Patents
Literature
52 results about "Rotational atherectomy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
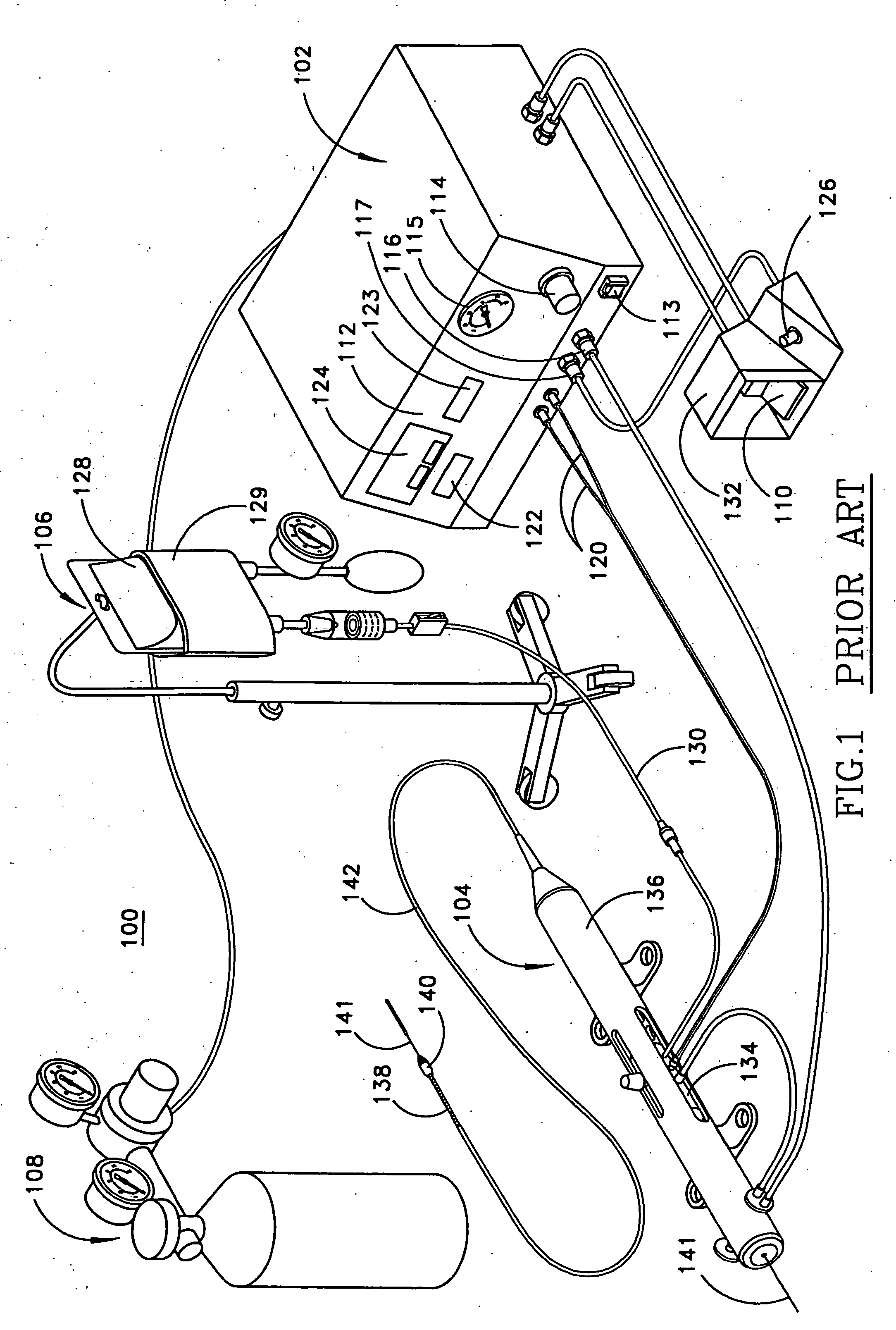
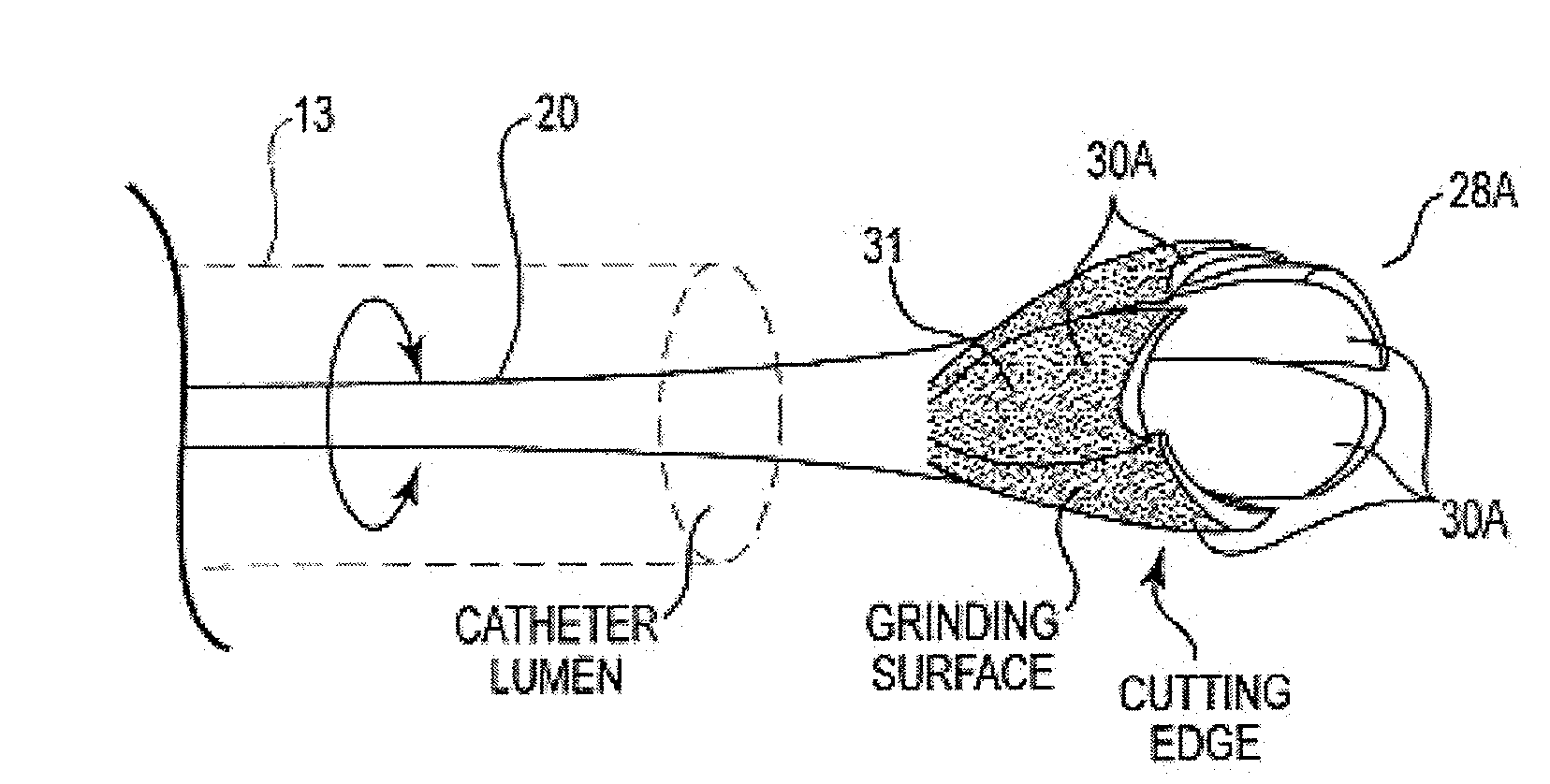
Rotational atherectomy is a procedure during which the plaque in your coronary arteries is ground into minuscule particles, which your body cleans from the bloodstream.
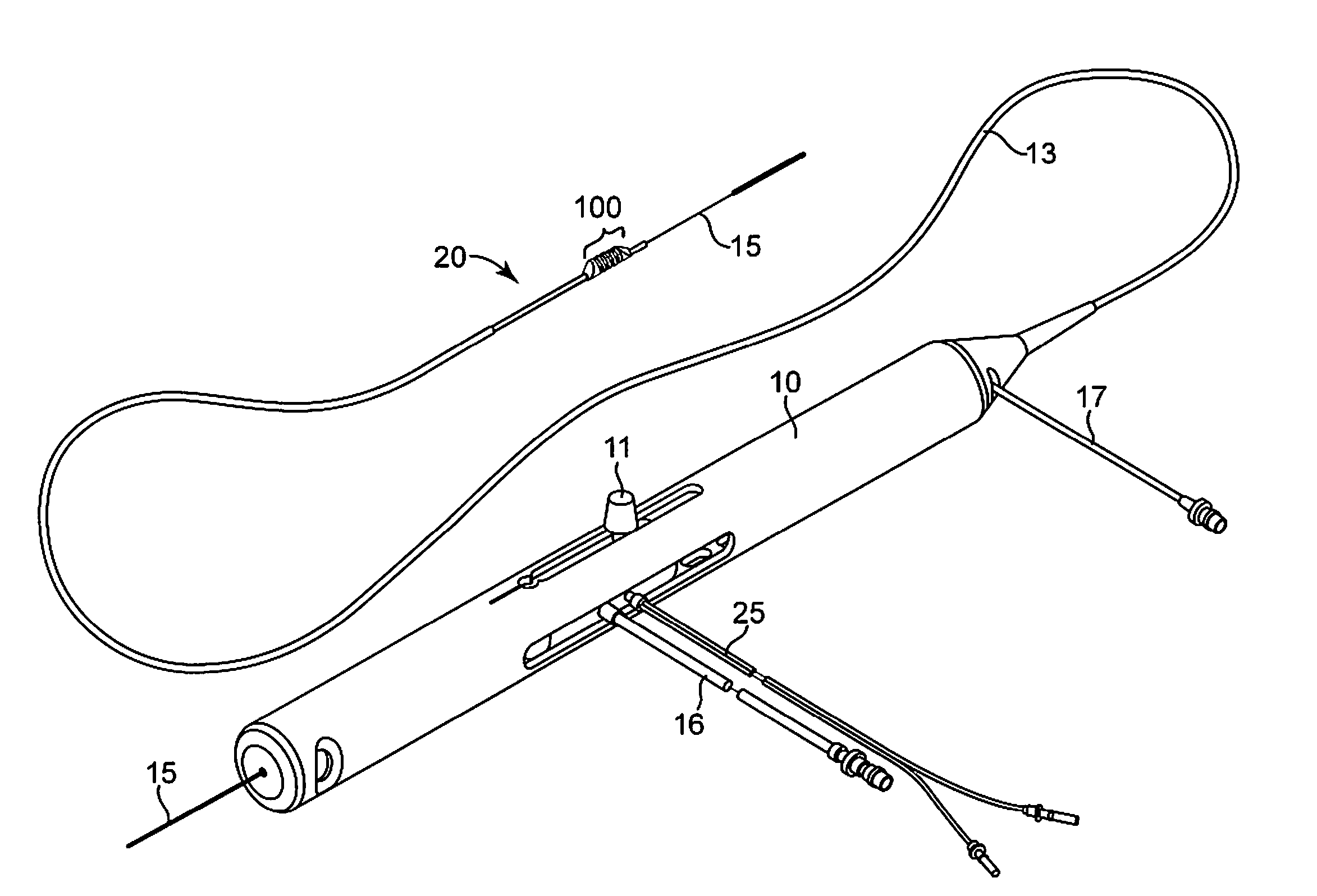
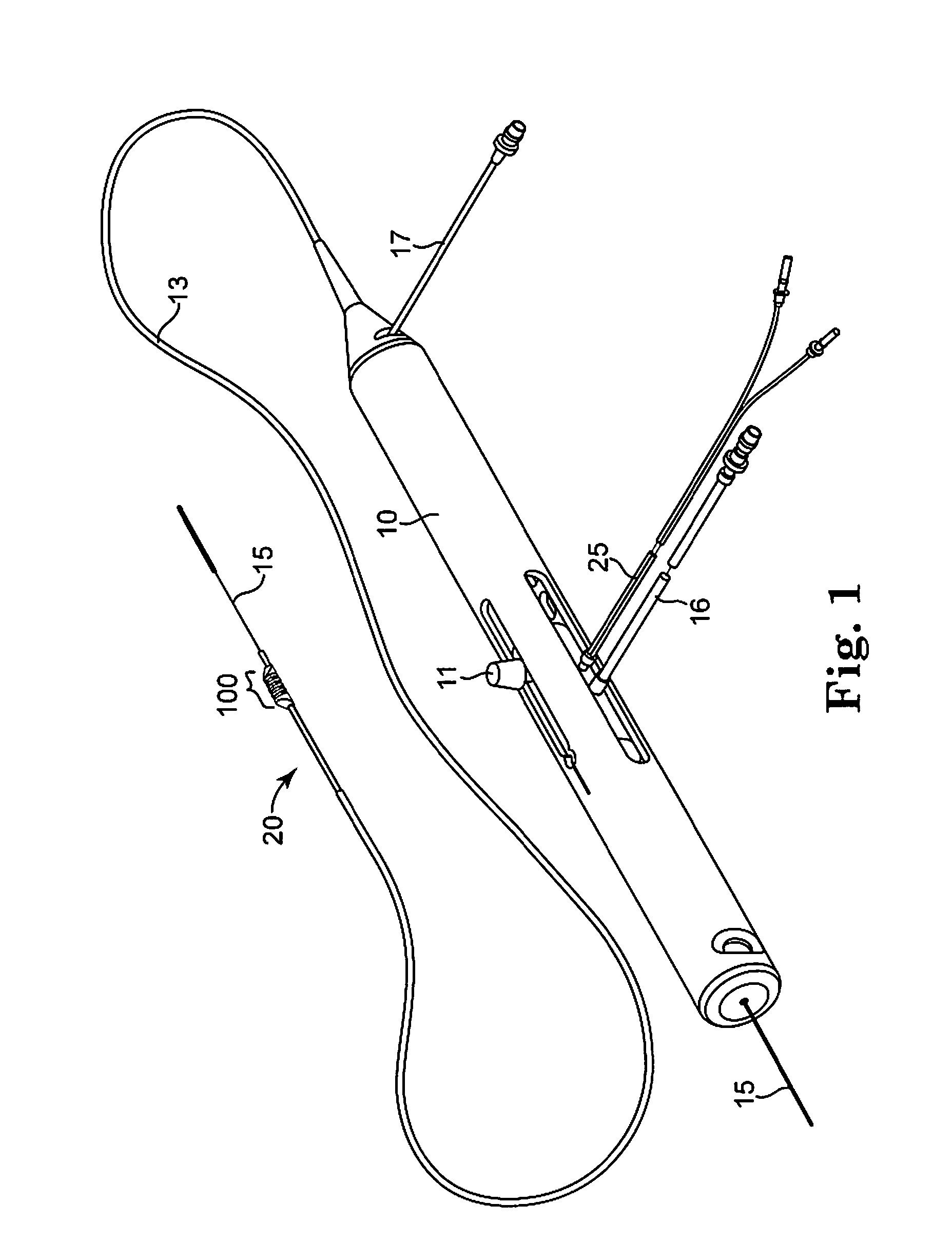
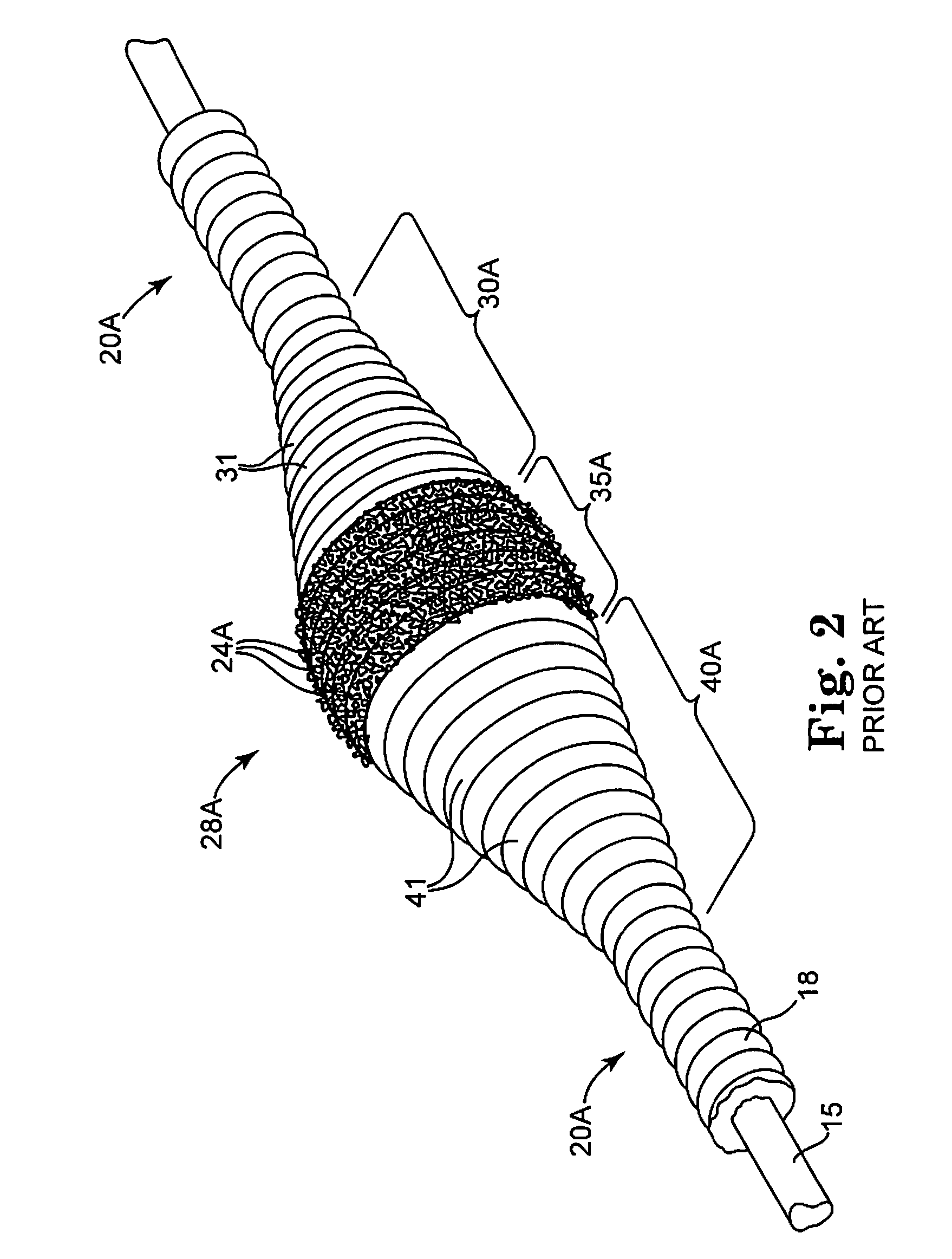
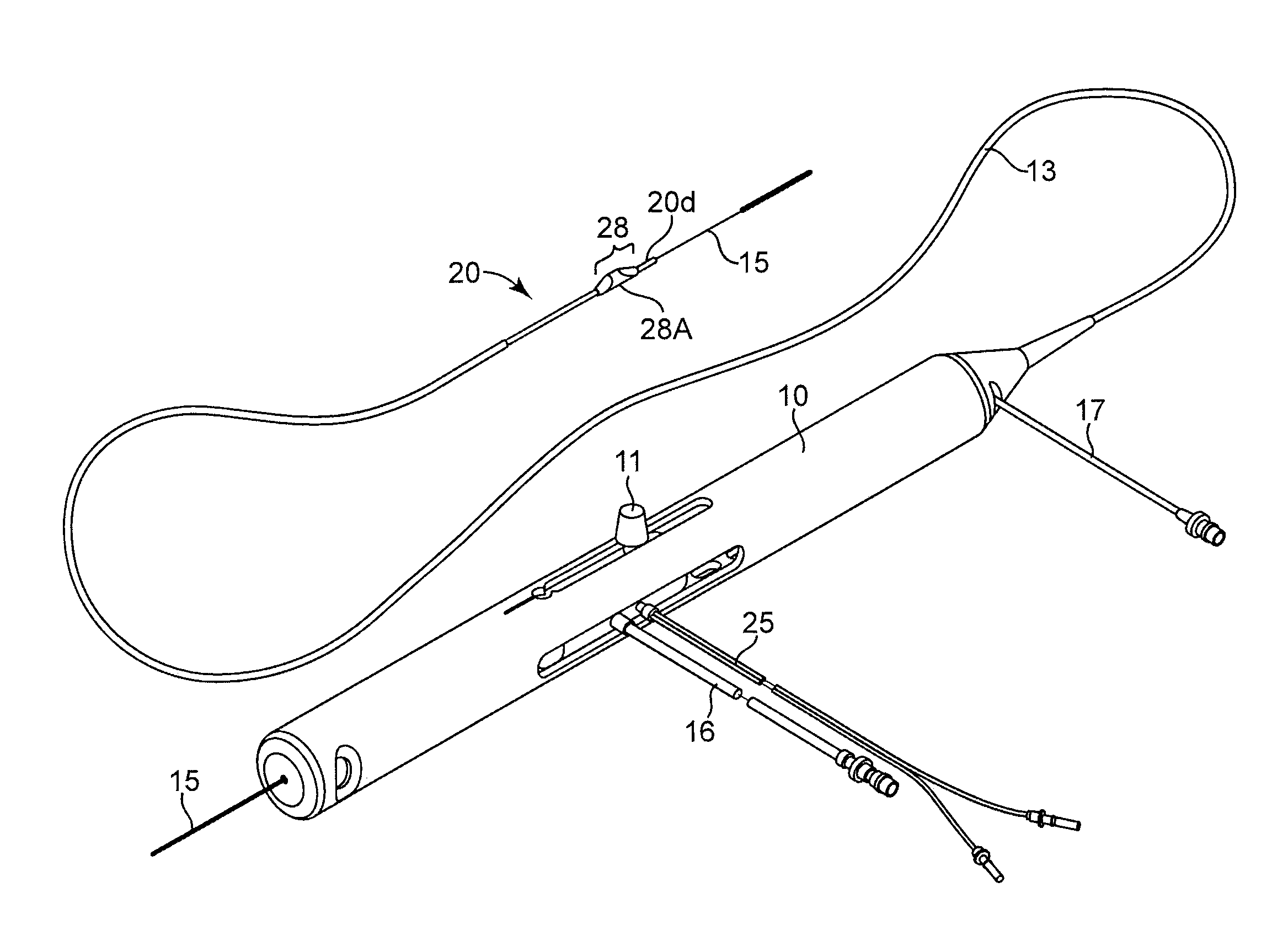
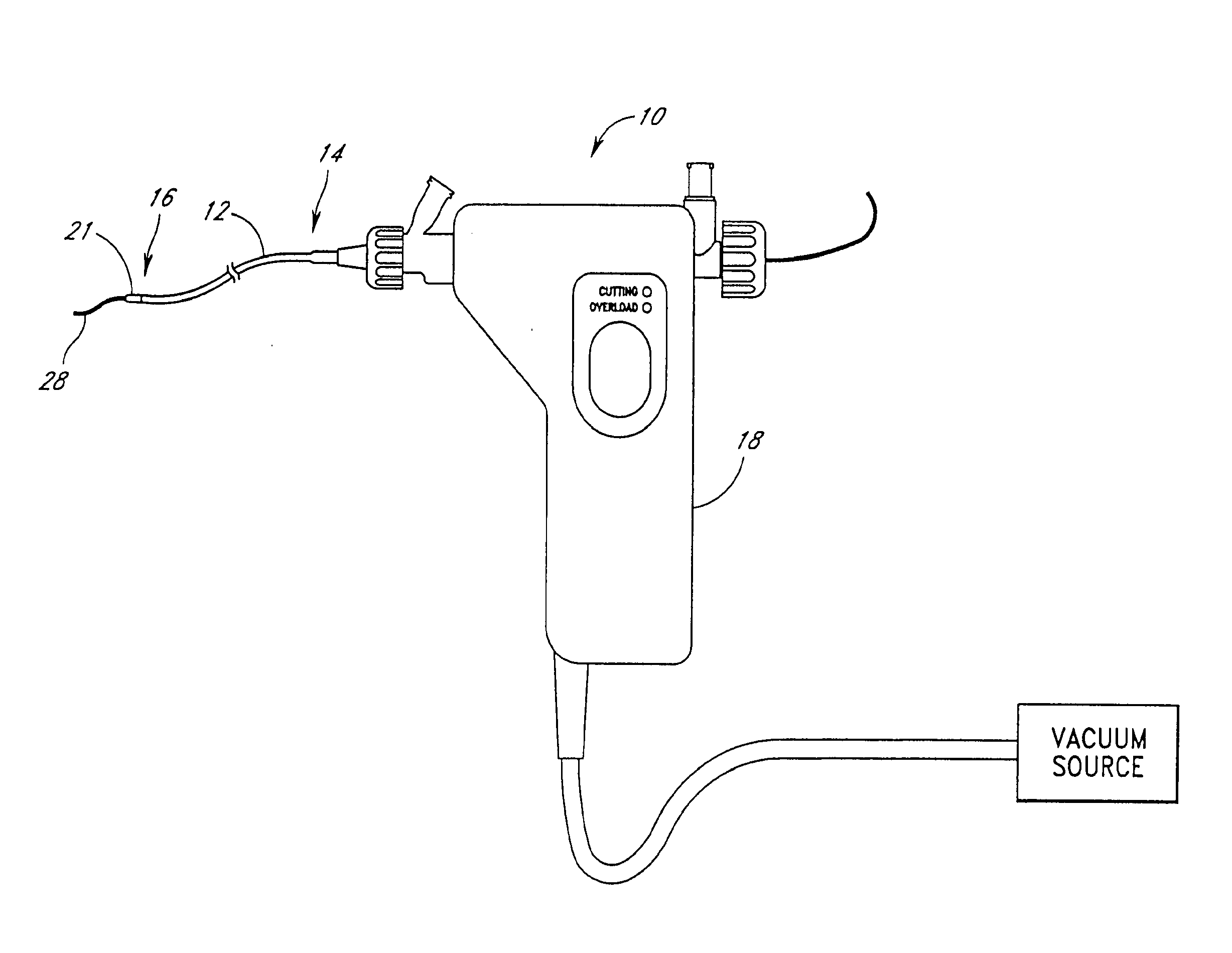
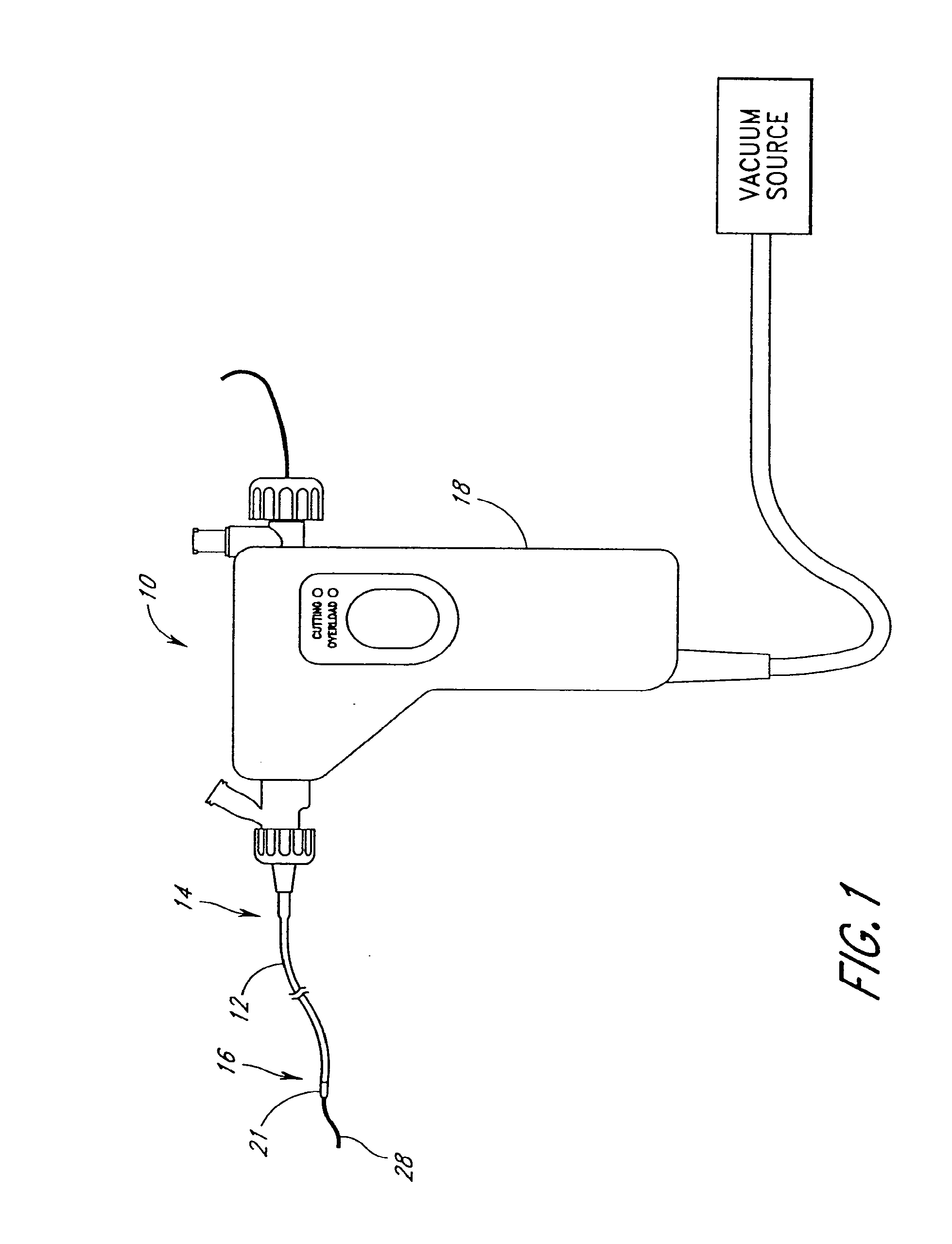
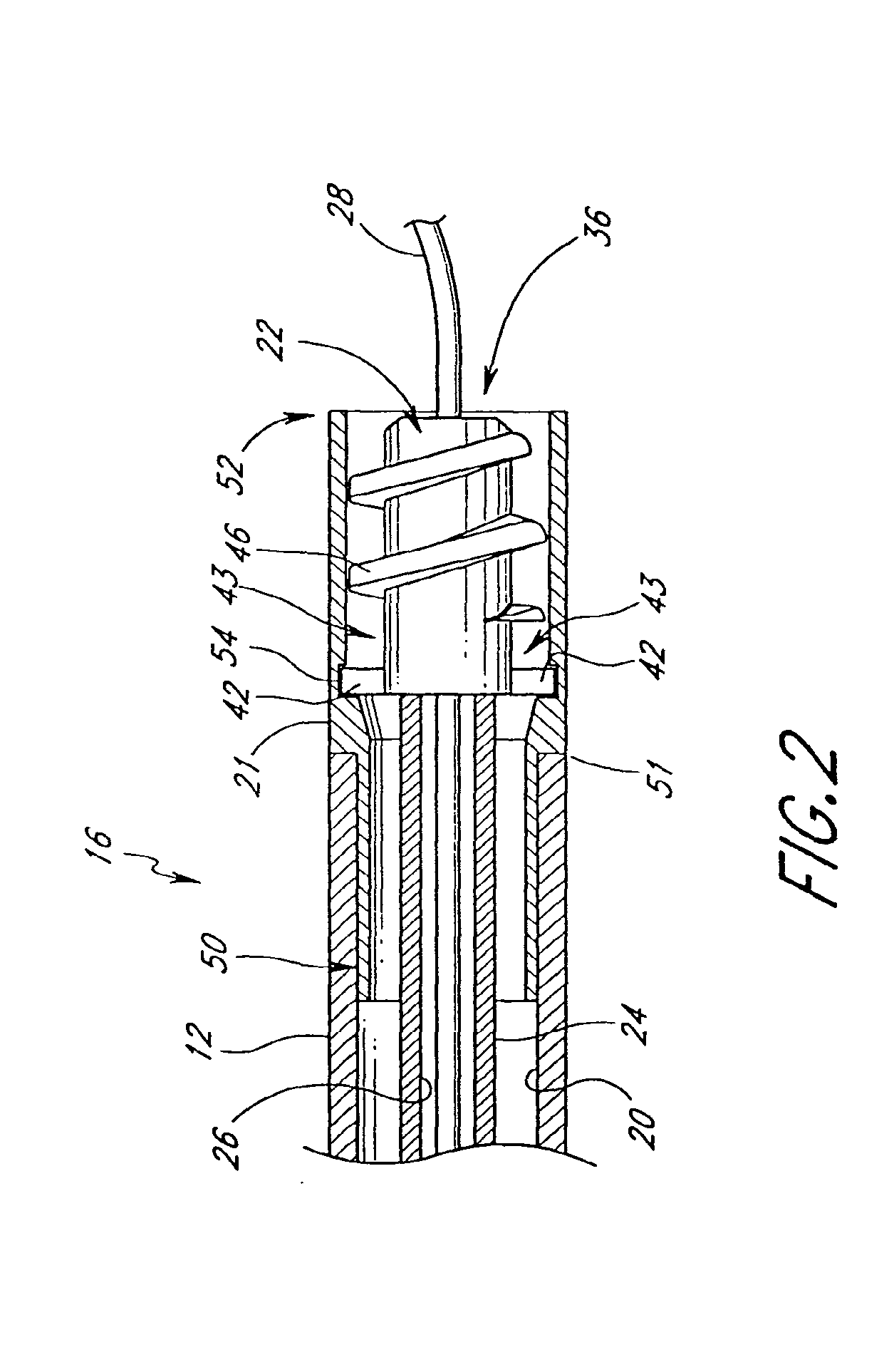
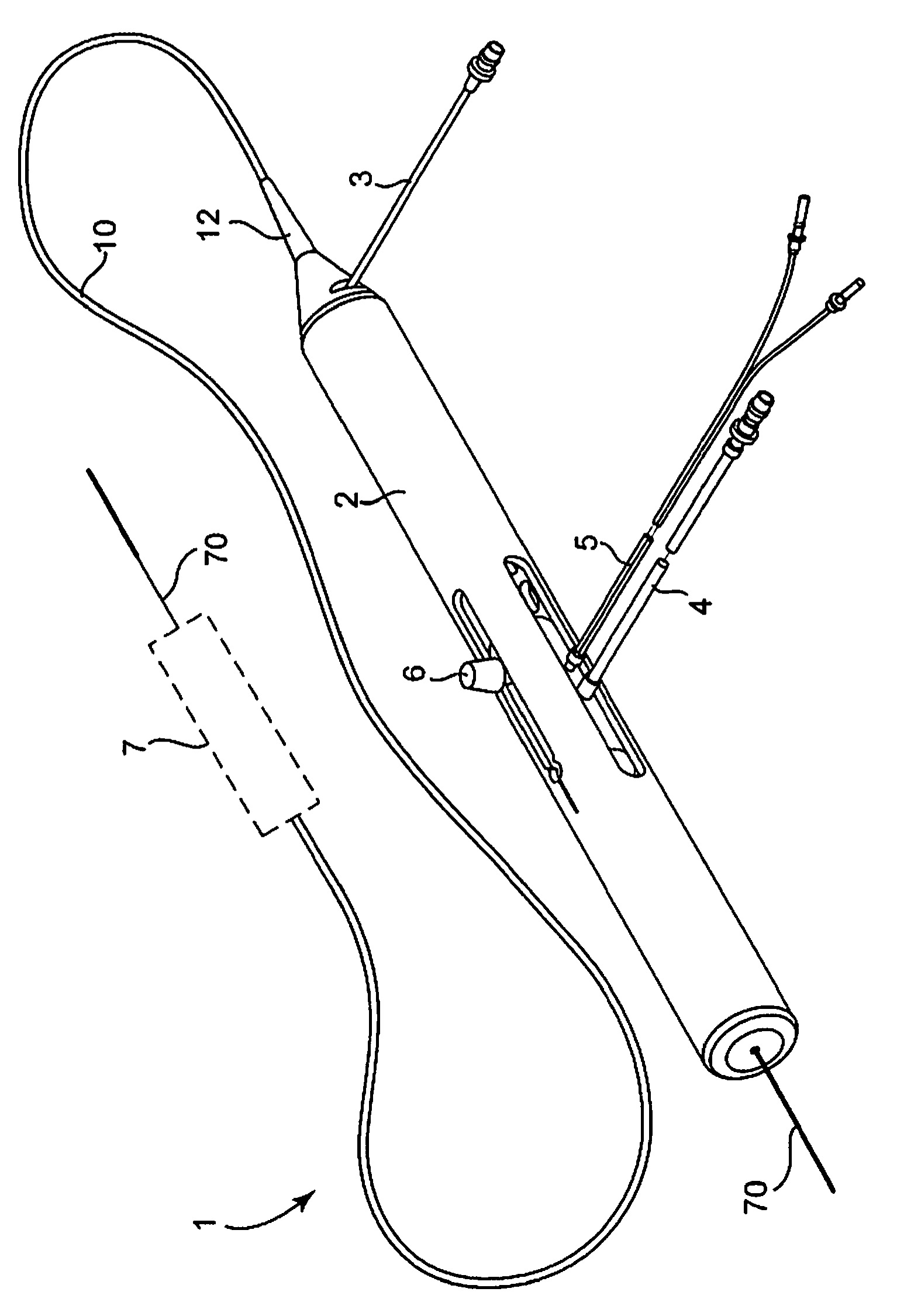
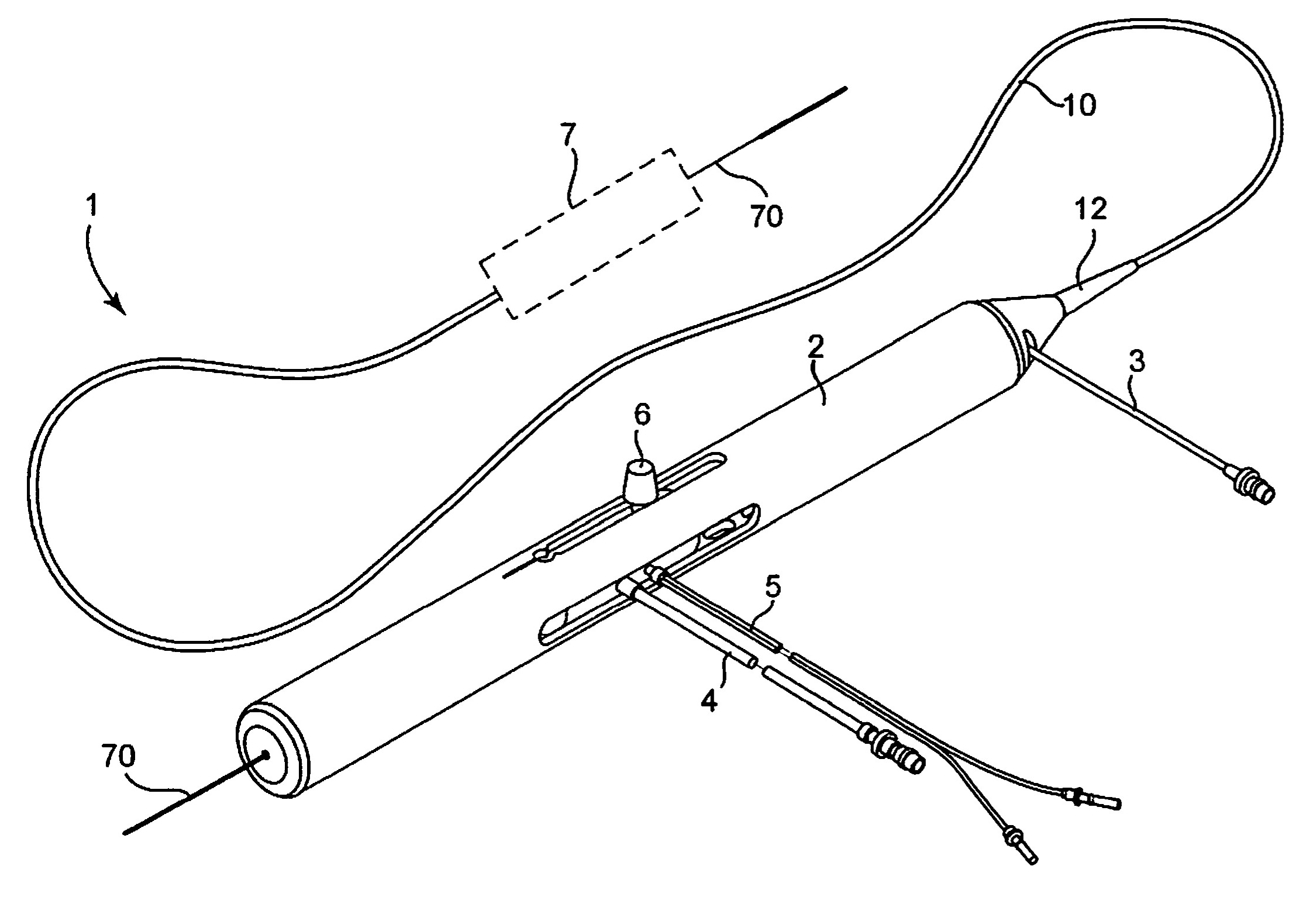
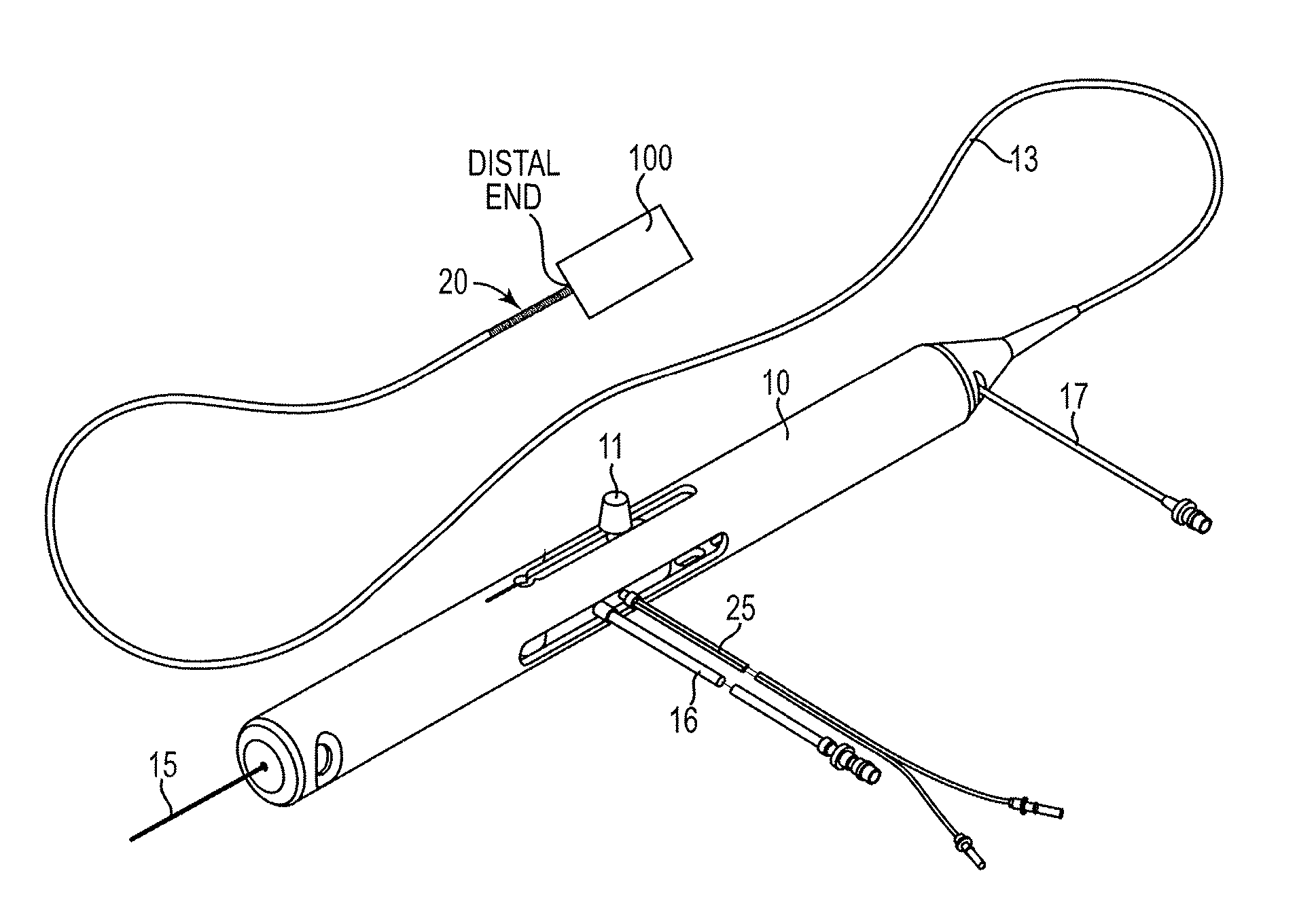
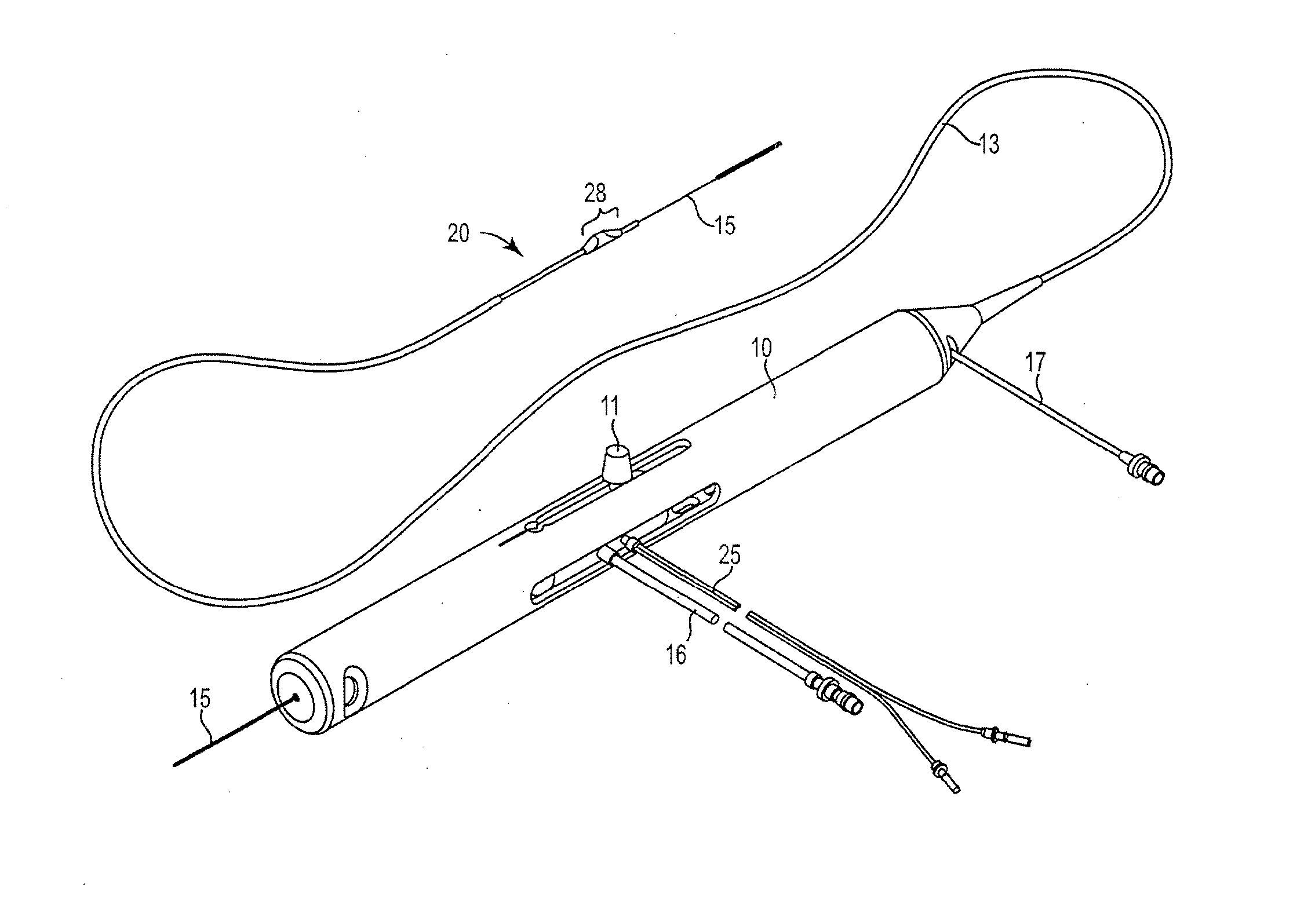
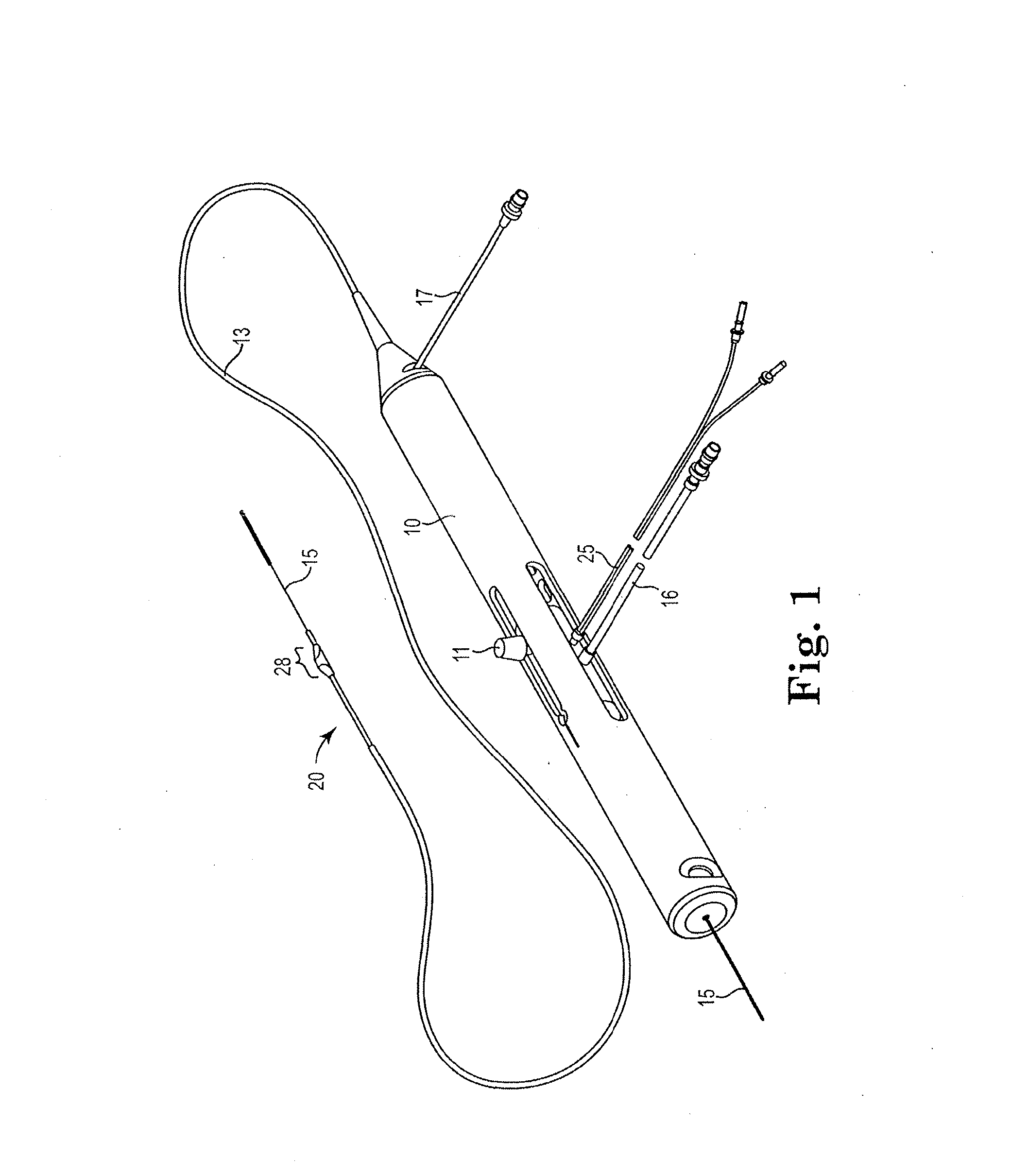
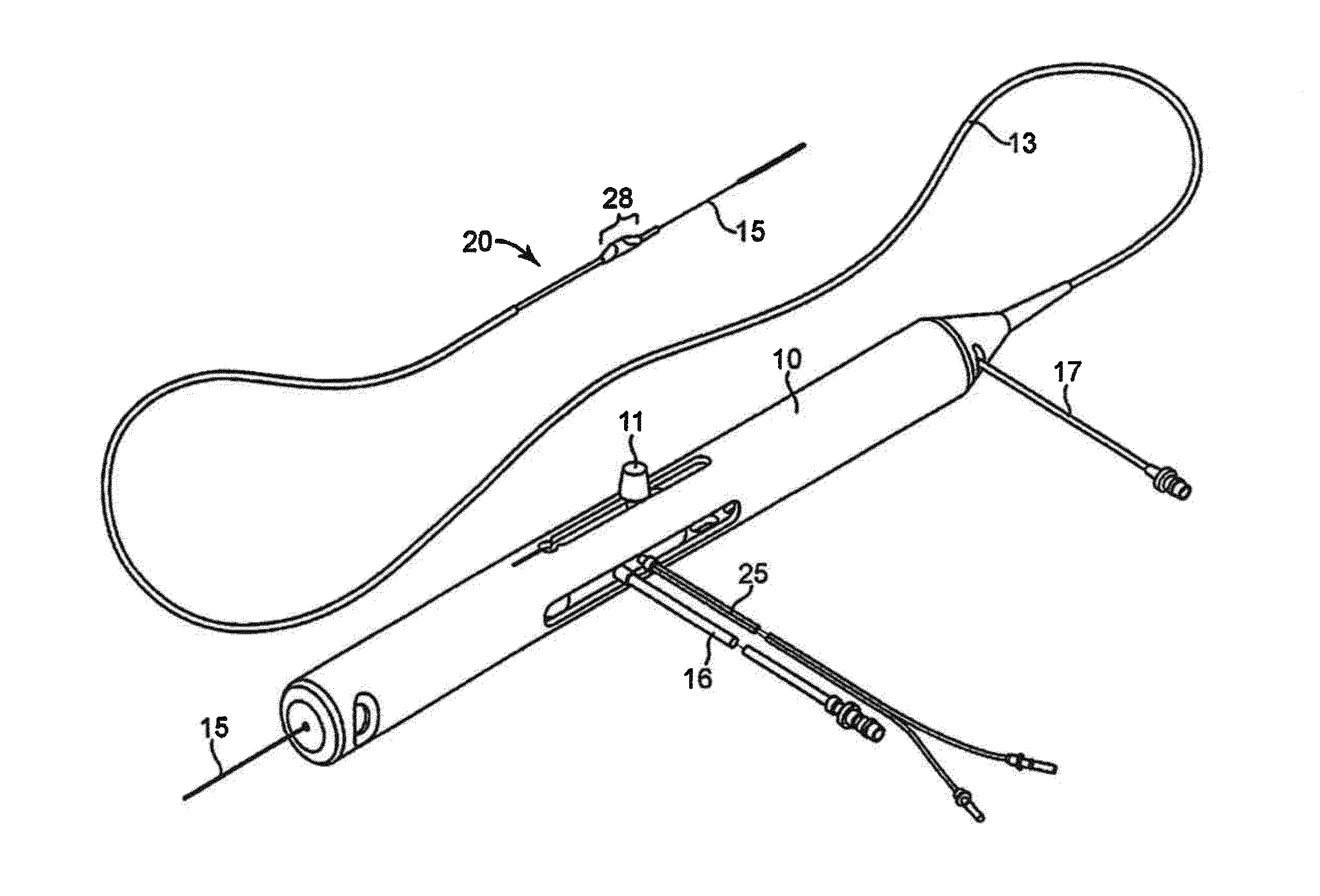
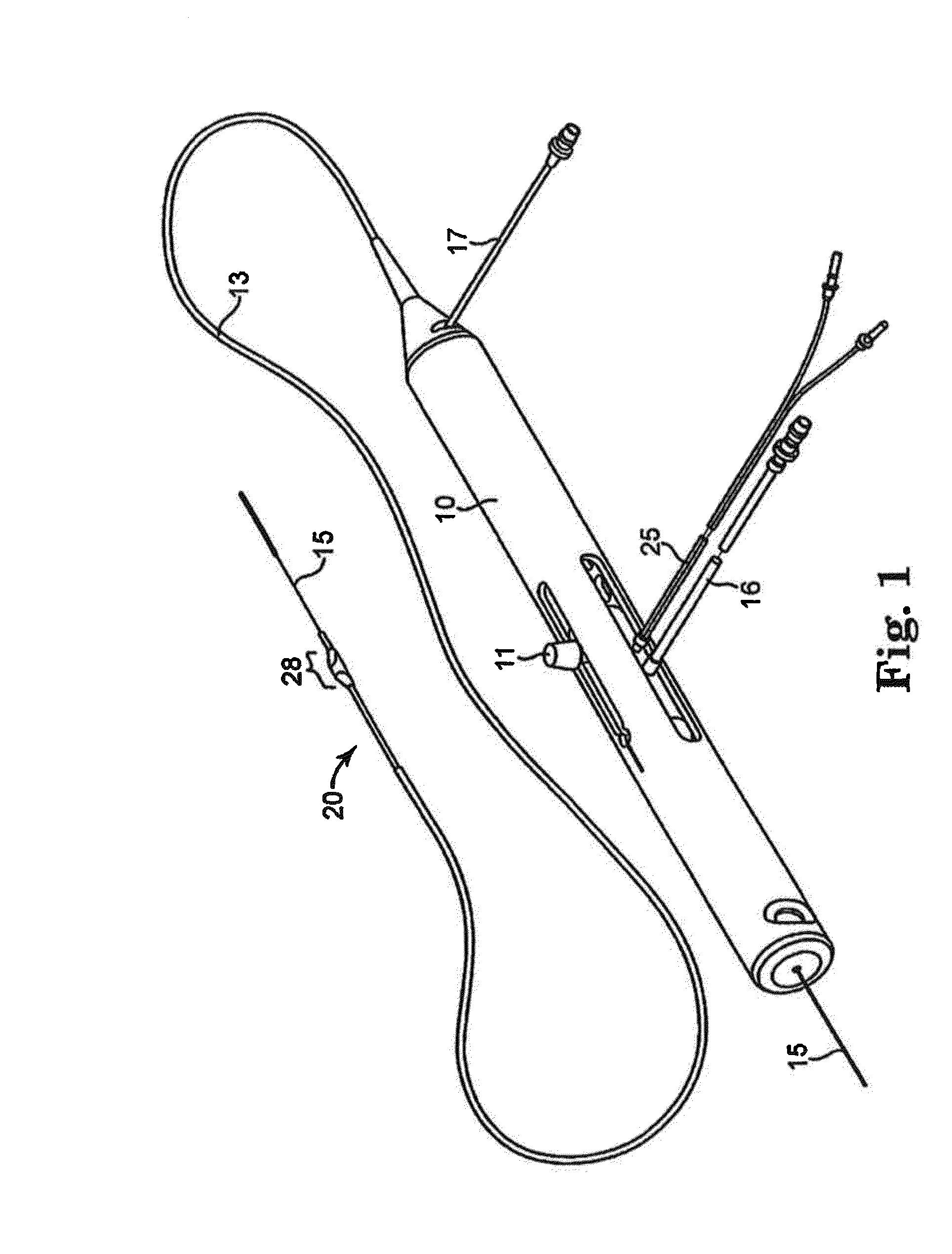
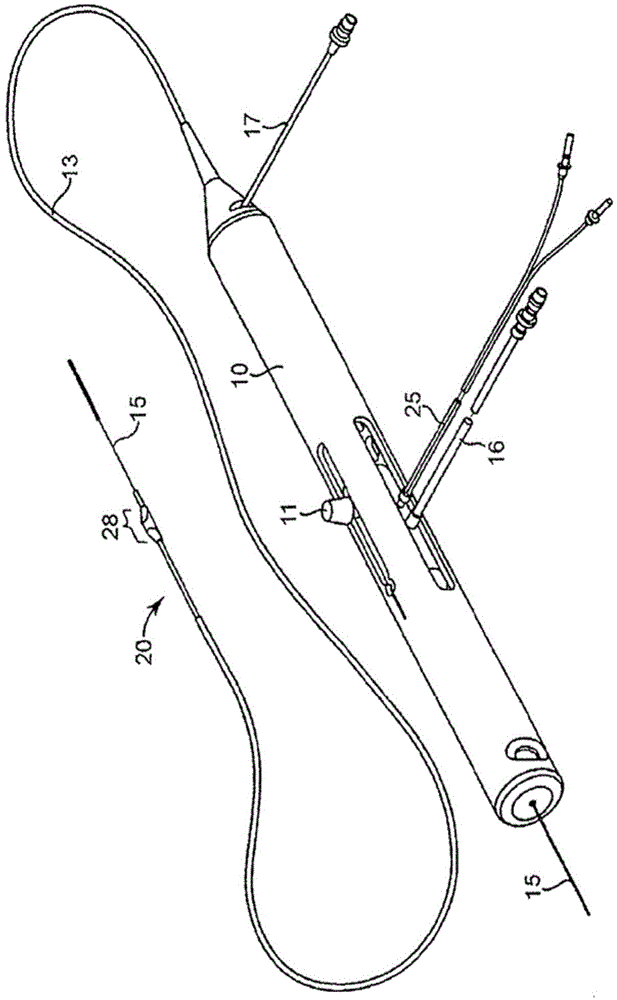
Rotational atherectomy system with stationary cutting elements
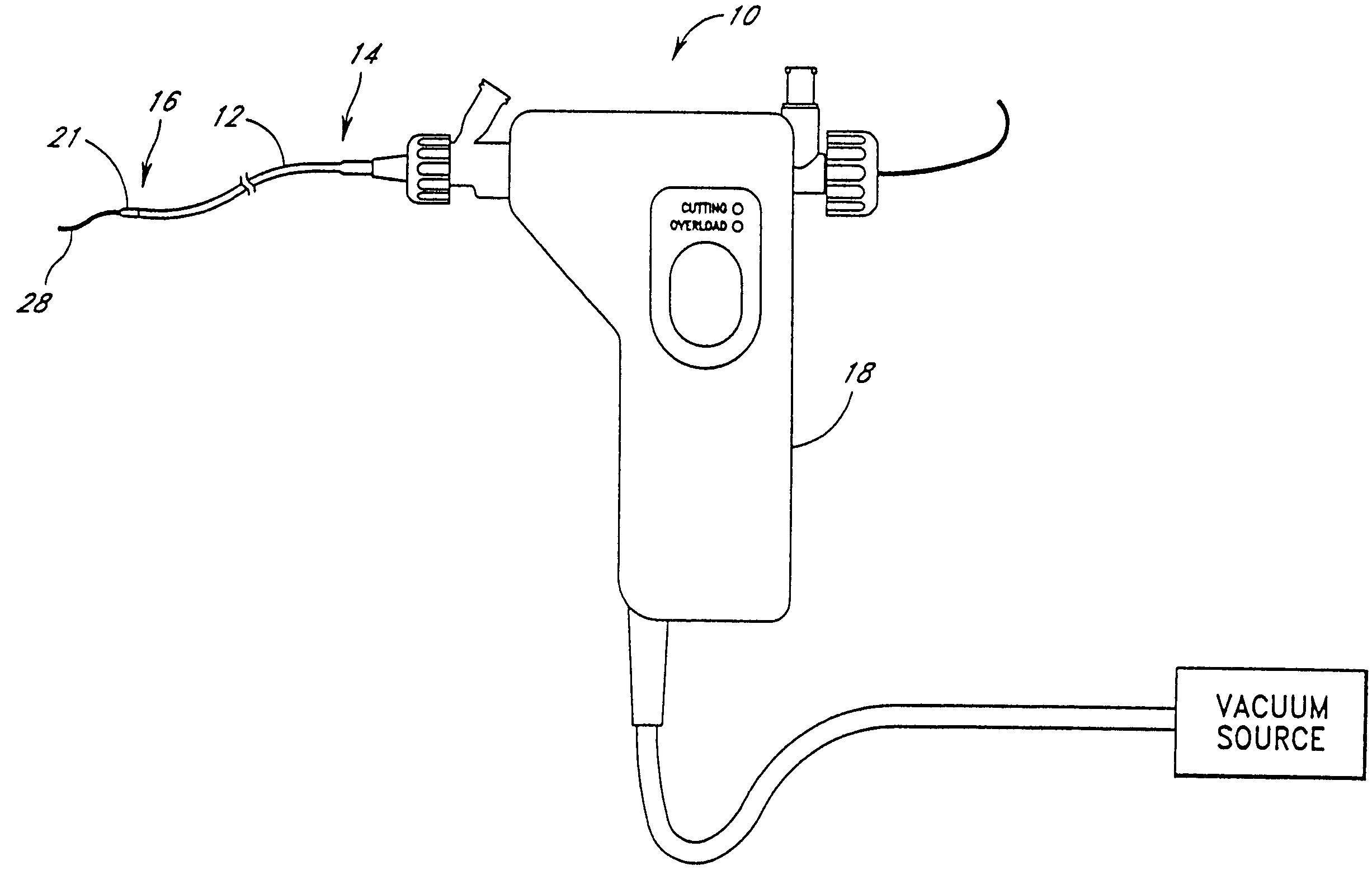
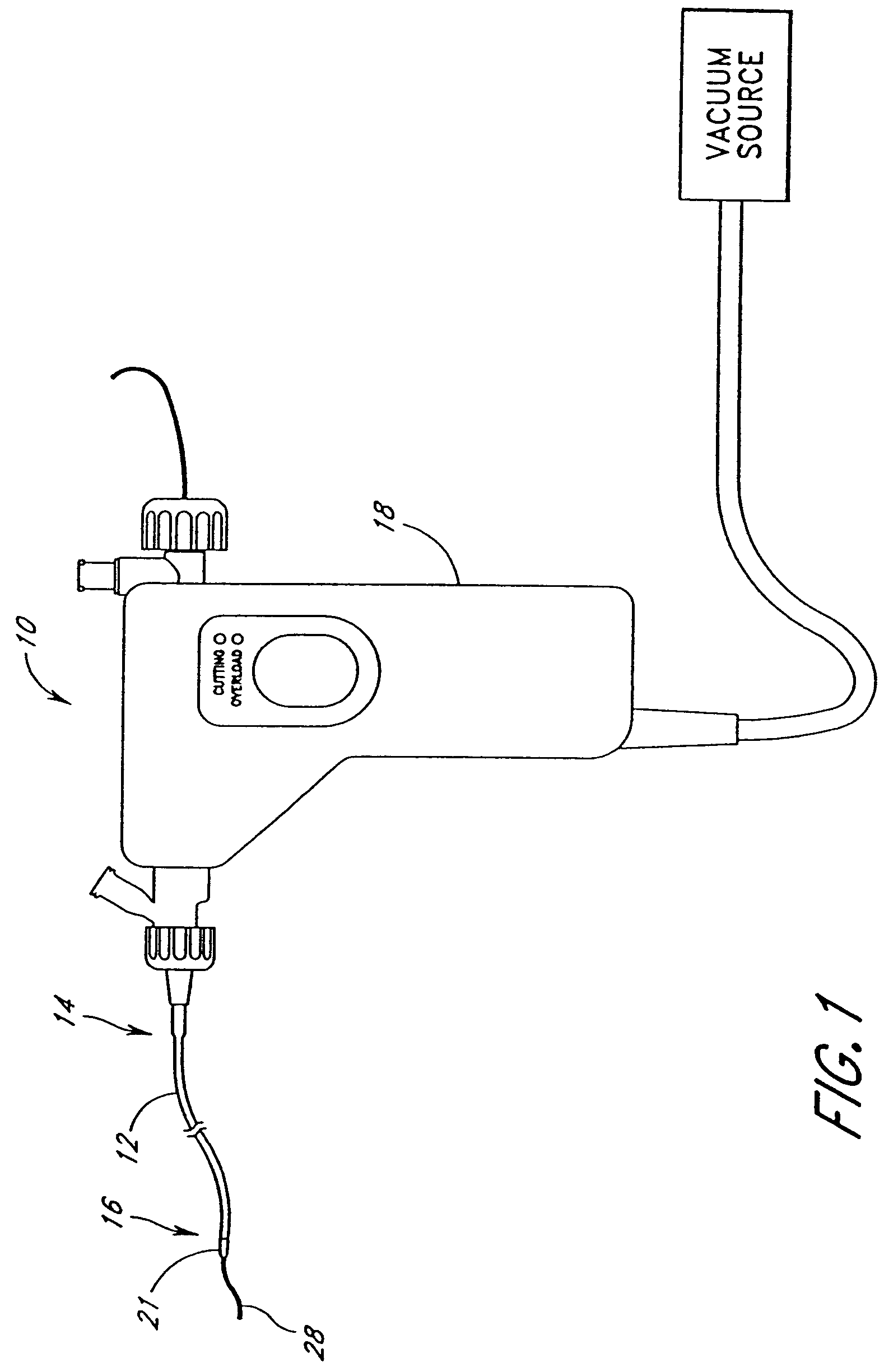
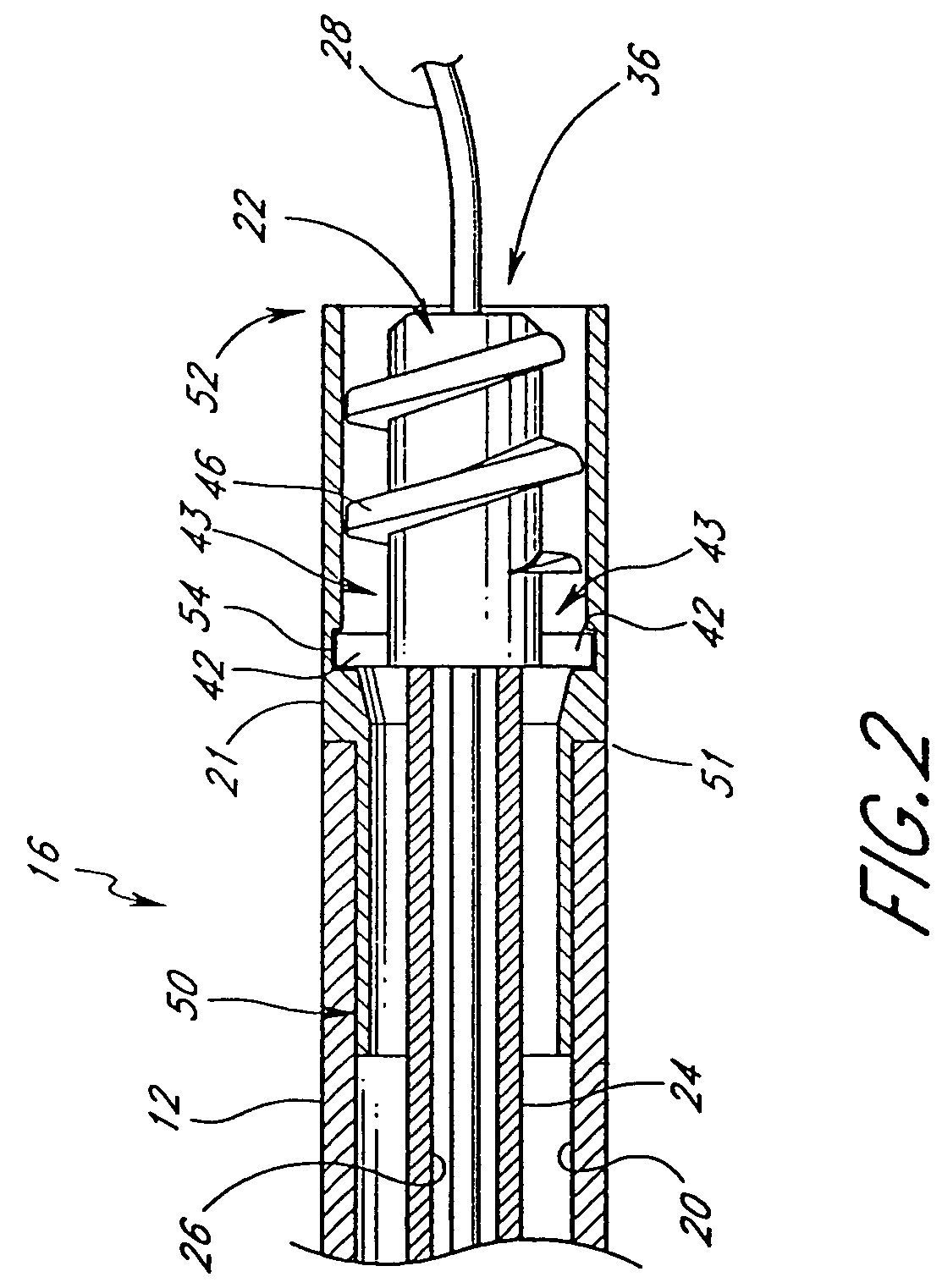
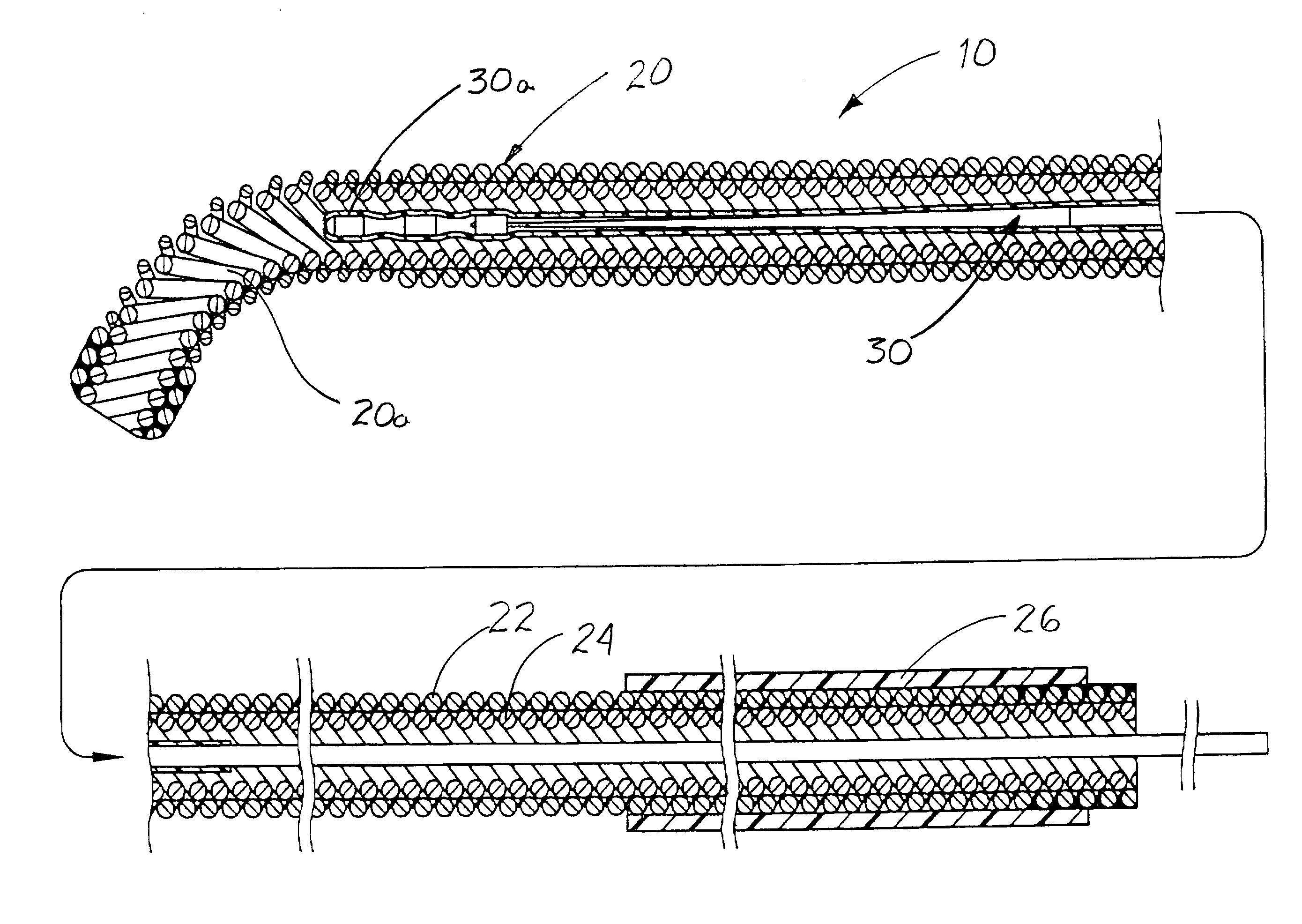
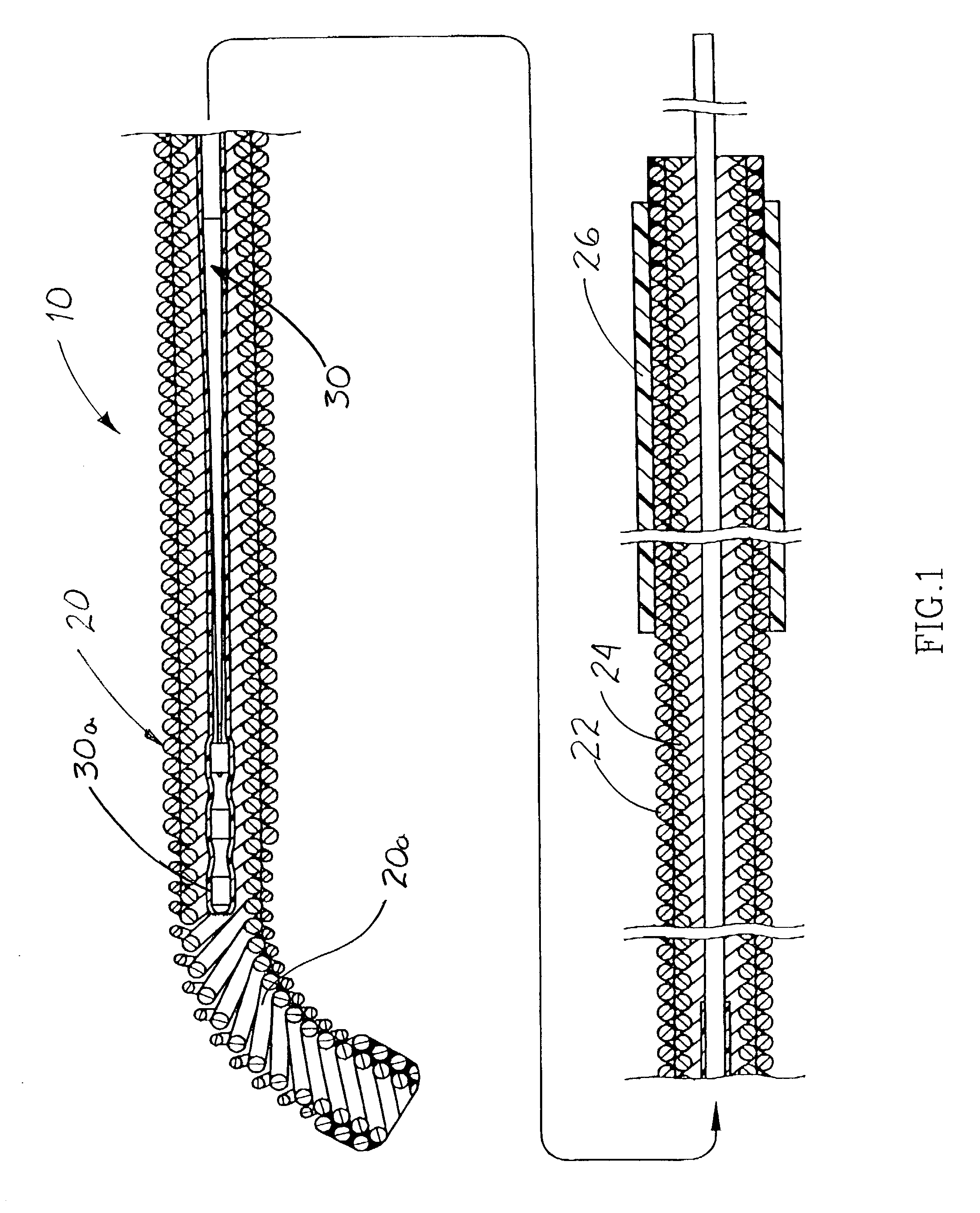
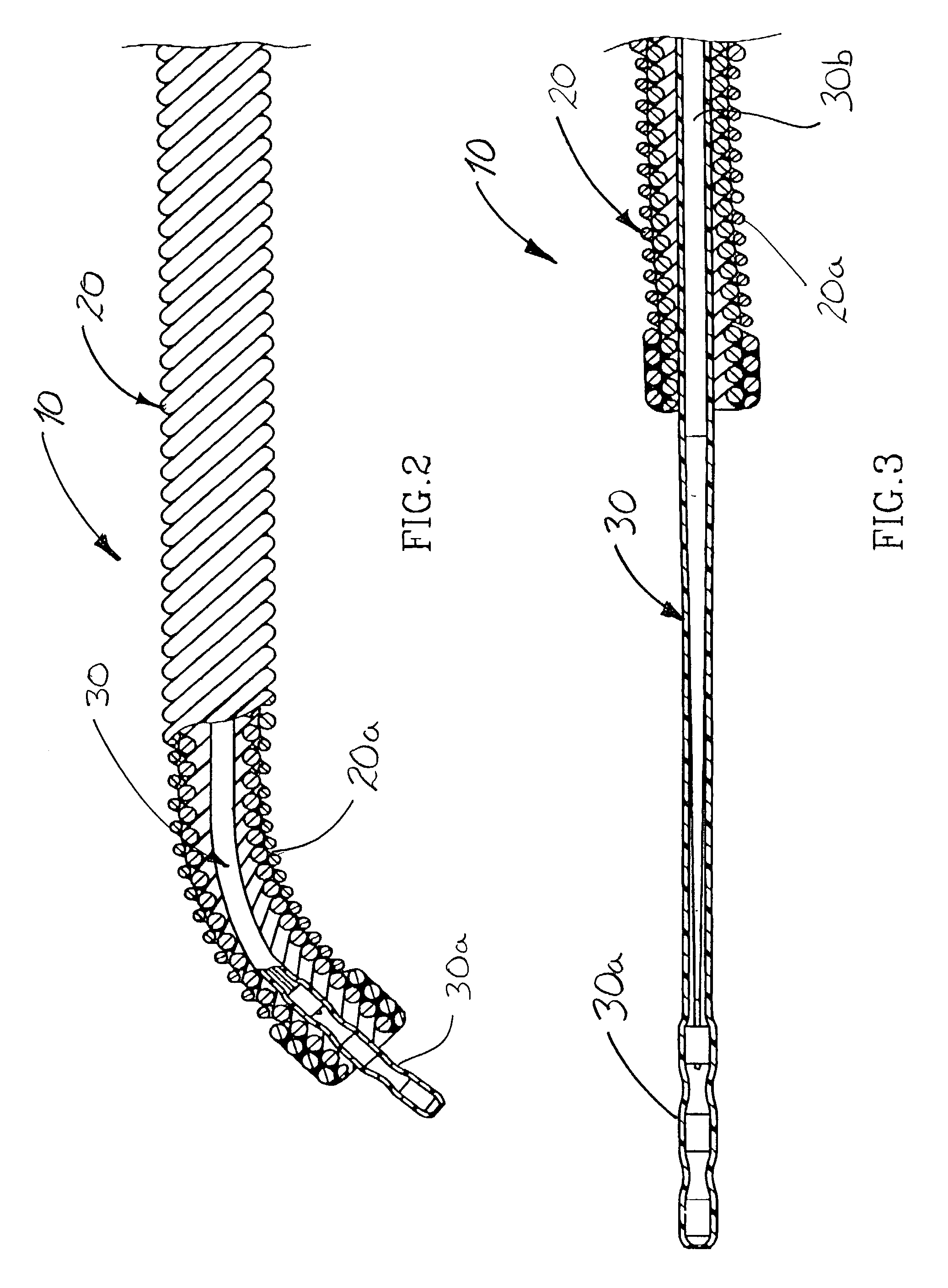
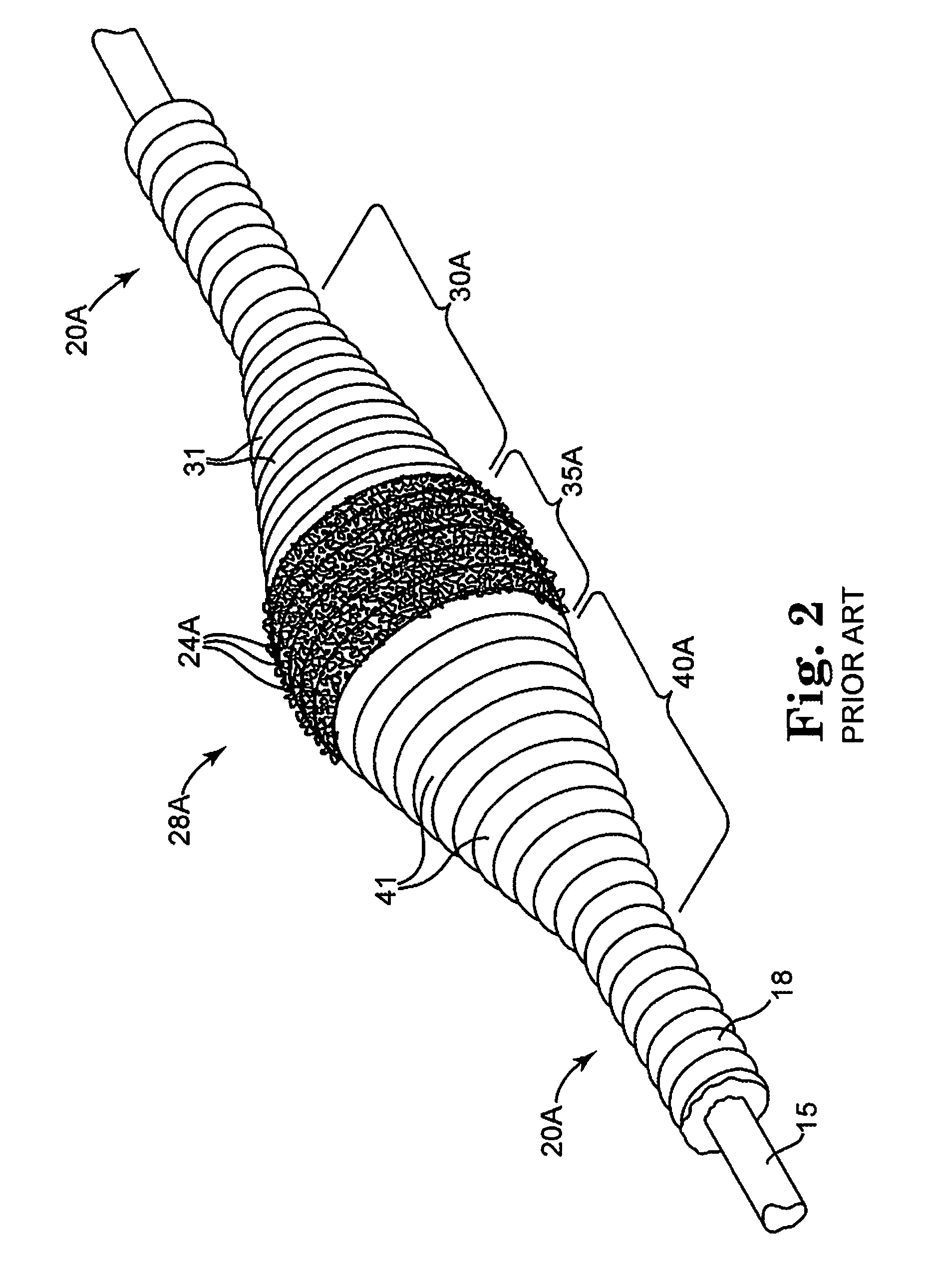
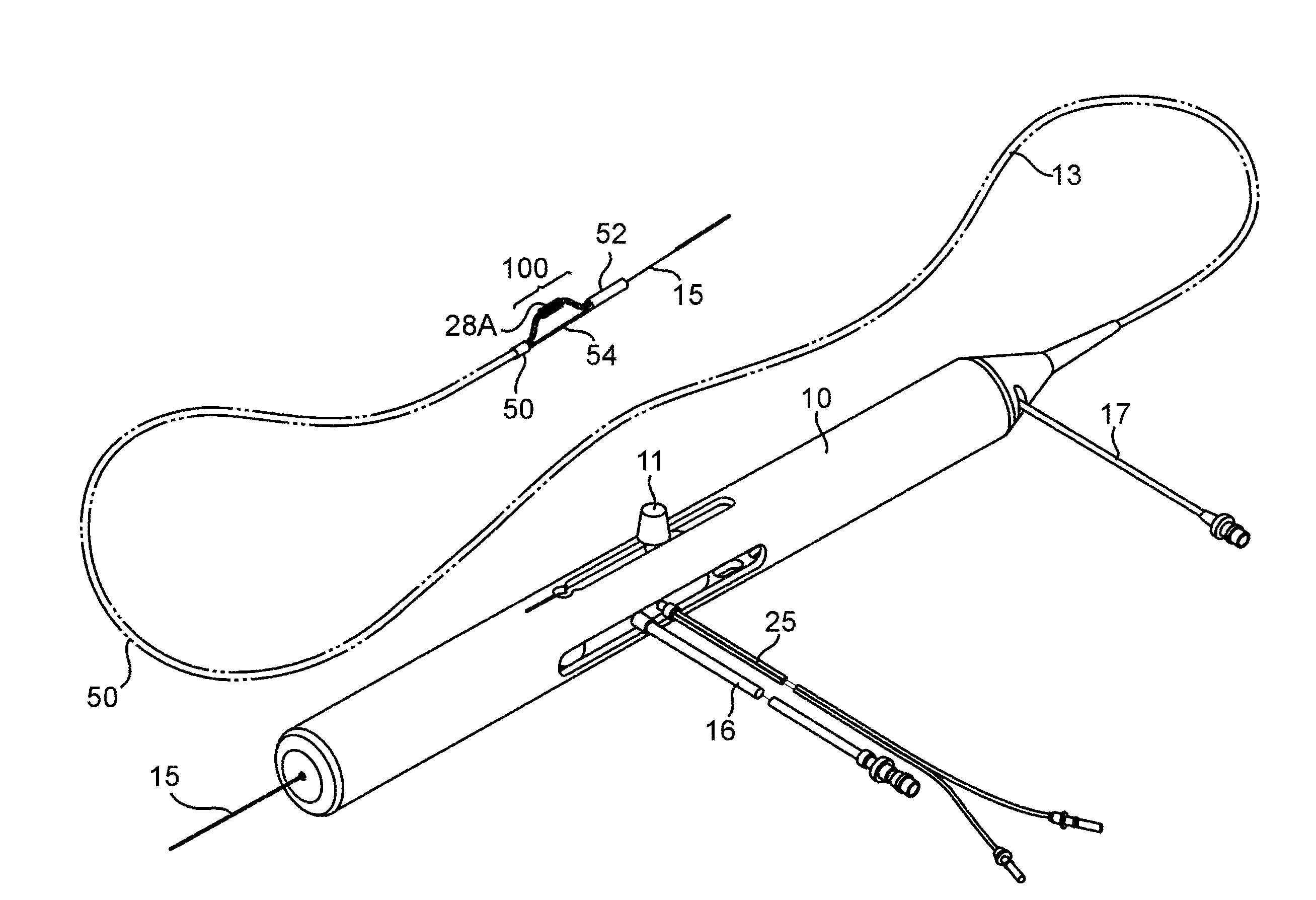
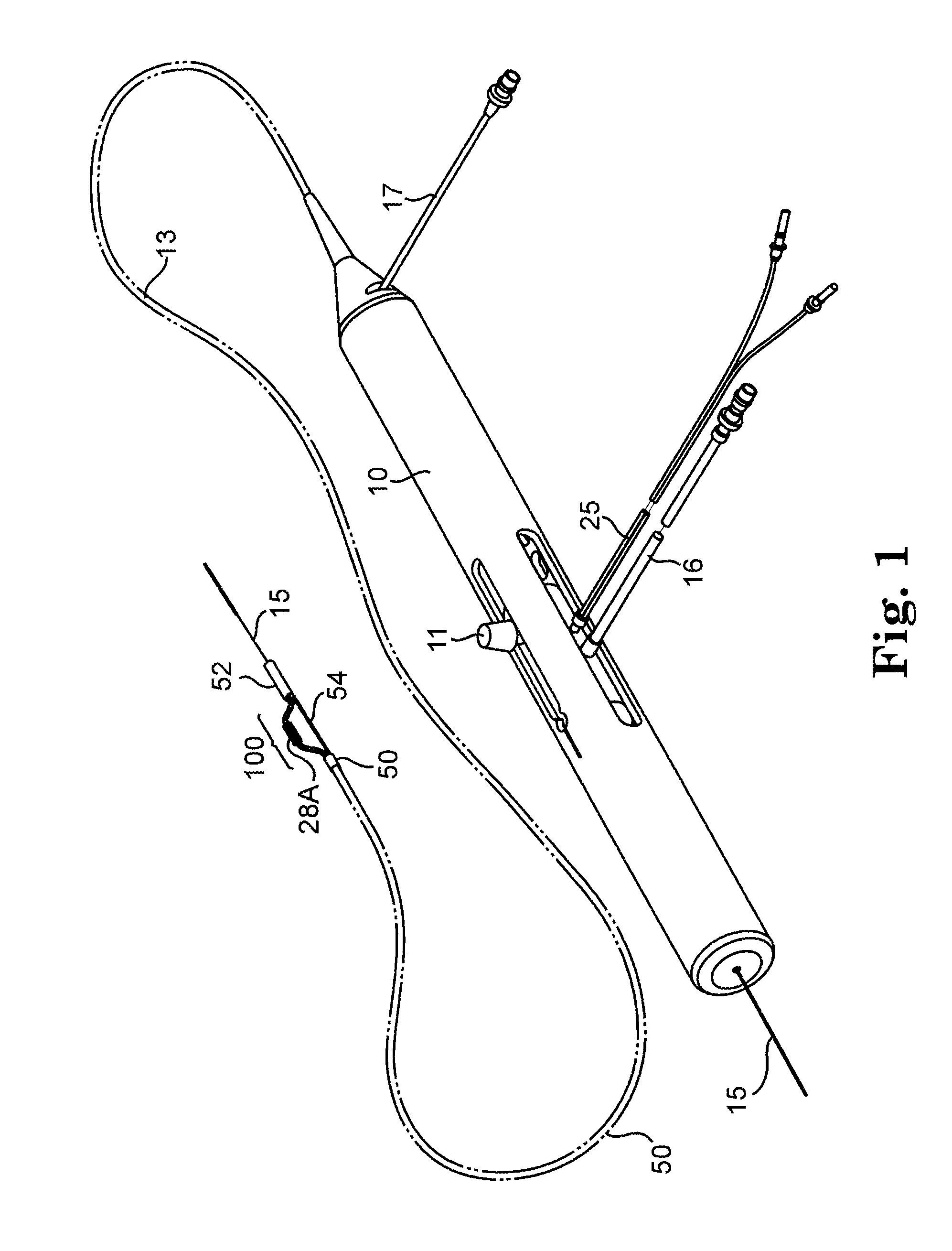
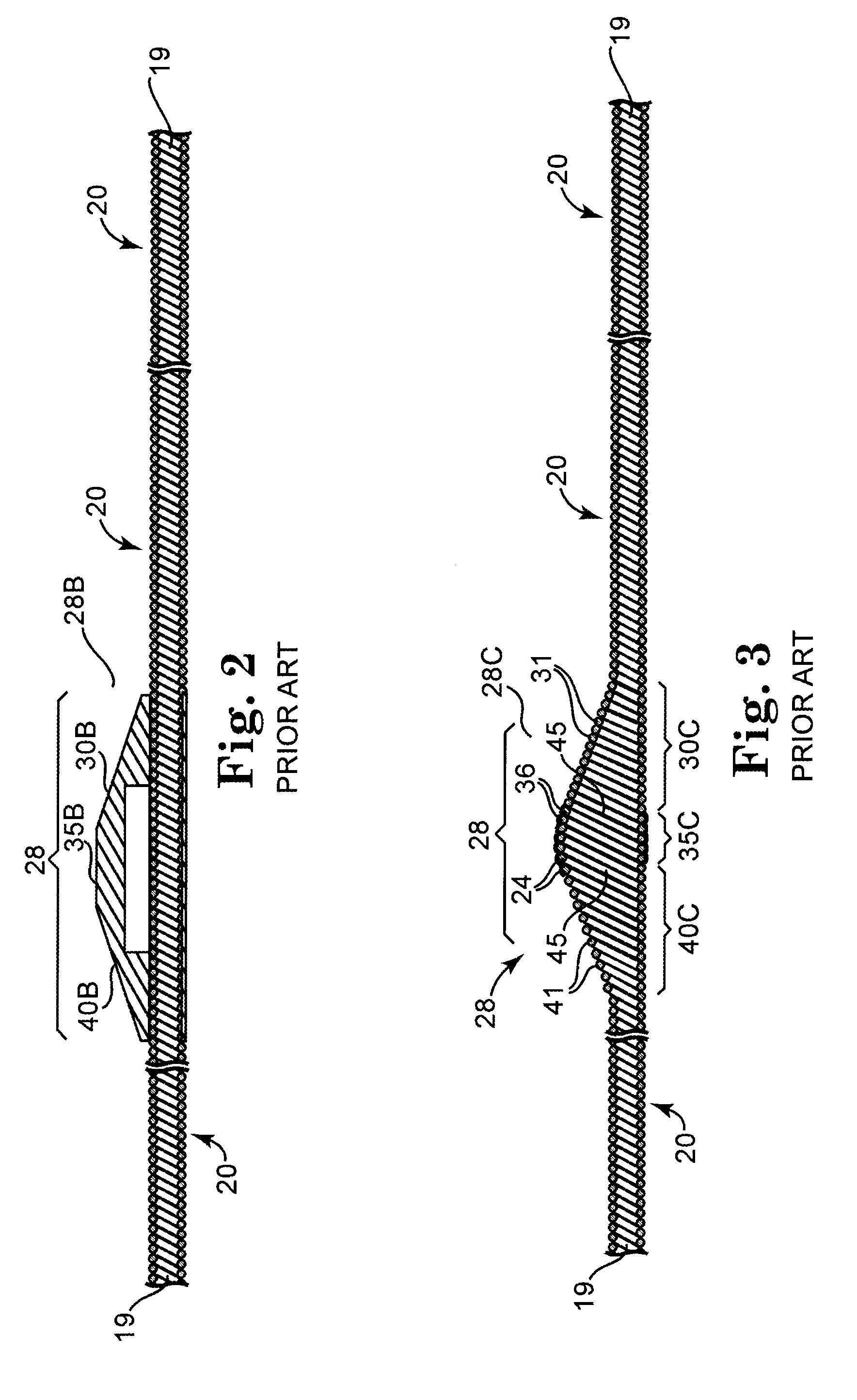
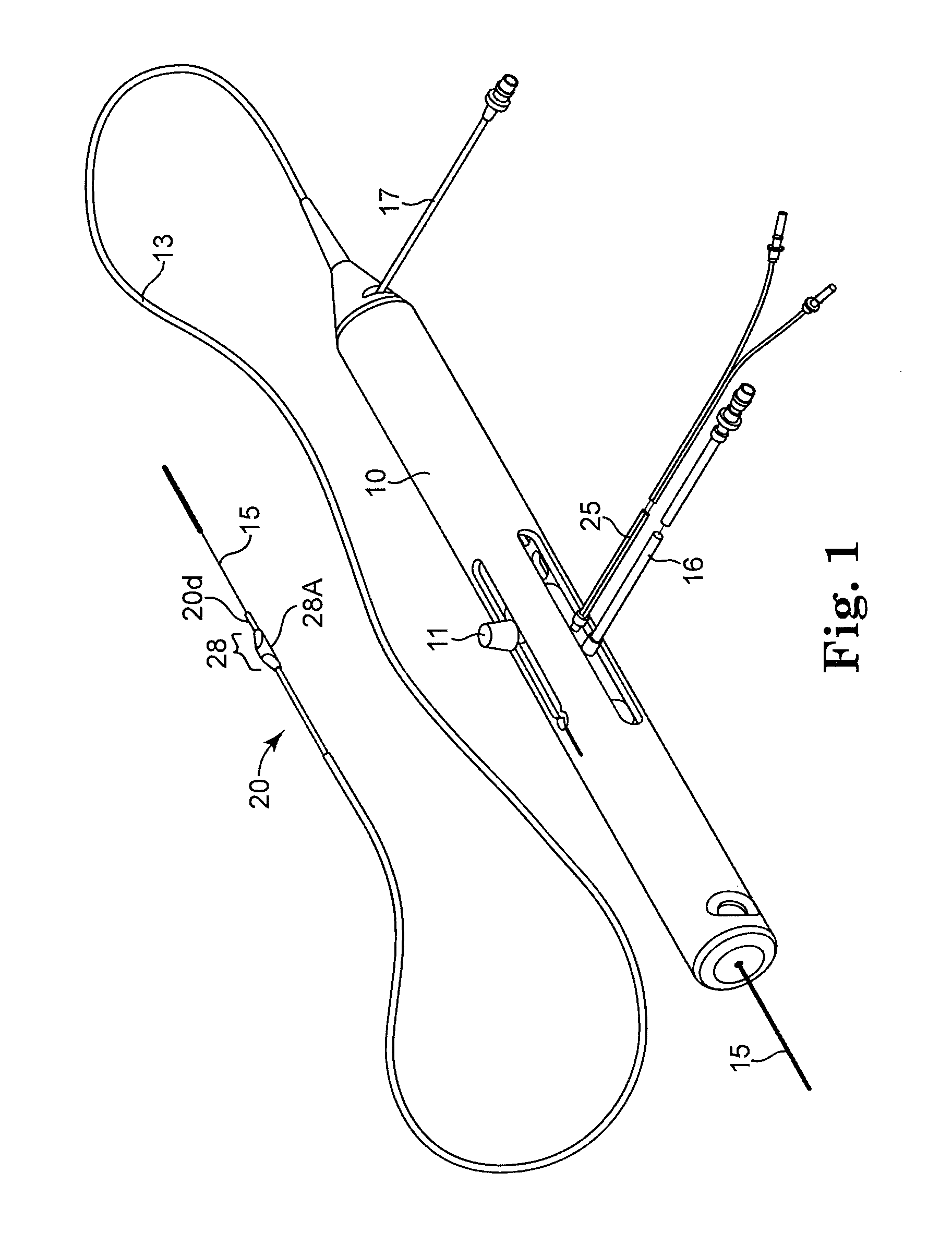
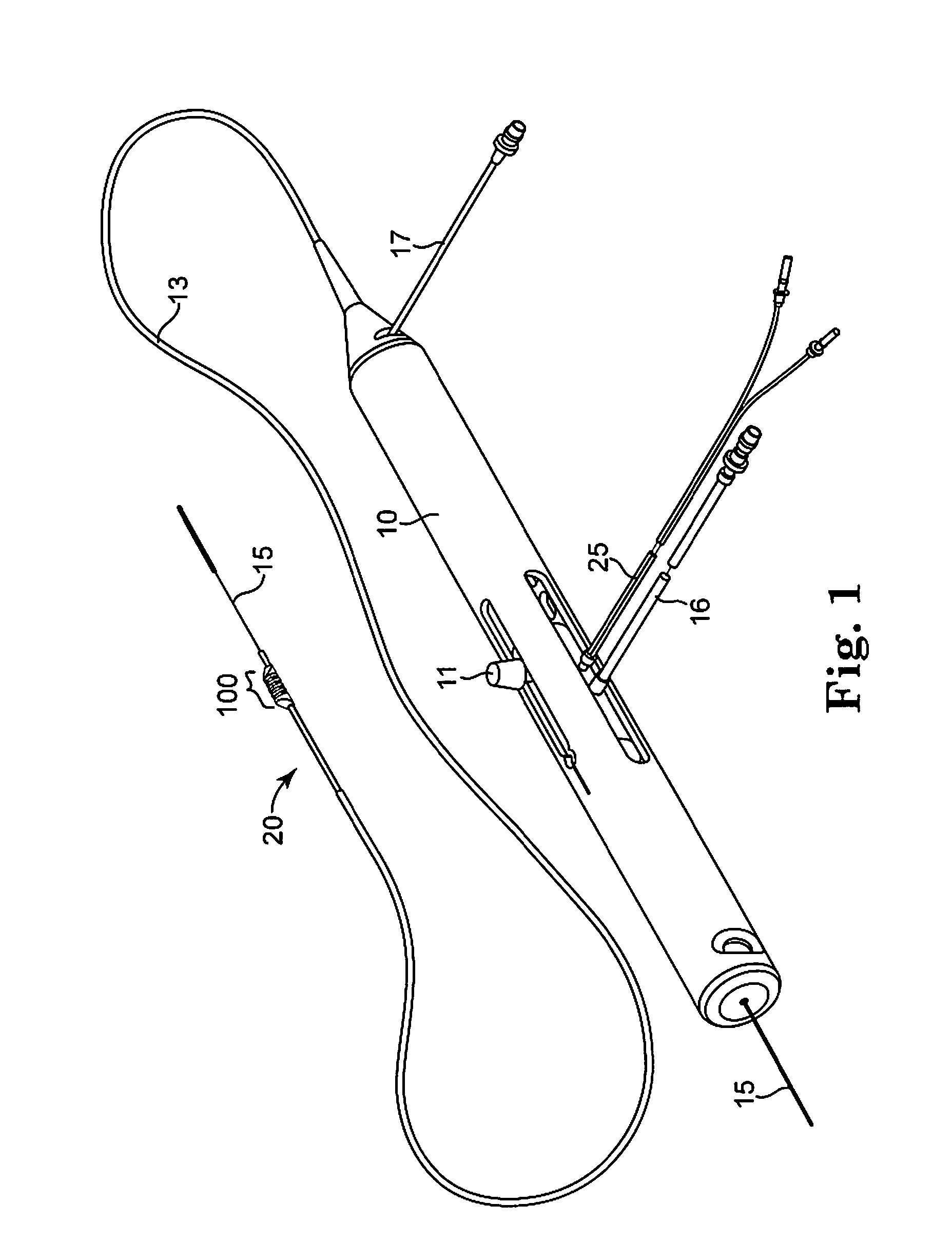
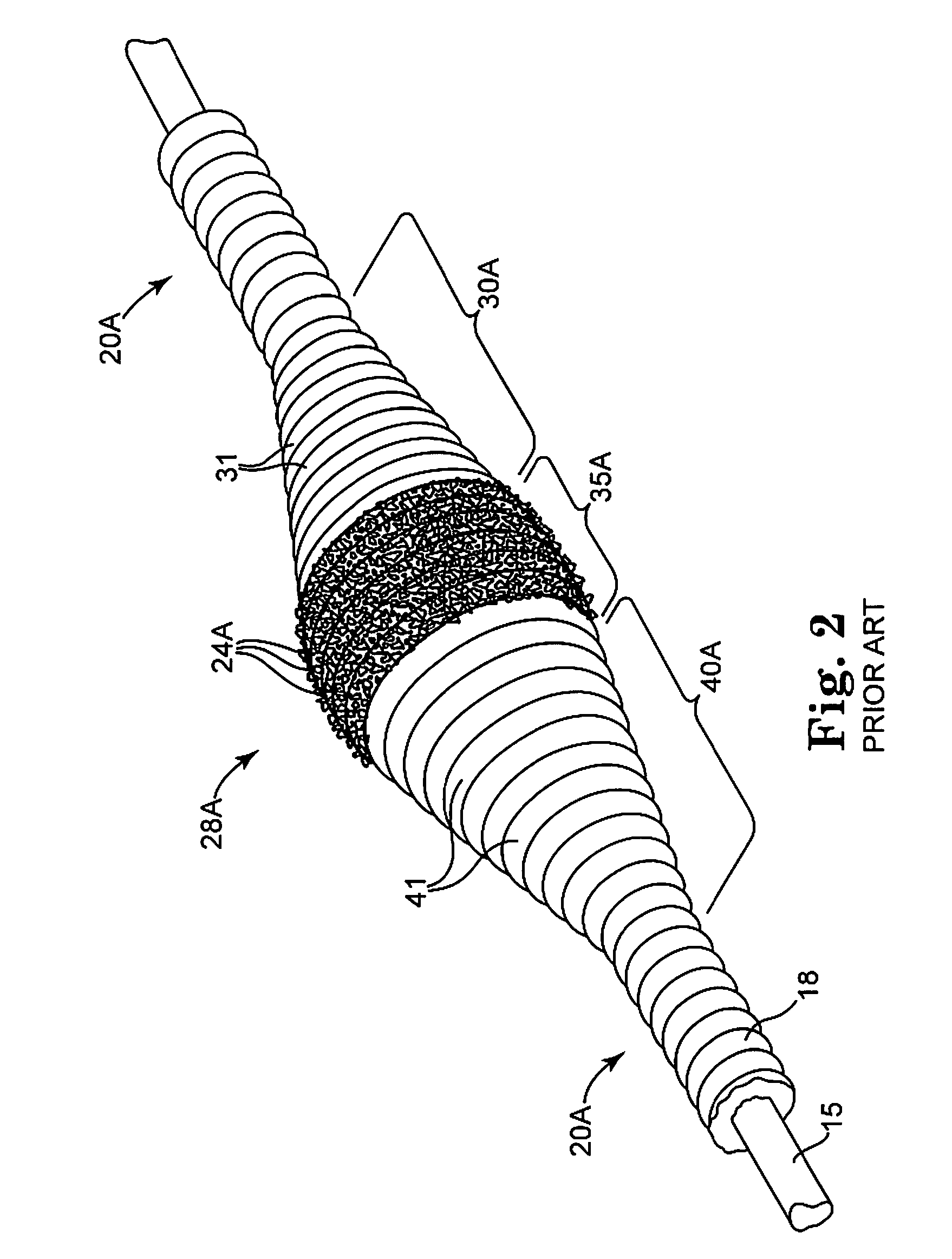
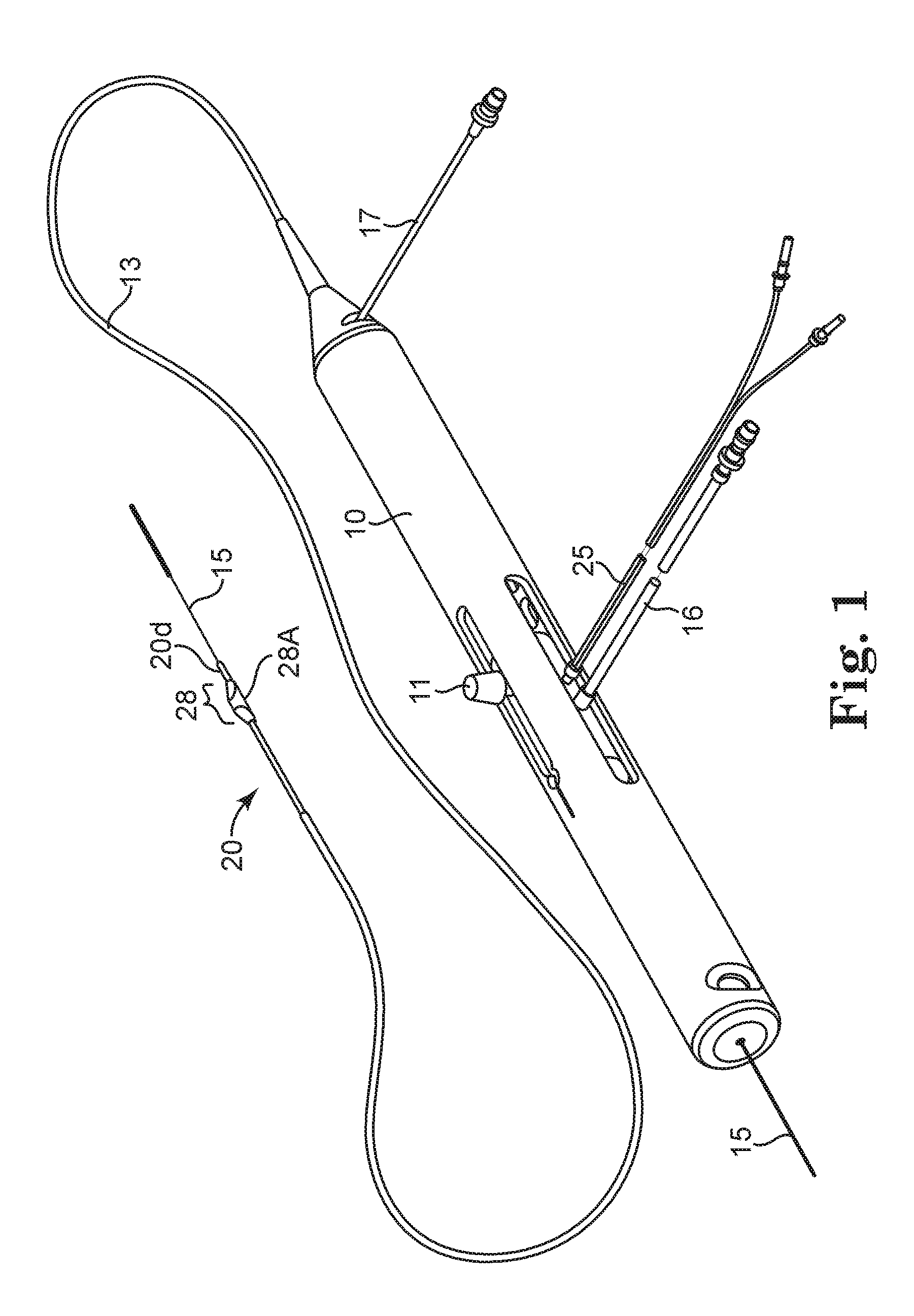
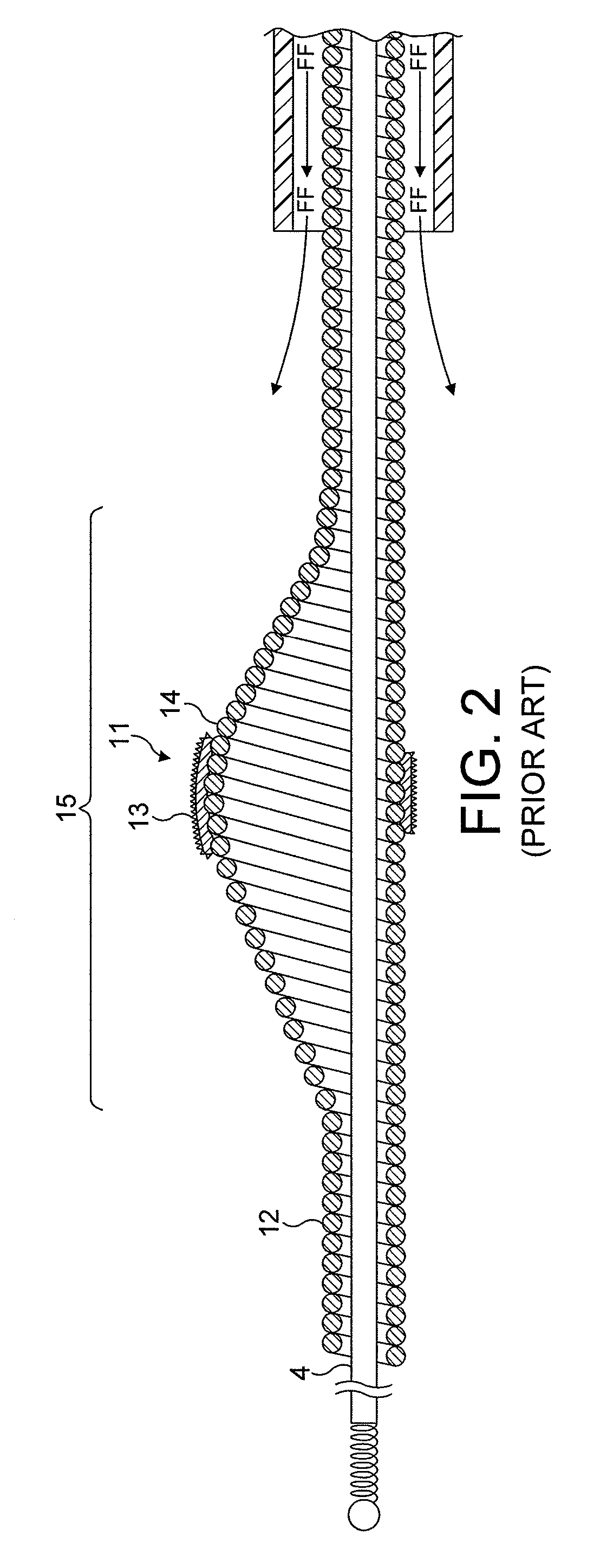
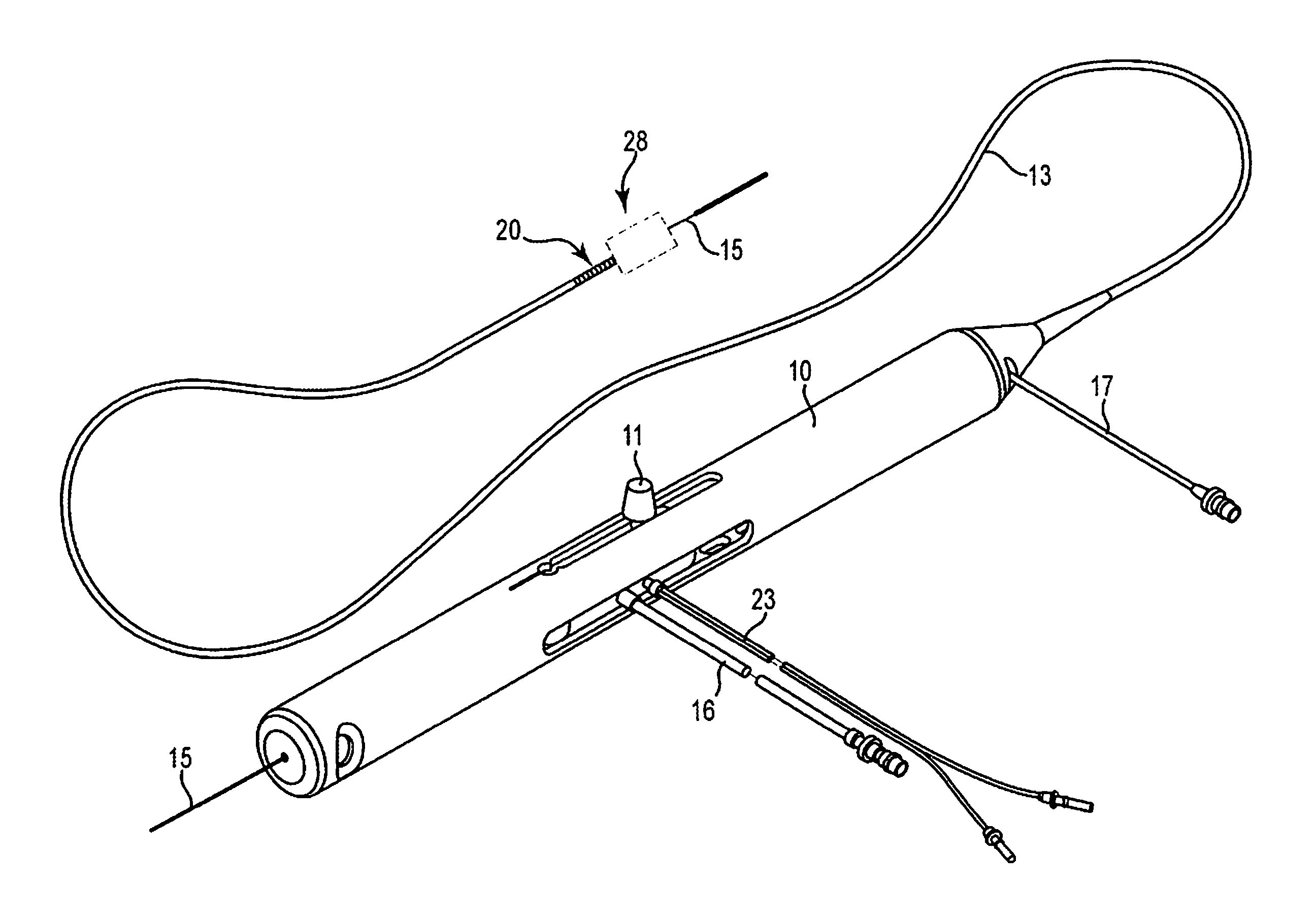
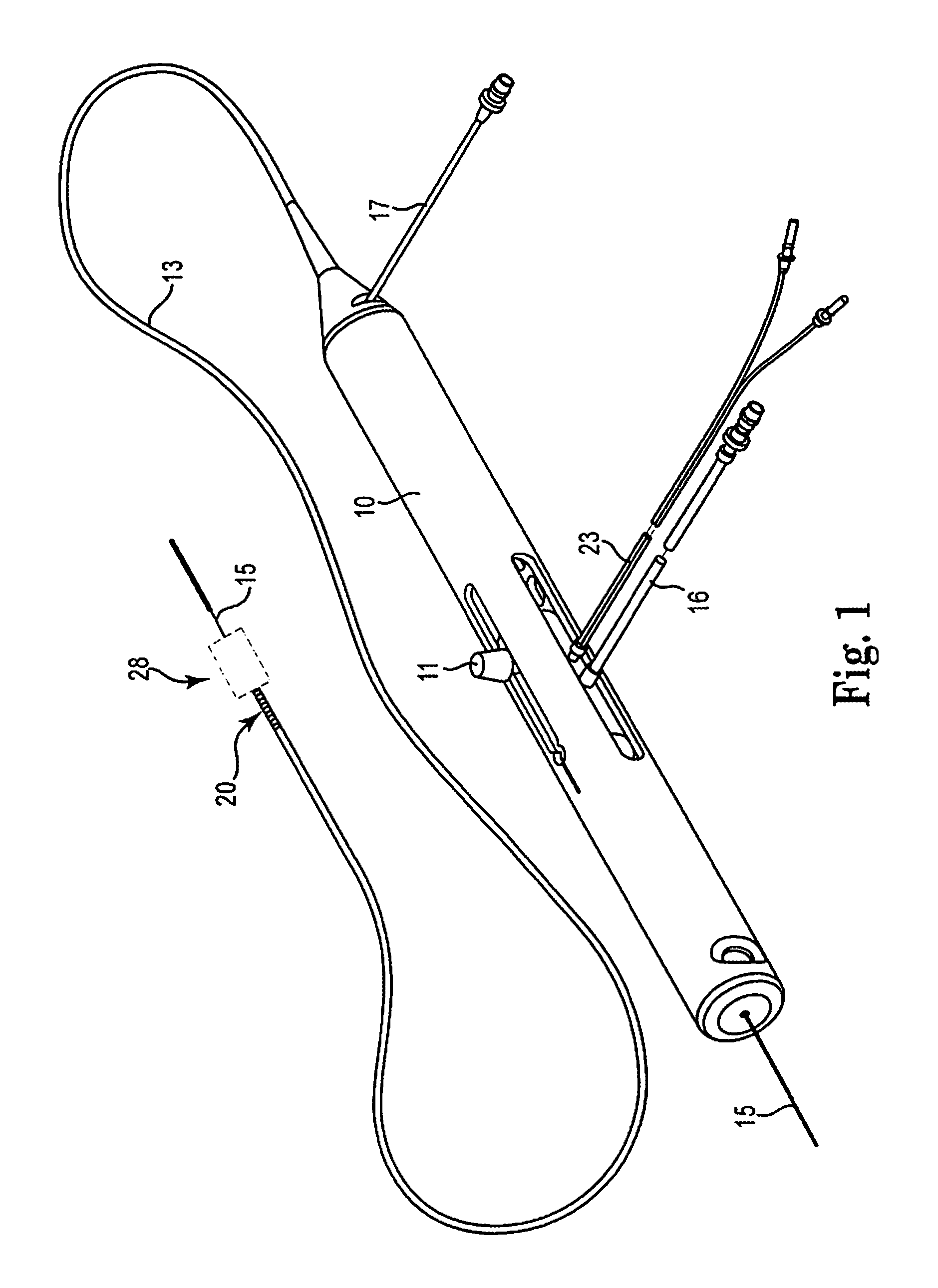
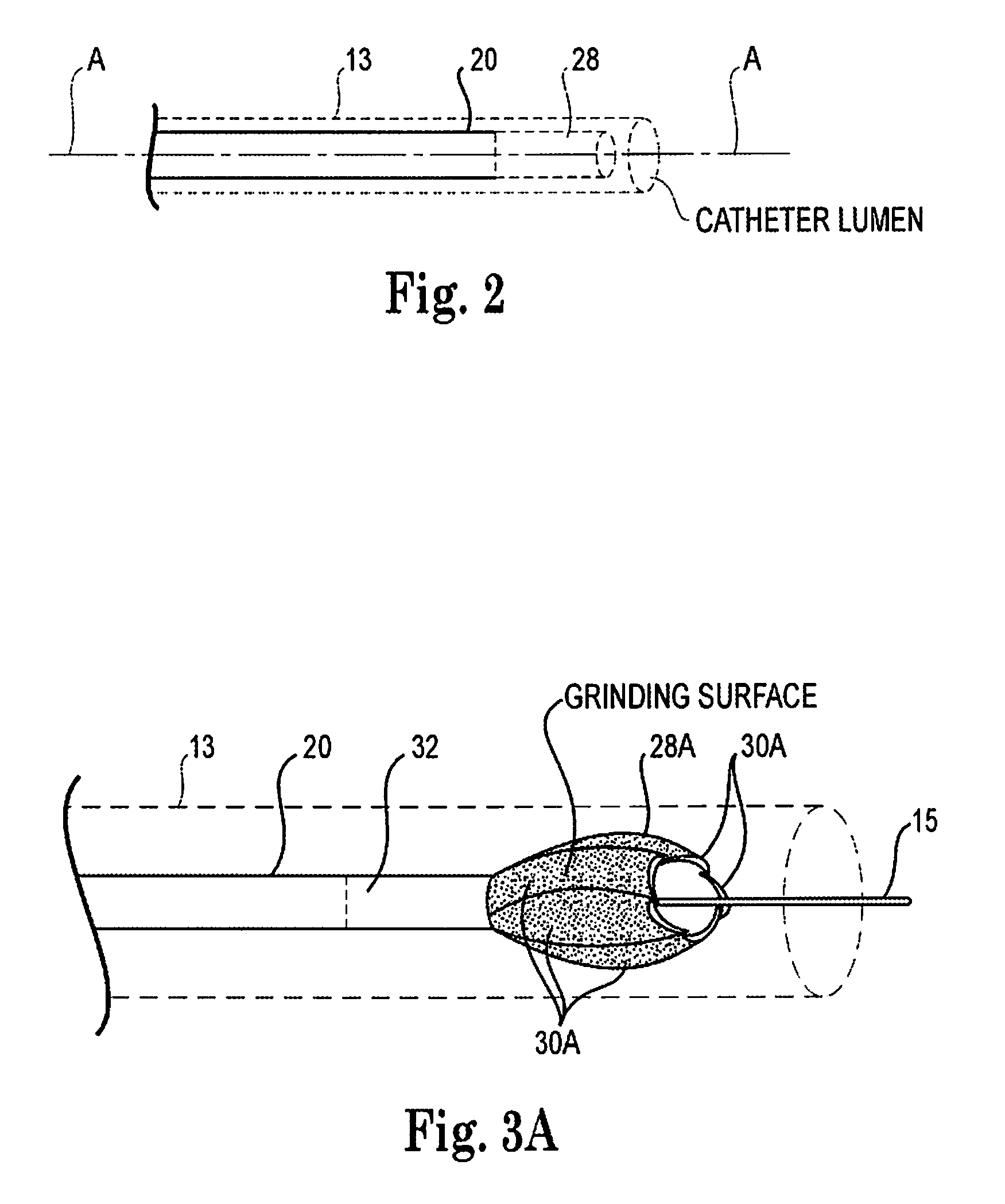
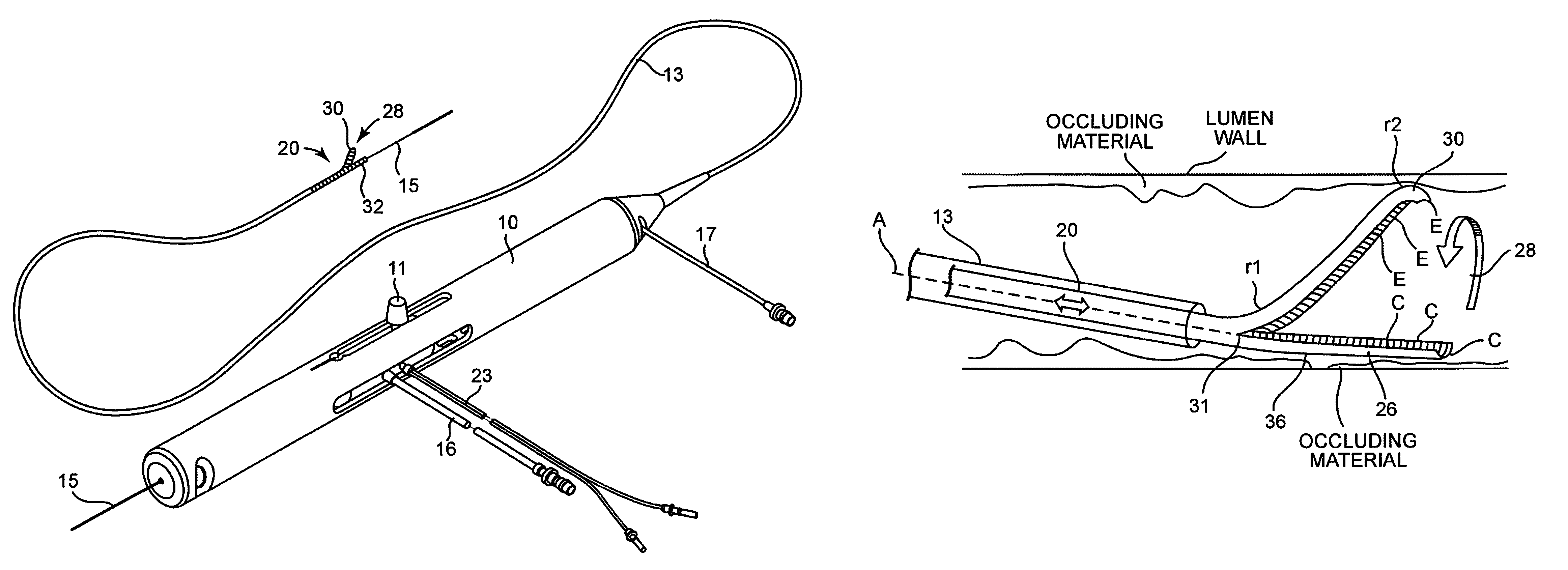
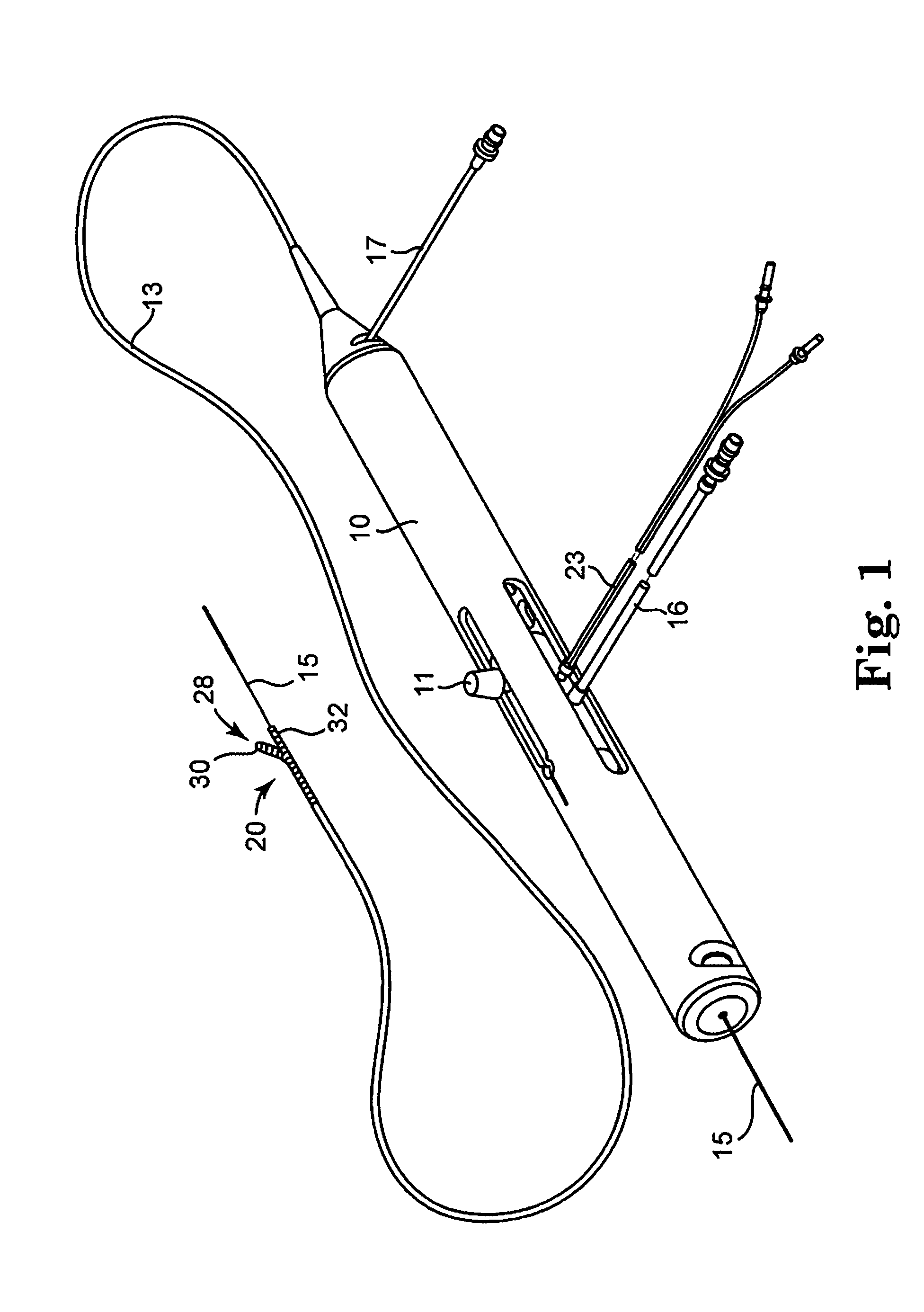
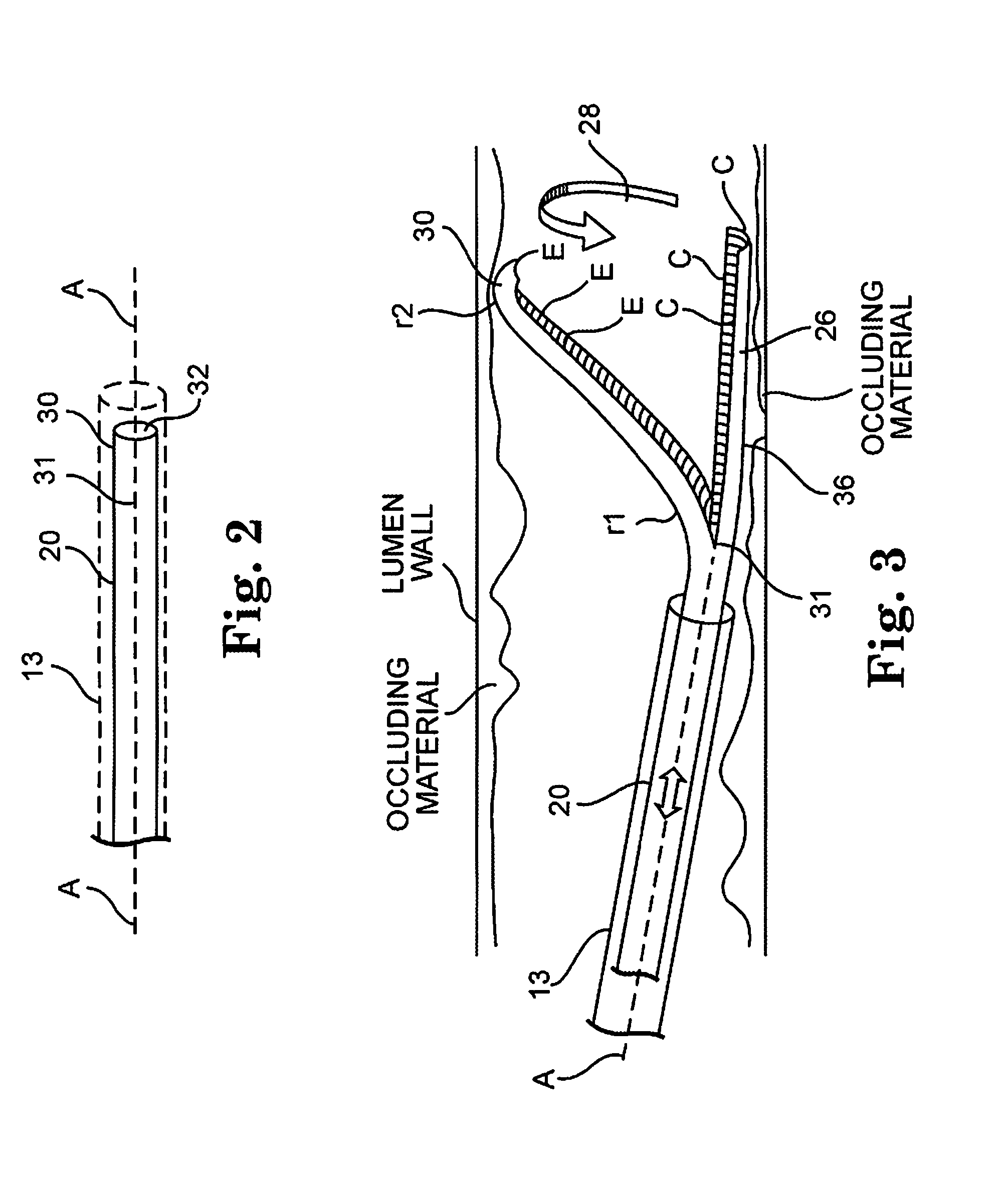
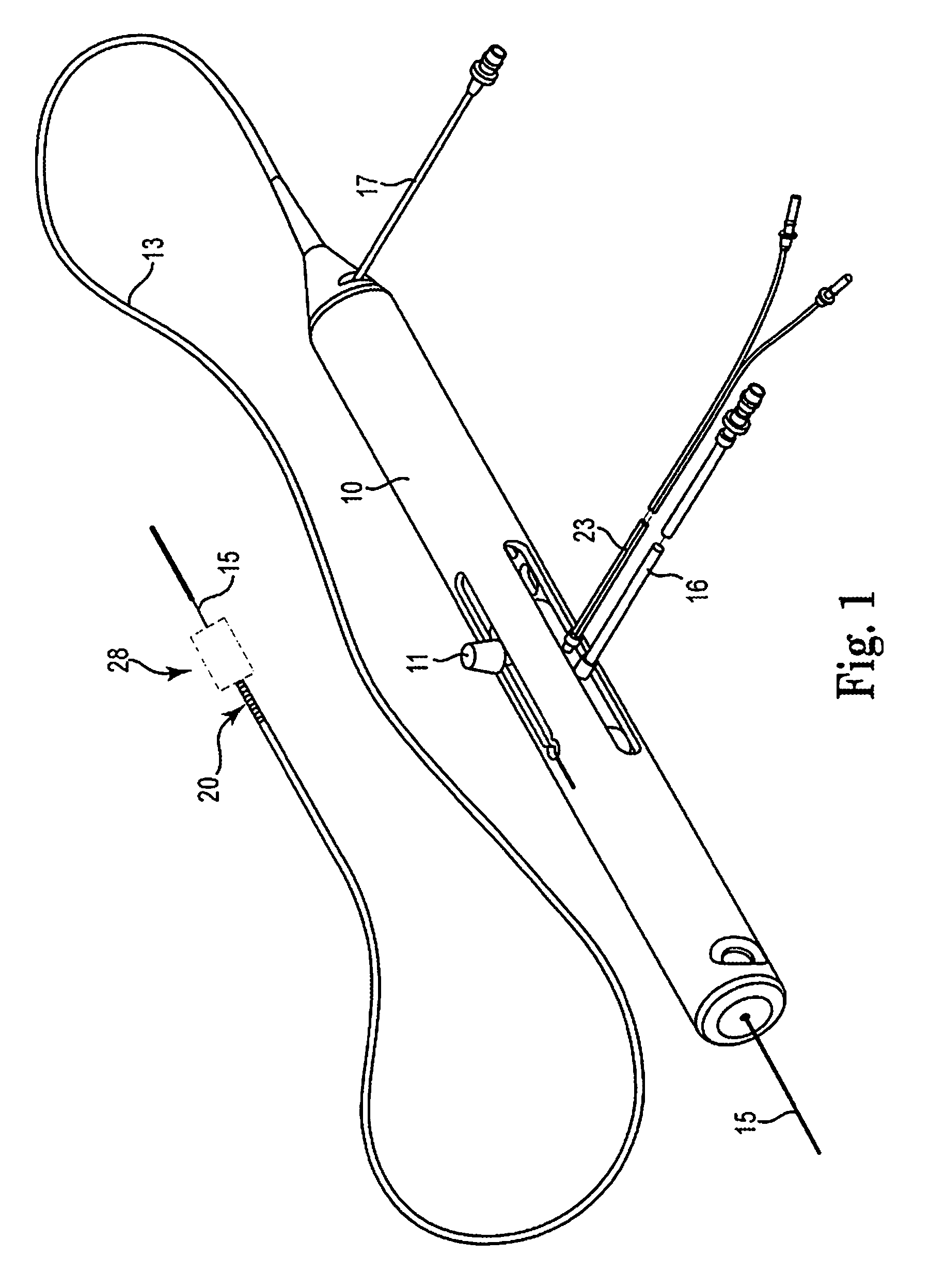
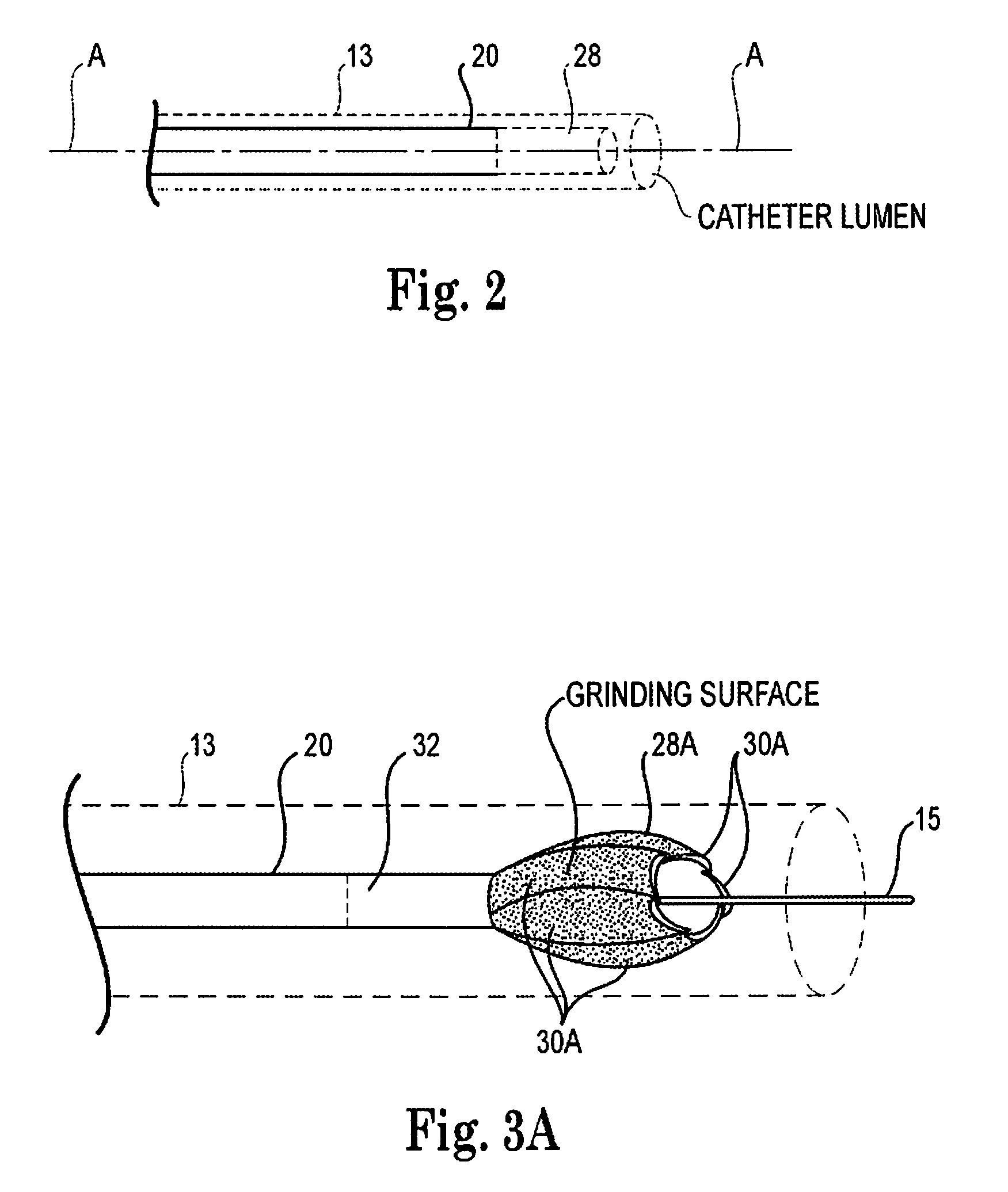
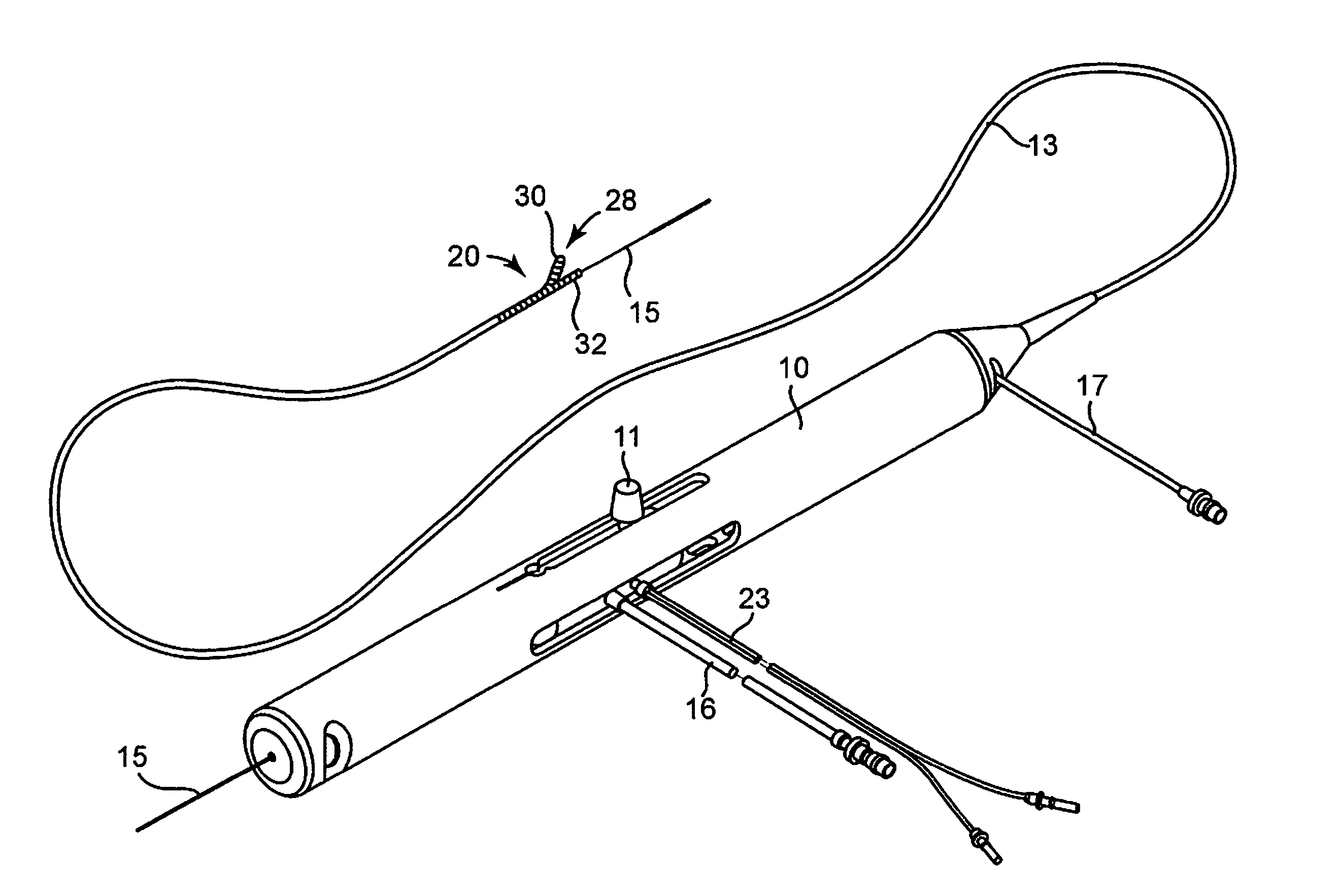
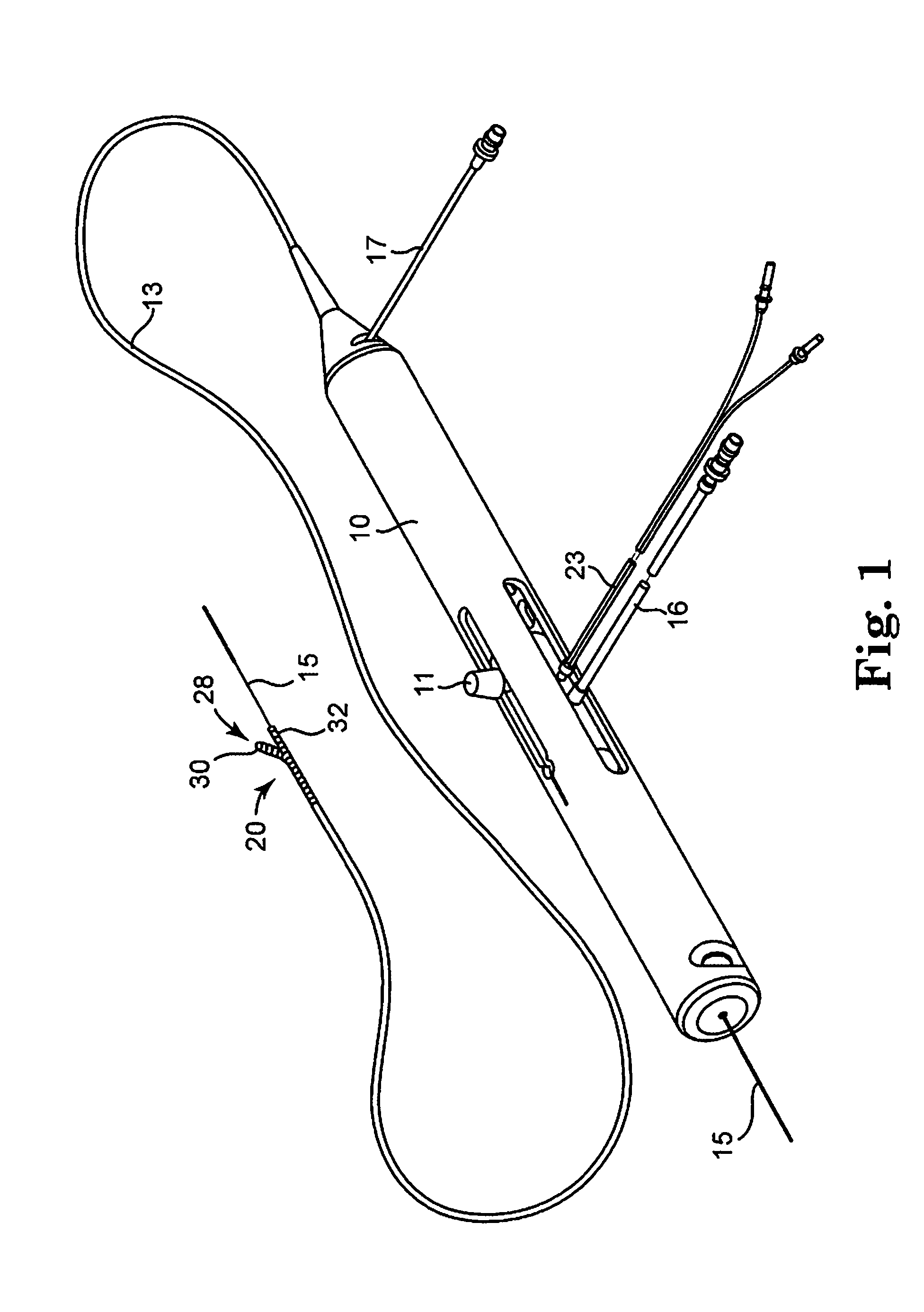
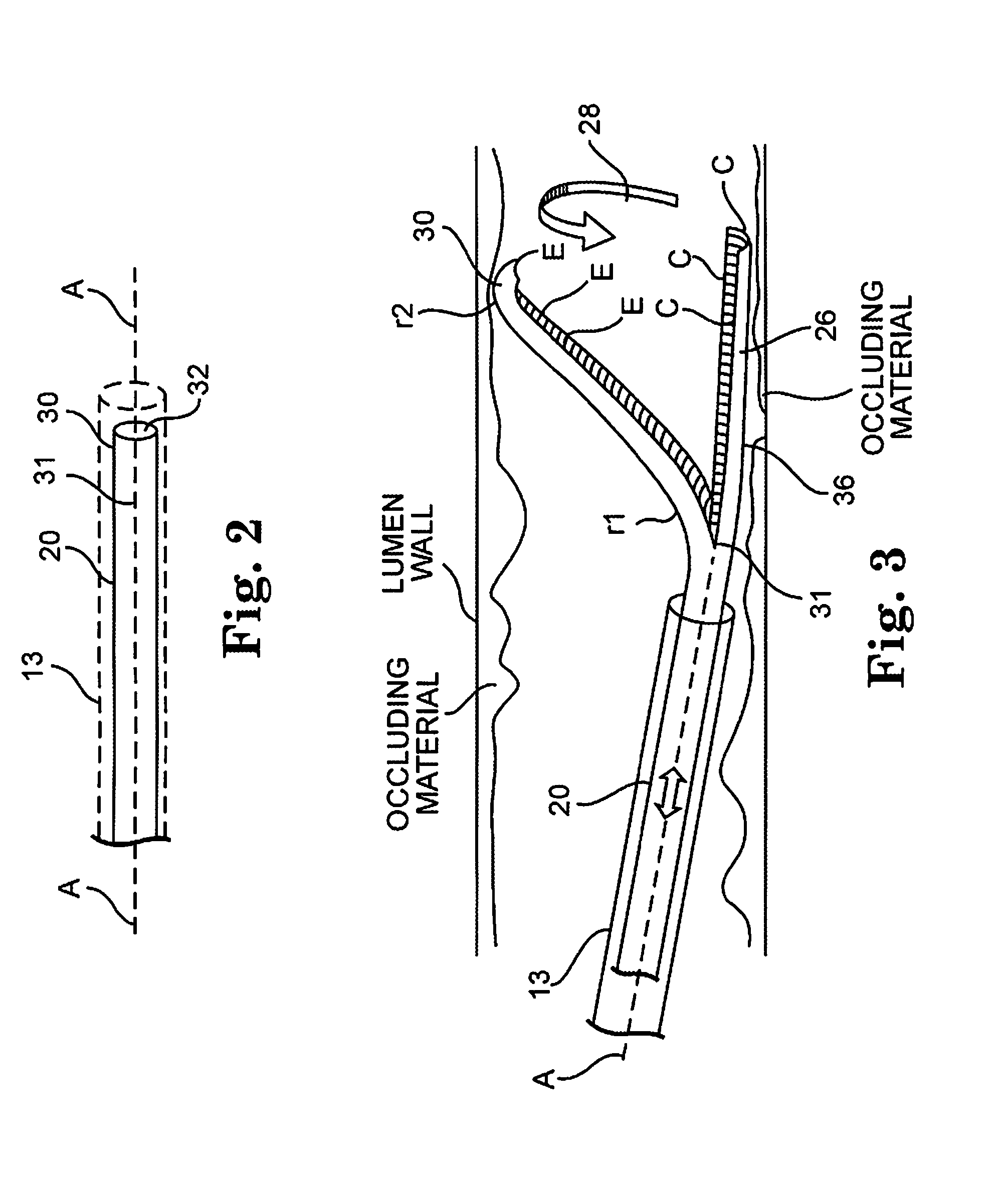
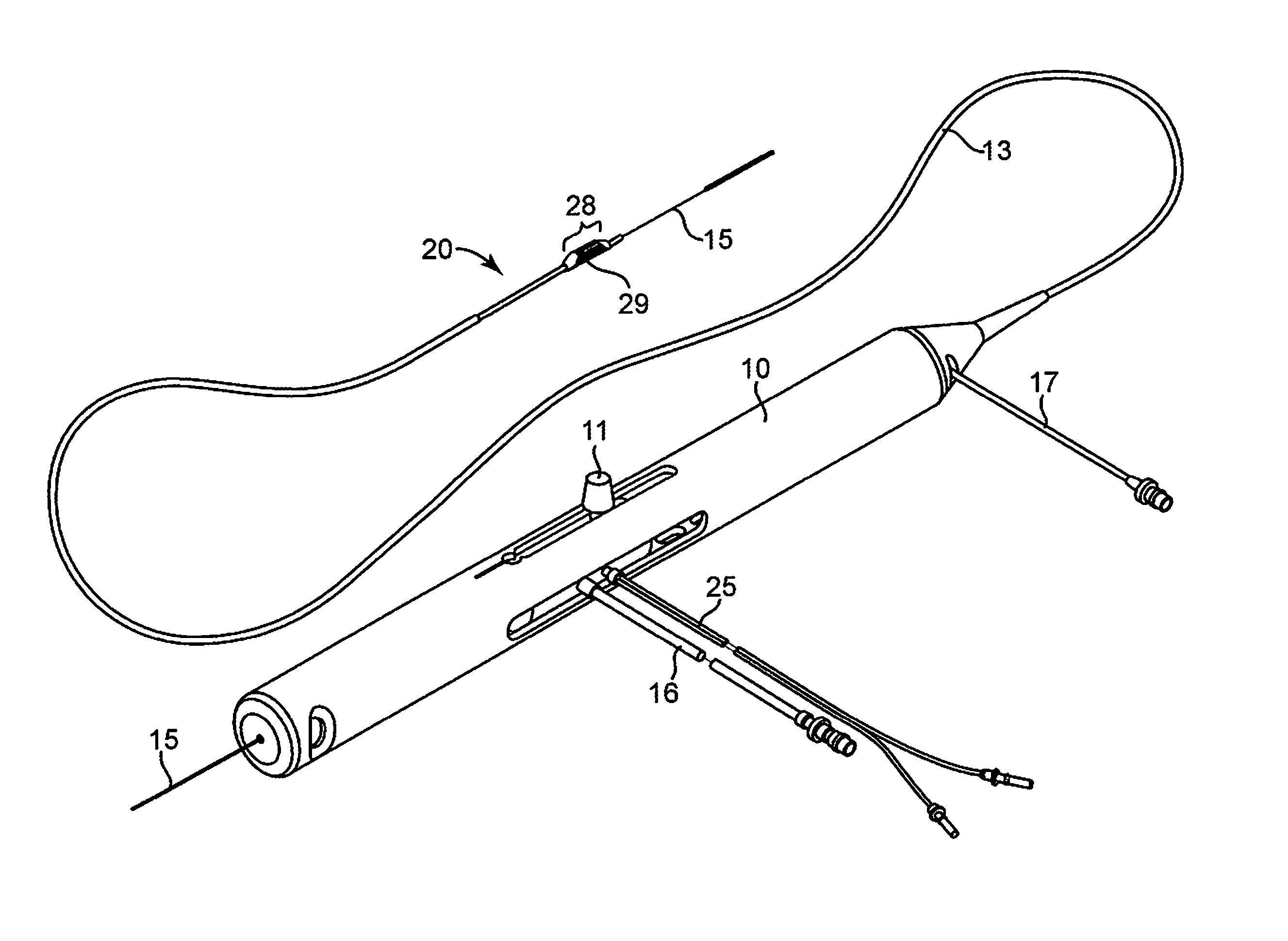
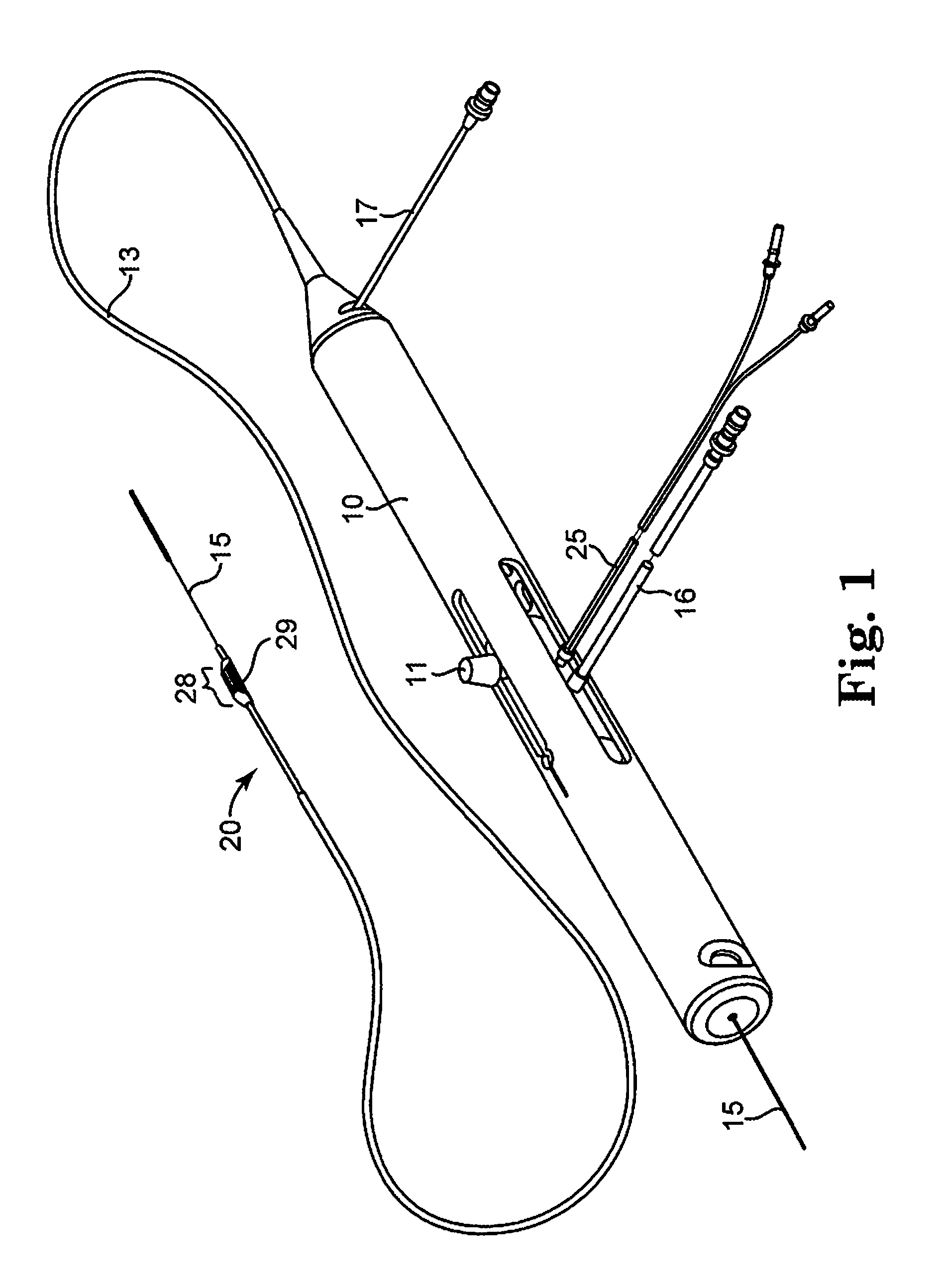
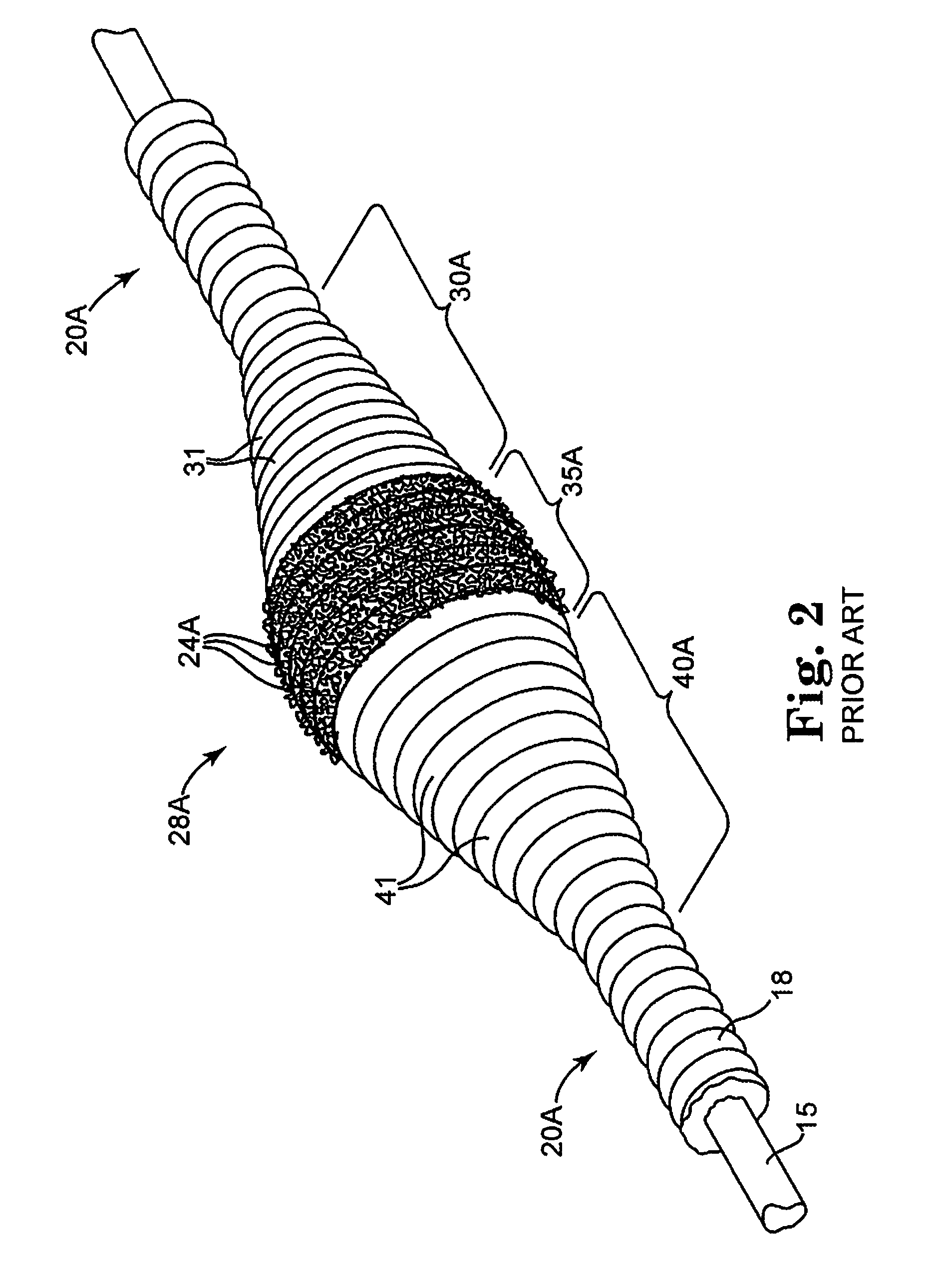
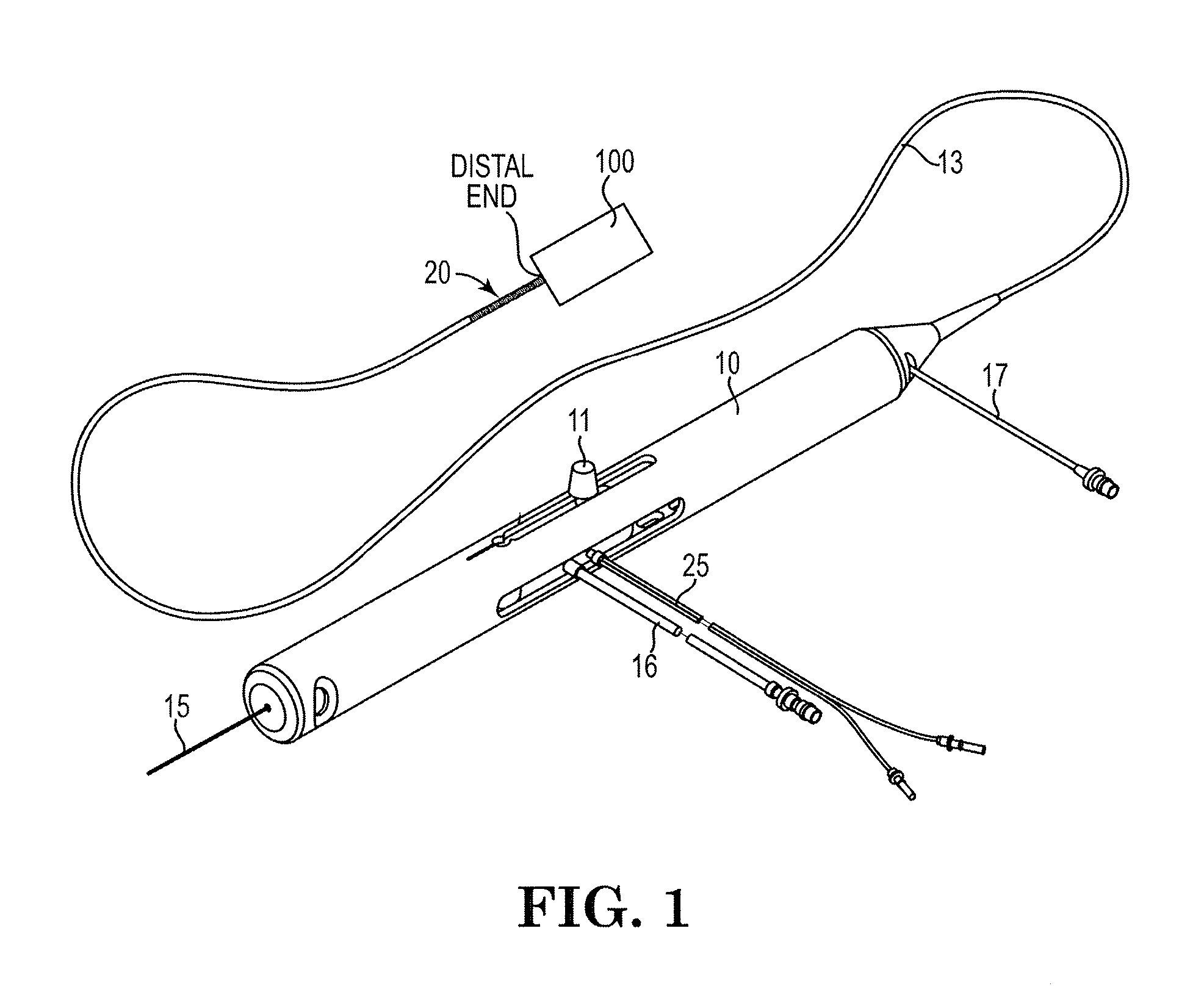
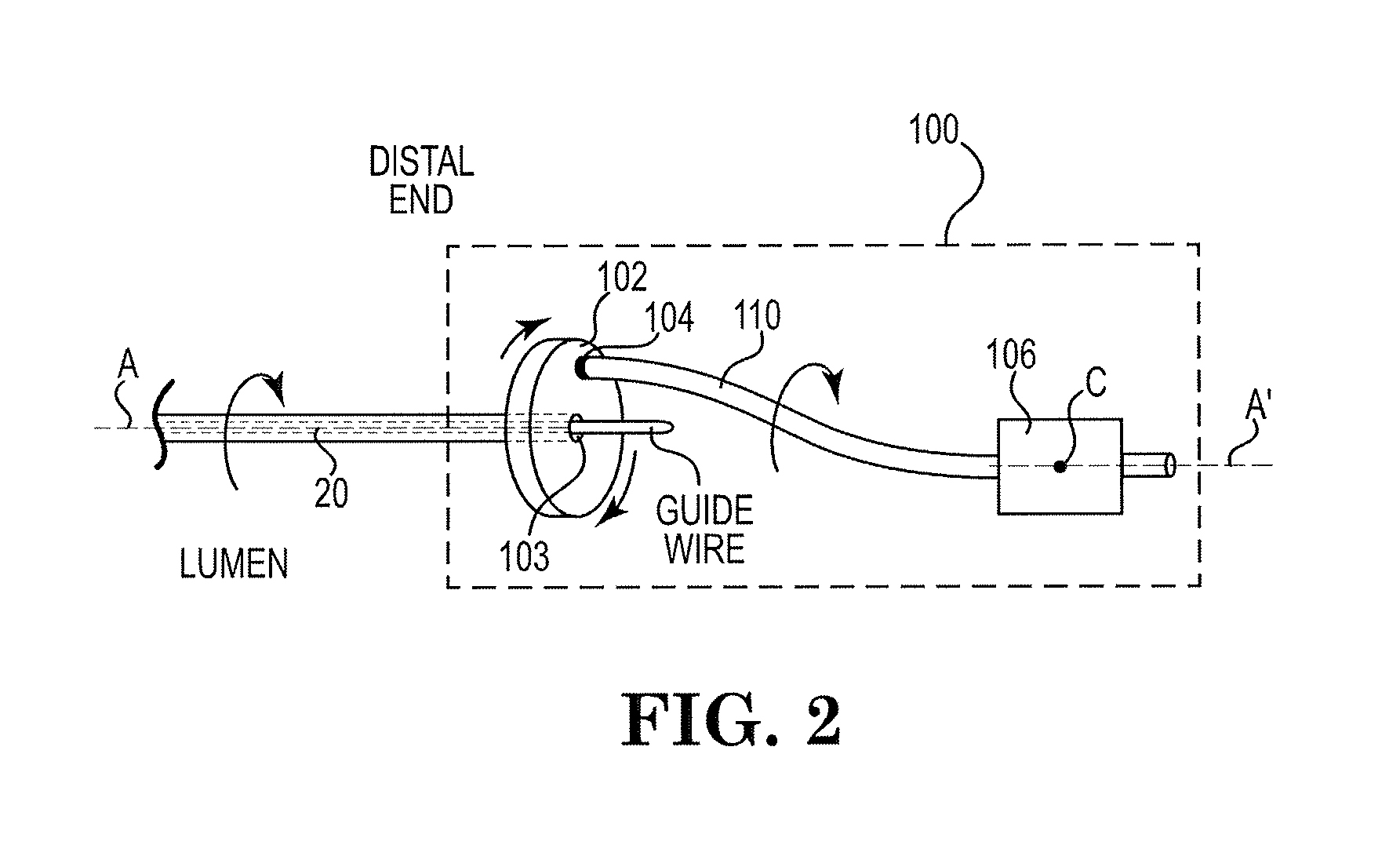
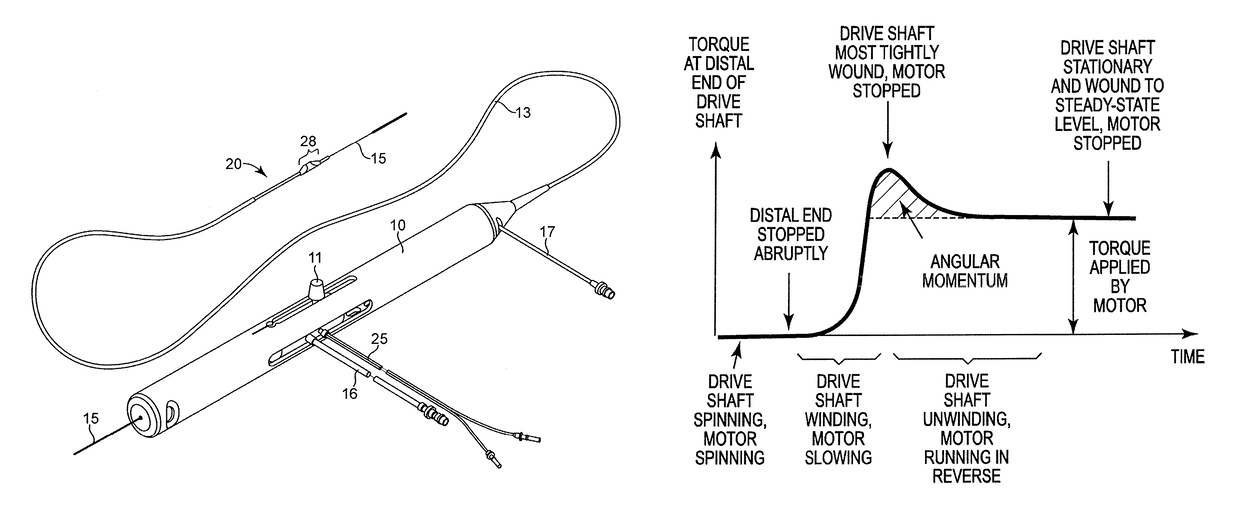
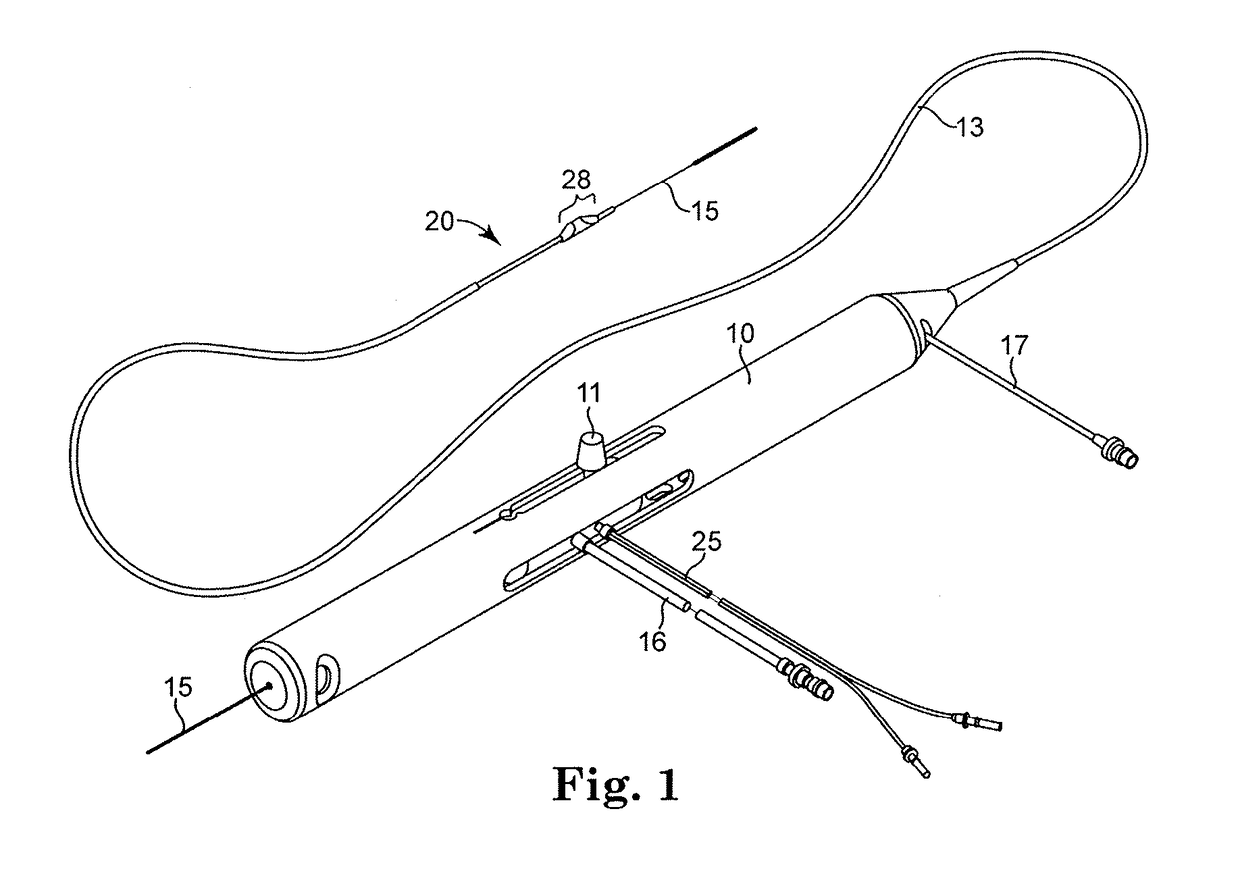
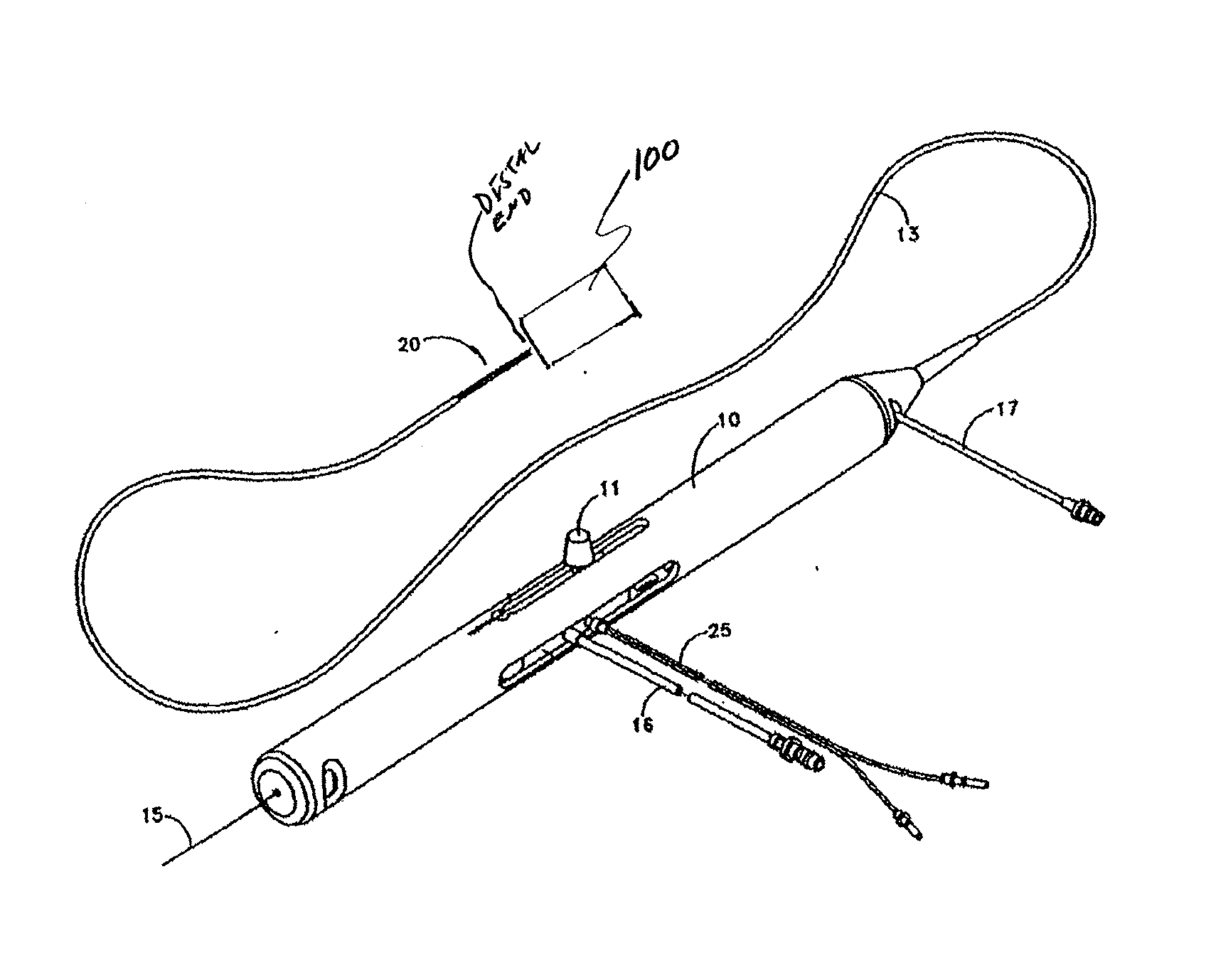
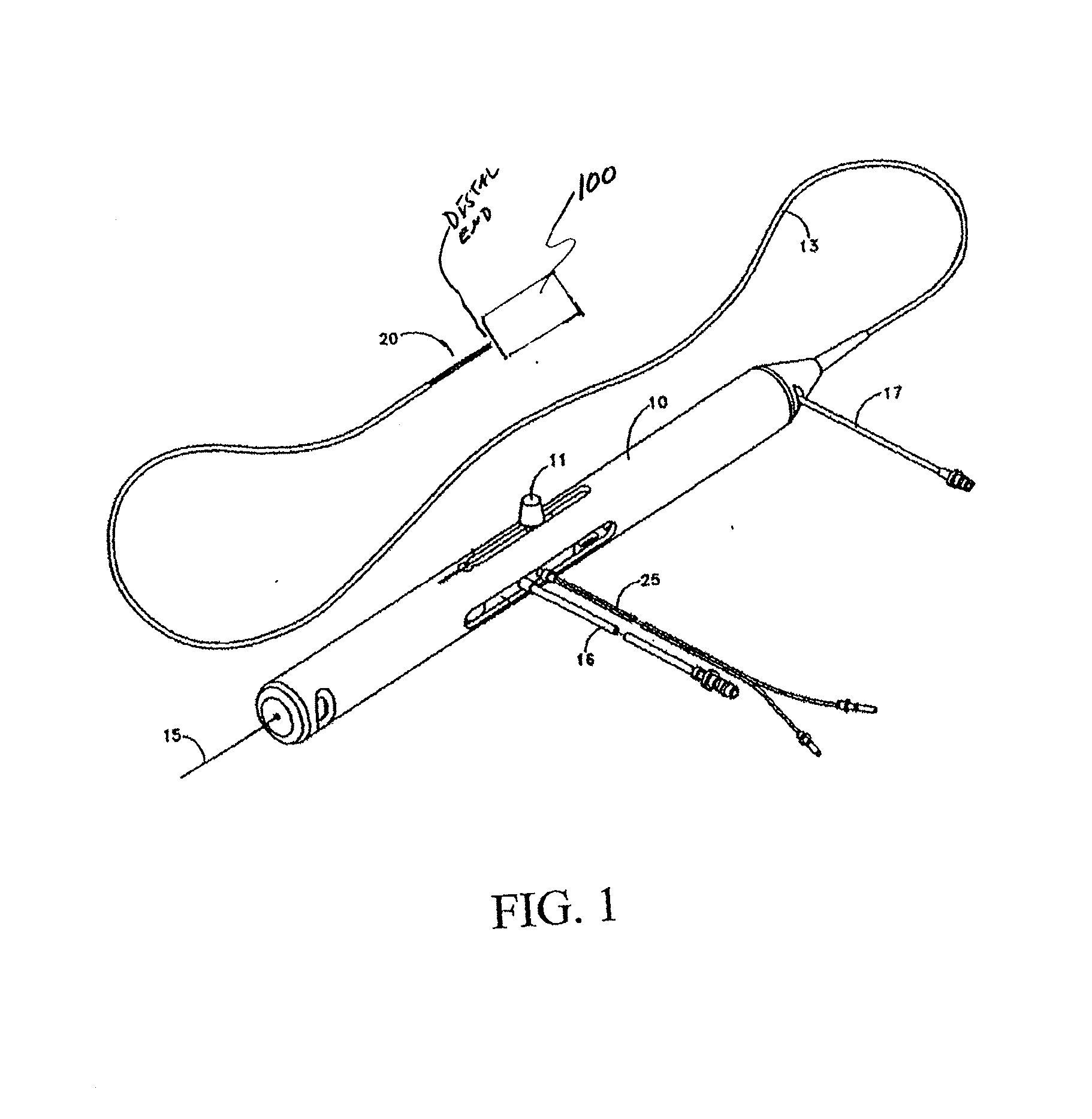
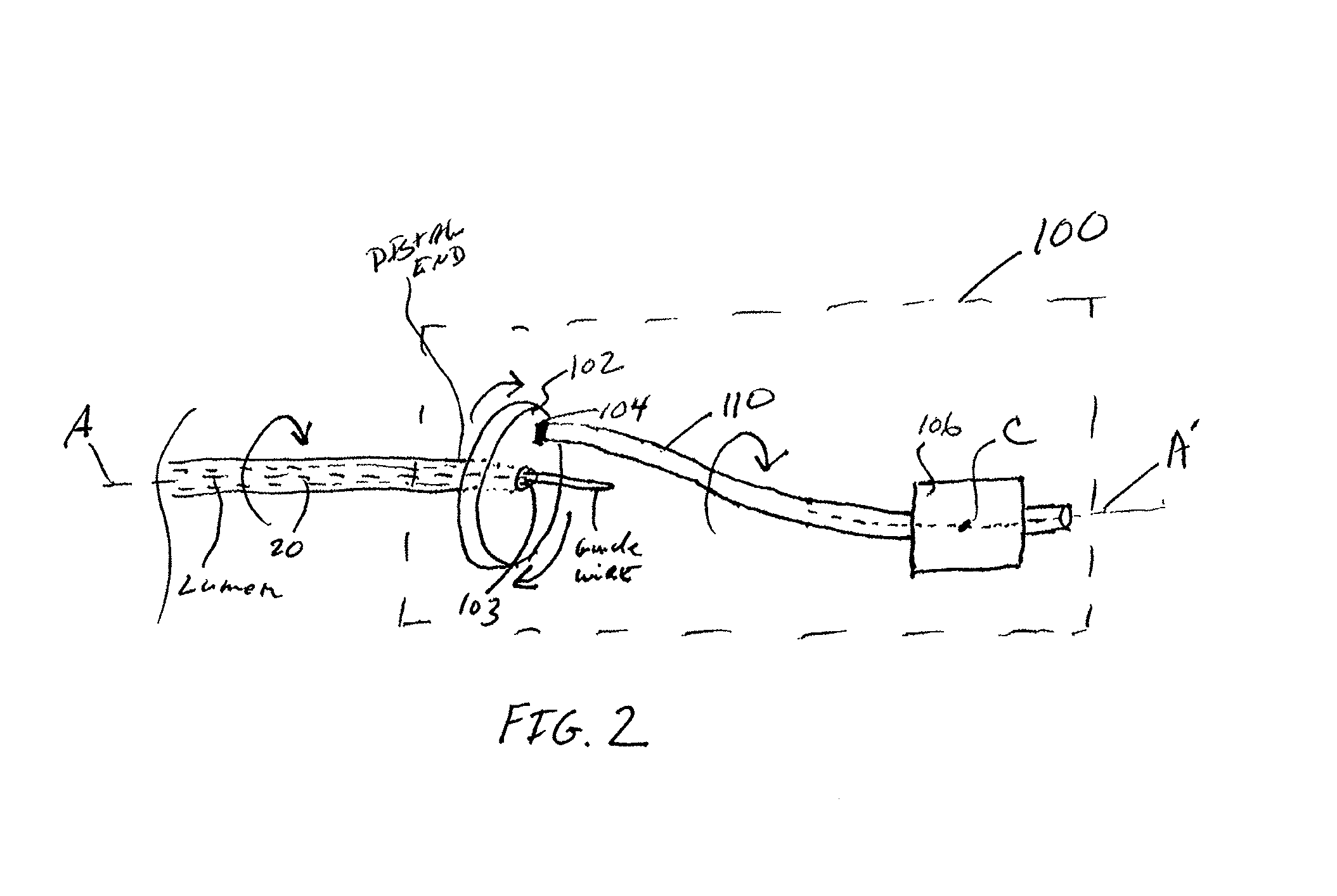
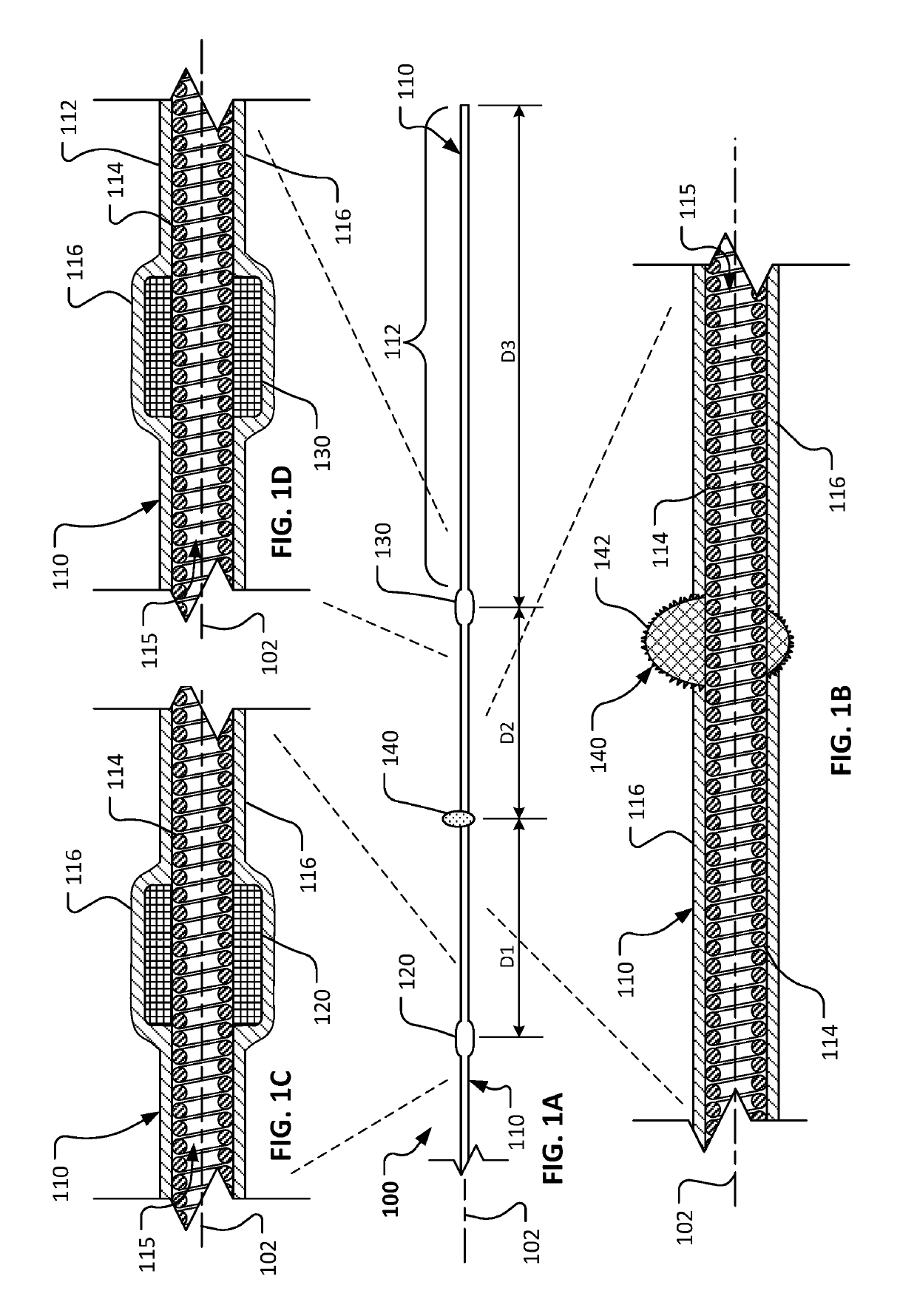
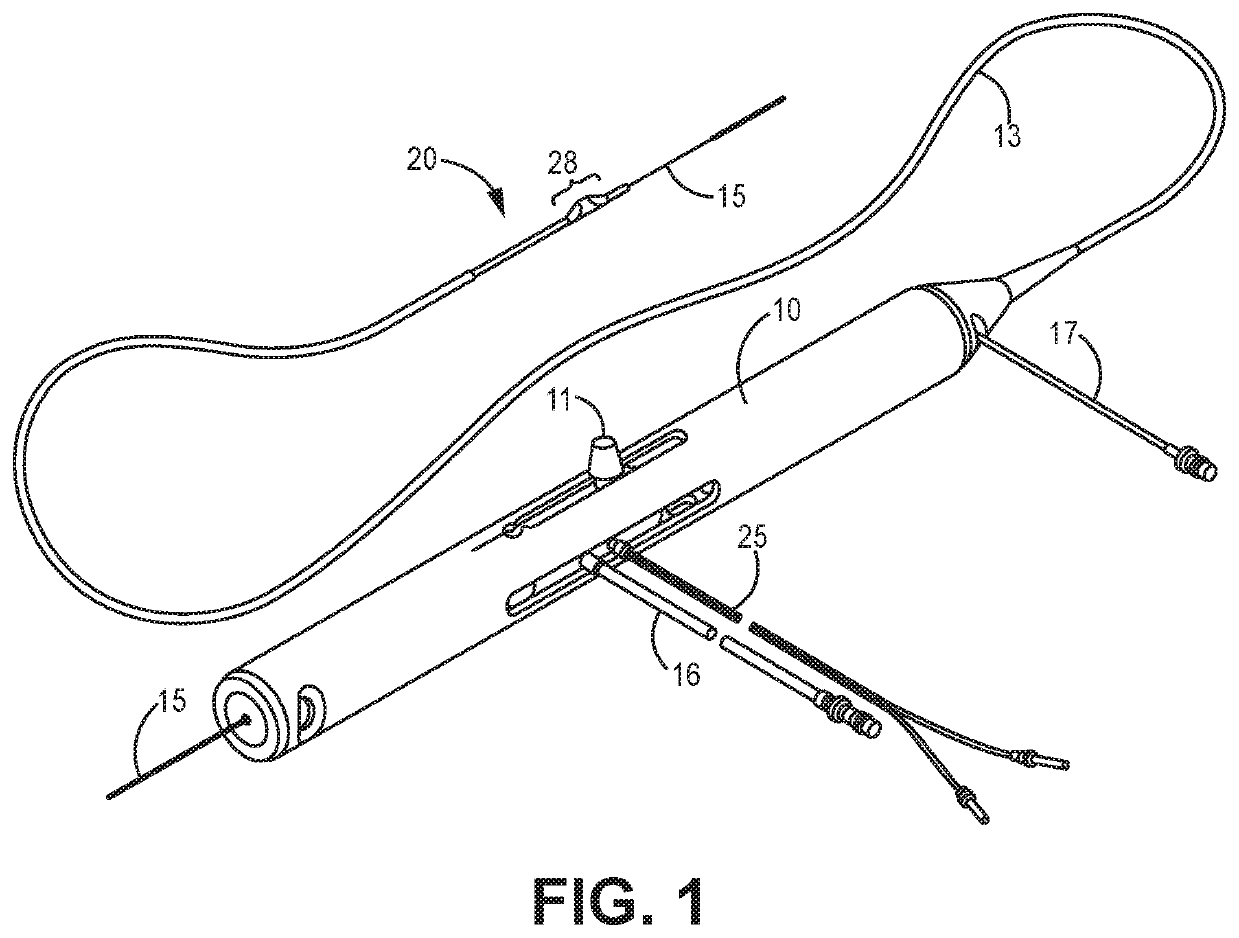
An elongate tubular body extends between a rotatable cutter and a control. The cutter is connected to the control with a rotatable element. A vacuum is applied through an annular passage defined between the tubular body and the rotatable element. The cutter has at least one radial projection which cooperates with at least one stationary element on the tubular body to cut material drawn into the tubular body. Material that has been processed by the cutter is aspirated through the tubular body for disposal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
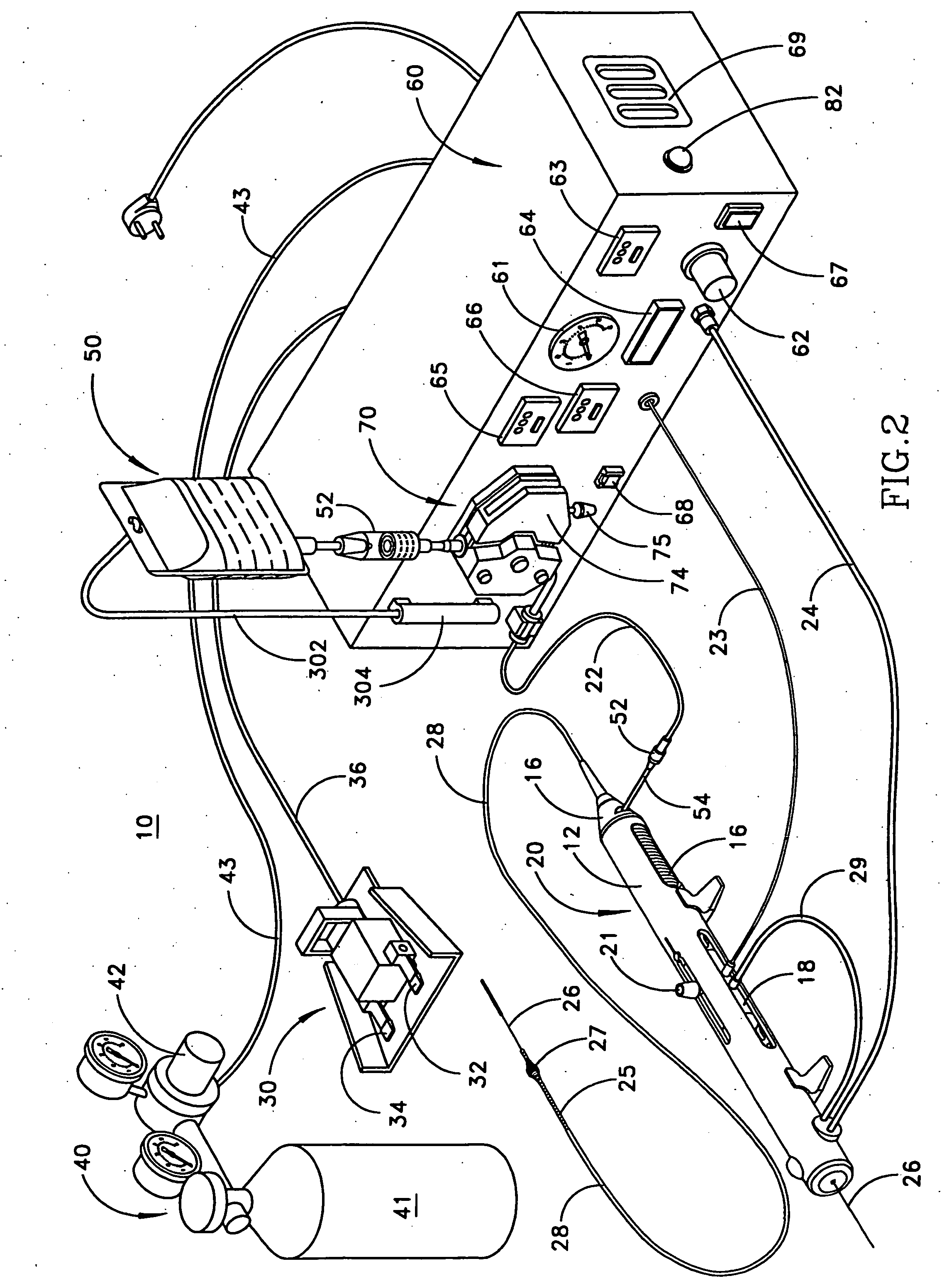
High torque, low profile intravascular guidewire system
A guidewire system is disclosed for performing a rotational atherectomy procedure, wherein the system includes a core wire having an elongated wire body defining a flexible distal portion and a more rigid medial portion, and a torquing sheath for positioning the core wire, the torquing sheath having a normally curved, relatively flexible distal portion and an interior lumen dimensioned and configured to accommodate the core wire, wherein the medial portion of the core wire is sufficiently rigid to straighten the normally curved distal portion of the torquing sheath when it is extended therethrough.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy device and method to improve abrading efficiency
ActiveUS8632557B2Good curative effectConvenient restCannulasExcision instrumentsRotational axisStenotic lesion
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
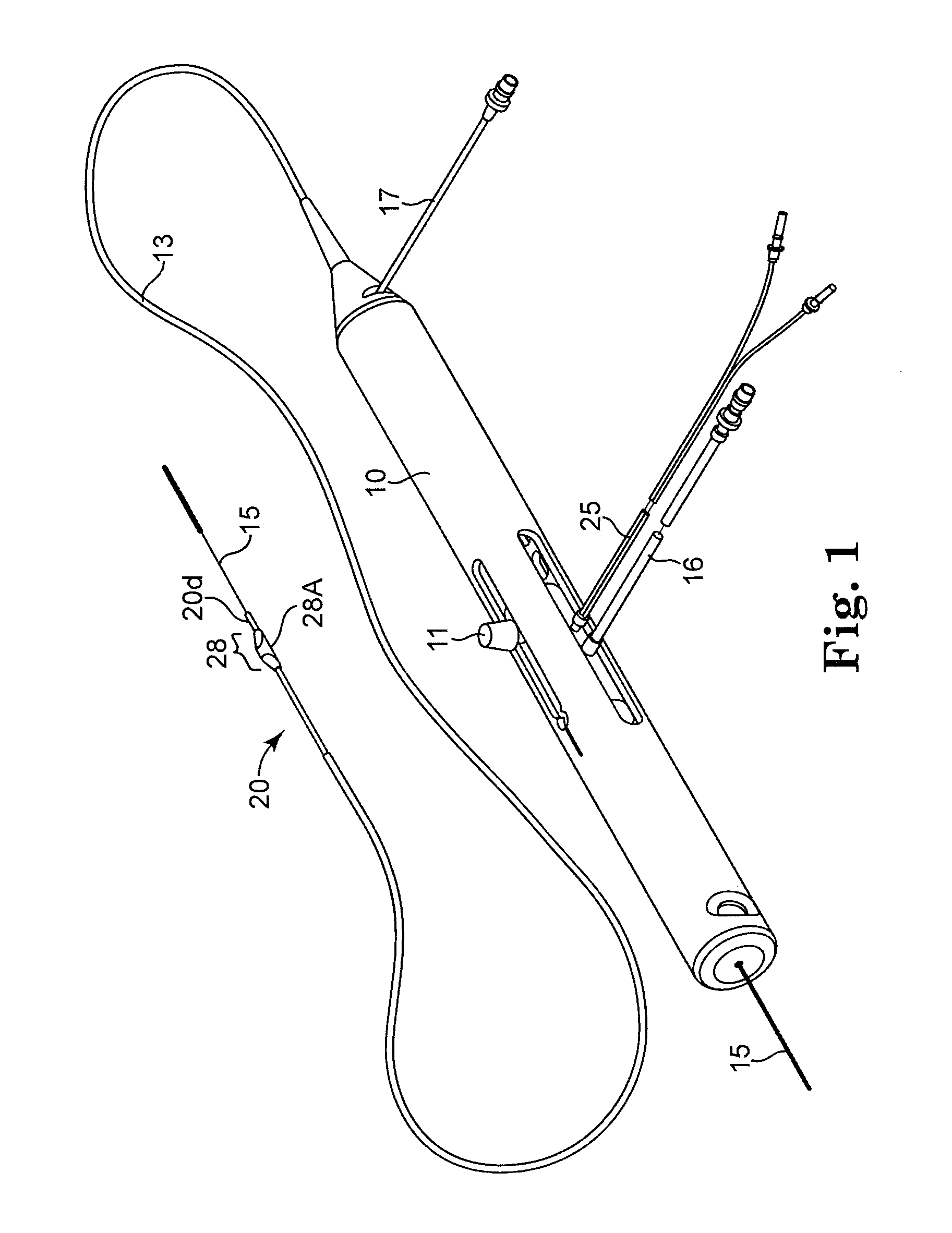
Directional rotational atherectomy device with offset spinning abrasive element
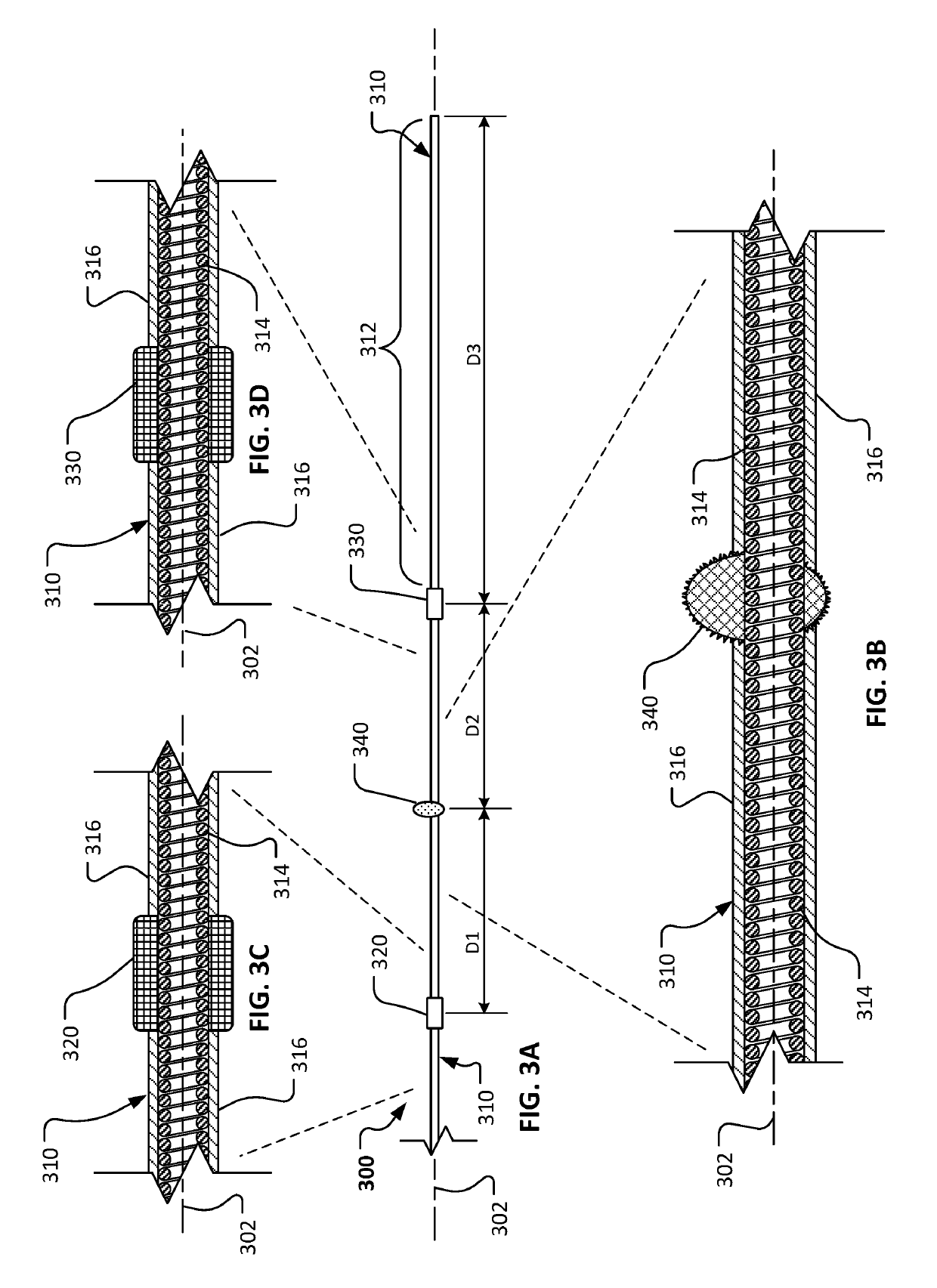
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with a pre-curved abrasive section disposed within a catheter that deforms the abrasive section to a substantially straight profile and, when the abrasive section is moved distally out of the catheter, the abrasive section resumes its pre-curved profile. Directional ablation is achieved by rotation of the drive shaft along its pre-curved axis as the abrasive section is urged against a portion of the lumen wall.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
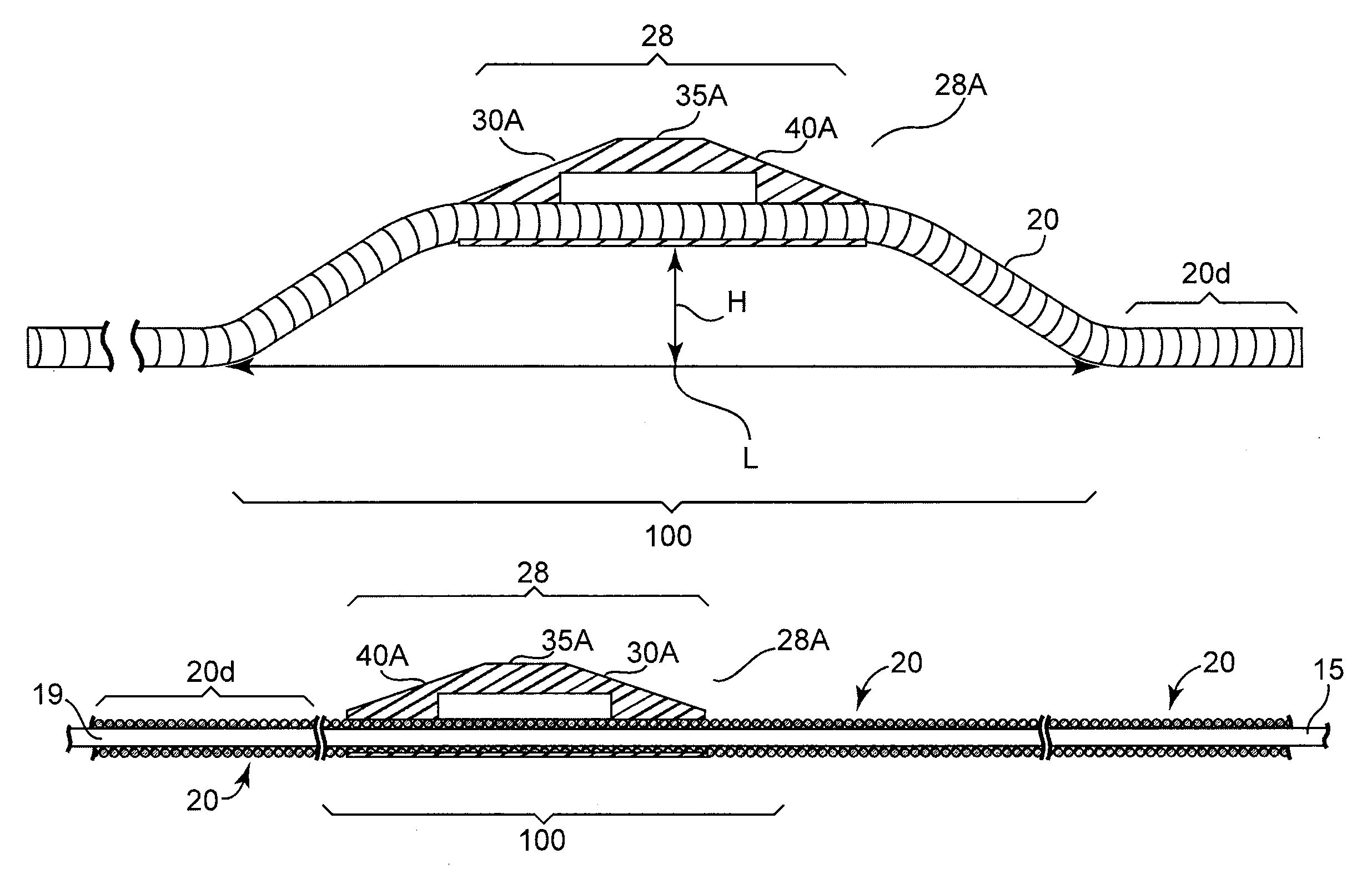
Rotational atherectomy segmented abrading head and method to improve abrading efficiency
ActiveUS20100211088A1Improve abilitiesConvenient restCannulasExcision instrumentsRotational axisStenotic lesion
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method having, in various embodiments, a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft comprising an eccentric abrading head comprising at least one eccentric abrading cylindrical segments attached to the drive shaft and in spaced proximity with proximal and a distal conical segments. Each individual abrading segment, comprises a first tissue removing surface, typically an abrasive coating on the outer surface, that is designed to abrade calcified, hard tissue and abrasive coating on the leading and trailing surfaces designed to abrade non-calcified, soft tissue. Each abrading segment, as well as the abrading head comprising the collective segments, has a center of mass spaced radially from the rotational axis of the drive shaft, facilitating the ability of the device to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged abrading head when operated at high speeds.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy device with pre-curved drive shaft
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with an abrasive section within a pre-curved section of the drive shaft. The device may further comprise a concentric or eccentric enlarged diameter section that is at least partially covered with abrasive material to comprise the abrasive section. The abrasive section may further comprise an abrasive crown or burr mounted to the drive shaft. The pre-curved drive shaft allows smaller diameter and / or massive abrasive regions to be used while sweeping larger diameters during high-speed rotation. The pre-curved region is substantially straightened for insertion into vasculature and placement adjacent stenosis by insertion of the guide wire. Removal of guide wire proximally from the pre-curved region allows the drive shaft to return to its pre-curved form for ablation. Reinsertion of the guide wire beyond the pre-curved region straightens the drive shaft for ease of removal.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy segmented abrading head and method to improve abrading efficiency
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method having, in various embodiments, a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft comprising an eccentric abrading head comprising at least one eccentric abrading cylindrical segments attached to the drive shaft and in spaced proximity with proximal and a distal conical segments. Each individual abrading segment, comprises a first tissue removing surface, typically an abrasive coating on the outer surface, that is designed to abrade calcified, hard tissue and abrasive coating on the leading and trailing surfaces designed to abrade non-calcified, soft tissue. Each abrading segment, as well as the abrading head comprising the collective segments, has a center of mass spaced radially from the rotational axis of the drive shaft, facilitating the ability of the device to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged abrading head when operated at high speeds.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
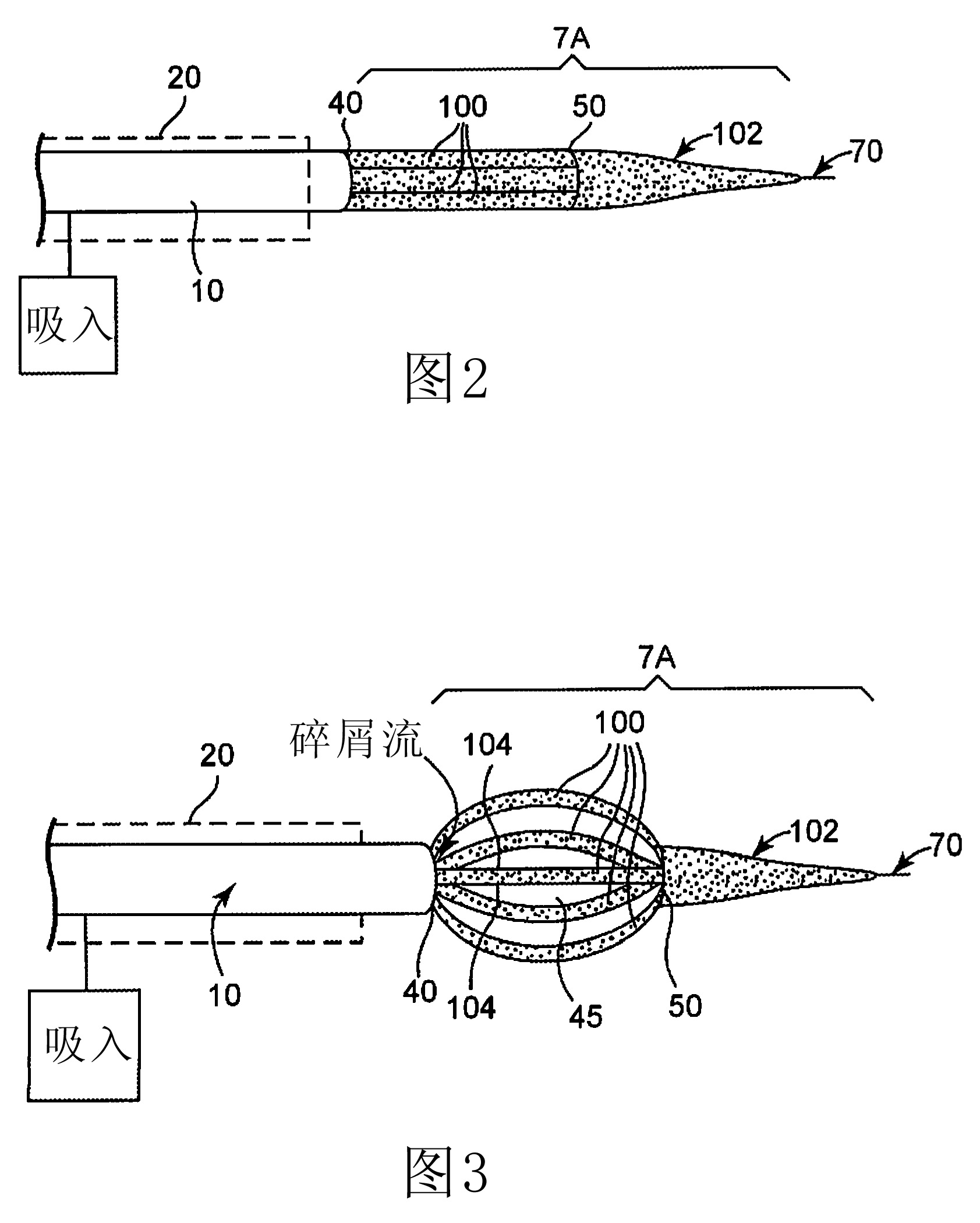
Abrasive nose cone with expandable cutting and sanding region for rotational atherectomy device
An rotational atherectomy apparatus for abrading tissue, comprising: a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft having a proximal end and a distal end opposite the proximal end; a nose cone operatively attached proximate the distal end of the drive shaft comprising a distal tapered section and a plurality of elongate, flexible members adjacent to the distal tapered section of the drive shaft, each member in the plurality being fixed at both a proximal end and a distal end opposite the proximal end; a proximal mount rotatable with the drive shaft and fixedly connected to the proximal ends of all the flexible members in the plurality; and a distal mount axially separated from the proximal mount and fixedly connected to the distal ends of all the flexible members in the plurality. When the axial separation of the proximal and distal mounts is reduced by pulling the distal tapered section proximally, each member in the plurality bows outward from the drive shaft and expands radially in an at least partially elliptical profile.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy system and methods of use
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Rotational atherectomy device with pre-curved drive shaft
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with an abrasive section within a pre-curved section of the drive shaft. The device may further comprise a concentric or eccentric enlarged diameter section that is at least partially covered with abrasive material to comprise the abrasive section. The abrasive section may further comprise an abrasive crown or burr mounted to the drive shaft. The pre-curved drive shaft allows smaller diameter and / or massive abrasive regions to be used while sweeping larger diameters during high-speed rotation. The pre-curved region is substantially straightened for insertion into vasculature and placement adjacent stenosis by insertion of the guide wire. Removal of guide wire proximally from the pre-curved region allows the drive shaft to return to its pre-curved form for ablation. Reinsertion of the guide wire beyond the pre-curved region straightens the drive shaft for ease of removal.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
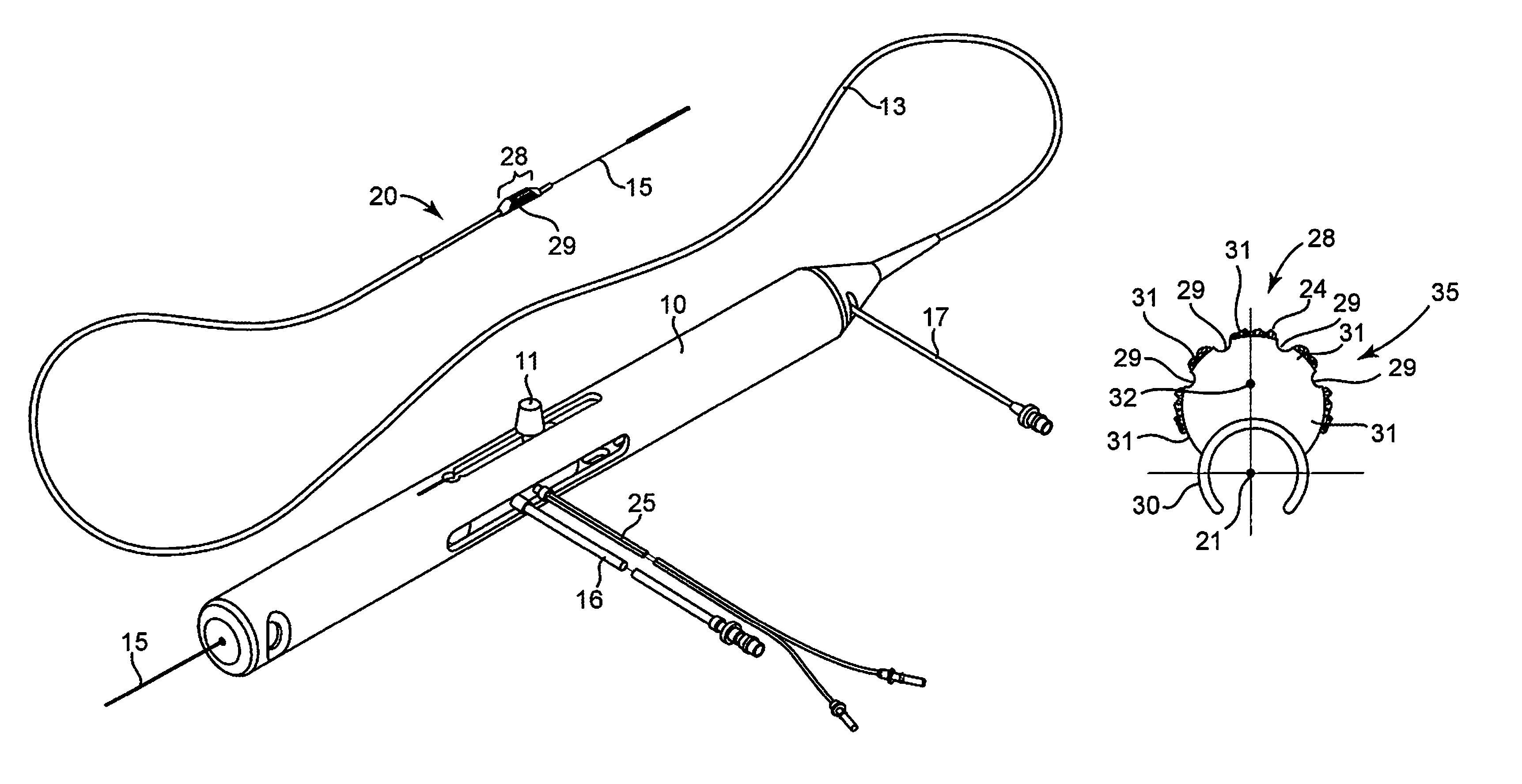
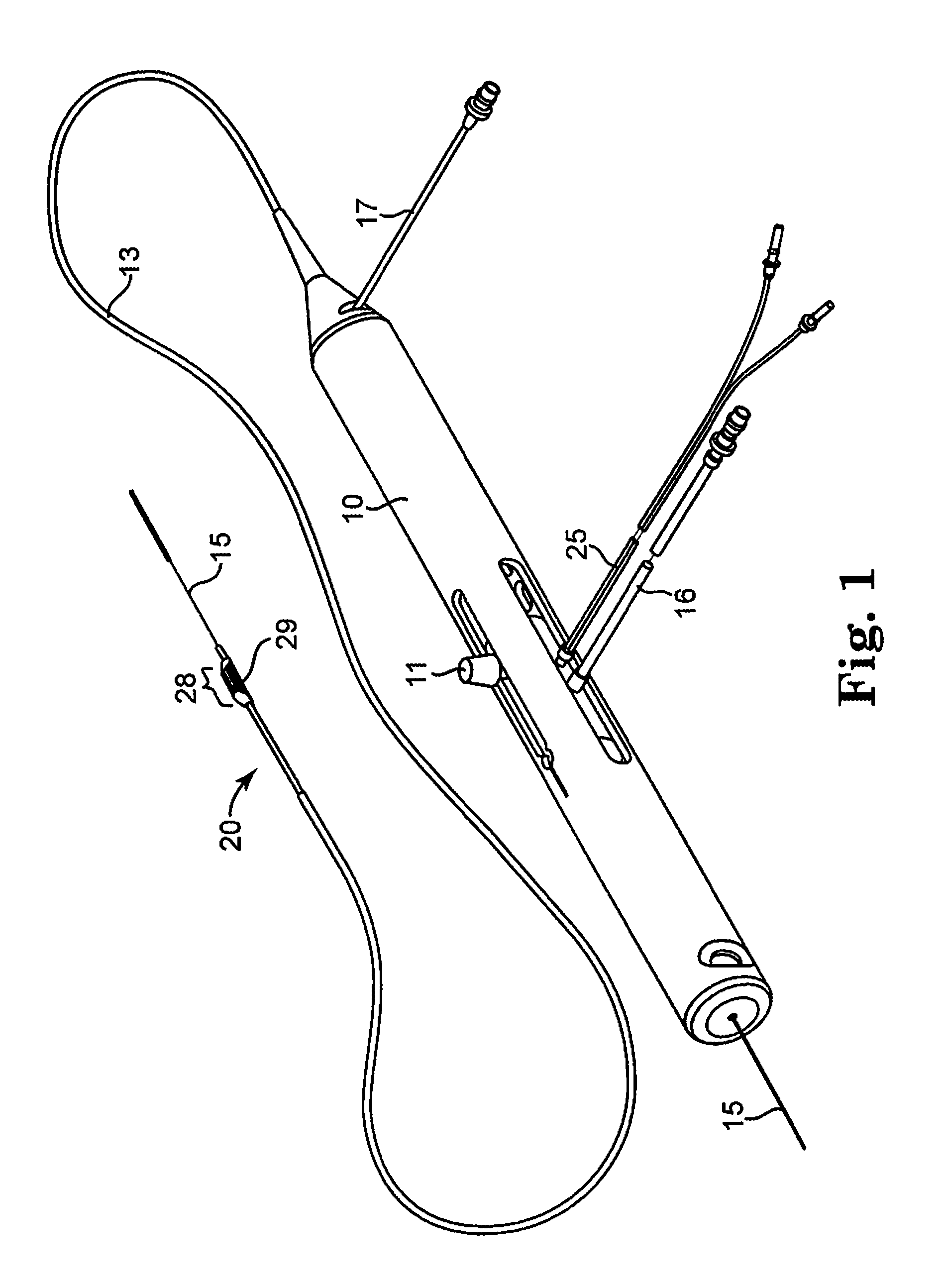
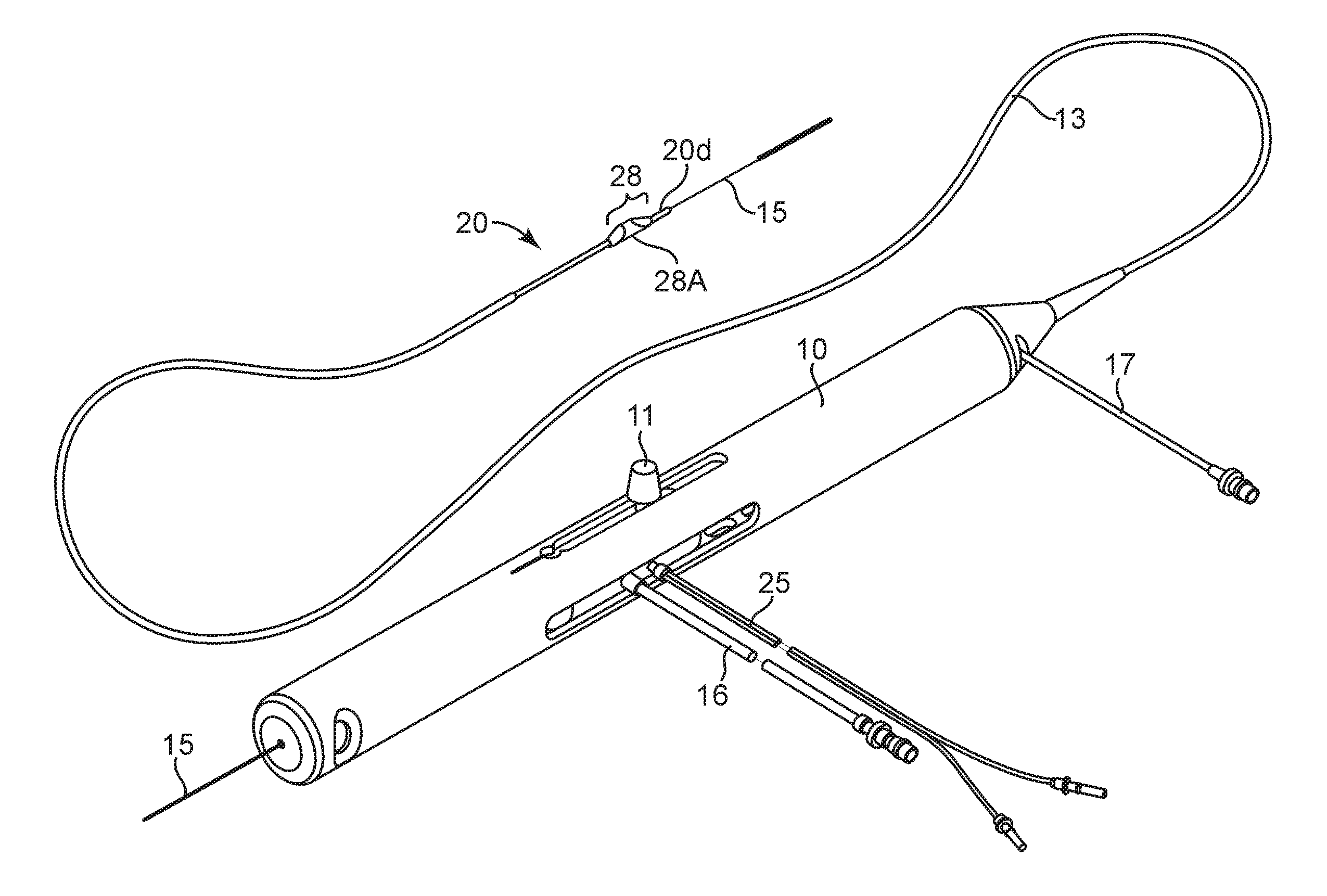
Rotational atherectomy system with enhanced distal protection capability and method of use
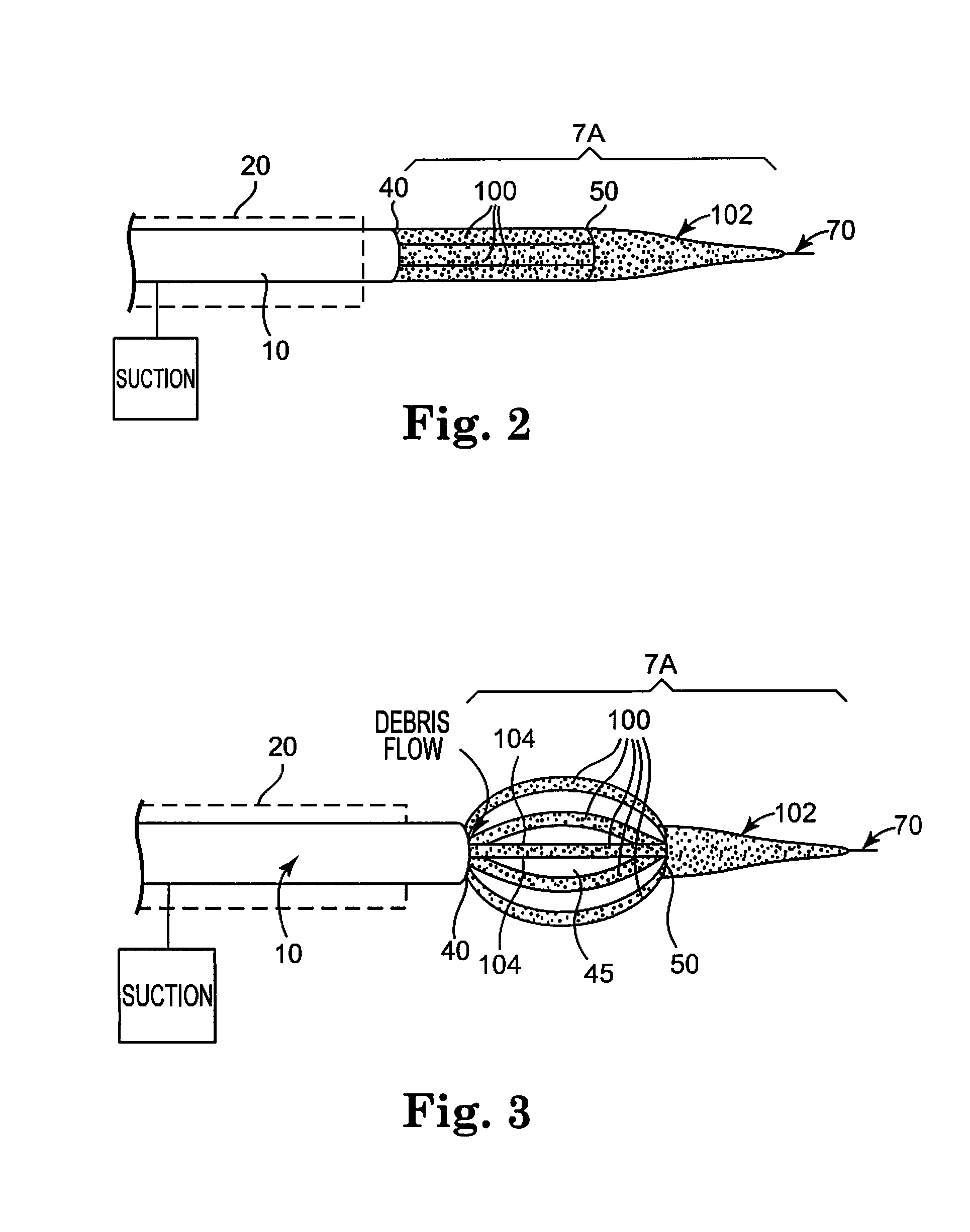
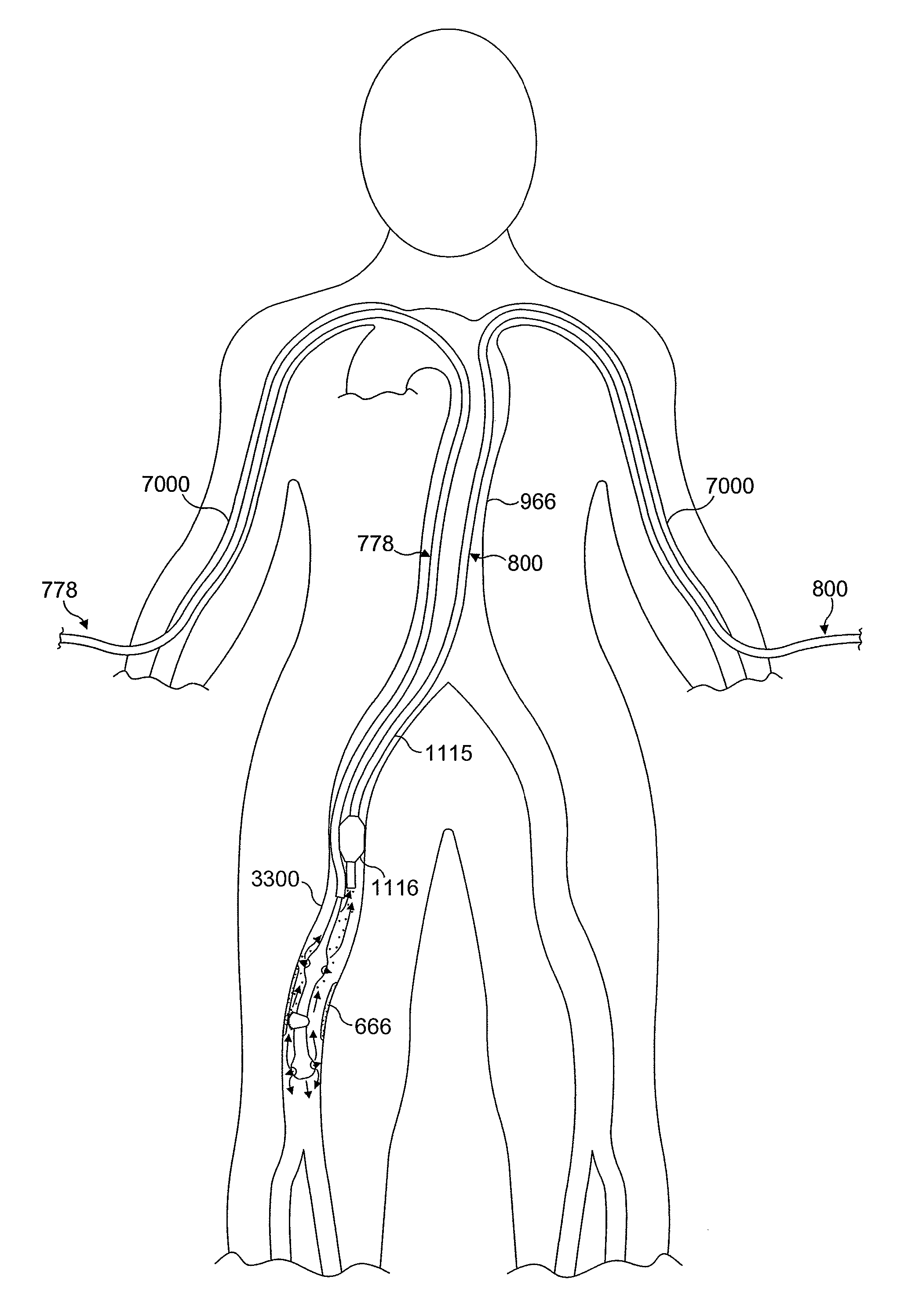
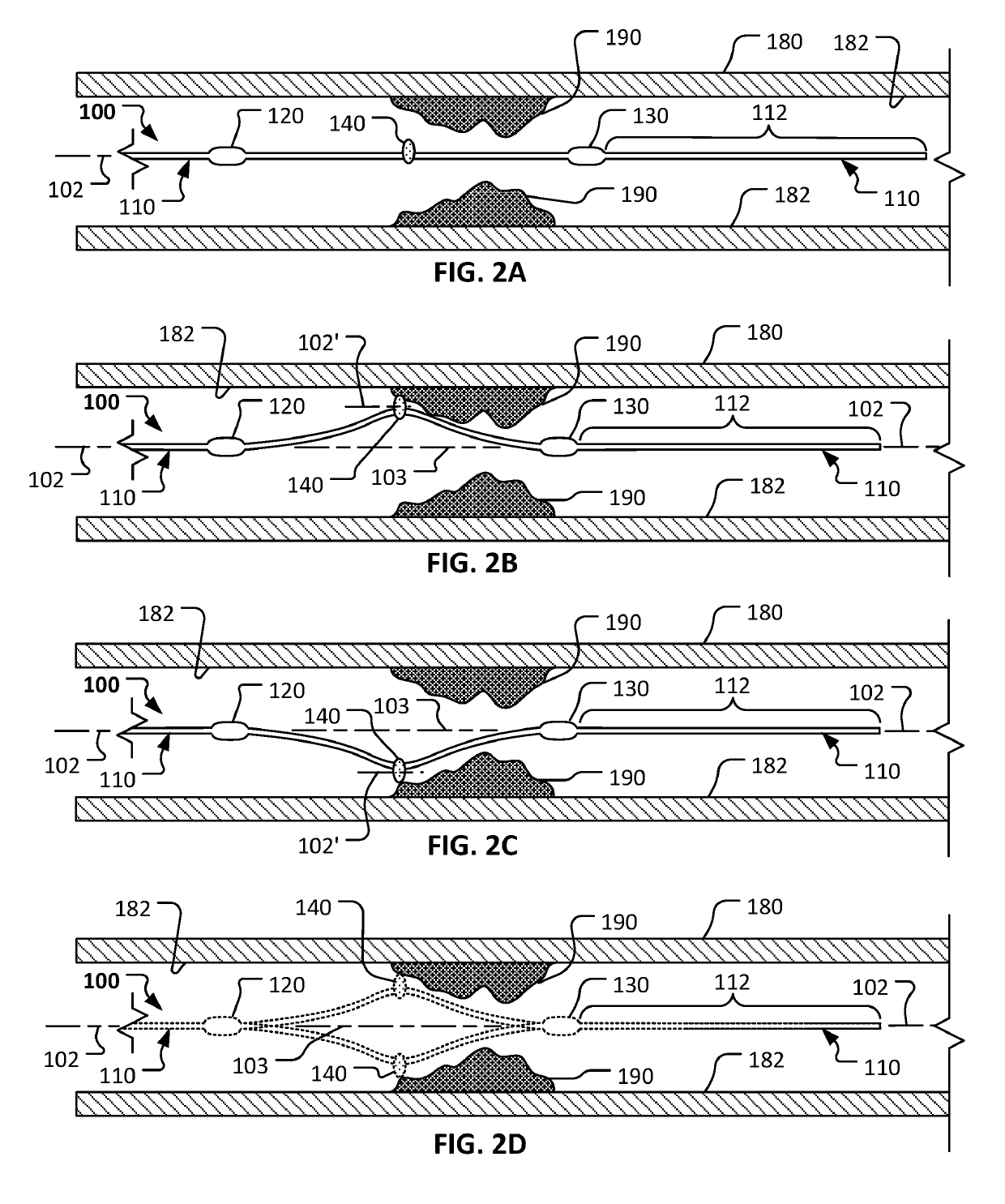
An atherectomy system for removing a stenotic lesion from within a vessel of a patient is disclosed. The system comprising an atherectomy device for reducing the lesion and a separate elongate drainage catheter for evacuating from the treated vessel embolic particles released into the vessel from the stenotic lesion during its reduction by the atherectomy device during an atherectomy procedure. The atherectomy device and the separate elongate drainage catheter are each configured for introduction into the patent's vasculature though separate openings in at least one peripheral artery of the patient.
Owner:CARDIOFLOW
Atherectomy device, system and method having a bi-directional distal expandable ablation element
ActiveUS20110144671A1Minimal profileCannulasExcision instrumentsBiomedical engineeringRotational atherectomy
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a bi-directional drive shaft with a flexible ablation element disposed at the distal end of the drive shaft. The flexible ablation element comprises a first retracted position for insertion into vasculature and a second expanded position for ablation, i.e., cutting, sanding and / or grinding. The ablation element comprises more than one flexible finger or blade which allows changing, in certain embodiments, of curvature radius to fit inside a deployment catheter and / or enlarge to the diameter of larger lumens, up to at least 9 mm in diameter. Bi-directional rotation of the expanded ablation element allows cutting in one rotational direction and grinding and / or sanding in the opposite rotational direction.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Split flexible tube biasing and directional atherectomy device and method
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method having a flexible, elongated, rotatable catheter tube that is split into two elements, a biasing element and a cutting element, distally and wherein the biasing element and cutting element are capable of forming a first and retracted position for insertion into a lumen and a second and expanded position for ablation. The biasing element is biased in the expanded position, thereby placing a biasing force against the lumen wall and pressing the cutting element against the opposite side of the lumen wall for directional cutting and / or grinding, either by rotation, axial translation, vibration or a combination thereof.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy system
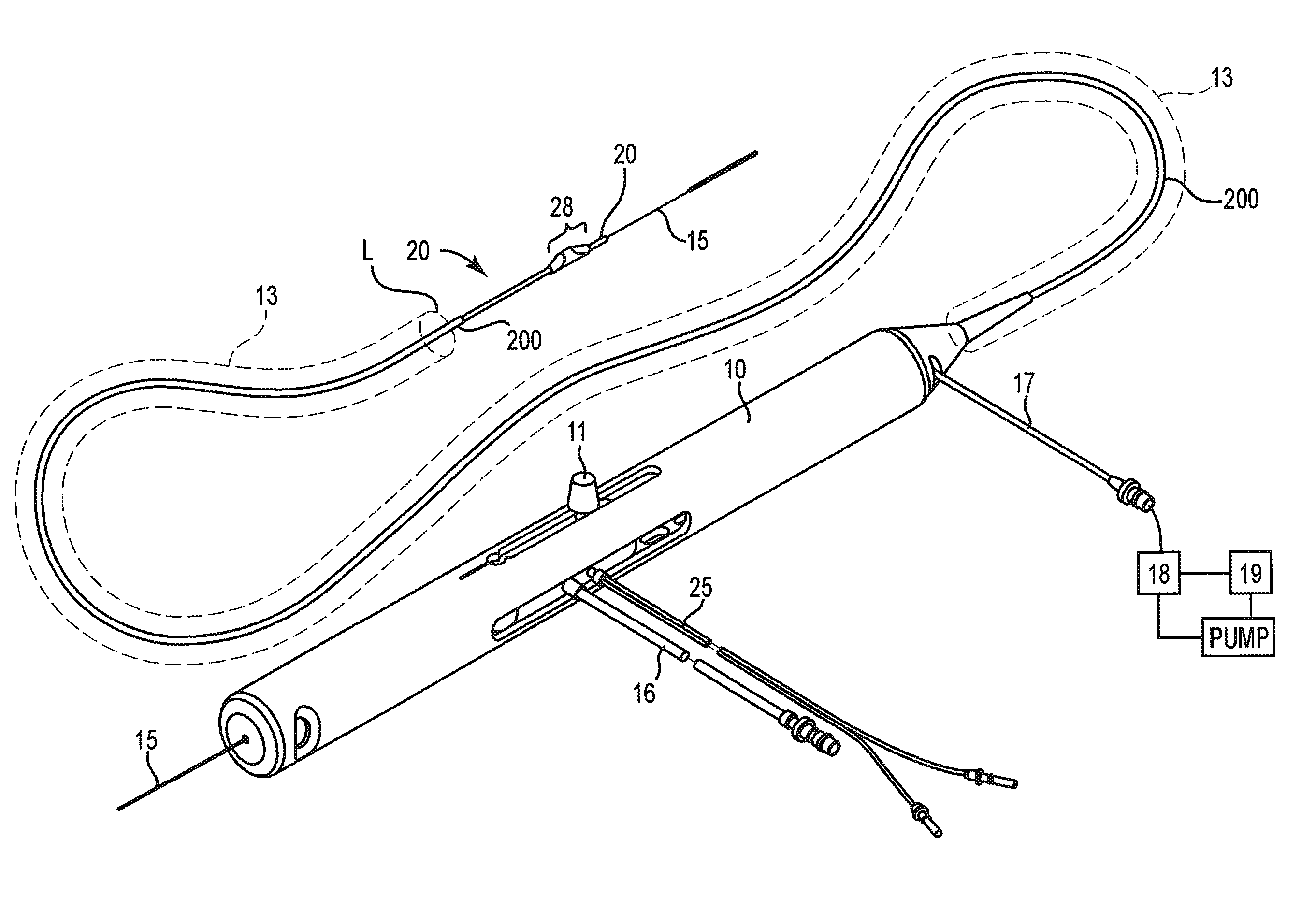
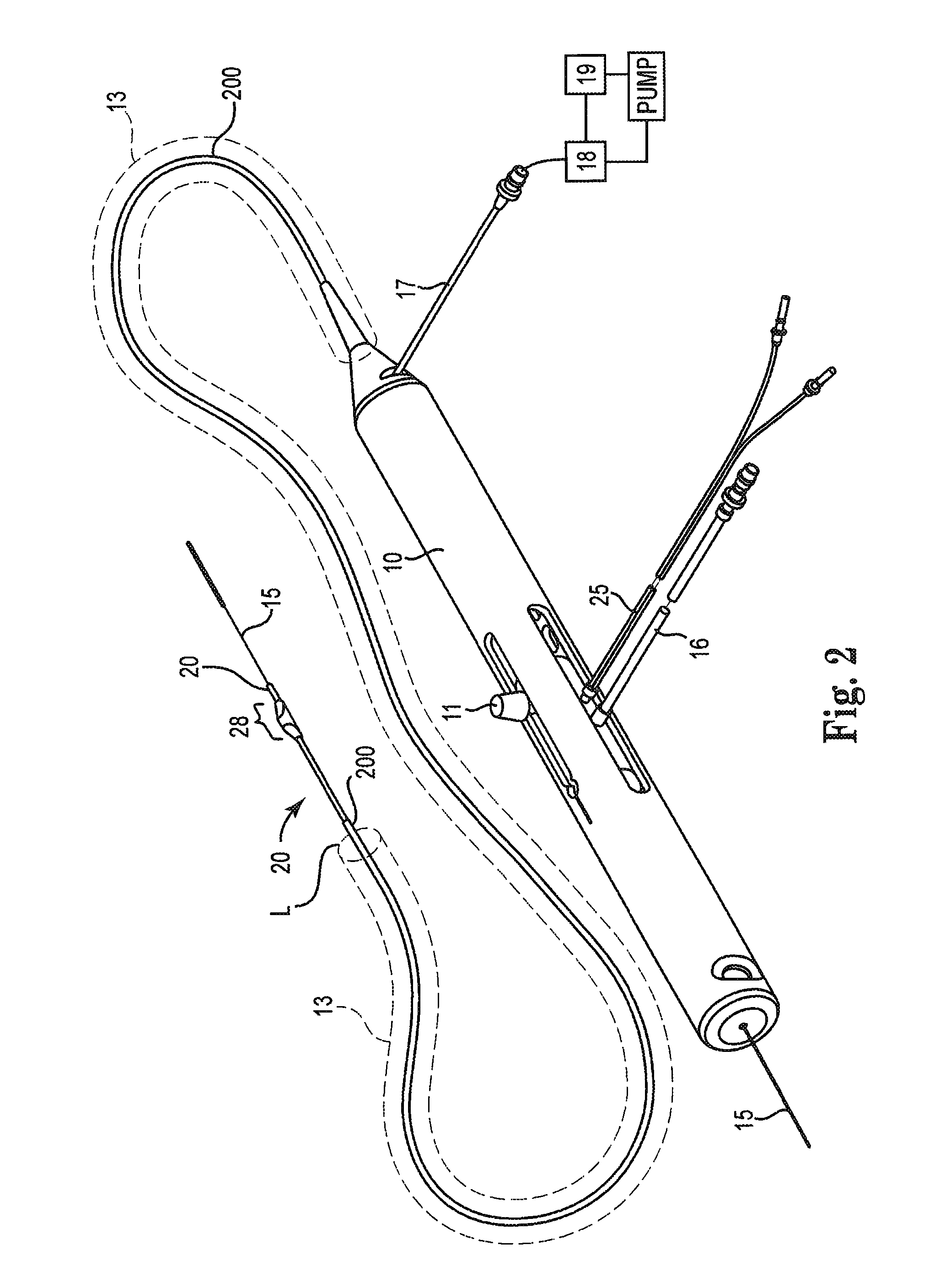
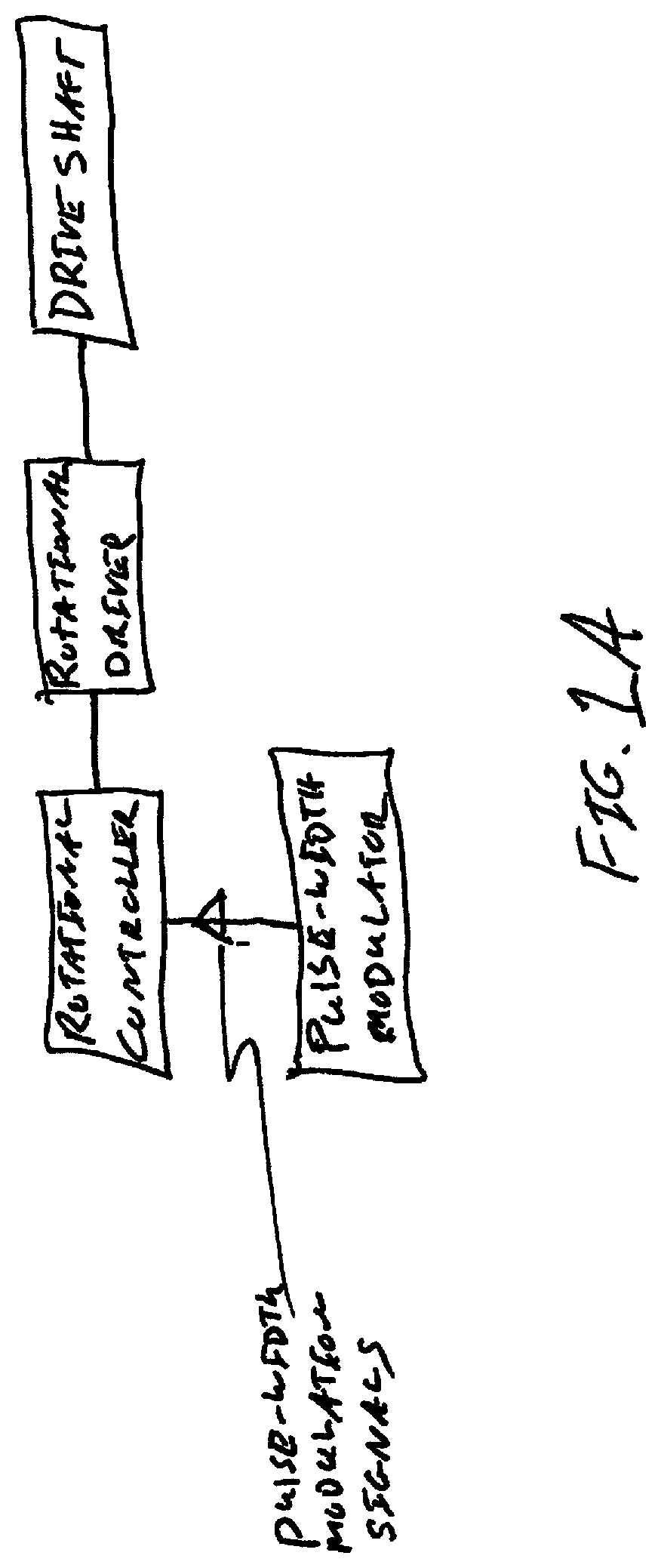
A method system and controller for controlling fluid flow in a rotational atherectomy device. A source of fluid is provided through a pump to the rotational atherectomy device, wherein the pump maintains the fluid flow at a minimal rate during a time period when a drive shaft of the device is not rotating. A first control is activated to increase a rate of the fluid flow and second control is activate to initiate a rotation of the drive shaft during another time period when the fluid flow is at the increased rate.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy device with pre-curved drive shaft
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with an abrasive section within a pre-curved section of the drive shaft. The device may further comprise a concentric or eccentric enlarged diameter section that is at least partially covered with abrasive material to comprise the abrasive section. The abrasive section may further comprise an abrasive crown or burr mounted to the drive shaft. The pre-curved drive shaft allows smaller diameter and / or massive abrasive regions to be used while sweeping larger diameters during high-speed rotation. The pre-curved region is substantially straightened for insertion into vasculature and placement adjacent stenosis by insertion of the guide wire. Removal of guide wire proximally from the pre-curved region allows the drive shaft to return to its pre-curved form for ablation. Reinsertion of the guide wire beyond the pre-curved region straightens the drive shaft for ease of removal.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Directional rotational atherectomy device with offset spinning abrasive element
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with a pre-curved abrasive section disposed within a catheter that deforms the abrasive section to a substantially straight profile and, when the abrasive section is moved distally out of the catheter, the abrasive section resumes its pre-curved profile. Directional ablation is achieved by rotation of the drive shaft along its pre-curved axis as the abrasive section is urged against a portion of the lumen wall.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Atherectomy device, system and method having a bi-directional distal expandable ablation element
ActiveUS8795304B2Minimal profileCannulasExcision instrumentsBiomedical engineeringRotational atherectomy
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a bi-directional drive shaft with a flexible ablation element disposed at the distal end of the drive shaft. The flexible ablation element comprises a first retracted position for insertion into vasculature and a second expanded position for ablation, i.e., cutting, sanding and / or grinding. The ablation element comprises more than one flexible finger or blade which allows changing, in certain embodiments, of curvature radius to fit inside a deployment catheter and / or enlarge to the diameter of larger lumens, up to at least 9 mm in diameter. Bi-directional rotation of the expanded ablation element allows cutting in one rotational direction and grinding and / or sanding in the opposite rotational direction.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Split flexible tube biasing and directional atherectomy device and method
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method comprising a flexible, elongated, rotatable catheter tube that is split into two elements, a biasing element and a cutting element, distally and wherein the biasing element and cutting element are capable of forming a first and retracted position for insertion into a lumen and a second and expanded position for ablation. The biasing element is biased in the expanded position, thereby placing a biasing force against the lumen wall and pressing the cutting element against the opposite side of the lumen wall for directional cutting and / or grinding, either by rotation, axial translation, vibration or a combination thereof.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy device and method to improve abrading efficiency
ActiveUS20100292720A1Good curative effectConvenient restCannulasExcision instrumentsRotational axisStenotic lesion
The invention provides a rotational atherectomy system, device and method having, in various embodiments, a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft with at least one eccentric abrading head attached thereto, wherein the abrading head comprises at least one groove thereon. The eccentric grooved abrading comprises a tissue removing surface—typically an abrasive surface and / or at least one groove. Preferably the eccentric enlarged abrading head has a center of mass spaced radially from the rotational axis of the drive shaft, facilitating the ability of the device to open the stenotic lesion to a diameter substantially larger than the outer diameter of the enlarged abrading head when operated at high speeds. The groove(s) provide improved efficacy in the abrasion of non-calcified and / or soft tissue as well as provide a means for breaking the hydraulic wedge between the abrading head and the stenotic tissue.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
High-speed rotational atherectomy system, device and method for localized application of therapeutic agents to a biological conduit
InactiveUS20120046600A1Minimizing unwanted systemic exposureMinimizing accompanying undesirable side effectMedical devicesExcision instrumentsDrive shaftHigh speed rotational atherectomy
The invention provides a system, device and method for localized application of therapeutic agents within a biological conduit. A preferred biological conduit comprises a blood vessel. A preferred device comprises a high-speed rotational atherectomy device having, in various embodiments, a flexible, elongate non-rotatable therapeutic agent delivery sheath having a lumen therethrough and a flexible, elongated, rotatable, drive shaft with at least one flexible eccentric enlarged abrading head disposed within lumen of the delivery sheath. The operator may actuate a controlled amount or dose of one or more therapeutic agents to release from the distal end of the delivery sheath lumen during high-speed rotation of the drive shaft. The therapeutic agent(s) is thus released into a turbulent fluidic environment resulting from high-speed rotation and orbital motion of the eccentric abrading head, which aids to drivingly urge the therapeutic agent(s) radially through the boundary layer of fluid flow in the conduit and into the target region of the conduit wall.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Abrasive nose cone with expandable cutting and sanding region for rotational atherectomy device
InactiveCN102056556ASurgical instrument detailsExcision instrumentsEngineeringRotational atherectomy
An rotational atherectomy apparatus for abrading tissue, comprising: a flexible, elongated, rotatable drive shaft having a proximal end and a distal end opposite the proximal end; a nose cone operatively attached proximate the distal end of the drive shaft comprising a distal tapered section and a plurality of elongate, flexible members adjacent to the distal tapered section of the drive shaft, each member in the plurality being fixed at both a proximal end and a distal end opposite the proximal end; a proximal mount rotatable with the drive shaft and fixedly connected to the proximal ends ofall the flexible members in the plurality; and a distal mount axially separated from the proximal mount and fixedly connected to the distal ends of all the flexible members in the plurality. When theaxial separation of the proximal and distal mounts is reduced by pulling the distal tapered section proximally, each member in the plurality bows outward from the drive shaft and expands radially in an at least partially elliptical profile.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Devices, systems and methods for an oscillating crown drive for rotational atherectomy
The present invention is directed in various methods, devices and systems relating to rotational atherectomy. More specifically, an oscillating driver is connected to a drive shaft, or torque transfer tube, with abrasive element mounted thereon. The result provides a rotational working diameter for the rotating abrasive element that is larger than its resting diameter. Generally, the preferred abrasive element is concentric in profile and / or with center of mass collinear with the drive shaft's rotational axis. However, eccentric abrasive elements, both in terms of offsetting center of mass and / or geometric eccentricity may also be employed.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
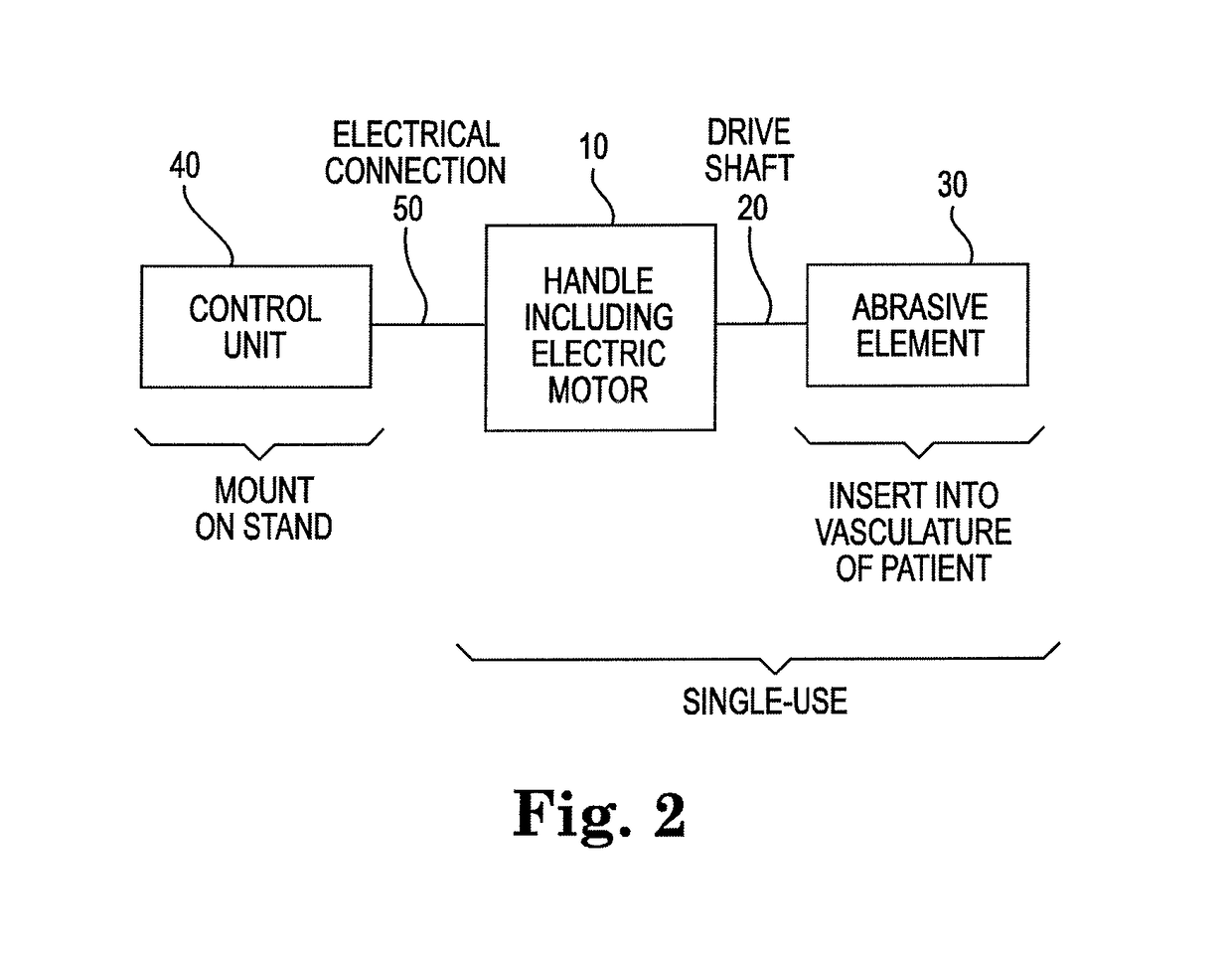
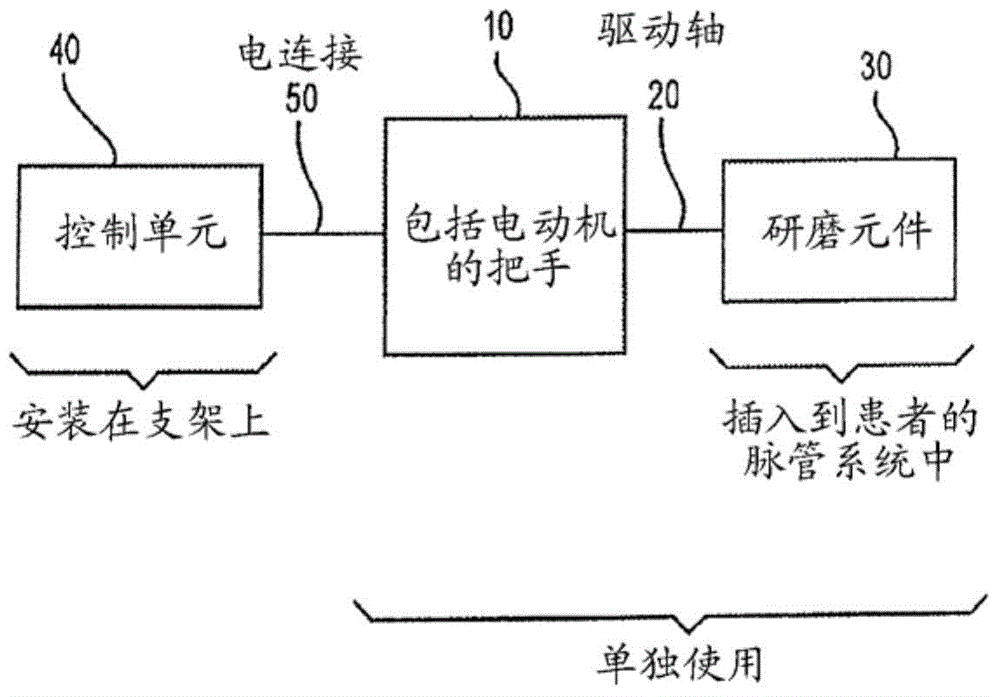
Spin-to-open atherectomy device with electric motor control
ActiveUS10052122B2Length of drive to shortenIncrease the outer diameterDiagnosticsExcision instrumentsControl electronicsSpins
A rotational atherectomy system is disclosed, comprising: an elongated, flexible spin-to-open drive shaft having a distal end for insertion into a vasculature of a patient and having a proximal end opposite the distal end remaining outside the vasculature of the patient; a concentric or eccentric abrasive element, preferably a solid crown, attached to the drive shaft proximate the distal end of the drive shaft; an electric motor rotatably coupled to the proximal end of the drive shaft, the electric motor being capable of rotating the drive shaft in a spin-to-open direction; and control electronics for monitoring and controlling the rotation of the electric motor. When an obstruction at the distal end is detected by the applied torque and / or current reaching a predetermined maximum allowed level and with the drive shaft opened to a maximum allowed outer diameter, power to the motor is eliminated.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Devices, systems and methods for an oscillating crown drive for rotational atherectomy
The present invention is directed in various methods, devices and systems relating to rotational atherectomy. More specifically, an oscillating driver is connected to a drive shaft, or torque transfer tube, with abrasive element mounted thereon. The result provides a rotational working diameter for the rotating abrasive element that is larger than its resting diameter. Generally, the preferred abrasive element is concentric in profile and / or with center of mass collinear with the drive shaft's rotational axis. However, eccentric abrasive elements, both in terms of offsetting center of mass and / or geometric eccentricity may also be employed.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Methods, devices and systems for slow rotation of drive shaft driven atherectomy systems
The present system is directed in various embodiments to methods, devices and systems for rotational atherectomy procedures. More specifically, embodiments comprise a rotational driver with rotational drive shaft and abrasive element attached thereto, the rotational driver being controlled by the rotational controller to rotate at unsustained low rotational speeds and / or rotational direction.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
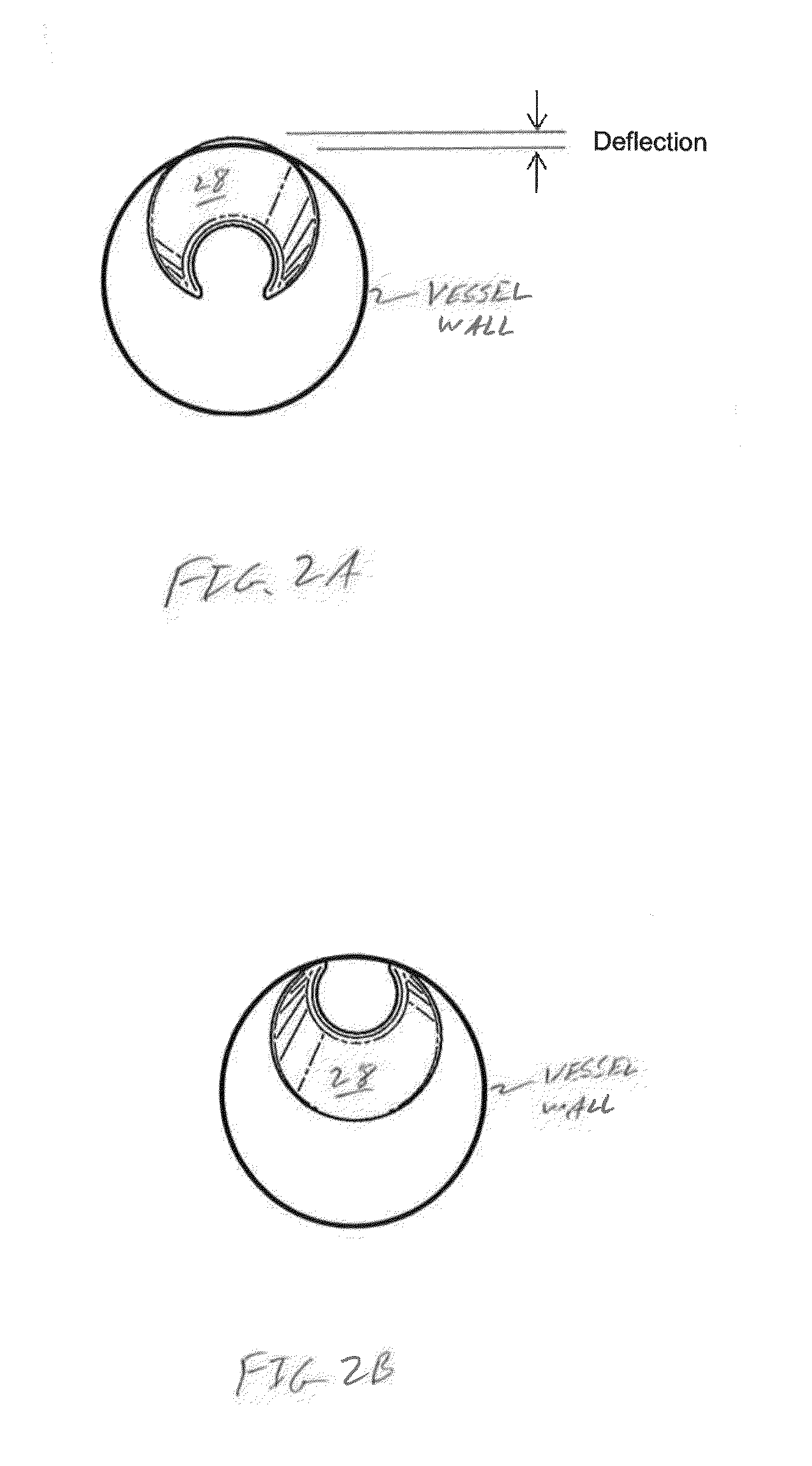
Methods and systems for disrupting calcified walls of biological conduits and calcified lesions therein
ActiveUS20160242805A1Improve complianceImprove lesionExcision instrumentsAbrasive surgical cuttersCalcificationThree vessels
The present system is directed in various embodiments to rotational atherectomy systems and methods generally. More specifically, a method for methodically softening and otherwise disrupting calcification located within atherosclerotic plaque, lesion or occlusion and / or within the wall of a biological conduit or lumen. For example, calcification within the occlusion and / or intimal and / or medial layer walls of a blood vessel, e.g., an artery, may be methodically softened or otherwise disrupted with various embodiments of the present invention. The softening and / or disruption of the calcification in the walls of the exemplary artery is accomplished in conjunction with abrading removal of any occlusion located on the interior surface of the exemplary artery and, therefore, located within the artery's lumen. This result is achieved by use of at least one eccentric head that, during high-speed rotation within the exemplary lumen, has been found to produce a combination of a low-frequency orbital motion comprising a force that is exerted against the lumen wall, with concomitant deflection of same, and / or a high-frequency pulsatile frequency, also with concomitant exertion of force against the lumen wall and deflection of same. These force-driven deflections produce a series of shockwaves within the layers of the exemplary artery's wall layers, resulting in systematic disruptions of any calcification within the intimal and / or medial layers of the subject artery. In addition, any calcification within the occlusion is also softened and disrupted. Thus, as this process proceeds, the compliance of the vessel, as well as the lesion itself, is increased.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Controller for an atherectomy device
A rotational atherectomy system may include an elongated, flexible drive shaft having a distal end for insertion into a vasculature of a patient and having a proximal end opposite the distal end remaining outside the vasculature of the patient, an electric motor rotatably coupled to the proximal end of the drive shaft, the electric motor being capable of rotating the drive shaft, and control electronics, wherein the control electronics comprise a computer readable storage medium in communication with a processor, the computer readable storage medium having software stored thereon for monitoring and controlling the rotation of the electric motor and for monitoring and controlling delivery of saline to the drive shaft.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Abrasive elements for rotational atherectomy systems
ActiveUS20170348018A1Improve grinding efficiencyExcision instrumentsAbrasive surgical cuttersRestenosisStenotic lesion
The present disclosure is generally directed to novel bead geometries that can provide improved sanding efficiencies in rotational atherectomy procedures. The abrasive elements disclosed herein may open stenotic lesions to diameters that are substantially larger than the maximum diameter of the abrasive element. In some embodiments, the abrasive elements may open stenotic lesions to diameters that are substantially larger than the maximum diameter of the sheath from which the abrasive element is delivered through. In some embodiments the abrasive elements are configured to expand when the abrasive elements are rotated at high speeds. In some embodiments, the abrasive elements have local centers of mass that are positioned at opposite diagonal ends. Accordingly, the abrasive elements disclosed herein may have improved sanding ranges, reduce treatment times, and prevent re-stenosis.
Owner:BARD PERIPHERAL VASCULAR
Atherectomy devices and methods
ActiveUS10478217B2Enhanced atherectomy performanceRemove and reduce stenotic lesionBalloon catheterExcision instrumentsStenotic lesionEngineering
This document describes rotational atherectomy devices and systems for removing or reducing stenotic lesions in blood vessels by rotating an abrasive element within the vessel to partially or completely remove the stenotic lesion material.
Owner:CARDIOFLOW
Methods, devices and systems for slow rotation of drive shaft driven atherectomy systems
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com