Patents
Literature
22066 results about "Amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
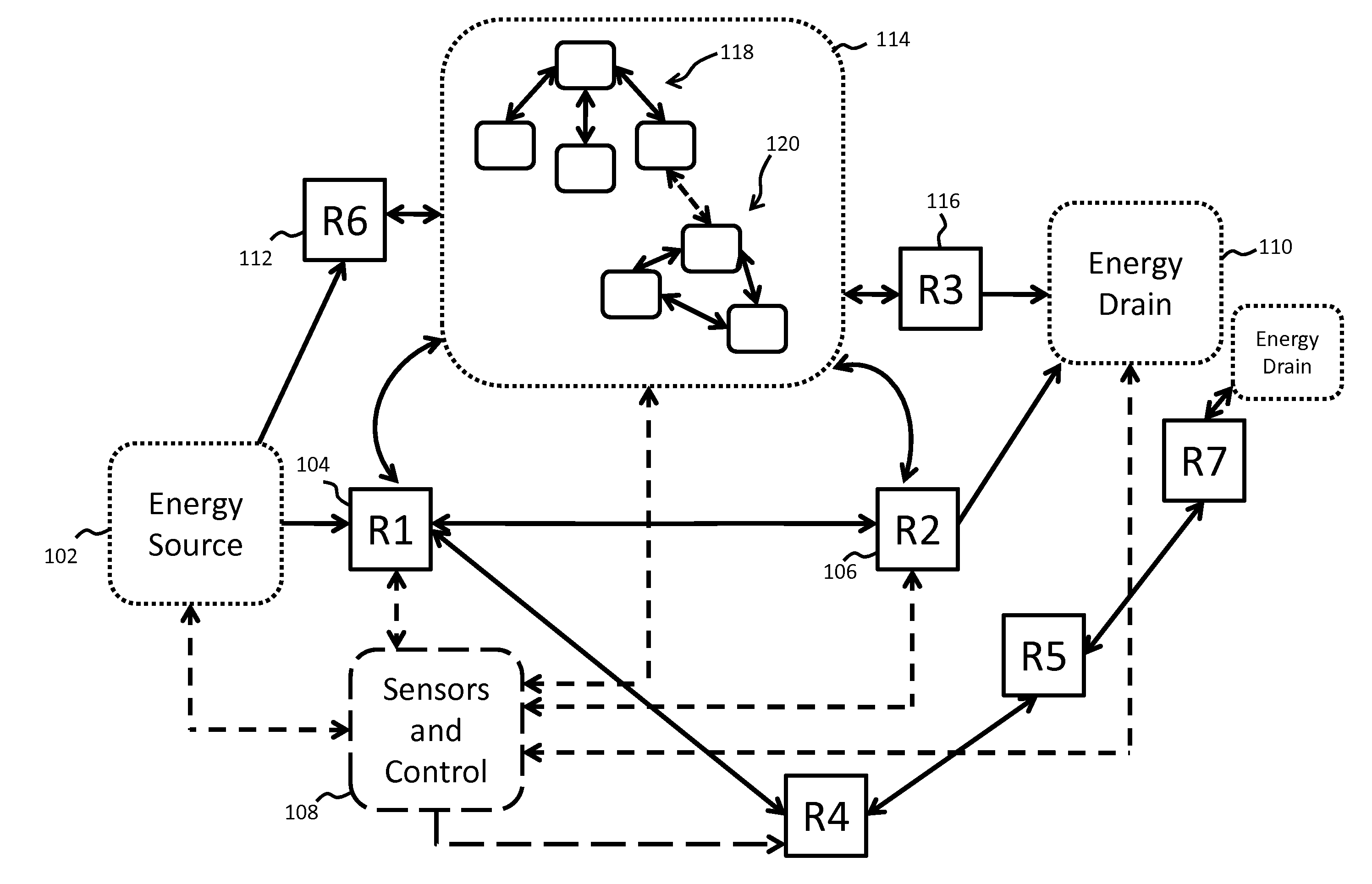
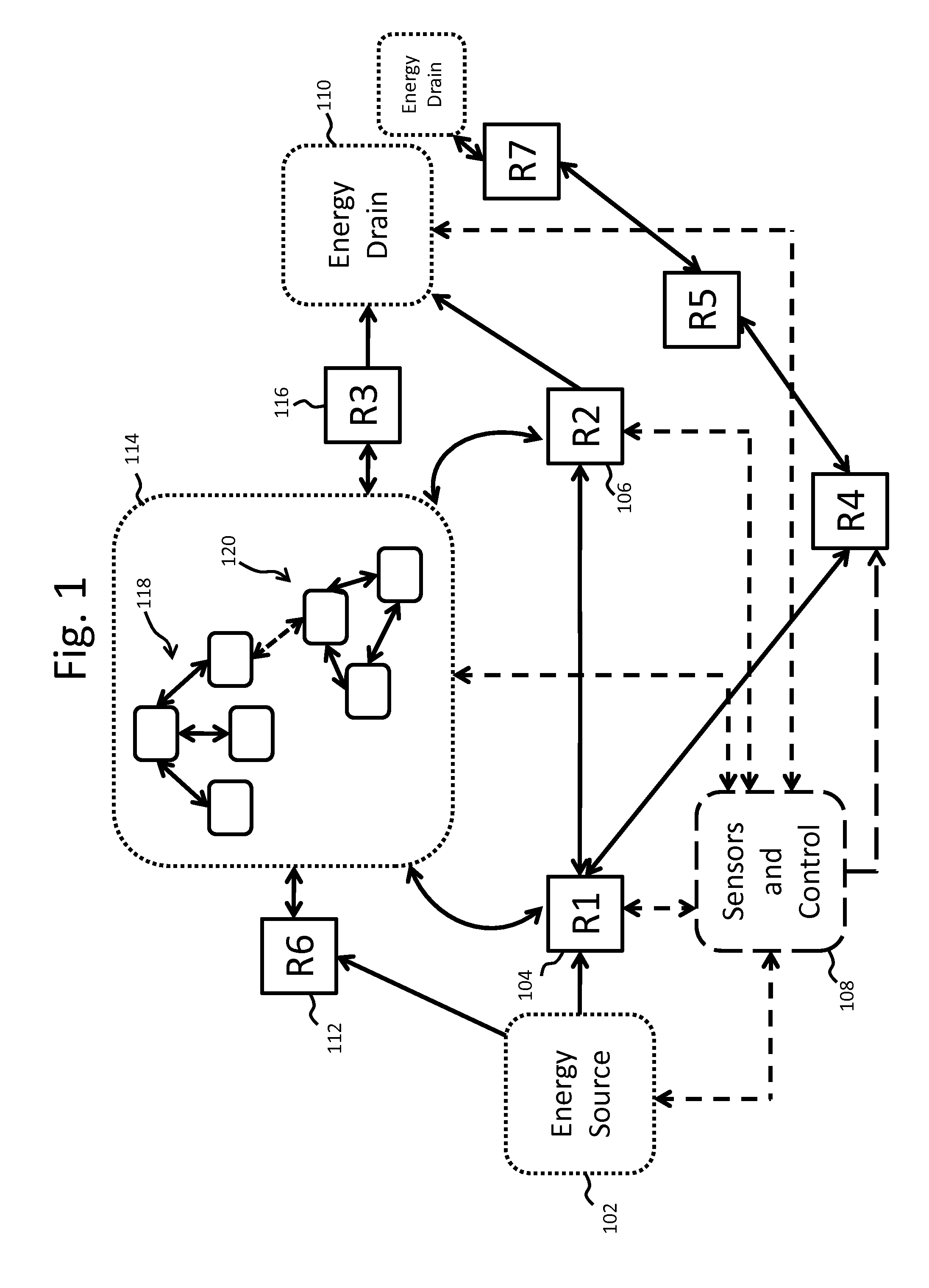
Tunable wireless power architectures
ActiveUS20130033118A1Tune performanceCharging stationsElectromagnetic wave systemEnergy transferPower Architecture
Described herein are improved configurations for a wireless power transfer. The parameters of components of the wireless energy transfer system are adjusted to control the power delivered to the load at the device. The power output of the source amplifier is controlled to maintain a substantially 50% duty cycle at the rectifier of the device.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
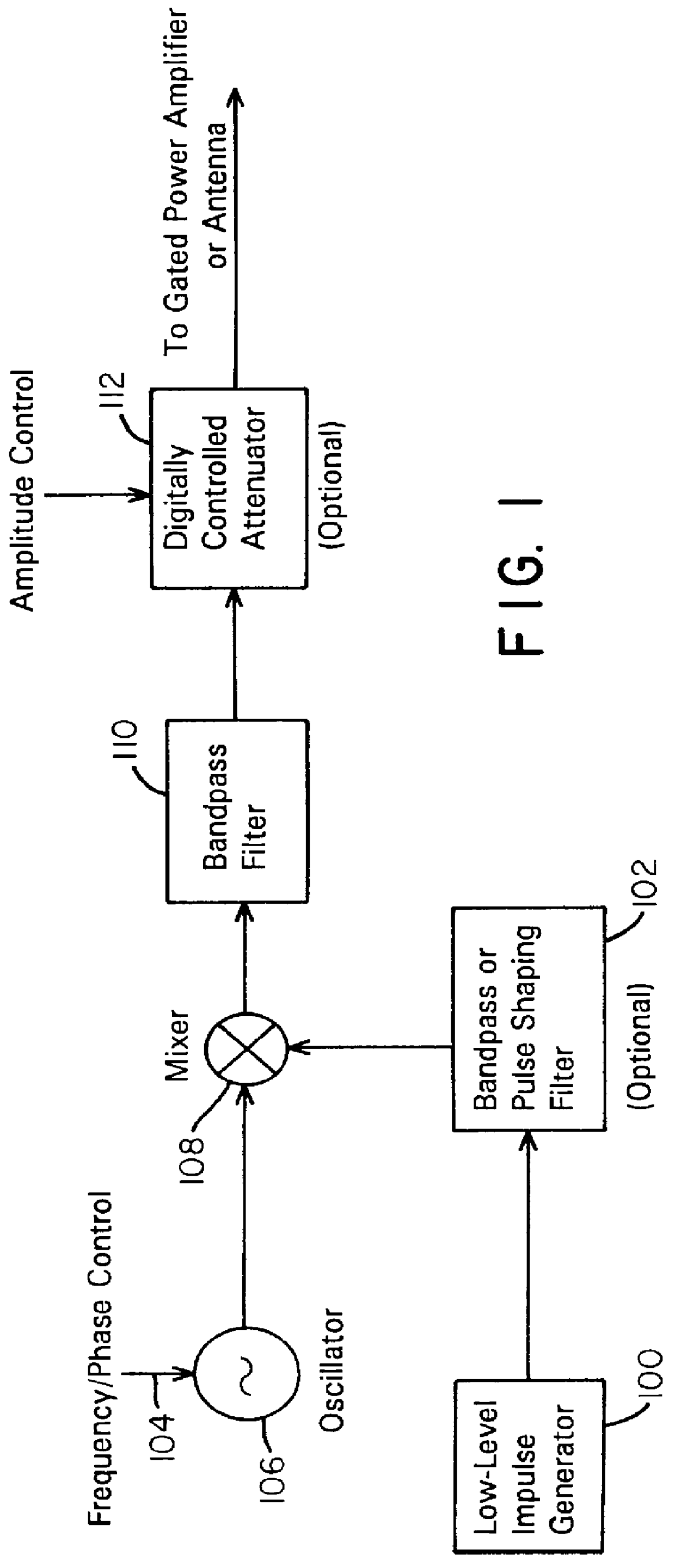
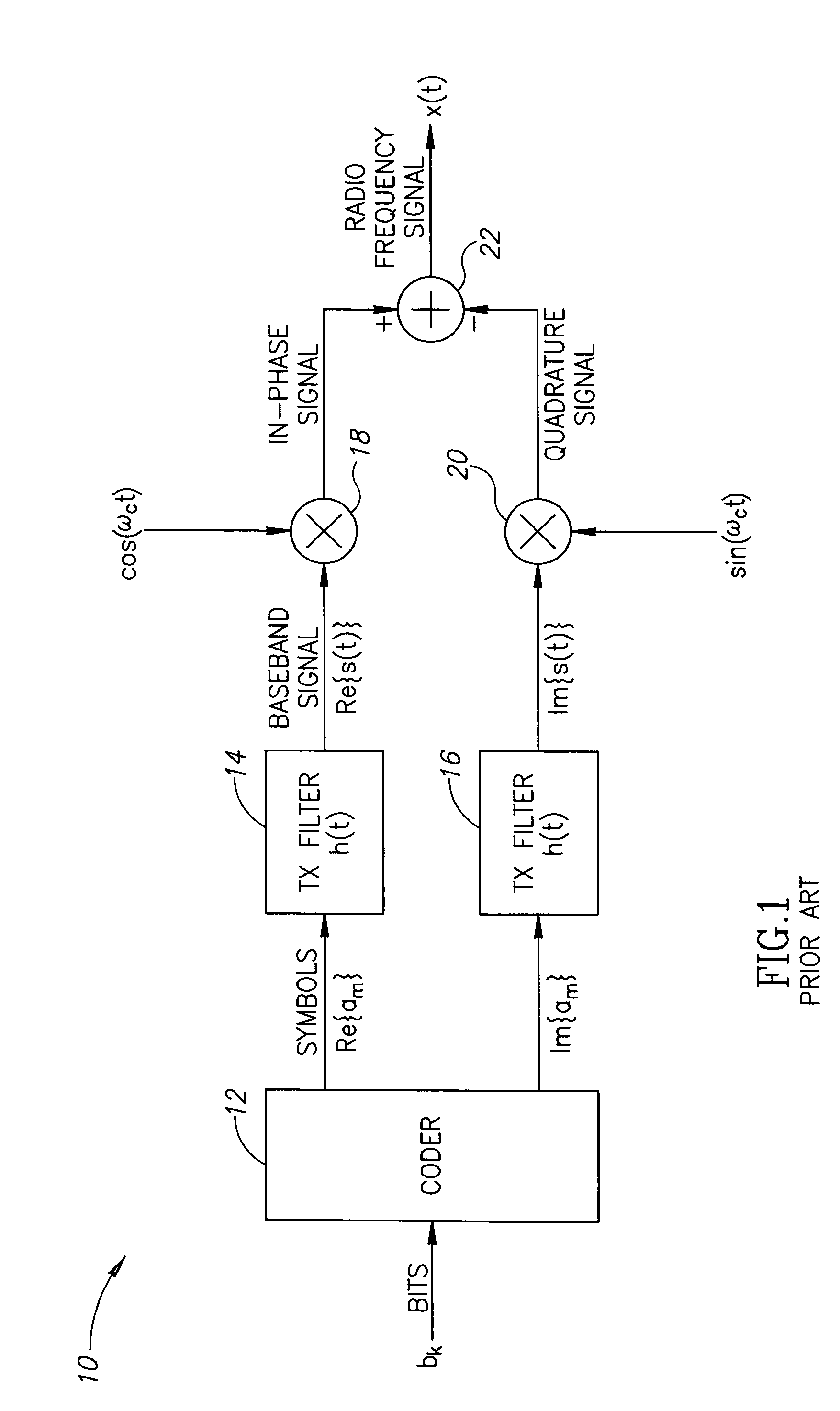
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
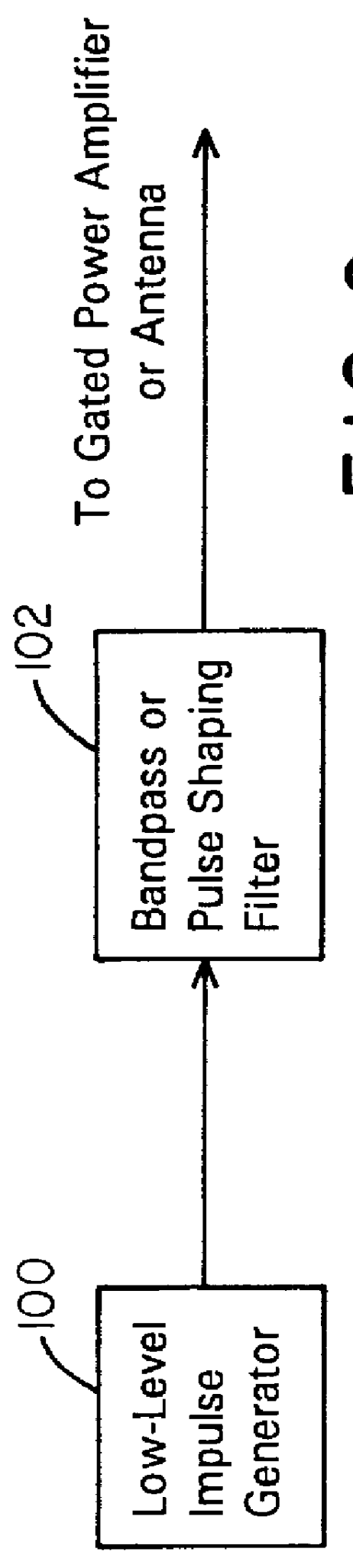
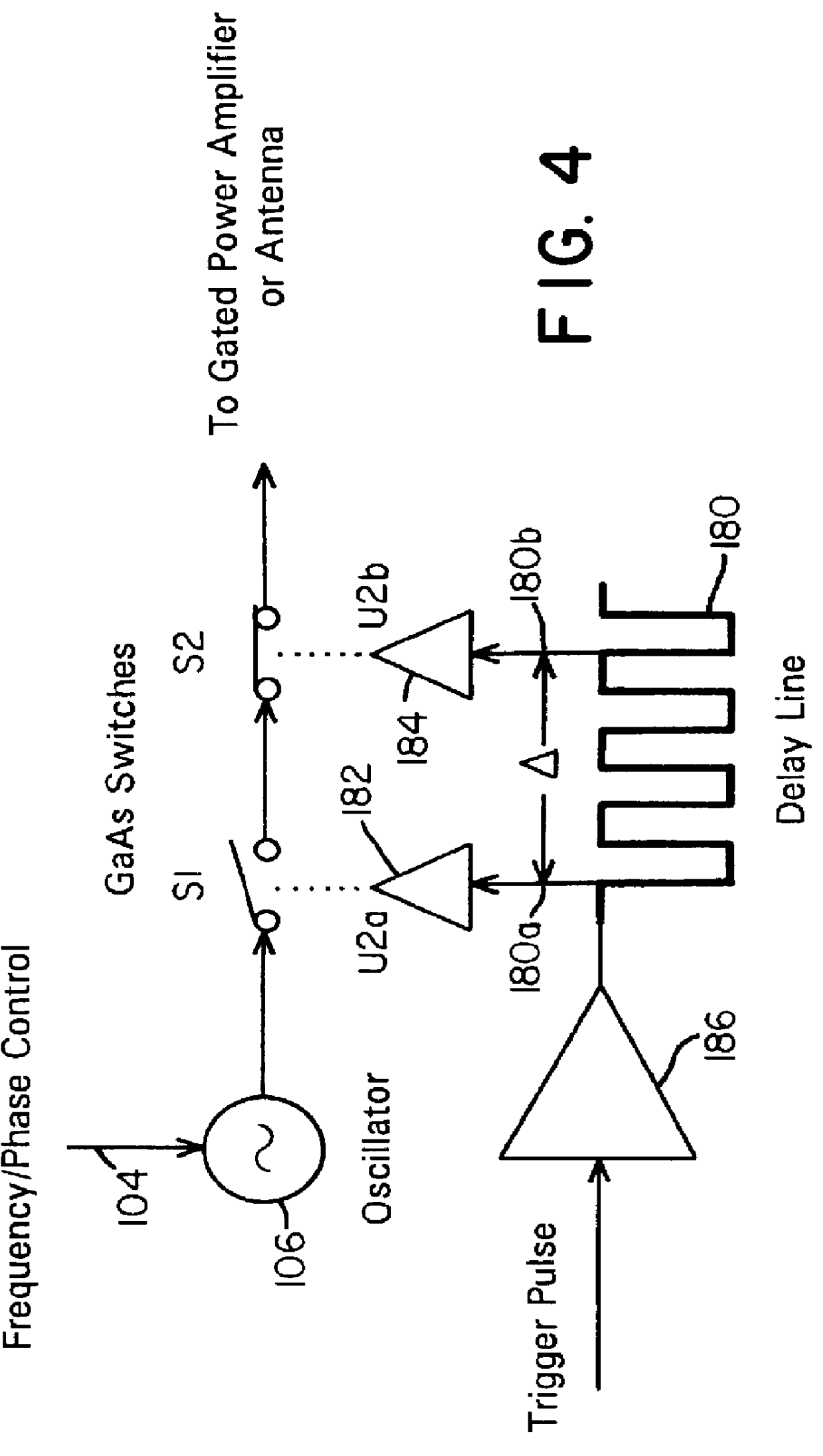
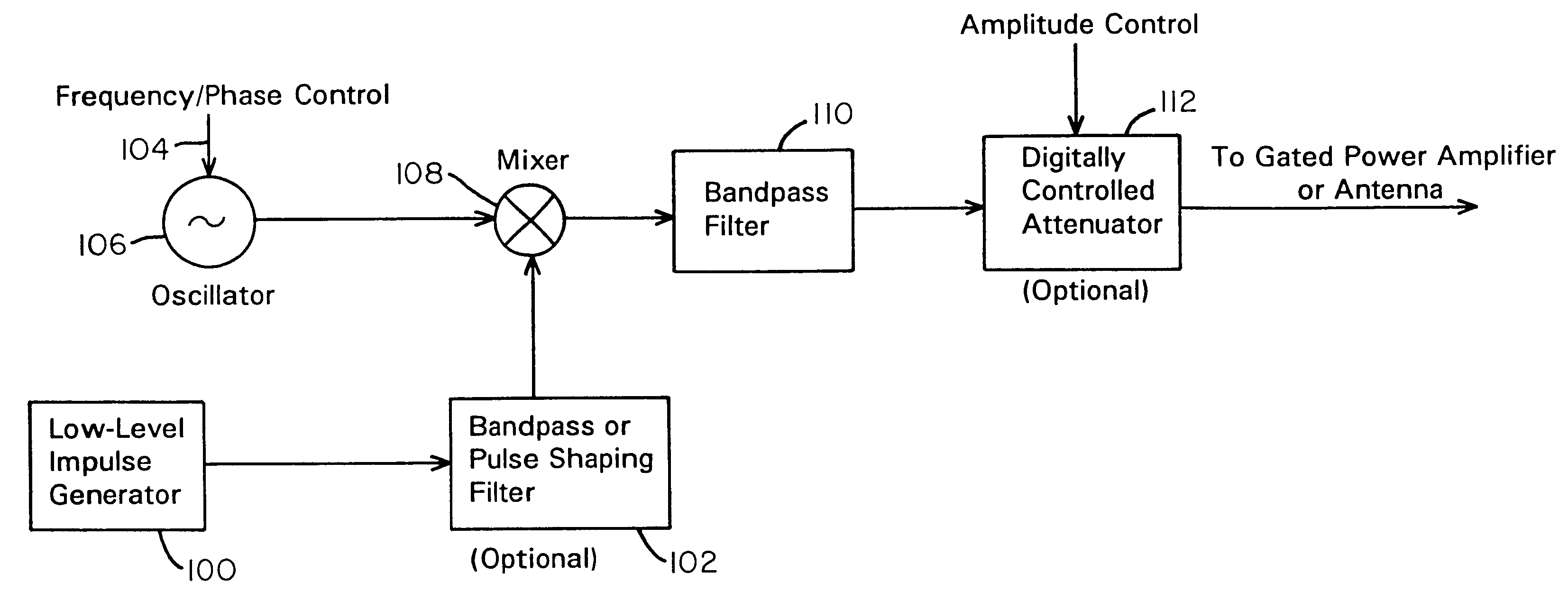
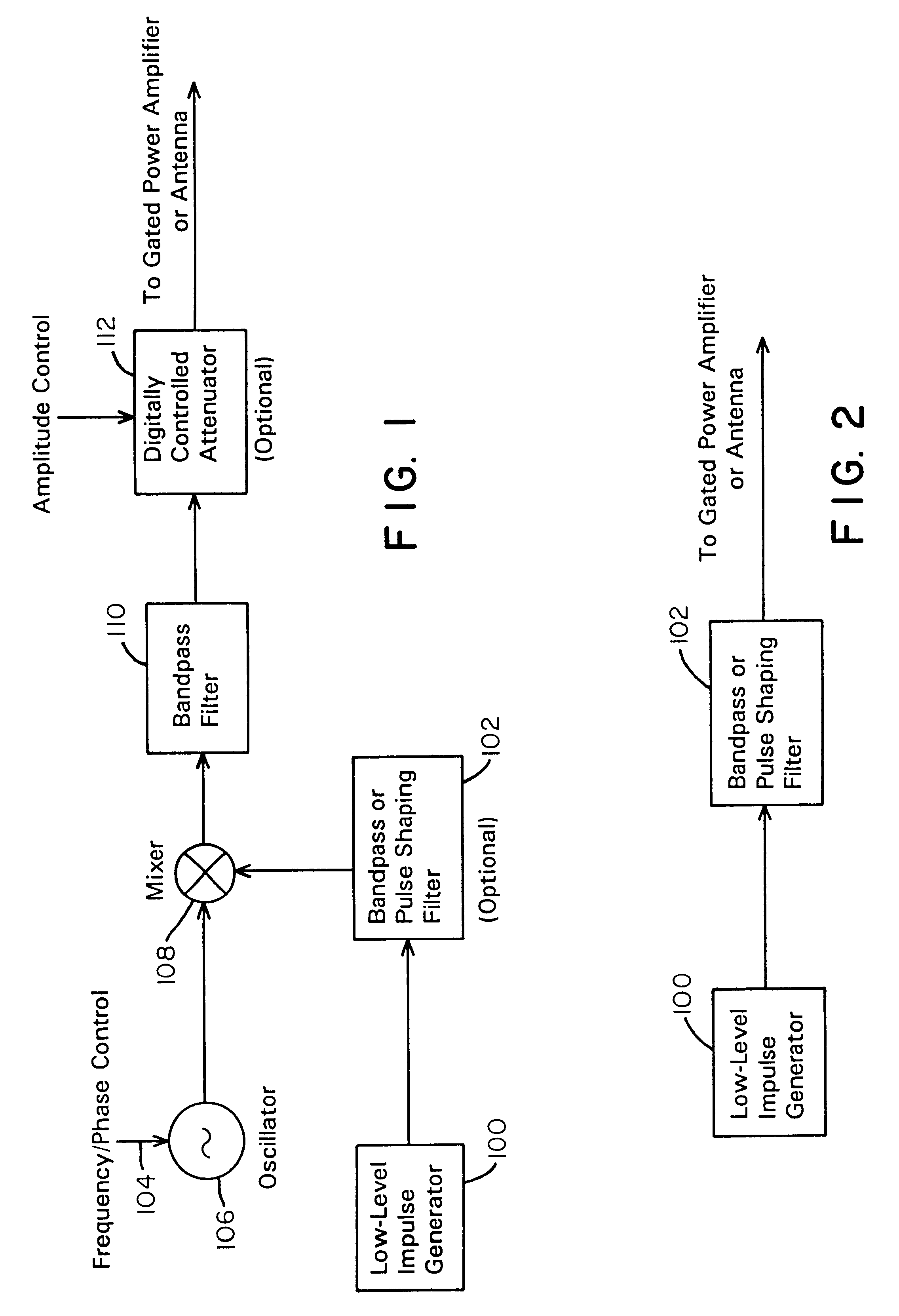
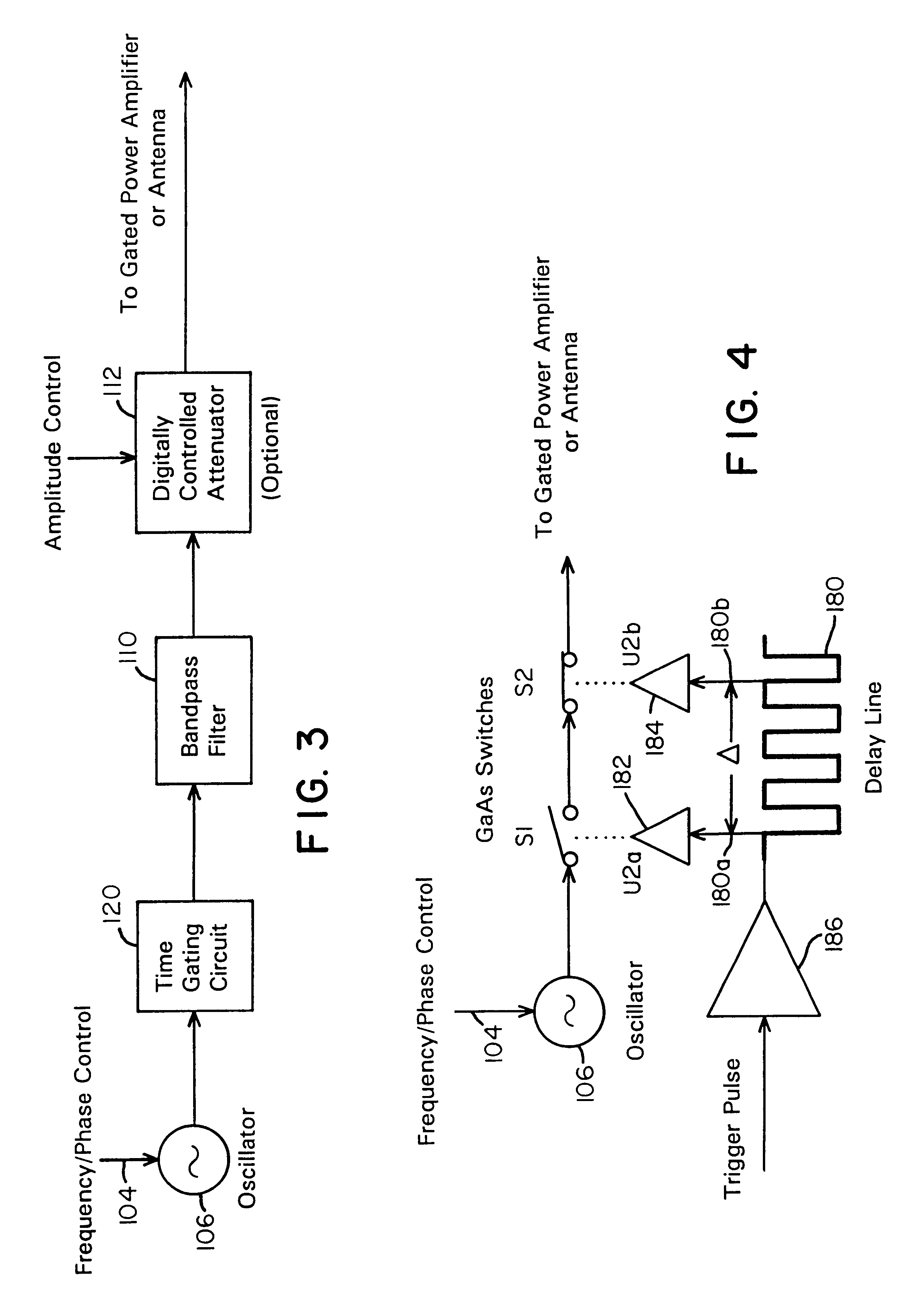
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Head end receiver for digital data delivery systems using mixed mode SCDMA and TDMA multiplexing
InactiveUS7050419B2Improve performance(SNR) ratioTransmission control/equlisationMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsDigital dataDOCSIS
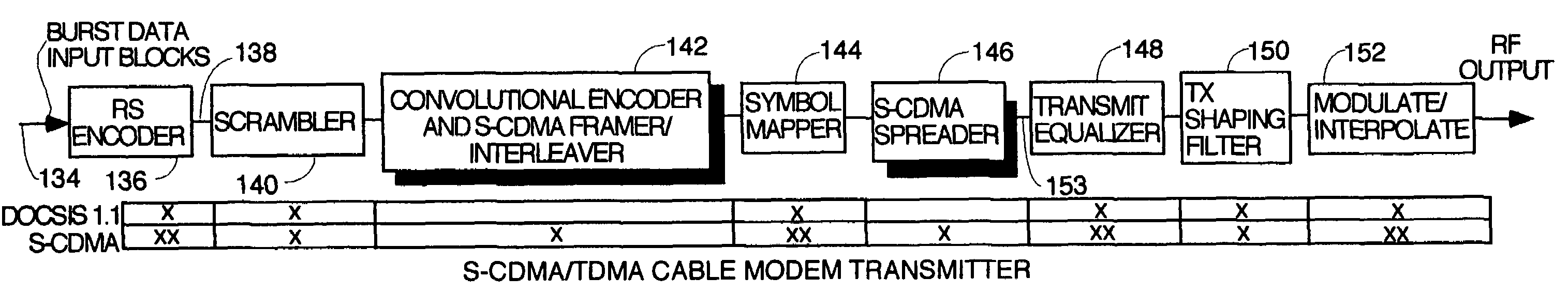
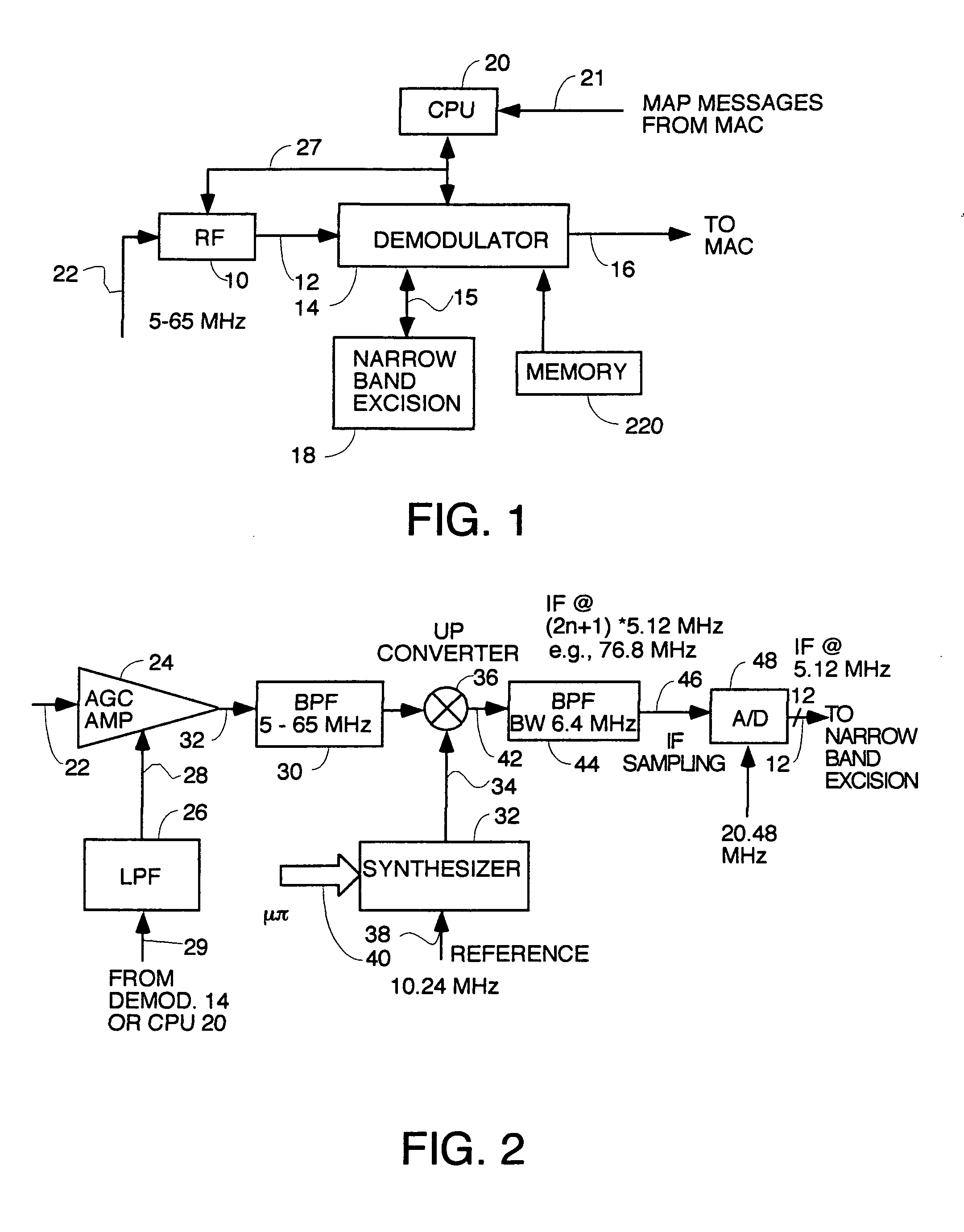
A pipelined digital data receiver for a cable TV headend which is capable of receiving DOCSIS 1.0 or 1.1 or advanced PHY TDMA or SCDMA bursts having programmable symbol rates and programmable modulation types as well as a host of other burst parameters such at Trellis code modulation on or off, scrambling on or off, various values for Reed-Solomon T number and codeword length. The receiver has an RF section to filter and digitize incoming RF signals. It also has an input section to detect impulse noise and do match filtering and despread SCDMA bursts. A timing recovery section recovers the symbol clock and detects the start of bursts and collisions. A rotational amplifier and equalizer calculate and track gain, phase and frequency offsets and correct symbols and calculates equalization coefficients. A decoder section decodes TCM and non TCM bursts, and a Reed-Solomon decoder section reconstructs RS codewords and uses them to error correct the payload data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Receiver controller for wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20120299542A1Electromagnetic wave systemTransducer detailsElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
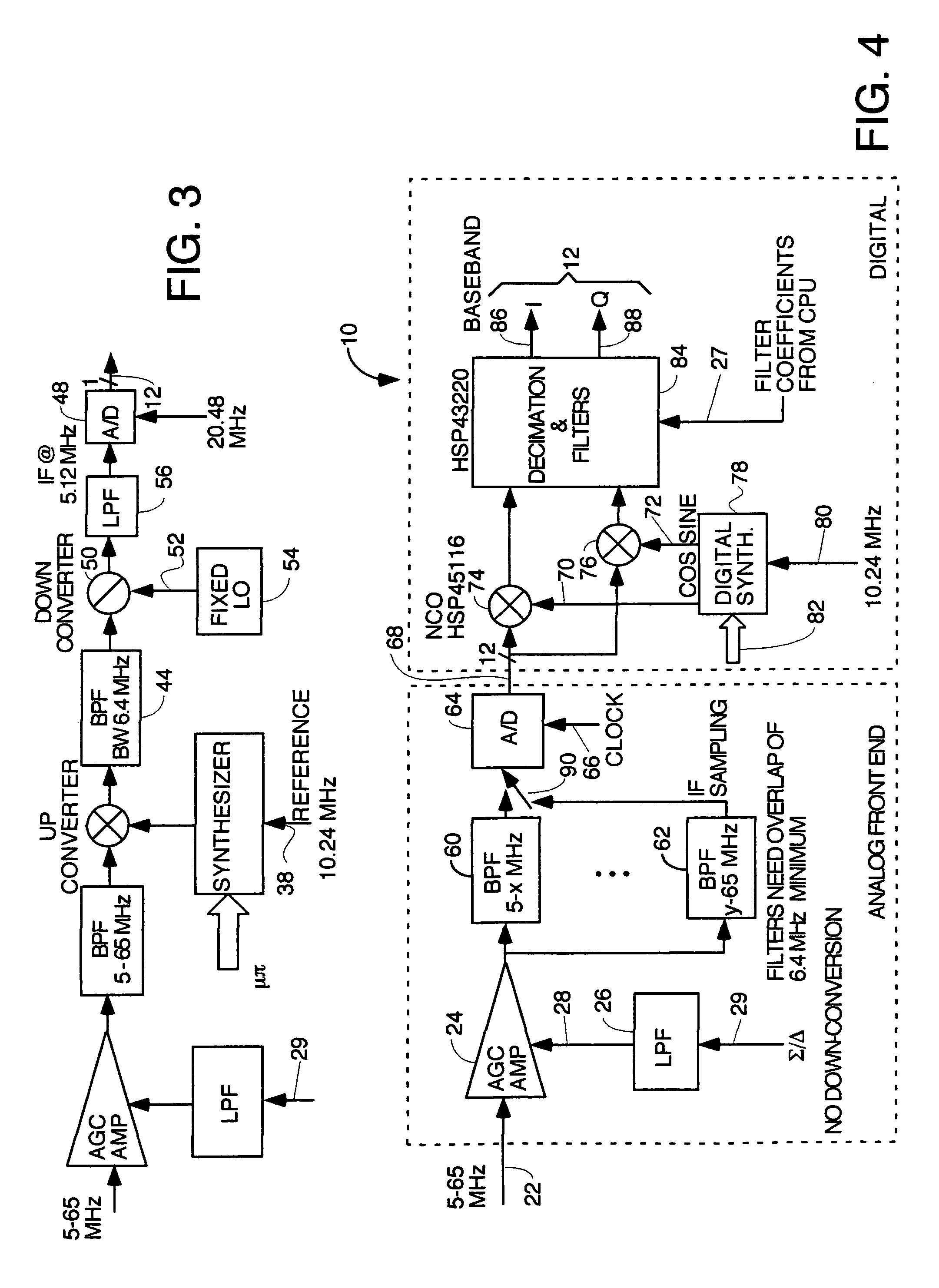
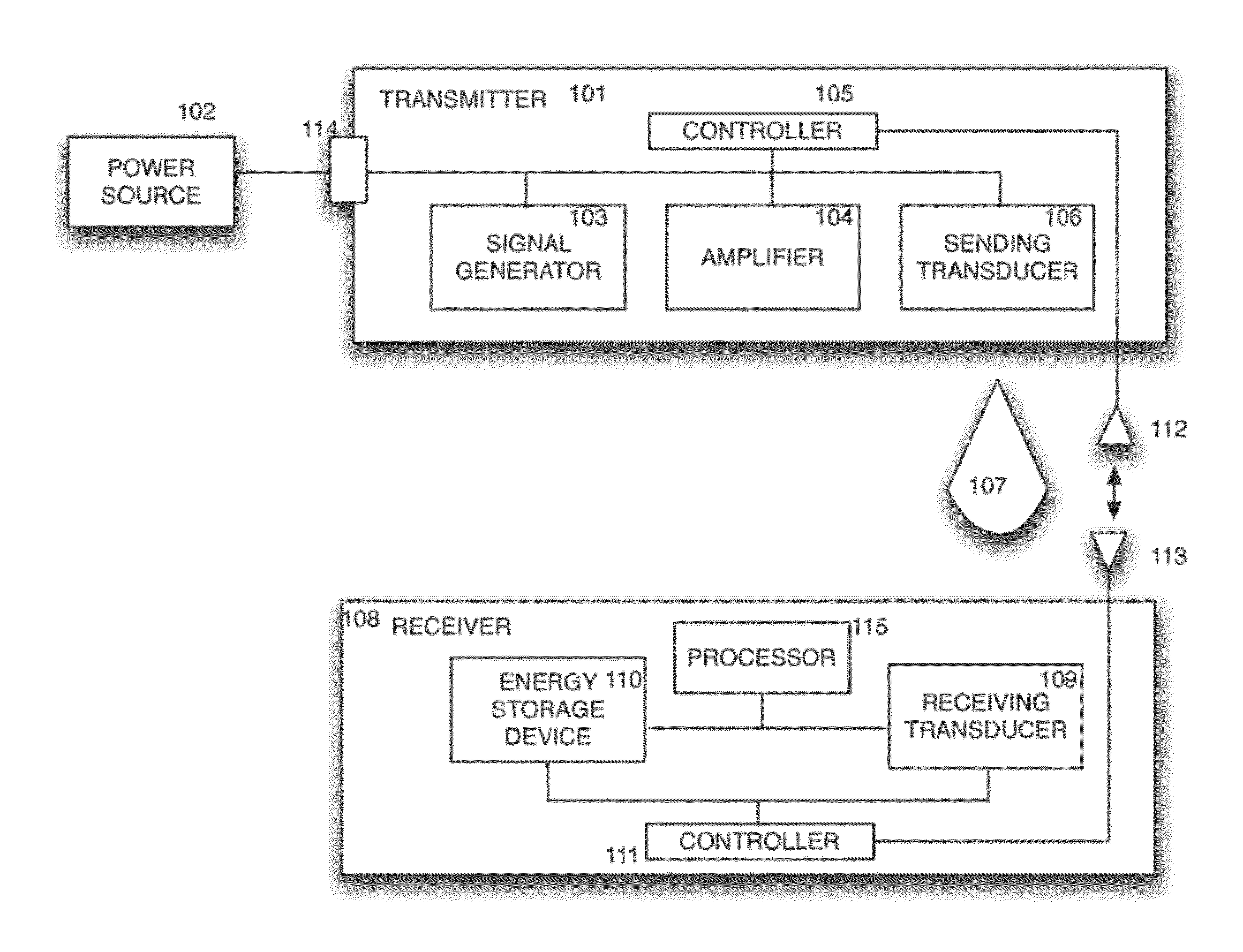
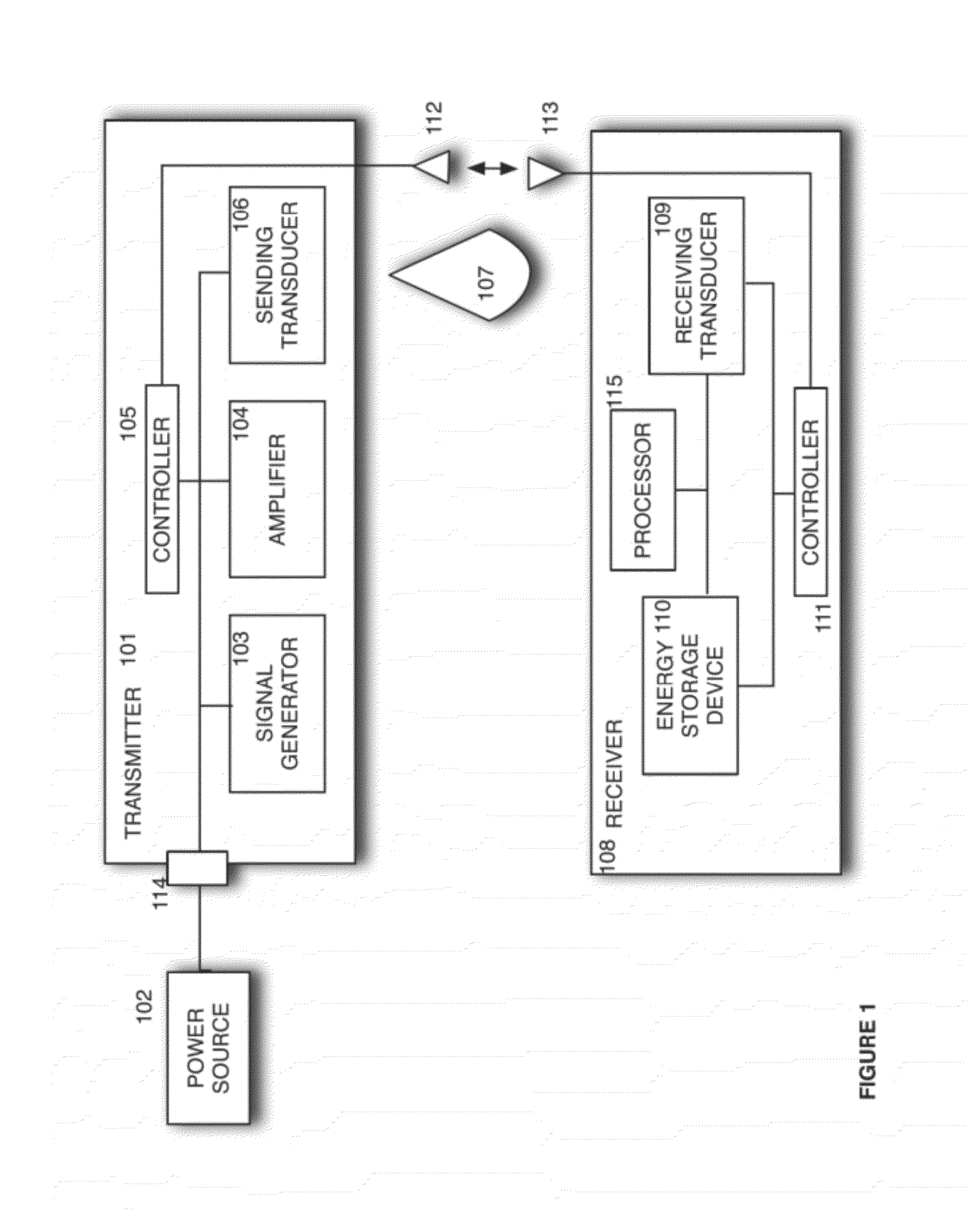
A signal generator generates an electrical signal that is sent to an amplifier, which increases the power of the signal using power from a power source. The amplified signal is fed to a sender transducer to generate ultrasonic waves that can be focused and sent to a receiver. The receiver transducer converts the ultrasonic waves back into electrical energy and stores it in an energy storage device, such as a battery, or uses the electrical energy to power a device. In this way, a device can be remotely charged or powered without having to be tethered to an electrical outlet.
Owner:UBEAM
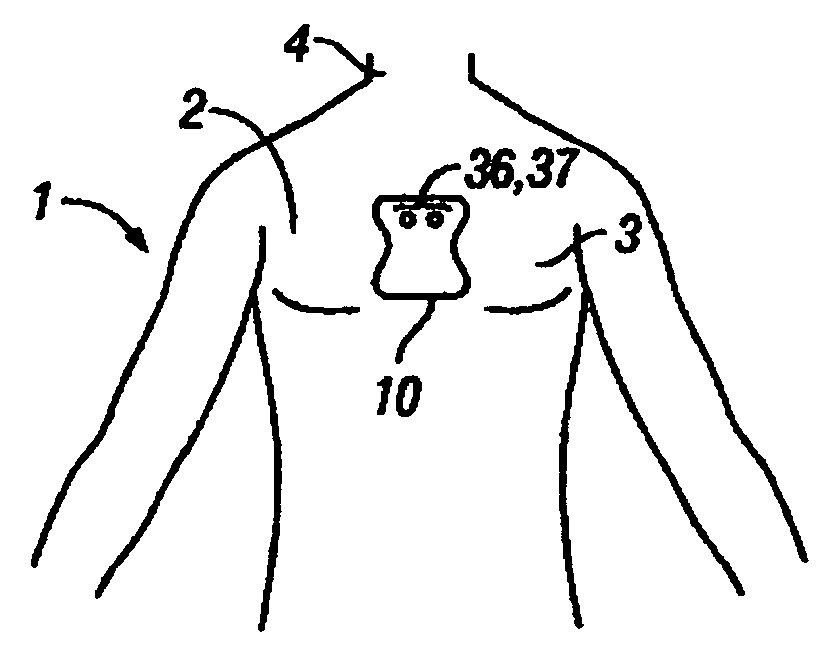
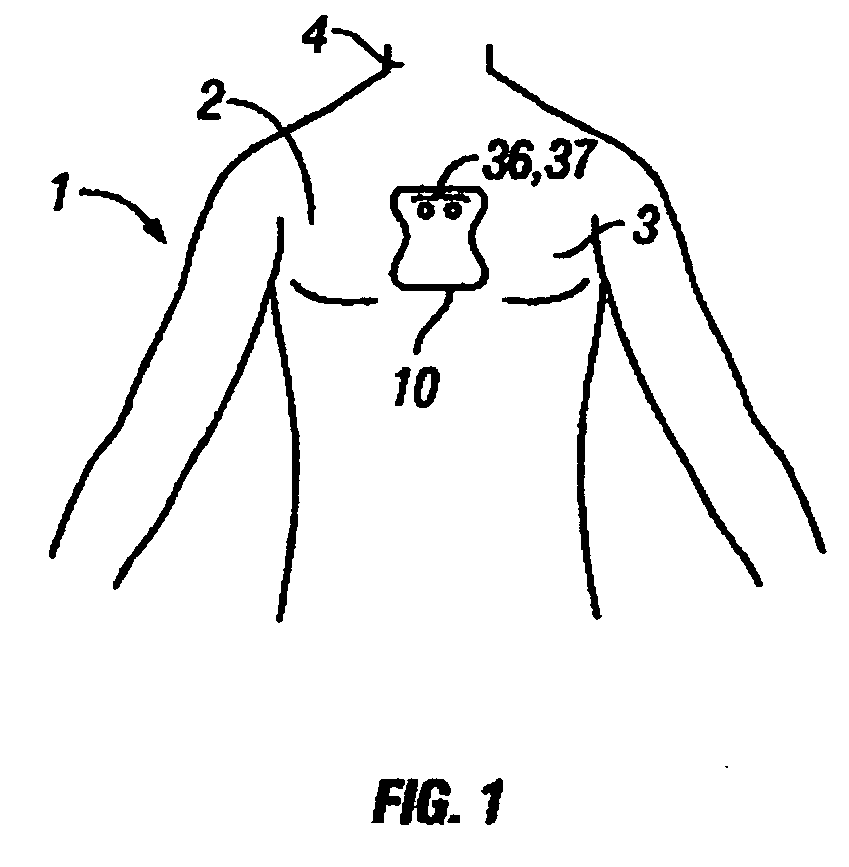
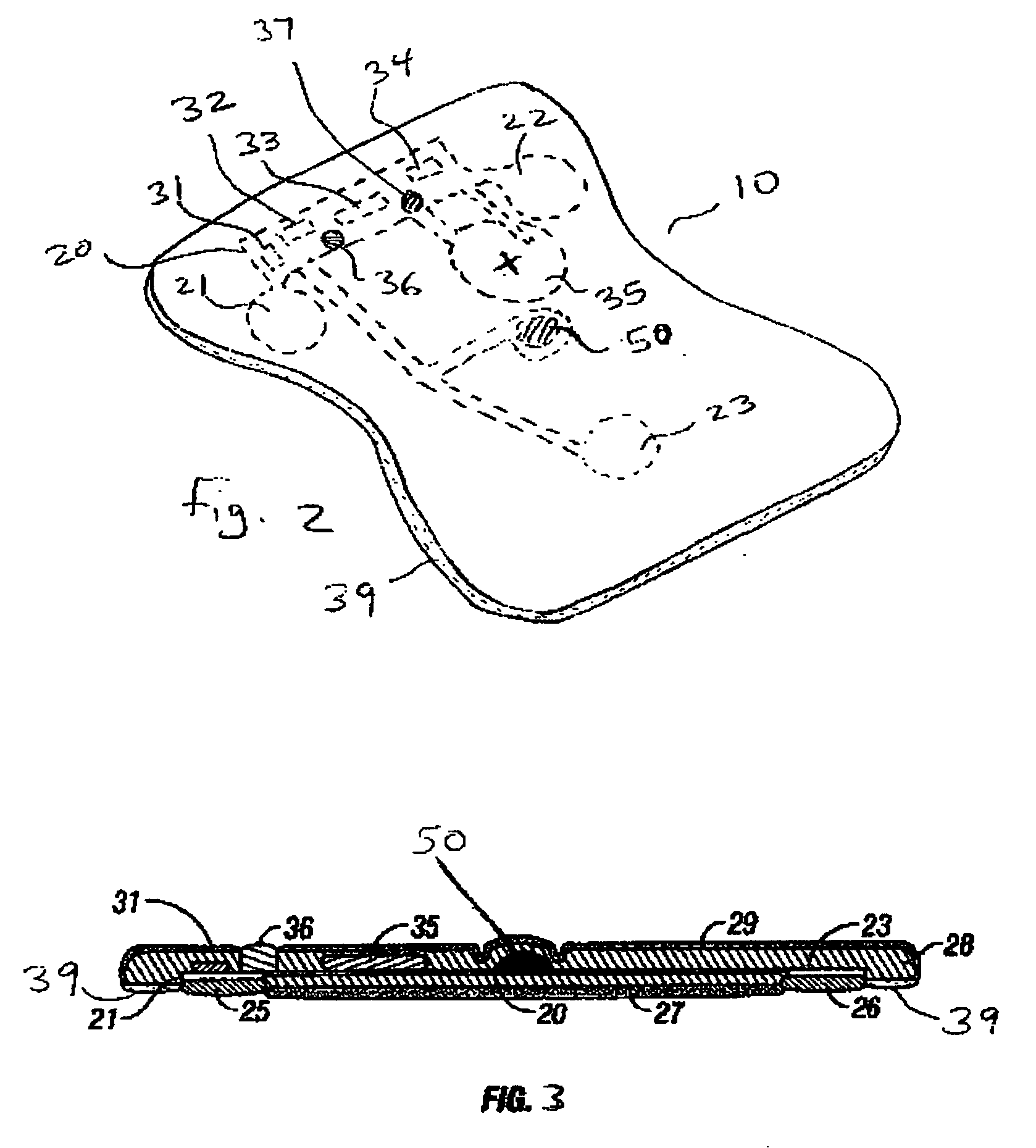
Disposable extended wear heart monitor patch
InactiveUS20060224072A1Easy diagnosisMinimizing contaminationElectrocardiographySensorsWireless transmissionNon invasive
The invention provides a disposable sensor patch for non-invasive monitoring and recording of infrequent cardiac events. The patch is thin and flexible for comfortable wear on the person's chest for automatic analysis and recording of ECG. The patch is inexpensive and simple for self-administration. The patch incorporates a battery, ECG amplifier, and a processor for analyzing ECG waveform and recording events. A software algorithm searches for a cardiac abnormality. The patch is designed for continuous long-term wear exceeding 3 days for diagnostic monitoring and exceeding 14 days for event detection. In one embodiment a preformatted report is automatically generated by the patch for wireless transmission to a reporting device such as a generic printer or a wireless network system. The patch may also incorporate a marker switch to correlate recorded ECG data with the patient's perception of a cardiac event.
Owner:CARDIOVU
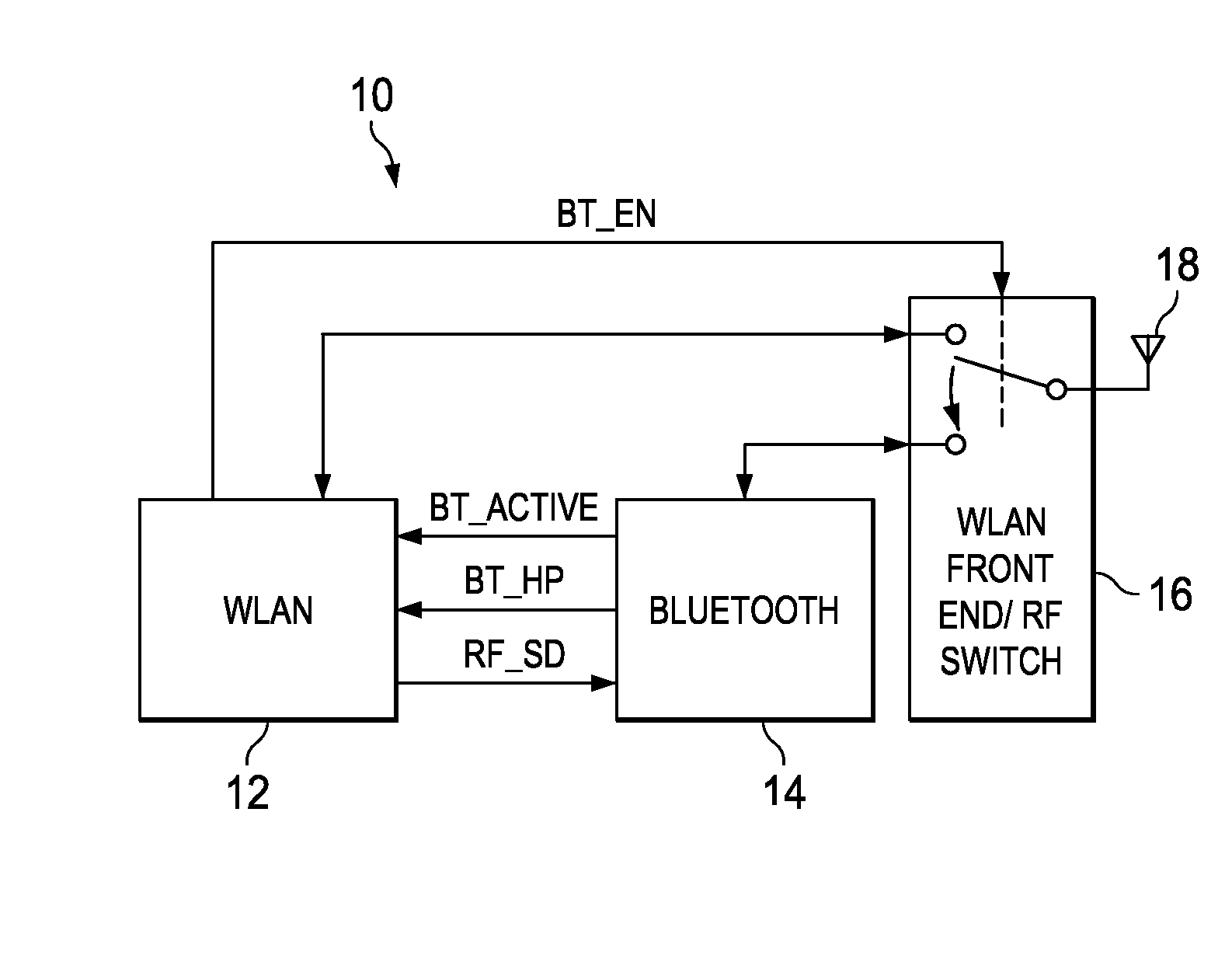
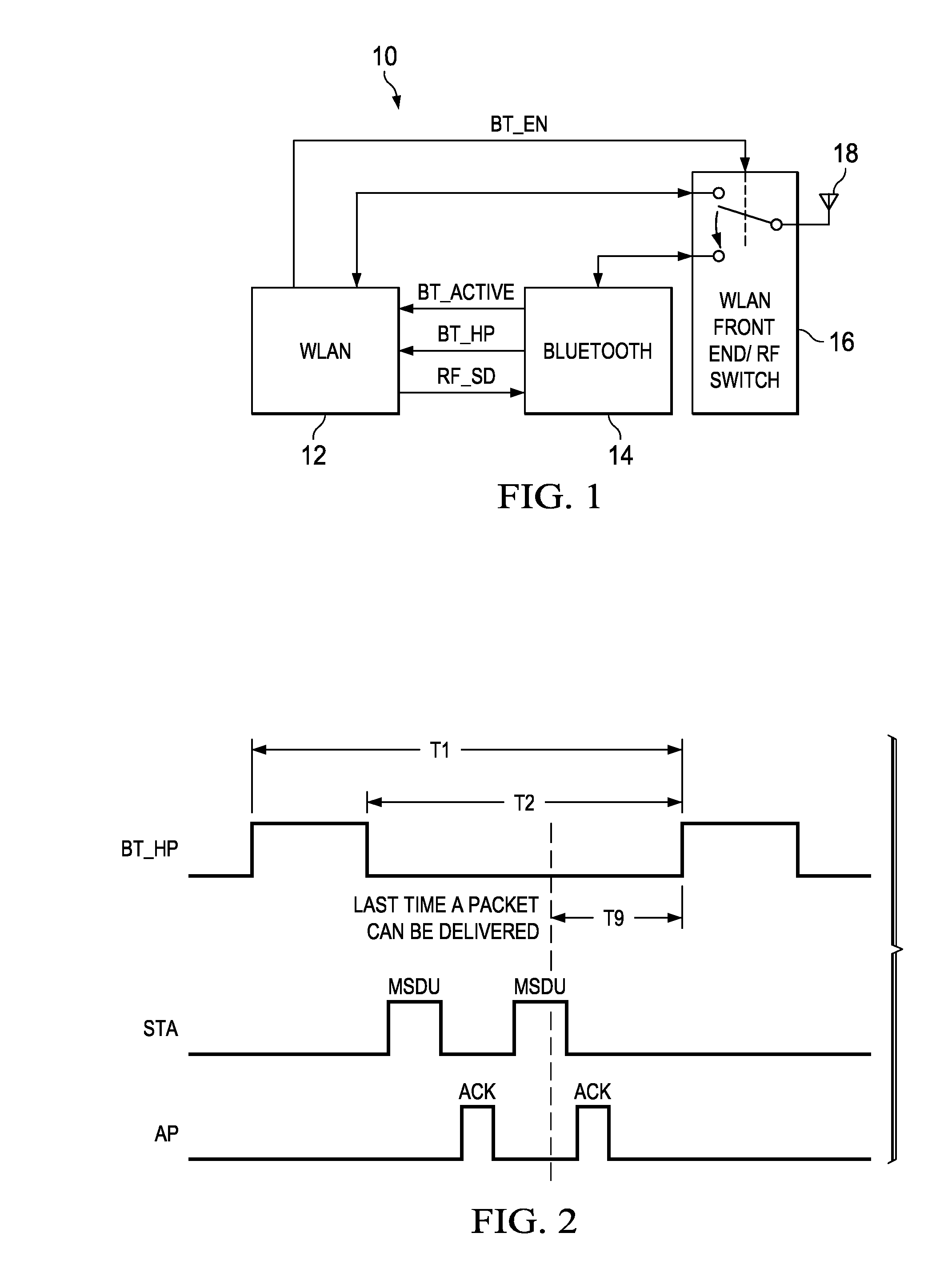
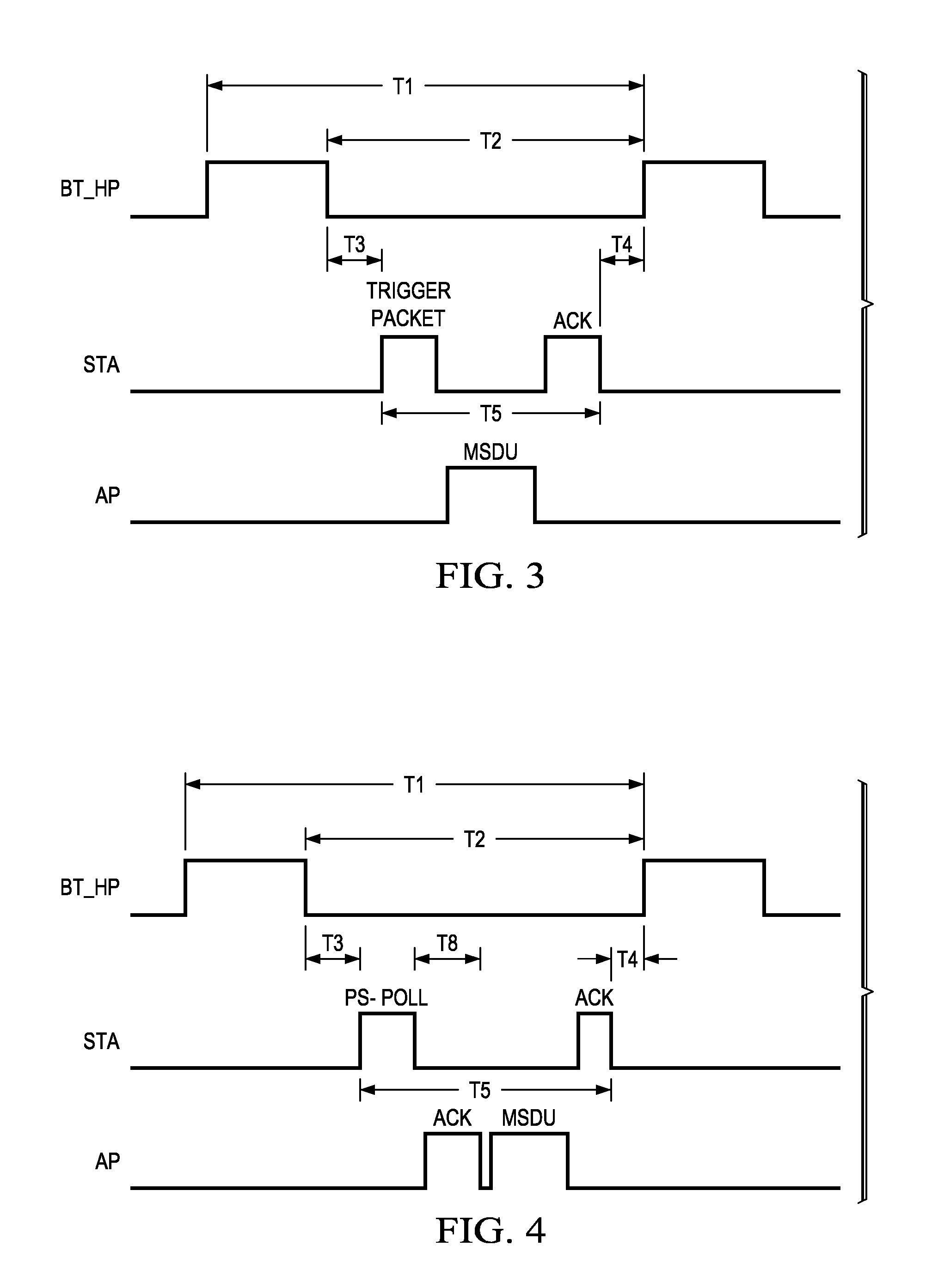
Apparatus for and method of bluetooth and wireless local area network coexistence using a single antenna in a collocated device
ActiveUS20090137206A1Clean voice” performanceSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTransfer mode
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of providing a mechanism for achieving coexistence between a Bluetooth system and WLAN system collocated in the same communications device such as a mobile terminal. The coexistence mechanism of the present invention functions to monitor WLAN and Bluetooth system activity, determine the access priority of both WLAN and Bluetooth systems, predict Bluetooth high priority packet transmission patterns, allocate bandwidth to both the Bluetooth and WLAN systems in accordance with the traffic patterns predicted, and switch the antenna and control the Bluetooth and WLAN power amplifiers when required.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
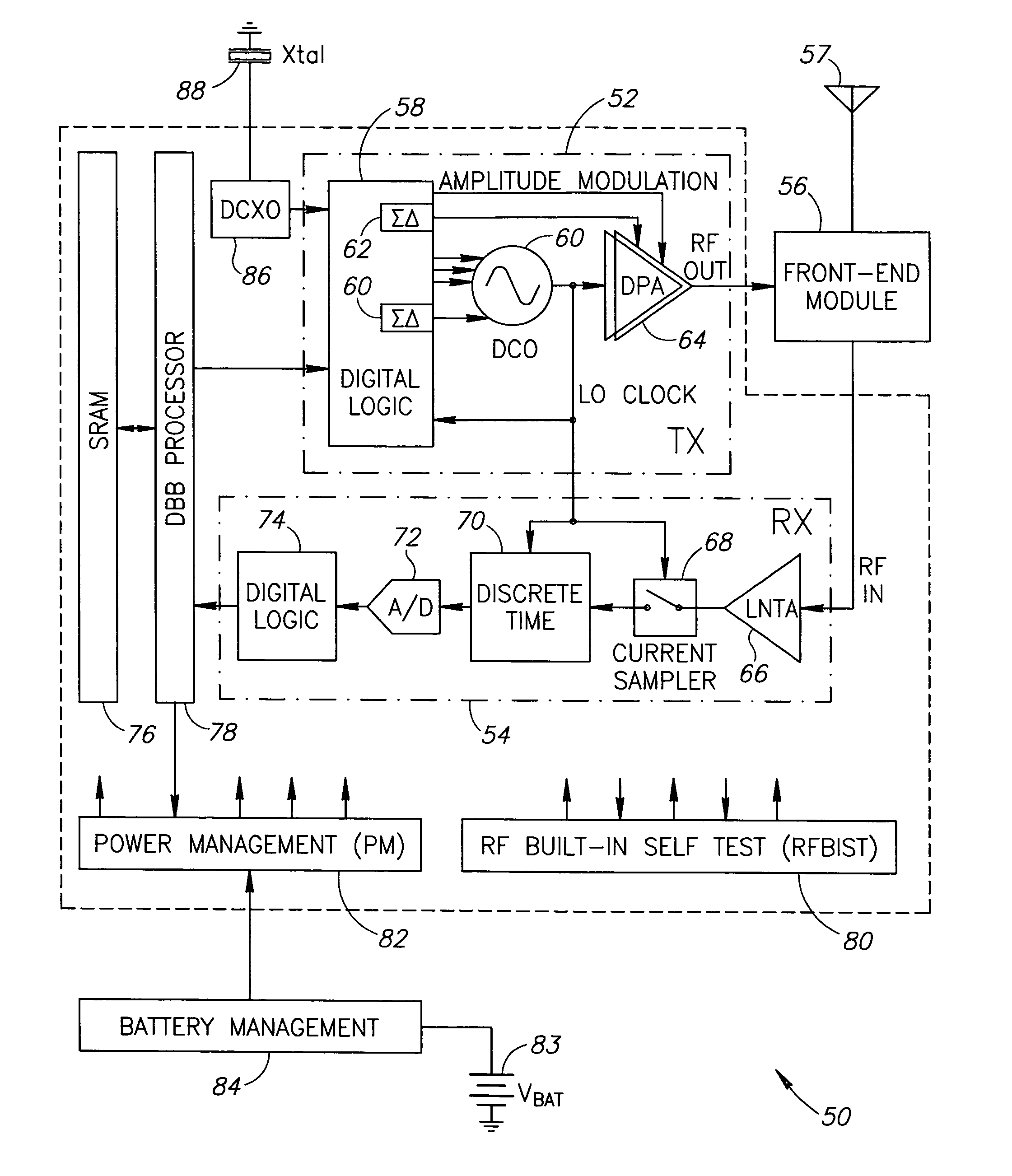
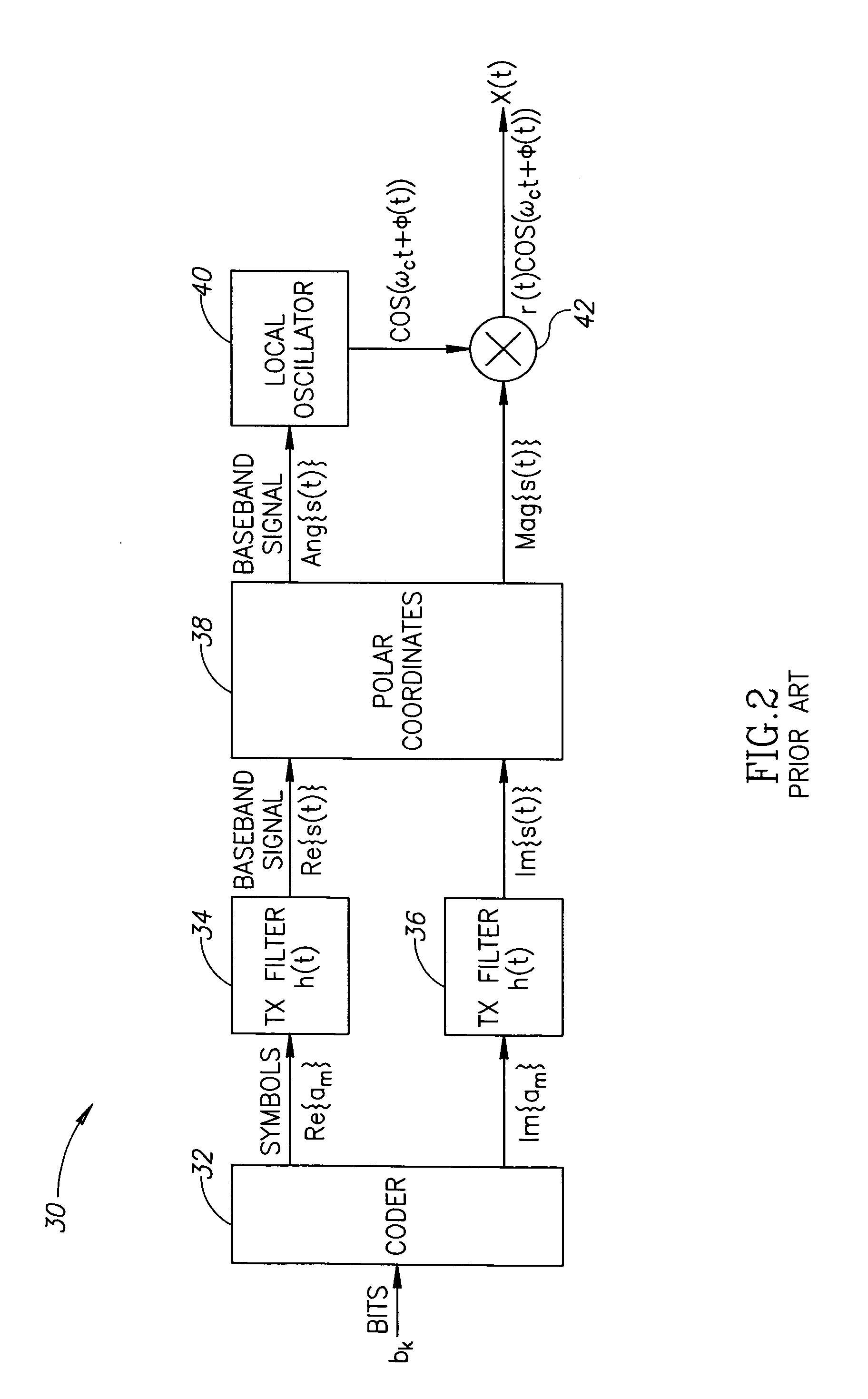
Hybrid polar/cartesian digital modulator
ActiveUS20060038710A1Reconfigurable analogue/digital convertersAnalogue conversionControl powerEngineering
A novel apparatus and method for a hybrid Cartesian / polar digital QAM modulator. The hybrid technique of the present invention utilizes a combination of an all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL) that features a wideband frequency modulation capability and a digitally controlled power amplifier (DPA) that features interpolation between 90 degree spaced quadrature phases. This structure is capable of performing either a polar operation or a Cartesian operation and can dynamically switch between them depending on the instantaneous value of a metric measured by a thresholder / router. In this manner, the disadvantages of each modulation technique are avoided while the benefits of each are exploited.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
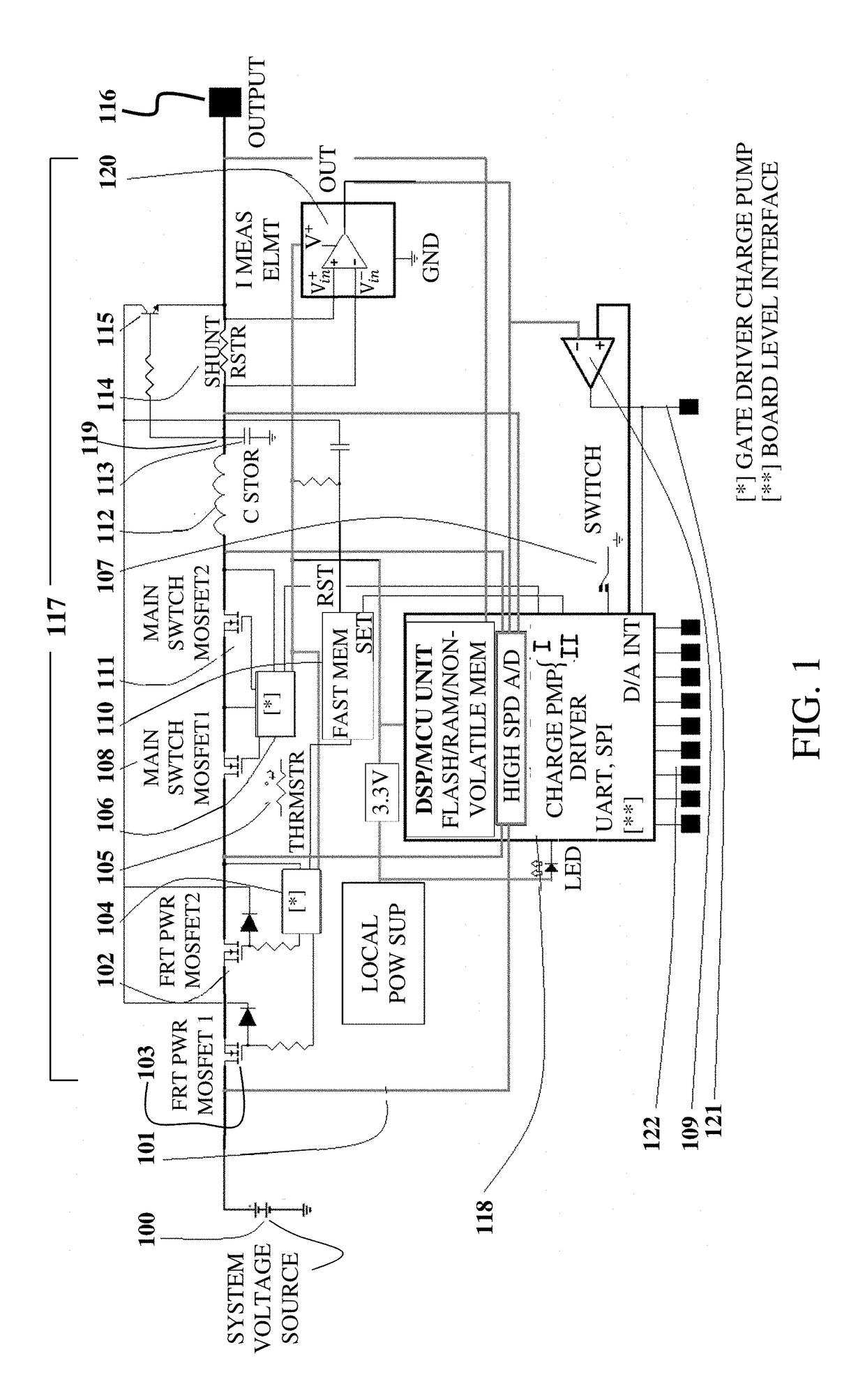
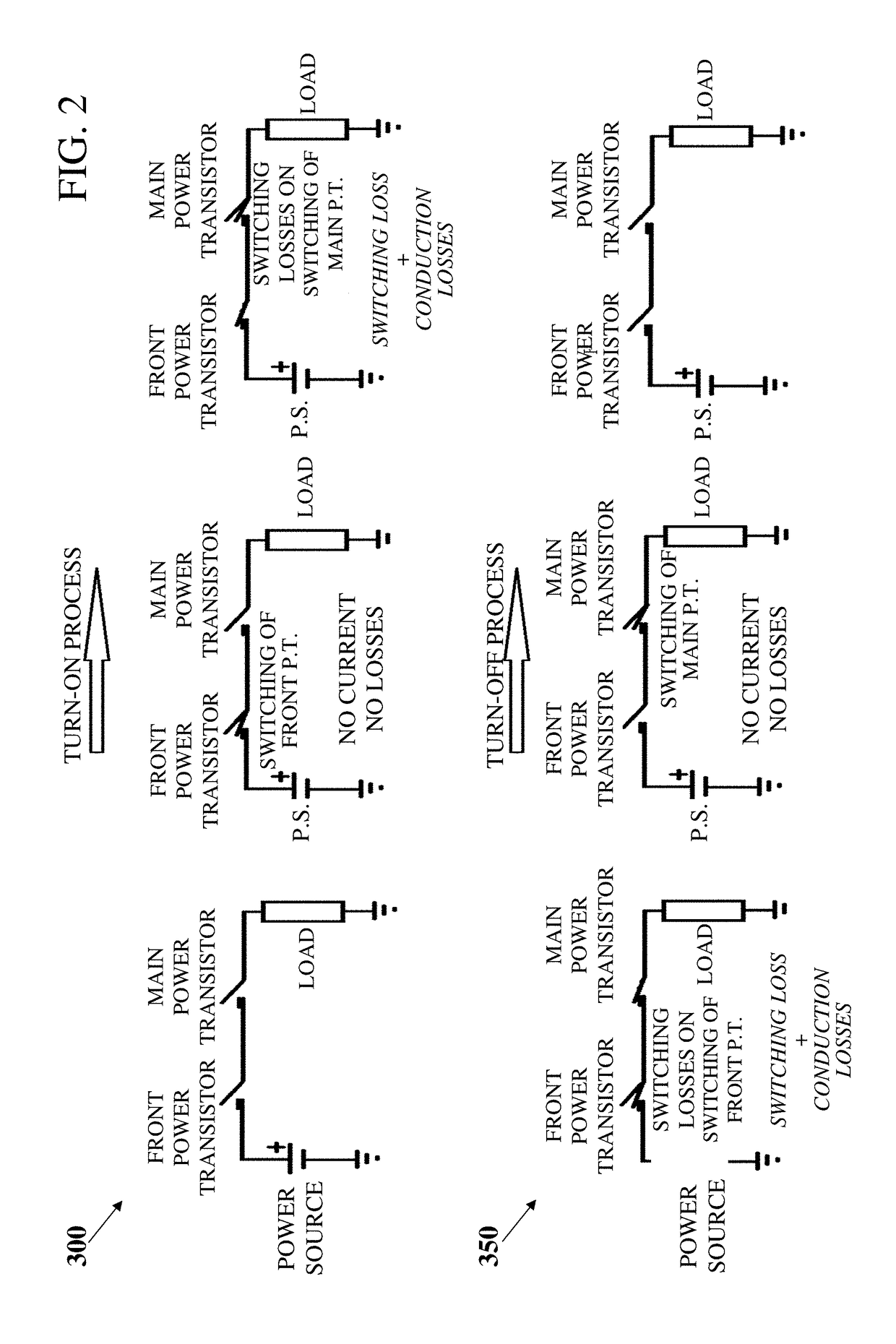
Automatic, Highly Reliable, Fully Redundant Electronic Circuit Breaker That Reduces or Prevents Short-Circuit Overcurrent
A programmable power (PPSE) switching element including a front power transistor, a main switching transistor, and at least one reverse current blocking transistor in series, a gate of each of which is connected to a gate driver; an inductor and a shunt resistor connected in series with the transistors; a charge storage capacitor connected between ground and a junction located between the inductor and the shunt resistor; a high-speed NPN transistor, a collector of which is connected to the front power transistor and an emitter of which is connected to an output of the main switching transistor via the shunt resistor; a current measurement element in parallel to the shunt resistor; a voltage amplifier; and a high-speed MCU.
Owner:REDLER TECH LTD
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
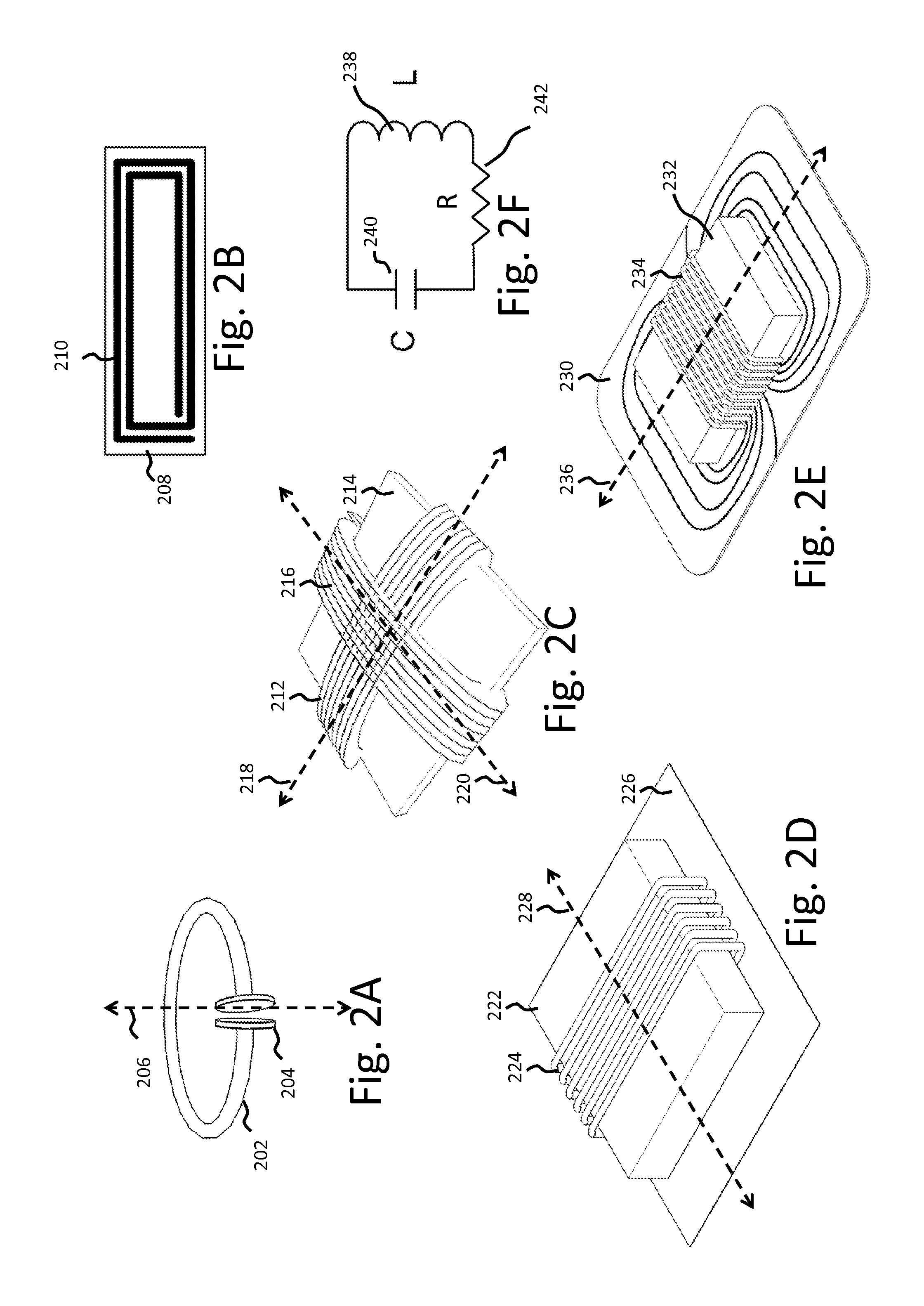
Wireless power transmission system and associated devices
A wireless power transmission system comprises: a power transmitter, which includes a power amplifier that provides a sinusoidal waveform in the frequency range of about 20 to 500 kHz; a first loop antenna producing an alternating magnetic field within a selected area; a power receiver, which includes a second loop antenna located at least partially within the alternating magnetic field of the first antenna; and an electricity-consuming device connected to the output of the power receiver. Both transmitter and receiver preferably contain a capacitive circuit element to optimize tuning, which may be discrete capacitors or may rely on the self capacitance of the antenna(s). Applications of the system include: wirelessly powered lights for fans, boats, aquariums, display cases, etc.; wirelessly powered sensors and other devices for use with captive animals; and systems for transmitting useful power through construction materials to devices on the other side of walls or other structures.
Owner:MESIBOV STEVEN
Adaptive antenna optimization network
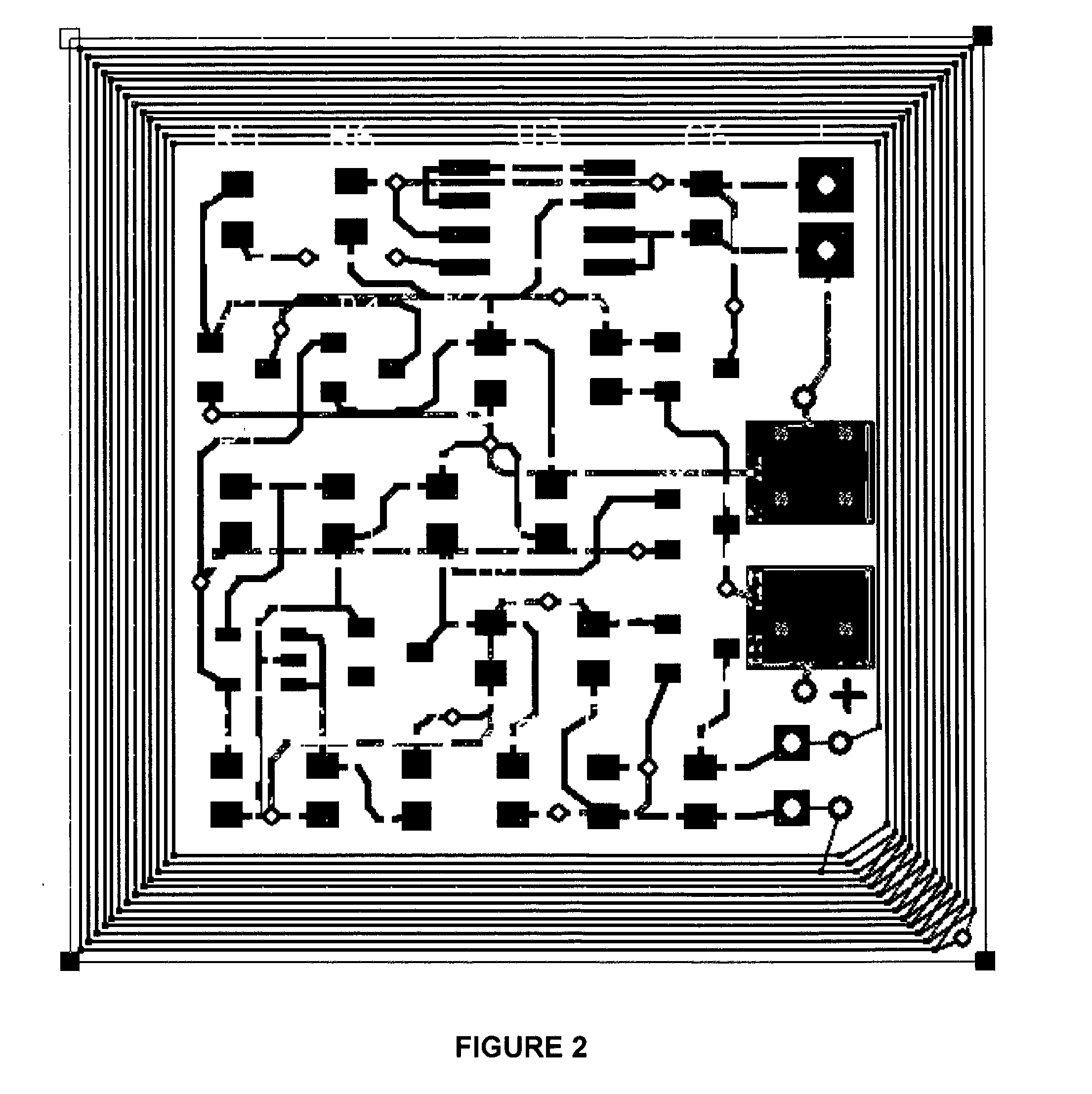
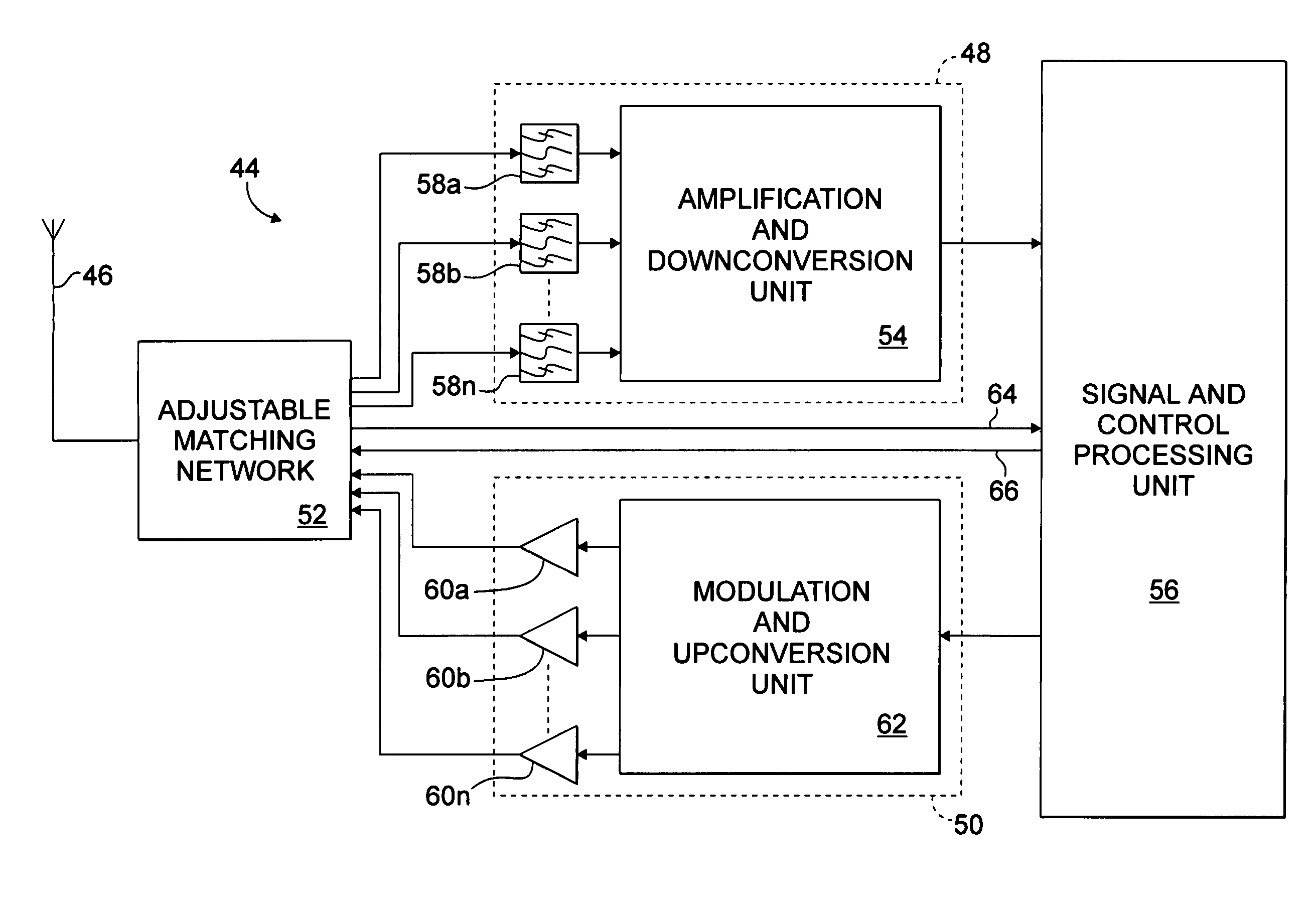
InactiveUS6961368B2Low costMinimal spacePower amplifiersAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency bandSelf adaptive
An adjustable matching network is provided for a wireless communications device transmitting and receiving signals in multiple frequency bands via an antenna. The adjustable matching network selectively connecting the antenna to a select power amplifier corresponding to a selected transmit frequency band and automatically matching the impedance of the antenna to the select power amplifier. The adjustable matching network also selectively connecting the antenna to a select bandpass filter corresponding to a selected receive frequency band and automatically matching the impedance of the antenna to the select bandpass filter.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Methods and apparatus for filtering an optical fiber
InactiveUS6222970B1Improve responseReduce sensitivityCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh energyPhotonics
Filtering of optical fibers and other related devices. High-energy methods for depositing thin films directly onto the ends of optical fibers can be used to produce high-quality, high-performance filters in quantity at a reasonable cost. These high-quality filters provide the high performance needed for many demanding applications and often eliminate the need for filters applied to wafers or expanded-beam filtering techniques. Having high-quality filters applied directly to optical fiber and faces permits production of high-performance, micro-sized devices that incorporate optical filters. Devices in which these filters may be used include spectroscopic applications including those using fiber optic probes, wavelength division multiplexing, telecommunications, general fiber optic sensor usage, photonic computing, photonic amplifiers, pump blocking and a variety of laser devices.
Owner:CIRREX SYST
Tunable wireless energy transfer systems
ActiveUS8643326B2Effective levelingImprove performanceMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferAudio power amplifier
Described herein are improved configurations for a wireless power transfer. A power source for driving a resonator includes a switching amplifier. The duty cycle of the switching amplifier may be adjusted as well as optionally inductors and / or capacitors of the circuit to improve the efficiency of power transfer from the power source to the resonators when the parameters of the resonant load change.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
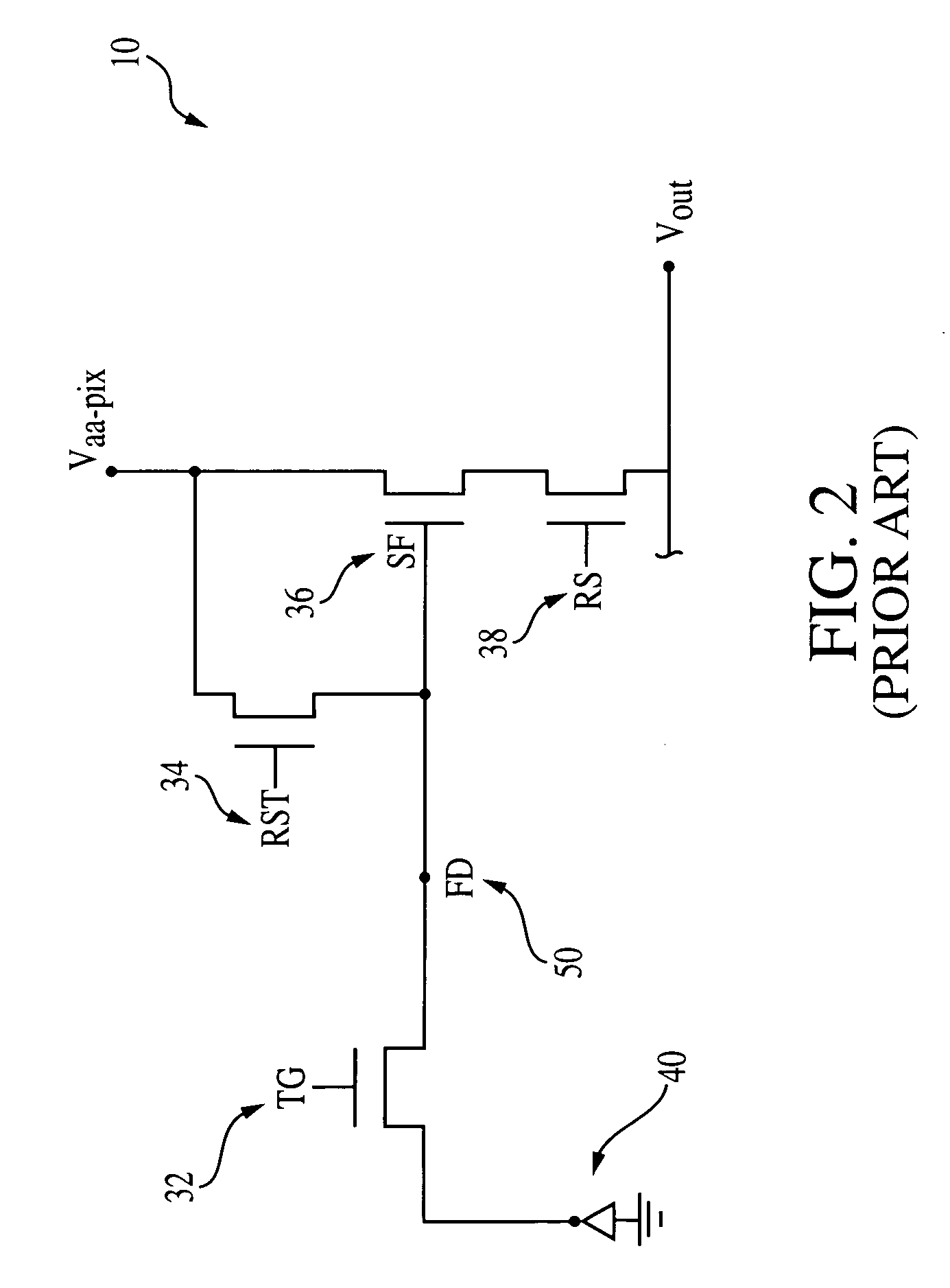
Storage pixel sensor and array with compression
InactiveUS6512544B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceSemiconductor
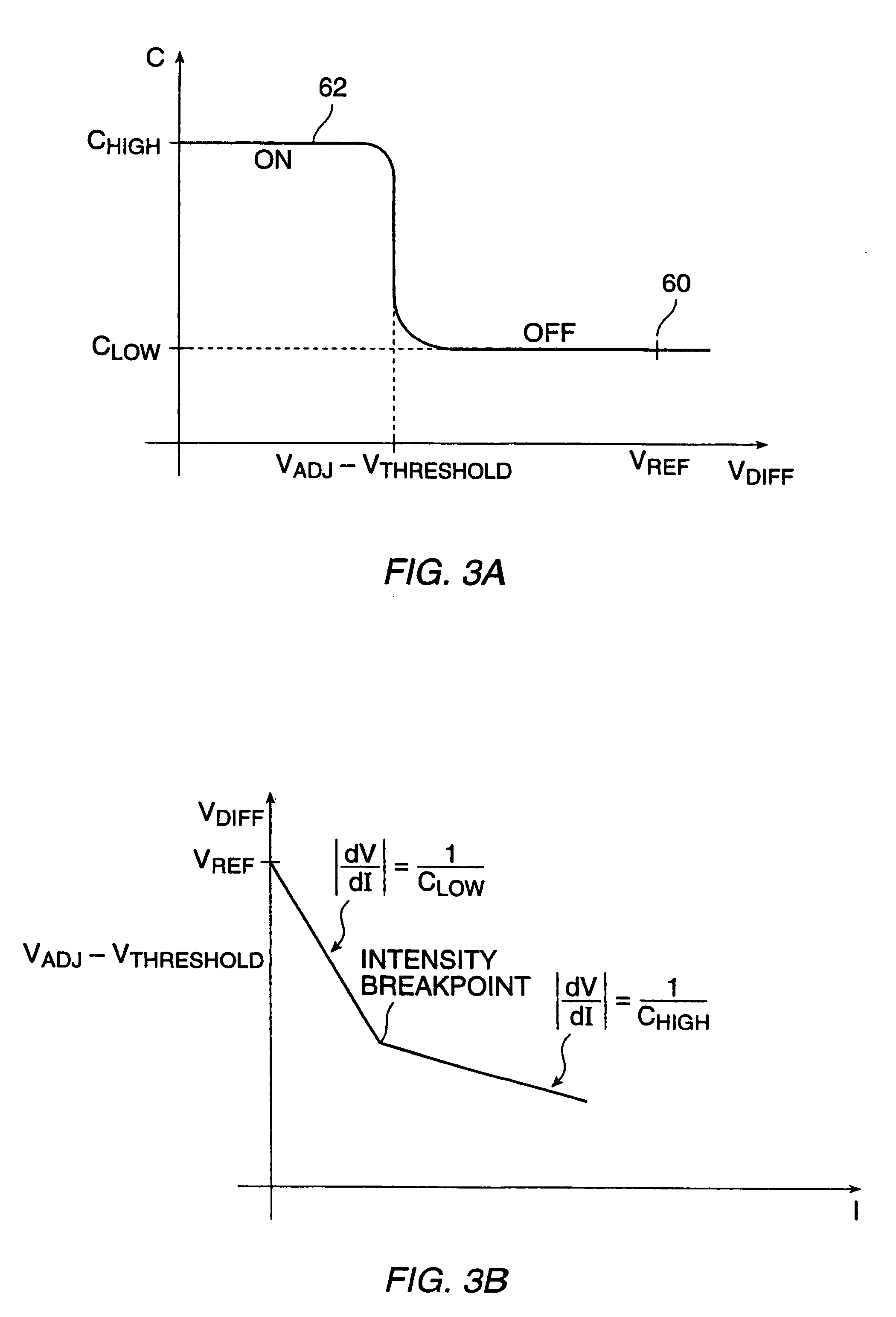
A storage pixel sensor disposed on a semiconductor substrate comprises a photosensor. At least one nonlinear capacitive element is coupled to the photosensor. At least one nonlinear capacitive element is arranged to have a compressive photocharge-to-voltage gain function. An amplifier has an input coupled to the nonlinear capacitor and an output. Other, non-capacitive elements may be employed to produce a compressive photo-charge-to-voltage gain having at least one breakpoint.
Owner:FOVEON
Echo detection and self-excitation elimination method for electromagnetic wave common-frequency amplifying repeater system
ActiveCN102130698AAchieve full power transmissionReduced transceiver isolationRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringEcho detectionMechanical engineering
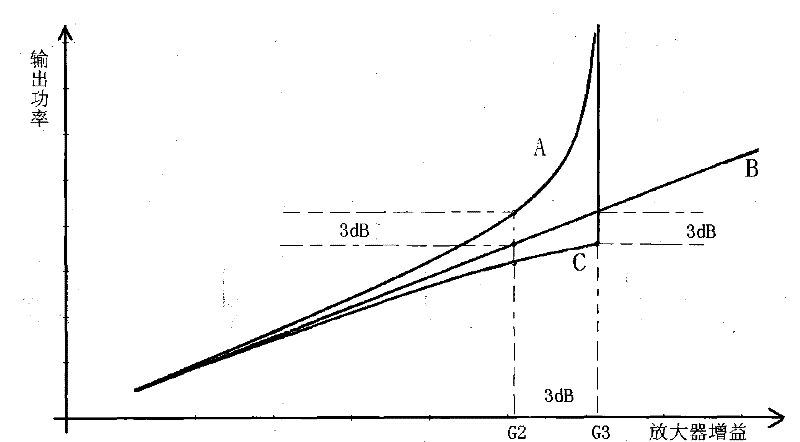
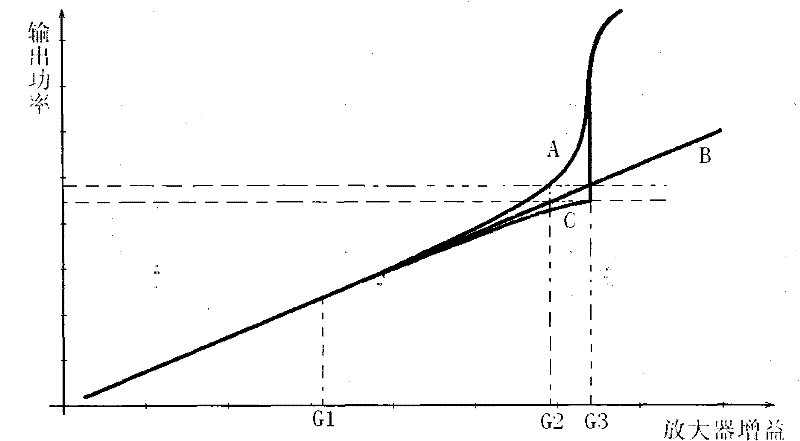
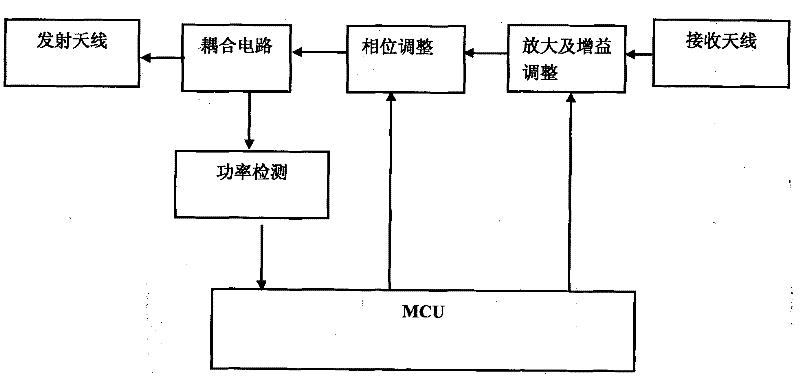
The invention relates to an echo detection and self-excitation elimination method for an electromagnetic wave common-frequency amplifying repeater system. By using the method, a relationship among grains of an amplifier, a phase when returned electromagnetic wave signals reach a receiving antenna and the output power of the amplifier in the electromagnetic wave common-frequency amplifying repeater system is discovered. According to the relationship, the magnitude of echo signals can be detected effectively, the output power of the amplifier is improved, the self-excitation of the amplifier resulting from the echo signals is avoided, the requirements on isolations of a forward antenna and a backward antenna are reduced, the system grains are improved, and the coverage area is increased. The method is suitable for all electromagnetic wave common-frequency amplifying repeater systems, such as communication repeaters, data television repeaters and the like.
Owner:深圳市佳贤通信科技股份有限公司
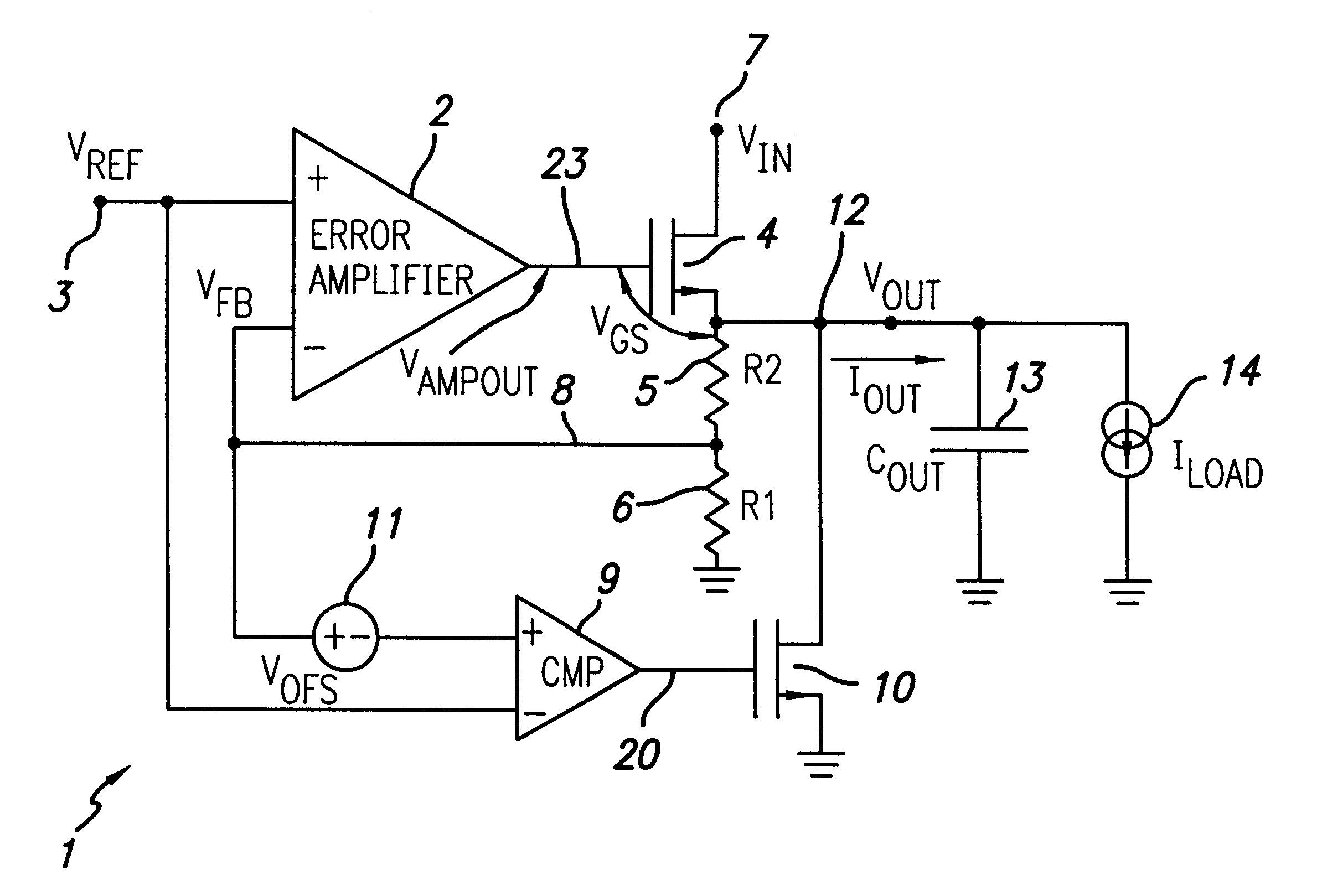
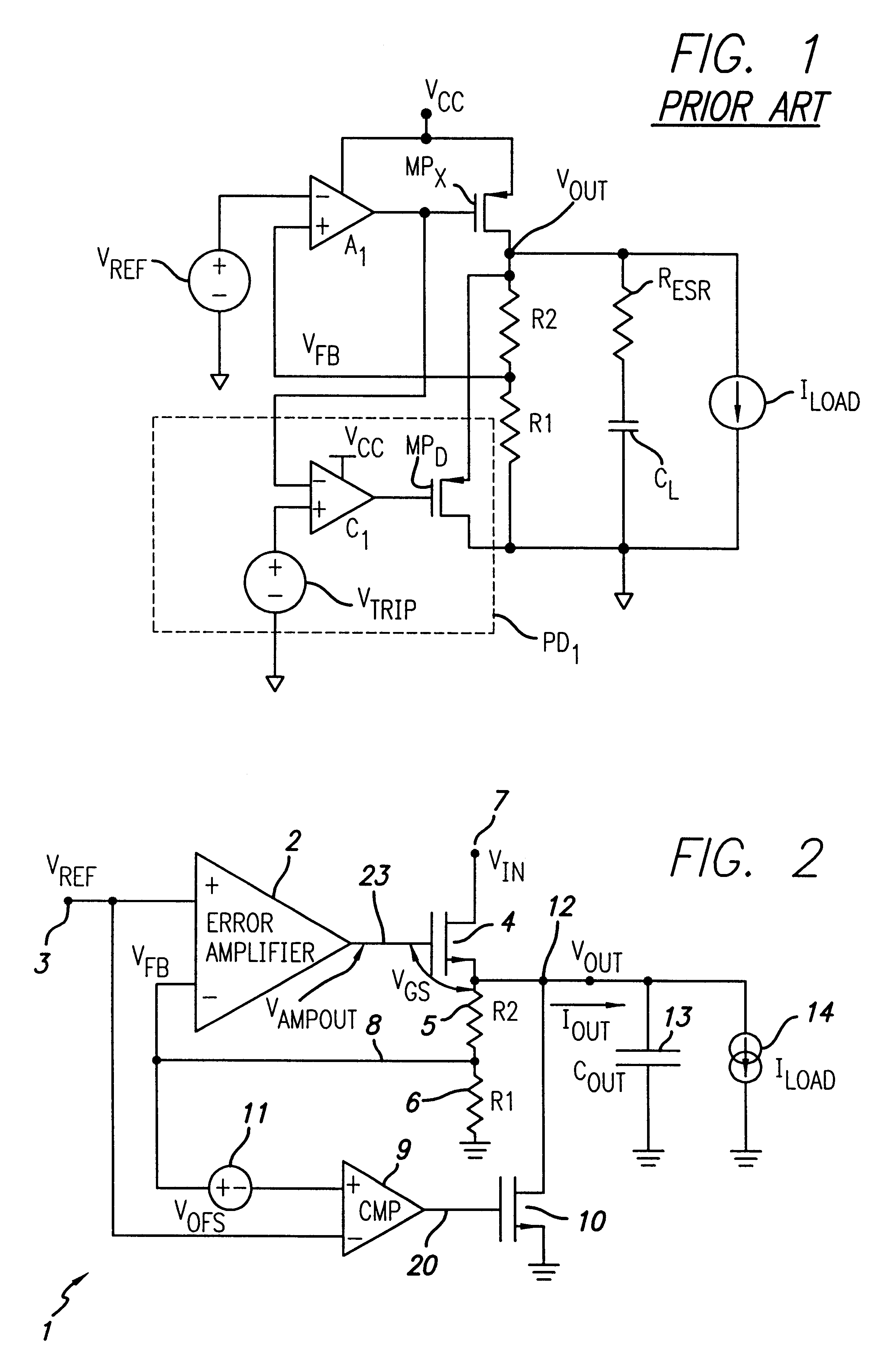
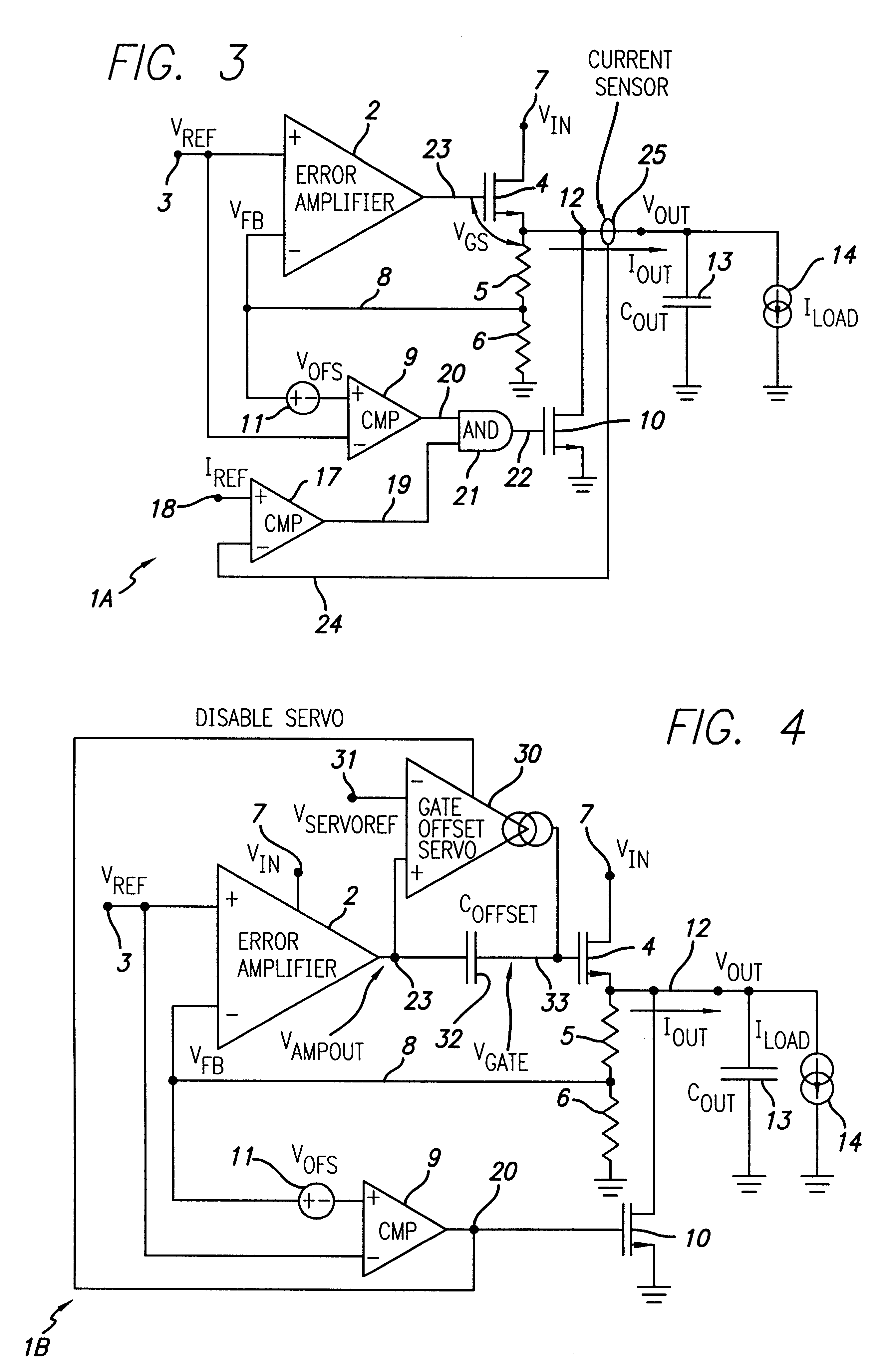
Overvoltage sensing and correction circuitry and method for low dropout voltage regulator
InactiveUS6201375B1Reduce severityEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentArrangements responsive to excess voltageOvervoltageElectrical conductor
Owner:BURR-BROWN CORPORATION
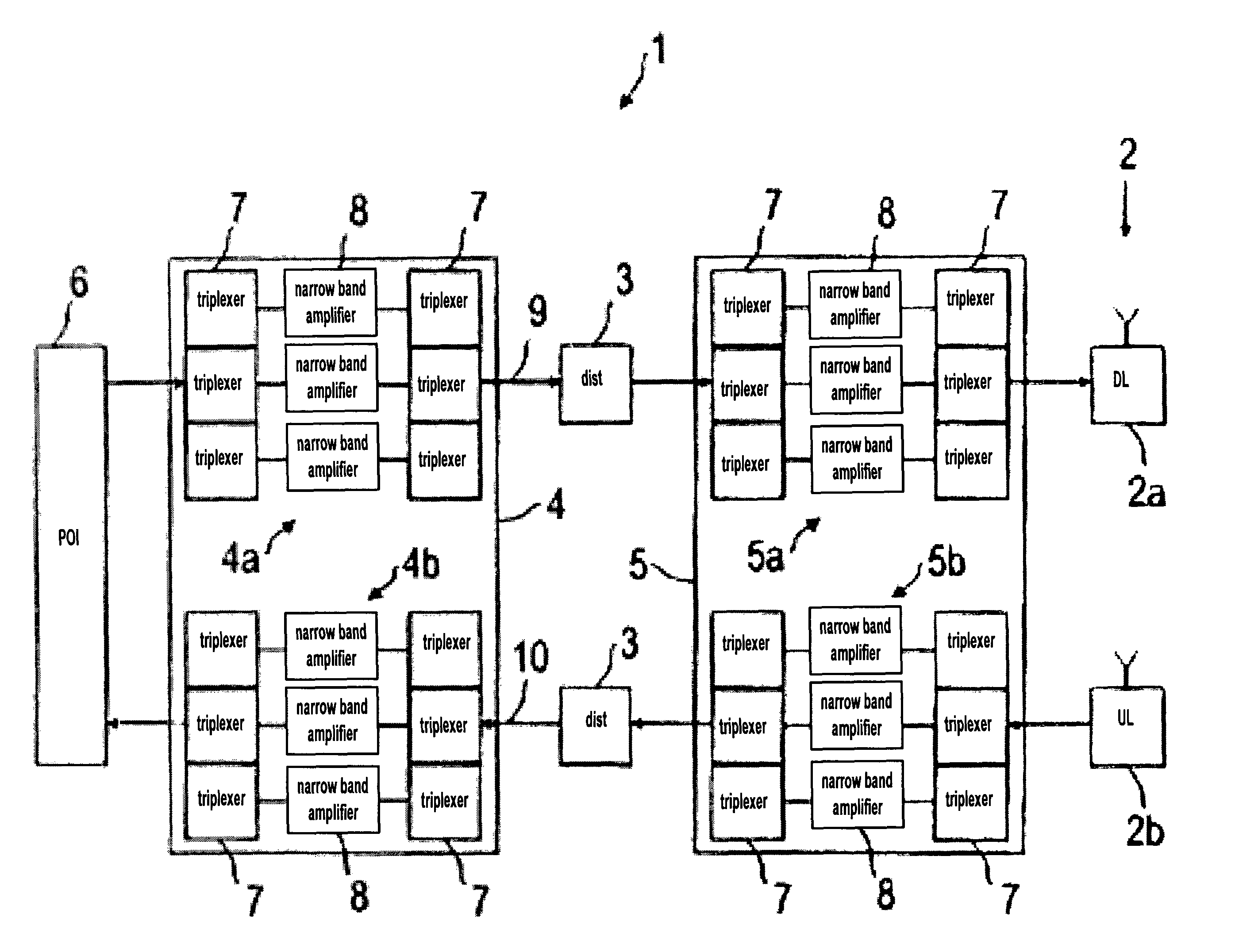
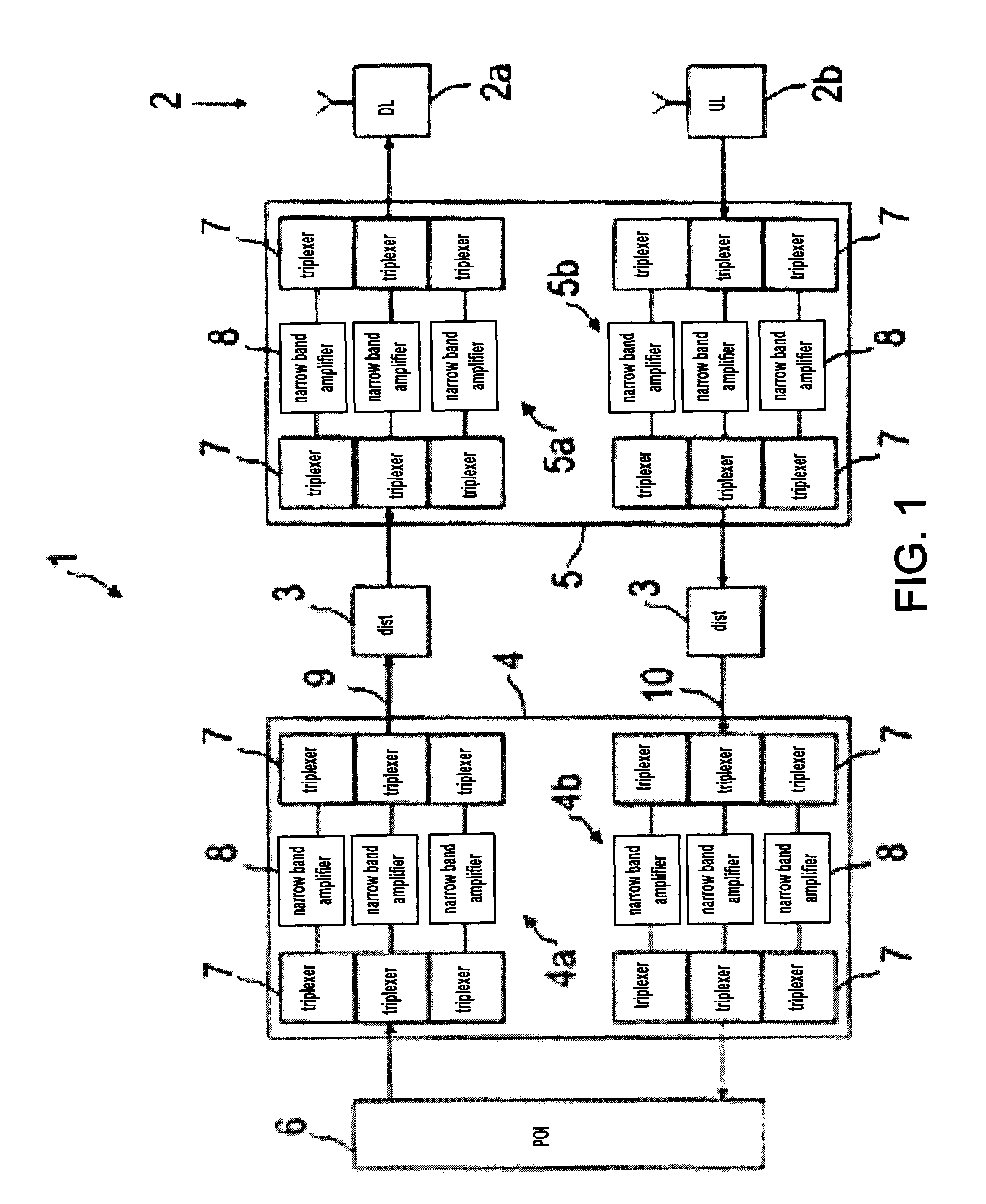
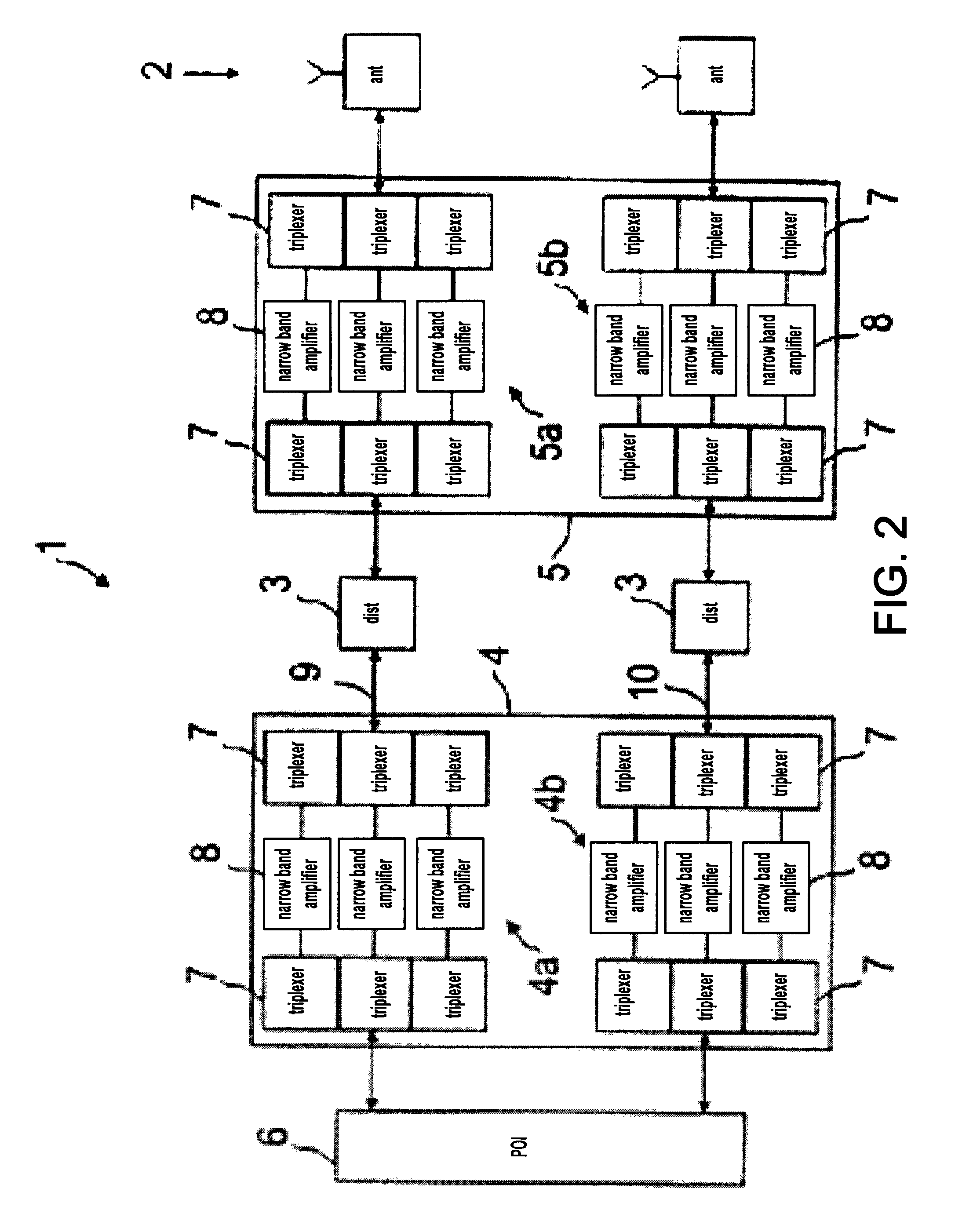
Radio frequency network
ActiveUS8428033B2Avoid intermodulationsReduce sizeFrequency-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesAudio power amplifierDistributed antenna system
Owner:RFS TECH INC
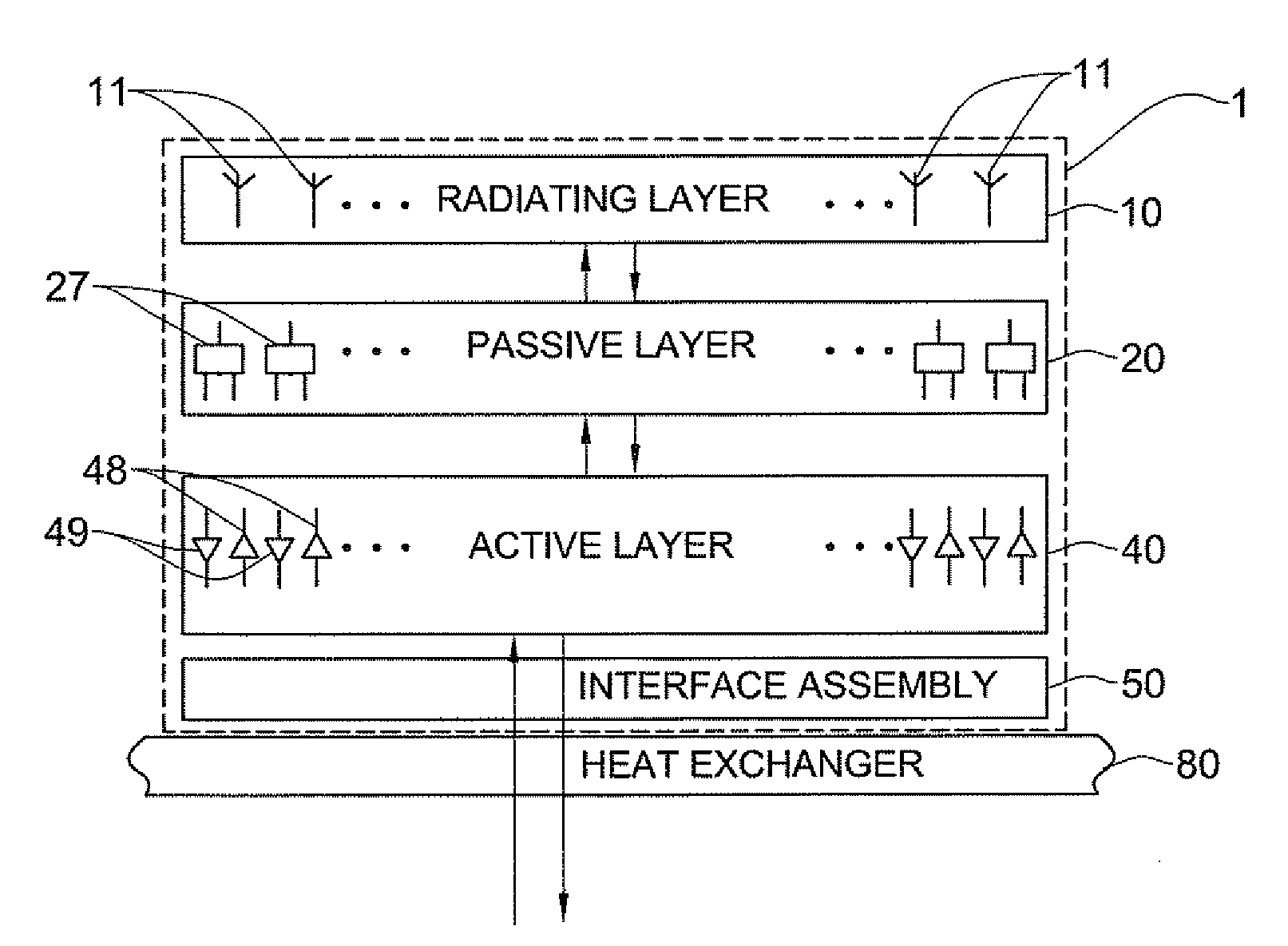
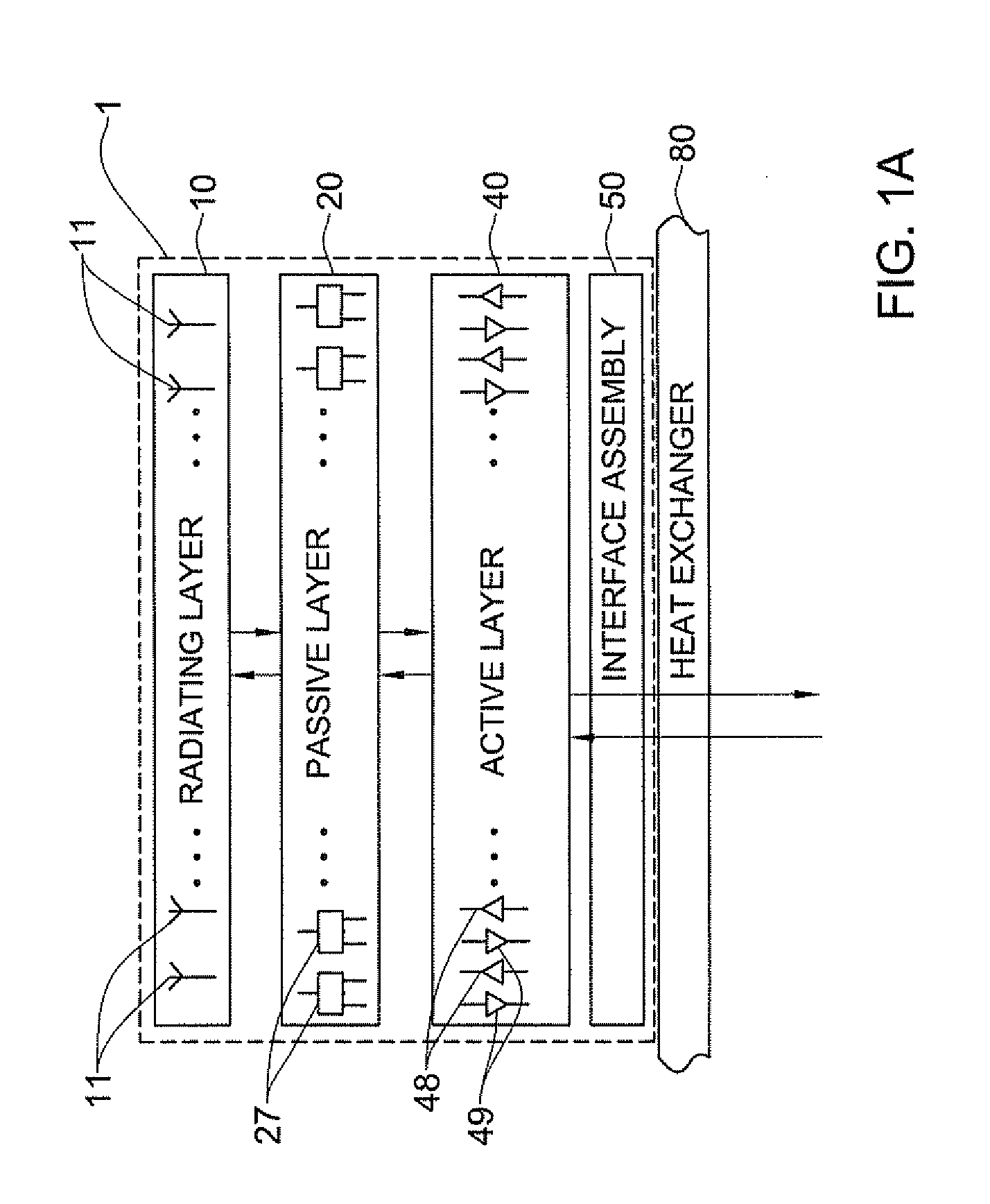
Phased array antenna and method for producing thereof
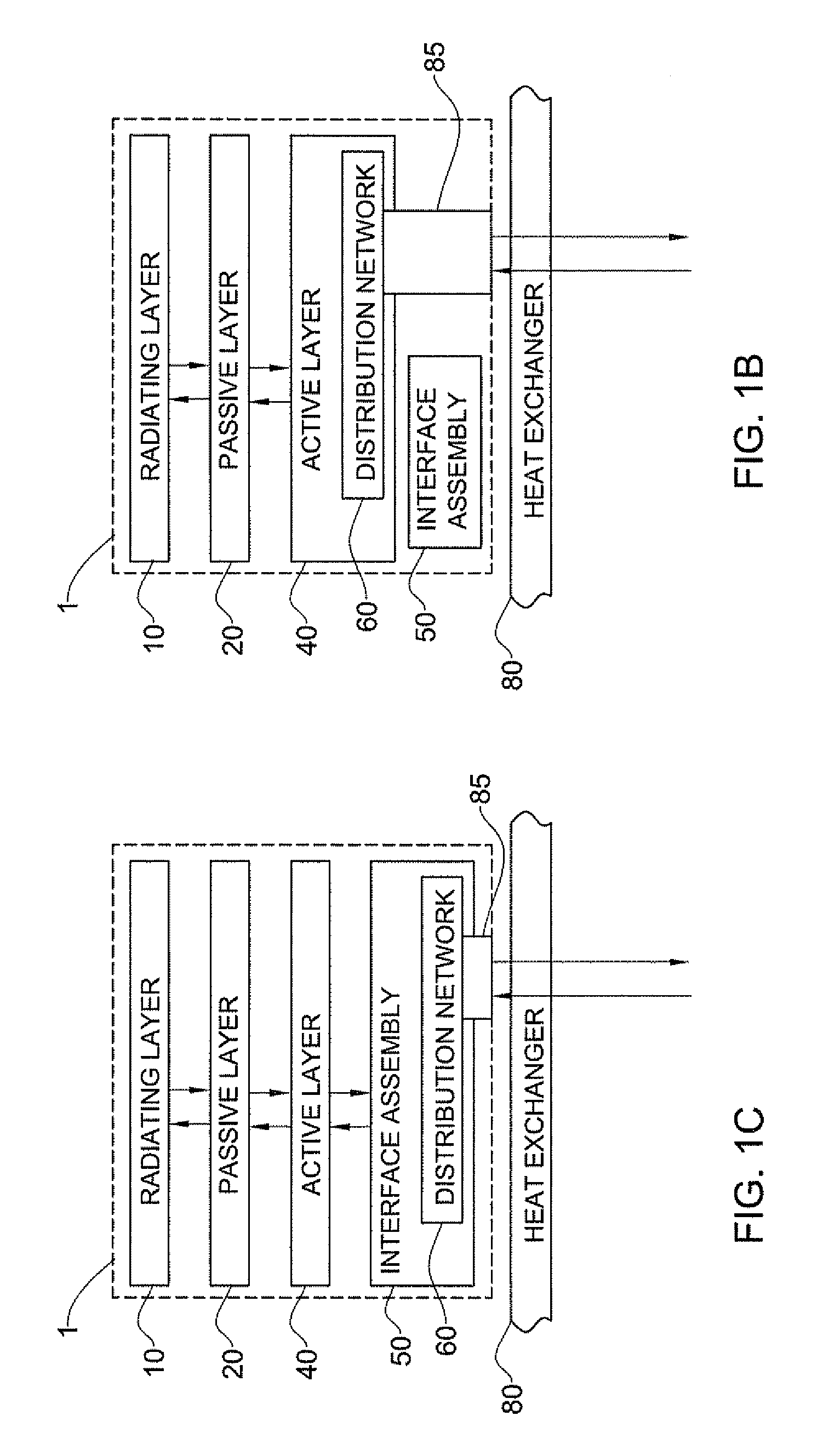
A vertically stacked array antenna structure is described. The structure comprises a radiating layer, a passive layer disposed under said radiating layer, an active layer disposed under said passive layer, and an interface assembly. The radiating layer comprises an array of radiating elements. The passive layer has only passive components. At least a part of the passive components includes an array of RF duplexers corresponding to the array of radiating elements. The active layer comprises RF amplifiers. The interface assembly comprises at least one metallic frame which is in direct thermal coupling with the RF amplifiers. The interface assembly is configured for providing thermal communication of the active layer with a heat exchanger.
Owner:ELTA SYST LTD
Single mode optical fiber
InactiveUS6334019B1High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5 mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20 mu, and may be as large as 50 mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibres, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fiber may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
Method and apparatus for treating hemodynamic disfunction
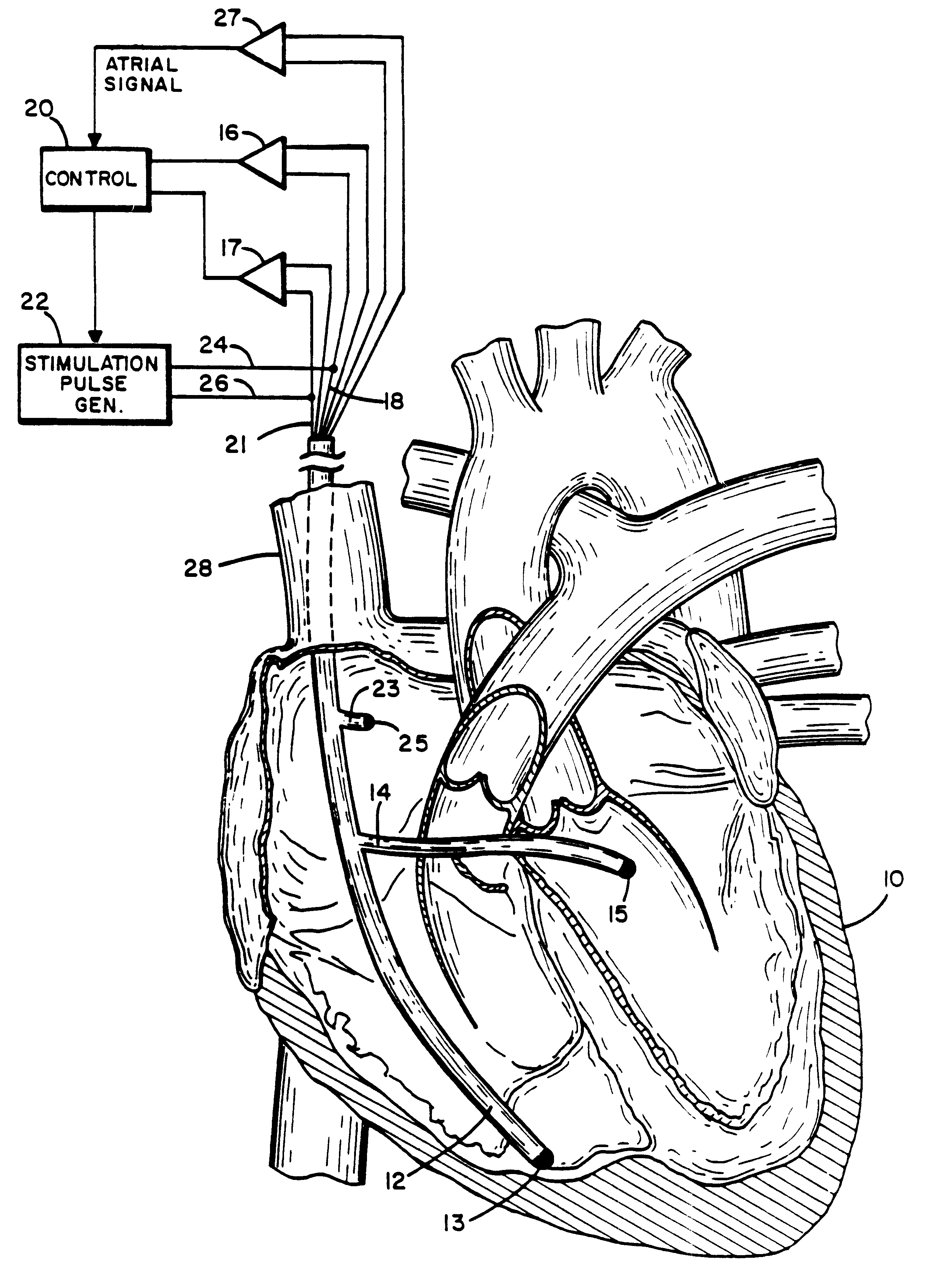
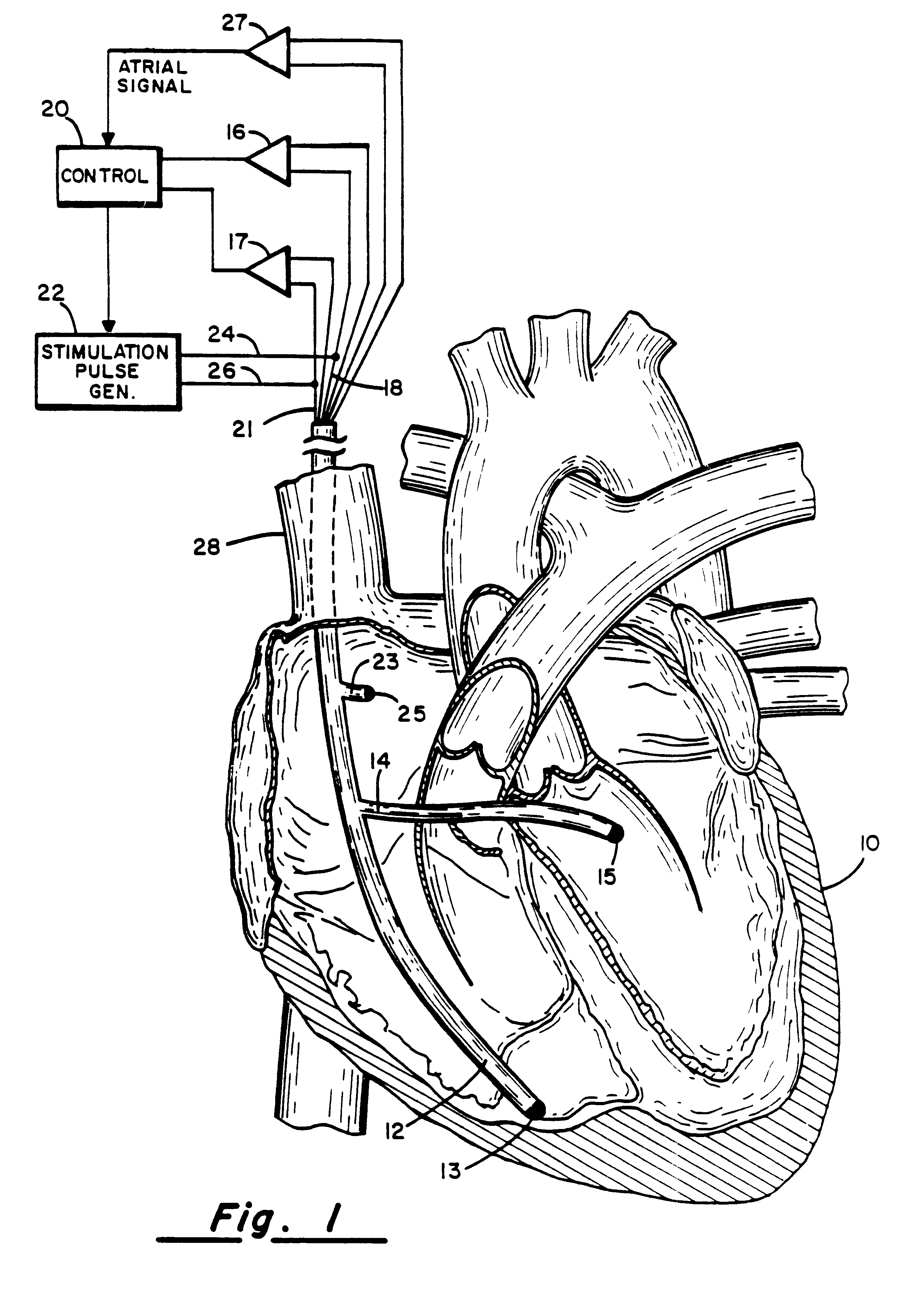
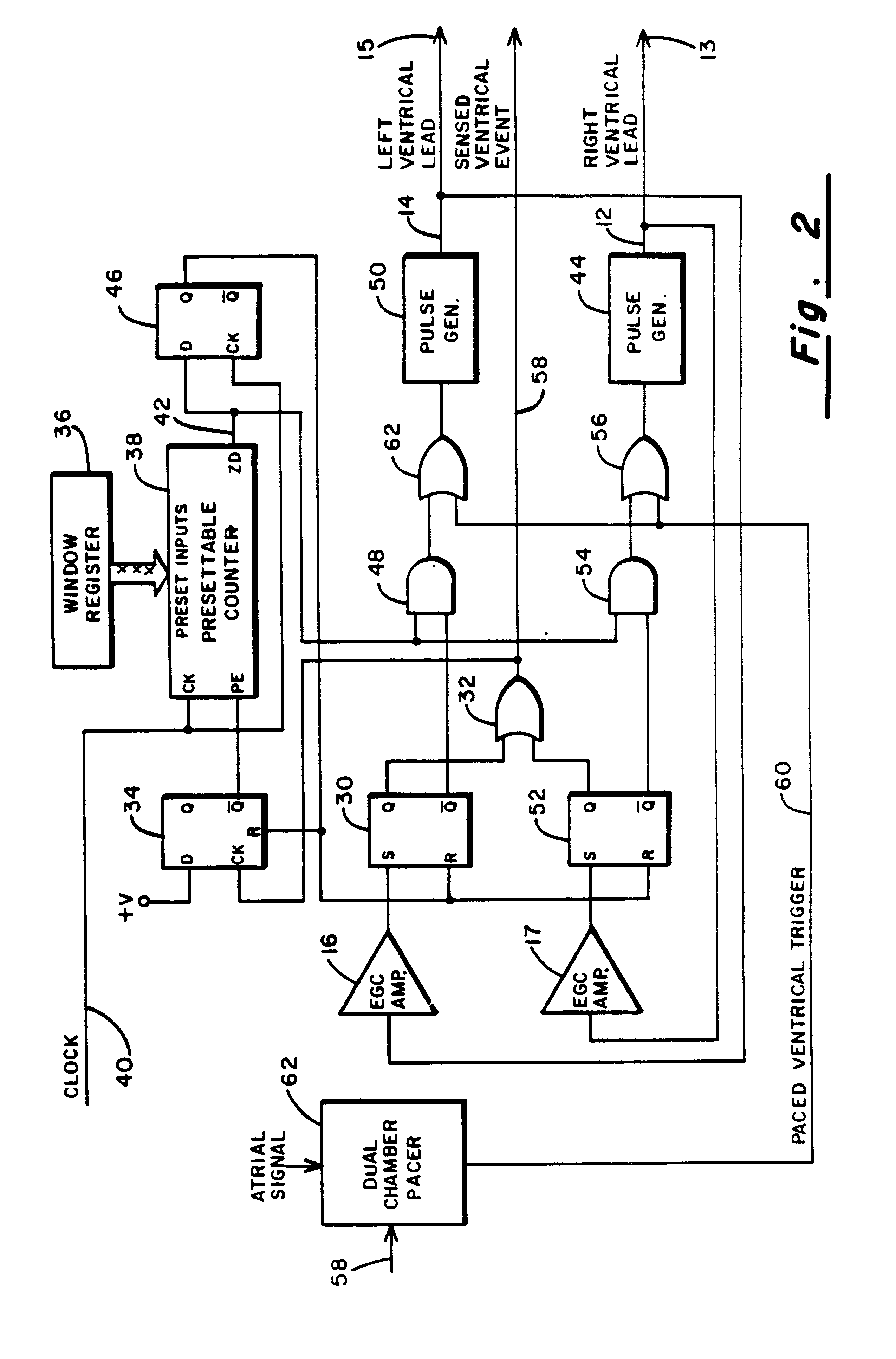
A method of treating hemodynamic disfunction by simultaneously pacing both ventricles of a heart. At least one ECG amplifier is arranged to separately detect contraction of each ventricle and a stimulator is then activated for issuing stimulating pulses to both ventricles in a manner to assure simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, thereby to assure hemodynamic efficiency. A first ventricle is stimulated simultaneously with contraction of a second ventricle when the first fails to properly contract. Further, both ventricles are stimulated after lapse of a predetermined A-V escape interval. One of a pair of electrodes, connected in series, is placed through the superior vena cava into the right ventricle and a second is placed in the coronary sinus about the left ventricle. Each electrode performs both pacing and sensing functions. The pacer is particularly suitable for treating bundle branch blocks or slow conduction in a portion of the ventricles.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
MP3 doorbell chime system
InactiveUS20070008081A1Level of customizationSound producing devicesElectric/electromagnetic audible signallingMicrocontrollerDoorbell
A door chime system includes a microcontroller having a processor and a data memory for storing digital sound files. The microcontroller includes an input and an output representative of digital sound files; a door chime actuator having an output responsive to the depression of the doorbell electrically connected to the input of said microcontroller and an amplifier stage for converting a one of said digital sound files into sound. The output from the microcontroller representative of a digital sound file is supplied to the input of the amplifier stage responsive to the door chime output.
Owner:HEATH & CO LTD
High dynamic range pixel amplifier
ActiveUS20050224843A1Increase capacitanceReduce capacitanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceEngineering
A pixel cell with increased dynamic range is formed by providing a floating diffusion region having a variable capacitance, controlled by at least one gate having source and drain regions commonly connected to the floating diffusion region. The gate has an intrinsic capacitance which, when the gate is activated, is added to the capacitance of the floating diffusion region, providing a low conversion gain readout. When the gate is off, the floating diffusion region capacitance is minimized, providing a high conversion gain readout. The gate may also be selectively switched to mid-level. At mid-level, a mid-level conversion gain, which is between the high and low conversion gains, readout is provided, but the gate still provides some capacitance to prevent the floating diffusion region from saturating.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
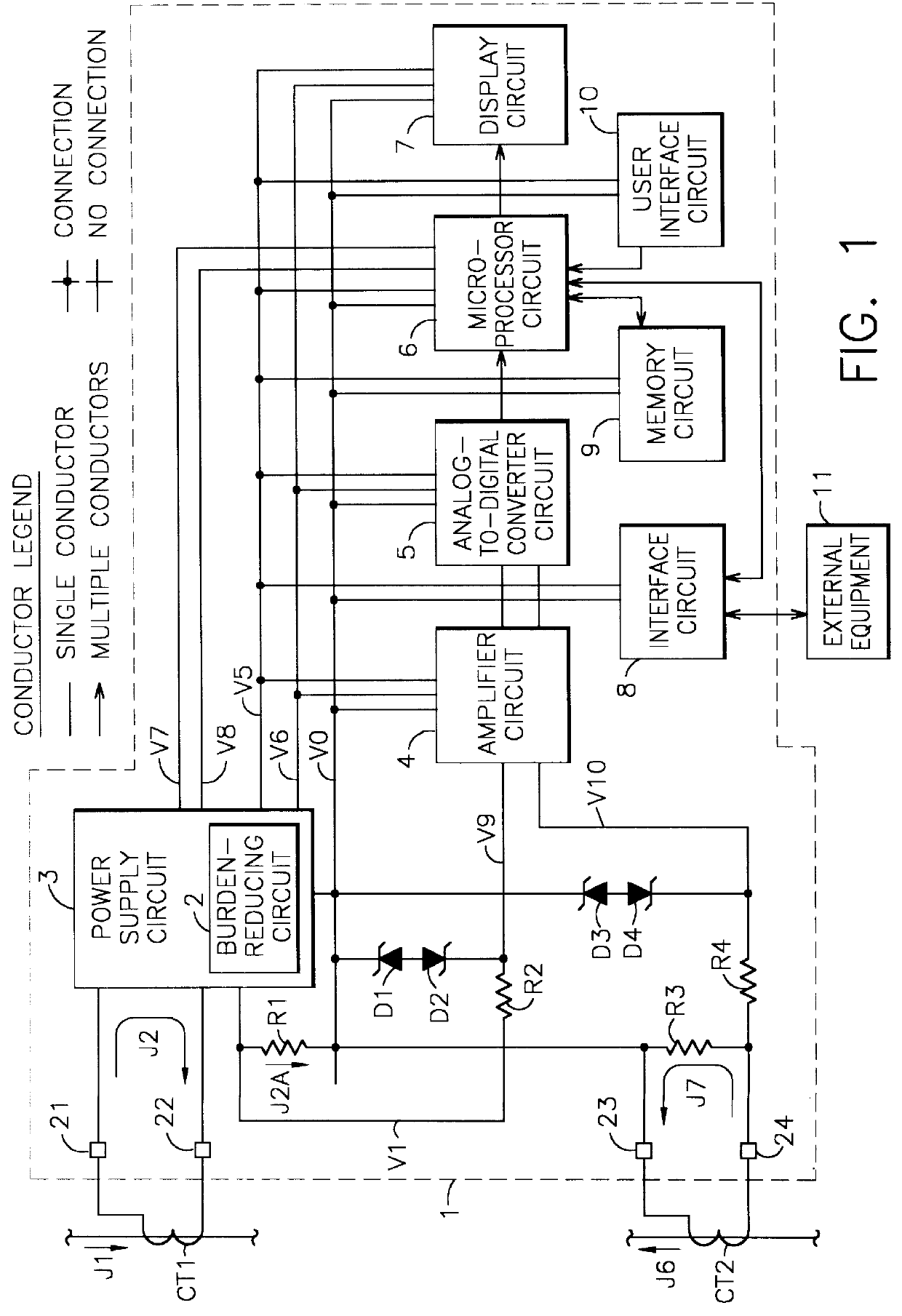
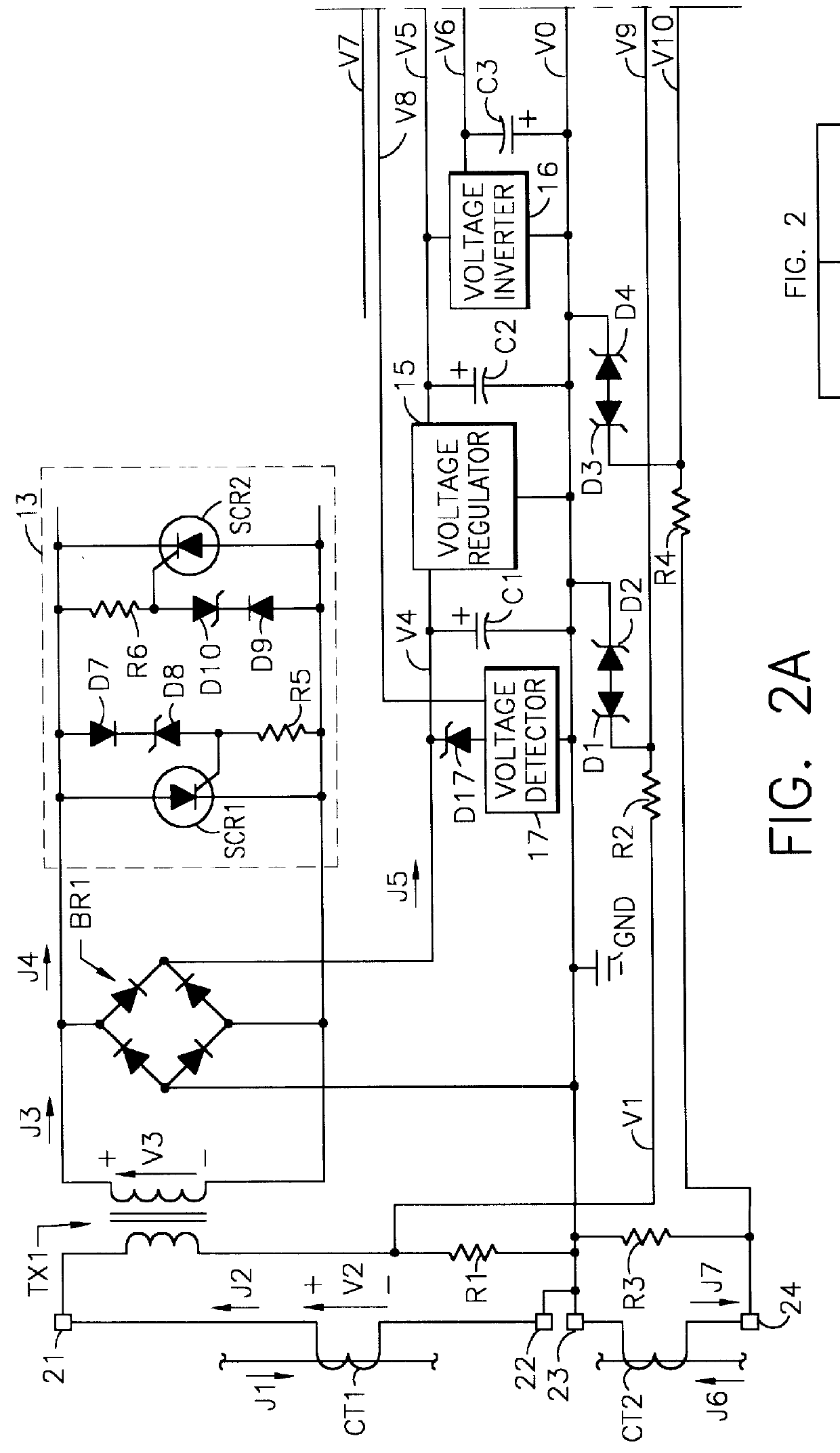
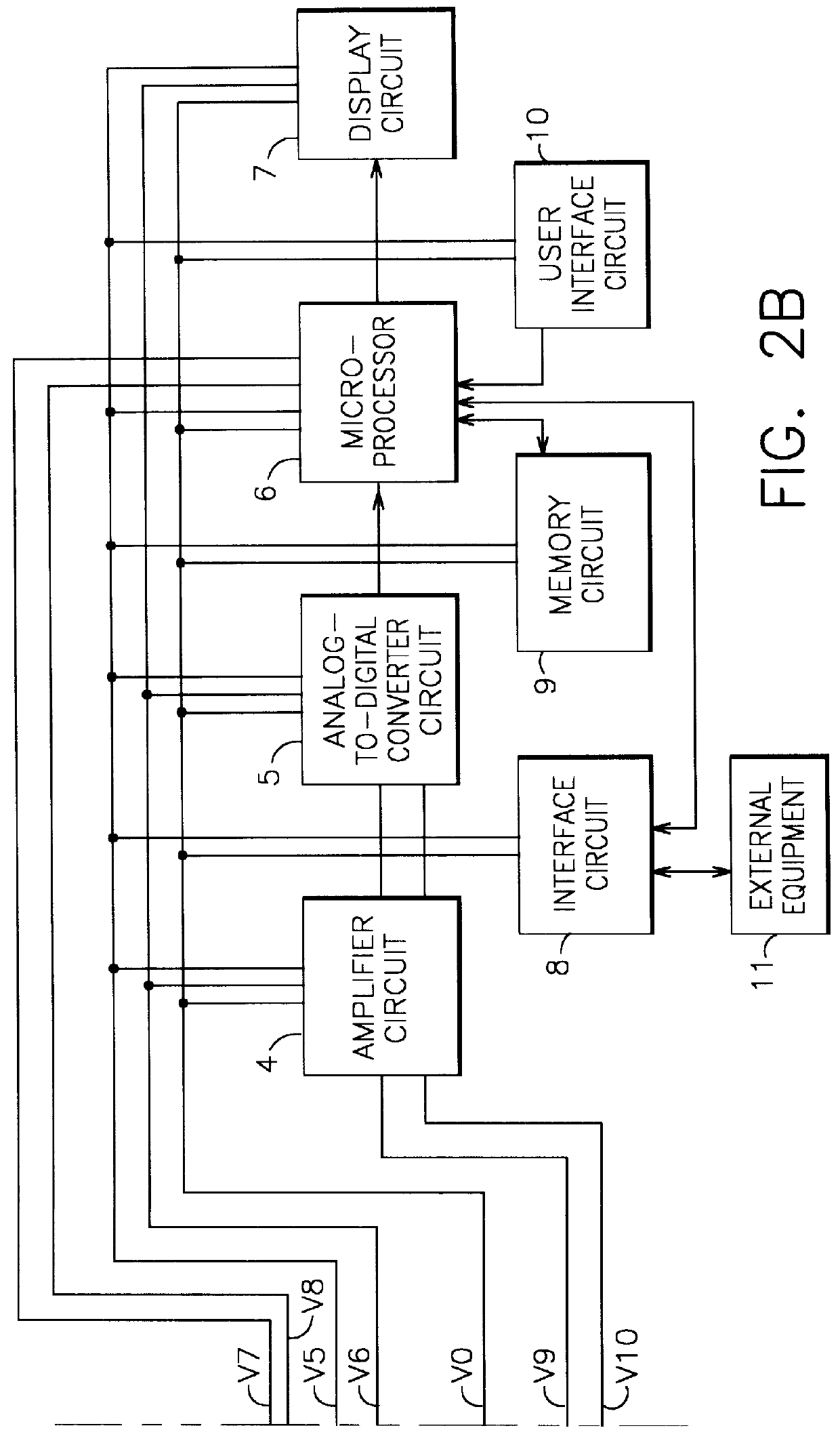
Self-powered current monitor
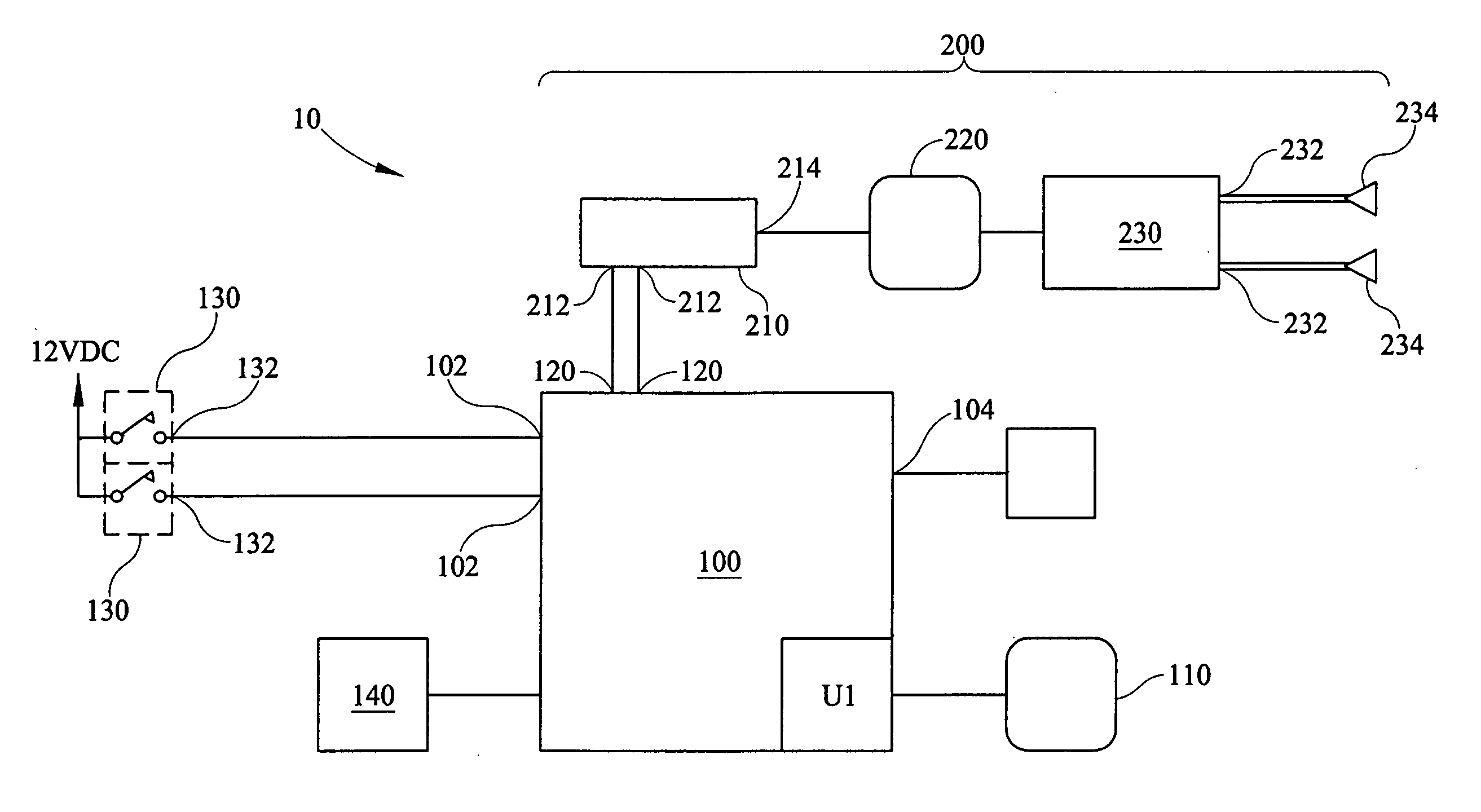
A self-powered current monitor for monitoring current in electric power systems. Various data relating to input currents may be displayed, such as current magnitude, current demand, and harmonics levels. Operating power is derived from one or more of the input currents. The power supply configuration may include a burden-reducing means to reduce the burden on input current sources during sampling of the input currents. The self-powered current monitor (1) includes a power supply section (3), input resistors (R1 and R3), an analog-to-digital converter circuit (5), a microprocessor circuit (6), a memory circuit (9), and a display circuit (7). Optional features include a burden-reducing circuit (2), input circuit protective elements (D1, D2, D3, D4, R2, and R4), an amplifier circuit (4), a user interface circuit (10), and an interface circuit (8) for communication to other equipment.
Owner:EDEL THOMAS G
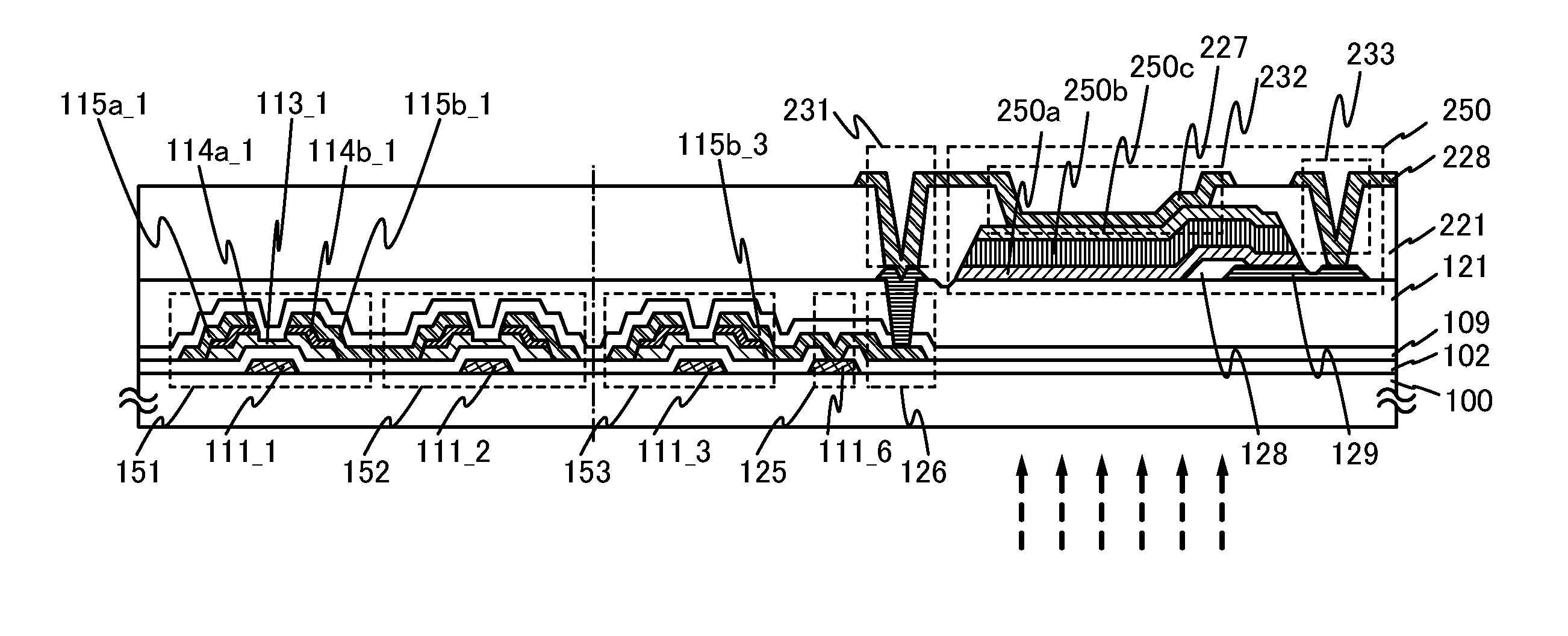
Photosensor and display device
ActiveUS20100134735A1Good reproducibilitySmall display unevennessTransistorStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitIndium
Thin film transistors including an oxide semiconductor containing indium, gallium, and zinc are easily arranged in a matrix over a large substrate and have small characteristic variations. With amplifier circuits and driver circuits of display elements which include the thin film transistors including an oxide semiconductor containing indium, gallium, and zinc with small characteristic variations, intensity distribution of light received by the photodiodes arranged in a matrix is converted into electrical signals with high reproducibility and output, and the display elements arranged in a matrix can be uniformly driven.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
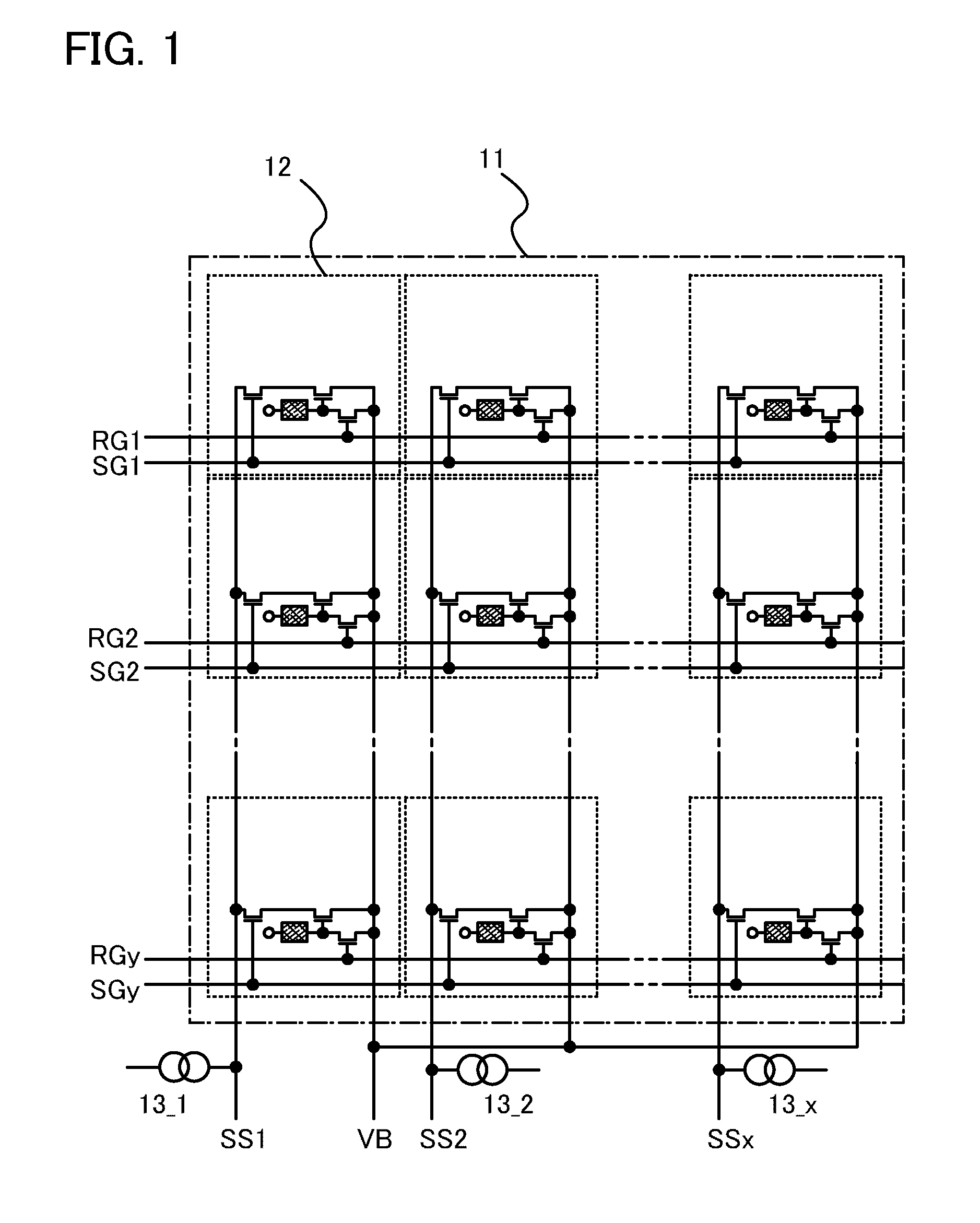
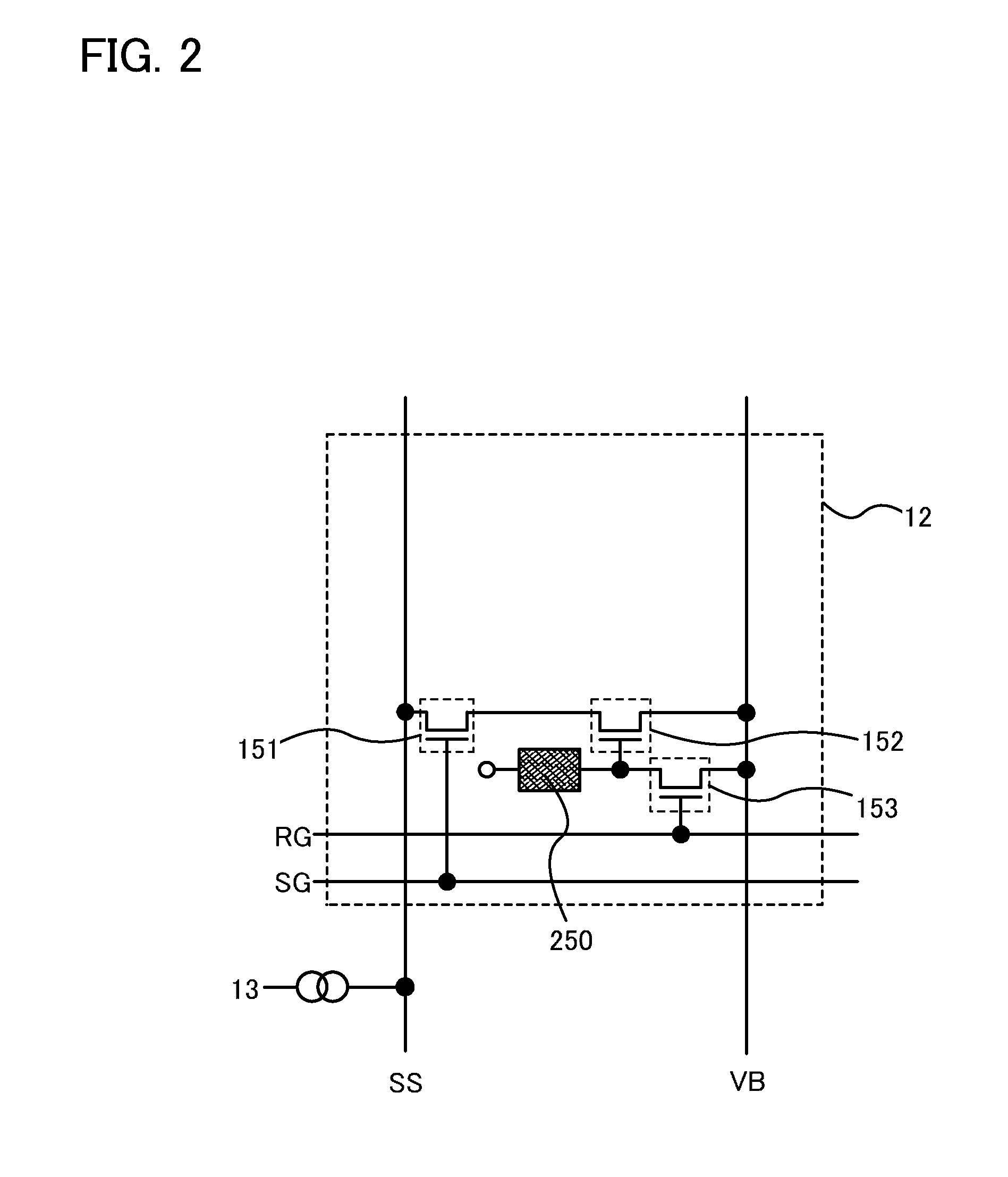
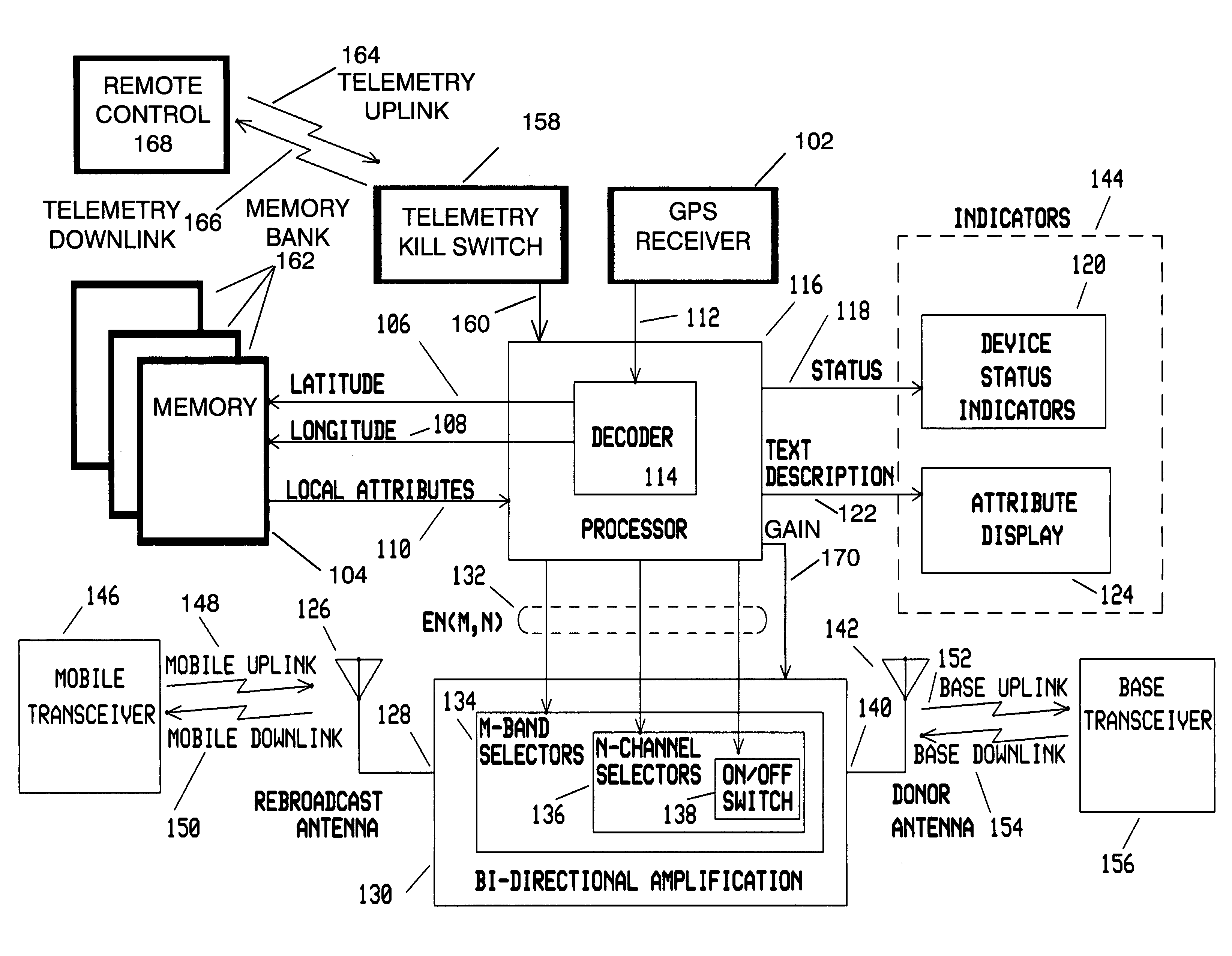
Intelligent signal booster
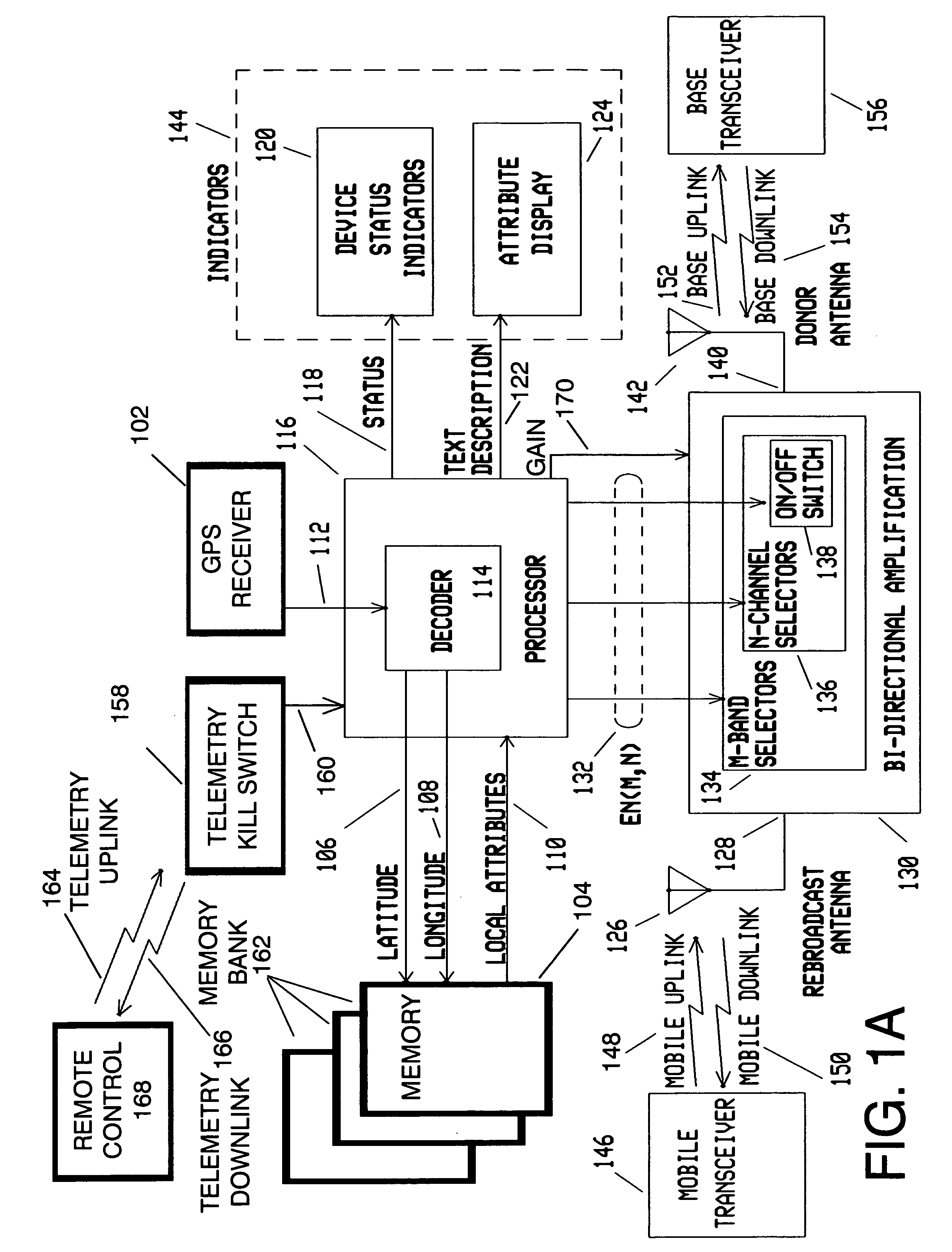
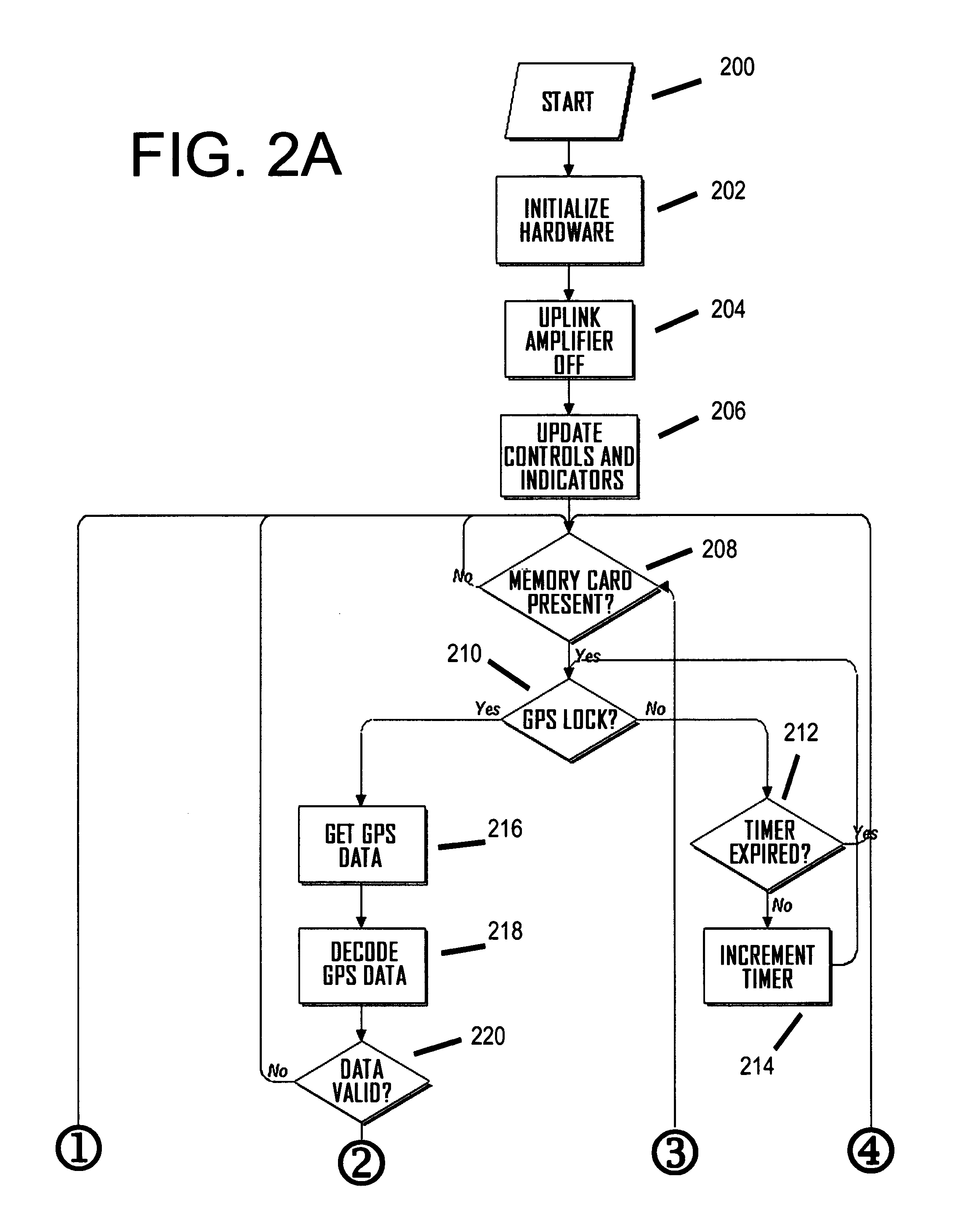
The invention is a device for multi-band, multi-channel, wireless communications that automatically provides signal amplification when and where necessary, and that automatically avoids harmful interference to base stations and other parts of the communications infrastructure. The device is especially suitable for, but not limited to, cellular and PCS bands and channels. The invention is a unique combination of an adjustable gain, bidirectional amplifier, a GPS receiver, a processor, and one or more removable, non-volatile, updatable memory devices. Alternatively, the memory can be an internal device accessible via an electronic port such as a USB. In either case, the memory stores comprehensive information that determines if amplification is necessary at a particular location sensed by the GPS receiver. Because the memory devices are updatable, they therefore provide protection against piracy and unauthorized and improper use. As an added measure of protection for the wireless networks, the device includes a dedicated apparatus that permits a service technician to remotely deactivate it in the event of a malfunction.
Owner:RAINES JEREMY KEITH +1
Implantable medical devices and related methods
Implantable medical devices and associated methods are disclosed. In one implementation, the implantable medical device comprises a conductive housing and a remote electrode that is mechanically coupled to the conductive housing by a lead body. An amplifier is electrically connected to the remote electrode and the conductive housing for providing a signal representative of a voltage difference between the remote electrode and the conductive housing. In some methods in accordance with the present invention, the implantable medical device is implanted in an implant site overlaying one half of a rib cage of a human body. The implantable medical device produces a signal representative of the voltage difference between the remote electrode and the conductive housing and the signal is transmitted to a receiver located outside the human body.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
High efficiency medical nebulizer
A pneumatic nebulizer that produces a high volume of aerosols for inhalent delivery of medications and other constituencies. High pressure gas formed into a gas jet is passed through a thin choked region of fluid that is entrailed and impinged upon an aerosol amplifier which creates a spray whose aerosol components are directed up through vents to an aerosol outlet for delivery. Larger-sized liquid particles are caused to pool up in a region surrounding the aerosol amplifer and then drip down back into the liquid medication reservoir.
Owner:MERCURY ENTERPRISES
Encapsulation of independent transmissions over internal interface of distributed radio base station
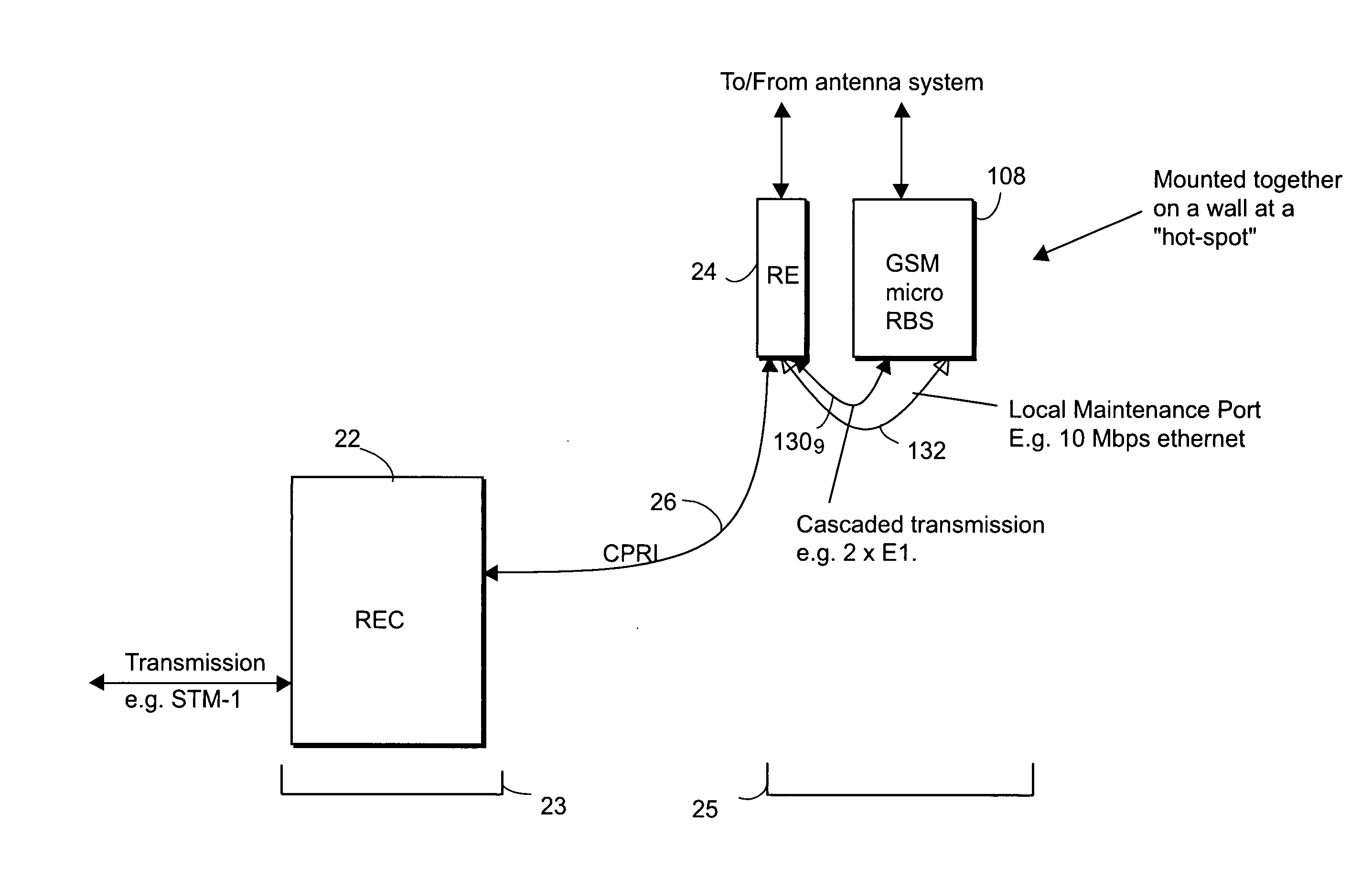
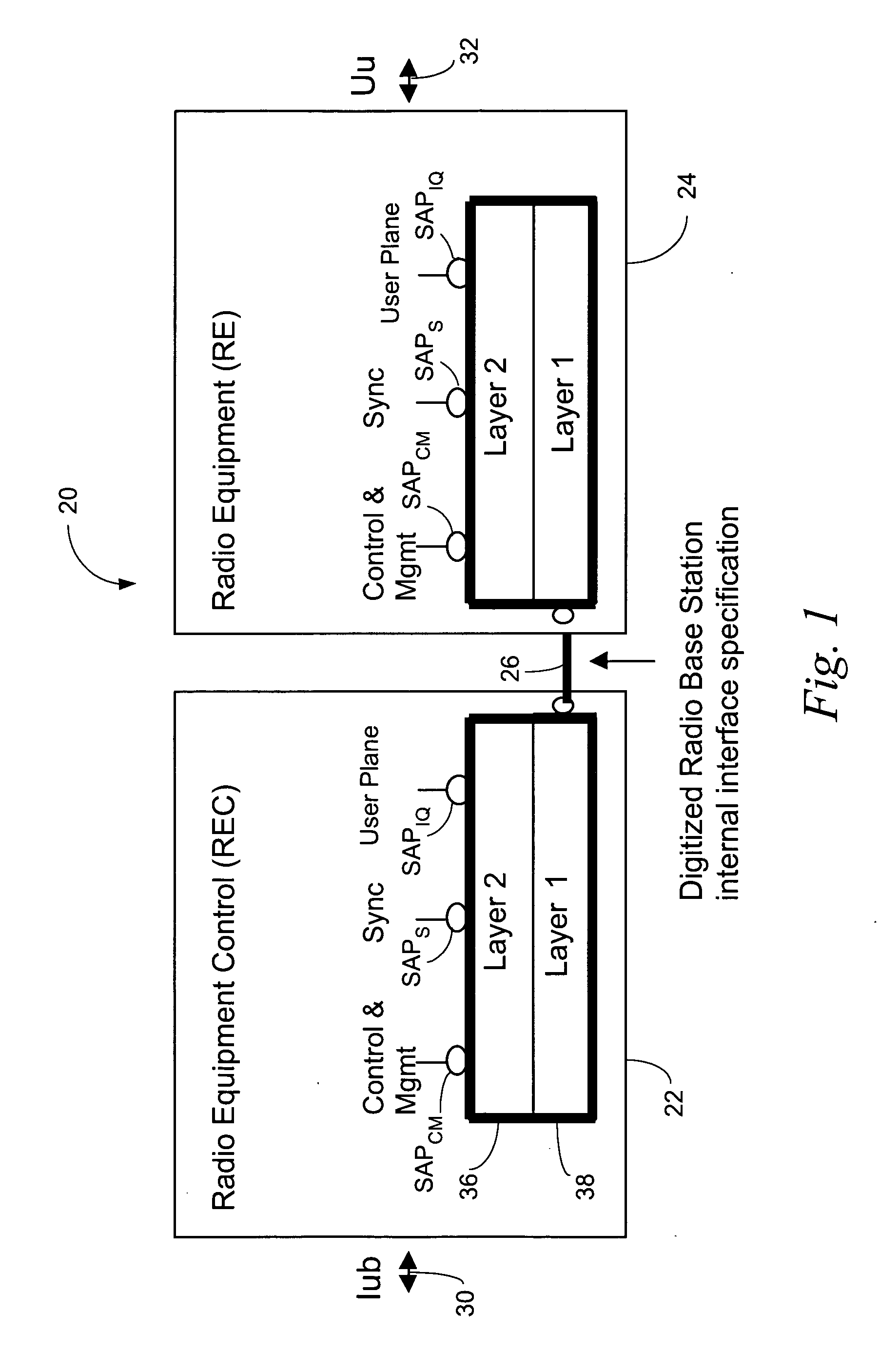
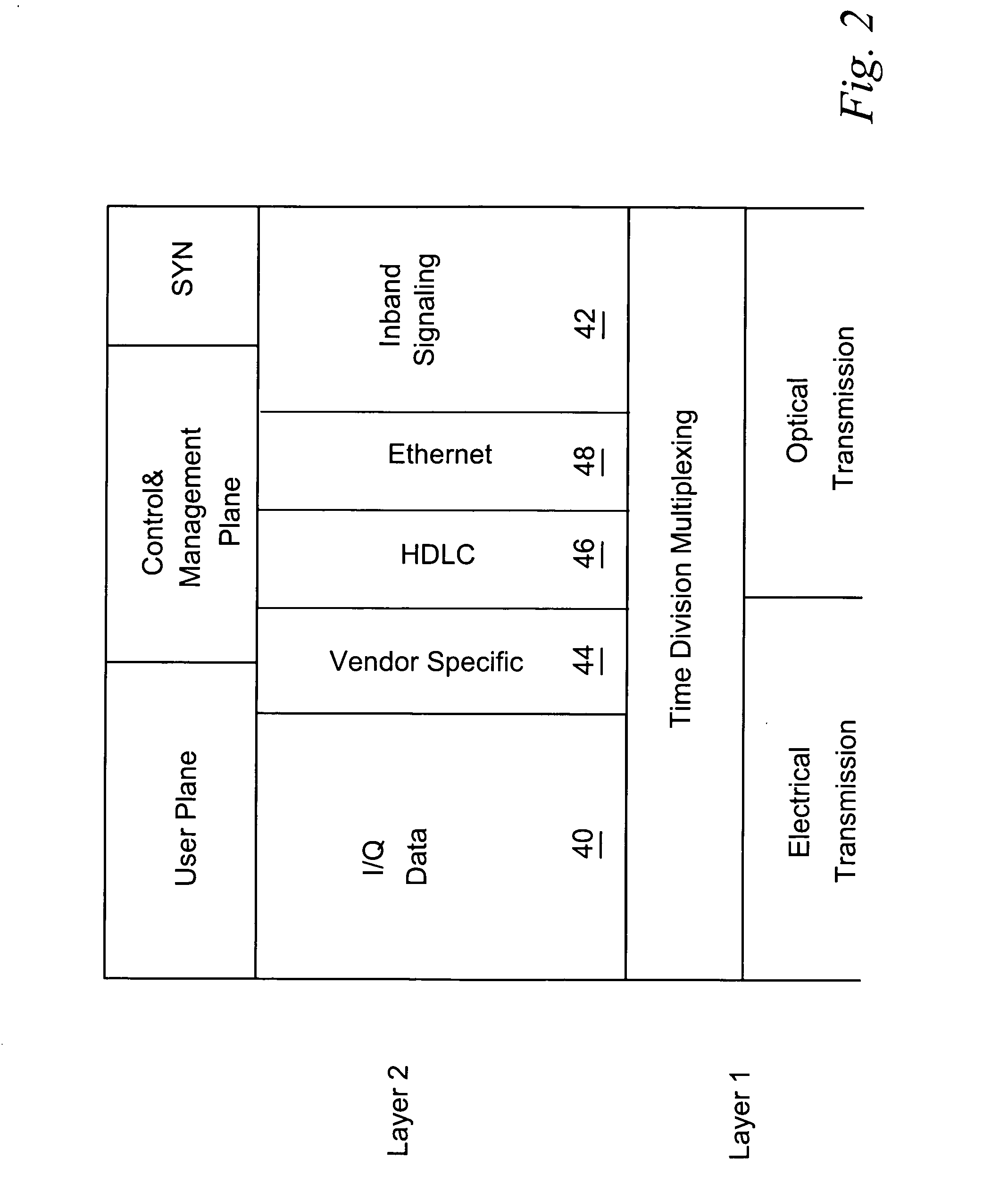
ActiveUS20050105552A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexRadio equipmentEngineering
A distributed radio base station (20) comprises a radio equipment controller (REC) (22) situated at a main site (23) and a radio equipment (RE) (24) situated at a remote site (25). A remote unit (102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 124) configured to engage in direct communications with the radio equipment controller (REC) is also situated at the remote site (25). An internal interface (26) connects the radio equipment controller (REC) and the radio equipment (RE). Advantageously, the internal interface (26) also encapsulates the direct communications between the radio equipment controller (REC) (22) and the remote unit, thereby obviating a separate physical link between the radio equipment controller (REC) and the remote unit. A new physical link (130) transmits, between the radio equipment (RE) and the remote unit, the direct communications between the radio equipment controller (REC) and the remote unit which are encapsulated over the internal interface (26). The remote unit can take various differing forms, including that of an antenna (102) with remote electrical tilt control; a tower mounted amplifier (TMA) (104); a Transmission network unit (106); a separate radio base station (108) which is co-located at the remote site; a proprietary equipment unit (110); or even one or more cascaded radio equipments (RE) (124).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
High frequency module
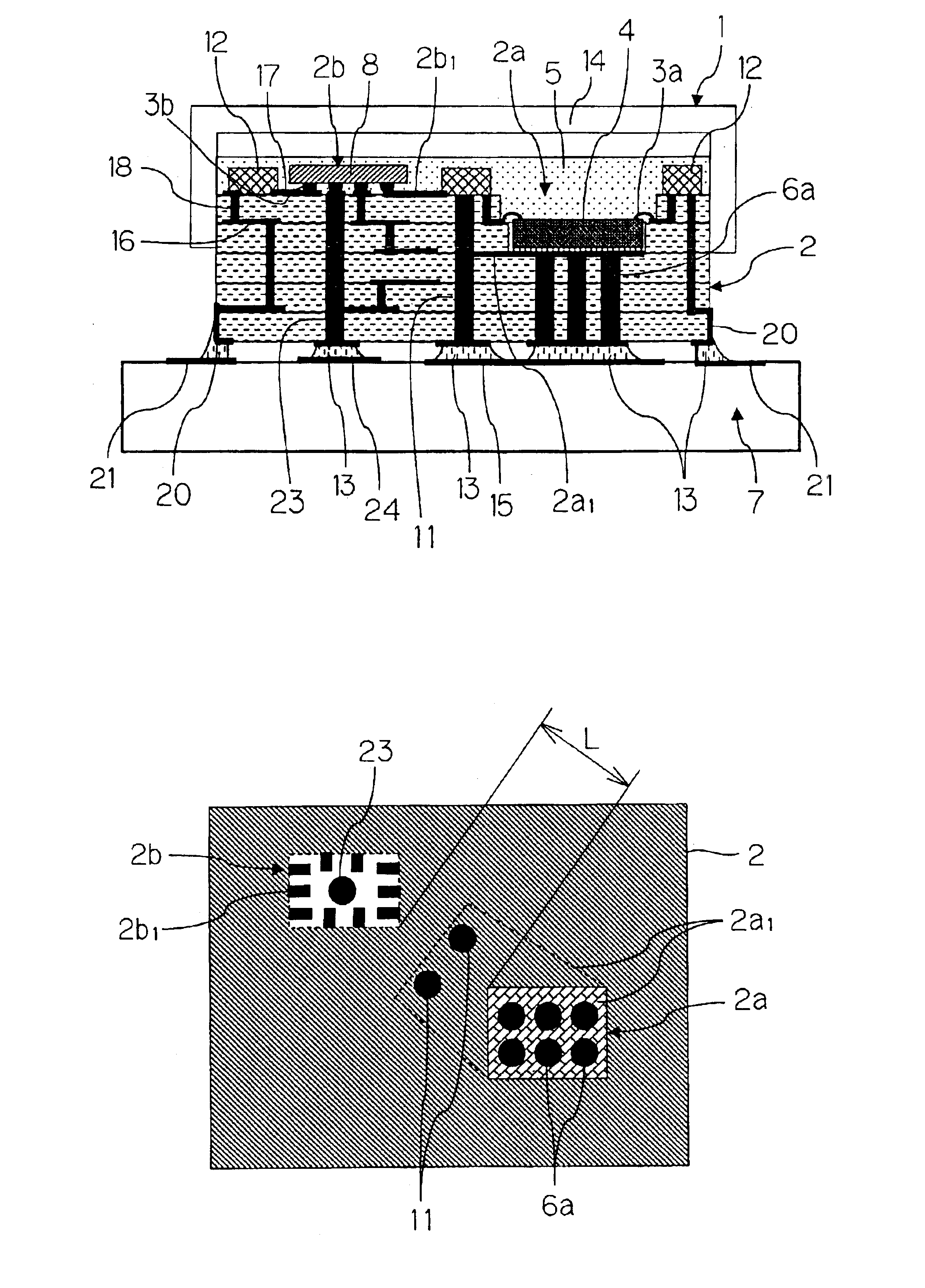
InactiveUS6873529B2Low costImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSurface acoustic wave
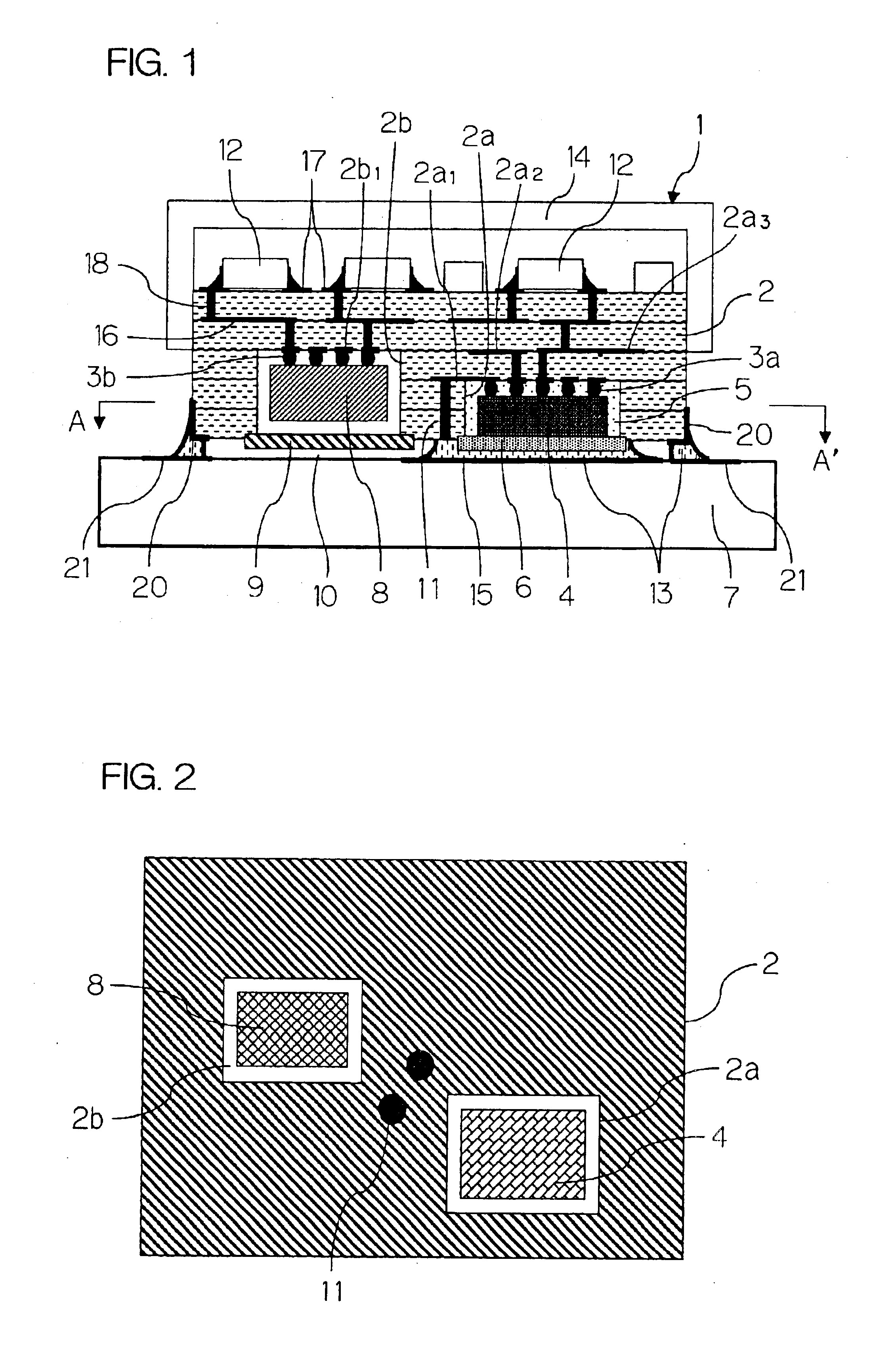
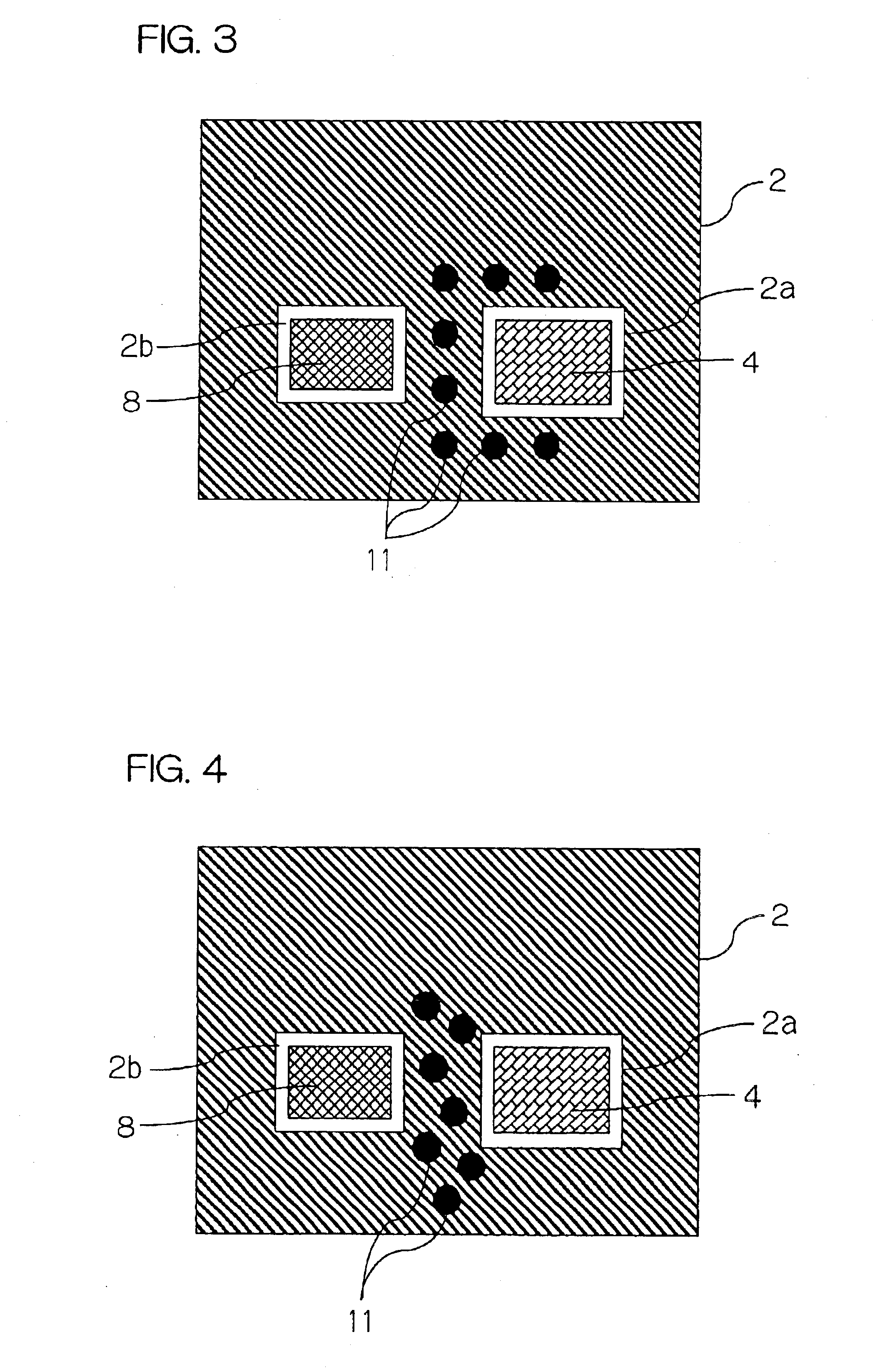
There is presented a high frequency module, in which a recess 2a for mounting power amplifier device is formed on a lower surface of a dielectric substrate 2, and a recess 2b for mounting surface acoustic wave filter is formed on an upper surface of the dielectric substrate 2, and a power amplifier device 4 and a surface acoustic wave filter 8 are mounted through conductive bumps 3a and 3b on the recesses 2a and 2b, respectively. In addition, a through-hole conductor 11 whose one end is exposed at the lower surface of the dielectric substrate 2 is provided between the recesses 2a and 2b. The exposed end of the through-hole conductor 11 is attached to a thermal dissipation conductor 15 on an upper surface of an external electric circuit board 7 through a brazing material 13.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
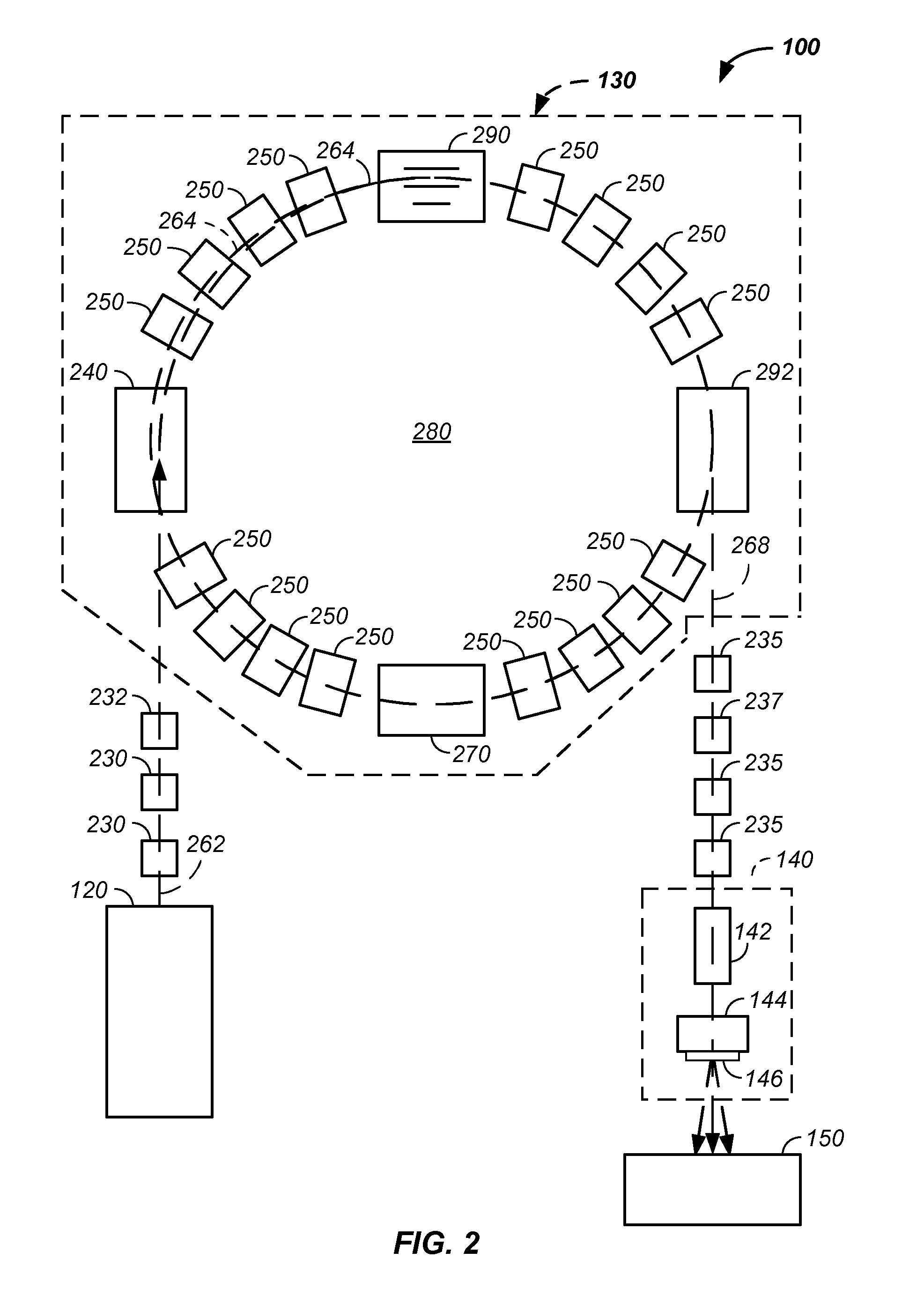
RF accelerator method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS20100060209A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLow voltageCharged particle radiotherapy
The invention comprises a radio-frequency accelerator method and apparatus used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. An RF synthesizer provides a low voltage RF signal, that is synchronized to the period of circulation of protons in the proton beam path, to a set of integrated microcircuits, loops, and coils where the coils circumferentially enclose the proton beam path in a synchrotron. The integrated components combine to provide an accelerating voltage to the protons in the proton beam path in a size compressed and price reduced format. The integrated RF-amplifier microcircuit / accelerating coil system is operable from about 1 MHz, for a low energy proton beam, to about 15 MHz, for a high energy proton beam.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com