Patents
Literature
380 results about "Native valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
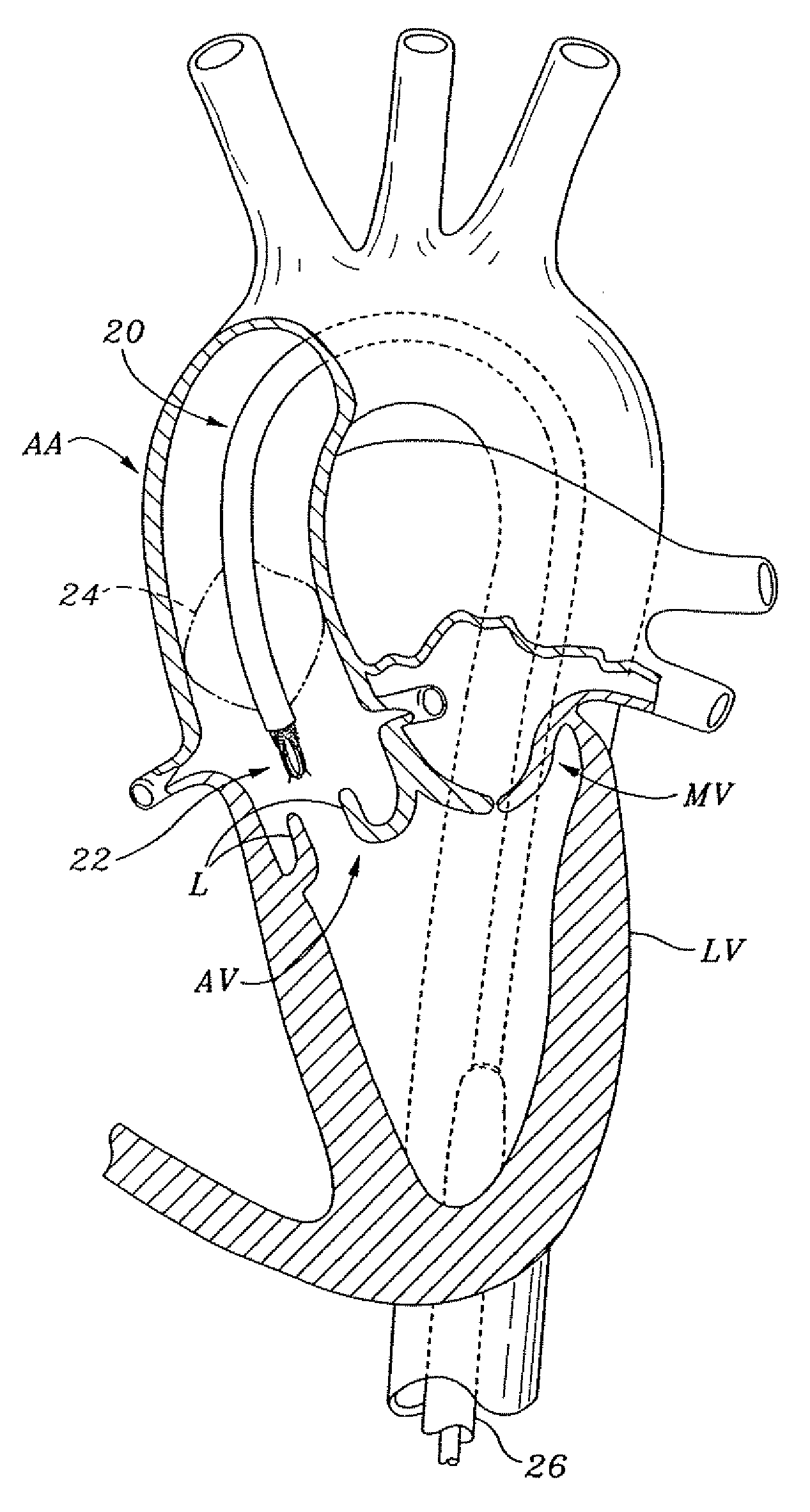
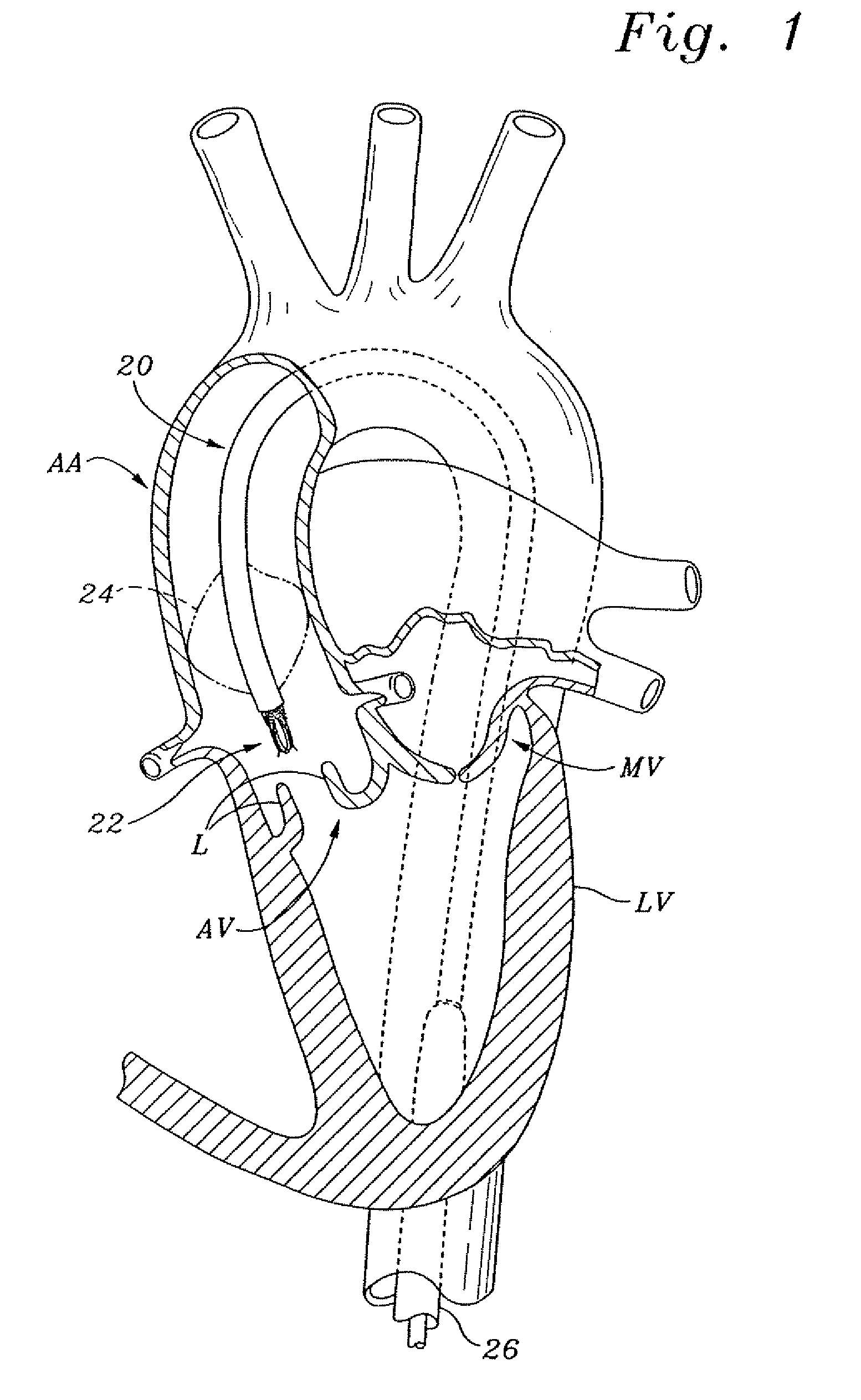
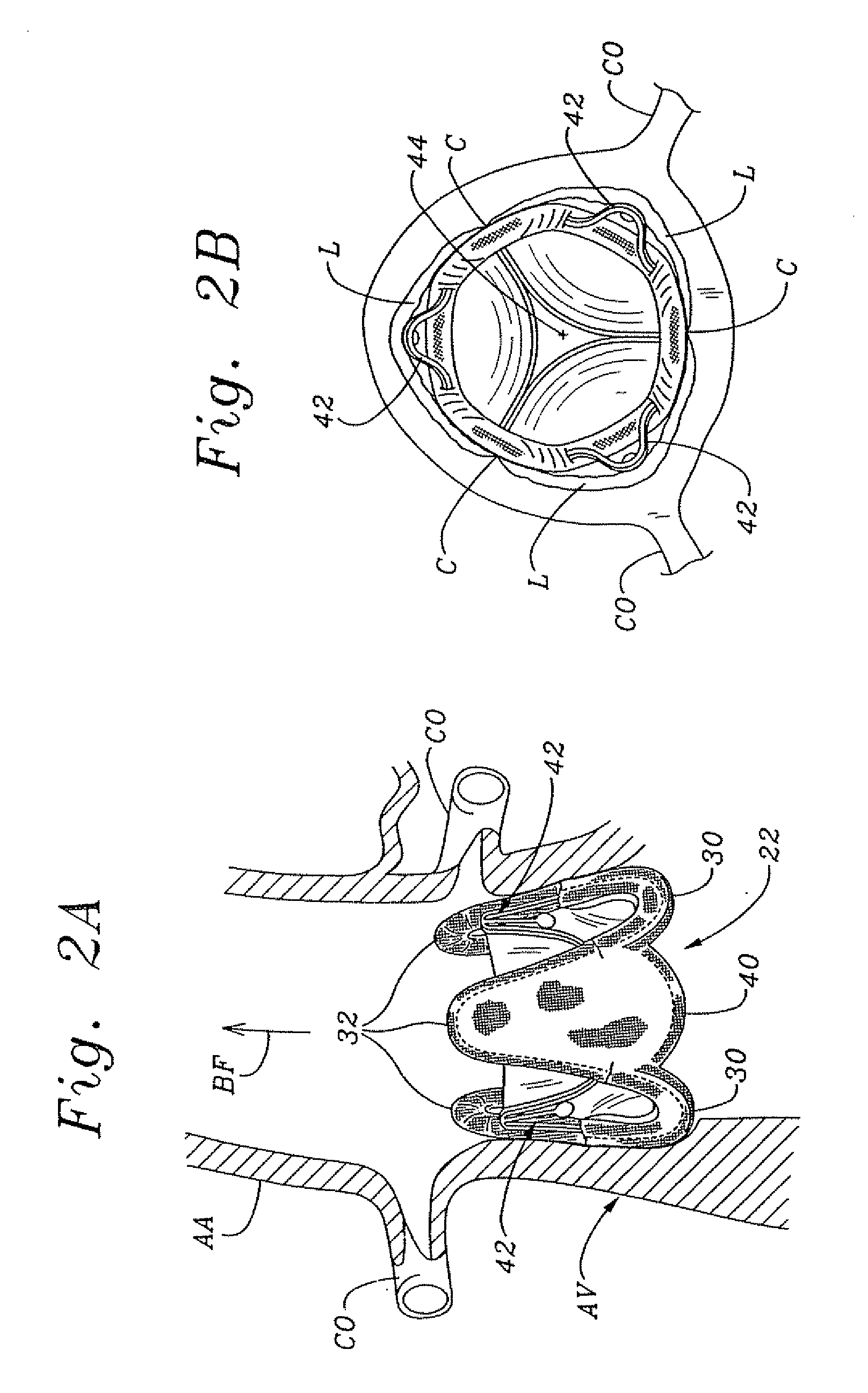
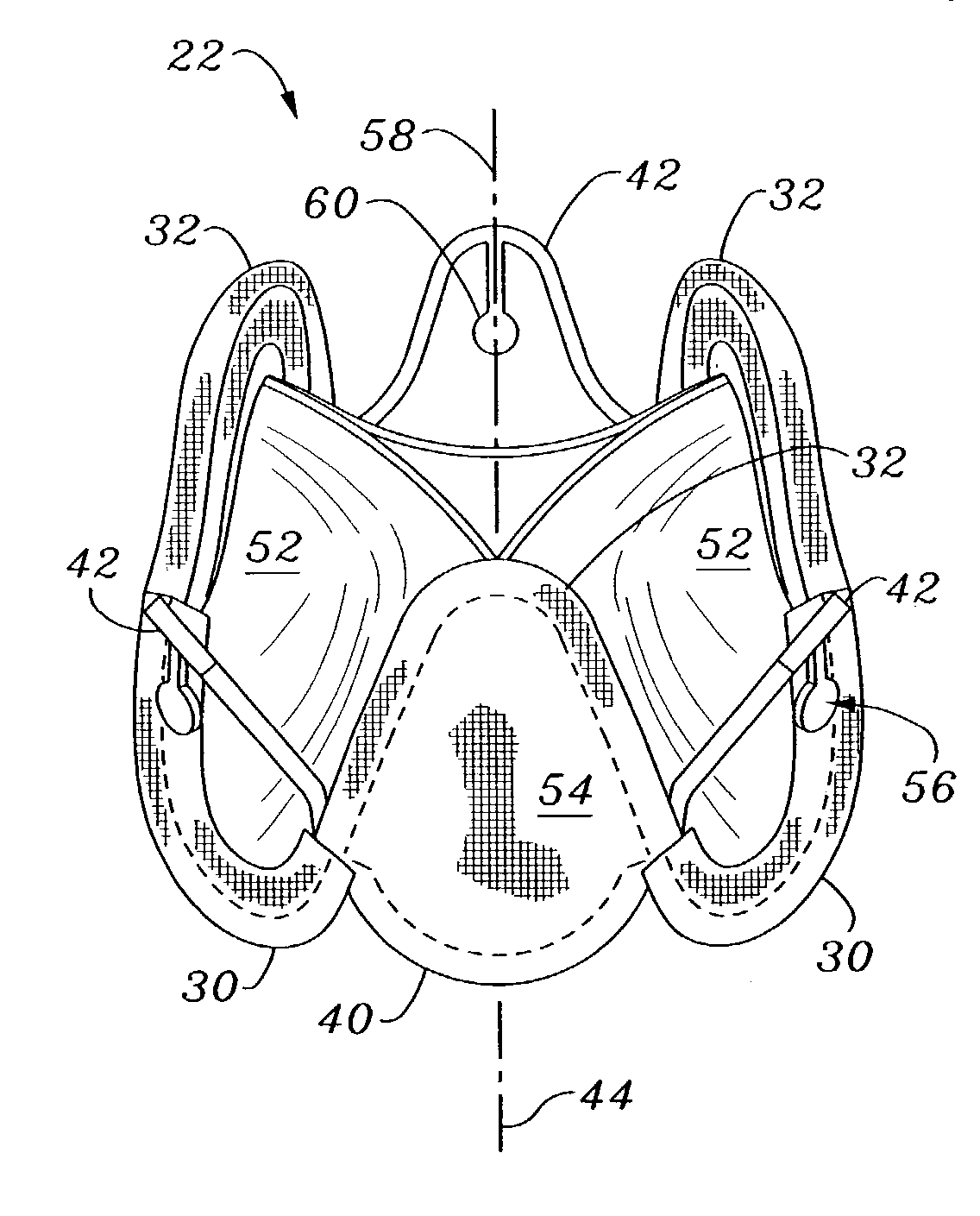
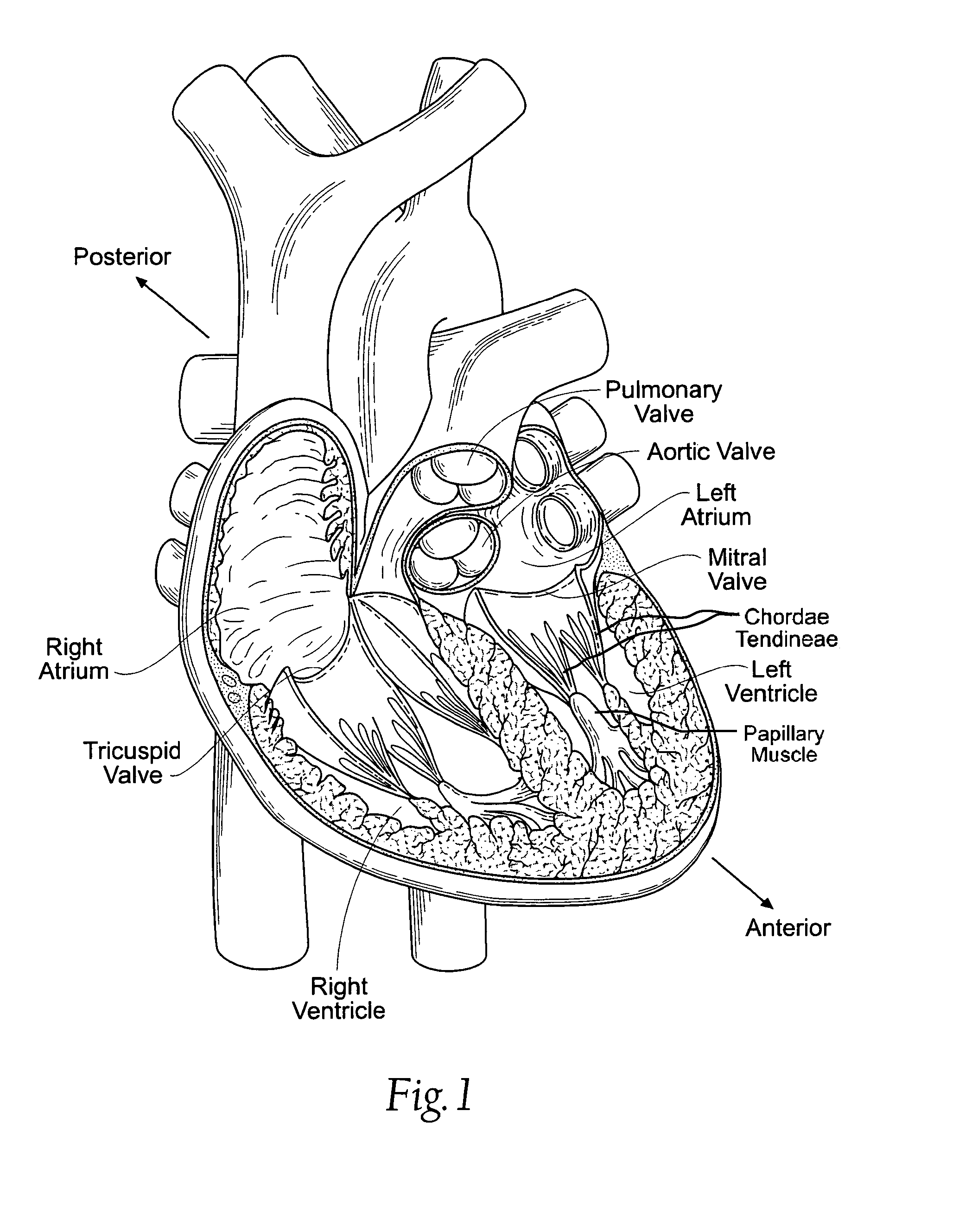
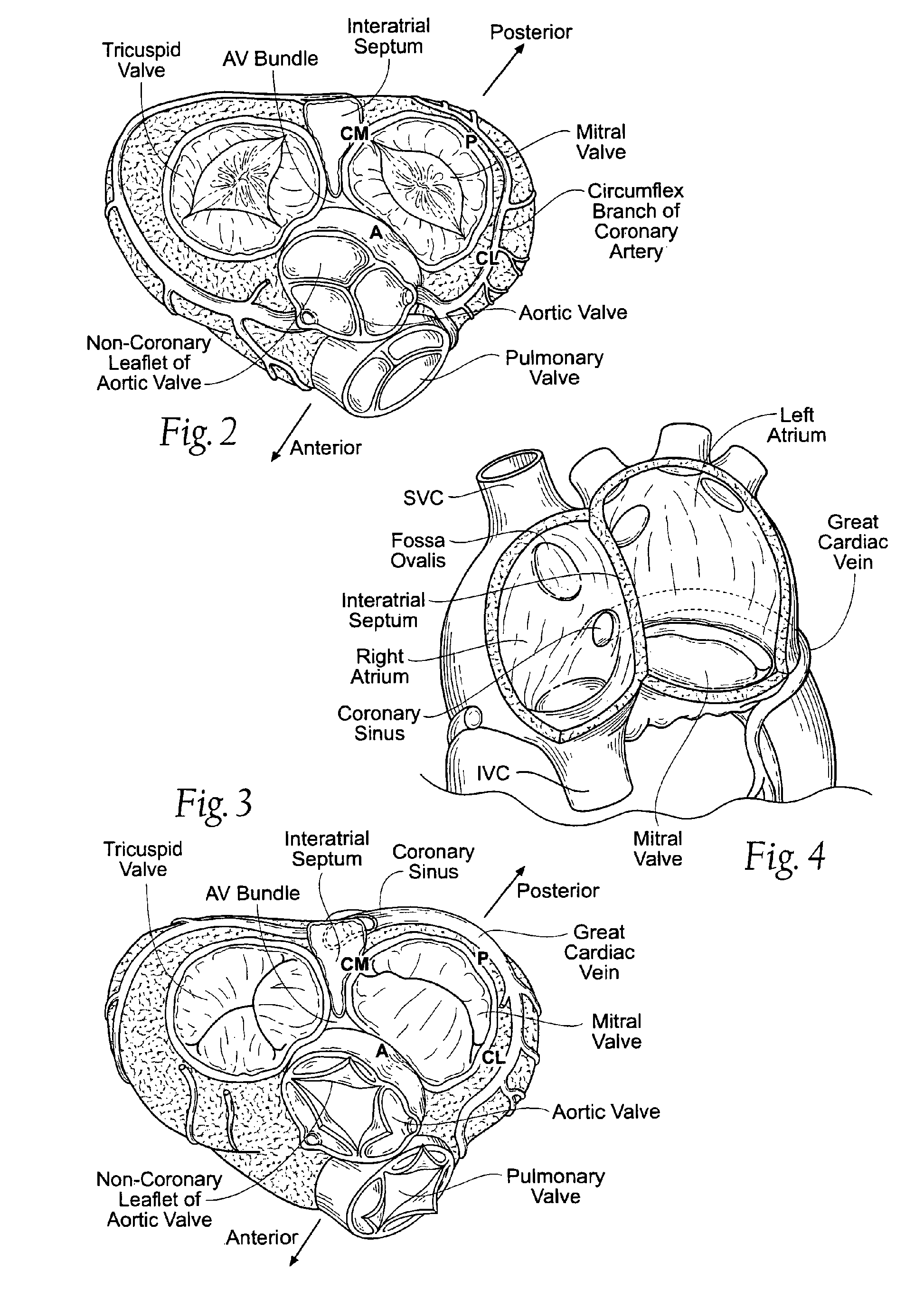
Native valve is what the patient is born with as compared to a prosthetic valve. It is the regurgitant lesion which predisposes to native valve endocarditis and the most common organism (s) are the viridans group since there is transient bacteremia every time someone chews/brushes their teeth.
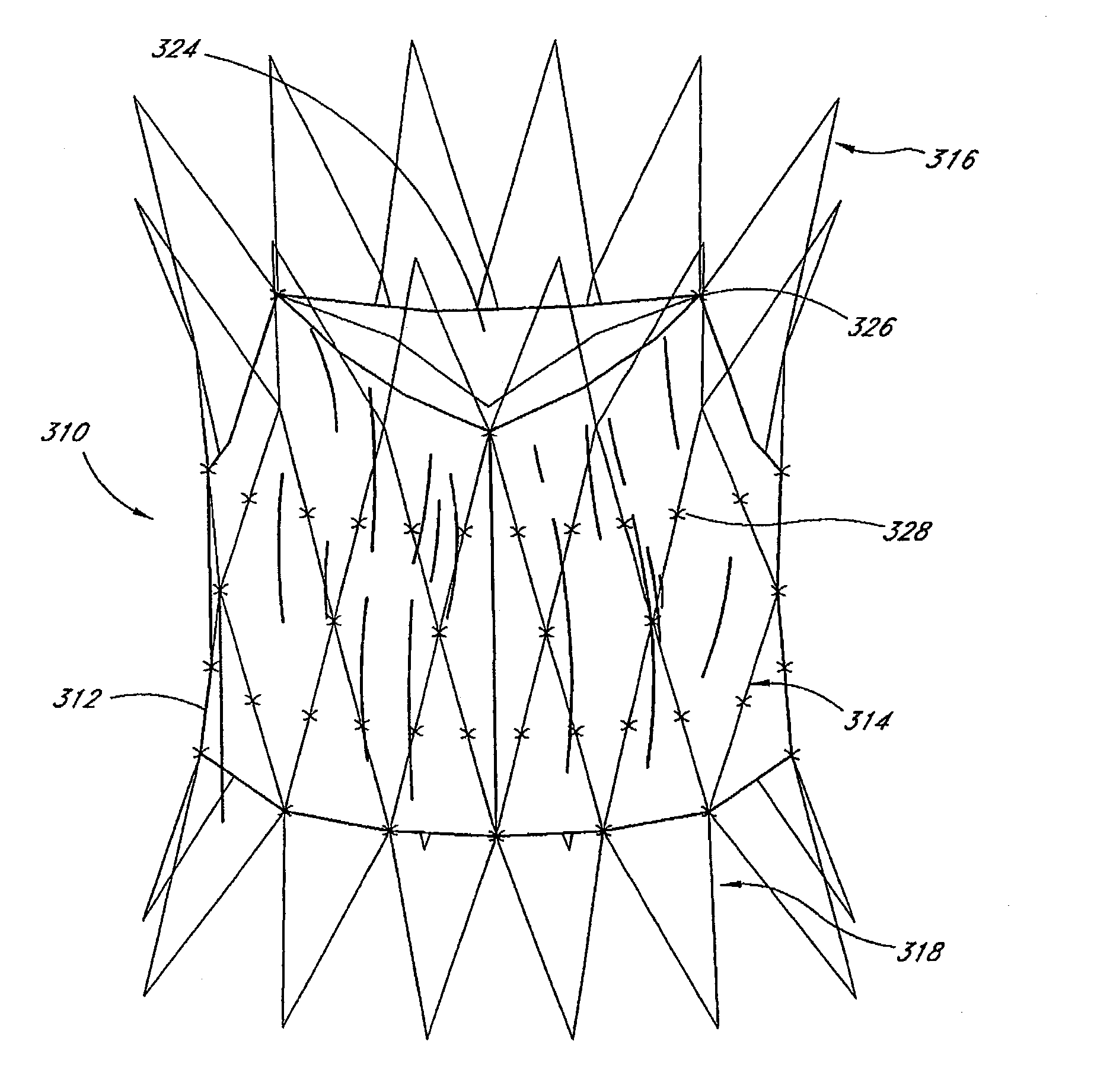
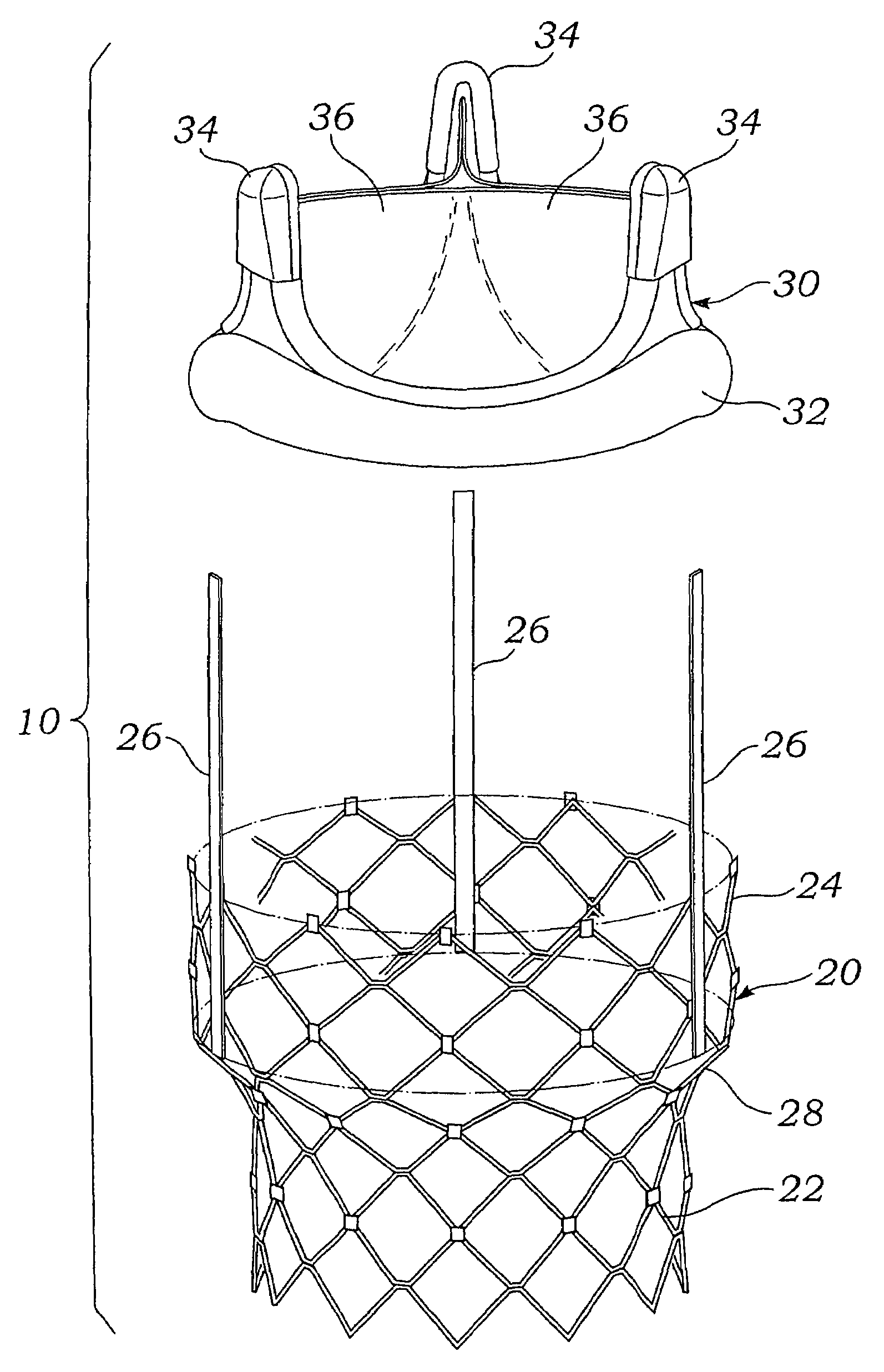
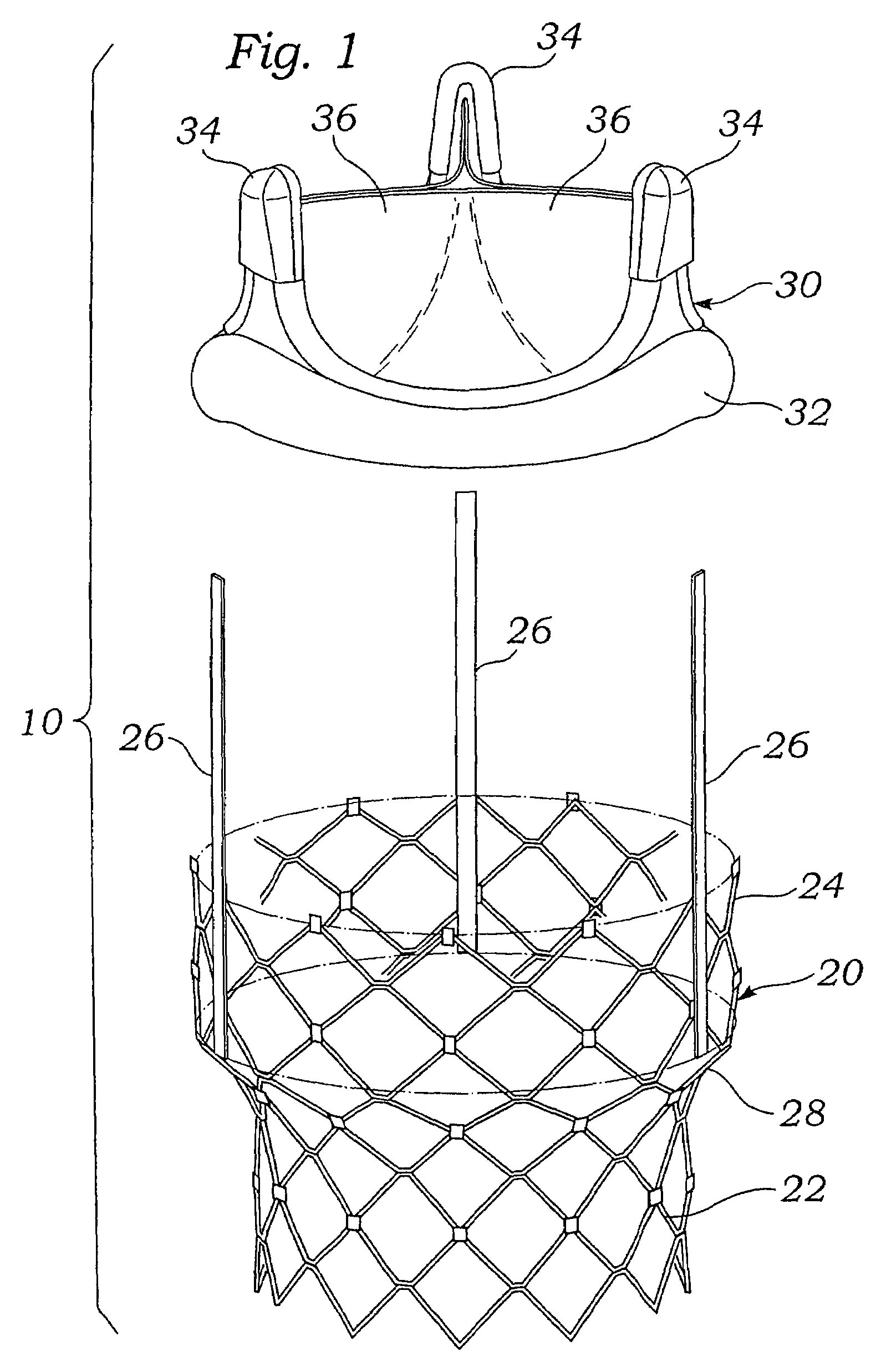
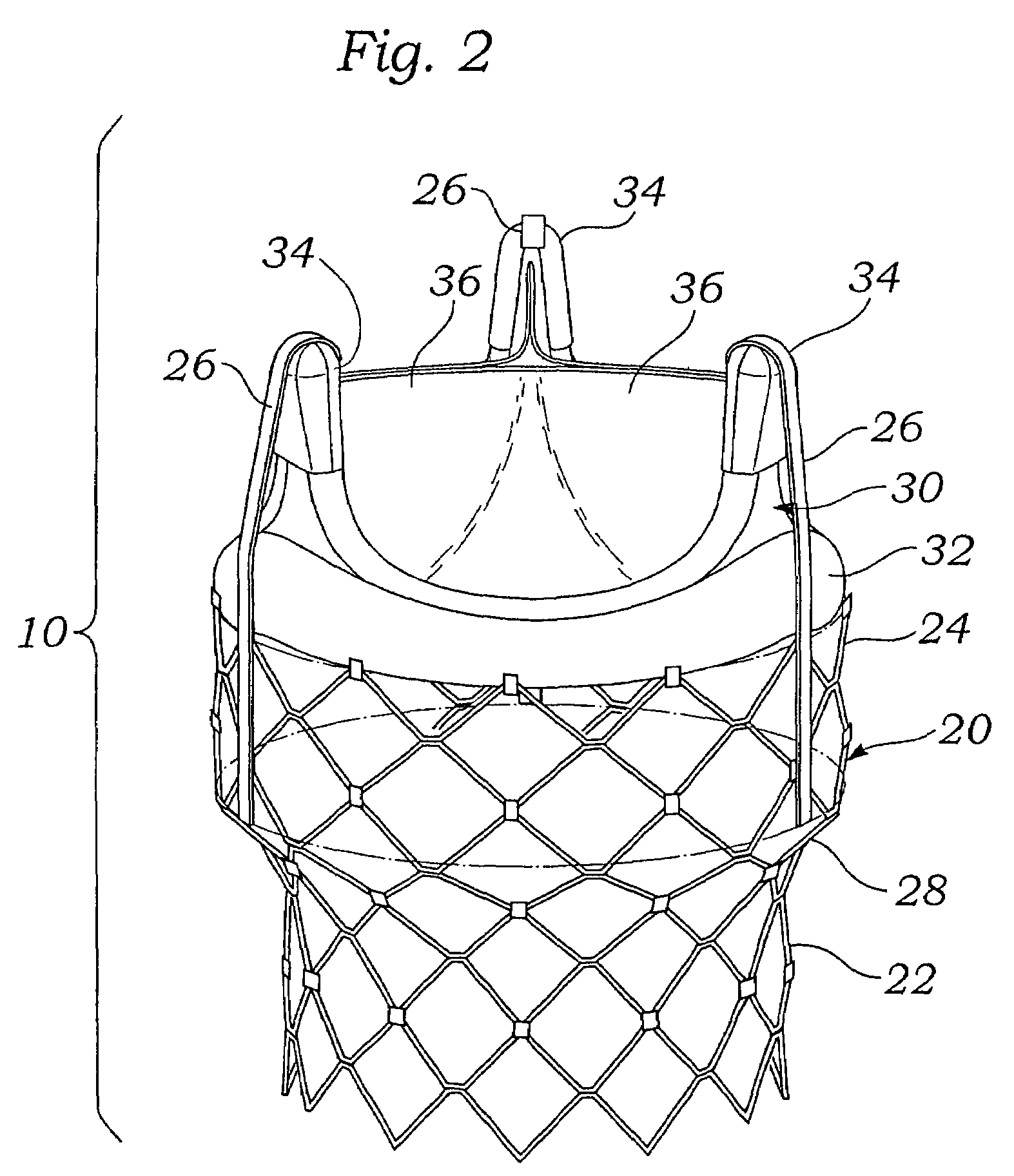
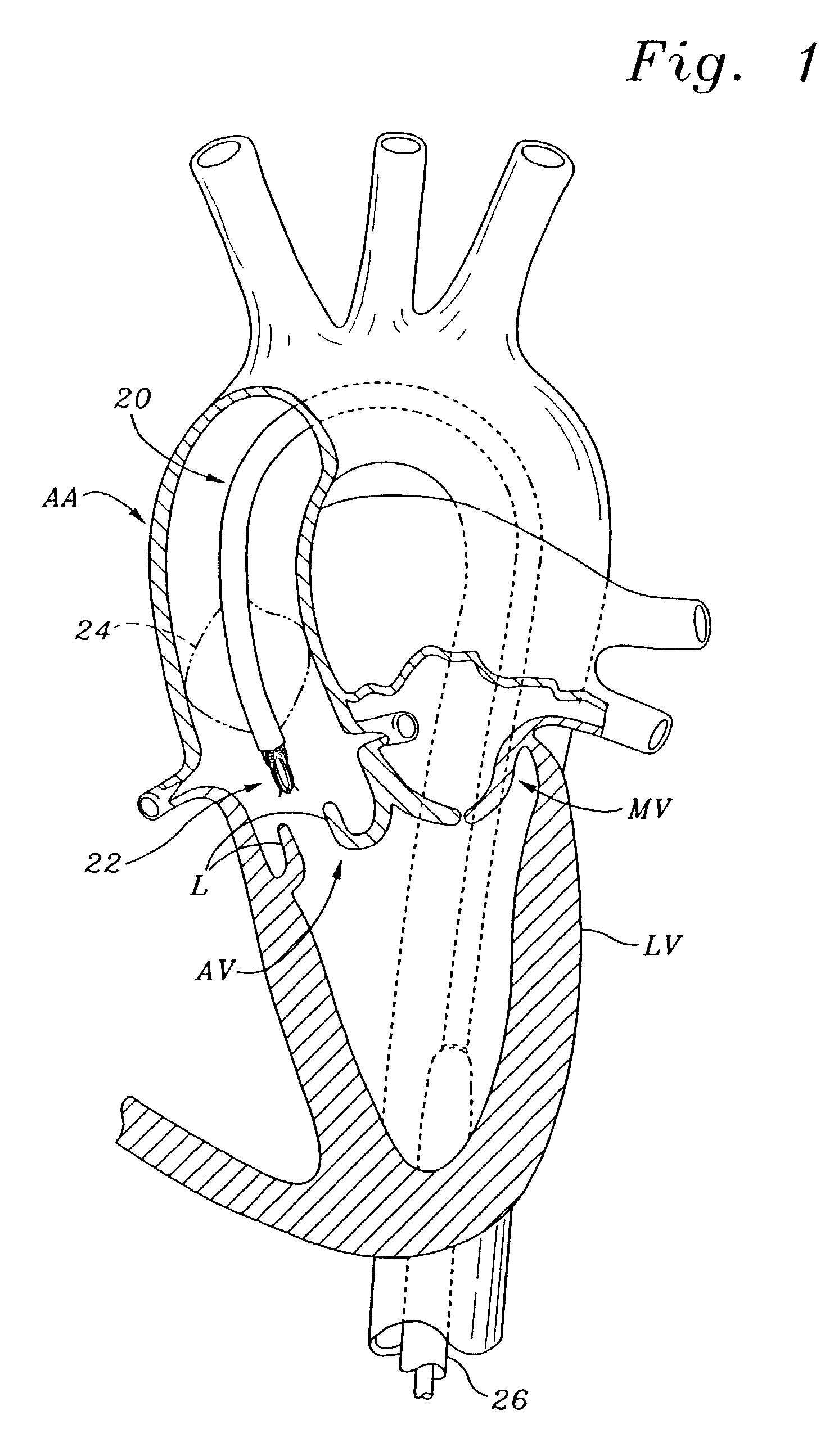
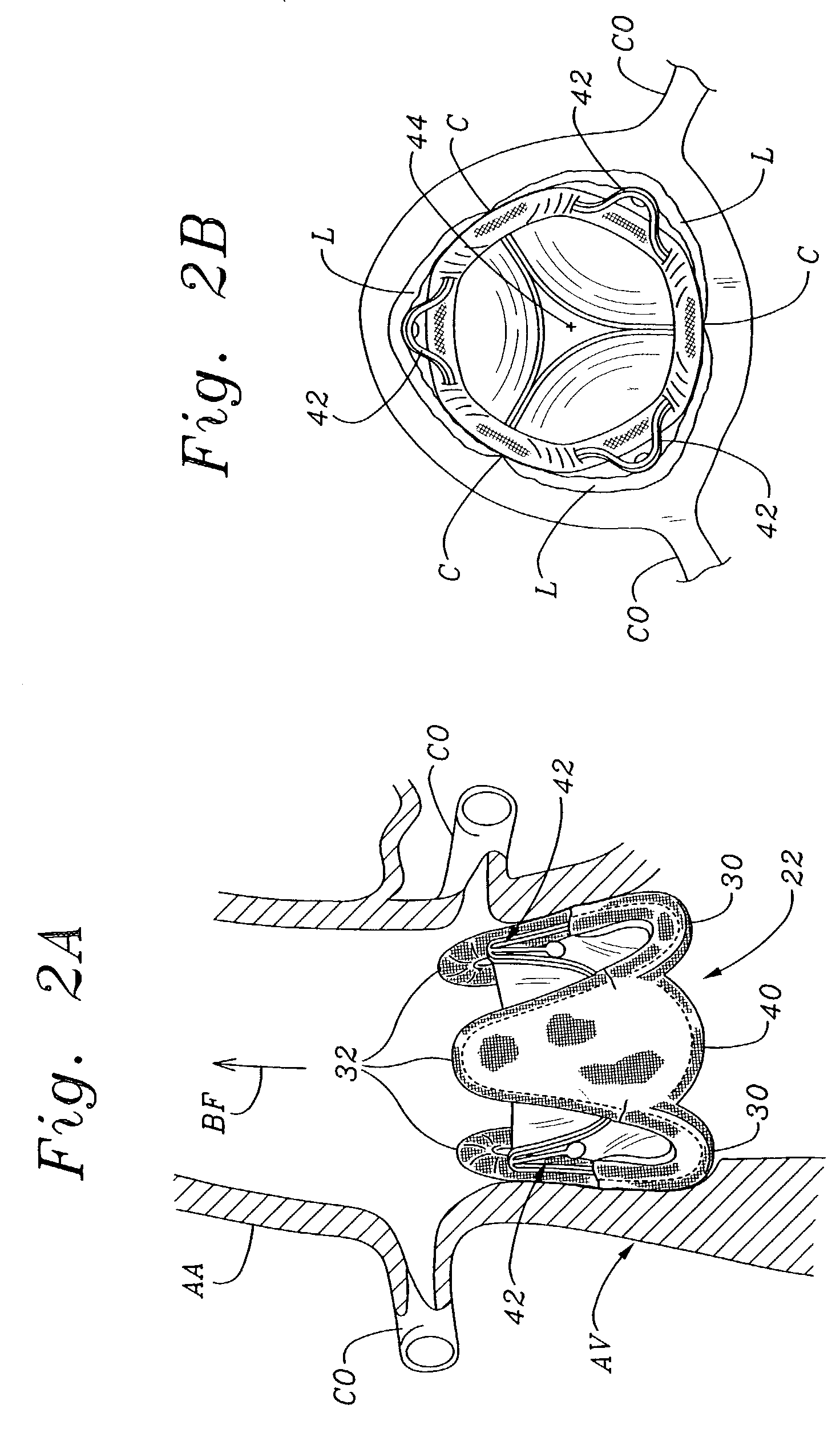
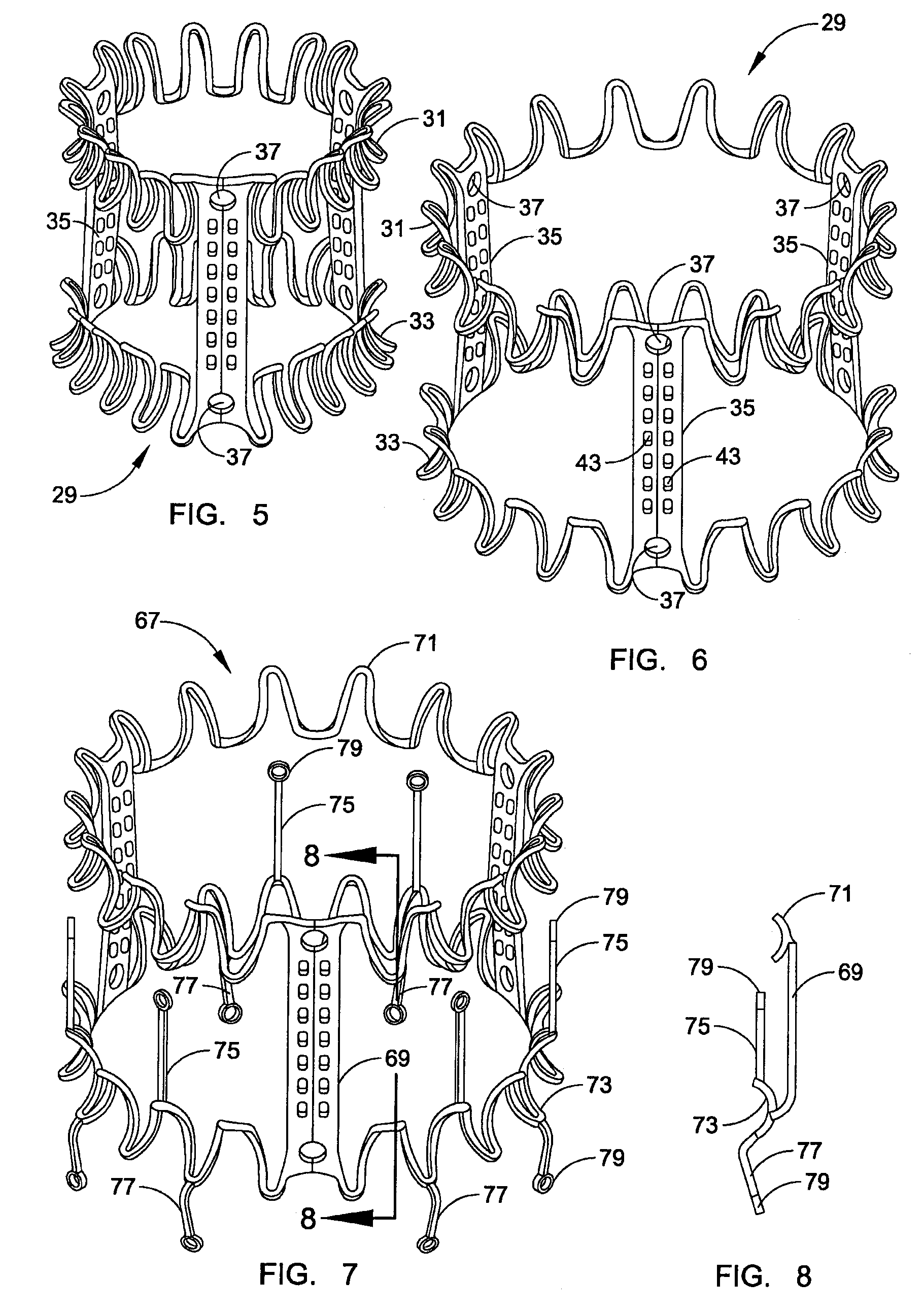
Prosthetic valve for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS7018406B2Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisCommissure
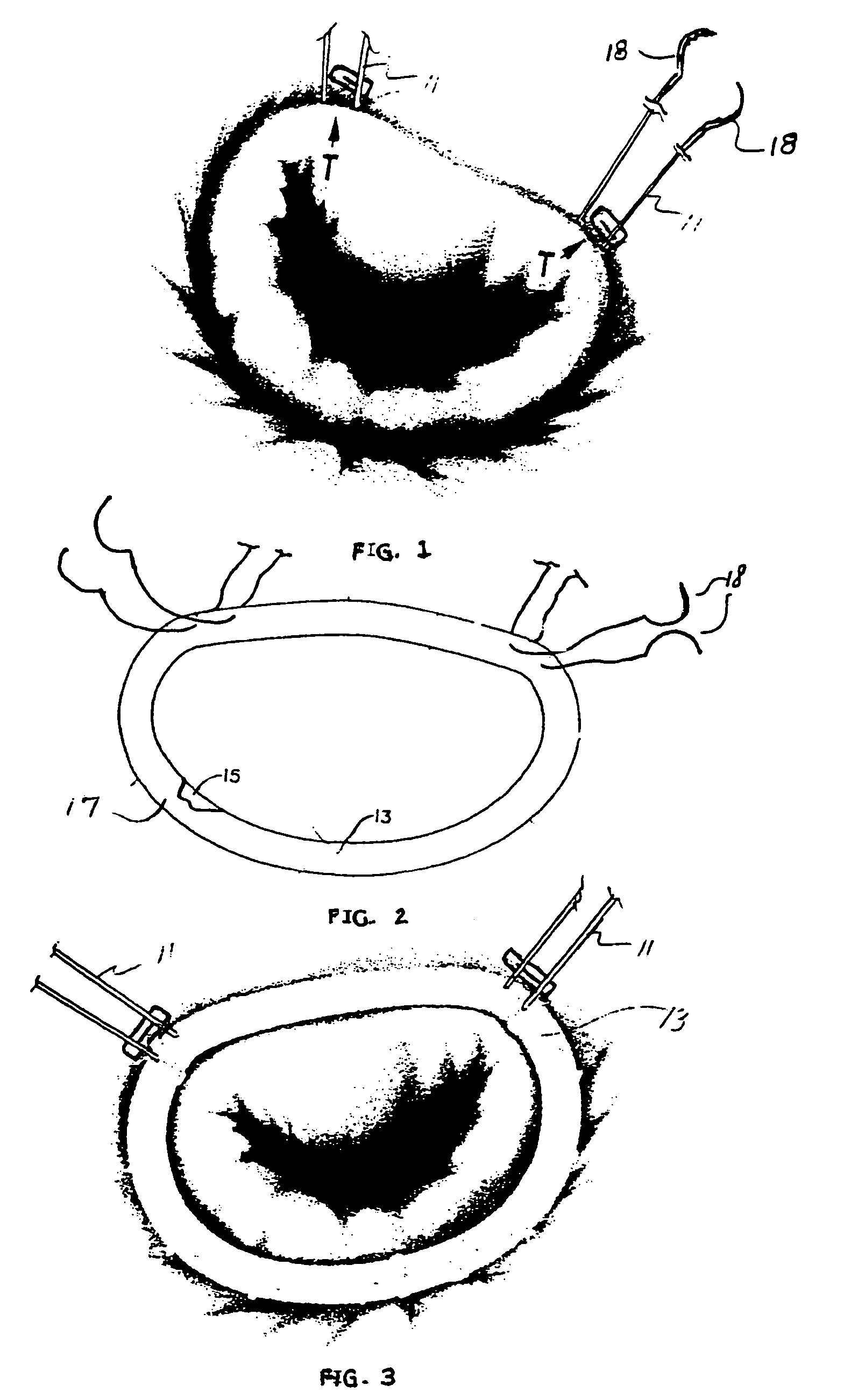
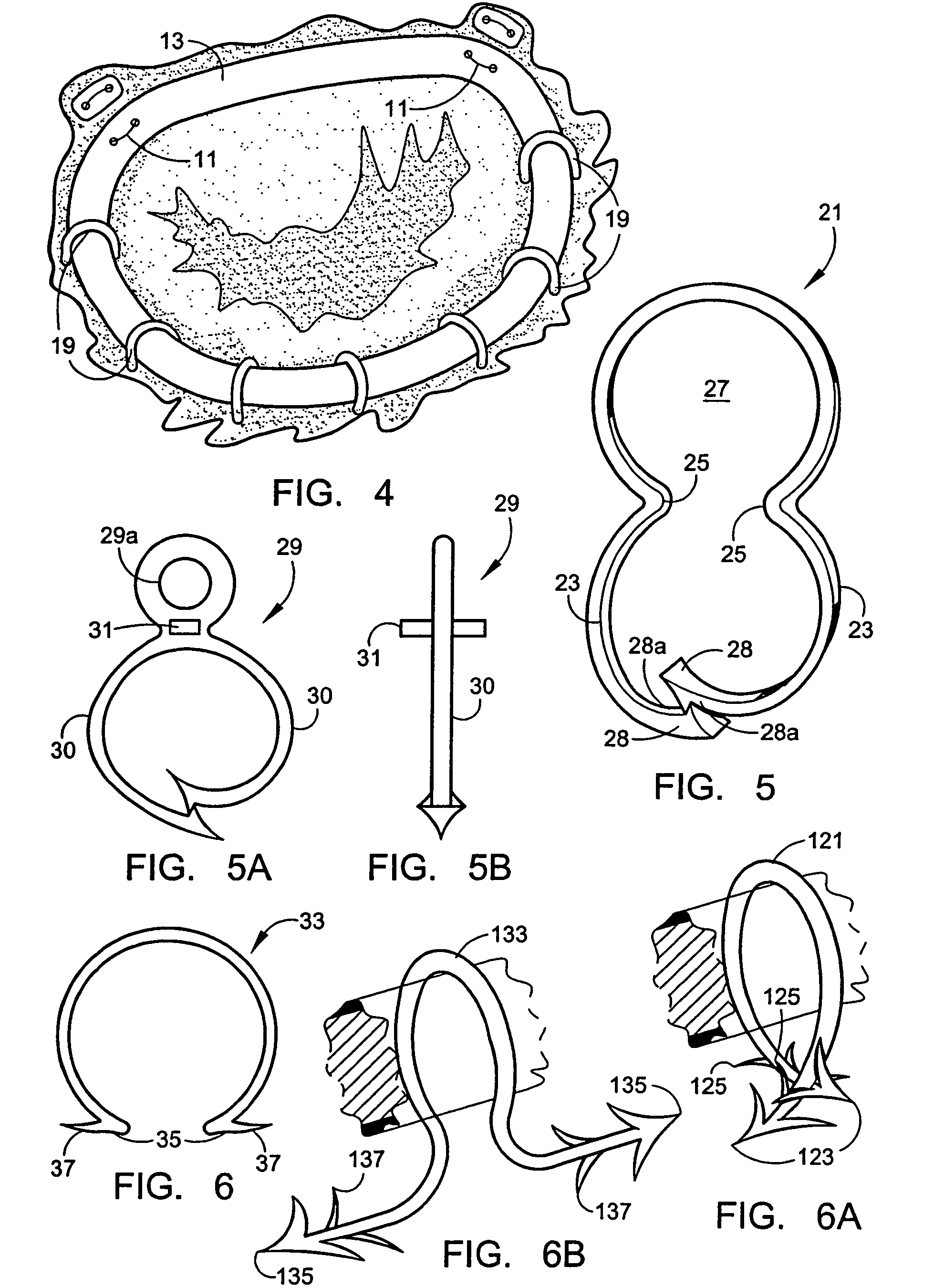
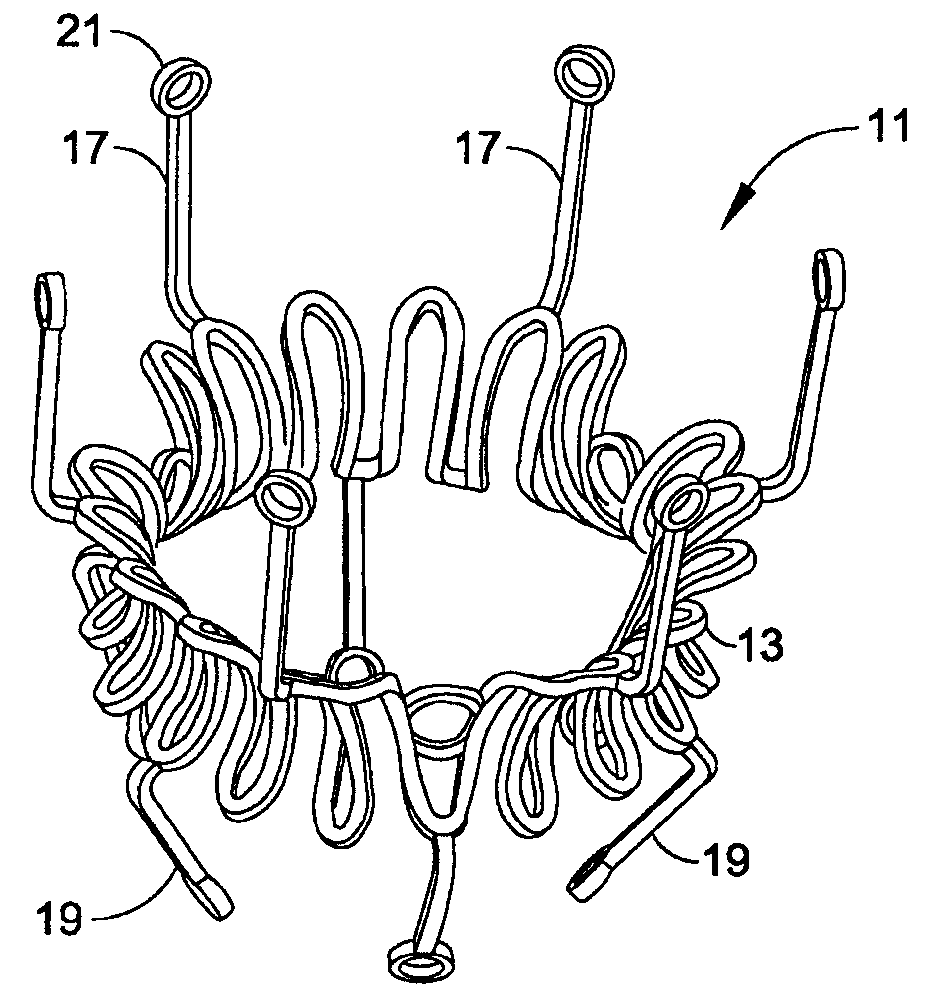
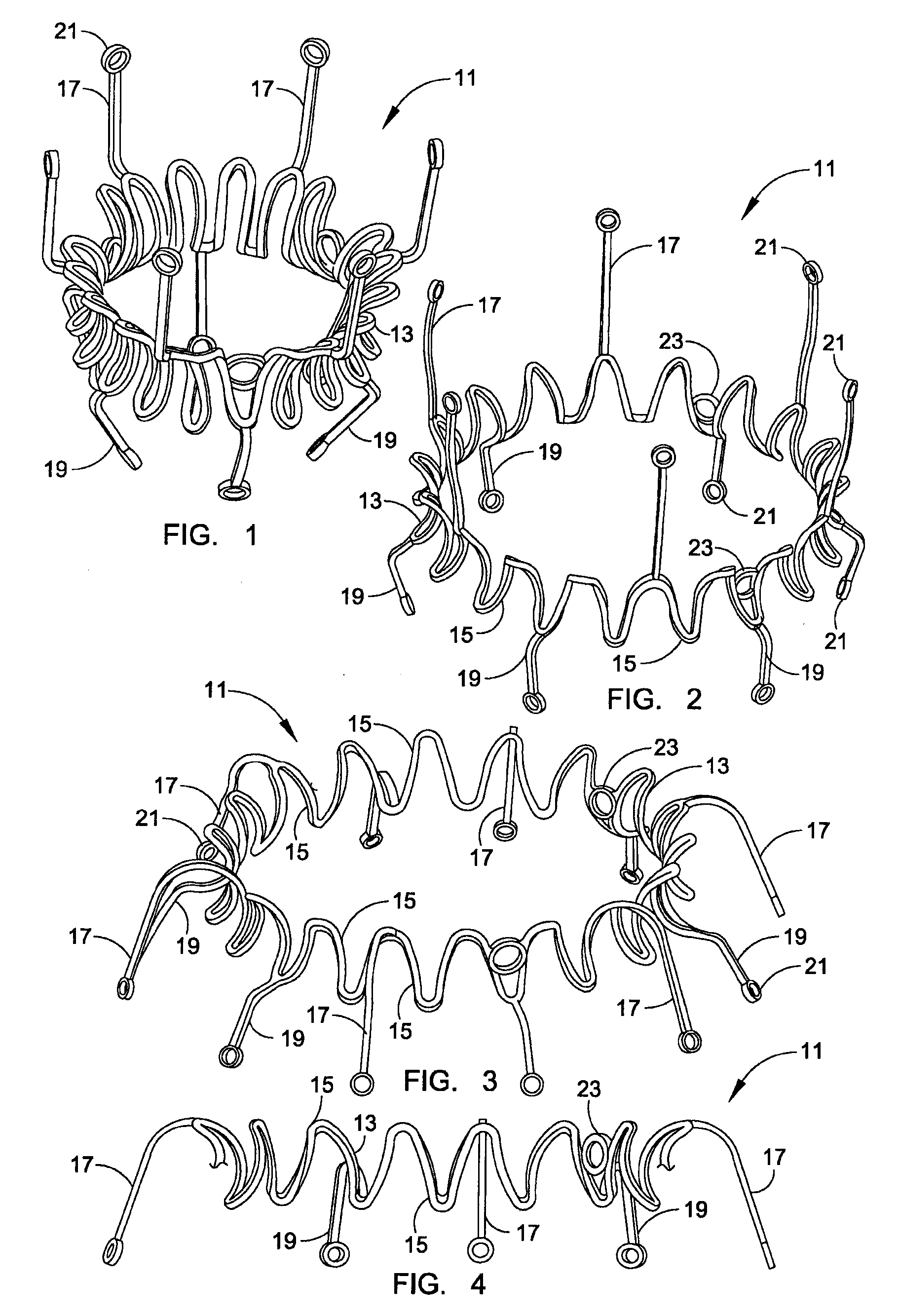
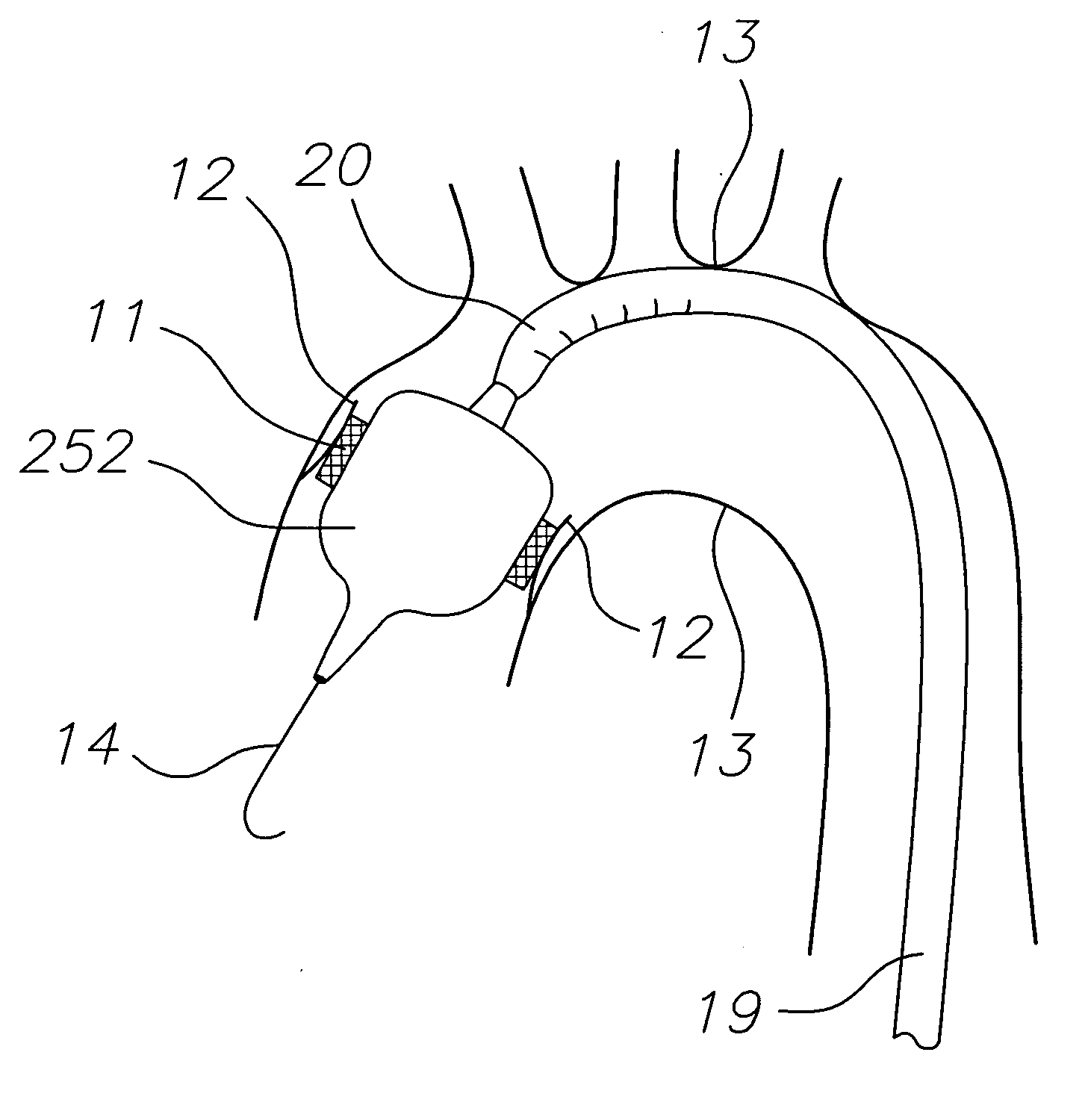
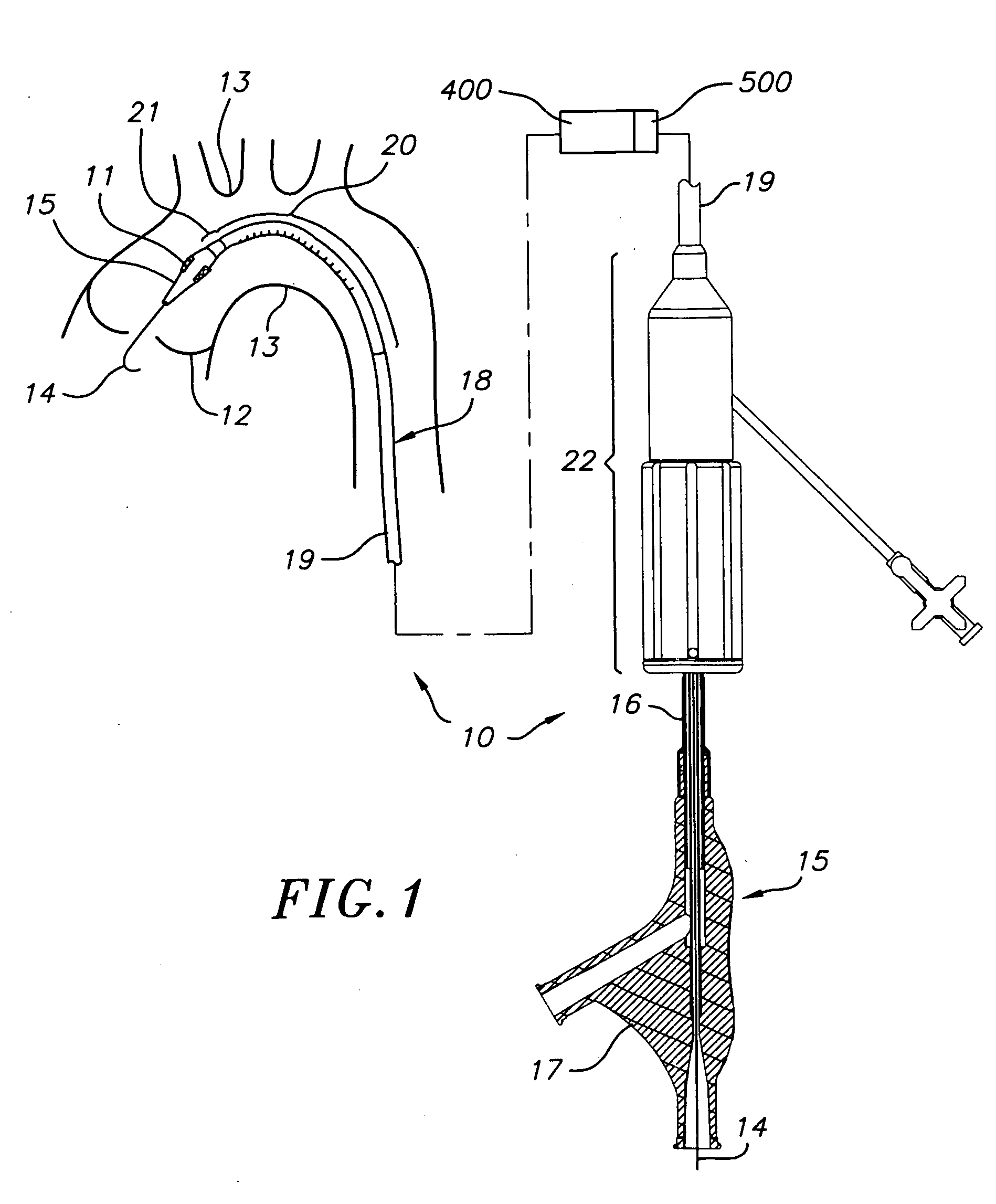
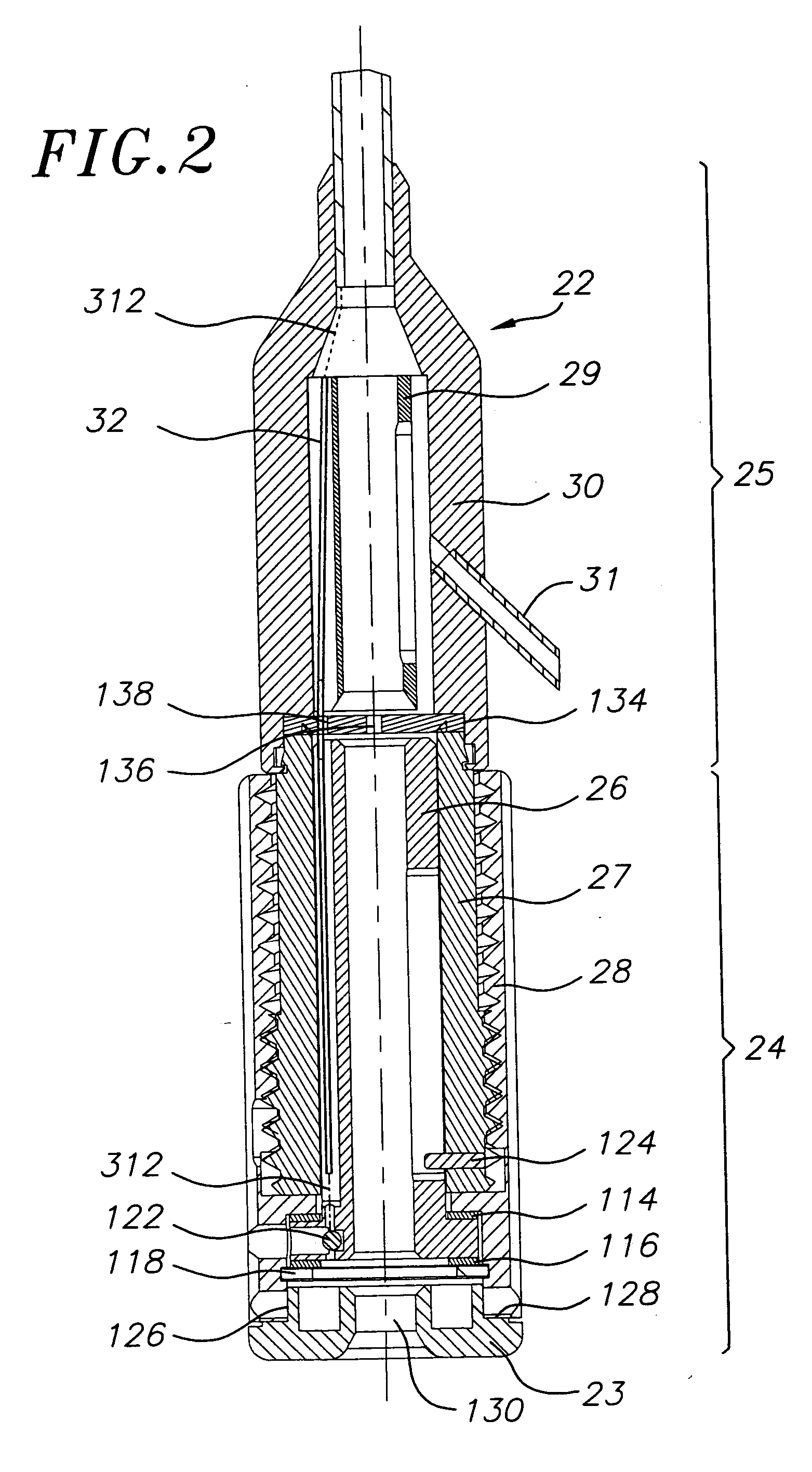
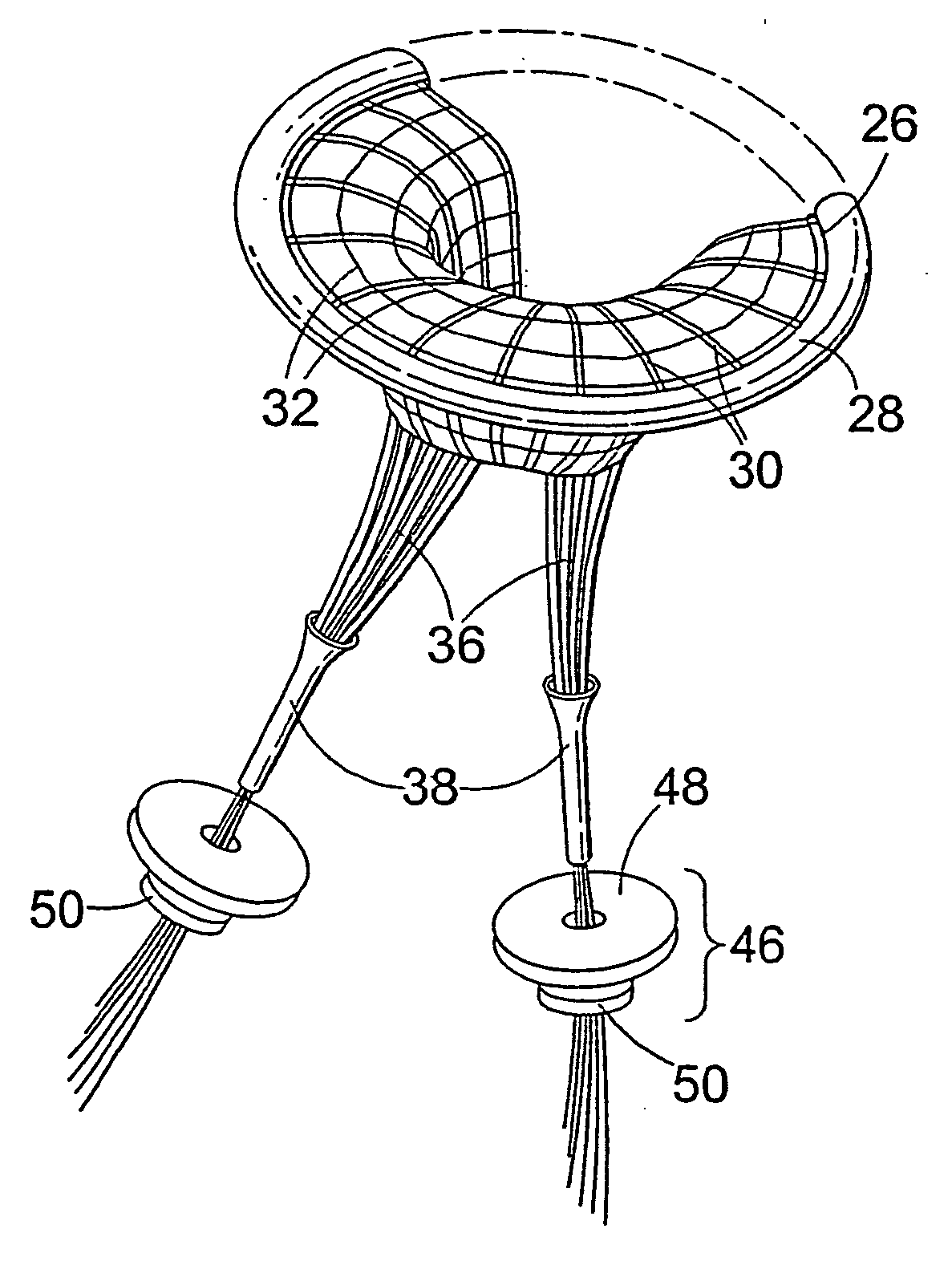
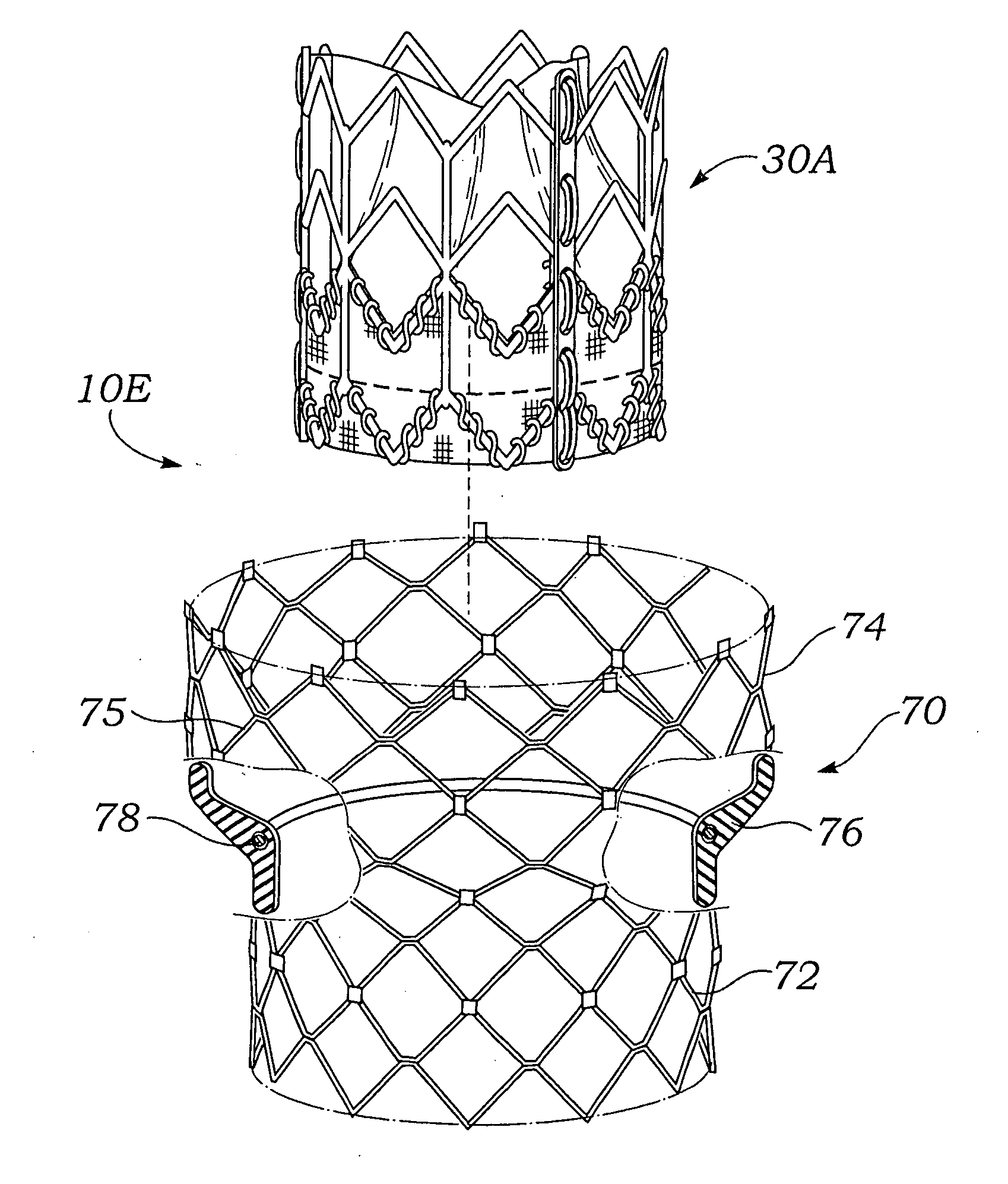
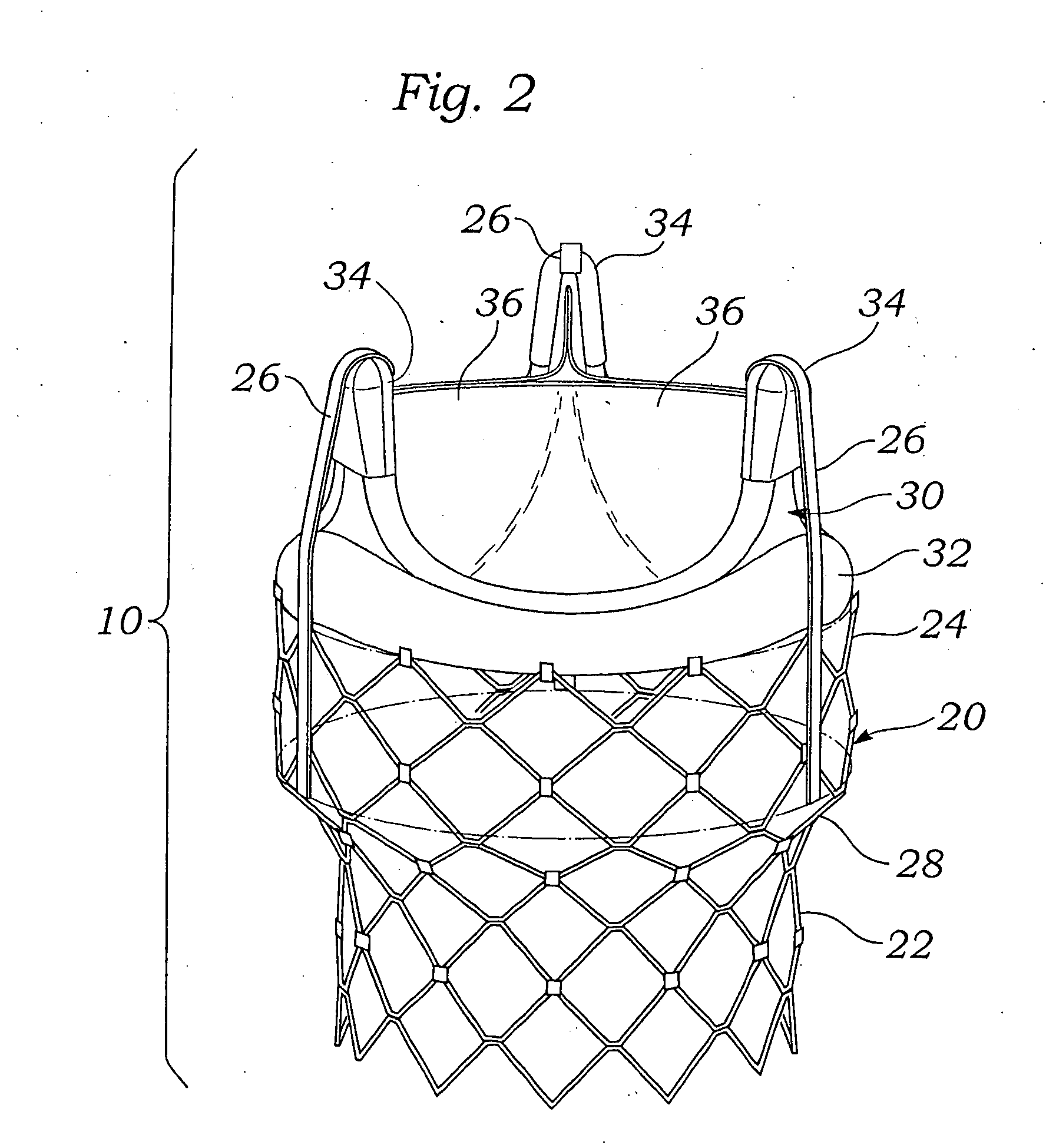
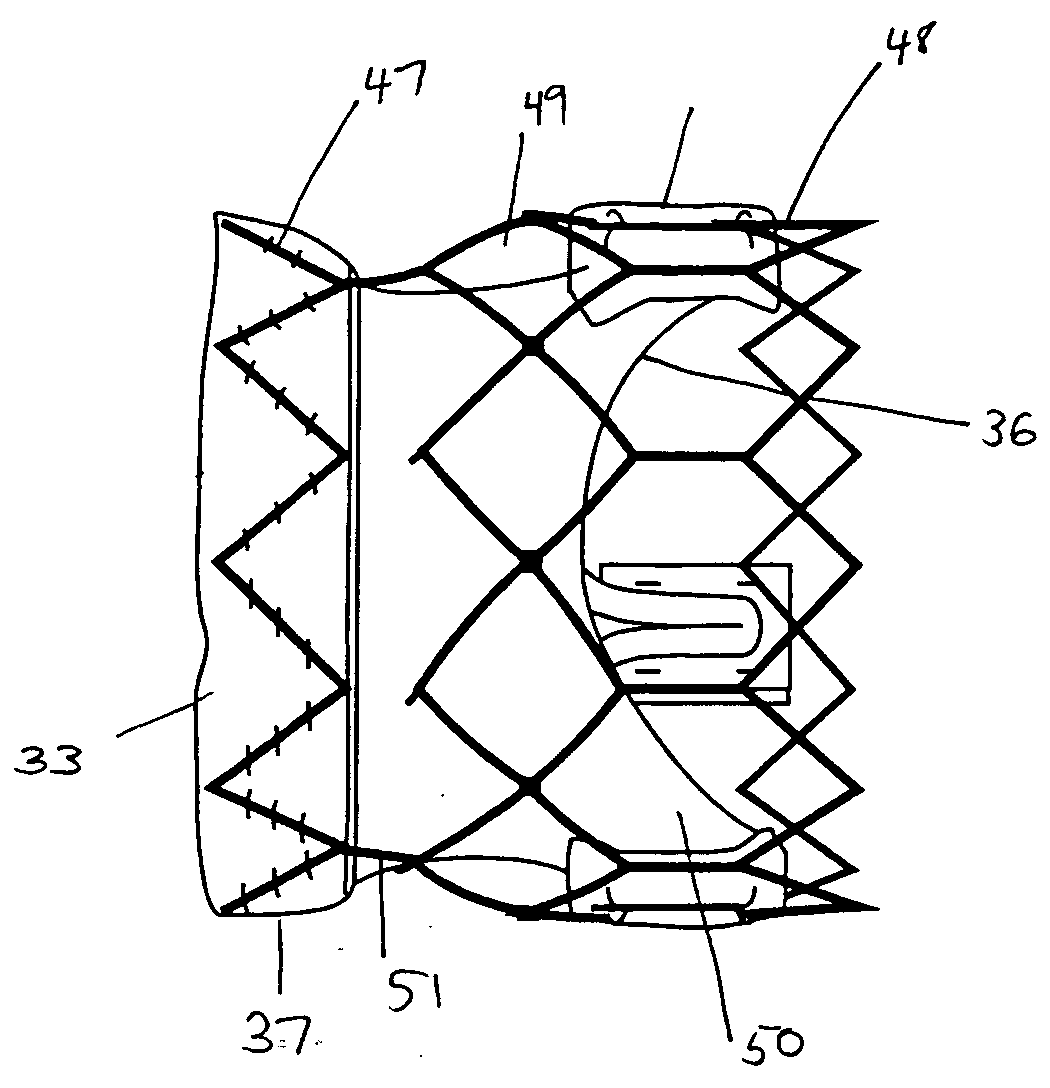
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchor may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand within the deficient native valve, and the anchor engages the lumen wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Implantation system for annuloplasty rings
InactiveUS7485142B2Good coaptation of leafletImprove hemodynamic functionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEffective lengthShape-memory alloy
Methods for reconfiguring an atrioventricular heart valve that may use systems comprising a partial or complete annuloplasty rings proportioned to reconfigure a heart valve that has become in some way incompetent, a pair of trigonal sutures or implantable anchors, and a plurality of staples which may have pairs of legs that are sized and shaped for association with the ring at spaced locations along its length. These systems permit relative axial movement between the staples and the ring, whereby a patient's heart valve can be reconfigured in a manner that does not deter subtle shifting of the native valve components. Shape-memory alloy material staples may have legs with free ends that interlock following implantation. Annuloplasty rings may be complete or partial and may be fenestrated. One alternative method routes a flexible wire, preferably of shape-memory material, through the bights of pre-implanted staples. Other alternative systems use linkers of shape-memory material having hooked ends to interengage with staples or other implanted supports which, following implantation, decrease in effective length and pull the staples or other supports toward one another so as to create desired curvature of the reconfigured valve. These linkers may be separate from the supports or may be integral with them and may have a variety of shapes and forms. Various of these systems may be implanted non-invasively using a delivery catheter.
Owner:QUICKRING MEDICAL TECH LTD
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS20090005863A1Minimally invasiveSufficient flexibilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
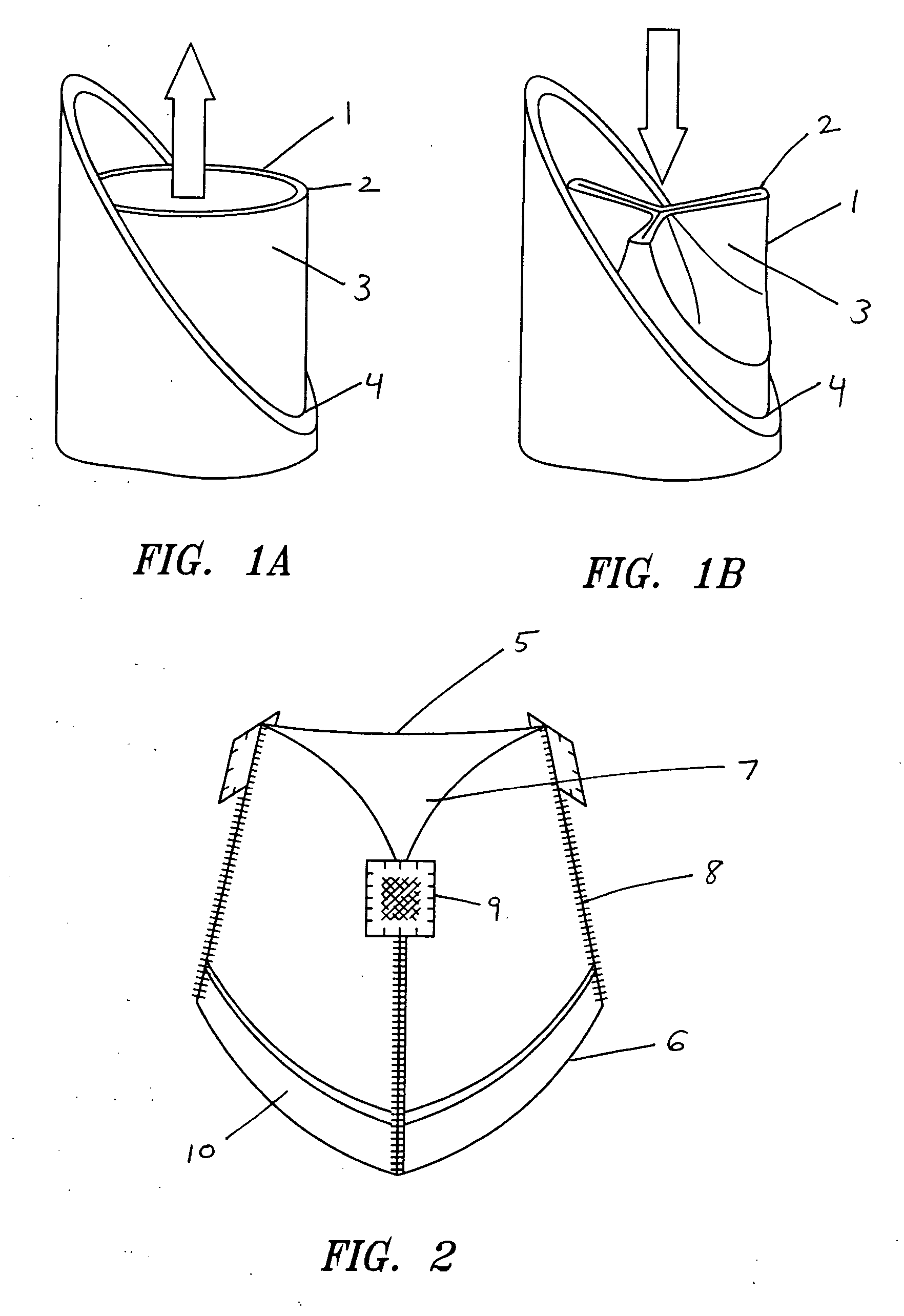
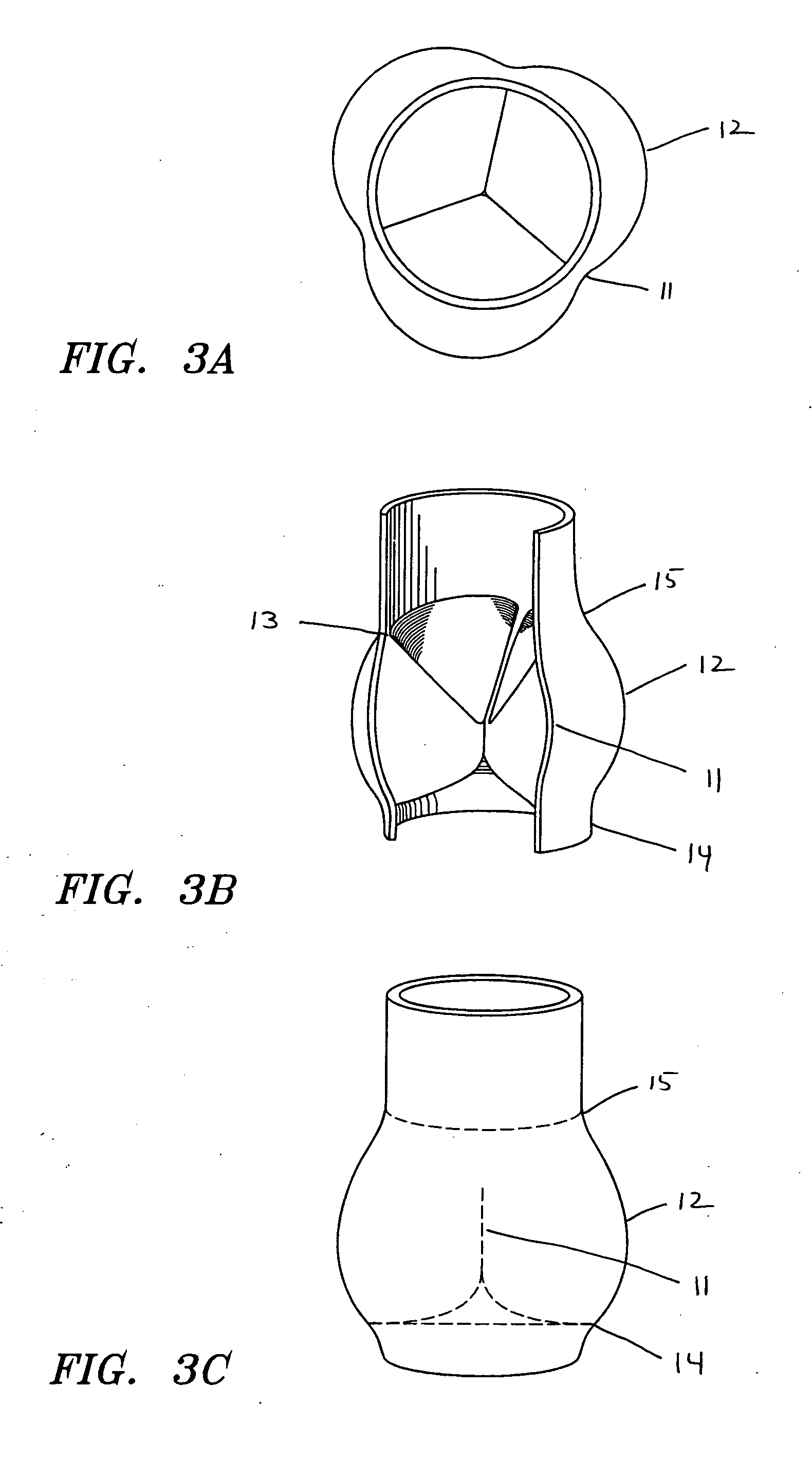
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Non-cylindrical prosthetic valve system for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS20070043435A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesCoronary arteriesProsthesis
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable prosthesis frame. If desired, one or more expandable anchors may be used. The prosthesis frame, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the prosthesis frame may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. The prosthesis frame is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthesis frame expands to an expanded position such that the valve and prosthesis frame expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. The prosthesis frame has a non-cylindrical configuration with a preset maximum expansion diameter region about the valve opening to maintain the preferred valve geometry. The prosthesis frame may also have other regions having a preset maximum expansion diameter to avoid blockage of adjacent structures such as the coronary ostia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
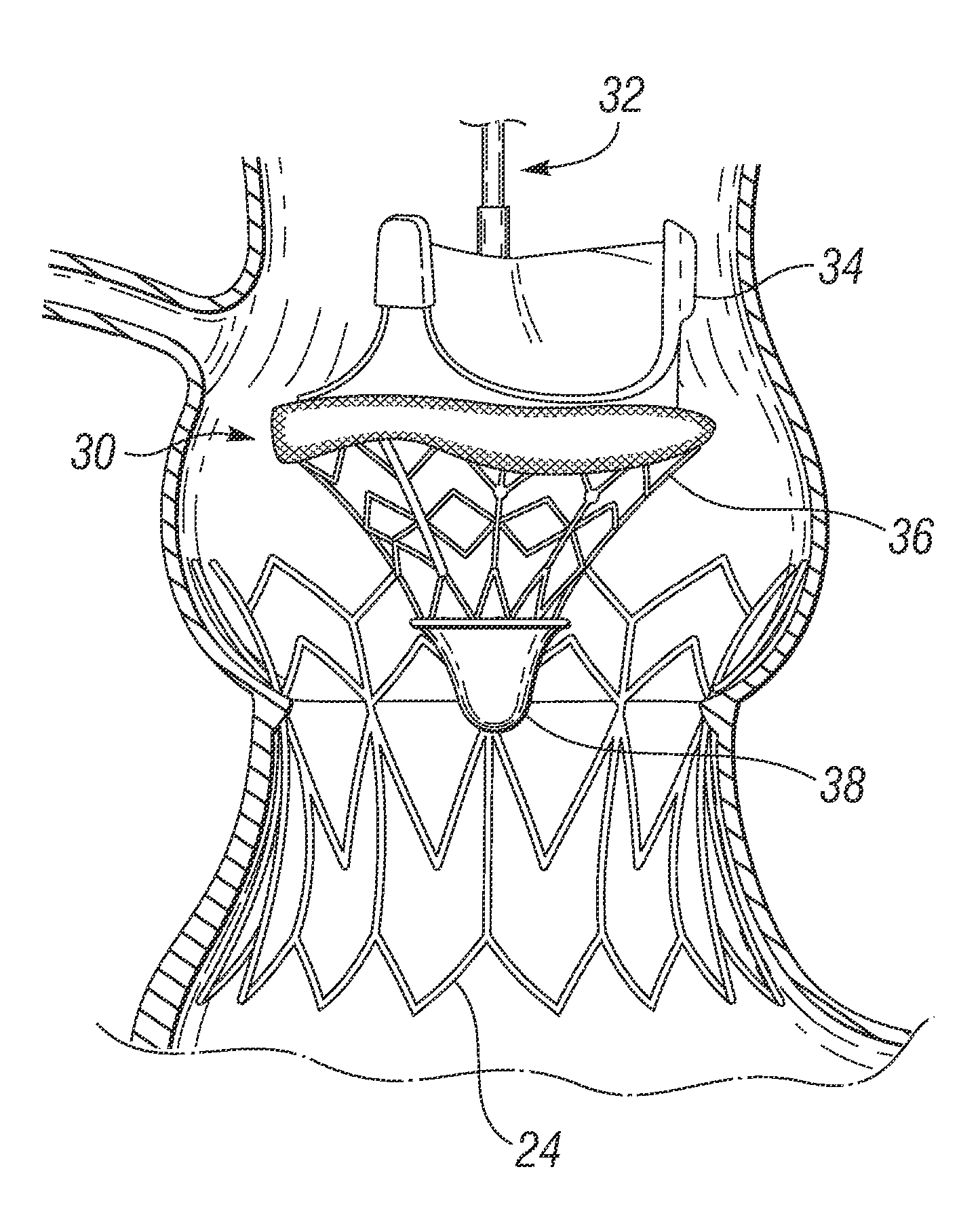
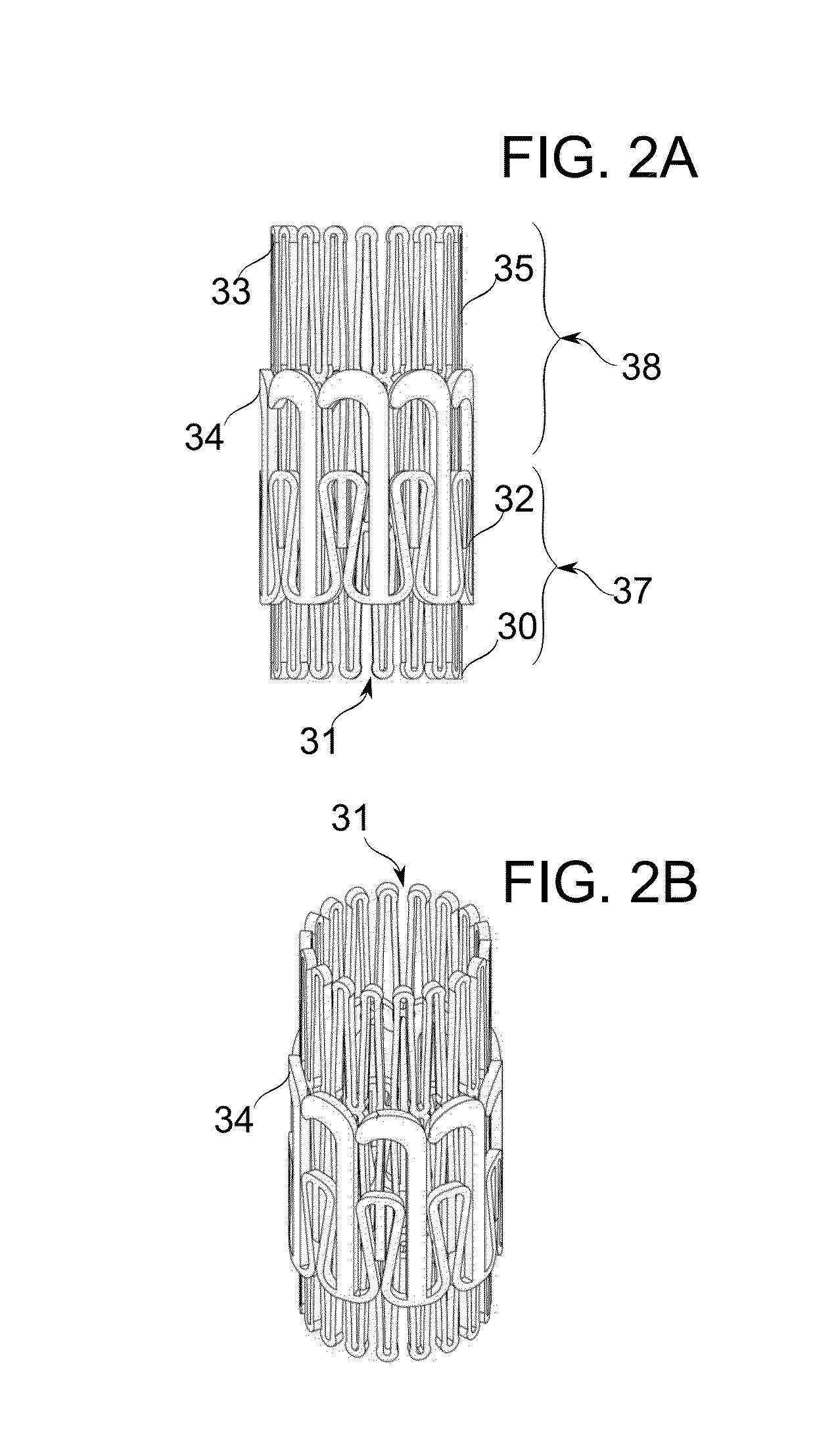
Heart valve delivery system
ActiveUS20070005131A1Easy to navigateIncrease thrustBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthetic heartBalloon catheter
A delivery system for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to a native valve site within the human vasculature. The prosthetic valve is disposed on a balloon at the end of a balloon catheter. The balloon catheter passes through a delivery sleeve assembly and handle. A pull wire travels from the handle to a distal end of the delivery sleeve assembly. Actuation of the handle pulls on the pull wire, which causes openings in a slotted tube of the delivery sleeve assembly to close, thus causing the delivery sleeve assembly to bend. A stretchable cover is placed over the slotted tube for biasing the steerable catheter toward a straight position. Once advanced to the native valve site, the prosthetic valve is deployed by inflating the balloon.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Mitral valve prosthesis
The present invention relates to a mitral valve prosthesis comprising flexible leaflet-like elements with curved coapting surfaces and means for maintaining continuity of the valve when inserted into the mitral annulus, which mimics the continuity between the papillary muscles, the chordae tendineae, the mitral valve leaflets and the mitral annulus of a natural valve. The present invention also relates to a method of fitting such a prosthesis to heart of a patient.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Methods for rapid deployment of prosthetic heart valves
ActiveUS20060287717A1Quickly and easily replacingUse minimizedStentsAnnuloplasty ringsInsertion stentCoupling
A two-stage or component-based valve prosthesis that can be quickly and easily implanted during a surgical procedure is provided. The prosthetic valve comprises a support structure that is deployed at a treatment site. The prosthetic valve further comprises a valve member configured to be quickly connected to the support structure. The support structure may take the form of a stent that is expanded at the site of a native valve. If desired, the native leaflets may remain and the stent may be used to hold the native valve open. In this case, the stent may be balloon expandable and configured to resist the powerful recoil force of the native leaflets. The support structure is provided with a coupling means for attachment to the valve member, thereby fixing the position of the valve member in the body. The valve member may be a non-expandable type, or may be expandable from a compressed state to an expanded state. The system is particularly suited for rapid deployment of heart valves in a conventional open-heart surgical environment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
System and method for transapical delivery of an annulus anchored self-expanding valve
ActiveUS20080140189A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemStentsBalloon catheterLimited accessCardiac muscle
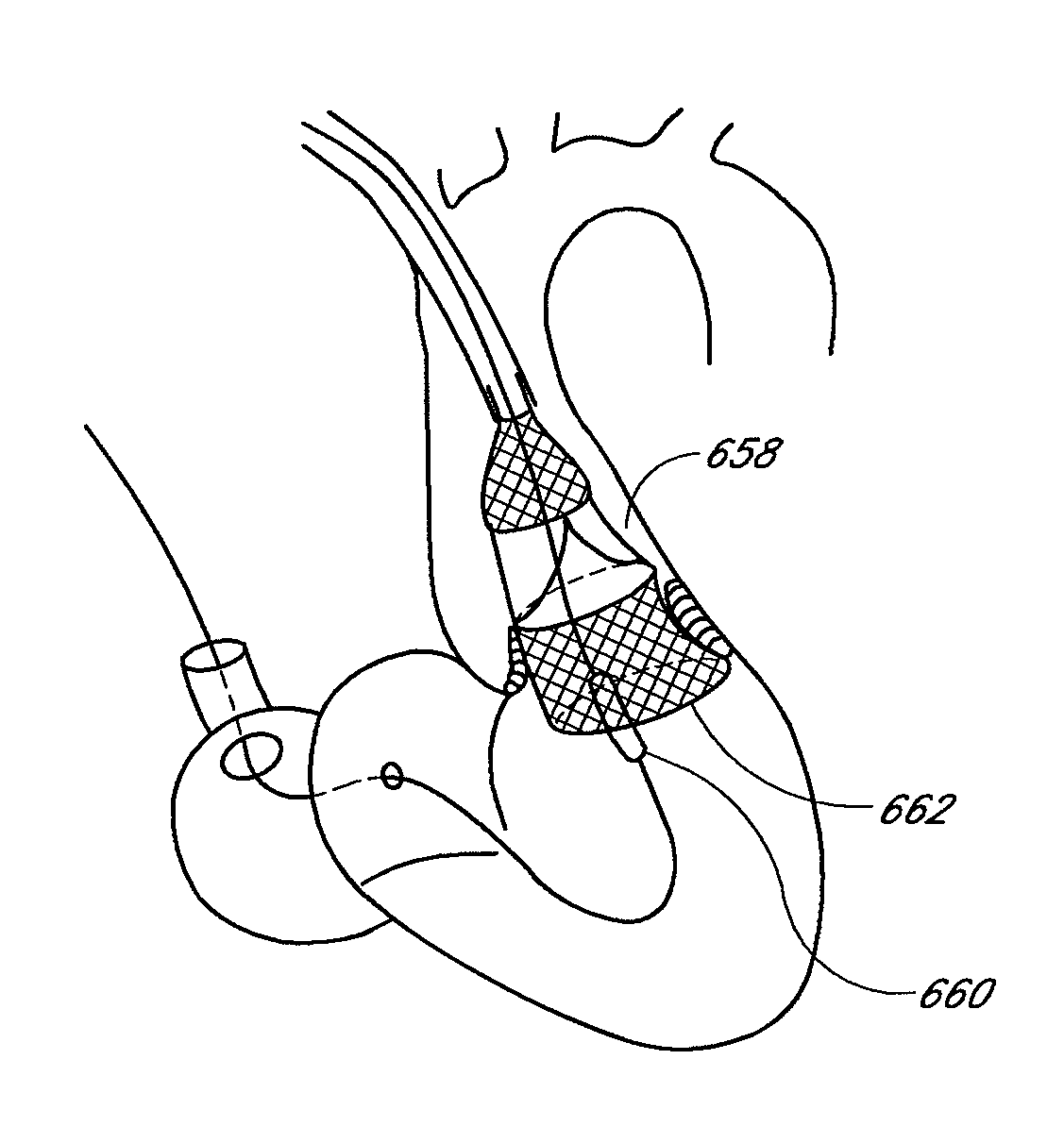
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable prosthesis frame. The valve may be delivered transluminally or transmyocardially using a thorascopic or other limited access approach using a delivery catheter. Preferably, the initial partial expansion of the valve is performed against the native valve annulus to provide adequate anchoring and positioning of the valve as the remaining portions of the valve expand. The valve may be delivered using a retrograde or antegrade approach. When delivered using a retrograde approach, a delivery catheter with a pull-back sheath may be used, while antegrade delivery is preferably performed with a delivery catheter with a push-forward sheath that releases the proximal end of the valve first.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Devices, systems, and methods for supplementing, repairing, or replacing a native heart valve leaflet
Devices, systems and methods supplement, repair, or replace a native heart valve. The devices, systems, and methods employ an implant that, in use, extends adjacent a valve annulus. The implant includes a mobile neoleaflet element that occupies the space of at least a portion of one native valve leaflet. The implant mimics the one-way valve function of a native leaflet, to resist or prevent retrograde flow. The implant restores normal coaptation of the leaflets to resist retrograde flow, thereby resisting eversion and / or prolapse, which, in turn, reduces regurgitation.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050096738A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:CALI DOUGLAS S +1
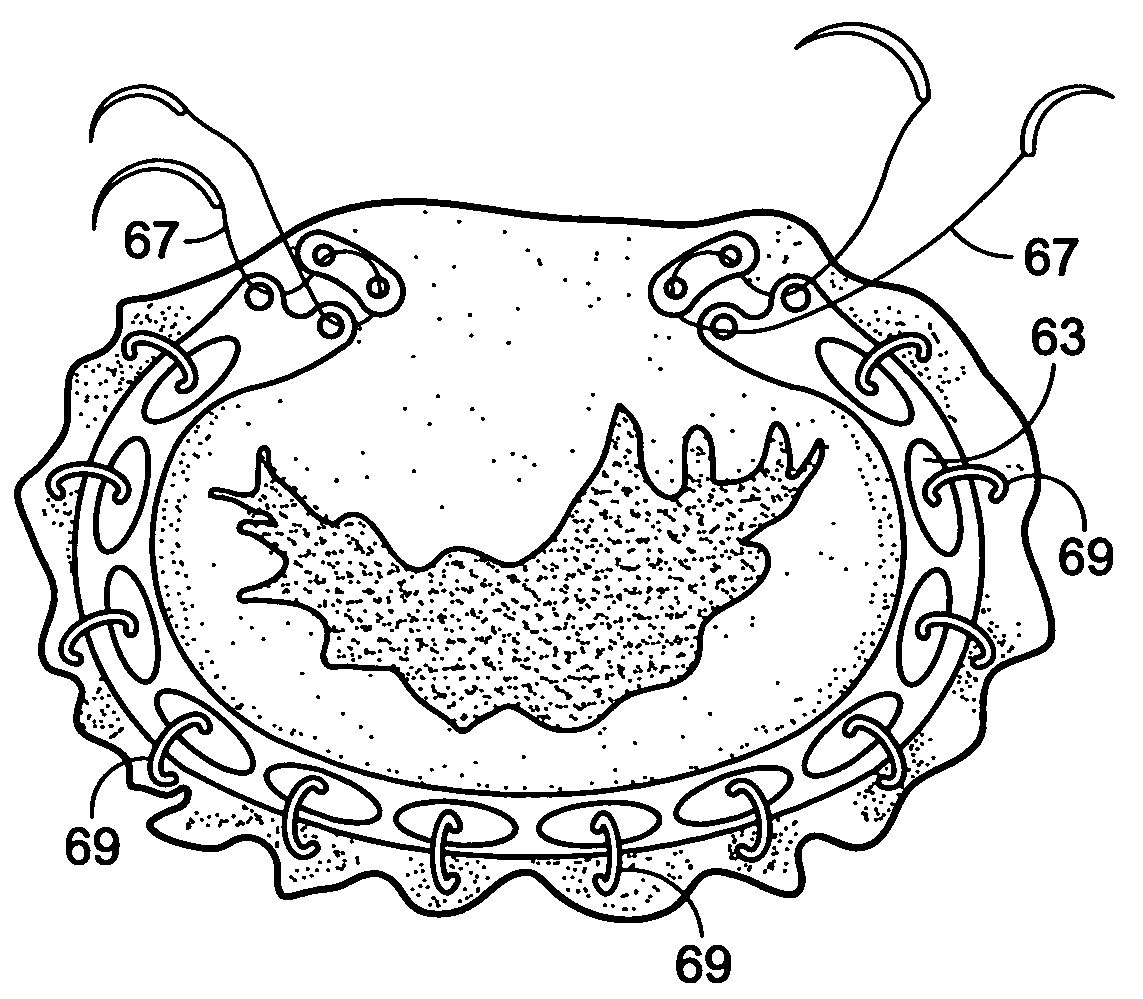
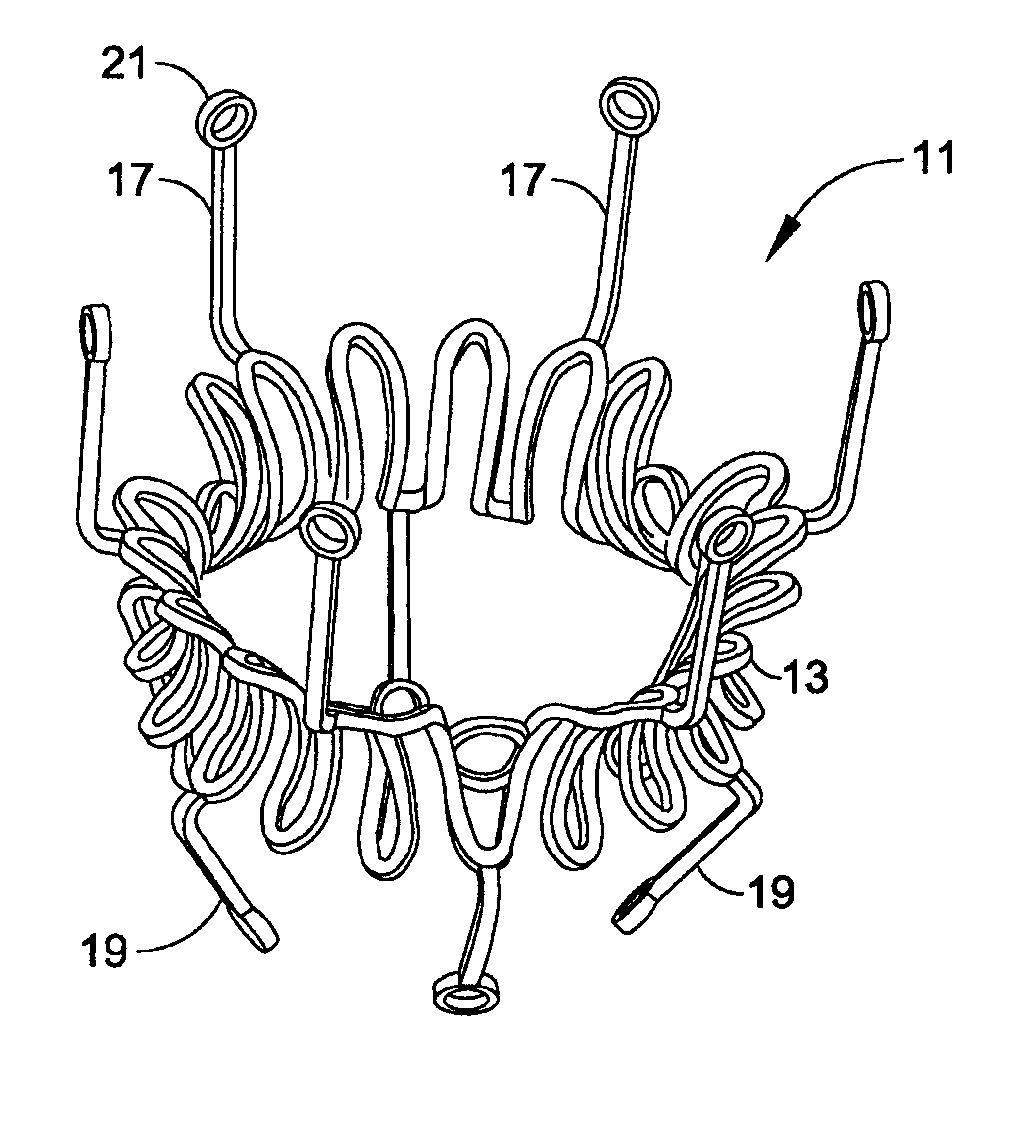
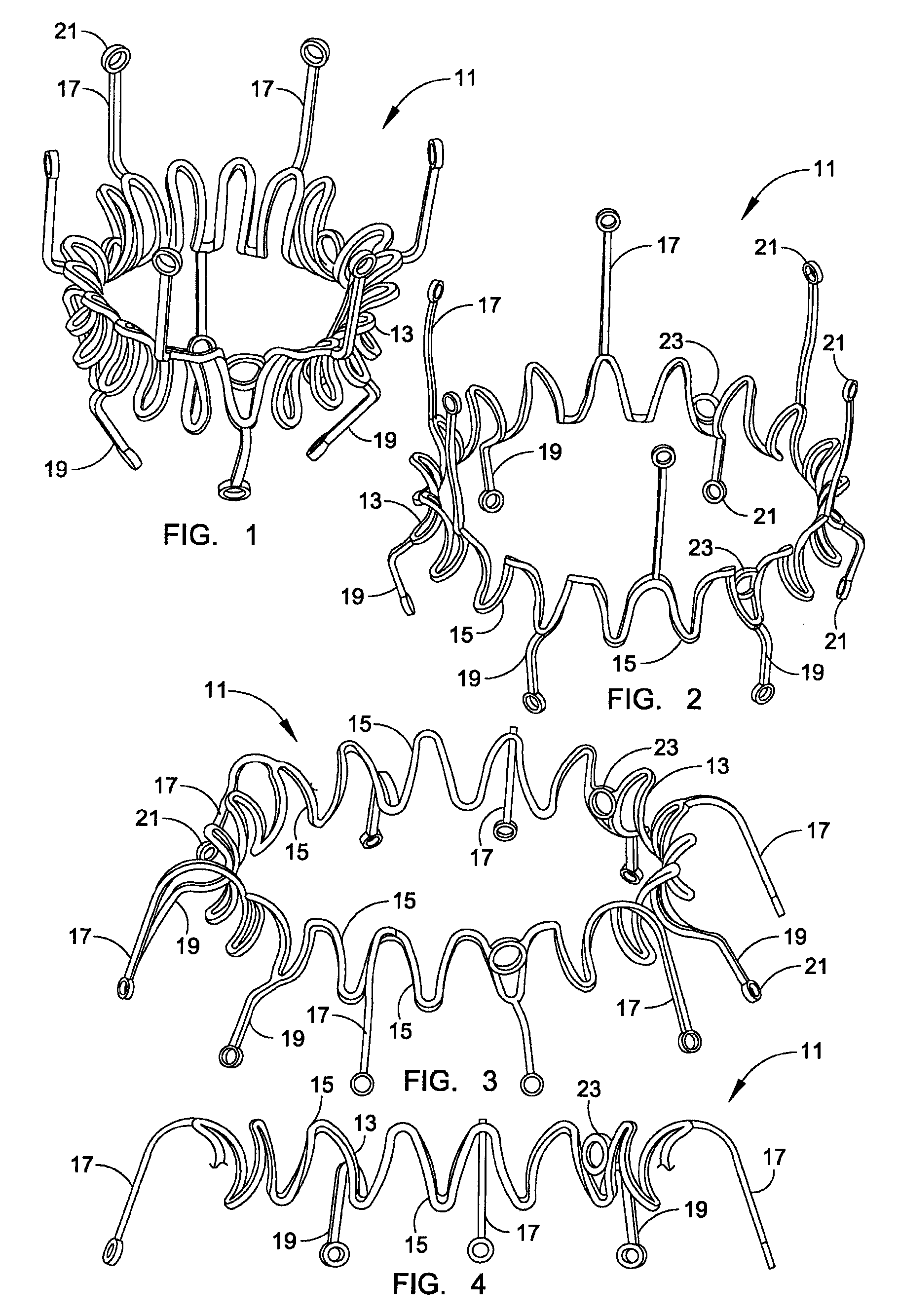
Prosthetic mitral valve with tissue anchors
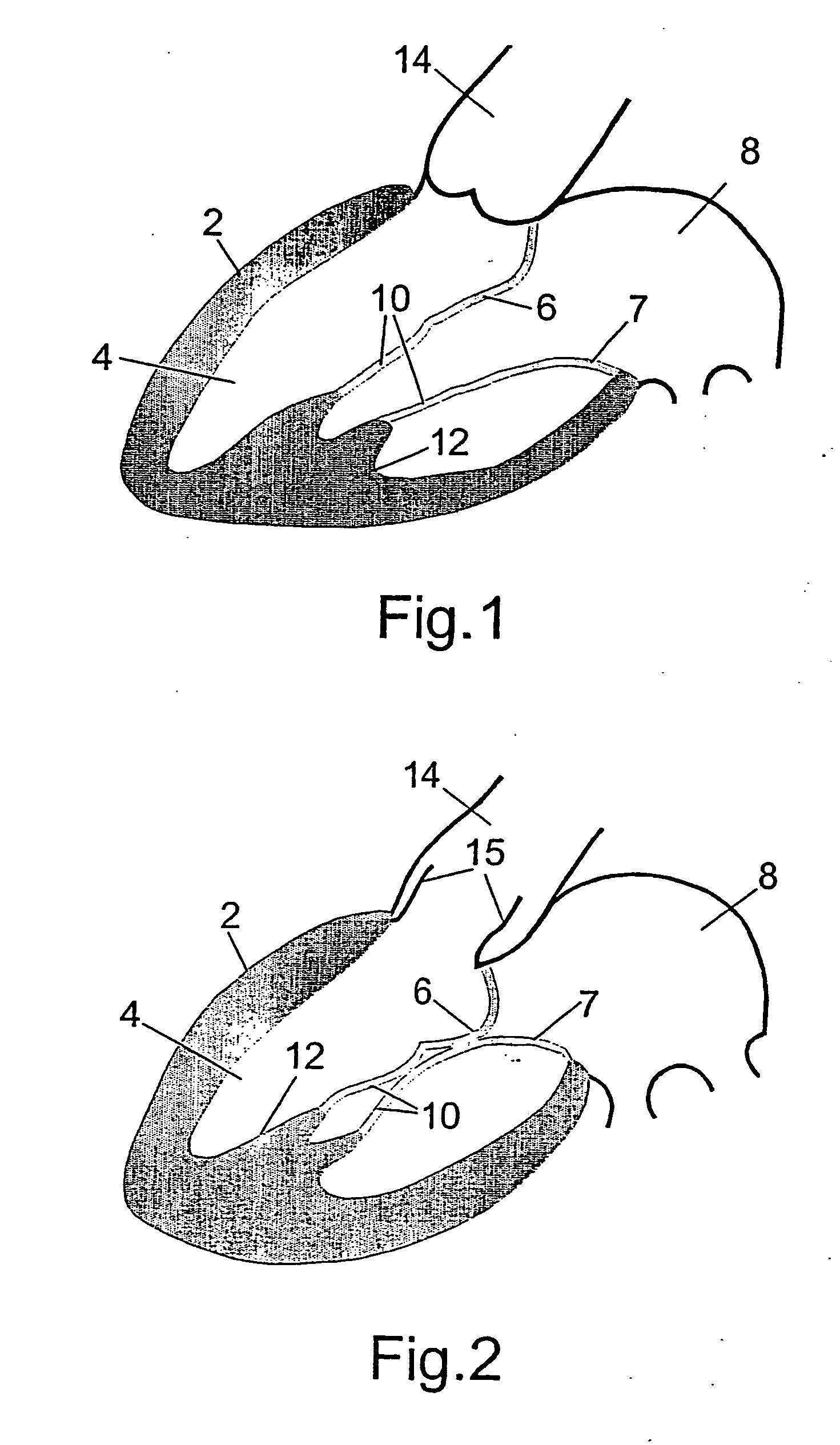
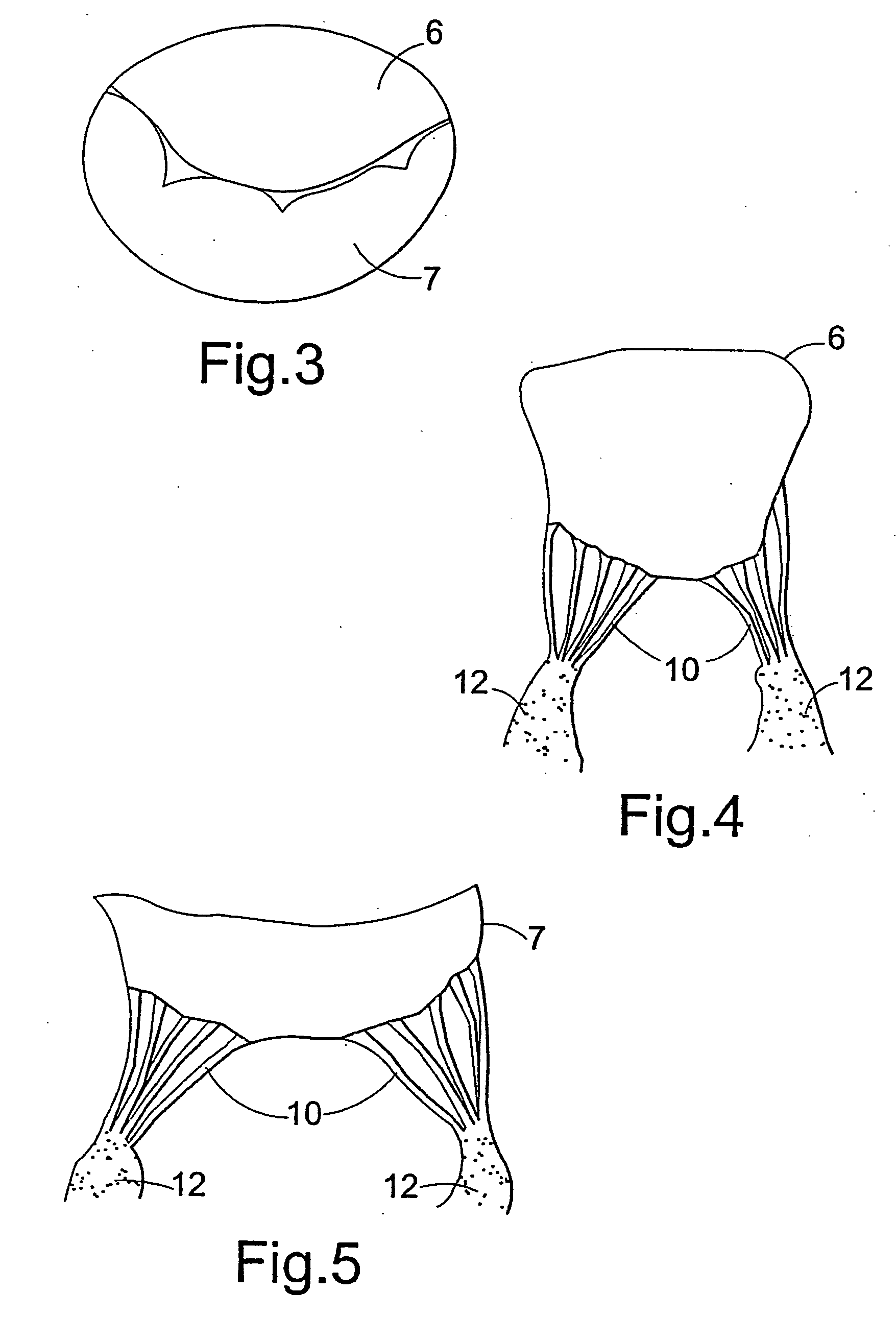
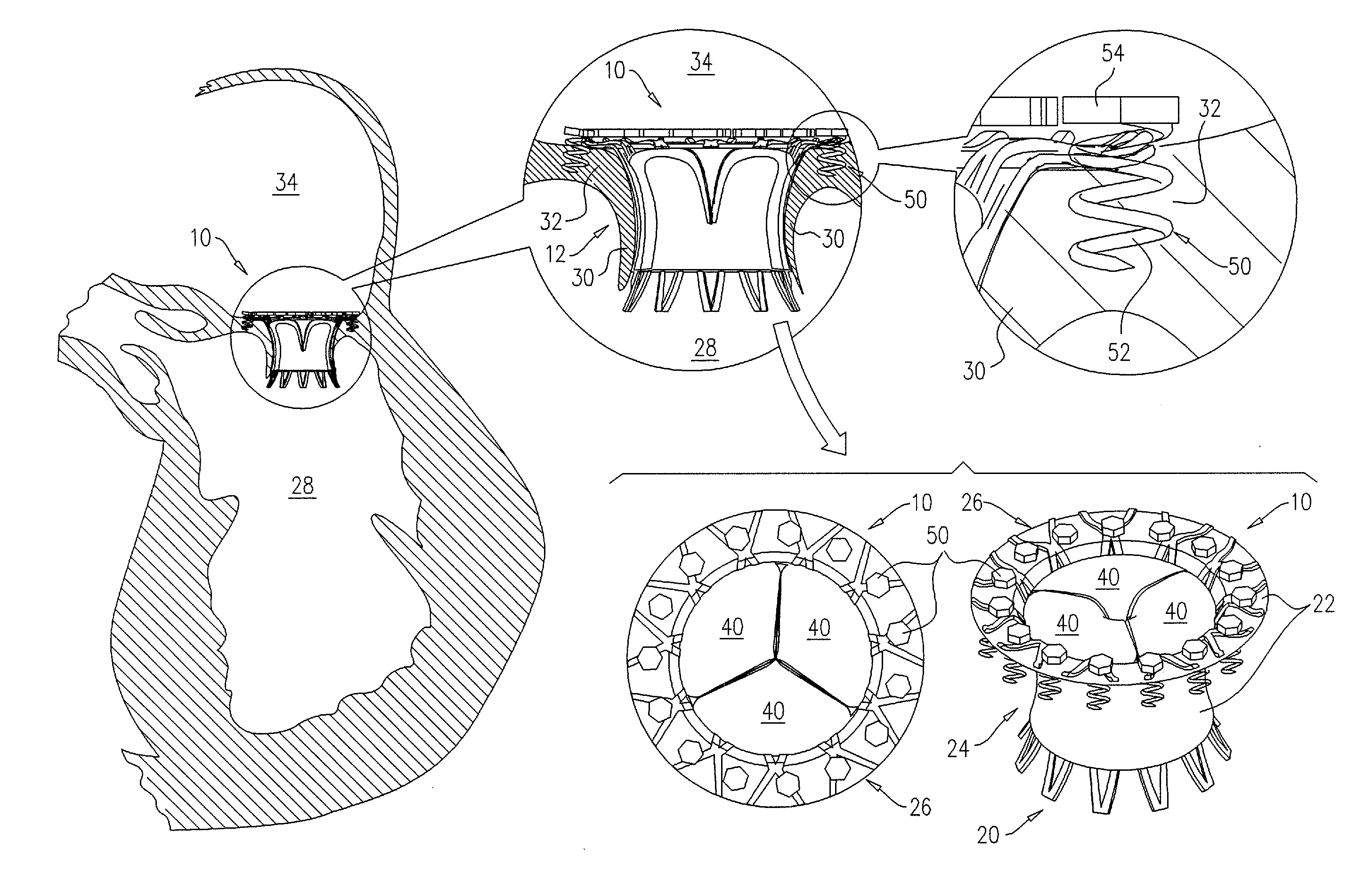
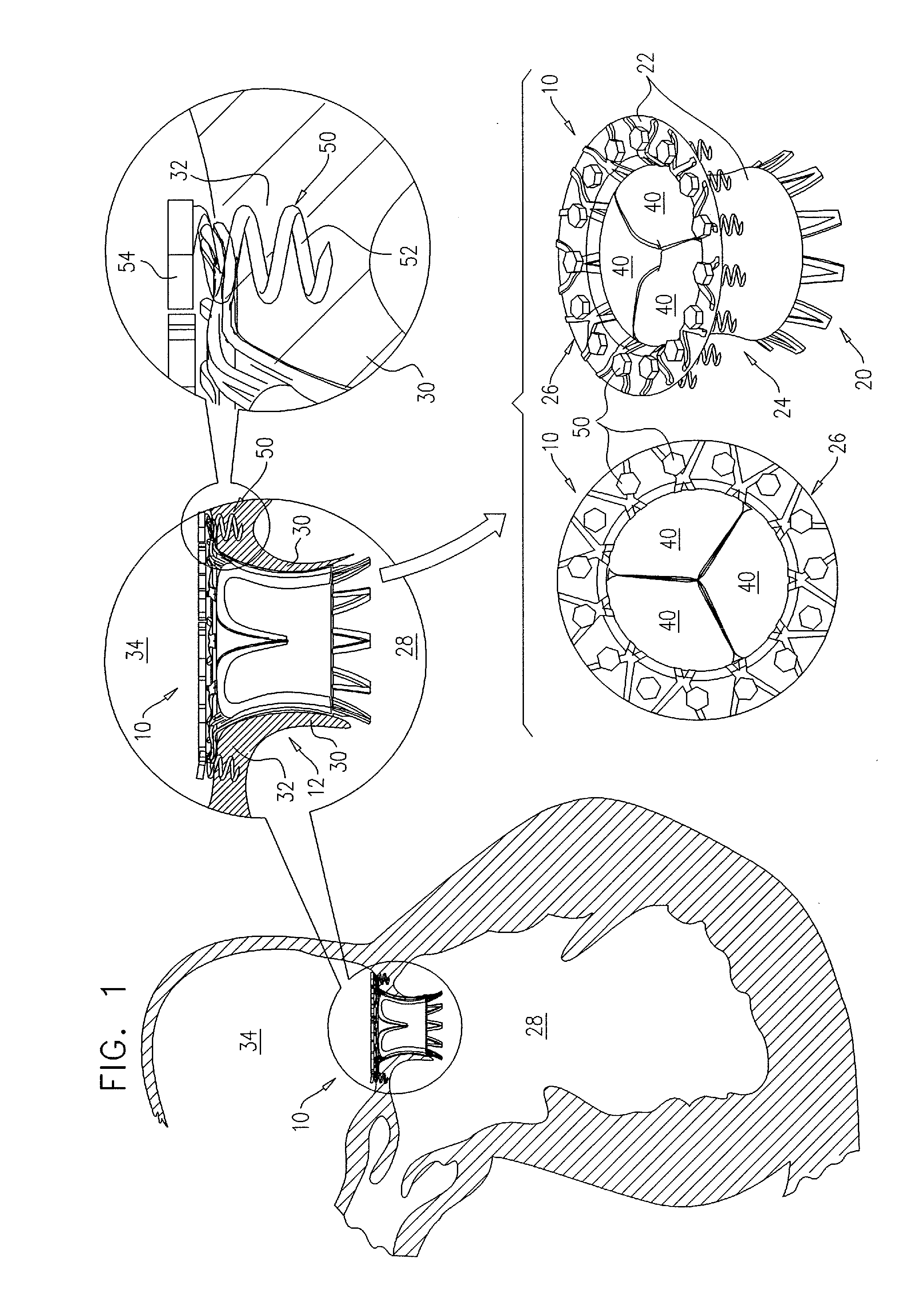
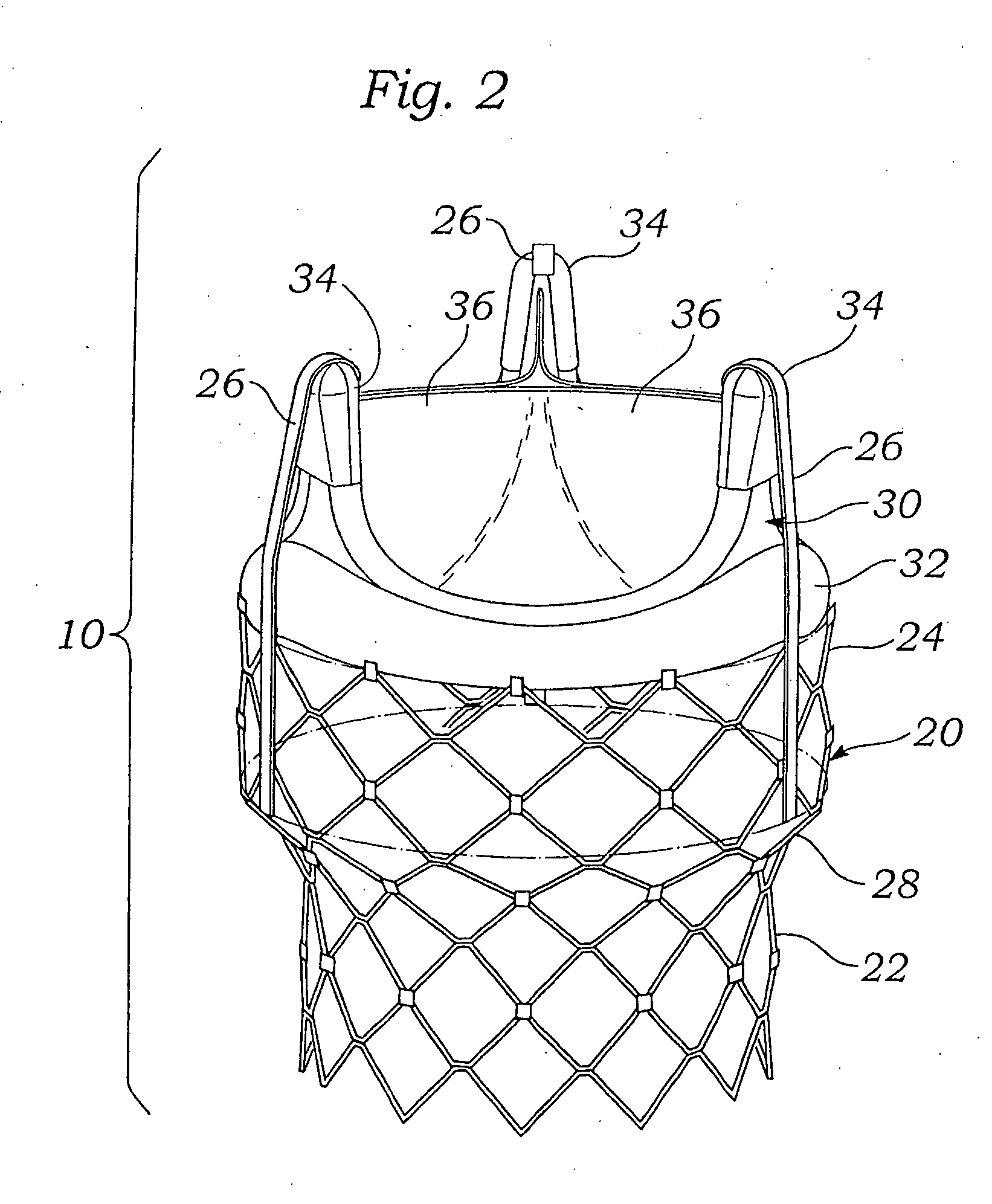
Apparatus and methods are described including a prosthetic atrioventricular valve (10) for coupling to a native atrioventricular valve (12). The prosthetic valve includes a support frame (20) and a covering (22), which at least partially covers the support frame. The support frame and the covering are shaped so as to define a downstream skirt (24). A plurality of prosthetic leaflets (40) are coupled to at least one element selected from the group consisting of the support frame and the covering. An elongated anchoring member (152) is positioned around the downstream skirt in a subvalvular space (150), such that the anchoring member presses native leaflets (30) of the native valve against the downstream skirt, thereby anchoring the prosthetic valve to the native valve. Other applications are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050075584A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:CALI DOUGLAS S
Methods for rapid deployment of prosthetic heart valves
ActiveUS7708775B2Quickly and easily replacingUse minimizedStentsAnnuloplasty ringsCouplingProsthetic heart
A two-stage or component-based valve prosthesis that can be quickly and easily implanted during a surgical procedure is provided. The prosthetic valve comprises a support structure that is deployed at a treatment site. The prosthetic valve further comprises a valve member configured to be quickly connected to the support structure. The support structure may take the form of a stent that is expanded at the site of a native valve. If desired, the native leaflets may remain and the stent may be used to hold the native valve open. In this case, the stent may be balloon expandable and configured to resist the powerful recoil force of the native leaflets. The support structure is provided with a coupling means for attachment to the valve member, thereby fixing the position of the valve member in the body. The valve member may be a non-expandable type, or may be expandable from a compressed state to an expanded state. The system is particularly suited for rapid deployment of heart valves in a conventional open-heart surgical environment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050075719A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050075724A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:SVANIDZE OLEG +1
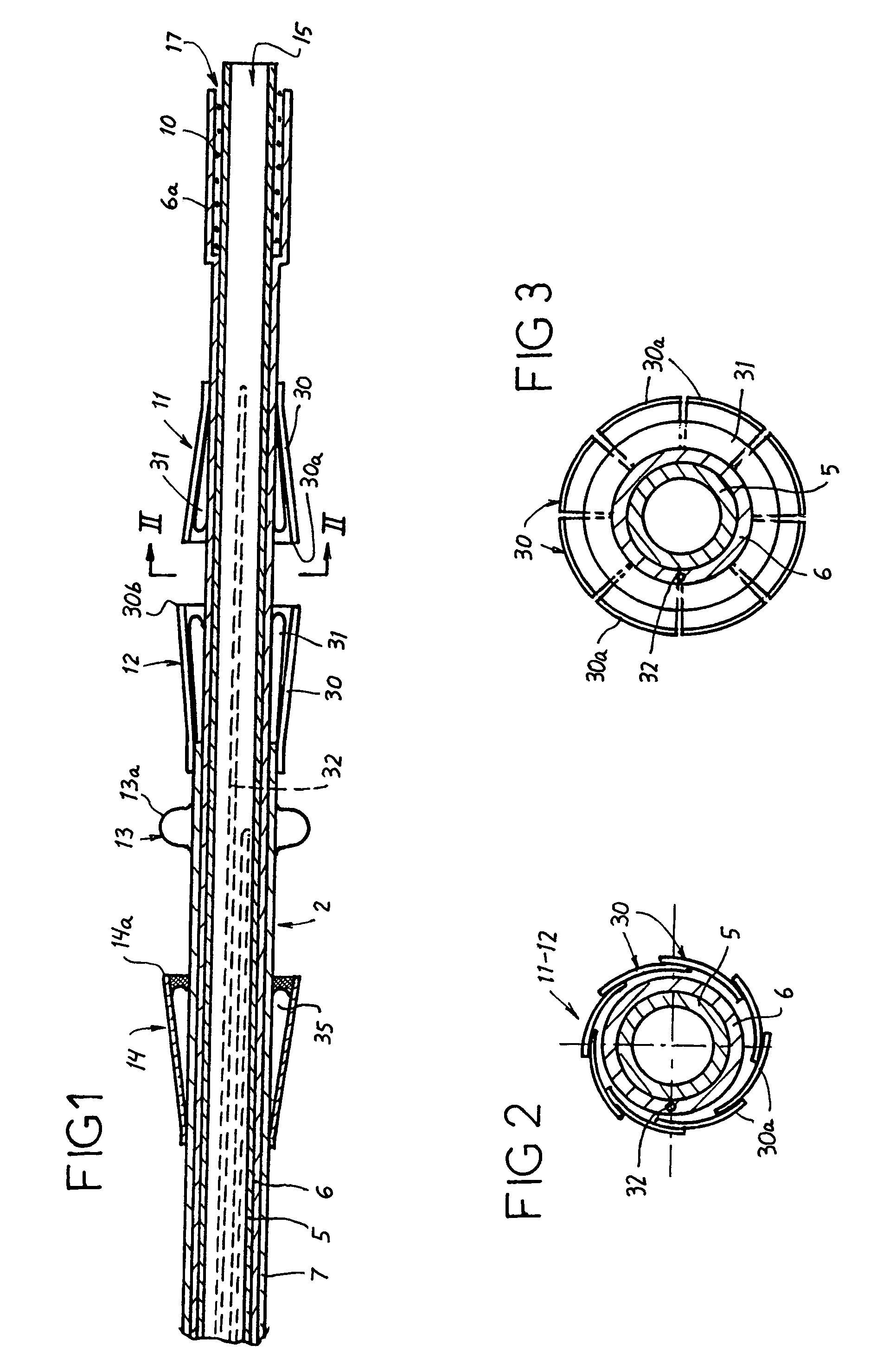
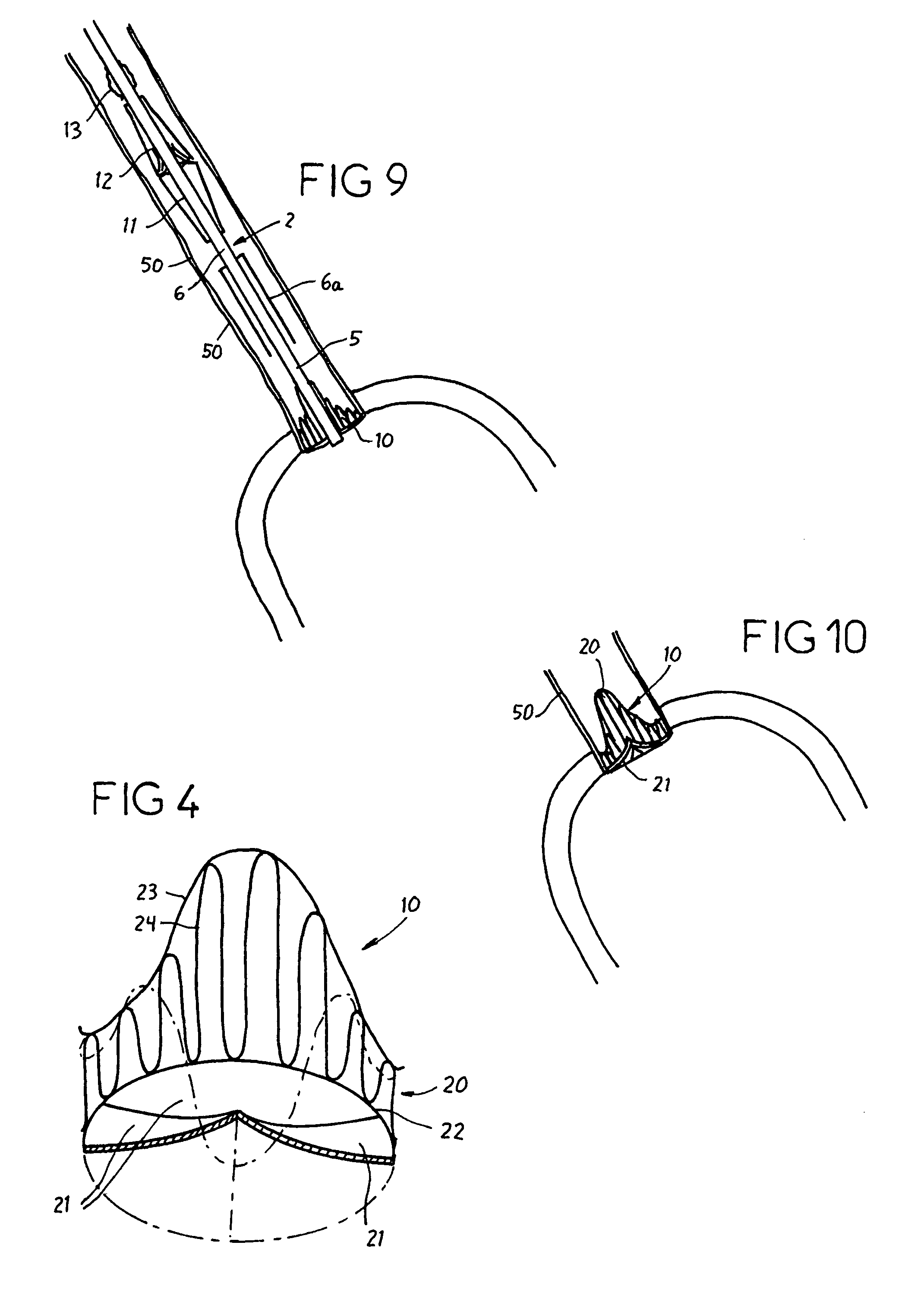
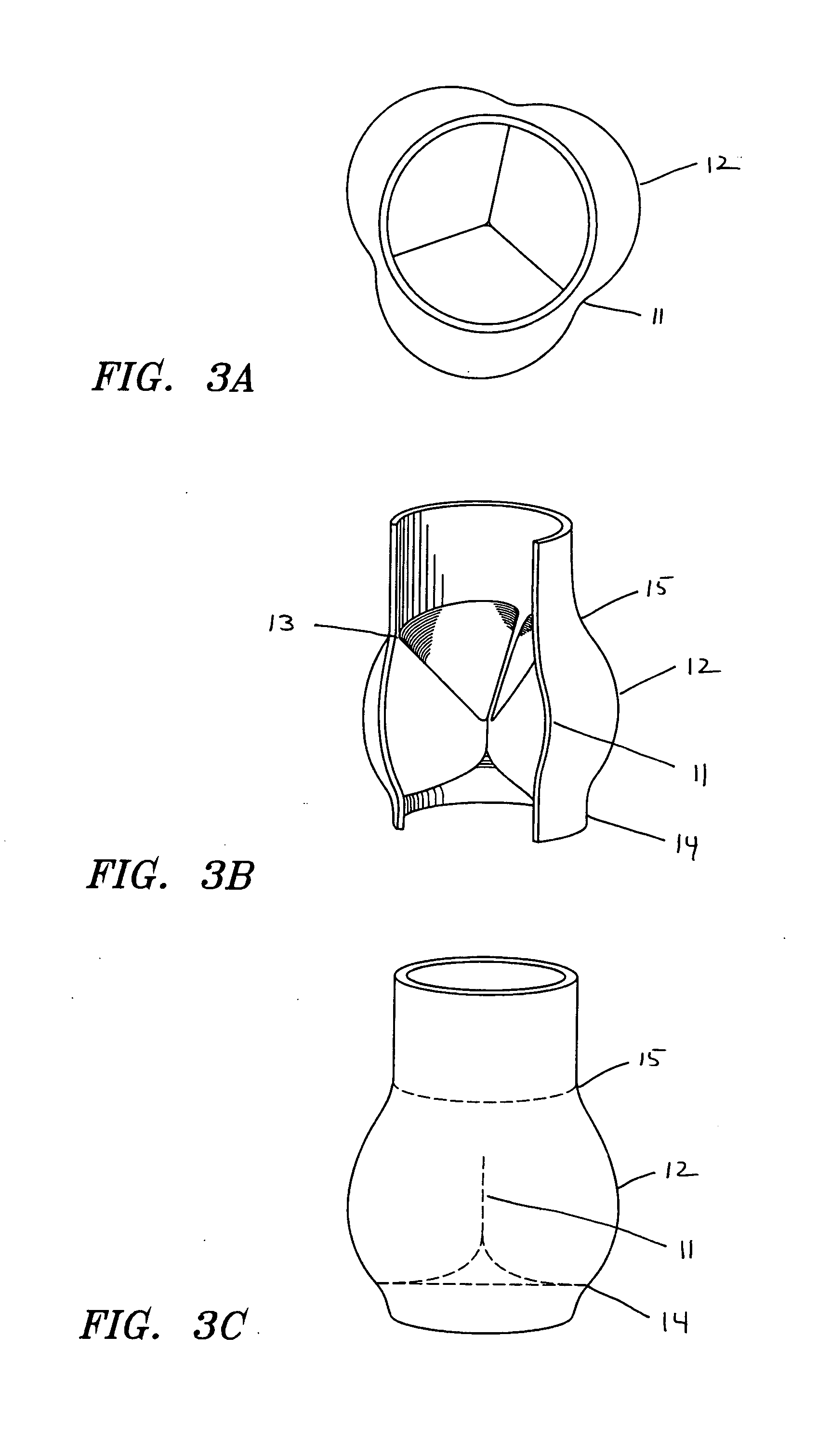
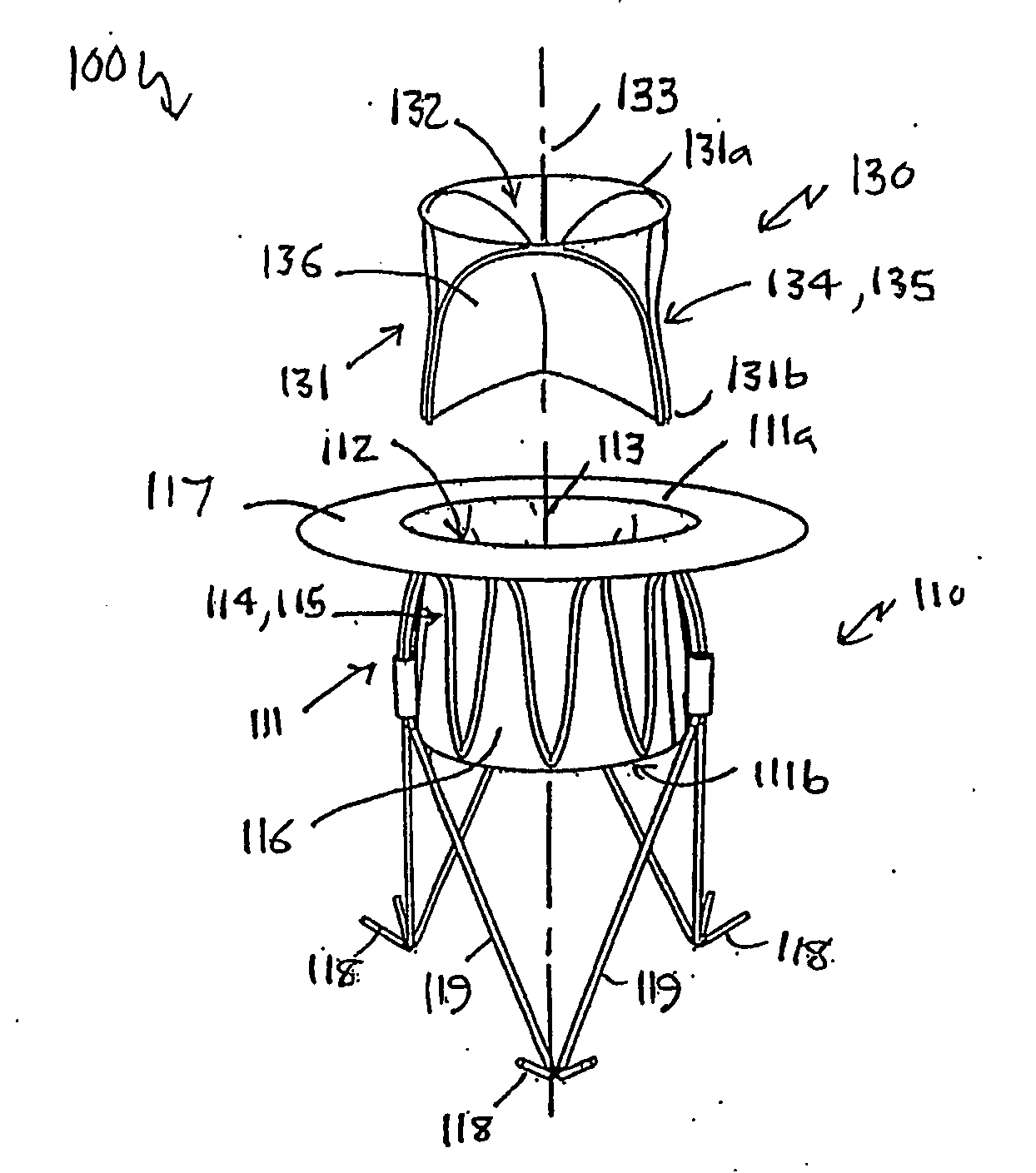
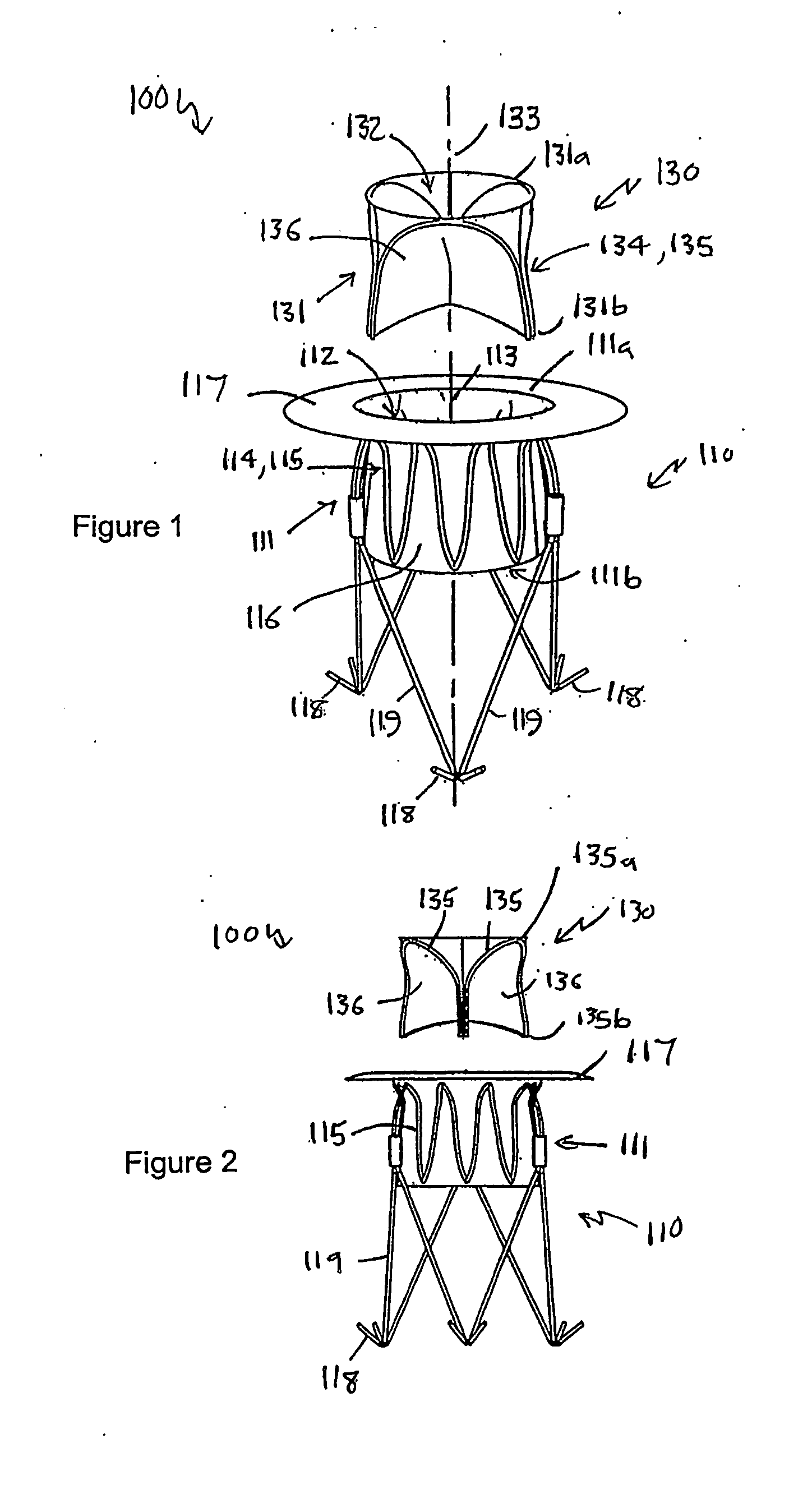
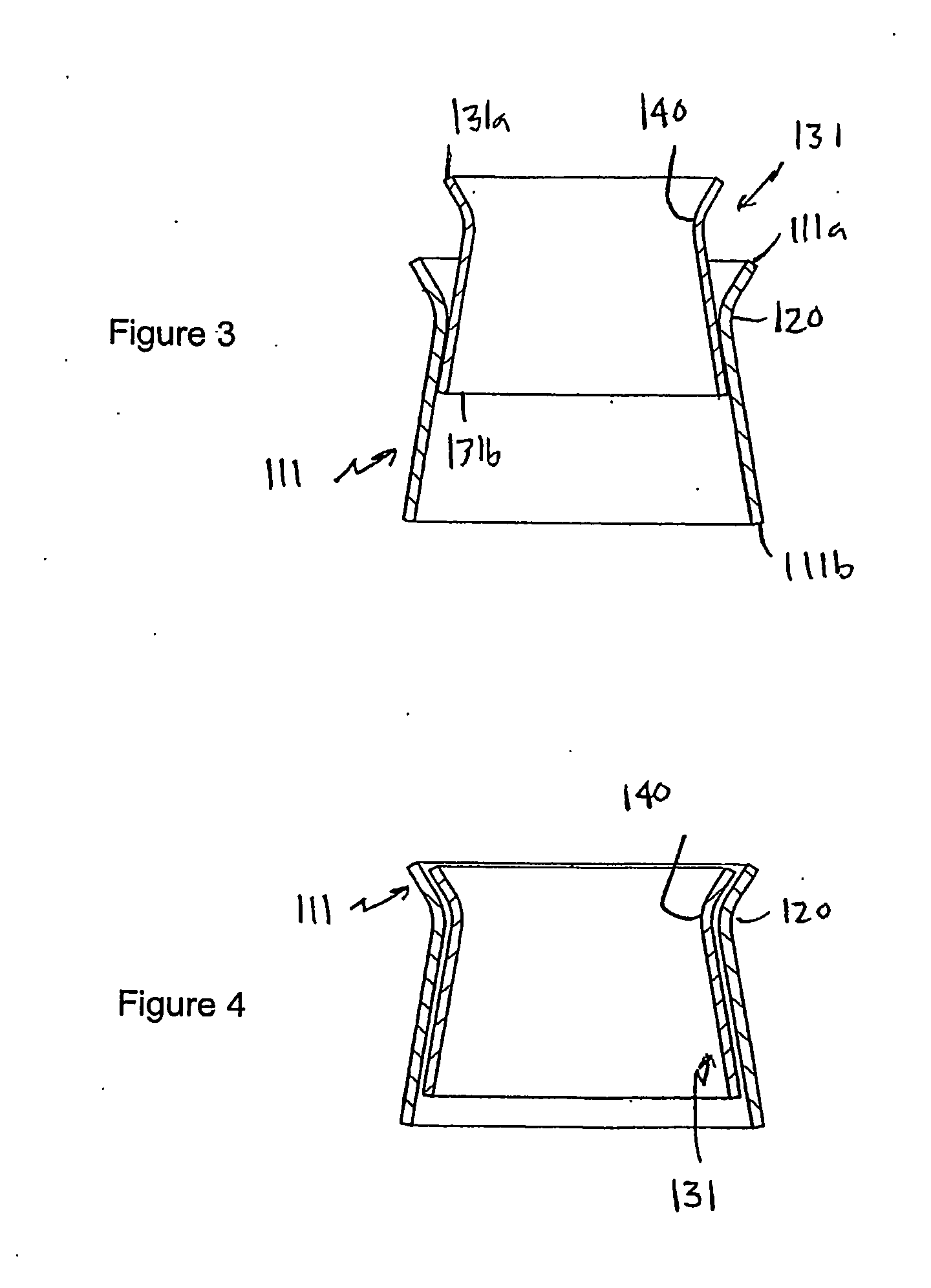
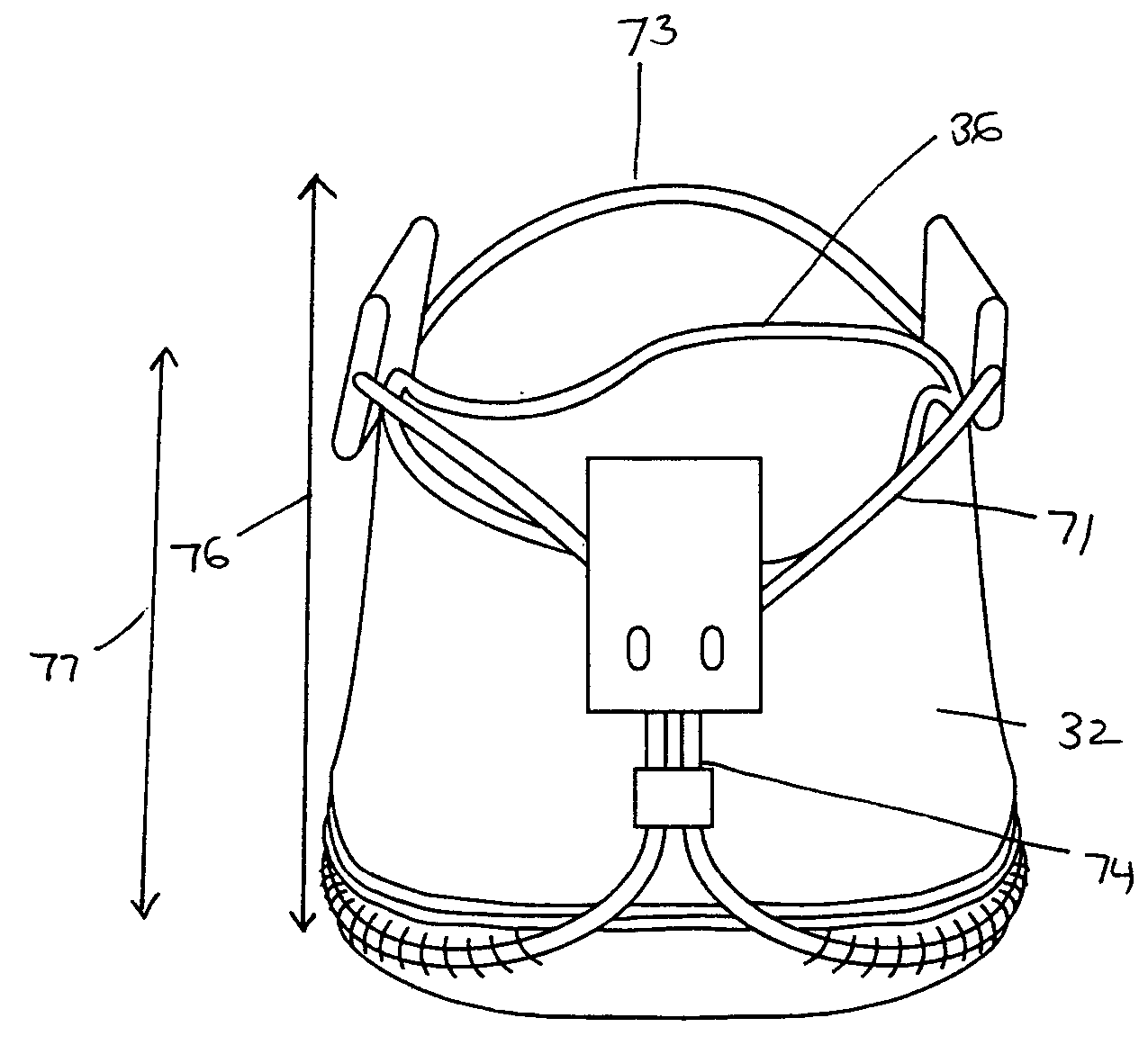
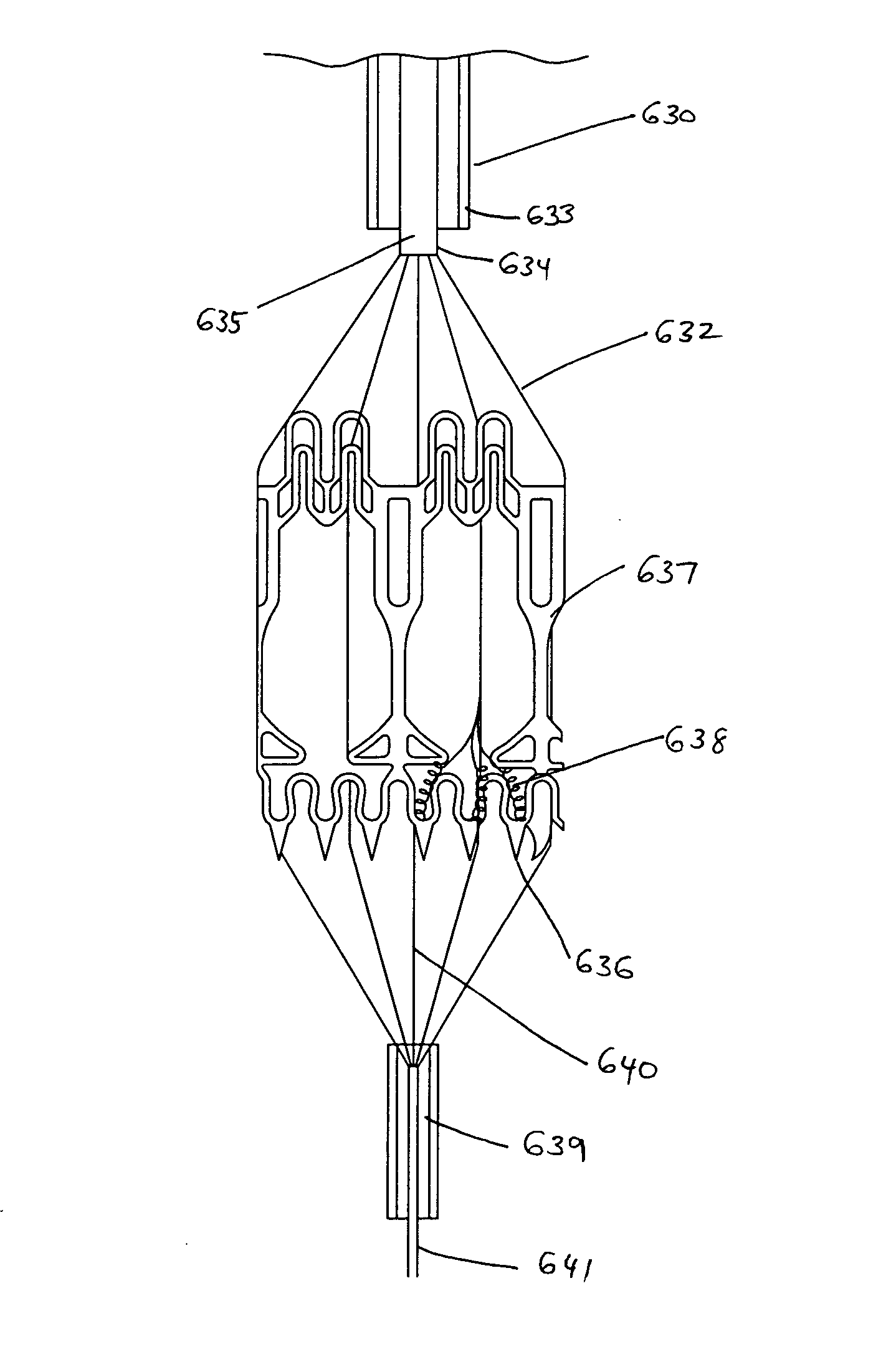
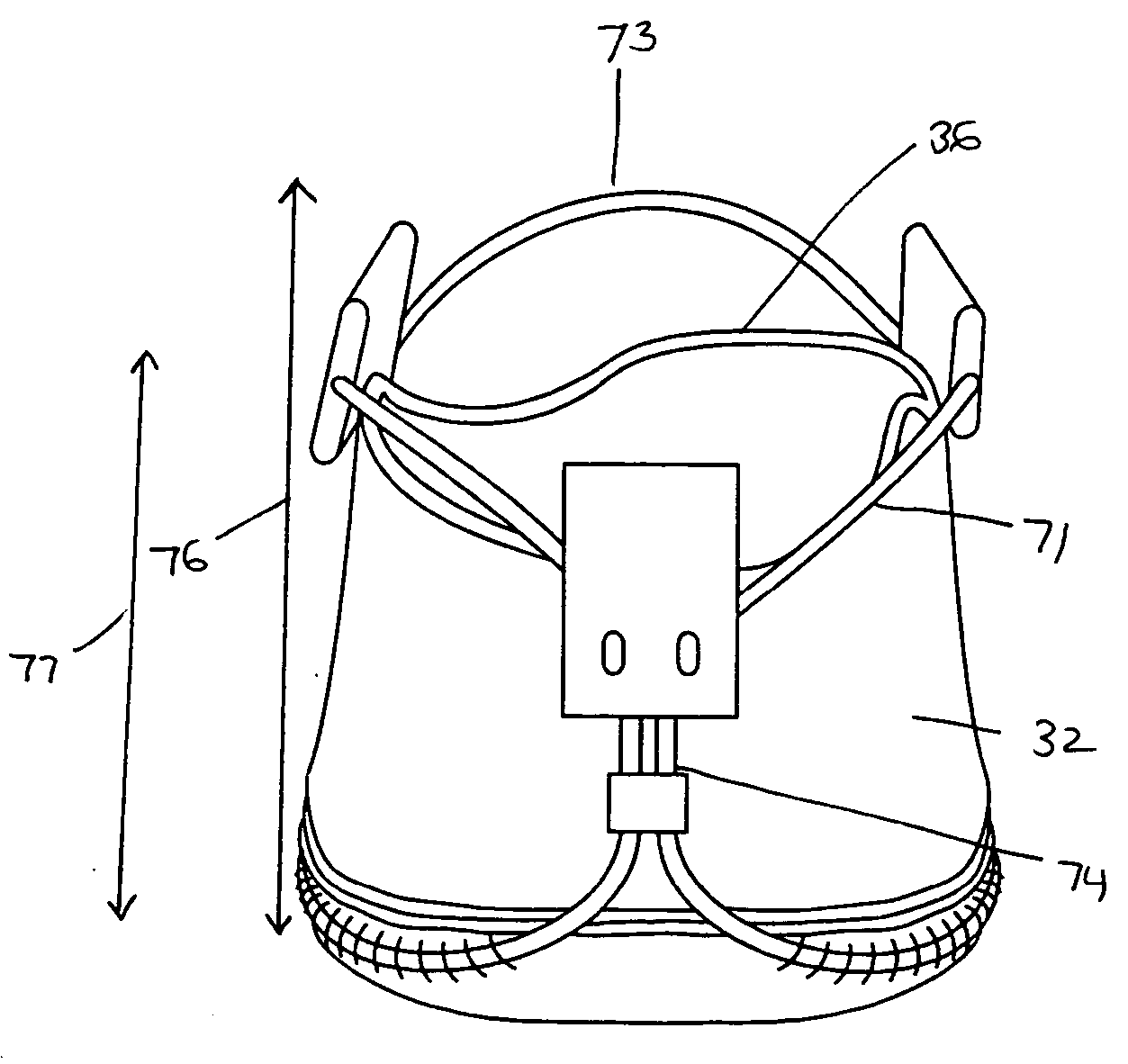
Heart valve prosthesis and method
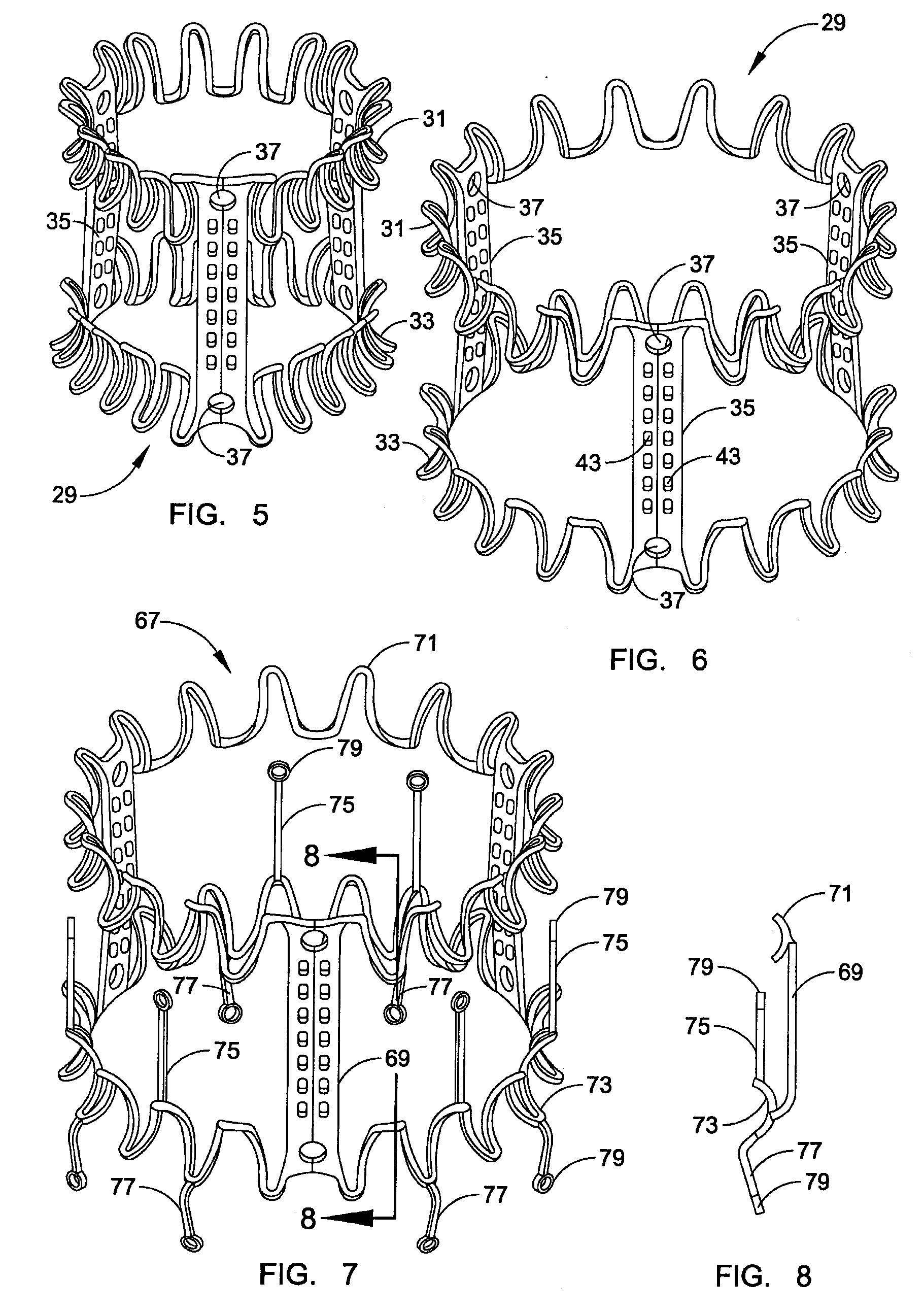
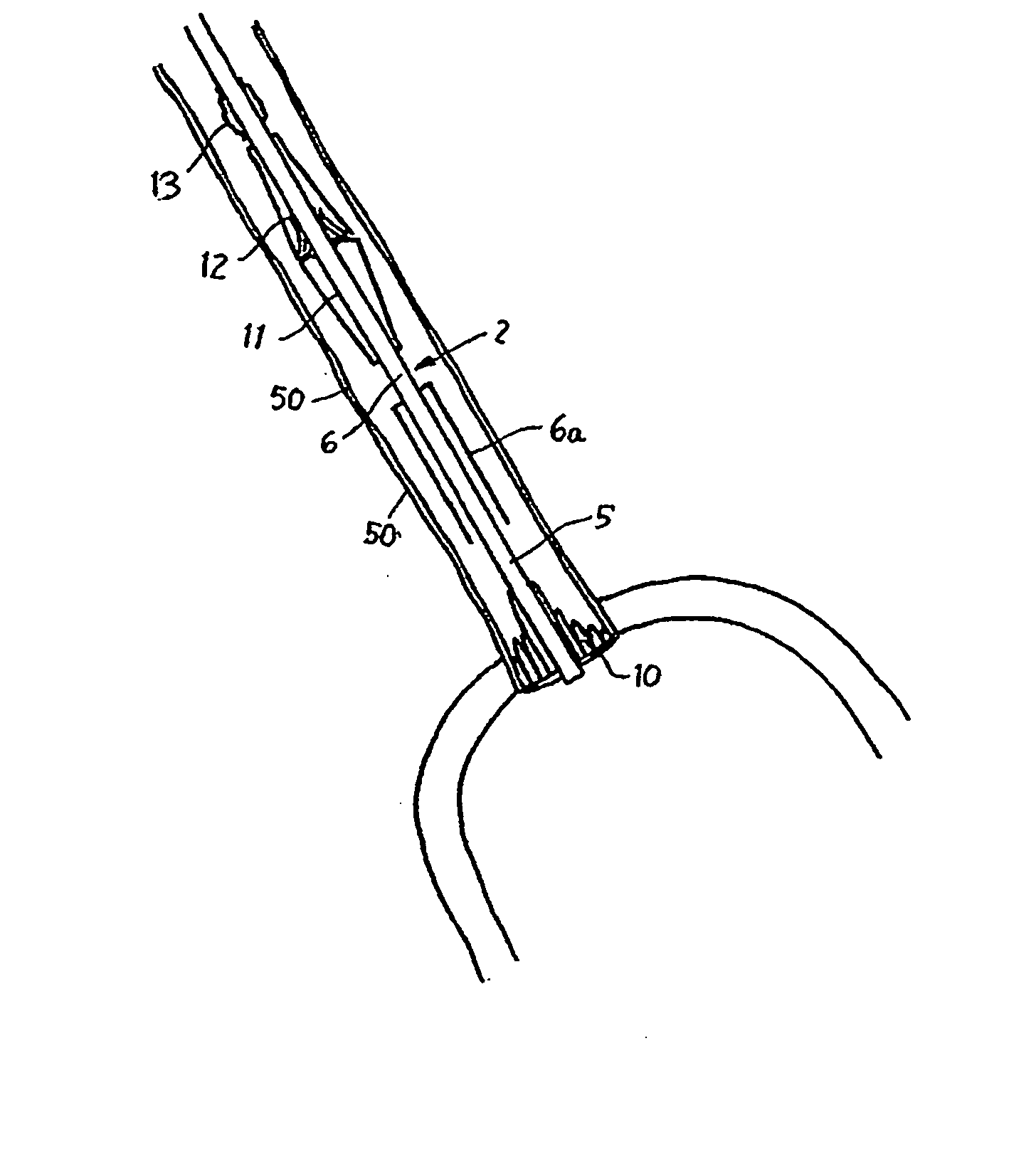
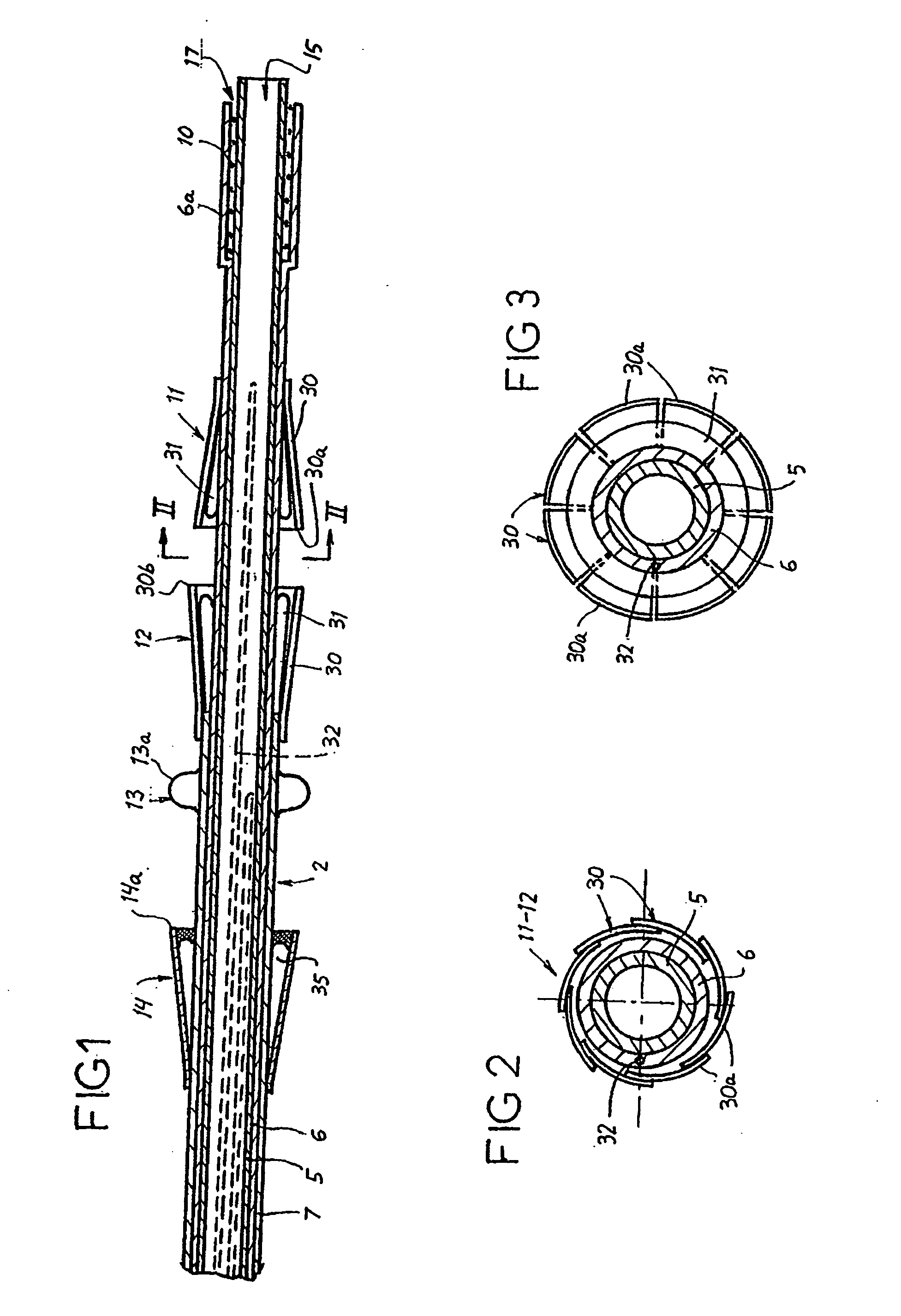
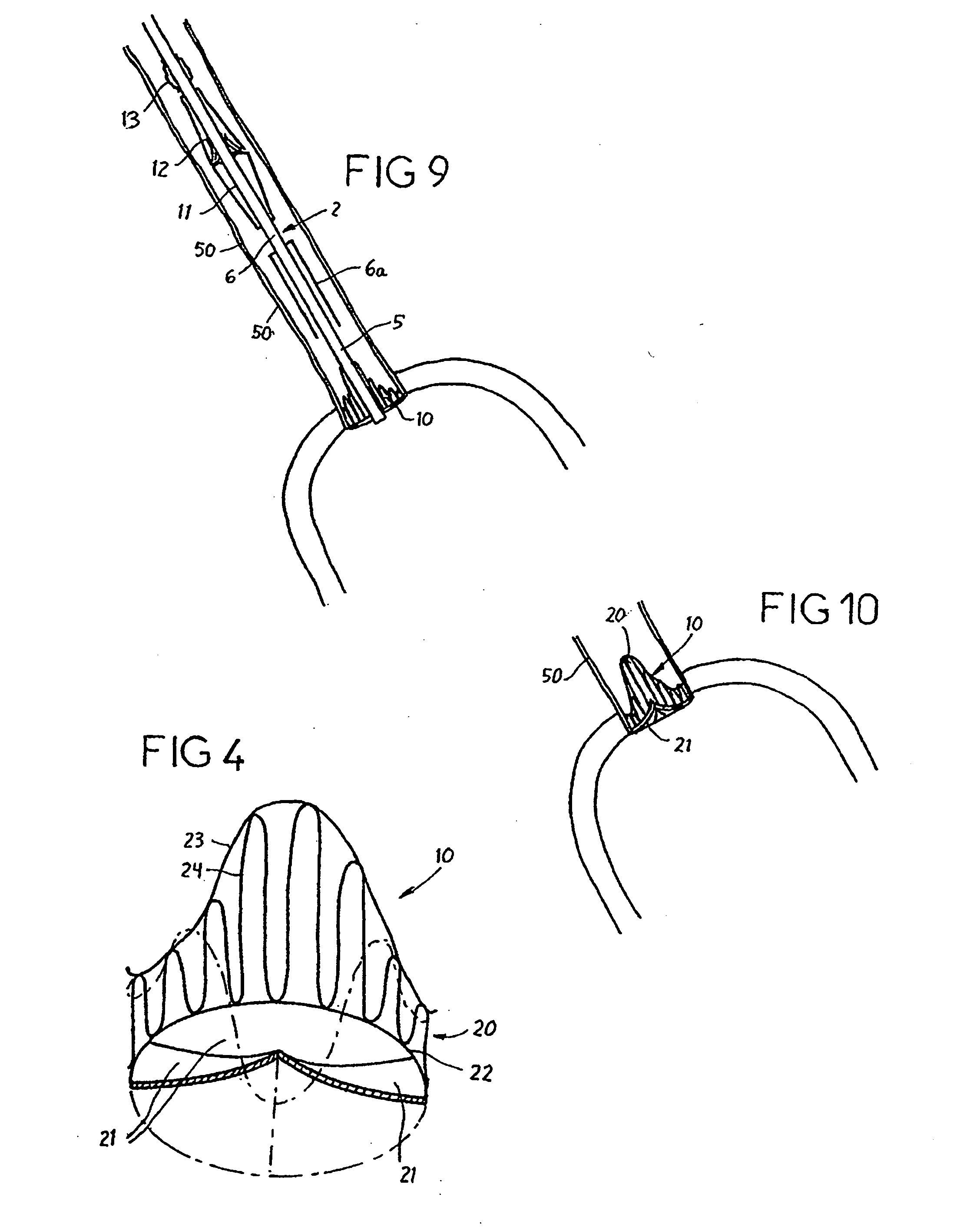
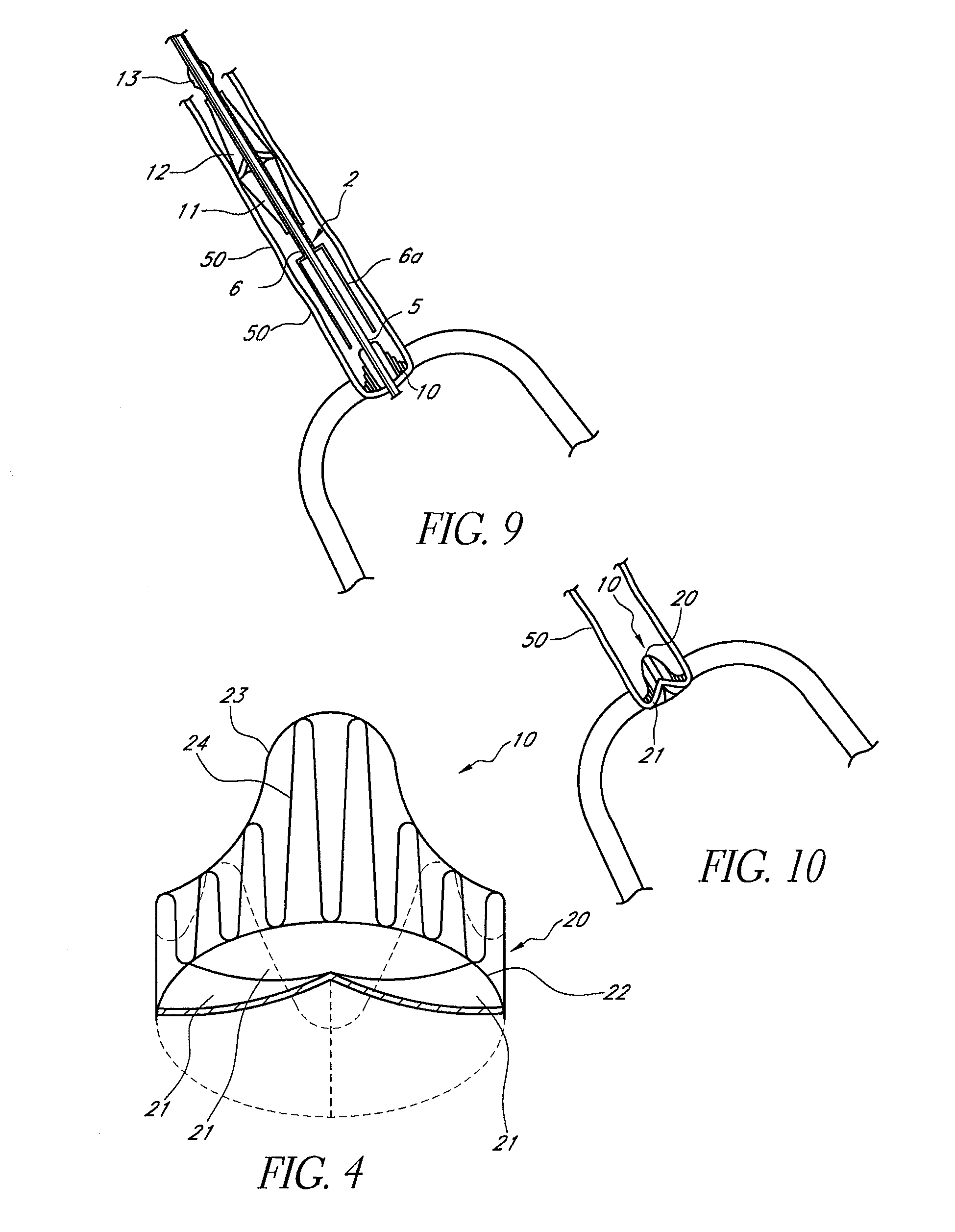
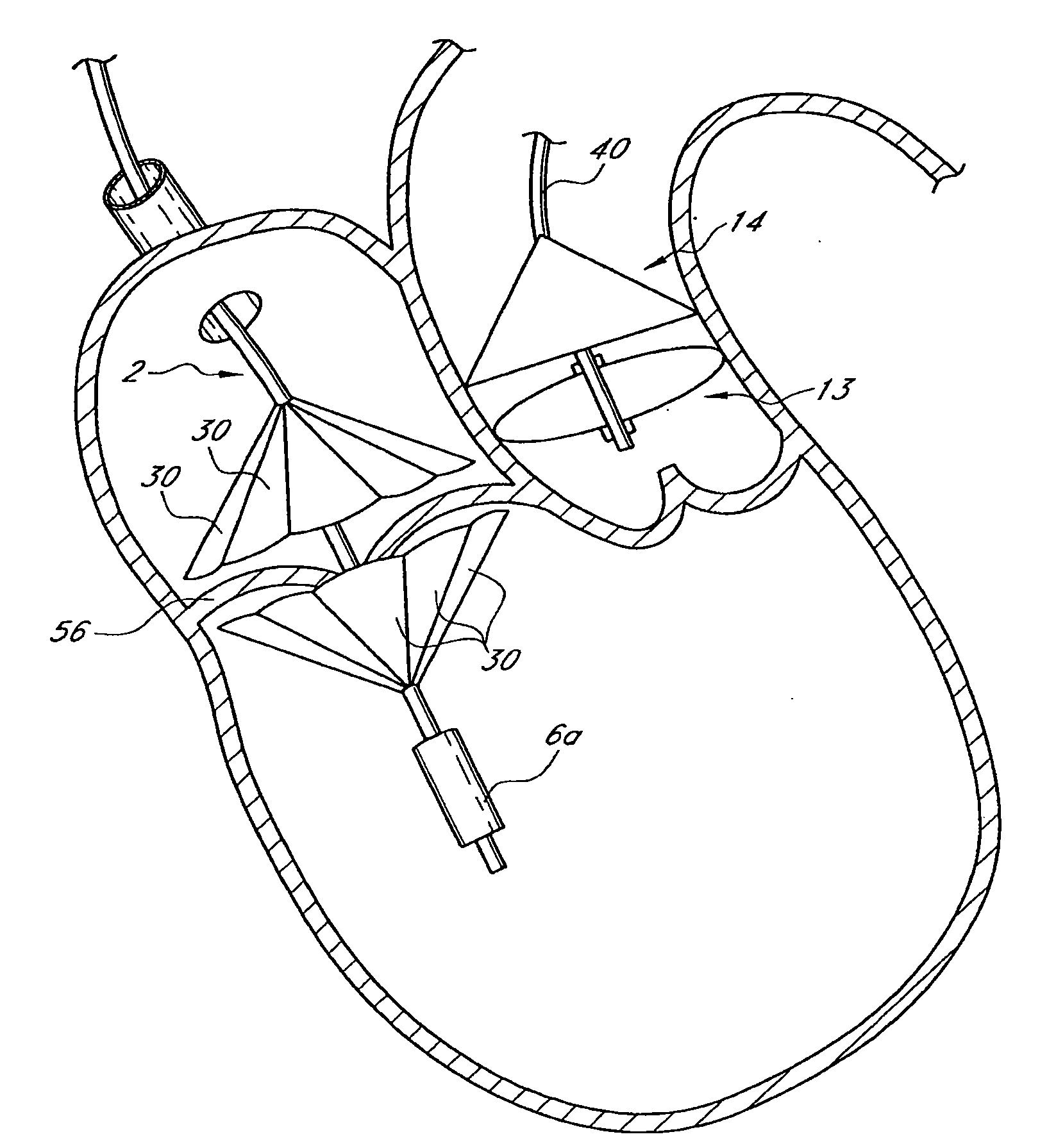
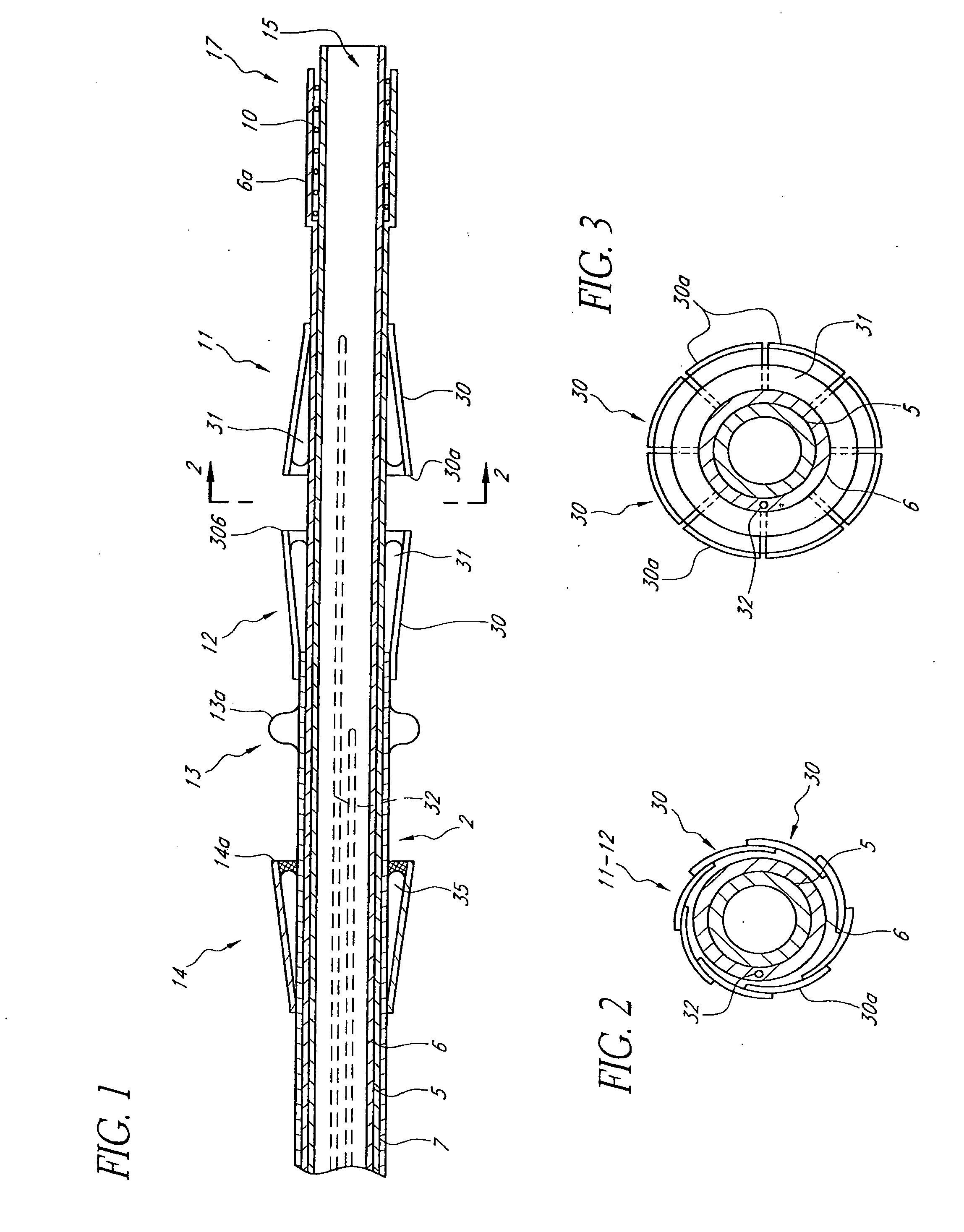
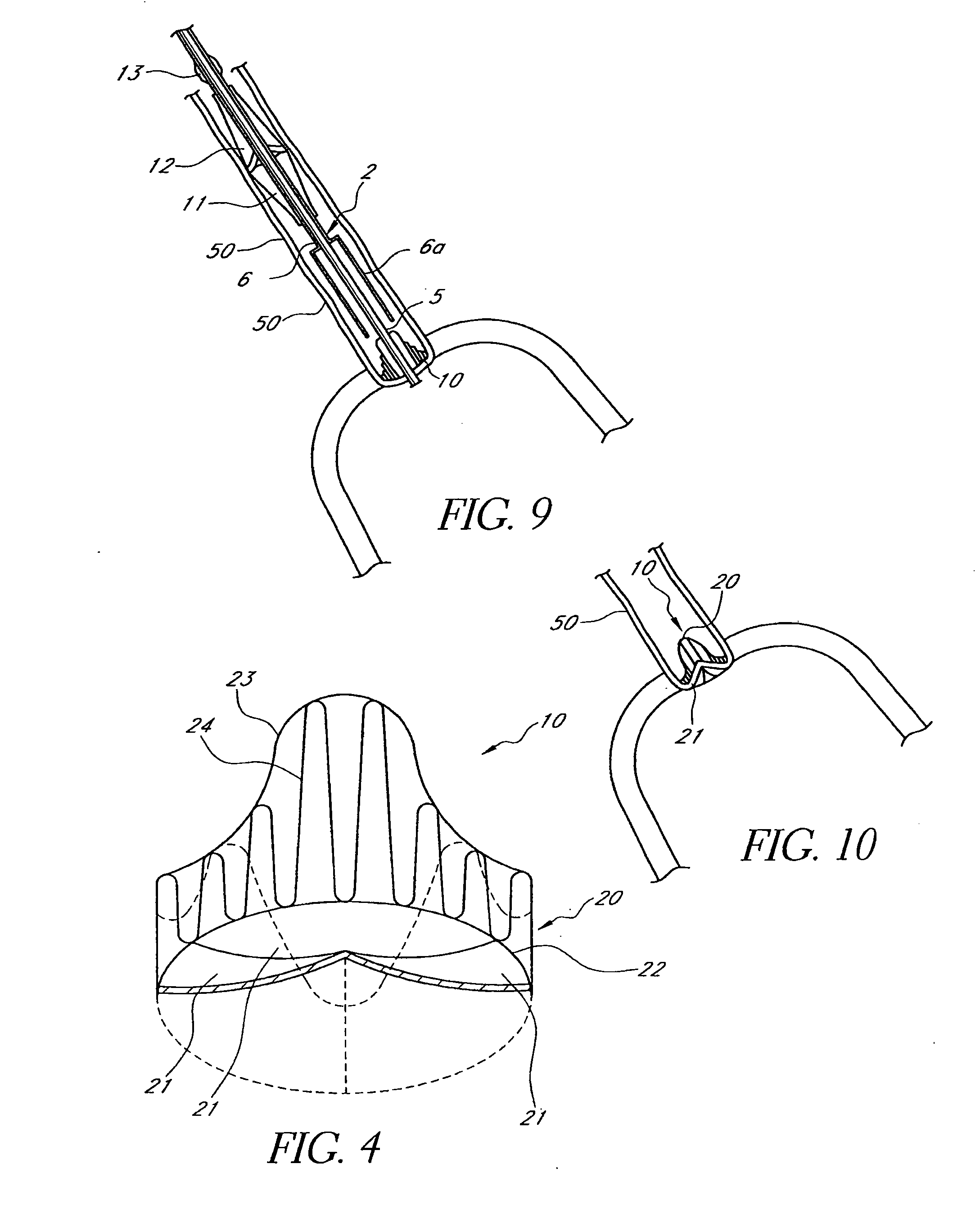
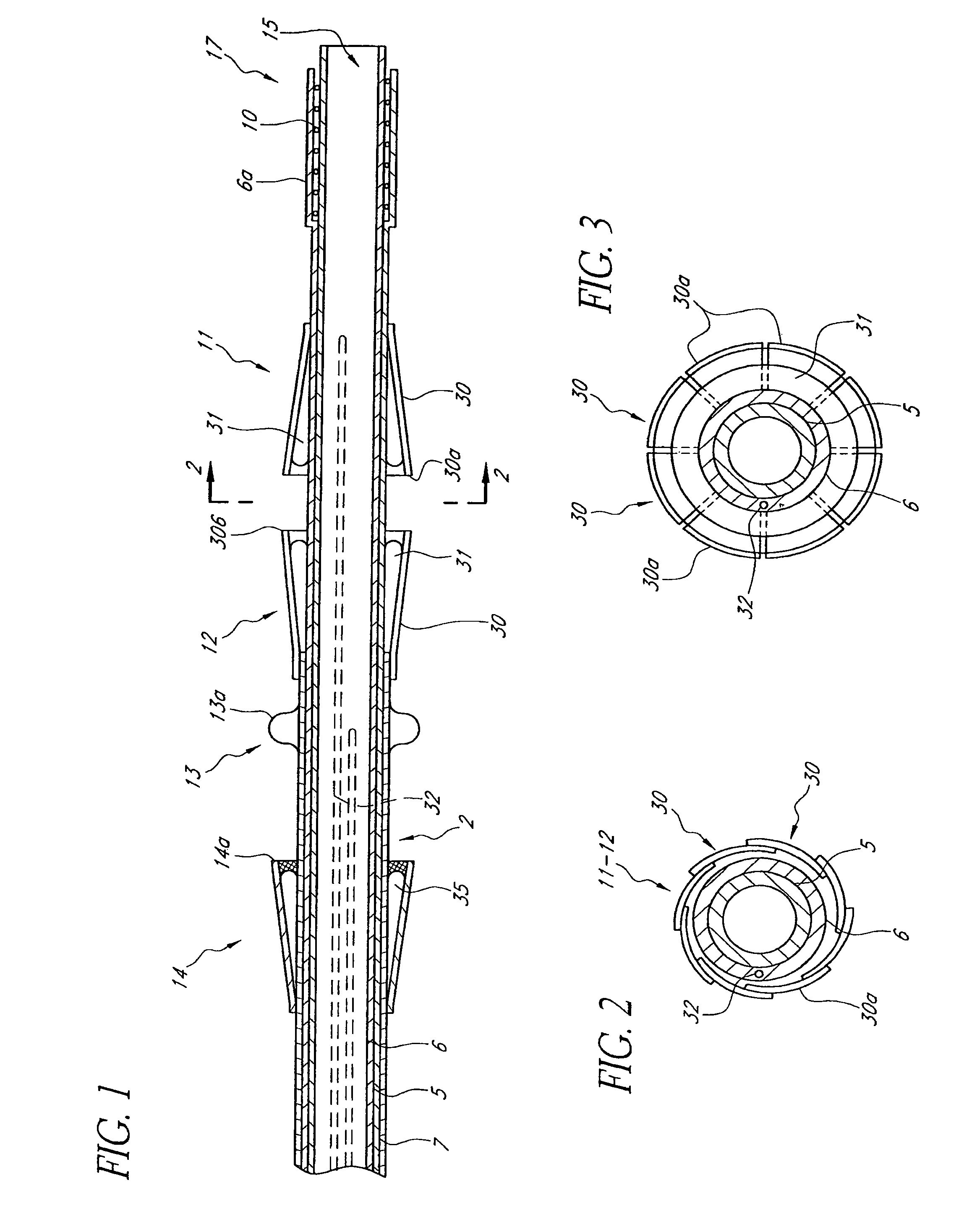
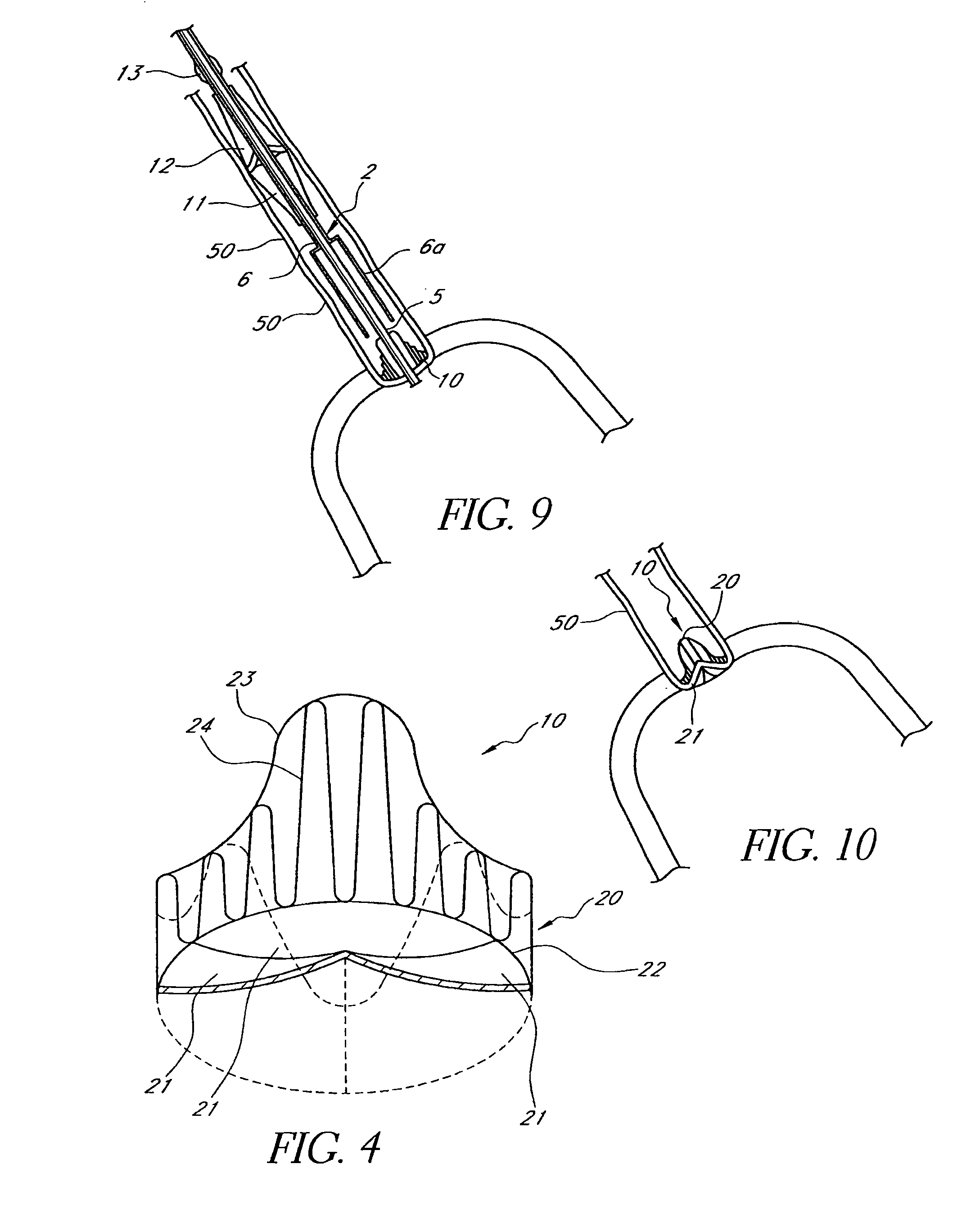
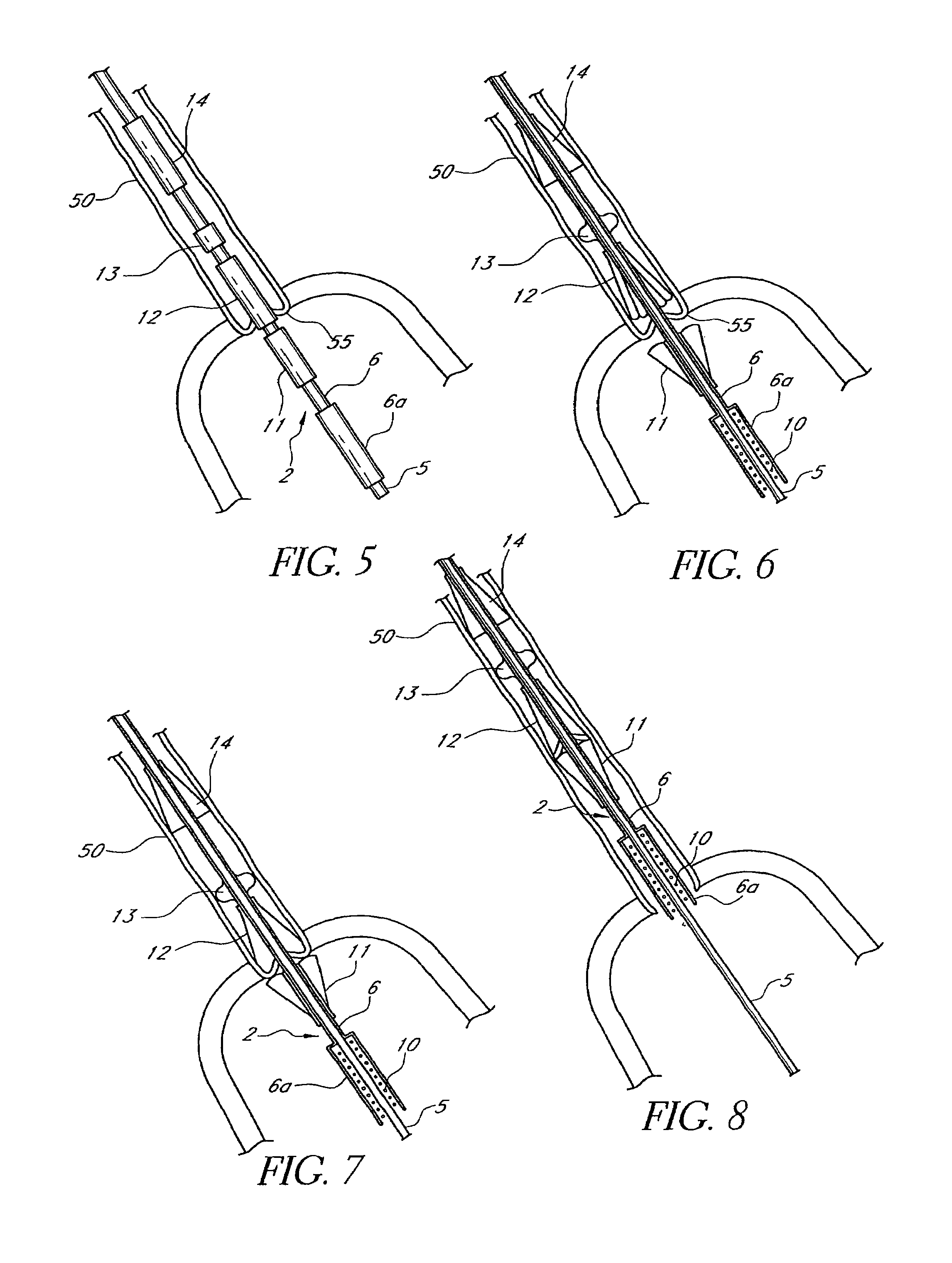
A heart valve prosthesis (100) comprises a housing component (110) and a valve component (130). The housing component (110) comprises a housing body (111) having a housing passage (112) extending therethrough. The housing body (111) is configured to be located in, or adjacent to and communicating with, a native valve orifice (16) of a heart (10) and to engage structure of the heart (10) to fix the housing body (111) in relation to the valve orifice (161). The housing component (111) is collapsible for delivery via catheter (2). The valve component (130) comprises a valve body (131) having a valve passage (132) extending therethrough. The valve body (131) is configured to be fixed within the housing passage (112) with the valve passage (132) extending along the housing passage (112). One or more flexible valve elements (131) is / are secured to the valve body and extend across the valve passage (132) for blocking blood flow in a first direction through the valve passage (132) whilst allowing blood flow in the opposing direction. The valve component (130) is collapsible for delivery via catheter (2) separate to the housing component (110). An associated method of replacing a failed or failing heart valve utilising the heart valve prosthesis (100) is also disclosed.
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
ActiveUS20050075731A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Prosthetic heart valves
A prosthetic heart valve (10) (e.g., a prosthetic aortic valve) is designed to be somewhat circumferentially collapsible and then re-expandable. The collapsed condition may be used for less invasive delivery of the valve into a patient. When the valve reaches the implant site in the patient, it re-expands to normal operating size, and also to engage surrounding tissue of the patient. The valve includes a stent portion (200) and a ring portion (100) that is substantially concentric with the stent portion but downstream from the stent portion in the direction of blood flow through the implanted valve. When the valve is implanted, the stent portion engages the patient's tissue at or near the native valve annulus, while the ring portion engages tissue downstream from the native valve site (e.g., the aorta).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Rapid deployment prosthetic heart valve
ActiveUS20060287719A1For quick replacementMinimize timeStentsAnnuloplasty ringsCouplingProsthetic heart
A two-stage or component-based valve prosthesis that can be quickly and easily implanted during a surgical procedure is provided. The prosthetic valve comprises a support structure that is deployed at a treatment site. The prosthetic valve further comprises a valve member configured to be quickly connected to the support structure. The support structure may take the form of a stent that is expanded at the site of a native valve. If desired, the native leaflets may remain and the stent may be used to hold the native valve open. In this case, the stent may be balloon expandable and configured to resist the powerful recoil force of the native leaflets. The support structure is provided with a coupling means for attachment to the valve member, thereby fixing the position of the valve member in the body. The valve member may be a non-expandable type, or may be expandable from a compressed state to an expanded state. The system is particularly suited for rapid deployment of heart valves in a conventional open-heart surgical environment.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Prosthetic Valve for Transluminal Delivery
InactiveUS20100004740A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesVenous accessImplantation Site
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchors may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. A radial restraint, comprising a wire, thread or cuff, may be used to ensure expansion does not exceed the preset diameter. The valve support may optionally comprise a drug elution component. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. A blood pump may be inserted into the catheter to ensure continued blood flow across the implantation site during implantation procedure. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. Insertion of the catheter may optionally be performed over a transseptally delivered guidewire that has been externalized through the arterial vasculature. Such a guidewire provide dual venous and arterial access to the implantation site and allows additional manipulation of the implantation site after arterial implantation of the prosthetic valve. Additional expansion stents may be delivered by venous access to the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Minimally-invasive heart valve with cusp positioners
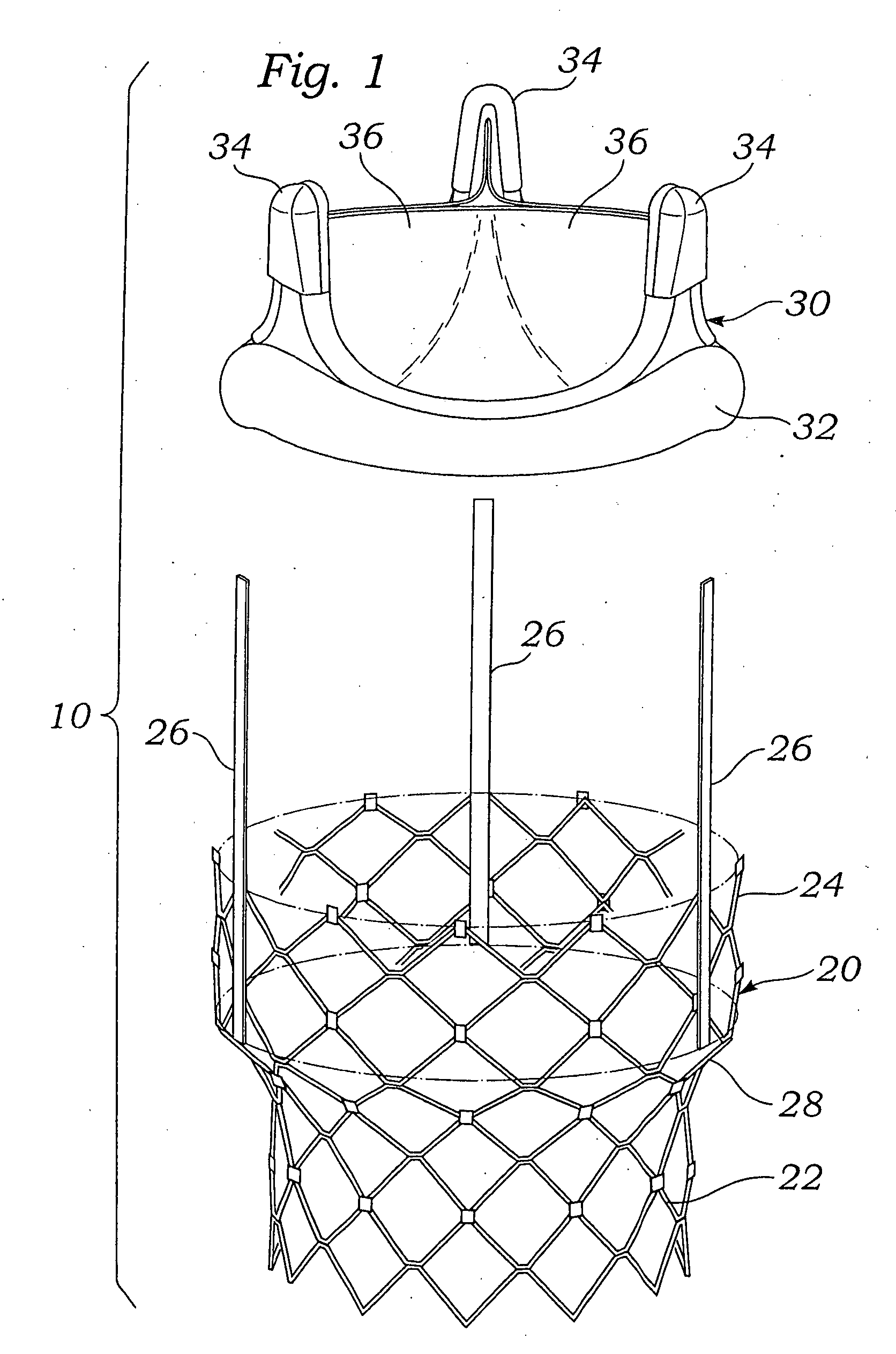
A prosthetic heart valve having an internal support frame with a continuous, undulating leaflet frame defined therein. The leaflet frame has three cusp regions positioned at an inflow end intermediate three commissure regions positioned at an outflow end thereof. The leaflet frame may be cloth covered and flexible leaflets attached thereto form occluding surfaces of the valve. The support frame further includes three cusp positioners rigidly fixed with respect to the leaflet frame and located at the outflow end of the support frame intermediate each pair of adjacent commissure regions. The valve is desirably compressible so as to be delivered in a minimally invasive manner through a catheter to the site of implantation. Upon expulsion from catheter, the valve expands into contact with the surrounding native valve annulus and is anchored in place without the use of sutures. In the aortic valve position, the cusp positioners angle outward into contact with the sinus cavities, and compress the native leaflets if they are not excised, or the aortic wall if they are. The support frame may be formed from a flat sheet of Nitinol that is bent into a three-dimensional configuration and heat set. A holder having spring-like arms connected to inflow projections of the valve may be used to deliver, reposition and re-collapse the valve, if necessary.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Minimally-invasive heart valve with cusp positioners
A prosthetic heart valve having an internal support frame with a continuous, undulating leaflet frame defined therein. The leaflet frame has three cusp regions positioned at an inflow end intermediate three commissure regions positioned at an outflow end thereof. The leaflet frame may be cloth covered and flexible leaflets attached thereto form occluding surfaces of the valve. The support frame further includes three cusp positioners rigidly fixed with respect to the leaflet frame and located at the outflow end of the support frame intermediate each pair of adjacent commissure regions. The valve is desirably compressible so as to be delivered in a minimally invasive manner through a catheter to the site of implantation. Upon expulsion from catheter, the valve expands into contact with the surrounding native valve annulus and is anchored in place without the use of sutures. In the aortic valve position, the cusp positioners angle outward into contact with the sinus cavities, and compress the native leaflets if they are not excised, or the aortic wall if they are. The support frame may be formed from a flat sheet of Nitinol that is bent into a three-dimensional configuration and heat set. A holder having spring-like arms connected to inflow projections of the valve may be used to deliver, reposition and re-collapse the valve, if necessary.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS7837727B2Sufficient flexibilitySevere size constraintHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Sigmoid valve and method for its percutaneous implantation
A multi-leaflet valve adapted to serve as a prosthesis for diseased native valve of a mammal is incorporated in self-expandable or inflatable endovascular stents or stents to form a combination which is introduced on a catheter with a guide wire into the circulatory system of the mammal to replace the diseased native valve. Once the combination is at the desired location the stent is caused to expand and affix itself to the patient's vessel wall. The prosthetic valve has the shape of a truncated cone that has an inflow and an outflow orifice with leaflets forming the outflow orifice and forming a plurality of commissures. A first flexible circular support is affixed in a substantially circular fashion around the truncated cone in proximity of the inflow orifice, and a second flexible circular support is affixed at the location of the commissures to form a circle around the truncated cone in proximity of the outflow orifice. The circular supports maintain the shape of the valve during the surgical implantation procedure and thereafter.
Owner:THE INT HEART INST OF MONTANA FOUND
Quick-connect prosthetic heart valve and methods
ActiveUS8308798B2Quickly and easily replacingUse minimizedBalloon catheterHeart valvesCouplingInsertion stent
A heart valve prosthesis that can be quickly and easily implanted during a surgical procedure is provided. The prosthetic valve has a base stent that is deployed at a treatment site, and a valve component configured to quickly connect to the base stent. The base stent may take the form of a self- or balloon-expandable stent that expands outward against the native valve with or without leaflet excision. The valve component has a non-expandable prosthetic valve and a self- or balloon-expandable coupling stent for attachment to the base stent, thereby fixing the position of the valve component relative to the base stent. The prosthetic valve may be a commercially available to valve with a sewing ring and the coupling stent attaches to the sewing ring. The system is particularly suited for rapid deployment of heart valves in a conventional open-heart surgical environment. A catheter-based system and method for deployment is provided.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050075712A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsEar treatmentEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:BIANCUCCI BRIAN +1
Prosthetic mitral valve
A prosthetic mitral valve with a frame comprises at least one arm shaped to deploy among a region of chordae tendineae of the native mitral valve to deflect these chords in order to pull the native valve leaflets around the frame to avoid paravalvular leaks. The frame may be made from two parts that are connected by sutures. The prosthetic valve may be deployed by a catherer comprising a deployment clamp attached to the valve frame where the deployment clamp is actuable to induce rotation of the frame.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050075730A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:MYERS KEITH E +2
Minimally invasive valve replacement system
InactiveUS20050075720A1Reduce and eliminate needShorten the timeStentsHeart valvesEngineeringDelivery system
Methods and systems for minimally invasive replacement of a valve. The system includes a collapsible valve and anchoring structure, devices and methods for expanding the valve anchoring structure, adhesive means to seal the valve to the surrounding tissue, a catheter-based valve sizing and delivery system, native valve removal means, and a temporary valve and filter assembly to facilitate removal of debris material. The valve assembly comprises a valve and anchoring structure for the valve, dimensioned to fit substantially within the valve sinus.
Owner:NGUYEN TUOC TAN +1
Prosthetic valve for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS8016877B2Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisCommissure
A method for deploying a prosthetic valve assembly is provided. The prosthetic valve assembly replaces a deficient native valve and comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary oslia. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com