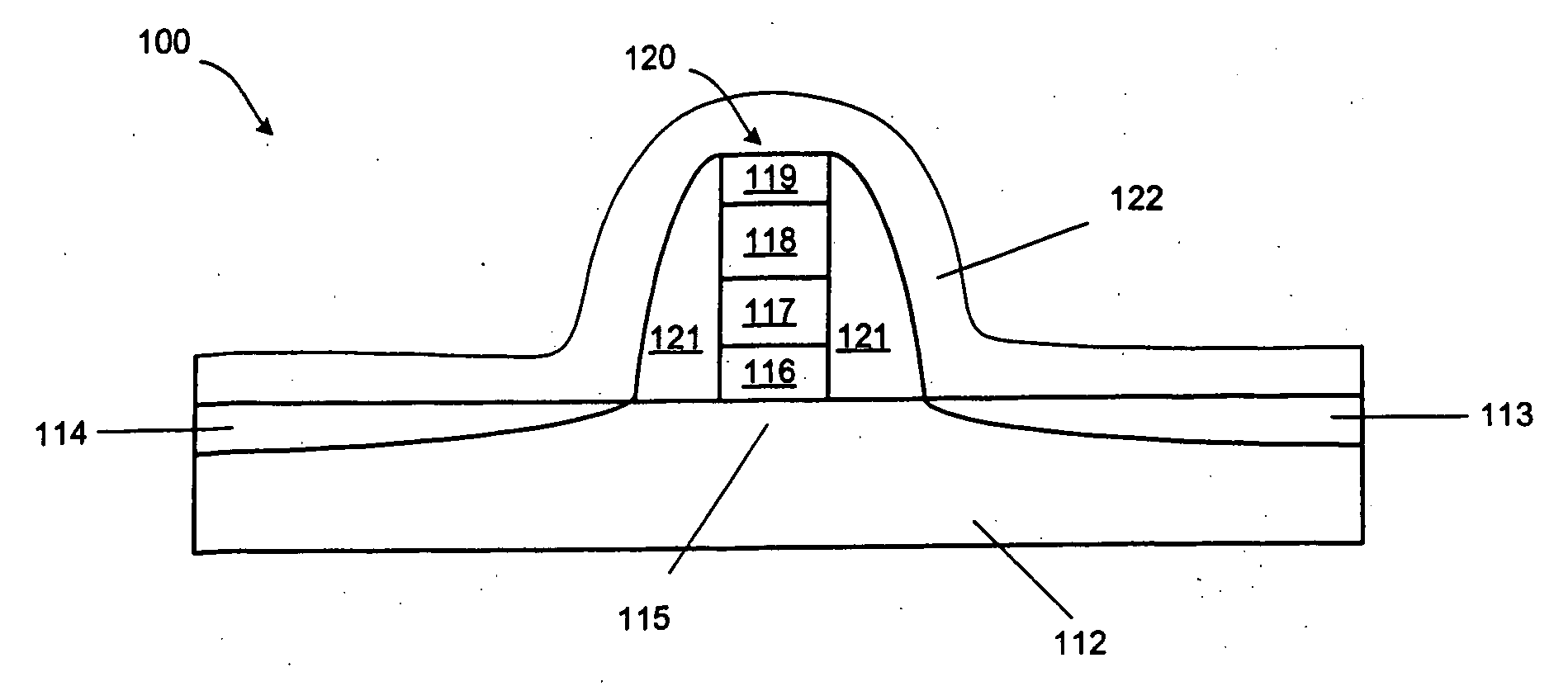
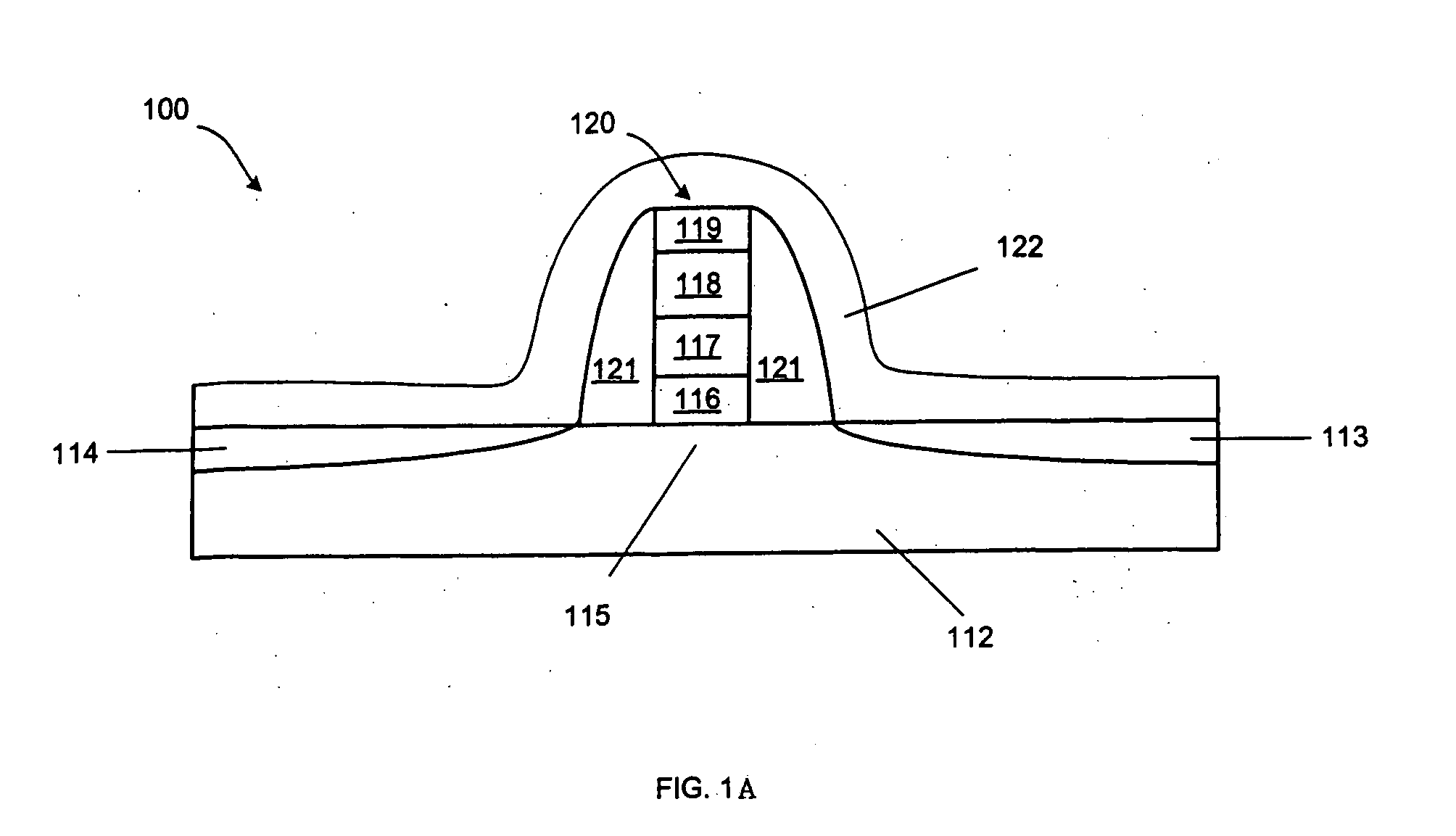
METHOD FOR FABRICATION OF SEMIPOLAR (Al, In, Ga, B)N BASED LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
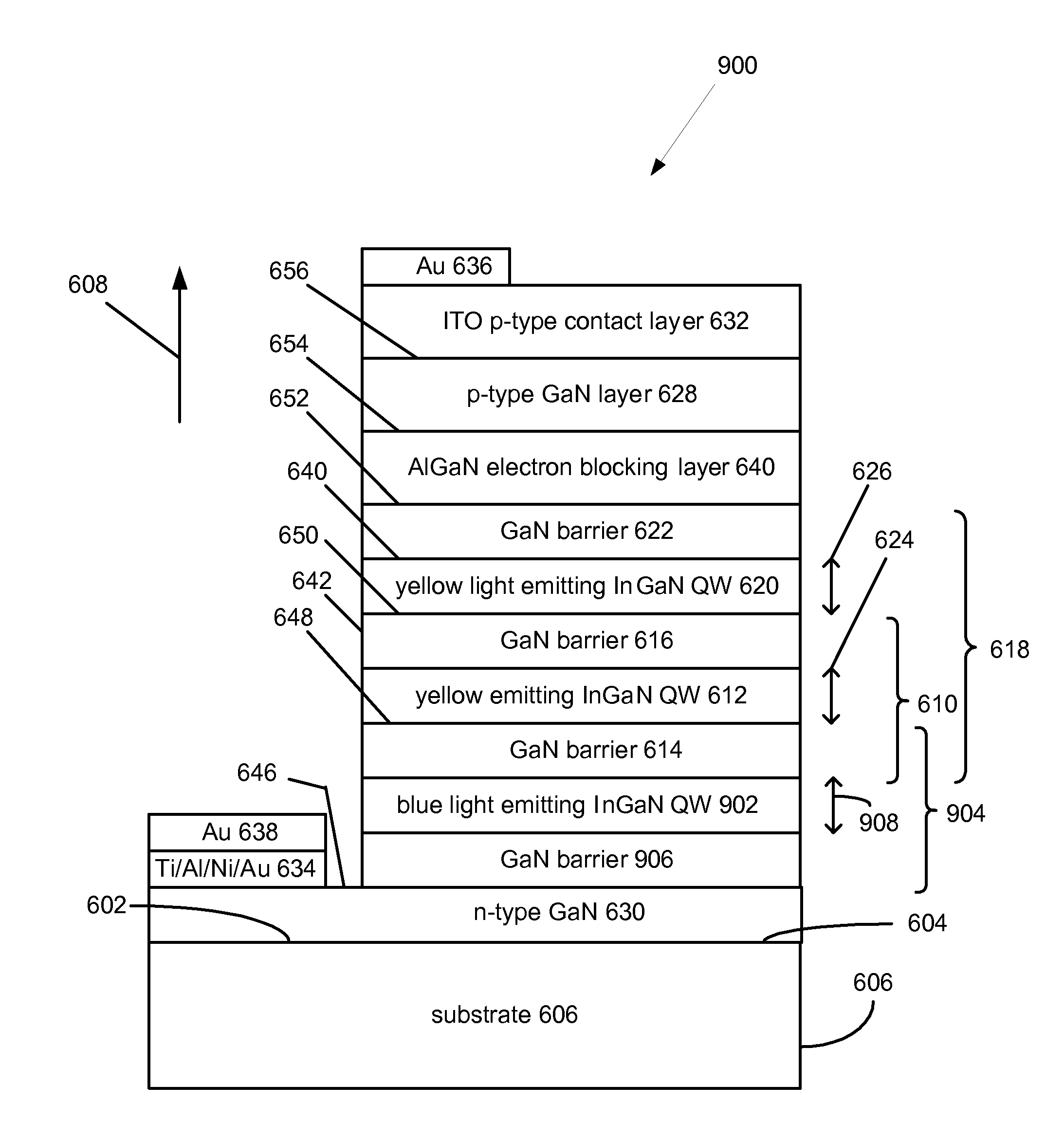
A yellow Light Emitting Diode (LED) with a peak emission wavelength in the range 560-580 nm is disclosed. The LED is grown on one or more III-nitride-based semipolar planes and an active layer of the LED is composed of indium (In) containing single or multi-quantum well structures. The LED quantum wells have a thickness in the range 2-7 nm. A multi-color LED or white LED comprised of at least one semipolar yellow LED is also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
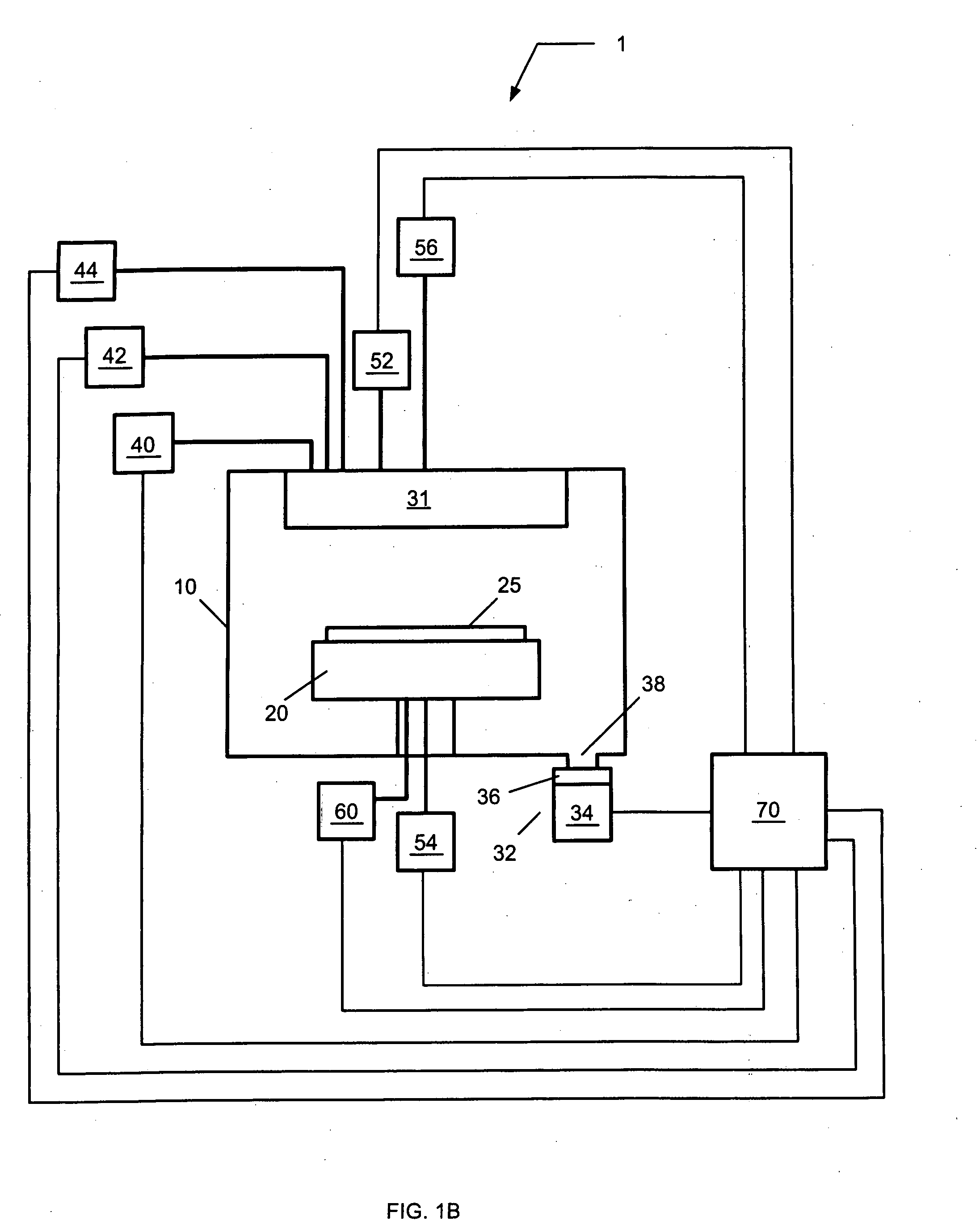
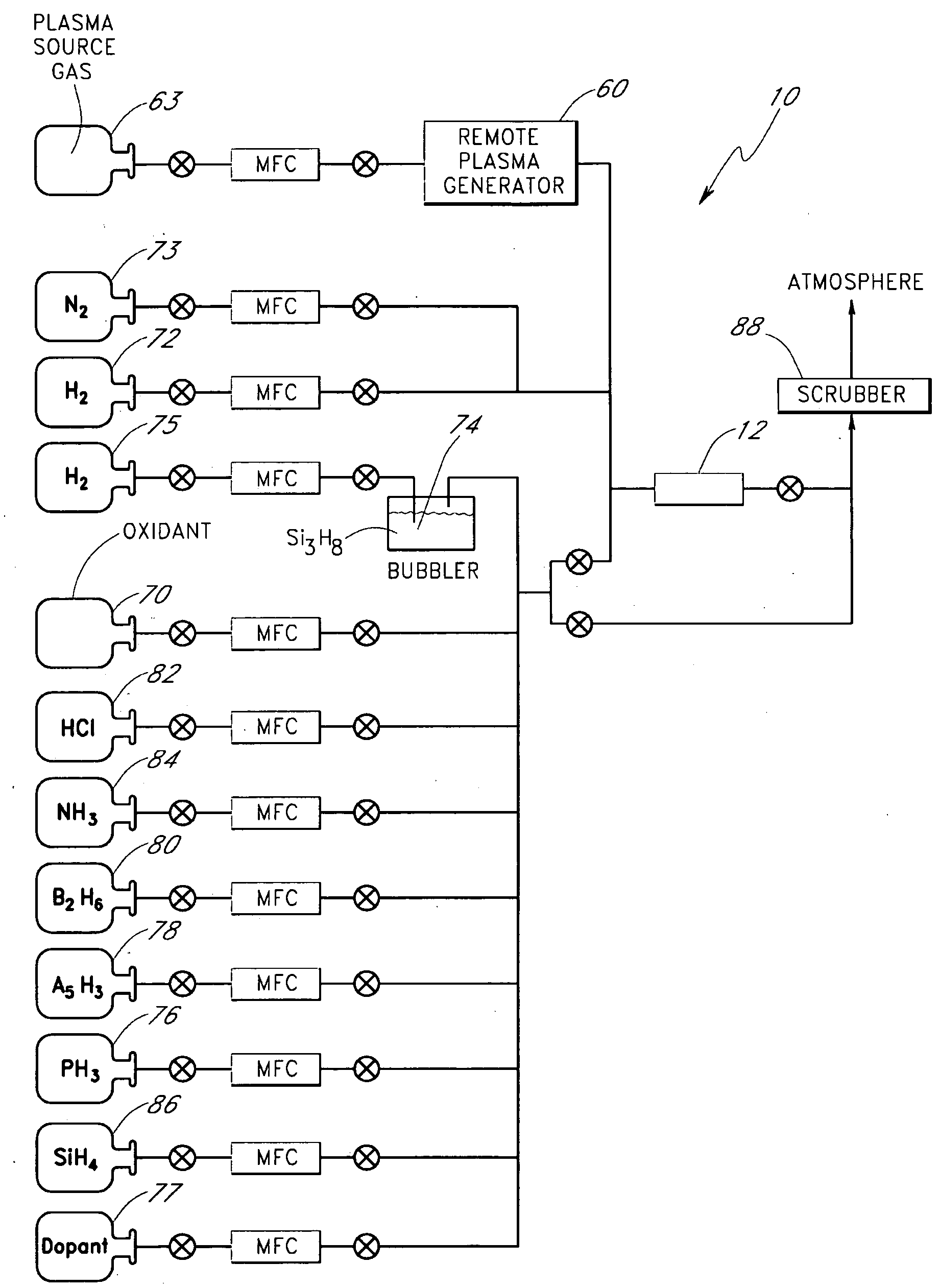
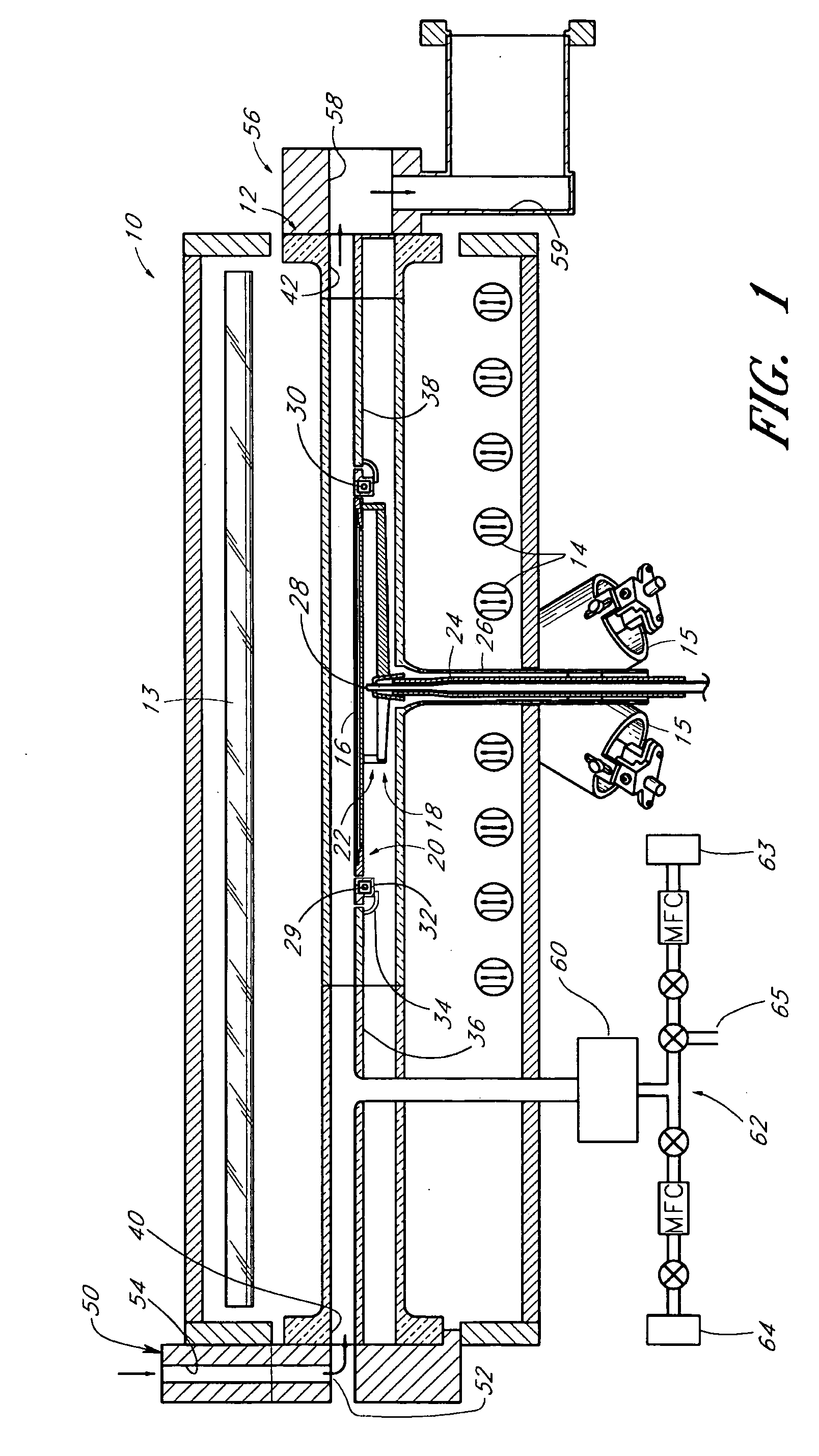
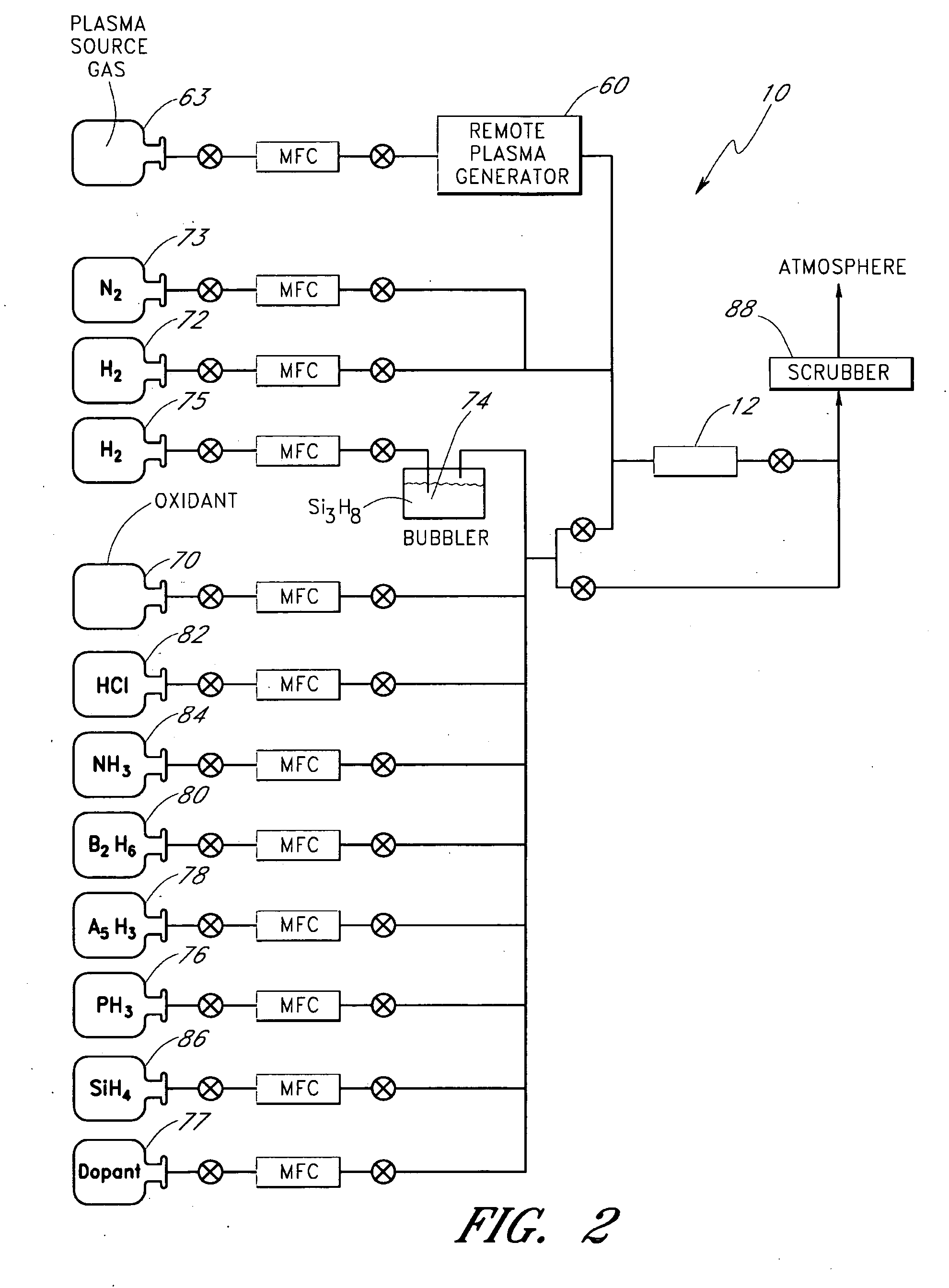
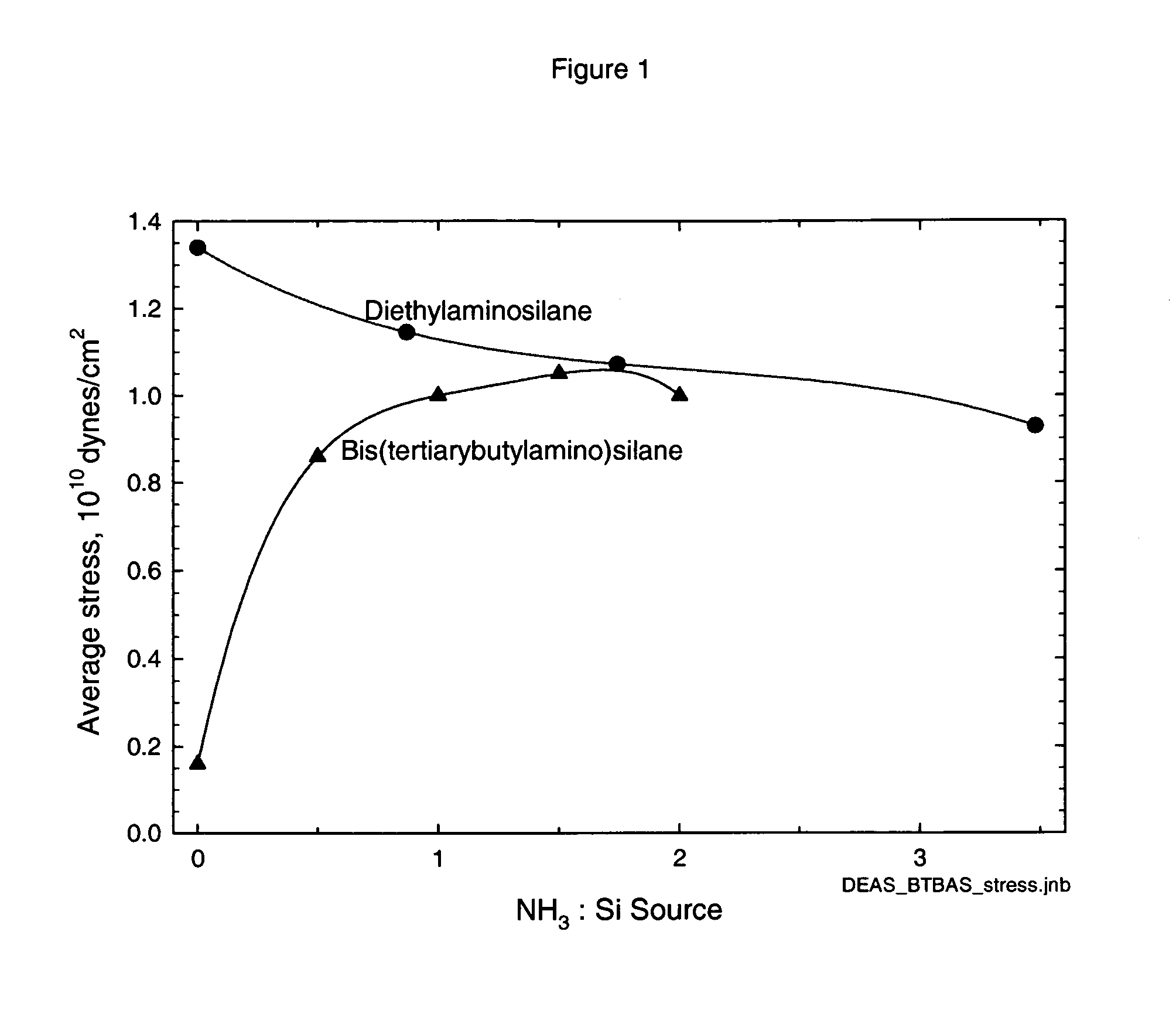
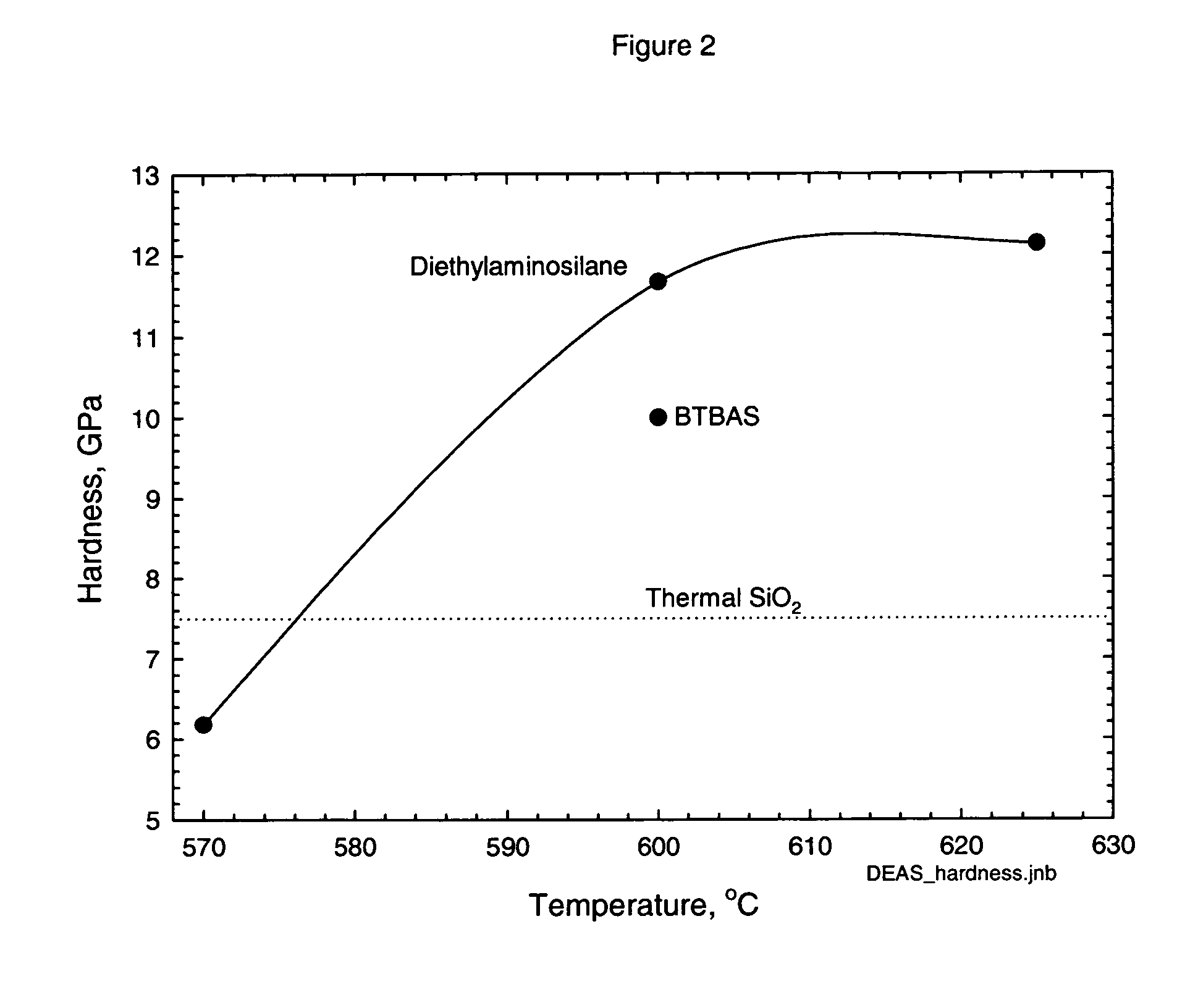
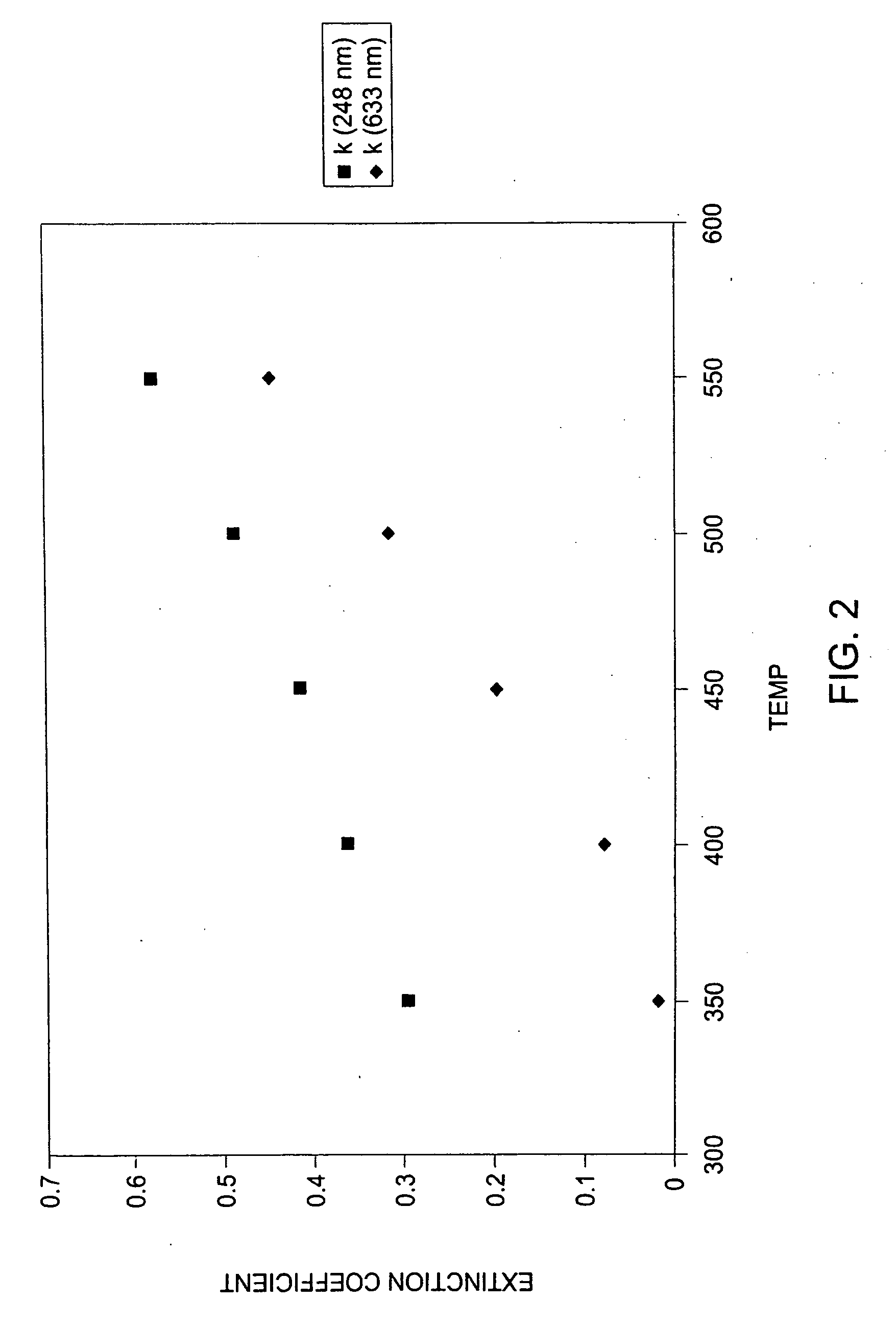
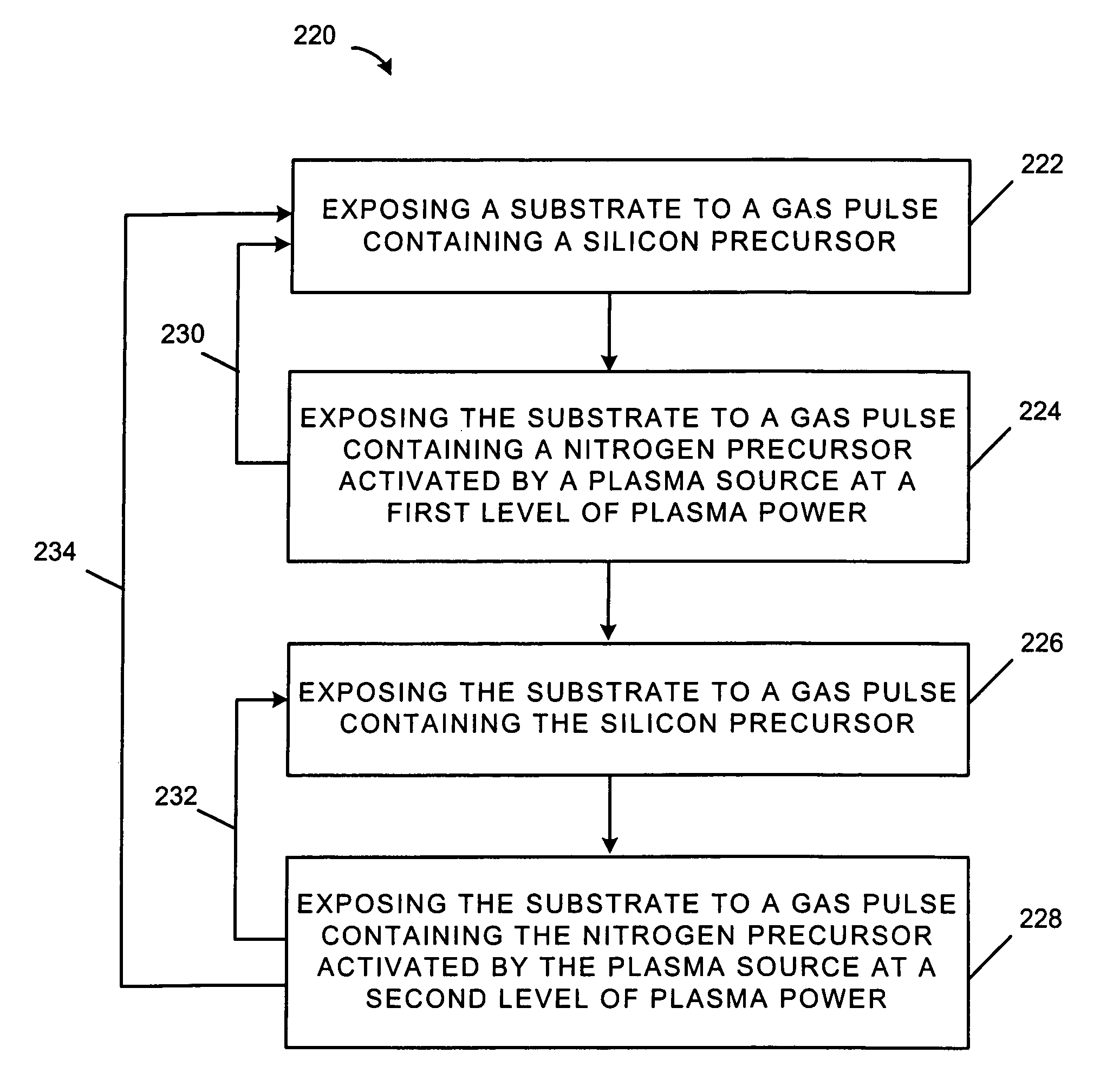
Method for forming strained silicon nitride films and a device containing such films
A method for forming a strained SiN film and a semiconductor device containing the strained SiN film. The method includes exposing the substrate to a gas including a silicon precursor, exposing the substrate to a gas containing a nitrogen precursor activated by a plasma source at a first level of plasma power and configured to react with the silicon precursor with a first reactivity characteristic, and exposing the substrate to a gas containing the nitrogen precursor activated by the plasma source at a second level of plasma power different from the first level and configured to react with the silicon precursor with a second reactivity characteristic such that a property of the silicon nitride film formed on the substrate changes to provide the strained silicon nitride film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
High stress nitride film and method for formation thereof
ActiveUS20060199357A1Increase the tensile stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDopantNitrogen
A silicon nitride film is formed on a substrate in a reaction chamber by introducing trisilane and a reactive nitrogen species into the chamber in separate pulses. A carbon precursor gas is also flowed into the chamber during introduction of the trisilane and / or during introduction of the reactive nitrogen species, or in pulses separate from the trisilane and reactive nitrogen species pulses. The carbon is used as a dopant in the silicon nitride film and advantageously allows a high stress silicon nitride film to be formed.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Nonvolatile memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
In a novel nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NixOy, NbxOy, TixOy, HFxOy, AlxOy, MgxOy, CoxOy, CrxOy, VxOy, ZnxOy, ZrxOy, BxNy, and AlxNy. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors. The memory cell of the present invention can be used as a rewriteable memory cell or a one-time-programmable memory cell, and can store two or more data states.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Semiconductor light emitting element, and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS6303405B1Quality improvementImprove electricitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser lightHeat stress
A semiconductor light emitting element of nitride compound semiconductors excellent in cleavability, heat radiation and resistance to leakage is made by epitaxially grow a nitride compound semiconductor layers on a substrate of sapphire, for example, and thereafter separating the substrate. For separating the substrate, there are a technique using a abruption mechanism susceptible to a stress such as a "lift-off layer" and a recesses on a substrate. A technique using laser light to cause a local dense heat stress at the abruption mechanism is effective. A nitride compound semiconductor obtained by separating the substrate may be used as a new substrate to epitaxially grow high-quality nitride compound semiconductors thereon.
Owner:ALPAD CORP
Low Temperature Deposition of Silicon-Containing Films
ActiveUS20100304047A1Low deposition temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesLow temperature depositionDeposition temperature
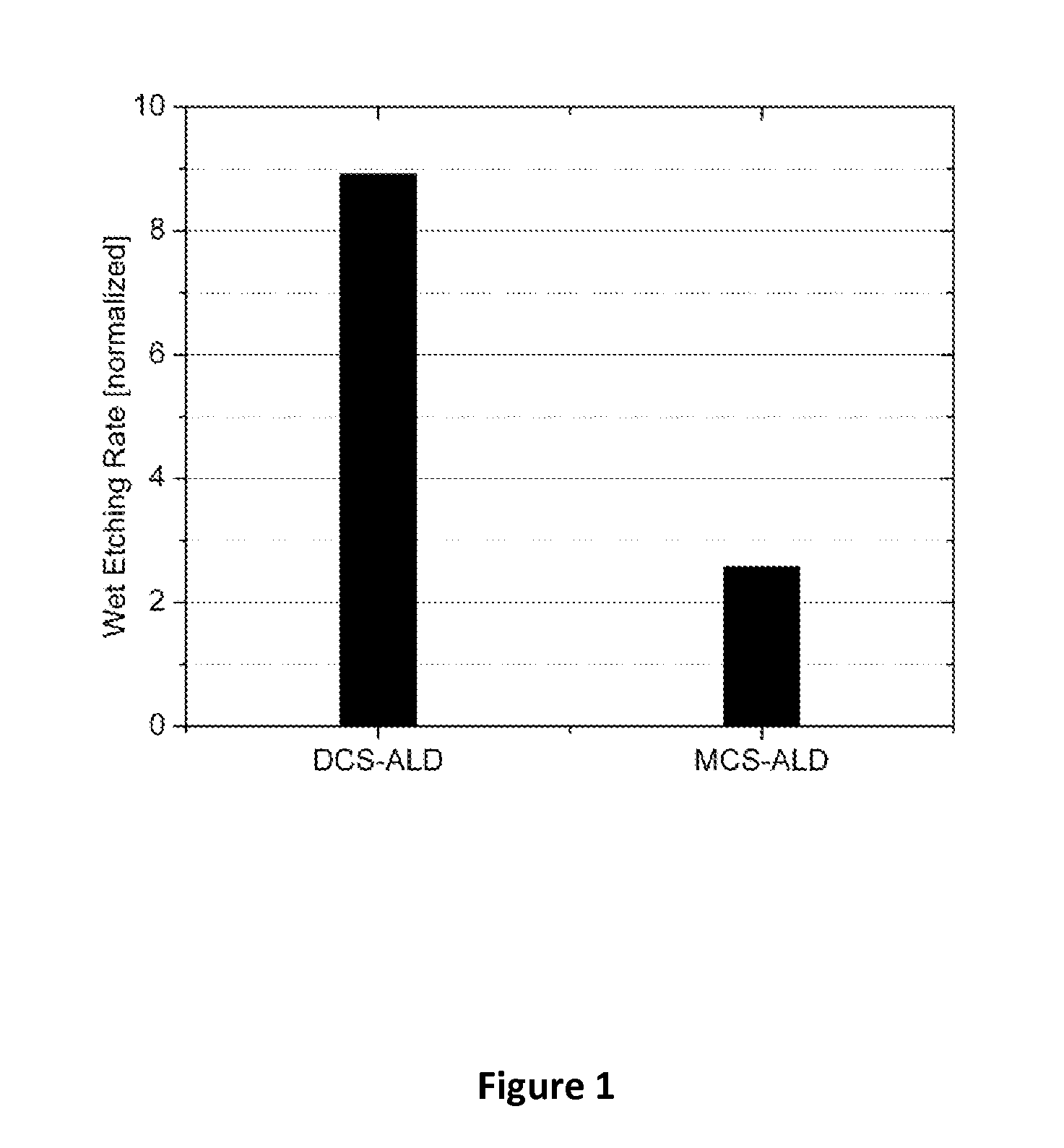
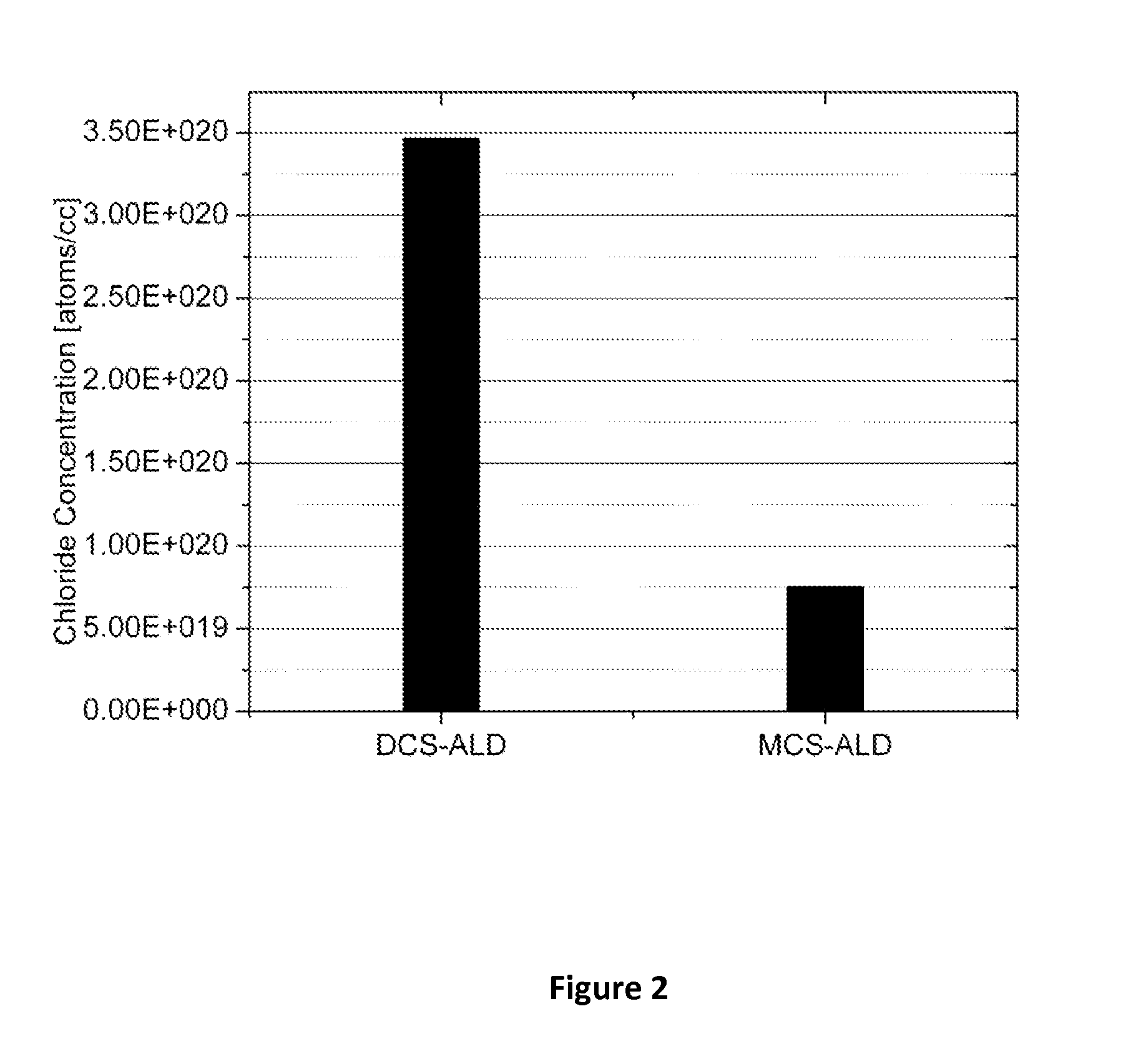
This invention discloses the method of forming silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, silicon oxide, carbon-doped silicon nitride, carbon-doped silicon oxide and carbon-doped oxynitride films at low deposition temperatures. The silicon containing precursors used for the deposition are monochlorosilane (MCS) and monochloroalkylsilanes. The method is preferably carried out by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and plasma enhanced cyclic chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Atomic layer deposition using metal amidinates
ActiveUS20060141155A1Improve conductivityReduce the temperatureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHydrogenWater vapor
Metal films are deposited with uniform thickness and excellent step coverage. Copper metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of copper(I) NN′-diisopropylacetamidinate vapor and hydrogen gas. Cobalt metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of cobalt(II) bis(N,N′-diisopropylacetamidinate) vapor and hydrogen gas. Nitrides and oxides of these metals can be formed by replacing the hydrogen with ammonia or water vapor, respectively. The films have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in narrow holes. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Ald metal oxide deposition process using direct oxidation
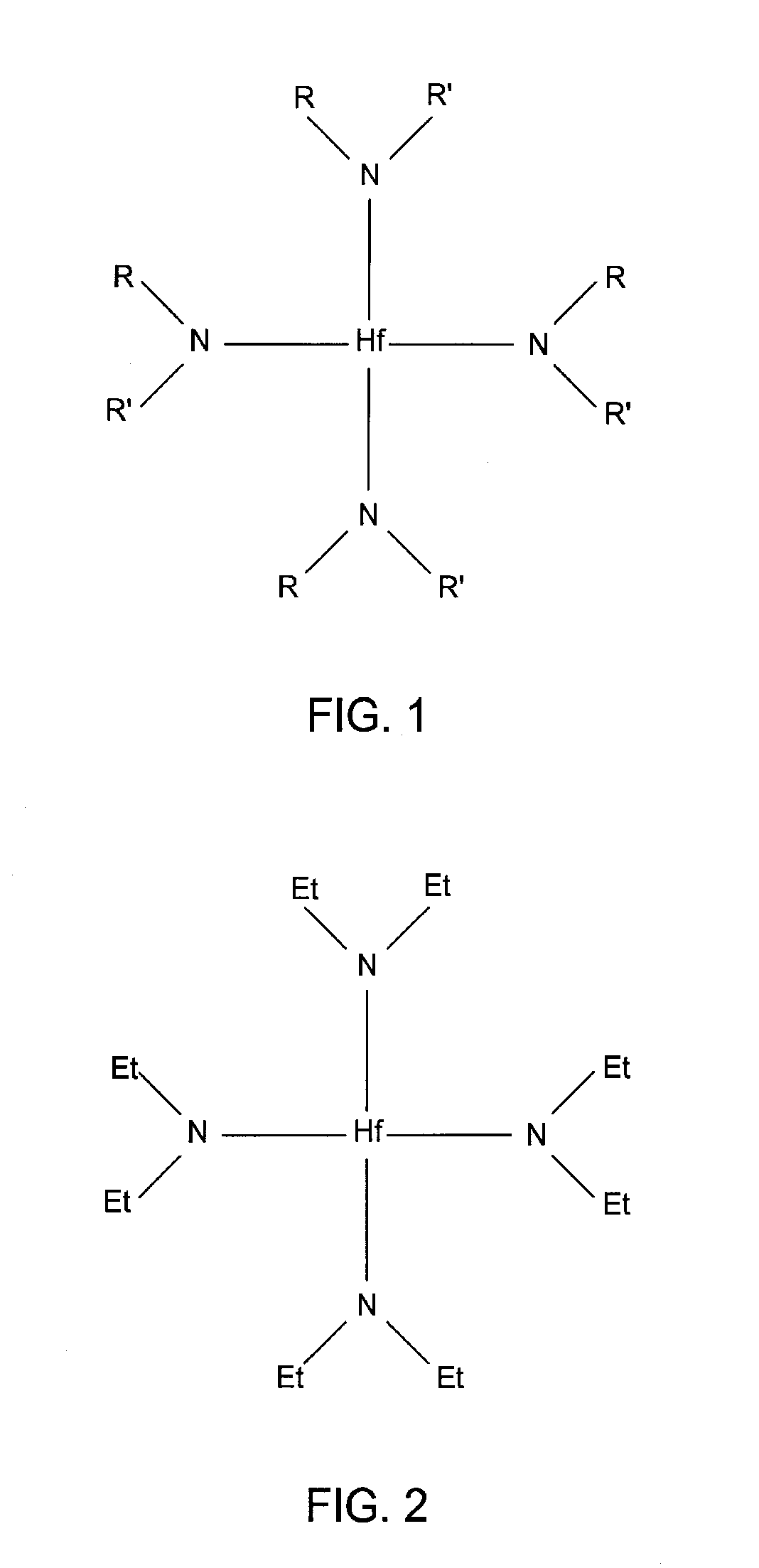
InactiveUS20070059948A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenHafnium
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for forming hafnium materials, such as oxides and nitrides, by sequentially exposing a substrate to hafnium precursors and active oxygen or nitrogen species (e.g., ozone, oxygen radicals, or nitrogen radicals). The deposited hafnium materials have significantly improved uniformity when deposited by these atomic layer deposition (ALD) processes. In one embodiment, an ALD chamber contains an expanding channel having a bottom surface that is sized and shaped to substantially cover a substrate positioned on a substrate pedestal. During an ALD process for forming hafnium materials, process gases form a vortex flow pattern while passing through the expanding channel and sweep across the substrate surface. The substrate is sequentially exposed to chemical precursors that are pulsed into the process chamber having the vortex flow.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Thin films
InactiveUS20050181555A1Quality improvementHigh dielectric constantSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon oxide
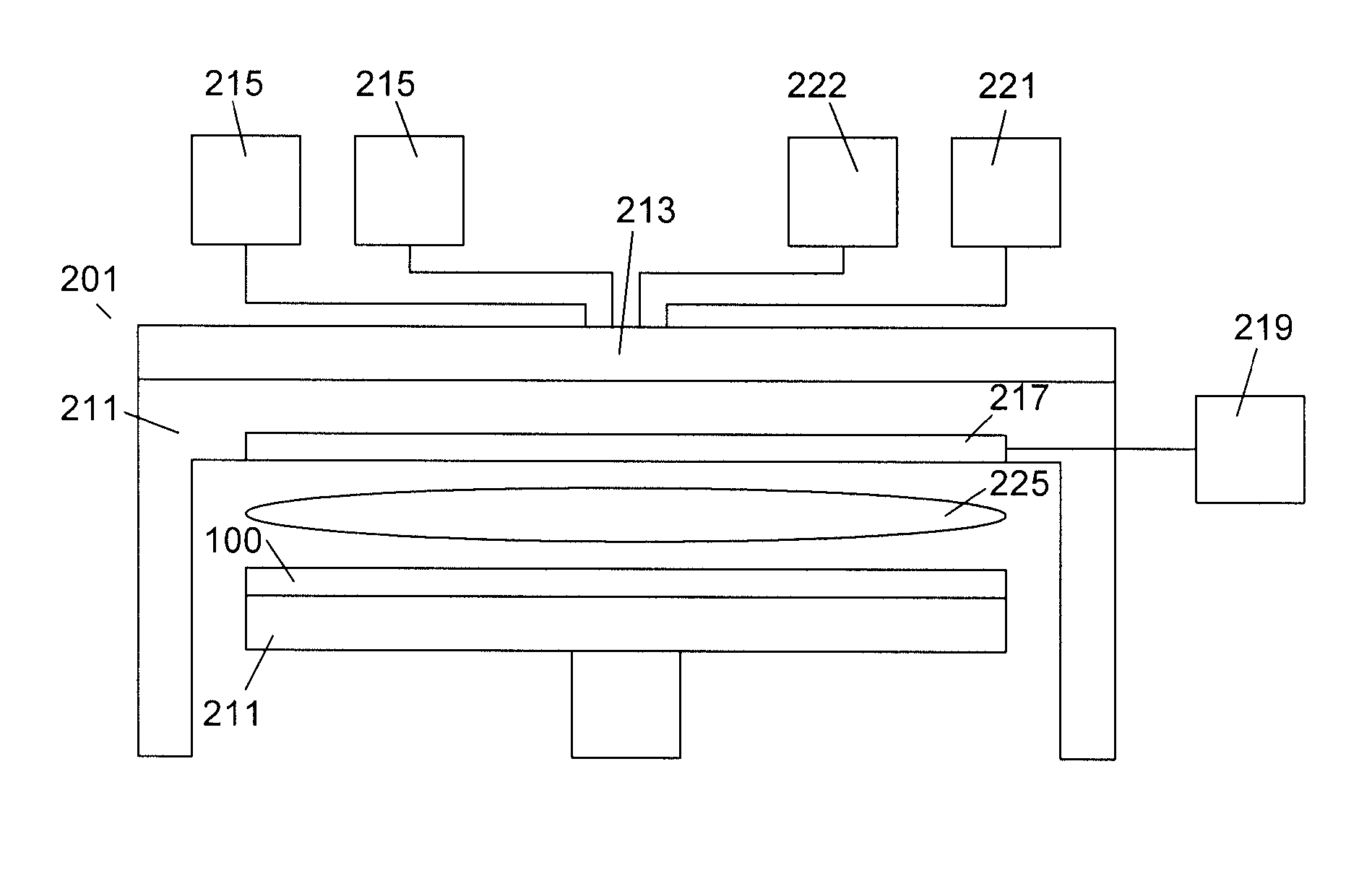
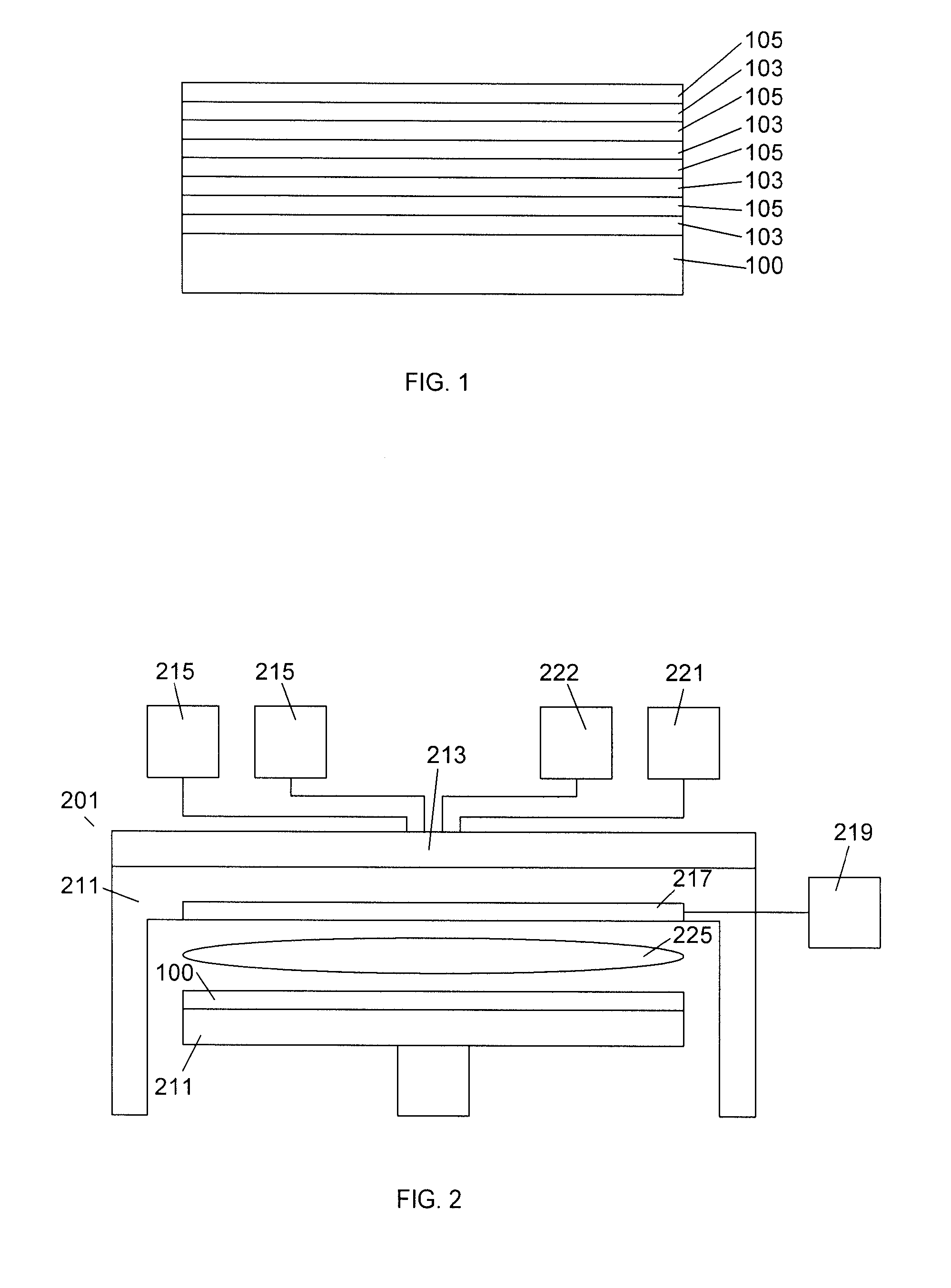
Thin films are formed by formed by atomic layer deposition, whereby the composition of the film can be varied from monolayer to monolayer during cycles including alternating pulses of self-limiting chemistries. In the illustrated embodiments, varying amounts of impurity sources are introduced during the cyclical process. A graded gate dielectric is thereby provided, even for extremely thin layers. The gate dielectric as thin as 2 nm can be varied from pure silicon oxide to oxynitride to silicon nitride. Similarly, the gate dielectric can be varied from aluminum oxide to mixtures of aluminum oxide and a higher dielectric material (e.g., ZrO2) to pure high k material and back to aluminum oxide. In another embodiment, metal nitride (e.g., WN) is first formed as a barrier for lining dual damascene trenches and vias. During the alternating deposition process, copper can be introduced, e.g., in separate pulses, and the copper source pulses can gradually increase in frequency, forming a transition region, until pure copper is formed at the upper surface. Advantageously, graded compositions in these and a variety of other contexts help to avoid such problems as etch rate control, electromigration and non-ohmic electrical contact that can occur at sharp material interfaces. In some embodiments additional seed layers or additional transition layers are provided.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method to increase the compressive stress of PECVD silicon nitride films
ActiveUS20060269692A1Increase silicon nitride compressive stressReduce defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningHydrogenDevice material
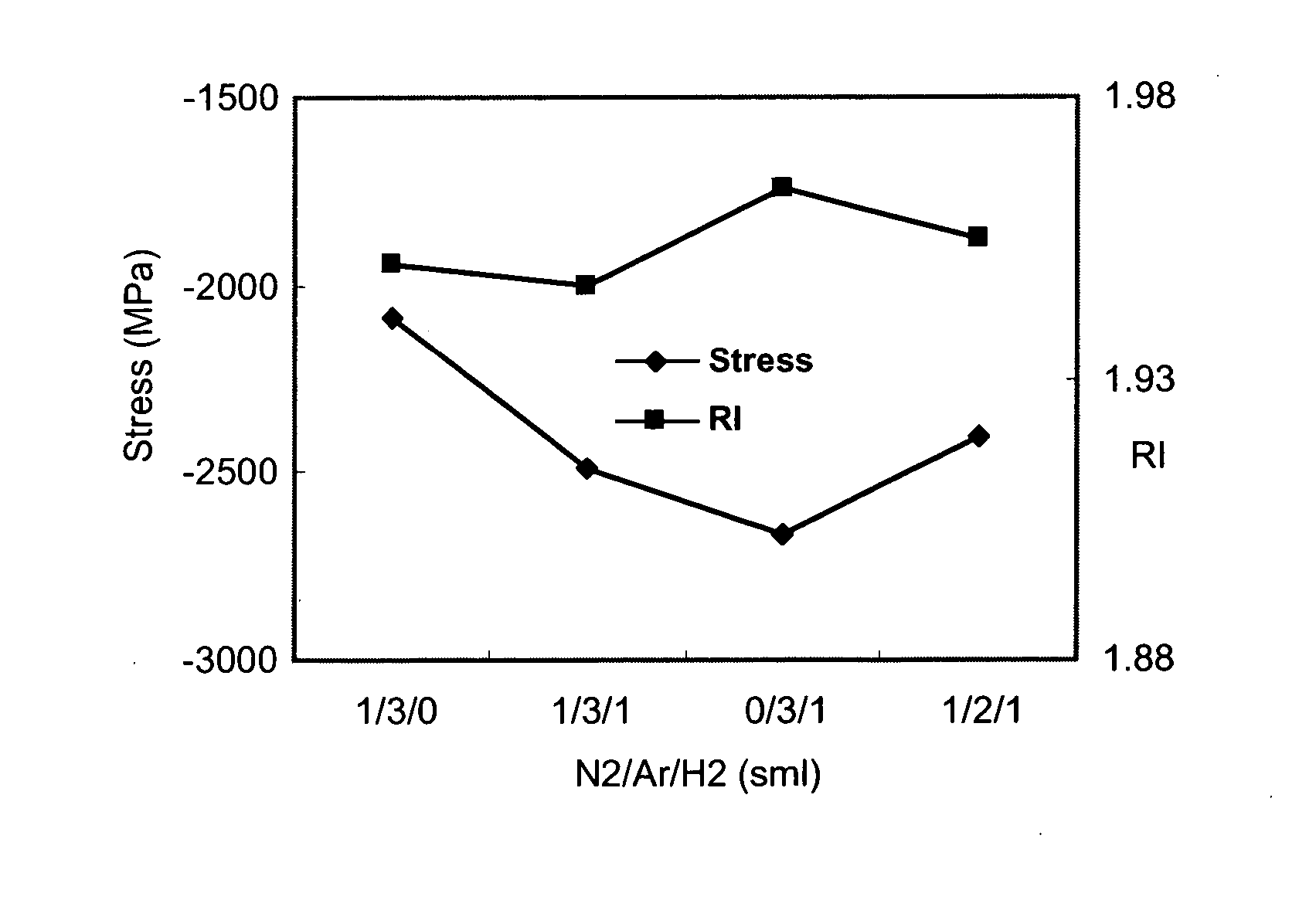
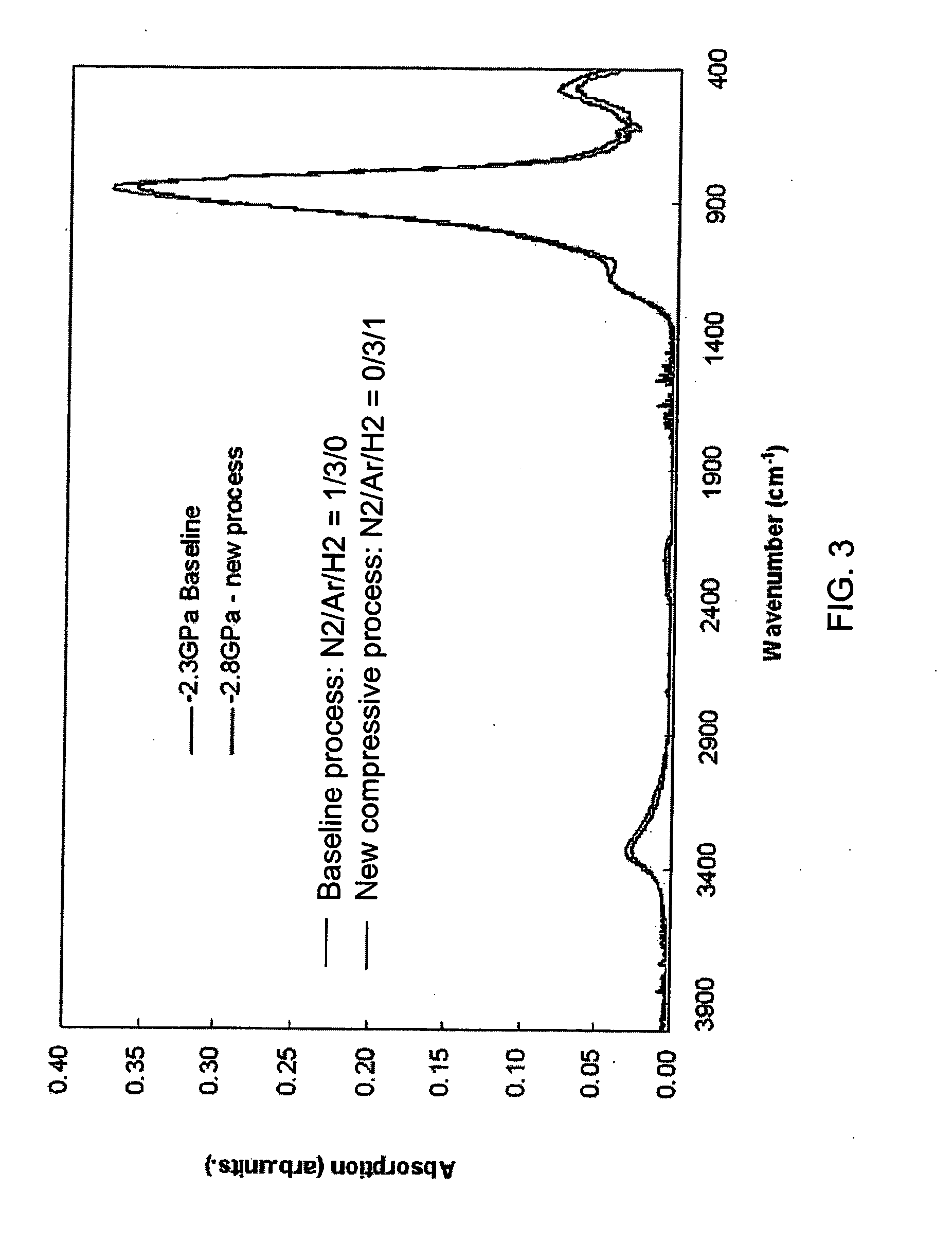
Compressive stress in a film of a semiconductor device may be controlled utilizing one or more techniques, employed alone or in combination. A first set of embodiments increase silicon nitride compressive stress by adding hydrogen to the deposition chemistry, and reduce defects in a device fabricated with a high compressive stress silicon nitride film formed in the presence of hydrogen gas. A silicon nitride film may comprise an initiation layer formed in the absence of a hydrogen gas flow, underlying a high stress nitride layer formed in the presence of a hydrogen gas flow. A silicon nitride film formed in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention may exhibit a compressive stress of 2.8 GPa or higher.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ampoule with a thermally conductive coating
ActiveUS20080149031A1Improve temperature uniformityChemical vapor deposition coatingConductive coatingCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention provide an apparatus and a process for generating a chemical precursor used in a vapor deposition processing system. The apparatus includes a canister (e.g., ampoule) having a sidewall, a top, and a bottom encompassing an interior volume therein, inlet and outlet ports in fluid communication with the interior volume, and a thermally conductive coating disposed on or over the outside surface of the canister. The thermally conductive coating is more thermally conductive than the outside surface of the canister. The thermally conductive coating may contain aluminum, aluminum nitride, copper, brass, silver, titanium, silicon nitride, or alloys thereof. In some embodiments, an adhesion layer (e.g., titanium or tantalum) may be disposed between the outside surface of the canister and the thermally conductive coating. In other embodiments, the canister may contain a plurality of baffles or solid heat-transfer particles to help evenly heat a solid precursor therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Precursors for CVD silicon carbo-nitride films
ActiveUS20060258173A1Easy to movePromote formationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesRoom temperature
Classes of liquid aminosilanes have been found which allow for the production of silicon carbo-nitride films of the general formula SixCyNz. These aminosilanes, in contrast, to some of the precursors employed heretofore, are liquid at room temperature and pressure allowing for convenient handling. In addition, the invention relates to a process for producing such films. The classes of compounds are generally represented by the formulas: and mixtures thereof, wherein R and R1 in the formulas represent aliphatic groups typically having from 2 to about 10 carbon atoms, e.g., alkyl, cycloalkyl with R and R1 in formula A also being combinable into a cyclic group, and R2 representing a single bond, (CH2)n, a ring, or SiH2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
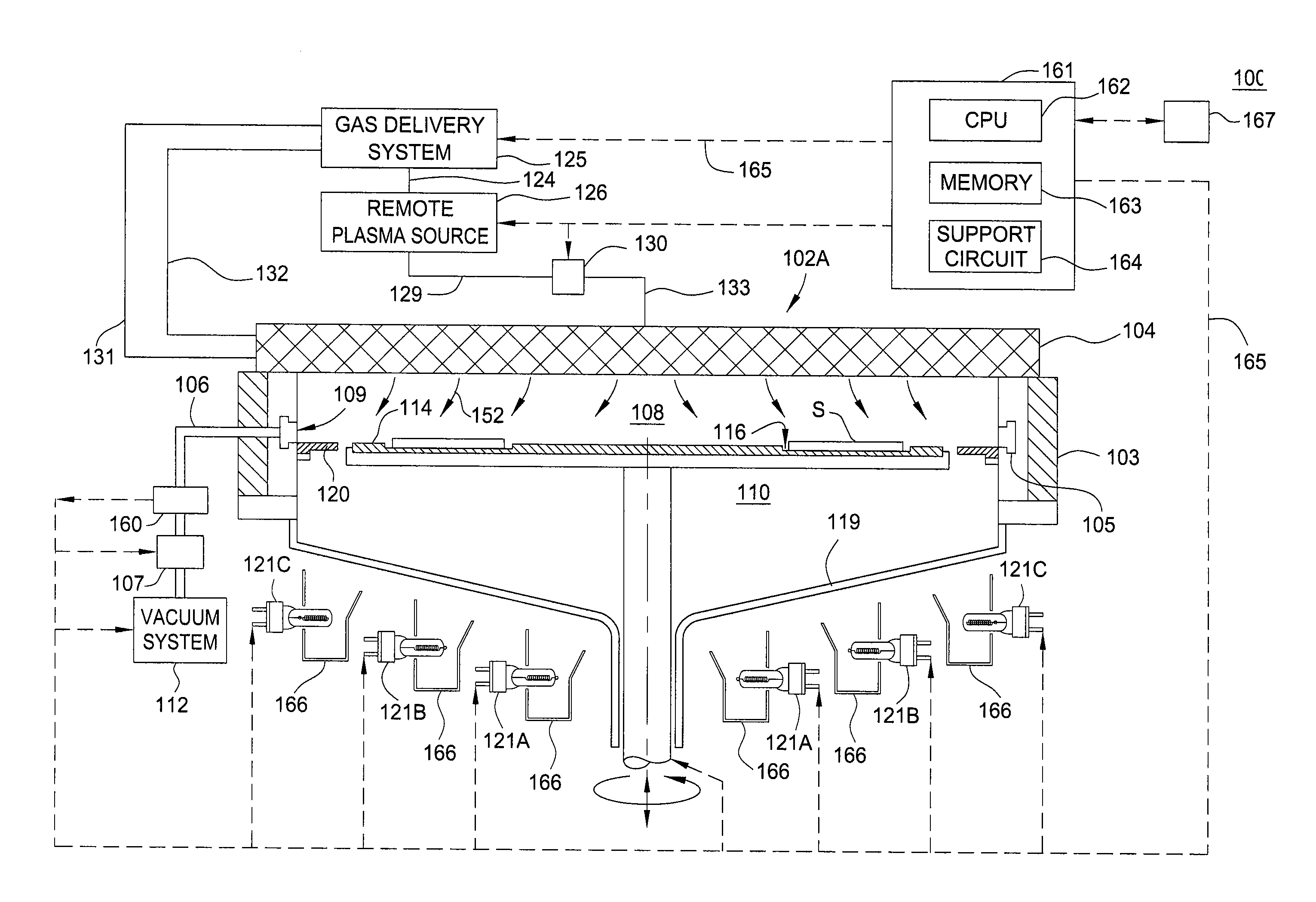
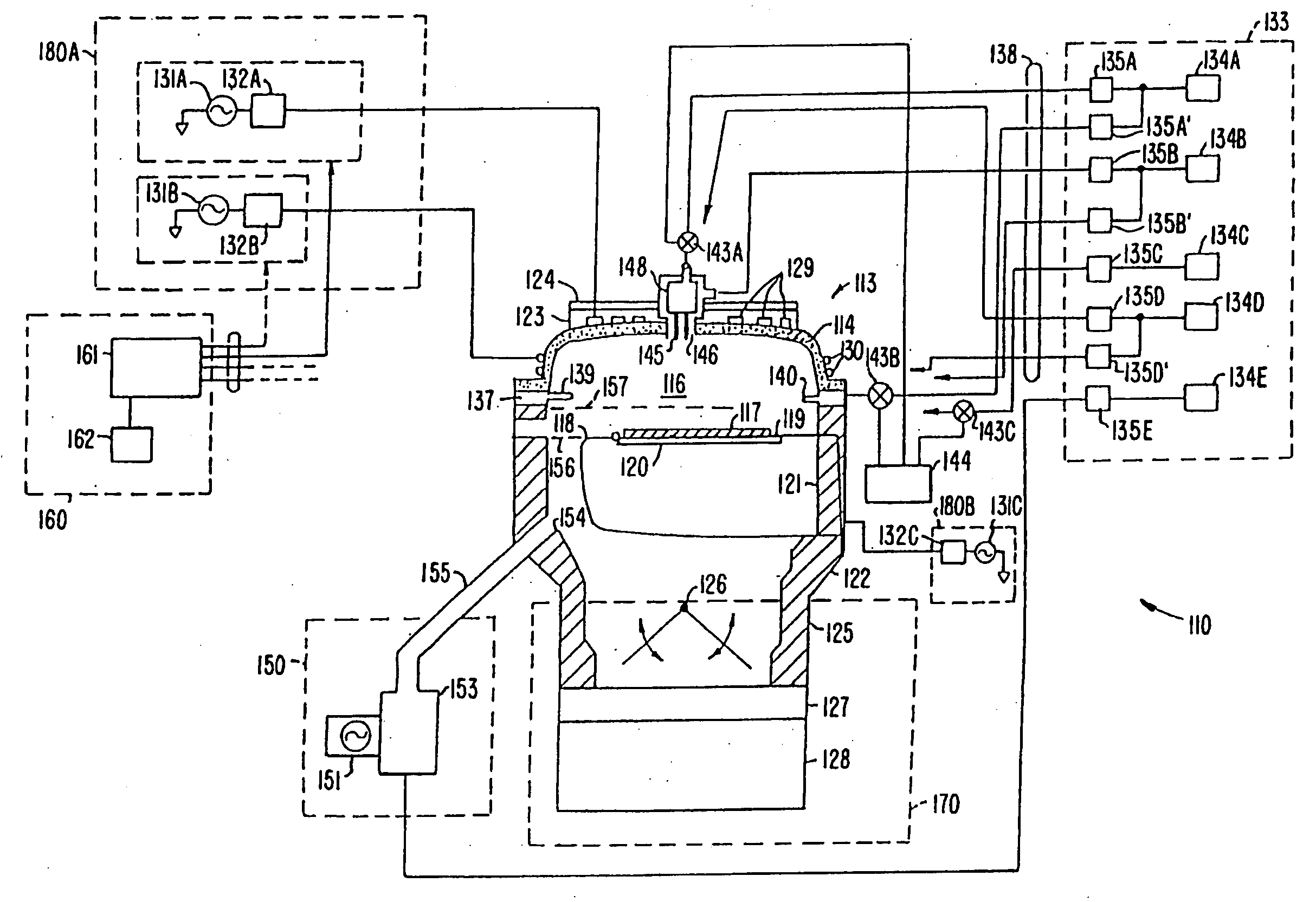
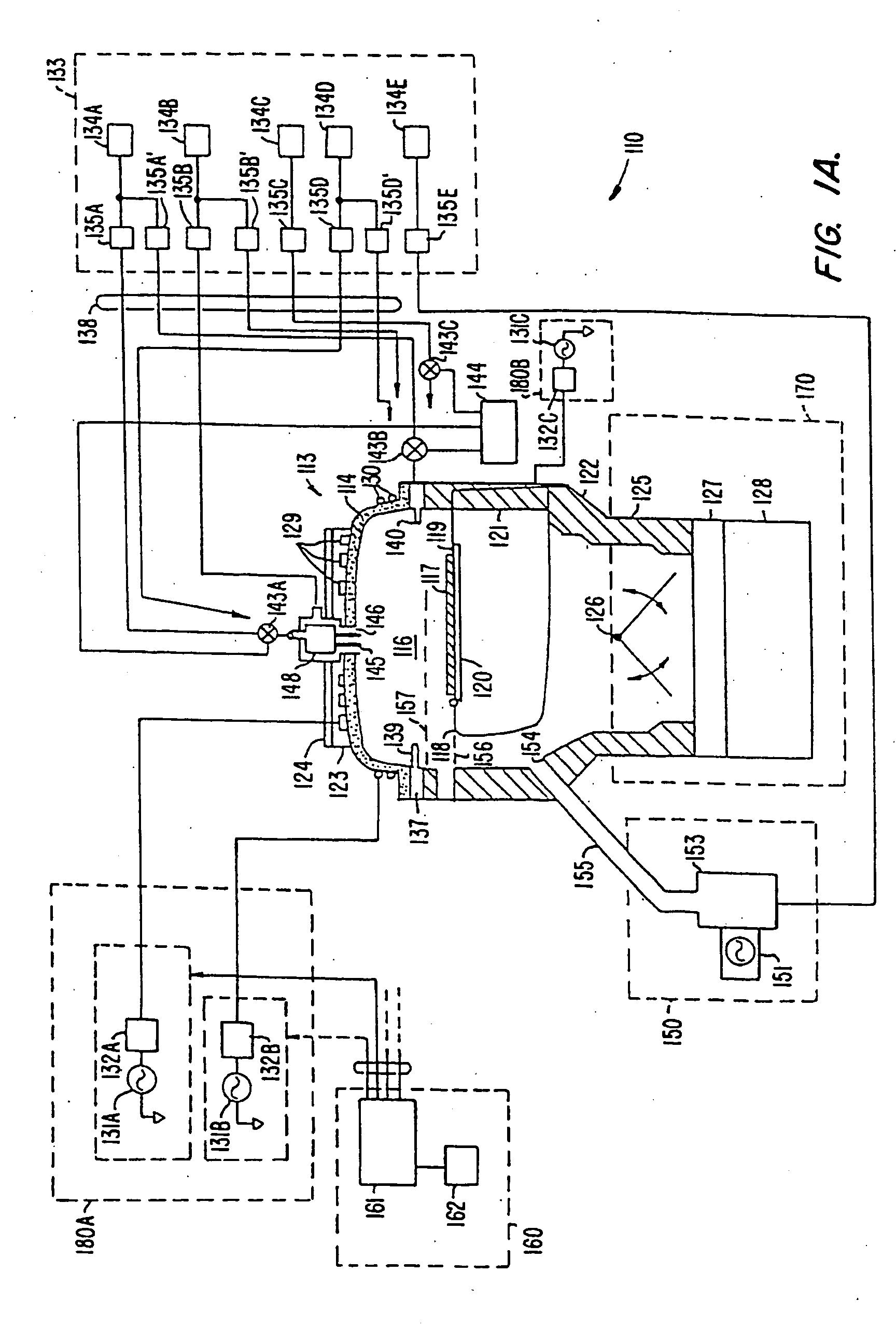
Closed loop mocvd deposition control
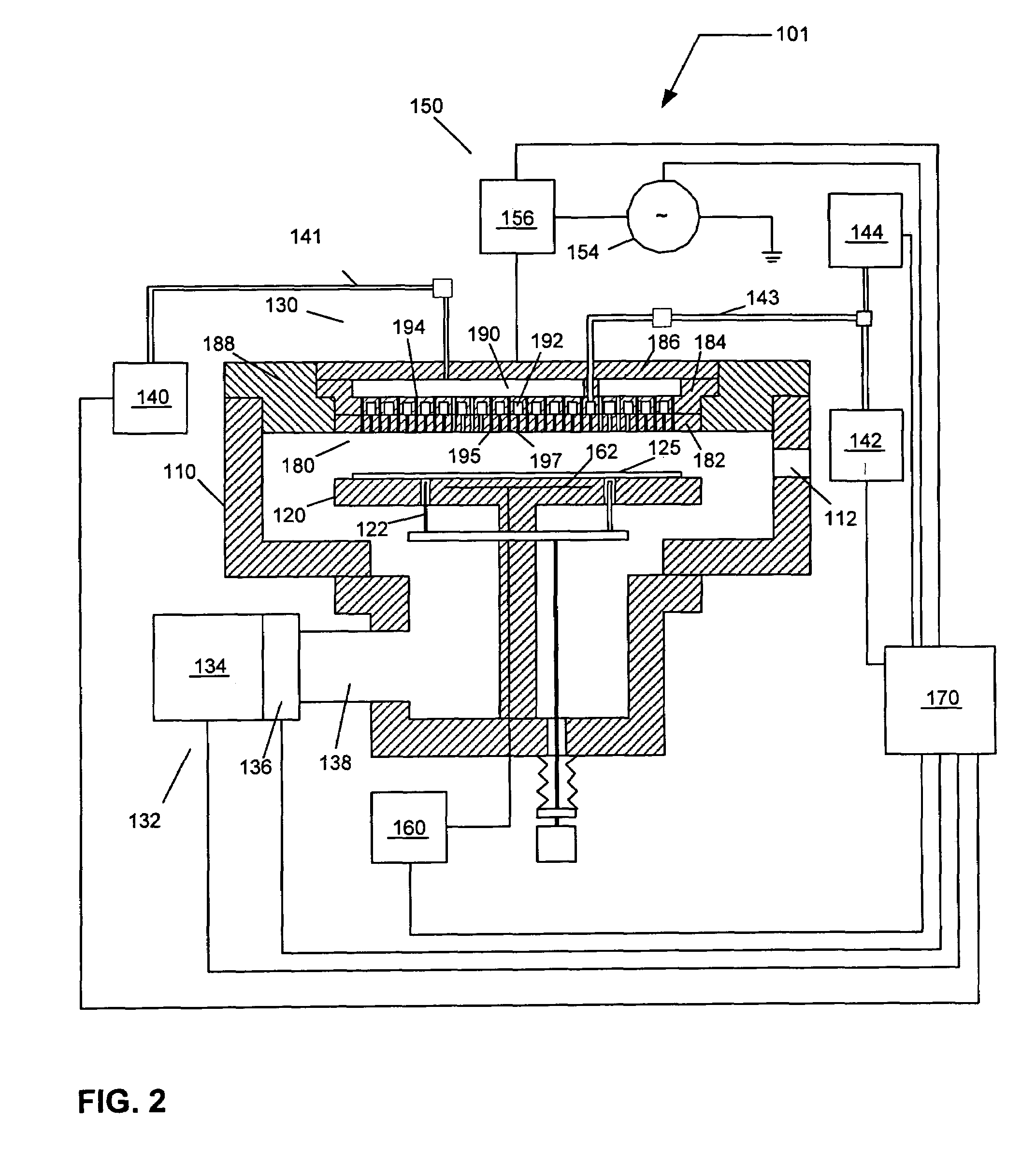
InactiveUS20110308453A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseControl system
A method and apparatus are provided for monitoring and controlling substrate processing parameters for a cluster tool that utilizes chemical vapor deposition and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition. In one embodiment, a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) process is used to deposit a Group III-nitride film on a plurality of substrates within a processing chamber. A closed-loop control system performs in-situ monitoring of the Group III-nitride film growth rate and adjusts film growth parameters as required to maintain a target growth rate. In another embodiment, a closed-loop control system performs in-situ monitoring of film growth parameters for multiple processing chambers for one or more film deposition systems.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
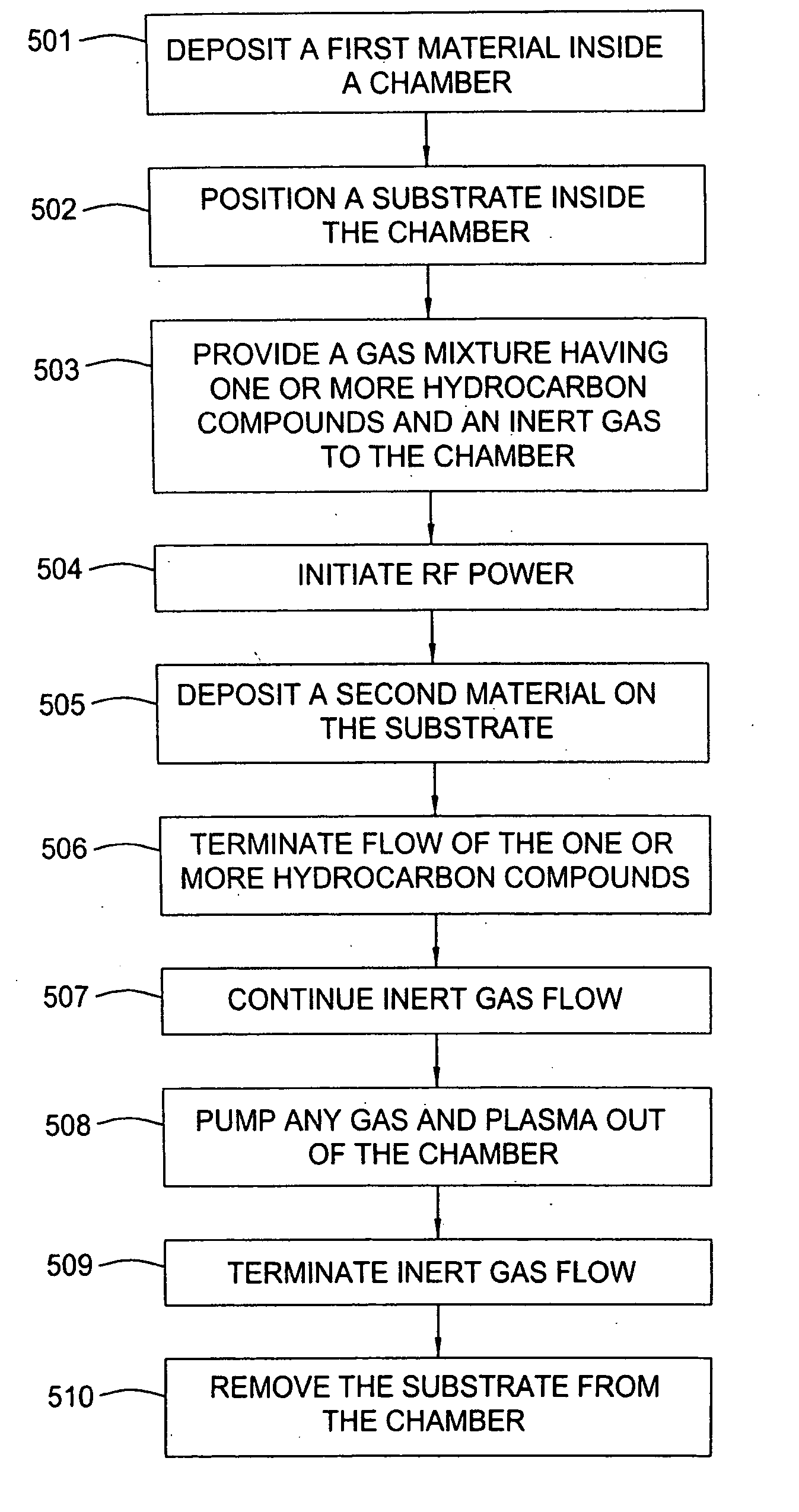
PECVD oxide-nitride and oxide-silicon stacks for 3D memory application
ActiveUS8076250B1Improve bonding interfaceAvoid layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMaterials science3d memory
A layer stack of different materials is deposited on a substrate in a single plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition processing chamber while maintaining a vacuum. A substrate is placed in the processing chamber and a first processing gas is used to form a first layer of a first material on the substrate. A plasma purge and gas purge are performed before a second processing gas is used to form a second layer of a second material on the substrate. The plasma purge and gas purge are repeated and the additional layers of first and second materials are deposited on the layer stack.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
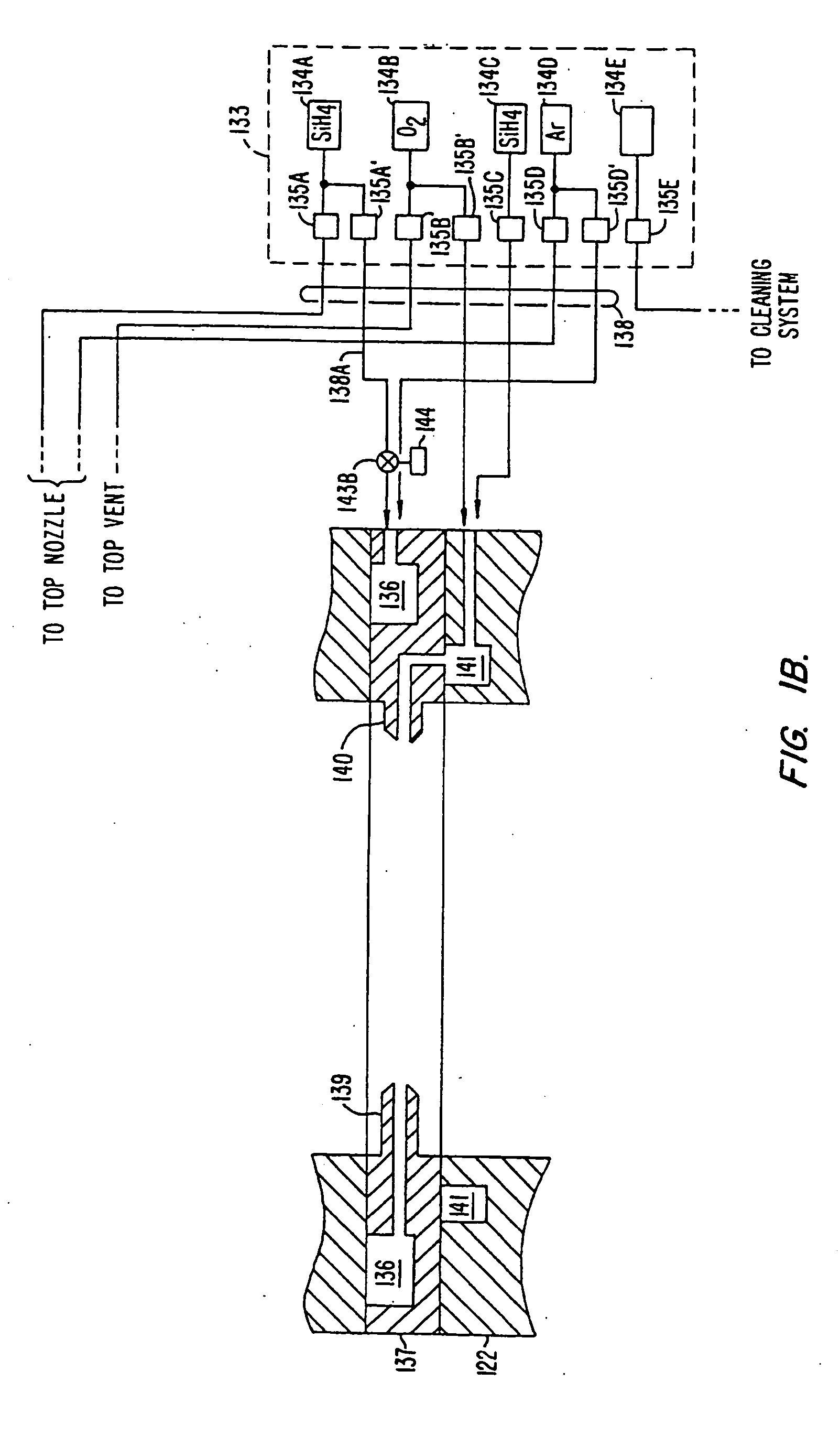
HDP-CVD seasoning process for high power HDP-CVD gapfil to improve particle performance
InactiveUS20050250340A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanesSilicon oxide
A method of operating a substrate processing chamber that includes, prior to a substrate processing operation, flowing a seasoning gas comprising silane and oxygen into said chamber at a flow ratio of greater than or equal to about 1.6:1 oxygen to silane to deposit a silicon oxide film over at least one aluminum nitride nozzle exposed to an interior portion of the chamber. Also, a substrate processing system that includes a housing, a gas delivery system for introducing a seasoning gas into a vacuum chamber, where the gas delivery system comprises one or more aluminum nitride nozzles exposed to the vacuum chamber, a controller and a memory having a program having instructions for controlling the gas delivery system to flow a seasoning gas that has an oxygen to silane ratio greater than or equal to about 1.6:1 to deposit a silicon oxide film on the aluminum nitride nozzles.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Atomic layer deposition of metal oxynitride layers as gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20060051925A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricHafnium
A metal oxynitride layer formed by atomic layer deposition of a plurality of reacted monolayers, the monolayers comprising at least one each of a metal, an oxide and a nitride. The metal oxynitride layer is formed from zirconium oxynitride, hafnium oxynitride, tantalum oxynitride, or mixtures thereof. The metal oxynitride layer is used in gate dielectrics as a replacement material for silicon dioxide. A semiconductor device structure having a gate dielectric formed from a metal oxynitride layer is also disclosed.
Owner:AHN KIE Y +1
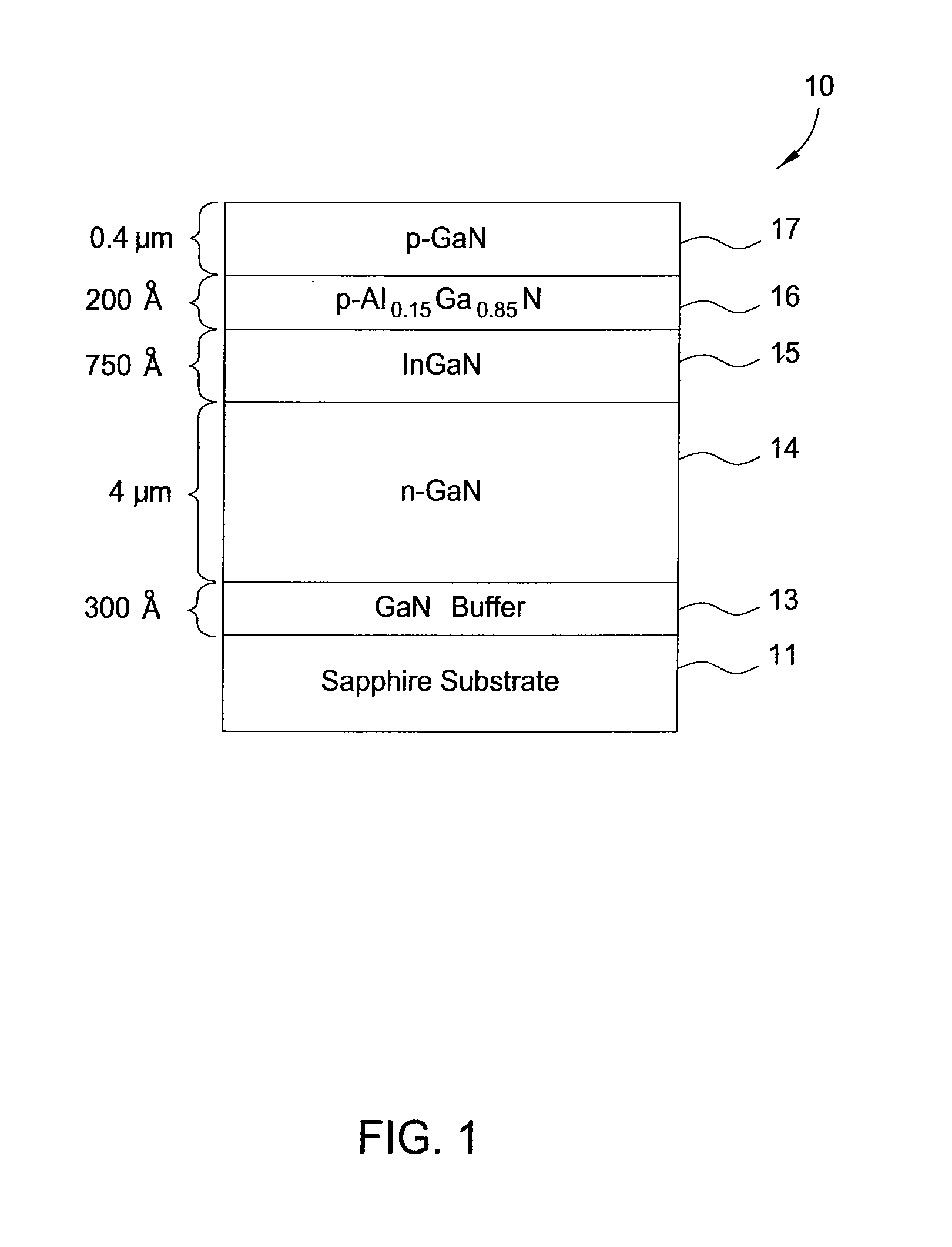
Homoepitaxial gallium-nitride-based light emitting device and method for producing
A light emitting device, such as a light emitting diode or a laser diode. The light emitting device comprises a light emitting semiconductor active region disposed on a substrate. The substrate comprises an optical absorption coefficient below about 100 cm−1 at wavelengths between 700 and 465 nm a GaN single crystal having a dislocation density of less than 104 per cm2 and an optical absorption coefficient below about 100 cm−1 at wavelengths between 700 and 465 nm. A method of making such a light emitting device is also provided.
Owner:SLT TECH +1
Vehicle, display device and manufacturing method for a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7335573B2Simple processBroad visionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDisplay deviceLight emitting device
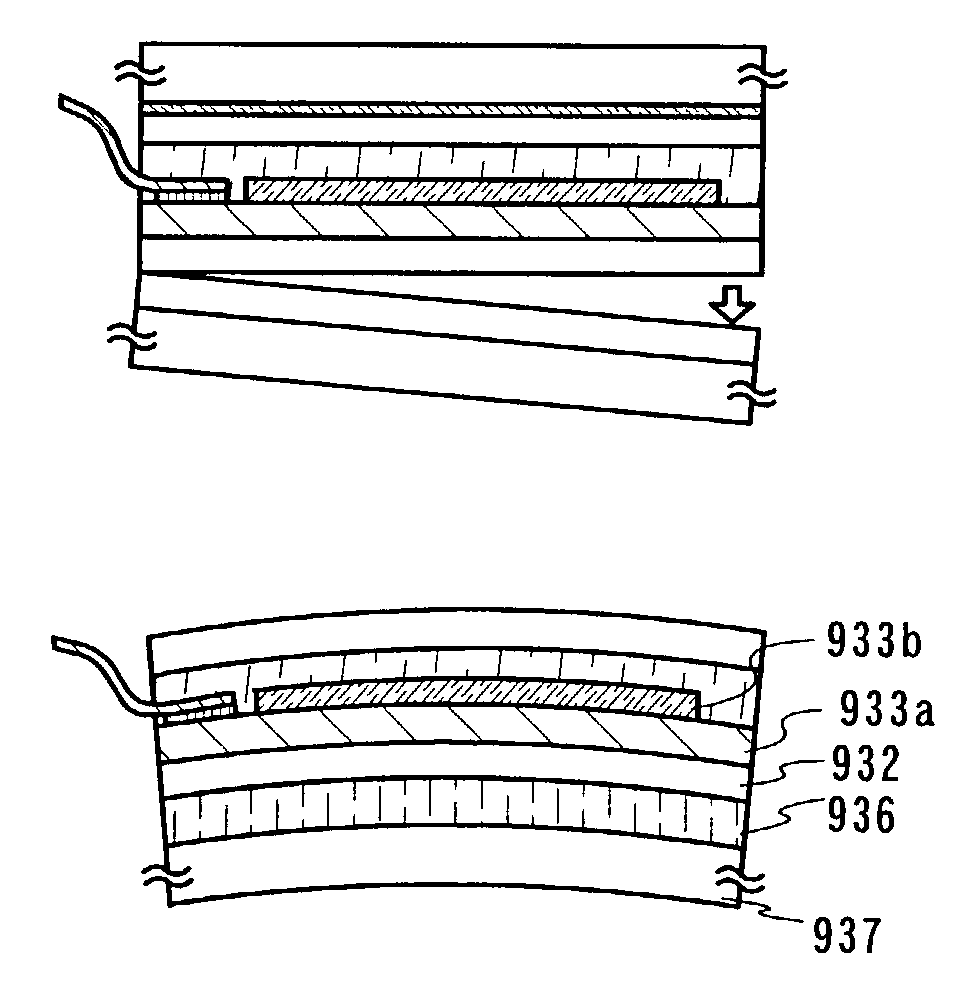
To provide a semiconductor device in which a layer to be peeled is attached to a base having a curved surface, and a method of manufacturing the same, and more particularly, a display having a curved surface, and more specifically a light-emitting device having a light emitting element attached to a base with a curved surface. A layer to be peeled, which contains a light emitting element furnished to a substrate using a laminate of a first material layer which is a metallic layer or nitride layer, and a second material layer which is an oxide layer, is transferred onto a film, and then the film and the layer to be peeled are curved, to thereby produce a display having a curved surface.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Metal nitride carbide deposition by ALD
InactiveUS7410666B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogen halideCorrosive chemical
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
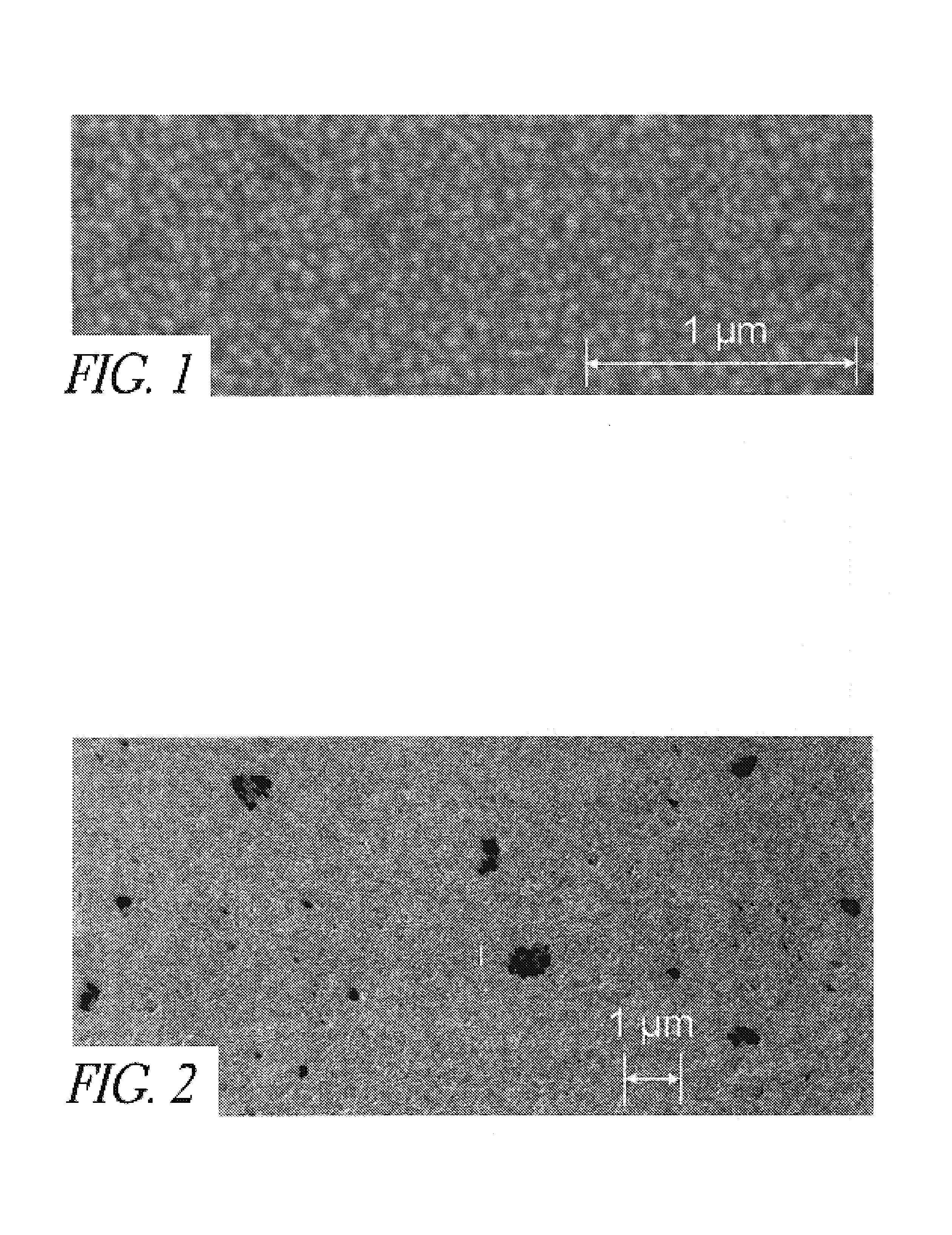
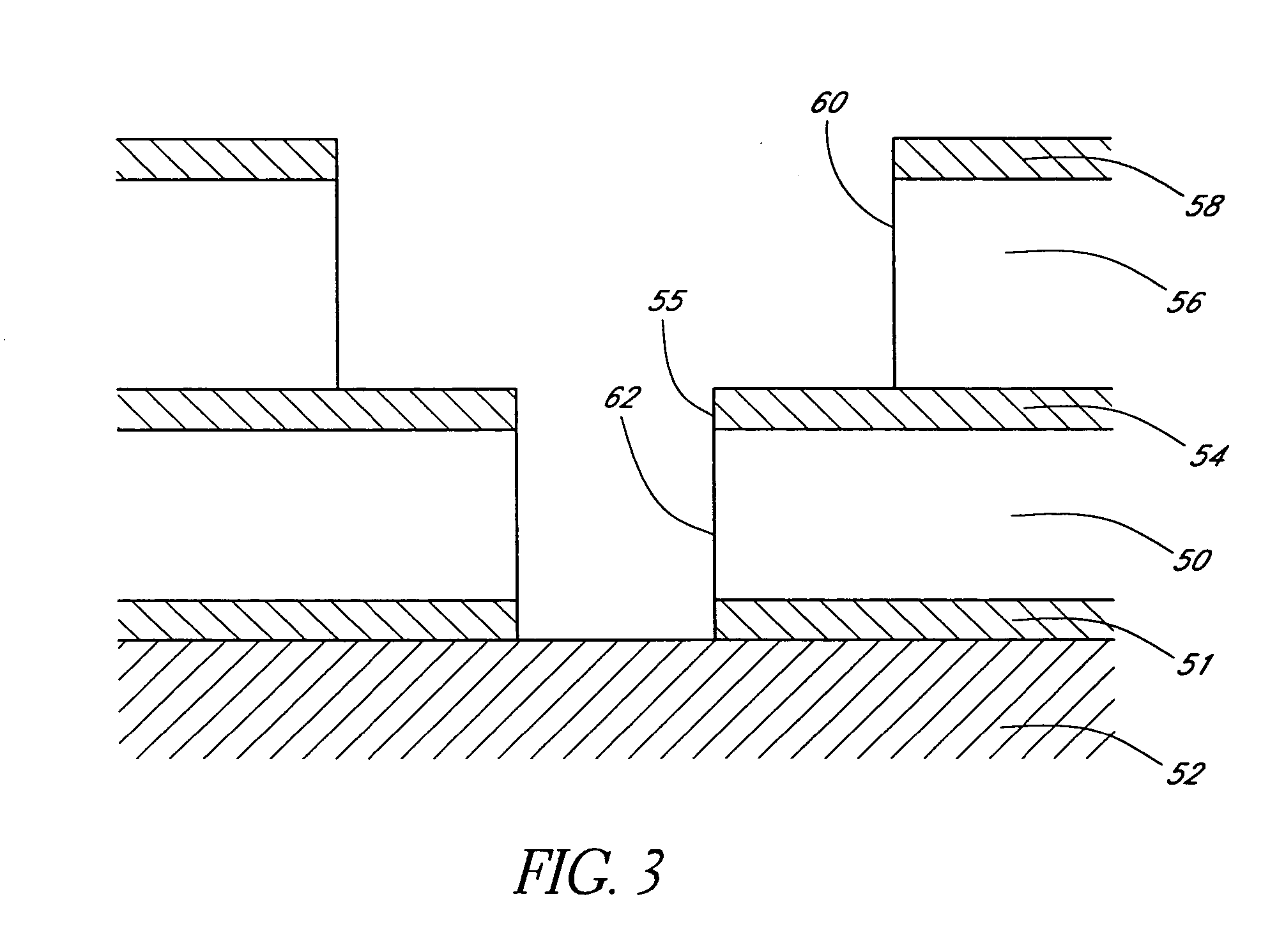
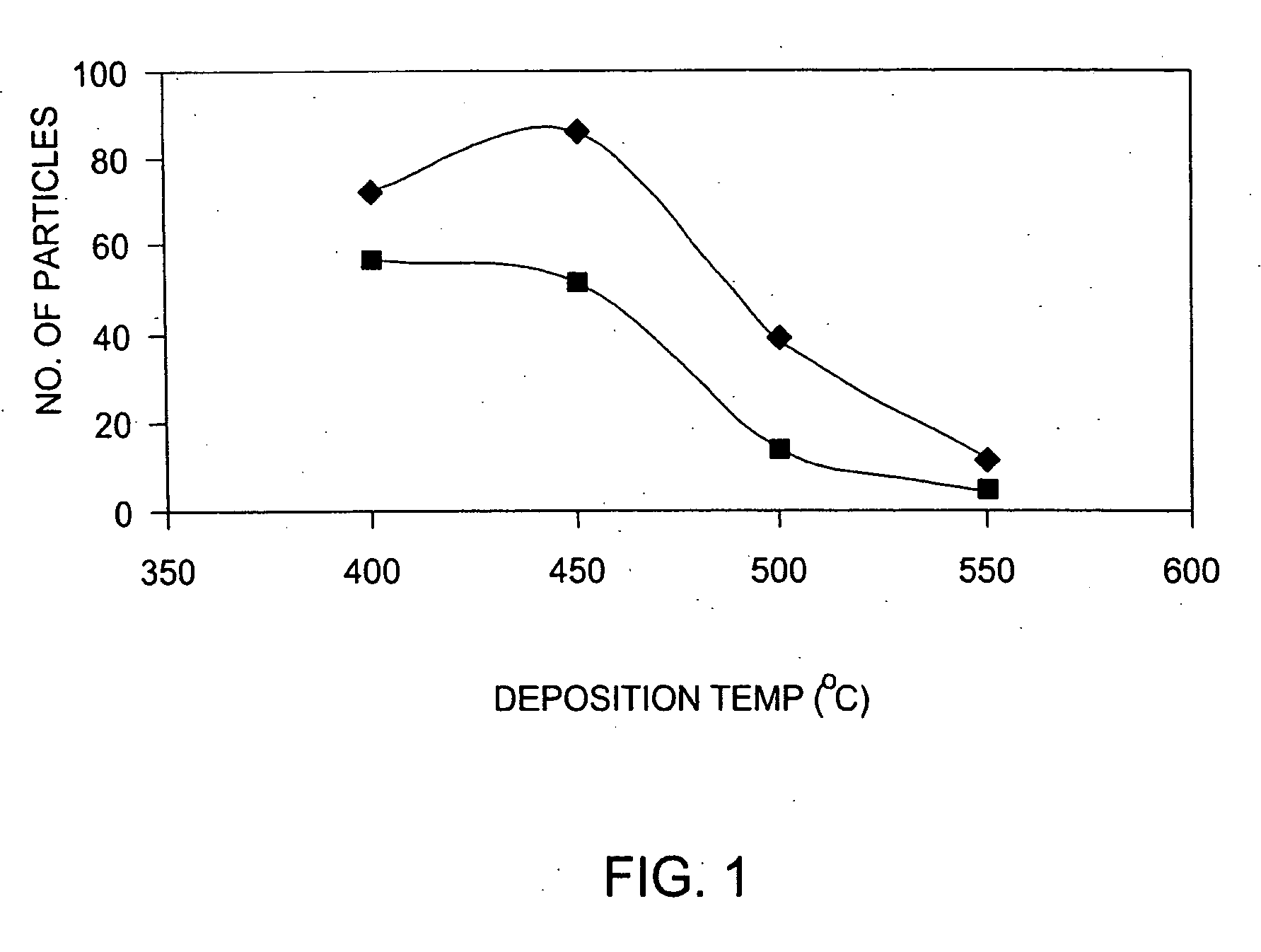
Methods for the reduction and elimination of particulate contamination with CVD of amorphous carbon
InactiveUS20060014397A1Minimal defect formationReduce particle pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesVariable thicknessMicroparticle
A method is provided for forming an amorphous carbon layer, deposited on a dielectric material such as oxide, nitride, silicon carbide, carbon doped oxide, etc., or a metal layer such as tungsten, aluminum or poly-silicon. The method includes the use of chamber seasoning, variable thickness of seasoning film, wider spacing, variable process gas flows, post-deposition purge with inert gas, and post-deposition plasma purge, among others, to make the deposition of an amorphous carbon film at low deposition temperatures possible without any defects or particle contamination.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Method for forming strained silicon nitride films and a device containing such films
ActiveUS7651961B2Vacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenNitride
A method for forming a strained SiN film and a semiconductor device containing the strained SiN film. The method includes exposing the substrate to a gas including a silicon precursor, exposing the substrate to a gas containing a nitrogen precursor activated by a plasma source at a first level of plasma power and configured to react with the silicon precursor with a first reactivity characteristic, and exposing the substrate to a gas containing the nitrogen precursor activated by the plasma source at a second level of plasma power different from the first level and configured to react with the silicon precursor with a second reactivity characteristic such that a property of the silicon nitride film formed on the substrate changes to provide the strained silicon nitride film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method of forming a metal carbide or metal carbonitride film having improved adhesion
InactiveUS7645484B2Improve adhesionFacilitate depositionChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueGas phaseDecomposition
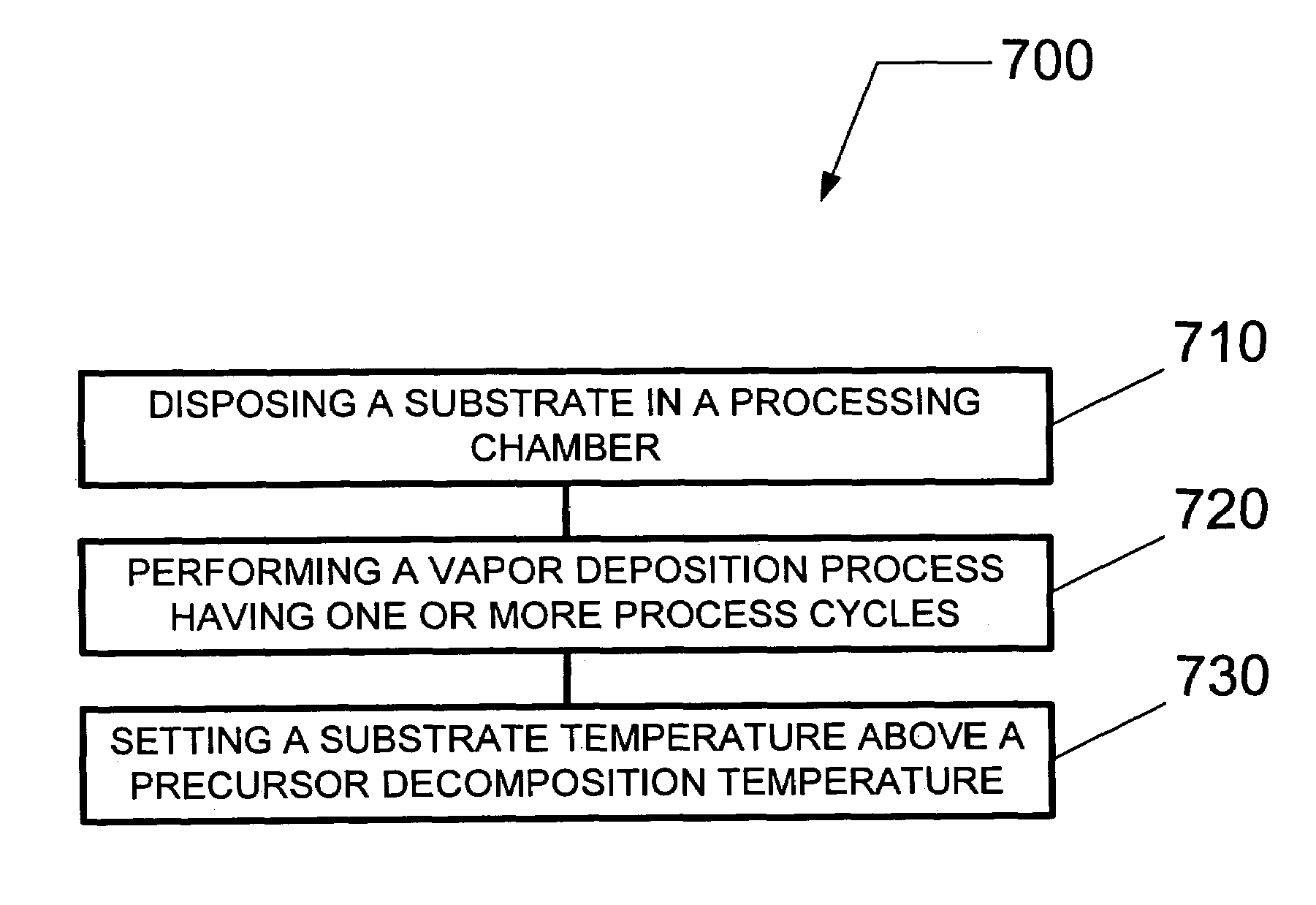
A method for forming a metal carbide or metal carbonitride film on a substrate using a vapor deposition process. The method includes comprises introducing a first process material, such as a film precursor, to the substrate followed by introducing a second process material, such as a film reducing agent, to the substrate, whereby plasma can be formed during the introduction of the second process material in order to assist reduction of the first process material on the substrate. Additionally, the temperature of the substrate is elevated to a value approximately equal to or greater than the decomposition temperature of the first process material in order to improve adhesion properties for the metal carbide or metal carbonitride film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com