Patents
Literature
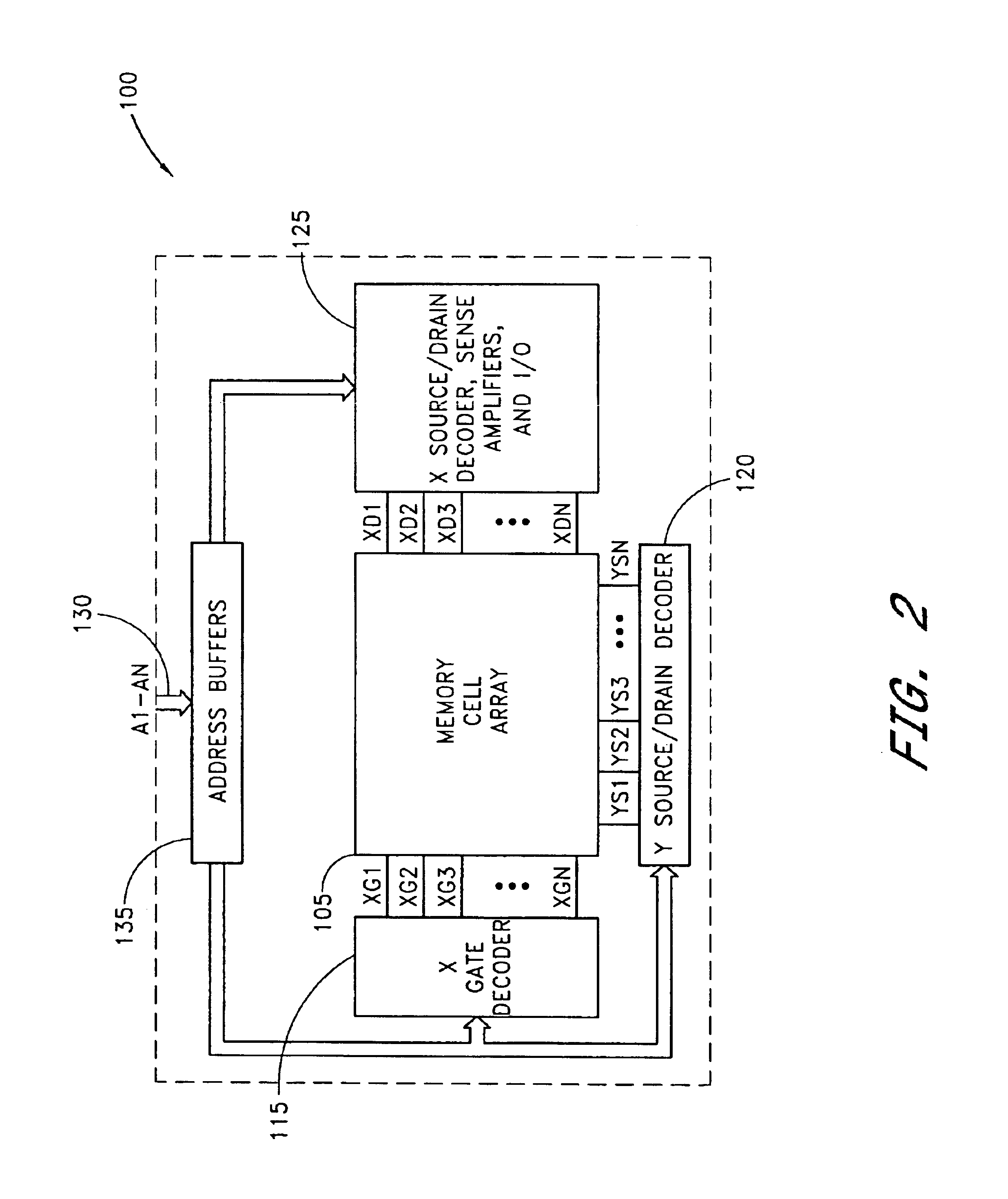
6525 results about "Memory array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
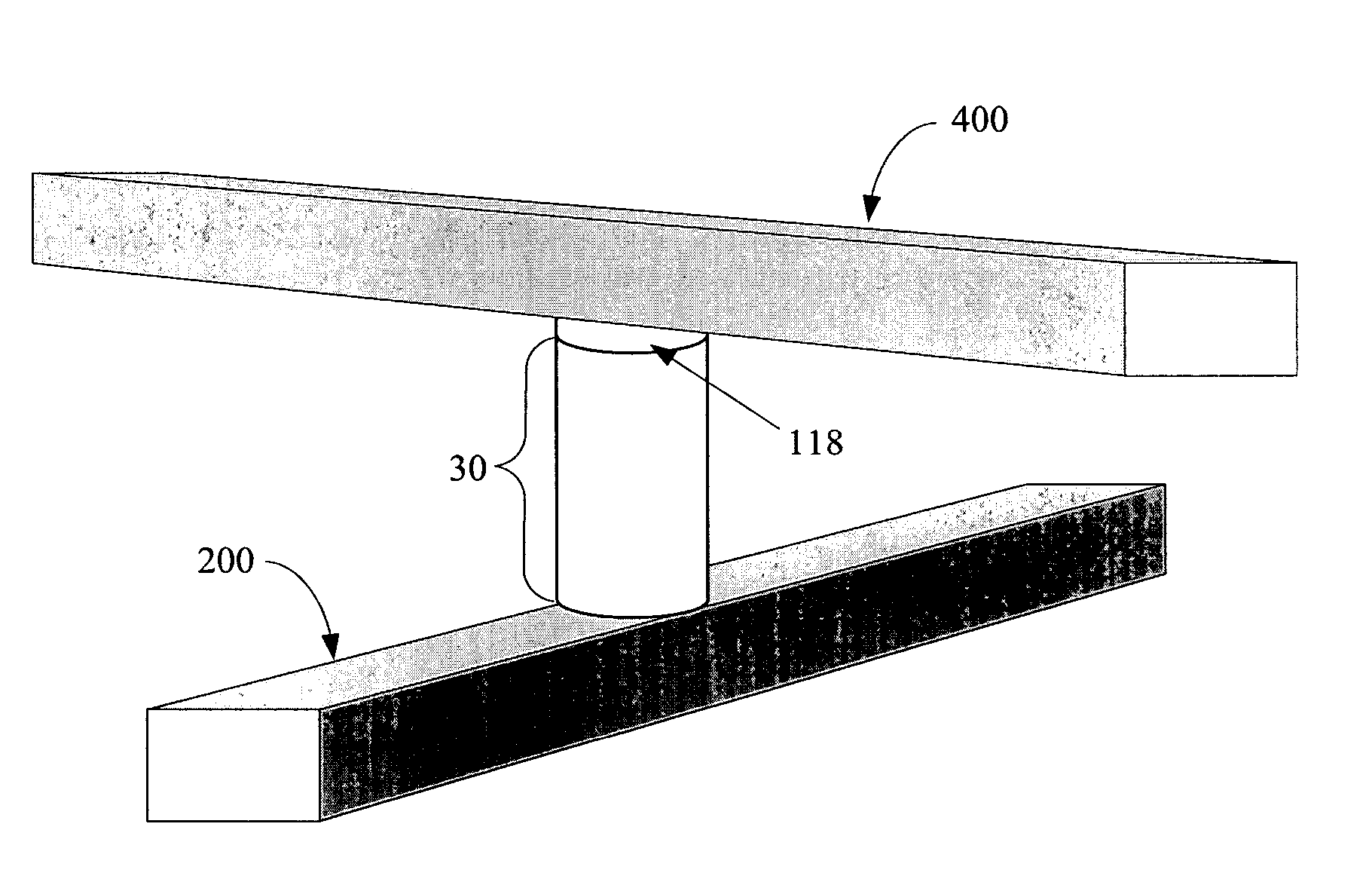
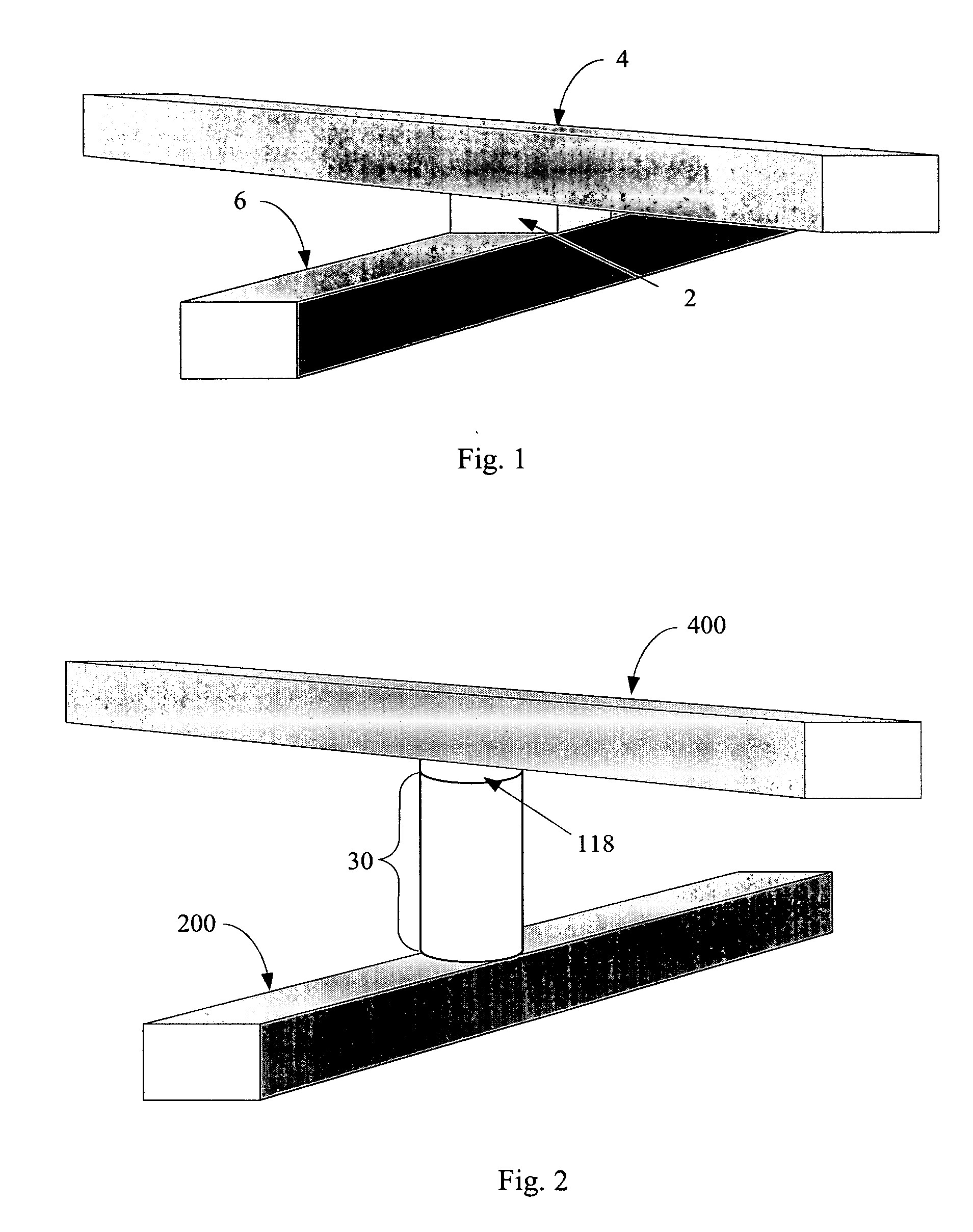
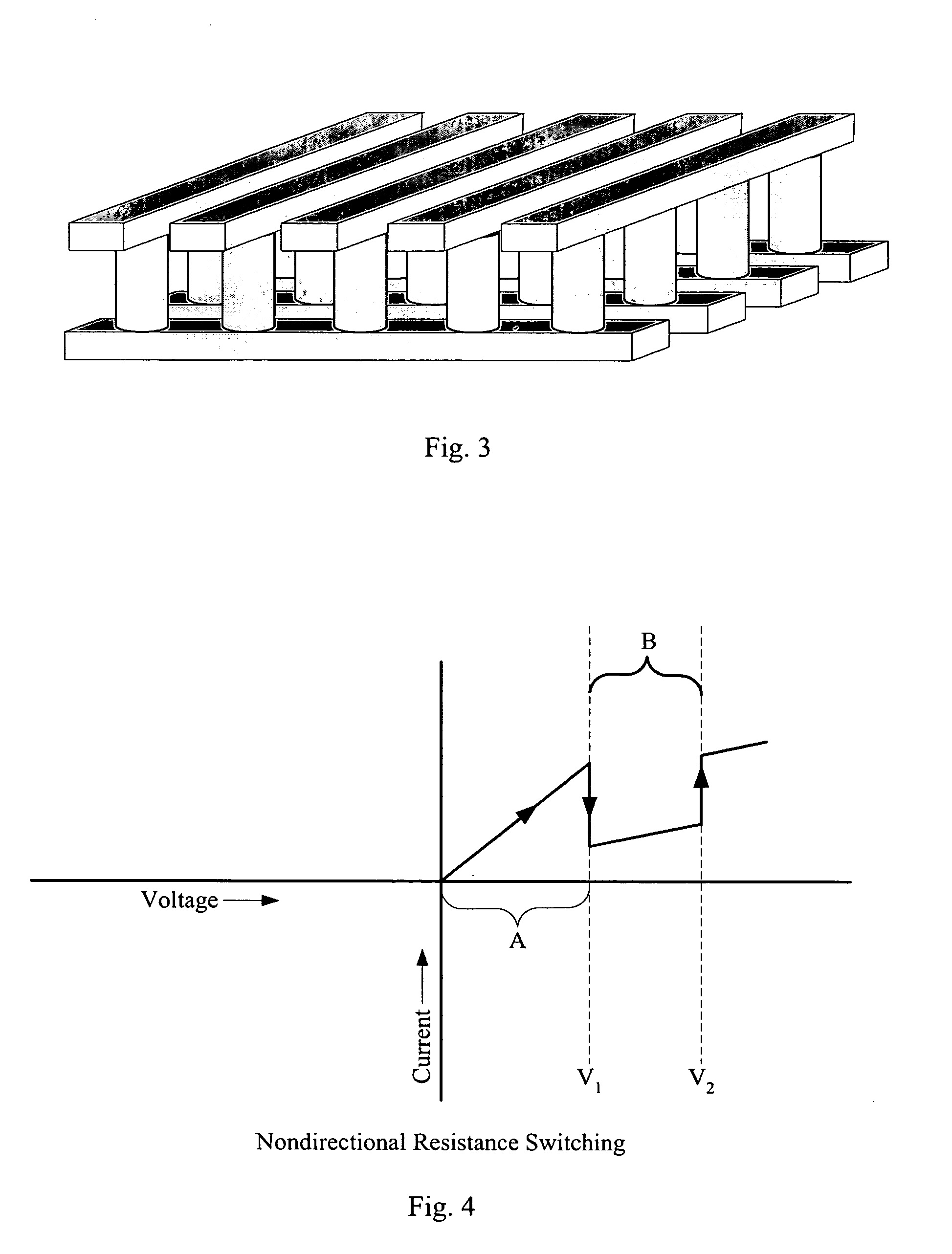
Rewriteable memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
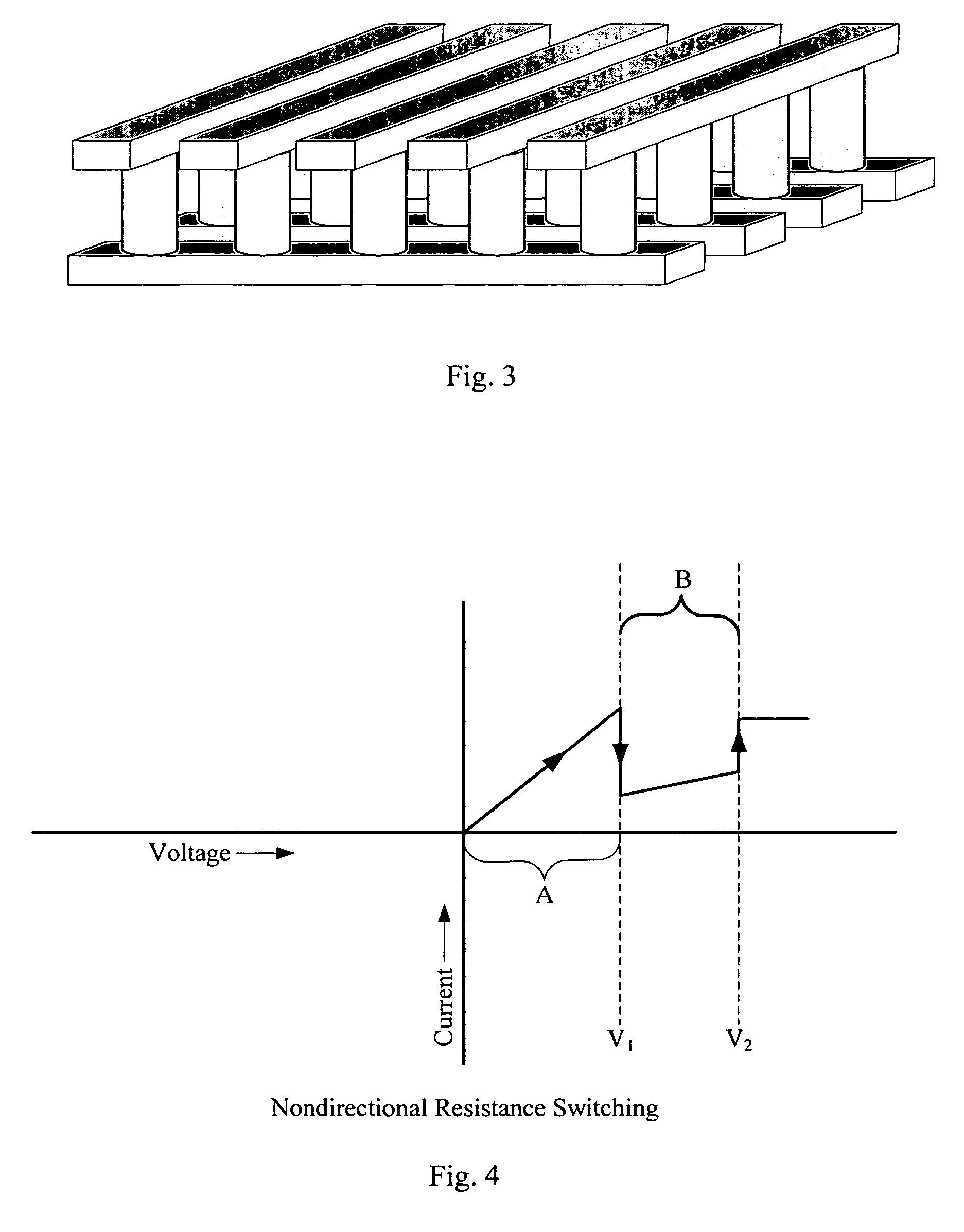
In a novel rewriteable nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NiO, Nb2O5, TiO2, HfO2, Al2O3, MgOx, CrO2, VO, BN, and AlN. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
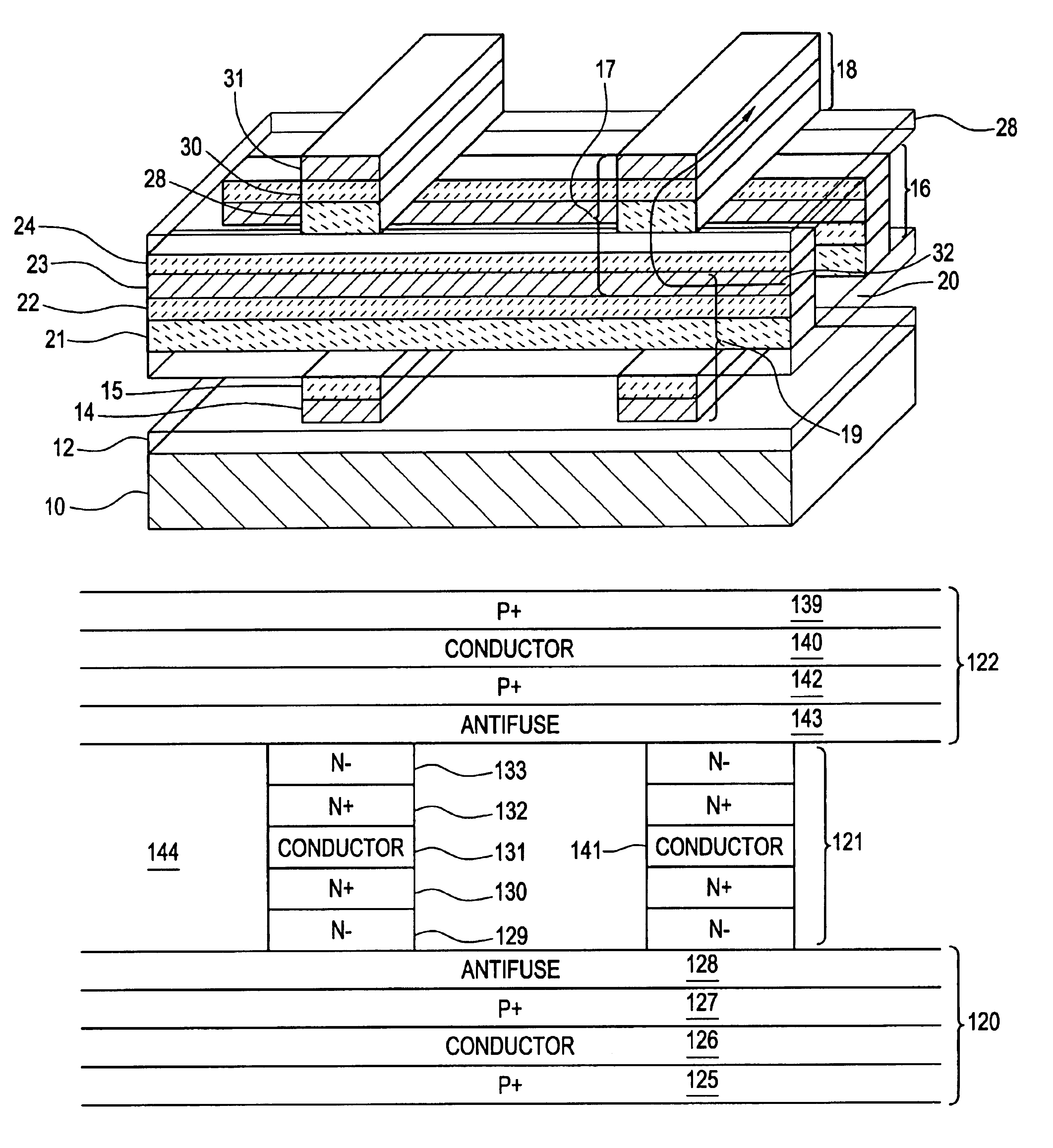
Nonvolatile memory on SOI and compound semiconductor substrates and method of fabrication
A nonvolatile memory array is provided. The array includes an array of nonvolatile memory devices, at least one driver circuit, and a substrate. The at least one driver circuit is not located in a bulk monocrystalline silicon substrate. The at least one driver circuit may be located in a silicon on insulator substrate or in a compound semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
In a novel nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NixOy, NbxOy, TixOy, HFxOy, AlxOy, MgxOy, CoxOy, CrxOy, VxOy, ZnxOy, ZrxOy, BxNy, and AlxNy. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors. The memory cell of the present invention can be used as a rewriteable memory cell or a one-time-programmable memory cell, and can store two or more data states.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
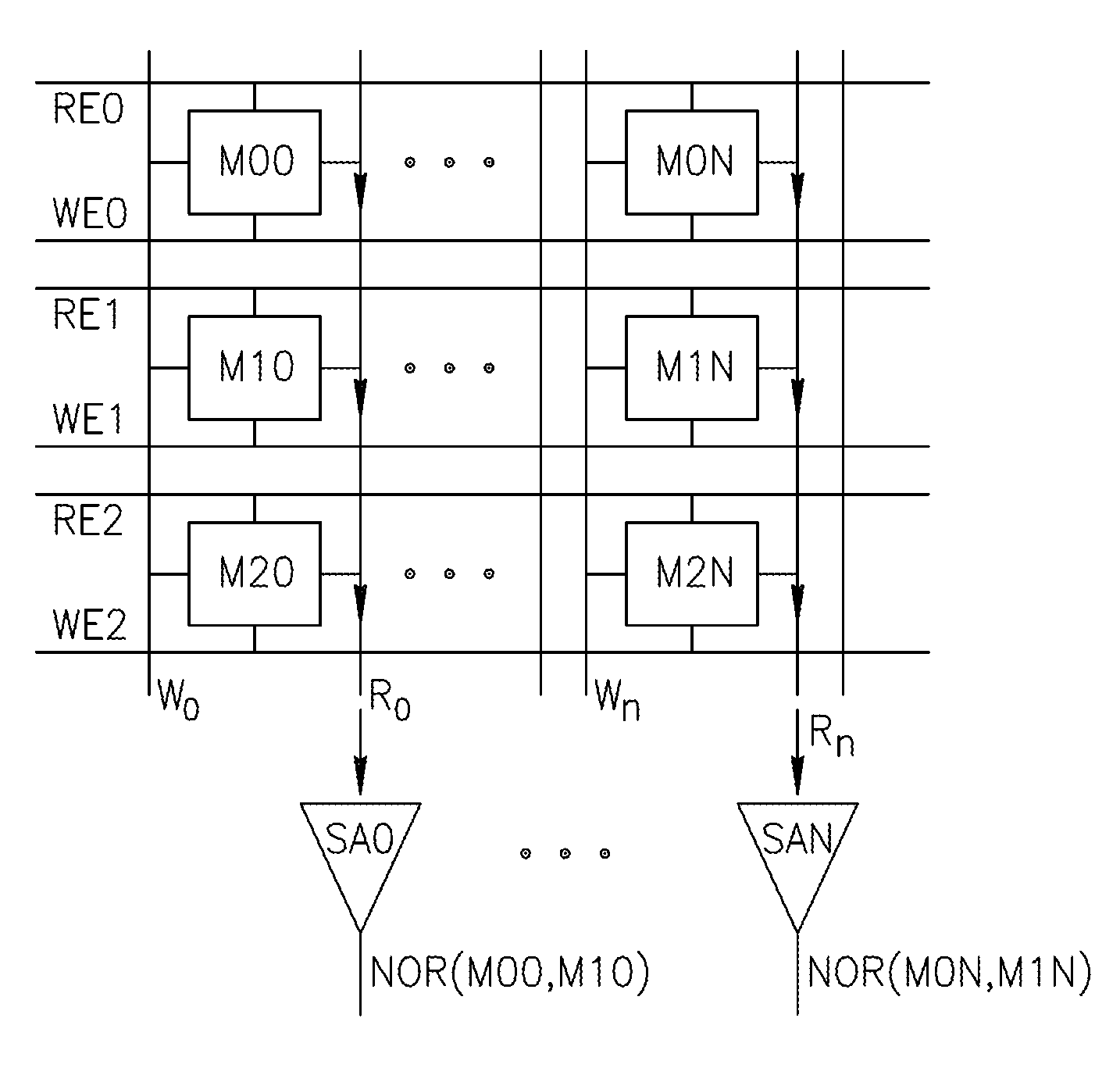
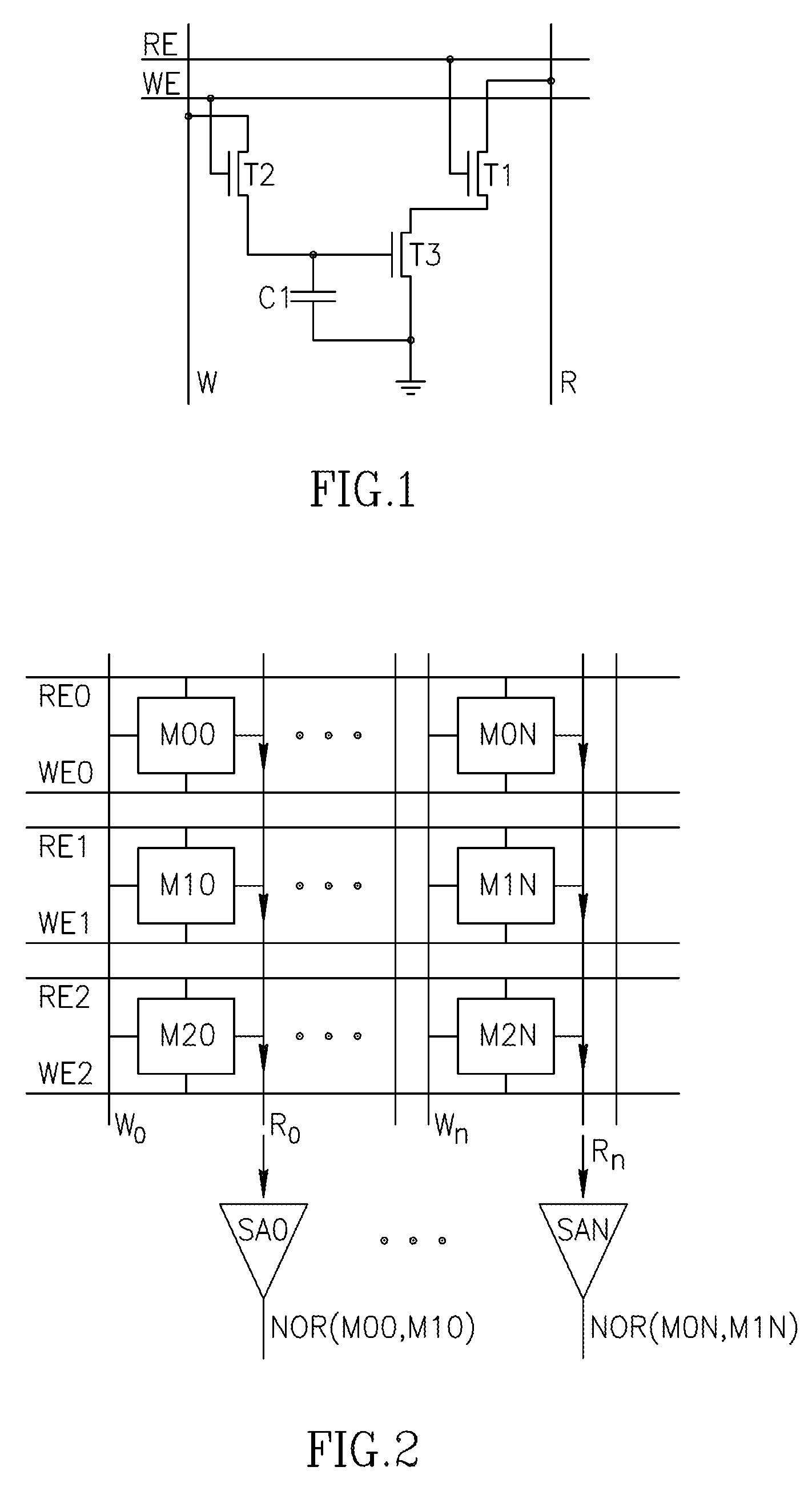
Using storage cells to perform computation
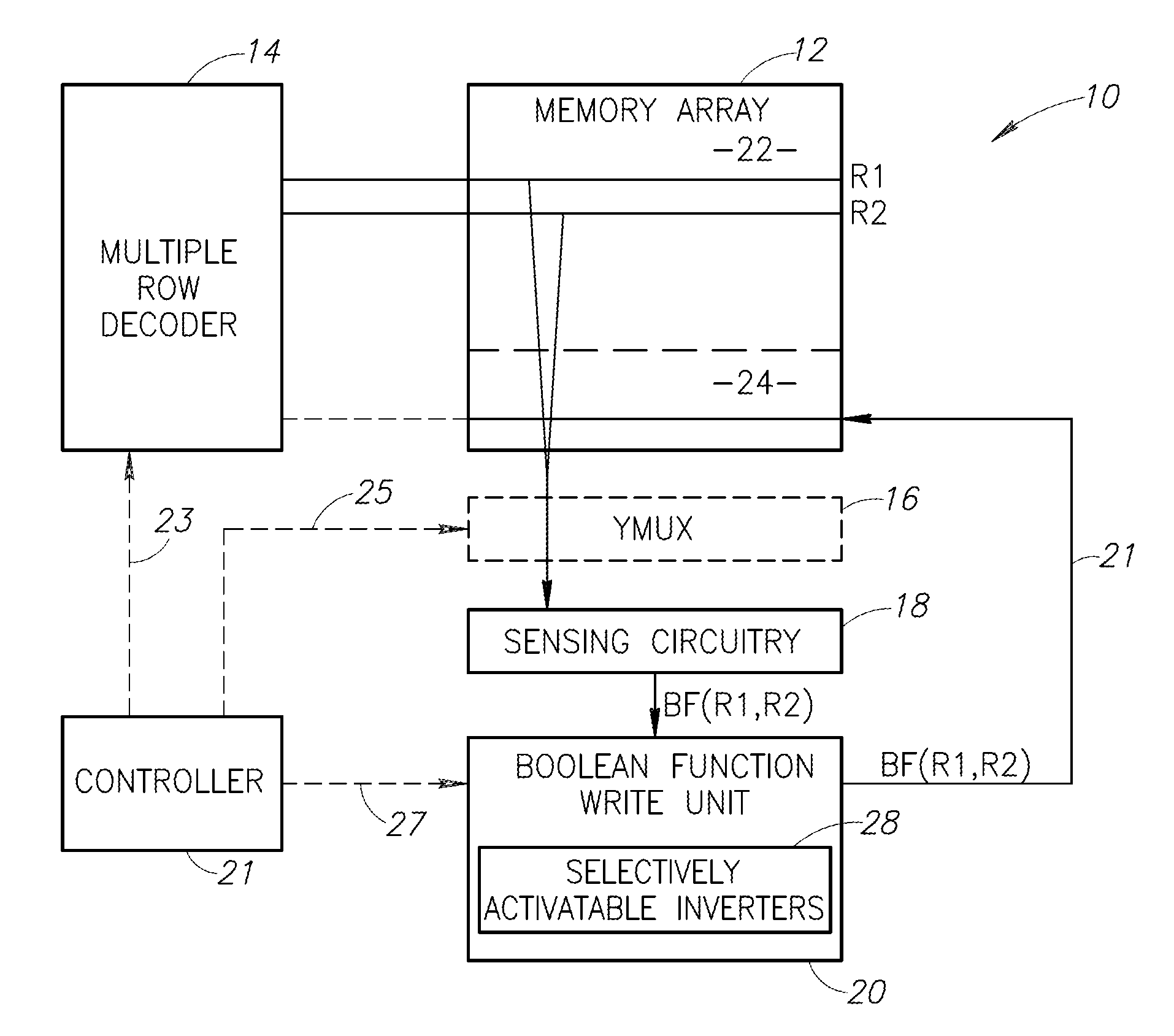
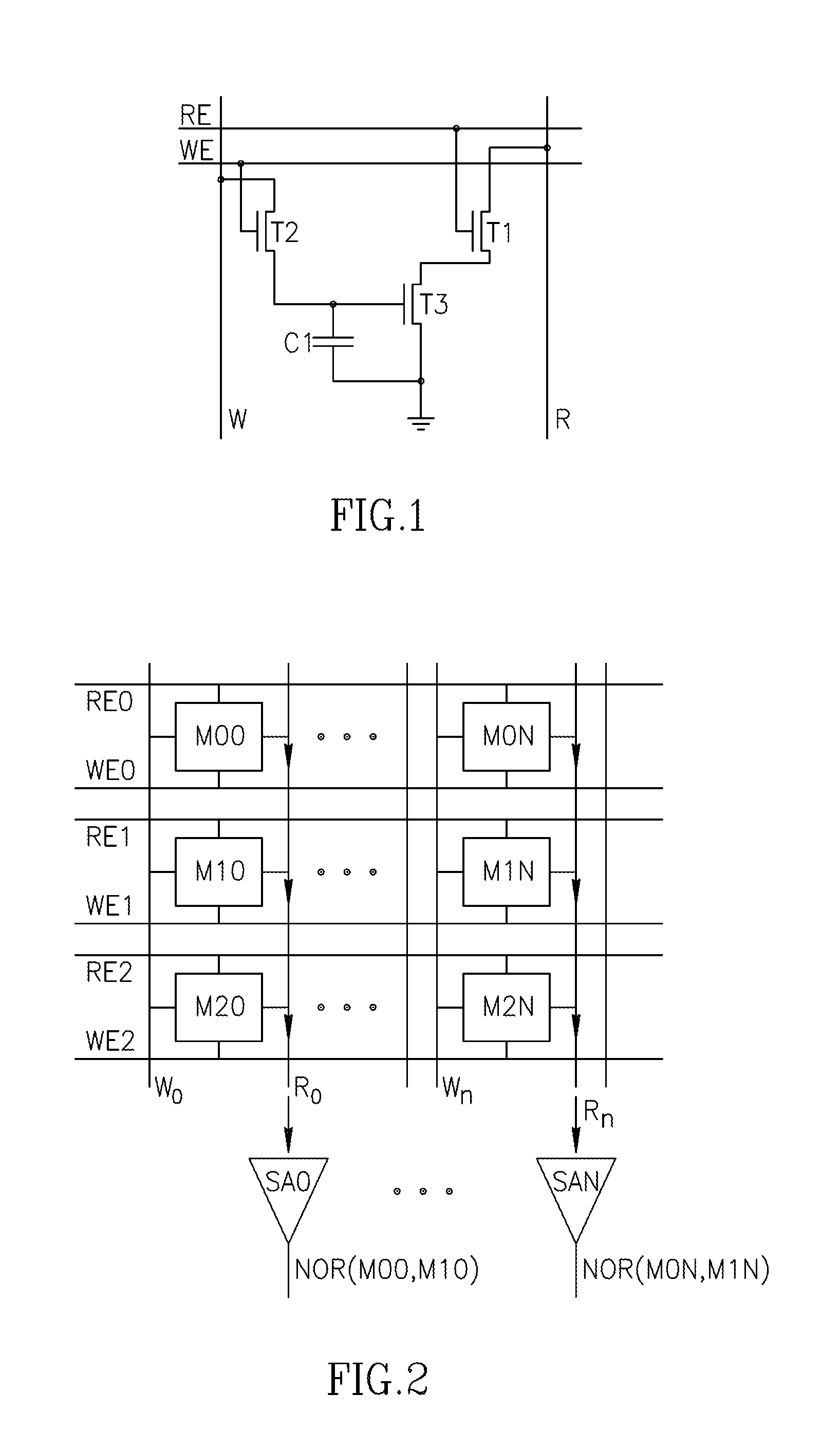
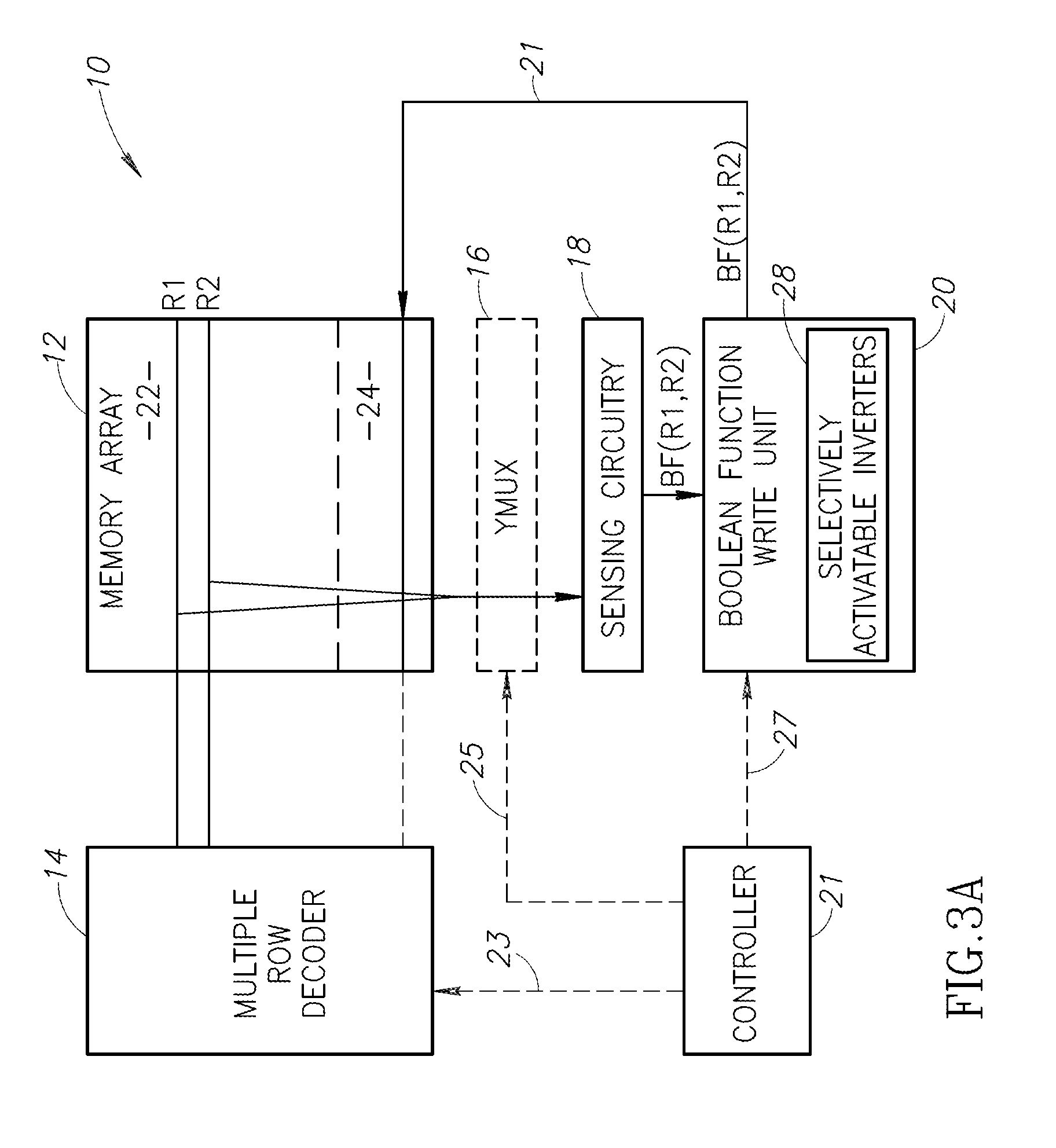
An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells. Another embodiment shows a content addressable memory (CAM) unit without any in-cell comparator circuitry.
Owner:GSI TECH
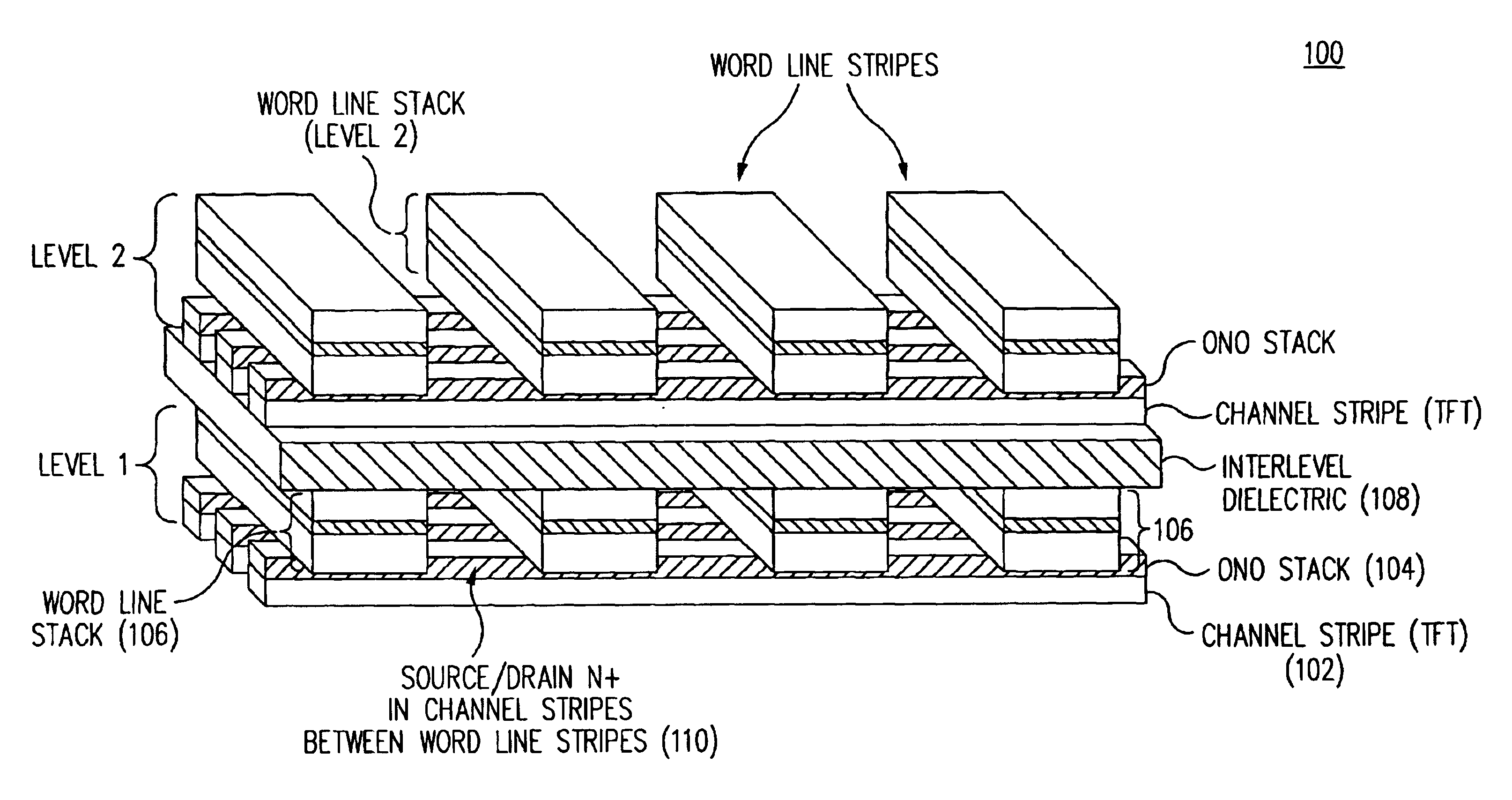
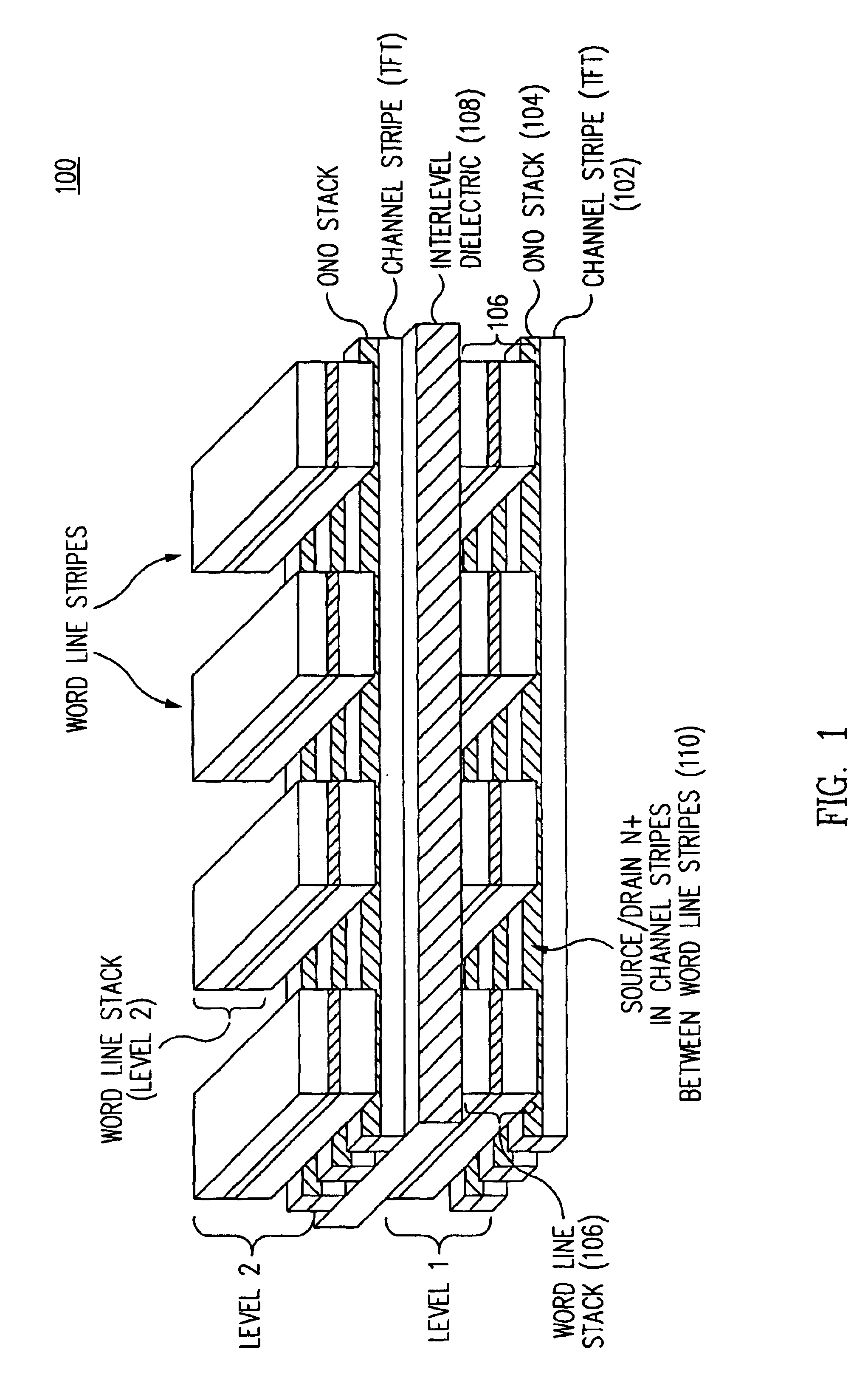
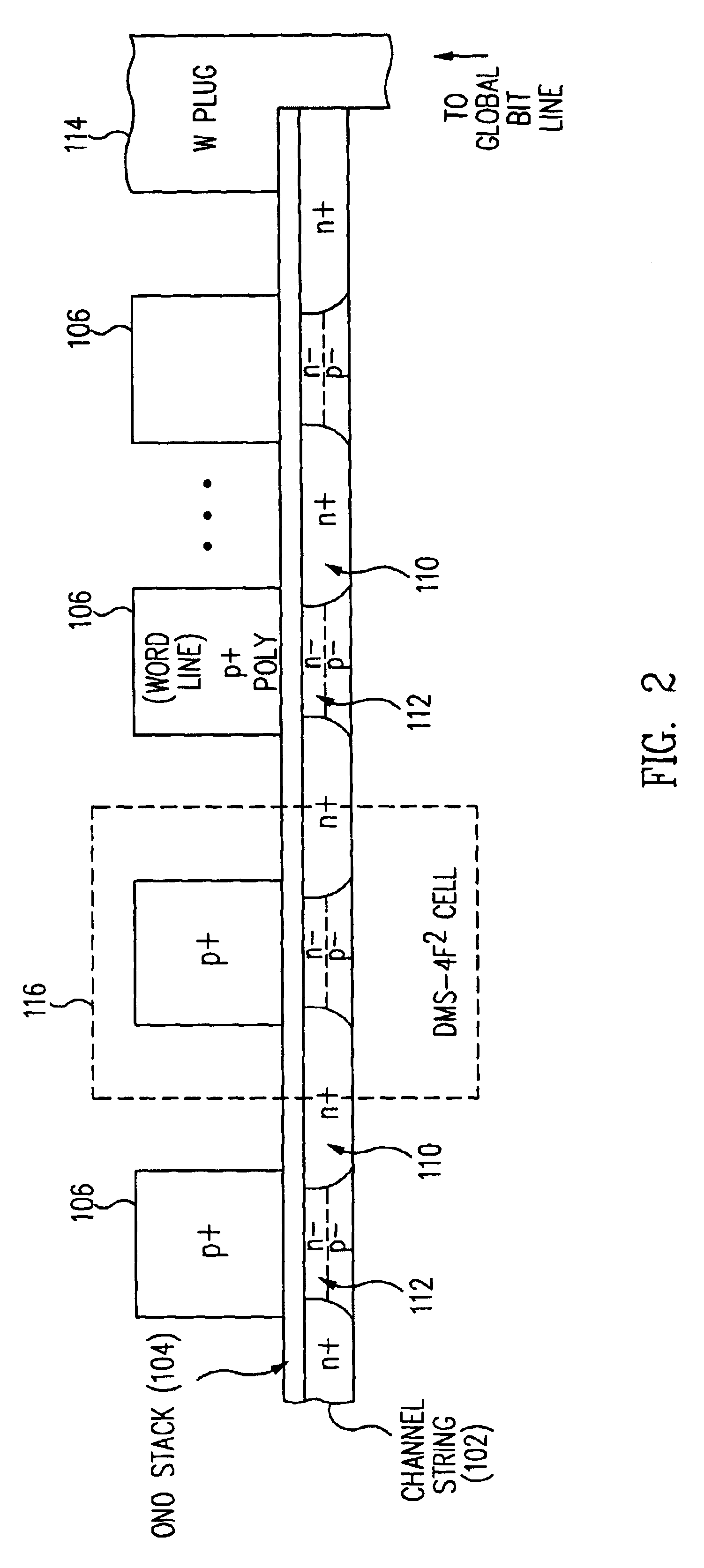
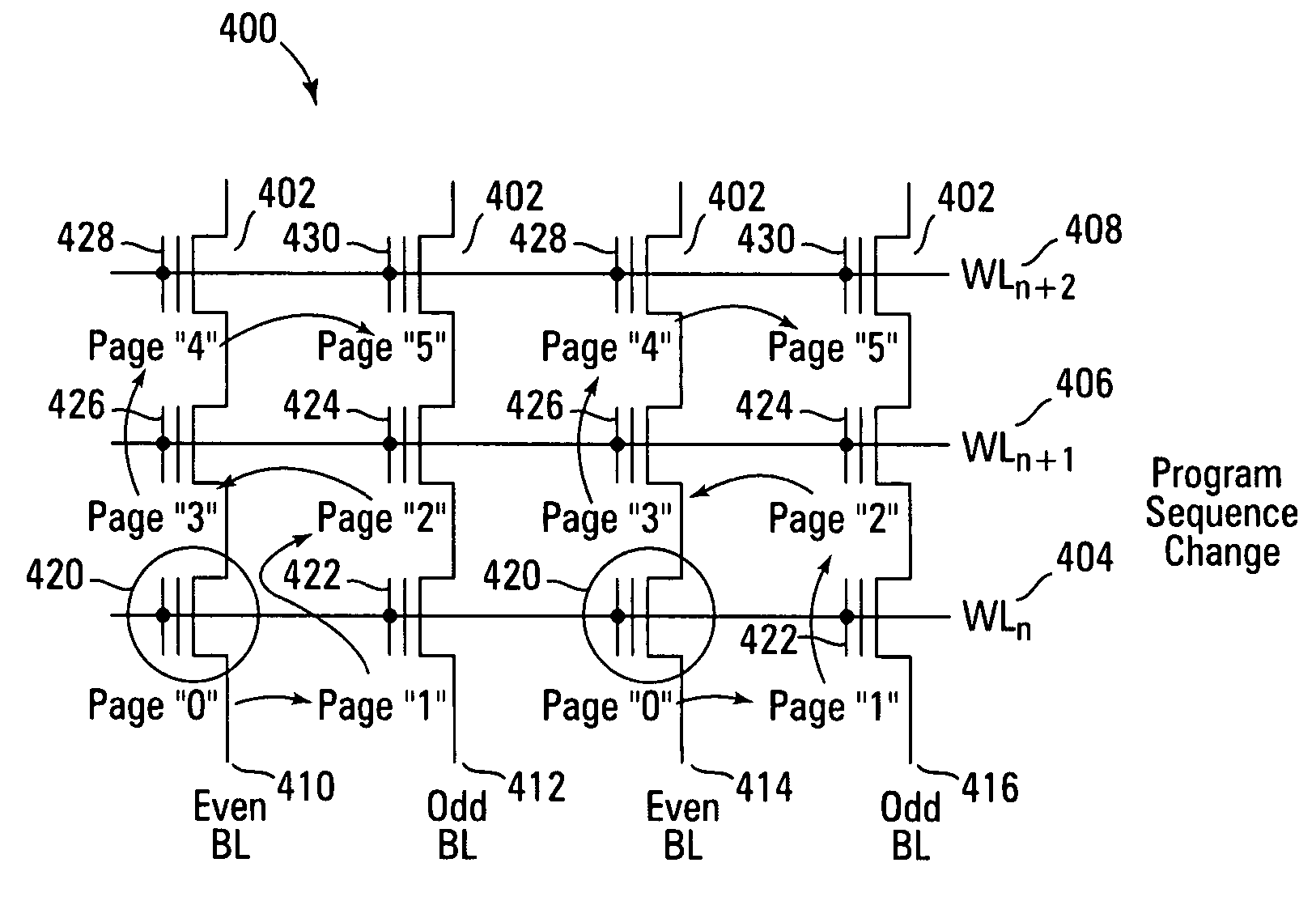
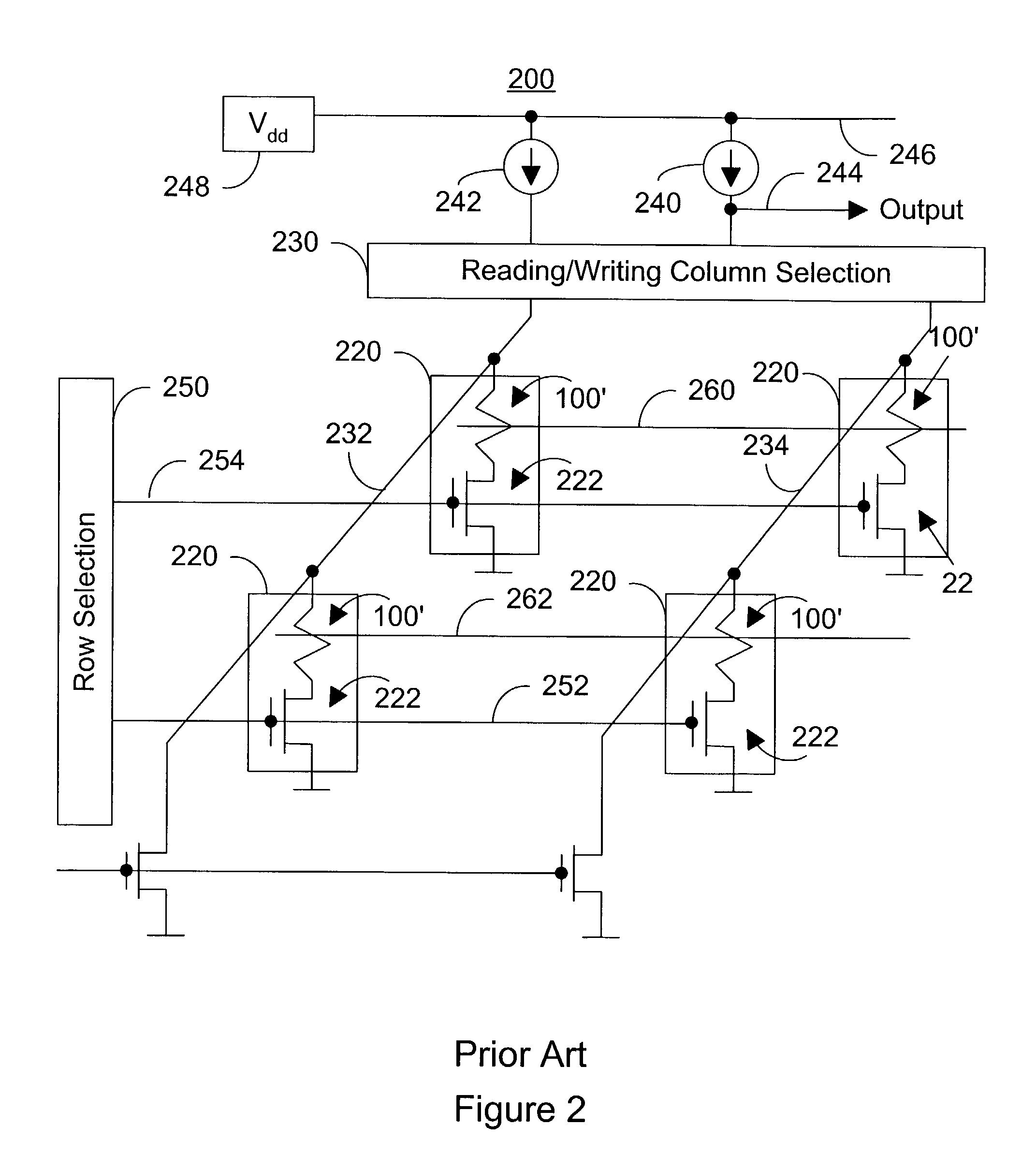
Method for fabricating programmable memory array structures incorporating series-connected transistor strings
InactiveUS7005350B2Reduce in quantityDense memory arraySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineComputer architecture
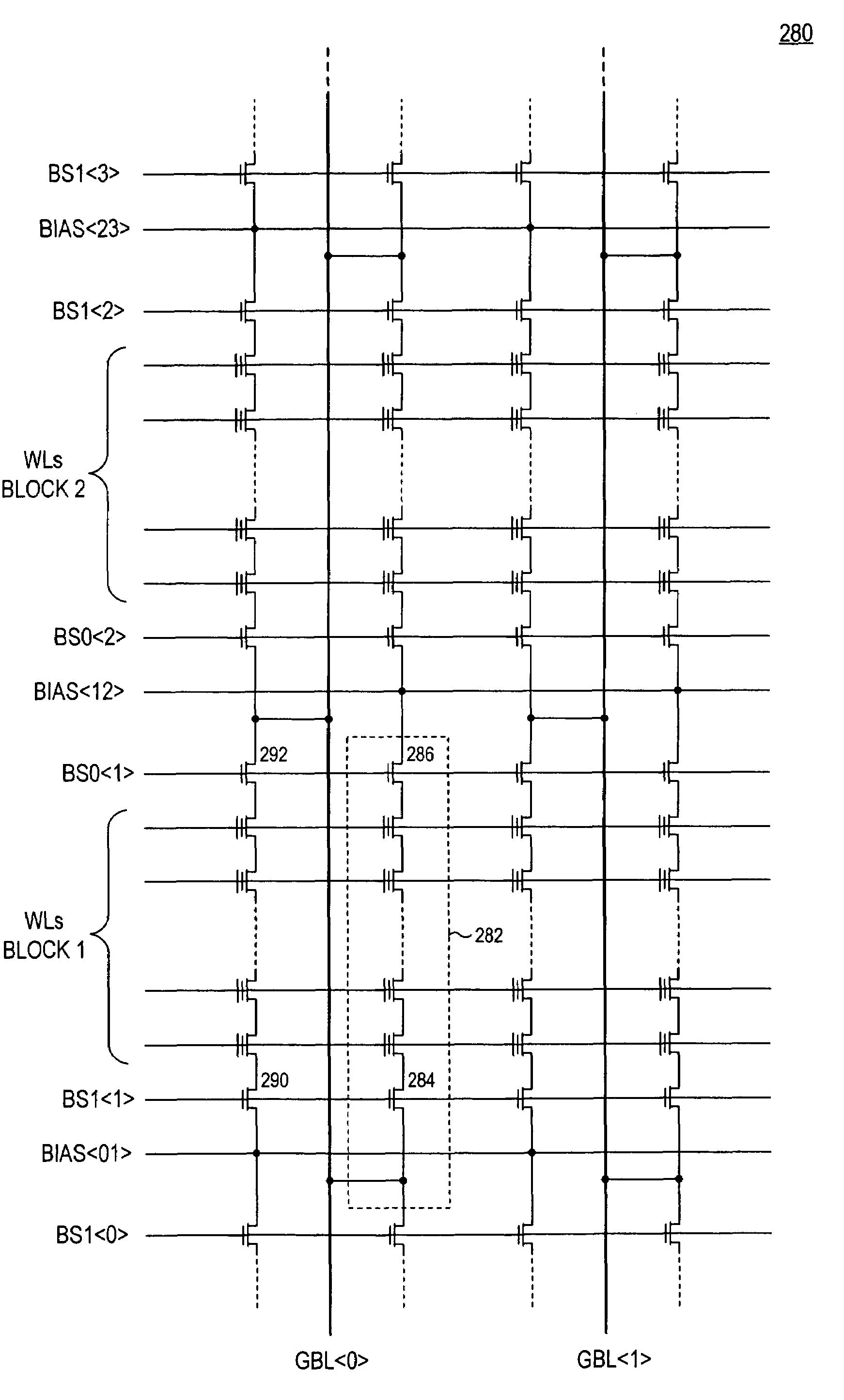
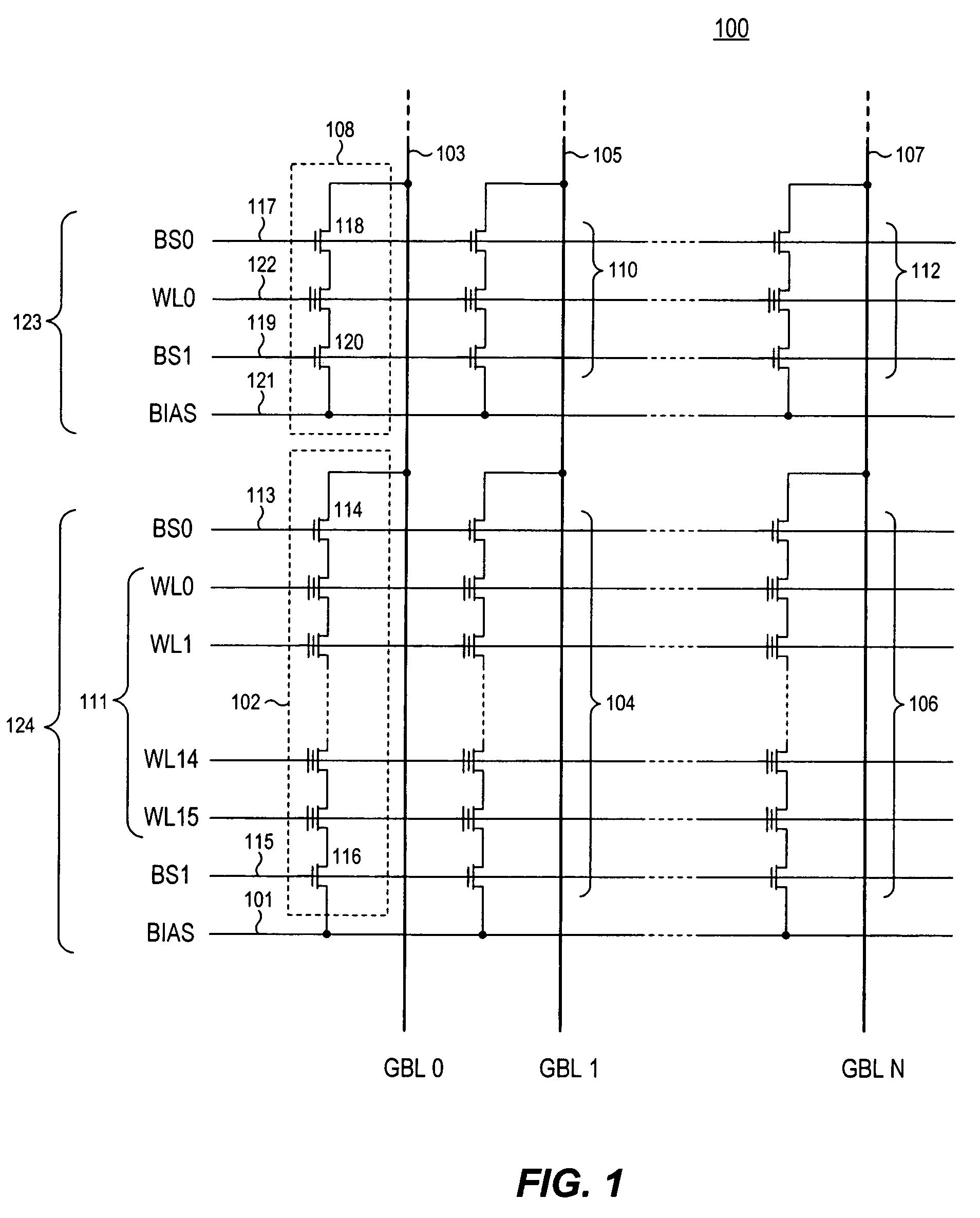
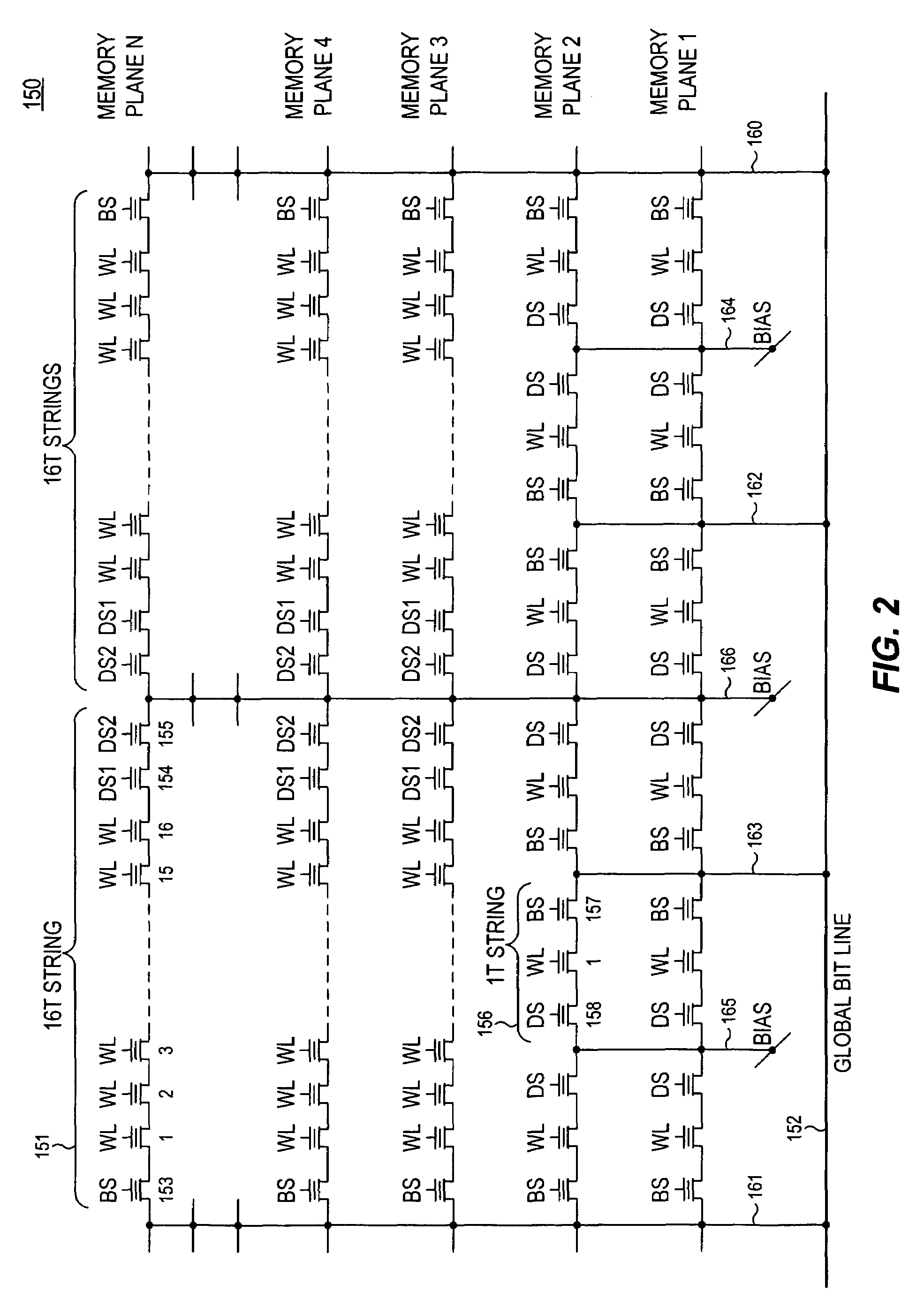
A three-dimensional flash memory array incorporates thin film transistors having a charge storage dielectric arranged in series-connected NAND strings to achieve a 4F2 memory cell layout. The memory array may be programmed and erased using only tunneling currents, and no leakage paths are formed through non-selected memory cells. Each NAND string includes two block select devices for respectively coupling one end of the NAND string to a global bit line, and the other end to a shared bias node. Pairs of NAND strings within a block share the same global bit line. The memory cells are preferably depletion mode SONOS devices, as are the block select devices. The memory cells may be programmed to a near depletion threshold voltage, and the block select devices are maintained in a programmed state having a near depletion mode threshold voltage. NAND strings on more than one layer may be connected to global bit lines on a single layer. By interleaving the NAND strings on each memory level and using two shared bias nodes per block, very little additional overhead is required for the switch devices at each end of the NAND strings. The NAND strings on different memory levels are preferably connected together by way of vertical stacked vias, each preferably connecting to more than one memory level. Each memory level may be produced with less than three masks per level.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Programming method to reduce gate coupling interference for non-volatile memory
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
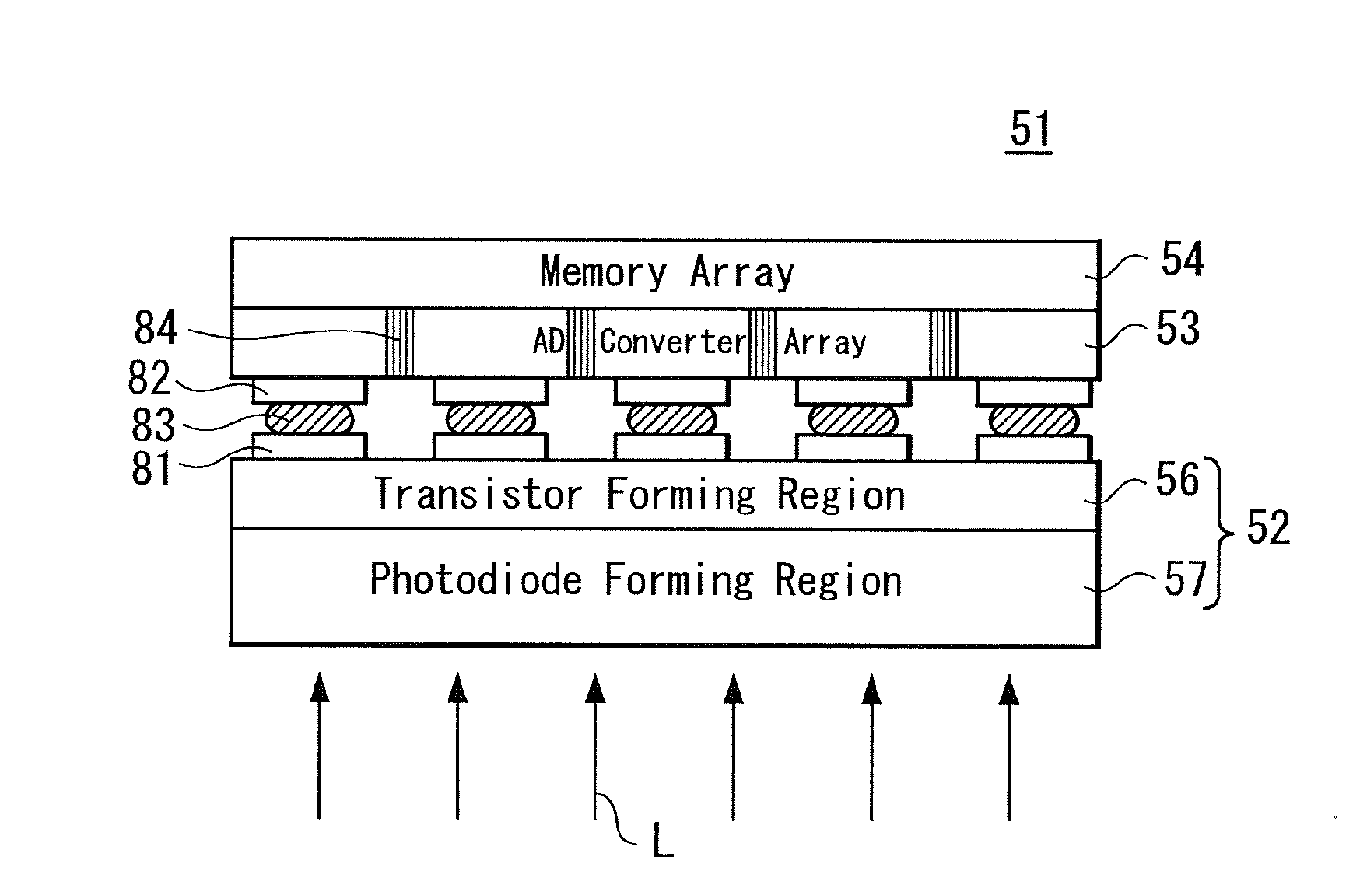
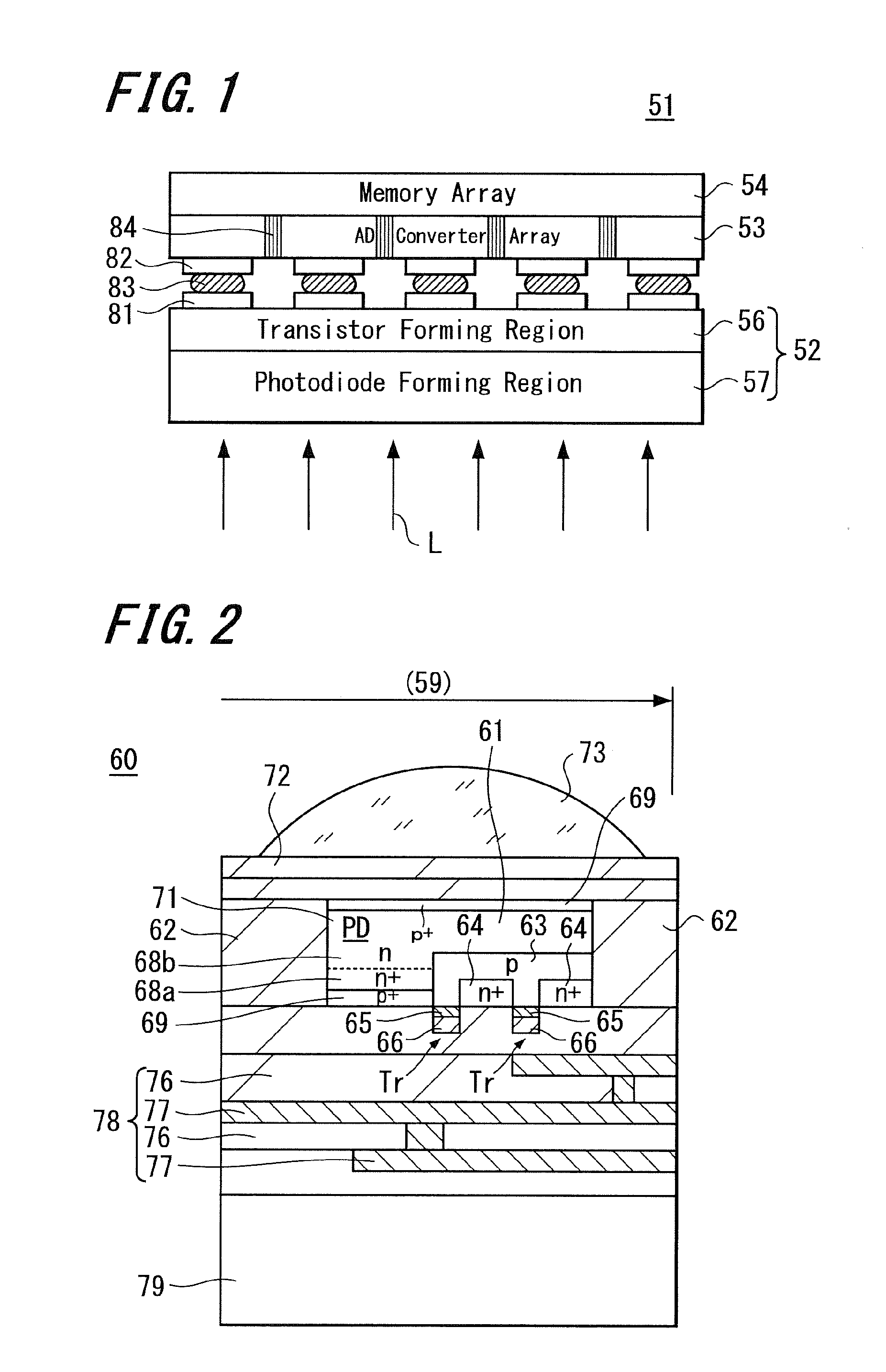
Semiconductor image sensor module and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100276572A1Increase the aperture ratioIncrease profitTransistorTelevision system detailsCMOSSemiconductor chip
A CMOS type semiconductor image sensor module wherein a pixel aperture ratio is improved, chip use efficiency is improved and furthermore, simultaneous shutter operation by all the pixels is made possible, and a method for manufacturing such semiconductor image sensor module are provided. The semiconductor image sensor module is provided by stacking a first semiconductor chip, which has an image sensor wherein a plurality of pixels composed of a photoelectric conversion element and a transistor are arranged, and a second semiconductor chip, which has an A / D converter array. Preferably, the semiconductor image sensor module is provided by stacking a third semiconductor chip having a memory element array. Furthermore, the semiconductor image sensor module is provided by stacking the first semiconductor chip having the image sensor and a fourth semiconductor chip having an analog nonvolatile memory array.
Owner:SONY CORP
Processor Arrays Made of Standard Memory Cells
Owner:GSI TECH
Dram-like nvm memory array and sense amplifier design for high temperature and high endurance operation
InactiveUS20110267883A1Improve threshold voltage sensing marginLarge silicon areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
A DRAM-like non-volatile memory array includes a cell array of non-volatile cell units with a DRAM-like cross-coupled latch-type sense amplifier. Each non-volatile cell unit has two non-volatile cell devices with respective bit lines and source lines running in parallel and laid out perpendicular to the word line associated with the non-volatile cell unit. The two non-volatile cell devices are programmed with erased and programmed threshold voltages as a pair for storing a single bit of binary data. The two bit lines of each non-volatile cell unit are coupled through a Y-decoder and a latch device to the two respective inputs of the latch-type sense amplifier which provides a large sensing margin for the cell array to operate properly even with a narrowed threshold voltage gap. Each non-volatile cell device may be a 2 T FLOTOX-based EEPROM cell, a 2 T flash cell, 11 T flash cell or a 1.5 T split-gate flash cell.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
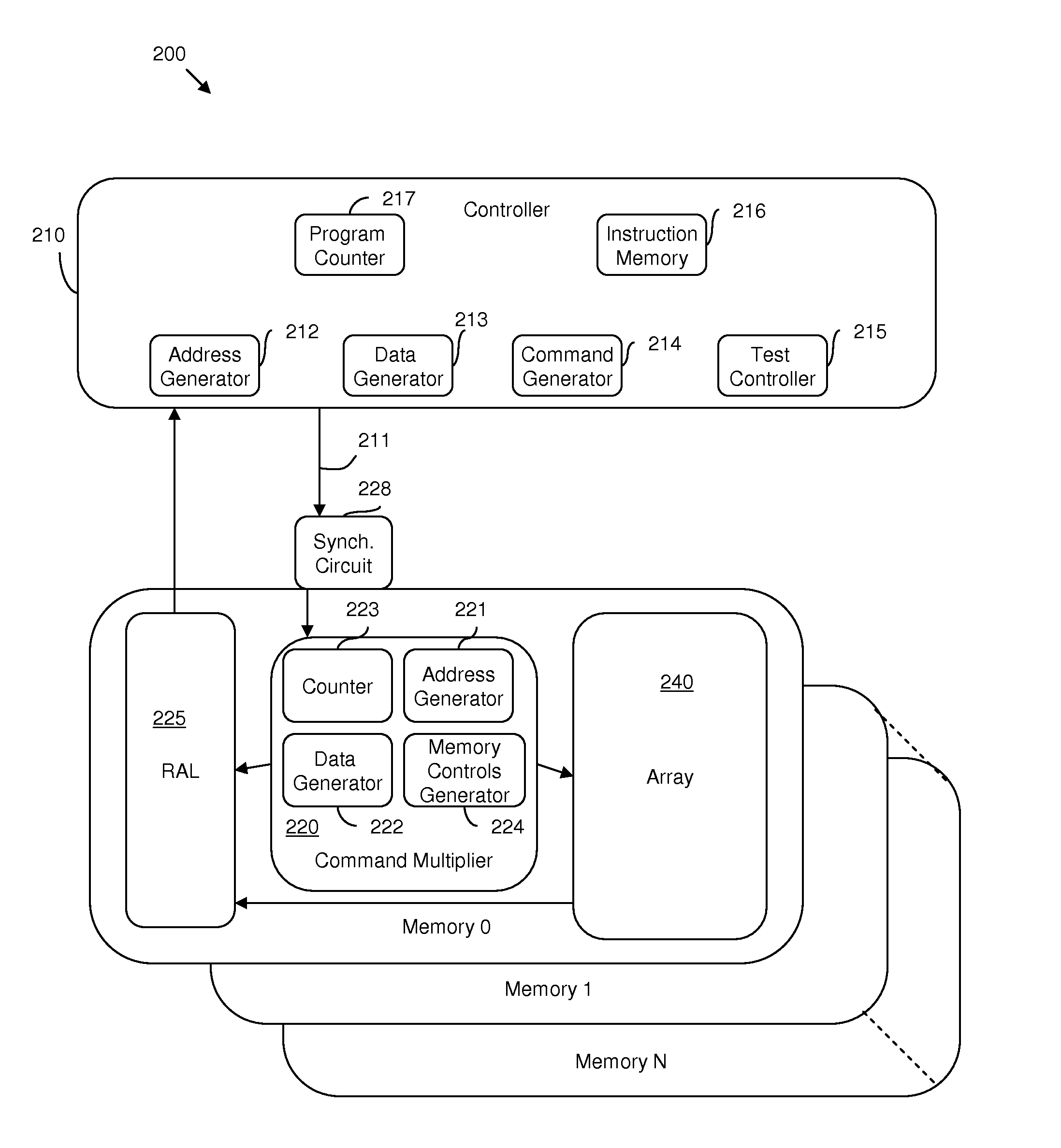
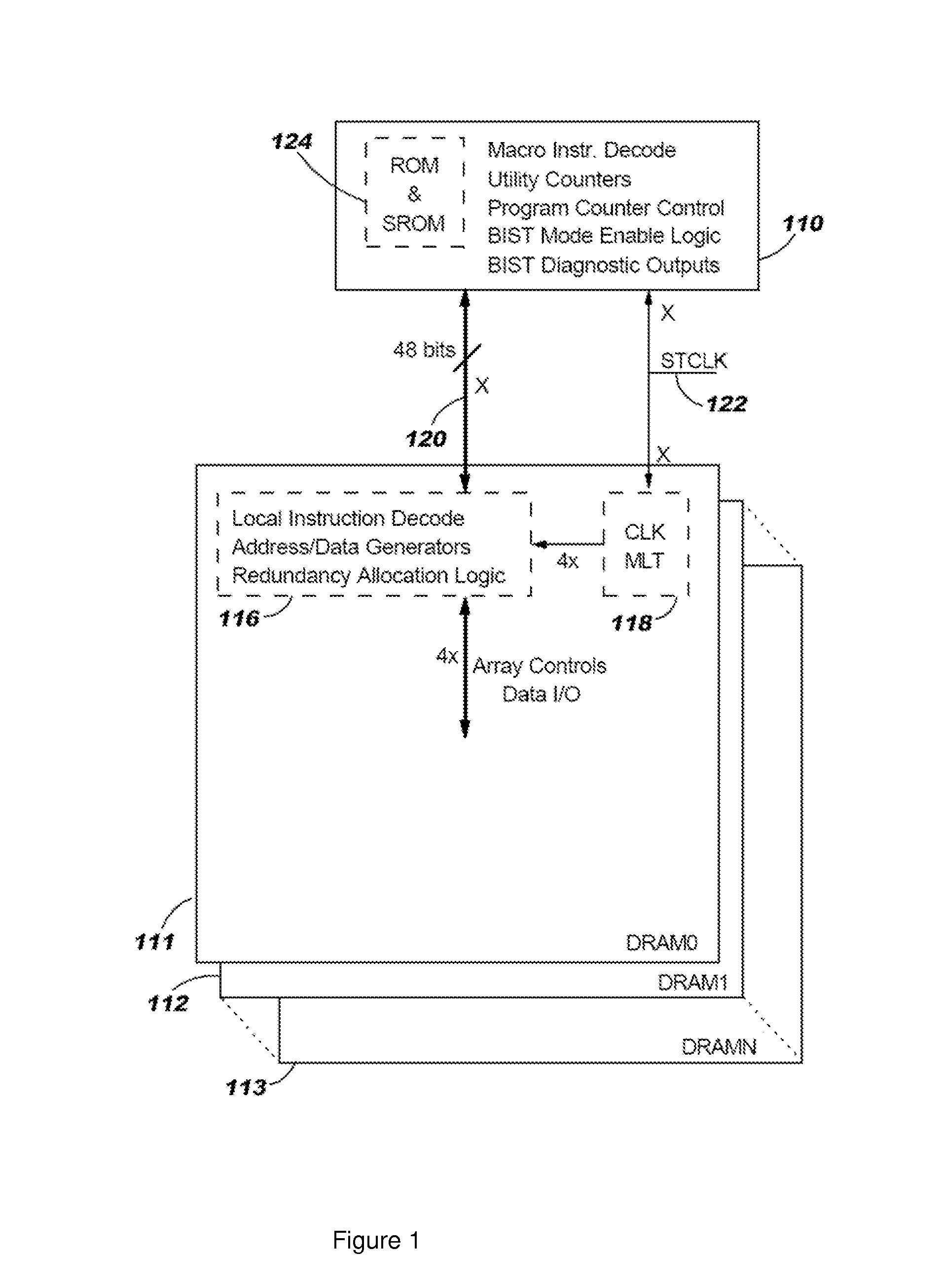
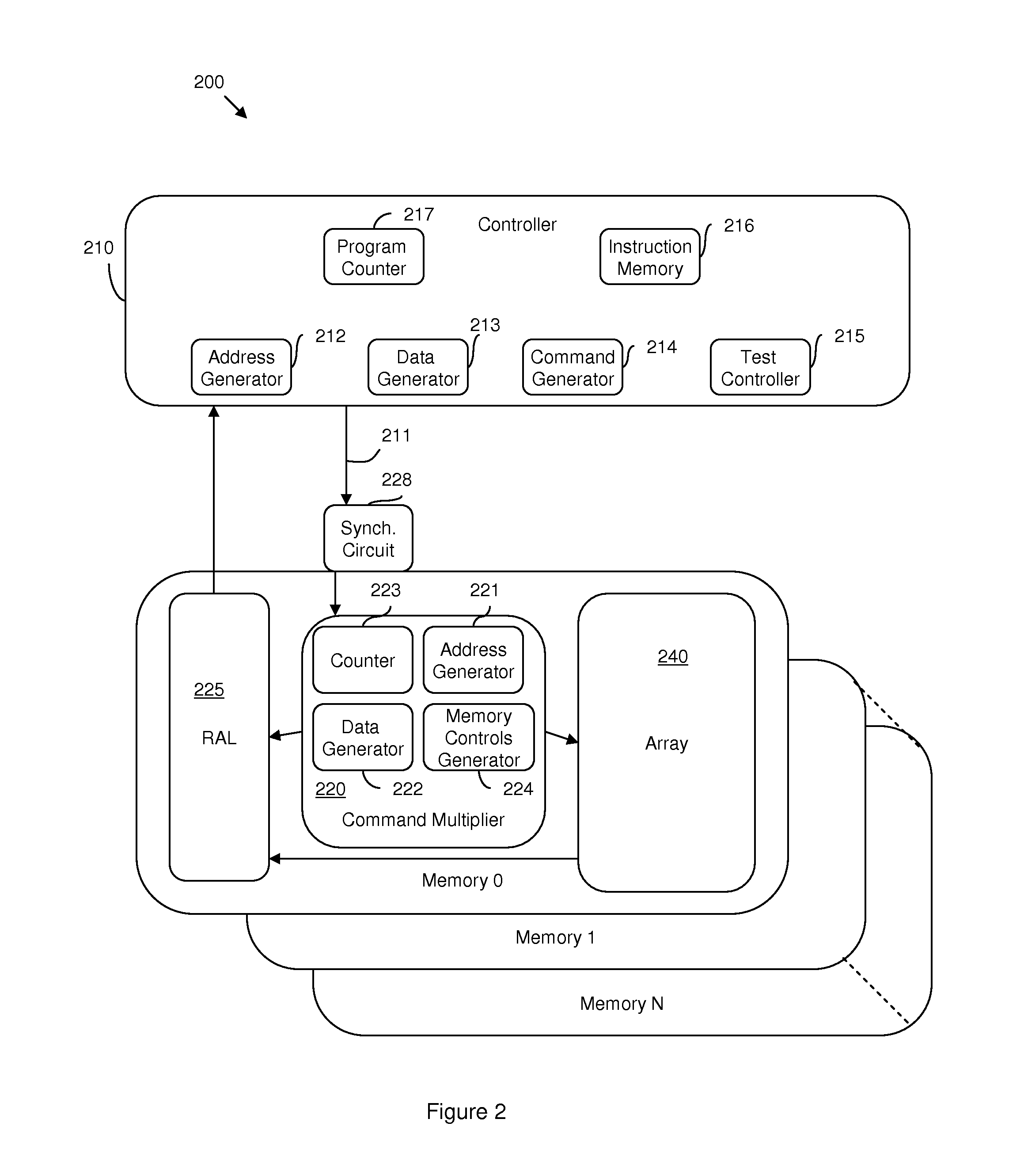
Hybrid built-in self test (BIST) architecture for embedded memory arrays and an associated method
ActiveUS20080178053A1Reduce frequencyMore test pattern flexibilityElectronic circuit testingFunctional testingSpecific testNormal mode
Disclosed are embodiments of a built-in self-test (BIST) architecture that incorporates a standalone controller that operates at a lower frequency to remotely perform test functions common to a plurality of embedded memory arrays. The architecture also incorporates command multipliers that are associated with the embedded memory arrays and that selectively operate in one of two different modes: a normal mode or a bypass mode. In the normal mode, instructions from the controller are multiplied so that memory array-specific test functions can be performed locally at the higher operating frequency of each specific memory array. Whereas, in the bypass mode, multiplication of the instructions is suspended so that memory array-specific test functions can be performed locally at the lower operating frequency of the controller. The ability to vary the frequency at which test functions are performed locally, allows for more test pattern flexibility.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
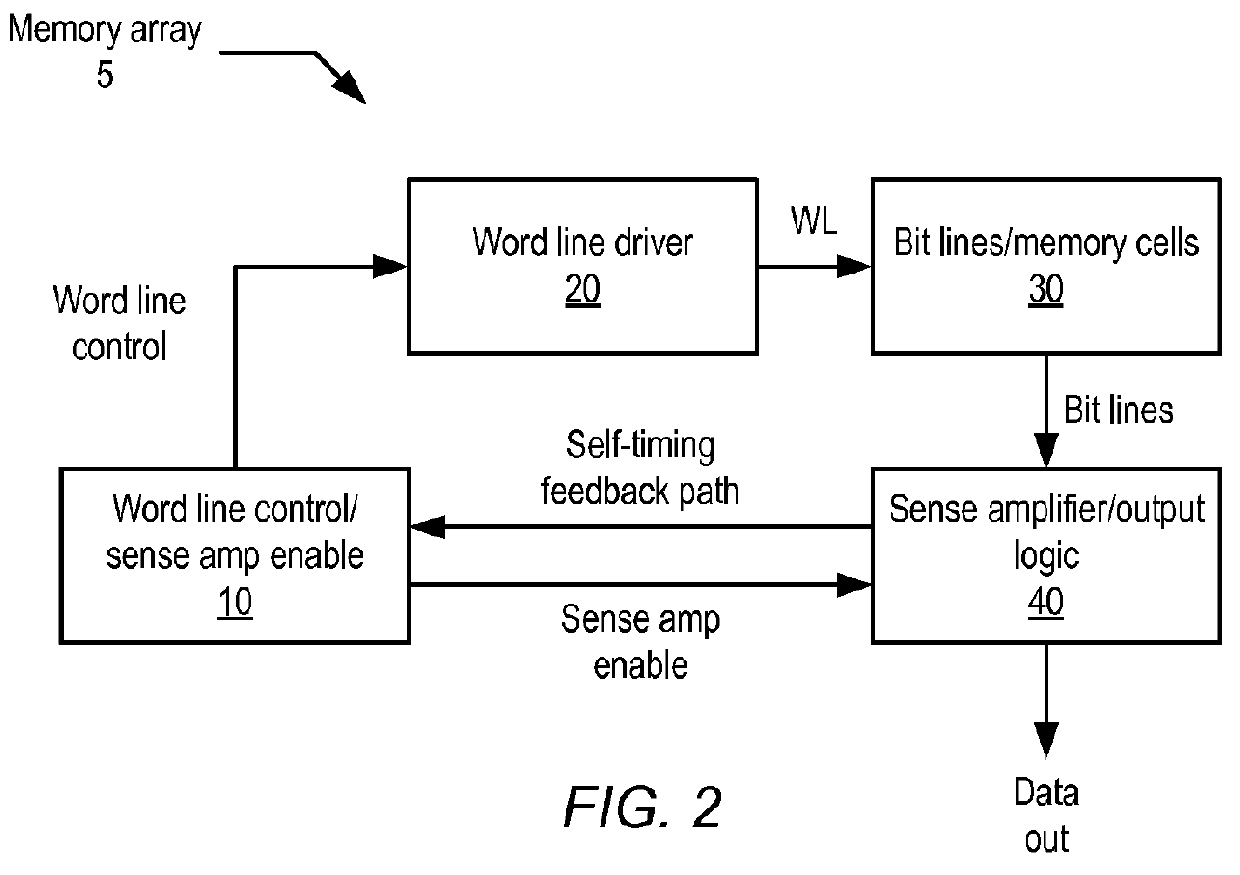
Sense amplifier and sense amplifier latch having common control
A sense amplifier of a memory array may be provided to amplify data presented from storage cells of the memory array. Additionally, a sense amplifier latch may be provided to store data received from the sense amplifier. The sense amplifier may be enabled for operation by a sense amplifier enable signal that is distinct from a clock signal. Moreover, the latch enable signal of the sense amplifier latch may be controlled by the sense amplifier enable signal, such that the sense amplifier latch opens in response to activation of the sense amplifier and closes in response to deactivation of the sense amplifier.
Owner:APPLE INC
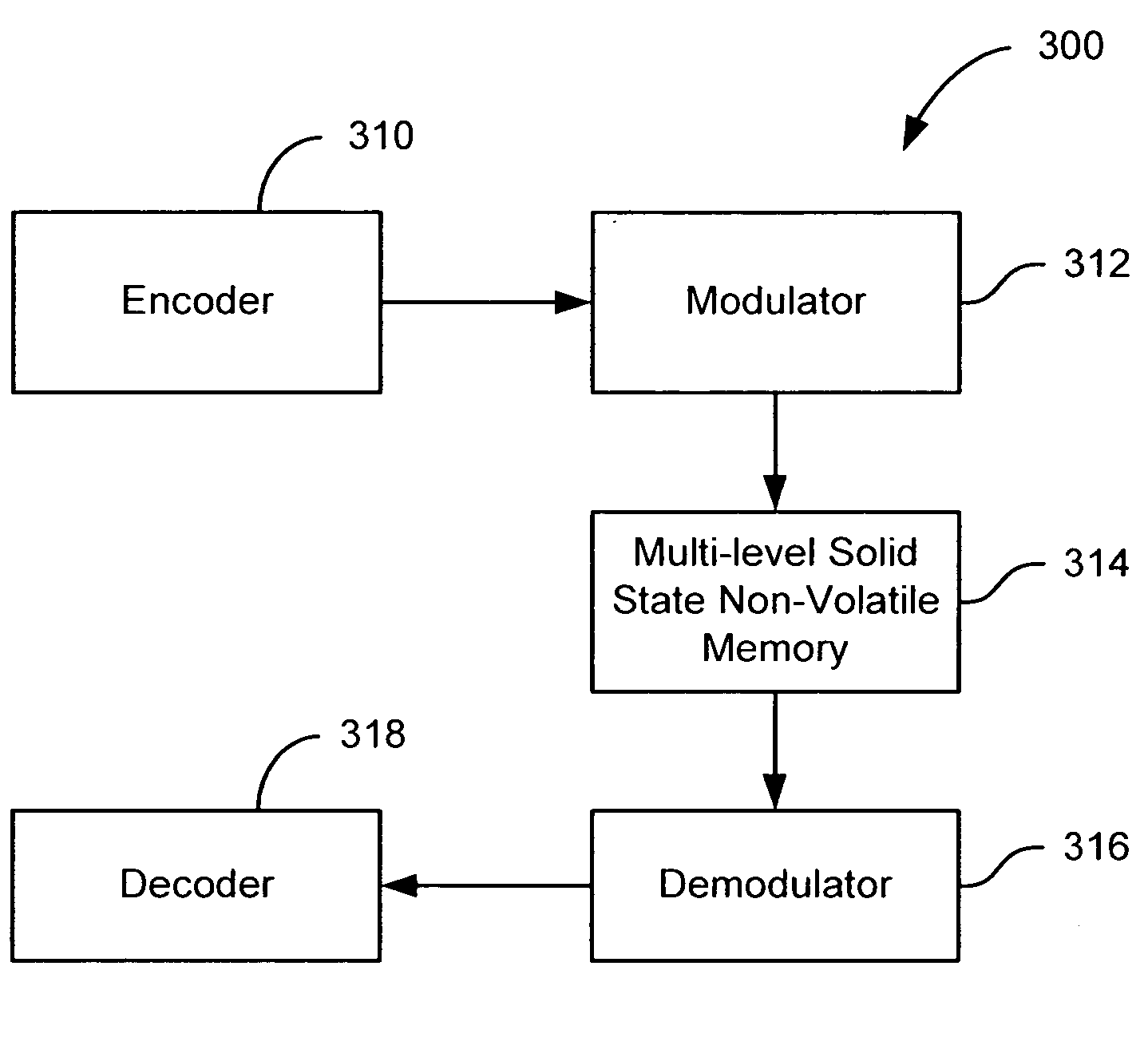
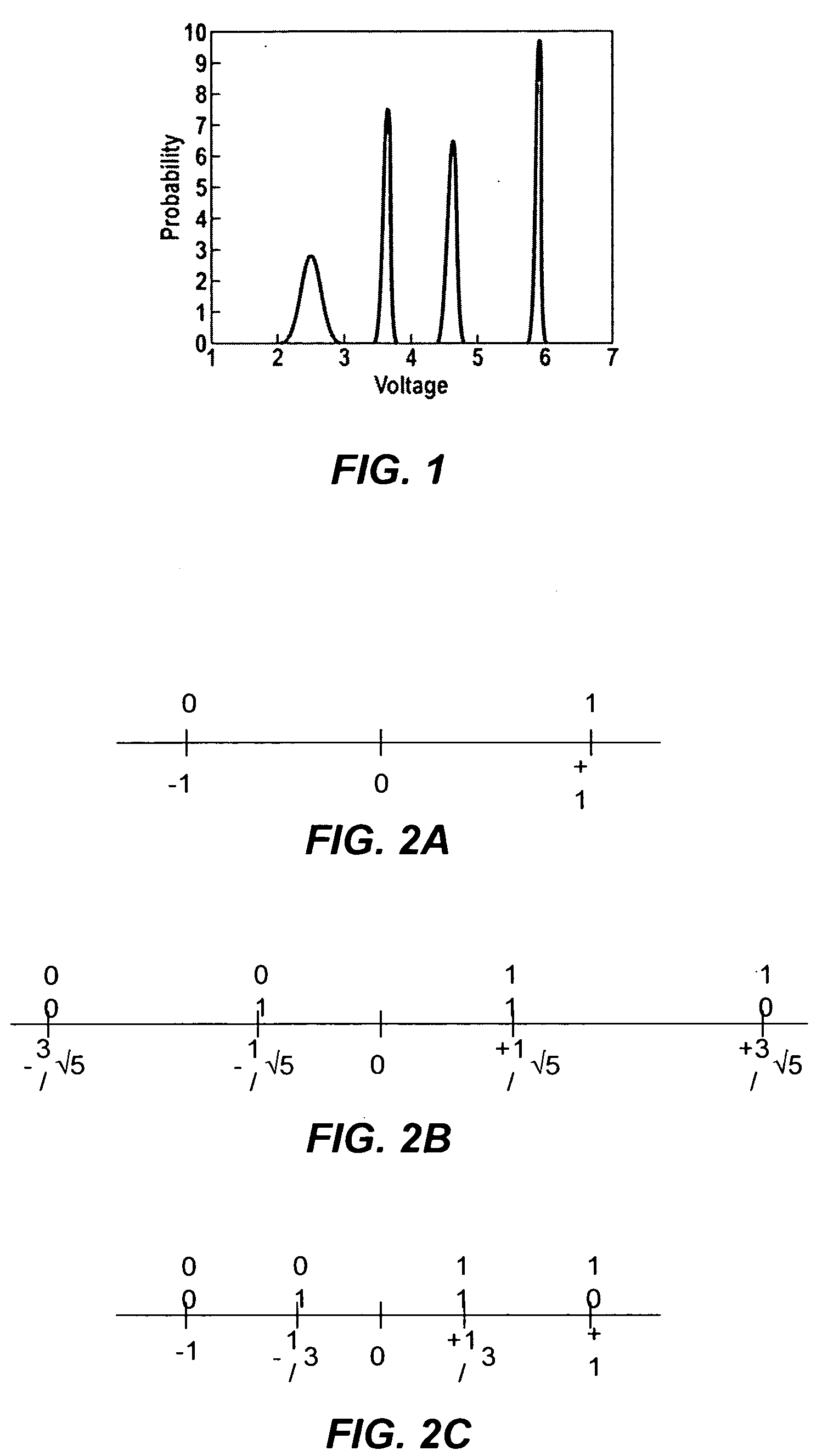
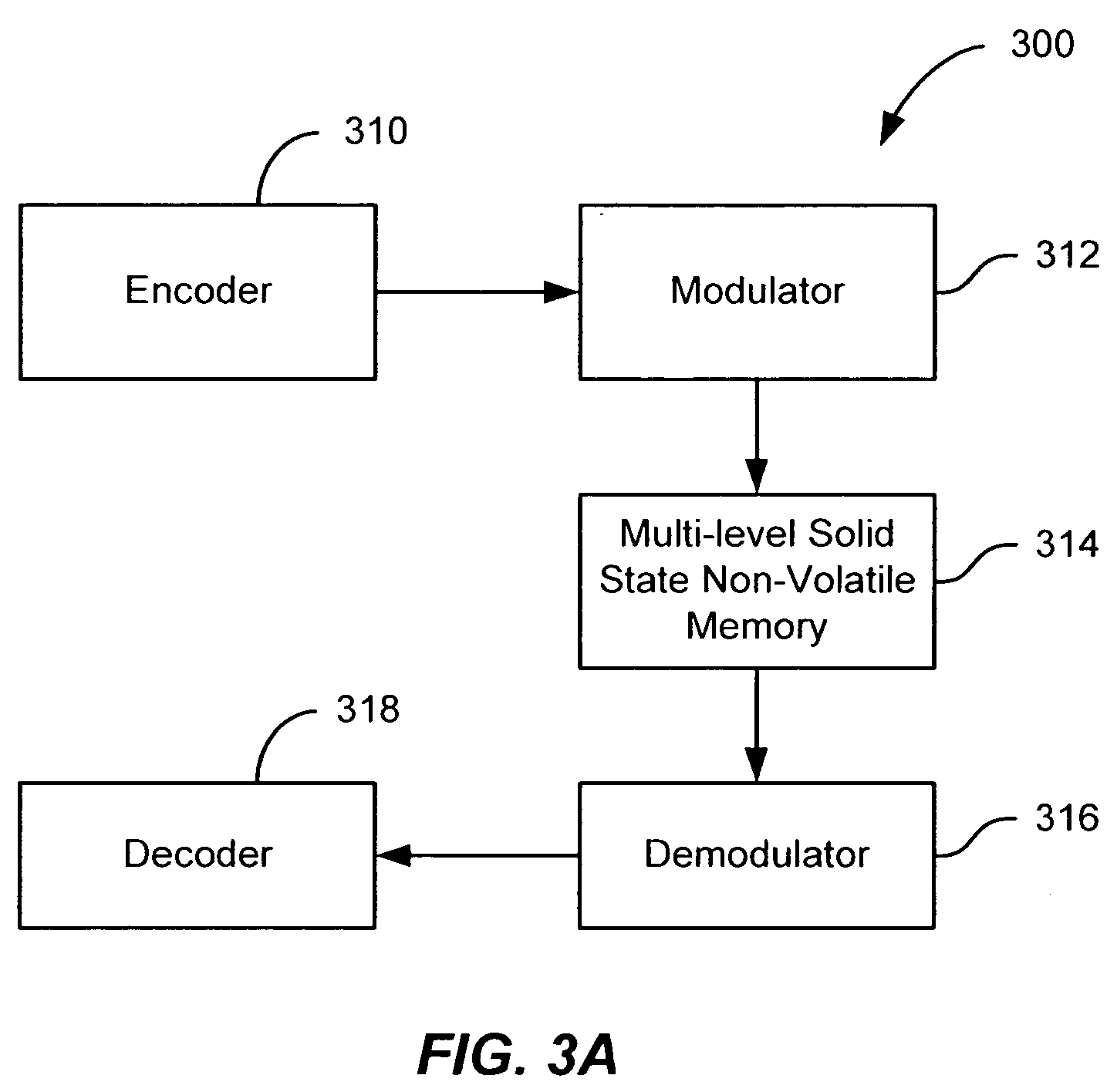
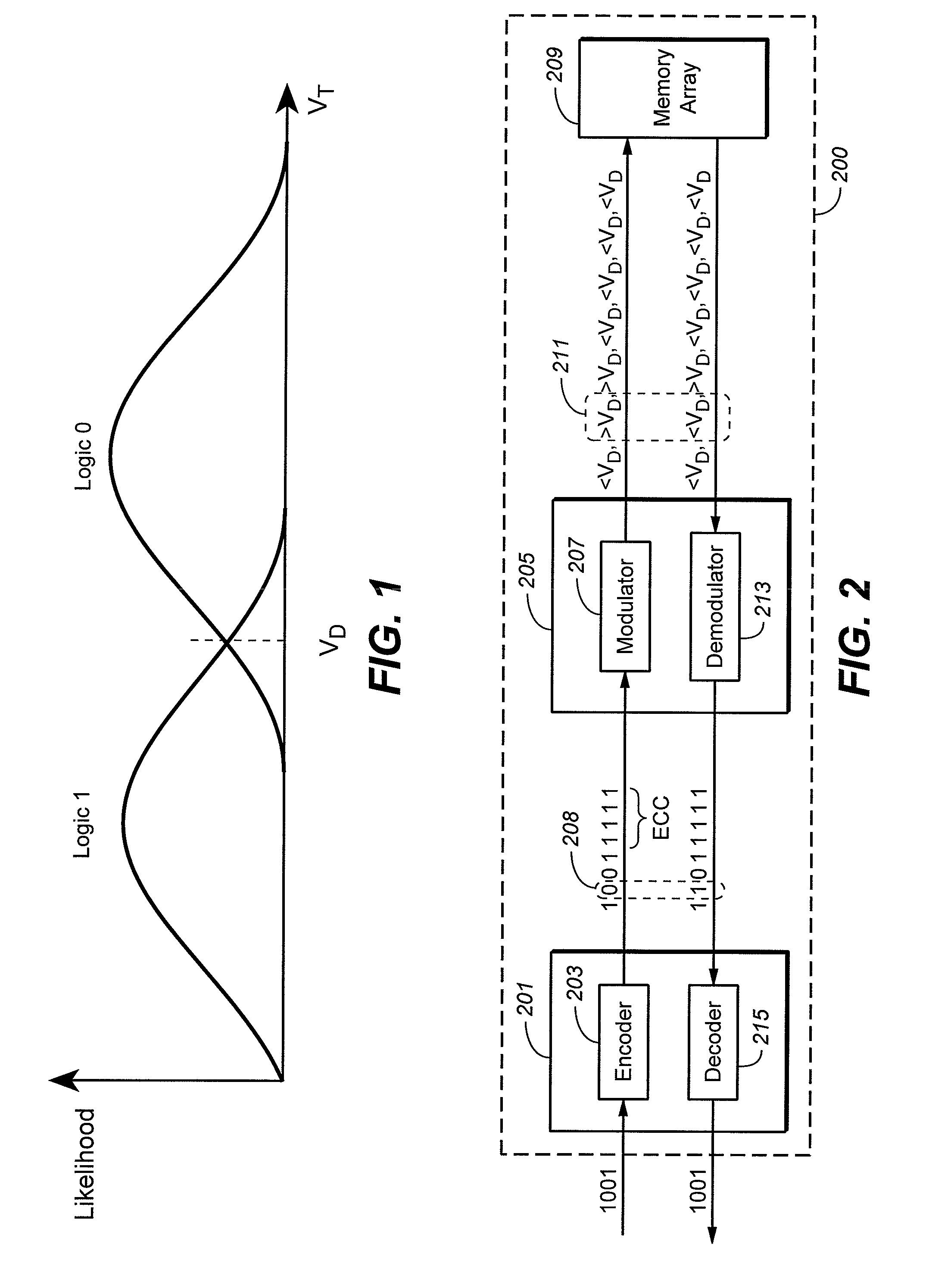
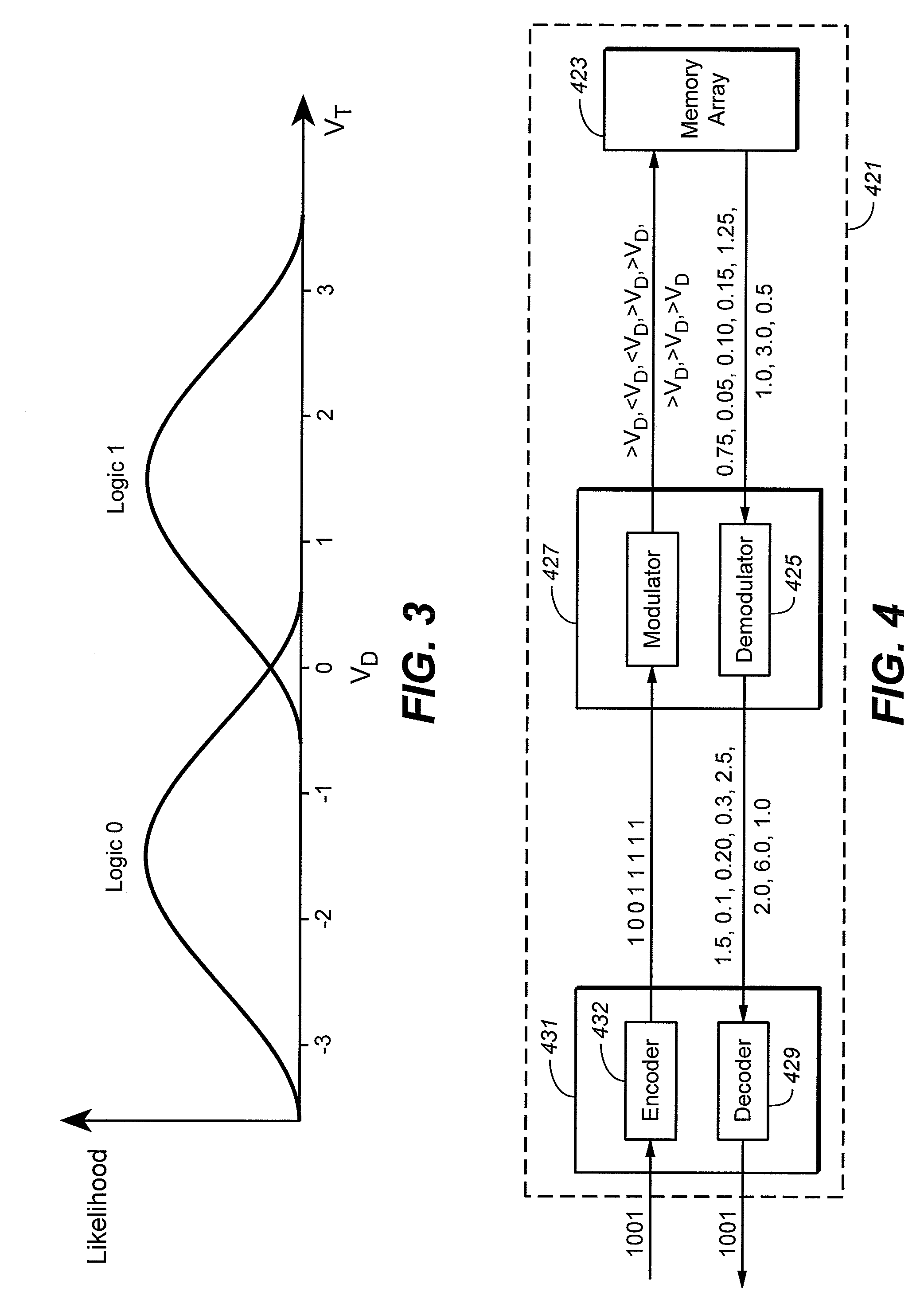
Flash memory with coding and signal processing
A solid state non-volatile memory unit includes, in part, an encoder, a multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array adapted to store data encoded by the encoder, and a decoder adapted to decode the data retrieved from the memory array. The memory array may be a flash EEPROM array. The memory unit optionally includes a modulator and a demodulator. The data modulated by the modulator is stored in the memory array. The demodulator demodulates the modulated data retrieved from the memory array.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
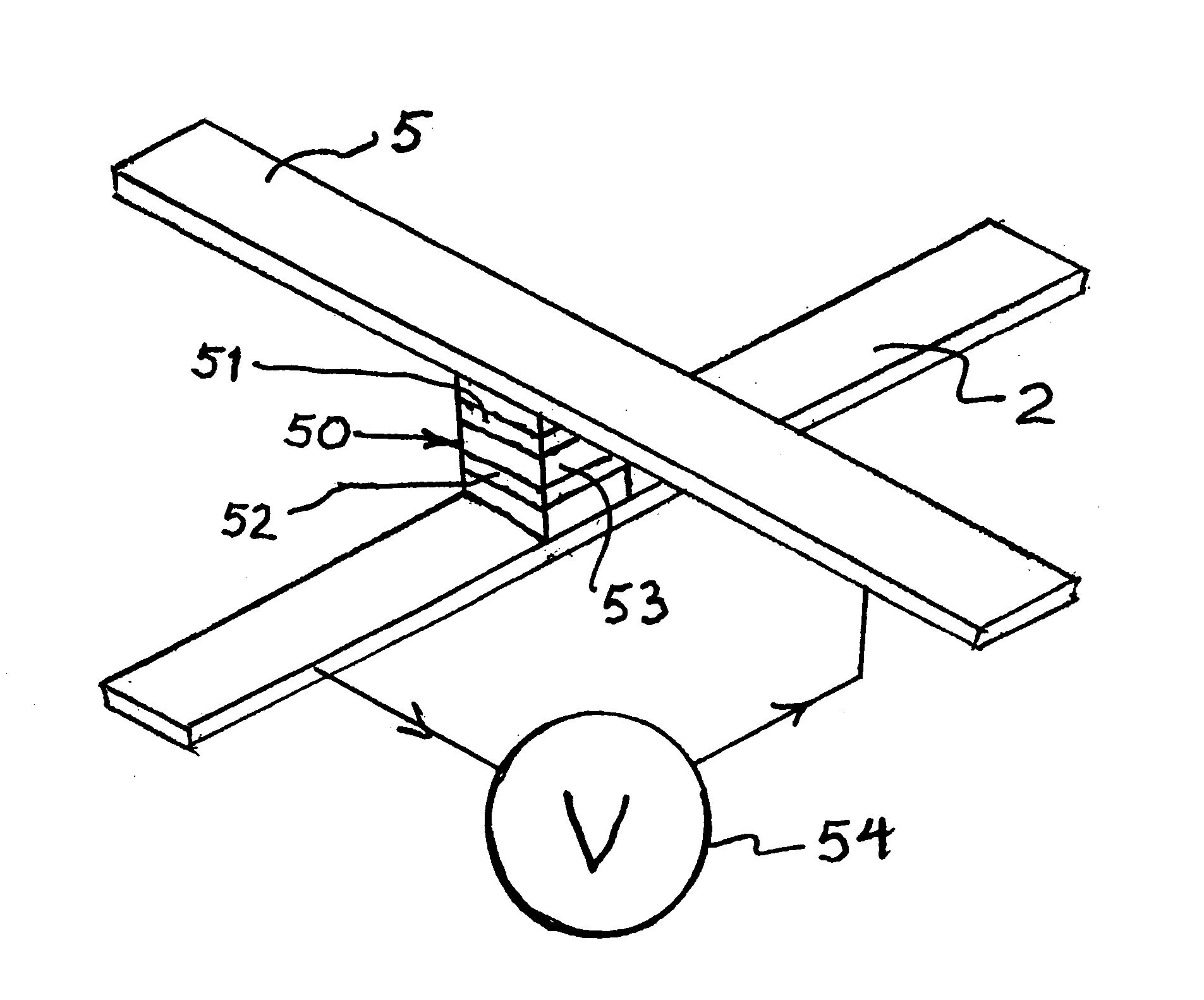
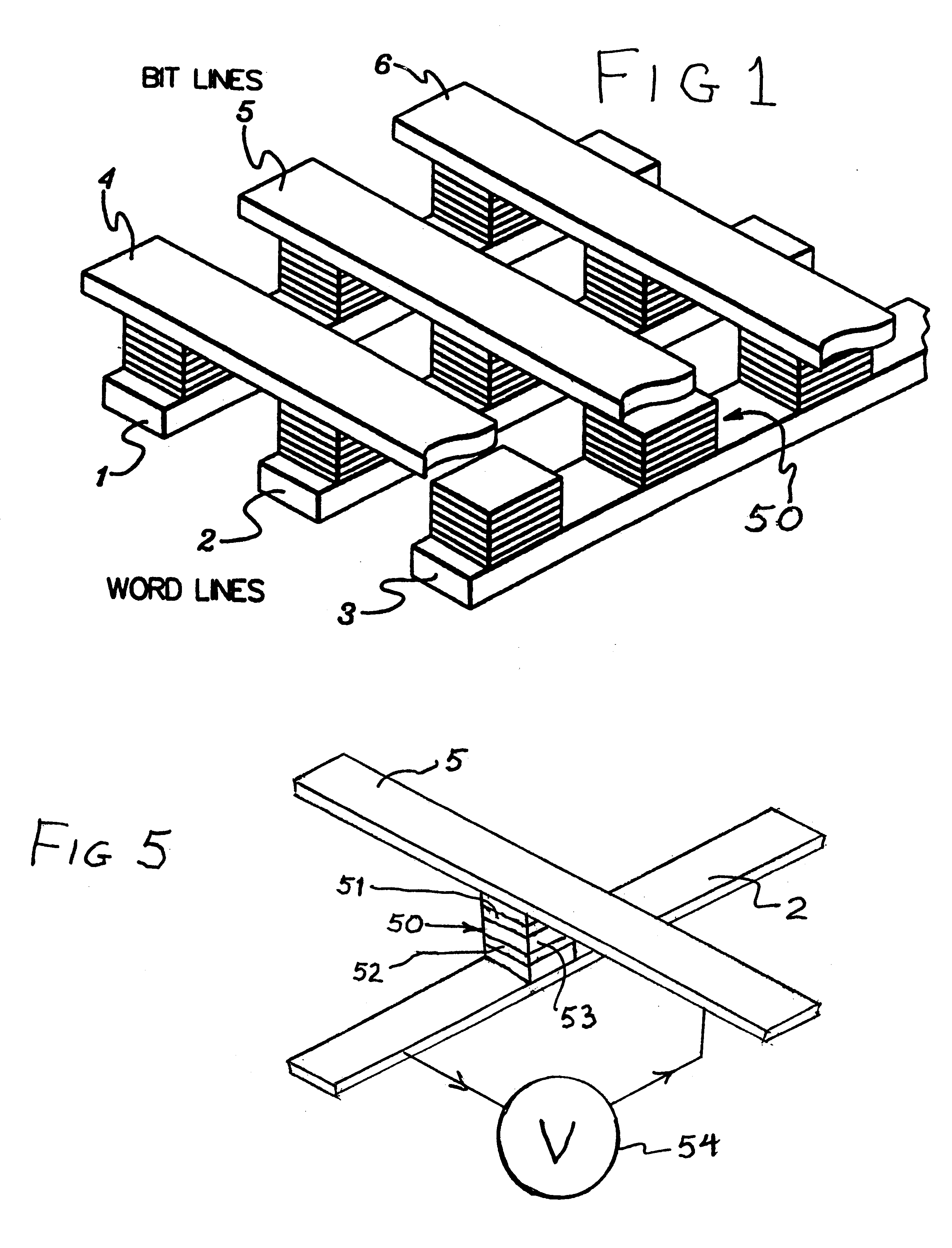
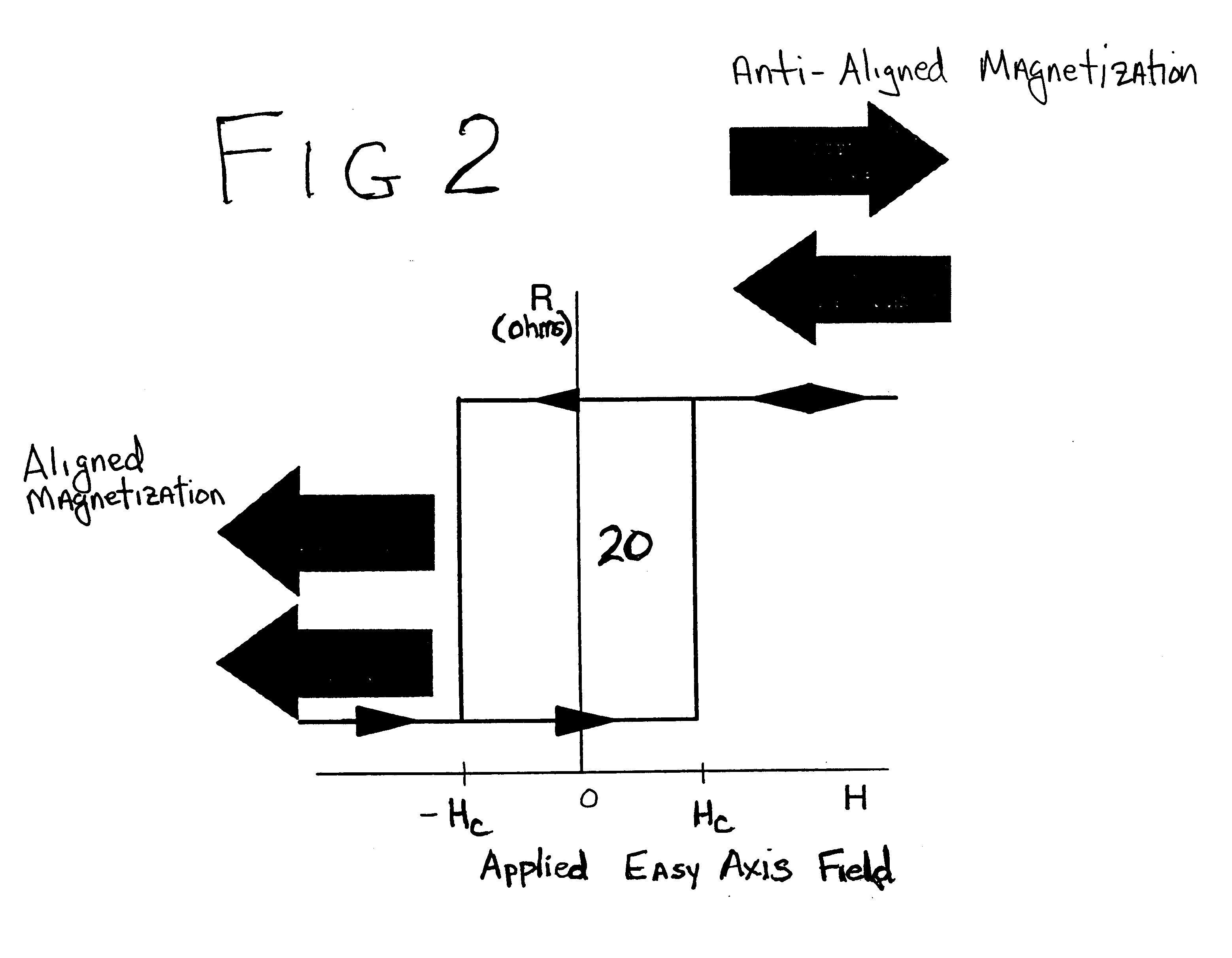
Thermally-assisted magnetic random access memory (MRAM)
It is important to ensure good selectivity of a single magnetic tunnel junction storage cell within a memory array without affecting nearby storage cells. For this purpose, this memory array of storage cells preferably comprises a) an array of electrically conducting bit lines and electrically conducting word lines which form intersections therebetween, b) a storage cell disposed at each of said intersections, each storage cell comprising at least one reversible magnetic region or layer characterized by a magnetization state which can be reversed by applying thereto a selected external magnetic field, said reversible magnetic layer comprising a material whose magnetization state is more easily reversed upon a change in the temperature thereof, and c) a temperature change generator for changing the temperature of said reversible magnetic layer of only a selected one of said array of storage cells at any moment. To select a cell, it is preferable to select a cell by using a brief pulse of tunnelling current between the intersecting bit and word lines at that cell in order to provide sufficient Joule heating to facilitate a change in the magnetization state of its reversible magnetic layer, which preferably comprises a ferrimagnetic material.
Owner:IBM CORP
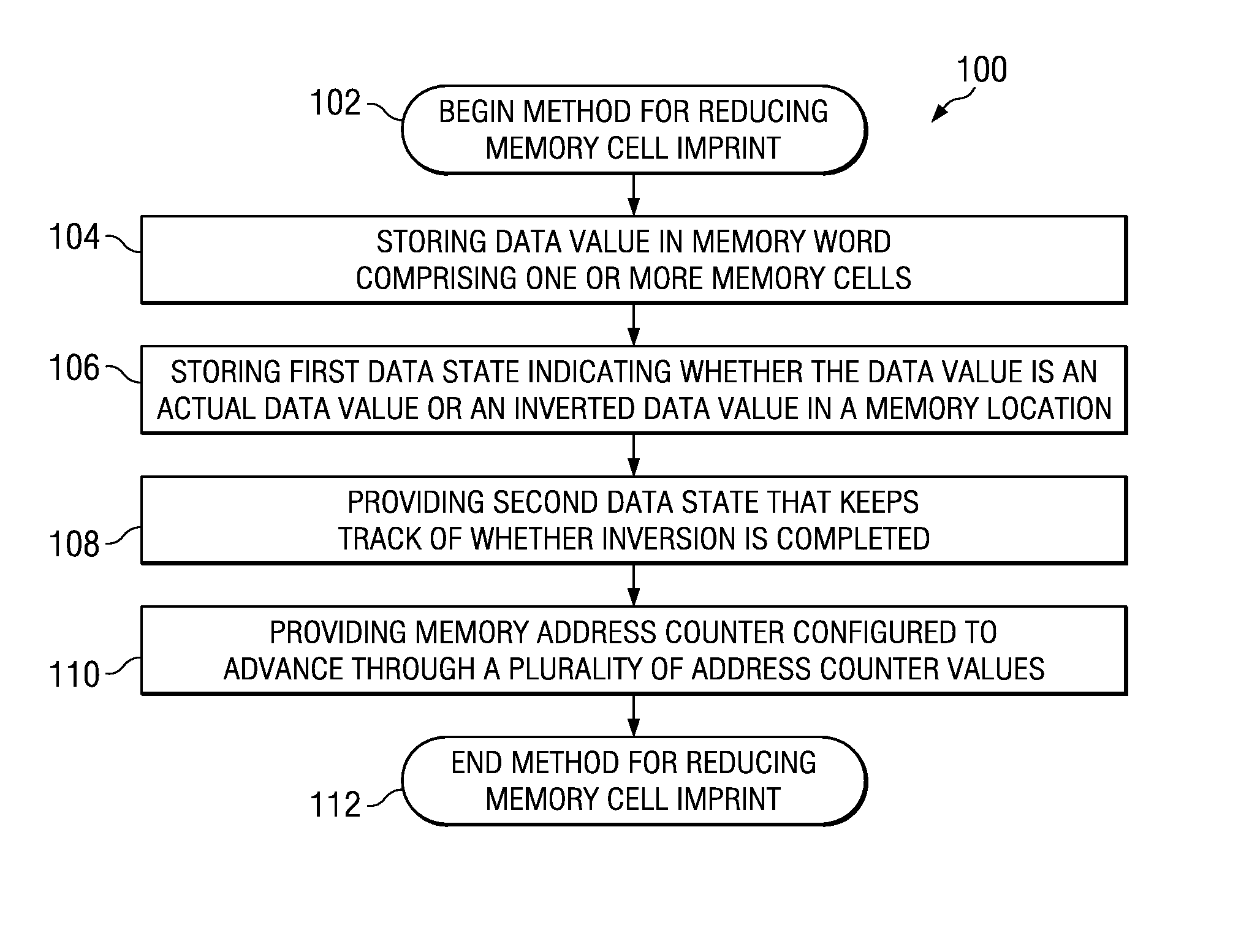
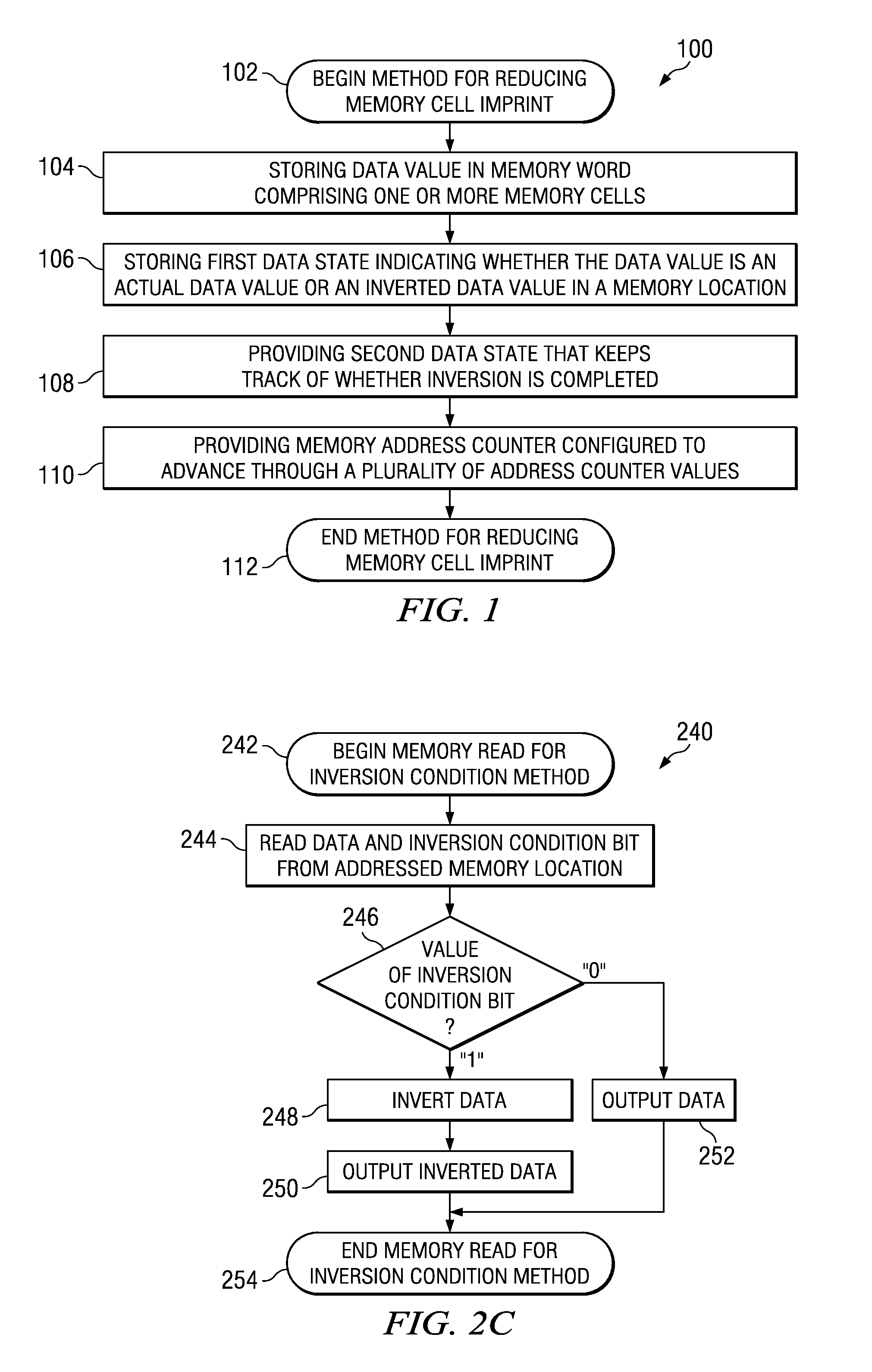
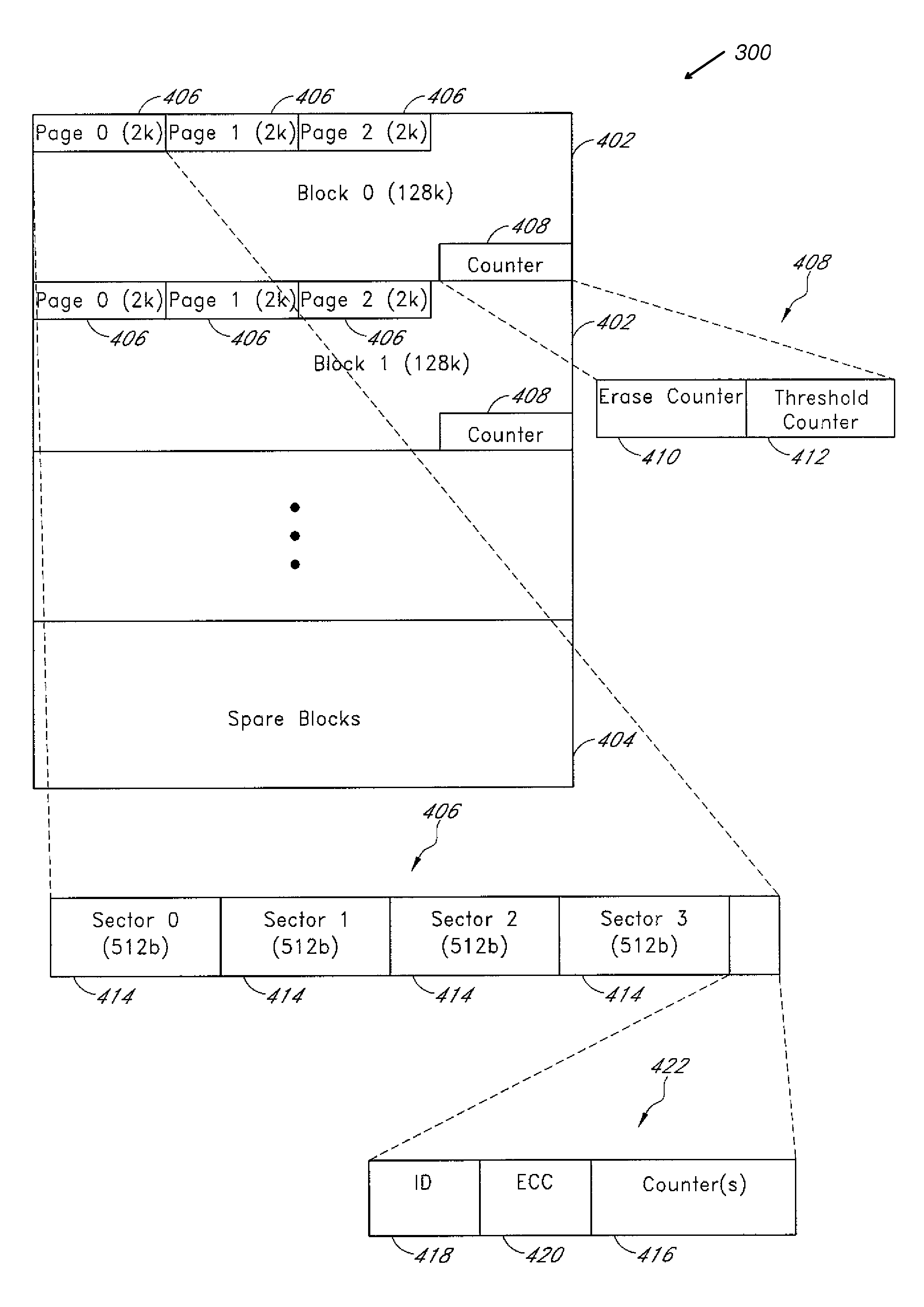
Technique for memory imprint reliability improvement
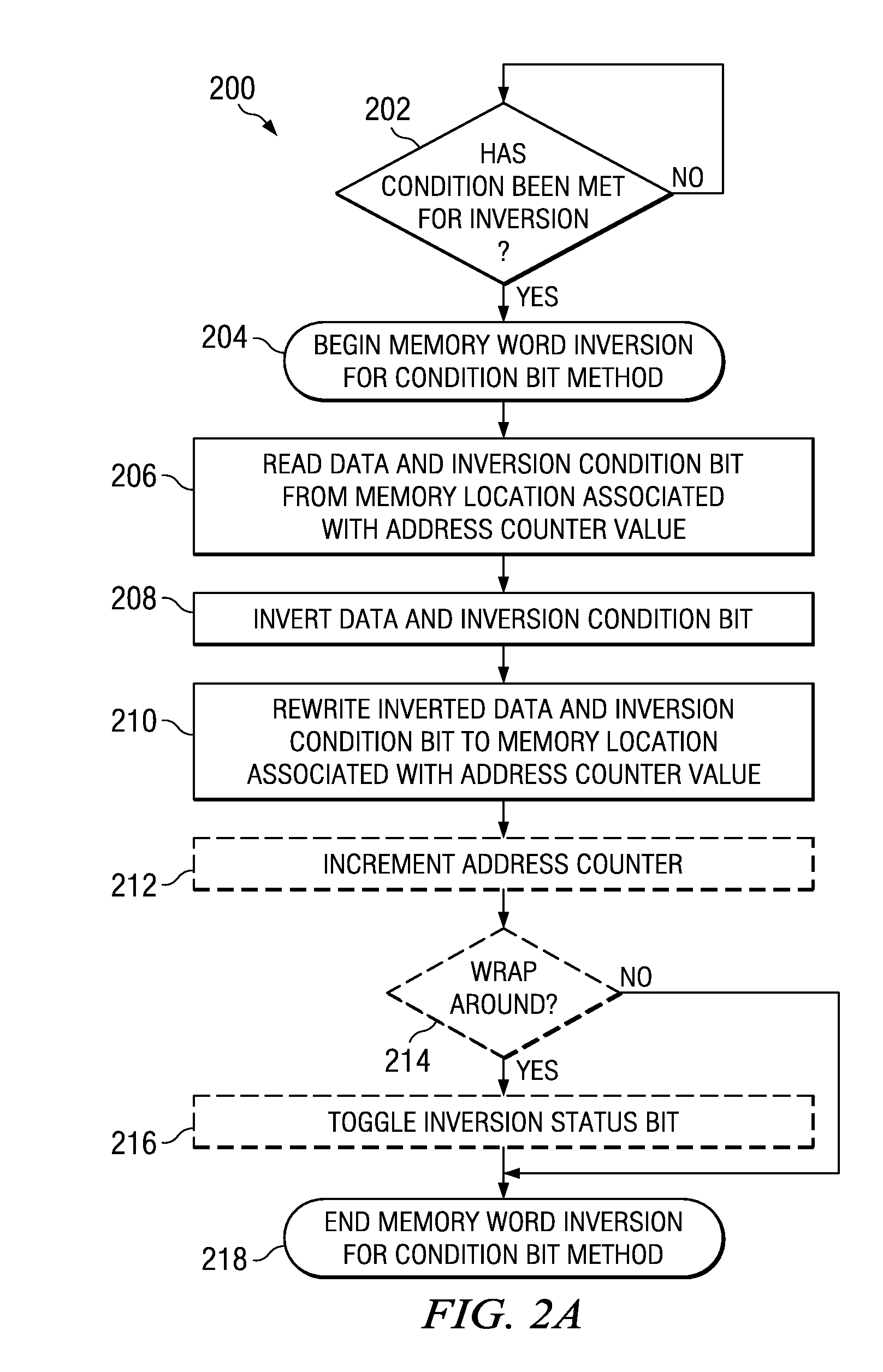
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of reducing imprint of a memory cell. The method comprises adding an inversion condition bit operably associated with one or more memory cells storing a memory word. The inversion condition bit indicates whether the memory word represents an actual payload or an inversion of the actual payload. The inversion condition bit and memory word are selectively toggled by a control circuitry. Inversion is performed by reading the inversion condition bit and memory word and rewriting the memory word back to the one or more memory cells in an inverted or non-inverted state, depending on an inversion condition bit. The inversion condition bit is then written to the inversion status bit value. The memory address is incremented, and the inversion status data state is toggled once the address counter addresses the entire memory array. Other methods and circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Integrated circuit including memory array incorporating multiple types of NAND string structures
ActiveUS7177191B2High densityGood flexibilitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDevice formParallel computing
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Charge sharing in a tcam array
A memory cell includes a storage capacitor, a read line, and a storage transistor, where the storage transistor is connected to the read line and is subject to activation by a charge in the storage capacitor. An in-memory processor includes a memory array which stores data, and an activation unit to activate at least two cells in a column of the memory array at generally the same time, thereby to generate a Boolean function output of the data of the at least two cells, wherein each of the at least two cells includes at least a storage capacitor, a storage transistor and a read line, where the storage transistor is connected to the read line and subject to activation by a charge in the storage capacitor.
Owner:GSI TECH
Flash memory storage system and method
ActiveUS20070061502A1Overcome disadvantagesEqually distributedMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesParallel computingStorage cell
A flash memory storage system includes a memory array containing a plurality of memory cells and a controller for controlling the flash memory array. The controller dedicates a first group of memory cells to operate with a first number of bits per cell and a second, separate group of memory cells to operate with a second number of bits per cell. A mechanism is provided to apply wear leveling techniques separately to the two groups of cells to evenly wear out the memory cells.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Electromechanical memory array using nanotube ribbons and method for making same
InactiveUS6919592B2Nanoelectromechanical switchesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringNanotube
Electromechanical circuits, such as memory cells, and methods for making same are disclosed. The circuits include a structure having electrically conductive traces and supports extending from a surface of the substrate, and nanotube ribbons suspended by the supports that cross the electrically conductive traces, wherein each ribbon comprises one or more nanotubes. The electro-mechanical circuit elements are made by providing a structure having electrically conductive traces and supports, in which the supports extend from a surface of the substrate. A layer of nanotubes is provided over the supports, and portions of the layer of nanotubes are selectively removed to form ribbons of nanotubes that cross the electrically conductive traces. Each ribbon includes one or more nanotubes.
Owner:NANTERO
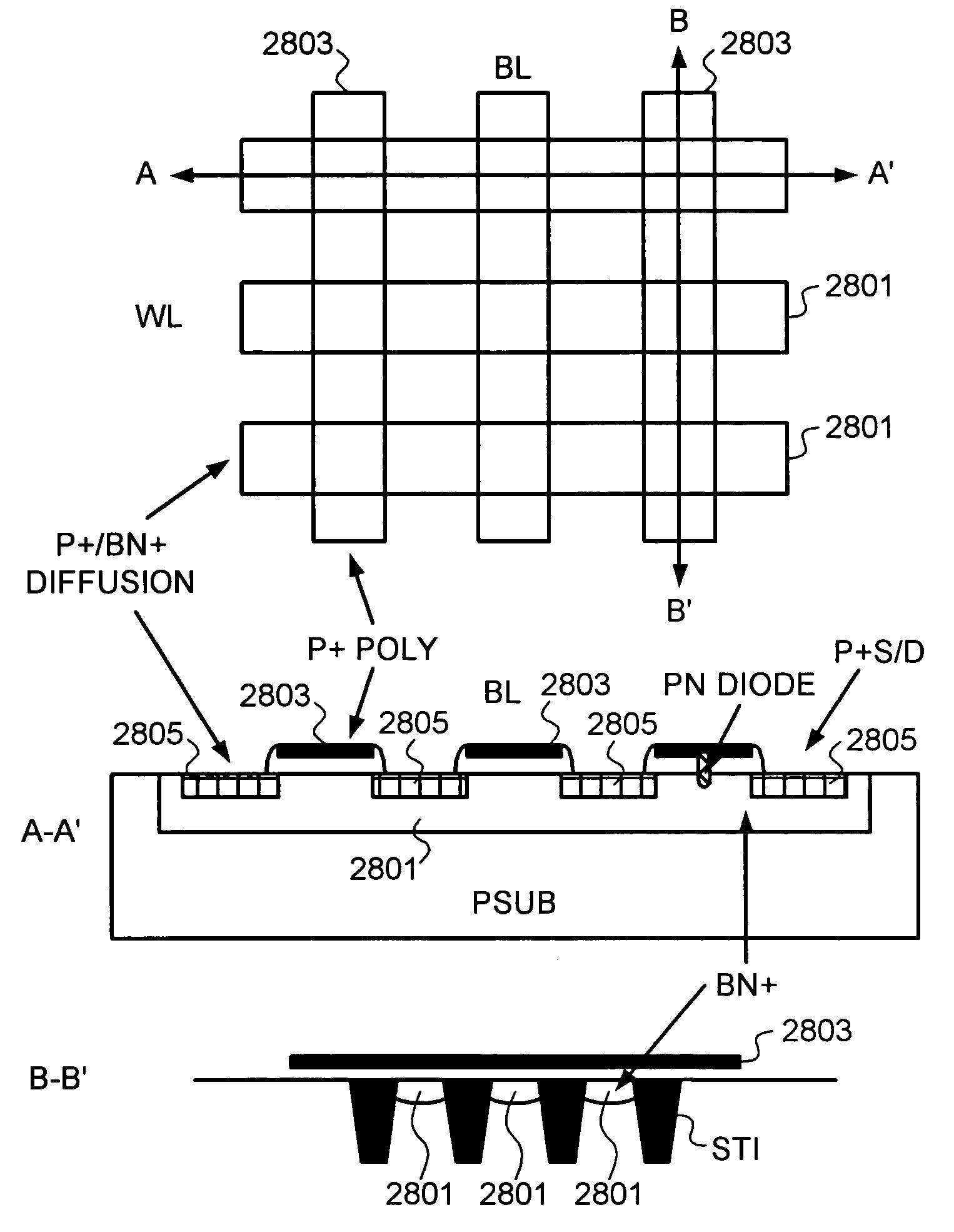
High density semiconductor memory cell and memory array using a single transistor and having counter-doped poly and buried diffusion wordline
A programmable memory cell comprised of a transistor located at the crosspoint of a column bitline and a row wordline is disclosed. The transistor has its gate formed from the column bitline and its source connected to the row wordline. The memory cell is programmed by applying a voltage potential between the column bitline and the row wordline to produce a programmed p+ region to form a p-n diode in the substrate underlying the gate of the transistor. Further, the wordline is formed from a buried diffusion N+ layer while the column bitline is formed from a counterdoped polysilicon layer.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Structure and method for biasing phase change memory array for reliable writing
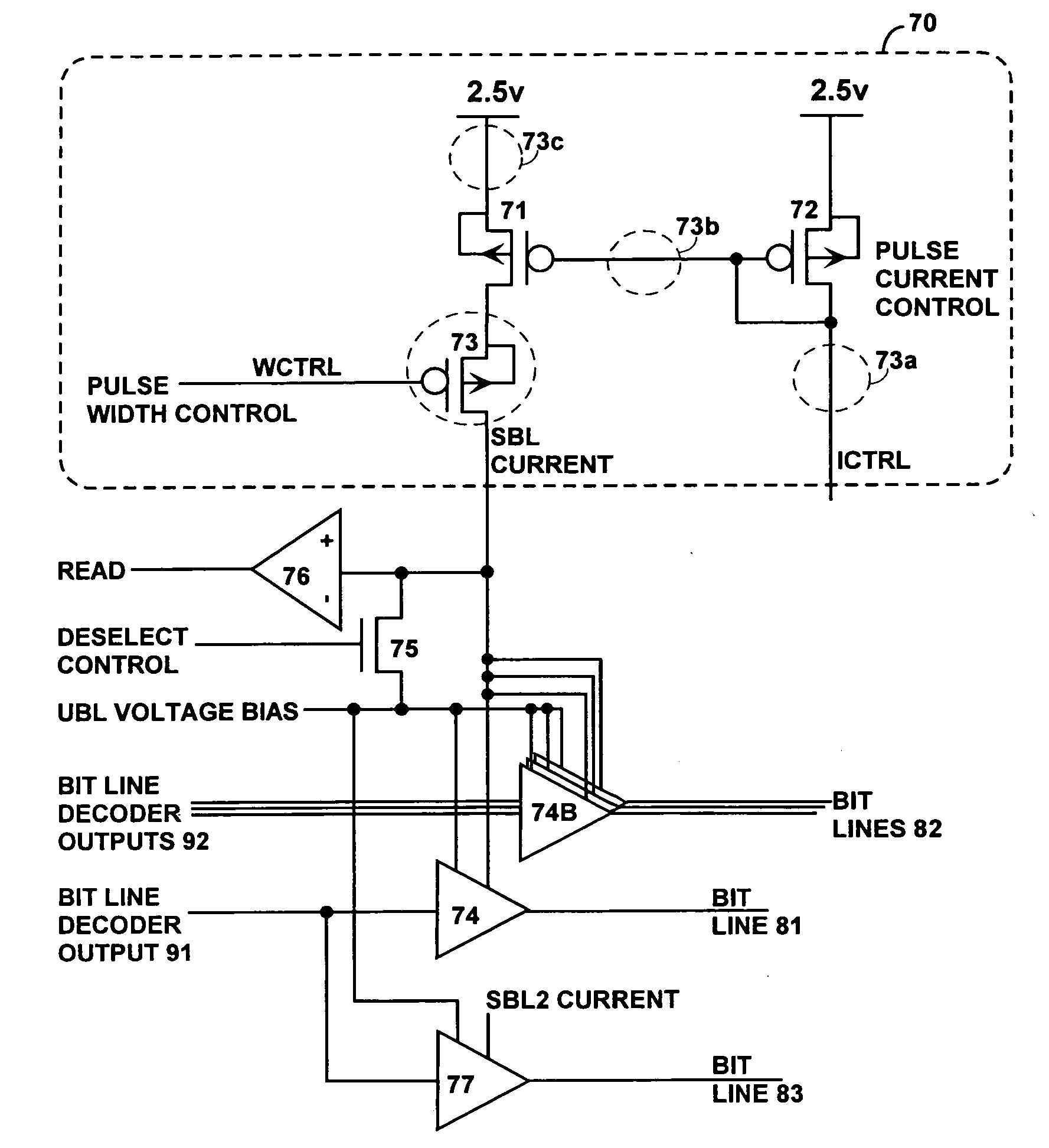
ActiveUS20060157679A1Minimize leakage currentReduce the possibilitySolid-state devicesDigital storageBit linePhase-change memory
A memory array having memory cells comprising a diode and a phase change material is reliably programmed by maintaining all unselected memory cells in a reverse biased state. Thus leakage is low and assurance is high that no unselected memory cells are disturbed. In order to avoid disturbing unselected memory cells during sequential writing, previously selected word and bit lines are brought to their unselected voltages before new bit lines and word lines are selected. A modified current mirror structure controls state switching of the phase change material.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Floating gate transistor with horizontal gate layers stacked next to vertical body
Vertical body transistors with adjacent horizontal gate layers are used to form a memory array in a high density flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM) or a logic array in a high density field programmable logic array (FPLA). The transistor is a field-effect transistor (FET) having an electrically isolated (floating) gate that controls electrical conduction between source regions and drain regions. If a particular floating gate is charged with stored electrons, then the transistor will not turn on and will provide an indication of the stored data at this location in the memory array within the EEPROM or will act as the absence of a transistor at this location in the logic array within the FPLA. The memory array or the logic array includes densely packed cells, each cell having a semiconductor pillar providing shared source and drain regions for two vertical body transistors that have control gates overlaying floating gates distributed on opposing sides of the semiconductor pillar. Both bulk semiconductor and silicon-on-insulator embodiments are provided. If a floating gate transistor is used to store a single bit of data or to represent a logic function, an area of only 2F<2 >is needed per respective bit of data or bit of logic, where F is the minimum lithographic feature size.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
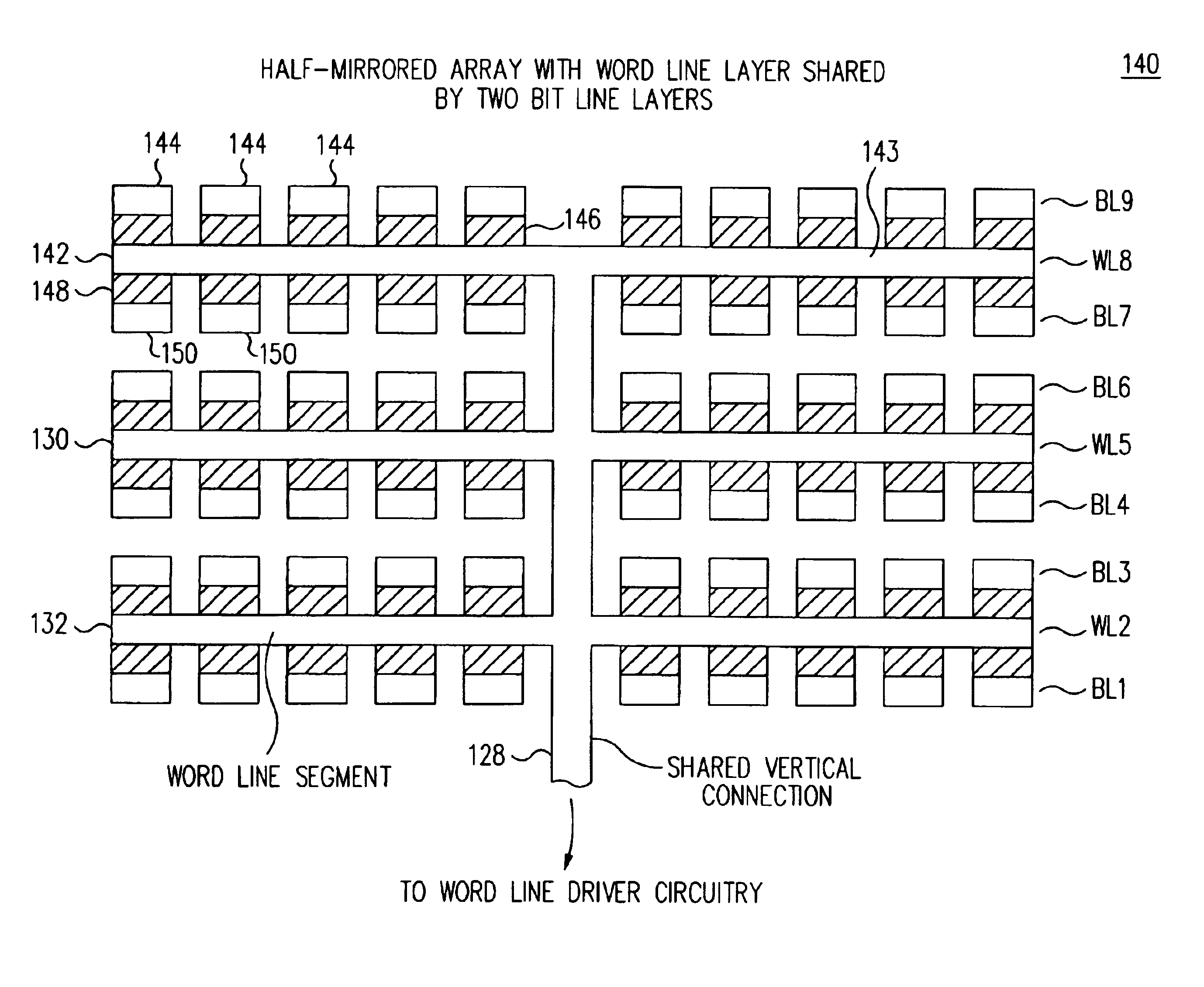
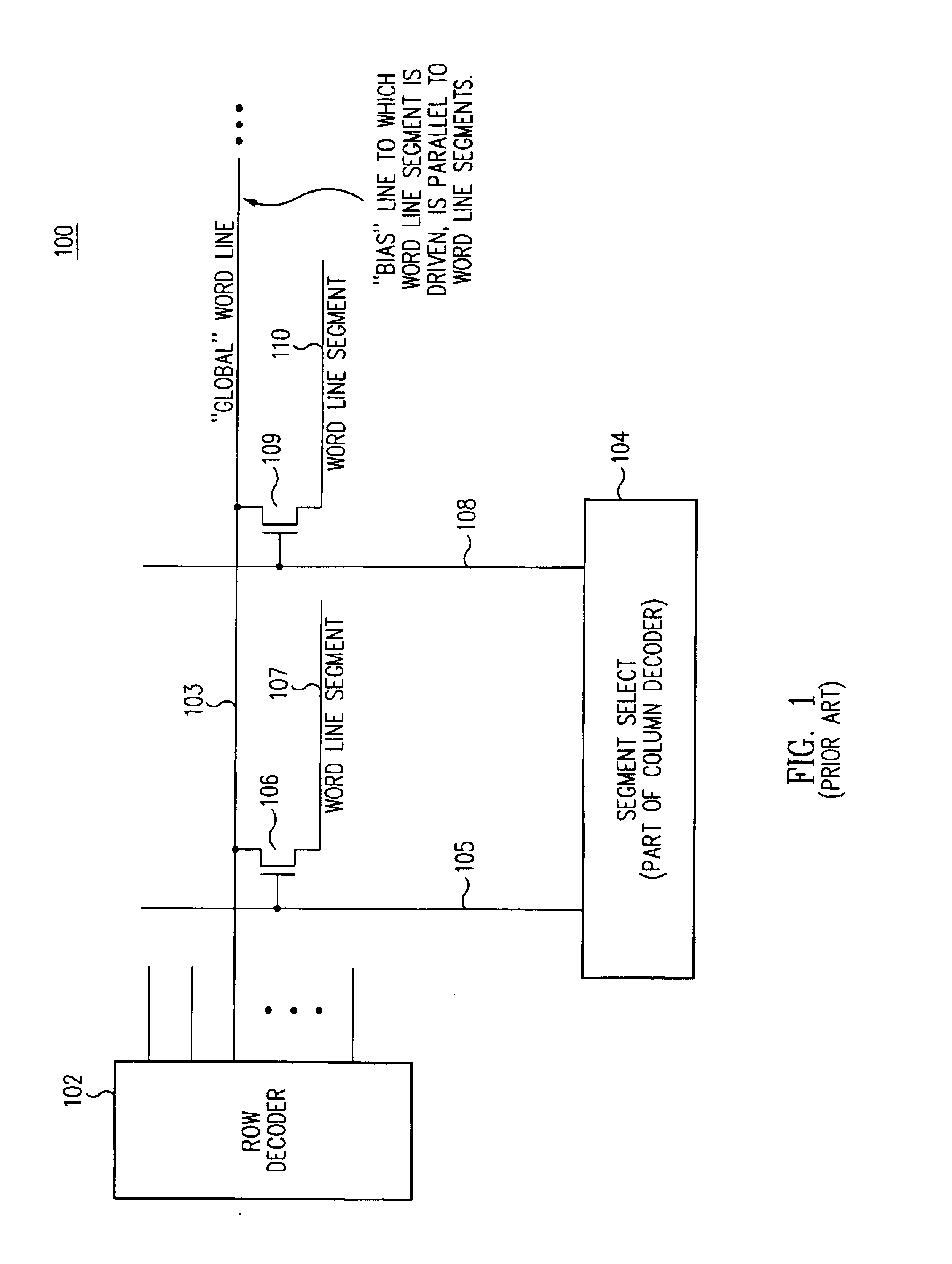
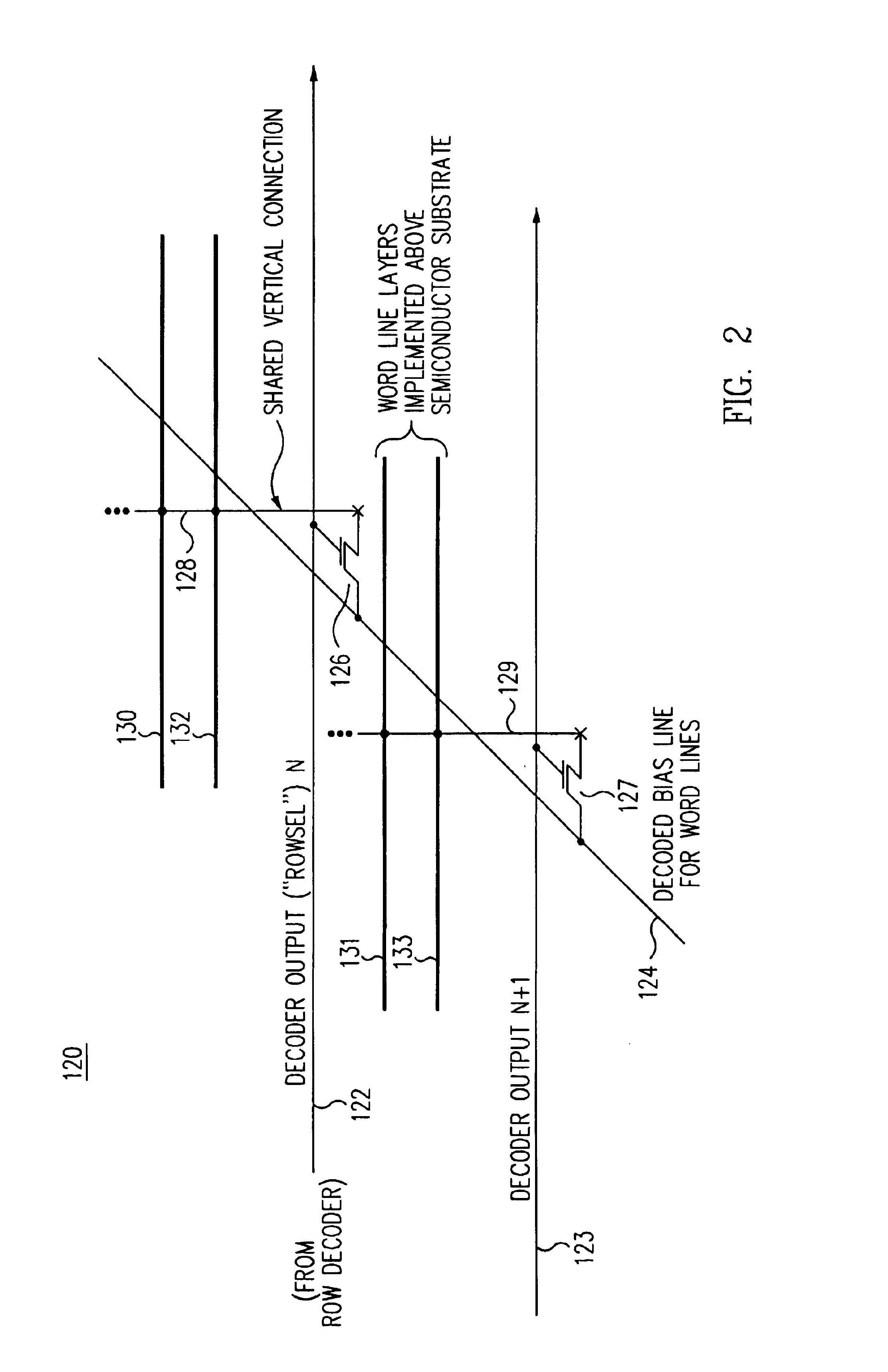
Word line arrangement having multi-layer word line segments for three-dimensional memory array
InactiveUS6879505B2Reduce stress timeDecreasing fan-outSolid-state devicesDigital storageDriver circuitLine driver
A three-dimensional (3D) passive element memory cell array provides short word lines while still maintaining a small support circuit area for efficiency. Short, low resistance word line segments on two or more word line layers are connected together in parallel to form a given word line without use of segment switch devices between the word line segments. A shared vertical connection preferably connects the word line segments together and connects to a word line driver circuit disposed generally below the array near the word line. Each word line driver circuit preferably couples its word line either to an associated one of a plurality of selected bias lines or to an unselected bias line associated with the driver circuit, which selected bias lines are themselves decoded to provide for an efficient multi-headed word line decoder.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
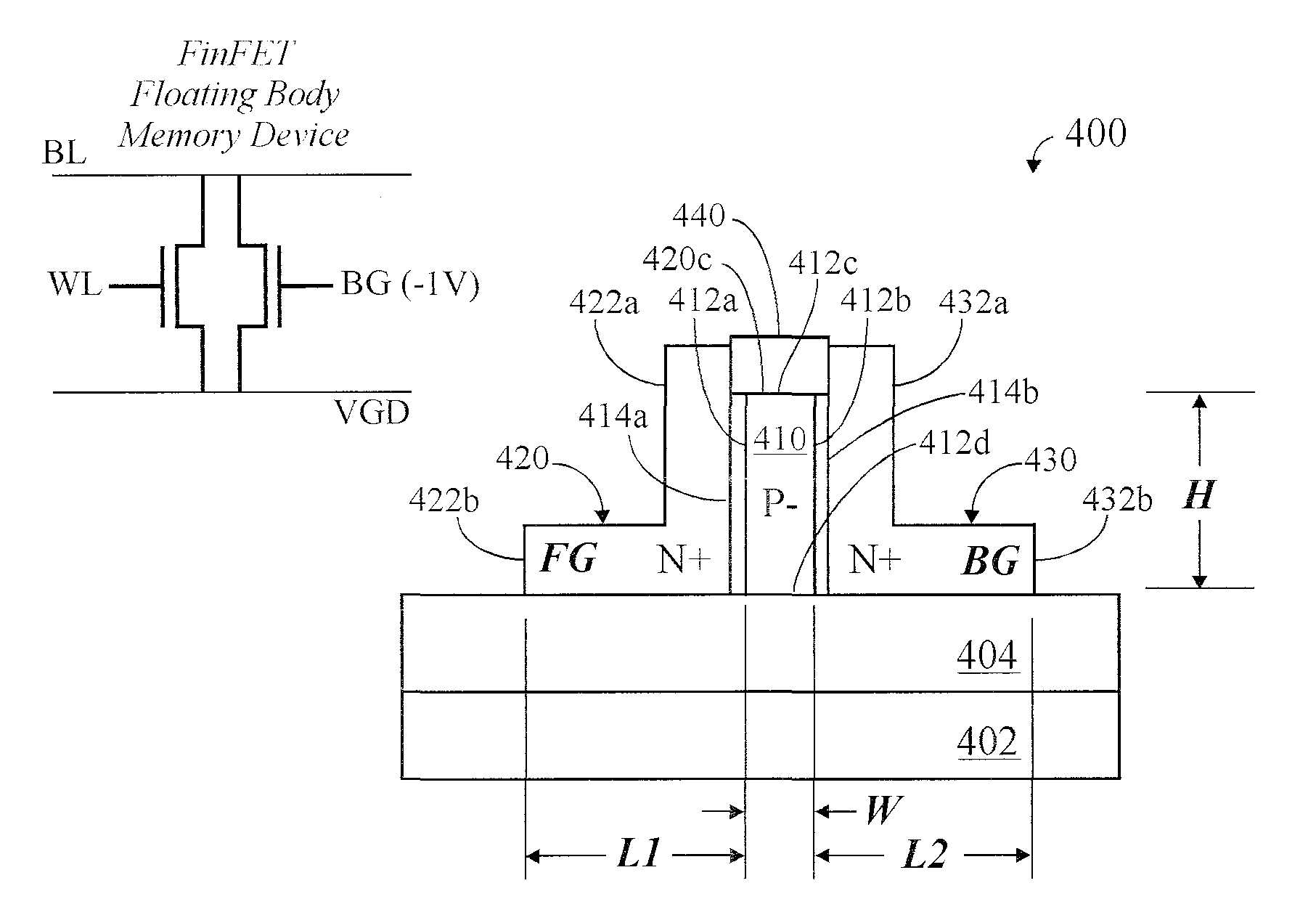
Finfet memory device with dual separate gates and method of operation
InactiveUS20090108351A1Conductivity alteredEnlarging and constricting channelTransistorSolid-state devicesVolatile memoryMemory array
A FinFET device comprises a front gate (FG) and a separate back gate (BG) disposed on opposite sides of the fine. The fin structure may act as a floating body of a volatile memory cell. The front and back gates may be doped with the same or opposite polarity, and may be biased oppositely. A plurality of FinFETs may be connected in a memory array with single column erase, or double column erase capability.
Owner:IBM CORP
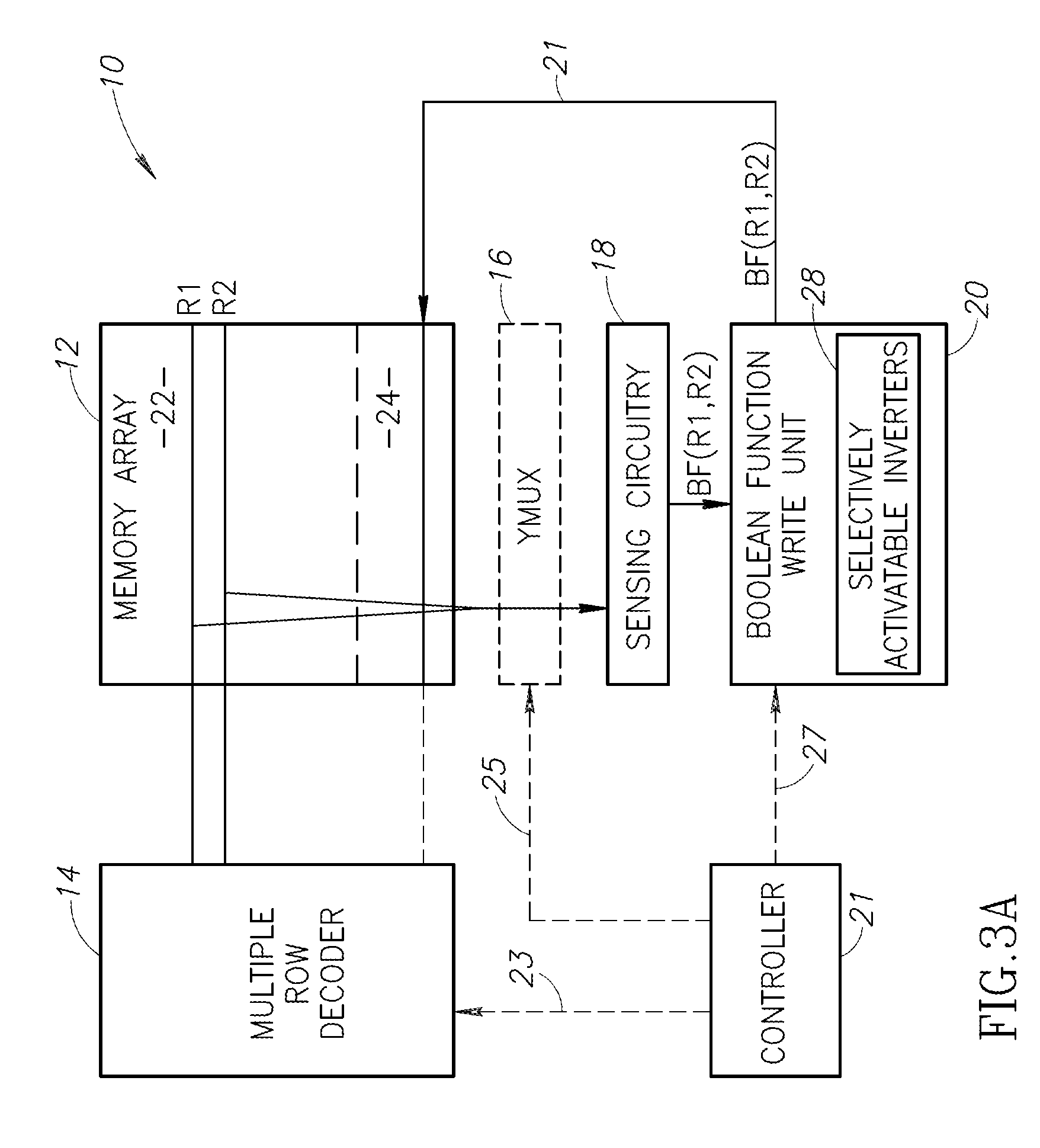
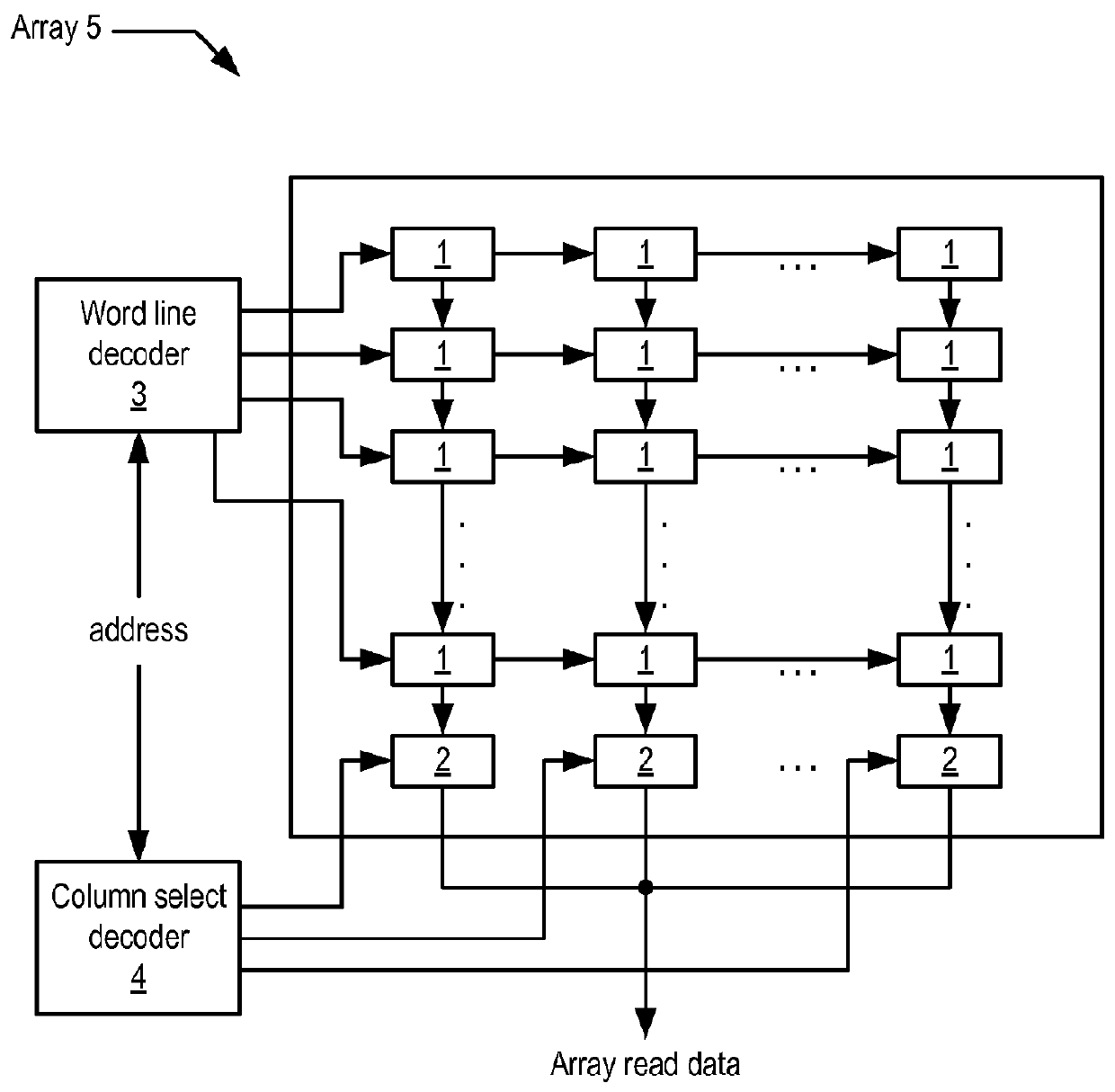
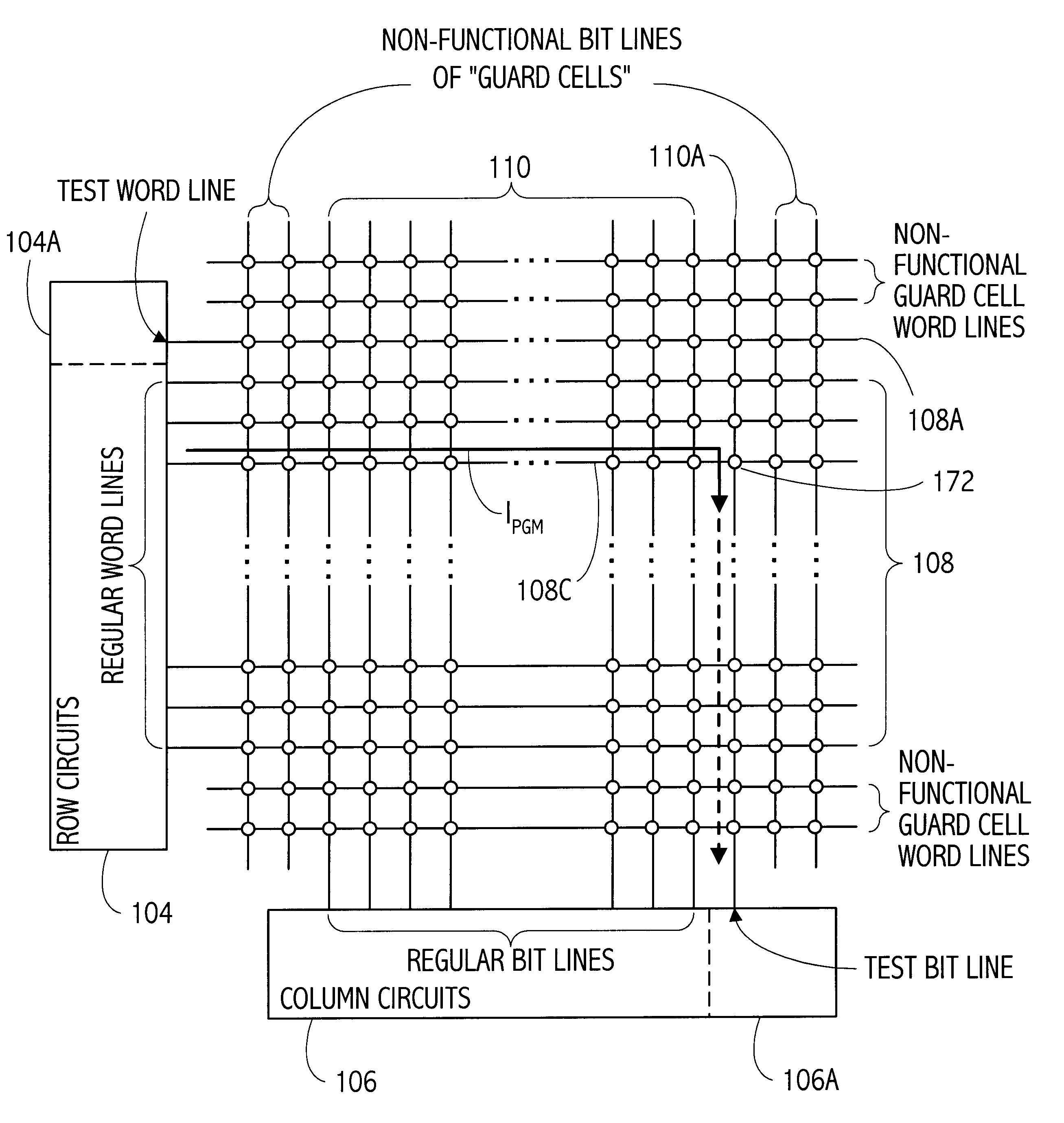
Memory array organization and related test method particularly well suited for integrated circuits having write-once memory arrays
In a preferred integrated circuit embodiment, a write-once memory array includes at least one test bit line which provides a respective test memory cell at the far end of each respective word line relative to its word line driver, and further includes at least one test word line which provides a respective test memory cell at the far end of each respective bit line relative to its bit line driver. An intra-layer short between word lines may be detected, such as during manufacturing testing, by biasing adjacent word lines to different voltages and detecting whether any leakage current flowing from one to another exceeds that normally accounted for by the memory cells and other known circuits. Intra-layer bit line shorts and inter-layer word line and bit line shorts may also be similarly detected. An "open" in a word line or bit line may be detected by trying to program the test memory cell at the far end of each such word line or bit line. If successfully programmed, the continuity of each word line and bit line is assured, and the programming circuitry for each word line and bit line is also known to be functional.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
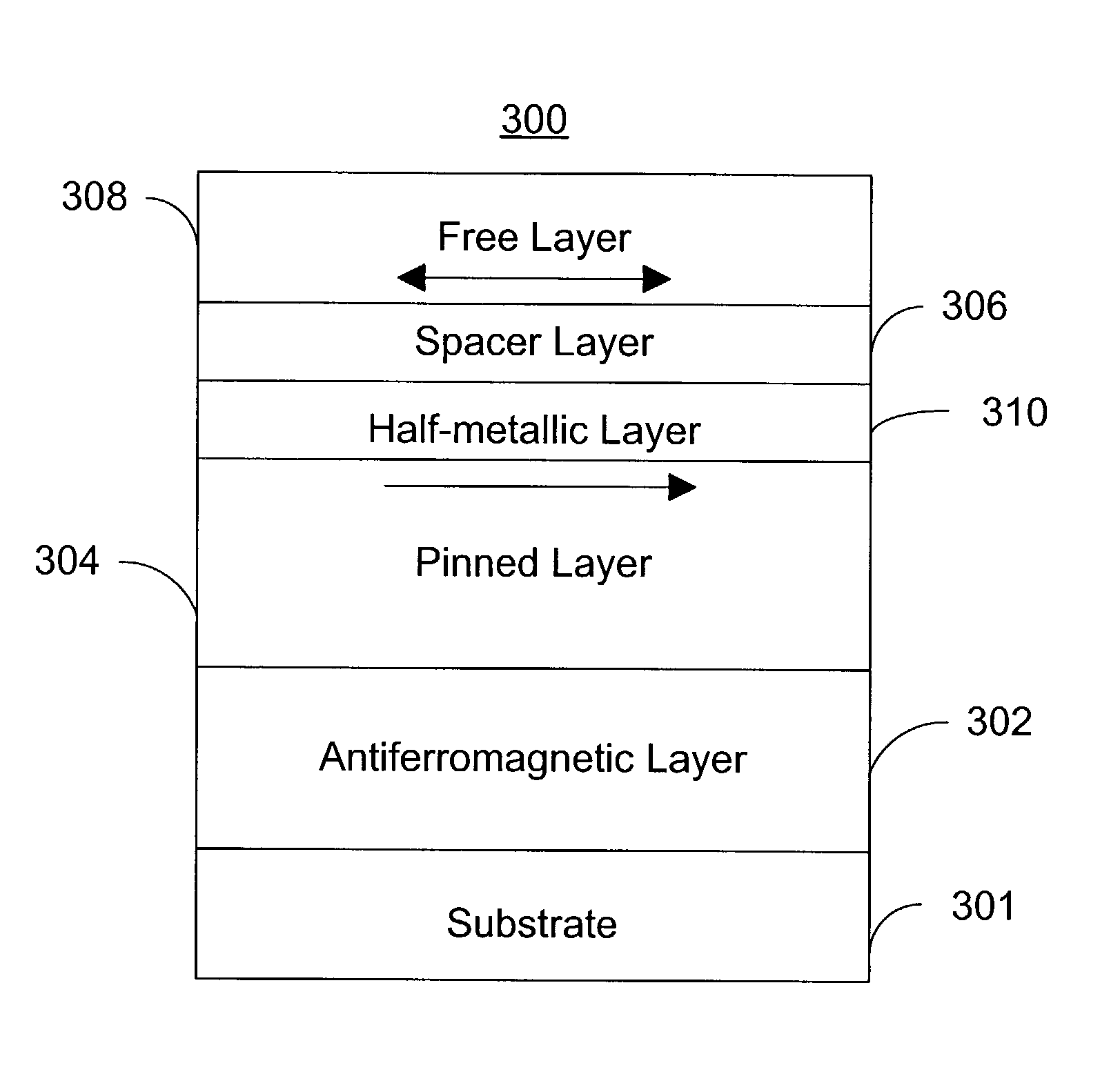
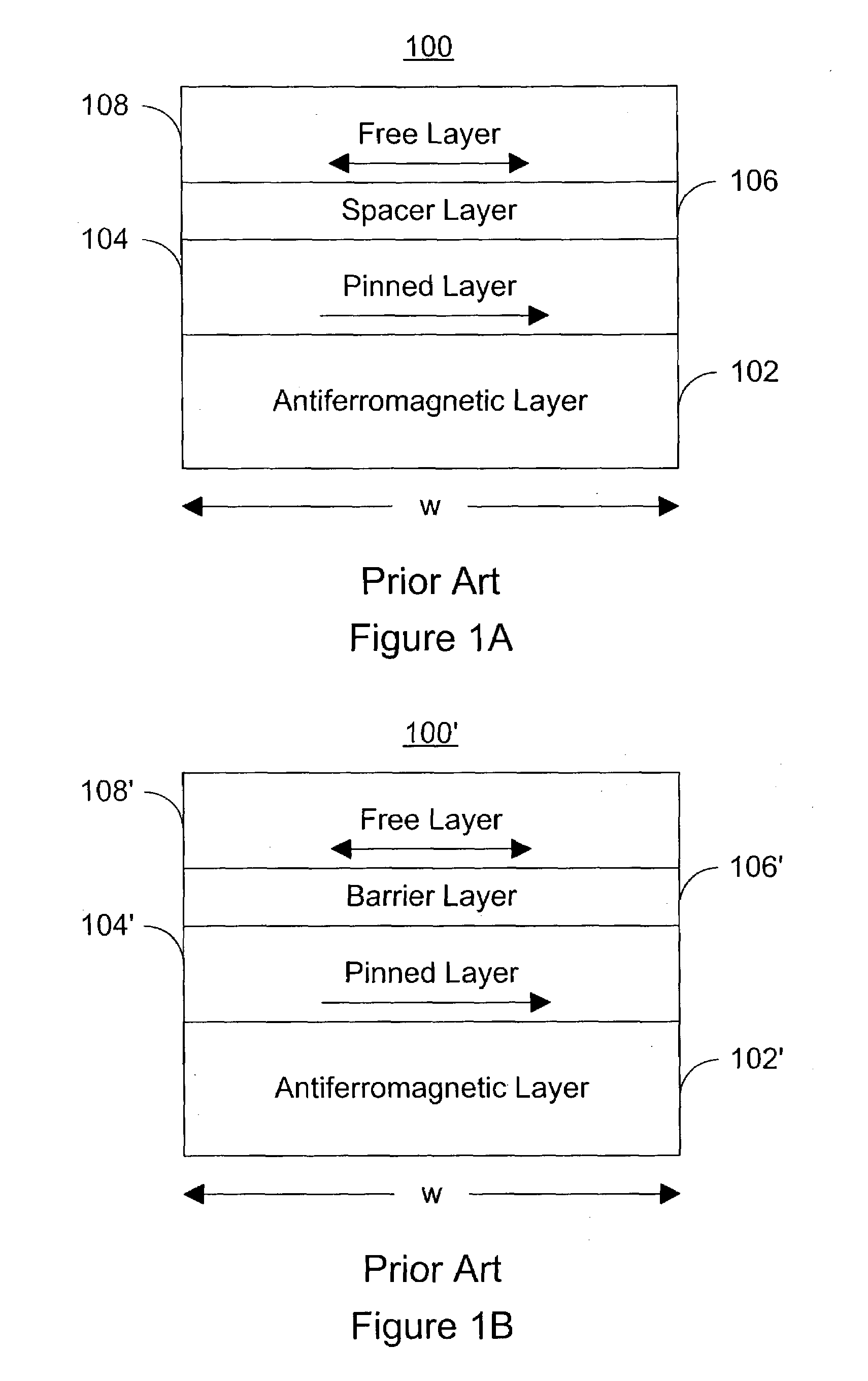
Magnetic element utilizing spin-transfer and half-metals and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6958927B1Reduce high switching currentReduce power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityHalf-metal
A magnetic element that can be used in a memory array having high density includes a pinned layer, a half-metallic material layer, a spacer (or a barrier) layer and a free layer. The half-metallic material layer is formed on the pinned layer and preferably has a thickness that is less than about 100 Å. The half-metallic material layer can be formed to be a continuous layer or a discontinuous on the pinned layer. The spacer (or barrier) layer is formed on the half-metallic material layer, such that the spacer (or barrier) layer is nonmagnetic and conductive (or insulating). The free layer is formed on the spacer (or barrier) layer and has a second magnetization that changes direction based on the spin-transfer effect when a write current passes through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
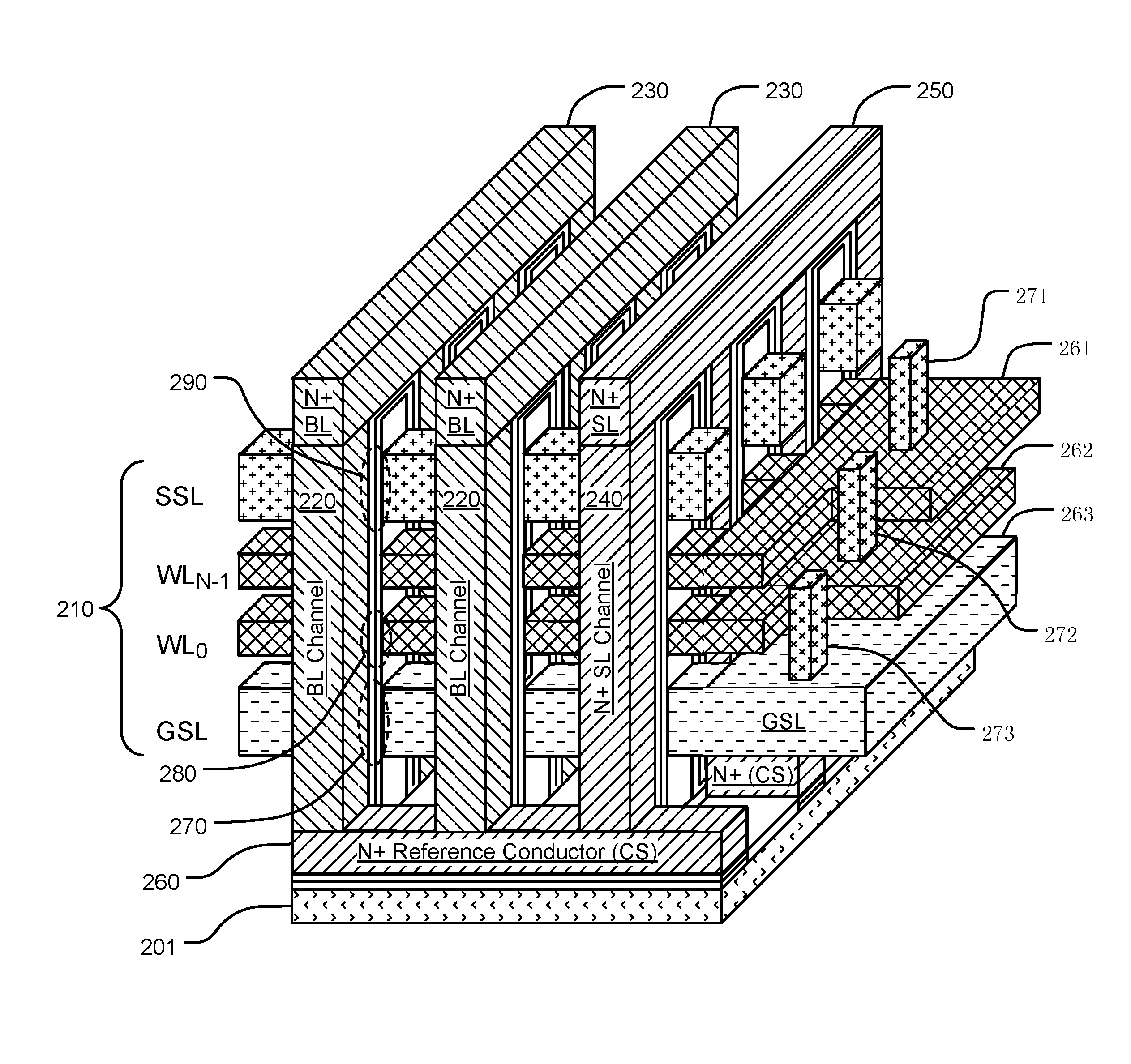
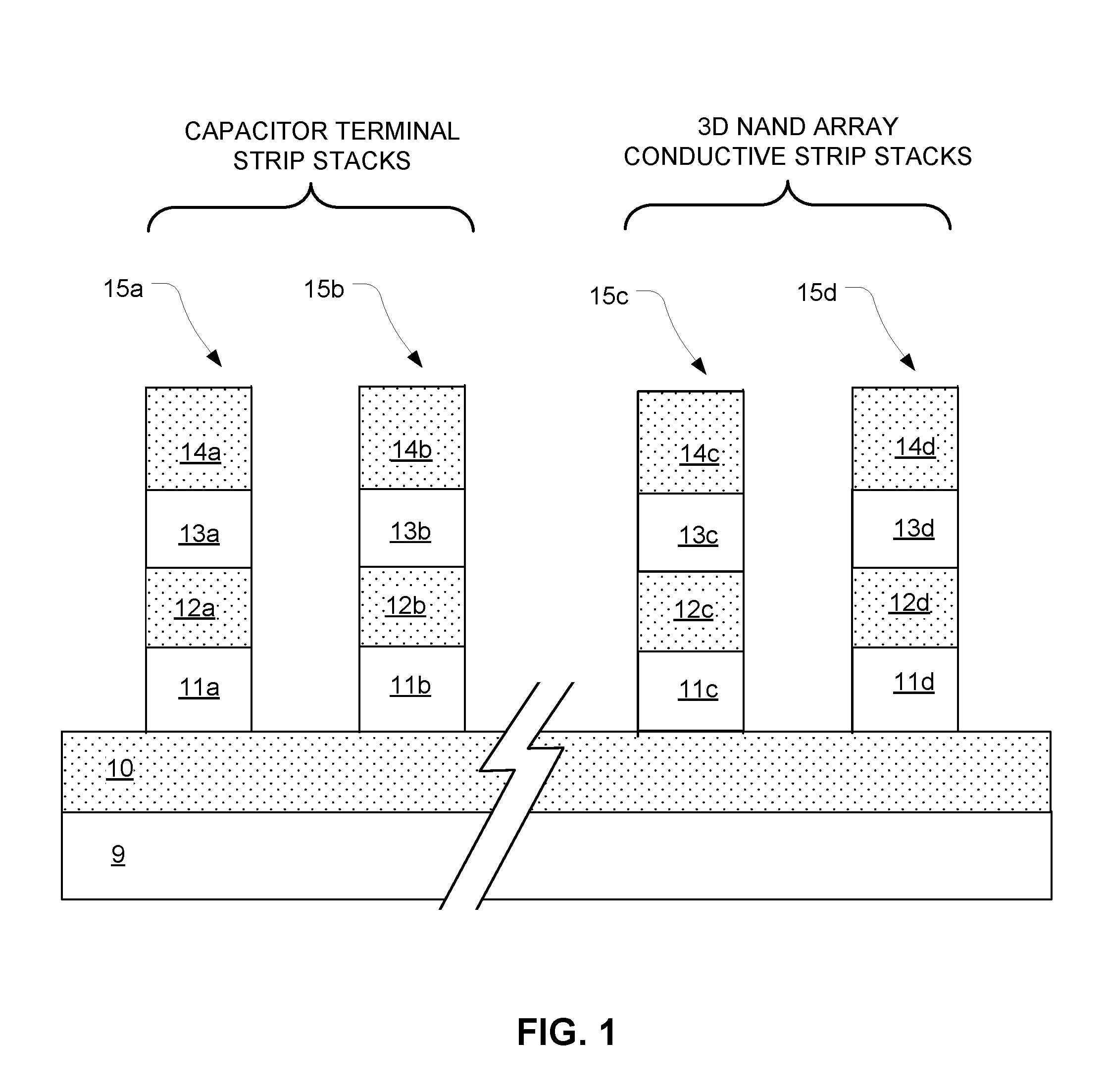
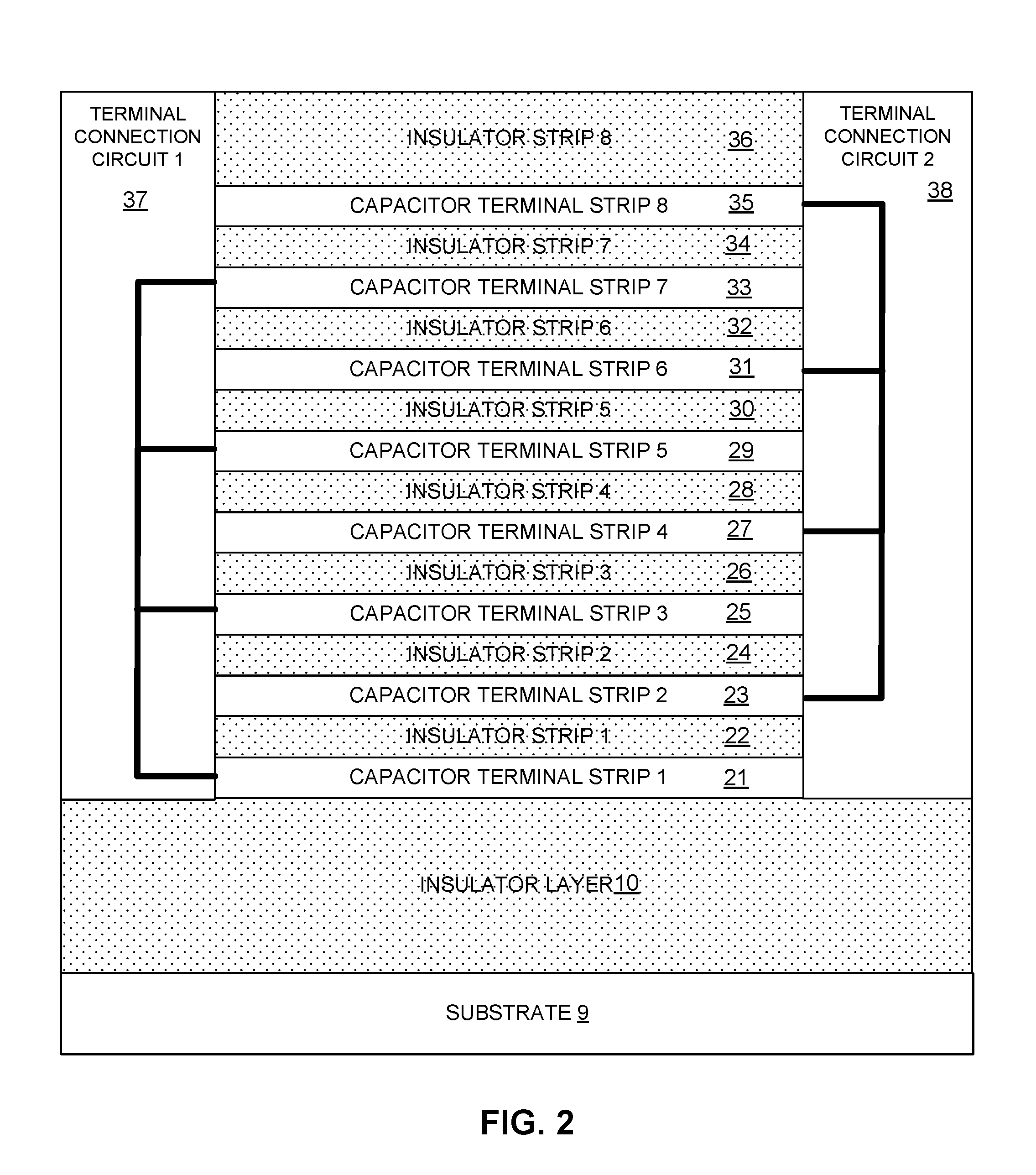
Capacitor With 3D NAND Memory
An integrated circuit includes a 3D NAND memory array with a stack of conductive strips and a capacitor with a stack of capacitor terminal strips. Multiple conductive strips in the stack of conductive strips, and multiple capacitor terminal strips of the stack of capacitor terminal strips, share a same plurality of plane positions relative to the substrate. Different plane positions in the same plurality of plane positions characterize different capacitor terminal strips in the stack of capacitor terminal strips and different conductive strips in the stack of conductive strips, and a same plane position characterizing both a conductive strip in the stack of conductive strips and a capacitor terminal strip in the stack of capacitor terminal strips indicates that the conductive strip and the capacitor terminal strip have a same vertical position relative to each other.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
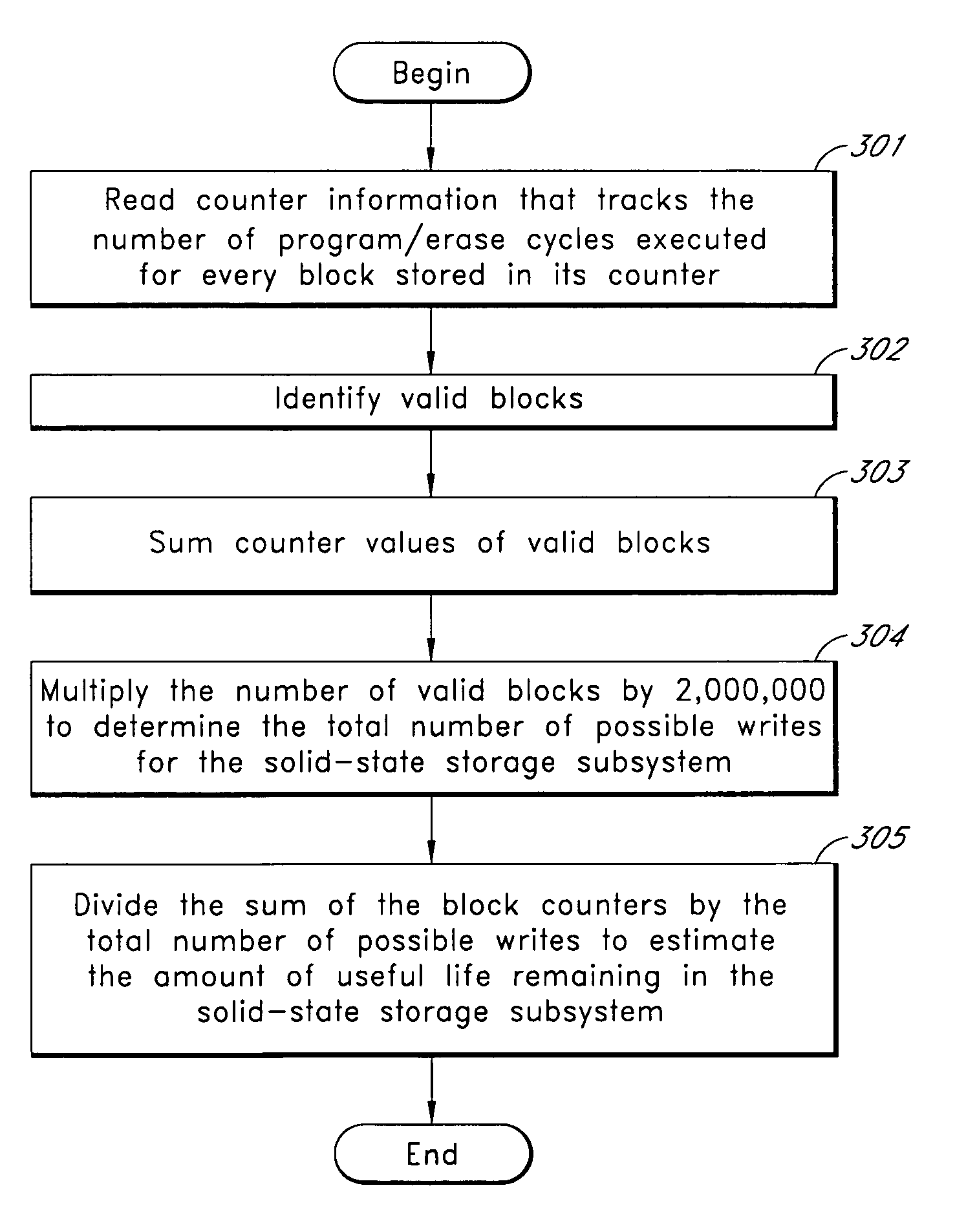
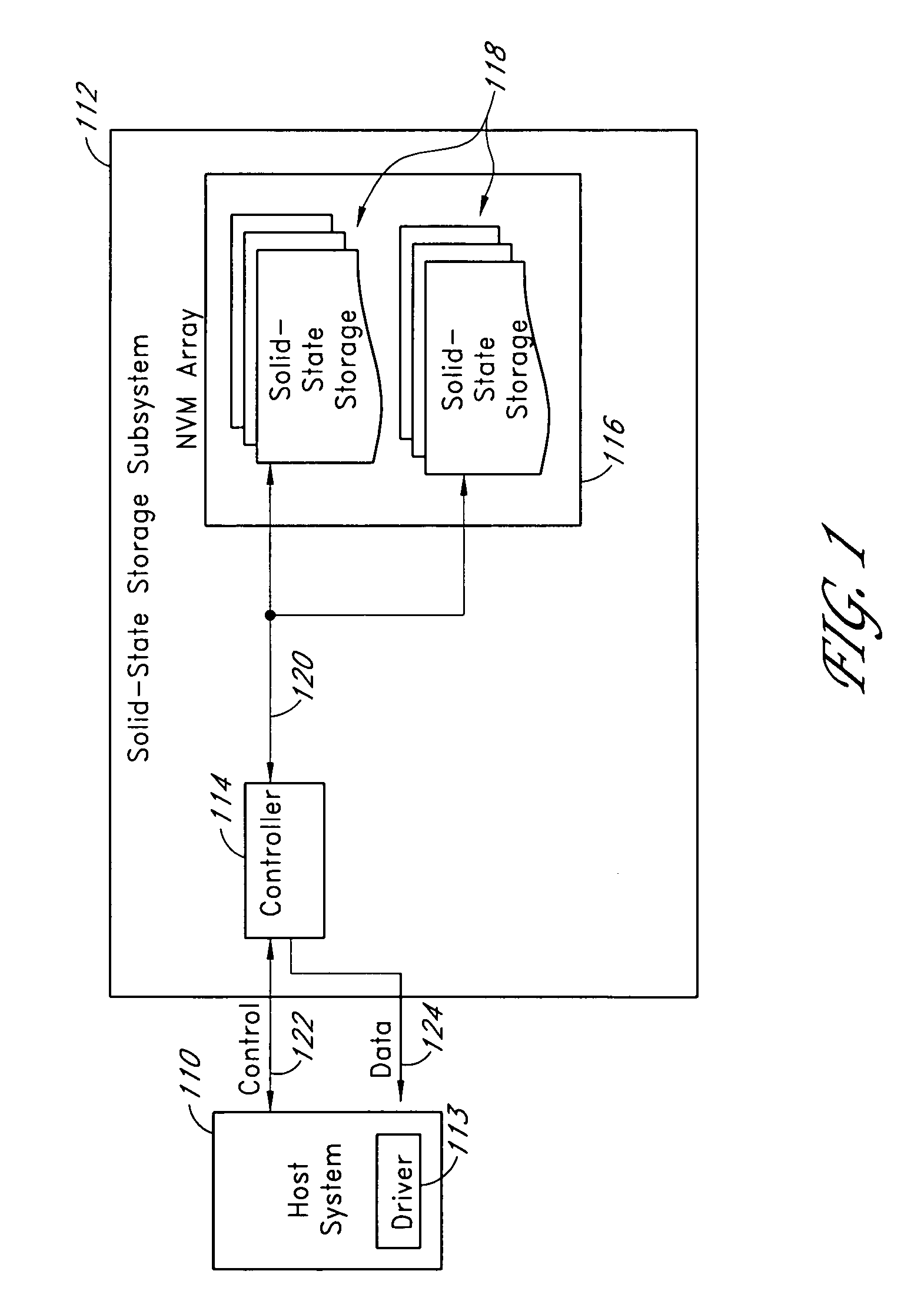
Systems and methods for measuring the useful life of solid-state storage devices
ActiveUS20070260811A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesSolid-state storageSystem maintenance
A non-volatile solid-state storage subsystem, such as a non-volatile memory device, maintains usage statistics reflective of the wear state, and thus the remaining useful life, of the subsystem's memory array. A host system reads the usage statistics information, or data derived therefrom, from the subsystem to evaluate the subsystem's remaining life expectancy. The host system may use this information for various purposes, such as to (a) display or report information regarding the remaining life of the subsystem; (b) adjust the frequency with which data is written to the subsystem; and / or (c) select the type(s) of data written to the subsystem.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
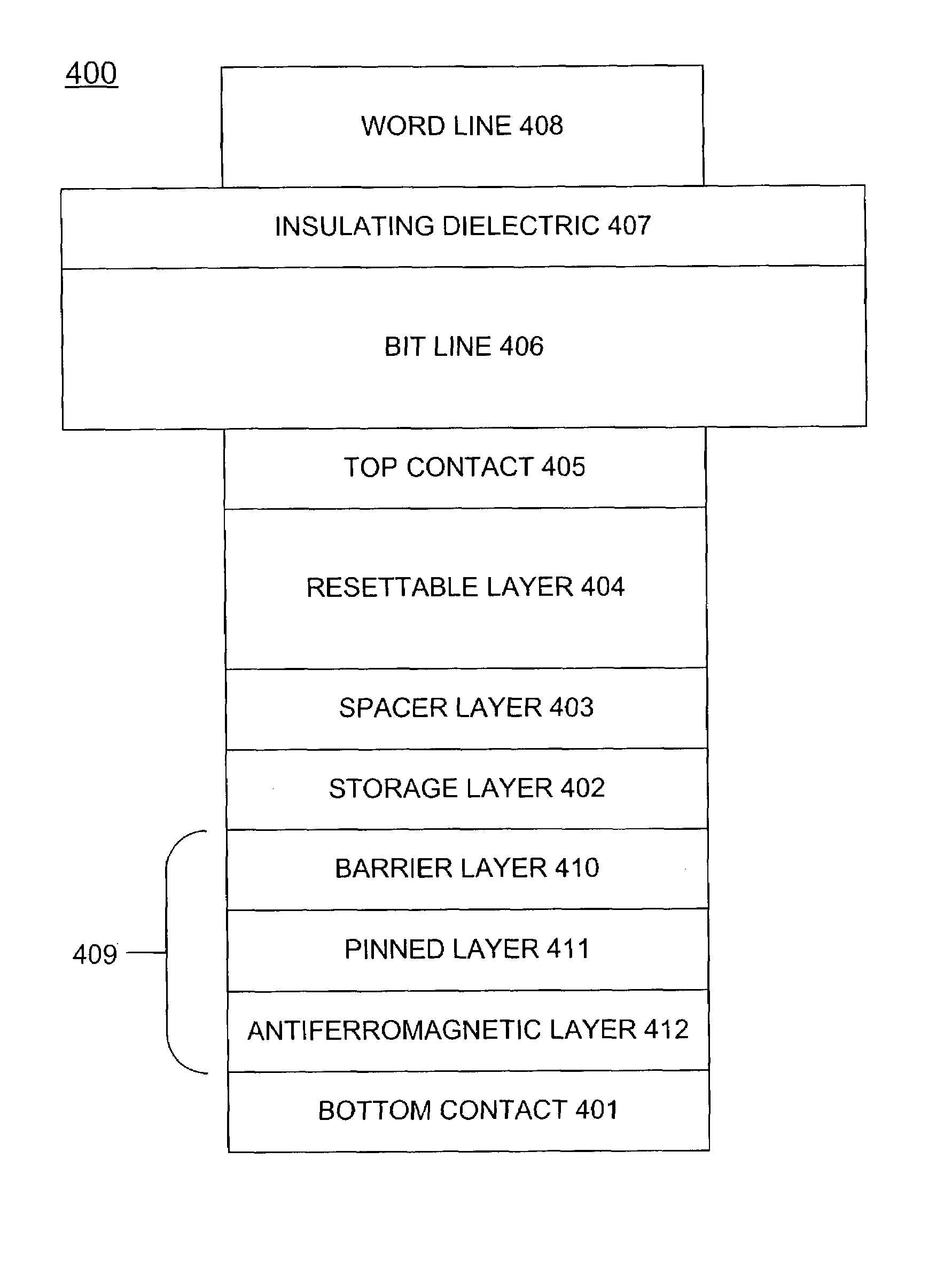
Spin-transfer multilayer stack containing magnetic layers with resettable magnetization
InactiveUS7190611B2Minimizing densityReduce process complexityGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesHigh densitySpin transfer
A magnetic element for a high-density memory array includes a resettable layer and a storage layer. The resettable layer has a magnetization that is set in a selected direction by at least one externally generated magnetic field. The storage layer has at least one magnetic easy axis and a magnetization that changes direction based on the spin-transfer effect when a write current passes through the magnetic element. An alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure formed from a tunneling barrier layer, a pinned magnetic layer and an antiferromagnetic layer that pins the magnetization of the pinned layer in a predetermined direction. Another alternative embodiment of the magnetic element includes an additional multilayer structure that is formed from a tunneling barrier layer and a second resettable layer having a magnetic moment that is different from the magnetic moment of the resettable layer of the basic embodiment.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Systems and methods for measuring the useful life of solid-state storage devices
ActiveUS7653778B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesSolid-state storageLife time
A non-volatile solid-state storage subsystem, such as a non-volatile memory device, maintains usage statistics reflective of the wear state, and thus the remaining useful life, of the subsystem's memory array. A host system reads the usage statistics information, or data derived therefrom, from the subsystem to evaluate the subsystem's remaining life expectancy. The host system may use this information for various purposes, such as to (a) display or report information regarding the remaining life of the subsystem; (b) adjust the frequency with which data is written to the subsystem; and / or (c) select the type(s) of data written to the subsystem.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
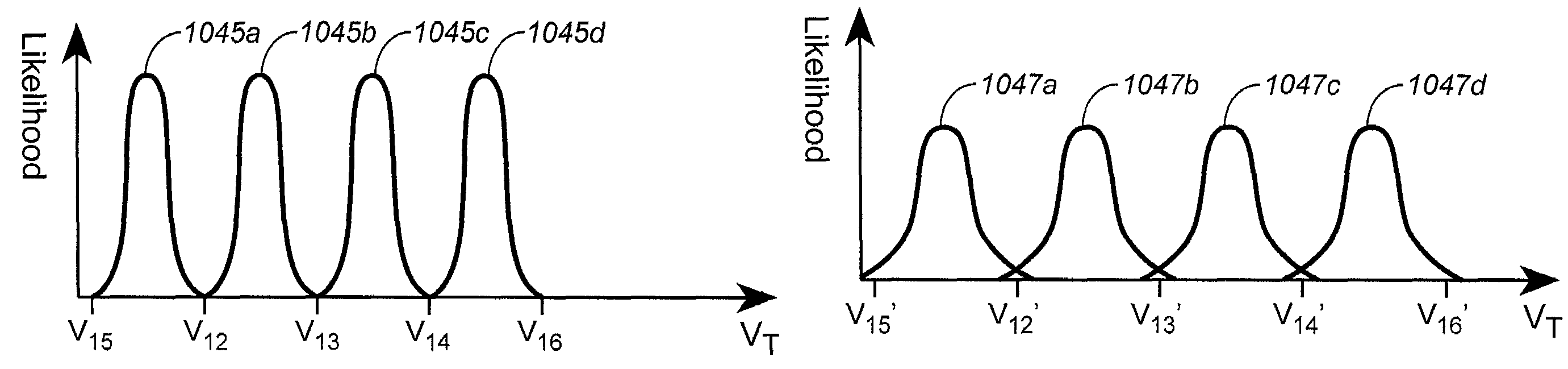
Nonvolatile memory with variable read threshold
Data is read from a nonvolatile memory array using one or more read voltages that are adjusted during memory life. Programming target voltages and read voltages may be adjusted together over memory life to map memory states to an increasingly wide threshold window. Individual memory states are mapped to sub-ranges that are made wider, reducing errors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com