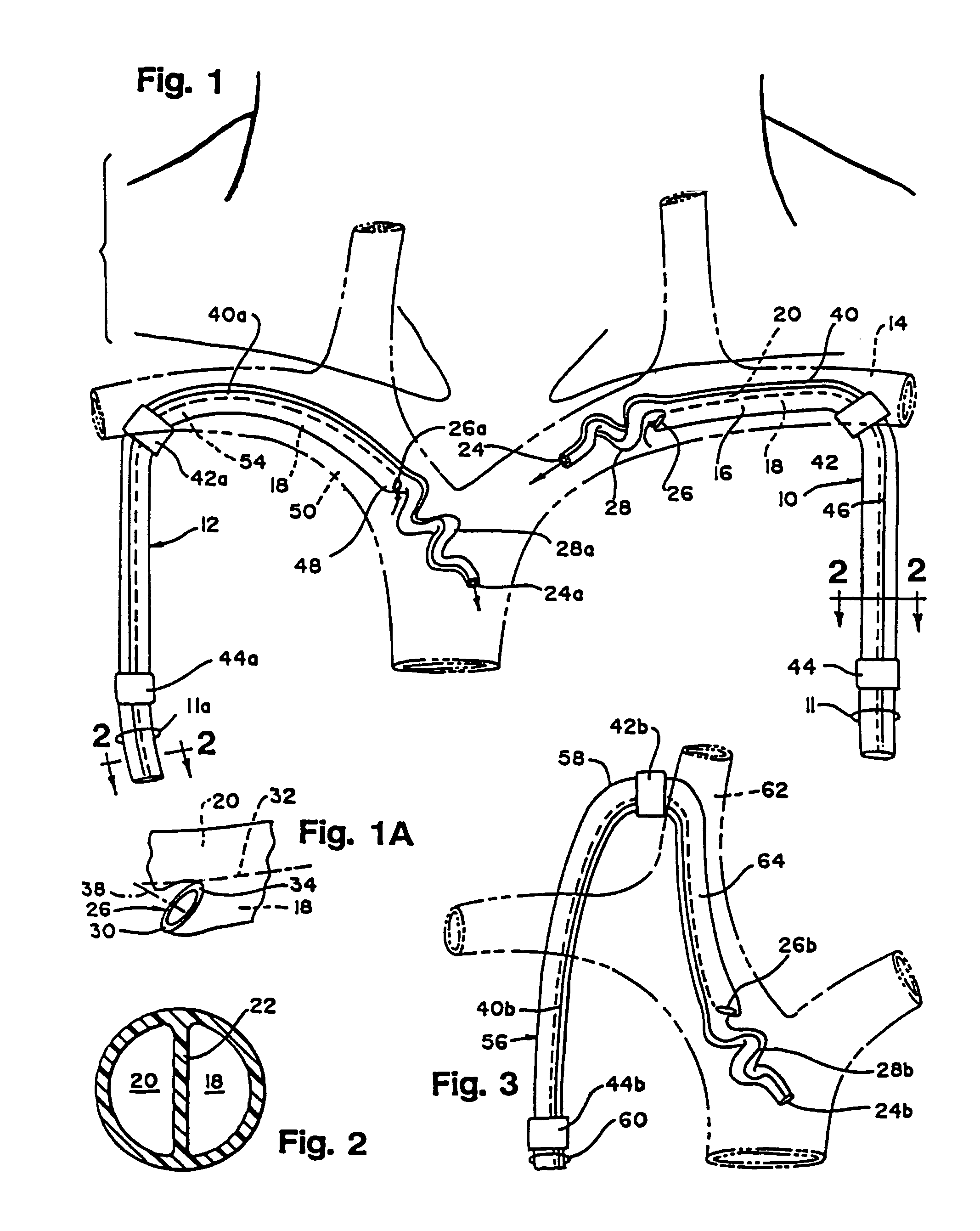
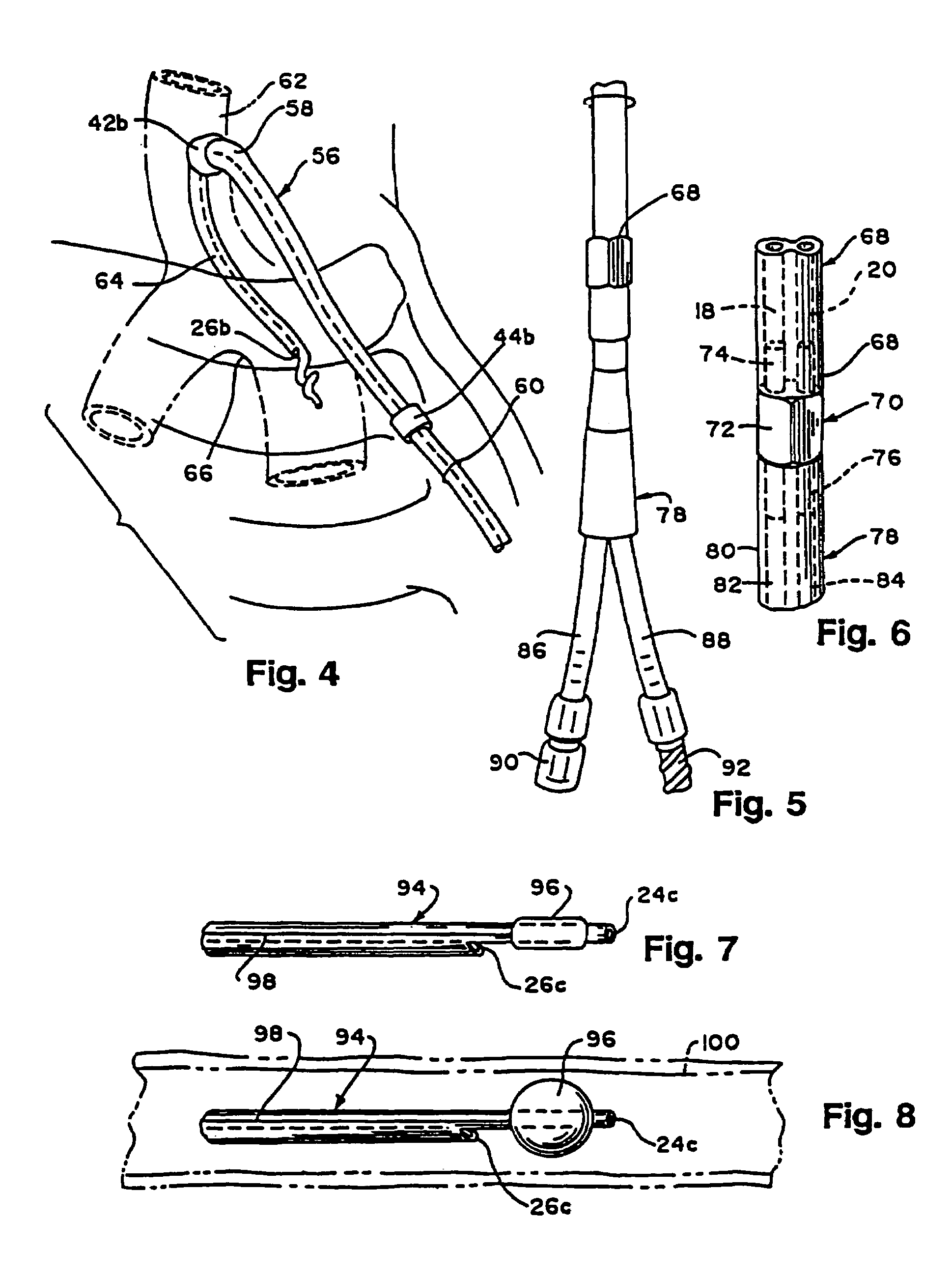
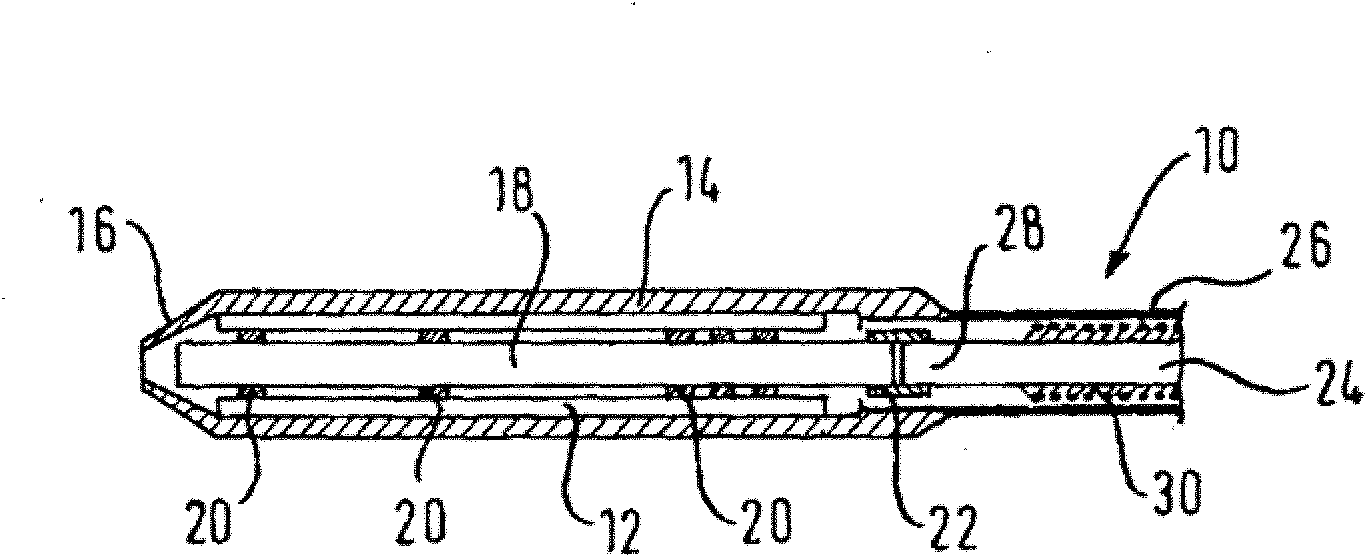
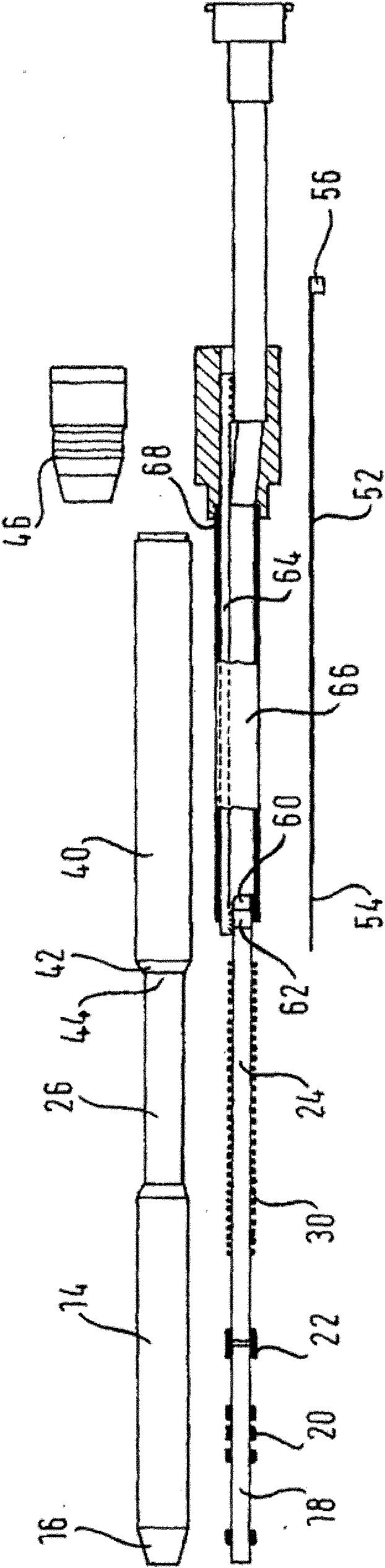
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Distal catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
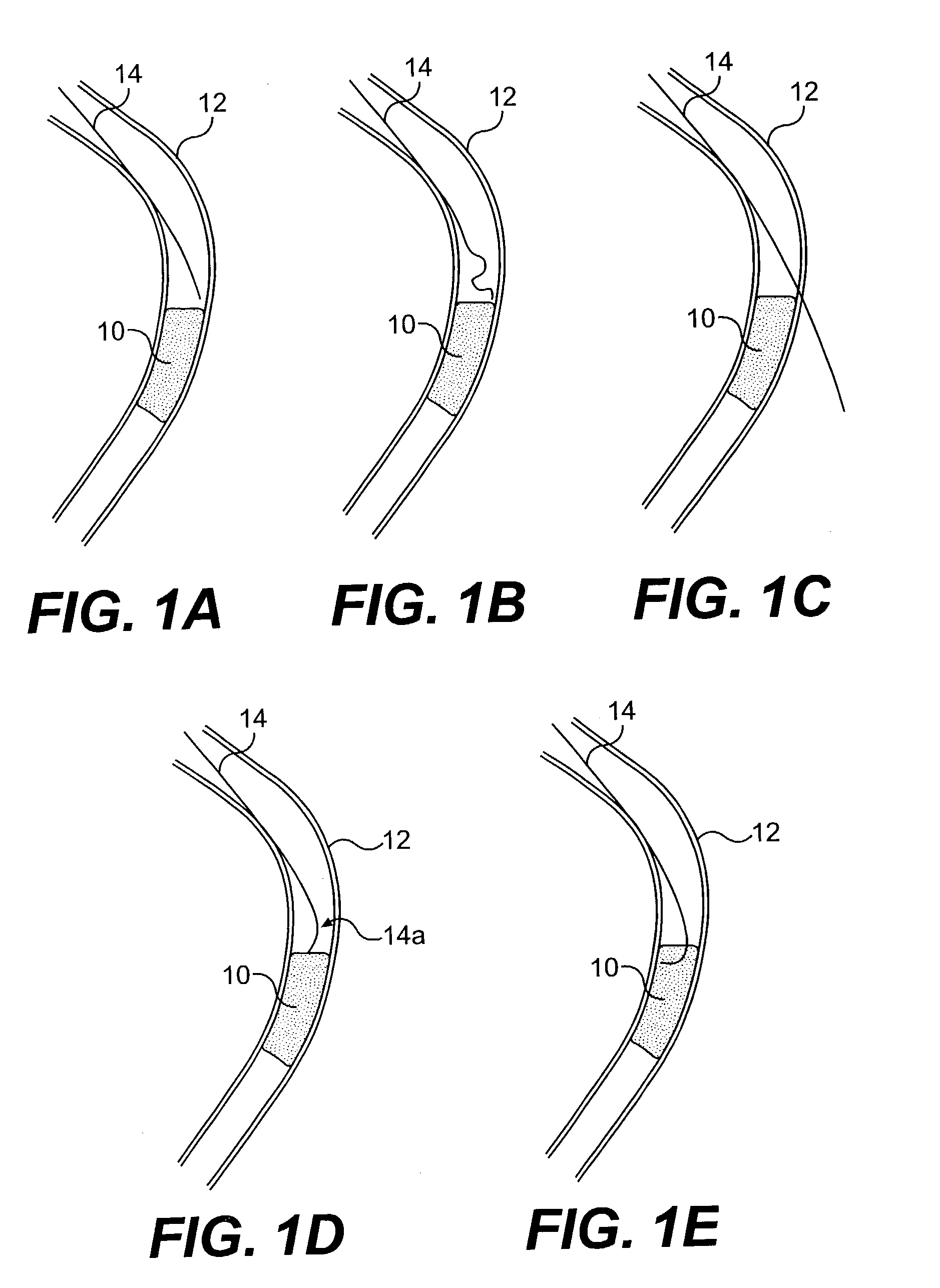
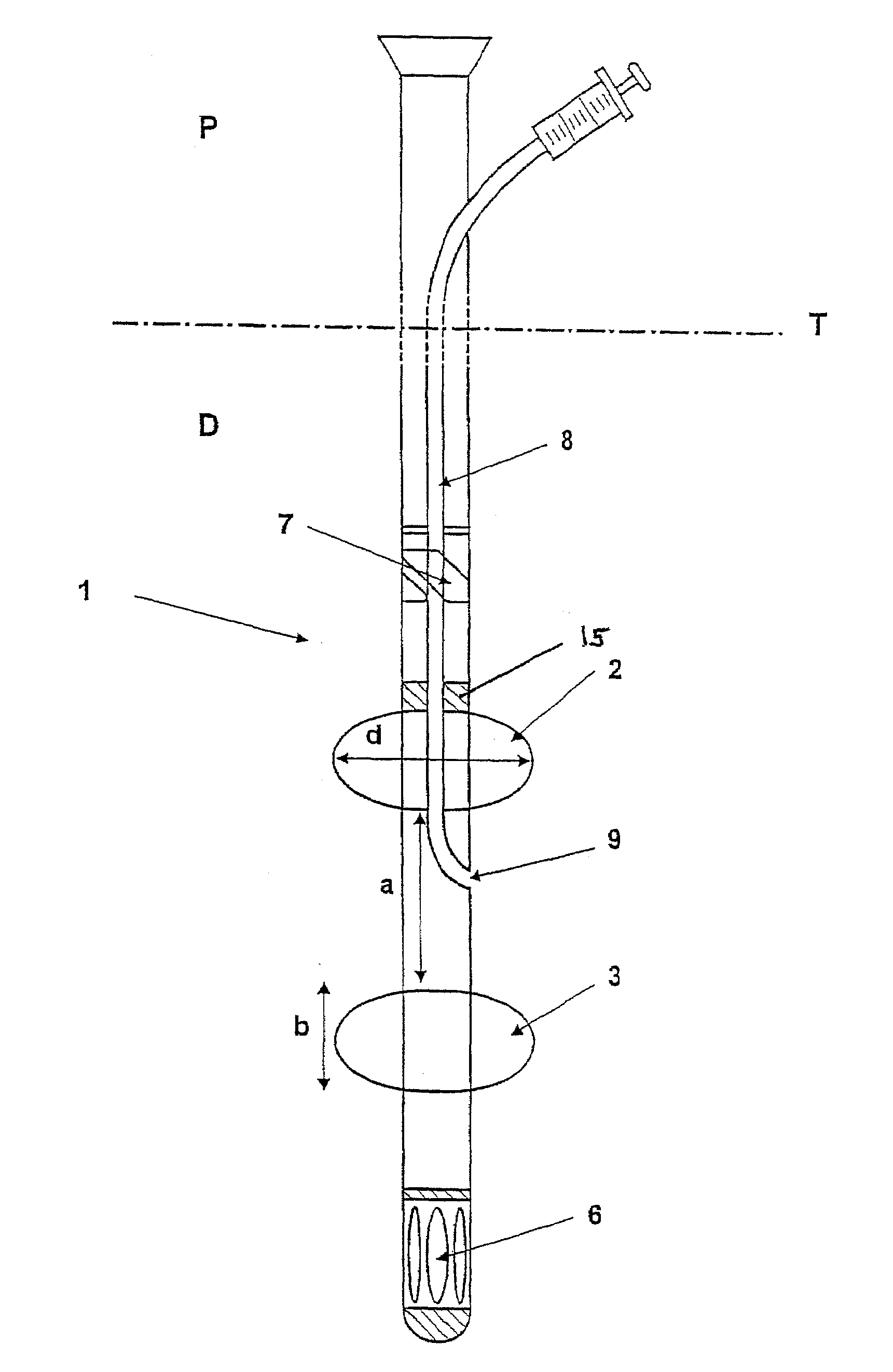
Adjustable multi-balloon local delivery device
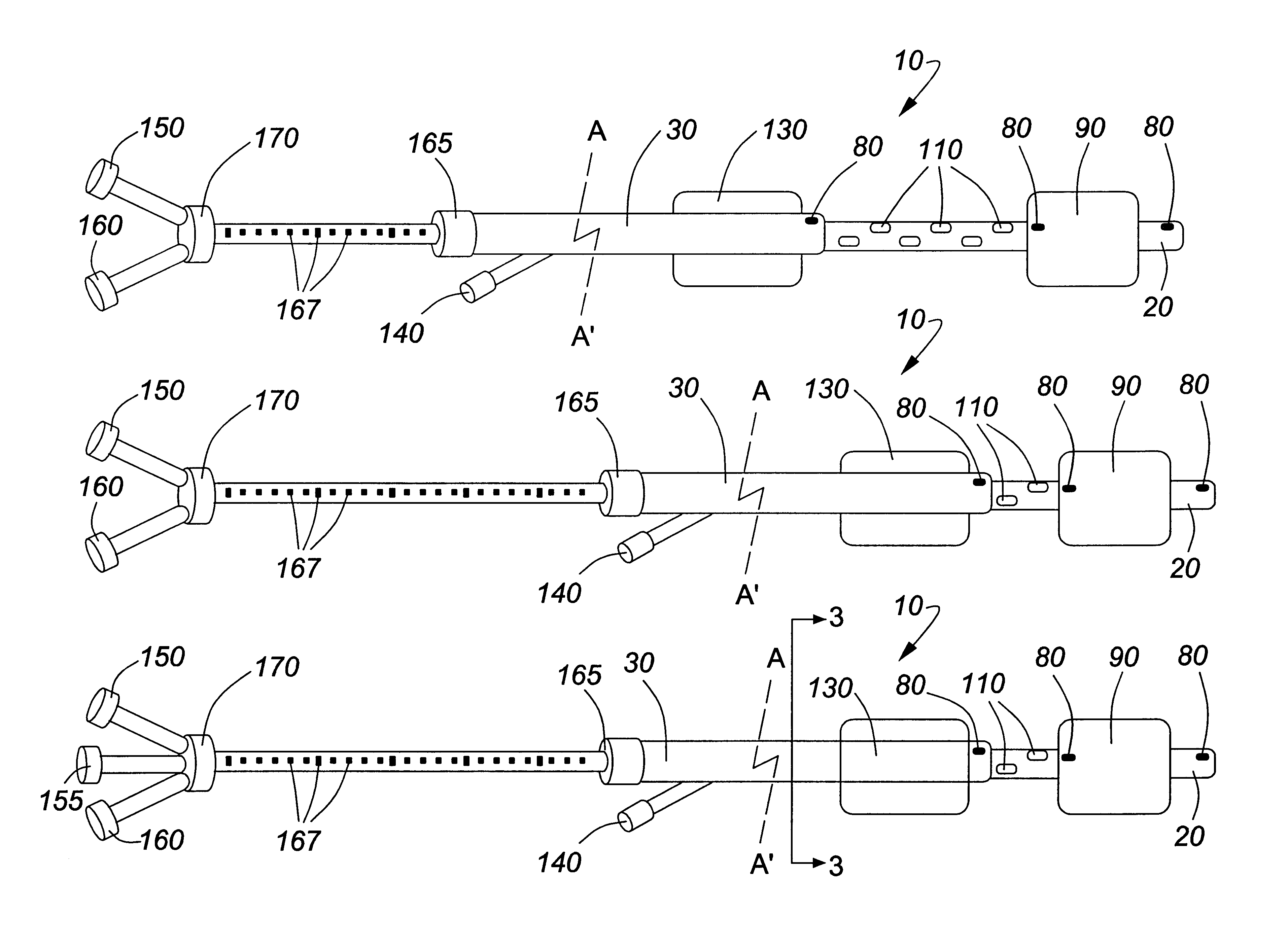
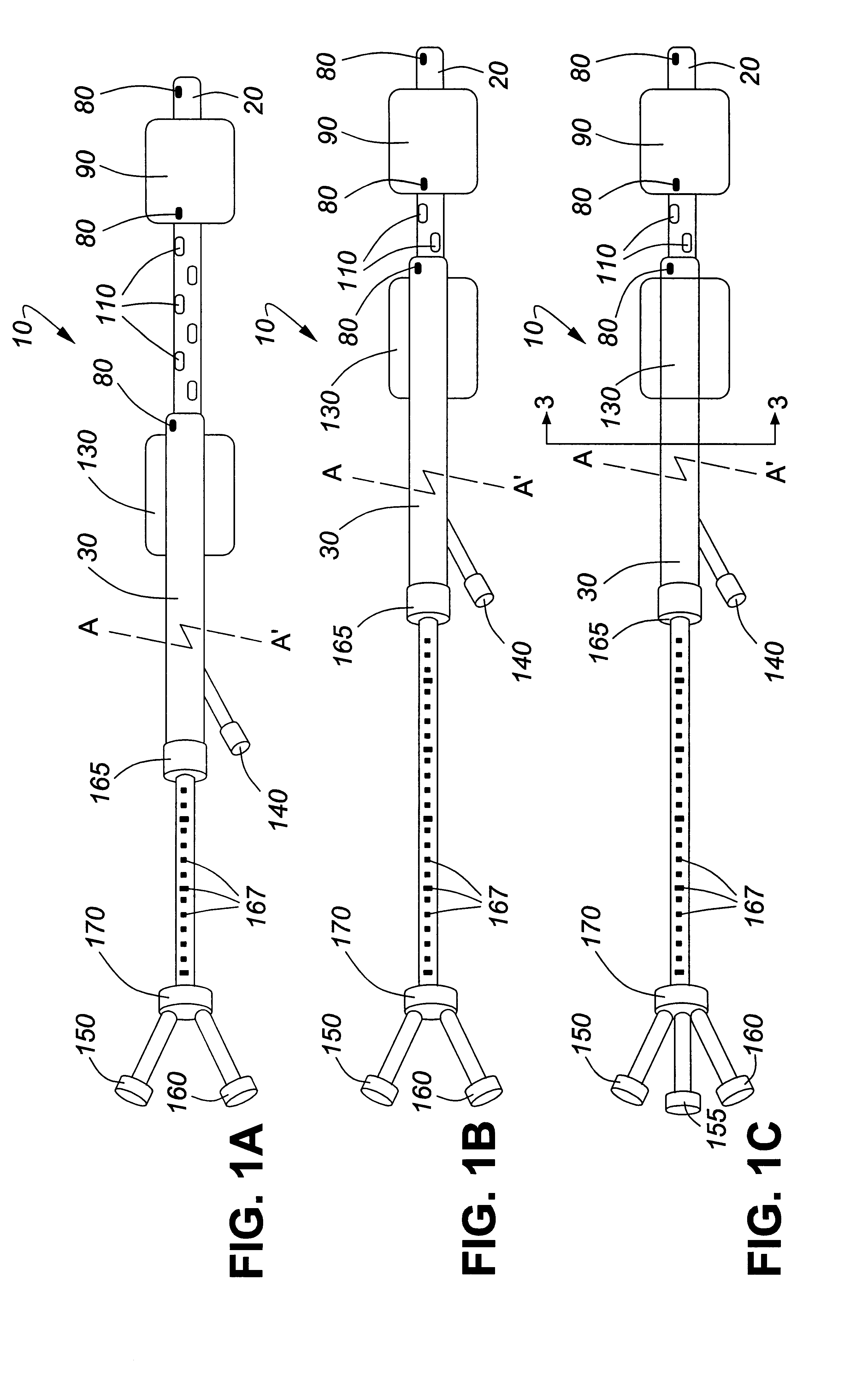
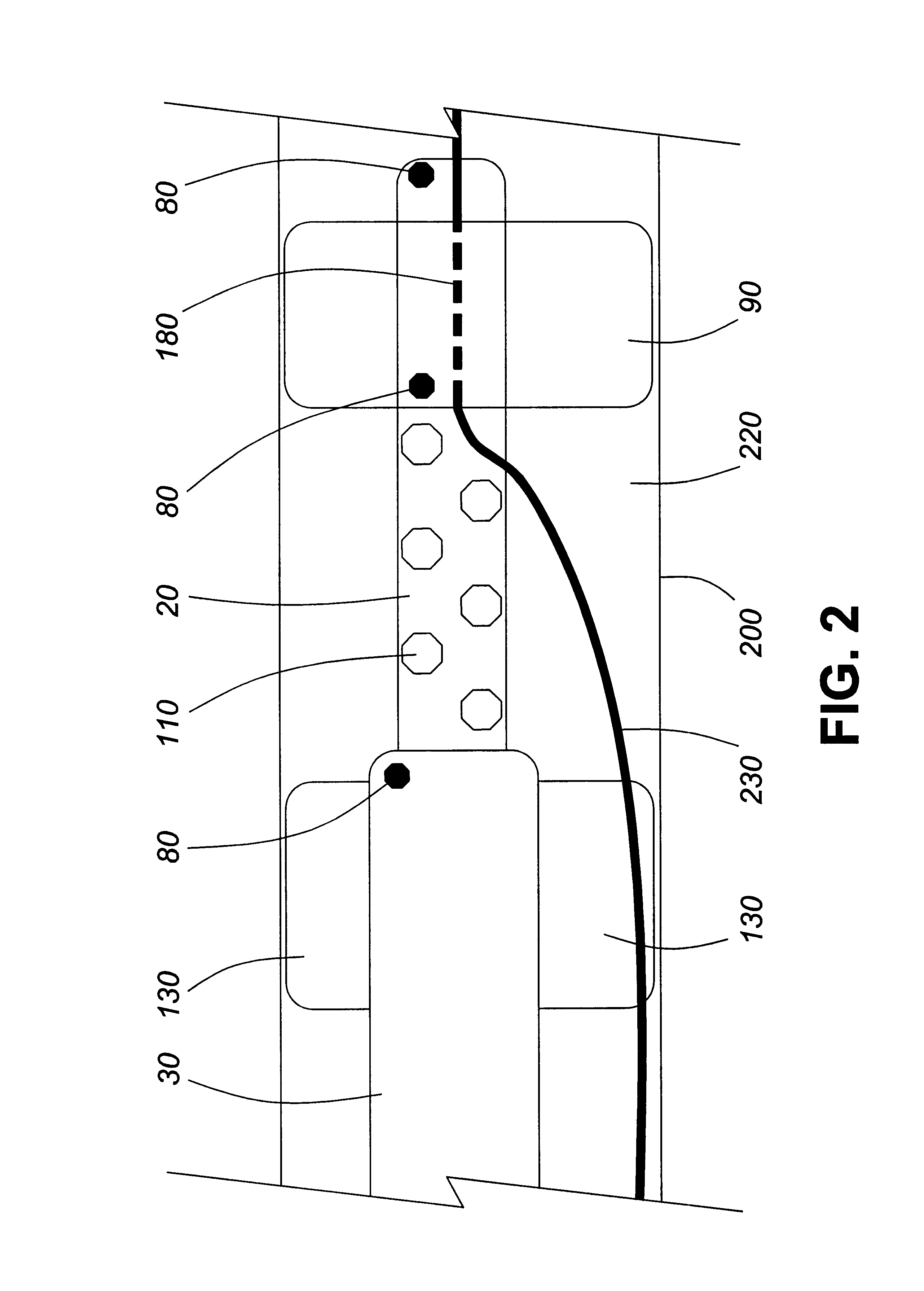
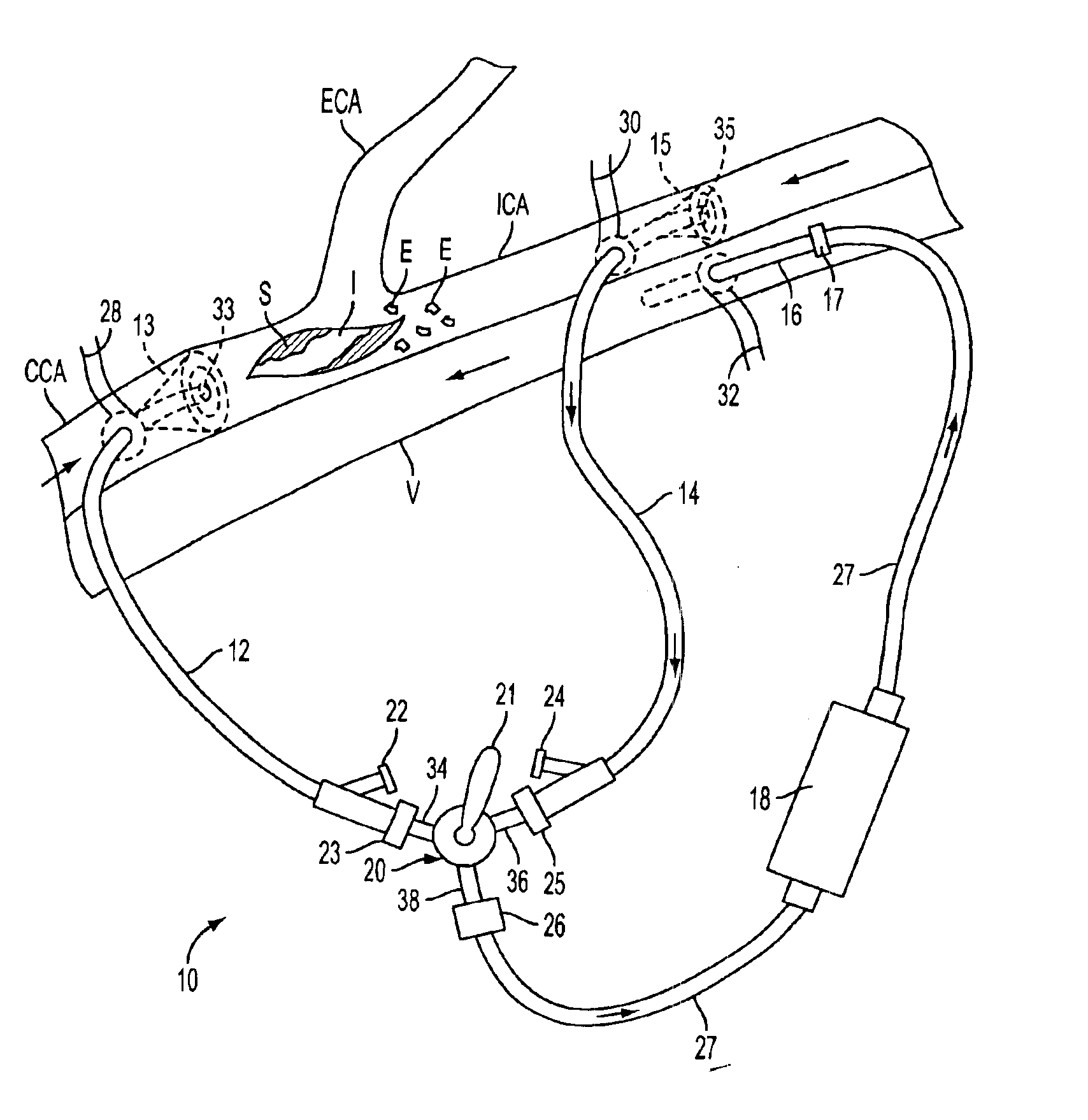
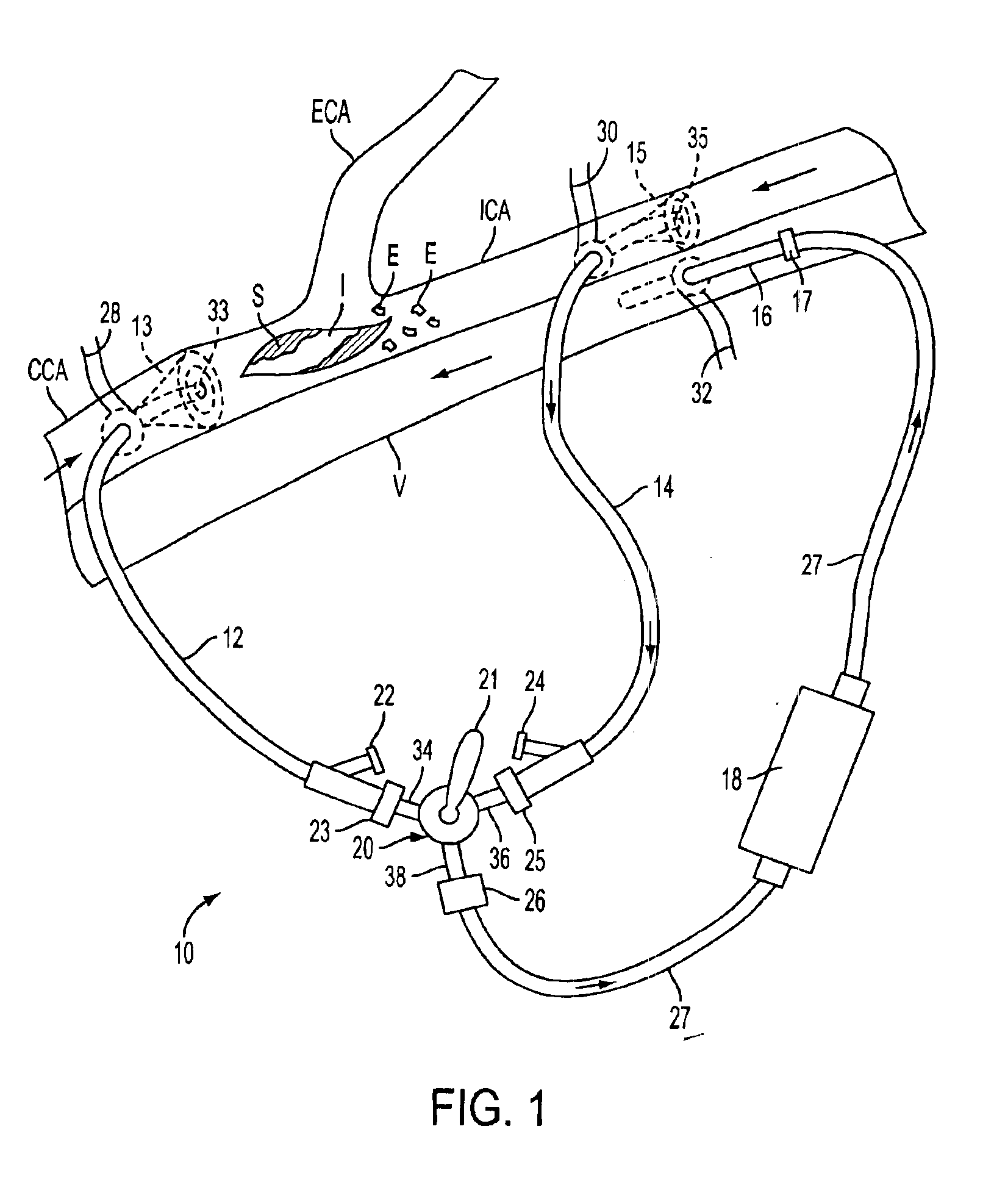
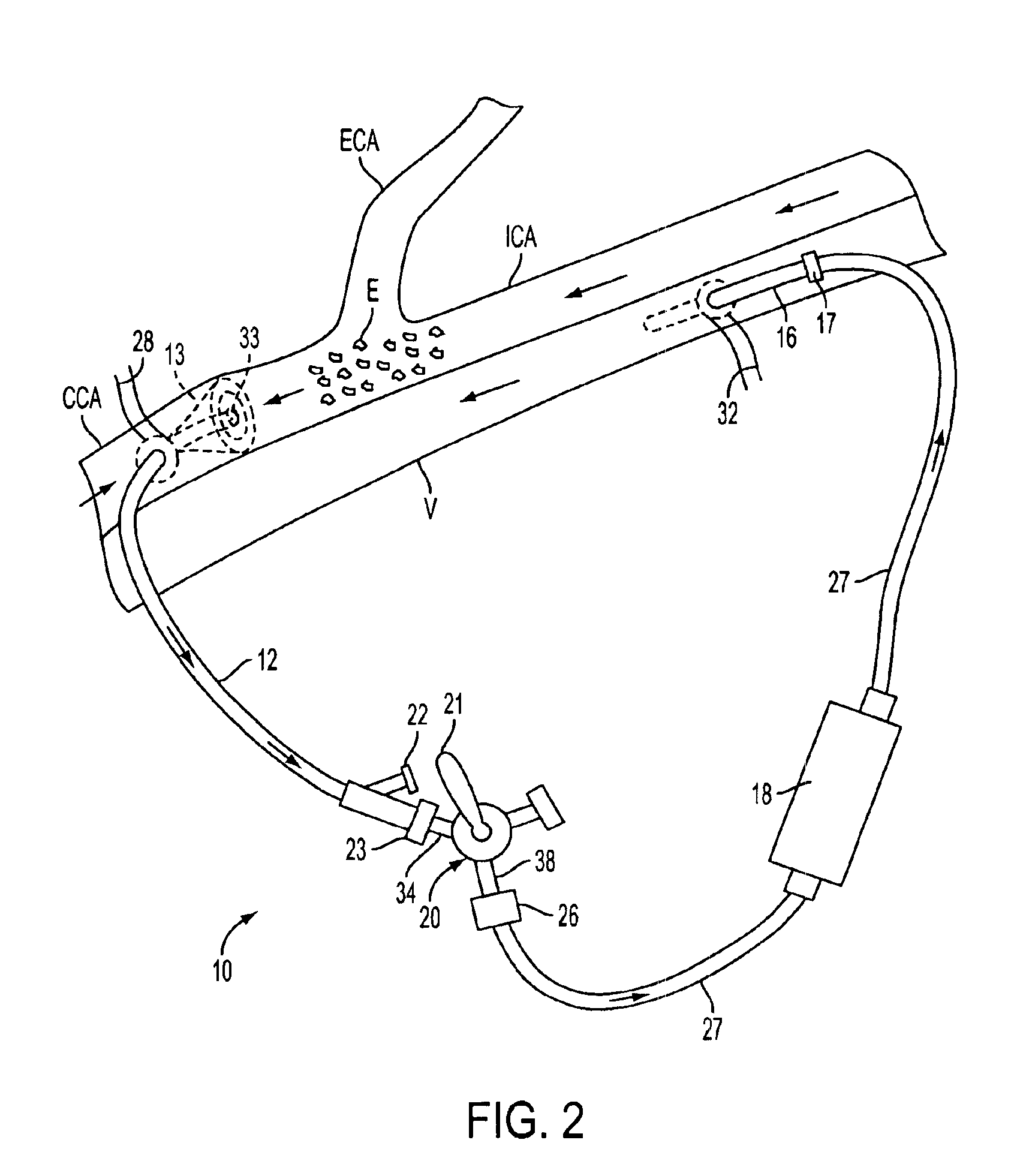
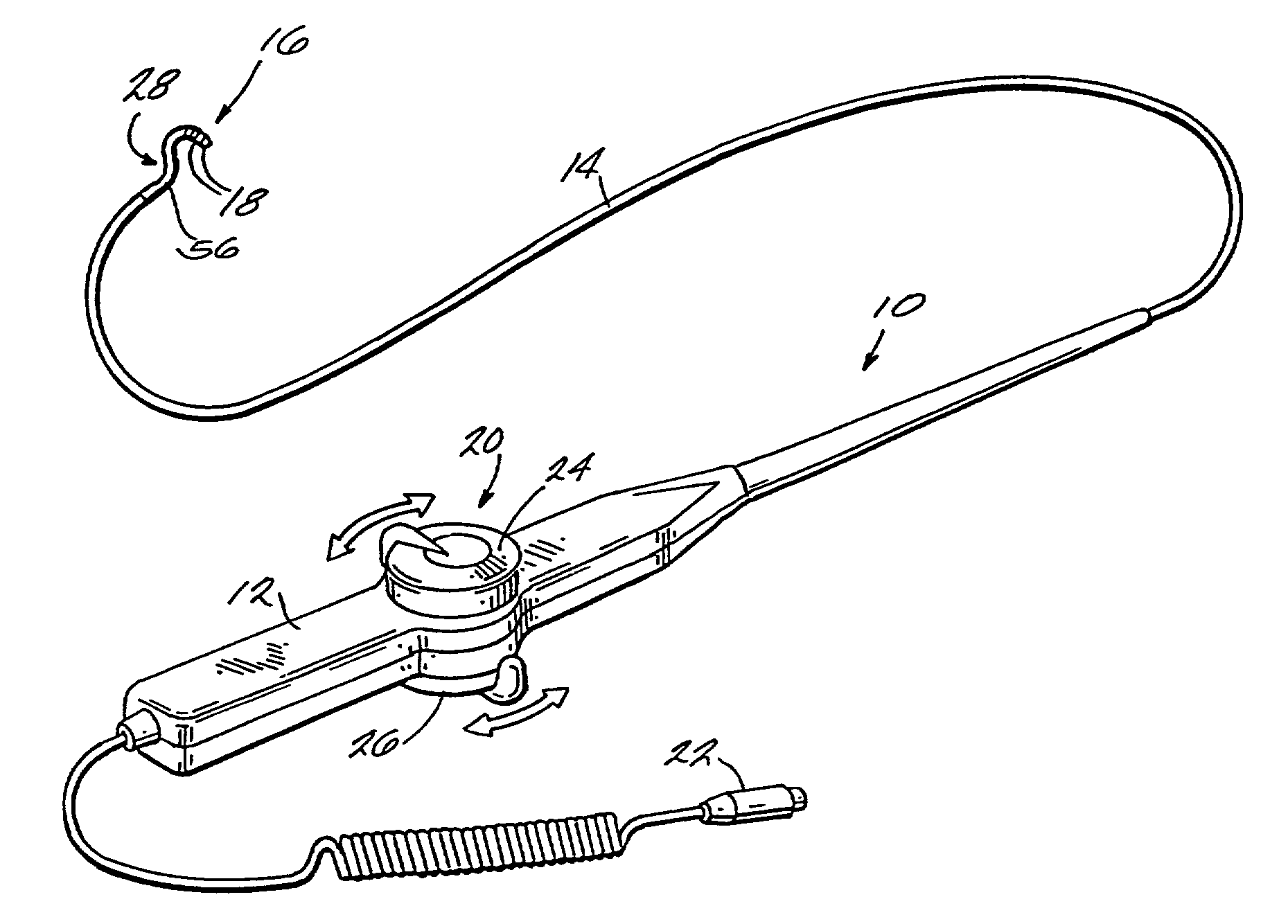
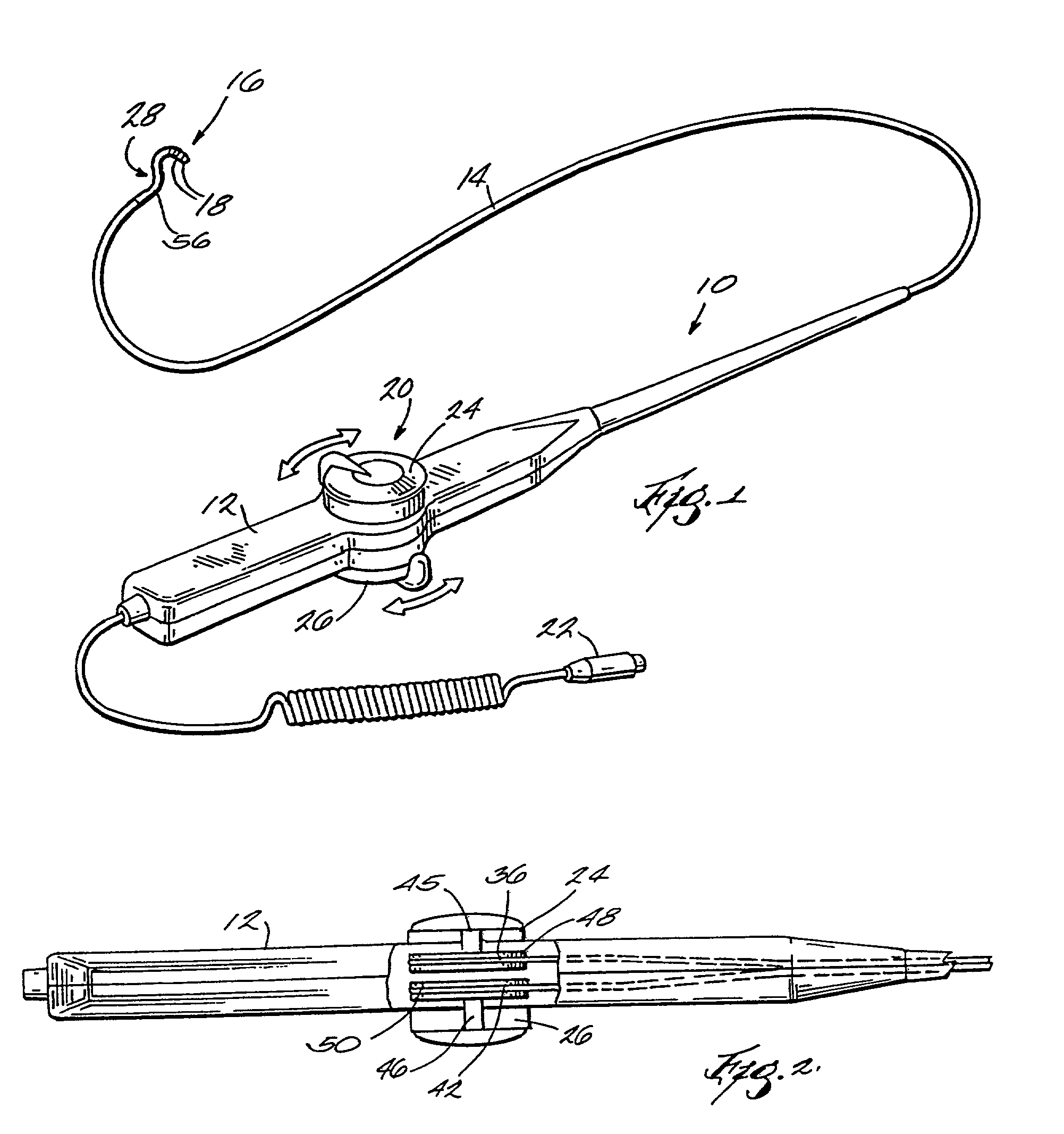
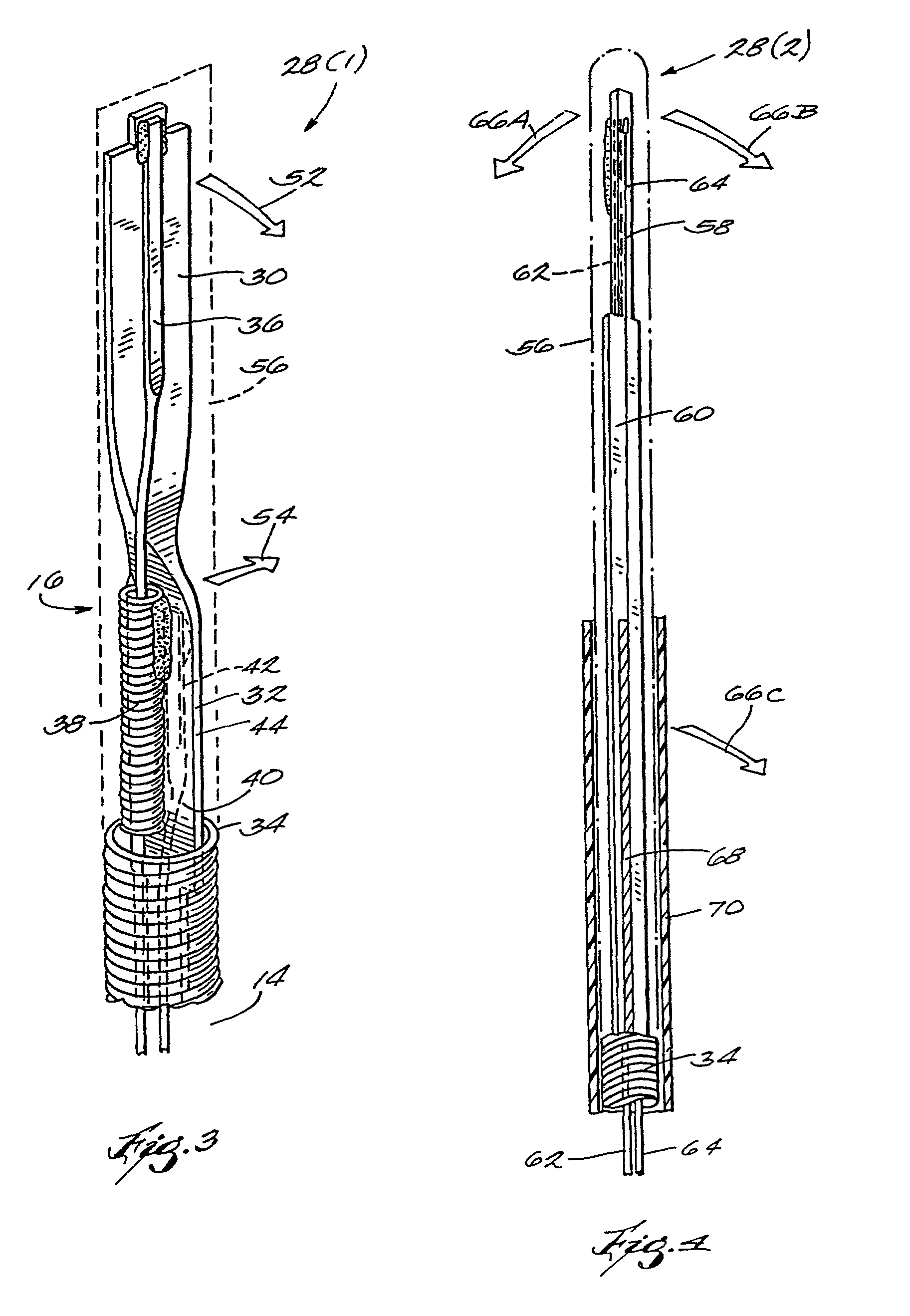
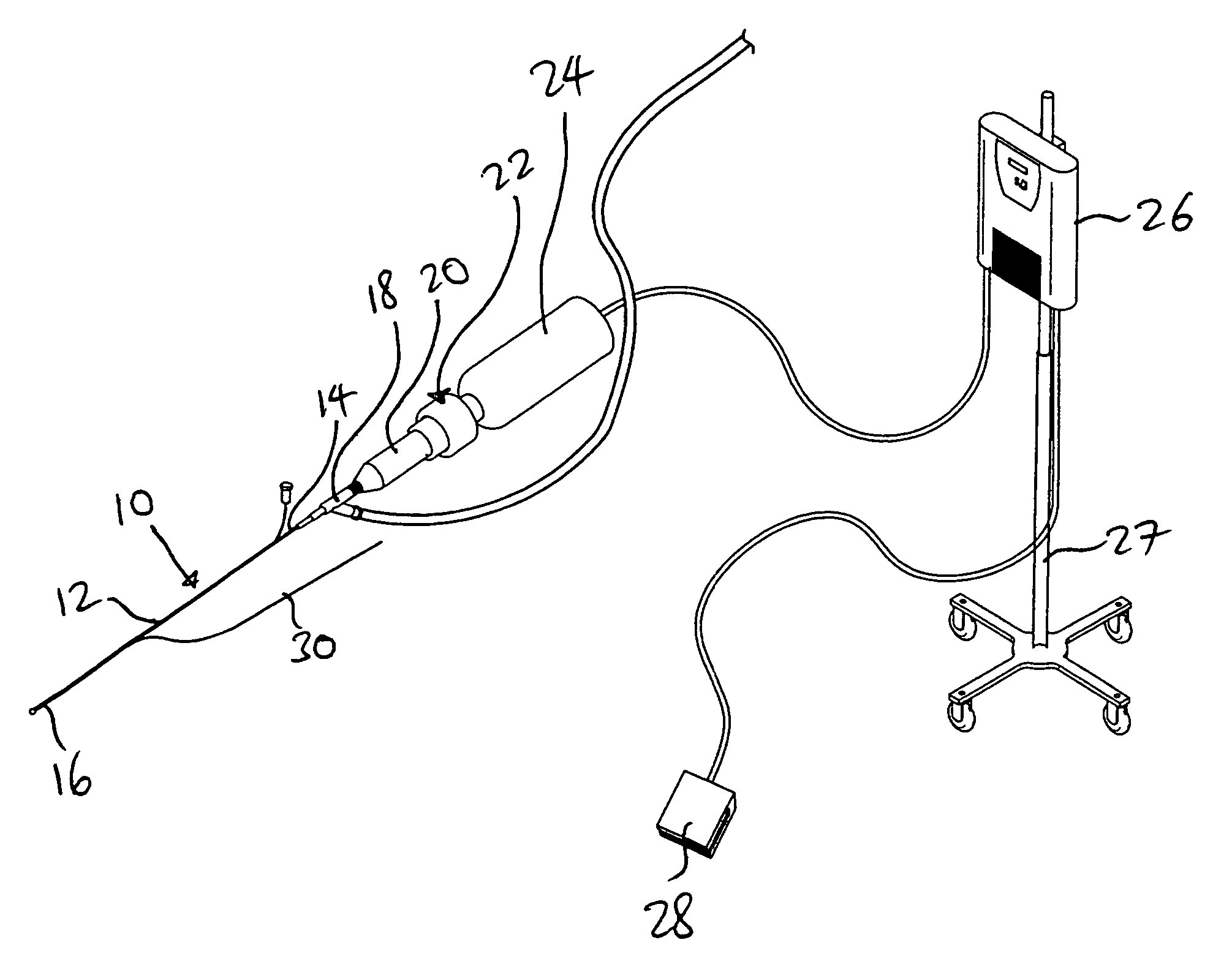
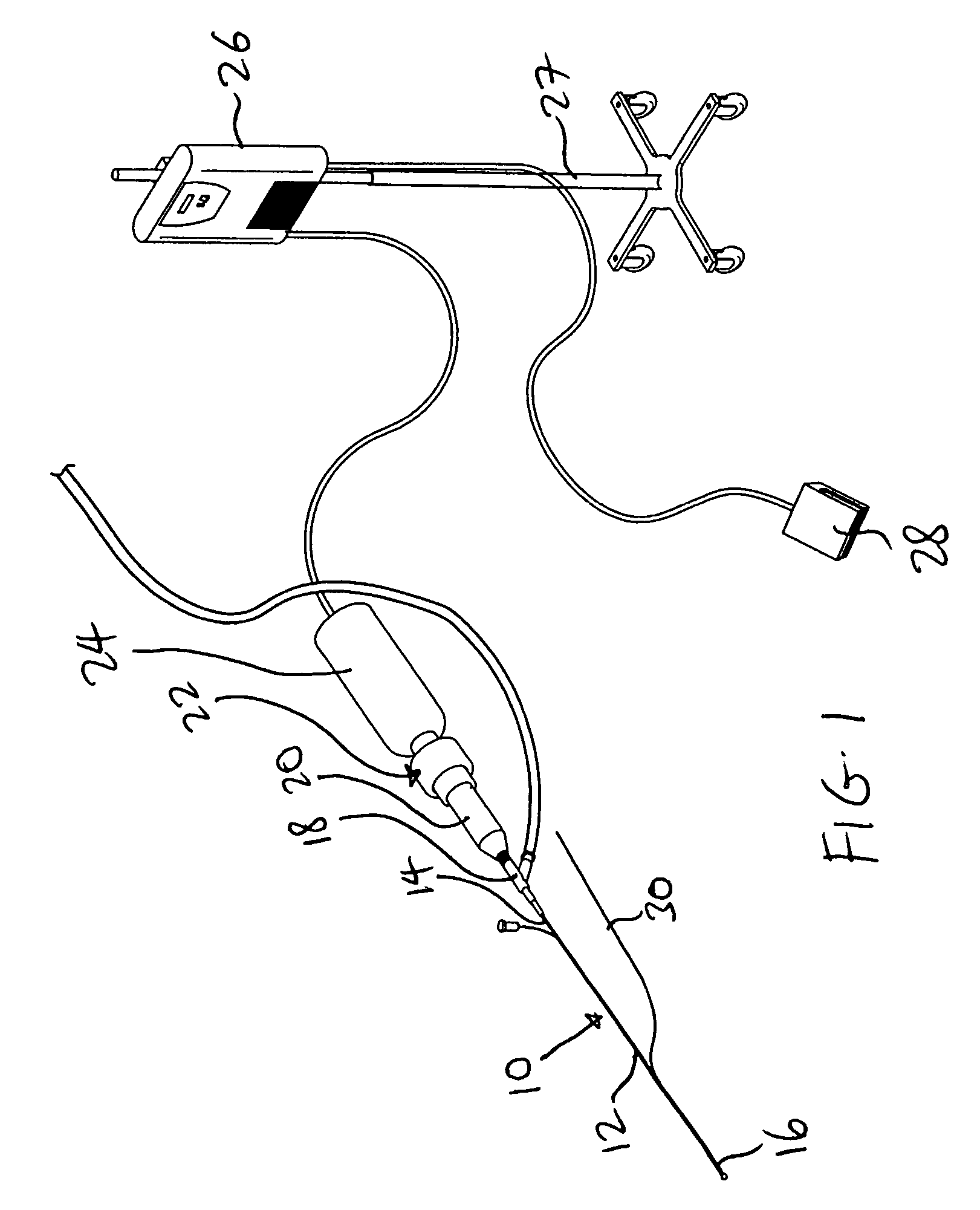
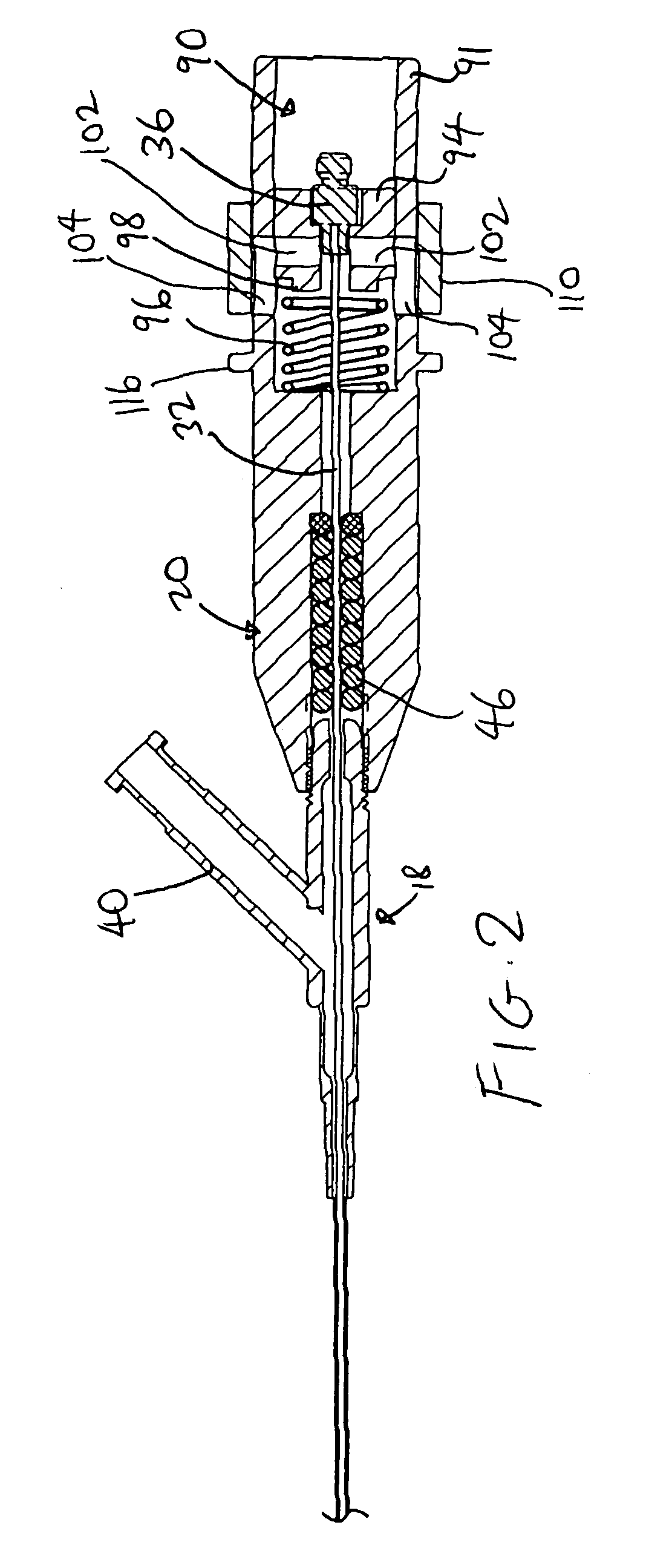
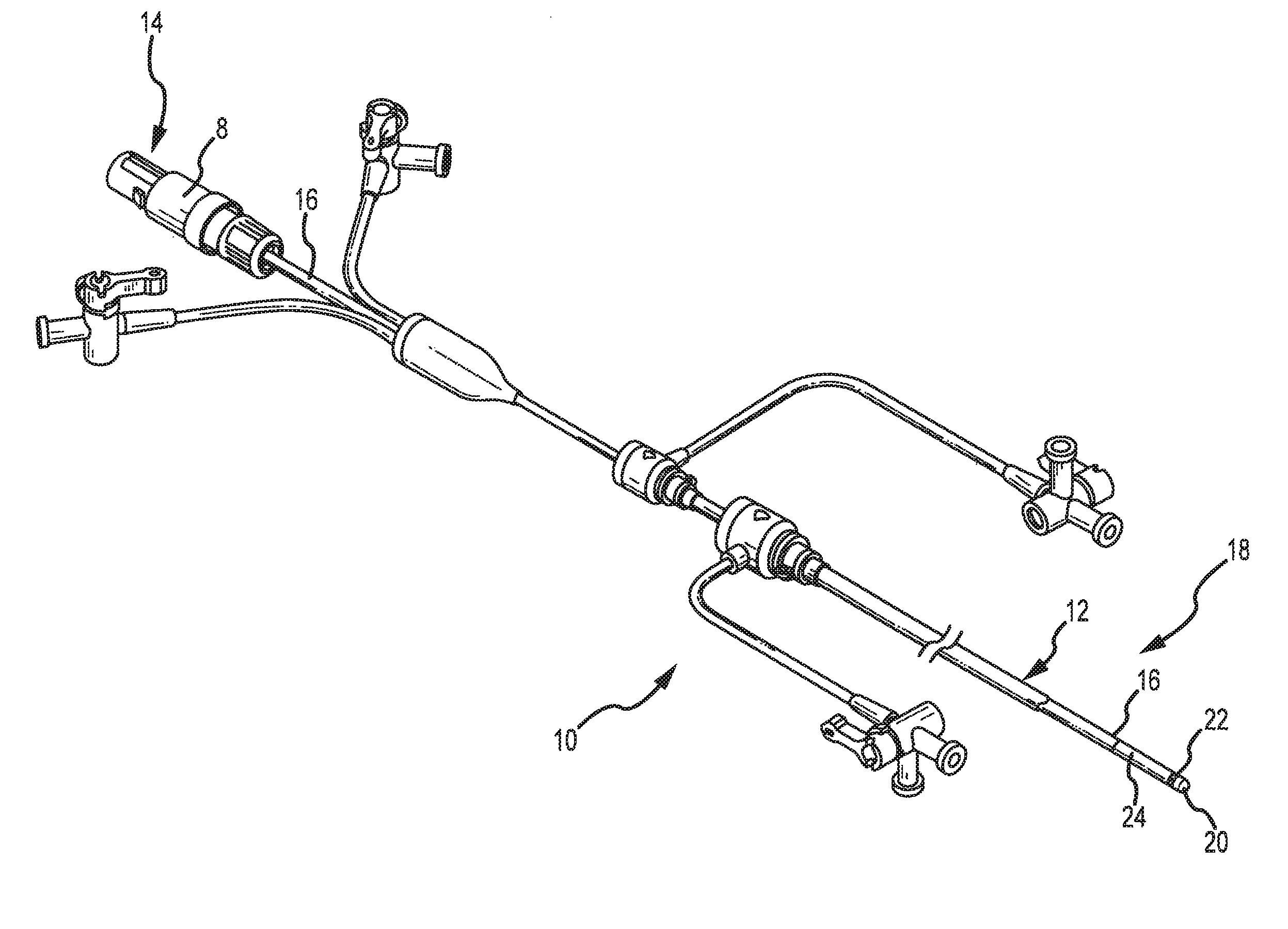
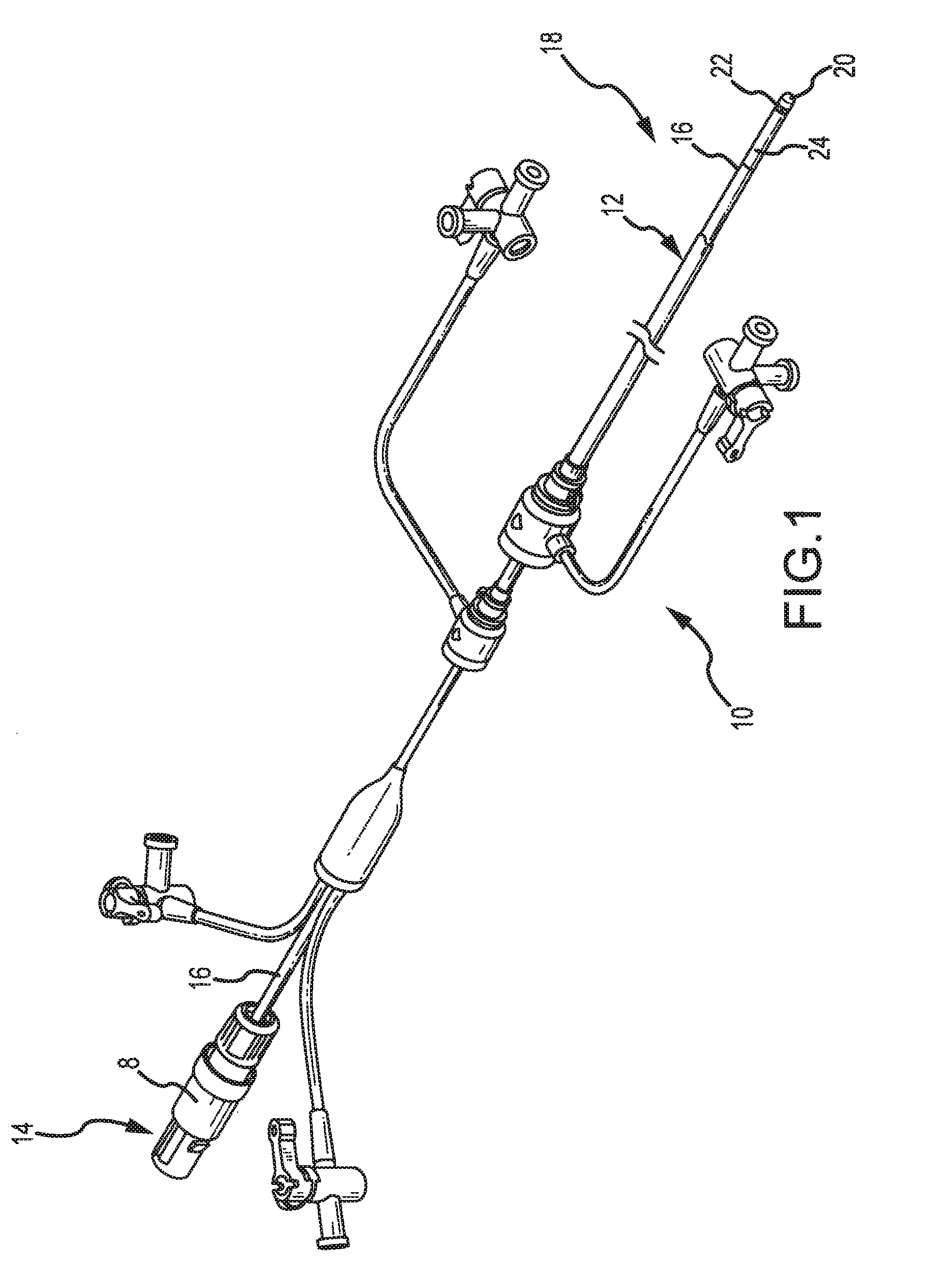
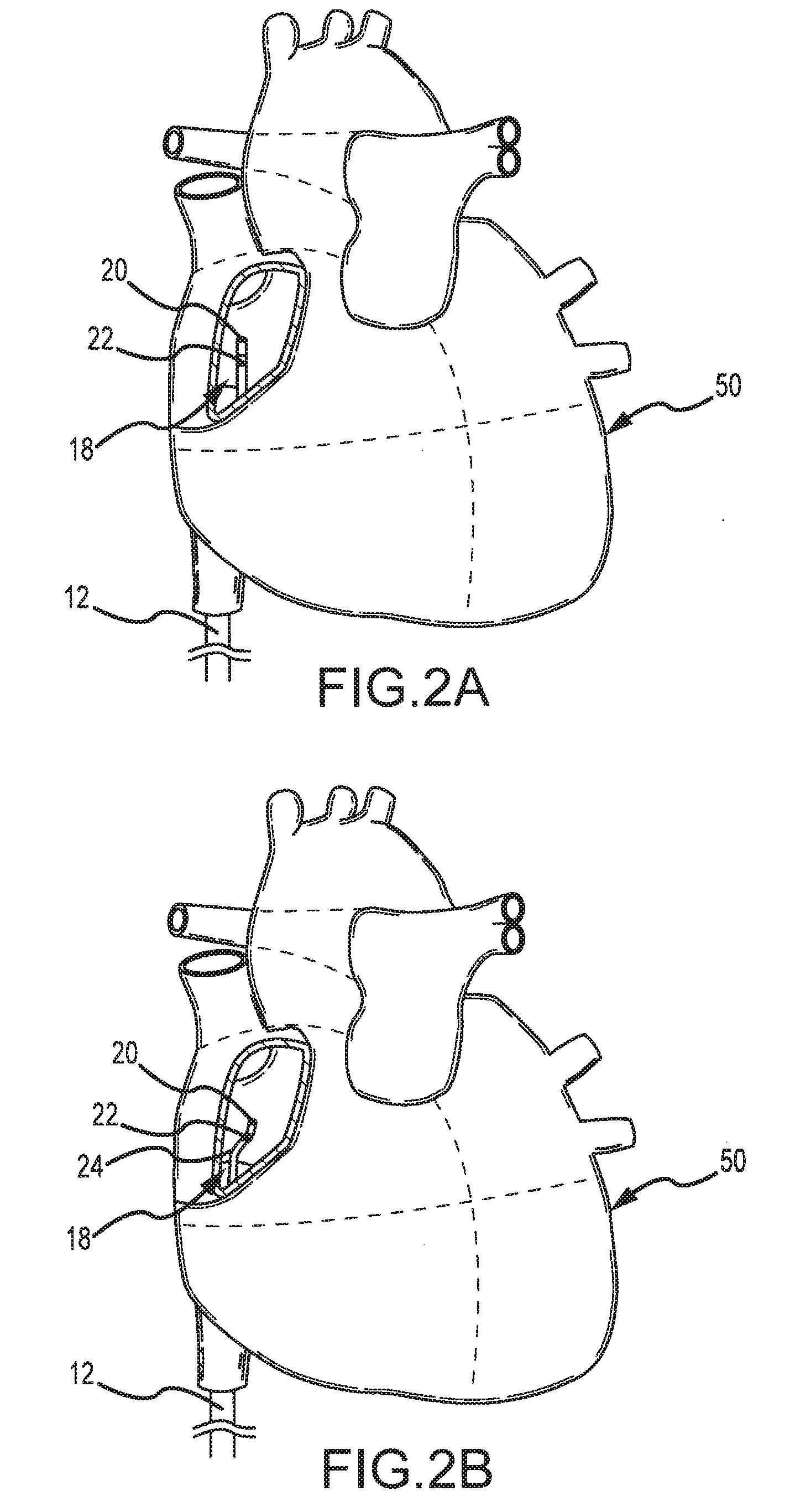
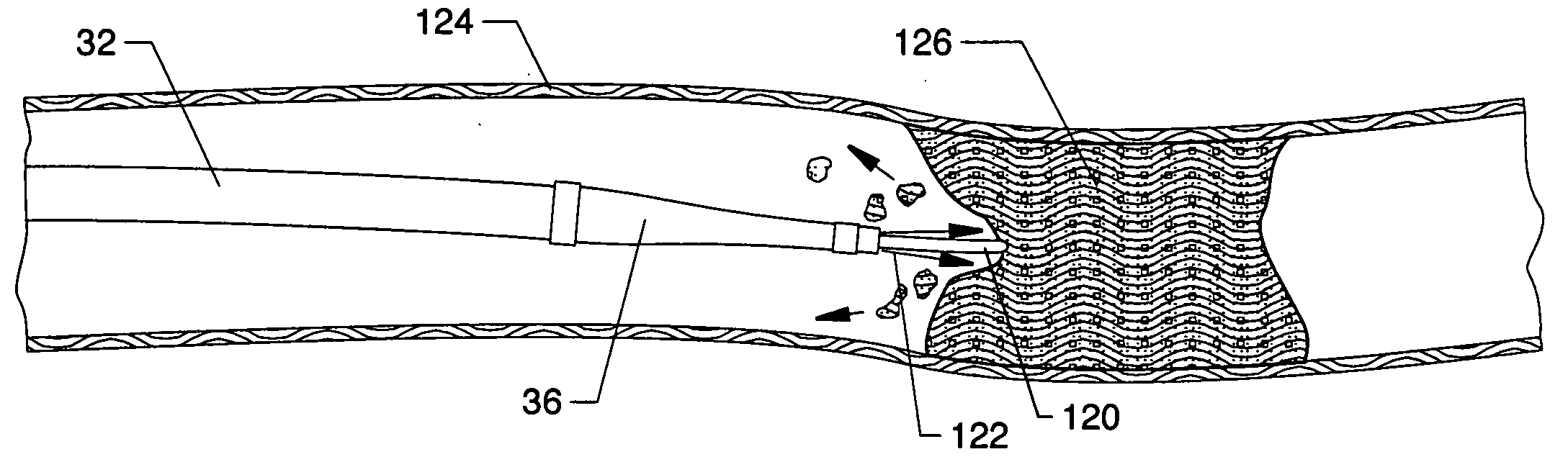
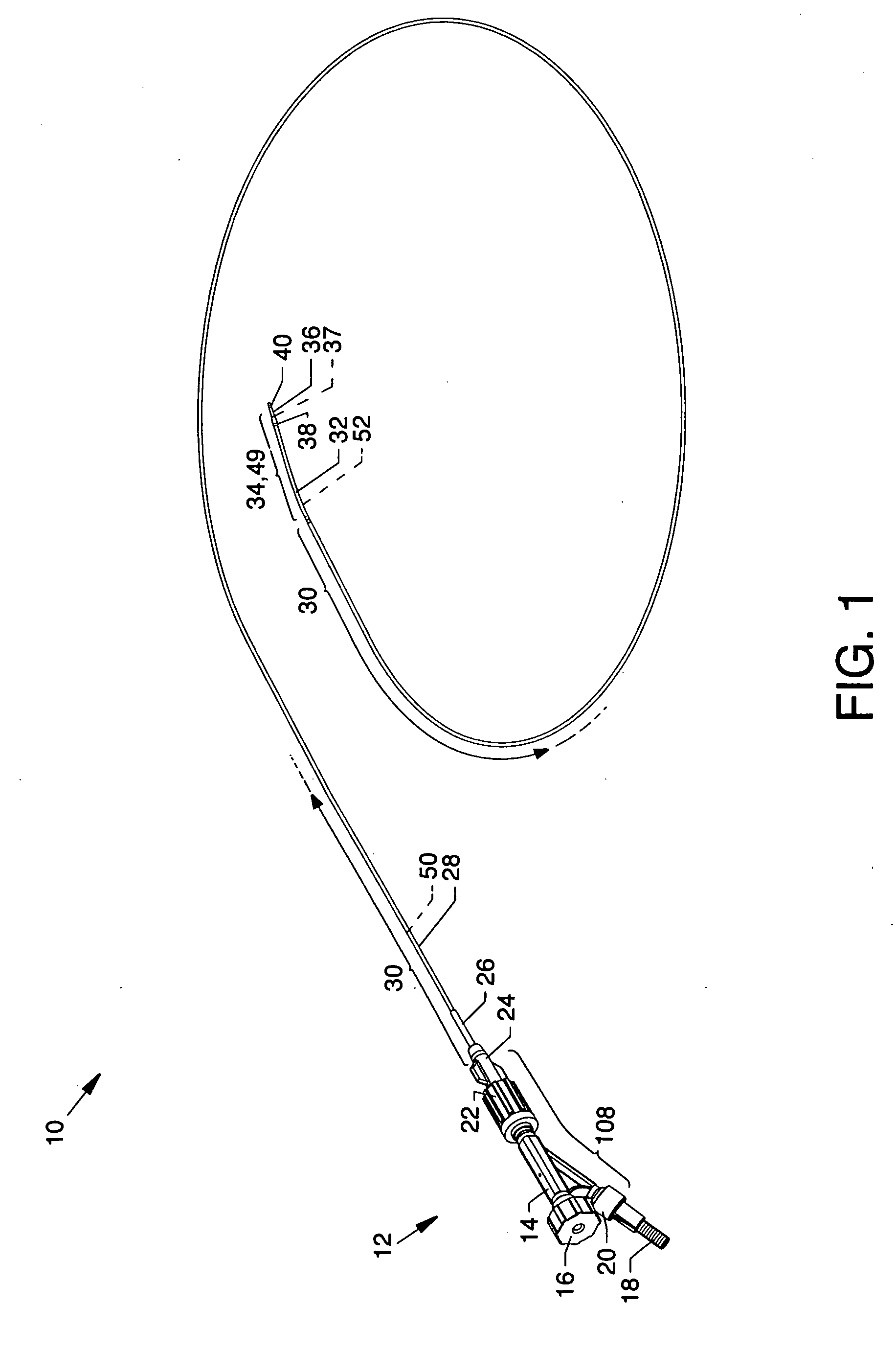
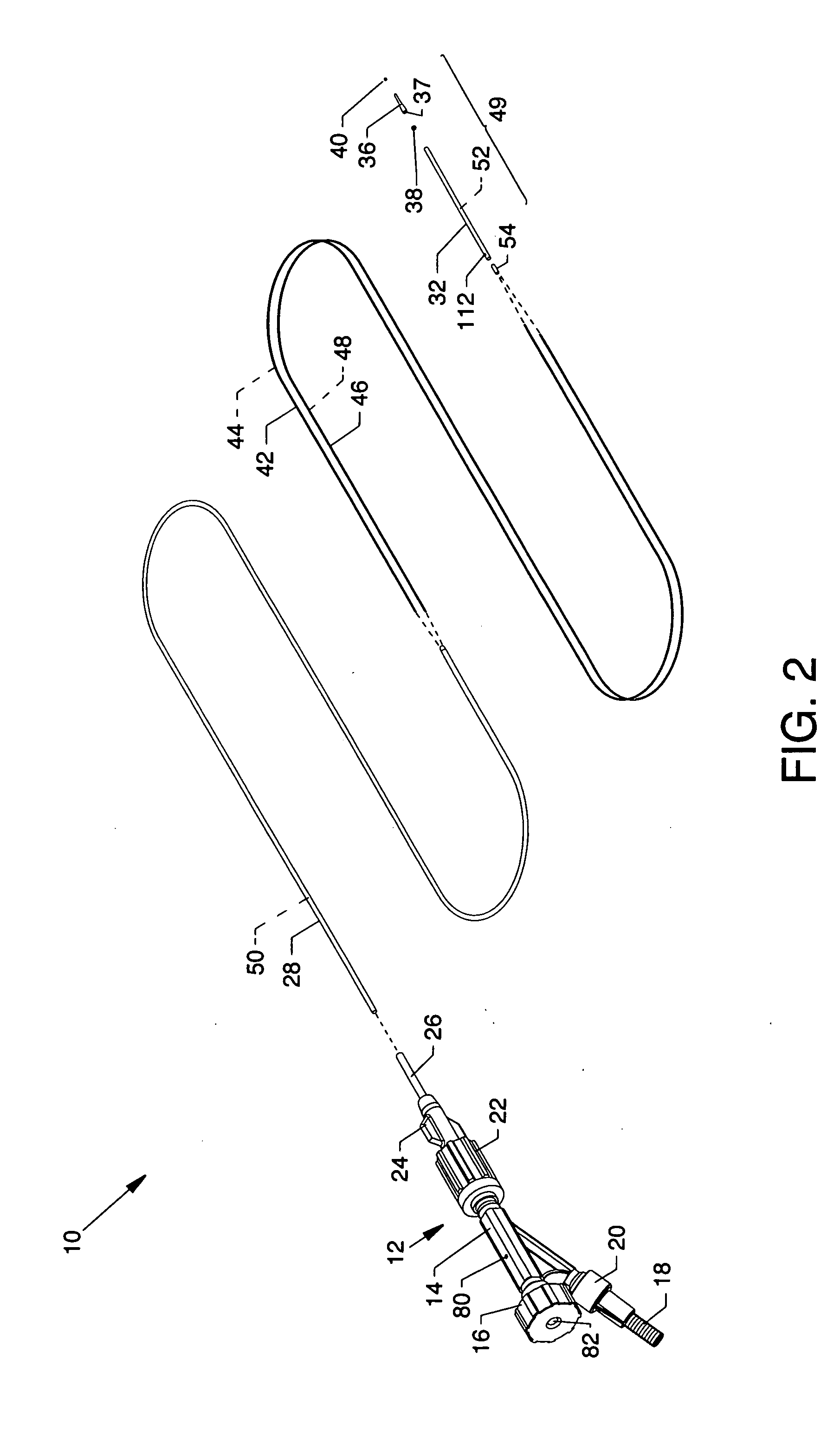
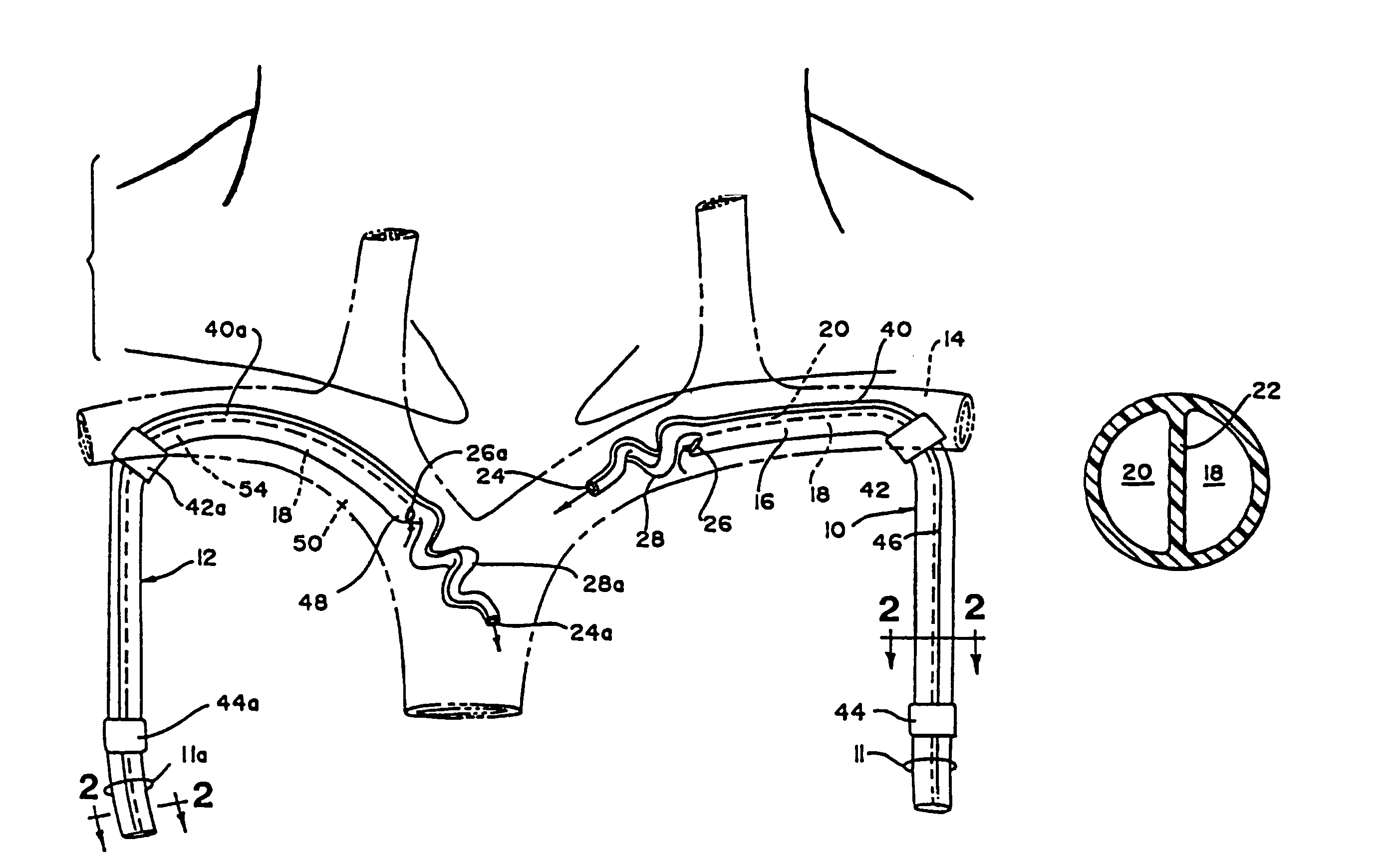
The present invention pertains to a local delivery device comprising a distal catheter unit and a proximal catheter unit which may be positioned by sliding over the distal catheter unit. Both the distal and the proximal catheter units have separate inflatable occluding balloons. The slidable positioning of the catheter units in relation to each other provides for variable inter-balloon distances, which in turn provides for a variably sized occlusion region in a hollow tubular organ, for example a vessel. Dispersed on the catheter shaft between the two occluding balloons are multiple infusion ports through which therapeutic agents may be delivered to an occluded region of a hollow tubular organ. The local delivery device may further comprise a quantifying device for determining the distance between the two occluding balloons. Therefore, precise adjustment of the inter-balloon distance permits controlled delivery of therapeutics to a discreet length of the hollow tubular organ wall.
Owner:OTTAWA HEART INST RES
Guide wire control catheters for crossing occlusions and related methods of use
InactiveUS20040102719A1Simplify the viewing processStentsBalloon catheterPercutaneous angioplastyThree vessels
A wire control catheter for aligning and guiding a guide wire through a lesion in a vessel is provided. The wire control catheter includes a shaft having a guide wire lumen and a control wire lumen. A control wire passes through the control wire lumen and is used in combination with an articulation structure to deflect or curve a distal tip portion of the catheter. The distal catheter shaft may include a centering device for centering the catheter within the vessel. The distal catheter shaft also may include a pre-dilation balloon for dilating the lesion prior to performing angioplasty or other treatment on the lesion. Additionally, a sliding sheath catheter may be used to provide additional support to the guide wire. The sliding sheath catheter is sized to fit within the guide wire lumen of the control catheter and to allow the guide wire to pass through it. A method of treatment of a blood vessel includes inserting a guide wire into the blood vessel and advancing a control catheter over the guide wire until the distal tip of catheter is near the occlusion in the blood vessel. The tip of the catheter then is deflected via a control wire and an articulation structure. The guide wire is then advanced across the occlusion. The control catheter also may be advanced across the occlusion simultaneously with the guide wire or subsequent to the guide wire crossing. Prior to crossing the occlusion, the wire control catheter may be centered using a centering device. Subsequent to crossing the occlusion, the occlusion may be pre-dilated with a pre-dilation balloon of the wire control catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
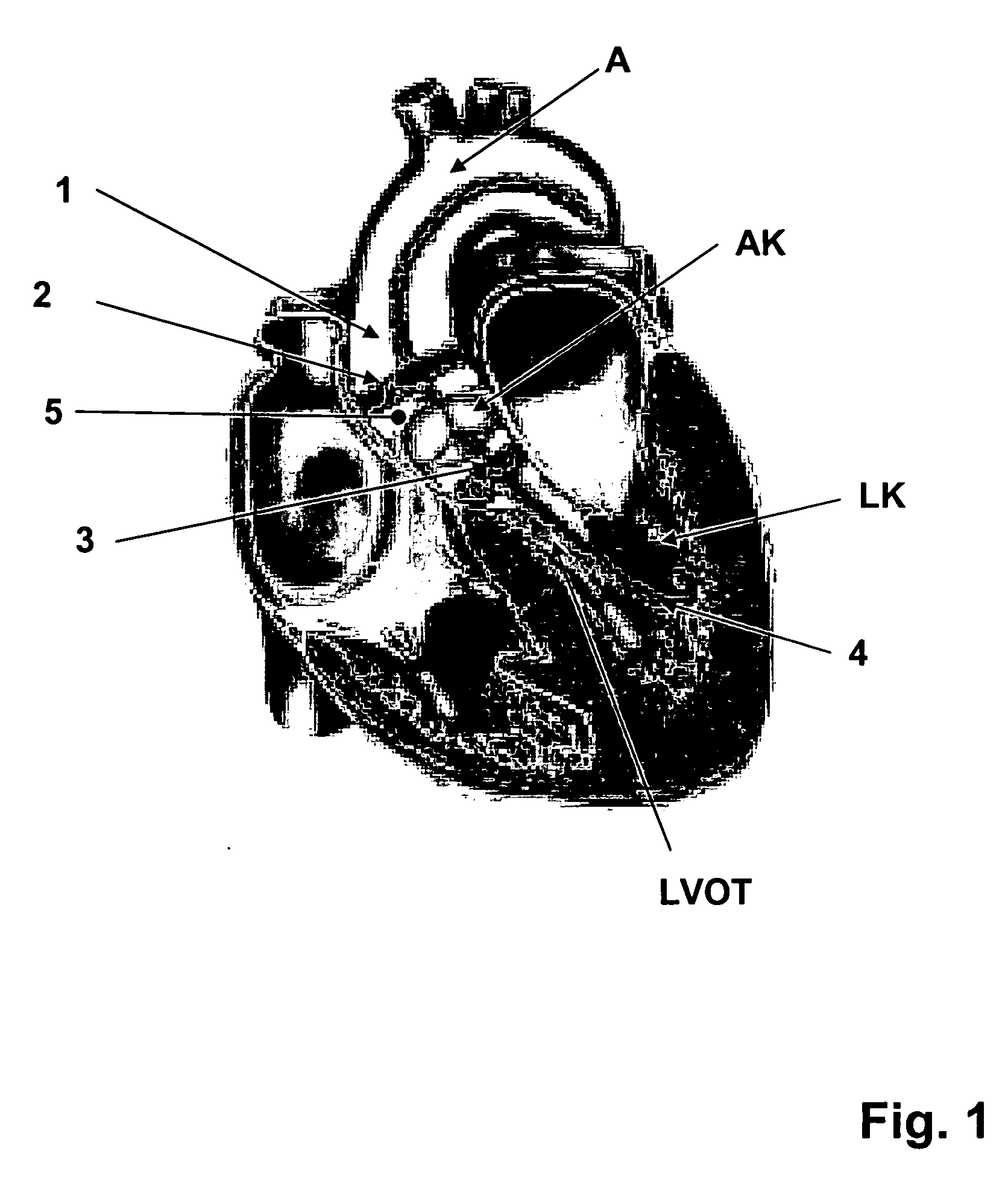
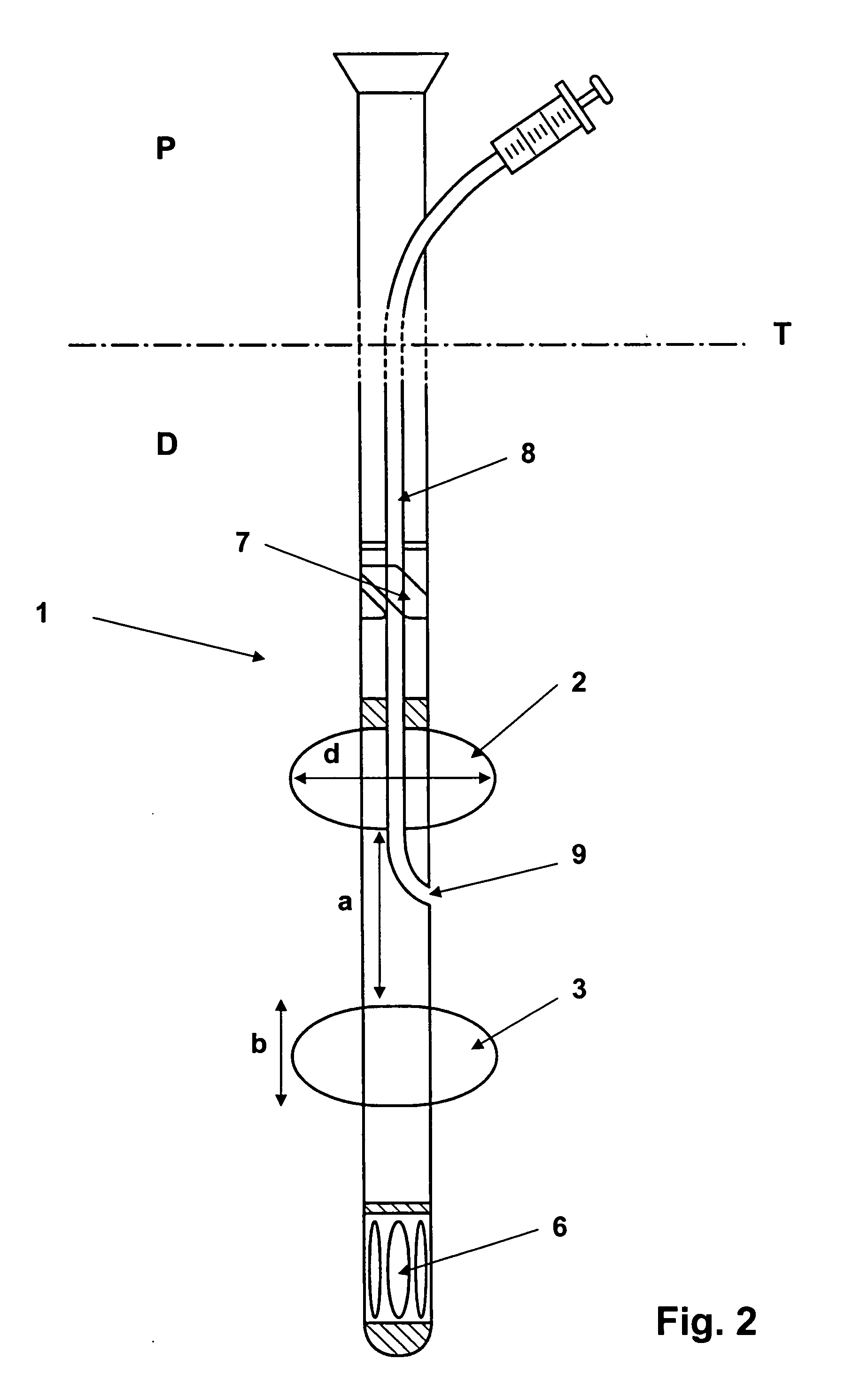
Device for minimally invasive intravascular aortic valve extraction
InactiveUS7338467B2Minimally invasiveThe equipment is easy to operateStentsMedical devicesPerfusionBlood vessel
A perfusion catheter includes at least one perfusion channel and at least two dilation units disposed at a distance from each other at the distal catheter region in the longitudinal extension of the catheter. Both of the at least two dilation units are projected through by the perfusion catheter and form, in an inflated state, an at least practically fluid-tight occlusion with the aortic wall. At least the dilation unit disposed on the proximal side has at least one passage through which an auxiliary catheter can be introduced in a fluid-tight manner. The perfusion catheter may have a working channel with an outlet opening in the region between the two dilation units and through which at least one auxiliary catheter can be introduced for aortic valve ablation.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
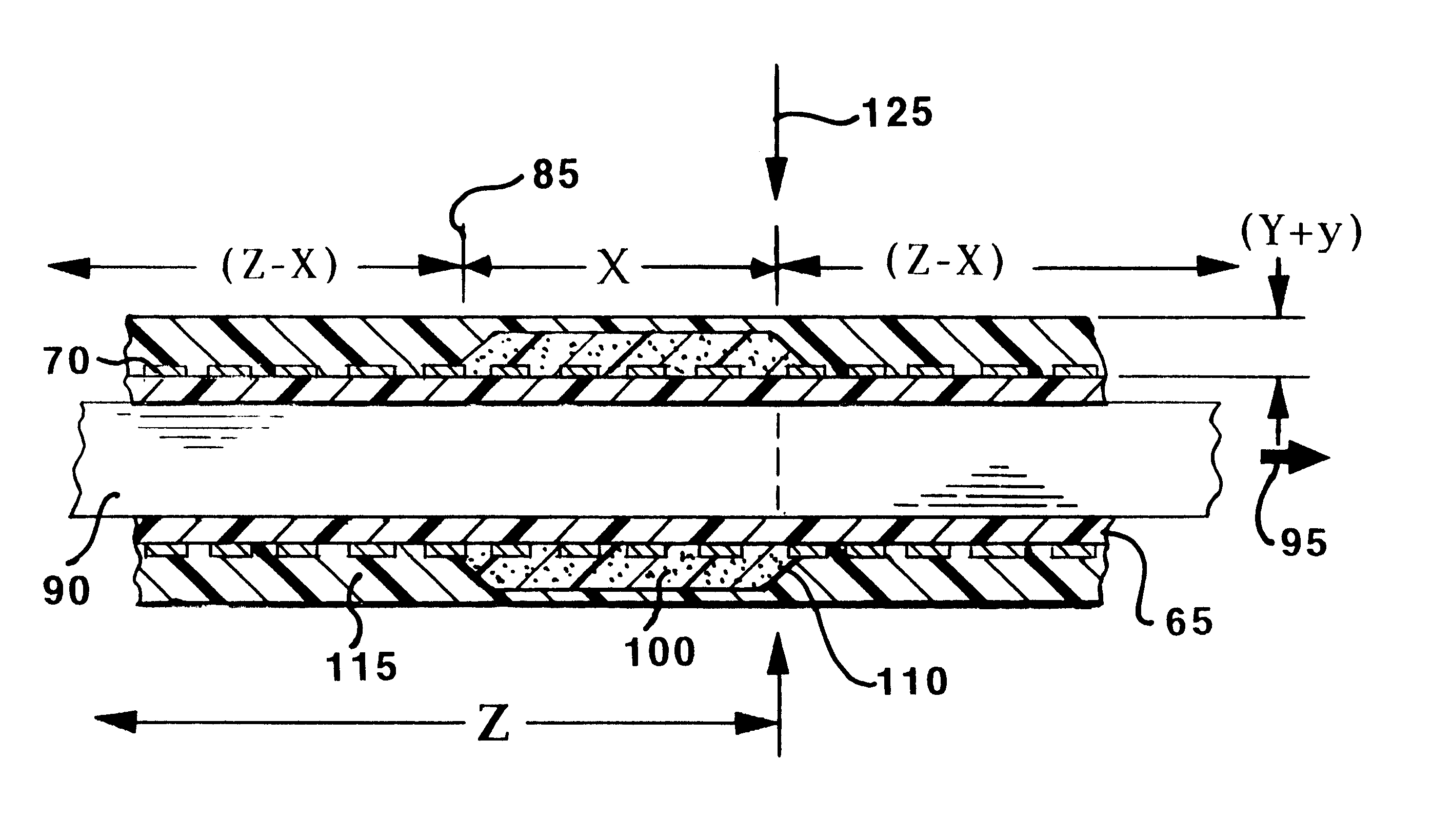
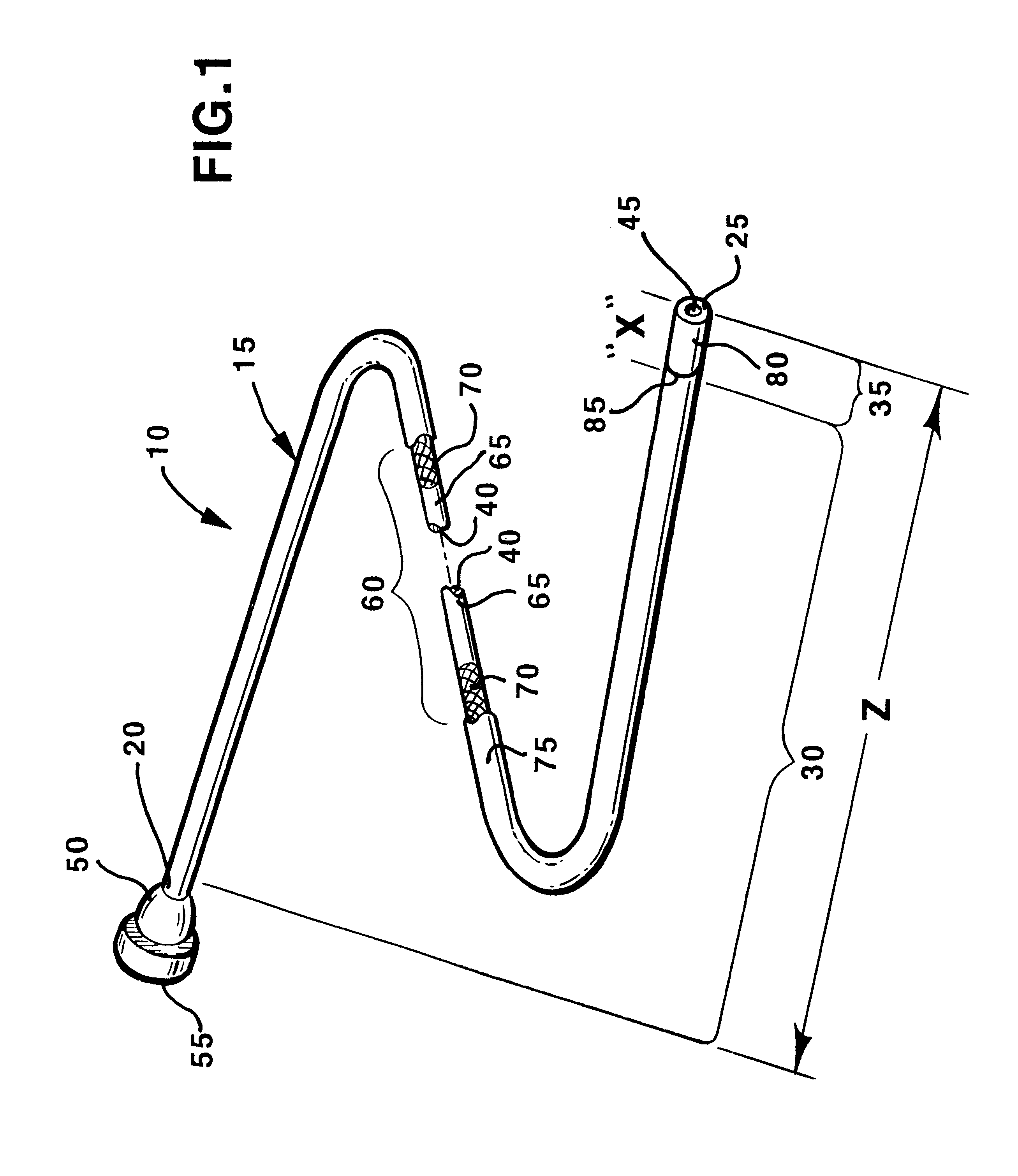
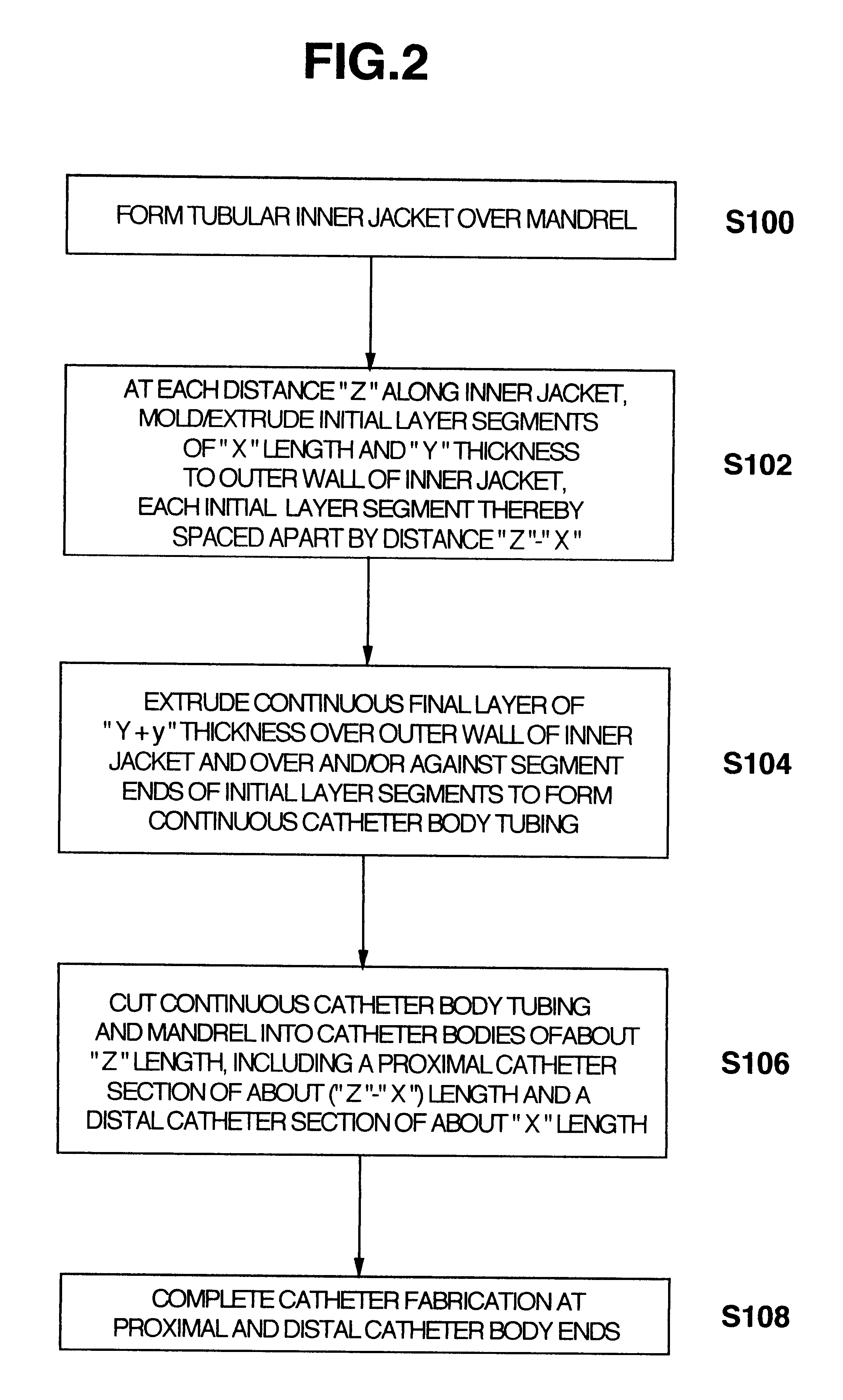
Multiple segment catheter and method of fabrication
Methods of fabricating medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing other devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes and particularly methods for fabricating such catheters with catheter bodies having catheter sections of differing flexibility are disclosed. Such catheter bodies having a proximal catheter body end and a distal catheter body end and formed of a proximal section and at least one distal section that have differing flexibilities are formed in a process comprising the steps of: (1) forming a continuous tubular inner jacket preferably of an inner liner and a reinforcement layer; (2) forming initial layer segments having an initial layer thickness along the length of the inner jacket from a material of first durometer hardness, whereby each initial layer segment is separated by a separation distance: (3) forming a final layer of a material of second durometer hardness with a second layer thickness over the tubular inner jacket along the separation distances and over and / or against the proximal and distal initial layer ends of the initial layer segments to form a continuous catheter body tubing; (4) severing the continuous catheter body tubing into catheter body lengths including a proximal catheter section formed of the material of second hardness and a distal catheter section of the material of first hardness; and (5) completing the catheter fabrication at the proximal catheter body end and the distal catheter body end. Centerless grinding of the catheter body or body tubing, formation of Intermediate catheter body sections, distal soft tips, and discontinuities in the reinforcement layer formed prior to step (2) are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and methods for removing emboli during a surgical procedure
Methods and apparatus for removing emboli during an endarterectomy procedure are provided. The present invention provides a proximal catheter disposed proximal to a stenosis and a distal catheter disposed distal to the stenosis. Each catheter may selectively communicate with a venous return catheter via a manifold having a setting controlled by a physician. Blood flows into an aspiration lumen of the distal catheter and is reperfused into a remote vein via the venous return catheter. Additionally, emboli generated during the procedure are removed via an aspiration lumen of the proximal catheter, and filtered blood then is reperfused into the remote vein.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
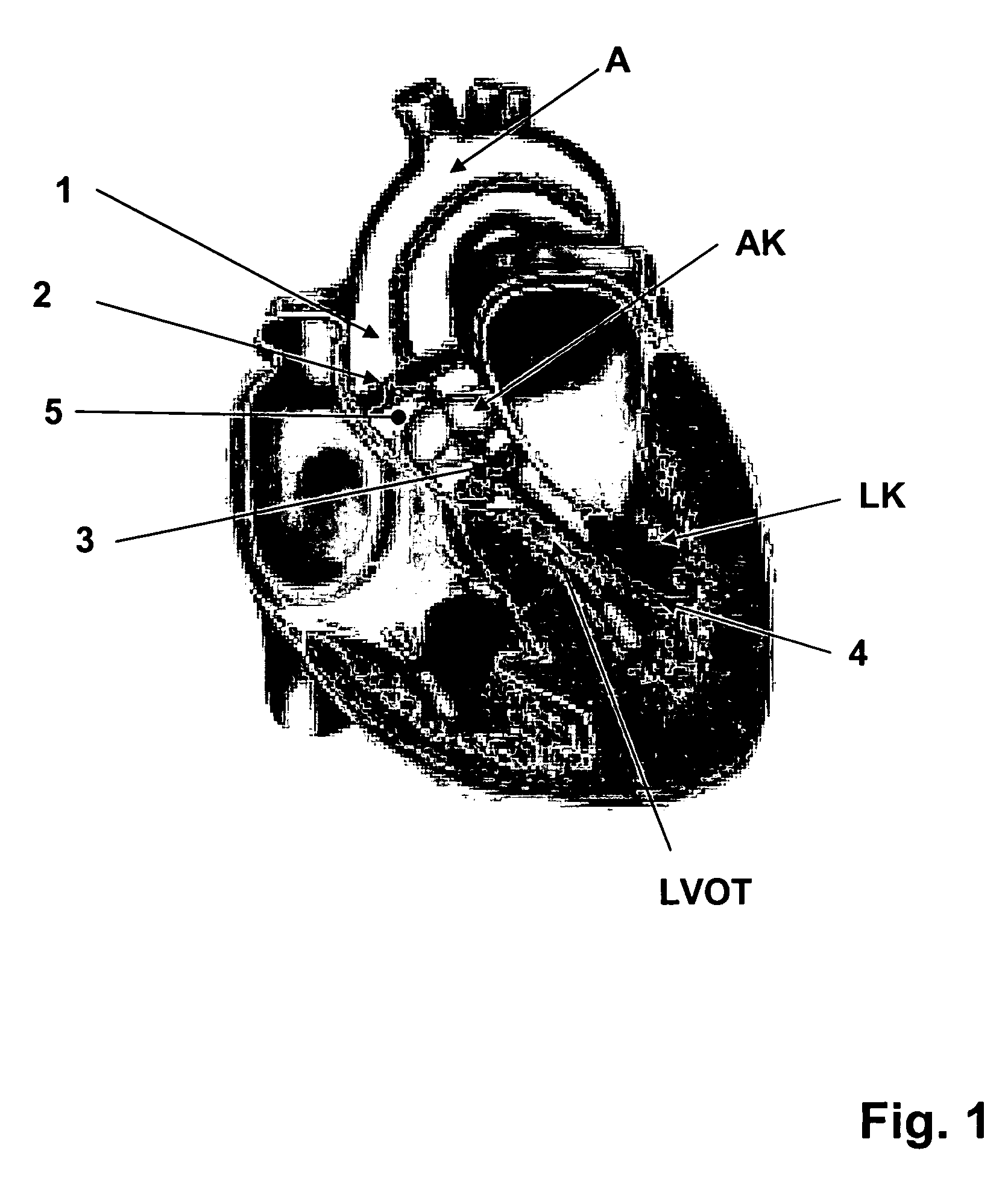
Method and apparatus for performing catheter-based annuloplasty using local plications
ActiveUS8460371B2Complicated surgical procedure can be avoidedImprove the quality of lifeSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsMitral valve leafletCatheter device
The present invention relates to minimally invasive methods and apparatus for performing annuloplasty. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for performing annuloplasty includes creating a first plication in the tissue near a mitral valve of a heart, using at least a first plication element, and creating a second plication in the tissue near the mitral valve such that the second plication is substantially coupled to the first plication. In another aspect, an apparatus for performing annuloplasty includes a distal catheter portion having a sidewall defining a lumen, anchor delivery structure disposed in the lumen, and al least one anchor supported on the anchor delivery structure. The anchor delivery structure is movable from a first position wherein the anchor is disposed within the lumen, to a second position wherein the anchor is moved through an opening.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Cardiac vein lead and guide catheter
InactiveUS6871085B2Easy steeringSmall sizeTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsWalking around obstaclesDistal segment
A guide catheter and medical lead are provided wherein the lead may be used as a pull wire to steer the guide catheter. The guide catheter is provided with a flexible distal segment and the lead is provided with a distal engaging member, which may also serve as an electrode. The distal engaging member interacts with the distal catheter end such that traction applied to the proximal lead end causes flexion of the distal segment of the catheter to advance the flexible distal segment between a non-flexed position and a flexed position, allowing the catheter to be steered around obstacles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Improved Catheters
Catheters having a tapered, atraumatic distal tip are provided. In one embodiment, the outer surface of the distal portion of the catheter has a generally non-cylindrical and substantially triangular cross-sectional configuration. The inner surface cross-sectional configuration of the distal portion of the catheter may match the outer surface, or it may have a cylindrical or oval configuration. The terminal orthogonal surface of the distal catheter tip is chamfered or rounded or contoured. In another embodiment, inner and / or outer catheter surfaces have a three dimensional surface conformation and may be dimpled or grooved. The grooves may be generally liner or curved or helical or in a spiral configuration. Dimpled and / or grooved surface discontinuities may be provided in connection with and in addition to lubricious coatings, surfaces, and the like.
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Assemblies for creating compound curves in distal catheter regions
InactiveUS7008401B2Swiftly and accurately steerEasy steeringMedical devicesSurgical instrument detailsBiomedical engineeringBody surface
Compound steering assemblies, usable in both diagnostic and therapeutic applications, enable a physician to swiftly and accurately steer the distal section of the catheter in multiple planes or complex curves to position and maintain ablation and / or mapping electrodes in intimate contact with an interior body surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Connector for securing ultrasound catheter to transducer
ActiveUS7758510B2Spread the wordLimiting and minimizing the impact of undesirable external forcesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTransducerAcoustic wave
An ultrasound system has an ultrasound transducer having a transducer housing and a horn provided at the distal end of the transducer housing, an ultrasound transmission member, a sonic connector that is connected to the horn and the proximal end of the ultrasound transmission member, and a catheter knob having a proximal end that is coupled to the distal end of the transducer housing. The catheter knob has a proximal bore that houses the sonic connector. The system also includes a nesting piece that is retained inside the proximal bore of the catheter knob. The nesting piece can be moved from a first position where the sonic connector is received inside the nesting piece to a second position where the sonic connector is separated from the nesting piece when ultrasound energy is being propagated through the ultrasound transmission member.
Owner:FLOWCARDIA
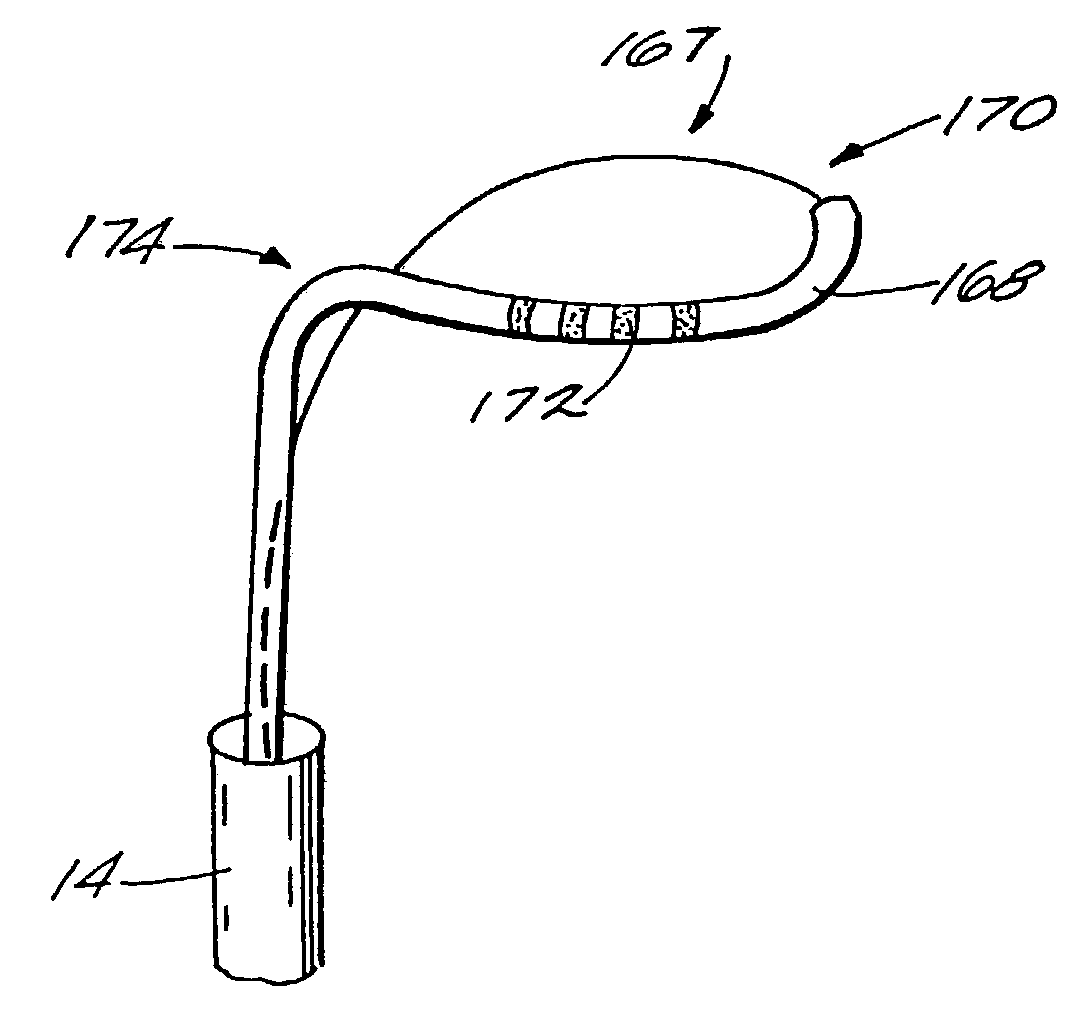
Slit valves bridging between the tip and distal side wall of catheter tubes and methods
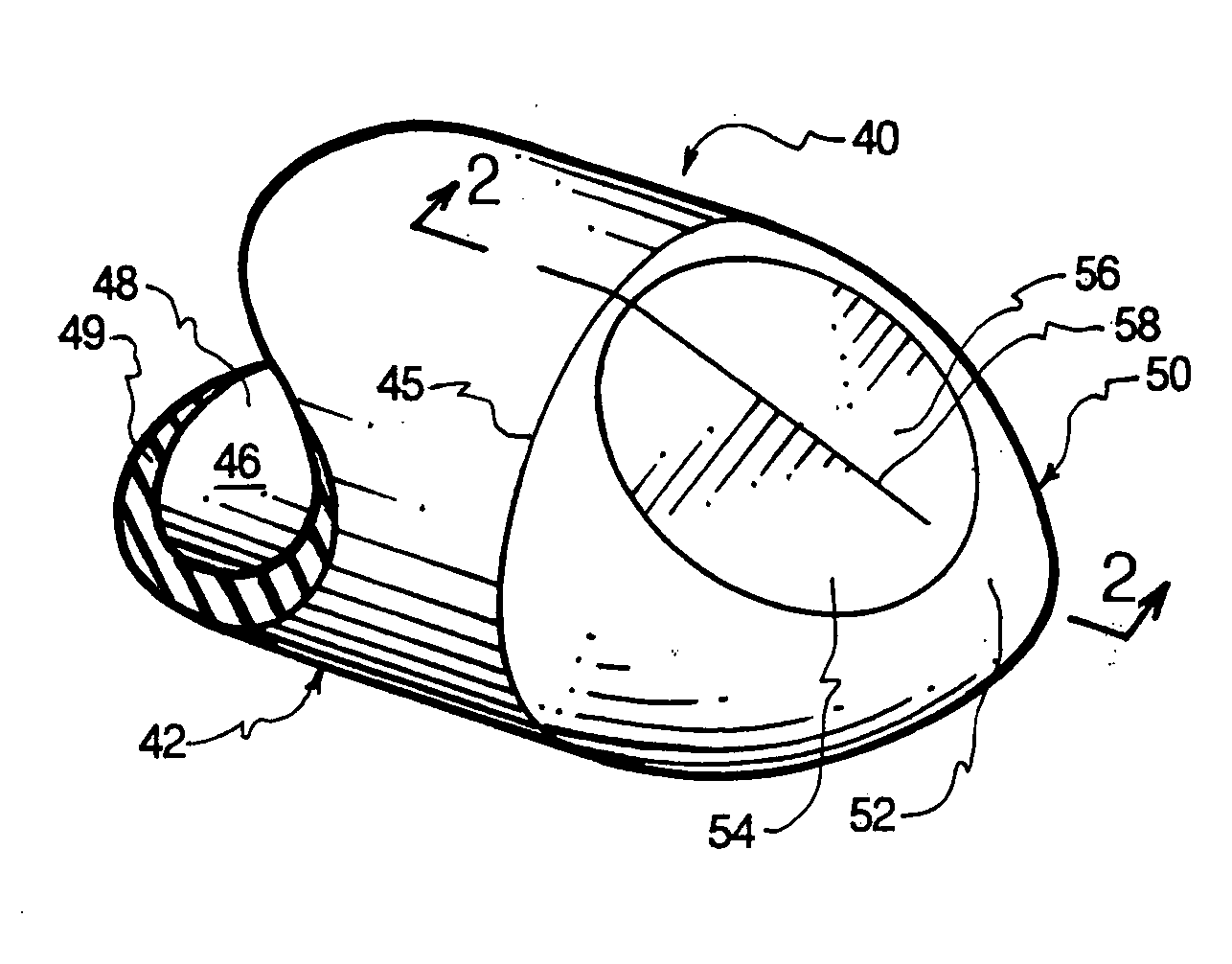
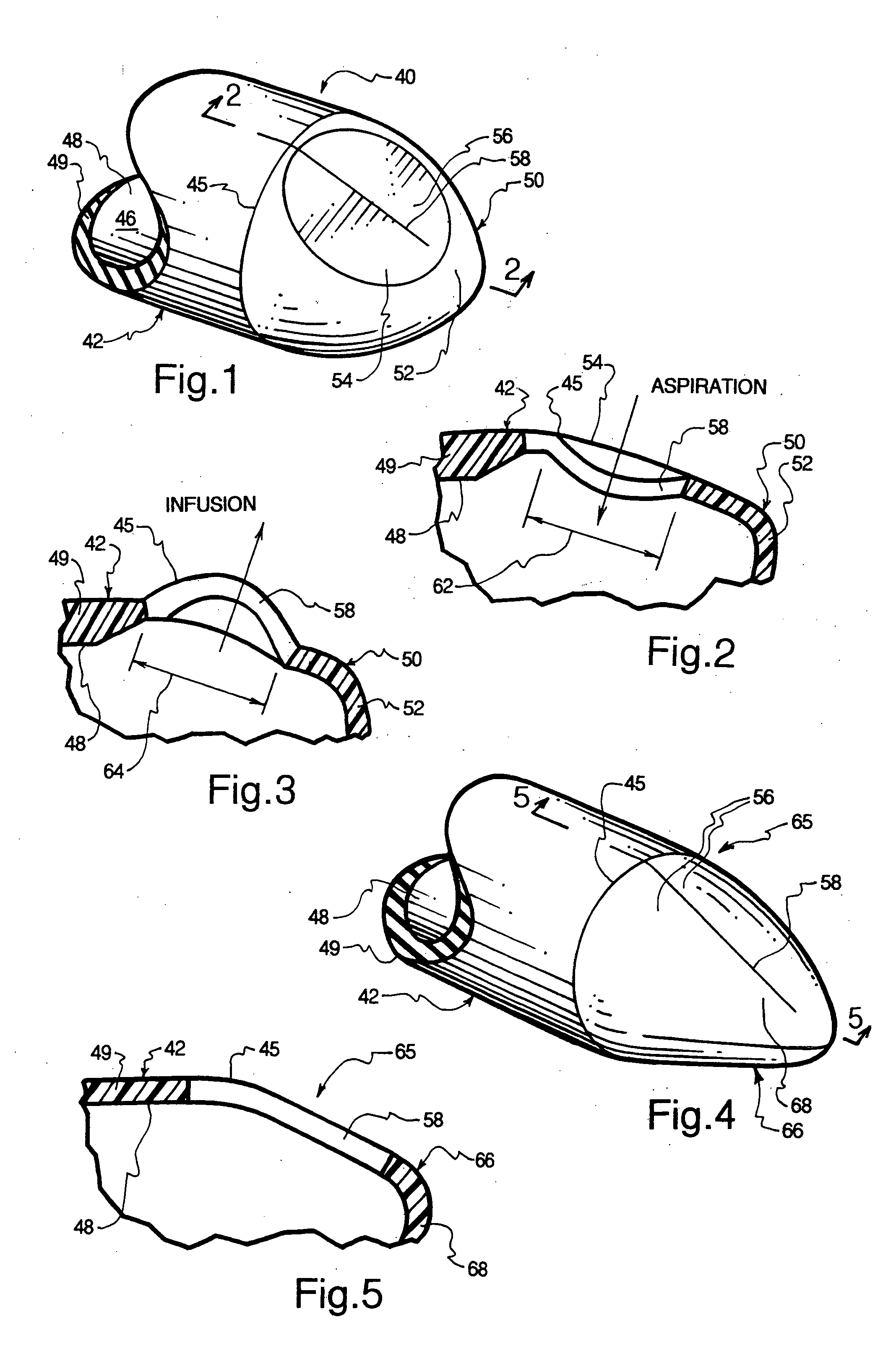
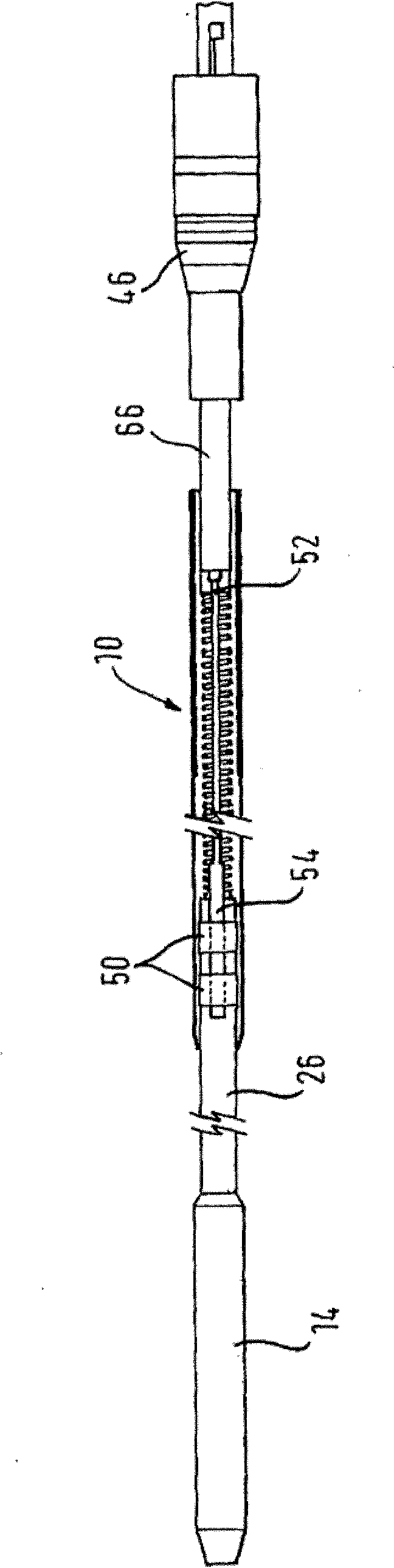
InactiveUS20050283122A1Reduce interferenceReduce occlusionCatheterIntravenous devicesVALVE PORTDistal catheter
Slit valves are disclosed which are placed in normally closed distal catheter tips so as to extend somewhat into the wall at the distal ends of catheter tubes whereby different rates of flow through the slit valves are achieved for aspiration and infusion, respectively.
Owner:NORDGREN CORP
Embolectomy device
An embodiment is a catheter comprising a first elongate shaft having a proximal end, a distal end and a first lumen therethrough, a wire having a proximal end and a distal end at least partially disposed in the first elongate shaft, the distal end extending distally from the first elongate shaft, and a motion control apparatus connected to the proximal end of the wire, further comprising a device attached to the distal end of the wire for changing the shape of an embolus, wherein the device is configured to change the shape of the embolus to unclog a distal catheter lumen.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Assemblies for creating compound curves in distal catheter regions
InactiveUS7011655B2Swiftly and accurately steerEasy steeringMedical devicesCatheterBiomedical engineeringBody surface
Compound steering assemblies, usable in both diagnostic and therapeutic applications, enable a physician to swiftly and accurately steer the distal section of the catheter in multiple planes or complex curves to position and maintain ablation and / or mapping electrodes in intimate contact with an interior body surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device for minimally invasive intravascular aortic valve extraction
The present invention is distinguished by a perfusion catheter being provided comprising at least one perfusion channel designed as a hollow channel and at least two dilation units disposed at a distance from each other at the distal catheter region in the longitudinal extension of the catheter, both the dilation units being projected through by the perfusion catheter and forming in an inflated state an at least practically fluid-tight occlusion with the aortic wall, of which the dilation units at least said dilation unit disposed on the proximal side is provided with at least one passage through which at least one auxiliary catheter can be introduced aortic valve ablation in a fluid-tight manner and / or the perfusion catheter is provided with a working channel which is provided with an outlet opening in the region between the two dilation units and through which at least one auxiliary catheter can be introduced for aortic valve ablation.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Embolectomy device
An embodiment is a catheter comprising a first elongate shaft having a proximal end, a distal end and a first lumen therethrough, a wire having a proximal end and a distal end at least partially disposed in the first elongate shaft, the distal end extending distally from the first elongate shaft, and a motion control apparatus connected to the proximal end of the wire, further comprising a device attached to the distal end of the wire for changing the shape of an embolus, wherein the device is configured to change the shape of the embolus to unclog a distal catheter lumen.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Guide wire control catheter for crossing occlusions and related methods of use
A wire control catheter for aligning and guiding a guide wire through a lesion in a vessel is provided. The wire control catheter includes a shaft having a guide wire lumen and a control wire lumen. A control wire passes through the control wire lumen and is used in combination with an articulation structure to deflect or curve a distal tip portion of the catheter. The distal catheter shaft may include a centering device for centering the catheter within the vessel. The distal catheter shaft may also include a pre-dilation balloon for dilating the lesion prior to performing angioplasty or other treatment on the lesion. A method of treatment of a blood vessel includes inserting a guide wire into the blood vessel and advancing a control wire over the guide wire until the distal tip of the catheter is near the occlusion in the blood vessel. The tip of the catheter then is deflected via a control wire and an articulation structure. The guide wire is then advanced across the occlusion. The control wire also may be advanced across the occlusion simultaneously with the guide wire or subsequent to the guide wire crossing. Prior to crossing the occlusion, the wire control catheter may be centered using a centering device. Subsequent to crossing the occlusion, the occlusion may be pre-dilated with a pre-dilation balloon of the wire control catheter.
Owner:VASCULAR SOLUTIONS +1
Magnetic navigation systems with dynamic mechanically manipulatable catheters
InactiveUS20060247522A1Efficiently and predictably navigatedMedical devicesCatheterNavigation systemTarget tissue
Systems and methods are provided for magnetically and mechanically navigating catheters. The system comprises a catheter that includes an elongated flexible catheter body having a distal end configured to be mechanically actuated to assume a non-compliant curved geometry. The distal end can be mechanically actuated in one of any number of manners. The catheter further comprises a magnetically responsive element and an operative element carried by the distal catheter end. The system further comprises a magnetic navigation system configured for applying a magnetic force to the magnetic element to deflect the distal catheter end. A method of using the system may comprise introducing the catheter within an anatomical cavity, mechanically actuating the distal catheter end to assume the curved geometry within the anatomical cavity, placing the operative element adjacent a target tissue site within the anatomical cavity, and performing a medical procedure on the target tissue site with the operative element. The magnetic navigation system can be used during catheter navigation and / or to firmly place the operative element against the target tissue site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Microcatheter system
A system for use in a vascular procedure includes a guidewire dimensioned to remotely access a neurovascular space, a microcatheter for positioning over the guidewire, an interventional treatment element for passage within the catheter member of the microcatheter, and an outer guide positionable over the catheter member of the microcatheter upon removal of the catheter hub. The microcatheter includes an elongated catheter member and a catheter hub. The catheter member defines a longitudinal axis and has a longitudinal length and with proximal and distal ends. The catheter hub is connected to the proximal end of the catheter member and is dimensioned and adapted to be selectively released from the catheter member. The outer guide is advanceable over the catheter member of the microcatheter after the catheter hub is released from the catheter member to a location proximate the lesion. The interventional treatment element is adapted to perform treatment on the lesion within the vasculature
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Spiral centering catheter
InactiveUS20050171592A1Through simpleAvoiding adverse lumen contactStentsBalloon catheterDistal portionStent deployment
A catheter with proximal and distal ends having a spiral centering device attached near the catheter distal end. The spiral centering device has at least one spiral strut having a proximal end and a distal end. The spiral centering device resiliently tends to center the distal end portion of the catheter, steering the catheter away from the vessel wall during insertion through the vasculature and toward the treatment site. The spiral centering catheter may facilitate access to tortuous anatomy by preventing the distal catheter tip from catching on irregularities in the lumenal surface. If a stent is provided on the catheter, the spiral centering catheter may also facilitate uniform stent expansion by stabilizing the catheter during stent deployment.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
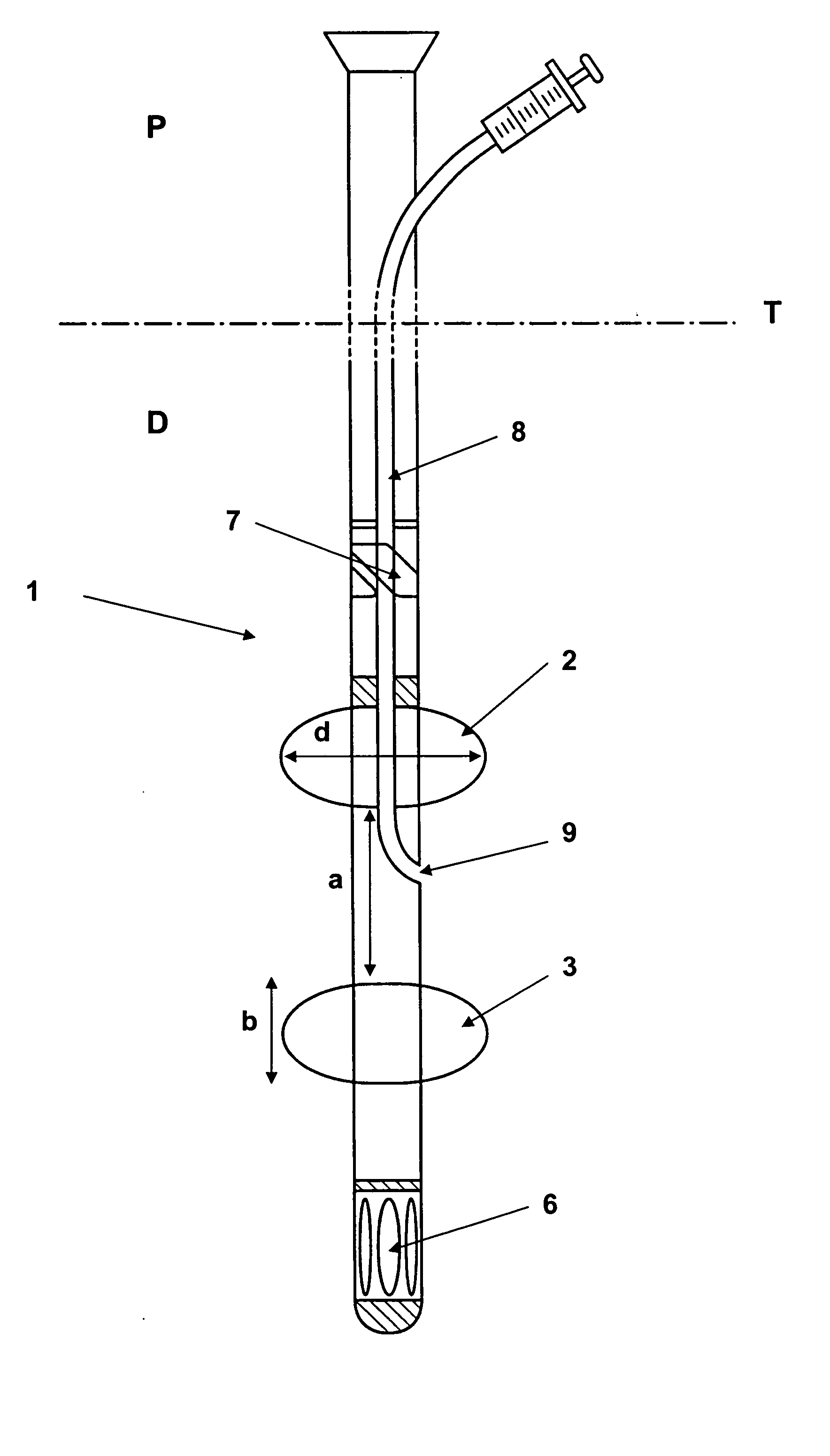
Catheter
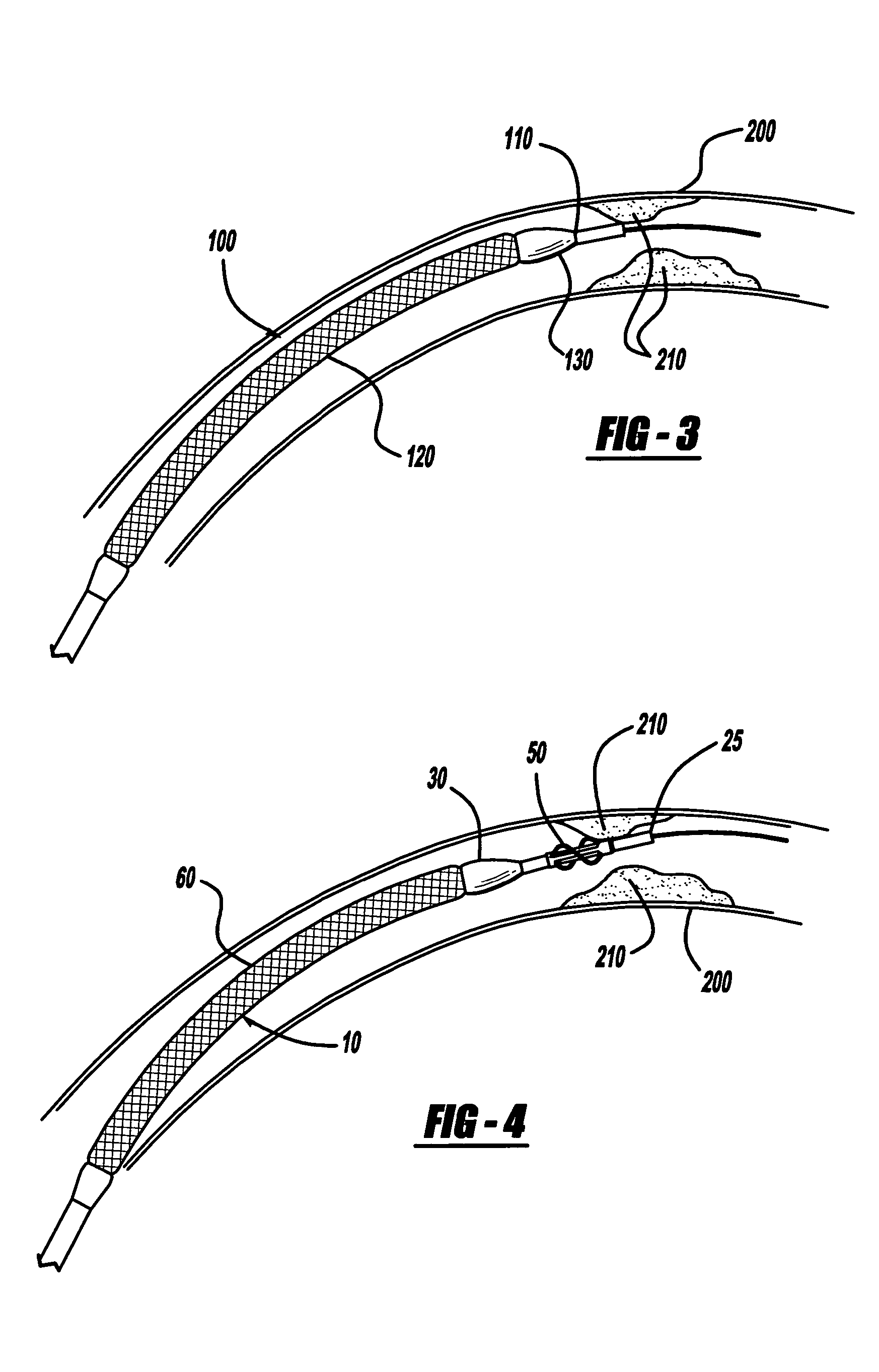
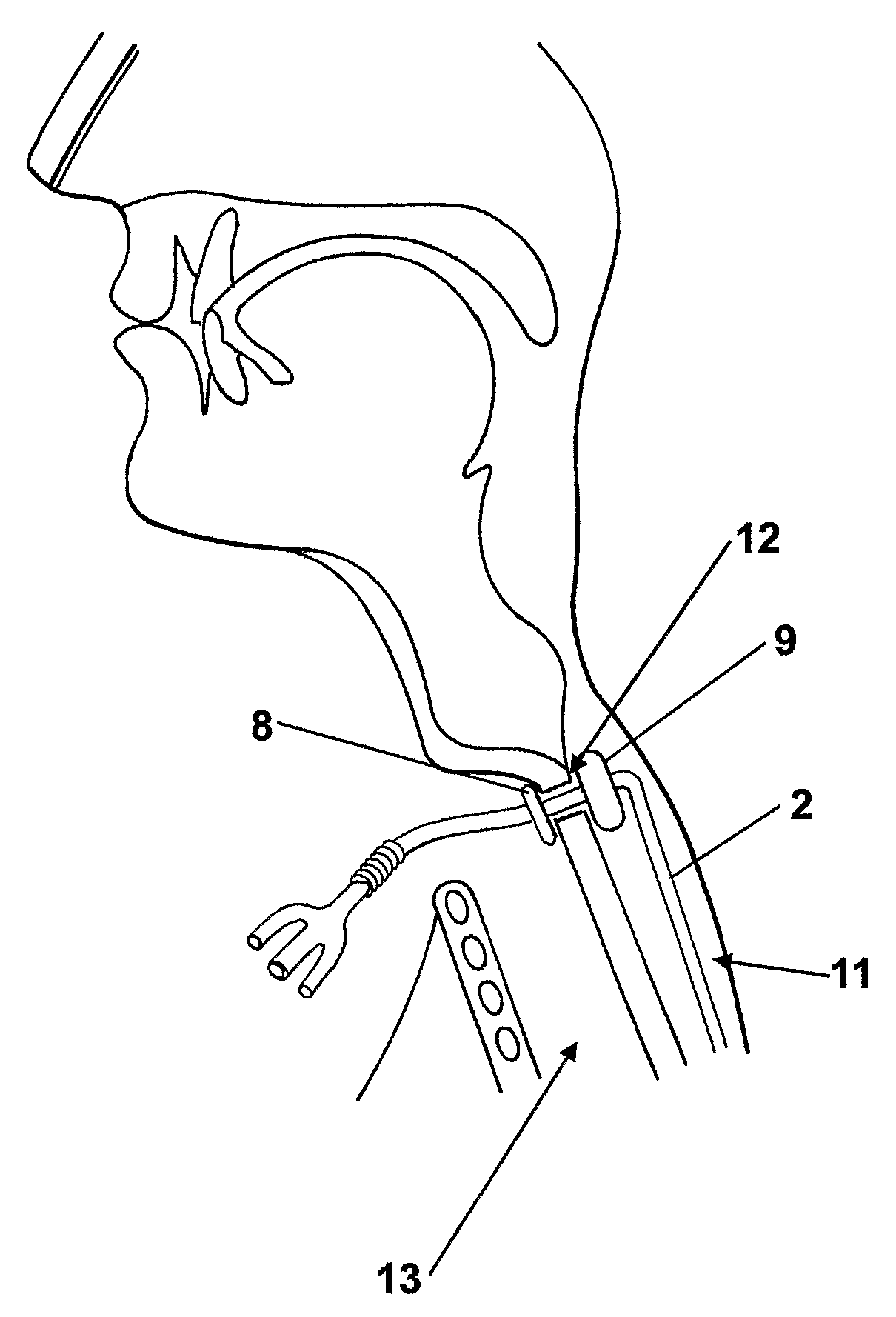
InactiveUS20090171280A1Comfortable to wearFew infectionRespiratorsStentsTracheo-oesophageal fistulaCatheter device
A tracheo-oesophageal fistula catheter (1) comprises an elongate conduit (2) having a proximal and a distal end, the conduit (2) comprising a plurality of lumens commencing adjacent to the proximal end; means (8, 9) for substantially sealing a tracheo-oesophageal fistula, the means being attached to the conduit (2) adjacent to the proximal end and comprising two elements (8, 9) to be placed on either side of the fistula; and at least one expandable balloon (7) attached to the conduit (2) adjacent to the distal end, and in fluid connection with at least one of said lumens; wherein at least one lumen is a gastric lumen, the gastric lumen extending along the full length of the conduit and having an outlet (6) at the distal end of the conduit (2), and wherein at least one element of the means for sealing the fistula comprises an expandable balloon in fluid connection with at least one of said lumens.
Owner:CITY HOSPITALS SUNDERLAND NHS TRUST
Deflectable catheter with distal deflectable segment
ActiveUS7985215B2Enhance and maximize sizeElectrocardiographyCatheterOut of plane motionProximal point
A guidable, or steerable, or deflectable catheter is provided that includes a proximal portion and a distal portion for insertion into a body cavity. A selectively deflectable segment having an anisotropic bending stiffness for deflection in individual planes is incorporated into the distal portion of the catheter shaft. Upon actuation of pull wires, the distal deflectable segment may be deflected to move / sweep the distal catheter tip through a sweeping plane. The anisotropic bending stiffness of the distal deflectable segment permits in-plane movement of the distal catheter tip in the sweeping plane while resisting any out-of-plane movements. In one arrangement, stiffening elements are selectively disposed within the distal deflectable segment such that the out-of-plane bending stiffness is largely increased and greater than the in-plane bending stiffness for deflection in the sweeping plane. In another arrangement, the cross section of a distal deflectable segment is altered to produce anisotropic area inertias of moment about its centroidal axes, and thus anisotropic bending stiffnesses.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Implantable anti-clogging device for maintenance of cerebrospinal fluid shunt patency
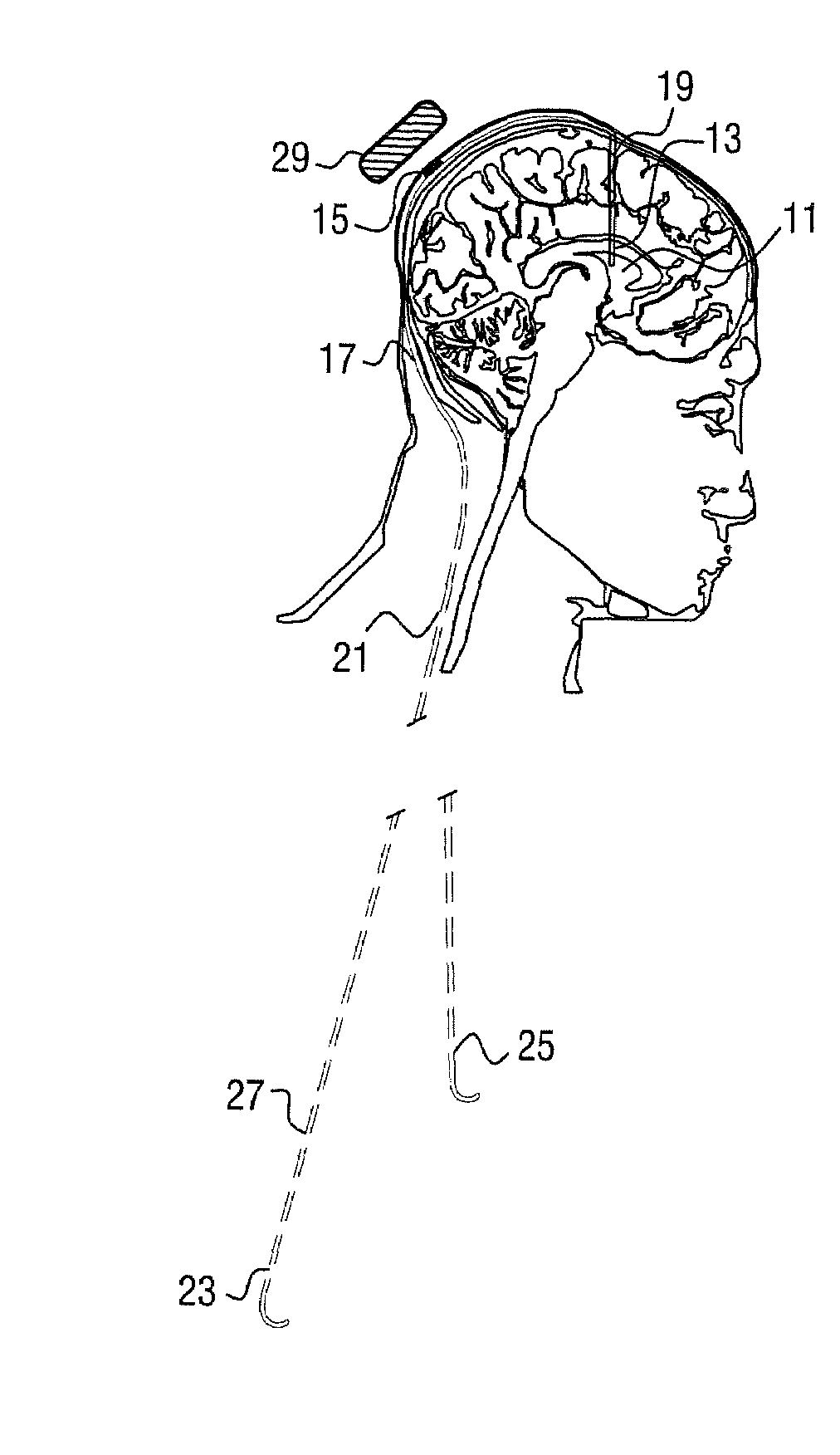
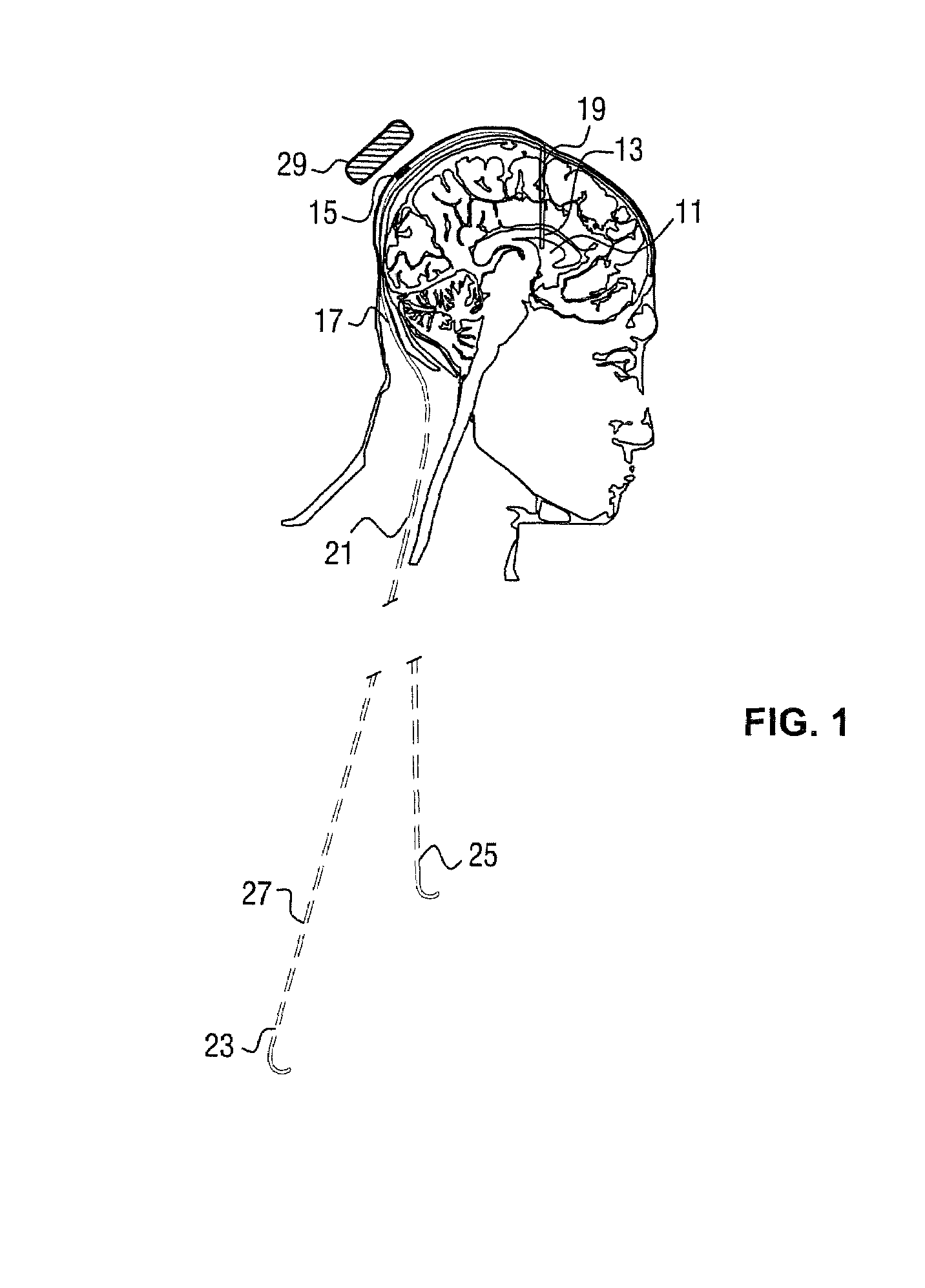
Cerebrospinal fluid shunts (implantable devices for diversion of excess fluid from the brain to other body cavities) used to treat hydrocephalus often malfunction. A common etiology of shunt malfunction is obstruction of the distal catheter tip by accumulating particulate matter such as fat or proteinaceous debris. The proposed implantable device maintains the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid shunt with mechanical energy which serves to “scrub” the catheter lumen of particulate debris. The proposed device accomplishes this by housing a source of mechanical energy which is coupled to the external aspect of the catheter, itself traversing through a bore in the device. The energy source secondarily induces a waveform in the cerebrospinal fluid flowing through the catheter. The fluid waveform exerts shearing forces on the catheter wall and serves to disrupt the formation and accumulation of debris that potentially could occlude the shunt catheter, thereby maintaining patency of the shunt.
Owner:OSBORN BRETT +1
Balloon catheter with kink resistant distal segment
InactiveUS20050107821A1Stay flexibleProvide kink resistanceStentsBalloon catheterBalloon catheterDistal segment
A rapid exchange balloon catheter has a kink resistant distal catheter segment just proximal of the balloon with a kink resisting member to provide pushability and kink resistance while maintaining flexibility. The kink resistant distal segment allows the rapid exchange guidewire tube to be shortened for a more rapid guidewire exchange.
Owner:INNOVATIONAL HLDG LLC
Intrajugular catheter
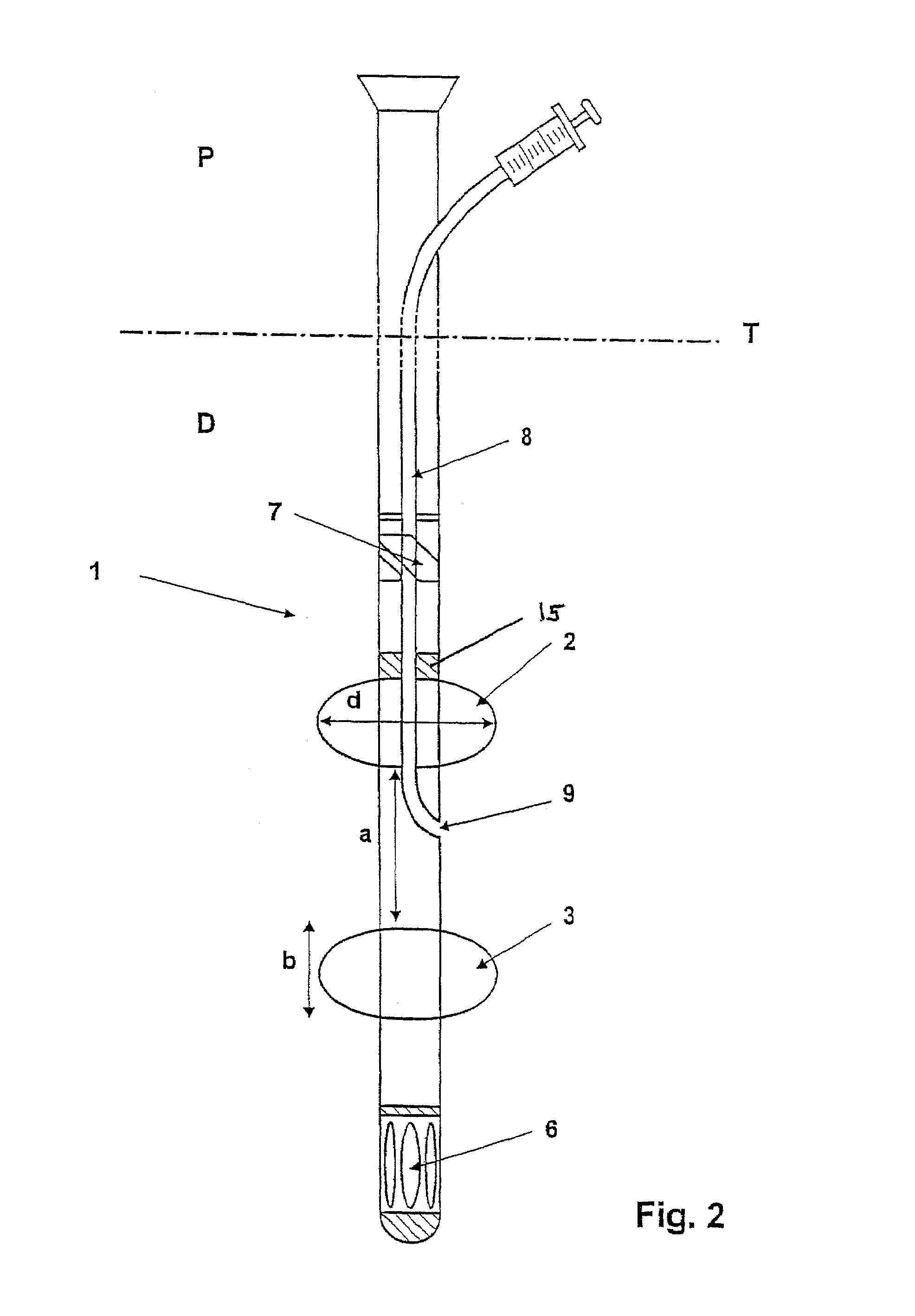
A catheter for insertion into a vascular system of a patient and for directing fluid flow includes a catheter body having a longitudinal axis and longitudinally spaced proximal and distal catheter ends with an intermediate catheter portion defined therebetween. An intermediate catheter outlet in the catheter body is located in the intermediate catheter portion and is spaced longitudinally from the proximal and distal catheter ends. A first lumen is defined within the catheter body and has longitudinally spaced proximal and distal first lumen ends with a reversing bend located therebetween, the first lumen providing fluid communication between the proximal catheter end and the intermediate catheter outlet. The reversing bend is located longitudinally between the intermediate catheter outlet and the distal catheter end. The reversing bend directs fluid flow to turn approximately 180° as the fluid flows through the first lumen. A method of using the catheter is also described.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Forwardly directed fluid jet crossing catheter
ActiveUS20080312672A1EfficaciousContact safetyCannulasFluid jet surgical cuttersJet flowTotal occlusion
The present invention provides a forwardly directed fluid jet crossing catheter having a distally directed cylindrical flow fluid jet stream to cross a chronic total occlusion. The distal end of the device includes a formable catheter tip region having flexible internal components. Low and high pressure cavities are formed substantially by joined proximal and distal catheter tubes having an adhesive plug seal in common therebetween which partially defines one end of each of the low pressure and high pressure cavities. A guidewire tube and a high pressure tube are aligned along and within the low pressure and high pressure cavities and through the adhesive plug seal. The high pressure tube openly terminates in the high pressure cavity, whereby pressurized fluid transfers from the high pressure cavity in the guidewire tube entry hole to subsequently pass along the guidewire lumen and co-located guidewire to exit as a cylindrical fluid jet stream.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
Multiple lumen catheter for hemodialysis
InactiveUS7695450B1Reduce the possibilityProtects the delicate intimal tissuesMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesVeinHemodialysis
A catheter for hemodialysis comprises a flexible catheter tube defining a plurality of separate lumens. The catheter defines an arc angle of generally U-shape in its natural, unstressed configuration. Thus, the catheter may be implanted with a distal catheter portion residing in a vein of the patient, the distal catheter portion being of substantially the shape of the vein in its natural, unstressed condition. Also, a proximal catheter portion resides in a surgically created tunnel extending from the vein and through the skin of the patient, this section of the catheter also being typically in its natural, unstressed condition. Thus blood may be removed from the vein through one lumen of the catheter, and blood may be returned to the vein through another lumen of the catheter, while the catheter is subject to long term indwelling in the body. Improved results are achieved because of the lack of mechanical stress in the shape of the catheter, which stress causes the catheter to press unduly against adjacent tissues.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Catheter delivery device
A catheter delivery device for a self-expanding stent including a distal catheter component, a distal sheath disposed over the stent, a proximal catheter shaft defining a tube; a proximal sheath connected to the distal sheath defining a lumen containing the catheter shaft, an open distal end suitable to receive the proximal end of the distal catheter component side-by-side with the distal end of the catheter shaft and; a casing tube surrounding the catheter shaft having a distal end telescopically receiving the proximal end of the distal sheath.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
System and method for low profile occlusion balloon catheter
ActiveUS10368872B2Deescalating the vibrating and pulsing effectsBalloon catheterOcculdersOcclusion catheterBalloon catheter
An occlusion catheter system includes an inflation catheter member and an occlusion balloon. The proximal and distal balloon ends are connected to the inflation catheter between the proximal and distal catheter ends. A distal pressure sensor is attached to the inflation catheter member between the proximal balloon end and the atraumatic tip. An inflatable spine is connected to the inflation catheter. The proximal spine end is connected to the inflation catheter near the proximal balloon end and the distal spine end is connected to the inflation catheter near the distal balloon end. The occlusion balloon and the inflatable spine are configured to define blood flow channels with the internal surface and the external balloon surface when the occlusion catheter system is at least partially positioned in the vessel and the occlusion balloon and the inflatable spine are in a partially inflated configuration.
Owner:PRYTIME MEDICAL DEVICES INC
Electroactive polymer actuated cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS20080125690A1Reduce in quantityAvoid possibilityWound drainsMedical devicesInternal pressureVentricular catheters
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt comprises a ventricular catheter and an electroactive polymer actuated valve for regulating the drainage rate of CSF from the brain ventricle of a patient. The shunt system also comprises a distal catheter for discharge of the CSF to a separate location in the patient's body such as the peritoneal cavity or atrium of the heart. The electroactive polymer actuated valve regulates the flow rate of CSF through a predetermined threshold pressure, which can be adjusted and programmed externally from the patient's body by means of an external control unit signal, as well as through a signal indicated by an internal sensor or an electroactive polymer transducer. The sensor also communicates a signal to the external control unit for indicating the internal pressure at a single location or multiple locations throughout the fully implanted shunt assembly.
Owner:ANITEAL LAB
Consolidated atherectomy and thrombectomy catheter
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com