Patents
Literature
4652 results about "Shape-memory alloy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
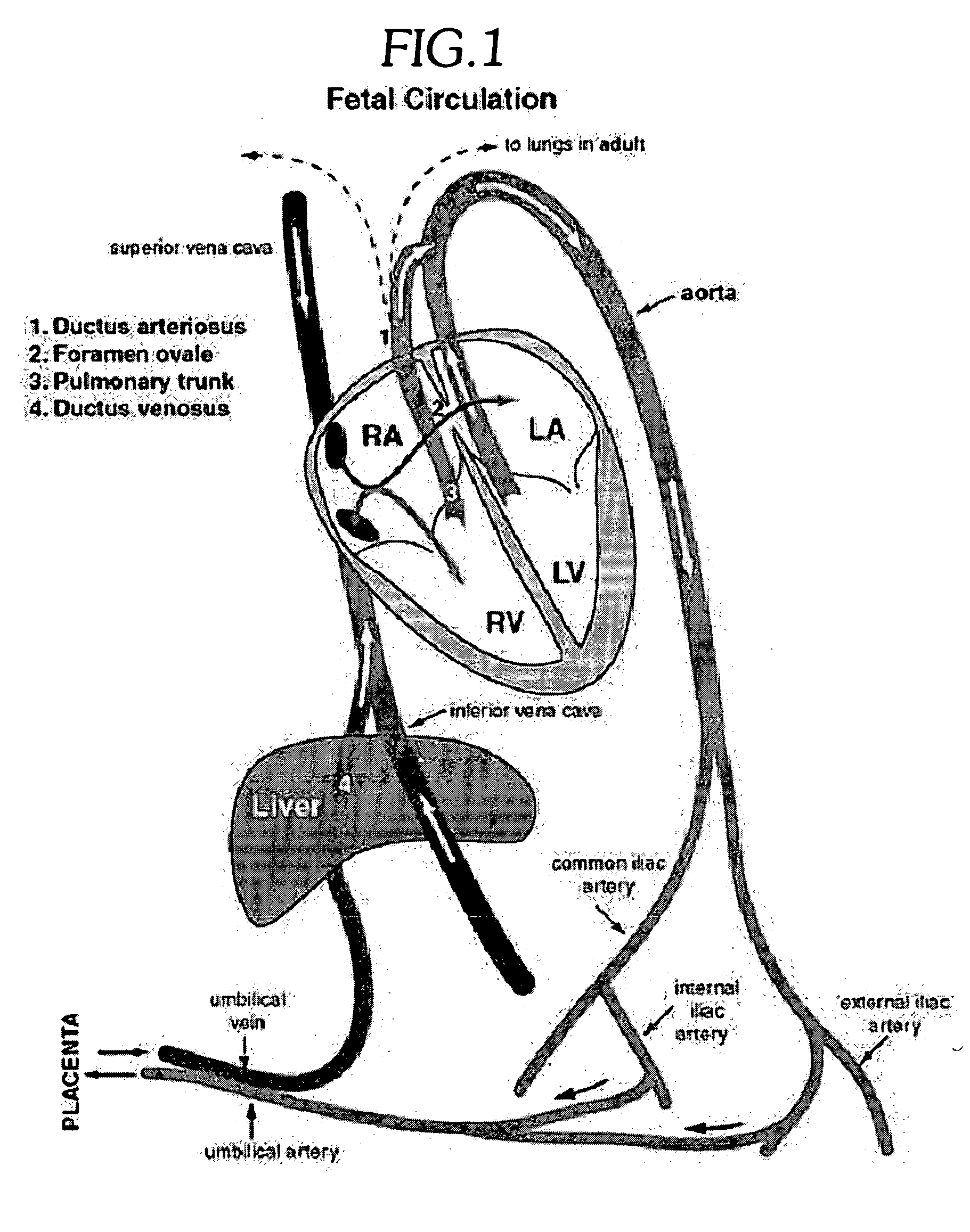
A shape-memory alloy is an alloy that can be deformed when cold but returns to its pre-deformed ("remembered") shape when heated. It may also be called memory metal, memory alloy, smart metal, smart alloy, or muscle wire.
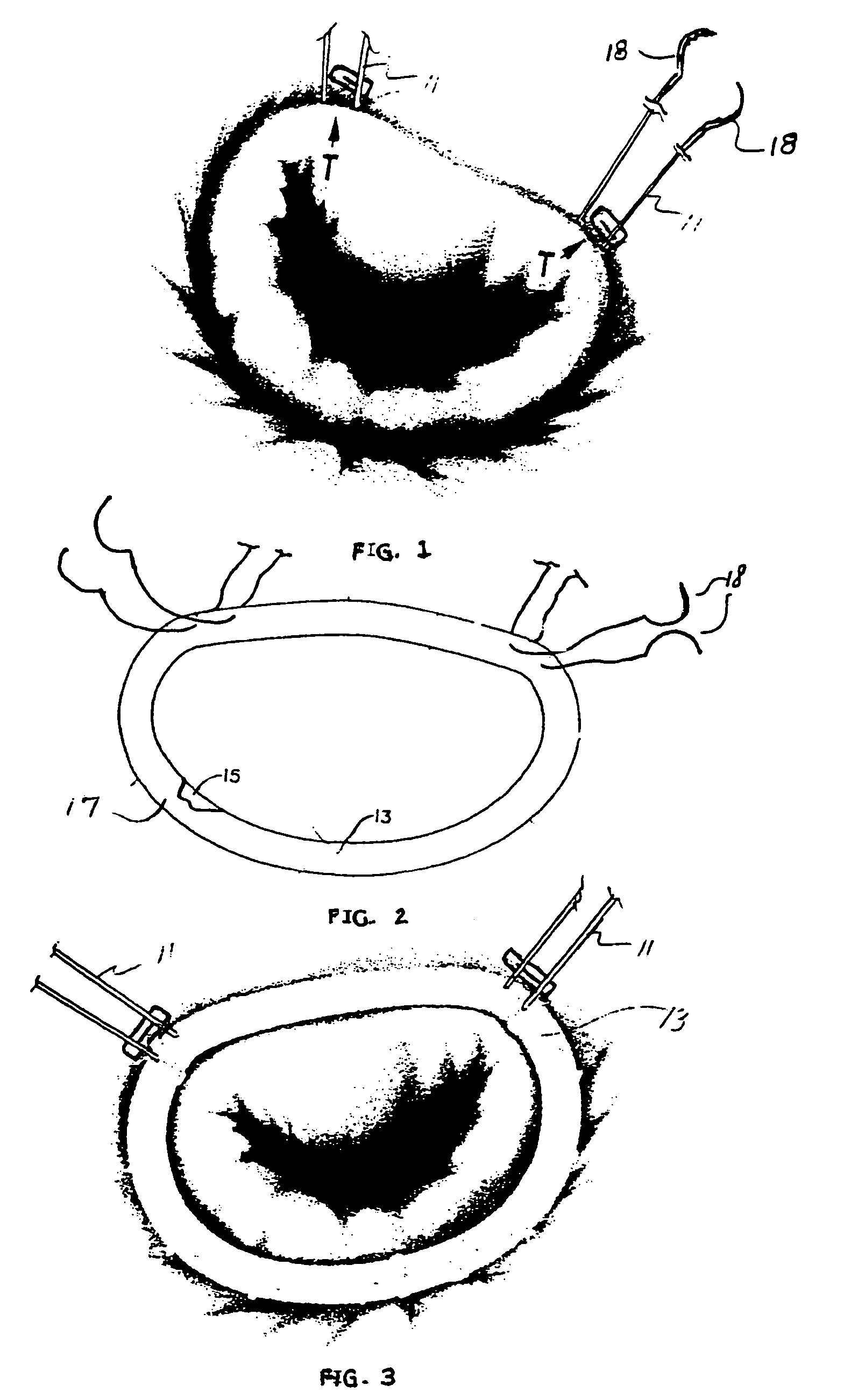
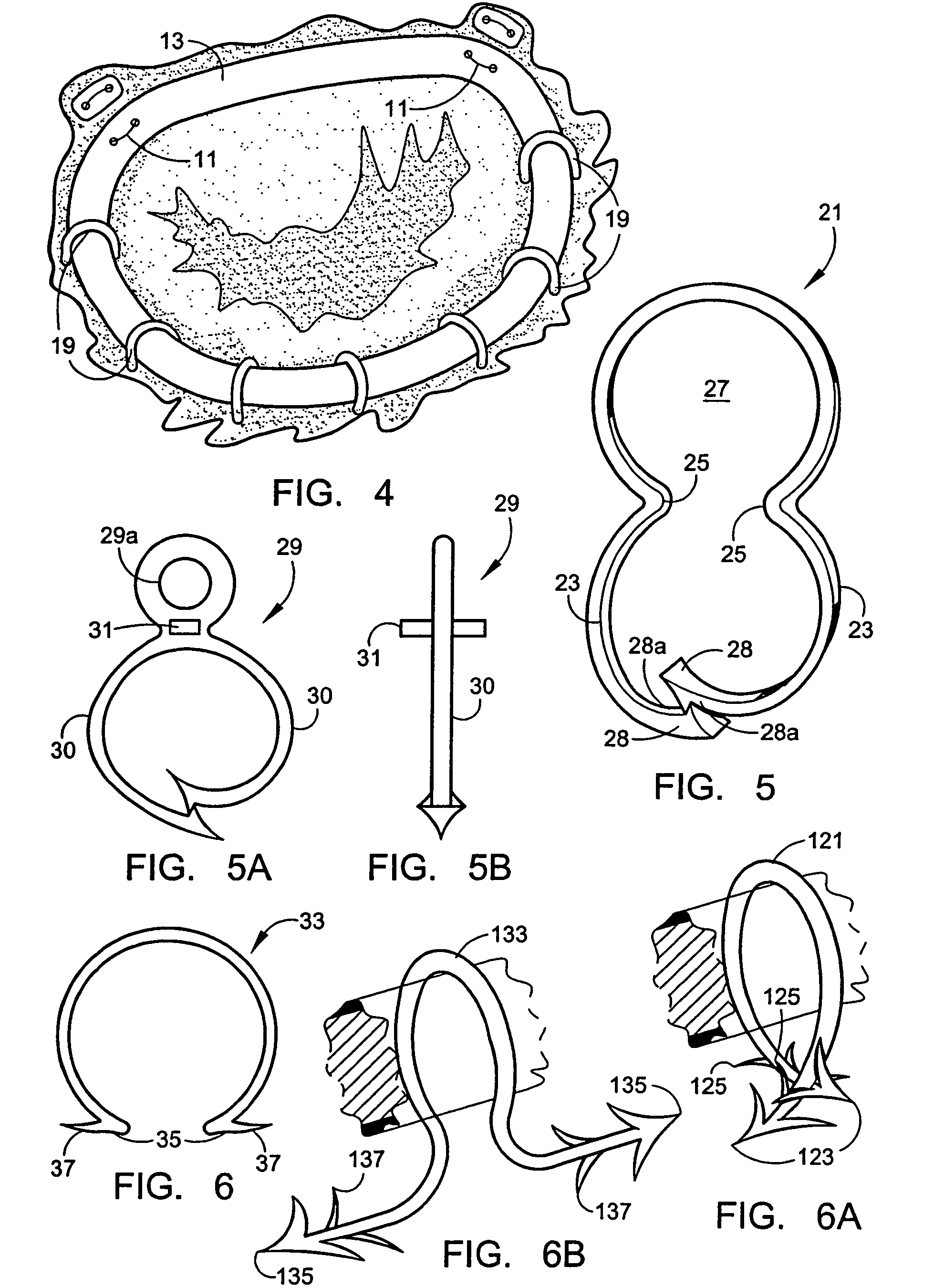
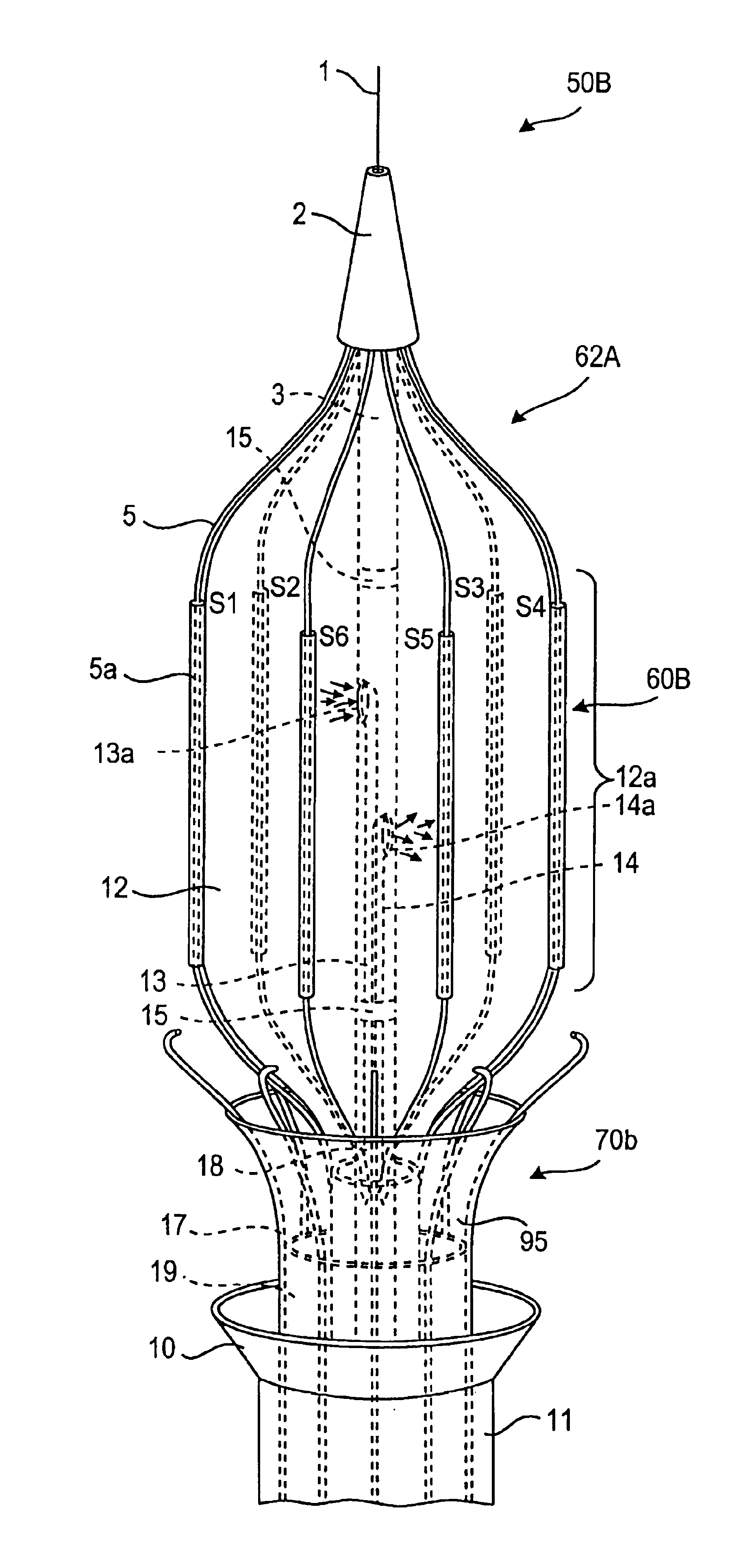
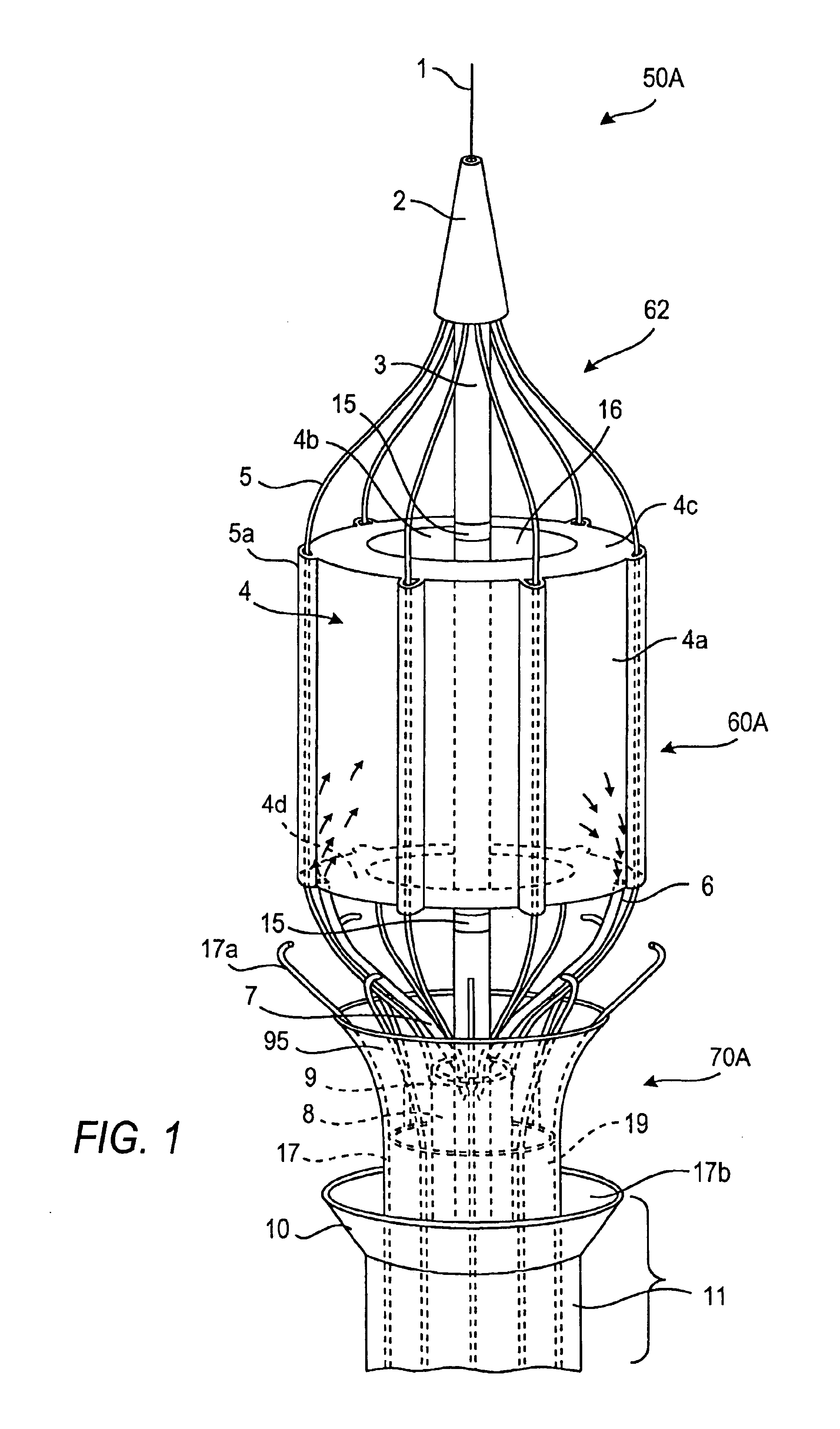
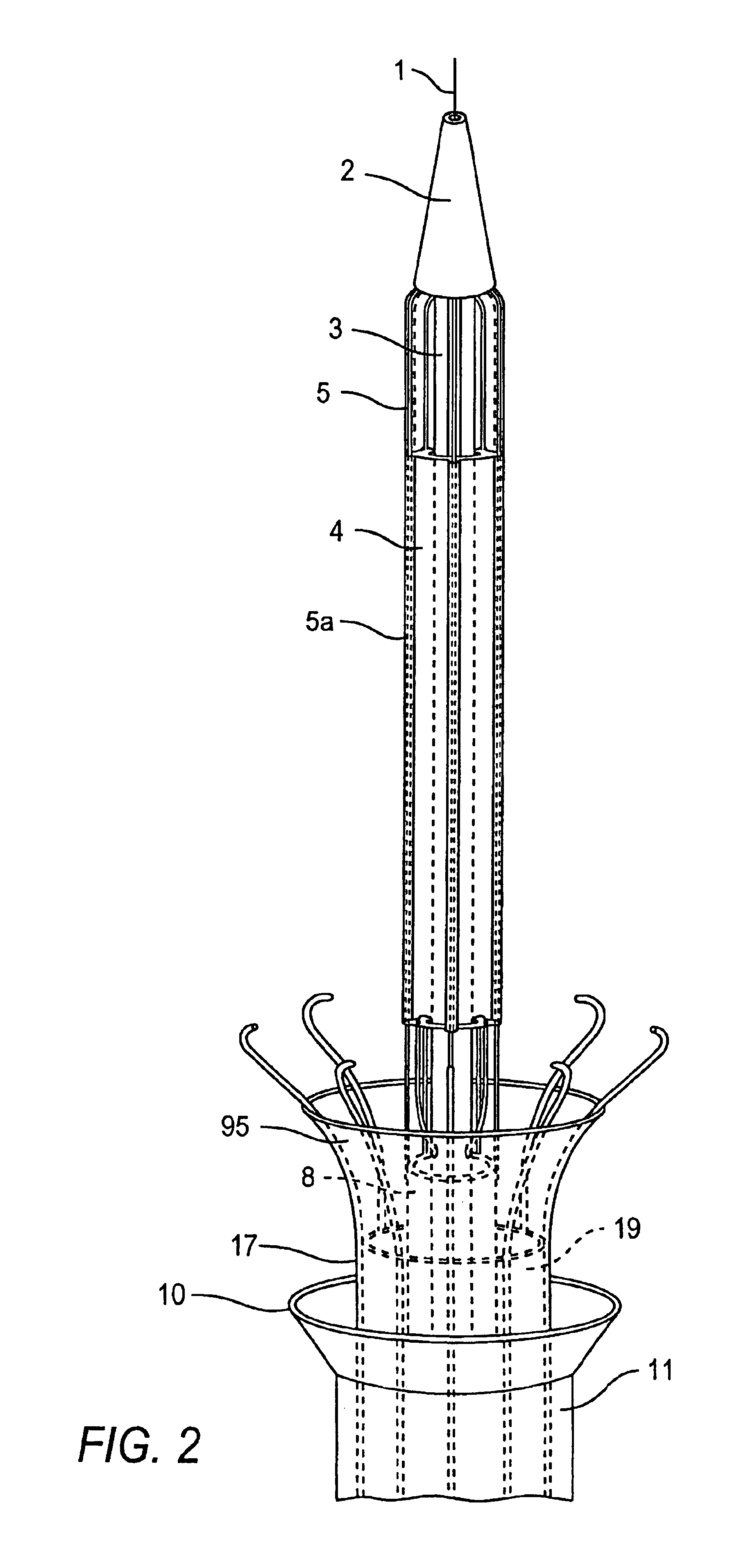
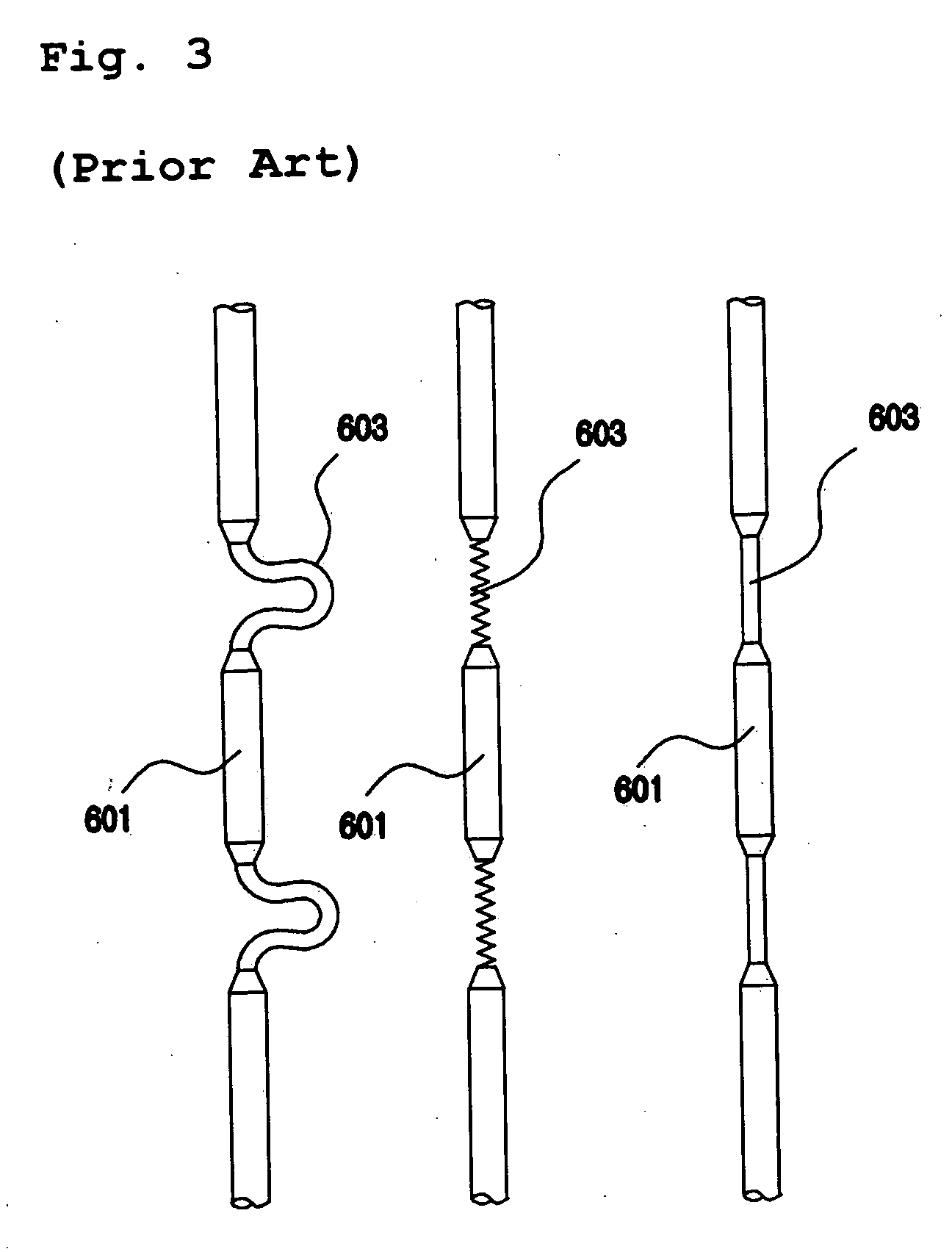
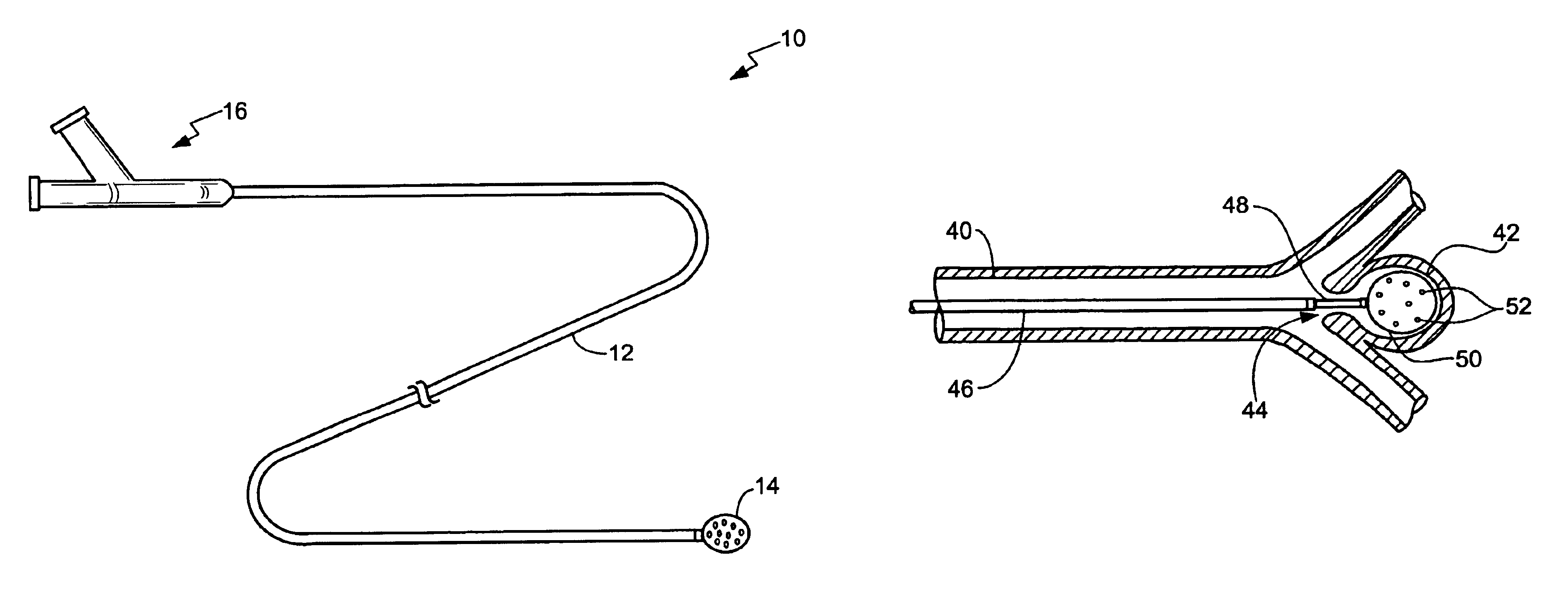
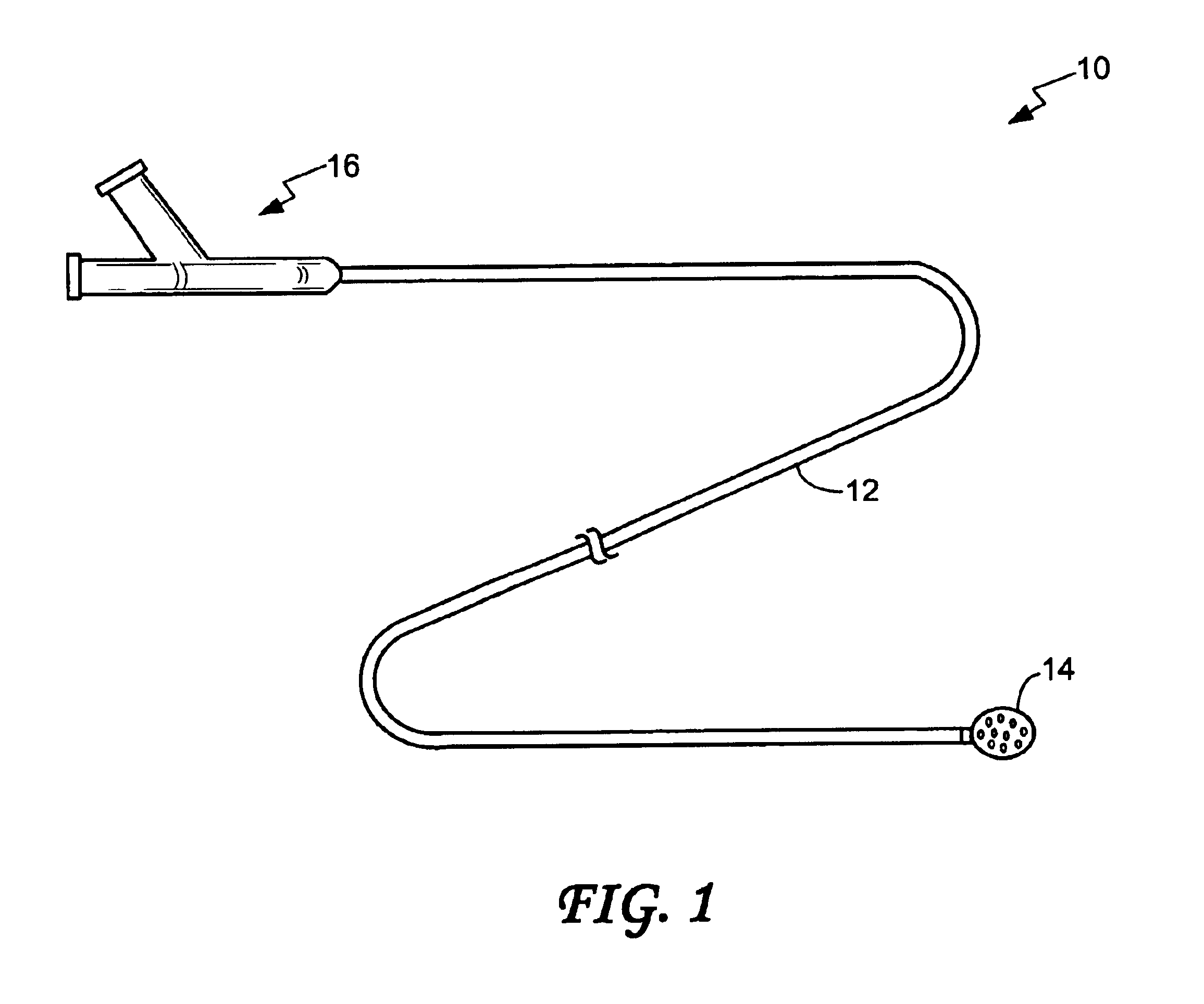
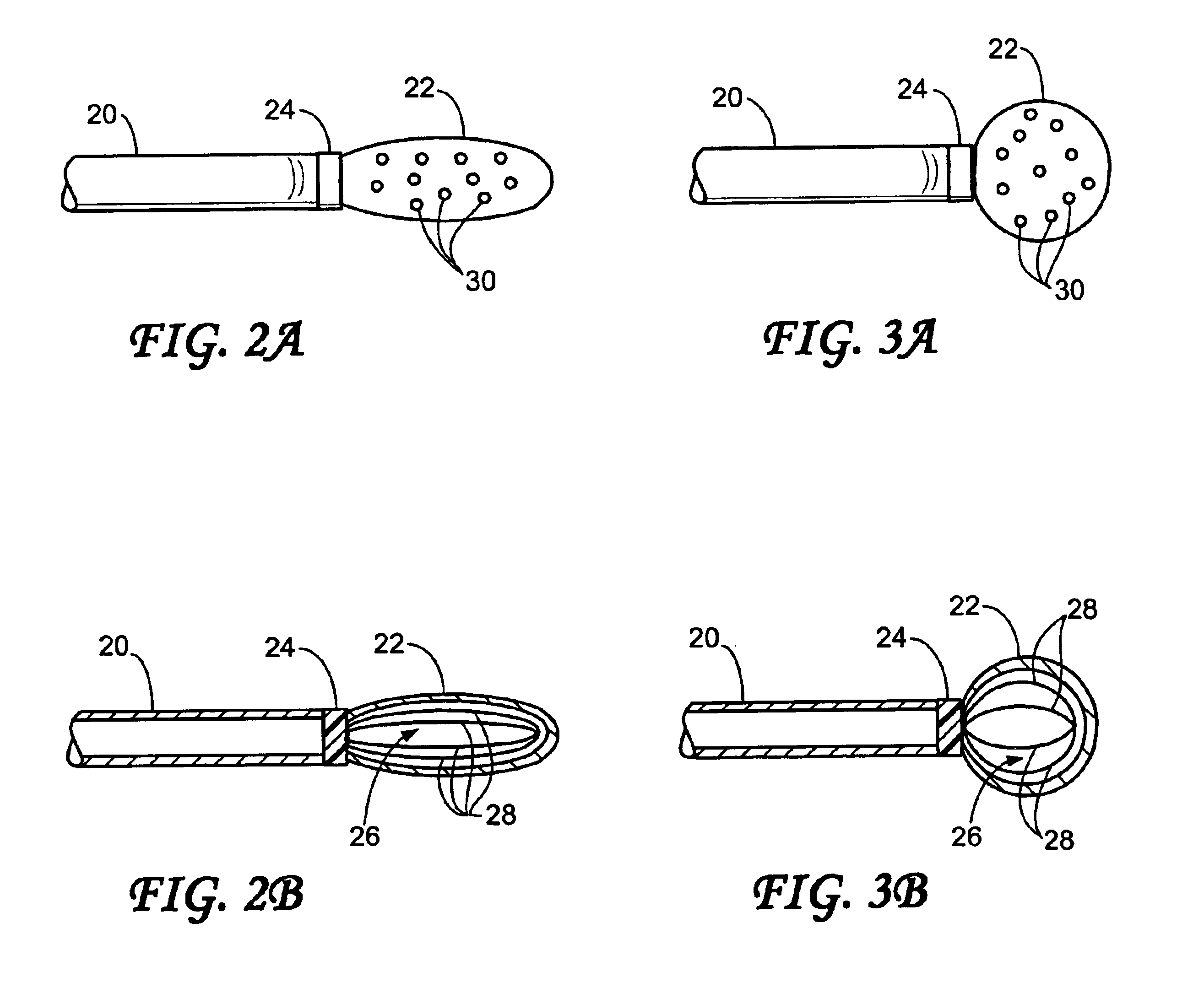
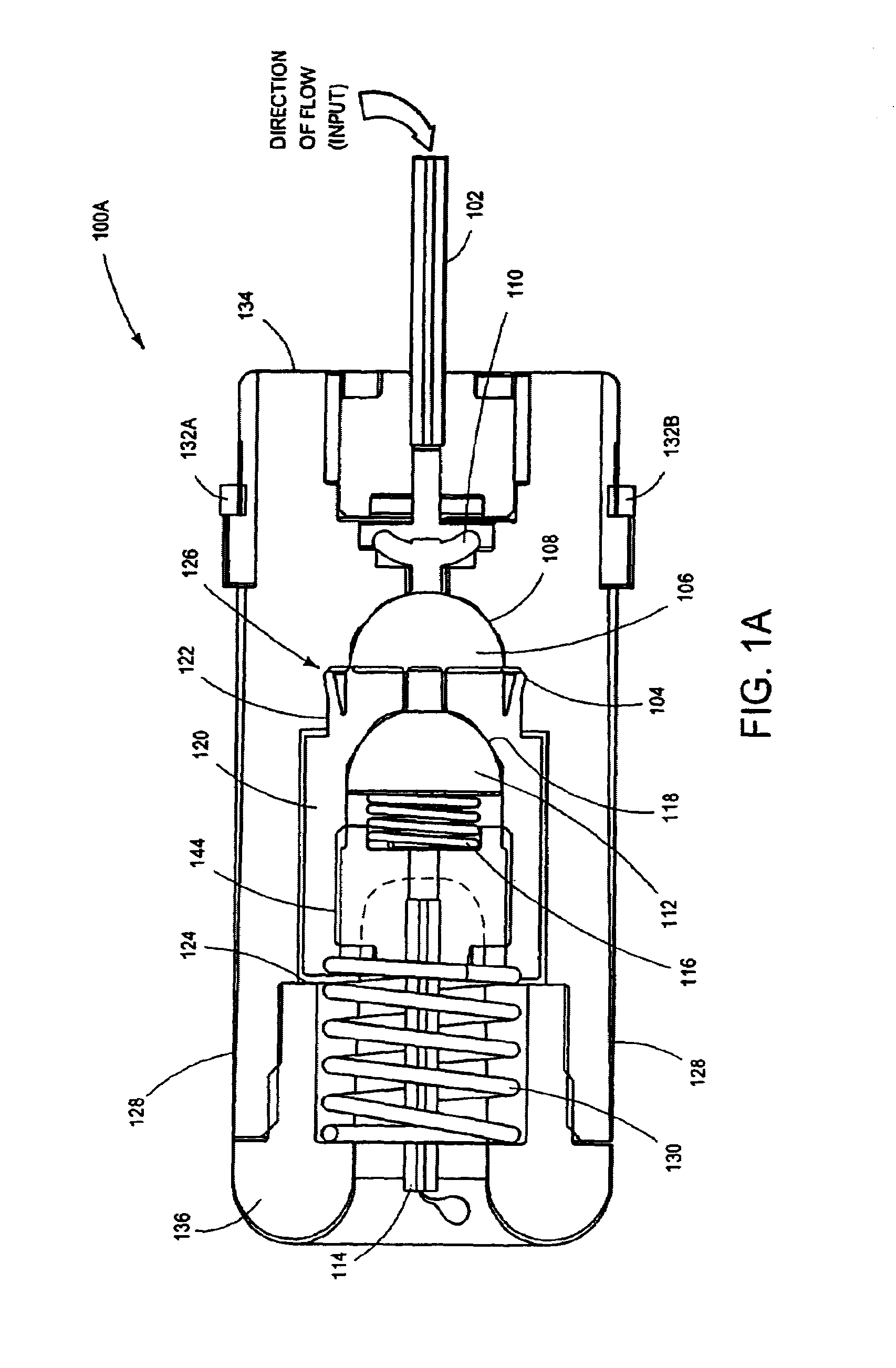
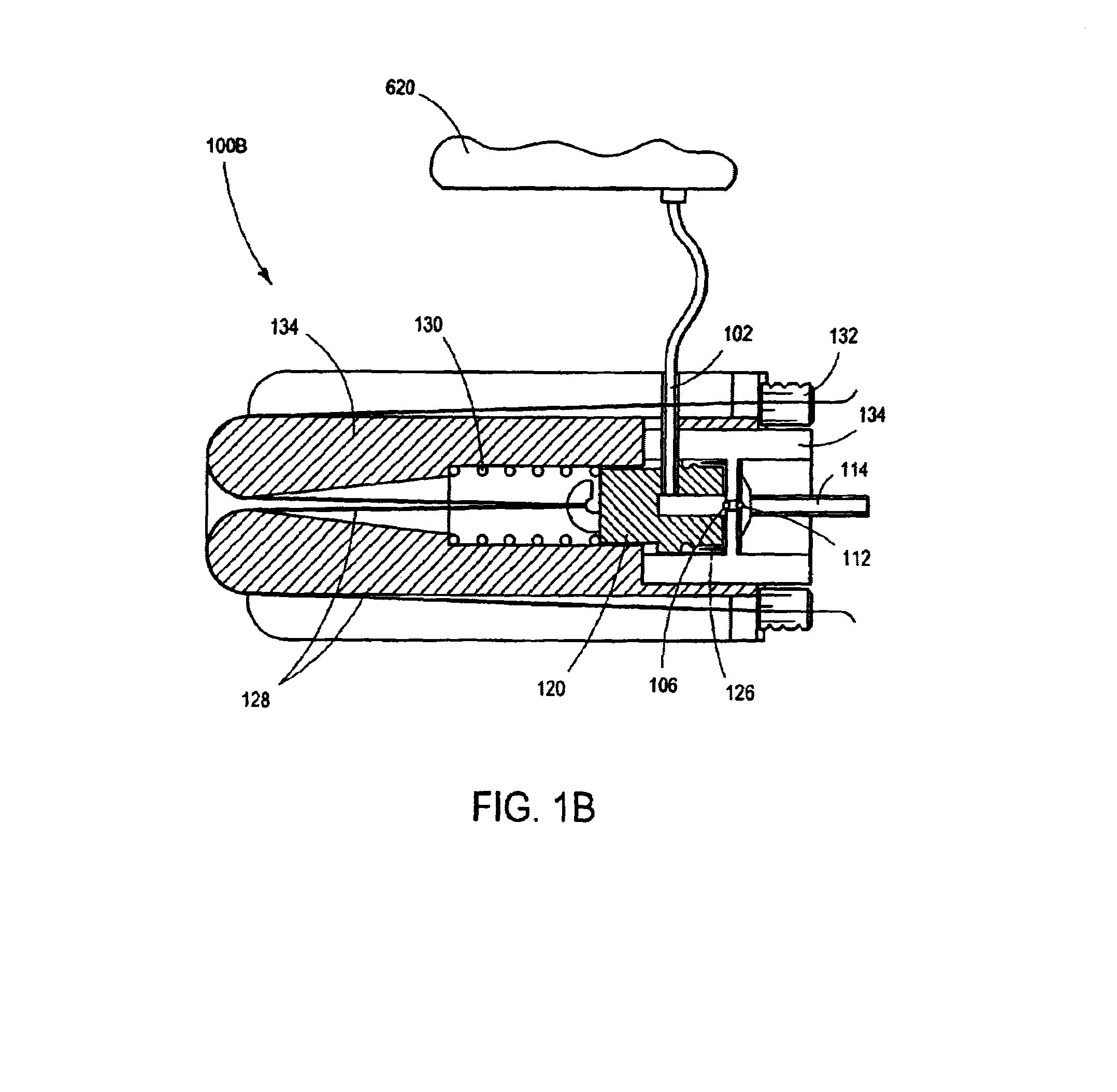
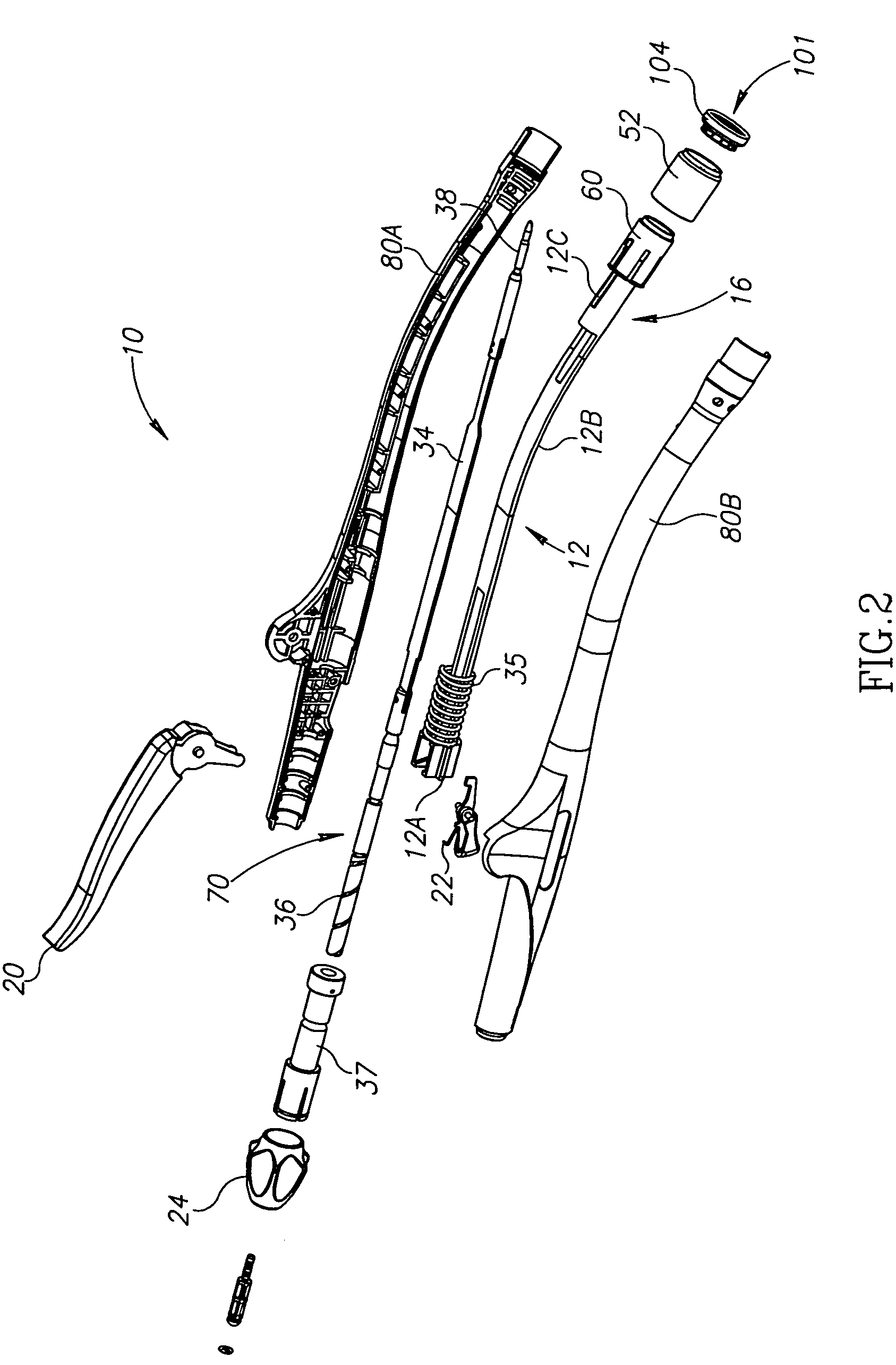
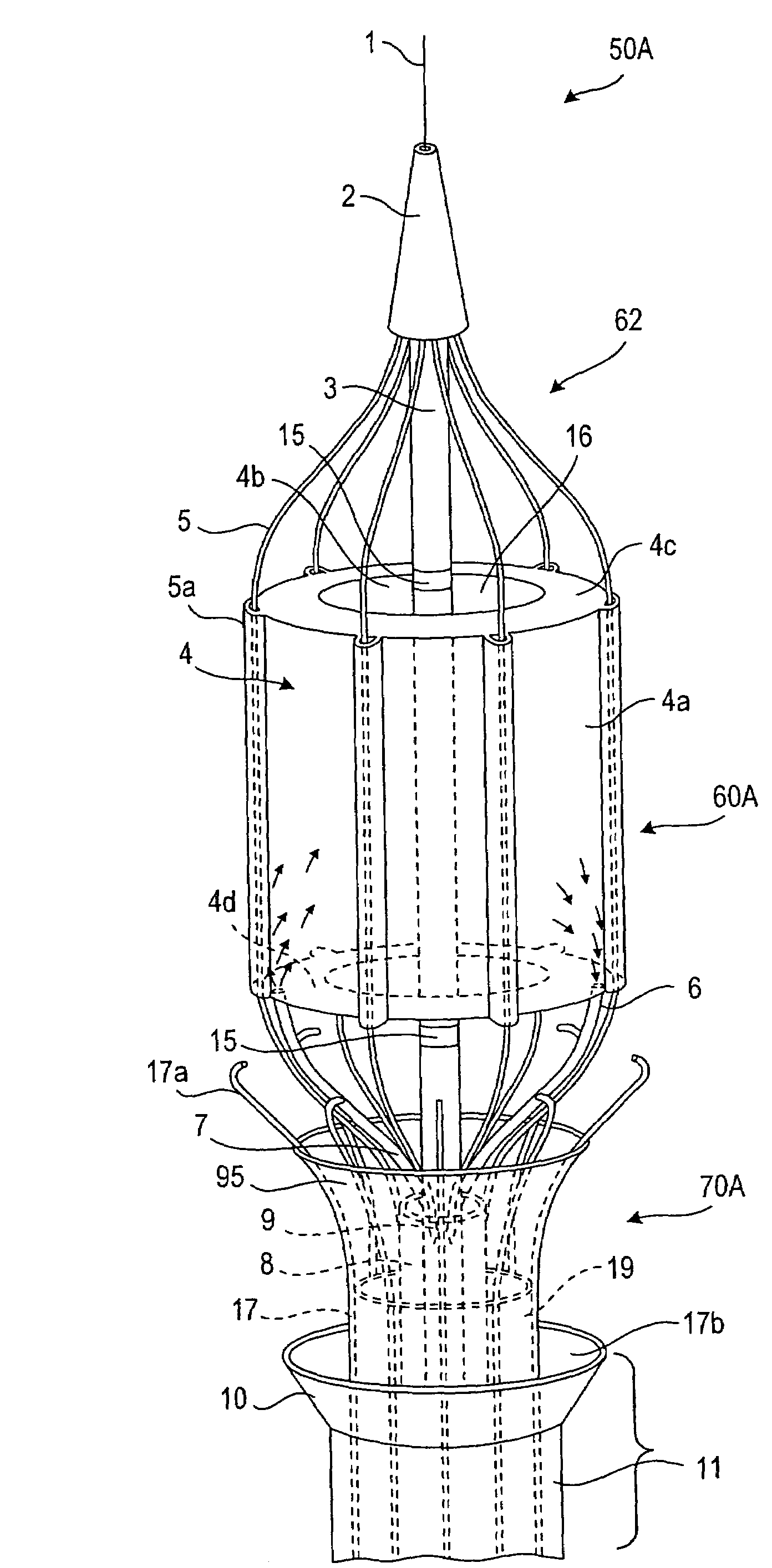
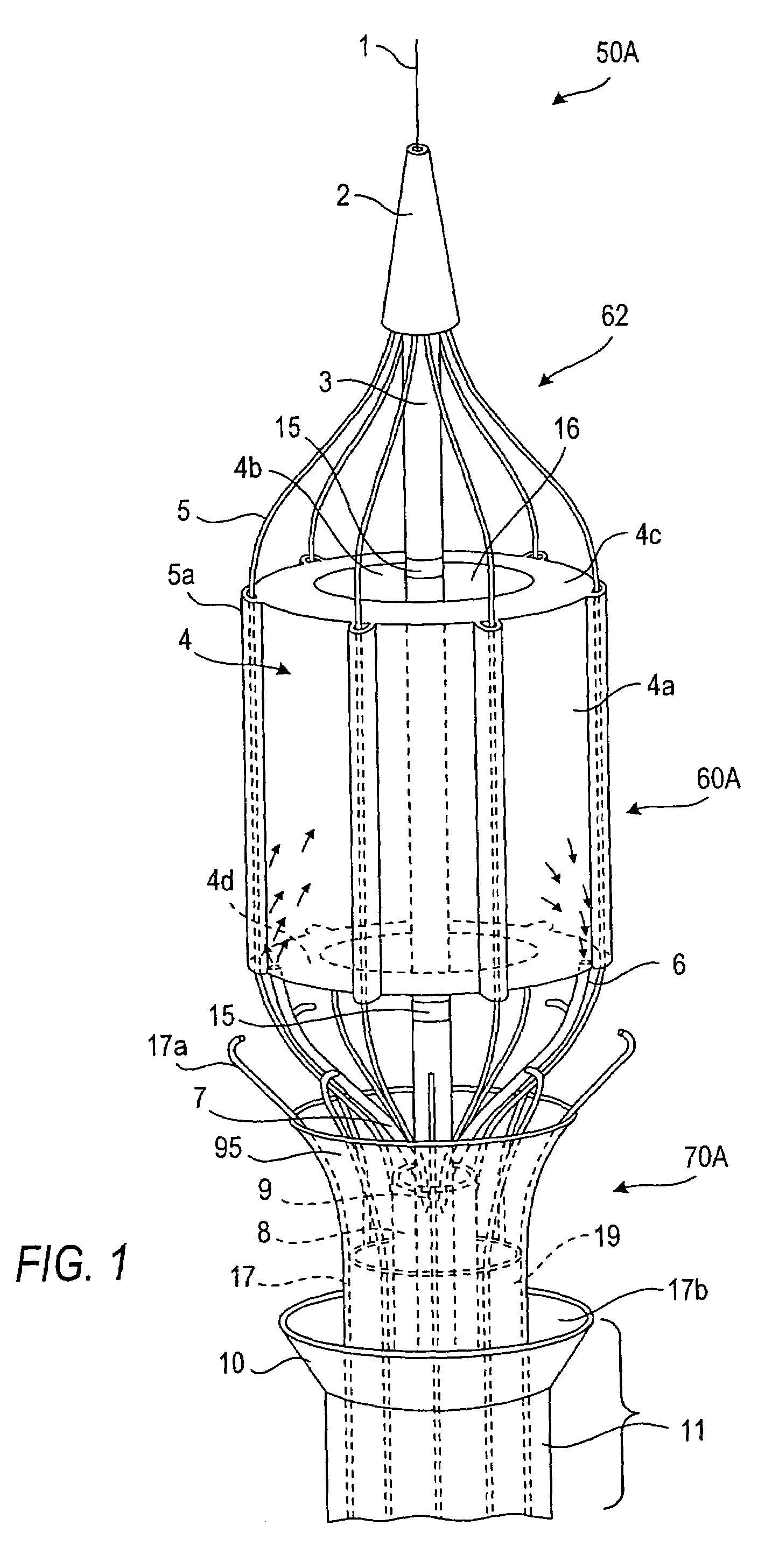
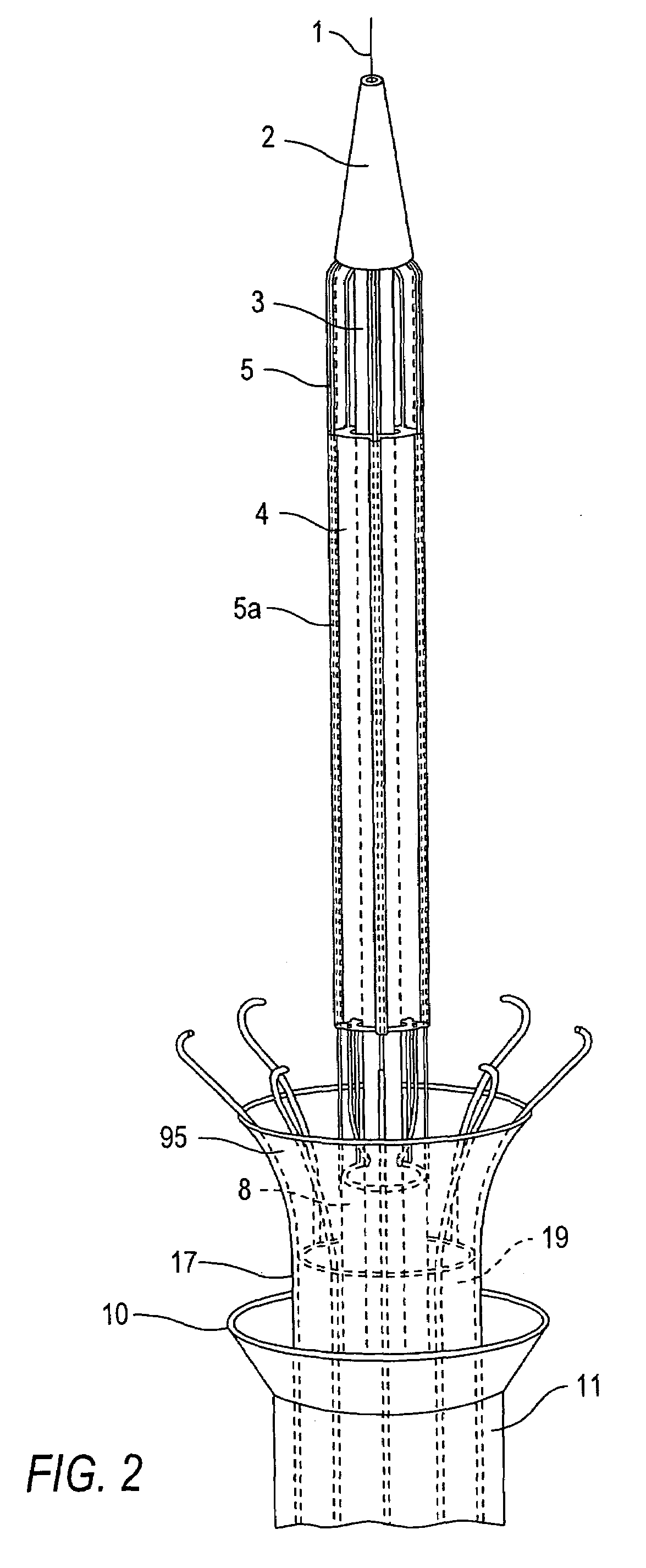
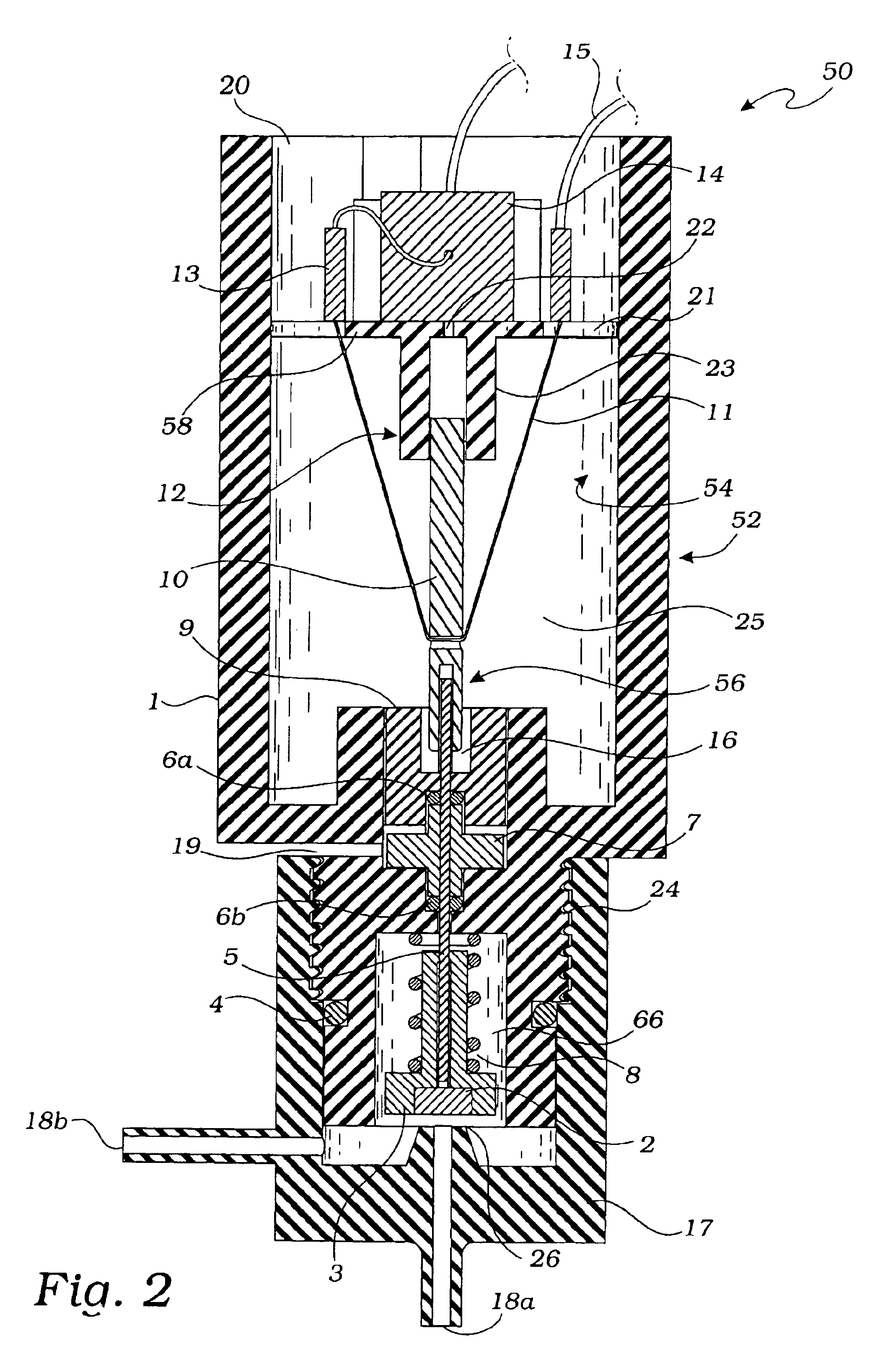
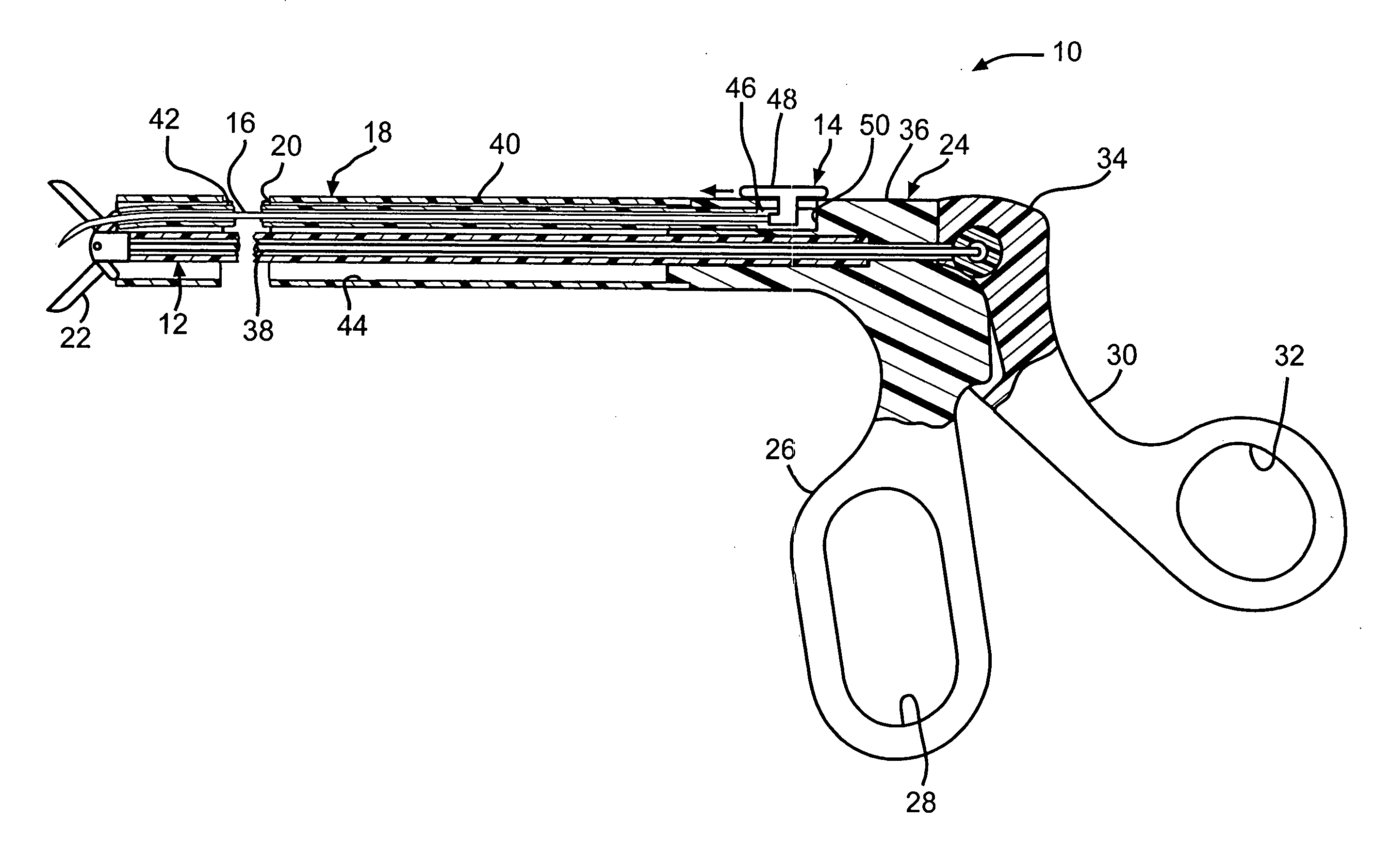
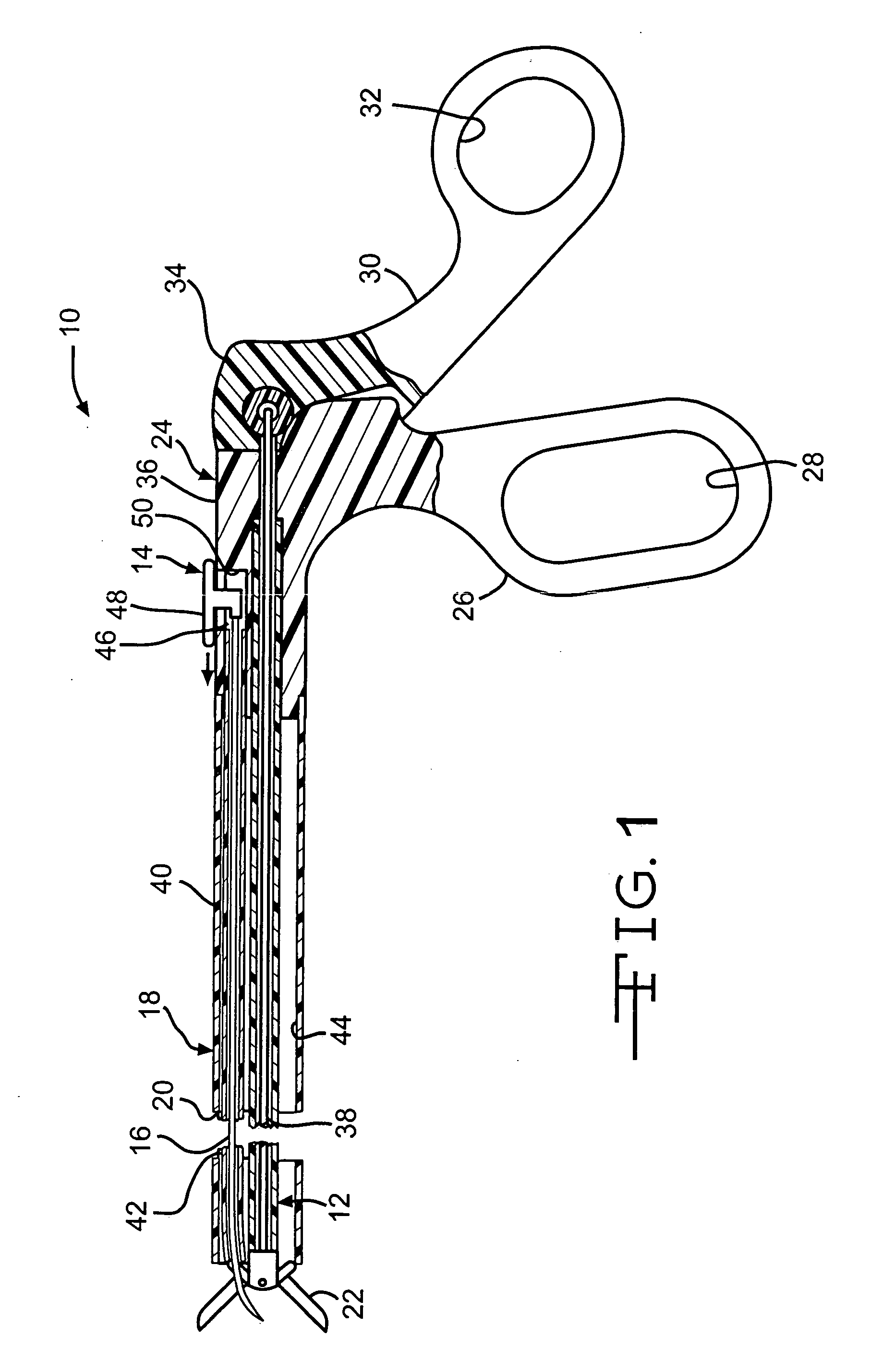
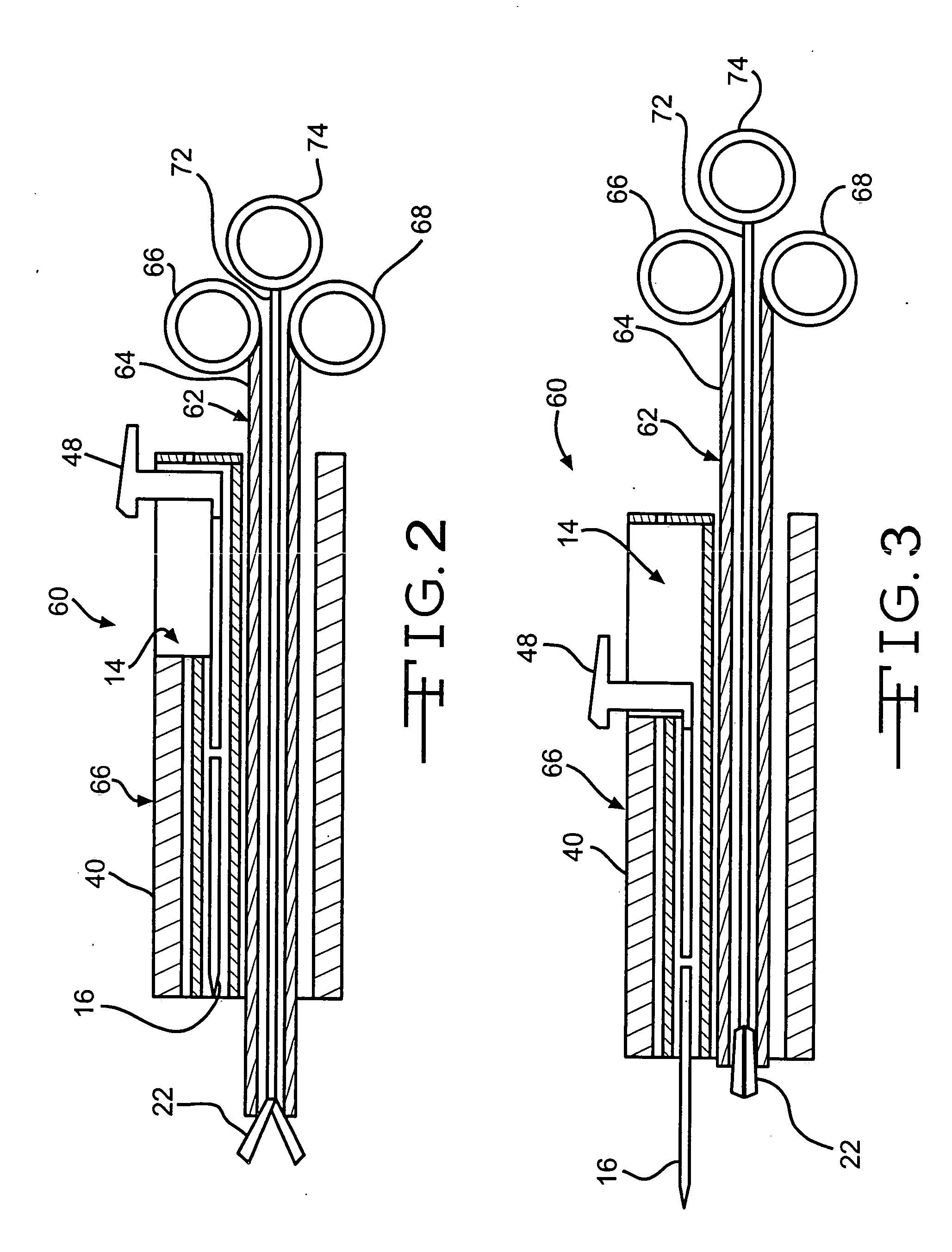
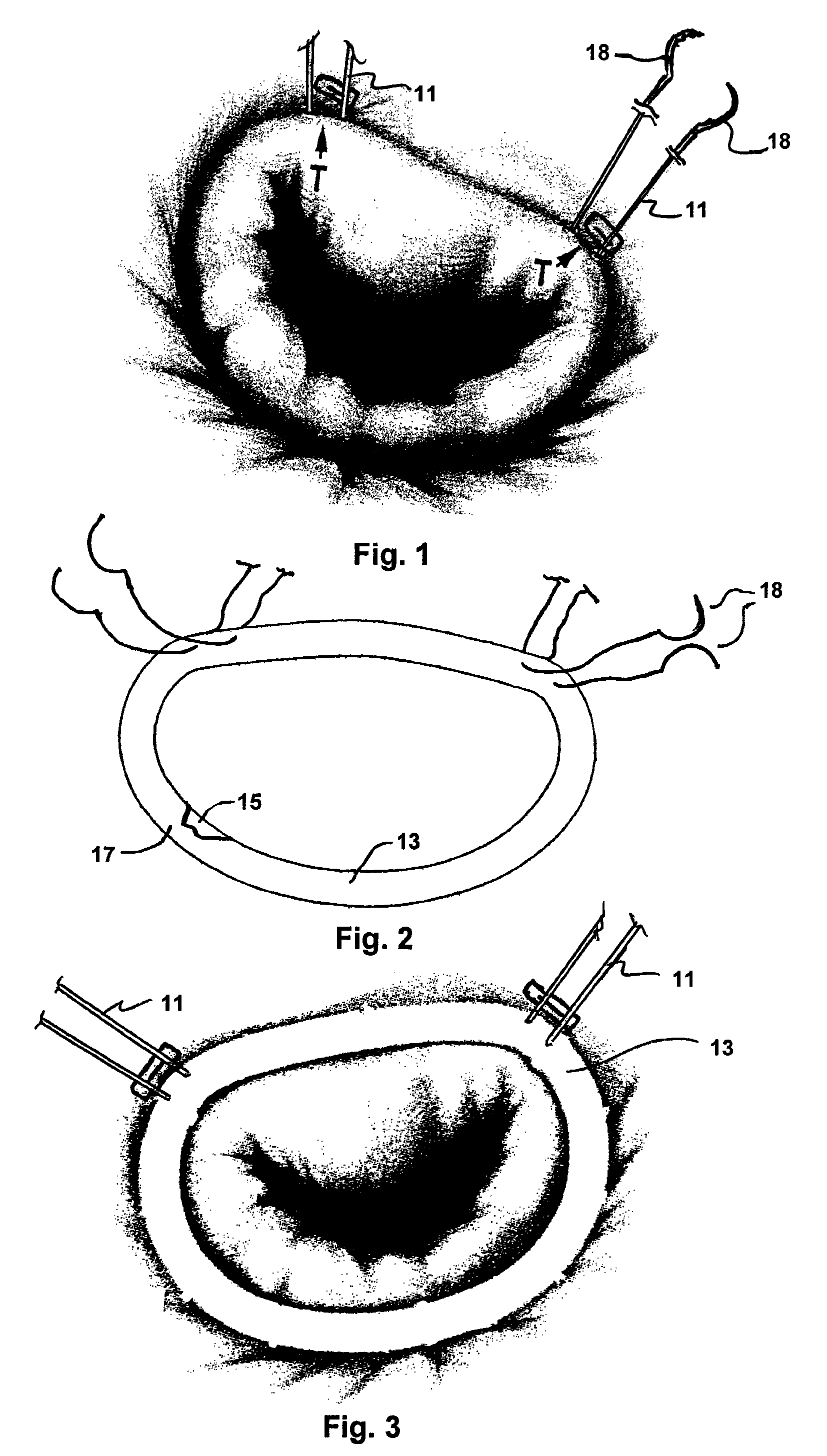
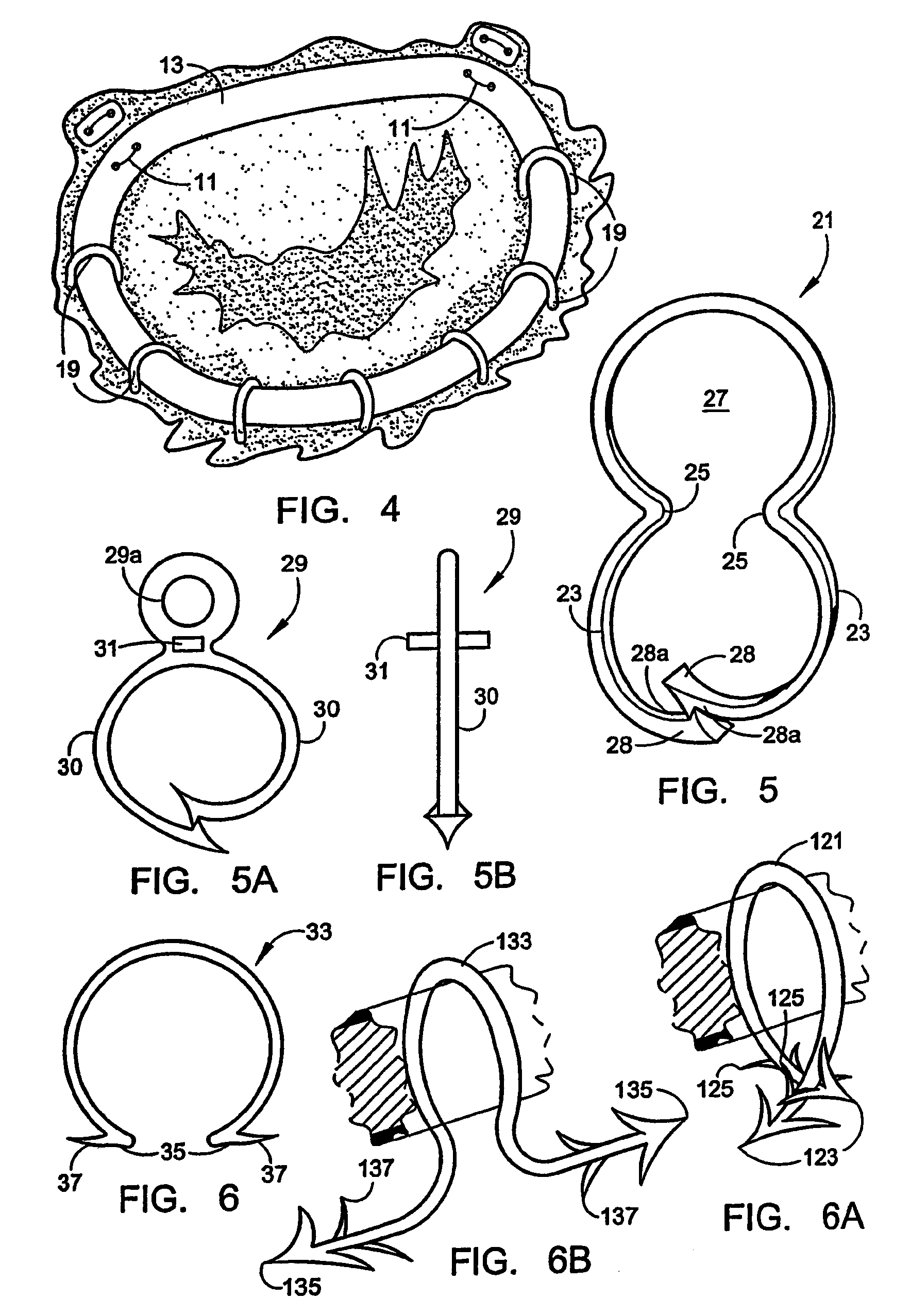
Intussusception and anastomosis apparatus
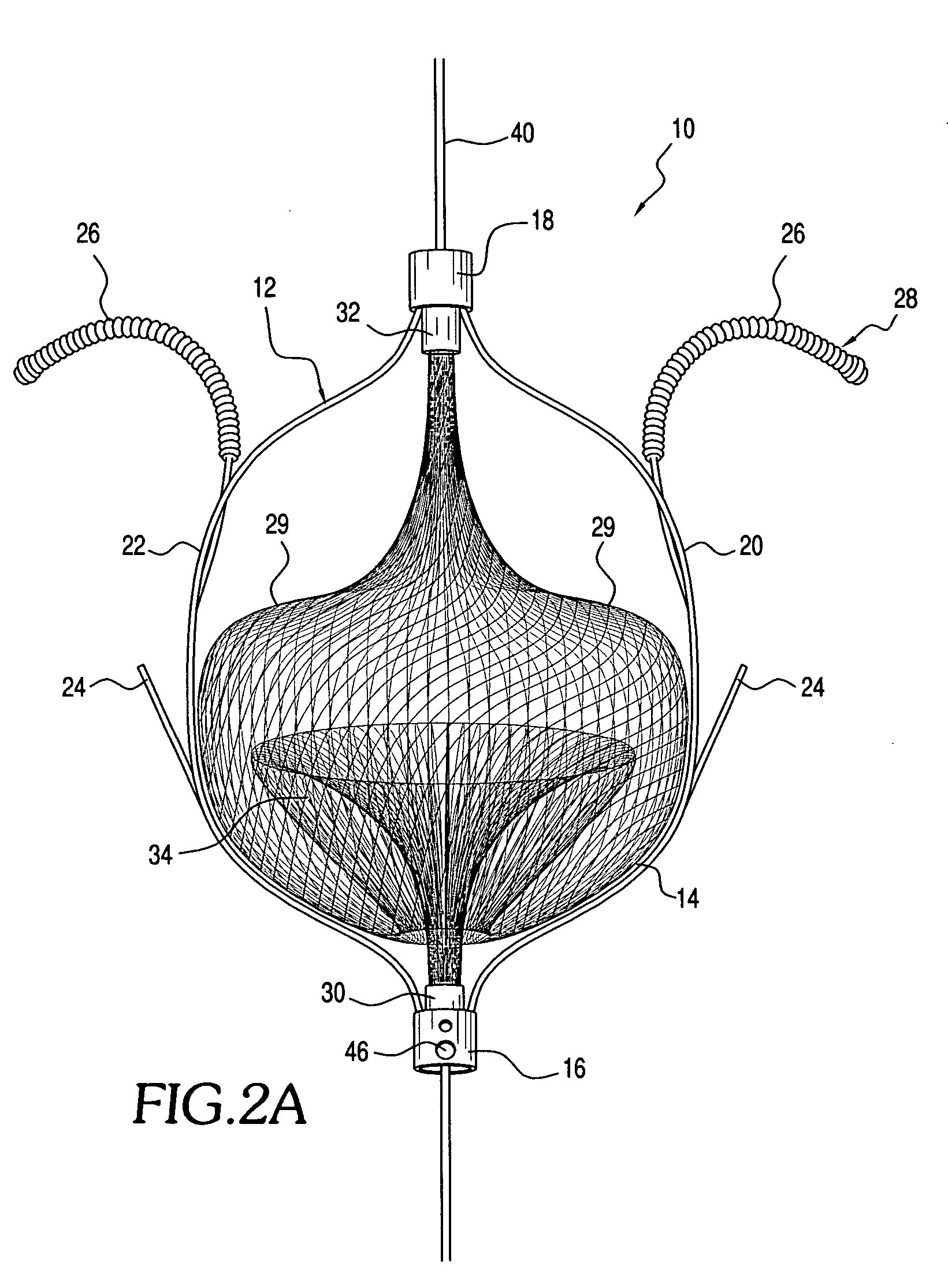
Apparatus for intratubular intussusception and anastomosis of a hollow organ portion including a cylindrical enclosure, coaxial intratubular intussusception device, for intussusception and clamping means. The apparatus also includes an intratubular anastomosis apparatus for joining organ portions after intussusception thereof with an anastomosis ring and crimping support element. The ring is formed of a shape memory alloy wire, for crimping adjacent organ portions against the crimping support element so as to cause anastomosis therebetween. The ring assumes a plastic or malleable state, at a lower temperature and an elastic state at a higher temperature. The apparatus further includes the crimping support element for intratubular insertion so as to provide a support for crimping the organ portions against the support element. The apparatus additionally includes a surgical excising means, for excising an intussuscepted organ portion, after crimping adjacent intussuscepted organ walls against the crimping support element with the anastomosis ring.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
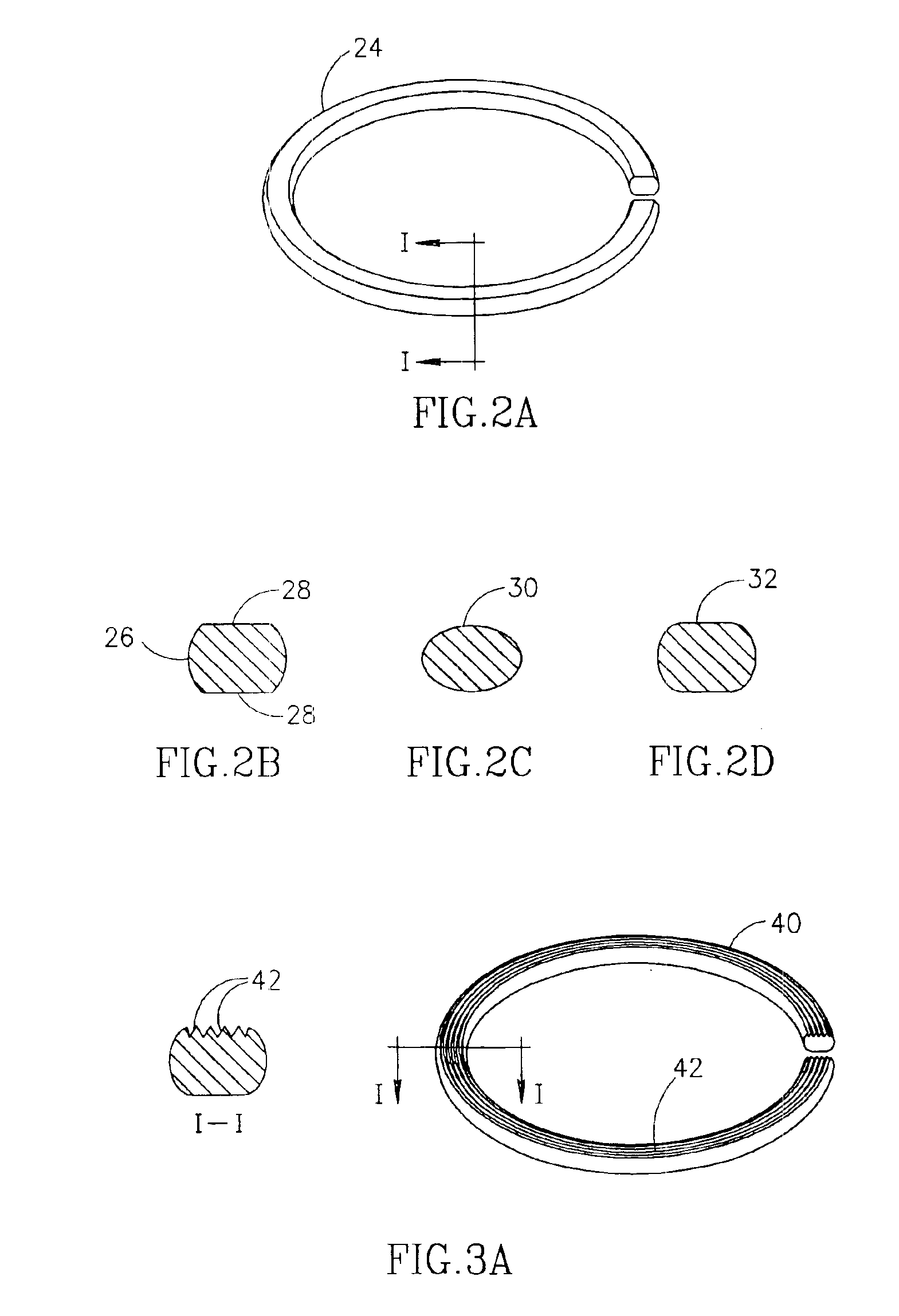
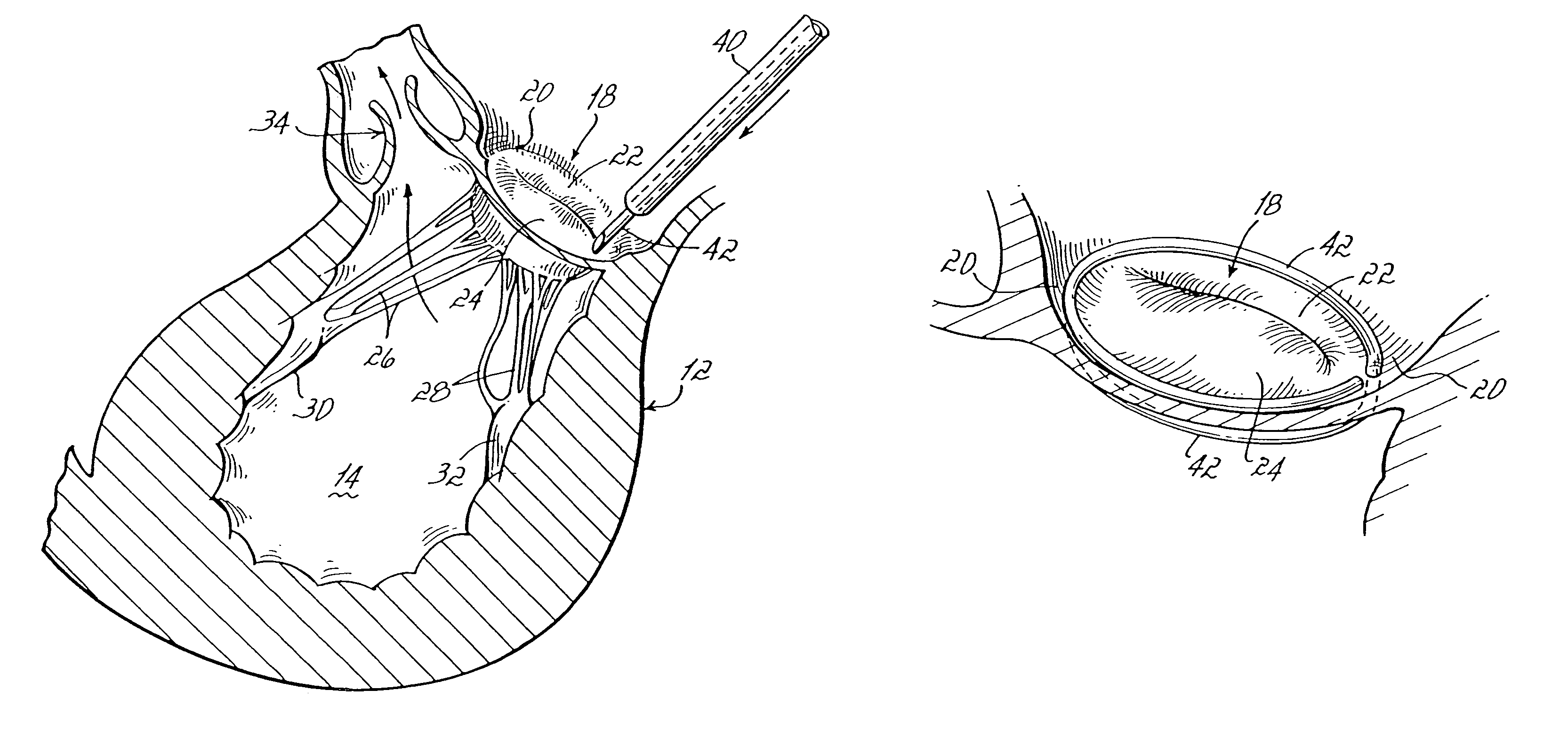
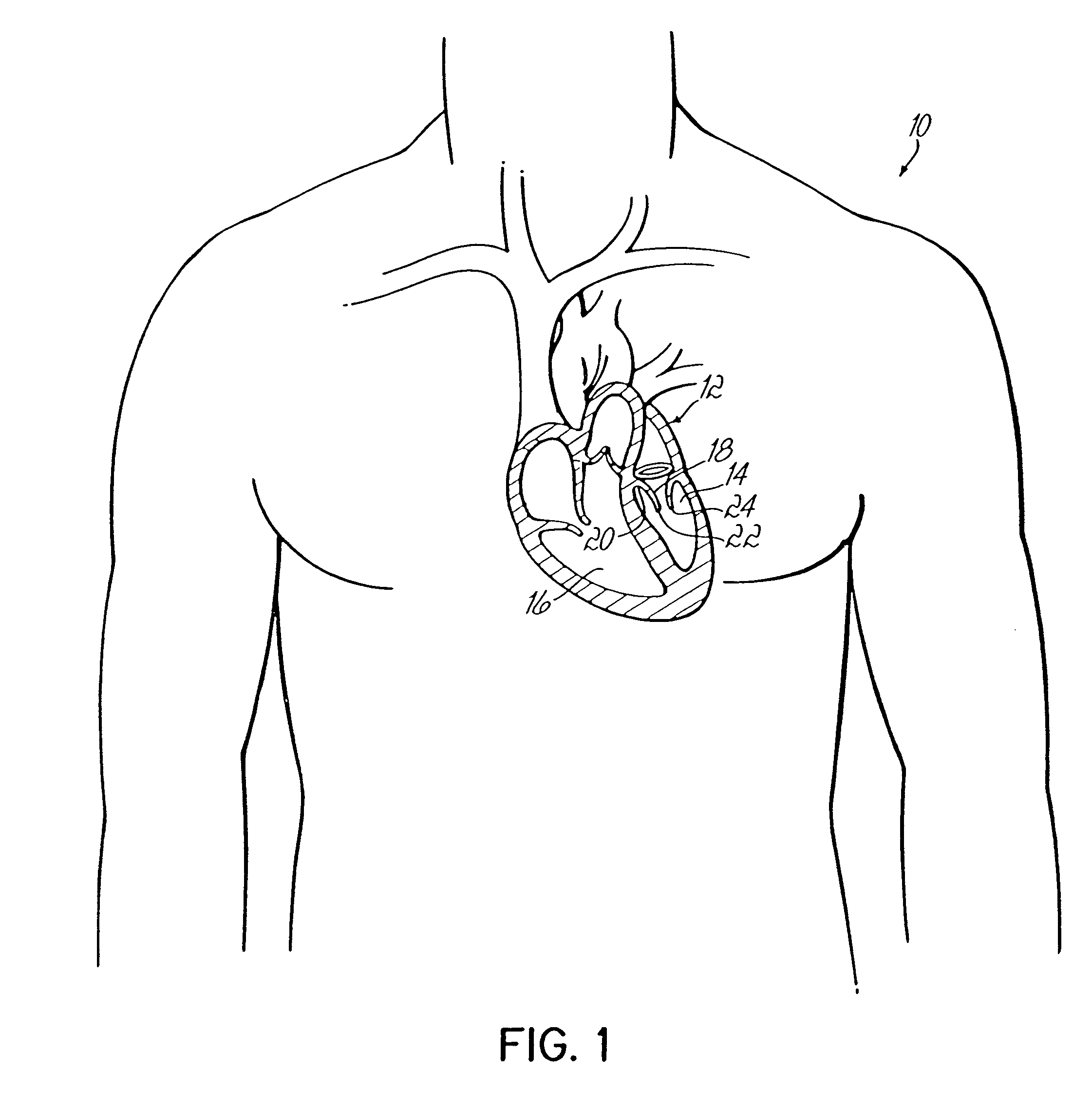
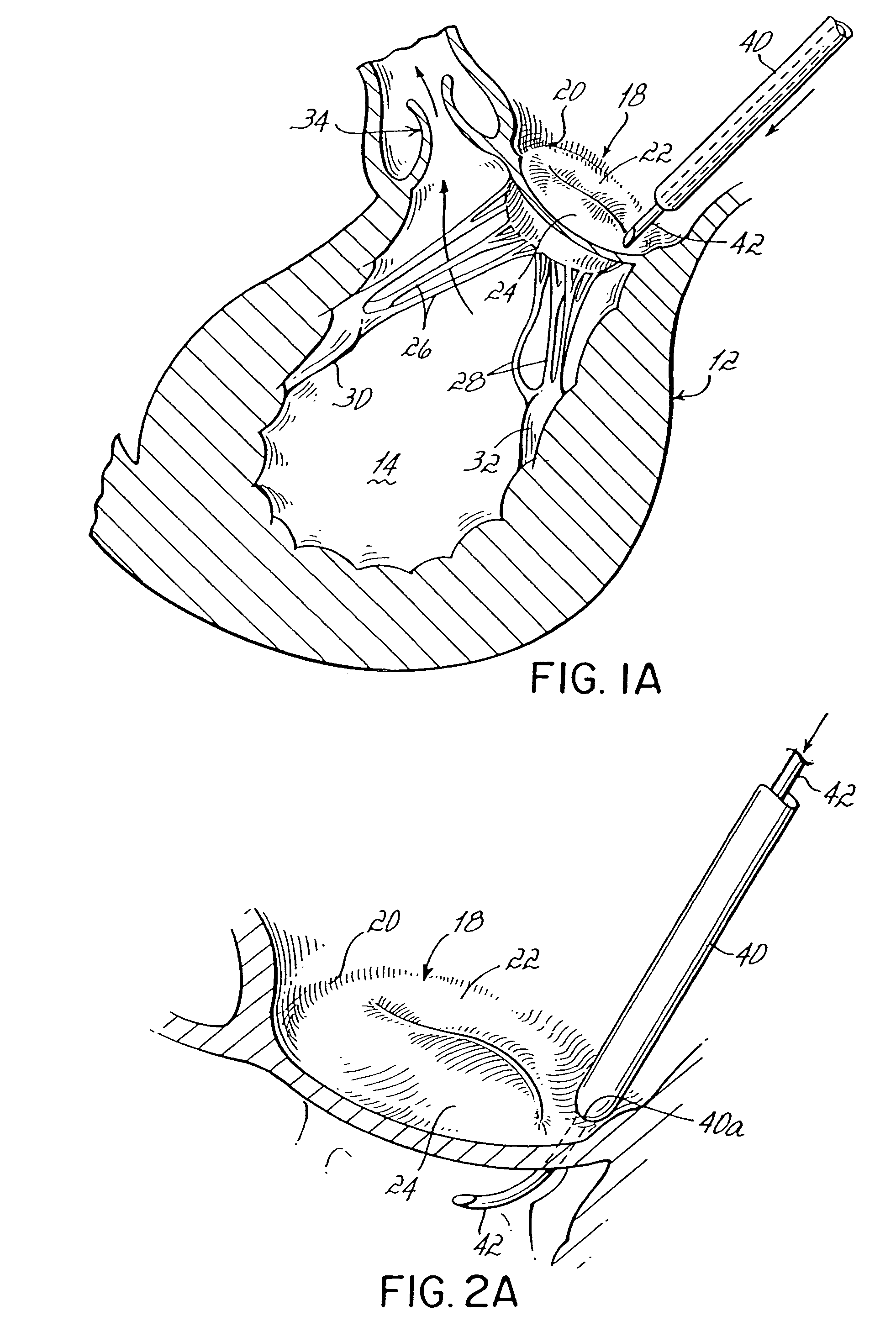
Implantation system for annuloplasty rings
InactiveUS7485142B2Good coaptation of leafletImprove hemodynamic functionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEffective lengthShape-memory alloy
Methods for reconfiguring an atrioventricular heart valve that may use systems comprising a partial or complete annuloplasty rings proportioned to reconfigure a heart valve that has become in some way incompetent, a pair of trigonal sutures or implantable anchors, and a plurality of staples which may have pairs of legs that are sized and shaped for association with the ring at spaced locations along its length. These systems permit relative axial movement between the staples and the ring, whereby a patient's heart valve can be reconfigured in a manner that does not deter subtle shifting of the native valve components. Shape-memory alloy material staples may have legs with free ends that interlock following implantation. Annuloplasty rings may be complete or partial and may be fenestrated. One alternative method routes a flexible wire, preferably of shape-memory material, through the bights of pre-implanted staples. Other alternative systems use linkers of shape-memory material having hooked ends to interengage with staples or other implanted supports which, following implantation, decrease in effective length and pull the staples or other supports toward one another so as to create desired curvature of the reconfigured valve. These linkers may be separate from the supports or may be integral with them and may have a variety of shapes and forms. Various of these systems may be implanted non-invasively using a delivery catheter.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
Device and method employing shape memory alloy
InactiveUS6916159B2Low costSmall size and weightTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementShape-memory alloyEngineering
Owner:THERASENSE
Multi-fastener surgical apparatus and method
A fastener preferably made from a shape memory alloy is provided which can access internal tissue or other synthetic material by catheter delivery through an endovascular pathway. After the fastener is deployed through layers of tissue or other material, it assumes a shape that automatically applies to the layers of tissue or other material an appropriate hemostatic compression which is relatively independent of tissue or material thickness. The fastener is a suitable replacement for conventional non bio-absorbable sutures and staples in certain clinical applications. The shape, method of deployment, and low force requirements make the disclosed apparatus suitable for endosurgical procedures where access to the wound site is limited. A method for deploying the fastener is also provided.
Owner:ONUX MEDICAL
Methods for delivering, repositioning and/or retrieving self-expanding stents
InactiveUS6837901B2Deployment securityRule out the possibilityStentsSurgeryShape-memory alloyCatheter device
Methods for delivery and deploying a stent formed of a shape memory alloy to a desired position in a tubular area of the body, and / or for repositioning and / or retrieving a stent formed of a two-way shape memory alloy. An arrangement is provided by which the temperature of the stent is locally adjusted during delivery, repositioning and / or retrieval in a safe and controlled manner by engagement with an expandable and collapsible thermal transfer member situated on a catheter assembly.
Owner:INTEK TECH
Intratubular anastomosis apparatus
An intratubular anastomosis apparatus for joining organ portions of a hollow organ after intussusception which includes an anastomosis ring, and a crimping support element. The anastomosis ring includes a length of a wire formed of a shape memory alloy for crimping adjacent organ portions against the crimping support element so as to cause anastomosis. The anastomosis ring and the shape memory alloy assumes a plastic state, when at a first, lower temperature and an elastic state, when reaching at least a second, higher temperature. The crimping support element provides a support for crimping the organ portions against the support element. Using the anastomosis ring and crimping support element of the present invention reduces the risk of leakage and no staples or sutures remain within the anastomosed organ portion.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
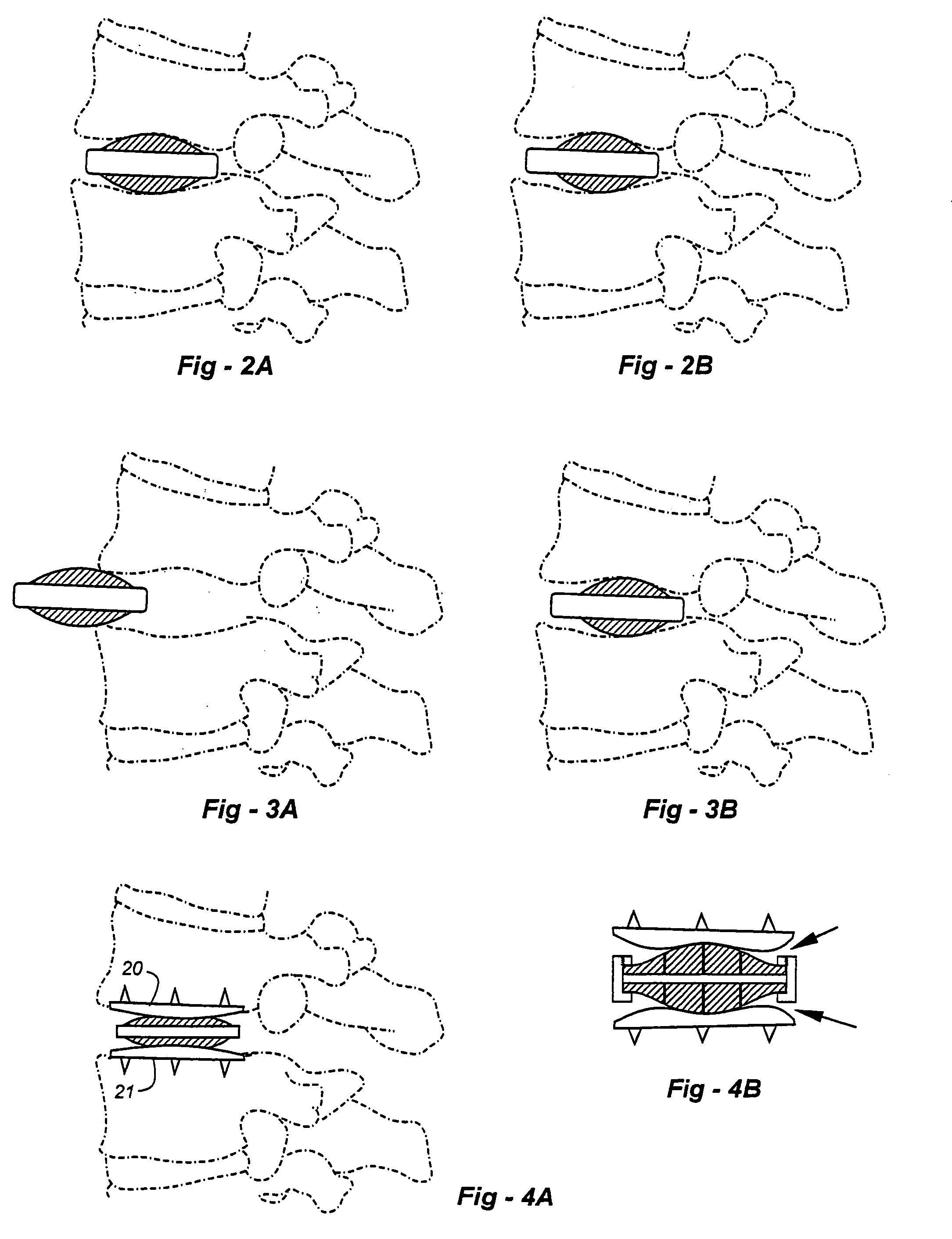
Bio-flexible spinal fixation apparatus with shape memory alloy
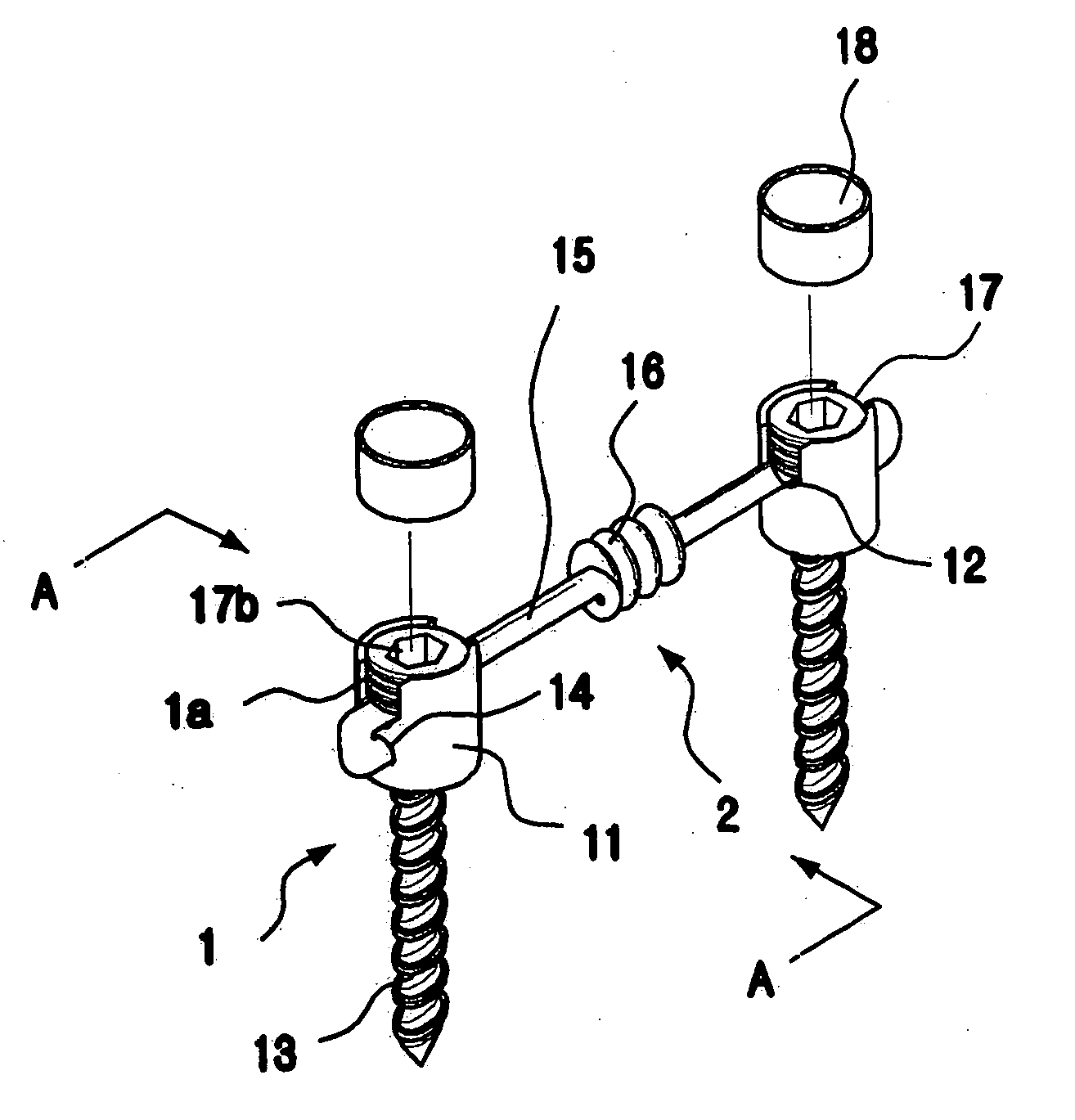
ActiveUS20060064090A1Easily simply achieveAccurate operationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsShape-memory alloyEngineering
The present invention relates to a spinal fixation apparatus having a segment flexible rod for connecting pedicle screws and a transverse link for spacing out the rods, which are made from a shape memory alloy, thereby easily and simply connecting the rods and the pedicle screws. According to the present invention, it can easily and simply fit the rods to the misaligned pedicle screw, even if it may be a failure of alignment of the pedicle screws in surgery. Also, it can easily set up the transverse link on a pair of the longitudinal rods, even if the longitudinal rods are declined or are not in parallel.
Owner:PARK KYUNG WOO
Device and method for intralumenal anastomosis
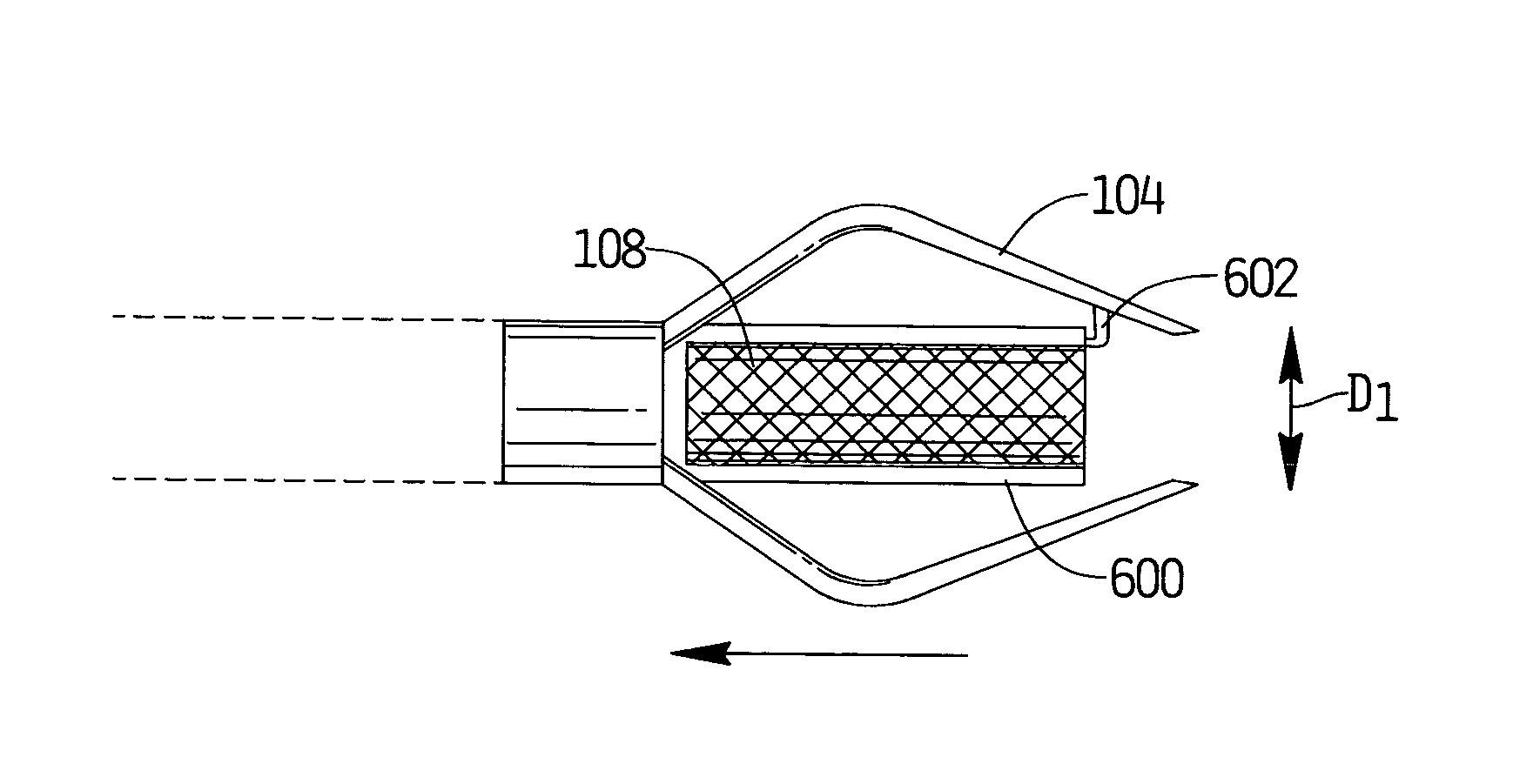
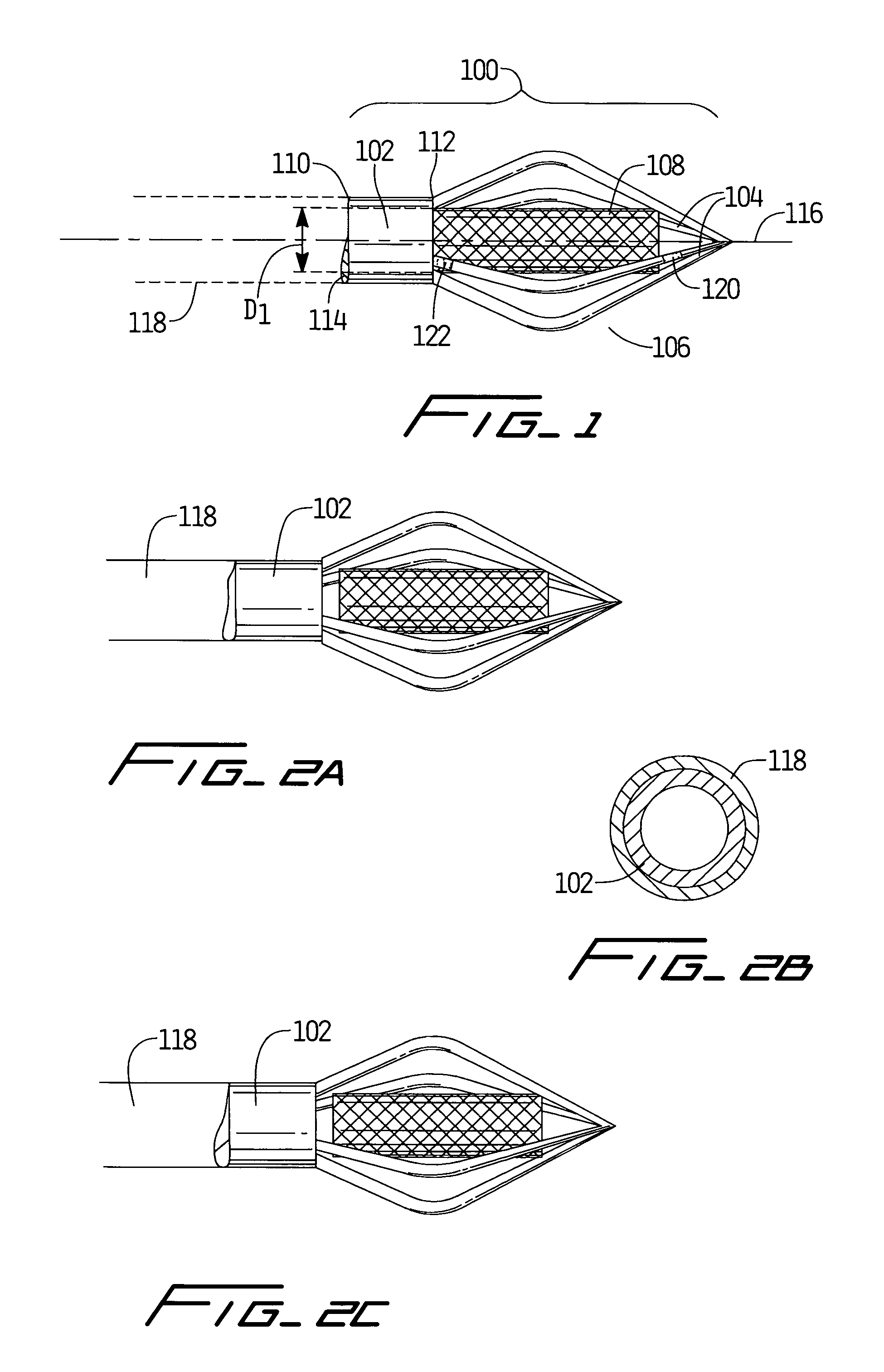
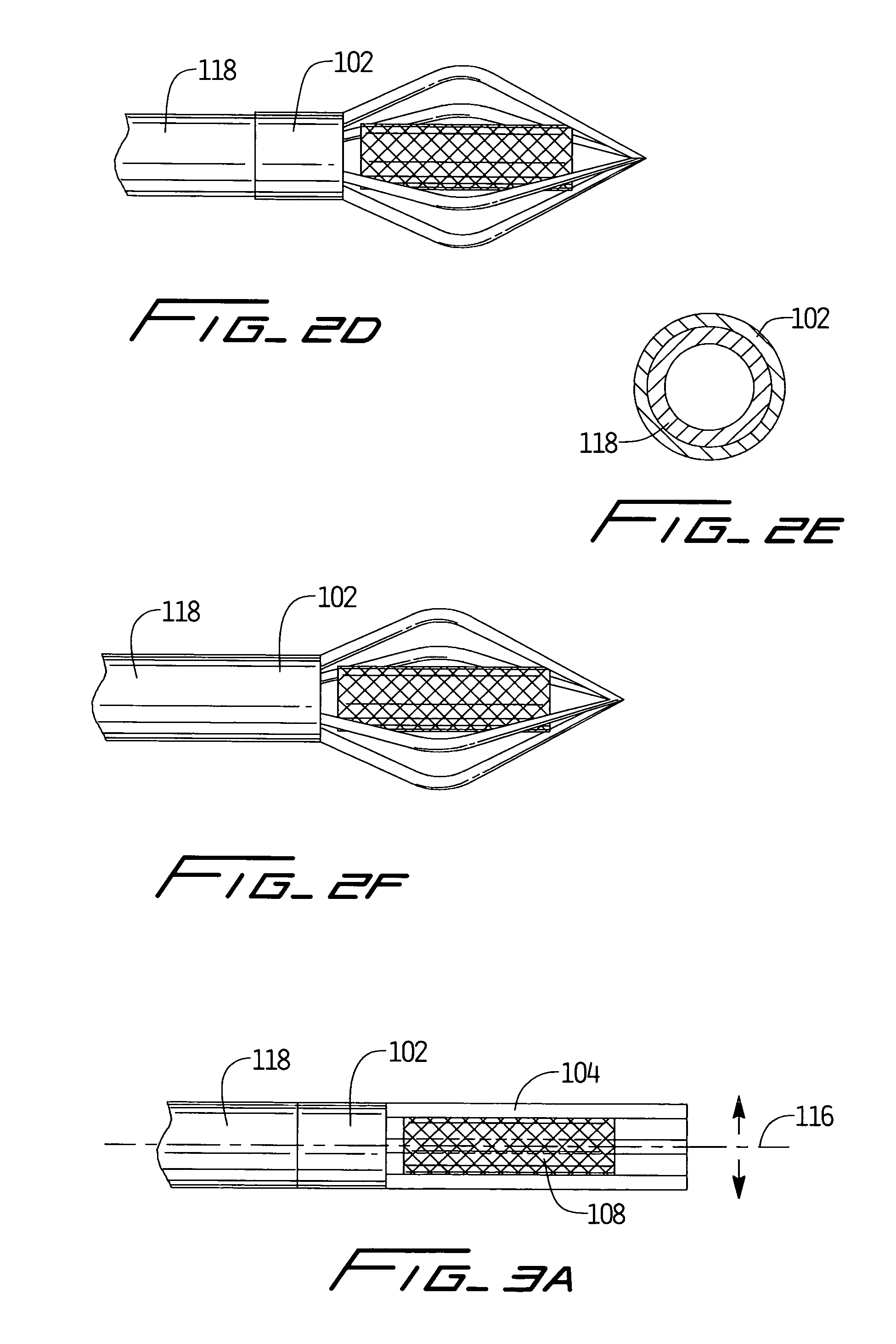
An anastomosis device formed from a Shape Memory Alloy (SME) wire that is annealed into a tight coil (e.g., flat coil, helical coil, cylindrical coil) that is subsequently substantially straightened (e.g., straight, longitudinally stretched spring-like shape) for being constrained within an elongate member of an anastomosis introducer instrument. After positioning and holding two tissue walls of adjacent lumens into apposition with a distally presented grasper of the instrument, a piercing tip of the anastomosis device is dispensed and inserted through the tissue walls before being allowed to relax to its tight coil shape, thereby forming the anastomosis attachment. The anastomosis device is released from the anastomosis introducer instrument, such as by fully dispensing its proximal end. Thereby, efficient single lumen anastomosis of gastrointestinal, bilatory, or other vessels may be achieved with a minimum of laparoscopic punctures, or perhaps performed fully as an endoscopic procedure.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Embolic balloon
An embolic balloon assembly is disclosed herein. The assembly includes a detachable balloon system which expands while aspirating a quantity of surrounding blood to occlude a vessel or aneurysm. The balloon has a distensible membrane having a plurality of orifices throughout its surface. Within the distensible membrane is a plurality of expandable members made from a shape memory alloy, e.g., Ni—Ti alloy, which expand upon application of a stimulus. Alternatively, the expandable members or a single expandable wire may be inserted separately into the distensible membrane. Once the balloon begins to expand, internal pressure within a volume defined by the distensible membrane begins to drop, forcing the device to aspirate a quantity of surrounding blood inside the volume which then begins to coagulate by stasis or some stimulus. The balloon may be configured to automatically release into the aneurysm or vessel or it may be released by a detachable joint.
Owner:SAADAT VAHID
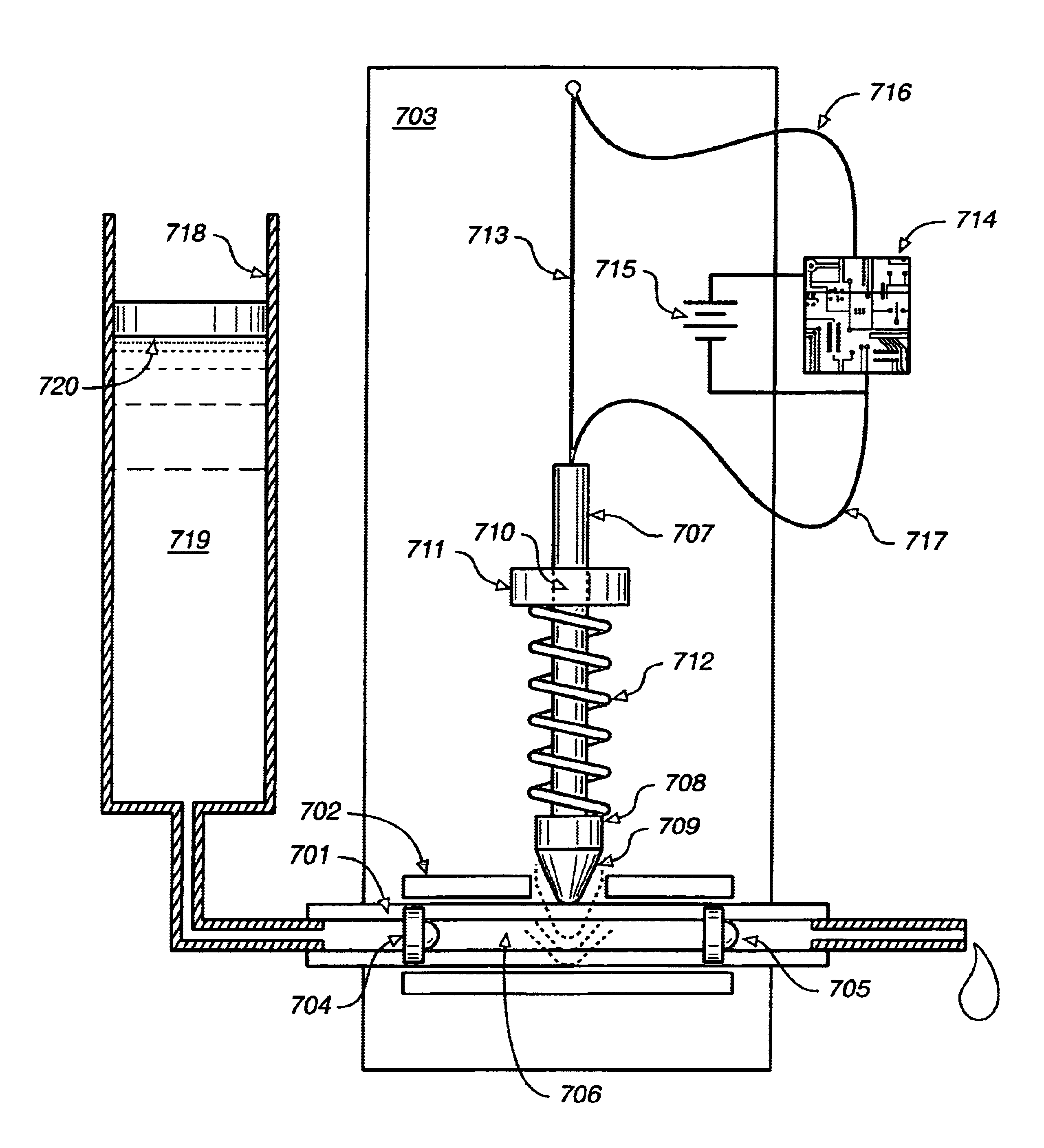
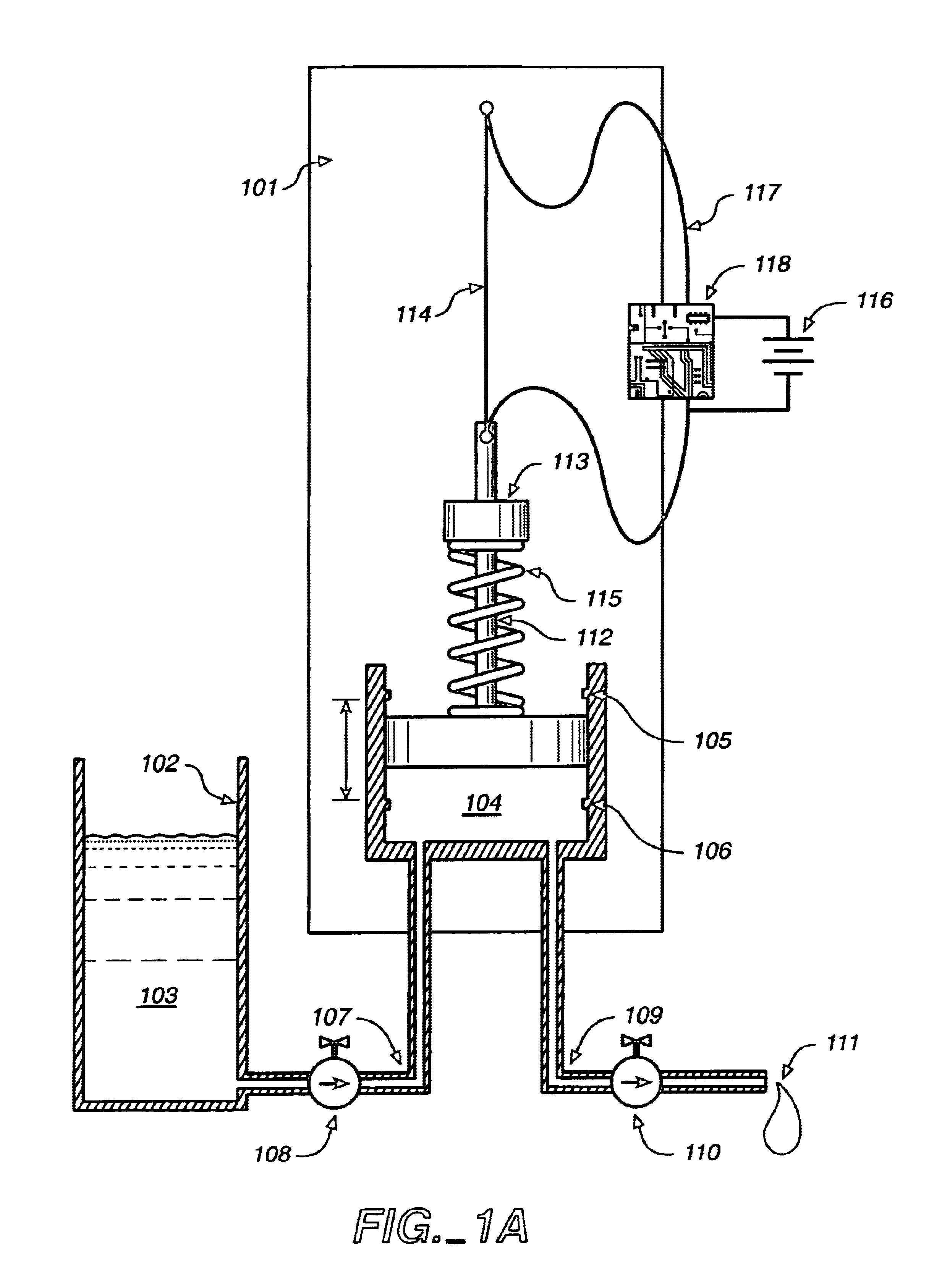
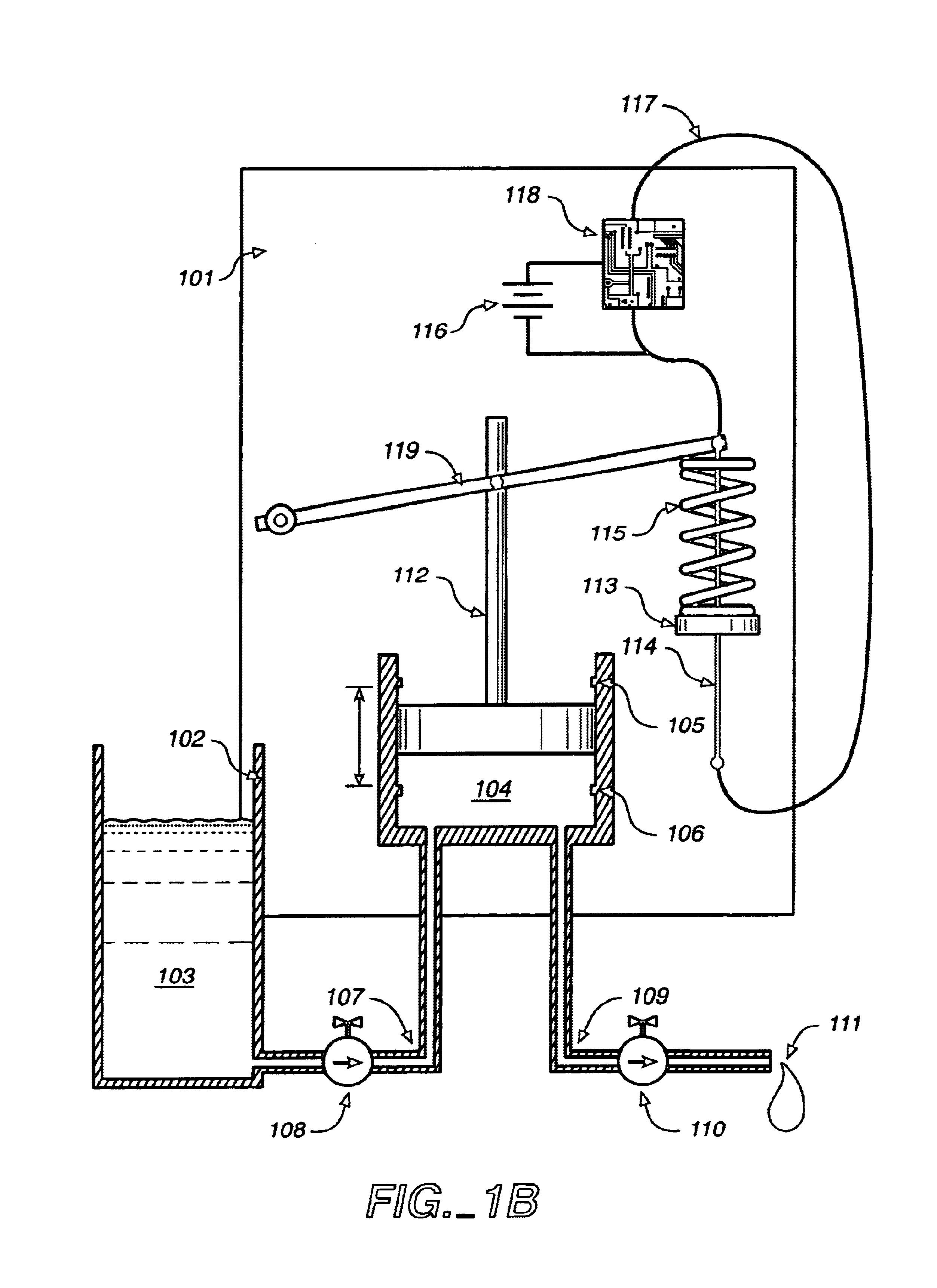
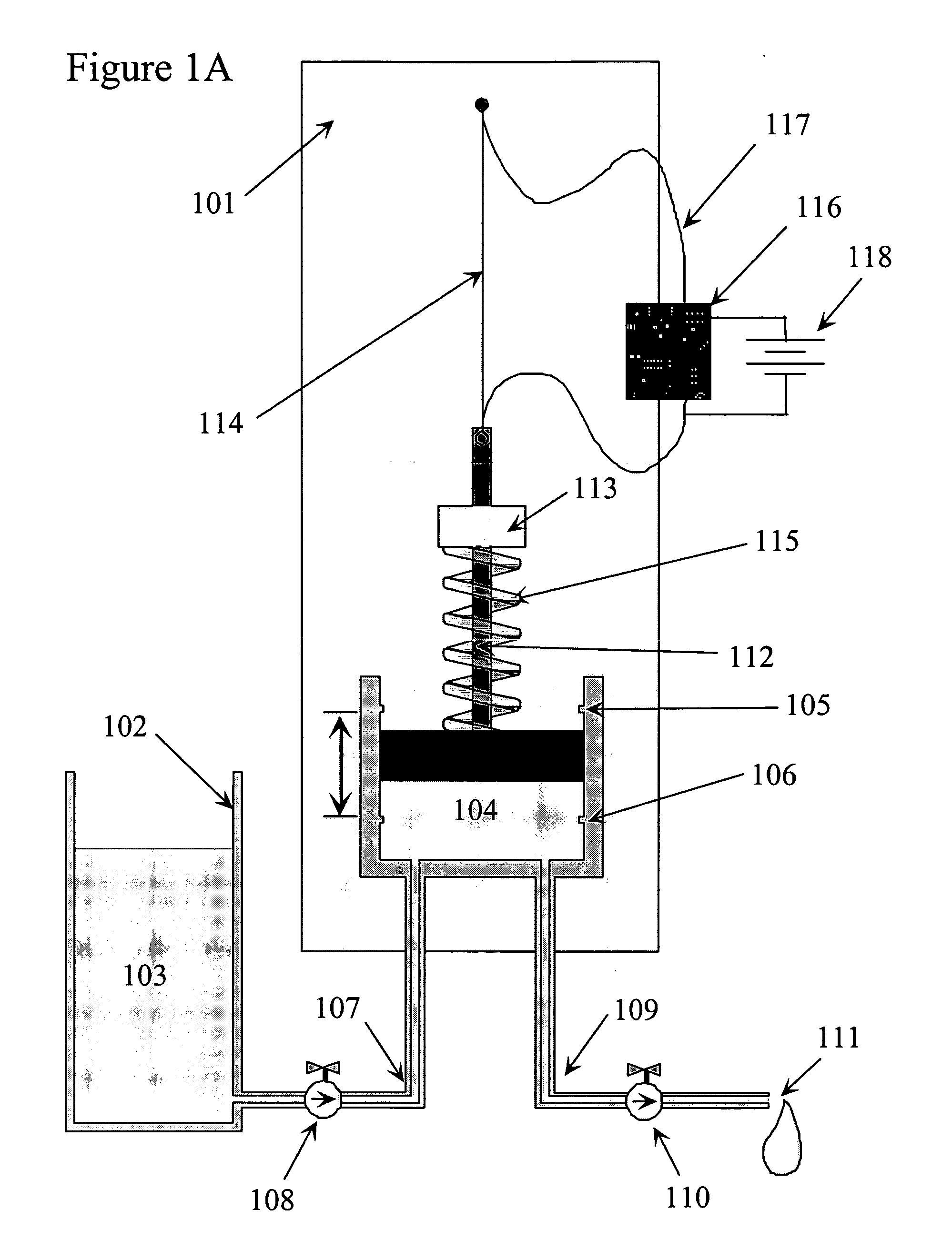
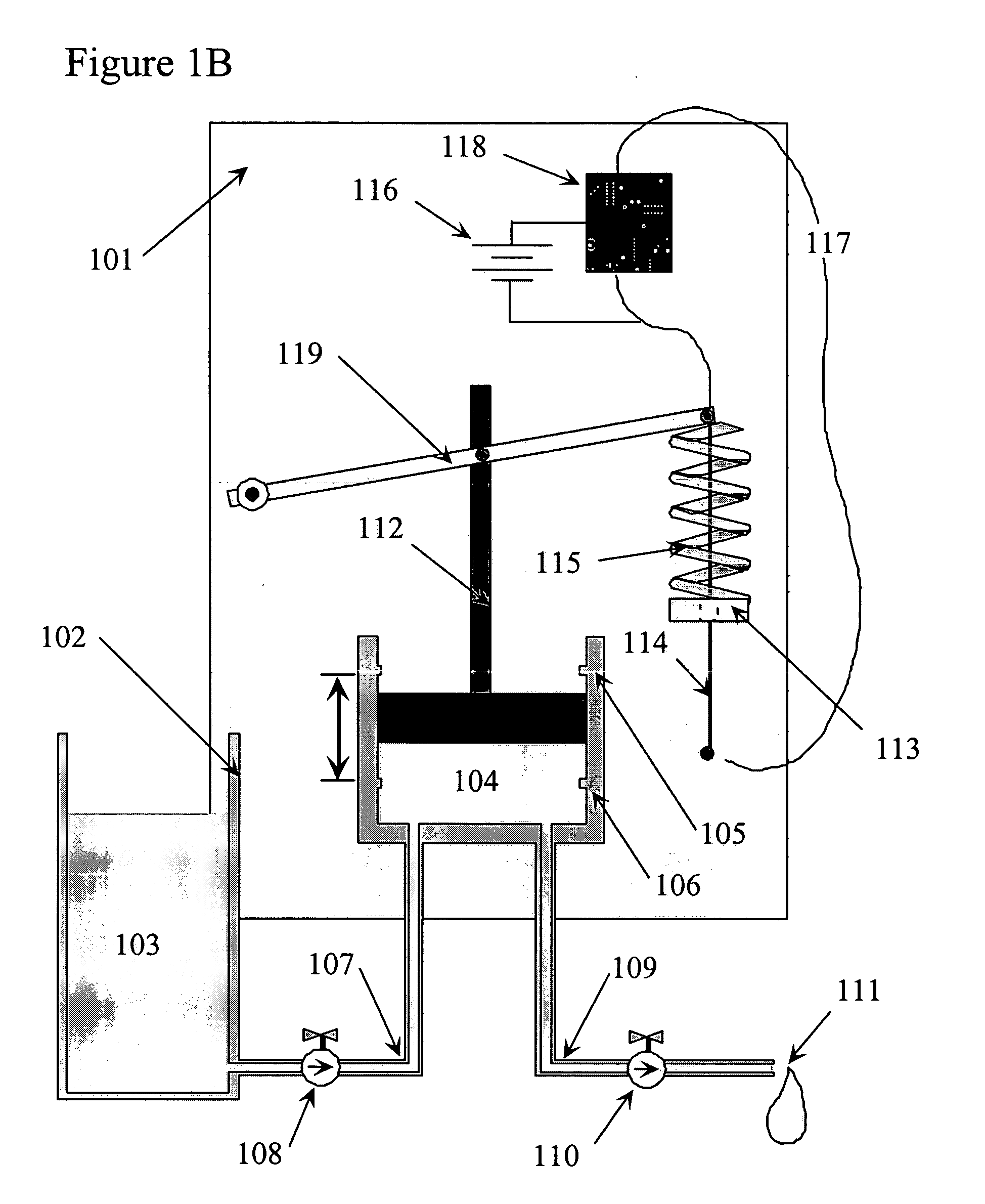
Shape memory alloy wire driven positive displacement micropump with pulsatile output
InactiveUS7052251B2Reliable outputLow costFlexible member pumpsMedical devicesControl electronicsShape-memory alloy
Apparatuses and methods for pumping fluid are disclosed. An exemplary apparatus is a miniature pump that includes a shape memory wire that obtains a plastic condition below a transformation temperature and has a memorized shape such that the shape memory wire produces a work stroke by returning to the memorize shape at least at the transformation temperature. A spring biased against the shape memory wire is deflected by the work stroke to deform the shape memory wire from the memorized shape below the transformation temperature. A fluid pump is coupled to the shape memory wire and driven by the biased spring and shape memory wire to produce a fluid flow. The miniature pump can be incorporated into a self-contained infusion device in the form of a compact self-adhesive patch including a fluid reservoir, control electronics and power supply that is place directly at the infusion site of a user.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
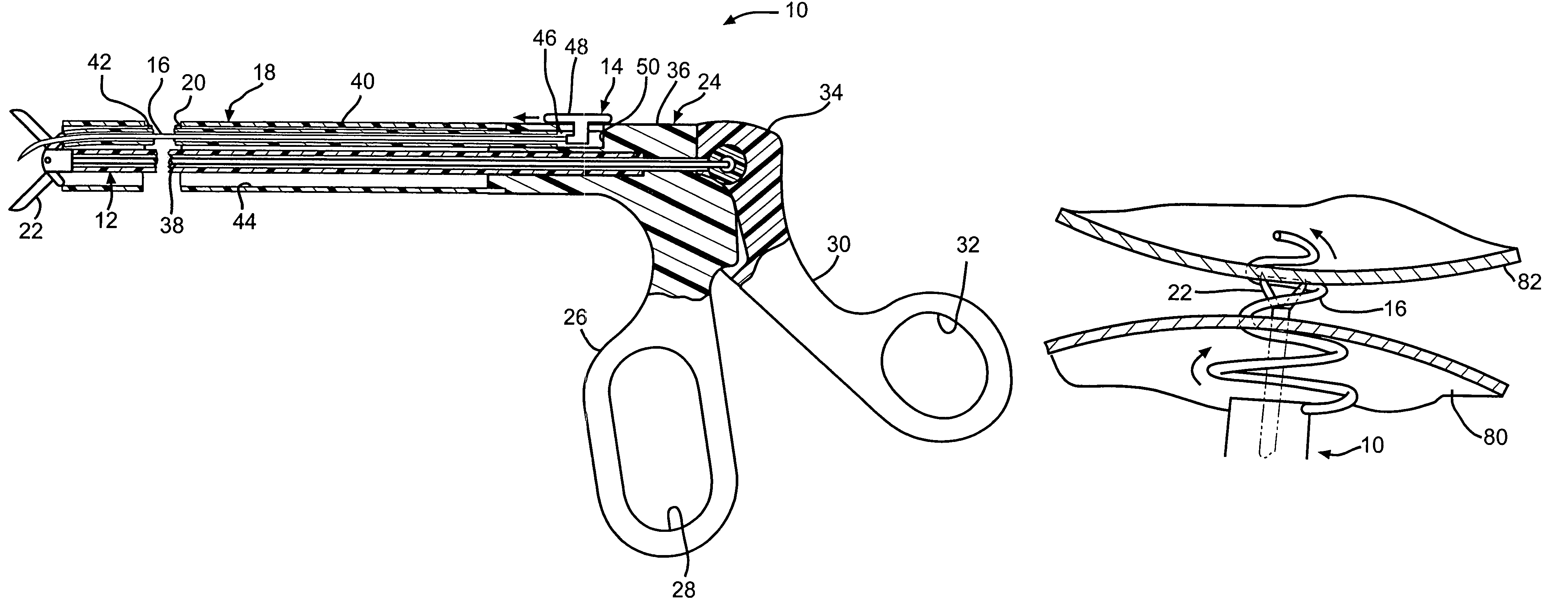
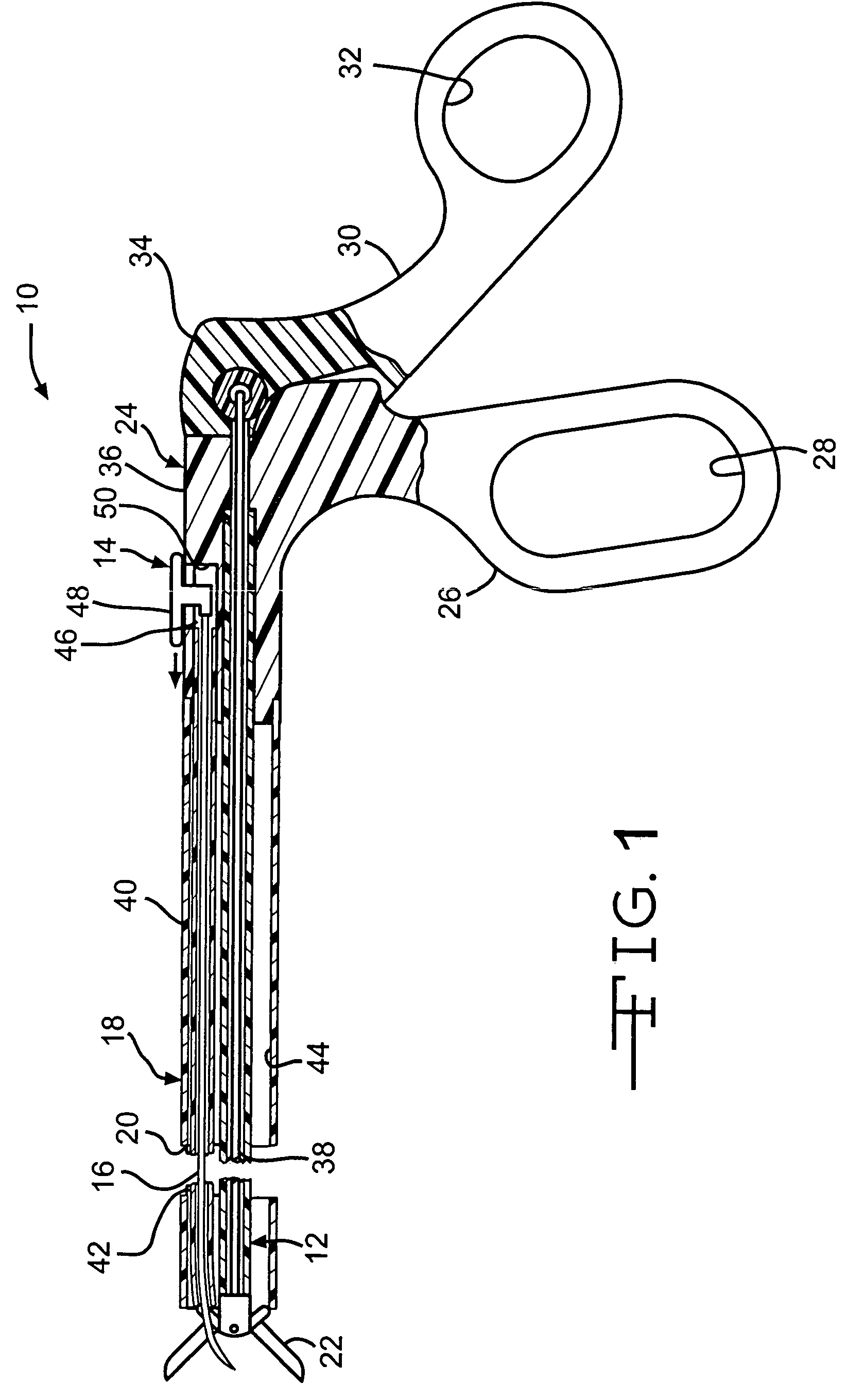
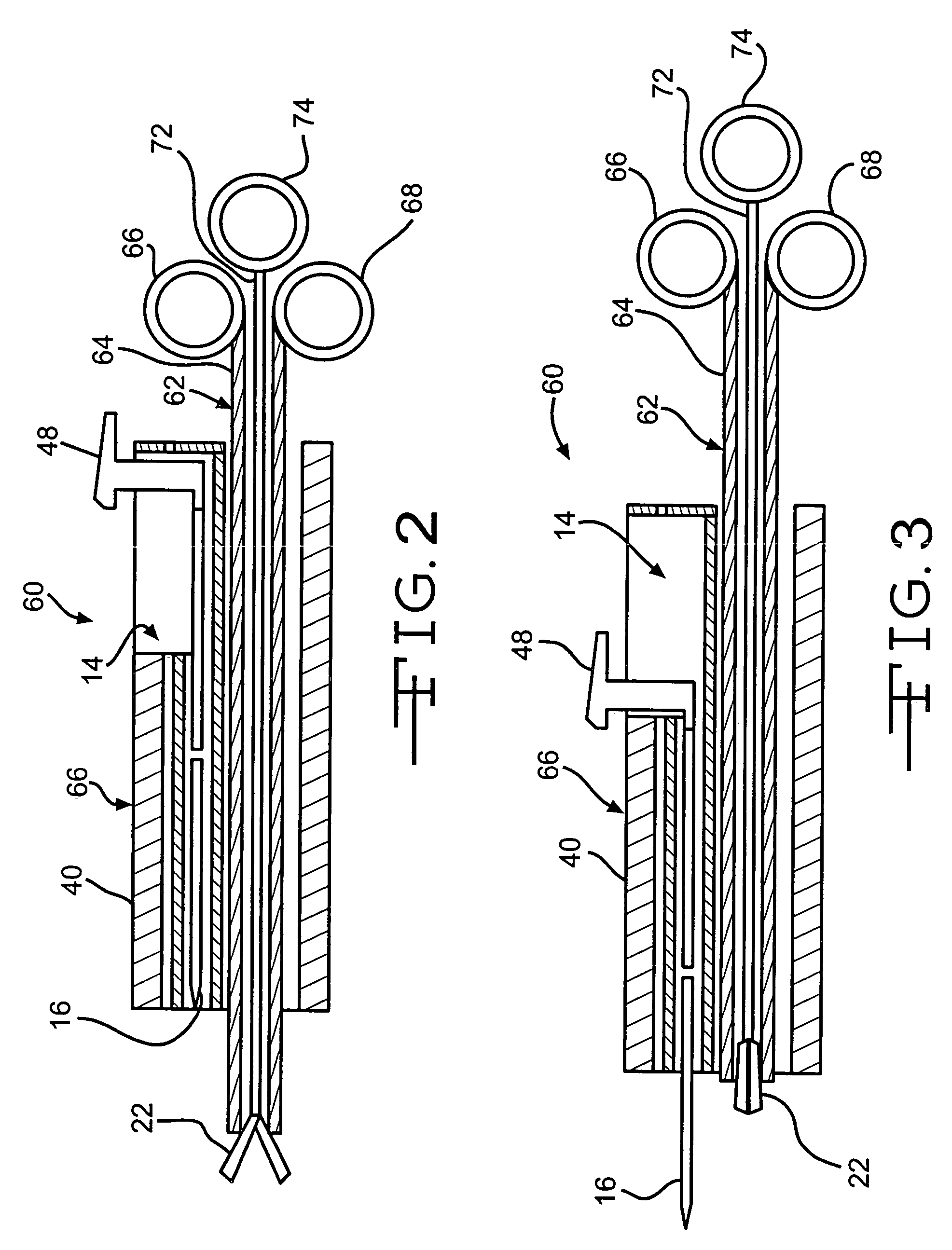
Surgical clip applicator device
The present invention, discloses an anastomosis clip applicator device for applying a surgical clip, formed at least partly of a shape memory alloy, to press together adjacent wall portions of adjacent hollow organ portions so as to effect anastomosis therebetween. The applicator device includes: gripping apparatus for gripping a surgical clip, a release mechanism, associated with the gripping apparatus, and tissue cutting apparatus, operatively associated with the gripping apparatus. There is also apparatus for activating the gripping apparatus, the release mechanism and the cutting apparatus, so as to introduce and apply the surgical clip into adjacent hollow organ portions, such that the surgical clip compresses together the adjacent walls of the hollow organ portions, and thereafter causes the cutting apparatus to perforate the adjacent pressed together organ walls to provide patency through the joined portions of the hollow organ.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Annuloplasty devices and related heart valve repair methods
InactiveUS6964684B2Facilitate engagement and retentionReduce frictionAnnuloplasty ringsSurgeryShape-memory alloyHeart valve repair
Devices for repairing and replacing a heart valve in various embodiments, the devices include at least first and second support rings connected together in a coiled configuration to abut opposite sides of a valve annulus. A replacement valve may be secured to the coil-shaped device. Various alternative fastening systems include suture fastening systems, mechanical fastening systems, shape memory alloy fastening systems and other fastening systems relying only on the resilience between adjacent coils. A method generally includes inserting a first end of the coil-shaped member through a valve annulus, rotating a first ring of the coil-shaped member into position on one side of the valve annulus and positioning at least a second ring of the coil-shaped member on an opposite side of the valve annulus.
Owner:MEDTENTIA INT LTD OY
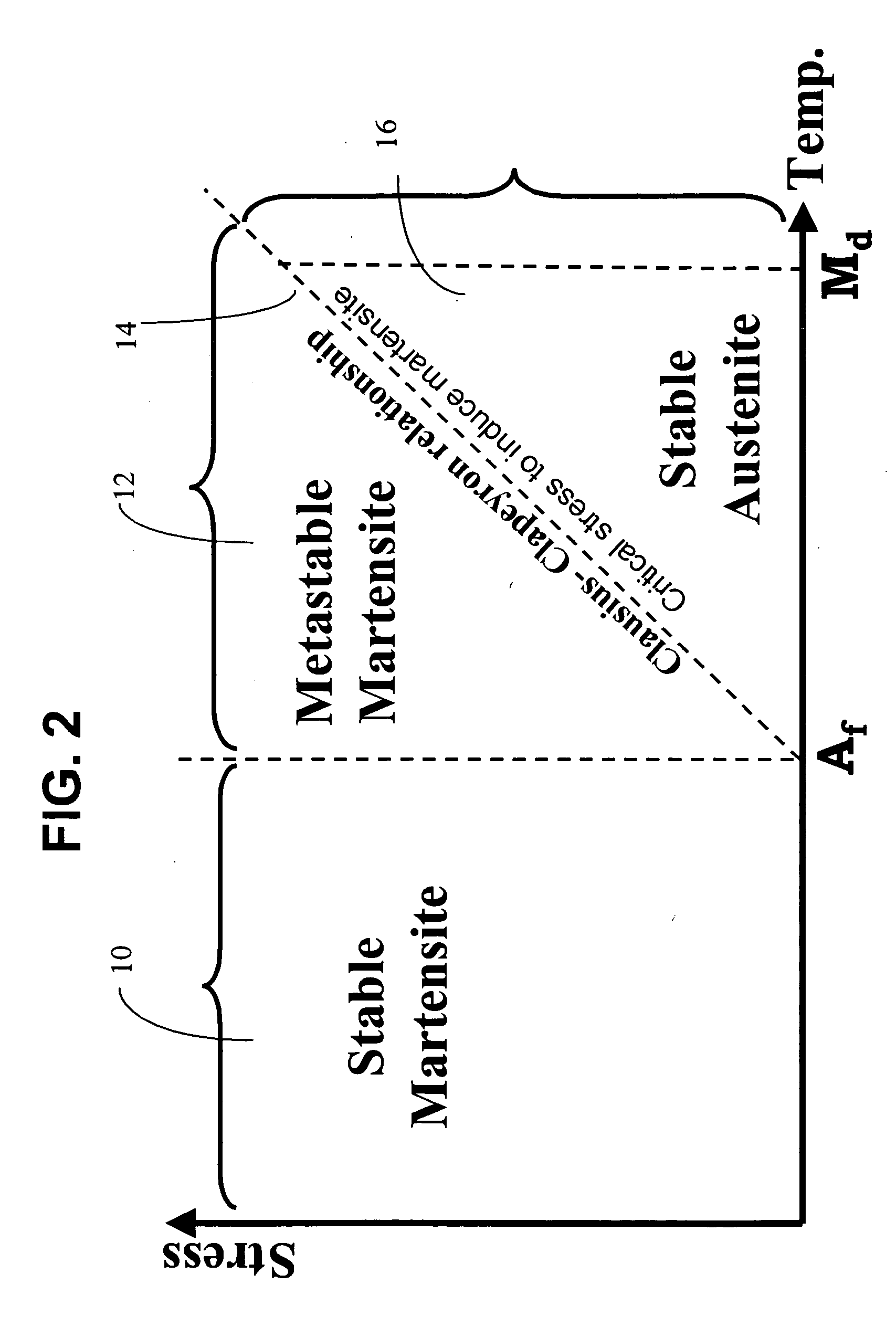
Medical devices formed from shape memory alloys displaying a stress-retained martensitic state and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20050043757A1Good body shapePromote recoverySuture equipmentsDental implantsManufactured formShape-memory alloy
A method is disclosed for utilizing a deformable article of manufacture formed at least partly of a shape memory alloy. The method includes the steps of deforming the article from a first predetermined configuration to a second predetermined configuration while the shape memory alloy is, at least partially, in its stable martensitic state and at a first temperature. A resisting force is applied to the deformed article of manufacture using a restraining means and the article is heated from the first temperature to a second temperature in the presence of the resisting force. The stable martensitic state is transformed to a metastable stress-retained martensitic state. The resisting force is then removed allowing the alloy to transform to its austenitic state and the shape of the article to be restored substantially to its first configuration. Devices primarily medical devices operative by employing this method are also disclosed.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Embolic filtering method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060009799A1Obstruct passageEncourage and facilitate growth of tissueAnnuloplasty ringsDilatorsVenous bloodCardiac defects
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
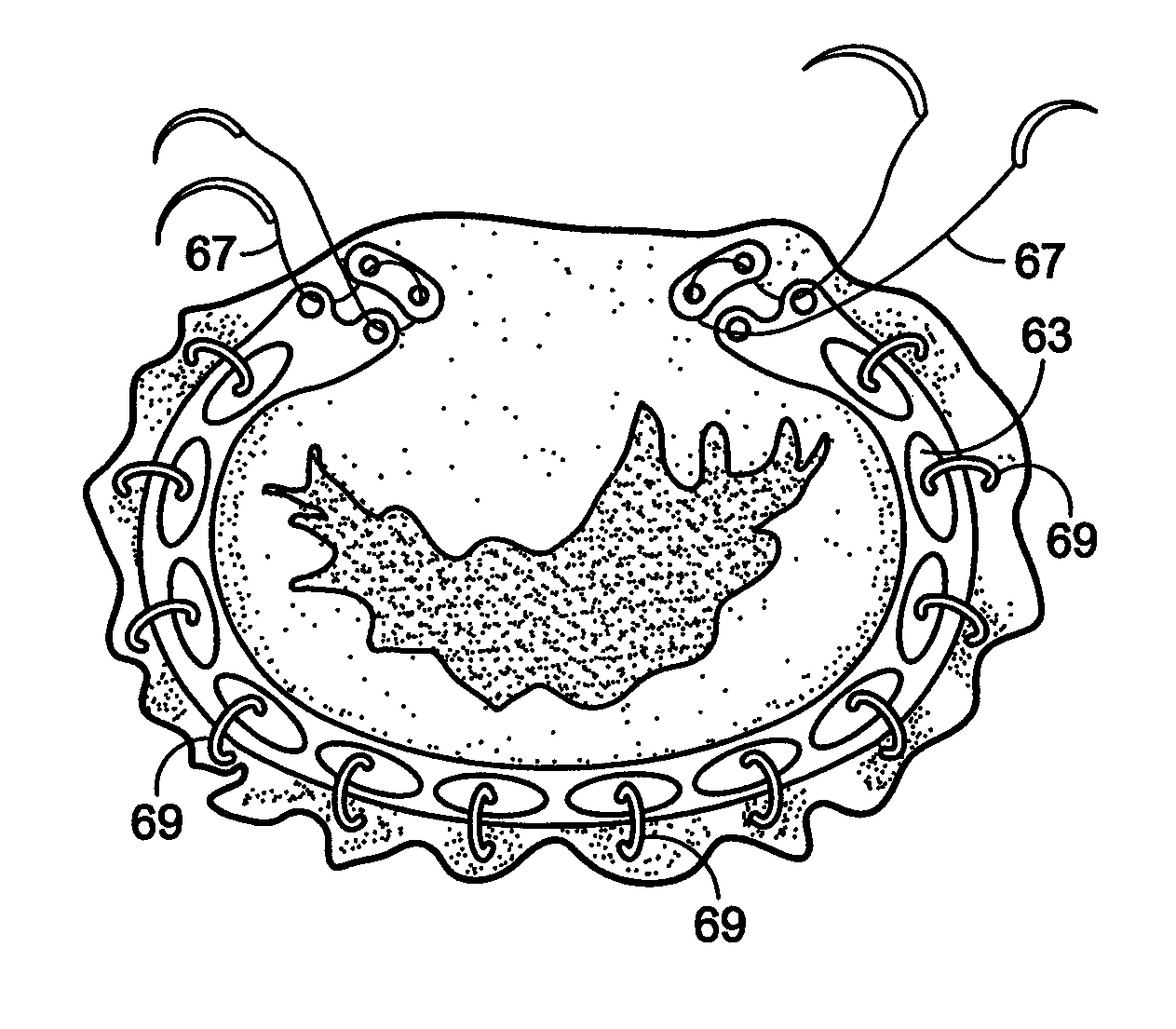
Compression anastomosis ring assembly and applicator for use therewith
InactiveUS7527185B2Reduced dimensionIncrease rangeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsOrgan wallShape-memory alloy
A compression anastomosis ring (CAR) assembly for use in joining severed organ wall portions of a hollow organ. The assembly comprises a first portion which includes an anvil assembly and a second portion which comprises a bottom ring, at least one ring element, and at least one spring element formed of a shape-memory alloy. The at least one spring element provides a restorative force and is in compressive force contact with the bottom ring and the tissue to be joined is positioned between the anvil ring and the bottom ring. A plurality of needles on one of the ring elements is operative, upon application of a closure force, to pierce the tissue and the anvil ring, holding the anvil ring to the second portion of the CAR assembly. An applicator for applying the CAR assembly and a method for using the assembly and applicator are taught.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
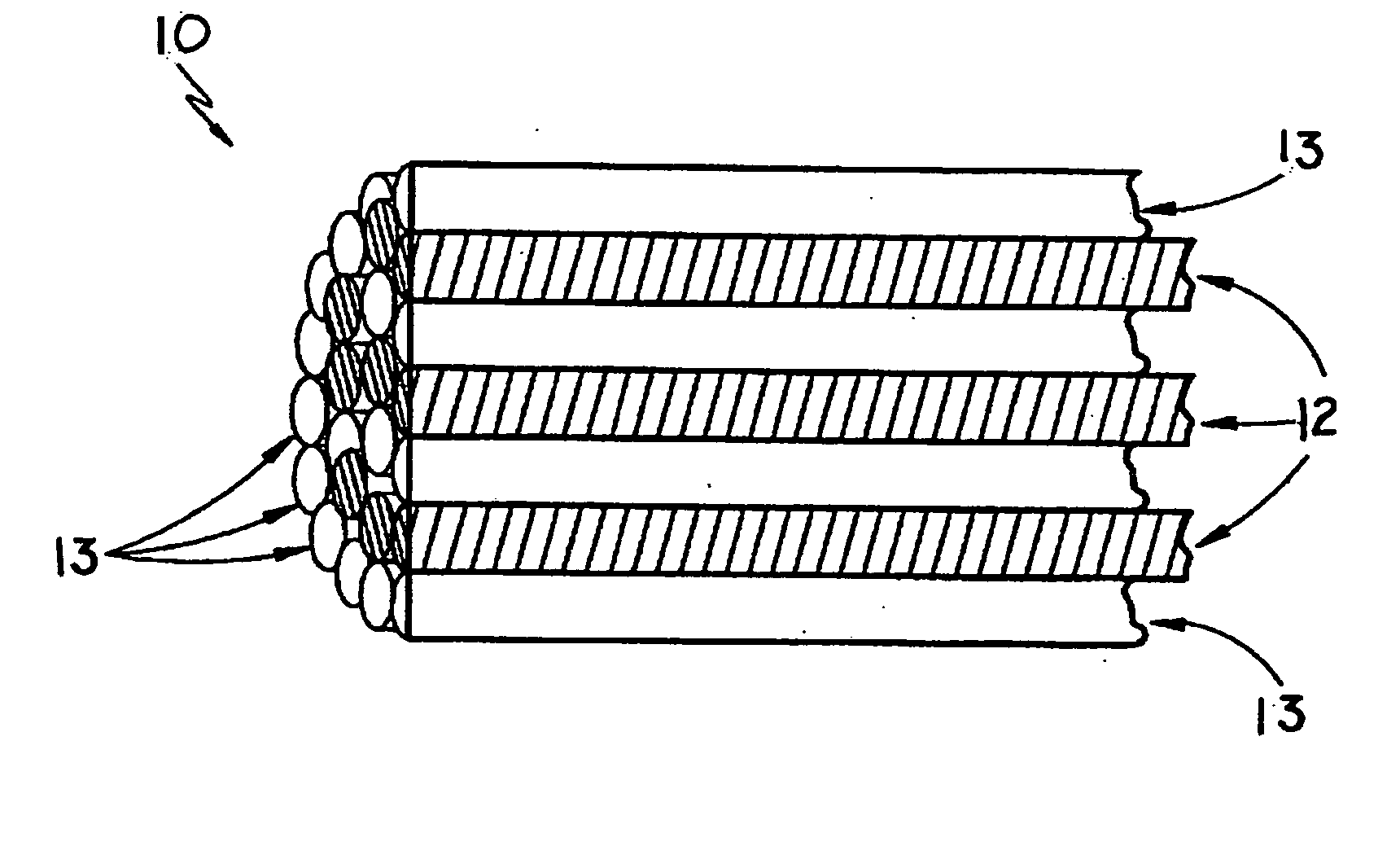
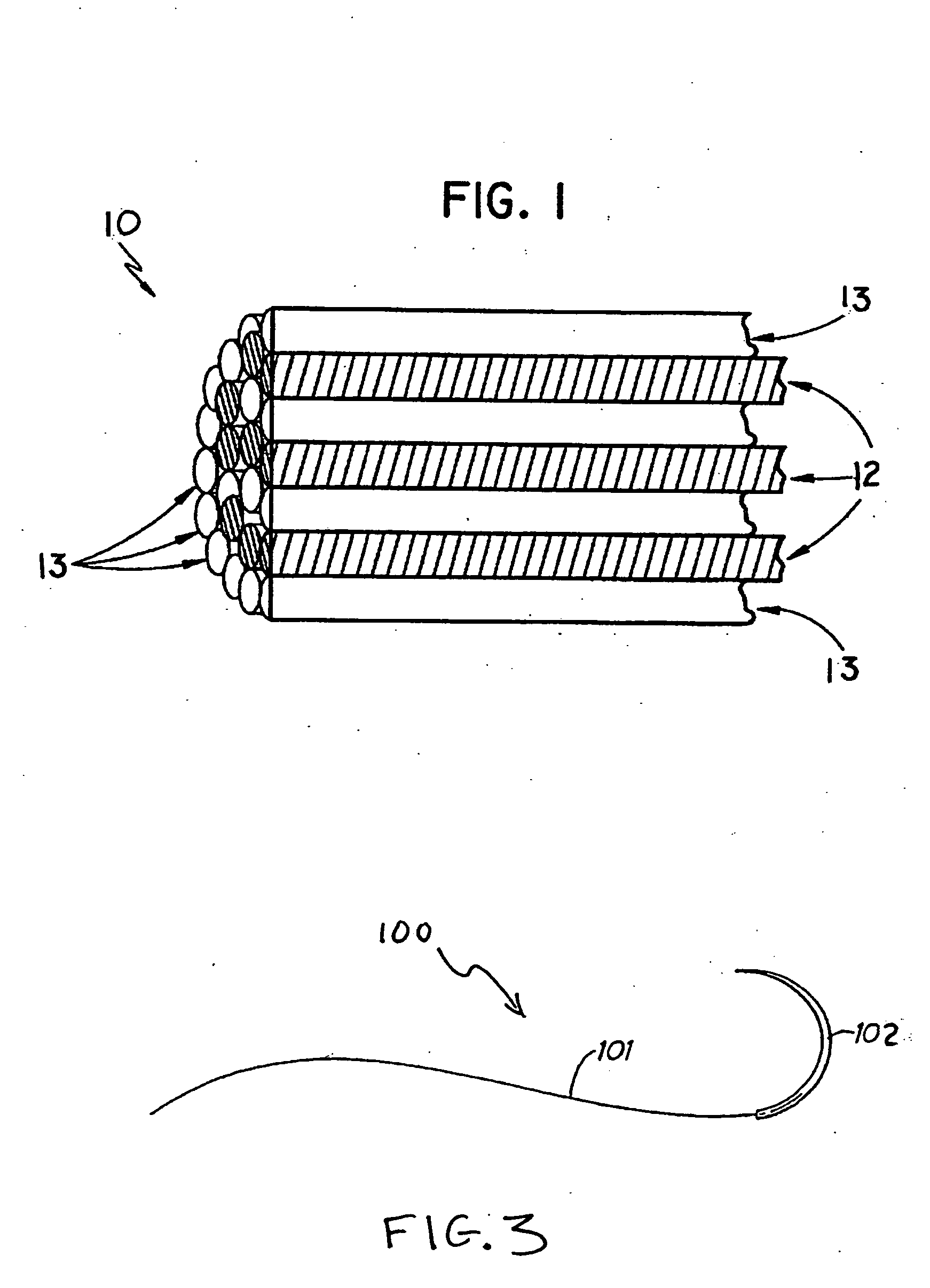
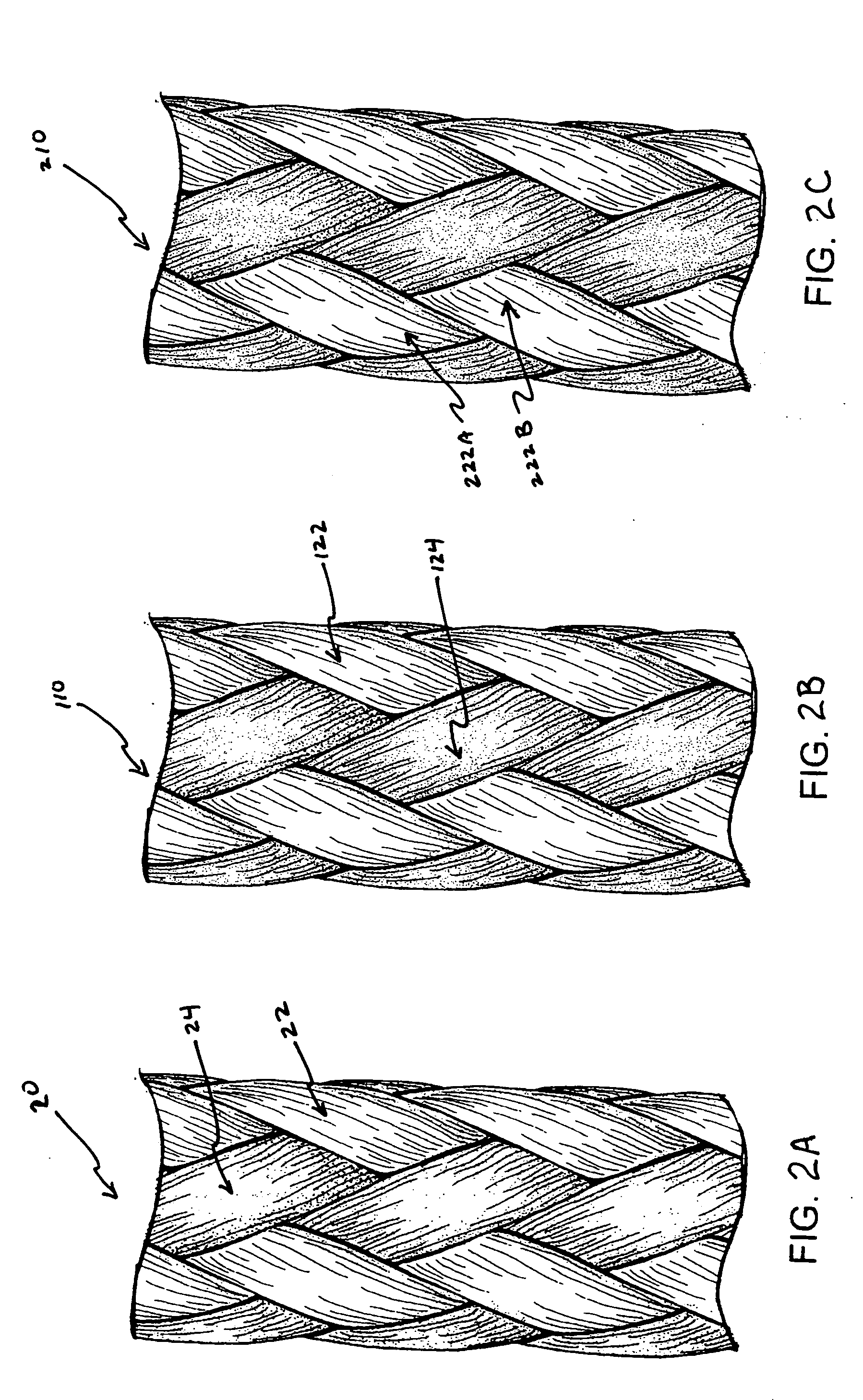
Yarns containing filaments made from shape memory alloys
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus for delivering, repositioning and/or retrieving self-expanding stents
Apparatus for delivering and deploying a stent formed of a shape memory alloy to a desired position in a tubular area of the body, and / or for repositioning and / or retrieving a stent formed of a two-way shape memory alloy. An arrangement is provided by which the temperature of the stent is locally adjusted during delivery, repositioning and / or retrieval in a safe and controlled manner by engagement with an expandable and collapsible thermal transfer member situated on a catheter assembly.
Owner:INTEK TECH
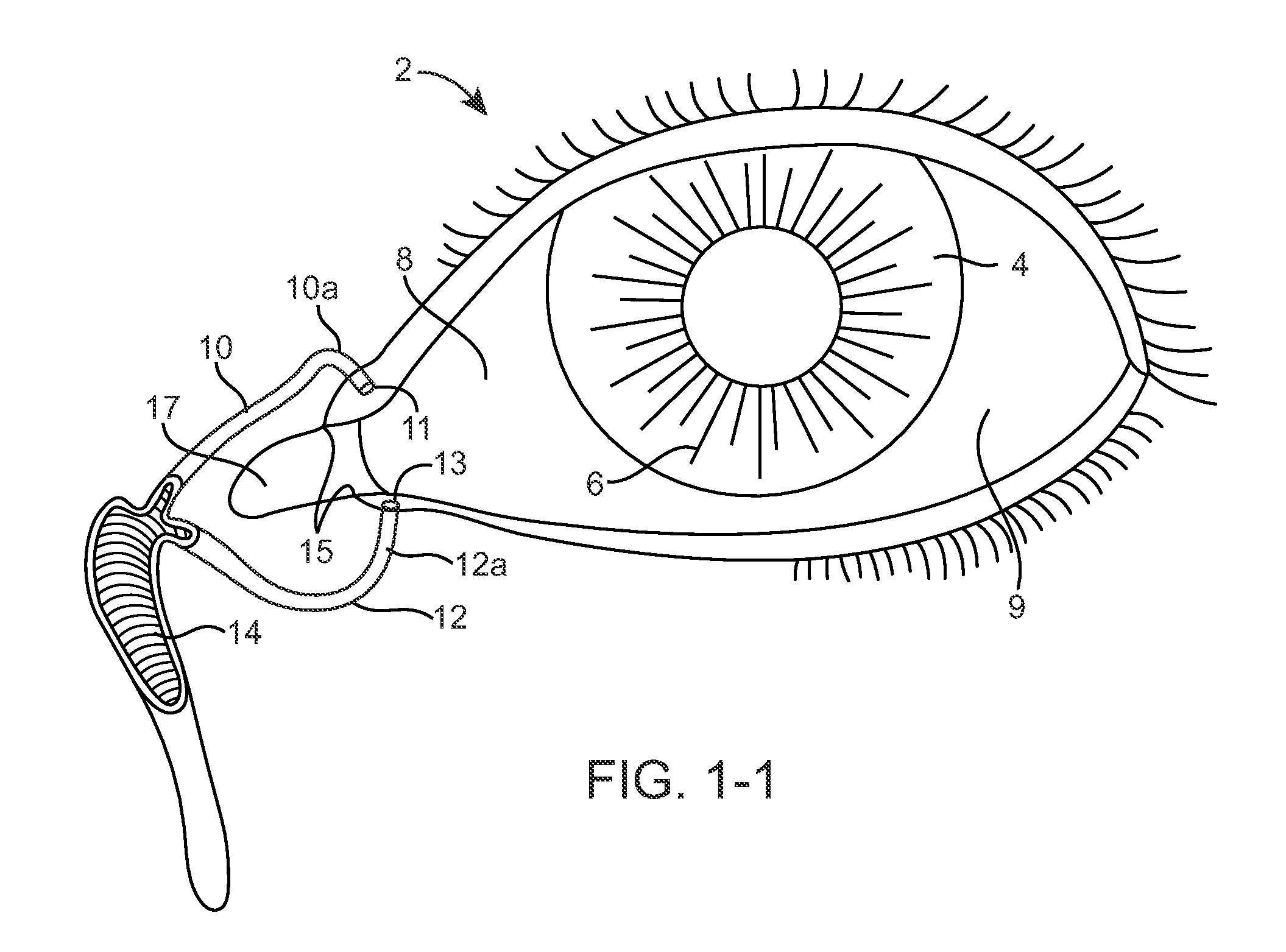
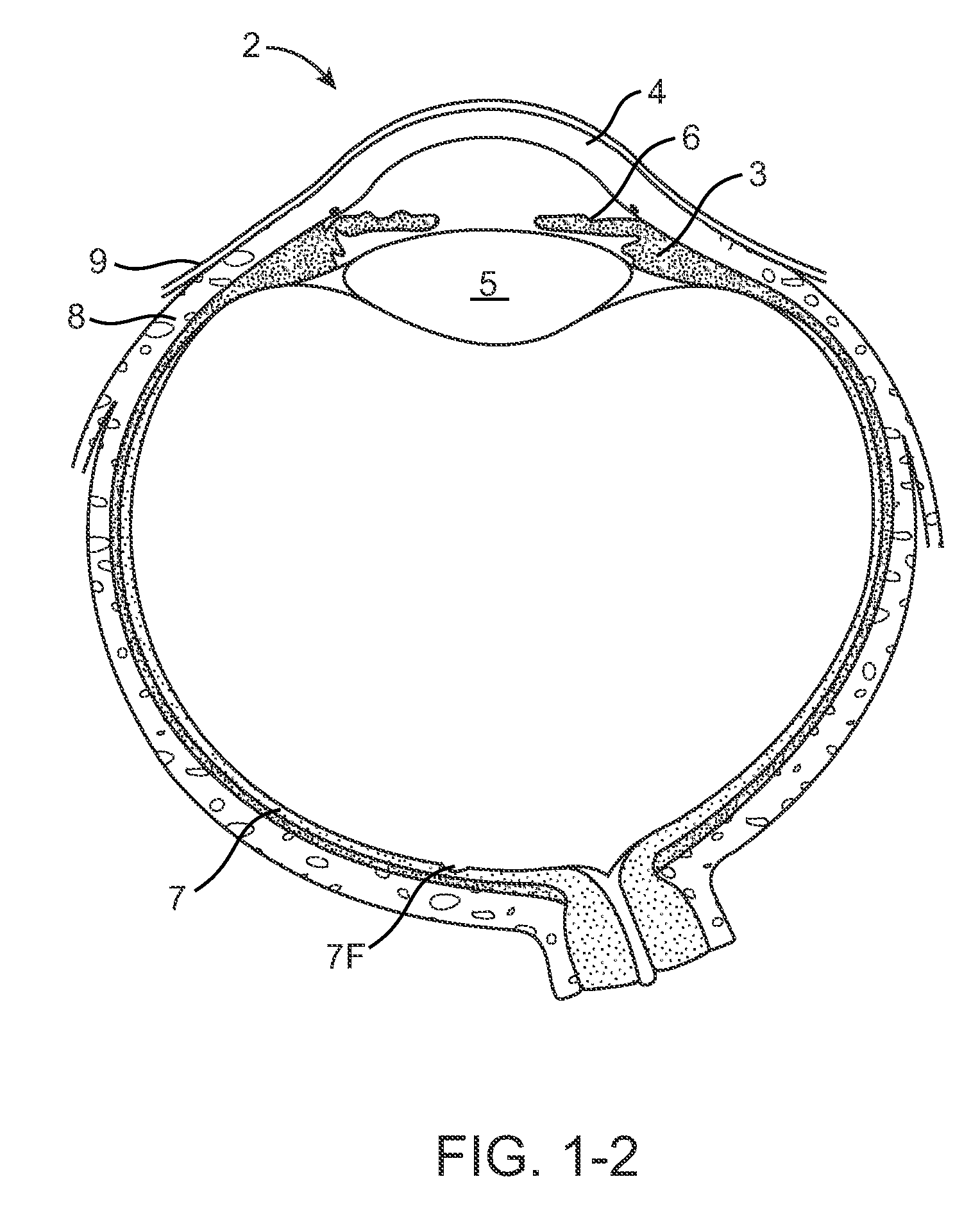
Nasolacrimal Drainage System Implants for Drug Therapy
ActiveUS20070243230A1Reduce deliveryAvoid flowAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderShape-memory alloyImplanted device
Implant devices, systems and methods for insertion into a punctum of a patient optionally comprises a drug core and a sheath body disposed over the drug core. The drug core includes a therapeutic agent deliverable into the eye, and the sheath defines at least one exposed surface of the drug core. The exposed surface(s) of the drug core may contact a tear or tear film fluid and release the therapeutic agent at therapeutic levels over a sustained period when the implant is implanted for use. The implant may include a retention element to retain the drug core and sheath body near the punctum, optionally comprising a shape memory alloy that can resiliently expand. An occlusive element may be attached to the retention element to at least partially occlude tear flow through the canalicular lumen.
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
Prosthetic components with partially contained compressible resilient members
InactiveUS7066958B2Improve protectionEliminate shear stressJoint implantsSpinal implantsElastomerShape-memory alloy
One or more rigid components associated with an articulating bone are used to encase, encapsulate, contain, or otherwise protect a compressible / resilient member. The embodiments are applicable not only to artificial disc replacement (ADR) devices, but also to joint situations including total knee and hip arthroplasty. The cushion elements in the preferred embodiments include synthetic rubbers, hydrogels, elastomers, and other polymeric materials such as viscoelastic polymers and foam polyurethanes. The invention effectively combines the advantages of such materials (cushioning, shape memory, and expansion after insertion in the case of hydrogels), while providing increased protection, particularly the elimination of shear stresses. When applied to an ADR, the invention also minimizes the risk of extrusion.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
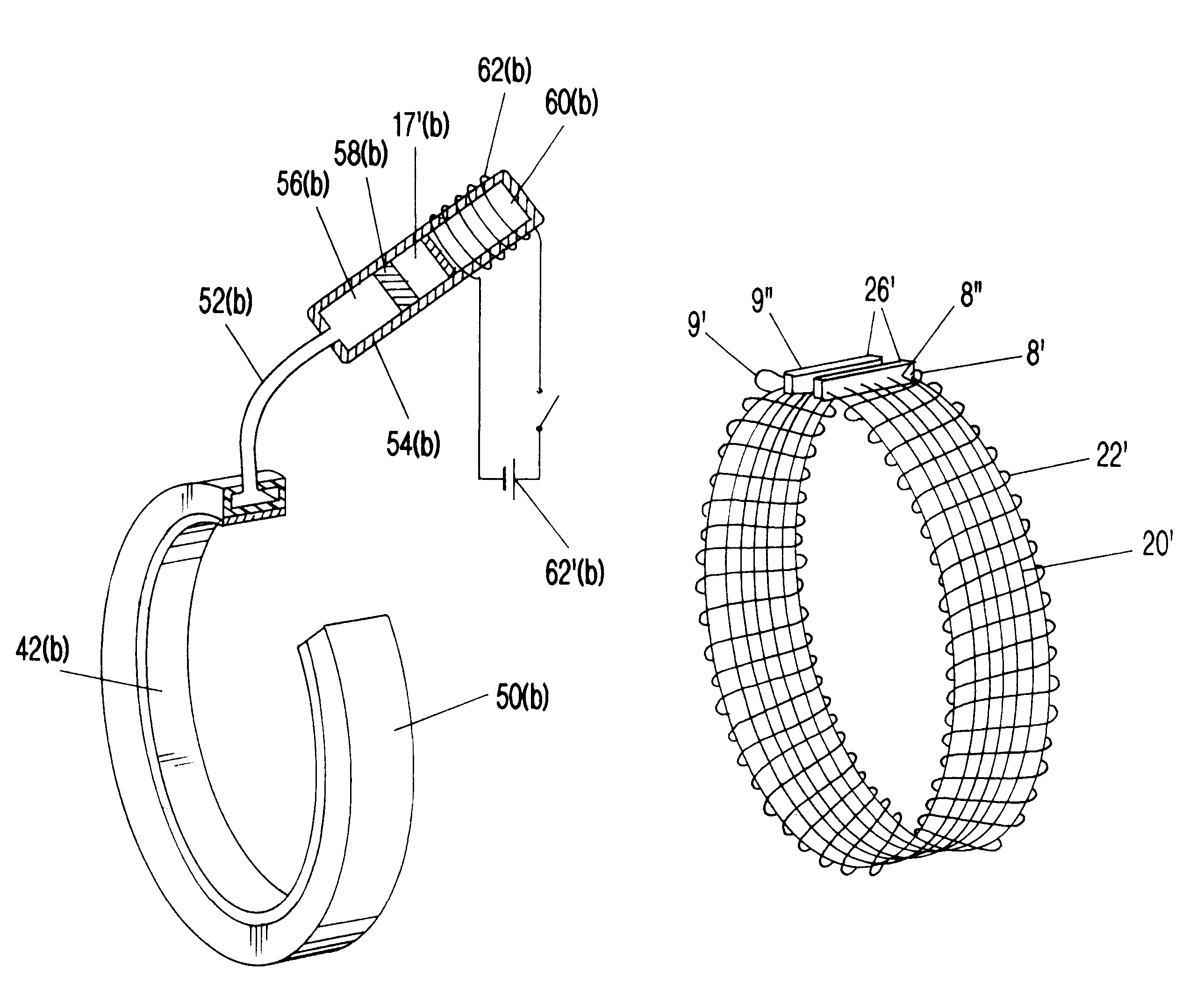
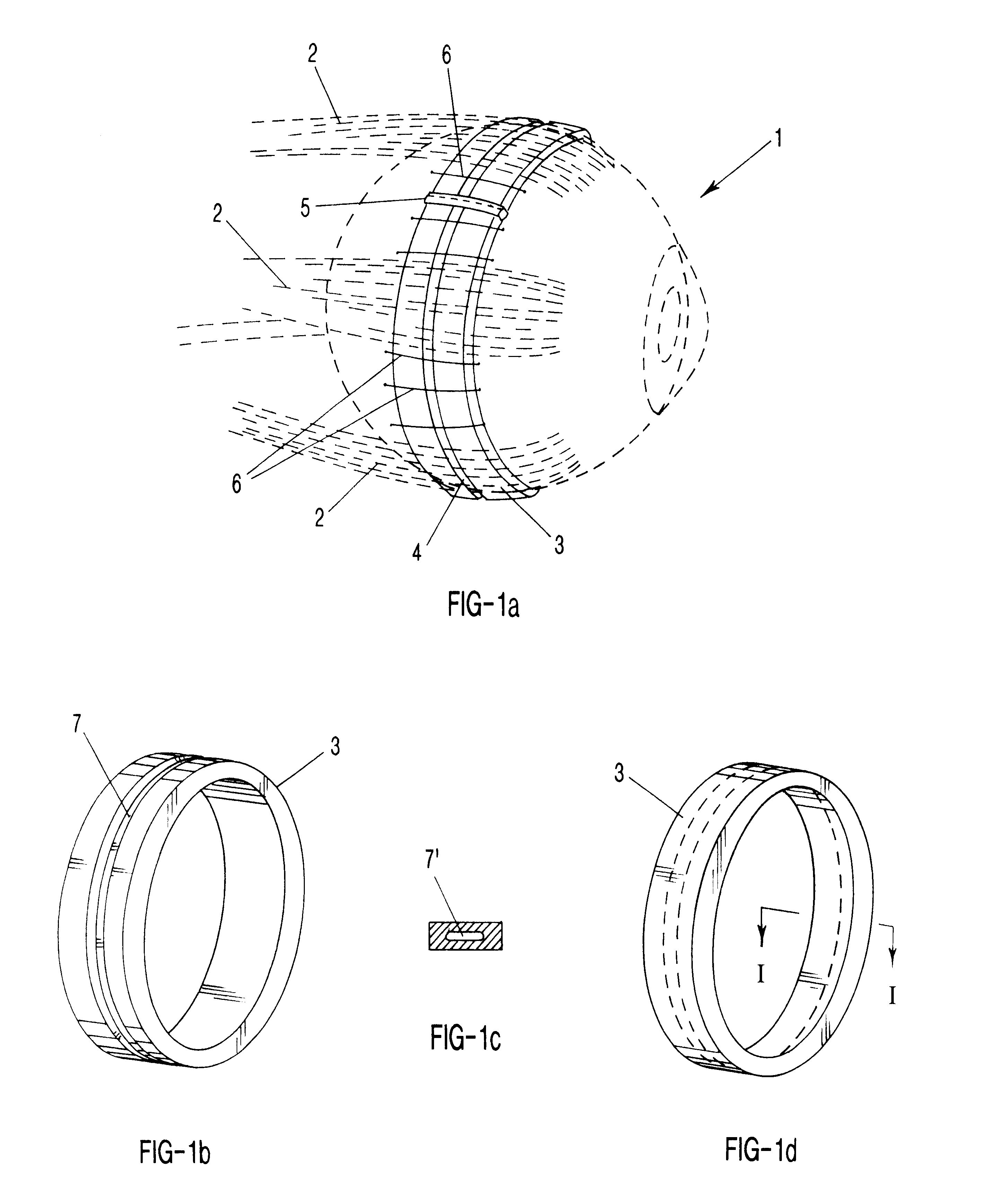
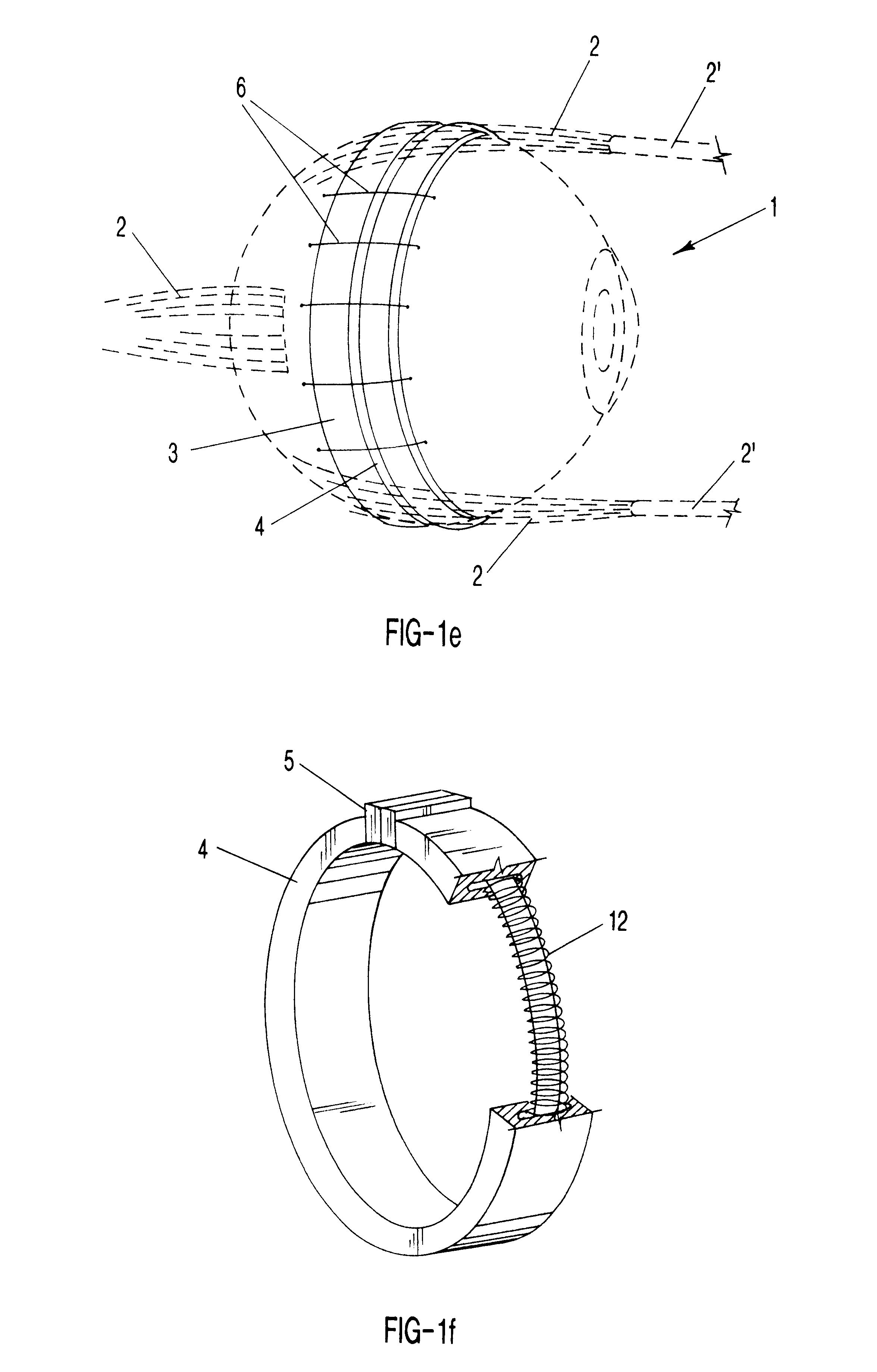
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
Method and apparatus for caged stent delivery
InactiveUS7169172B2Shorten exchange timeReduce frictionStentsEar treatmentCage deviceShape-memory alloy
A method and apparatus for caged stent delivery is provided herein. The device can be used to position and deliver any type of stent to a preselected treatment site within an intraluminal cavity. The device comprises a tubular portion, a plurality of arms attached to the distal end of the tubular portion, and a mechanism to open the arms. In operation, the caged device carries a stent in a constricted form to the treatment site for deployment. The arms of the cage are then opened, the stent released and deployed, and the device withdrawn. Several methods are provided to open the arms, including various pullwires, a piston, an electrolytic joint, and an activator. The arms may be constructed of a shape memory alloy and opened when shape memory behavior is effected. The device may be used with conventional catheters or used with a stent-loaded guidewire.
Owner:LEVINE MARC ALAN
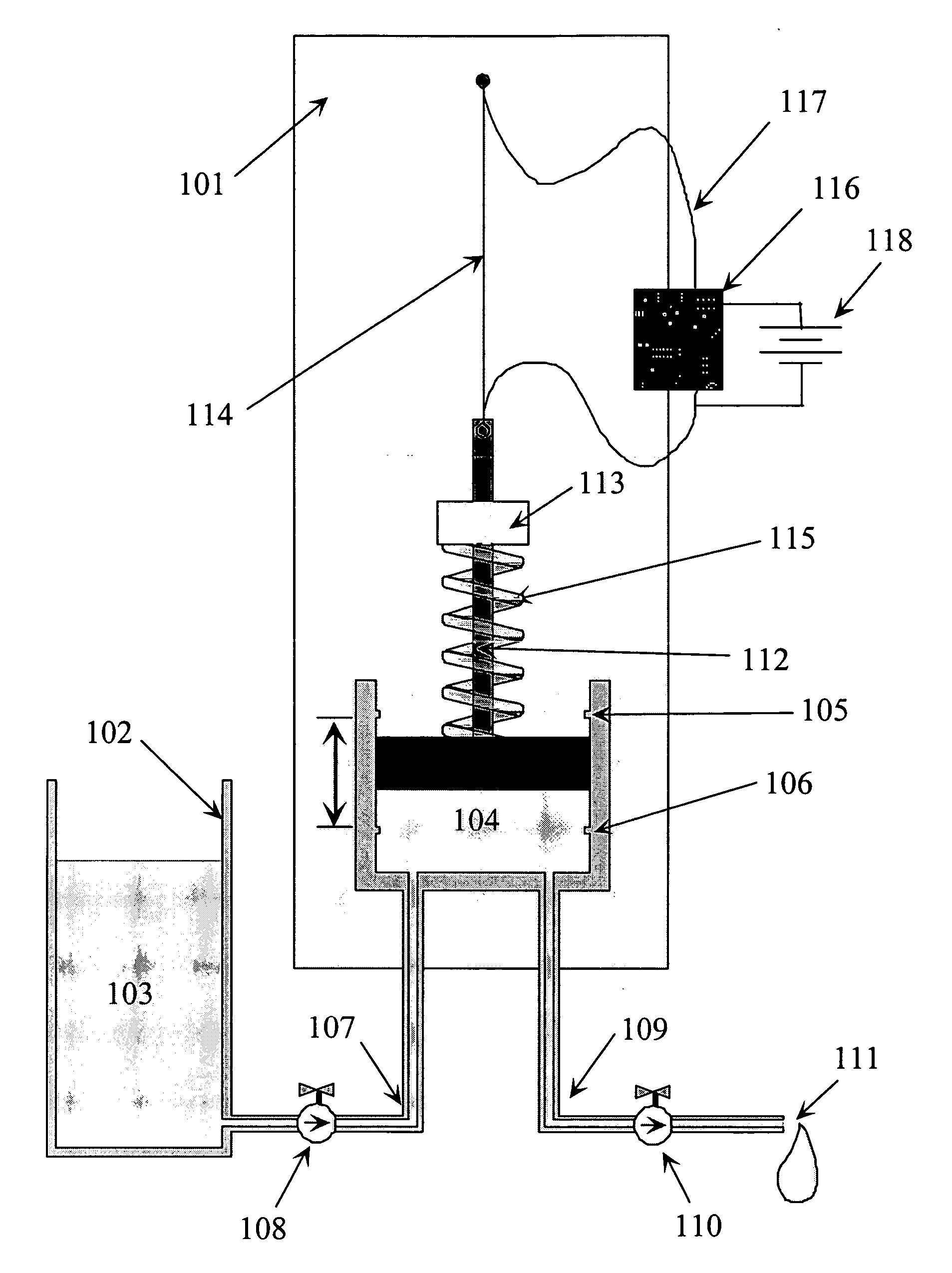
Fluid delivery device, system and method
ActiveUS20040115067A1Low costSmall sizeTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementShape-memory alloyAlloy
A system for the metering and delivery of small discrete volumes of liquid is comprised of a small or minimal number of inexpensive components. One such component is a movable member, such as a miniature precision reciprocating displacement pump head, which is driven by an actuator that comprises a shape memory alloy material. The operating mechanism of the system is of little or minimal complexity. The system facilitates the precise metering and delivery of the small discrete volumes of liquid. Potential applications for the system include subcutaneous, long-term, automated drug delivery, for example, the delivery of insulin to a person with diabetes. In such an application, the small, simple and inexpensive nature of the invention would allow for its use as both a portable and a disposable system.
Owner:THERASENSE
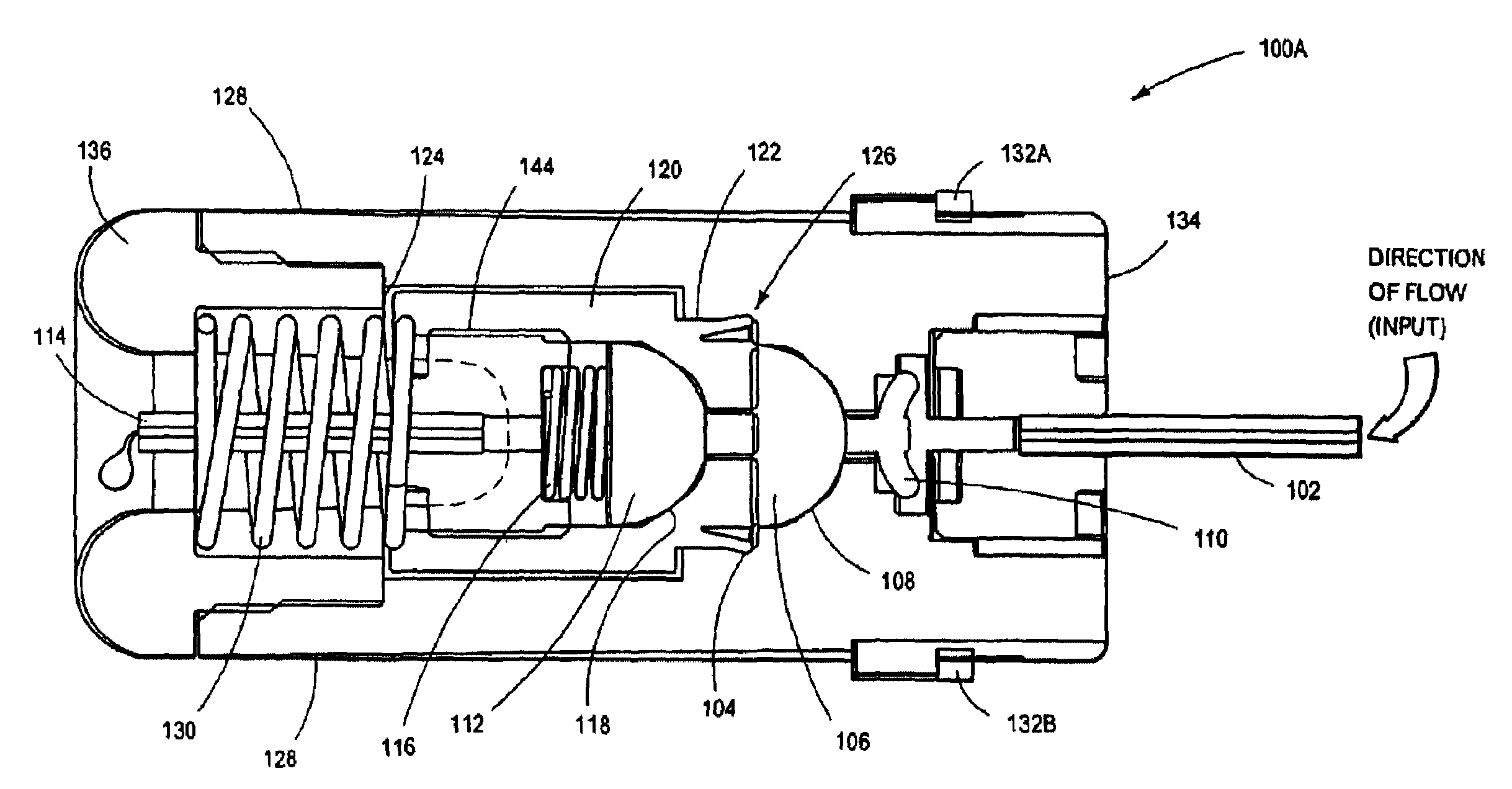
Memory wire actuated control valve
InactiveUS6843465B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesDomestic plumbingElectricityFluid control
A memory wire actuated control valve comprises a memory wire actuator operatively coupled to a fluid control valve. The memory wire actuator includes a housing having an interior cavity enclosing an electrical platform assembly, an activation wire and a transfer mechanism. The activation wire is formed of a shape memory alloy, often called a “memory wire” or “muscle wire.” The activation wire is electrically connected to the electrical platform and mechanically coupled to the transfer mechanism. The actuator is activated by conducting electrical current through the activation wire causing the wire to contract thereby actuating the transfer mechanism. The transfer mechanism is operable coupled to the fluid control valve such that actuated and de-actuating the transfer mechanism open and closes the valve.
Owner:SCOTT LOREN W
Surgical spacer with shape control
An interspinous spacer for placement between adjacent spinous processes includes a flexible, fillable container (e.g., a bag or balloon) for containing a material that is compressible during end use, for example, silicone after curing. The container is impermeable to the material it will be filled with. A structural mesh, for example, made of PET fabric and interwoven shape-memory alloy wire, provides structure for and containment of the container, as well as shape control. The material can be injected into the container through an optional conduit, for example, a one-way valve.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Stressed material and shape memory material MEMS devices and methods for manufacturing
Disclosed is a MEMS device which comprises at least one shape memory material such as a shape memory alloy (SMA) layer and at least one stressed material layer. Examples of such MEMS devices include an actuator, a micropump, a microvalve, or a non-destructive fuse-type connection probe. The device exhibits a variety of improved properties, for example, large deformation ability and high energy density. Also provided is a method of easily fabricating the MEMS device in the form of a cantilever-type or diaphragm-type structure.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Balloon expandable crush-recoverable stent device
InactiveUS20060020324A1Improve radial strengthKeep openStentsBlood vesselsLocking mechanismInsertion stent
An intraluminal, balloon expandable stent for implantation in a body lumen is disclosed. The present invention provides a lumen support stent with an unobstructed through-lumen for use in a blood vessel. A constraining mechanism is provided for securely maintaining the stent in the collapsed condition during delivery. The stent is preferably formed with a series of interconnected slide and lock mechanisms for permitting movement from a collapsed condition to an expanded condition and inhibiting radial recoil from the expanded condition. The stent may be formed from a shape memory alloy for providing crush-recovery after deployment.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
Apparatus and methods for treating bone
ActiveUS20070055274A1Increased radialIncreasing diameter of coilInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsFiberBobbin
Implants and methods for bone treatment, preferably minimally invasive treatment, including repositioning of vertebrae may comprise insertion of a bobbin having a wire, string, thread or band, coiled around the bobbin. During coiling, the diameter of the bobbing / band complex may increase. Such increase in diameter can push against the inner side of the endplates of the vertebral body, and augment the vertebral body to its original height. The implant may also take the form of a coiled sleeve which when inserted into the vertebral body is uncoiled. The force of the uncoiling sleeve pushes against the inner side o the endplates of the vertebral body, restoring the vertebral body to its original height. The implant may also take the form of fibrous masses comprised of a thread or other relatively thin structure, for example a fiber or strand, of any biocompatible material having desired characteristics, for example a shape memory alloy, titanium, stainless steel, another metal or metal alloy, a ceramic, a composite or any combination thereof. The, strand, thread or other fiber may be coiled, woven, matted, tangled or otherwise formed into a wool-like mass or body having a desired configuration. Expansion of the expandable member within the vertebral body or other bone may reposition the fractured bone to a desired height and augment the bone to maintain the desired height. A bone cement or other filler can be added to further treat and stabilize the vertebral body or other bone.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Mitral valve device using conditioned shape memory alloy
A mitral valve annulus reshaping device includes at least a portion that is formed of a biocompatible shape memory alloy SMA having a characteristic temperature, Af, that is preferably below body temperature. The device is constrained in an unstable martensite (UM) state while being introduced through a catheter that passes through the venous system and into the coronary sinus of the heart. The reshaping device is deployed adjacent to the mitral valve annulus of the heart as it is forced from the catheter. When released from the constraint of the catheter, the SMA of the device at least partially converts from the UM state to an austenitic state and attempts to change to a programmed shape that exerts a force on the adjacent tissue and modifies the shape of the annulus. The strain of the SMA can be varied when the device is within the coronary sinus.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
Device and method for intralumenal anastomosis
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Implantation system for annuloplasty rings
ActiveUS8123801B2Good coaptation of leafletEliminate riskSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEffective lengthShape-memory alloy
Methods for reconfiguring an atrioventricular heart valve may use systems comprising a partial or complete fenestrated annuloplasty ring proportioned to reconfigure a heart valve that has become in some way incompetent, and a plurality of staples which may have pairs of legs that are sized and shaped for association with the ring at spaced locations along its length. These systems permit relative axial movement between the staples and the ring, whereby a patient's heart valve can be reconfigured in a manner that does not deter subtle shifting of the native valve components. Shape-memory alloy material staples may have legs with free ends that interlock following implantation. One alternative is to use flexible rings that will bend in the plane of the ring as the heart beats. Other alternative systems use linkers of shape-memory material having hooked ends to interengage with staples or other implanted supports which, following implantation, decrease in effective length and pull the staples or other supports toward one another so as to create desired curvature of the reconfigured valve. These linkers may be separate from the supports or may be integral with them and may have a variety of shapes and forms. Various of these systems may be implanted non-invasively using a delivery catheter.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com