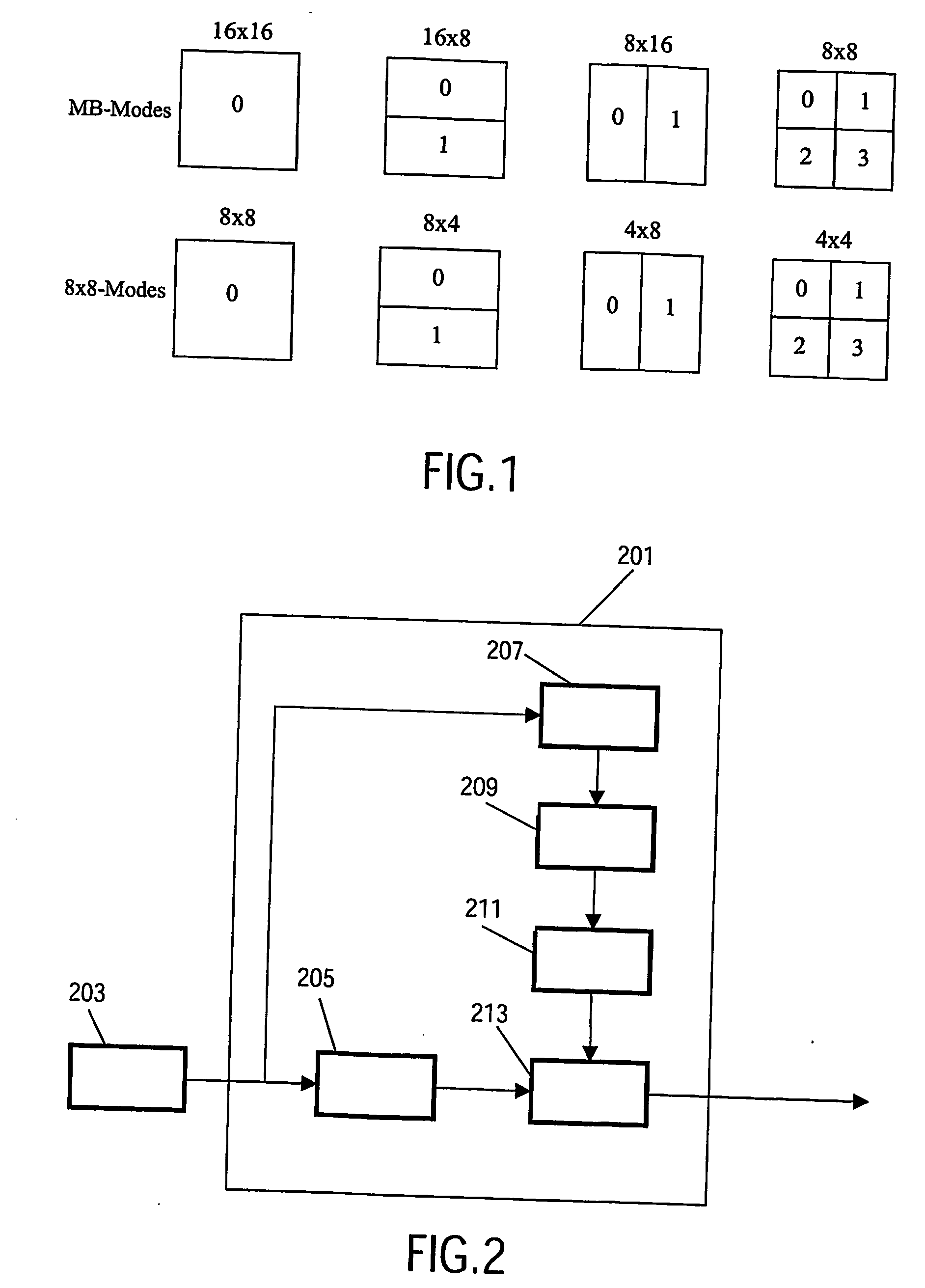
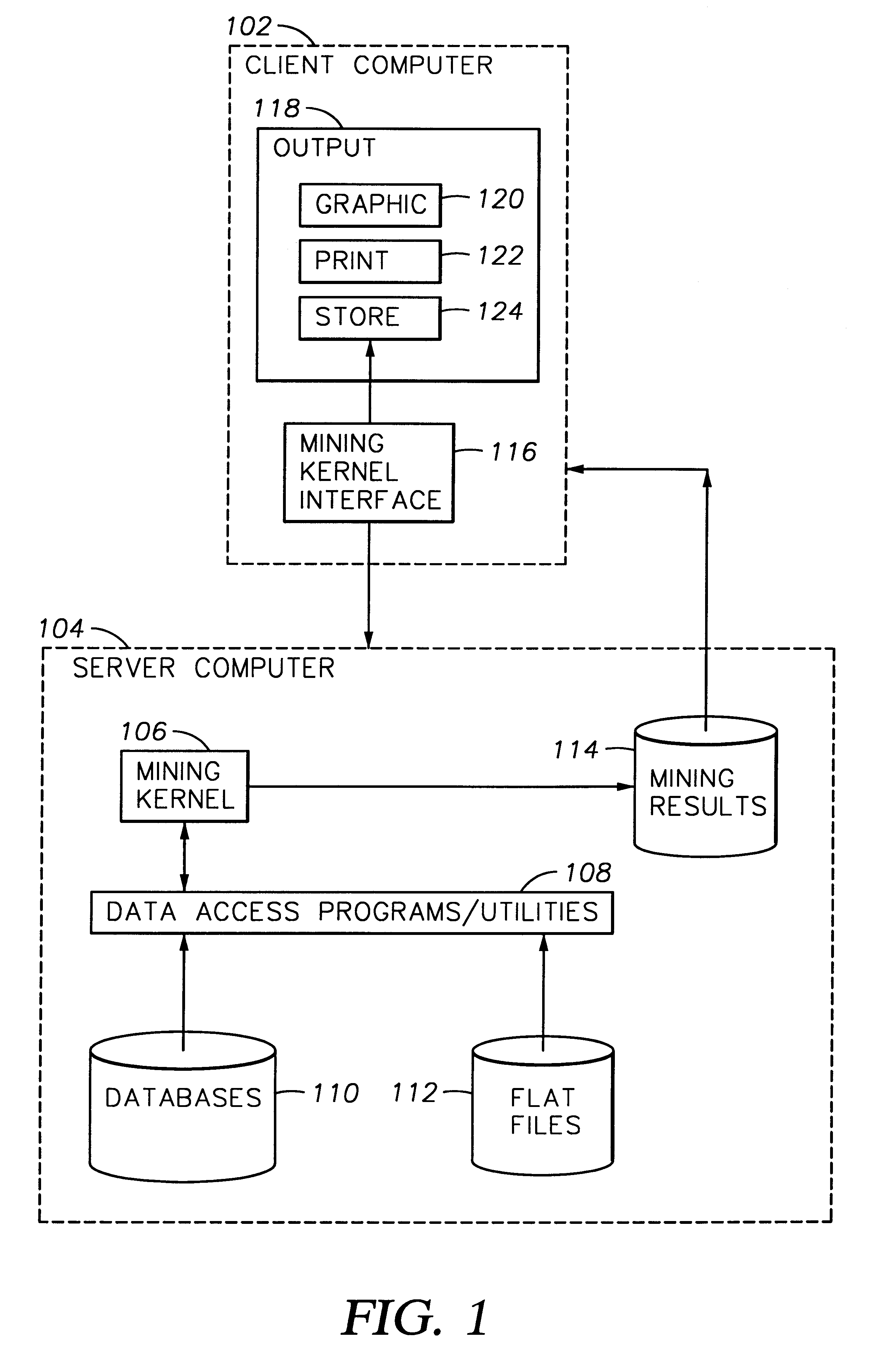
Patents
Literature
1024 results about "ENCODE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) is a public research project which aims to identify functional elements in the human genome.
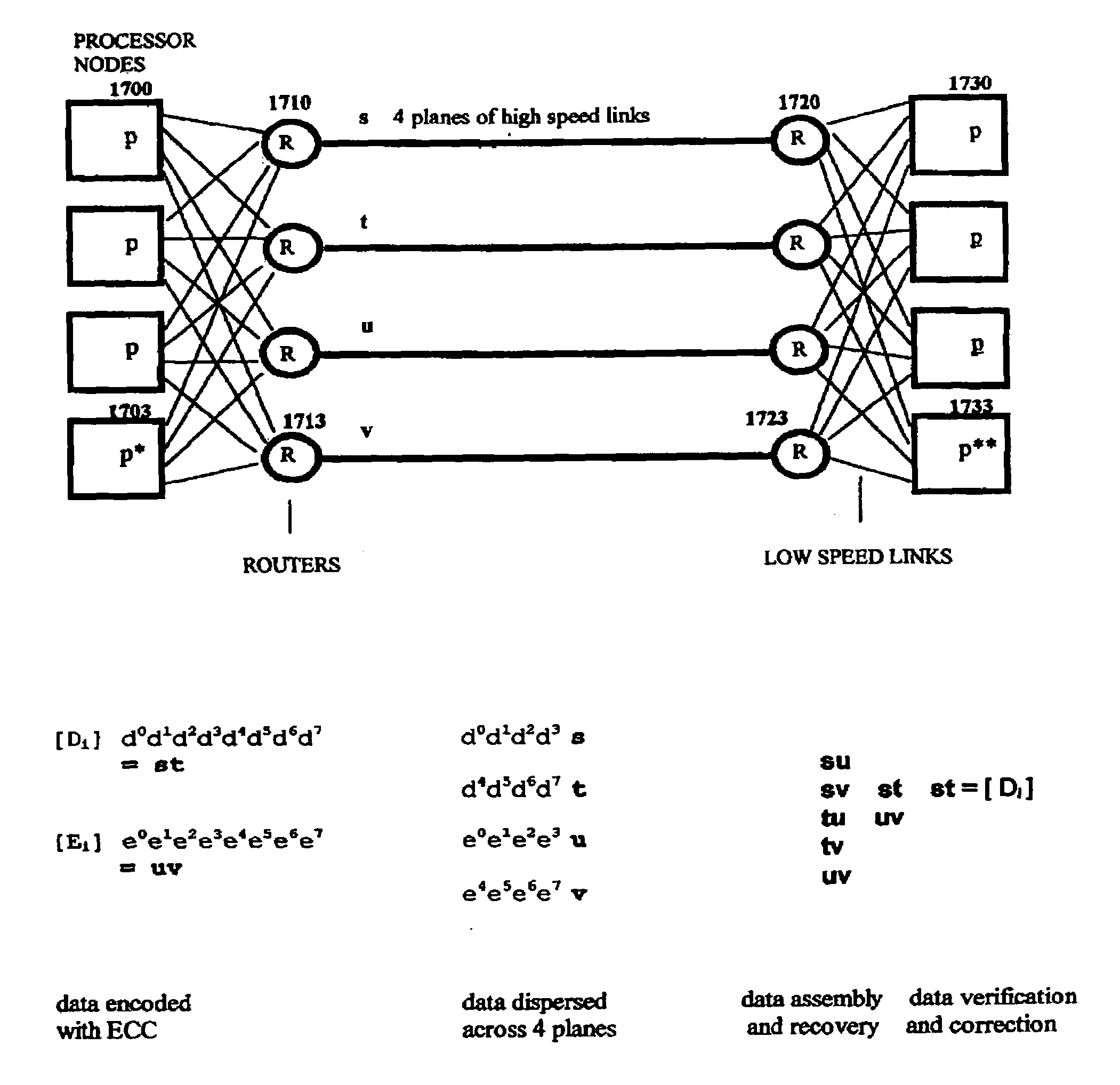
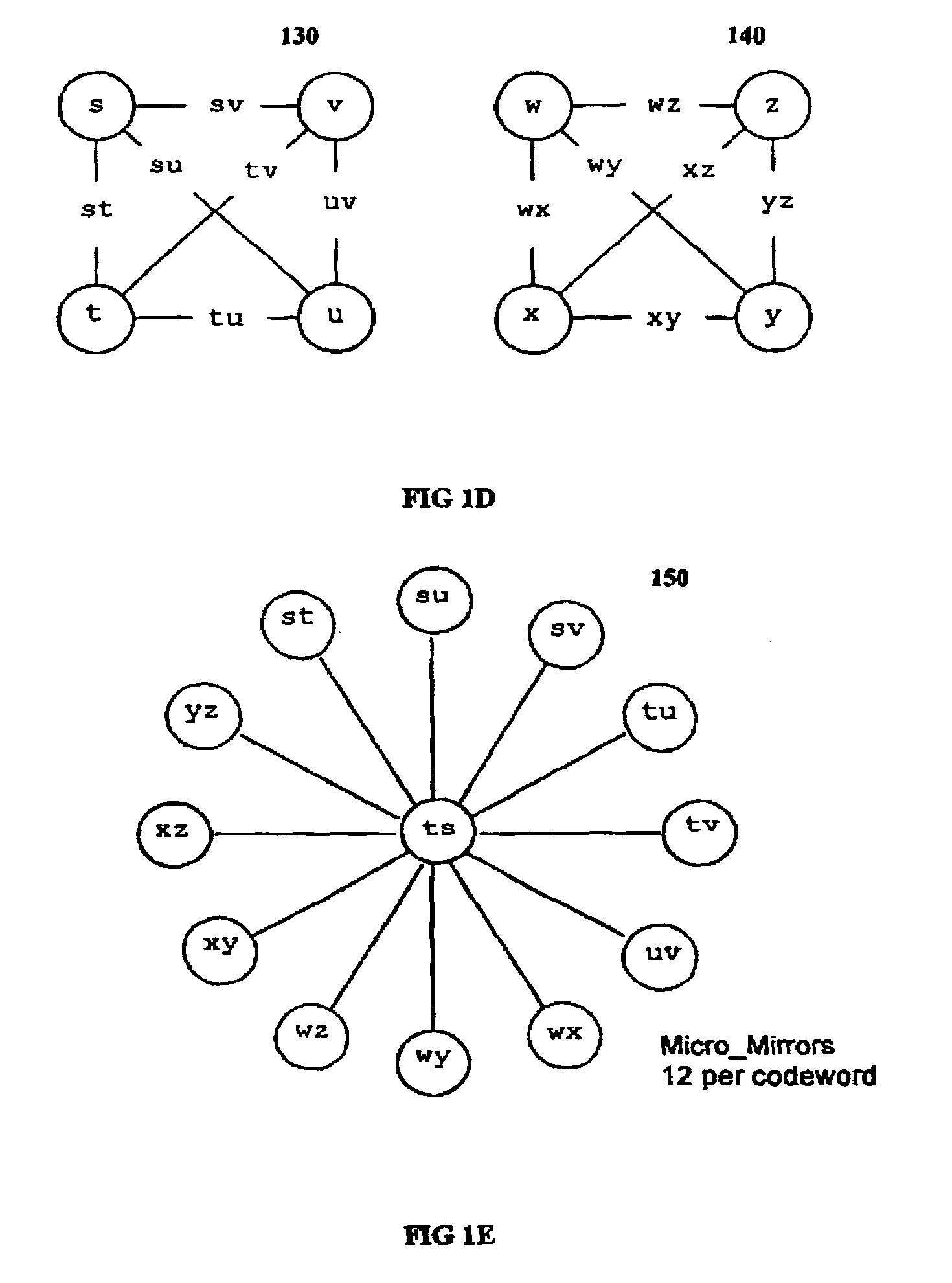
Multi-dimensional data protection and mirroring method for micro level data
ActiveUS7103824B2Detection errorLow common data sizeCode conversionCyclic codesData validationData integrity
The invention discloses a data validation, mirroring and error / erasure correction method for the dispersal and protection of one and two-dimensional data at the micro level for computer, communication and storage systems. Each of 256 possible 8-bit data bytes are mirrored with a unique 8-bit ECC byte. The ECC enables 8-bit burst and 4-bit random error detection plus 2-bit random error correction for each encoded data byte. With the data byte and ECC byte configured into a 4 bit×4 bit codeword array and dispersed in either row, column or both dimensions the method can perform dual 4-bit row and column erasure recovery. It is shown that for each codeword there are 12 possible combinations of row and column elements called couplets capable of mirroring the data byte. These byte level micro-mirrors outperform conventional mirroring in that each byte and its ECC mirror can self-detect and self-correct random errors and can recover all dual erasure combinations over four elements. Encoding at the byte quanta level maximizes application flexibility. Also disclosed are fast encode, decode and reconstruction methods via boolean logic, processor instructions and software table look-up with the intent to run at line and application speeds. The new error control method can augment ARQ algorithms and bring resiliency to system fabrics including routers and links previously limited to the recovery of transient errors. Image storage and storage over arrays of static devices can benefit from the two-dimensional capabilities. Applications with critical data integrity requirements can utilize the method for end-to-end protection and validation. An extra ECC byte per codeword extends both the resiliency and dimensionality.
Owner:HALFORD ROBERT
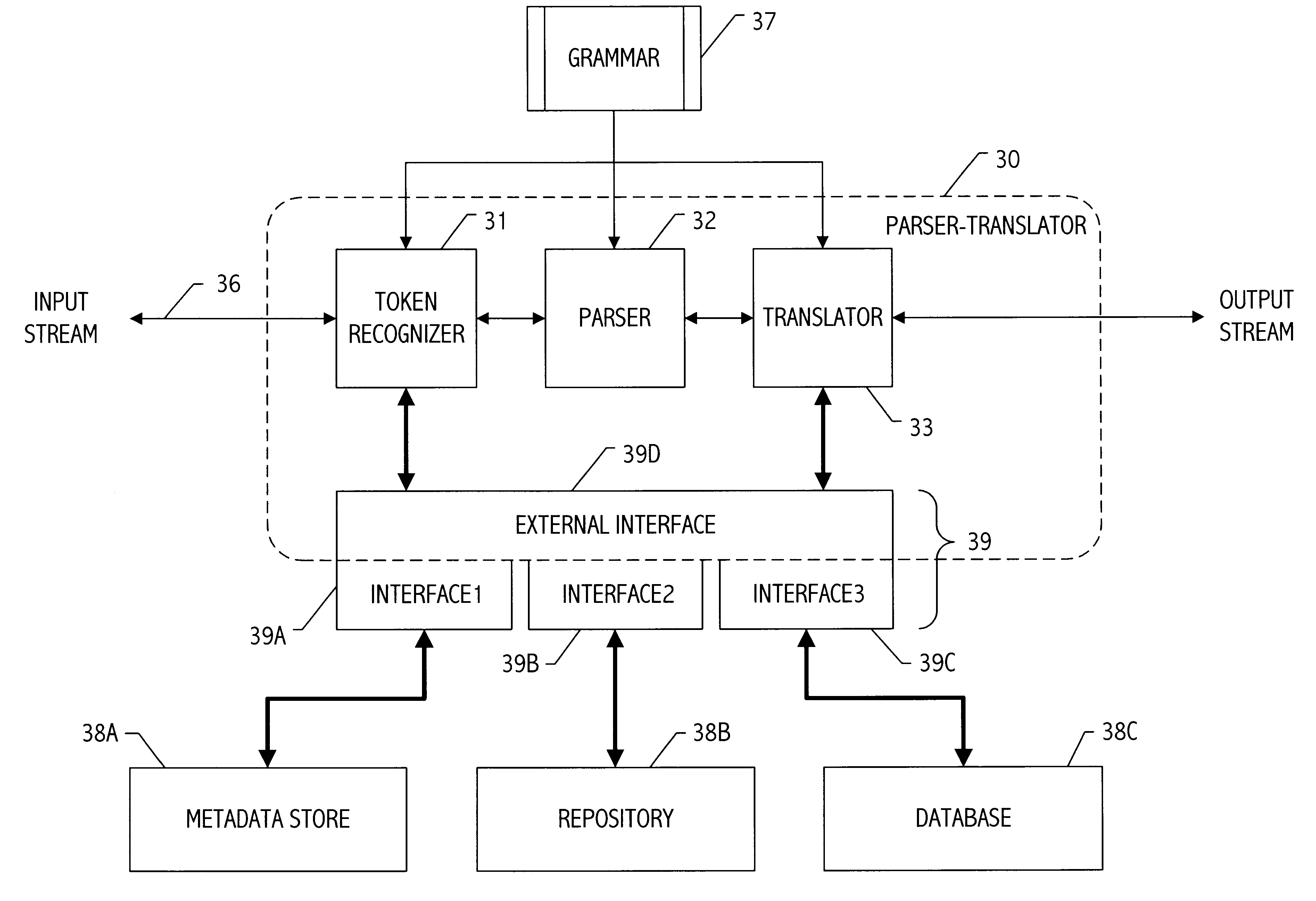
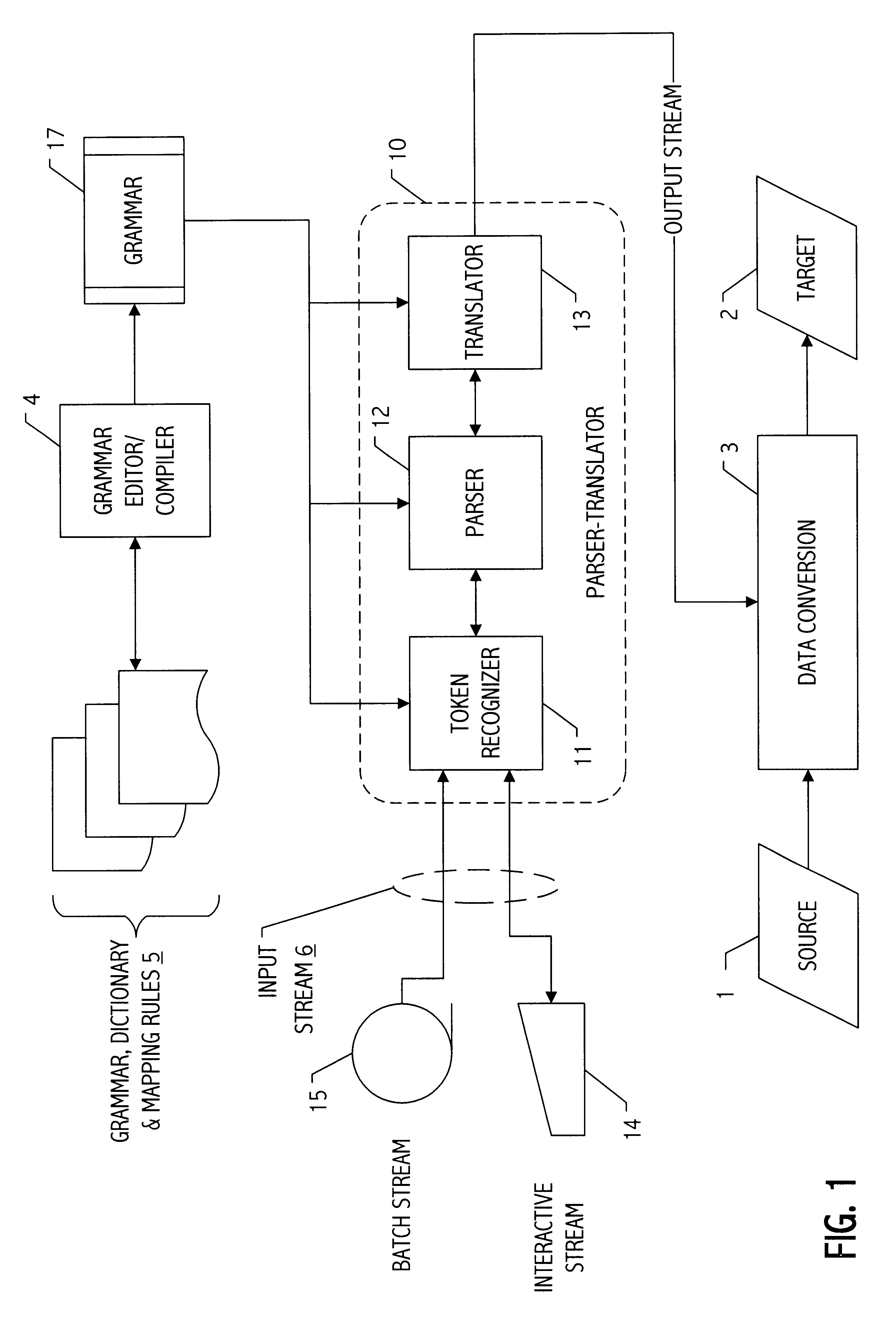
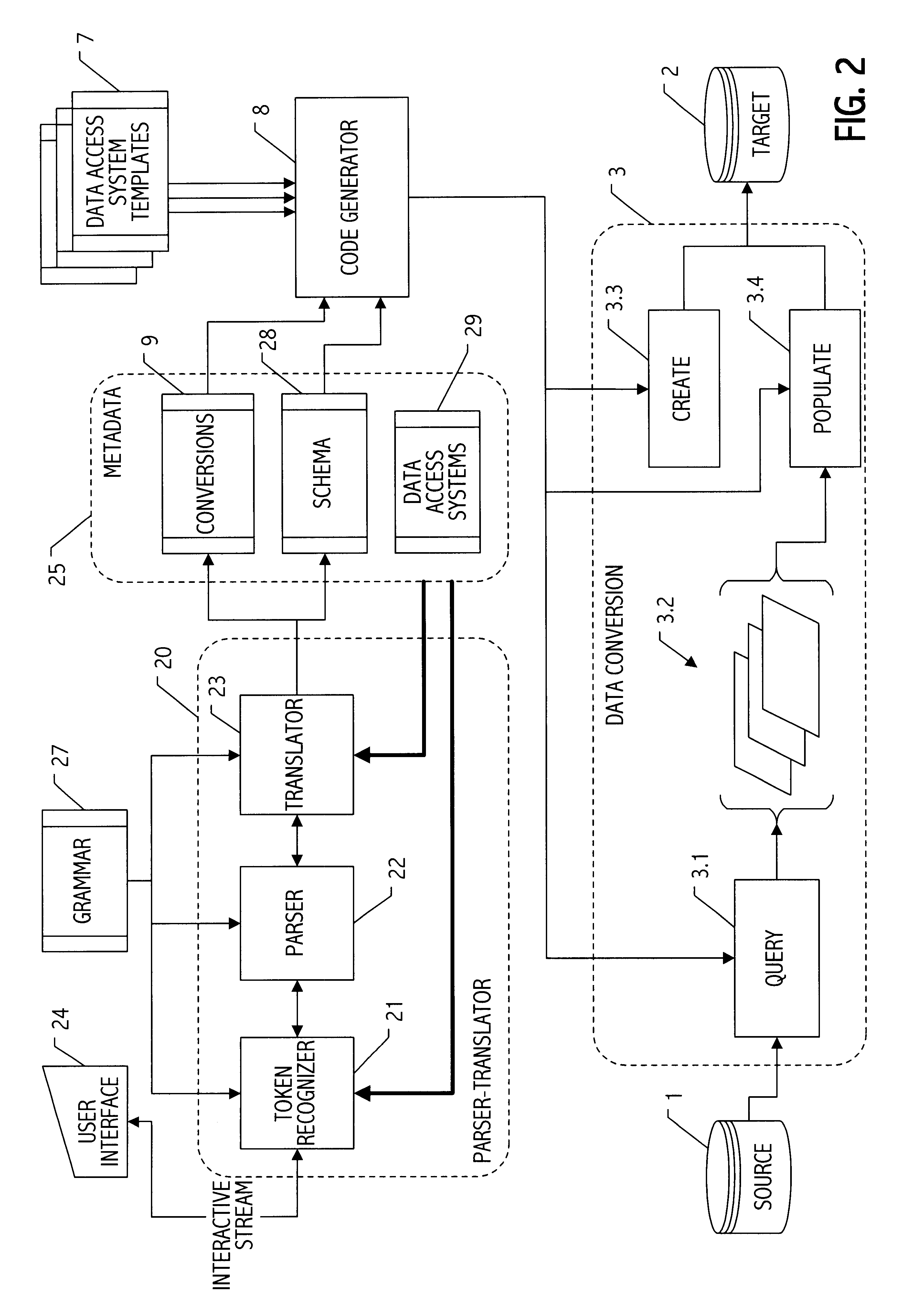
Parser translator system and method
A parser-translator technology allows a user to specify complex test and / or transformation statements in a high-level user language, to ensure that such test and / or transformation statements are well-formed in accordance with a grammar defining legal statements in the user language, and to translate statements defined by the user into logically and syntactically correct directives for performing the desired data transformations or operations. Using the parser-translator technology, a user can focus on the semantics of the desired operations and need not be concerned with the proper syntax of a language for a particular system. Instead, grammars (i.e., data) define the behavior of a parser-translator implementation by encoding the universe of statements (e.g., legal test and / or transformation statements) and by encoding translations appropriate to a particular data processing application (e.g., a data conversion program, etc.). Some parser-translator implementations described herein interface dynamically with other systems and / or repositories to query for information about objects, systems and states represented therein, and / or their respective interfaces. Some grammars described herein encode sensitivity to an external context. In this way, context-sensitive prompting and validation of correct specification of statements is provided. A combination of parser technology and dynamic querying of external system state allows users to build complex statements (e.g., using natural languages within a user interface environment) and to translate those complex statements into statements or directives appropriate to a particular data processing application.
Owner:VERSATA
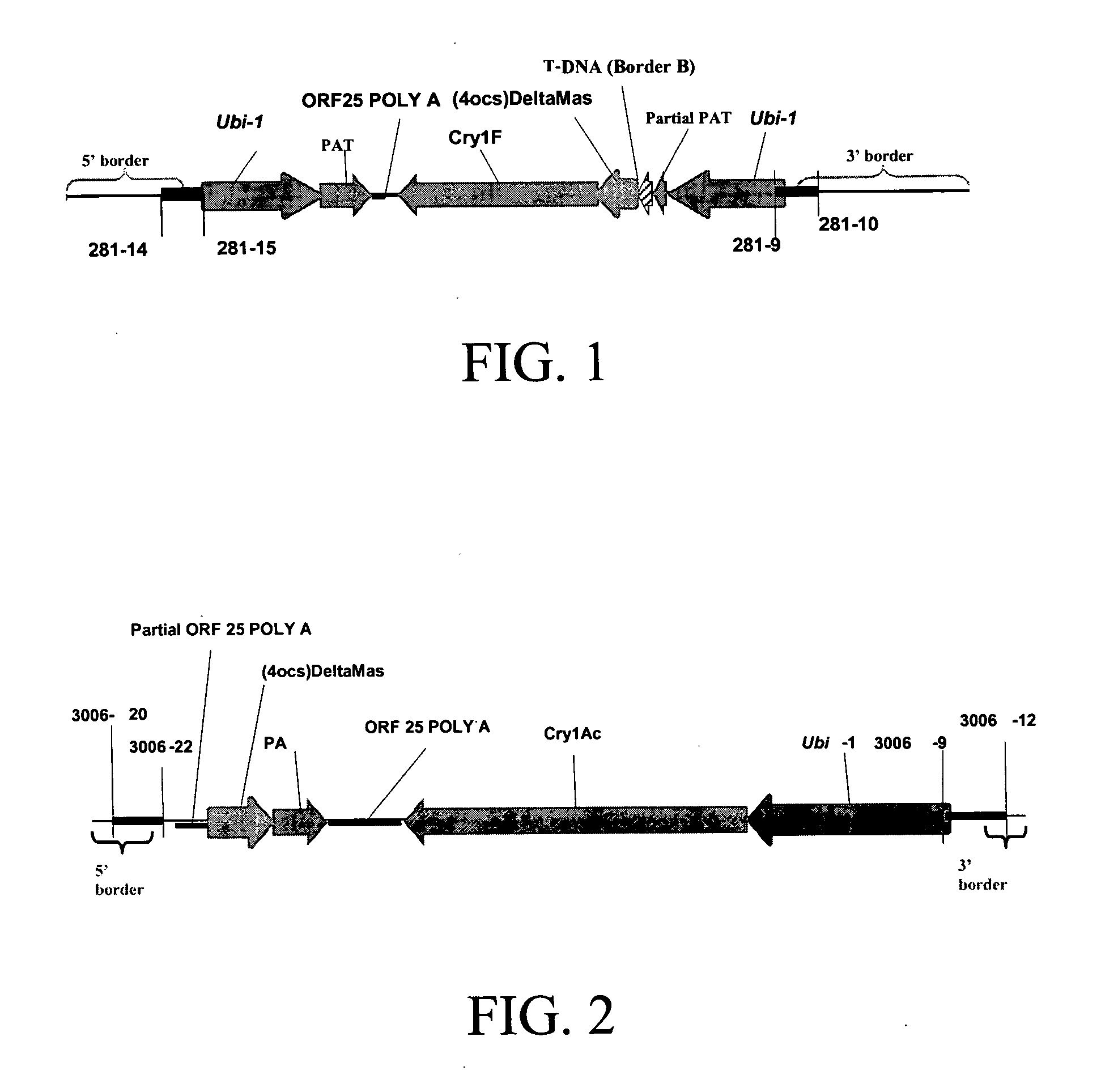
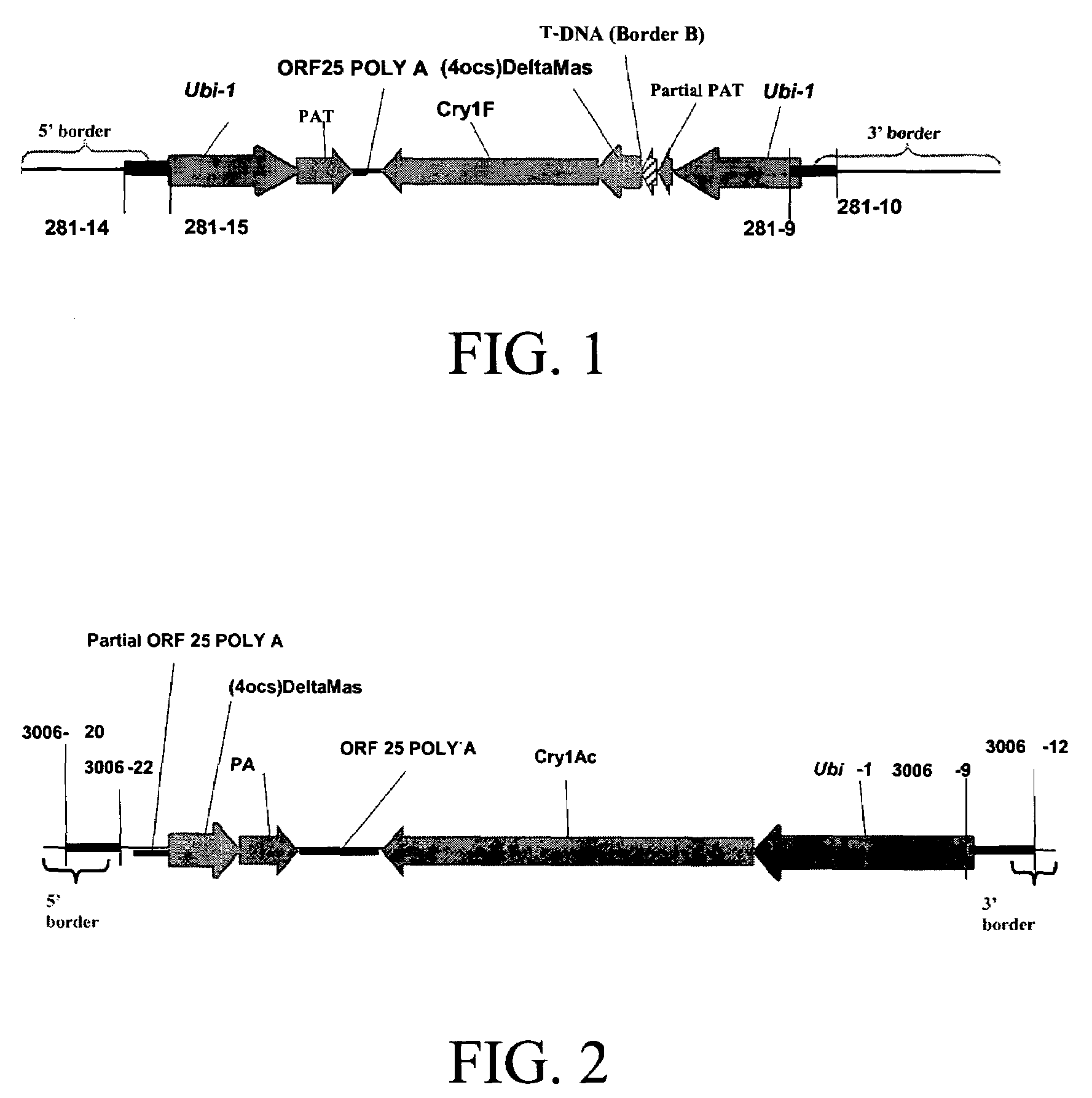
Cry1F and Cry1AC transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
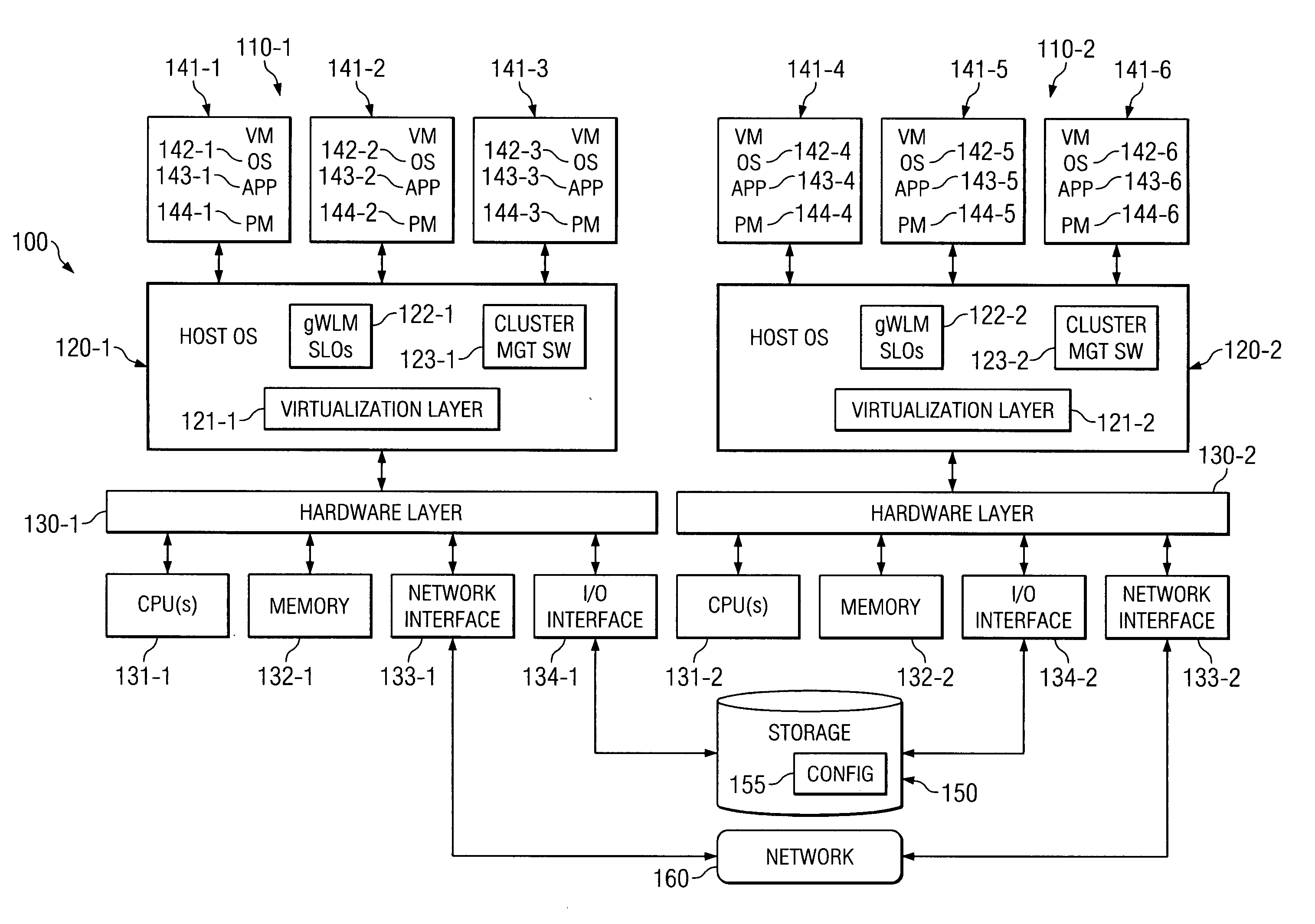
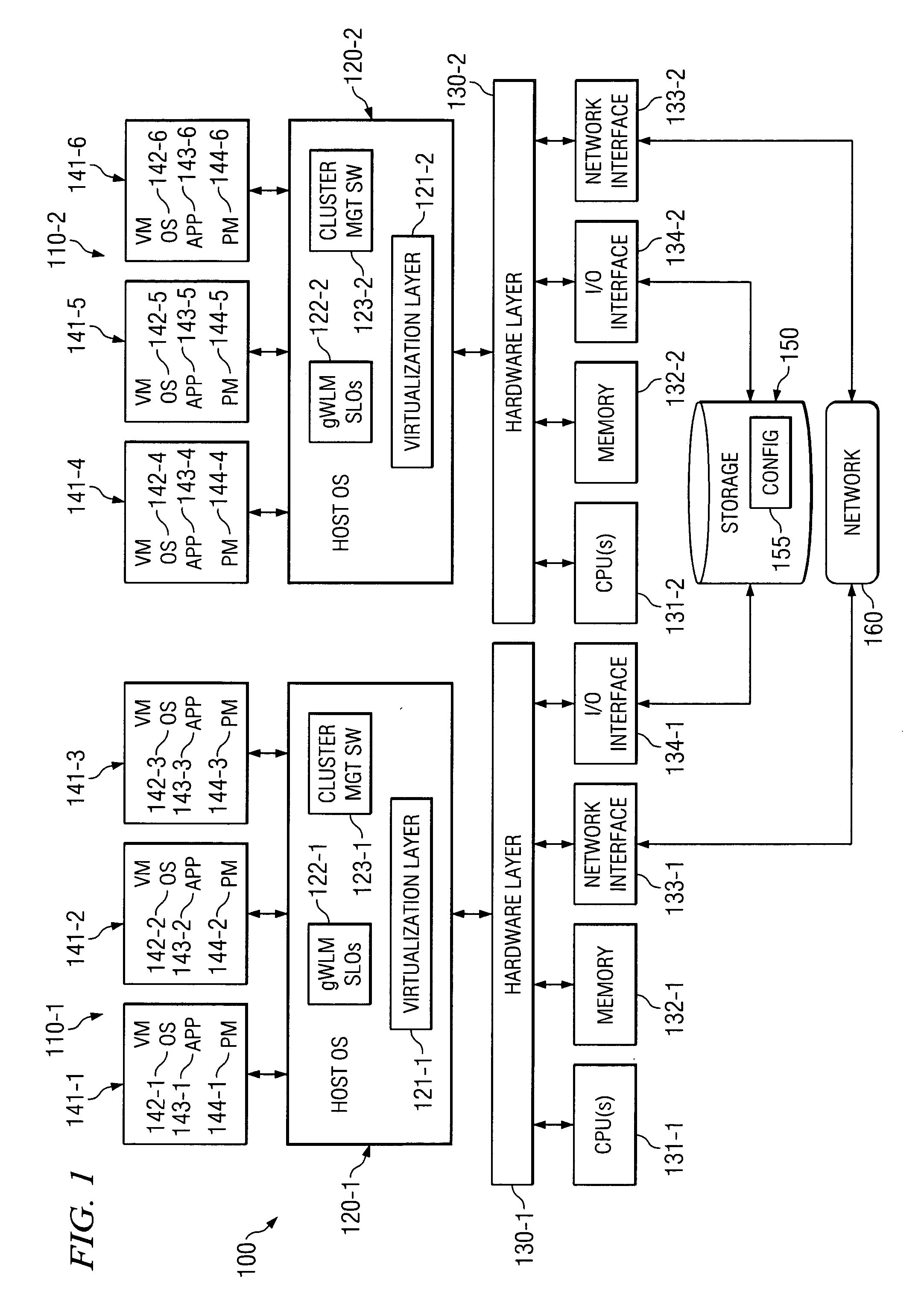
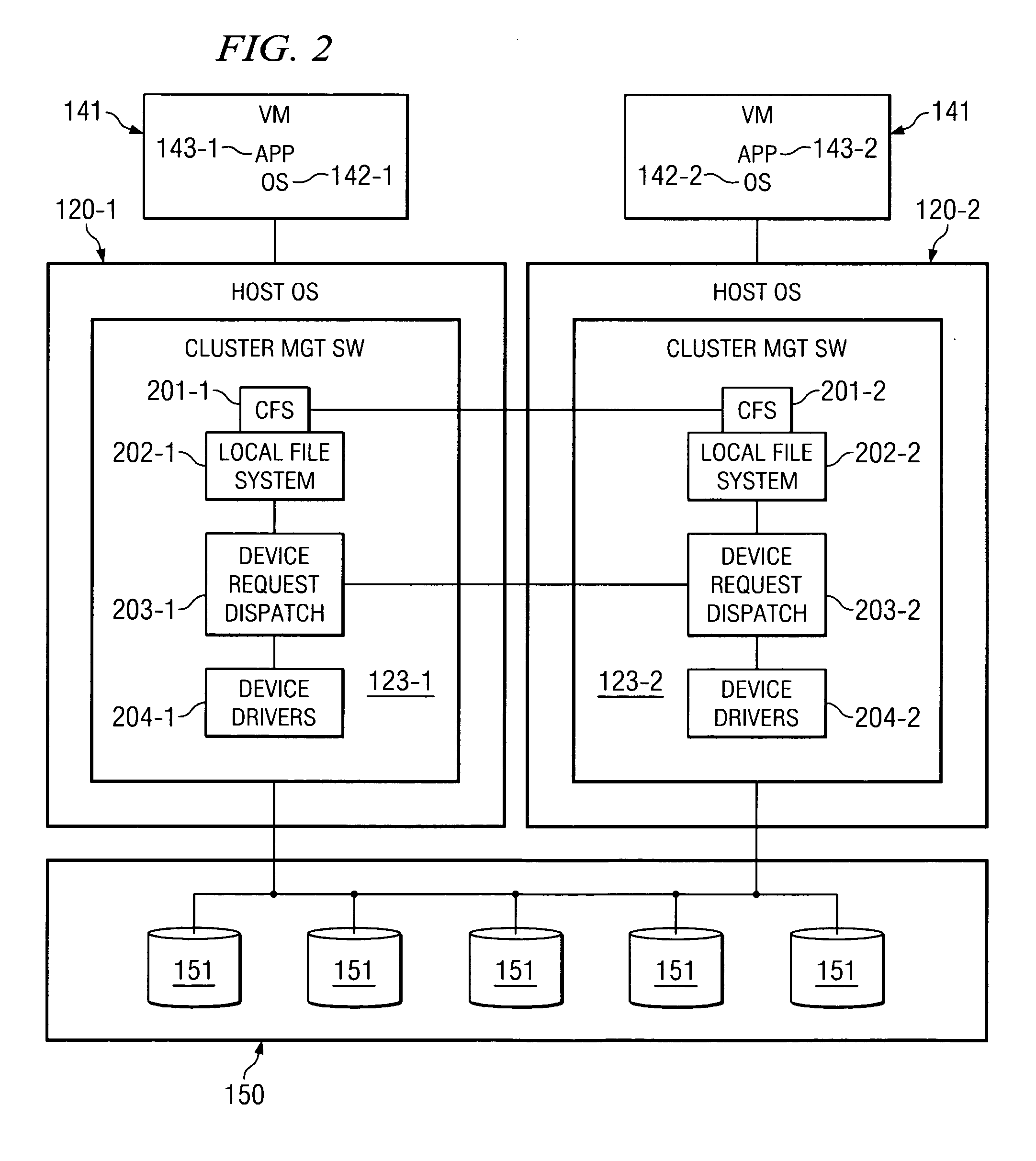
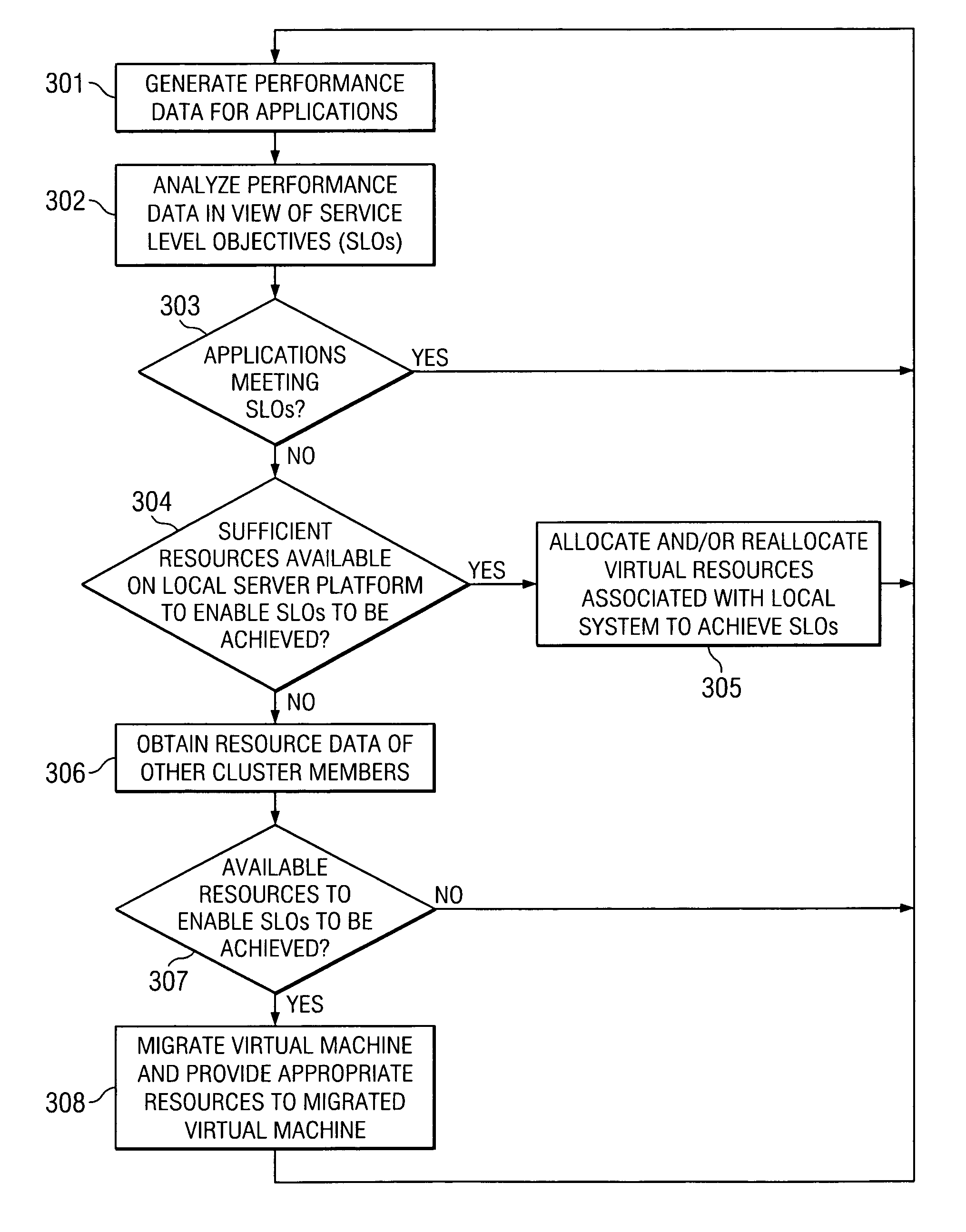
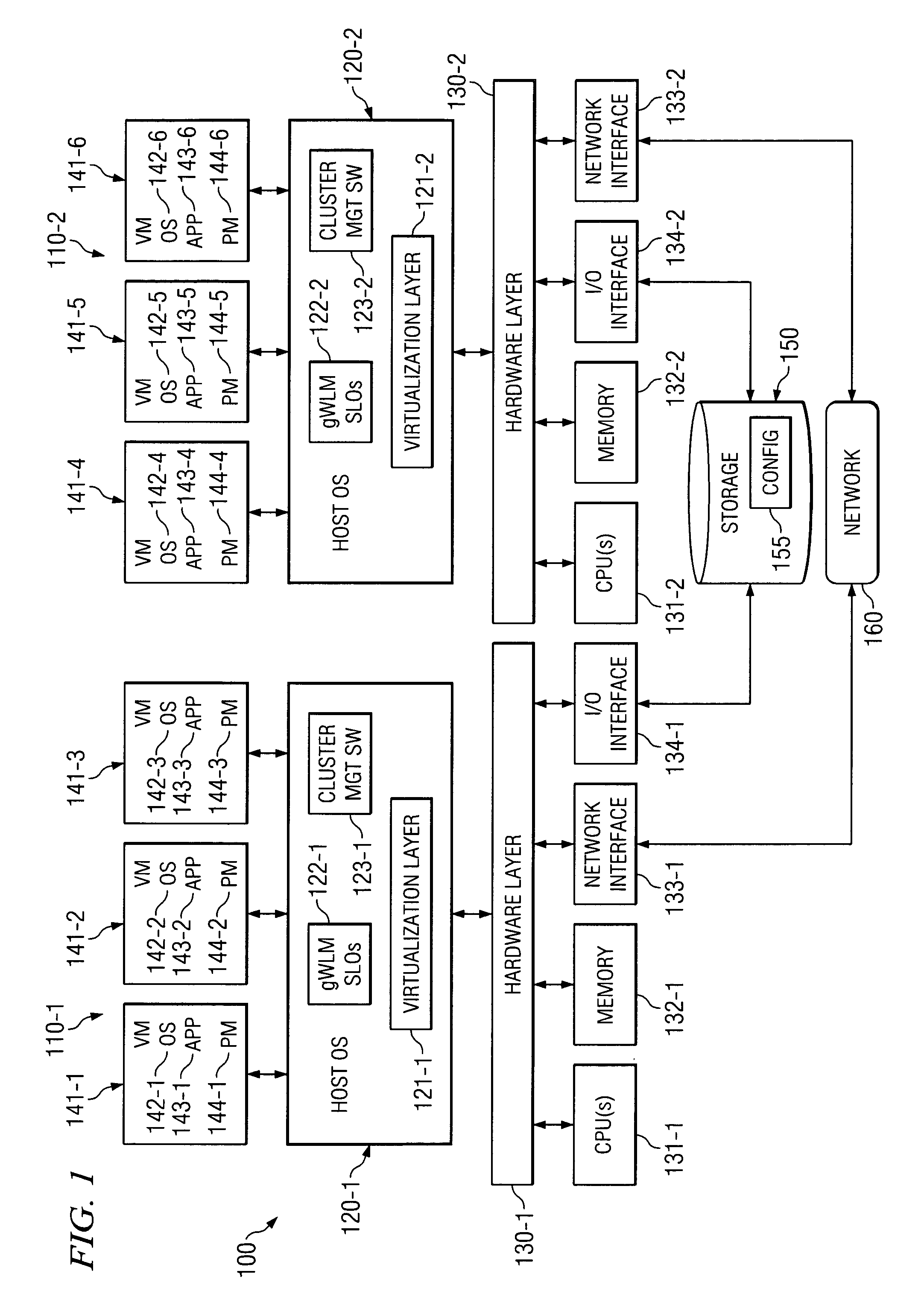
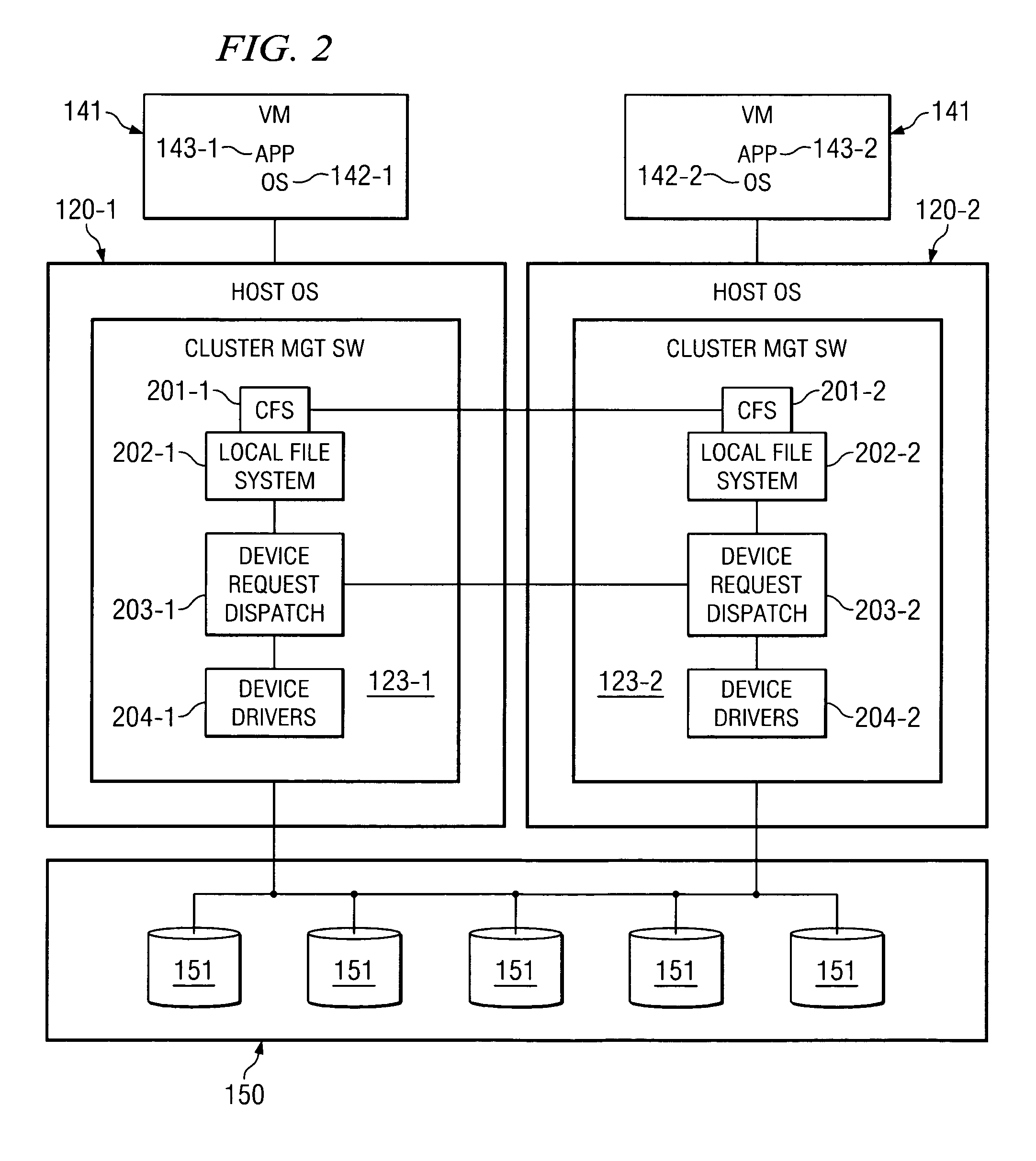
System and method for migrating virtual machines on cluster systems
ActiveUS20060195715A1Satisfactory operationError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsManagement processCluster systems
In one embodiment, a method comprises executing a plurality of virtual machines on a plurality of nodes of a cluster computing system, wherein at least one application is executed within each of the plurality of virtual machines, generating data that is related to performance of applications in the virtual machines, analyzing, by a management process, the data in view of parameters that encode desired performance levels of applications, and migrating, by the management process, a virtual machine on a first node to a second node of the plurality of nodes in response to the analyzing.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
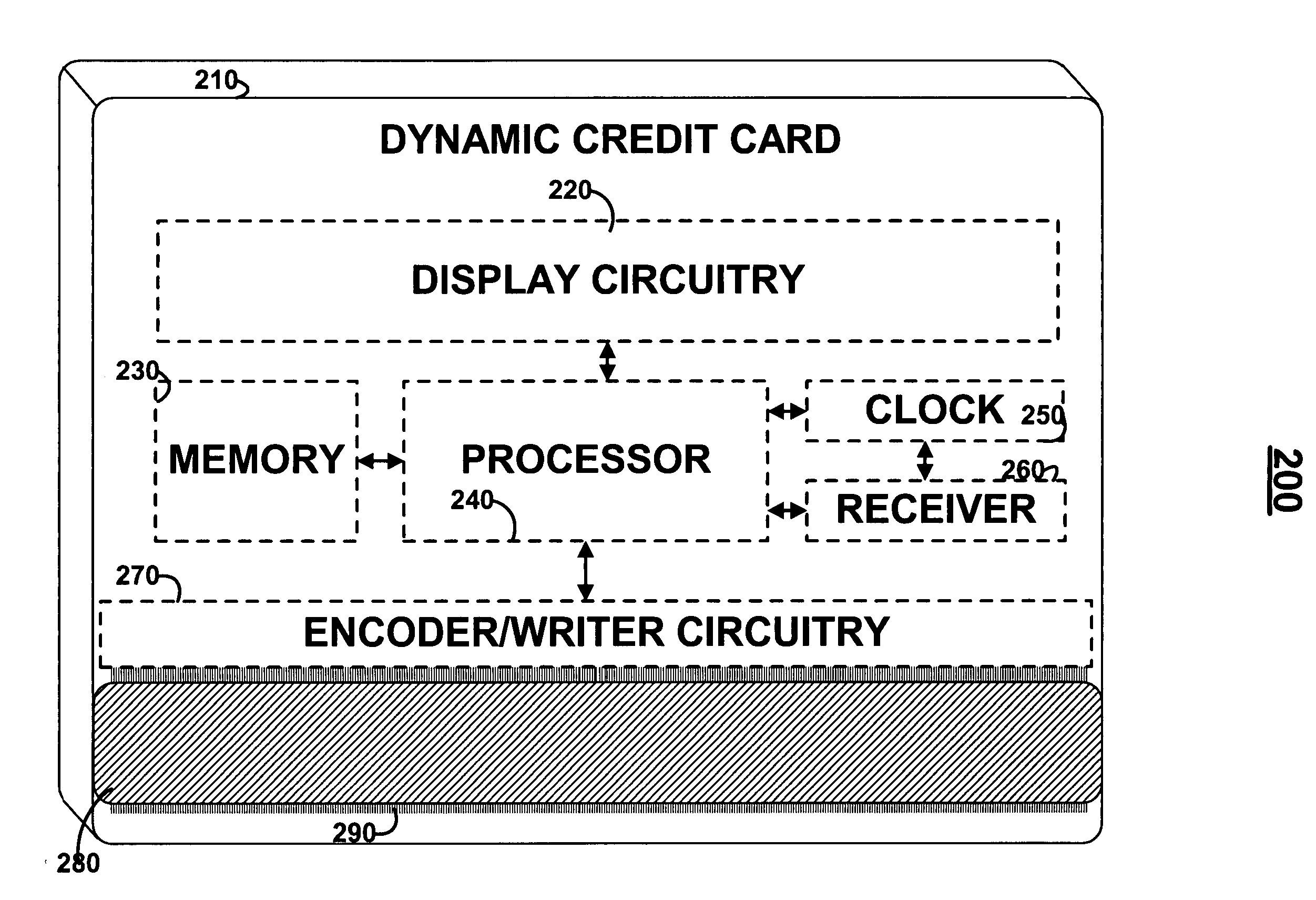
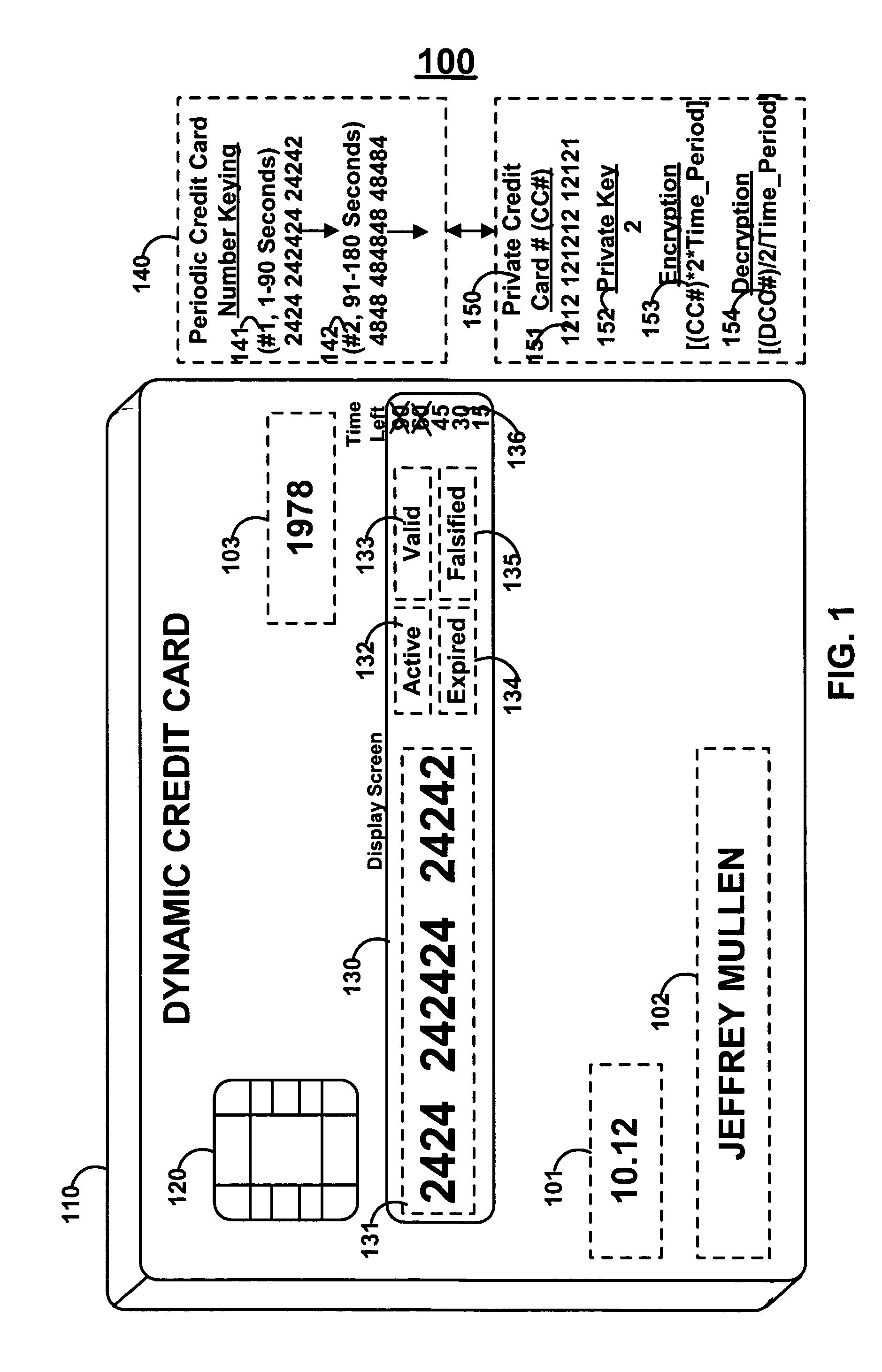
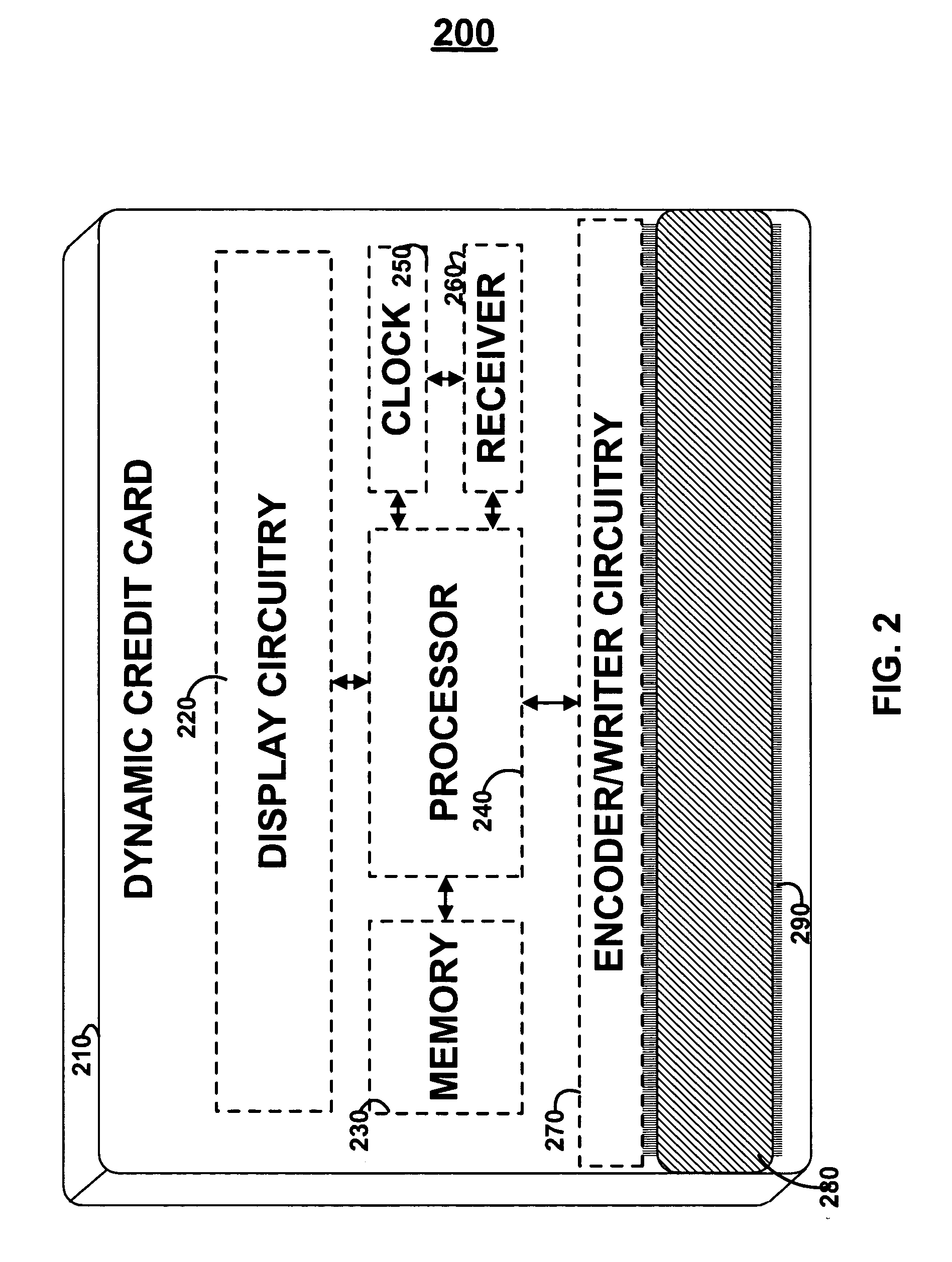
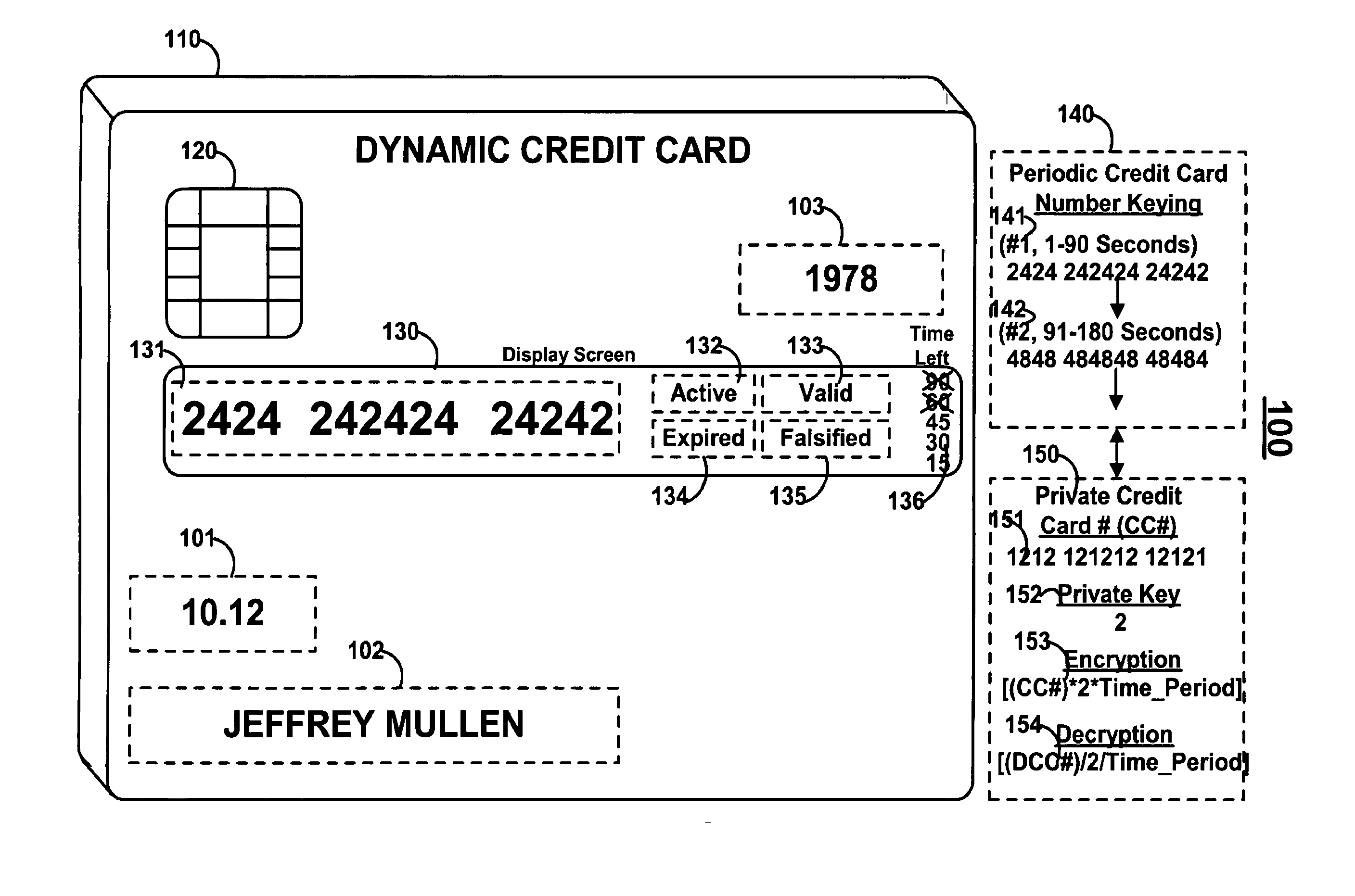
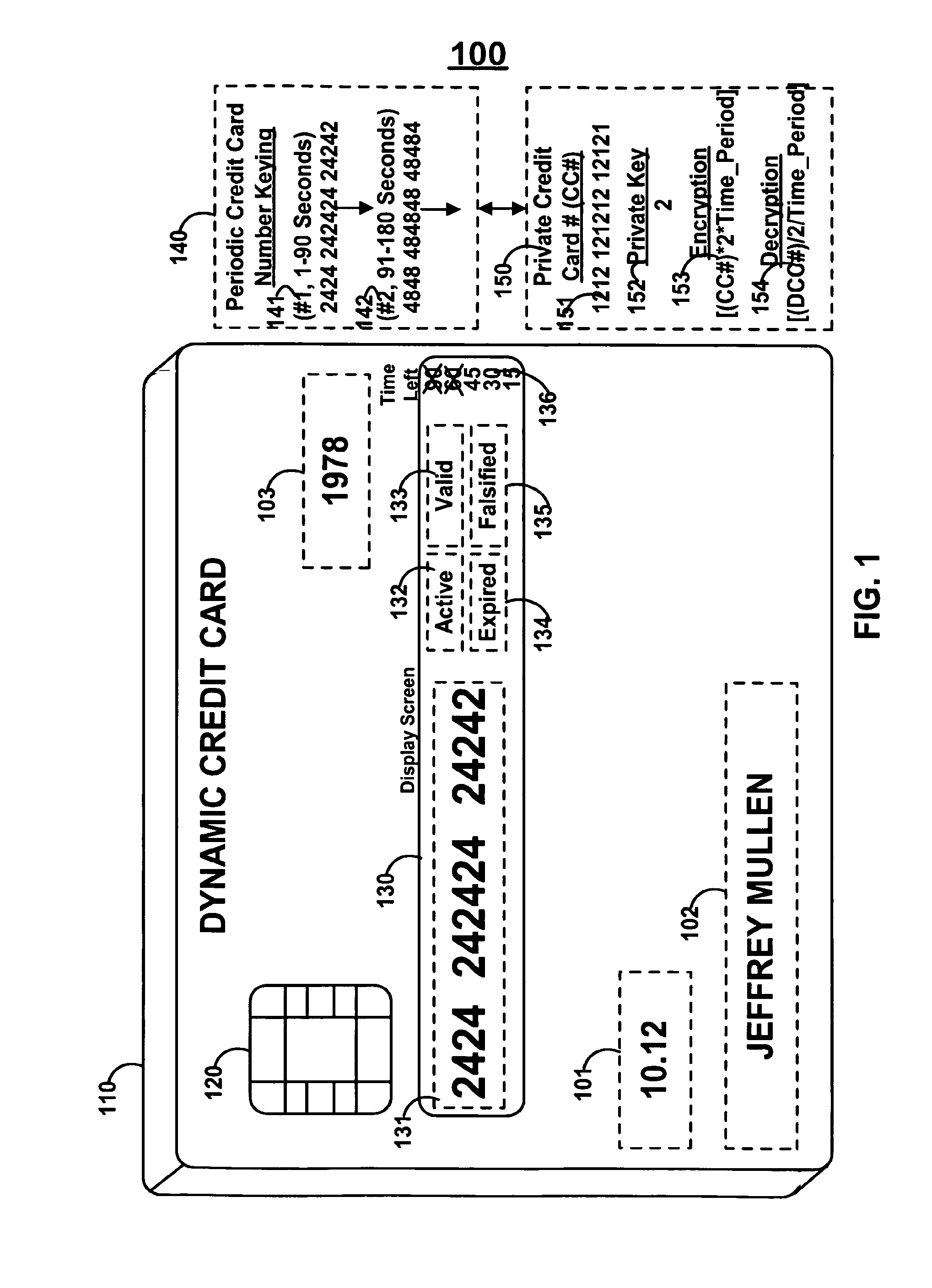
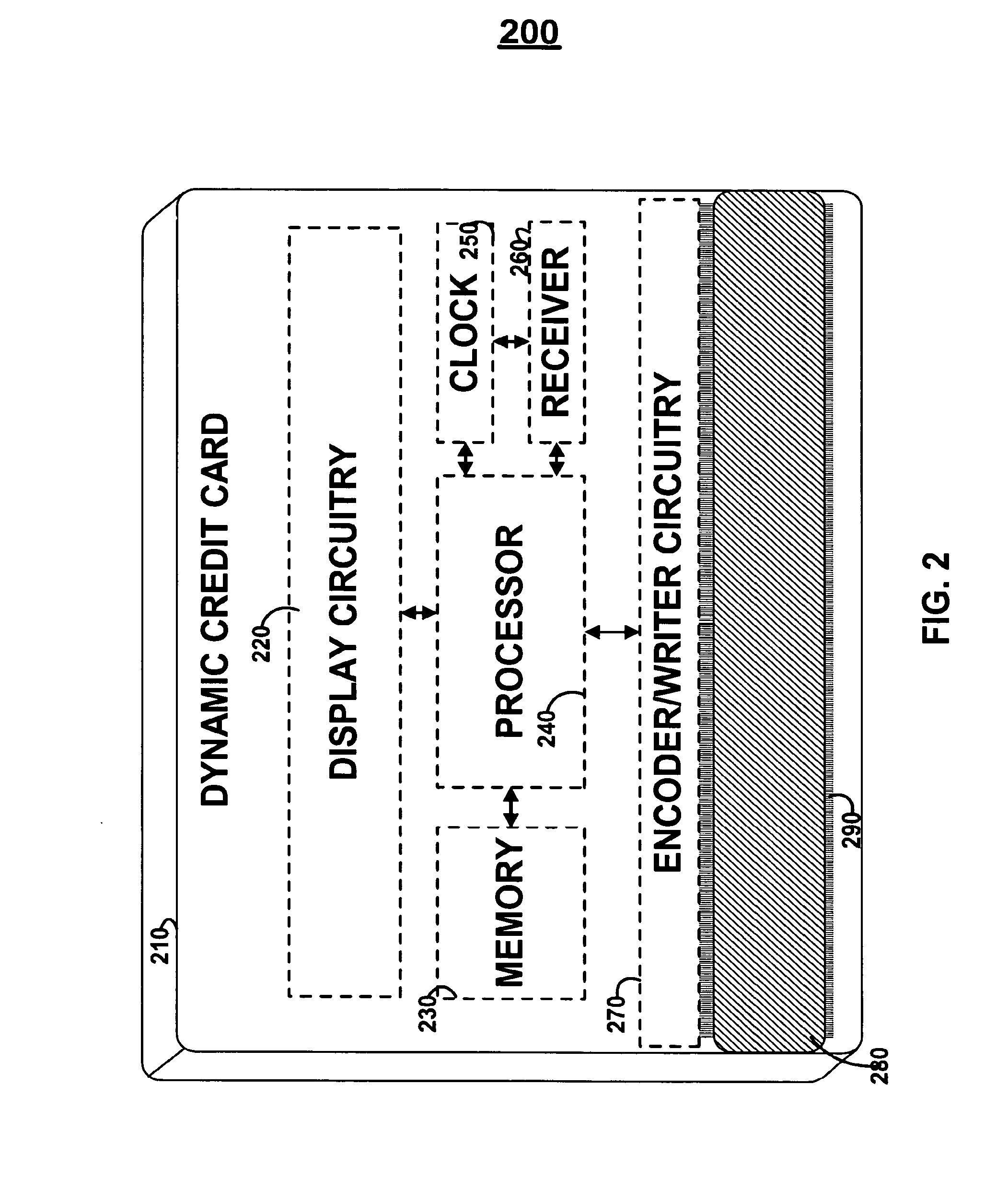
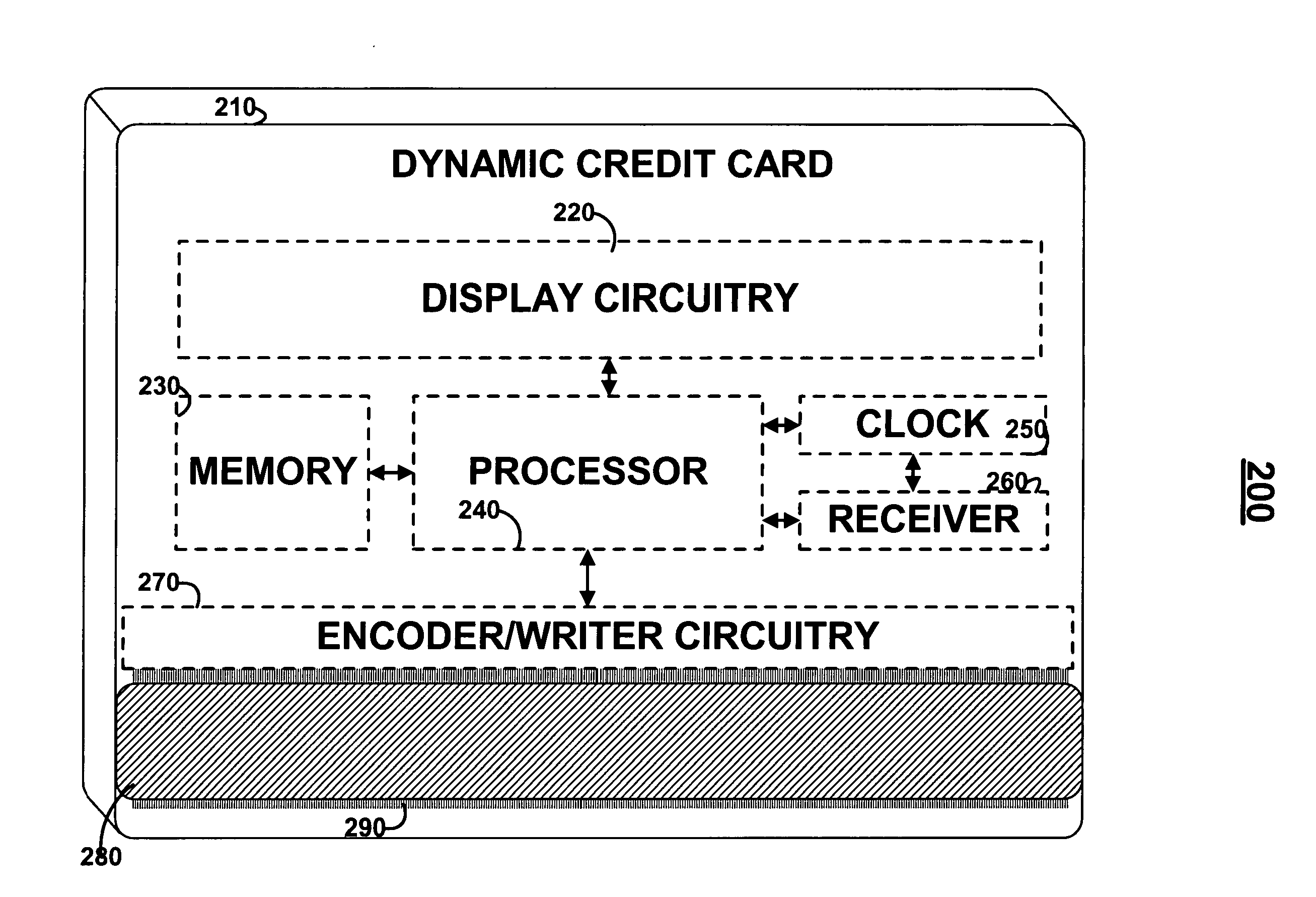
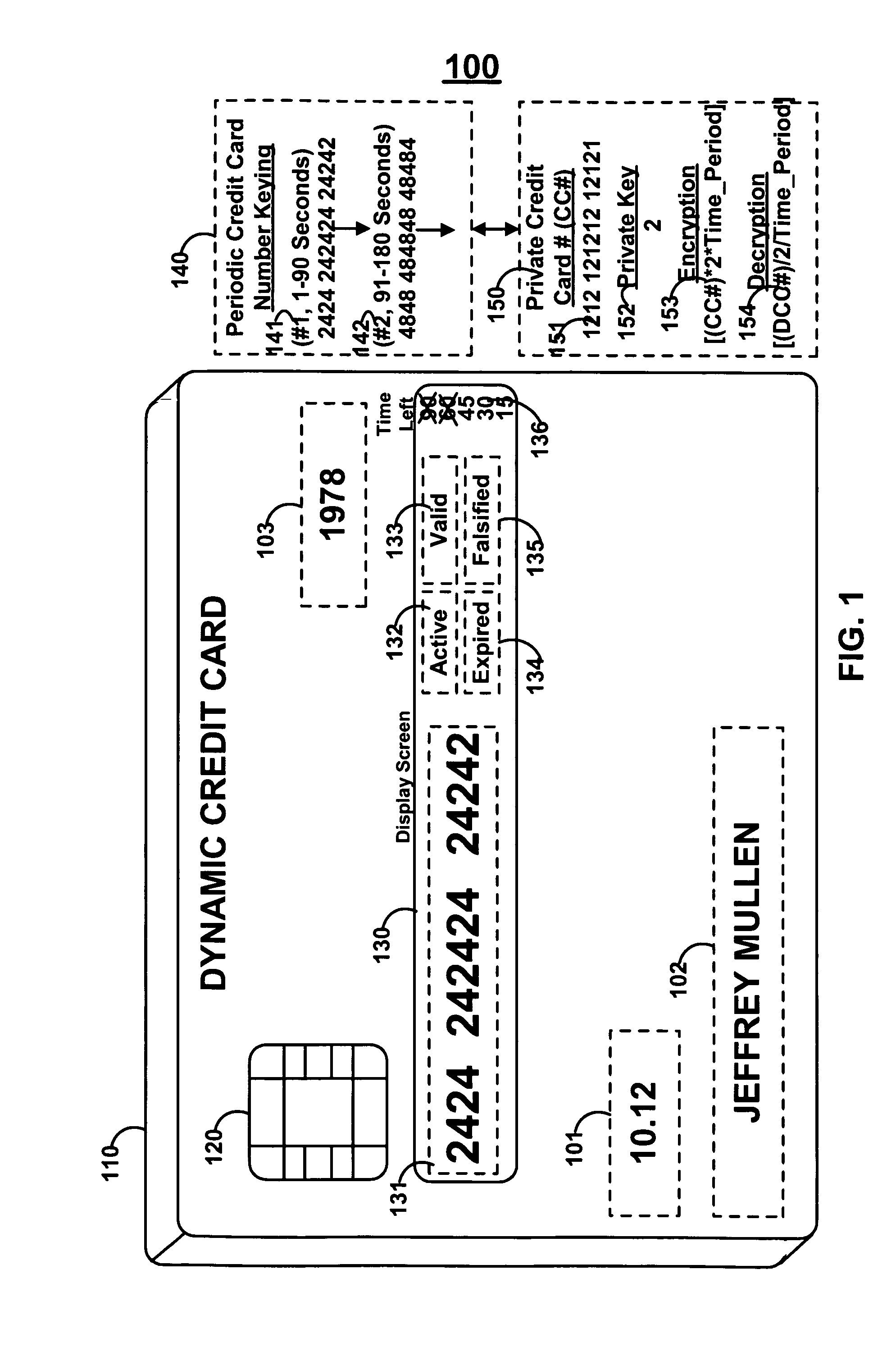
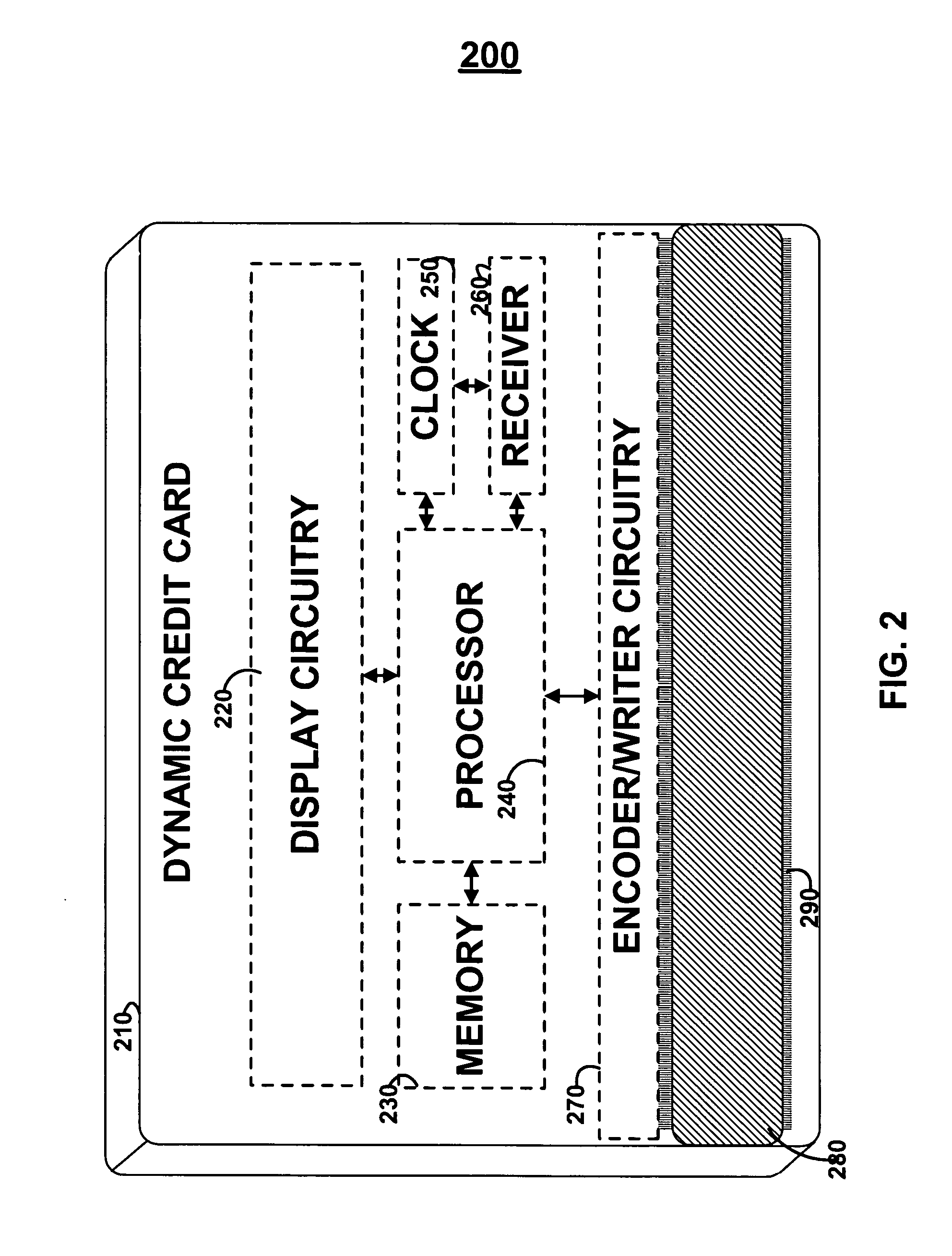
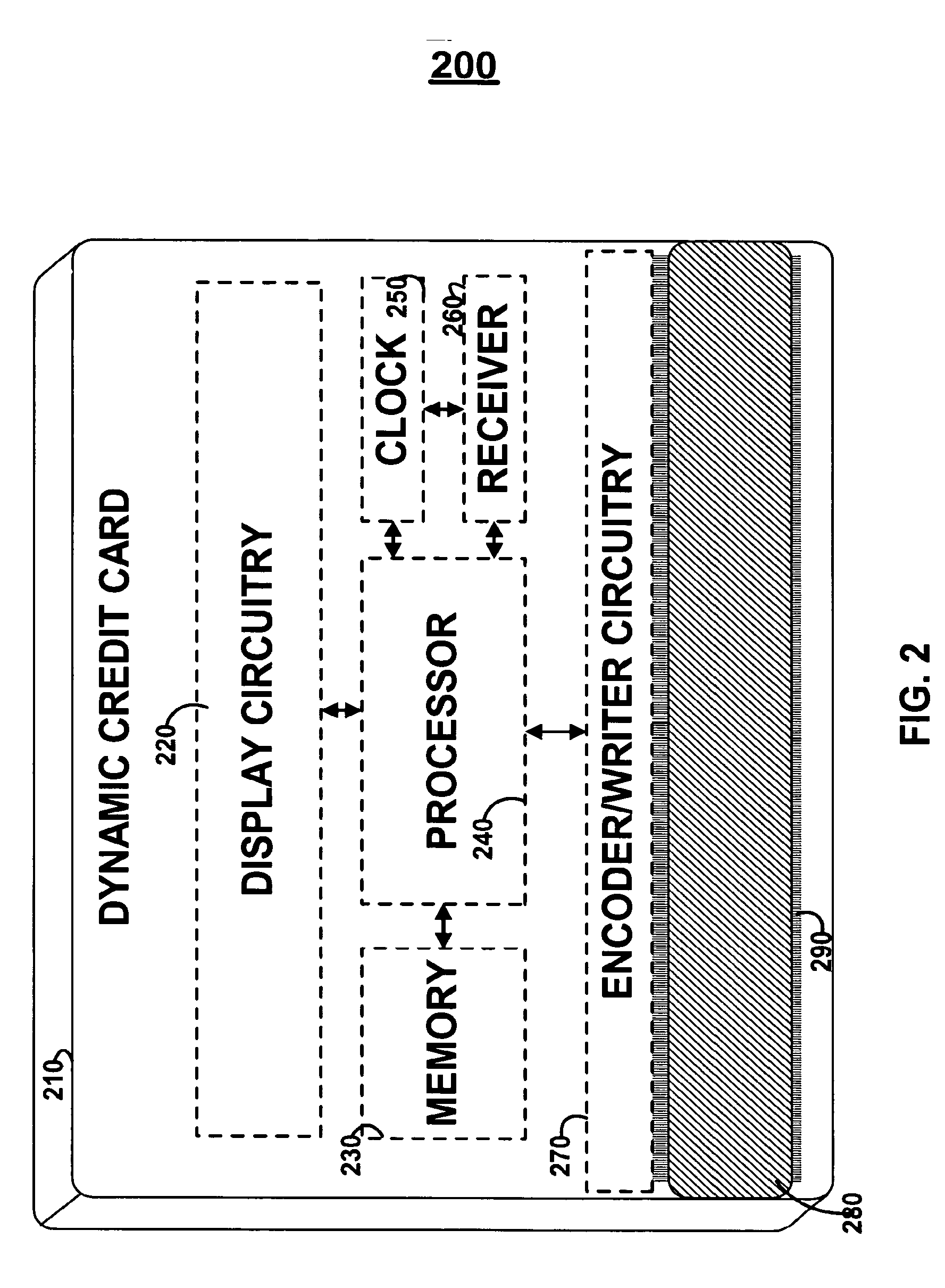
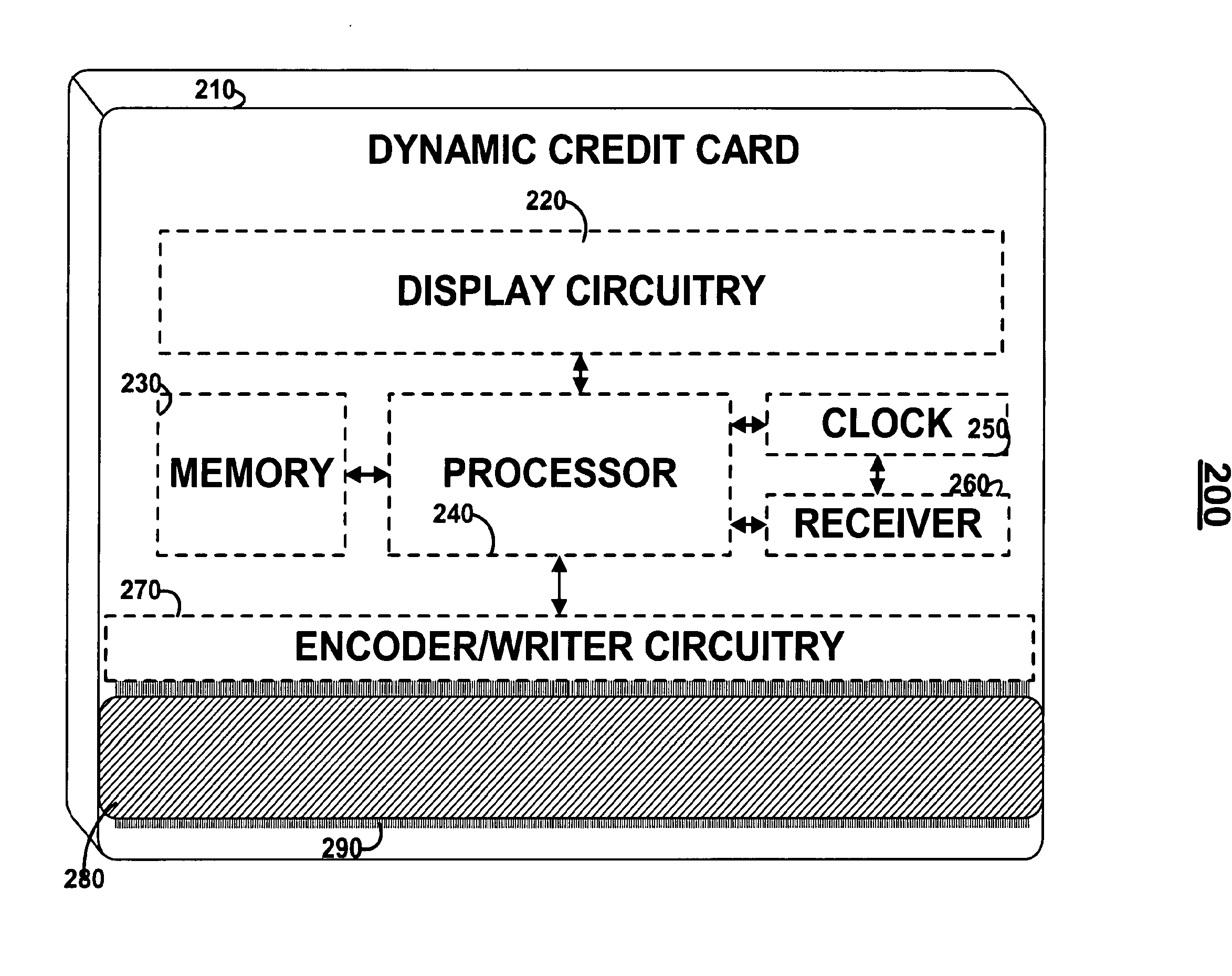
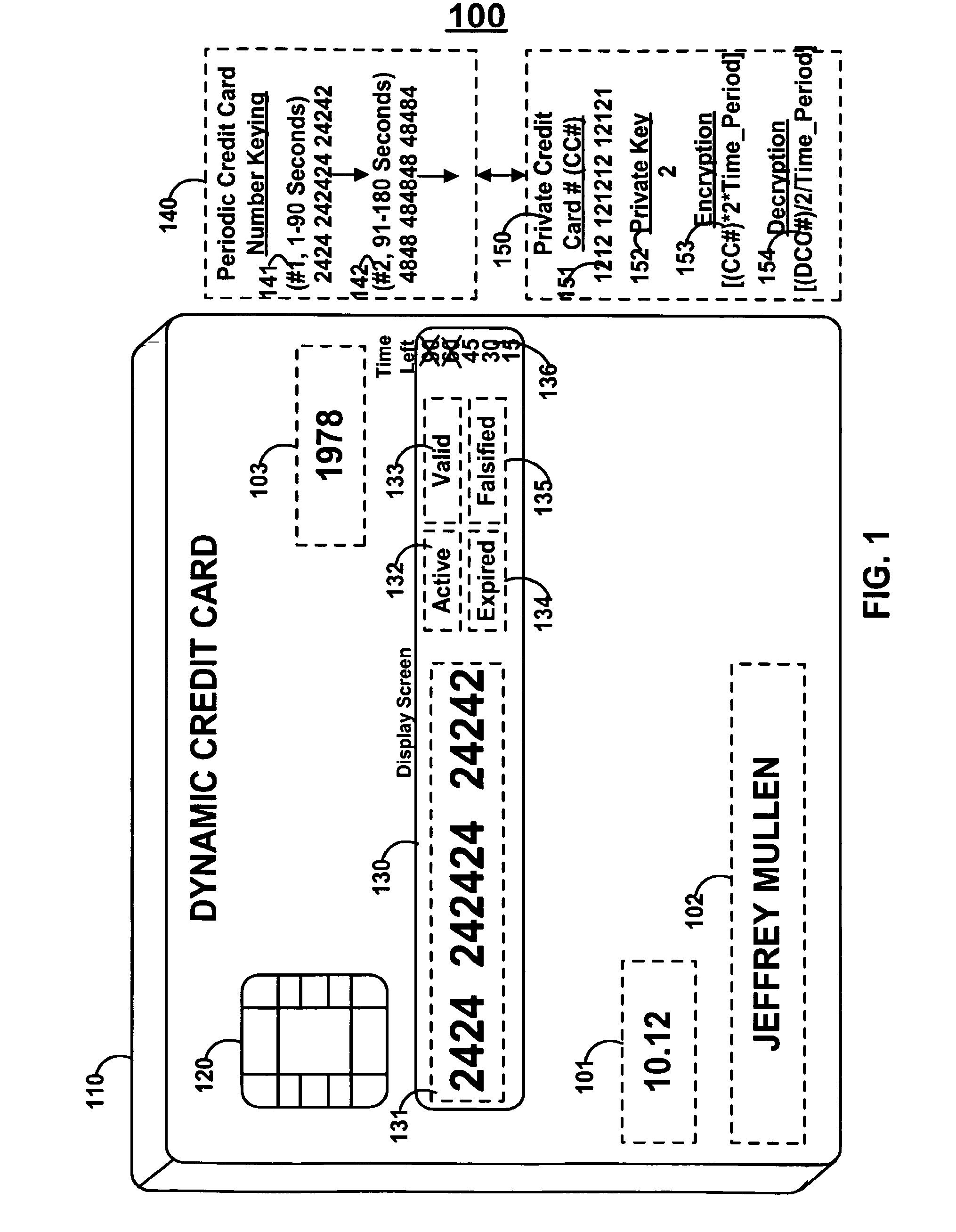
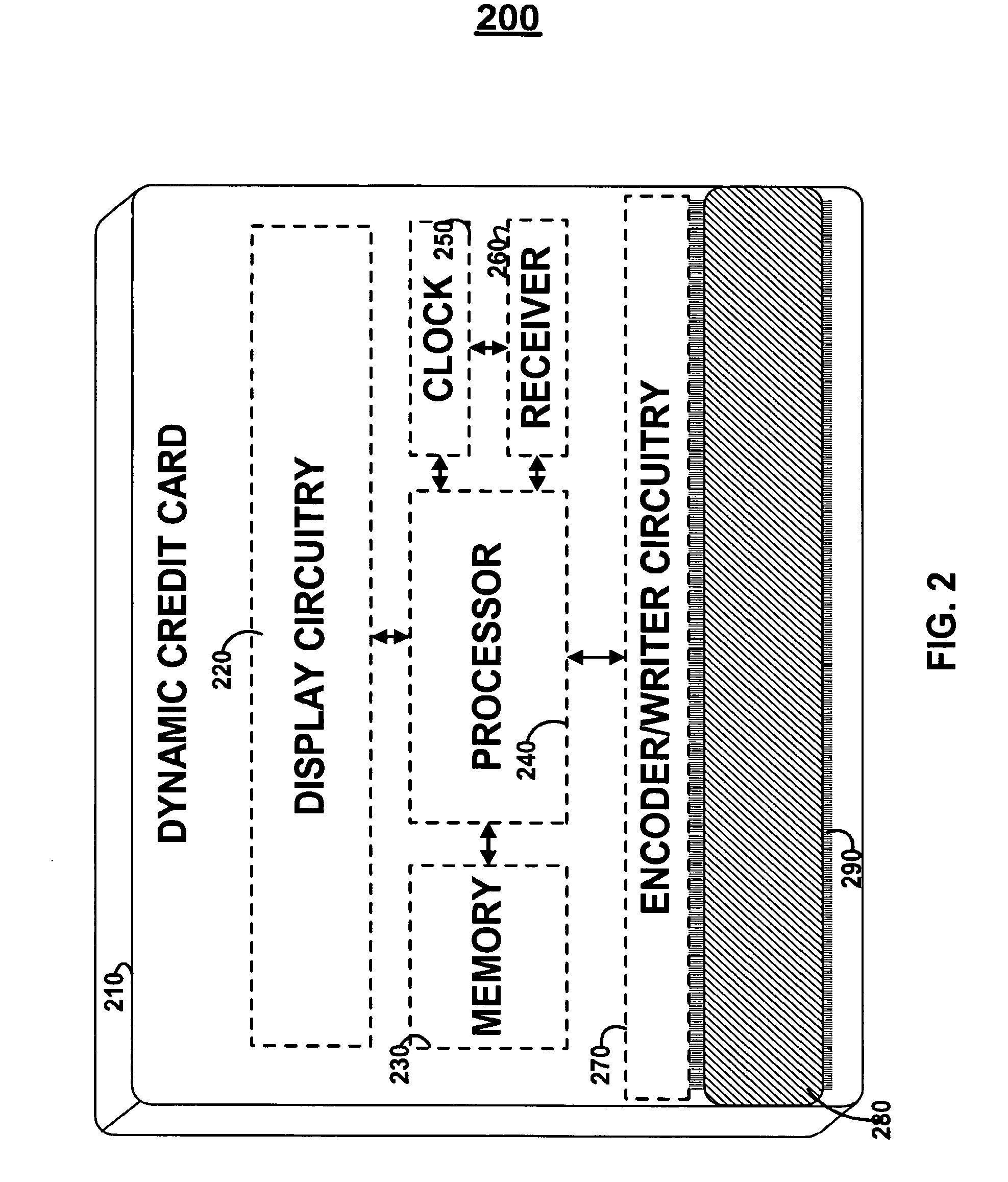
Dynamic credit card with magnetic stripe and embedded encoder and methods for using the same to provide a copy-proof credit card
A dynamic credit card is provided in which a secure credit card number (e.g., a secret / hidden credit card number) is encoded based on a timing signal (e.g., an internal counter) to provide a dynamic credit card number. This dynamic number may be displayed to a user via a display (e.g., so that online purchases can be made) or written onto a magnetic stripe such that the number may be processed by traditional credit card merchants (e.g., swiped). At a remote facility, the dynamic number may be decoded based on time (and / or a counter / key number / equation) or the facility may have the secure number and perform the same function as the dynamic credit card (e.g., encode using time data as a parameter to the encoding equation) and compare the resultant dynamic number to the dynamic number received. Thus, a dynamic credit card number may change continually or periodically (e.g., every sixty seconds) such that credit card numbers may not be copied by thieves and used at later times. A dynamic verification code may be utilized in addition to, or in lieu of, a dynamic credit card number.
Owner:DYNAMICS
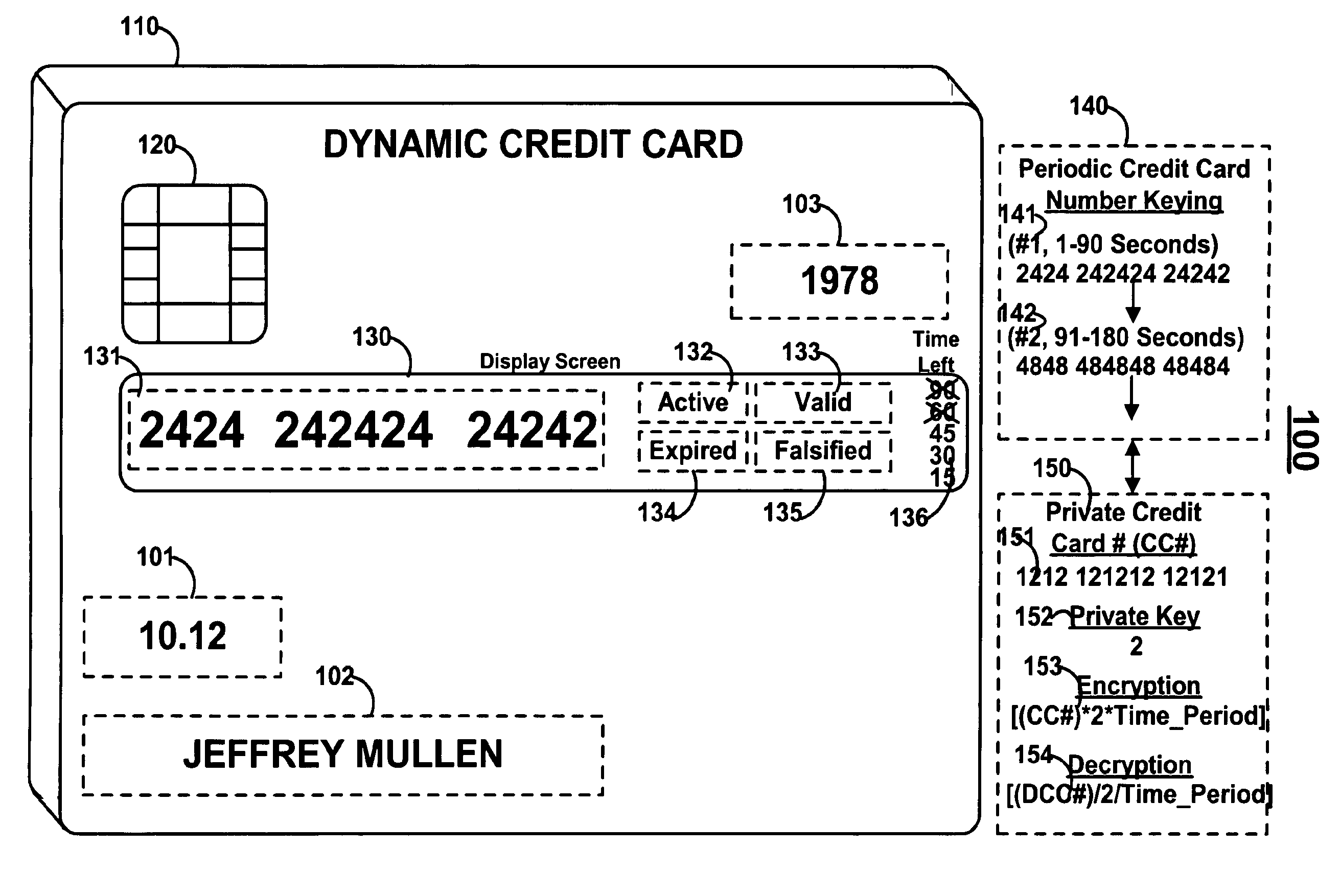
Dynamic credit card with magnetic stripe and embedded encoder and methods for using the same to provide a copy-proof credit card
A dynamic credit card is provided in which a secure credit card number (e.g., a secret / hidden credit card number) is encoded based on a timing signal (e.g., an internal counter) to provide a dynamic credit card number. This dynamic number may be displayed to a user via a display (e.g., so that online purchases can be made) or written onto a magnetic stripe such that the number may be processed by traditional credit card merchants (e.g., swiped). At a remote facility, the dynamic number may be decoded based on time (and / or a counter / key number / equation) or the facility may have the secure number and perform the same function as the dynamic credit card (e.g., encode using time data as a parameter to the encoding equation) and compare the resultant dynamic number to the dynamic number received. Thus, a dynamic credit card number may change continually or periodically (e.g., every sixty seconds) such that credit card numbers may not be copied by thieves and used at later times. A dynamic verification code may be utilized in addition to, or in lieu of, a dynamic credit card number.
Owner:DYNAMICS
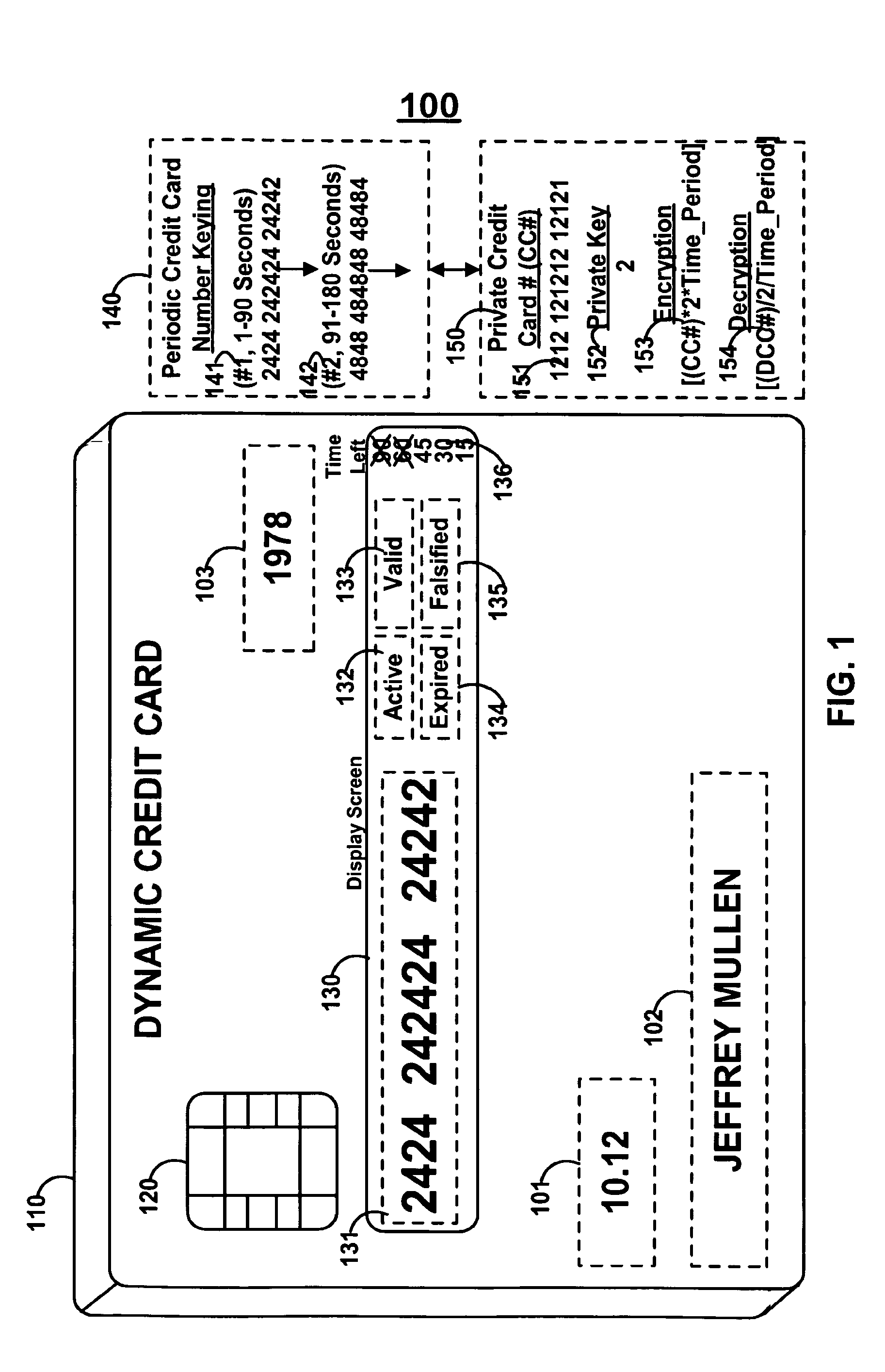
Dynamic credit card with magnetic stripe and embedded encoder and methods for using the same to provide a copy-proof credit card
A dynamic credit card is provided in which a secure credit card number (e.g., a secret / hidden credit card number) is encoded based on a timing signal (e.g., an internal counter) to provide a dynamic credit card number. This dynamic number may be displayed to a user via a display (e.g., so that online purchases can be made) or written onto a magnetic stripe such that the number may be processed by traditional credit card merchants (e.g., swiped). At a remote facility, the dynamic number may be decoded based on time (and / or a counter / key number / equation) or the facility may have the secure number and perform the same function as the dynamic credit card (e.g., encode using time data as a parameter to the encoding equation) and compare the resultant dynamic number to the dynamic number received. Thus, a dynamic credit card number may change continually or periodically (e.g., every sixty seconds) such that credit card numbers may not be copied by thieves and used at later times. A dynamic verification code may be utilized in addition to, or in lieu of, a dynamic credit card number.
Owner:DYNAMICS
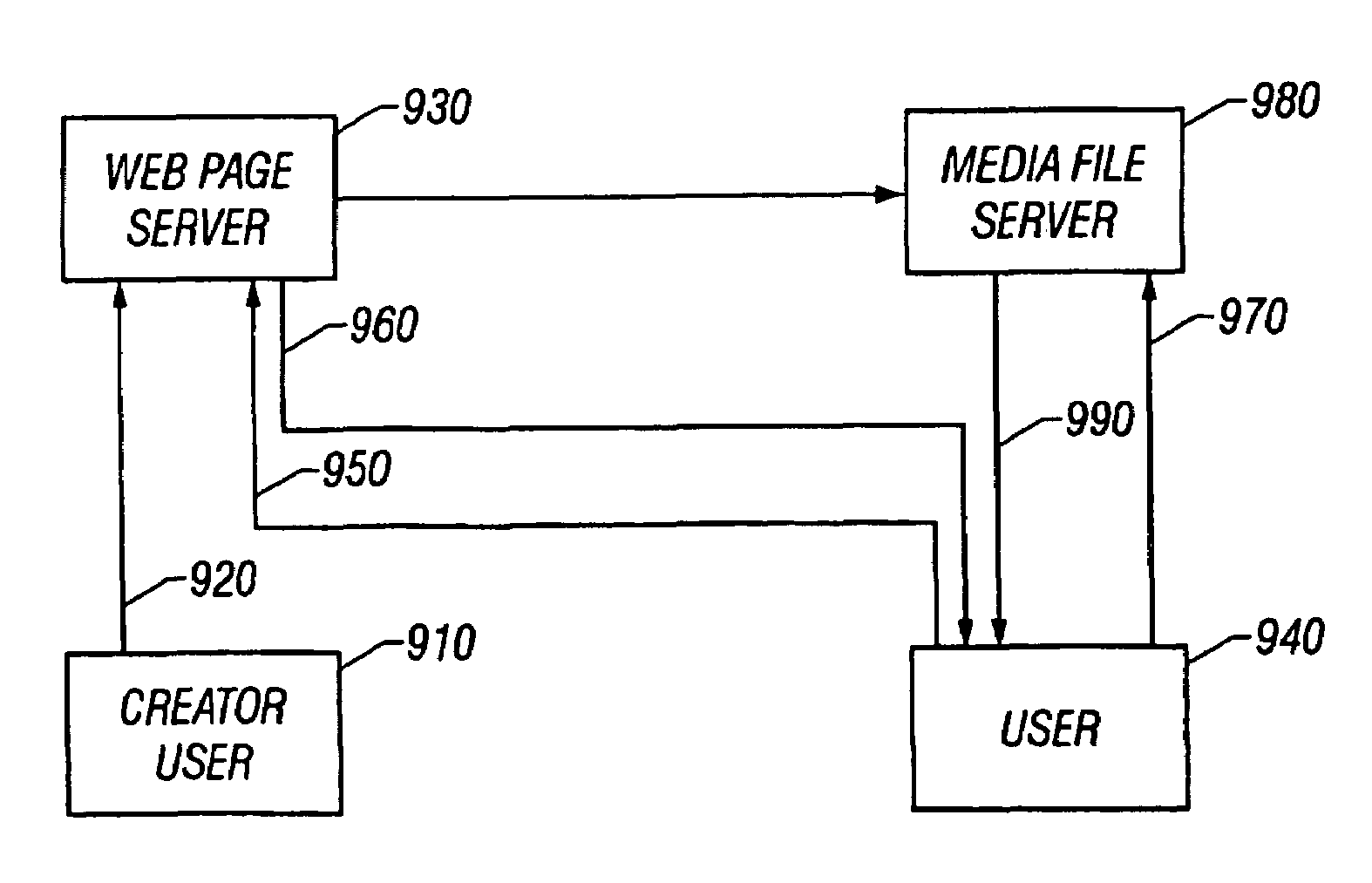
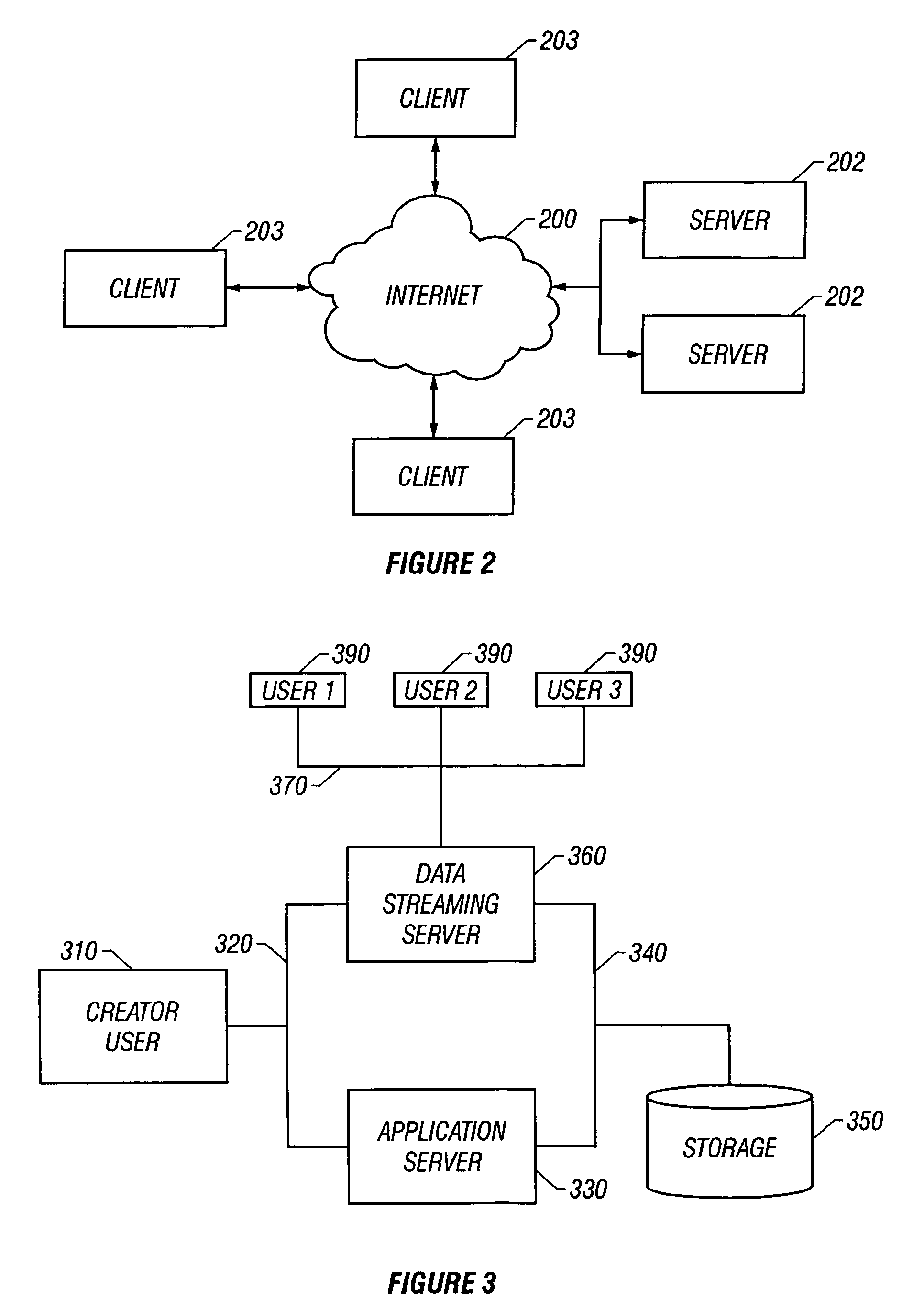
System and method for creating and posting media lists for purposes of subsequent playback
InactiveUS7069310B1Create quicklyEasy to processDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionDigital signal processingENCODE
A method and apparatus for creating and posting media is provided. For example, the invention allows a user to quickly create, signal process, encode, and transfer media files to a server for storage, posting, distribution, and retrieval. Thus, media such as audio, video, display, photo, spreadsheet, Web Clips, and HTML pages can be combined into a media file for uploading to a server and accessed from listings posted at web sites. In accordance with embodiments, a user downloads and installs a plug-in at the user's client computer. The user then registers and logs onto the server to perform various tasks. For example, the user can create a combined audio and photo media file at the client computer, in accordance with server based control parameters received from the system server. The plug-in then allows the user to perform digital signal processing and encoding of the media file at the client computer. After the file is encoded, it may be uploaded to a server for storage, posting, distribution, and retrieval. A file management system provides copies and listings of the file to other servers and web sites as permitted. Thus, other user having access to the database or web site lists via other client computers may select the file for retrieval. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, an information management system provides file and file list rankings based upon selection or click through of files and file listings.
Owner:POST MEDIA SYST LLC
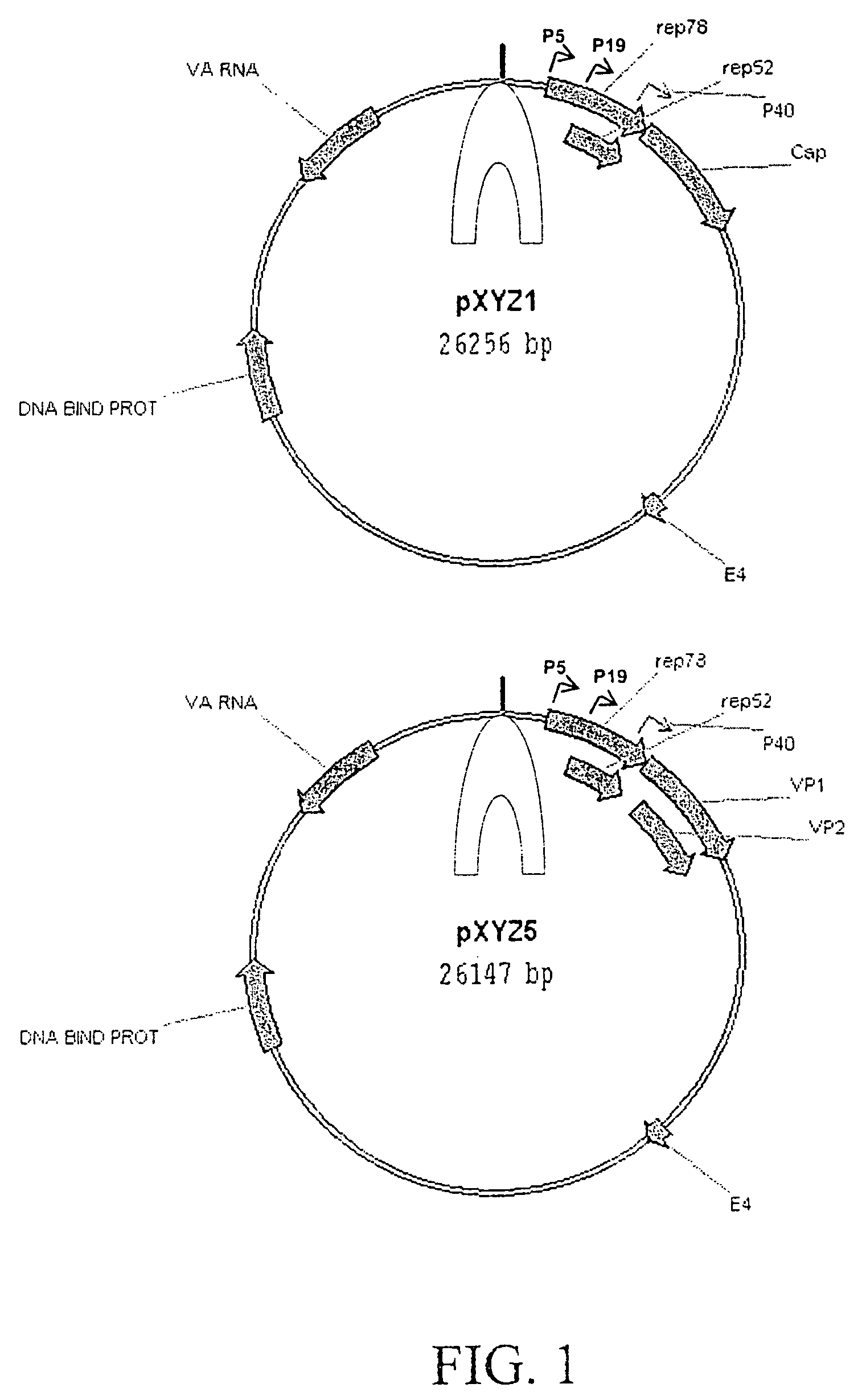
Production of pseudotyped recombinant AAV virions
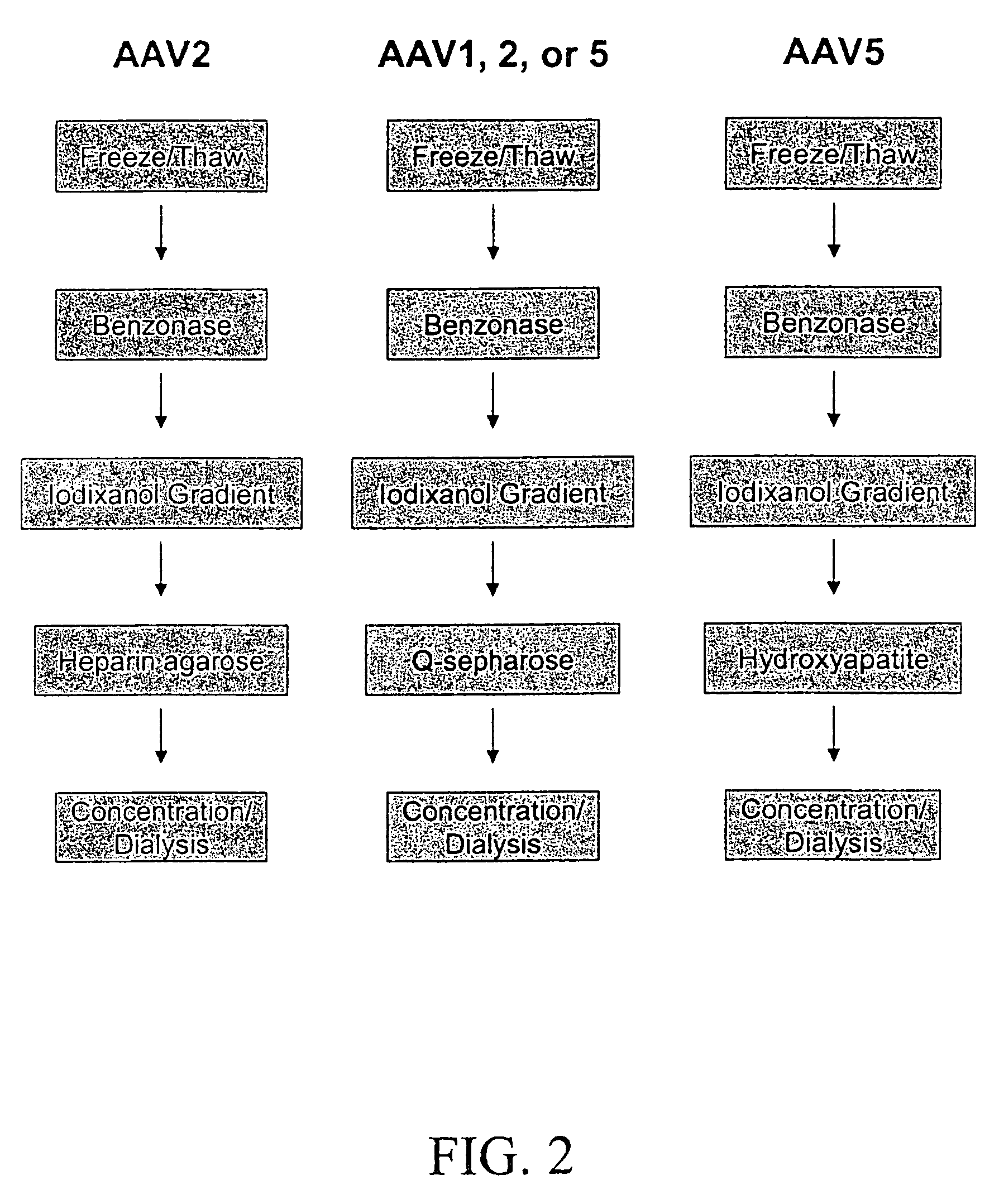
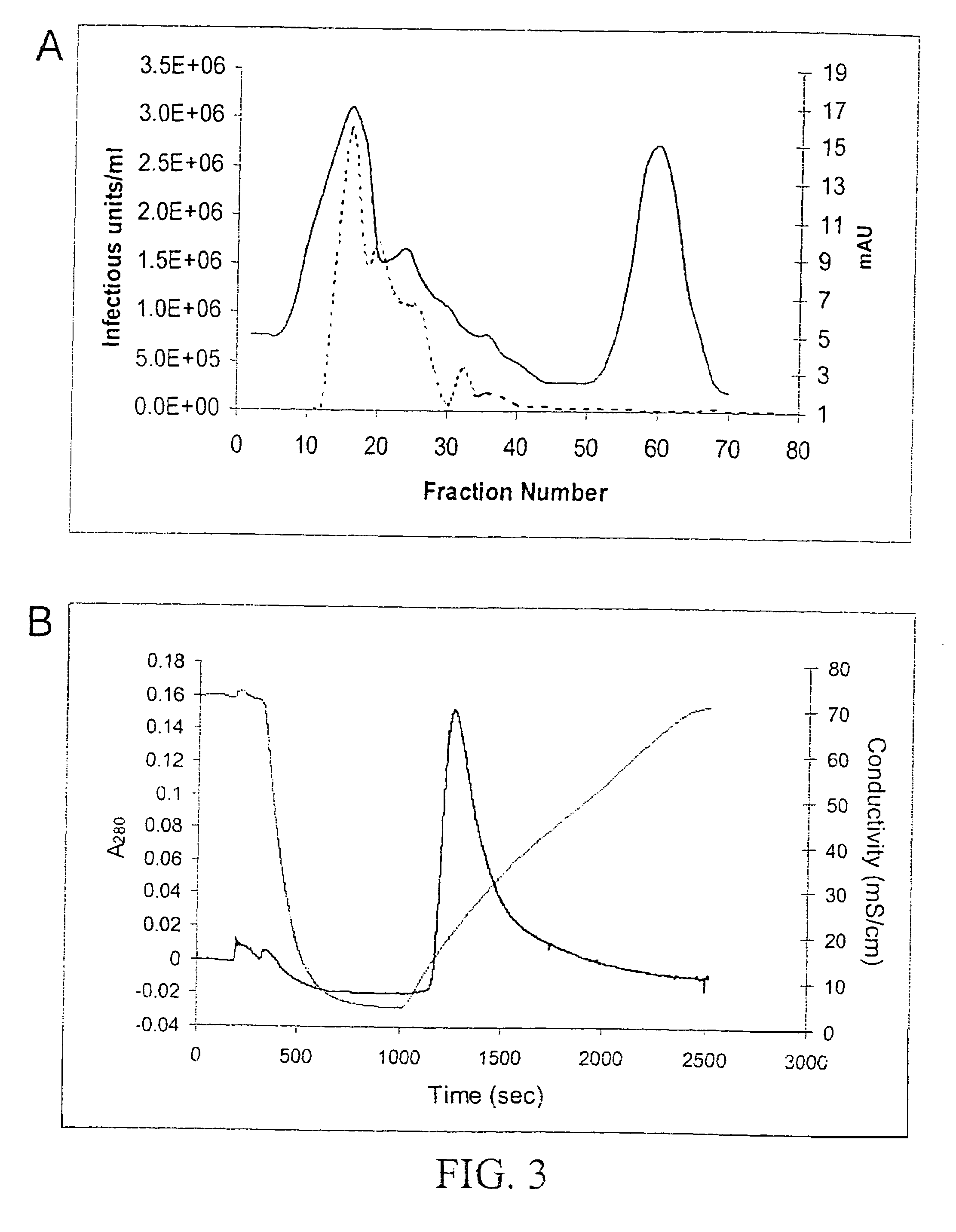
InactiveUS7094604B2Highly purified and concentratedEfficient and large-scale productionVectorsSugar derivativesPurification methodsSerotype
Vectors that encode Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Rep and Cap proteins of different serotypes and Adenovirus transcription products that provide helper functions were used to produce pseudotyped recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions. Purification methods generated pseudotyped rAAV virion stocks that were 99% pure with titers of 1×1012–1×1013 vector genomes / ml.
Owner:UNIVIRSITY OF FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
System and method for migrating virtual machines on cluster systems
ActiveUS7730486B2Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsManagement processCluster systems
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
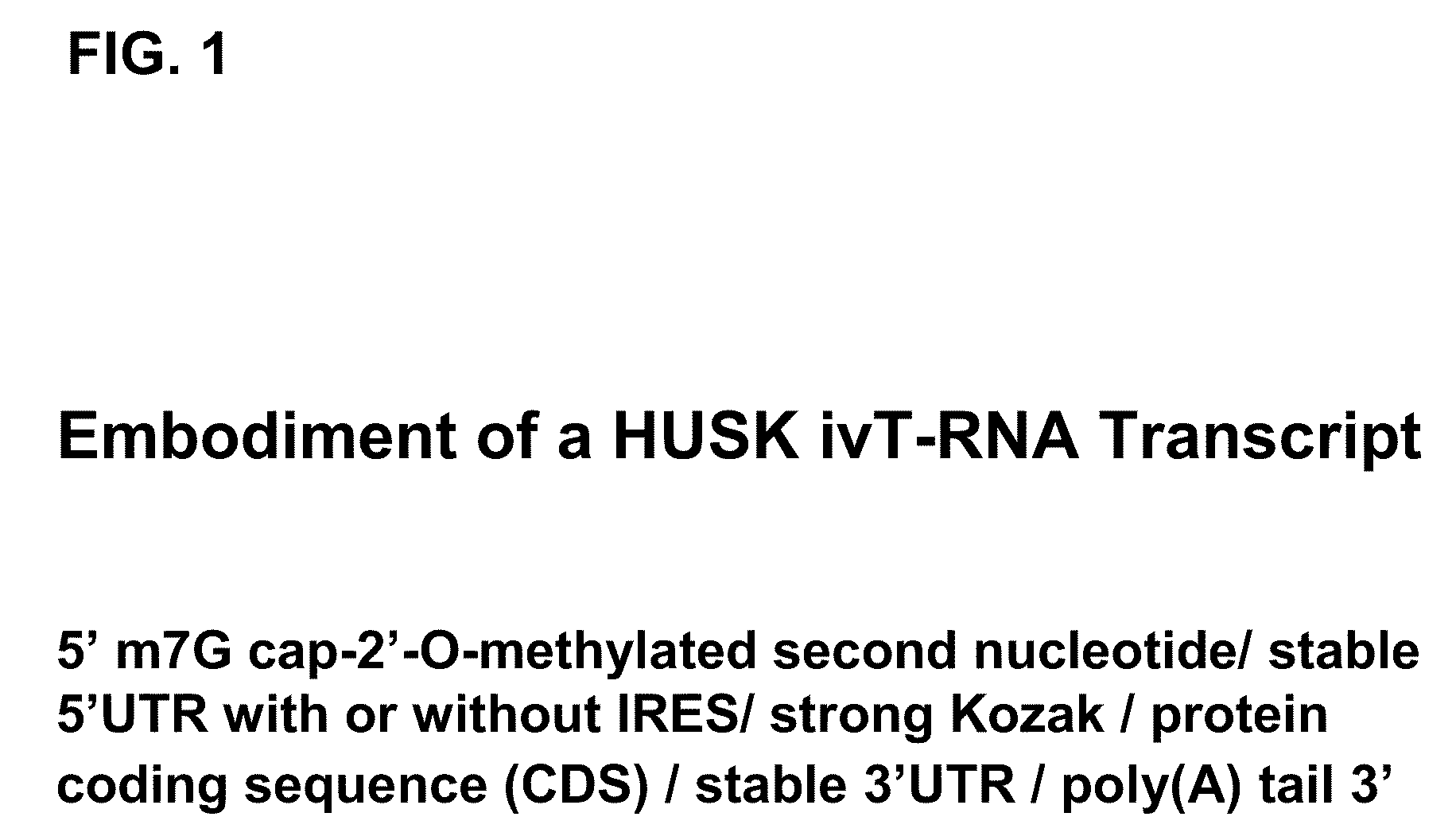
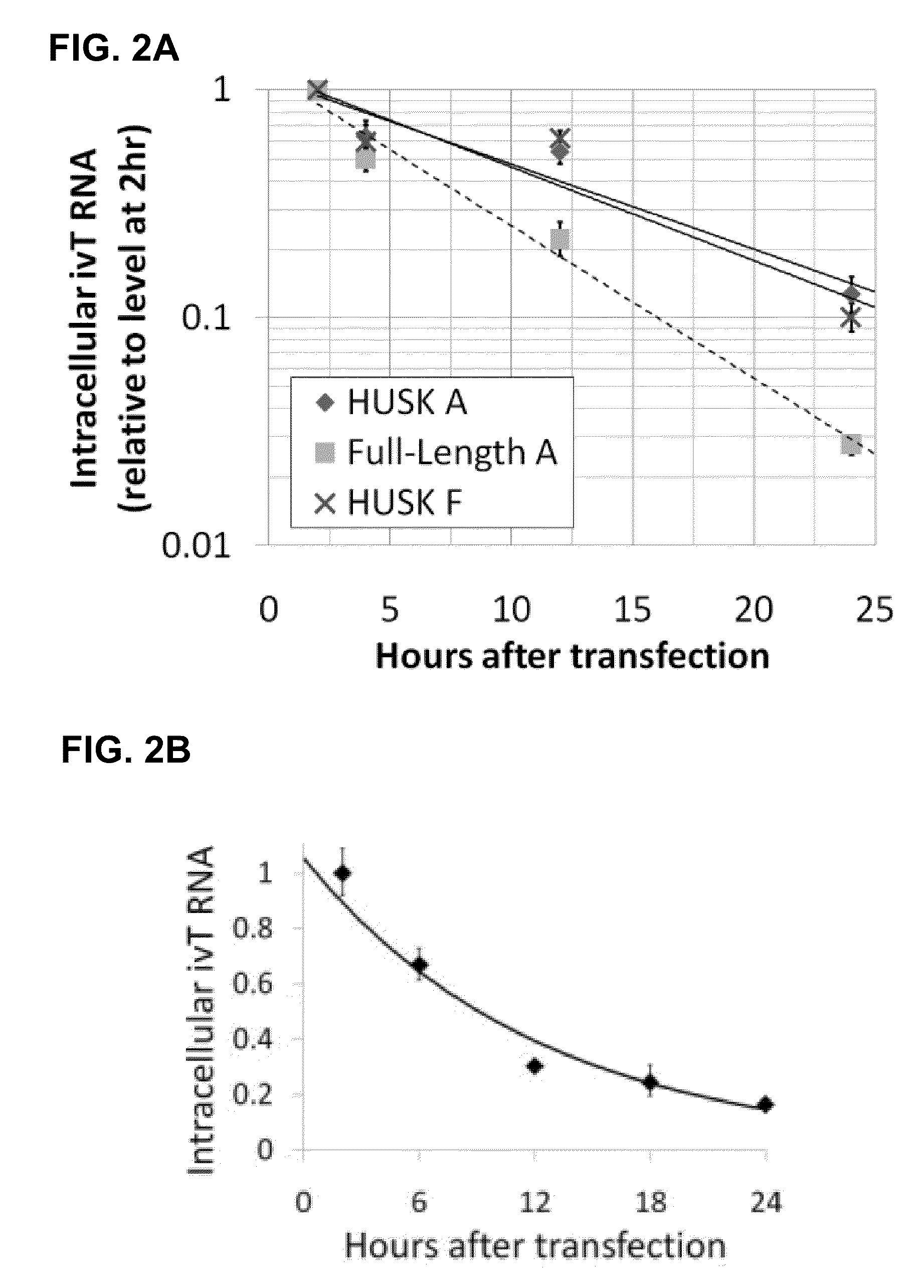
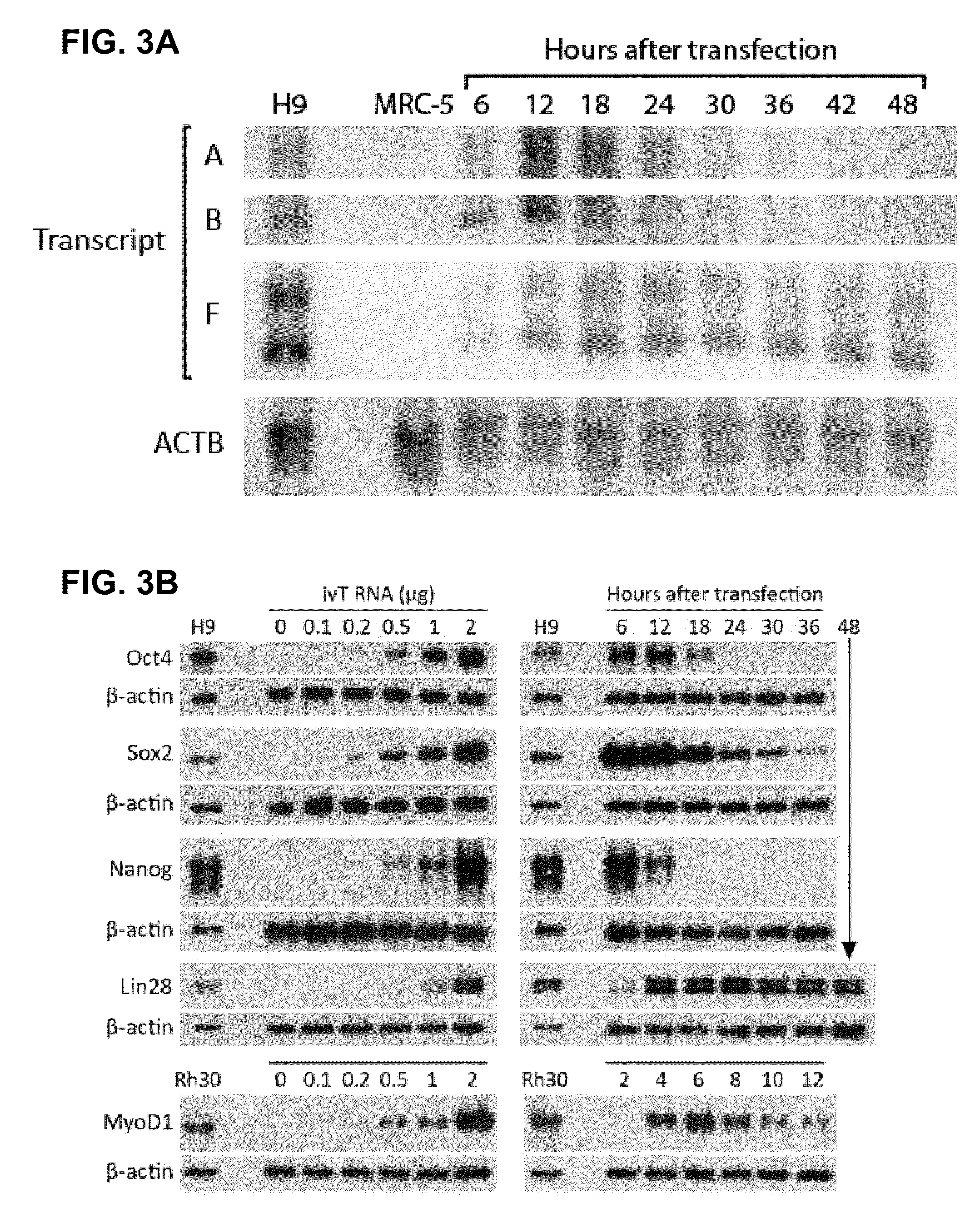
Innate immune suppression enables repeated delivery of long RNA molecules
InactiveUS20100273220A1Suppressing innate immune responseReduce expressionSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsENCODETransient transfection
The present invention relates in part to methods for suppressing the innate immune response of a cell to transfection with an exogenous nucleic acid, to methods for increasing expression of a protein encoded by an exogenous nucleic acid by repeated delivery of the exogenous nucleic acid to a cell, and to methods of changing the phenotype of a cell by differentiating, transdifferentiating or dedifferentiating cells by repeatedly delivering one or more nucleic acids that encode defined proteins. A method is provided for extended transient transfection by repeated delivery of an in vitro-transcribed RNA (“ivT-RNA”) to a cell to achieve a high and sustained level of expression of a protein encoded by an ivT-RNA transcripts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Self-processing plants and plant parts
The invention provides polynucleotides, preferably synthetic polynucleotides, which encode processing enzymes that are optimized for expression in plants. The polynucleotides encode mesophilic, thermophilic, or hyperthermophilic processing enzymes, which are activated under suitable activating conditions to act upon the desired substrate. Also provided are “self-processing” transgenic plants, and plant parts, e.g., grain, which express one or more of these enzymes and have an altered composition that facilitates plant and grain processing. Methods for making and using these plants, e.g., to produce food products having improved taste and to produce fermentable substrates for the production of ethanol and fermented beverages are also provided.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
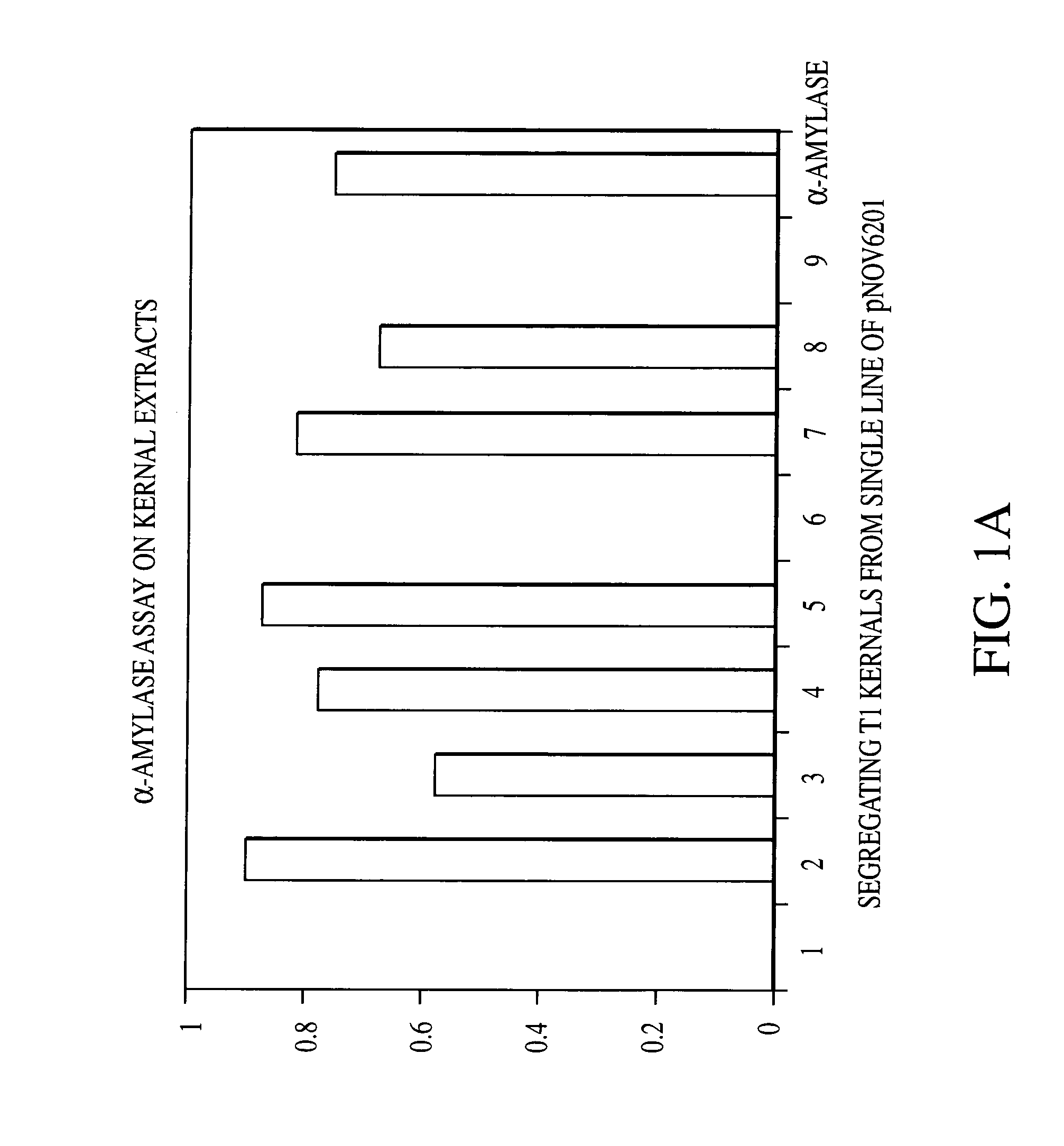
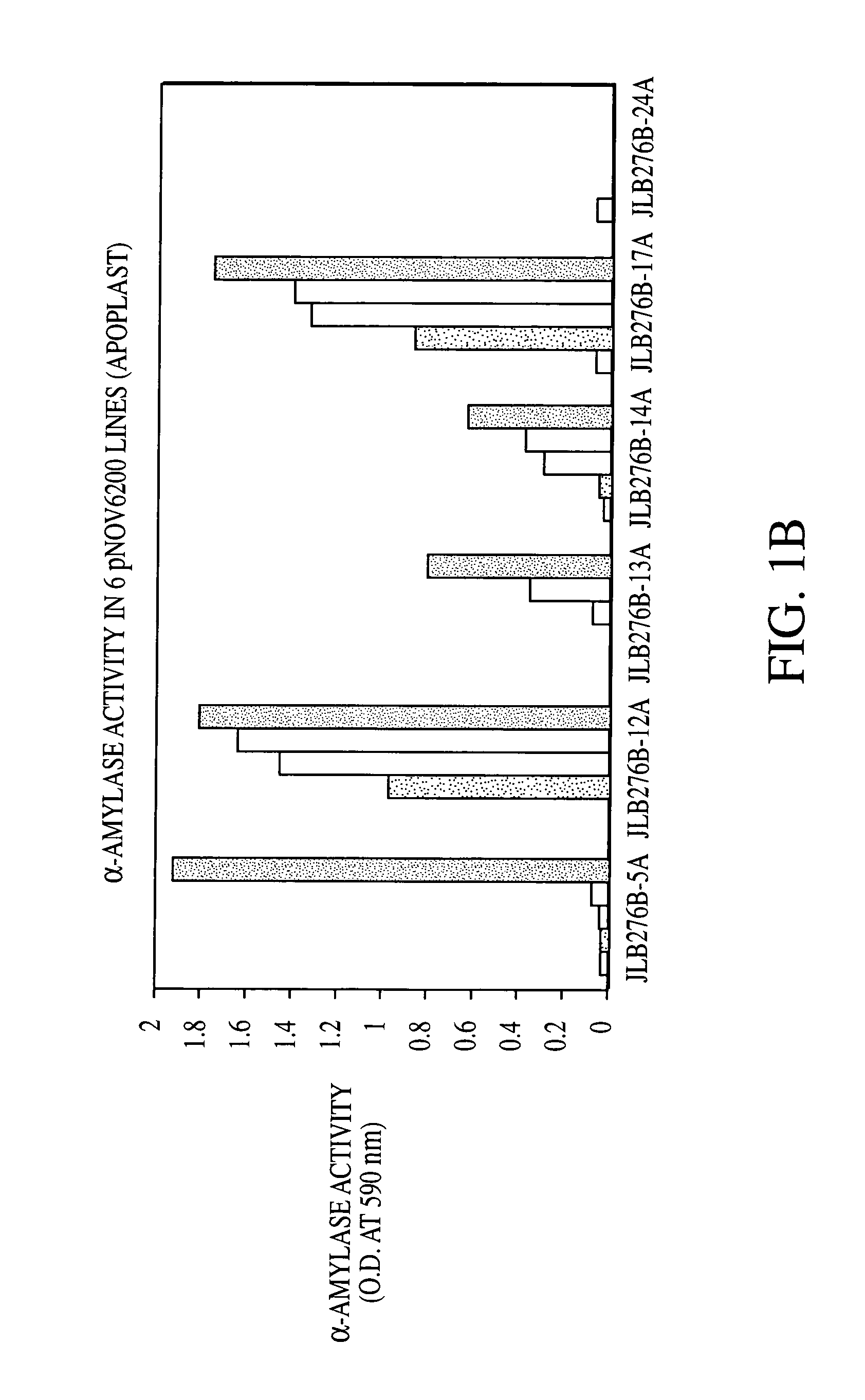
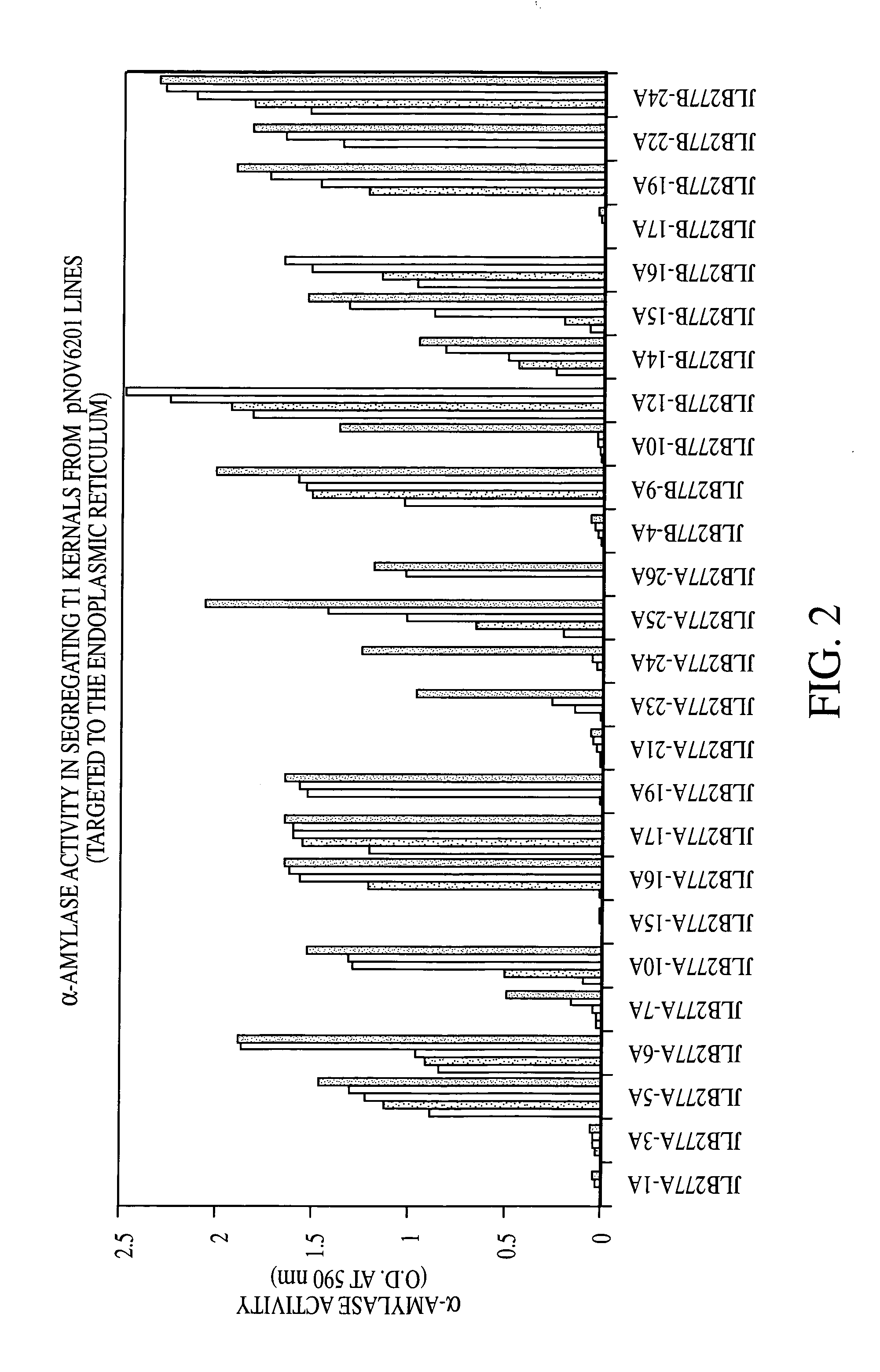
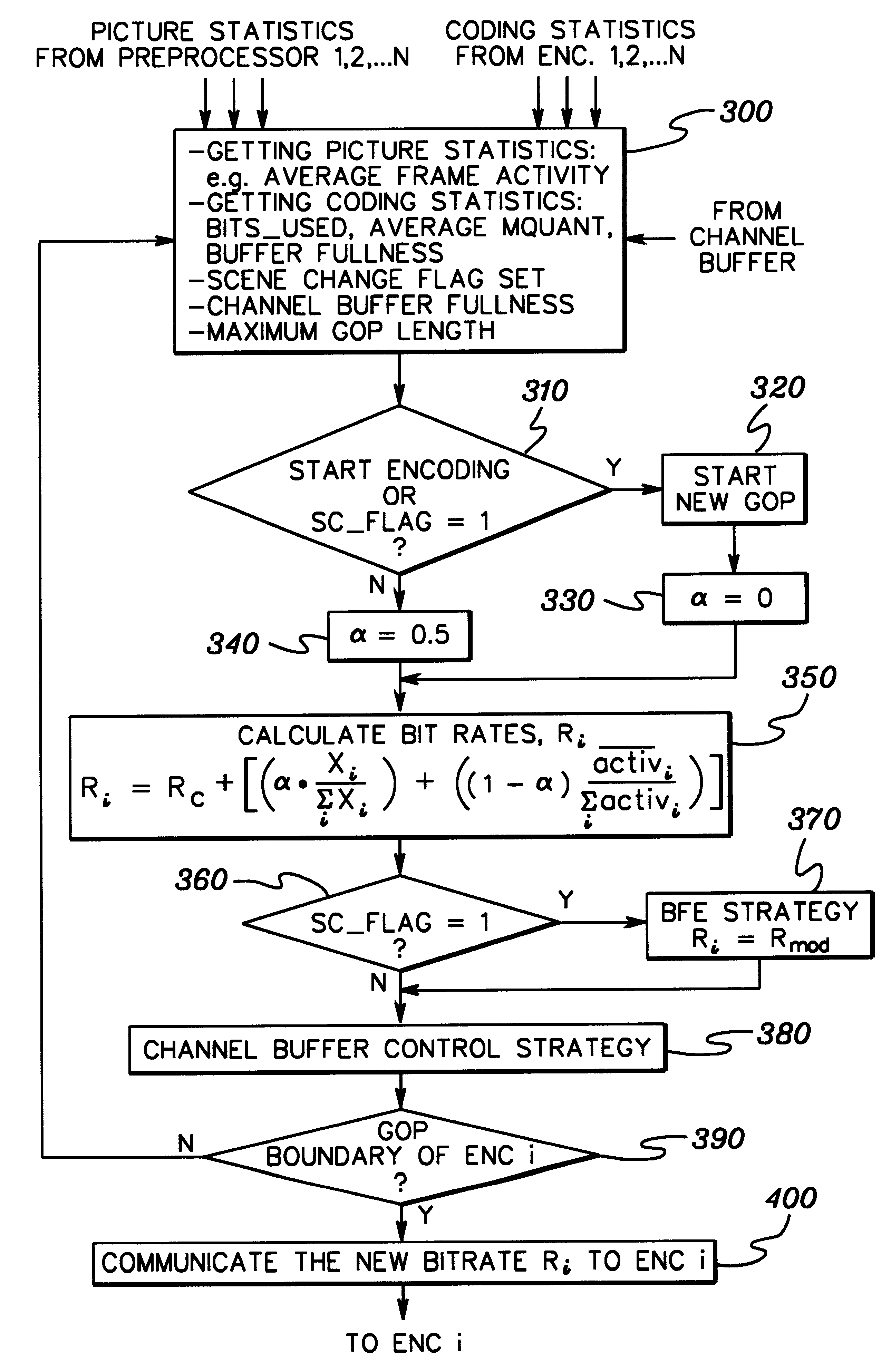
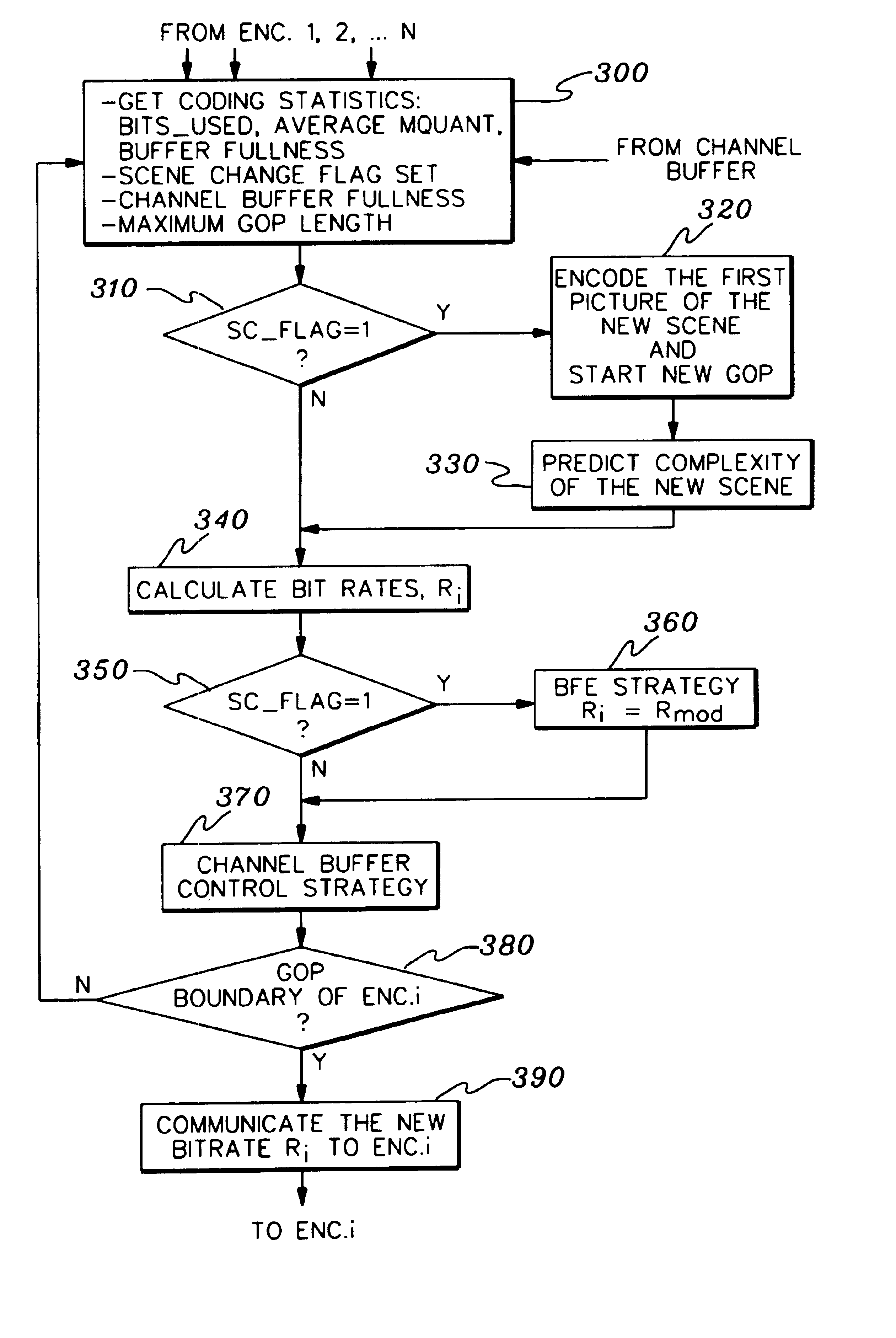
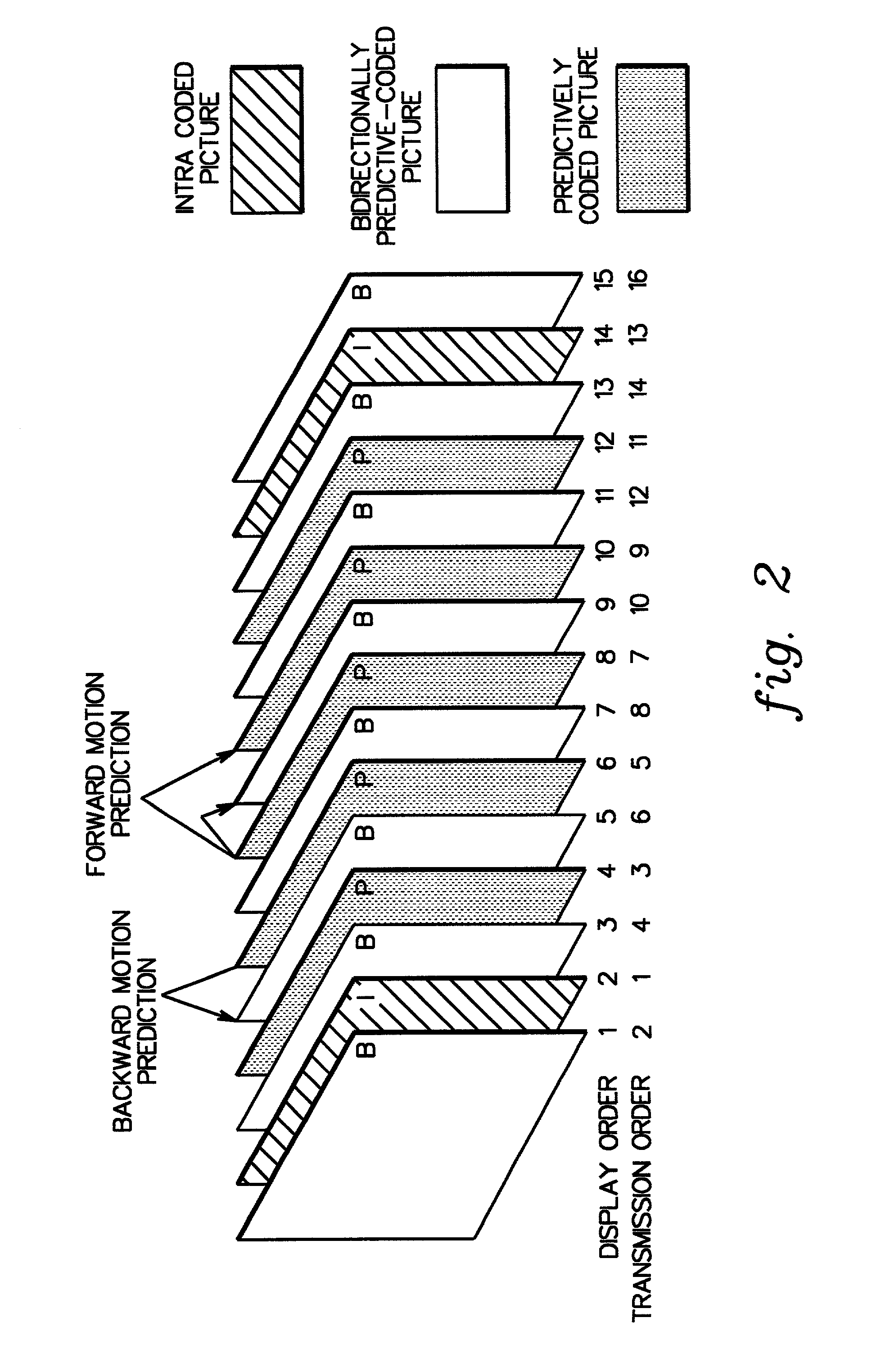
Adaptively encoding multiple streams of video data in parallel for multiplexing onto a constant bit rate channel
InactiveUS6859496B1Configuration highRapid responsePulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingFrame based
A control strategy is provided for dynamically encoding multiple streams of video data in parallel for multiplexing onto a constant bit rate channel. The control strategy allows individual encode bit rates to be dynamically adjusted for each video data stream based in part on relative complexity of the multiple streams of video data, as well as fullness of compressed video data buffers and a channel buffer coupled between the encoders and the constant bit rate channel. The control strategy includes analyzing the multiple streams of video to determine relative complexity thereof, encoding the multiple streams of video frames in parallel, and dynamically adapting encoding of at least one stream of the video frames based on the relative complexity of the video frames. The bit rate for each stream of video frames is only changed at GOP boundaries, or if a scene change occurs. The calculated bit rate is preferably further modified based upon buffer fullness.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cry1F and Cry1Ac transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
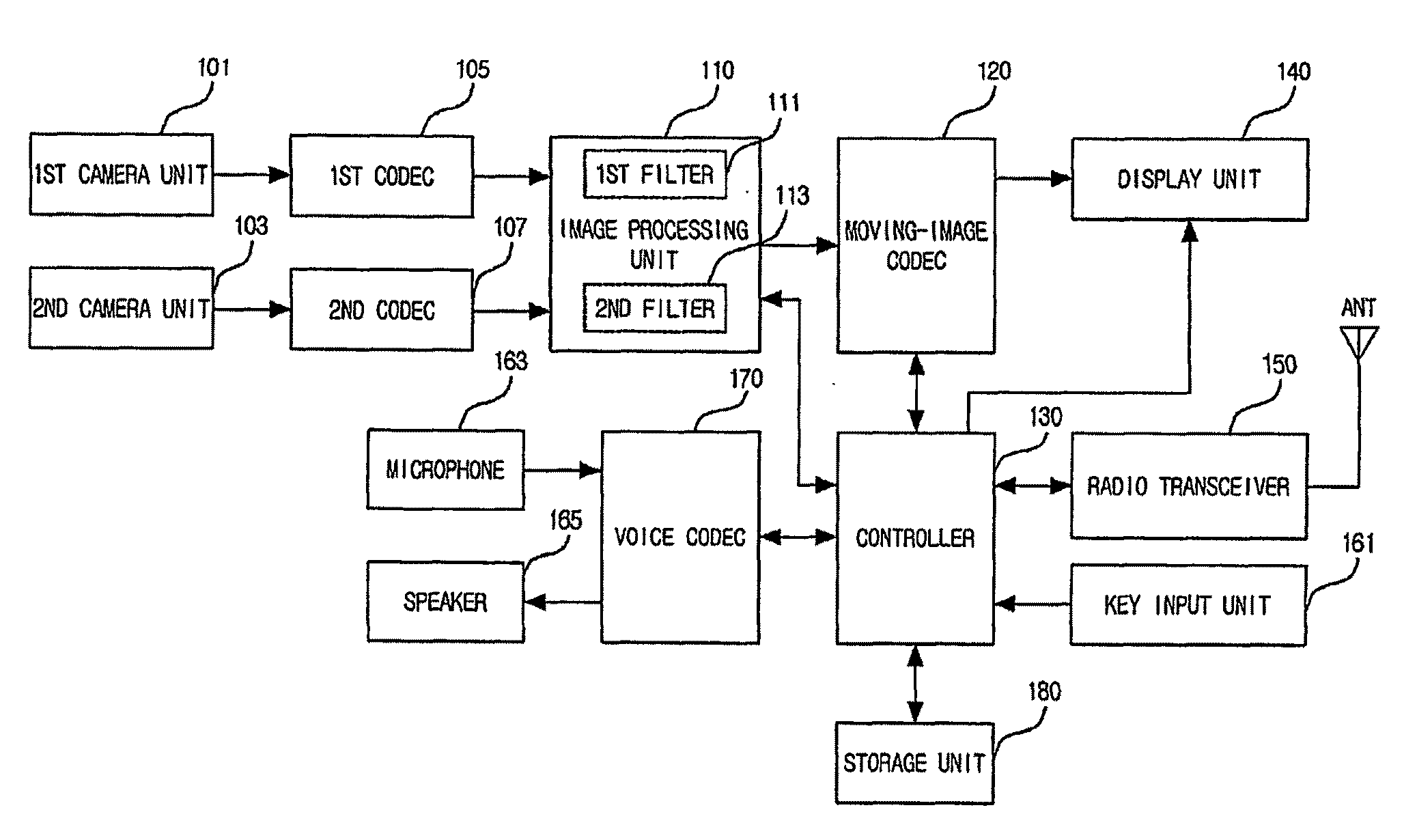
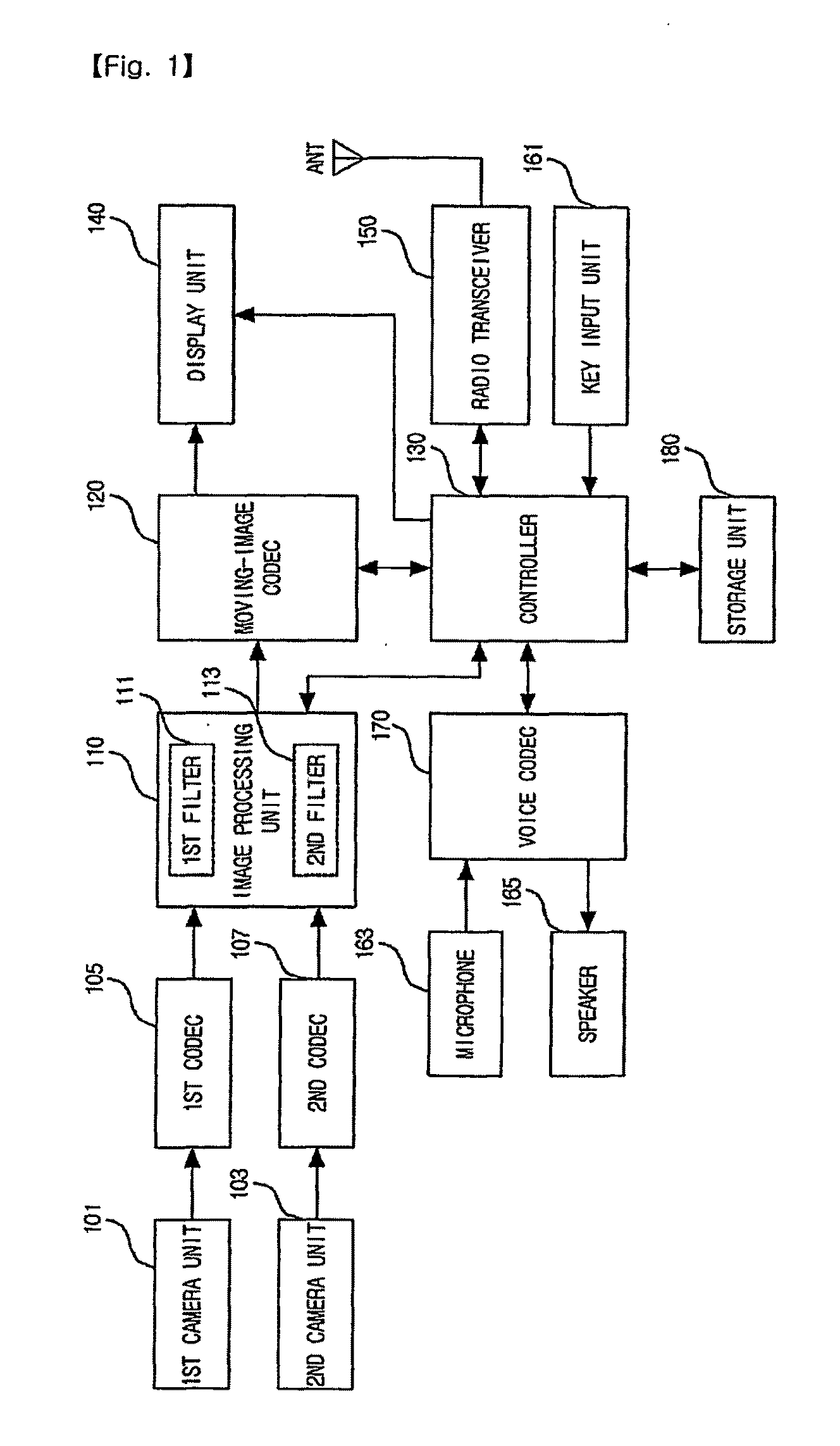
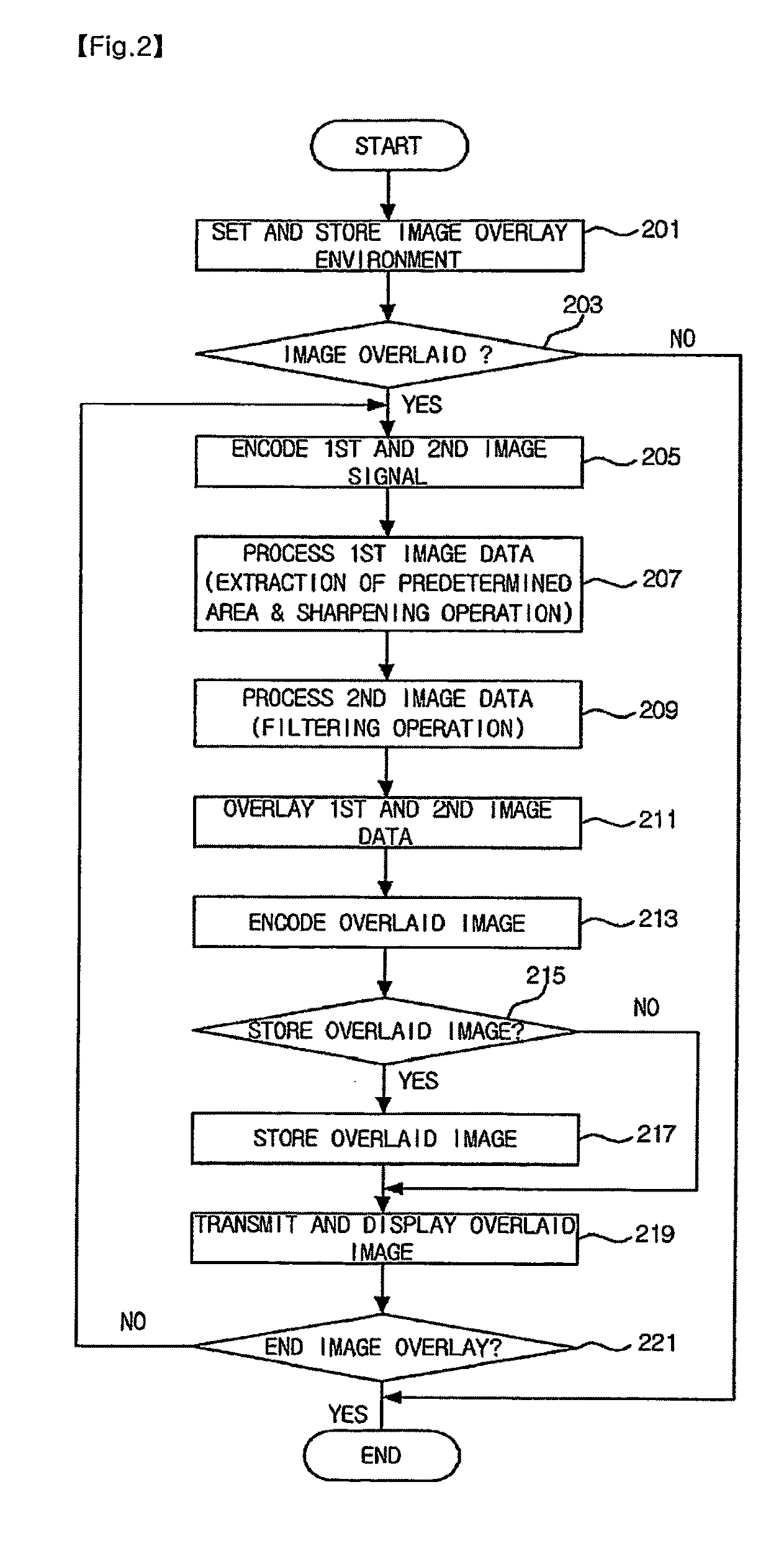
Portable device having image overlay function and method of overlaying image in portable device
Disclosed are a portable device having an image overlay function and a method of overlaying images in the portable device, which can photograph a plurality of images within areas having no overlapping regions between the areas in real time, and can overlay the photographed images. A first camera unit photographs a first area, and a second camera unit photographs a second area which does not overlap with the first area. A first codec and a second codec encode a first area image and a second area image, respectively, which have been obtained by photographing the first area and the second area. An image processing unit overlays the encoded first area image and the encoded second area image. Therefore, it is possible to photograph a plurality of subjects existing in at least two areas having no overlapping regions between the two areas in real time, to overlay the photographed images, and to transmit the overlaid image to a portable device of a counterpart for video telephone communication.
Owner:KT TECH
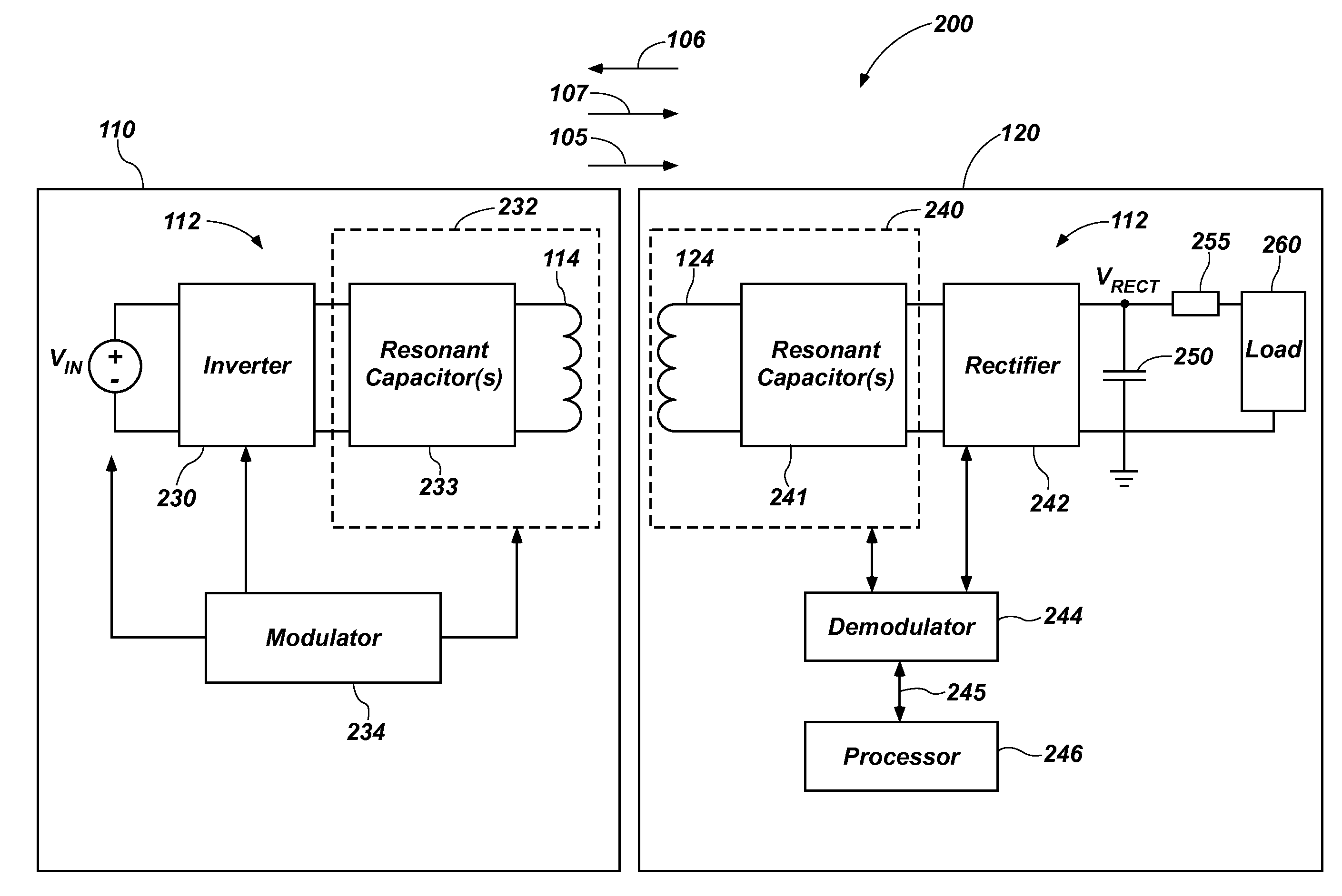
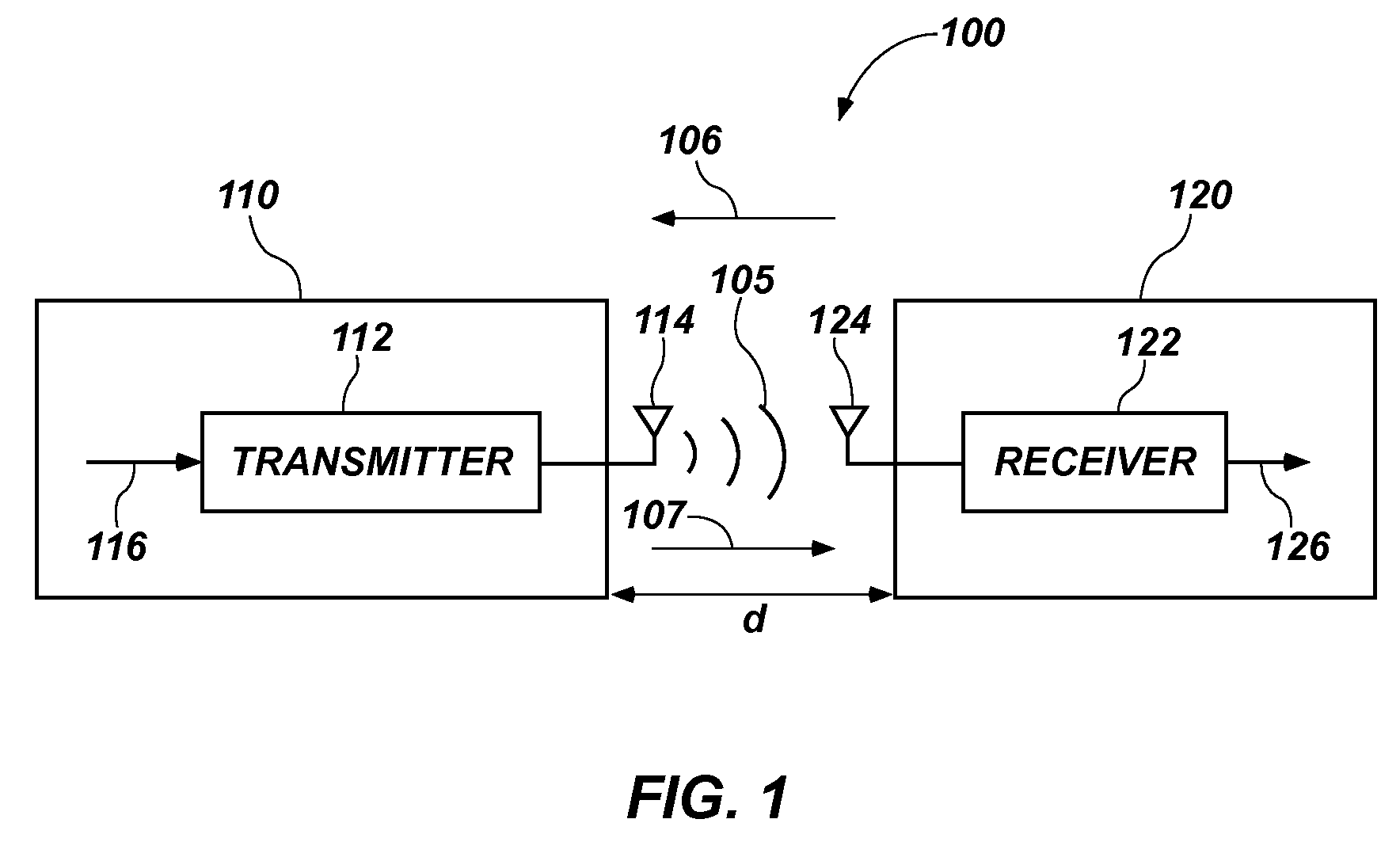
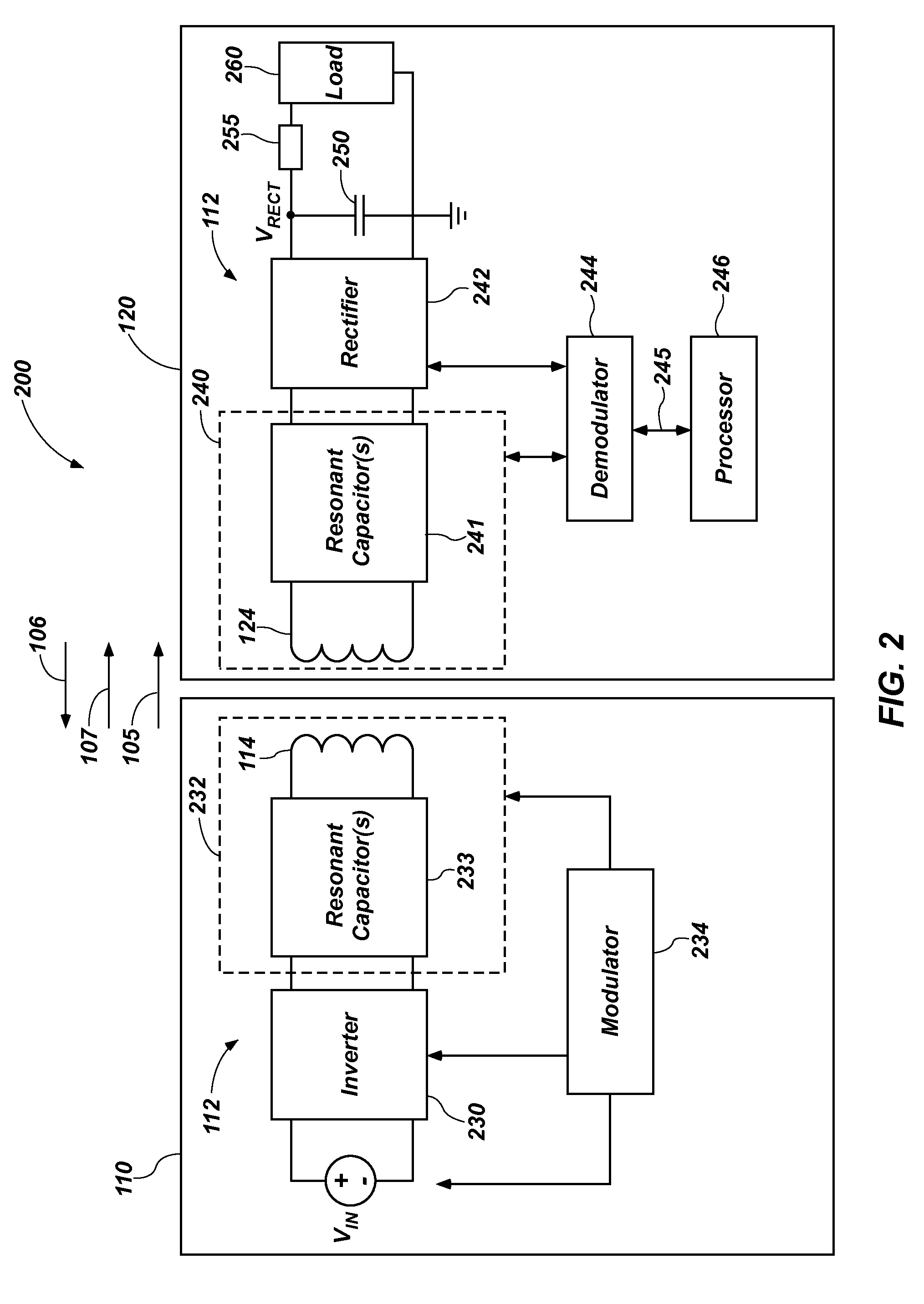
Apparatus, system, and method for back-channel communication in an inductive wireless power transfer system
An inductive wireless power transfer device comprises a transmitter that comprises a transmit coil configured to generate a wireless power signal to a coupling region in response to an input voltage, and a modulator configured to modulate the wireless power signal and encode data with the wireless power signal to establish a back-channel communication link from the transmitter to a receiver. An inductive wireless power receiving device comprises a receiver that comprises a receive coil configured to generate a time varying signal in response to receiving a modulated wireless power signal from a transmitter in a coupling region, and a demodulator configured to demodulate the modulated wireless power signal from an established back-channel communication link from the transmitter to a receiver. Related inductive wireless power transfer systems and methods for back-channel communication from the transmitter to the receiver of an inductive wireless power transfer system are disclosed.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
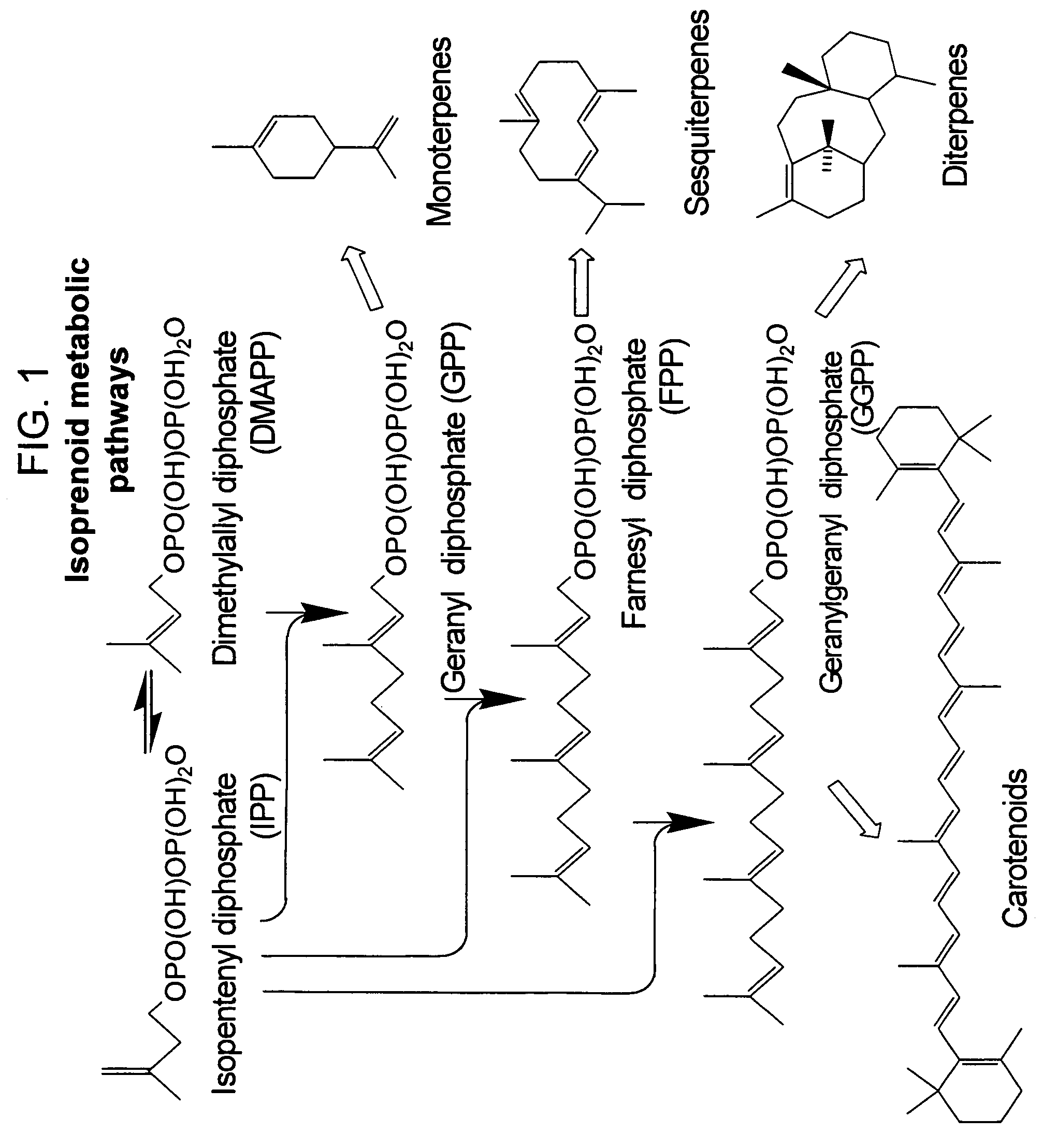
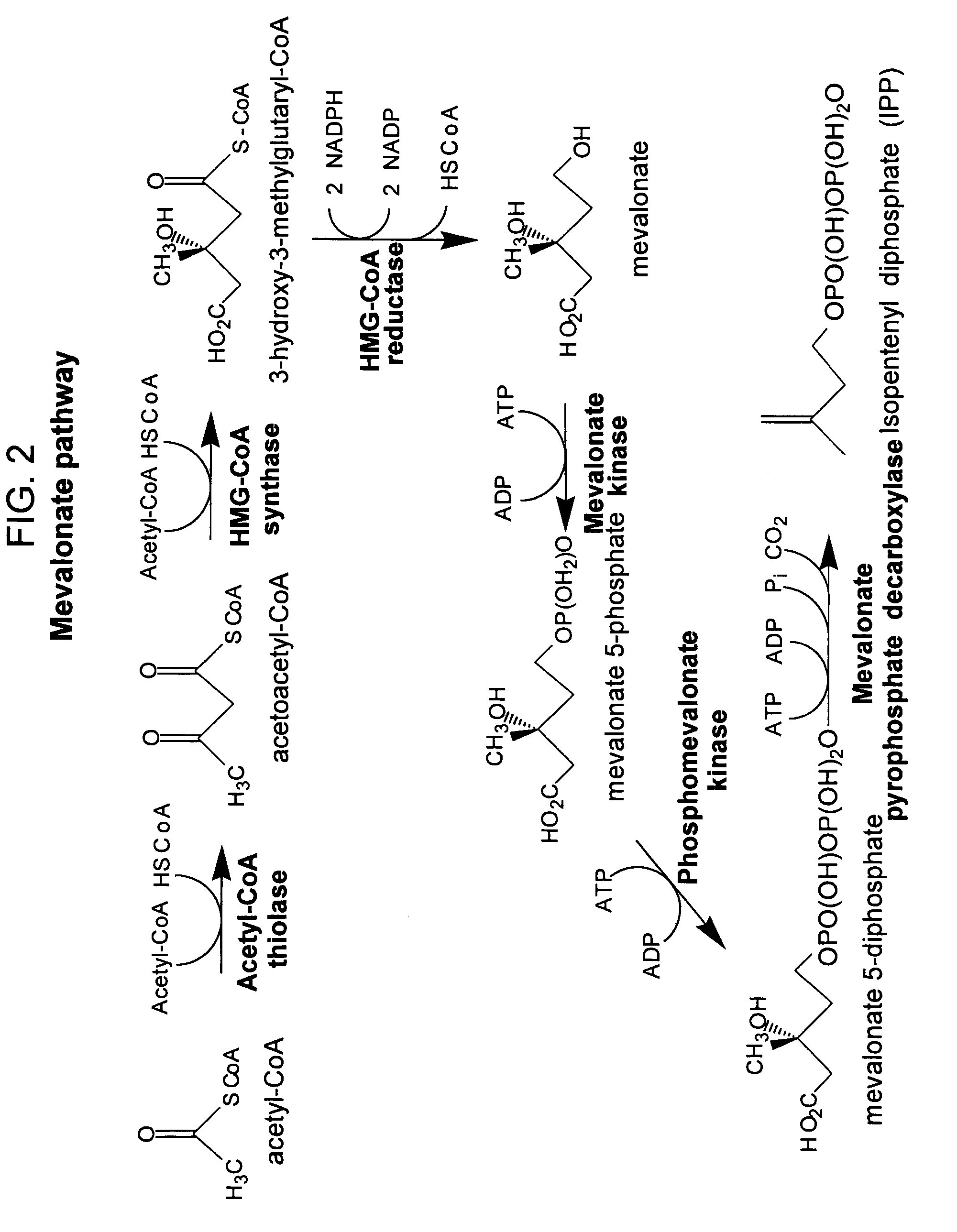
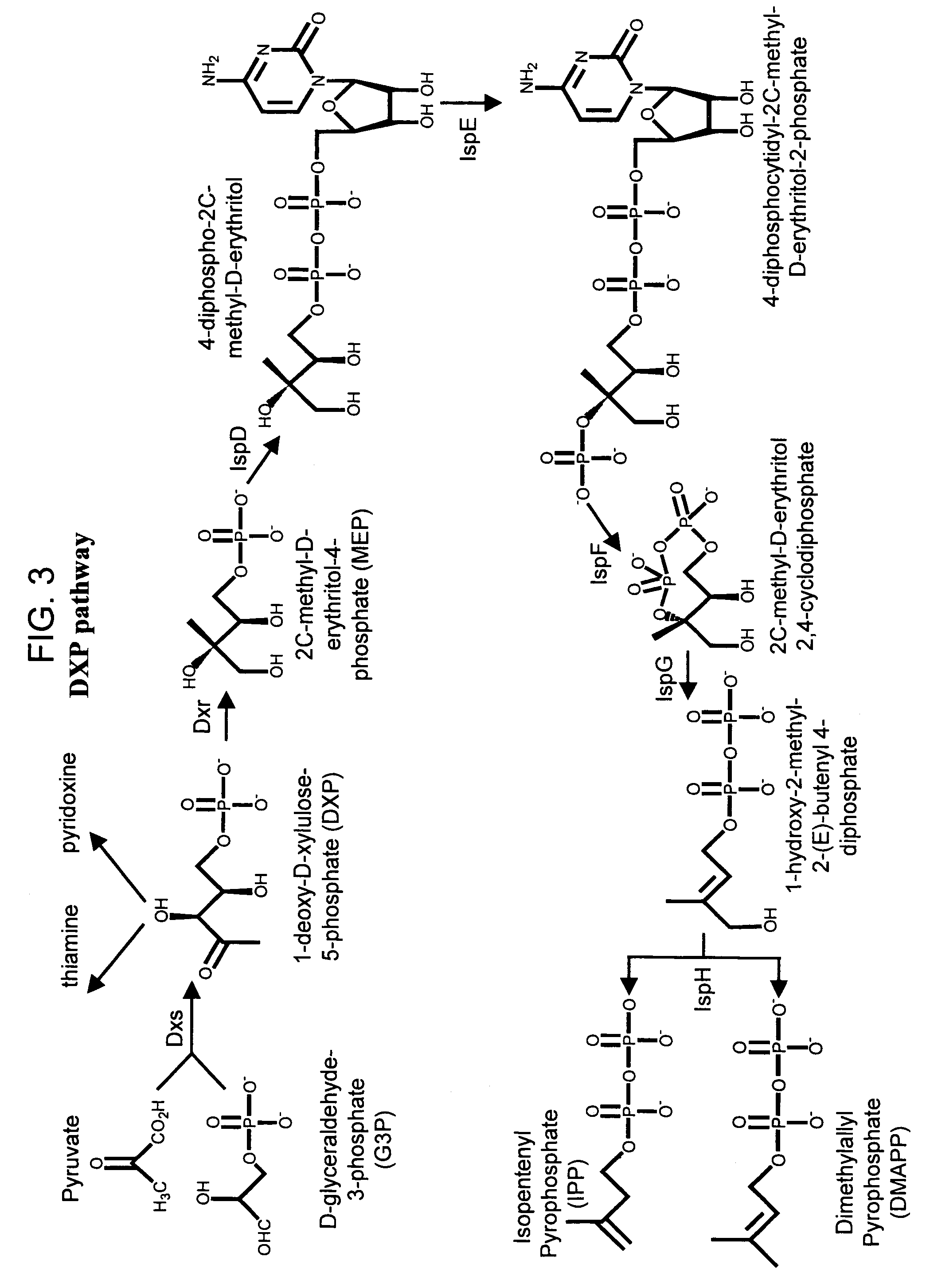
Method for enhancing production of isoprenoid compounds
The present invention provides methods of producing an isoprenoid or an isoprenoid precursor in a genetically modified host cell. The methods generally involve modulating the level of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) in the cell, such that the level of HMG-CoA is not toxic to the cell and / or does not substantially inhibit cell growth, but is maintained at a level that provides for high-level production of mevalonate, IPP, and other downstream products of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid pathway, e.g., polyprenyl diphosphates and isoprenoid compounds. The present invention further provides genetically modified host cells that are suitable for use in a subject method. The present invention further provides recombinant nucleic acid constructs for use in generating a subject genetically modified host cell, including recombinant nucleic acid constructs comprising nucleotide sequences encoding one or more mevalonate pathway enzymes, and recombinant vectors (e.g., recombinant expression vectors) comprising same. The present invention further provides methods for identifying nucleic acids that encode HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) variants that provide for relief of HMG-CoA accumulation-induced toxicity. The present invention further provides methods for identifying agents that reduce intracellular accumulation of HMG-CoA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
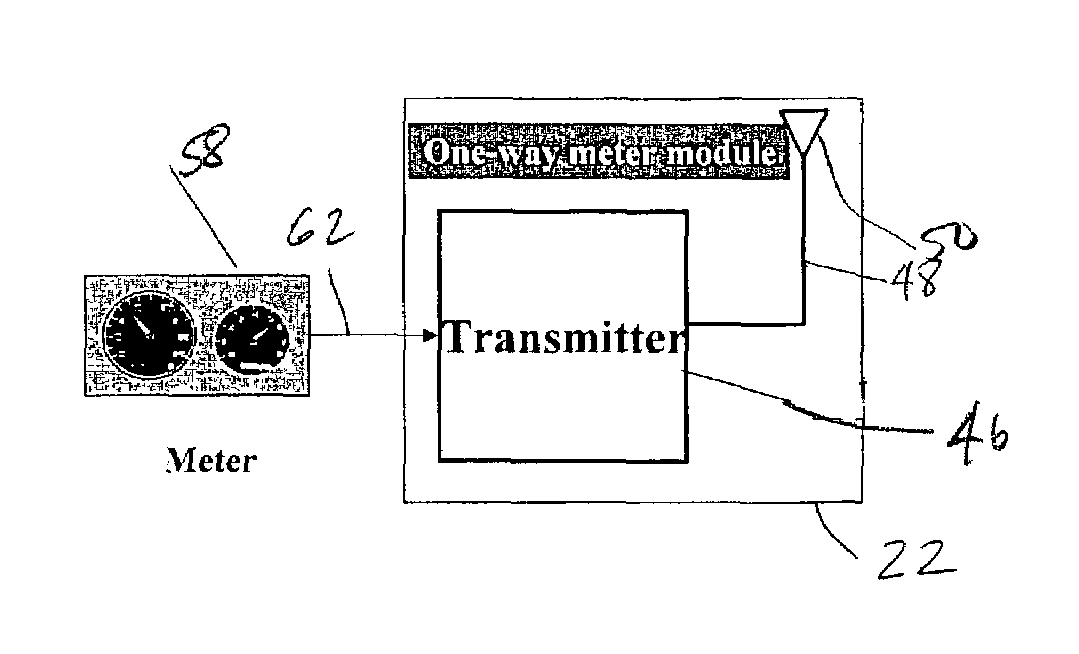
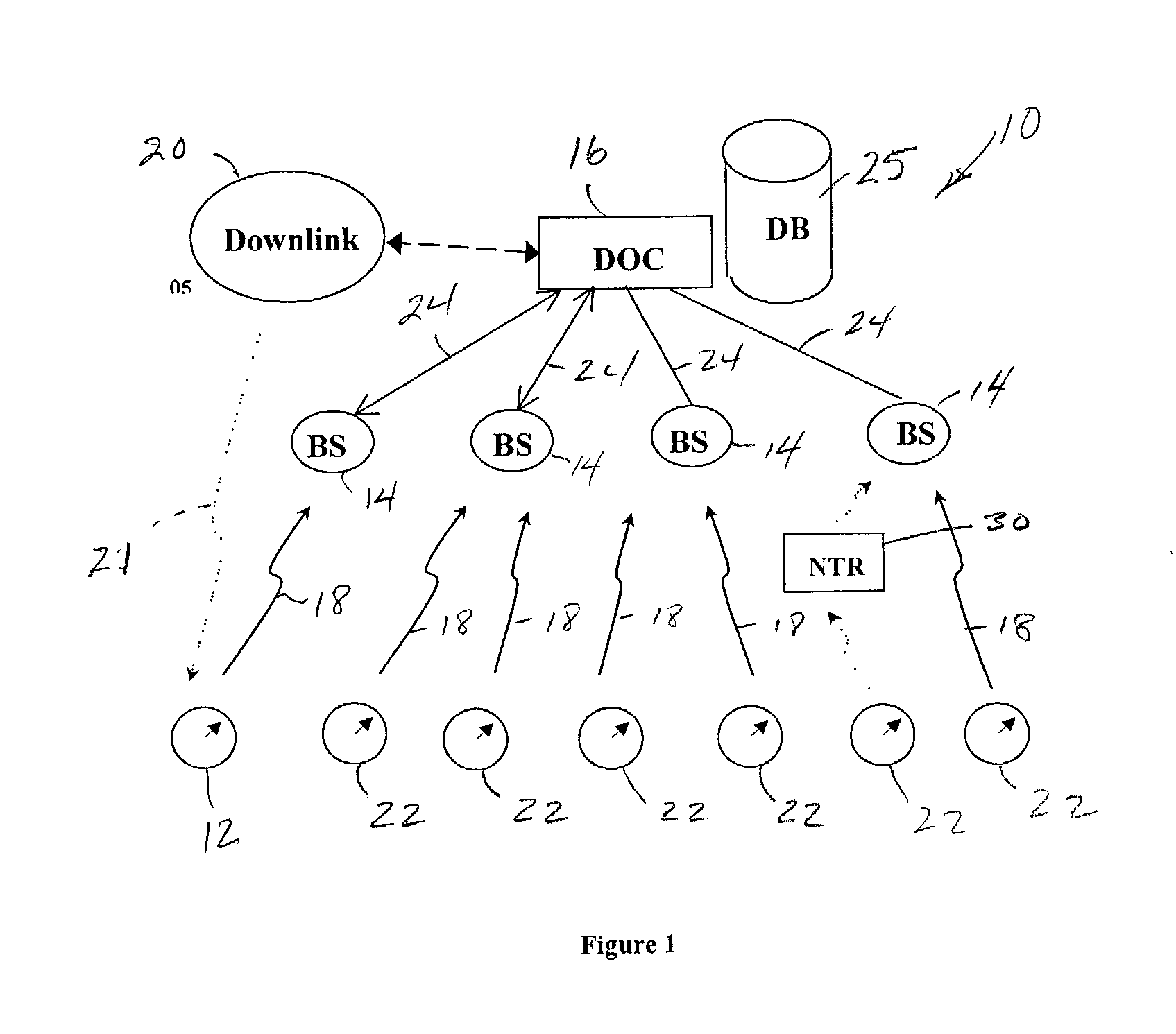
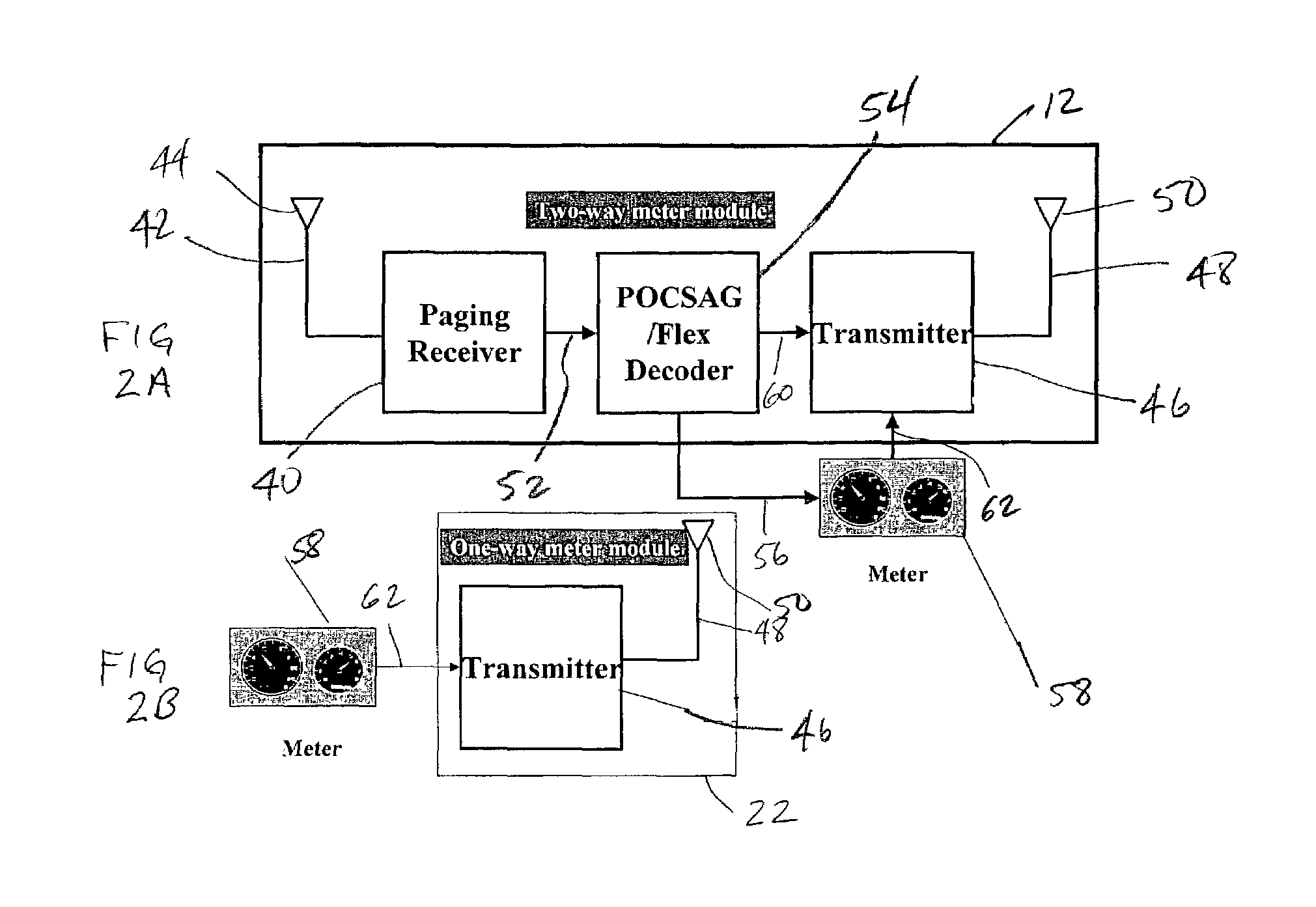
Modular wireless fixed network for wide-area metering data collection and meter module apparatus
InactiveUS7012546B1Increase flexibilityIncrease capacityElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusTransceiverData acquisition
A one way direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications wide-area network is the data collection channel (uplink) of an automatic meter reading (AMR) system, and a paging network, or other suitable communication channel is the optional forward (downlink) channel. The communications network may include one-way meter modules (transmitters) each communicatively coupled to a corresponding electric, gas or water utility meter, and may include two-way meter modules (transceivers) each coupled to such a corresponding utility meter. The meter modules monitor, store, encode and periodically transmit metering data via radio signals (air messages) in an appropriate RF channel. Metering data air messages are collected by a network of receiver Base Stations (BS) and forwarded to a Data Operations Center (DOC), which acts as a metering data gateway. The reception range of each base station is typically over 5 miles in urban areas, allowing sparse infrastructure deployment for a wide variety of metering data collection applications.
Owner:SENSUS USA
Control strategy for dynamically encoding multiple streams of video data in parallel for multiplexing onto a constant bit rate channel
InactiveUS6956901B2Improve picture qualityRapid responseTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexingData stream
A control strategy is provided for dynamically encoding multiple streams of video data in parallel for multiplexing onto a constant bit rate channel. The control strategy is a single pass strategy which allows individual encode bit rates to be dynamically adjusted for each video data stream based on part in relative complexity of the multiple streams of video data, as well as fullness of compressed video data buffers and a channel buffer coupled between the encoders and the constant bit rate channel. The control strategy includes encoding the multiple streams of video frames in parallel, and dynamically adapting encoding of at least one stream of the video frames based on relative complexity of the video frames. The bit rate for each stream of video frames is only changed at GOP boundaries, or if a scene change occurs. The calculated bit rate is preferably further modified based upon buffer fullness.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
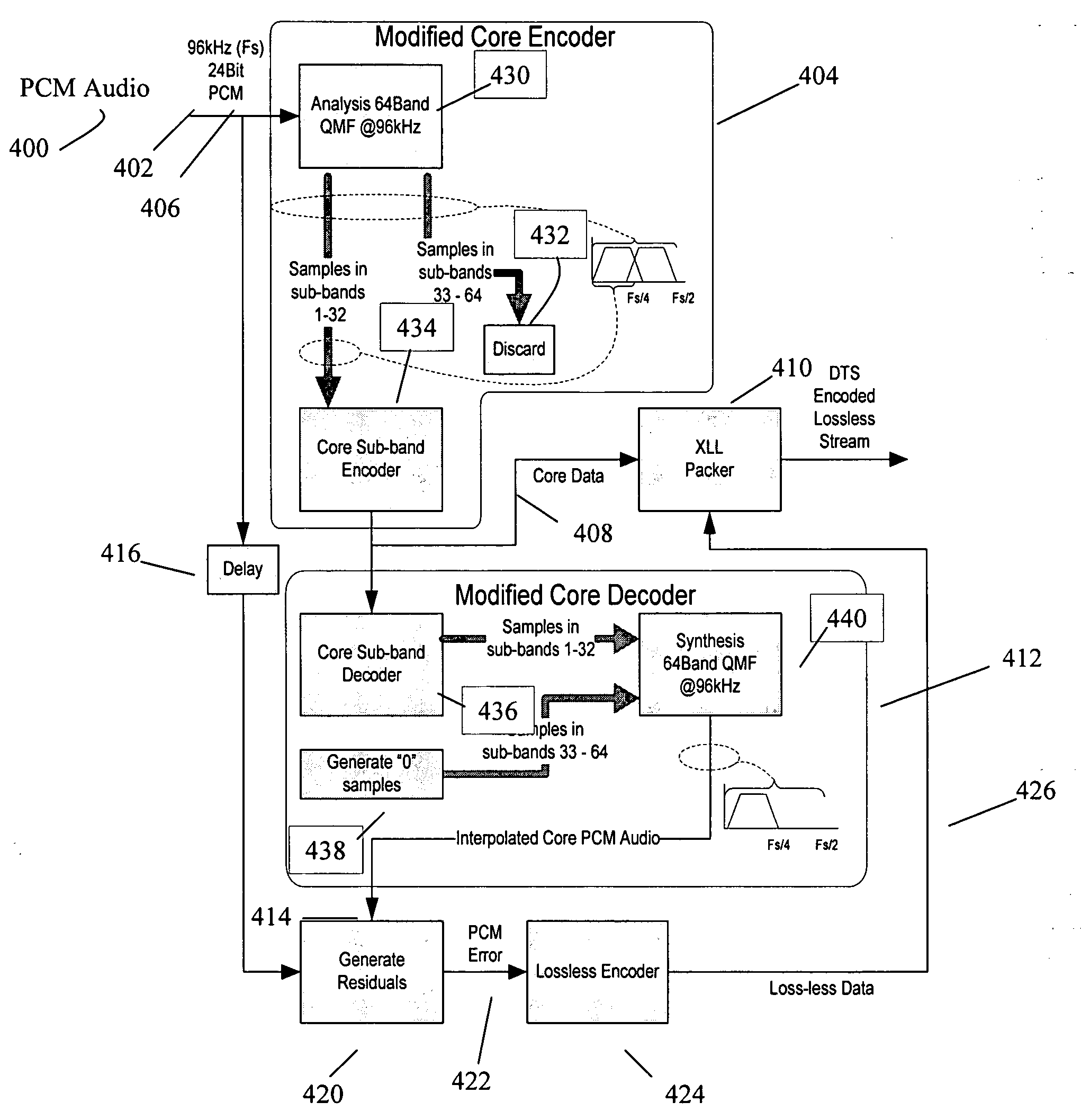
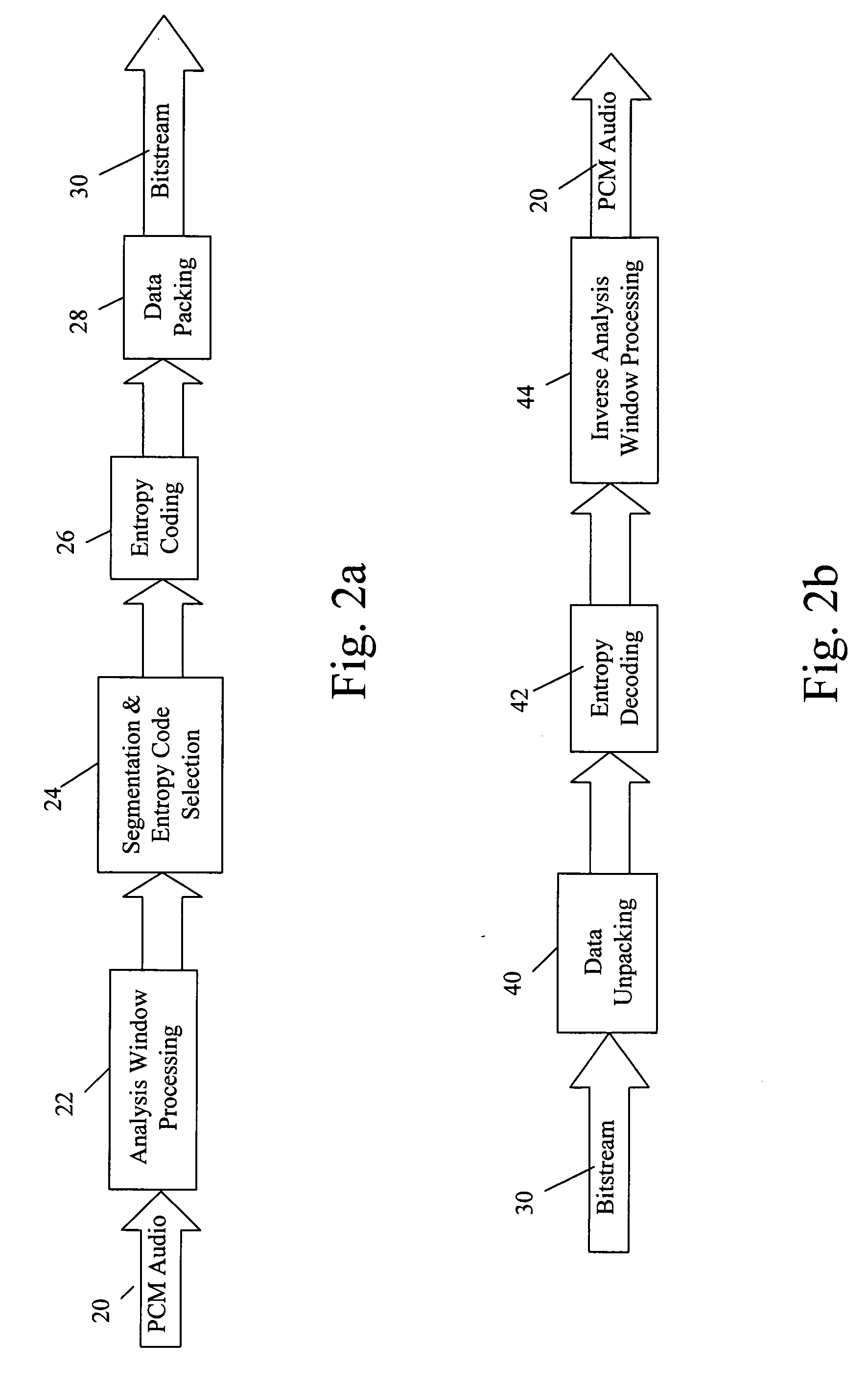
Lossless multi-channel audio codec using adaptive segmentation with random access point (RAP) and multiple prediction parameter set (MPPS) capability
ActiveUS20080215317A1Reduce transient effectsReduce encoded frame payloadBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisENCODEComputer science
A lossless audio codec encodes / decodes a lossless variable bit rate (VBR) bitstream with random access point (RAP) capability to initiate lossless decoding at a specified segment within a frame and / or multiple prediction parameter set (MPPS) capability partitioned to mitigate transient effects. This is accomplished with an adaptive segmentation technique that fixes segment start points based on constraints imposed by the existence of a desired RAP and / or detected transient in the frame and selects a optimum segment duration in each frame to reduce encoded frame payload subject to an encoded segment payload constraint. In general, the boundary constraints specify that a desired RAP or detected transient must lie within a certain number of analysis blocks of a segment start point. In an exemplary embodiment in which segments within a frame are of the same duration and a power of two of the analysis block duration, the RAP and / or transient constraints set a maximum segment duration to ensure the desired conditions. RAP and MPPS are particularly applicable to improve overall performance for longer frame durations.
Owner:DTS
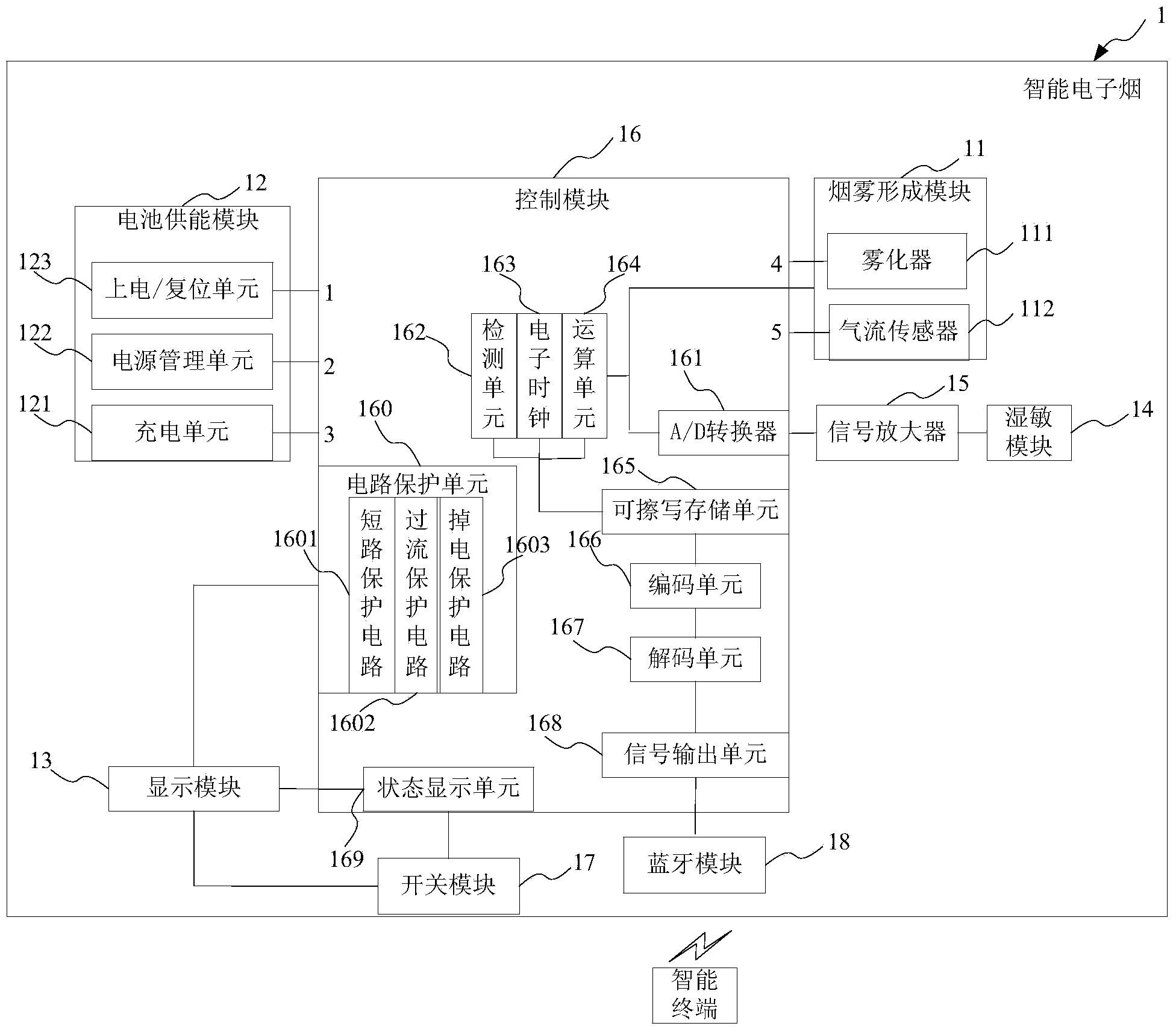
Intelligent electronic cigarette
ActiveCN103653261AMonitor usage in real timeGet smoking parametersTobacco devicesElectricityWireless communication protocol
The invention provides an intelligent electronic cigarette which comprises a wireless communication module and a control module. The control module is respectively and electrically connected with a smoke generating module, a battery energy supplying module and the wireless communication module, and used for controlling the intelligent electronic cigarette to calculate smoking parameters, generated in the use process, of the human body, encode and decode the generated smoking parameters into smoking parameter signals meeting the wireless communication protocol, and carry out data interaction with an intelligent terminal in real time or in a timing mode through the wireless communication module. The control module comprises an encoding unit, a decoding unit and a signal output unit, wherein the encoding unit is used for encoding the smoking parameters into a smoking parameter file meeting the wireless communication protocol, the decoding unit is used for decoding the smoking parameter file into the smoking parameter signals, and the signal output unit is used for transmitting the smoking parameter signals. According to the intelligent electronic cigarette, the user use conditions can be monitored in real time, a complete use log can be created, and the smoking parameters are transmitted to the intelligent terminal in a wireless mode so that the intelligent electronic cigarette can conveniently carry out the data interaction with the intelligent terminal in real time or in the timing mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI TOBACCO GRP CO LTD
Distributed control strategy for dynamically encoding multiple streams of video data in parallel for multiplexing onto a constant bit rate channel
InactiveUS7085322B2Simplifying and economizing design of systemEliminate needPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMultiplexingData stream
A distributed control strategy is provided for dynamically encoding multiple streams of video data in parallel for multiplexing onto a constant bit rate channel. The control strategy is a single pass strategy which allows individual encode bit rates to be dynamically adjusted for each video data stream based in part on relative complexity of the multiple streams of video data, as well as fullness of compressed video data buffers coupled between the encoders and the constant bit rate channel. The control strategy includes encoding the multiple streams of video frames in parallel using multiple encoders, exchanging one or more statistics between the encode processes using an exchange interface, and dynamically adapting encoding of at least one stream of the video frames using the exchanged statistics based on relative complexity of the video frames.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Meter system designed to run singulated test sensors
ActiveUS20080034834A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricitySystems design
A test system comprises a sensor container and a testing device. The sensor container has a base and a lid. The container encloses a plurality of test sensors therein. The container includes a calibration label attached thereto. The label includes electrical contacts located thereon that encode calibration information onto the calibration label. The testing device has a sensor-container opening formed thereon. The sensor-container opening has an auto-calibration feature located therein. The auto-calibration feature is external to the testing device. The auto-calibration feature includes calibration elements to communicate with the electrical contacts on the calibration label. The testing device determines the calibration information encoded on the calibration label in response to the calibration elements engaging the electrical contacts. A portion of the sensor container remains external to the meter while the encoded calibration information is being determined.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
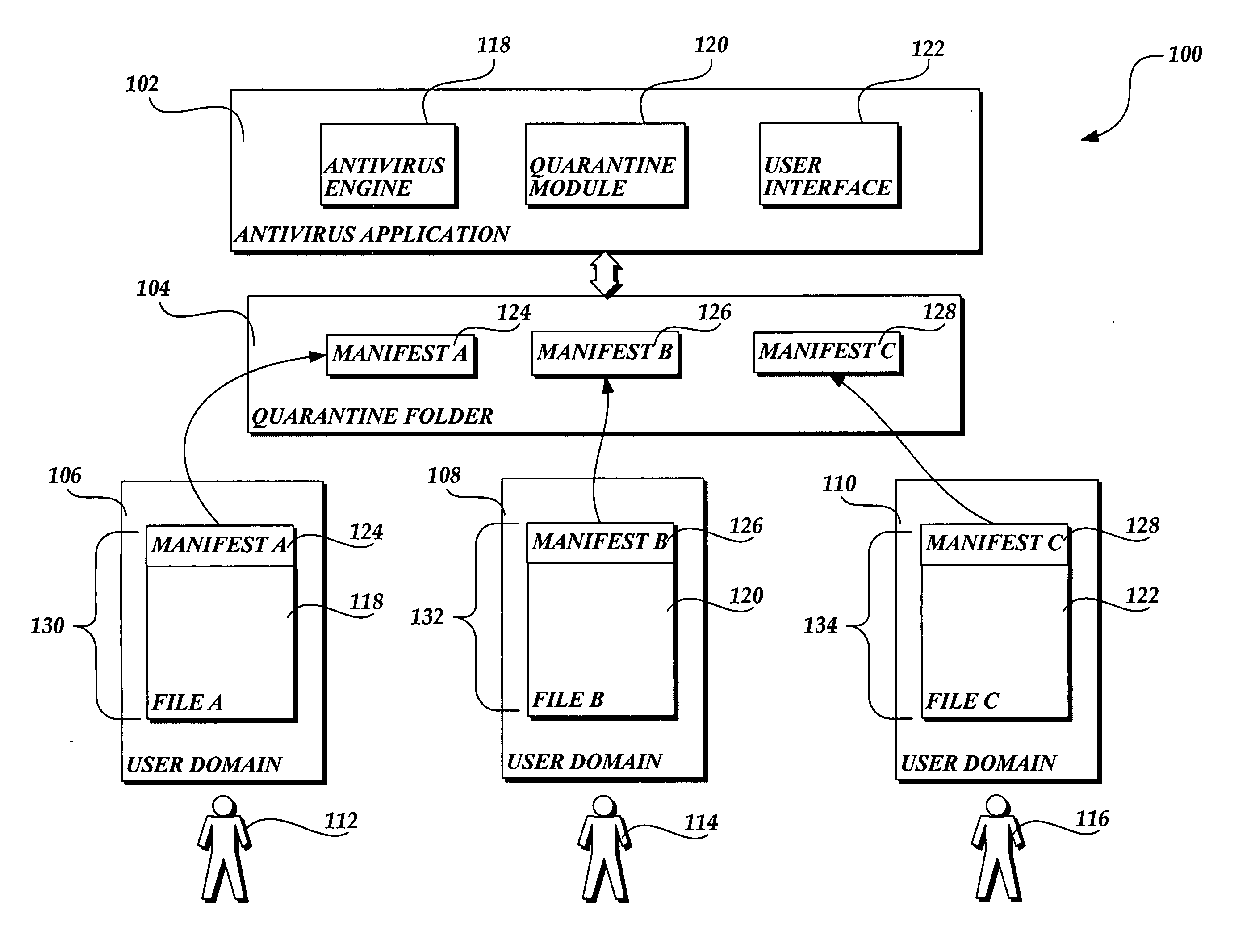
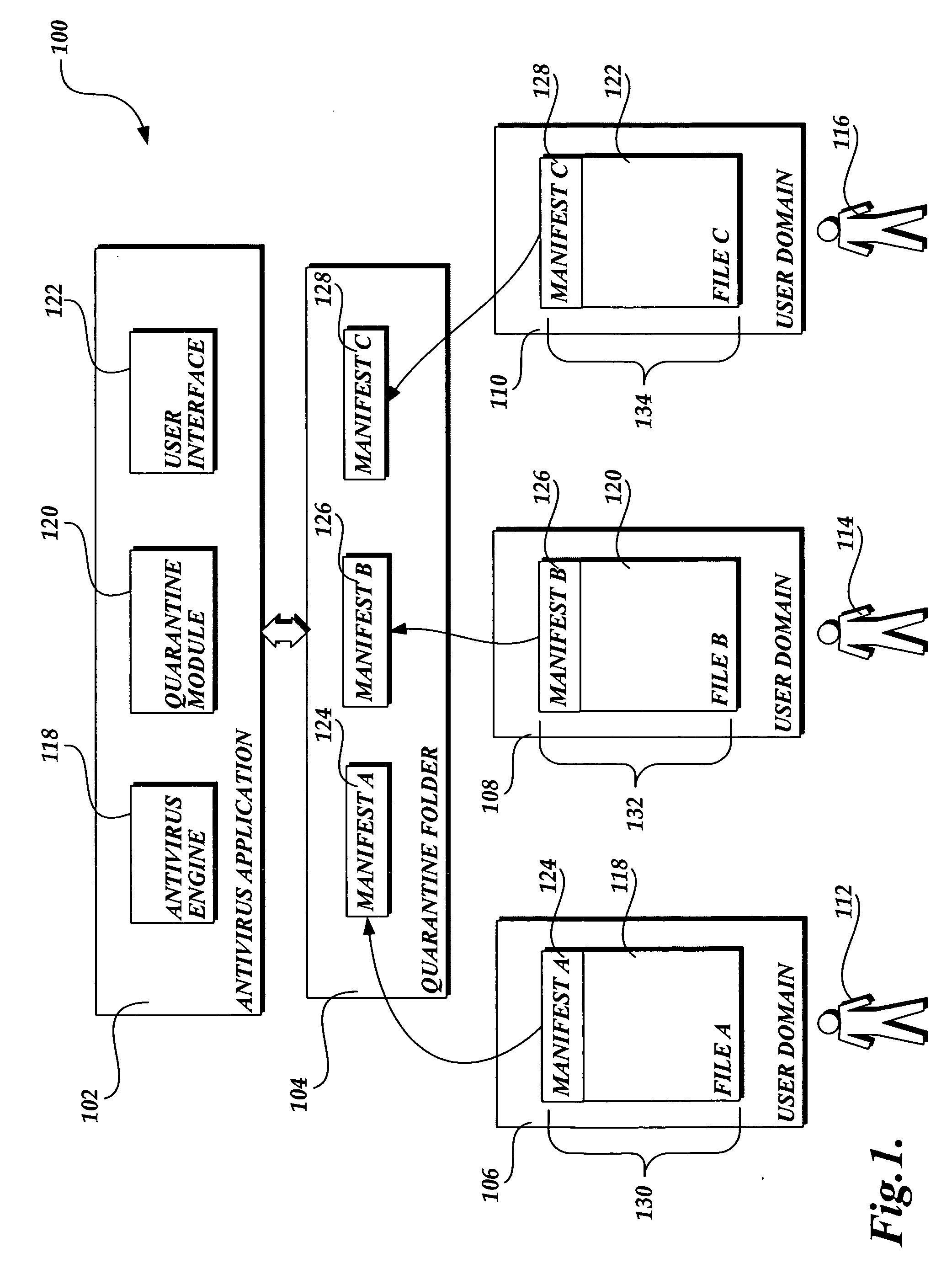
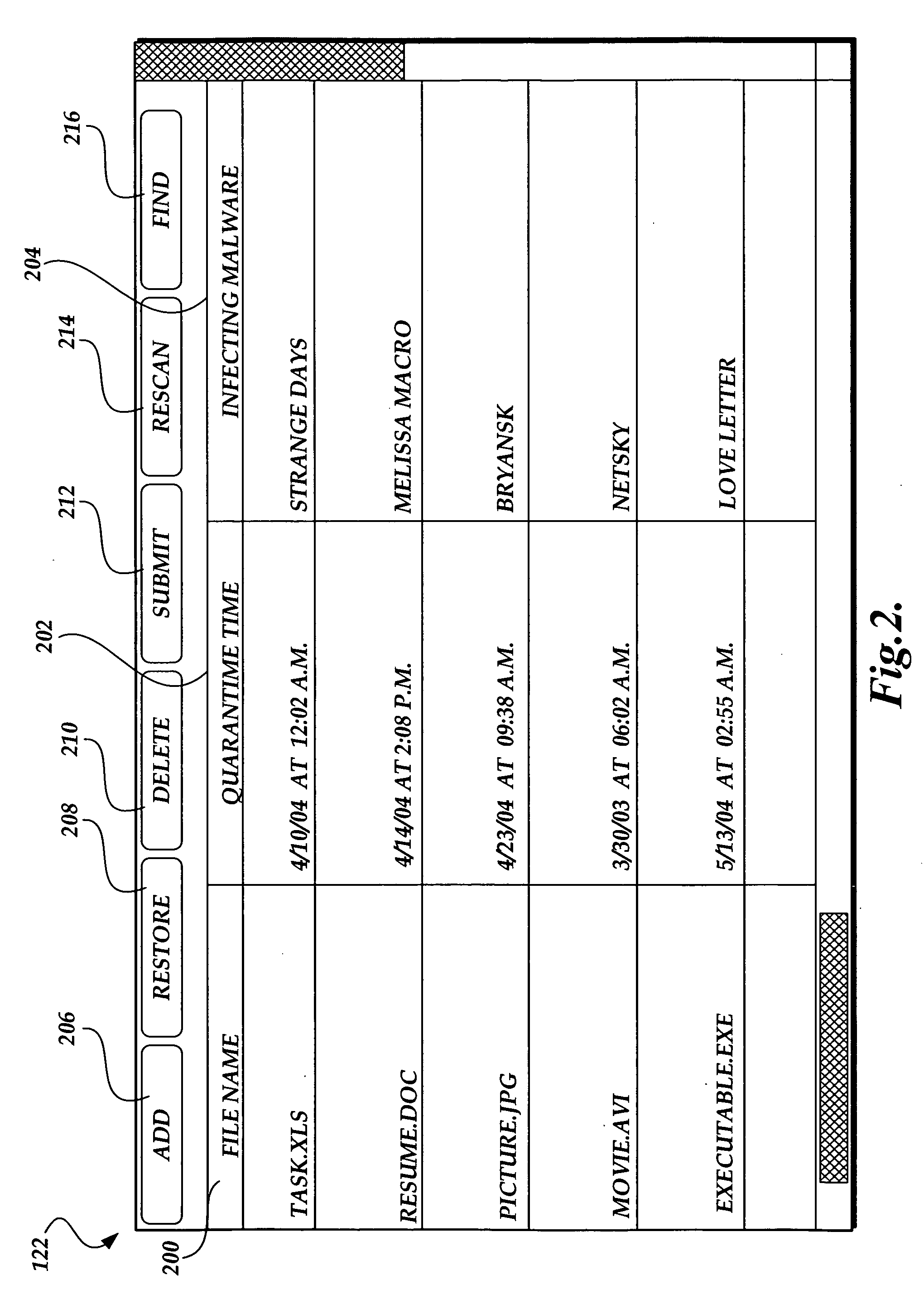
Privacy friendly malware quarantines
The present invention provides a system, method, and computer-readable medium for quarantining a file. Embodiments of the present invention are included in antivirus software that maintains a user interface. From the user interface, a user may issue a command to quarantine a file or the quarantine process may be initiated automatically by the antivirus software after malware is identified. When a file is marked for quarantine, aspects of the present invention encode file data with a function that is reversible. Then a set of metadata is identified that describes attributes of the file including any heightened security features that are used to limit access to the file. The metadata is moved to a quarantine folder, while the encoded file remains at the same location in the file system. As a result, the encoded file maintains the same file attributes as the original, non-quarantined file, including any heightened security features.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
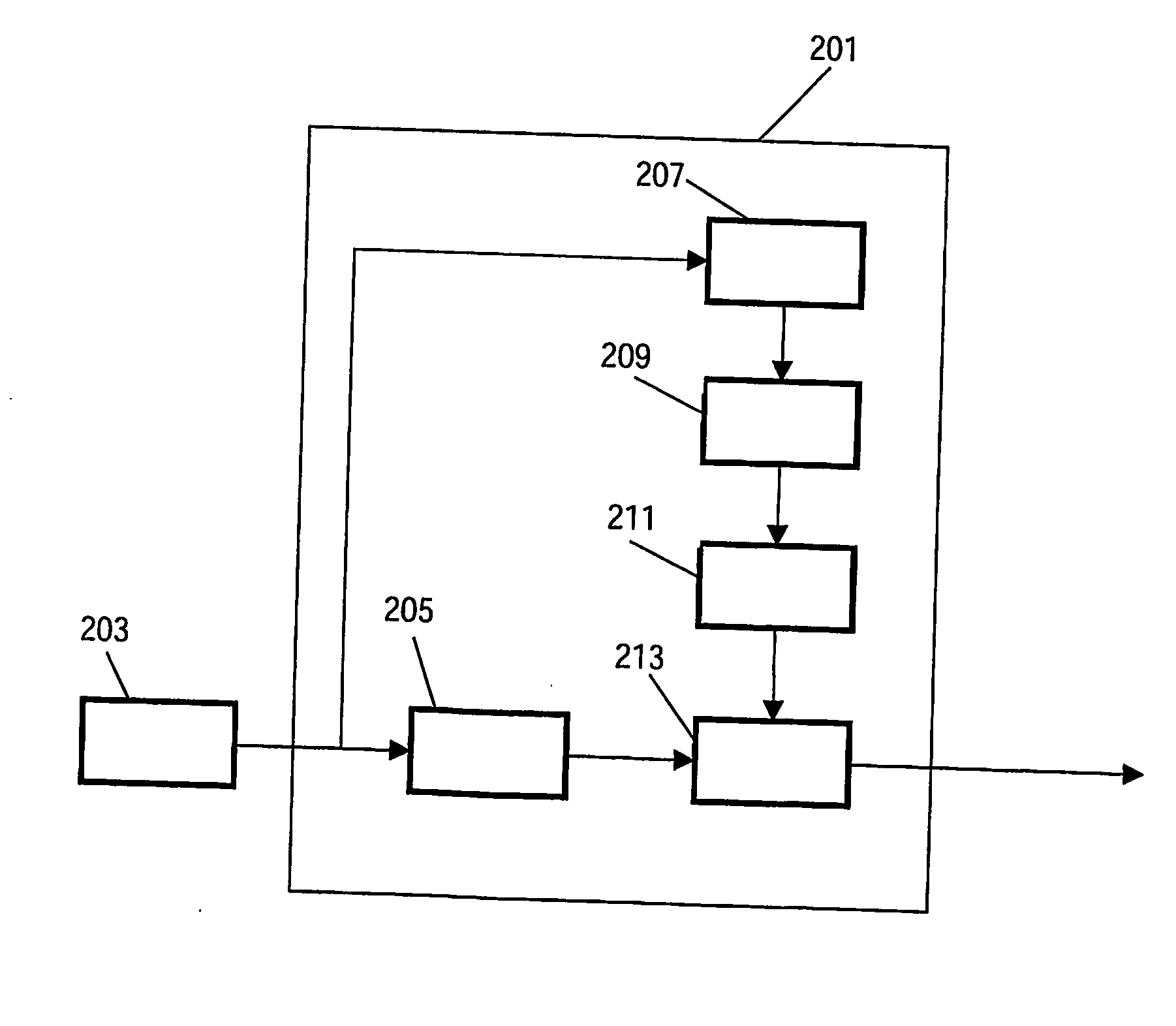
Video encoding
InactiveUS20060165163A1Improve performanceReduce lossesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
The invention relates to a video encoder (201) for encoding a video signal. The video encoder comprises a segmentation processor (207) which divides the picture into picture regions. Preferably, picture regions having a high degree of flatness or uniformity are determined in this way. A characteristics processor (209) determine a spatial frequency characteristic for each picture region, and a coding controller (211) selects an encoding block size, such as a prediction block size for motion estimation, in response to the spatial frequency characteristic. An encode processor (213) encodes the picture using the selected encoding block size. Specifically, increasing block sizes are selected for increasing degrees of uniformity or flatness indicated by the spatial frequency characteristic. Thereby, an increasing proportion of high frequency components and a consistent choice of encoding block sizes are maintained, and thus the coding artefacts from many encoders having variable prediction block sizes is reduced. The invention is particularly suitable for H.264 and similar encoders.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
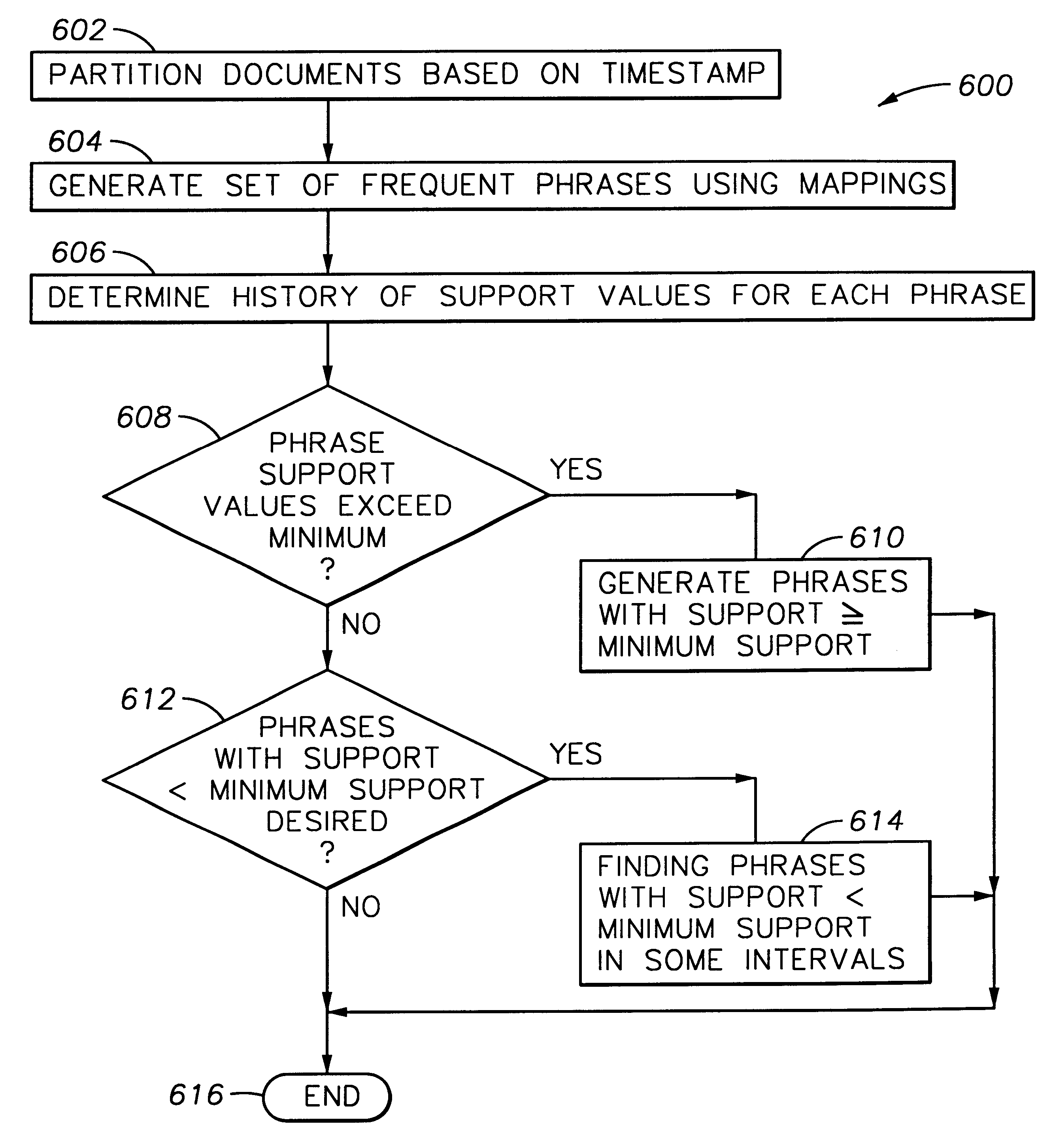
Method and apparatus for partitioning a database upon a timestamp, support values for phrases and generating a history of frequently occurring phrases
A method and apparatus for mining text databases, employing sequential pattern phrase identification and shape queries, to discover trends. The method passes over a desired database using a dynamically generated shape query. Documents within the database are selected based on specific classifications and user defined partitions. Once a partition is specified, transaction IDs are assigned to the words in the text documents depending on their placement within each document. The transaction IDs encode both the position of each word within the document as well as representing sentence, paragraph, and section breaks, and are represented in one embodiment as long integers with the sentence boundaries. A maximum and minimum gap between words in the phrases and the minimum support all phrases must meet for the selected time period may be specified. A generalized sequential pattern method is used to generate those phrases in each partition that meet the minimum support threshold. The shape query engine takes the set of phrases for the partition of interest and selects those that match a given shape query. A query may take the form of requesting a trend such as "recent upwards trend", "recent spikes in usage", "downward trends", and "resurgence of usage". Once the phrases matching the shape query are found, they are presented to the user.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dynamic encoding algorithms and inline message decryption
InactiveUS7096355B1Prevent copyingKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePlaintextThird party
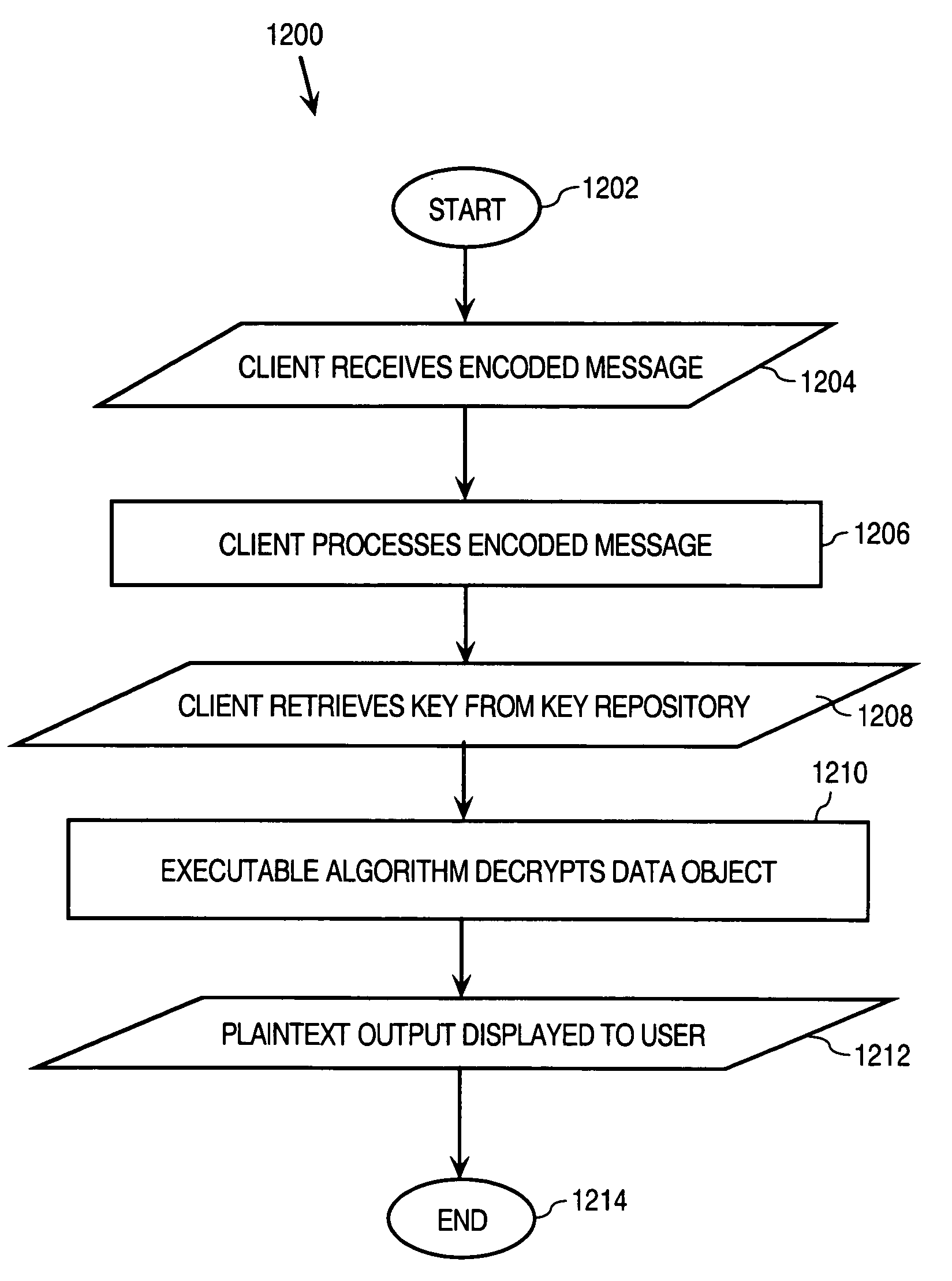
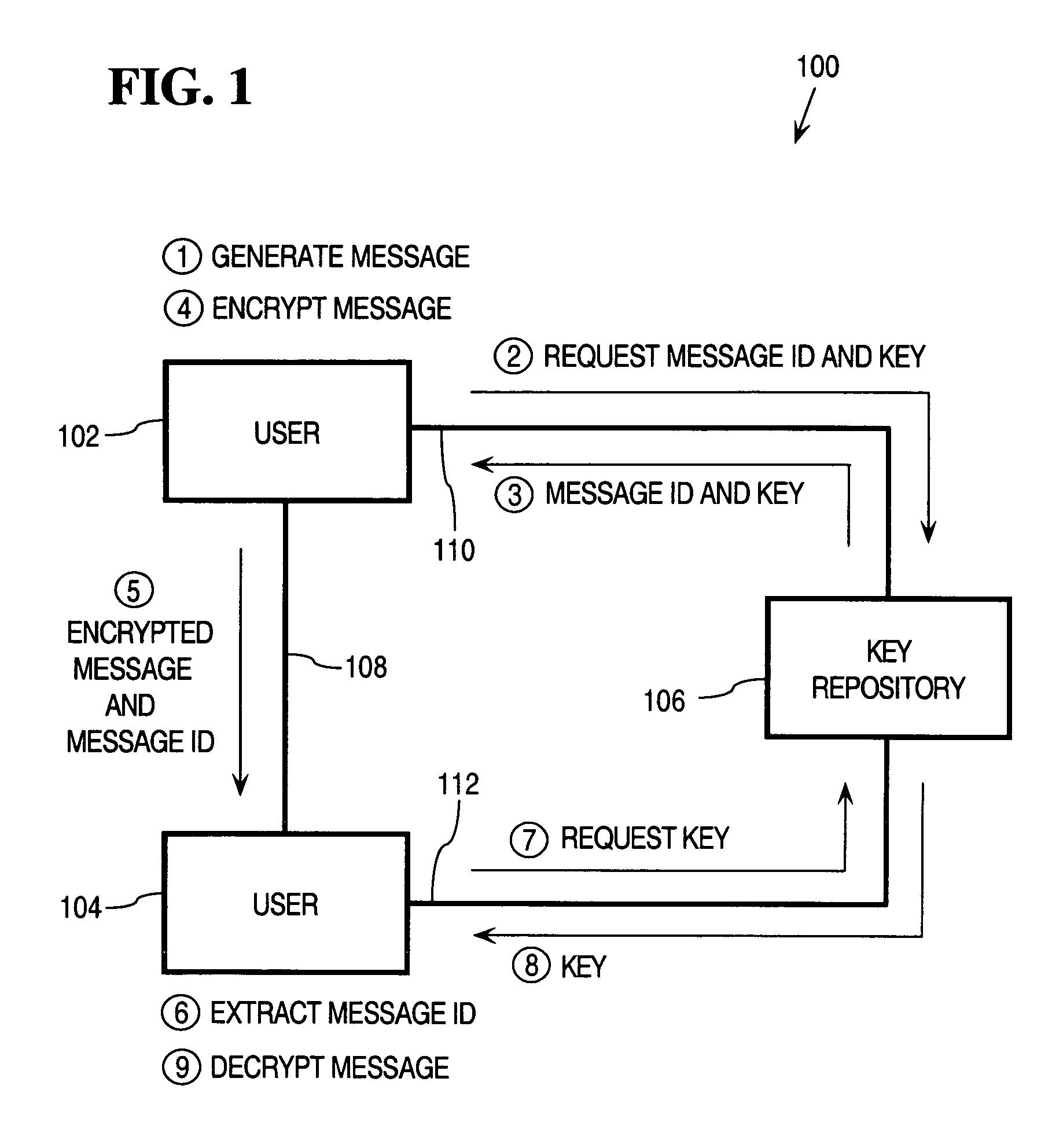
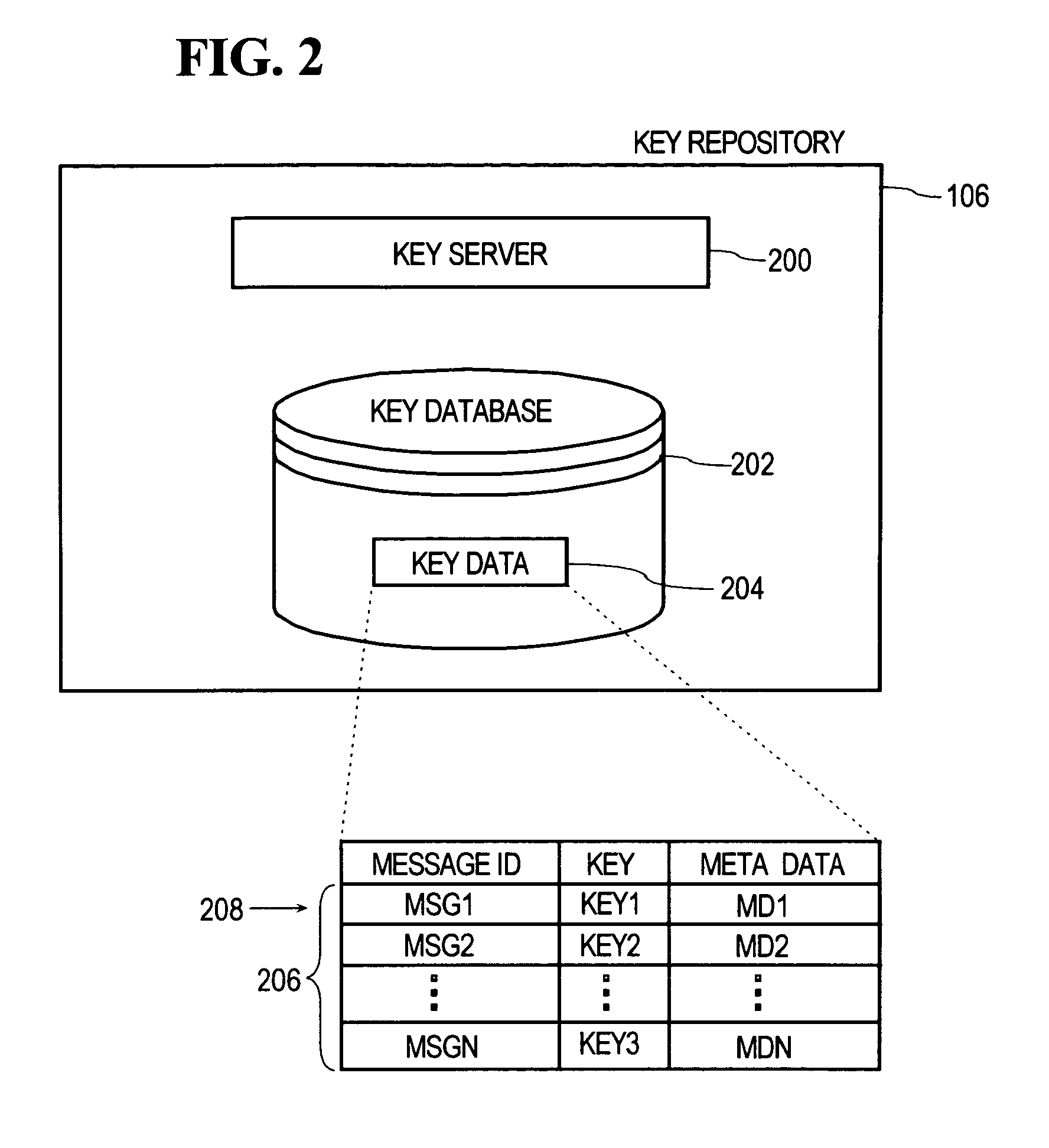
In general, data exchanged between users is protected using any of various encoding approaches. An example of encoding is encryption, but any kind of encoding may be used. The data used to encrypt the data exchanged between the users, referred to as a “key”, is maintained only in a key repository. Users must obtain a key from the key repository to either encode or decode, encrypt or decrypt data, after which the user's copy of the key is destroyed or otherwise rendered inoperable. A key management policy is employed to control access to the keys maintained by the key repository. Encoding algorithms may be dynamically changed over time. Users may negotiate different algorithms to be used with specific users or messages. Thus, different algorithms may be used between different sets of users depending upon what the member users of those sets negotiate among themselves. The frequency at which algorithms are changed may also be separately negotiated between users. The frequency may vary depending, for example, upon the perceived risk of intrusion by unauthorized third parties, the content of the messages being transmitted, or both. According to an inline message decryption approach, an encoded message is provided to a user in a form that enables the user's client to process the encoded message using conventional client tools and obtain the cleartext message. This eliminates the need for a user's client to be aware of the particular encoding algorithm used to encode the message. Various embodiments of the inline message decryption approach include: a) in-situ decryption; b) remote decryption; and c) data uploading. An approach is also provided for exchanging data between nodes in a network using sets of associated URLs.
Owner:CHECK POINT SOFTWARE TECH INC
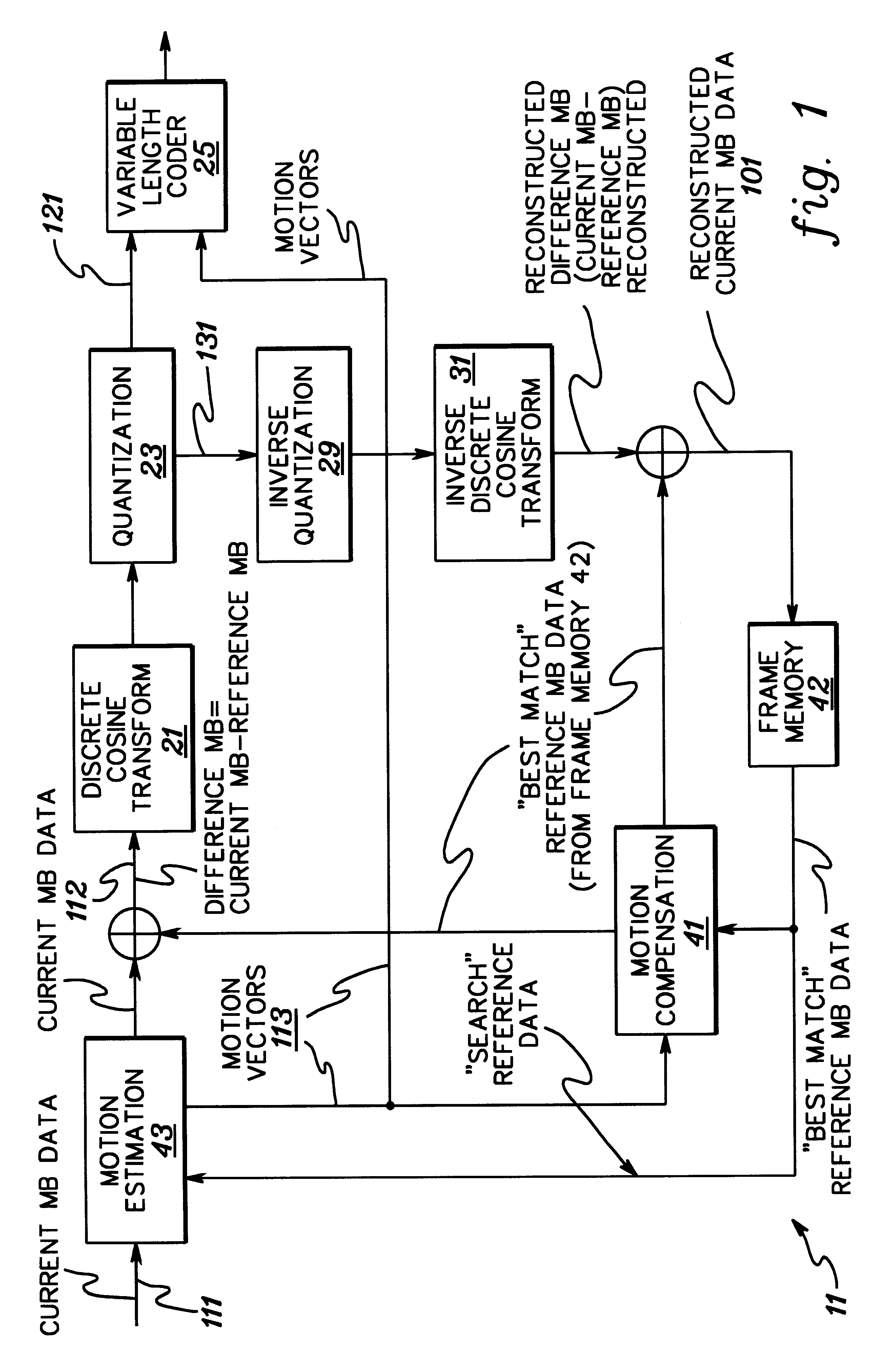
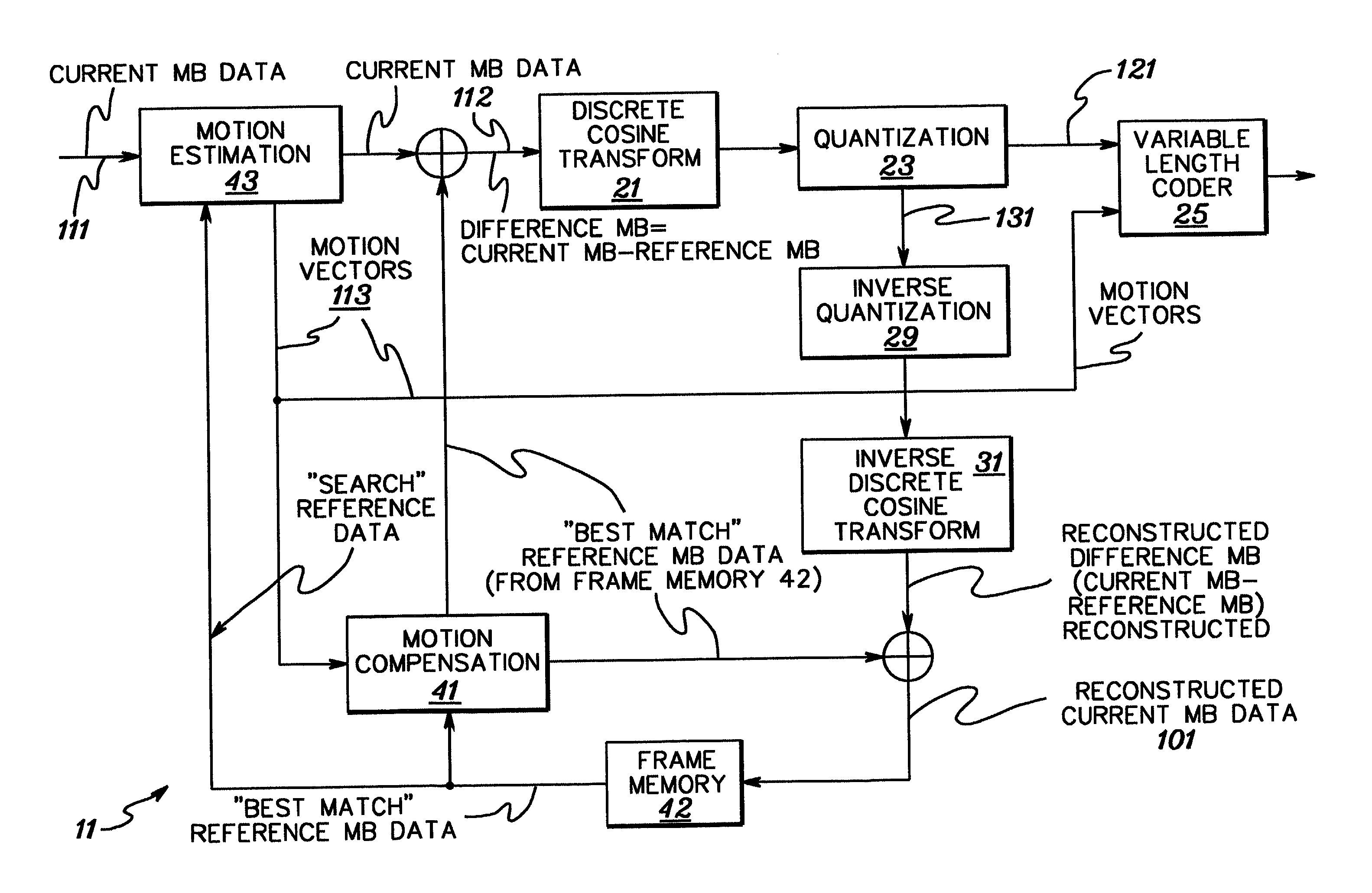
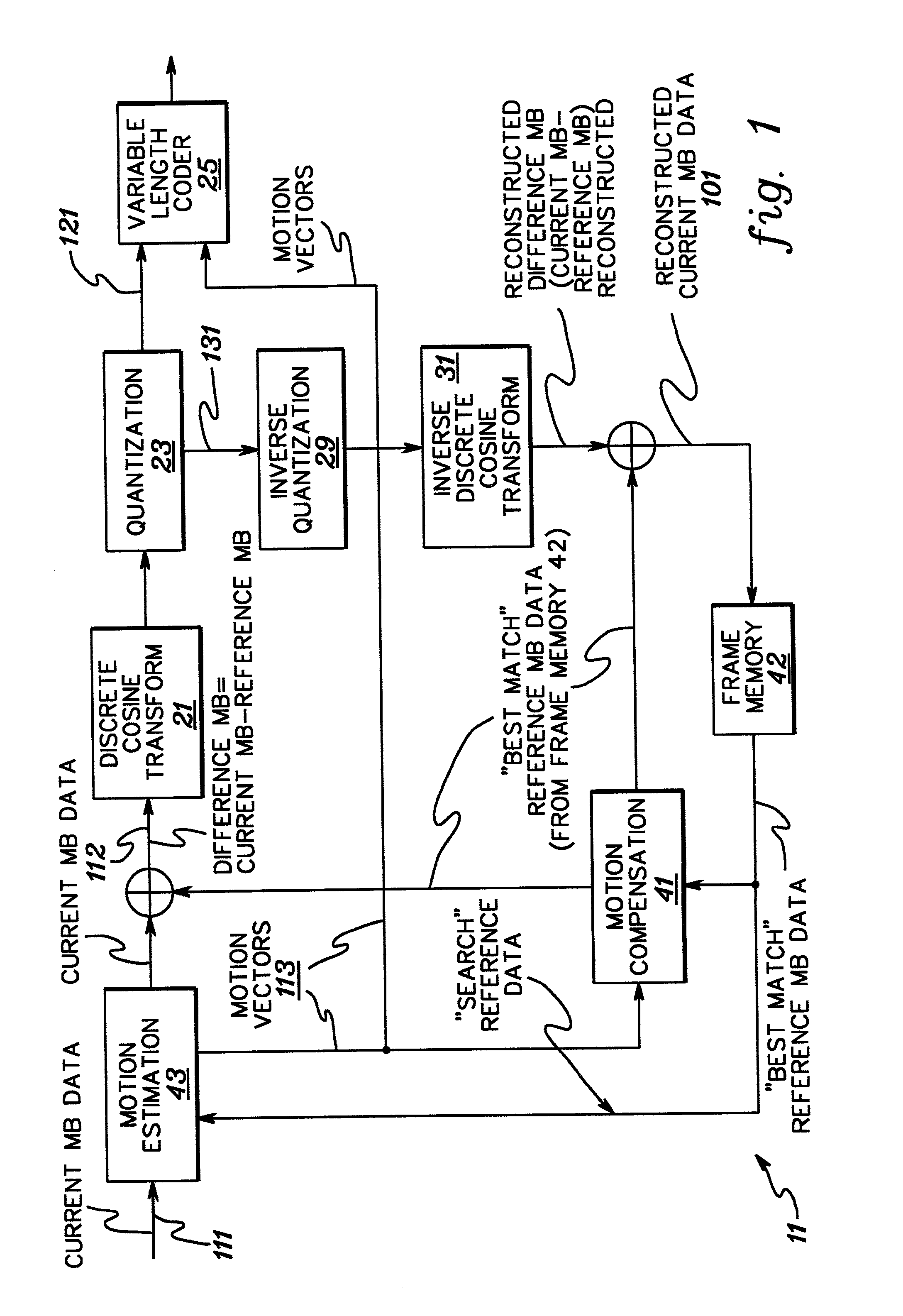
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding digital video data
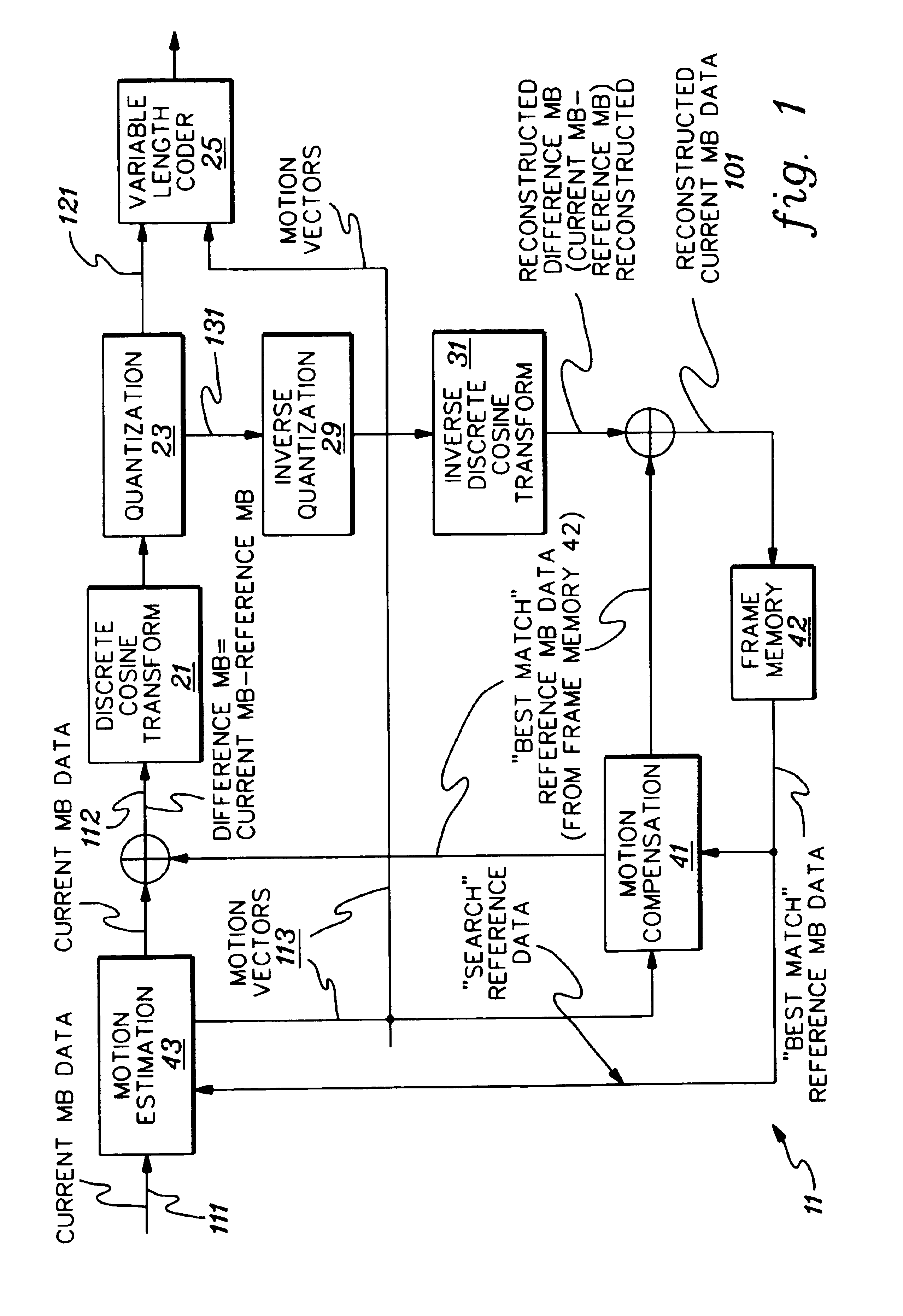
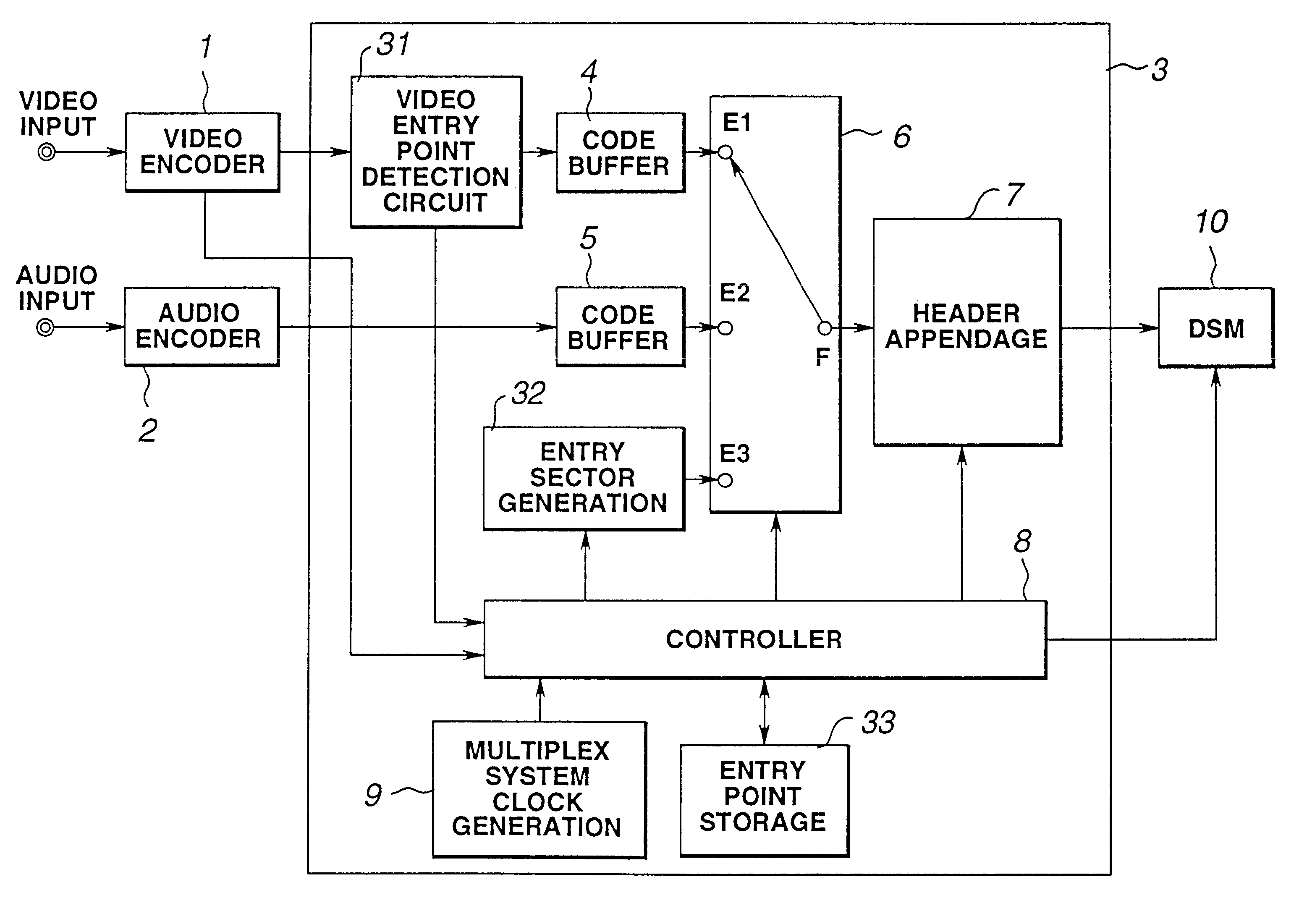
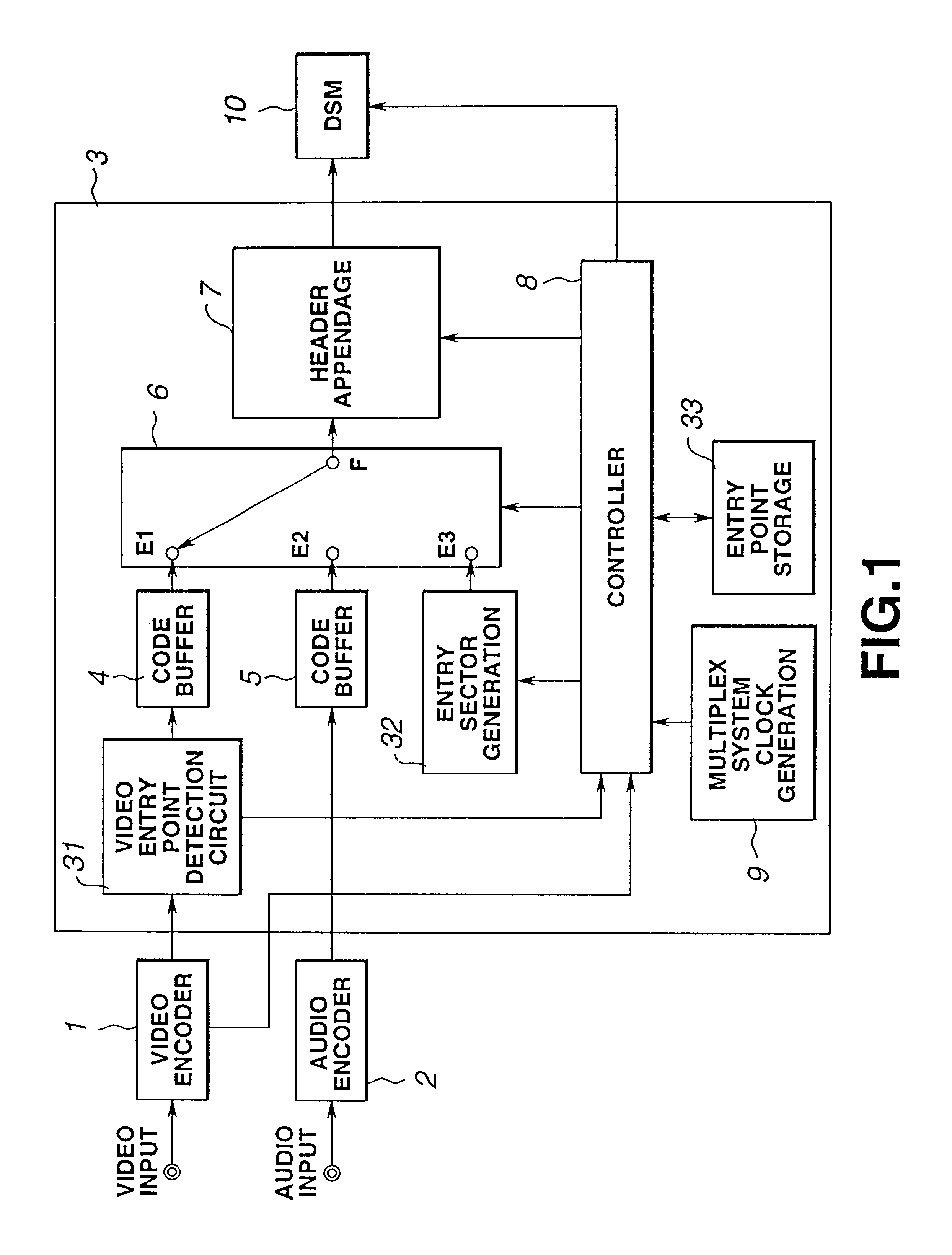
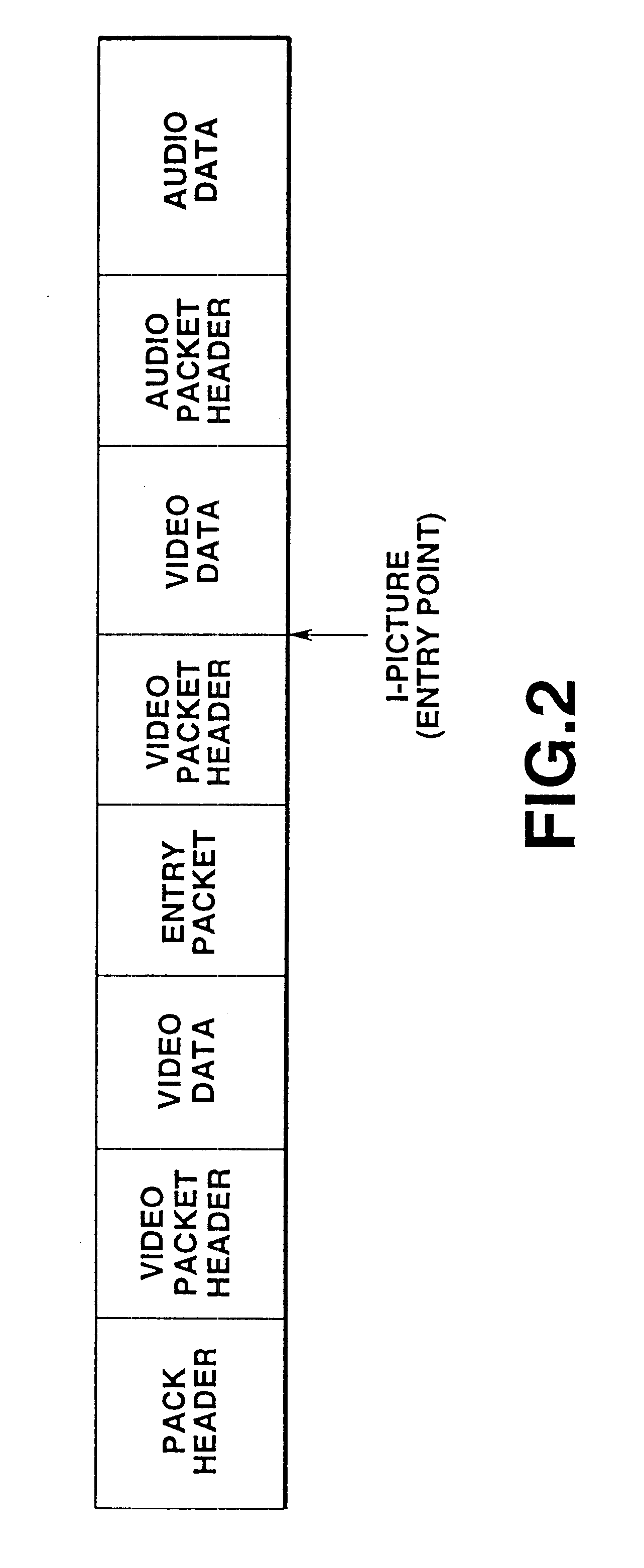
InactiveUS6363212B1Low and high search speedHigh and low speed reproductionTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
Digital video data encoder and decoder operate to enable the low and high speed reproduction of variable rate encoded digital video data by reproducing and decoding intraframe encoded frames that are identified by previously reproduced intraframe encoded frames. In the encoder, digital video data is variable rate encoded, for example, intraframe and interframe encoded, entry points (i.e., beginning positions) of selected encoded video data are identified and which represent video frames that occur at predetermined intervals of time (e.g., 1, 2 and 4 seconds) in the video picture. Entry point data that identify these positions are generated and added to the encoded video data before the video data is recorded on a record medium. When the encoded data is reproduced from the record medium, the entry point data is extracted therefrom and stored, and a successive intraframe encoded frame identified by the extracted entry point data is reproduced and decoded. The invention further provides for a record medium having thereon the encoded digital video data, and also provides for an encoder and corresponding decoder which encode and decode, respectively, digital still image and audio data in which entry points refer to each of the still images and also to particular intervals of time of the audio data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com