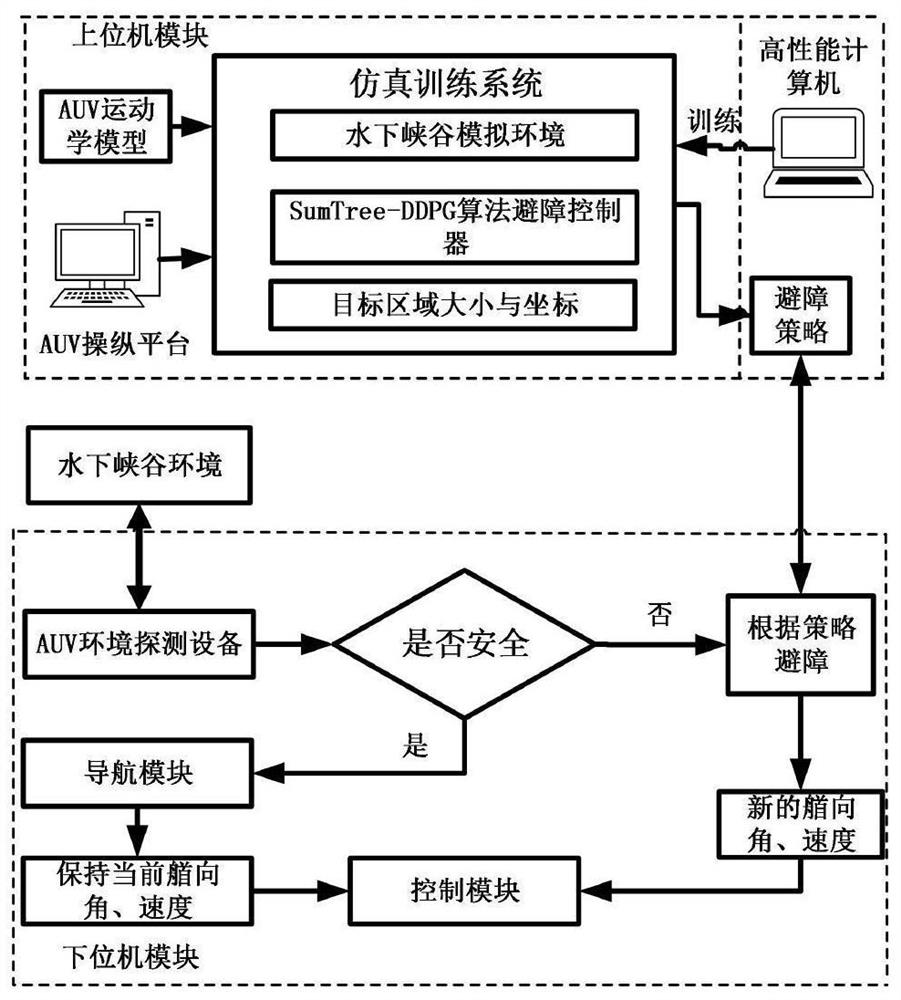
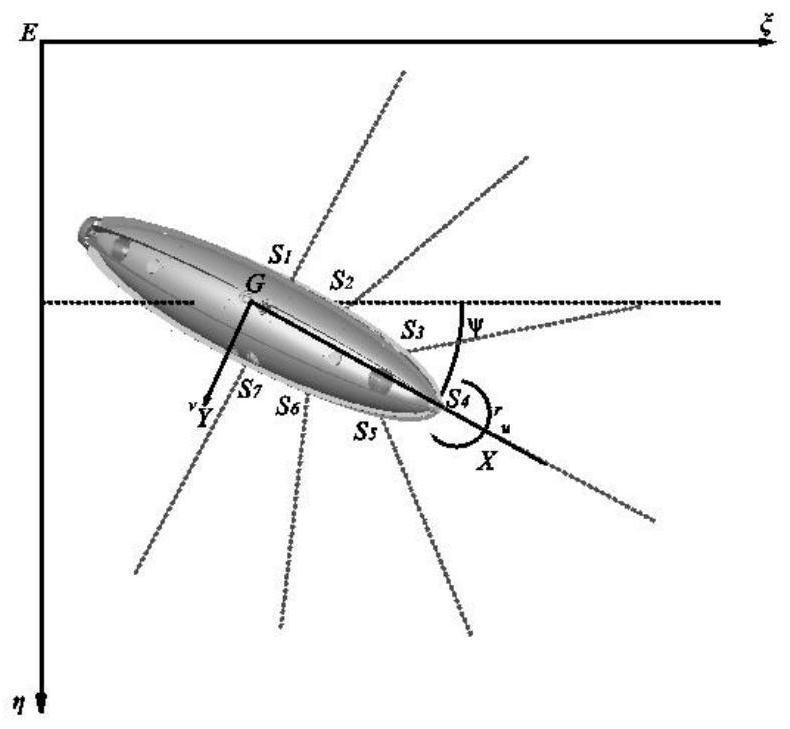
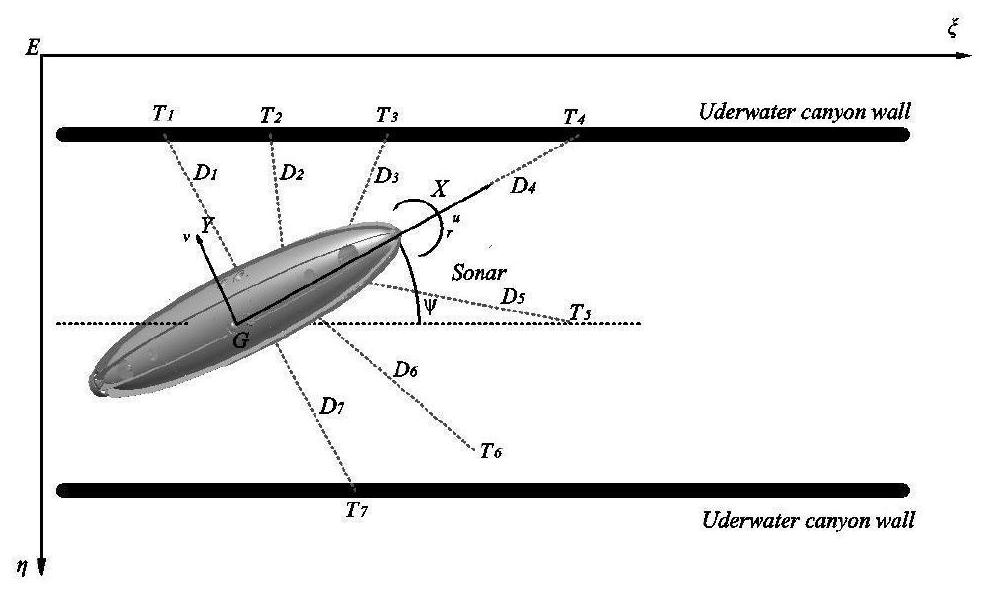
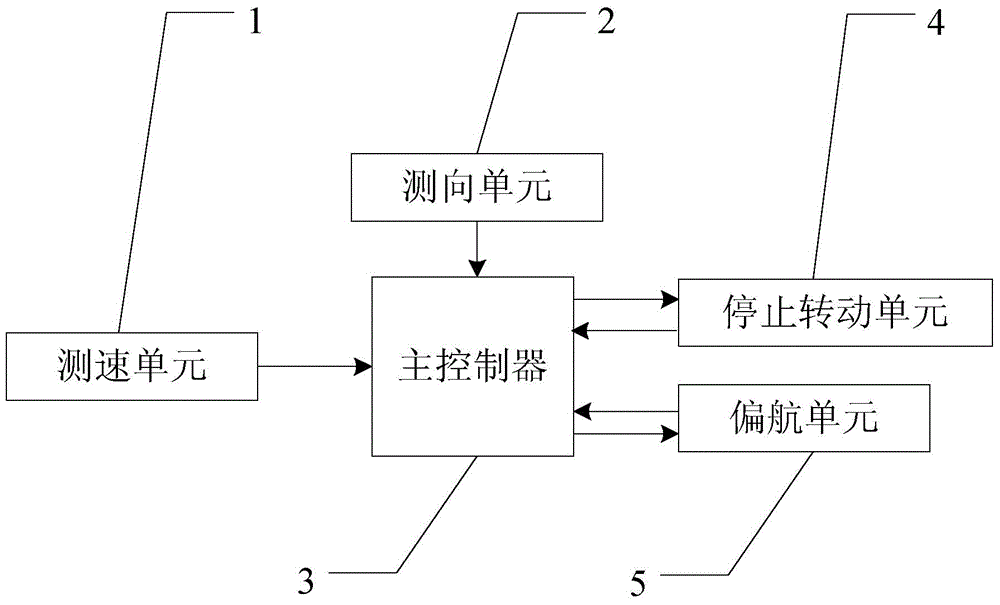
Patents
Literature
1229 results about "Yaw" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
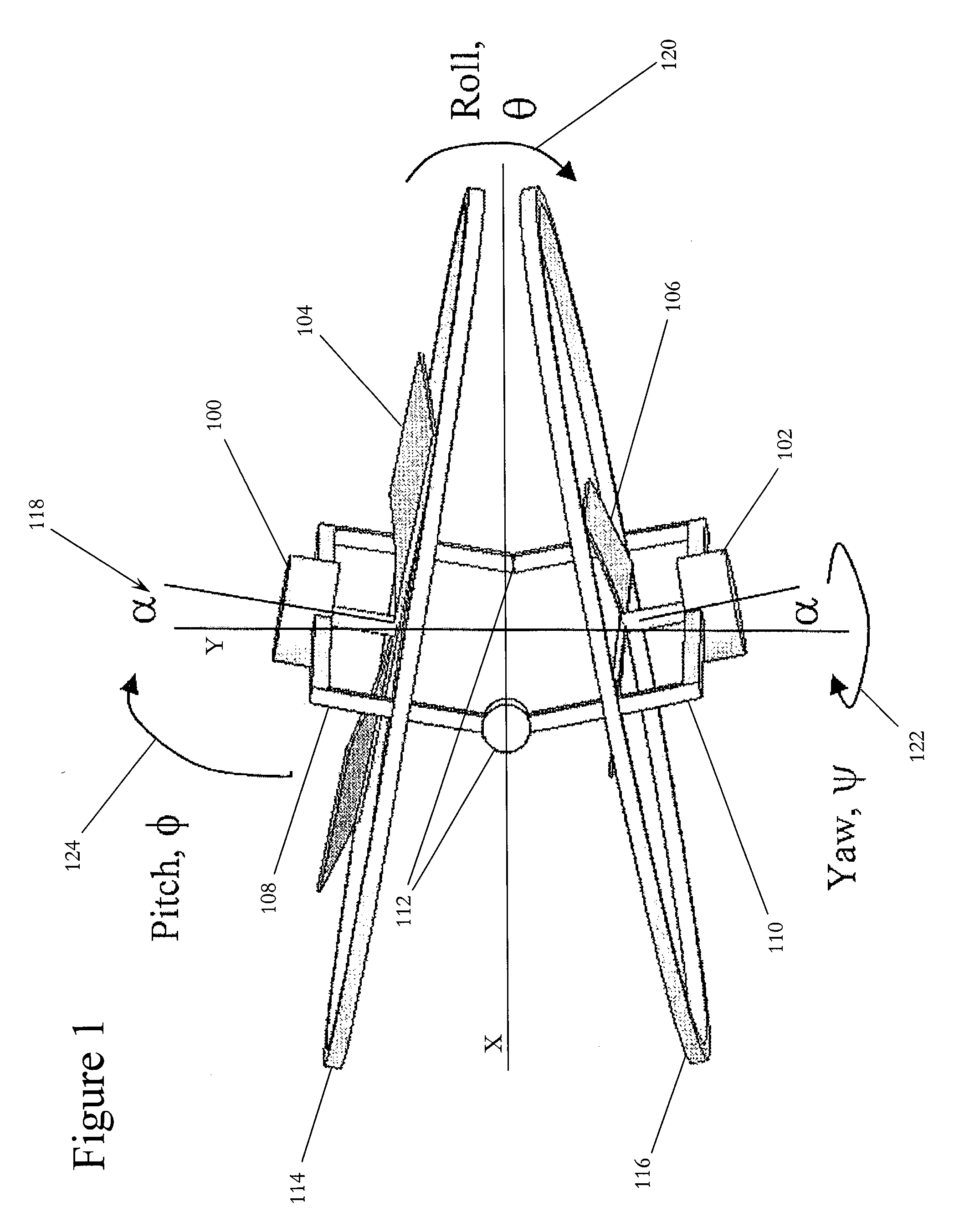
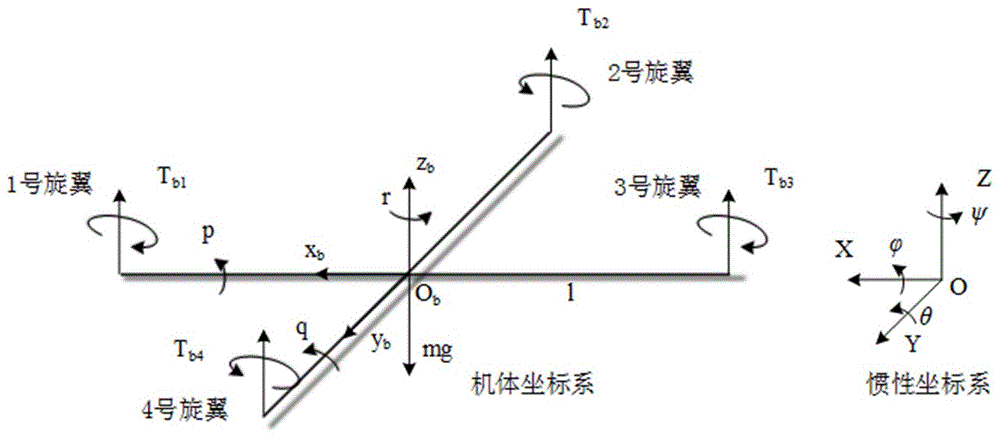
A yaw rotation is a movement around the yaw axis of a rigid body that changes the direction it is pointing, to the left or right of its direction of motion. The yaw rate or yaw velocity of a car, aircraft, projectile or other rigid body is the angular velocity of this rotation, or rate of change of the heading angle when the aircraft is horizontal. It is commonly measured in degrees per second or radians per second.
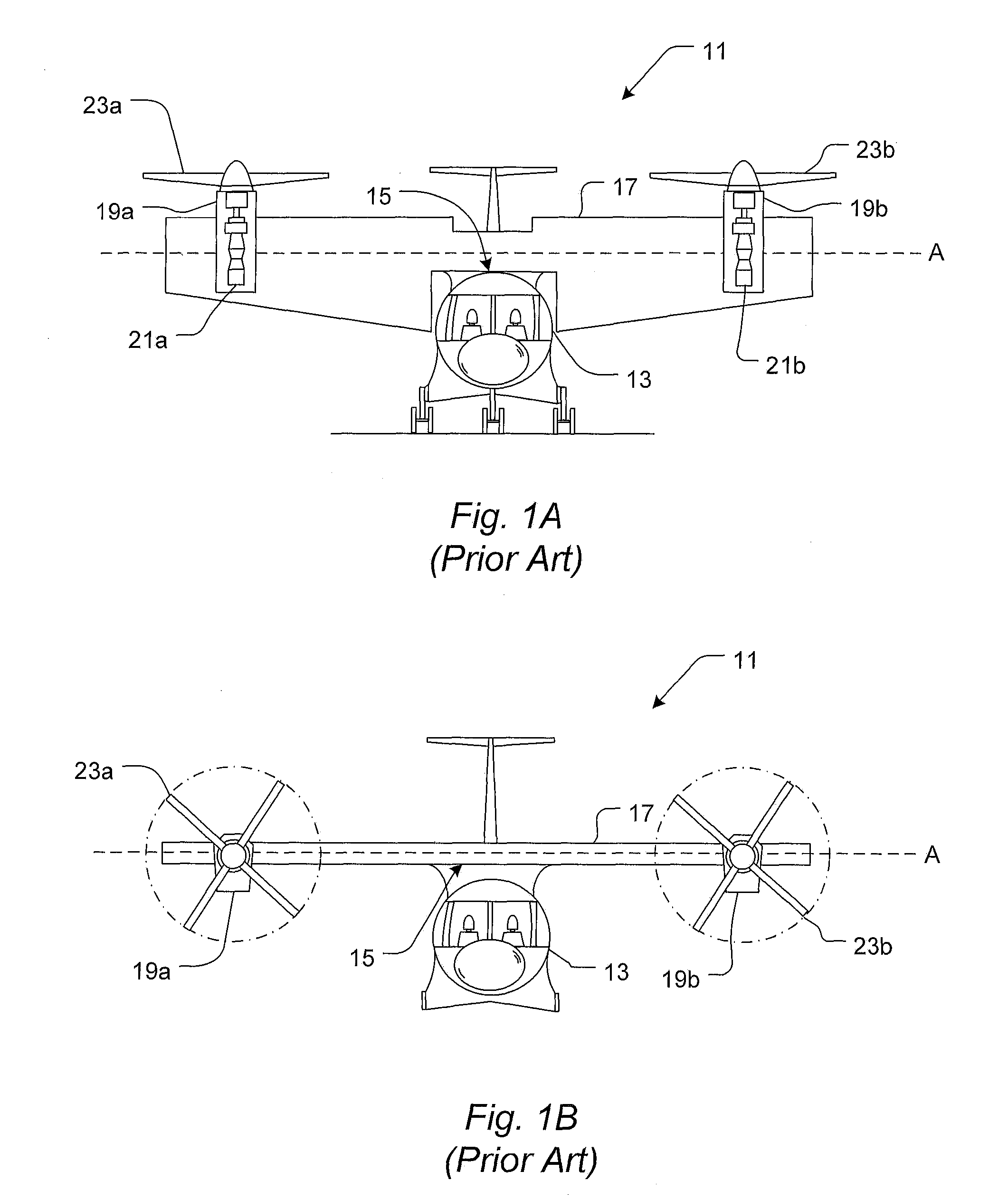
Aircraft and torque transmission
InactiveUS6467726B1Satisfactory stability and controllabilityReduce rotationAircraft navigation controlToothed gearingsFlight directionGear wheel
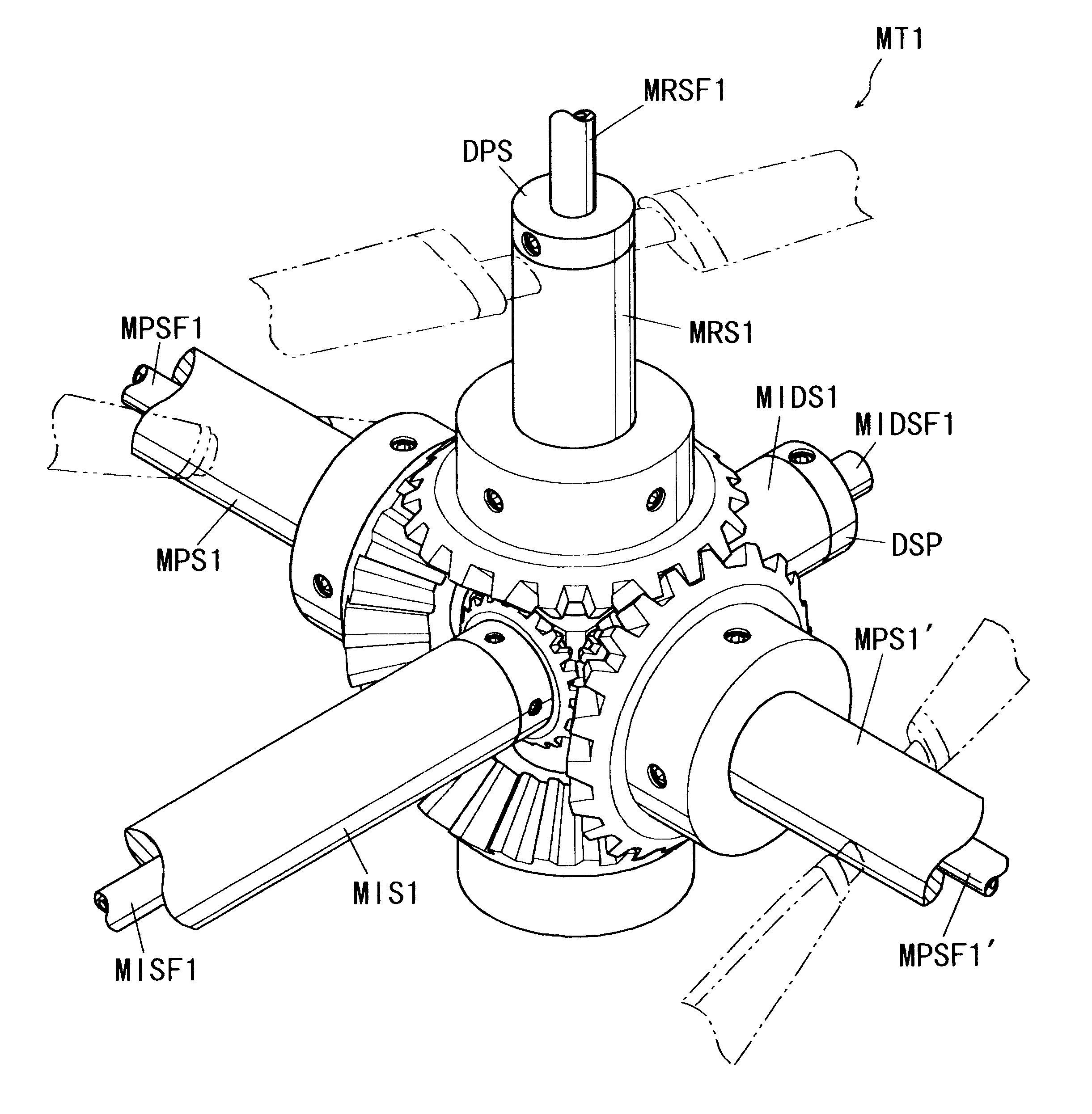
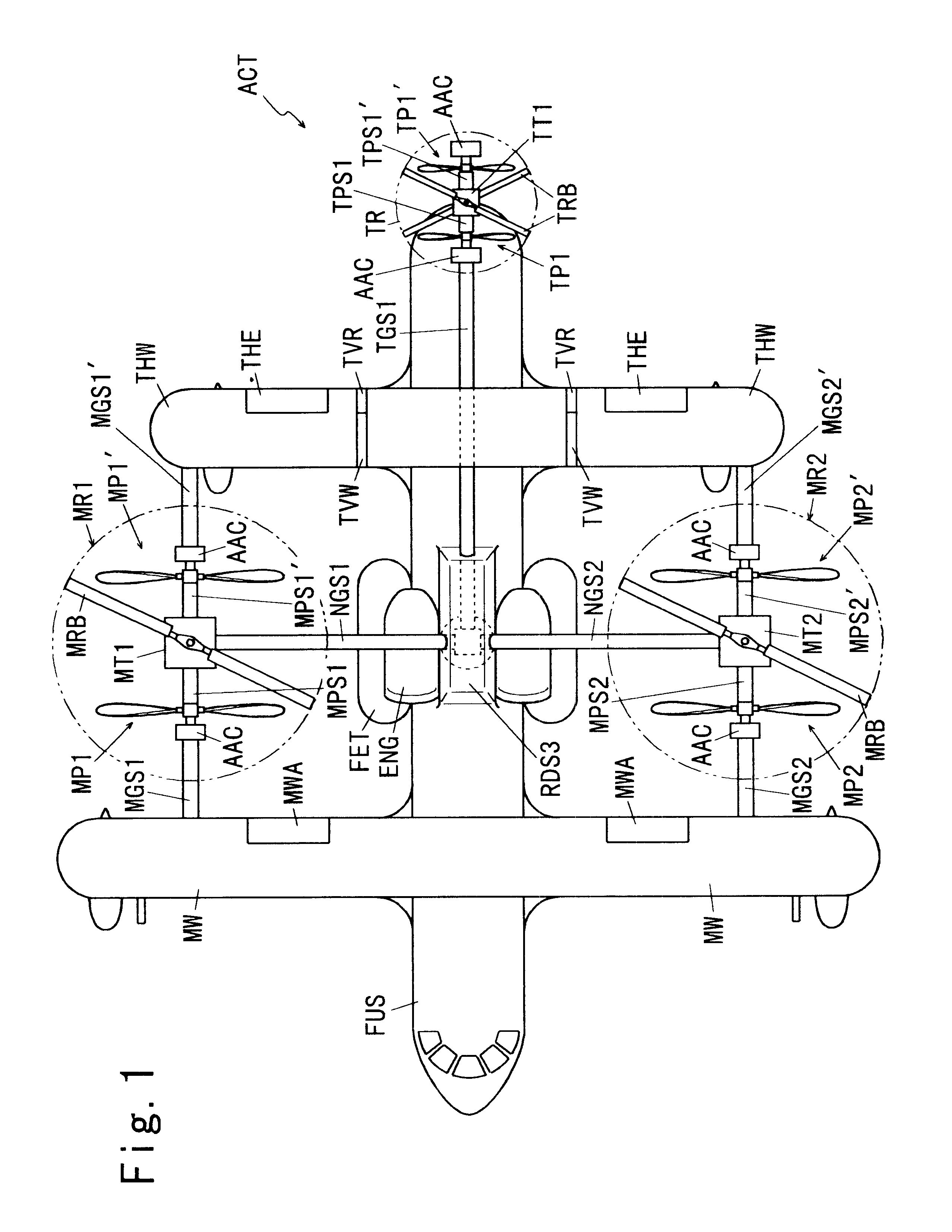
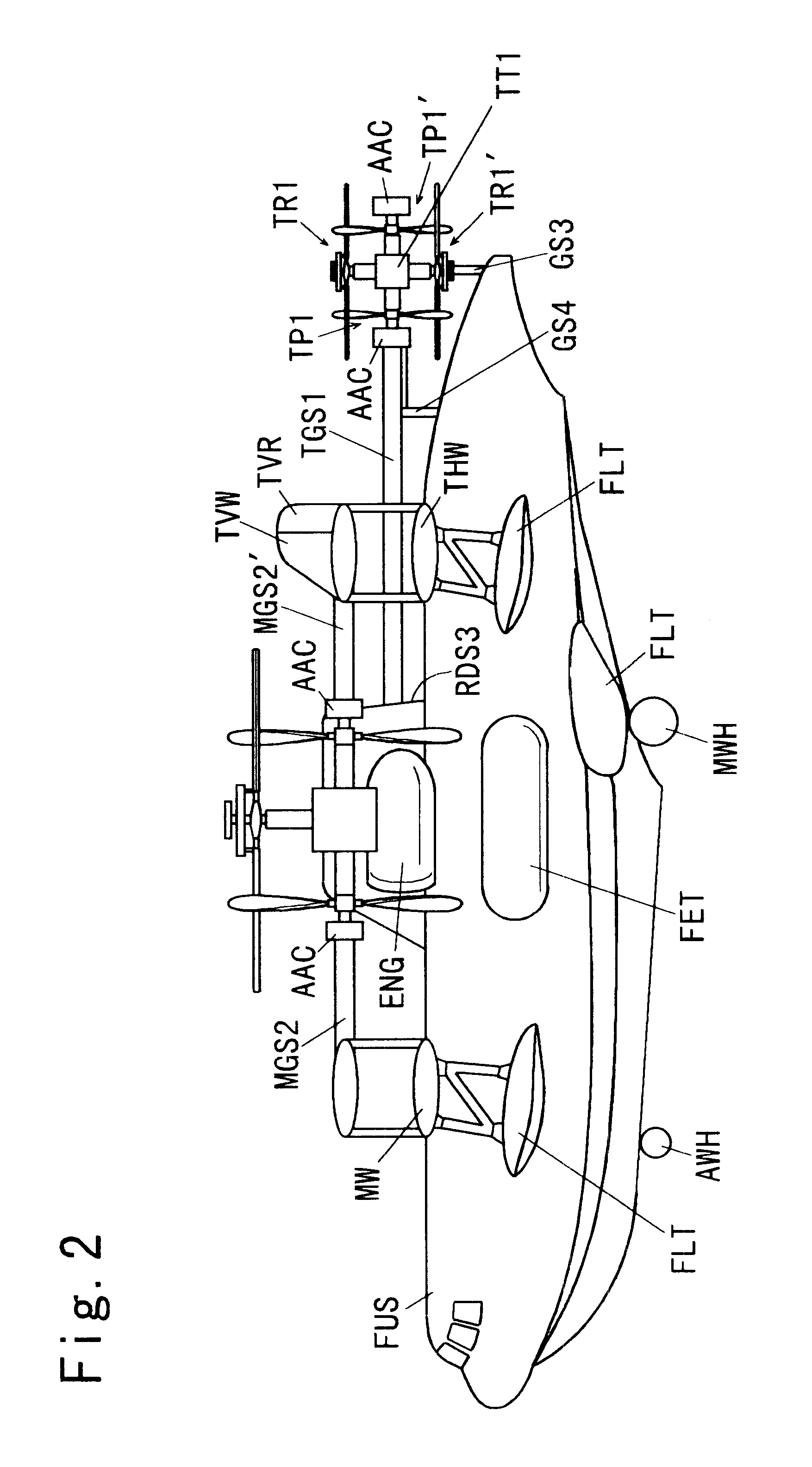
An aircraft including an airframe having a fuselage which extends longitudinally, and having fixed wings including a main wing, a horizontal tail wing and a vertical tail wing. A propeller-rotor torque transmission has a bevel gear which transmits the rotation of an input shaft simultaneously to a propeller shaft and to a rotor shaft. An engine gearbox supplies the above-mentioned input shaft with rotationalal motive power. The aircraft further includes a propeller collective pitch controller, a rotor collective pitch controller, an engine power controller which controls the output of the above-mentioned engine gearbox for the purpose of changing the rotational speed of the input shaft, and a flight control system having a directional (yaw) control system which controls the flight direction of the aircraft by controlling the positions of the above-mentioned control surfaces.
Owner:HOSODA ROKURO
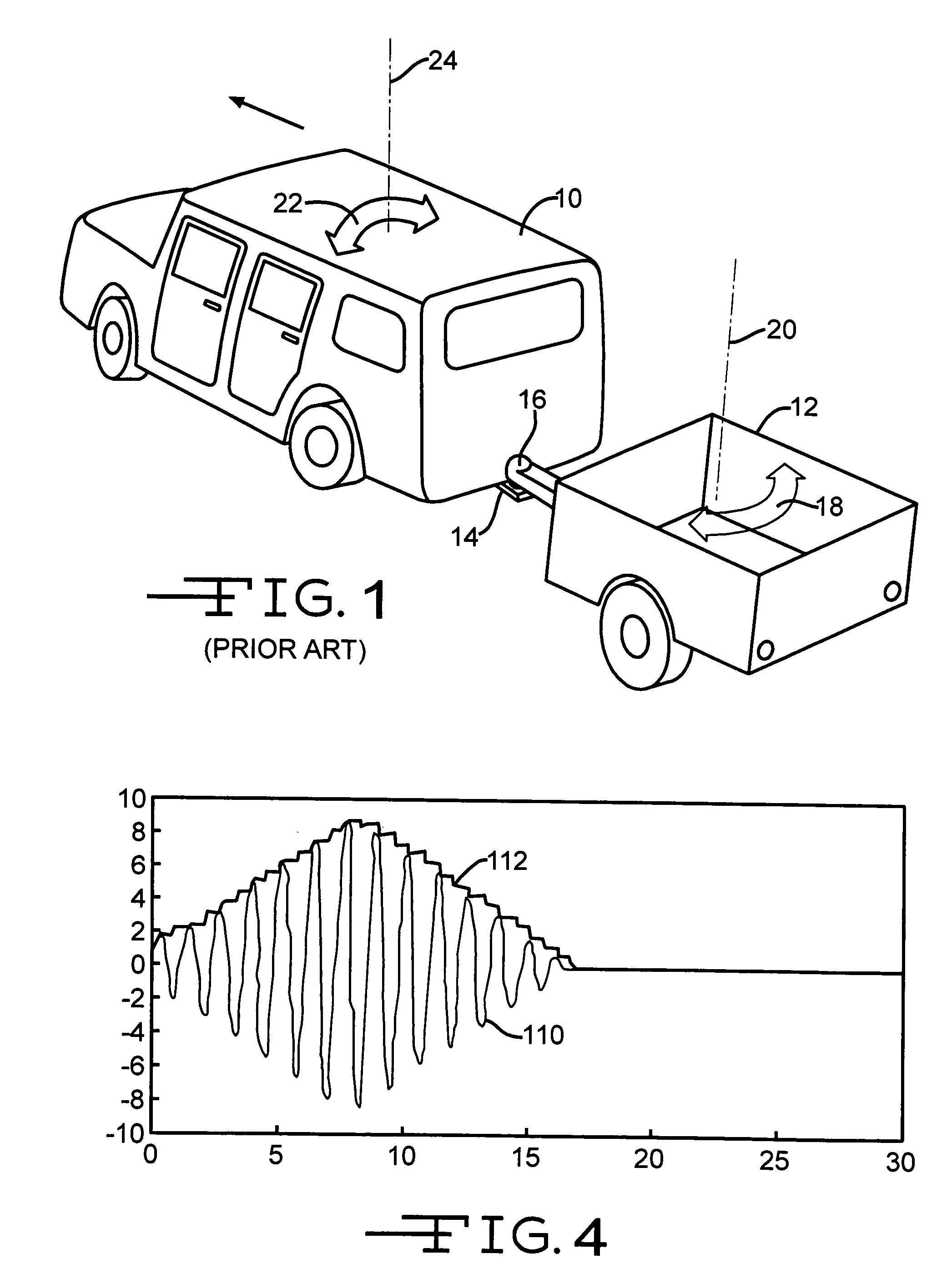
Method and apparatus for detecting and correcting trailer induced yaw movements in a towing vehicle
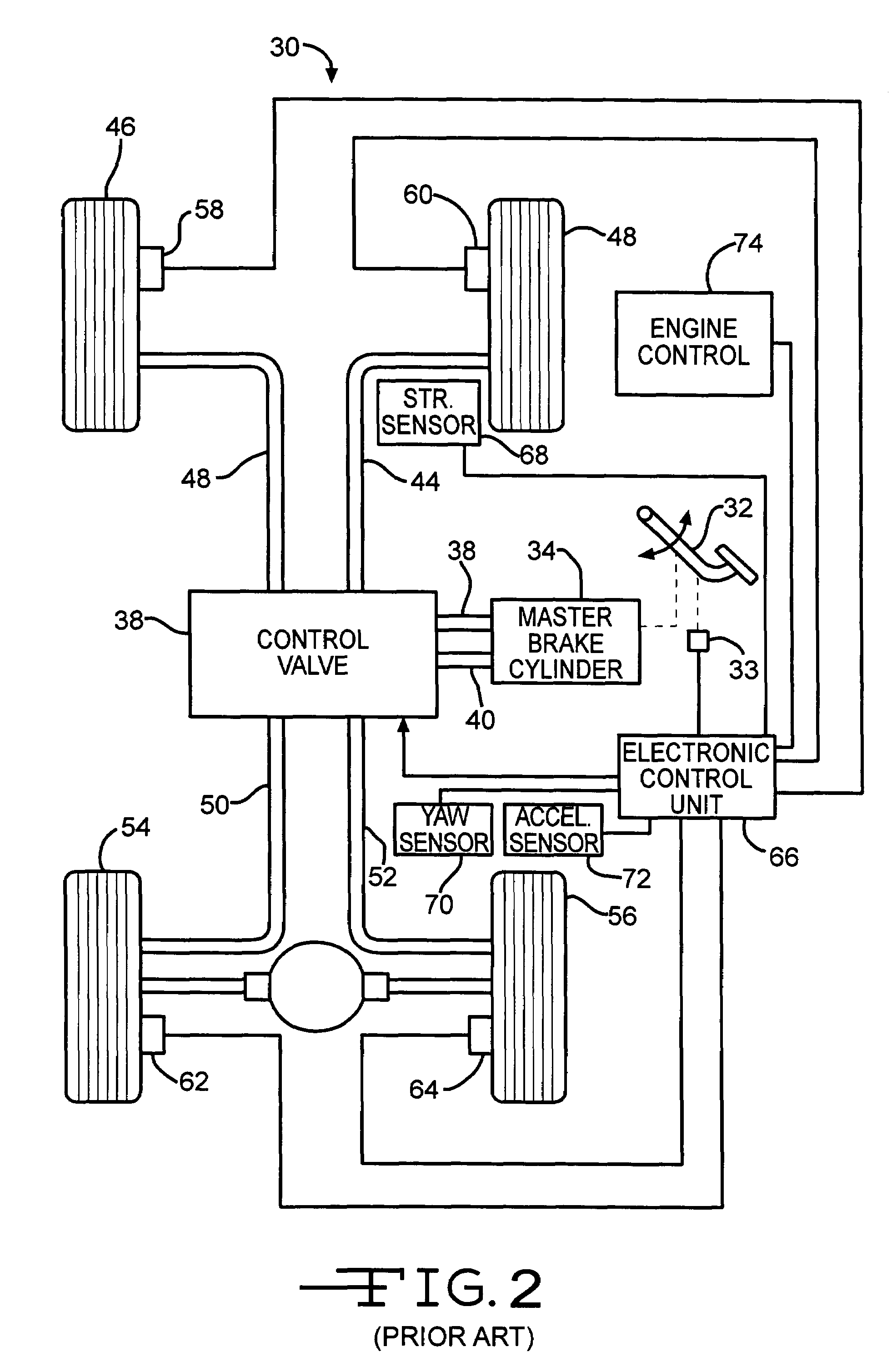
InactiveUS7272481B2Reduce yaw rateReduce relative motionAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsControl theoryMechanical engineering
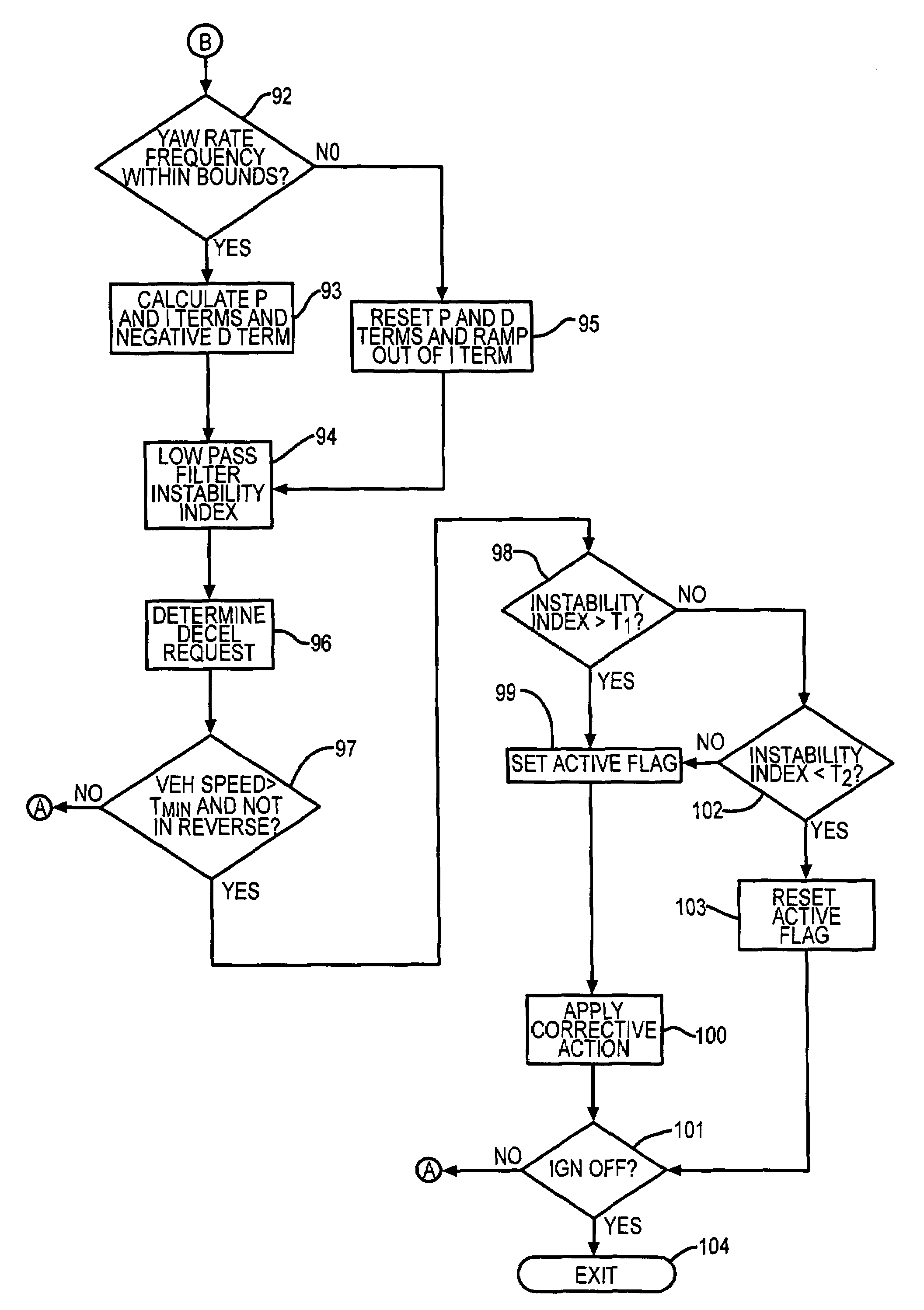
An apparatus and method for determining the presence of excessive yaw rate in a vehicle by calculating an instability index that is a function of the vehicle yaw rate and generating an excessive yaw rate signal when the instability index exceeds a yaw rate threshold.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
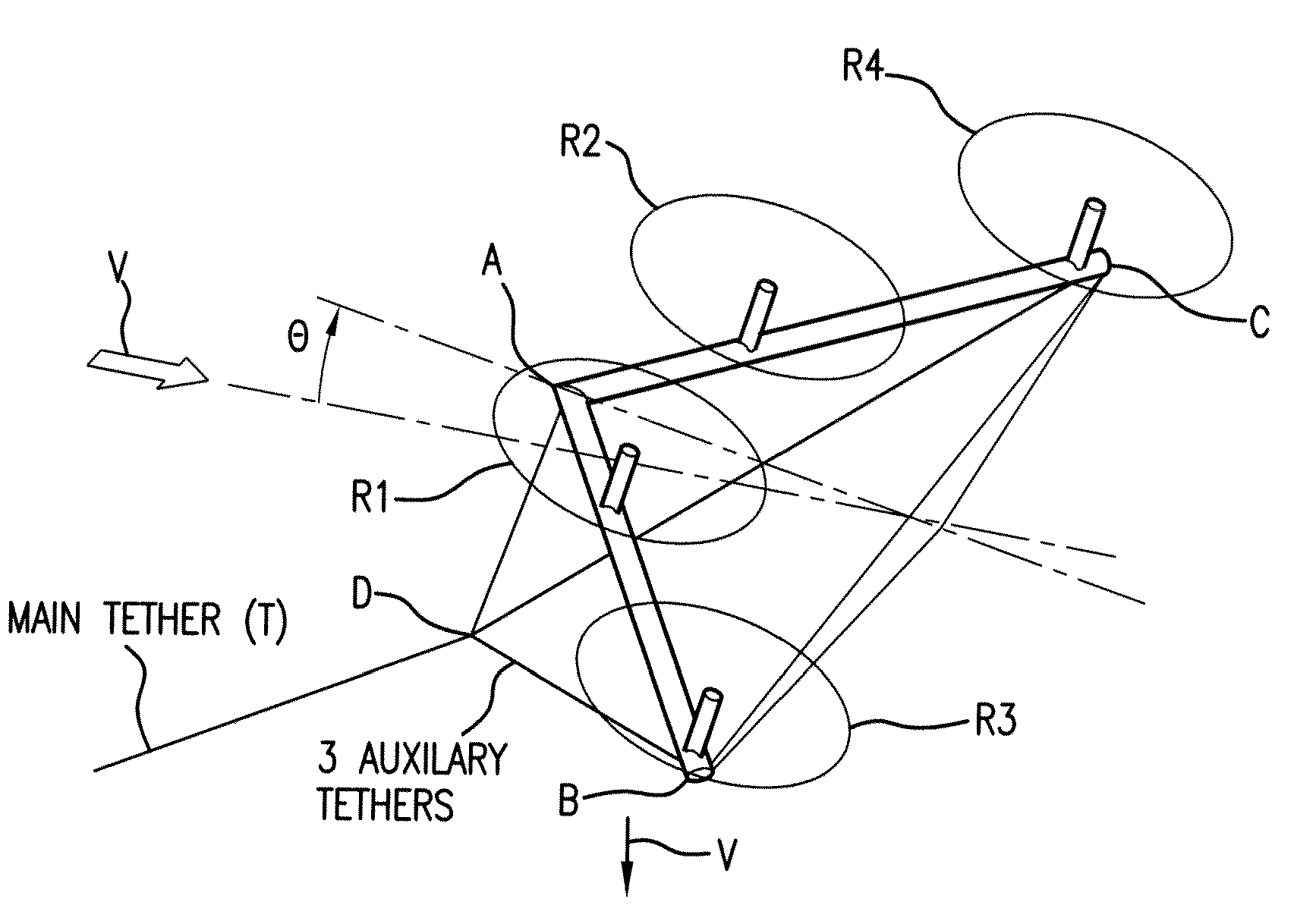
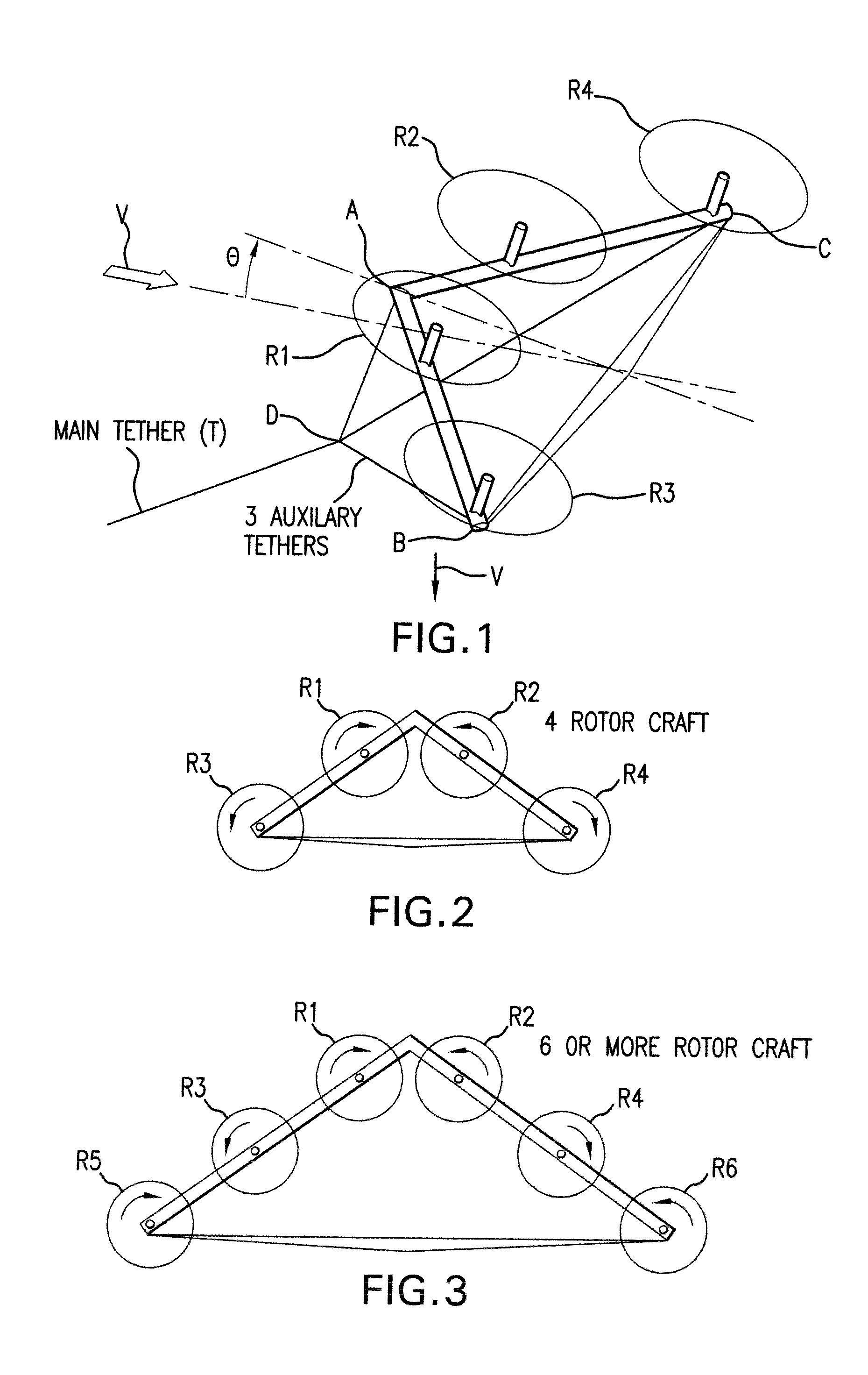
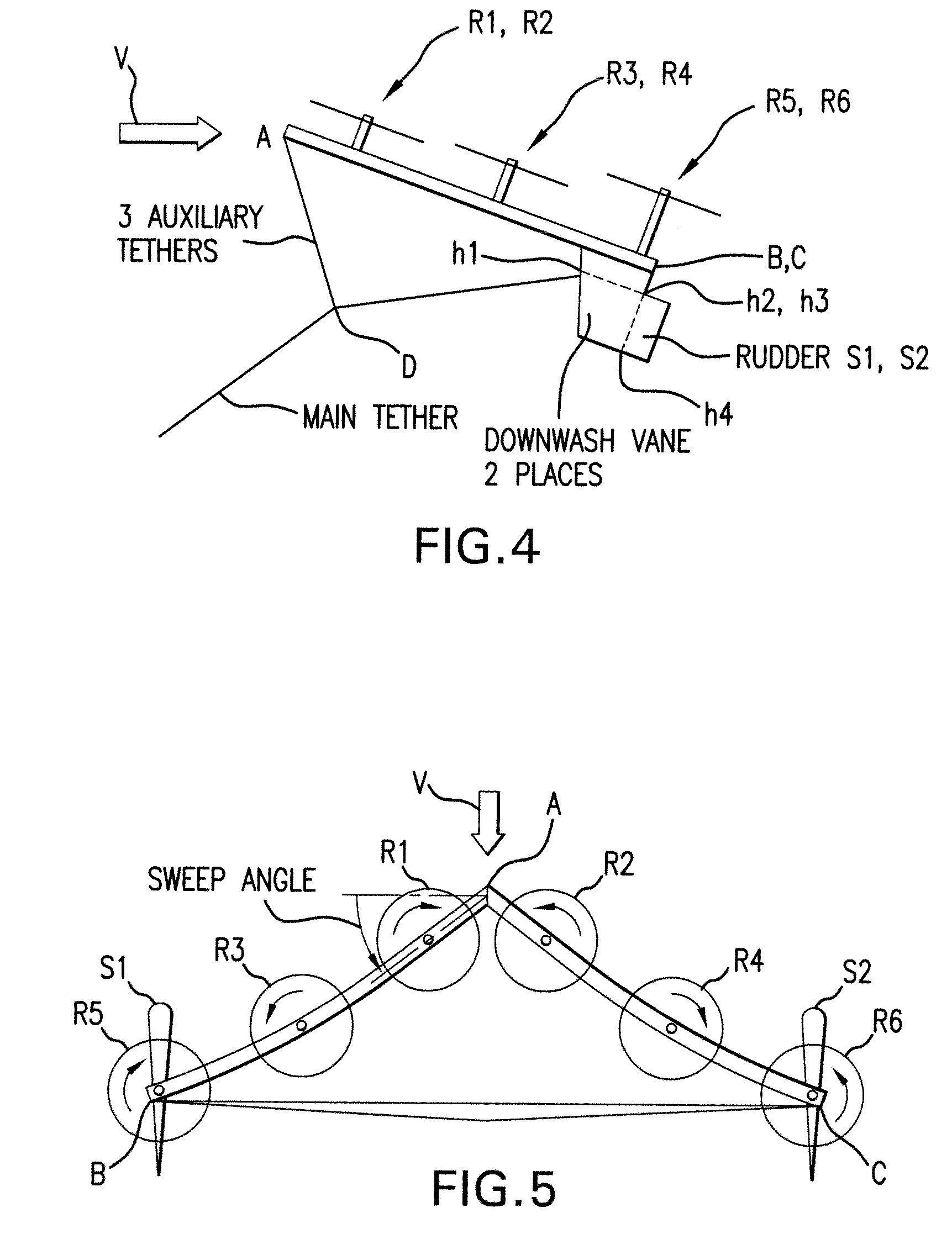
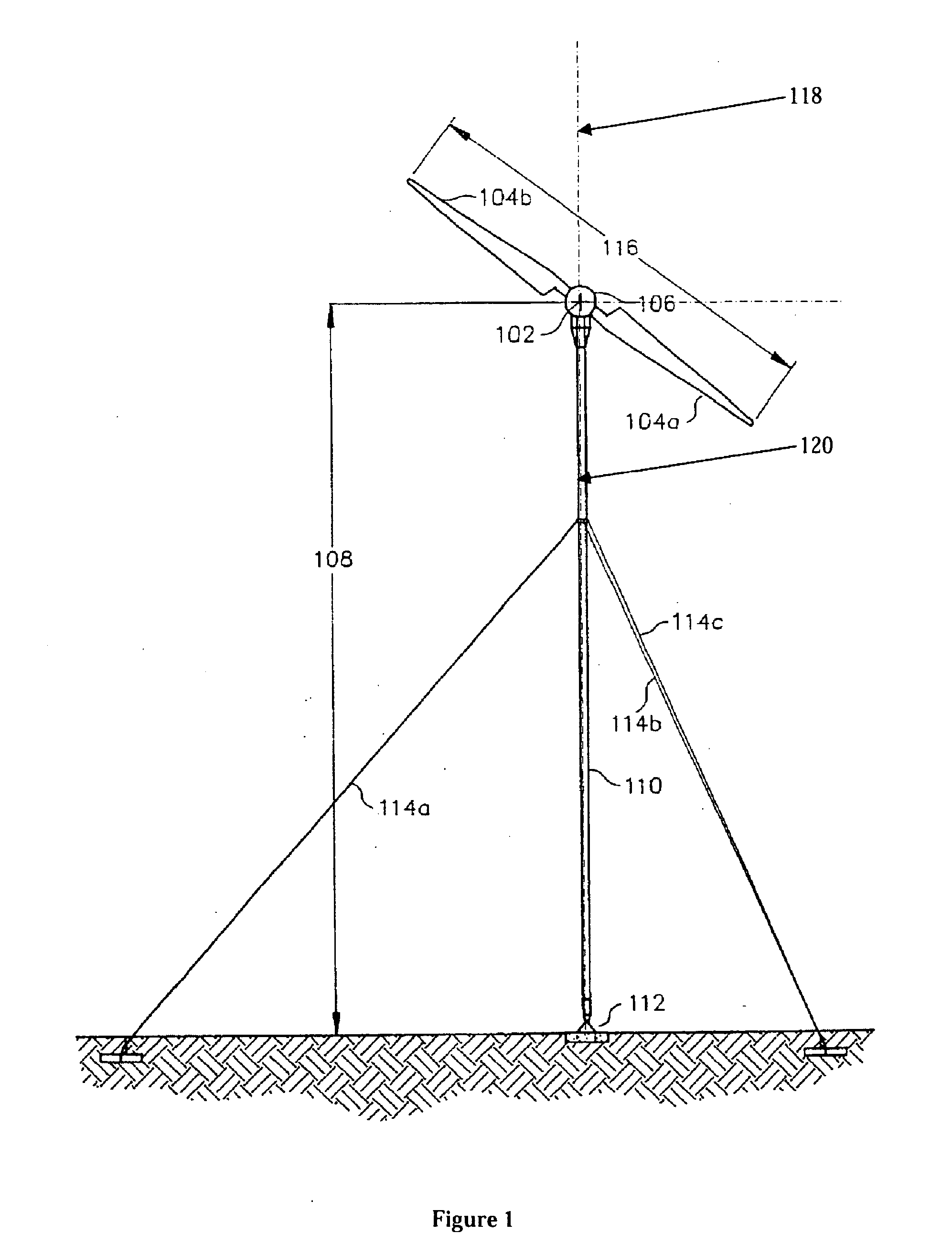
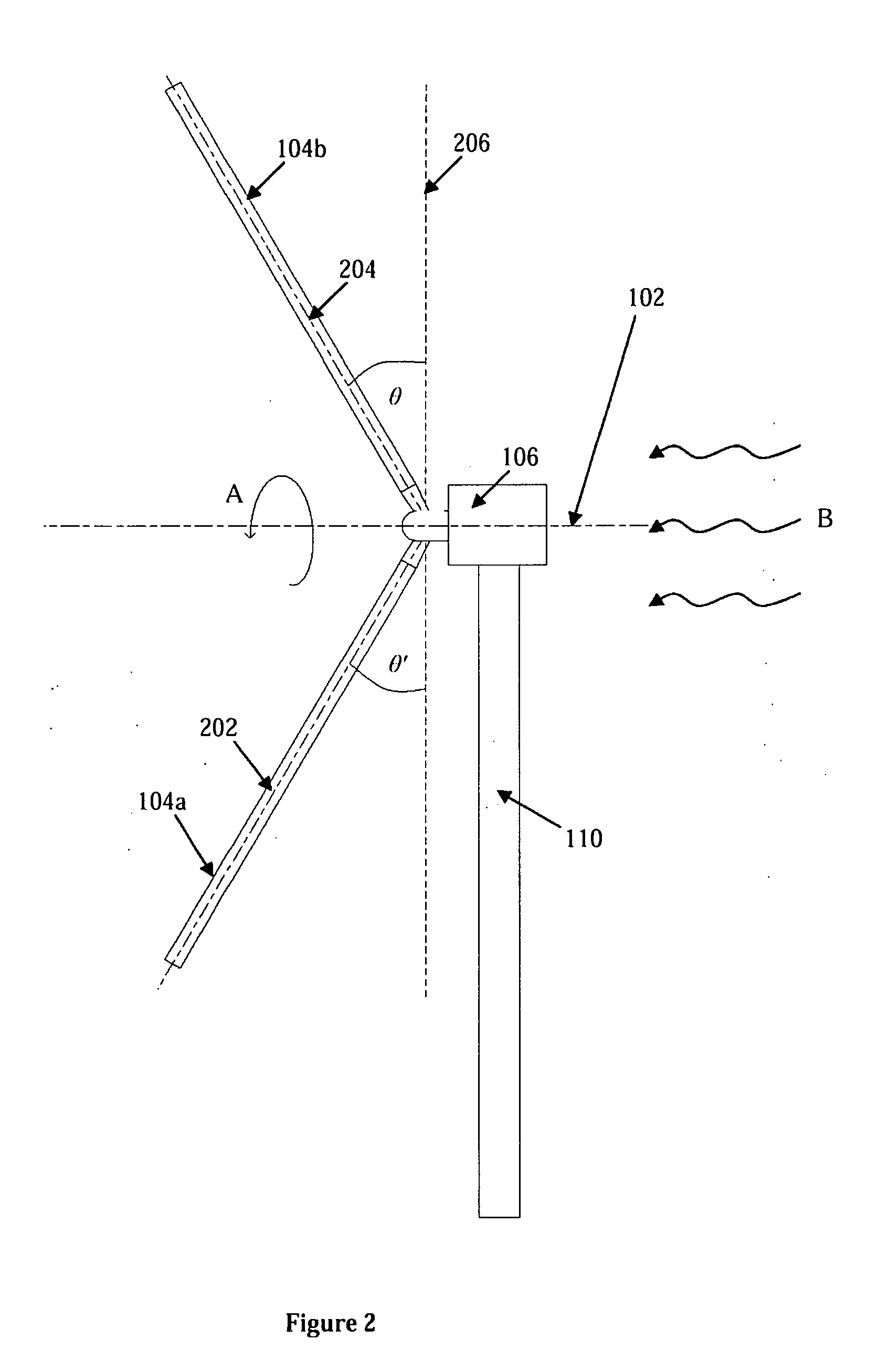
Tethered airborne wind-driven power generator
InactiveUS20110057453A1Reduce stressImprove power production efficiencyWind energy with electric storageMachines/enginesWind drivenInstability
A tethered airborne wind-driven power generation device providing, in various embodiments, a main tether and plurality of auxiliary tethers, feedback controls for continuously adjusting pitch, roll and yaw, and a Vee-shaped configuration for disposing rotors along the frame of the device. The auxiliary tethers avoid slack and resultant transient instability, and the Vee-shaped rotor disposition takes advantage of upwash or any other aerodynamic benefit from the rotors adjacent to it, to improve efficiency.
Owner:ROBERTS BRYAN WILLIAM
System and method for autonomous navigation of a tracked or skid-steer vehicle
ActiveUS20120179322A1Programme-controlled manipulatorPosition fixationMarine navigationPosition sensor
An autonomous navigation system for a tracked or skid-steer vehicle is described. The system includes a path planner (54) that computes a series of waypoint locations specifying a path to follow and vehicle location sensors (82). A tramming controller (60) includes a waypoint controller (62) that computes vehicle speed and yaw rate setpoints based on vehicle location information from the vehicle location sensor and the locations of a plurality of neighbouring waypoints, and a rate controller (64) that generates left and right track speed setpoints from the speed and yaw rate setpoints. A vehicle control interface actuates the vehicle controls in accordance with the left and right track speed setpoints.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Dynamic detection method for preventing wagon from turning towards one side on bending road and pre-warning apparatus
InactiveCN101350137AAccurate speedExact heightDetection of traffic movementRolloverMeasurement device
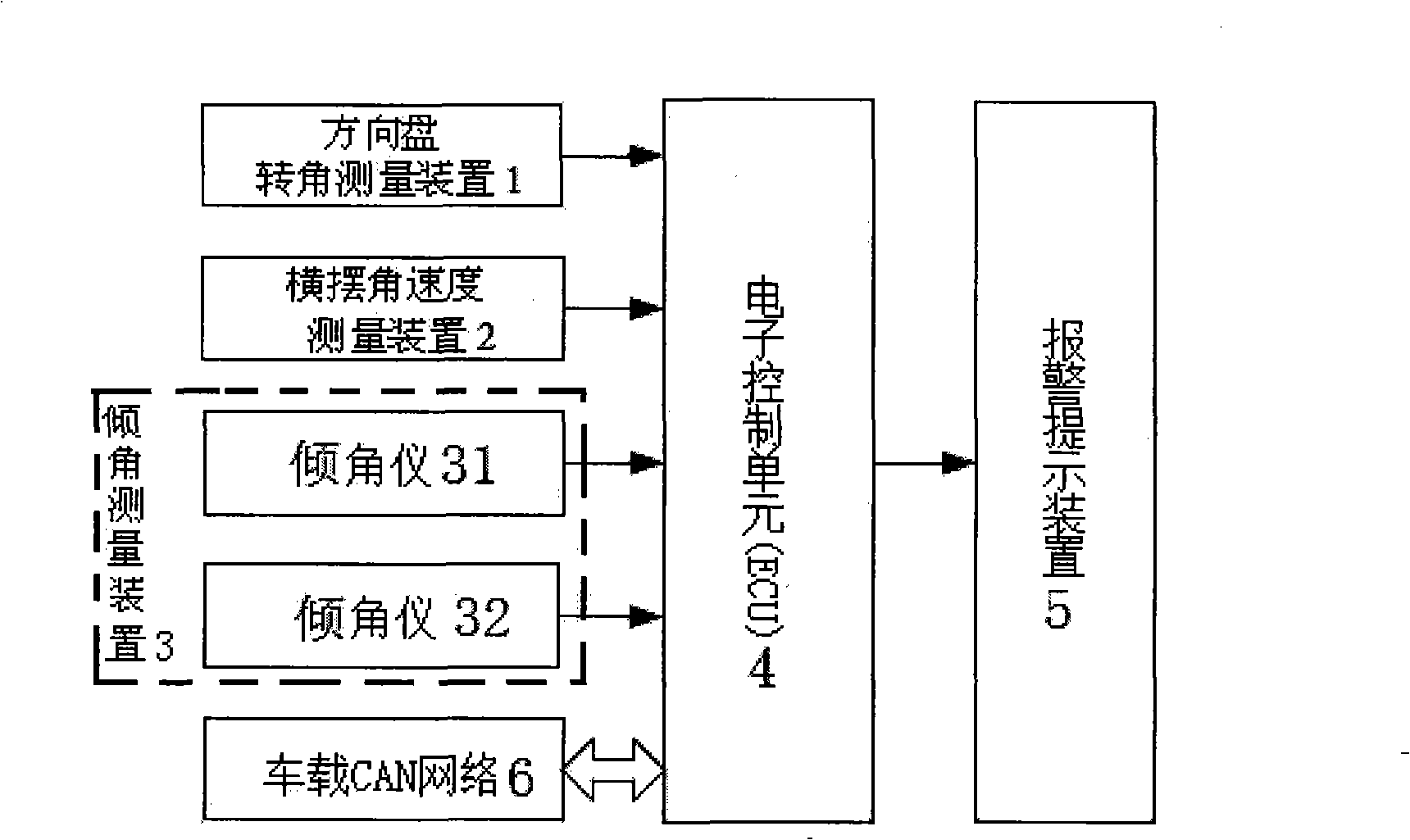
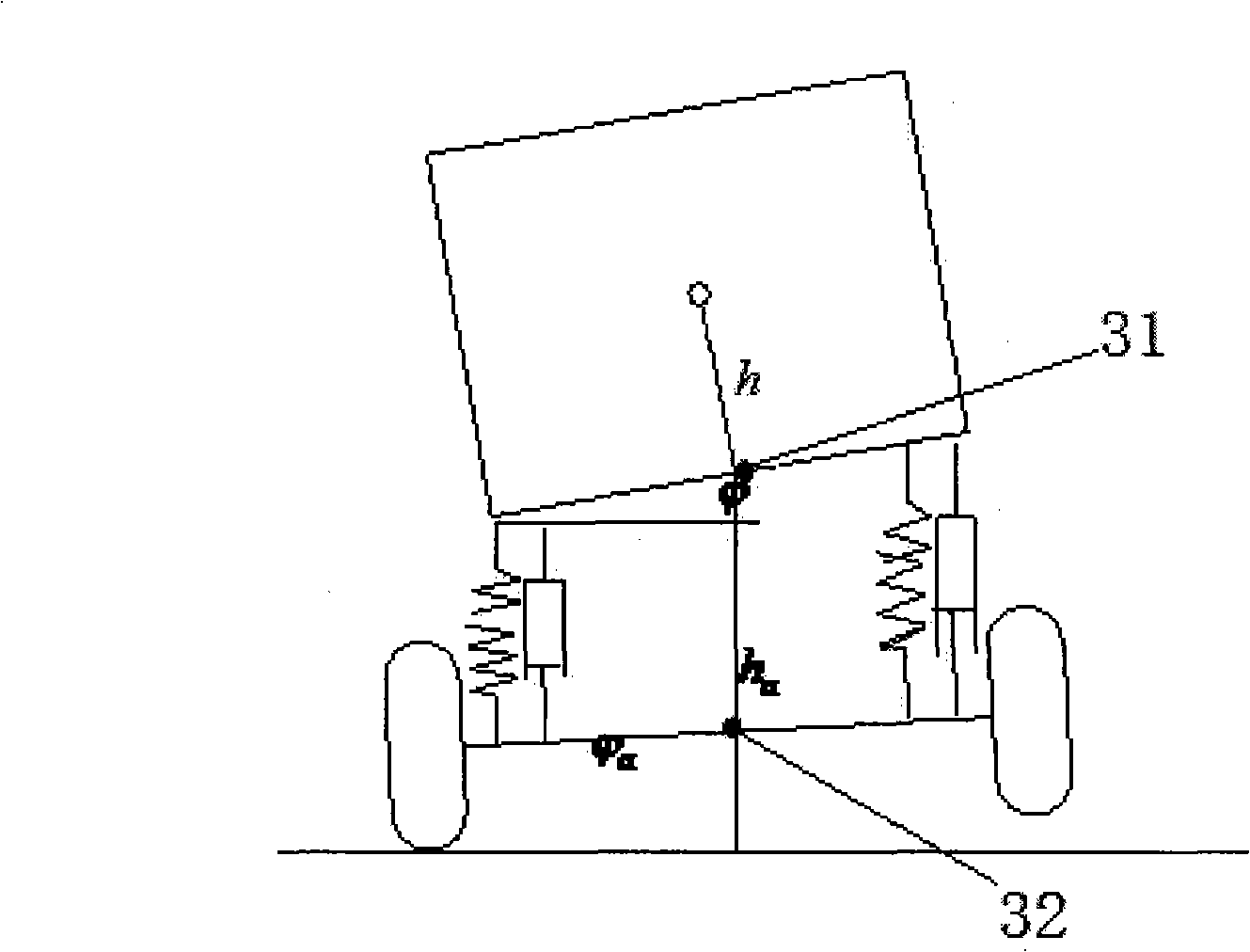
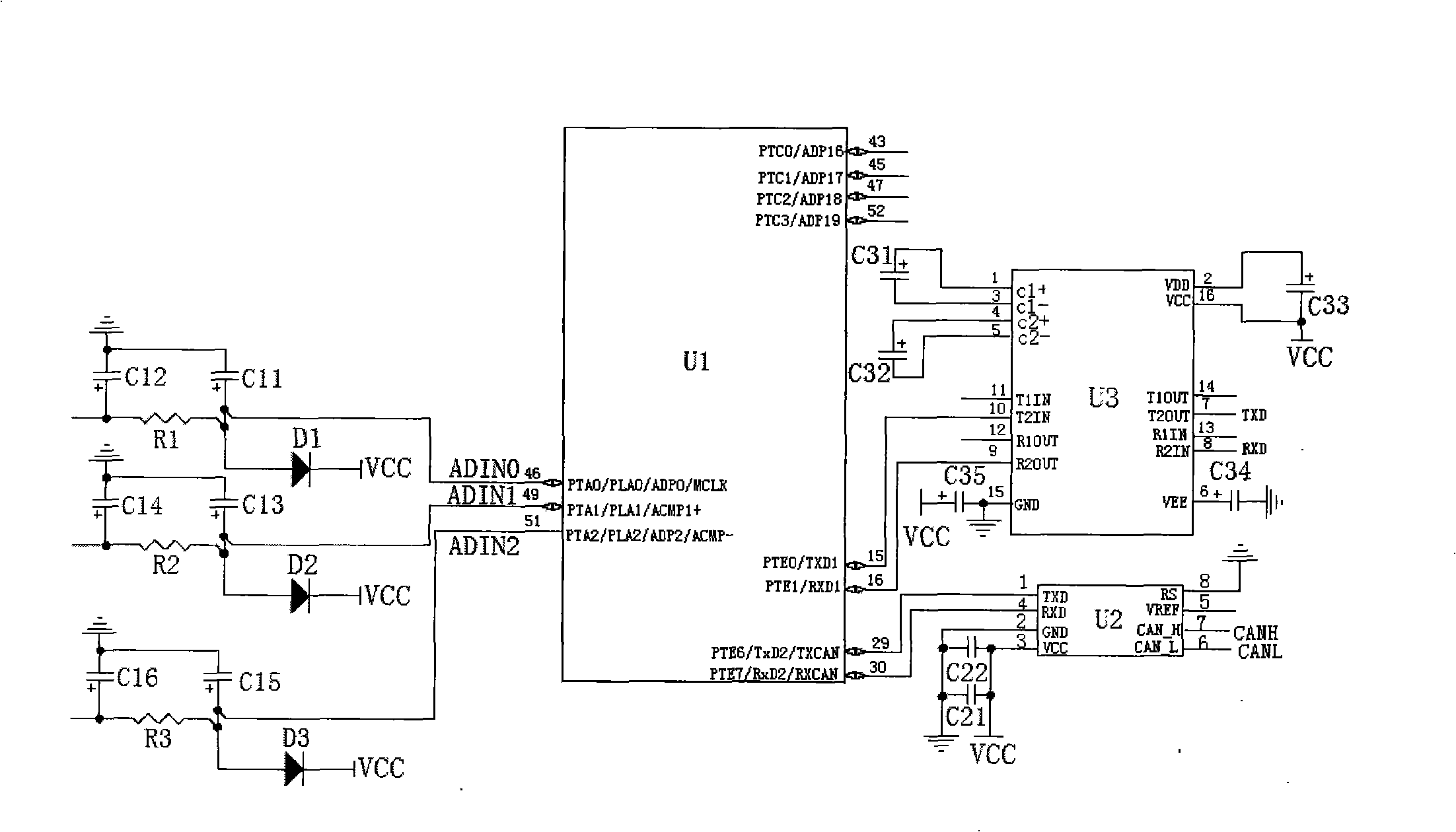
The invention relates to a rollover prevention dynamic detection method for a wagon on a curved conduit and a warning device. The method comprises the following steps: 1, installing a rollover prevention dynamic detection method for a wagon on a curved conduit which comprises a steering wheel rotation angle measuring device, a yaw angle velocity measuring device, an inclination angle measuring device and an electronic control unit which comprises a single chip microcomputer, wherein a solidification program of the single chip microcomputer is equipped with a centroid height dynamic detection algorithm module and a rollover prevention warning algorithm module, and a rollover alarming range is arranged in the rollover prevention warning algorithm module. 2, collecting steering wheel rotation angle singles, vertical yaw angle velocity measuring singles of the wagon, side-tipping angle singles of a carriage of the wagon, the side-tipping angle singles of a rear shaft of the wagon and vertical speed singles of the wagon. 3, a lateral acceleration and a centroid height of the wagon is counted through the centroid height dynamic detection algorithm module. 4, counting a rollover acceleration threshold value through the rollover prevention warning algorithm module according to the centroid height. 5, sending a corresponding alarm command according to a difference value of the lateral acceleration and the rollover acceleration threshold value of the wagon and the reset rollover alarm range.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Thrust vectoring
InactiveUS20070018034A1Reduces forward thrustPromote productionAircraft navigation controlCosmonautic vehiclesAttitude controlFlight vehicle
Thrust vectoring enhances aircraft and spacecraft maneuverability. The propulsion systems of aircraft, using gas turbine engines, and spacecraft, using solid or liquid rockets, generate compressed gases that are directed through a nozzle to generate forward thrust. This patent describes opening ports to release gases from aircraft and spacecraft in a direction other than the direction of forward propulsion. By altering the direction of gas flows leaving the craft pitch, roll, yaw and attitude control is obtained. To control gas flow from ports a variable throat thrust vectoring nozzle is described. Independent operation of ports, rotational nozzles, laterally moving flaps and rotational vanes assists the thrust vectoring of gases leaving aircraft or spacecraft ports. The ability to direct gases enhances maneuverability during vertical takeoff and landing, forward flight and space flight.
Owner:DICKAU JOHN EUGENE
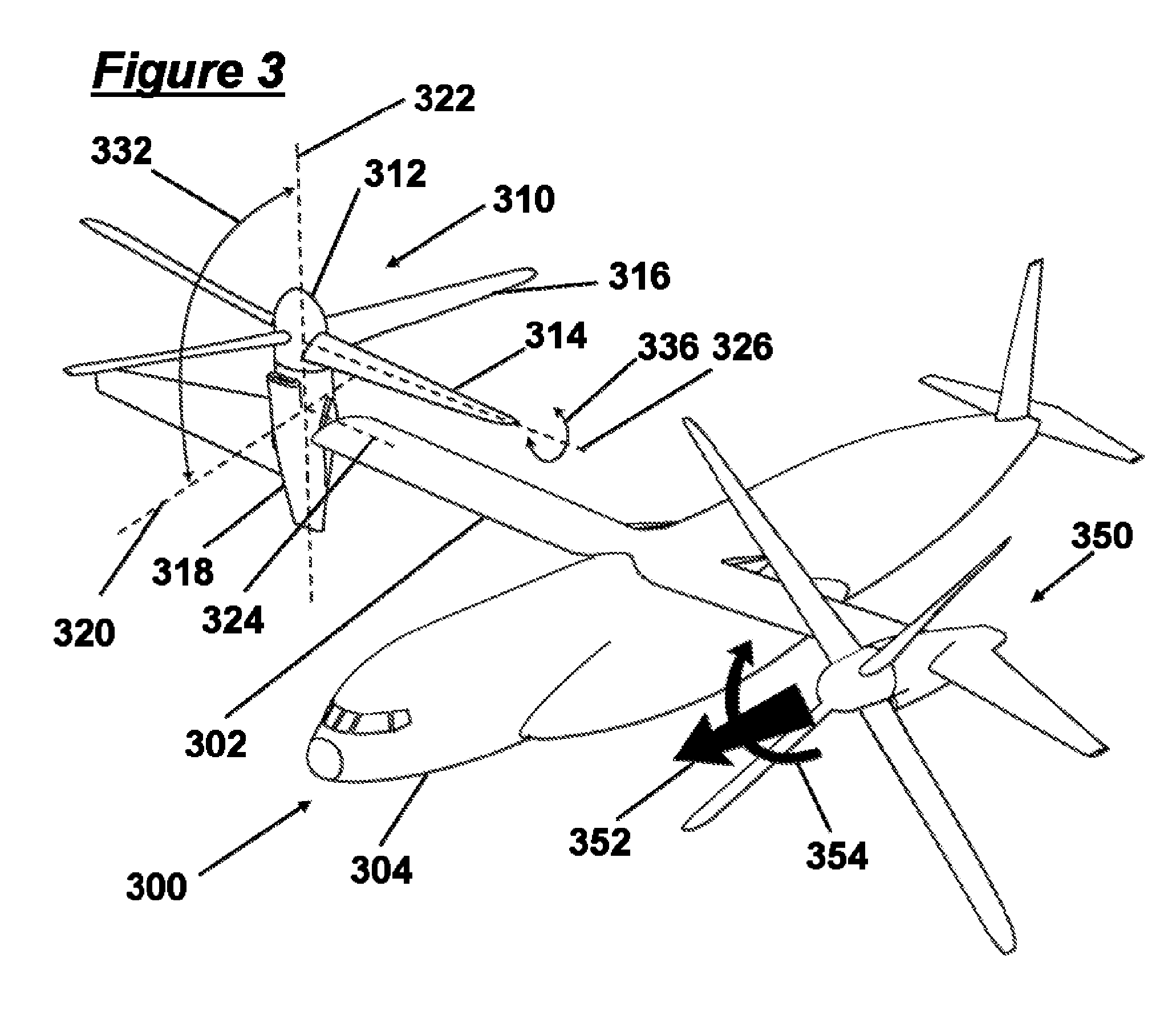
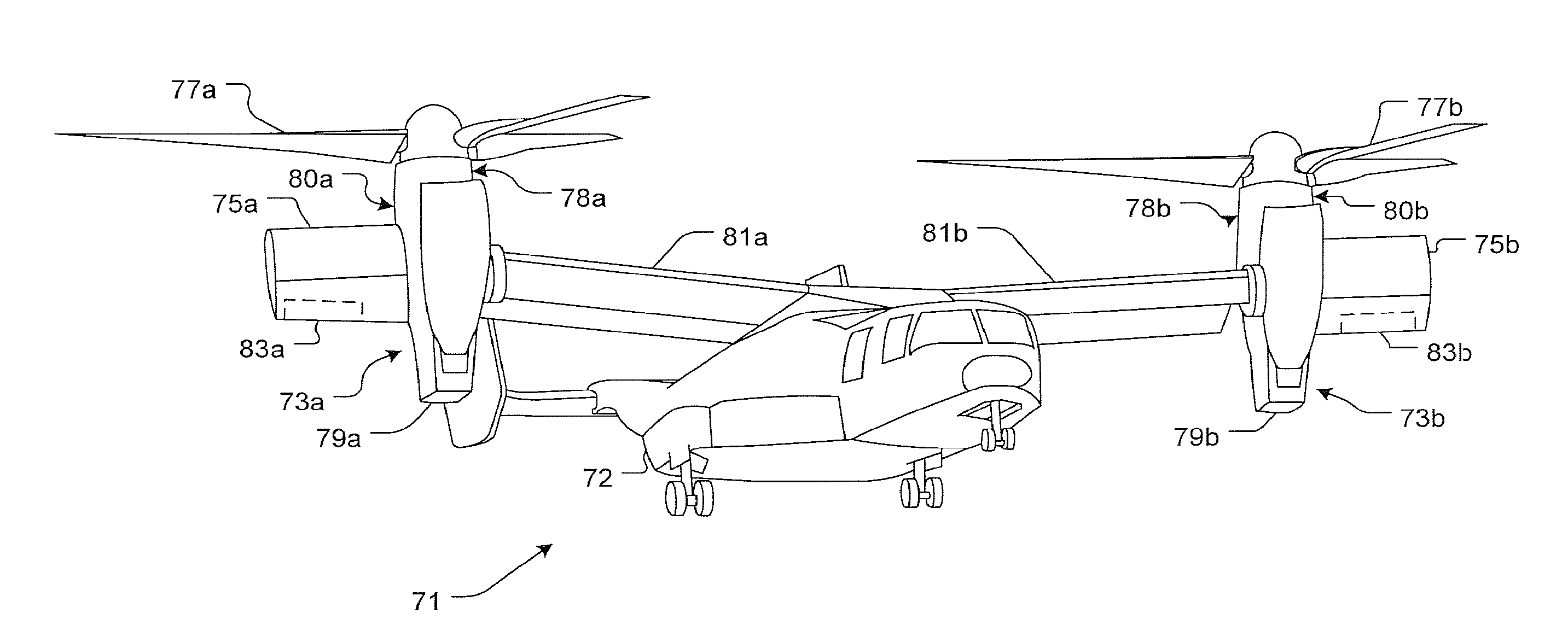
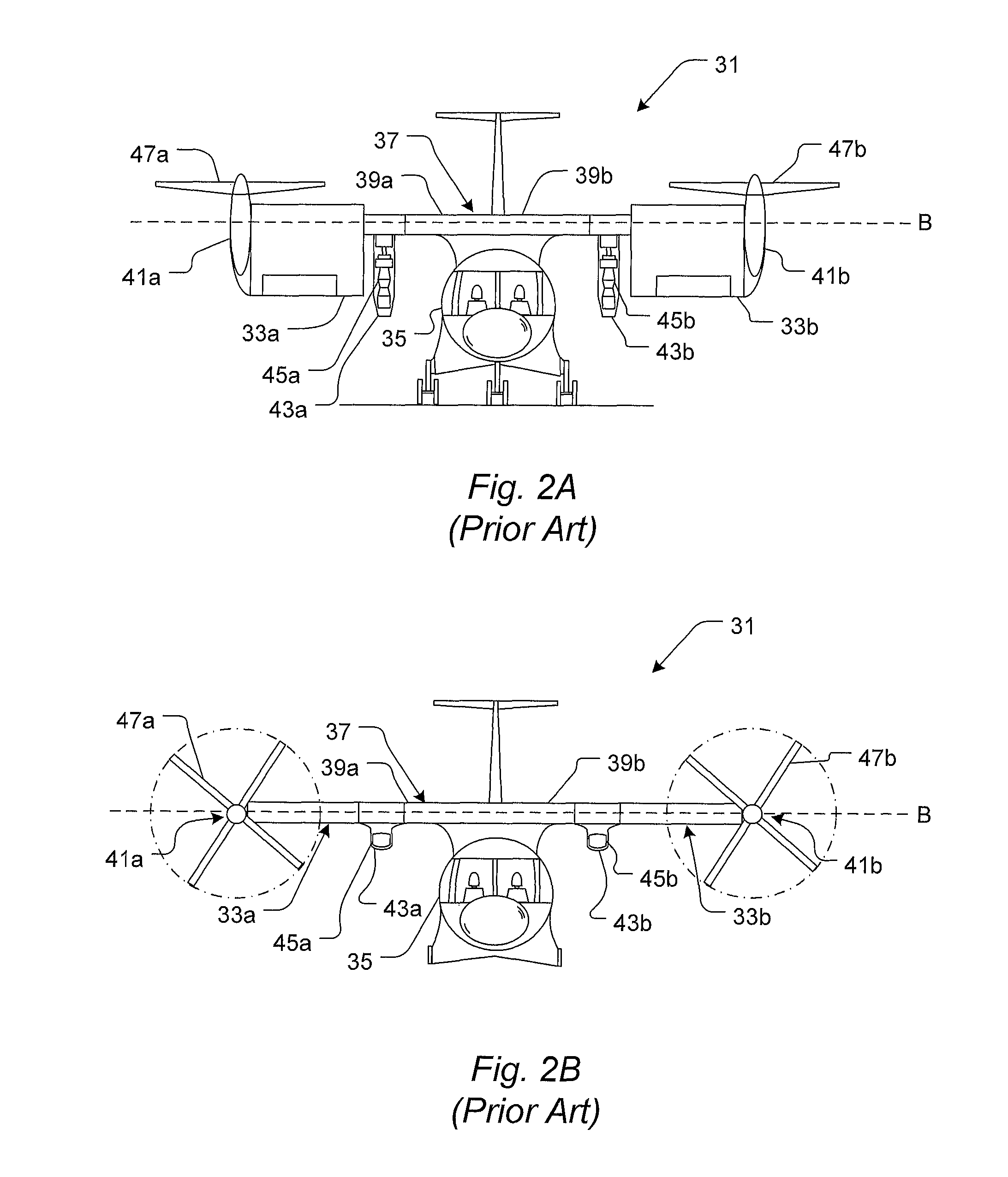
Tilt Actuation for a Rotorcraft
ActiveUS20090256026A1Reduce loadContinued controlPower plant arrangements/mountingAircraft stabilisationNacelleActuator
An aircraft is equipped with hingeless rotors on tilting nacelles, and the tilt angles of the nacelles are controlled using either or both of an actuator and a mast moment generated by a hingeless rotor. An aircraft with two or more rotors on tilting nacelles can achieve control of yaw orientation by differential tilt of its nacelles or masts. Hingeless rotors can be manipulated to control a tilt angle of a mast by changing the rotor blade pitch to produce a mast moment. The rotor and nacelle tilt of a tiltrotor rotorcraft can be controlled and effected in order to manipulate the yaw orientation and flight mode of a rotorcraft such as a tiltrotor. The use of mast moment to control nacelle tilt angle can reduce tilt actuator loads and allows for the control of nacelle tilt even in the event of an actuator failure.
Owner:KAREM AIRCRAFT INC
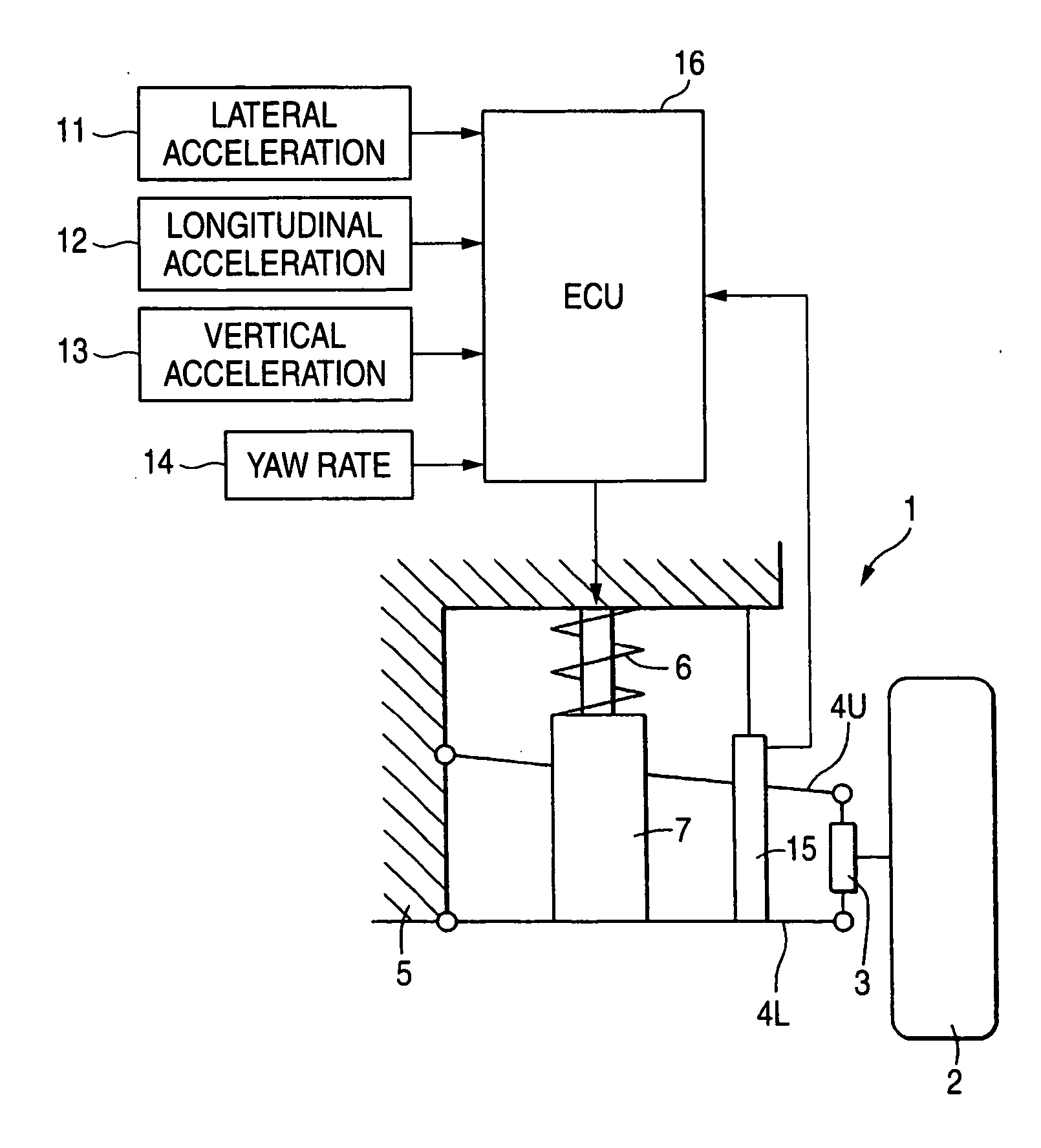
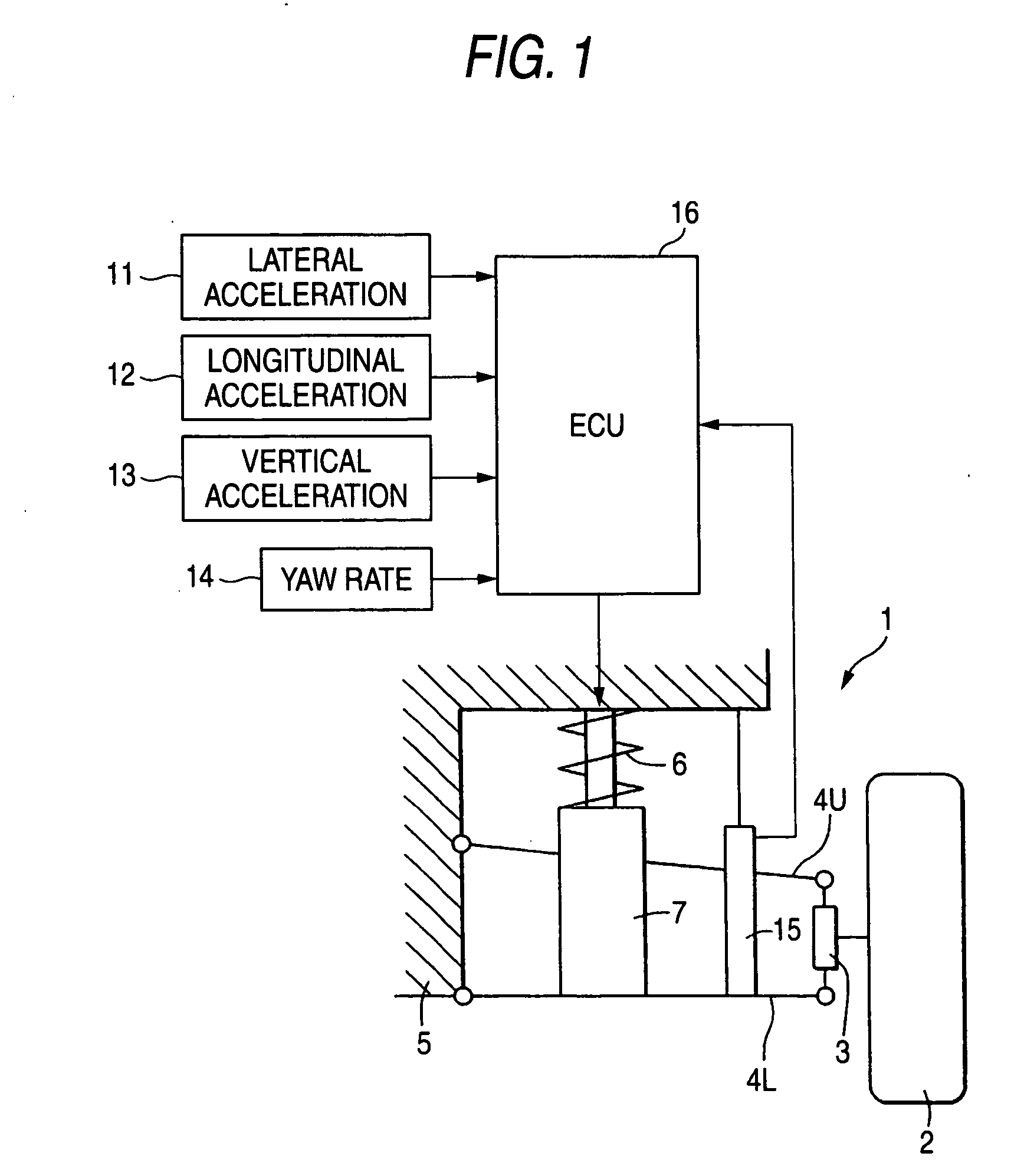
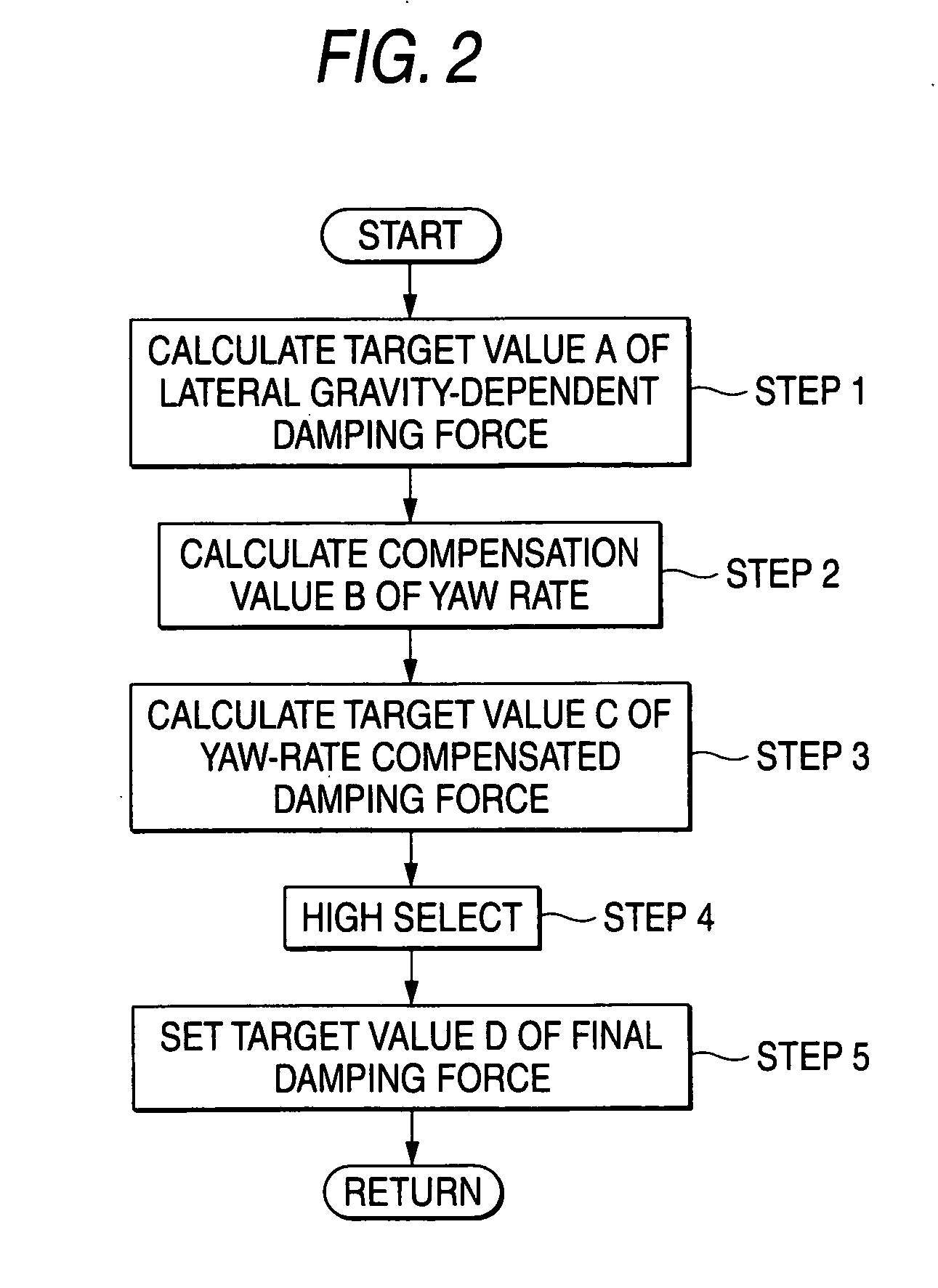
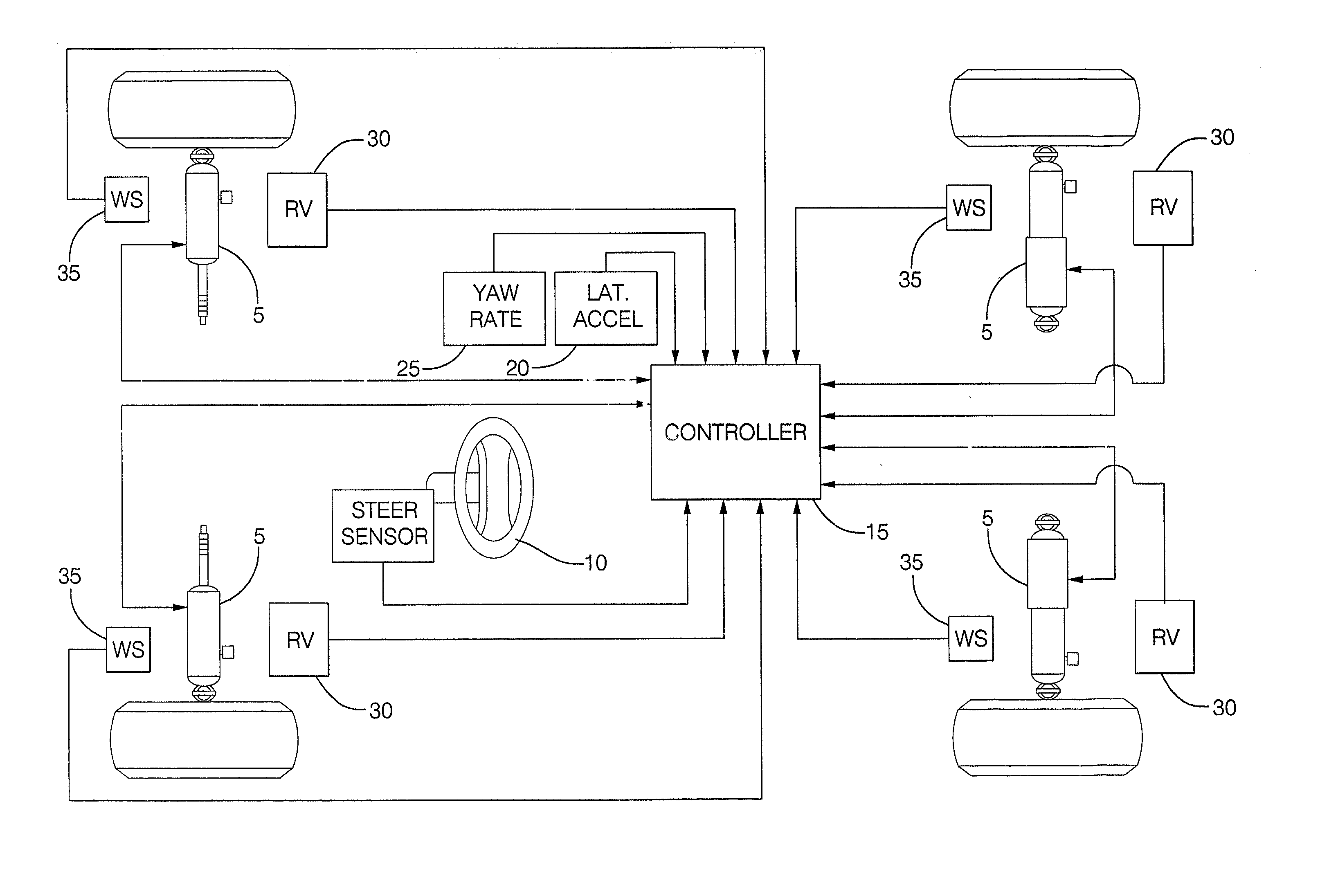
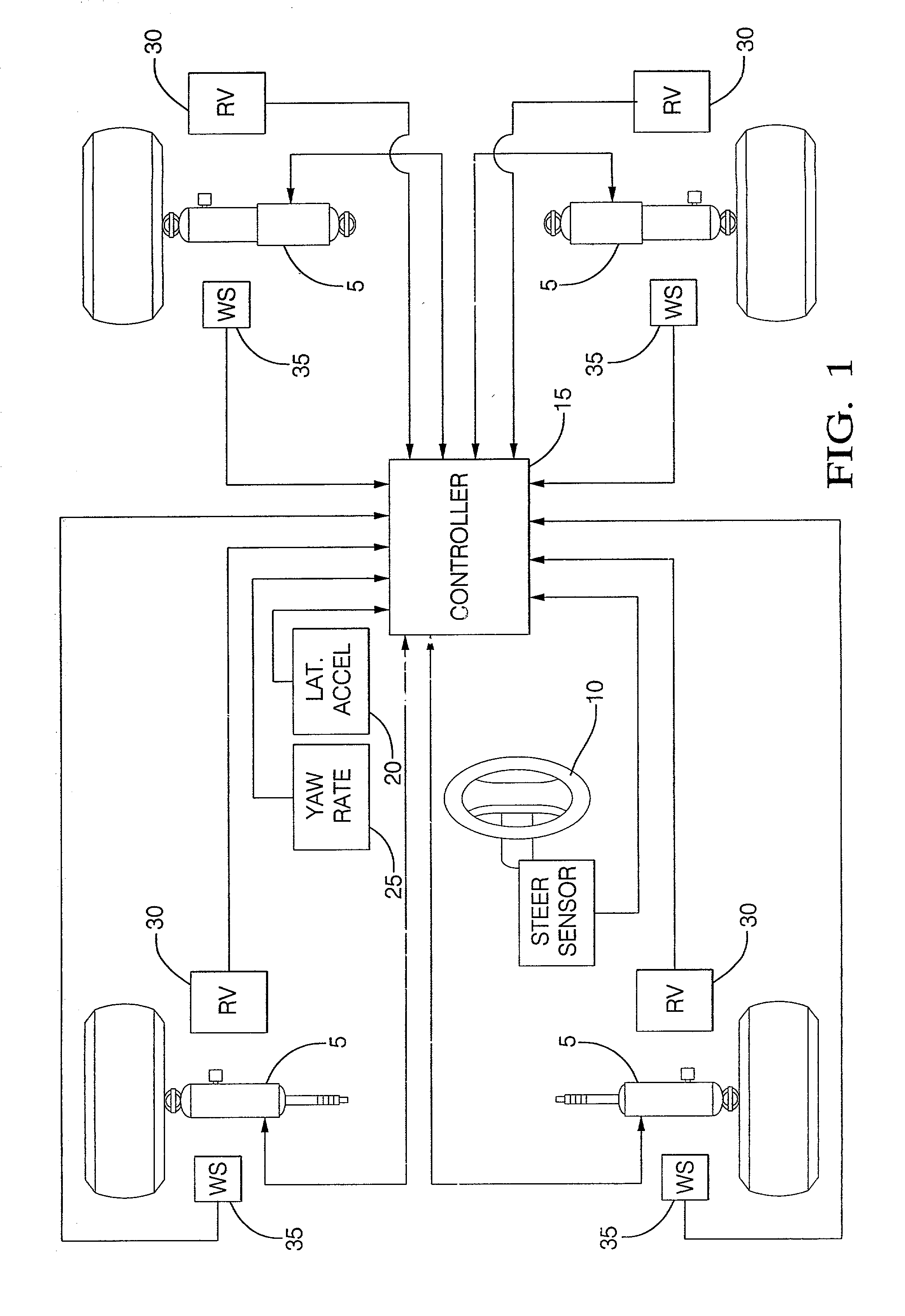
Control system for adjustable damping force damper
ActiveUS20060224287A1Good precisionWithout a deterioration of a high responsibilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesControl systemTarget control
A control system for an adjustable damping force damper of a suspension apparatus of a vehicle, includes a lateral acceleration detecting unit detecting a lateral acceleration of the vehicle at a gravity point thereof, a yaw rate detecting unit detecting a yaw rate of the vehicle and a control unit controlling a damping force of the damper. The control unit calculates a first target damping force based on an output of the lateral acceleration detecting unit, calculates a second target damping force based on a lateral acceleration at an axel position which is estimated by an output of the yaw rate detecting unit, compares an absolute value of the first target damping force with that of the second target damping force and sets a target controlling value of the damping force in accordance with the first or second target damping force which has a larger absolute value.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
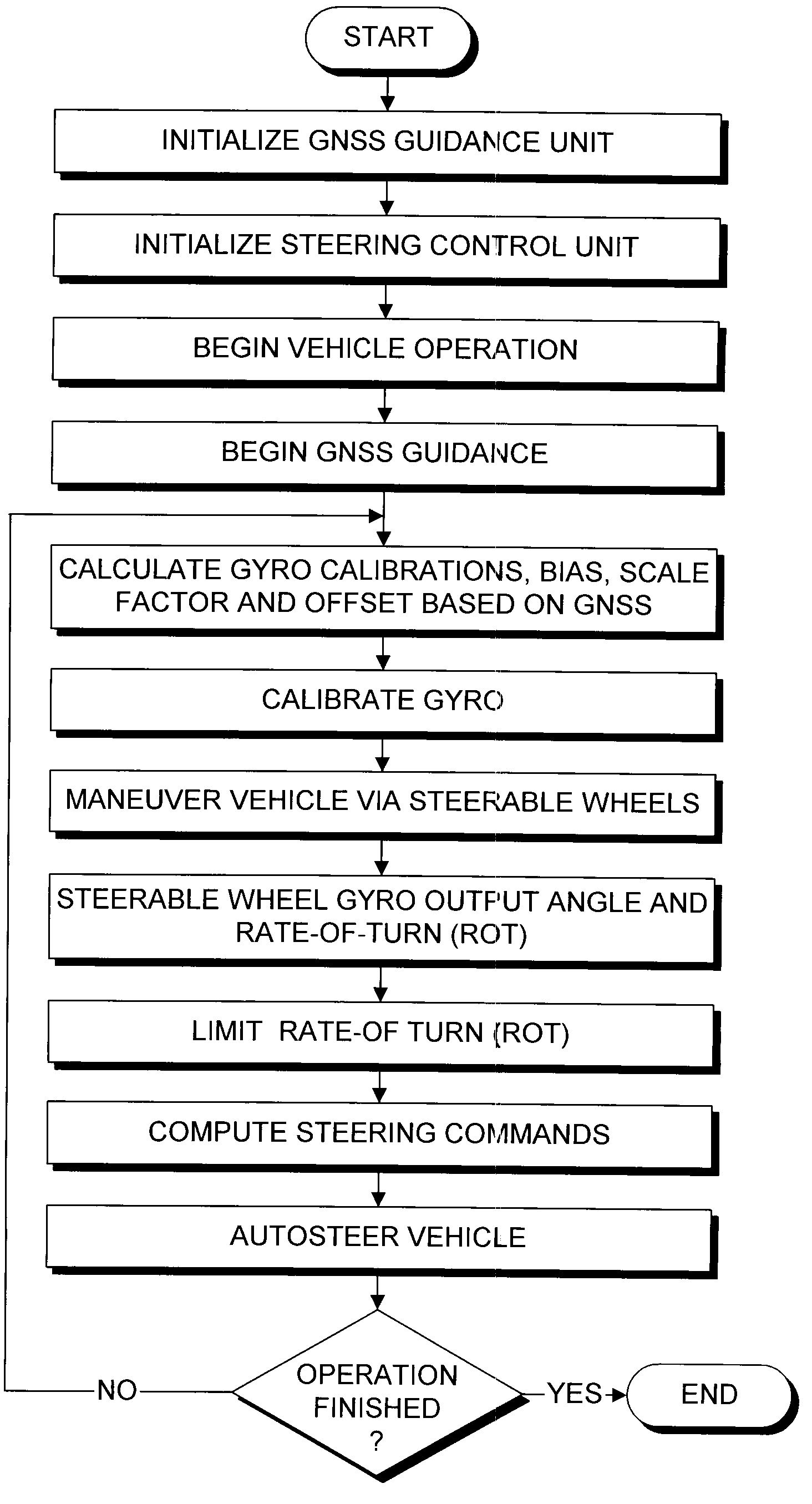
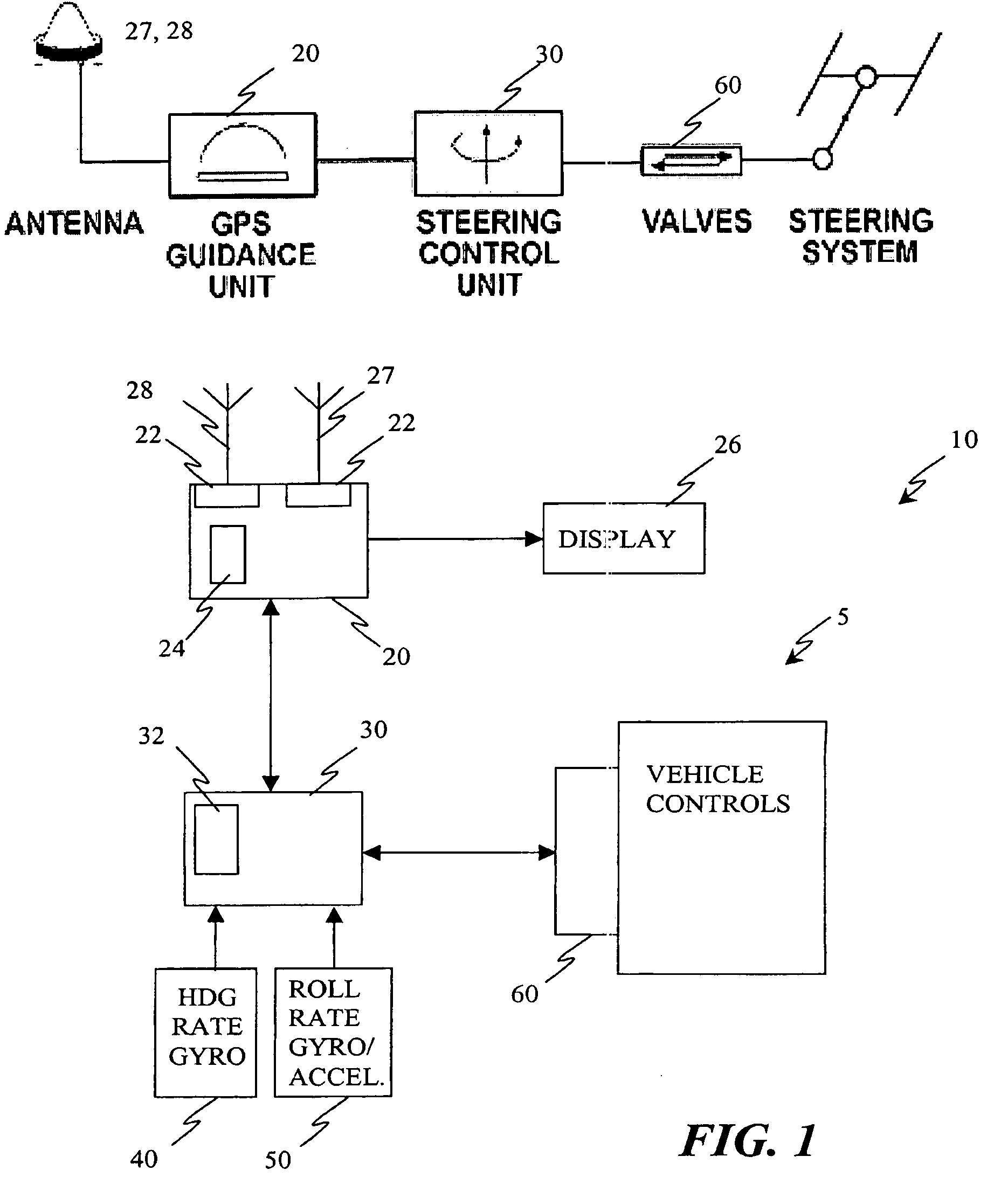
Satellite based vehicle guidance control in straight and contour modes
ActiveUS20090099730A1Steering initiationsDigital data processing detailsControl theoryTracking error
A method for steering an agricultural vehicle comprising: receiving global positioning system (GPS) data including position and velocity information corresponding to at least one of a position, velocity, and course of the vehicle; receiving a yaw rate signal; and computing a compensated heading, the compensated heading comprising a blend of the yaw rate signal with heading information based on the GPS data. For each desired swath comprising a plurality of desired positions and desired headings, the method also comprises: computing an actual track and a cross track error from the desired swath based on the compensated heading and the position; calculating a desired radius of curvature to arrive at the desired track with a desired heading; and generating a steering command based on the desired radius of curvature to a steering mechanism, the steering mechanism configured to direct the vehicle.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Wing extension control surface
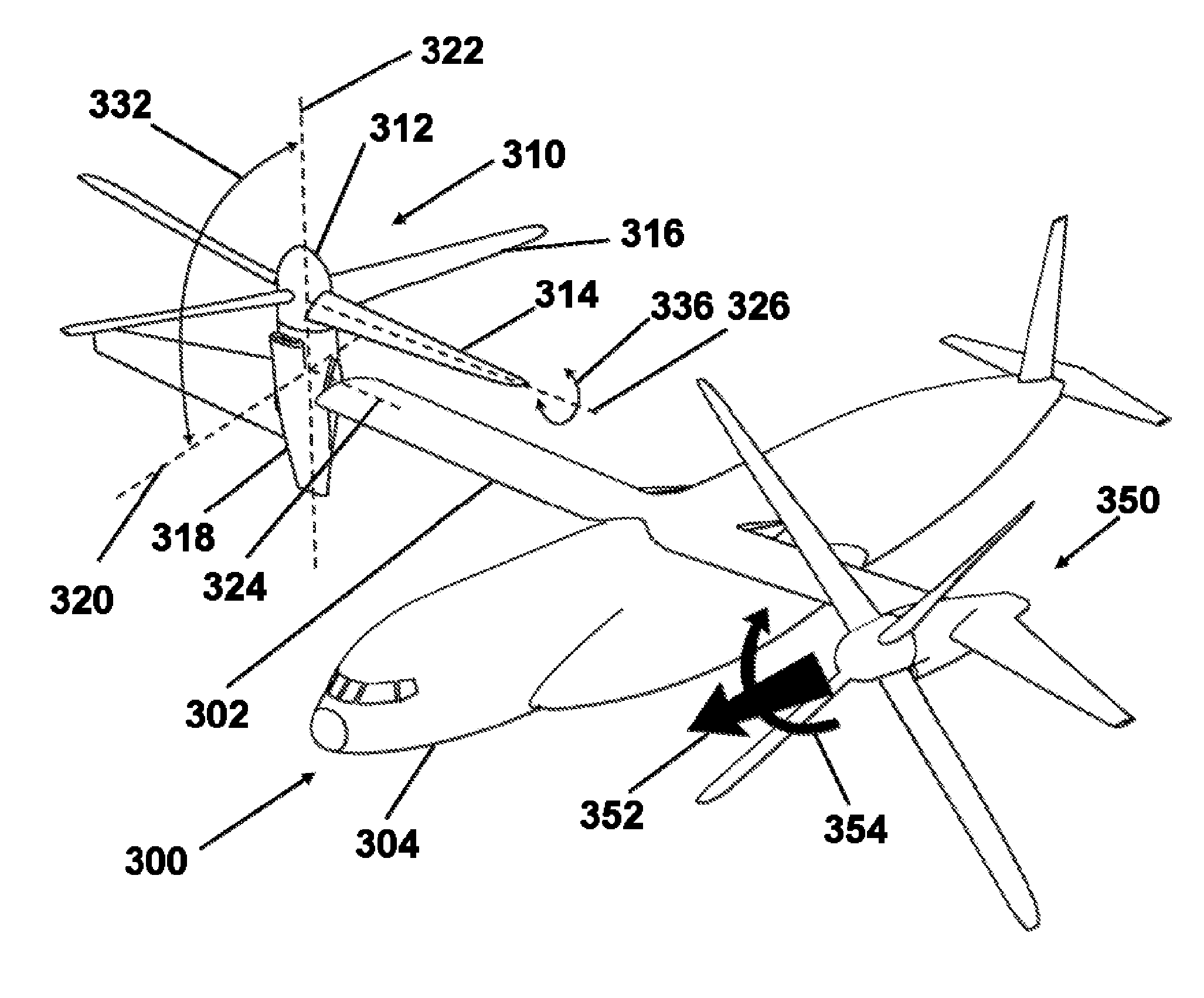
A tiltrotor aircraft includes a rotatable nacelle that supports a rotor assembly and is pivotally attached to the air-craft's fuselage. A wing extension attaches to an outboard section of the nacelle. The wing extension provides additional yaw control during helicopter mode and additional lift during airplane mode. A method for controlling at least a portion of yaw movement includes positioning the rotor assembly in helicopter mode, creating rotor wash with the rotor assembly, and pivotally rotating the wing extension in the rotor wash.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
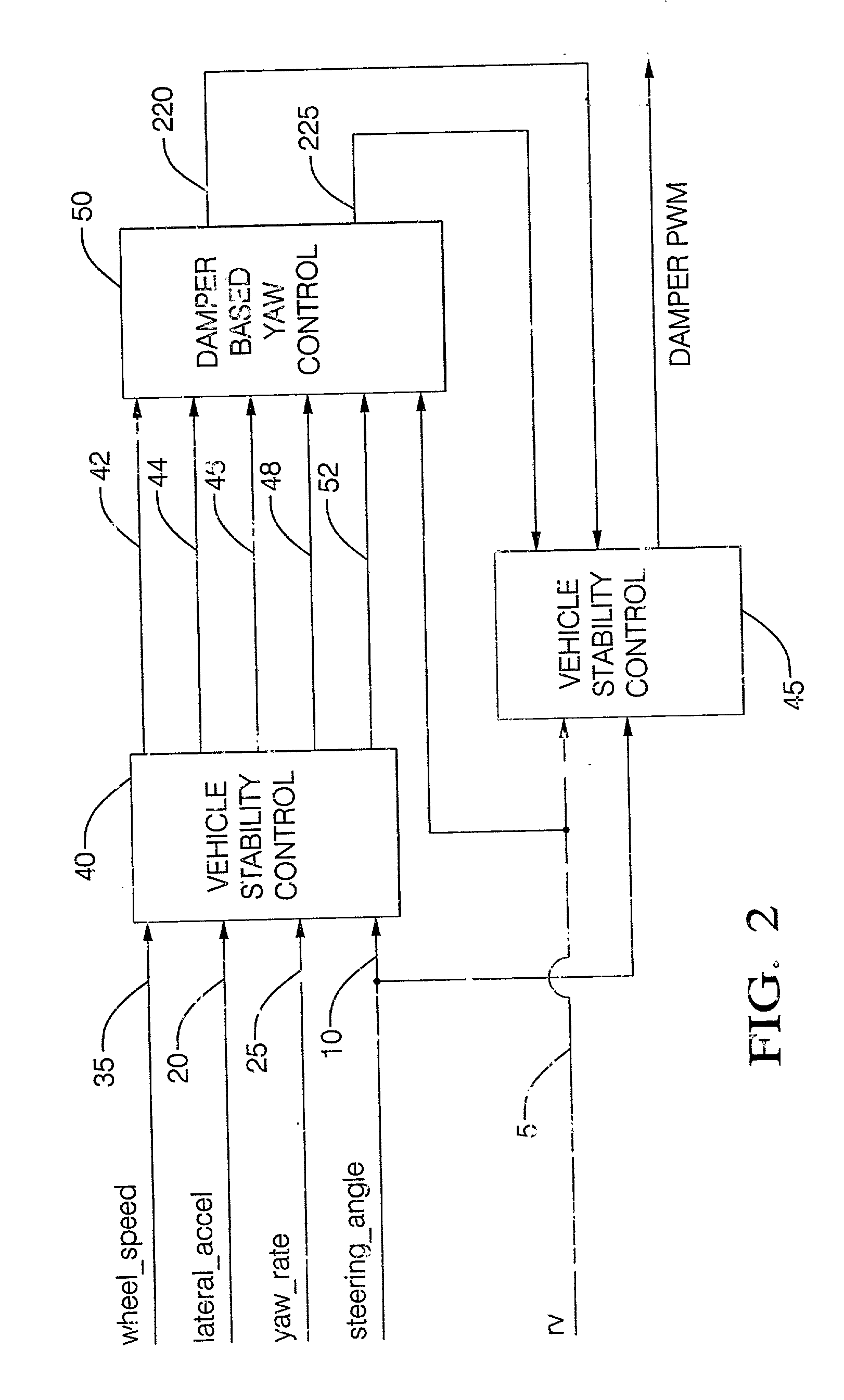
Damper based vehicle yaw control
InactiveUS20020128760A1Improve vehicle responseImprove stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesTime derivativeYaw control
Controllable dampers are used to improve vehicle responses and stability during severe vehicle handling maneuvers. A total handling damping value for the vehicle is derived, preferably from the greatest of a yaw rate error value, a lateral acceleration value and a time derivative of lateral acceleration value. In addition, a control ratio of front axle roll damping to total roll damping is derived, preferably from the yaw rate error value, an oversteer / understeer indication and possibly vehicle speed. From these values, handling damping values are derived for each wheel of the vehicle and blended with damping values for the same wheels derived from suspension component movement to determine a corner damping command for each controllable damper. Preferably, the damping values derived from suspension component movement are shifted away from damping control of the vehicle body toward handling damping control when yaw rate error is large in magnitude.
Owner:BWI +1
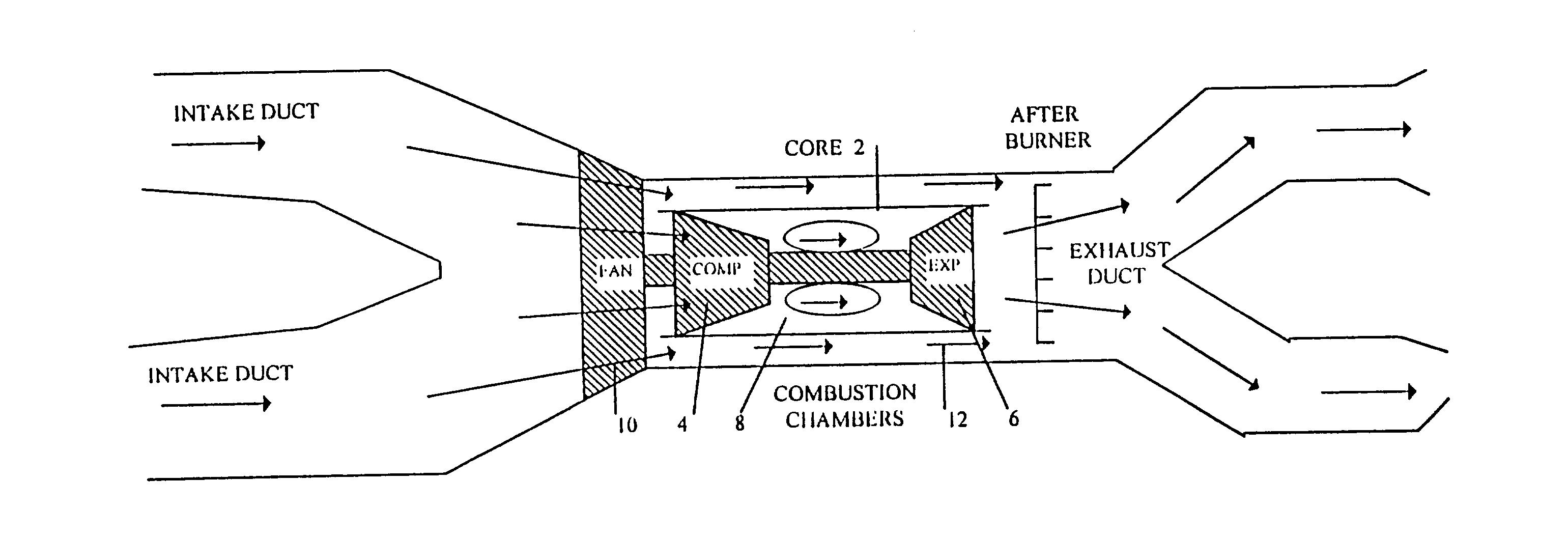
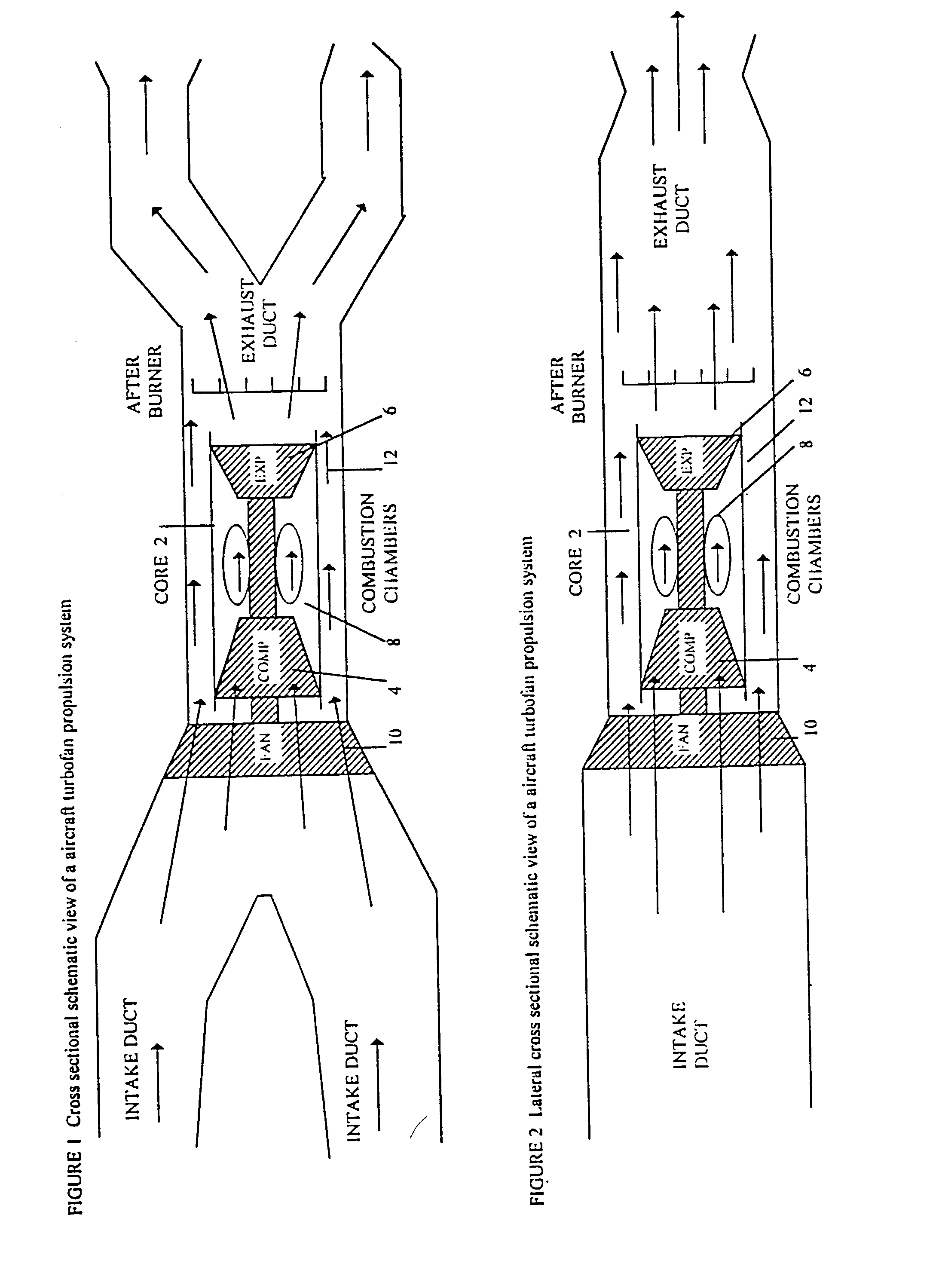
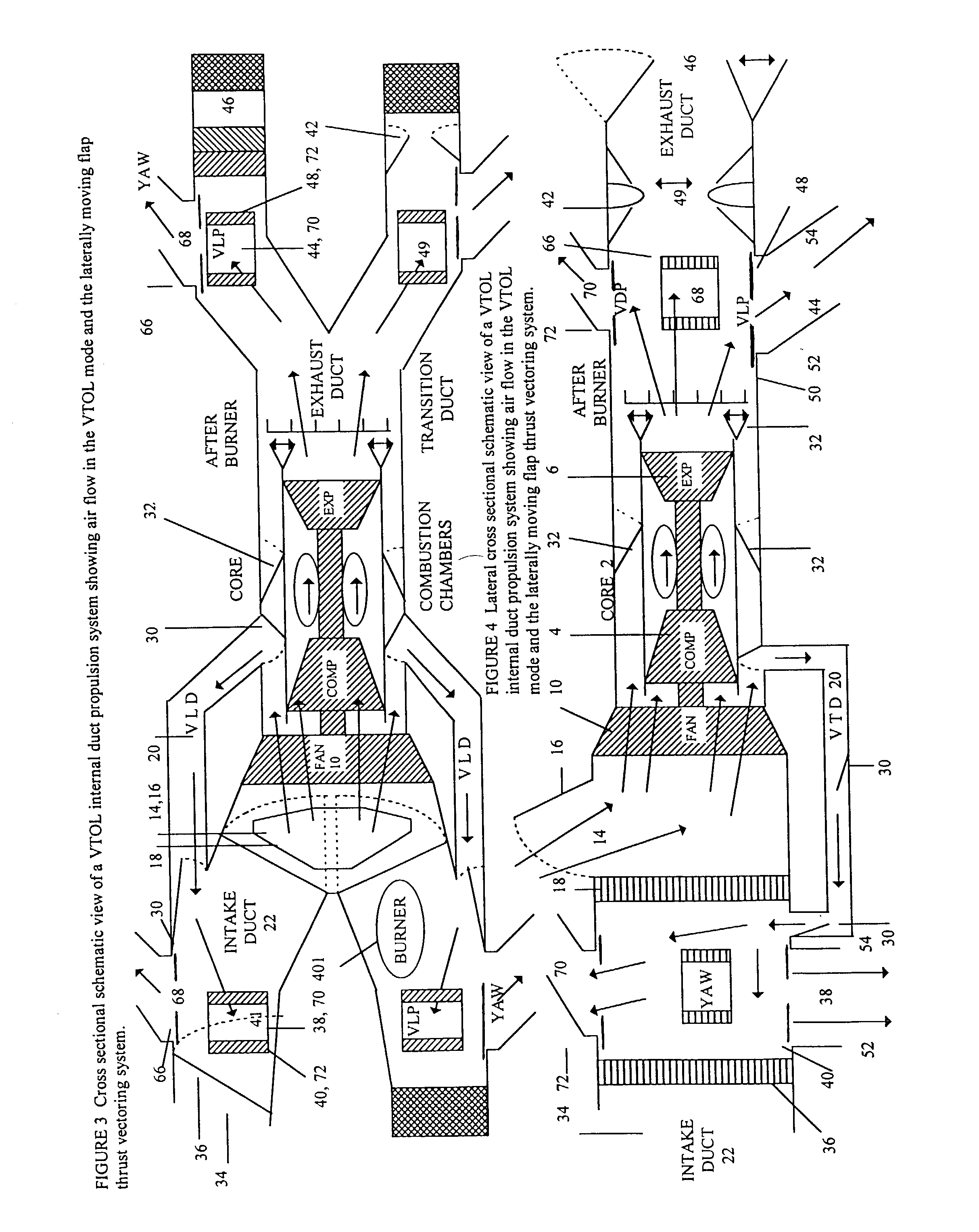
VTOL aircraft propulsion systems and forward flight thrust vectoring
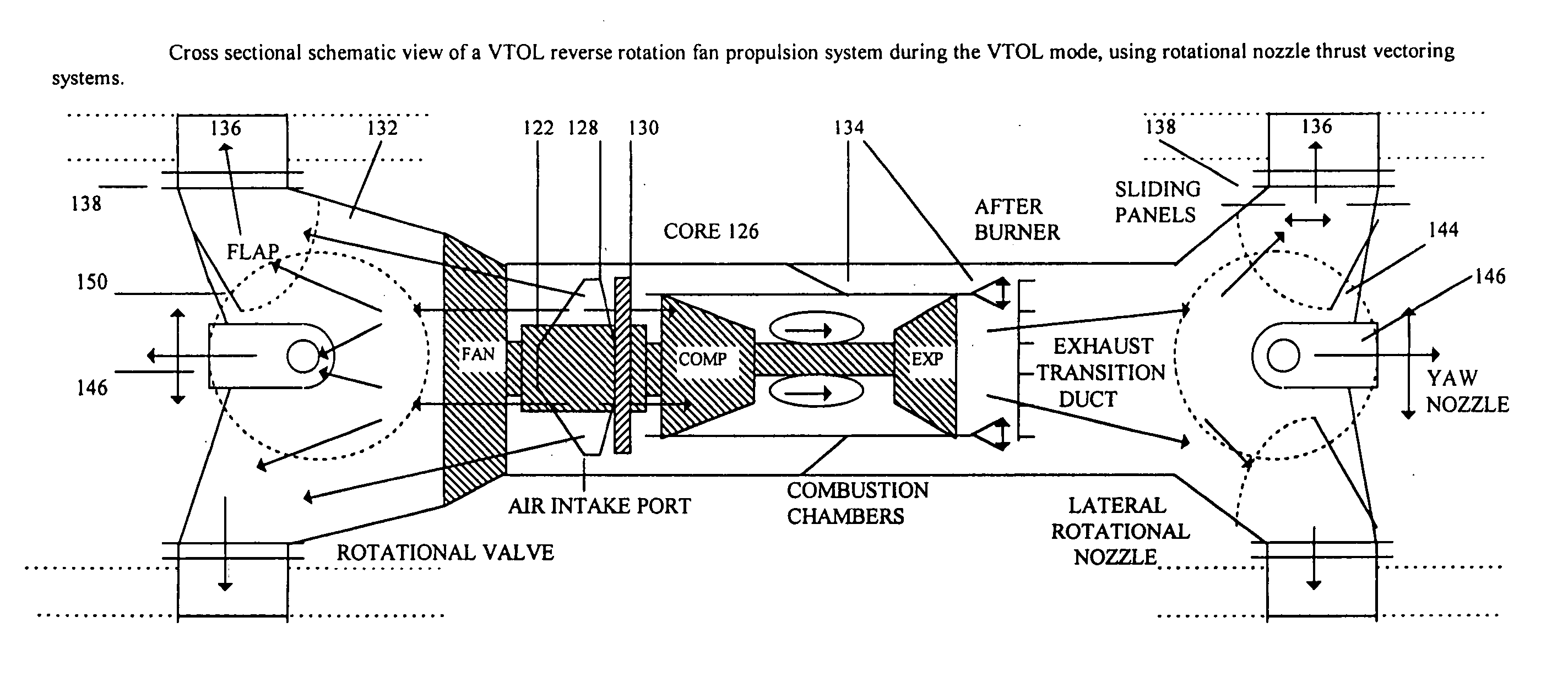
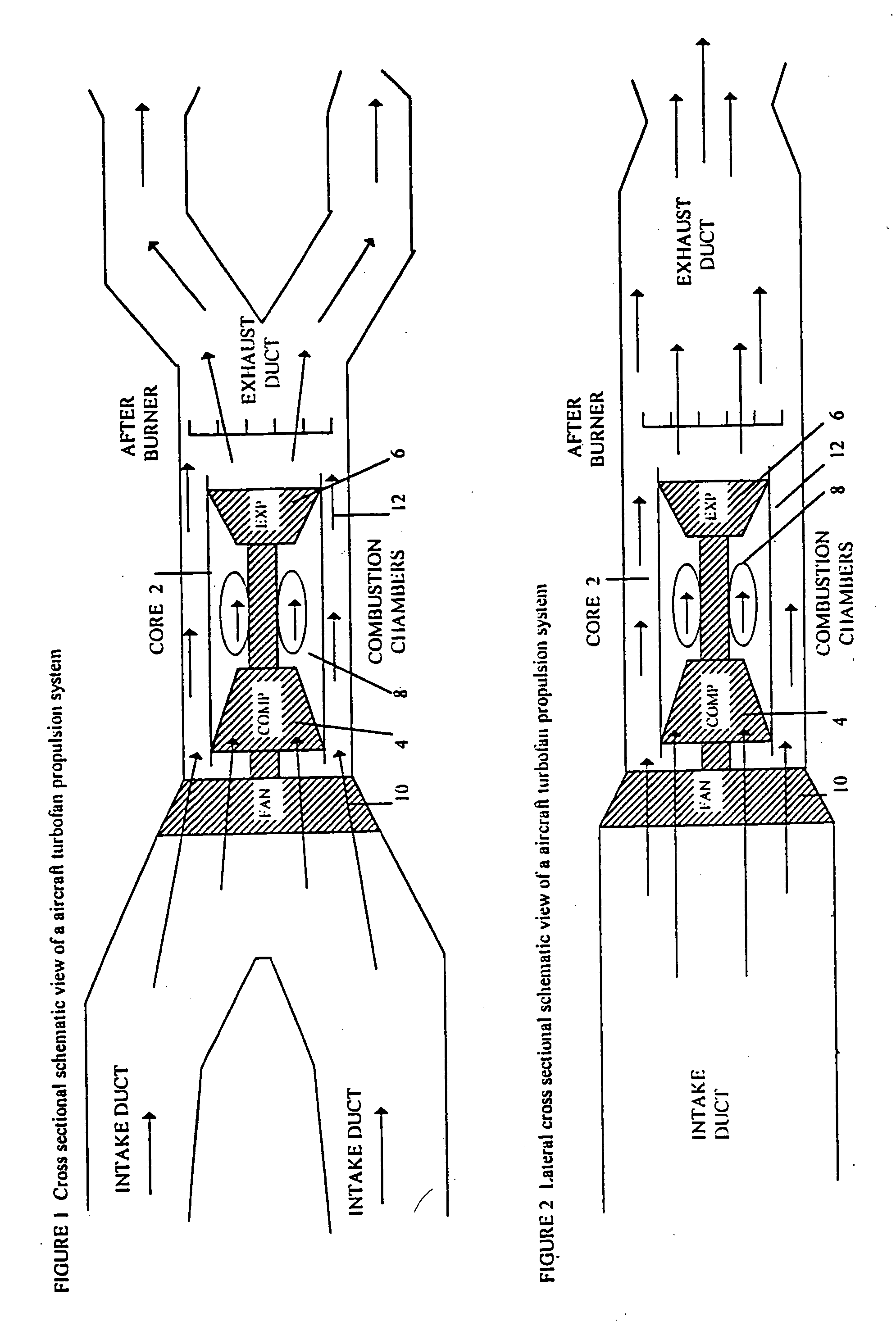
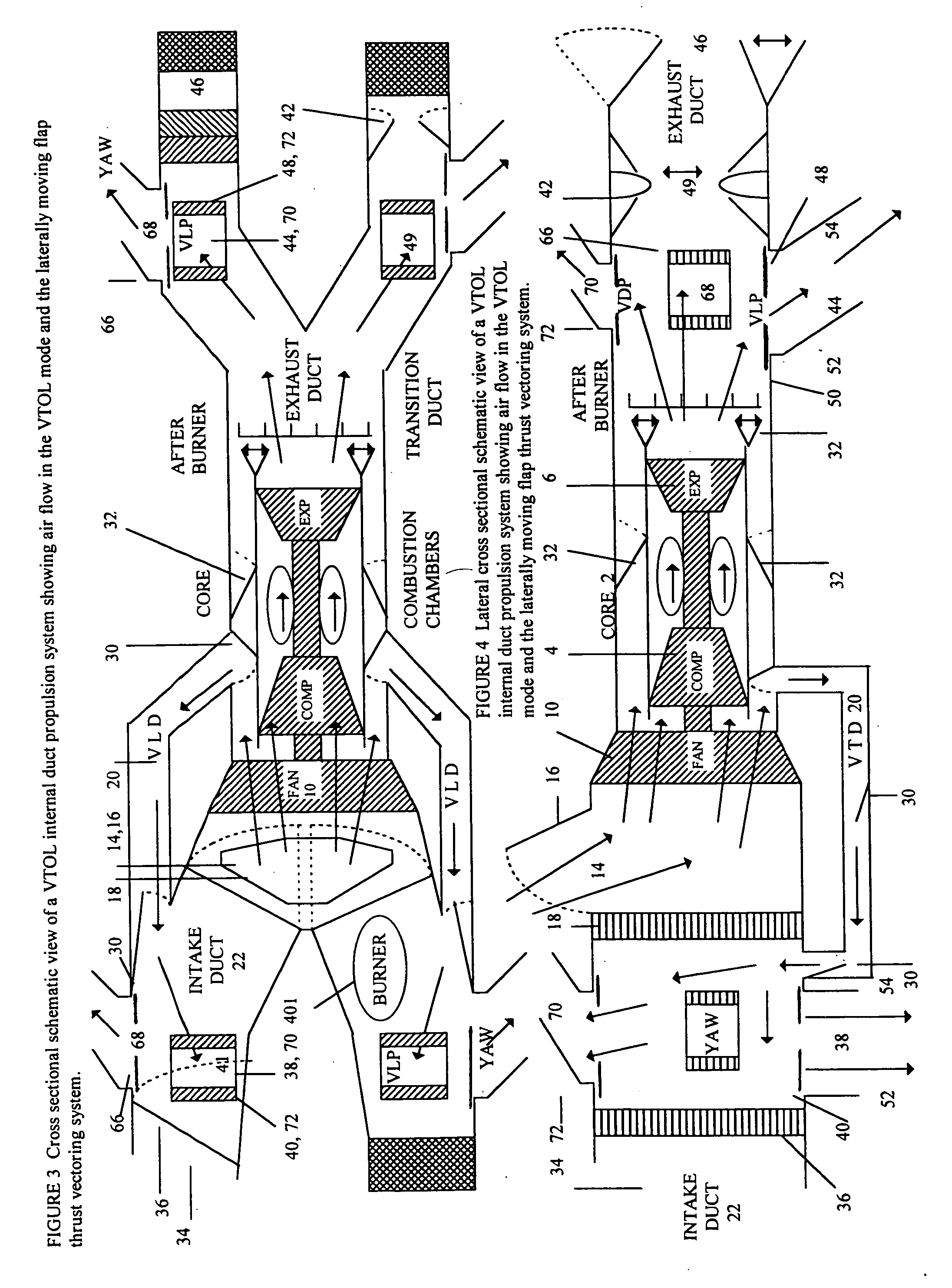
This invention describes vertical take off and landing (VTOL) propulsion systems that develop a forward flow of air through the air intake ducts during vertical takeoff and landing. This forward air flow in the air intake ducts is developed by a internal duct system, reversing the rotation of the fan, or altering the blade pitch of a variable pitch fan. This invention describes thrust vectoring systems for controlling aircraft direction, attitude, pitch, roll, yaw and rotation during VTOL and forward flight. Rotational nozzles are described to function in a independent but coordinated manner to control the aircraft during VTOL and forward flight. A thrust vectoring variable throat converging diverging exhaust duct nozzle is described. A movable radar absorbing or reflecting grid may be located in the air intake duct. The radar grid is movable to increase aircraft speed and engine efficiency when the aircraft is not operating in a radar threat situation. The described VTOL propulsion systems and thrust vectoring methods are applied to a aircraft with a internal combustion engine.
Owner:DICKAU JOHN EUGENE
Counter-rotational inertial control of rotorcraft
A rotorcraft with two counter-rotating rotors and method for inertially controlling the rotorcraft. The rotorcraft includes a hinged frame configured such that at least one inter-rotor angle of the two counter-rotating rotors is controlled by at least one actuated hinge of the hinged frame and the rotational axes of the two counter-rotating rotors are substantially collinear when the actuated hinge is in a fully open position. The sum of the magnitudes of torque applied to the two counter-rotating rotors is varied to control the lift of the rotorcraft. The difference of the magnitudes of torque applied to the two counter-rotating rotors is varied to control the yaw of the rotorcraft. The at least one inter-rotor angle is varied using the at least one actuated hinge to control the pitch and / or roll of the rotorcraft.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Blade control system
A wind turbine system for blade control which employs means for adjusting the pitch and yaw of the blades rotating about an axis and the resulting speed of the blades powering a wind turbine. The control system selectively resists movement of said blades to a different incline position based on a comparison of the measured rotational speed with a target speed value, the target speed value being determined based on an energy output level for said turbine. The control system includes at least one adjustable hydraulic actuator for movement of said blades to a different incline position.
Owner:DEERING KENNETH JAMES
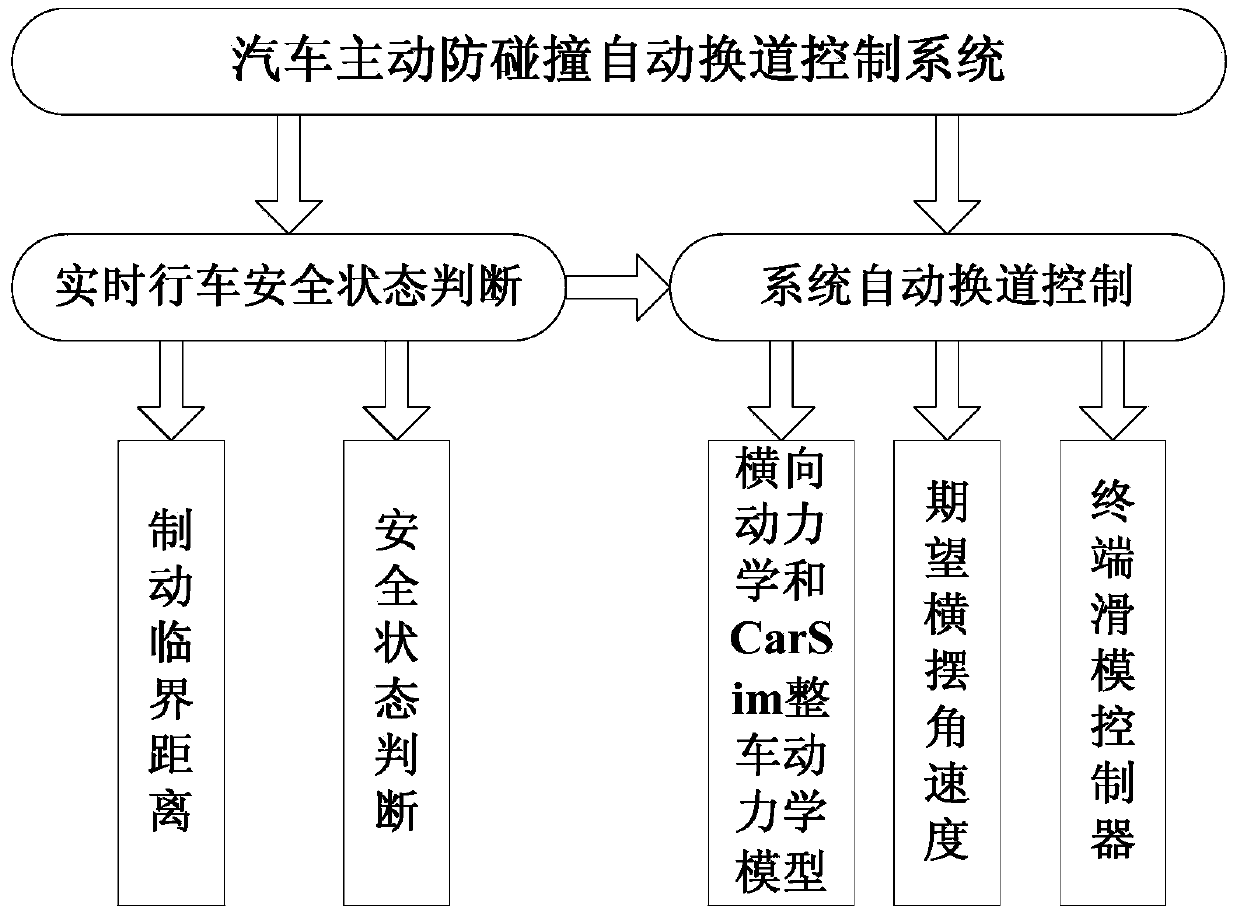
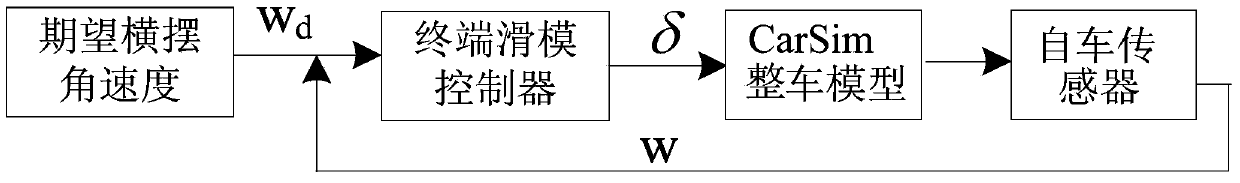
Automobile active anti-collision automatic lane change control system and operating method thereof
InactiveCN104176054AProtection securitySmooth changeExternal condition input parametersAutomatic control systemsAutomatic controlControl system
The invention discloses an automobile active anti-collision automatic lane change control system and an operating method thereof. The system comprises a real-time driving safety state judging module and an automatic lane change control module which are connected with each other; the real-time driving safety state judging module comprises a critical braking distance calculation module and a safety state judging module unit; the automatic lane change control module comprises a lateral dynamics and CarSim vehicle dynamics model establishing module, an expected yaw velocity acquiring module and a design terminal sliding formwork lane change controller module. The method includes two steps of driving safety state judgment and automatic lane change control. The system and method adopt pedestrians in front as the study objects of active anti-collision, whether driving is in the dangerous state or not can be judged by calculating the critical braking distance and corresponded automatic control is performed, the smoothness and operating stability during lane change are guaranteed, and safety of the pedestrians in front is guaranteed.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
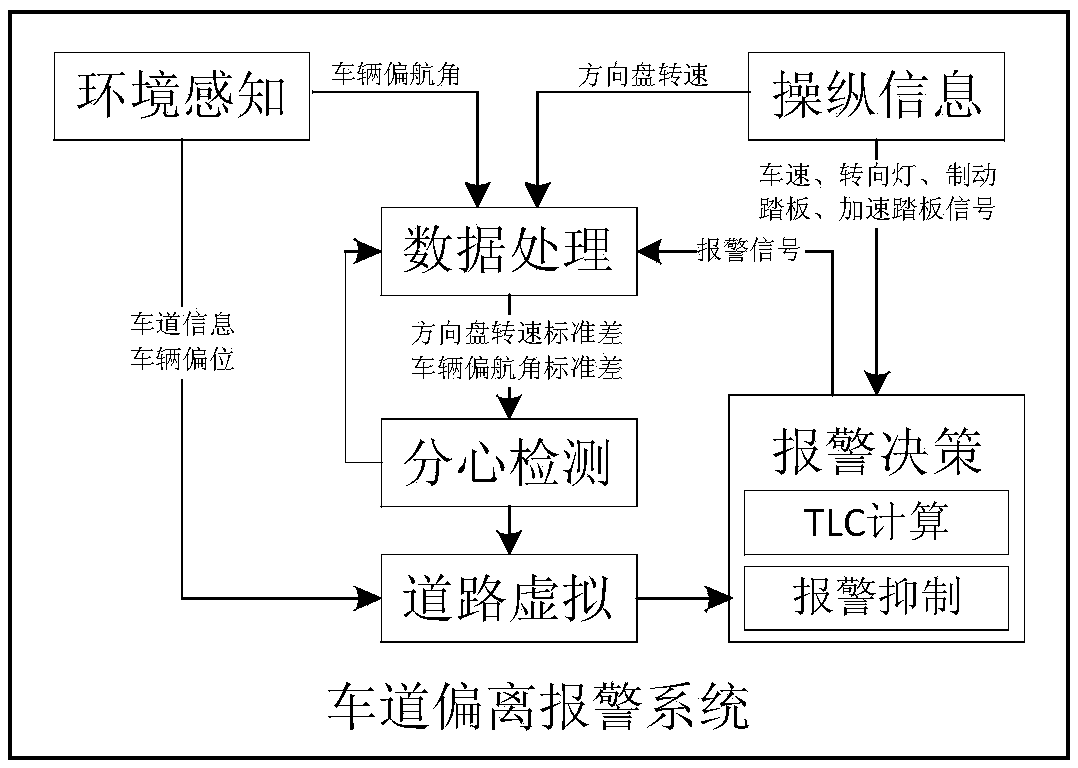
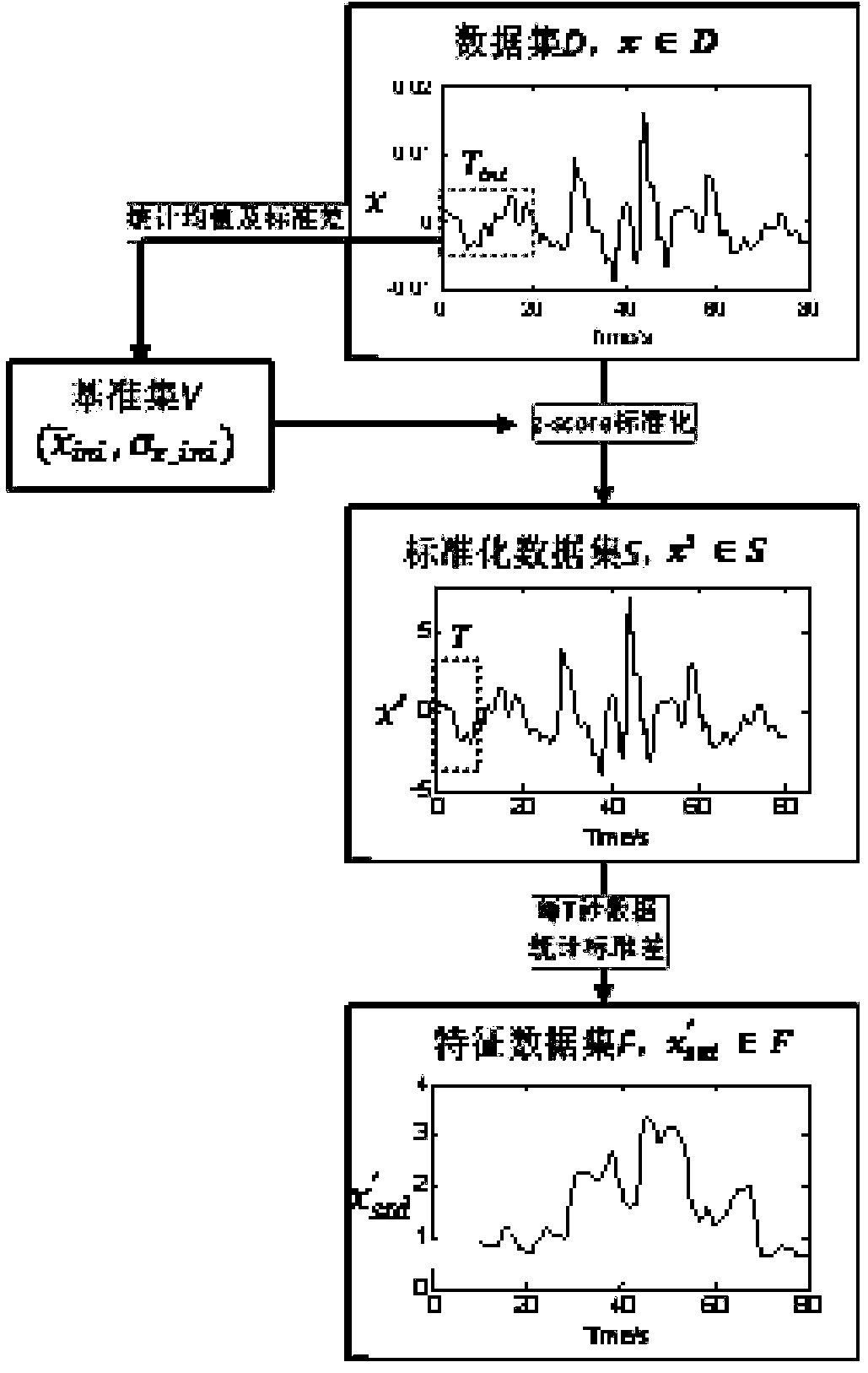
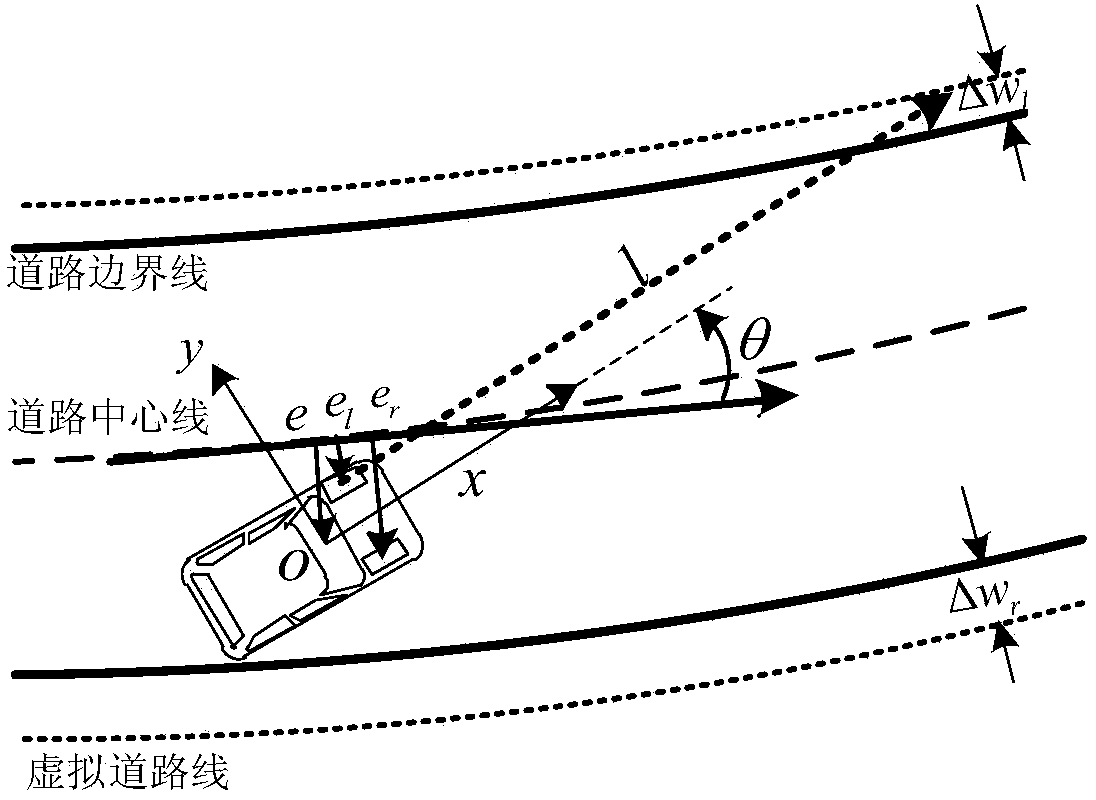
Lane departure alarming method and system with driving distraction state considered
InactiveCN103661375AAdjust system parameters in real timeIncrease driving distraction detection functionExternal condition input parametersSignalling/lighting devicesInformation controlSteering wheel
Provided is a lane departure alarming method with a driving distraction state considered. The method comprises the steps that whether a driver is in a distracted driving state at present is judged according to the traveling track of an automobile and the operation information of the driver; distinguished alarming strategies are provided according to the detecting result of distracted driving, and when driving distraction is not detected, the time for lane departure alarming is delayed. A lane departure alarming system for achieving the method comprises an environment sensing unit, an information control unit, a data processing unit, a distraction detecting unit, a road virtual unit and an alarm decision making unit. The yaw angle of the automobile and the rotating speed signal of a steering wheel are acquired from the environment sensing unit and the information control unit, corresponding standard deviation statistical data can be obtained after data processing, and driving distraction detection is conducted. The alarm decision making unit makes alarm decisions, and judges whether the current alarm signal is restrained or not. The lane departure alarming method and system can provide the distraction driver with timely lane departure alarm, and meanwhile avoid frequent false alarm to the focused driver so that disturbing to the driver can be reduced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
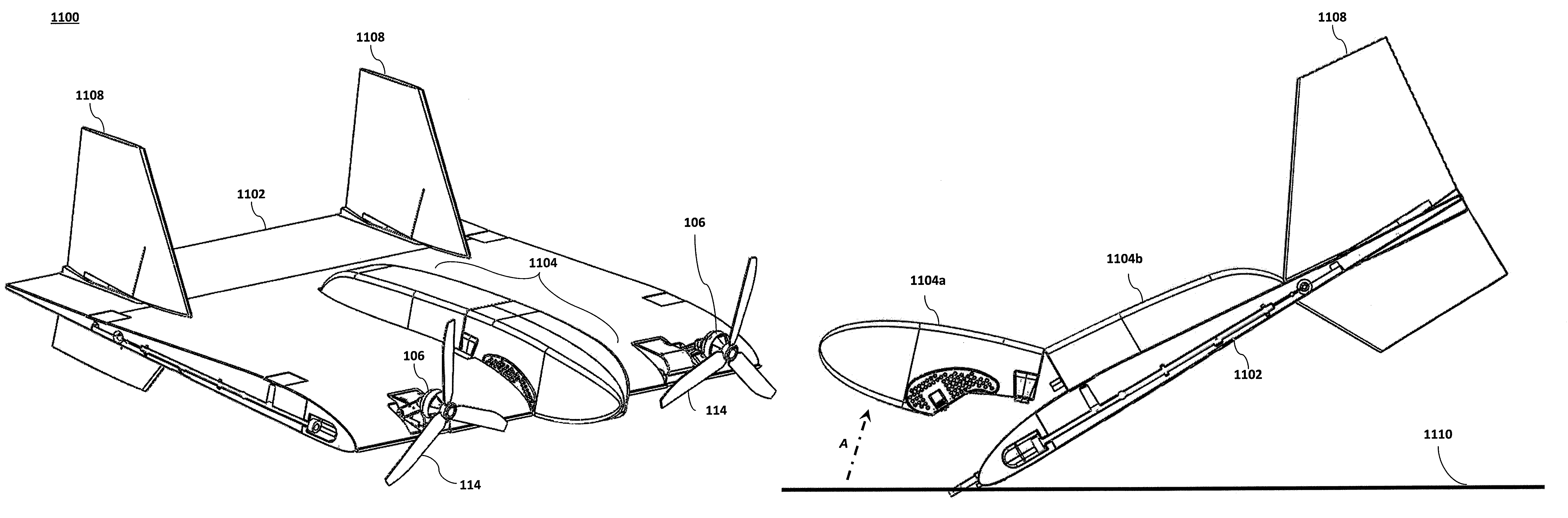
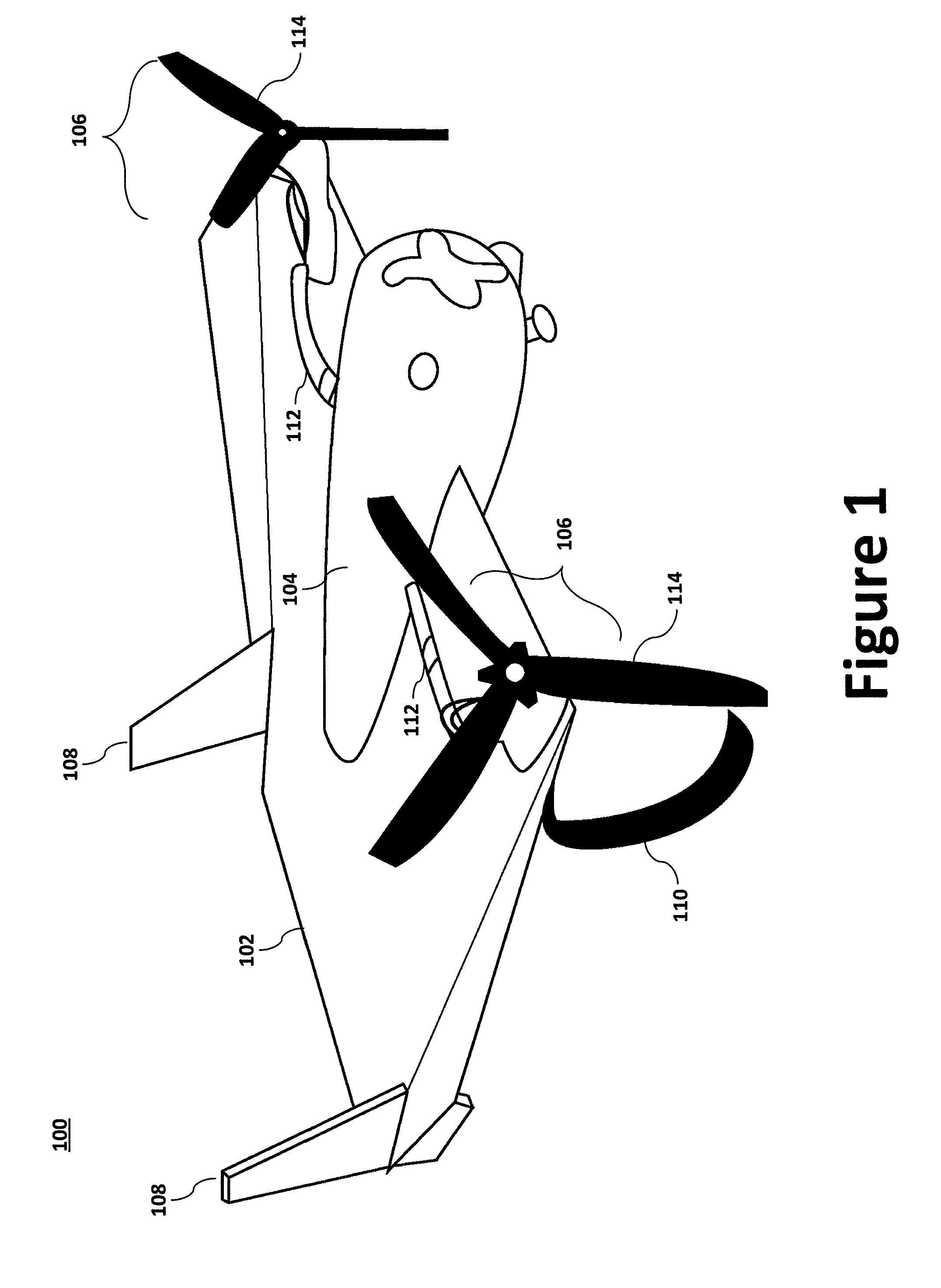
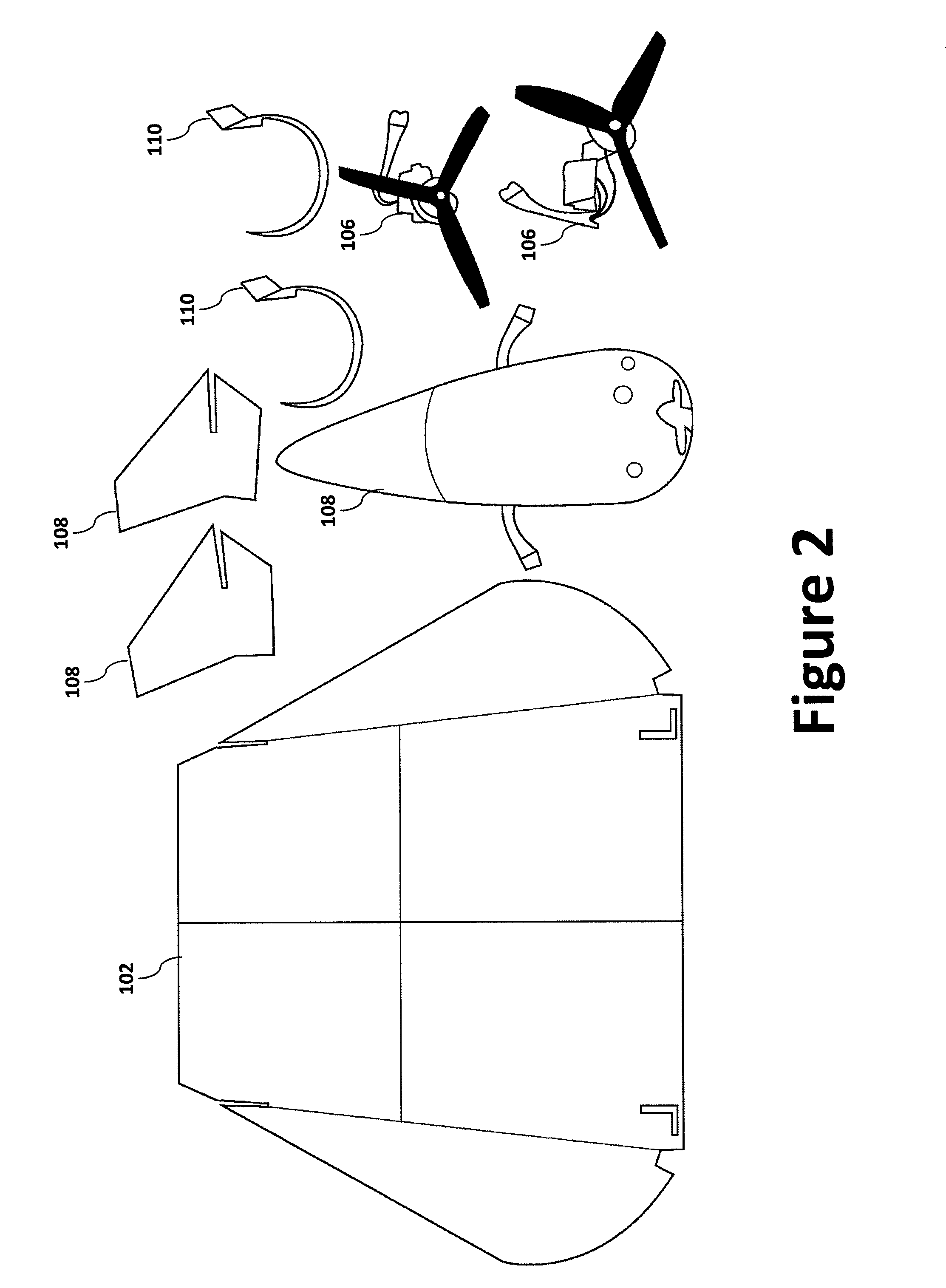
Modular miniature unmanned aircraft with vectored-thrust control
An aircraft for unmanned aviation is described. The aircraft includes an airframe, a pair of fins attached to a rear portion of the airframe, a pair of dihedral braces attached to a bottom portion of the airframe, a first thrust-vectoring (“T / V”) module and a second T / V module, and an electronics module. The electronics module provides commands to the two T / V modules. The two T / V modules are configured to provide lateral and longitudinal control to the aircraft by directly controlling a thrust vector for each of the pitch, the roll, and the yaw of the aircraft. The use of directly articulated electrical motors as T / V modules enables the aircraft to execute tight-radius turns over a wide range of airspeeds.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Steer-by-wire system and stability control method thereof
ActiveCN107512305AExact gear ratioRealize variable transmission ratio controlSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlSteering wheelFeedback controller
The invention provides a steer-by-wire system and a stability control method thereof. The steer-by-wire system comprises a steering wheel module, a front wheel steering module and an ECU electronic control unit, wherein the ECU electronic control unit comprises a variable transmission ratio controller, a fuzzy self-adaptive PID controller and a full state feedback controller. The stability control method is as follows: the variable transmission ratio controller calculates an ideal transmission ratio at the moment according to a steering wheel rotation angle signal and a vehicle speed signal, to obtain an ideal front wheel rotation angle at the moment; the full state feedback controller of an automobile calculates a compensation rotation angle of front wheels according to a yaw rate signal and a lateral acceleration signal of the automobile, to realize the outer ring control of the steer-by-wire system; and finally the fuzzy self-adaptive PID controller is designed, to realize the inner ring control of the steer-by-wire system. The operating stability of the automobile is effectively improved through the coordinated control of inner and outer rings of the steer-by-wire system.
Owner:NANJING AUTOMOBILE GROUP CORP
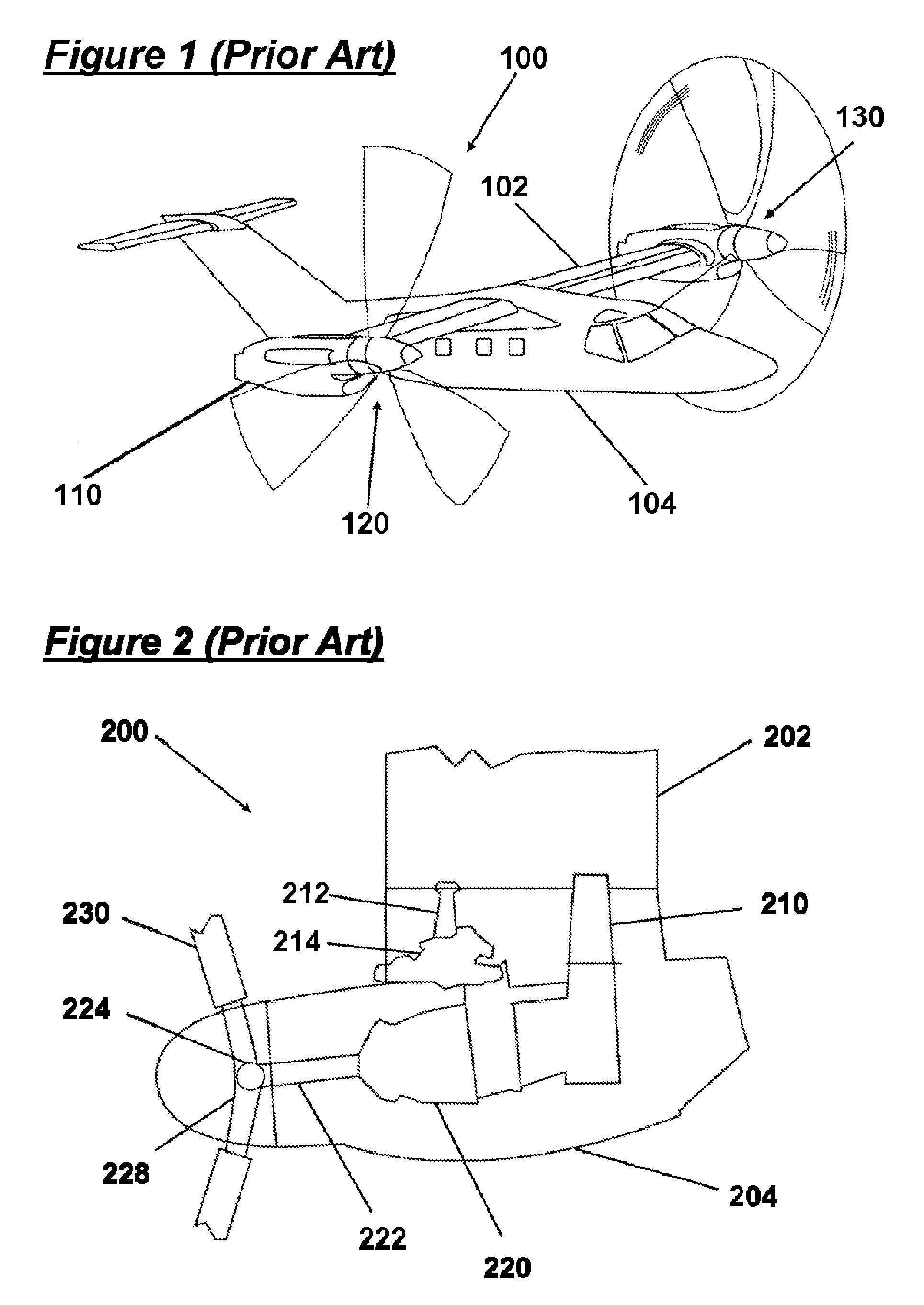
Counter rotating ducted fan flying vehicle
A flying vehicle having a pair of counter rotating propeller blades which provide lift for the vehicle when the vehicle is in a flight mode of operation. The counter rotating blades have in flight adjustable pitch and are connected to a control and steering system in the cockpit of the vehicle. A gas turbine engine located in the aft section of the vehicle is connected through a drive shaft and transmission to the counter rotating propeller blades When the vehicle transitions to the flight mode, the user has aircraft controls available in the cockpit to make the transitions from a driver to a pilot in a short time period. Yaw pedals located on the floor board of the cockpit as well as a pitch control handle and the steering wheel allow the user to steer and control the altitude of the vehicle when the vehicle is in the flight mode.
Owner:ROADABLE AIRCRAFT INTL
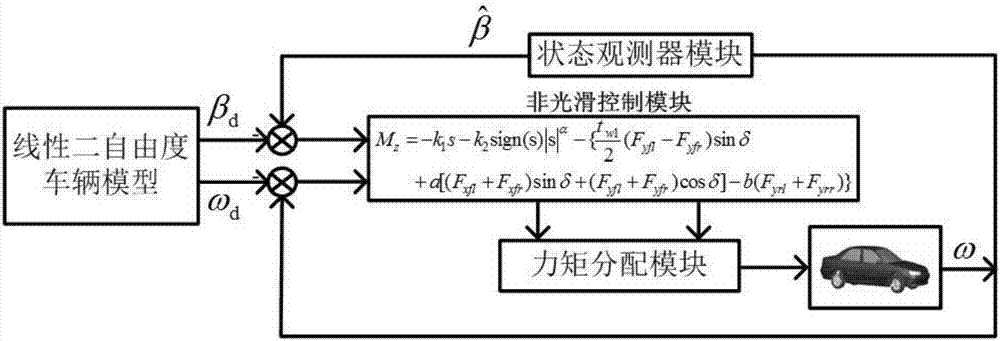
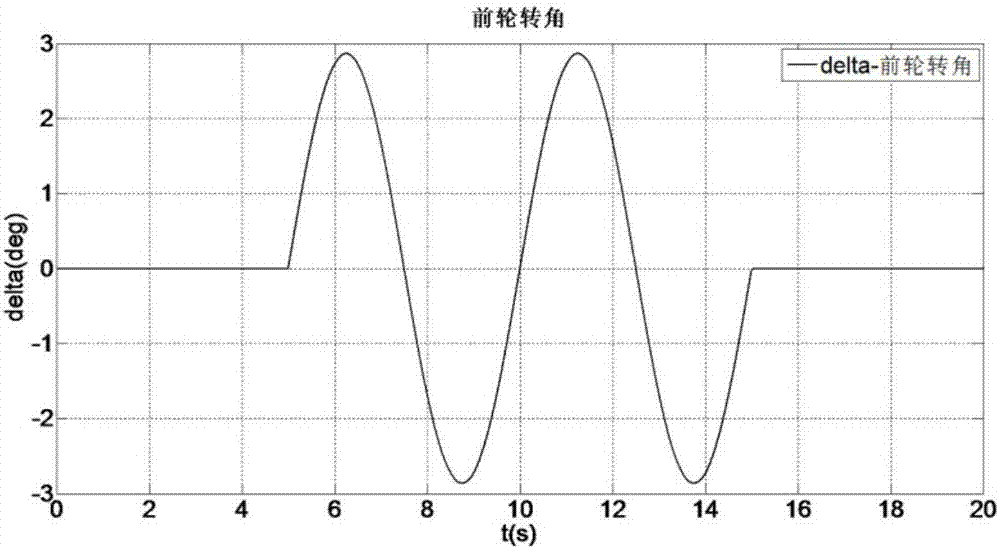
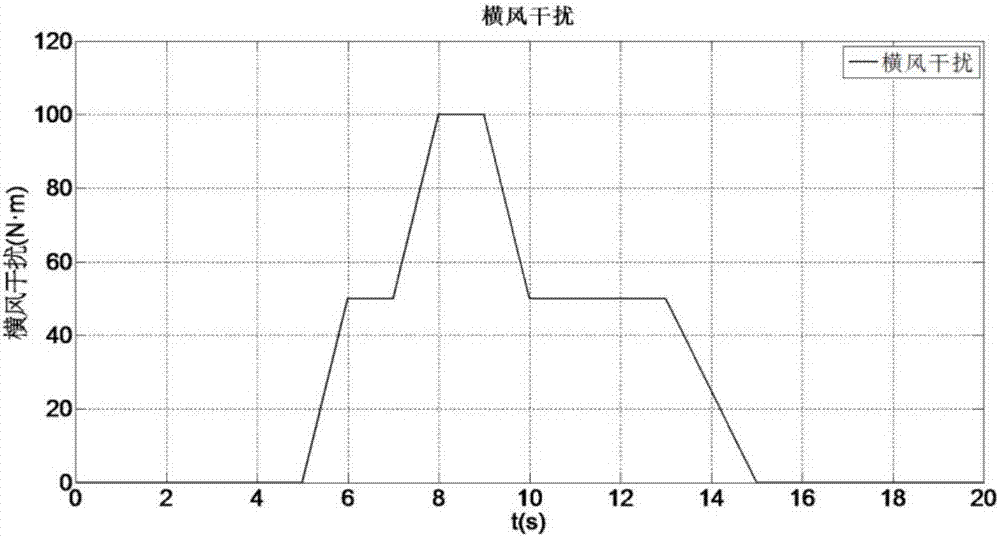
Non-smooth technique-based direct yaw moment control method of electric vehicles
InactiveCN107139775ALow costFast convergenceGeometric CADSpeed controllerVehicle dynamicsState observer
The invention discloses a non-smooth technique-based direct yaw moment control method of electric vehicles. By means of the method, the vehicle stability under extreme driving circumstances can be increased under the conditions of external disturbances and system uncertainty. The method comprises the following main steps: (1) building a linear two-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamic model and a seven-degree-of-freedom whole vehicle dynamic model; 2, calculating the ideal yaw velocity and ideal side slip angle of the vehicles through the linear two-degree-of-freedom model, and constructing a state observer to observe the actual side slip angle of the vehicles; 3, designing a non-smooth control module controlled by yaw moment on the basis of non-smooth control technique; and 4, distributing the yaw moment by using a moment distributing module, thereby realizing the stable control of the vehicles. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that (1) the system has fast convergence performance and better disturbance-resistant performance; and (2) a chattering phenomenon is effectively avoided while good robust performance is obtained at the same time.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
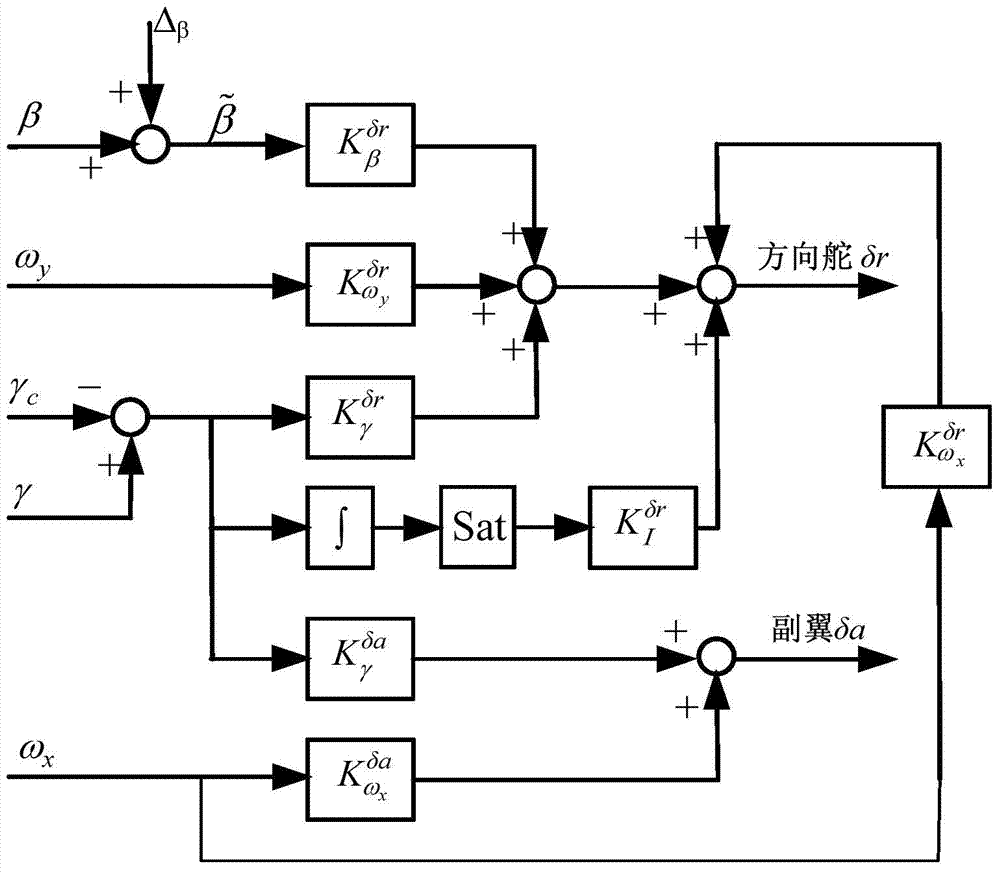
Hypersonic speed aircraft control method capable of suppressing constant deviation influence of sideslip angle signal
ActiveCN103587681ASteady state error zeroHigh control precisionActuated automaticallyAdaptive controlEngineeringOmega
The invention discloses a hypersonic speed aircraft control method capable of suppressing the constant deviation influence of a sideslip angle signal. The method comprises the following steps: (1) measuring the yaw angle speed omega y and the roll angle speed omega x of an aircraft in real time by utilizing an inertial measurement unit, and acquiring a roll angle gamma and a sideslip angle by utilizing the inertial measurement unit and a sensor; (2) calculating a deviation signal of the gamma and a roll angle instruction gamma c, integrating a deviation signal Delta gamma, and performing the amplitude limiting on the deviation signal, so as to obtain a roll angle integrated signal; (3) amplifying the roll angle integrated signal and the omega y, generating a control instruction, and feeding the control instruction back to a rudder of the aircraft; amplifying the omega x, generating a control instruction I and feeding the control instruction I back to an aileron of the aircraft; amplifying the Delta gamma, generating a control instruction II and feeding the control instruction II back to the rudder / aileron of the aircraft; (4) adding all the control instructions which are fed back to the rudder to serve as a general control instruction of the rudder, and controlling the rudder to track the general control instruction through a servo system on the aircraft; adding all the control instructions I fed back to the aileron to serve as a general control instruction I of the aileron, and controlling the aileron to track the general control instruction through the servo system on the aircraft.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF LAUNCH VEHICLE TECH
Stability integrated control method for intelligent wheel and electric driven automobile
ActiveCN106985813AIdeal yaw moment responseAchieve independent driveGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationDriver/operatorSteering wheel
The invention discloses a stability integrated control method for an intelligent wheel and electric driven automobile. According to the stability integrated control method, a cooperative control method and a generalized internal model control method are utilized to design and develop the automobile stability control method based on the yaw velocity and the mass center side slip angle; and a drive signal, a brake signal and steering wheel angle driving demand which are provided by a driver and measured or estimated automobile state information serve as input, and through a stability integrated control algorithm and cooperative control over three stability intervention modes, ideal yaw moment response is obtained, control over the automobile is finally converted into independent control over wheels, all the wheels can achieve independent drive, brake and steering, and system robustness of the automobile is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
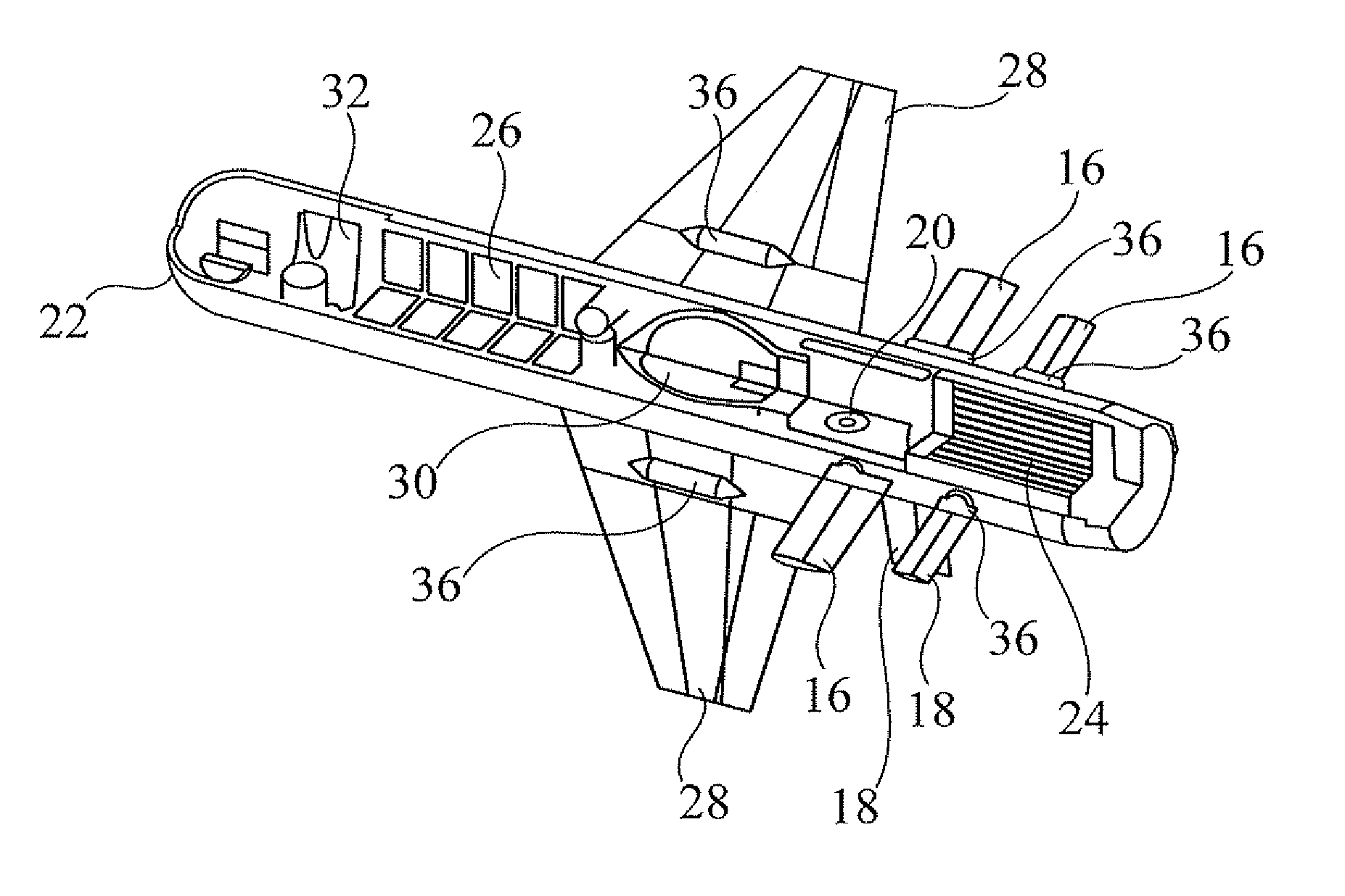
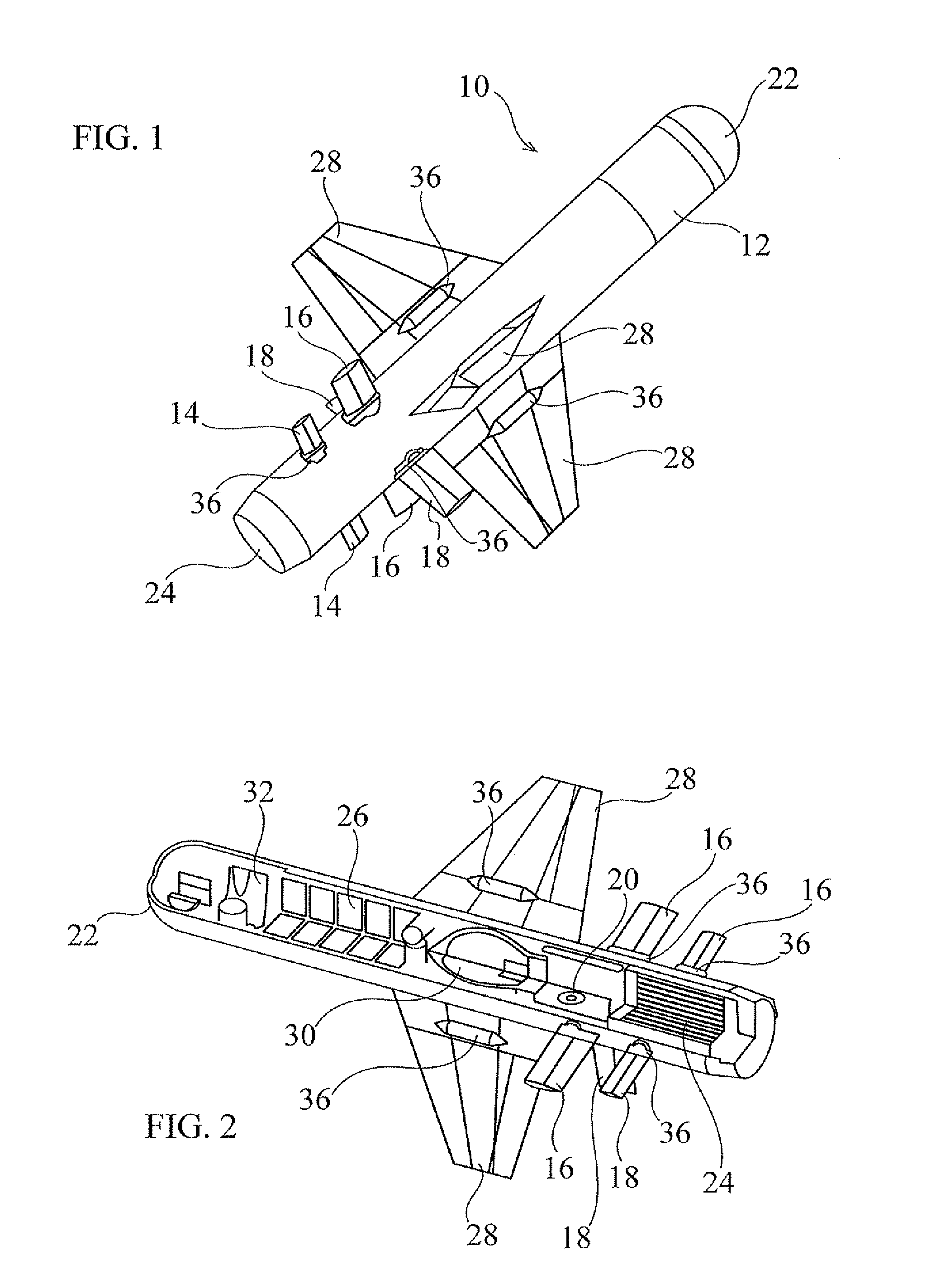
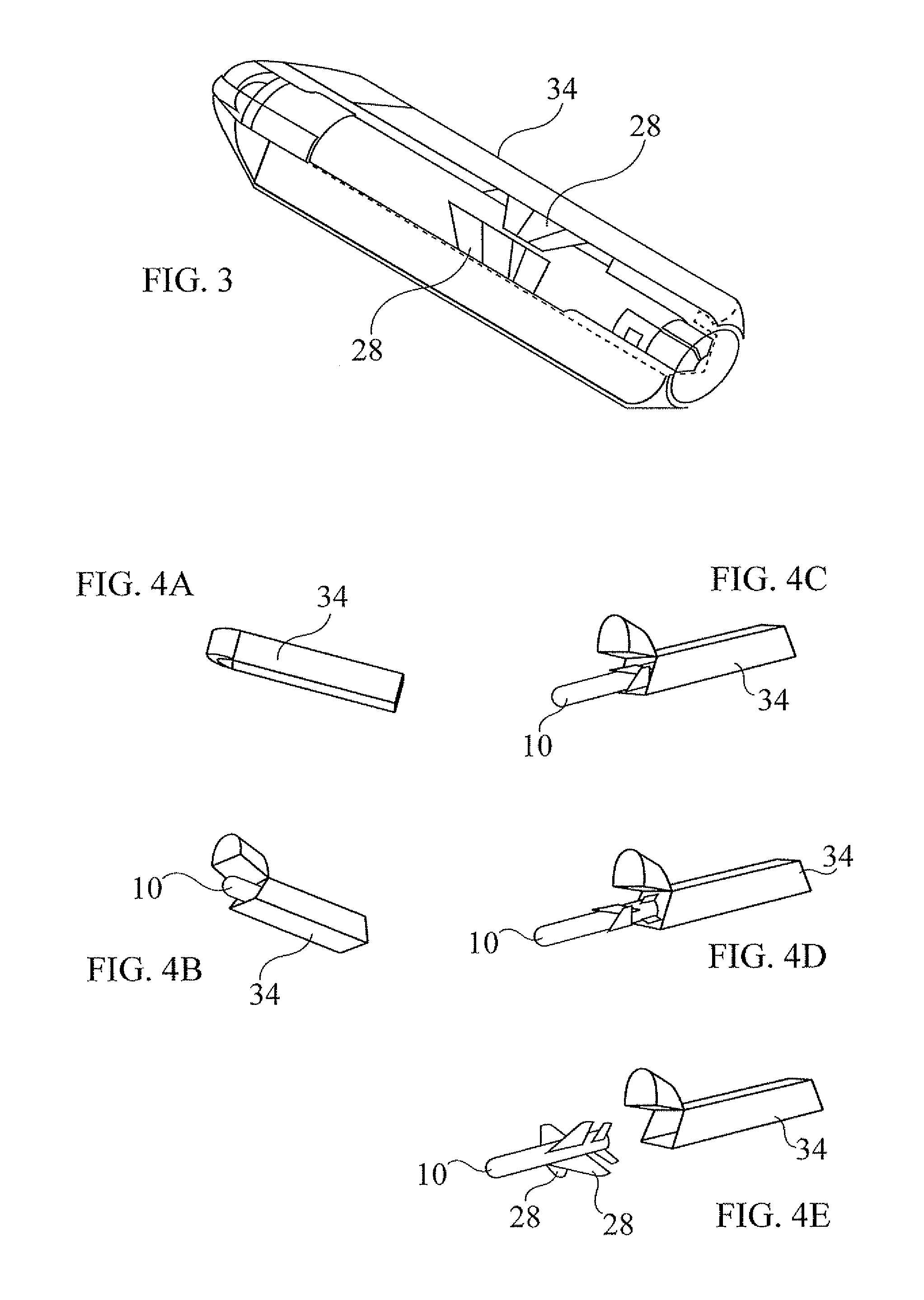
Miniature missile
A miniature lightweight high-maneuverability missile (10) has a missile body (12) with three sets of at least two aerodynamic control surfaces (14, 16, 18) for independent control of roll, pitch and yaw of the missile. Each set of control surfaces (14, 16, 18) is independently controlled by a corresponding actuator (20) deployed within the missile body (12). Other preferred features include selection of an elevation angle of incidence at a target, and switching between explosive and kinetic modes of operation.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
Precision thrust/sun tracking attitude control system for gimbaled thruster
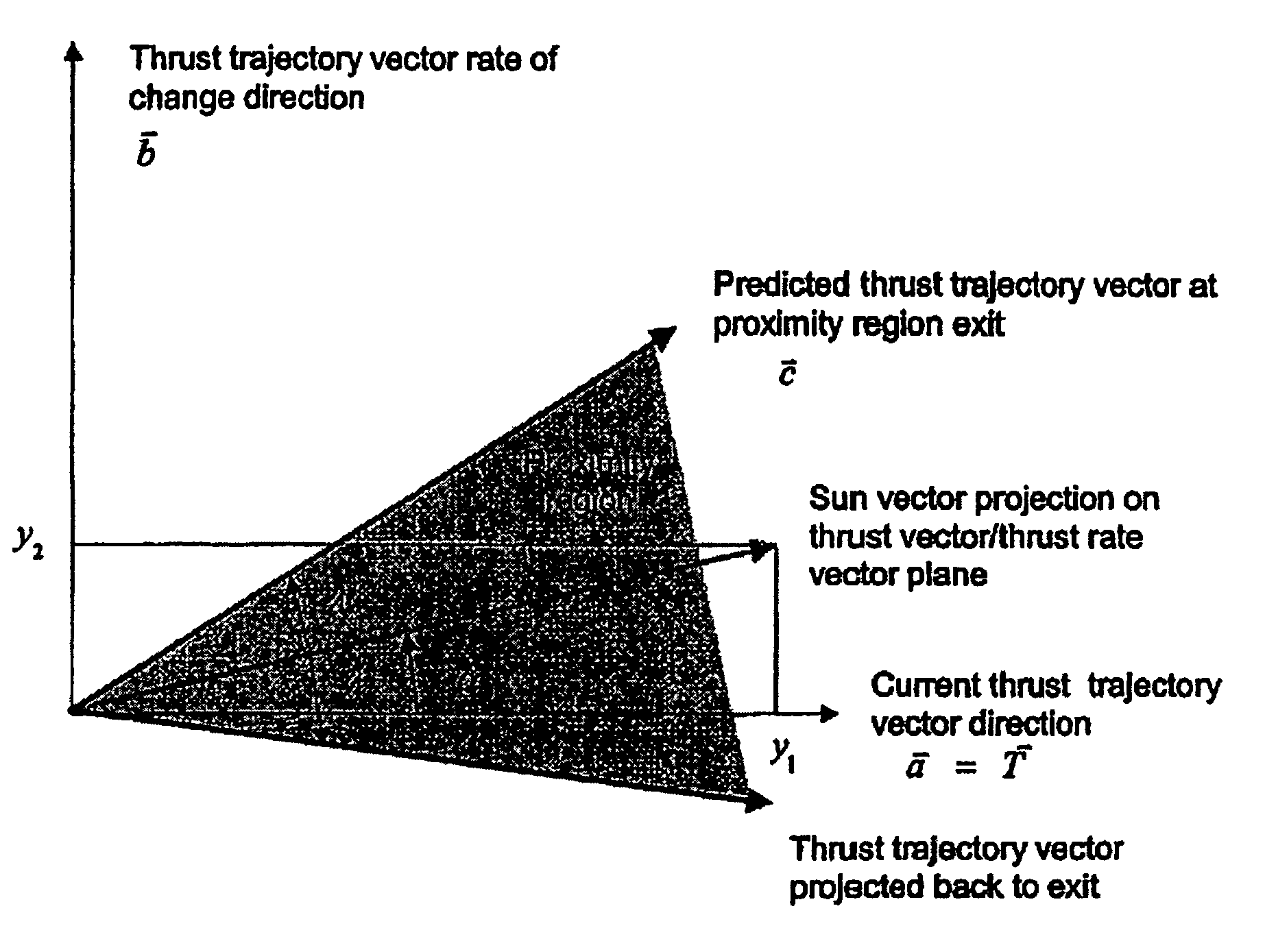
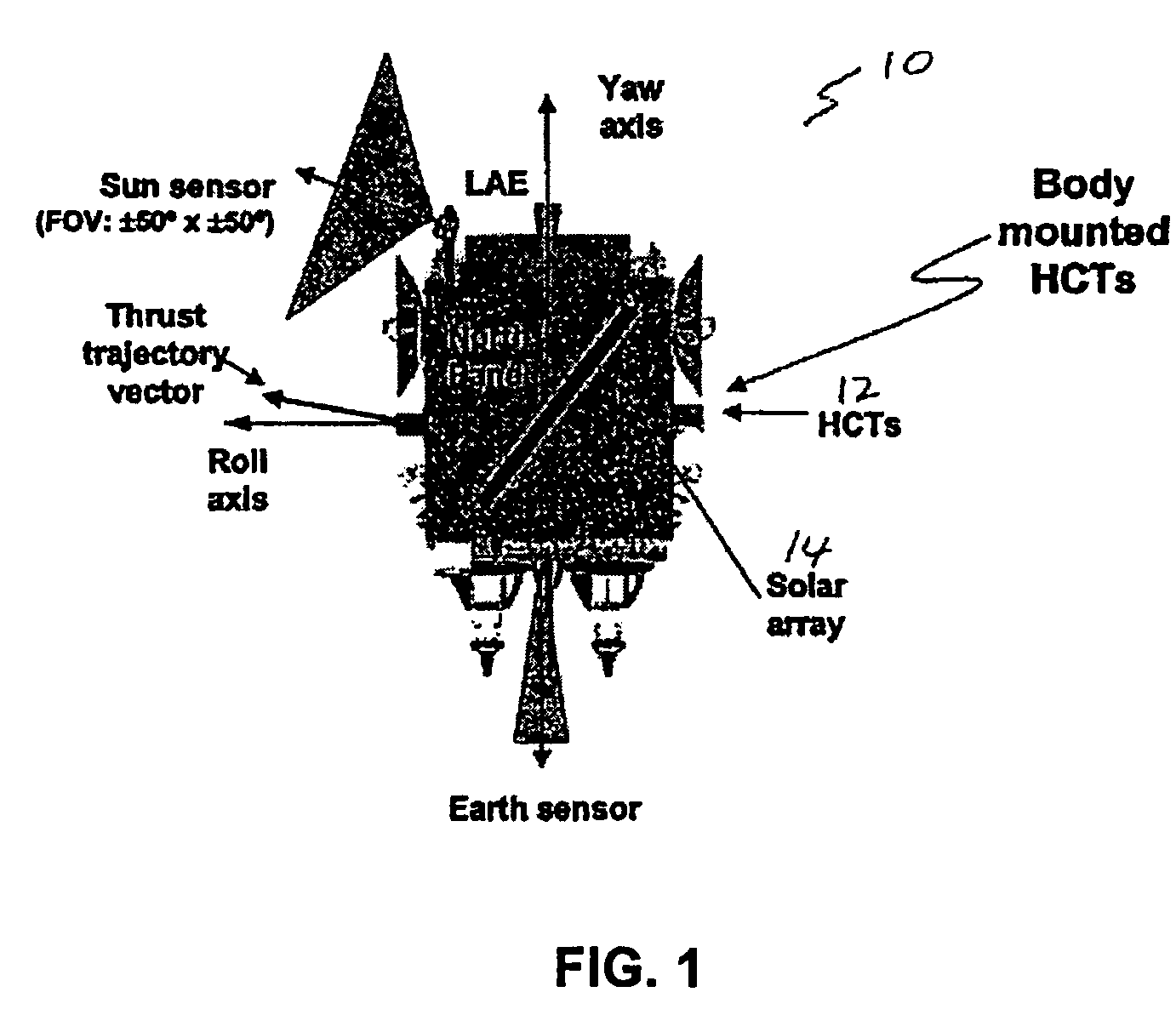
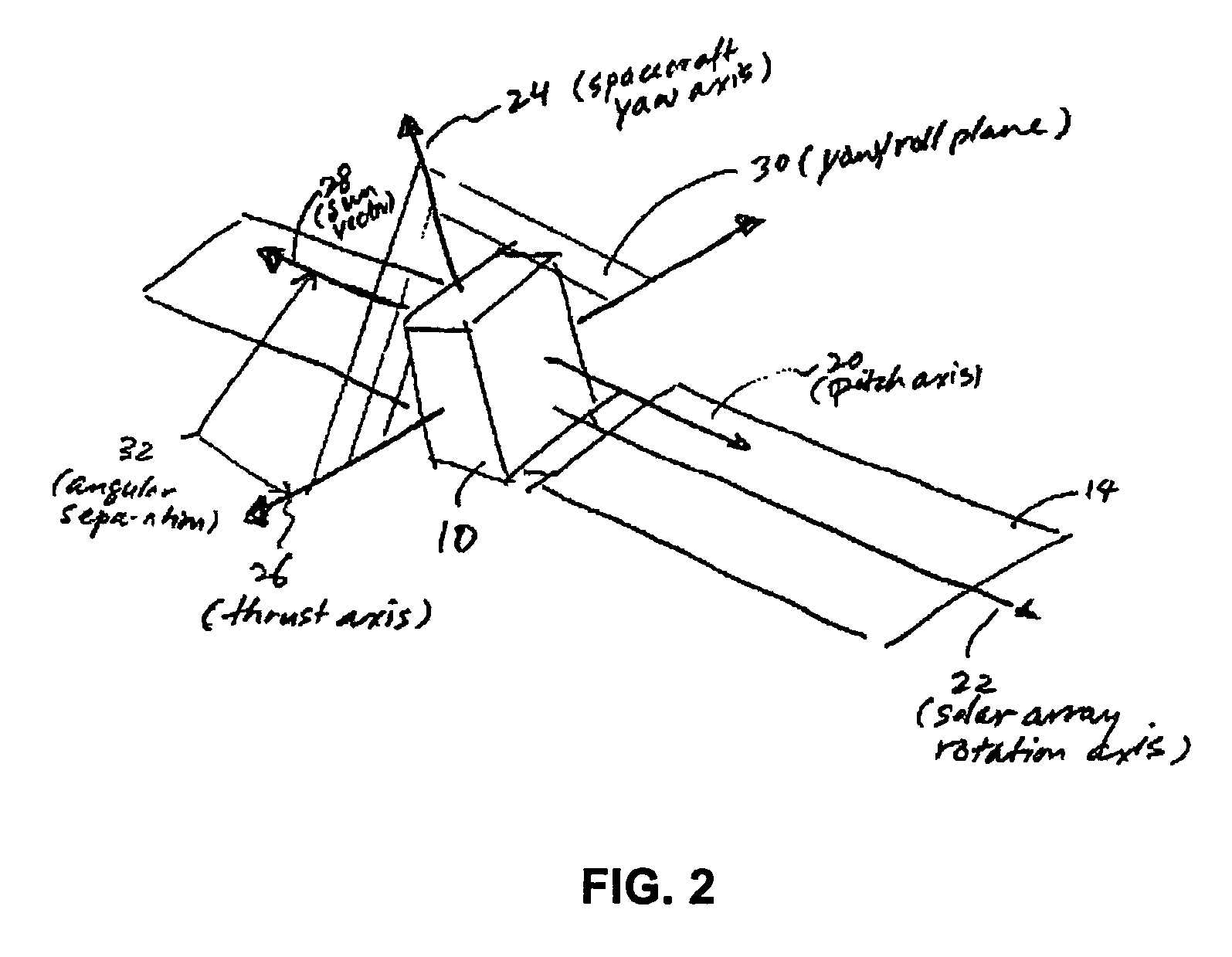
InactiveUS7464898B1Improve performanceCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemOperation mode
A system for providing precision thrust and sun tracking attitude control is provided. The system determines a proximity region and alternately engages either an ideal operational mode or a predictive operational mode based on whether a thrust trajectory vector is in the proximity region in order to provide attitude control. The proximity region is determined based on an angle between the thrust trajectory vector and a sun vector. For example, the angle is about 20-30 degrees. The system engages the predictive operational mode when the thrust trajectory vector enters the proximity region. When in the predictive operational mode, the system periodically re-calculates the thrust trajectory vector and determines where the thrust trajectory vector will exit the proximity region. Based on the determination with respect to where the thrust trajectory vector will exit the proximity region, the system provides appropriate attitude control adjustment with respect to gimbaled thrusters and solar arrays so as to reduce sun-pointing errors and keep the sun in a predetermined yaw / roll plane. The system can be used in a spacecraft including a satellite.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
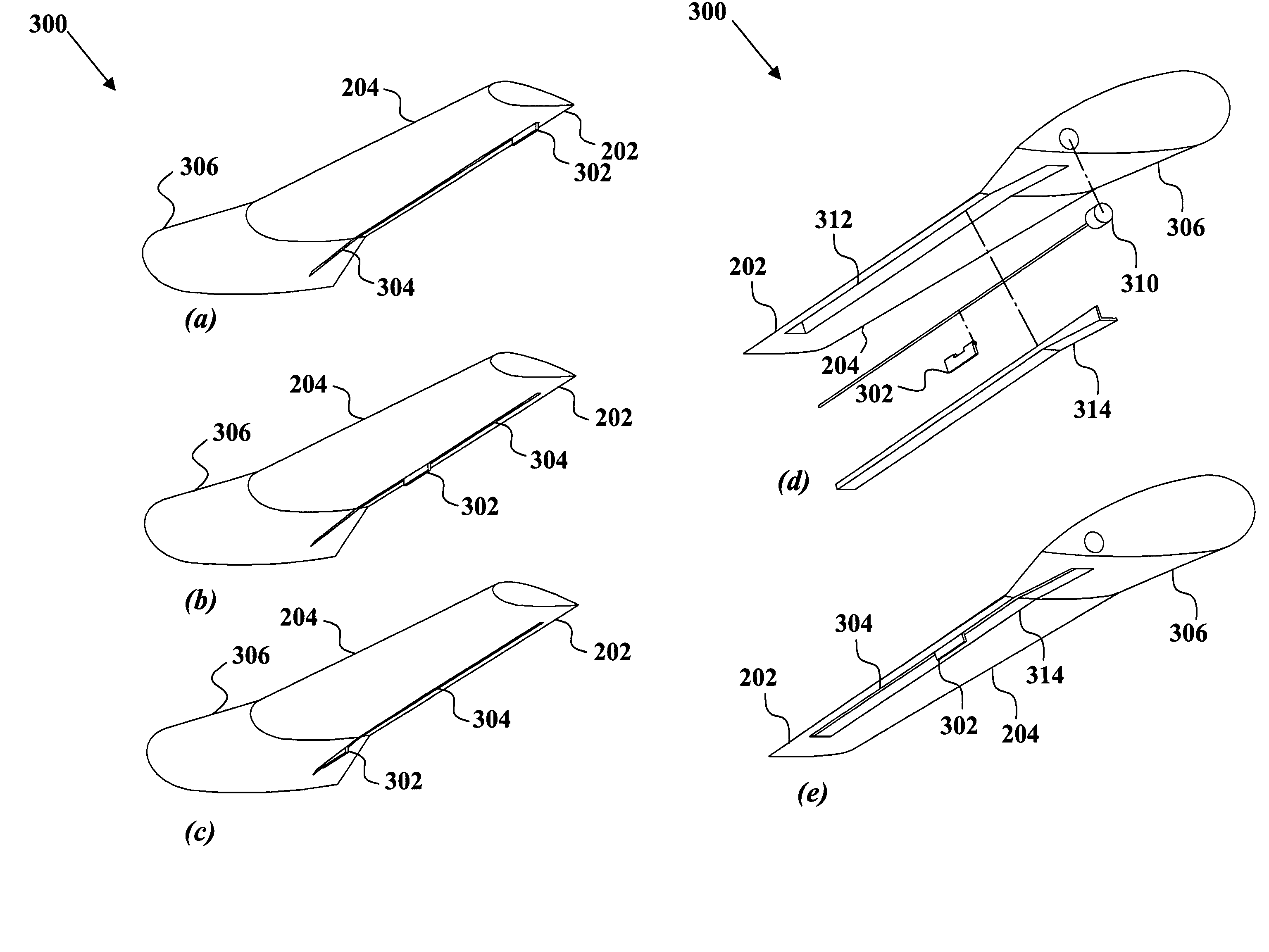
Translating active Gurney flap to alleviate aircraft wake vortex hazard
InactiveUS7740206B2Quick changeMinimizing wake vortex hazardsInfluencers by generating vorticesWing adjustmentsActuatorTrailing edge
A wake vortex alleviator is provided. The wake vortex alleviator produces rapid variations in the position of vortices emanating from aerodynamic surfaces by using an active flap that moves span-wise back and forth along the outboard section of the surface. Rapidly moving the flap back and forth in a slot at an appropriate frequency will cause the vortex to oscillate, resulting in interaction between other vortices and subsequent destruction much earlier than it would occur naturally. The slot is positioned near the aerodynamic surface trailing edge and generally transverse to a chord line of the aerodynamic surface. The flap can be moved using a variety of actuators to position, translate and stow the flap. The oscillation frequency and position are guided by information feedback according variations in lift in the aerodynamic surface, such as wind gusts. The flaps can control yaw, roll and pitch of the aerodynamic surface.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Flight control method of QUAV (Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)
InactiveCN106444826AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove operational efficiencyPosition/course control in three dimensionsControl mannerAttitude control
The invention provides a flight control method of a QUAV. The method comprises the following steps that S10) a dynamical model and a dynamic equation of the QUAV are established; and S20) a compound control based control manner is designed to control four independent control channels converted from the dynamic equation in the step S10), control manners for the four channels include height PID, tumbling ADRC, pitching ADRC and yaw EACS-PID respectively, and conversion of control quantities is controlled to adjust the rotating speed of the four rotors and further achieve attitude control. Via the method of the invention, the QUAV adapts to the external environment change, yaw EACS-PID can realize adaptive adjustment of control parameters, tumbling ADRC and pitching ADRC can resist to interference more actively, height PID can be used to maintain high anti-interference capability and robustness and avoid the process from being too complex, the processor load of the QUAV is reduced, and the operation efficiency of hardware is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Adaptive vehicle control system with driving style recognition based on vehicle left/right turns
InactiveUS20100023216A1Steering initiationsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorControl system
An adaptive vehicle control system that classifies a driver's driving style based on left / right-turn maneuvers. A process determines if the vehicle has started a turn if the yaw rate is greater than a first yaw rate threshold, and determines a vehicle heading angle based on the yaw rate and a sampling time if the vehicle has started a turn. The process then determines whether the vehicle maneuver has been completed by determining if the yaw rate is less than a second yaw rate threshold. The process then determines that the completed maneuver was a left / right-turn maneuver if the yaw rate is less than a third yaw rate threshold over the sampling time and the vehicle heading angle is within a heading angle range for a time period less than a predetermined time threshold. In one non-limiting embodiment, the heading angle range is between 75° and 105°.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Path planning obstacle avoidance control method for autonomous underwater vehicle in large-scale continuous obstacle environment
ActiveCN112241176AFast convergenceReal-time obstacle avoidance capabilityAltitude or depth controlComputer control systemModular design
The invention relates to a path planning obstacle avoidance control method for an autonomous underwater vehicle in a large-scale continuous obstacle environment. The invention relates to the technicalfield of underwater robot path obstacle avoidance planning, and the method comprises the steps: building a large-scale continuous obstacle simulation training environment, building the state and action of a deep reinforcement learning neural network through employing obstacle avoidance sensor information as the input and the navigation speed and yaw angular speed as the output, for a multi-targetstructure of a motion planning obstacle avoidance control process, performing modular design on a reward function, and in order to avoid system instability caused by sparse rewards, setting continuous rewards are set in combination with an artificial potential field method. According to the method, obstacle avoidance training is carried out on the autonomous underwater vehicle by utilizing an improved depth deterministic strategy gradient algorithm, and an obstacle avoidance strategy obtained by training is written into a robot lower computer control system; when the autonomous underwater vehicle runs in an underwater canyon, obstacle avoidance is carried out by using an obstacle avoidance strategy learned by training, and the autonomous underwater vehicle safely reaches a target area.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Wind-driven power generator yaw control method and module and control device based on control module
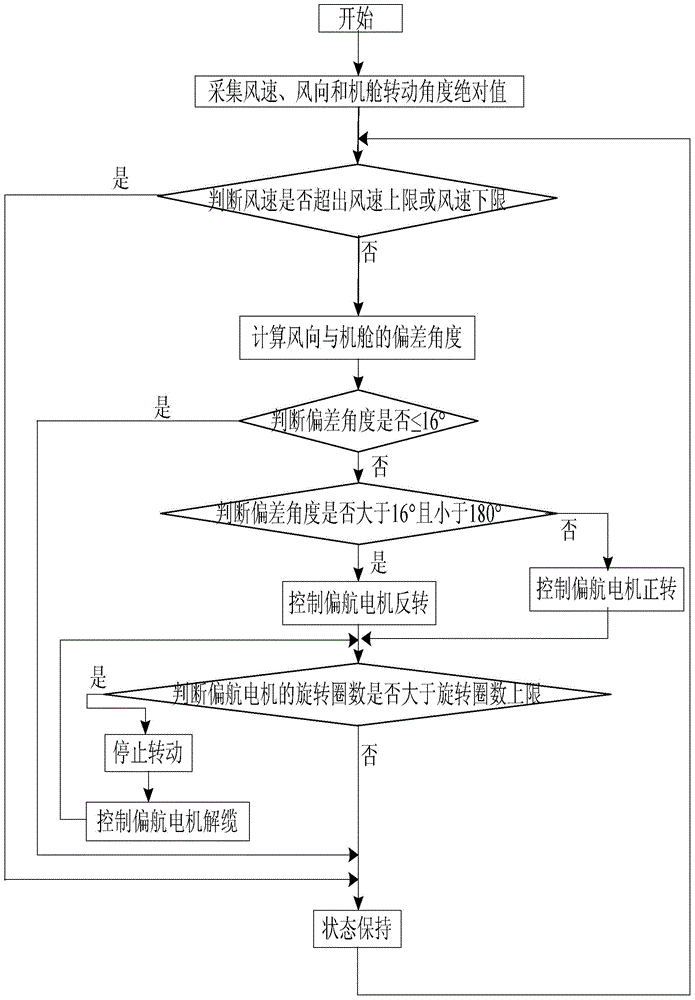
ActiveCN104912733AExtend your lifeGuaranteed utilizationWind motor controlMachines/enginesNacelleElectric machine
The invention discloses a wind-driven power generator yaw control method and module and a control device based on the control module, relates to the wind-driven power generator yaw control technology, and aims to solve the problem that the instantaneous wind direction interferes yaw control to allow a yaw unit to be started frequently, and unstable current output, difficulty in control and cabin service life lowering are caused. If wind speed exceeds a set value range or the deviation angle of the wind direction and a cabin is not larger than 16 degrees, the yaw unit keeps the state; if the deviation angle ranges between 16 degrees and 180 degrees, a yaw motor rotates reversely, or else the yaw motor rotates forwardly, and wind-driven power generator yaw control is achieved. The wind-driven power generator yaw control module is embedded into the control device based on the module. The yaw unit has a delay starting function and adopts error control, interference caused by the instantaneous wind speed is prevented, wind energy utilization rate is guaranteed, the situations of frequent starting and control difficulty caused by zero alignment are avoided, and cabin service life can be prolonged. The control method and module and the control device are applicable to wind-driven power generator yaw control.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Small-size aircraft system based on cradle head
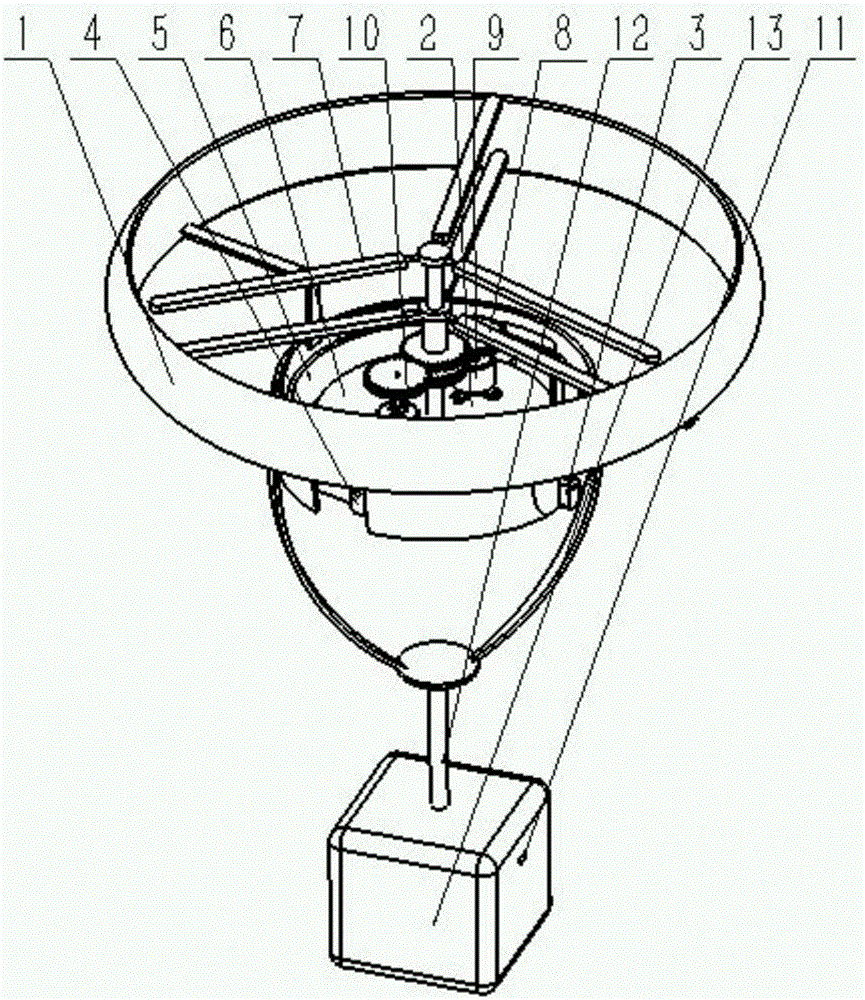
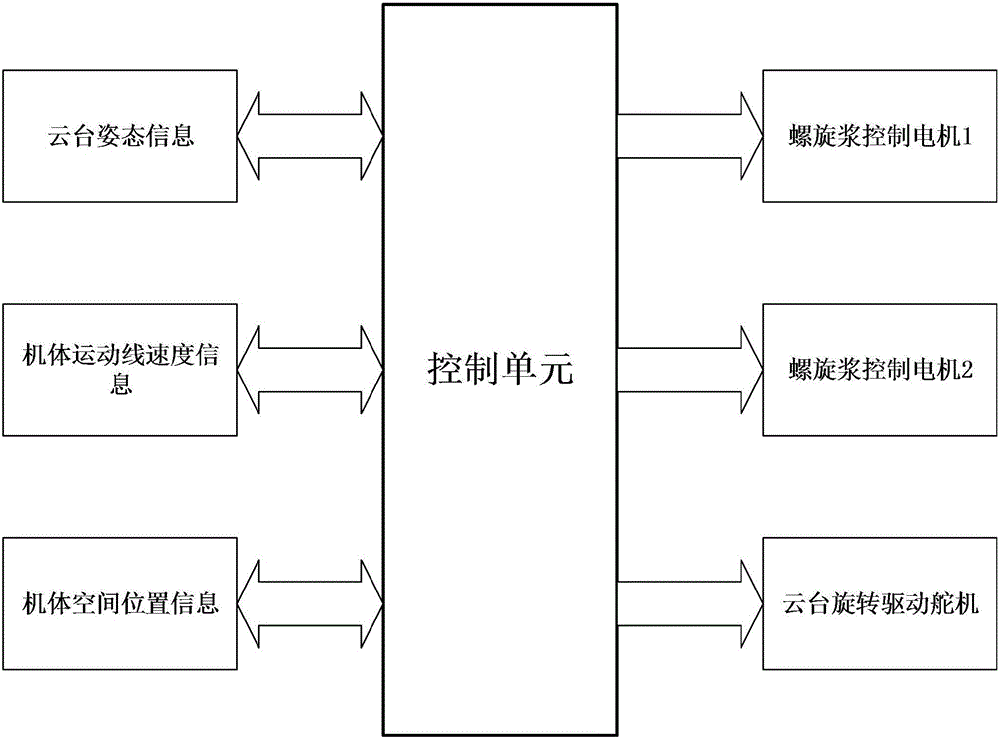
InactiveCN105857595AEasy to controlImprove anti-interference abilityRotocraftFlight vehiclePropeller
The invention discloses a small-size aircraft system based on a cradle head, comprising a rack, a sensor box, a cradle head rolling rudder, a cradle head pitching rudder, a cradle head outer framework, a cradle head inner framework, an upper airscrew, a lower airscrew, an upper airscrew drive motor, a lower airscrew drive motor, a control unit, a telescopic rod and a pod. The aircraft system can realize complete control on the pose of an aircraft by pose adjustment on the cradle head and control on the revolving speed of the airscrews; the yaw angle of an aircraft body is controlled by reaction torque which is generated by the differential rotation of the upper and lower airscrews; the pitching angle and the rolling angle of the airscrews are realized by the rudders driving the cradle head to rotate; control on a spatial position is realized by the airscrew drive motors and pose adjustment on the cradle head. The small-size aircraft system is simple and reliable in design, and clear and explicit in structure; while expanding the existing rotor-type flight structure and control schemes, the small-size aircraft system is also a superior space carrier vehicle, and has considerable practical value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com