Patents
Literature
624 results about "Tubular stenosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
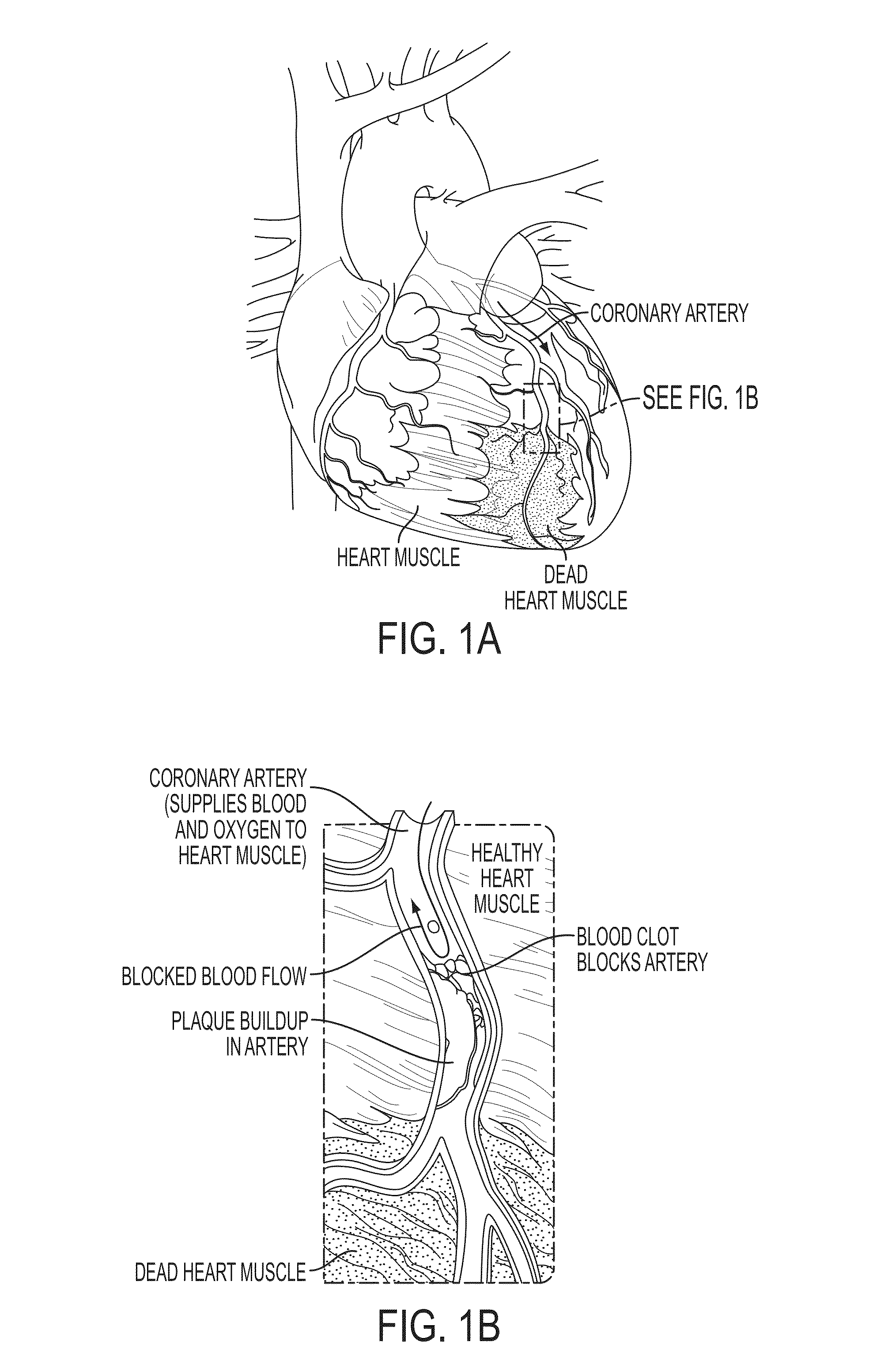
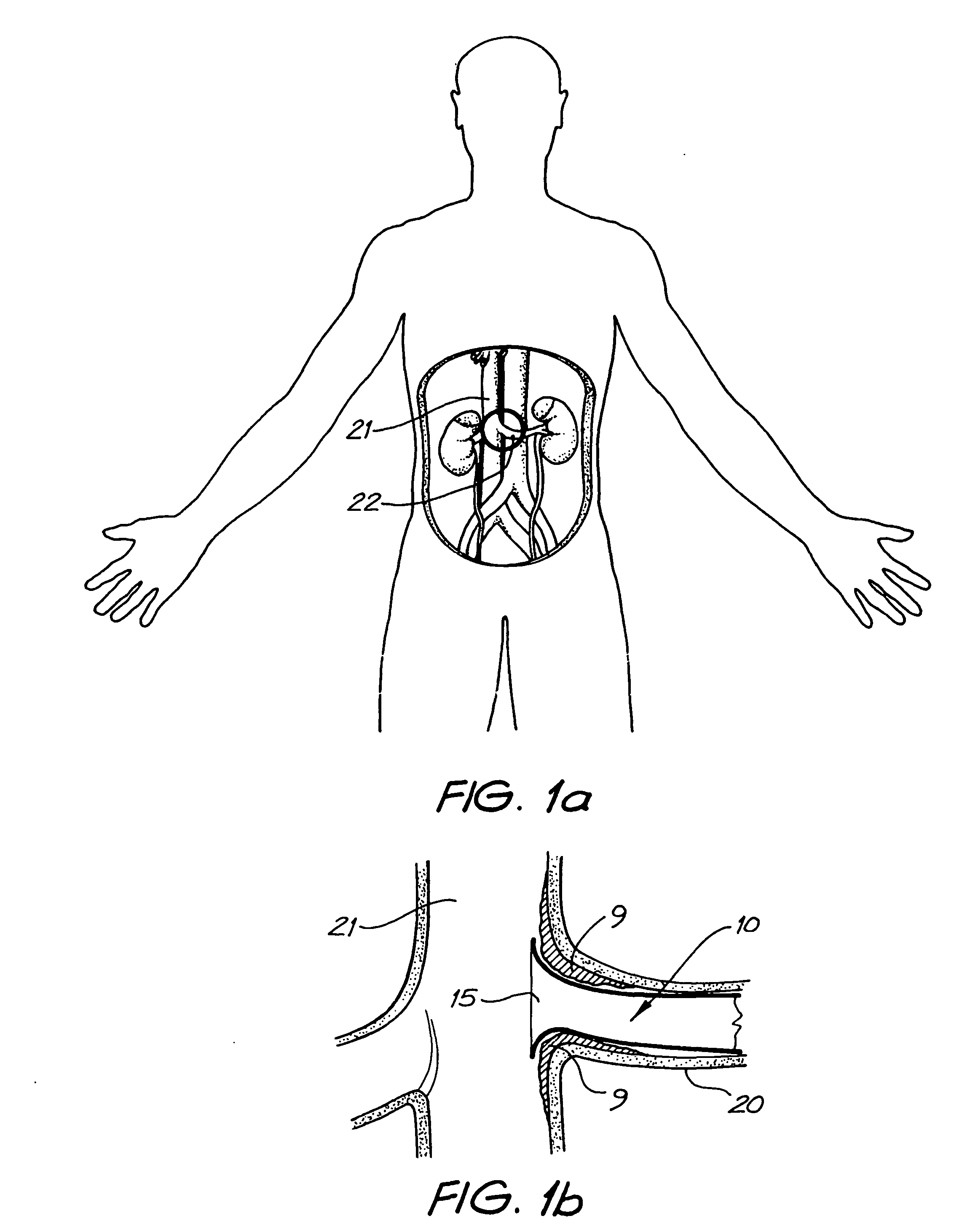
A stenosis is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
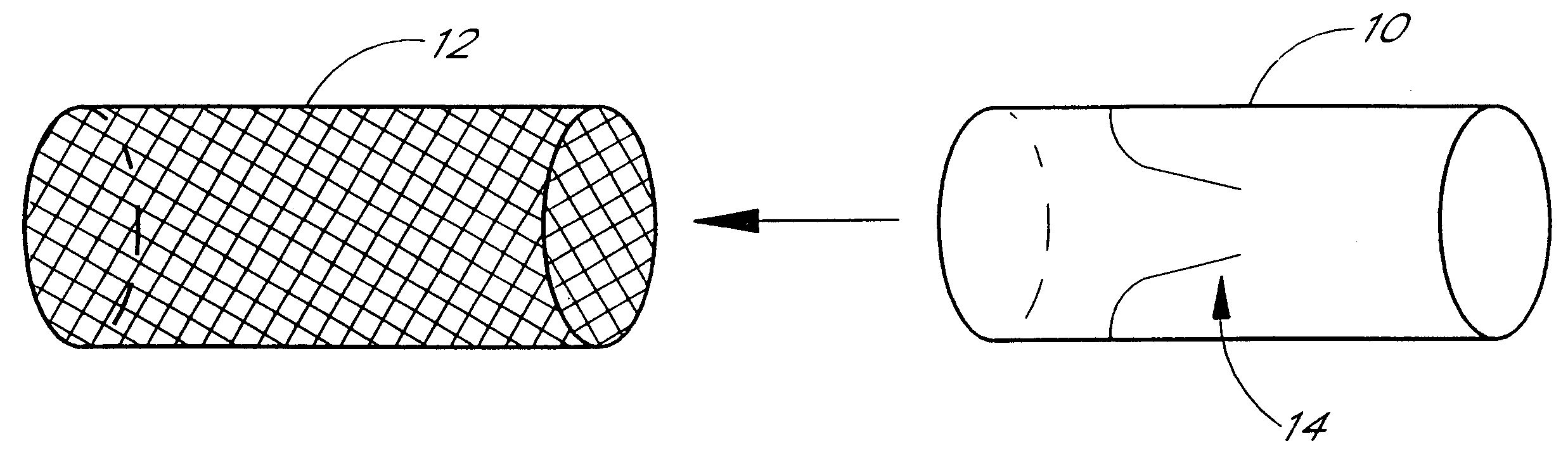
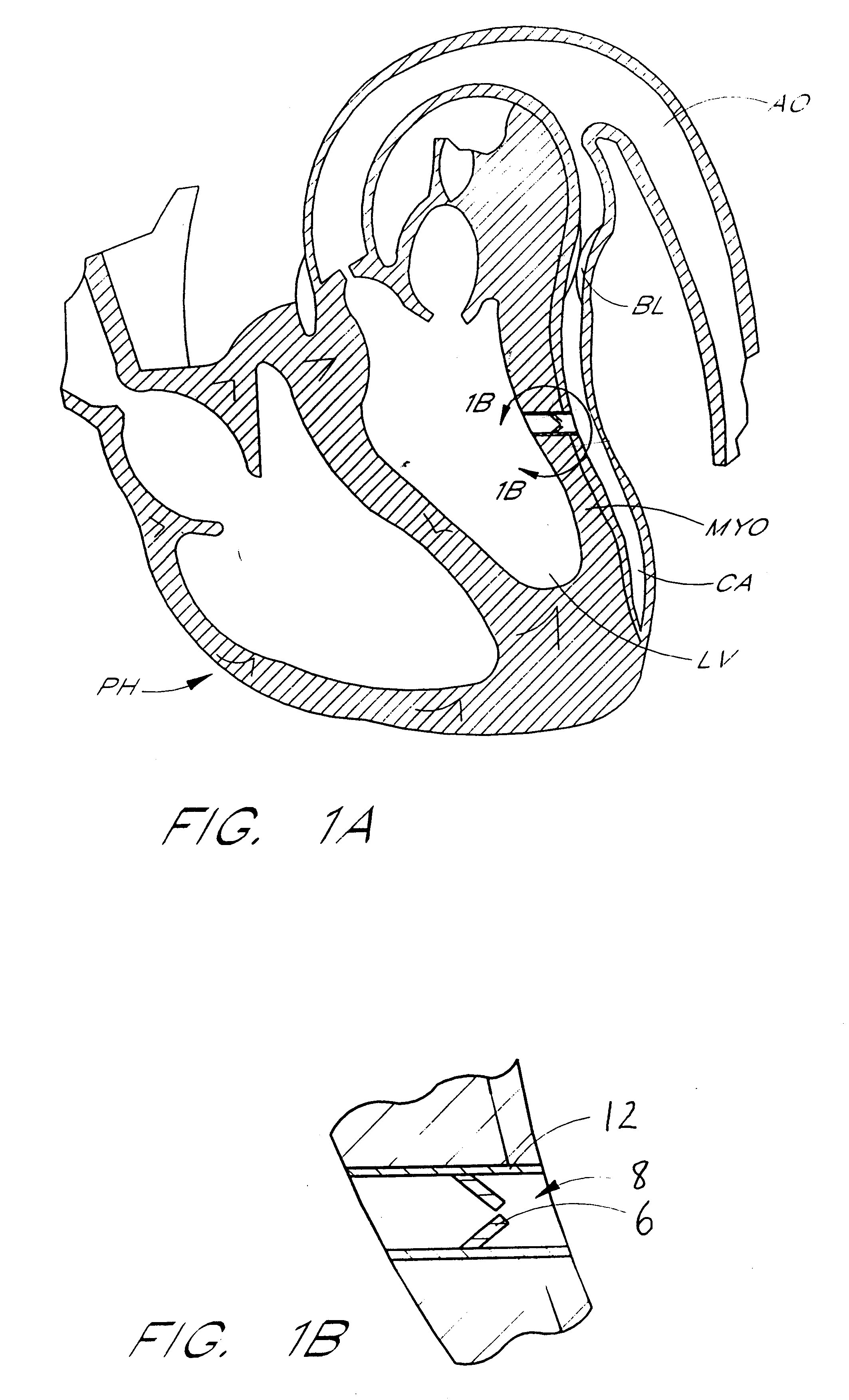
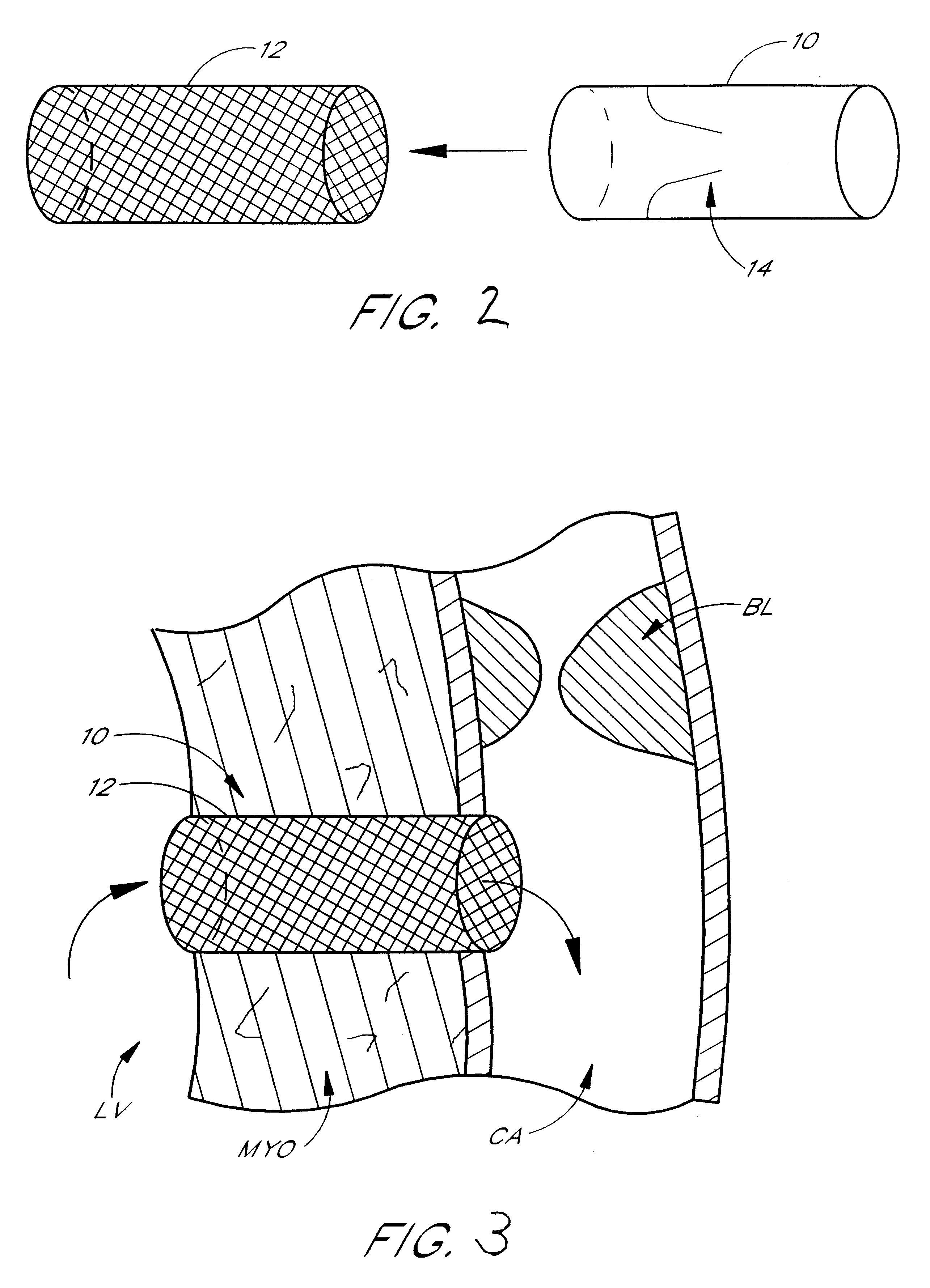
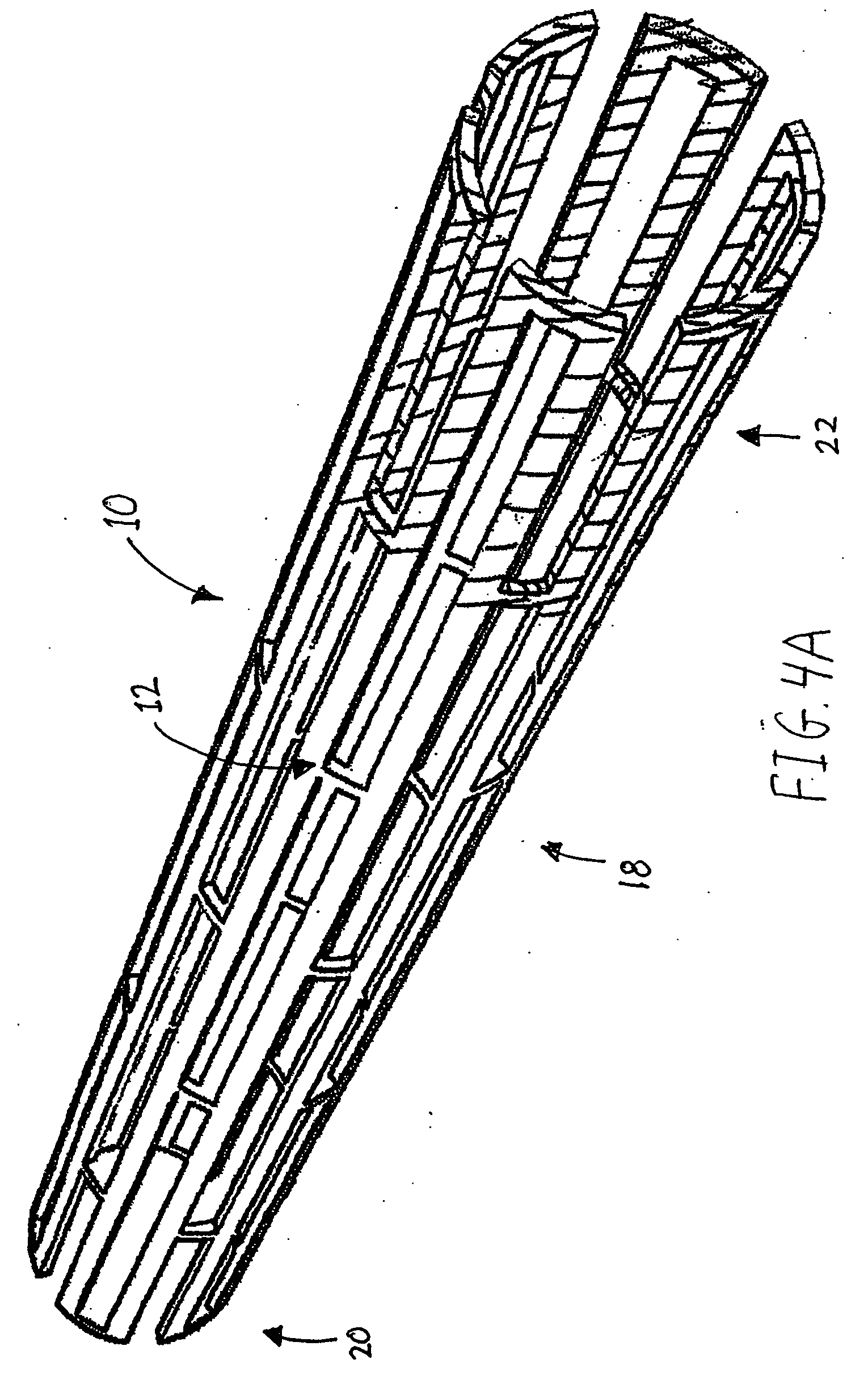
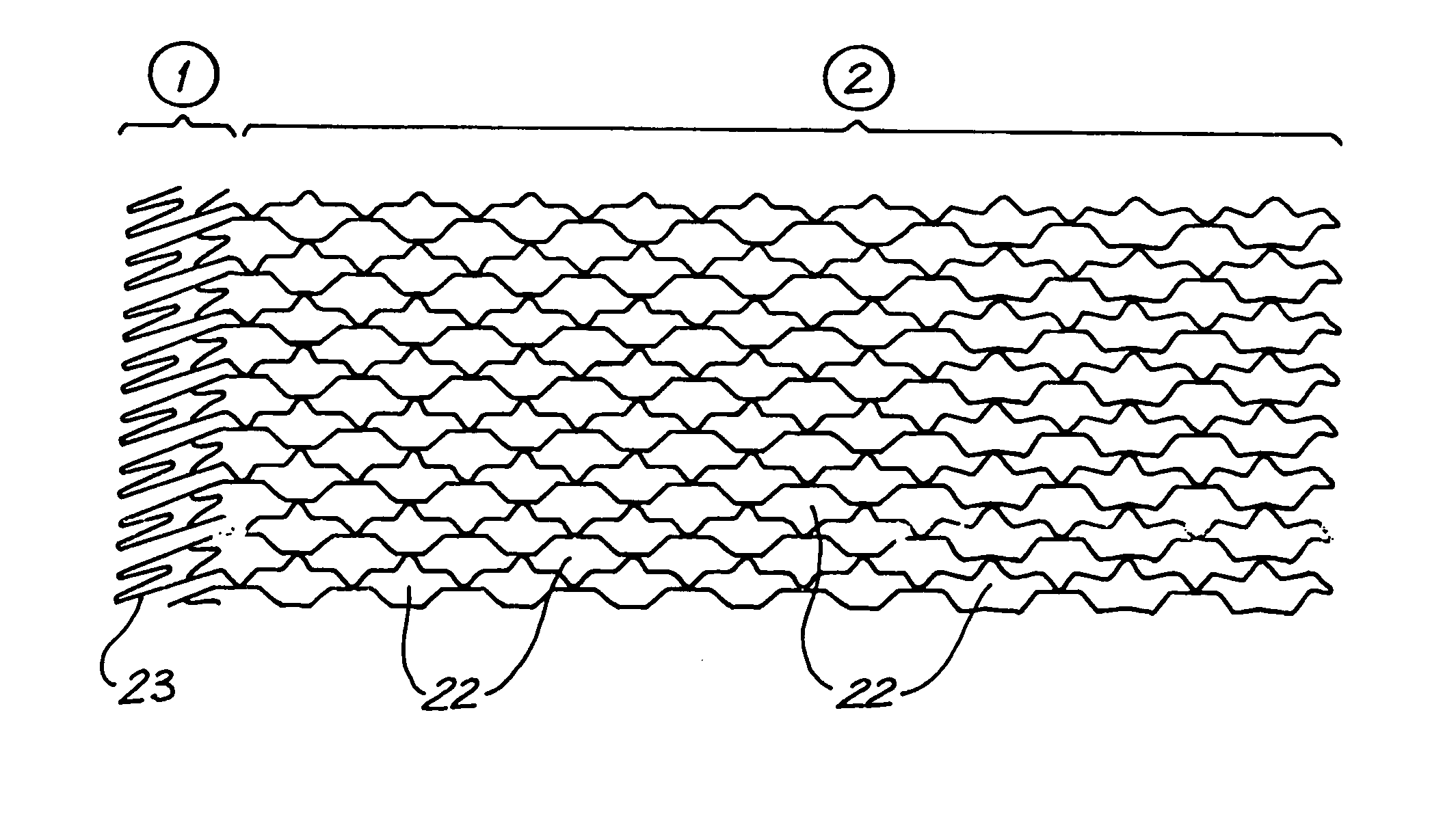
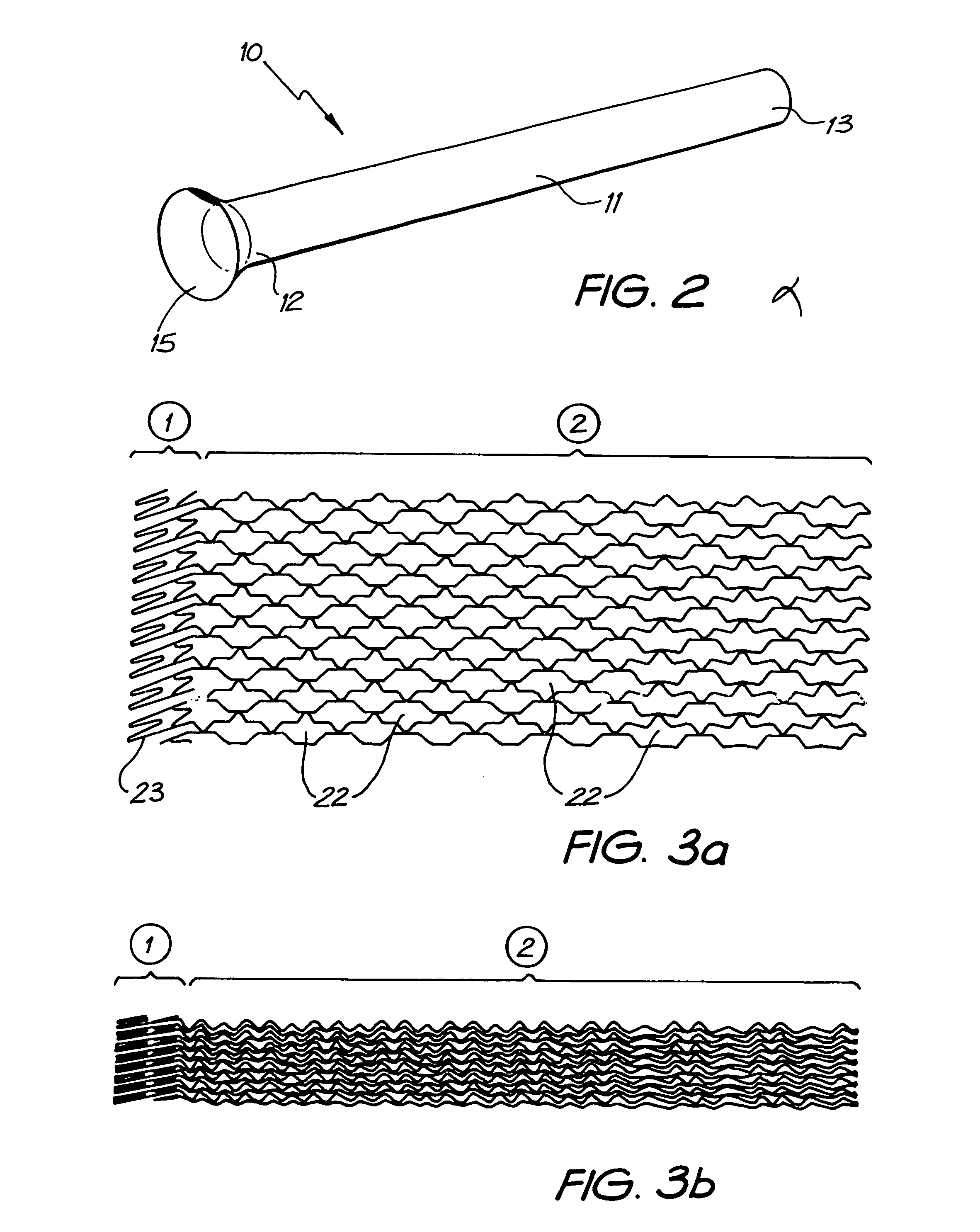
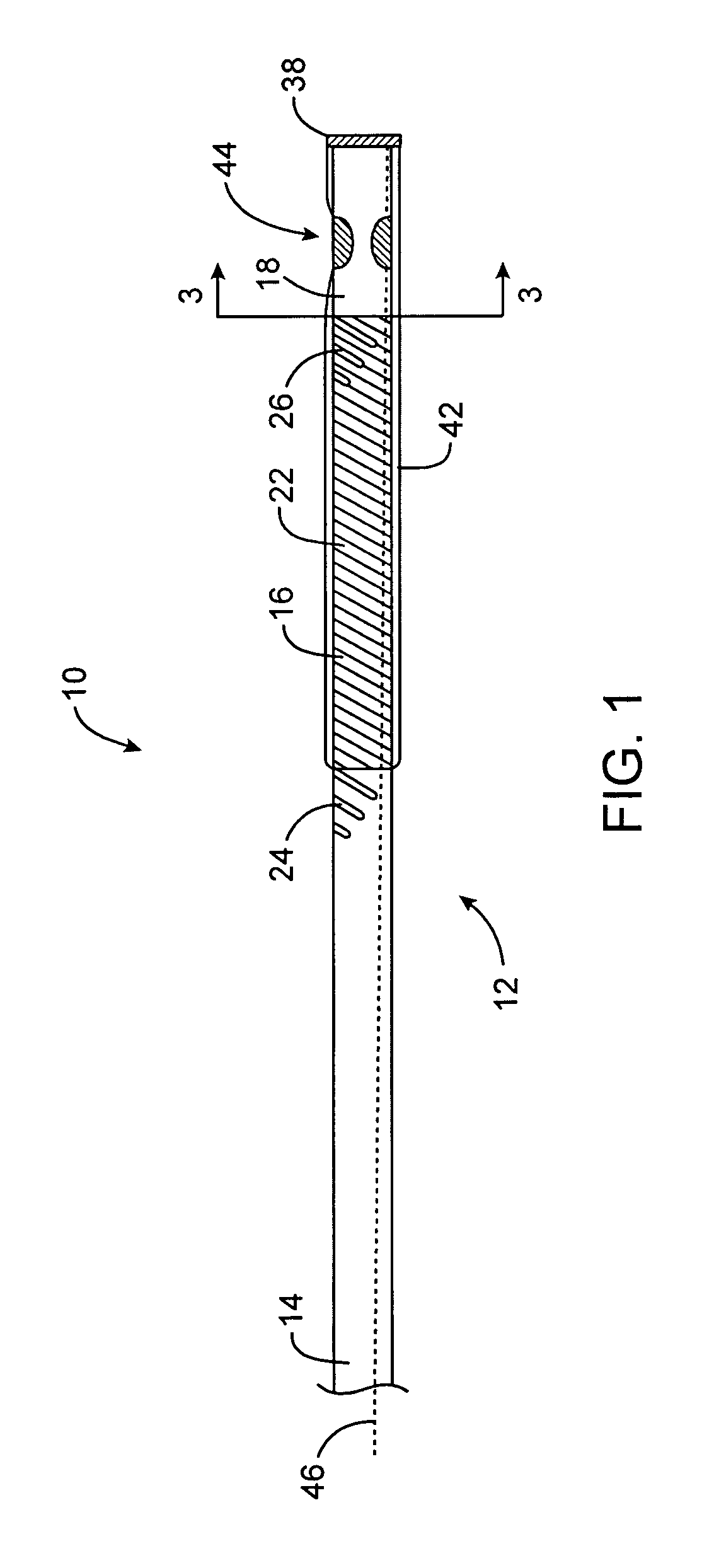
Expandable supportive endoluminal grafts
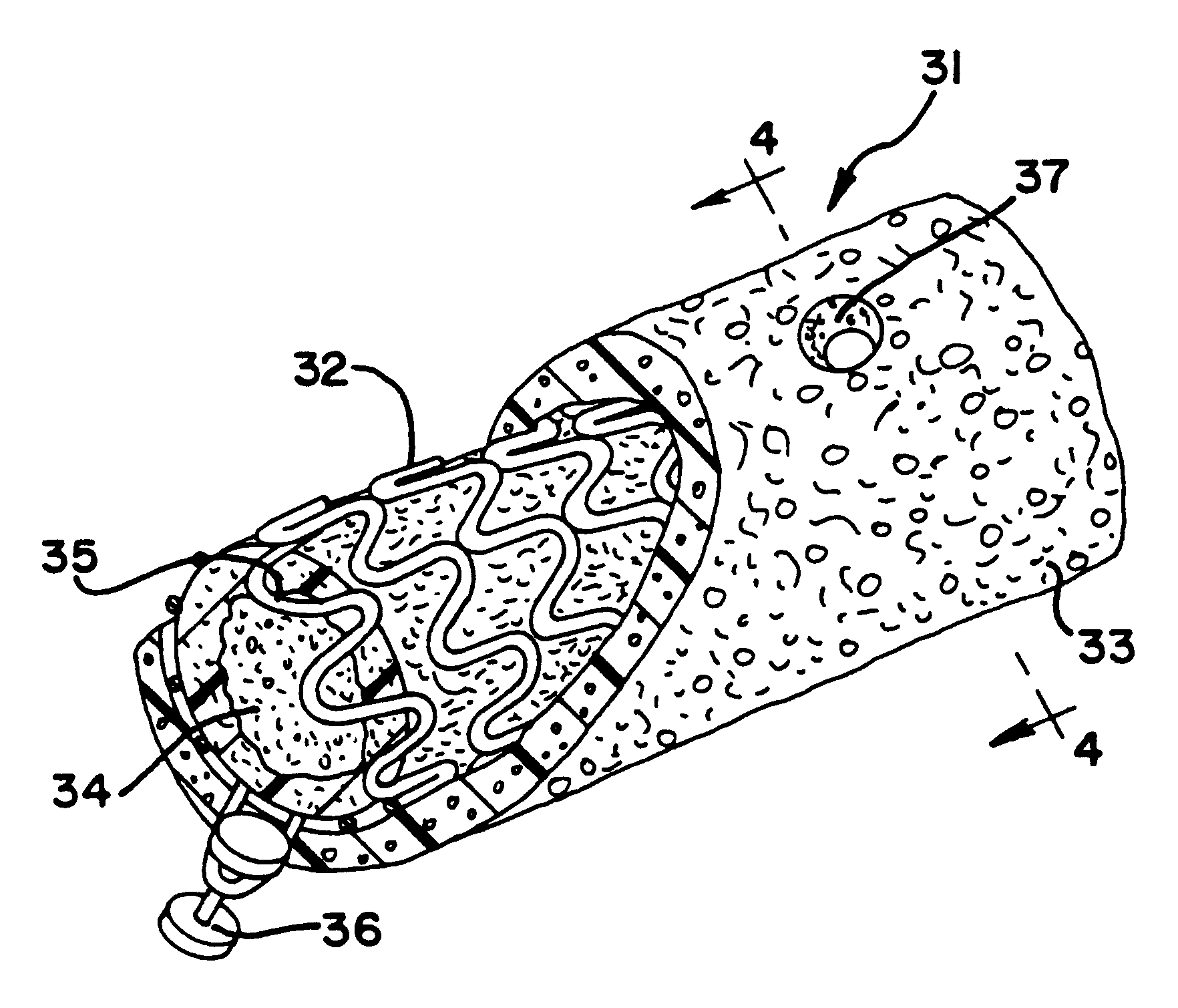
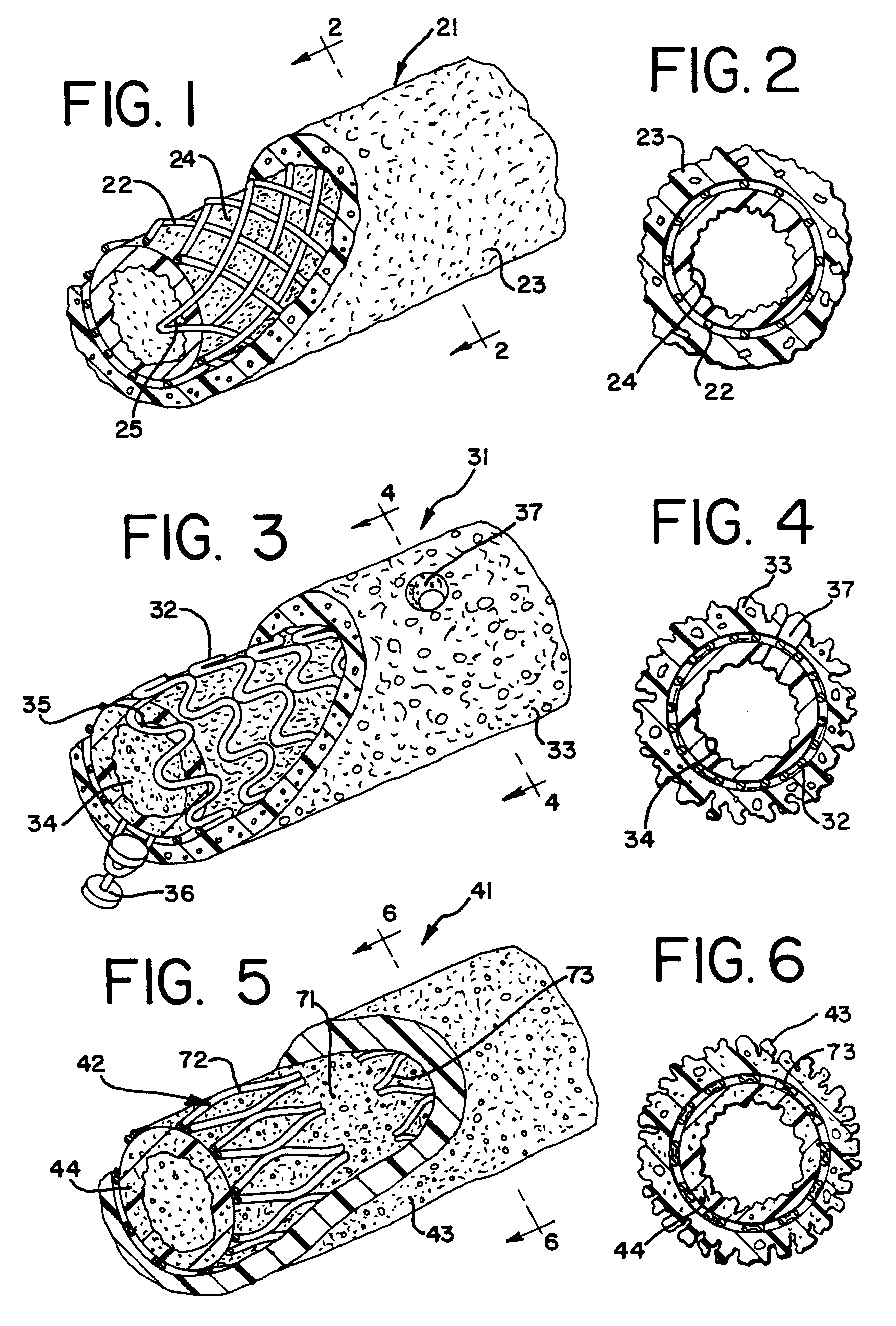
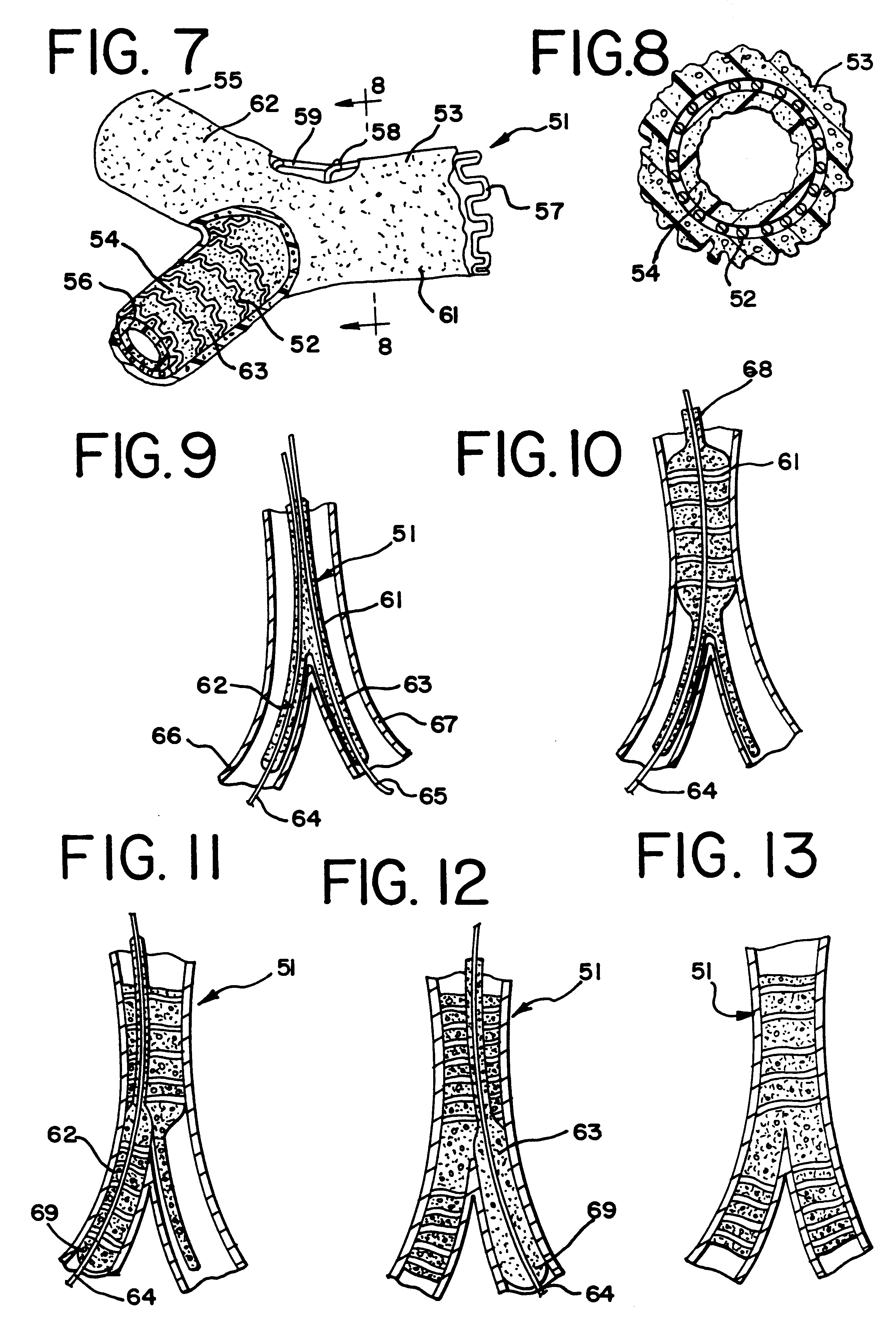
An endoluminal graft which is both expandable and supportive is provided either in a longitudinal form or in a bifurcated form. The graft expands between a first diameter and a second, larger diameter. The support component is an expandable stent endoprosthesis. A cover, liner, or a liner, or both a cover and a liner are applied to the endoprosthesis in the form of a stretchable wall material that is porous, elastomeric and biocompatible in order to allow normal cellular invasion upon implantation, without stenosis, when the expandable and supportive graft is at its second diameter. Preferably, the elastomeric wall material is a polycarbonate urethane.
Owner:LIFEPORT SCI
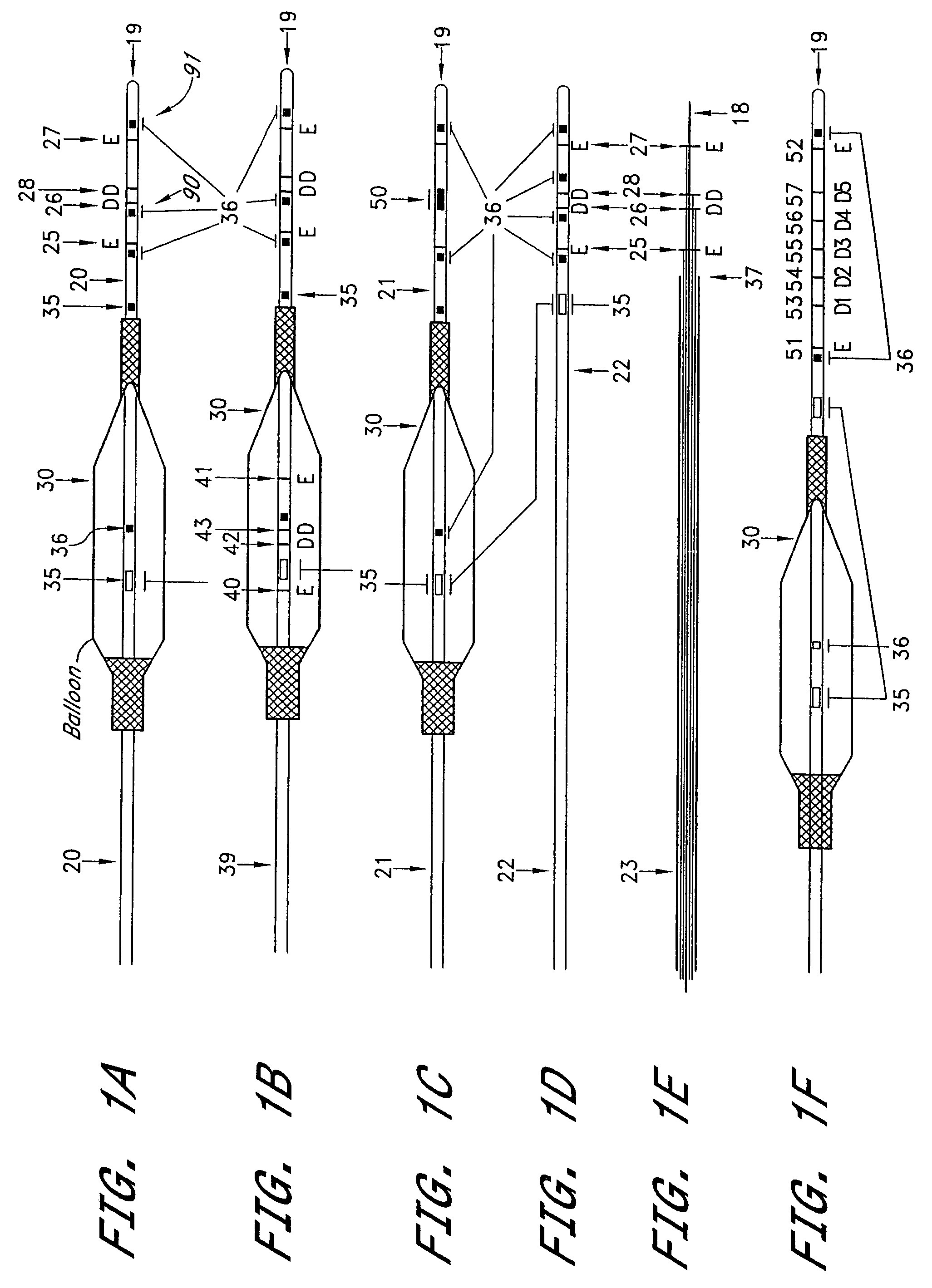
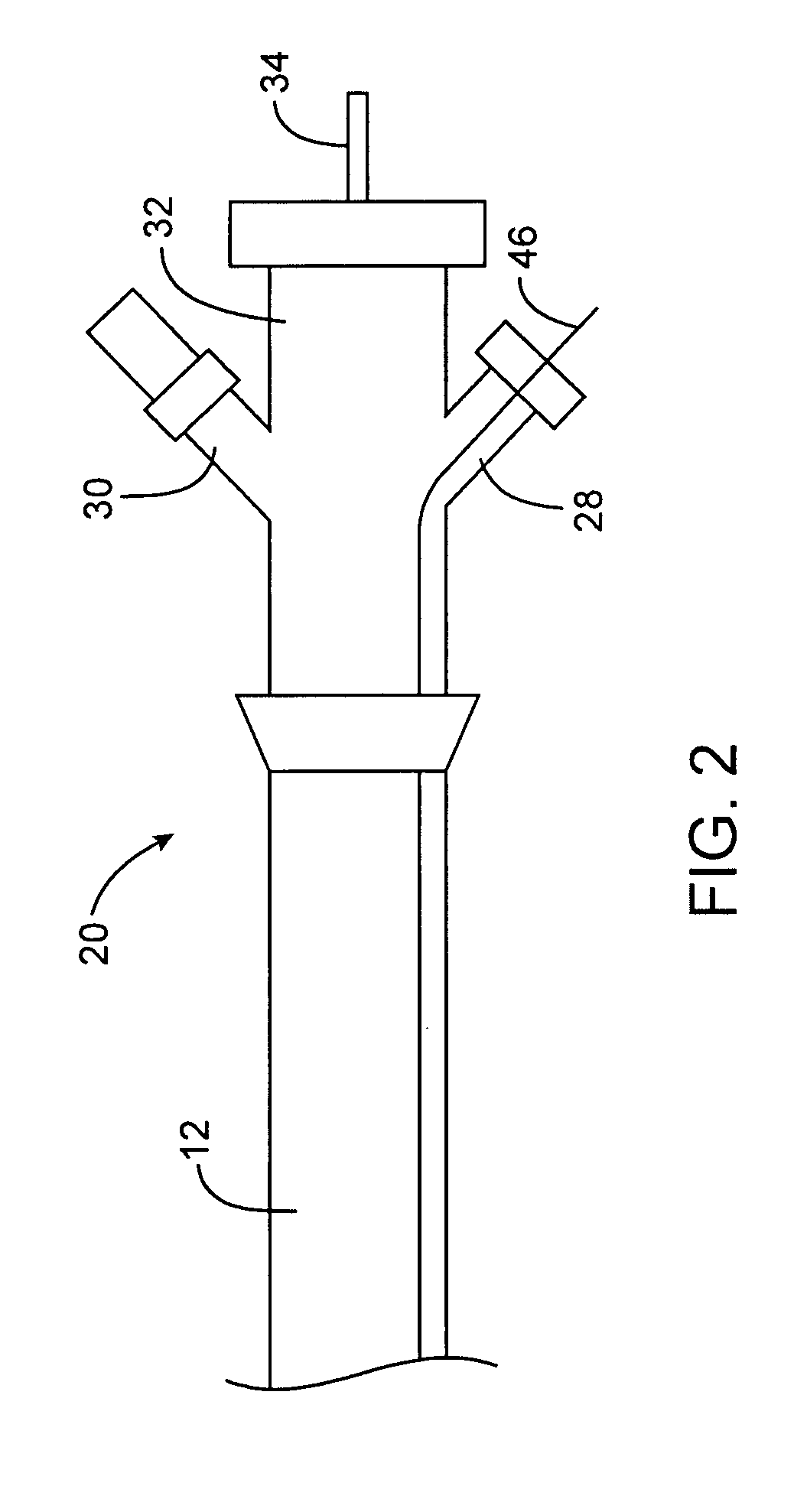
Guidewire for crossing occlusions or stenoses
InactiveUS20060074442A1Easy to controlFacilitate occlusionCannulasGuide wiresCoronary arteriesThrombus
A deflectable and torqueable hollow guidewire device is disclosed for removing occlusive material and passing through occlusions, stenosis, thrombus, plaque, calcified material, and other materials in a body lumen, such as a coronary artery. The hollow guidewire generally comprises an elongate, tubular guidewire body that has an axial lumen. A mechanically moving core element is positioned at or near a distal end of the tubular guidewire body and extends through the axial lumen. Actuation of the core element (e.g., oscillation, reciprocation, and / or rotation) creates a passage through the occlusive or stenotic material in the body lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
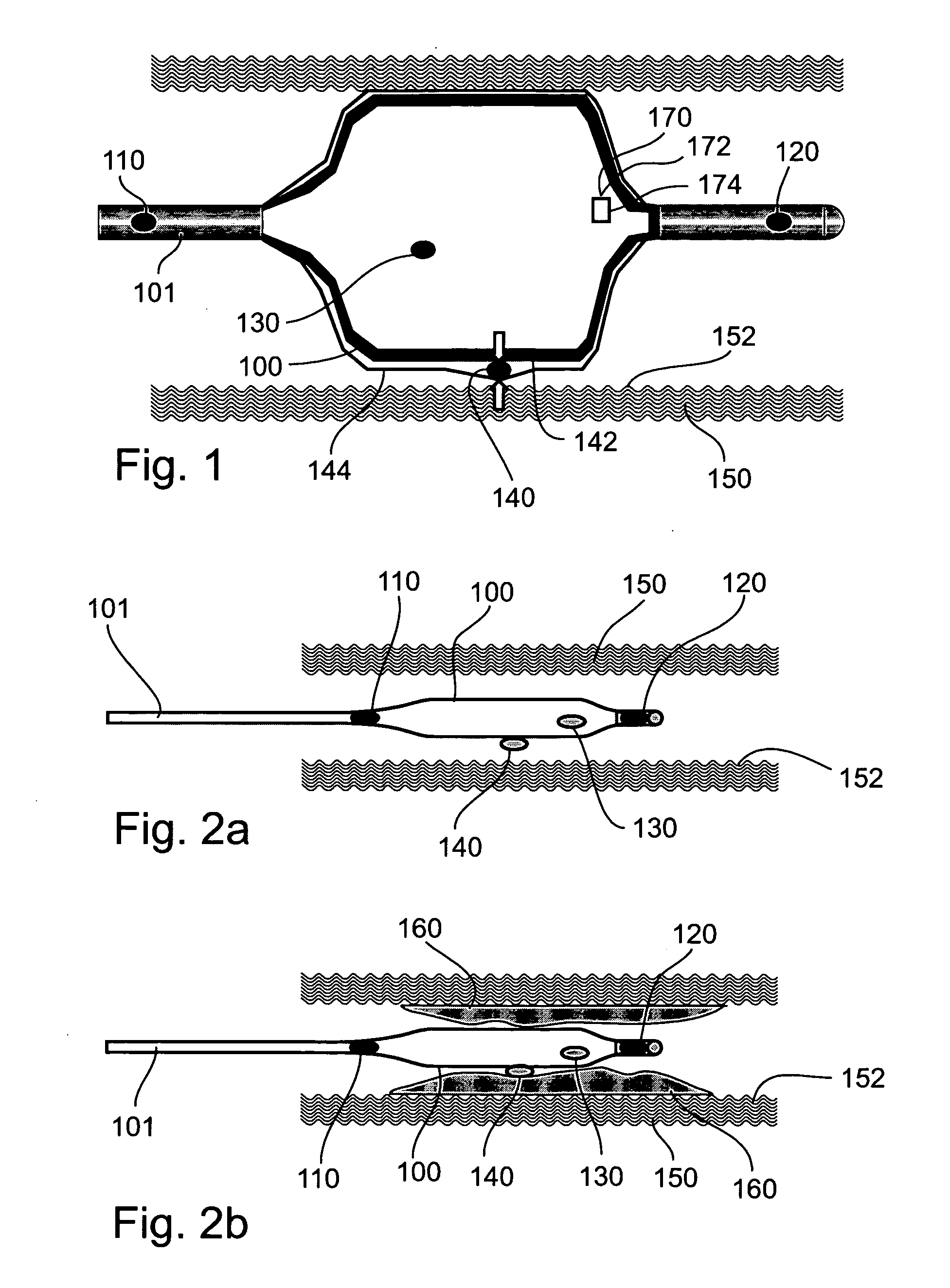
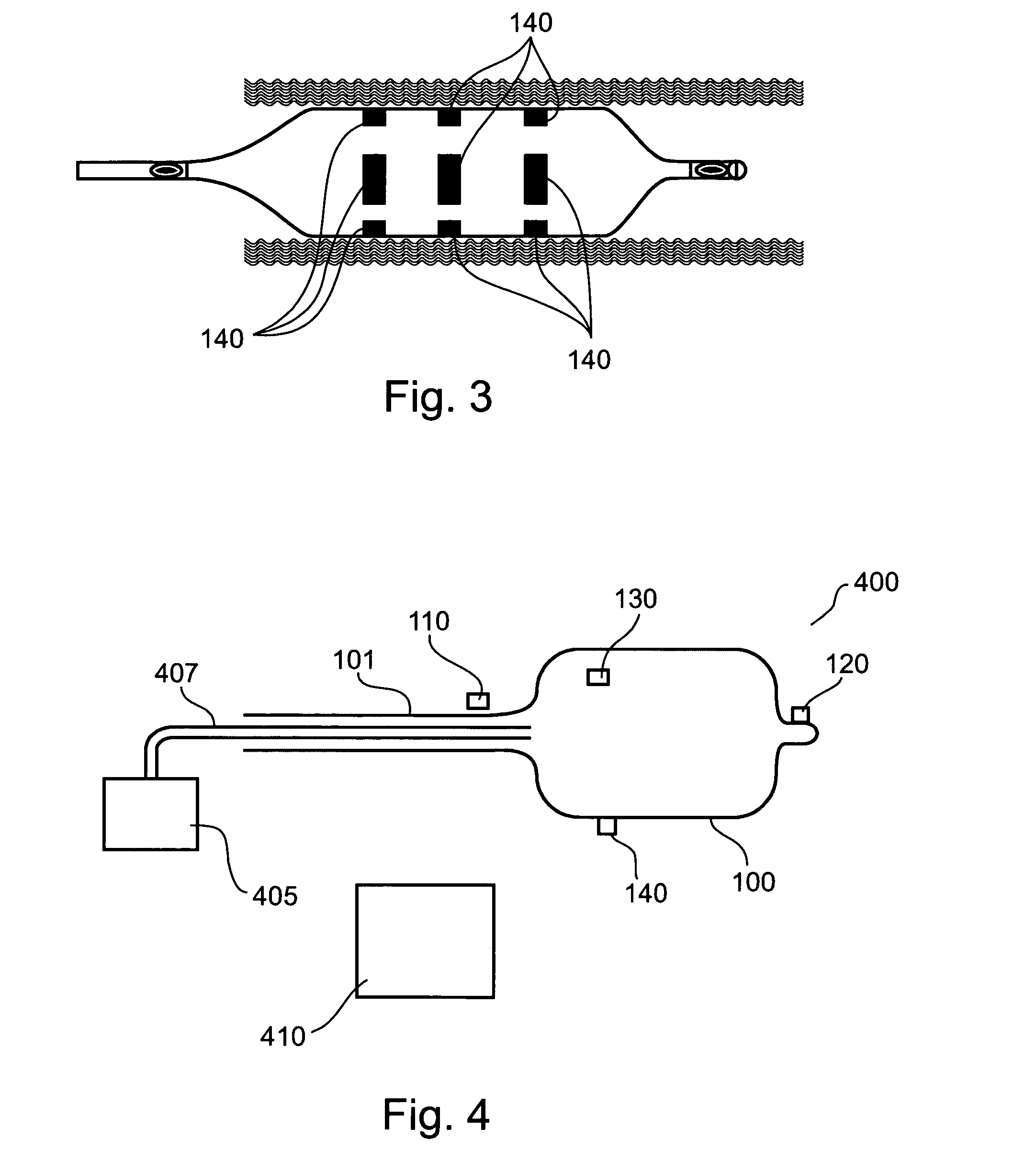
Medical device for treating a heart valve insufficiency or stenosis
A medical device for treating a heart valve insufficiency, with an endoprosthesis which can be introduced into a patient's body and expanded to secure a heart valve prosthesis in the patient's aorta with a catheter. In an embodiment, the endoprosthesis has a plurality of positioning arches configured to be positioned with respect to a patient's aorta and a plurality of retaining arches to support a heart valve prosthesis. The endoprosthesis includes a collapsed mode during the process of introducing it into the patient's body and an expanded mode when it is implanted. The endoprosthesis may be introduced into a patient's body and expanded via a catheter. In an embodiment, the catheter has first and second slide mechanisms configured to independently manipulate first and second sleeve elements to sequentially expand the endoprosthesis from the collapsed mode to the expanded mode.
Owner:JENAVALVE TECH INC
Emboli protection devices and related methods of use
ActiveUS7374560B2Improve visualizationStopping normal blood flowStentsDilatorsRetrograde FlowEmbolization material
An evacuation sheath assembly and method of treating occluded vessels which reduces the risk of distal embolization during vascular interventions is provided. The evacuation sheath assembly includes an elongated tube defining an evacuation lumen having proximal and distal ends. A proximal sealing surface is provided on a proximal portion of the tube and is configured to form a seal with a lumen of a guided catheter. A distal sealing surface is provided on a distal portion of the tube and is configured to form a seal with a blood vessel. Obturator assemblies and infusion catheter assemblies are provided to be used with the evacuation sheath assembly. A method of treatment of a blood vessel using the evacuation sheath assembly includes advancing the evacuation sheath assembly into the blood vessel through a guide catheter. Normal antegrade blood flow in the blood vessel proximate to the stenosis is stopped and the stenosis is treated. Retrograde blood flow is induced within the blood vessel to carry embolic material dislodged during treating into the evacuation sheath assembly. If necessary to increase retrograde flow, the coronary sinus may be at least partially occluded. Alternatively, antegrade flow may be permitted while flow is occluded at the treatment site.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Conduit with valved blood vessel graft
Disclosed is a conduit that provides a bypass around an occlusion or stenosis in a coronary artery. The conduit is a tube adapted to be positioned in the heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a heart chamber and a coronary artery, at a site distal to the occlusion or stenosis. The conduit has a section of blood vessel attached to its interior lumen which preferably includes at least one naturally occurring one-way valve positioned therein. The valve prevents the backflow of blood from the coronary artery into the heart chamber.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC +1
System and method for measuring cross-sectional areas and pressure gradients in luminal organs
The invention comprises a system, catheter and method for measuring the cross-sectional areas and pressure gradients in any hollow organ, such as, for example, blood vessels. One embodiment of such a system includes: an impedance catheter capable of being introduced into a targeted site; a solution delivery source; a constant current source; a balloon inflation control device; and a data acquisition and processing system that receives conductance and / or pressure gradient data from the catheter and calculates the cross-sectional area of the targeted site. In one embodiment, the catheter has an inflatable balloon along its longitudinal axis, thereby enabling the breakup of any materials causing stenosis at the targeted site and / or distention and delivery of an optional stent into the targeted site.
Owner:ELECTRO CAT
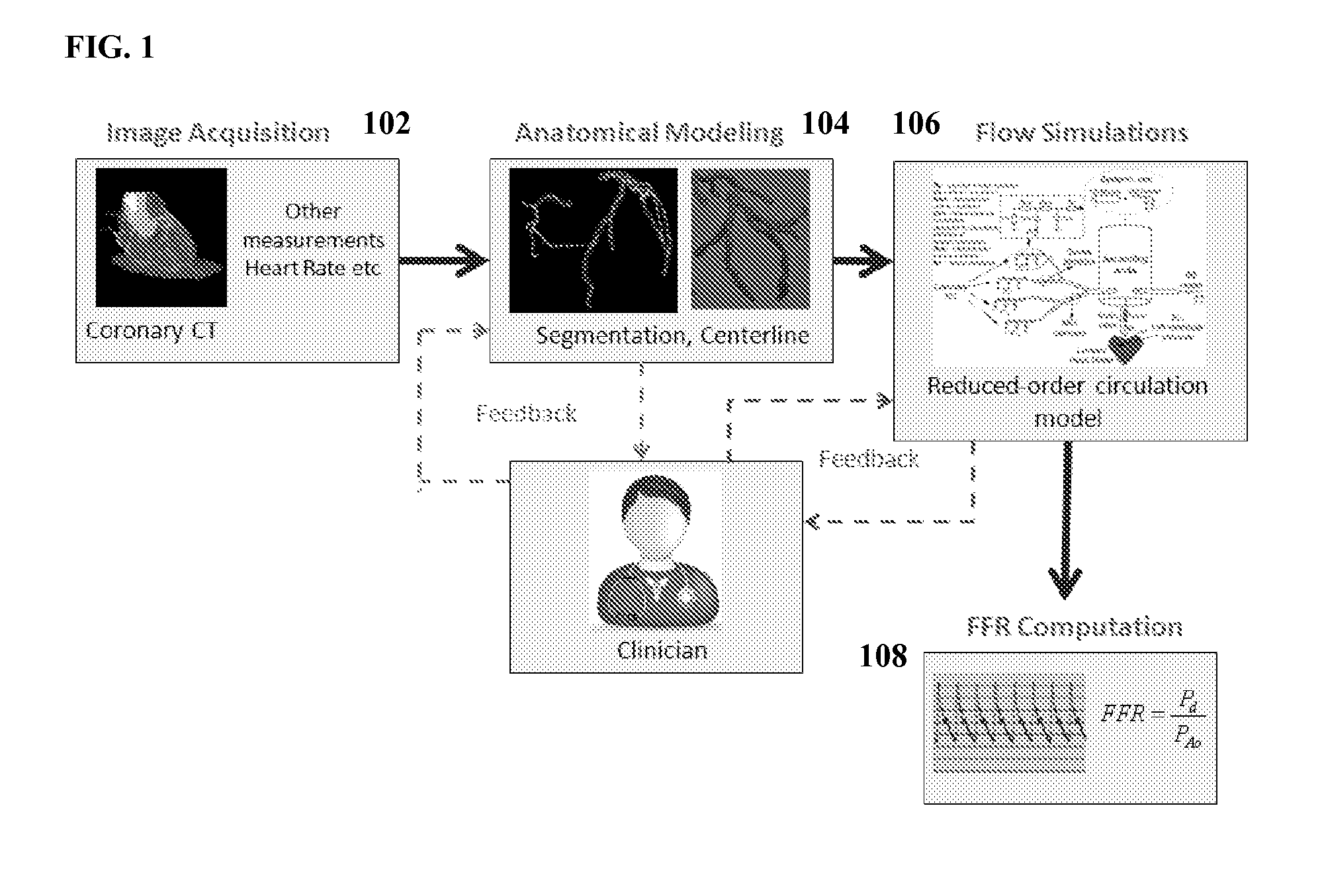
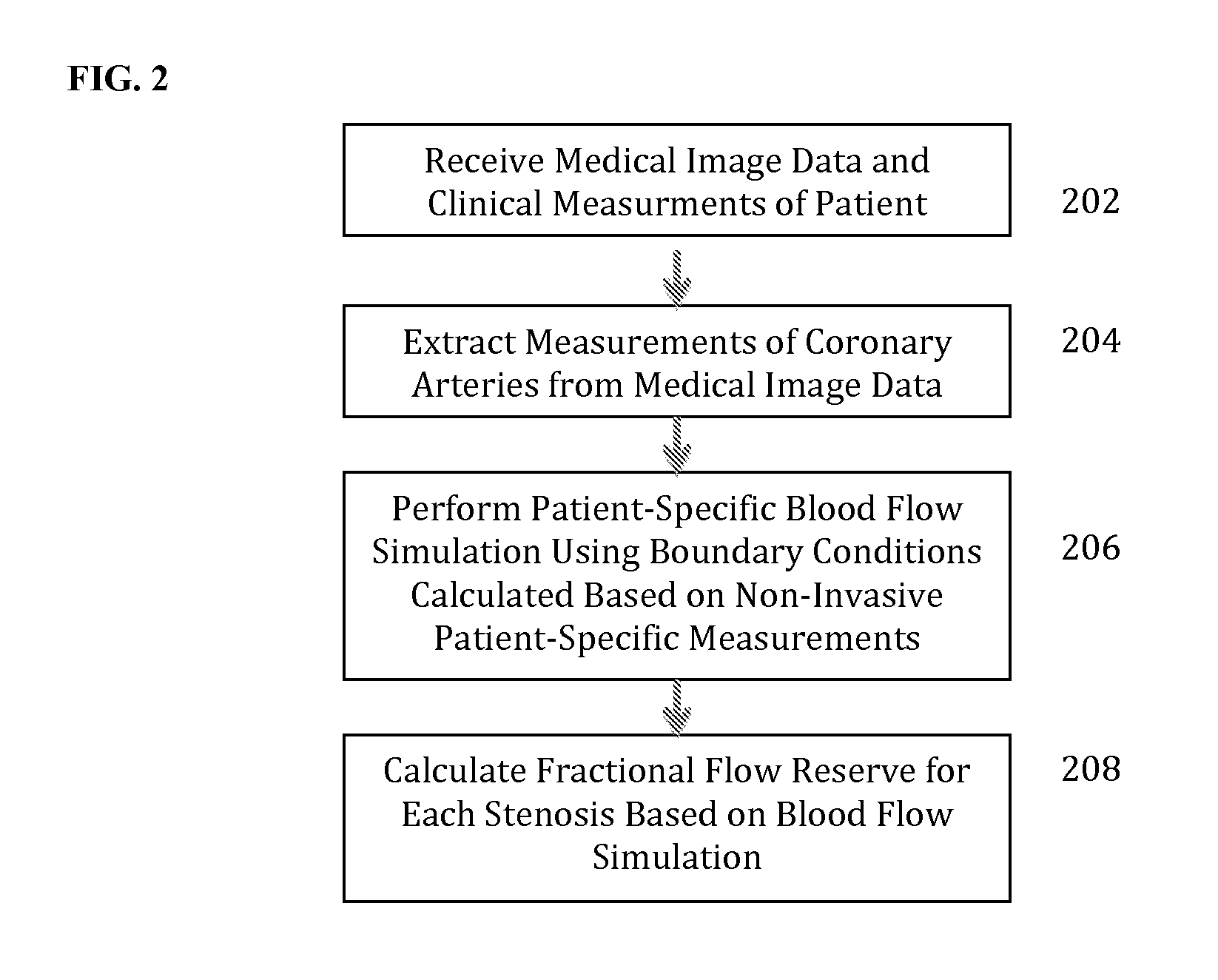
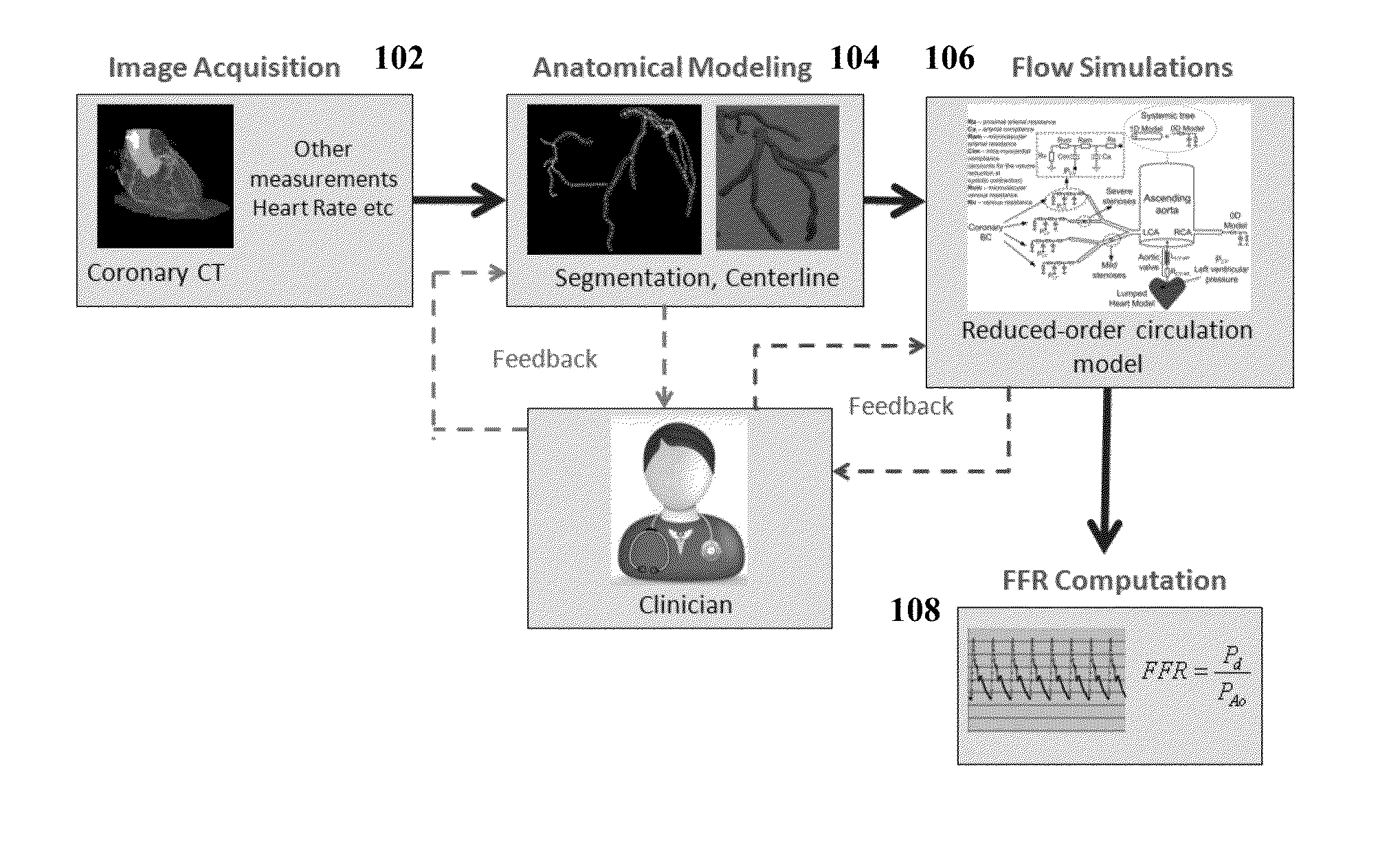
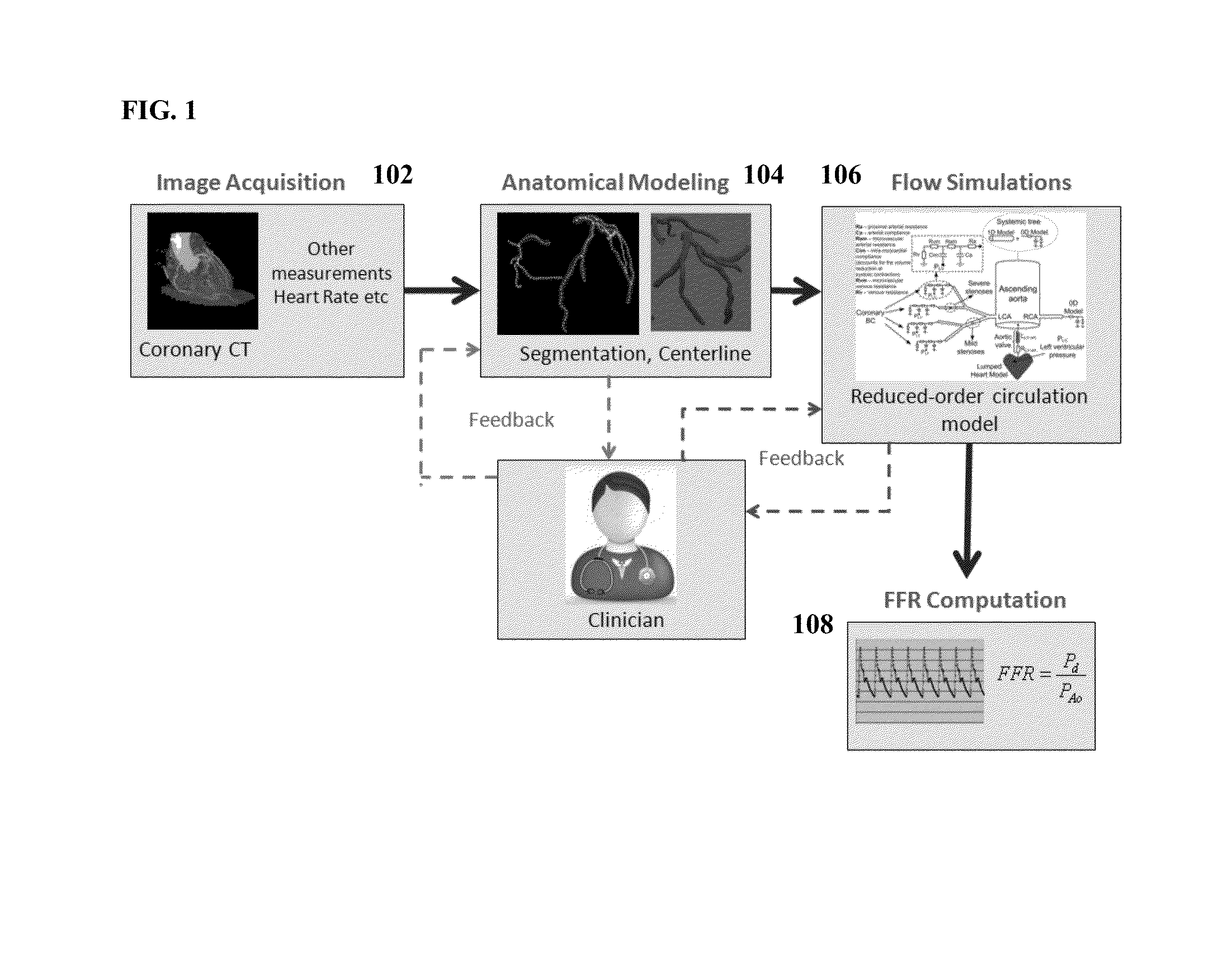
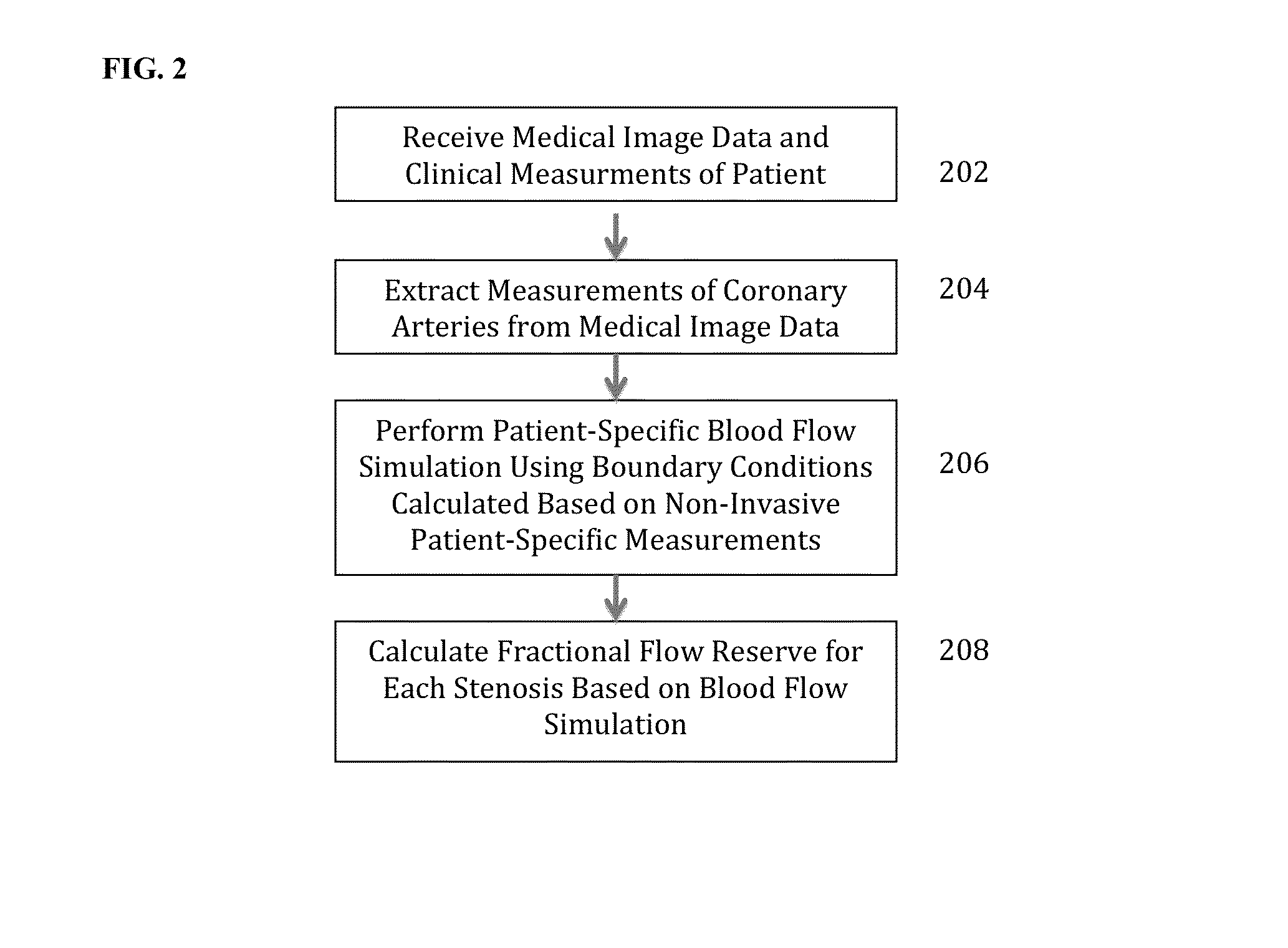
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
InactiveUS20130246034A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
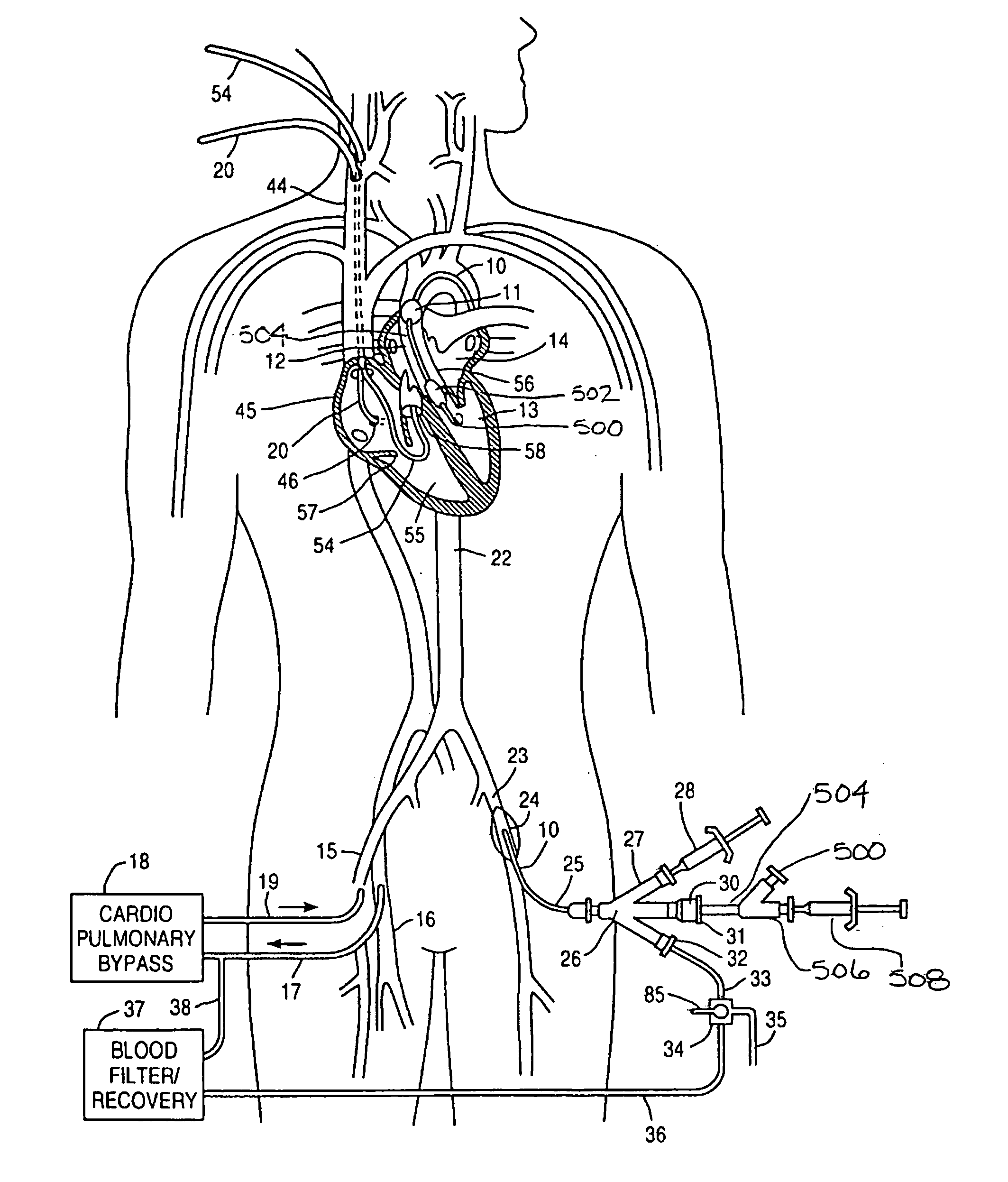
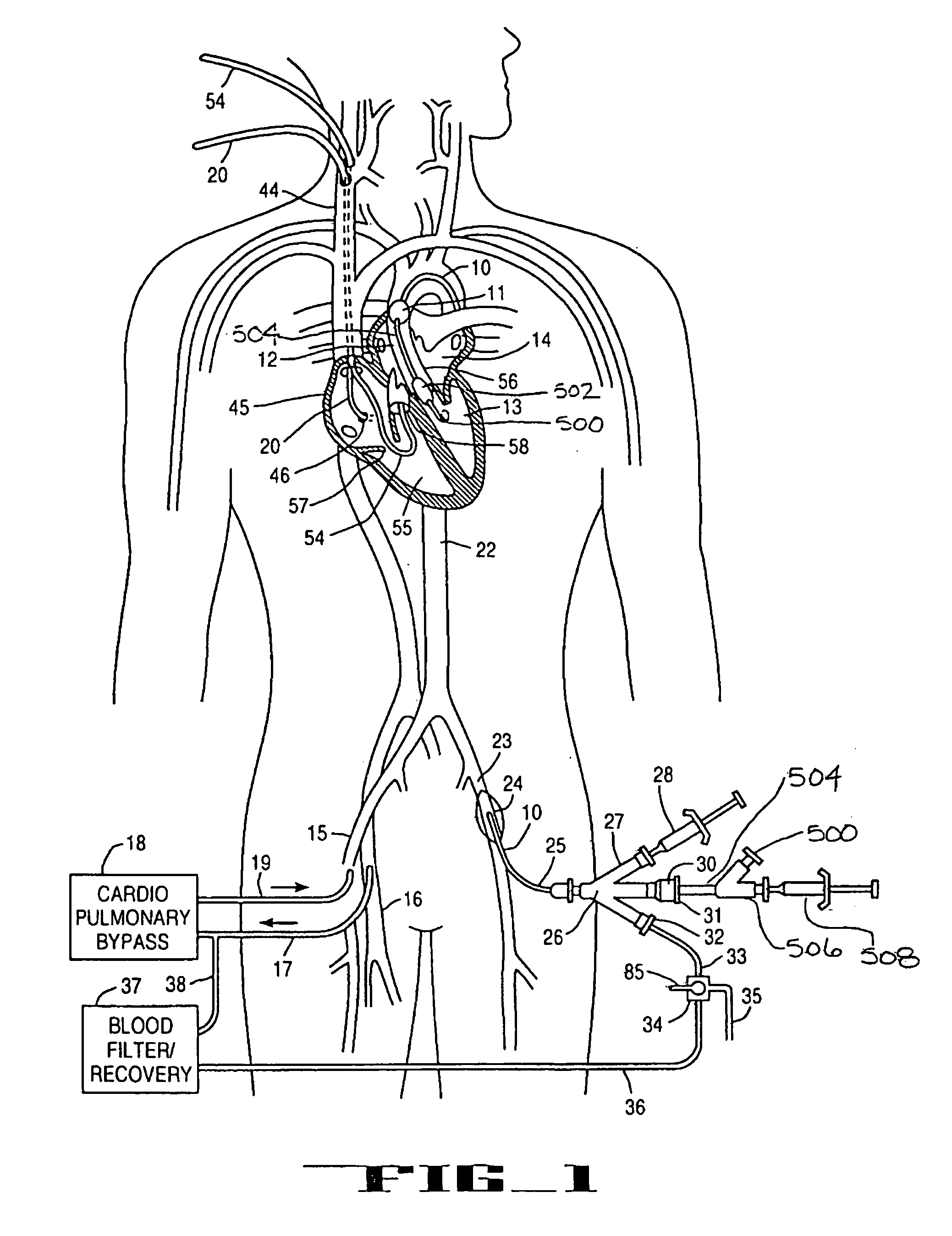
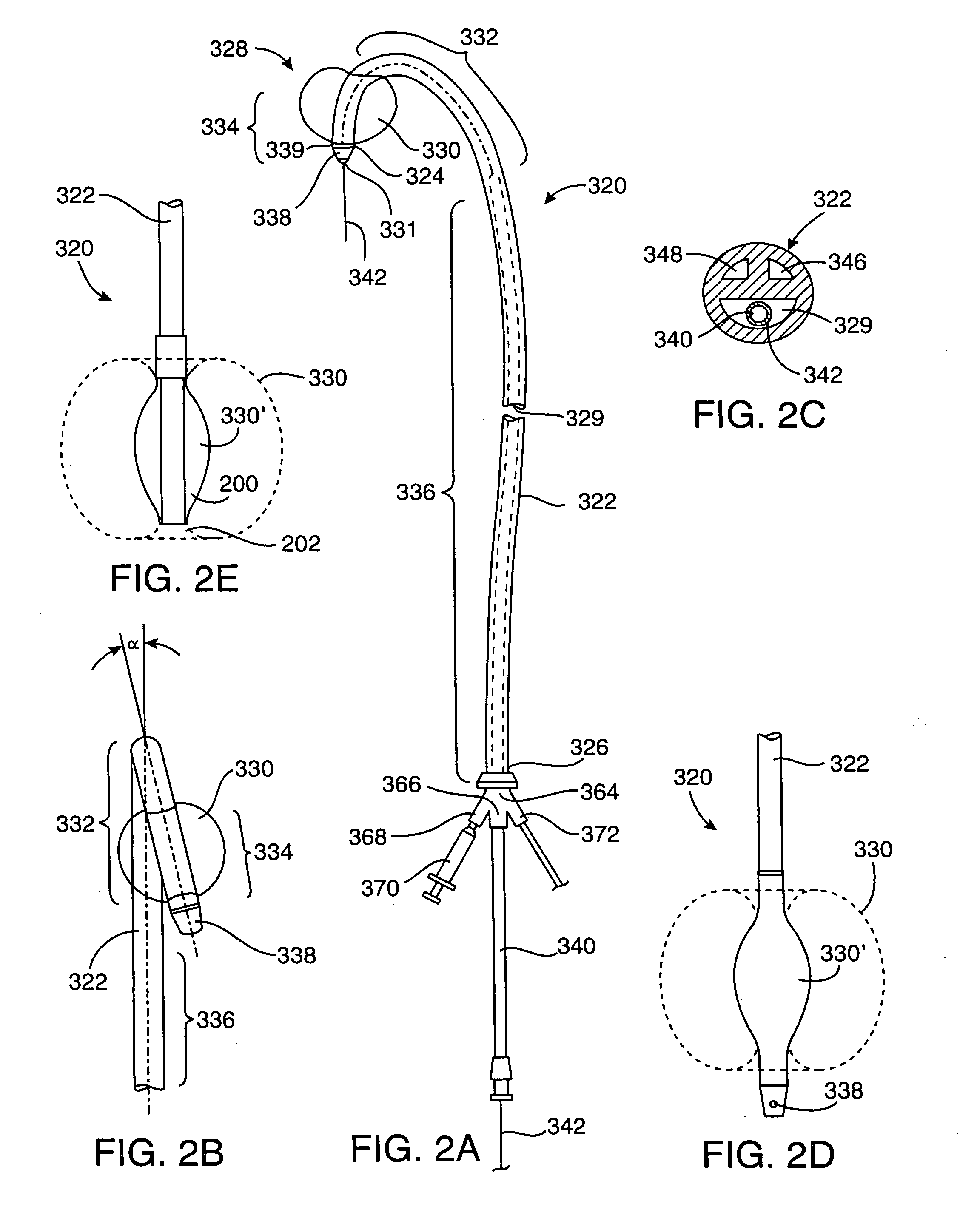
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
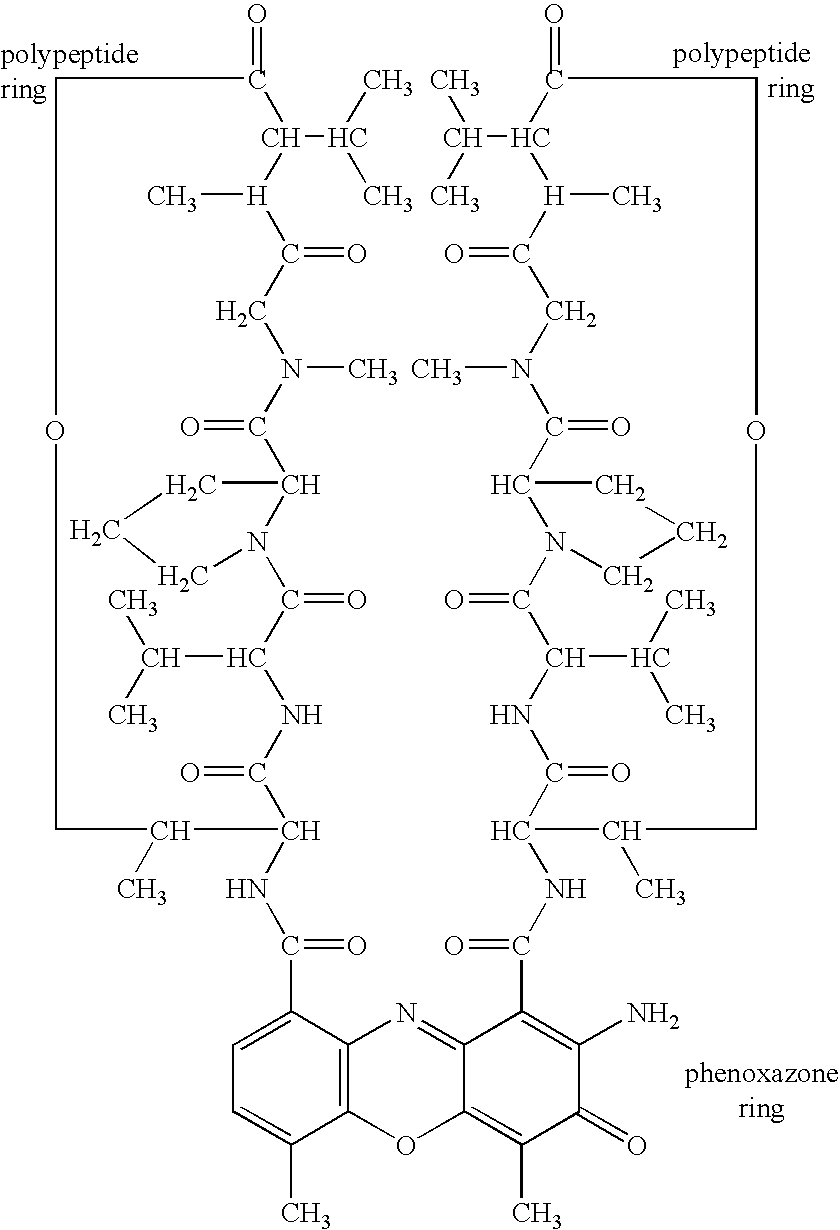
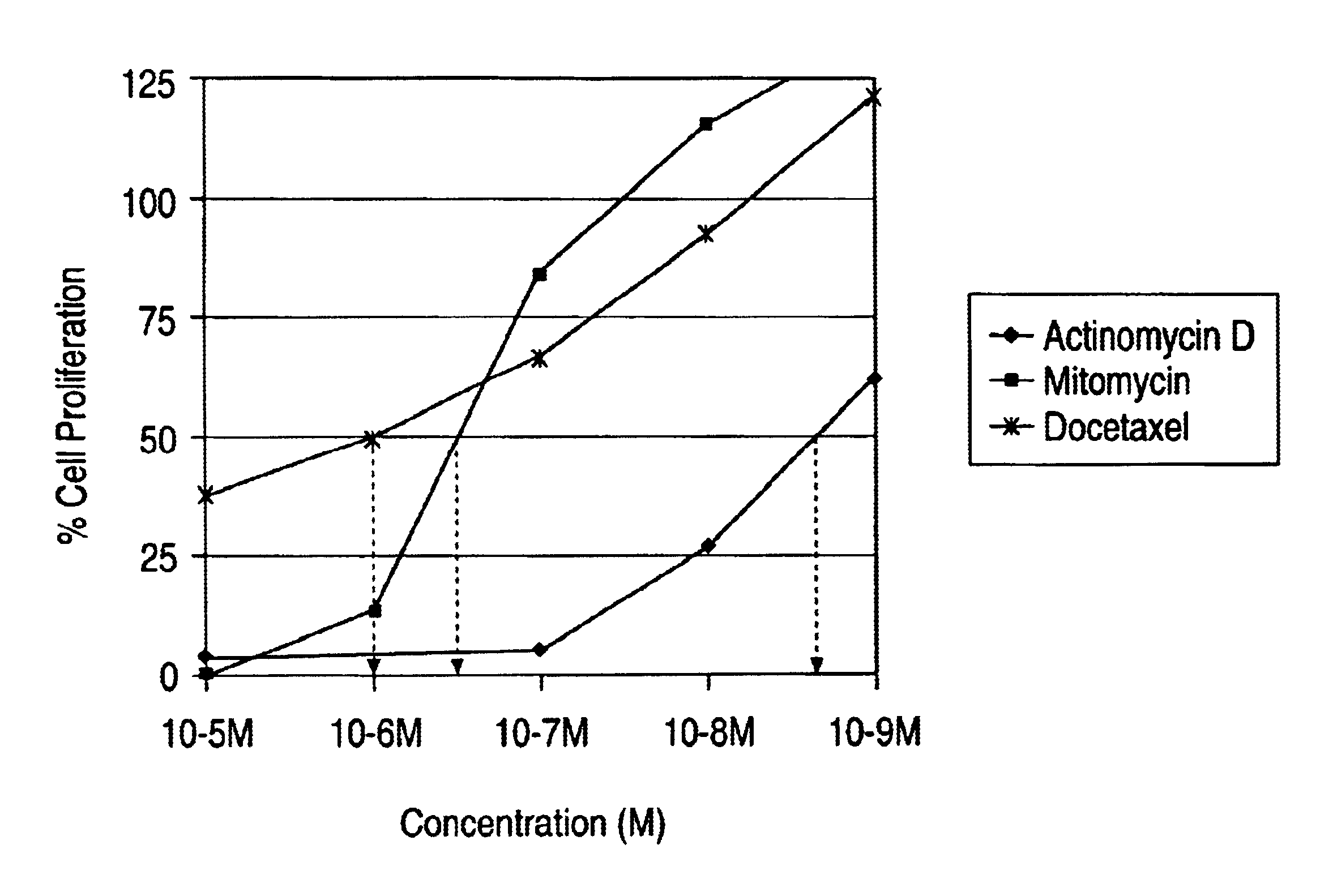
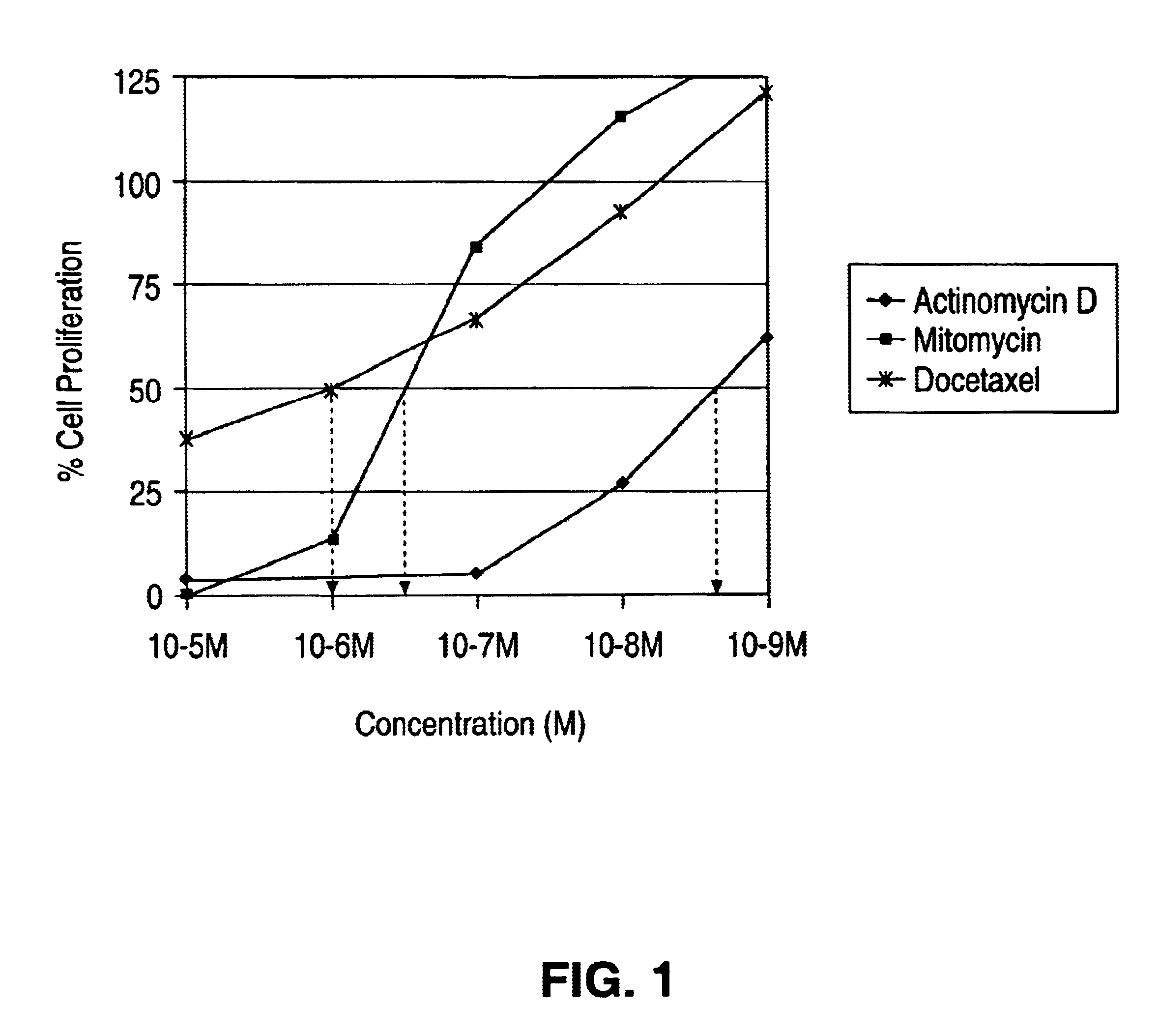
Actinomycin D for the treatment of vascular disease
A composition, comprising actinomycin D, is locally or systemically administered for the treatment of a blood vessel, such as caused by recurring stenosis or restenosis following vascular trauma or disease.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Pulmonary vein valve implant
InactiveUS20050273160A1Reduced likelihoodReduce severityStentsBronchiPulmonary vasculatureAtrial cavity
The present invention involves placing a valve between the left atrium and the lung to prevent regurgitant flow from increasing the pulmonary pressures, which may lead to pulmonary edema and congestion. Mitral stenosis or poor synchronization of the mitral valve may add additional pressures to the left atrium thus raising the pulmonary pressures and leading to congestion in the lung vasculature. By blocking the additional pressures from the mitral regurgitant flow from reaching the pulmonary circulation, the left atrium may act as a sealed vessel to allow additional aortic output. The valve placement can be intralumenal or attached to the ostium of the atrium. The device can be placed via the vascular conduits or through a surgical procedure into the pulmonary circulation. One or more devices may be placed in each of the four pulmonary veins. Additionally only one, two, three or all four veins may be implanted with the valve as desired by the physician.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
Endoluminal prosthetic device
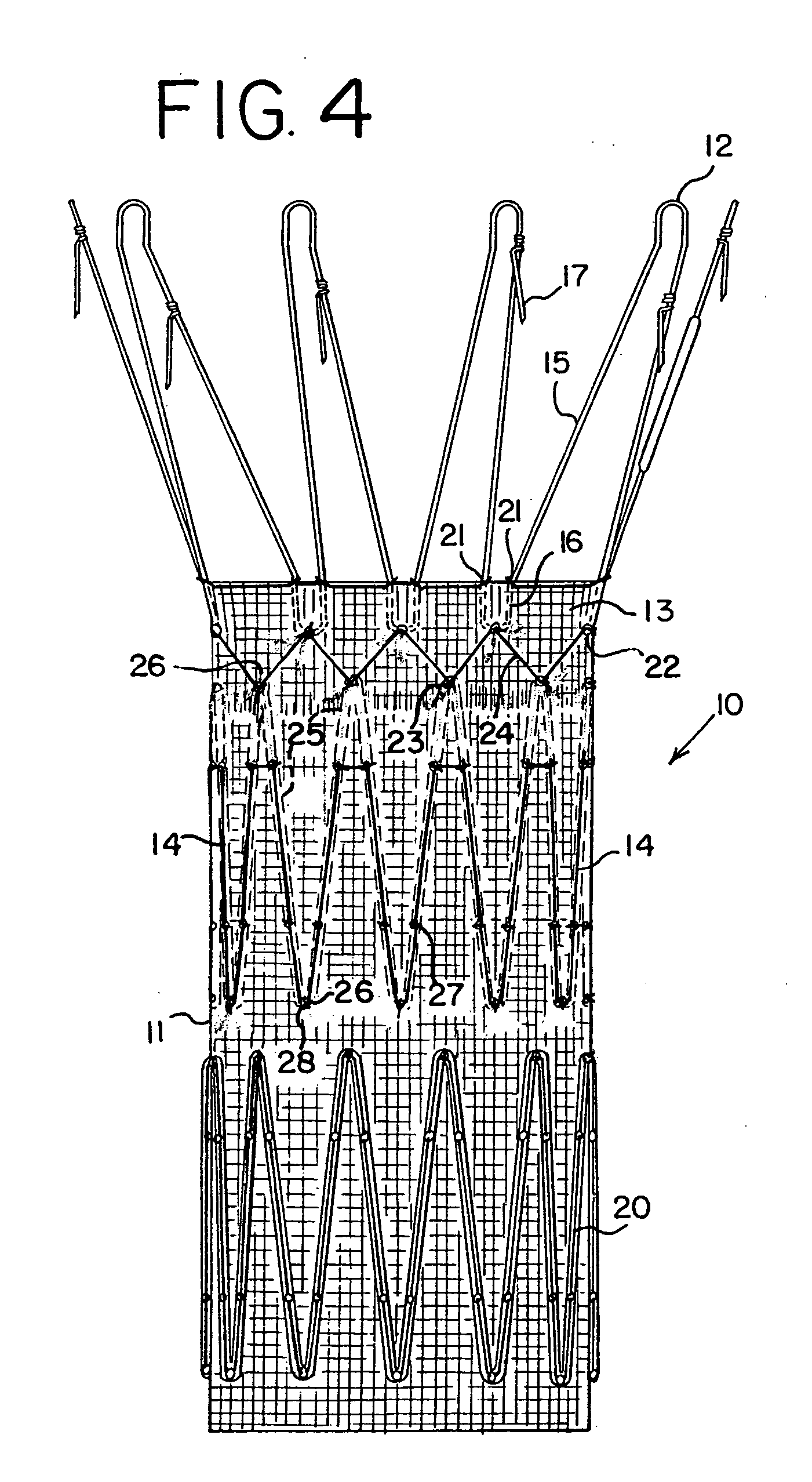
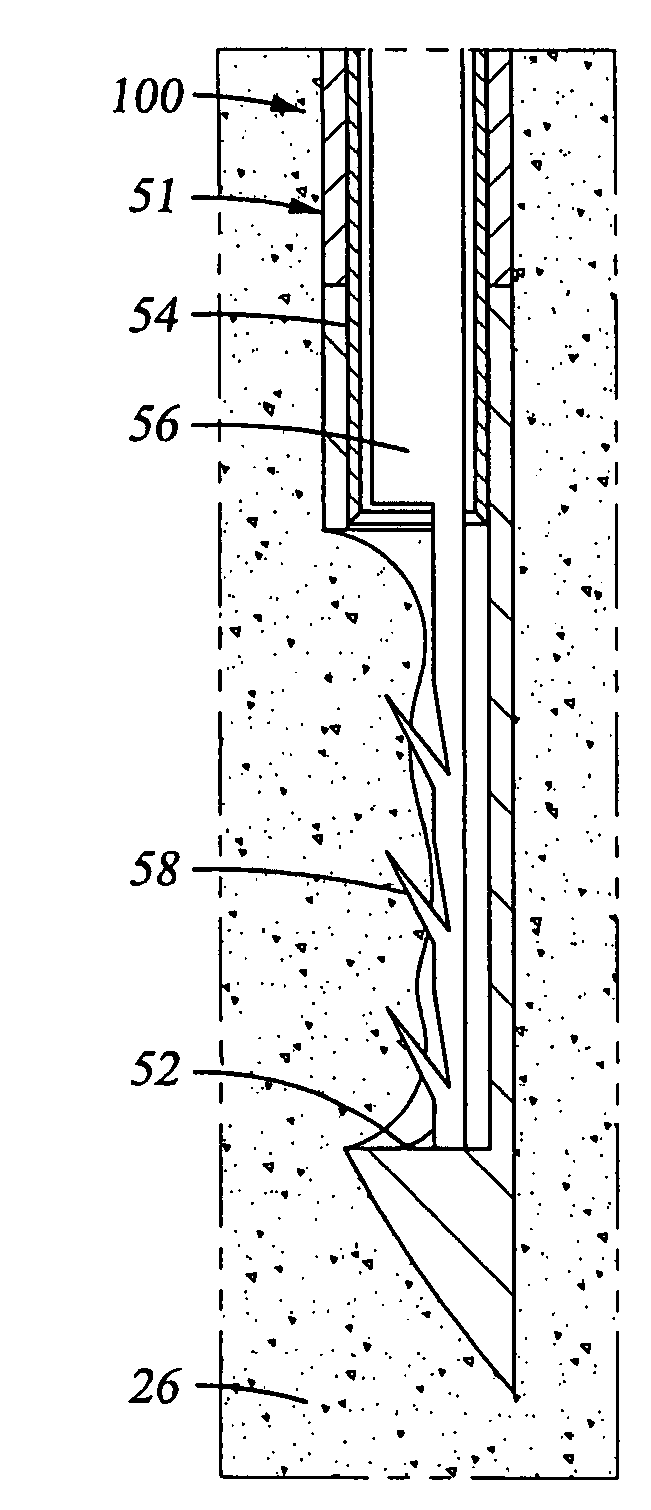
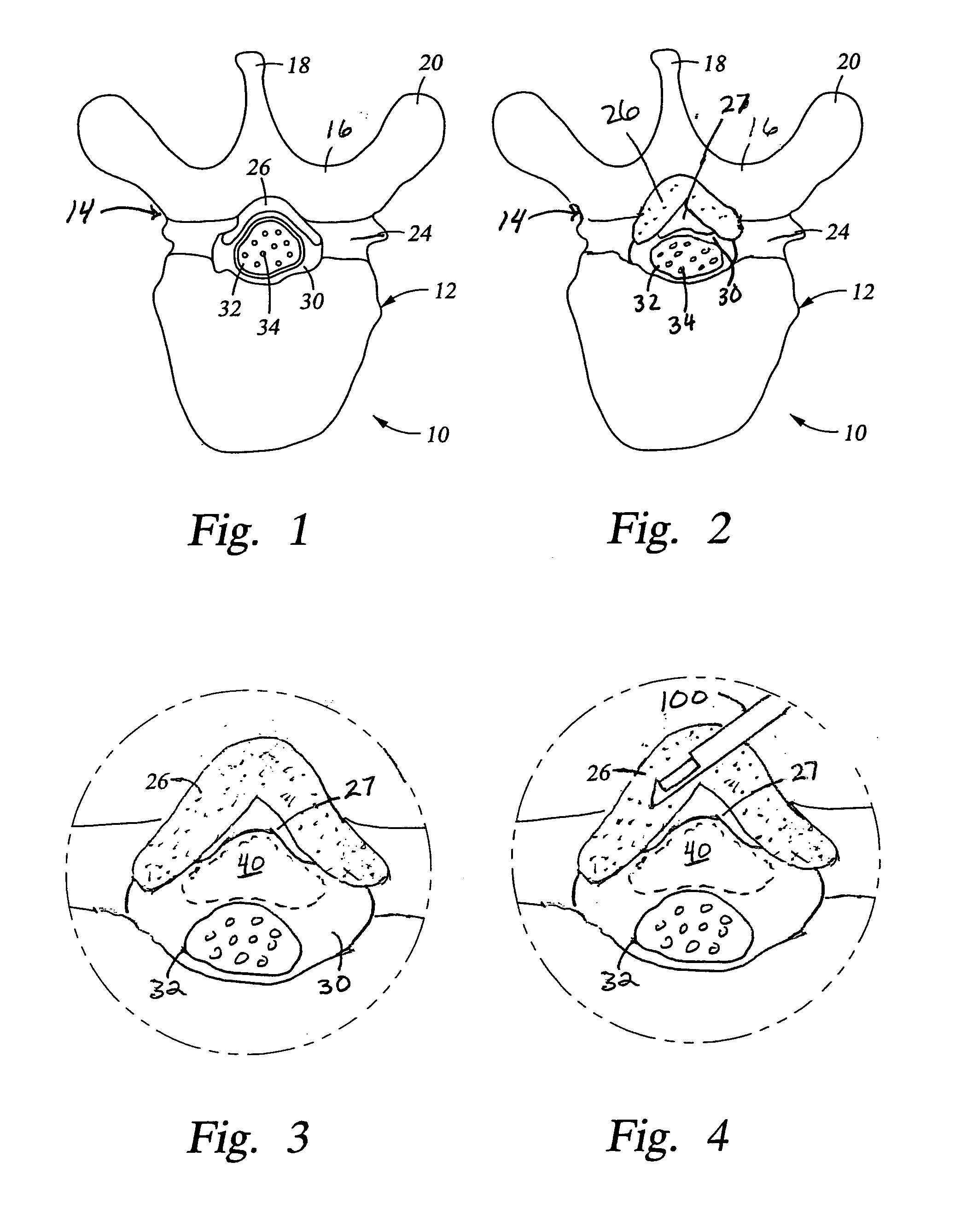
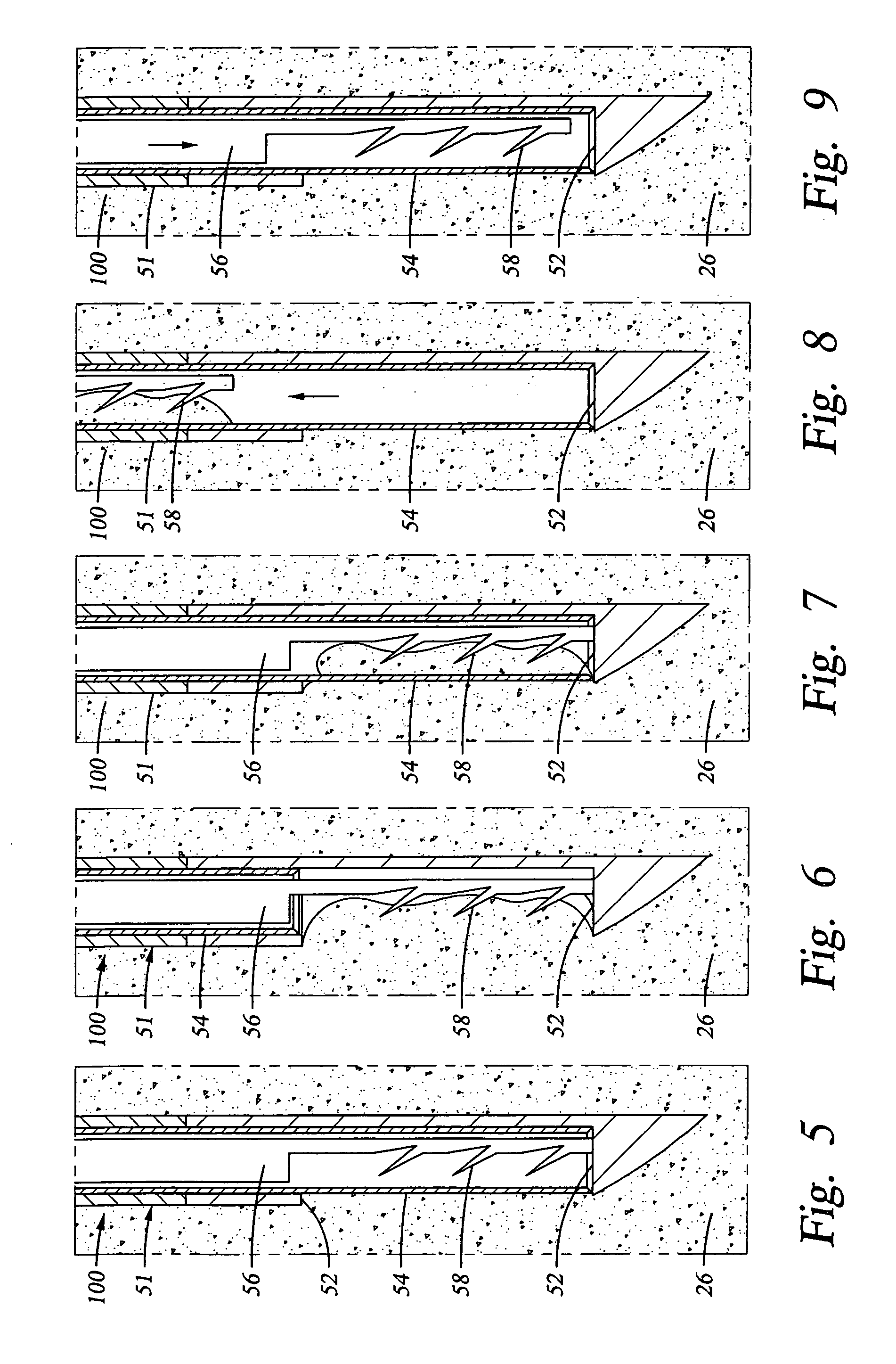
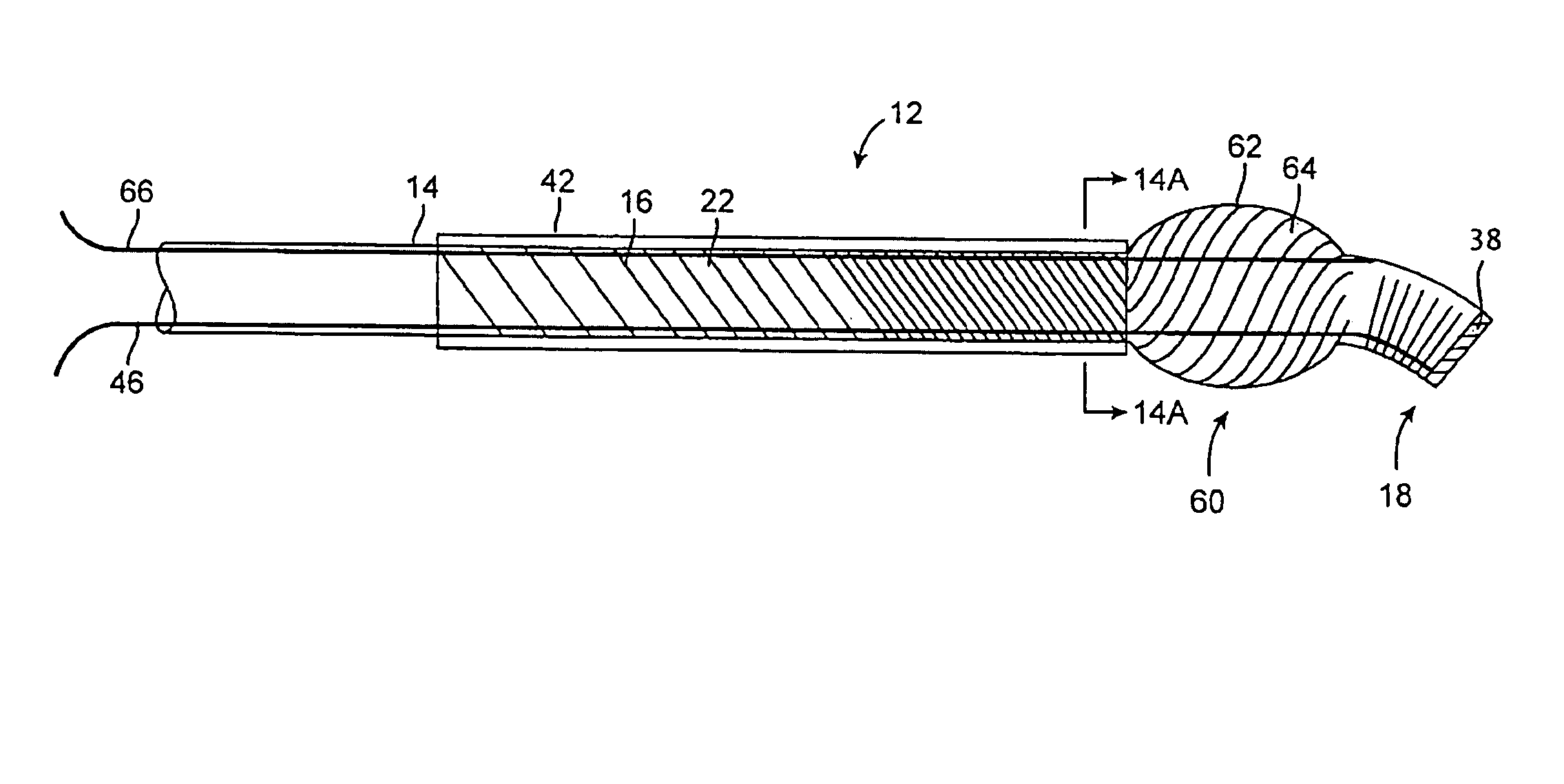
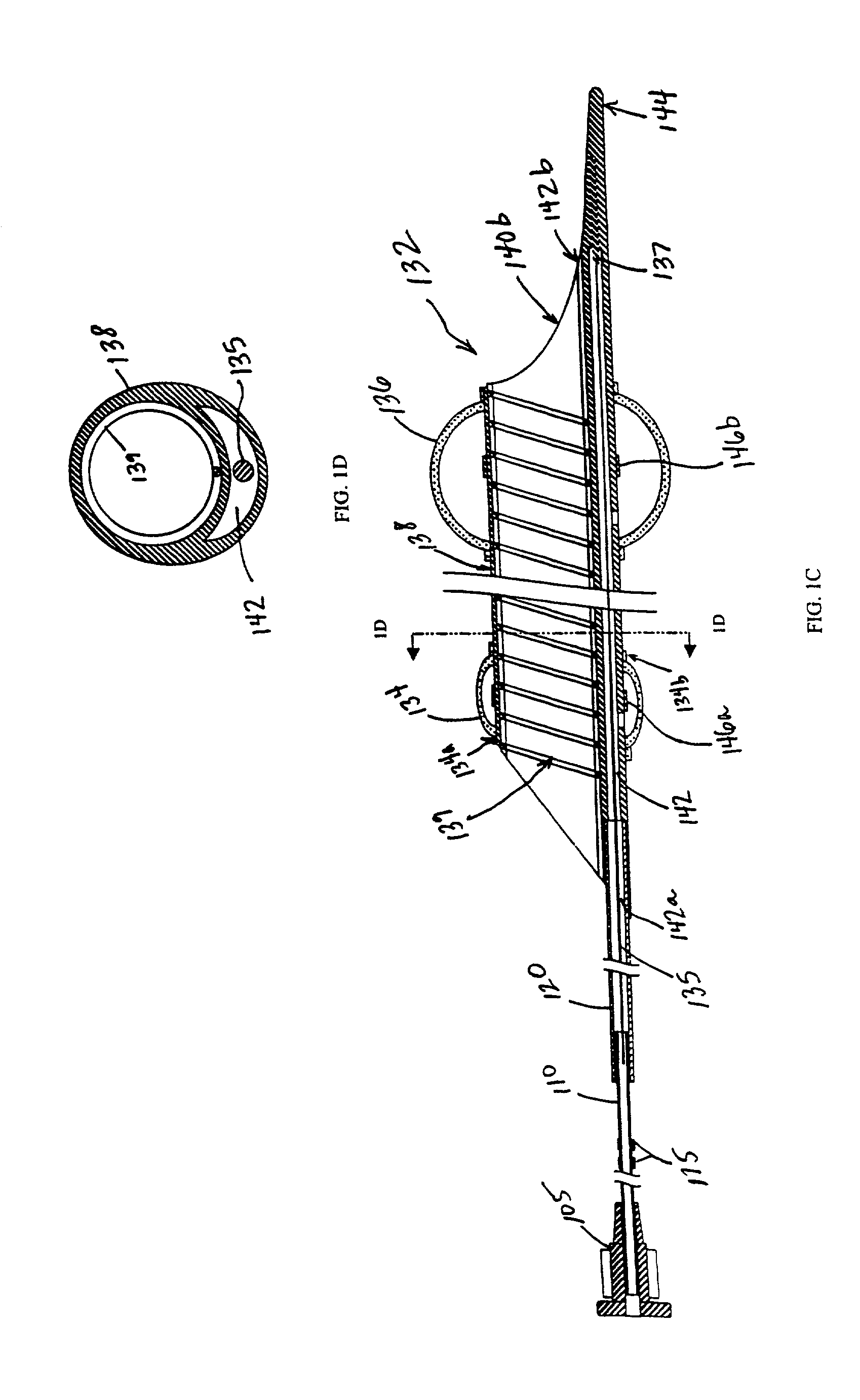
An endoluminal prosthetic device for placement in a body lumen is formed by stitching stents to a graft. A first or anchoring stent is used for securing a graft made of biocompatible material that forms at least one lumen. There is also a second stent. The first and second stents each include a plurality of struts and apices between the struts. At least two of the apices in each of the first and second stents are secured to the graft by stitches. A running suture links at least one stitch of the first stent and one stitch of the second stent. The running suture linking the first stent and the second stent adds strength to the stitches and better secures the first stent to the device. The endoluminal prosthetic device may be used in an aortic vessel to treat stenoses or aneurysms.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Aspiration method
InactiveUS20030009146A1Fast and efficient aspirationReduce amountBalloon catheterGuide wiresSaphenous veinsSaphenous vein graft
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
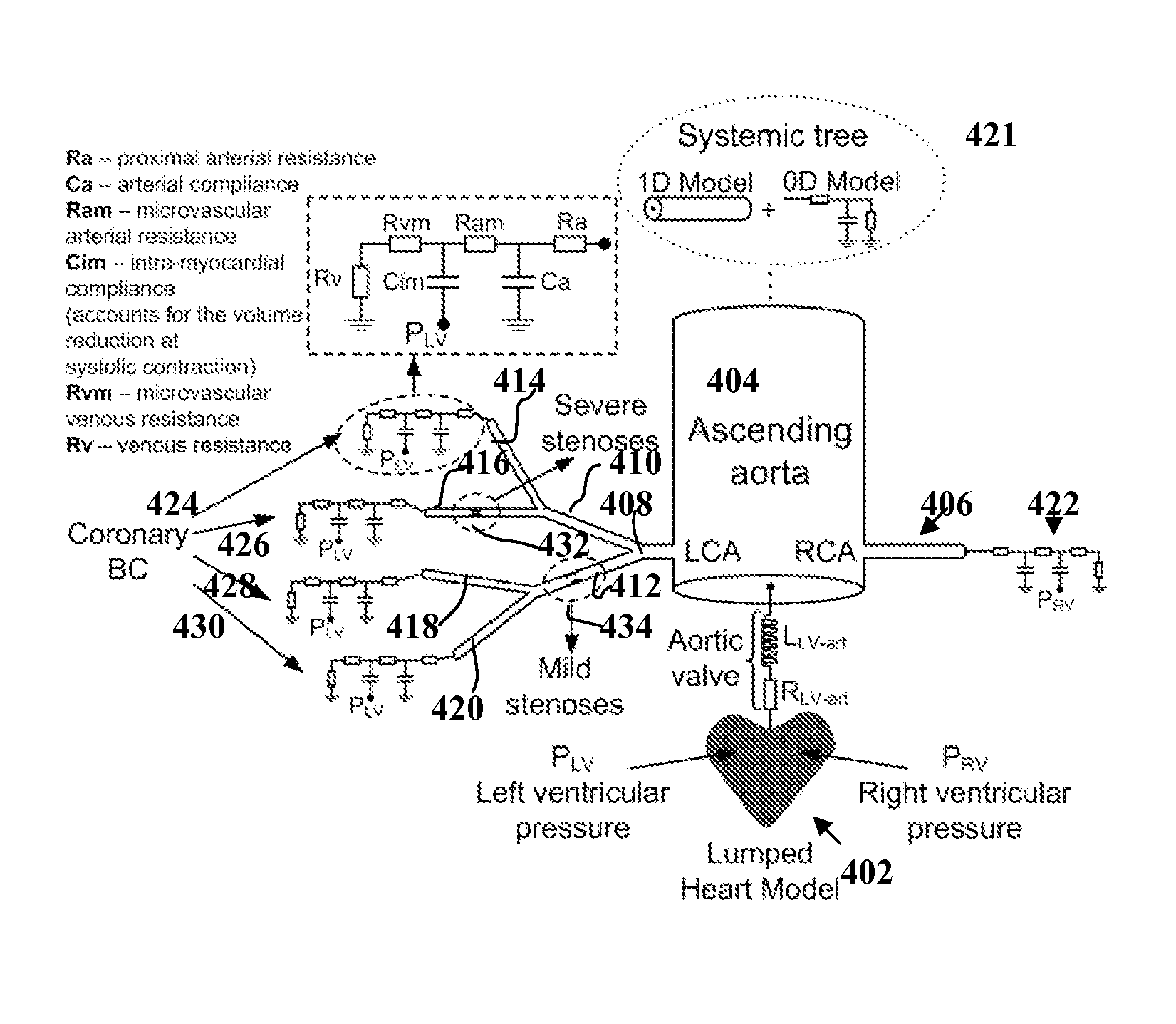
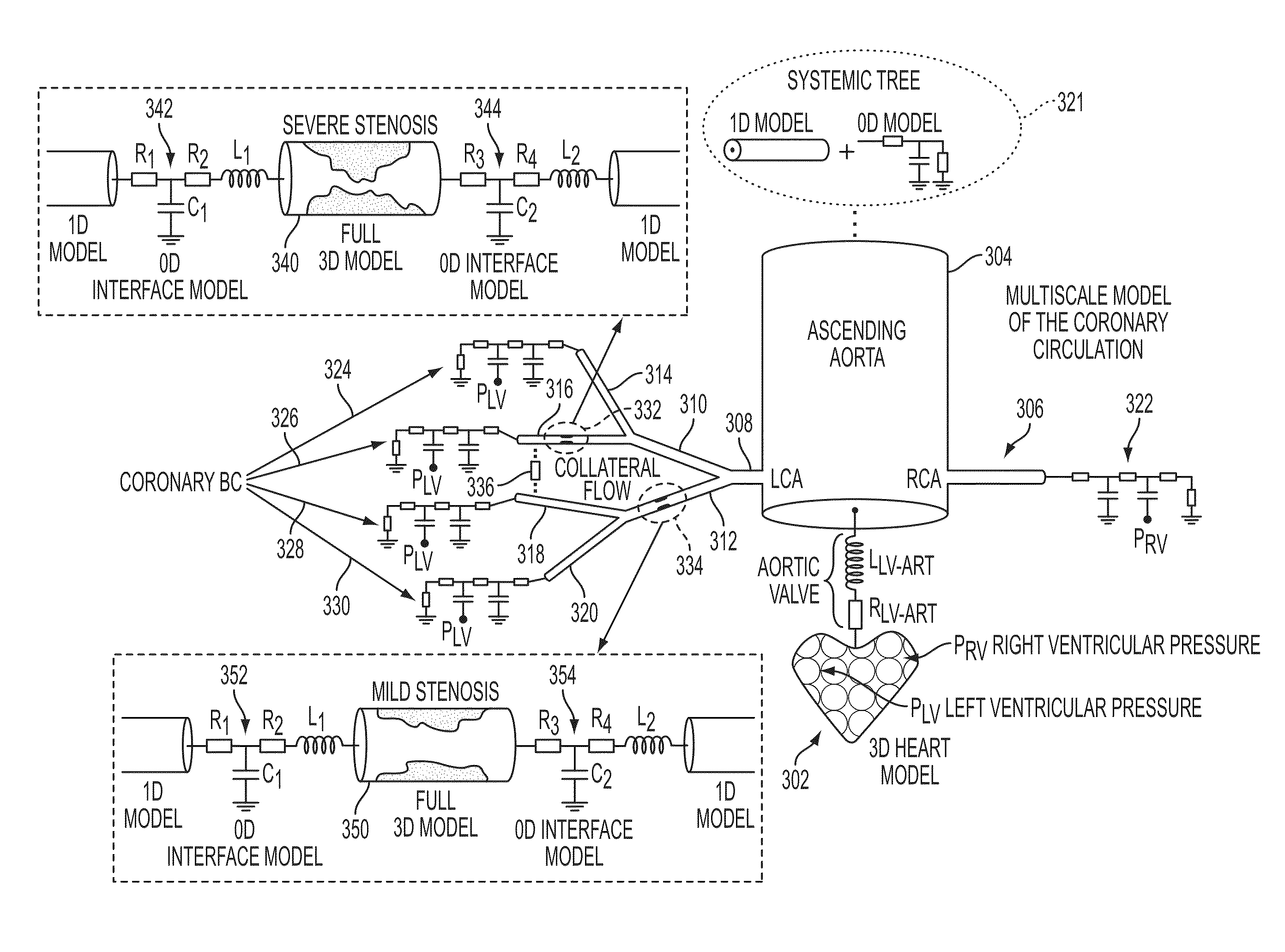
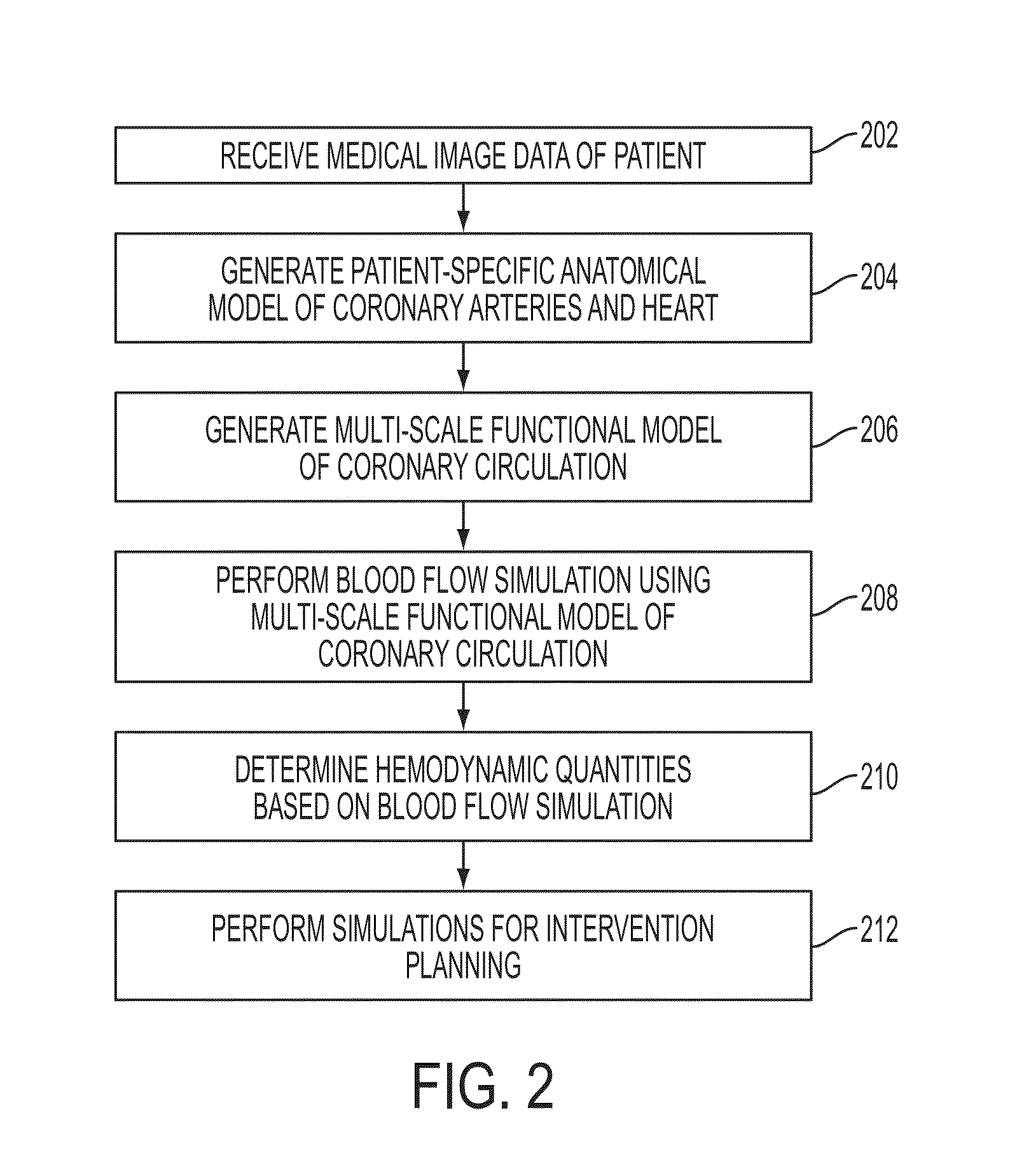
Method and System for Multi-Scale Anatomical and Functional Modeling of Coronary Circulation
ActiveUS20130132054A1Improve predictive performanceImprove clinical managementChemical property predictionChemical structure searchCoronary arteriesIntervention planning
A method and system for multi-scale anatomical and functional modeling of coronary circulation is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of coronary arteries and the heart is generated from medical image data of a patient. A multi-scale functional model of coronary circulation is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model. Blood flow is simulated in at least one stenosis region of at least one coronary artery using the multi-scale function model of coronary circulation. Hemodynamic quantities, such as fractional flow reserve (FFR), are computed to determine a functional assessment of the stenosis, and virtual intervention simulations are performed using the multi-scale function model of coronary circulation for decision support and intervention planning.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
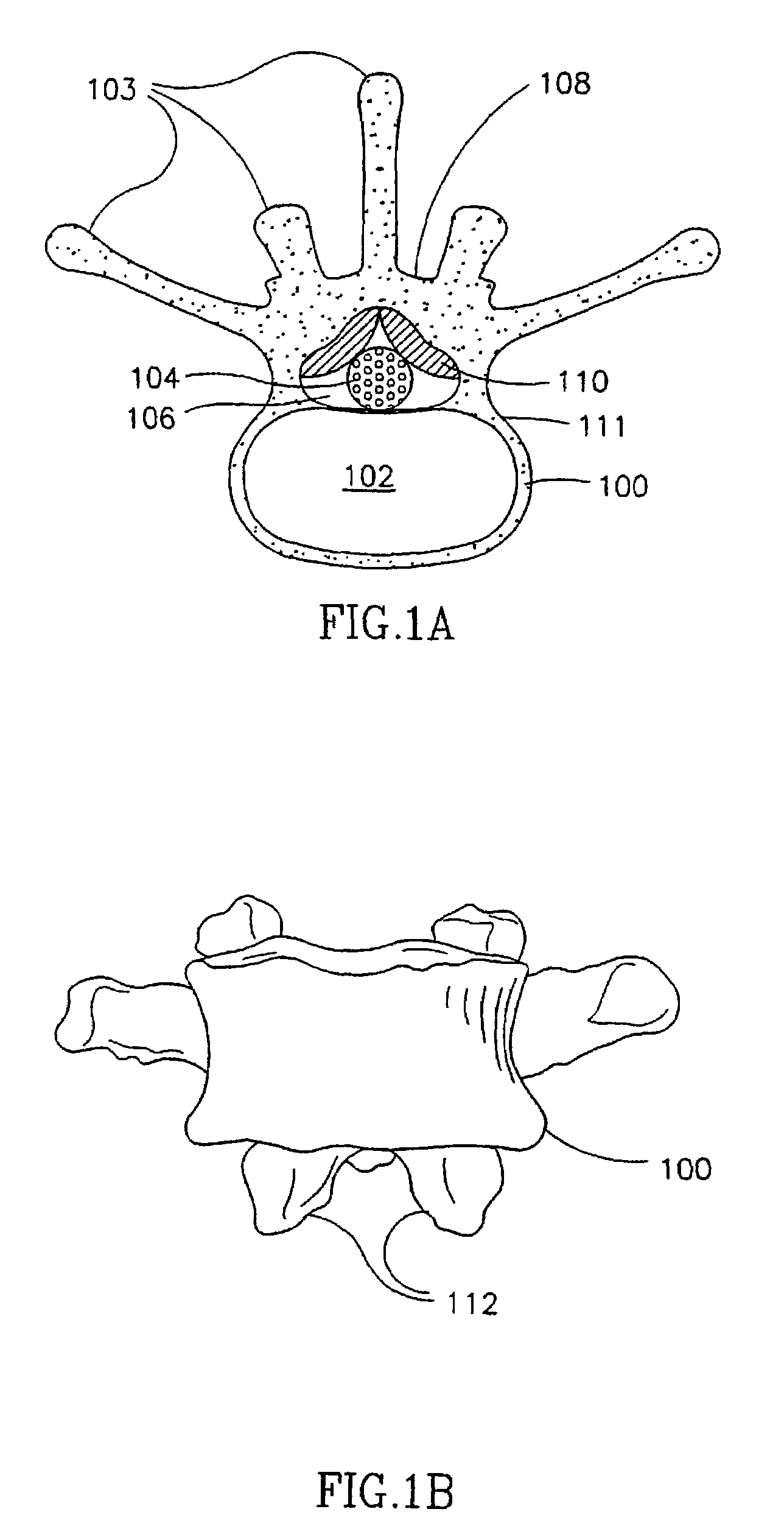
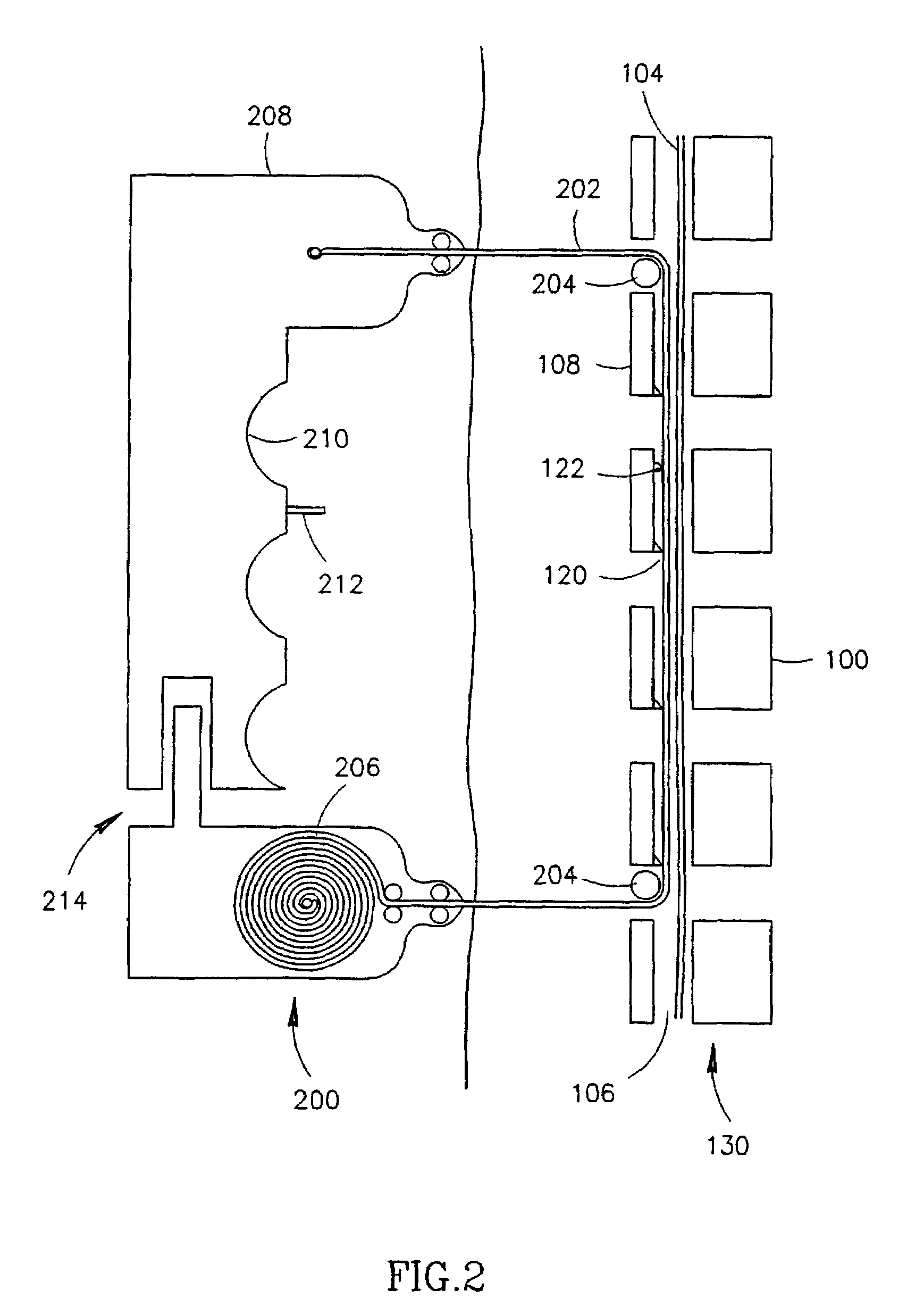
Method and apparatus for spinal procedures
InactiveUS7189240B1Assist in removeExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsSpinal columnSpinal stenosis
A method of treating spinal stenosis, in which a rasp is brought through a part of a spinal channel and then axially moved so that the rasp removes a stenosis in the spinal channel. Optionally, a shield protects a spinal cord or other sensitive tissues in the spinal channel.
Owner:KYPHON
Medical devices with nanoporous layers and topcoats
The present invention relates generally to medical devices with therapy eluting components and methods for making same. More specifically, the invention relates to implantable medical devices having at least one porous layer, and methods for making such devices, and loading such devices with therapeutic agents. A mixture or alloy is placed on the surface of a medical device, then one component of the mixture or alloy is generally removed without generally removing the other components of the mixture or alloy. In some embodiments, a porous layer is adapted for bonding non-metallic coating, including drug eluting polymeric coatings. A porous layer may have a random pore structure or an oriented or directional grain porous structure. One embodiment of the invention relates to medical devices, including vascular stents, having at least one porous layer adapted to resist stenosis or cellular proliferation without requiring elution of therapeutic agents. The invention also includes methods, devices, and specifications for loading of drugs and other therapeutic agents into nanoporous coatings.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC +1
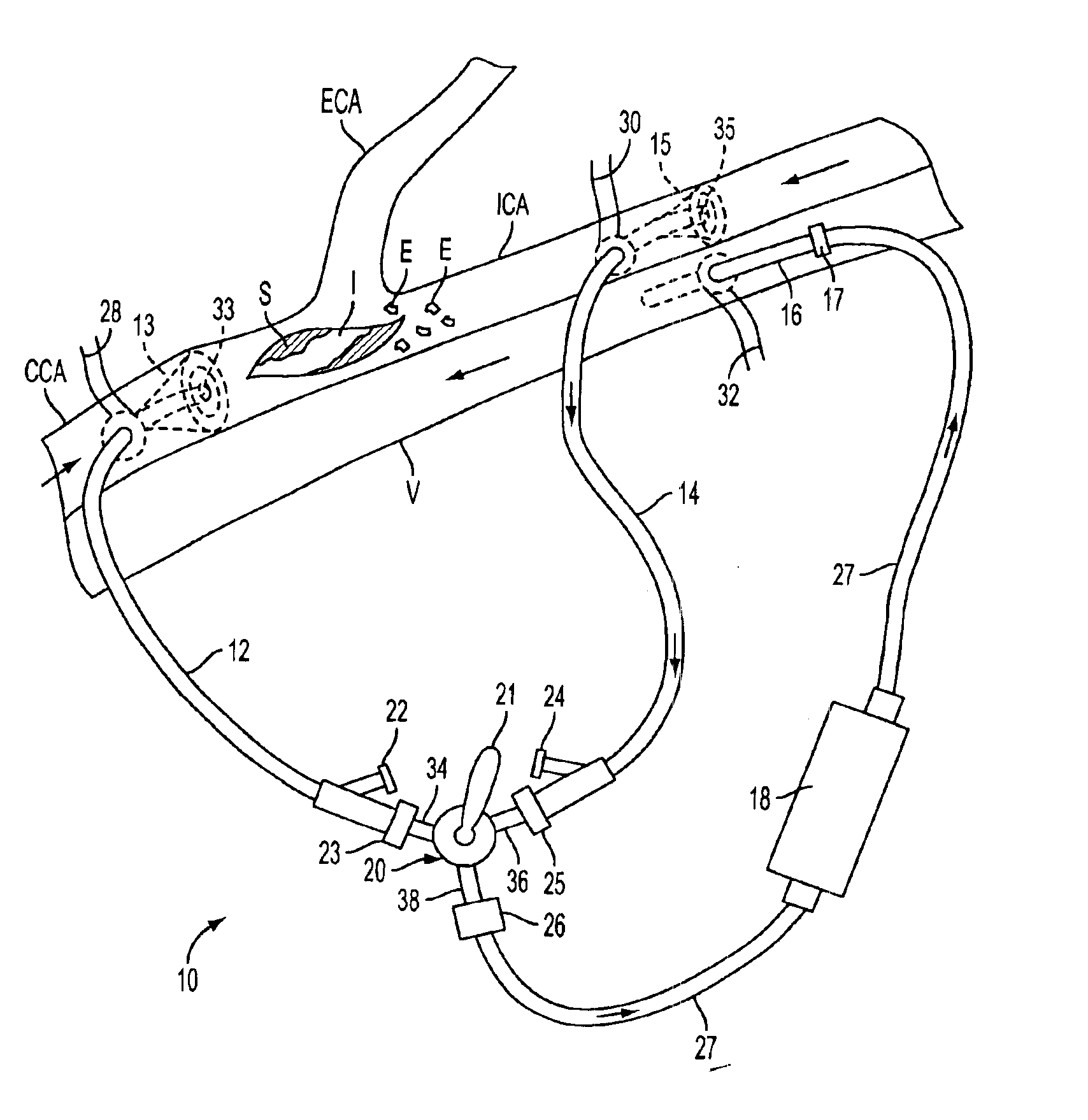
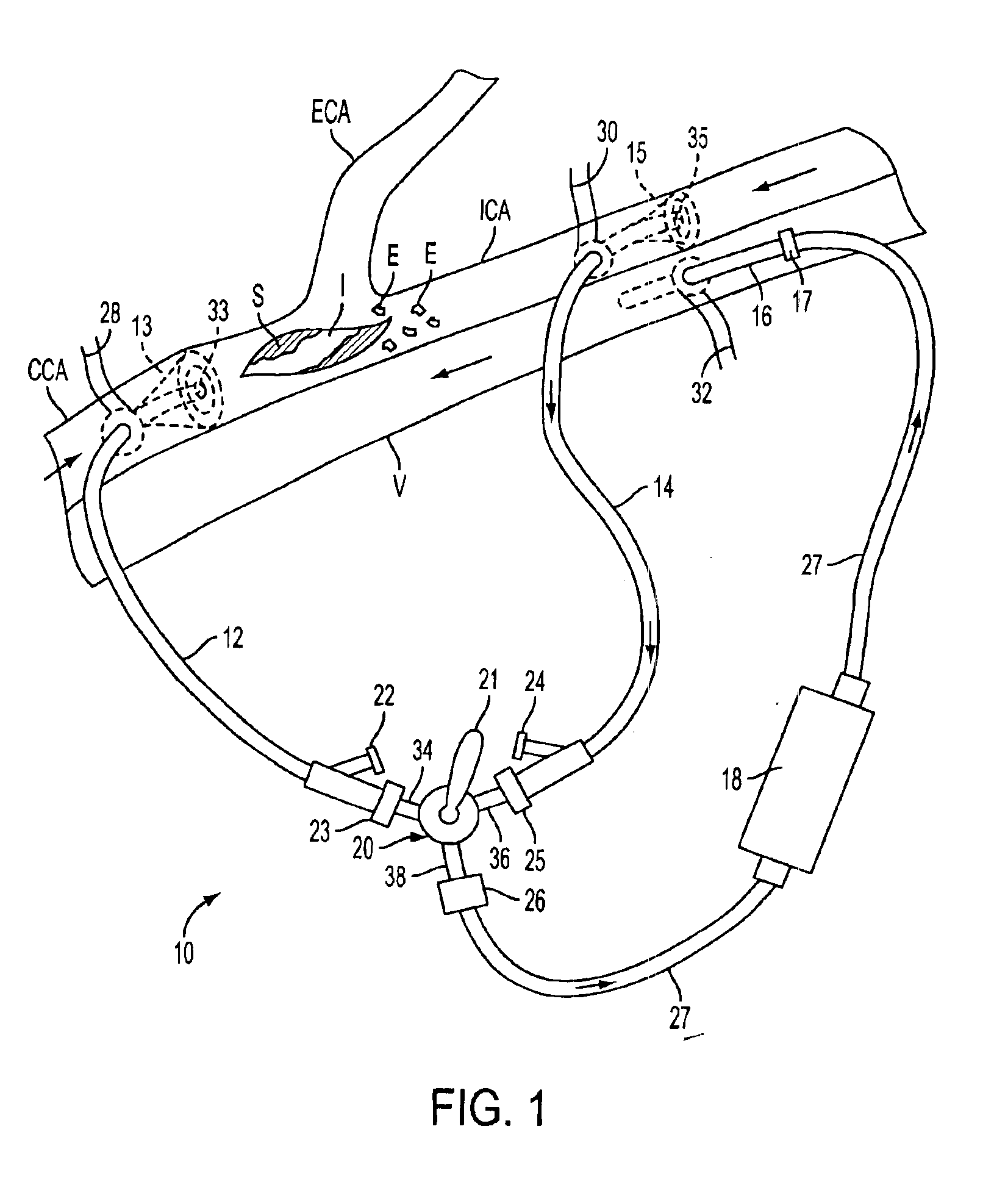
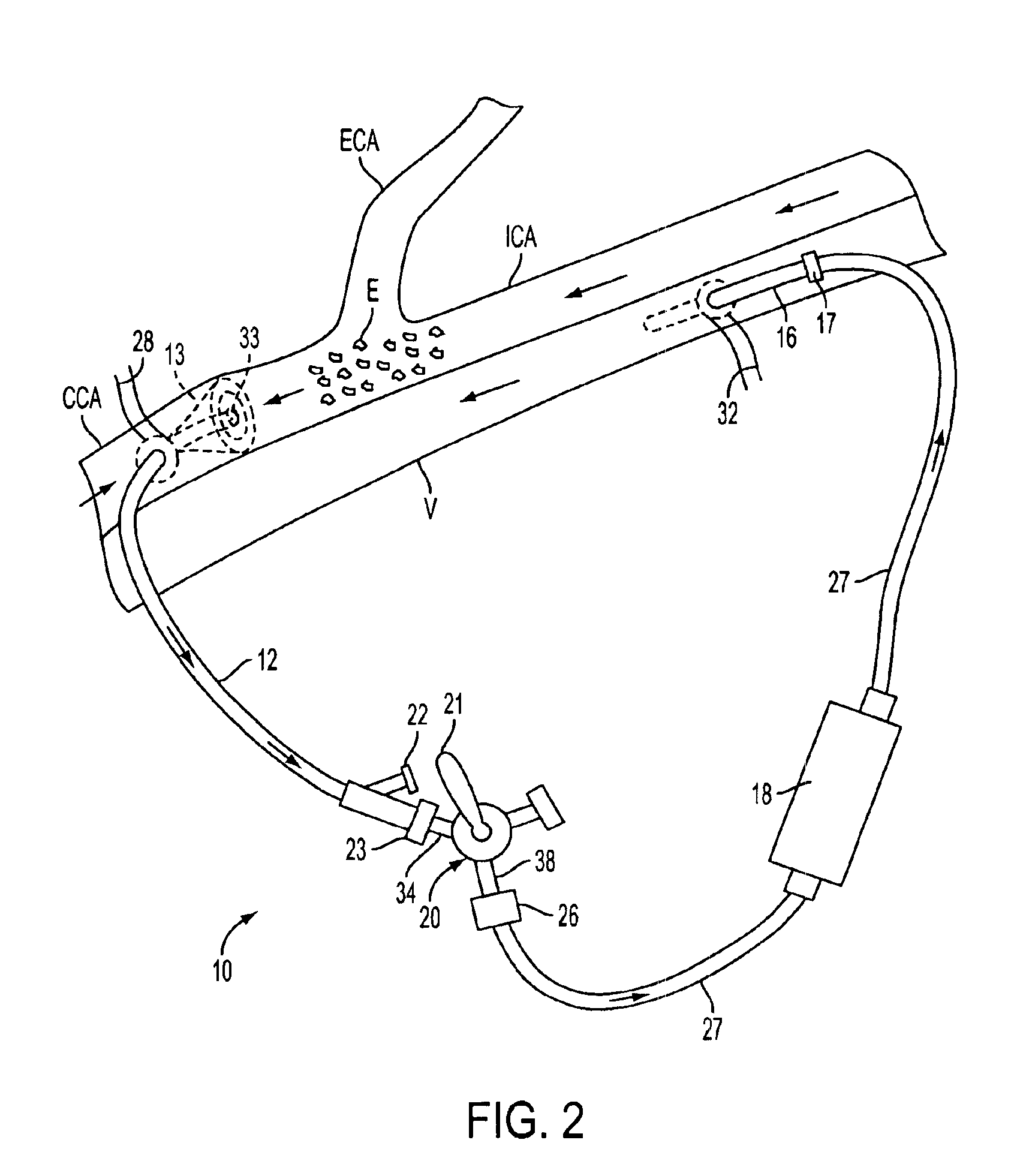
Apparatus and methods for removing emboli during a surgical procedure
Methods and apparatus for removing emboli during an endarterectomy procedure are provided. The present invention provides a proximal catheter disposed proximal to a stenosis and a distal catheter disposed distal to the stenosis. Each catheter may selectively communicate with a venous return catheter via a manifold having a setting controlled by a physician. Blood flows into an aspiration lumen of the distal catheter and is reperfused into a remote vein via the venous return catheter. Additionally, emboli generated during the procedure are removed via an aspiration lumen of the proximal catheter, and filtered blood then is reperfused into the remote vein.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
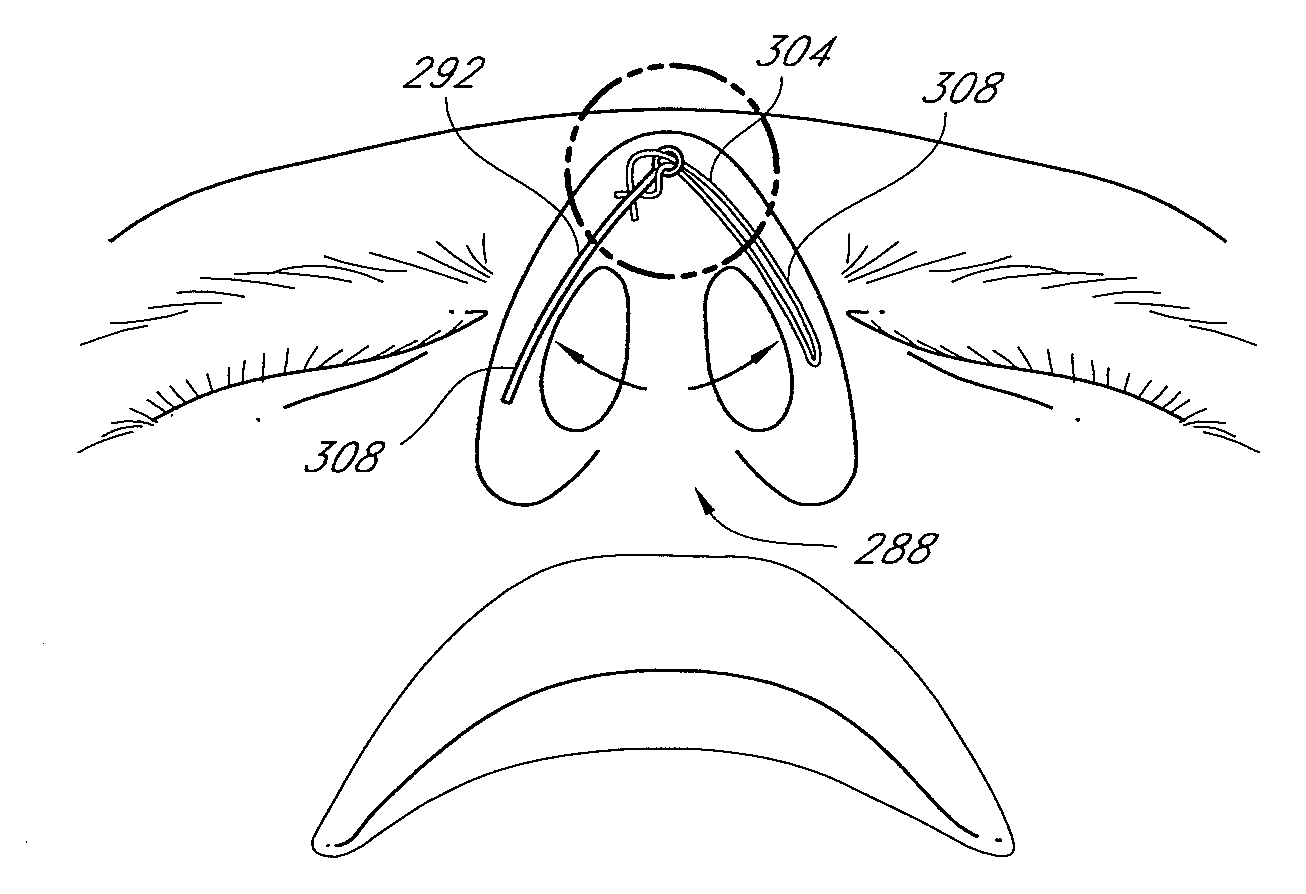
Methods and devices for rhinoplasty and treating internal valve stenosis
ActiveUS20080027480A1Increase the cross-sectional areaIncrease exposureSuture equipmentsNose implantsNasal cavityMitral valve stenosis
Methods and devices for rhinoplasty and treating nasal valve stenosis are disclosed herein. The nasal valve acts as a flow-limiter and can contribute to airway obstruction if resistance within the nasal valve is excessive. In one embodiment, a system for treating nasal valve stenosis includes a first elongate implant and a second elongate implant configured to support the nasal valves when implanted. The implants can be coupled together by connecting elements, such as eyelets, tethers, complementary socket joints, and button-rivet supports.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Non-invasive systems and methods for determining fractional flow reserve
Non-invasive systems and methods for determining fractional flow reserve. At least one method of determining fractional flow reserve within a luminal organ of the present disclosure comprising the steps of positioning a monitoring device external to a luminal organ and near a stenosis, the monitoring device capable of determining at least one characteristic of the stenosis, operating the monitoring device to determine the at least one characteristic of the stenosis, and determining fractional flow reserve at or near the stenosis based upon the at least one characteristic determined by the monitoring device.
Owner:KASSAB GHASSAN S +1
Feature quantification from multidimensional image data
Techniques, hardware, and software are provided for quantification of extensional features of structures of an imaged subject from image data representing a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image. In one embodiment, stenosis in a blood vessel may be quantified from volumetric image data of the blood vessel. A profile from a selected family of profiles is fit to selected image data. An estimate of cross sectional area of the blood vessel is generated based on the fit profile. Area values may be generated along a longitudinal axis of the vessel, and a one-dimensional profile fit to the generated area values. An objective quantification of stenosis in the vessel may be obtained from the area profile. In some cases, volumetric image data representing the imaged structure may be reformatted to facilitate the quantification, when the structural feature varies along a curvilinear axis. A mask is generated for the structural feature to be quantified based on the volumetric image data. A curve representing the curvilinear axis is determined from the mask by center-finding computations, such as moment calculations, and curve fitting. Image data are generated for oblique cuts at corresponding selected orientations with respect to the curvilinear axis, based on the curve and the volumetric image data. The oblique cuts may be used for suitable further processing, such as image display or quantification.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Spinal ligament modification kit
InactiveUS20060036211A1Prevent leakageUse minimizedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A method for treating stenosis in a spine comprises percutaneously accessing the epidural space in a stenotic region of interest, compressing the thecal sac in the region of interest to form a safety zonem, inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone, using the tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis; and utilizing imaging to visualize the position of the tool during at least a part of the reduction step. A tissue excision system for performing percutaneous surgery, comprises a cannula comprising a tissue-penetrating member having a distal end defining an aperture on one side thereof, an occluding member slidably received on or in the cannula and closing the aperture when the occluding member is adjacent the cannula distal end, means for engaging adjacent tissue via the aperture, and cutting means for resecting a section of the engaged tissue.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Stent
A stent (10) which may be used in the treatment of stenosis and particularly ostial stenosis. The stent (10) includes a flange member (15) which engages the surrounding wall of an ostium and anchors the stent (10) in its target vessel. A delivery system for a stent (10) is also disclosed, the delivery system including a membrane (109) or a compression member to hold an intraluminal stent (101) in a first radially compressed state until said stent (101) is delivered to a target site.
Owner:COCKS GRAEME +1
Method of and system for intravenous volume tomographic digital angiography imaging
InactiveUS6075836AQuality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersData acquisition
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
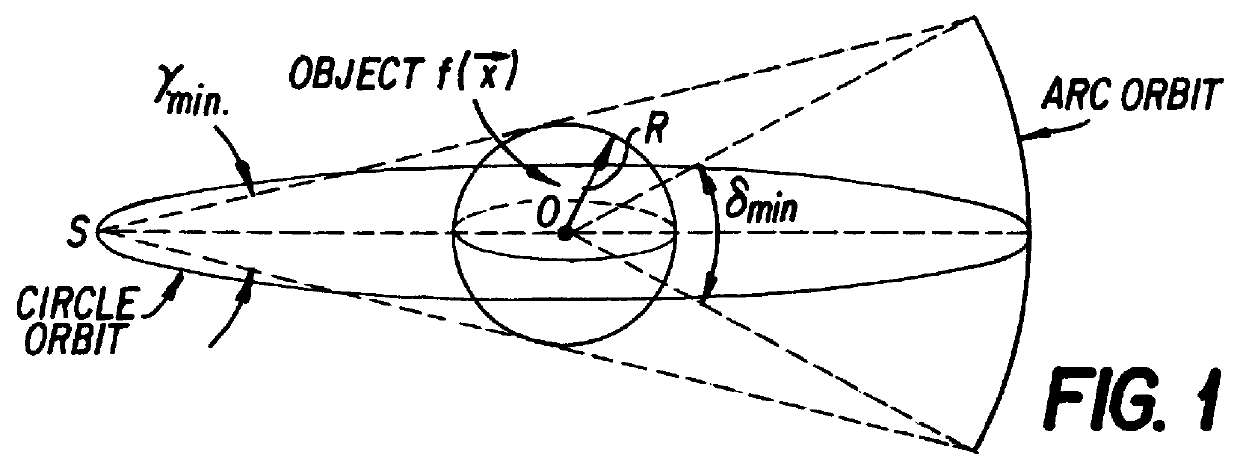
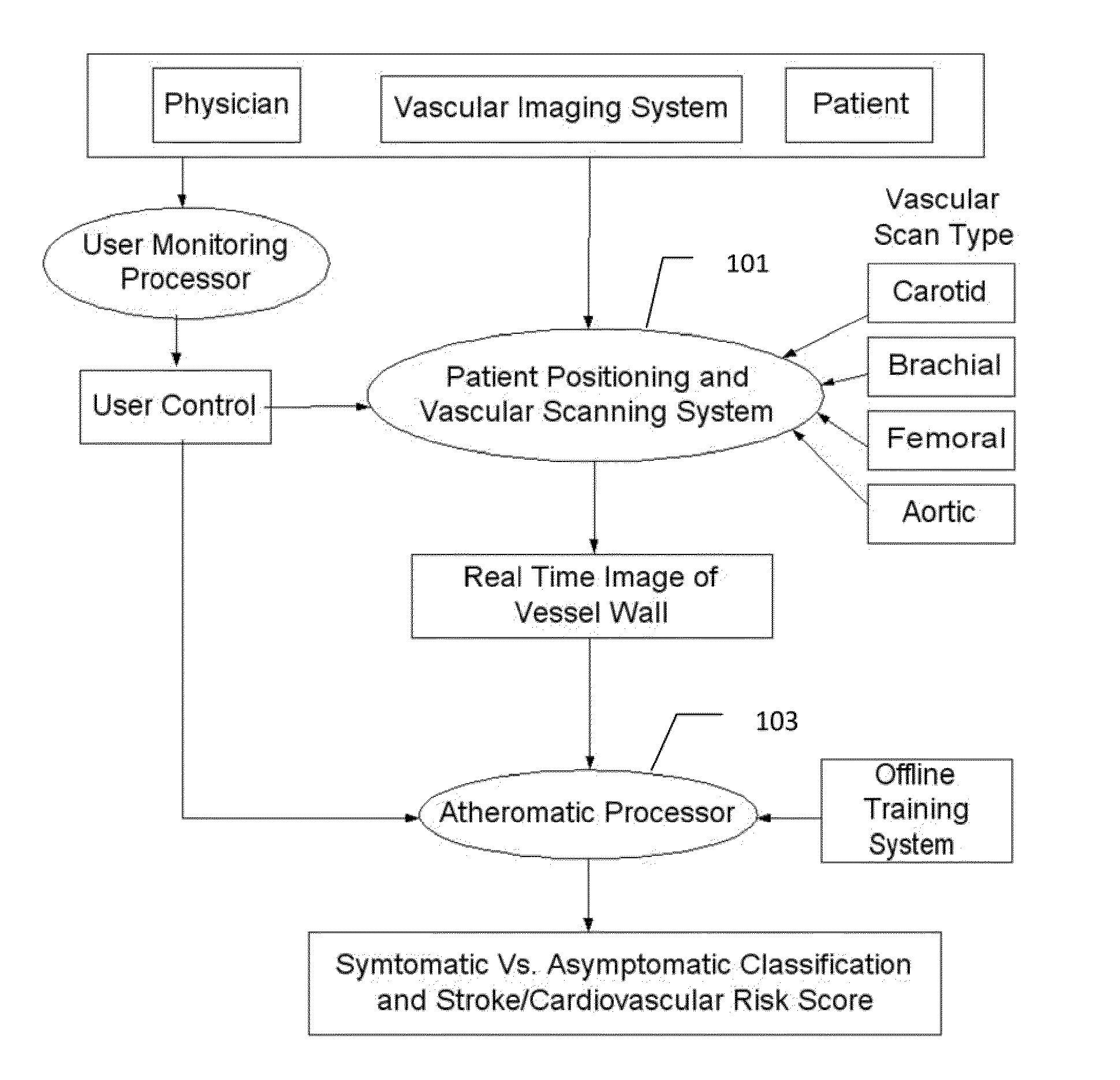
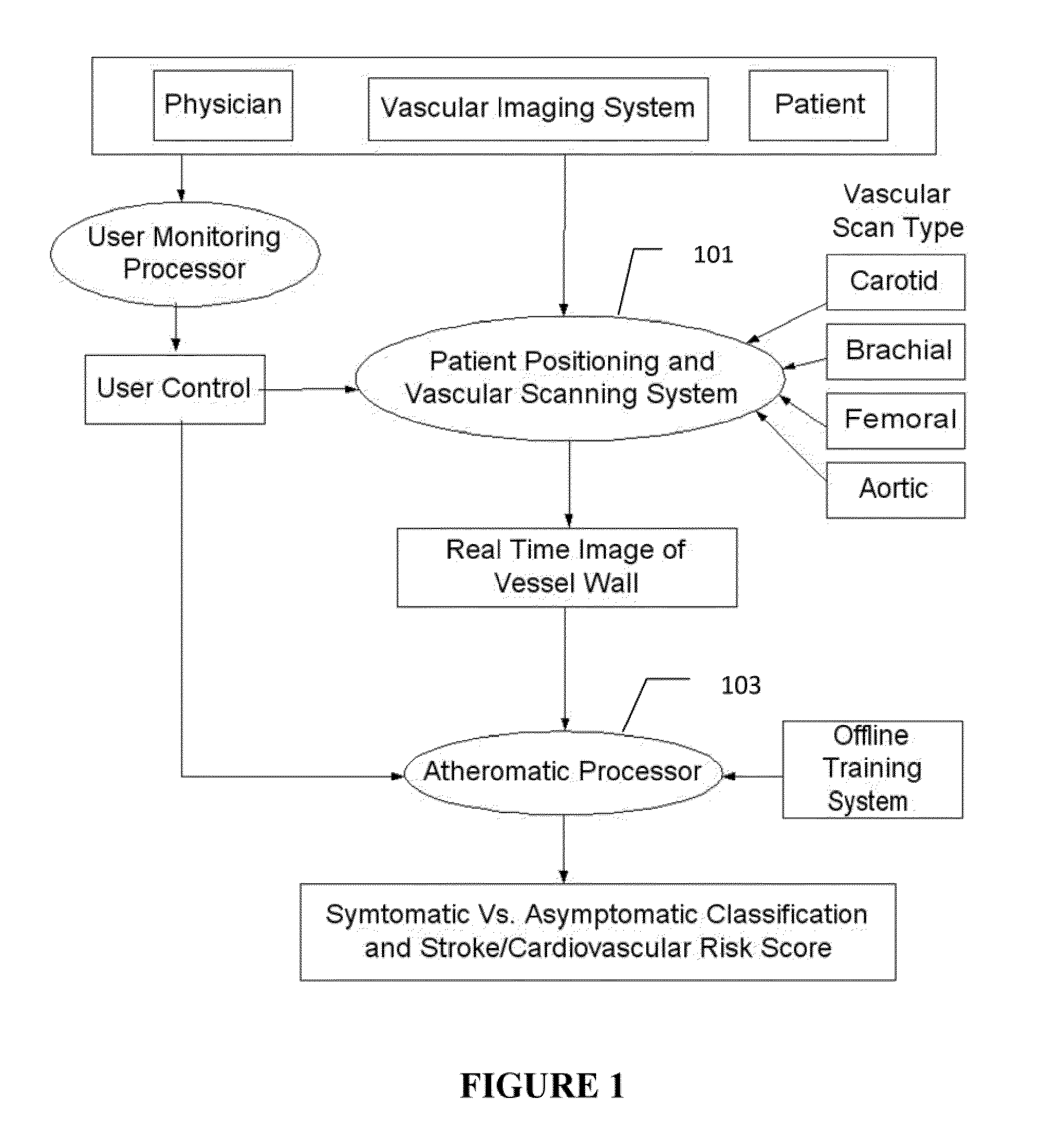
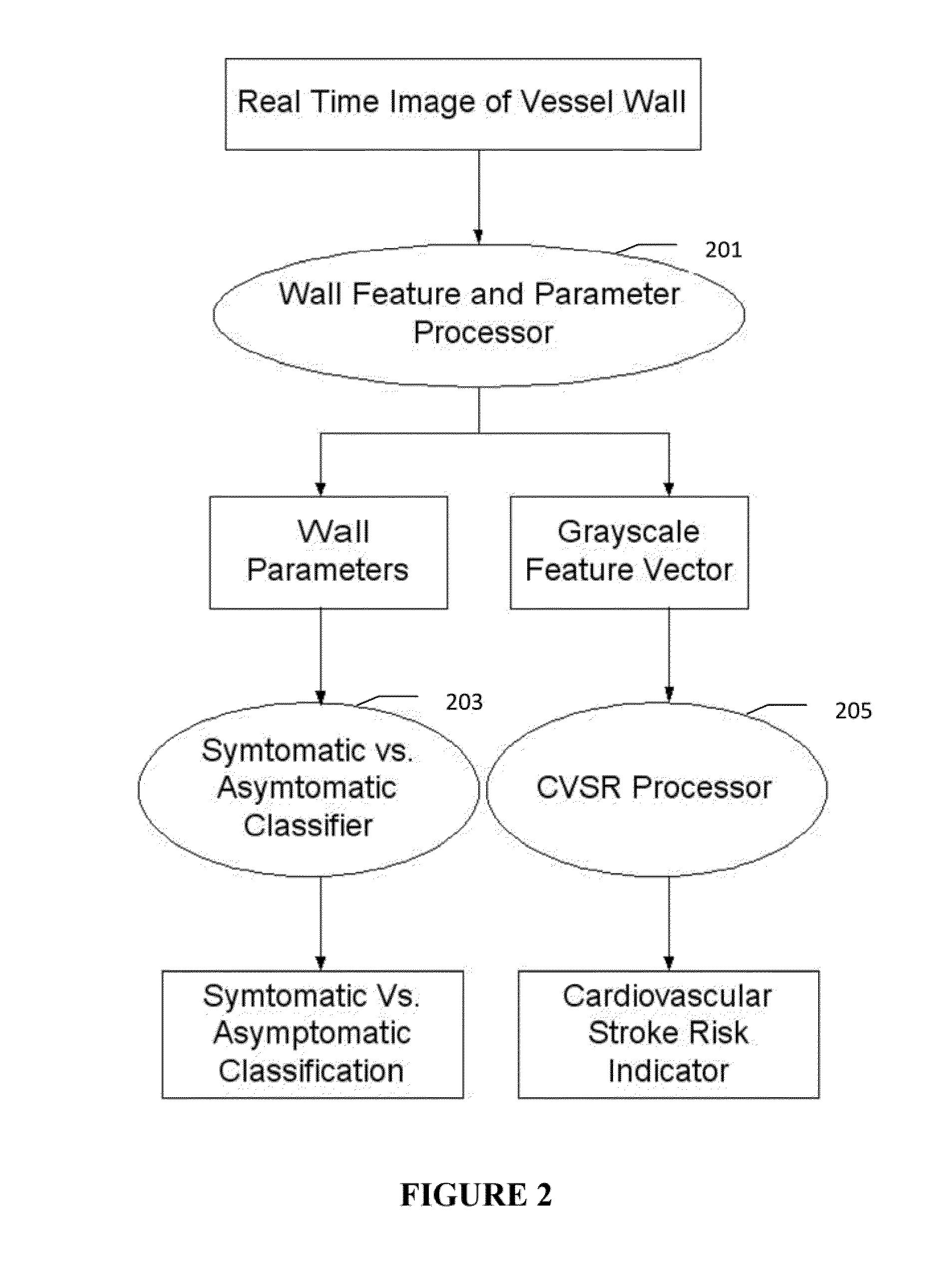
Imaging based symptomatic classification and cardiovascular stroke risk score estimation
InactiveUS20110257545A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementGround truthCross modality
Characterization of carotid atherosclerosis and classification of plaque into symptomatic or asymptomatic along with the risk score estimation are key steps necessary for allowing the vascular surgeons to decide if the patient has to definitely undergo risky treatment procedures that are needed to unblock the stenosis. This application describes a statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular stroke risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which computes: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line from the Database of similar Atherosclerotic Wall Region images. The off-line Classifier is trained from the significant features from (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability, selected using t-test. Symptomatic ground truth information about the training patients is drawn from cross modality imaging such as CT or MR or 3D ultrasound in the form of 0 or 1. Support Vector Machine (SVM) supervised classifier of varying kernel functions is used off-line for training. The Atheromatic™ system is also demonstrated for Radial Basis Probabilistic Neural Network (RBPNN), or Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier or Decision Trees (DT) Classifier for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification. The obtained training parameters are then used to evaluate the test set. The system also yields the cardiovascular stroke risk score value on the basis of the four set of wall features.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
ActiveUS20140058715A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Spinal ligament modification
ActiveUS20060036272A1Prevent leakageUse minimizedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A method for treating stenosis in a spine comprises percutaneously accessing the epidural space in a stenotic region of interest, compressing the thecal sac in the region of interest to form a safety zonem, inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone, using the tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis; and utilizing imaging to visualize the position of the tool during at least a part of the reduction step. A tissue excision system for performing percutaneous surgery, comprises a cannula comprising a tissue-penetrating member having a distal end defining an aperture on one side thereof, an occluding member slidably received on or in the cannula and closing the aperture when the occluding member is adjacent the cannula distal end, means for engaging adjacent tissue via the aperture, and cutting means for resecting a section of the engaged tissue.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
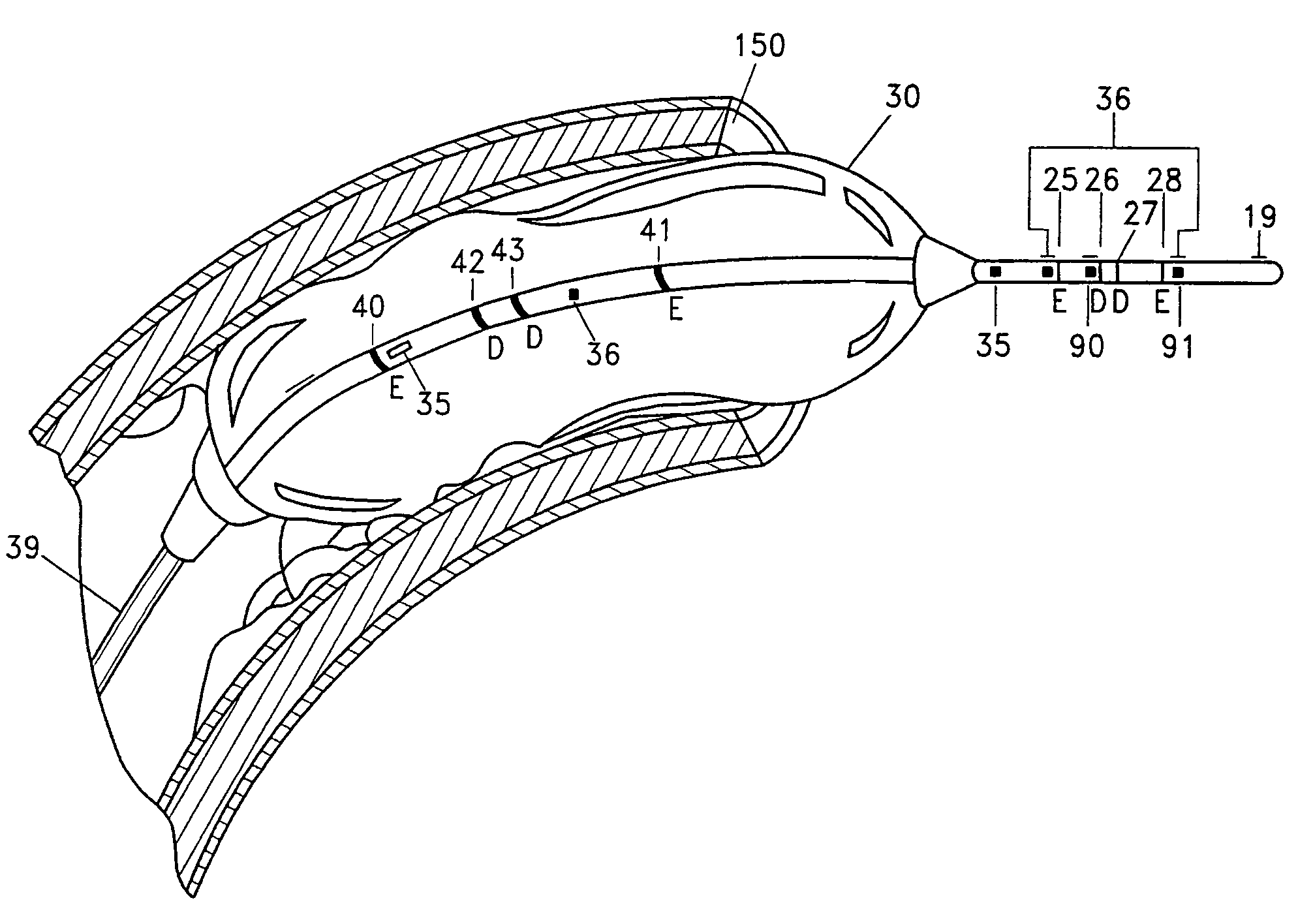
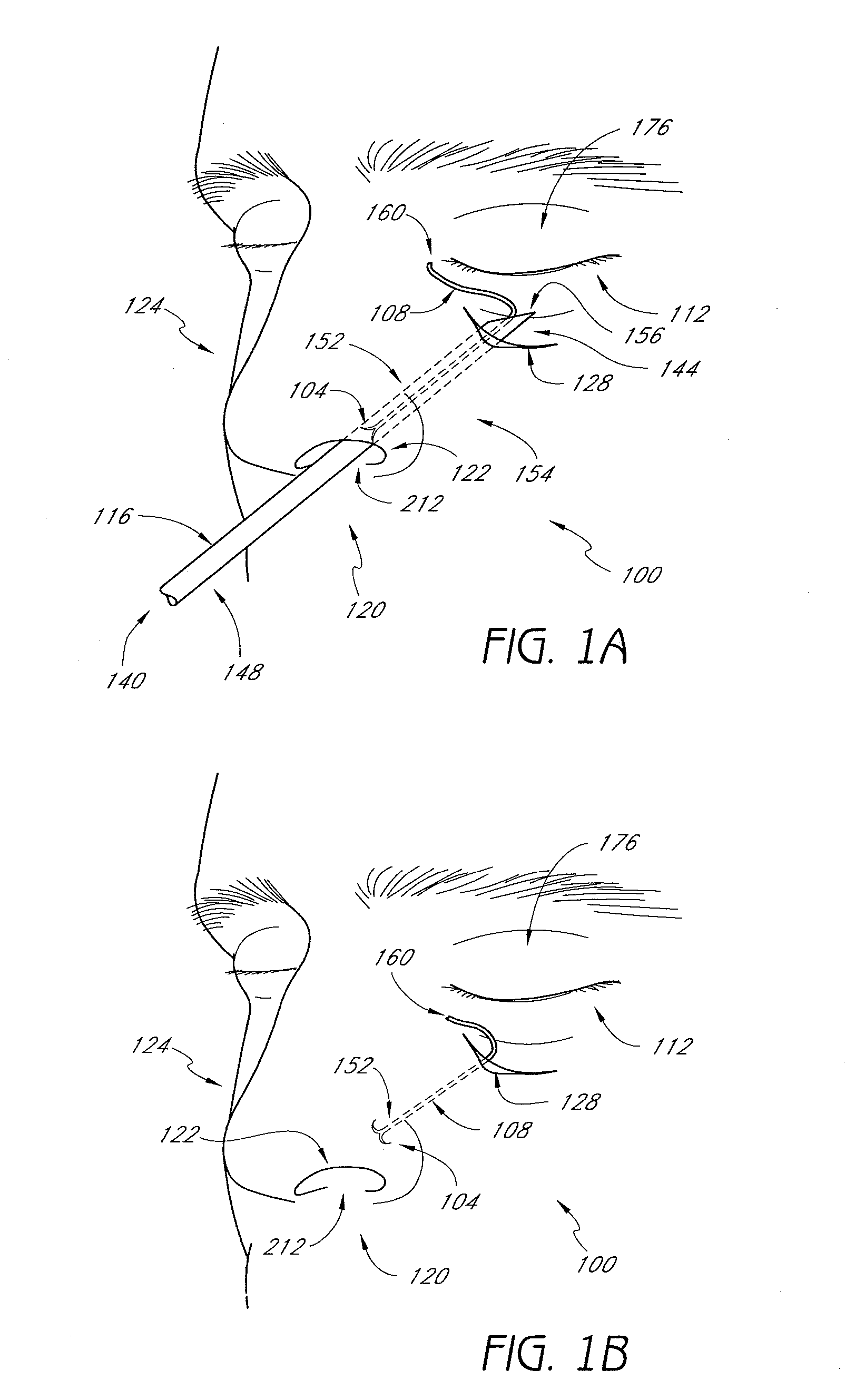
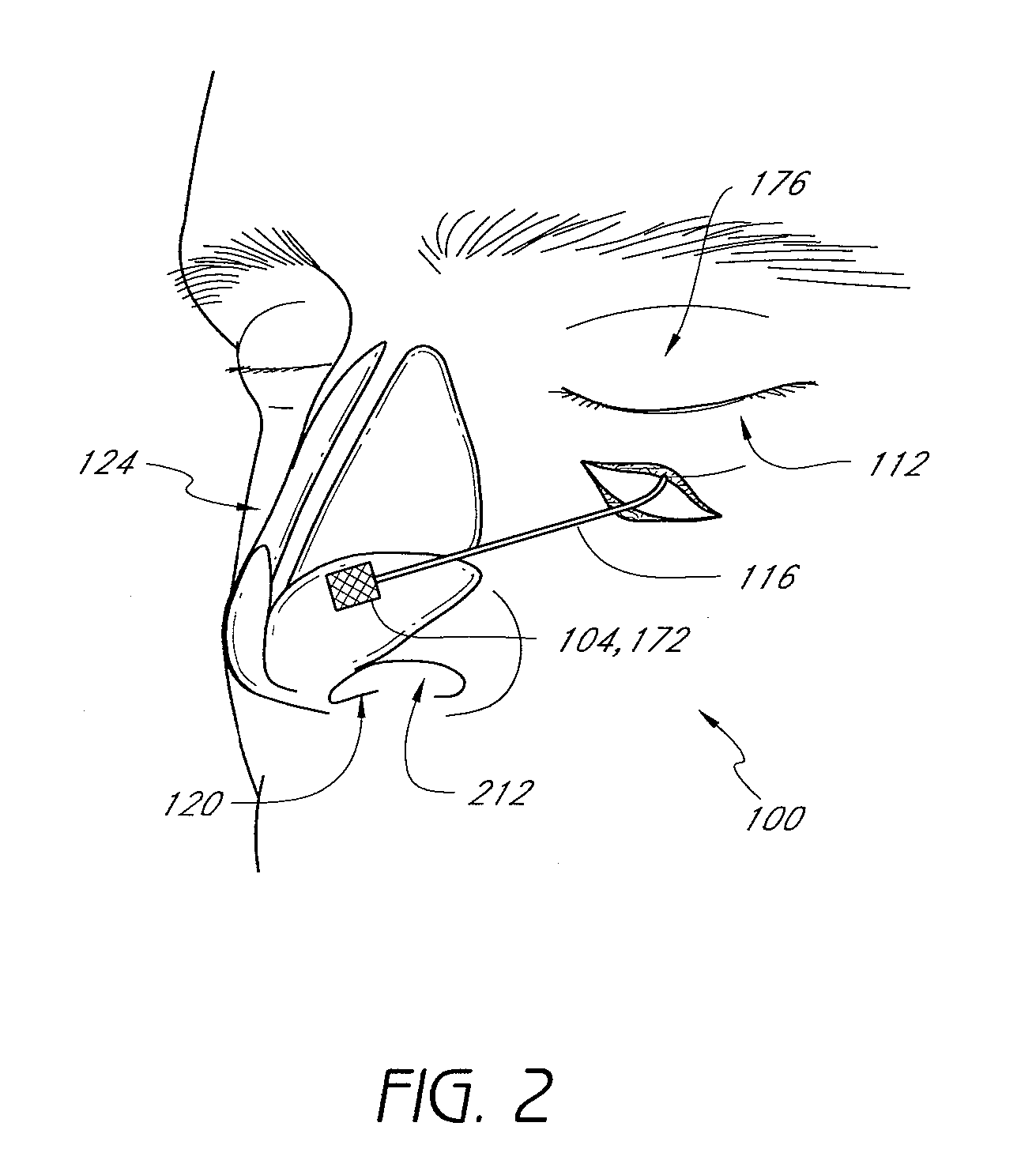
Steerable distal support system
InactiveUS7381198B2Sufficient maneuverabilitySufficient torqueabilitySurgeryMedical devicesSupporting systemMedicine
A steerable distal support system for accessing stenosis, partial occlusions, or complete occlusions within a body lumen. The steerable distal support system generally includes an elongate member that comprises a proximal portion, a more flexible intermediate portion and a deflectable distal tip. The deflectable distal tip is at a distal end of the elongate body to facilitate directionality and positioning of the steerable distal support system to the target site. Optionally, an expandable centering assembly may be disposed on the steerable support assembly to center and anchor the steerable support assembly within the body lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device, system, and method for detecting, localizing, and characterizing plaque-induced stenosis of a blood vessel
InactiveUS20060106321A1Easy constructionSimple in useOrgan movement/changes detectionPerson identificationVulnerable plaqueCompressibility
The present invention is of system, device, and method for detection, localization, and characterization of plaque-induced stenosis of a blood vessel. More particularly, the present invention relates to a balloon catheter having an expandable balloon insertable into a blood vessel, which balloon comprises a plurality of pressure sensors operable to detect stenosis of the vessel, and further operable to report degrees of compressibility of stenotic regions of plaque within the vessel, thereby distinguishing between standard and vulnerable plaque.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
Guidewire with multiple radiopaque marker sections
An over-the-wire balloon catheter has a radiopaque marker thereon at a known distance from a distal end of the catheter. An elongated flexible guide wire has a plurality of longitudinally spaced radiopaque markers on a distal portion thereof, with adjacent markers on the guide wire being longitudinally spaced at a distance equal to the known distance between the distal end of the catheter and its radiopaque marker. The guide wire is advanced through an artery until one of its markers is positioned at a desired location relative to a stenosis. Subsequently, the balloon catheter is advanced over the guide wire until the radiopaque marker of the catheter is in a predetermined position relationship to the radiopaque marker of the guide wire which has aligned on the stenosis. The cooperating radiopaque markers of the guide wire and catheter thus allow the balloon member of the catheter to be positioned relative to the stenosis in a timely fashion without the need to constantly inject fluoroscopic dye to view the stenosis.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Emboli protection devices and related methods of use
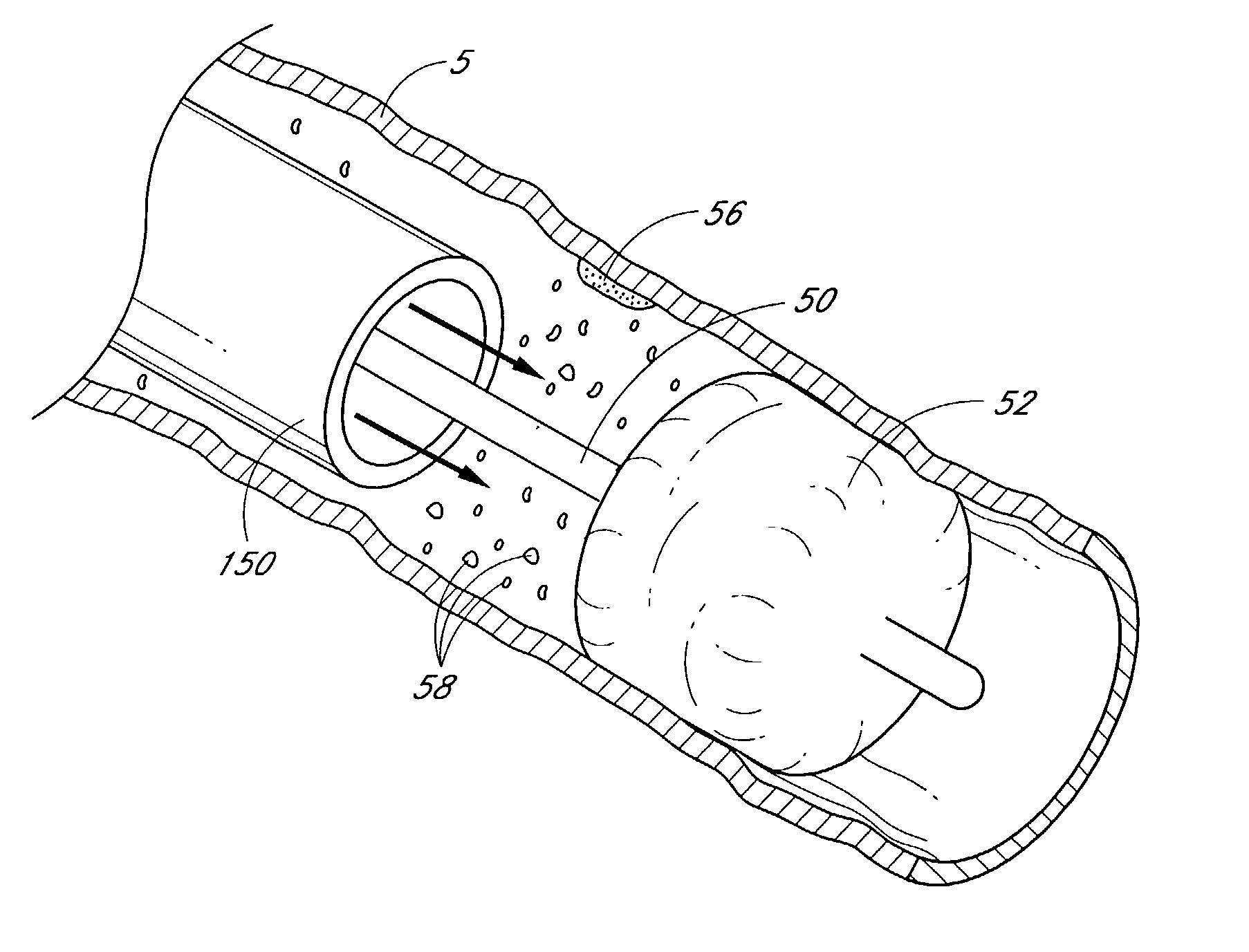
An evacuation sheath assembly and method of treating occluded vessels which reduces the risk of distal embolization during vascular interventions is provided. The evacuation sheath assembly includes an elongated tube defining an evacuation lumen having proximal and distal ends. A proximal sealing surface is provided on a proximal portion of the tube and is configured to form a seal with a lumen of a guided catheter. A distal sealing surface is provided on a distal portion of the tube and is configured to form a seal with a blood vessel. Obturator assemblies and infusion catheter assemblies are provided to be used with the evacuation sheath assembly. A method of treatment of a blood vessel using the evacuation sheath assembly includes advancing the evacuation sheath assembly into the blood vessel through a guide catheter. Normal antegrade blood flow in the blood vessel proximate to the stenosis is stopped and the stenosis is treated. Retrograde blood flow is induced within the blood vessel to carry embolic material dislodged during treating into the evacuation sheath assembly. If necessary to increase retrograde flow, the coronary sinus may be at least partially occluded. Alternatively, antegrade flow may be permitted while flow is occluded at the treatment site.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Expandable supportive endoluminal grafts
Owner:LIFEPORT SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com