Patents
Literature
448 results about "Millimeter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The millimetre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI unit symbol mm) or millimeter (American spelling) is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one thousandth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length. Therefore, there are one thousand millimetres in a metre. There are ten millimetres in a centimetre.
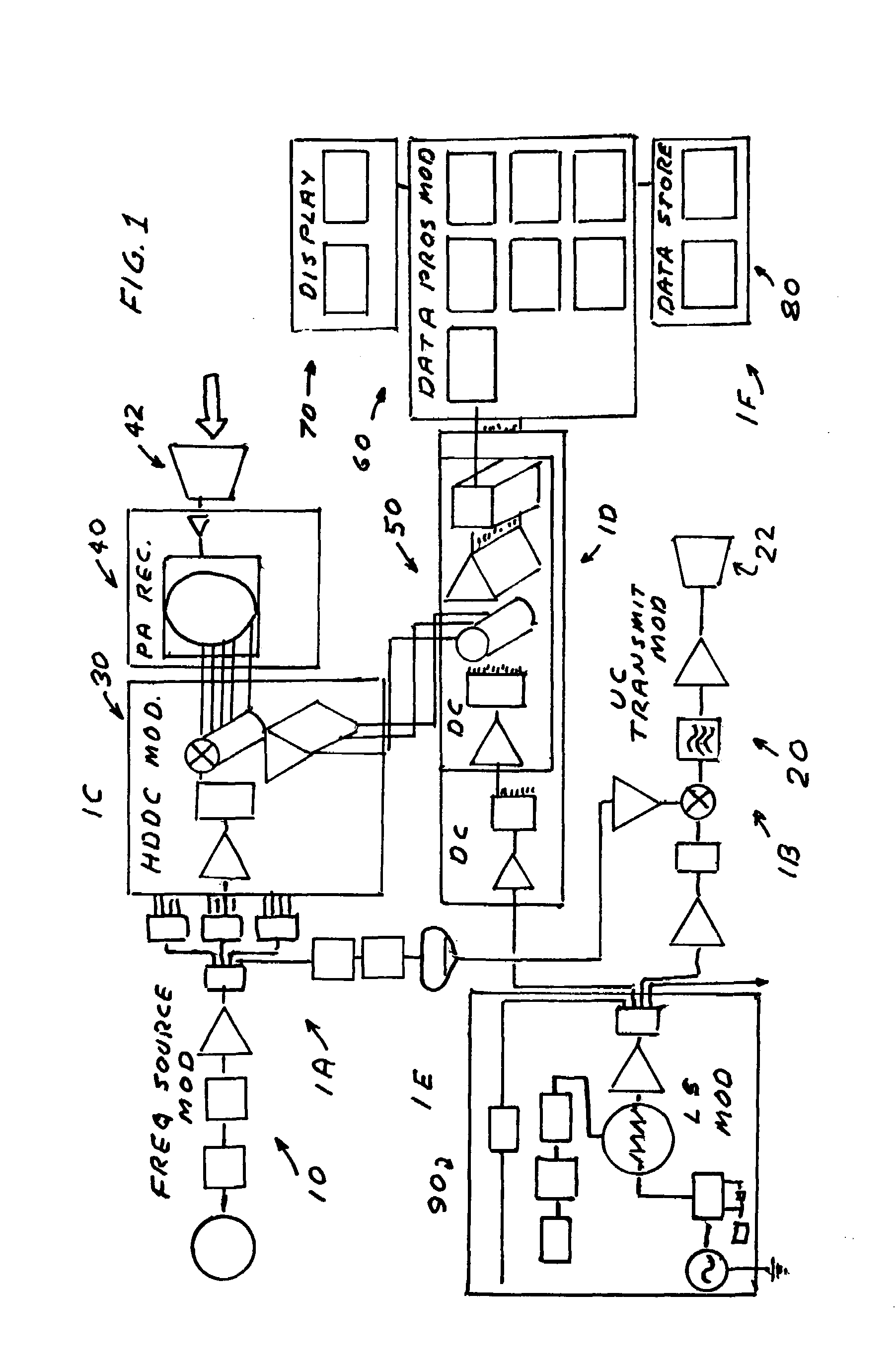
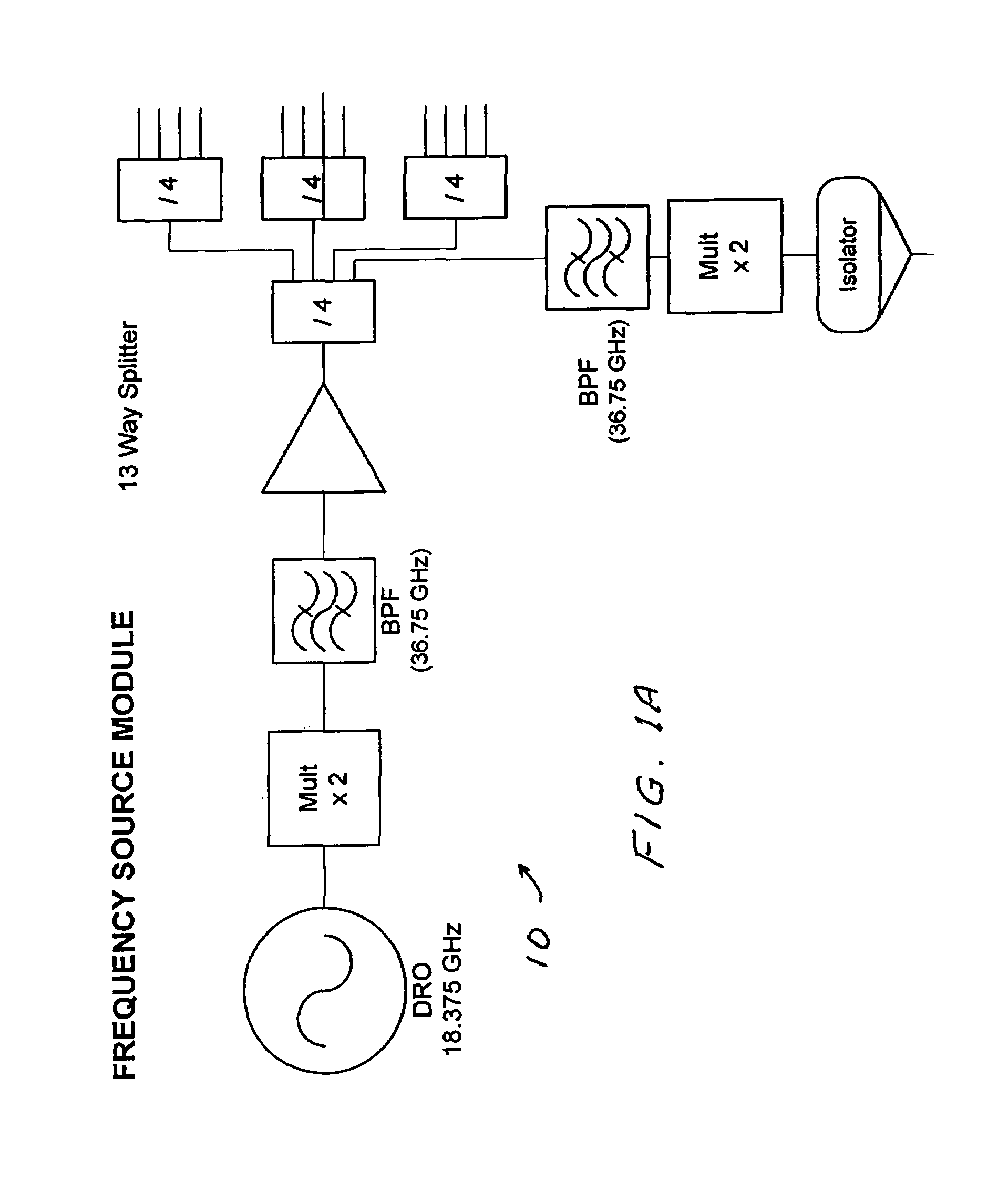
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
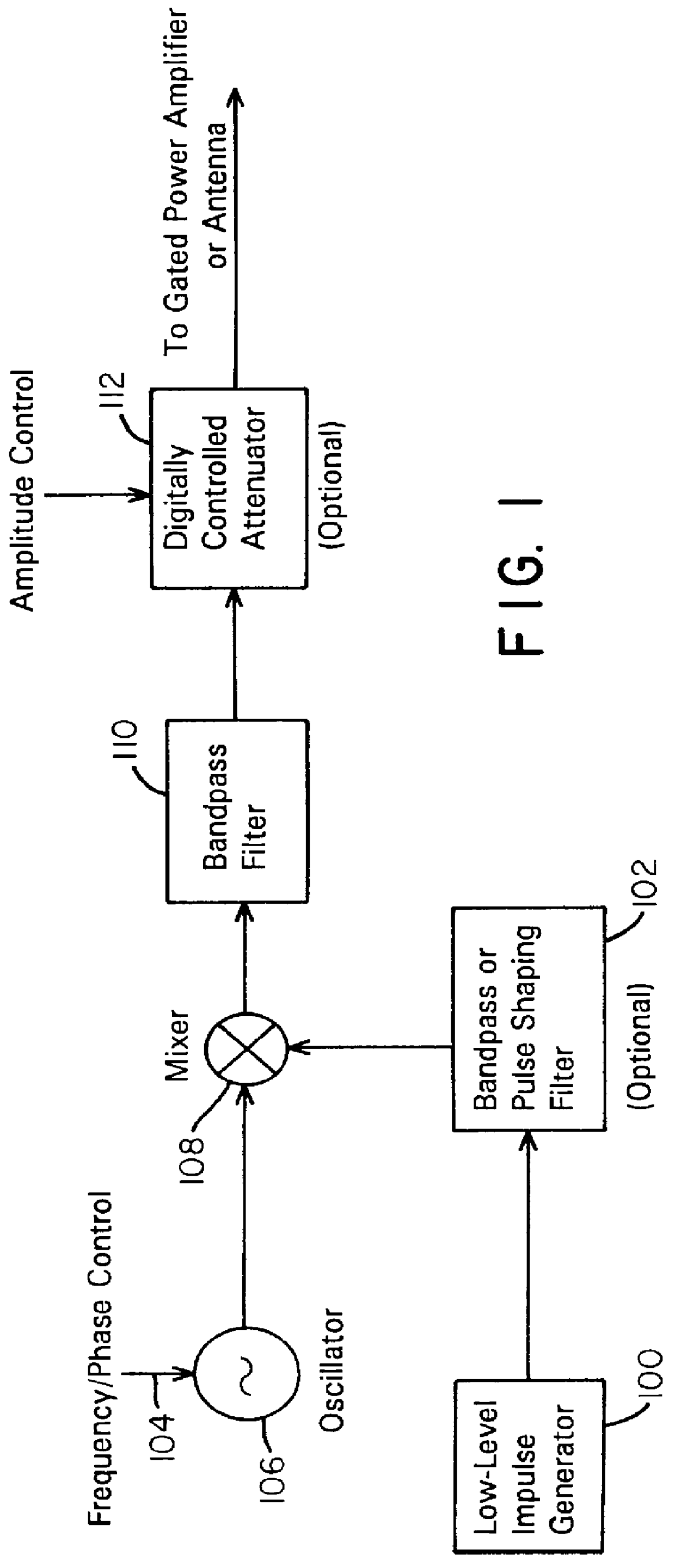
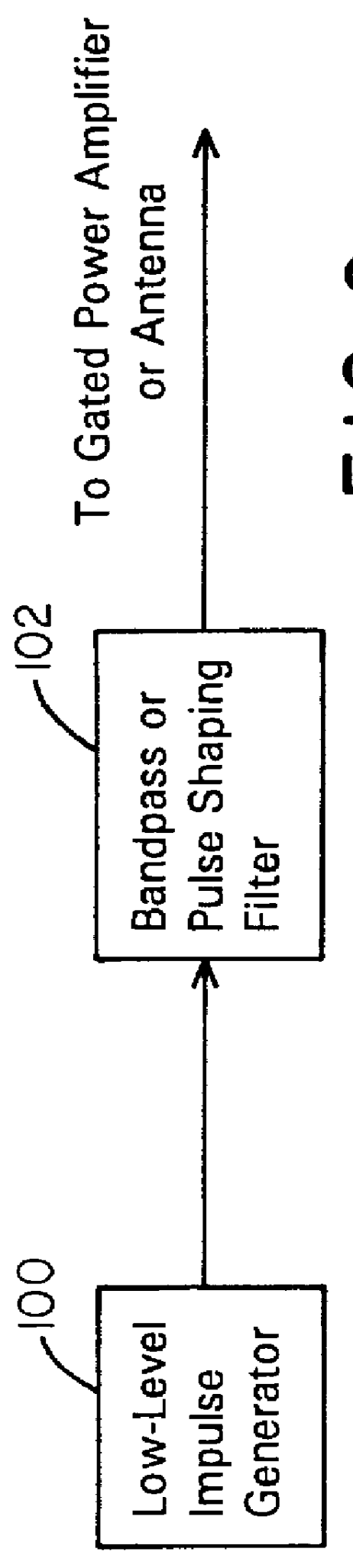
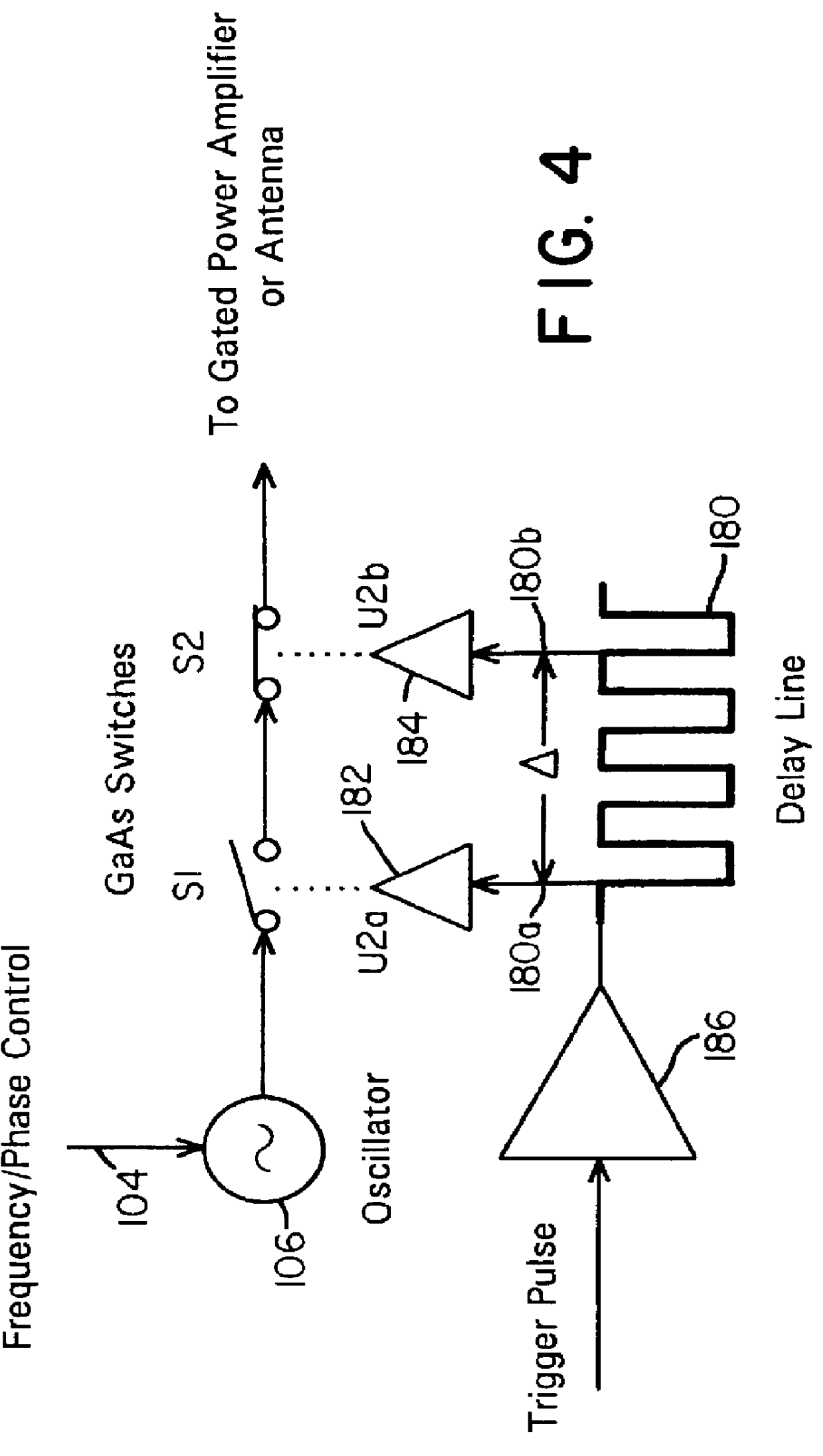
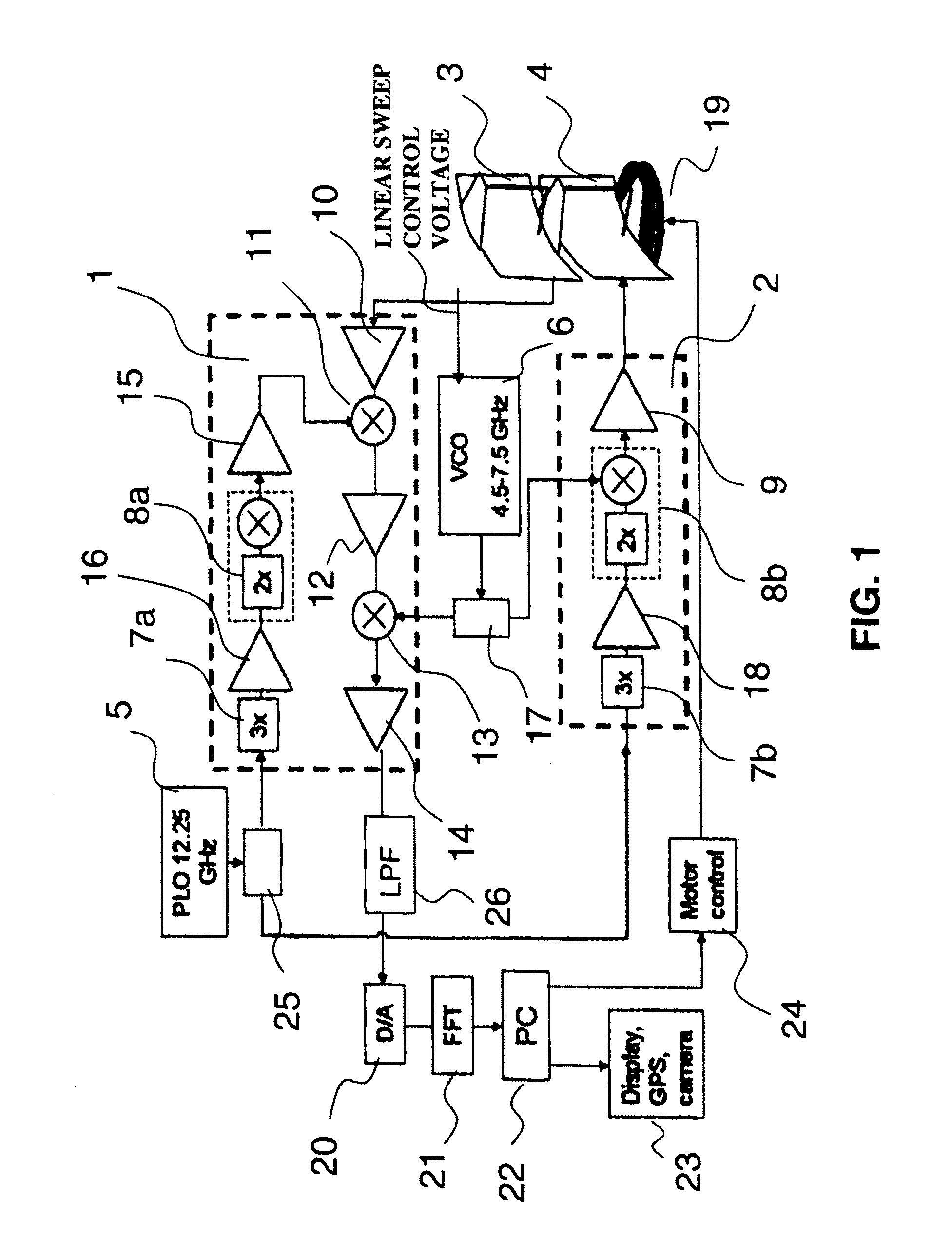
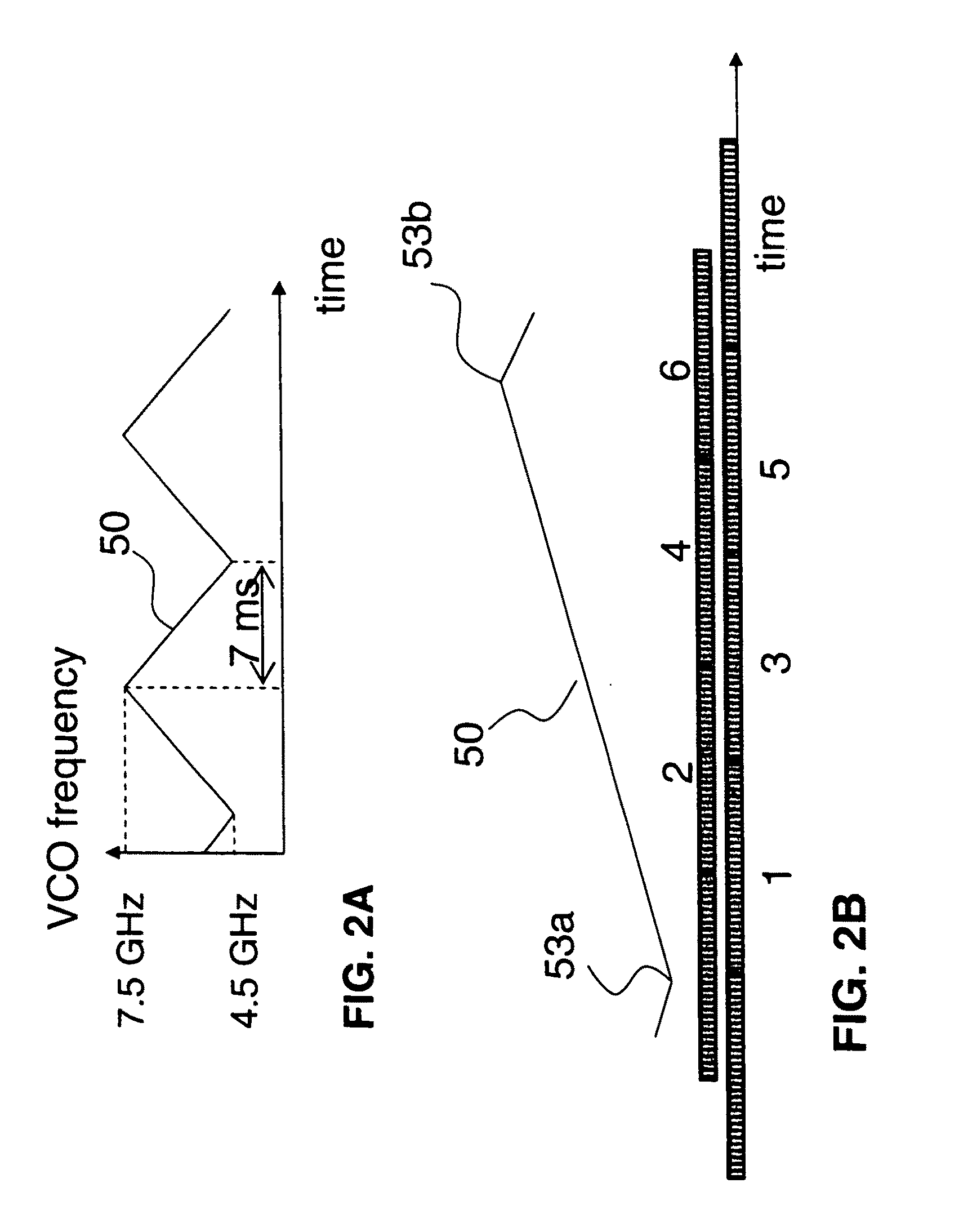
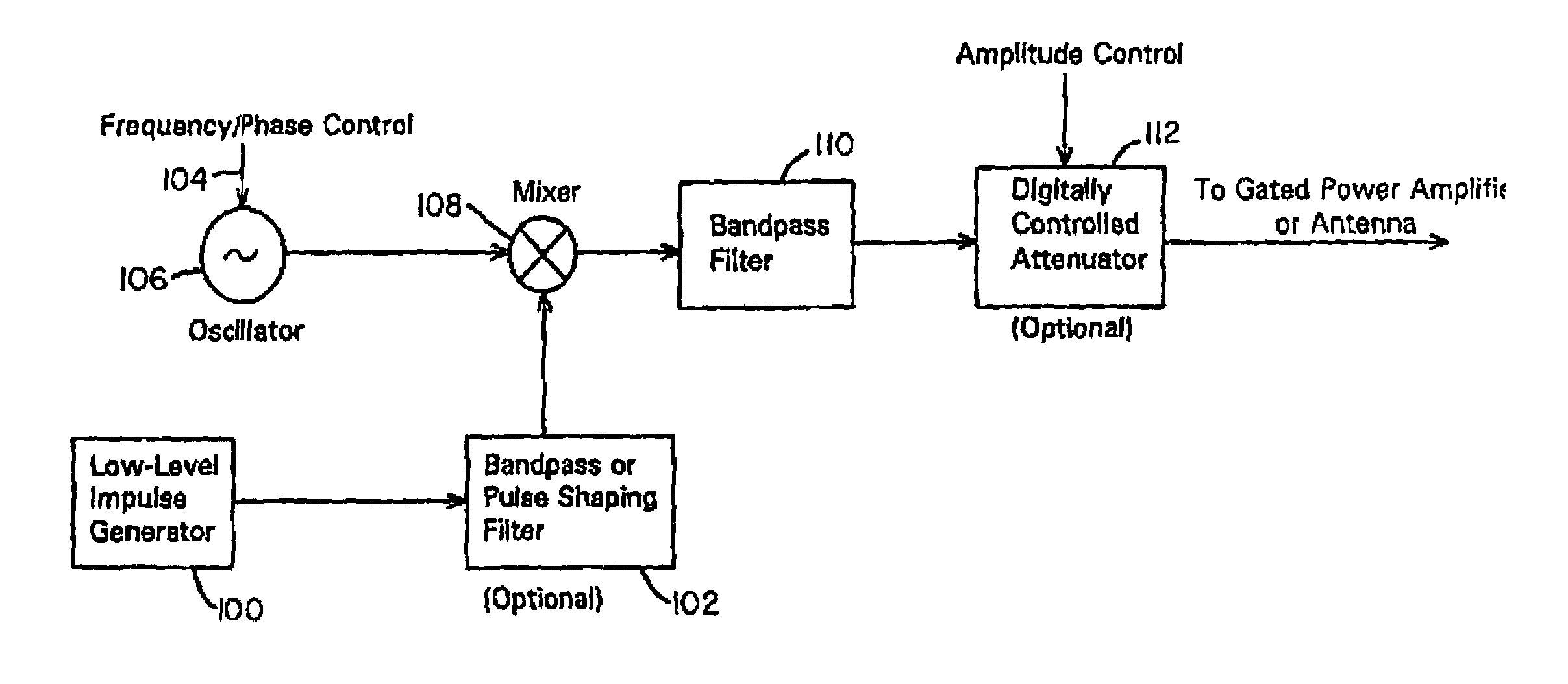
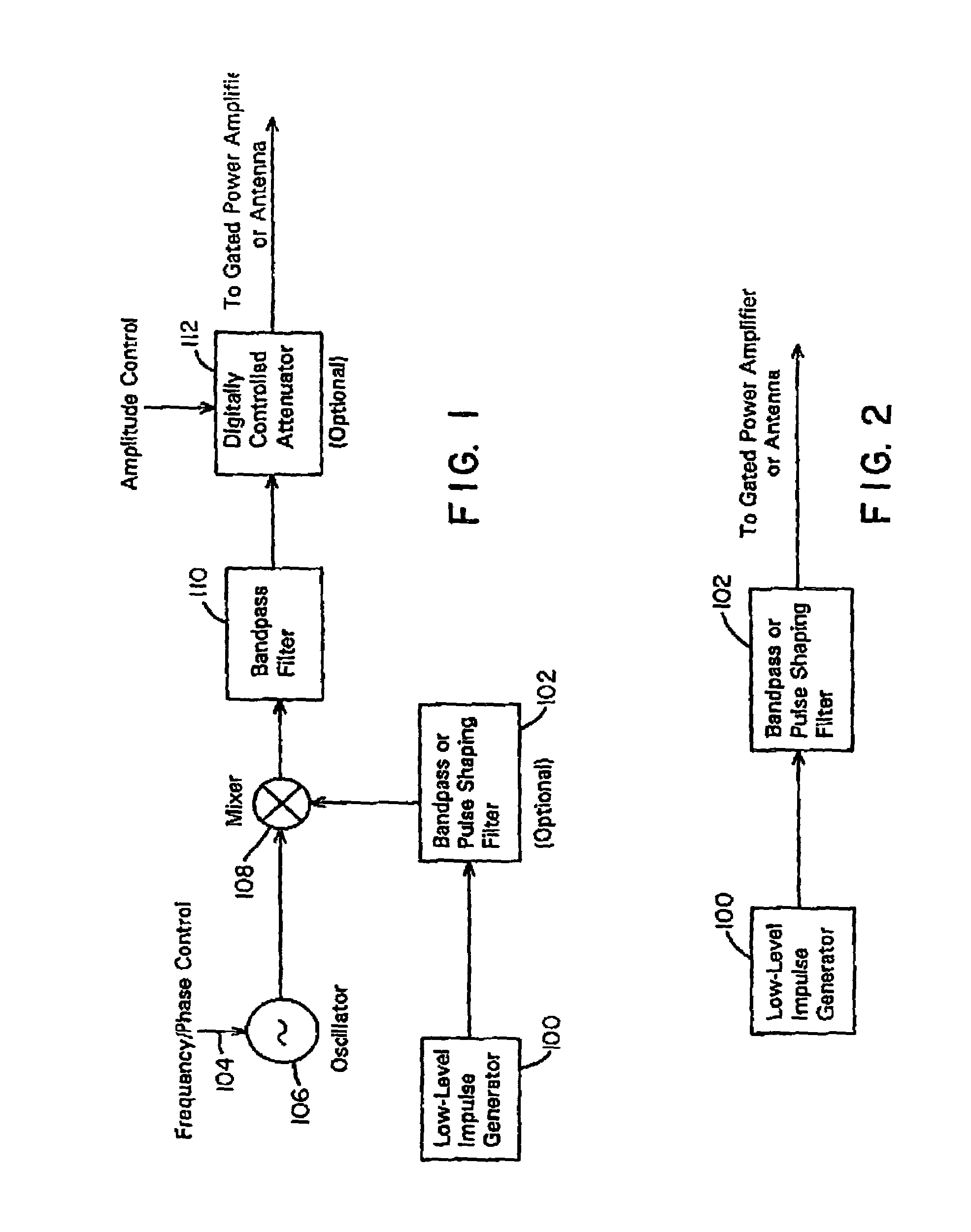
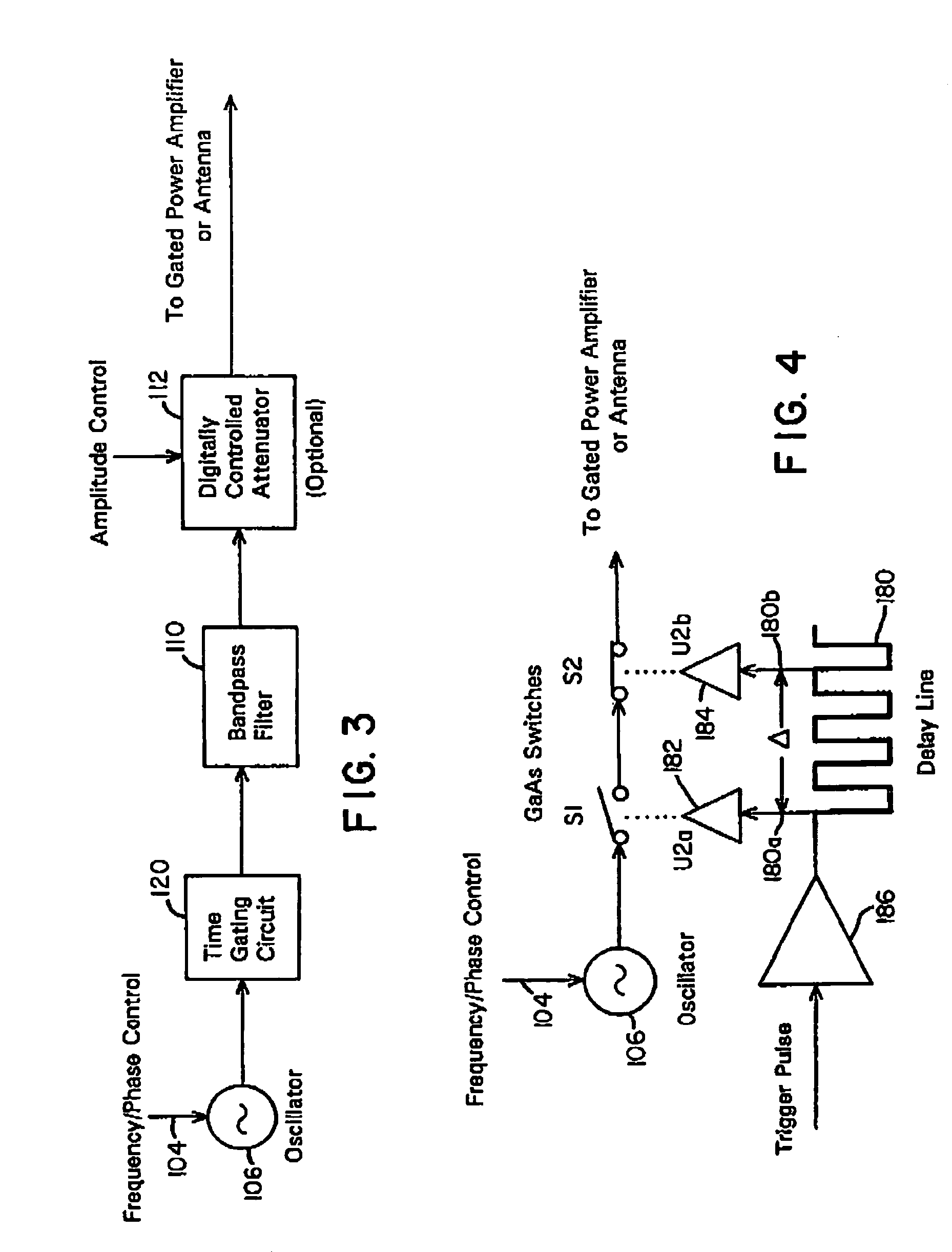
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Antenna for radio frequency identification
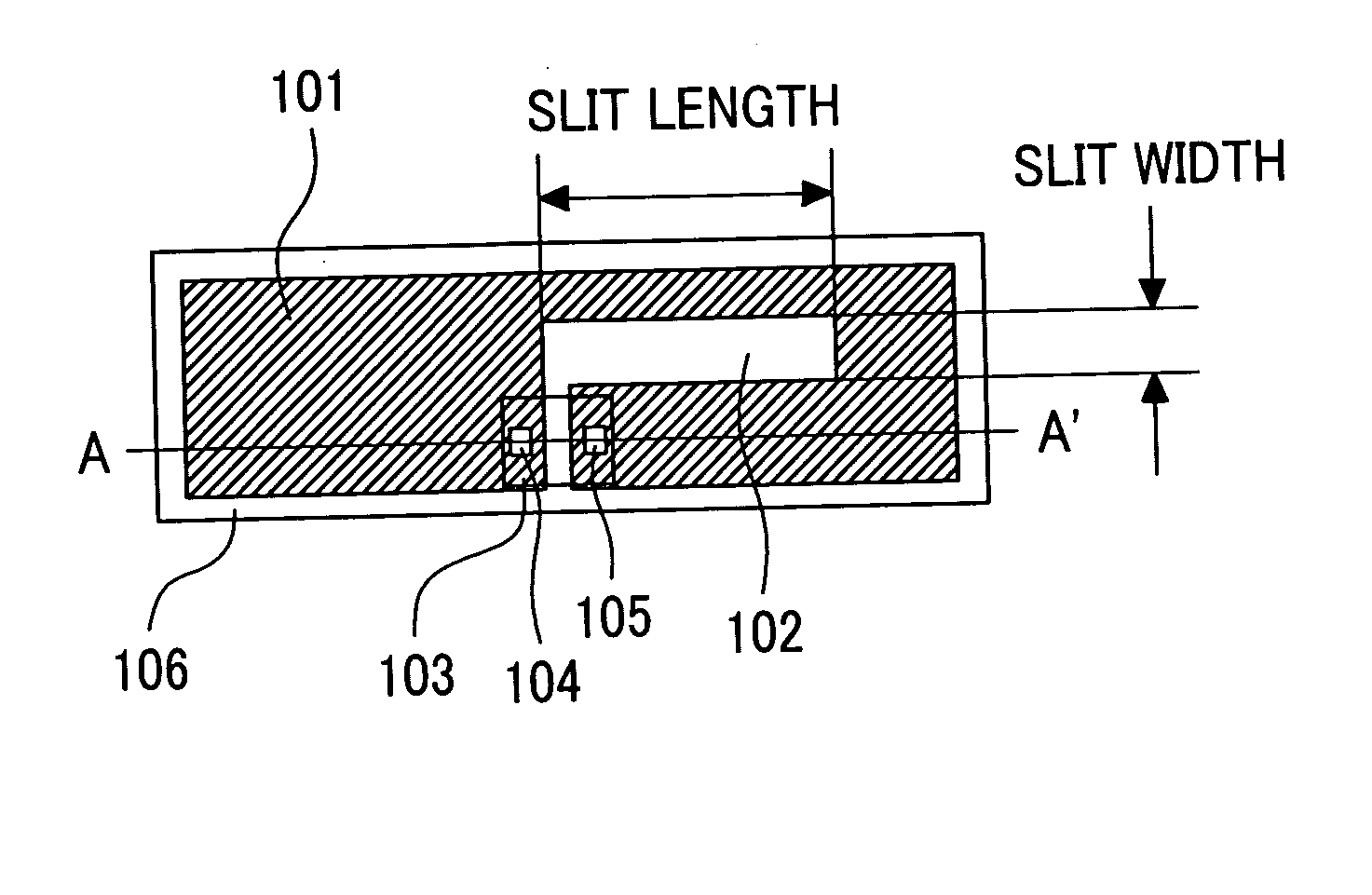
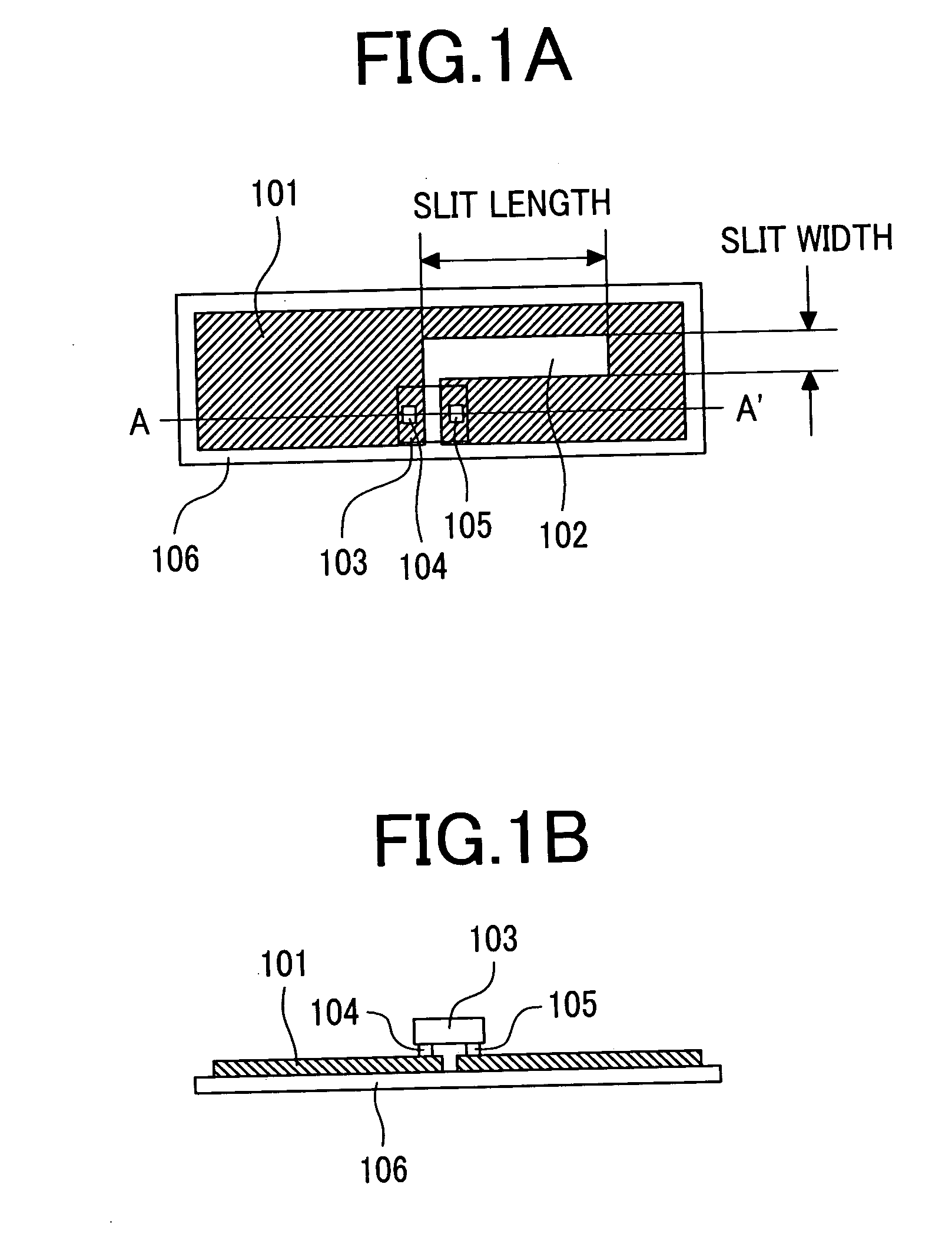
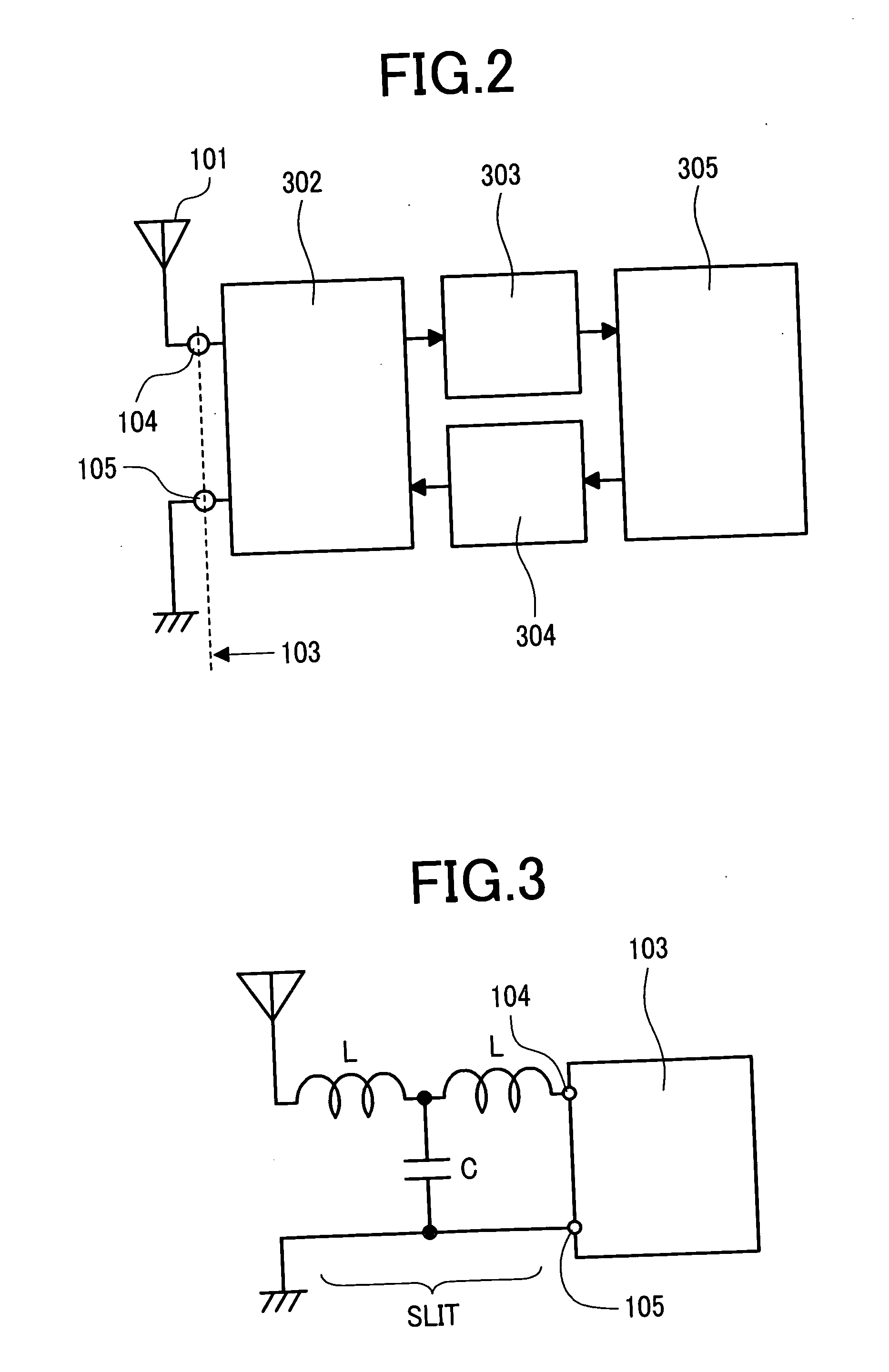
InactiveUS20050134460A1Integrated and compact antennaSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMillimeterPhysics
To provide an antenna shape devised to be integrated and compact. The antenna connected to an IC chip that performs wireless identification includes a slit that separates two connection points with respect to the IC chip, in which a length of the slit is approximately 3 millimeters, and a width of the slit is in a range of from 0.8 millimeter to 1.4 millimeters.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
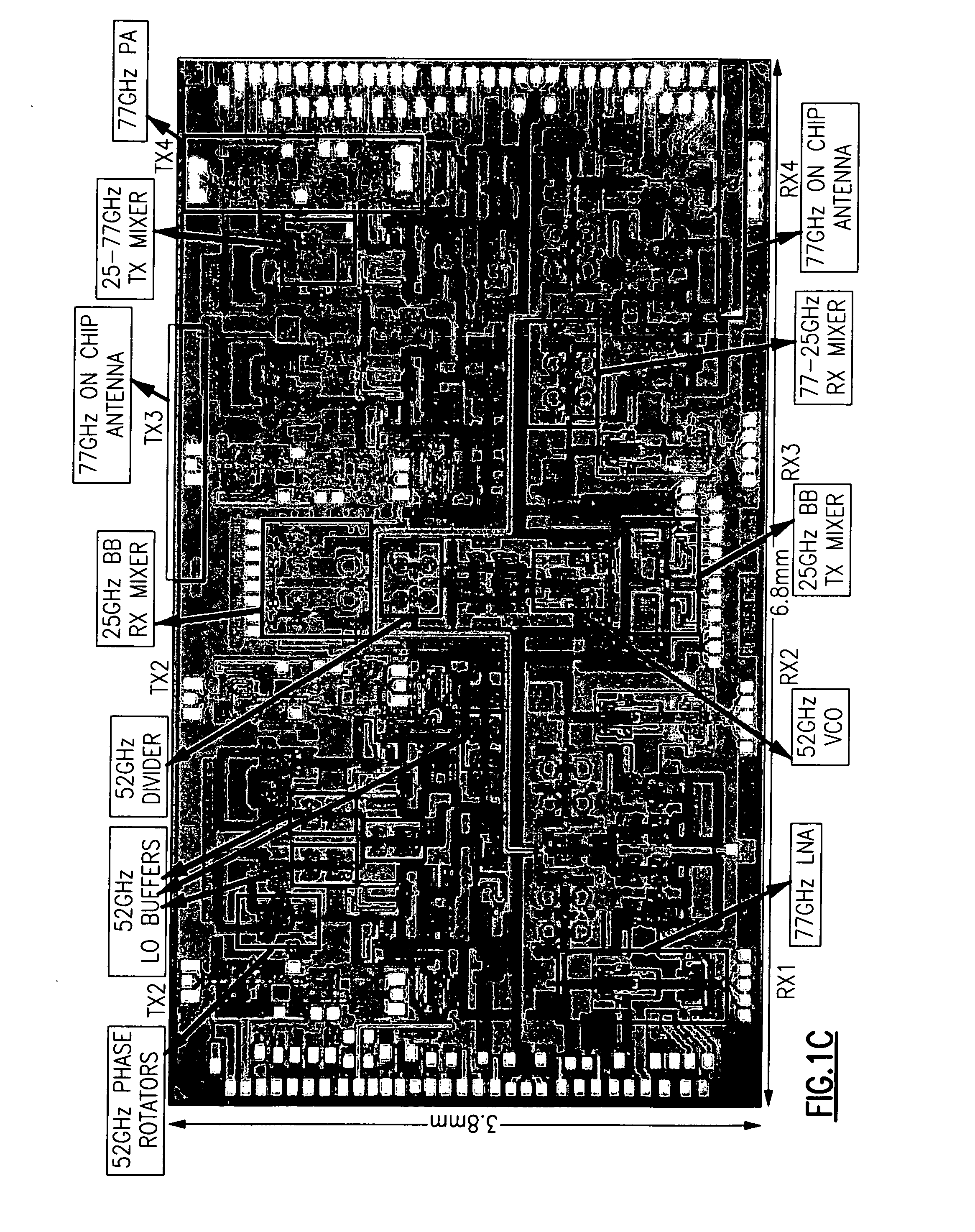
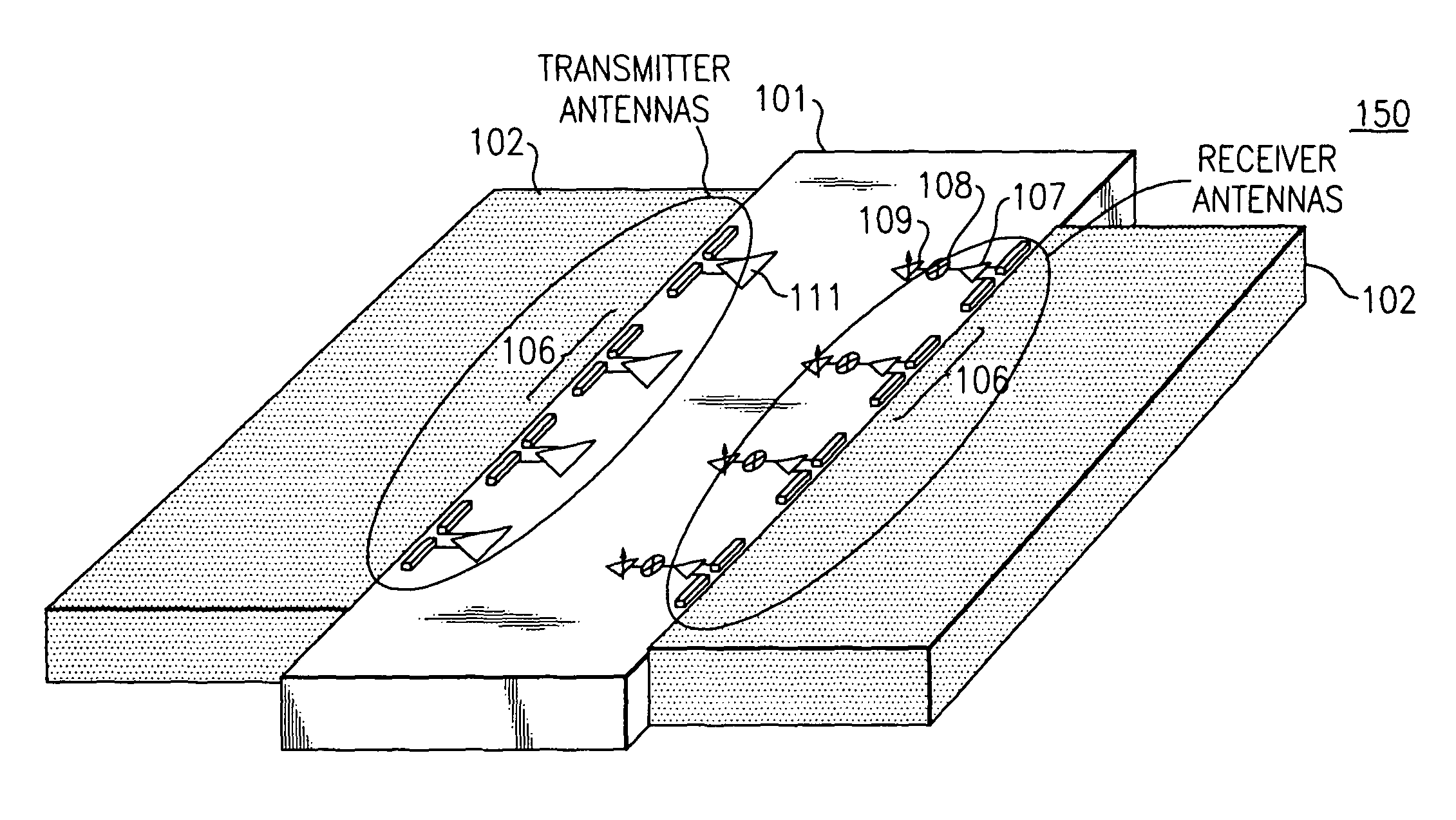
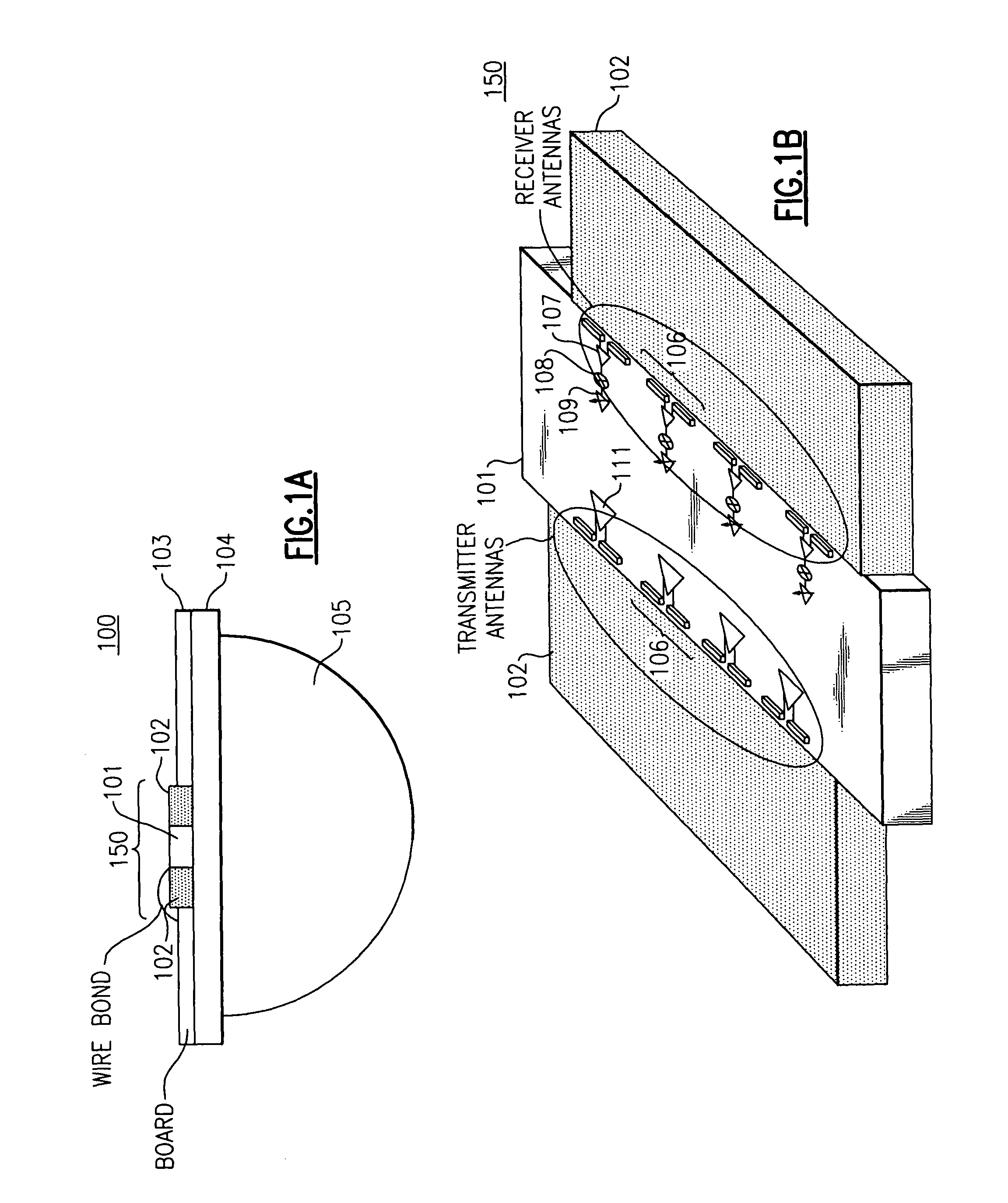
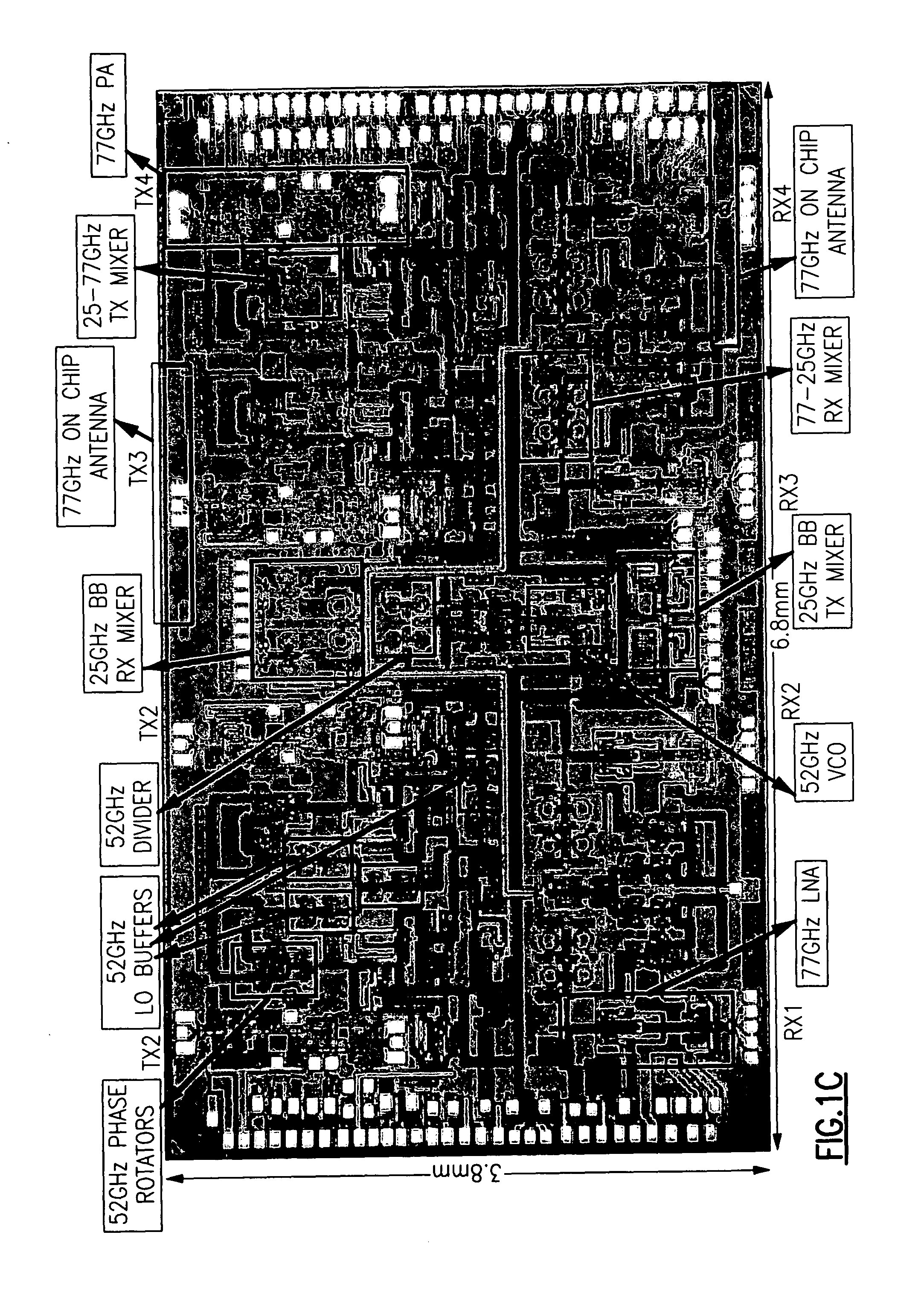
Mm-wave fully integrated phased array receiver and transmitter with on-chip antennas
ActiveUS20100231452A1Facilitate transmissionEasy to receiveWave based measurement systemsAntenna feed intermediatesMillimetre waveAntenna element
A phased array mm-wave device includes a substrate, a mm-wave transmitter integrated onto the substrate configured to transmit a mm-wave signal and / or a mm-wave receiver integrated onto the substrate and configured to receive a mm-wave signal. The mm-wave device also includes a phased array antenna system integrated onto the substrate and including two or more antenna elements. The phased array mm-wave device also includes one or more dielectric lenses. A distributed mm-wave distributed combining tree circuit includes at least two pairs of differential transconductors with regenerative degeneration and accepts at least two differential input signals. Two mm-wave loopback methods measure the phased array antenna patterns and the performance of an integrated receiver transmitter system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
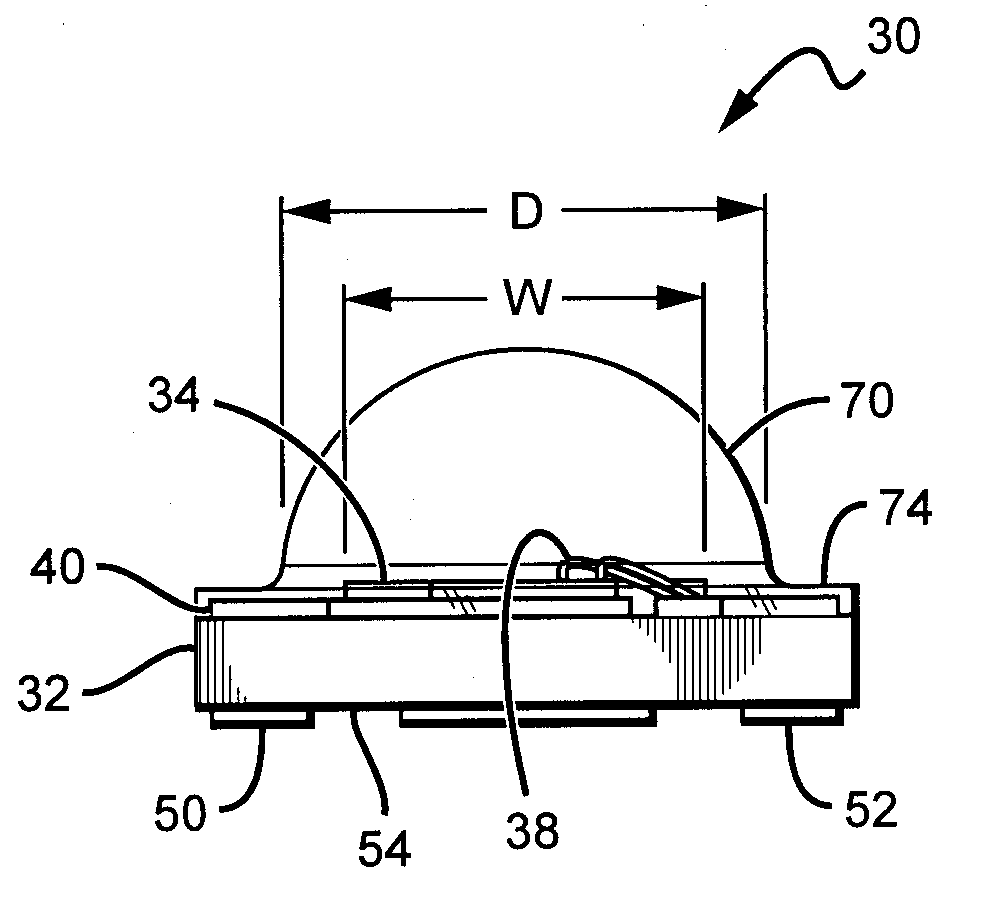
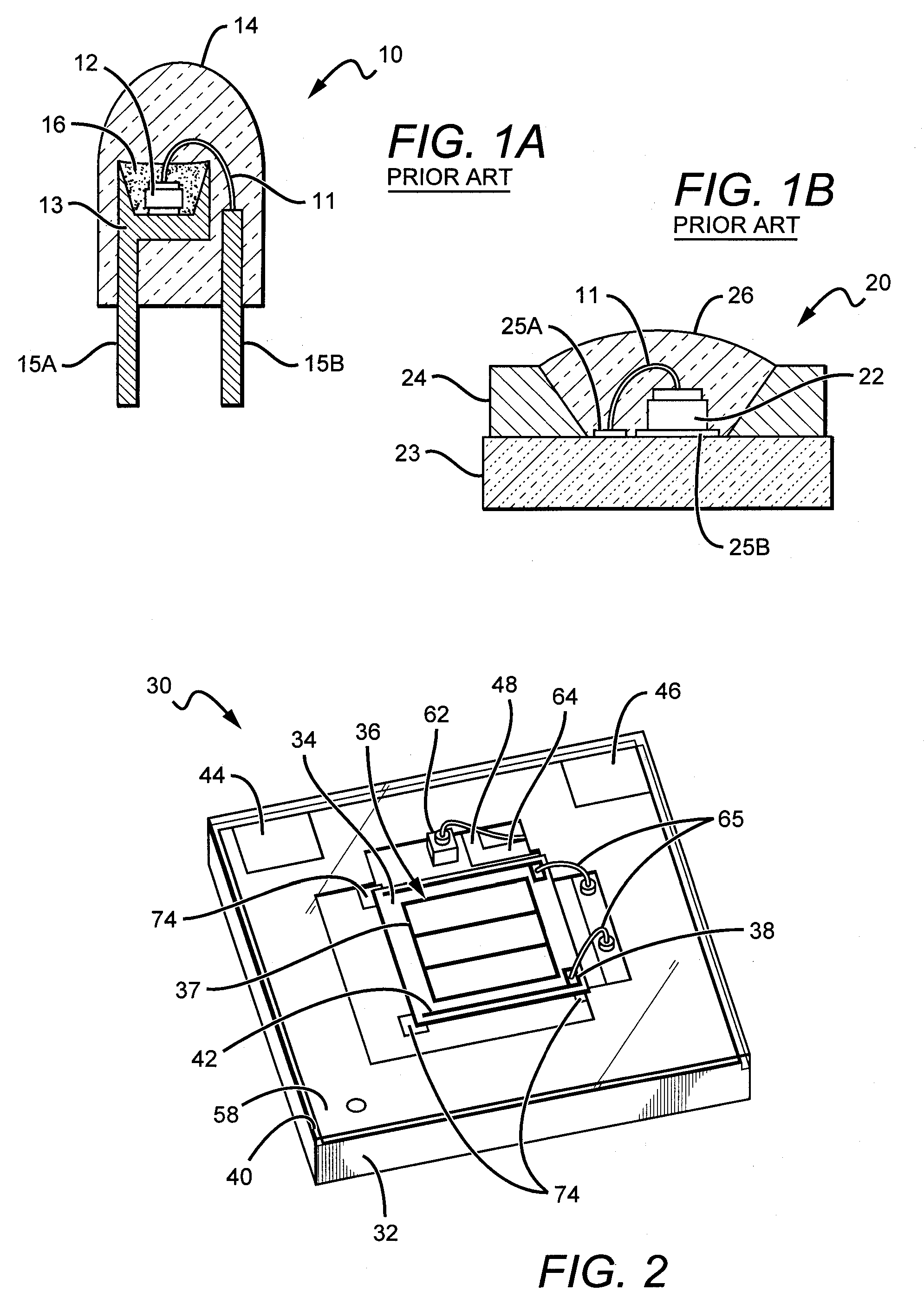
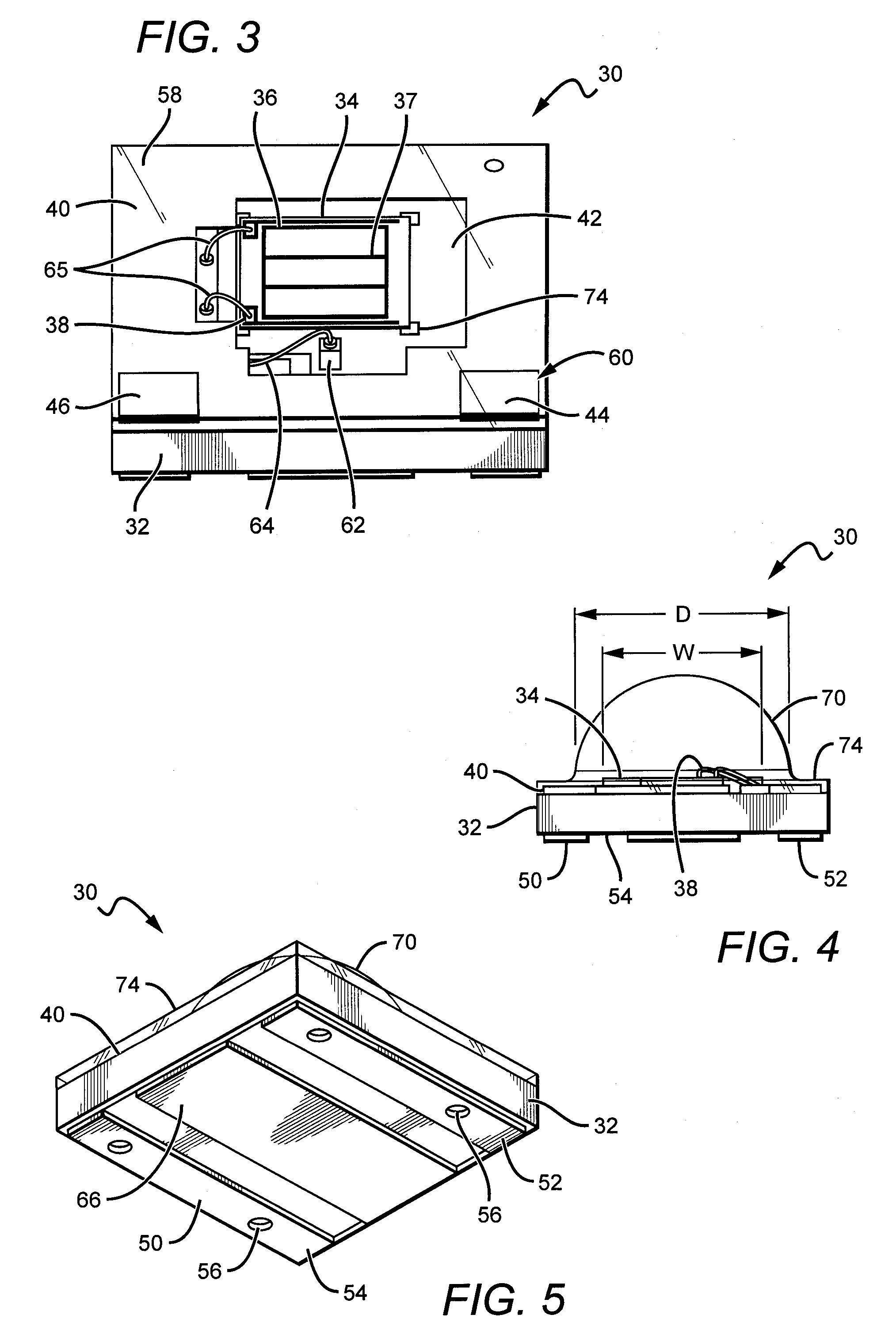
LED package with increased feature sizes
A light emitter package having increased feature sizes for improved luminous flux and efficacy. An emitter chip is disposed on a submount with a lens that covers the emitter chip. In some cases, the ratio of the width of the light emitter chip to the width of said lens in a given direction is 0.5 or greater. Increased feature sizes allow the package to emit light more efficiently. Some packages include submounts having dimensions greater than 3.5 mm square used in conjunction with larger emitter chips. Materials having higher thermal conductivities are used to fabricate the submounts, providing the package with better thermal management.
Owner:CREELED INC
Mm-wave fully integrated phased array receiver and transmitter with on-chip antennas
A phased array mm-wave device includes a substrate, a mm-wave transmitter integrated onto the substrate configured to transmit a mm-wave signal and / or a mm-wave receiver integrated onto the substrate and configured to receive a mm-wave signal. The mm-wave device also includes a phased array antenna system integrated onto the substrate and including two or more antenna elements. The phased array mm-wave device also includes one or more dielectric lenses. A distributed mm-wave distributed combining tree circuit includes at least two pairs of differential transconductors with regenerative degeneration and accepts at least two differential input signals. Two mm-wave loopback methods measure the phased array antenna patterns and the performance of an integrated receiver transmitter system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Imaging millimeter wave radar system
InactiveUS7019682B1Linear waveguide fed arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumDisplay device
An imaging millimeter wave radar system. The system includes a millimeter wave transmitter transmitting a frequency scanned millimeter beam that is narrow in the scanned direction and wide in a direction perpendicular to the scanned direction. The system includes a receive antenna and a Rotman type lens for forming a one-dimensional image in the perpendicular direction of targets in the antennas field of view based on millimeter wave radiation reflected from the targets. A computer creates a two dimensional image based on the scanning direction of the transmit beam of the transmit antenna and the one dimensional image from the receive antenna. Distance to the target is determined based on difference in frequency of the transmit signal and the receive signal. Thus, a three dimensional view of the systems field of view is determined by the system. This view can be displayed on a monitor using color to represent target distance. In a preferred embodiment the scanned direction is the vertical direction and the receive antenna forms a horizontal image from signals reflected from targets in the field of view. In this preferred embodiment the transmit antenna is a variable frequency millimeter wave single channel wave guide antenna operating in the 78 GHz to 81 Ghz spectral range to produce a scanning range of 10 degrees and a scanning rate of 60 Hz. The receive antenna is a multi-channel (176 channels) strip-line antenna also operating in the 78 GHz to 81 GHz spectral range, which with the Rotman lens, provides 192 horizontal pixel resolution.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Patch antenna with wide bandwidth at millimeter wave band
InactiveUS20110057853A1Suppress signal leakageReduce size and manufacturing costSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrically long antennasGround planeWide band
Provided is a millimeter wave band patch antenna. The patch antenna includes a multi-layer substrate, at least one metal pattern layer, an antenna patch, a ground layer, and a plurality of vias. In the multi-layer substrate, a plurality of dielectric layers are stacked. The metal pattern layer is disposed between the dielectric layers except for a center region of the multi-layer substrate. The antenna patch is disposed on an upper surface of the multi-layer substrate in the center region. The ground layer is disposed on a lower surface of the multi-layer substrate opposing to the upper surface. The vias is disposed around the center region through the dielectric layers for electrically connecting the metal pattern layer to the ground layer. The center region, which is surrounded by the ground layer and the vias, functions as a resonator.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Millimeter wave imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6353224B1Maximises emissionEmission reductionGeological detection using milimetre wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansMillimetre waveLength wave
Millimeter wave imaging apparatus for use, in articular, as an indoor security system to identify objects concealed under the clothing of a person in a background scene, including means for generating a millimetric temperature contrast between the person to be imaged and the surroundings in scene. This may be a "hot" or "cold" source for producing a flux, and a relatively smaller flux respectively, of incoherent millimeter wavelength radiation. The apparatus may also include at least one partial ellipsoid reflective enclosure for reflecting millimeter wavelength radiation emitted from the "hot" and "cold" source so as to generate non-localized and uniform illumination of the person. The enclosure may have a metallic inner surface on which a dimpled pattern may be embossed to diffuse the millimeter wavelength radiation reflected from the metallic inner surface. The apparatus also includes one or more millimeter wavelength imaging cameras for detecting the millimeter wavelength radiation at one or more millimeter wave center frequencies, which may be mounted inside or outside the reflective enclosure. An image of the objects may be generated on a television monitor from the detected radiation.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
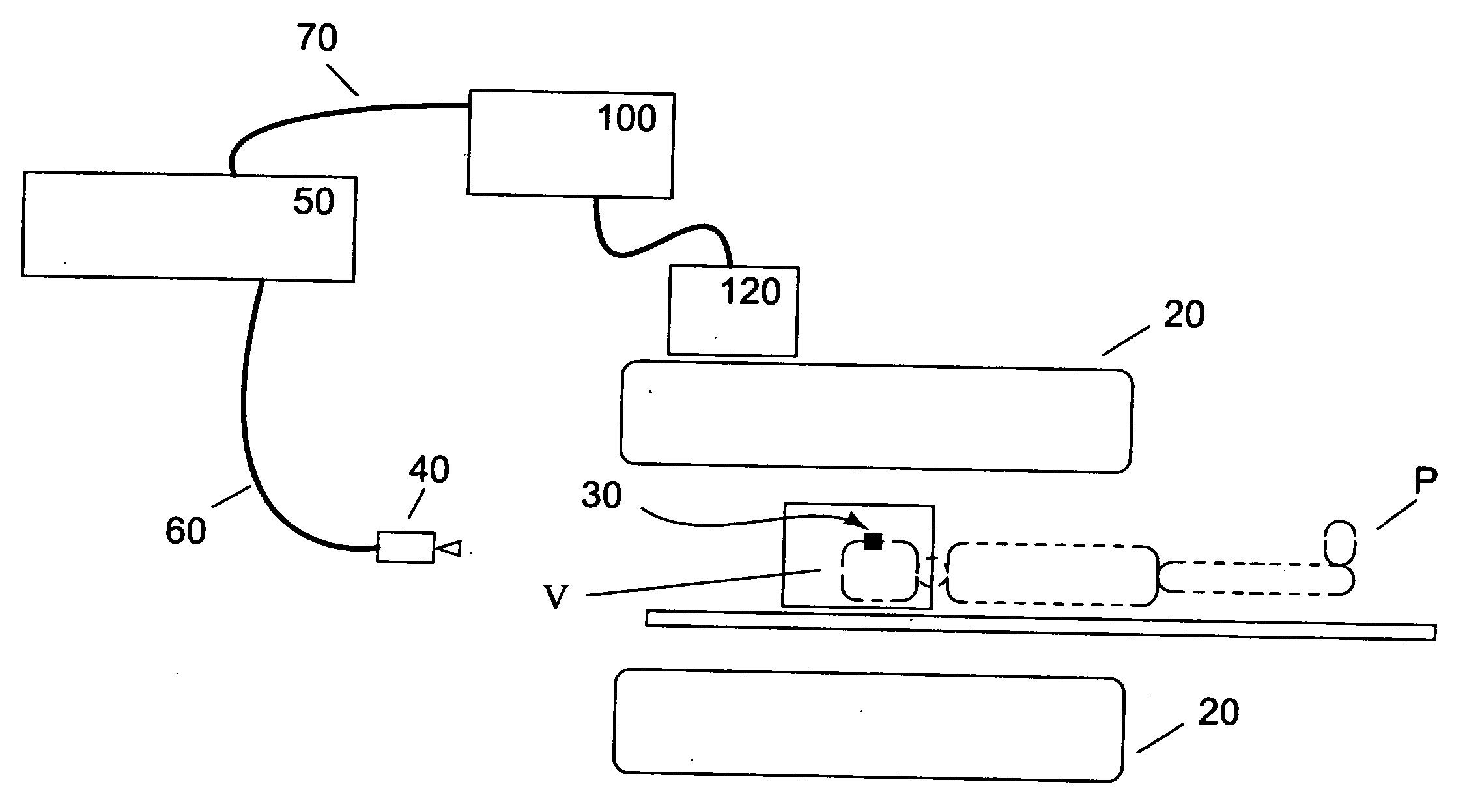
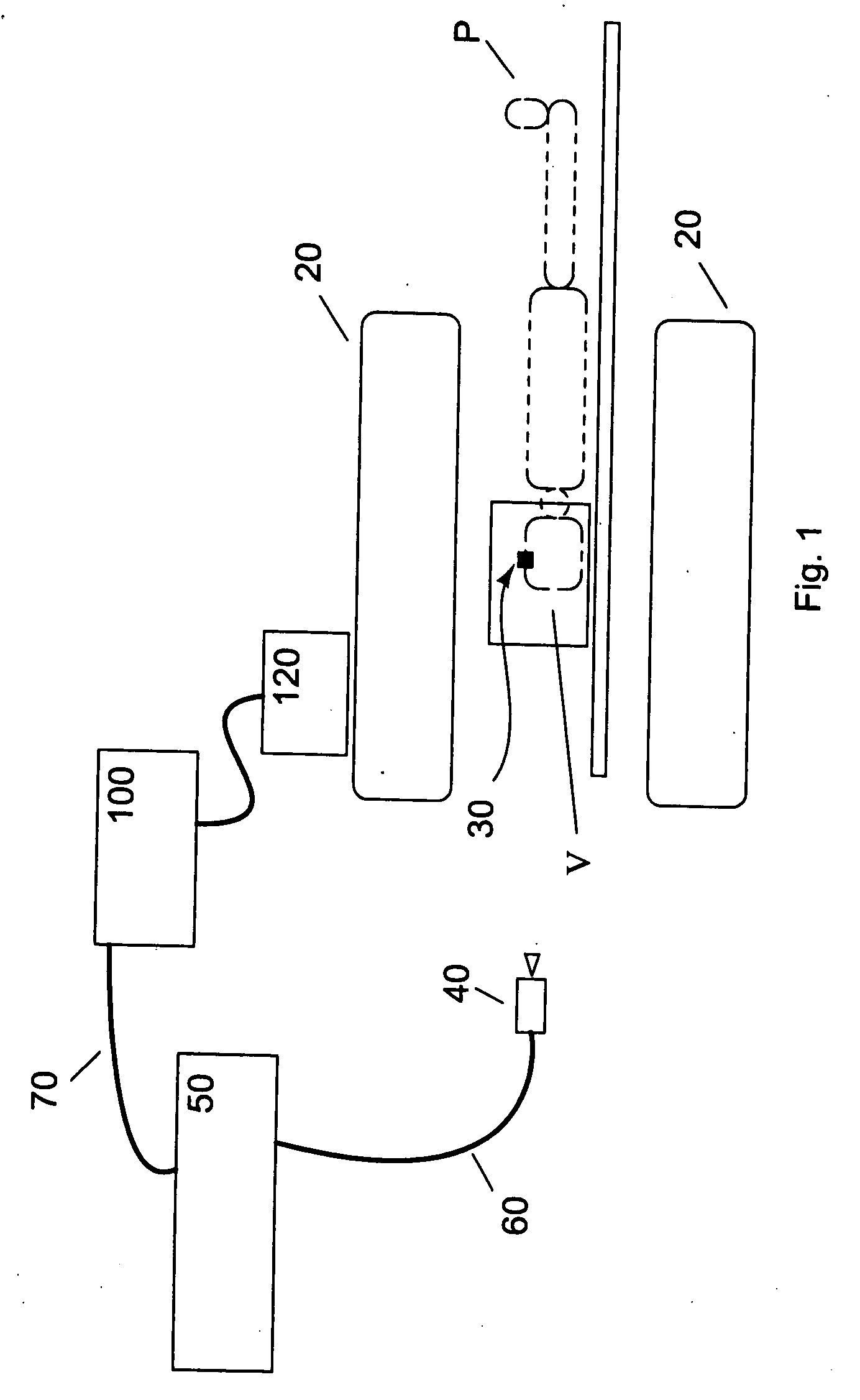
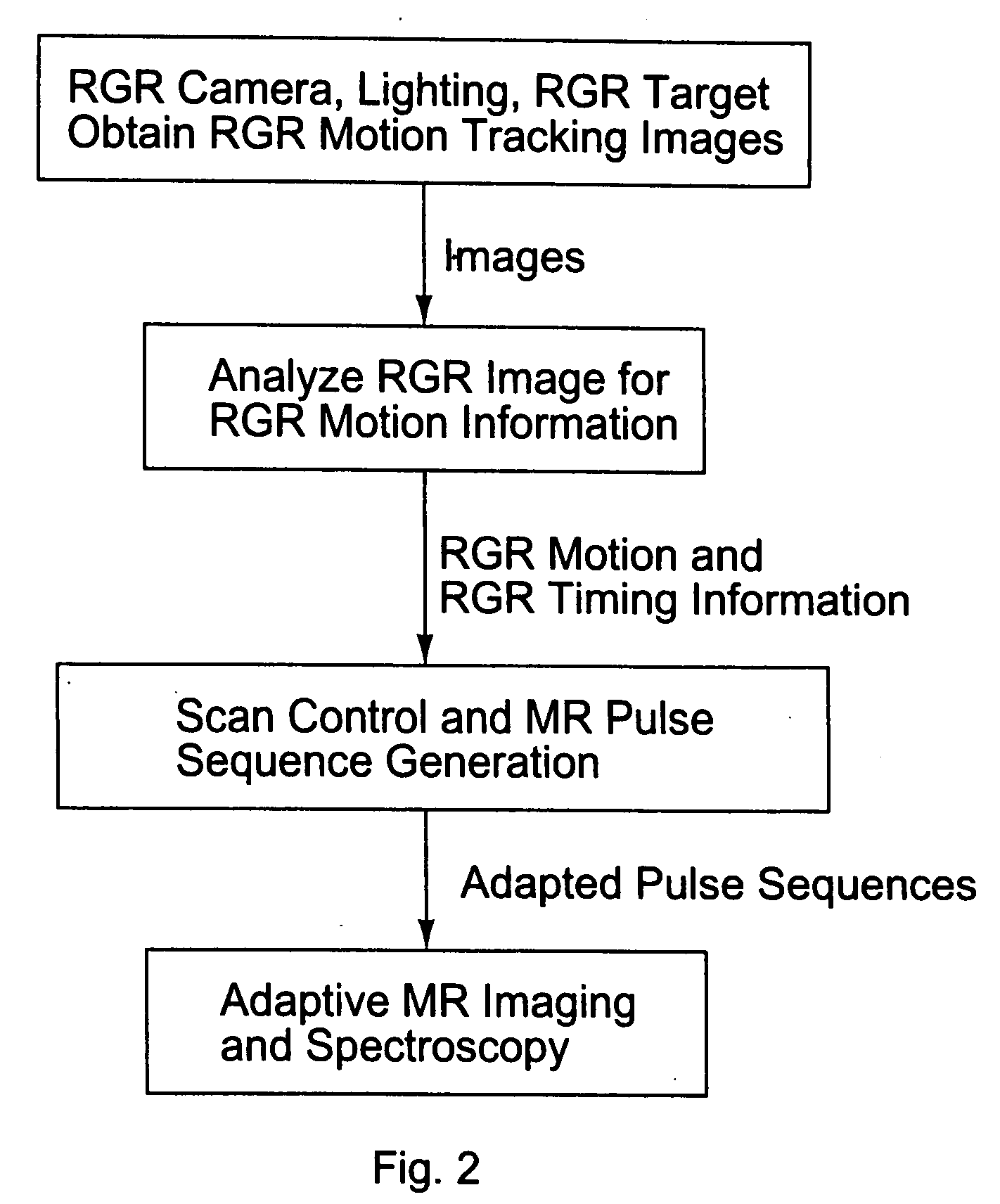
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070280508A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingUsability
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
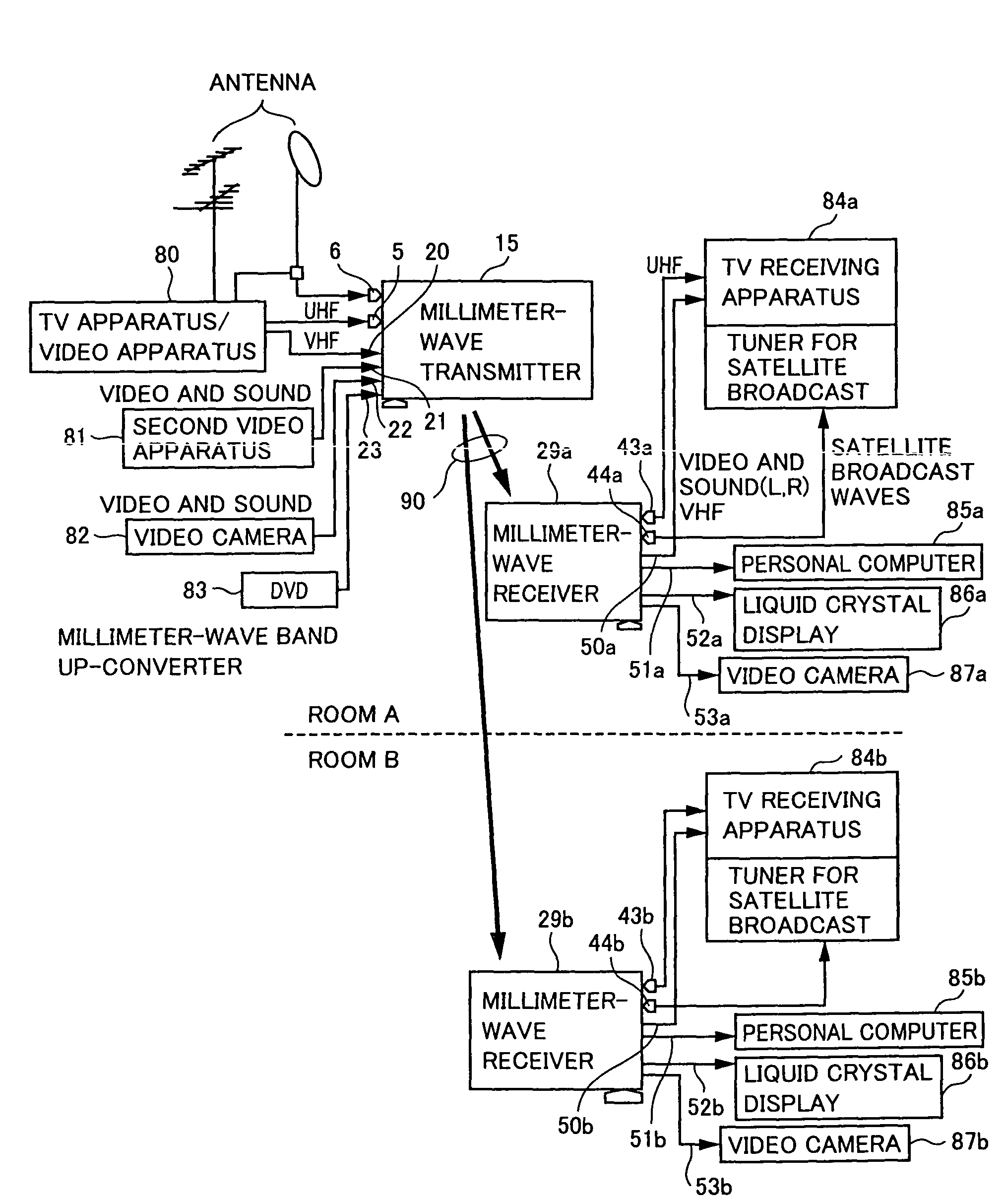
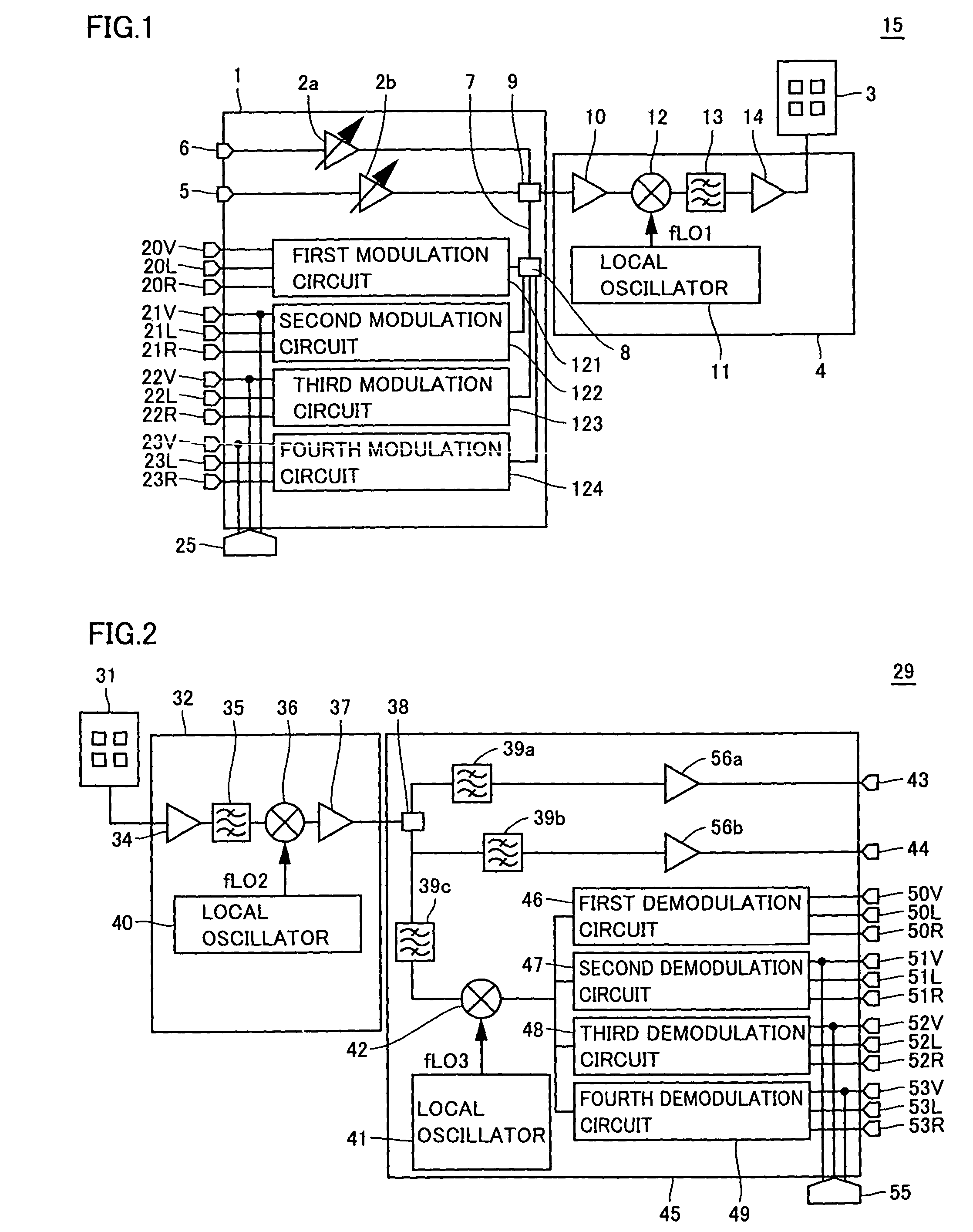
Radio communication apparatus, transmitter apparatus and receiver apparatus
InactiveUS7697574B2Improve frequency stabilityTelevision system detailsActive radio relay systemsMultiplexingSignal wave
The present invention provides a radio communication device, a transmitter and a receiver capable of handling a plurality of signal waves. A radio communication device has a millimeter-wave transmitter (15) and a millimeter-wave receiver (29). Millimeter-wave transmitter (15) includes a multiplexing circuit (1), a millimeter-wave up-converter (4) and an antenna (3), and the millimeter-receiver includes an antenna (31), a millimeter-wave down-converter (32) and an output processing circuit (45). The signal waves dedicated to the user are modulated by a modulation circuit (121 to 124) so as to be allocated between the ground broadcast waves and satellite broadcast waves. The frequencies are multiplexed in an intermediate frequency band, after that, the multiplexed frequencies are converted into a millimeter-wave band and the resultant is transmitted. On the reception side, the multiplexed waves are down-converted, separated to signal waves and demodulated.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
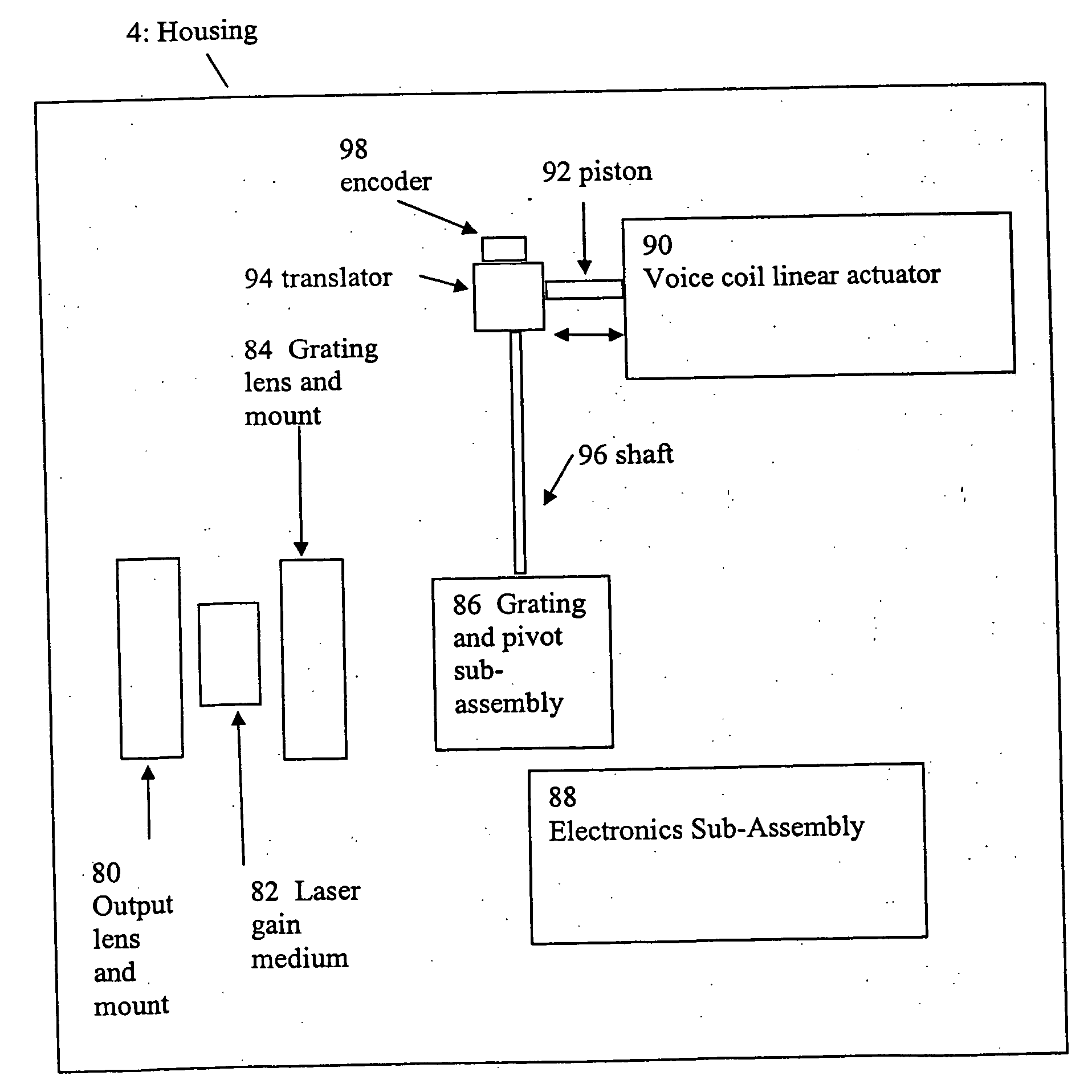
External cavity tunable compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070030865A1Reduce usageImprove cooling effectLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Millimeter-wave-band radio communication method in which both a modulated signal and an unmodulated carrier are transmitted to a system with a receiver having plural receiving circuits
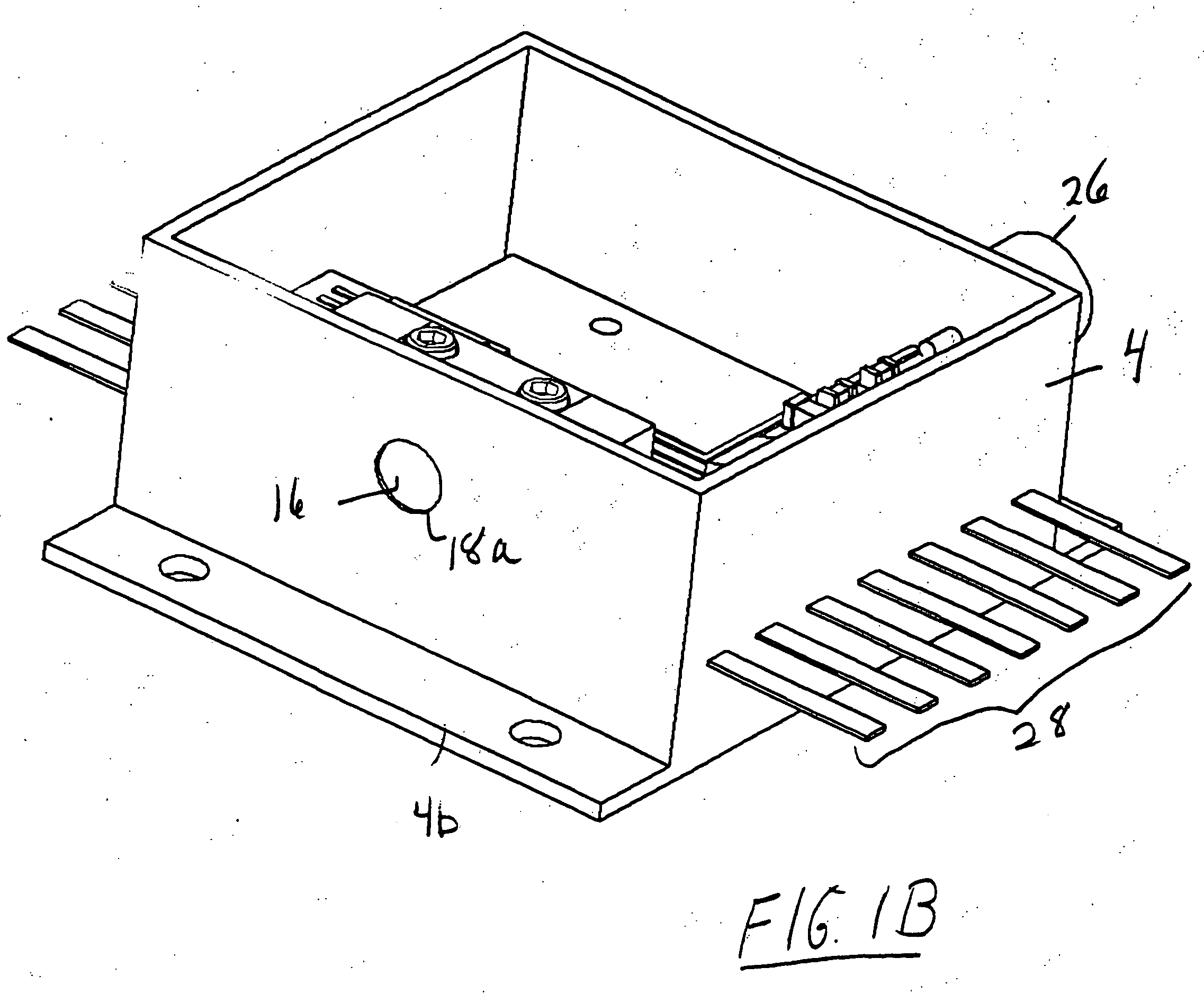
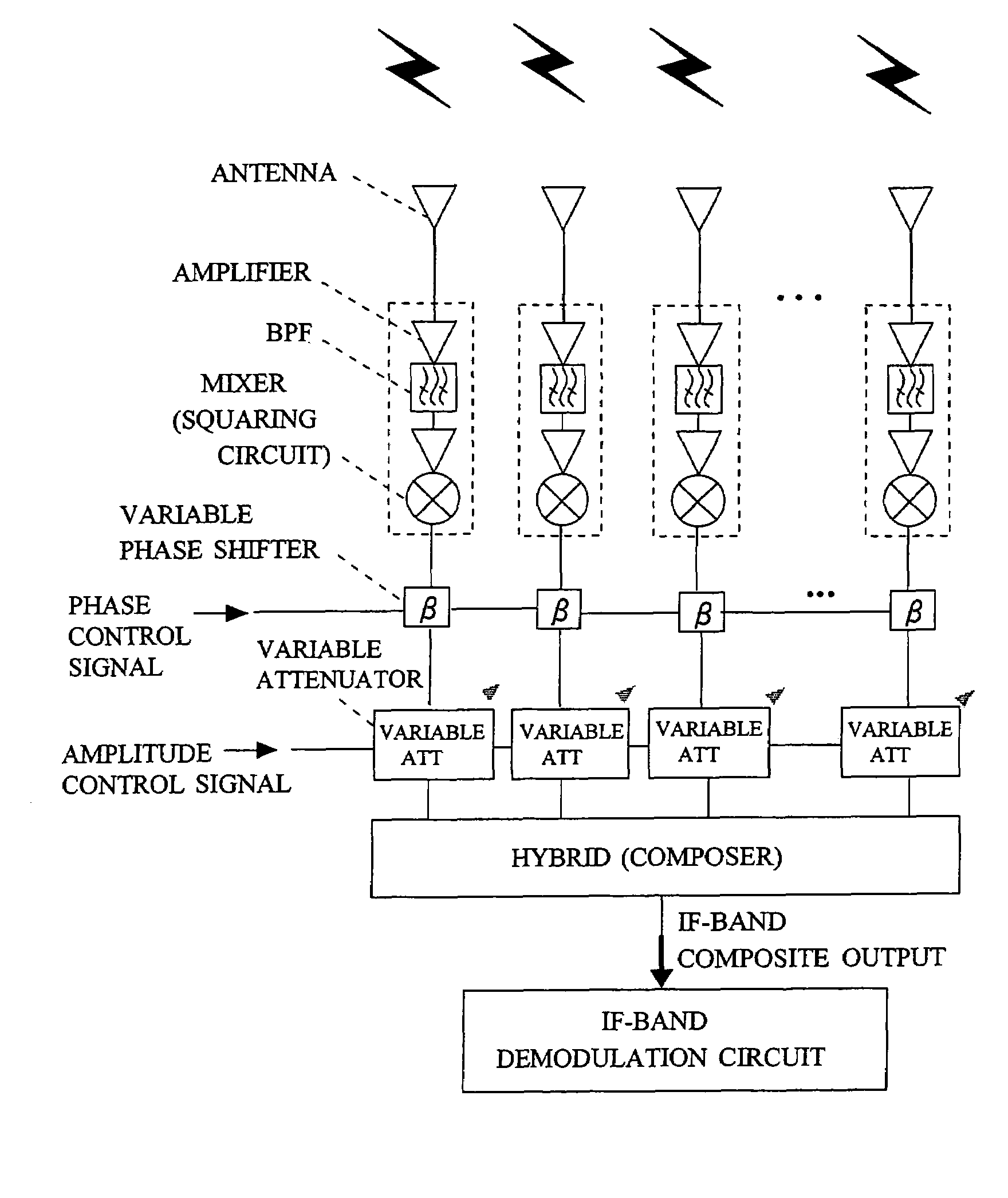
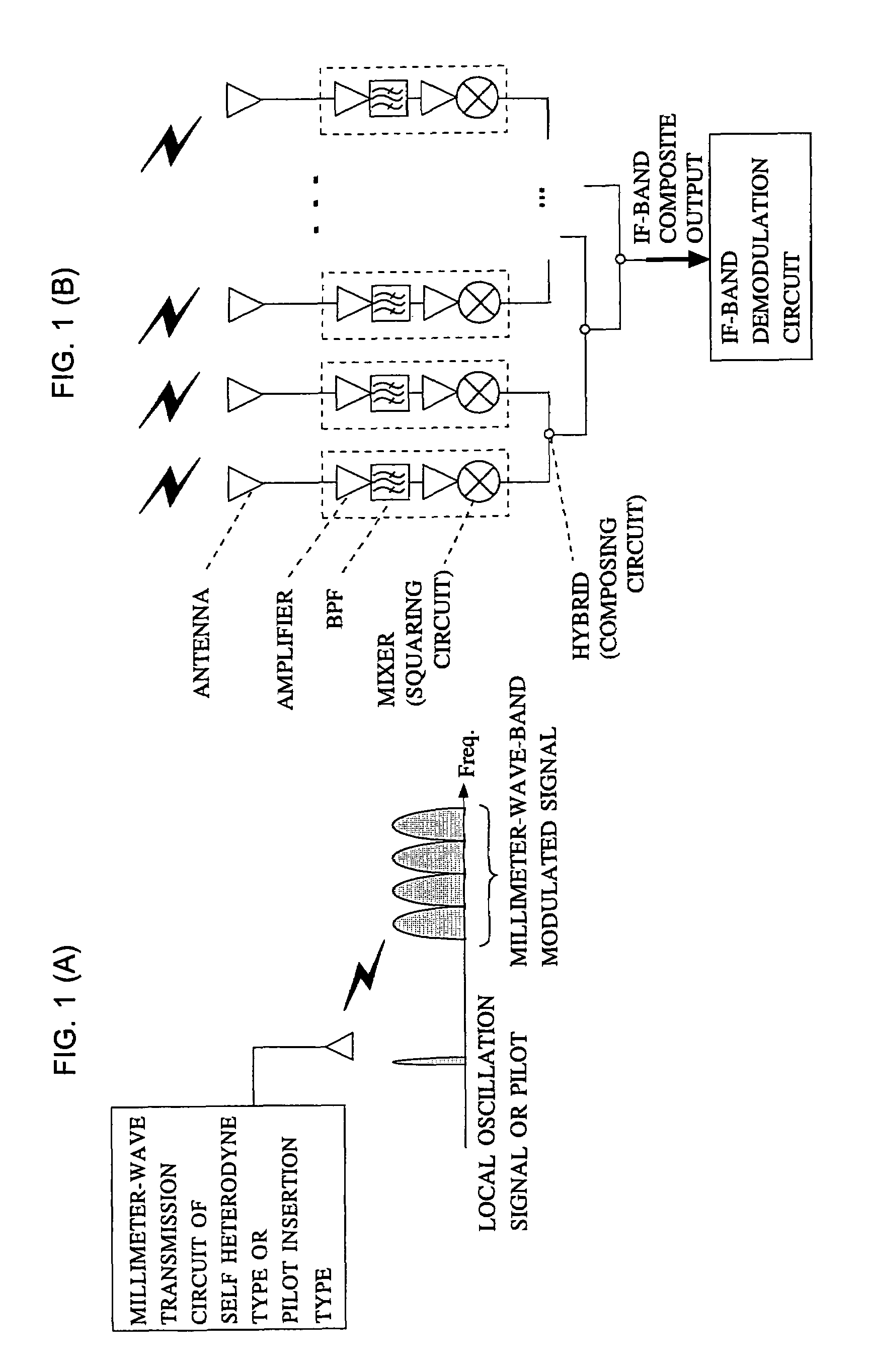
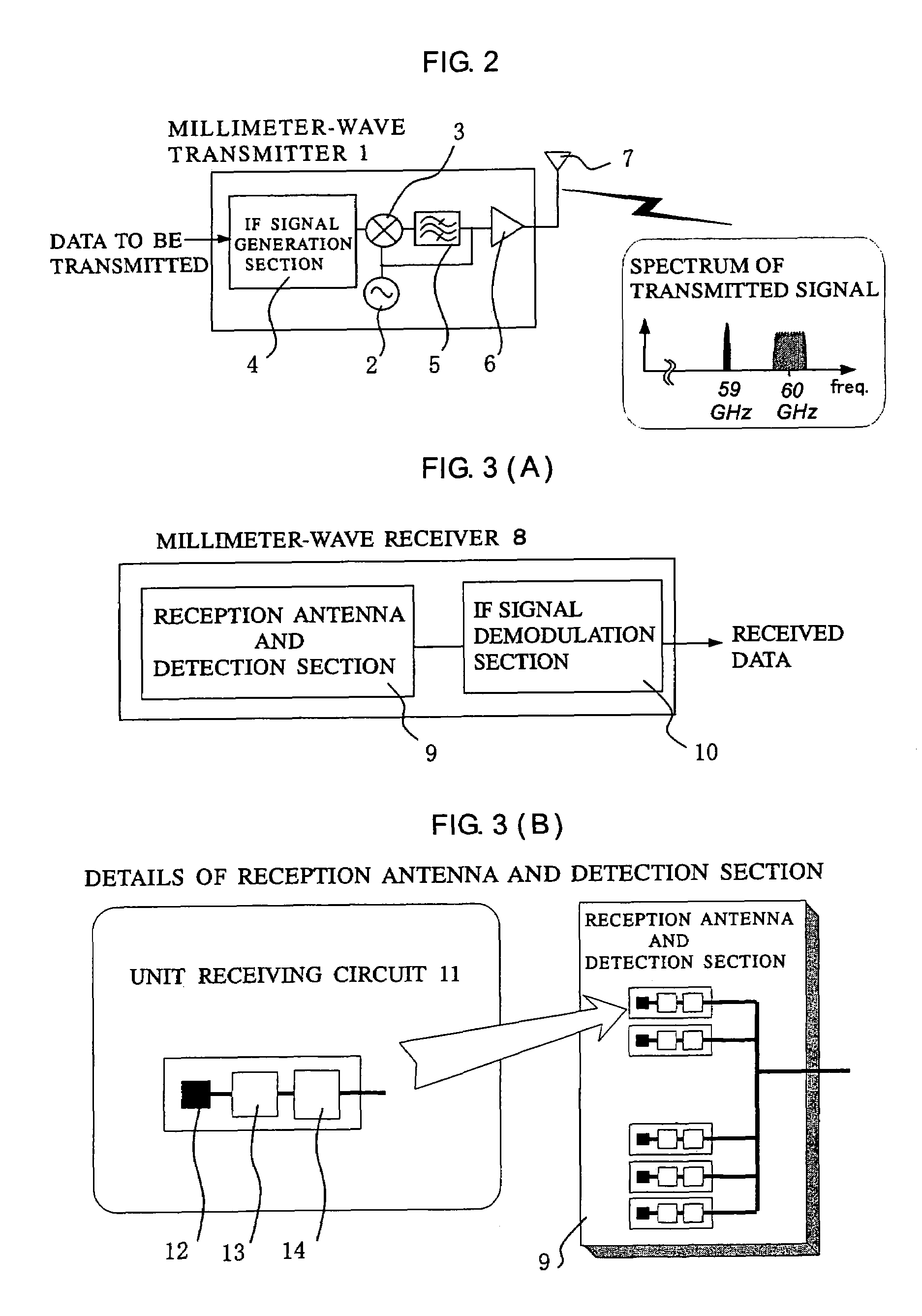
InactiveUS7599672B2Quality improvementEasy to useSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentPhase noiseWide beam
A receiver receives an RF-band modulated signal transmitted from a transmitter, as well as an un-modulated carrier also transmitted from the transmitter and having a phase noise characteristic coherent with that of the modulated signal, and a product of the two components is generated to thereby restore an IF-band transmission source signal. In the receiver, a small planar antenna having a broad beam characteristic such as a single-element patch antenna is combined with an amplifier and a mixer circuit, which are formed on a micro planar circuit by an MMIC technique, so as to form a unit receiving circuit. A plurality of such unit receiving circuits are disposed on the receiver at intervals smaller than a wavelength corresponding to an IF band, and detection outputs from the unit receiving circuits are power-mixed. Thus, the receiver serves as a high-gain antenna having a detection function, and can realize a broad beam radiation characteristic comparable to that of a single-element antenna. The composed IF-band composite output is demodulated in an IF-band demodulation circuit. The present invention enables construction of a low-cost radio communication system, transmission of high-quality signals, and production of a wide beam antenna which has a high gain and which is convenient for use.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
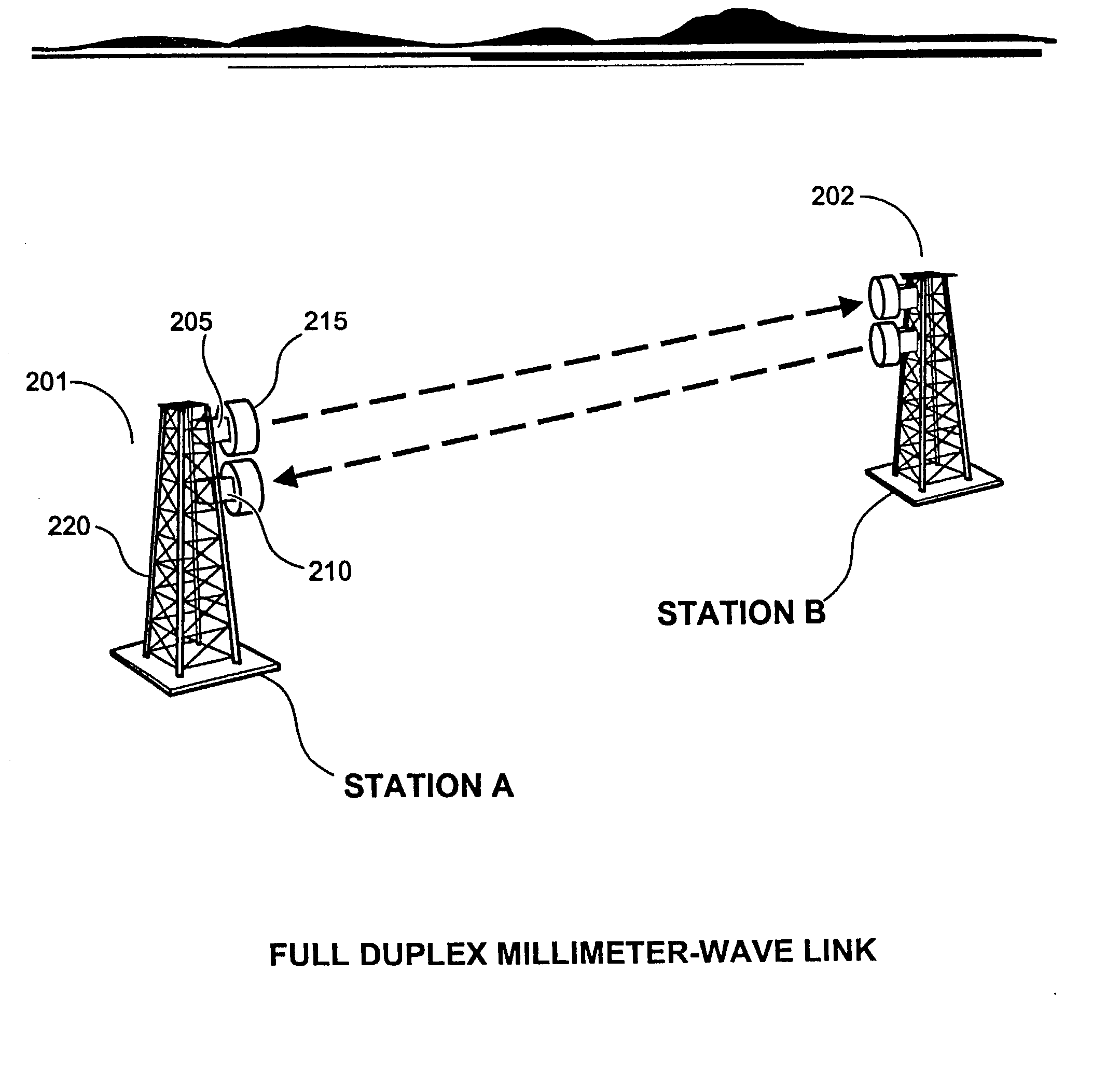
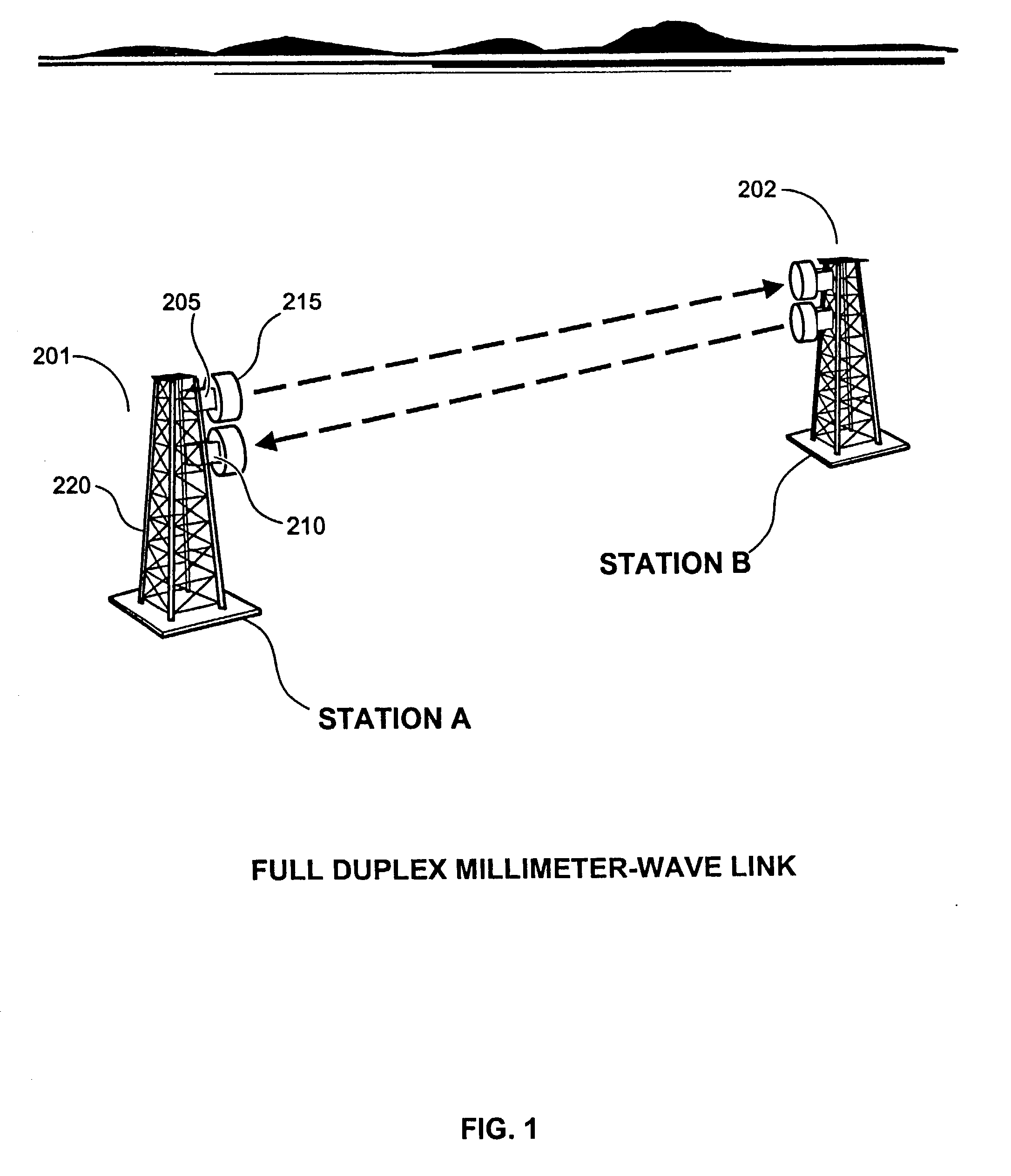
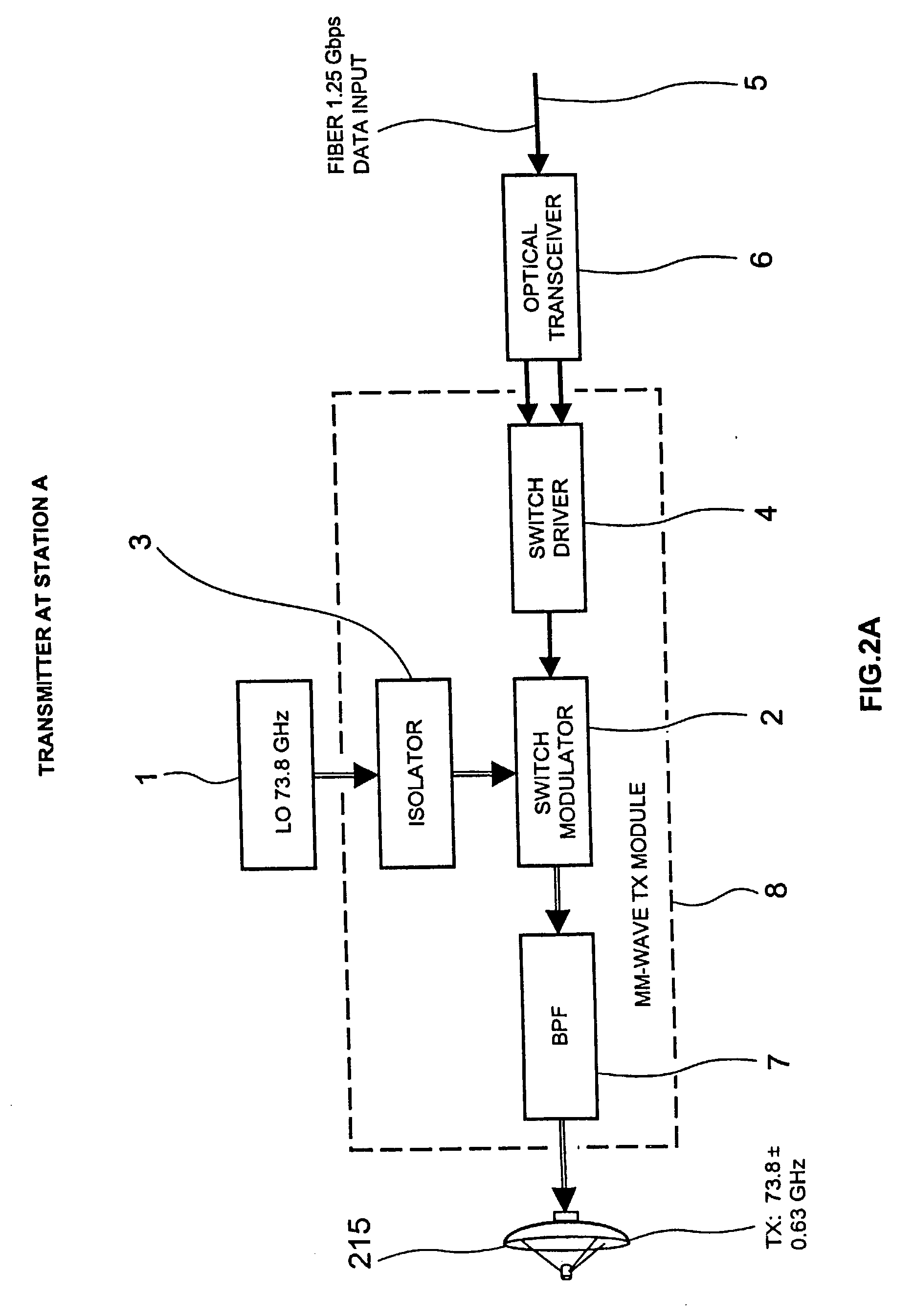
High data rate wireless communication system
InactiveUS20030224801A1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverTelecommunications link
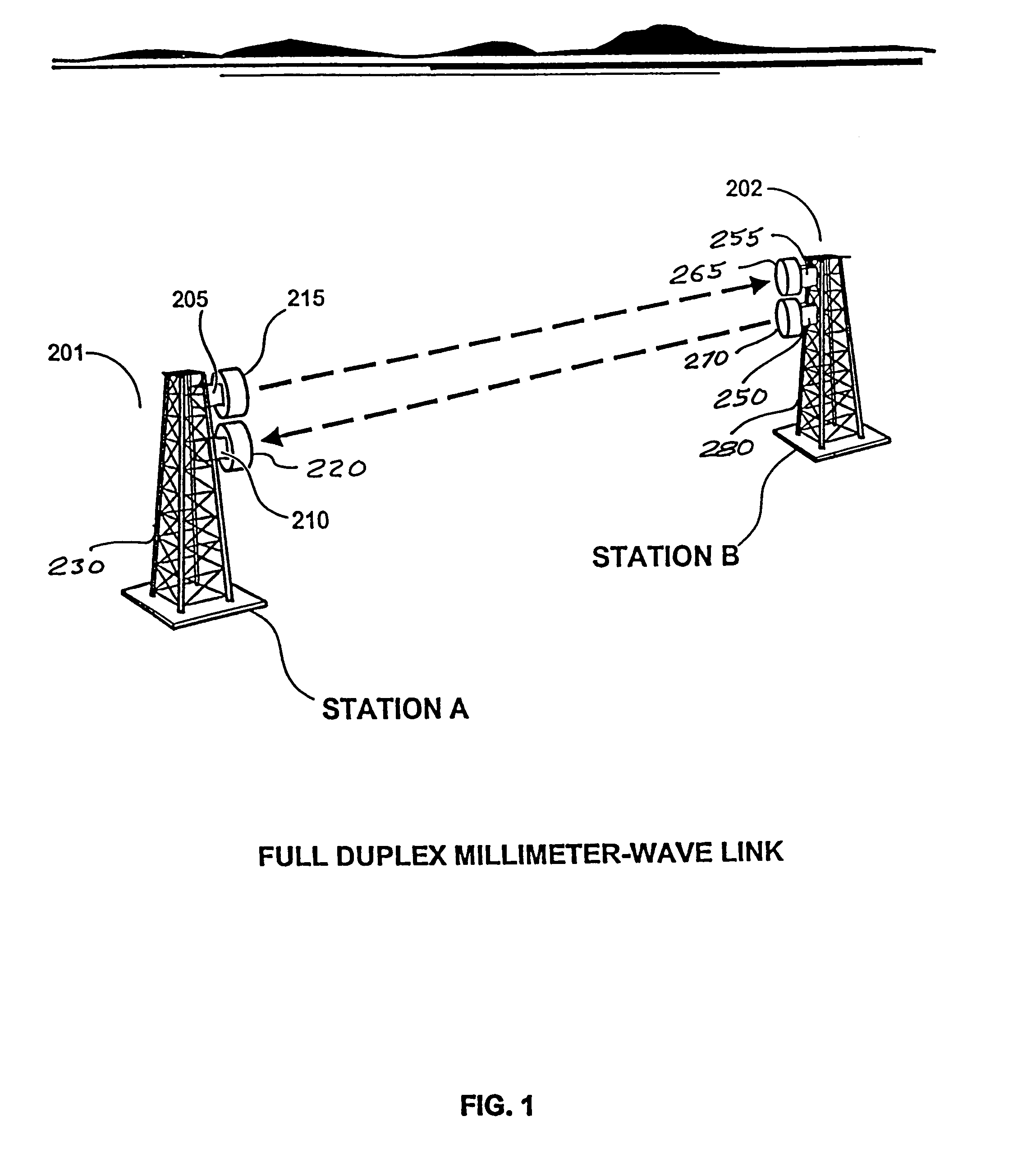
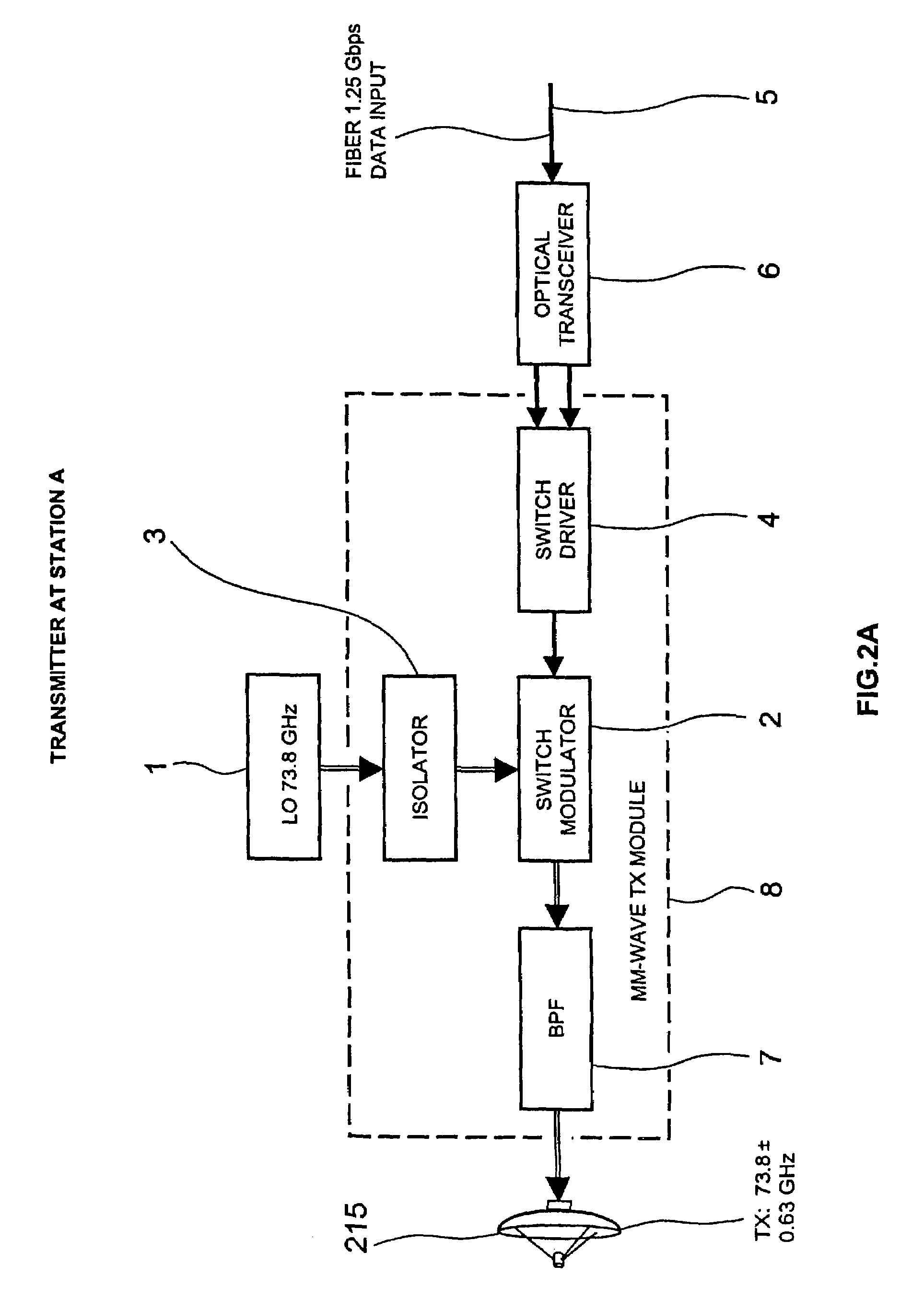
A high data rate communication system operating at frequencies greater than 70 MHz and at data rates of about 1.25 Gbps or greater. Preferred embodiments include modulators with a resonant LC circuit including a diode which is back-biased for "off" (i.e., no transmit) and forward biased for "on" (or transmit). The modulator is a part of high performance transceivers for wireless, millimeter wave communications links. A preferred embodiment provides a communication link of more than eight miles which operates within the 71 to 76 GHz portion of the millimeter spectrum and provides data transmission rates of 1.25 Gbps with bit error rates of less than 10<-10 >. A first transceiver transmits at a first bandwidth and receives at a second bandwidth both within the above spectral range. A second transceiver transmits at the second bandwidth and receives at the first bandwidth. The transceivers are equipped with antennas providing beam divergence small enough to ensure efficient spatial and directional partitioning of the data channels so that an almost unlimited number of transceivers will be able to simultaneously use the same spectrum. In a preferred embodiment the first and second spectral ranges are 71.8+ / -0.63 GHz and 73.8+ / -0.63 GHz and the half power beam width is about 0.2 degrees or less. Preferably, a backup transceiver set is provided which would take over the link in the event of very bad weather conditions. In other embodiments especially useful for mobile applications at least one of the transceivers include a GPS locator.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Millimeter wave surface imaging radar system
InactiveUS20110199254A1Ample scan coverageReliable and effective FOD detectionAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar imagingMillimetre wave
A short range millimeter wave surface imaging radar system. The system includes electronics adapted to produce millimeter wave radiation scanned over a frequency range of a few gigahertz. The scanned millimeter wave radiation is broadcast through a frequency scanned transmit antenna to produce a narrow transmit beam in a first scanned direction (such as the vertical direction) corresponding to the scanned millimeter wave frequencies. The transmit antenna is scanned to transmit beam in a second direction perpendicular to the first scanned direction (such as the horizontal or the azimuthal direction) so as to define a two-dimensional field of view. Reflected millimeter wave radiation is collected in a receive frequency scanned antenna co-located (or approximately co-located) with the transmit antenna and adapted to produce a narrow receive beam approximately co-directed in the same directions as the transmitted beam in approximately the same field of view. Computer processor equipment compares the intensity of the receive millimeter radar signals for a pre-determined set of ranges and known directions of the transmit and receive beams as a function of time to produce a radar image of at least a desired portion of the field of view. In preferred embodiment the invention is mounted on a truck and adapted as a FOD finder system to detect and locate FOD on airport surfaces.
Owner:TREX AVIATION
Ultra-wideband receiver and transmitter
InactiveUS7209523B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorExtensibilityBandpass filtering
A waveform-adaptive ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitter and noise-tracking UWB receiver for use in communications, object detection and radar applications. In one embodiment, the output of an oscillator is gated by a low-level impulse generator either directly or through an optional filter. In a special case of that embodiment wherein the oscillator is zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, the low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The low-level impulse signal can be generated digitally. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry data, or may be used in object detection or ranging applications. The power amplifier may be gated to provide a power-efficient UWB transmitter. The UWB transmitter exhibits well defined and controllable spectral characteristics. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Millimeter wave communications system with a high performance modulator circuit
InactiveUS7065326B2Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsMillimeter wave communication systemsFrequency spectrum
A high data rate communication system operating at frequencies greater than 70 MHz and at data rates of about 1.25 Gbps or greater. Preferred embodiments include modulators with a resonant LC circuit including a diode which is back-biased for “off” (i.e., no transmit) and forward biased for “on” (or transmit). The modulator is a part of high performance transceivers for wireless, millimeter wave communications links. A preferred embodiment provides a communication link of more than eight miles which operates within the 71 to 76 GHz portion of the millimeter spectrum and provides data transmission rates of 1.25 Gbps with bit error rates of less than 10−10 . A first transceiver transmits at a first bandwidth and receives at a second bandwidth both within the above spectral range. A second transceiver transmits at the second bandwidth and receives at the first bandwidth. The transceivers are equipped with antennas providing beam divergence small enough to ensure efficient spatial and directional partitioning of the data channels so that an almost unlimited number of transceivers will be able to simultaneously use the same spectrum. In a preferred embodiment the first and second spectral ranges are 71.8+ / −0.63 GHz and 73.8+ / −0.63 GHz and the half power beam width is about 0.2 degrees or less. Preferably, a backup transceiver set is provided which would take over the link in the event of very bad weather conditions. In other embodiments especially useful for mobile applications at least one of the transceivers include a GPS locator.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
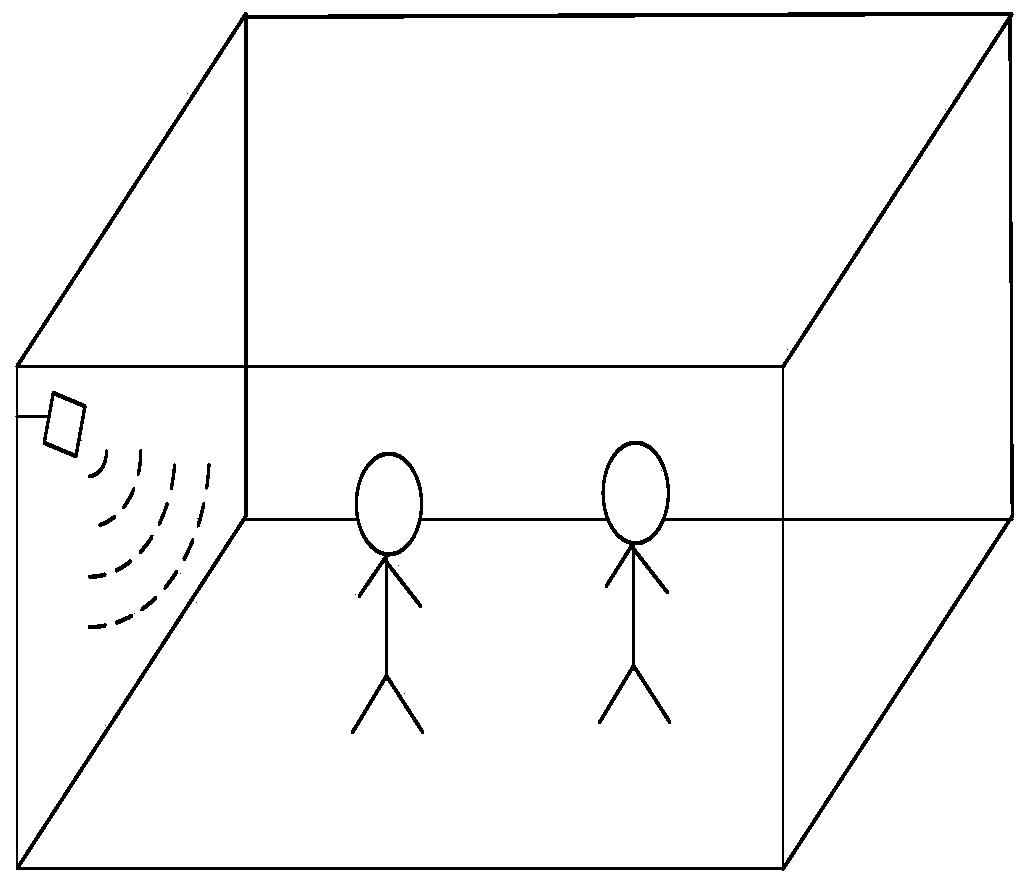
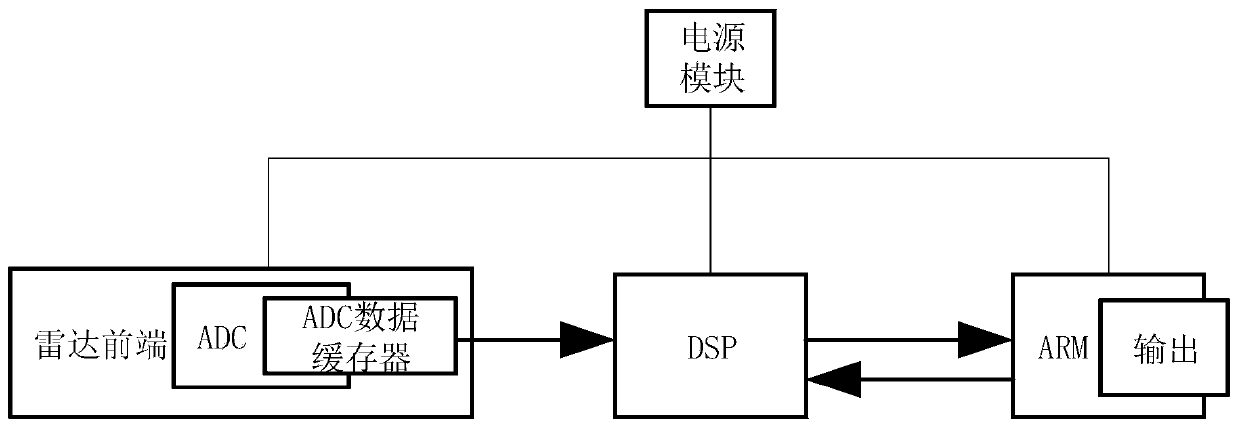
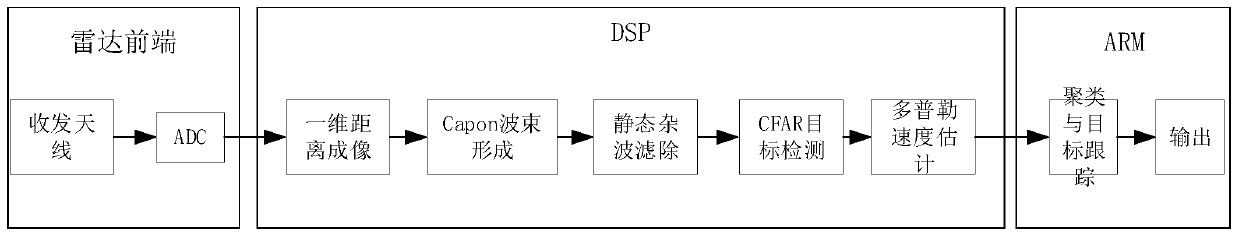
Personnel detection and counting system based on millimeter wave radar
ActiveCN110118966AEasy to detectAchieve countRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingData set
The invention provides a personnel detection and counting system based on a millimeter wave radar, wherein the millimeter wave radar is installed at a set position of a monitoring area, the millimeterwave radar transmits millimeter wave band radio frequency signals to the monitoring area through a multi-transmitting and multi-receiving antenna of the millimeter wave radar and receives echo signals at the same time, the echo signals are subjected to frequency mixing with the transmitted signals and then subjected to down-conversion to obtain beat intermediate frequency signals, and the beat intermediate frequency signals are sampled to obtain an echo sampling sequence. A digital signal processor reads the echo sampling sequence and performs signal processing to obtain a detected point cloud data set. An ARM processor reads the point cloud data set, meanwhile, Kalman filtering tracking is carried out on the point cloud data, continuous observation of states and the number of a pluralityof human body moving targets is achieved, the positions and the number of people in the monitoring area are obtained, and the number of people in the monitoring area is counted. The personnel detection and counting system based on the millimeter wave radar can track at least 20 targets simultaneously, provide the position and speed information of the targets, effectively judge the state of the targets and give early warning in time.
Owner:长沙莫之比智能科技有限公司
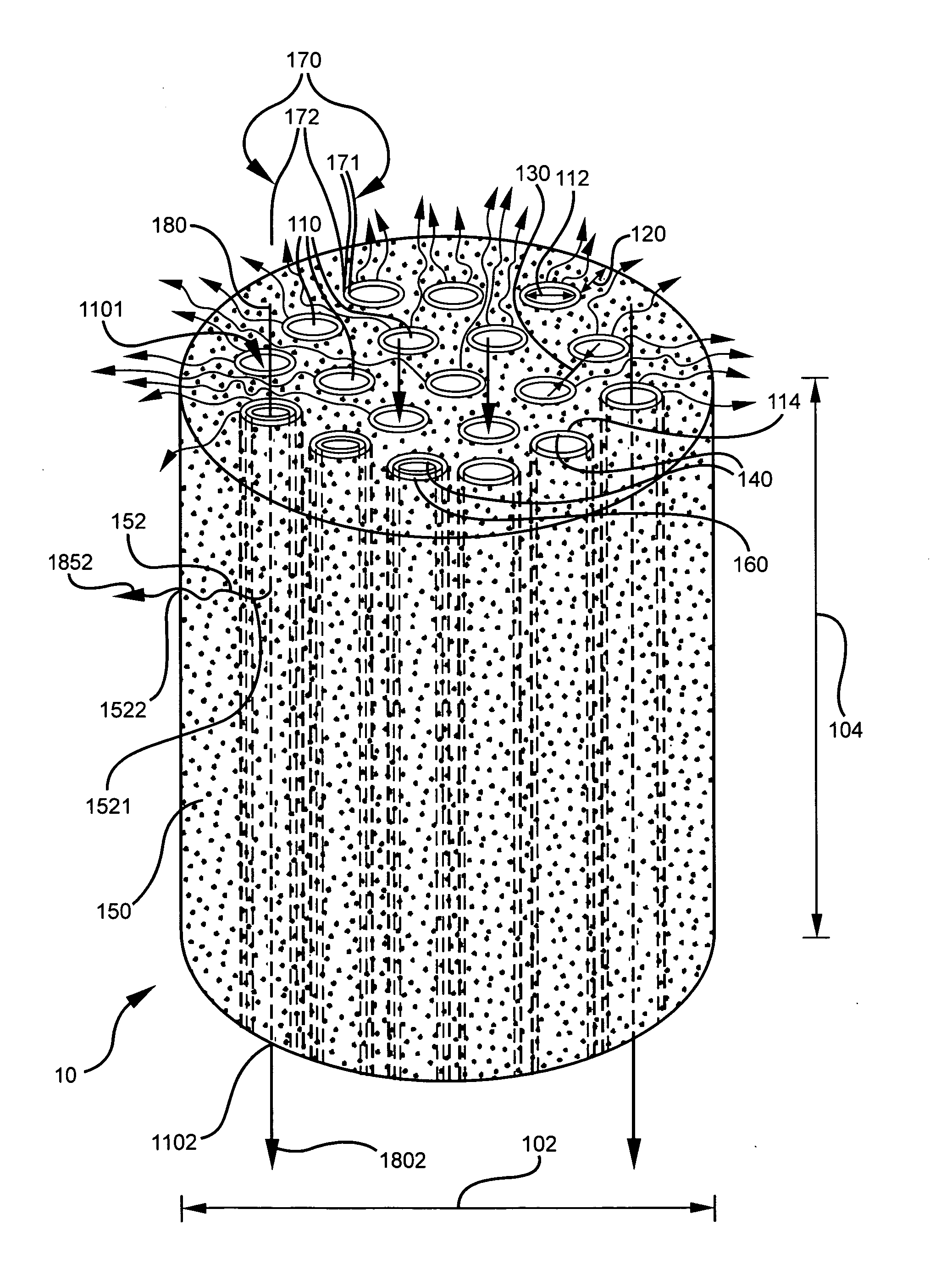
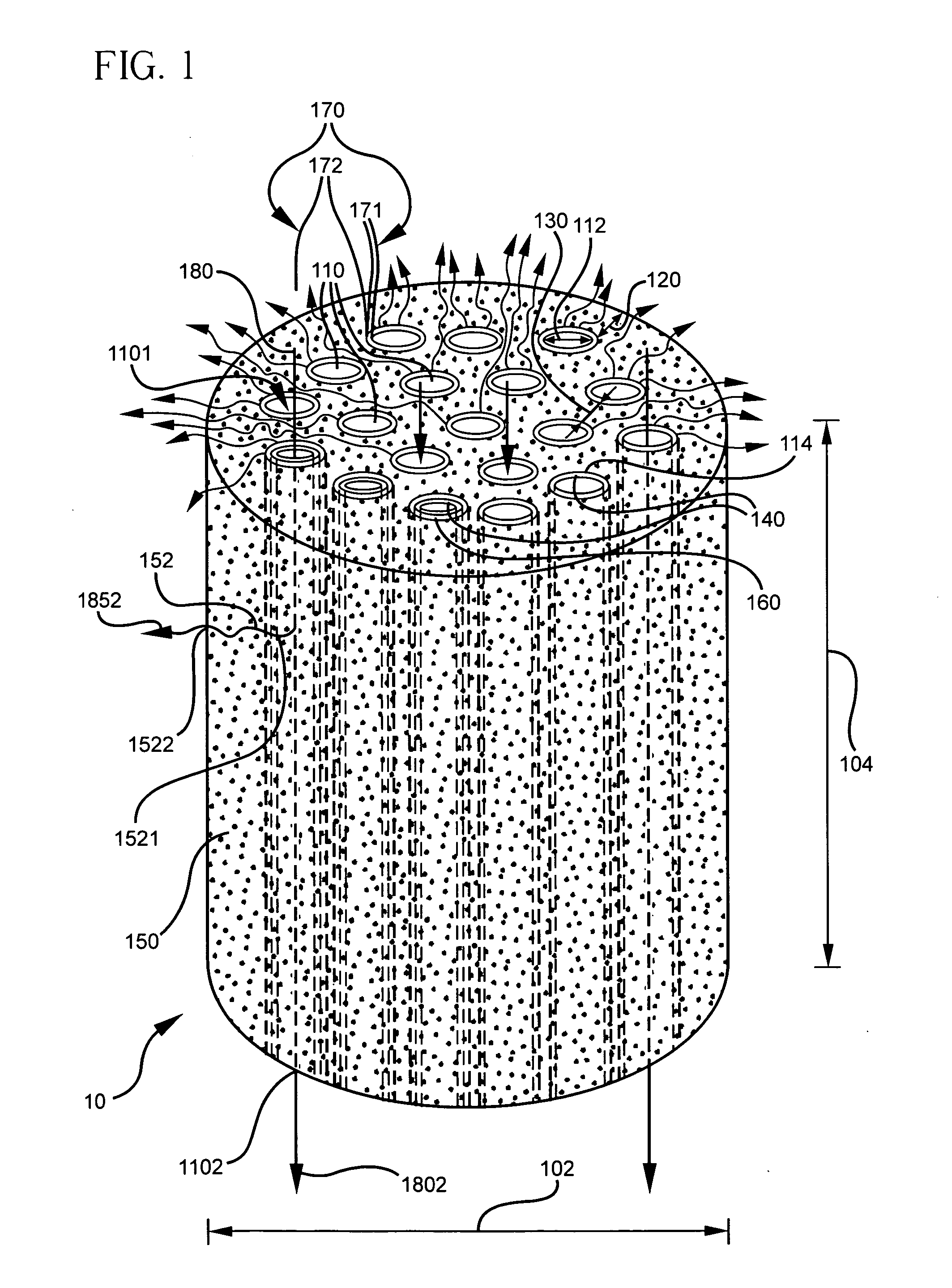
Honeycomb structure
InactiveUS20060292334A1Good dispersionHigh strengthPhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle filtrationFiberWhiskers
A honeycomb structure having multiple honeycomb units united through a seal material layer, wherein each honeycomb unit has multiple through holes arranged side by side in a longitudinal direction and separated from each other by the wall surfaces of the through holes, is disclosed. The honeycomb units include at least: ceramic particles; and at least one of inorganic fibers and whiskers. At least one of the honeycomb units has a cross section perpendicular to a longitudinal direction thereof, the cross section having an area greater than or equal to about 5 cm2 and less than or equal to about 50 cm2. The flatness of the exterior wall of each of the honeycomb units is about 0.1 mm to about 1.5 mm.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
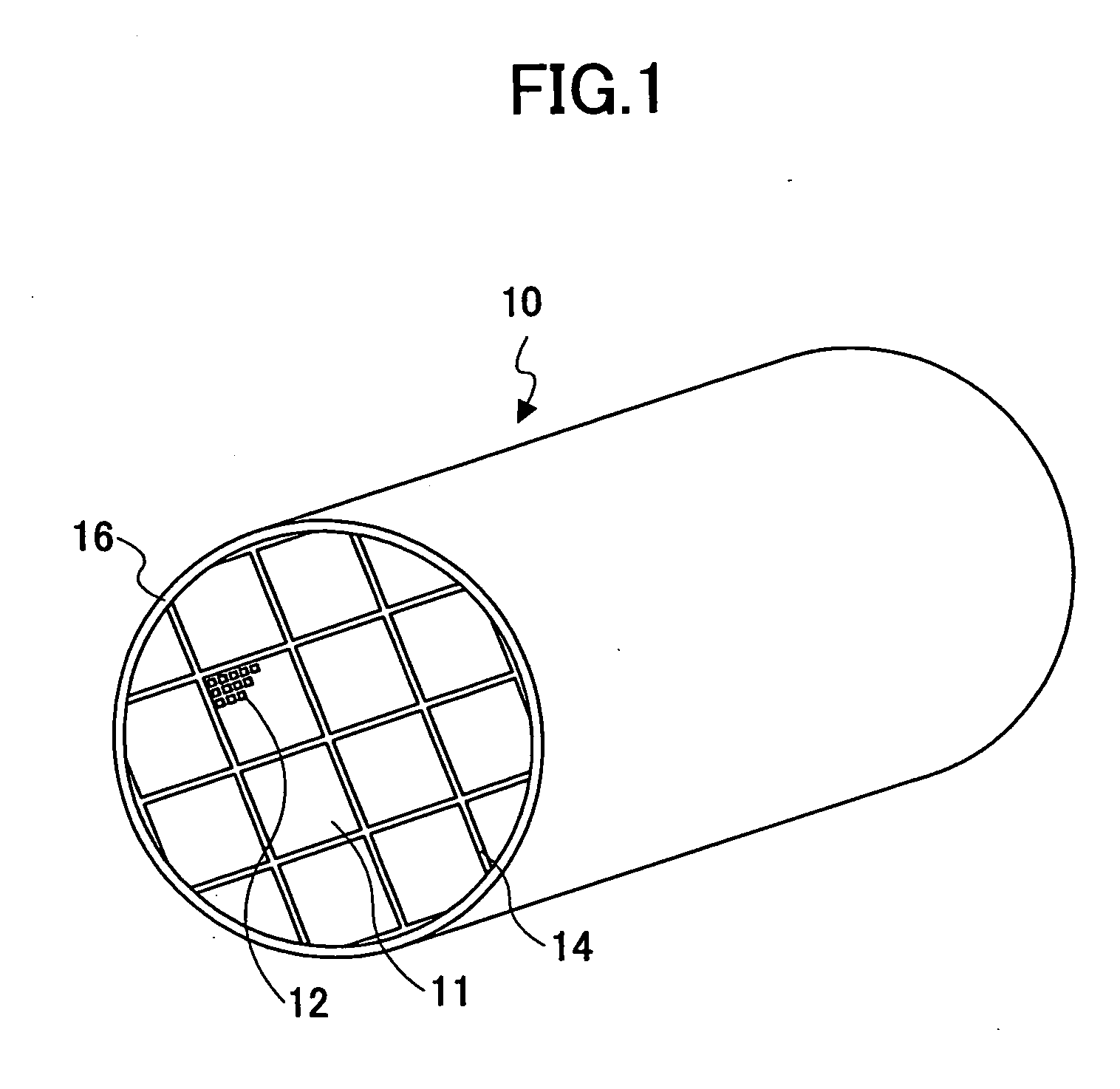
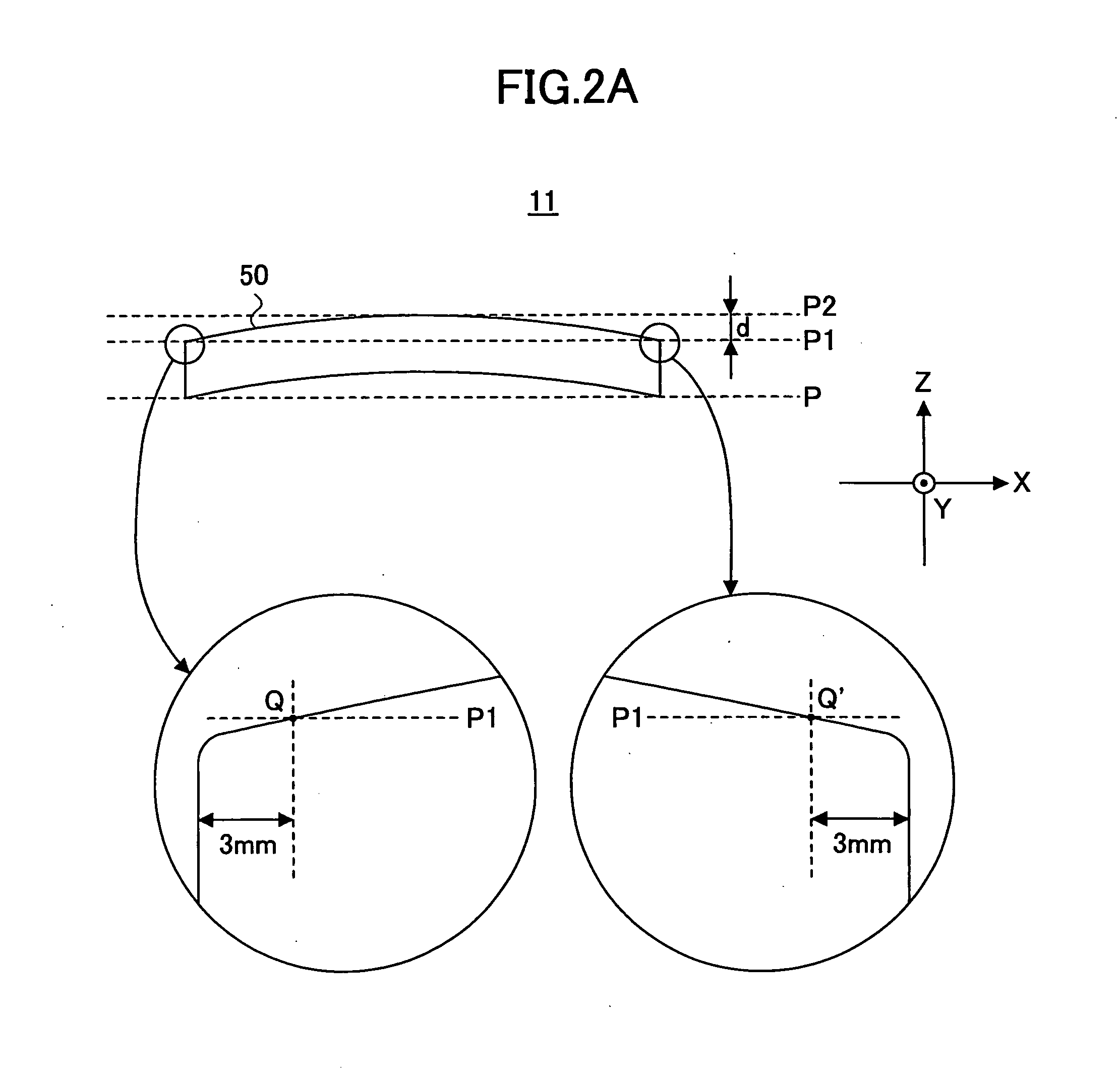
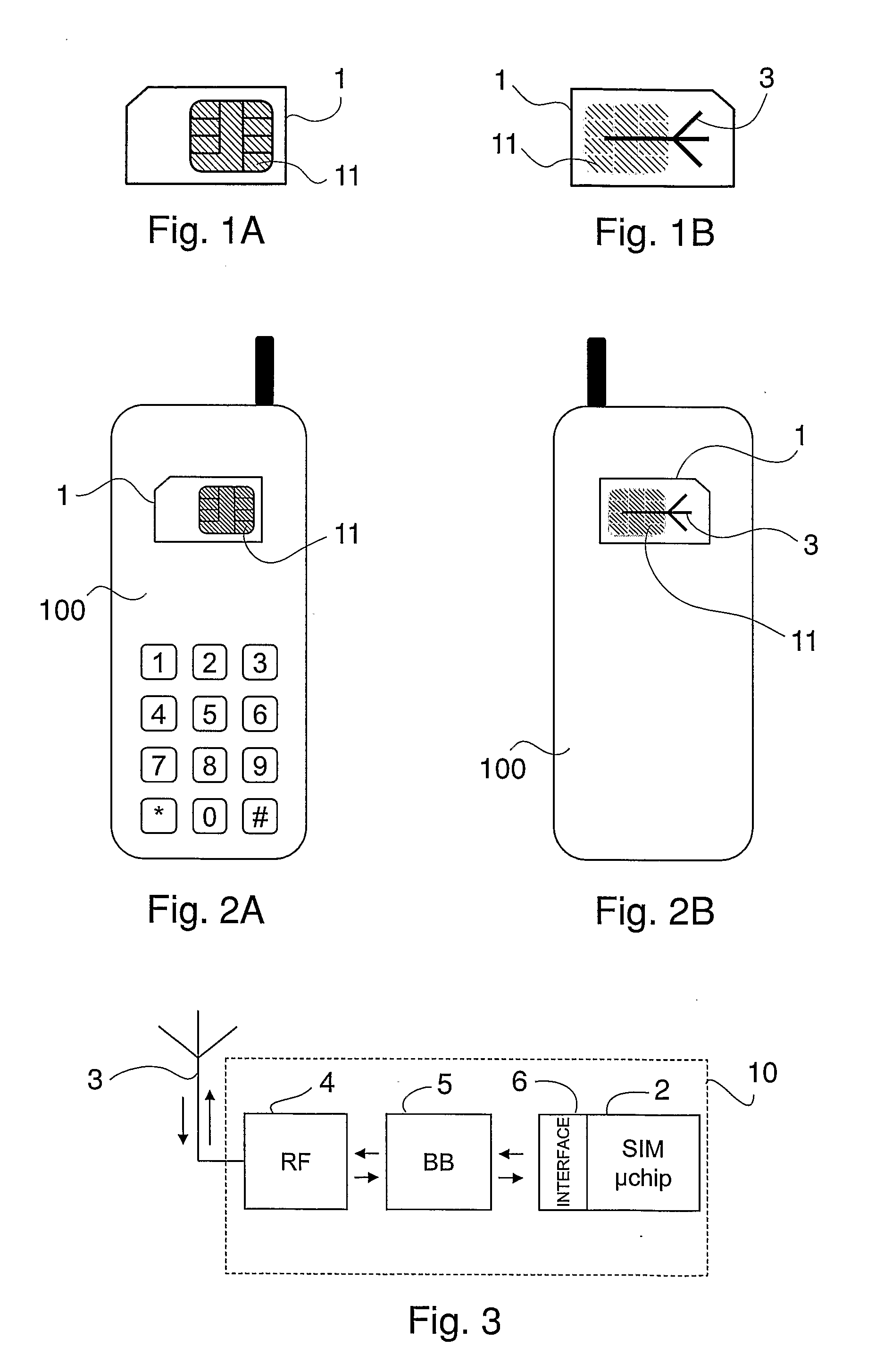
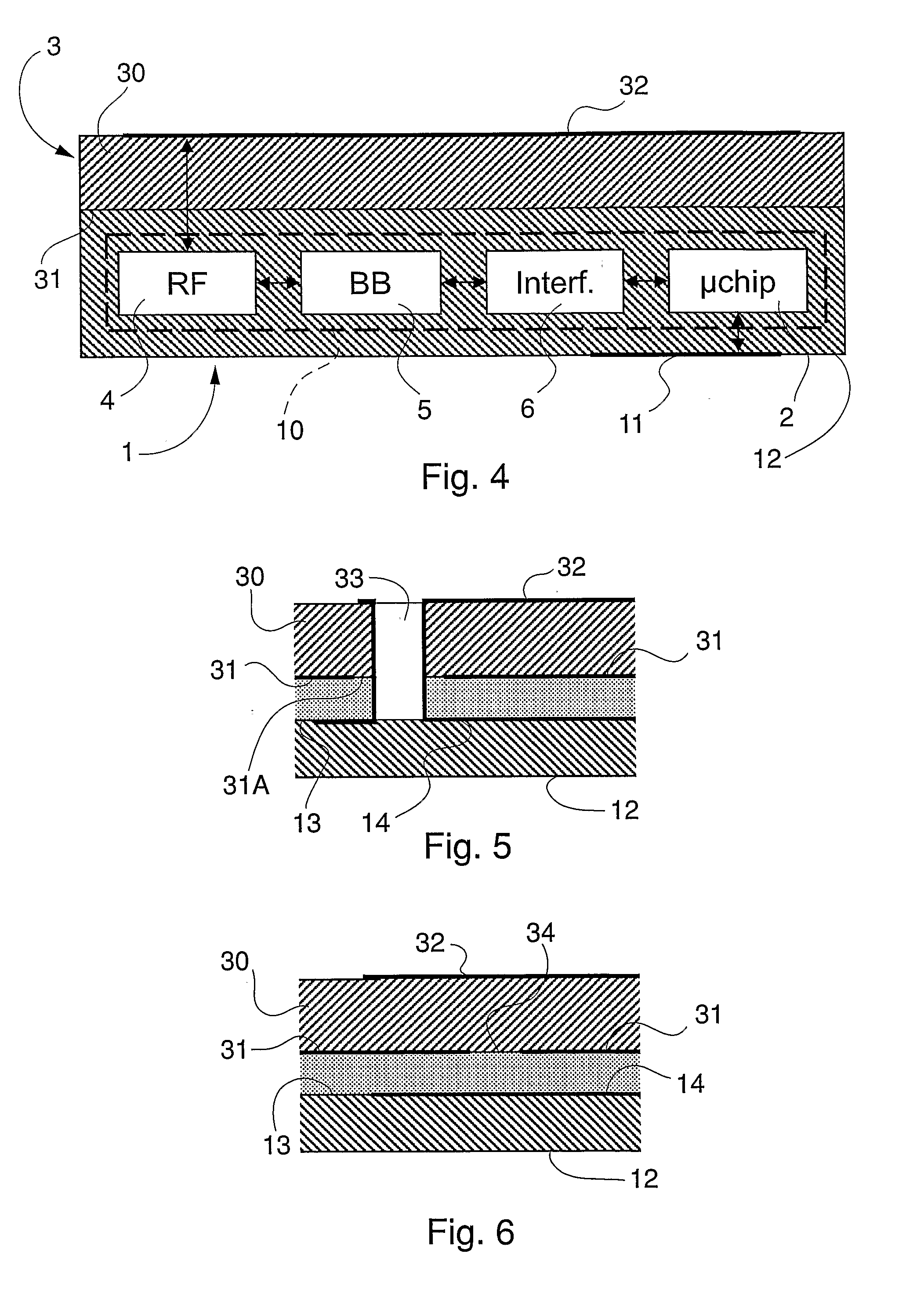
Subscriber Identification Card Performing Radio Transceiver Functionality for Long Range Applications
InactiveUS20070213096A1Low powerLong distanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentTransceiverMillimetre wave
A subscriber identification card performing radio transceiver functionality for long-range applications incorporates a radio transceiver including an antenna formed on a card surface, an RF module and a base-band module. The antenna and the transceiver operate in the microwave / millimetre waves frequency range. This allows meeting the dimensional constraints imposed by the plug-in size and attaining a long-range operation. At least the base-band module might be integrated within the same chip executing standard security related functions for the terminal.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA +1
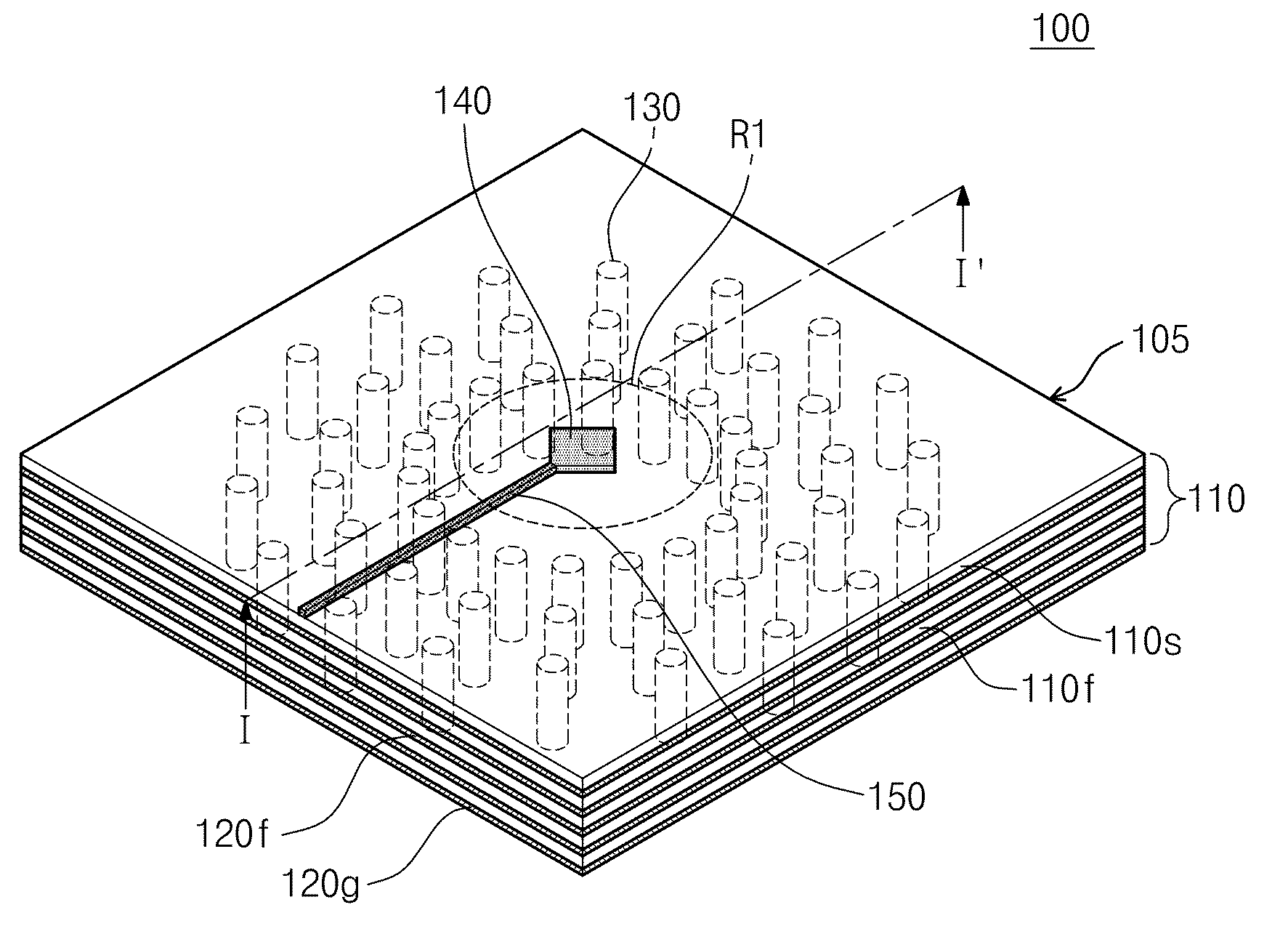
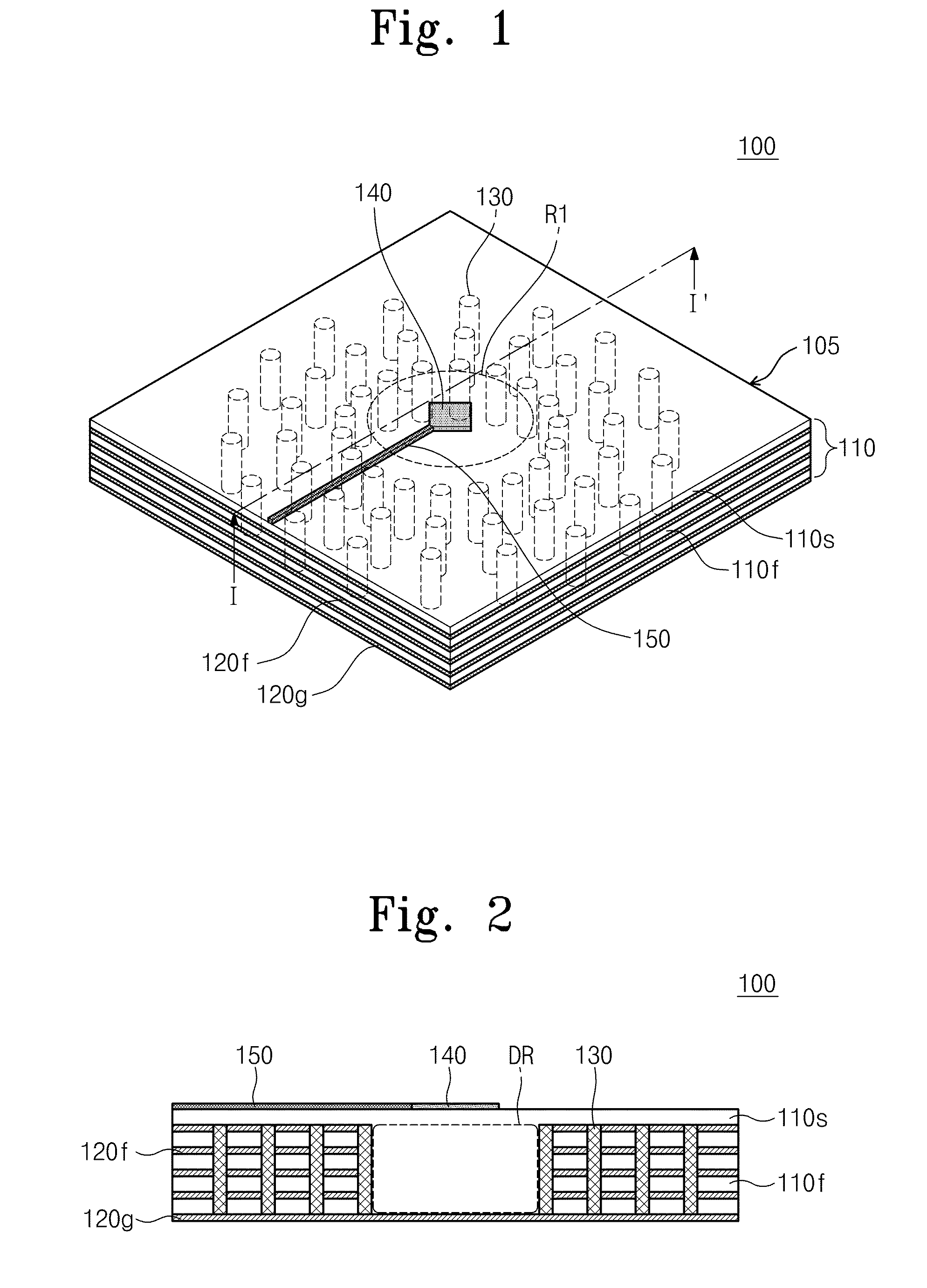
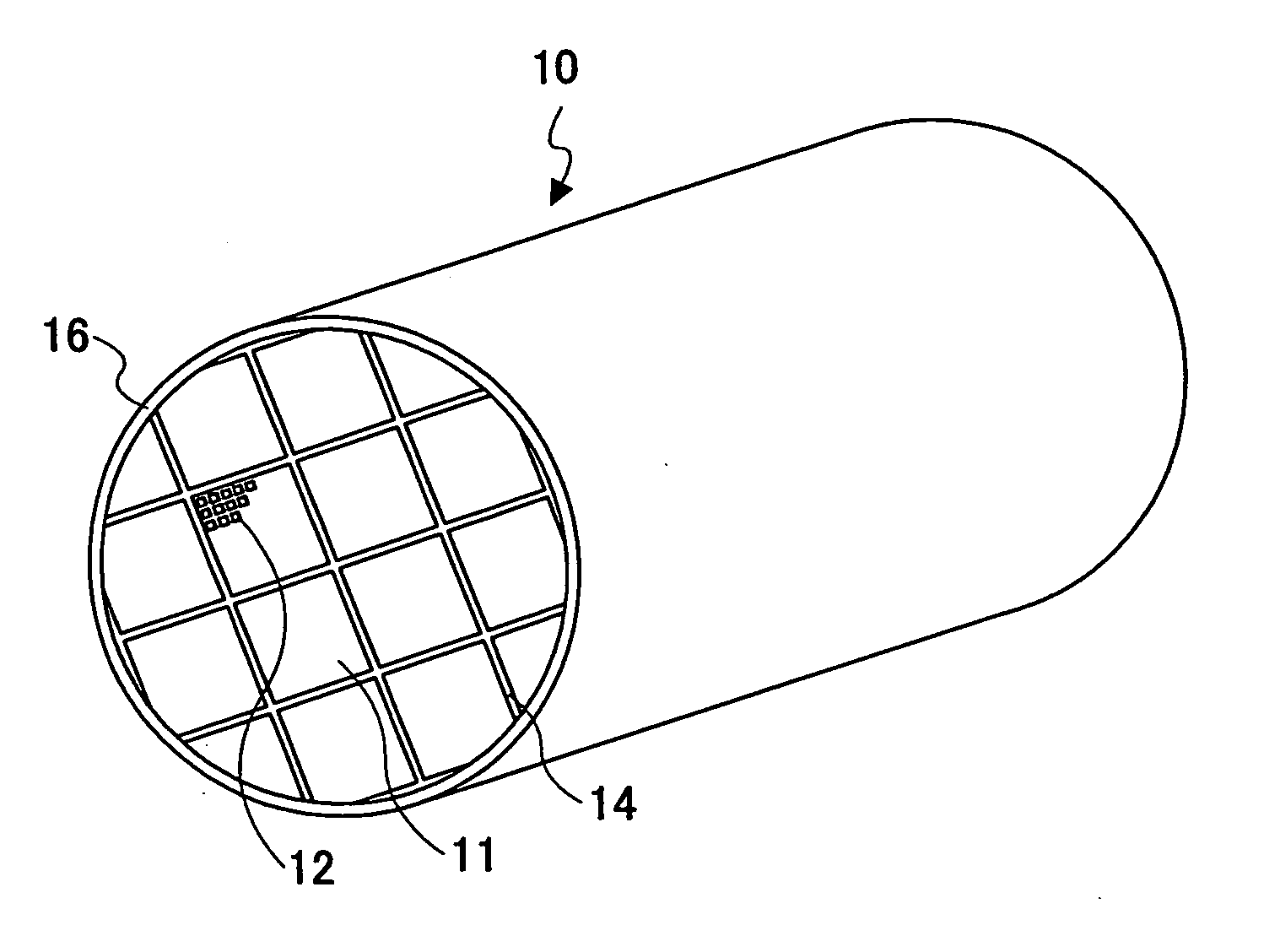
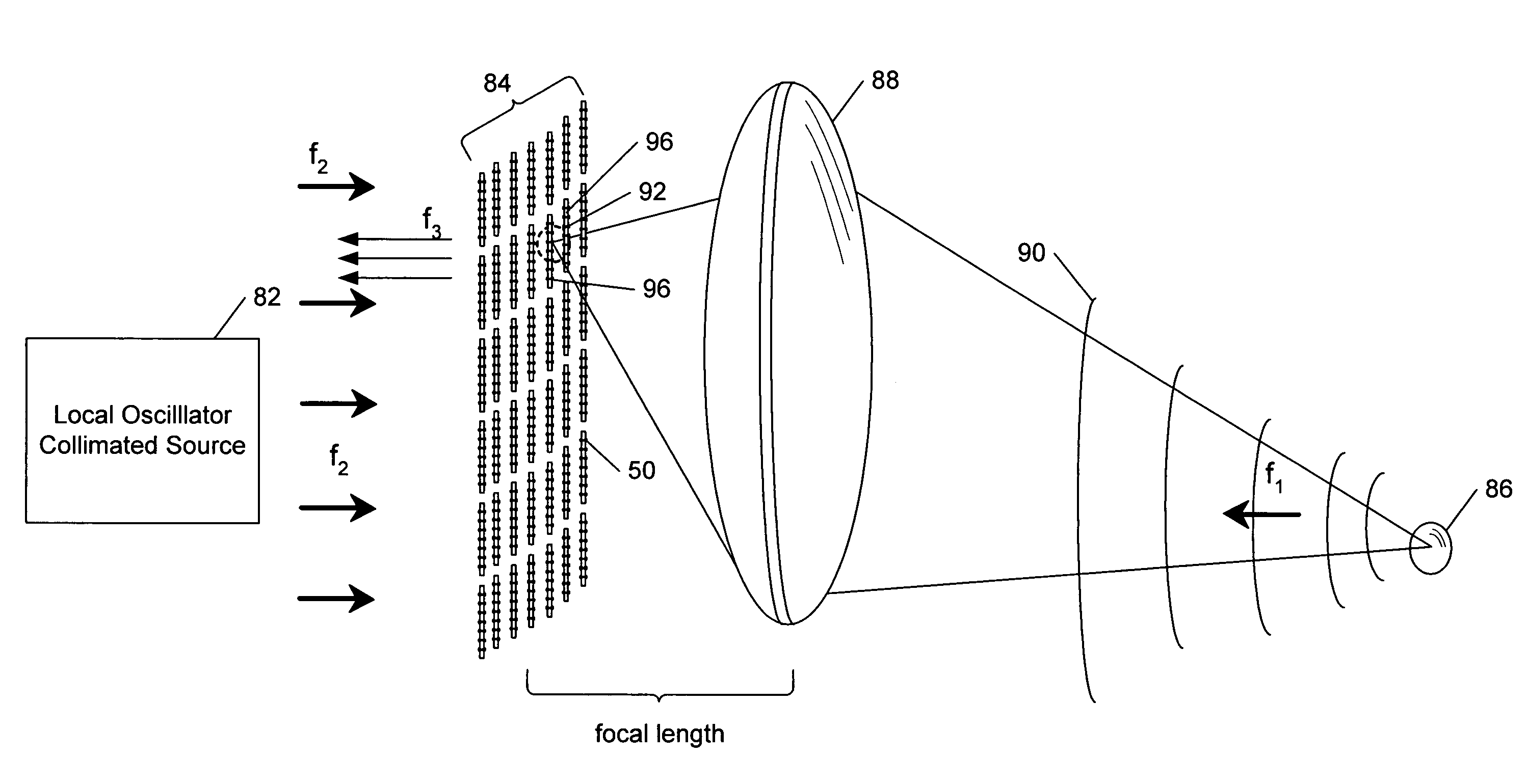
Focal plane array for THz imager and associated methods
ActiveUS6943742B2Antenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysDual frequencyElectromagnetic spectrum
A high-frequency imaging system for the millimeter and submillimeter radiation includes a high frequency lens to image an object at its focal plane. The object emits electromagnetic radiation at a first frequency above the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum. A local oscillator generates an electromagnetic beam at a second frequency to illuminate a plurality of dual-frequency antennas at the focal plane of the lens. Intermodulation of first and second frequencies generates a signal distribution of a third frequency over the focal plane, which represents an image. Also, a method of providing an image at the third frequency of an object emitting electromagnetic radiation at a first frequency is provided. The method includes imaging the electromagnetic radiation at the first frequency from each point of the object onto the focal plane. An electromagnetic beam is transmitted to illuminate all elements of the focal plane array.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High power diode laser having multiple emitters and method for its production
InactiveUS20080084905A1Simple and cost-efficient configurationIncrease powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser transmitterHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a high power laser diode comprising a plurality of laser light emitters (2) and a plurality of light collimating means (33), wherein each of the laser light emitters (2) defines, in a direction perpendicular to a direction of propagation (32) of an output laser beam, a fast axis (y) and a slow axis (x), and wherein each of the light collimating means is associated with a laser light emitter and configured for collimating the output laser beam at least in a fast axis (y) direction. In order to enable a simple and cost-efficient assembly of the diode laser with collimating means, having a layered structure consisting of a plurality of plane-parallel substrates. For this purpose, the diode laser comprises planar substrate means (10, 30) which serves to precisely define a distance between a respective laser light emitter (2) and an associated light collimating means to the order of one or several millimetres and to support the collimating means (33) such that the optical axis of said laser light emitters are parallel to each other and for defining a precise location of emitters on the planar substrate (10), preferably at predetermined distance in fast axis direction between said laser light emitters. The collimating means is an array or multiple single of micro-optical lenses having a rear side which is bonded to the upper surface of the planar spacer means. The submounts of the light emitters (2) are mounted to the planar substrate means (10, 30) and to a heatsink (6).
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
Polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane-electrode assembly for polymer electrolyte fuel cells and process for producing polymer electrolyte membrane
InactiveUS20060068258A1Good chemical stabilityHigh mechanical strengthNon-metal conductorsIon-exchanger regenerationMillimeterPolymer chemistry
A polymer electrolyte membrane comprises at least one layer of a perforated sheet having many through-holes formed substantially parallel to the thickness direction with an average cross-sectional area per hole ranging from 1×10−3 to 20 mm2, wherein the numerical aperture based on the through-holes ranges from 30 to 80%, and the through-holes are filled with an ion exchange resin.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
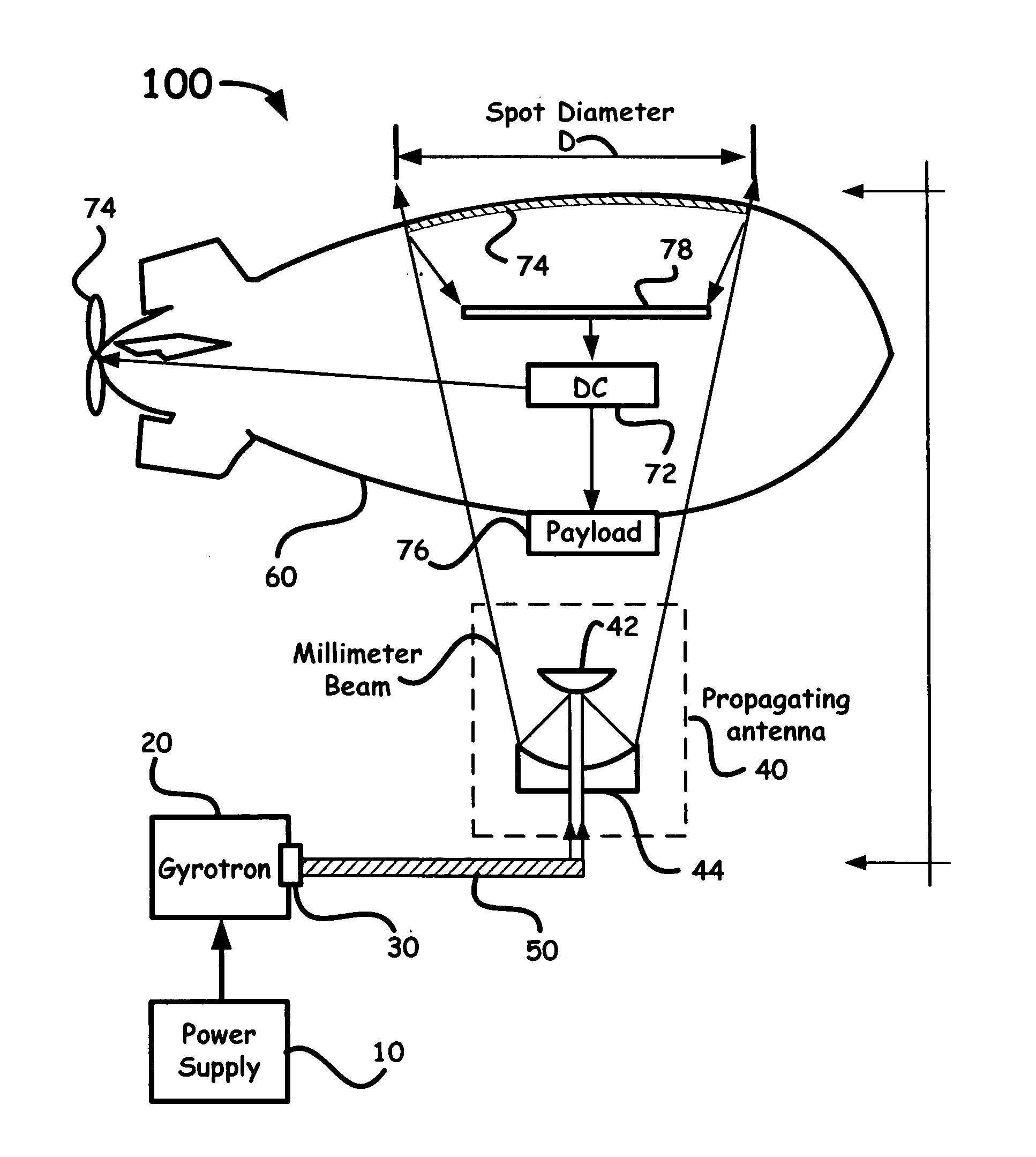
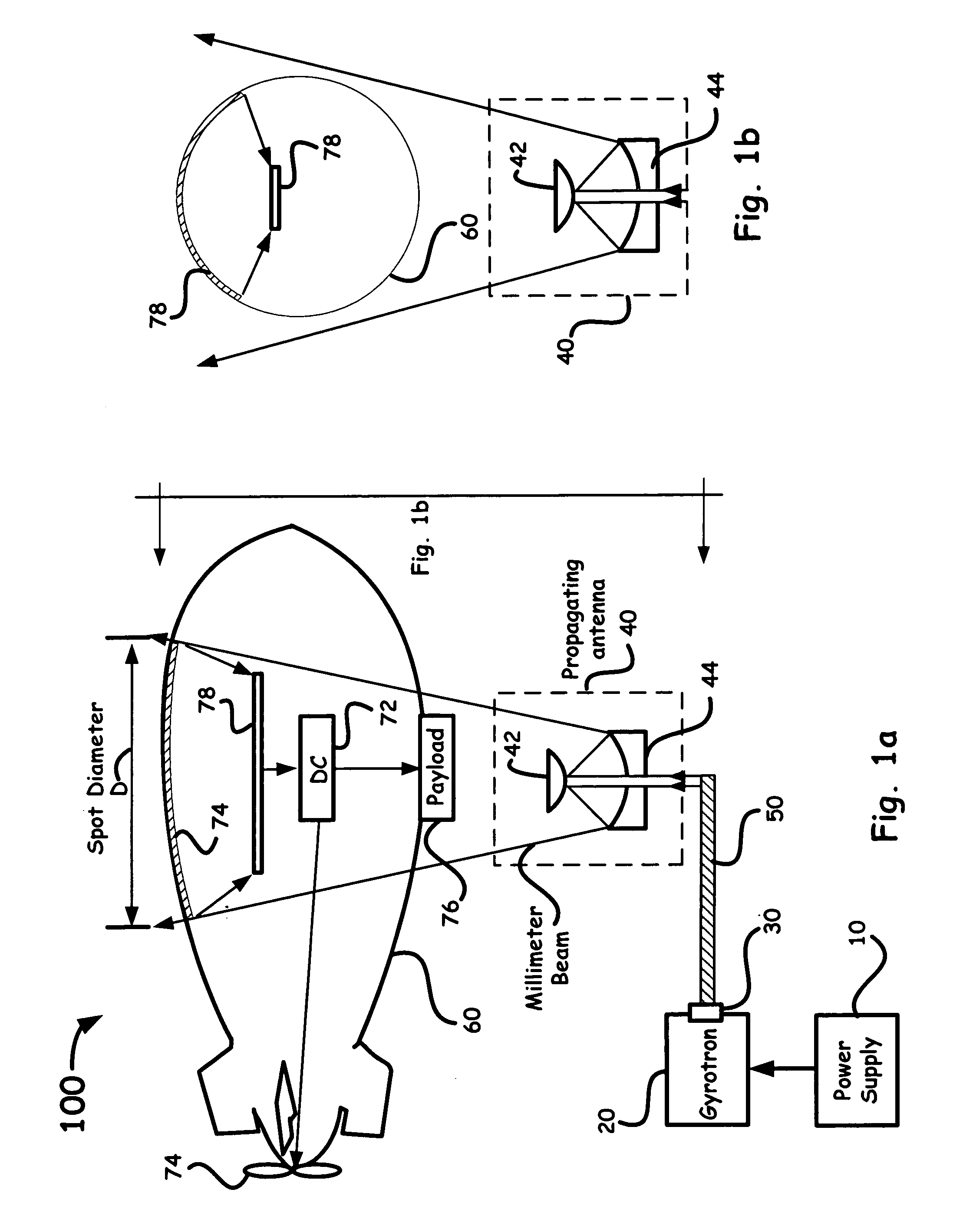
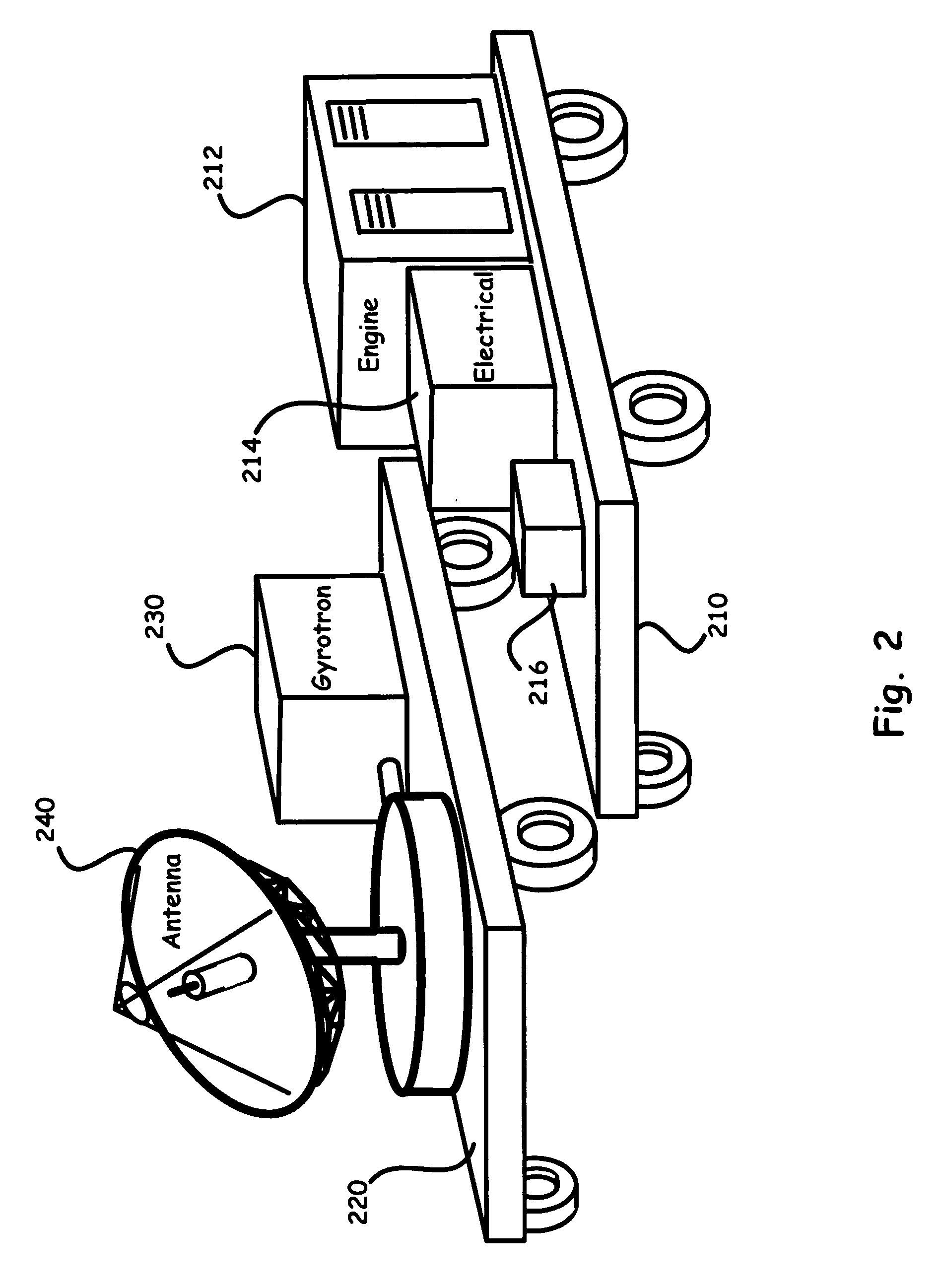
System using a megawatt class millimeter wave source and a high-power rectenna to beam power to a suspended platform
InactiveUS20040156400A1Laser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic wave systemEngineeringMillimeter
A system for beaming power to a high altitude platform is based upon a high power millimeter gyrotron source, optical transmission components, and a high-power receiving antenna (i.e., a rectenna) capable of rectifying received millimeter energy and converting such energy into useable electrical power.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
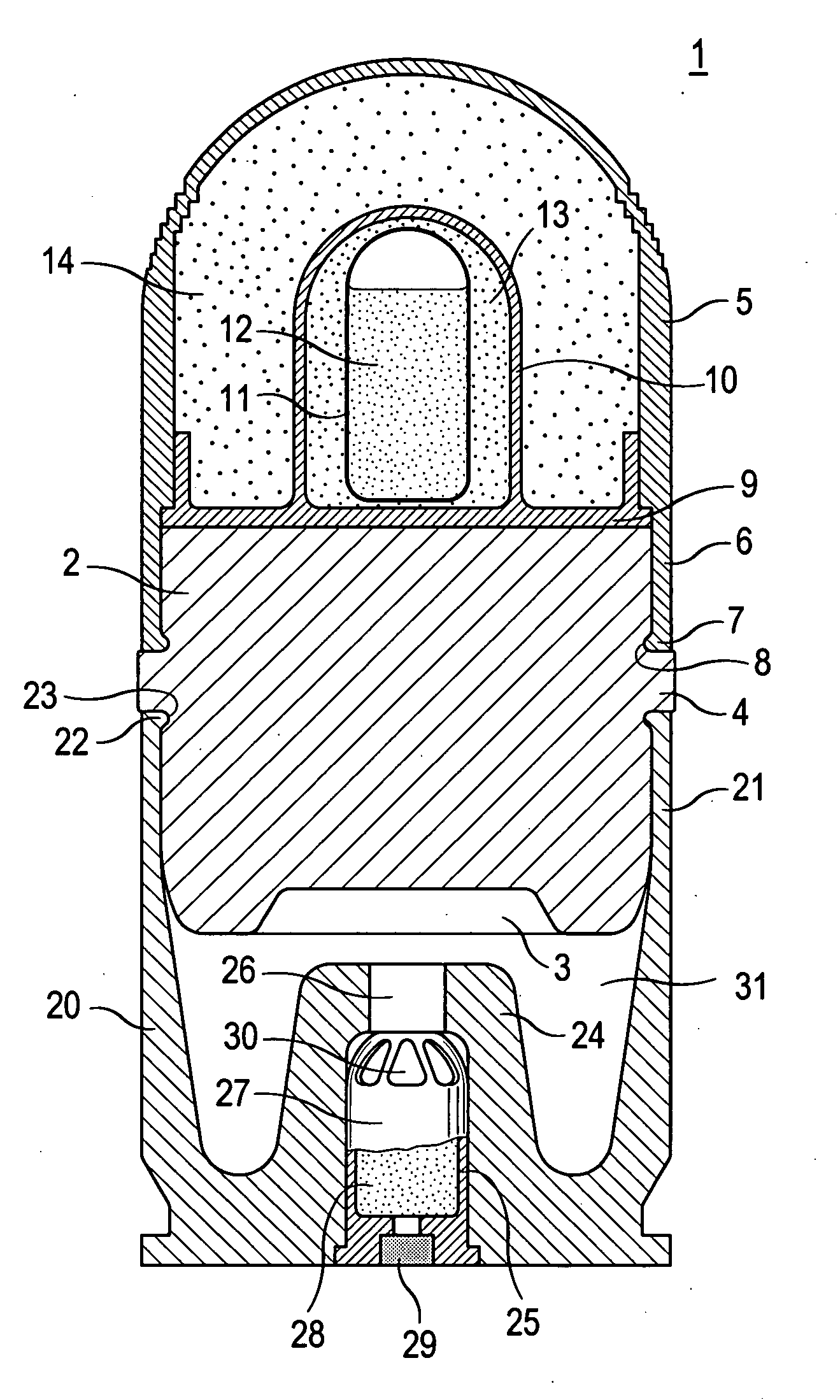
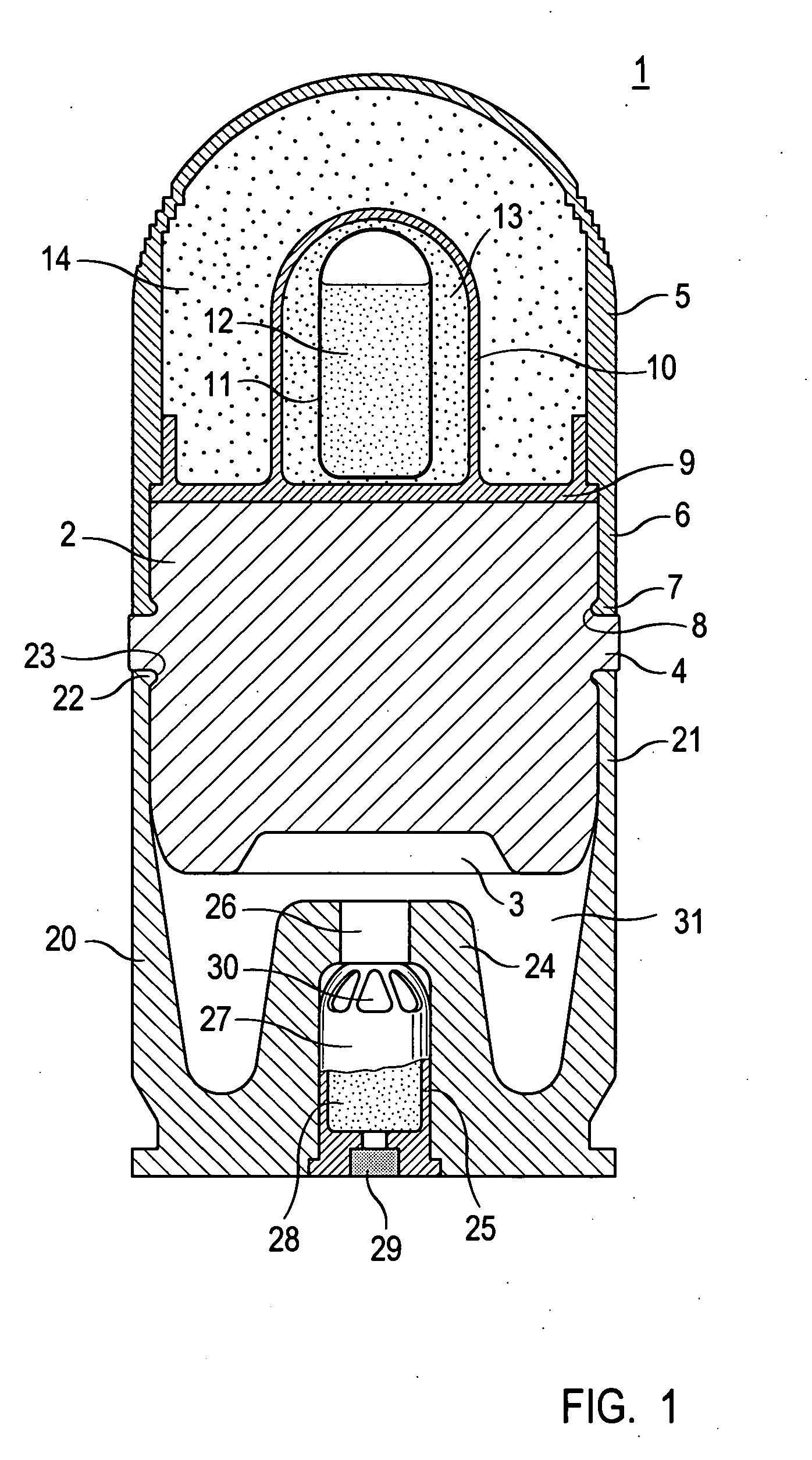
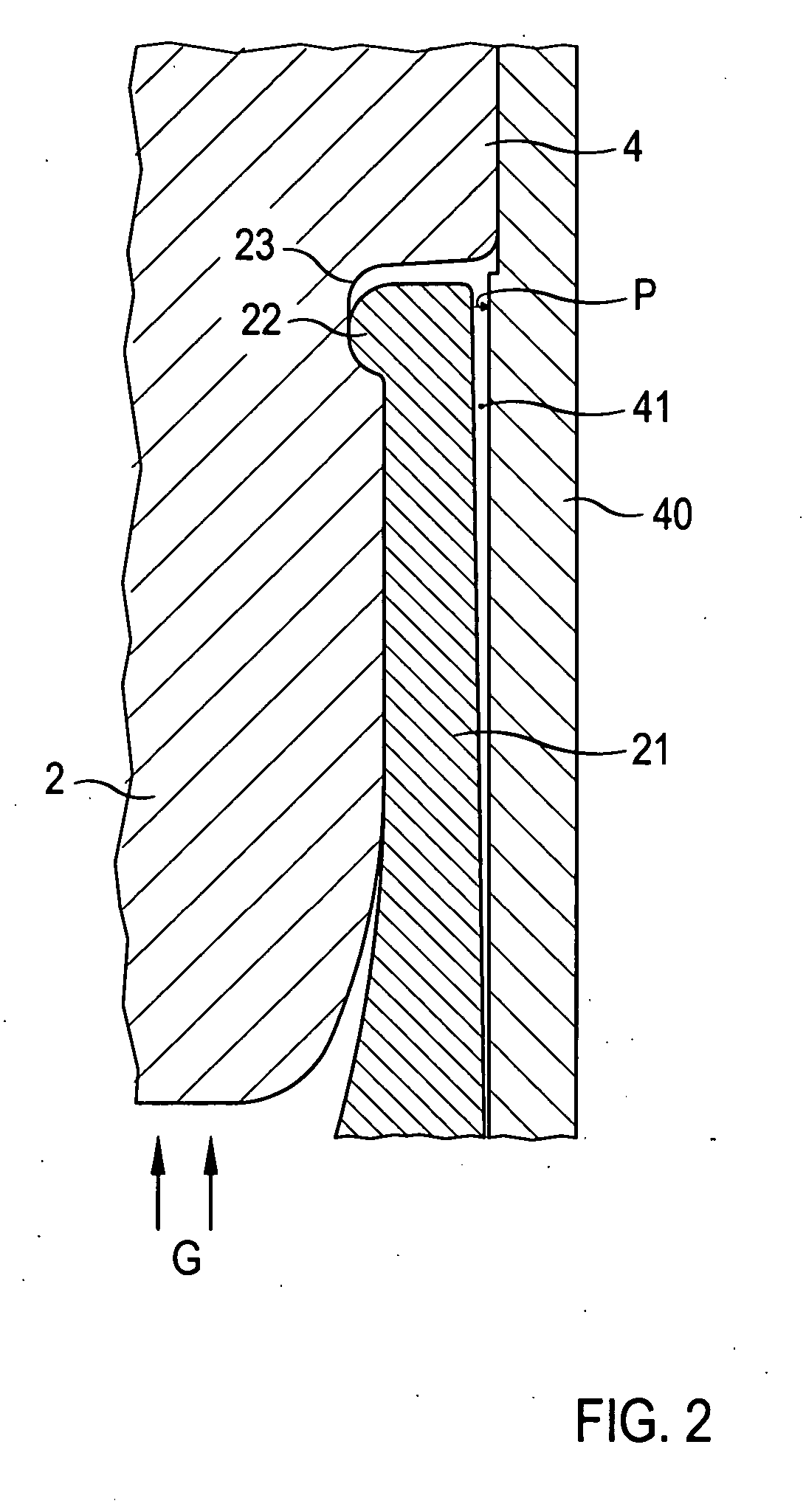
40 mm low cost cartridge
ActiveUS20060032393A1Easy to manufactureReduce manufacturing costAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringMillimeter
The cartridge-type training round consists of a projectile and a cartridge shell into which the projectile is inserted. The projectile includes a one-piece cylindrical central body (2) and a one-piece basin-shaped projectile tip (5) that is pressed onto the central body and engages a circumferential engagement bead (7) with a circumferential engagement slot (8) located in the central body (2). The cartridge shell (20) is a one-piece basin-shaped part; it is also pressed onto the central body (2) and engages a circumferential engagement bead (22) with a circumferential engagement slot (23) of the central body (2). A receiver recess (25) is provided in an approximately cylindrical projection (24) that is inserted centered from the base to receive the propulsive charge (28) and its igniter (29). The round is of simple design, and may be manufactured inexpensively owing to its simple parts that may be largely of plastic without loss of function.
Owner:NICO PYROTECHNIK HANNS JUERGEN DIERGEN
Antenna-feeder device and antenna
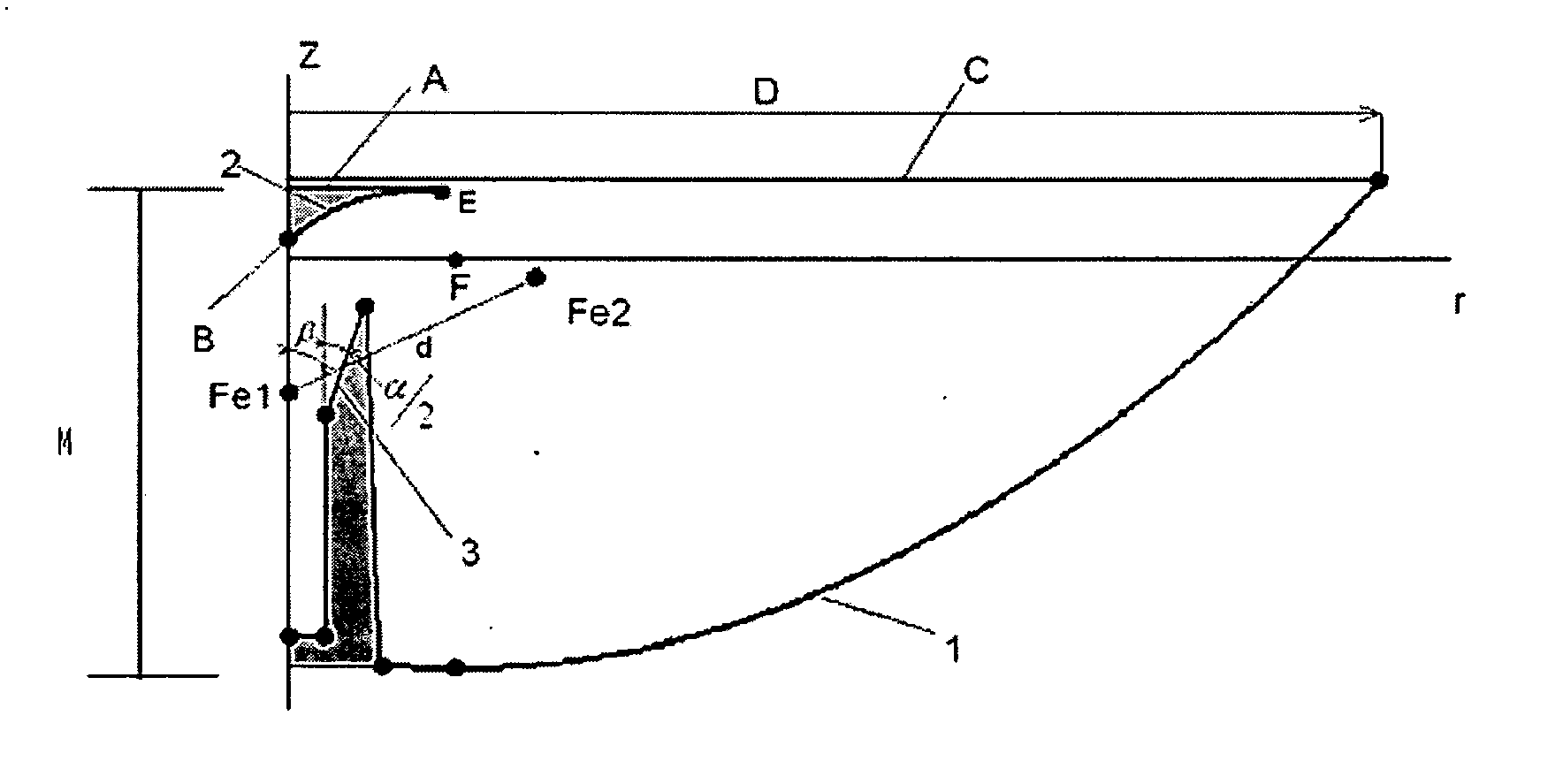
An antenna comprises: a main reflector being a body of revolution of arbitrary curve which axis diverges from axis of the revolution; a sub-reflector being a body of the revolution of arbitrary curve along the axis of revolution, having a circle and a vertex pointing to the main reflector and being placed between the circle and the main reflector; a radiator being located along the axis of revolution and being placed between the main reflector and the sub-reflector; and wherein the main reflector and the sub-reflector are: zm(r,D)=∑n=04∑m=06qmn,mDm-n+1rn,zs(r,D)=∑n=04∑m=06qsn,mDm-n+1rn,z, r are coordinates of the main reflector and the sub-reflector measured in millimeters, Index m corresponds to the main reflector, index s to the sub-reflector D is the main reflector diameter measured in millimeters.
Owner:AHN JIHO
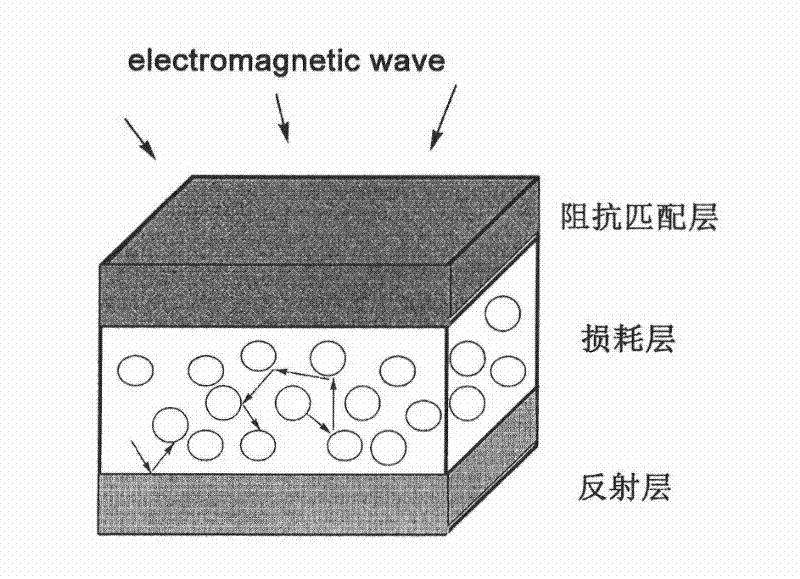
Three-layer composite wave-absorbing film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a three-layer composite wave-absorbing film and a preparation method thereof. The three-layer composite wave-absorbing film consists of an impedance matching layer, an absorption layer and a reflection layer, wherein the impedance matching layer consists of a dielectric material and an organic carrier; the absorption layer consists of magnetic particles and the organic carrier; the reflection layer consists of a carbon material with better electro-conductivity and the organic carrier; the thickness of the impedance matching layer is 0.1 to 0.3 millimetre (mm); the thickness of the absorption layer is 0.2 to 0.4 mm; and the thickness of the reflection layer is 0.1 to 0.3 mm. The preparation method of the three-layer composite wave-absorbing film comprises the following steps of: firstly, processing organic particles; secondly, uniformly dispersing the organic particles in an organic phase in a certain mode, and spreading to form a film; and finally, after a solvent of a first layer is completely volatilized, spreading a second layer and a third layer to form the three-layer composite wave-absorbing film. The three-layer composite wave-absorbing film has the advantages of high efficiency, light weight and low thickness, can be applied to electromagnetic shielding materials, and has a wide application prospect in ultra-thin radar wave-absorbing materials.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS +1
Filters and antennas for microwaves and millimetre waves, based on open-loop resonators and planar transmission lines
InactiveUS20070024399A1Good level of directivityGood level of polarisationResonatorsLoop antennasElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
Filter for microwaves and millimetER waves, characterised in that it comprises a planar transmission medium (1) that it includes a conductor strip (3), metallic ground plane (4) and dielectric substrate (2) and in that it includes at least one split rings resonator (5a, 5b, 5c, 5d, 5e and 5f)
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA
High separation area membrane module
InactiveUS20060090649A1Easy to separateReduce in quantityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesChannel densityEngineering
A ceramic monolithic multi-channel module support (10) has a module hydraulic diameter (102) in a range about 9 to 100 mm, an aspect ratio of the module hydraulic diameter (102) to a module length (104) greater than 1, a plurality of feed flow channels (110) distributed substantially in parallel over a module cross-section, the plurality of feed flow channels (110) having a size and shape defining a channel density in the range of about 50-800 channels / in2 (7.8-124 channels / cm2) in a module frontal area, a channel hydraulic diameter (112) in the range of about 0.5-3 mm, a rim distance (120) having a thickness greater than 1.0 mm (0.04 in), and a percent open frontal area (OFA) in the range of about 20-80%.
Owner:CORNING INC
Passive millimeter wave imaging system
ActiveCN101644770AHigh resolutionImaging time is shortRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow-pass filterMillimeter
The invention discloses a passive millimeter wave imaging system and relates to a millimeter wave imaging system. The passive millimeter wave imaging system solves the problems of long imaging time ofthe system, poor real-time property and low resolution of an obtained image caused by the way of focal plane array imaging of the existing millimeter wave imaging system. A metal reflection plate ofthe passive millimeter wave imaging system reflects electromagnetic waves radiated by a target to be tested onto a receiving antenna by aggregation via a medium lens, the received signals are processed by a millimeter wave band high-gain low-noise amplifier, a high-sensitivity square law detector, a low-pass filter and a low-frequency amplifier in sequence and then collected by a digital collection circuit, and the collected signals are transmitted into a computer for carrying out imaging processing. The passive millimeter wave imaging system is applicable to the field of security.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
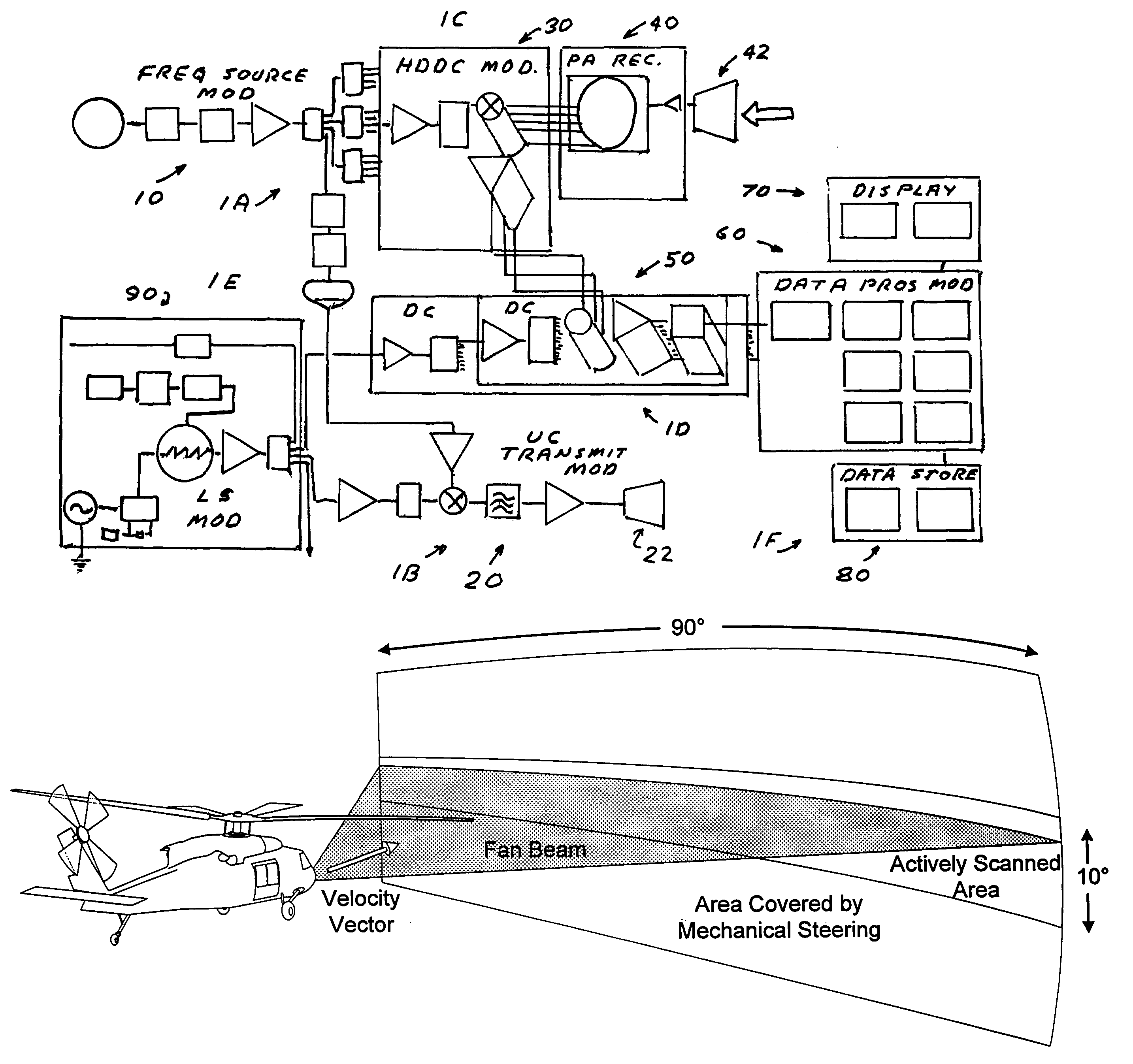
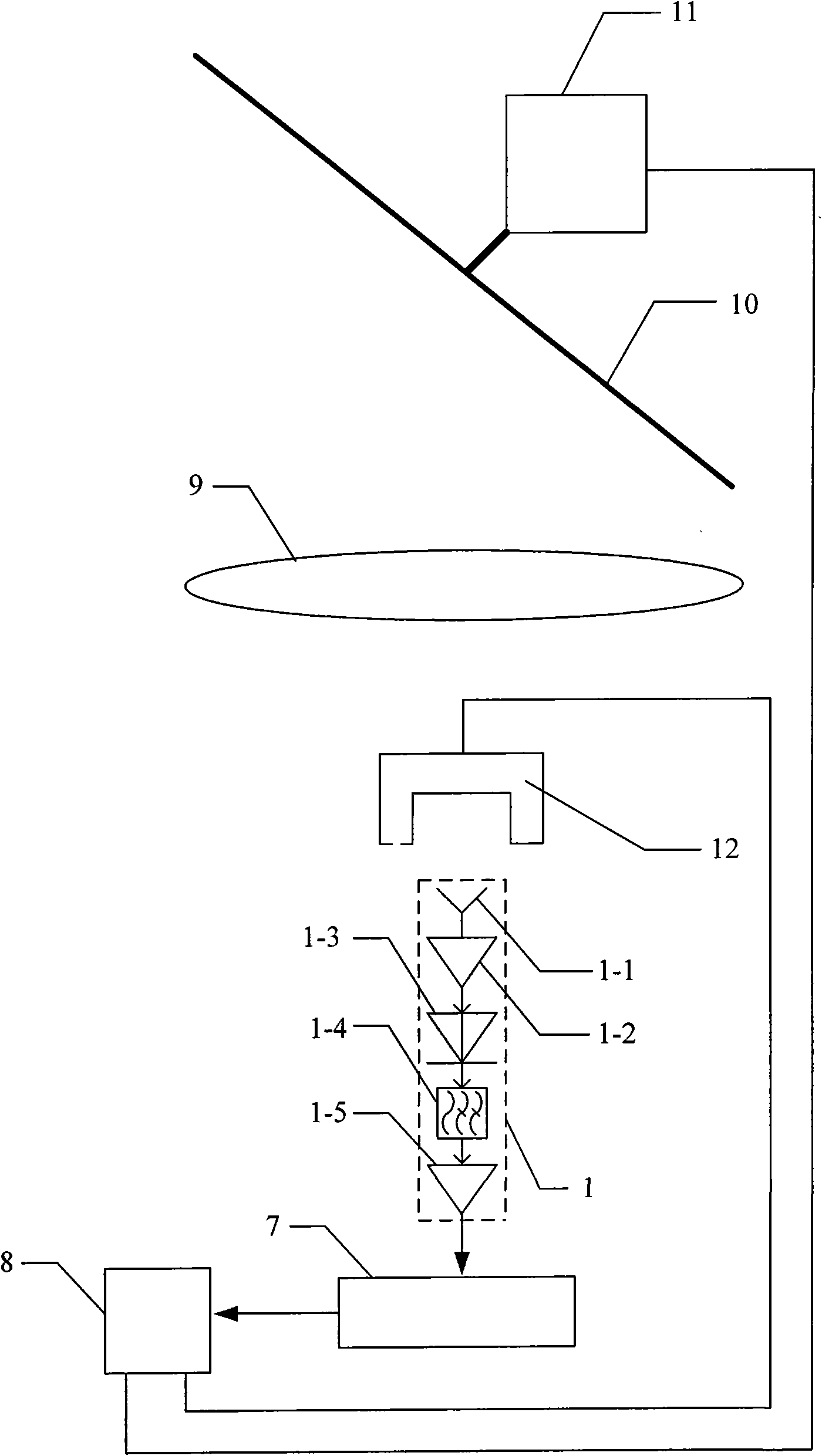
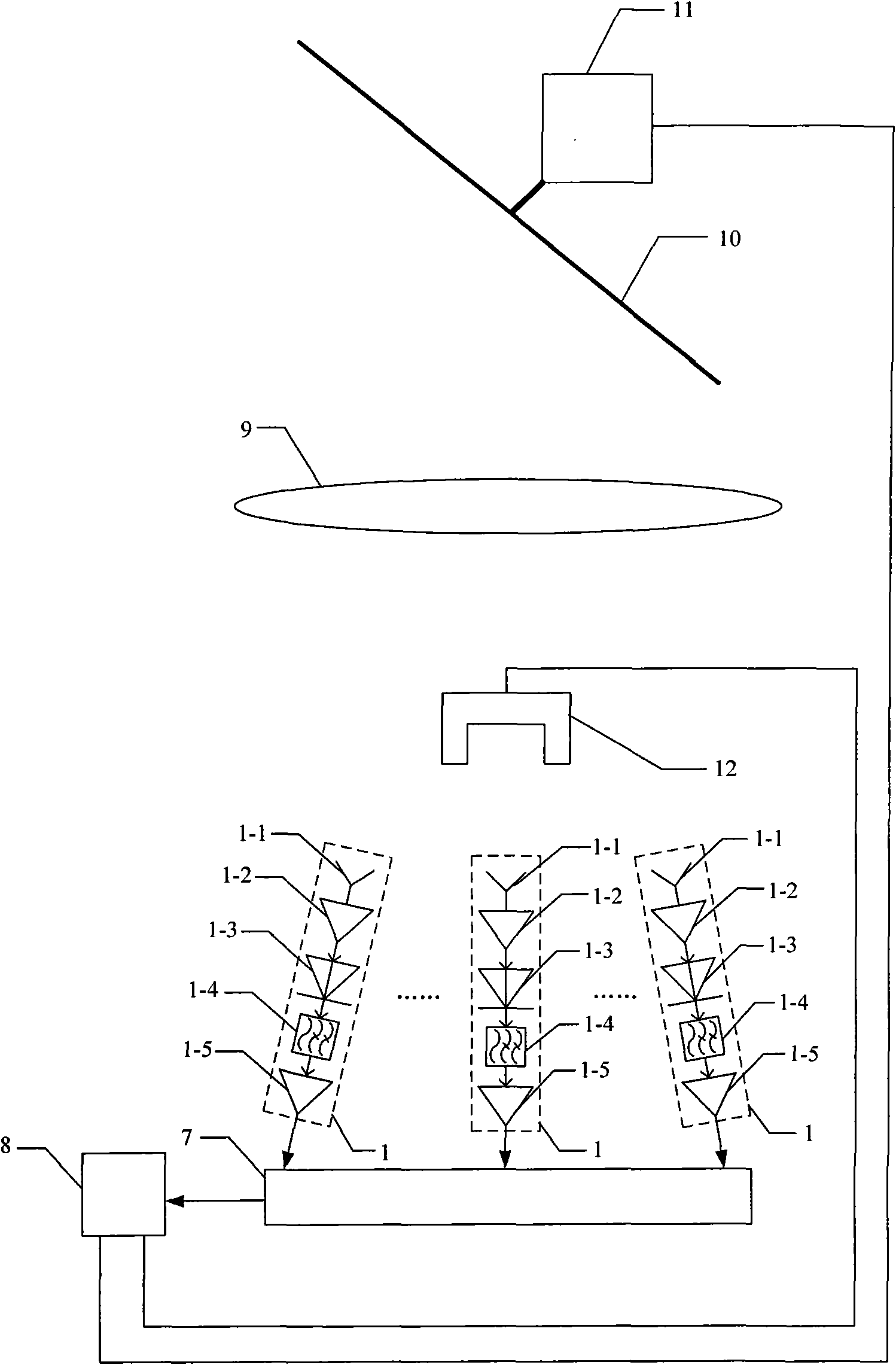
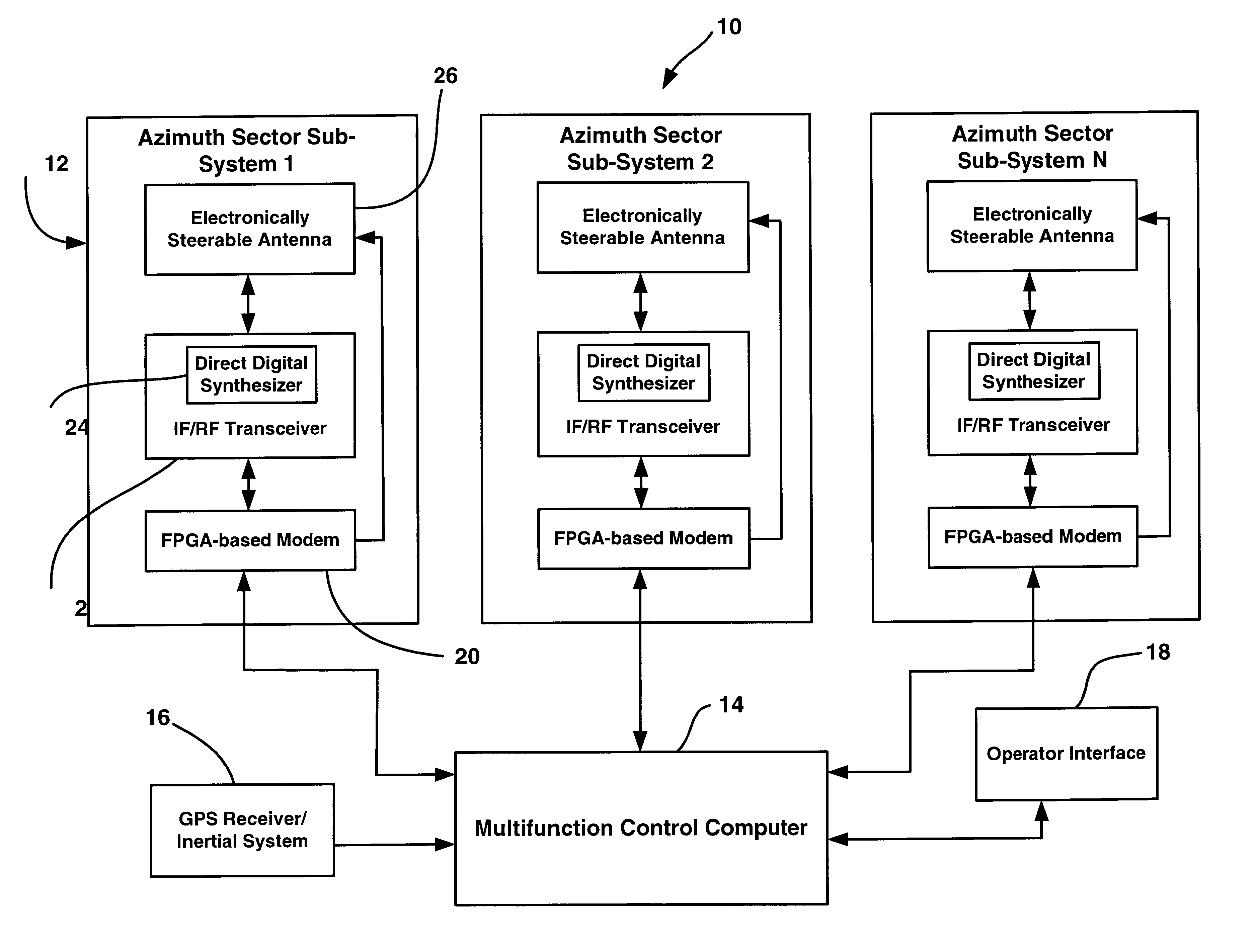
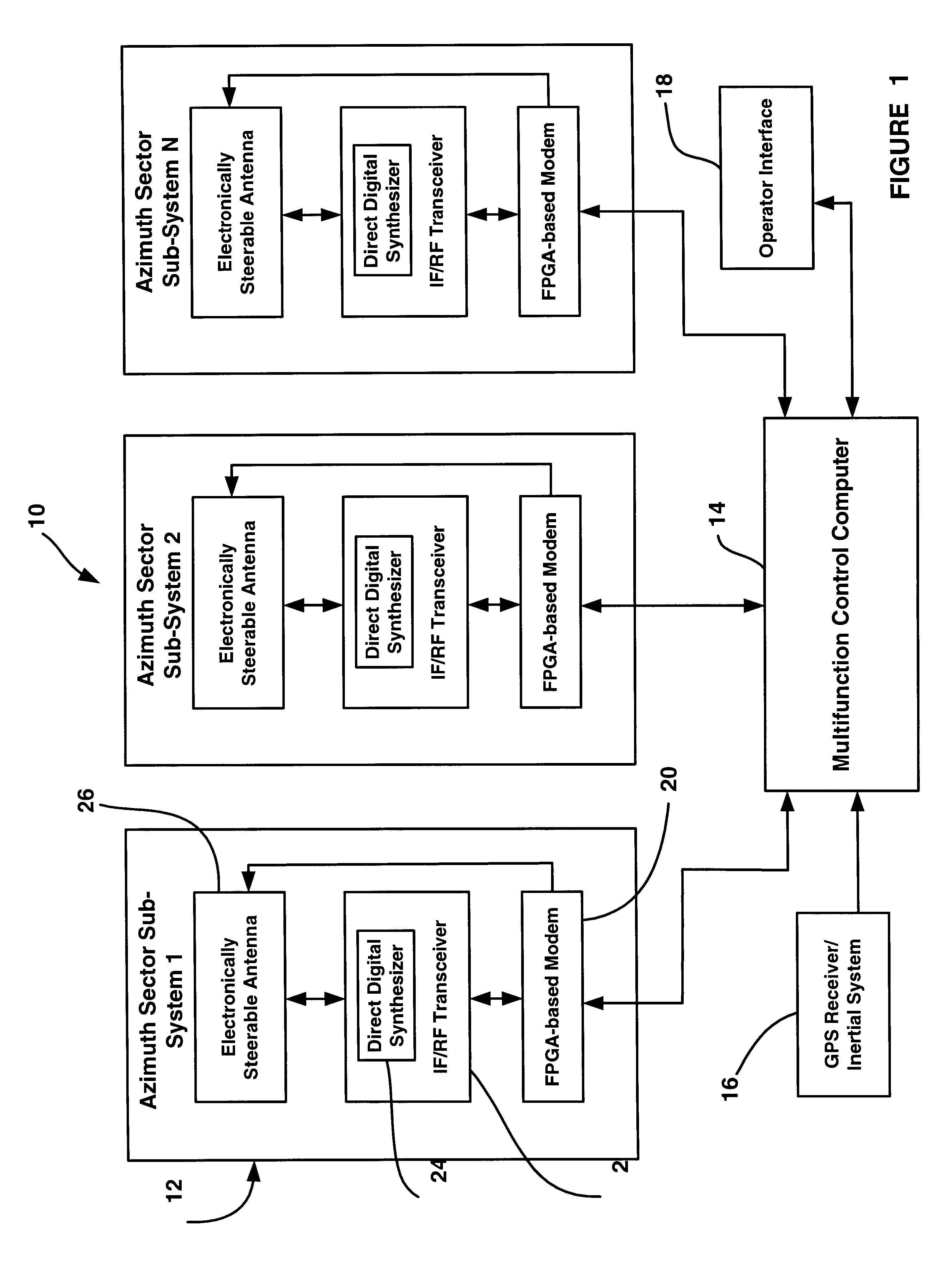
Multifunction millimeter-wave system for radar, communications, IFF and surveillance
InactiveUS6693580B1Communication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingDigital data
A multifunction millimeter-wave system (10) that provides simultaneous and prioritized active radar protection and surveillance, high digital data rate communications, interceptor missile guidance, passive surveillance and IFF interrogation for a military vehicle. The system (10) includes a multi-function control computer (14) that provides high level control functions. The system (10) also includes a plurality of azimuth sector sub-systems (12), each including a steerable antenna (26) that directs a millimeter-wave beam to a particular location within the area covered by the sector sub-system (12). Each sector sub-system (12) also includes an FPGA-based modem (20) that performs digital signal processing for the various system operations, such as signal modulation and demodulation. Each sector sub-system (12) also includes an IF / RF transceiver (22), including a direct digital synthesizer (24), for providing signal tuning and frequency up-conversion and down-conversion.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com