Patents
Literature
89 results about "Organ wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
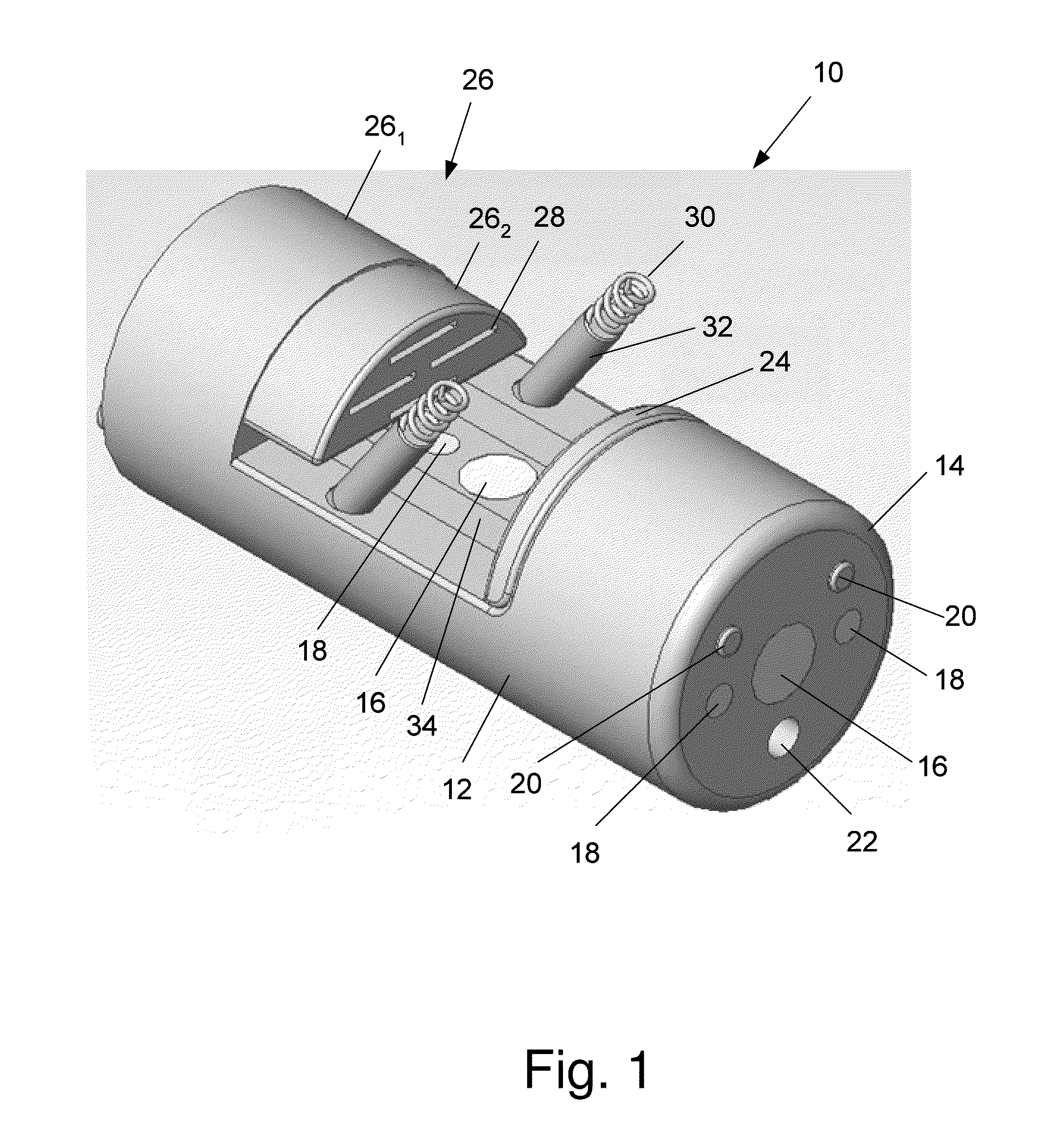
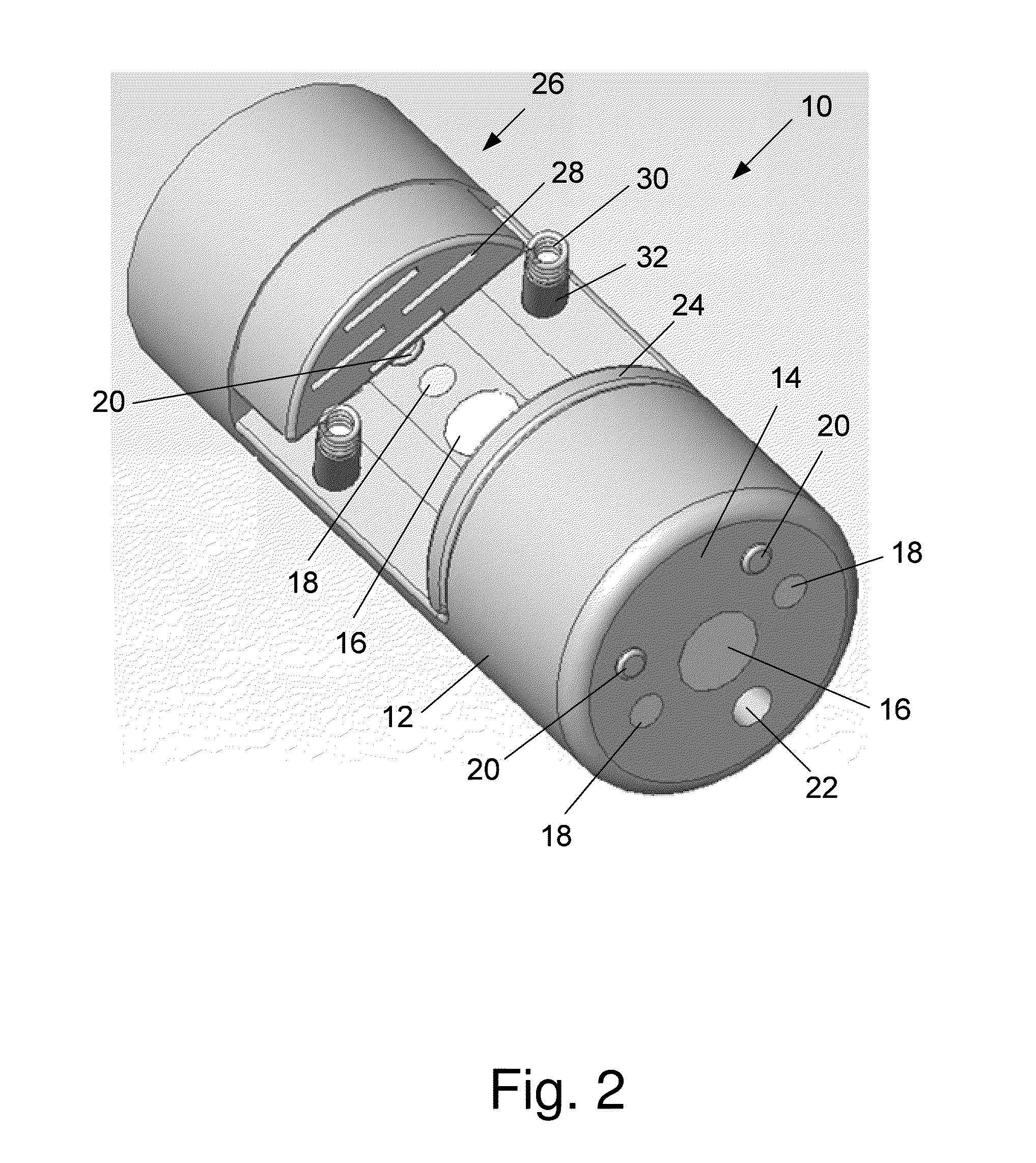
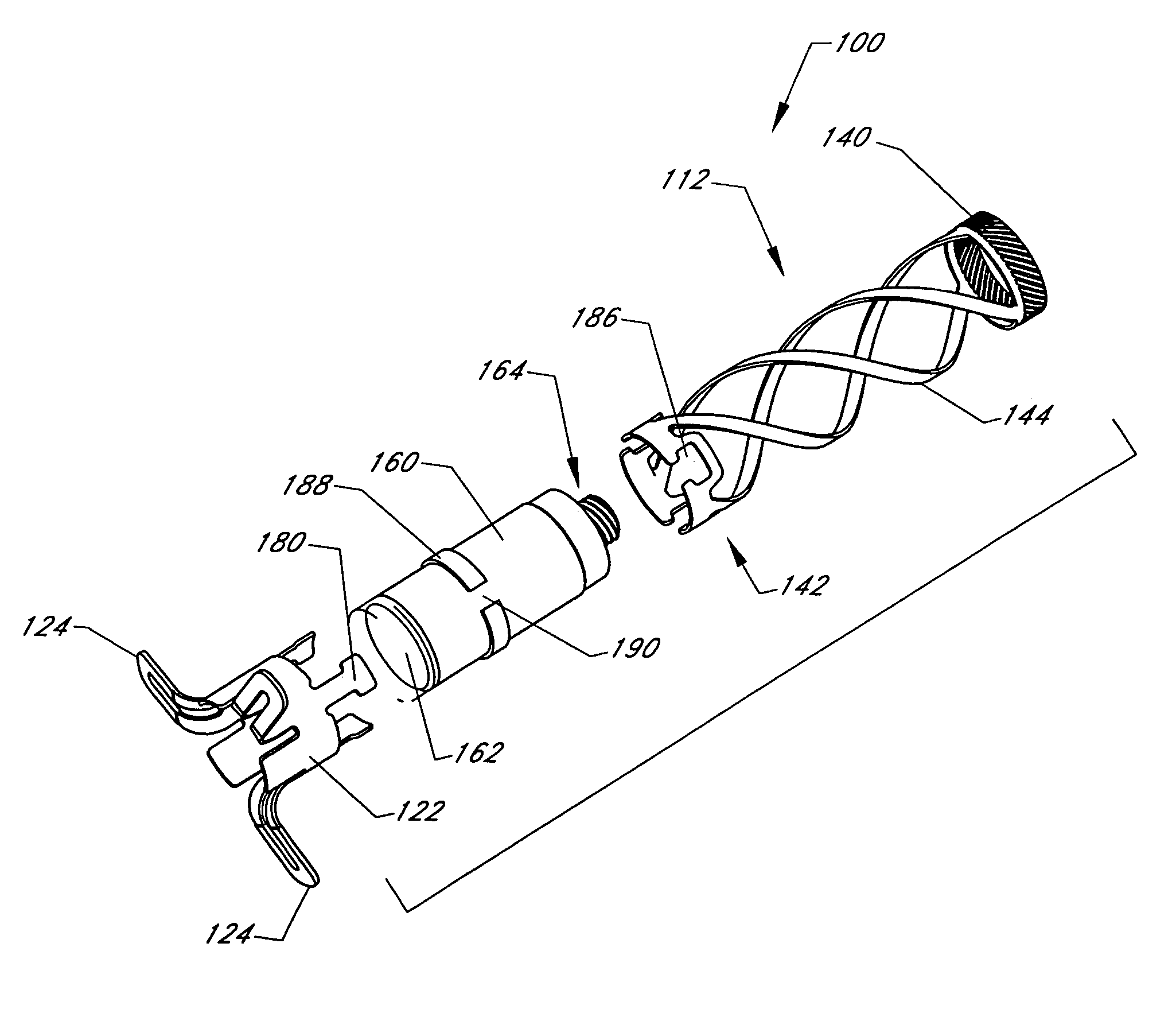
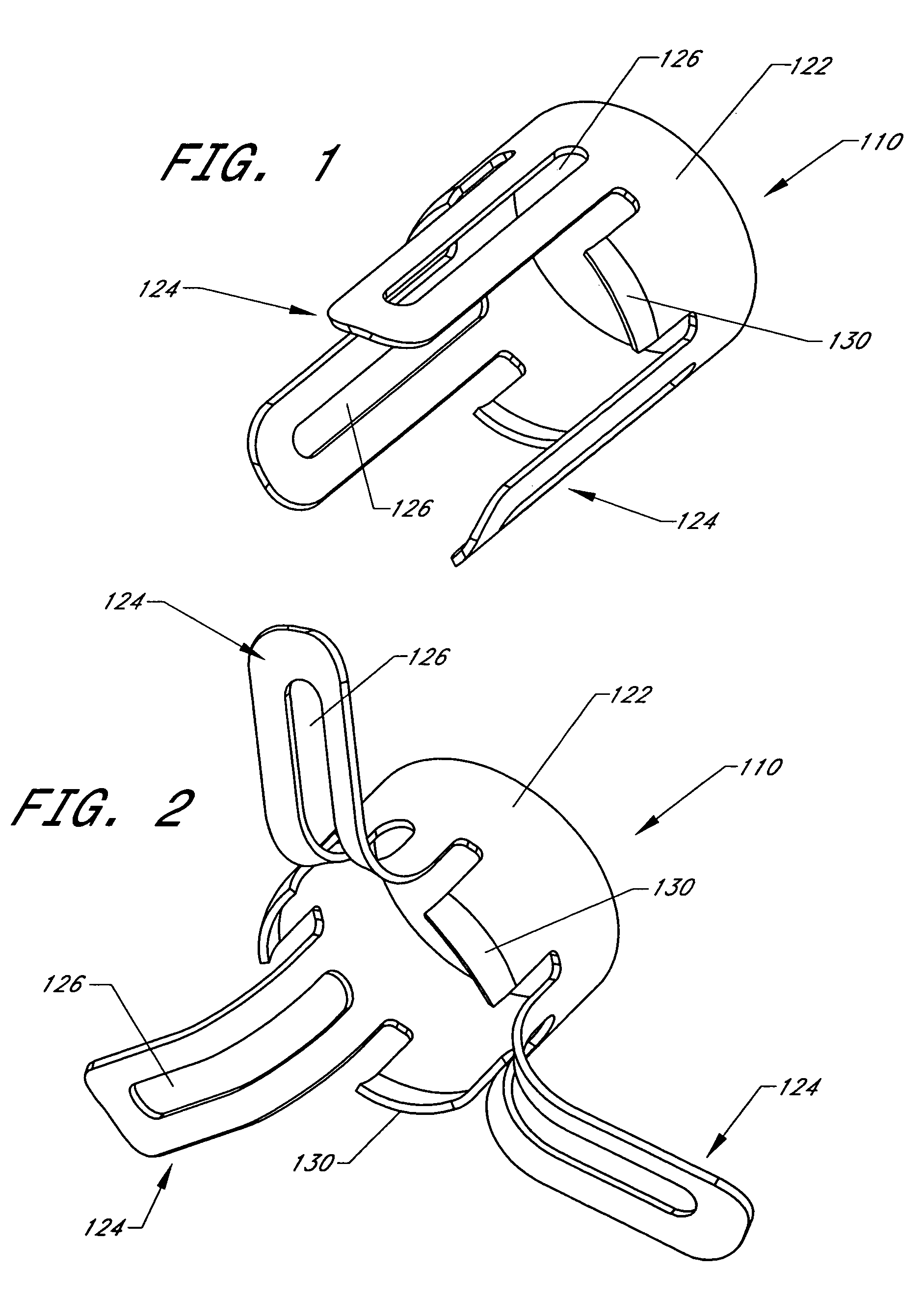
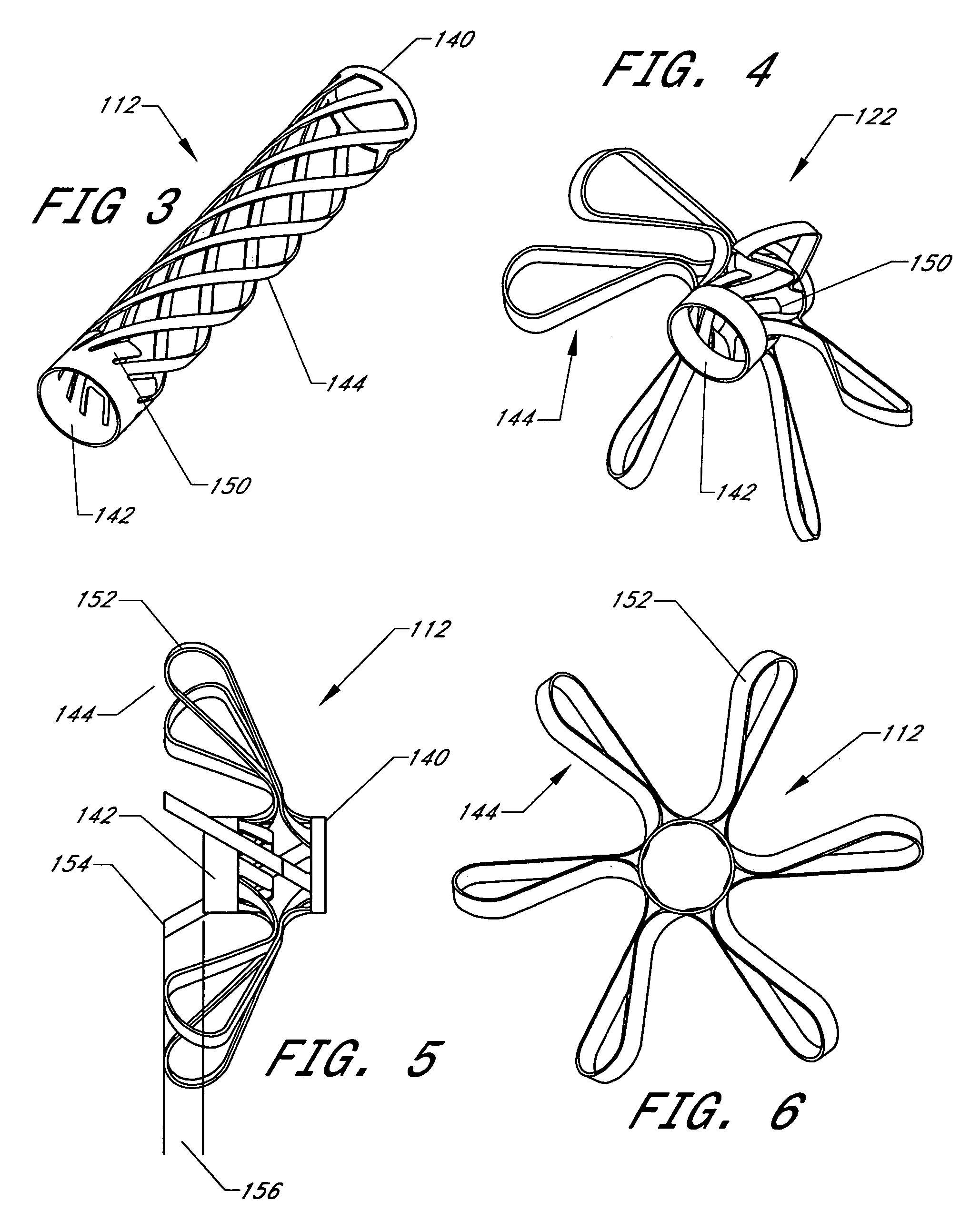
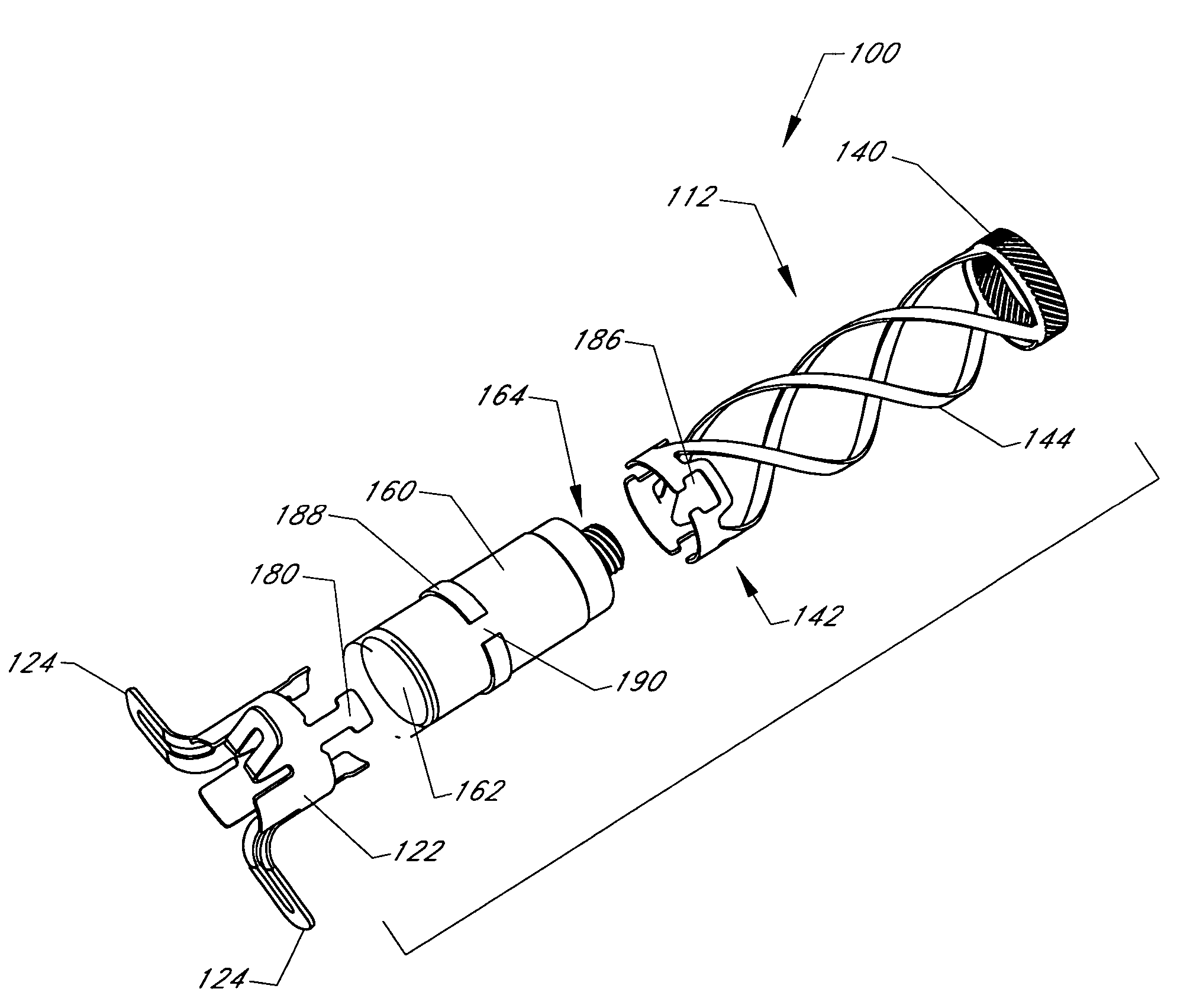
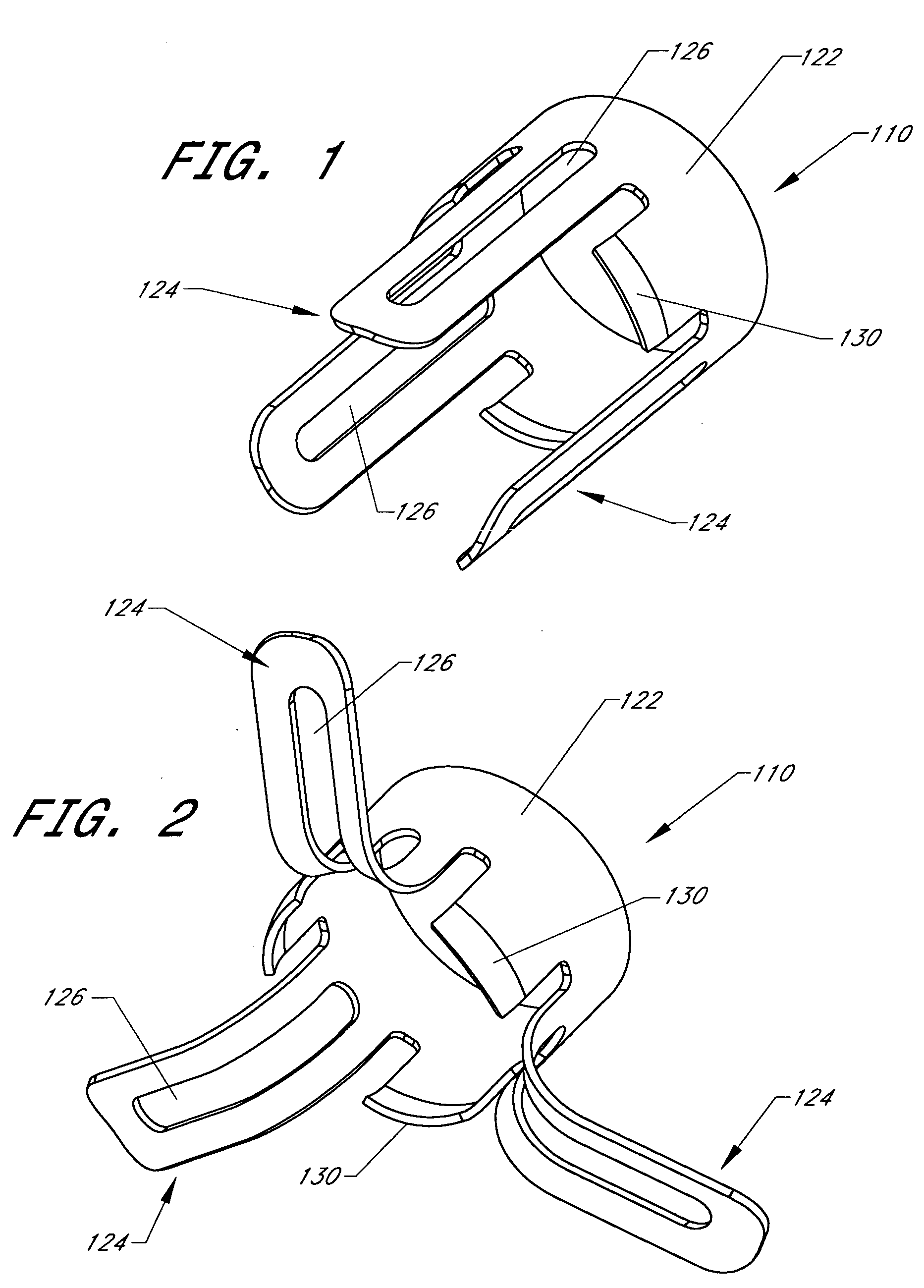
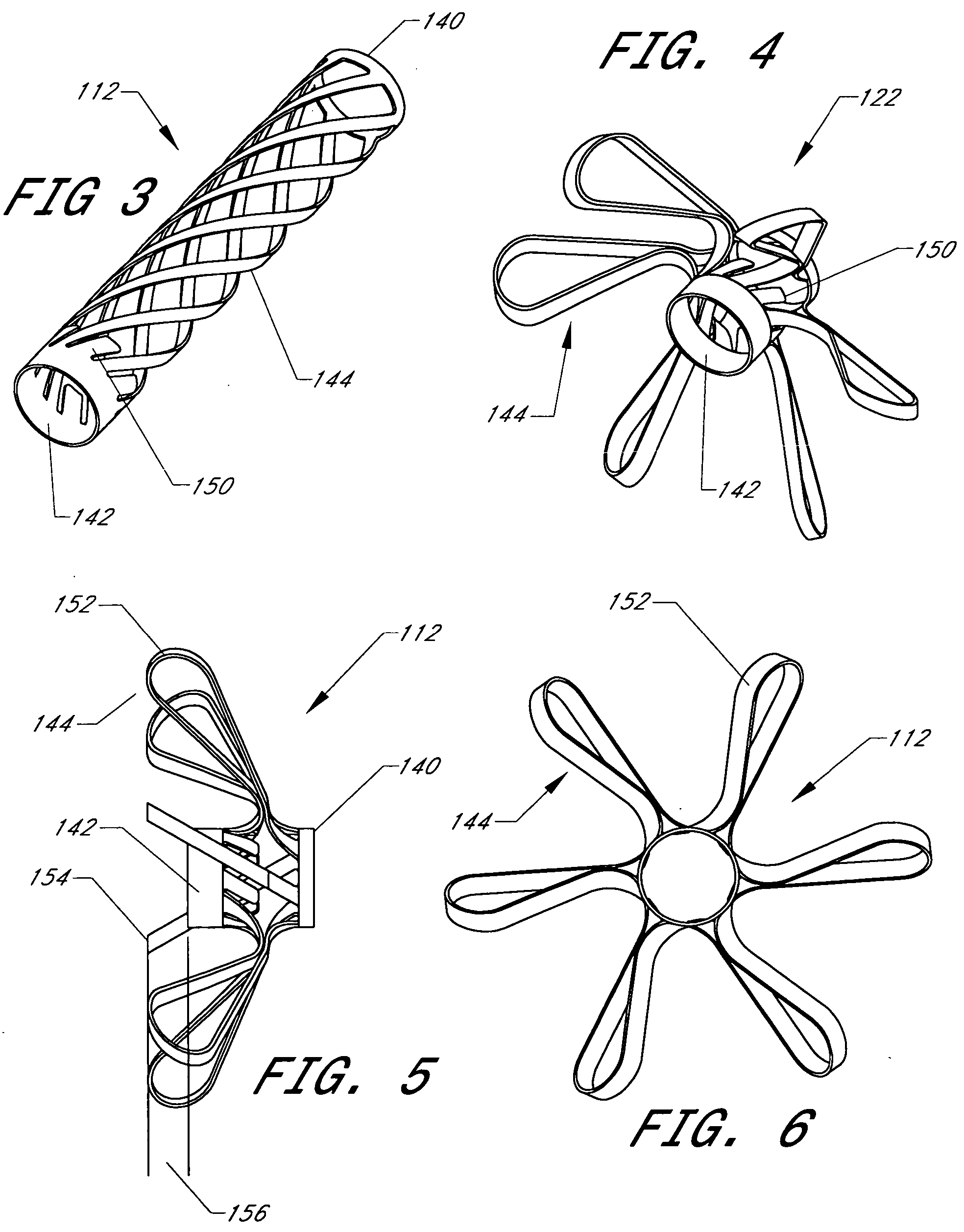
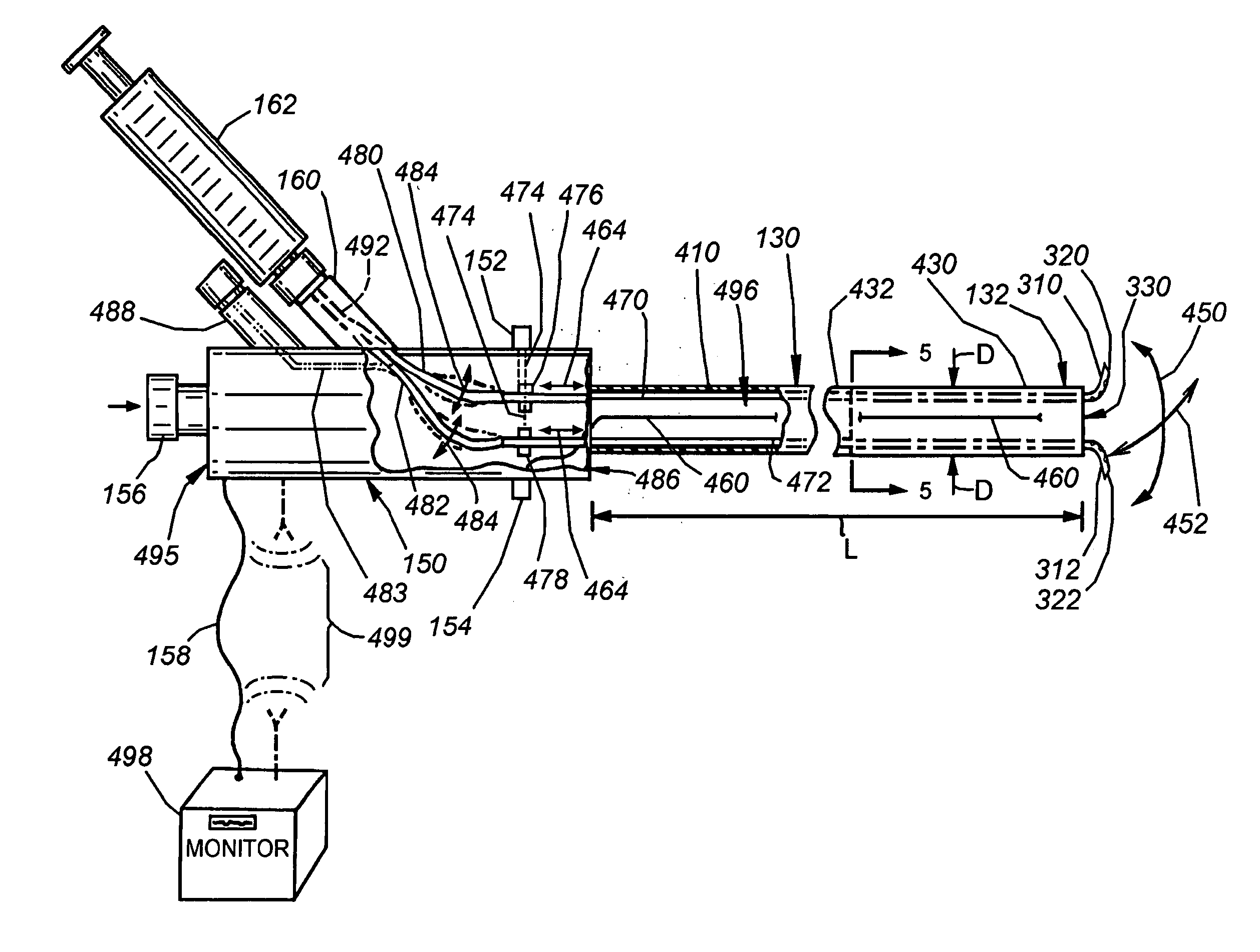
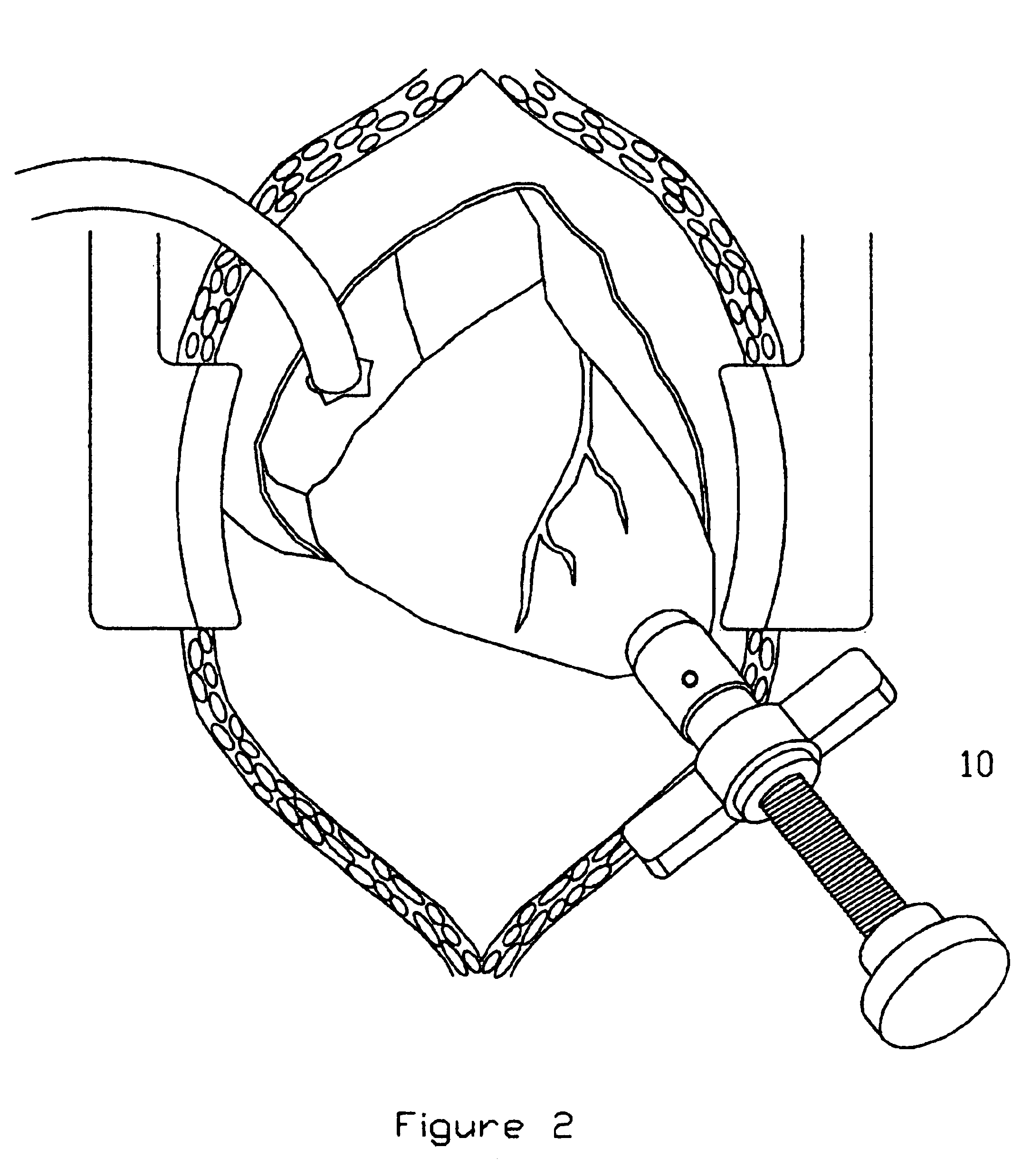
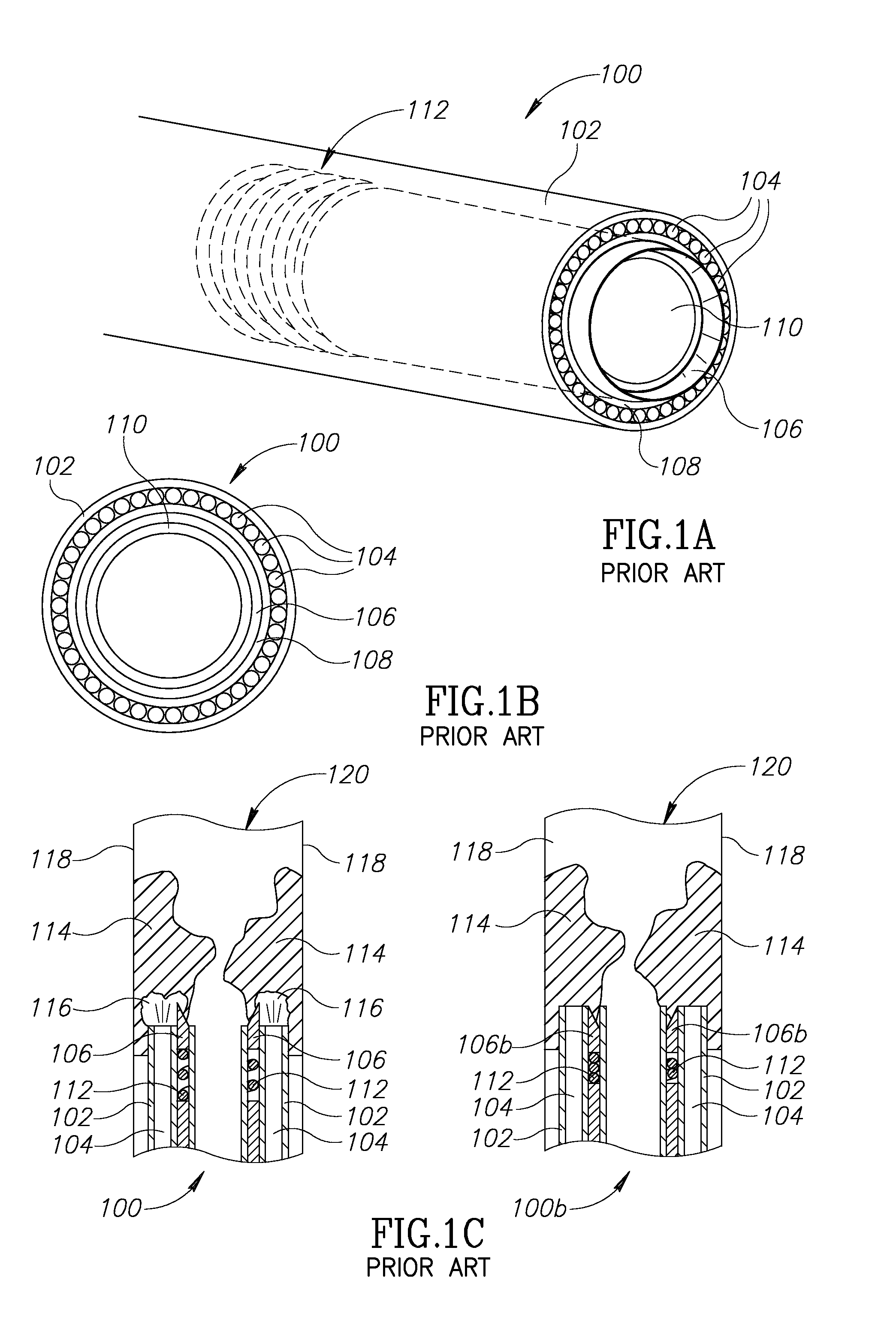
Intussusception and anastomosis apparatus
Apparatus for intratubular intussusception and anastomosis of a hollow organ portion including a cylindrical enclosure, coaxial intratubular intussusception device, for intussusception and clamping means. The apparatus also includes an intratubular anastomosis apparatus for joining organ portions after intussusception thereof with an anastomosis ring and crimping support element. The ring is formed of a shape memory alloy wire, for crimping adjacent organ portions against the crimping support element so as to cause anastomosis therebetween. The ring assumes a plastic or malleable state, at a lower temperature and an elastic state at a higher temperature. The apparatus further includes the crimping support element for intratubular insertion so as to provide a support for crimping the organ portions against the support element. The apparatus additionally includes a surgical excising means, for excising an intussuscepted organ portion, after crimping adjacent intussuscepted organ walls against the crimping support element with the anastomosis ring.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Endoscopic stapler having camera
The invention is a stapler device comprising an anvil and staple cartridge located in the distal tip of an endoscopic device. The staple cartridge is comprised of a fixed proximal portion and a moveable distal portion, which slides into said fixed portion. Means are provided for moving the anvil back and forth, such that the anvil pushes against the distal face of the staple cartridge thereby pushing the moveable portion of the staple cartridge into the fixed portion and causing the staples to be ejected from said staple cartridge passively without said staples moving. The stapler of the invention has two embodiments, a side fastening embodiment and a front fastening embodiment. The endoscopic device that comprises the stapler can be used to perform many different stapling tasks, e.g. closure of a hole in the wall of an internal organ.
Owner:MEDIGUS LTD
Device and method for endoluminal therapy
InactiveUS7666195B2Minimizing dilationMinimize timeSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesOrgan wallOrgan of Corti
A device and method for selectively engaging or penetrating a layer of a luminal organ wall where the luminal organ wall has a plurality of layers including an outermost layer and an innermost layer adjacent to the lumen of the organ. The device and method select one of the plurality of layers of the organ wall other than the innermost layer and deploy from within the lumen of the organ a tissue device through the innermost layer to a specific depth to engage or penetrate the selected one of the plurality of layers. The device and method may be employed to create luminal pouches or restrictive outlets. In a stomach organ, the device and methods may be employed to treat obesity by forming a gastric pouch with or without a restrictive outlet.
Owner:KELLEHER BRIAN +1
Surgical clip applicator device
The present invention, discloses an anastomosis clip applicator device for applying a surgical clip, formed at least partly of a shape memory alloy, to press together adjacent wall portions of adjacent hollow organ portions so as to effect anastomosis therebetween. The applicator device includes: gripping apparatus for gripping a surgical clip, a release mechanism, associated with the gripping apparatus, and tissue cutting apparatus, operatively associated with the gripping apparatus. There is also apparatus for activating the gripping apparatus, the release mechanism and the cutting apparatus, so as to introduce and apply the surgical clip into adjacent hollow organ portions, such that the surgical clip compresses together the adjacent walls of the hollow organ portions, and thereafter causes the cutting apparatus to perforate the adjacent pressed together organ walls to provide patency through the joined portions of the hollow organ.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
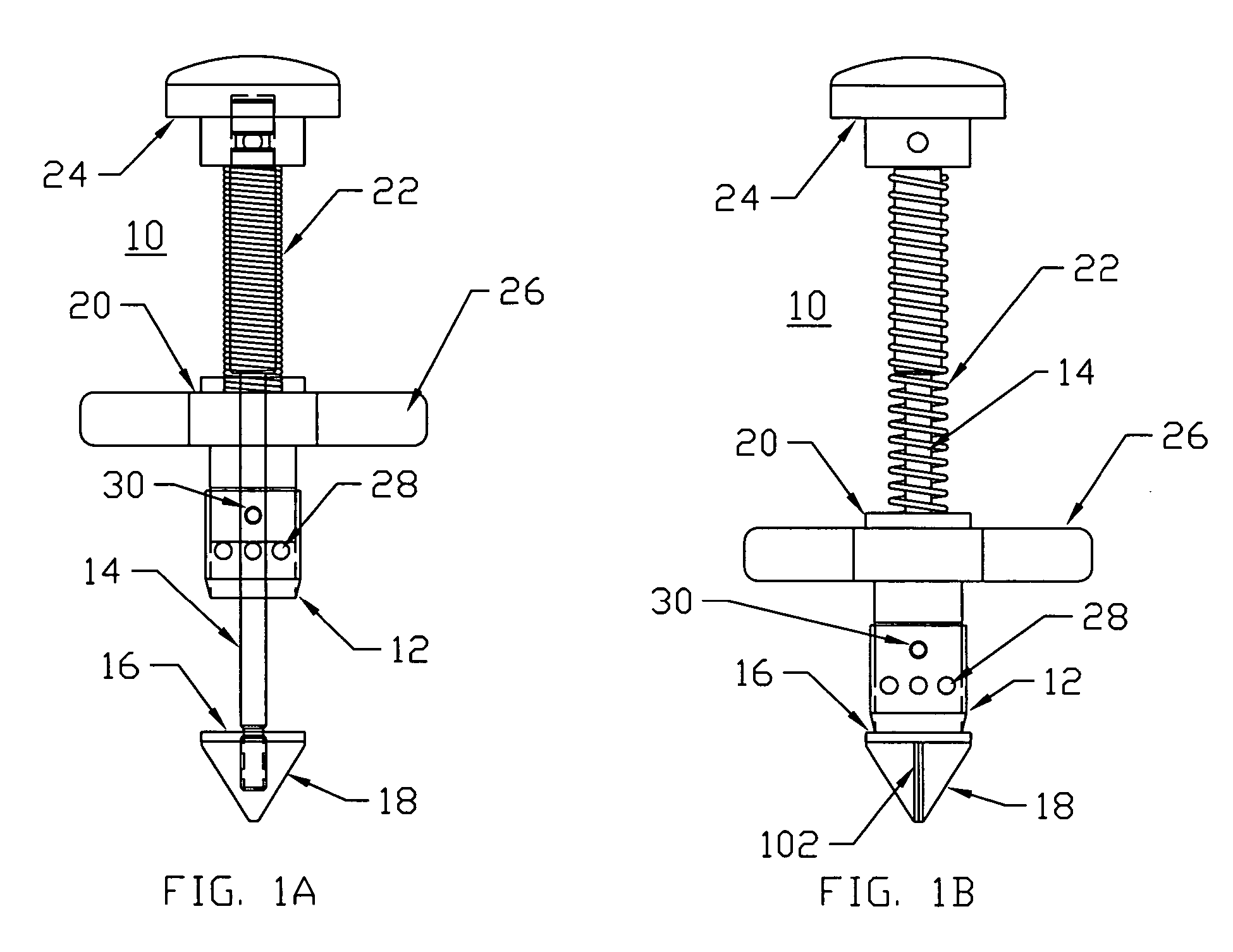
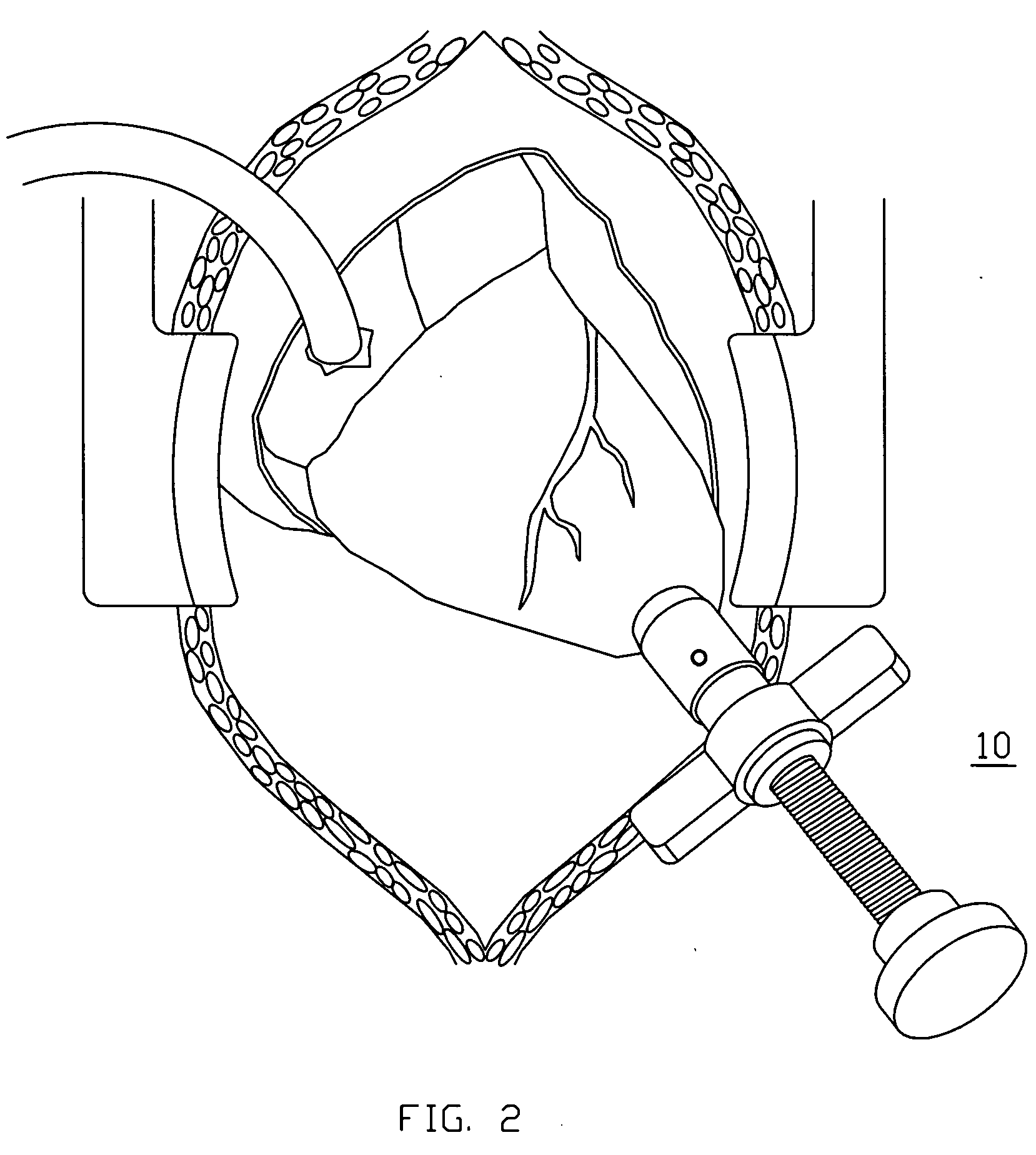
Cardiovascular anchoring device and method of deploying same
InactiveUS7149587B2Efficient deploymentElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesMeasurement deviceOrgan wall
An anchoring device and a delivery method thereof can effectively provide a means for securing an implant to a wall of an internal organ within a patient in a variety of clinical applications. In one embodiment, an anchoring device used to retain a cardiac pressure measurement device is provided. The device is implanted in the body by deforming it to a small cross section profile, sliding it through a low profile delivery device and ejecting from the delivery device at a targeted site. The anchoring mechanism, when ejected from the delivery device, reverts back to pre-formed configuration and engages opposite sides of an organ wall, thereby anchoring the implant in the organ wall.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Adjustable multi-balloon local delivery device
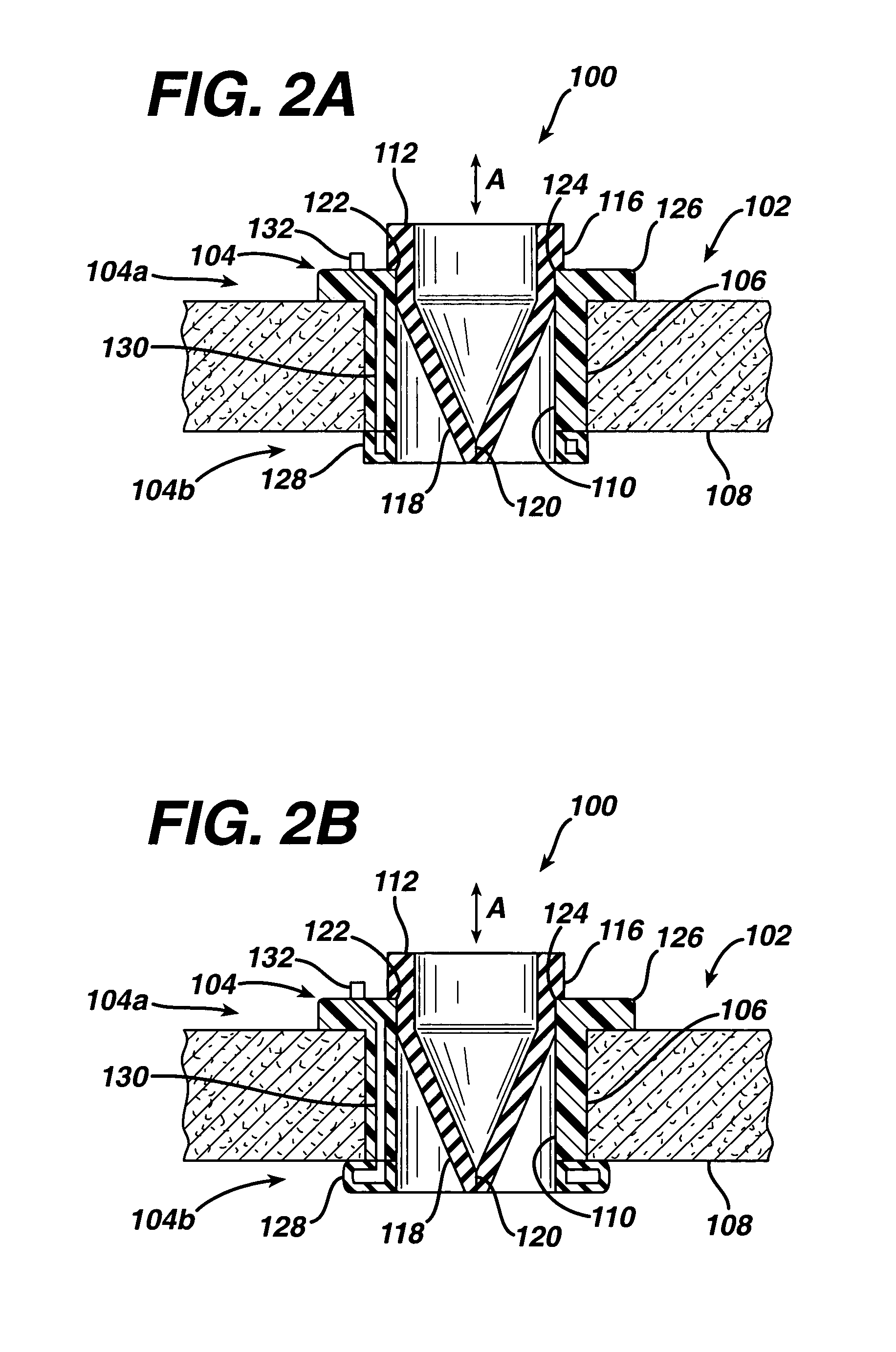
The present invention pertains to a local delivery device comprising a distal catheter unit and a proximal catheter unit which may be positioned by sliding over the distal catheter unit. Both the distal and the proximal catheter units have separate inflatable occluding balloons. The slidable positioning of the catheter units in relation to each other provides for variable inter-balloon distances, which in turn provides for a variably sized occlusion region in a hollow tubular organ, for example a vessel. Dispersed on the catheter shaft between the two occluding balloons are multiple infusion ports through which therapeutic agents may be delivered to an occluded region of a hollow tubular organ. The local delivery device may further comprise a quantifying device for determining the distance between the two occluding balloons. Therefore, precise adjustment of the inter-balloon distance permits controlled delivery of therapeutics to a discreet length of the hollow tubular organ wall.
Owner:OTTAWA HEART INST RES
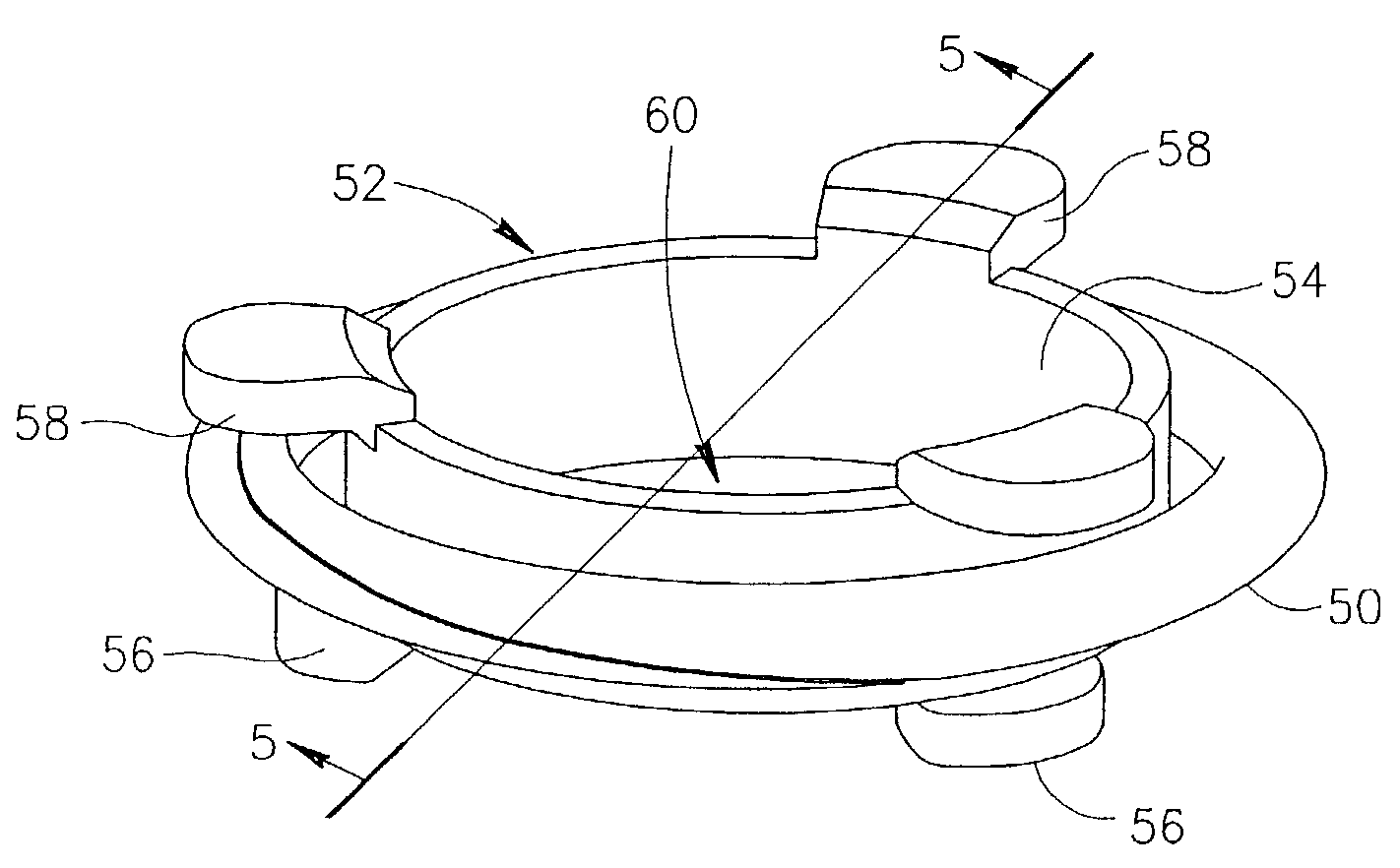
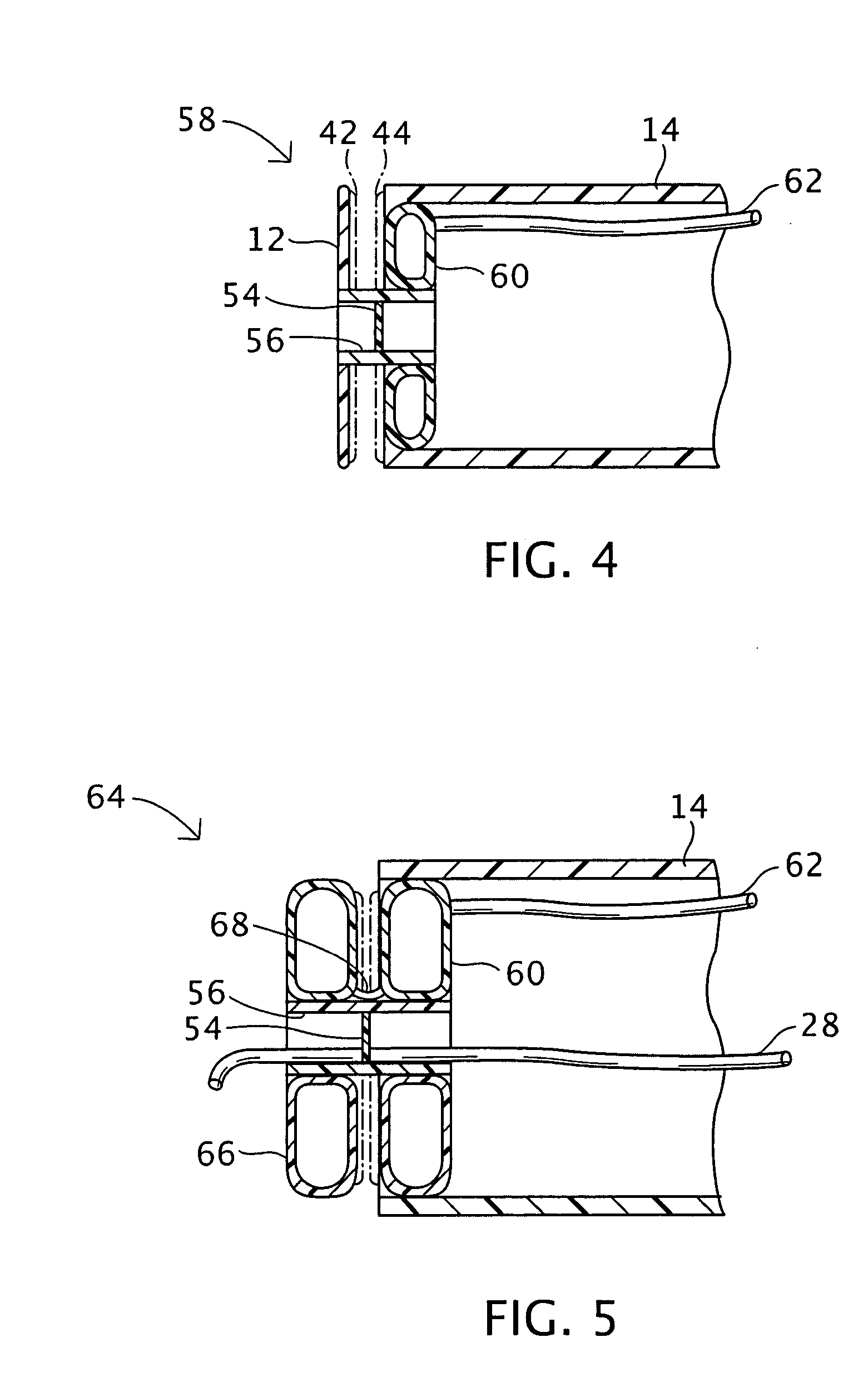
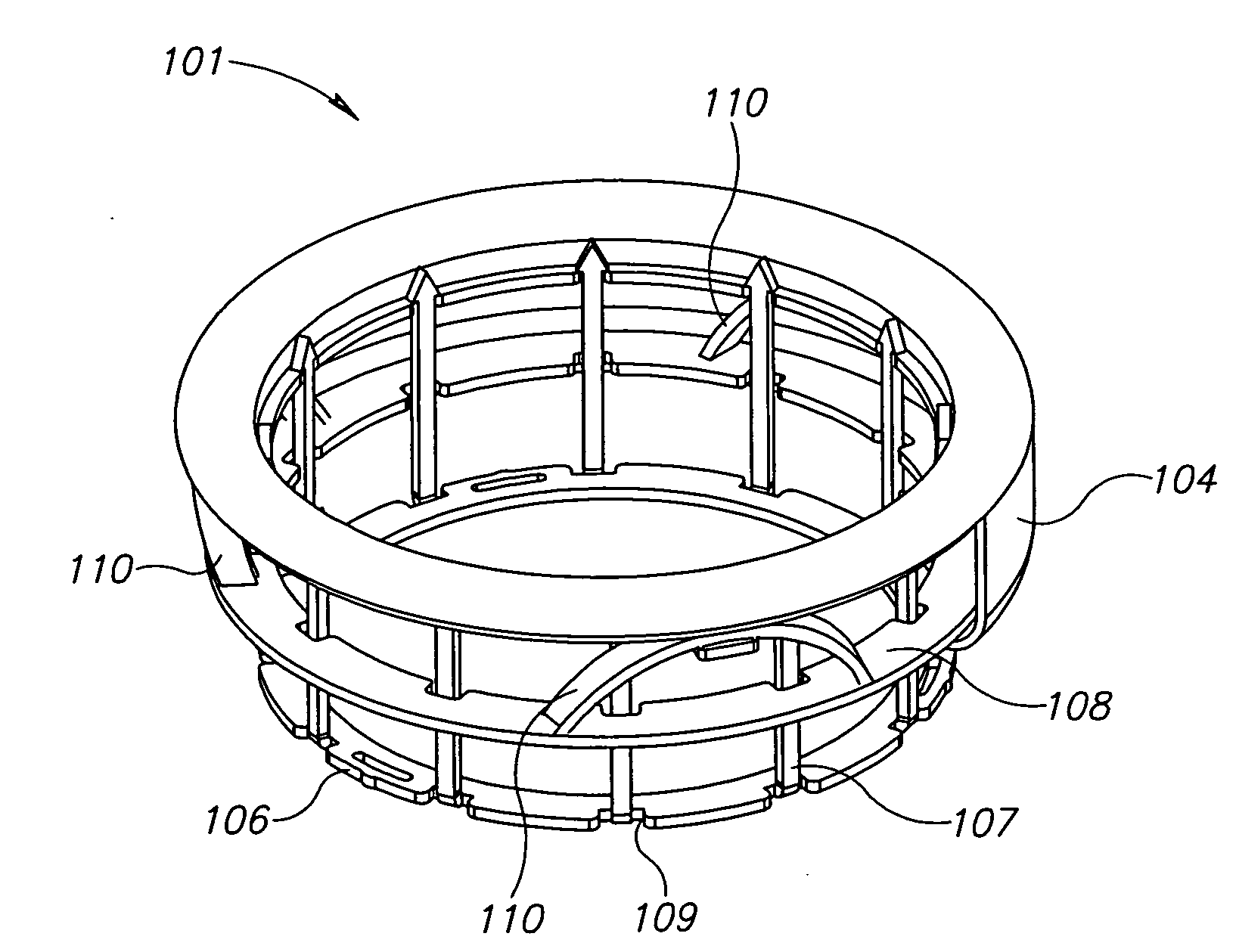
Compression anastomosis ring assembly and applicator for use therewith
InactiveUS7527185B2Reduced dimensionIncrease rangeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsOrgan wallShape-memory alloy
A compression anastomosis ring (CAR) assembly for use in joining severed organ wall portions of a hollow organ. The assembly comprises a first portion which includes an anvil assembly and a second portion which comprises a bottom ring, at least one ring element, and at least one spring element formed of a shape-memory alloy. The at least one spring element provides a restorative force and is in compressive force contact with the bottom ring and the tissue to be joined is positioned between the anvil ring and the bottom ring. A plurality of needles on one of the ring elements is operative, upon application of a closure force, to pierce the tissue and the anvil ring, holding the anvil ring to the second portion of the CAR assembly. An applicator for applying the CAR assembly and a method for using the assembly and applicator are taught.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Sealing plug for an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ
InactiveUS20060190036A1The way is simple and fastBleeding is stopped immediatelySurgical veterinaryProsthesisSurgical operationHuman body
The present invention relates to a sealing plug for an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ of an animal or human body, in particular a blood vessel, to a device for placing such a sealing plug in such an opening, to a surgery kit for percutaneously sealing an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ of an animal or human body, in particular a blood vessel, and to a method for percutaneously sealing of an opening in a wall of a vessel or hollow organ of an animal or human body.
Owner:UNIV TUBINGEN
Retrieval devices for anchored cardiovascular sensors
ActiveUS20070106328A1Efficient deploymentPharmaceutical delivery mechanismStaplesOrgan wallMeasurement device
An anchoring device and a delivery method thereof can effectively provide a means for securing an implant to a wall of an internal organ within a patient in a variety of clinical applications. In one embodiment, an anchoring device used to retain a cardiac pressure measurement device is provided. The device is implanted in the body by deforming it to a small cross section profile, sliding it through a low profile delivery device and ejecting from the delivery device at a targeted site. The anchoring mechanism, when ejected from the delivery device, reverts back to pre-formed configuration and engages opposite sides of an organ wall, thereby anchoring the implant in the organ wall.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
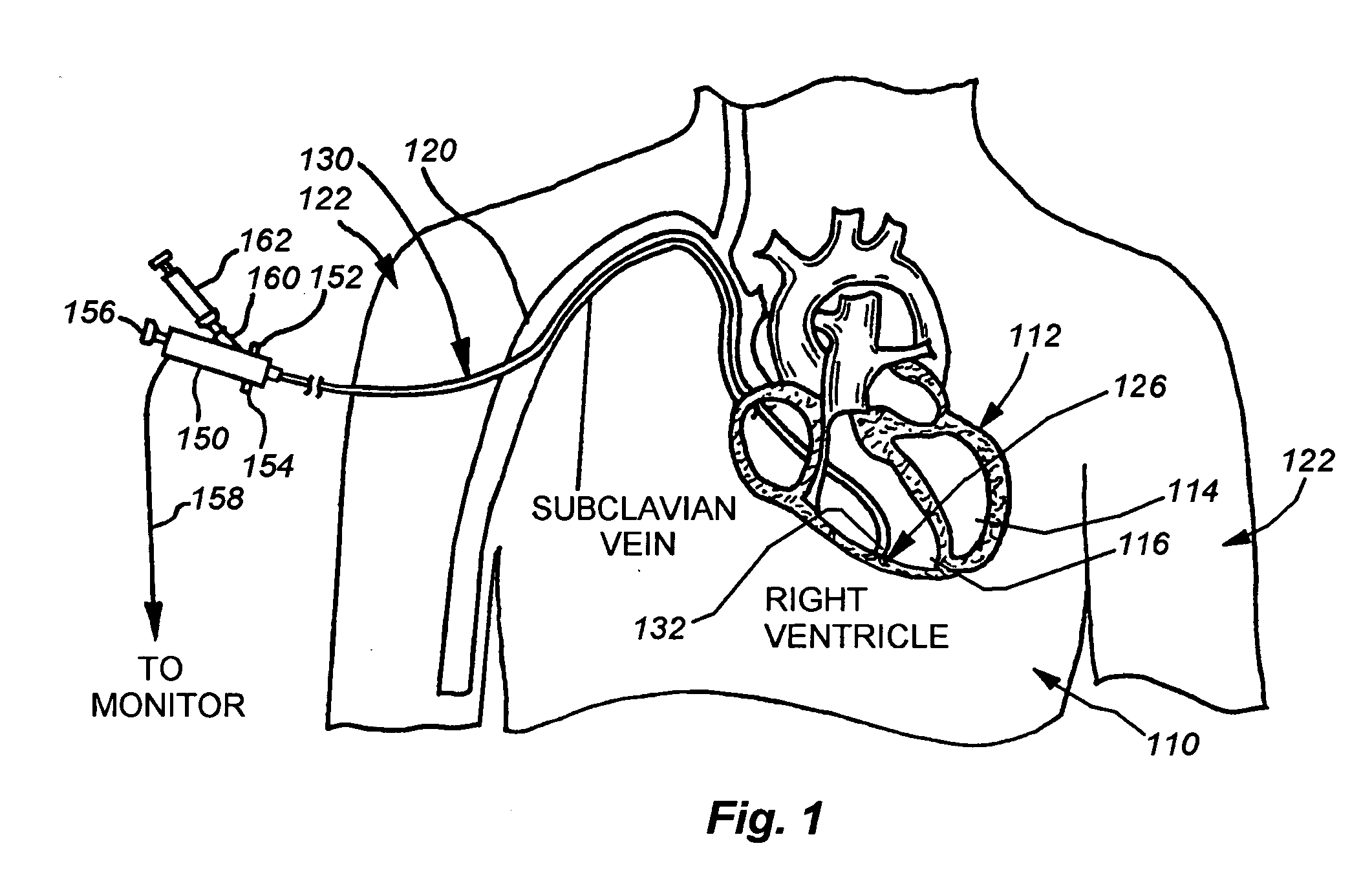
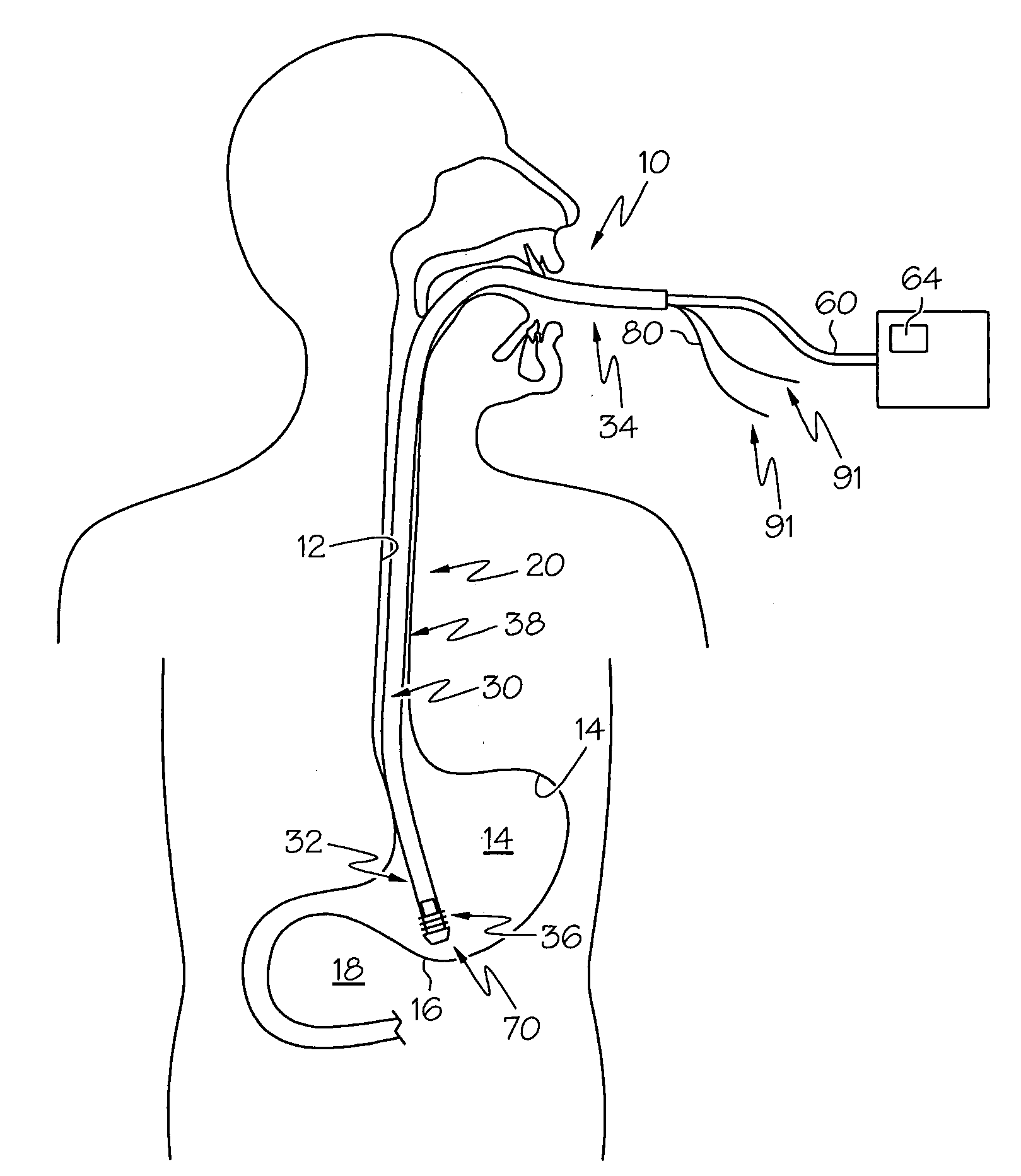
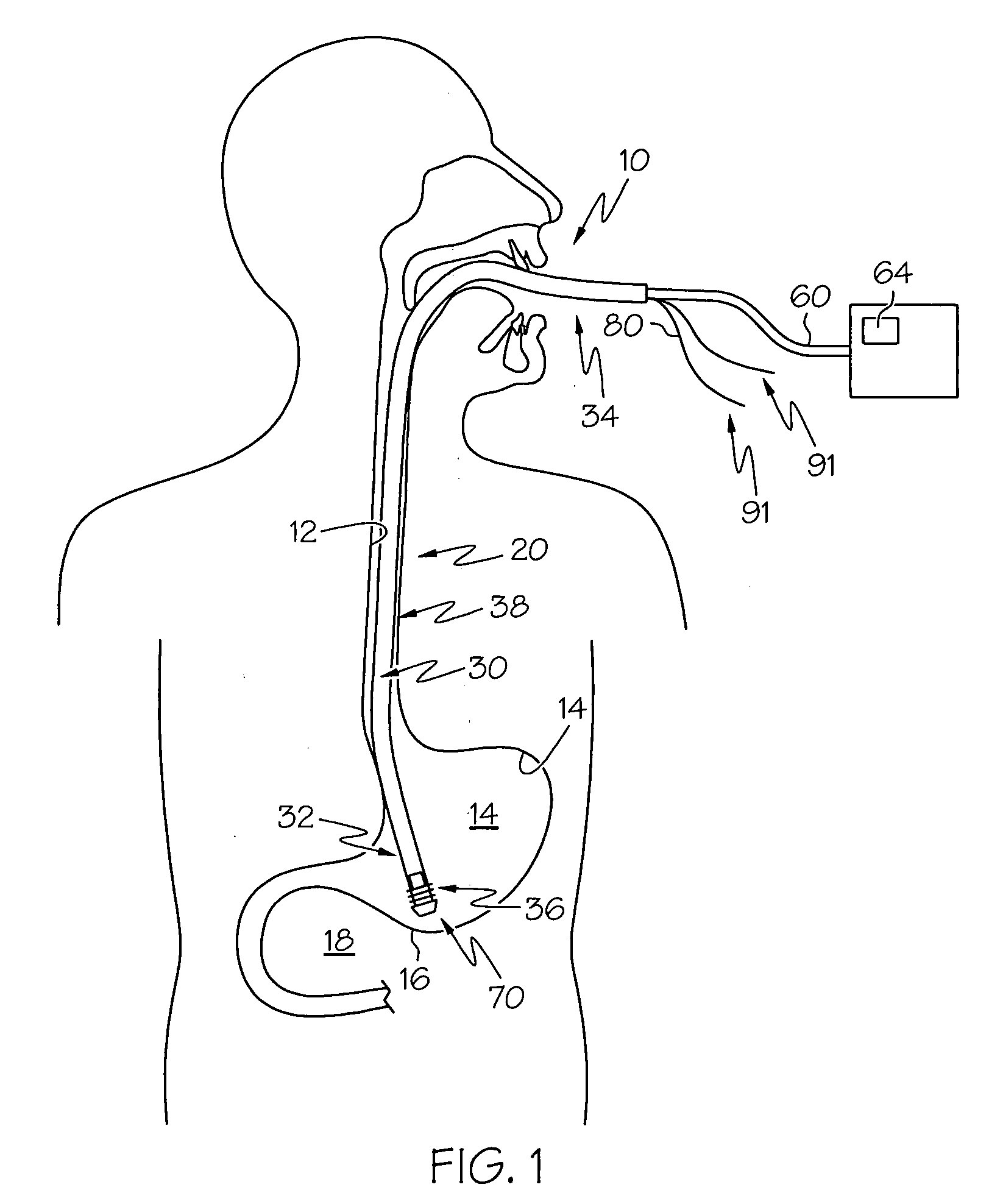
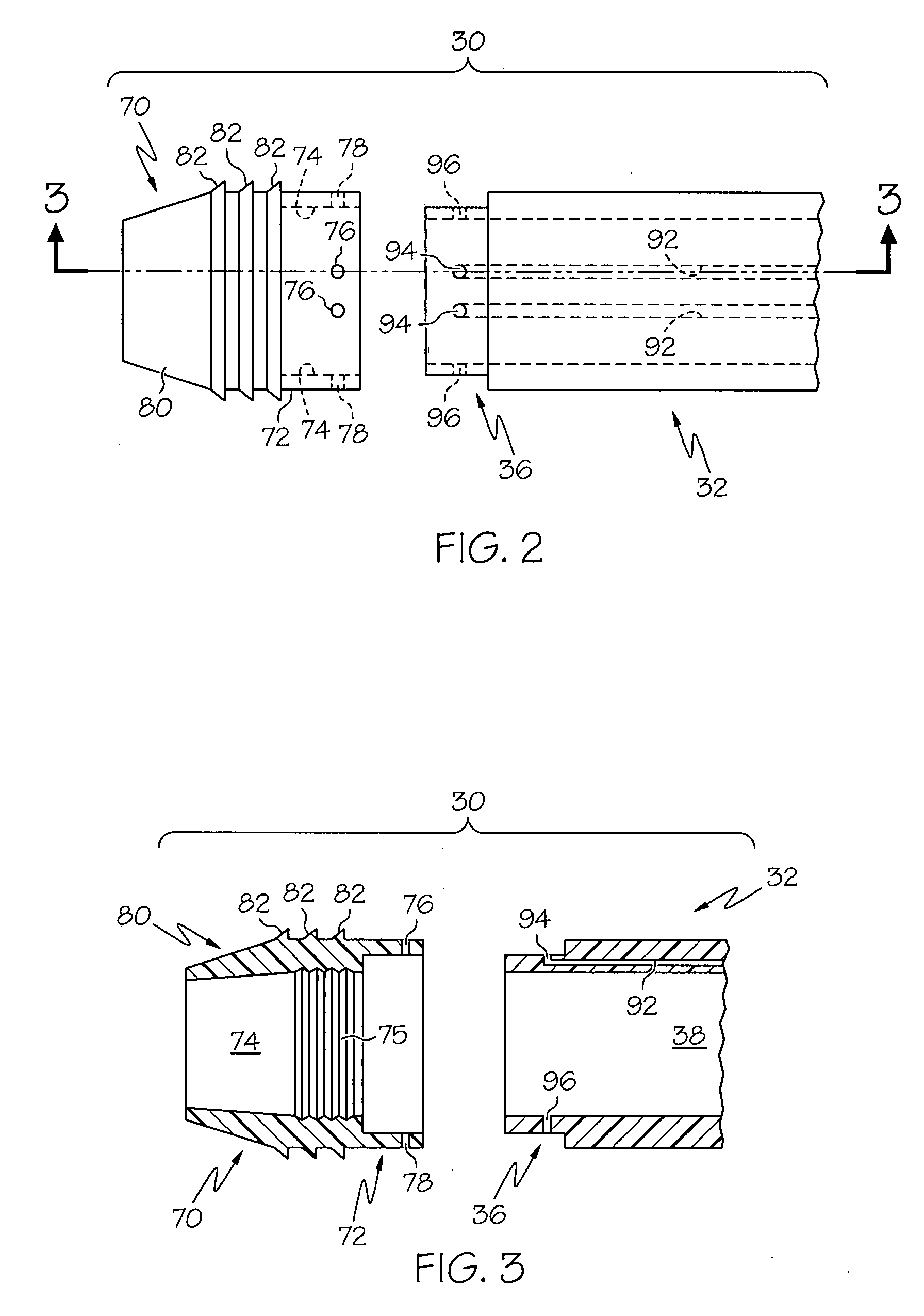
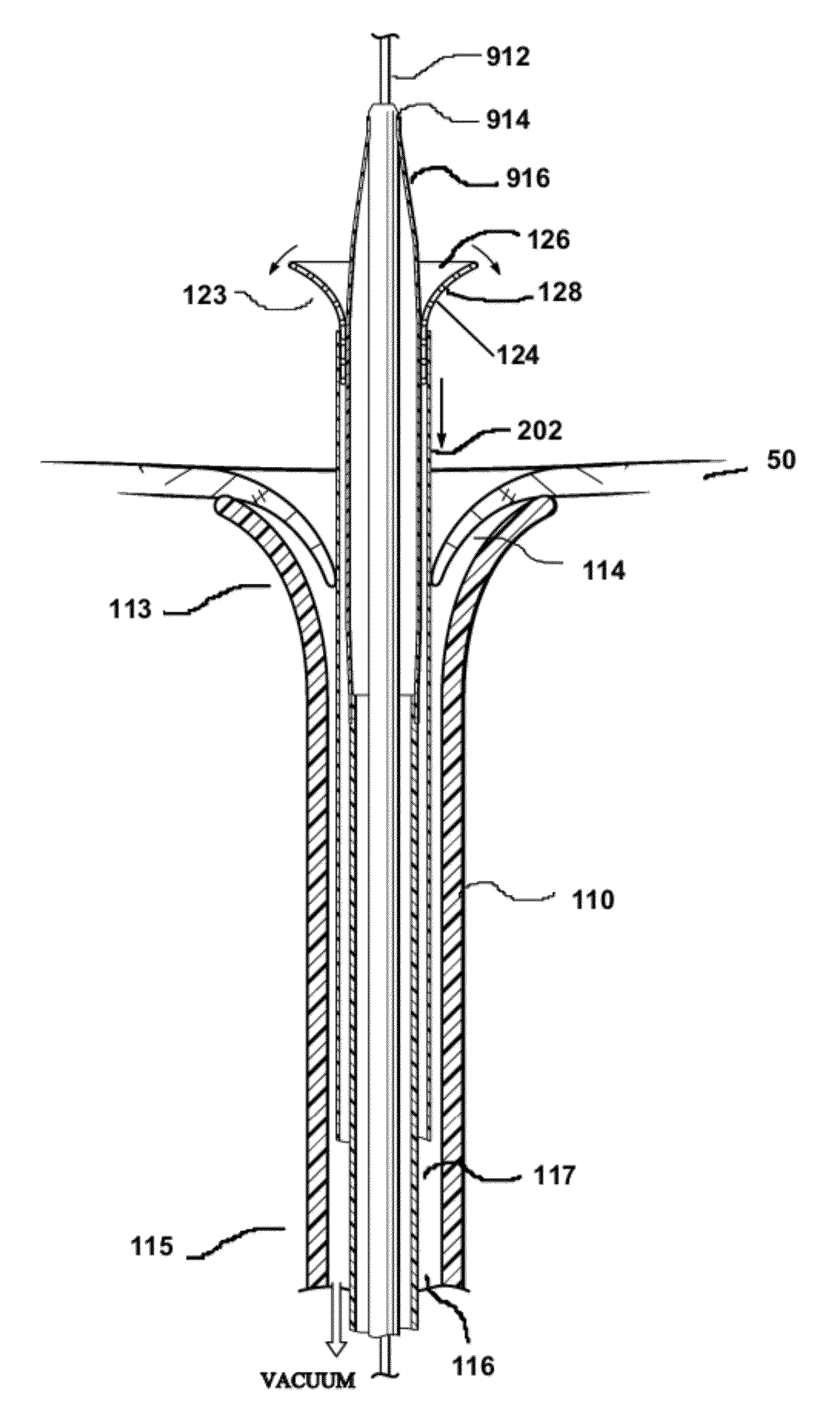
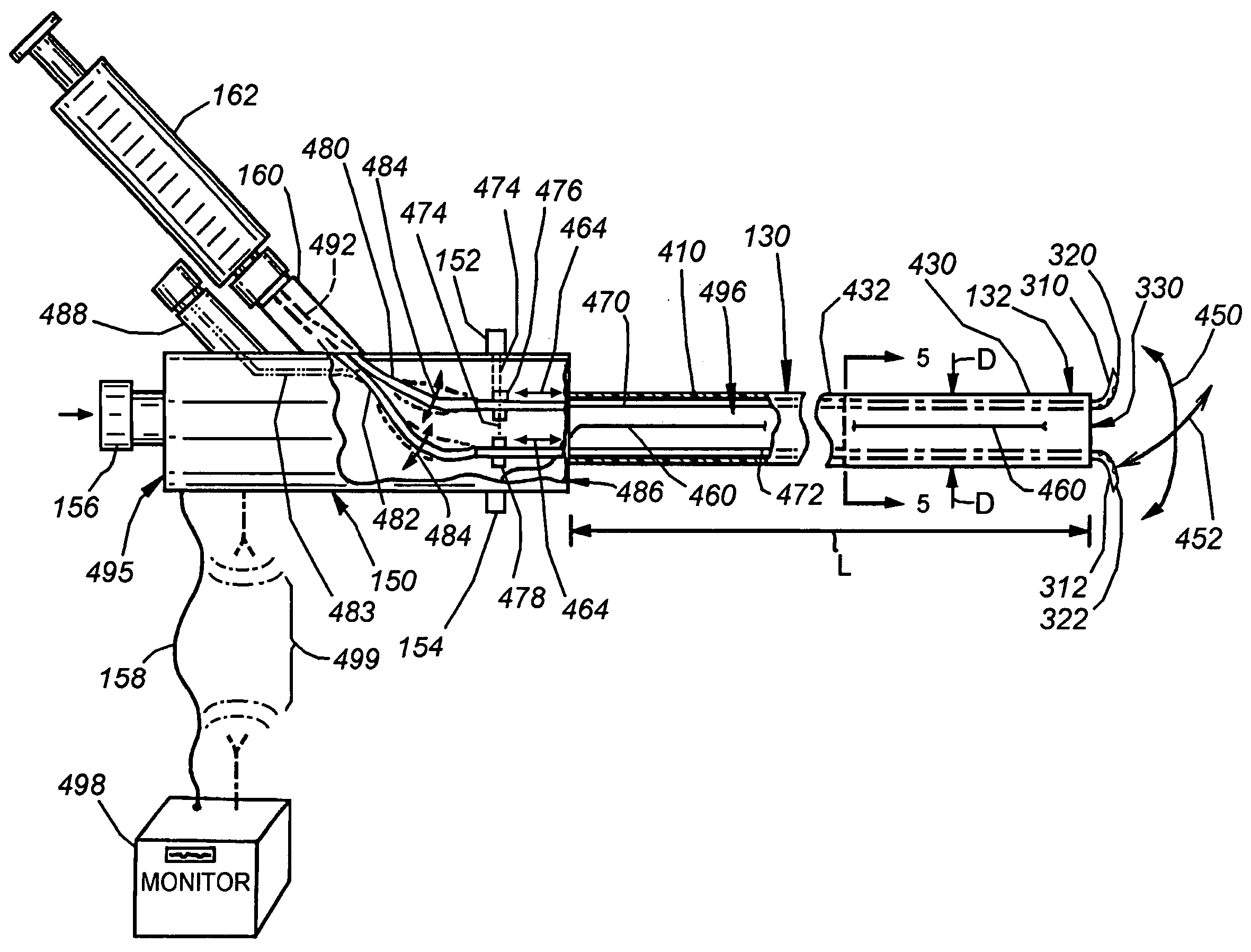
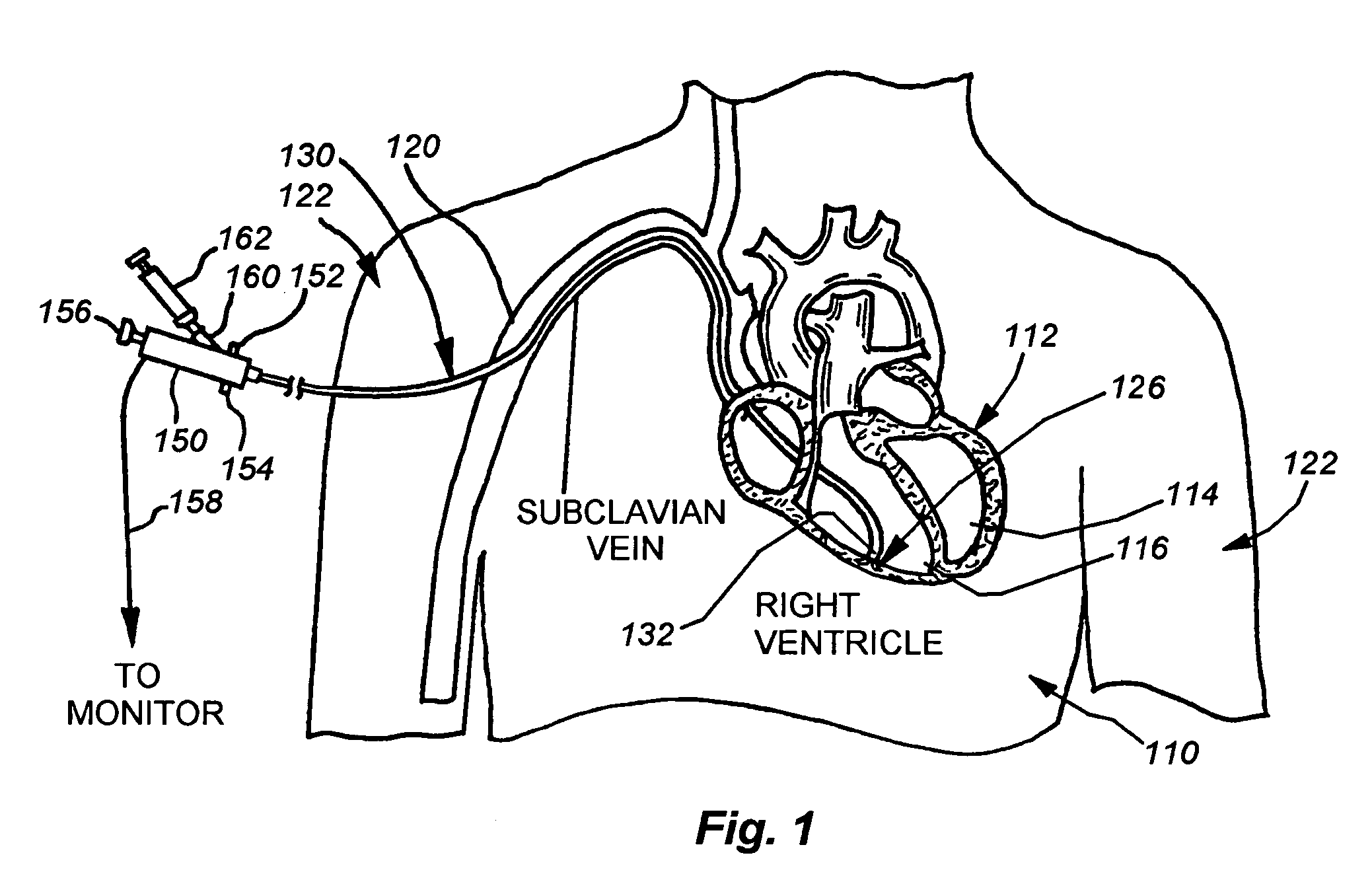
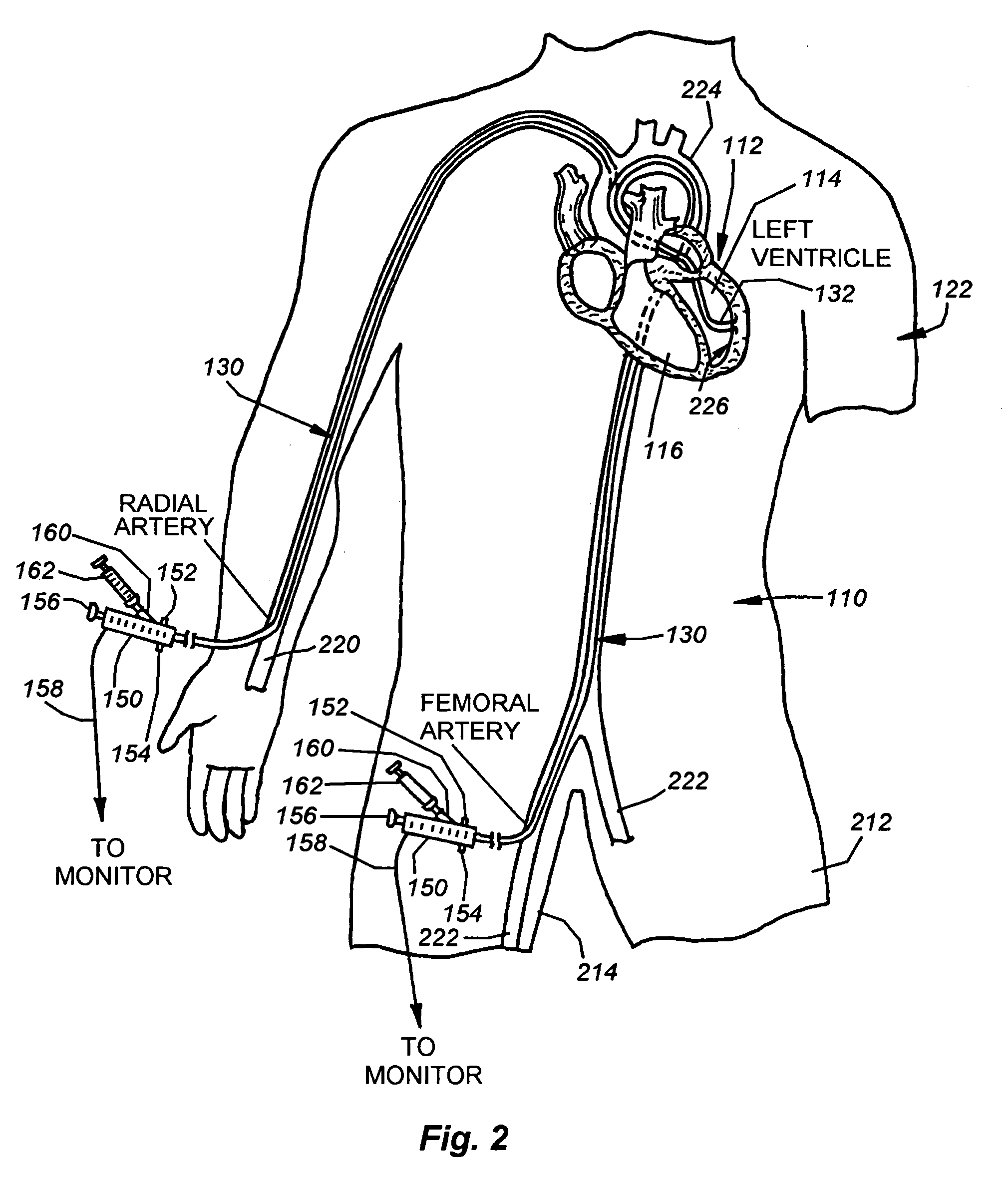
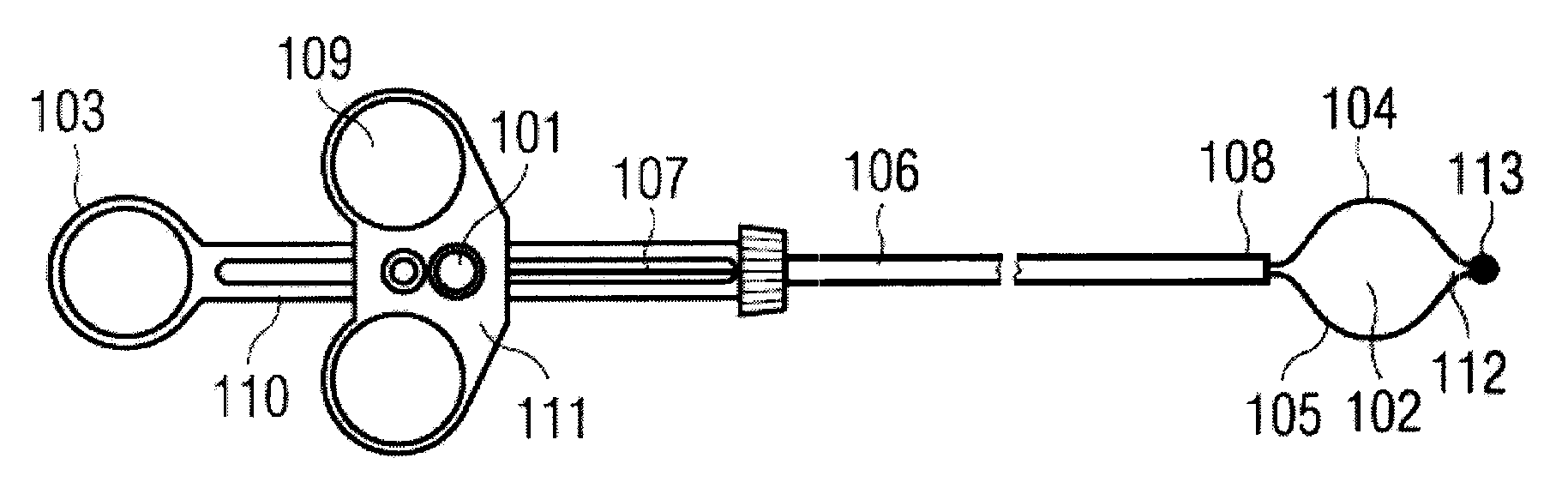
Catheter for introduction of medications to the tissues of a heart or other organ
ActiveUS20070005018A1Shorten the lengthOvercome disadvantagesMulti-lumen catheterInfusion syringesOrgan wallTreatment delivery
This invention overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art by providing a positionable, direct-injection catheters that can access a specific region of the heart or other organ. The catheter is provided with one or two needle shafts, which may be located within respective sheaths that extend axially along the interior of the lumen of a main catheter shaft. Each needle shaft carries, at a distal end thereof a penetrable element or “needle” that is normally retracted within the distal tip of the main shaft during travel to the target organ, but is subsequently deployed by action of a handle-mounted trigger mechanism to extend the needles into the organ's wall. Each extended needle is curved to relative to the shaft's axis to enter the organ wall in a flattened trajectory that both reduces the chance of puncture through the wall and anchors the needles into the wall during injection (for reduced chance of pullout under pressure). A plurality of apertures which provide for more complete agent delivery rapidly, while maintaining a low delivery velocity to effect treatment delivery in as short a period of time as possible without the problems caused by high velocity delivery. The needles are typically arranged to exit the tip at contralateral orientations relative to each other
Owner:TKEBUCHAVA TENGIZ
Device for providing intracardiac access in an open chest
ActiveUS7217277B2Improve handlingPrevent leakageSuture equipmentsCannulasDistal portionThoracic cavity
An access device for providing access into a hollow organ during an open surgical procedure. The access device includes: a body for insertion into an opening in a wall of the hollow organ, the body having a bore for passage of at least a distal portion of an instrument into an interior of the hollow organ; a valve disposed in the bore for allowing passage of the instrument and substantially preventing a fluid in the interior of the hollow organ from leaking outside the hollow organ; and a mechanism for securing the body to the wall of the hollow organ; wherein the body has a low-profile length in an axial direction of the bore.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Apparatus and method for a global model of hollow internal organs including the determination of cross-sectional areas and volume in internal hollow organs and wall properties
InactiveUS20090062684A1Ease of evaluationCorrection errorCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringThree vesselsVisceral organ
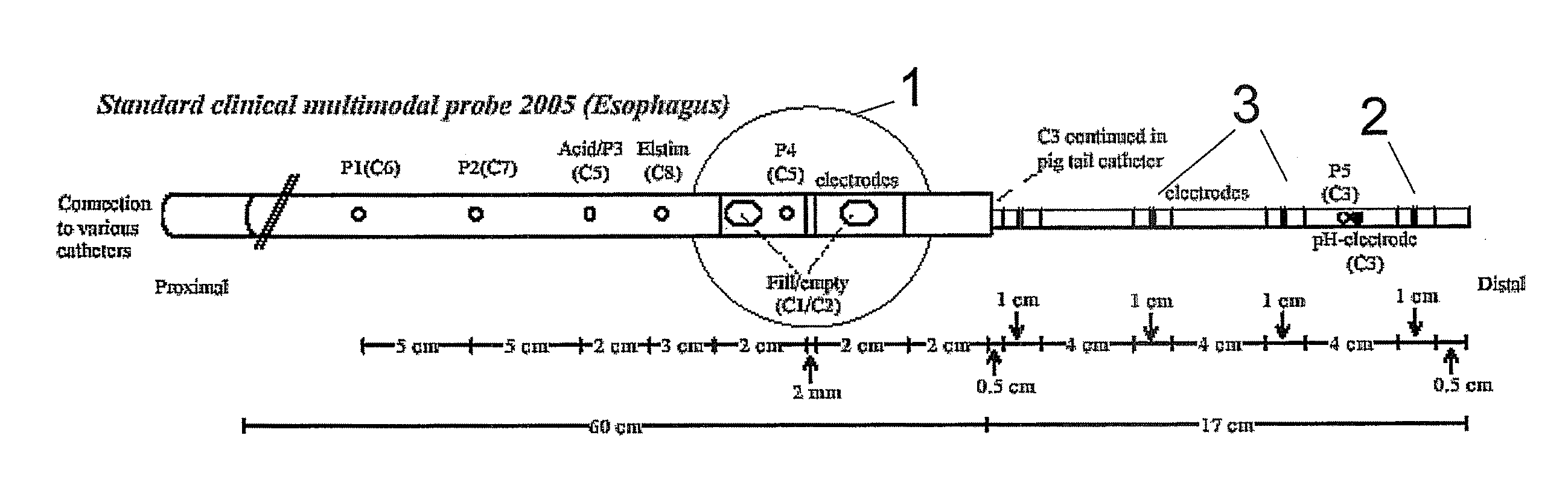
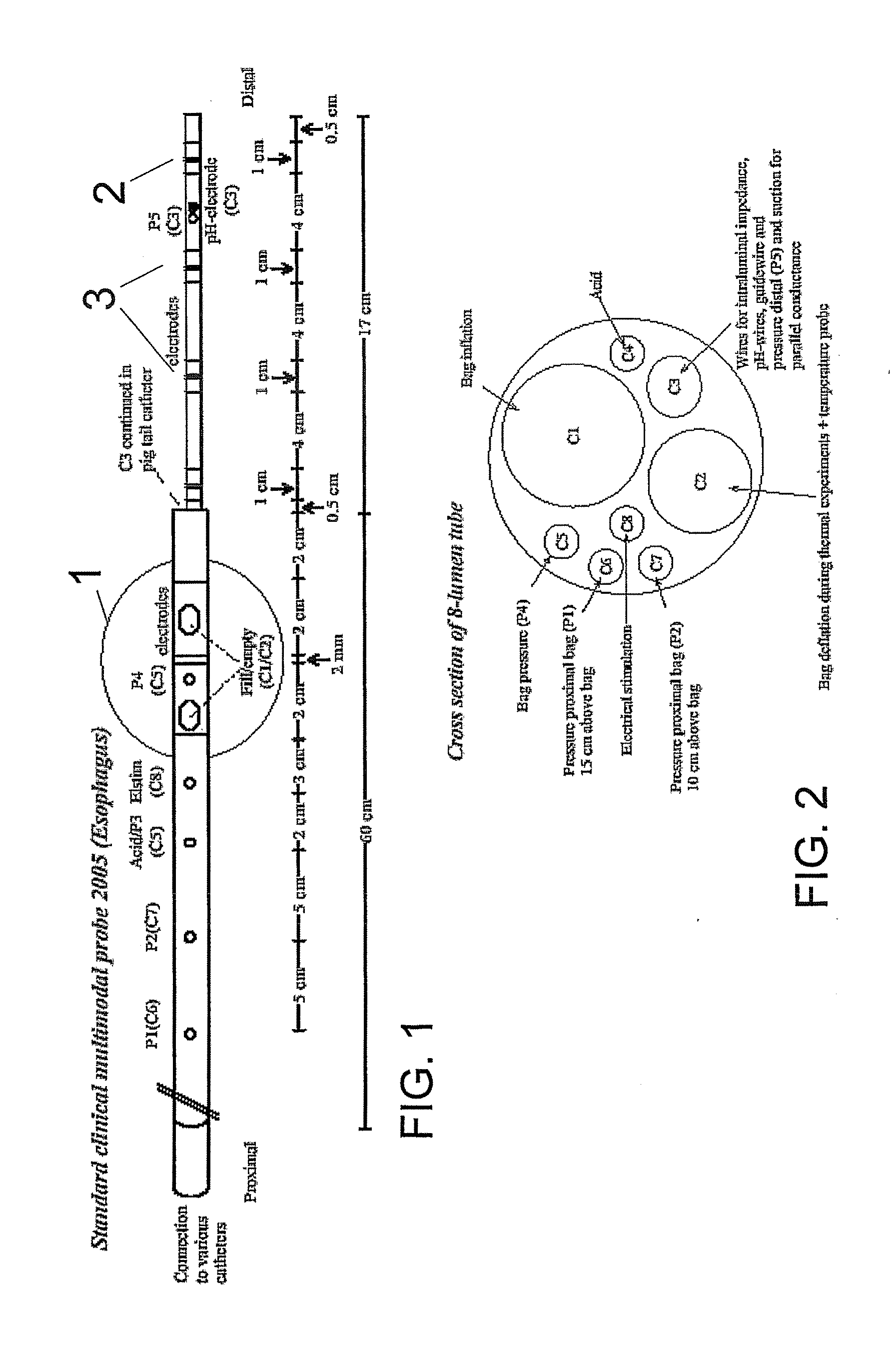
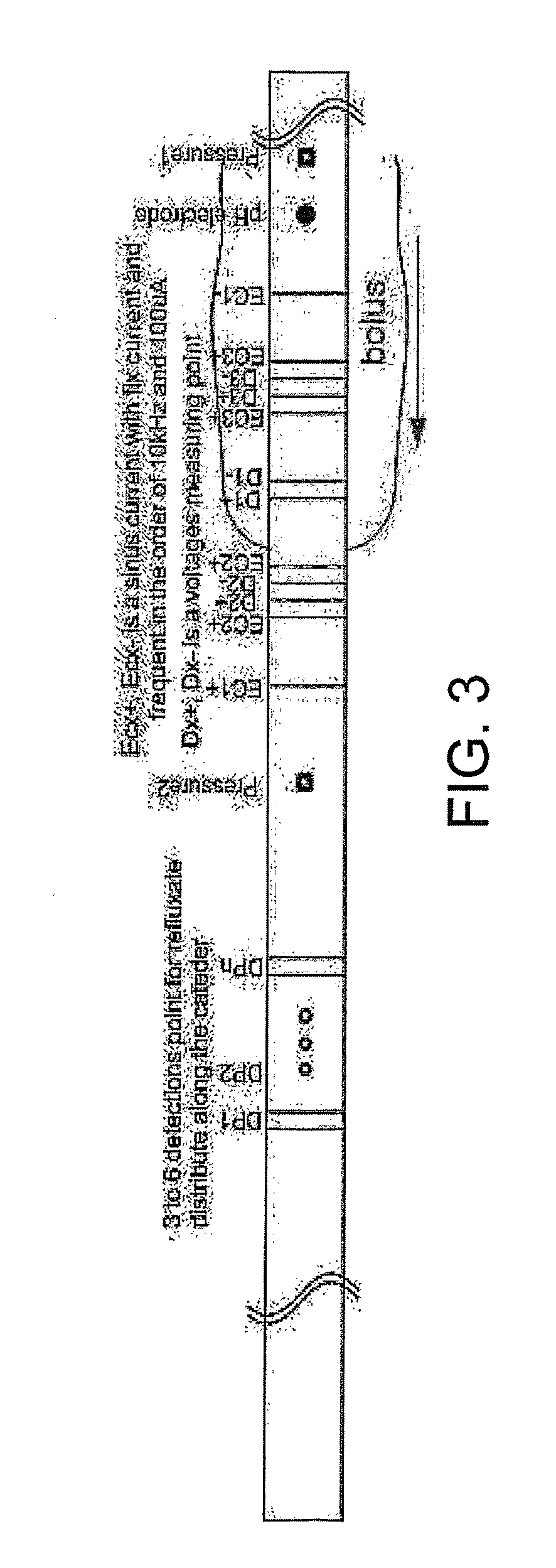
The present invention relates generally to medical measurement systems for evaluation of organ function and understanding symptom and pain mechanisms. This model takes into account a number of factors such as volume and properties of the fluid and the surrounding tissue. Particular emphasis is on a multifunctional probe that can provide a number of measurements including volume of refluxate in the esophagus and to what level it extents. The preferred embodiments of the invention relate to methods and apparatus for measuring luminal cross-sectional areas of internal organs such as blood vessels, the gastrointestinal tract, the urogenital tract and other hollow visceral organs and the volume of the flow through the organ. It can also be used to determine conductivity of the fluid in the lumen and thereby it can determine the parallel conductance of the wall and geometric and mechanical properties of the organ wall.
Owner:GREGERSEN ENTERPRISES 2005
Detachable distal overtube section and methods for forming a sealable opening in the wall of an organ
An overtube for use with an endoscopic surgical instrument. In various embodiments, the overtube may comprise a hollow tubular member that has an implantable tip detachably affixed to a distal end thereof. The implantable tip may have at least one retention member formed thereon to retain the tip within an organ wall. The implantable tip may further have a lumen extending therethrough to form a passageway through the organ wall. A plug member may be provided to selectively seal off the lumen within the implantable tip.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
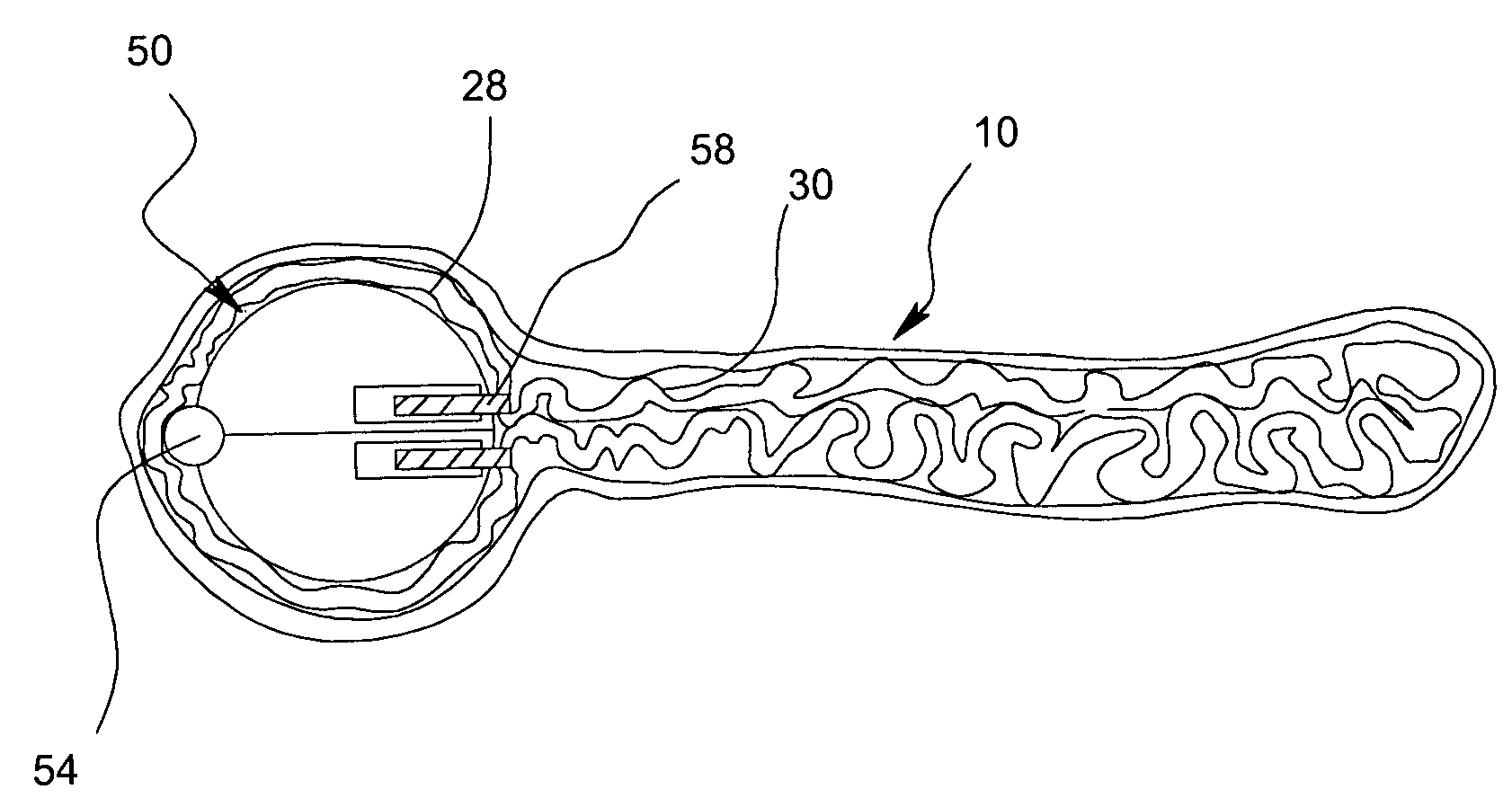
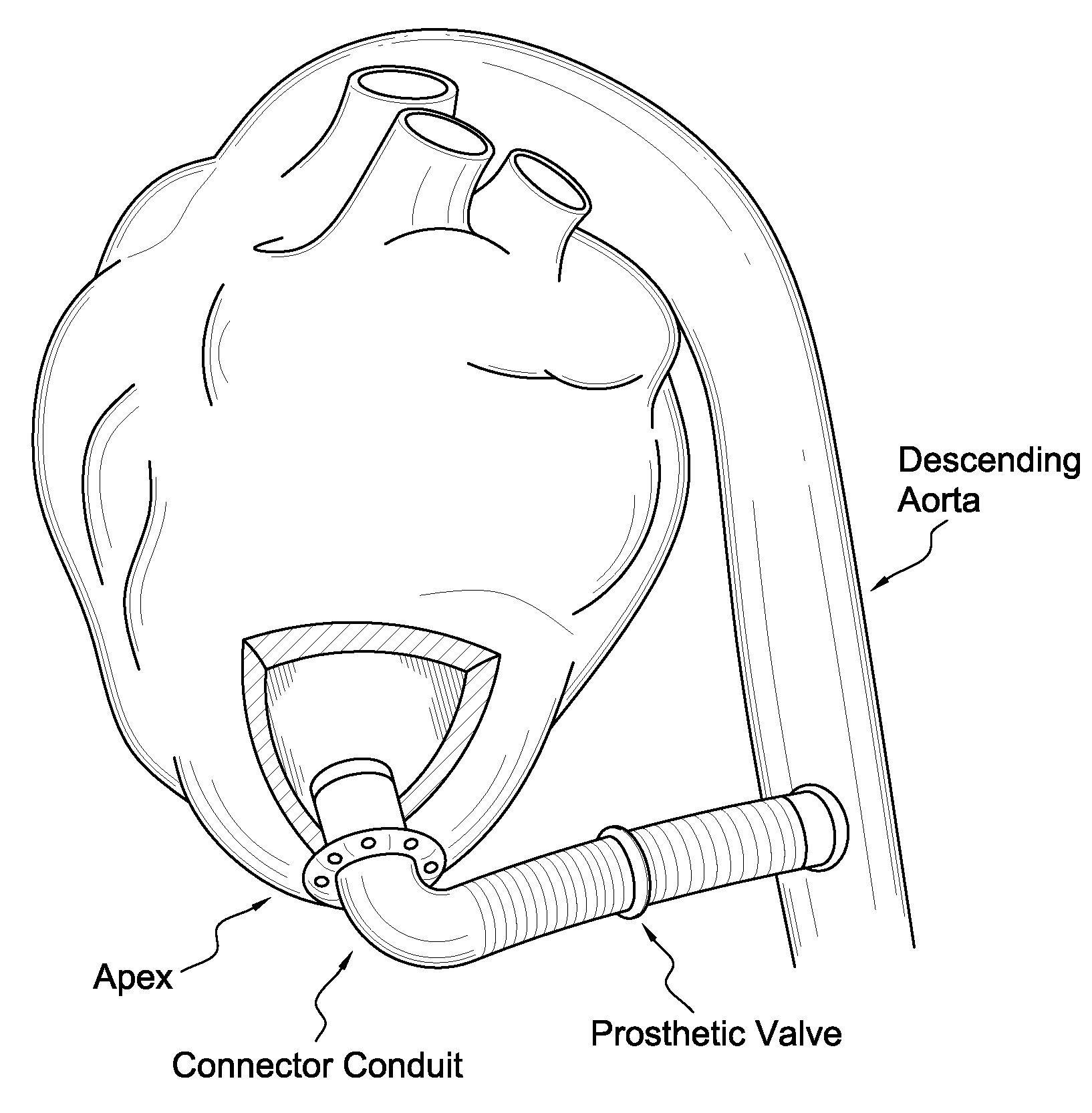
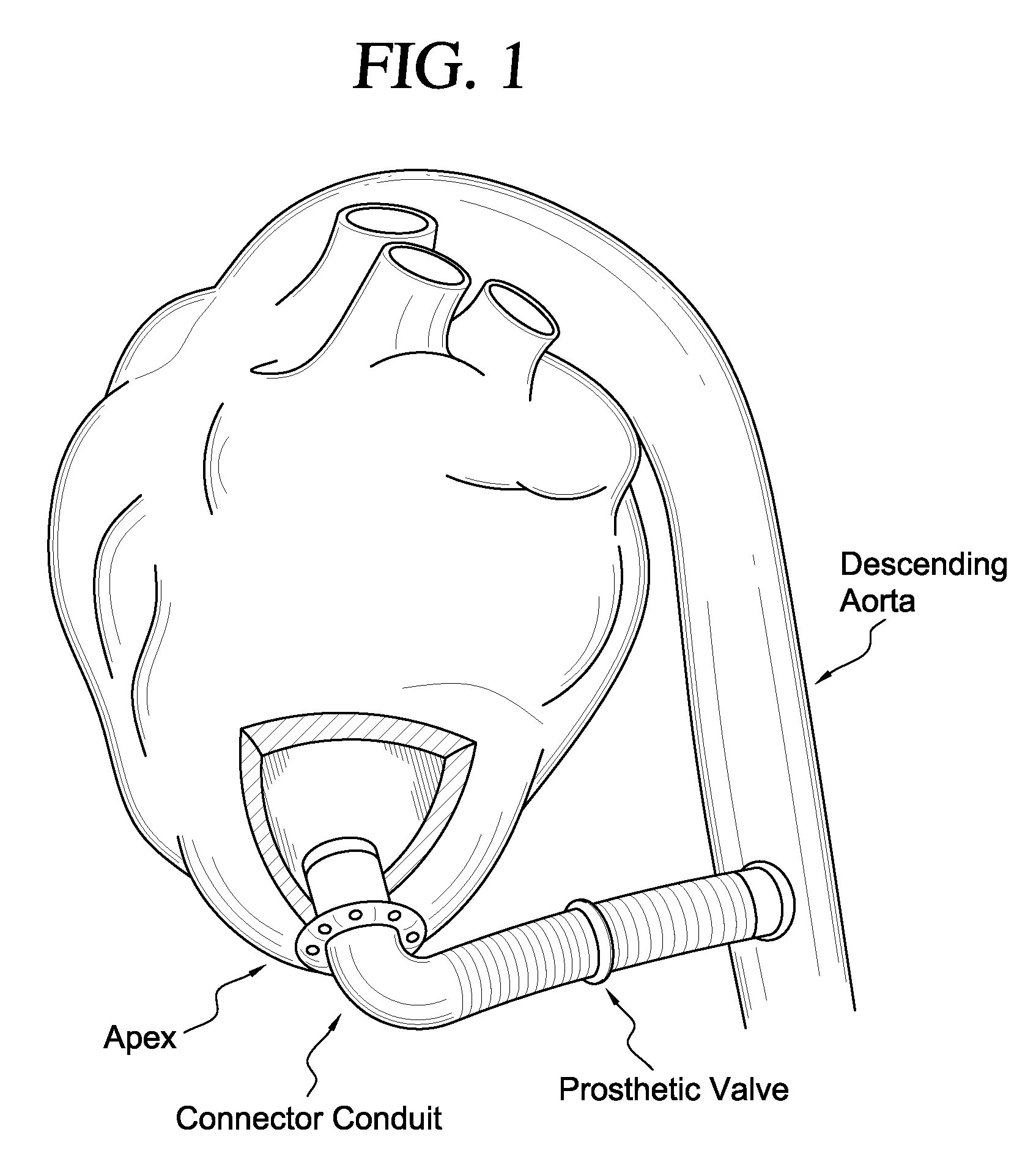
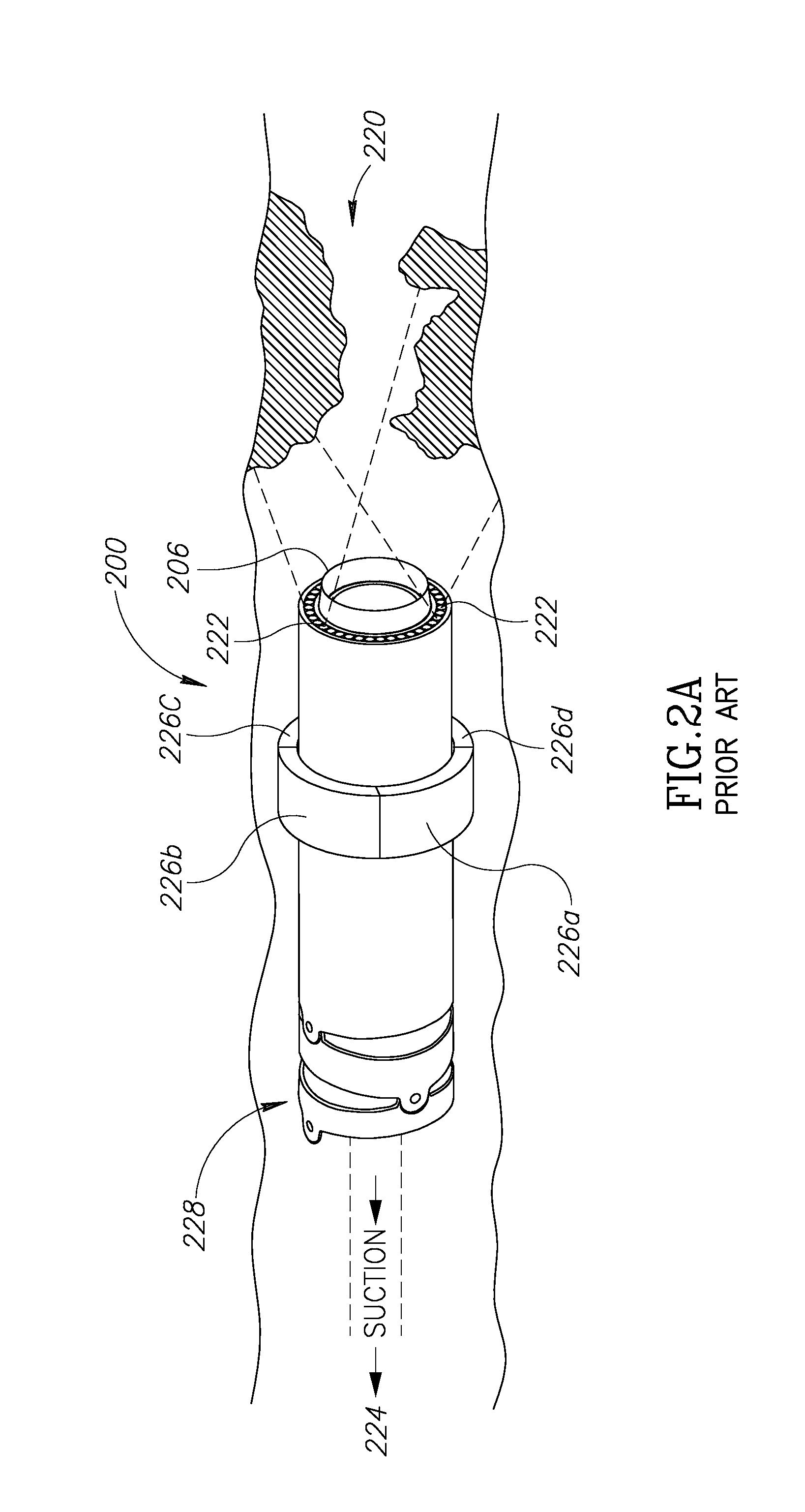
Apparatus and method for suturelessly connecting a conduit to a hollow organ
InactiveUS20070265643A1Avoid blood lossPrevent movementBlood vesselsWound clampsOrgan wallCoil spring
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for securing a connector conduit to a hollow organ. The method comprises forming a hole in a wall of the organ; inserting a connector conduit through the hole in the wall of the organ until a flange element comes into contact with the wall of the organ, the flange element being positioned on the connector conduit; and engaging a retention means with the wall of the organ to prevent movement of the connector conduit relative to the wall of the organ, the retention means being positioned on the connector conduit. Exemplary retaining means include a plurality of retaining pins positioned circumferentially around the connector conduit, a plurality of prongs positioned circumferentially around the connector conduit, a balloon positioned on the connector conduit, a torsion spring positioned on the connector conduit, a spiral spring positioned on the connector conduit, or combinations thereof.
Owner:CORREX
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS6863677B2Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Cannula Systems and Methods
Disclosed herein is a cannula assembly for directing the flow of material from an organ chamber, e.g., blood from the left chamber of the heart, and methods of placing the cannula assembly in fluidic communication with the chamber. The cannula assembly includes an elongate tubular member and a coupling assembly disposed at the distal end of elongate tubular member. The elongate tubular member includes a lumen extending from a distal opening at the distal end to a proximal opening at the proximal end. The coupling assembly includes a retaining element and a retention member configured to cooperate with each other and with the portion of the organ wall surrounding the opening in the wall to couple or anchor cannula system to the wall and to provide fluidic communication between the distal opening of the elongate tubular member and the organ chamber.
Owner:SPENCE PAUL A
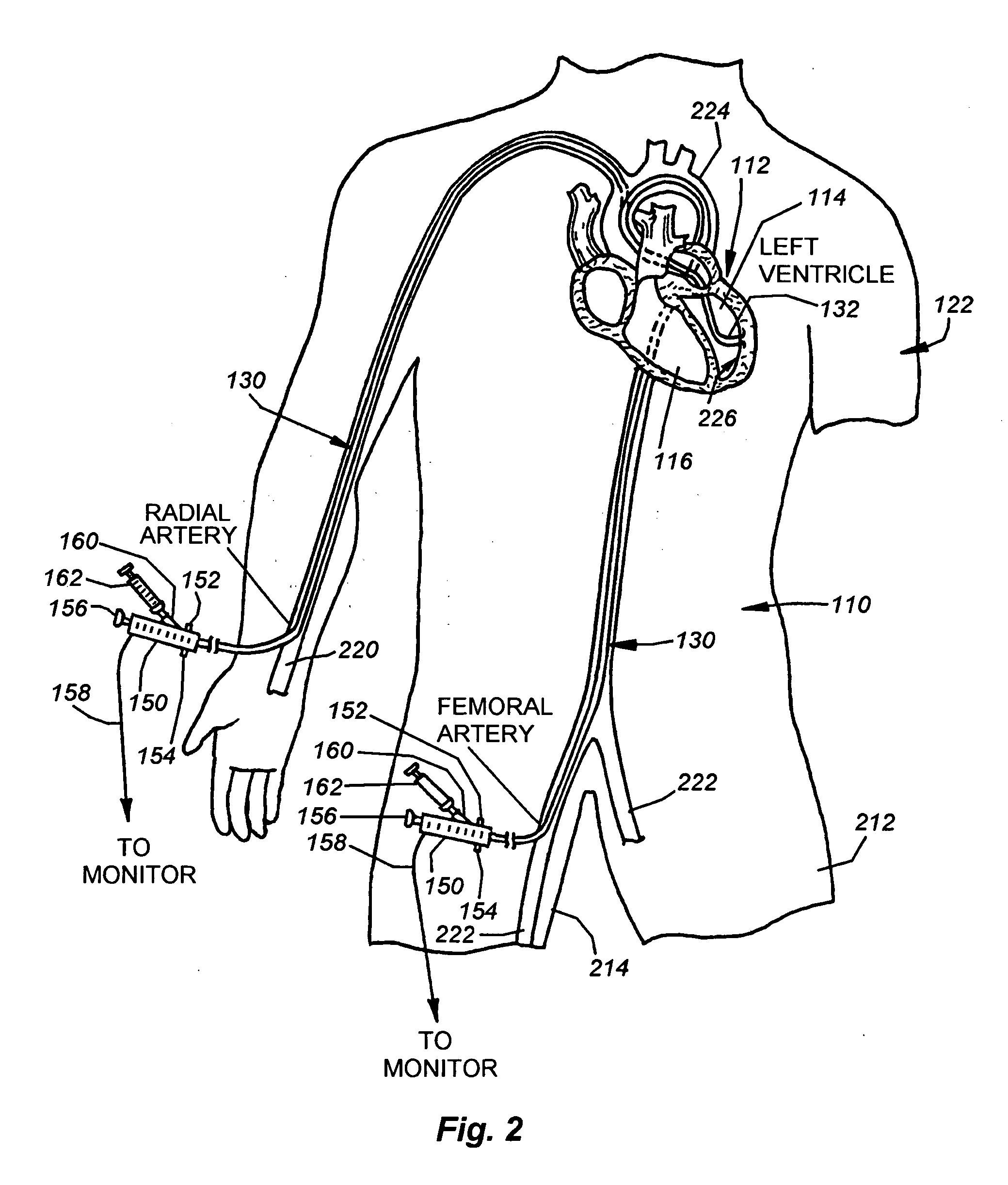
Catheter for introduction of medications to the tissues of a heart or other organ
ActiveUS7691086B2Shorten the lengthMinimizing abrasionMulti-lumen catheterInfusion syringesOrgan wallTreatment delivery
This invention overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art by providing a positionable, direct-injection catheters that can access a specific region of the heart or other organ. The catheter is provided with one or two needle shafts, which may be located within respective sheaths that extend axially along the interior of the lumen of a main catheter shaft. Each needle shaft carries, at a distal end thereof a penetrable element or “needle” that is normally retracted within the distal tip of the main shaft during travel to the target organ, but is subsequently deployed by action of a handle-mounted trigger mechanism to extend the needles into the organ's wall. Each extended needle is curved to relative to the shaft's axis to enter the organ wall in a flattened trajectory that both reduces the chance of puncture through the wall and anchors the needles into the wall during injection (for reduced chance of pullout under pressure). A plurality of apertures which provide for more complete agent delivery rapidly, while maintaining a low delivery velocity to effect treatment delivery in as short a period of time as possible without the problems caused by high velocity delivery. The needles are typically arranged to exit the tip at contralateral orientations relative to each other.
Owner:TKEBUCHAVA TENGIZ
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS20050154411A1Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M +1
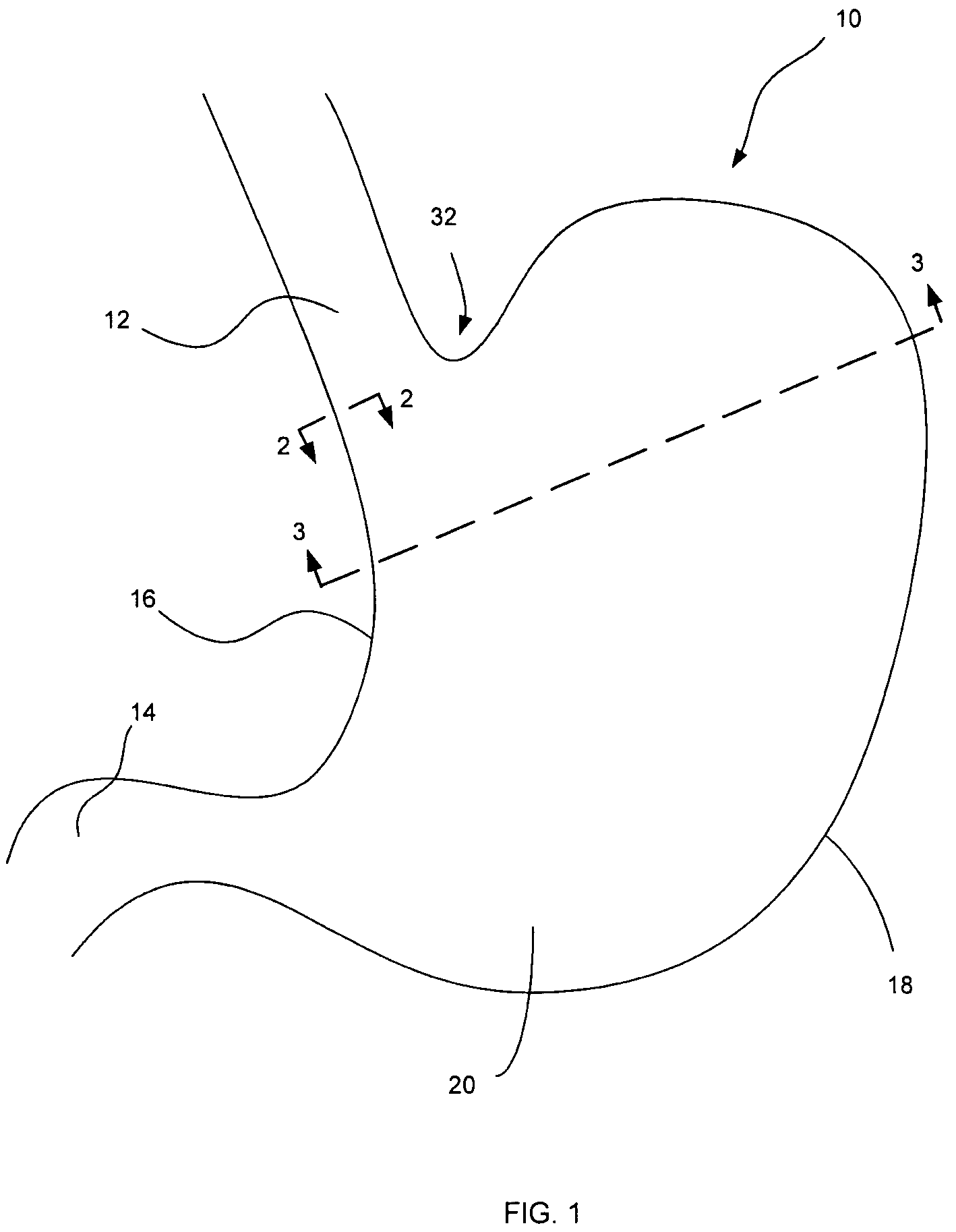
Surgical device and associated trans-organ surgical method
InactiveUS20060212063A1Easy to operateImprove performanceCannulasSurgical needlesAbdominal cavityOrgan wall
A tubular member is inserted into a natural body cavity such as the vagina or colon for retracting that internal organ to facilitate surgical access to the abdominal cavity through a wall of the organ. An end closure is formed with an aperture for the insertion of medical instruments. The tubular member is provided with a clamping element at the one end for holding the tubular member to the wall of the organ about an artificial opening incised into the organ wall.
Owner:WILK PATENT
Monopolar RF-Surgical Snares
ActiveUS20120172864A1Improve insulation performanceSurgical instruments for heatingOrgan wallConductive materials
Symmetrical and asymmetrical snares are used for endoscopically controlled methods by which tumors in hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract can be ensnared and RF-surgically removed from the organ wall for diagnostic and / or therapeutic purposes. These snares are characterised in that one of the two snare portions, in the case of asymmetrical snares the longer of the two snare portions, is completely electrically insulated or is made from electrically non-conductive material and that the other of the two snare portions is made from electrically conductive material and its surface is not electrically insulated. In one embodiment, the asymmetrical snare is characterised in that the long snare portion is so much flexurally stiffer than the short snare portion that it tensions the short snare portion like the string of a bow.
Owner:ENDOX FEINWERKTECHN
Compression anastomosis ring assembly and applicator for use therewith
InactiveUS20080015617A1Reduced dimensionIncrease the scope of applicationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsOrgan wallShape-memory alloy
A compression anastomosis ring (CAR) assembly for use in joining severed organ wall portions of a hollow organ. The assembly comprises a first portion which includes an anvil ring and a second portion which comprises a bottom ring, at least one ring element, and at least one spring element formed of a shape-memory alloy. The at least one spring element provides a restorative force and is in compressive force contact with the bottom ring and the tissue to be joined is positioned between the anvil ring and the bottom ring. A plurality of needles on one of the ring elements is operative, upon application of a closure force, to pierce the tissue and the anvil ring, holding the disk to the second portion of the CAR assembly. An applicator for applying the CAR assembly and a method for using the assembly and applicator are taught.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Extraluminal stent type prosthesis for anastomosis
An external stent type prosthesis is provided that is extraluminal, with at least one tubular member, interconnectable in an upper end, and inflatable by a balloon with a central lumen, single but with multiple projections in equal plurality of tubular members of the stent which is adjusted in its interior, for side-to-side, end-to-end, end-to-side anastomosis without clamping and sutureless, or with expeditious clamping and sutureless, where the vascular graft, or anastomotic trunk, or any other grafts, inserted in the lumen of the balloon and prosthesis, comprising a distensible mesh and after being coated with graft, this mesh is expansible by the balloon until the necessary gauge to keep the graft wall joined together and sealed in relation to the organ wall, that can contain a bag suture around the place where the anastomosis is made.
Owner:GRANJA FILHO LUIZ GONZAGA
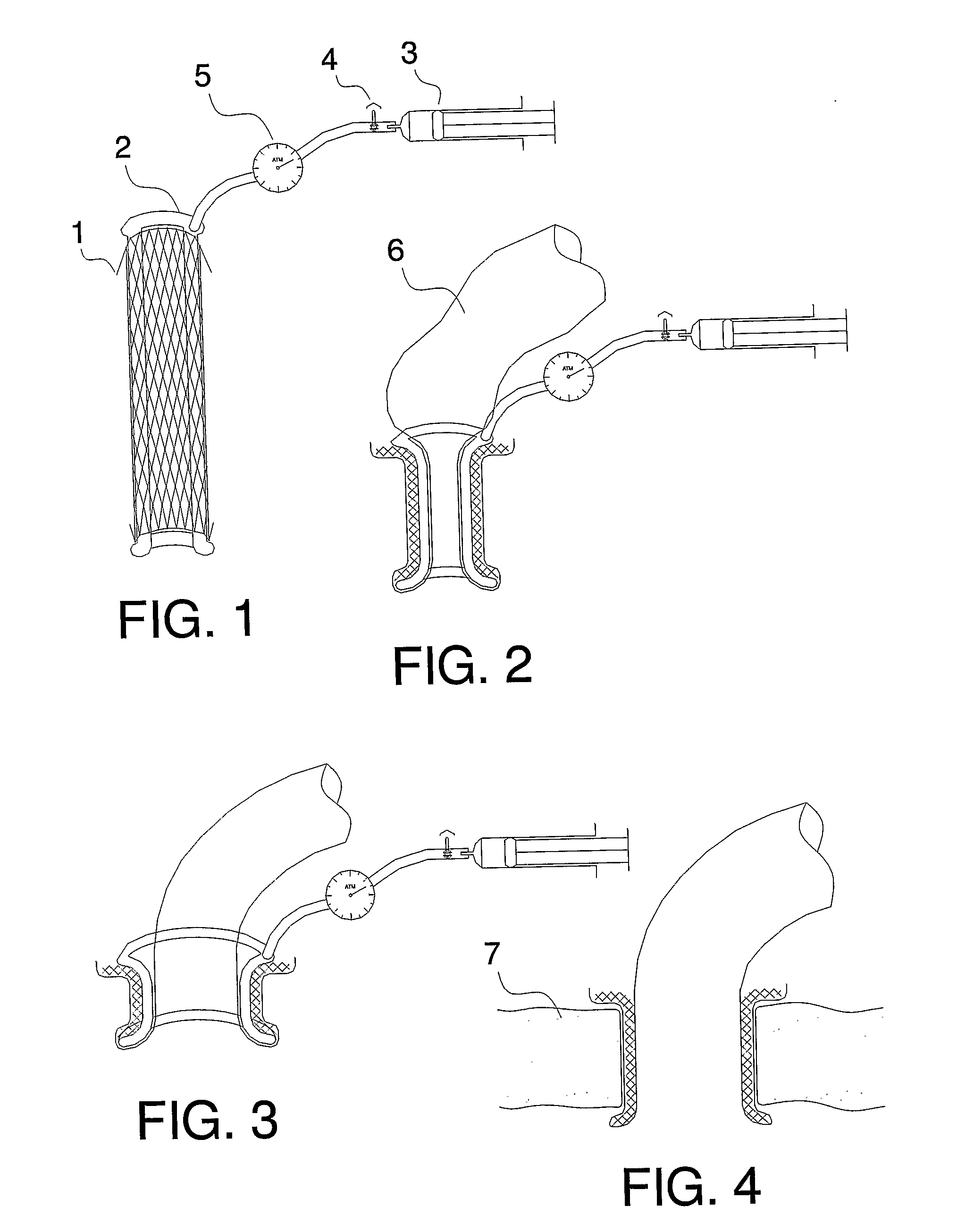
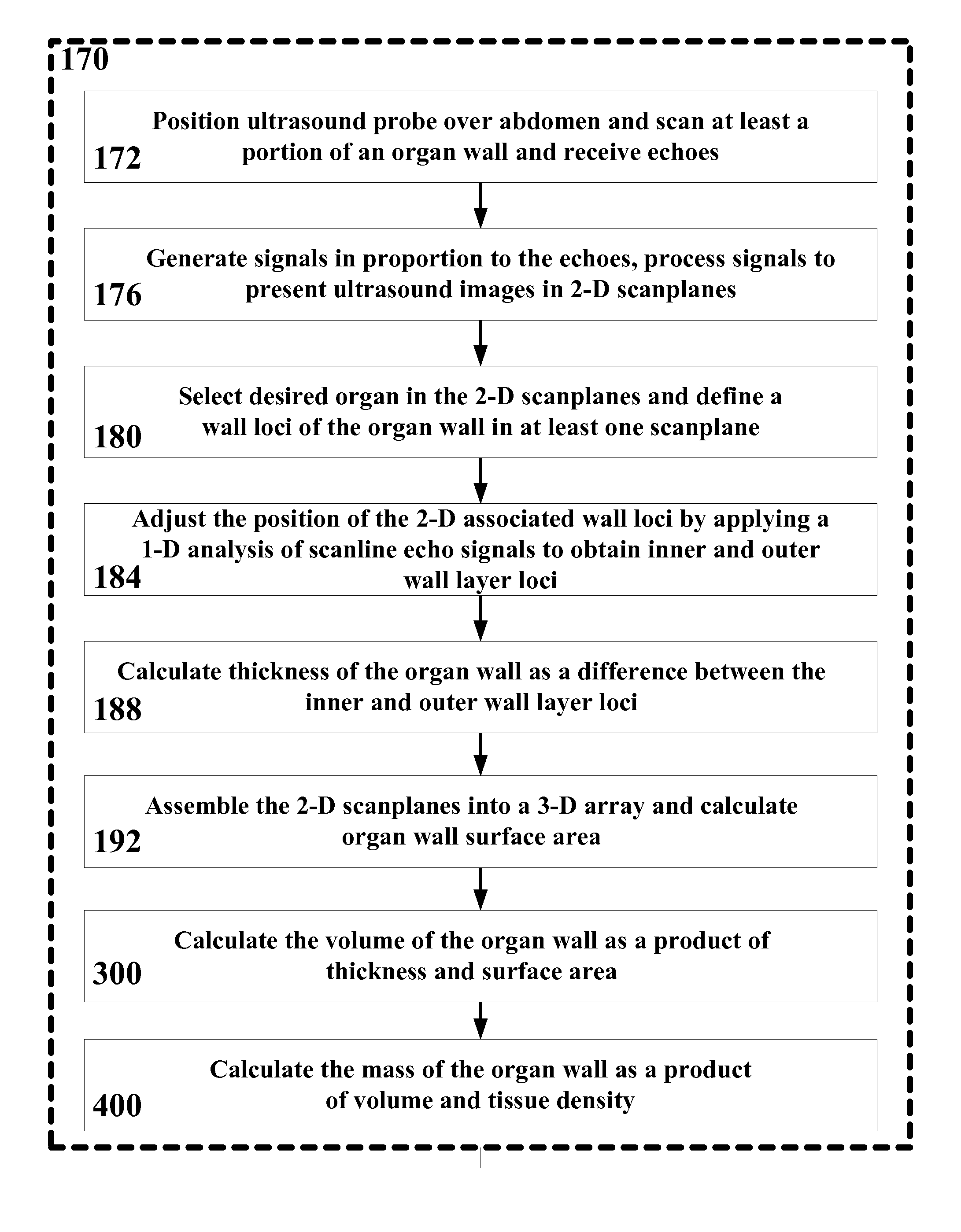
Ultrasound system and method for measuring bladder wall thickness and mass
An ultrasound transceiver scans an organ and processes the echogenic signals to produce three-dimensional, two-dimensional, and one-dimensional information of the organ. The 3-D, 2-D, and 1-D information is utilized to determine the thickness, surface area, volume, and mass of the organ wall.
Owner:VERATHON
Detachable distal overtube section and methods for forming a sealable opening in the wall of an organ
An overtube for use with an endoscopic surgical instrument. In various embodiments, the overtube may comprise a hollow tubular member that has an implantable tip detachably affixed to a distal end thereof. The implantable tip may have at least one retention member formed thereon to retain the tip within an organ wall. The implantable tip may further have a lumen extending therethrough to form a passageway through the organ wall. A plug member may be provided to selectively seal off the lumen within the implantable tip.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
System and method to identify and measure organ wall boundaries
ActiveUS20070276254A1Accurate detectionAccurate delineationImage enhancementImage analysisOrgan wallSonification
Systems and methods are described for acquiring, processing, and presenting boundaries of a cavity-tissue interface within a region-of-interest in an ultrasound image based upon the strength of signals of ultrasound echoes returning from structures within the region-of-interest. The segmentation of boundaries of cavity shapes occupying the region-of-interest utilizes cost function analysis of pixel sets occupying the cavity-tissue interface. The segmented shapes are further image processed to determine areas and volumes of the organ or structure containing the cavity within the region-of-interest.
Owner:VERATHON
Apparatus for treating an organ and related methods of use
Embodiments of the disclosure may include a method of treatment. The method of treatment may include advancing a medical device to a wall of an organ having a plurality of layers of tissue. The medical device may include an elongate tube having a proximal end and a distal end, a lumen extending therebetween, and an injector disposed within the lumen. The injector may be configured to deliver a substance to a location between first and second layers of tissue of the plurality of layers of tissue within the organ wall. In addition, the method may further include delivering the substance to the location, wherein, when delivered, the substance is configured to spatially separate a portion of the first and second layers of the tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
System and method to identify and measure organ wall boundaries
InactiveUS20080139938A1Accurate detectionAccurate delineationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementOrgan wallSonification
Systems and methods are described for acquiring, processing, and presenting boundaries of a cavity-tissue interface within a region-of-interest in an ultrasound image based upon the strength of signals of ultrasound echoes returning from structures within the region-of-interest. The segmentation of boundaries of cavity shapes occupying the region-of-interest utilizes cost function analysis of pixel sets occupying the cavity-tissue interface. The segmented shapes are further image processed to determine areas and volumes of the organ or structure containing the cavity within the region-of-interest.
Owner:YANG FUXING +2
Ultrasound system and method for measuring bladder wall thickness and mass
InactiveUS20100036252A1Improve accuracy and precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementTransceiverOrgan wall
An ultrasound transceiver scans an organ and processes the echogenic signals to produce three-dimensional, two-dimensional, and one-dimensional information of the organ. The 3-D, 2-D, and 1-D information is utilized to determine the thickness, surface area, volume, and mass of the organ wall.
Owner:VERATHON
Hybrid catheter apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20150359595A1Enhance separation debulkingImprove clinical efficacyEndoscopesCatheterOrgan wallLaser cutting
A hybrid catheter device for performing cutting action on a region of a tissue, using sequential laser and mechanical cutting processes, and incorporating an acoustic sensor on the end of the device, such that if a pulsed laser beam is used for the laser cutting, the absorption of that beam in the tissue being cut can provide information about the progress of the cut by means of the opto-acoustic effect. Other hybrid catheter devices incorporate blunt protrusions on the end of said device, but having sharp lateral edges, such that rotation of the catheter device generates mechanical cutting action in the tissue. The blunt protrusion ends prevents uncontrolled cutting in the forward motion. Other hybrid catheter devices enable controlled incisions into an organ wall, such as the duodenum, and held in place by means of an inflatable balloon. A dual-wavelength nail fungus treatment hybrid catheter is also shown.
Owner:EXIMO MEDICAL
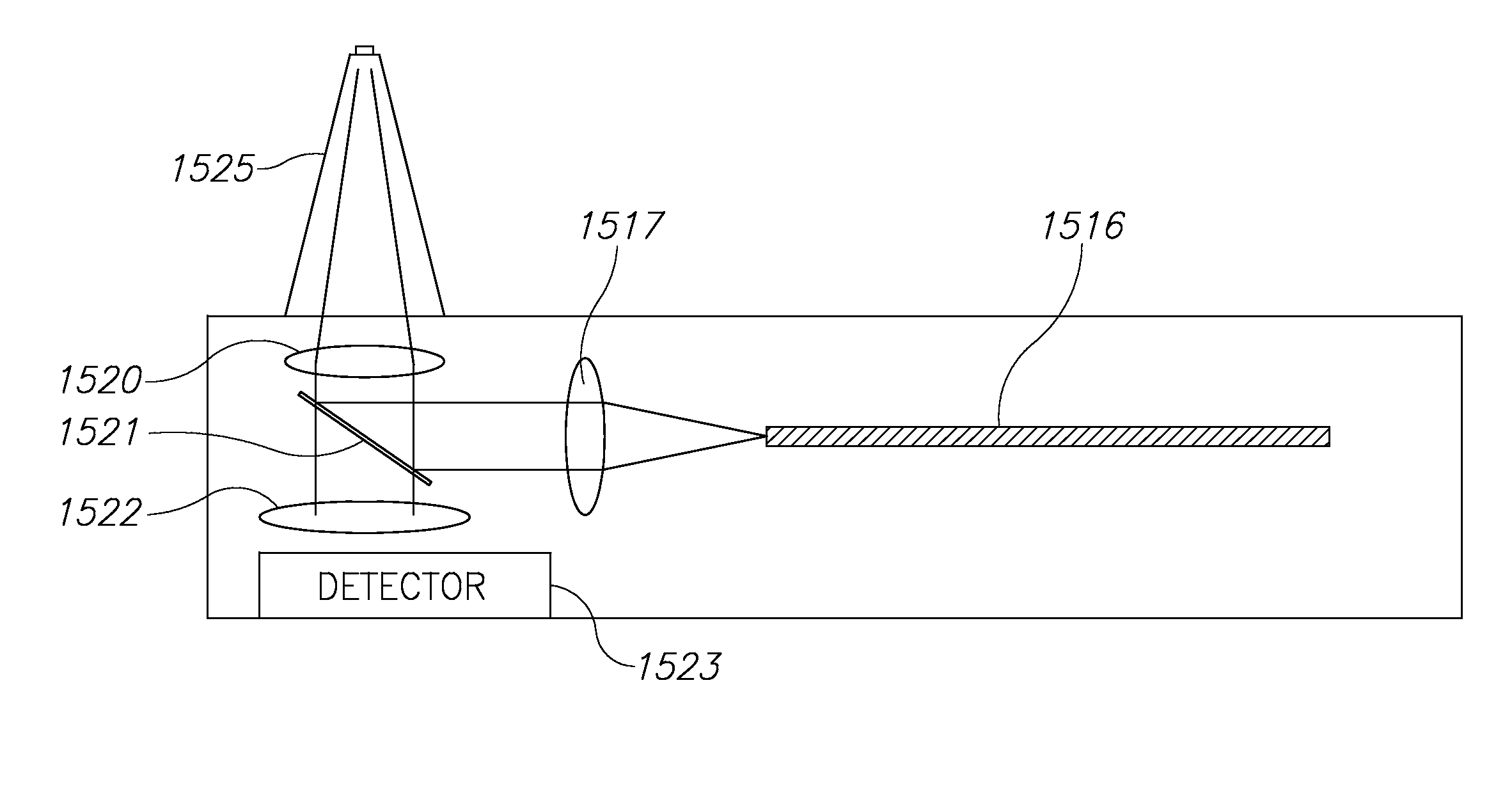
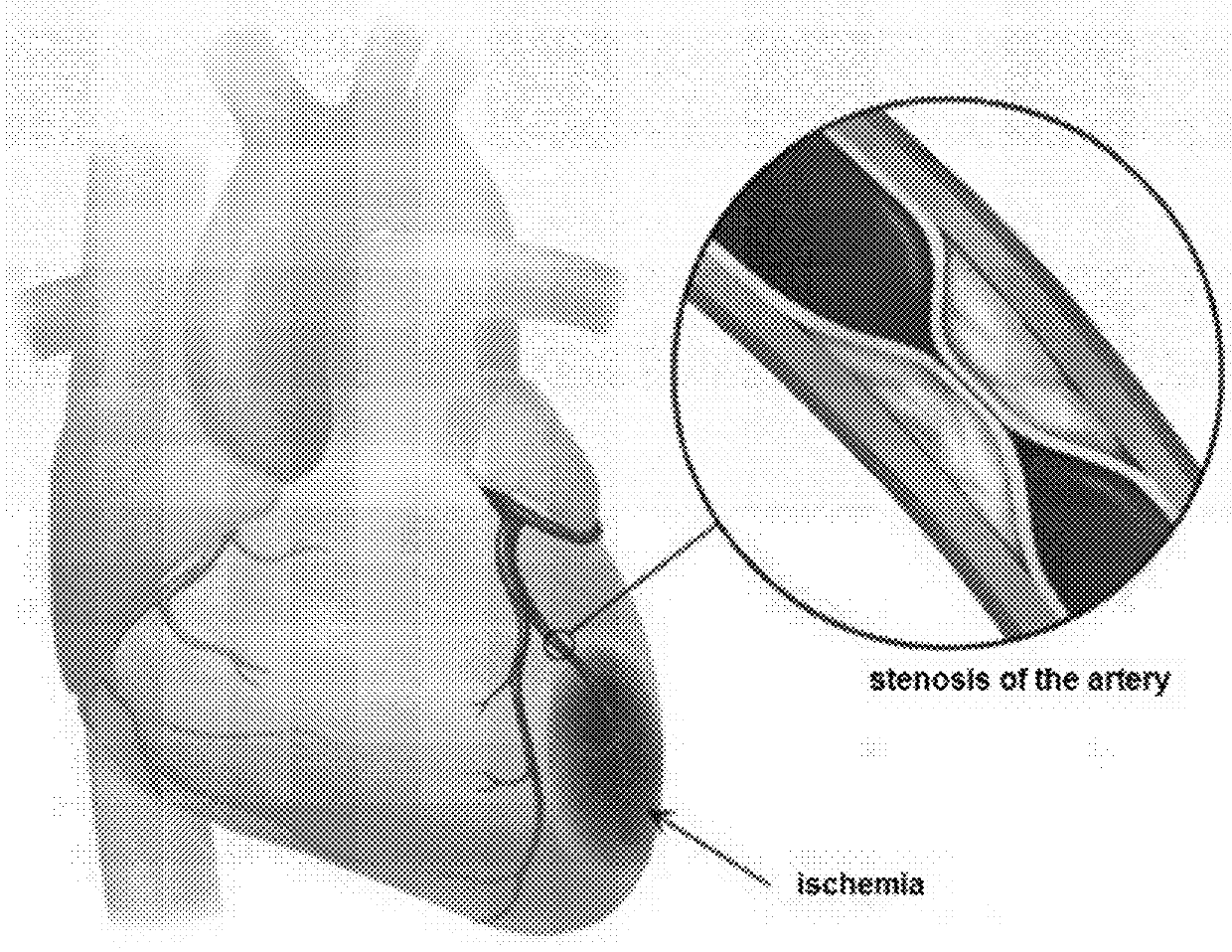
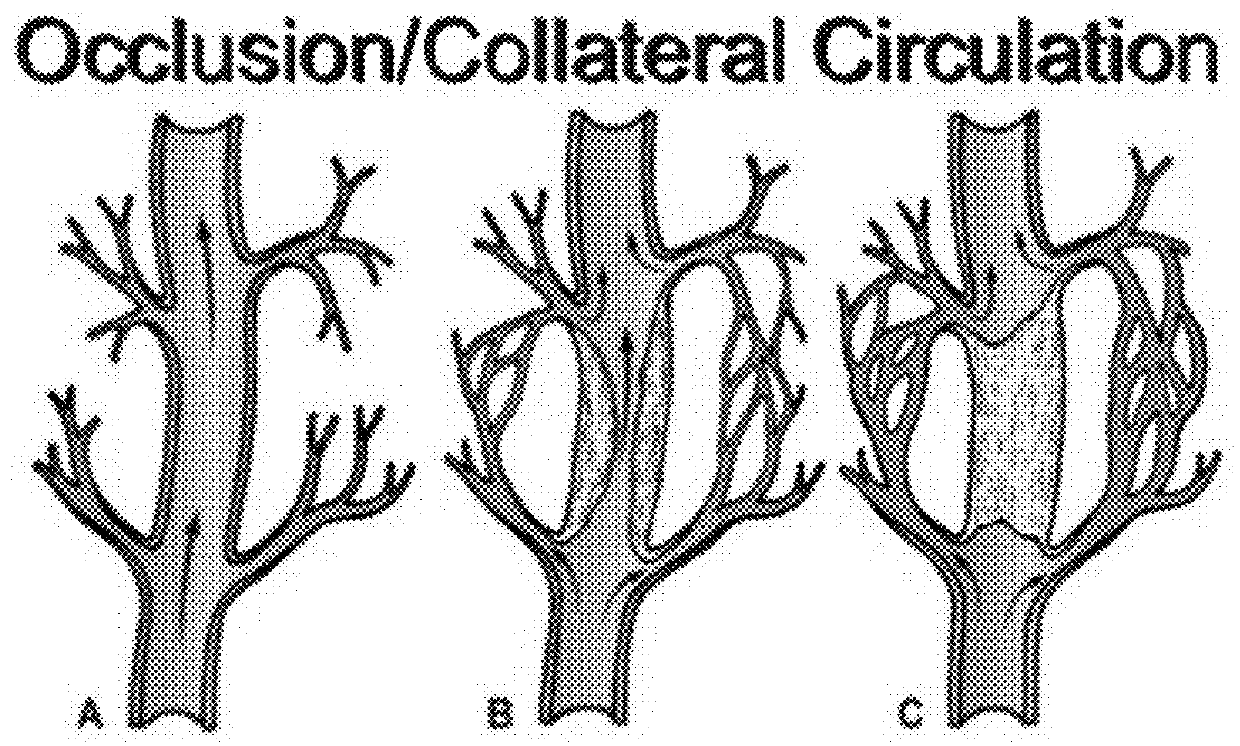
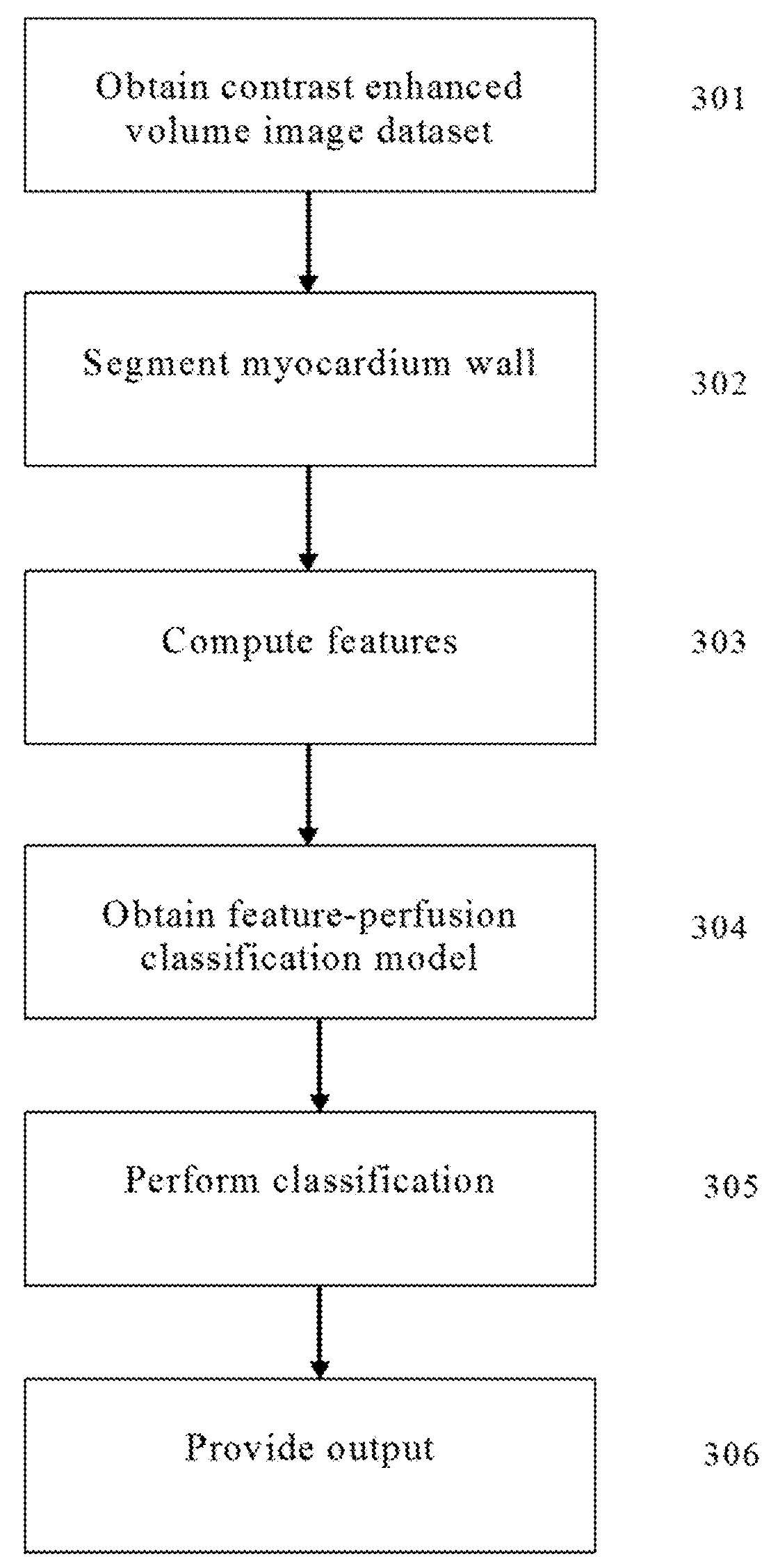
Method and System for Assessing Vessel Obstruction Based on Machine Learning
Methods and systems are provided for assessing the presence of functionally significant stenosis in one or more coronary arteries, further known as a severity of vessel obstruction. The methods and systems can implement a prediction phase that comprises segmenting at least a portion of a contrast enhanced volume image data set into data segments corresponding to wall regions of the target organ, and analysing the data segments to extract features that are indicative of an amount of perfusion experiences by wall regions of the target organ. The methods and systems can obtain a feature-perfusion classification (FPC) model derived from a training set of perfused organs, classify the data segments based on the features extracted and based on the FPC model, and provide, as an output, a prediction indicative of a severity of vessel obstruction based on the classification of the features.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com