Patents
Literature
35707 results about "Rotational axis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
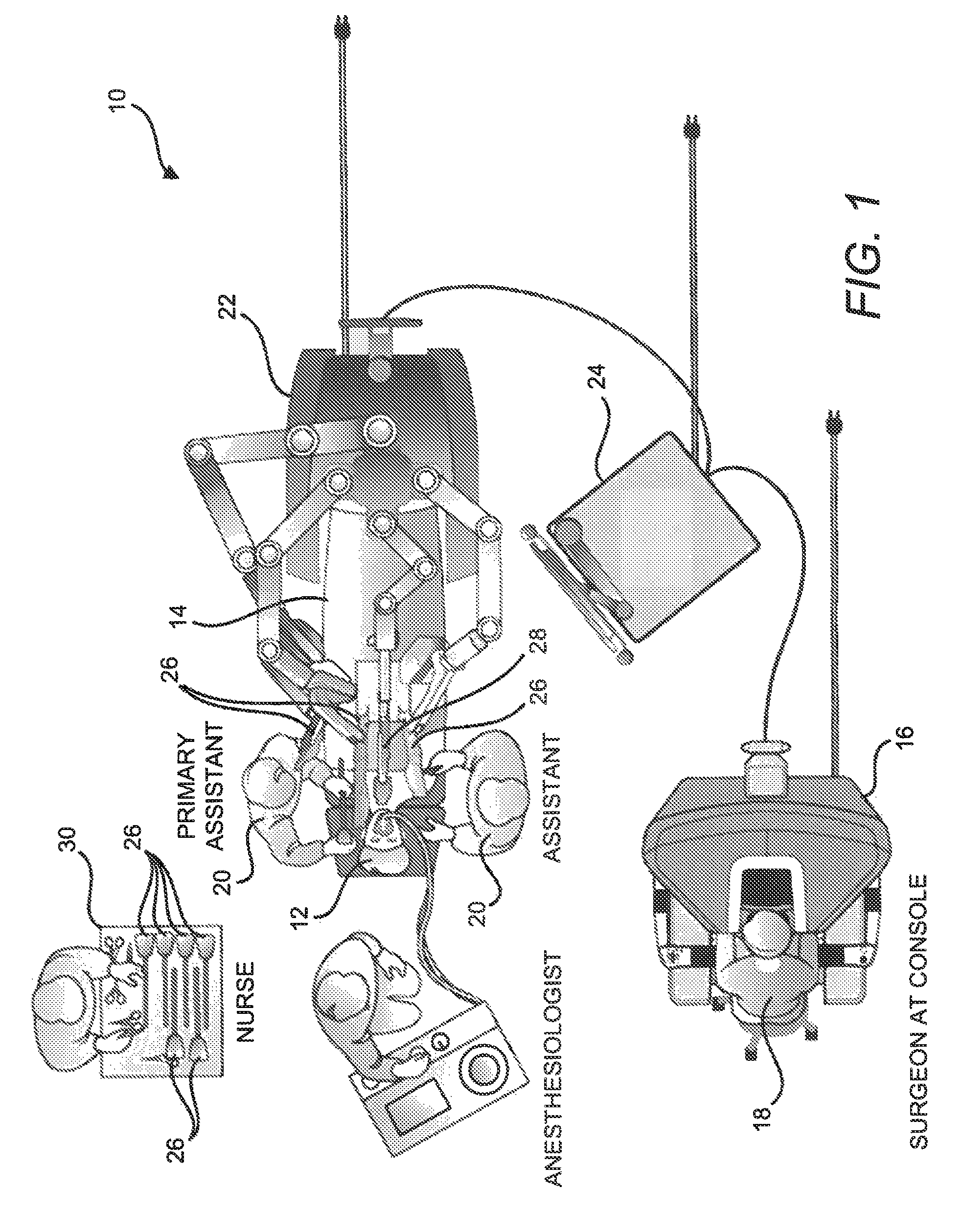
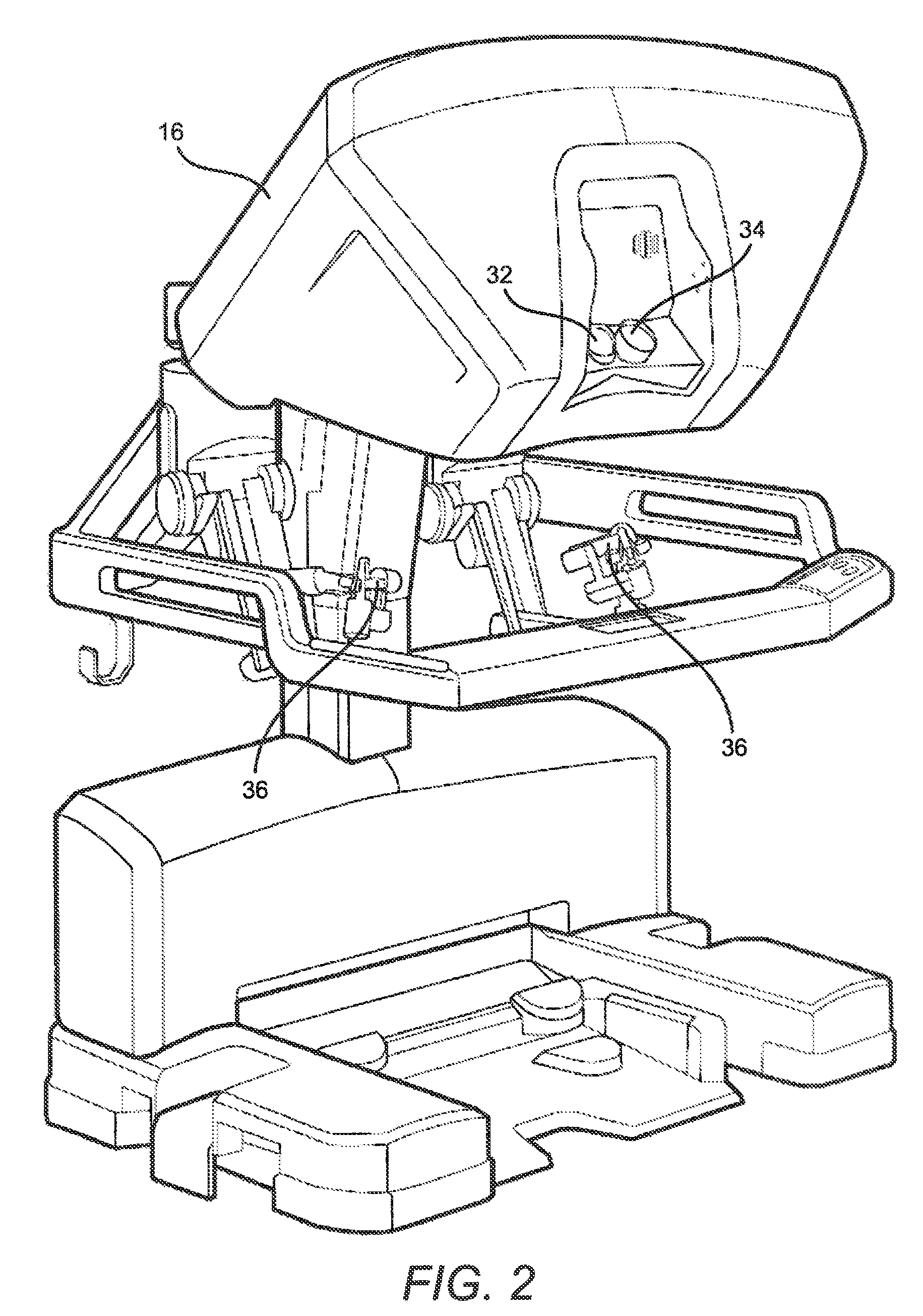
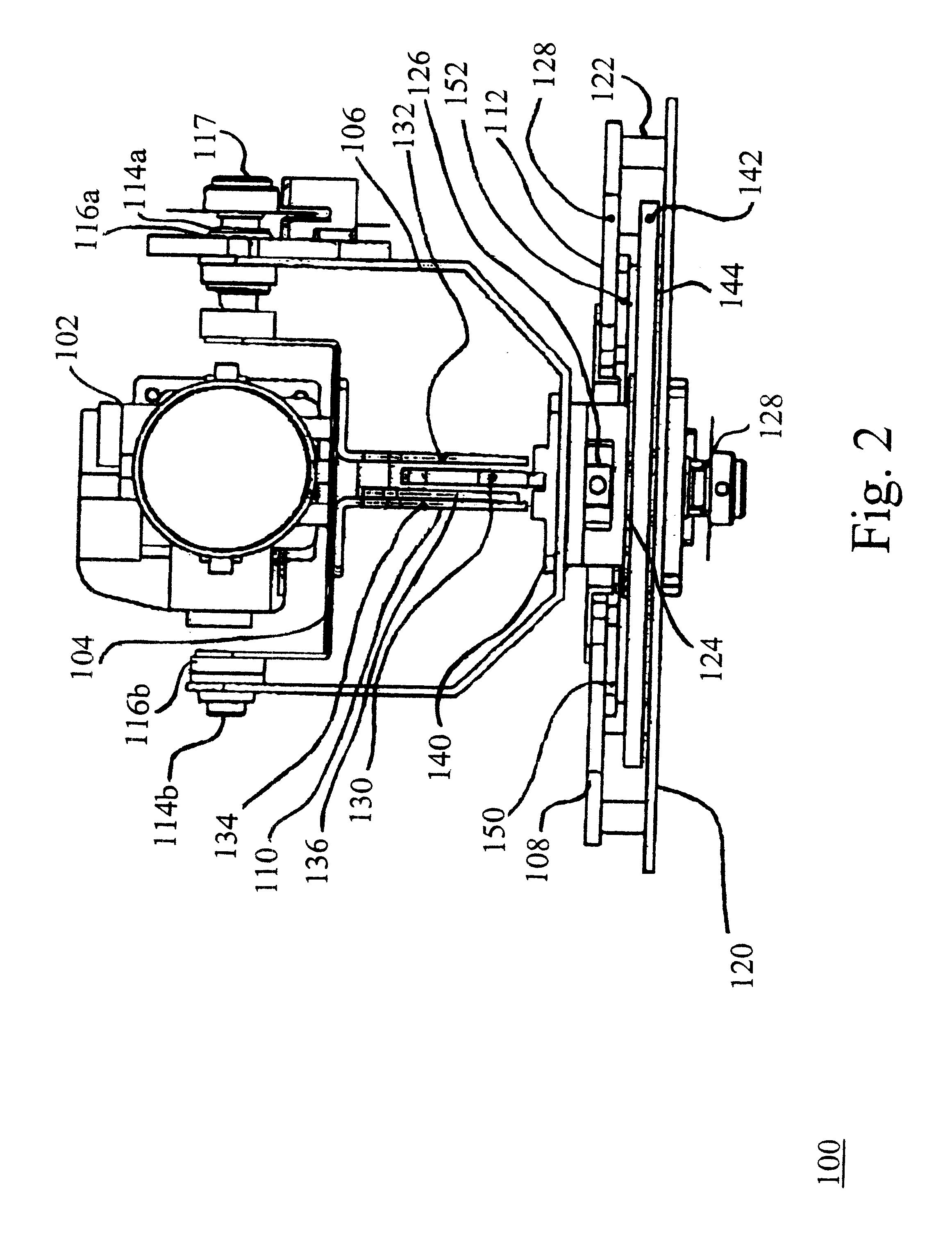
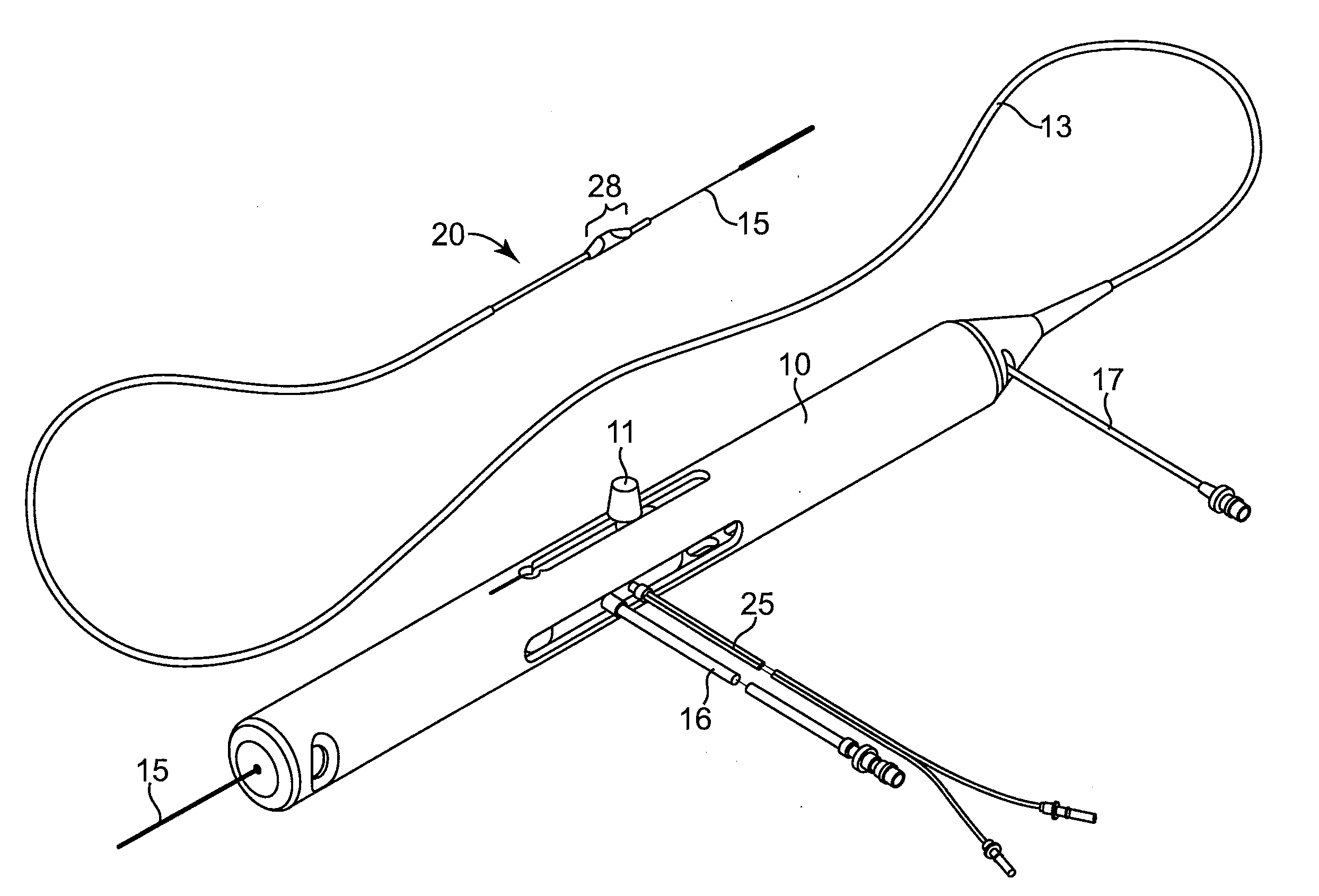
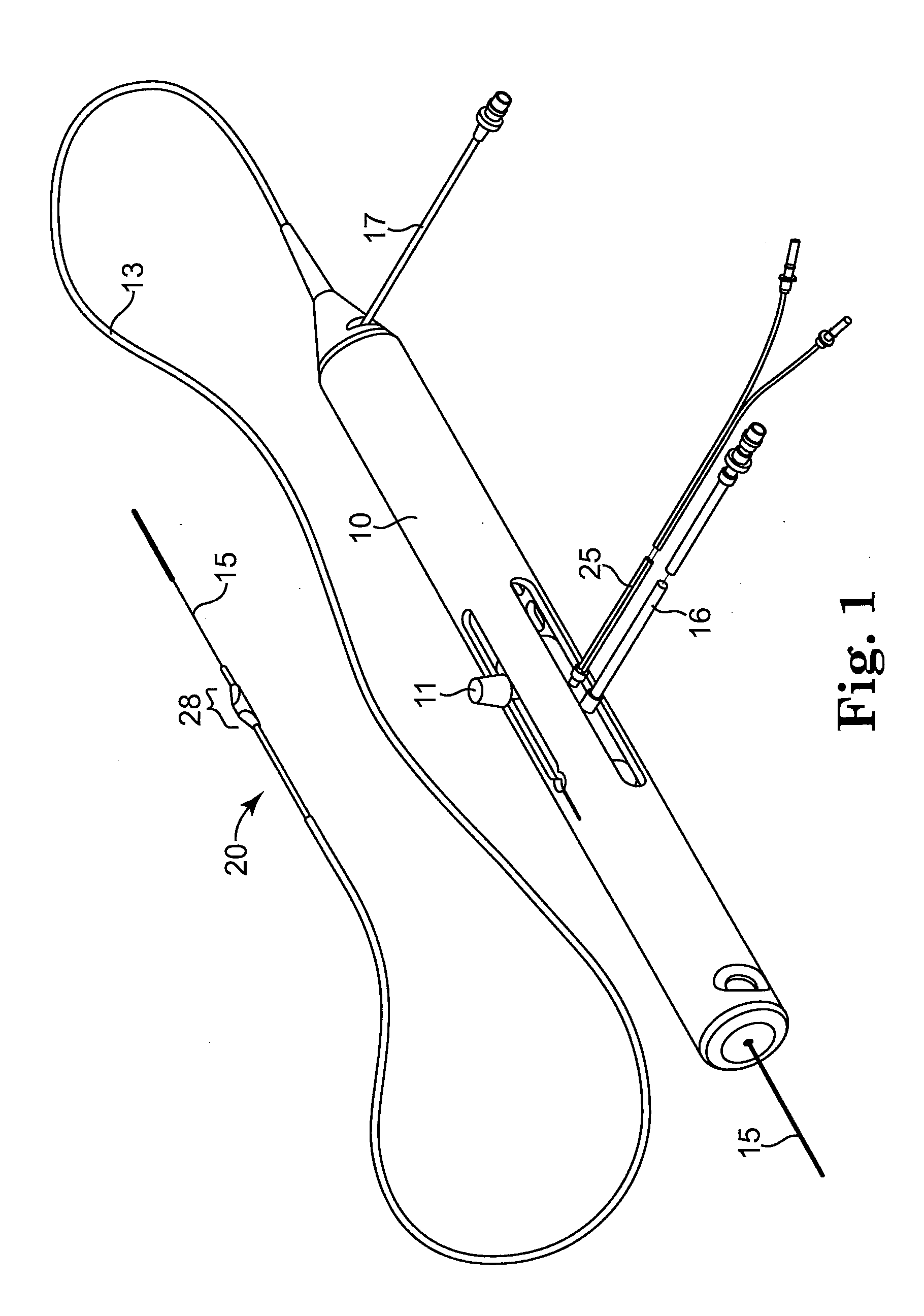
Sterile drape interface for robotic surgical instrument
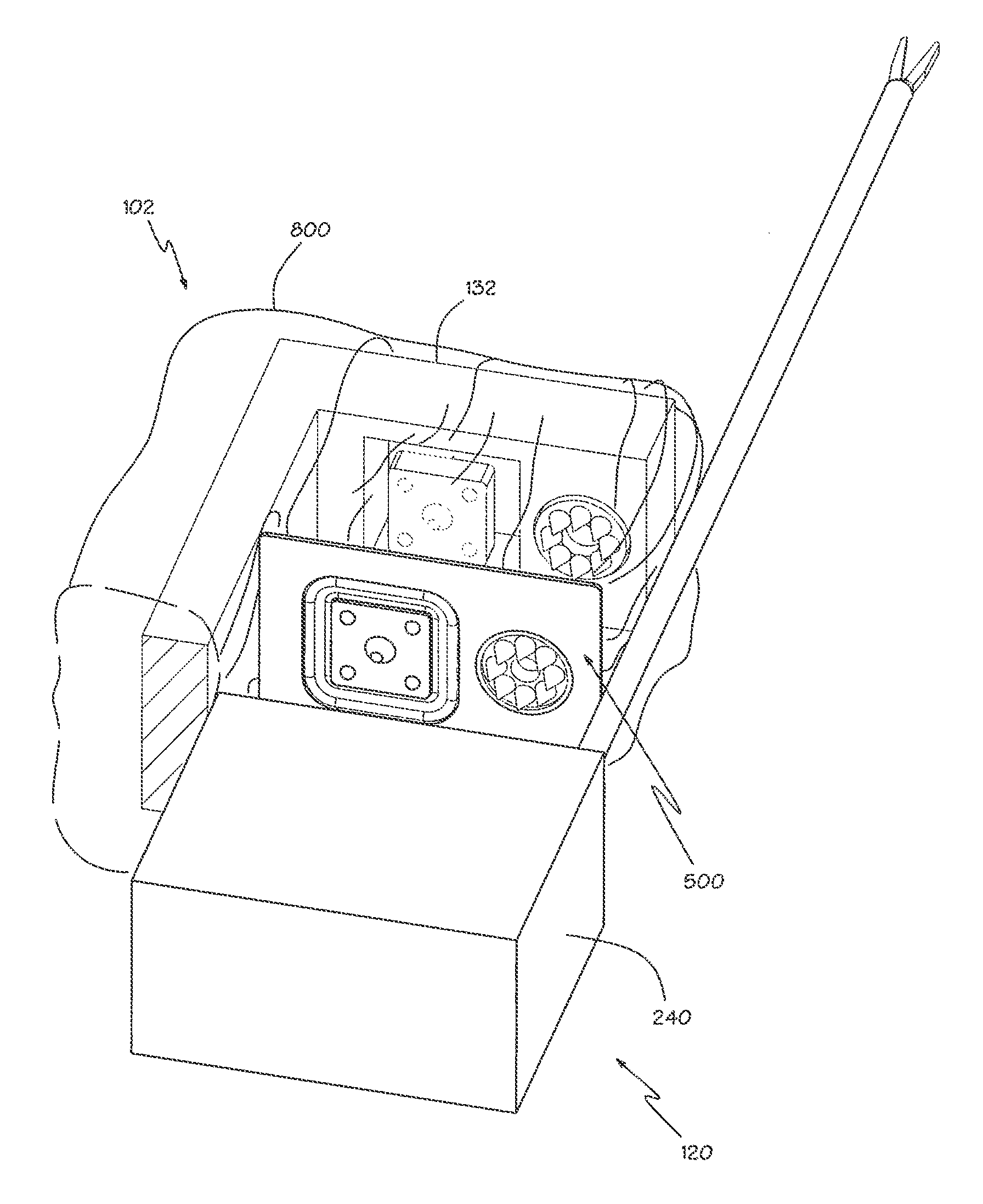
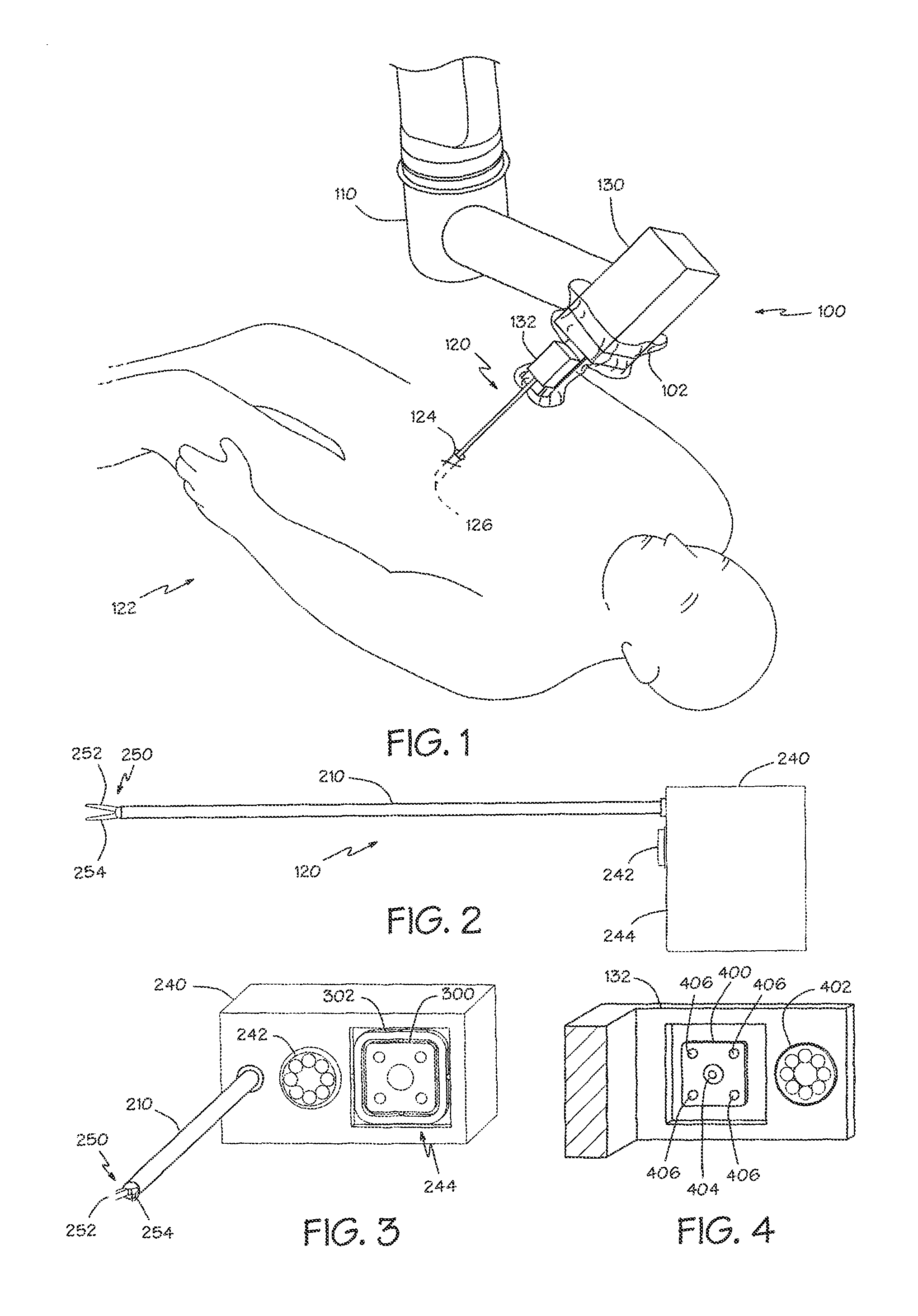
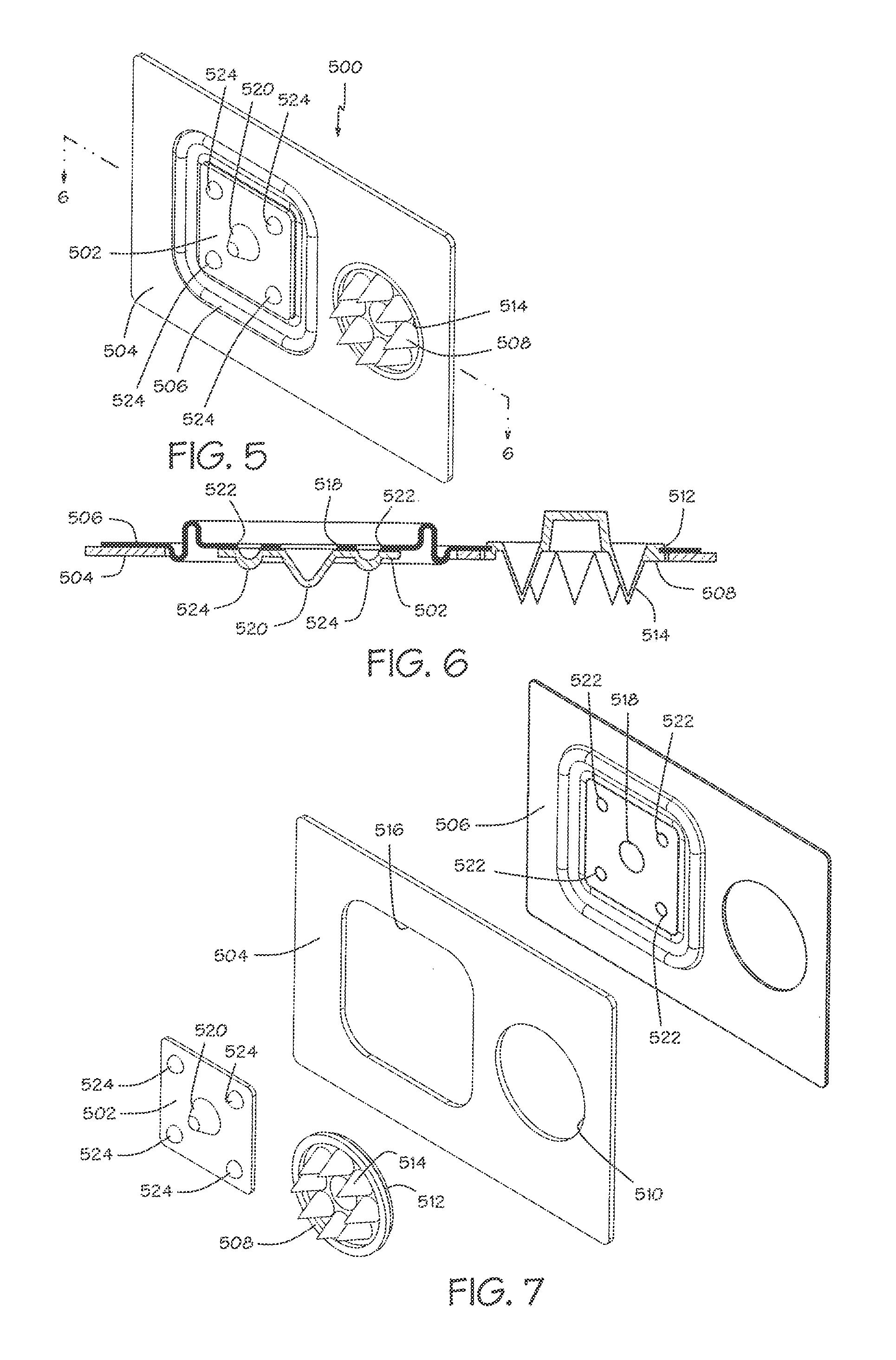
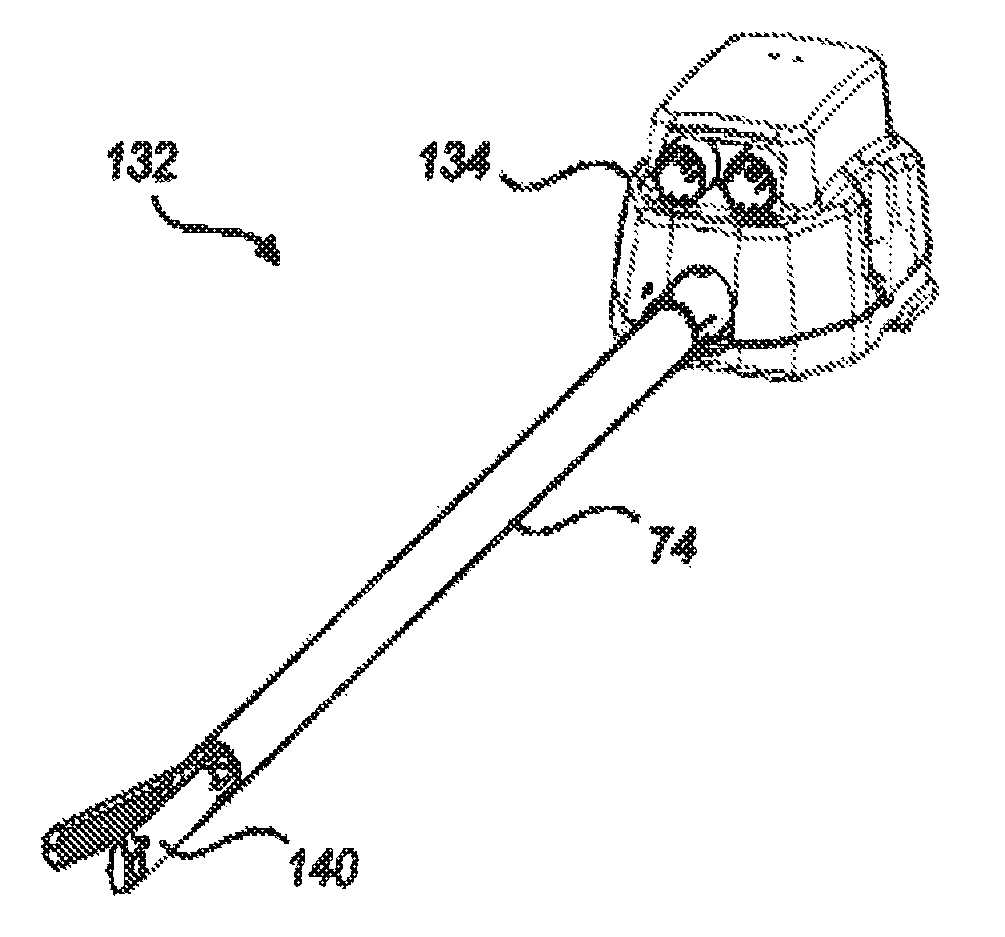
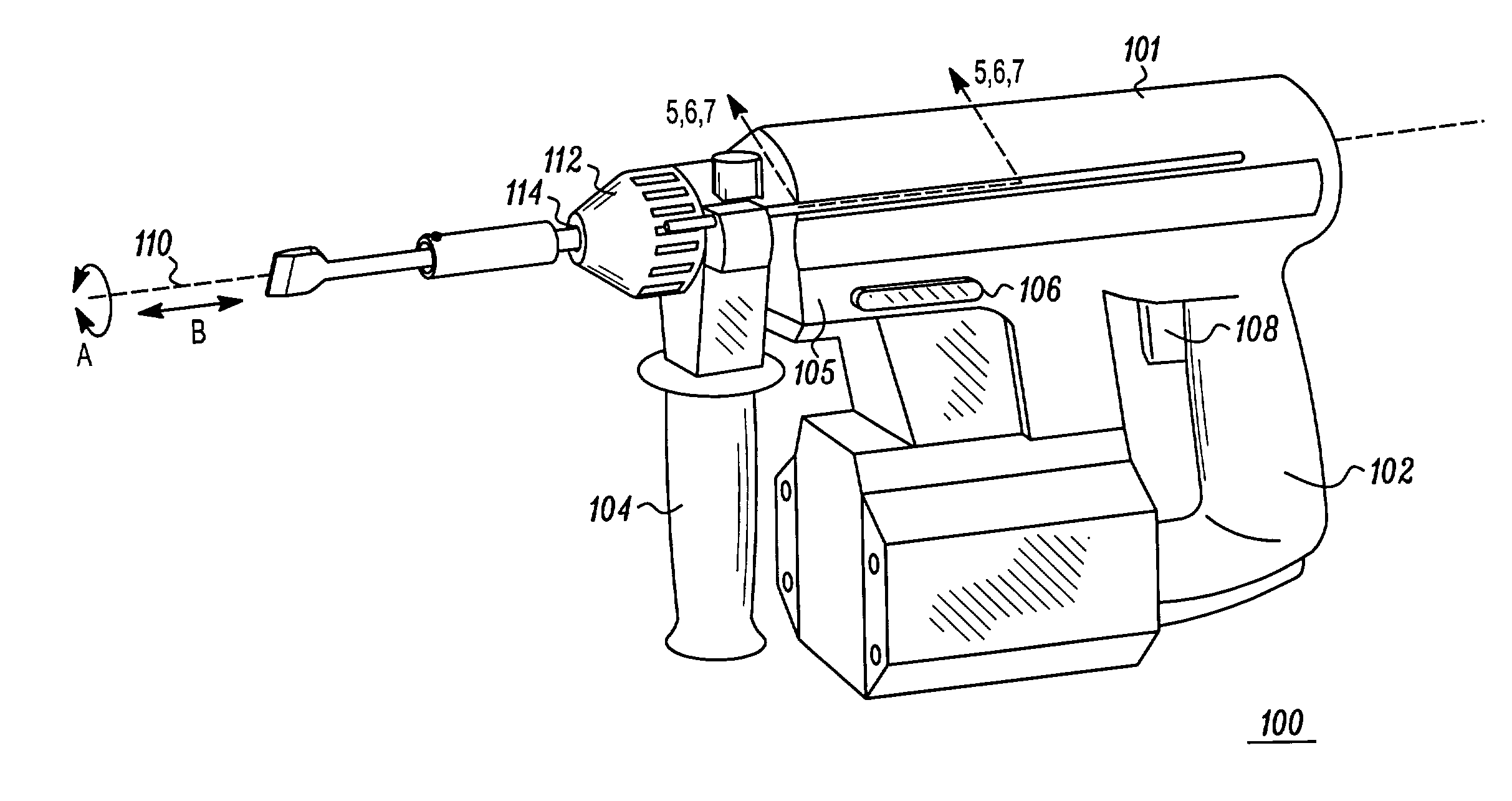
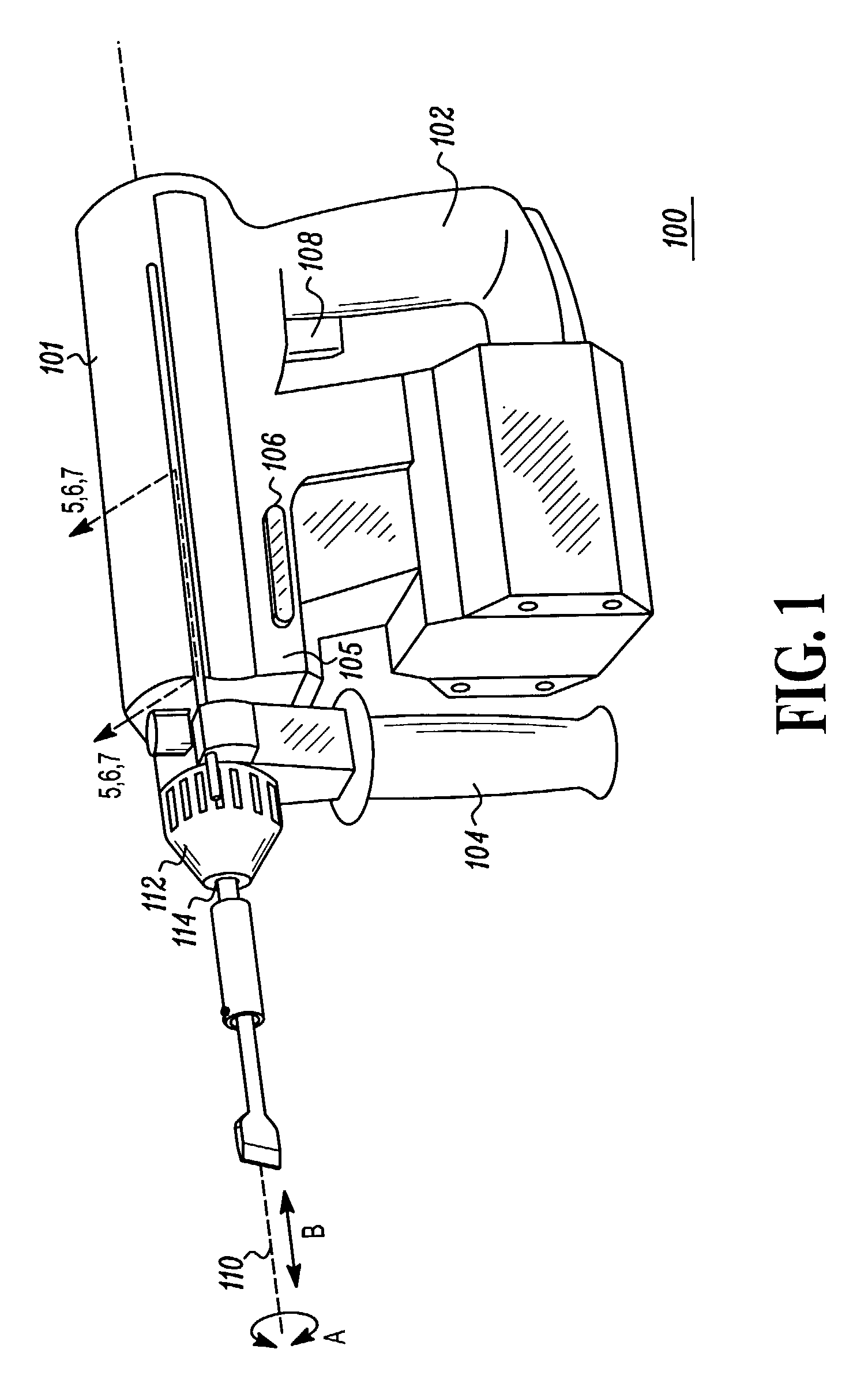
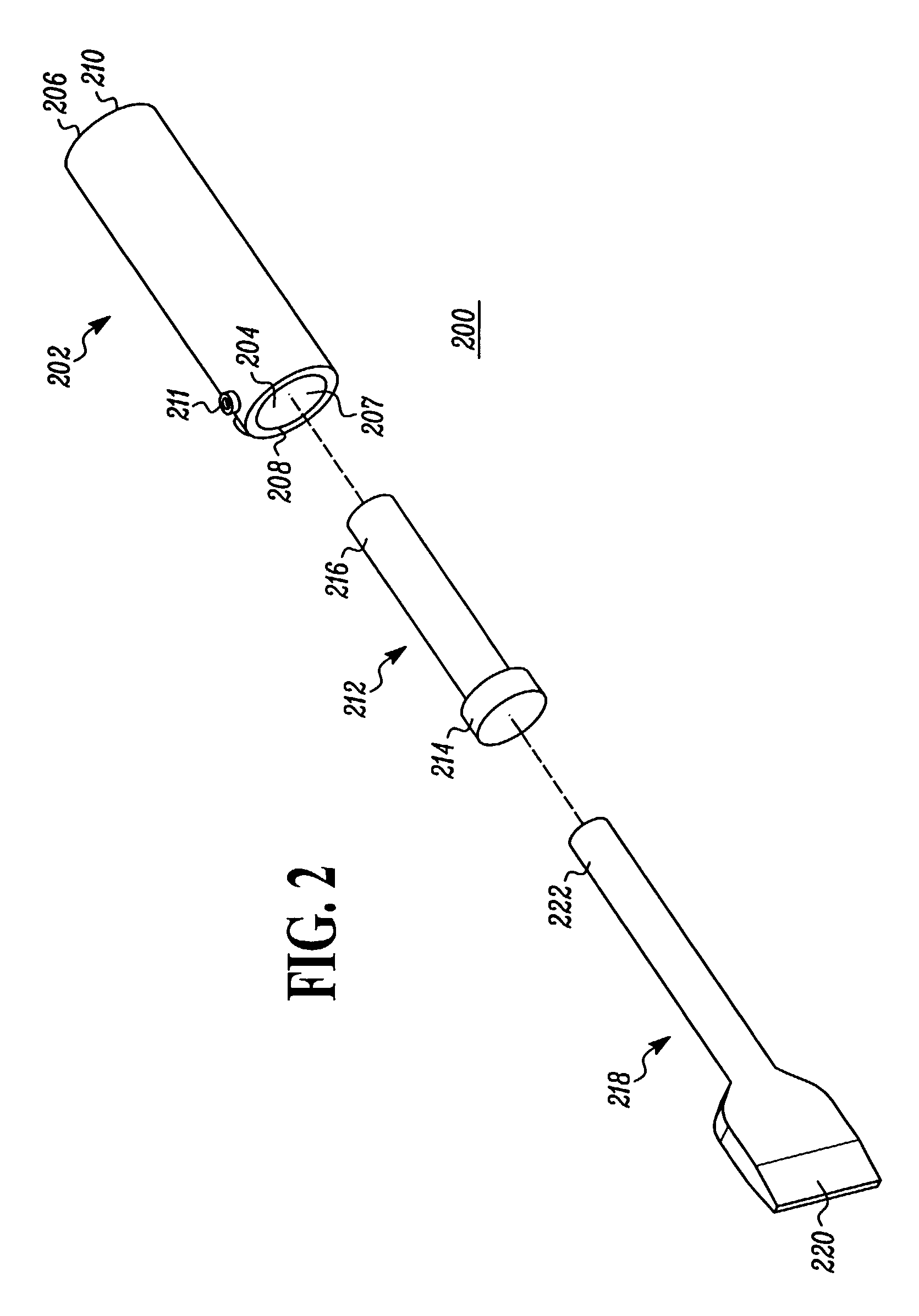
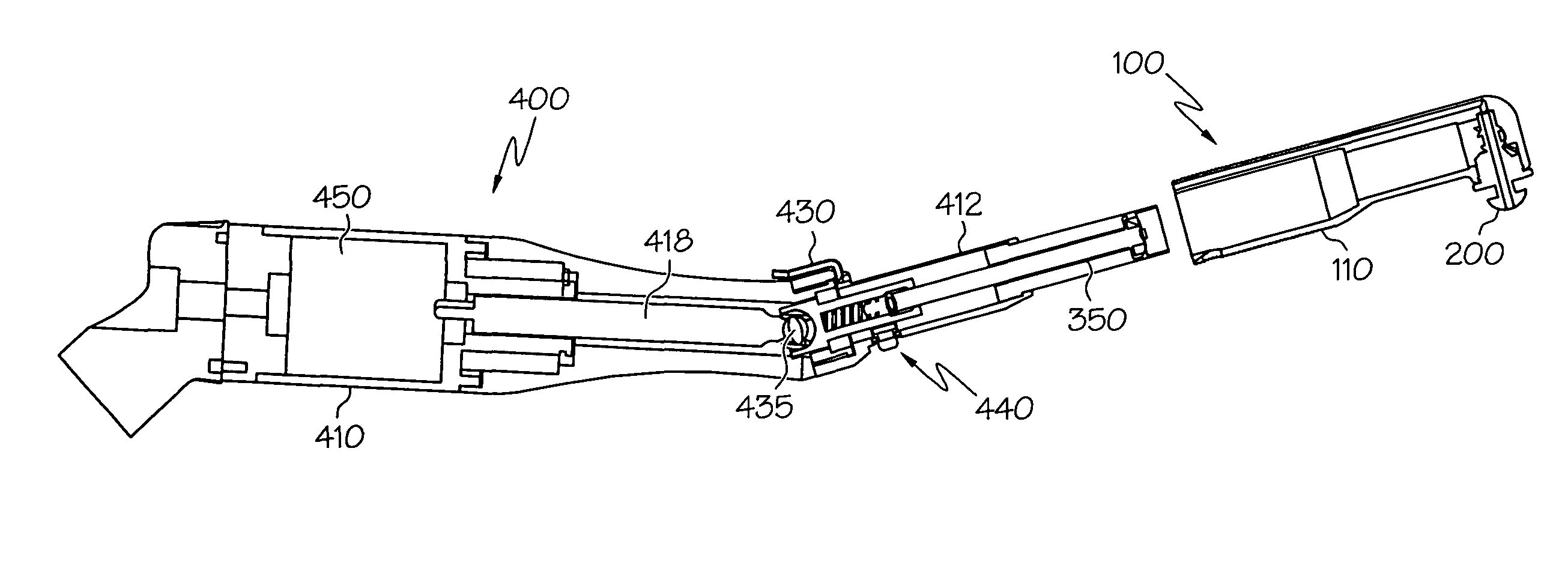
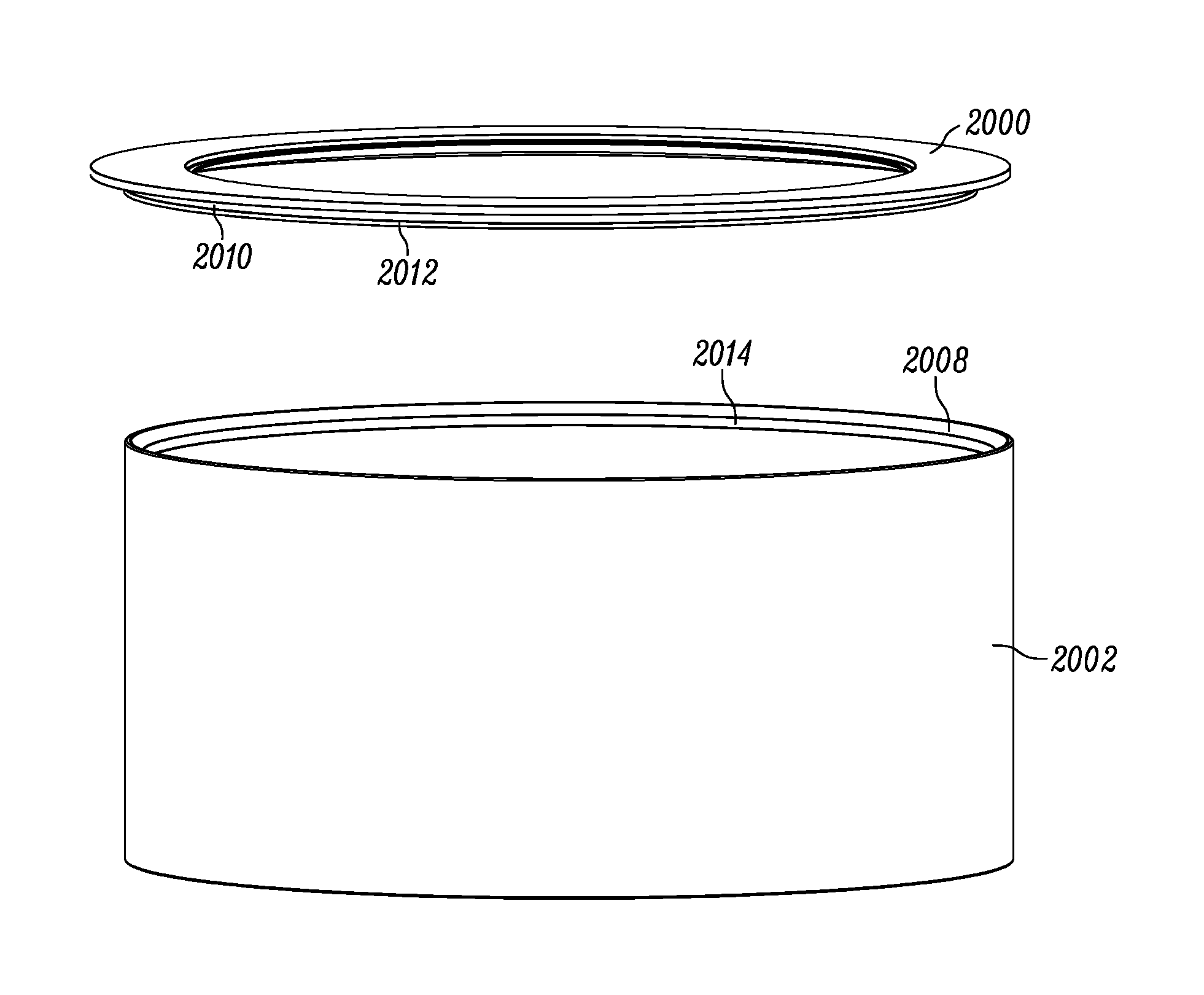
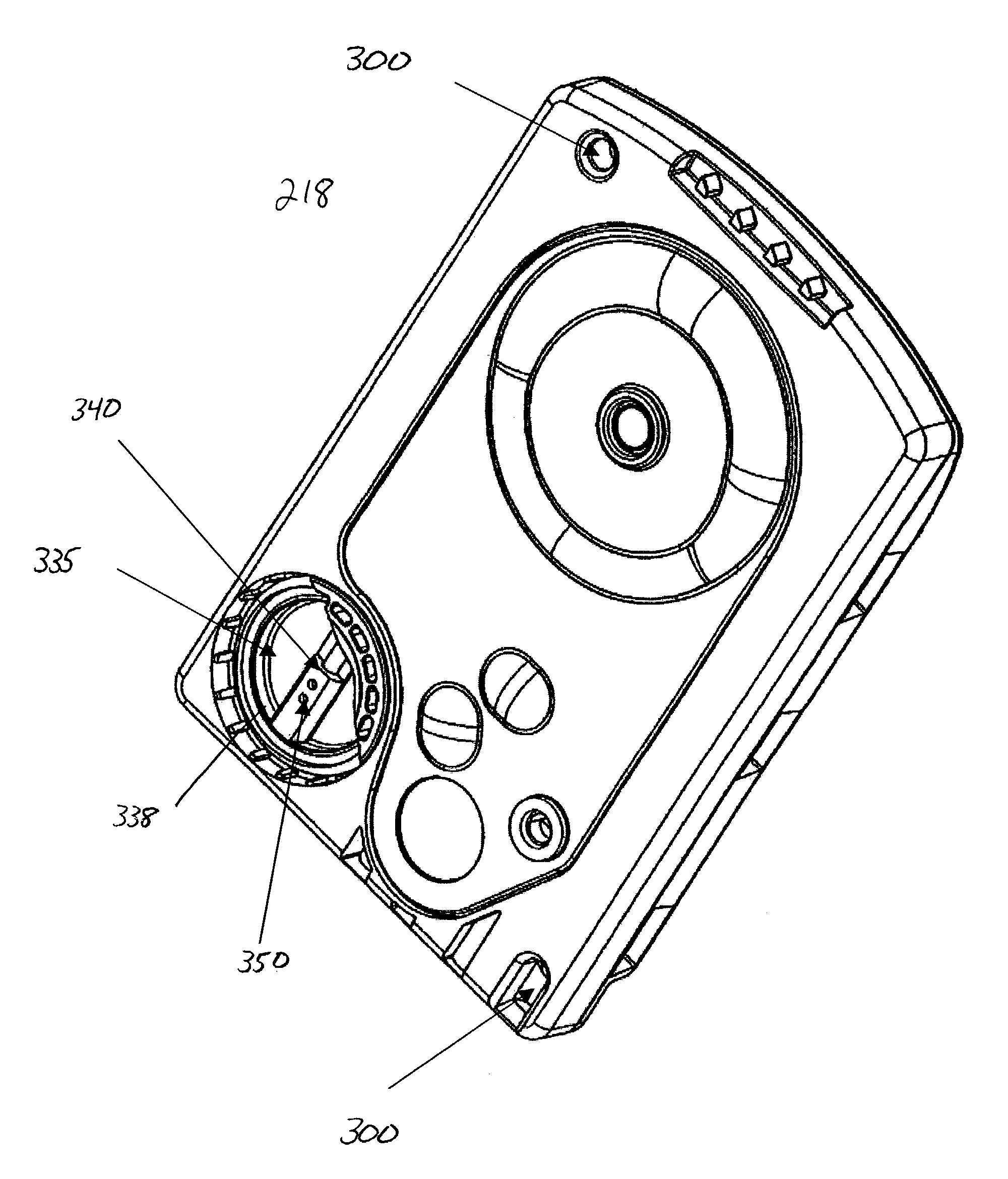
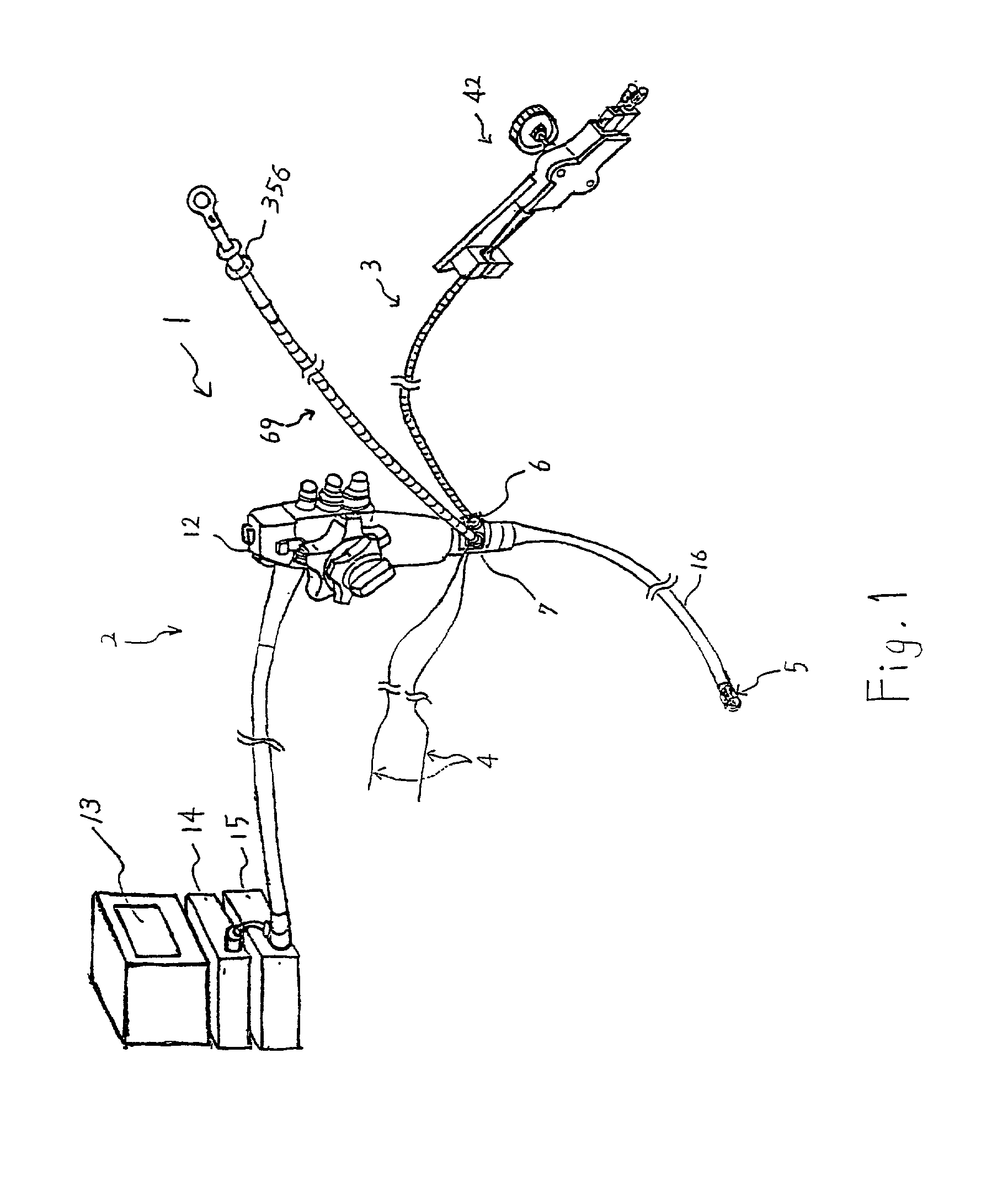
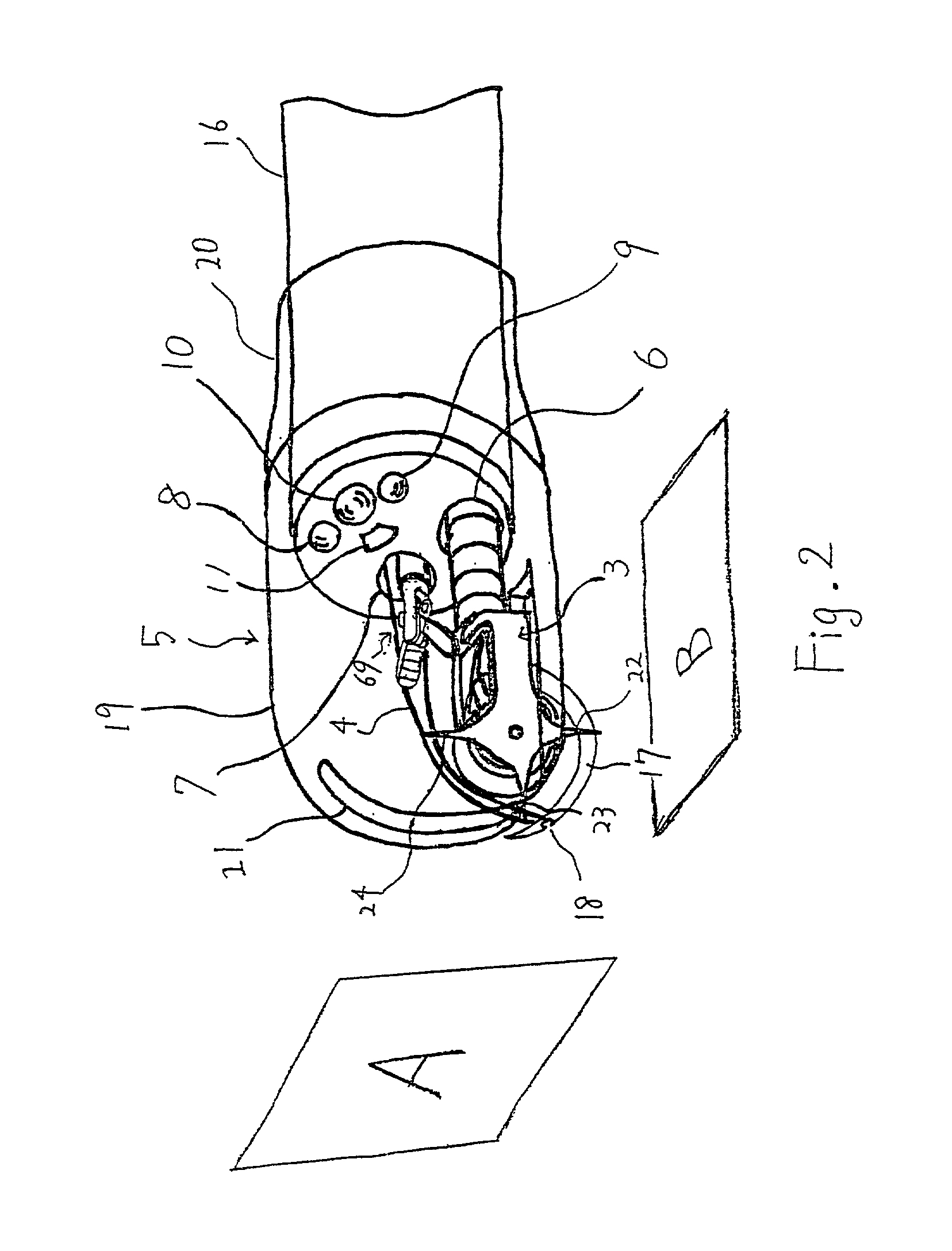
A robotic surgical system includes a sterile surgical instrument, a robotic surgical manipulator, and a sterile drape covering at least a portion of the robotic surgical manipulator. The surgical instrument has a proximal interface and a distal end effector. The proximal interface includes a gimbal assembly with two intersecting rotational axes coupled to the distal end effector. The robotic surgical manipulator has a drive plate that bears against the gimbal assembly. The drive plate has two degrees of rotational freedom about a center of motion that is coincident with an intersection of the axes of the gimbal assembly. The sterile drape includes a sterile sheet covers at least a portion of the robotic surgical manipulator, a frame bonded to the sterile sheet, an instrument interface that covers the drive plate of the robotic surgical manipulator, and a diaphragm that connects the instrument interface to the frame.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
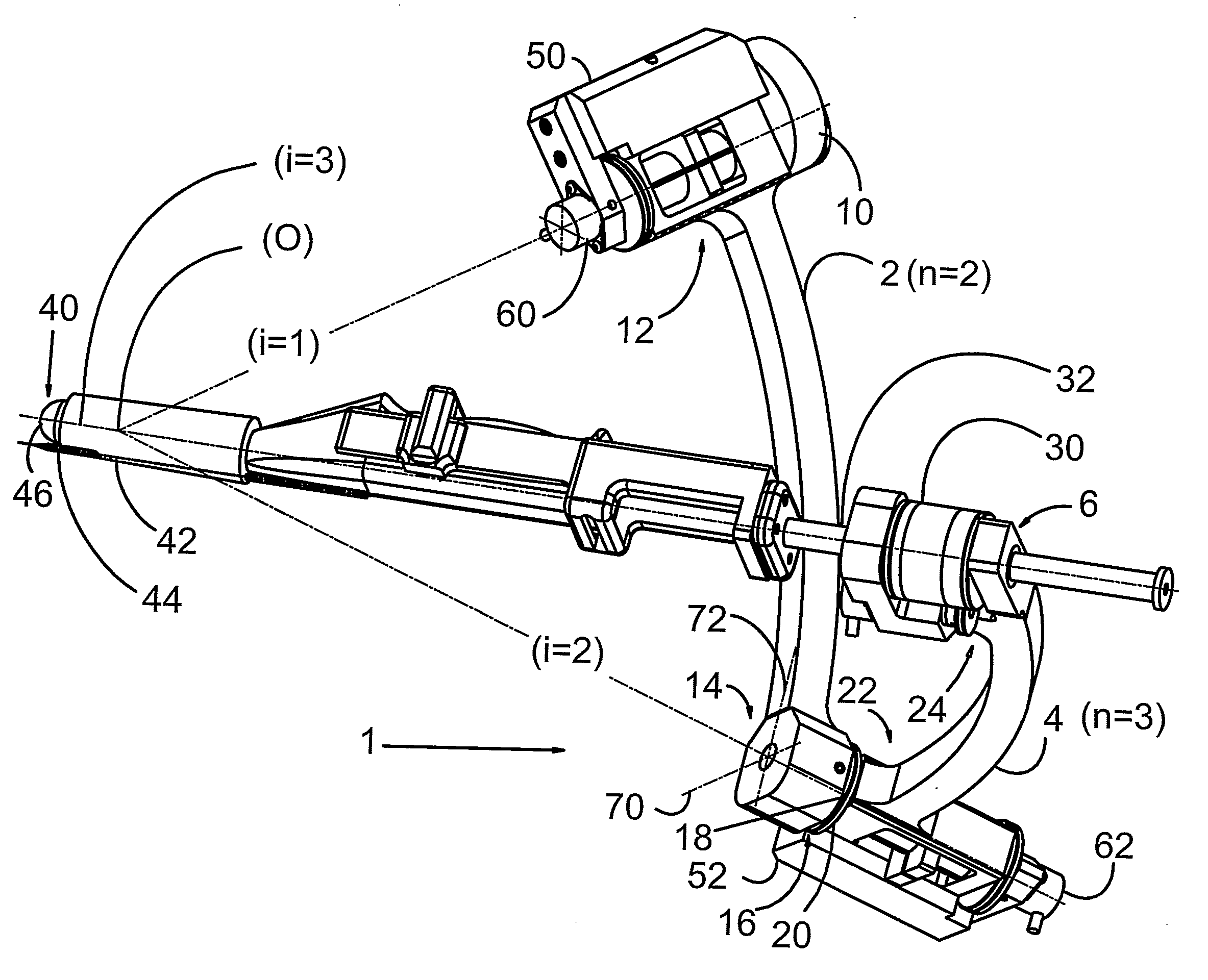
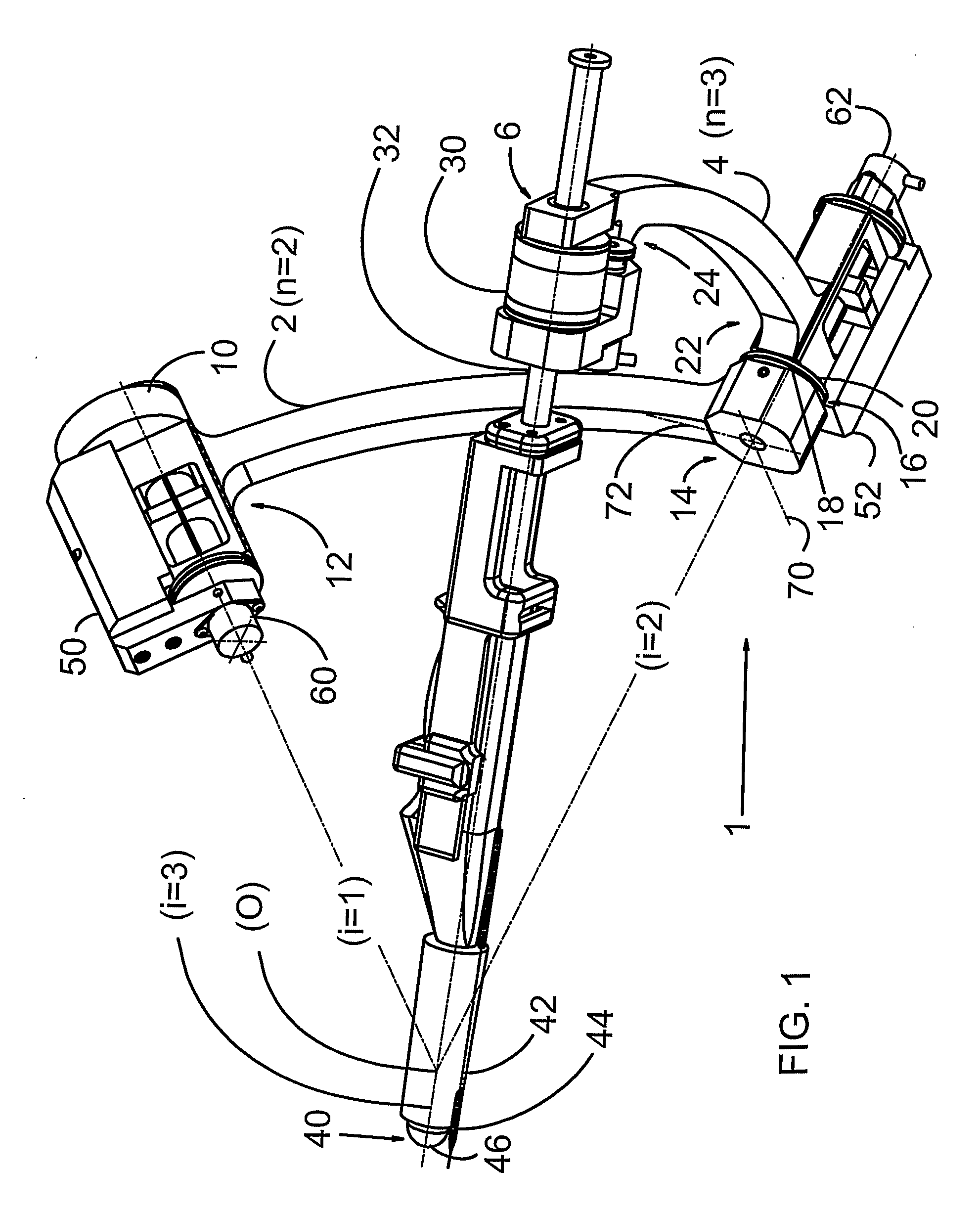
Motor interface for parallel drive shafts within an independently rotating member
ActiveUS8640788B2Force articulationIncrease clamping forceDrilling rodsConstructionsRotational axisDrive shaft
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
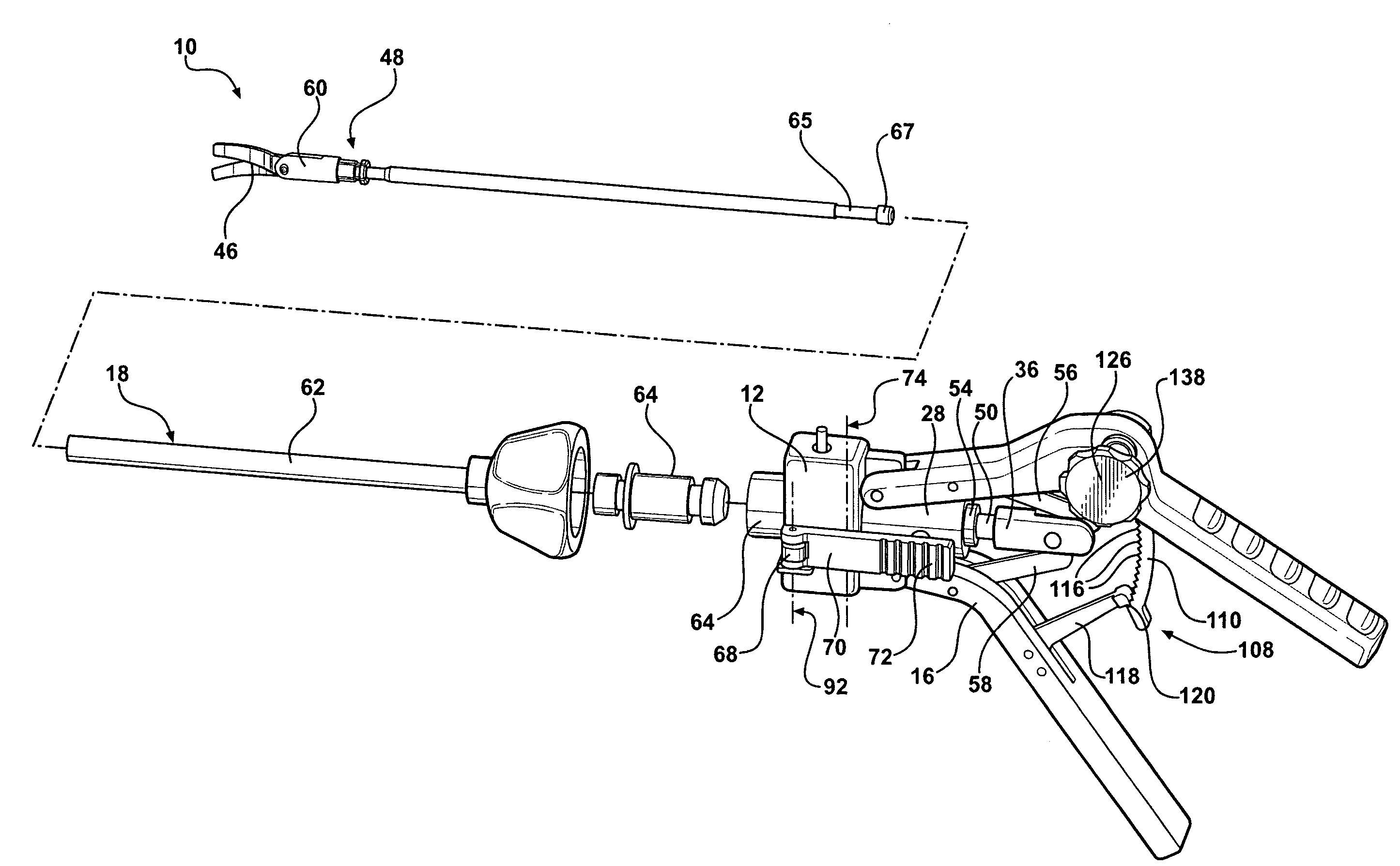
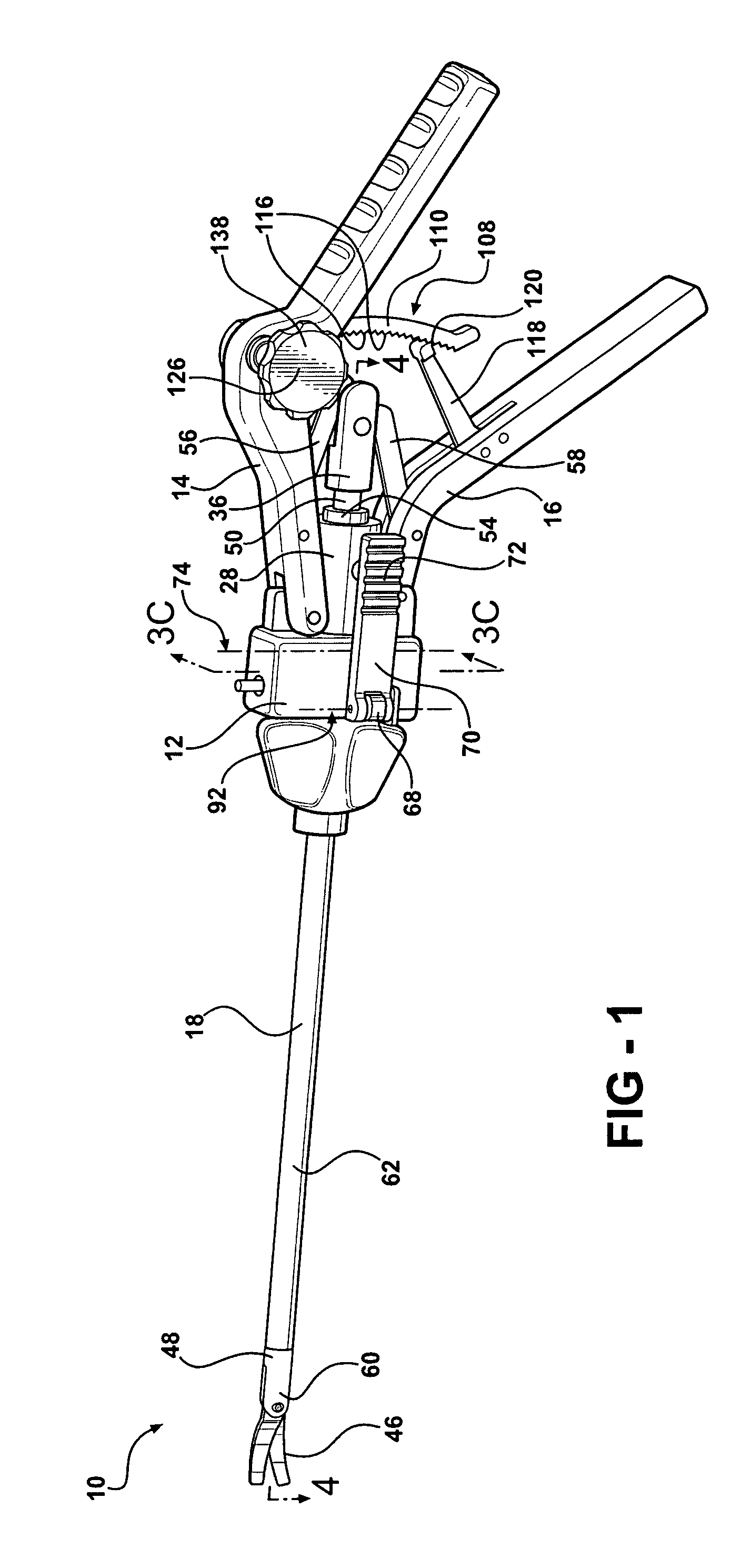
Forceps for performing endoscopic surgery
A surgical instrument for performing surgery includes a housing defining an axial bore. A lock is slidably disposed in the transverse bore to engage and disengage a tube adaptor. A latch extends from the lock to move the latch into and out of the axial bore. The lock and latch allow for interchangeability of tip assemblies inserted into the surgical instrument. A first and second handle are pivotally attached to the housing. A first ratchet member is rotatably attached to the first handle and includes serrated teeth. A second ratchet member extends from the second handle. The second ratchet member including a finger for engagement with the serrated tooth to prevent movement of said first handle relative to the second handle. The first ratchet member is rotatable about the rotational axis to disengage from the second ratchet member and allow the first handle to move relative to the second handle.
Owner:RF KINETICS
Manipulator
A manipulator includes a working unit comprising an operation command unit, horizontal roller and vertical rollers mounted thereon, drive pulleys rotatable in response to operation of the horizontal roller and the vertical roller, a connector, a first rotational axis disposed on a distal end of the connector, a second rotational axis extending perpendicularly to the first rotational axis, tubular members rotatably supported on a shaft providing the first rotational axis, and wires having rear and front portions trained around the drive pulleys and the tubular members, respectively. A drive mechanism operates about the first rotational axis in response to rotation of the tubular member, and an end effector operates about the second rotational axis in response to rotation of the tubular member.
Owner:TERUMO KK +1
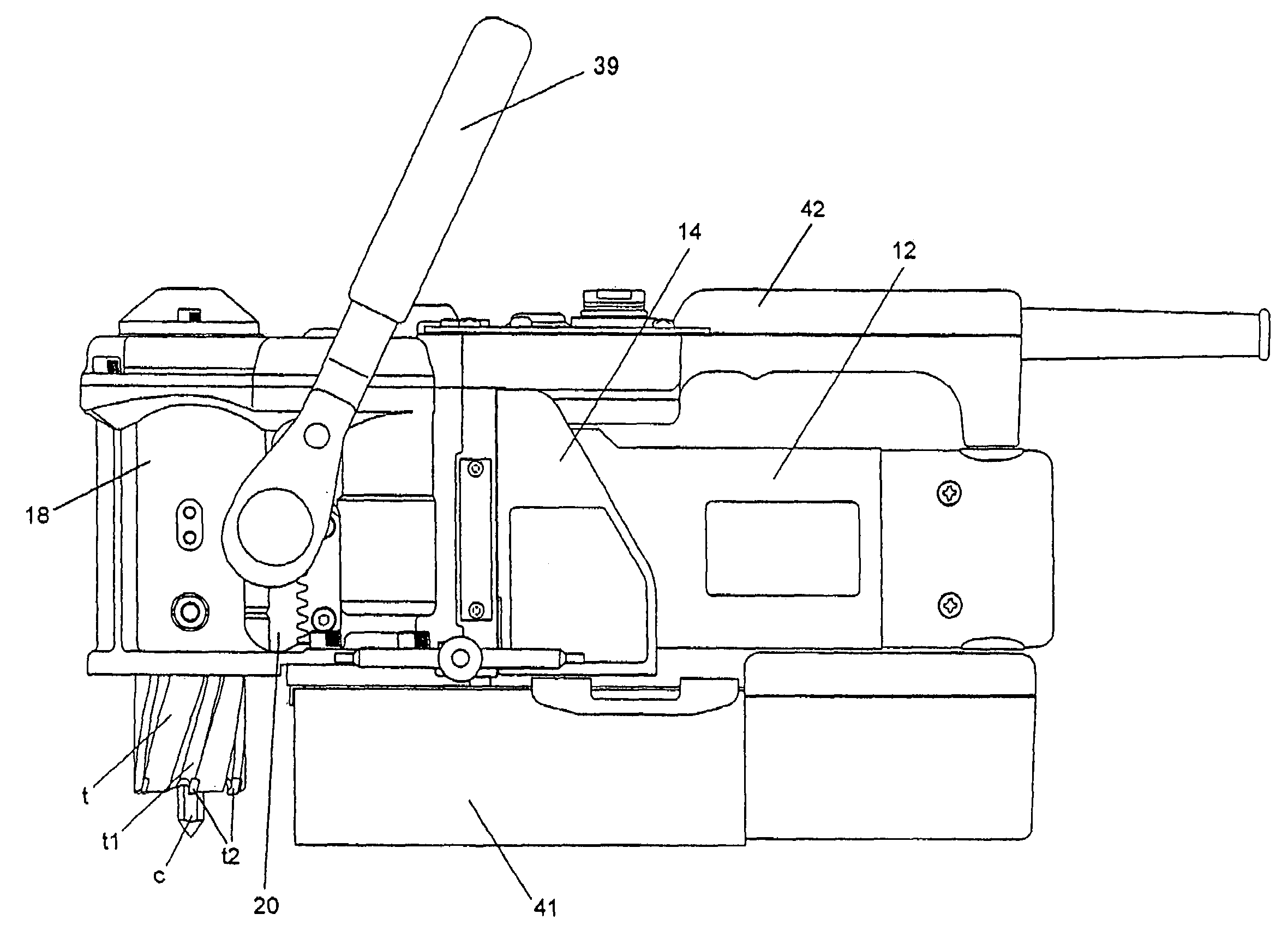
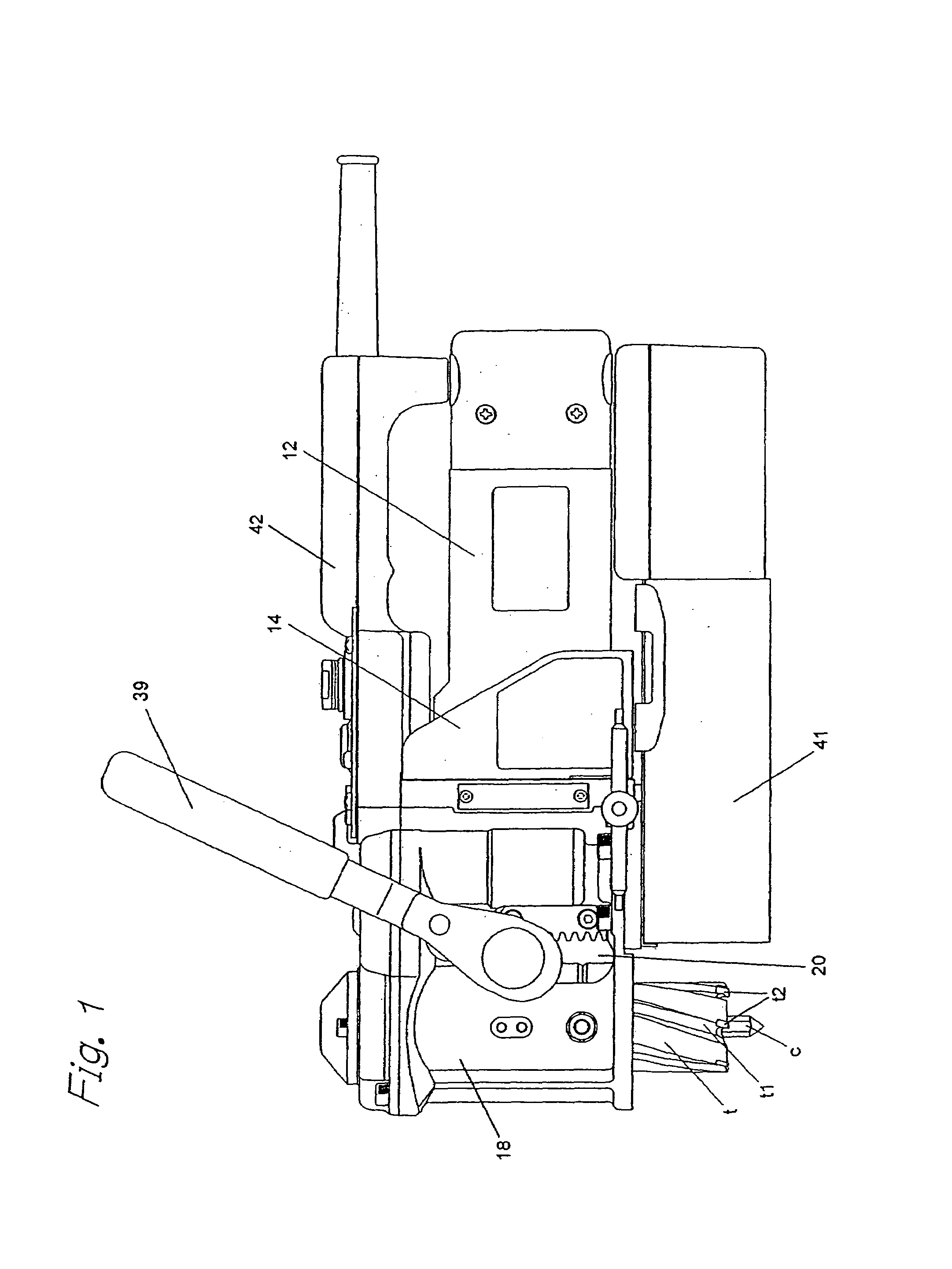
Hammer drill attachment
Power tools of the type under consideration include hammer drills, for example, which are electric or battery powered and includes two modes of operation: a rotation mode and a rotation-hammer mode. A manually operable selector lever enables the hammer drill to be selectively operated in one of the two modes by disengaging and engaging a hammer mechanism. In rotation-hammer mode, the drive shaft of the hammer drill rotates a tool element about a rotational axis and oscillates the tool element along a rotational axis. An attachment mountable within the chuck of a hammer drill prevents a tool element from rotating when the hammer drill is operating in rotation-hammer mode. The hammer drill attachment transfers hammer action, but not rotation, to the tool element. The hammer drill attachment enables dual function power tools to be operated in a hammer only mode to perform a function, for example, chiseling.
Owner:OROZCO JR EFREM
Prophy angle and adapter
A dental prophy angle includes a housing and a rotor. The housing defines a first bore and a second bore in communication with the first bore, and rotor is disposed within the second bore. The rotor includes a gearing system, and rotor includes a lock having a lock channel configured to receive a tip of a drive shaft. The housing includes a lock receiver for receiving the lock receiver permits rotation of the lock within the lock receiver and restrains linear movement of the lock in a direction substantially parallel to a rotational axis of the rotor.
Owner:AVID INC
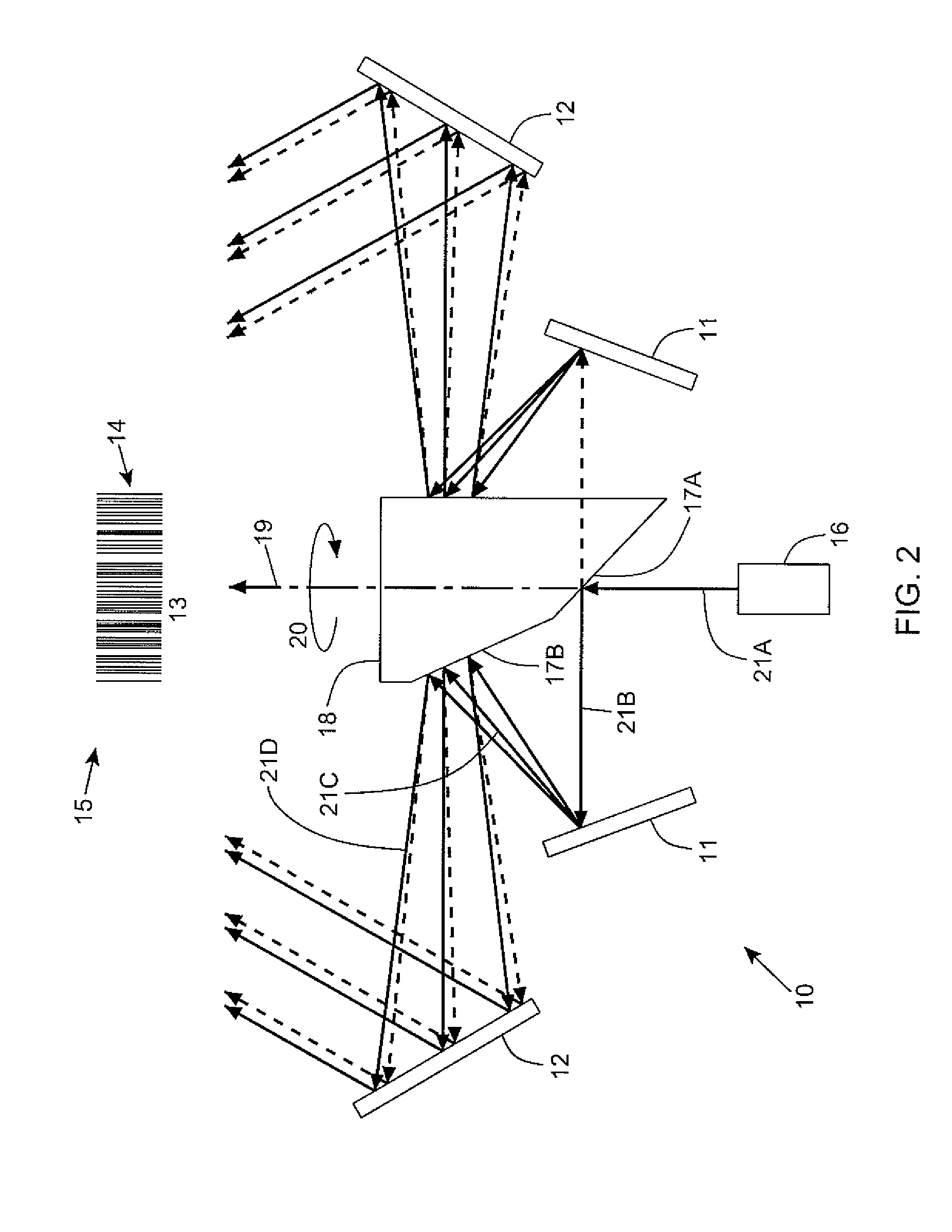
Laser scanning assembly having an improved scan angle-multiplication factor
InactiveUS8408469B2Increase multipleUniform collectionMirrorsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRotational axisAcute angle
A laser scanning system for generating a laser scanning pattern in a scanning field, while amplifying the scan-angle multiplication factor of rotating mirrors employed therein. The laser scanning system employs rotatable laser scanning assembly having an axis of rotation and first and second rotating mirrors with normal vectors that are coplanar with each other and said rotational axis, and which form an acute angle substantially less than 90 degrees so as to provide a laser scanning assembly with a scan angle multiplication factor that is greater than 2.0. A cluster of stationary mirrors mounted about the first and second rotating mirrors, for sweeping a laser beam off the cluster of stationary mirrors after a laser beam has been reflected off the first rotating mirror, then reflected off the second rotating mirror, and then directed outwardly towards an array of pattern mirrors, so as to generate a resultant laser scanning pattern within the scanning field.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR INC
Electric drill apparatus
InactiveUS7121773B2Reduce weight and sizeLow profileDrilling/boring measurement devicesThread cutting machinesRotational axisAnnular cutter
An electric drill apparatus having a low profile is provided which comprises an annular cutter, a motor for rotating the annular cutter, a rotary shaft assembly for rotating the annular cutter attached to its leading end about a rotating, a rotation reduction mechanism disposed between the motor and rotary shaft assembly for transmitting a driving force of the motor to the annular cutter through the rotary shaft assembly, a feed mechanism responsive to an operation of a manual handle, for moving the rotary shaft assembly along with a straight line to advance or retract the annular cutter attached to the rotary shaft assembly with respect to a workpiece, and an adhesion base for securing the electric drill apparatus to the workpiece. The annular cutter has a plurality of cutting blades comprised of cemented carbide tips fixed on its lower end, thereby it is capable of rotating at a high speed. The rotary shaft assembly has a rotating shaft which rotates in a direction different from that of a rotating shaft of the motor, thereby the drill apparatus has a low profile.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
Self-Centering Wafer Carrier System For Chemical Vapor Deposition
ActiveUS20160372321A1Increase probabilityQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseCarrier system
A self-centering wafer carrier system for a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reactor includes a wafer carrier comprising an edge. The wafer carrier at least partially supports a wafer for CVD processing. A rotating tube comprises an edge that supports the wafer carrier during processing. An edge geometry of the wafer carrier and an edge geometry of the rotating tube being chosen to provide a coincident alignment of a central axis of the wafer carrier and a rotation axis of the rotating tube during process at a desired process temperature.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Spin head, apparatus for treating substrate, and method for treating substrate
ActiveUS20100126539A1Prevent excessive speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using liquidsRotational axisCentrifugal force
Provided is a spin head supporting a substrate and rotating the substrate. The spin head includes a body, chuck pins installed on the body and moving between supporting positions where a substrate is supported and waiting positions providing space for loading / unloading of the substrate, and a chuck pin moving unit configured to move the chuck pins. The chuck pin moving unit includes a rotation rod coupled with each of the chuck pins, a pivot pin fixing the rotation rod to the body, and a driving member rotating the rotation rod about the pivot pin as a rotation shaft to move the chuck pin from the supporting position to the waiting position. When the body rotates, the rotation rod uses reverse centrifugal force to apply force to the chuck pin from the waiting position to the supporting position. The chuck pins include first pins and second pins that alternately chuck a substrate during a process.
Owner:SEMES CO LTD
Shaft mounted energy harvesting for wireless sensor operation and data transmission
InactiveUS20050017602A1Provide informationEfficiently transferring energyBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLine sensorRotational axis
A device for monitoring a rotating shaft is provided. The device measures strain in the shaft and provides angular velocity and torque in the shaft. The device includes a sensor, sensor conditioning circuitry, a microprocessor, and a transmitter, all located on a rotating shaft. The device obtains power by harvesting mechanical energy of the rotating shaft itself. Coils are provided rotating with the shaft and permanent magnets are mounted adjacent the rotating shaft so electrical energy is induced in the coils as they rotate through the magnetic field of the permanent magnets. A battery or capacitor is connected to the coils for storing energy. A microprocessor is connected to the sensors, the storage device, and the transmitter for managing power consumption and for monitoring the amount of electrical energy stored in the storage device and for switchably connecting the storage device to the transmitter when the stored energy exceeds a threshold.
Owner:LORD CORP
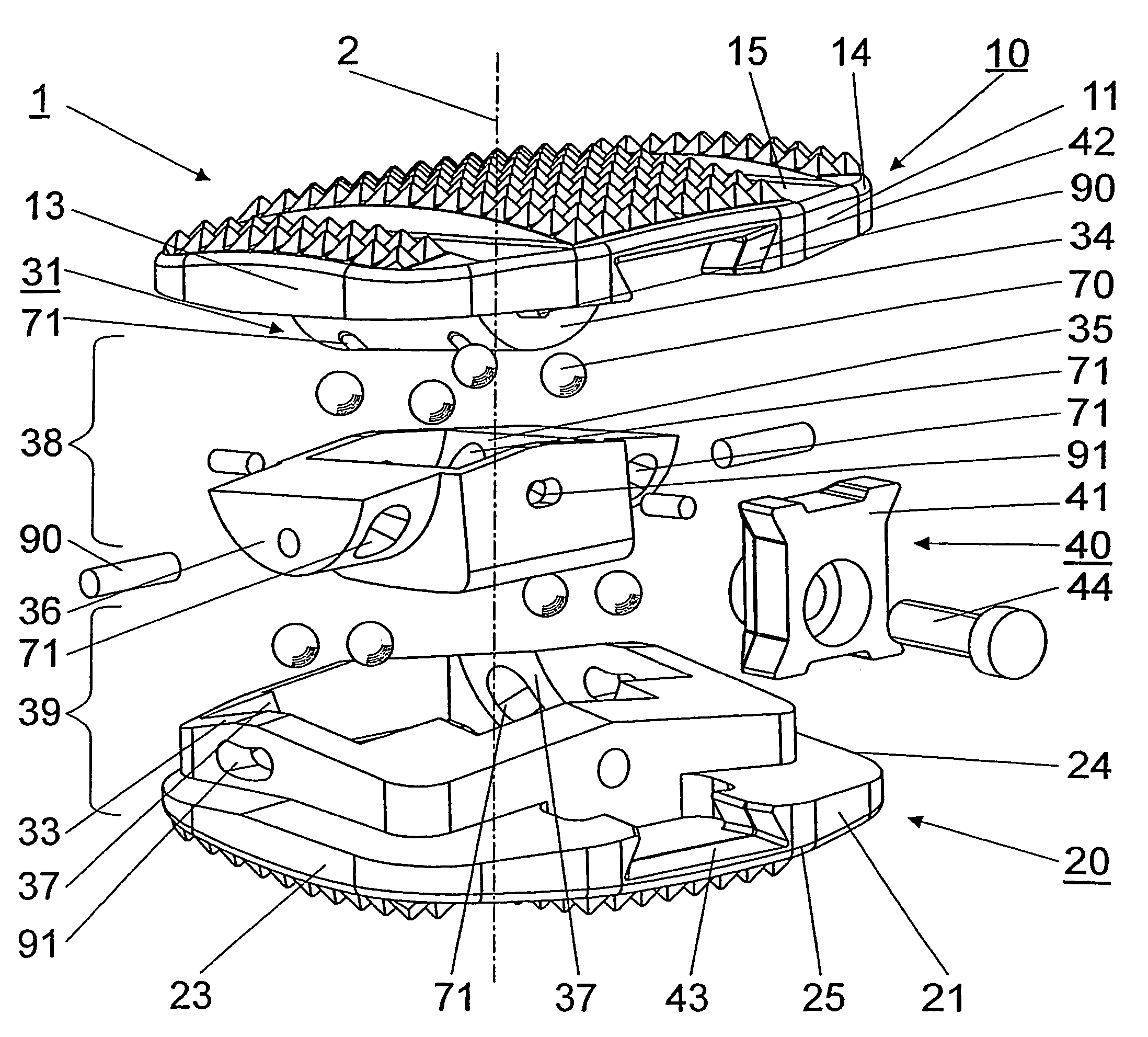
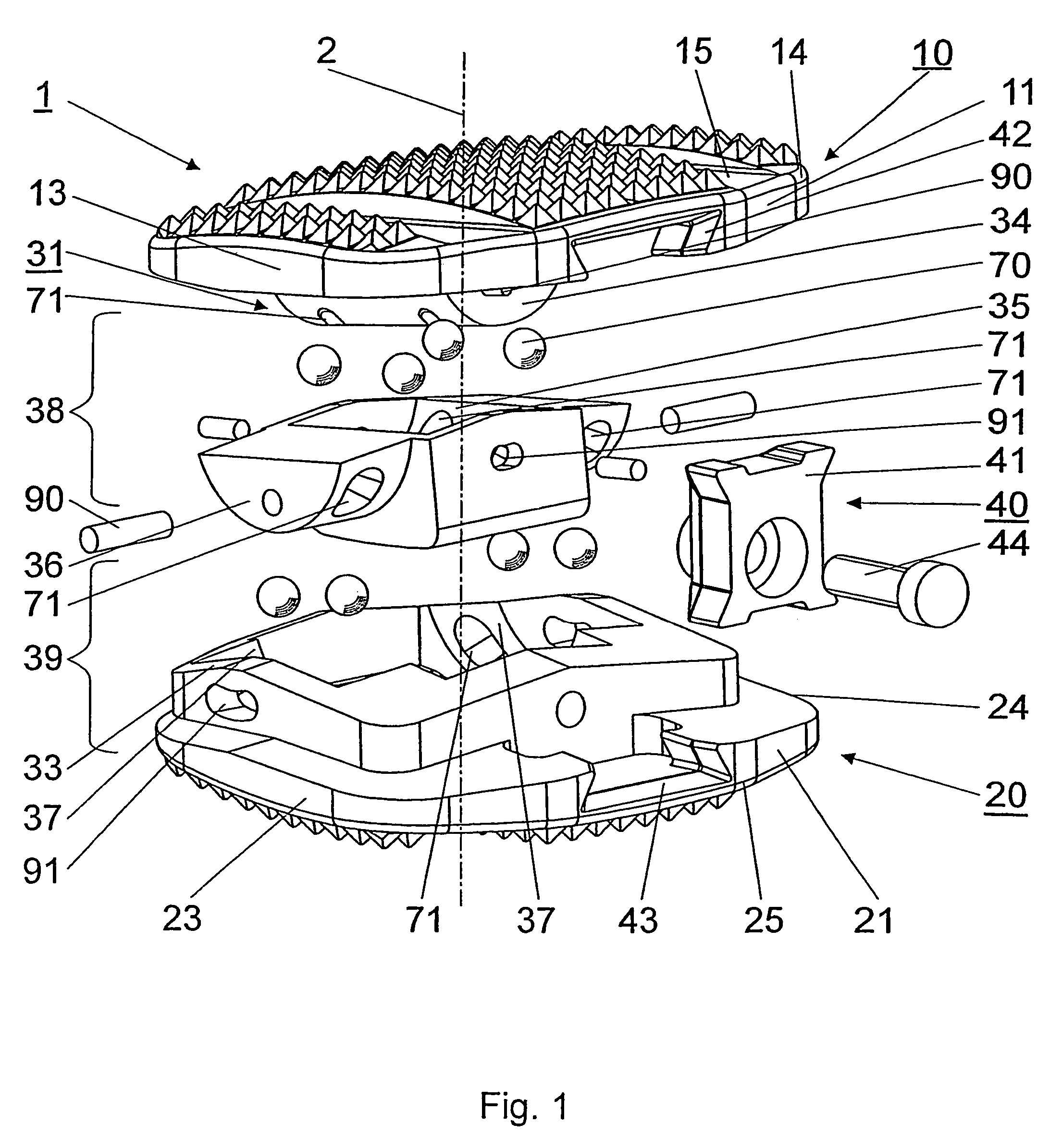
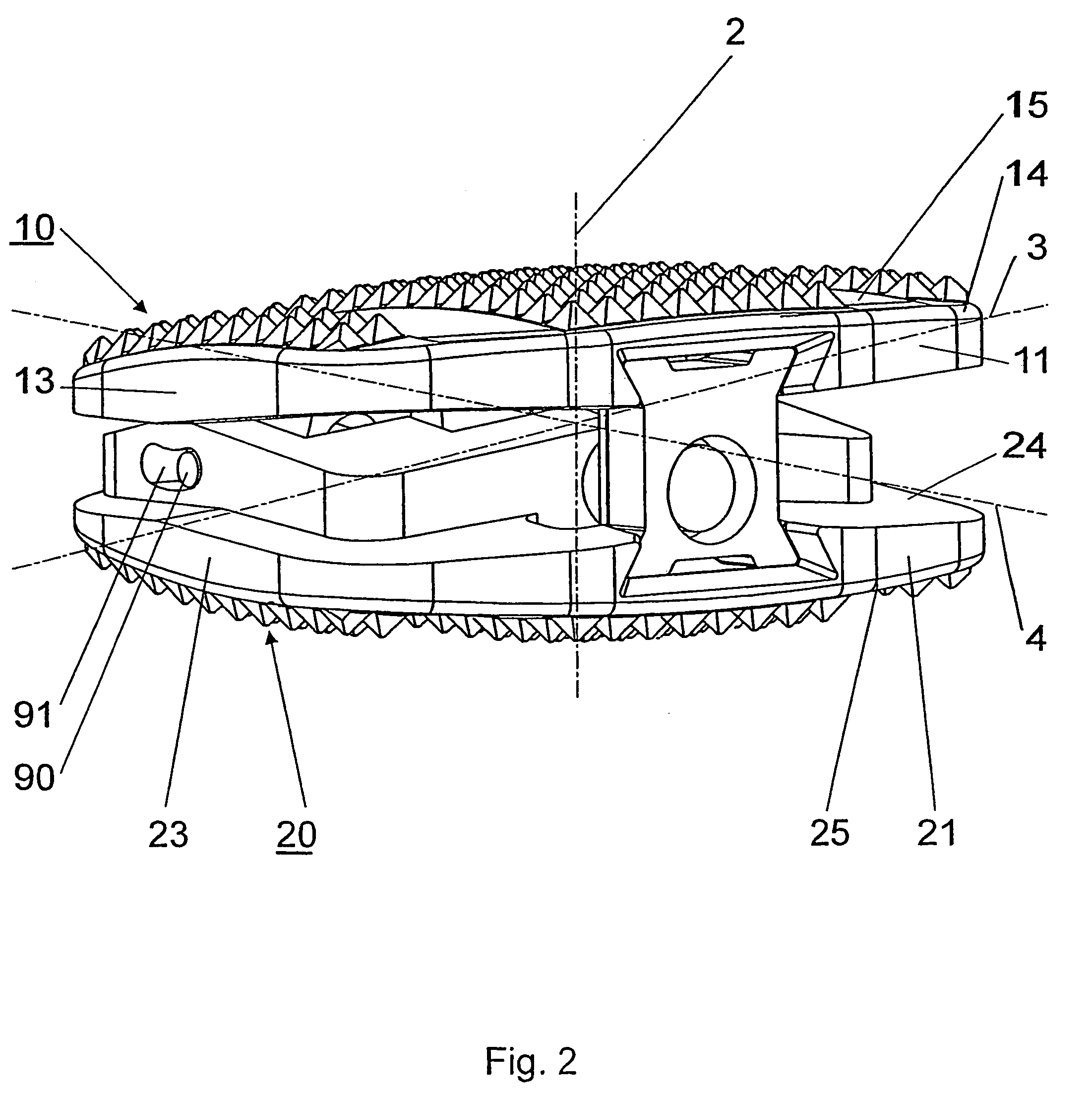
Intervertebral implant with joint parts mounted on roller bodies
InactiveUS7473276B2Relieves strain on the face jointsJoint implantsSpinal implantsRotational axisEngineering
An intervertebral implant (1), including an upper section (10) provided with a ventral side area (11), a dorsal side area (12), two lateral side areas (13,14), a top apposition surface (15) and a bottom surface (16), a lower section (20) provided with a ventral side area (21), a dorsal side area (22), two lateral side areas (23,24), a bottom apposition surface (25) and a top surface (26), wherein the two sections (10,20) are moveable in relation to each other by means of two joints (38;39) arranged between the two sections (10;20), and wherein each of the joints (38;39) has a swivel axle (3;4) and the two swivel axles (3;4) are arranged perpendicular to each other, each of the joints (38;39) comprises at least one axle (34;36) coaxial to the relevant swivel axle (3;4) and a bearing shell (35;37) receiving the axle (34;36), and roll bodies (70) are inserted between the axles (34;36) and the bearing shells (35;37).
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Surgical cassette having an aspiration pressure sensor
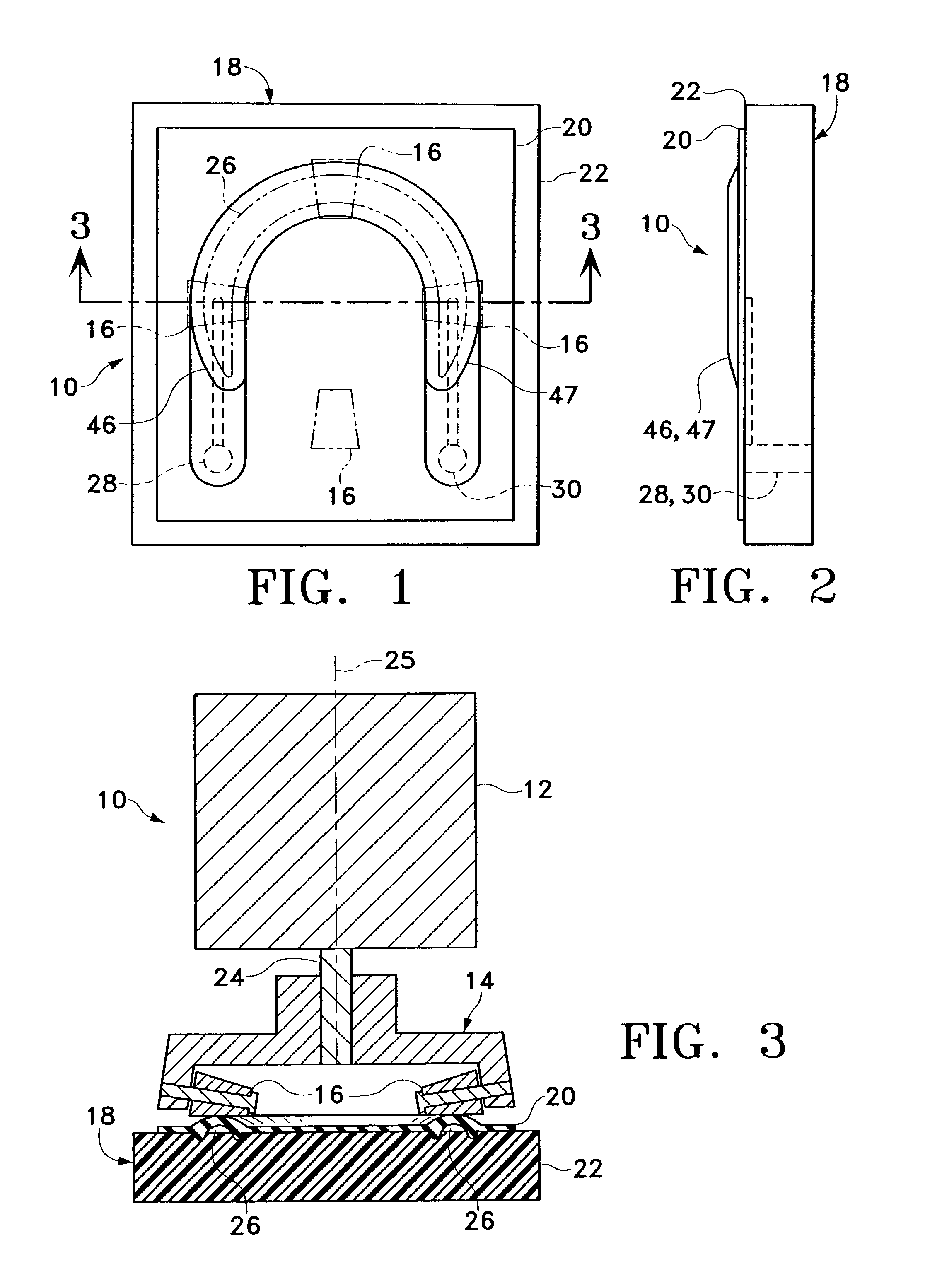
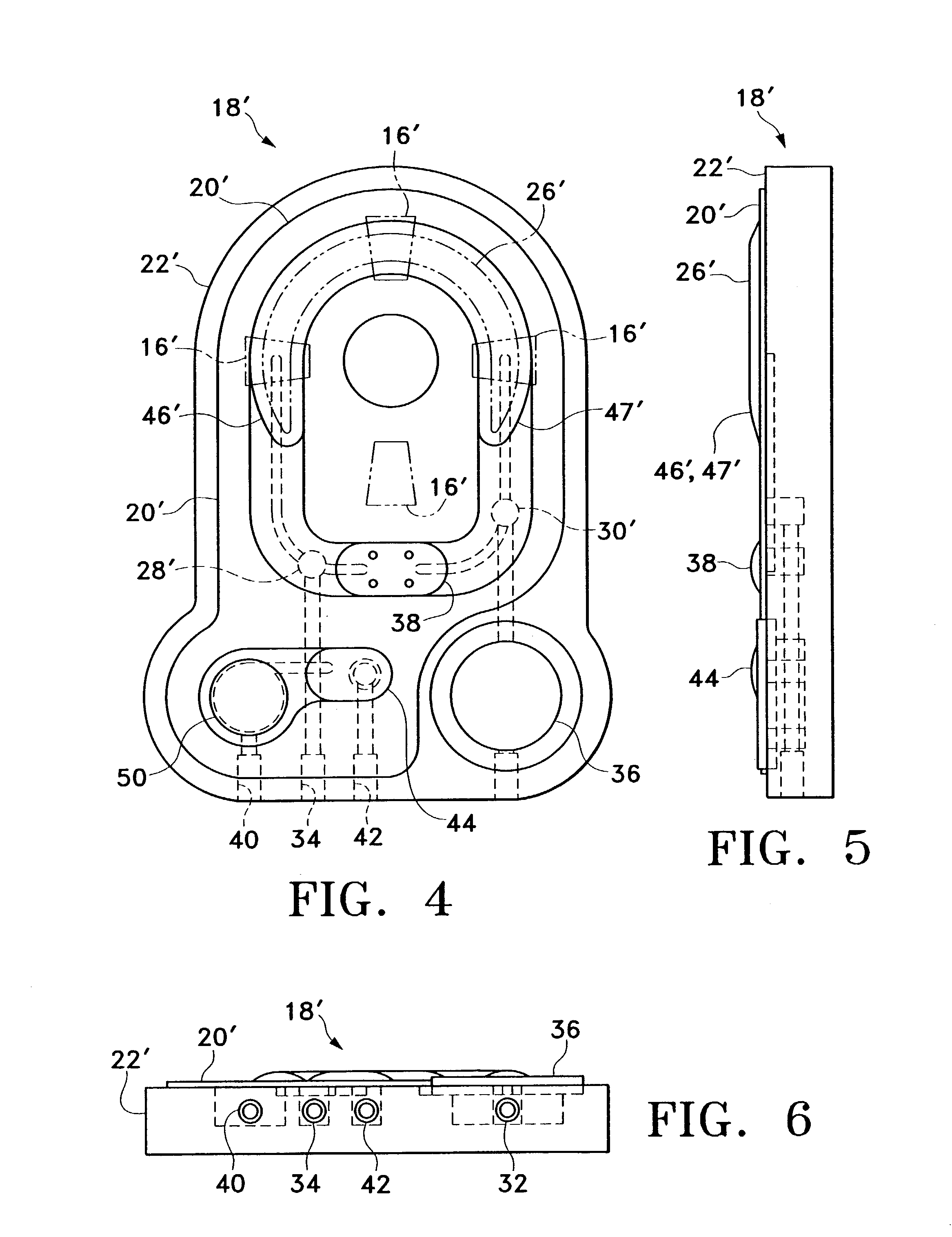
A cassette having a molded flow channel contained on an elastomeric sheet that is bonded or mechanically attached to a rigid substrate. The flow channel projects outwardly from the exterior of the cassette so that a peristaltic pump having pump head rollers mounted radially from the axis of rotation of the pump motor compress the elastomeric flow channels against the rigid substrate during operation.
Owner:ALCON INC
Suturing device for endoscope
InactiveUS7144401B2Avoid misalignmentPreventing the suturing device from dislocatingSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEndoscopic staplerRotational axis
A suturing device for an endoscope includes a curved needle rotatably attached on the distal end of the suturing device. A rotary member is provided on the rotation axis of the curved needle for rotating said curved needle and a connecting arm connects the curved needle to the rotary member. The center of curvature of the curved needle is aligned with the rotation axis of the curved needle and engaging means are provided at least at the pointed end of the curved needle for receiving thread.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC +1
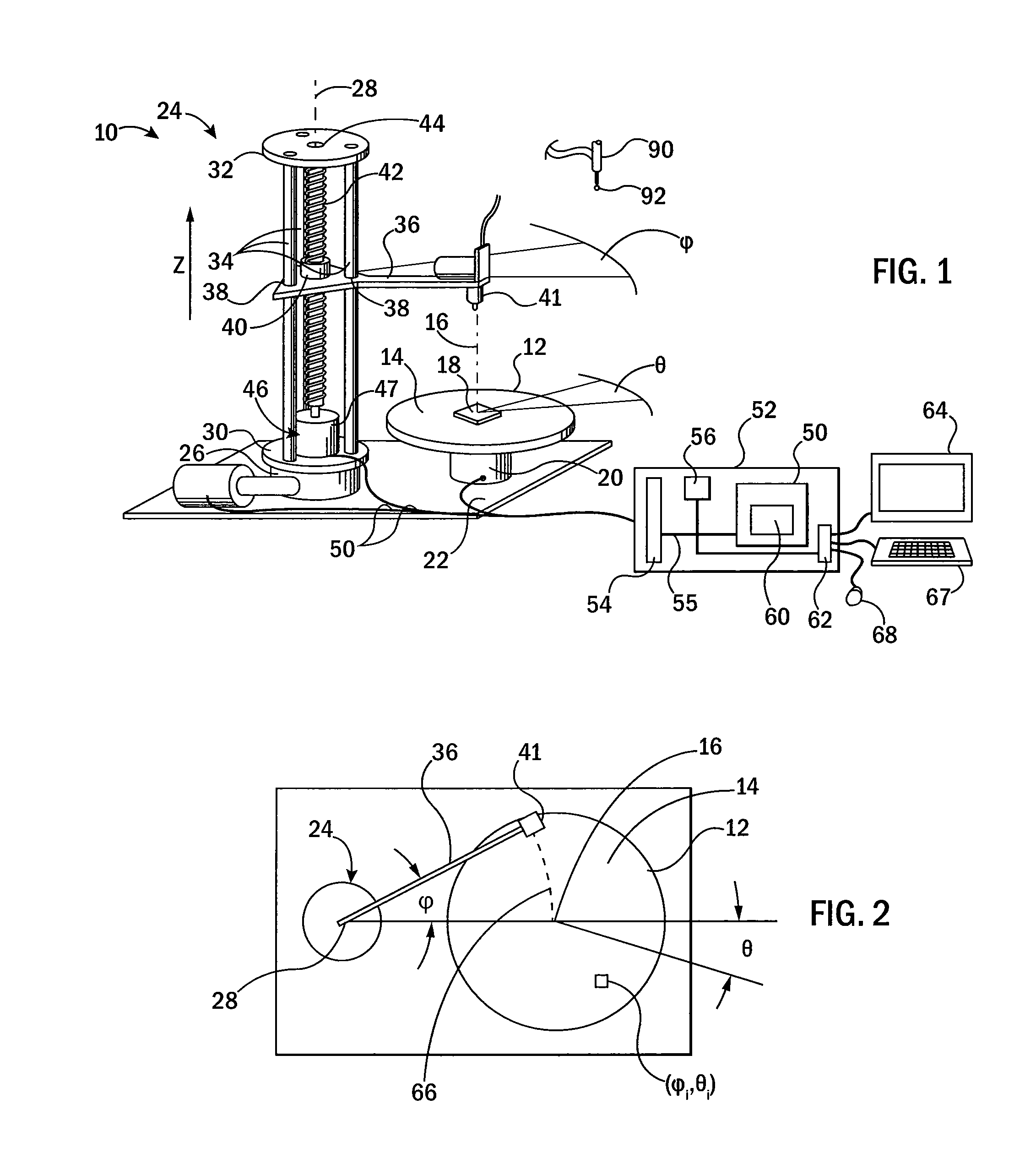
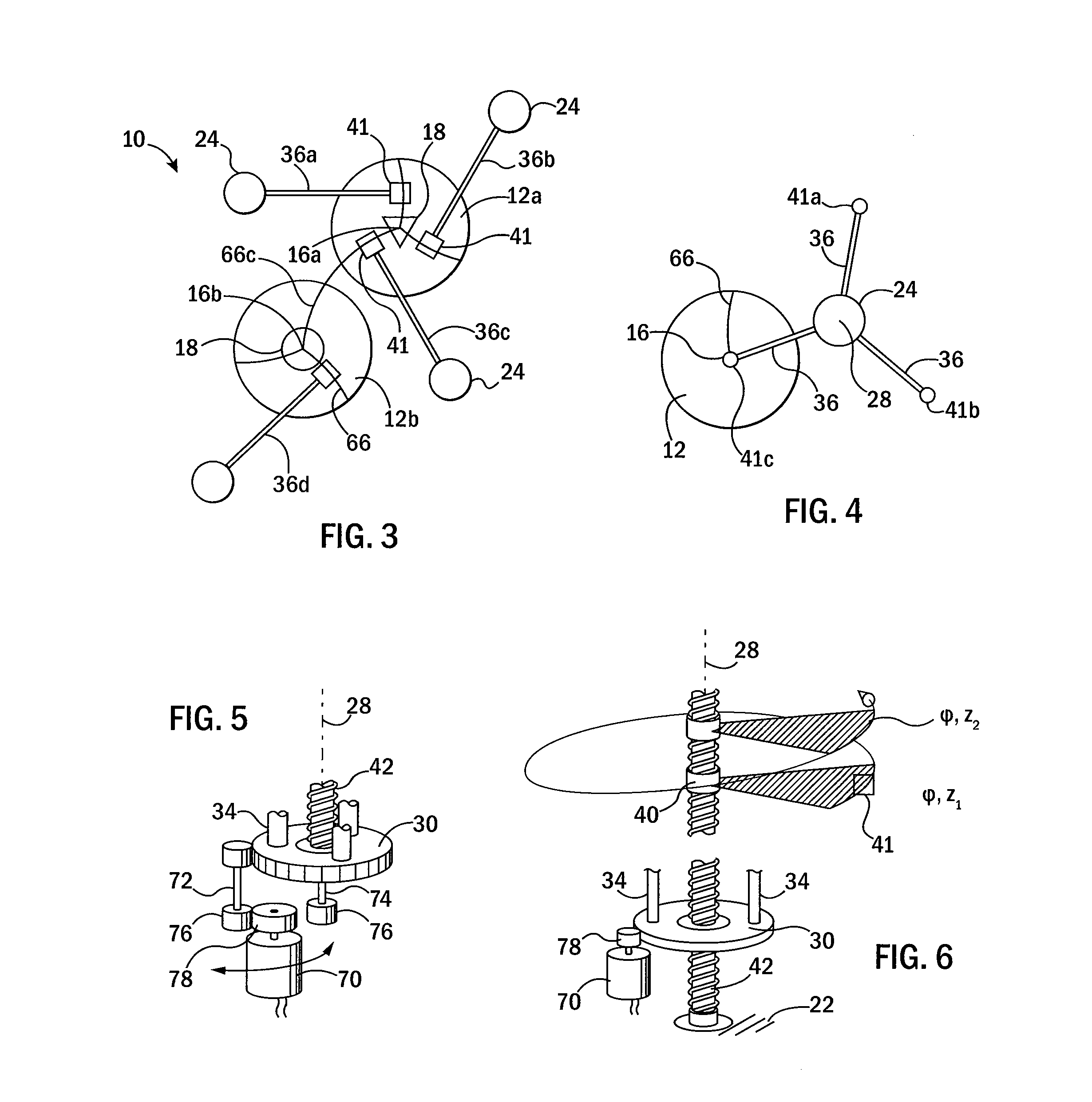
Apparatus for guiding a medical tool
InactiveUS20090234369A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesRotational axisCoupling
There is provided a guide apparatus for orienting a medical tool relative to and through a remote fulcrum or remote center of motion. The guide apparatus may comprise: at least one crank arm comprising at least a portion of a first hinged coupling for hinged coupling to a stabilizer; at least one link arm comprising at least a portion of a second hinged coupling for hinged coupling to the crank arm at a location spaced from the first hinged coupling; a tool holder for supporting a medical tool on the link arm at a location spaced from the first hinged coupling; wherein the rotational axes of the first and second hinged couplings intersect to define a remote fulcrum. The guide apparatus may be configured to be an open-loop spherical chain or a closed-loop spherical chain.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Rotating irradiation apparatus
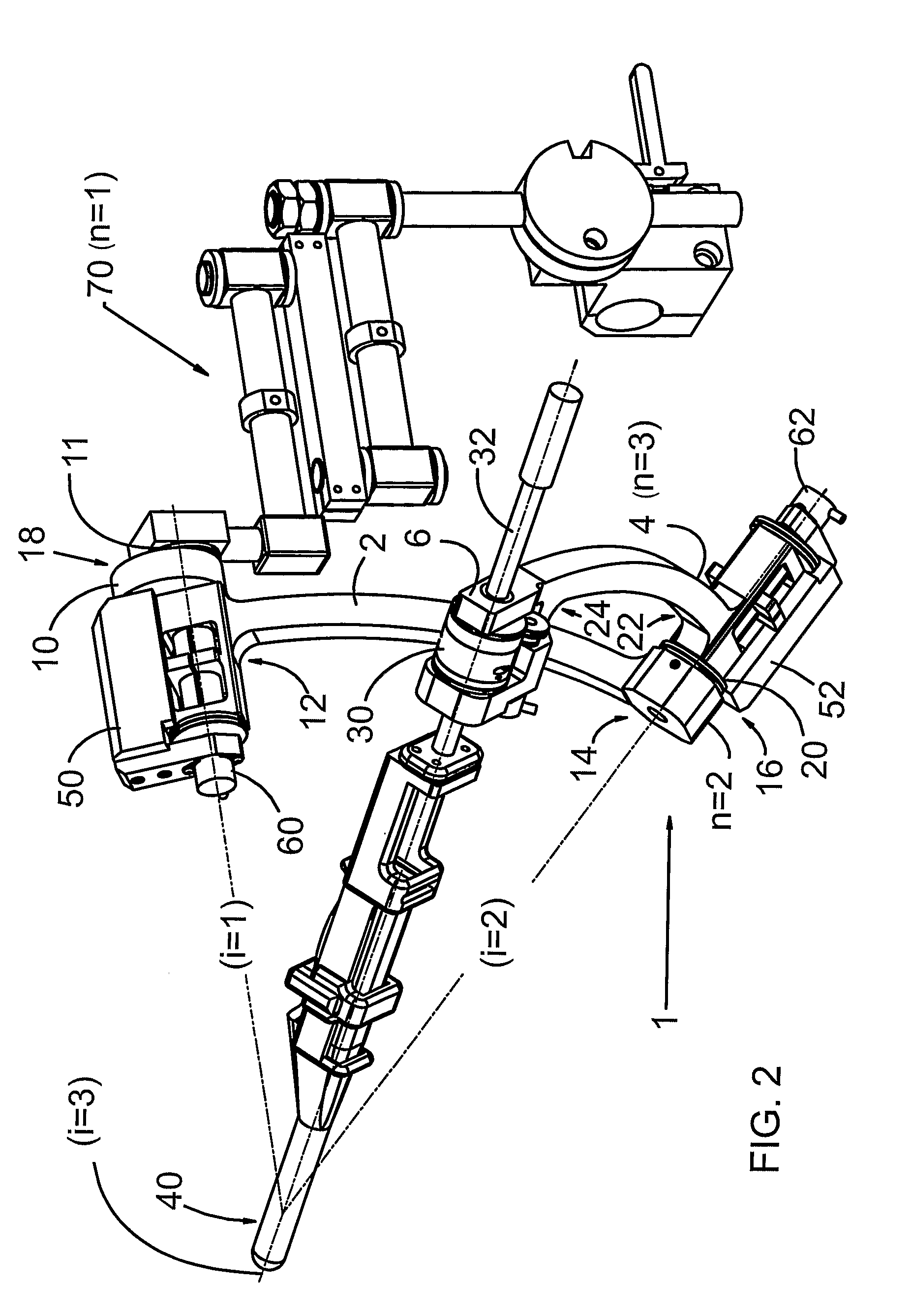
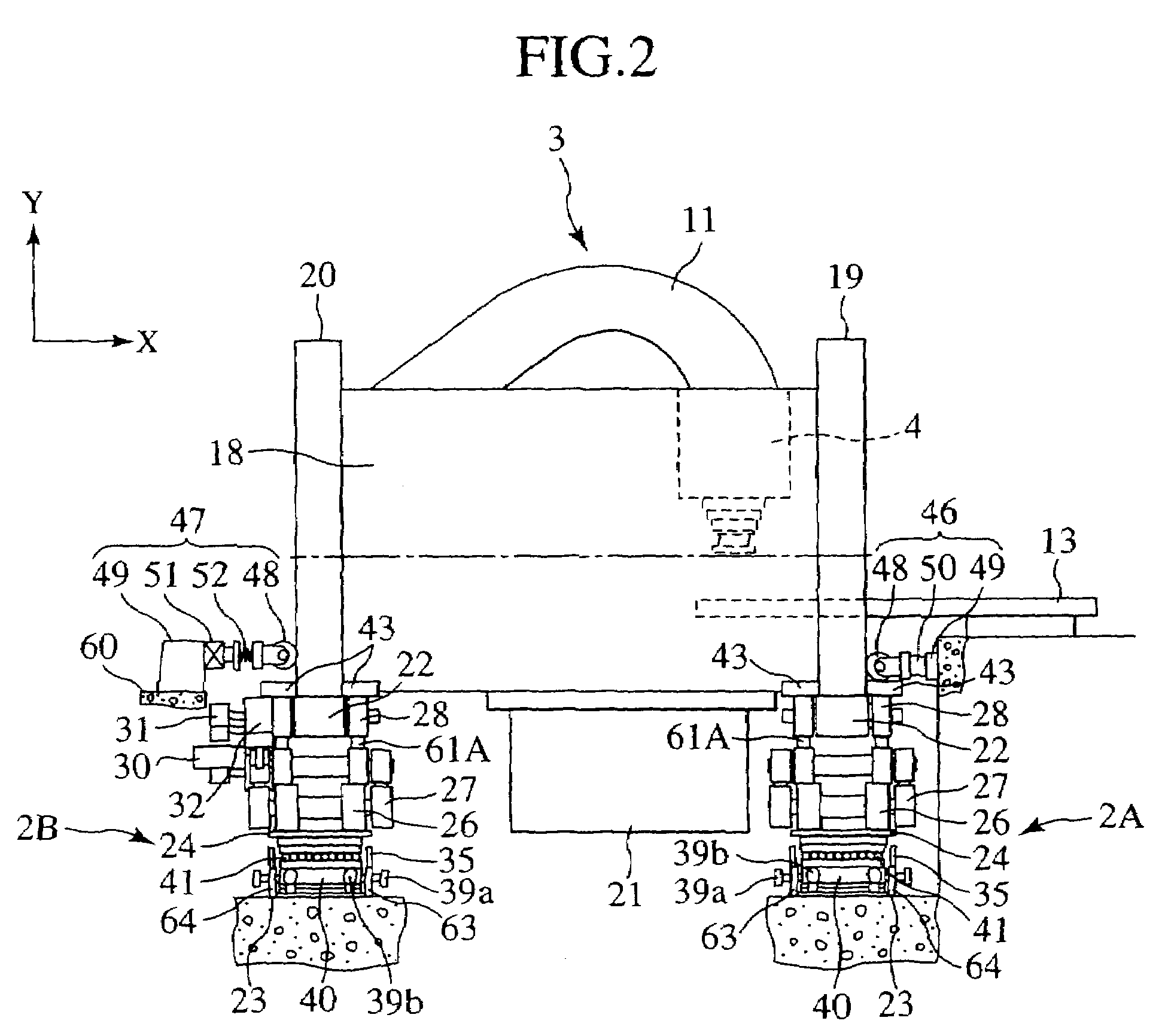
ActiveUS7381979B2Increase the number ofHigh positioning accuracyRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsParticle radiotherapyRotational axis
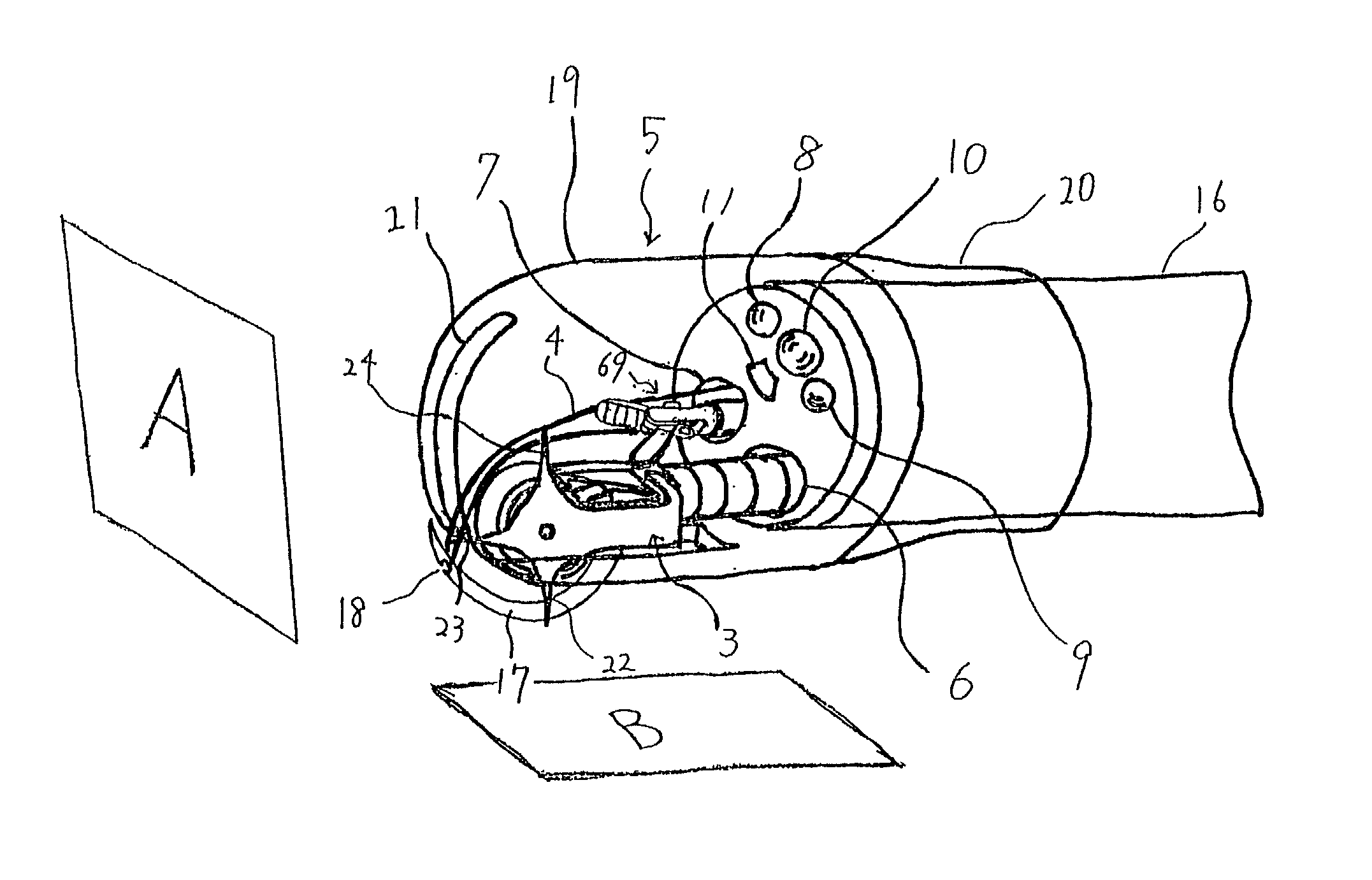
A rotating irradiation apparatus includes a rotating gantry 3 including a front ring 19 and a rear ring 20 and is provided with a beam delivery device 11 and an irradiation device 4. The beam delivery device 11 delivers an ion beam used for particle radiotherapy. Radial support devices 61A and 61B support the front ring 19 and radial support devices 61A and 61B support the rear ring 20. Each radial support device includes a linear guide 41, an upper support structure disposed above the linear guide 41, and a lower support structure disposed below the linear guide 41. The upper support structure is movably mounted on the lower support structure and is movable in the direction of the rotational axis of the rotating gantry 3.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
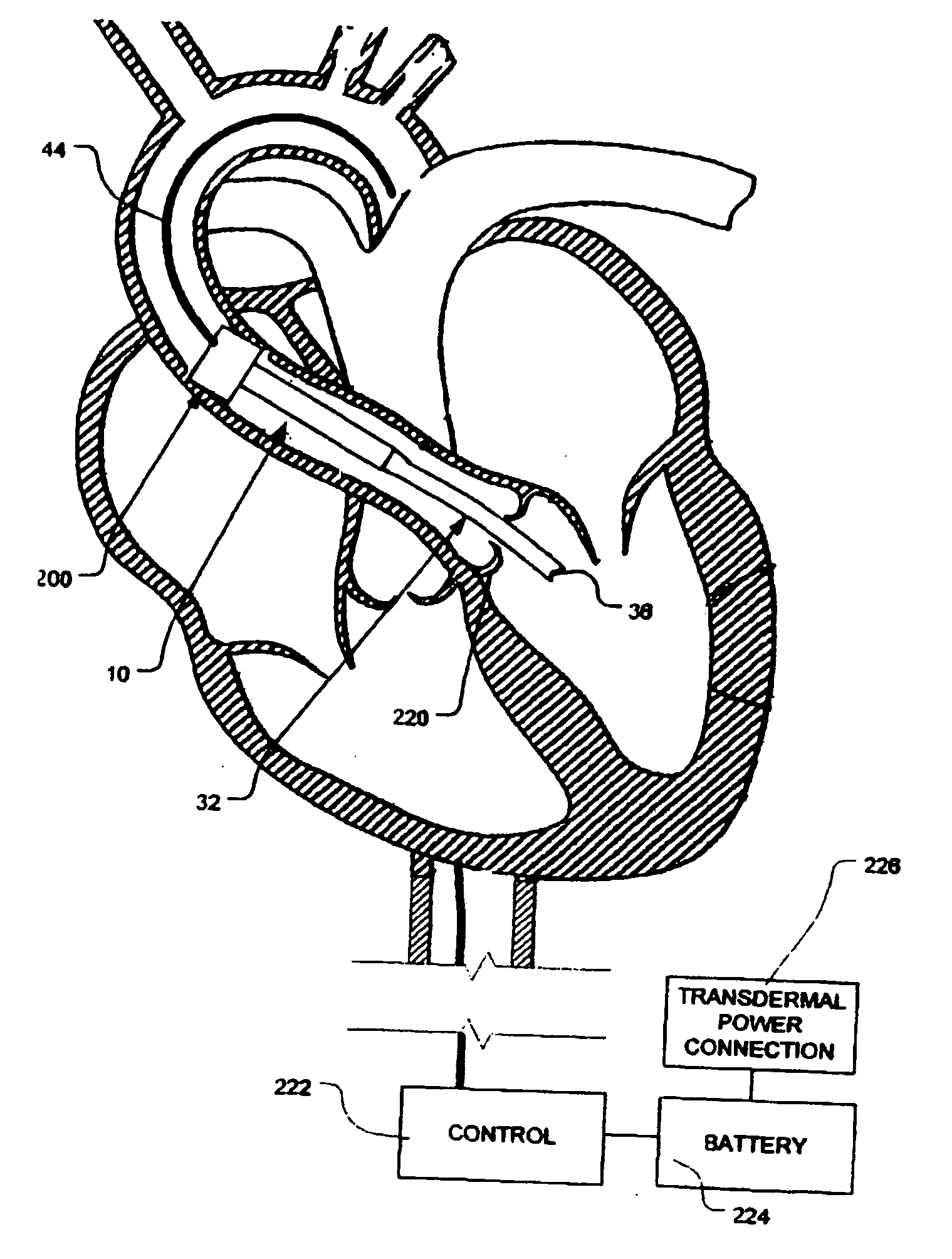
Intravascular ventricular assist device
One aspect of an intravascular ventricular assist device is an implantable blood pump where the pump includes a housing defining a bore having an axis, one or more rotors disposed within the bore, each rotor including a plurality of magnetic poles, and one or more stators surrounding the bore for providing a magnetic field within the bore to induce rotation of each of the one or more rotors. Another aspect of the invention includes methods of providing cardiac assistance to a mammalian subject as, for example, a human. Further aspects of the invention include rotor bodies having helical channels formed longitudinally along the length of the body of the rotor where each helical channel is formed between peripheral support surface areas facing radially outwardly and extending generally in circumferential directions around the rotational axis of the rotor.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Fiber tow treatment apparatus and system
In one embodiment, a fiber treatment system includes a rotatable nubbed roller including an axis of rotation, a surface, and a number of spaced apart nubs projecting away from the surface, the number of spaced apart nubs imparting a number of spaced apart openings in a fiber tow. In another embodiment, the fiber treatment system further includes an optionally rotatable spreader roller for flattening the fiber tow. In yet another embodiment, the loosened, but still continuous fiber tow is chopped by a downstream chopper to form short fibers with reduced tow sizes.
Owner:US COUNCIL FOR AUTOMOTIVE RES
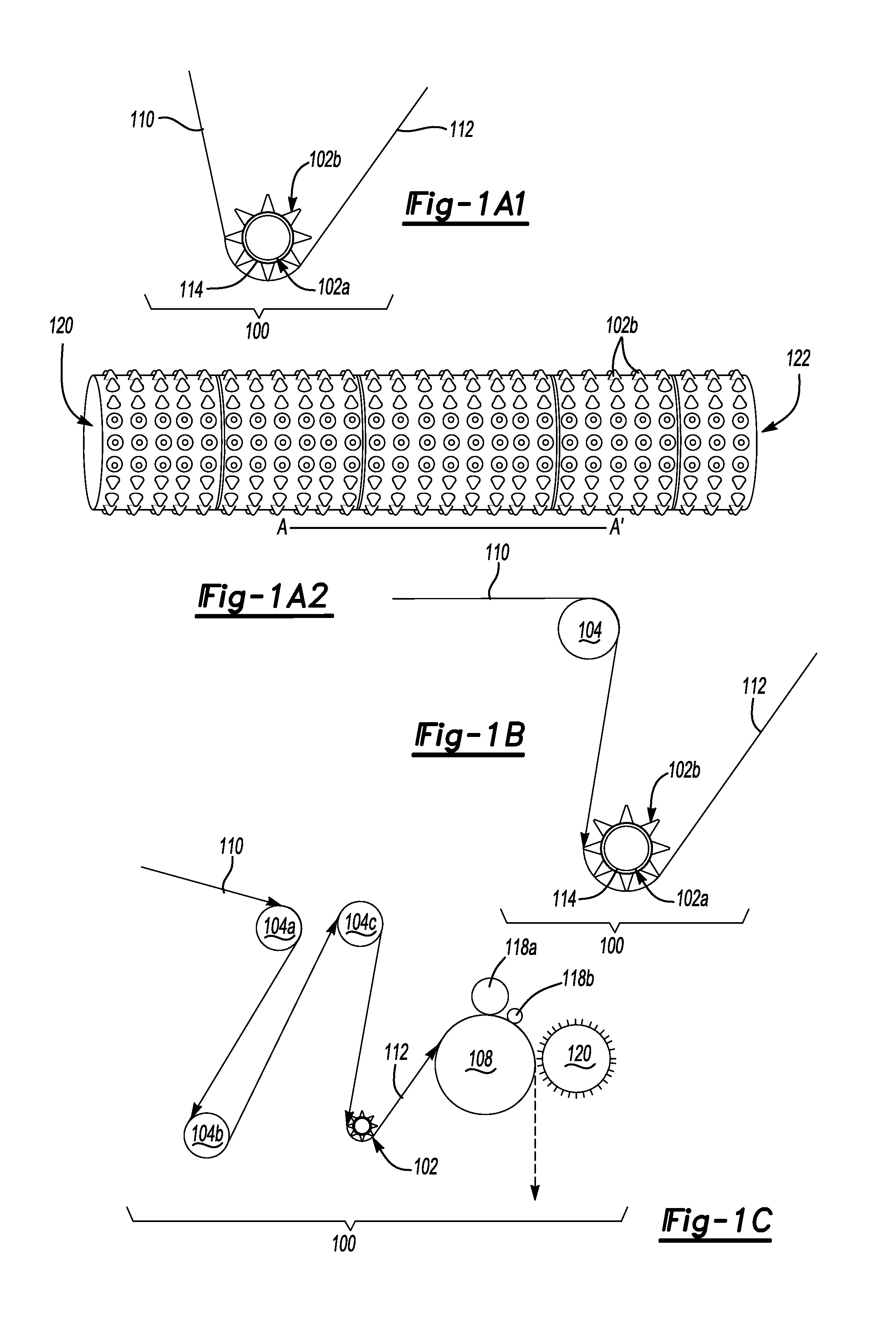
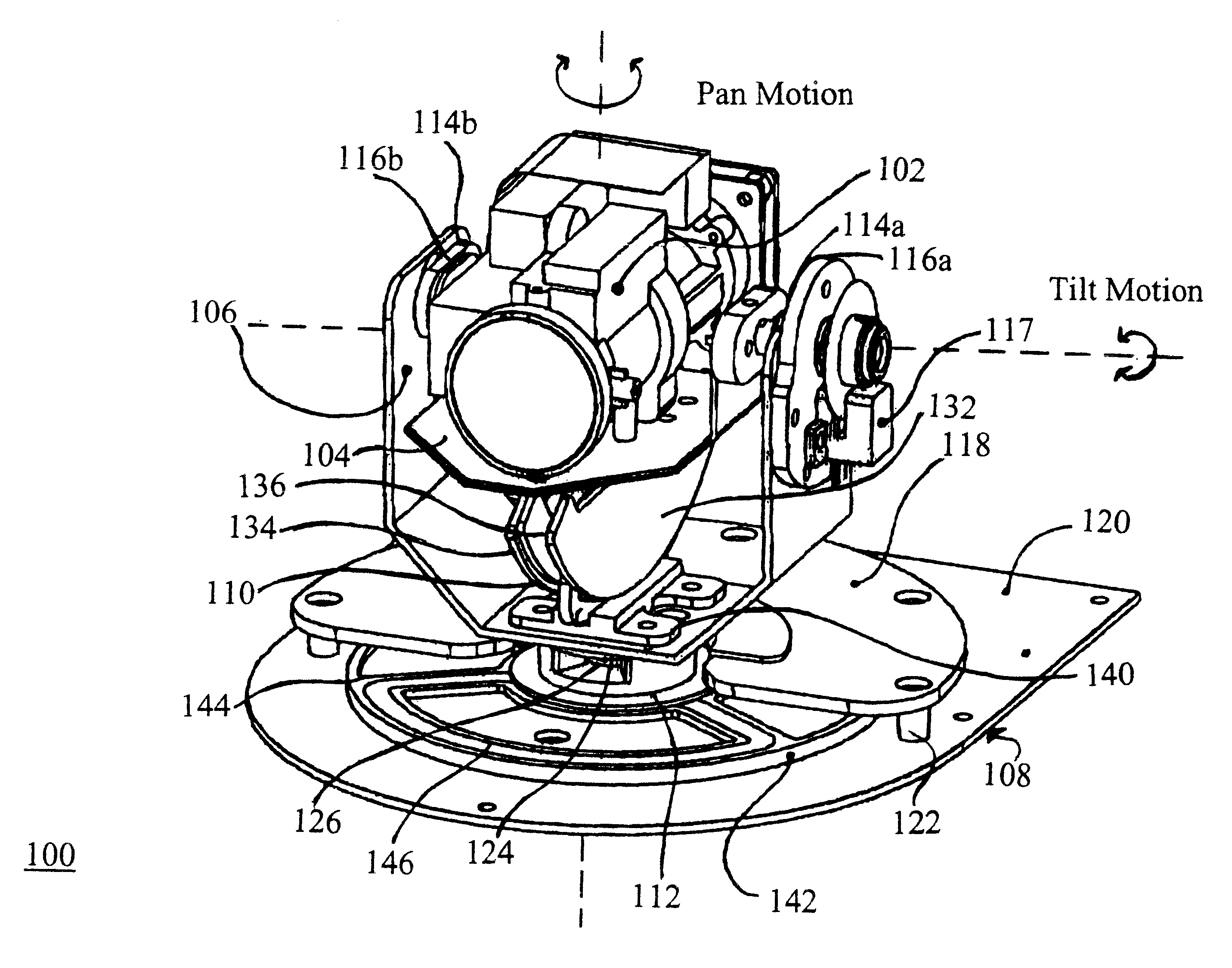
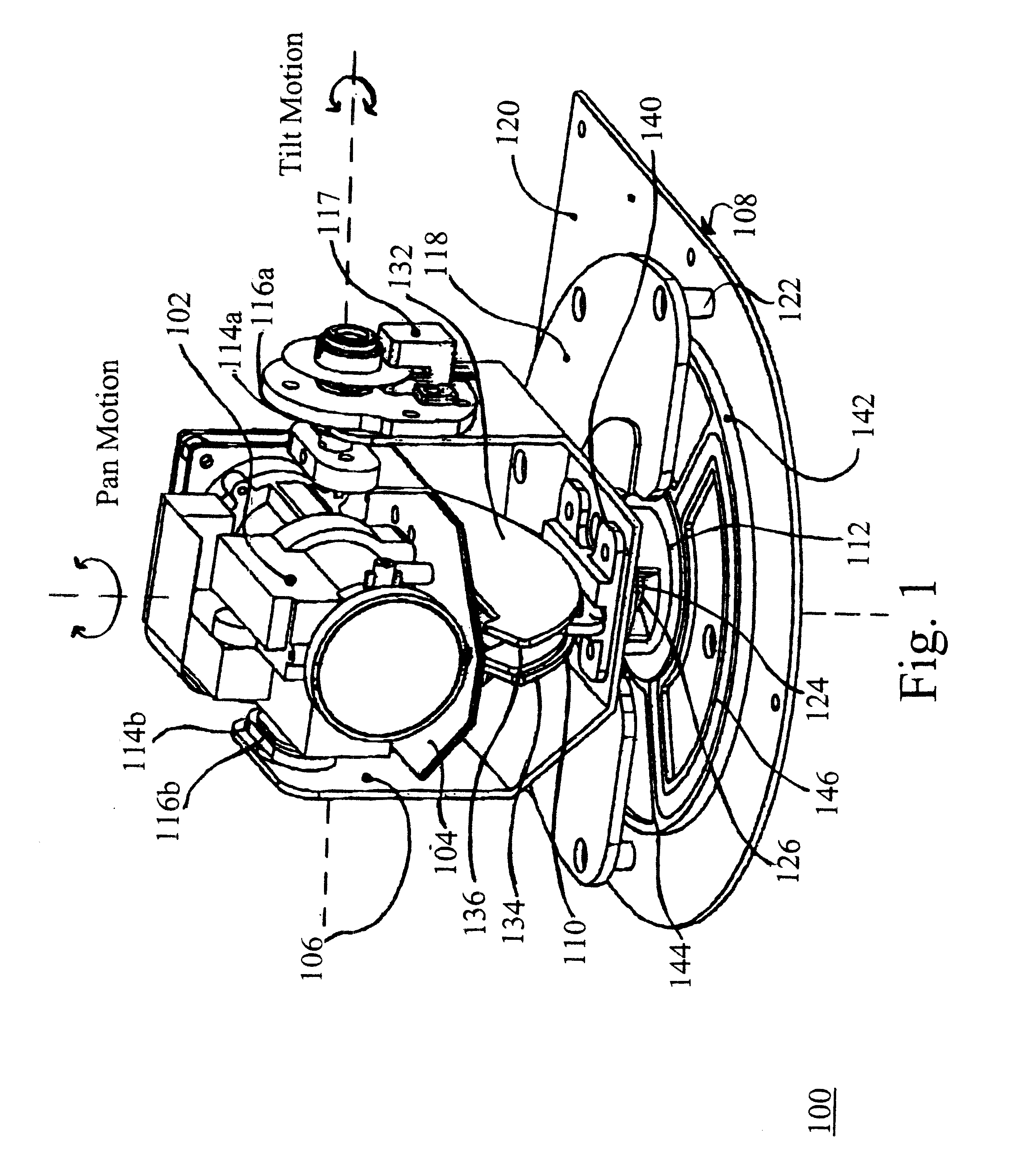
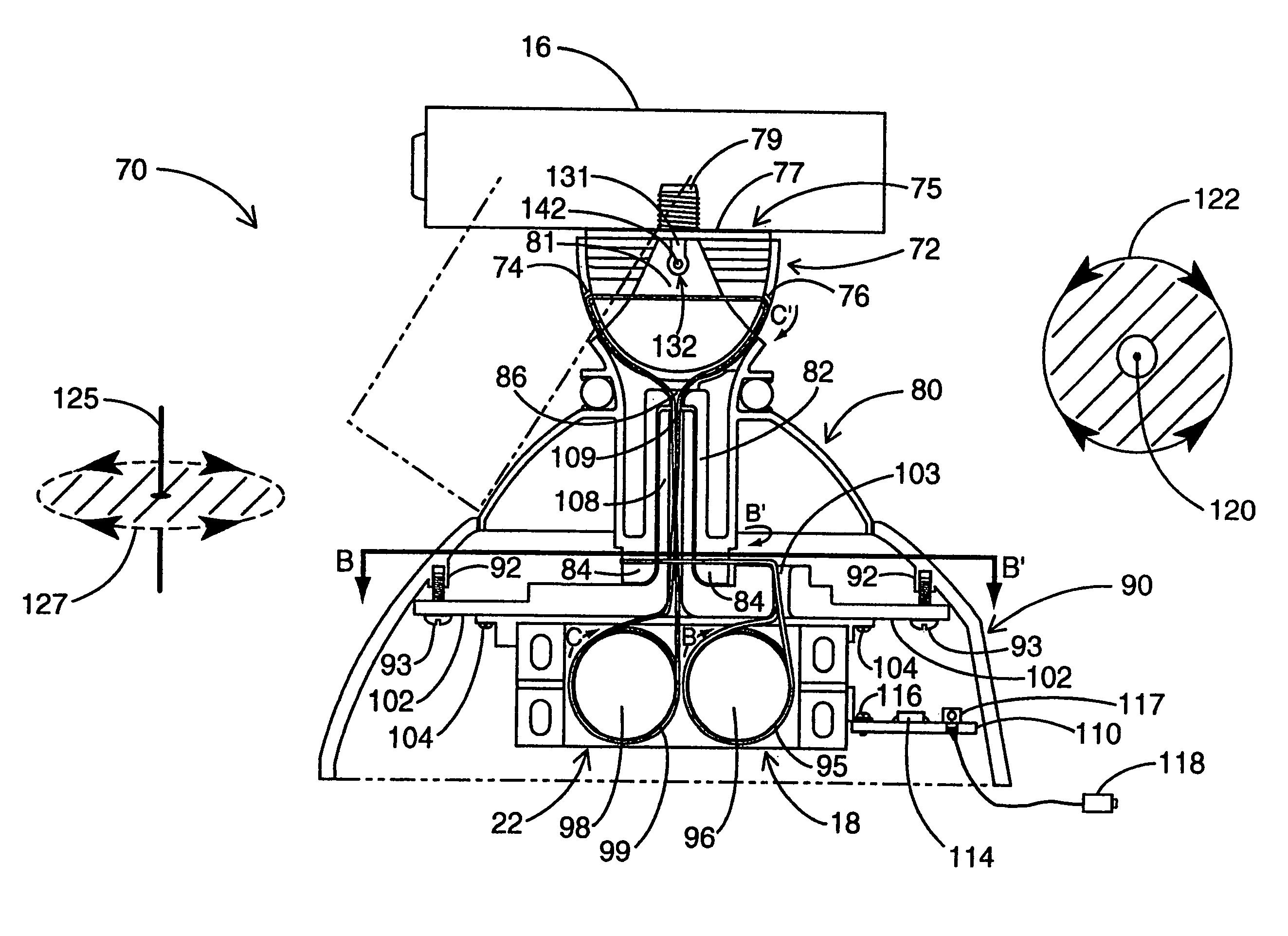
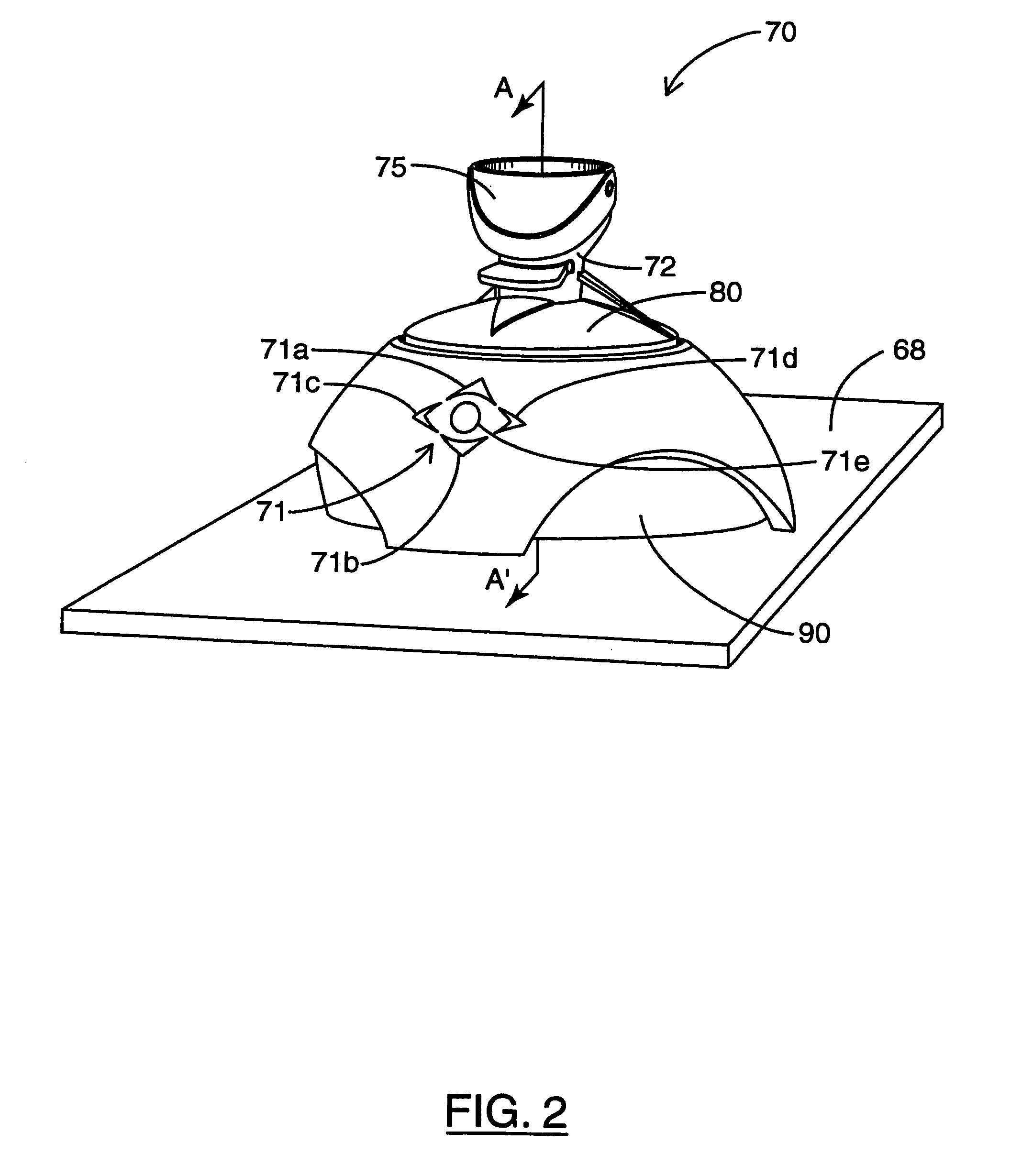
Device for rotatably positioning a camera or similar article about two orthogonal axes
A positioning device is provided for rotatably positioning a camera or other article about orthogonal rotational axes. The positioning device includes a carriage supported for rotation about a horizontal axis by a yoke. The yoke is in turn rotatably coupled to a base assembly for rotation of the yoke about a vertical axis. Rotation of the camera about the horizontal and vertical axes is respectively effected by first and second voice coil actuators, each comprising a pair of magnets and at least one coil to which current is supplied. The amplitude and direction of the current supplied to the coil determines the speed and direction of rotation of the camera. The second voice coil actuator preferably includes a coil assembly comprising two opposed coils. This design overcomes the angular range limitations associated with prior art voice coil actuators and enables rotation of the camera about an extended angular range. The device can be advantageously utilized for adjustment of the pan and tilt angles of a video camera in a conferencing system.
Owner:POLYCOM INC
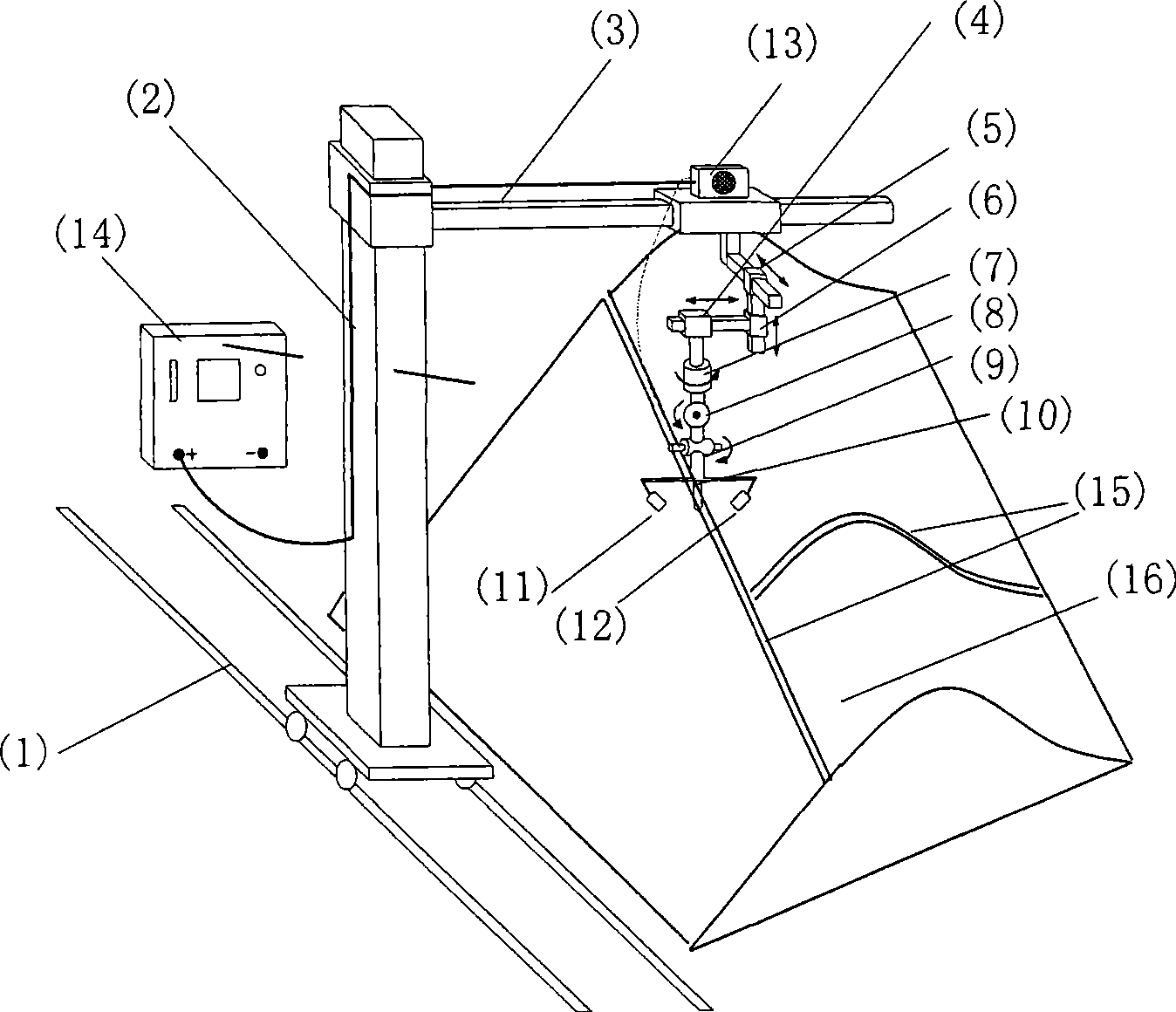
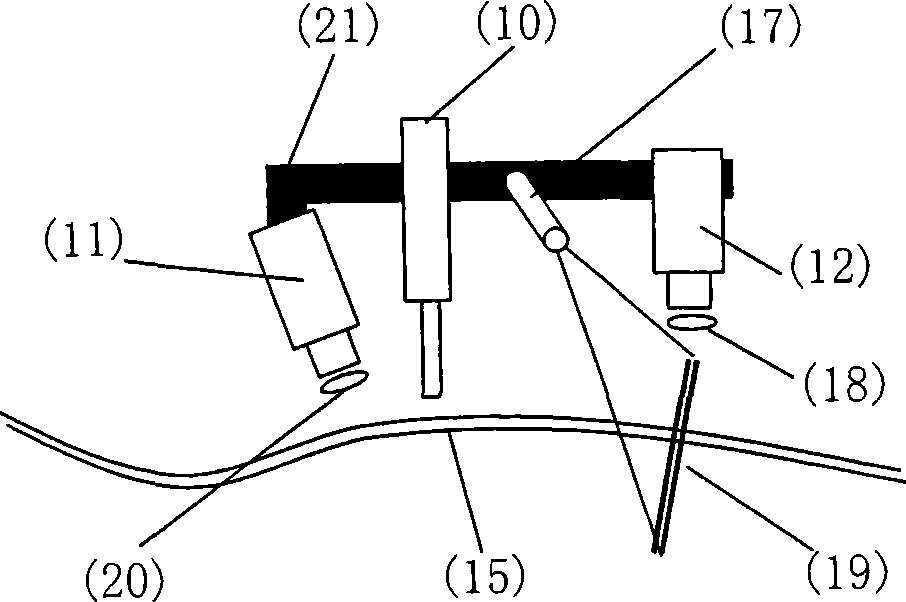
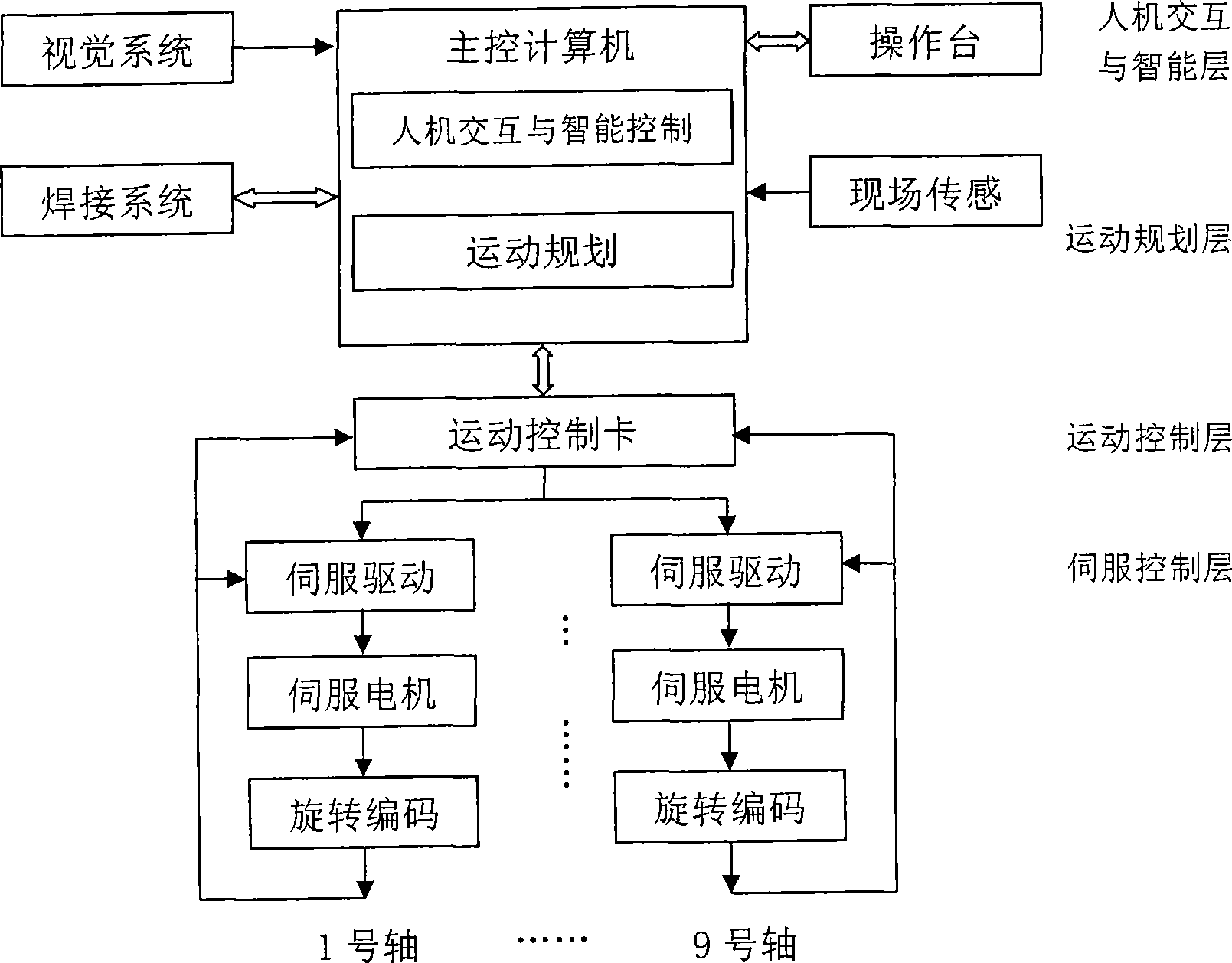
Intelligent robot welding device using large-scale workpiece
InactiveCN101456182AWith visual functionSimple motion controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorArc welding apparatusRotational axisRotational degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a large-sized workpiece welded intelligent robot device, relates to robot technology, in particular to the robot device based on visual control technology. The device consists of a robot body, a sensing system, a robot controller and a welding auxiliary mechanism. The welded robot is provided with nine moving shafts, including three macrographic moving translational moving shafts, three microscopic moving translational moving shafts and three rotating shafts. The robot body comprises a robot frame and a robot head which is arranged on a transverse arm of the robot frame, and the robot frame consists of the three macrographic moving translational moving shafts, namely a horizontal lead rail, an upright post and the transverse arm. The robot head consists of the three microscopic moving translational moving shafts, the three rotating shafts and a welding gun. The robot frame provides the large-scale three-dimensional movement of the robot; the precision of macrographic moving movement is compensated by the microscopic moving mechanisms of the robot head which also provides rotating freedom of motion. The robot device can meet the movement requirements of large scale and precise positioning for the welding operation of large-sized workpieces. Through the visual sensing technology and intelligent visual controlling technology, the device can improve the automatic welding quality and efficiency of the welded robot.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shaft seal and turbine using the same
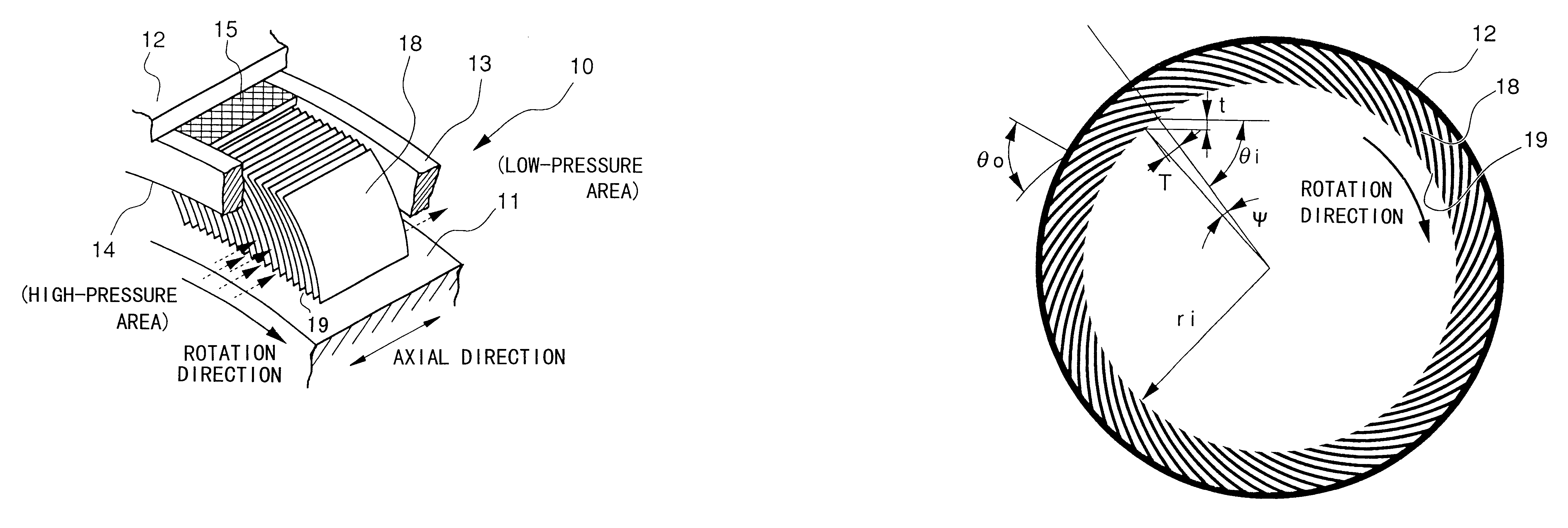
InactiveUS6343792B1High sealing capabilityReduce leakageEngine sealsPiston ringsGas turbinesEngineering
A shaft seal having a high abrasion resistance is disclosed, by which the leakage of the gas from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side can be reduced. In the shaft seal, flexible leaves are multi-layered to form a ring shape. The shaft seal is mainly arranged around the rotation shaft of a gas turbine or the like. The relevant turbine comprises a casing, a compressor, a rotation shaft, moving blades attached to the rotation shaft, and stationary blades attached to the casing in a manner such that the stationary blades face the moving blades, wherein the shaft seals are provided between a plurality of stationary blades and the rotation shaft wherein the leaves of each shaft seal contact the rotation shaft. Under the rated operating conditions, the top ends of the leaves slightly separate from the surface of the rotation shaft due to the dynamic pressure generated by the rotation of the rotation shaft. When the turbine is not operated, the top ends of the leaves contact the rotation shaft again due to the elastic restoring force of the leaves.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Multiple head automated composite laminating machine for the fabrication of large barrel section components
An aircraft part manufacturing device for automated composite lamination on a mandrel surface of a tool having a rotational axis includes a mechanical supporting structure that supports multiple material delivery heads. The tool is moveable and rotatable relative to the mechanical supporting structure. The mechanical supporting structure provides for axial translation of the material delivery heads relative to the mandrel surface while the mandrel surface is rotated for laying down courses of composite material over the entire mandrel surface of the tool. The position and movement of each of the plurality of material delivery heads is individually adjustable. Arm mechanisms provide motion of each material delivery head in a direction normal to the mandrel surface; rotation about an axis normal to the mandrel surface; circumferential position adjustment in a hoop direction relative to the mandrel surface; and axial position adjustment relative to the other material delivery heads.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Continuously variable transmission and method of controlling it
InactiveUS20050037876A1Shorten the axial lengthReduce widthGearingGearing controlRotational axisControl theory
To provide a continuously variable transmission and a control method thereof, allowing for control of the axial position of a movable sheave without a sensor for measuring the axial position of the movable sheave on a rotational shaft and for stable control with the movable sheave being held in position, without the increase in the size of mechanisms and power consumption. A continuously variable transmission in which, on a rotational shaft 1 thereof are mounted a fixed sheave 2 positioned in the axial direction and a movable sheave 3 slidable axially, so as to face each other, a motor is provided for driving the movable sheave, and a slide driving means 16 is provided for sliding the movable sheave 3 axially by the rotation of the motor, characterized in that: the motor is a step motor 6, and the step motor 6 and the slide drive means 16 are mounted coaxially with the rotational shaft 1.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
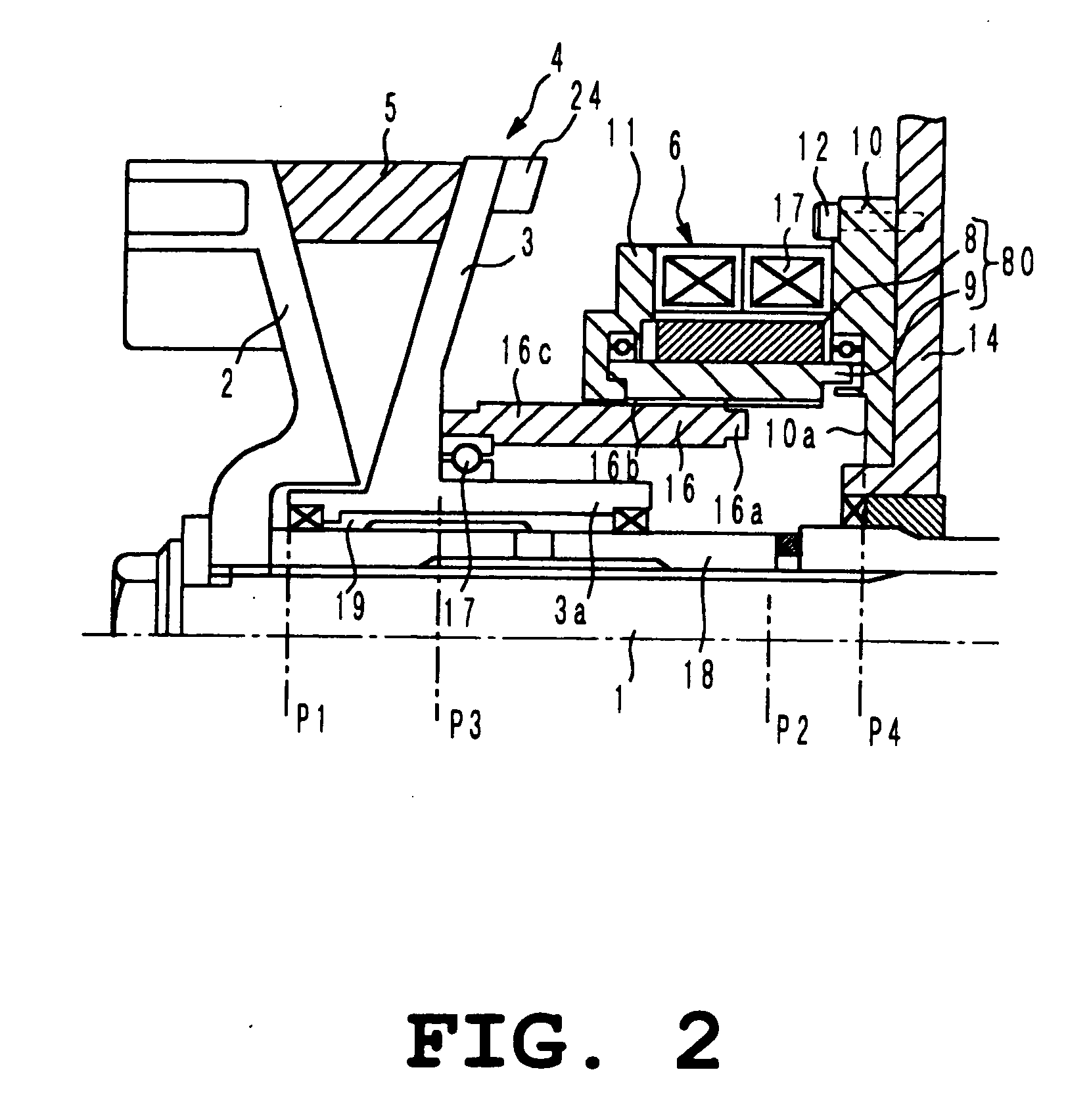
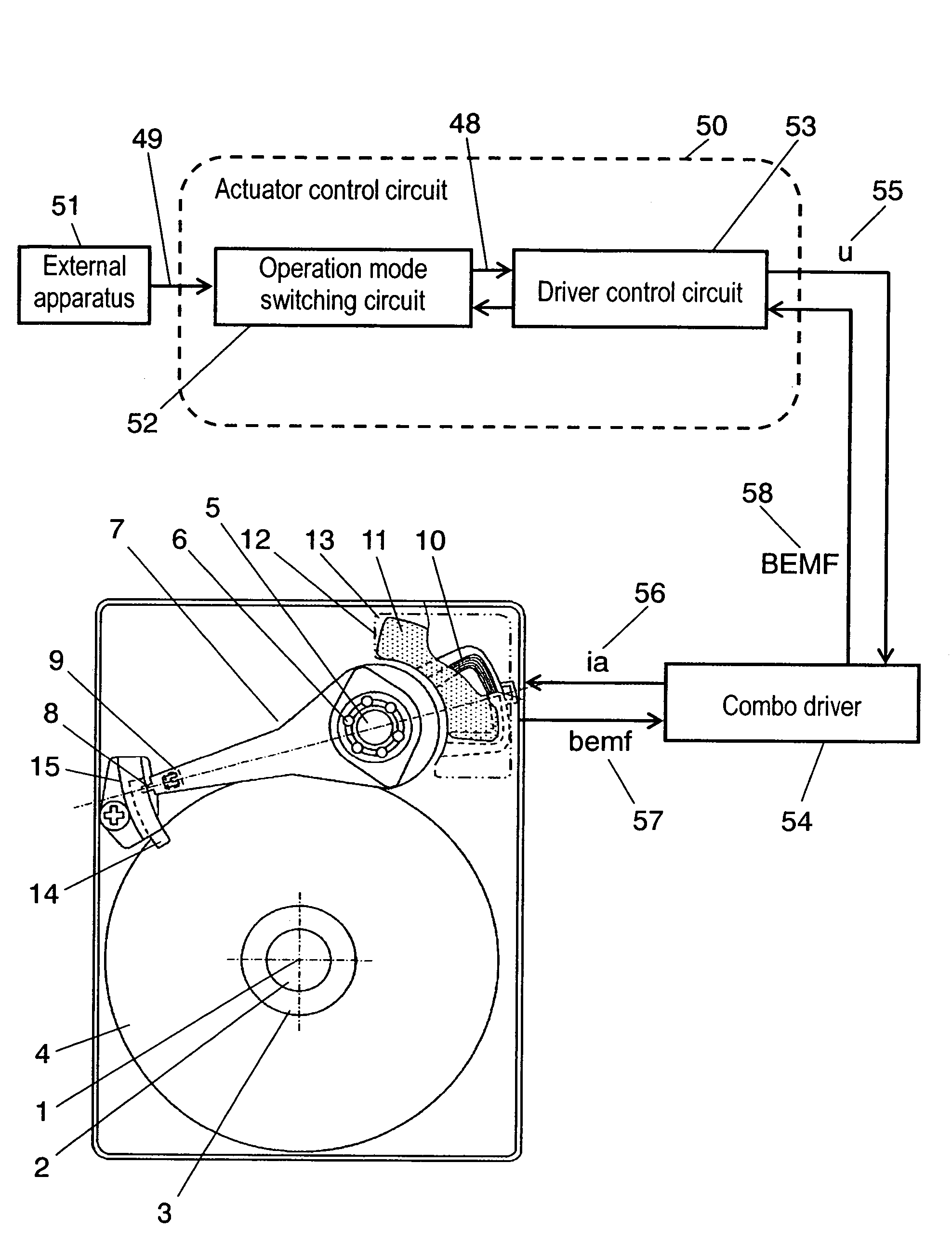
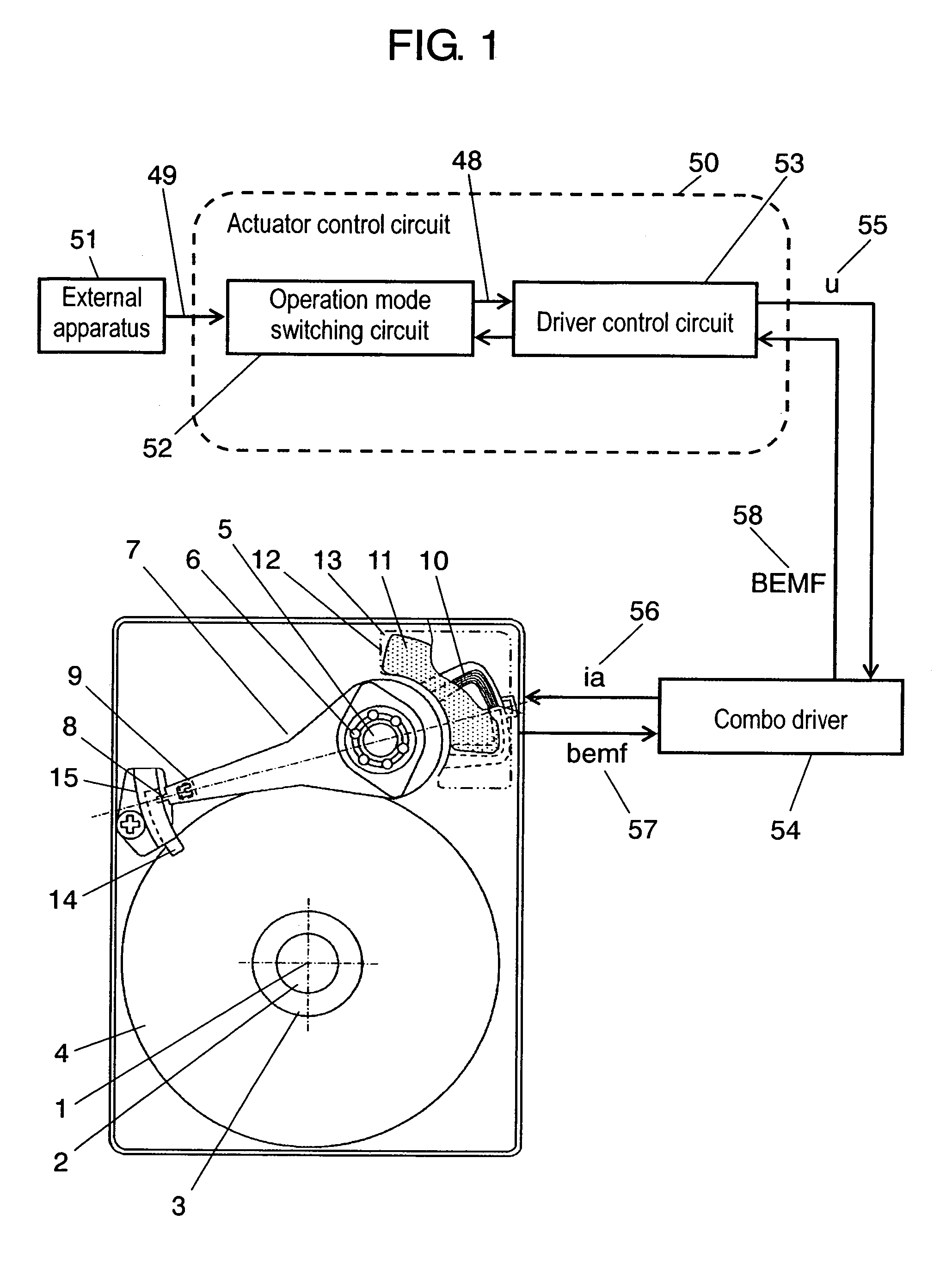
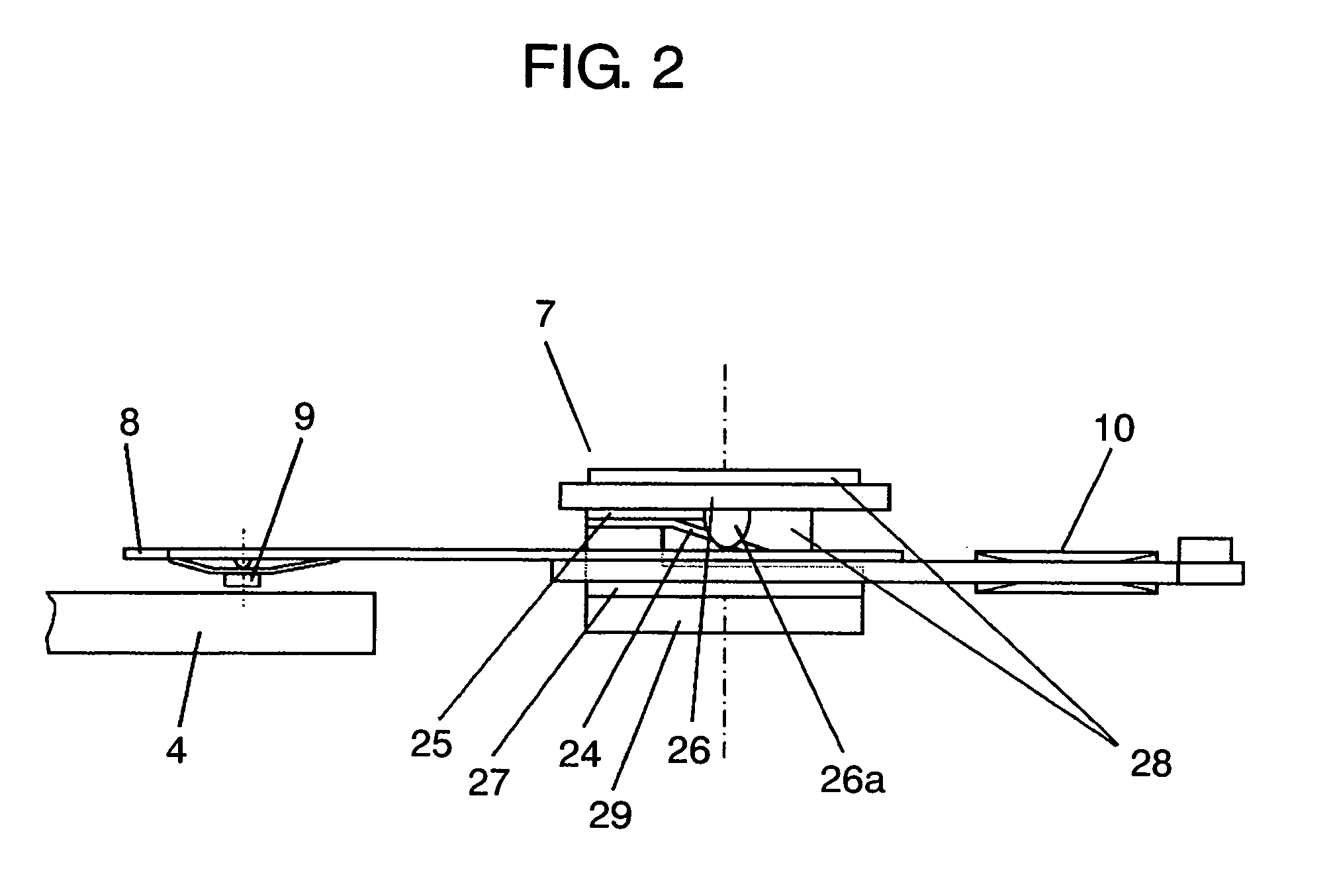
Method of controlling an actuator, and disk apparatus using the same method
InactiveUS7265929B2Power saving and downsizingReduce placementDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsDriving currentRepulsion force
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Apparatus and method for large area multi-layer atomic layer chemical vapor processing of thin films
An apparatus and method for large area high speed atomic layer chemical vapor processing wherein continuous and alternating streams of reactive and inert gases are directed towards a co-axially mounted rotating cylindrical susceptor from a plurality of composite nozzles placed around the perimeter of the processing chamber. A flexible substrate is mounted on the cylindrical susceptor. In one embodiment, the process reactor has four composite injectors arranged substantially parallel to the axis of rotation of the cylindrical susceptor. In the other embodiment, the susceptor cross section is a polygon with a plurality of substrates mounted on its facets. The reactor can be operated to process multiple flexible or flat substrates with a single atomic layer precision as well as high-speed chemical vapor processing mode. The atomic layer chemical vapor processing system of the invention also has provisions to capture unused portion of injected reactive chemical precursors downstream.
Owner:GADGIL PRASAD
Three-Dimensional Printing System Using Dual Rotation Axes
ActiveUS20130189435A1Promote sportsImprove throughputAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsRotational axisLinear motion
A 3-D printer system moves a printed tool over a print surface with a mechanism controlling a rotational angle of an arm holding the print tool and a revolutionary angle of axis of rotation of the printable area to eliminate the disadvantages of conventionally used linear motion mechanisms
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
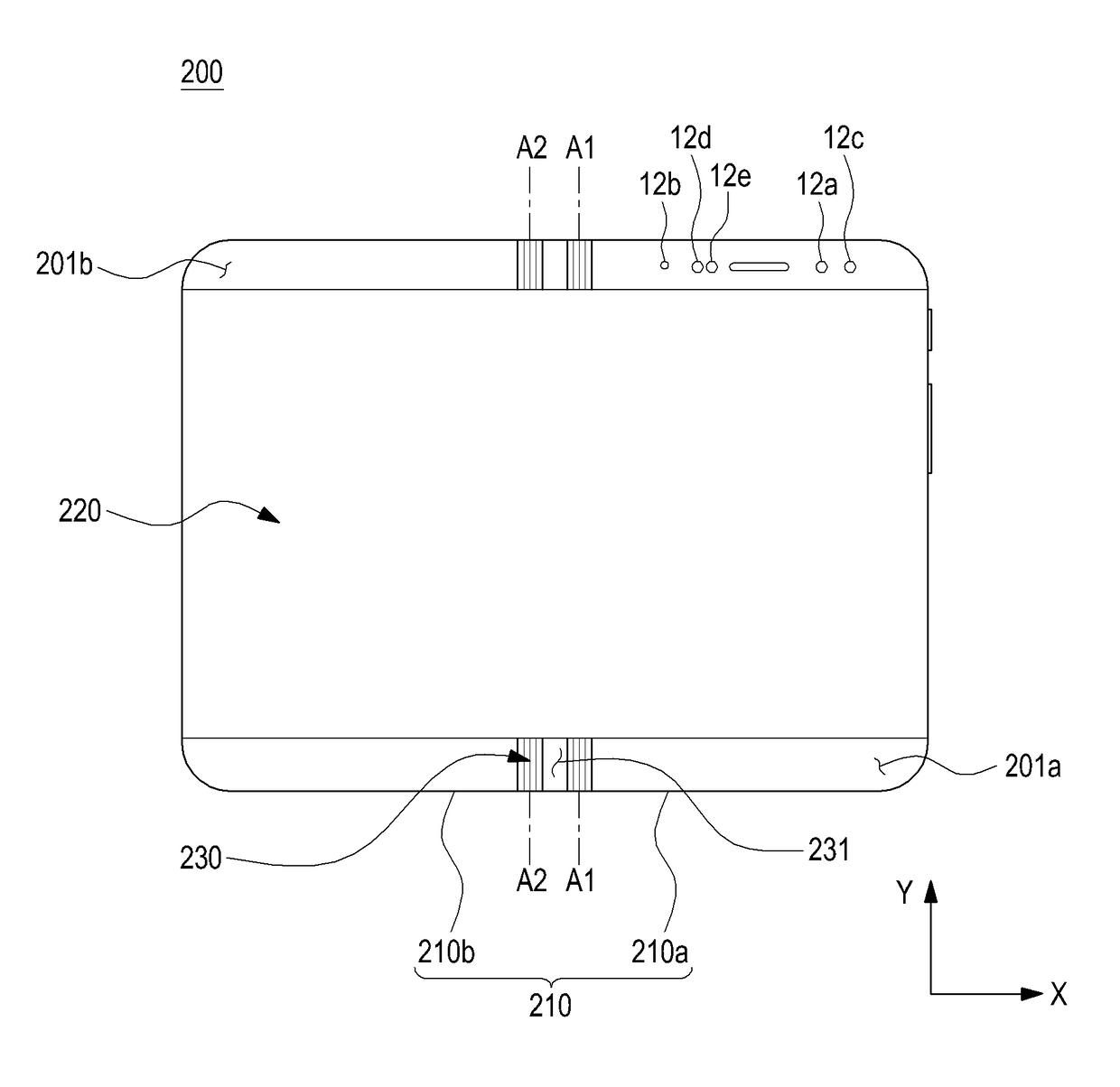
Electronic device including flexible display
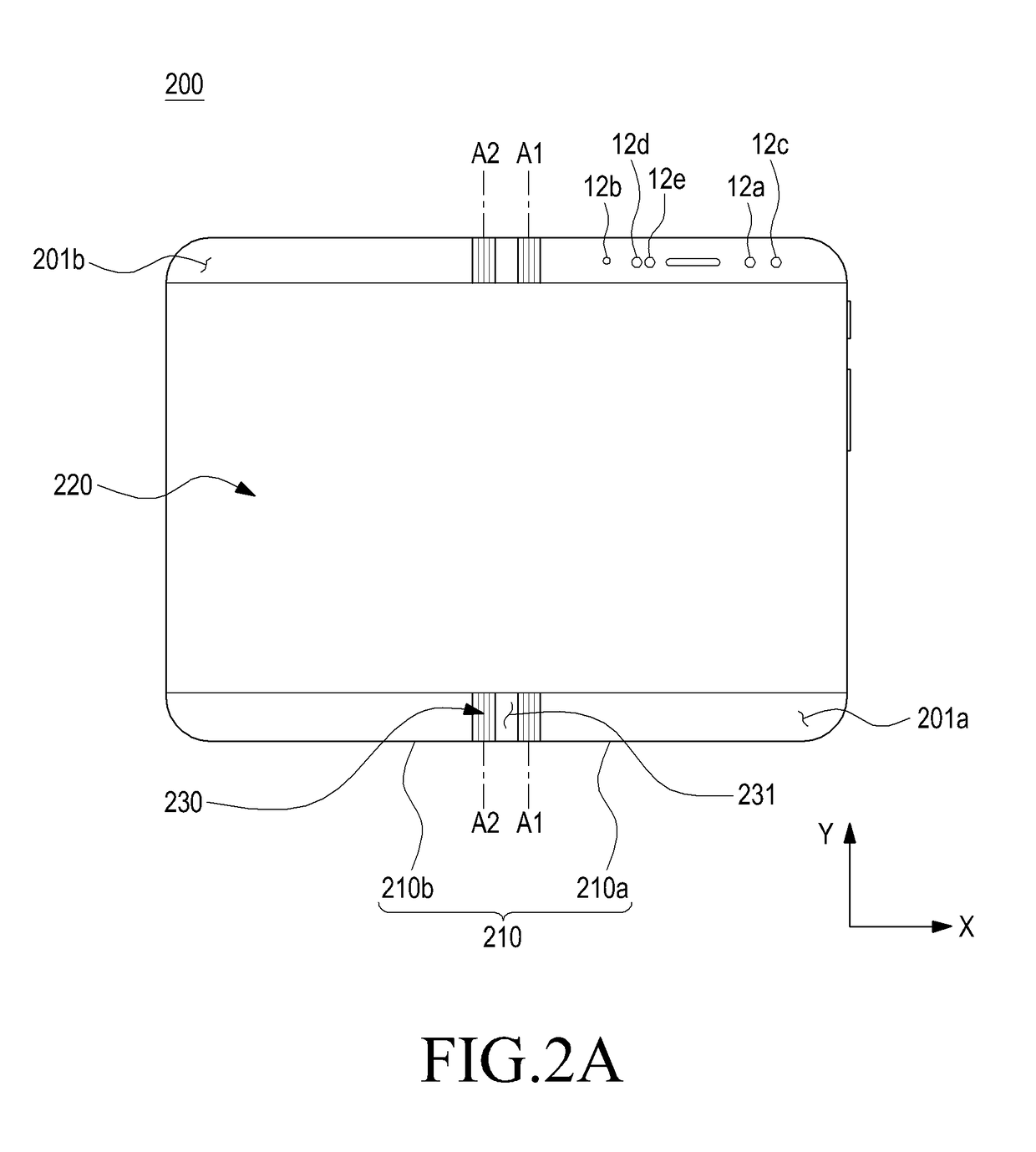
ActiveUS20180324964A1Linear bearingsCasings with display/control unitsRotational axisFlexible display
According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, an electronic device may comprise a first housing including a first surface and a second surface facing in a direction opposite the first surface, a second housing including a third surface and a fourth surface facing in a direction opposite the third surface, a hinge disposed between the first housing and the second housing configured to provide rotational motion between the first housing and the second housing, and a flexible display disposed from the first surface of the first housing across the hinge to the third surface of the second housing, at least part of the flexible display configured to form a curved surface as the hinge structure is folded, wherein the hinge may include dual-axis hinges configured to provide a first rotational axis allowing the first housing to rotate about the second housing and a second rotational axis allowing the second housing to rotate about the first housing and slides coupled with the first housing and the second housing and configured to provide sliding motion perpendicular to a lengthwise direction of the first housing and the second housing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for tracking a subject
An image tracking system for generating digitized image frames of a moving object using an image capture device and a position control device. The image capture device and determining a location value for an object image within each of the digitized image frames. The position control device is coupled to the image capture device to receive the location value of the object image and generates a plurality of control signals which are sent to the position manipulating device. The position control device also uses the plurality of control signals and generates a plurality of rotational movements which position the image capture device, such that the location value of the object image remains within a center region of each of the digitized image frames and such that rotation along different rotation axis occurs independently.
Owner:VERGHESE GILBERT
Eccentric abrading head for high-speed rotational atherectomy devices
ActiveUS20080306498A1Improve abilitiesMinimal traumaCannulasExcision instrumentsStenotic lesionRotational axis
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy device having, in various embodiments, a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with at least one flexible eccentric enlarged abrading head attached thereto. In other embodiments, the eccentric abrading head is not flexible or partially flexible. At least part of the eccentric enlarged cutting head has a tissue removing surface—typically an abrasive surface. In certain embodiments, the abrading head will be at least partially hollow. When placed within an artery against stenotic tissue and rotated at sufficiently high speeds the eccentric nature of the enlarged cutting head causes the cutting head and drive shaft to rotate in such a fashion as to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter substantially larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged cutting head. Preferably the eccentric enlarged cutting head has a center of mass spaced radially from the rotational axis of the drive shaft, facilitating the ability of the device to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter substantially larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged cutting head when operated at high speeds.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
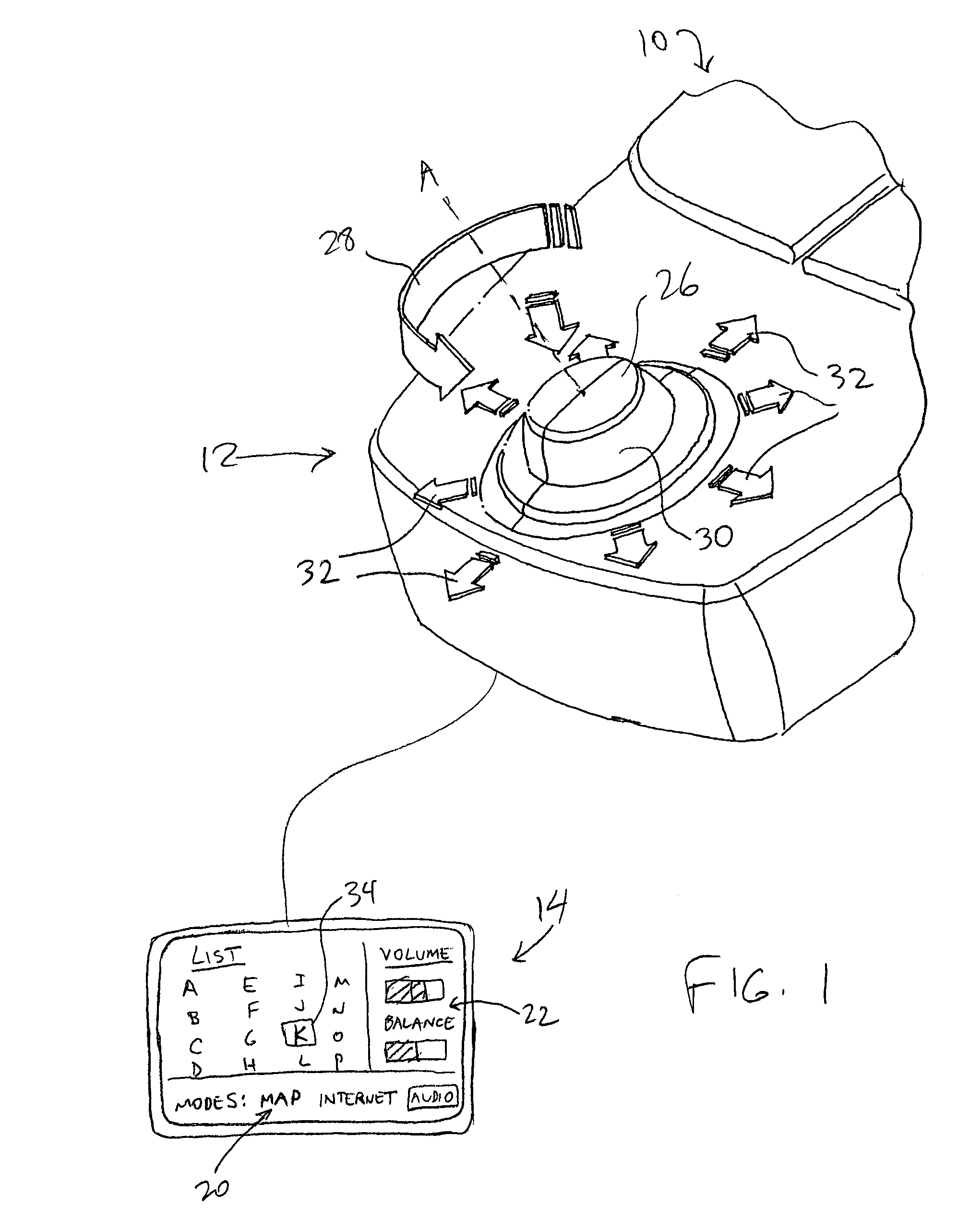
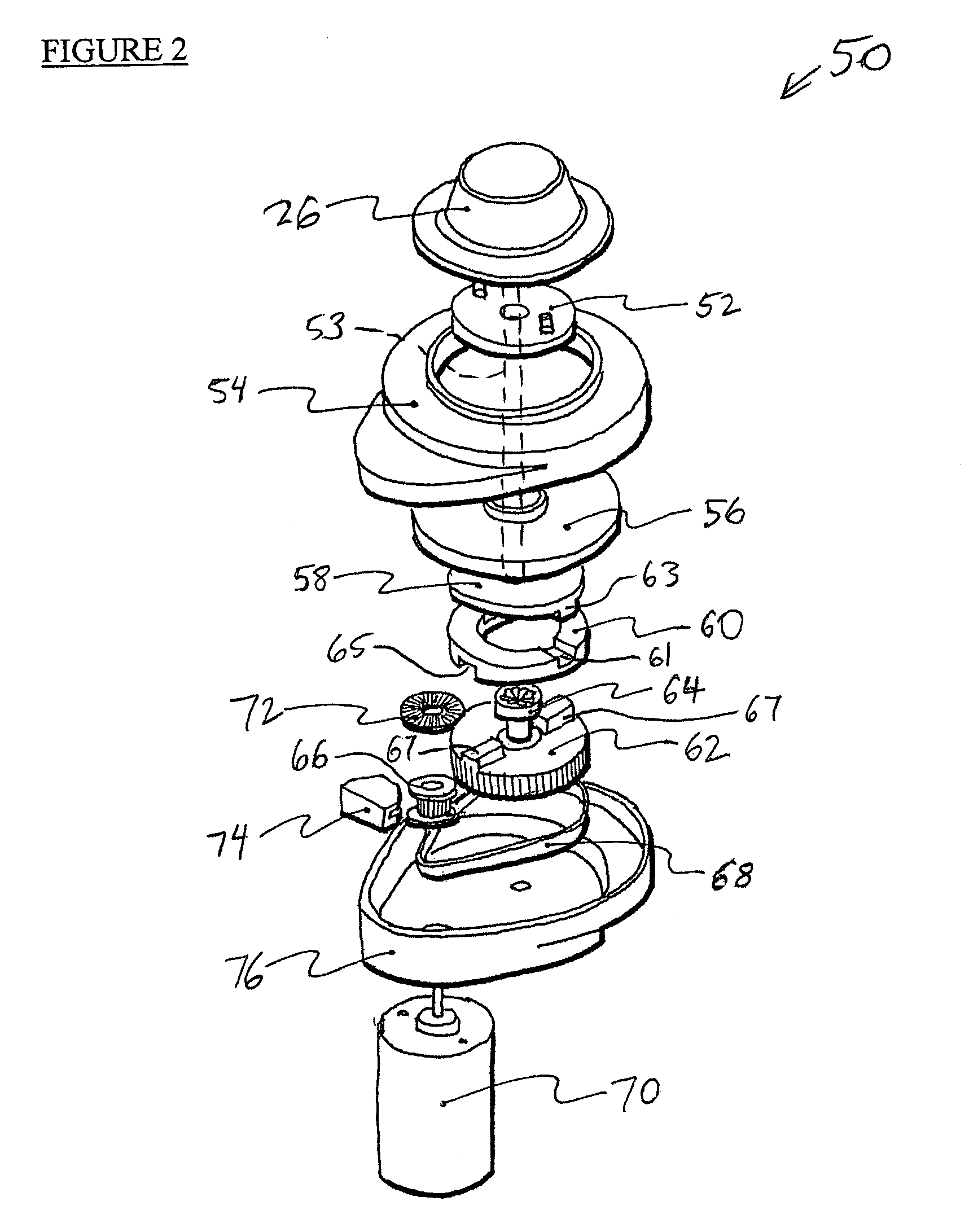
Mechanisms for control knobs and other interface devices
InactiveUS7038667B1Strong control functionGreat easeCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrical haptic/tactile feedbackRotational axisLinear motion
Mechanisms for a control knob or other interface device providing additional degrees of freedom for the knob. One embodiment provides a rotatable knob moveable also in a lateral plane approximately perpendicular to the axis of rotation. A mechanism providing the lateral motion can include a gate member and a plunger member that engages grooves in the gate member. A rotational sensor detects a rotational position and a lateral sensor can detect a lateral position of the knob. Another embodiment provides an actuator that includes a shaft that is coaxial with the axis of rotation and which can be moved linearly along the axis of rotation with respect to actuator housing to accommodate linear motion of the knob. In another embodiment, a gear assembly including two interlocked gears is provided to transmit rotational motion from the knob to the sensor, and the interlocked gears translate with respect to each other when the knob is translated along the rotational axis.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com