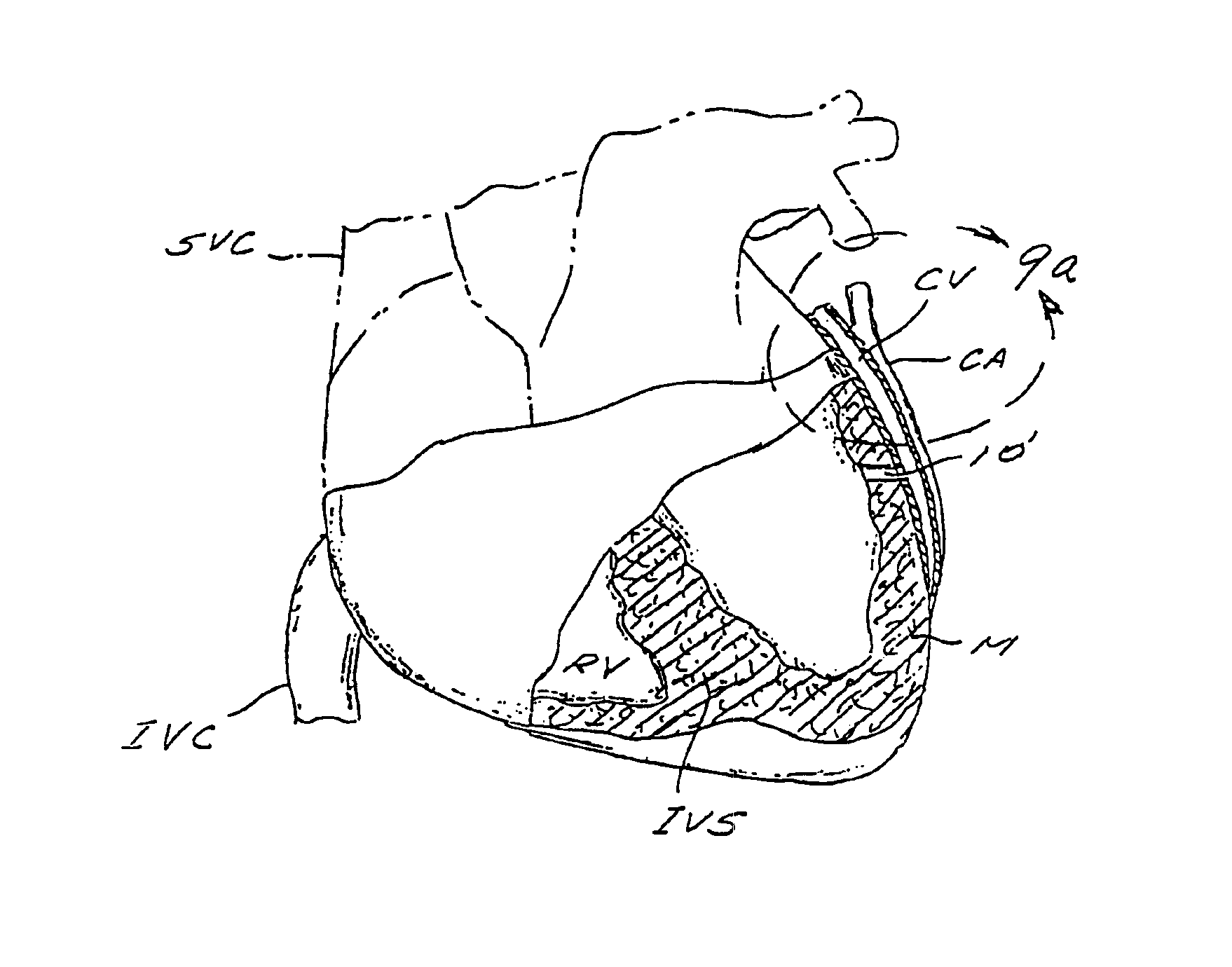
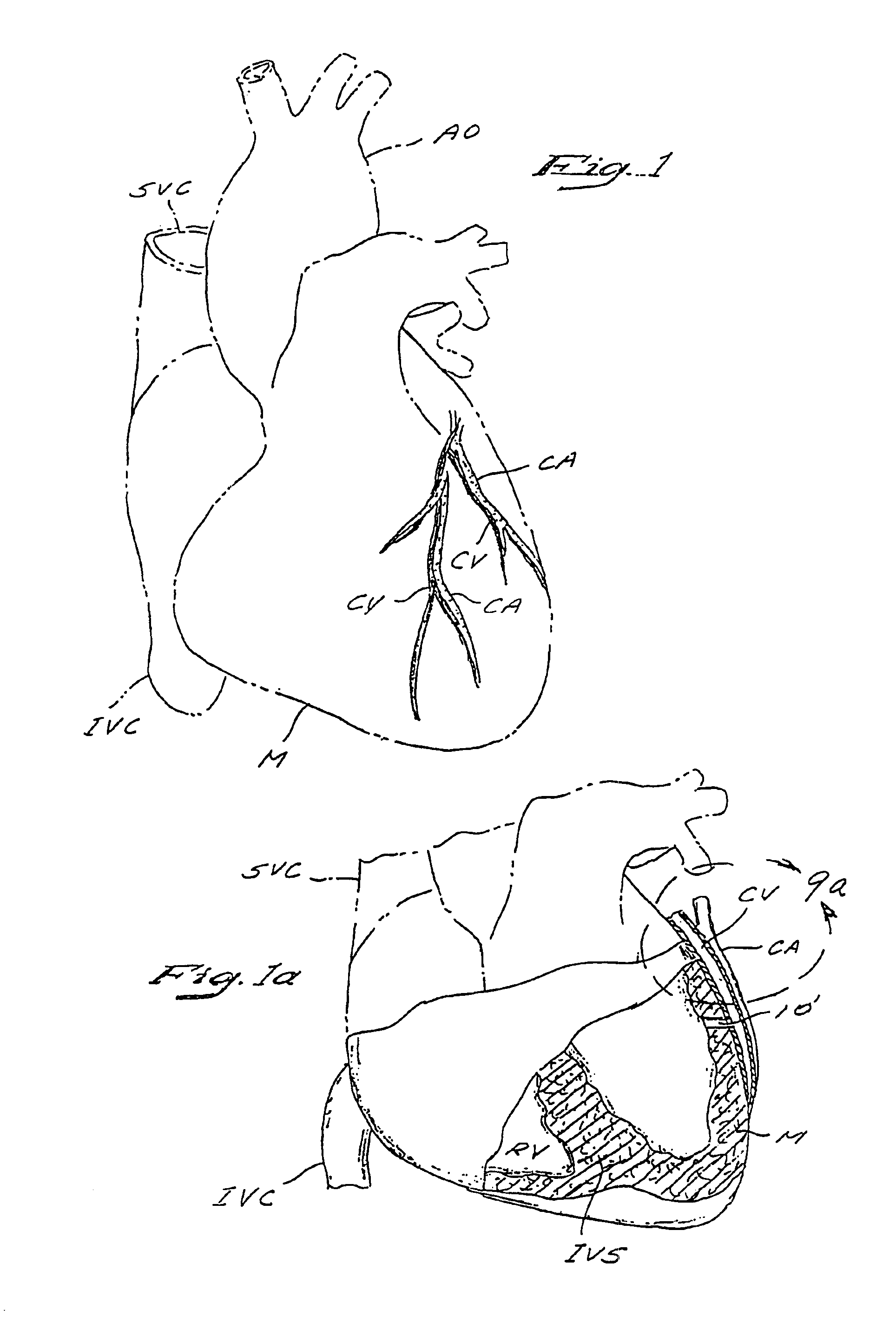
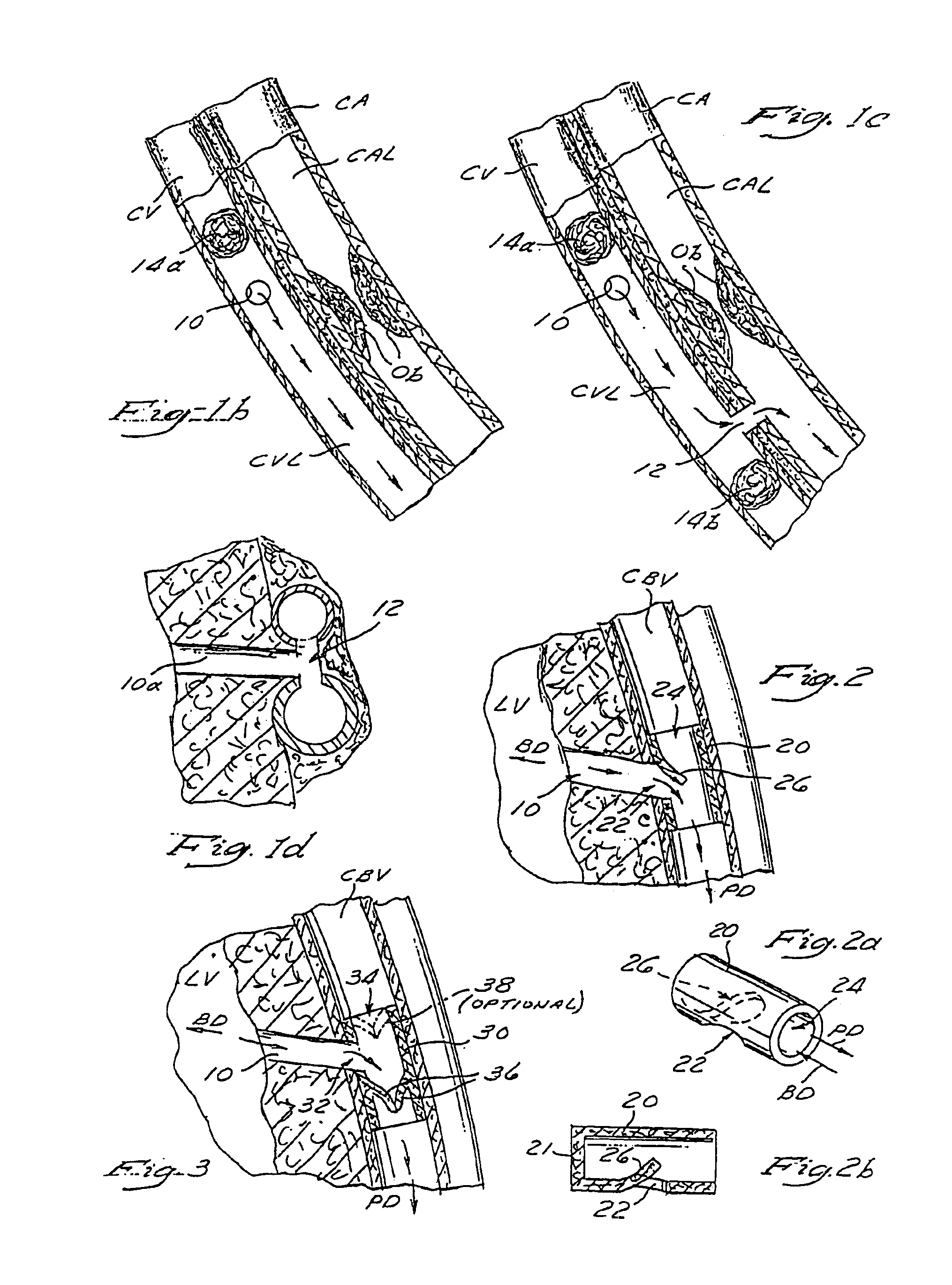
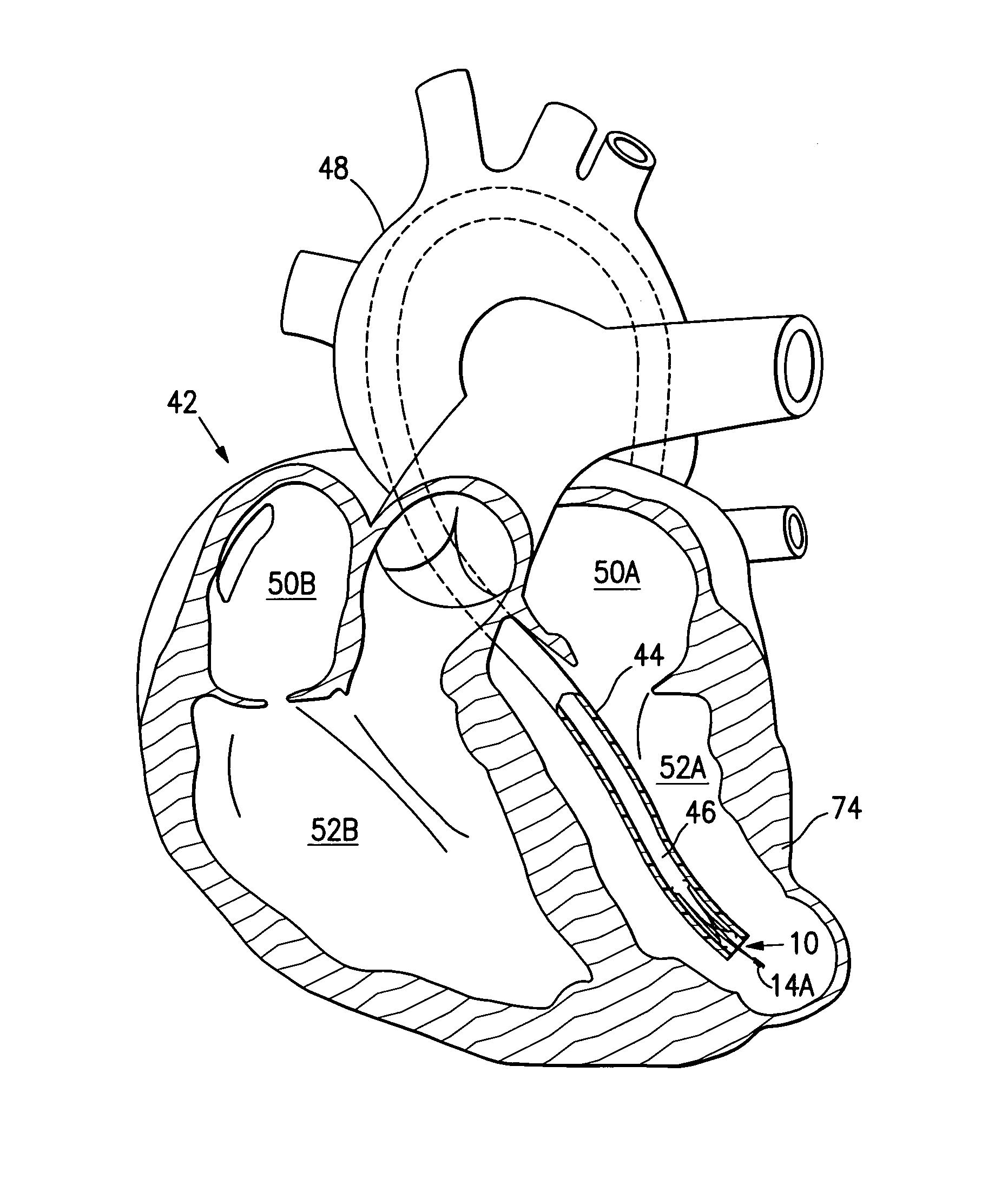
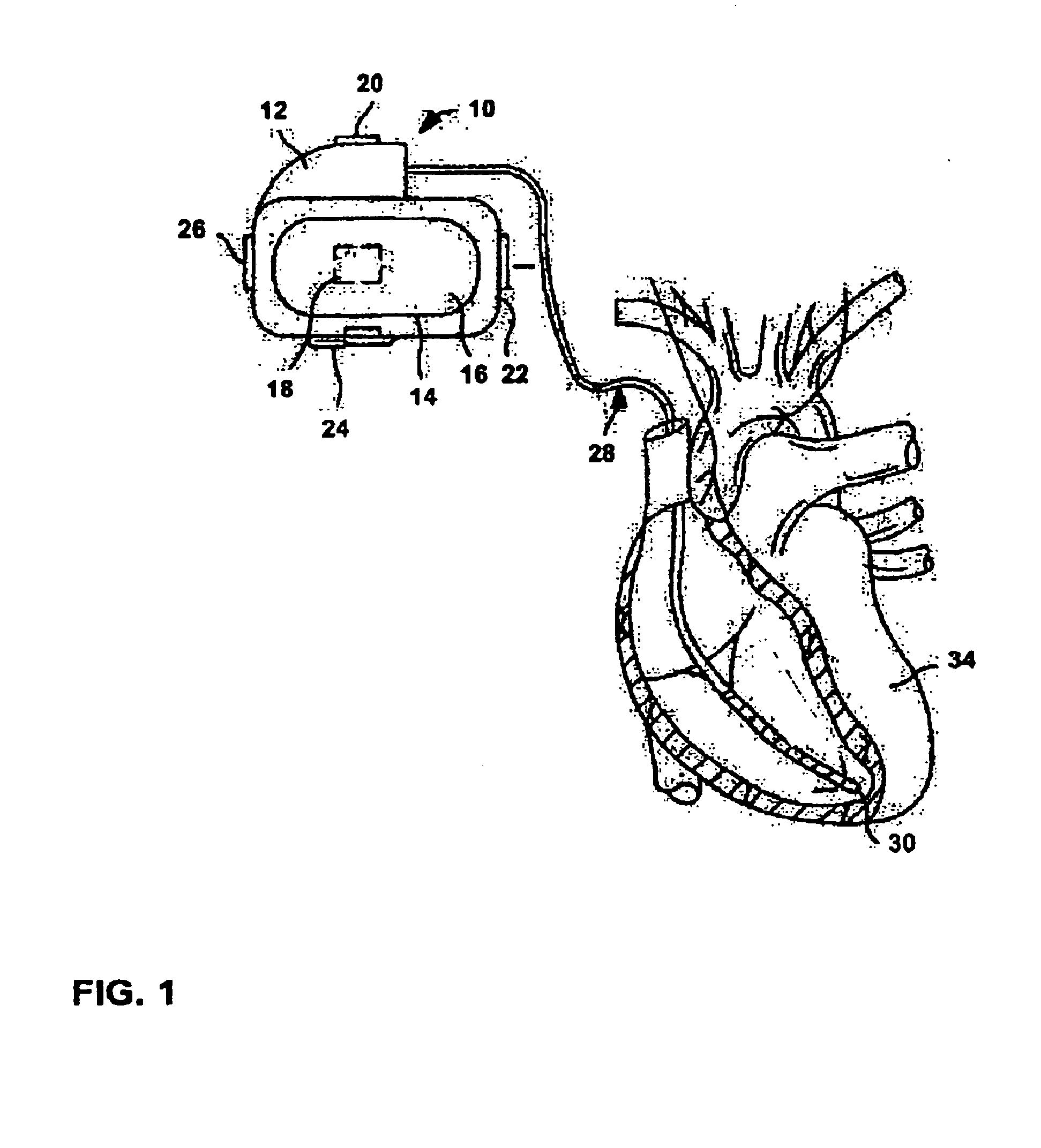
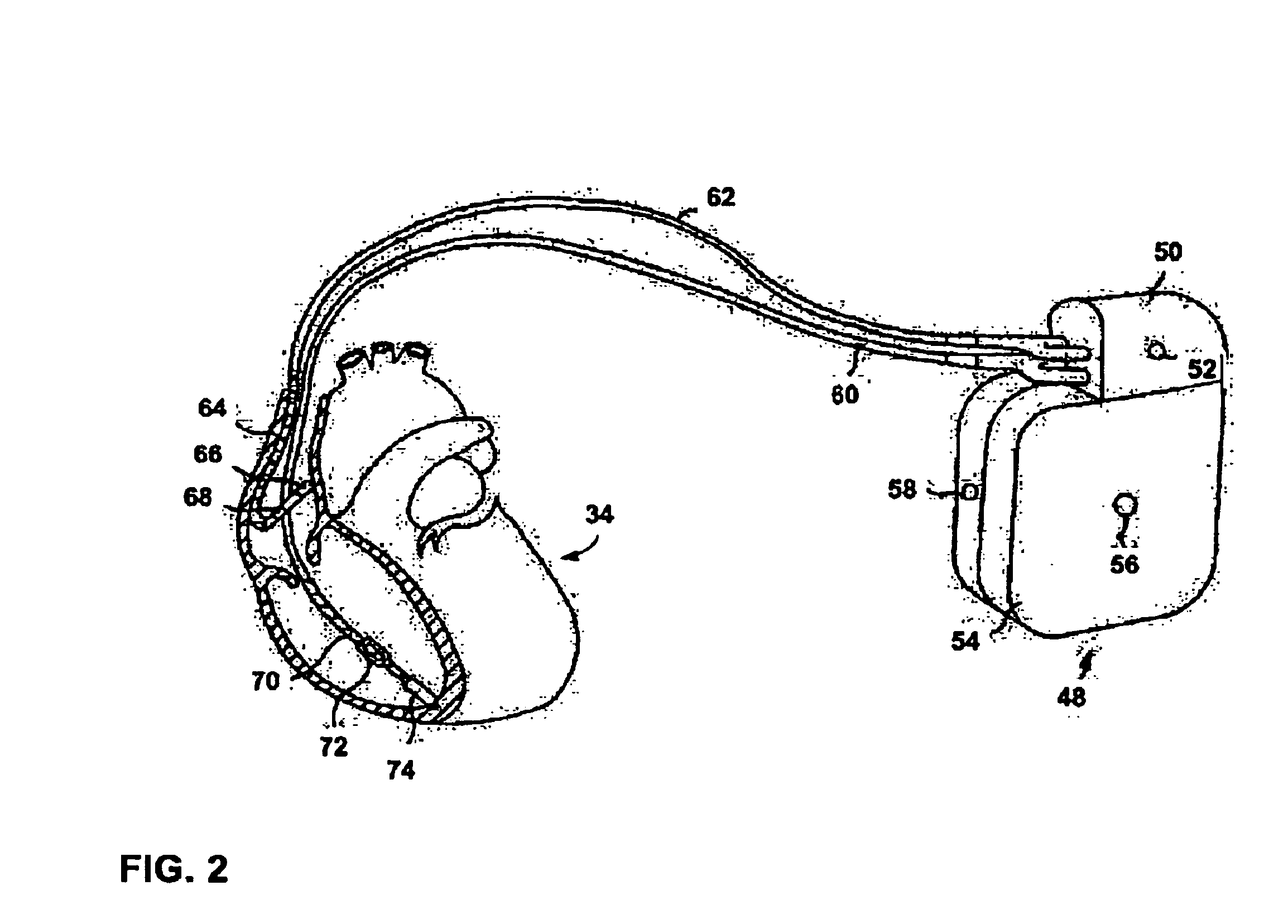
Patents
Literature
4328 results about "Cardiac muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscles, with the other two being skeletal and smooth muscles. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the walls of the heart. The myocardium forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the epicardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) joined together by intercalated discs, encased by collagen fibres and other substances that form the extracellular matrix.
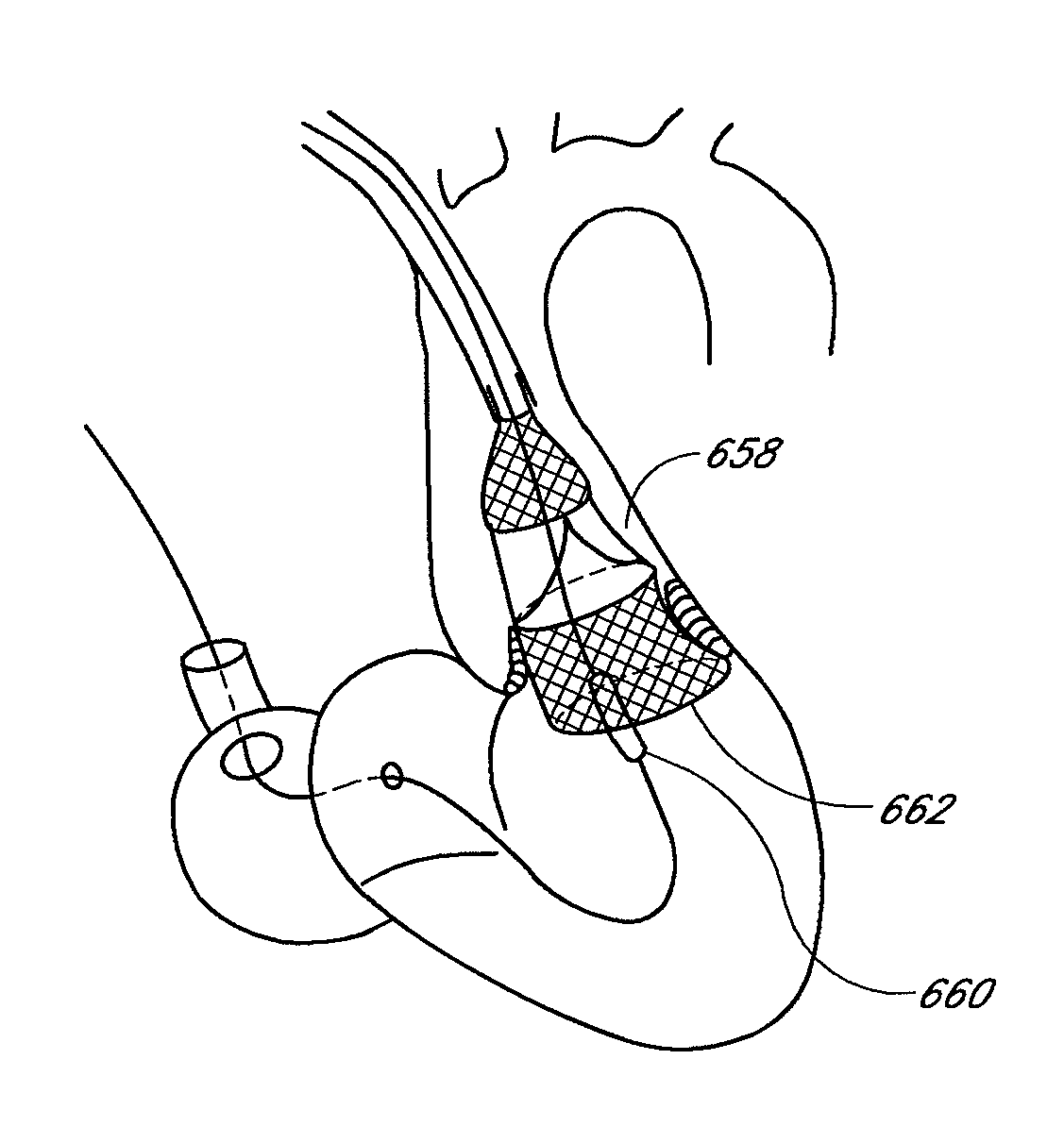
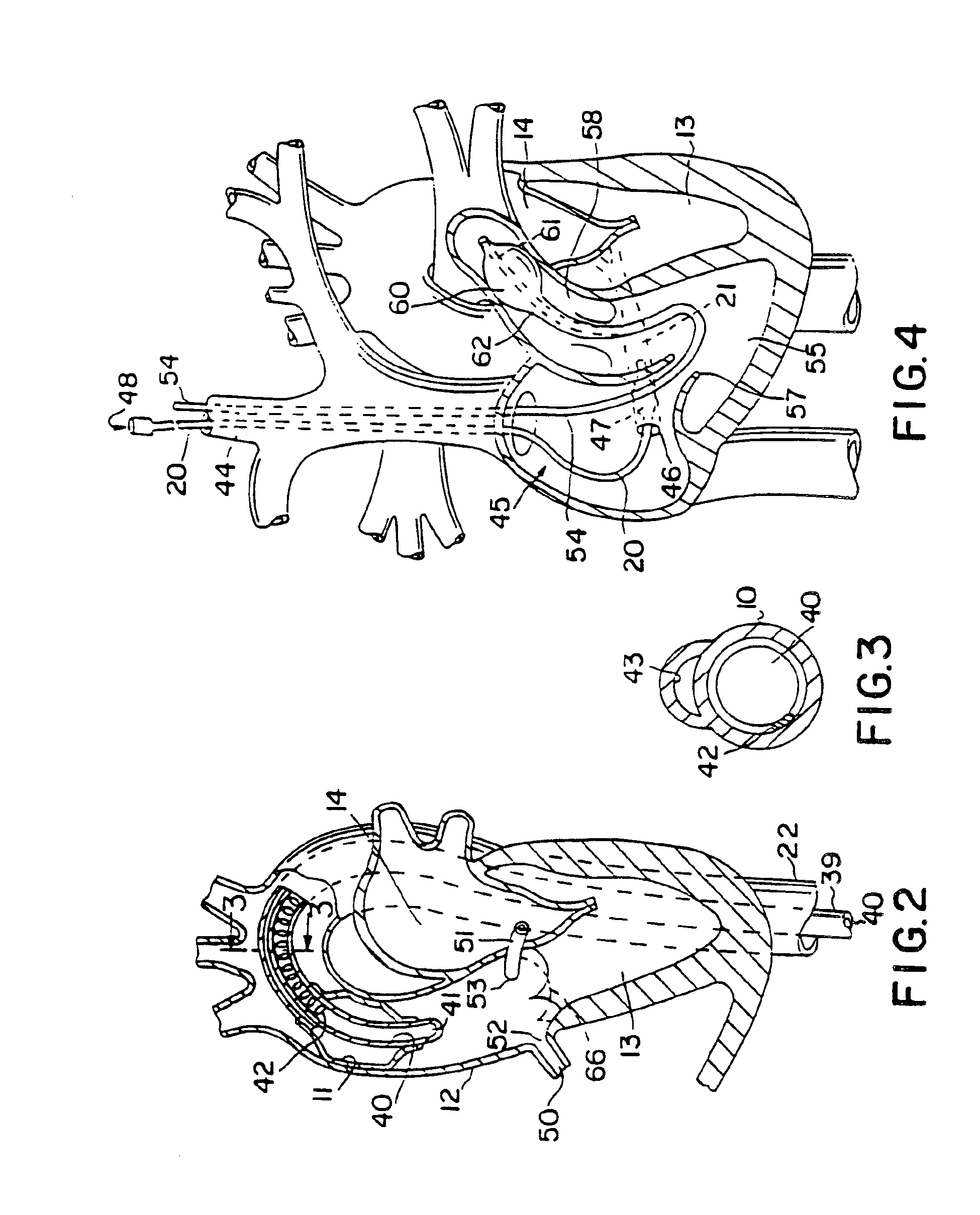
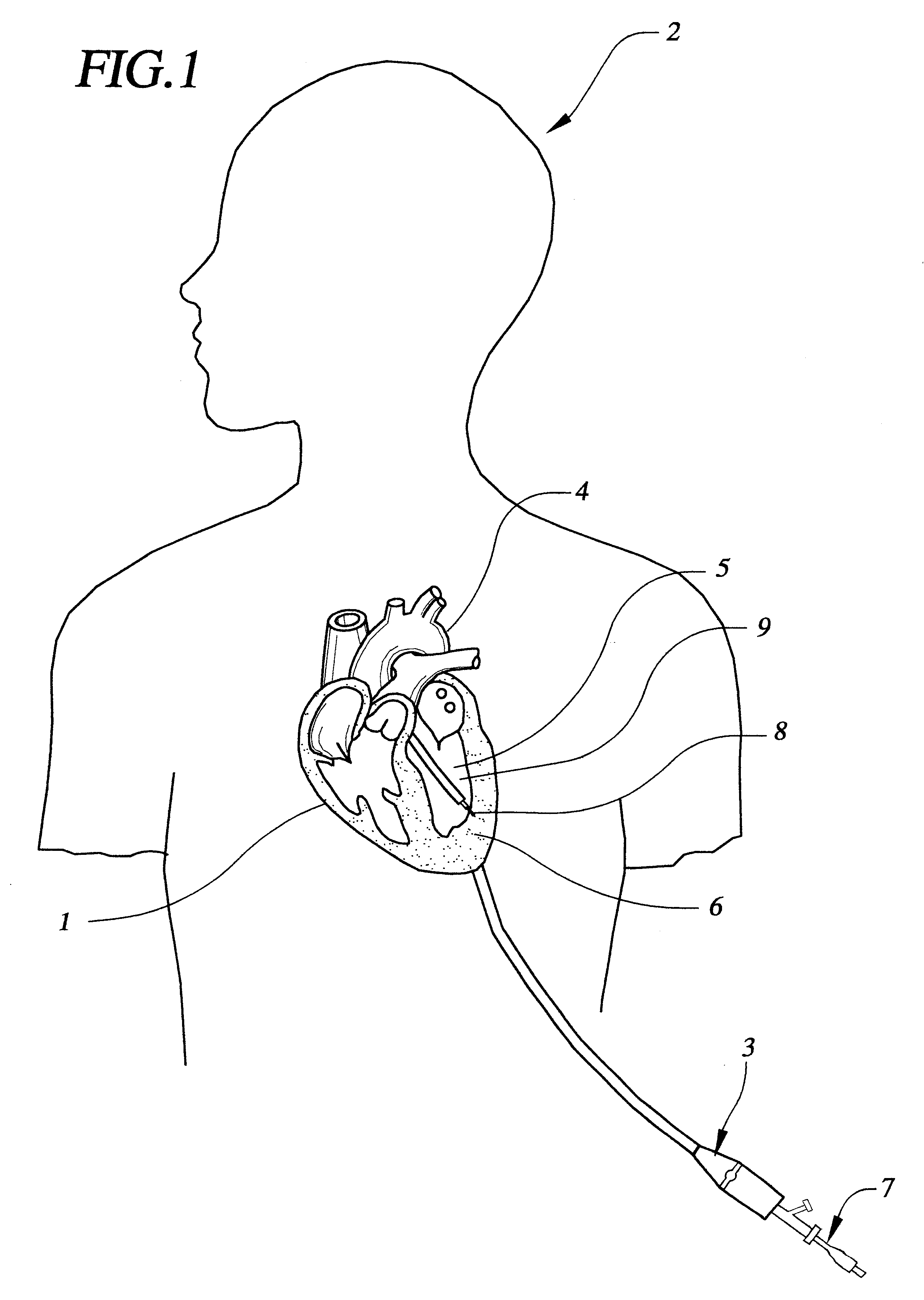
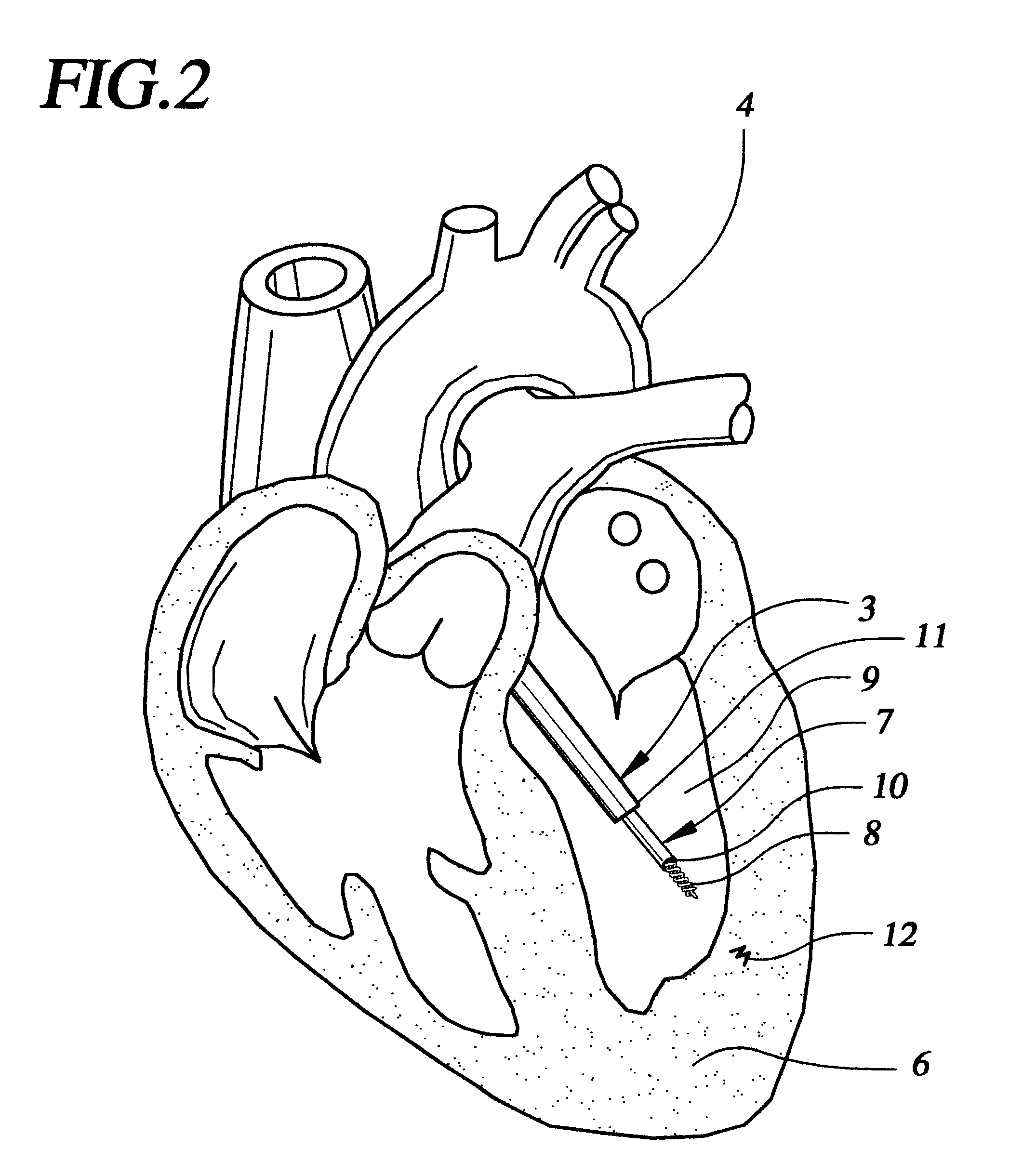
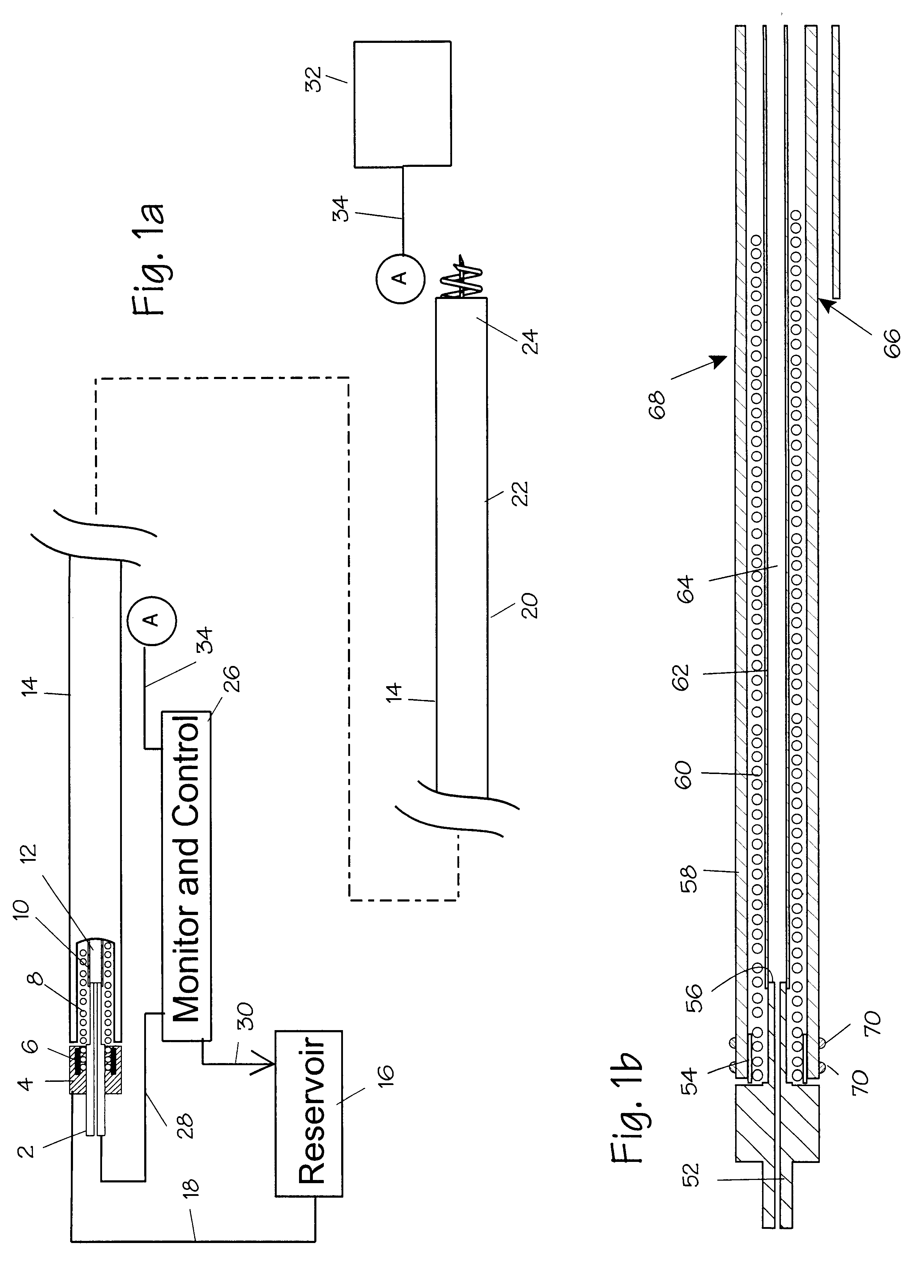
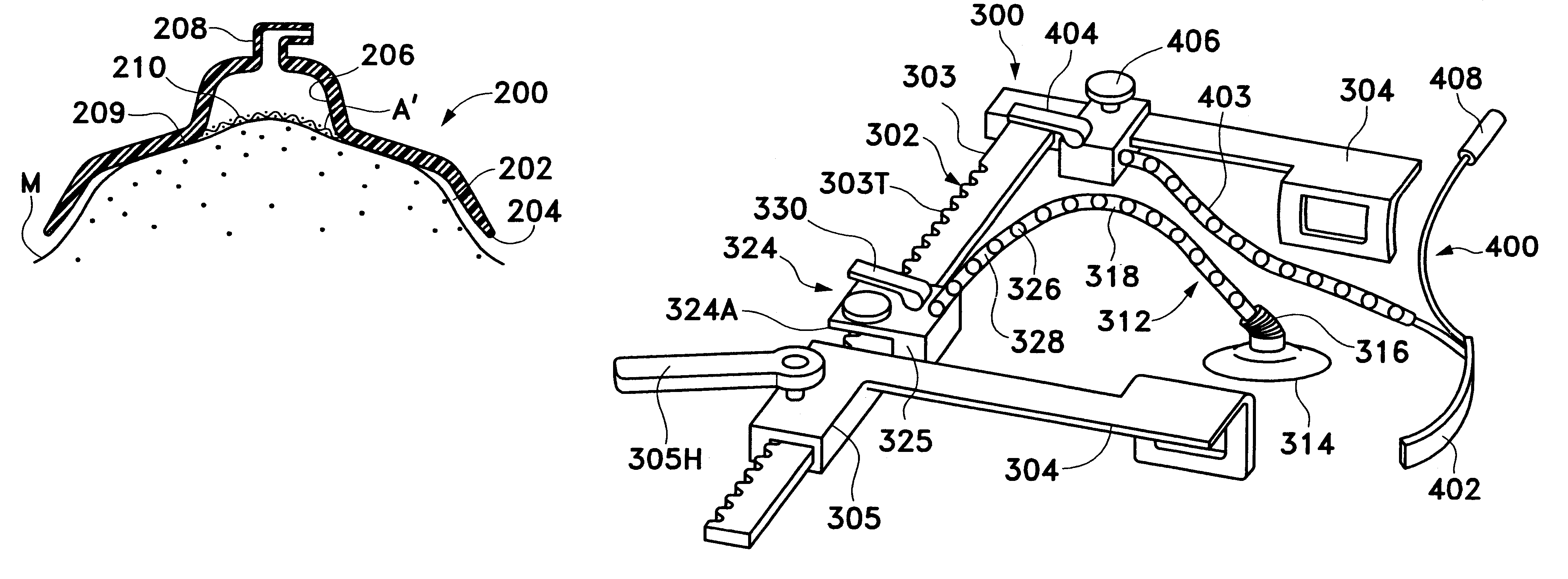
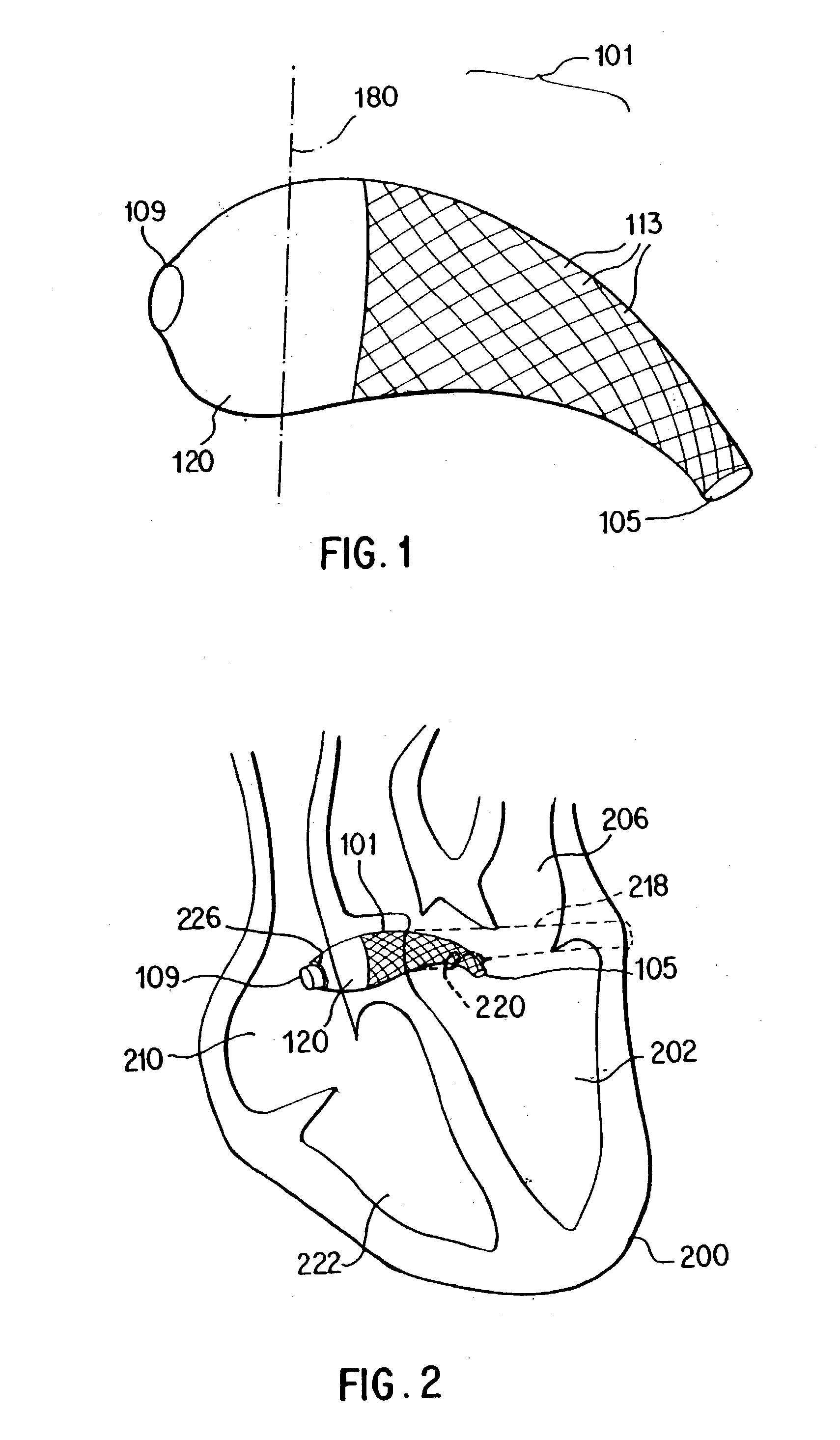
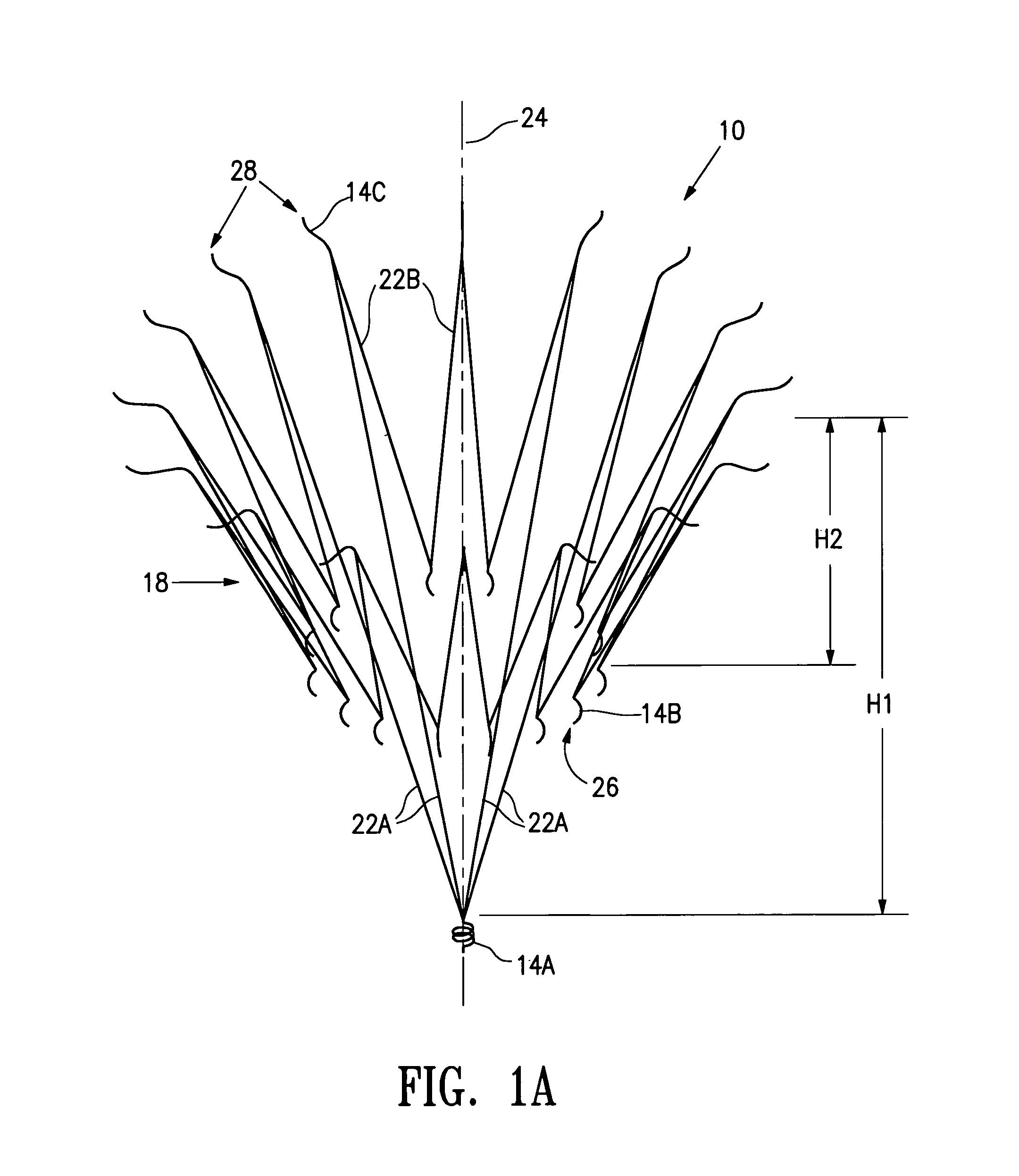
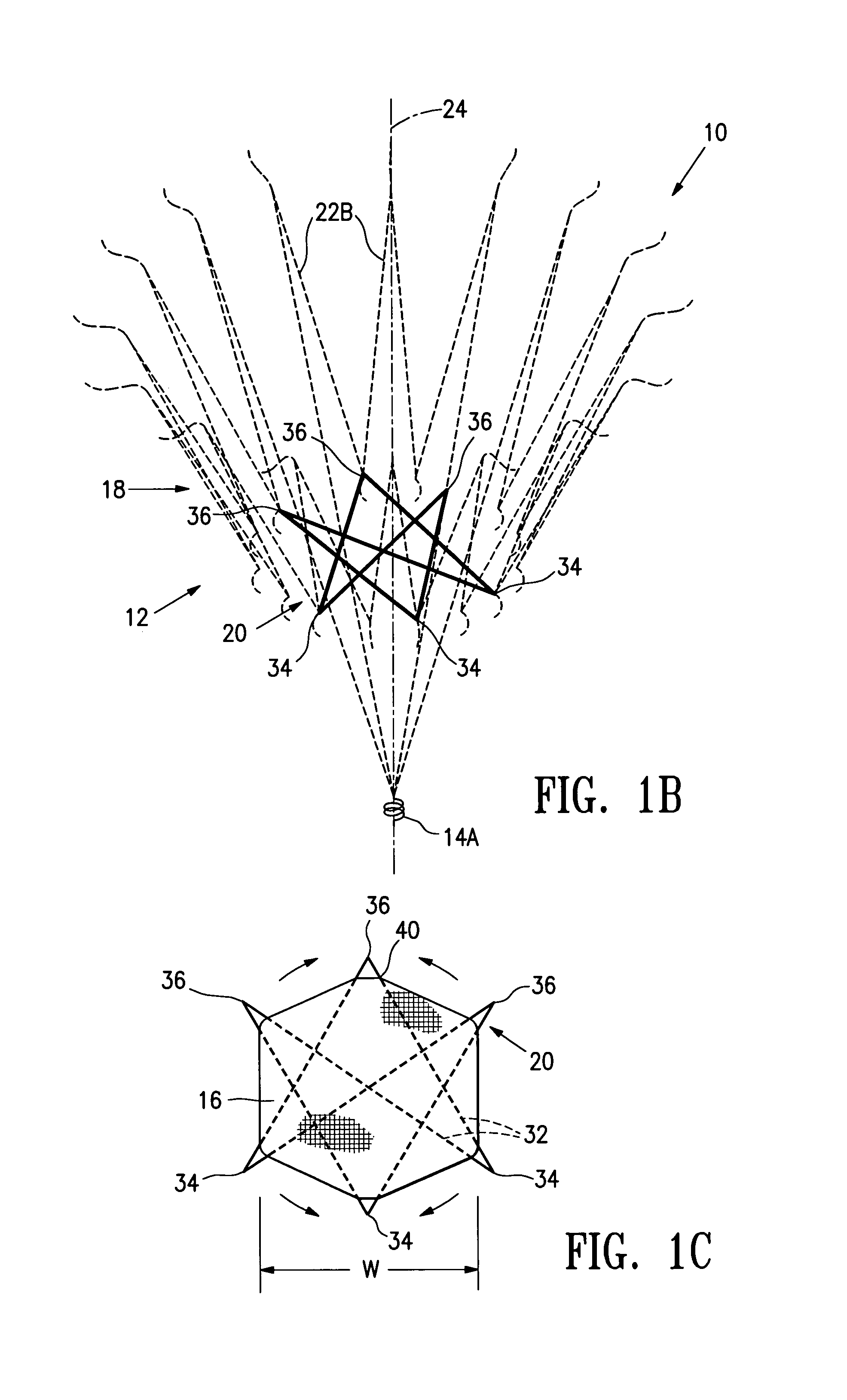
System and method for transapical delivery of an annulus anchored self-expanding valve
ActiveUS20080140189A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemStentsBalloon catheterLimited accessCardiac muscle
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable prosthesis frame. The valve may be delivered transluminally or transmyocardially using a thorascopic or other limited access approach using a delivery catheter. Preferably, the initial partial expansion of the valve is performed against the native valve annulus to provide adequate anchoring and positioning of the valve as the remaining portions of the valve expand. The valve may be delivered using a retrograde or antegrade approach. When delivered using a retrograde approach, a delivery catheter with a pull-back sheath may be used, while antegrade delivery is preferably performed with a delivery catheter with a push-forward sheath that releases the proximal end of the valve first.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
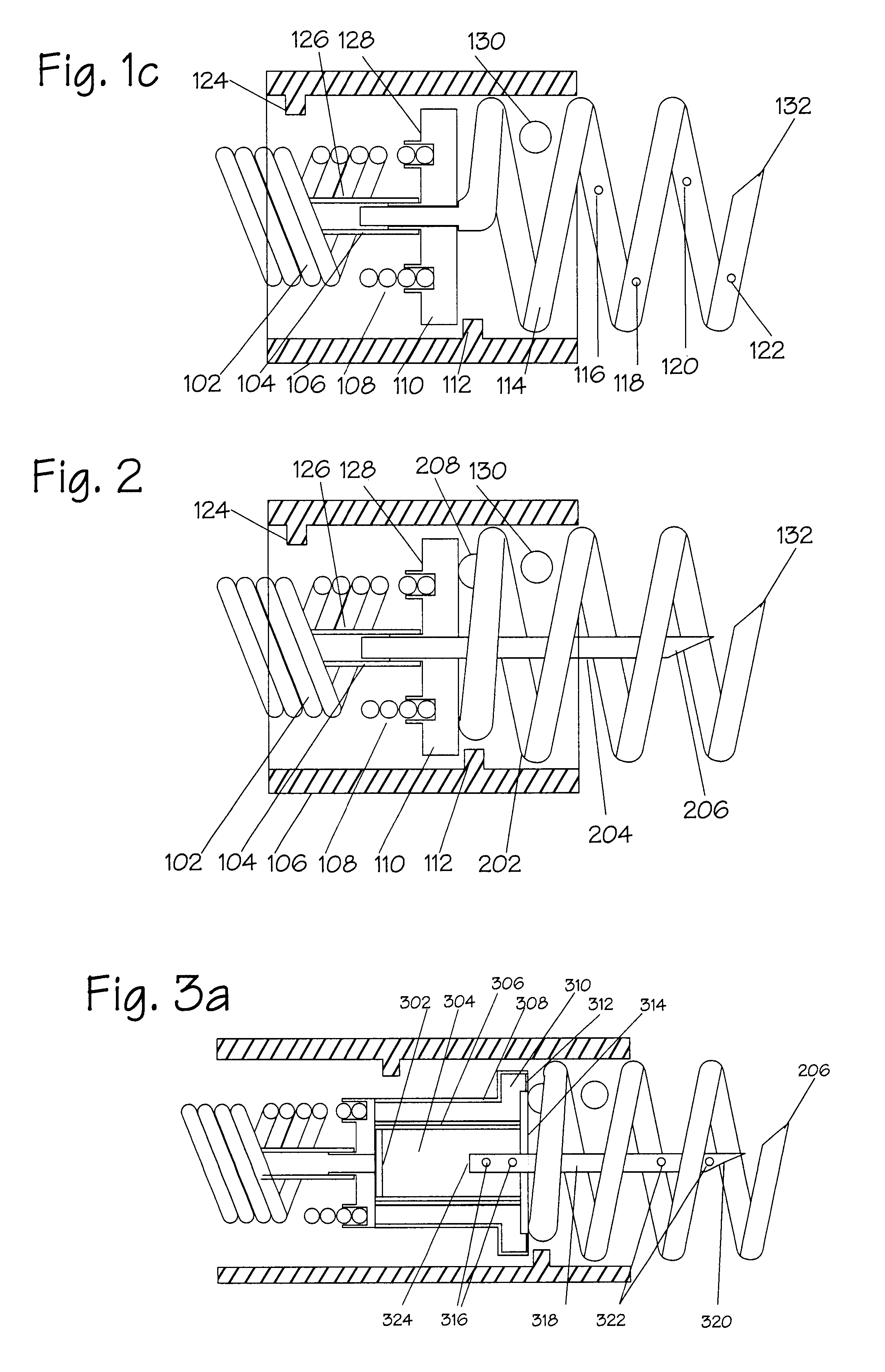
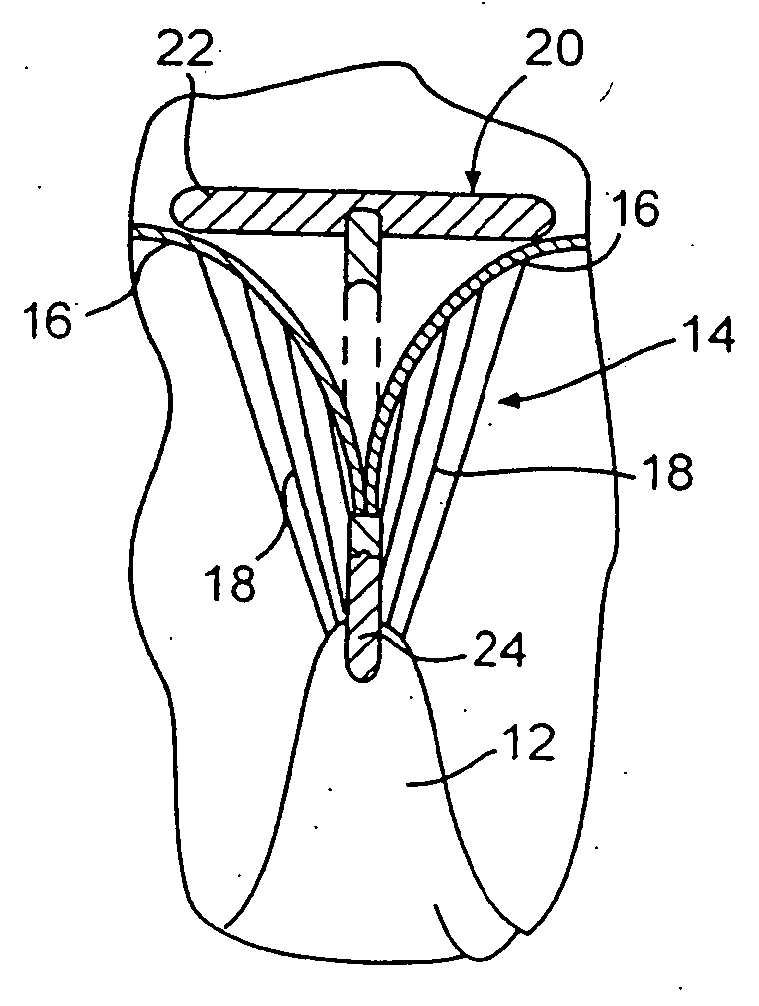
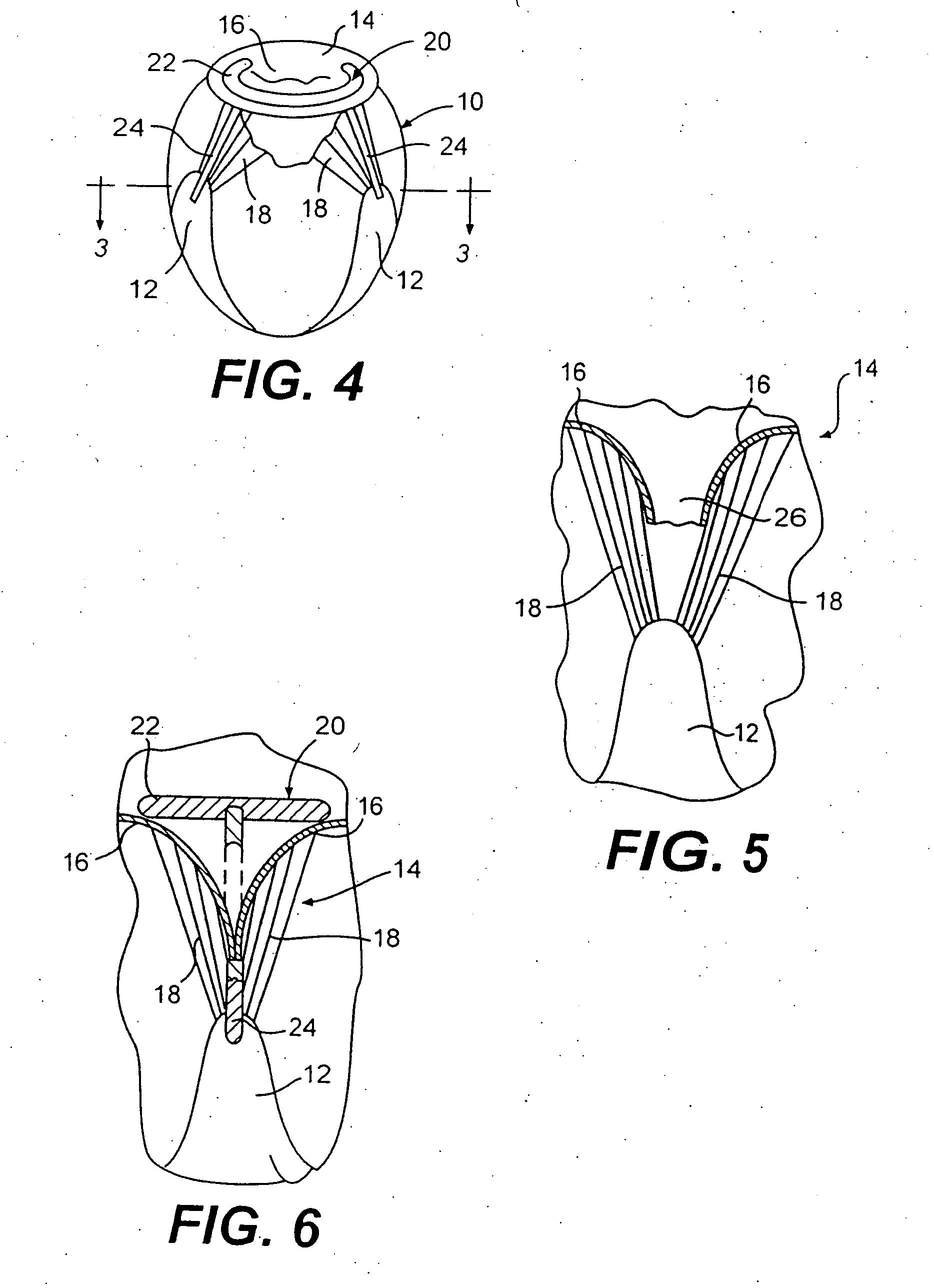
Heart valve annulus device and method of using same
InactiveUS6893459B1Minimize time-consume processShorten the timeHeart valvesProsthesisCardiac muscle
A method of implanting a universal heart valve prosthetic anchor device for receipt of a mating occluder. The anchor device includes a pair of rings axially shiftable from a retracted to a deployed position. The anchor device further formed with a plurality of flexible retaining elements received within the anchor rings and which are capable of laterally downwardly outward movement upon deployment of the rings. The deployment tool includes an elongated tubular housing mounted at its distal end with radially outwardly diverging tines for reversible engagement with the anchoring rings. A wire is telescoped through the tines for actuation of the fork thereby causing deployment of the anchoring rings. Once placed at the desired location within the heart muscle, the deployment tool is actuated causing the anchor device to shift axially thereby causing the retainers to deploy outwardly and upwardly to secure the valve anchor in place at the heart valve annulus shelf.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
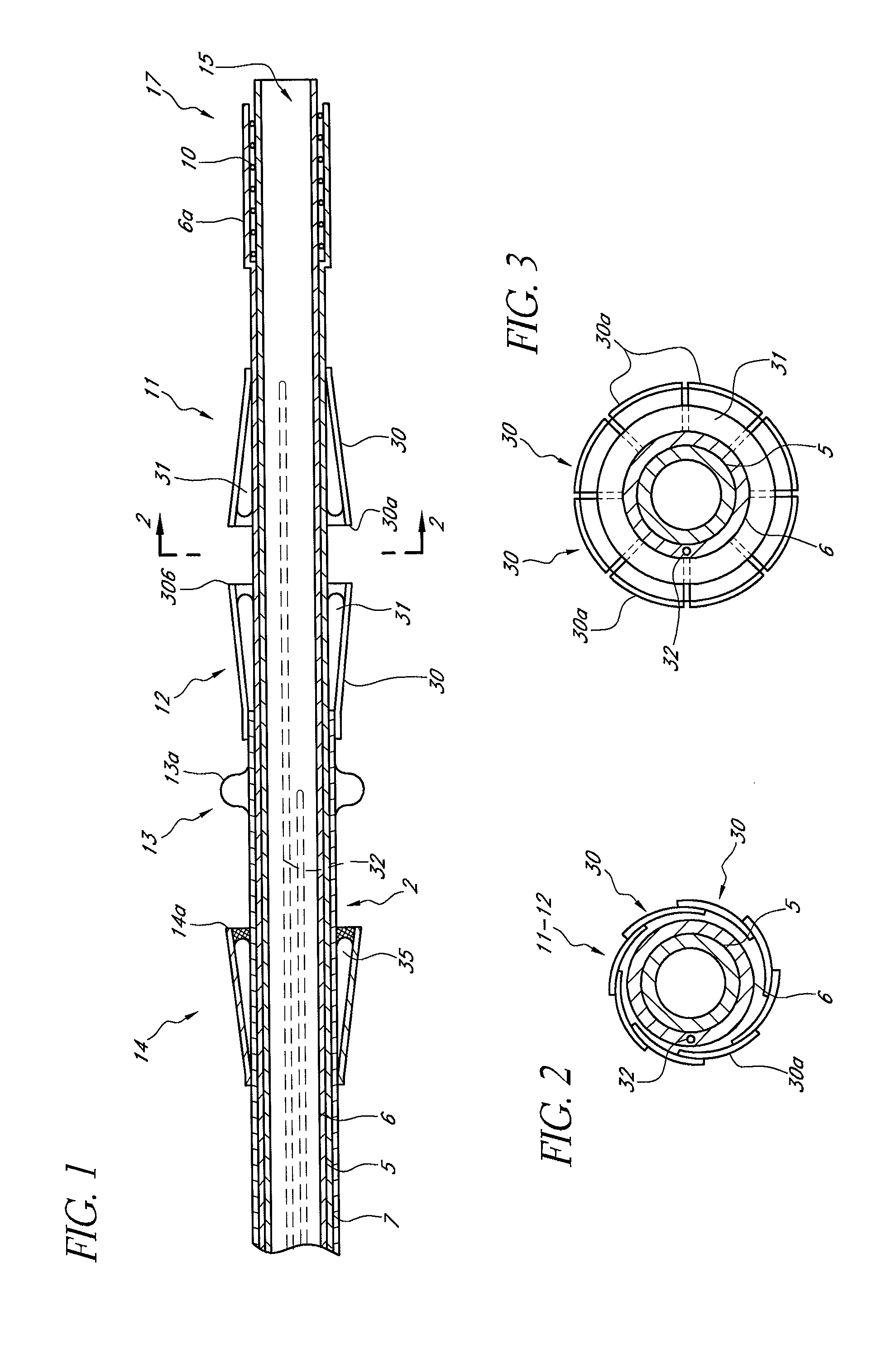
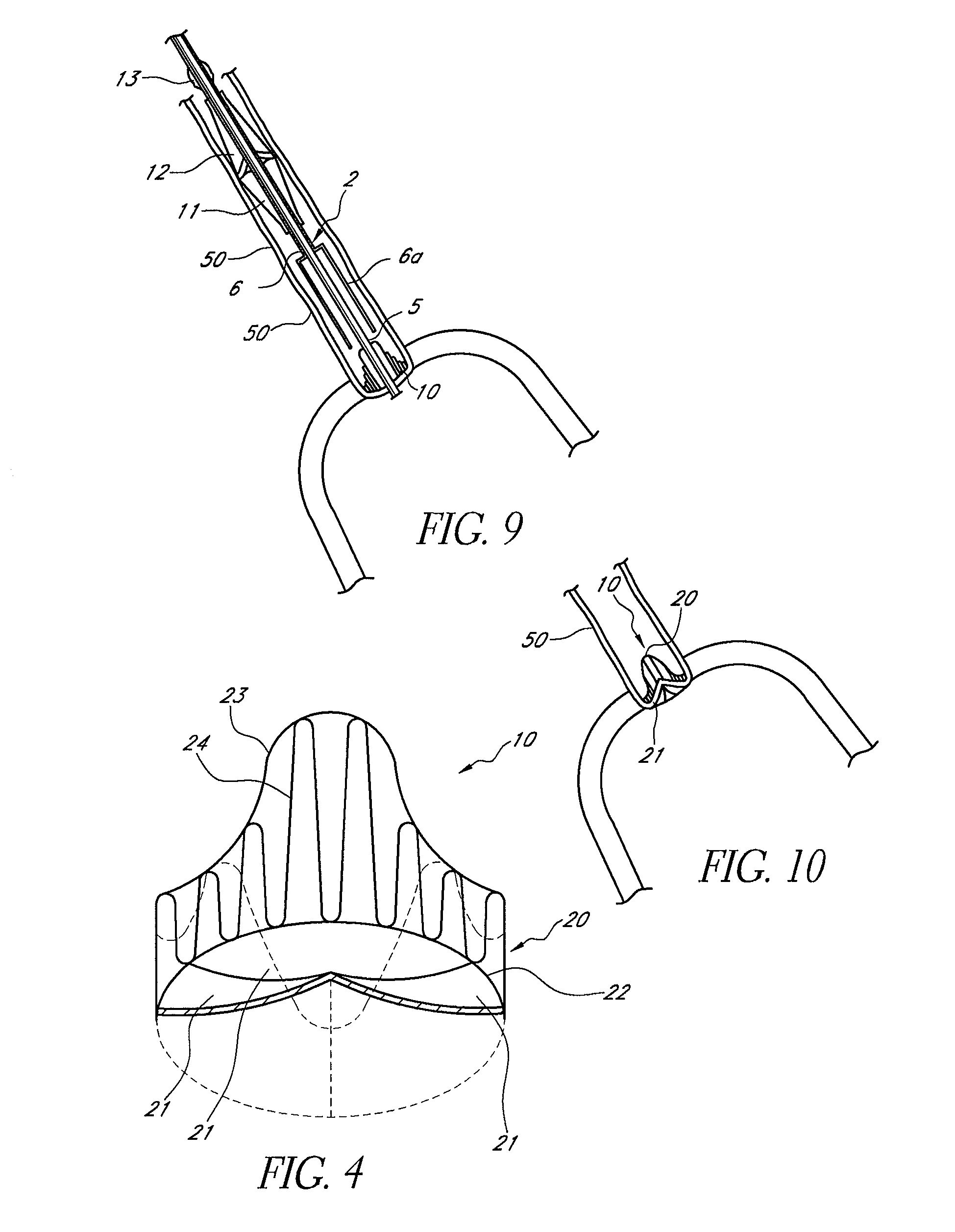
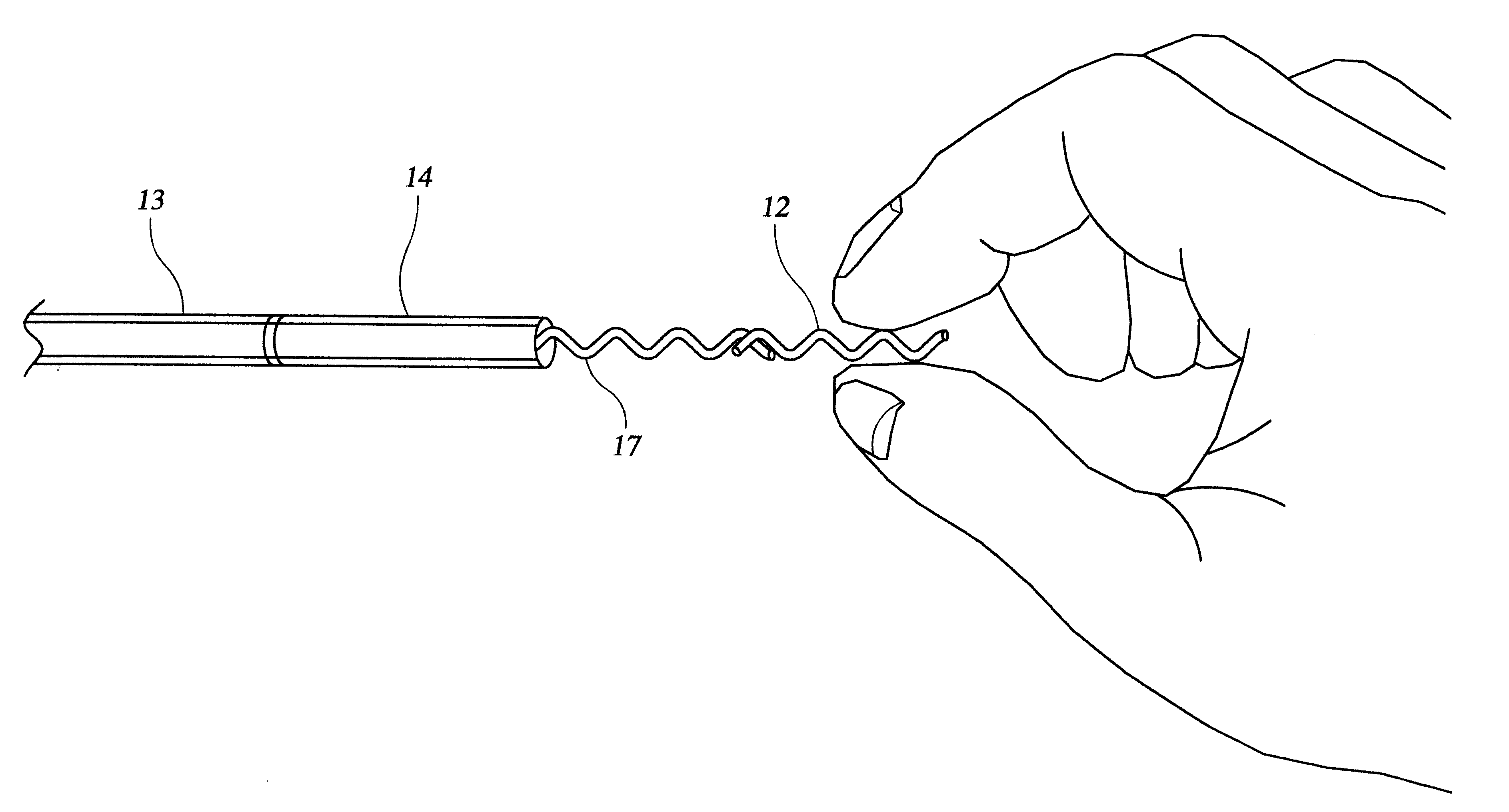
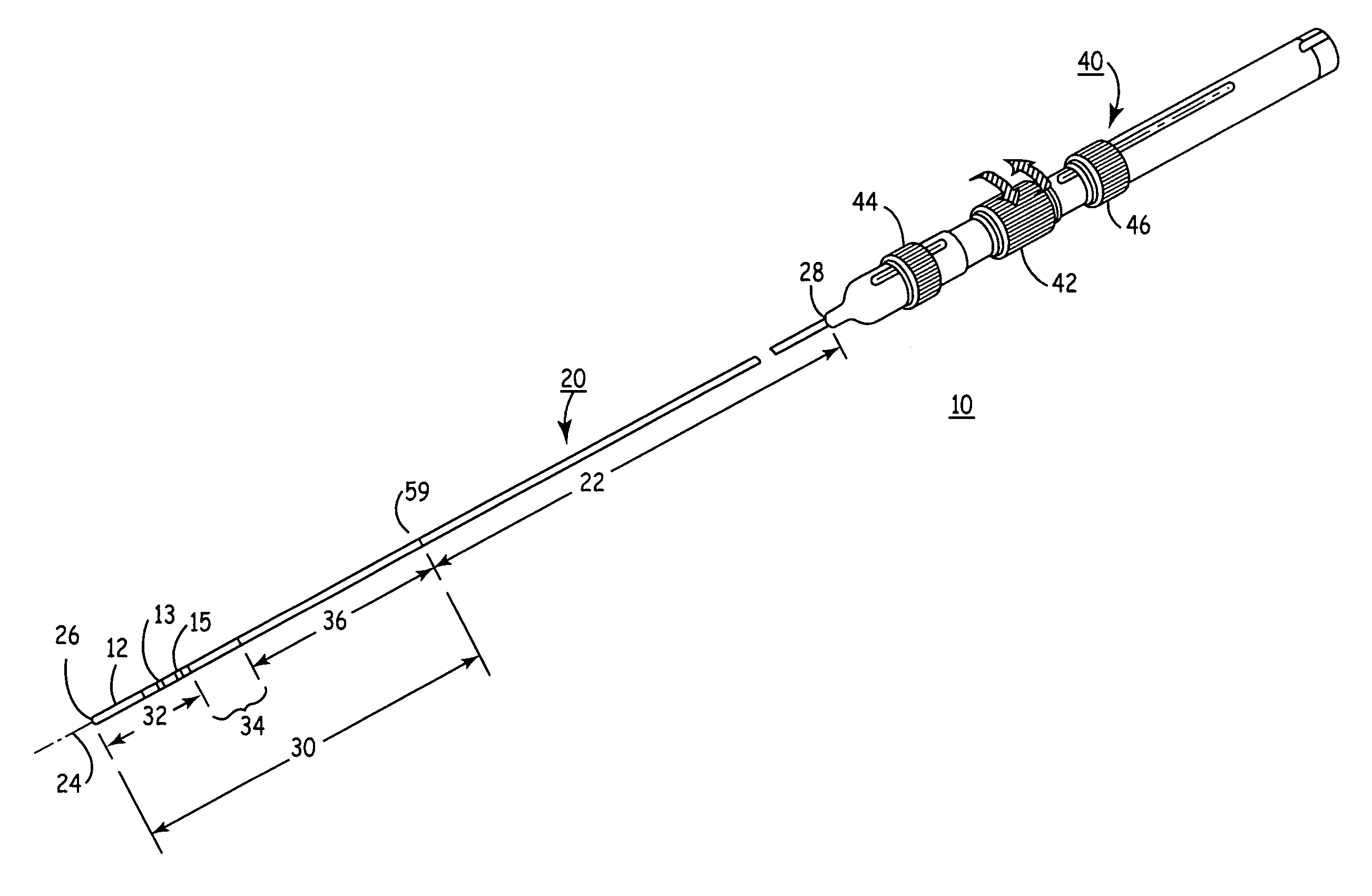
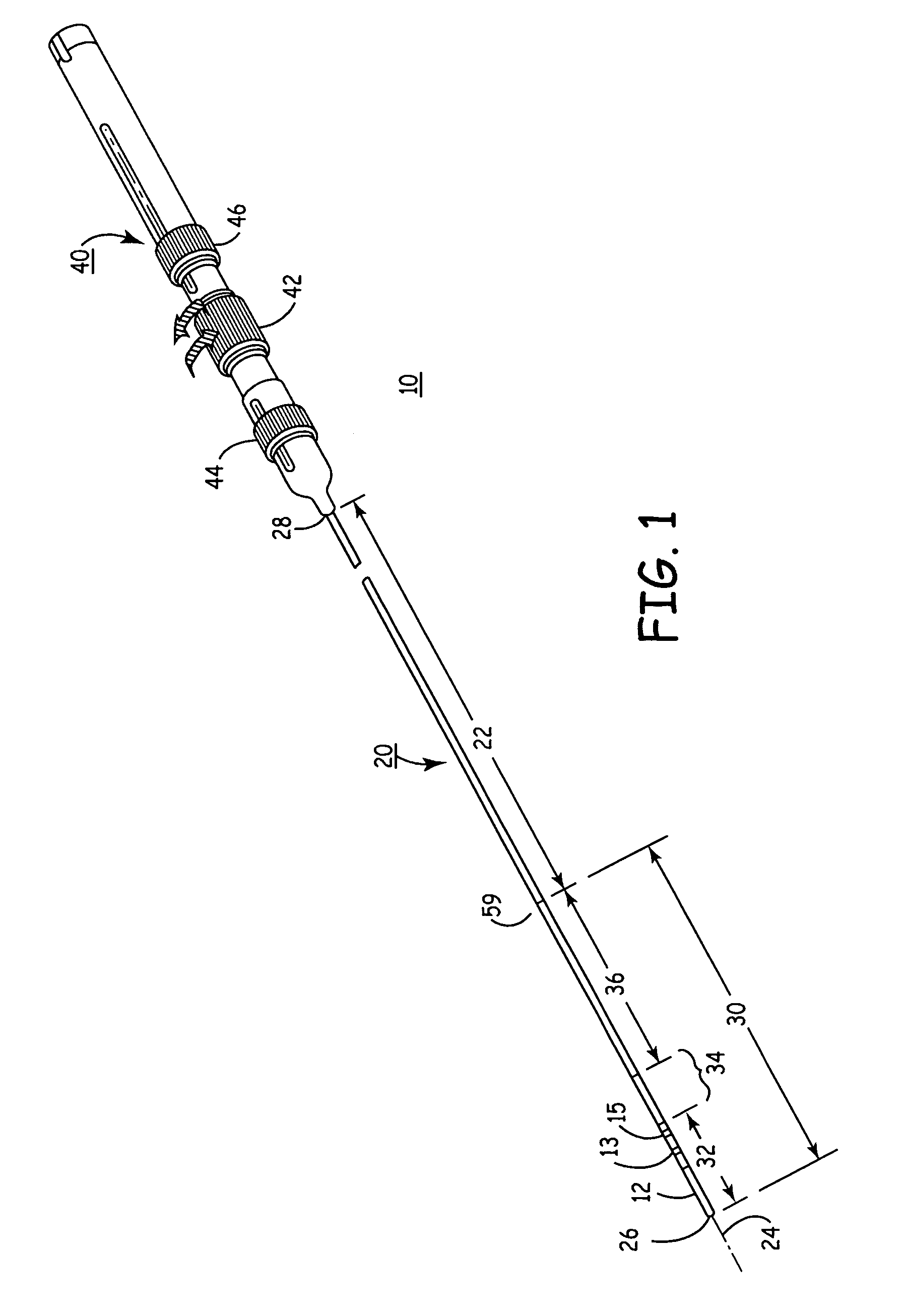
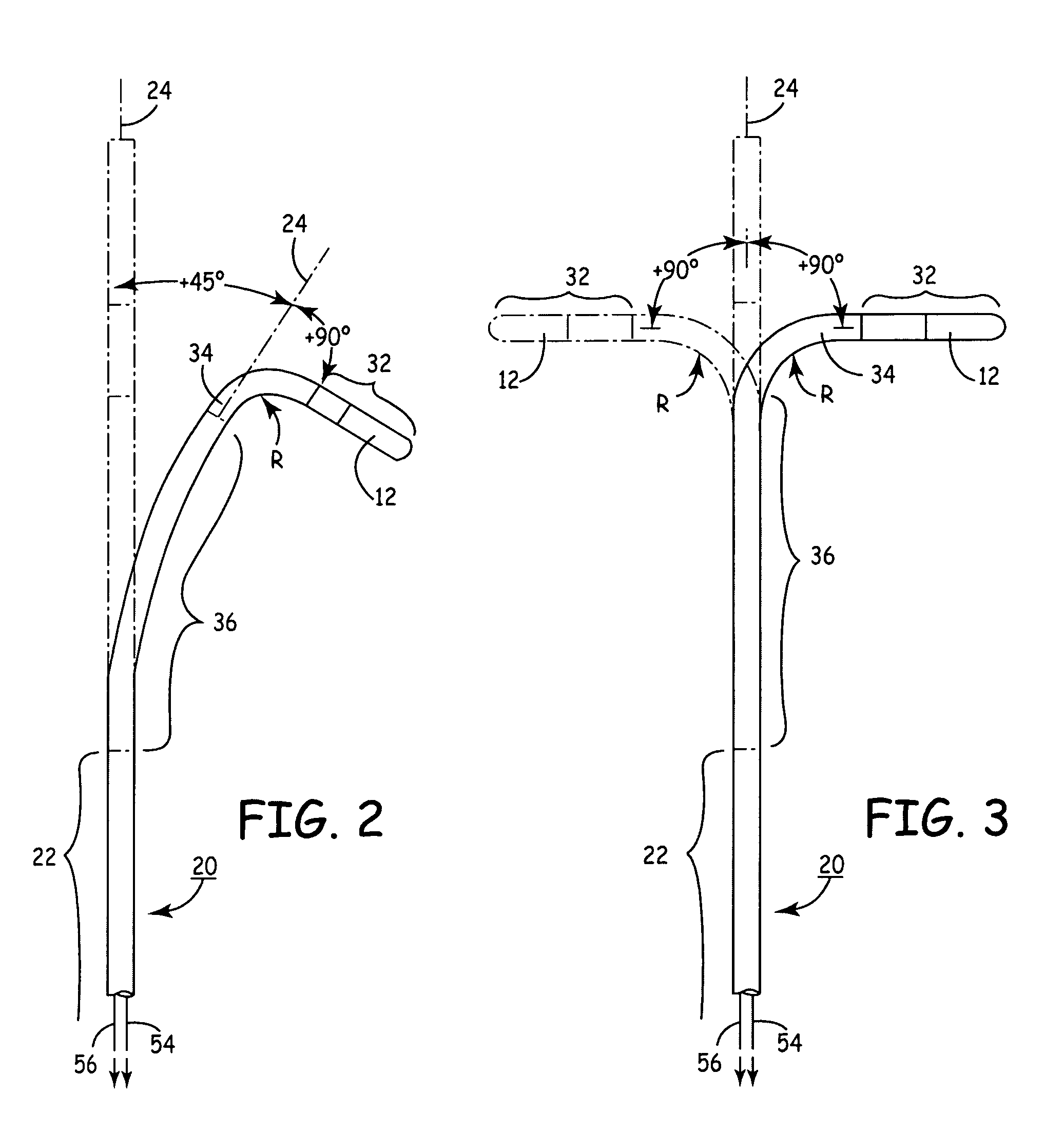
Rotatable lead introducer
Minimally invasive introducers and methods that can be used for rotationally securing devices within the human body. Introducers can include a distal element for releasably engaging a lead head controllable from a proximal control located outside of the body. An inner stem can extend between a proximal portion and a distal portion, and be pivotally and rotatably coupled to the distal lead engagement mechanism. An outer tube can be rotatably disposed over the inner stem and be flexibly coupled over the pivot to rotationally drive the distal element. A helical epicardial-myocardial lead electrode can be secured and oriented straight ahead and introduced through a port or small incision with the introducer in a straight configuration. The introducer can then be bent and rotated to screw the helical electrode into the heart.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
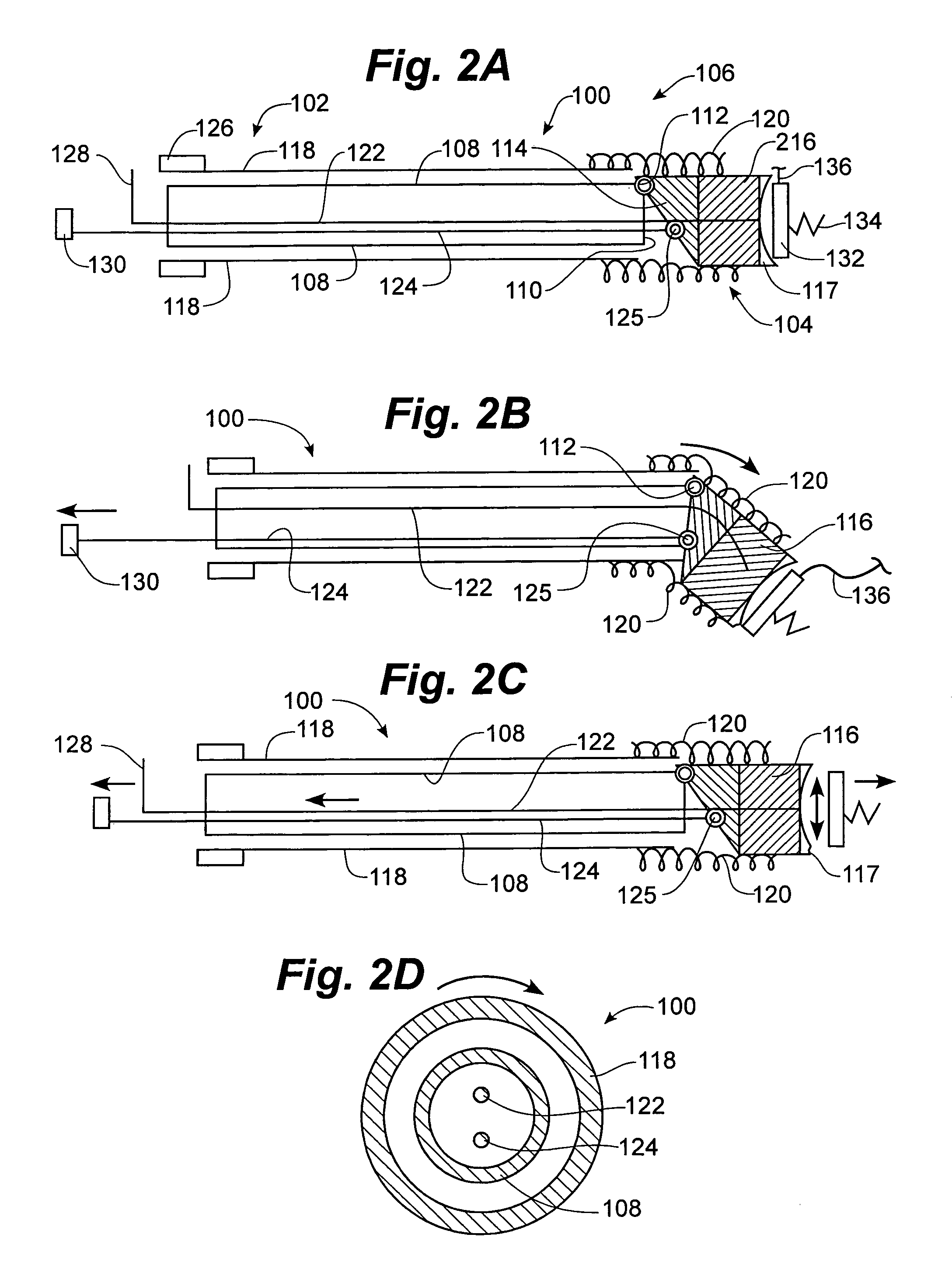
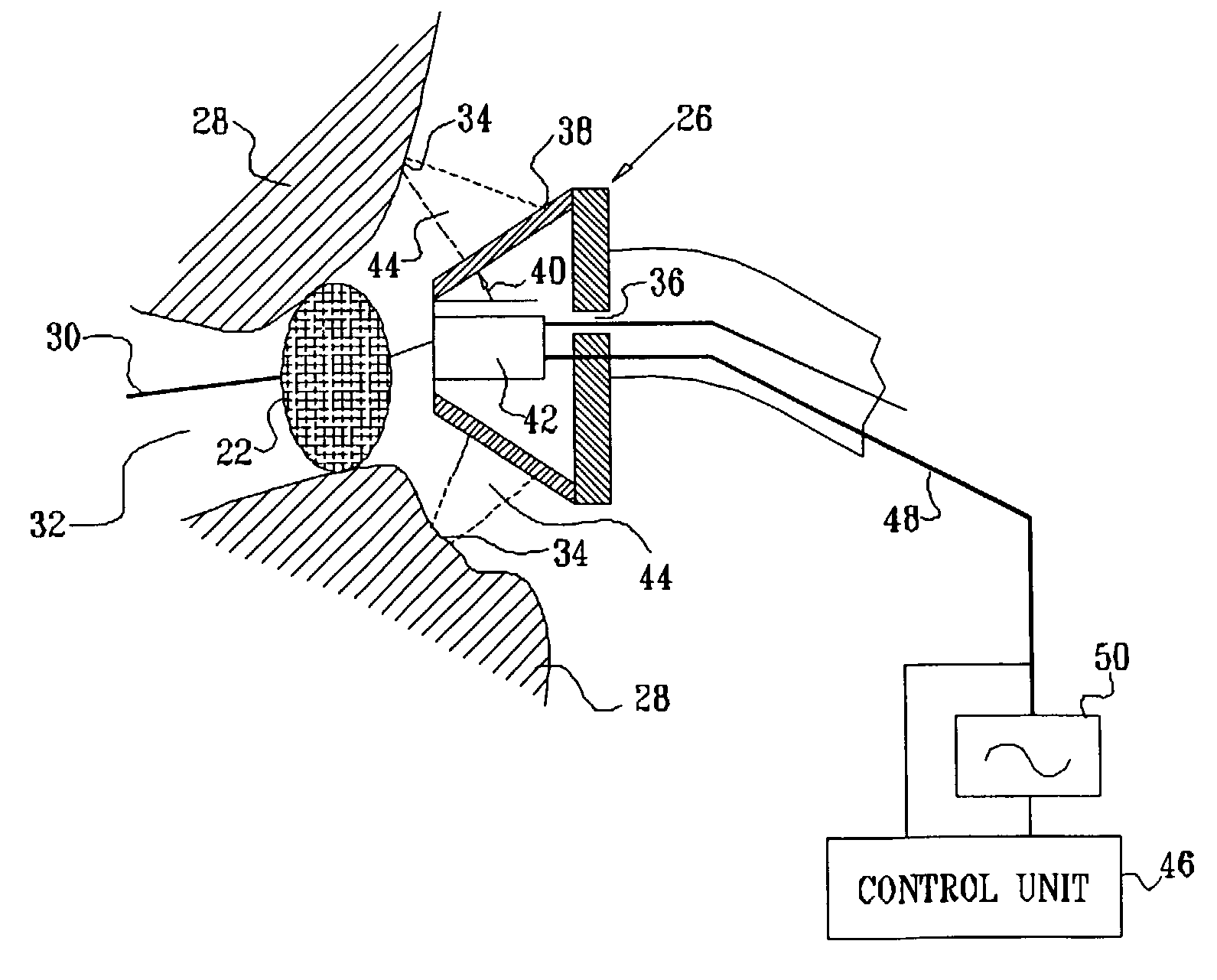
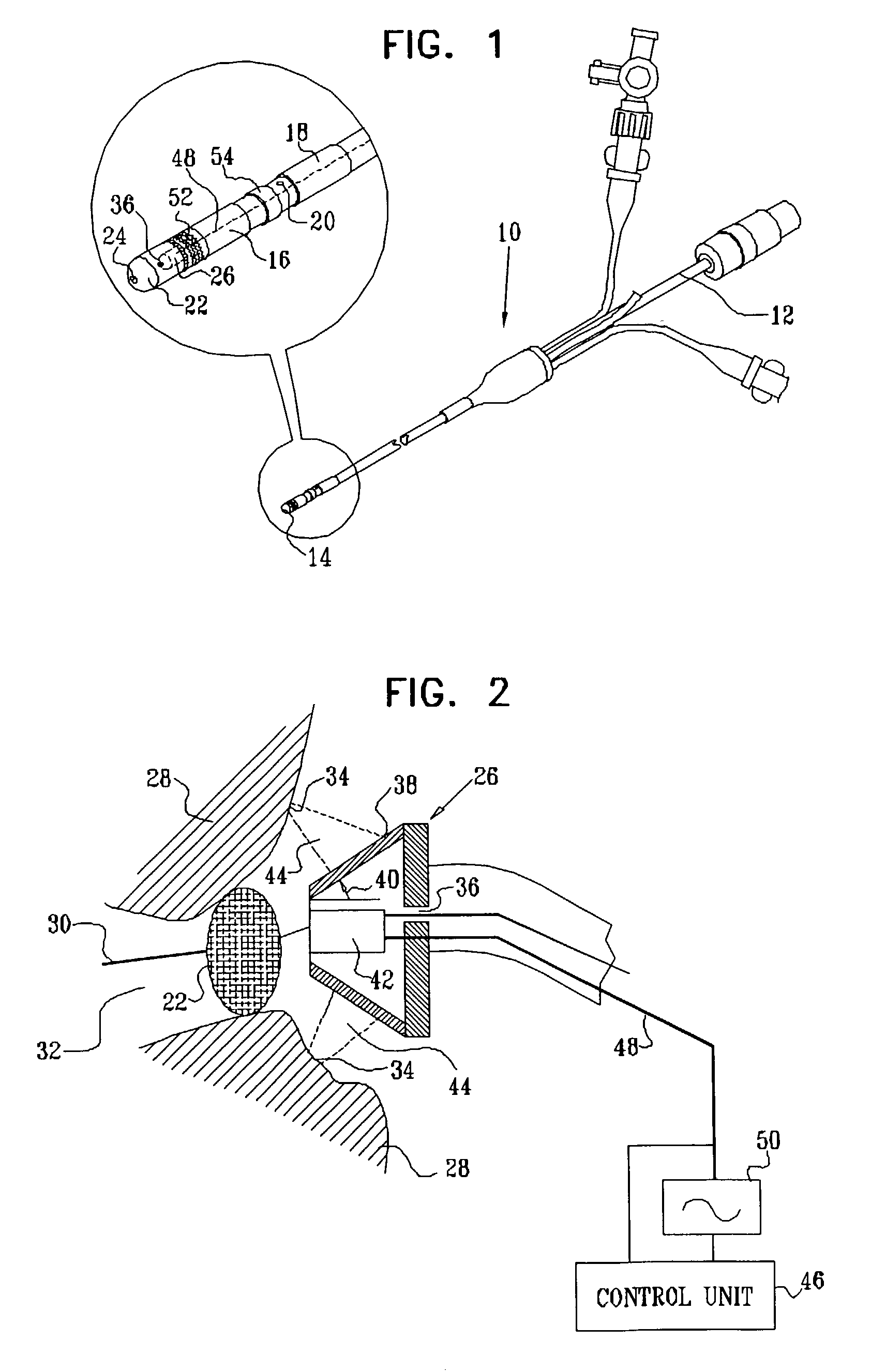
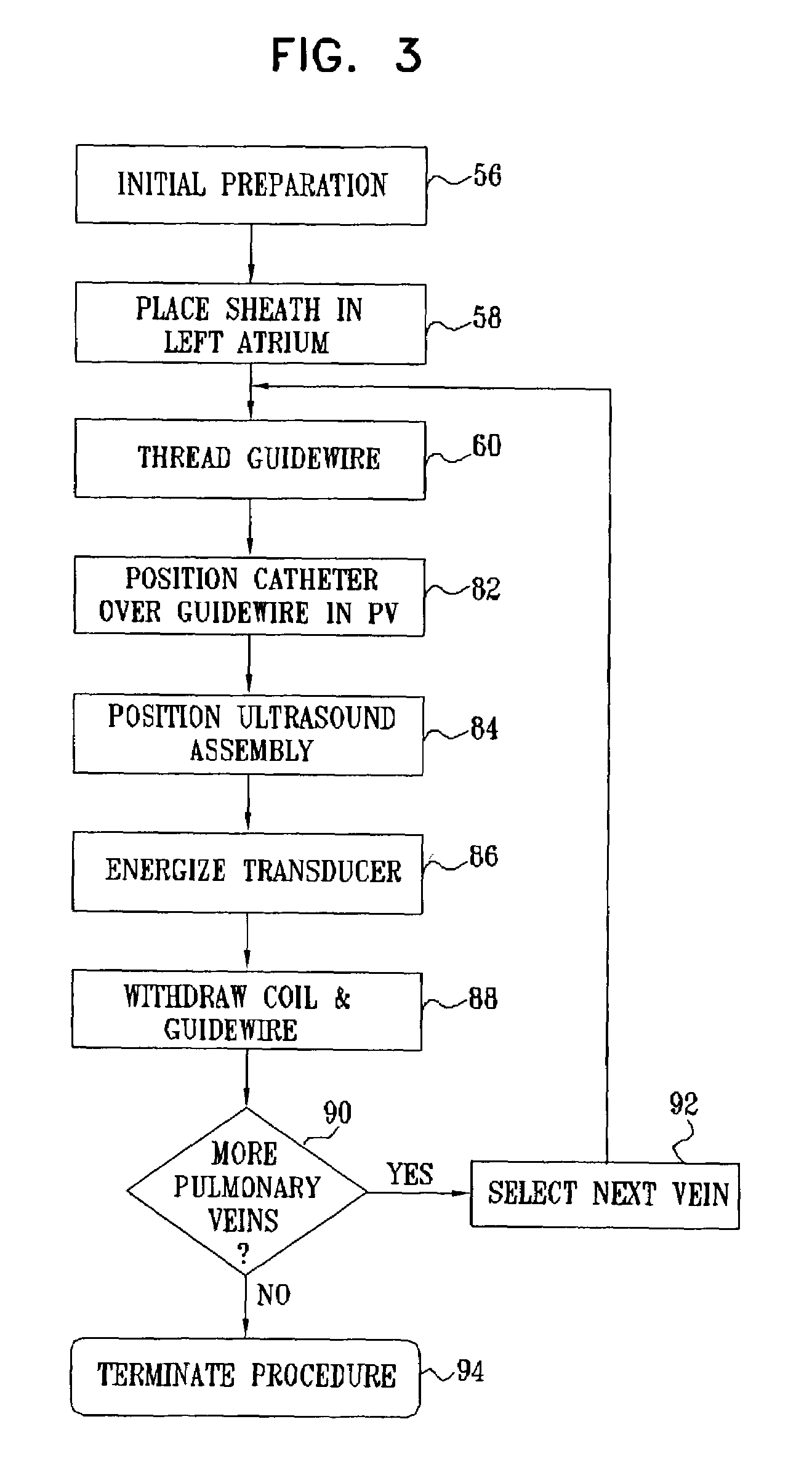
Ultrasound pulmonary vein isolation
A catheter introduction apparatus provides an ultrasound assembly for emission of ultrasound energy. In one application the catheter and the ultrasound assembly are introduced percutaneously, and transseptally advanced to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. An anchoring balloon is expanded to center an acoustic lens in the lumen of the pulmonary vein, such that energy is converged circumferentially onto the wall of the pulmonary vein when a transducer is energized. A circumferential ablation lesion is produced in the myocardial sleeve of the pulmonary vein, which effectively blocks electrical propagation between the pulmonary vein and the left atrium.
Owner:BIOSENSE
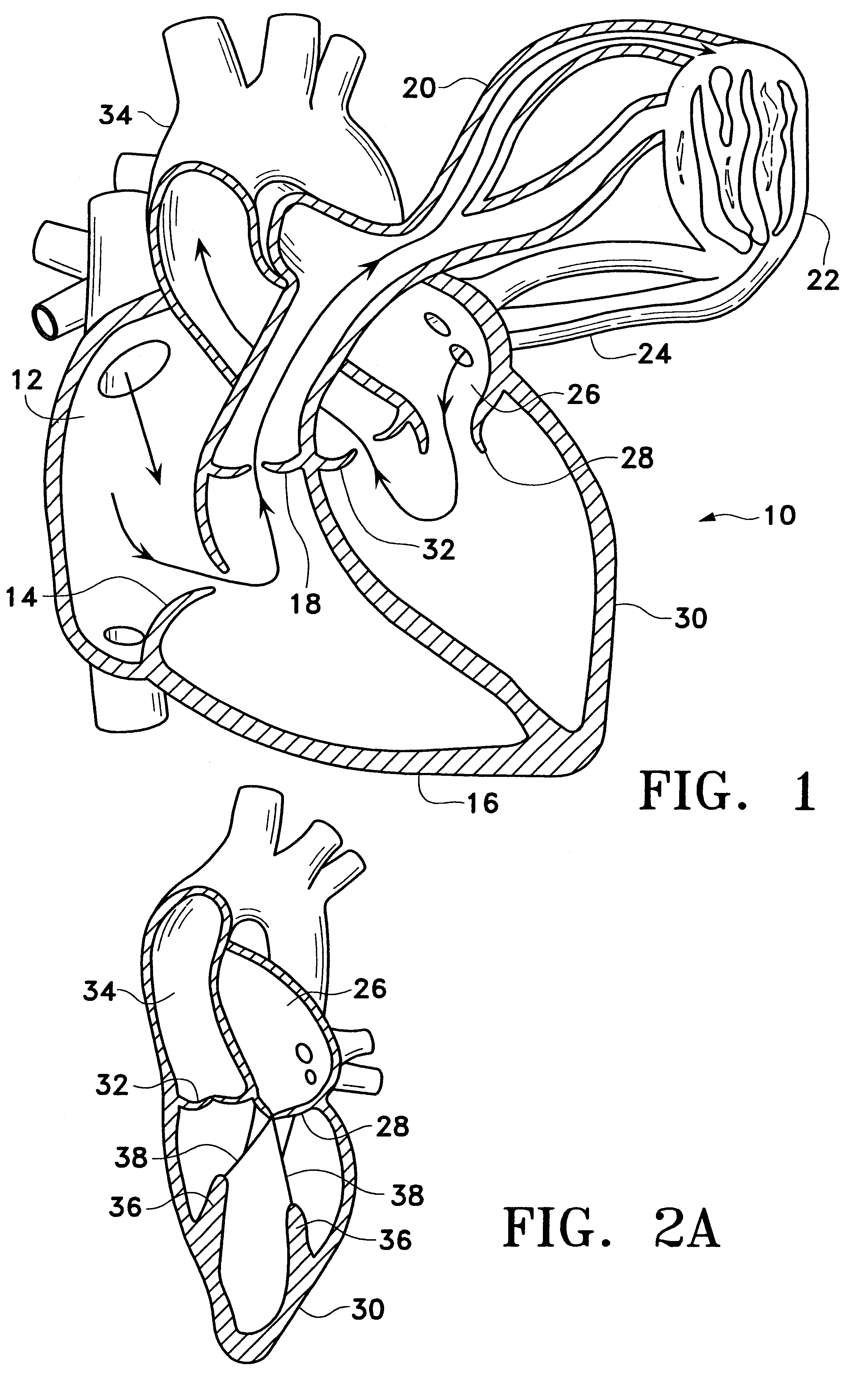
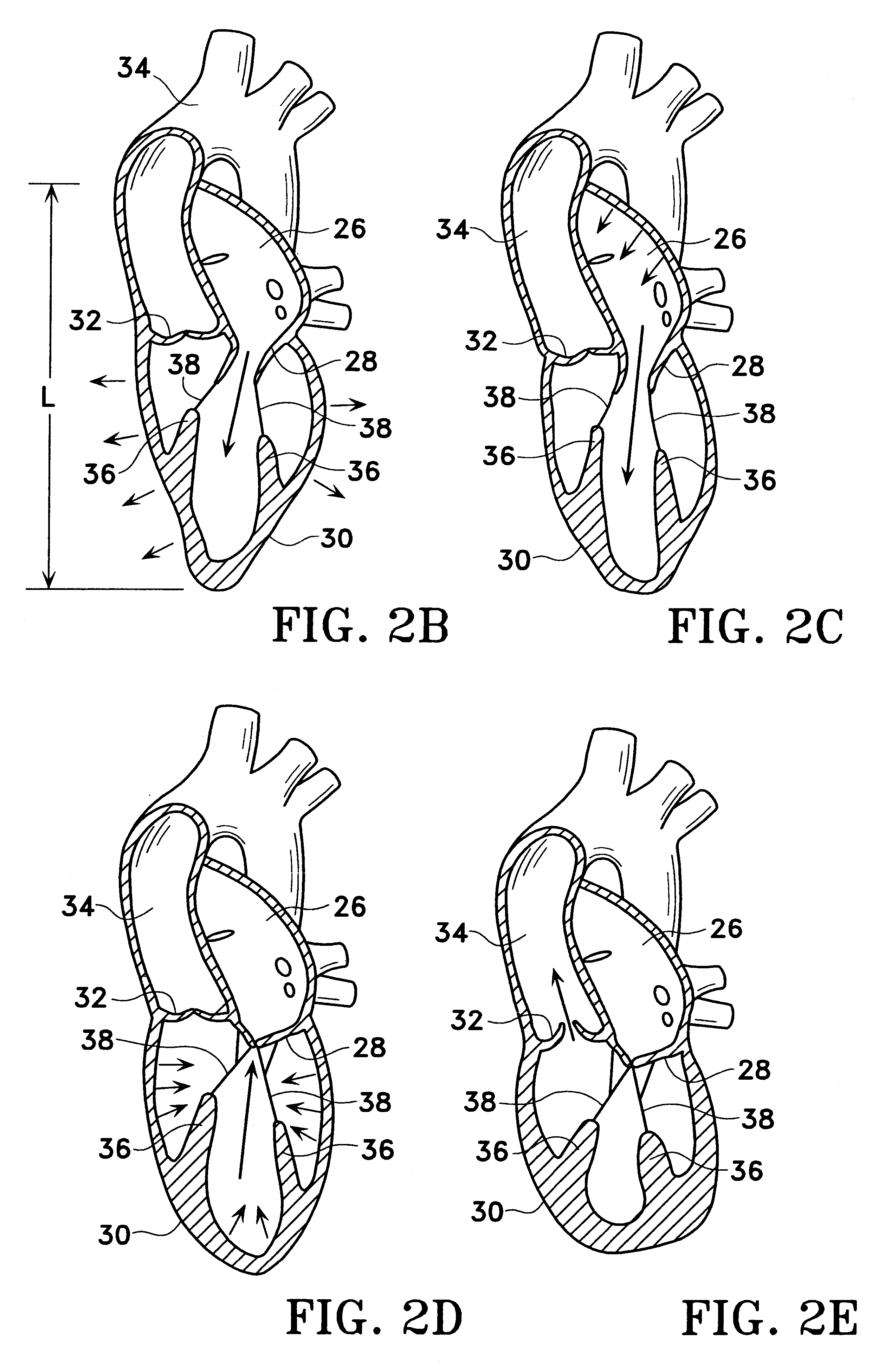
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS20050197694A1Reduce stressReduce/limit volumeSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Described are devices and methods for treating degenerative, congestive heart disease and related valvular dysfunction. Percutaneous and minimally invasive surgical tensioning structures offer devices that mitigate changes in the ventricular structure (i.e., remodeling) and deterioration of global left ventricular performance related to tissue damage precipitating from ischemia, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or other abnormalities. These tensioning structures can be implanted within various major coronary blood-carrying conduit structures (arteries, veins and branching vessels), into or through myocardium, or into engagement with other anatomic structures that impact cardiac output to provide tensile support to the heart muscle wall which resists diastolic filling pressure while simultaneously providing a compressive force to the muscle wall to limit, compensate or provide therapeutic treatment for congestive heart failure and / or to reverse the remodeling that produces an enlarged heart.
Owner:EXTENSIA MEDICAL
Anterior segment ventricular restoration apparatus and method
The symptoms of congenital heart failure are addressed in this surgical procedure for mounting a patch in the ventricle of the heart to reduce ventricular volume. Placement of the patch is facilitated by palpating a beating heart to identify akinetic, although normal appearing, tissue. The patch has an oval configuration facilitating return of the heart to a normal apical shape which enhances muscle fiber efficiency and a normal writhing pumping action. The patch includes a semi-rigid ring, and a circumferential rim to address bleeding. Patch placement is further enhanced by creating a Fontan neck and use of pledged sutures. Intraoperative vascularization and valve replacement is easily accommodated. Increased injection fraction, reduced muscle stress, improved myocardial protection, and ease of accurate patch placement are all achieved with this procedure.
Owner:CORRESTORE
System for cardiac procedures
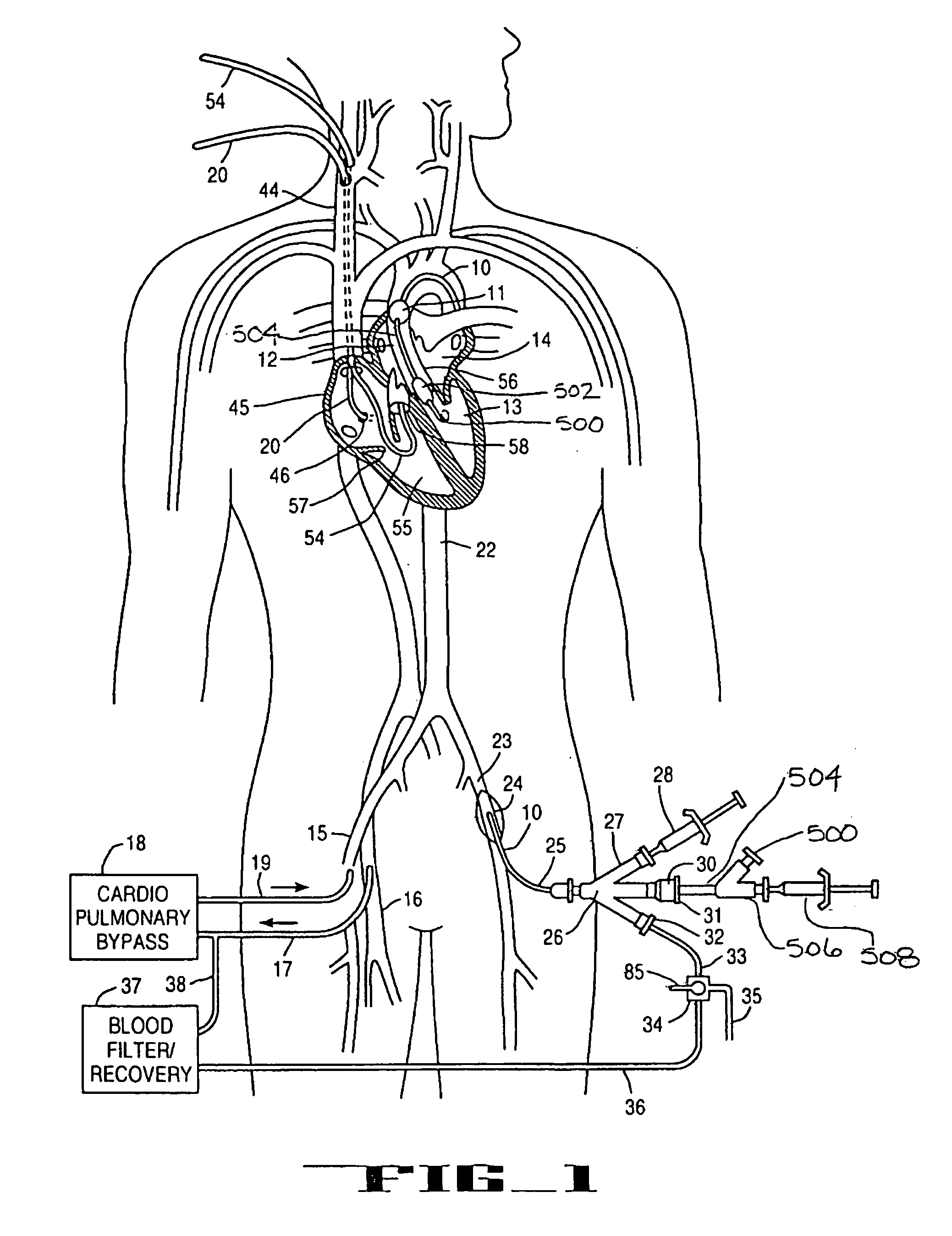
A system for accessing a patient's cardiac anatomy which includes an endovascular aortic partitioning device that separates the coronary arteries and the heart from the rest of the patient's arterial system. The endovascular device for partitioning a patient's ascending aorta comprises a flexible shaft having a distal end, a proximal end, and a first inner lumen therebetween with an opening at the distal end. The shaft may have a preshaped distal portion with a curvature generally corresponding to the curvature of the patient's aortic arch. An expandable means, e.g. a balloon, is disposed near the distal end of the shaft proximal to the opening in the first inner lumen for occluding the ascending aorta so as to block substantially all blood flow therethrough for a plurality of cardiac cycles, while the patient is supported by cardiopulmonary bypass. The endovascular aortic partitioning device may be coupled to an arterial bypass cannula for delivering oxygenated blood to the patient's arterial system. The heart muscle or myocardium is paralyzed by the retrograde delivery of a cardioplegic fluid to the myocardium through patient's coronary sinus and coronary veins, or by antegrade delivery of cardioplegic fluid through a lumen in the endovascular aortic partitioning device to infuse cardioplegic fluid into the coronary arteries. The pulmonary trunk may be vented by withdrawing liquid from the trunk through an inner lumen of an elongated catheter. The cardiac accessing system is particularly suitable for removing the aortic valve and replacing the removed valve with a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
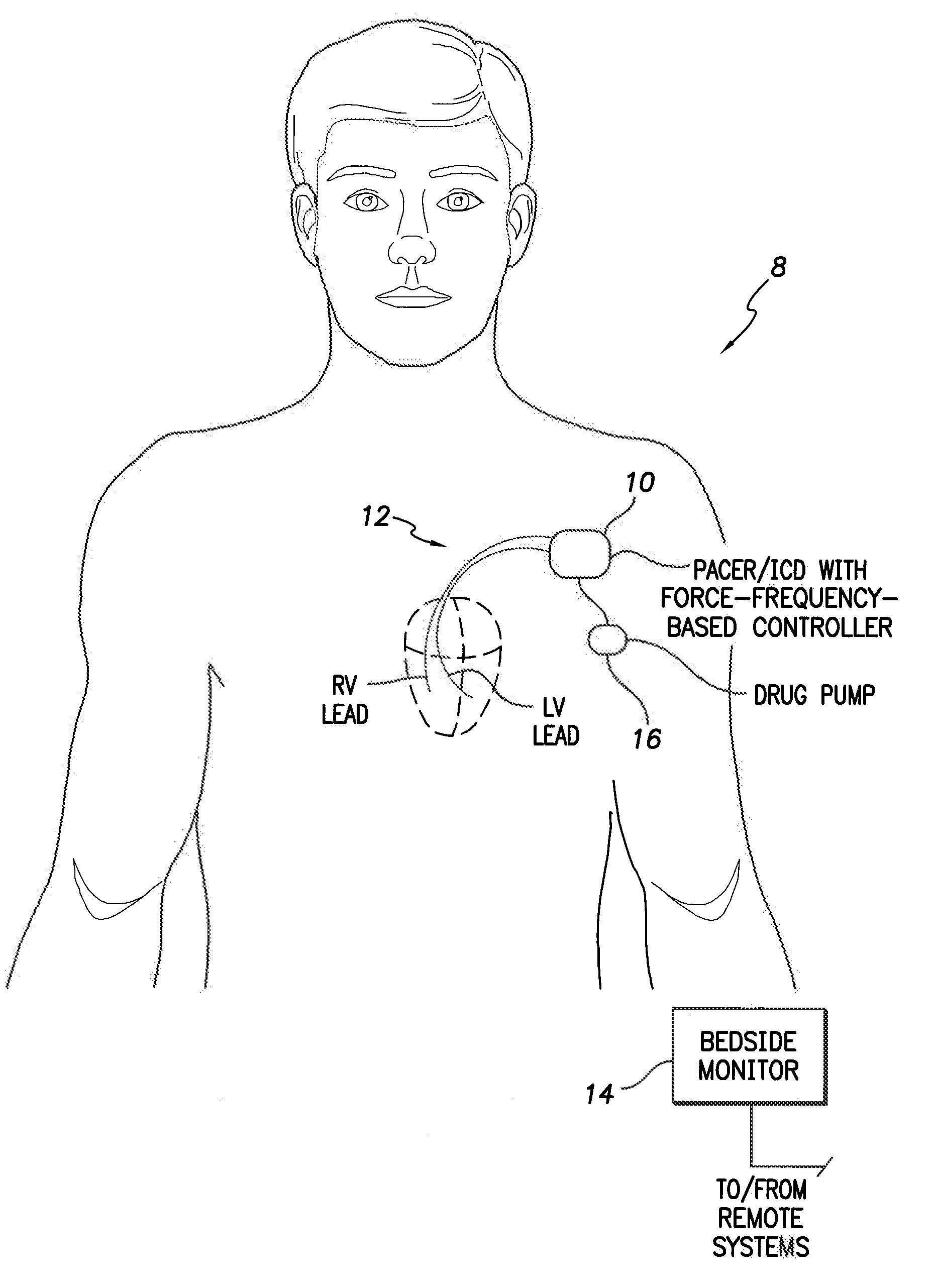
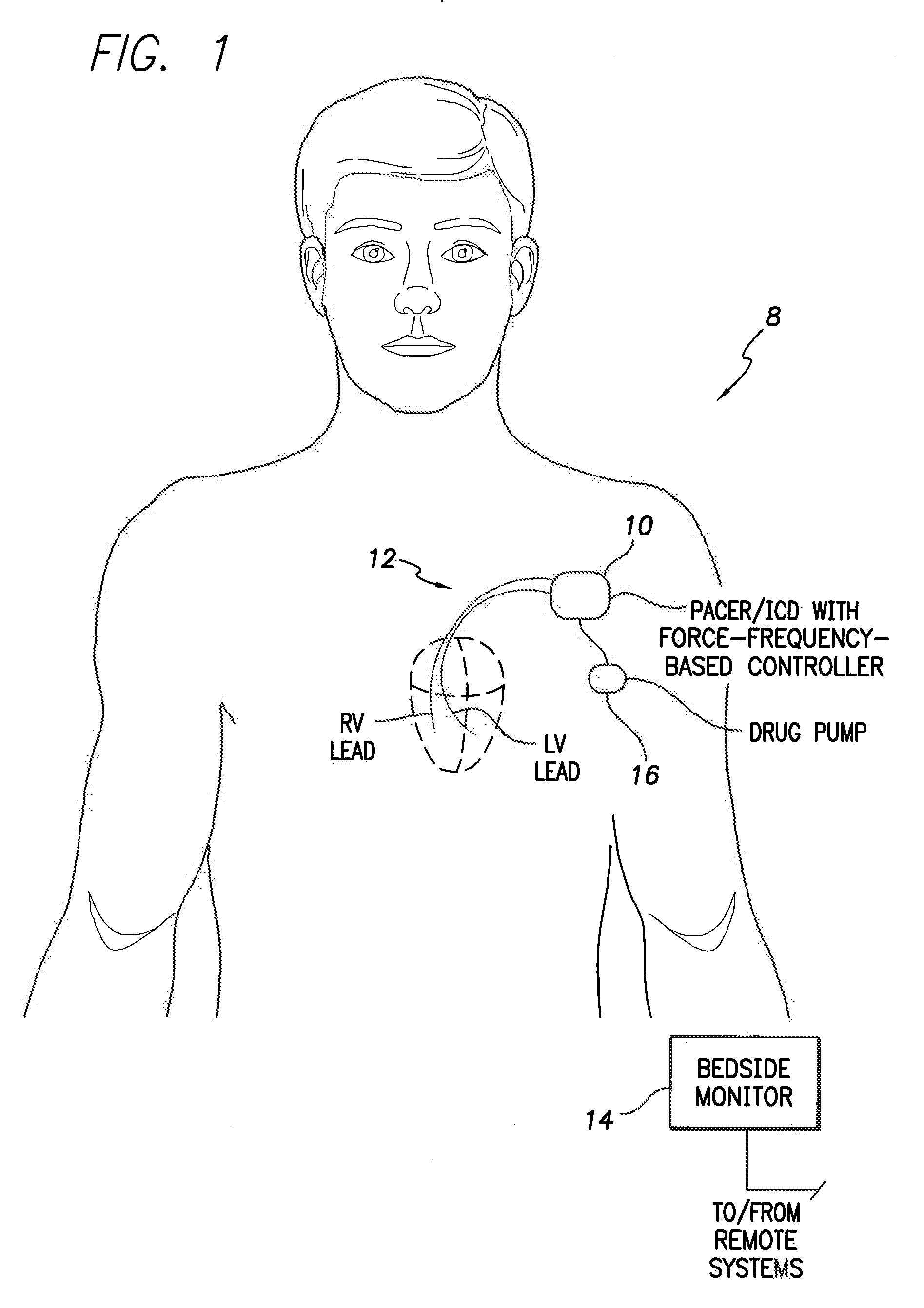
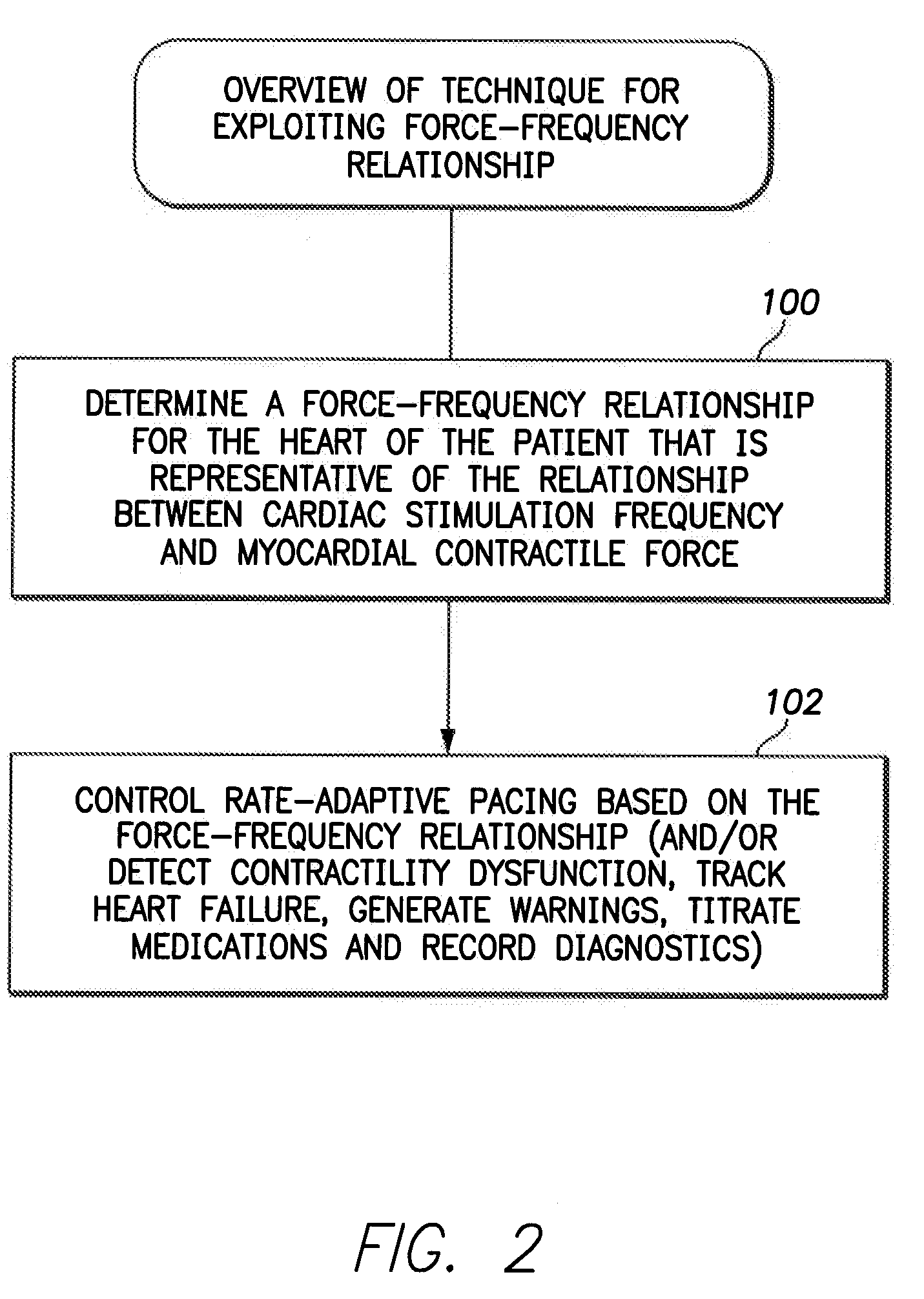
System and method for controlling rate-adaptive pacing based on a cardiac force-frequency relation detected by an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20100234906A1Reduce slopeDecrease in abscissaCatheterHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Techniques are provided for use in controlling rate-adaptive pacing within implantable medical devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs). In one example, a force-frequency relationship is determined for the heart of the patient, which is representative of the relationship between cardiac stimulation frequency and myocardial contractile force. To this end, various parameters are detected for use as surrogates for contractile force, including selected systolic pressure parameters and cardiogenic impedance parameters. Rate-adaptive pacing is then controlled based on the detected force-frequency relationship to, for example, deactivate rate-adaptive pacing if the slope and / or abscissa of the force-frequency relationship indicates significant contractility dysfunction within the patient. In other examples, rather than deactivating rate-adaptive pacing, control parameters are adjusted to render the rate-adaptive pacing less aggressive. In still other examples, trends in the slope and / or abscissa of the force-frequency relationship are monitored to detect contractility dysfunction and / or heart failure and titrate medications accordingly.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
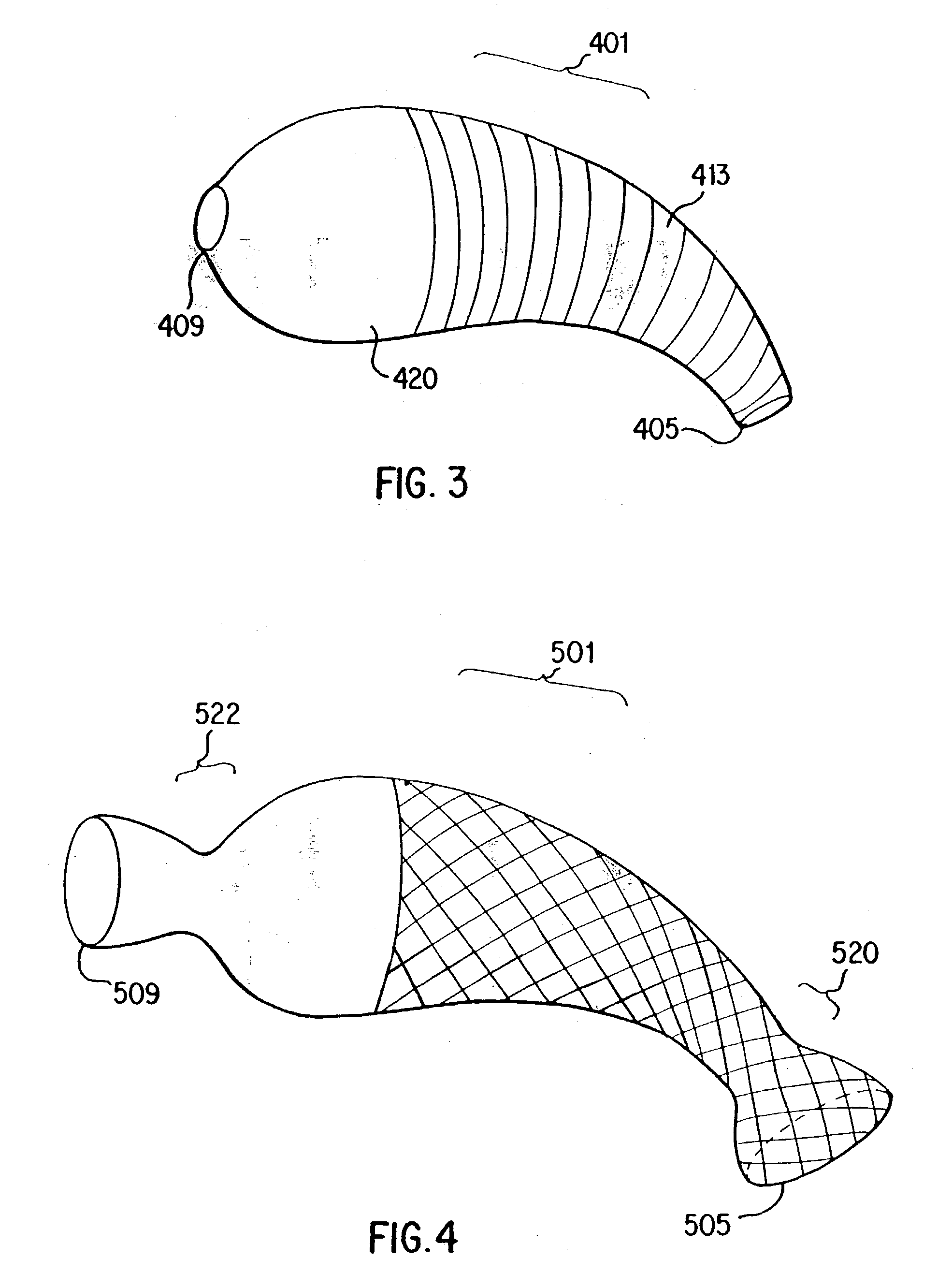
System and method for transapical delivery of an annulus anchored self-expanding valve
ActiveUS8747459B2Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemStentsBalloon catheterLimited accessCardiac muscle
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable prosthesis frame. The valve may be delivered transluminally or transmyocardially using a thorascopic or other limited access approach using a delivery catheter. Preferably, the initial partial expansion of the valve is performed against the native valve annulus to provide adequate anchoring and positioning of the valve as the remaining portions of the valve expand. The valve may be delivered using a retrograde or antegrade approach. When delivered using a retrograde approach, a delivery catheter with a pull-back sheath may be used, while antegrade delivery is preferably performed with a delivery catheter with a push-forward sheath that releases the proximal end of the valve first.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
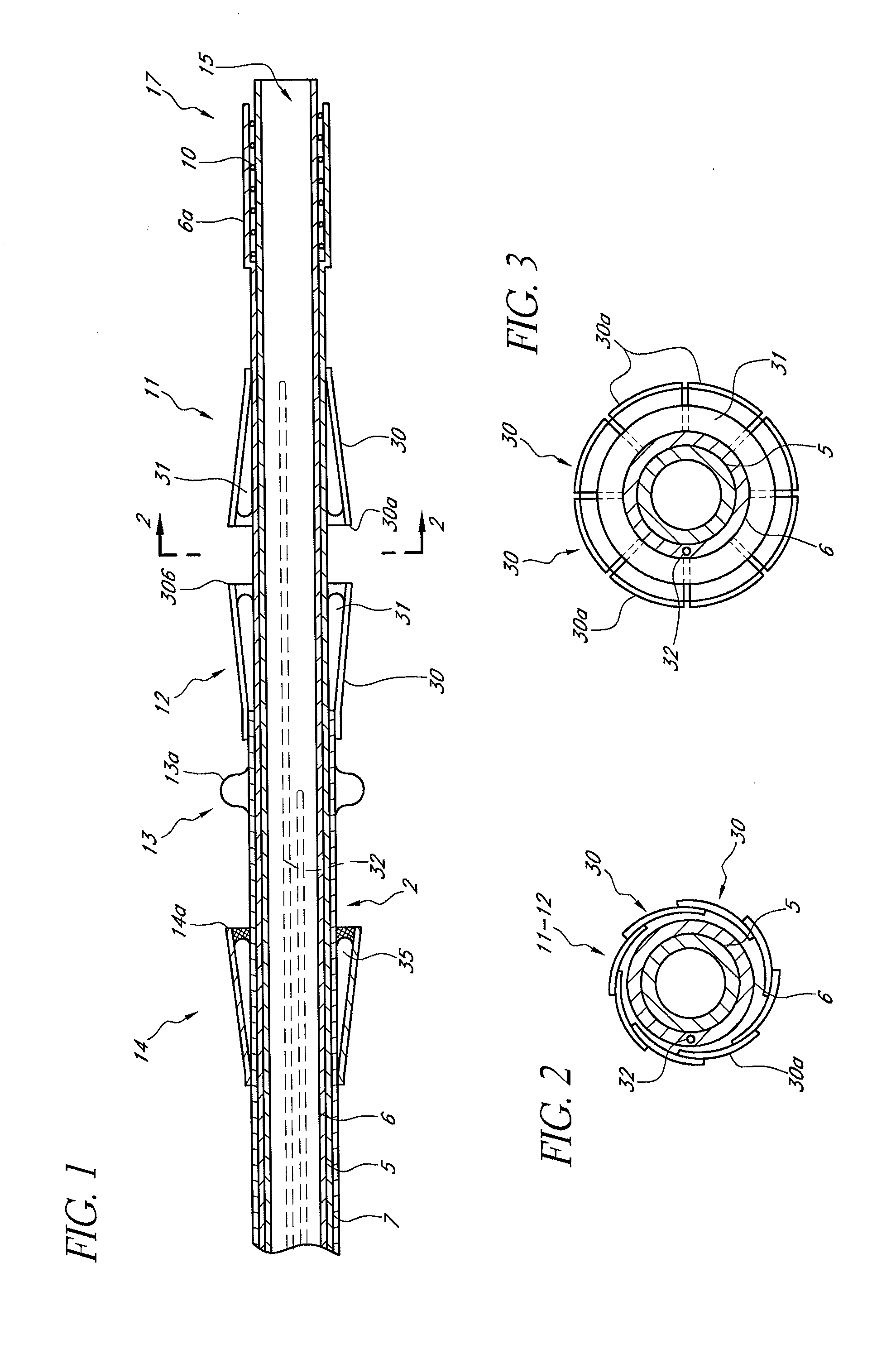
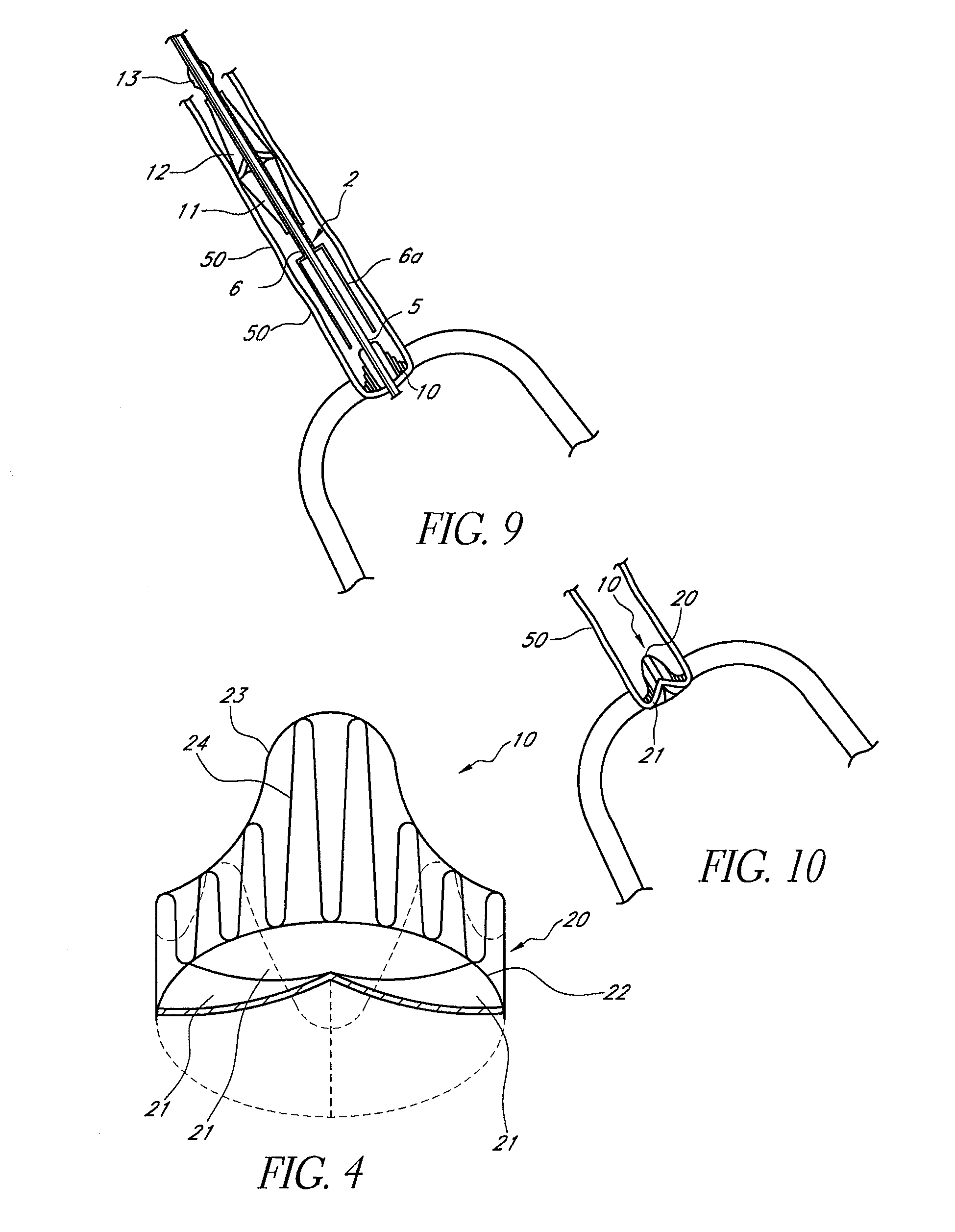
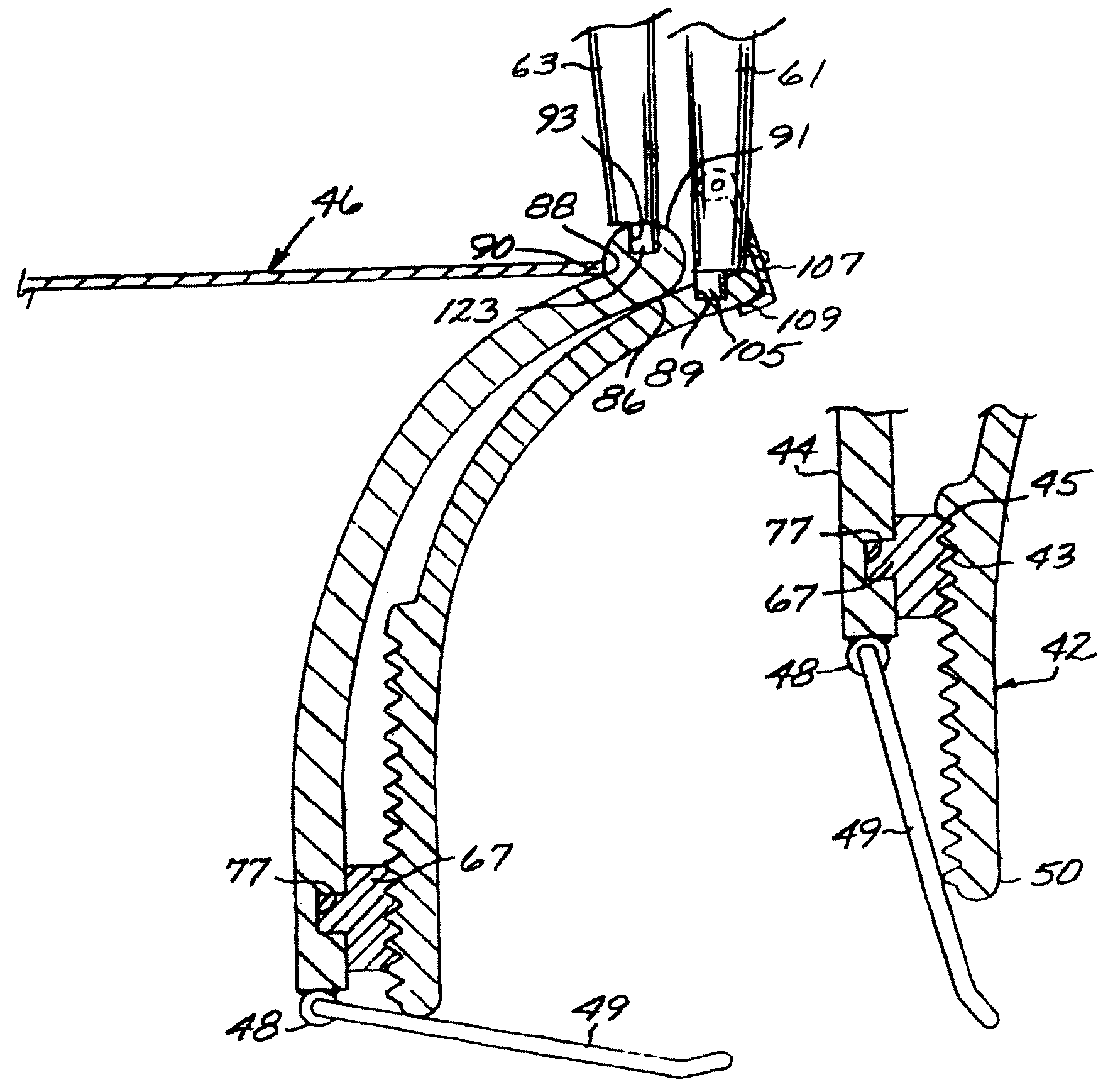
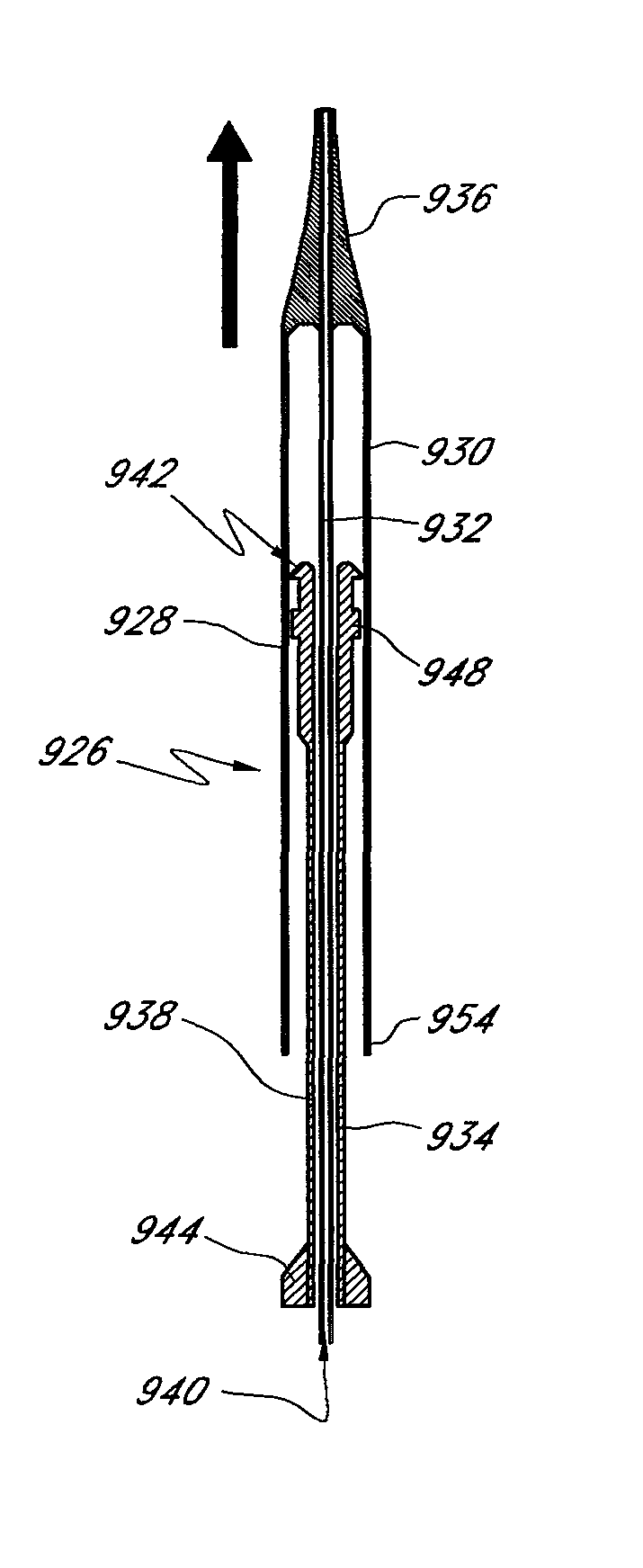
Implant delivery catheter system and methods for its use
Catheter systems and methods for implanting helical or dart-like implants into the myocardium or other body tissue. The catheter system includes a helix for fixing the distal end of the catheter to the myocardium, an implant held by the helix, mechanisms for driving the fixation helix into the myocardium, and mechanisms for driving the implant into the myocardium, removing the fixation helix and leaving the implant behind. The implant may be coated, filled, or made of a drug or drug eluting compound, or drug delivery matrix of any composition.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
Apparatus and methods for treating congestive heart failure
InactiveUS6076013AImprove efficiencyImproved ventricular functionEpicardial electrodesHeart valvesCardiac muscleVentricular function
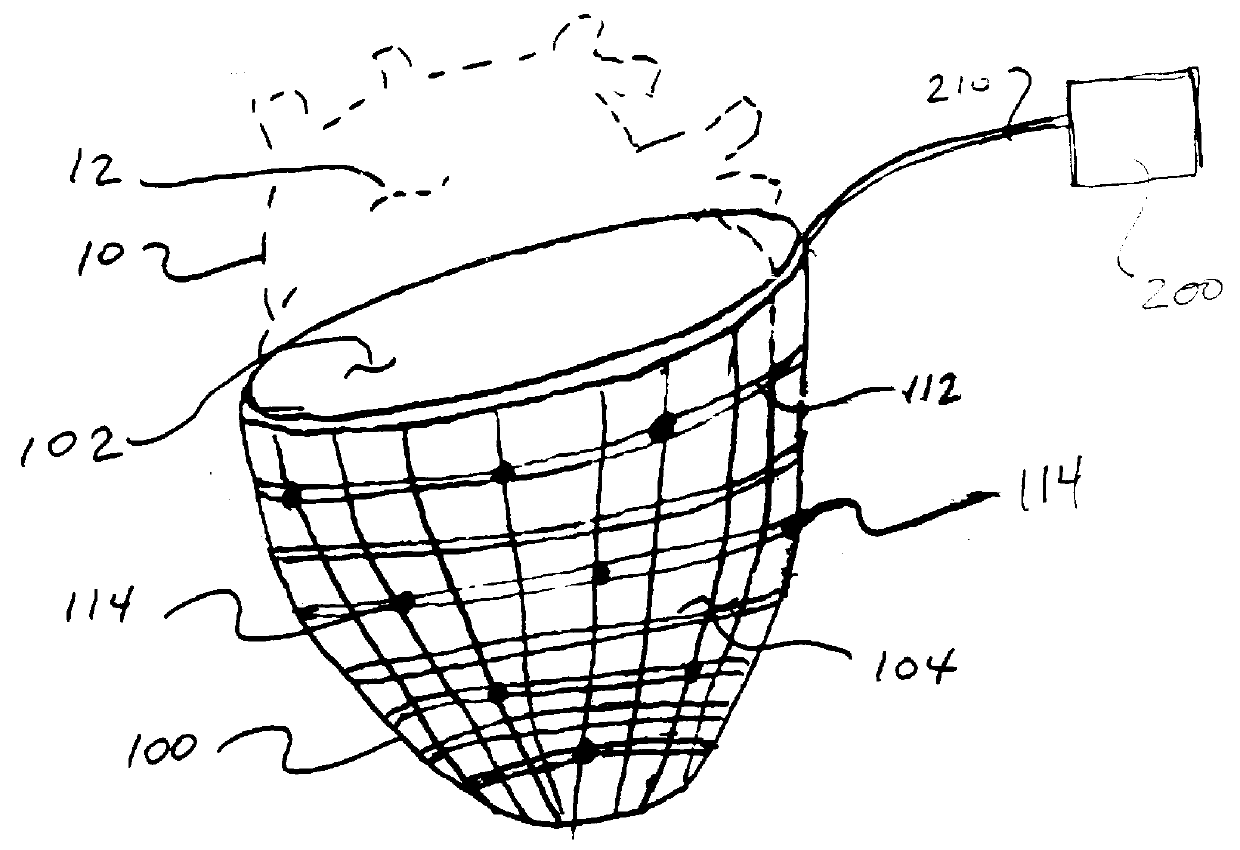
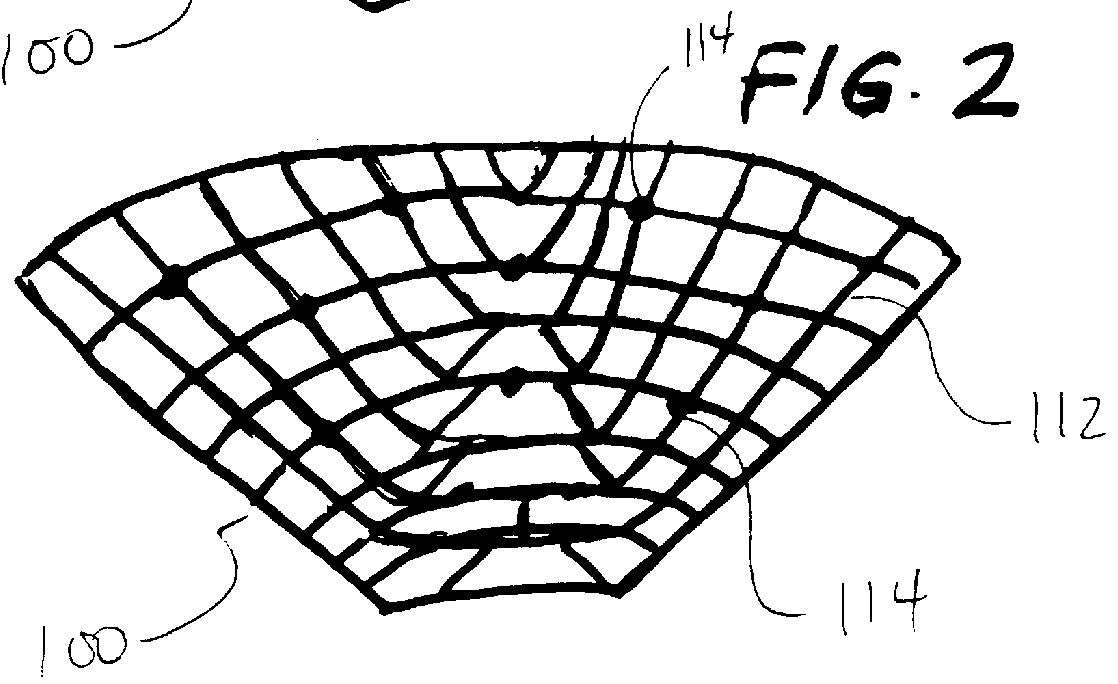
Apparatus and method for the treatment of congestive heart failure are disclosed that utilize a cuff that surrounds the heart and constrains cardiac dilation, while electrodes embedded in the cuff stimulate the myocardium to contractile function. An EKG signal can be processed to create an optimal pattern of selective stimulation of different areas of the heart at different times. An implantable circuit contains a power source and stimulation circuits. In some embodiments, a telemetry unit and an EKG collection circuit are also included. In accordance with the present disclosure, cuff limits the dilation of the heart and the stimulation electrodes enhance ventricular function by optimizing ventricular contractility.
Owner:BRENNAN EDWARD F +1
Prevention of myocardial infarction induced ventricular expansion and remodeling
ActiveUS20050080402A1Prevent further deteriorationInhibit swellingSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryCardiac muscleTherapeutic treatment
A method for direct therapeutic treatment of myocardial tissue in a localized region of a heart having a pathological condition. The method includes identifying a target region of the myocardium and applying material directly and substantially only to at least a portion of the myocardial tissue of the target region. The material applied results in a physically modification the mechanical properties, including stiffness, of said tissue. Various devices and modes of practicing the method are disclosed for stiffening, restraining and constraining myocardial tissue for the treatment of conditions including myocardial infarction or mitral valve regurgitation.
Owner:MYOMEND
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
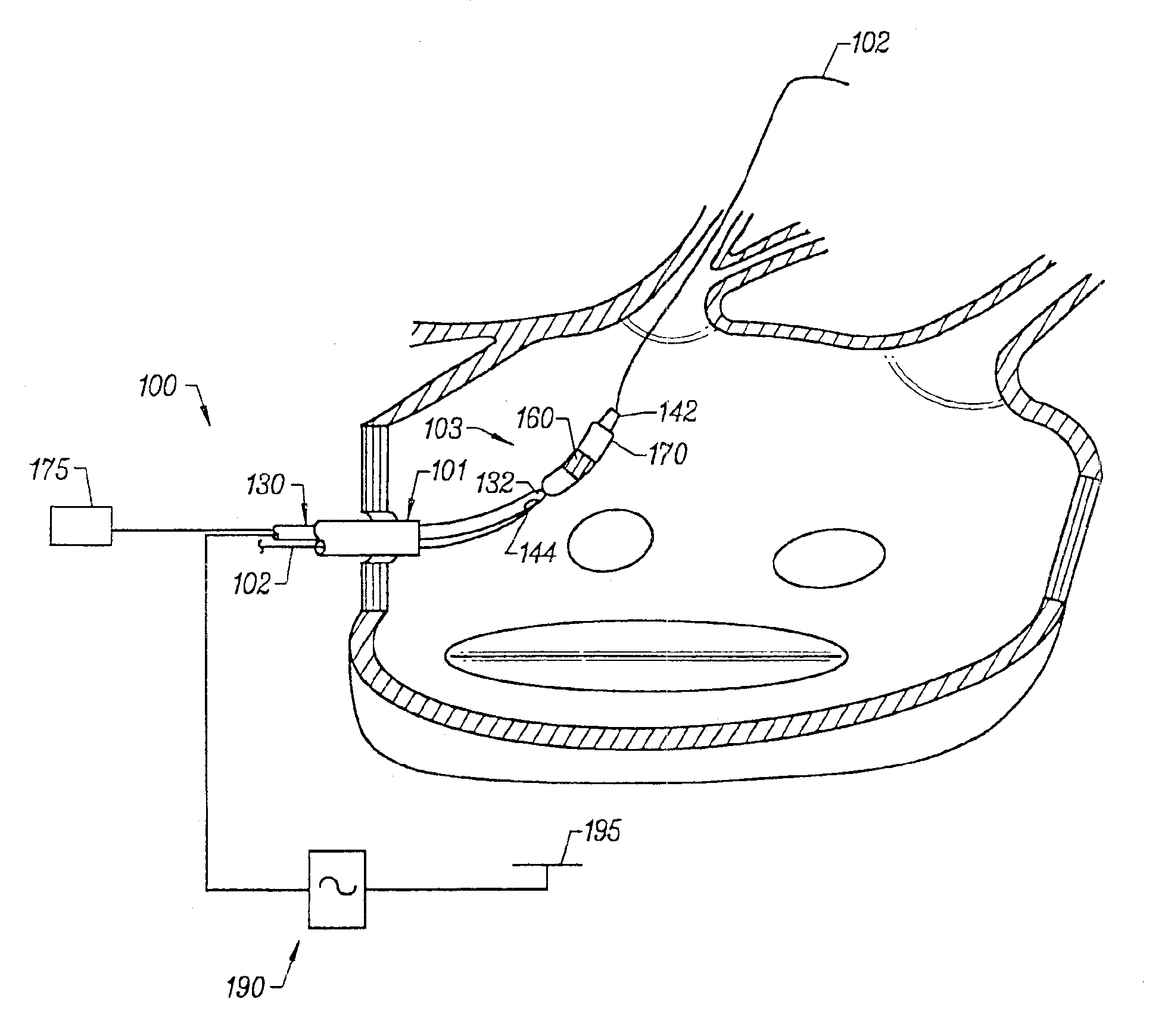
InactiveUS6926669B1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a about +180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Drug delivery catheters that attach to tissue and methods for their use
A drug delivery catheter suited for cardiac procedures including transmyocardial revascularization. The catheter includes a distal helical coil or other fixation and penetrating element, which can be operated from the proximal end of the catheter to engage and penetrate the myocardium. Once delivered to the inside of the heart, the catheter can be used to created several helical wounds in the myocardium, and also inject small doses of therapeutic agents to the wounds. The TMR accomplished by the procedure provides for large wound to penetration ratio, and limits the potential of perforating the heart wall.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
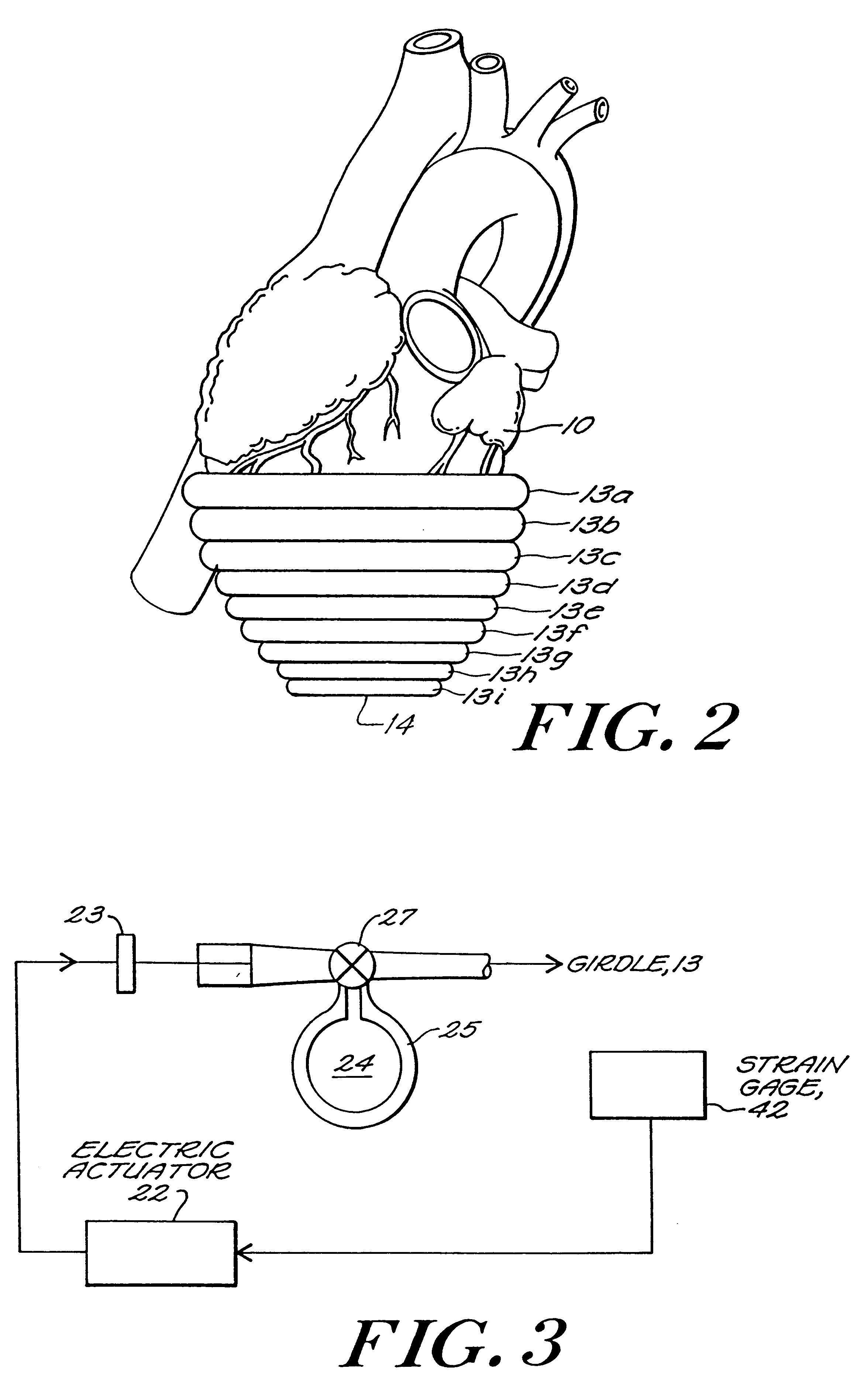
Passive girdle for heart ventricle for therapeutic aid to patients having ventricular dilatation
InactiveUS6224540B1Increased oxygen consumptionLarge increases in the tension-time integralHeart valvesControl devicesVentricular dilatationCardiac muscle
A passive girdle is wrapped around a heart muscle which has dilatation of a ventricle to conform to the size and shape of the heart and to constrain the dilatation during diastole. The girdle is formed of a material and structure that does not expand away from the heart but may, over an extended period of time be decreased in size as dilatation decreases.
Owner:ABIOMED
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS20050197692A1Decreasing wall stressReinforce wallSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Described are devices and methods for treating degenerative, congestive heart disease and related valvular dysfunction. Percutaneous and minimally invasive surgical tensioning structures offer devices that mitigate changes in the ventricular structure (i.e., remodeling) and deterioration of global left ventricular performance related to tissue damage precipitating from ischemia, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or other abnormalities. These tensioning structures can be implanted within various major coronary blood-carrying conduit structures (arteries, veins and branching vessels), into or through myocardium, or into engagement with other anatomic structures that impact cardiac output to provide tensile support to the heart muscle wall which resists diastolic filling pressure while simultaneously providing a compressive force to the muscle wall to limit, compensate or provide therapeutic treatment for congestive heart failure and / or to reverse the remodeling that produces an enlarged heart.
Owner:EXTENSIA MEDICAL
Devices and methods for accelerometer-based characterization of cardiac synchrony and dyssynchrony
InactiveUS20080021336A1Easy to identifyReduce power consumptionStentsElectrotherapyAccelerometerCardiac muscle
Systems and methods according to the invention employ an acceleration sensor to characterize the synchrony or dyssynchrony of the left ventricle. Patterns of acceleration related to myocardial contraction can be used to assess synchrony or dyssynchrony. Time-frequency transforms and coherence are derived from the acceleration. Information and numerical indices determined from the acceleration time frequency transforms and coherence can be used to find the optimal pacing location for cardiac resynchronization therapy. Similarly, the information can be used to optimize timing intervals including V to V and A to V timing.
Owner:CARDIOSYNC
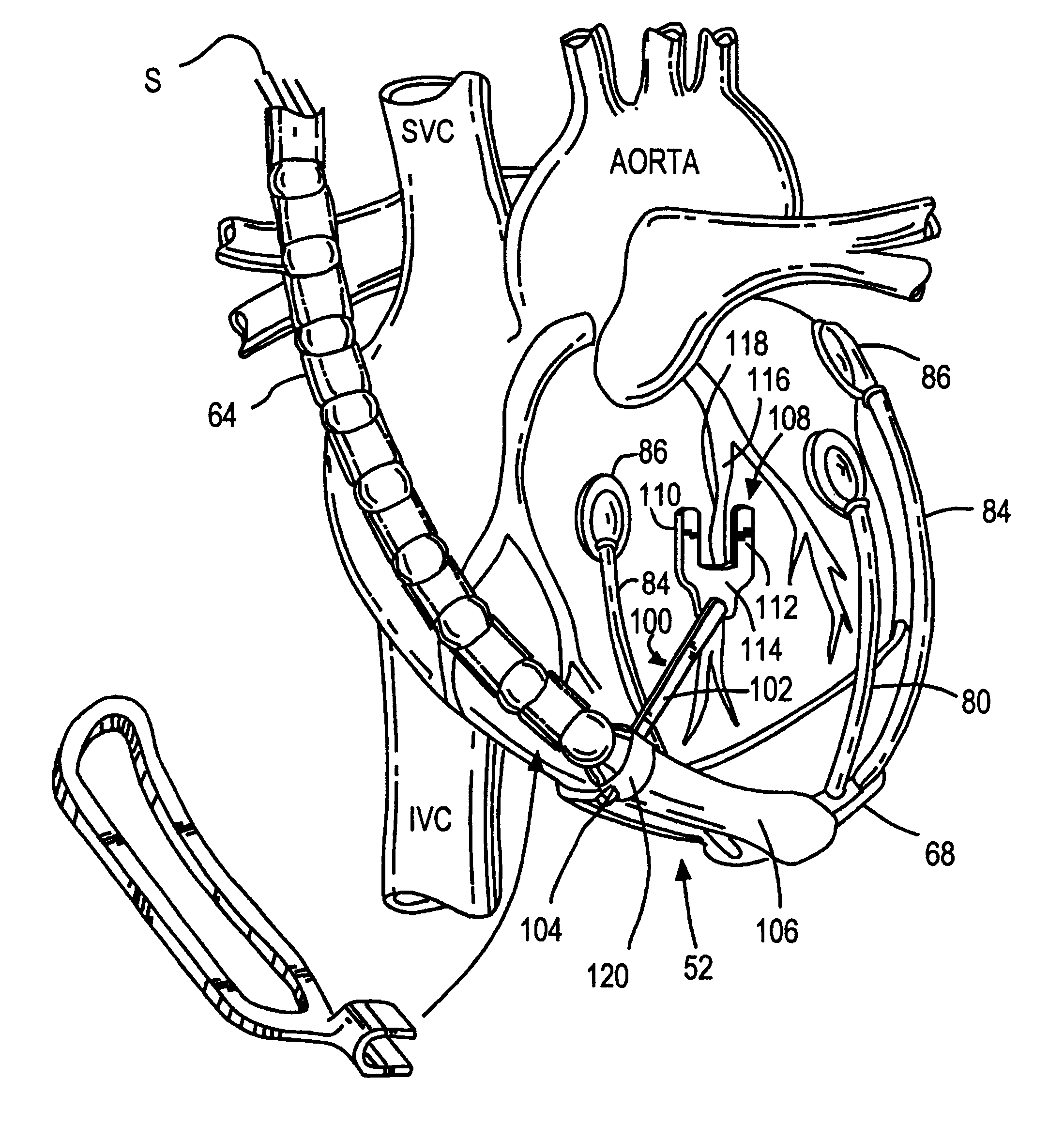
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
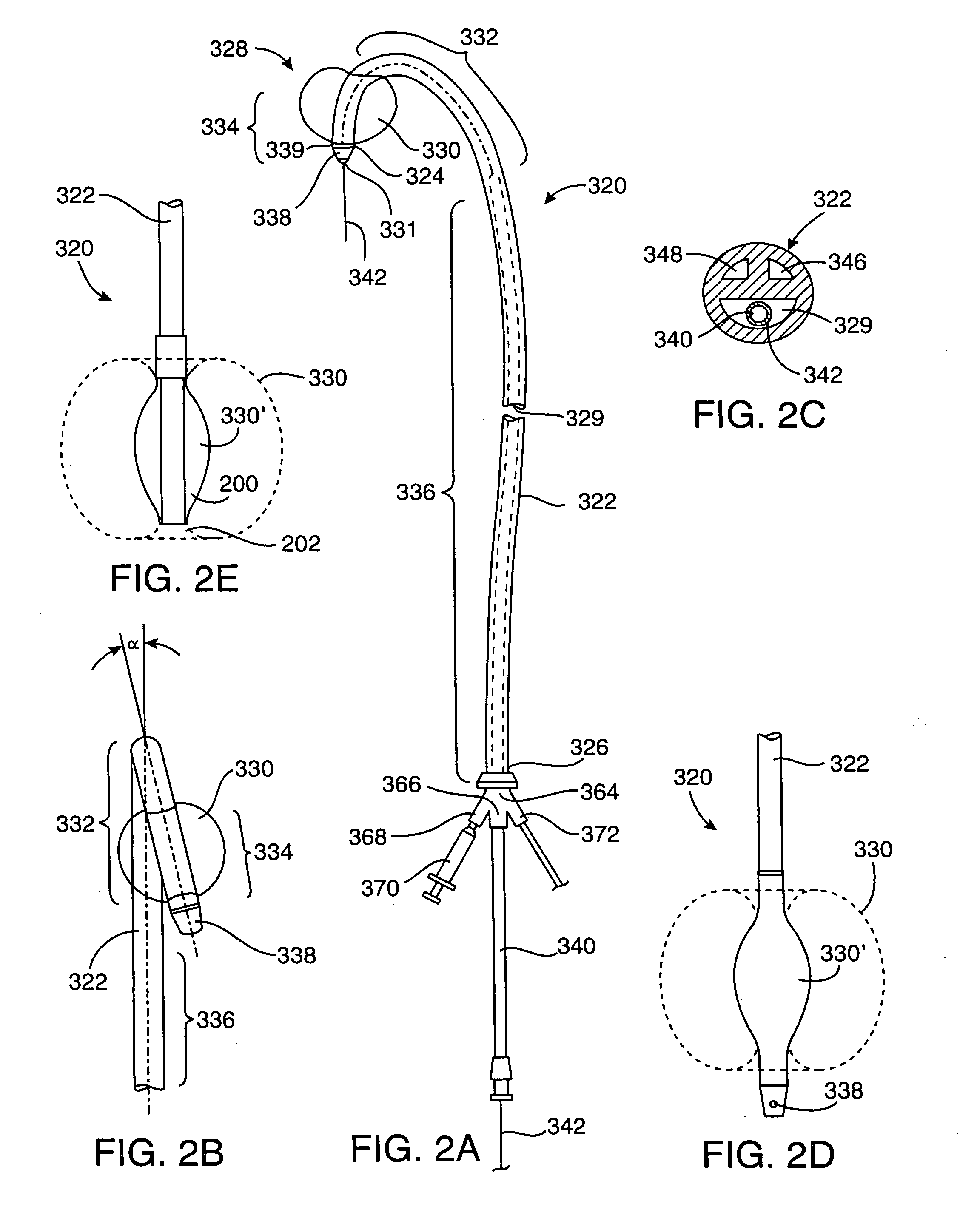
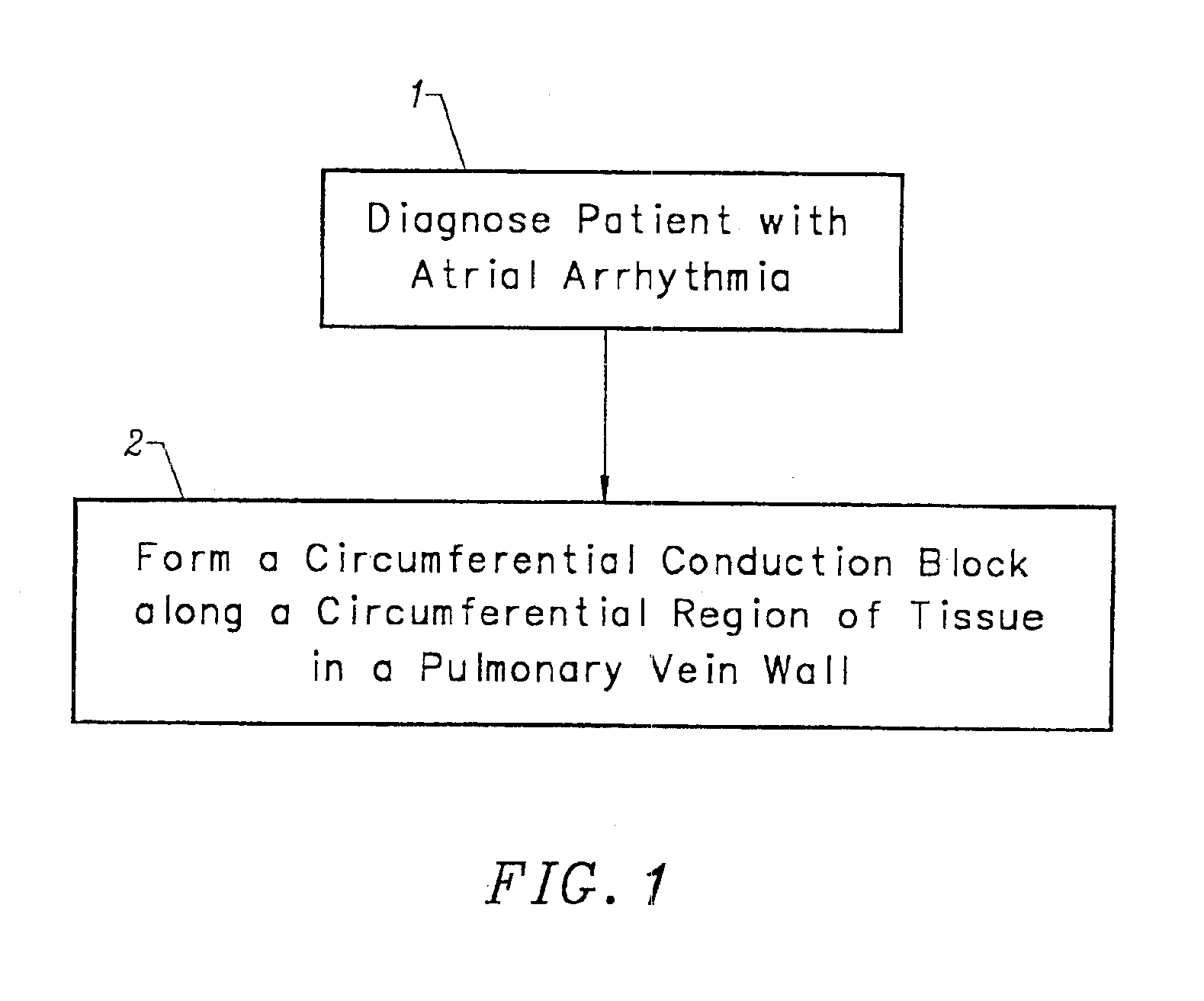
Device and method for forming a circumferential conduction block in a pulmonary vein
This invention is a method for treating a patient diagnosed with atrial arrhythmia by forming a circumferential conduction block along a circumferential path of tissue in a pulmonary vein wall that circumscribes the pulmonary vein lumen and transects the electrical conductivity of the pulmonary vein such that conduction is blocked along the longitudinal axis of the vein wall and into the left atrial wall. The method is performed to treat a patient with a focal arrythmogenic origin along the pulmonary vein wall by either ablating the focal origin or by isolating the focal origin from the atrial wall with the circumferential conduction block. The circumferential conduction block is also formed in a pulmonary vein in order to bridge the adjacent ends of two linear lesions, wherein each linear lesion is formed to extend between the pulmonary vein and another adjacent pulmonary vein in a less-invasive “maze”-type procedure. A circumferential ablation element in a circumferential ablation device assembly is used in a percutaneous translumenal catheter technique in order to form the circumferential conduction block in the pulmonary vein wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
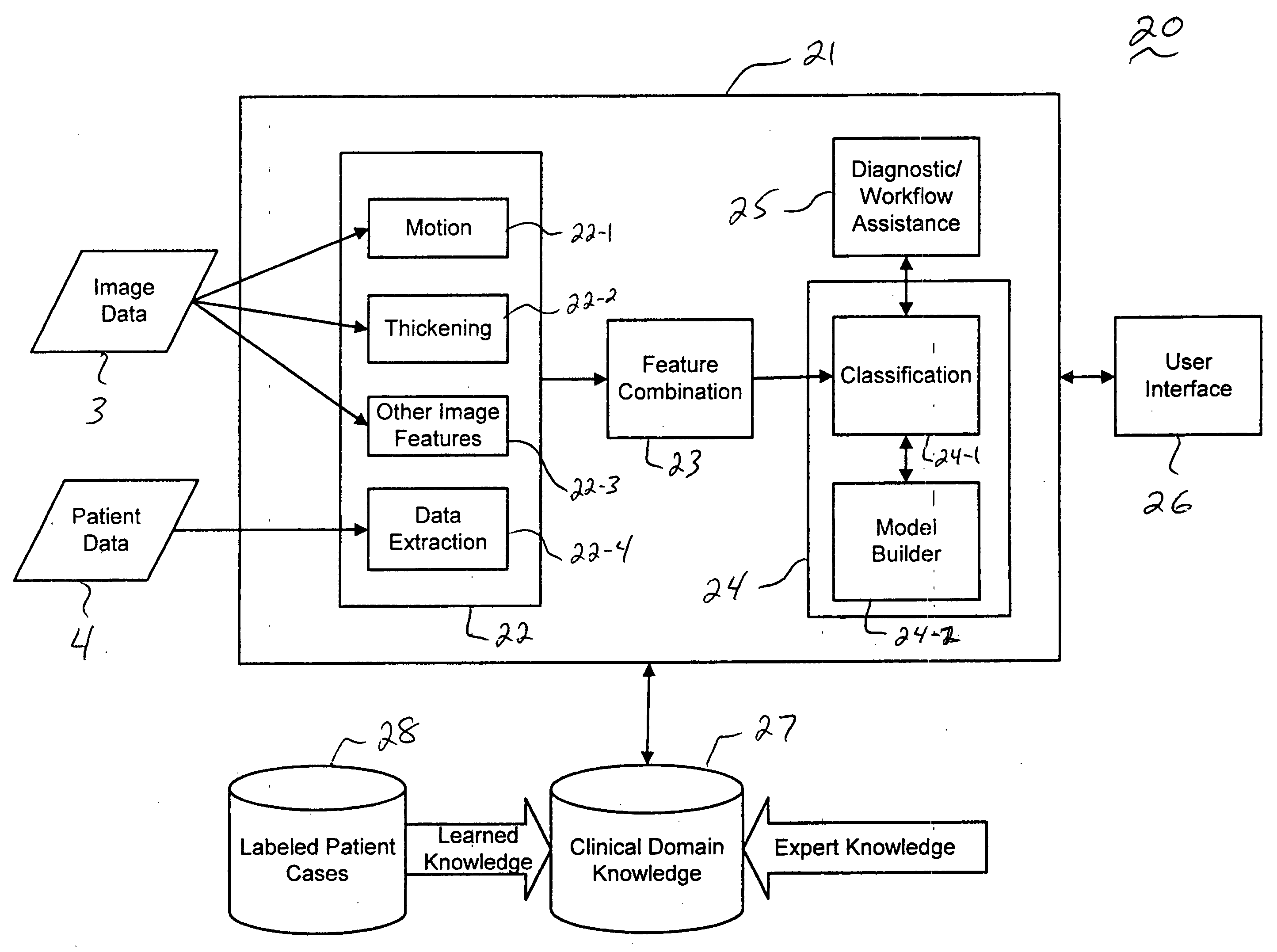
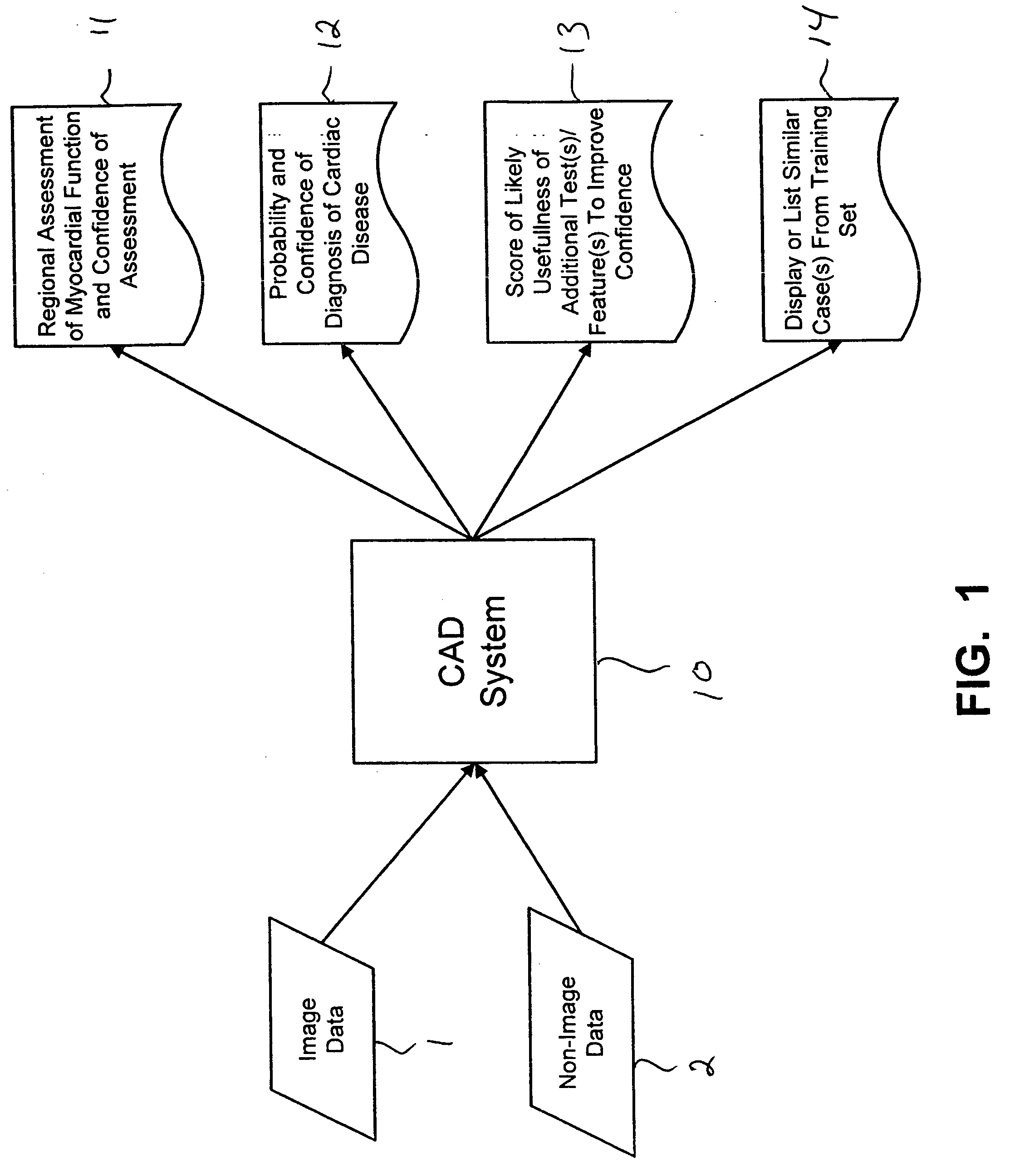
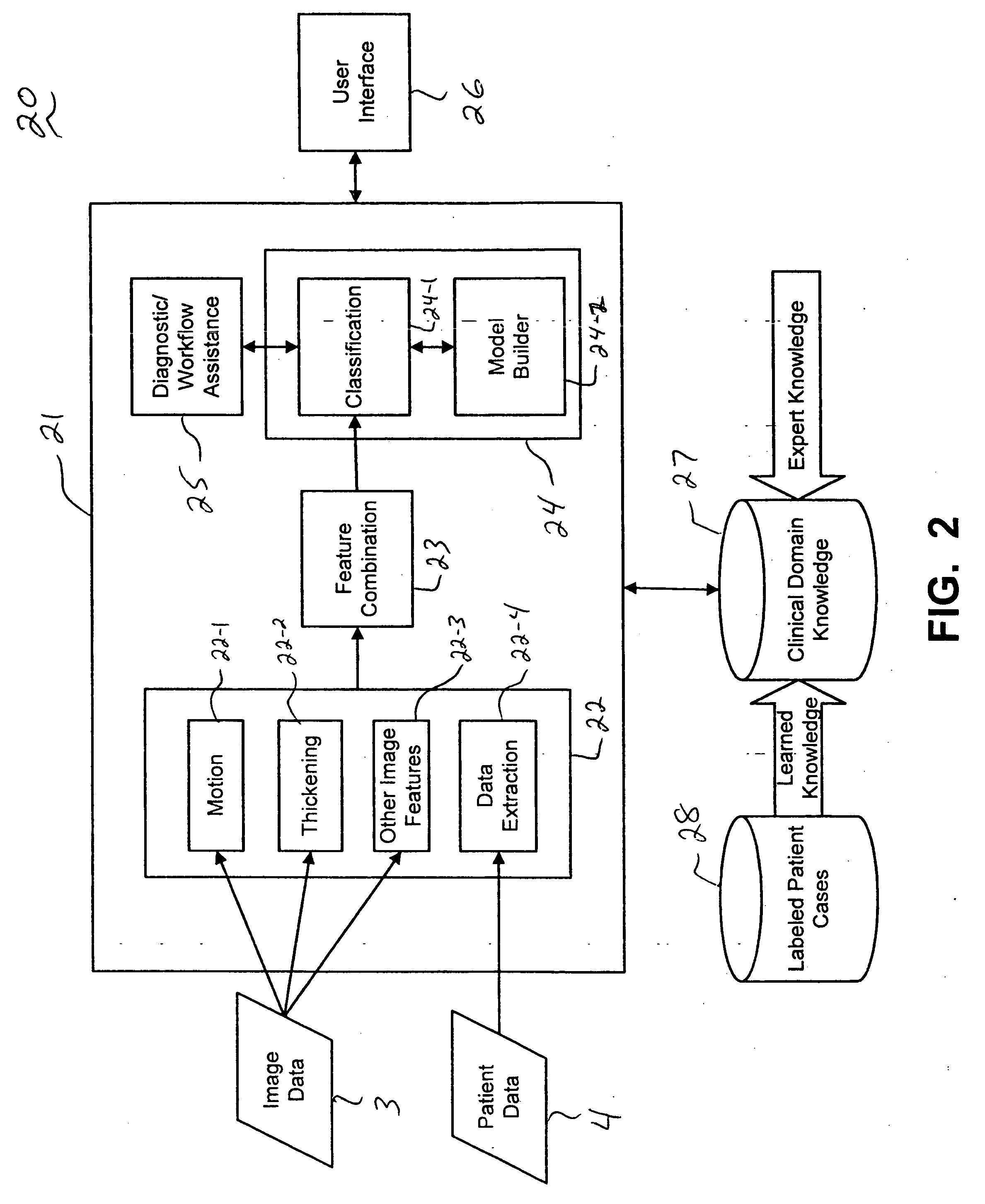
Systems and methods for providing automated regional myocardial assessment for cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20050059876A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedical recordAcquired characteristic
Systems and methods are provided for automated assessment of regional myocardial function using wall motion analysis methods that analyze various features / parameters of patient information (image data and non-image data) obtained from medical records of a patient. For example, a method for providing automatic diagnostic support for cardiac imaging generally comprises obtaining image data of a heart of a patient, obtaining features from the image data of the heart, which are related to motion of the myocardium of the heart, and automatically assessing regional myocardial function of one or more regions of a myocardial wall using the obtained features.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
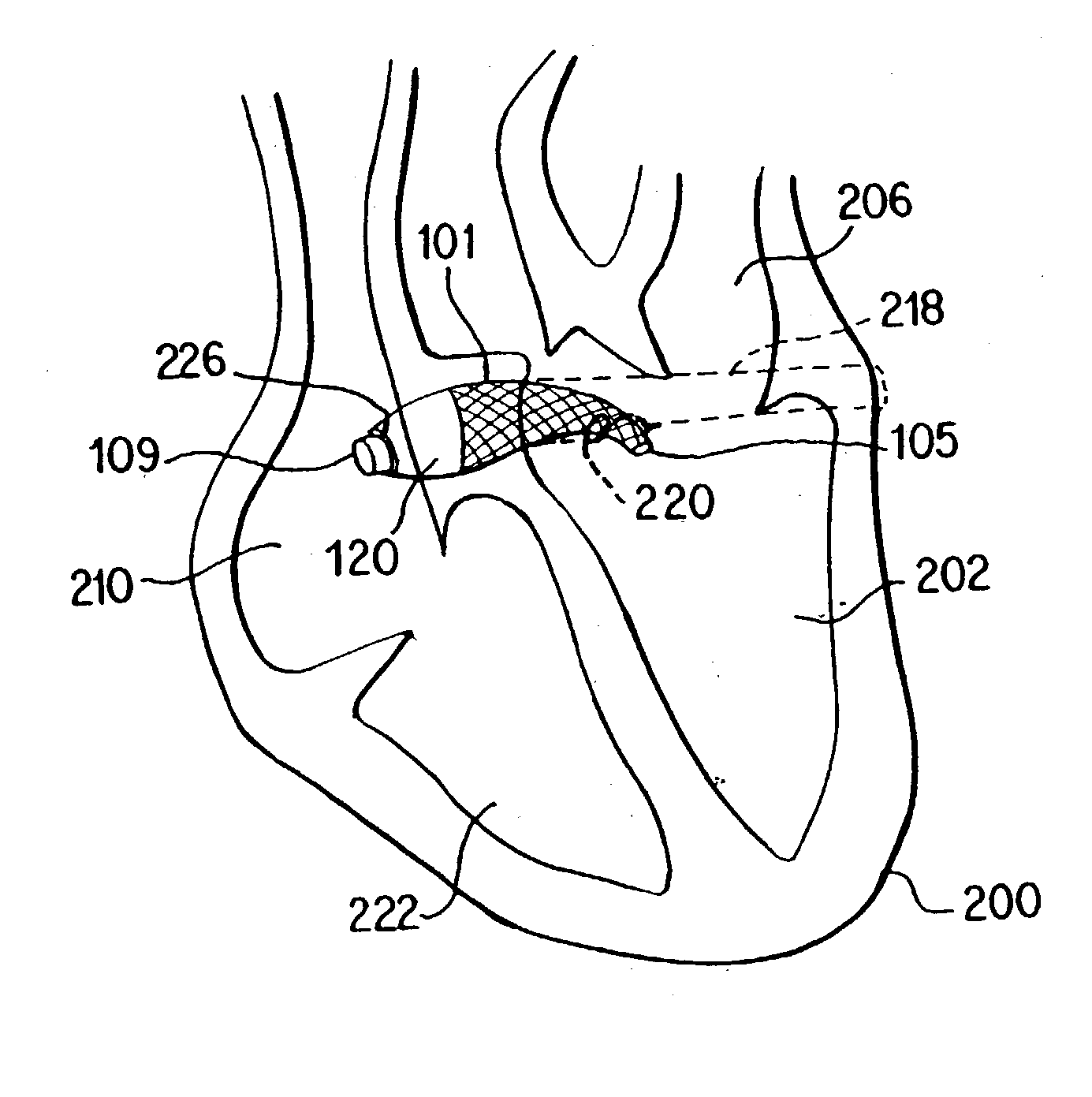
Stent for arterialization of the coronary sinus and retrograde perfusion of the myocardium
The present invention concerns a novel stent and a method for communicating oxygenated blood directly from the left ventricle to the coronary sinus to provide retrograde perfusion to the myocardium. The stent is placed substantially within the coronary sinus with its trailing end protruding into the right atrium and the leading end protruding into the left ventricle. The stent has a smaller passageway at or near the trailing (right ventricular) end and at or near the leading (left ventricle) end, and has a covering at the trailing end. The smaller passageway and the cover at the trailing end to promote retrograde flow into the venous system of the hear and specifically the myocardium of the left ventricle and to reduce a significant left-to-right shunt.
Owner:MARTIN ERIC C
Valve to myocardium tension members device and method
InactiveUS20060195012A1Improved chamber geometryFunction increaseSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsCardiac muscleEngineering
A device for heart valve repair including at least one tension member having a first end and second end. A basal anchor is disposed at the first end of the tension member and a secondary anchor at the second end. The method includes the steps of anchoring the basal anchor proximate a heart valve and anchoring the secondary anchor at a location spaced from the valve such that the chamber geometry is altered to reduce heart wall tension and / or stress on the valve leaflets.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
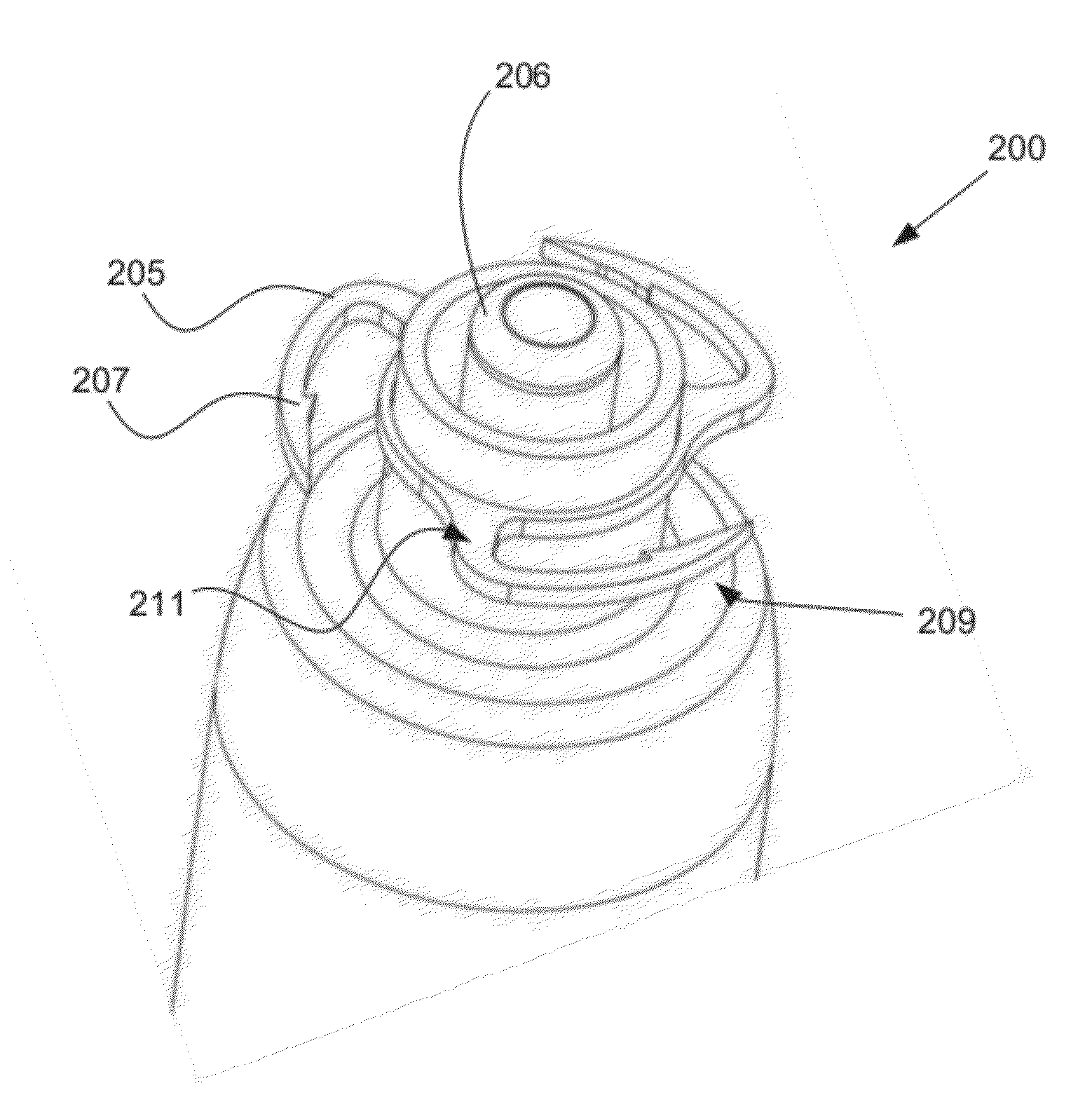
Leadless Pacemaker with Radial Fixation Mechanism
ActiveUS20120158111A1Reduce compressionTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesDistal portionCardiac muscle
A leadless cardiac pacemaker having a radial fixation mechanism is provided. The cardiac pacemaker can include fixation mechanism separate from a pacing electrode and having a diameter equal to or less than the outer diameter of the pacemaker. The fixation mechanism can allow the pacemaker to be inserted into tissue with less than 2 rotations of the pacemaker to place the pacing electrode in contact with the tissue. In some embodiments, the fixation mechanism can comprise a plurality of hooks or protrusions positioned near a distal portion of the pacemaker. The fixation mechanism(s) can be configured to penetrate the endocardium of the patient and reside mostly within the myocardium. Methods of delivering the leadless cardiac pacemaker into the heart are also provided.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for transmyocardial direct coronary revascularization
InactiveUS6929009B2Facilitate valvingShortening and thickeningEar treatmentCannulasVeinHeart chamber
Methods and apparatus for direct coronary revascularization wherein a transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary blood vessel to permit blood to flow therebetween. In some embodiments, the transmyocardial passageway is formed between a chamber of the heart and a coronary vein. The invention includes unstented transmyocardial passageways, as well as transmyocardial passageways wherein protrusive stent devices extend from the transmyocardial passageway into an adjacent coronary vessel or chamber of the heart. The apparatus of the present invention include protrusive stent devices for stenting of transmyocardial passageways, intraluminal valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, intracardiac valving devices for valving of transmyocardial passageways, endogenous tissue valves for valving of transmyocardial passageways, and ancillary apparatus for use in conjunction therewith.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for improving cardiac function
A method and a device for improving cardiac function are provided. The device is packaged in a collapsed state in an end of a catheter. Portions of a frame construction of the device spring outwardly when the catheter is withdrawn from the device. Anchoring formations on the frame construction secure the frame construction to a myocardium of the heart. A membrane secured to the frame construction then forms a division between volumes of an endocardial cavity of the heart on opposing sides of the membrane.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
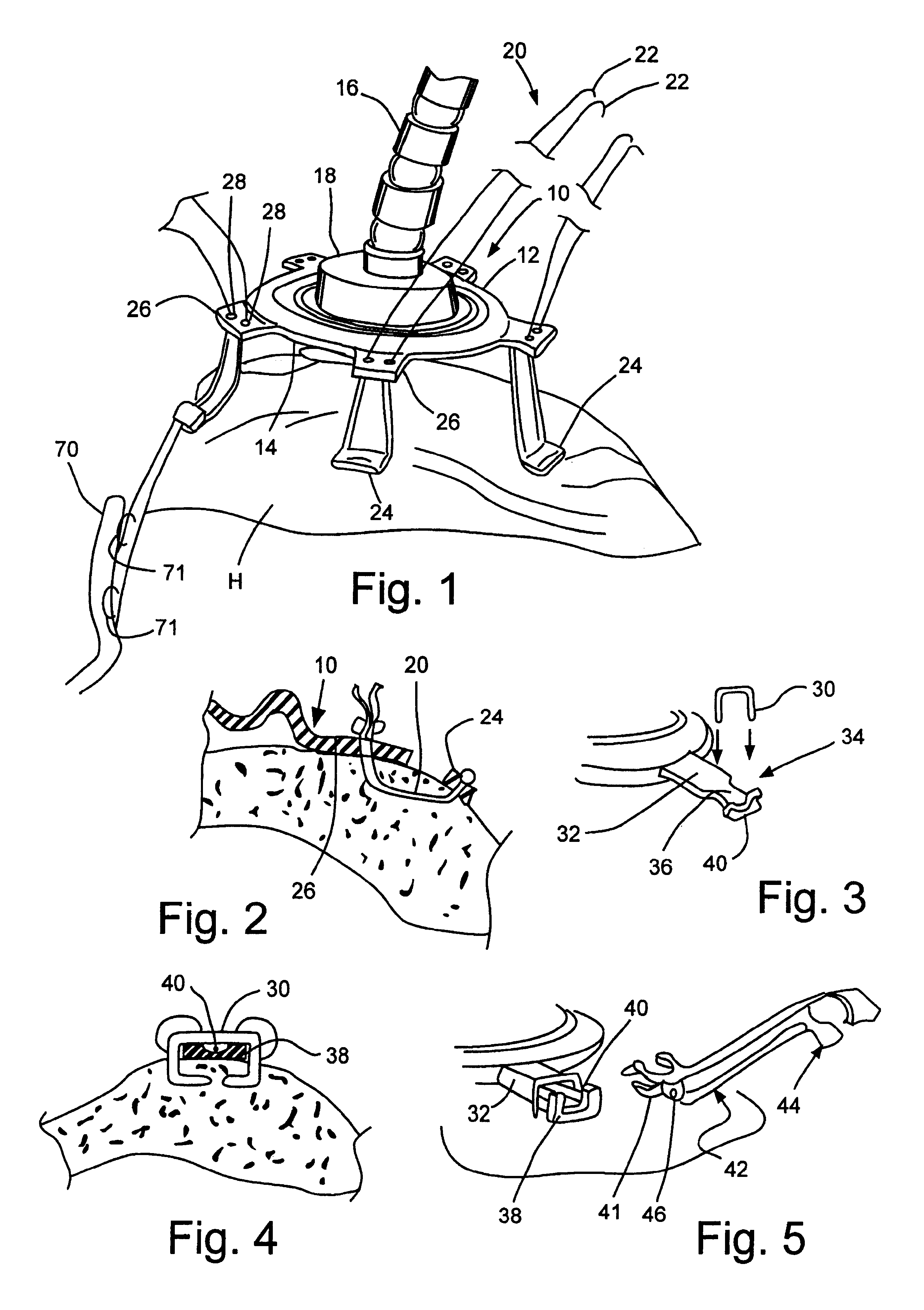
System to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
InactiveUS6390976B1Improve performanceImprove system performanceSuture equipmentsStaplesAdhesiveCardiac muscle
A system for manipulating and supporting a beating heart during cardiac surgery, including a gross support element for engaging and supporting the heart (the gross support element preferably including a head which is sized and shaped to cradle the myocardium of the left ventricle), a suspension head configured to exert lifting force on the heart when positioned near the apical region of the heart at a position at least partially overlying the right ventricle, and a releasable attachment element for releasably attaching at least one of the gross support element and the suspension head to the heart. The releasable attachment element can be a mechanical element (such as one or more staples or sutures) or an adhesive such as glue. Alternatively, the system includes a suspension head and a releasable attachment element for releasably attaching it to the heart, but does not include a gross support element.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Cardiac stimulation device for optimizing cardiac output with myocardial ischemia protection
InactiveUS6865420B1Reduce demandReduce detectionHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleIntracardiac Electrogram
A cardiac stimulation device and method detect myocardial ischemia and provide a response for alleviating the ischemia. Myocardial ischemia is detected by identifying changes in the ST-segment of the intracardiac electrogram (EGM) sensed using large sensing electrode surfaces created by electrically coupling one or more cardiac electrodes or by using larger surface area shocking coils. Myocardial ischemia monitoring is performed when stimulation parameters are adjusted for increasing cardiac output, causing an increased metabolic demand to be placed on the myocardium itself. When myocardial ischemia is detected, stimulation parameters are re-adjusted to reduce the demand placed on the myocardium and thereby alleviate the ischemia.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS20020061587A1Restoring functional integrityRestoring structuralBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac muscleCytokine
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
Ischemia detection
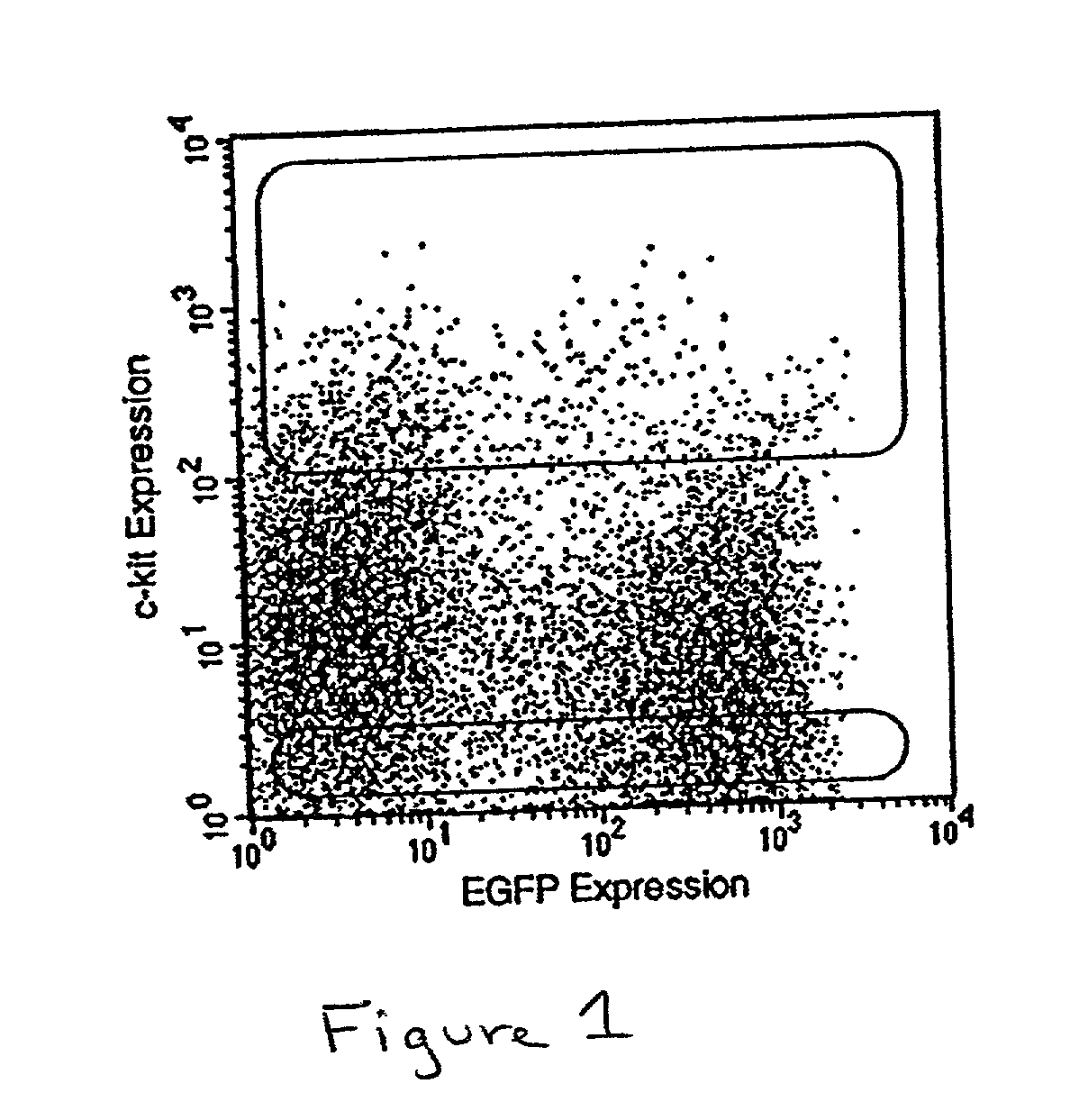
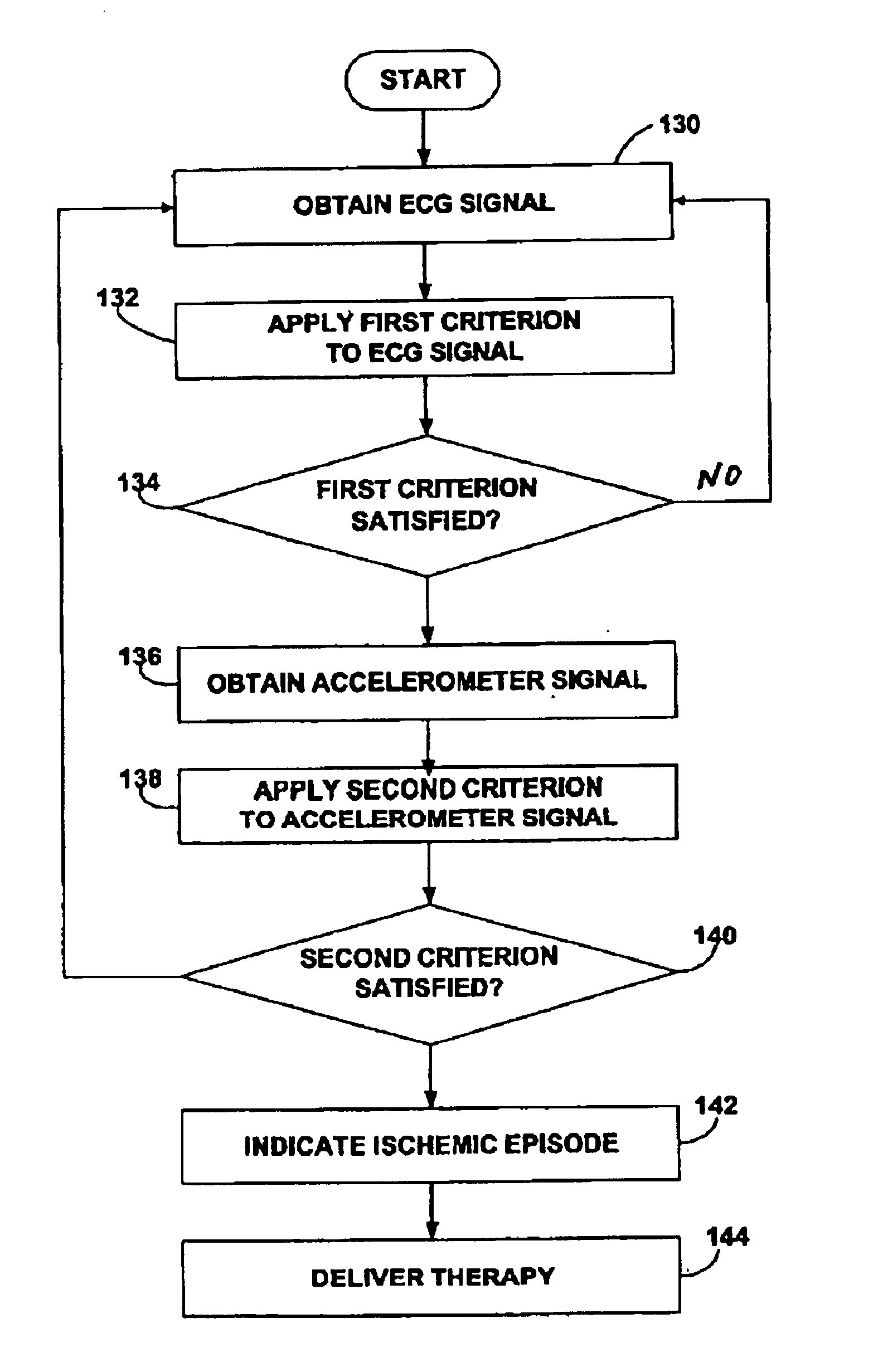
InactiveUS6937899B2Reliable detectionReliable treatmentElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerCardiac muscle
Techniques for detection and treatment of myocardial ischemia are described that monitor both the electrical and dynamic mechanical activity of the heart to detect and verify the occurrence of myocardial ischemia in a more reliable manner. The occurrence of myocardial ischemia can be detected by monitoring changes in an electrical signal such as an ECG or EGM, and changes in dynamic mechanical activity of the heart. Dynamic mechanical activity can be represented, for example, by a heart acceleration signal or pressure signal. The electrical signal can be obtained from a set of implanted or external electrodes. The heart acceleration signal can be obtained from an accelerometer or pressure sensor deployed within or near the heart. The techniques correlate contractility changes detected by an accelerometer or pressure sensor with changes in the ST electrogram segment detected by the electrodes to increase the reliability of ischemia detection.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com