Patents
Literature
106686 results about "Robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer— capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. Robots can be guided by an external control device or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed on the lines of human form, but most robots are machines designed to perform a task with no regard to their aesthetics.
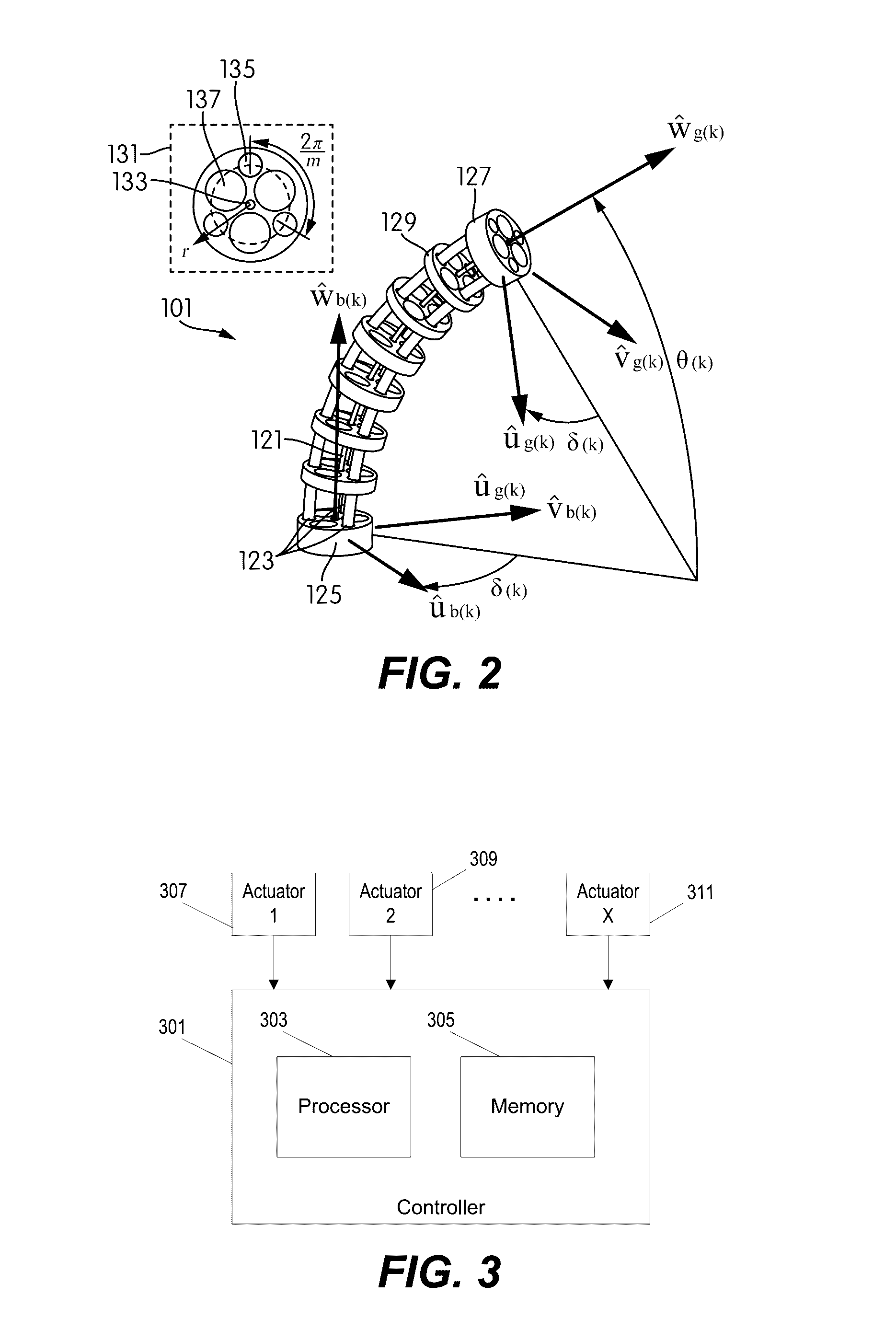
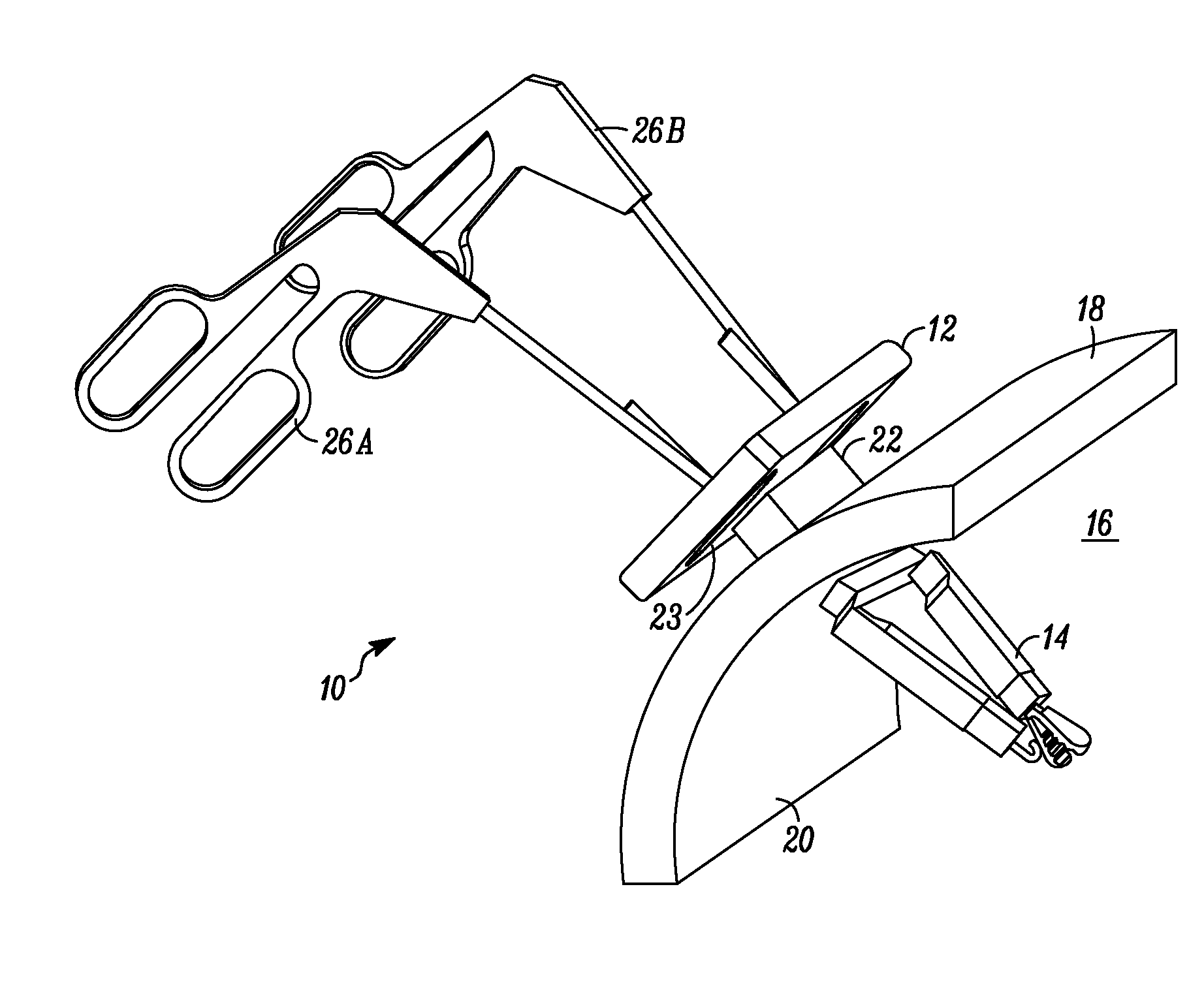
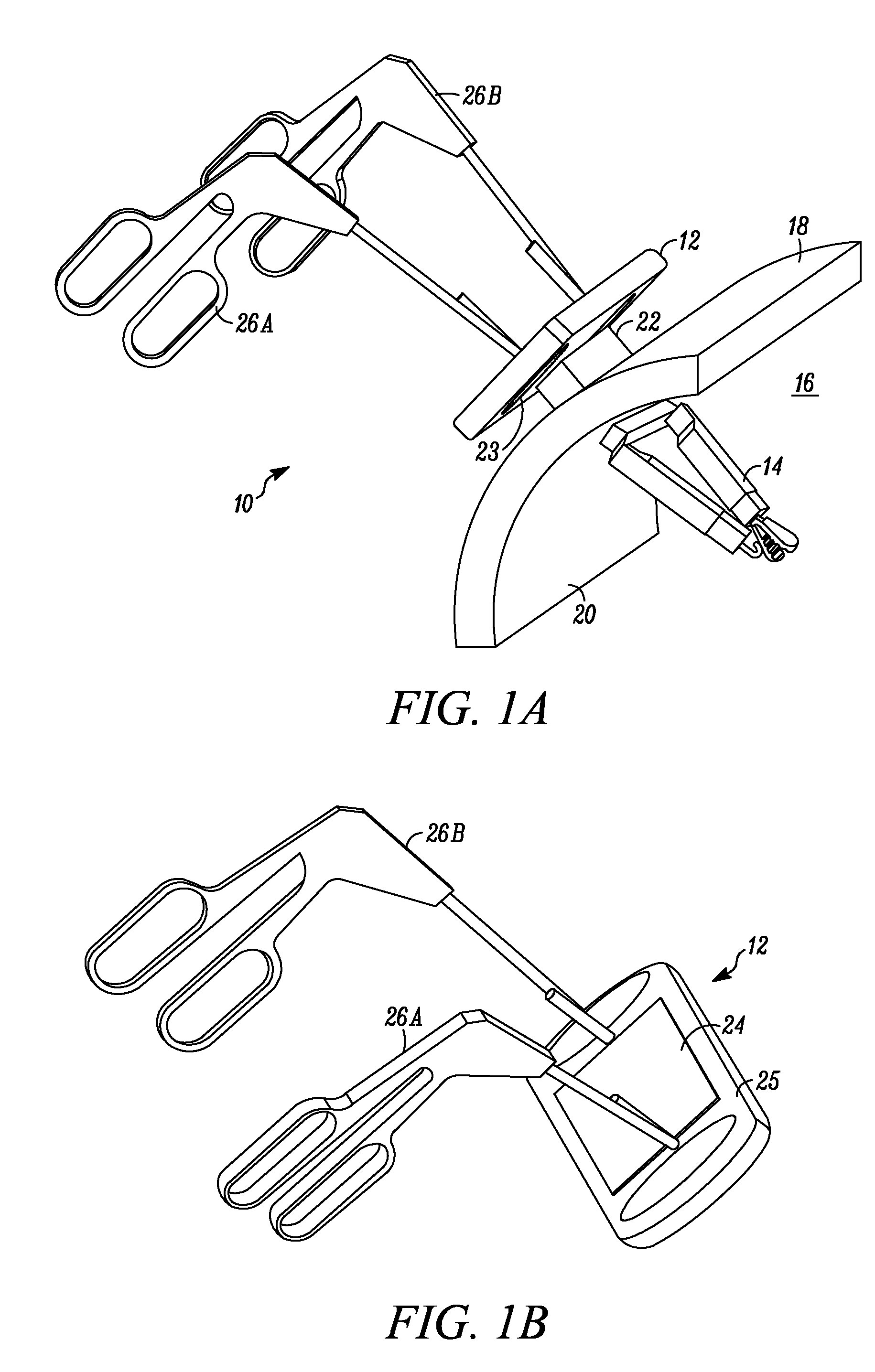
Platform link wrist mechanism
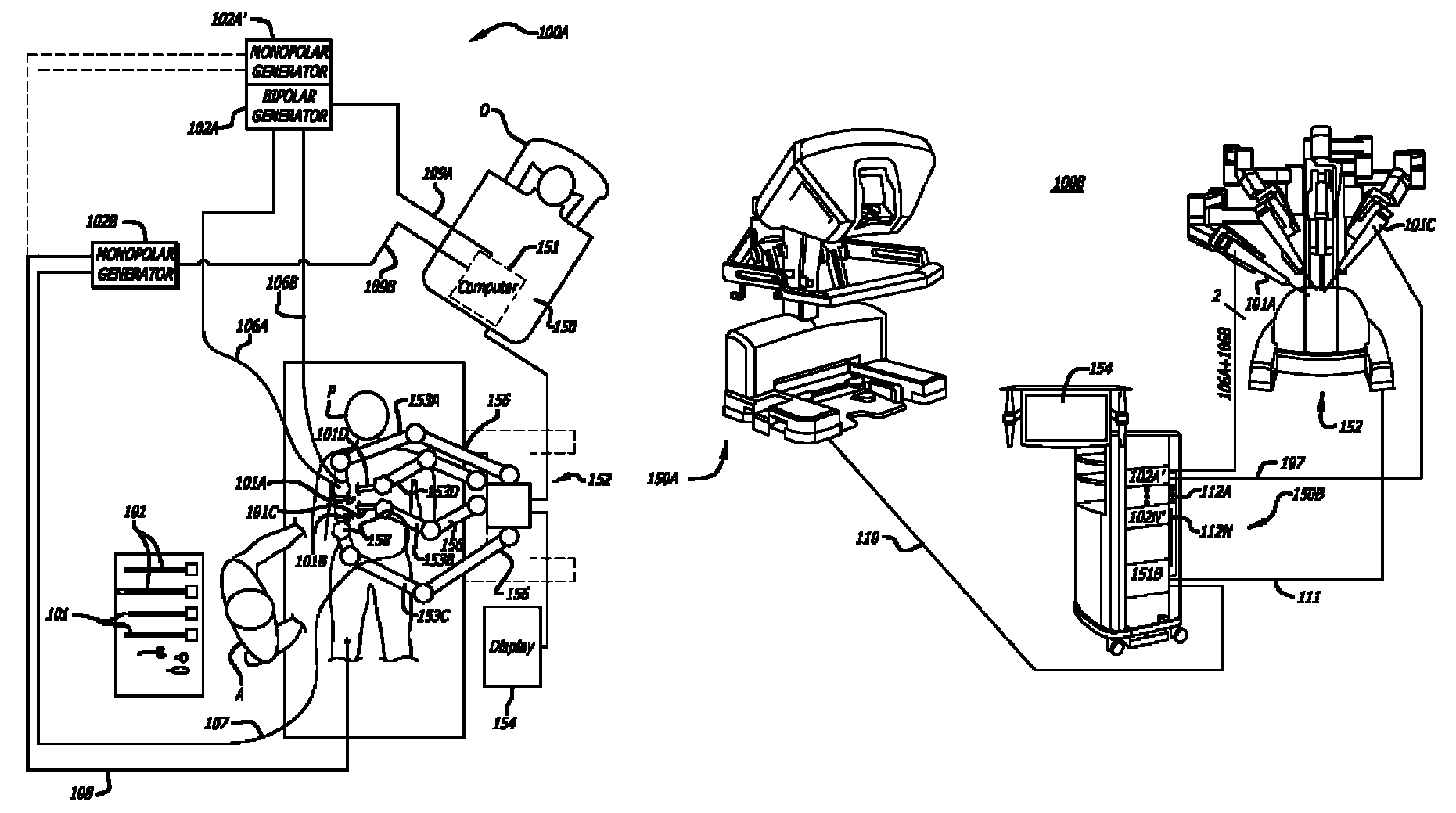
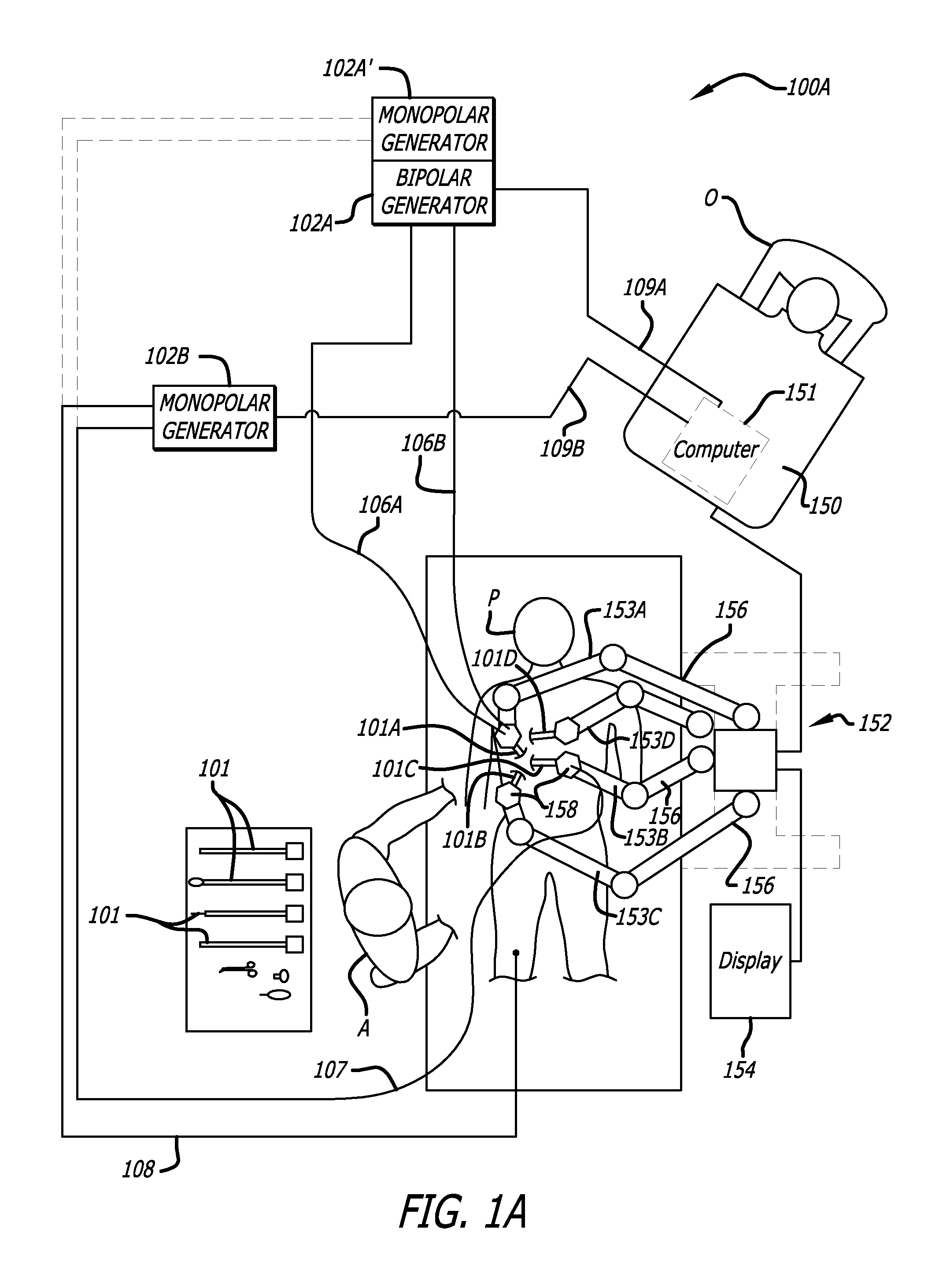
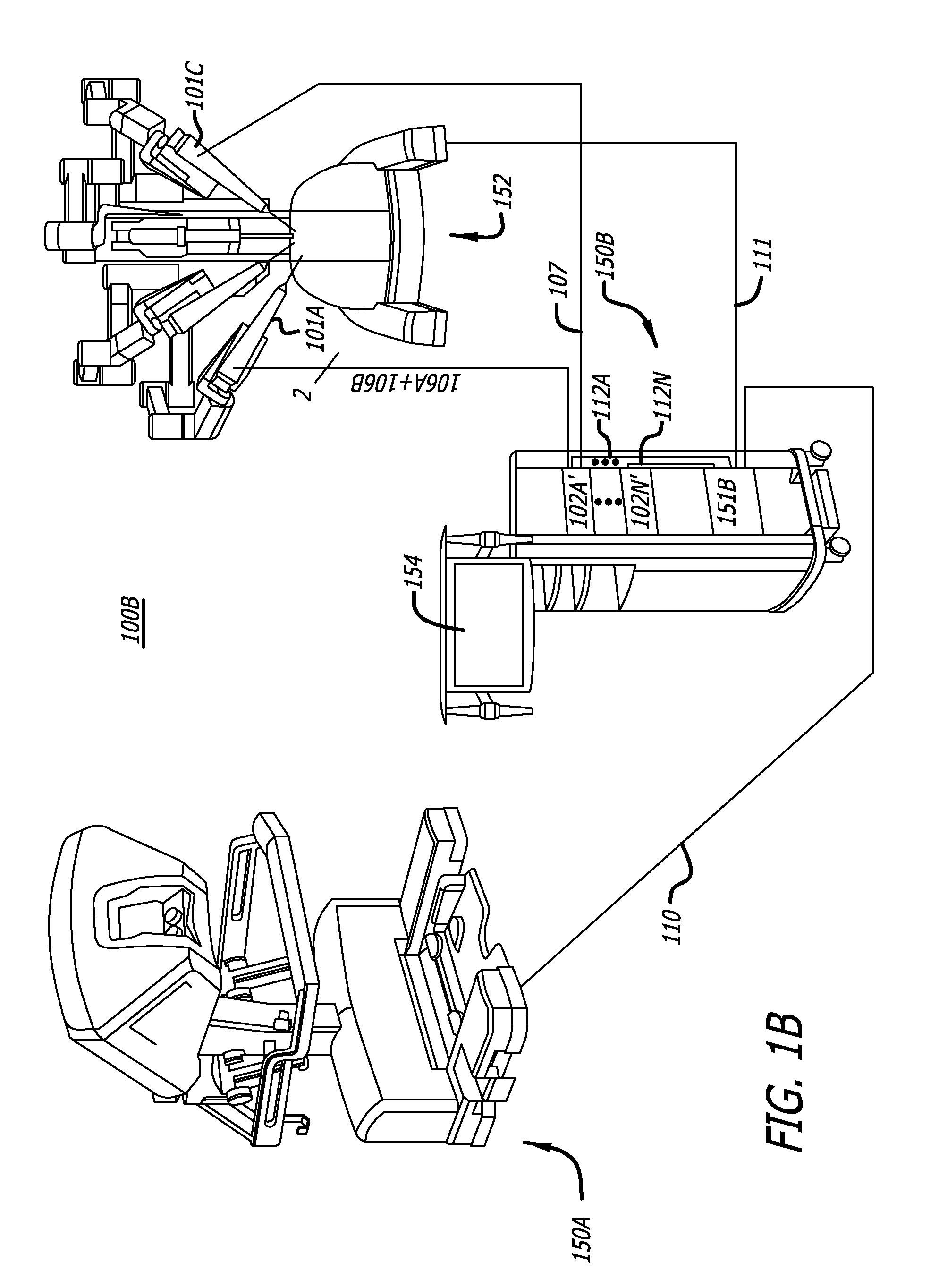
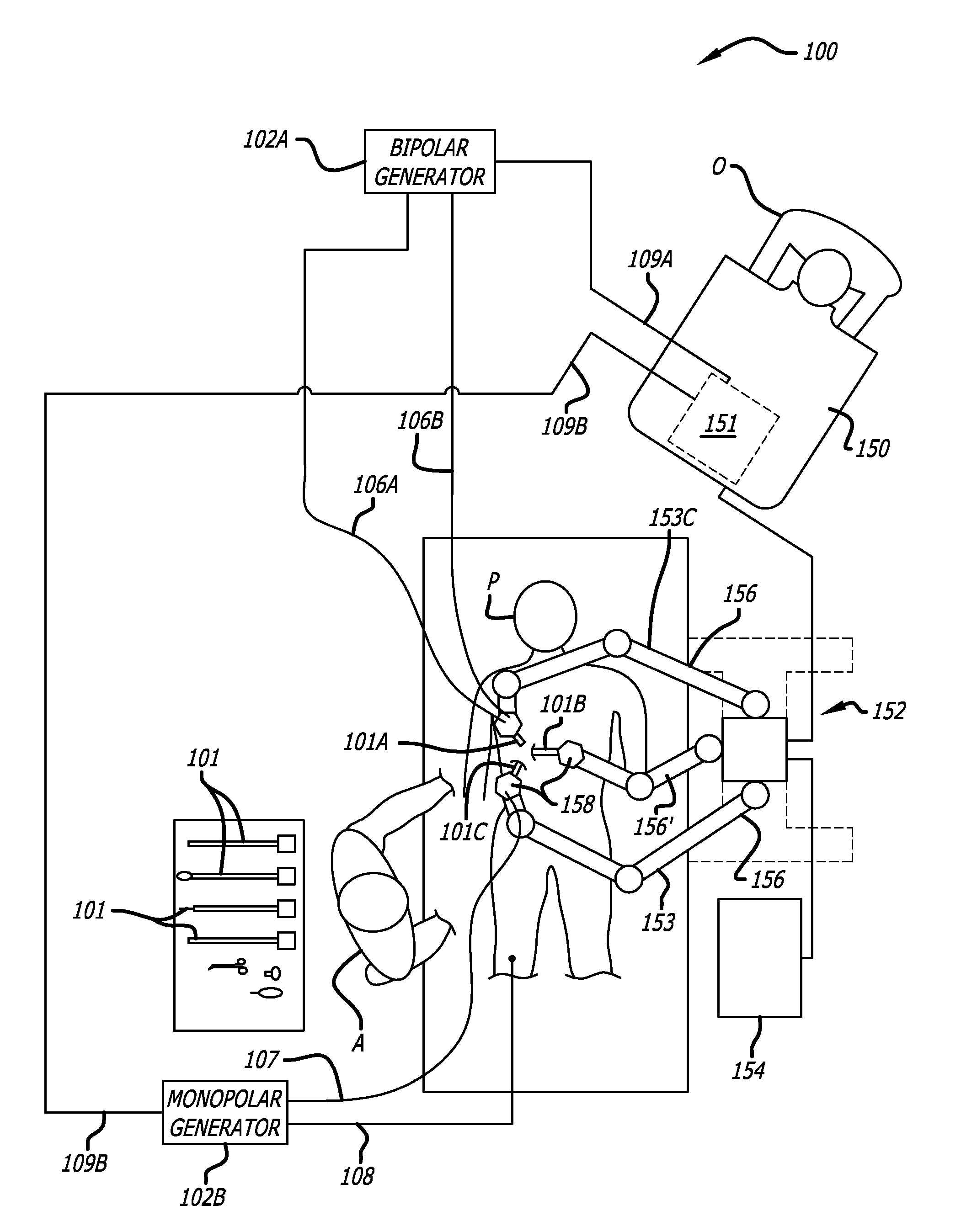
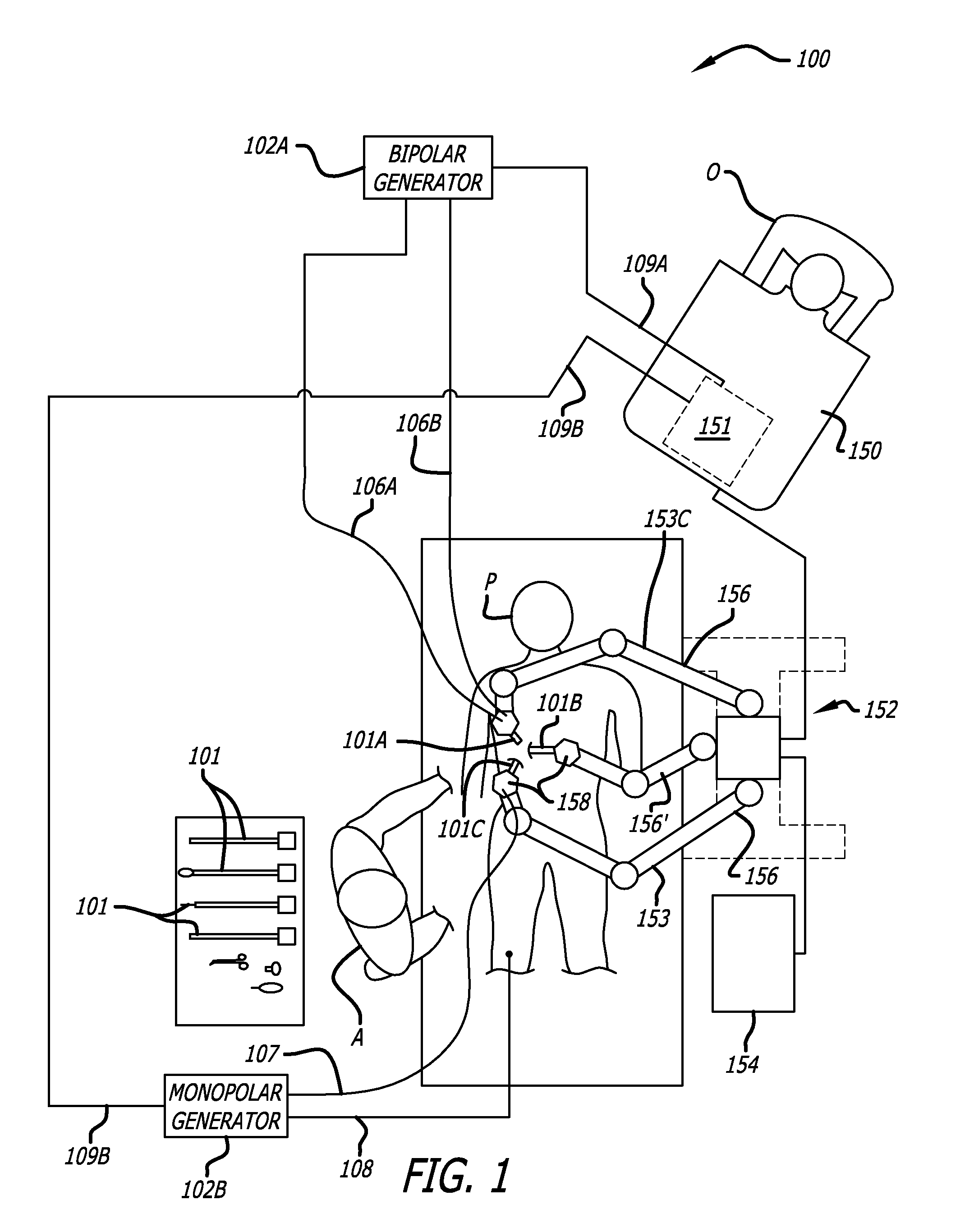
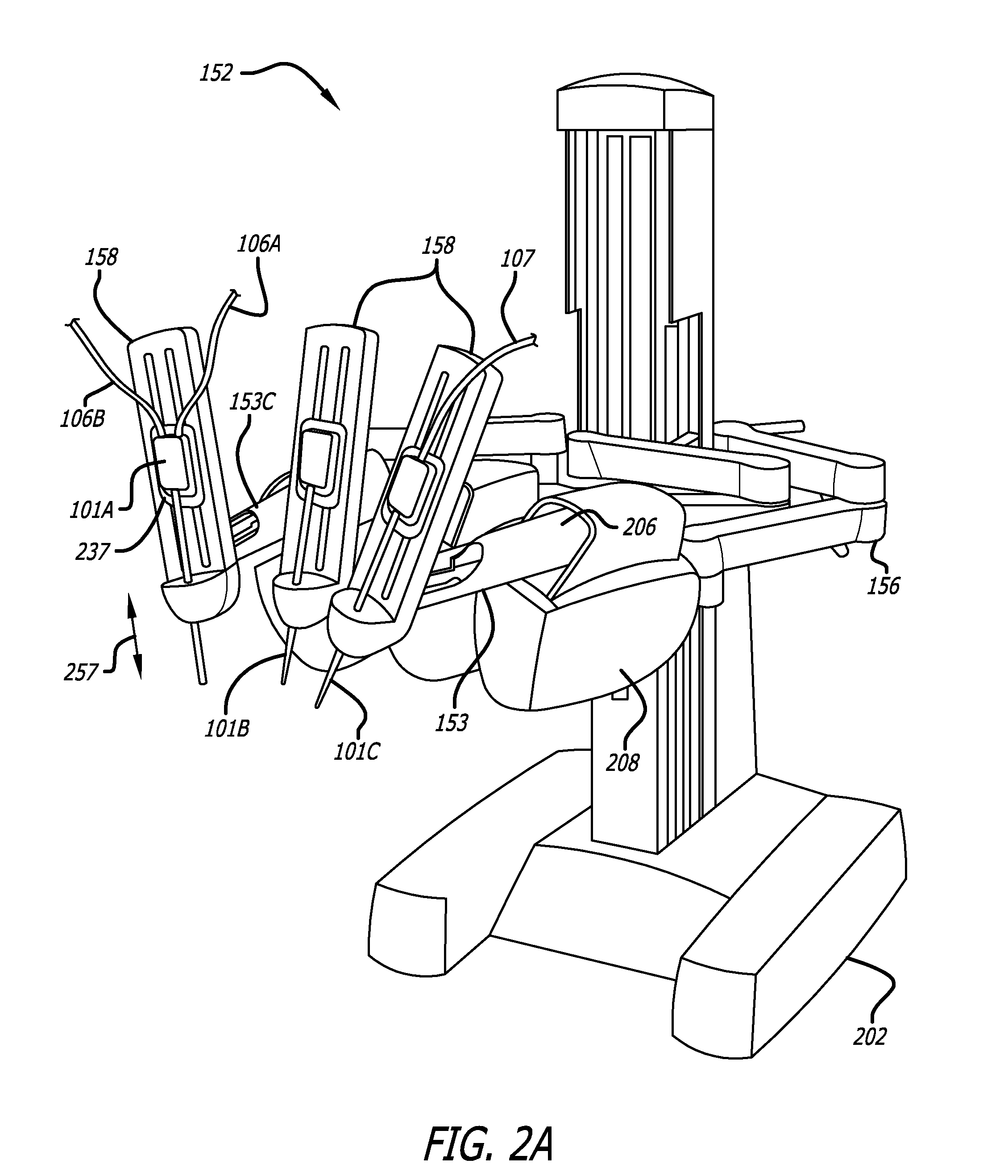
ActiveUS7691098B2Easy to controlSmooth rotationProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusSurgical operationEngineering
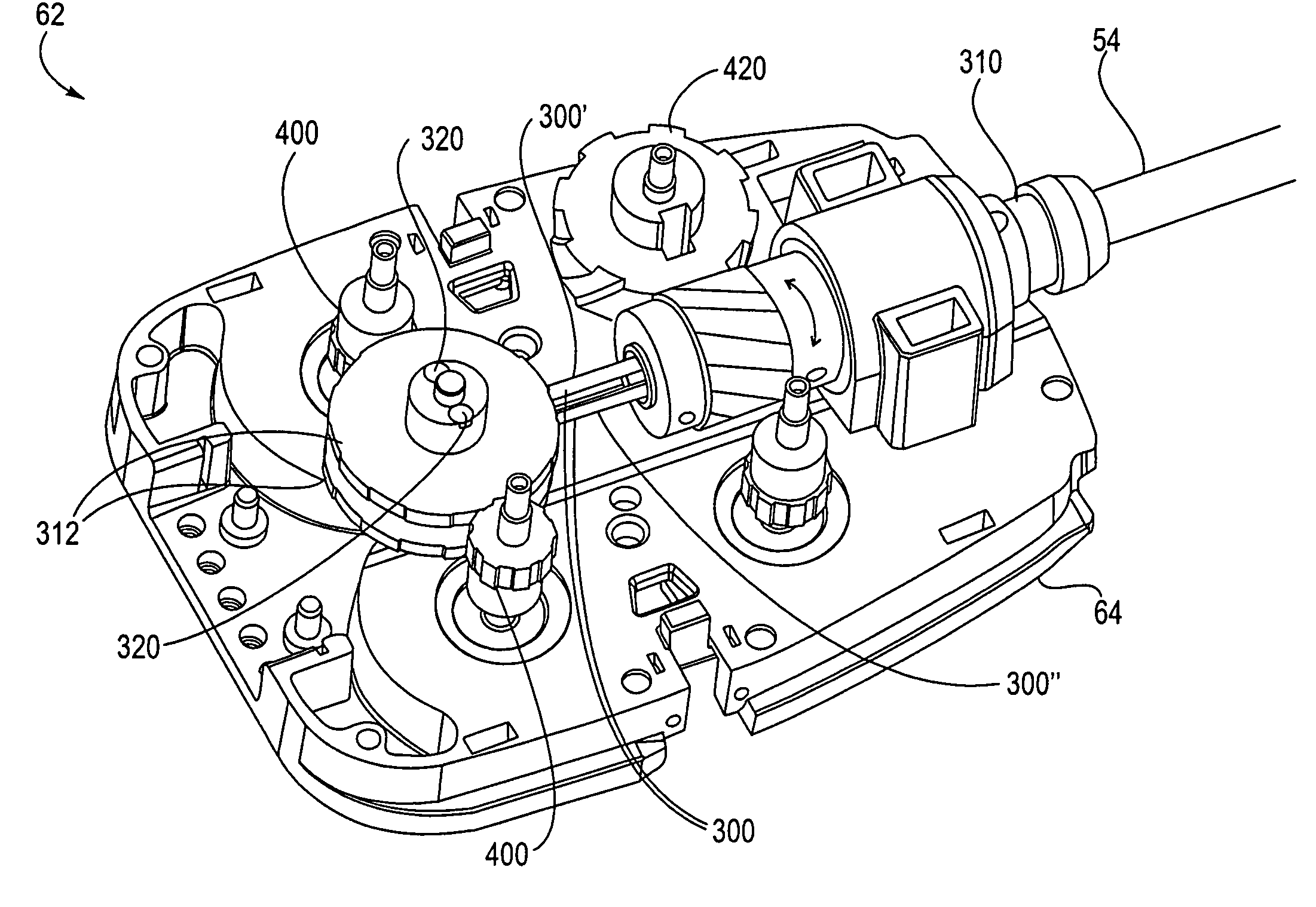
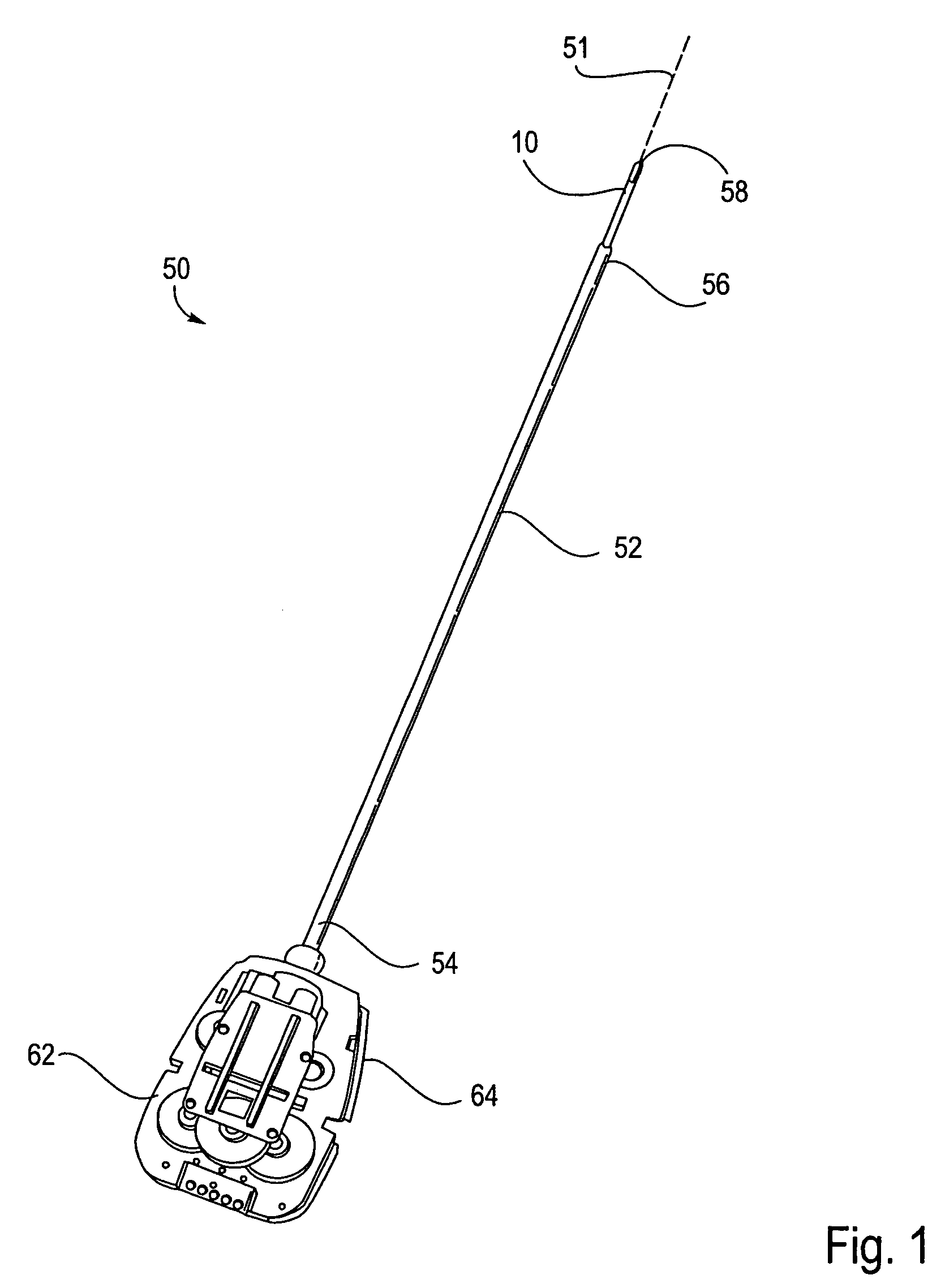
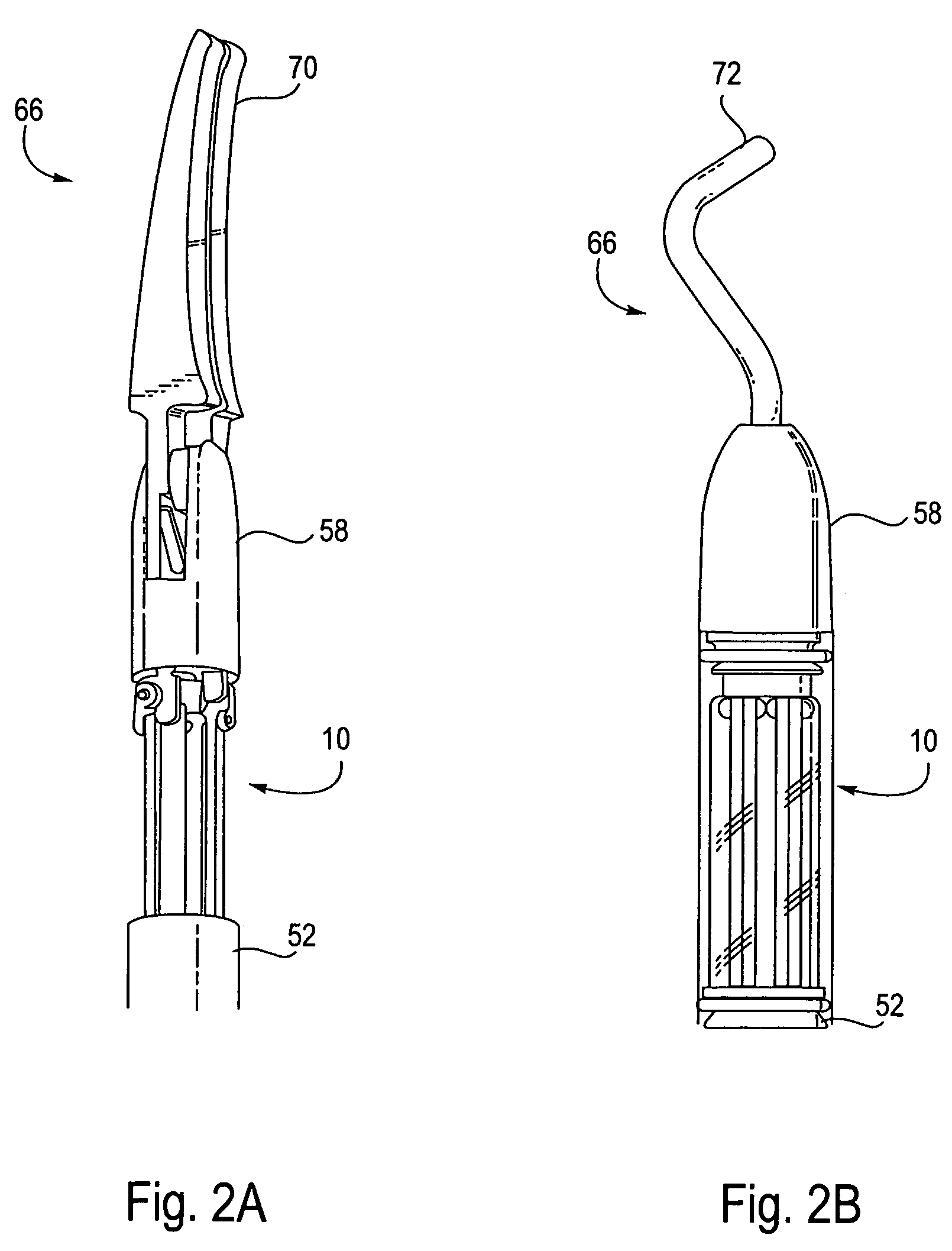
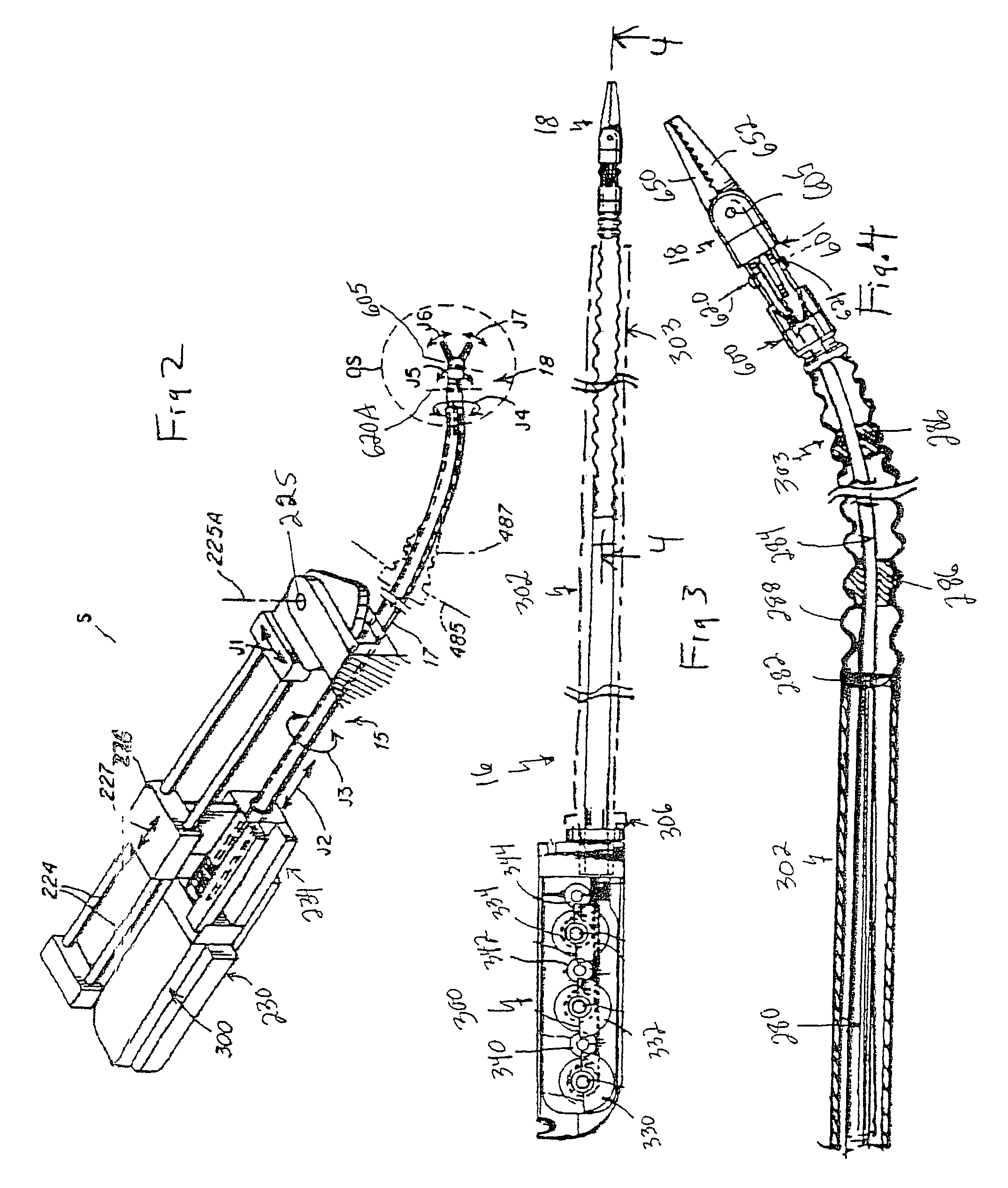
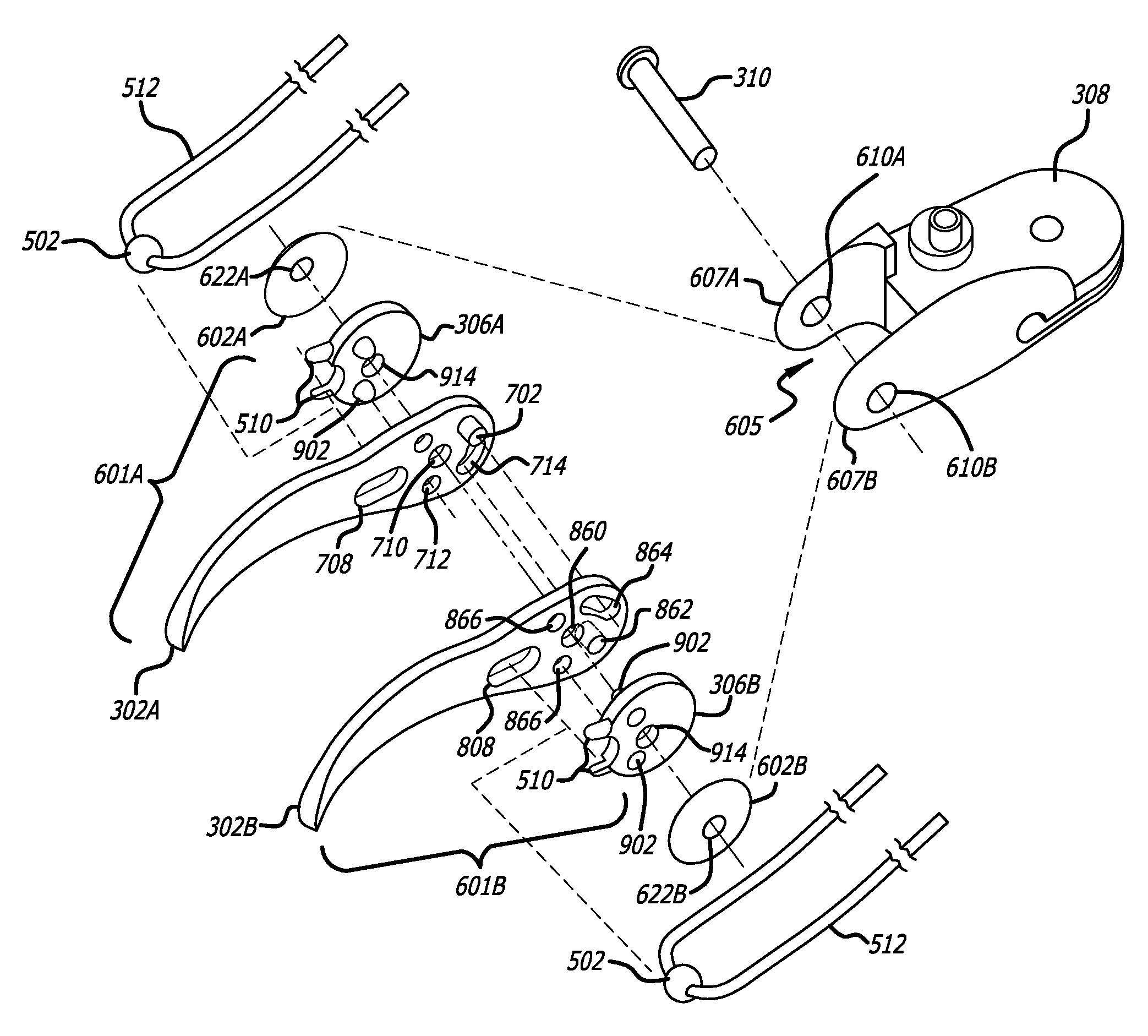
The present invention provides a robotic surgical tool for use in a robotic surgical system to perform a surgical operation. The robotic surgical tool includes a wrist mechanism disposed near the distal end of a shaft which connects with an end effector. The wrist mechanism includes a distal member configured to support the end effector, and a plurality of rods extending generally along an axial direction within the shaft and movable generally along this axial direction to adjust the orientation of the distal member with respect to the shaft. Advancement or retraction of a first rod generally along the axial direction tips the base through a first angle. The addition of a second angle allows the distal member to direct the end effector in essentially a compound angle. The robotic surgical tool may also include provisions for roll movement.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Robotic tool with monopolar electro-surgical scissors
InactiveUS6994708B2Reduce bleedingCoagulated bloodDiagnosticsSurgical scissorsSurgical operationElectrical conductor
The present invention provides robotic surgical instruments and systems that include electrosurgical cutting / shearing tools and methods of performing a robotic surgical procedure. The surgical instruments can advantageously be used in robotically controlled minimally invasive surgical operations. A surgical instrument generally comprises an elongate shaft having a proximal end and a distal end. An end effector, for performing a surgical operation such as cutting, shearing, grasping, engaging, or contacting tissue adjacent a surgical site, is coupleable to a distal end of the shaft. Preferably, the end effector comprises a pair of scissor-like blades for cooperatively shearing the tissue. A conductor electrically communicating with at least one blade delivers electrical energy to tissue engaged by the blades. An interface coupled to the proximal end of the shaft and removably connectable to the robotic surgical system is also included.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Robotically controlled surgical instruments
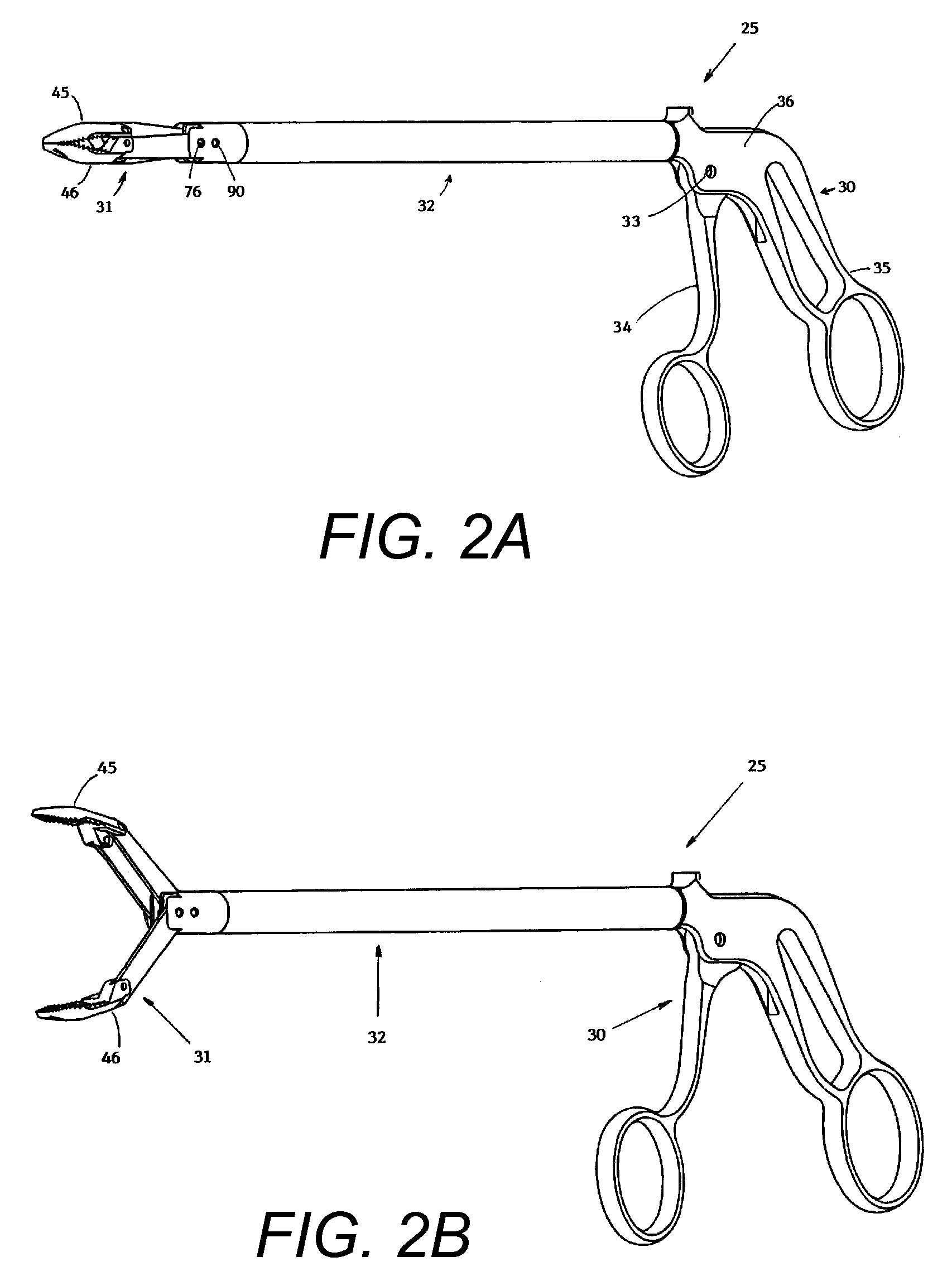
ActiveUS7699835B2High strengthIncreased leverageSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsEngineeringRobot control
A robotically controlled surgical instrument includes a first jaw and a second jaw used to grasp an item, and a drive mechanism that increases the force applied to the item grasped. The drive mechanism and the jaws can be provided with an accommodating mechanism that allows continued movement of the drive mechanism towards a locked position even after the jaws contact a larger item so that the drive mechanism can move to the locked position when grasping items of different sizes.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Surgical tool having electrocautery energy supply conductor with inhibited current leakage
InactiveUS7083615B2Low costEasy to manufactureDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingCapacitanceElectrical conductor
The present invention provides improved electrosurgical instruments and systems having electrocautery energy supply conductors that provide inhibited current leakage and methods of performing a robotically controlled minimally invasive surgical procedure while preventing unintended capacitive coupling. A surgical instrument generally comprises an elongate shaft having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an internal longitudinally extending passage. An electrocautery end effector is coupled to or disposed at the distal end of the shaft. An interface or tool base is coupled to or disposed at the proximal end of the shaft and removably connectable to the robotic surgical system. Typically, an independent electrical conductor extends from the interface to the end effector to transmit electrical energy to tissue engaged by the end effector. A sealed insulation tube extends within the passage and over the conductor. A separation is maintained between the sealed insulation tube and the conductor.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
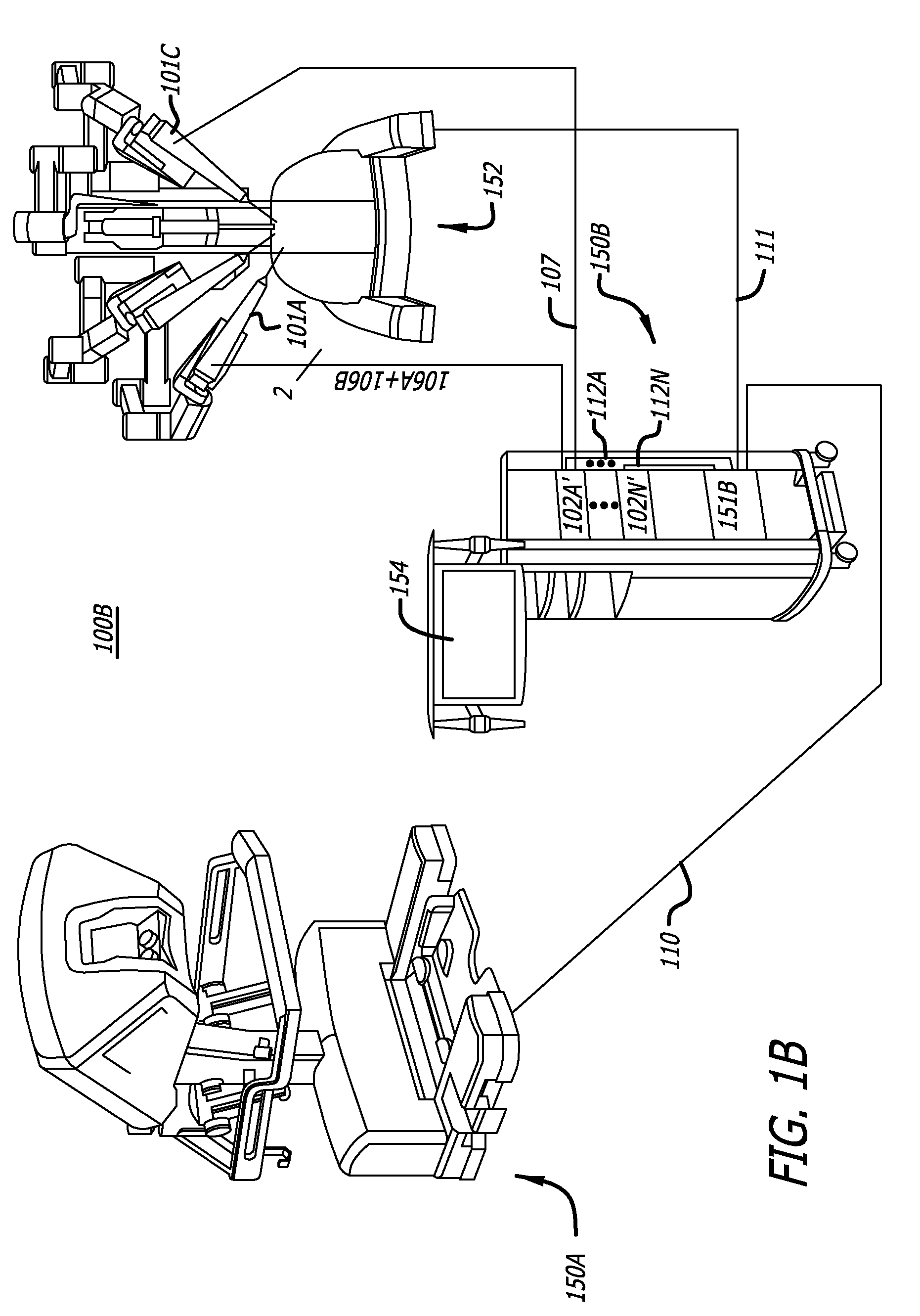
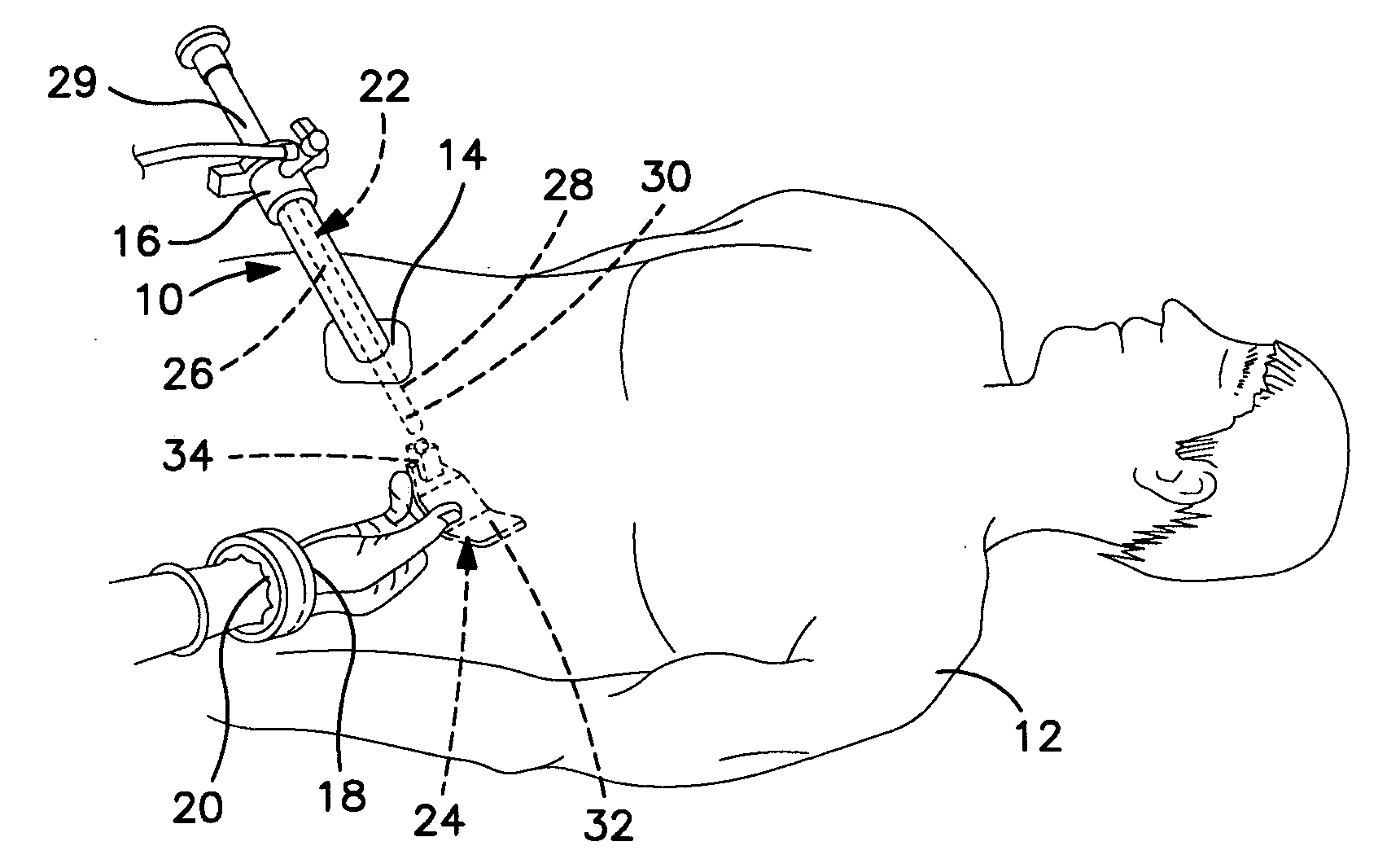
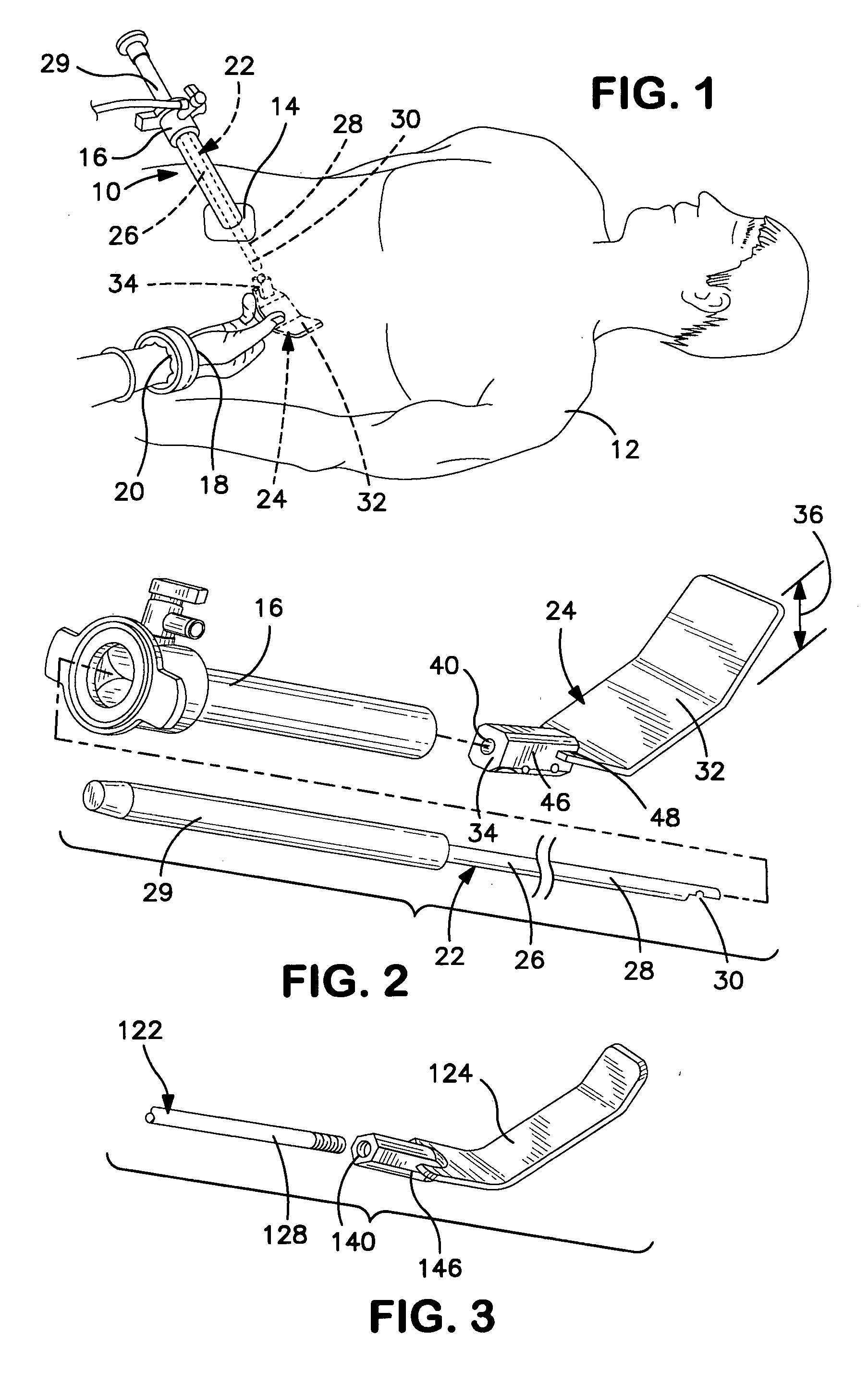
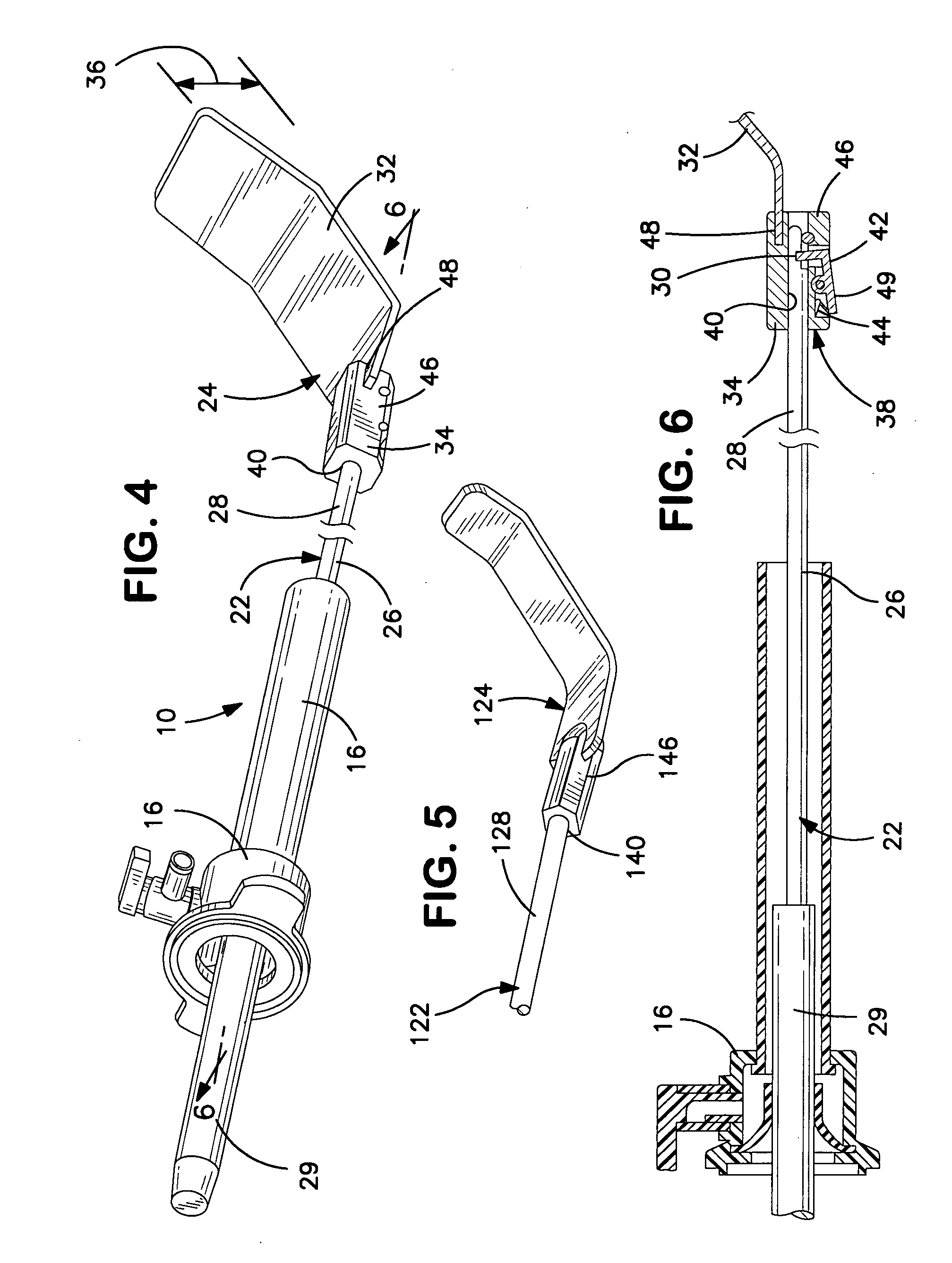
Sterile drape interface for robotic surgical instrument
A robotic surgical system includes a sterile surgical instrument, a robotic surgical manipulator, and a sterile drape covering at least a portion of the robotic surgical manipulator. The surgical instrument has a proximal interface and a distal end effector. The proximal interface includes a gimbal assembly with two intersecting rotational axes coupled to the distal end effector. The robotic surgical manipulator has a drive plate that bears against the gimbal assembly. The drive plate has two degrees of rotational freedom about a center of motion that is coincident with an intersection of the axes of the gimbal assembly. The sterile drape includes a sterile sheet covers at least a portion of the robotic surgical manipulator, a frame bonded to the sterile sheet, an instrument interface that covers the drive plate of the robotic surgical manipulator, and a diaphragm that connects the instrument interface to the frame.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Gentle touch surgical instrument and method of using same
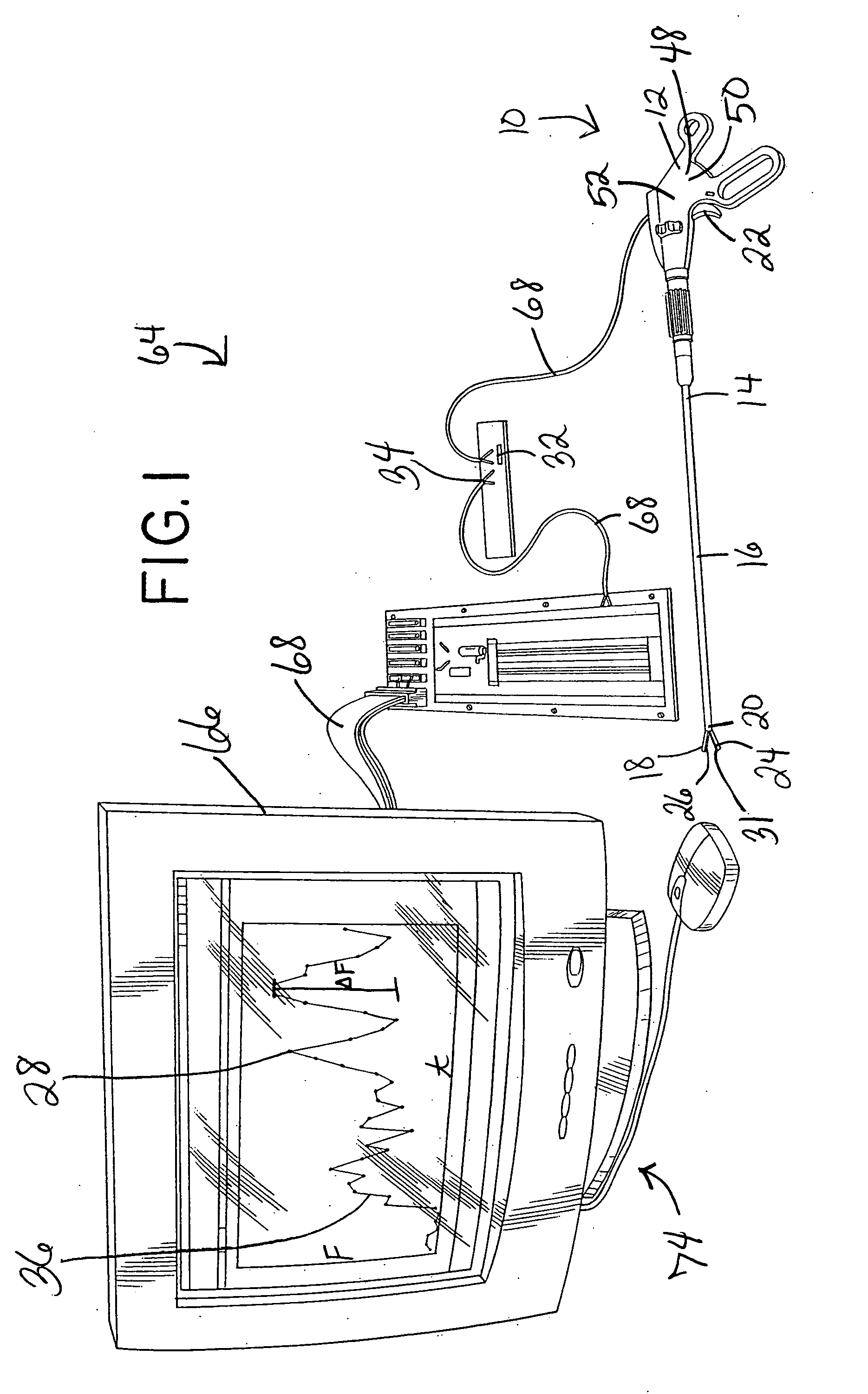
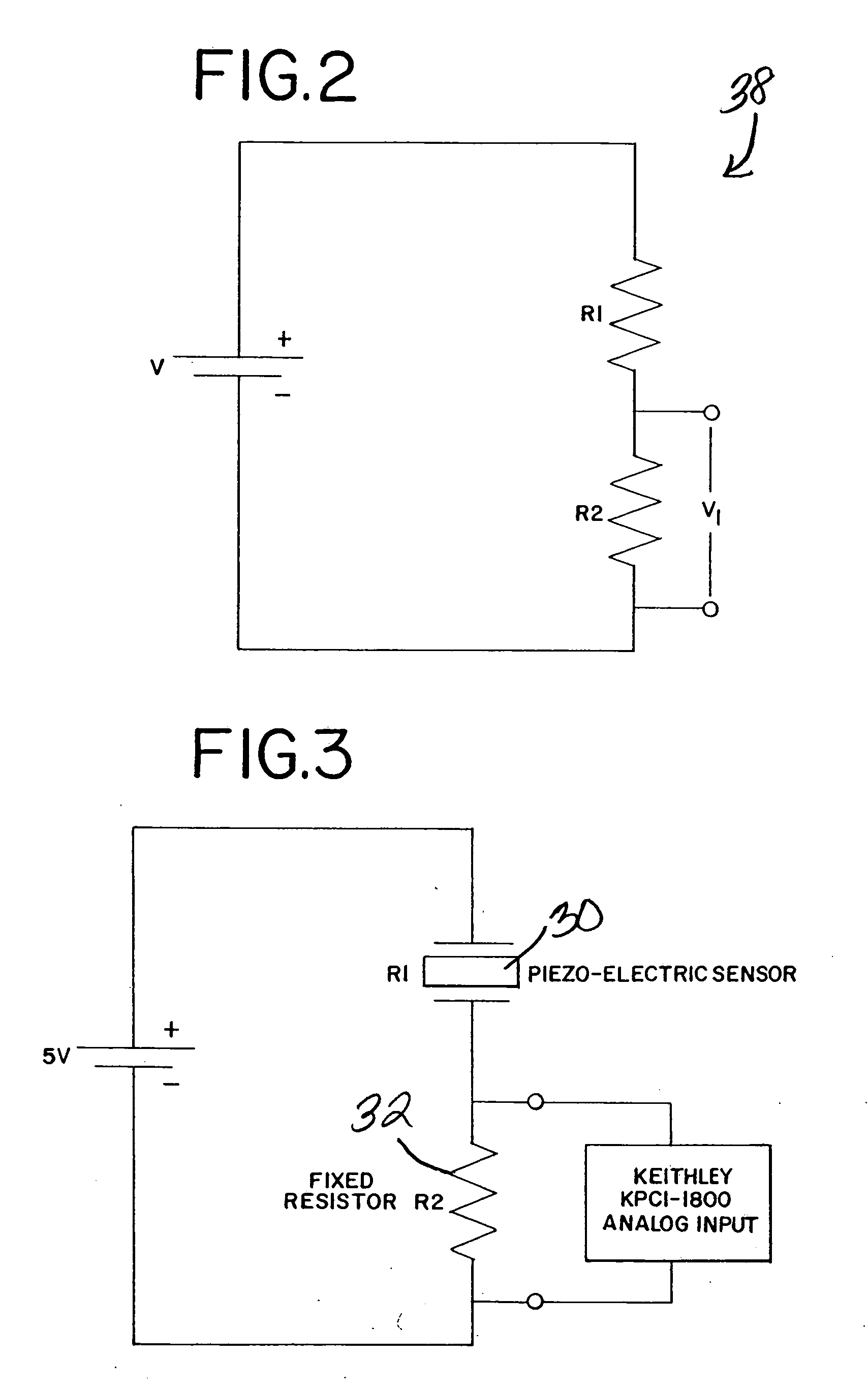
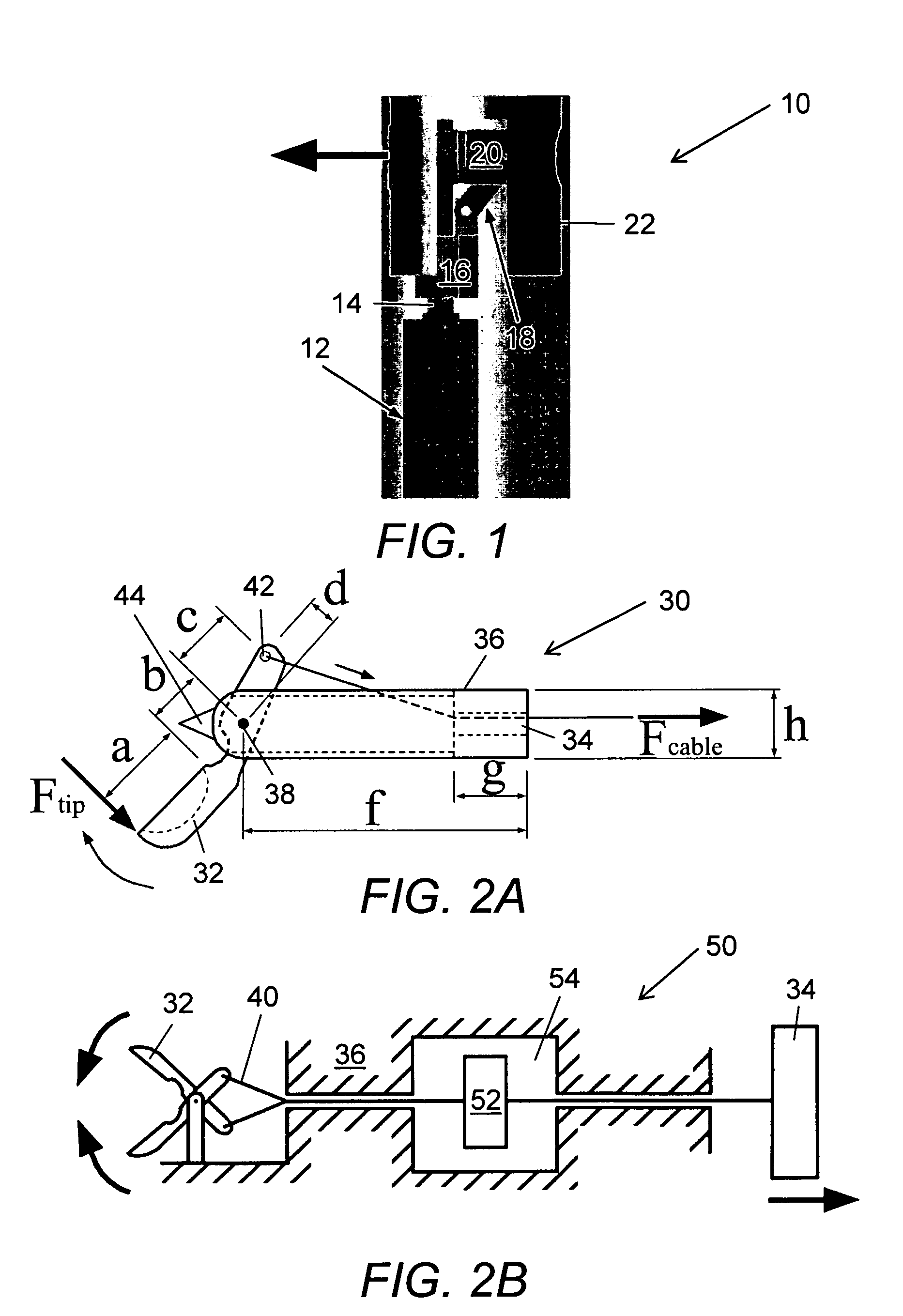
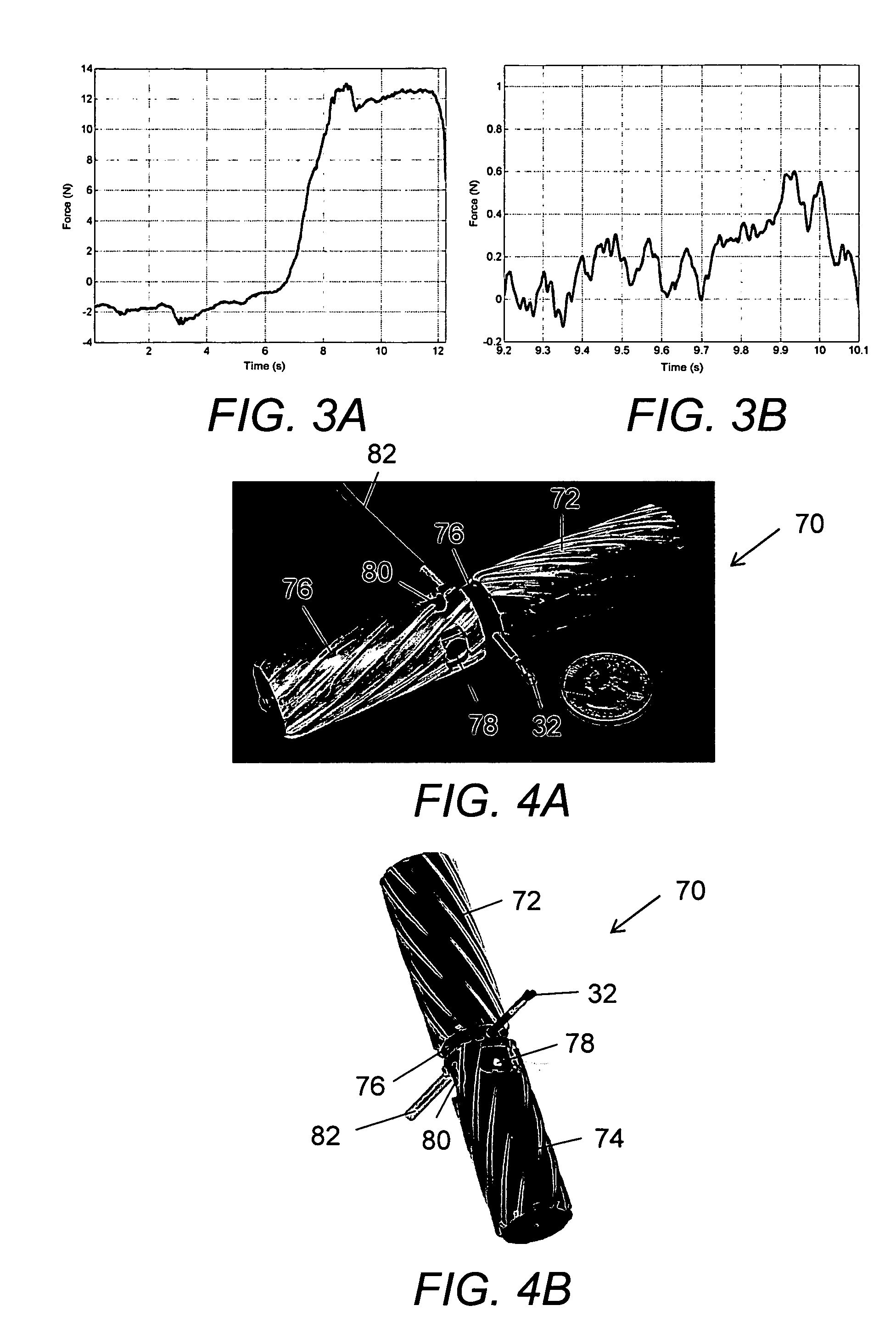
A surgical grasper is provided. The grasper comprises a handle, two jaws operably connected to the handle, which jaws can be actuated by the handle, and a sensor. A surgical grasper for use in robotic surgery is also provided. The grasper comprises a shaft, two jaws at a distal end of the shaft, which jaws can be actuated in response to a robot command, and a sensor. A method for measuring an amount of force being applied by a jaw of a grasper is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a grasper comprising a handle and two jaws operably connected to the handle, which jaws can be actuated by the handle; providing a sensor on the grasper; and, providing for measuring an amount of force being applied to the sensor. A method for measuring an amount of force being applied by a jaw of a grasper for use in robotic surgery is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a grasper for use in robotic surgery, the grasper comprising a shaft and two jaws at a distal end of the shaft, which jaws can be actuated responsive to a robot command; providing a sensor; and, providing for measuring an amount of force being applied to the sensor. A surgical feedback system is also provided. The surgical feedback system comprises a surgical grasper capable of taking a force measurement and a data concentrator coupled to the grasper via a wired or wireless interface using a first data transmission protocol with internal storage. A method for obtaining surgical feedback is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a surgical grasper capable of taking a force measurement; and, providing a data concentrator coupled to the grasper via a wired or wireless interface using a first data transmission protocol with internal storage.
Owner:TELESURGIX
Tool grip calibration for robotic surgery
ActiveUS7386365B2Limited tool lifeStringent manufacturing toleranceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringActuator
Telerobotic, telesurgical, and surgical robotic devices, systems, and methods selectively calibrate end effector jaws by bringing the jaw elements into engagement with each other. Commanded torque signals may bring the end effector elements into engagement while monitoring the resulting position of a drive system, optionally using a second derivative of the torque / position relationship so as to identify an end effector engagement position. Calibration can allow the end effector engagement position to correspond to a nominal closed position of an input handle by compensating for wear on the end effector, the end effector drive system, then manipulator, the manipulator drive system, the manipulator / end effector interfacing, and manufacturing tolerances.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Fusing and cutting surgical instrument and related methods
A surgical instrument can include a shaft having a proximal end and a distal end, and a wrist coupled to the distal end of the shaft and configured to articulate in multiple degrees of freedom coupled to the distal end of the shaft. The surgical instrument can further include an end effector supported by the wrist, wherein the end effector includes a cutting element and jaws configured to grip tissue and fuse tissue via electrosurgical energy. The surgical instrument can be configured for use with a teleoperated robotic surgical system that can include a patient side console configured to interface to actuate the surgical instrument and a surgeon side console configured to receive inputs from a surgeon to control the actuation of the surgical instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
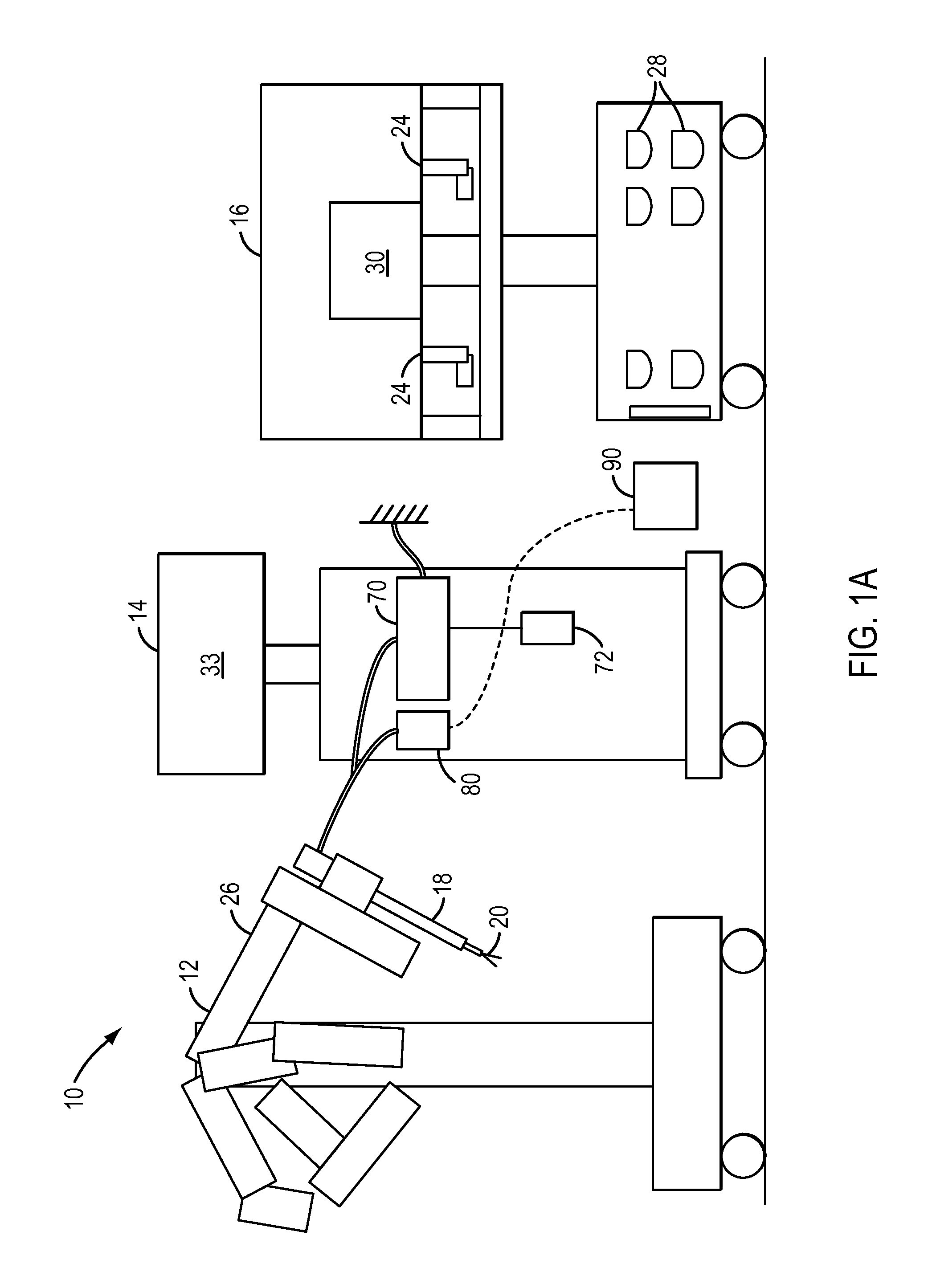
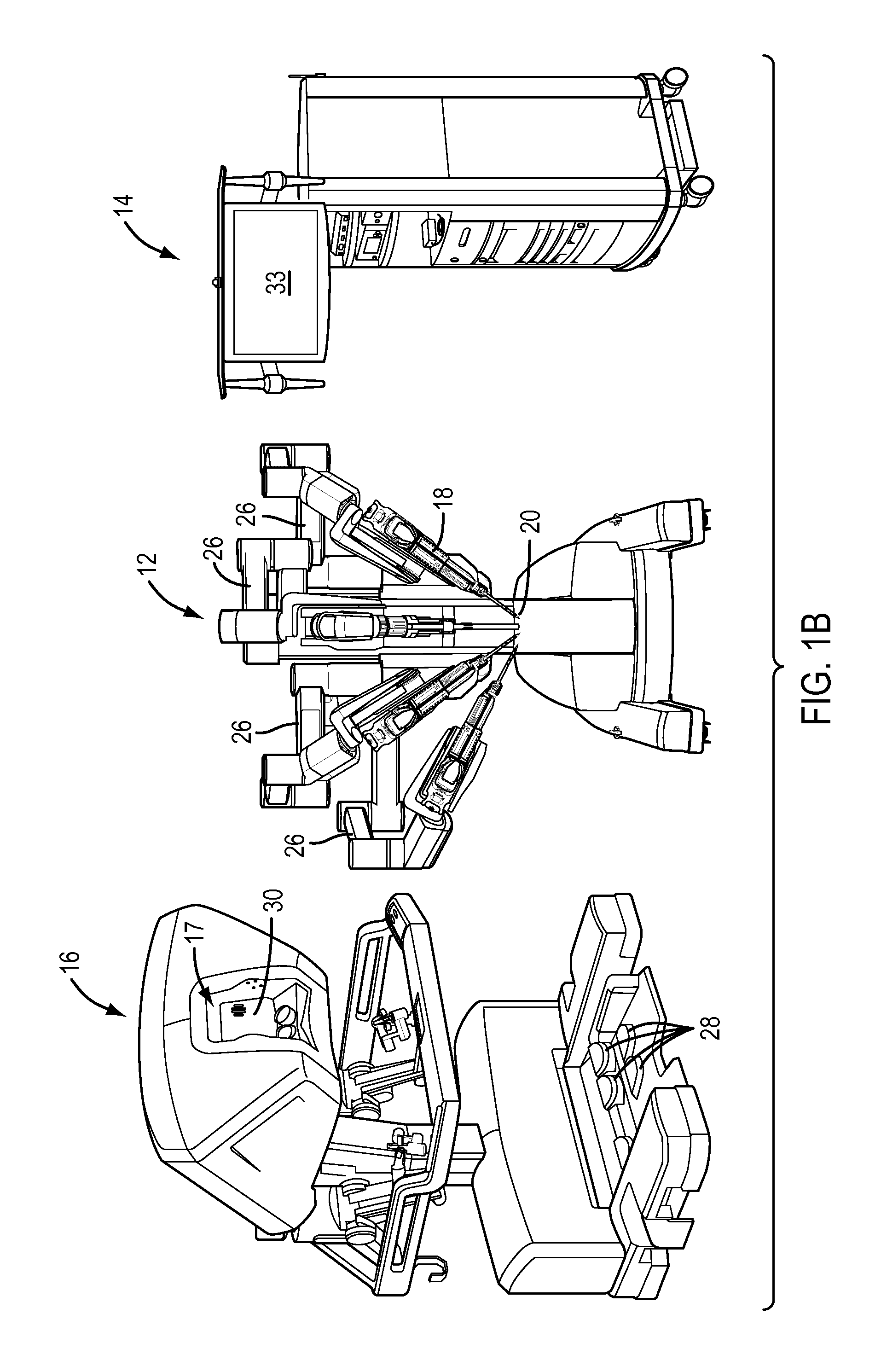
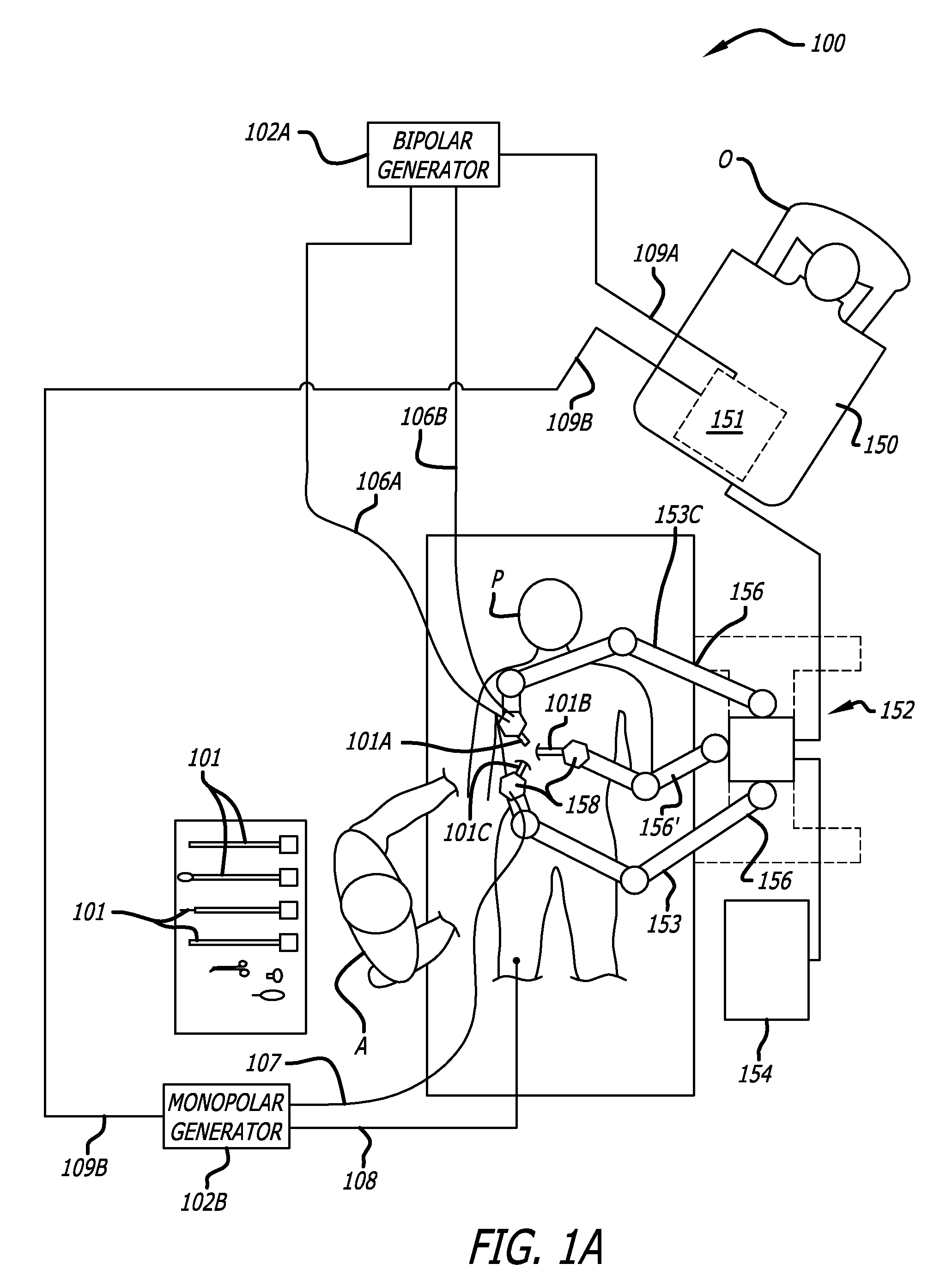
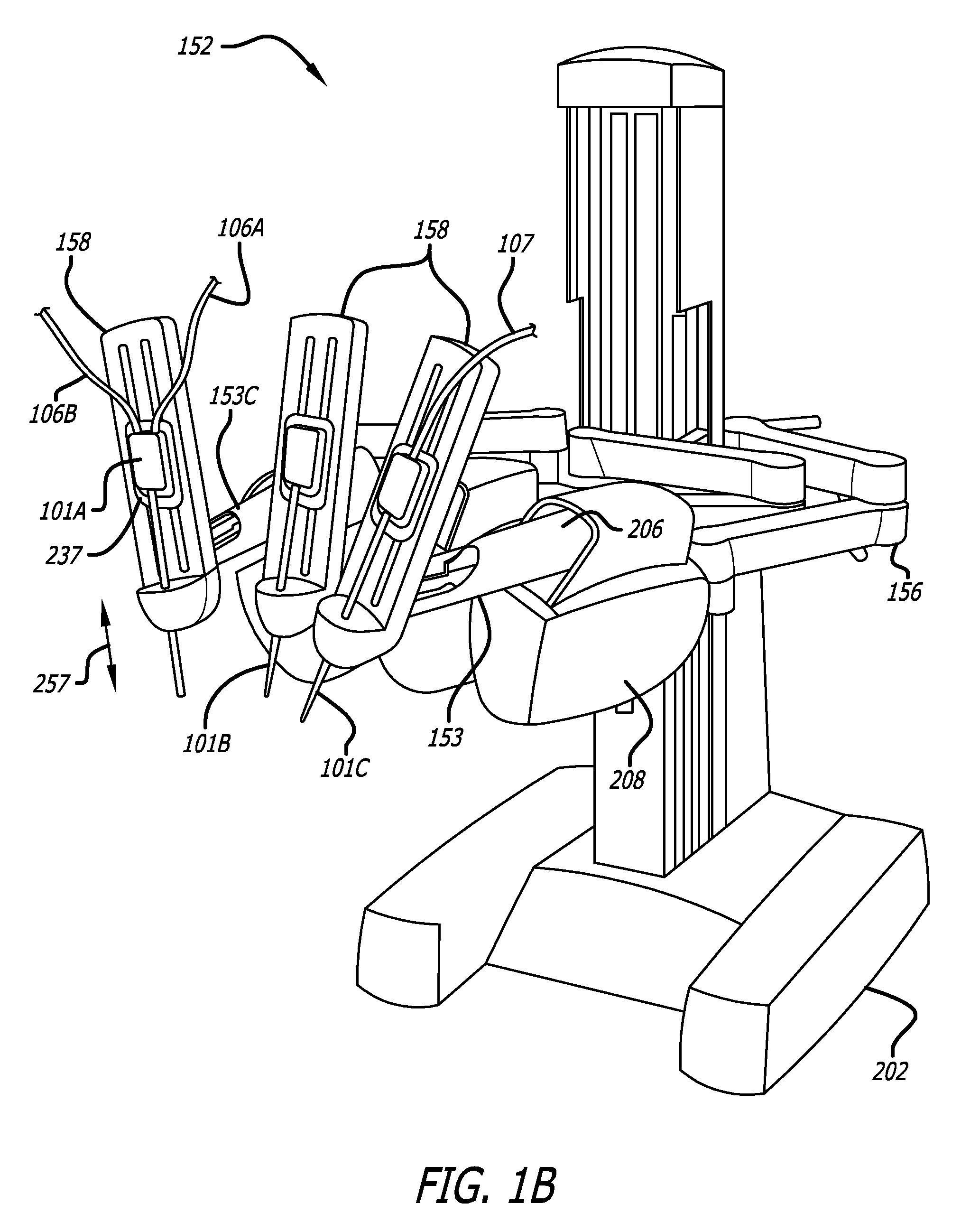
Ergonomic surgeon control console in robotic surgical systems
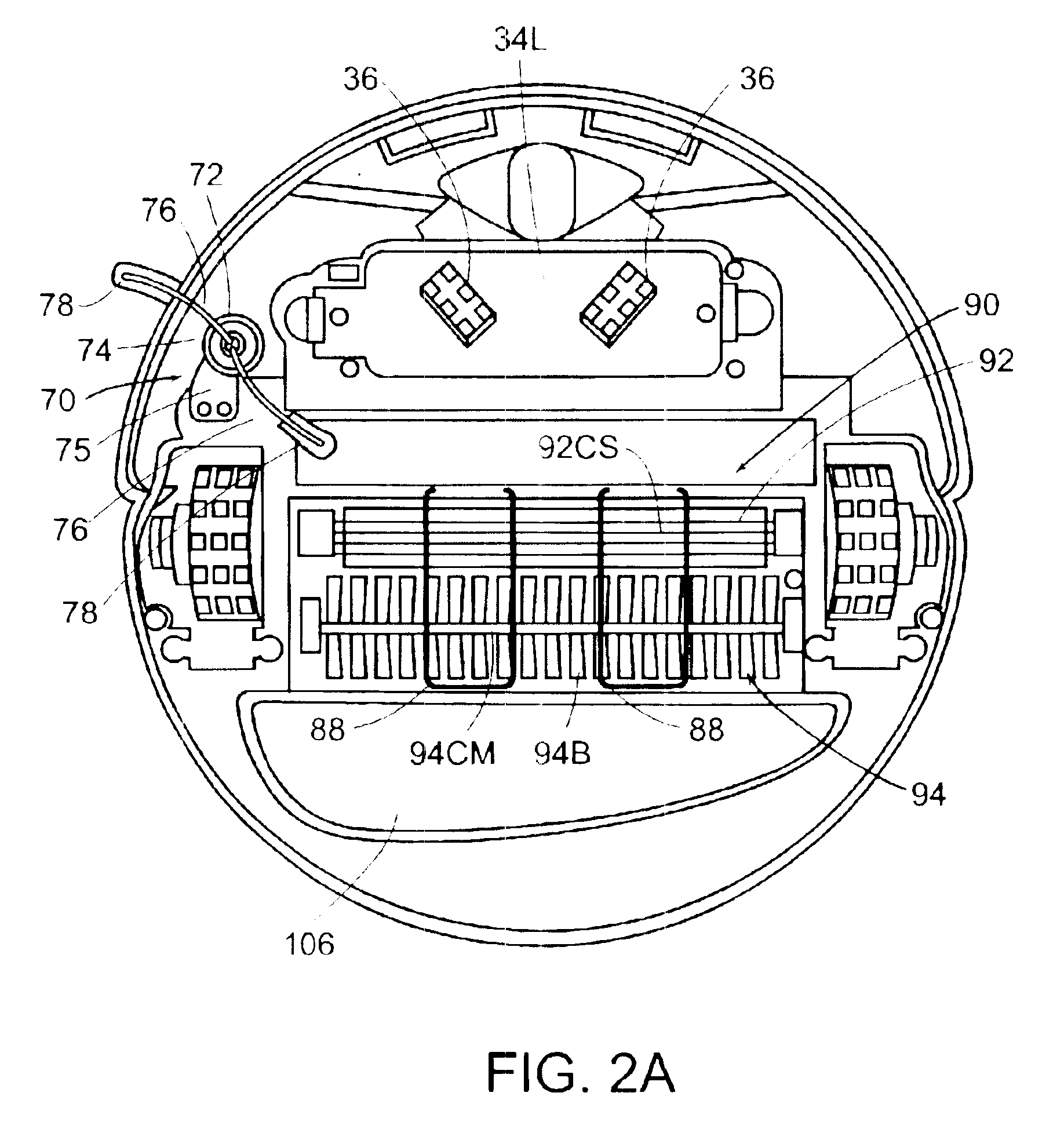
A control console to remotely control medical equipment is disclosed having a base with an ergonomically adjustable pedal system. The base further has an opening to receive the pedal system. The pedal system includes a moveable pedal tray with a pedal base. The tray includes a first left pedal assembly and a first right pedal assembly, and an upper tier having a second left pedal assembly and a second right pedal assembly respectively in alignment with and elevated above the first left pedal assembly and the first right pedal assembly. Rollers are rotatable coupled to the moveable pedal tray to allow it roll over a floor. A drive assembly is coupled between the moveable pedal tray and the base. The drive assembly applies a force to the to roll the moveable pedal tray over the floor within the opening of the base.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL +1
Robot for surgical applications
The present invention provides a micro-robot for use inside the body during minimally-invasive surgery. The micro-robot includes an imaging devices, a manipulator, and in some embodiments a sensor.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
User interfaces for electrosurgical tools in robotic surgical systems
A method for a minimally invasive surgical system is disclosed including capturing camera images of a surgical site; generating a graphical user interface (GUI) including a first colored border portion in a first side and a second colored border in a second side opposite the first side; and overlaying the GUI onto the captured camera images of the surgical site for display on a display device of a surgeon console. The GUI provides information to a user regarding the first electrosurgical tool and the second tool in the surgical site that is concurrently displayed by the captured camera images. The first colored border portion in the GUI indicates that the first electrosurgical tool is controlled by a first master grip of the surgeon console and the second colored border portion indicates the tool type of the second tool controlled by a second master grip of the surgeon console.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
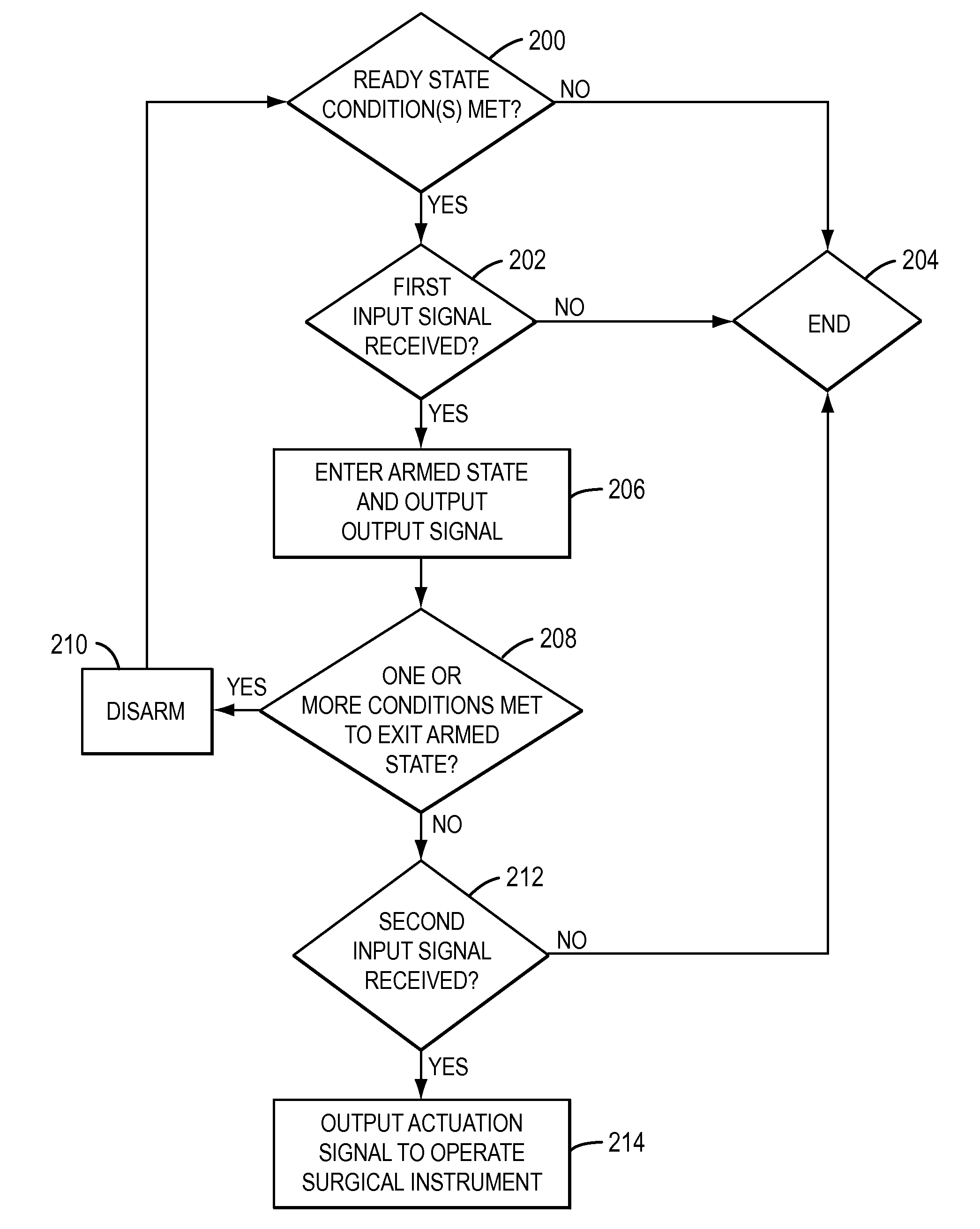
Positive control of robotic surgical instrument end effector
A method of controlling an operation of a robotically-controlled surgical instrument can include receiving a first input signal at a controller indicative of a user's readiness to actuate the surgical instrument to perform a surgical procedure, outputting an output signal from the controller to provide feedback to the user in response to the received first input signal, receiving a second input signal at the controller confirming the user's readiness to actuate the surgical instrument, outputting an actuation signal from the controller in response to receiving the second input signal, and actuating the surgical instrument to perform the surgical procedure based on the actuation signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
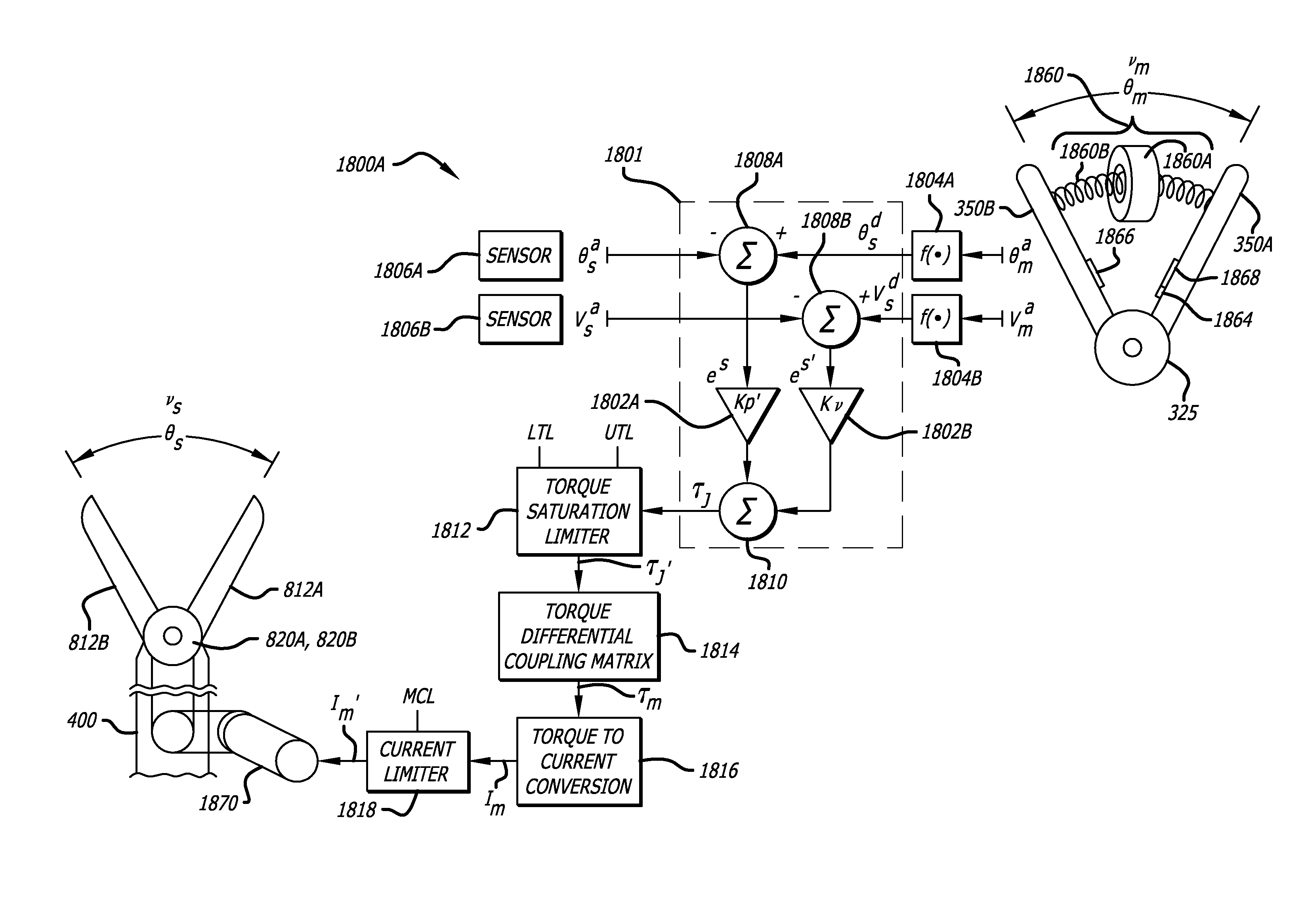
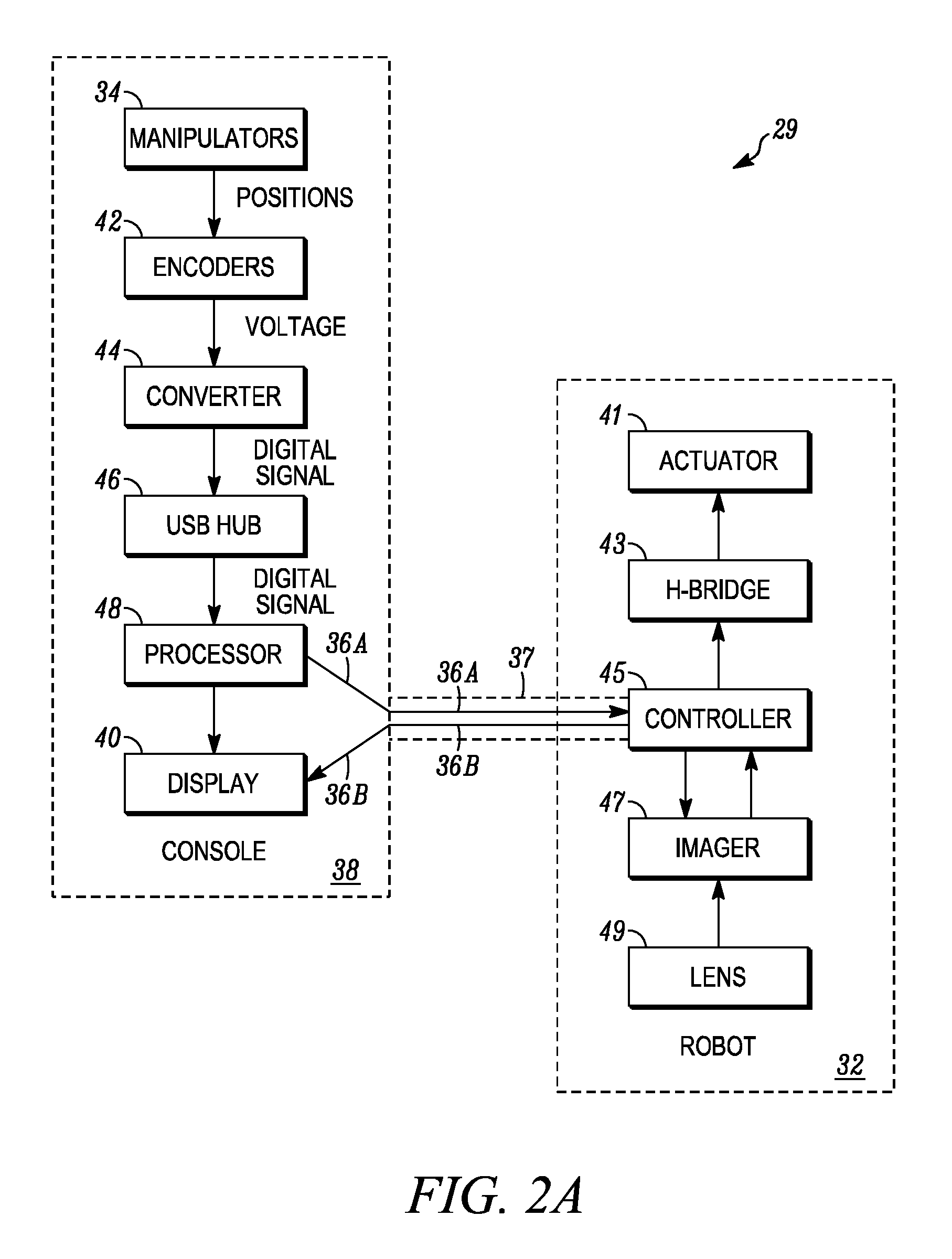
Maximum torque driving of robotic surgical tools in robotic surgical systems
ActiveUS9002518B2Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMaximum torqueMotor drive
In one embodiment of the invention, a control system for a robotic surgical instrument is provided including a torque saturation limiter, a torque to current converter coupled to the torque saturation limiter, and a motor coupled to the torque to current converter. The torque saturation limiter receives a desired torque signal for one or more end effectors and limits the desired torque to a range between an upper torque limit and a lower torque limit generating a bounded torque signal. The torque to current converter transforms a torque signal into a current signal. The motor drives an end effector of one or more end effectors to the bounded torque signal in response to the first current signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
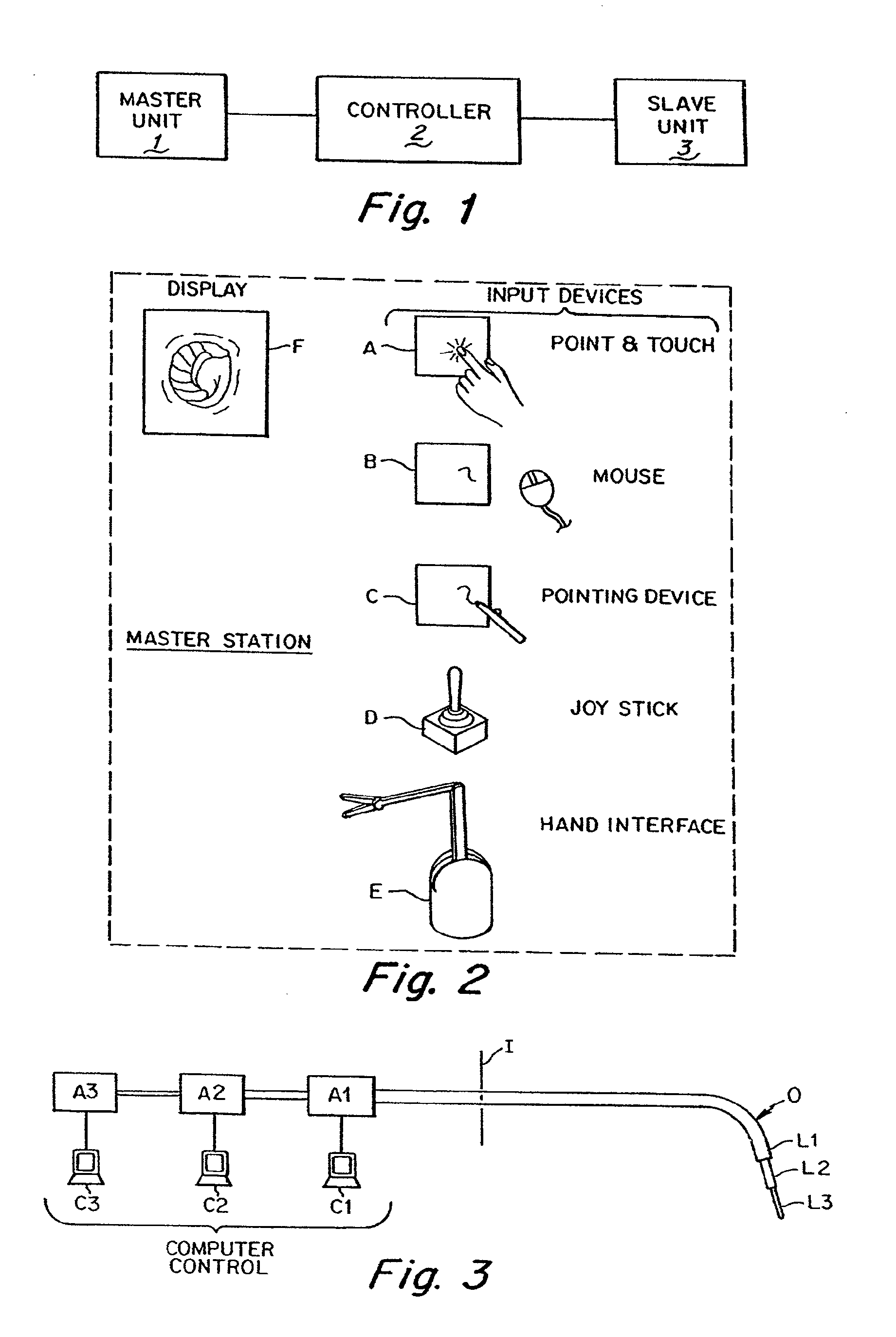
Repositioning and reorientation of master/slave relationship in minimally invasive telesurgery
InactiveUS7087049B2Easy SetupEasy to adjustDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringDegrees of freedom
The invention provides robotic surgical systems which allow selectable independent repositioning of an input handle of a master controller and / or a surgical end effector without corresponding movement of the other. In some embodiments, independent repositioning is limited to translational degrees of freedom. In other embodiments, the system provides an input device adjacent a manipulator supporting the surgical instrument so that an assistant can reposition the instrument at the patient's side.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
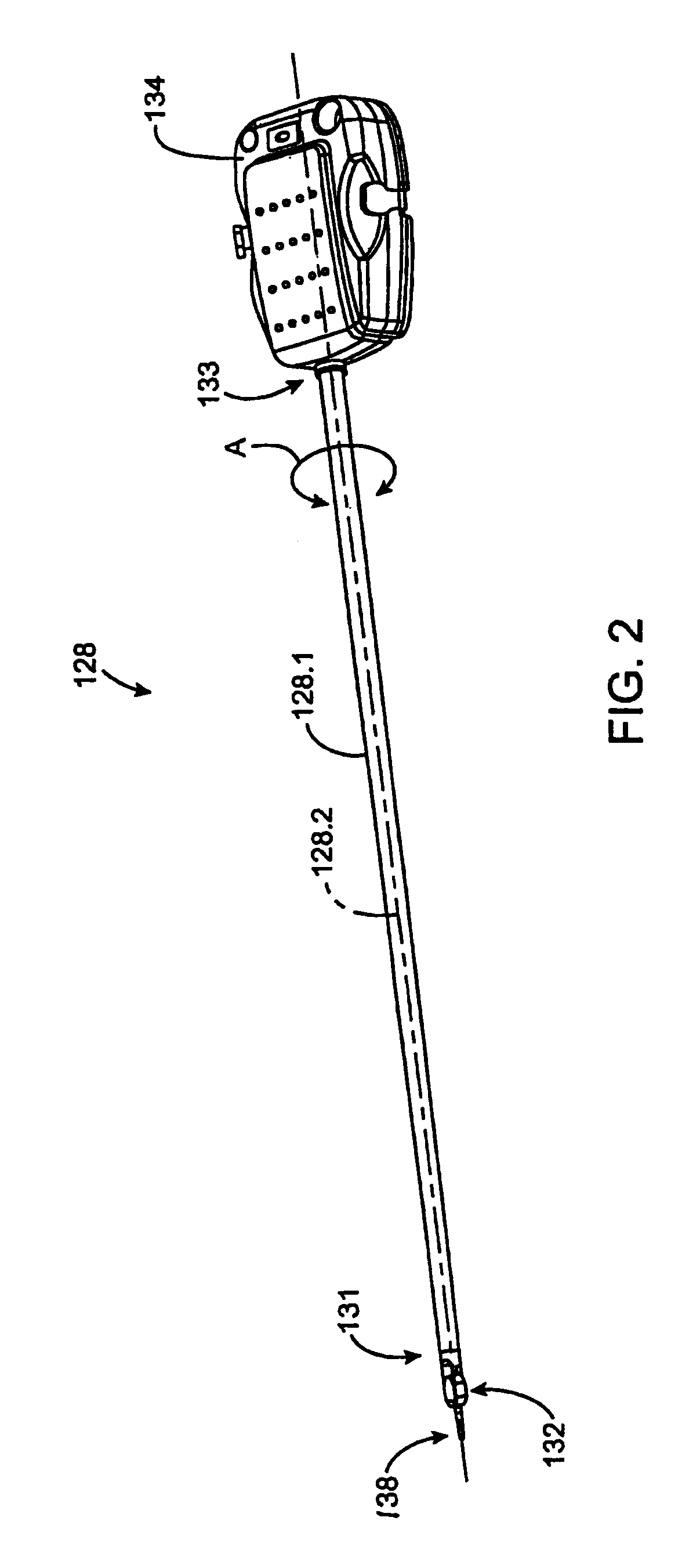
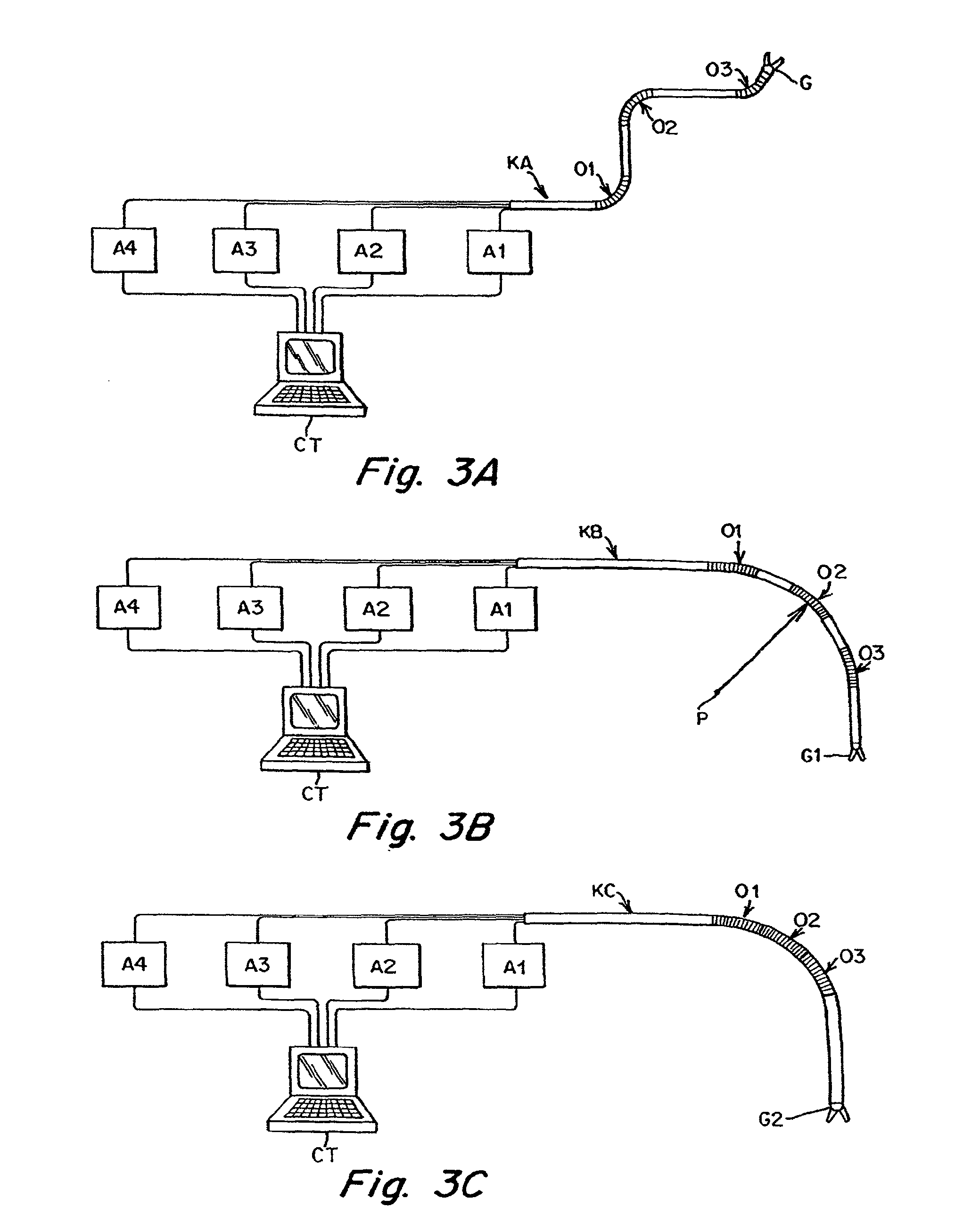
Interface assembly for controlling orientation of robotically controlled medical instrument
Interface assemblies for controlling an orientation of a working instrument of a robotic medical instrument system. A base member is coupled to a distal end of an instrument such as a robotically controllable catheter. A spacer element is retained between the base member and a platform member, which is movable relative to the base member about the spacer element. One or more control elements extending through a base member aperture can be used to control an orientation of the platform member and working instrument.
Owner:HANSEN MEDICAL INC
Wrist with decoupled motion transmission
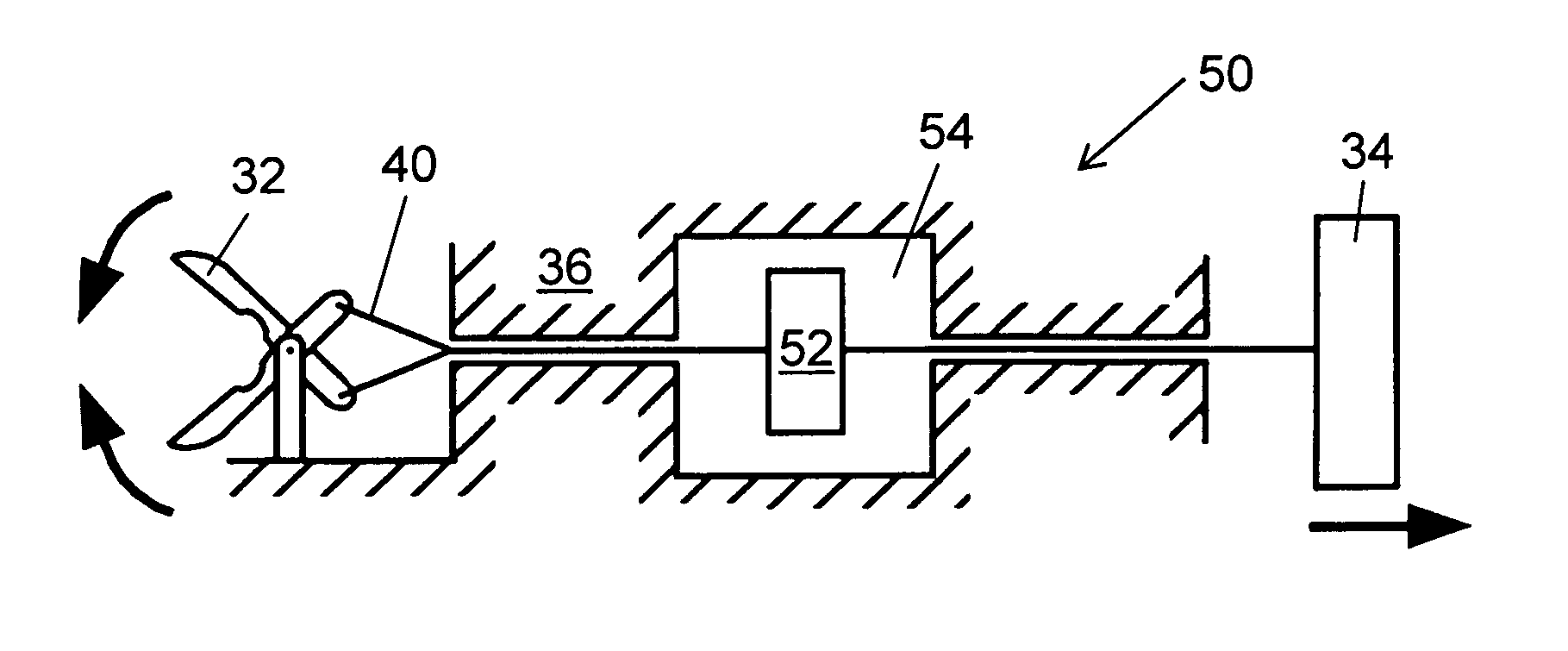
InactiveUS6969385B2Reduce inertiaImprove device performanceMechanical apparatusJointsEngineeringActuator
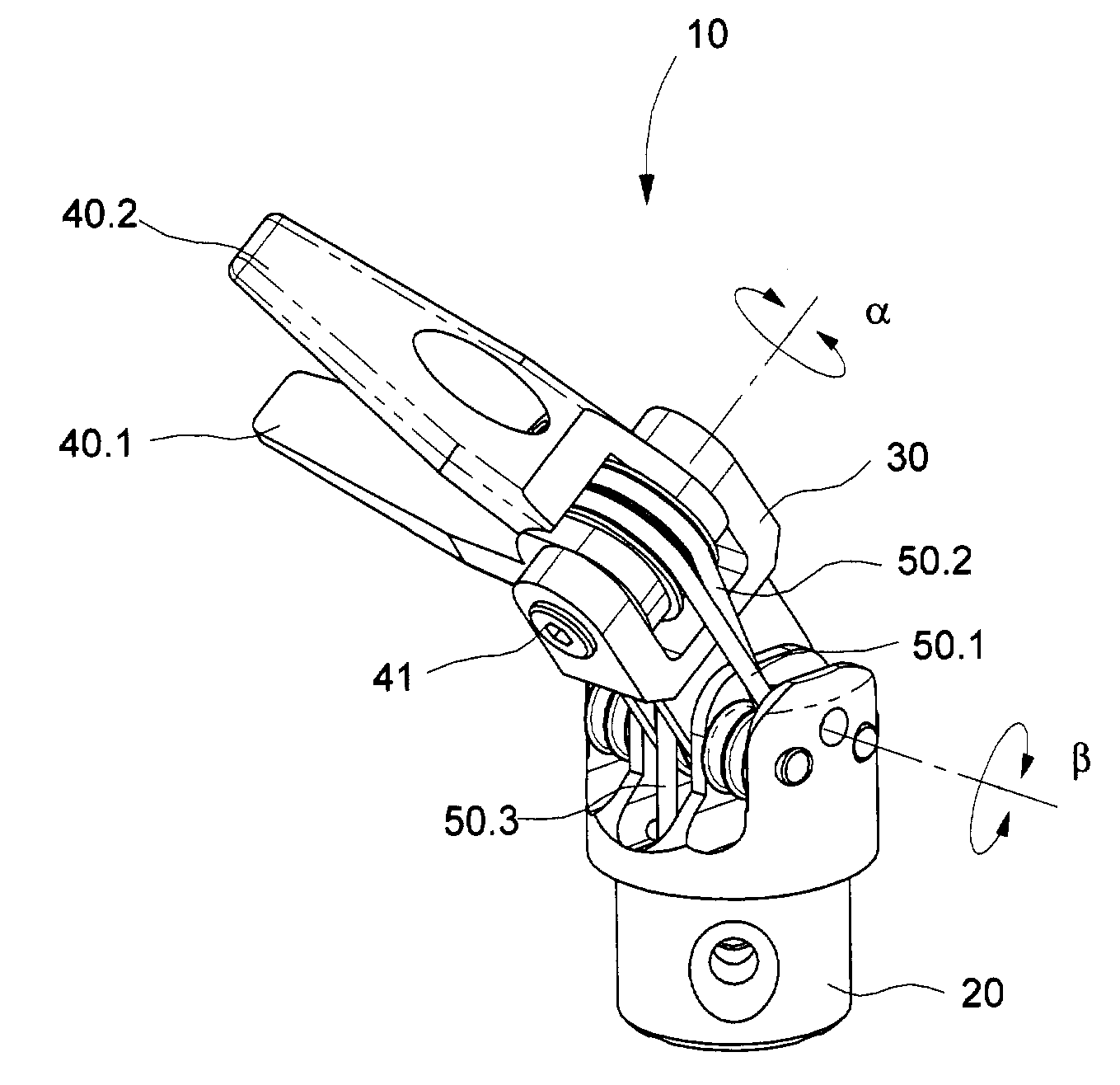
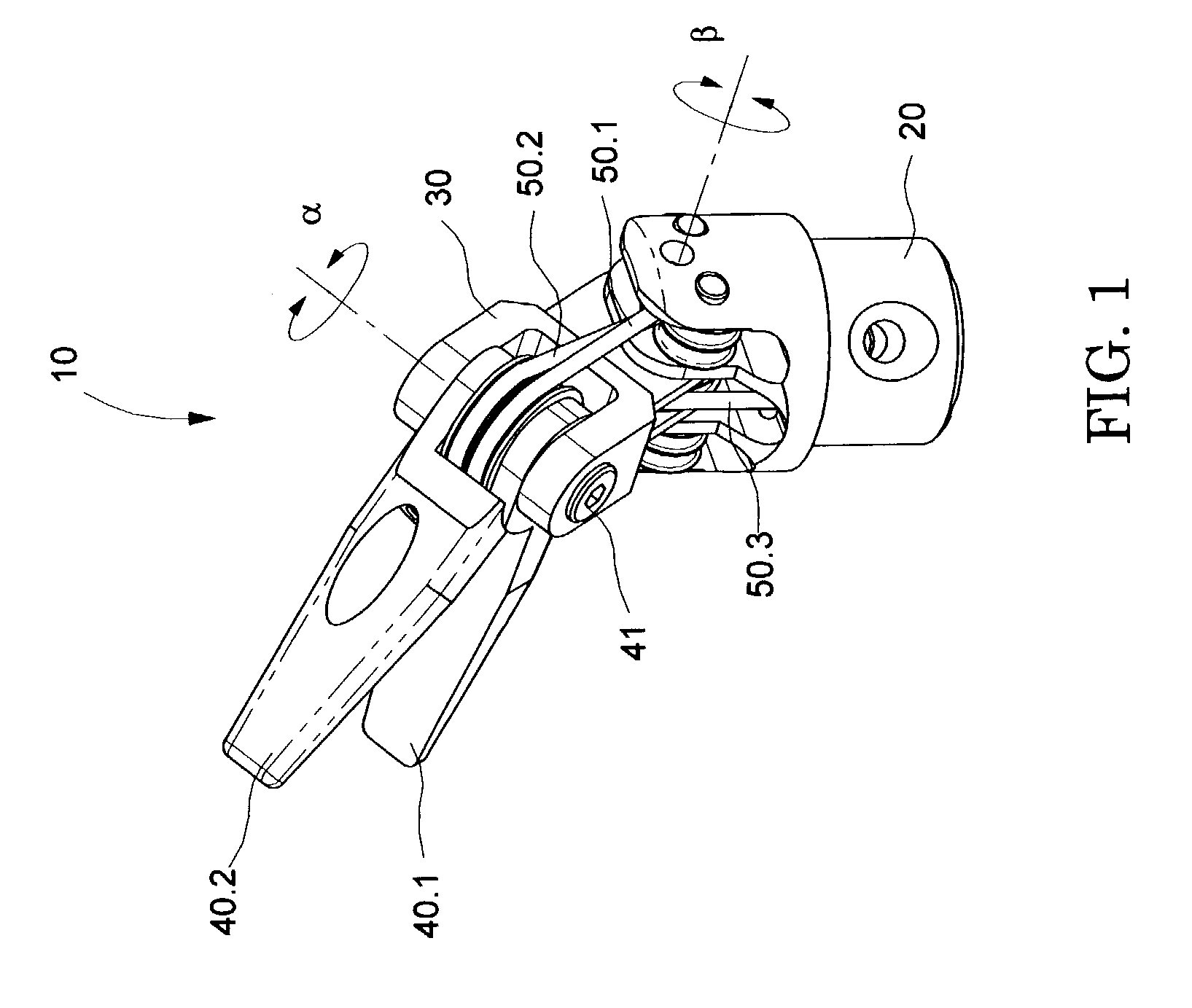
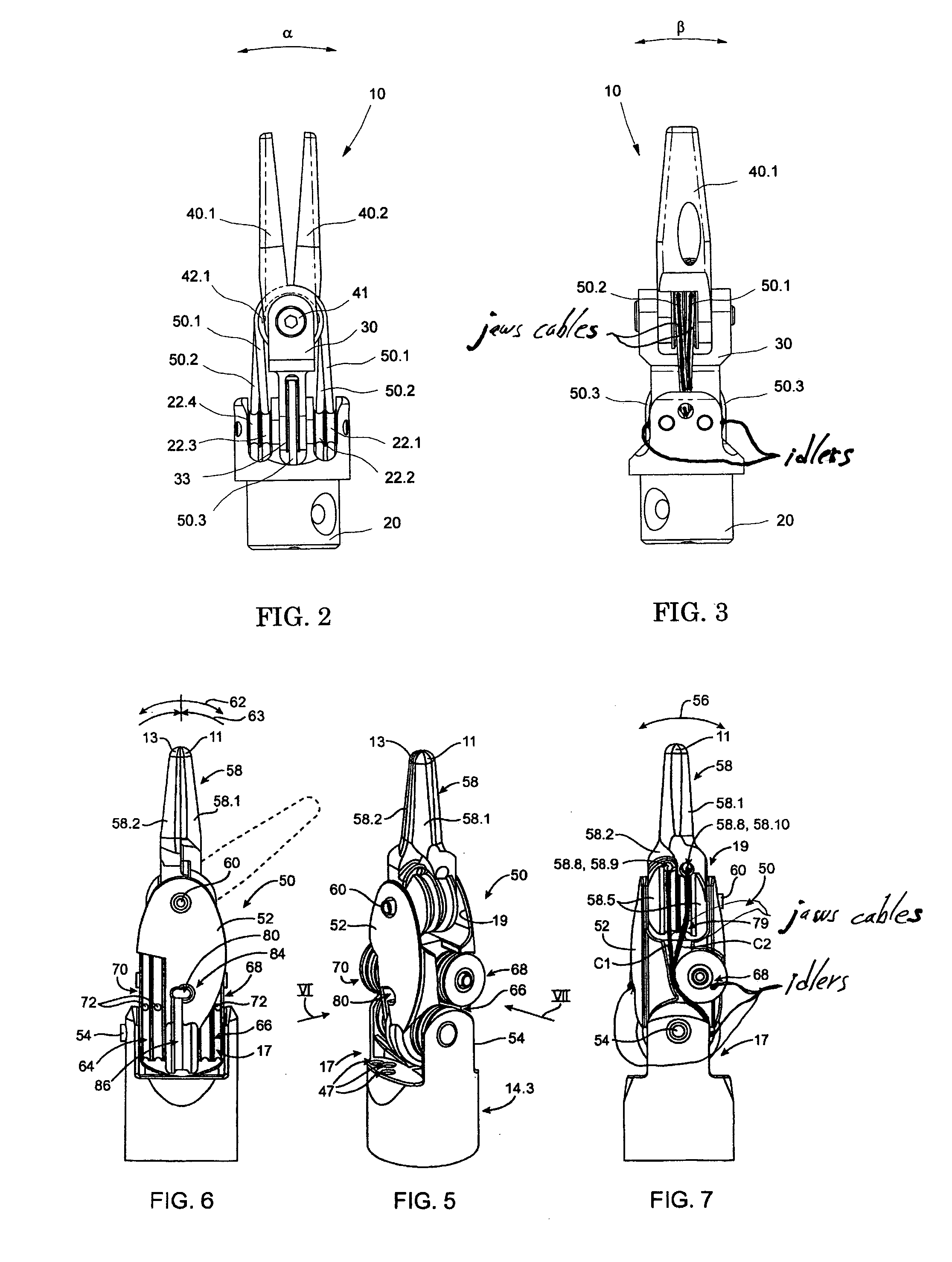
The present invention is a wrist mechanism and a method for making robotic devices in which the transmission of motion, force and / or torque around a revolute joint can be accomplished without coupling. This construction allows mounting the actuators on the base or lower elements of a mechanism, so that only linkage elements move the end-effector. Thus reducing inertia of the moving elements and increasing performance of the device. The decoupled motion of the end-effector or links is achieved by routing their transmission cables around idler pulleys placed parallel to the joint rotation axis on an optimal position such any stretch on the transmission cable is minimized. In particular, this construction can be use for robotic surgical tools that have two independently driven jaws, decoupled and orthogonal from its articulating wrist. This device may be used in grasping, cutting, suturing or alike operations.
Owner:MOREYRA MANUEL RICARDO
Maximum torque driving of robotic surgical tools in robotic surgical systems
ActiveUS20080046122A1Improve the level ofProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLower limitMaximum torque
In one embodiment of the invention, a control system for a robotic surgical instrument is provided including a torque saturation limiter, a torque to current converter coupled to the torque saturation limiter, and a motor coupled to the torque to current converter. The torque saturation limiter receives a desired torque signal for one or more end effectors and limits the desired torque to a range between an upper torque limit and a lower torque limit generating a bounded torque signal. The torque to current converter transforms a torque signal into a current signal. The motor drives an end effector of one or more end effectors to the bounded torque signal in response to the first current signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
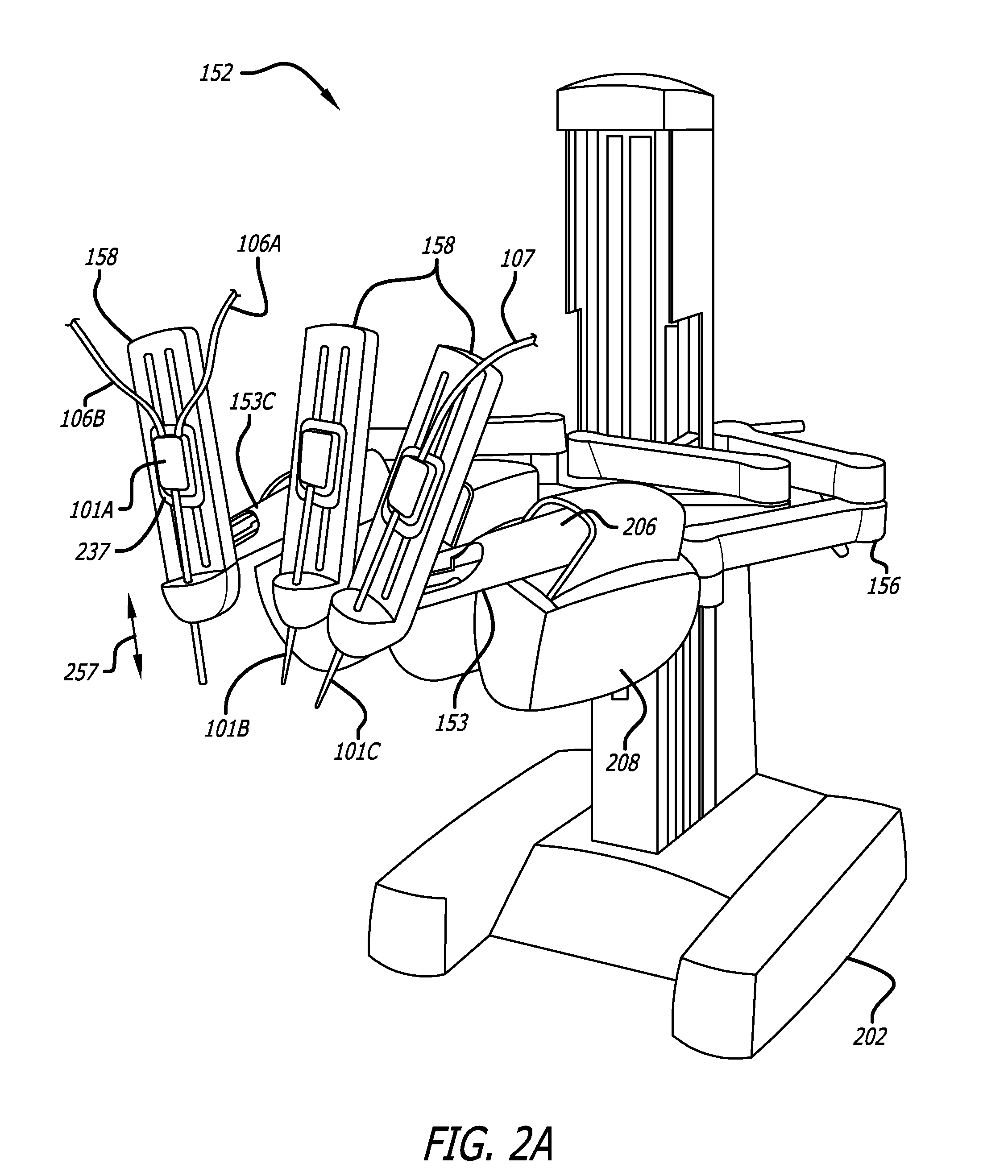
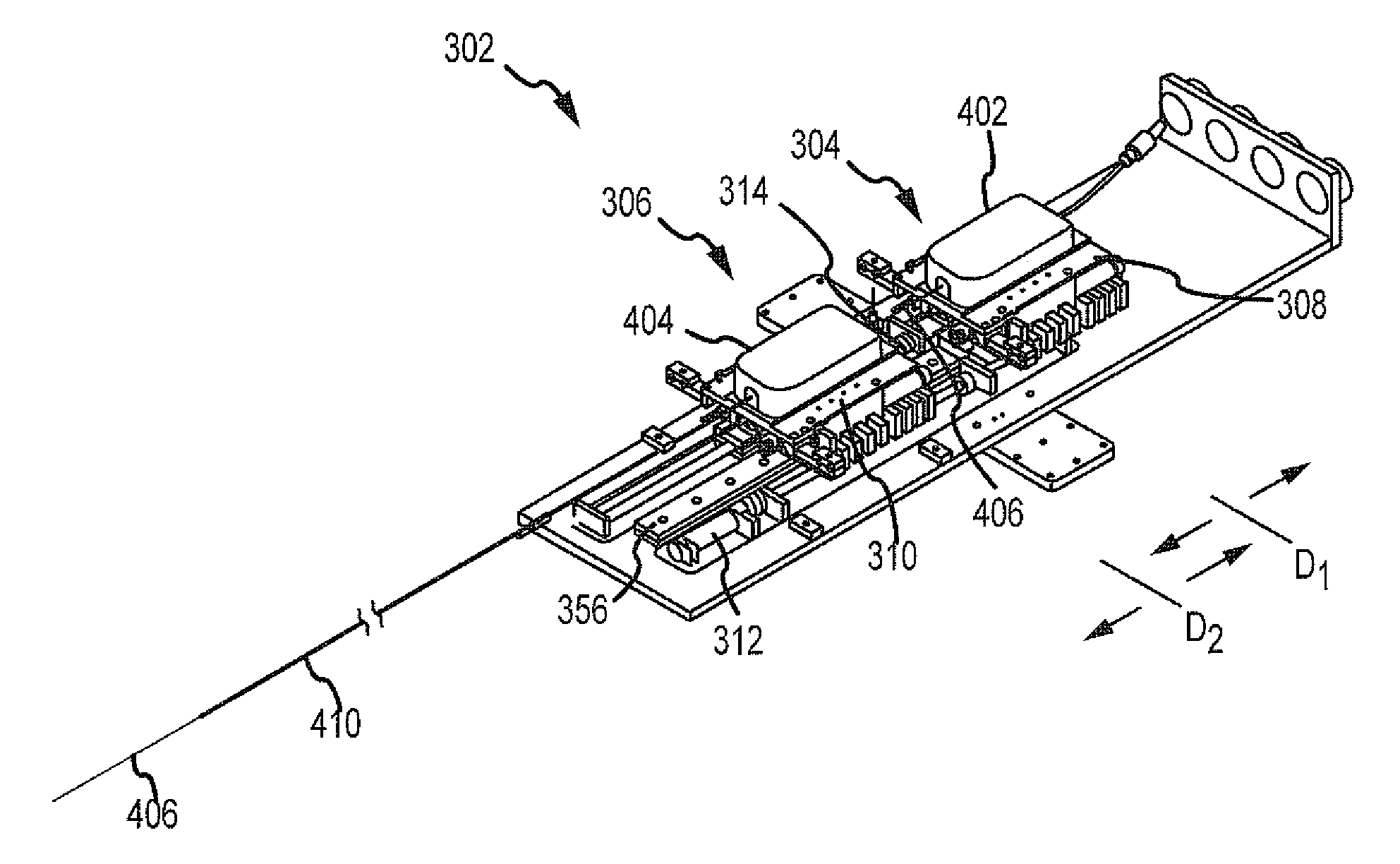
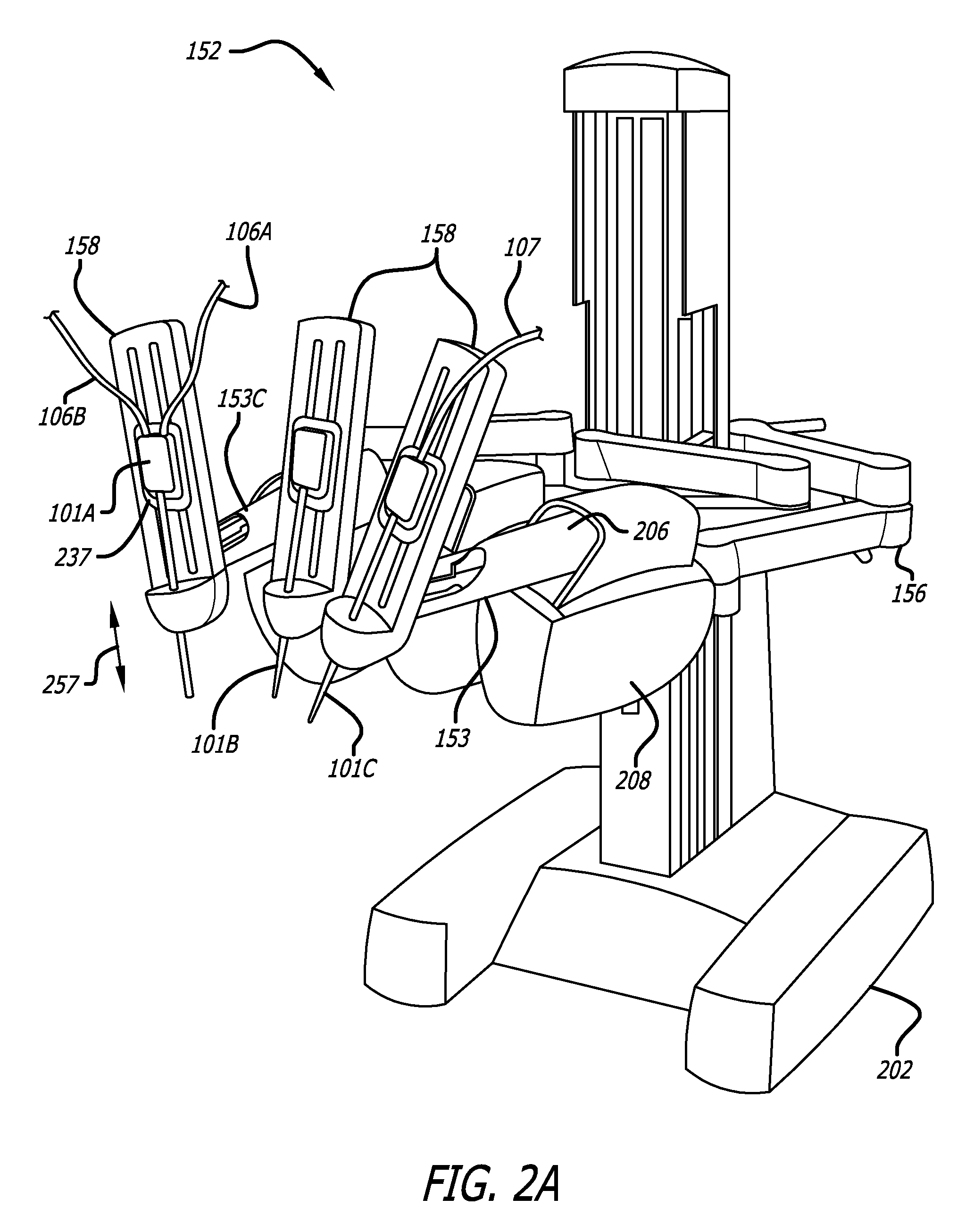
Robotic catheter manipulator assembly
ActiveUS8317744B2Minimize and eliminate procedural variabilityMinimize and eliminate exposureDiagnosticsMedical devicesEngineeringManipulator
A robotic catheter manipulator assembly may include a support member including a catheter manipulation base and a sheath manipulation base movable relative to each other and to the support member. Each respective manipulation base may be releasably connectable to a catheter cartridge and a sheath cartridge. A drive mechanism may be provided for moving the catheter and sheath manipulation bases relative to each other and to the support member. The manipulation base or the cartridge may include a first element engageable with a complementary second element slidably engaged with the other one of the manipulation base or the cartridge for controlling movement of a component connected to the cartridge. The cartridge, for example, may be a transseptal cartridge, a catheter cartridge or a sheath cartridge, and the component may respectively be a surgically insertable device such as a transseptal needle, a catheter or a sheath.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
End effector mechanism for a surgical instrument
Improved end effector mechanisms for a surgical instrument used in minimally invasive surgical instruments as well as instruments for general surgery or as part of robotically controlled end effectors. These end effector mechanisms include multiple grasping elements paired with drive links. Each grasping element also serves as a stabilizing link for the next most distal grasping element, forcing it to maintain its relative angle with respect to the opposing grasping elements.
Owner:SPECIALTY SURGICAL INSTR INC
Retractor system for internal in-situ assembly during laparoscopic surgery
A method of laparoscopic (or robotic) surgery, using a hand-port, comprising providing a trocar port operably disposed within a first abdominal incision opening of a patient, providing a hand-port operably disposed within a second abdominal incision opening, introducing an elongate positioner dimensioned to extend through the trocar, introducing a spatulate element through the hand port and joining the spatulate element to the positioner. The procedure further comprises removing an internal organ or other tissue from the operating area in order to make room and add visibility for the laparoscopic intervention, detaching the spatulate element from the positioner, and withdrawing the positioner through the trocar port and the spatulate through the hand port.
Owner:JOHNSTON WILLIAM
Two-piece end-effectors for robotic surgical tools
In one embodiment of the invention, a robotic surgical tool having opposing jaws, the working element of the robotic surgical tool is made of a different material from the drive element of the robotic surgical tool. The two elements may be manufactured independently and assembled together at a later stage. The material comprising each element may thus have properties more appropriate to the function each element plays in the robotic surgical tool. For example, the metal selected to comprise the blade of a surgical scissor may be corrosion resistant and capable of being sharpened to a high degree.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
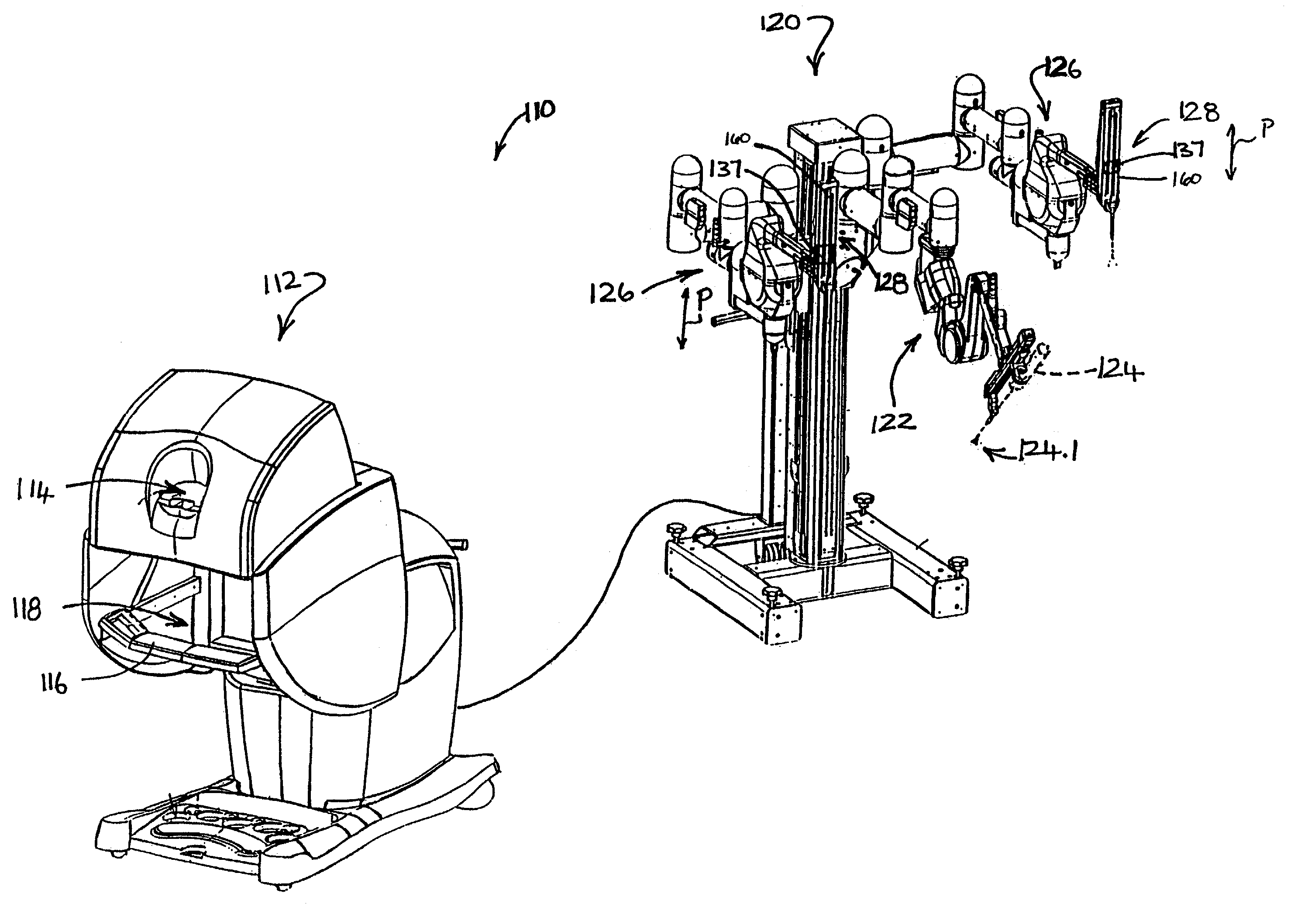
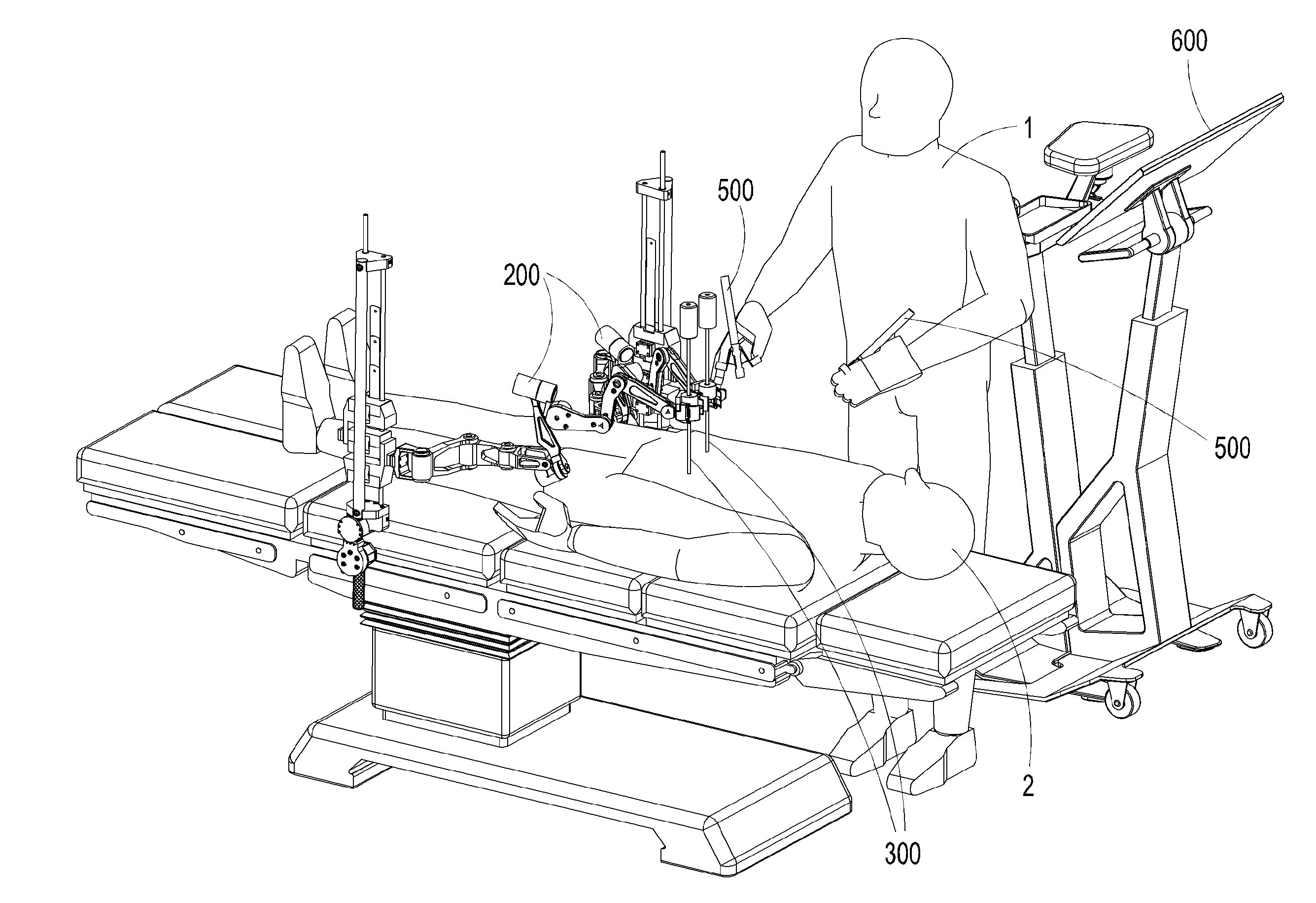
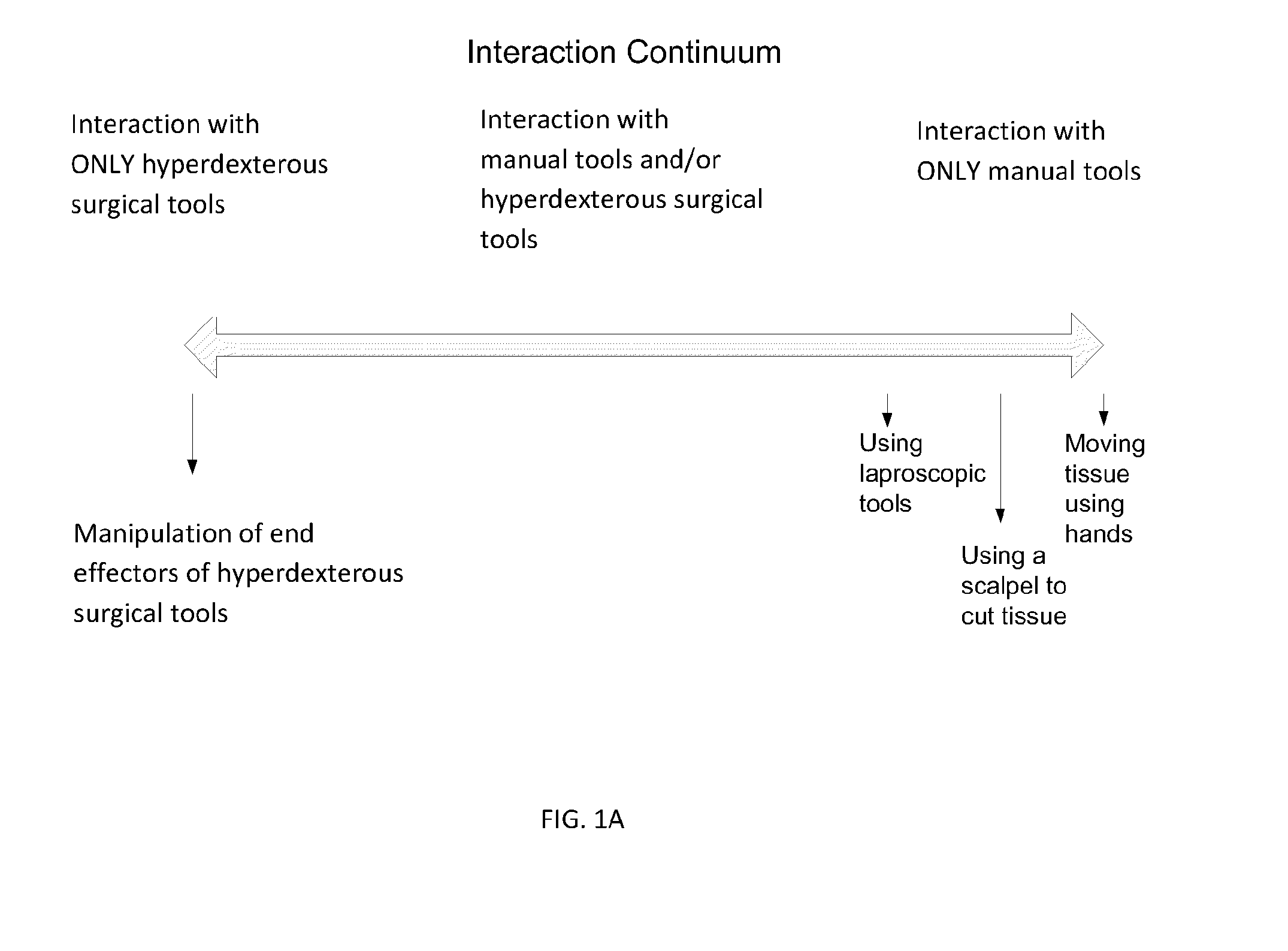
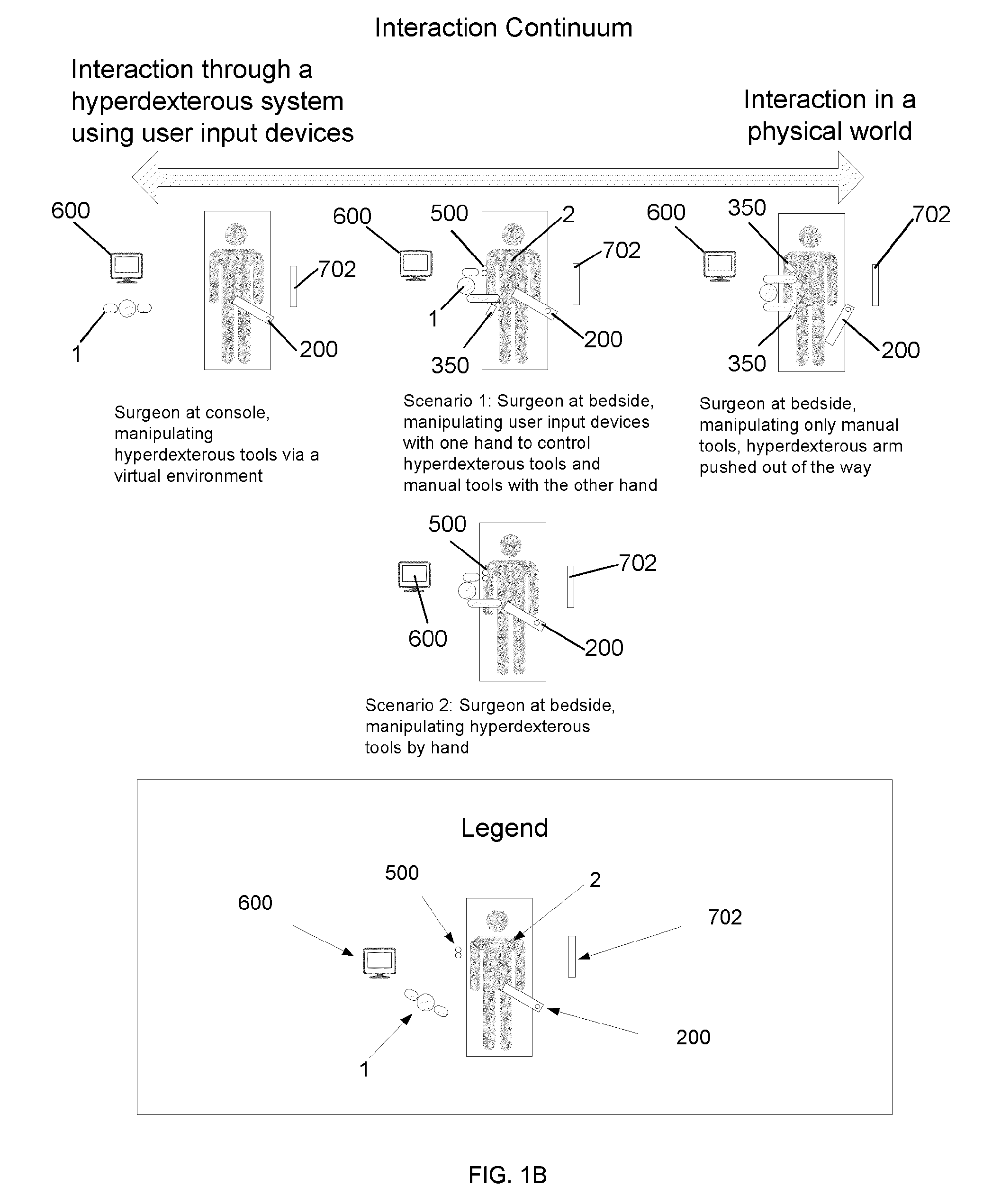
Hyperdexterous surgical system
InactiveUS20150025549A1Overcome deficienciesProvide flexibilityProgramme controlDiagnosticsControl signalElectronic control system
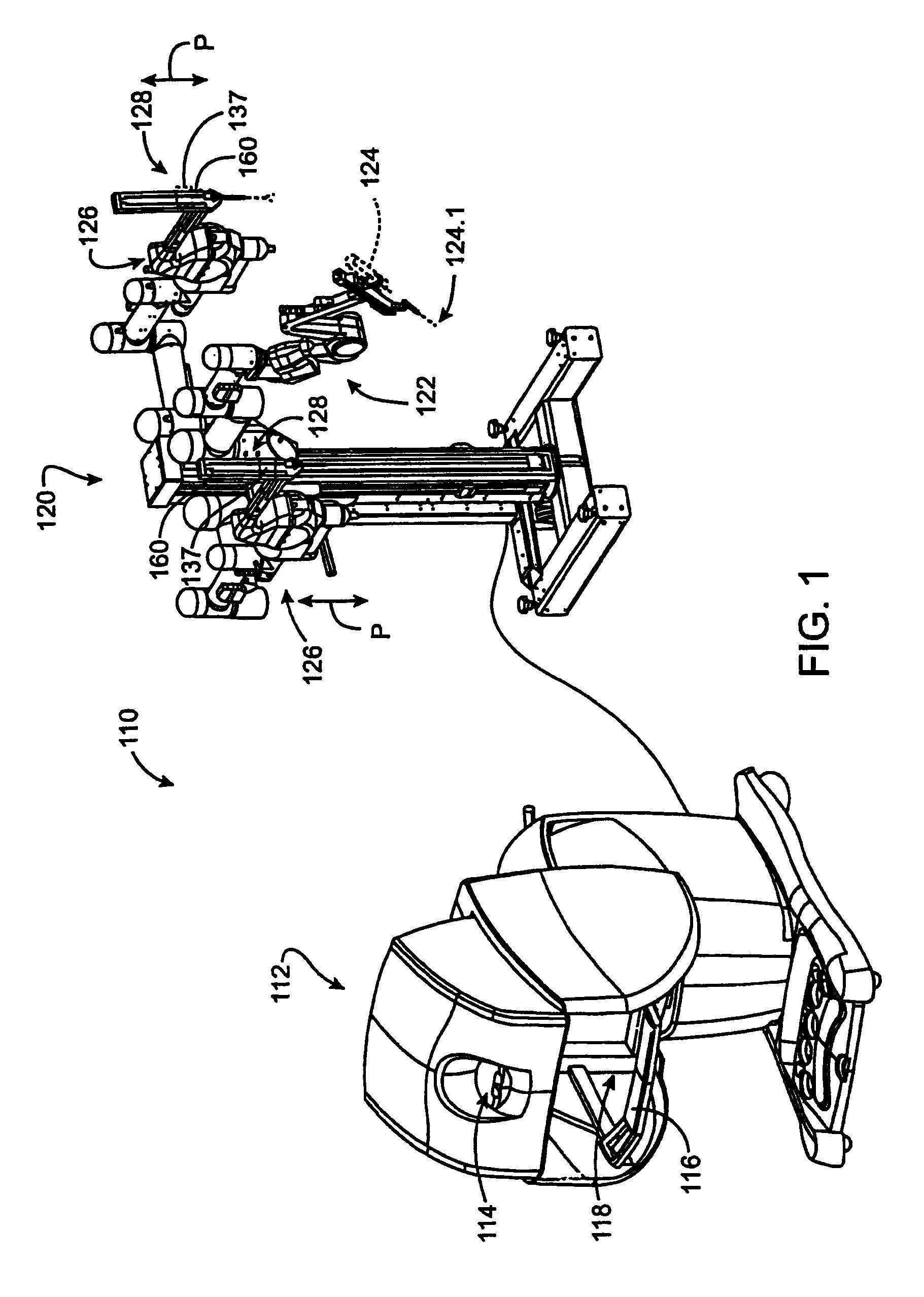
A hyperdexterous surgical system is provided. The system can include one or more surgical arms coupleable to a fixture and configured to support one or more surgical tools. The system can include an electronic control system configured to communicate electronically with the one or more robotic surgical tools. The control system can electronically control the operation of the one or more surgical tools. The system can include one or more portable handheld controllers actuatable by a surgeon to communicate one or more control signals to the one or more surgical tools via the electronic control system to operate the one or more surgical tools. The one or more portable handheld controllers can provide said one or more control signals from a plurality of locations of an operating arena, allowing a surgeon to be mobile during a surgical procedure and to remotely operate the one or more surgical tools from different locations of the operating arena.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
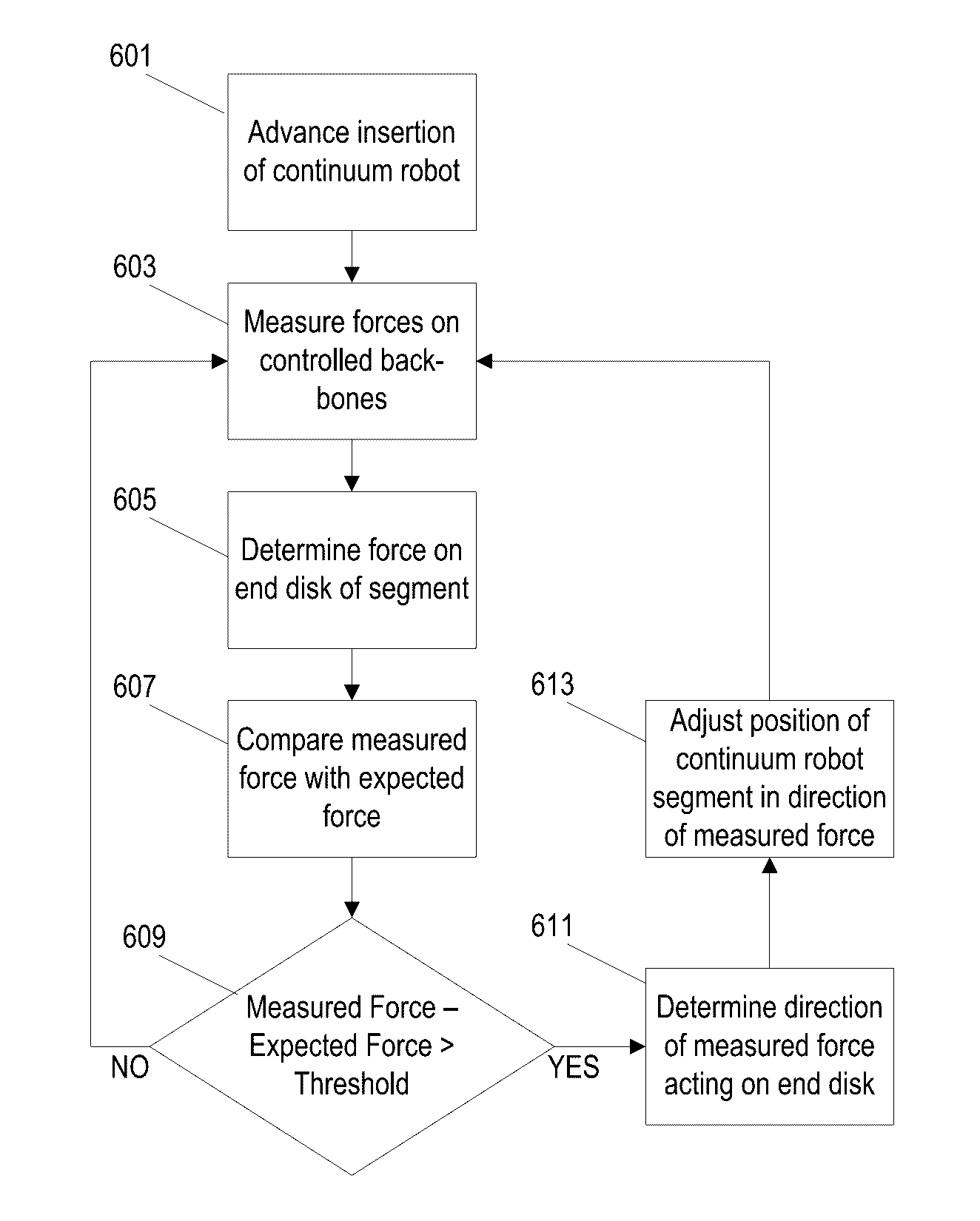
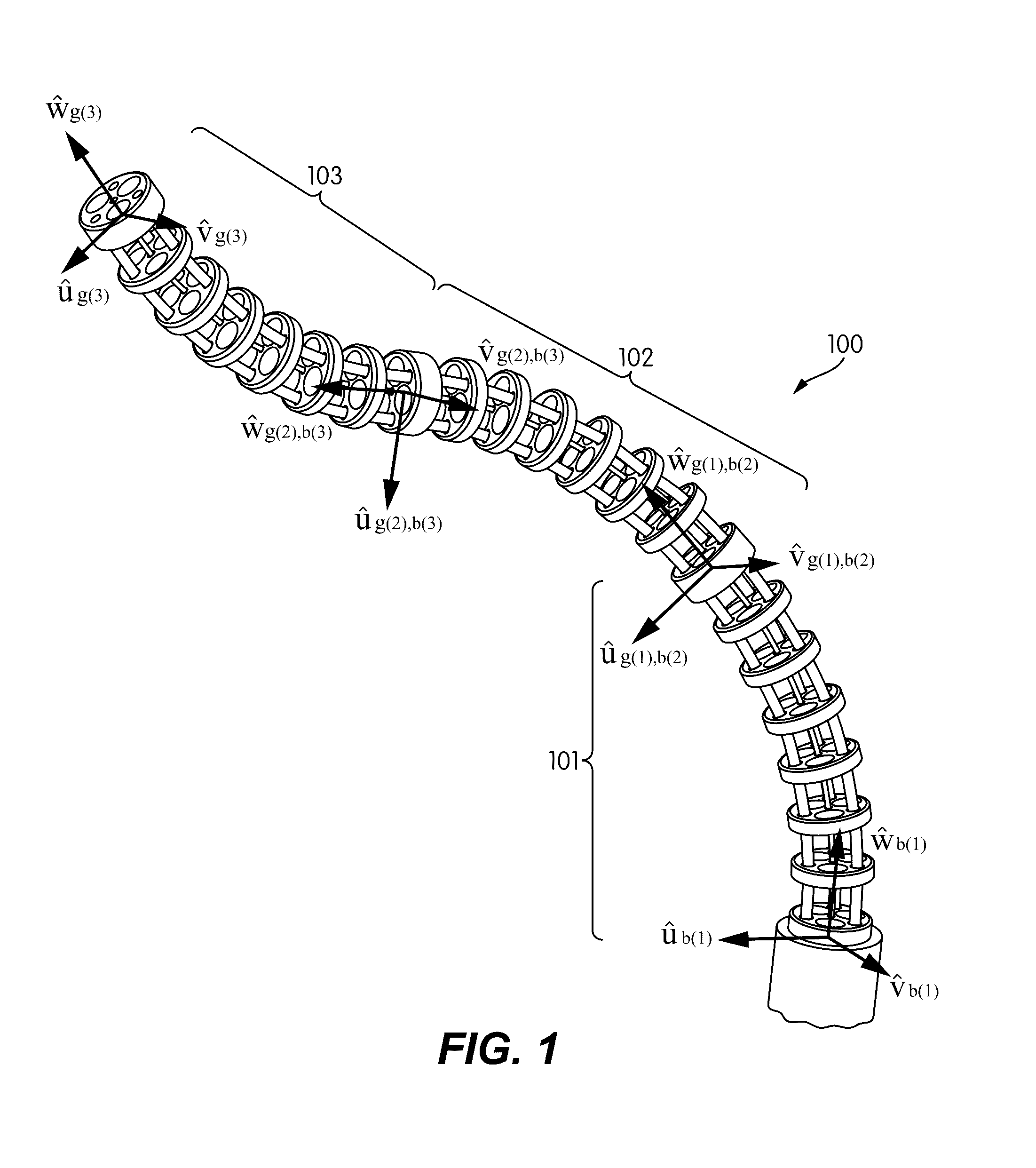
Systems and methods for safe compliant insertion and hybrid force/motion telemanipulation of continuum robots
ActiveUS9539726B2Easy to operateImprove stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringManipulator
Methods and systems are described for controlling movement of a continuum robot that includes a plurality of independently controlled segments along the length of the continuum robot. The continuum robot is inserted into a cavity of unknown dimensions or shape. A plurality of forces acting upon the continuum robot by the surrounding cavity are estimated. A positioning command indicating a desired movement of the distal end of the continuum robot is received from a manipulator control. The desired movement is augmented based, at least in part, on the estimated plurality of forces acting on the continuum robot such that movement is restricted to within safe boundaries of the surrounding cavity. The positioning of the continuum robot is then adjusted based on the augmented desired movement.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Apparatus and method of user interface with alternate tool mode for robotic surgical tools
ActiveUS20090088774A1Improve the level ofDiagnosticsSurgical systems user interfaceGrip forceEngineering
In one implementation, a method is disclosed in which a lock sensing mode is entered for a robotic surgical instrument. In the lock sensing mode, the degrees of freedom of movement in the robotic surgical instrument are switchably reduced. Further in the lock sensing mode, one or more end effectors of the robotic surgical instrument are switchably clamped together in the robotic surgical instrument. An increased level of torque may also be applied to the end effectors to increase a gripping force applied by the one or more end effectors in response to the reduced degrees of freedom of movement in the robotic surgical instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
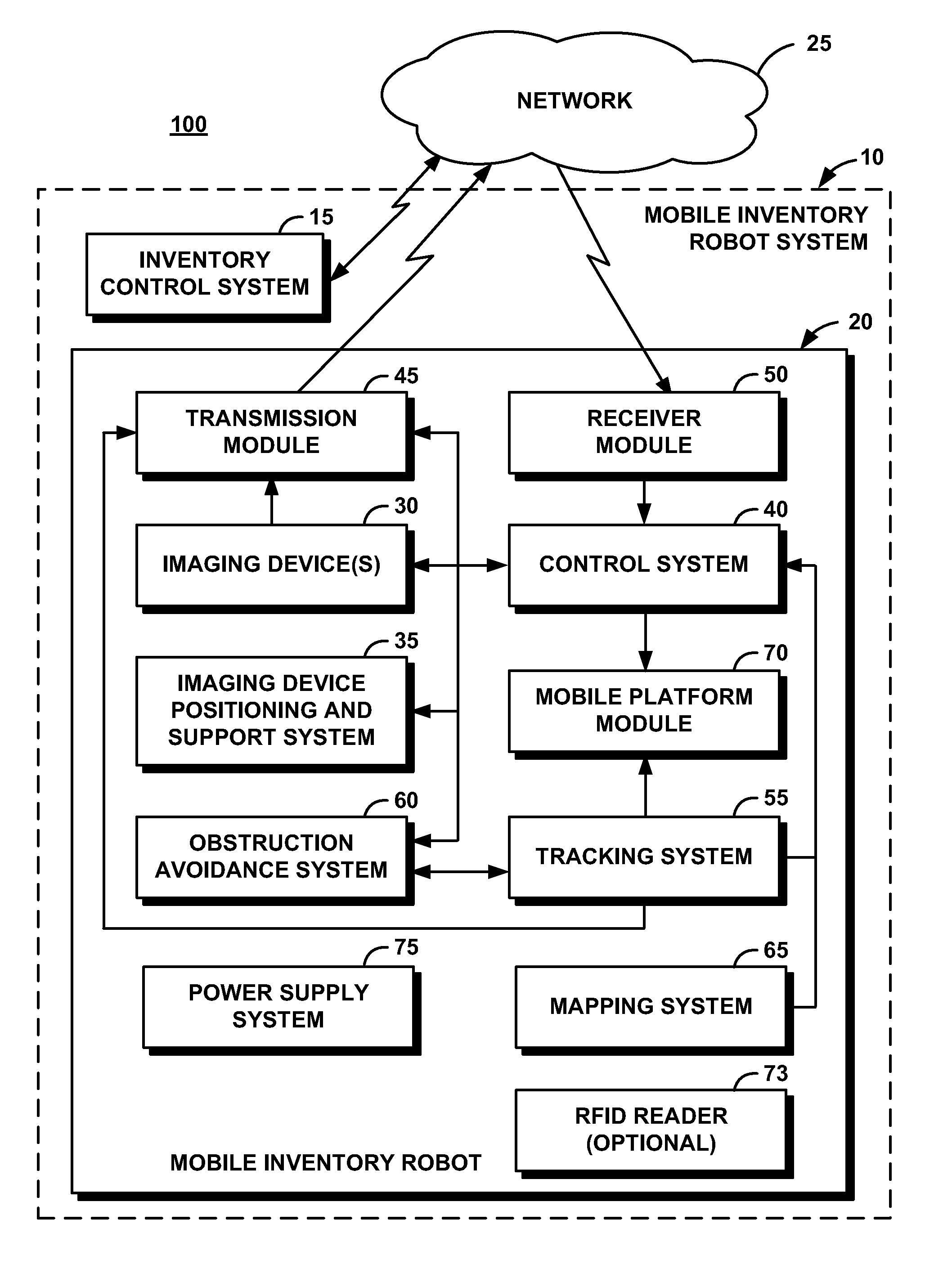
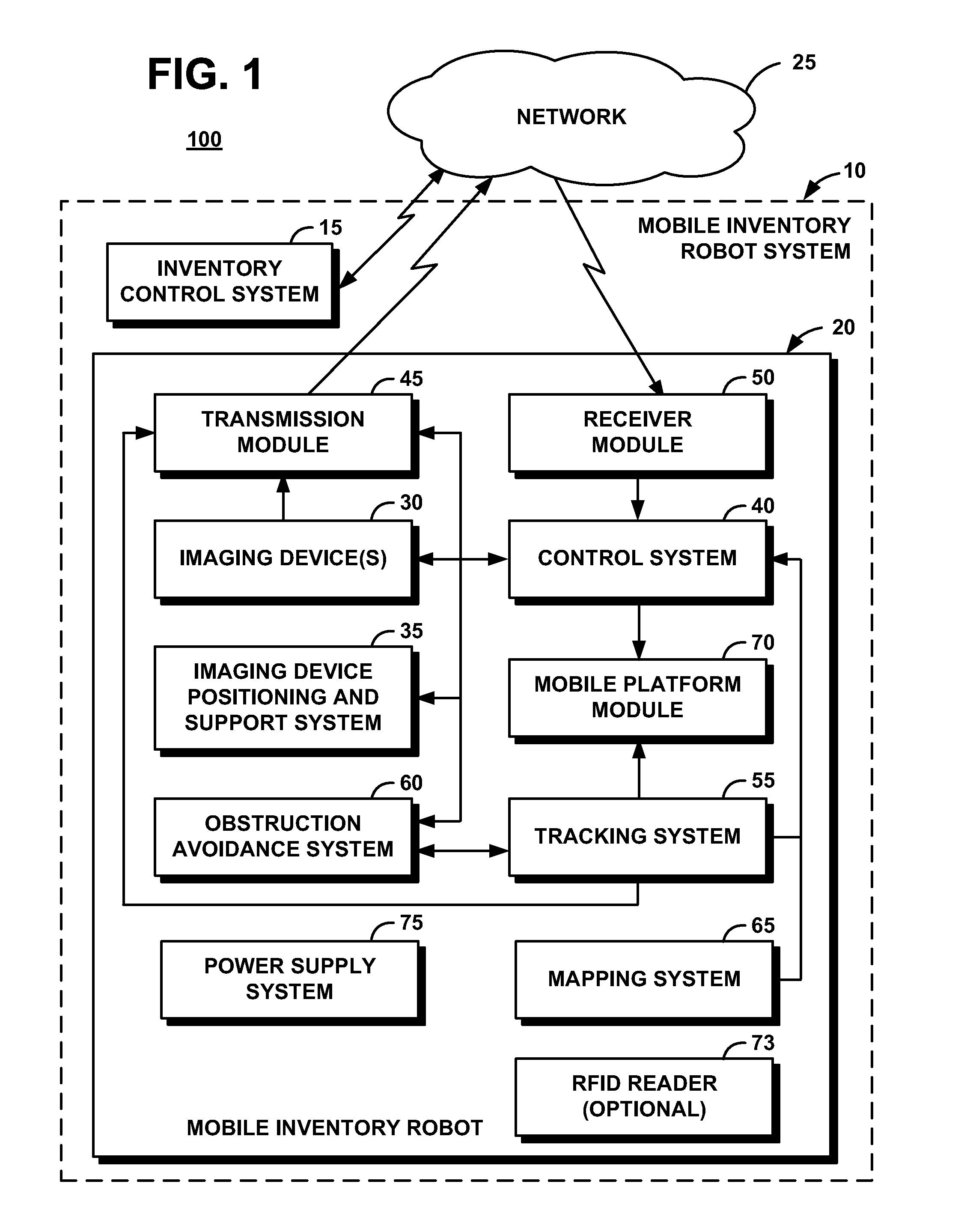
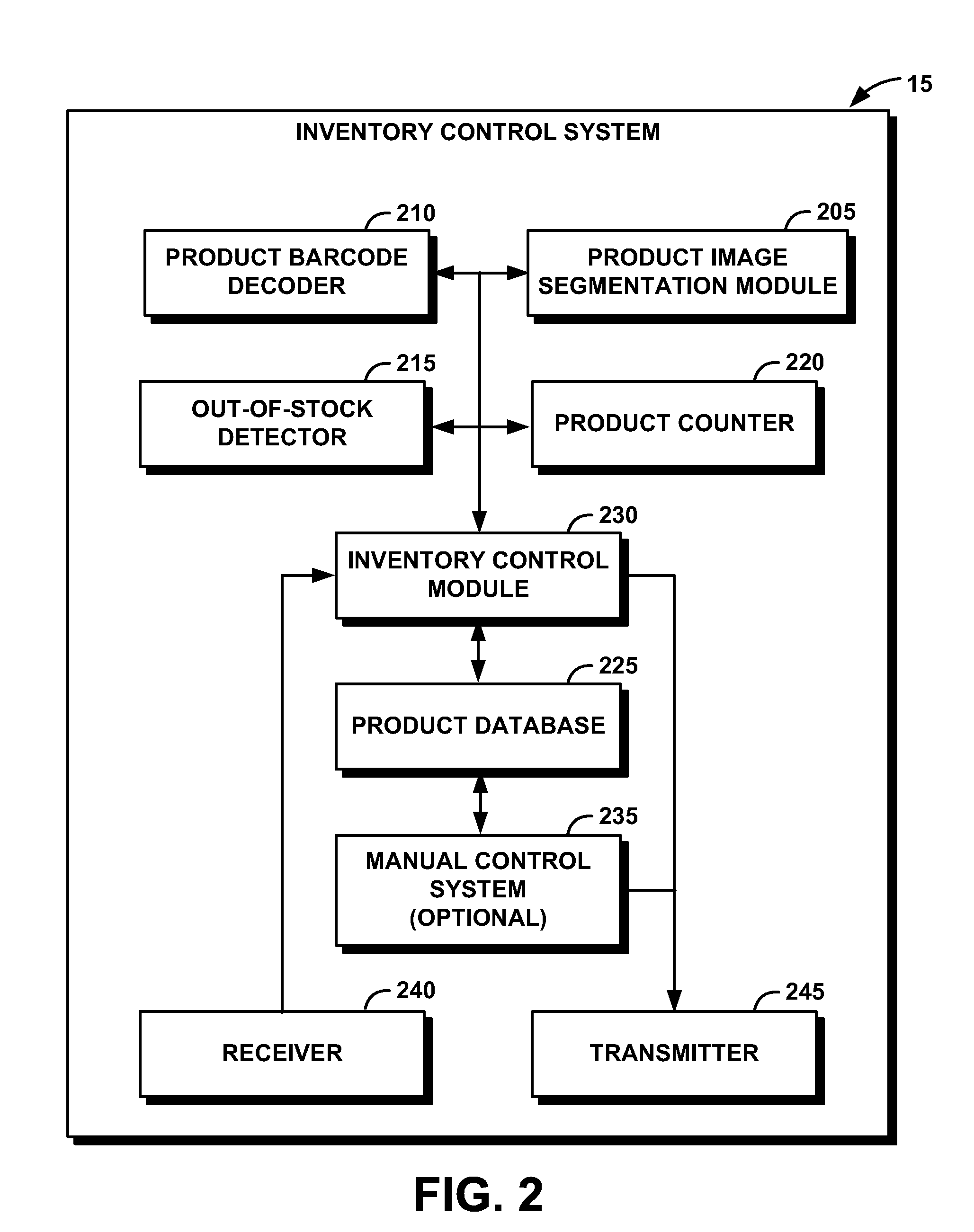
System and Method for Performing Inventory Using a Mobile Inventory Robot
InactiveUS20080077511A1Still image data retrievalVehicle position/course/altitude controlRobotic systemsBarcode
A mobile inventory robot system generates an inventory map of a store and a product database when a mobile inventory robot is manually navigated through the store to identify items on shelves, a location for each of the items on the shelves, and a barcode for each of the items. The system performs inventory of the items by navigating through the store via the inventory map, capturing a shelf image, decoding a product barcode from the captured shelf image, retrieving a product image for the decoded product barcode from the product database, segmenting the captured shelf image to detect an image of an item on the shelves, determining whether the detected image matches the retrieved image and, if not, setting an out-of-stock flag for an the item.
Owner:IBM CORP
Flexible instrument
A robotic medical system comprises a catheter having an elongated shaft with a plurality of flexible segments spaced apart along the catheter, and a drive unit coupled to the catheter. The catheter may have a plurality of cables respectively terminating at the flexible segments, in which case, the drive unit will be coupled to the plurality of cables. The robotic medical system further comprises a user interface remote from the drive unit and configured for generating at least one command, and an electric controller configured, in response to the command(s), for directing the drive unit to independently bend the flexible segments (e.g., three flexible segments).
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
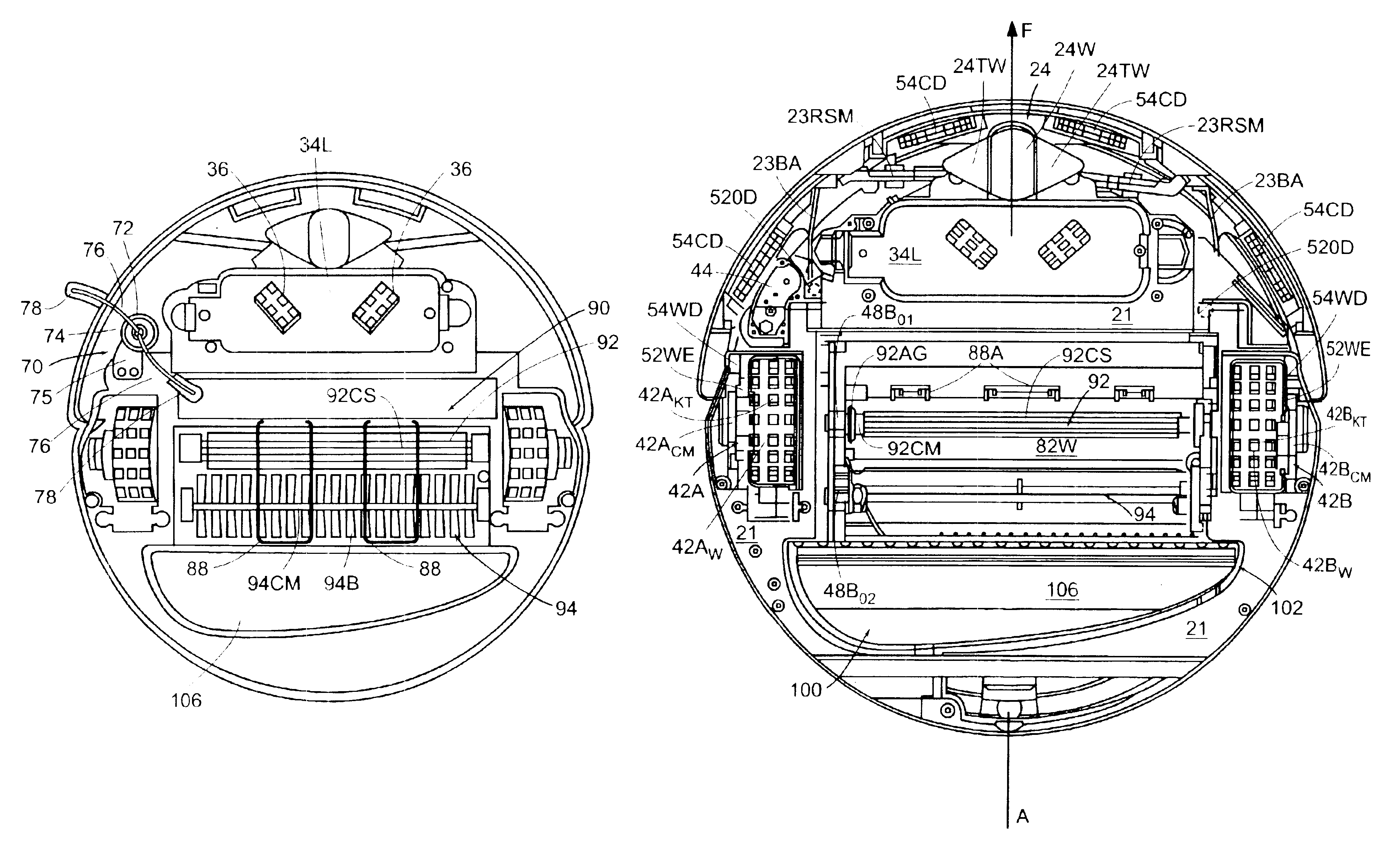
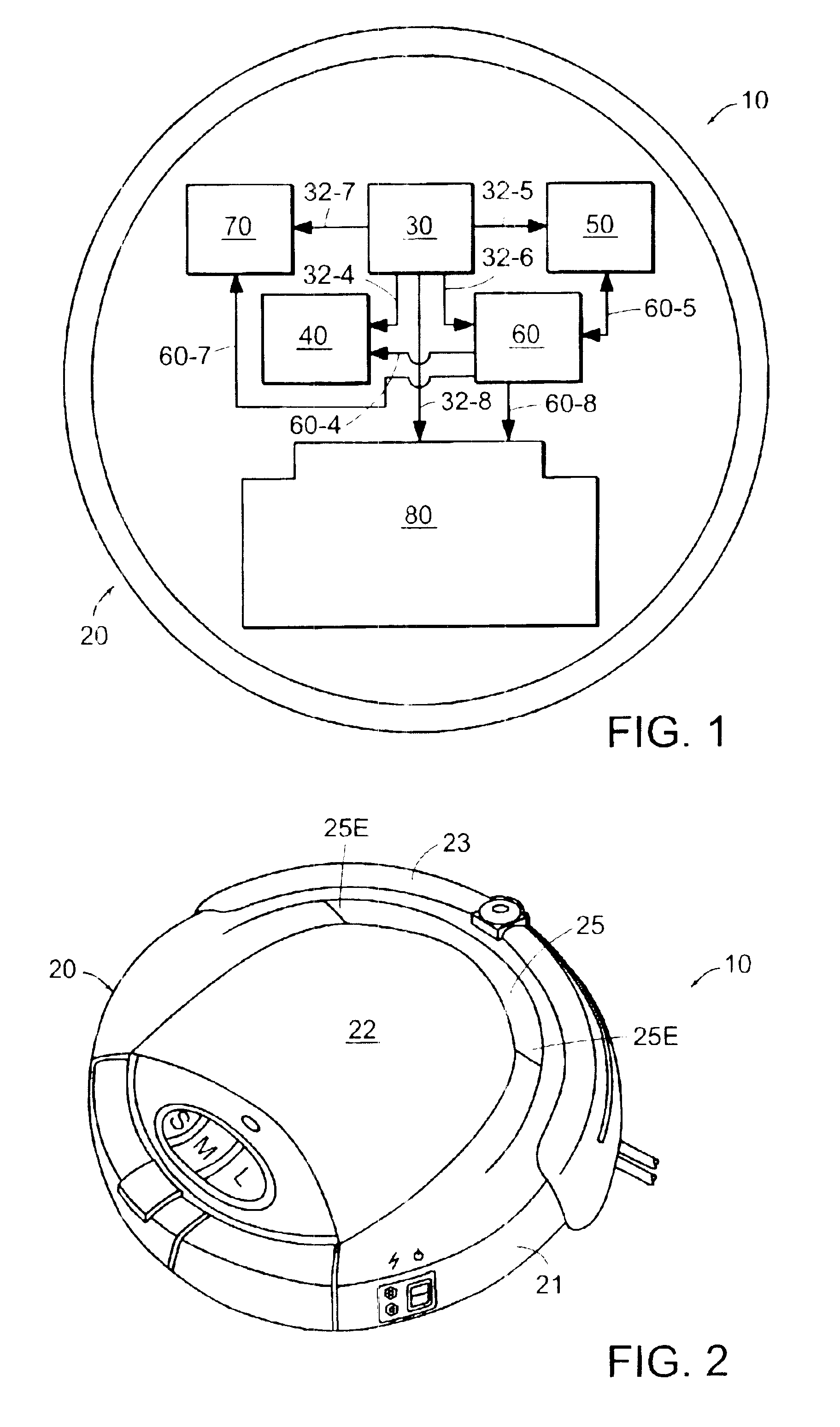
Autonomous floor-cleaning robot
InactiveUS6883201B2Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove efficiencyAutomatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlDual stageEngineering
Owner:IROBOT CORP
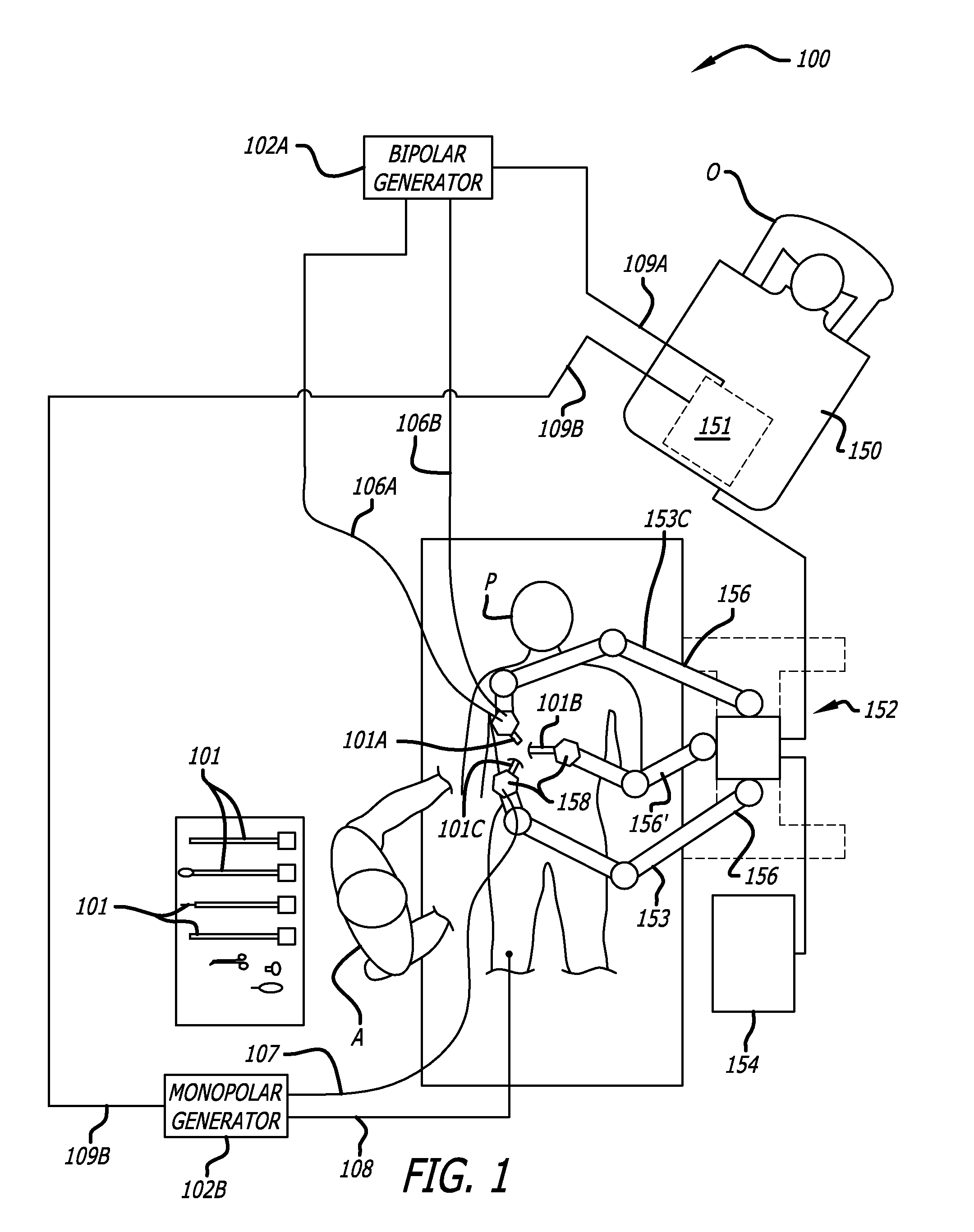
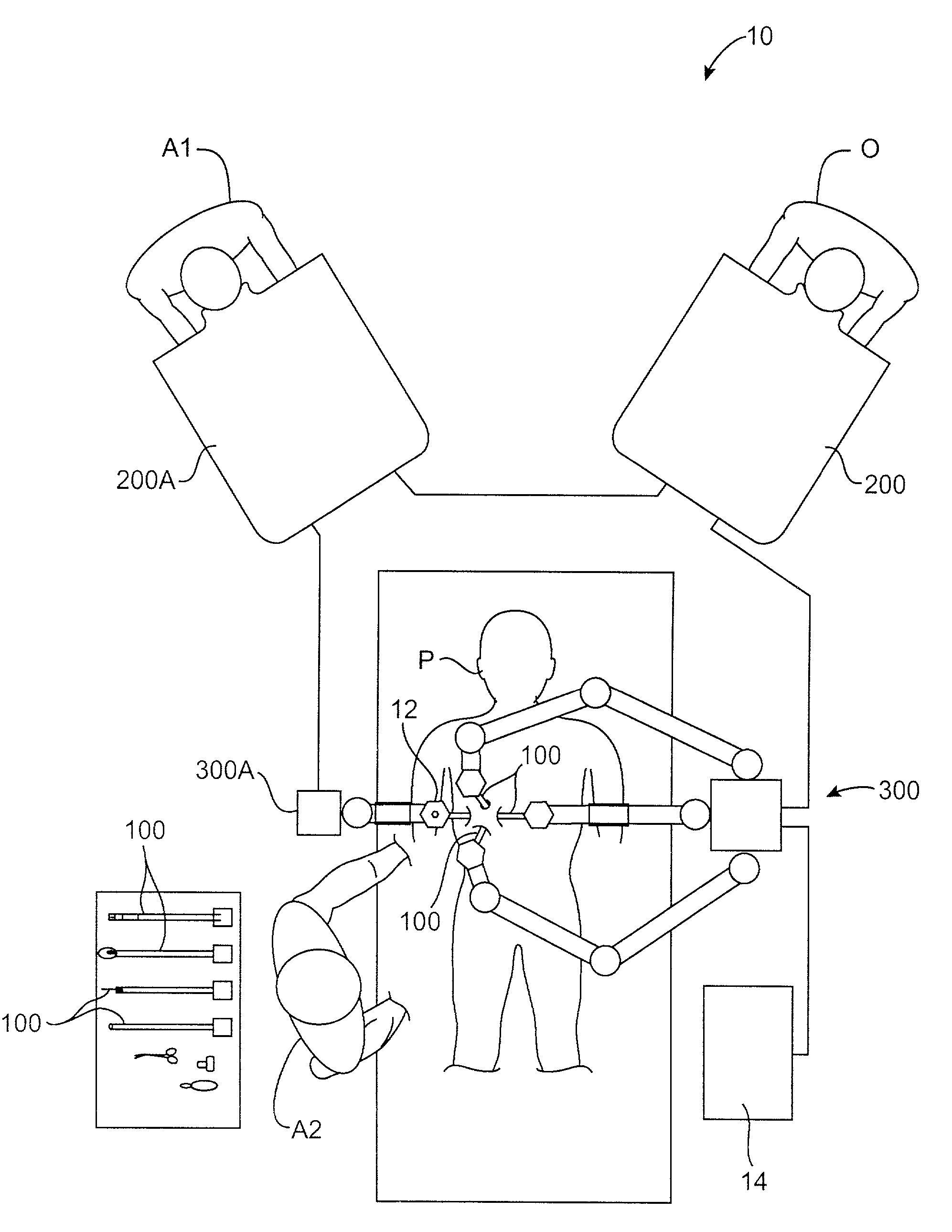
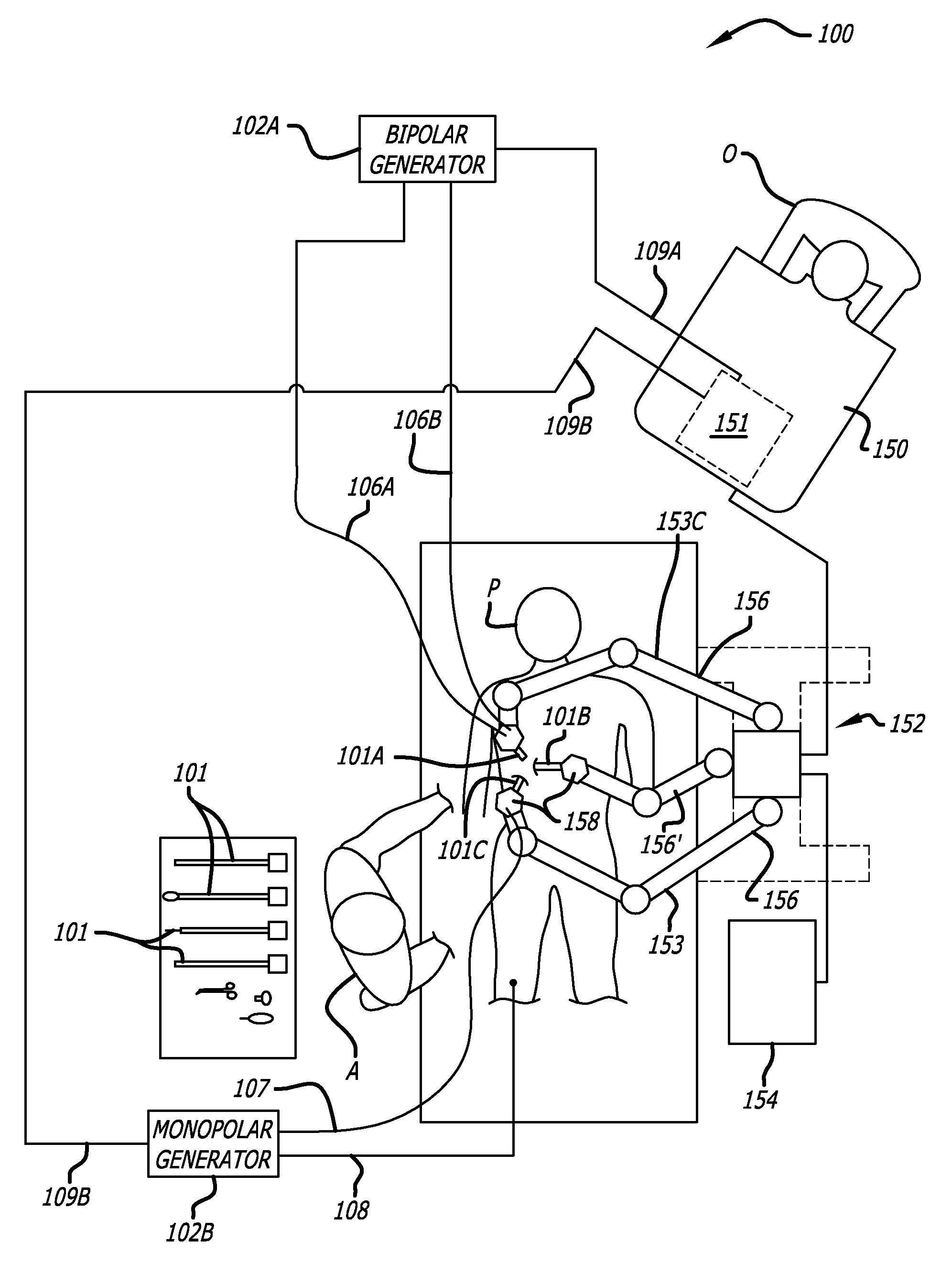
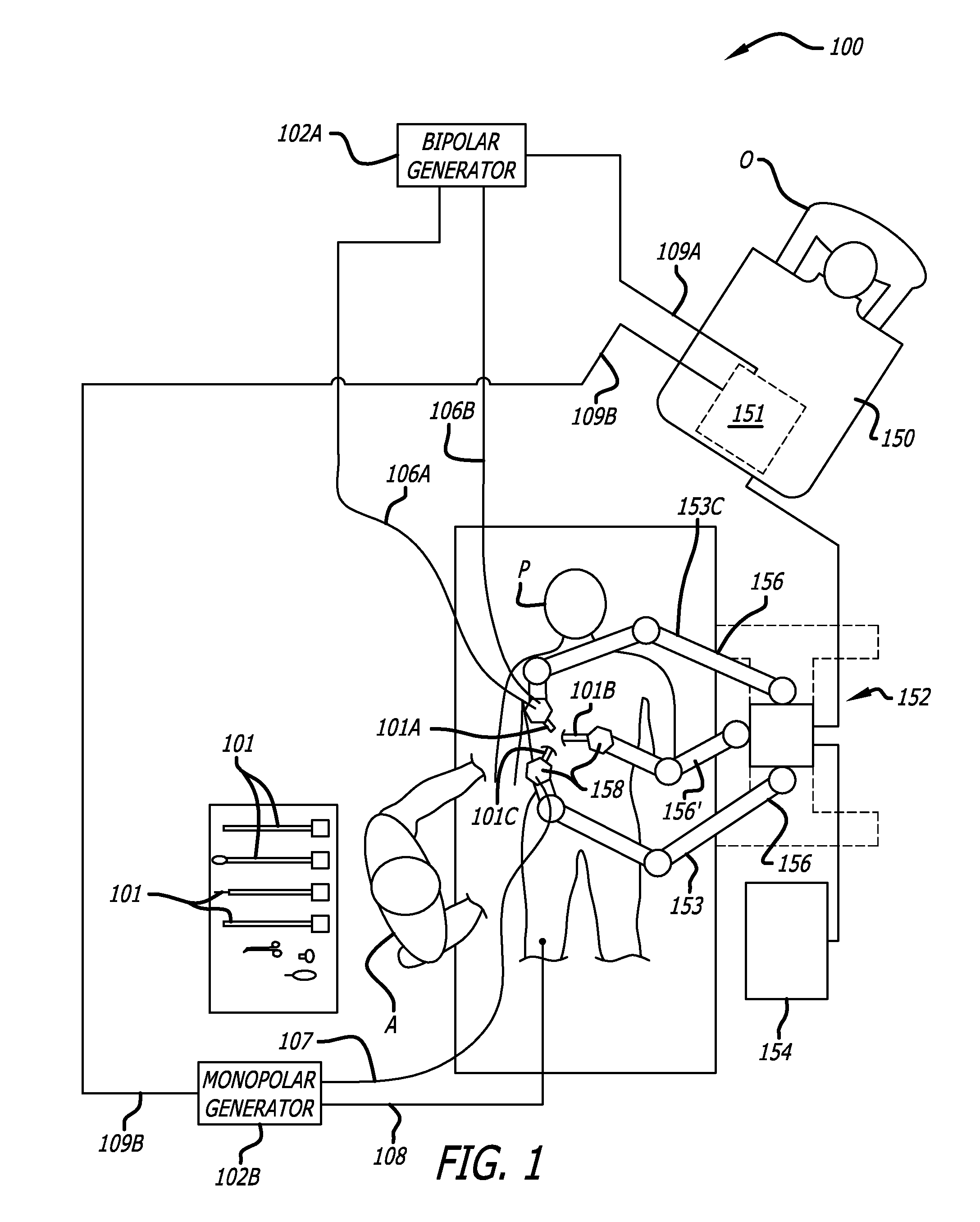
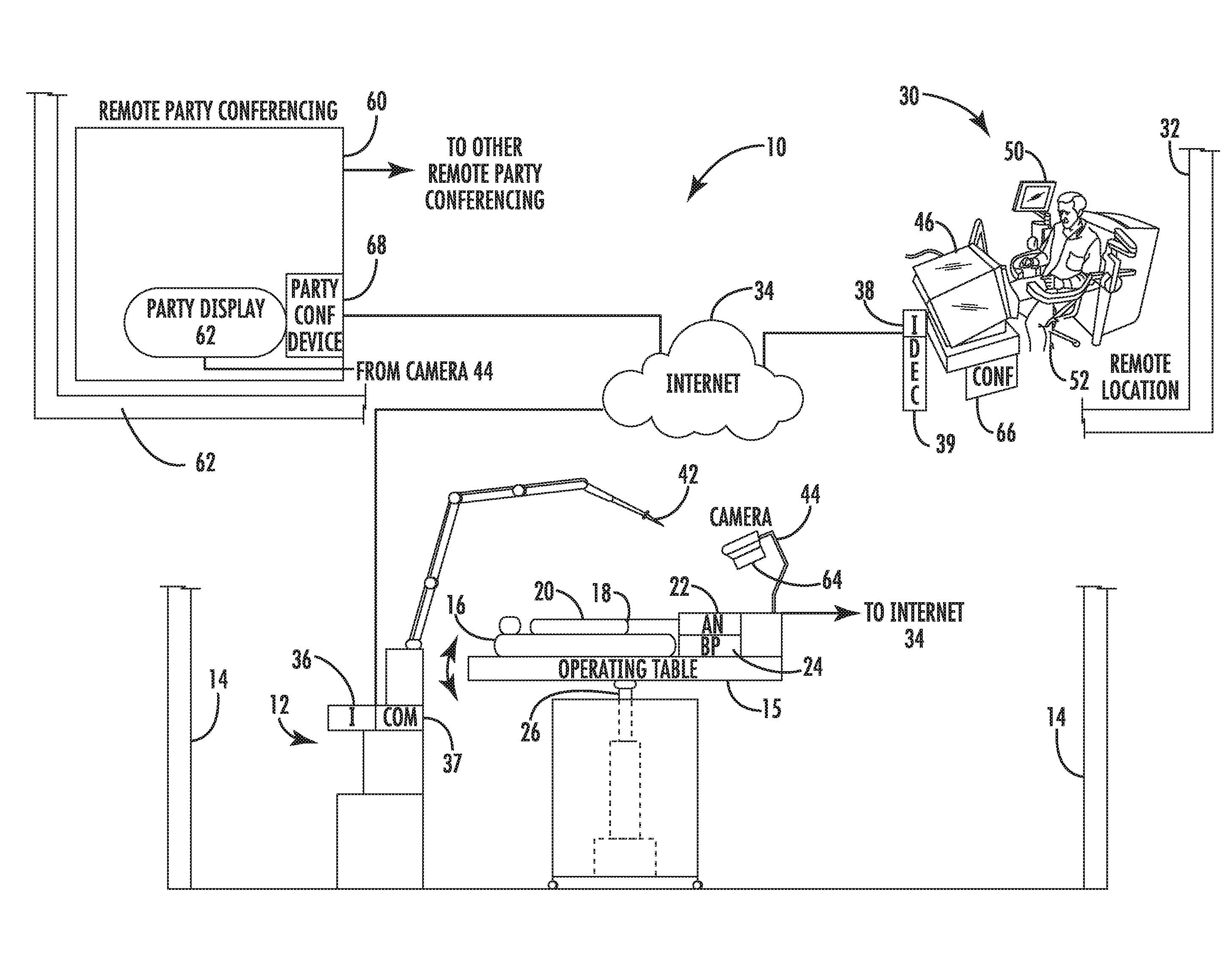
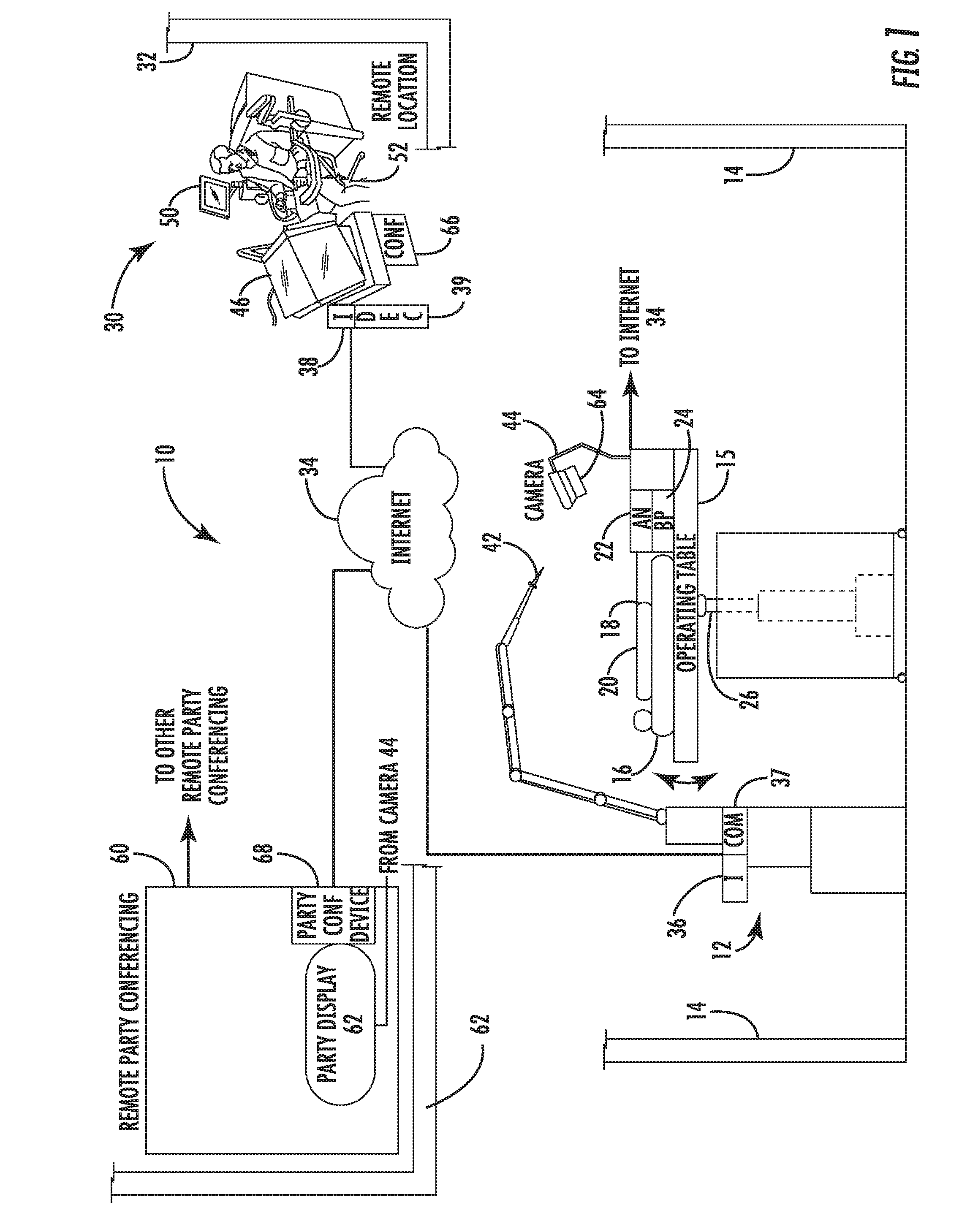
Telerobotic surgery system for remote surgeon training using remote surgery station and party conferencing and associated methods
A telerobotic surgery system for remote surgeon training includes a robotic surgery station at a first location in a first structure at a first geographic point. Harvested animal tissue is at the robotic surgery station. A remote surgeon station at a second location in a second structure is at a second geographic point remote from the first geographic point. A remote party conferencing station at a third location in a third structure is at a third geographic point remote from the first and second geographic points. A communications network couples the robotic surgery station, the remote surgeon station, and the remote party conferencing station so that a surgeon at the remote surgeon station is able to remotely train using the harvested animal tissue at the robotic surgery station and while conferencing with a party at the remote party conferencing station.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Methods, systems, and devices for surgical visualization and device manipulation
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Customizable Haptic Assisted Robot Procedure System with Catalog of Specialized Diagnostic Tips
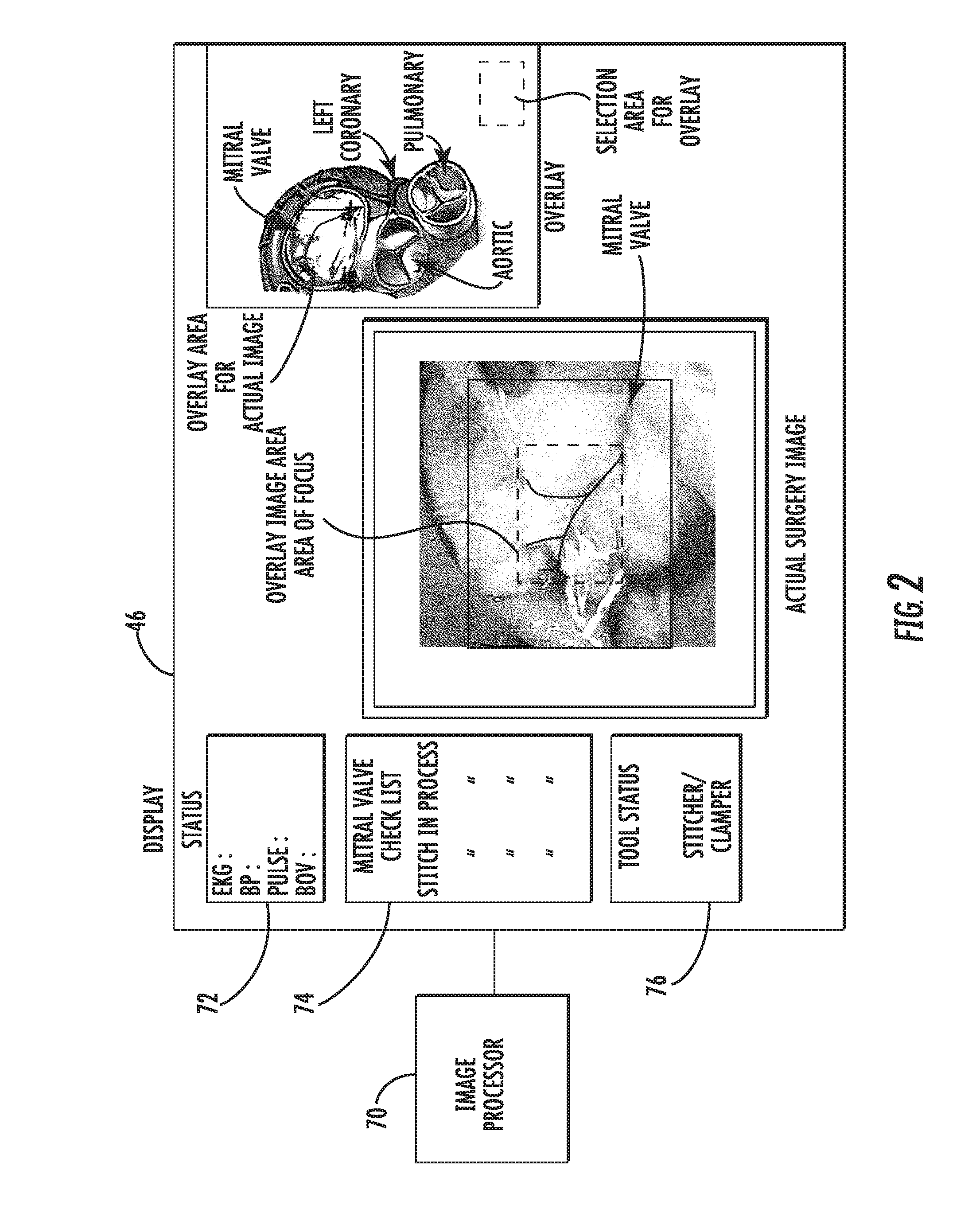
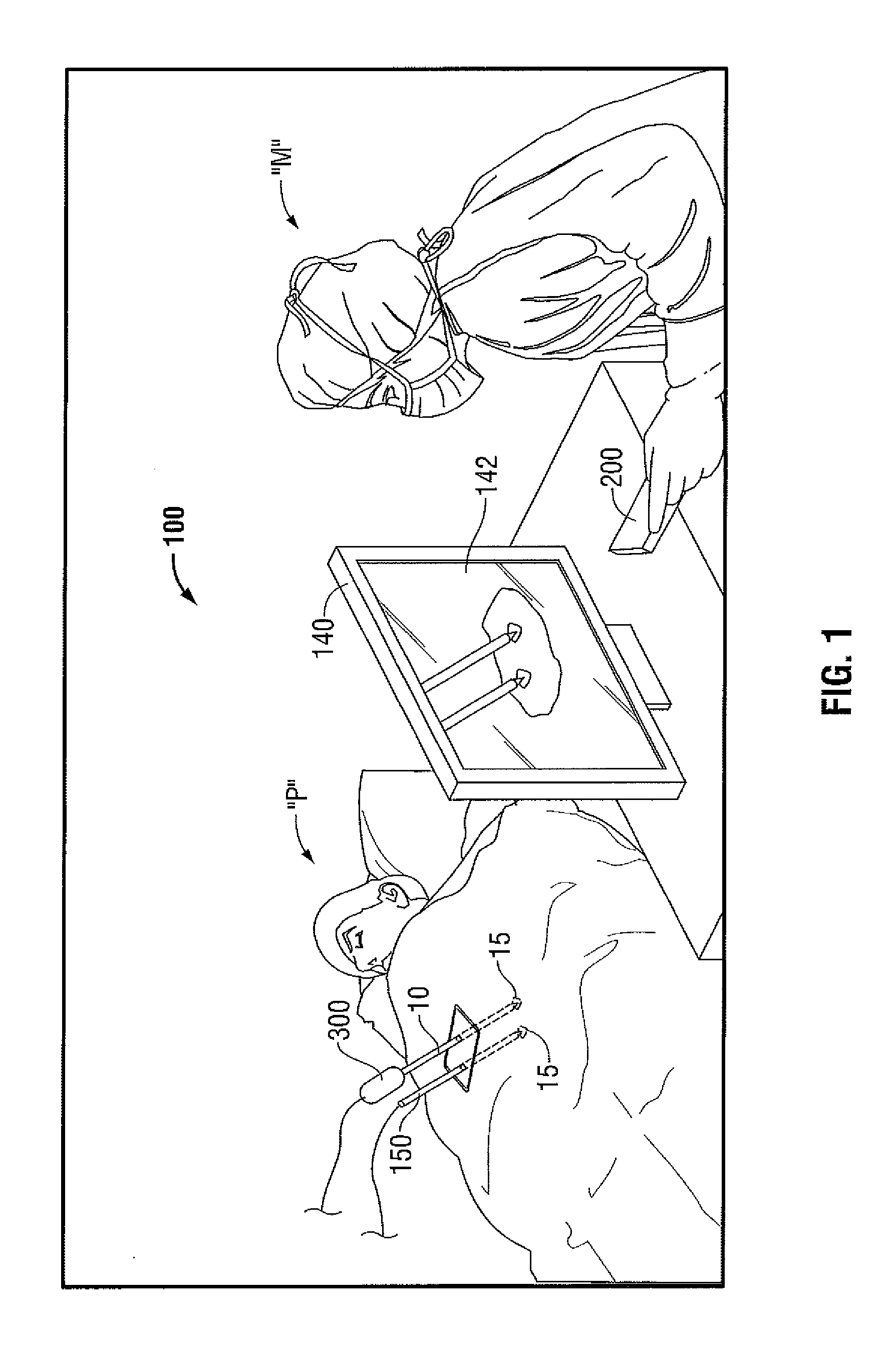
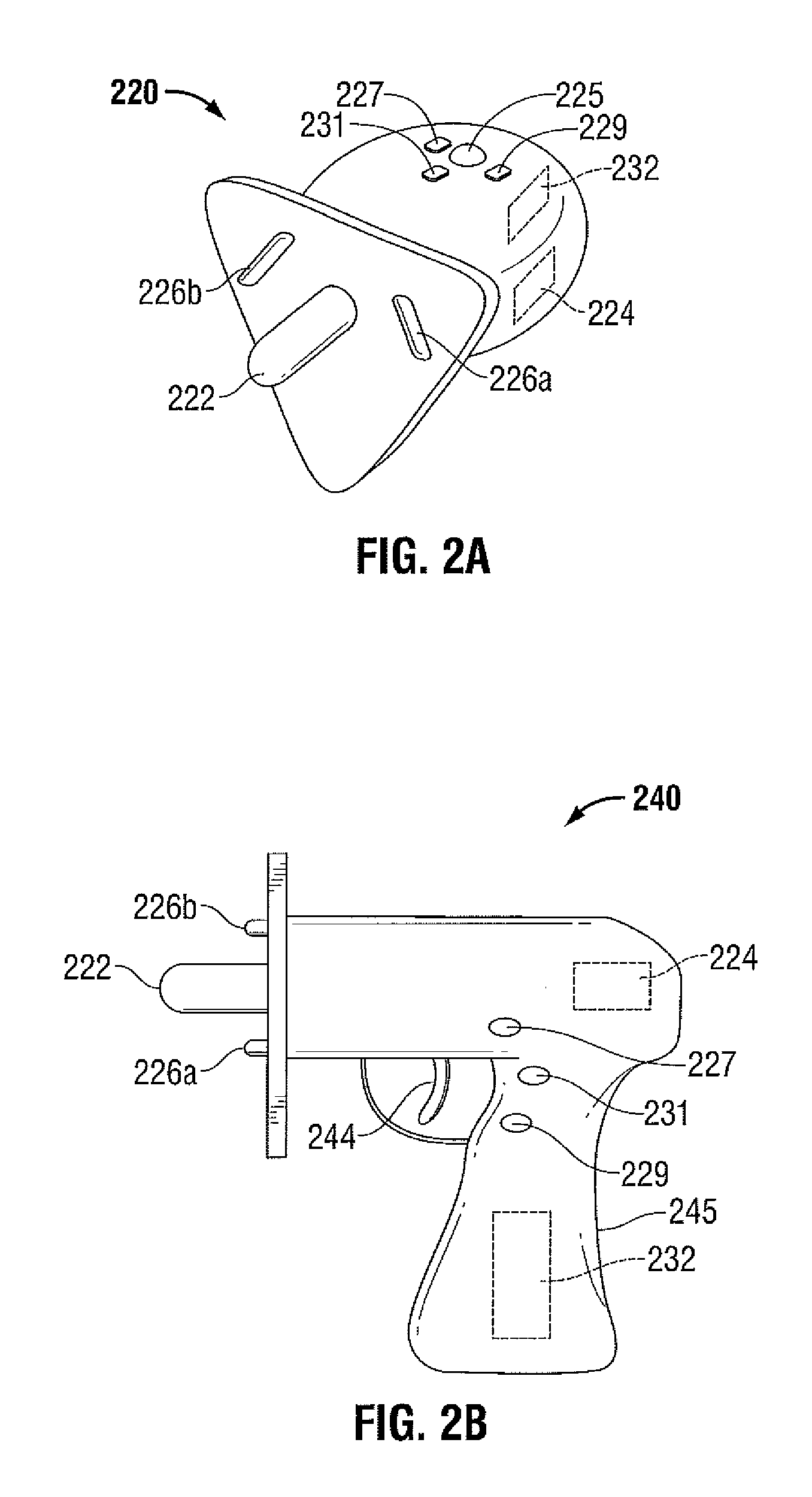
In accordance with the present disclosure, a system and method for using a remote control to control an electrosurgical instrument, where the remote controlled (RC) electrosurgical instrument has a universal coupling mechanism to allow switching between an interchangeable catalog of diagnostic tools. A controller within the base of the RC electrosurgical instrument identifies the type of disposable tip attached to the base. The controller, then, activates necessary features for use with the identified tip and deactivates any unnecessary features. A surgeon uses a remote with at least one momementum sensor to control the RC electrosurgical instrument 10. The surgeon rotates his hand mimicking movements of a handheld electrosurgical instrument, the movements of which are translated and sent to the RC electrosurgical instrument. The surgeon may use an augmented reality (AR) vision system to assist the surgeon in viewing the surgical site.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com