Patents
Literature
624 results about "Left ventricular size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
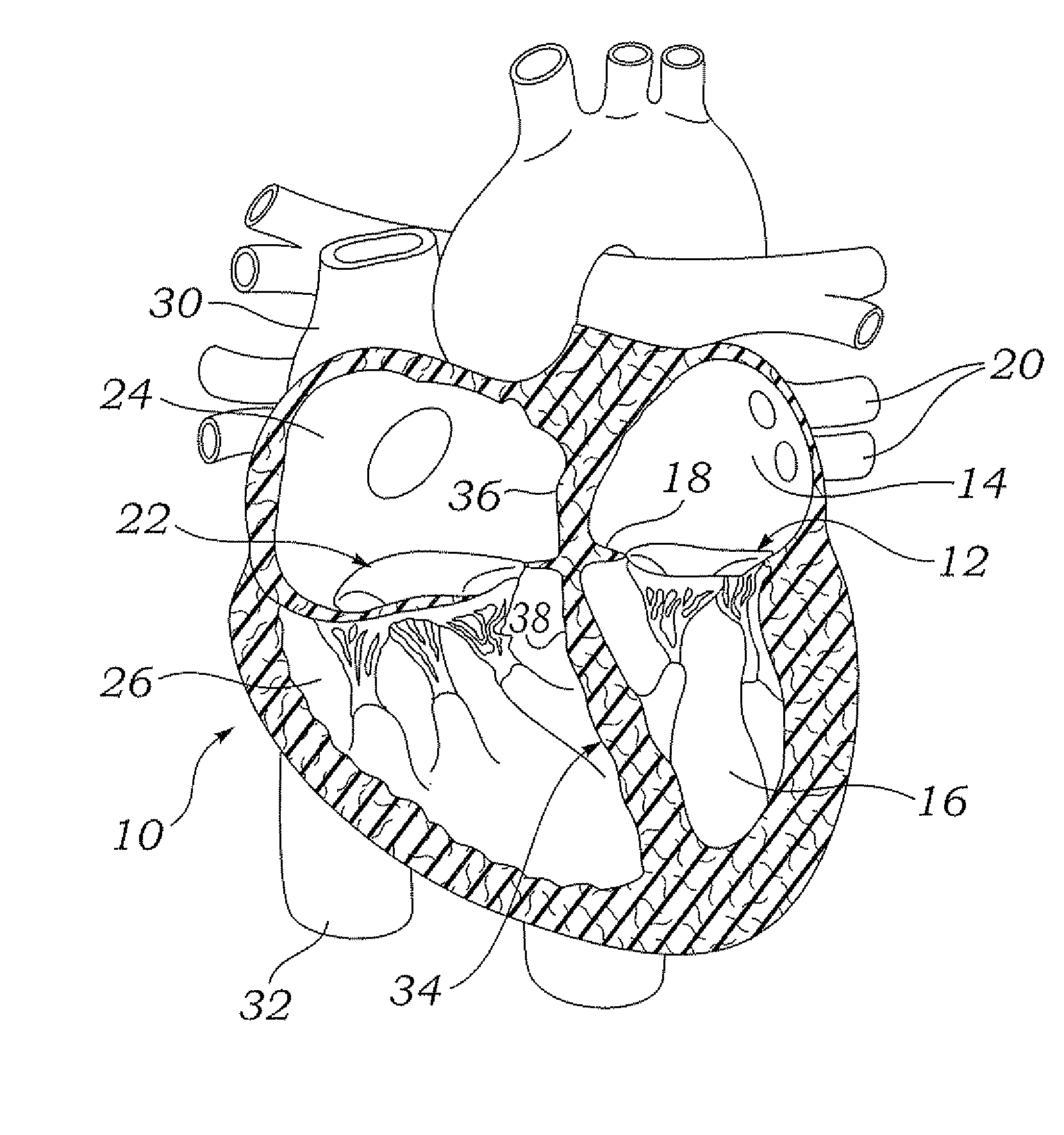
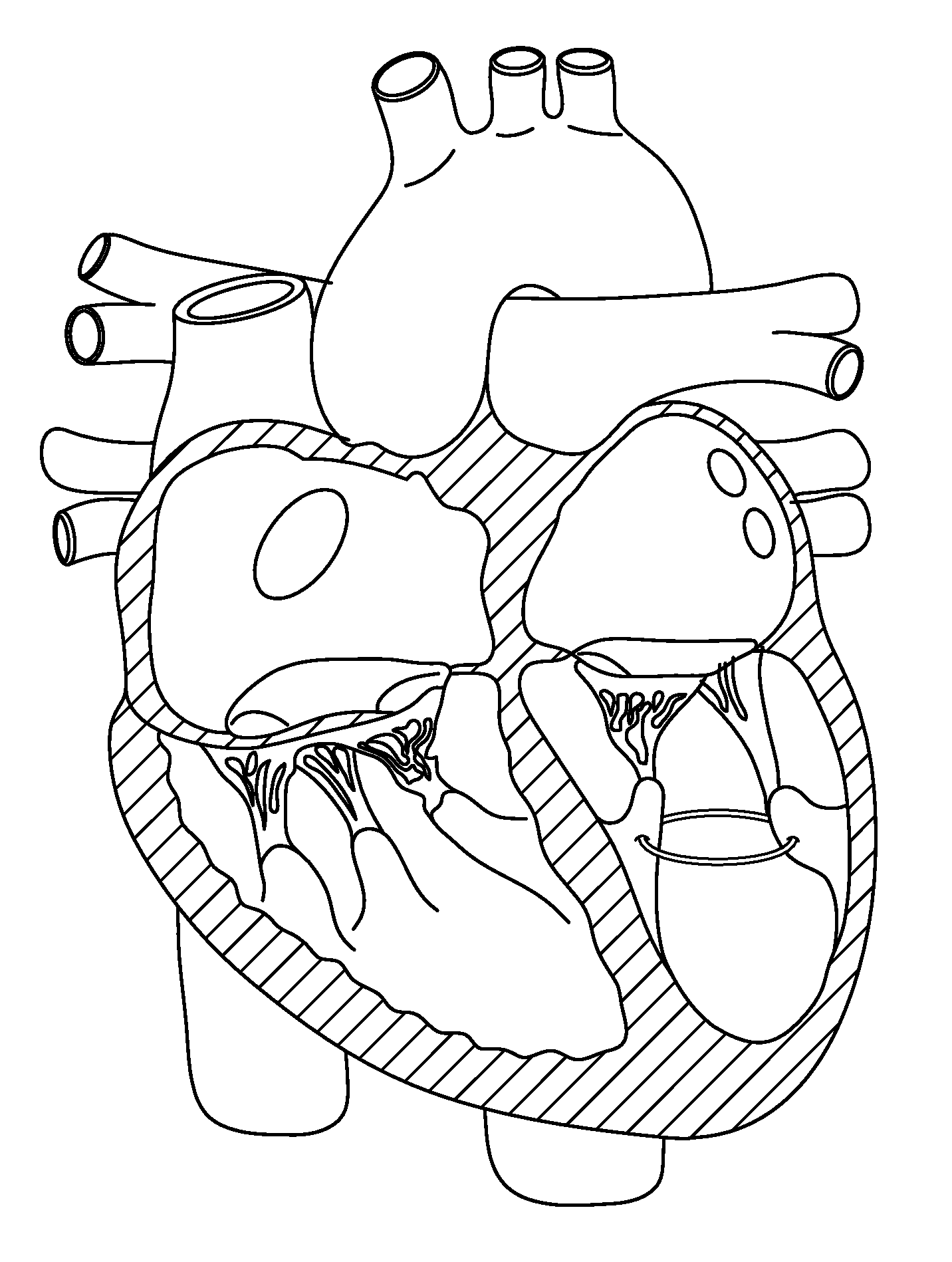
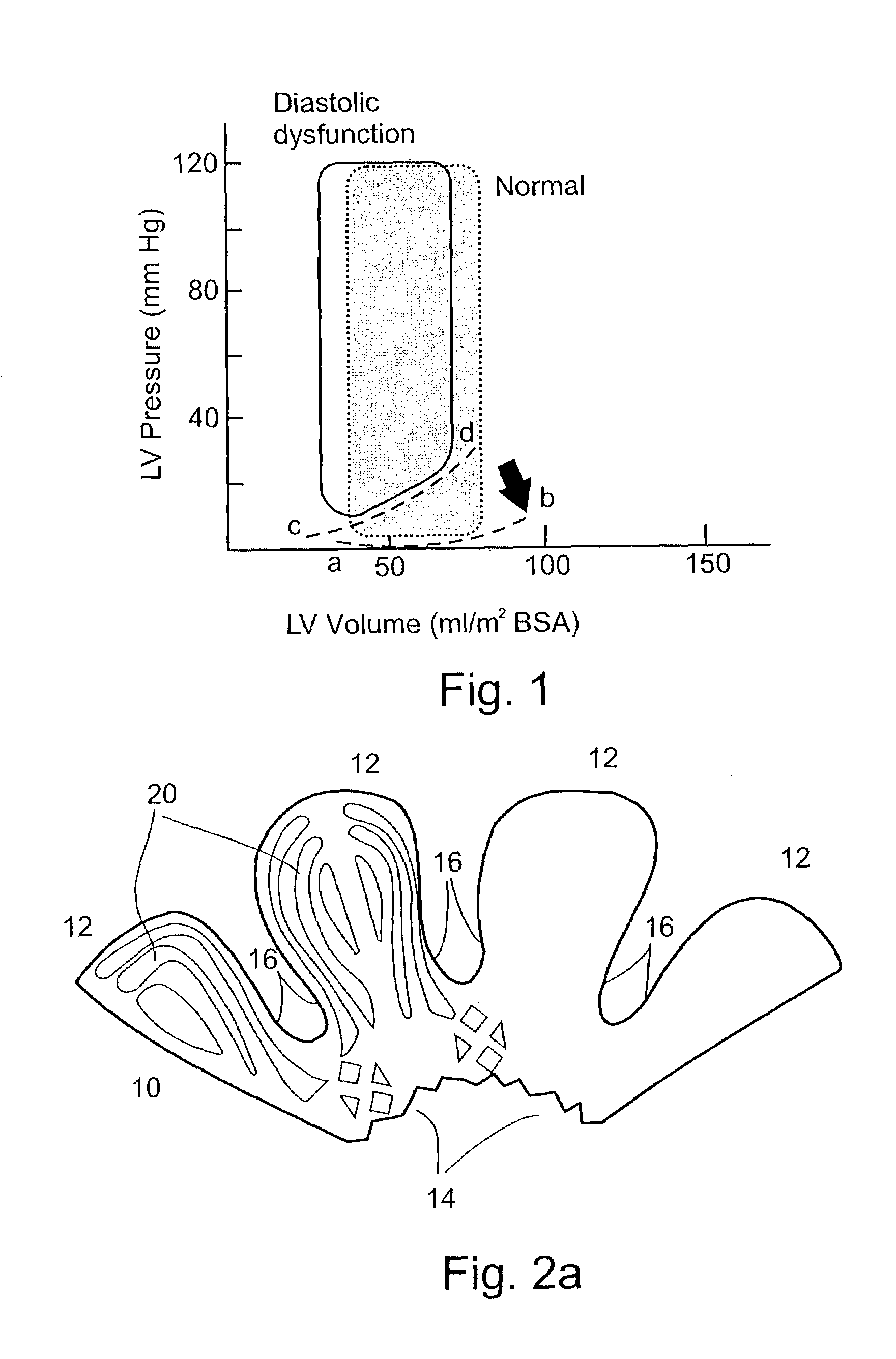
The mass of the left ventricle, as estimated by magnetic resonance imaging, averages 143 g ± 38.4 g, with a range of 87–224 g. The right ventricle is equal in size to that of the left ventricle, and contains roughly 85 millilitres (3 imp fl oz; 3 US fl oz) in the adult.
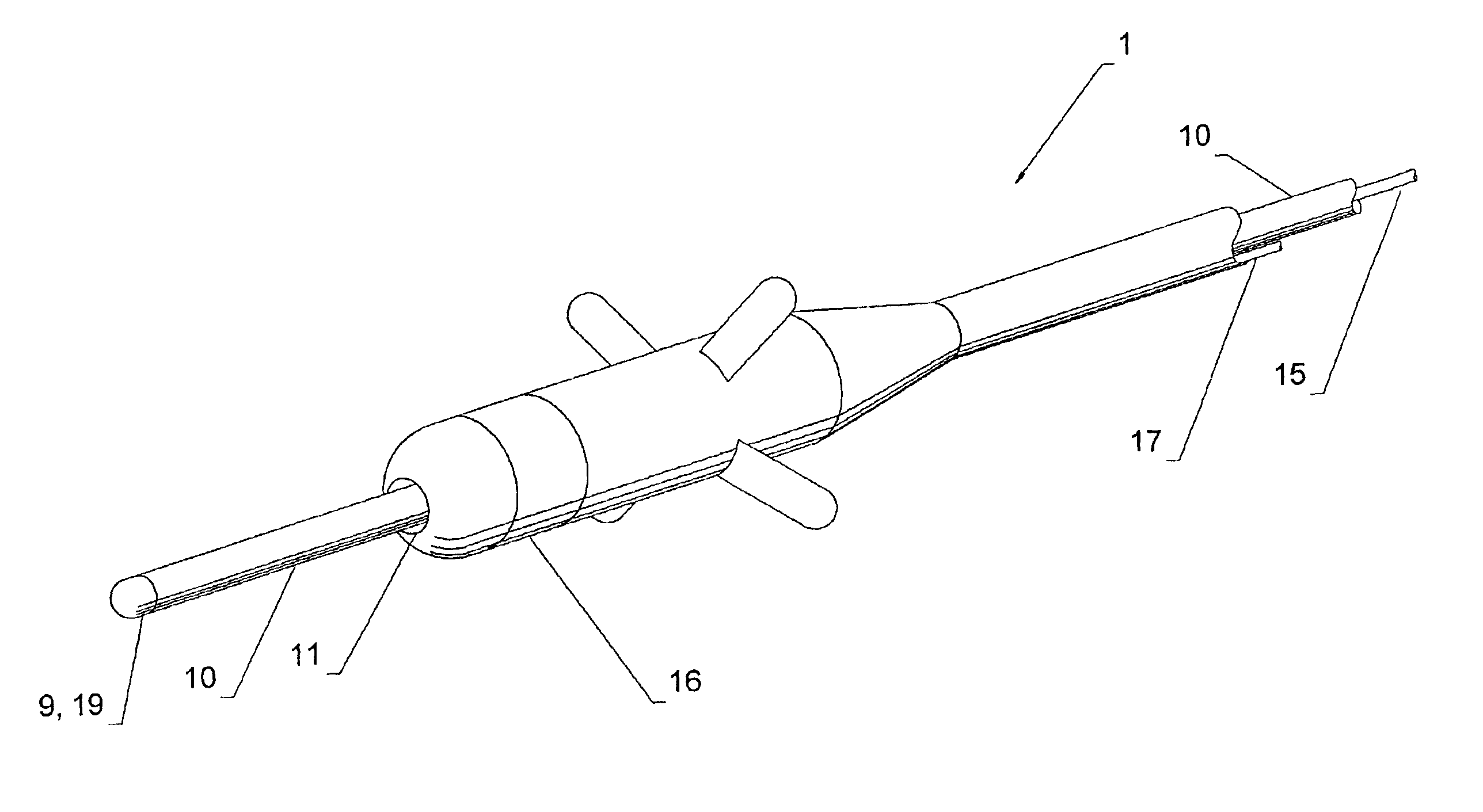
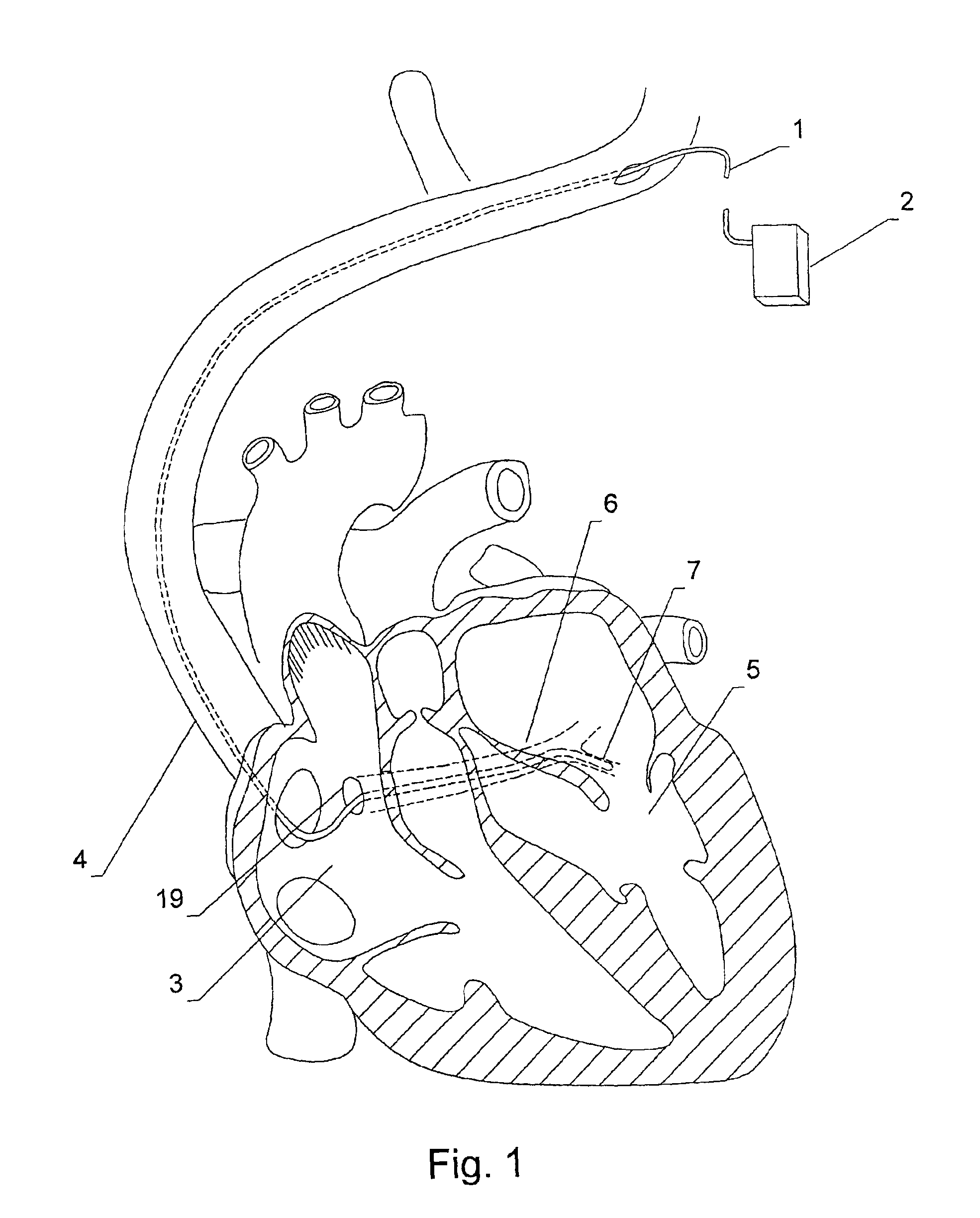
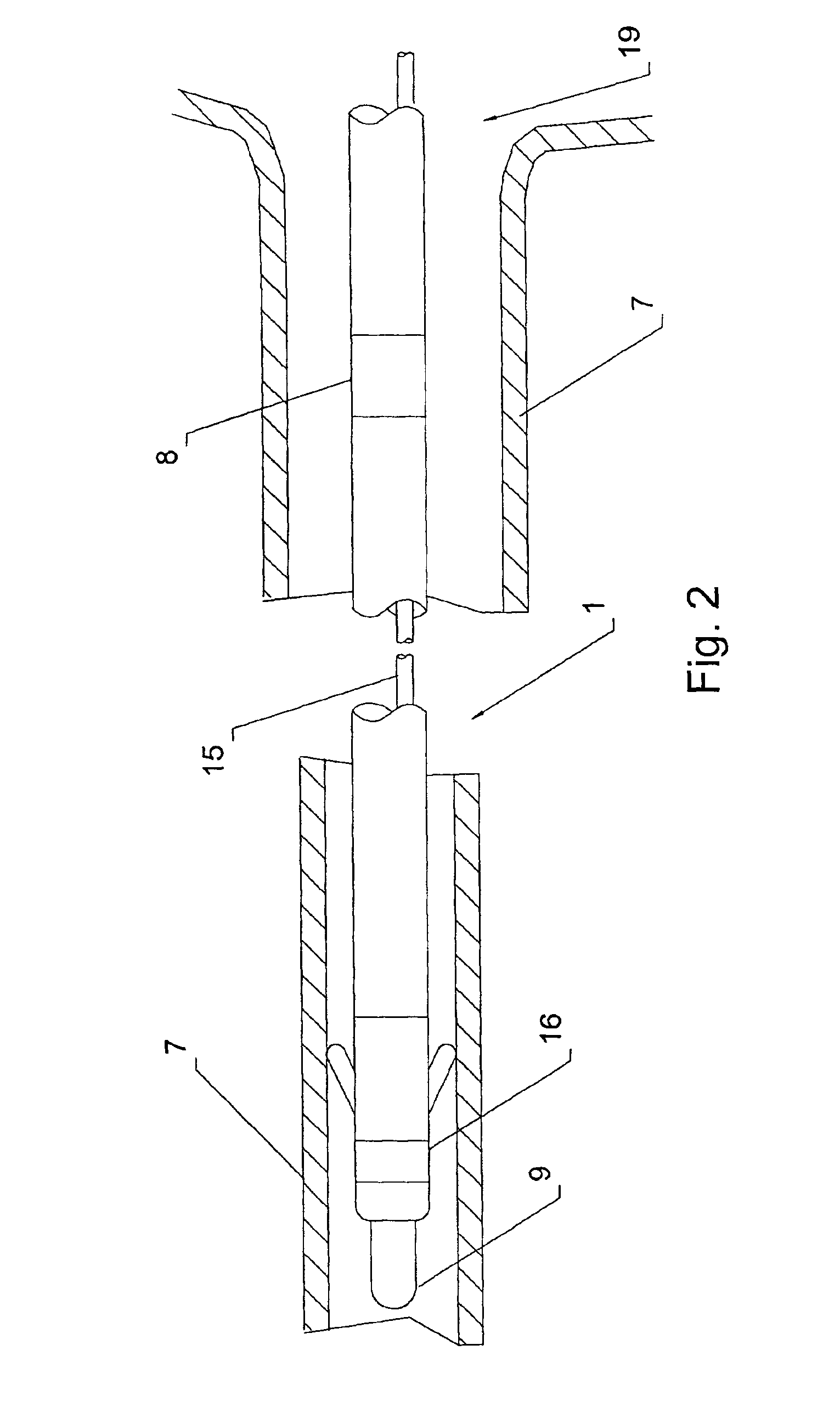
Systems for heart treatment
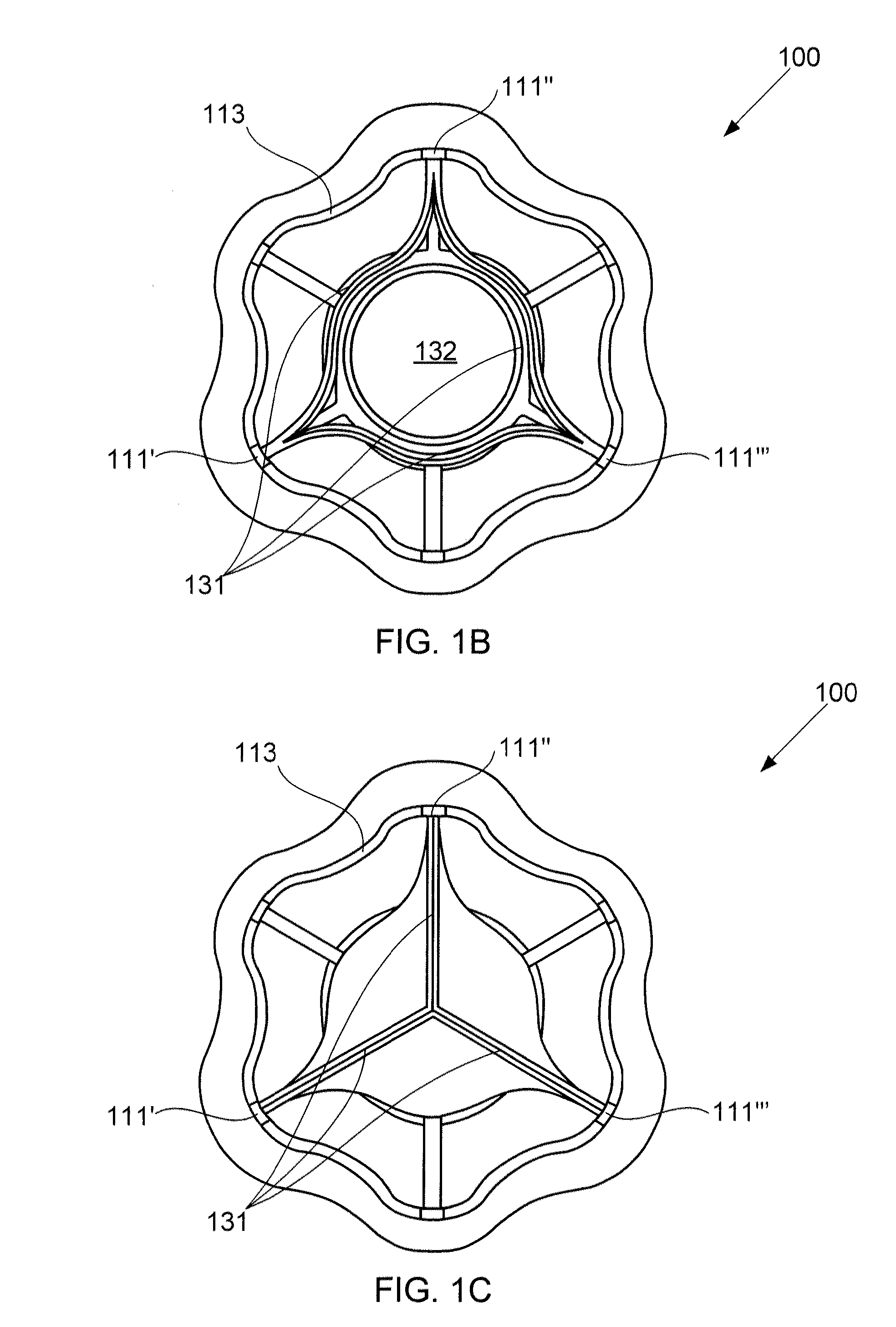
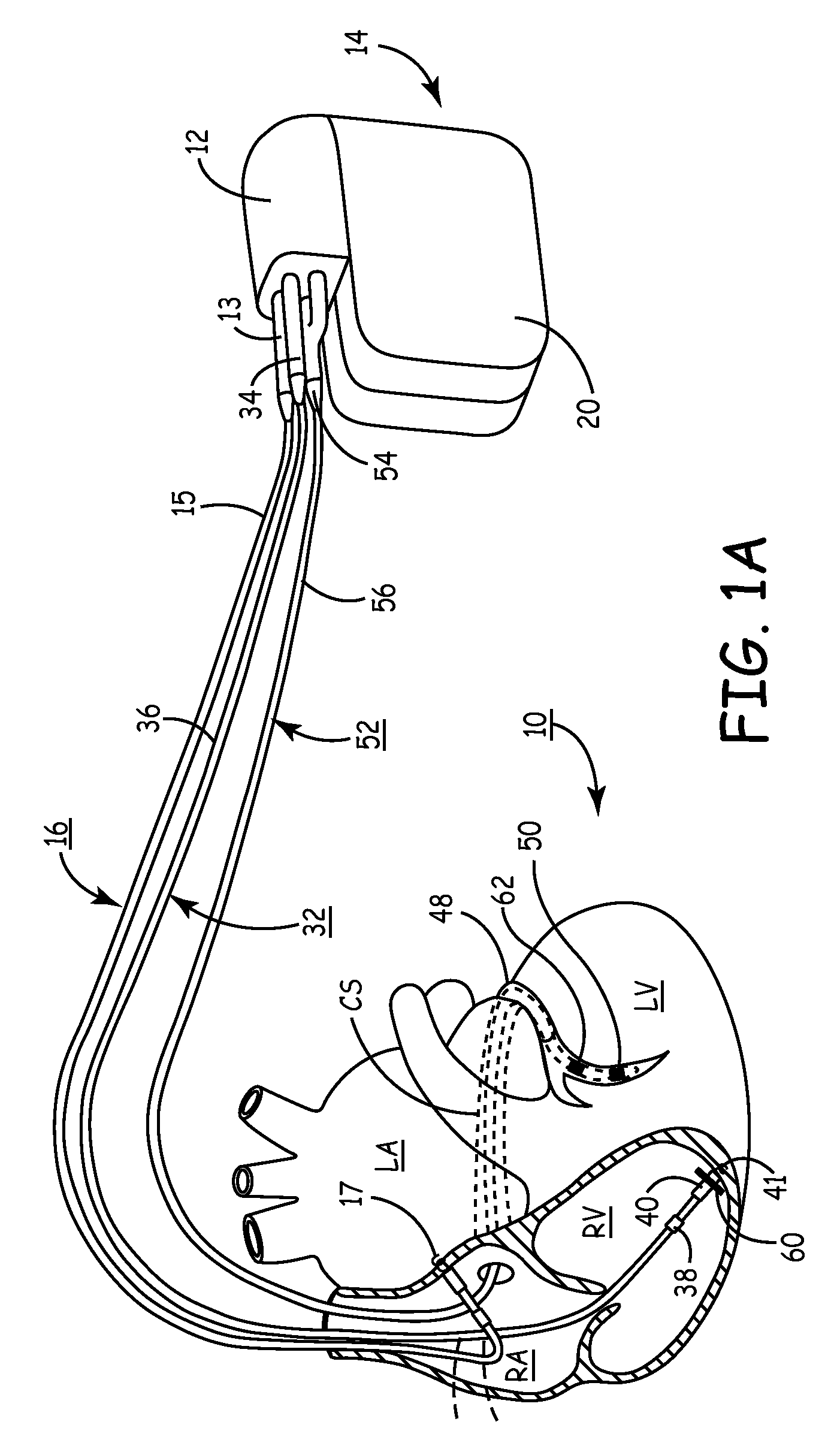
InactiveUS20050197694A1Reduce stressReduce/limit volumeSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
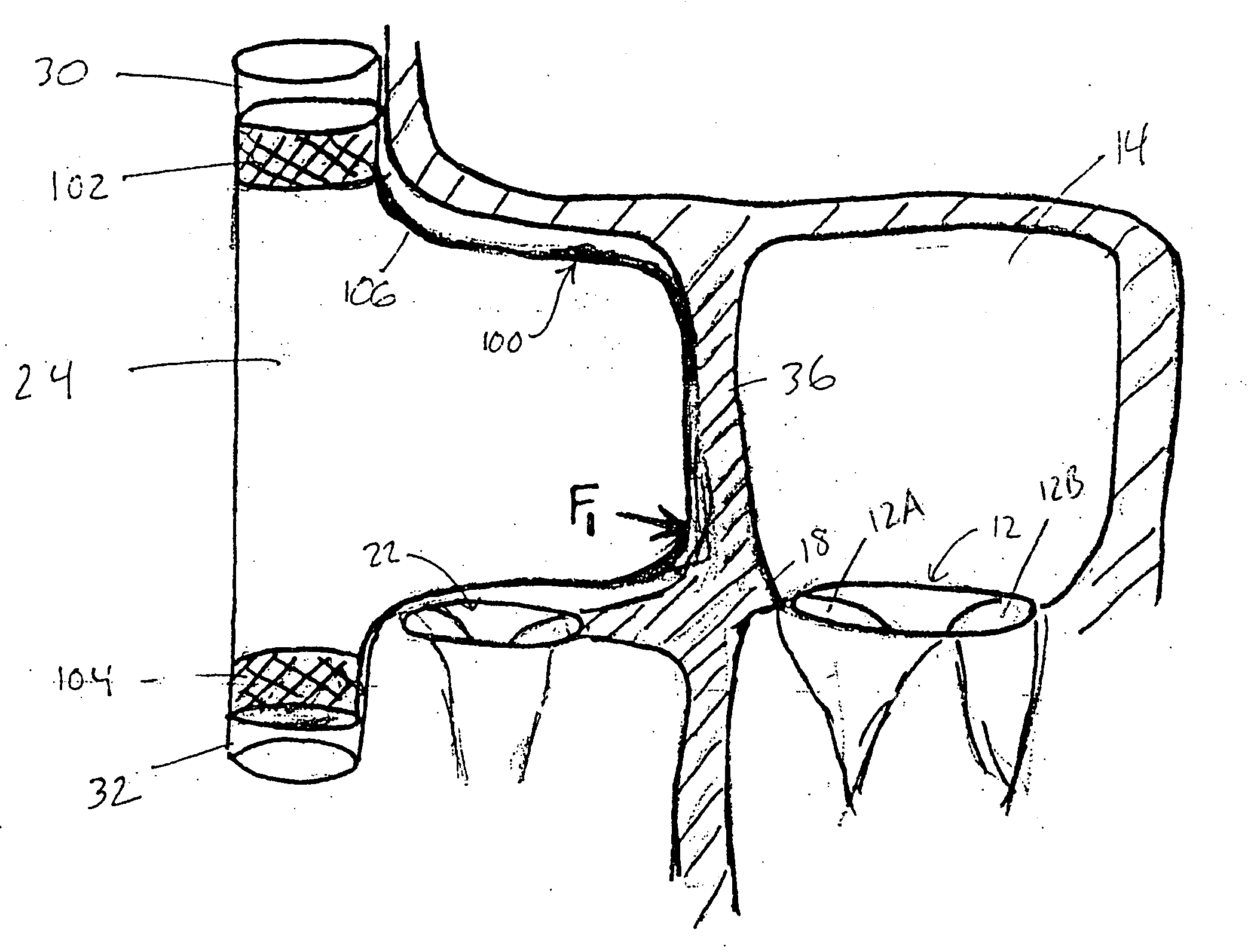
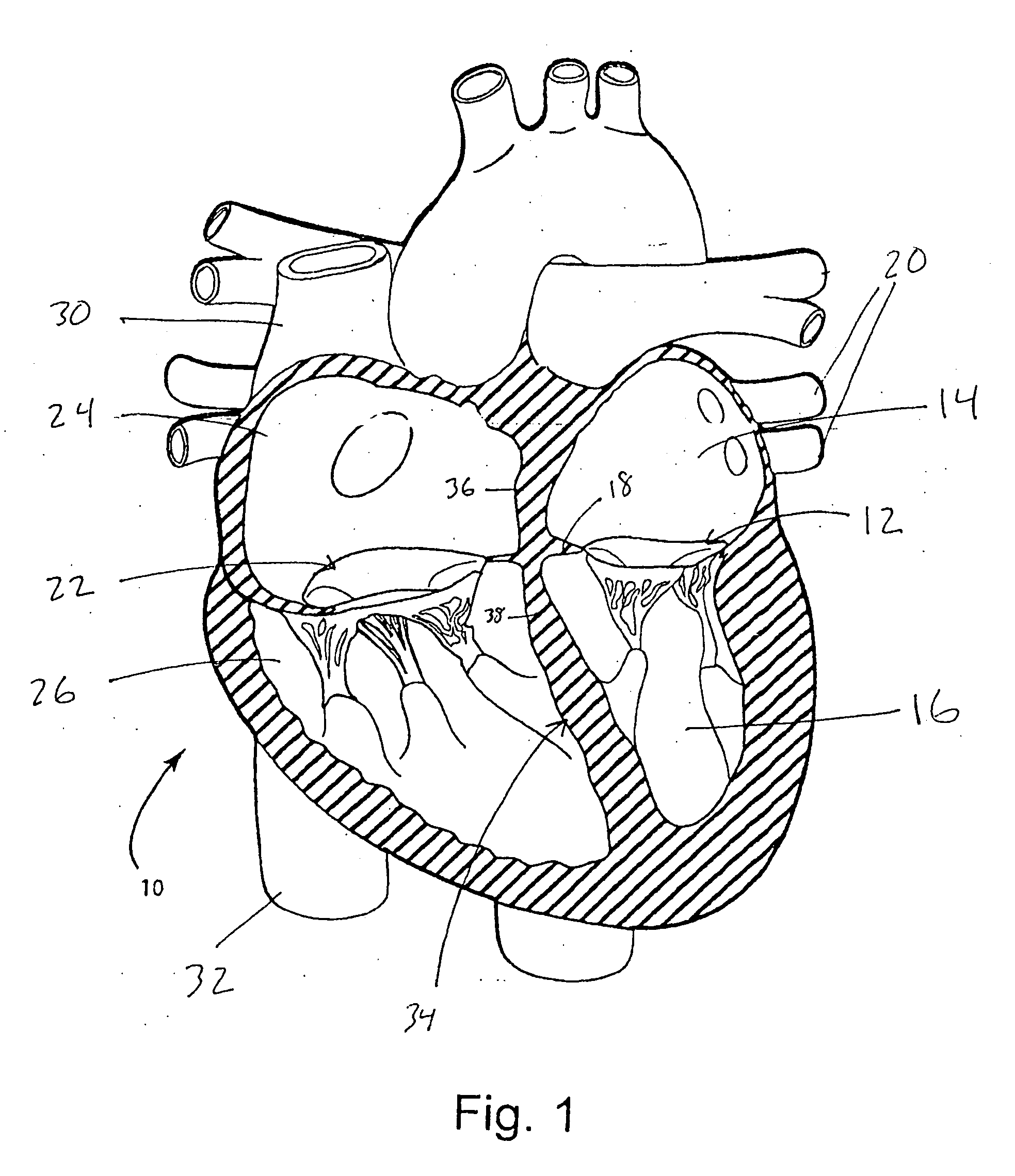
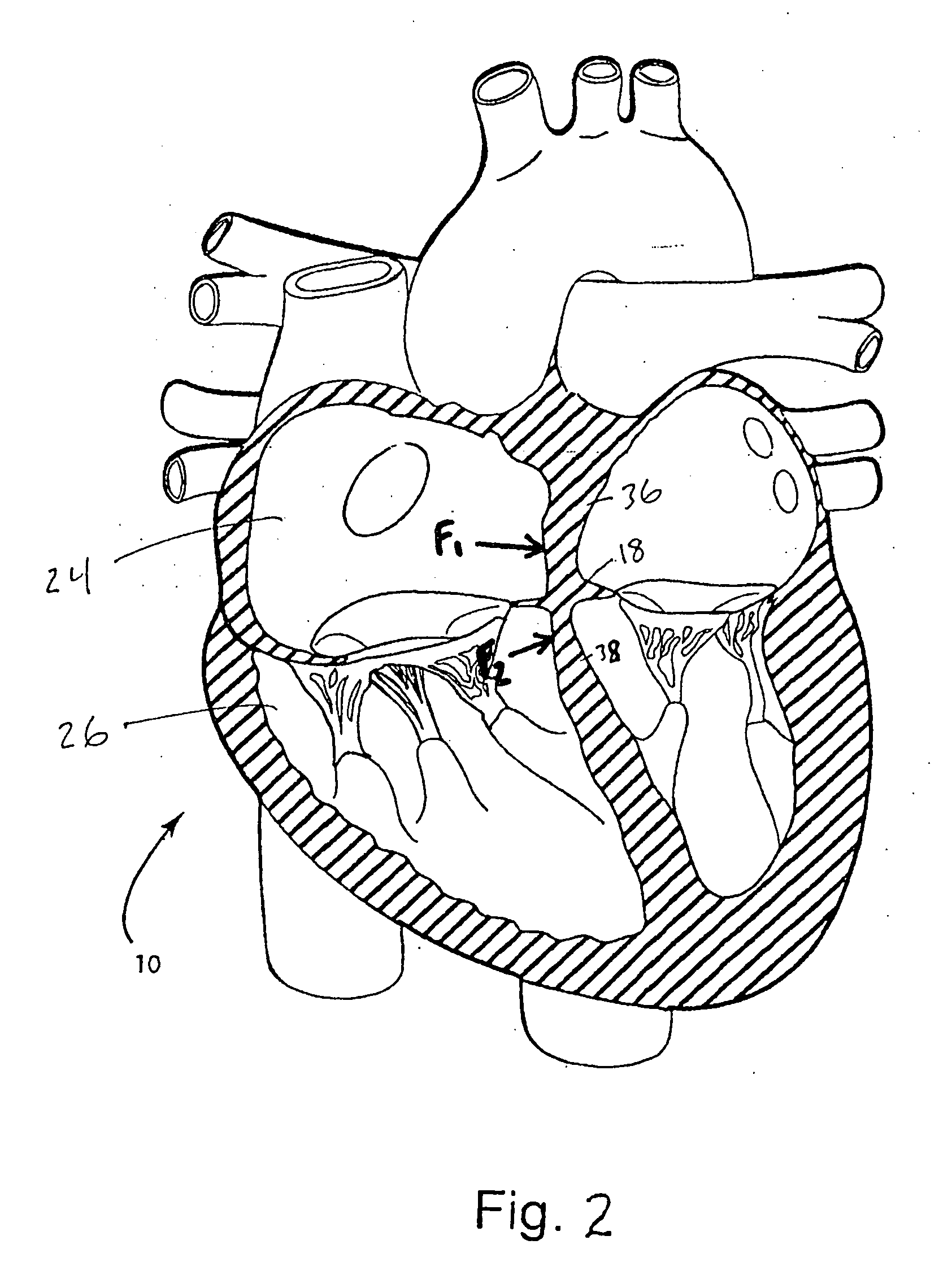
Described are devices and methods for treating degenerative, congestive heart disease and related valvular dysfunction. Percutaneous and minimally invasive surgical tensioning structures offer devices that mitigate changes in the ventricular structure (i.e., remodeling) and deterioration of global left ventricular performance related to tissue damage precipitating from ischemia, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or other abnormalities. These tensioning structures can be implanted within various major coronary blood-carrying conduit structures (arteries, veins and branching vessels), into or through myocardium, or into engagement with other anatomic structures that impact cardiac output to provide tensile support to the heart muscle wall which resists diastolic filling pressure while simultaneously providing a compressive force to the muscle wall to limit, compensate or provide therapeutic treatment for congestive heart failure and / or to reverse the remodeling that produces an enlarged heart.
Owner:EXTENSIA MEDICAL
Systems for heart treatment
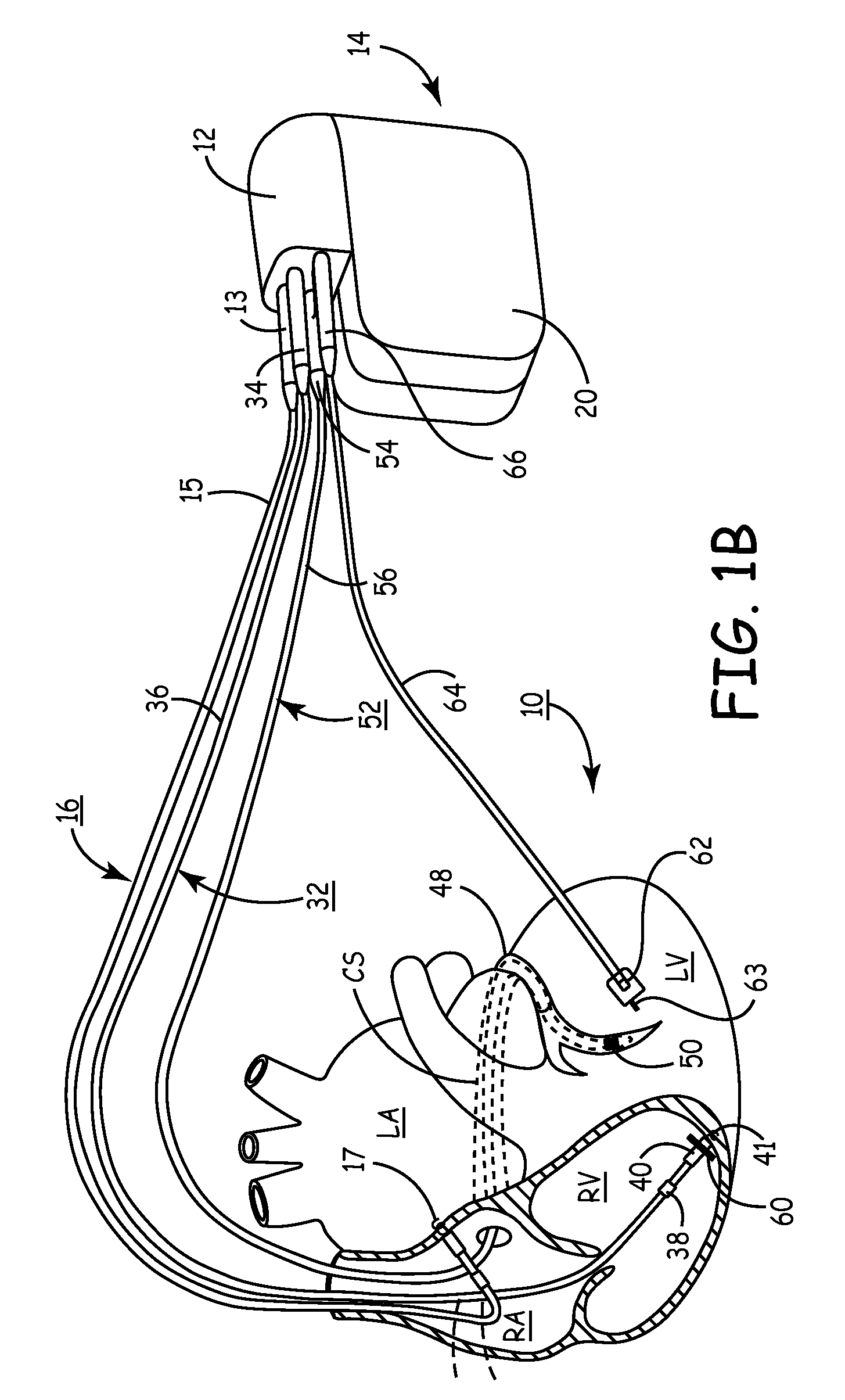
InactiveUS7144363B2Reduce stressReduce/limit volumeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Owner:BAY INNOVATION GROUP
Methods of implanting a mitral valve annuloplasty ring to correct mitral regurgitation
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
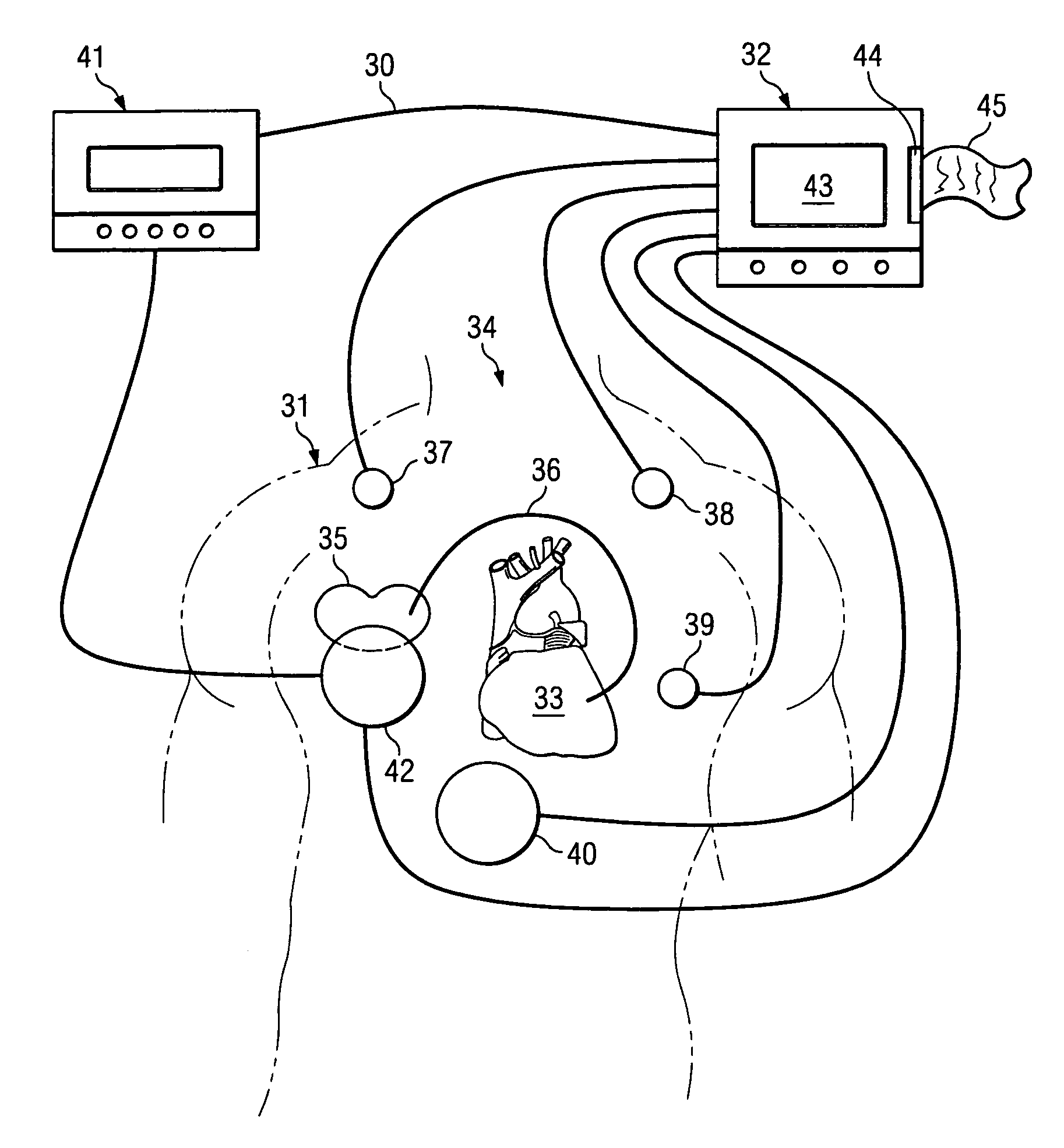
Method and apparatus for optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy based on left ventricular acceleration
InactiveUS6885889B2Good effectExtension of timeHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
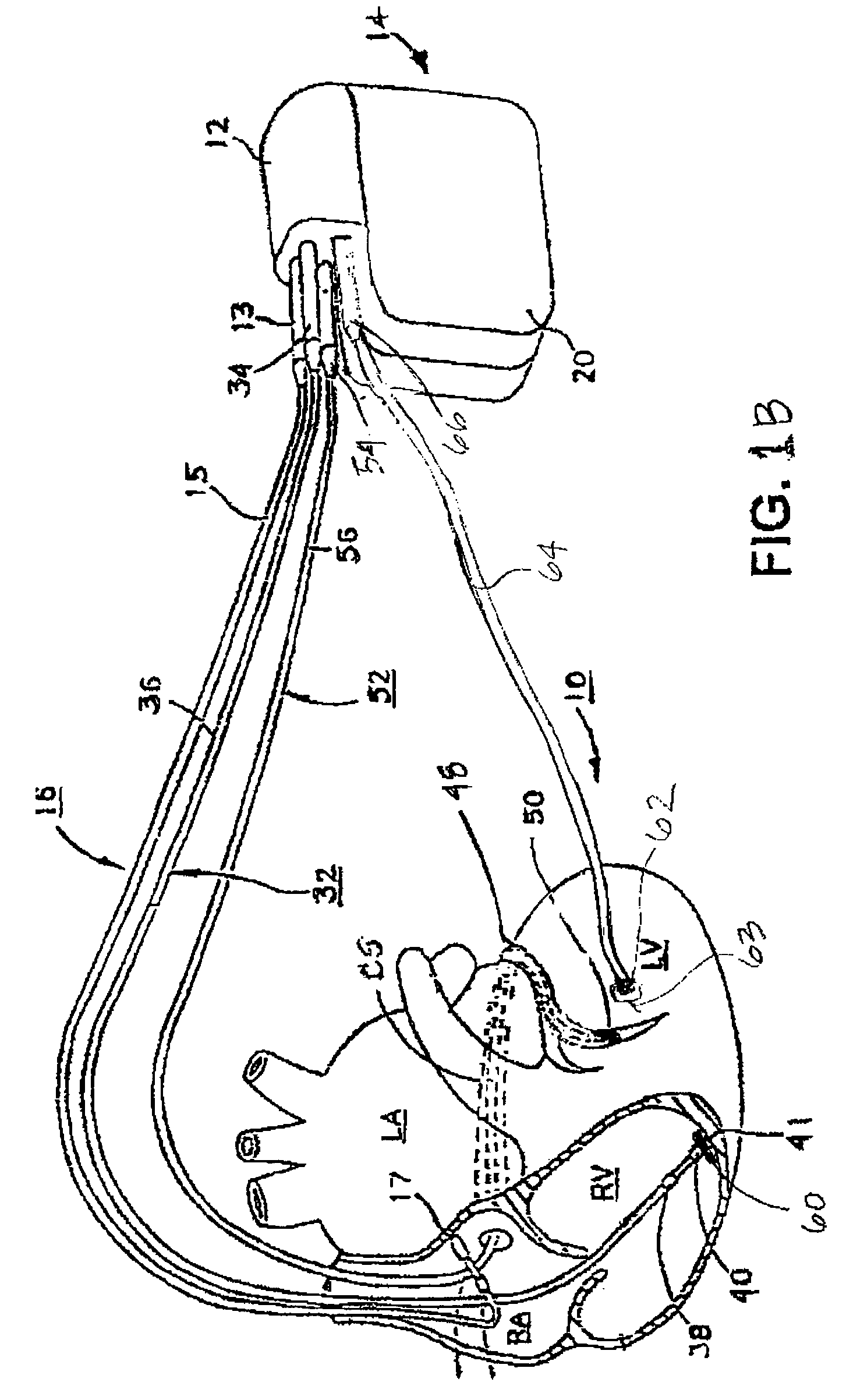
A system and method for monitoring left ventricular cardiac contractility and for optimizing a cardiac therapy based on left ventricular lateral wall acceleration (LVA) are provided. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads including a left ventricular epicardial or coronary sinus lead equipped with an acceleration sensor. The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of LVA during isovolumic contraction. A therapy optimization method evaluates the LVA during varying therapy settings and selects the setting(s) that correspond to a maximum LVA during isovolumic contraction. In one embodiment, the optimal inter-ventricular pacing interval for use in cardiac resynchronization therapy is determined as the interval corresponding to the highest amplitude of the first LVA peak during isovolumic contraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device and method for reshaping mitral valve annulus
InactiveUS20070061010A1Improve bindingReduce distanceStentsAnnuloplasty ringsAnterior leafletPosterior leaflet
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS20050197692A1Decreasing wall stressReinforce wallSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Described are devices and methods for treating degenerative, congestive heart disease and related valvular dysfunction. Percutaneous and minimally invasive surgical tensioning structures offer devices that mitigate changes in the ventricular structure (i.e., remodeling) and deterioration of global left ventricular performance related to tissue damage precipitating from ischemia, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or other abnormalities. These tensioning structures can be implanted within various major coronary blood-carrying conduit structures (arteries, veins and branching vessels), into or through myocardium, or into engagement with other anatomic structures that impact cardiac output to provide tensile support to the heart muscle wall which resists diastolic filling pressure while simultaneously providing a compressive force to the muscle wall to limit, compensate or provide therapeutic treatment for congestive heart failure and / or to reverse the remodeling that produces an enlarged heart.
Owner:EXTENSIA MEDICAL
Chronic performance control system for rotodynamic blood pumps
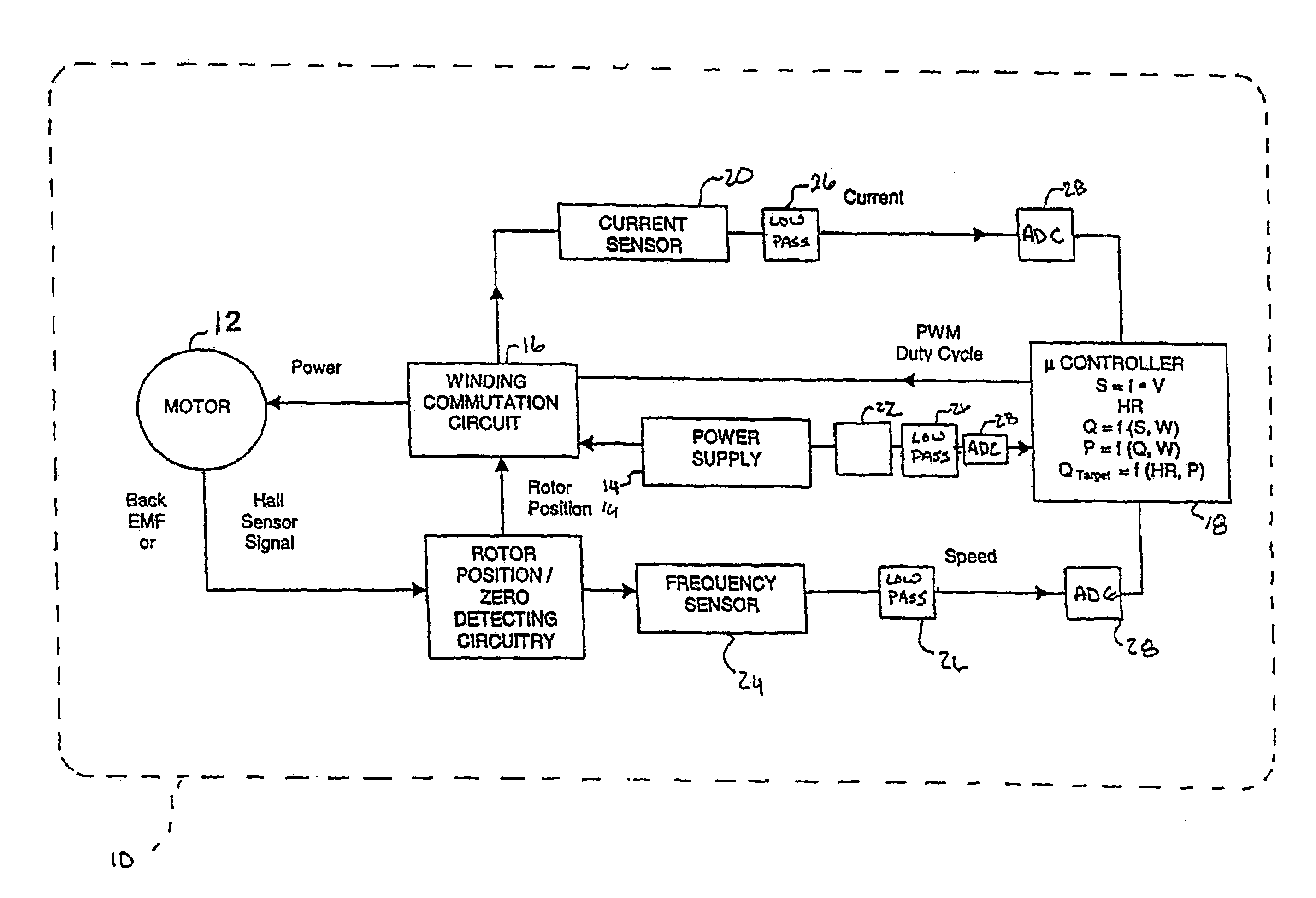
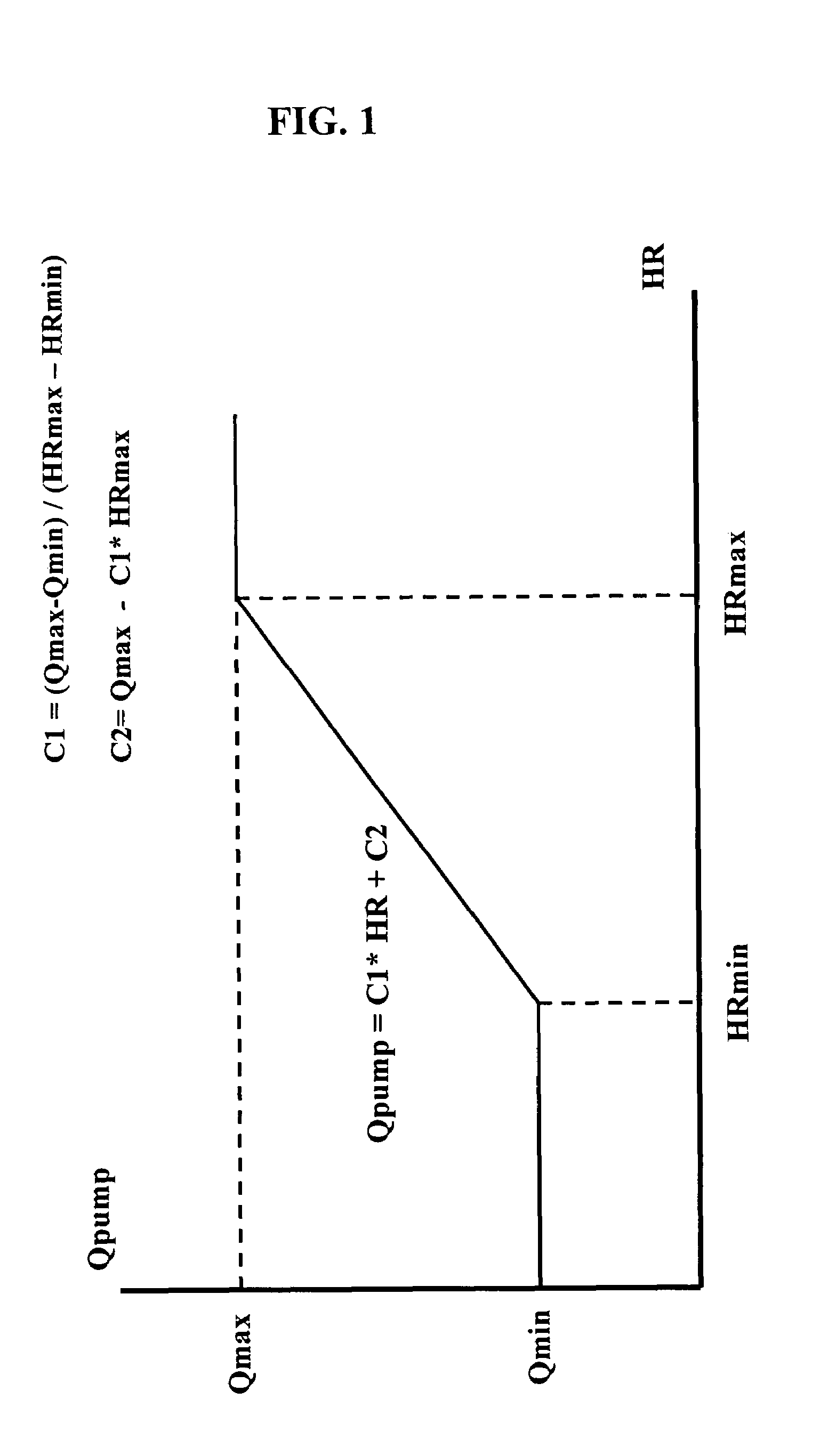
InactiveUS7645225B2Simple control circuitIncrease control flexibilityDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlMicrocontrollerMotor speed
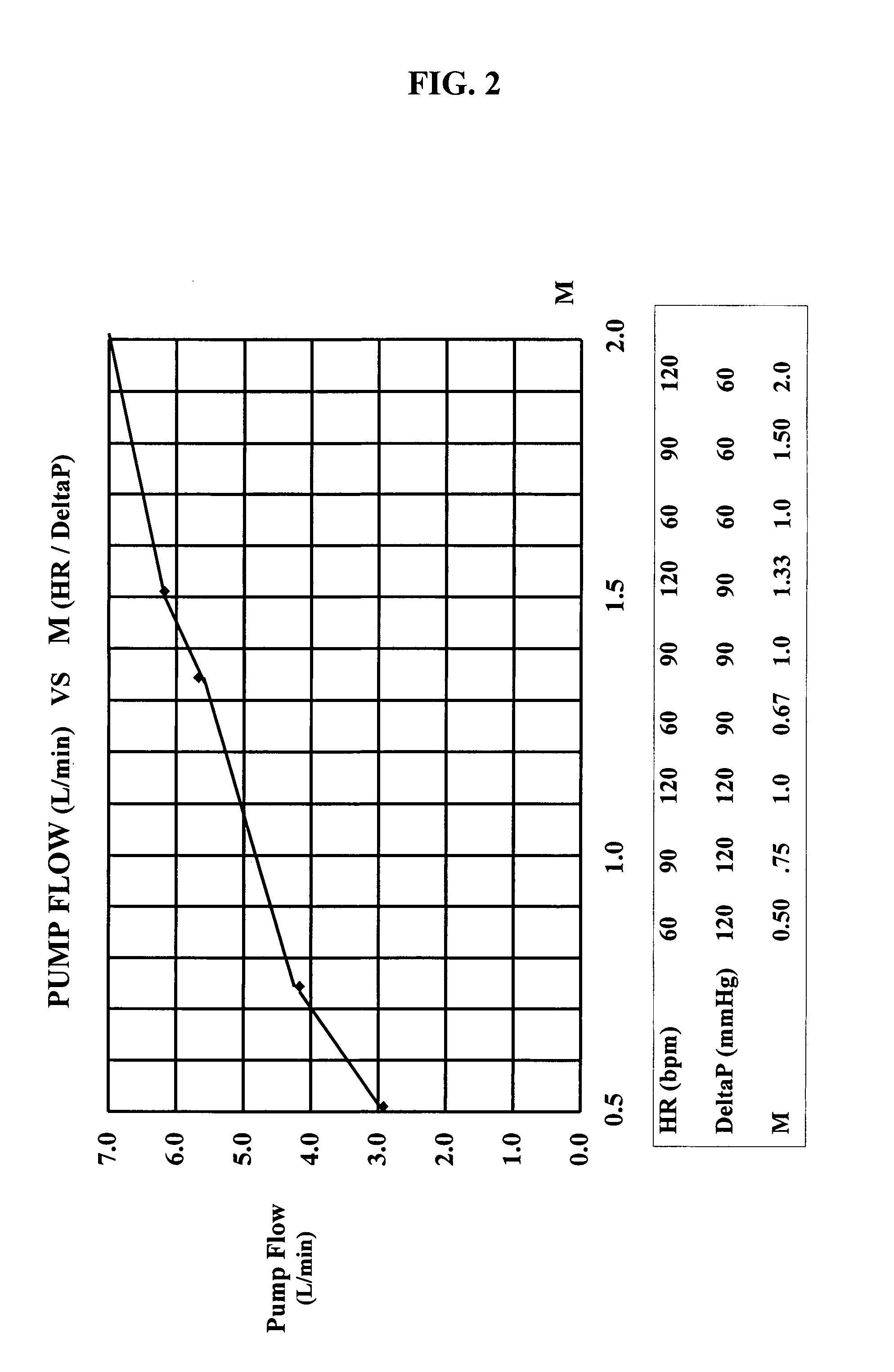
In a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) a rotodynamic blood pump (10) is powered by a brushless DC motor (12). A power supply (14) supplies power to the motor (12). Three feedback channels, one for each of voltage, current, and motor speed lead to a microcontroller or microprocessor (18). The three feedback waveforms are analyzed, and from these waveforms, motor input power, patient heart rate, current pump flow rate, and systemic pressure are determined. The microprocessor (18) then calculates a desired flow rate proportional to the patient heart rate. The microprocessor communicates a new power output to a commutation circuit (16), which regulates power to the motor (12). The pump (10) also includes safety checks that are prioritized over desired pump flow. These include prevention of ventricular suction, low pulsatility, minimum and maximum pump speed, minimum speed-relative pump flow, minimum absolute pump flow, minimum and maximum motor input power.
Owner:MEDVEDEV ALEXANDER +2
System and method for communicating information using encoded pacing pulses within an implantable medical system
InactiveUS7630767B1Facilitate communicationHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeLeft ventricular size
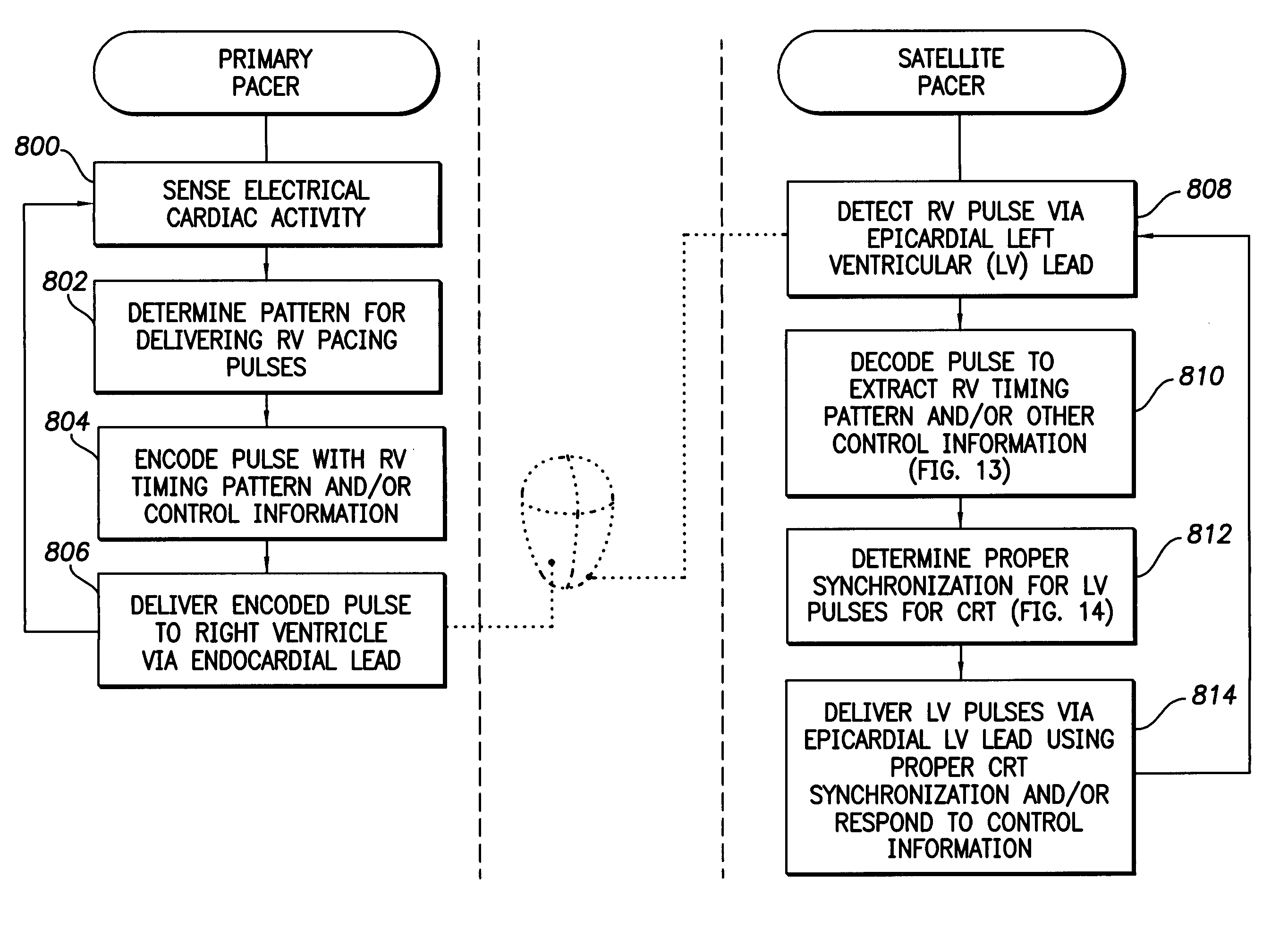
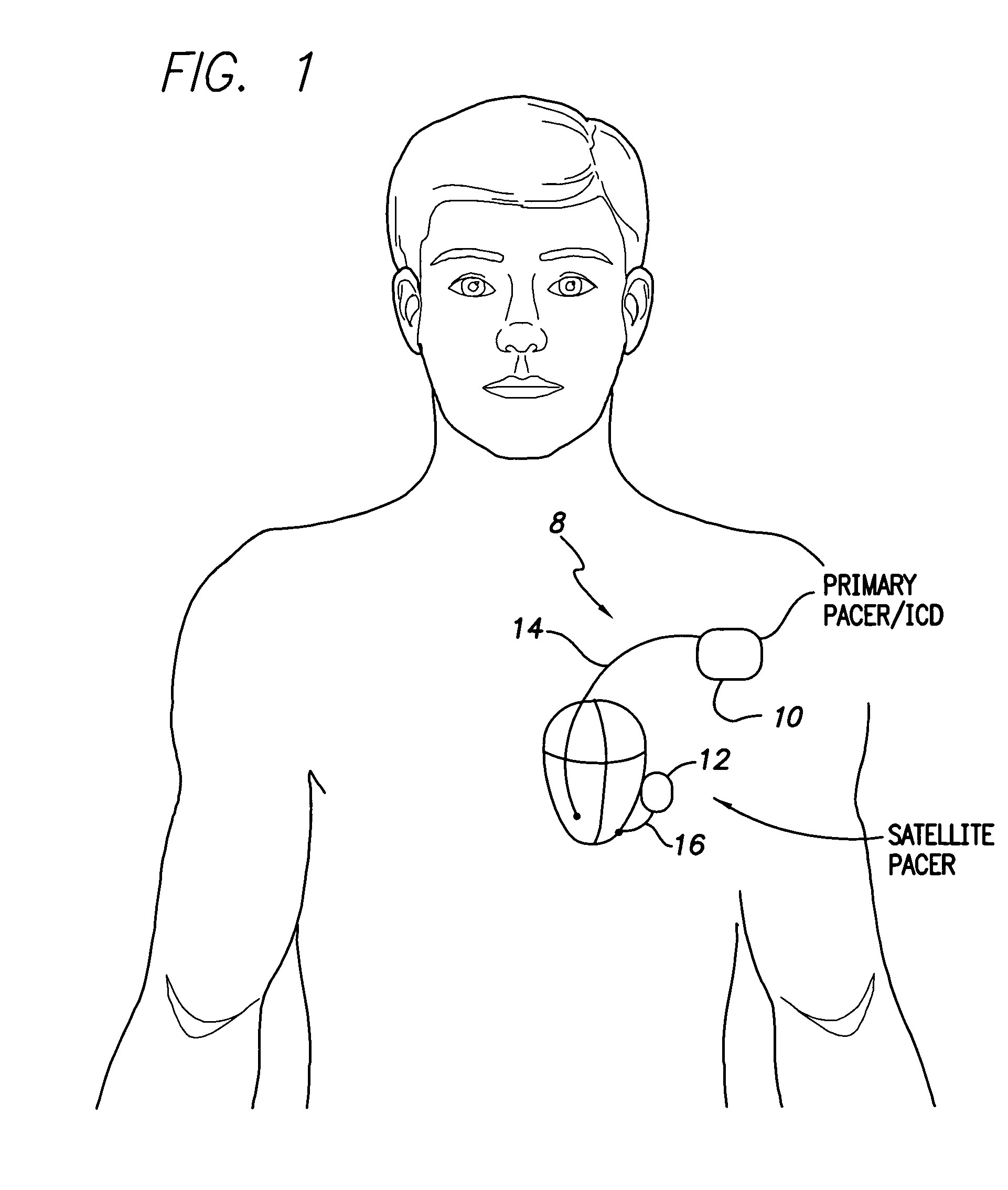
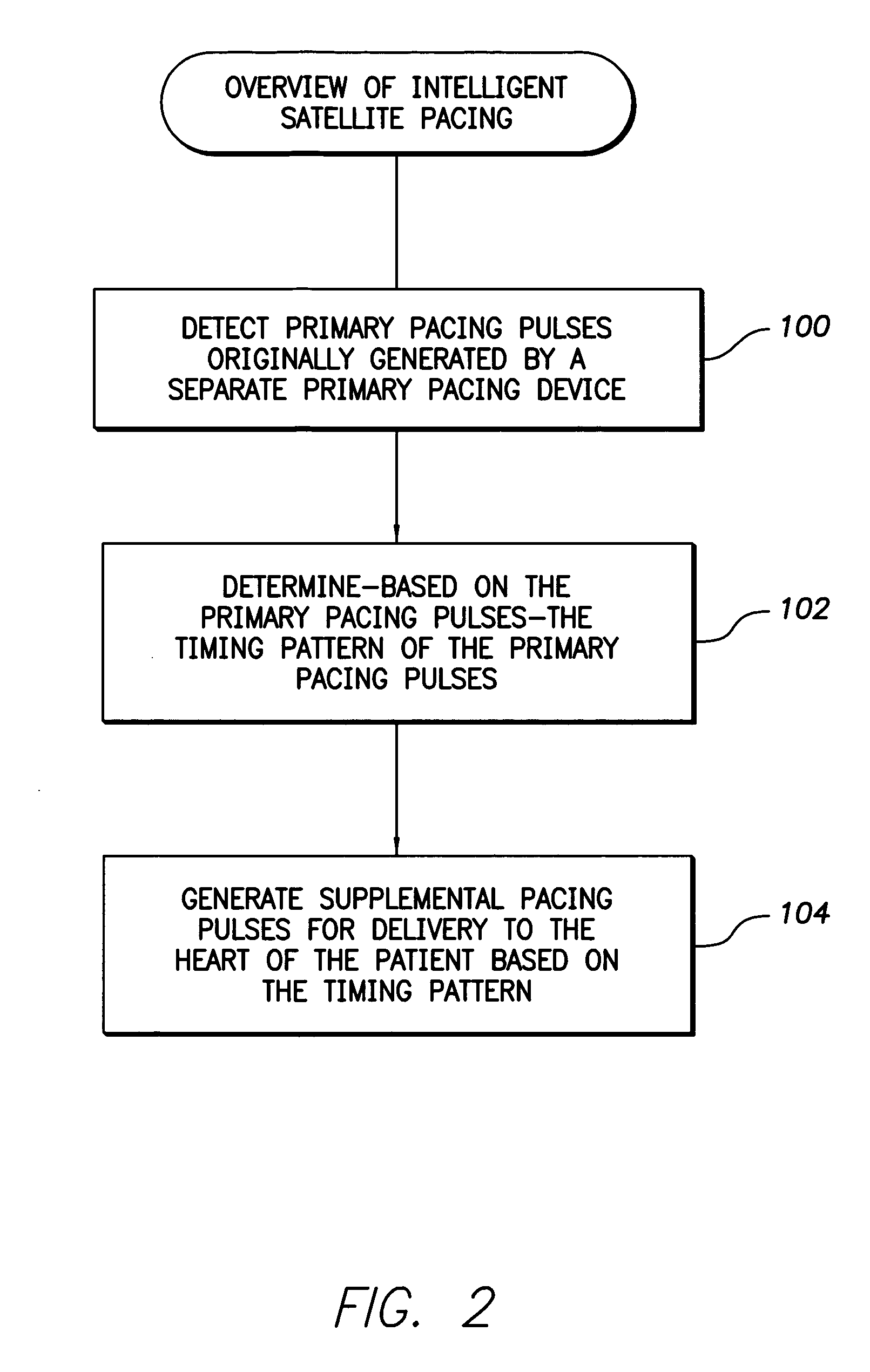
Techniques are provided for delivering cardiac pacing therapy to the heart of a patient using an epicardial left ventricular satellite pacing device in conjunction with primary pacemaker having at least a right ventricular pacing lead. In one embodiment described herein, right ventricular pulses generated by the primary pacemaker are detected by the satellite pacer and analyzed to determine the timing pattern employed by the primary pacemaker. The timing pattern is then used to specify the delivery times of epicardial left ventricular pulses so as to be synchronized with right ventricular pulses. In another embodiment described herein, the primary pacemaker modulates the right ventricular pulses to encode timing information, which is then detected and decoded by the satellite pacemaker. In this manner, biventricular pacing therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy, may be conveniently delivered using a non-biventricular pacemaker in combination with an epicardial satellite pacer.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods of implanting a mitral valve annuloplasty ring to correct mitral regurgitation
ActiveUS20050049698A1Reduce the impactReduce impactBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsStellite alloyMitral annuloplasty ring
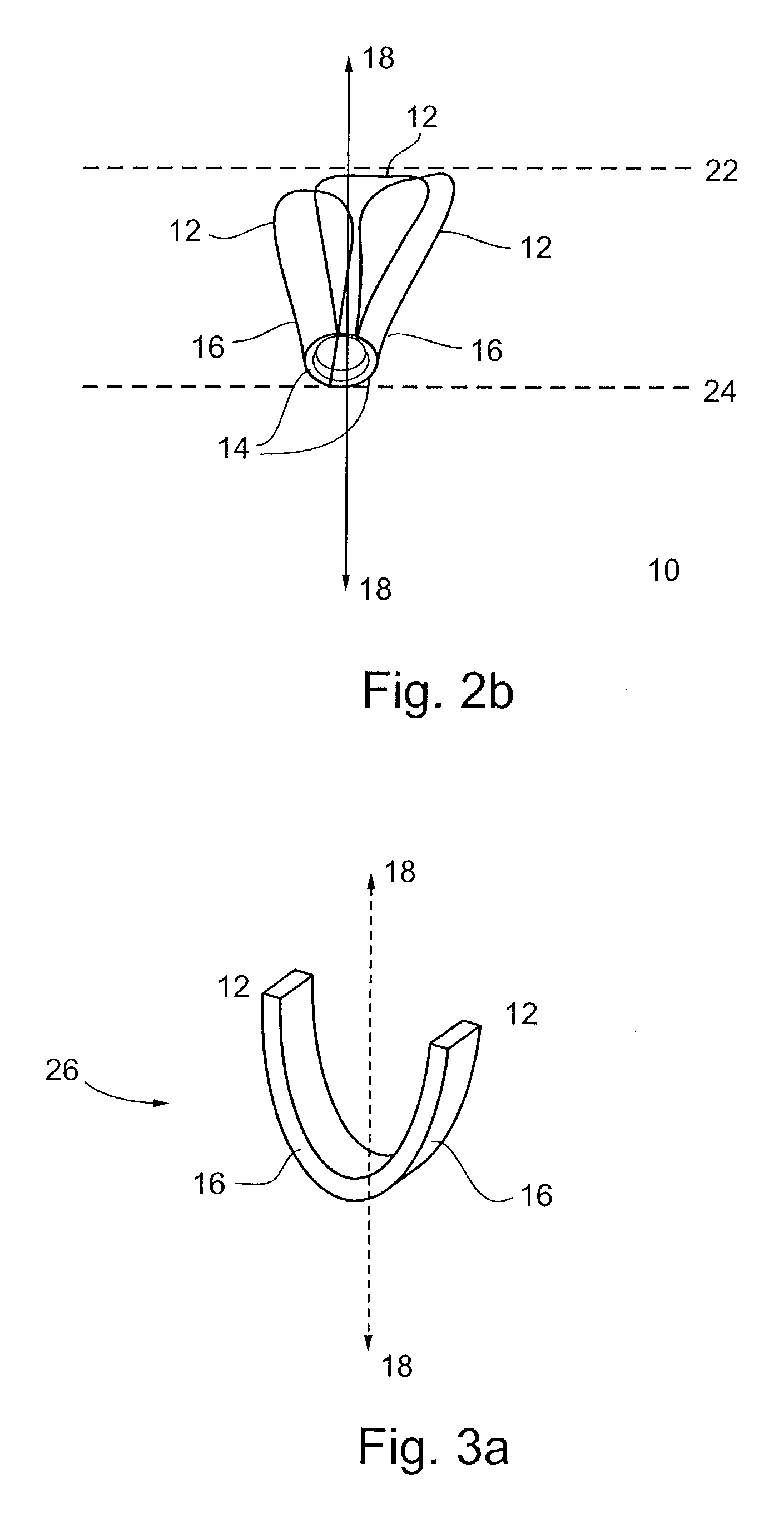
Methods of implanting an annuloplasty ring to correct maladies of the mitral annulus that not only reshapes the annulus but also reconfigures the adjacent left ventricular muscle wall. The ring may be continuous and is made of a relatively rigid material, such as Stellite. The ring has a generally oval shape that is three-dimensional at least on the posterior side. A posterior portion of the ring rises or bows upward from adjacent sides to pull the posterior aspect of the native annulus farther up than its original, healthy shape. In doing so, the ring also pulls the ventricular wall upward which helps mitigate some of the effects of congestive heart failure. Further, one or both of the posterior and anterior portions of the ring may also bow inward. The methods include securing the annuloplasty ring with the anterior portion against the annulus anterior aspect and the posterior portion against the annulus posterior aspect so that the ring posterior portion elevates and may also pull radially inward, the annulus posterior aspect and corrects the mitral regurgitation.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and Method for ReShaping Mitral Valve Annulus
ActiveUS20090076586A1Reduce regurgitationImprove bindingStentsDiagnosticsPosterior leafletLeft ventricular size
Devices and methods for reshaping a mitral valve annulus are provided. One preferred device is configured for deployment in the right atrium and is shaped to apply a force along the atrial septum. The device causes the atrial septum to deform and push the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve in a posterior direction for reducing mitral valve regurgitation. Another preferred device is deployed in the left ventricular outflow tract at a location adjacent the aortic valve. The device is expandable for urging the anterior leaflet toward the posterior leaflet. Another preferred device comprises a tether configured to be attached to opposing regions of the mitral valve annulus.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for assessing left ventricular function and optimizing cardiac pacing intervals based on left ventricular wall motion
A system and method for monitoring left ventricular (LV) lateral wall motion and for optimizing cardiac pacing intervals based on left ventricular lateral wall motion is provided. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads including a left ventricular epicardial or coronary sinus lead equipped with a motion sensor electromechanically coupled to the lateral wall of the left ventricle. The device receives and processes wall motion sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of systolic LV lateral wall motion or acceleration. An automatic pacing interval optimization method evaluates the LV lateral wall motion during varying pacing interval settings, including atrial-ventricular intervals and inter-ventricular intervals and selects the pacing interval setting(s) that correspond to LV lateral wall motion associated with improved cardiac synchrony and hemodynamic performance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Mechanical function marker channel for cardiac monitoring and therapy control
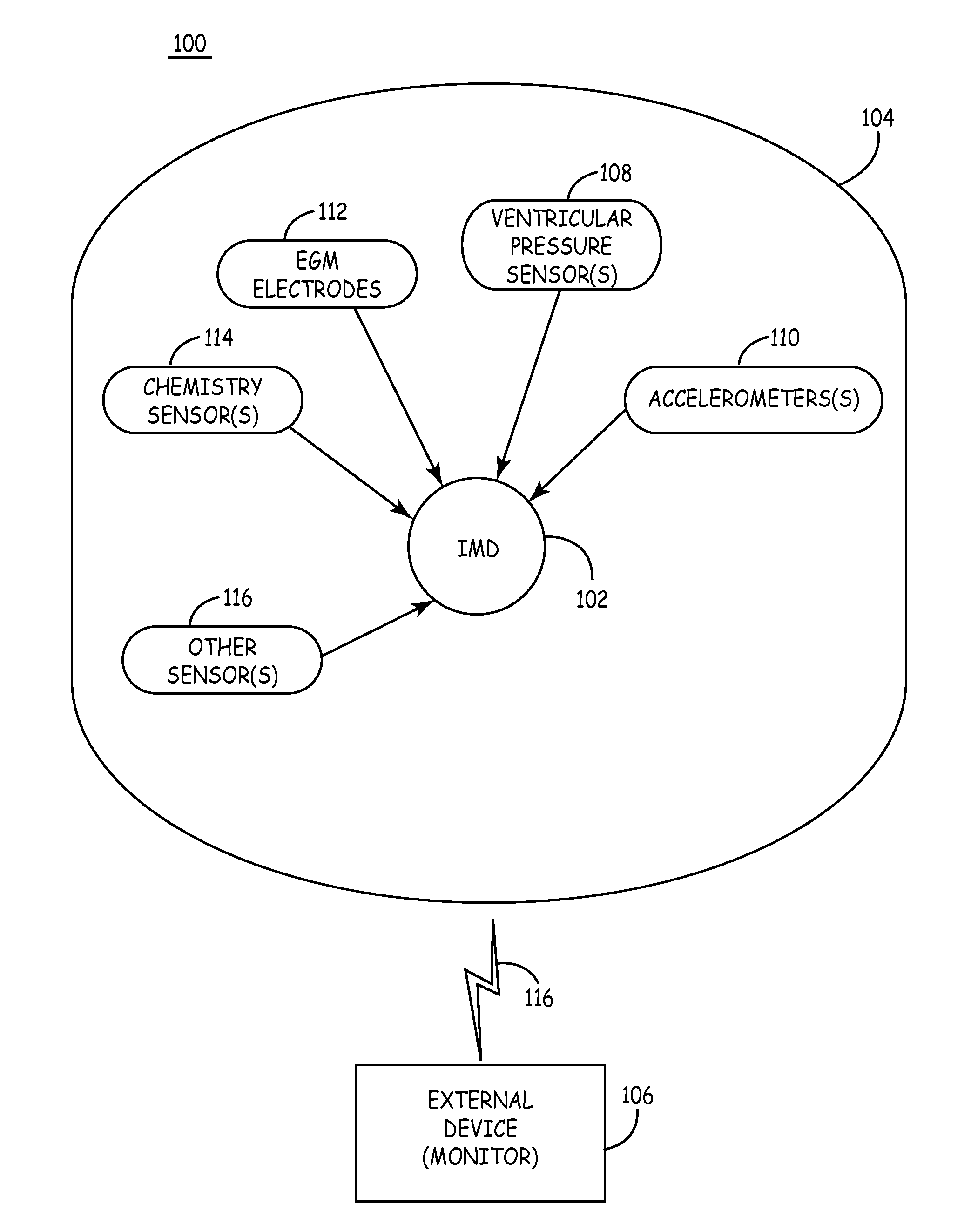
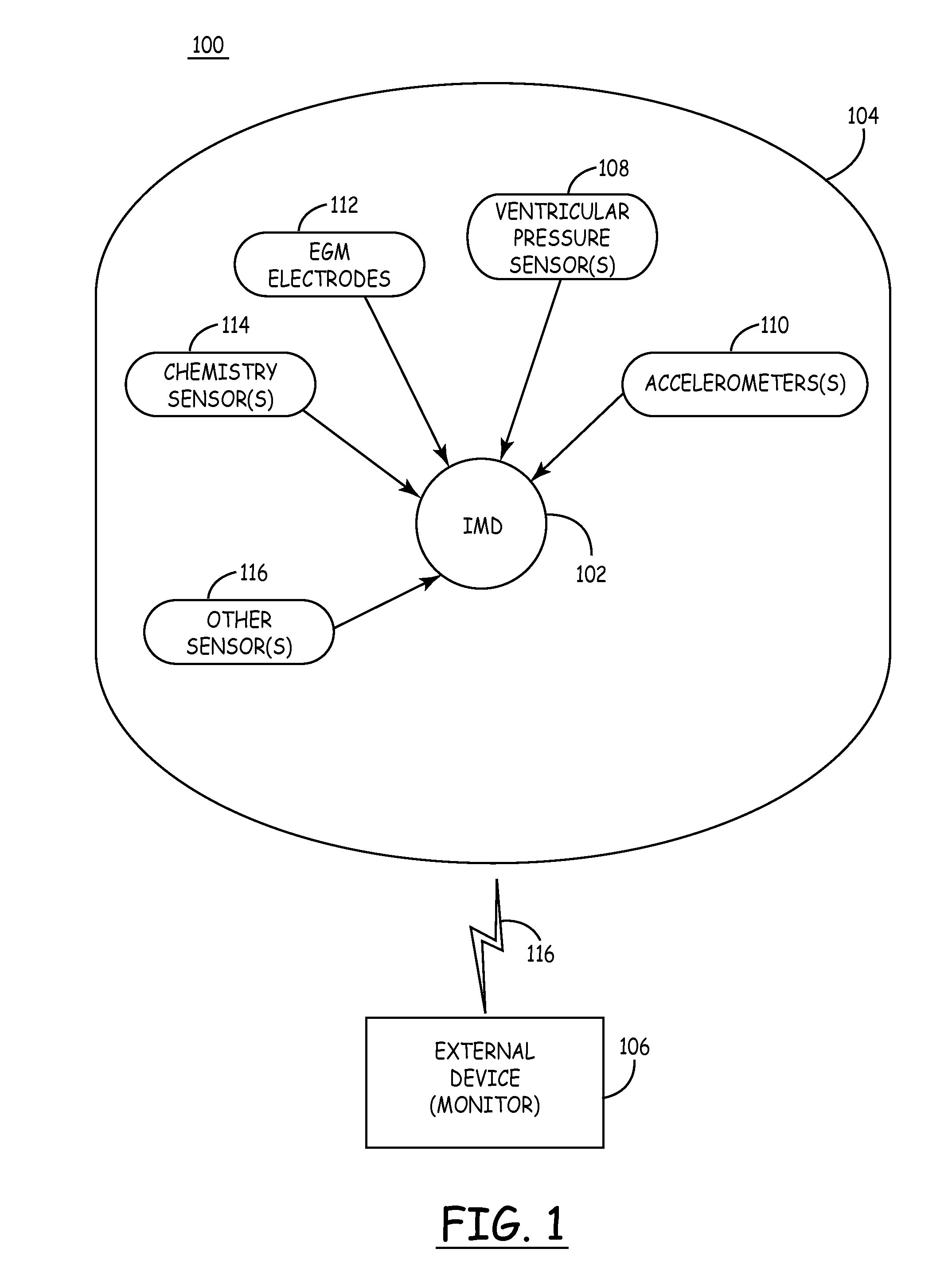
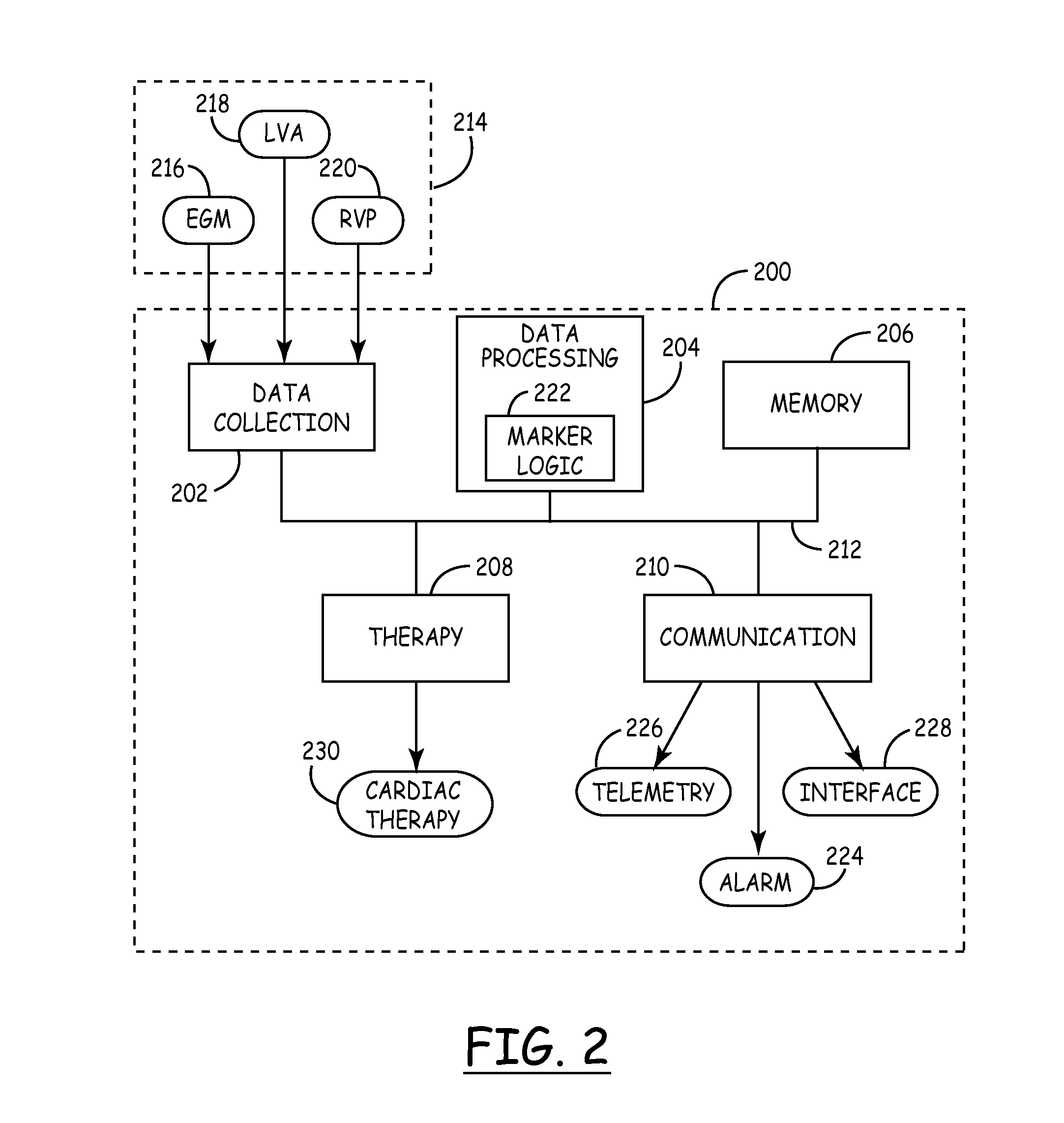
The implantable medical device (IMD) system disclosed here utilizes one or more cardiac sensors that measure mechanical characteristics of the heart, such as left ventricular acceleration or right ventricular pressure. The raw sensor data is collected and processed by the IMD, which derives one or more mechanical event marker signals from features, traits, and characteristics of the sensor data waveforms. The mechanical event marker signals are wirelessly transmitted to an external monitor device for display.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable pressure sensor with pacing capability
Devices and methods for left ventricular or biventricular pacing plus left ventricular pressure measurement. For example, a pacing lead having a combined electrode and pressure sensor assembly may be used for left ventricular (LV) pacing and pressure measurement. The assembly may include one or more electrodes, a pressure sensor, and a pressure transmission catheter. Such a pacing lead is particularly suitable for biventricular pacing and may be incorporated into a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) system, for example.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
Systems and Methods for Ranking and Selection of Pacing Vectors
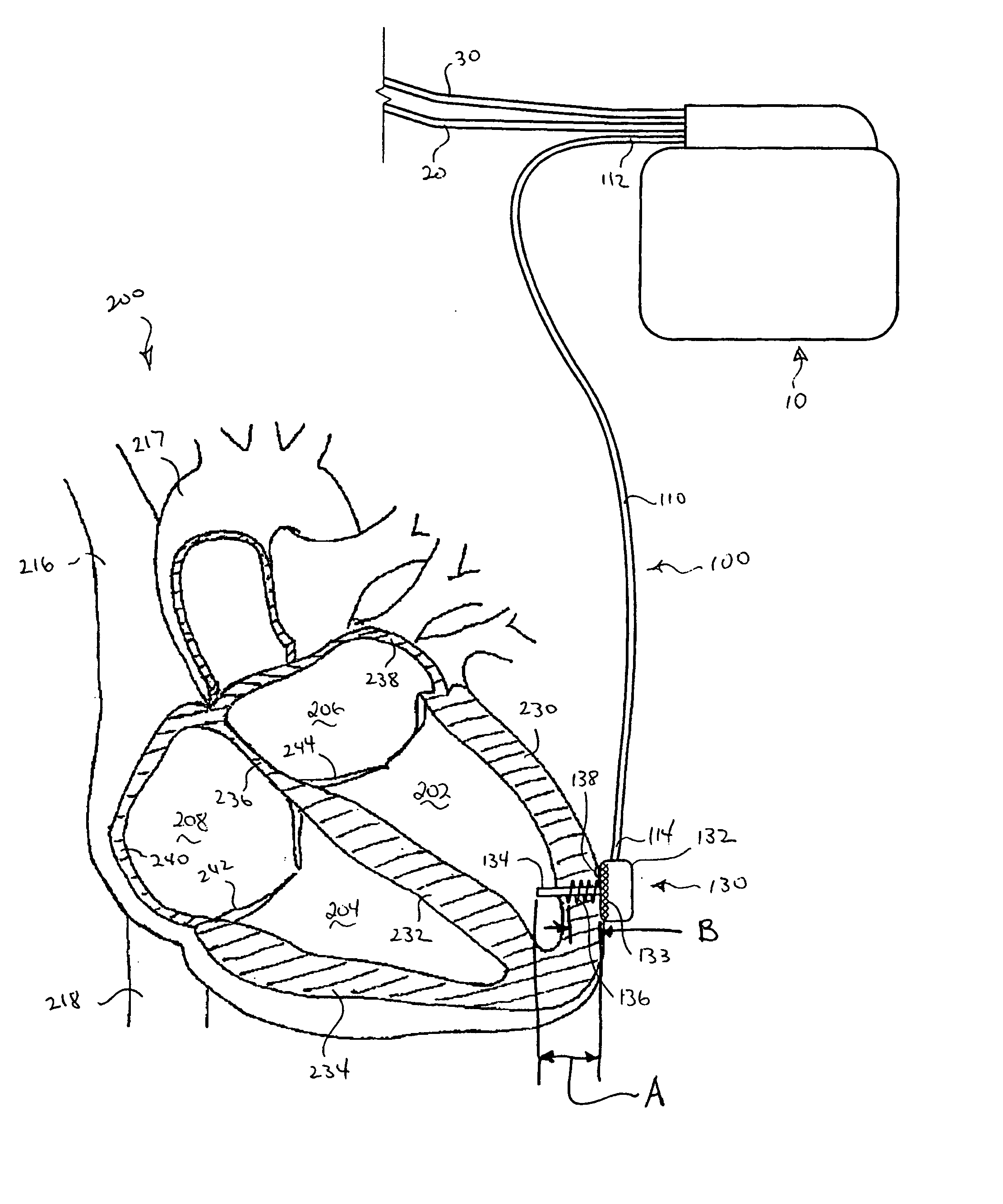
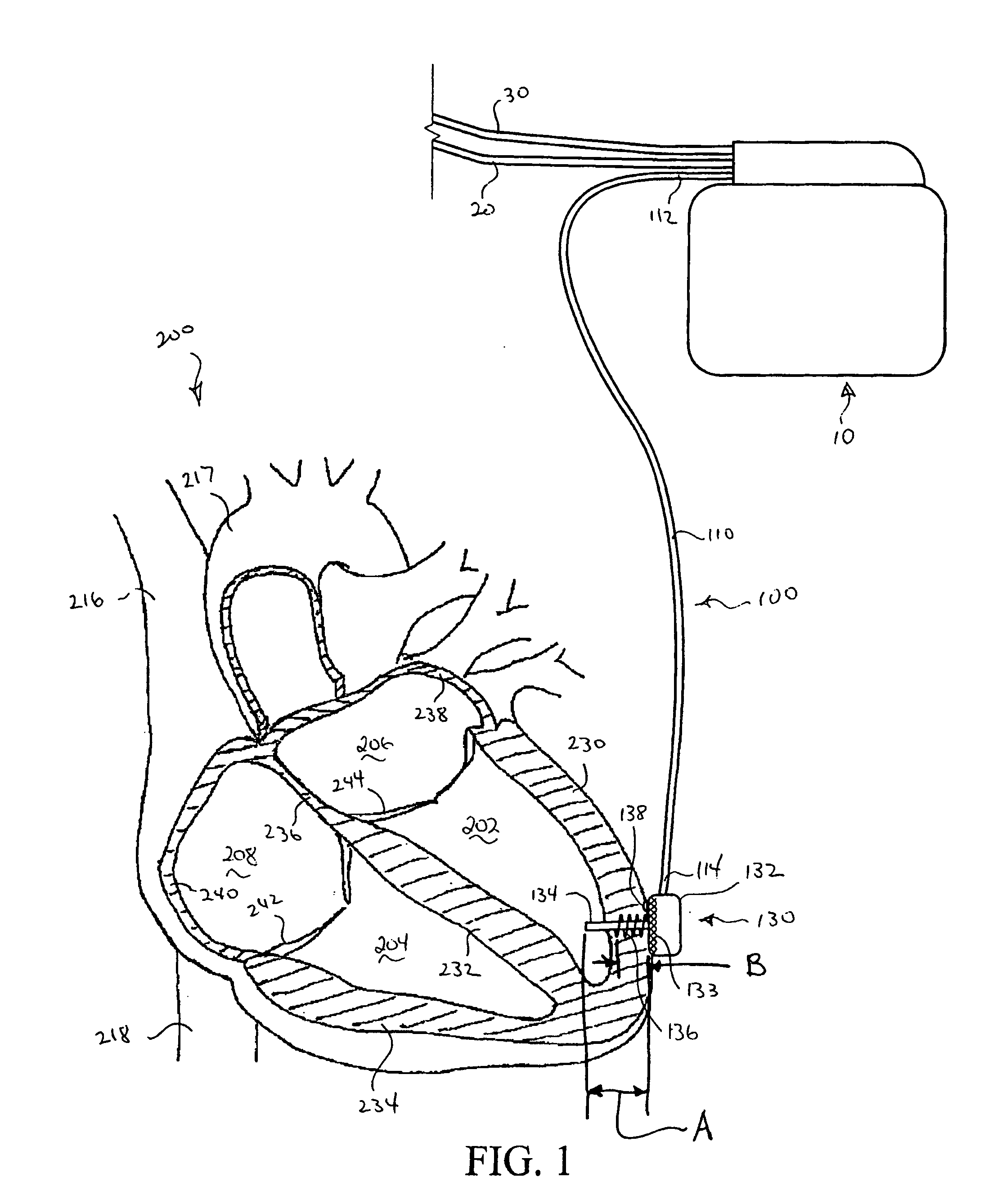
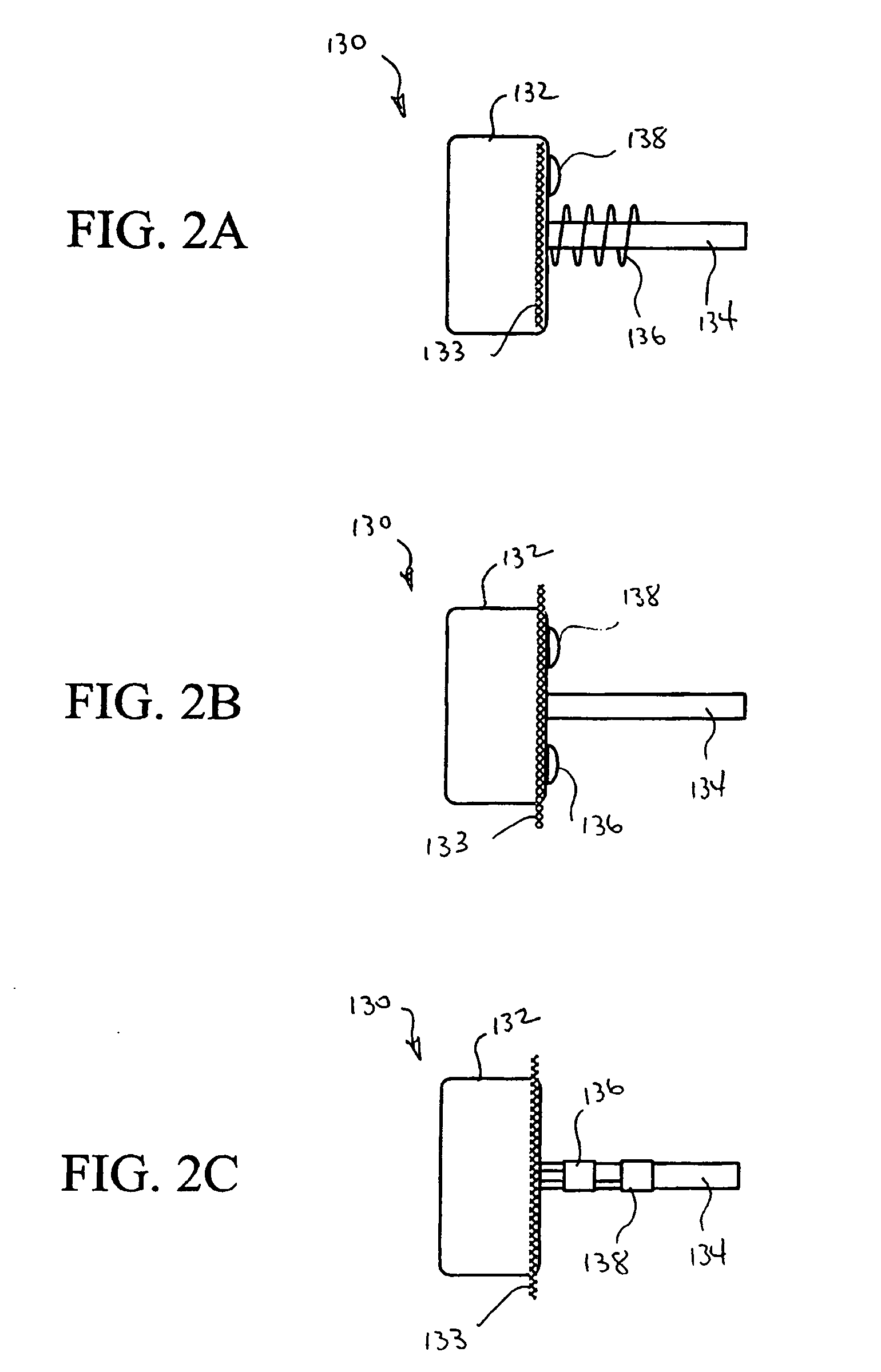
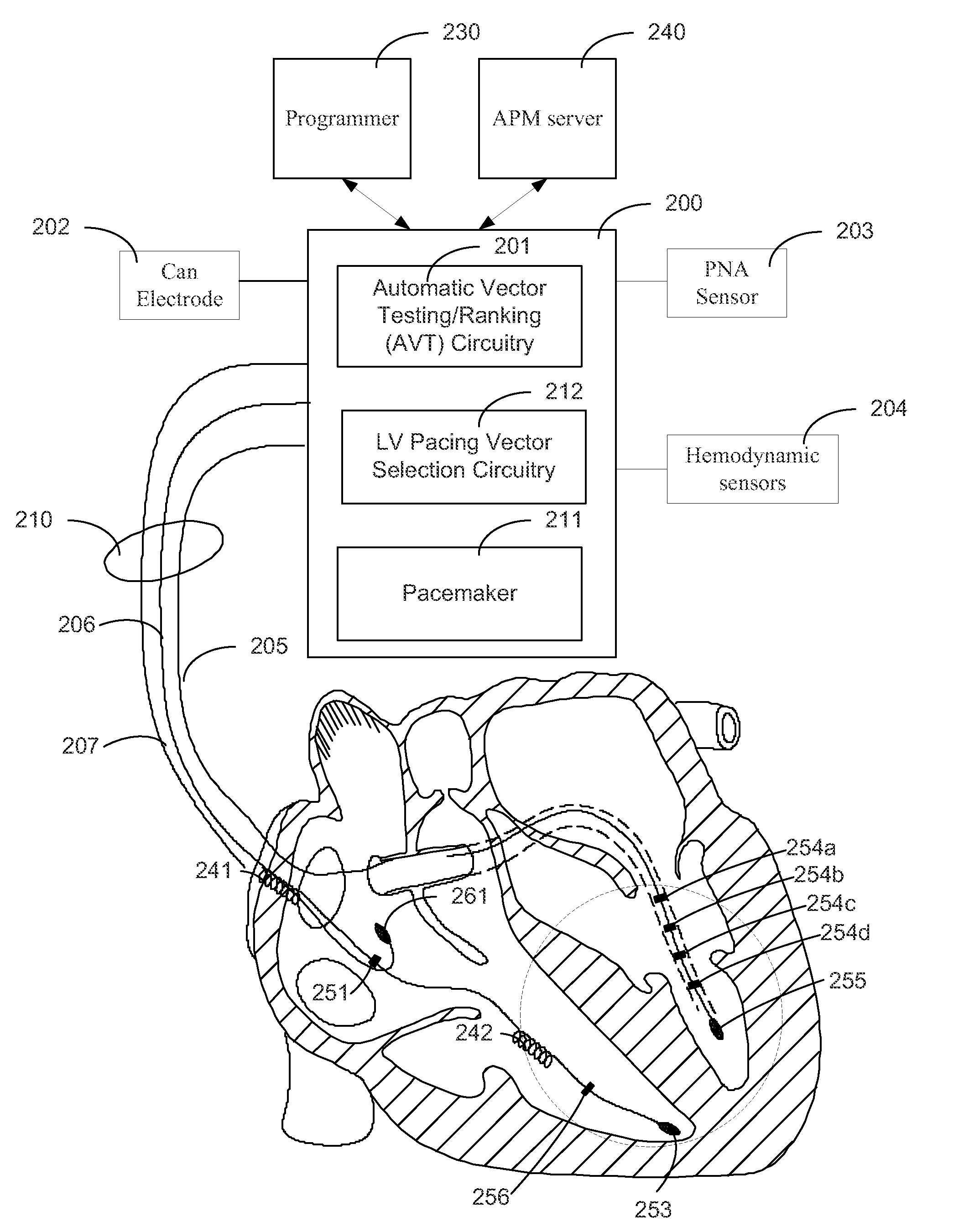
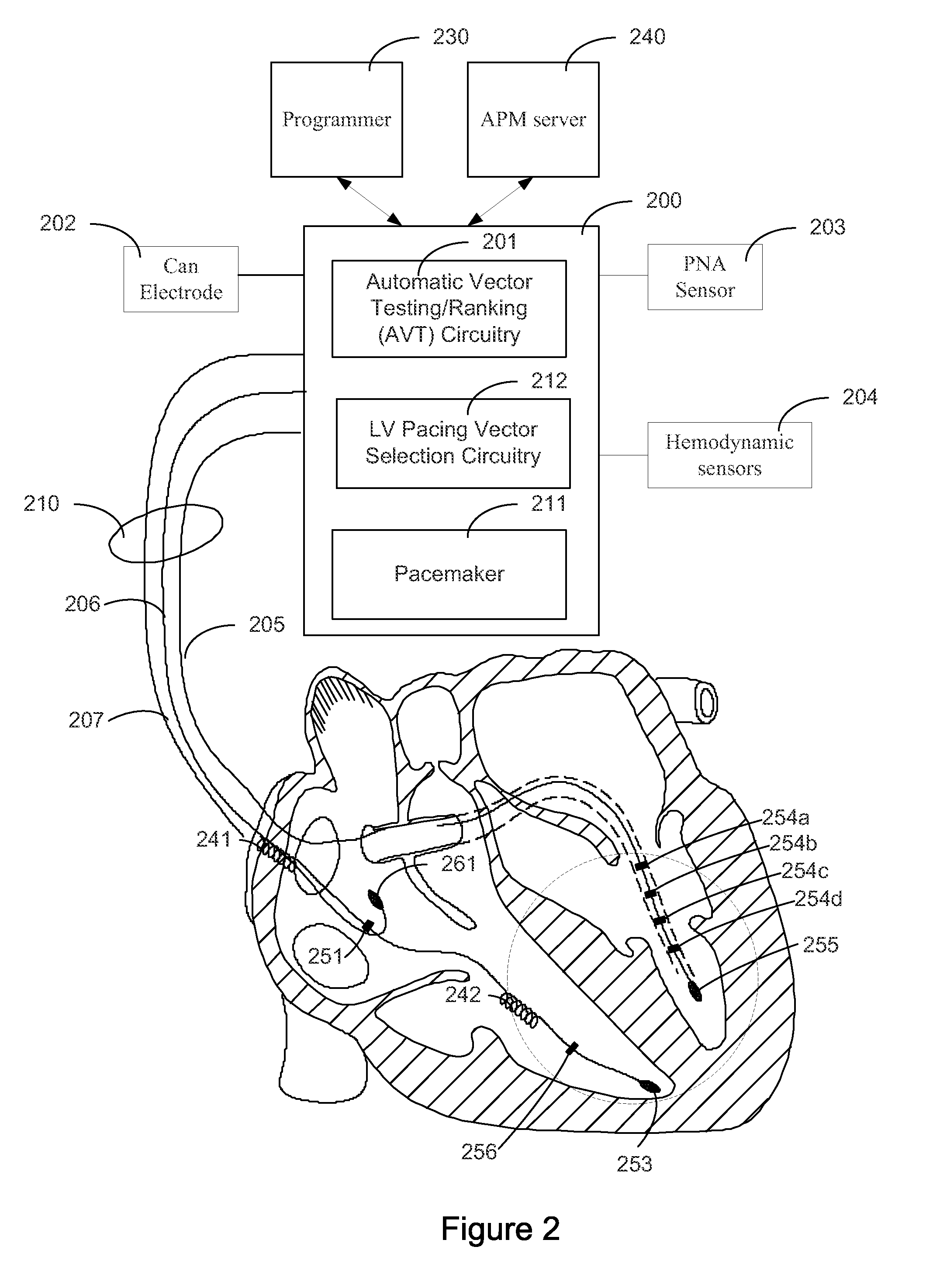
ActiveUS20110004264A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeHemodynamics
Approaches to rank potential left ventricular (LV) pacing vectors are described. Early elimination tests are performed to determine the viability of LV cathode electrodes. Some LV cathodes are eliminated from further testing based on the early elimination tests. LV cathodes identified as viable cathodes are tested further. Viable LV cathode electrodes are tested for hemodynamic efficacy. Cardiac capture and phrenic nerve activation thresholds are then measured for potential LV pacing vectors comprising a viable LV cathode electrode and an anode electrode. The potential LV pacing vectors are ranked based on one or more of the hemodynamic efficacy of the LV cathodes, the cardiac capture thresholds, and the phrenic nerve activation thresholds.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Patient identification for the pacing therapy using LV-RV pressure loop
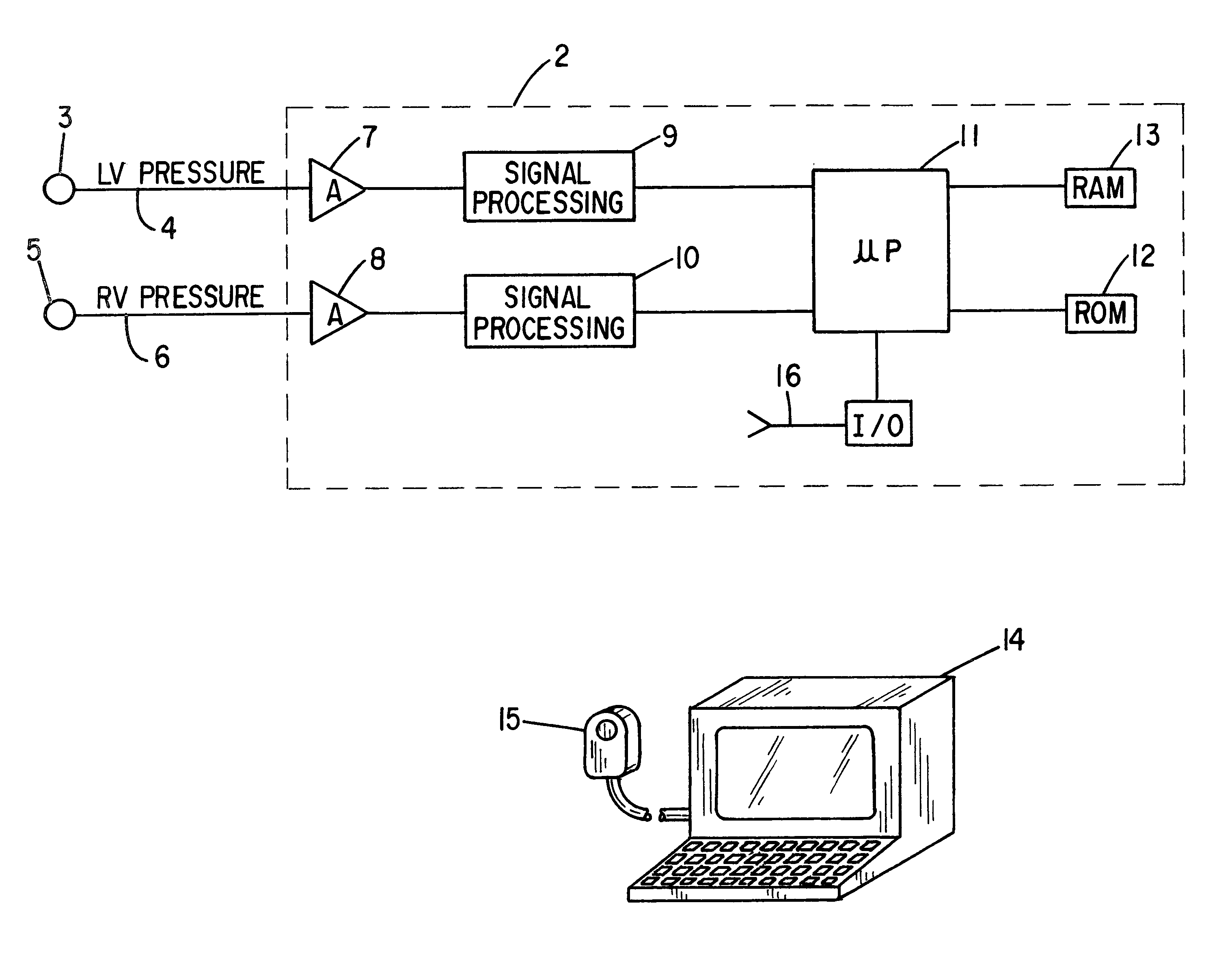
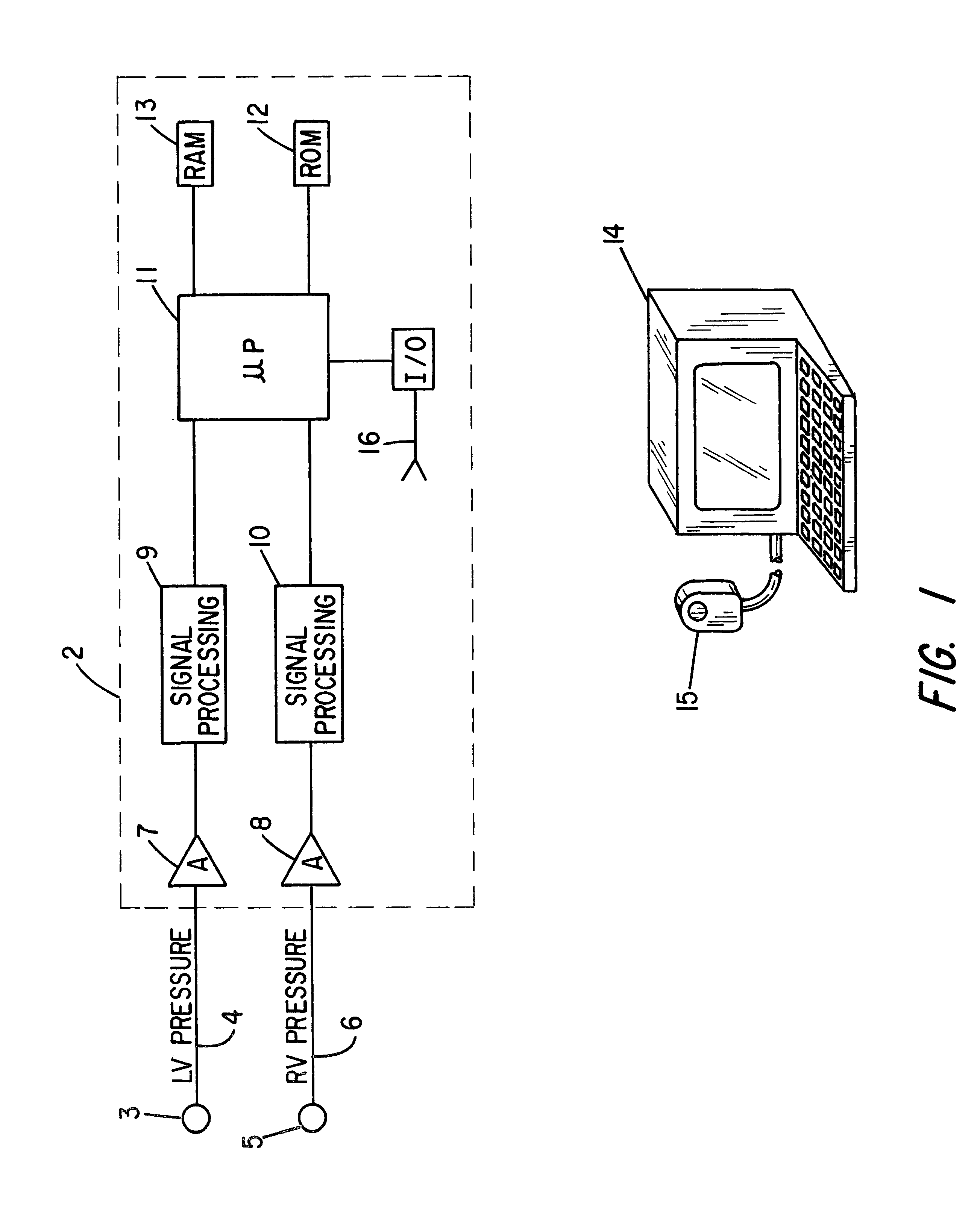
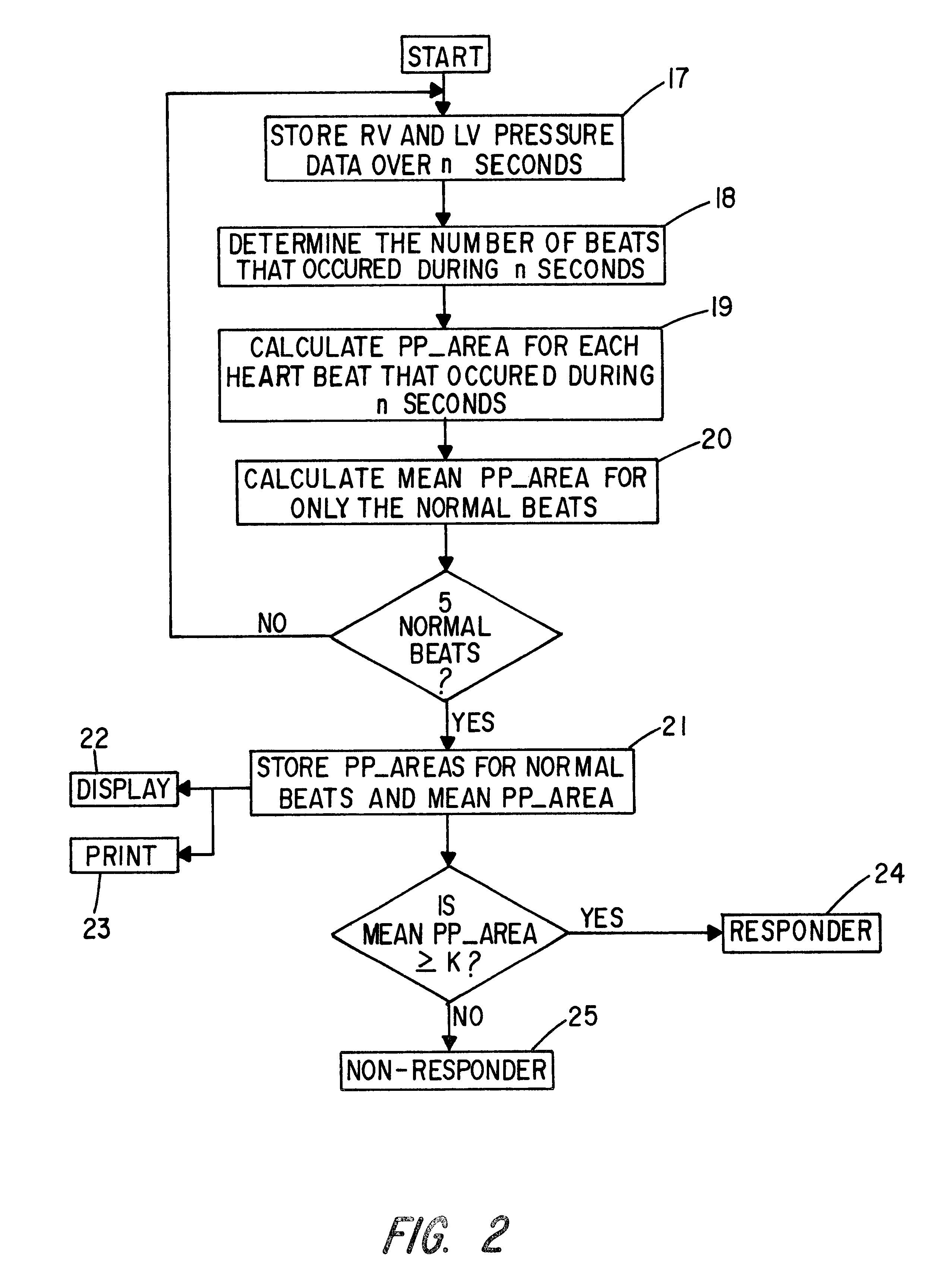
InactiveUS6280389B1Evaluation of blood vesselsCatheterLeft ventricular sizeCongestive heart failure chf
A method and apparatus for determining whether a patient with congestive heart failure (CHF) will benefit from pacing therapy through the use of an implantable cardiac rhythm management device. A patient's right ventricular and left ventricular pressures are measured, and the patient's PP_Area is calculated for each normal heartbeat that occurs during the testing period. Depending upon the value of the patient's mean PP_Area, it can be determined whether the patient will or will not respond well acutely to pacing therapy. A mean PP_Area value of greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold, which is about 0.3, indicates that the patient is a responder to pacing therapy, while a value of less than the predetermined threshold of about 0.3 indicates that the patient is a non-responder.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
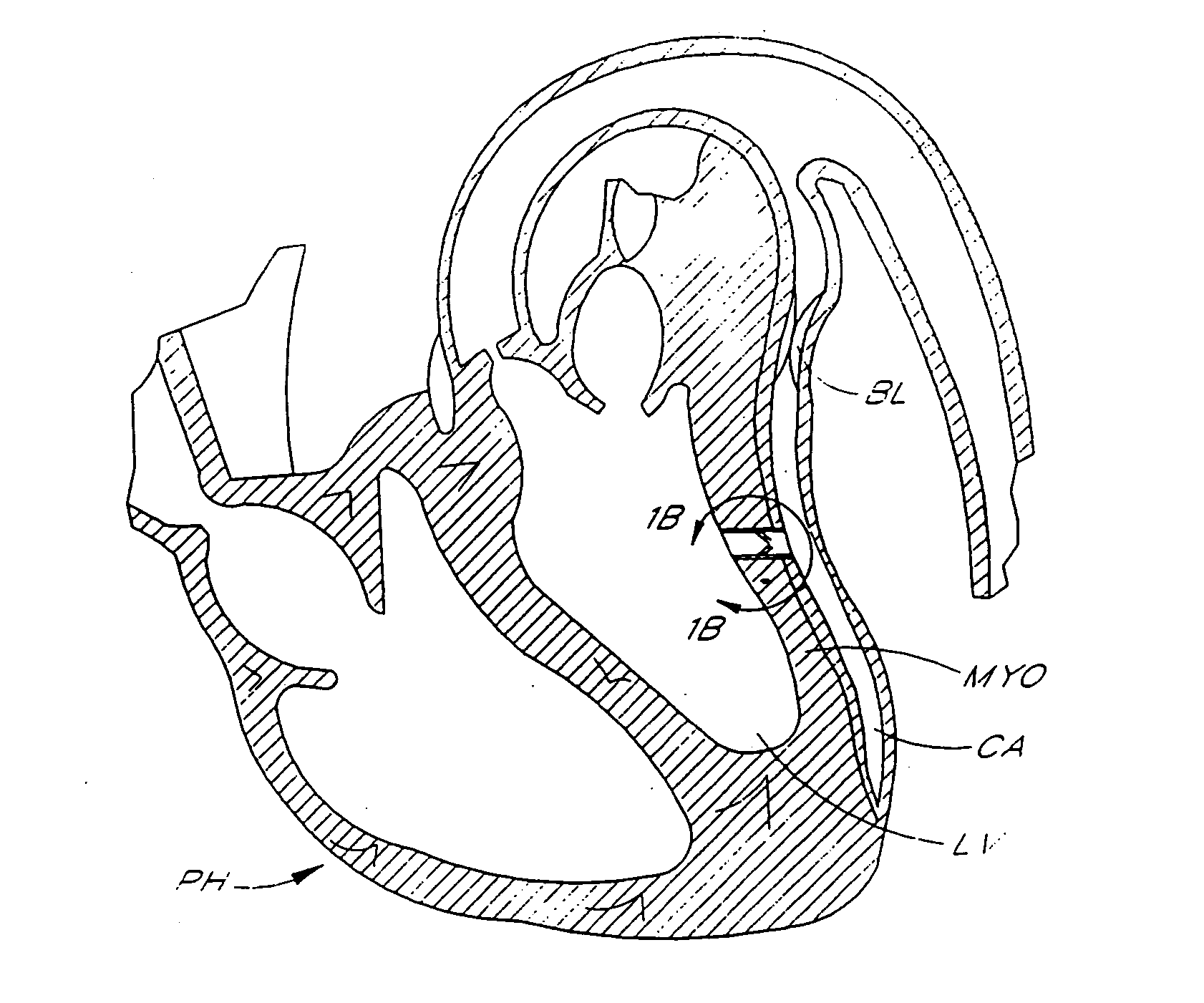
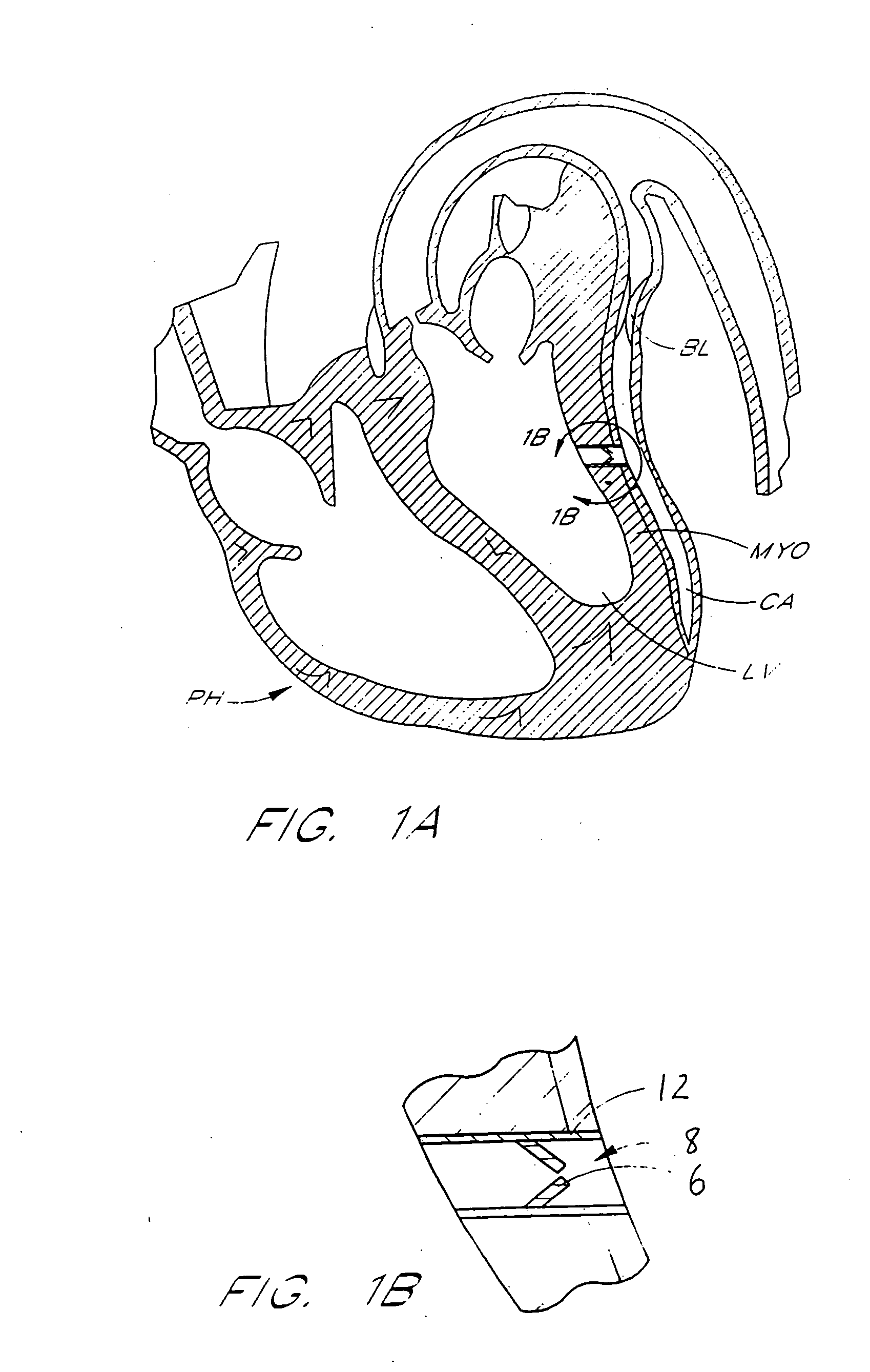
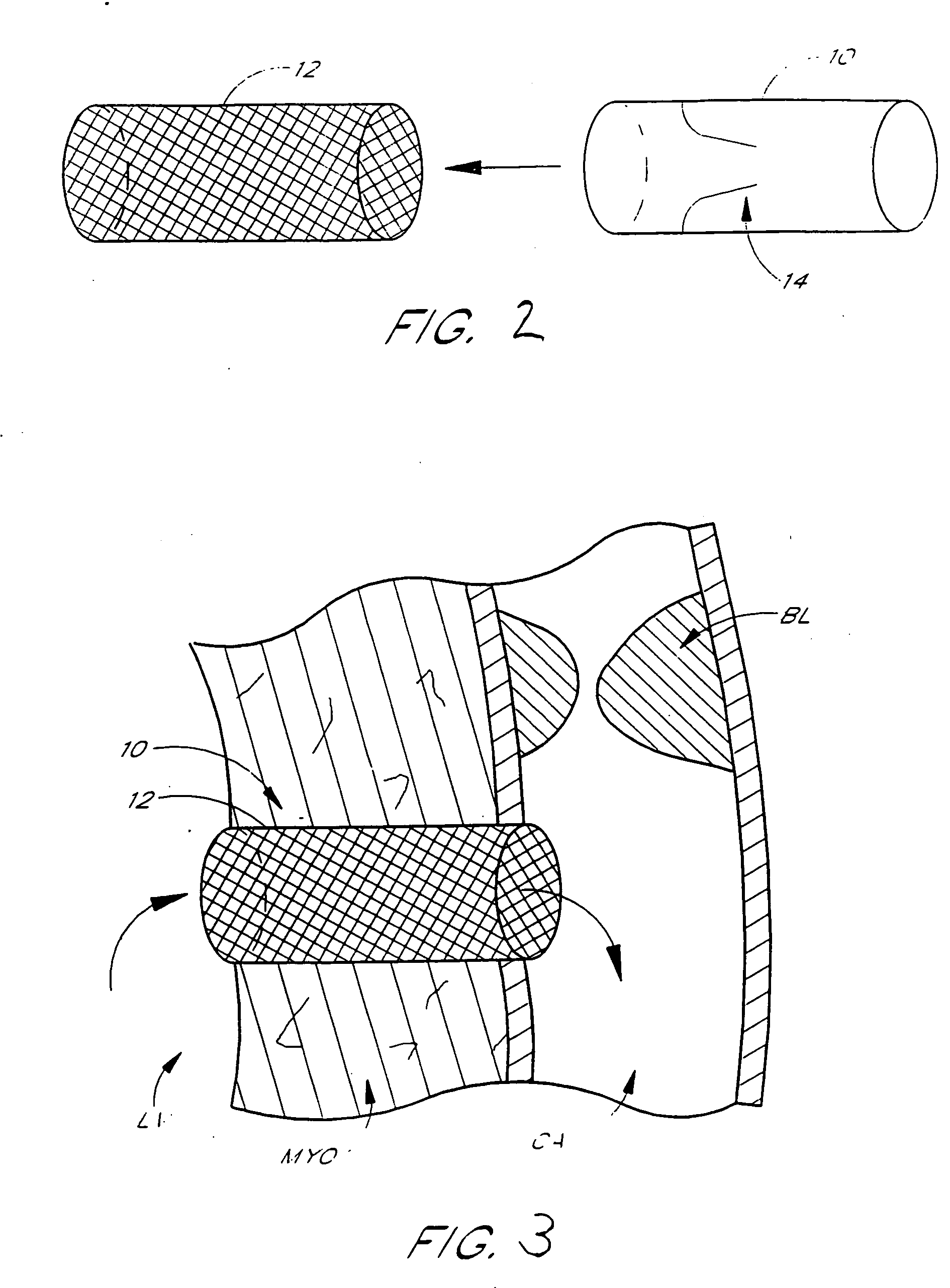
Method for percutaneous lateral access to the left ventricle for treatment of mitral insufficiency by papillary muscle alignment
InactiveUS20100210899A1Improve heart functionLower the volumeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizePapillary muscle
This invention relates to devices and methods for the therapeutic changing of the geometry of the left ventricle of the human heart. Specifically, the invention relates to the left-ventricular lateral wall introduction of an anchoring device to align the papillary muscles.
Owner:TENDYNE MEDICAL
In-vivo method and device for improving diastolic function of the left ventricle
InactiveUS7186210B2Function increaseReduce hydrostatic pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizeCardiac cycle
A method and device featuring at least one component providing a potential to kinetic converted elastic, magnetic repulsion, or, an elastic and magnetic repulsion, pushing, pulling, or, pulling and pushing, type of radially outward expansive force or pressure to an inner, outer, intermediate, and, combination thereof, wall region of the left ventricle, for reducing intraluminal hydrostatic pressure of the left ventricle (LV filling pressure) during the ventricular diastolic stage of the cardiac cycle, thereby, improving diastolic function of the left ventricle of the heart in subjects having a condition of diastolic heart failure (DHF), while minimally disturbing systolic function of the heart. The expansive force or pressure is in a range of about 5–40 mm Hg, whereby, left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is reduced down to the normal range of about 6–12 mm Hg, during ventricular diastole of the heart.
Owner:RELAXIS
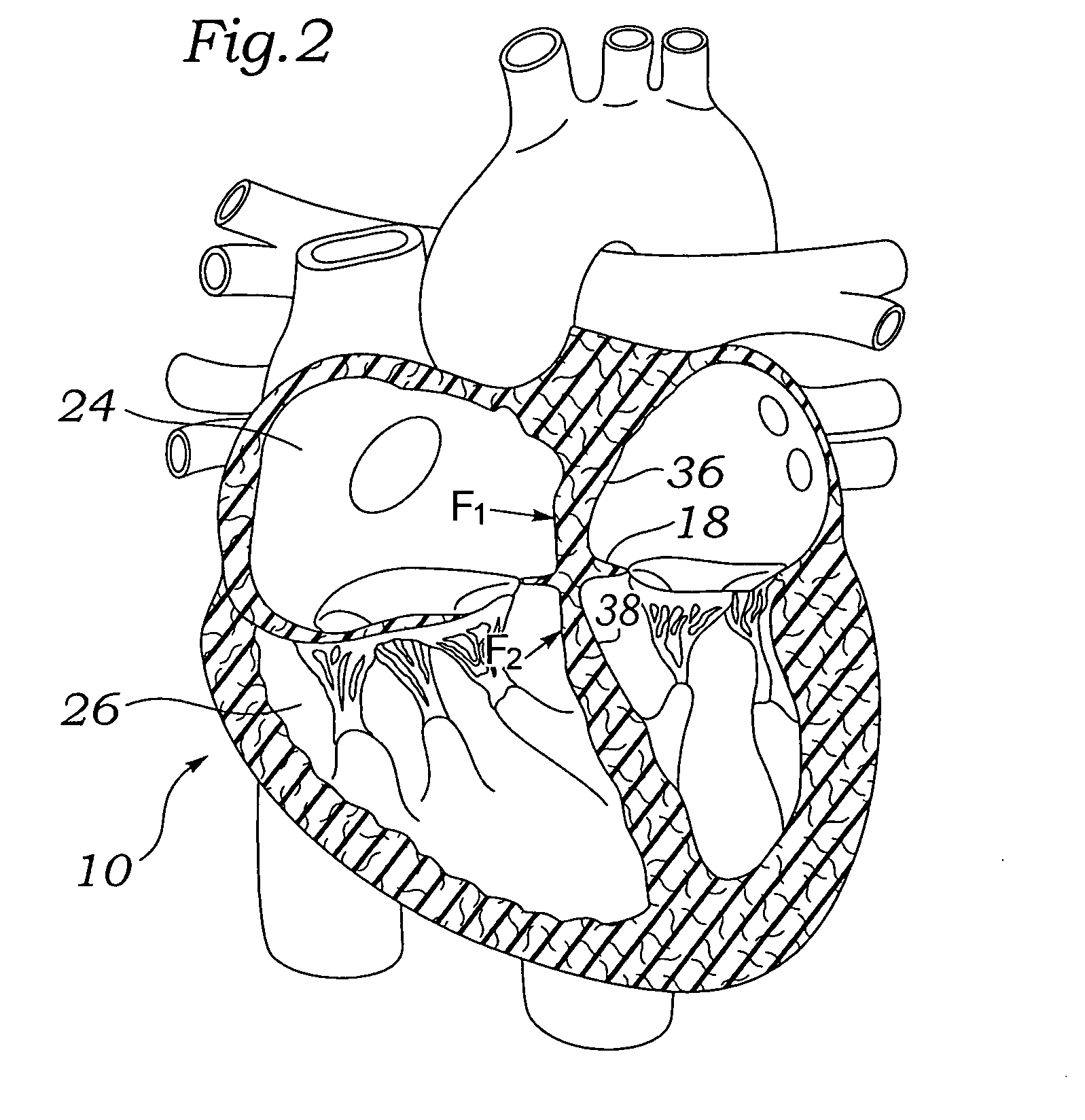
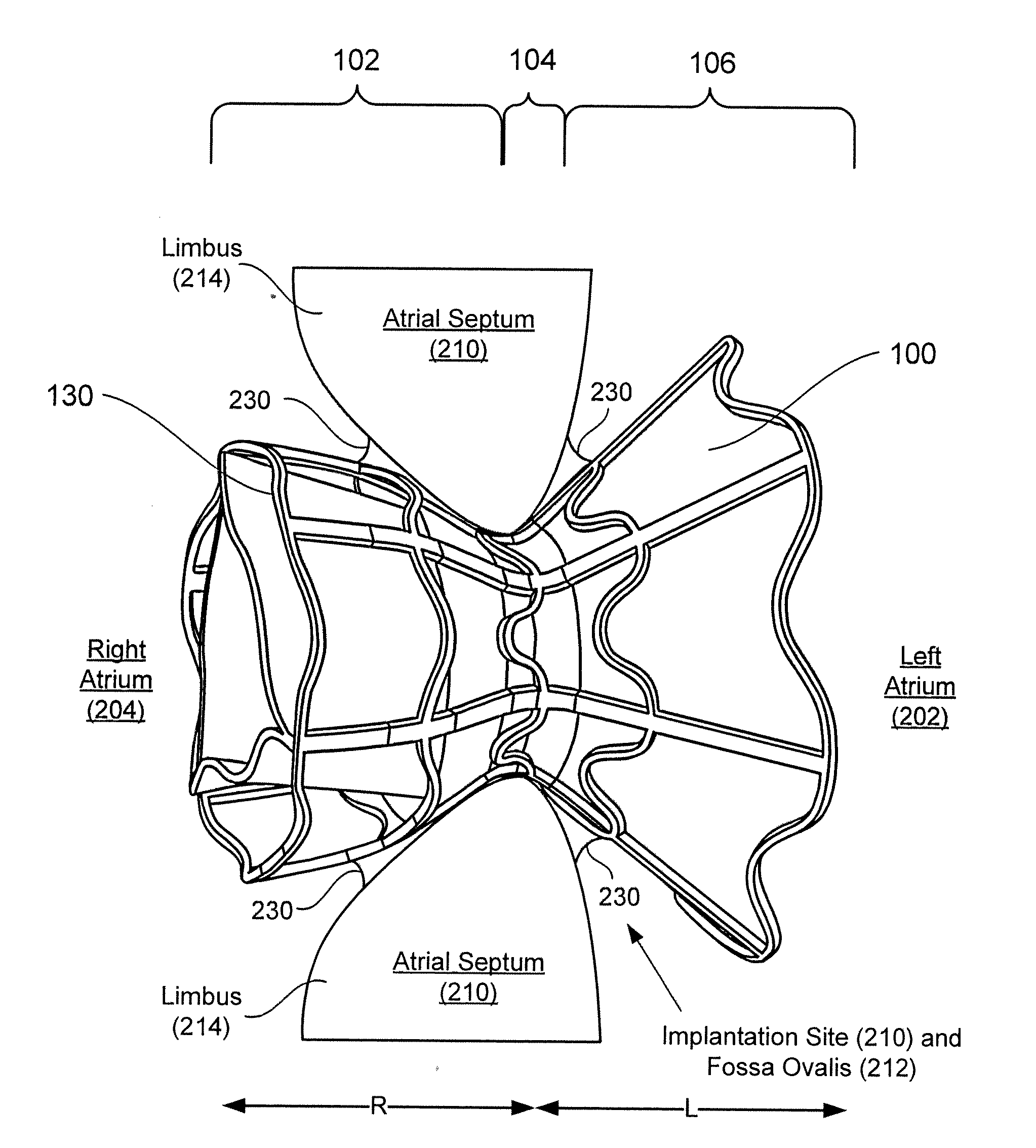
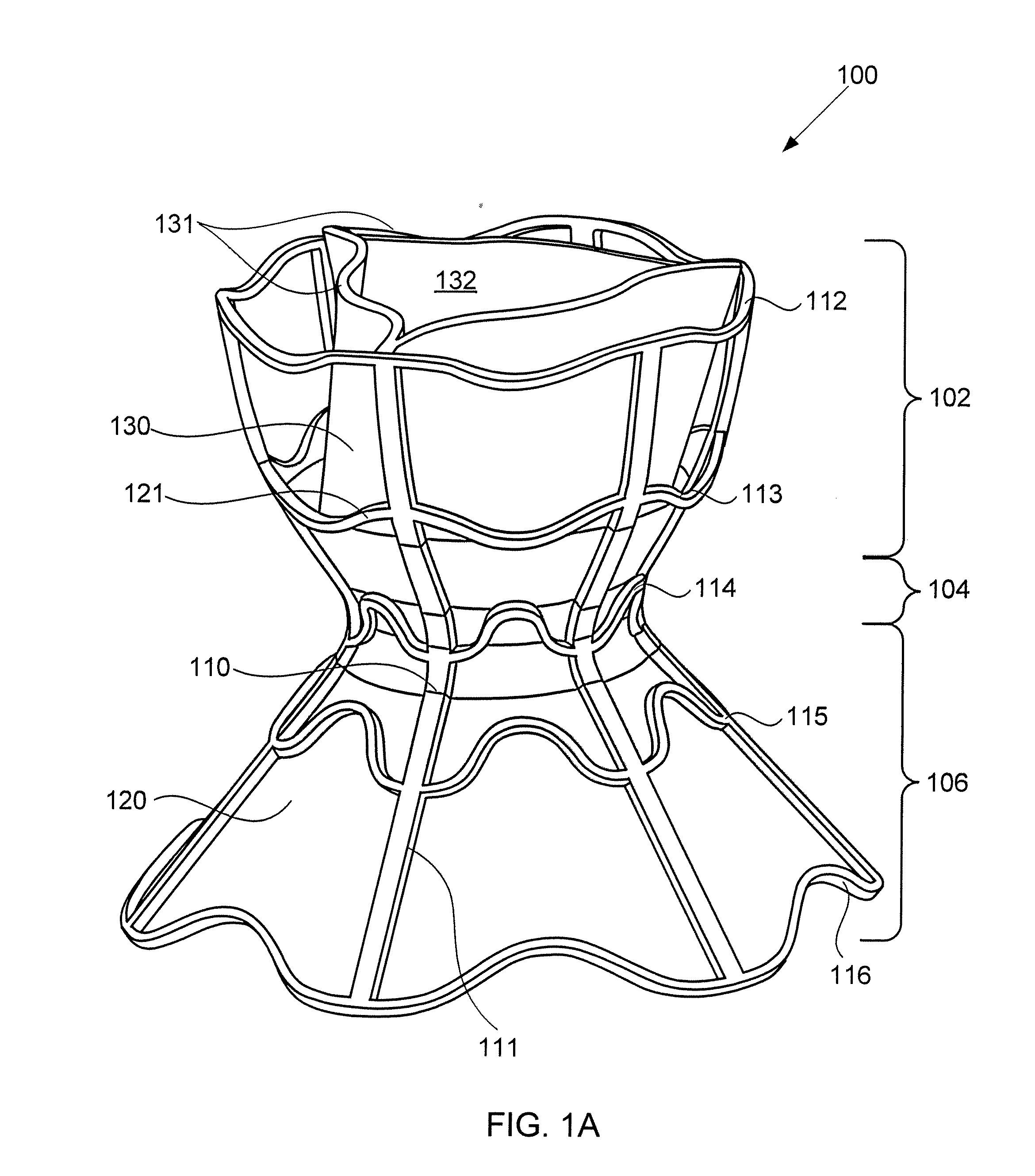
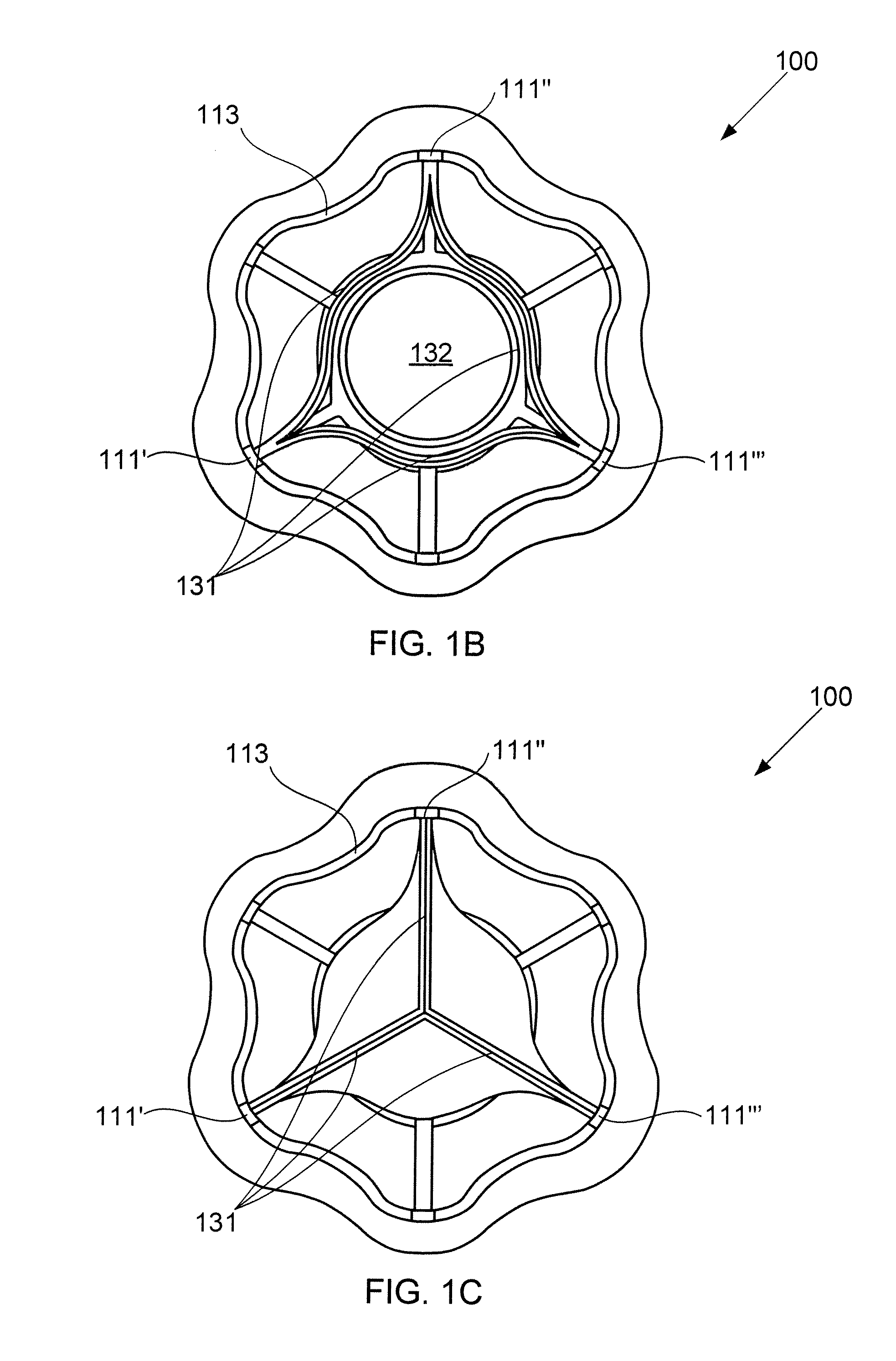
Devices for reducing left atrial pressure, and methods of making and using same
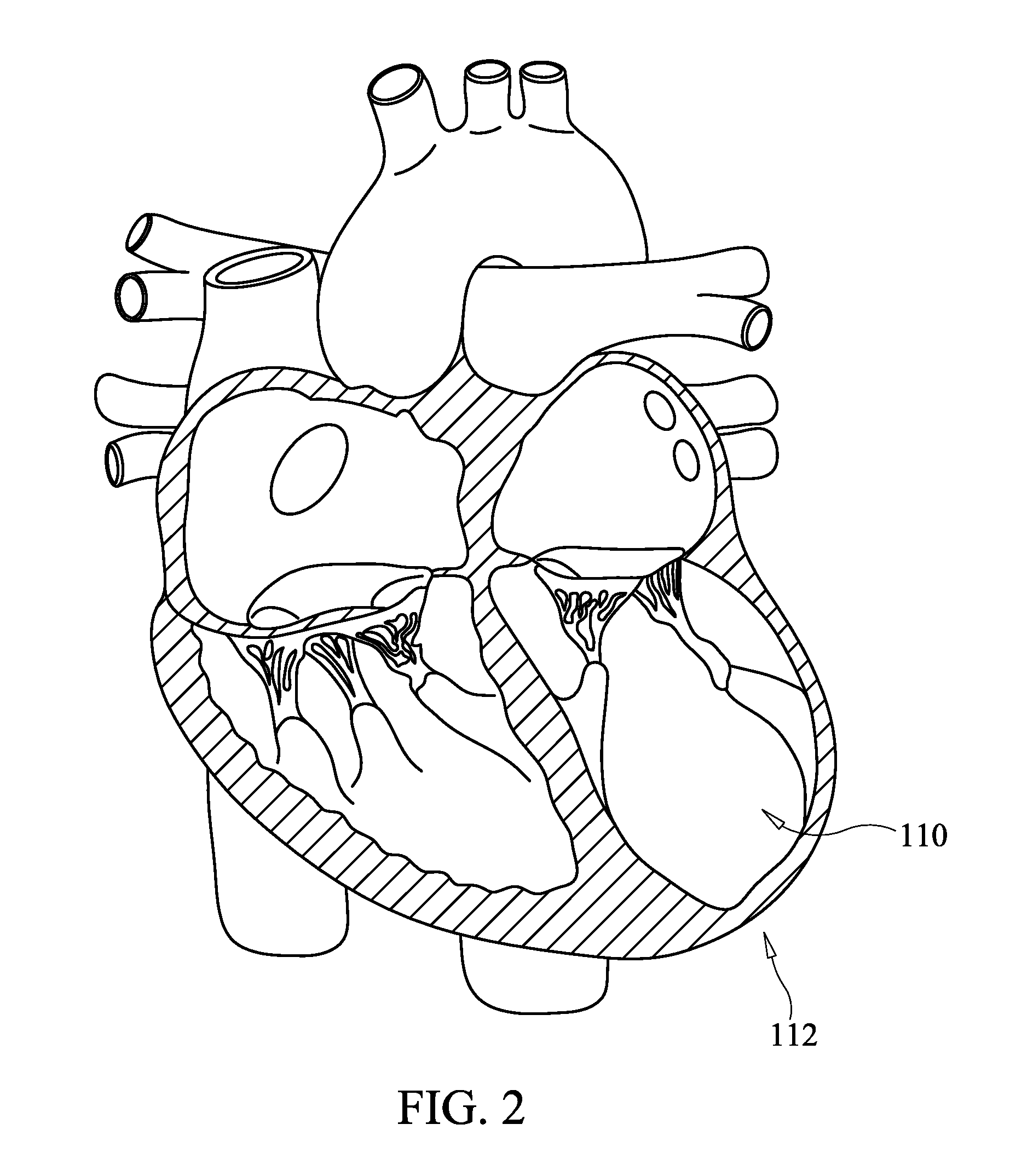
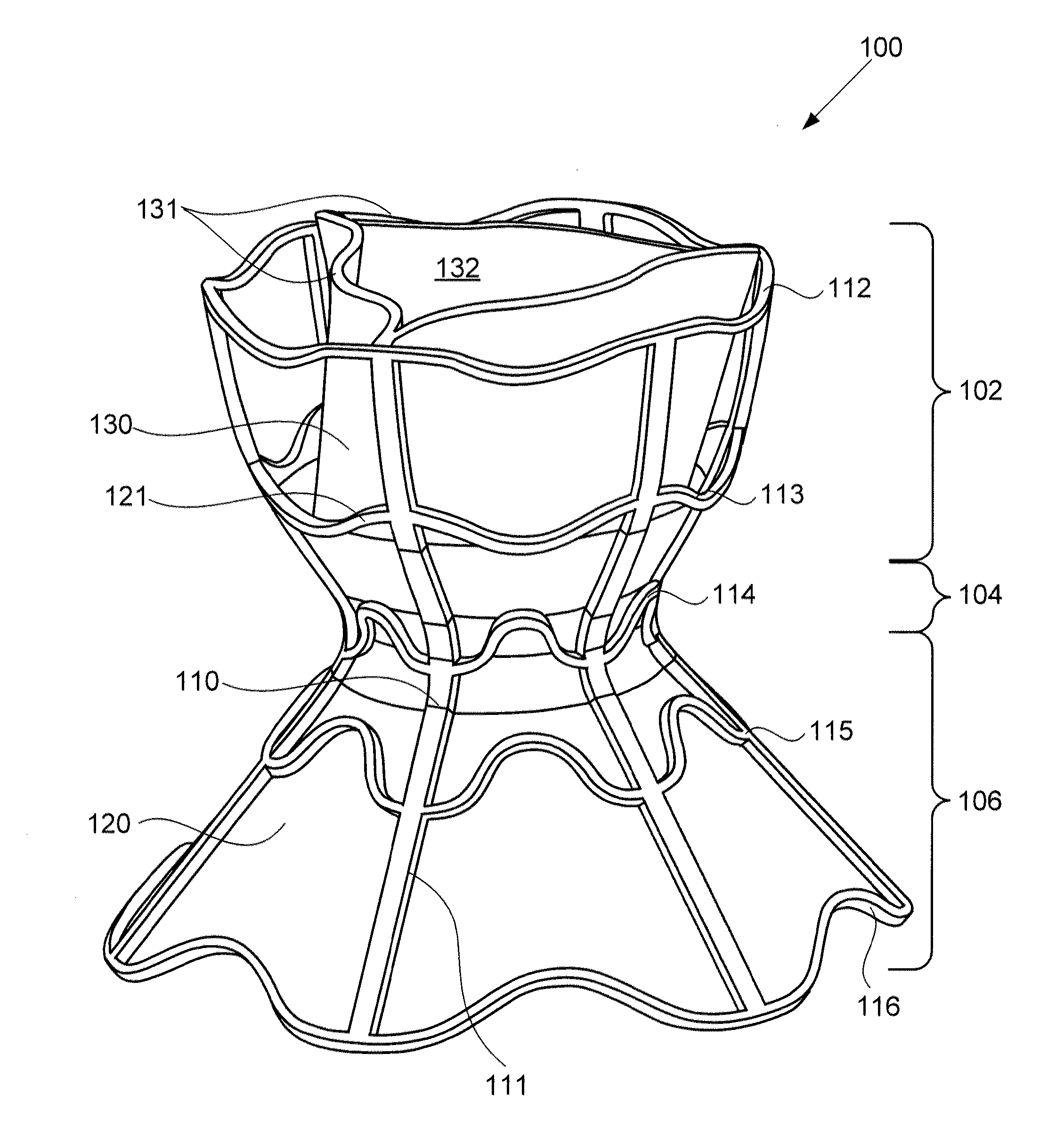
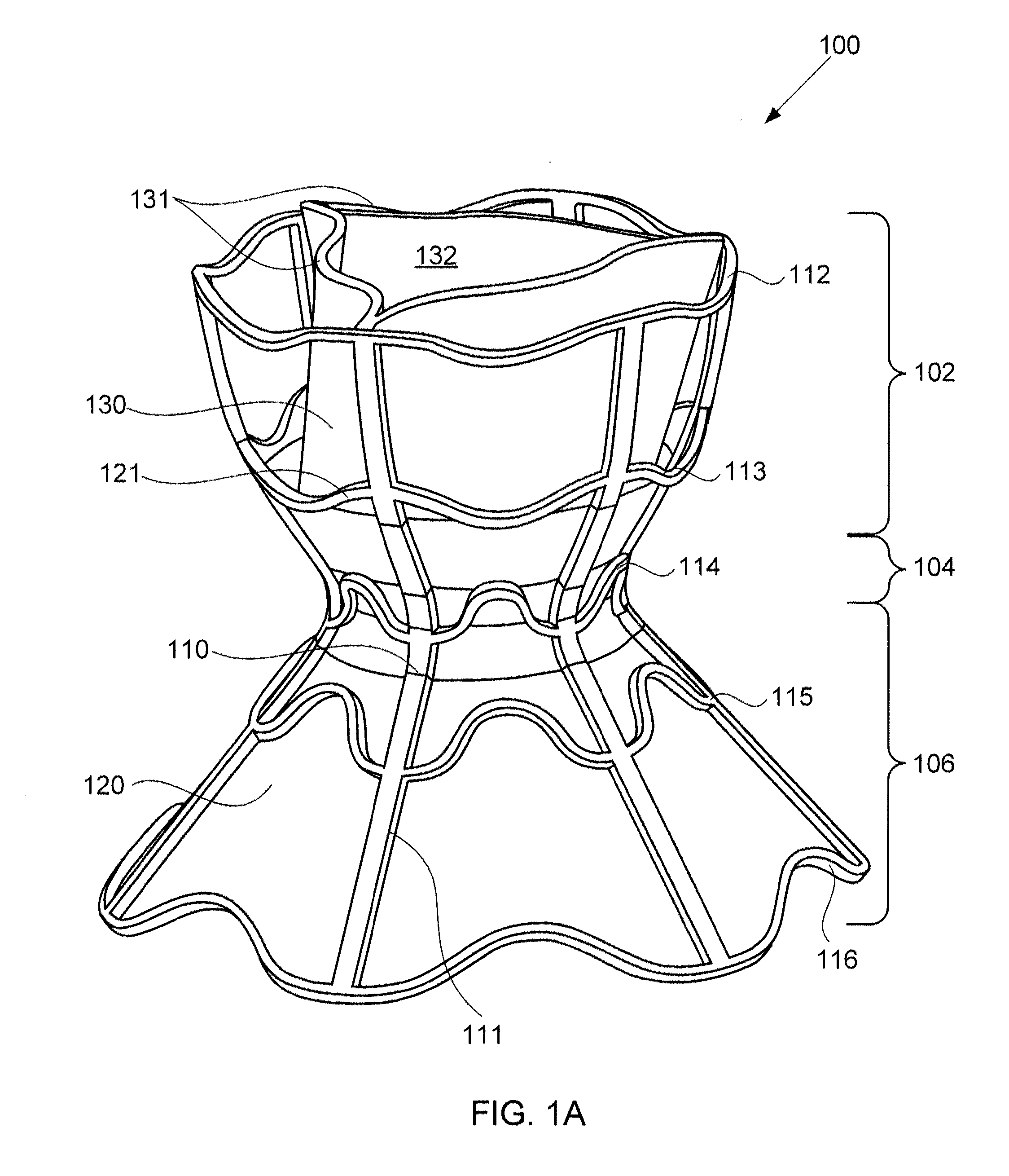
ActiveUS20120165928A1Reducing left atrial pressureIncrease cardiac outputHeart valvesSurgeryLeft ventricular sizeLeft atrial pressure
A device for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an hourglass-shaped stent comprising a neck region and first and second flared end regions, the neck region disposed between the first and second end regions and configured to engage the fossa ovalis of the patient's atrial septum; and a one-way tissue valve coupled to the first flared end region and configured to shunt blood from the left atrium to the right atrium when blood pressure in the left atrium exceeds blood pressure in the right atrium. The inventive devices may reduce left atrial pressure and left ventricular end diastolic pressure, and may increase cardiac output, increase ejection fraction, relieve pulmonary congestion, and lower pulmonary artery pressure, among other benefits. The inventive devices may be used, for example, to treat subjects having heart failure, pulmonary congestion, or myocardial infarction, among other pathologies.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Optimization method for cardiac resynchronization therapy
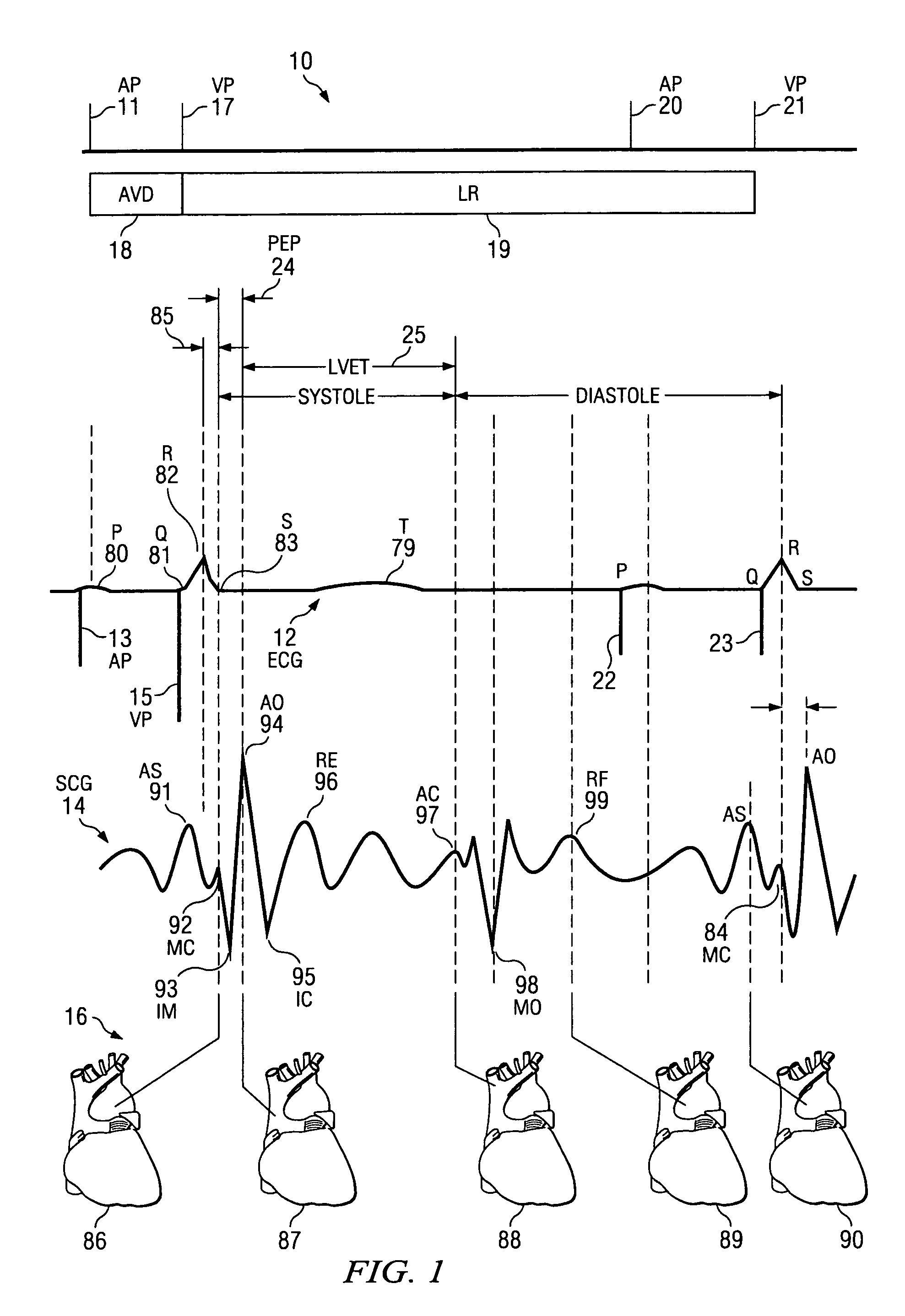
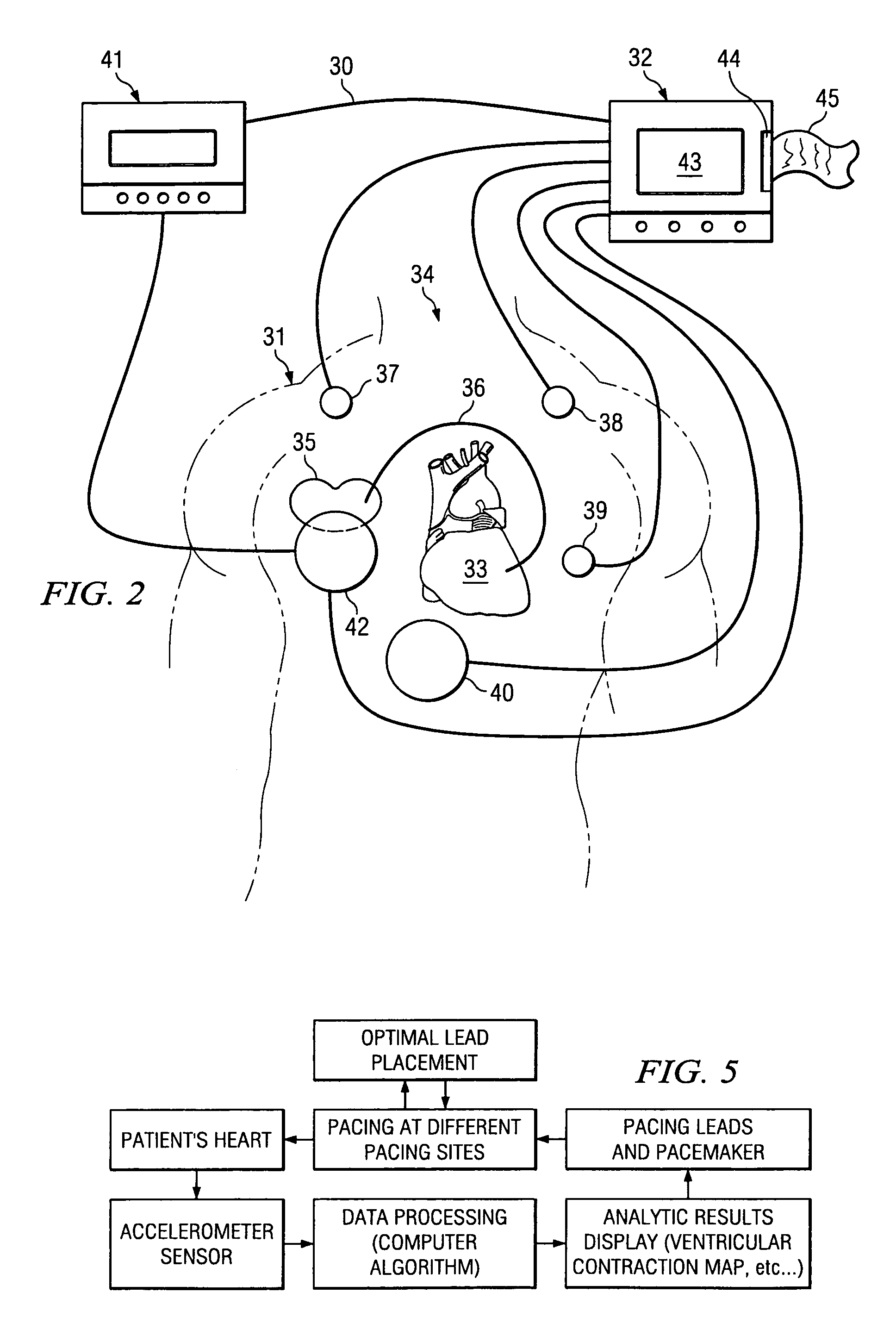
ActiveUS6978184B1Shortening of pre-ejection periodIncrease in rate of contractionInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
The patterns of contraction and relaxation of the heart before and during left ventricular or biventricular pacing are analyzed and displayed in real time mode to assist physicians to screen patients for cardiac resynchronization therapy, to set the optimal A-V or right ventricle to left ventricle interval delay, and to select the site(s) of pacing that result in optimal cardiac performance. The system includes an accelerometer sensor; a programmable pace maker, a computer data analysis module, and may also include a 2D and 3D visual graphic display of analytic results, i.e. a Ventricular Contraction Map. A feedback network provides direction for optimal pacing leads placement. The method includes selecting a location to place the leads of a cardiac pacing device, collecting seismocardiographic (SCG) data corresponding to heart motion during paced beats of a patient's heart, determining hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters based on the SCG data, repeating the preceding steps for another lead placement location, and selecting a lead placement location that provides the best cardiac performance by comparing the calculated hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters for each different lead placement location.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL +1
Method and apparatus for monitoring left ventricular work or power
A body implantable system employs a lead system having at least one electrode and at least one thermal sensor at a distal end. The lead system is implanted within a patient's heart in a coronary vein of the left ventricle. The thermal sensor can be attached to a catheter that is disposed within an open lumen of the lead system. The thermal sensor senses a coronary vein temperature. The coronary vein temperature can be measured at a detector / energy delivery system and used as an activity indicator to adaptively control pacing rate. The measured coronary vein temperature can be also used with a left ventricular flow measurement to determine hemodynamic efficiency of the heart. A detected change in hemodynamic efficiency can be used by the detector / energy delivery system to modify the delivery of electrical pulses to the lead system.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apical Papillary Msucle Attachment for Left Ventricular Reduction
InactiveUS20100185278A1Improve heart functionLower the volumeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizePapillary muscle
This invention relates to devices and methods for the therapeutic changing of the geometry of the left ventricle of the human heart. Specifically, the invention relates to the apical introduction of an anchoring device to align the papillary muscles.
Owner:TENDYNE MEDICAL
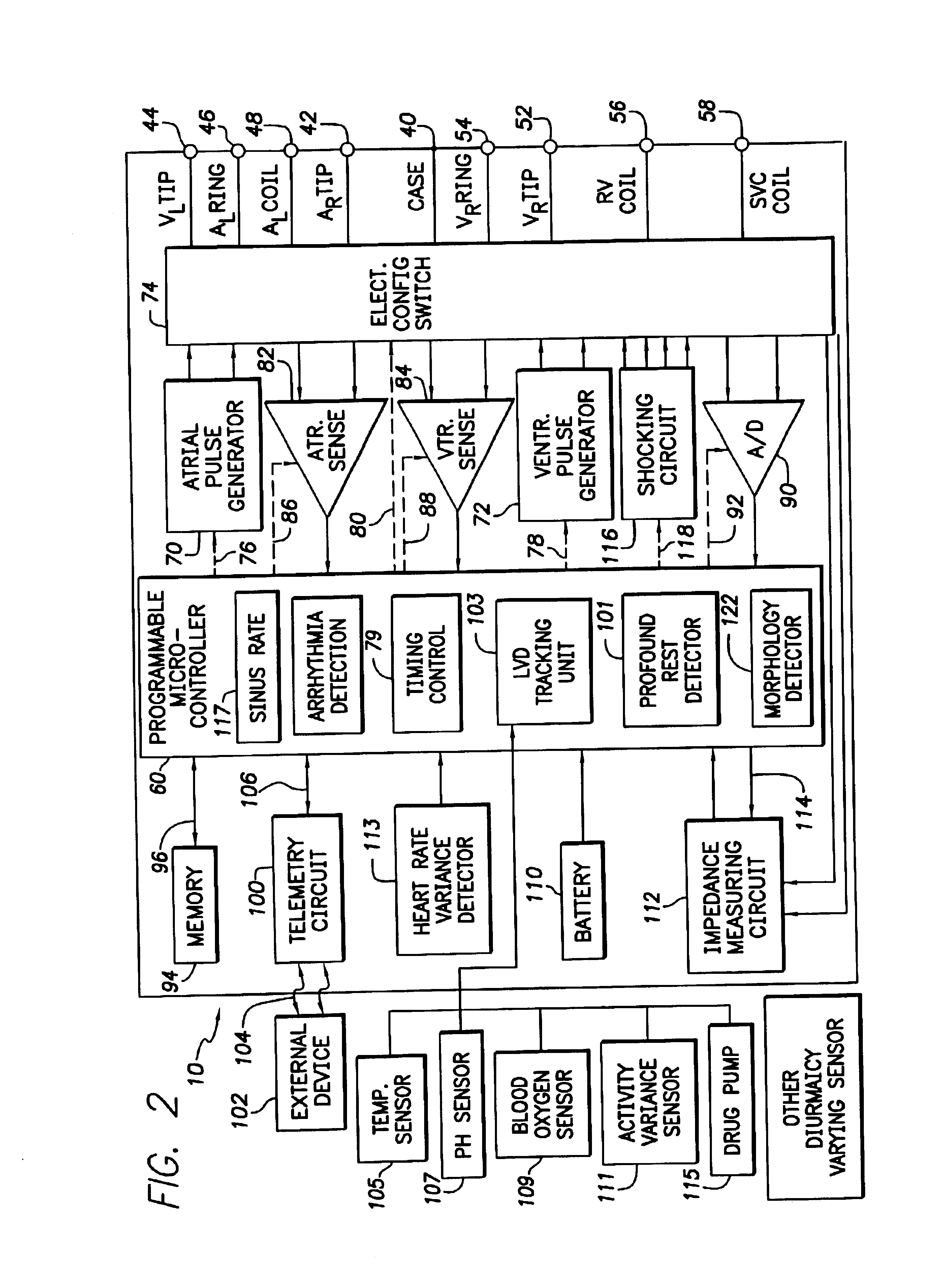
System and method for tracking progression of left ventricular dysfunction using implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS6922587B2Accurate and reliable assessmentAlter heart contractilityHeart stimulatorsPost extrasystolic potentiationCardiac pacemaker electrode
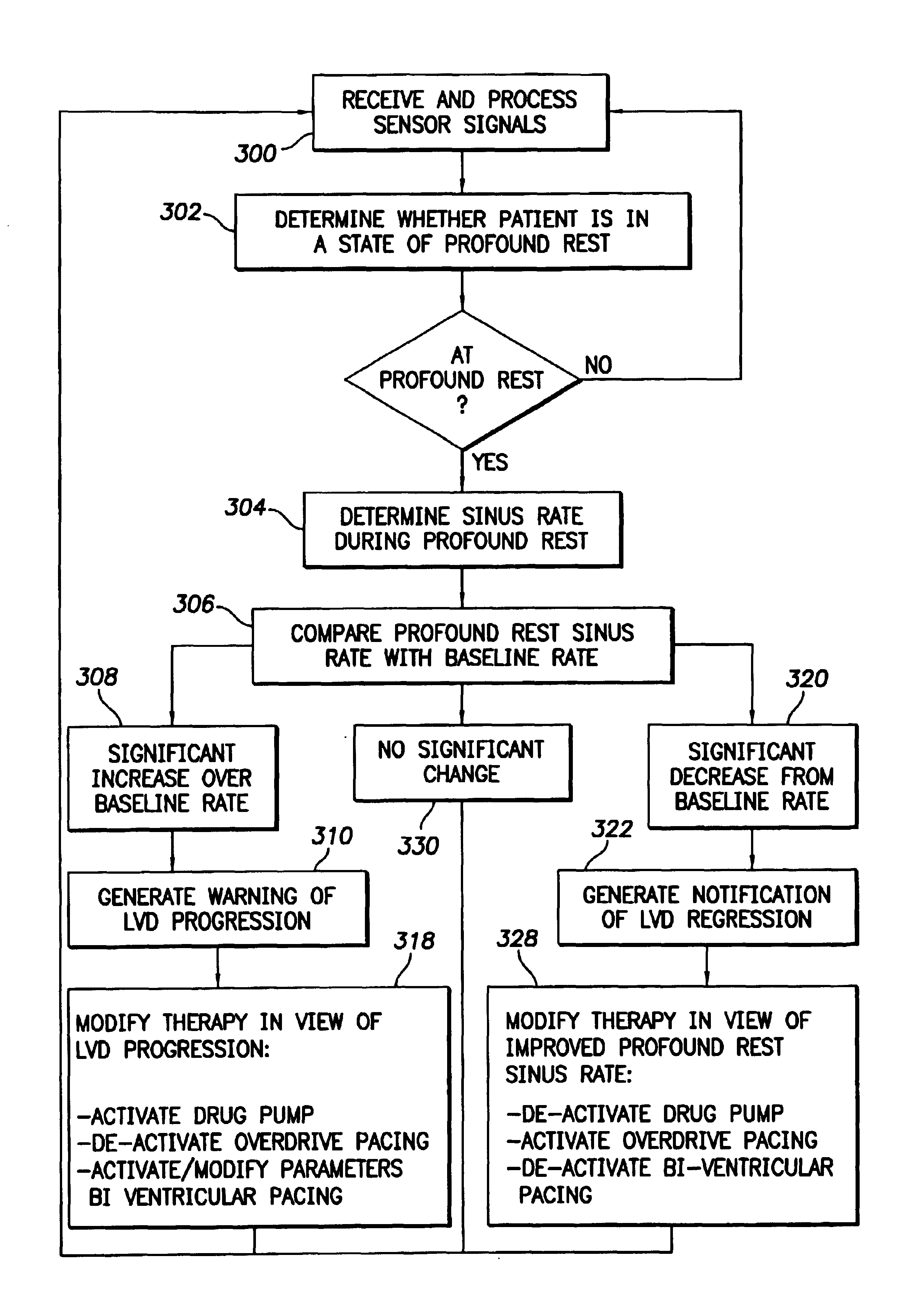
The progression or regression of left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) is automatically evaluated by a pacemaker or other implantable cardiac stimulation device by tracking changes in the resting sinus rate of the patient in which the device is implanted. The resting sinus rate is detected by first determining whether the patient is in a state of profound rest, such as sleep, then measuring the actual sinus rate during profound rest. Profound rest may be detected by using an activity variance sensor. An increase in the profound rest sinus rate over a period of several months indicates progression of LVD; whereas a decrease indicates regression. Appropriate LVD diagnostic information is recorded for subsequent review by a physician. Based on the progression or regression of LVD, the physician may then modify LVD drug therapy administered to the patient or may adjust control parameters of the pacemaker, such as overdrive pacing control parameters or control parameters affecting heart contractility via post-extrasystolic potentiation. If a drug pump is implanted within the patient for automatically delivering LVD drug therapy, the pacemaker controls the drug pump in view of any detected progression or regression of LVD. The technique may also be used to verify the efficacy of LVD drug therapy administered to the patient, whether delivered via an implanted drug pump or otherwise. Processing may be primarily performed within the implanted device itself or with an external programmer in communication with the implanted device. Activity state-based LVD tracking techniques are also set forth.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
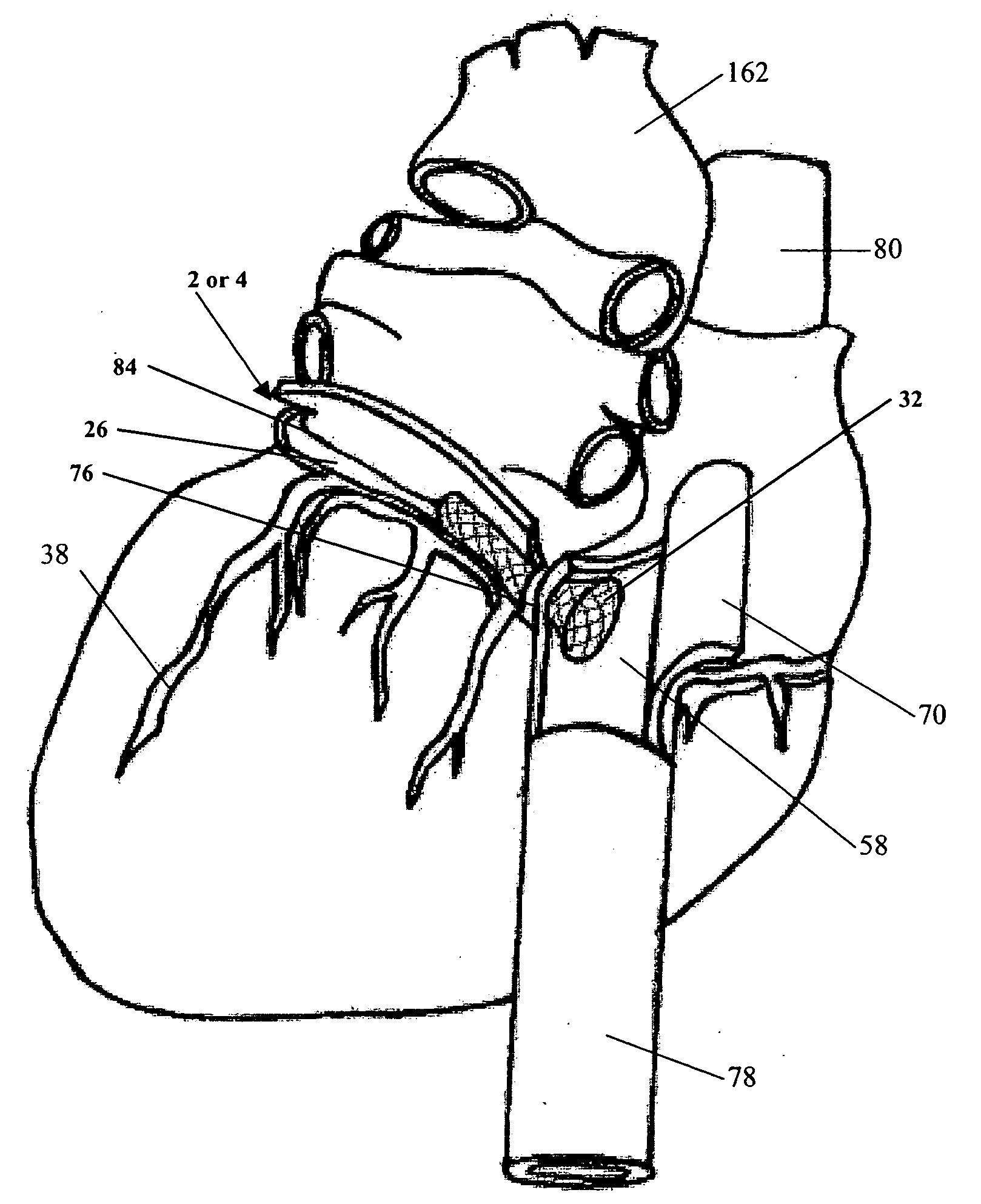
Left ventricular conduit with blood vessel graft
Disclosed is a conduit that provides a bypass around an occlusion or stenosis in a coronary artery. The conduit is a tube adapted to be positioned in the heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a heart chamber and a coronary artery, at a site distal to the occlusion or stenosis. The conduit has a section of blood vessel attached to its interior lumen which preferably includes at least one naturally occurring one-way valve positioned therein. The valve prevents the backflow of blood from the coronary artery into the heart chamber.
Owner:JENAVALVE TECH INC
Medical devices having superhydrophobic surfaces, superhydrophilic surfaces, or both
InactiveUS20070005024A1Reduce frictionLower resistanceMedical devicesCatheterUrinary catheterLeft ventricular size
According to an aspect of the invention, medical devices are provided, which have the following (a) one or more superhydrophobic surface regions, (b) one or more superhydrophilic surface regions having a durometer of at least 40 A, or (c) a combination of one or more superhydrophobic surface regions and one or more superhydrophilic surface regions having a durometer of at least 40 A. Such surfaces are created, for example, to provide reduced resistance to the movement of adjacent materials, including adjacent fluids and solids. Examples of medical device surface regions benefiting from the present invention include, for example, outside and / or inside (luminal) surfaces of the following: vascular catheters, urinary catheters, hydrolyser catheters, guide wires, pullback sheaths, left ventricular assist devices, endoscopes, airway tubes and injection needles, among many other devices.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Mechanical ventricular pacing capture detection for a post extrasystolic potentiation (PESP) pacing therapy using at least one lead-based accelerometer
InactiveUS20080234771A1Improve cardiac perfusionDecrease in cardiac performanceCatheterHeart stimulatorsPost extrasystolic potentiationAccelerometer
A system and method for monitoring at least one chamber of a heart (e.g., a left ventricular chamber) during delivery of extrasystolic stimulation to determine if the desired extra-systole (i.e., ventricular mechanical capture following refractory period expiration) occurs. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads such as epicardial, endocardial, and / or coronary sinus leads equipped with motion sensor(s). The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of chamber capture resulting from one or more pacing stimulus delivered closely following expiration of the refractory period. A threshold optimization method optionally evaluates capture and at least one of: runs an iterative routine to establish or re-establish chamber capture for the PESP therapy, sets a logical flag relating to chamber capture status and stores parameter(s) relating to successful chamber capture for one or more subsequent cardiac cycles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device and method for mitral valve repair
InactiveUS20100030330A1The implementation process is simpleLess criticalBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsPosterior leafletLeft ventricular size
Devices and methods for reshaping a mitral valve annulus are provided. One device according to the invention is configured for deployment in the right atrium and is shaped to apply a force along the atrial septum. The device causes the atrial septum to deform and push the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve in a posterior direction for reducing mitral valve regurgitation. Another embodiment of a device is deployed in the left ventricular outflow tract at a location adjacent the aortic valve. The device may be expandable for urging the anterior leaflet toward the posterior leaflet. Another embodiment of the device includes a first anchor, a second anchor, and a bridge, with the bridge having sufficient length to reach from the coronary sinus to the right atrium and / or superior or inferior vena cava. In a further embodiment a device includes a middle anchor positioned on the bridge between the distal and proximal anchors.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Devices for reducing left atrial pressure having biodegradable constriction, and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS20130030521A1Reducing left atrial pressureIncrease cardiac outputHeart valvesSurgeryLeft ventricular sizeLeft atrial pressure
A device for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an hourglass-shaped stent comprising a neck region and first and second flared end regions, the neck region disposed between the first and second end regions and configured to engage the fossa ovalis of the patient's atrial septum; and a one-way tissue valve coupled to the first flared end region and configured to shunt blood from the left atrium to the right atrium when blood pressure in the left atrium exceeds blood pressure in the right atrium. The inventive device may include a biodegradable material that biodegrades to offset flow changes caused by tissue ingrowth. The inventive device may reduce left atrial pressure and left ventricular end diastolic pressure, and may increase cardiac output, increase ejection fraction, relieve pulmonary congestion, and lower pulmonary artery pressure, among other benefits.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Method and apparatus for percutaneous delivery and deployment of a cardiovascular prosthesis
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Mechanical Ventricular Pacing Non-Capture Detection for a Refractory Period Stimulation (RPS) Pacing Therapy Using at Least One Lead-Based Accelerometer
InactiveUS20080269825A1Increase contractilityIncrease perfusionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
A system and method for monitoring at least one chamber of a heart (e.g., a left ventricular chamber) during delivery of a refractory period stimulation (RPS) therapy to determine if the desired non-capture (i.e., lack of ventricular mechanical capture due to refractory period stimulation) occurs. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads such as epicardial, endocardial, and / or coronary sinus leads equipped with motion sensor(s). The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of chamber capture due to pacing stimulus delivery, non-capture due to RPS therapy delivery, and / or contractile status based on the qualities of evoked response to pacing stimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Papillary Muscle Attachment for Left Ventricular Reduction
InactiveUS20090099410A1Reduce transventricular dimensionShorten the lengthSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsLeft ventricular sizePapillary muscle
The surgical implantation of a link, which may be in the form of a tether or a looped band, is proposed to connect and reduce the spacing between papillary muscles, to reduce dilation of the left ventricle. The implanted link thus improves heart function by reducing left ventricular failure.
Owner:MIAMI THE UNIV OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com