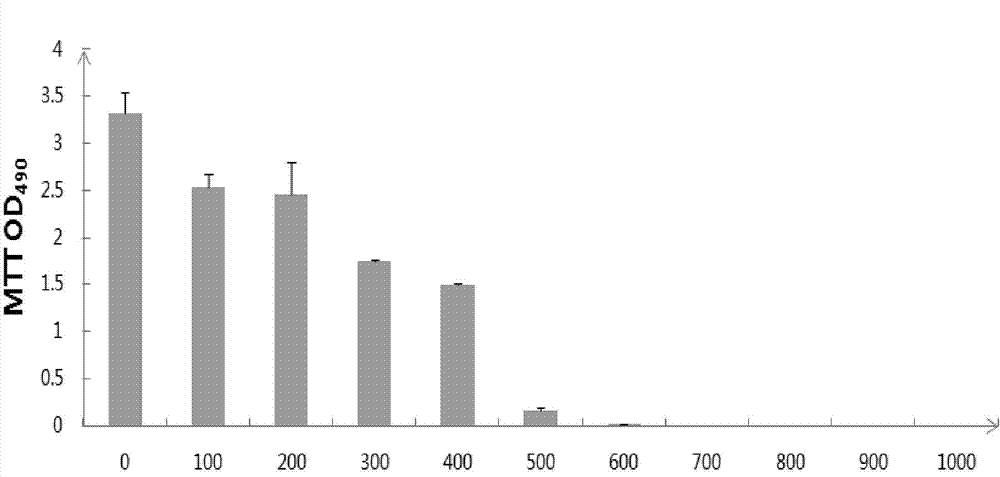
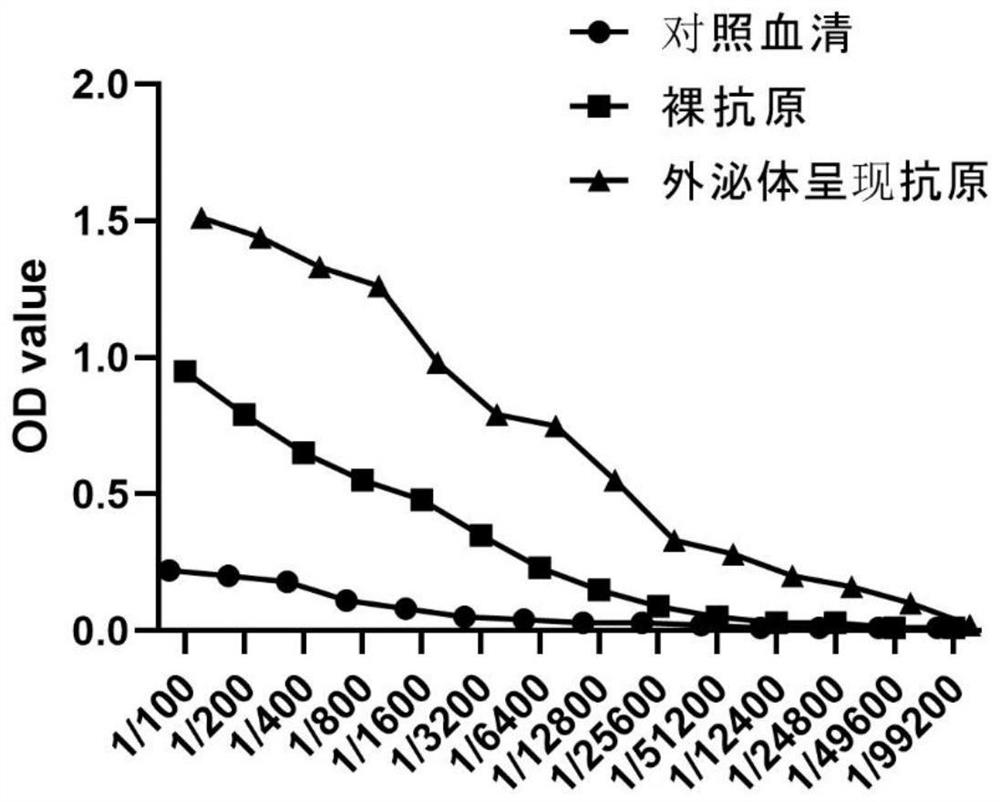
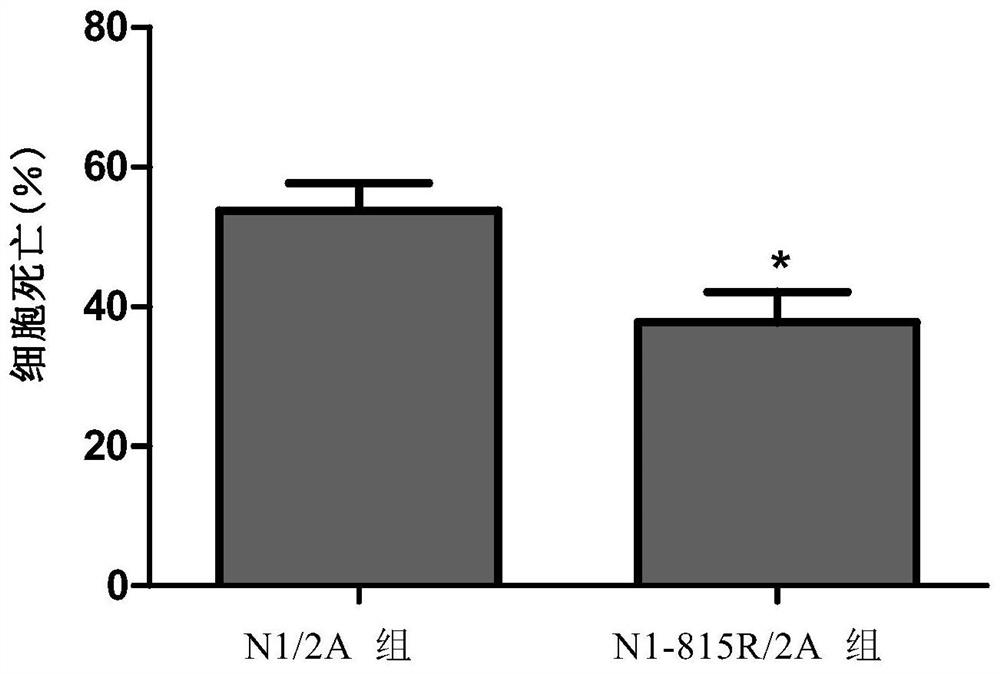
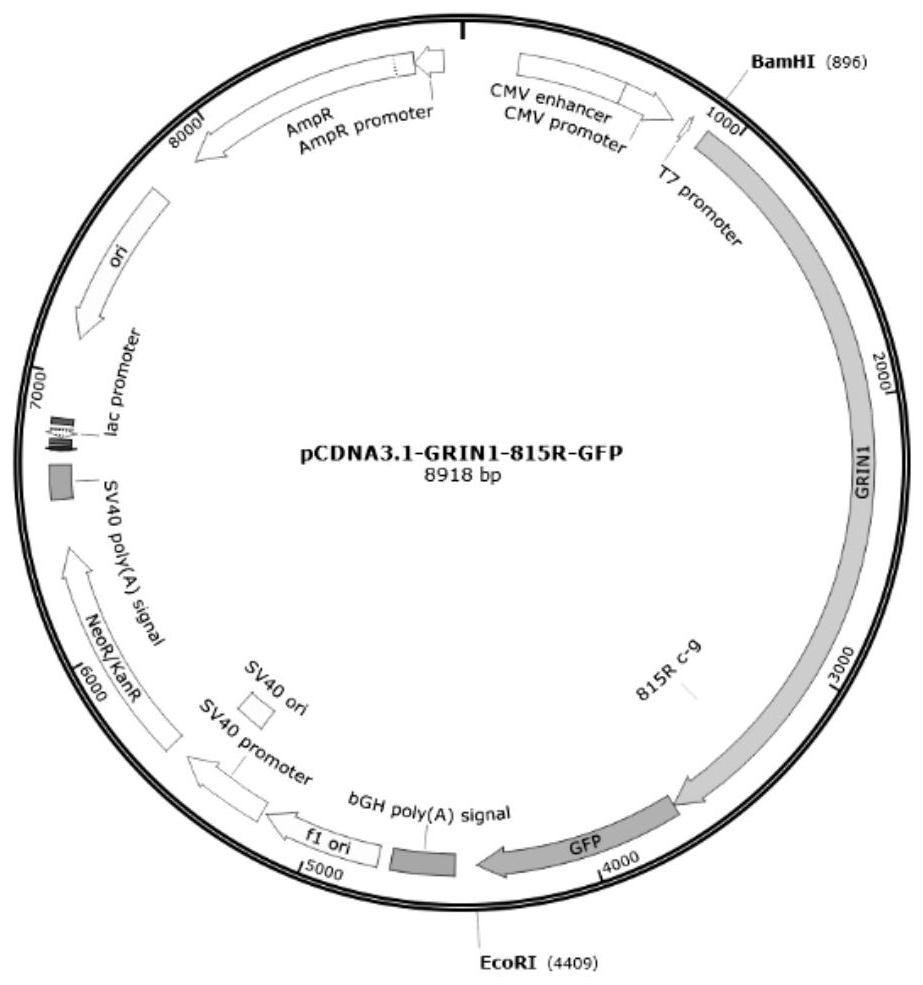
Patents
Literature
103 results about "Transient transfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
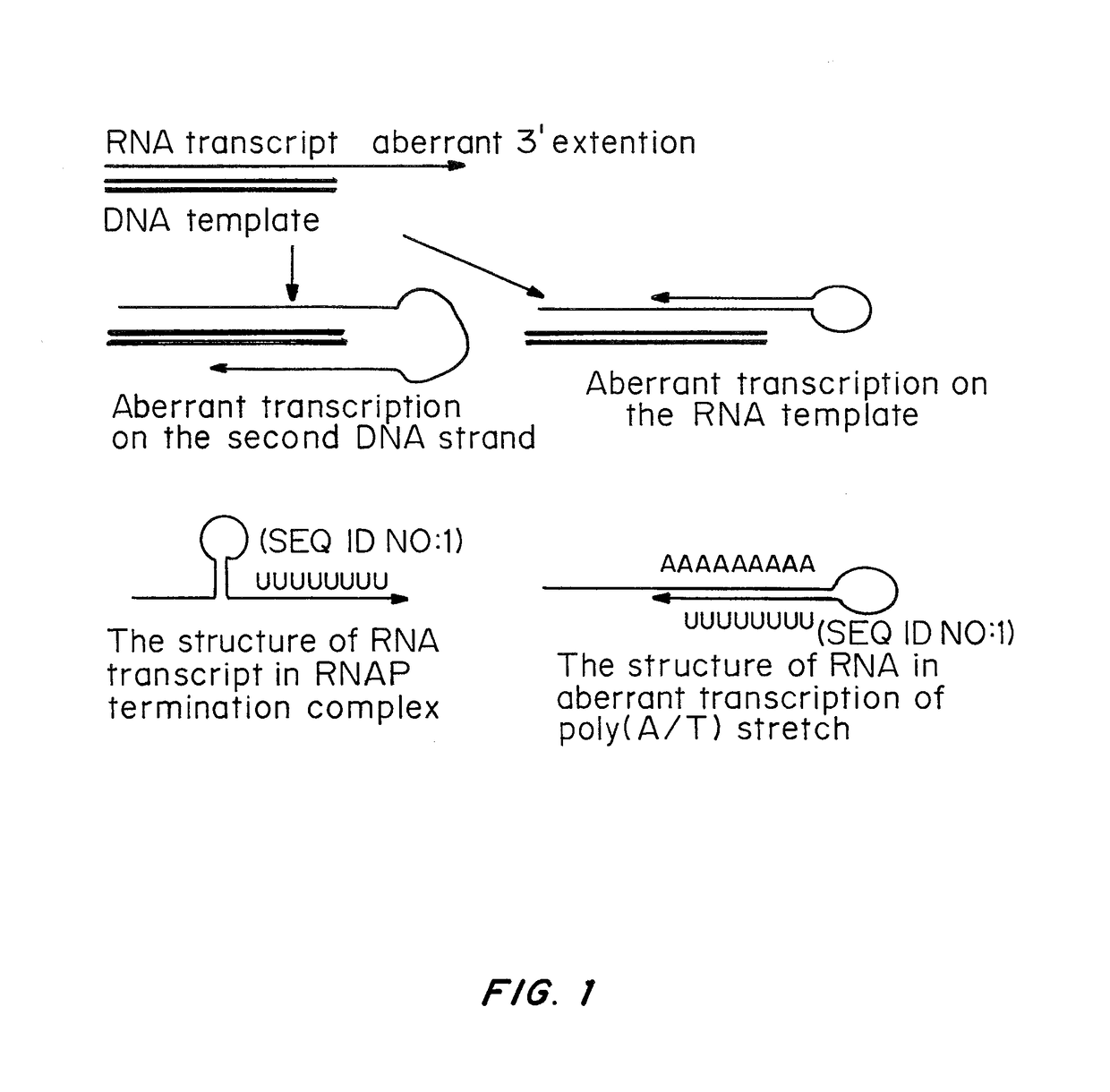
Transient transfection: When DNA is transfected into cultured cells, it is able to stay in those cells for about 2-3 days, but then will be lost (unless steps are taken to ensure that it is retained - see Stable transfection).
Transient Transfection with RNA
ActiveUS20080260706A1Lymphocyte transfectabilitySimilar efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDNA construct
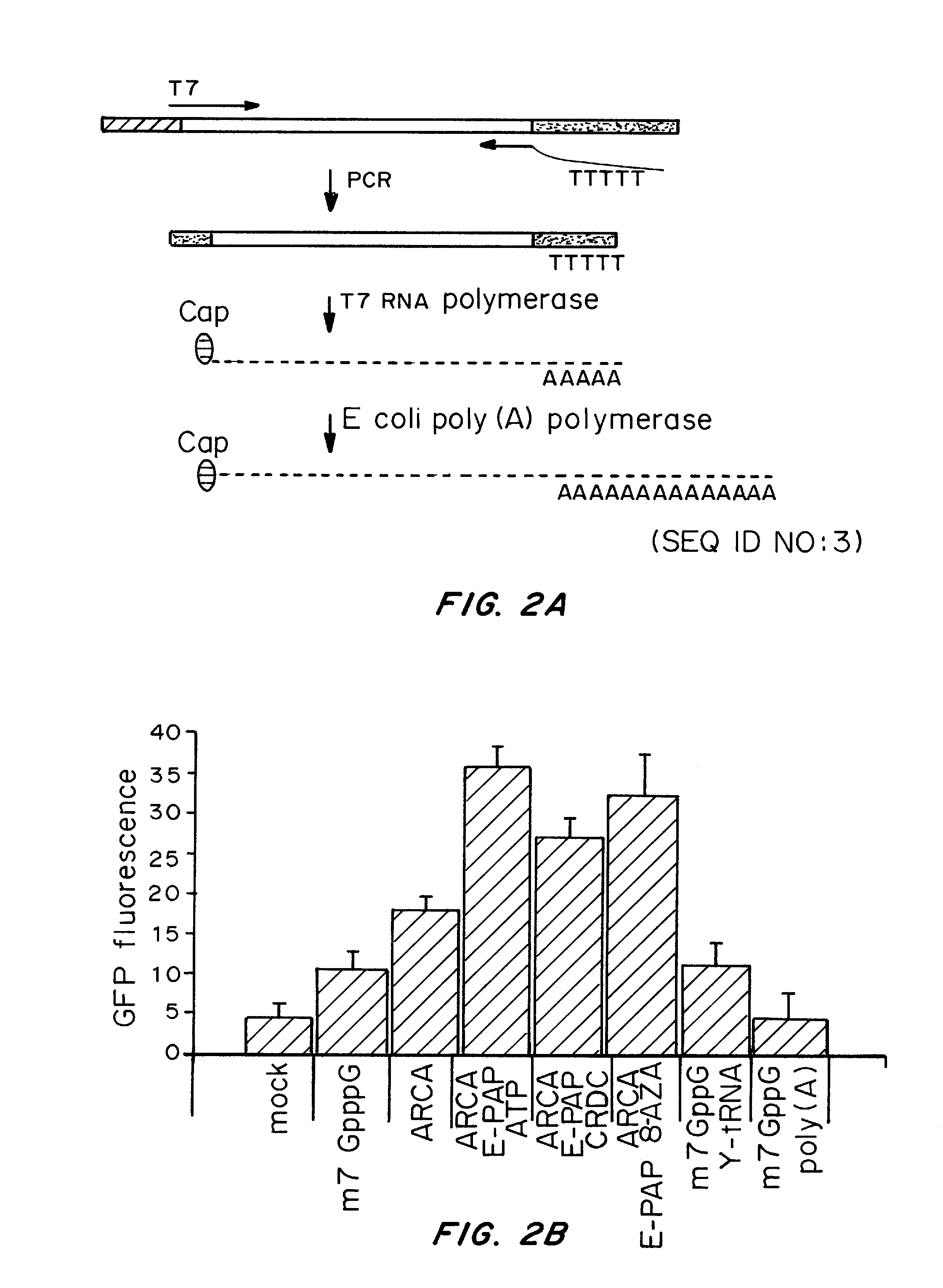
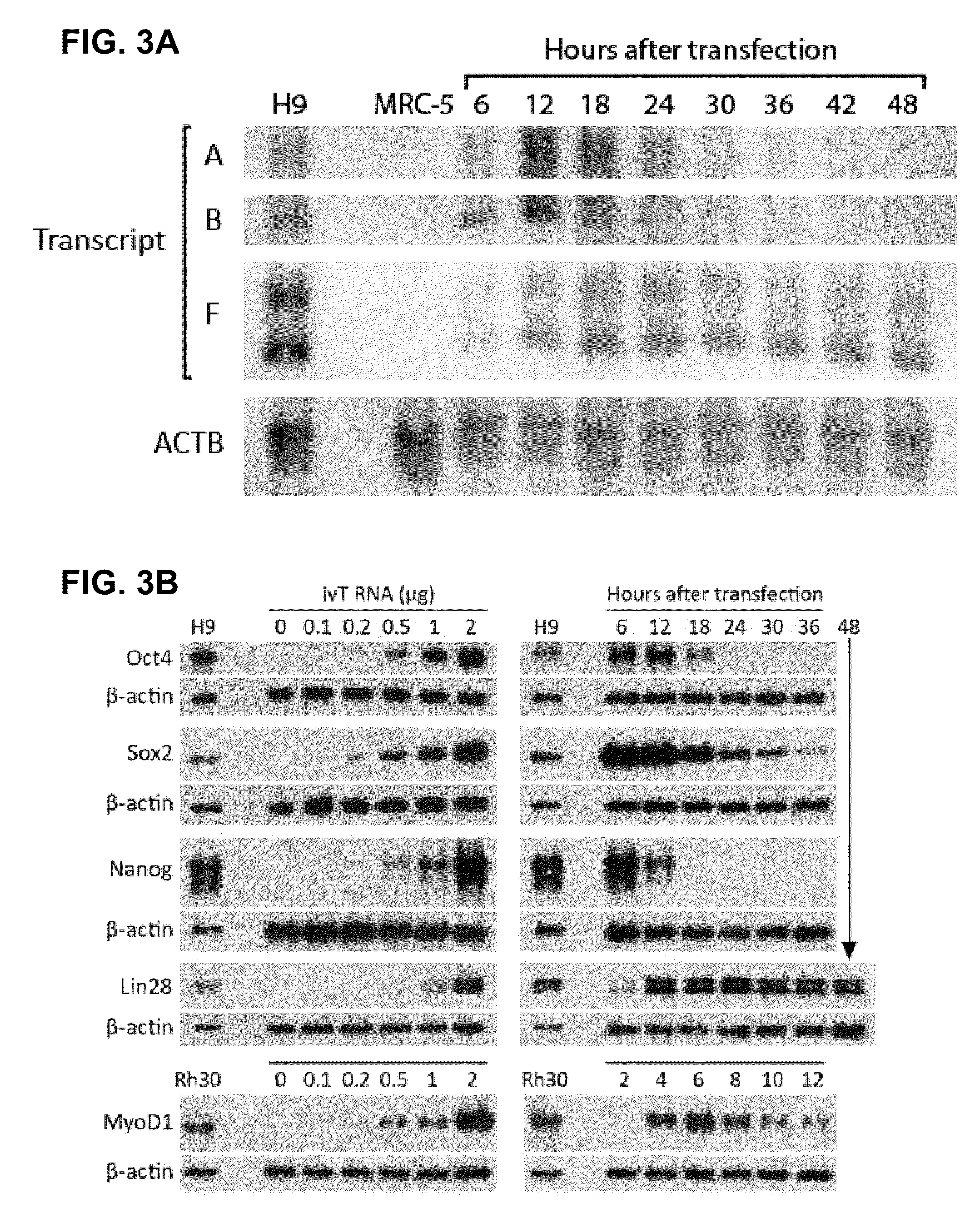
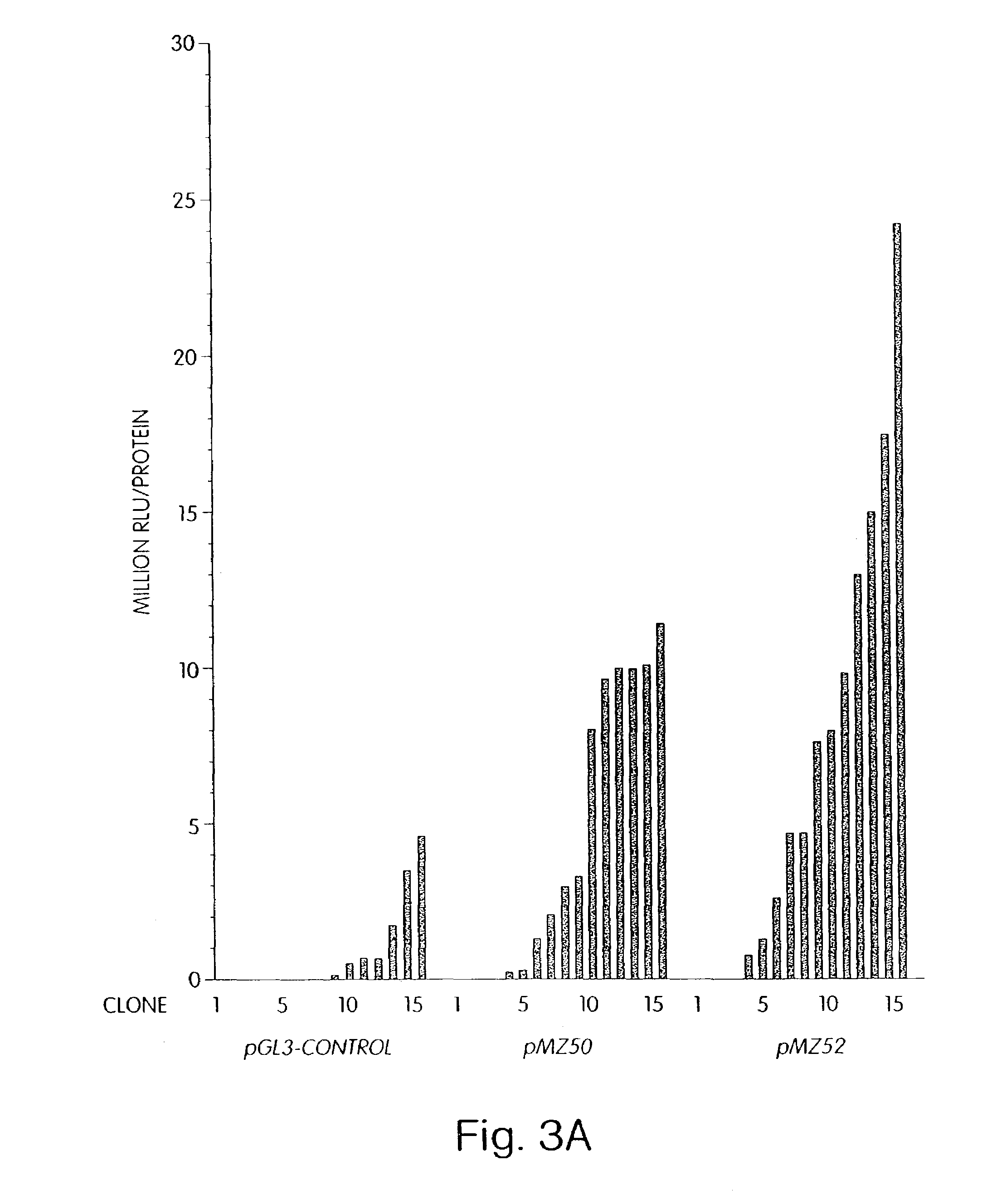
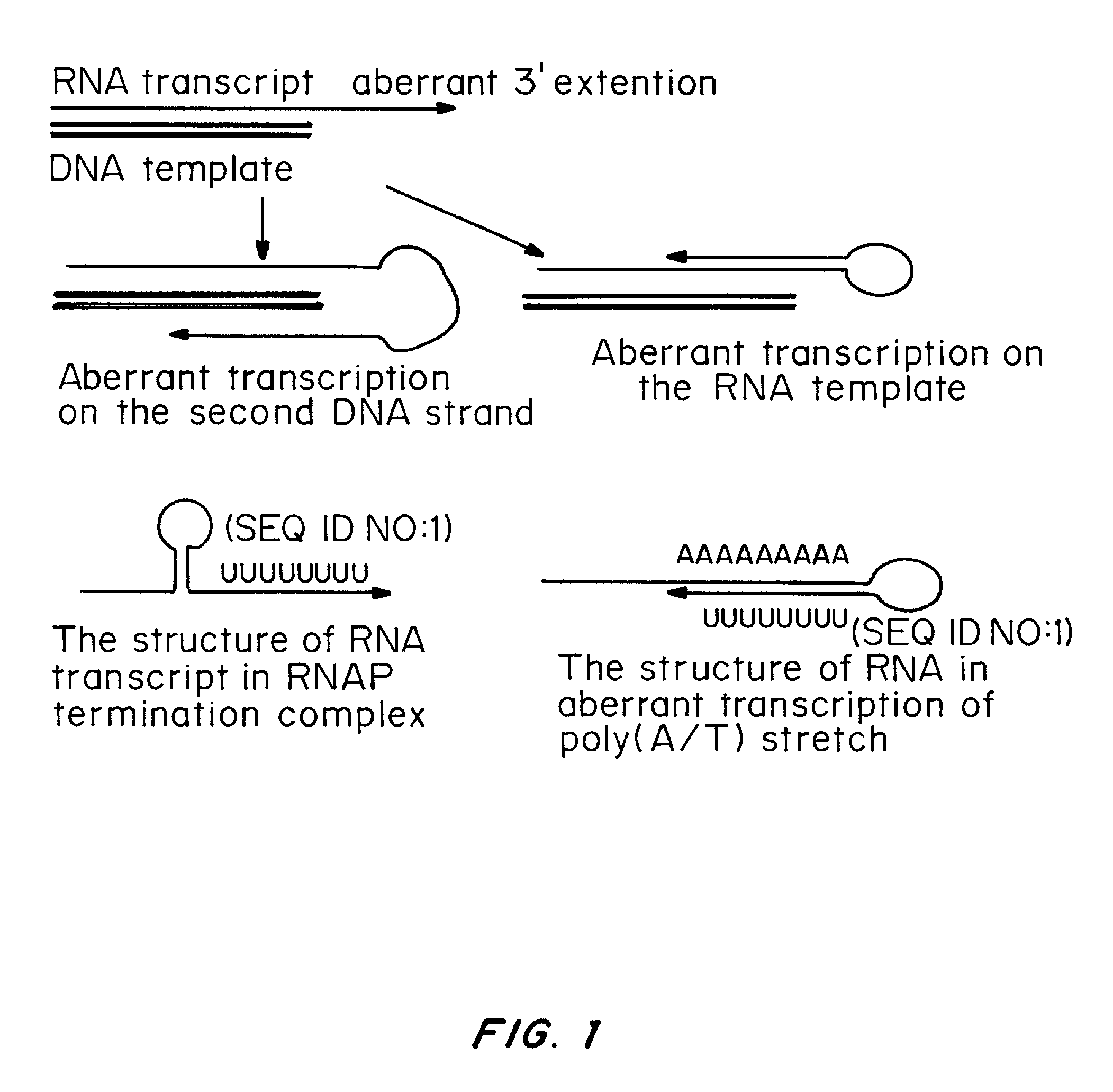
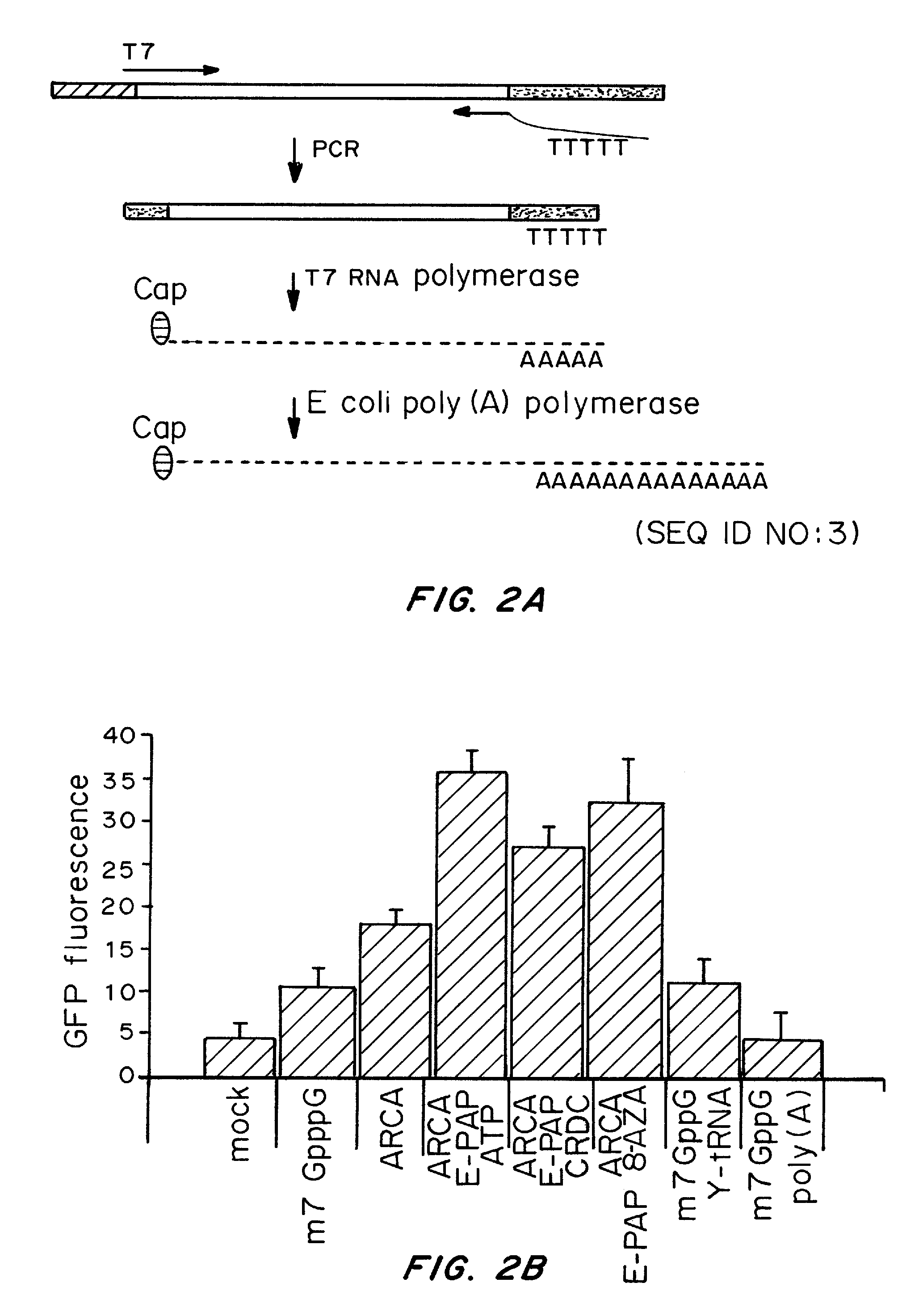
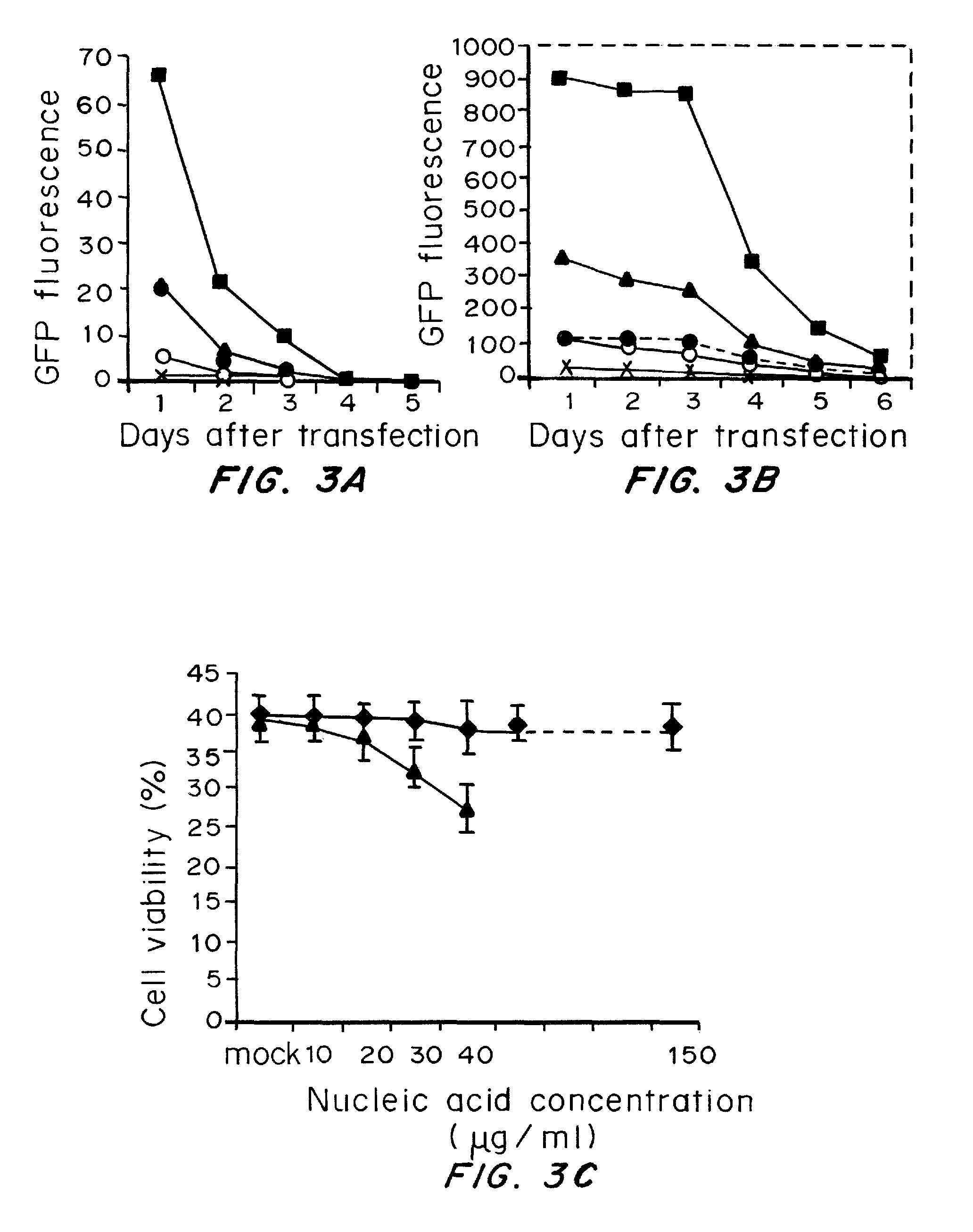
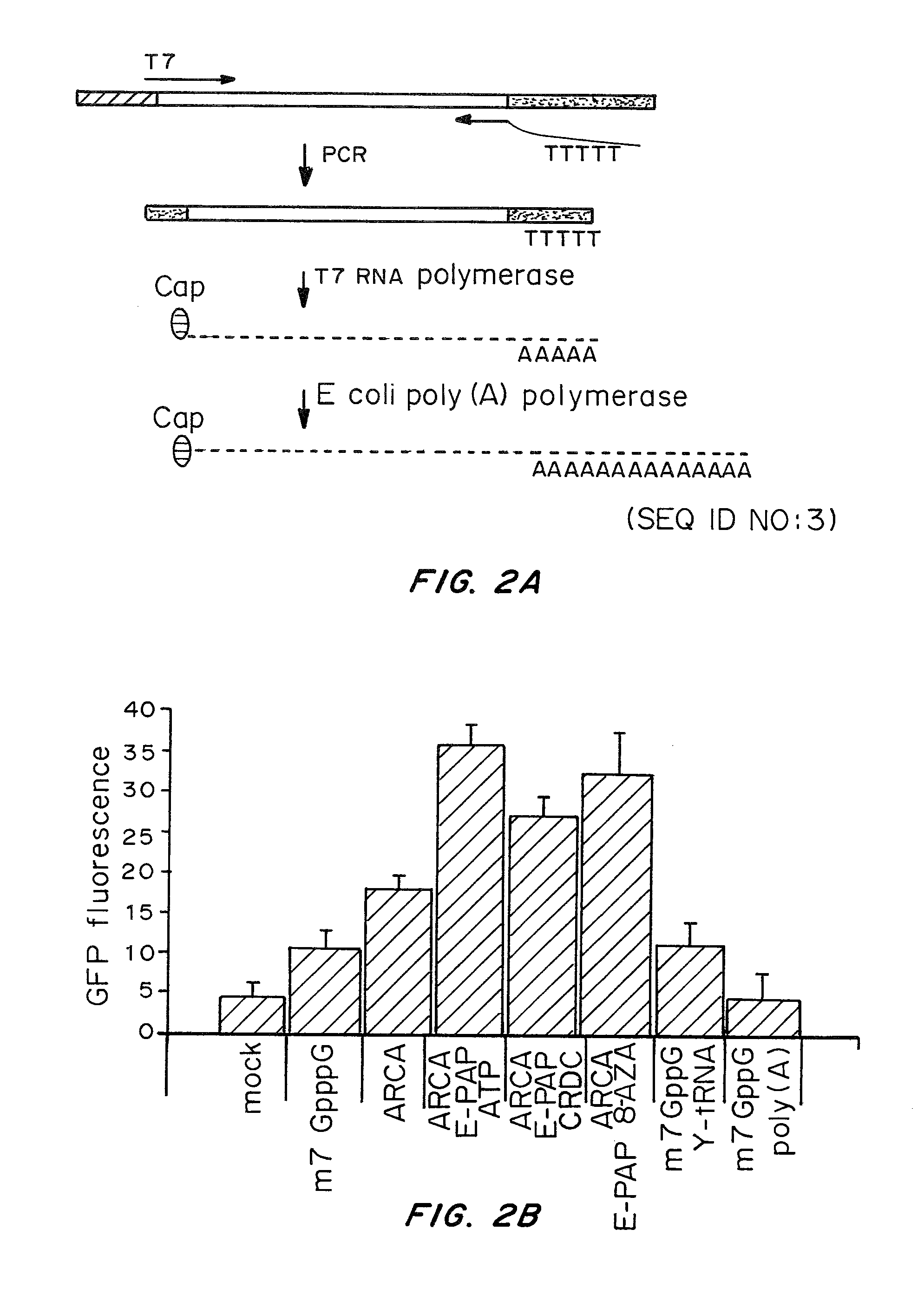
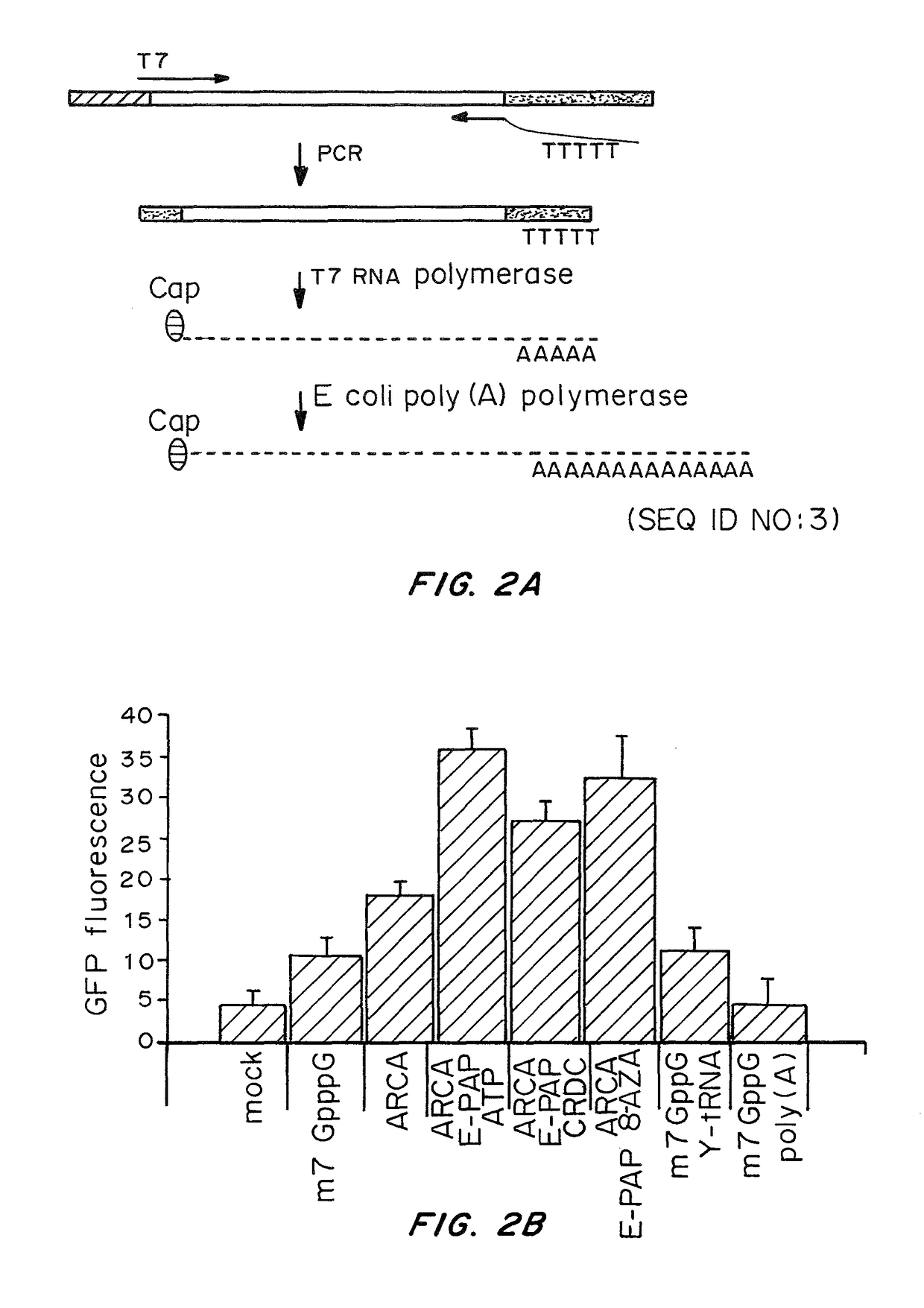
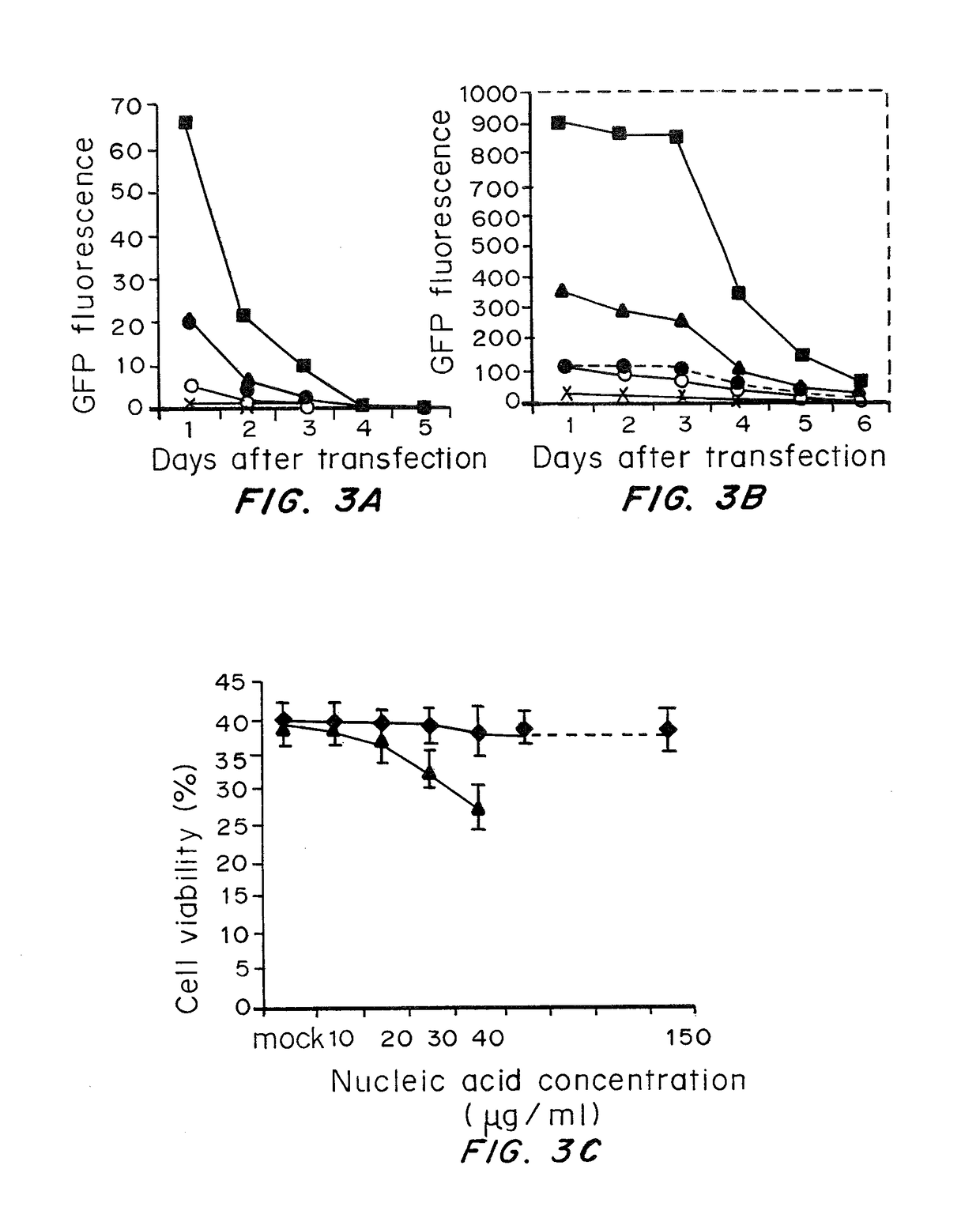
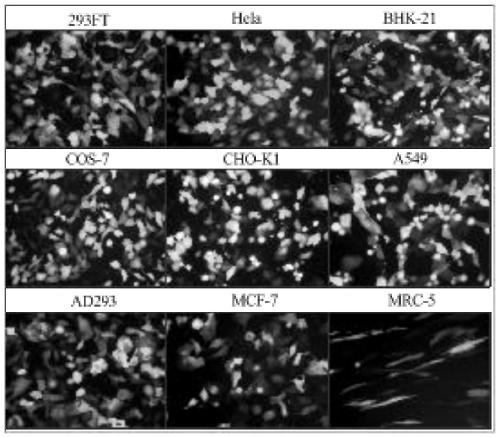
A method of mRNA production for use in transfection is provided, that involves in vitro transcription of PCR generated templates with specially designed primers, followed by polyA addition, to produce a construct containing 3′ and 5′ untranslated sequence (“UTR”), a 5′ cap and / or Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES), the gene to be expressed, and a polyA tail, typically 50-2000 bases in length. This RNA can efficiently transfect different kinds of cells. This approach results in increased efficiency (fidelity and productivity) of mRNA synthesis and is less time consuming because it does not require cloning, and also consequently eliminates the unwanted errors and effects related to RNA made on DNA templates obtained with cloning techniques. The results of transfection of RNAs demonstrate that RNA transfection can be very effective in cells that are exceedingly difficult to transfect efficiently with DNA constructs. Further, the levels of gene expression following mRNA transfection are consistent from cell to cell in an experiment and these levels can be controlled over a wide range simply by changing the amount of mRNA that is transfected, and without obvious cytotoxic effects due to the levels of RNA per se. Due to high efficiency the cells can be simultaneously transfected with multiple genetic constructs. The method can be used to deliver genes into cells not- or only poorly transfectable for DNA, in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Innate immune suppression enables repeated delivery of long RNA molecules
InactiveUS20100273220A1Suppressing innate immune responseReduce expressionSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsENCODETransient transfection
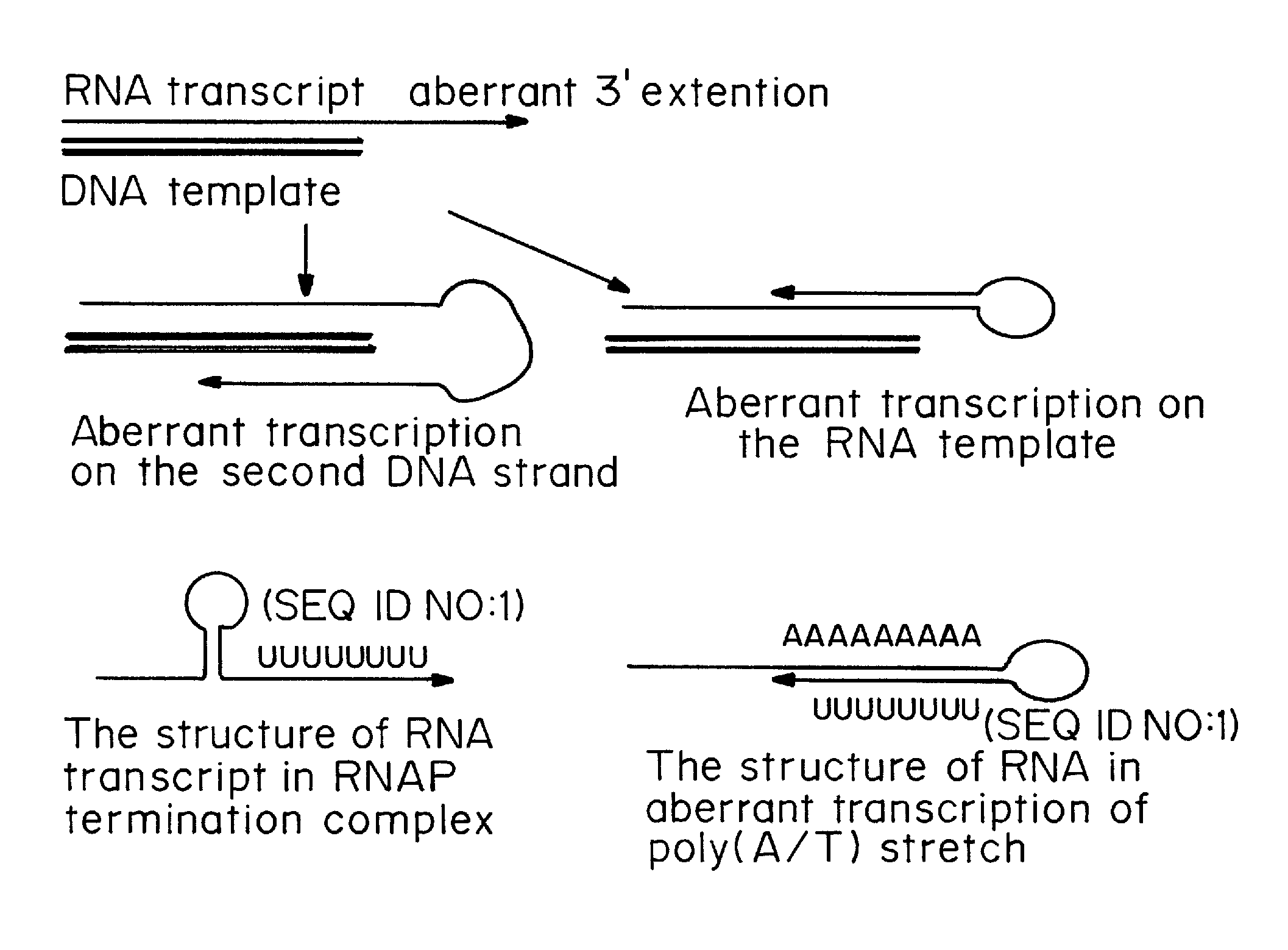
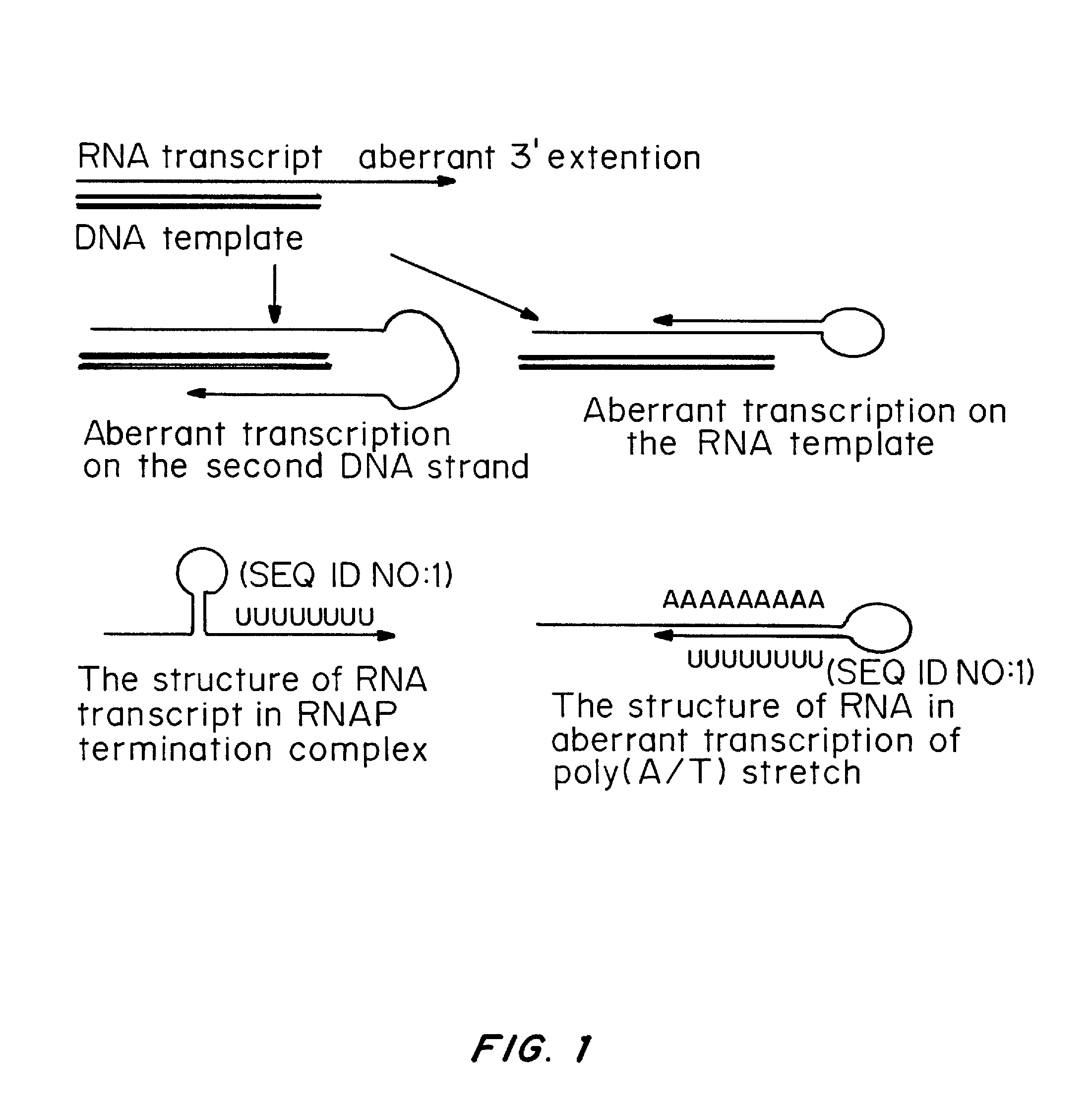
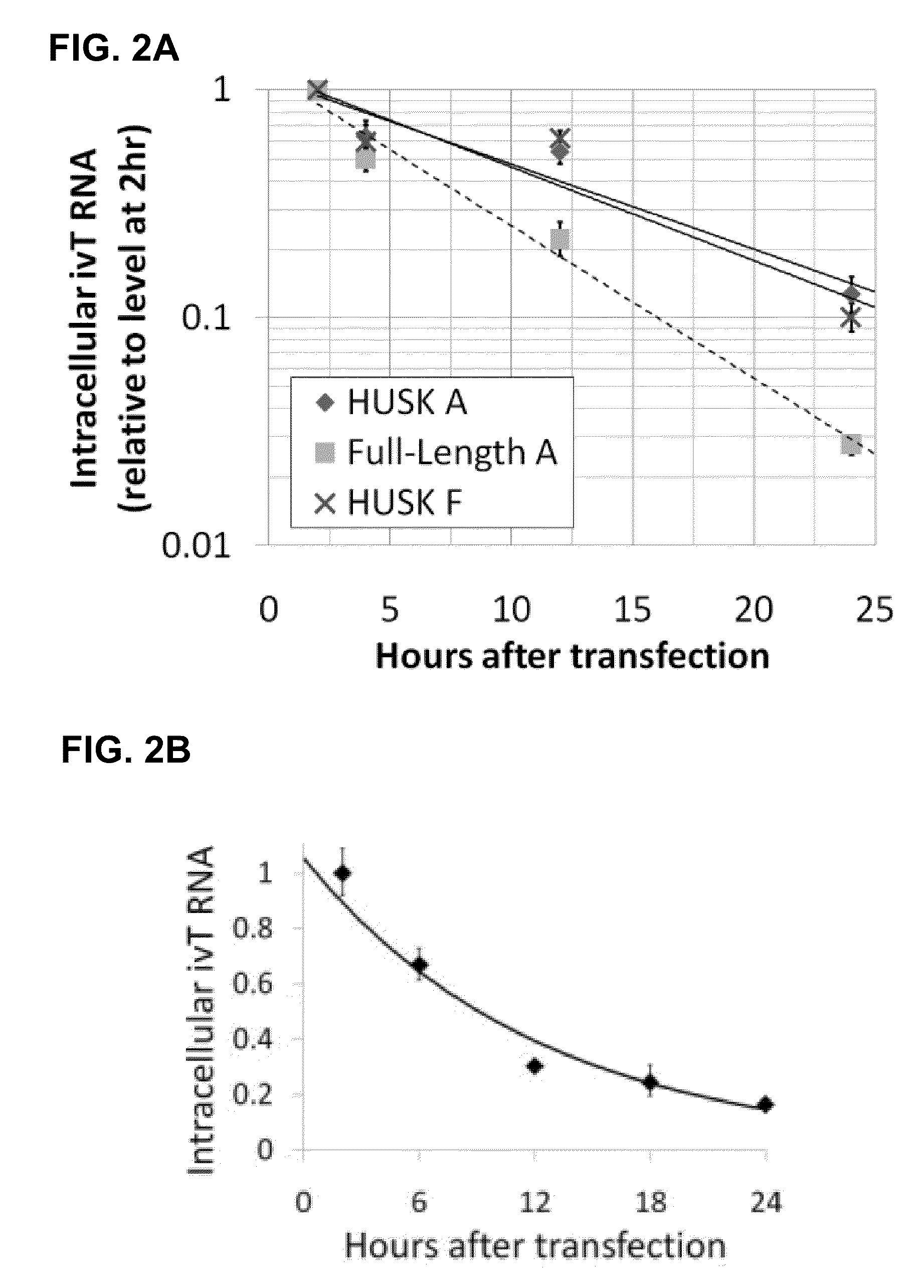
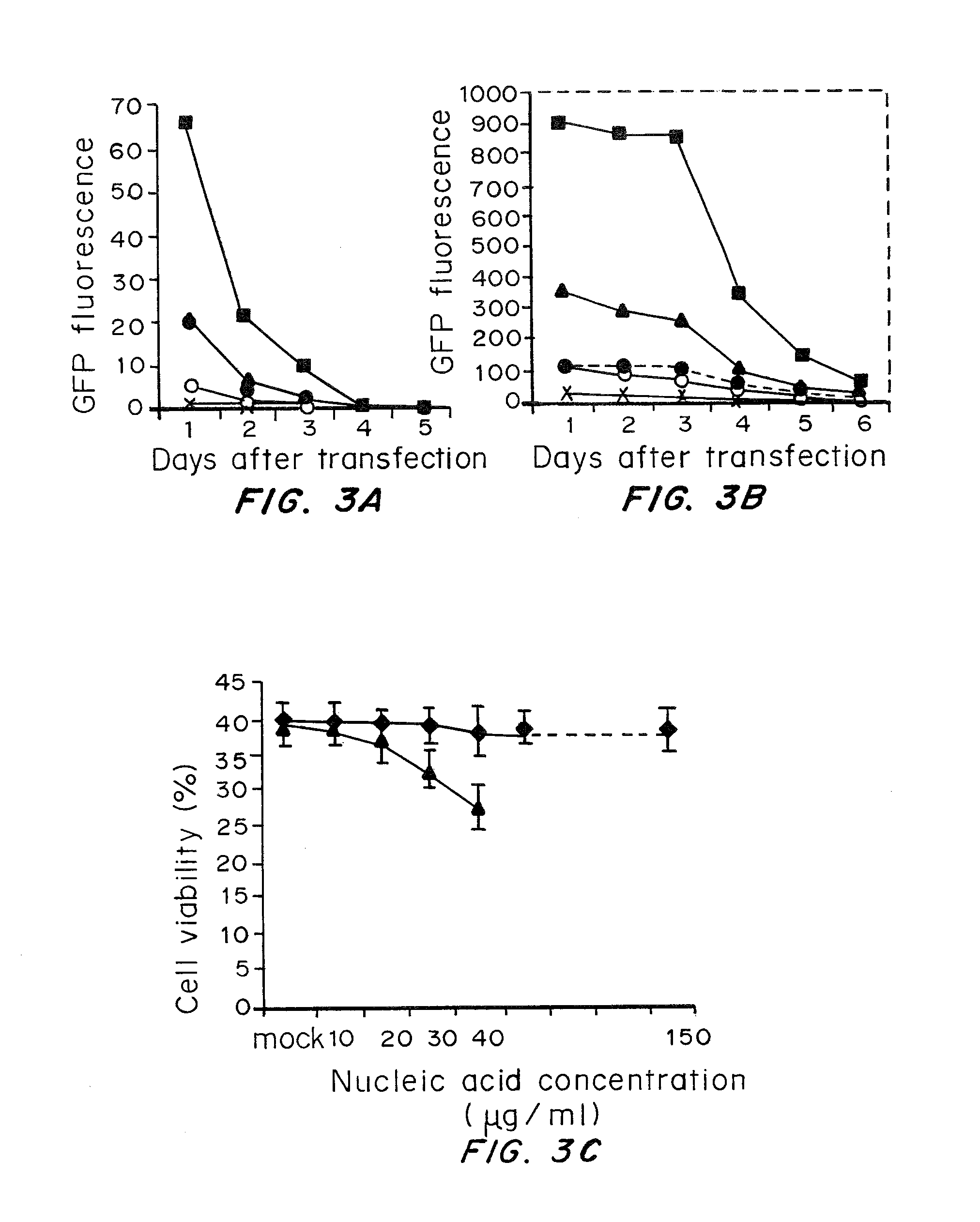
The present invention relates in part to methods for suppressing the innate immune response of a cell to transfection with an exogenous nucleic acid, to methods for increasing expression of a protein encoded by an exogenous nucleic acid by repeated delivery of the exogenous nucleic acid to a cell, and to methods of changing the phenotype of a cell by differentiating, transdifferentiating or dedifferentiating cells by repeatedly delivering one or more nucleic acids that encode defined proteins. A method is provided for extended transient transfection by repeated delivery of an in vitro-transcribed RNA (“ivT-RNA”) to a cell to achieve a high and sustained level of expression of a protein encoded by an ivT-RNA transcripts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Matrix attachment regions and methods for use thereof
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for transfecting eukaryotic cells with nucleic acid vectors. In particular, the invention relates to the uses of Matrix Attachment Region (MAR) elements to increase stable and transient transfection efficiency.
Owner:SELEXIS SA
Transient transfection with RNA
Owner:YALE UNIV
Enhanced production of recombinant proteins by transient transfection of suspension-growing mammalian cells
ActiveUS20050170450A1Increase transcriptional activityIncreasing nuclear importGenetically modified cellsVirus peptidesEpstein–Barr virusGene Variant
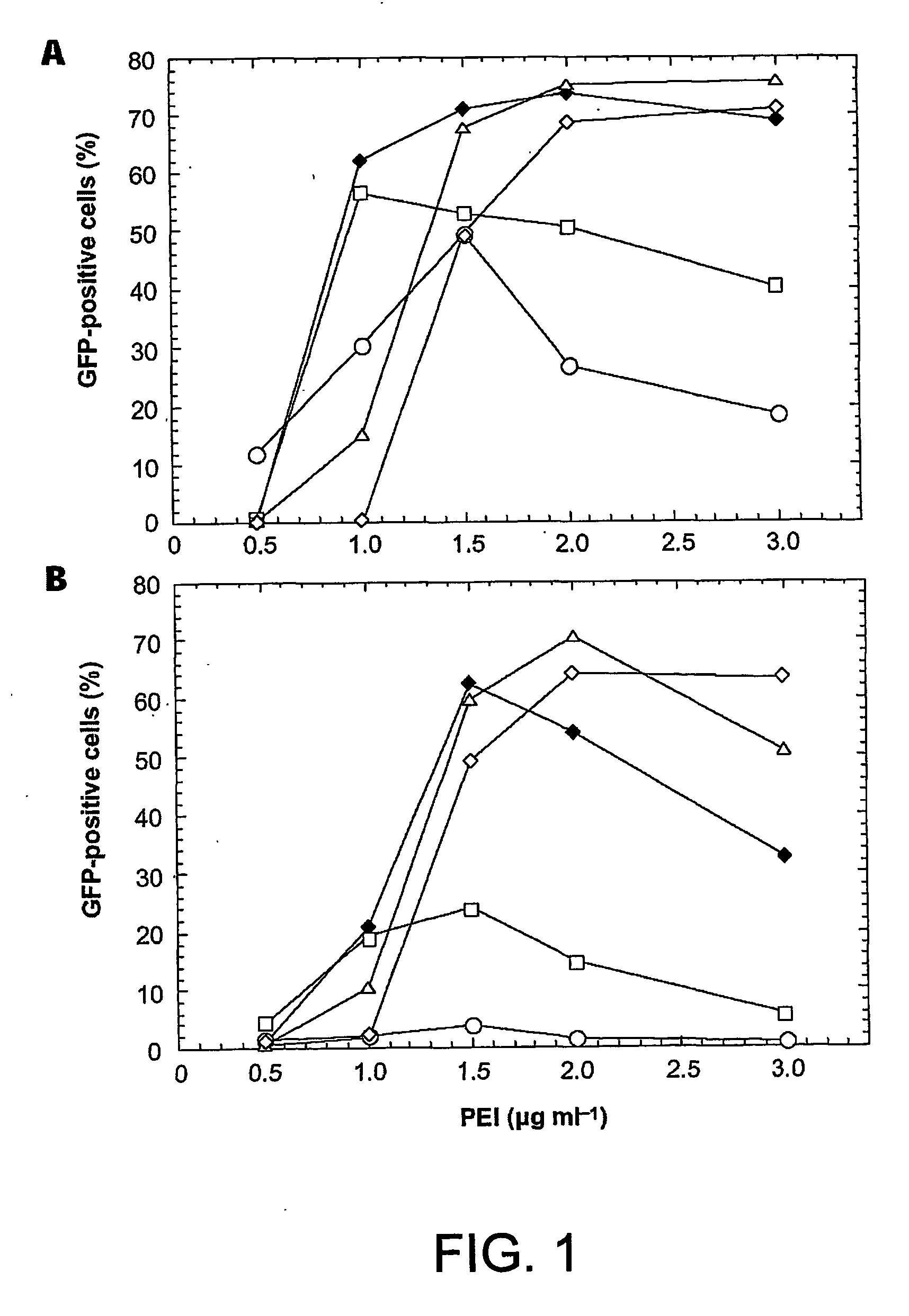
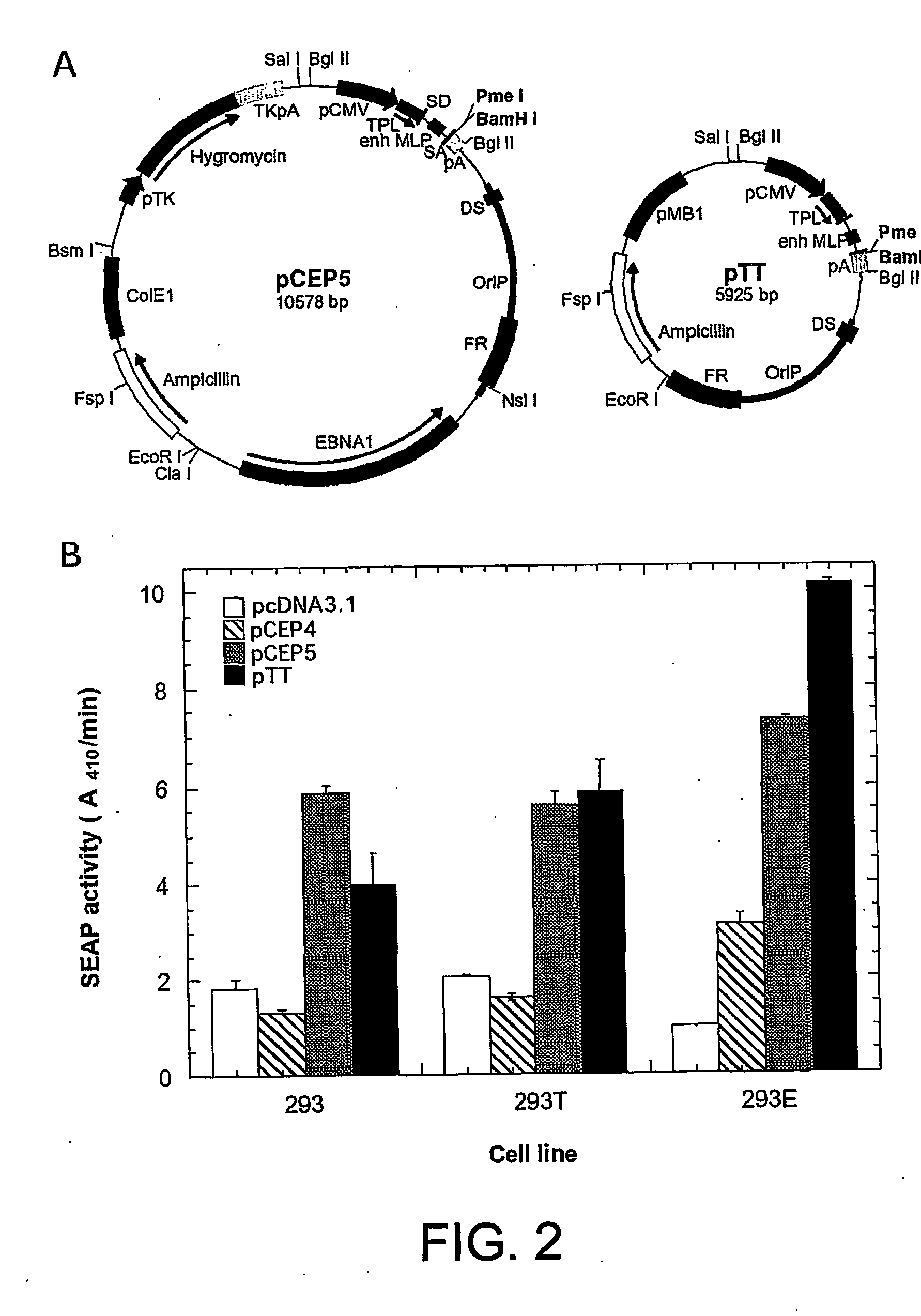
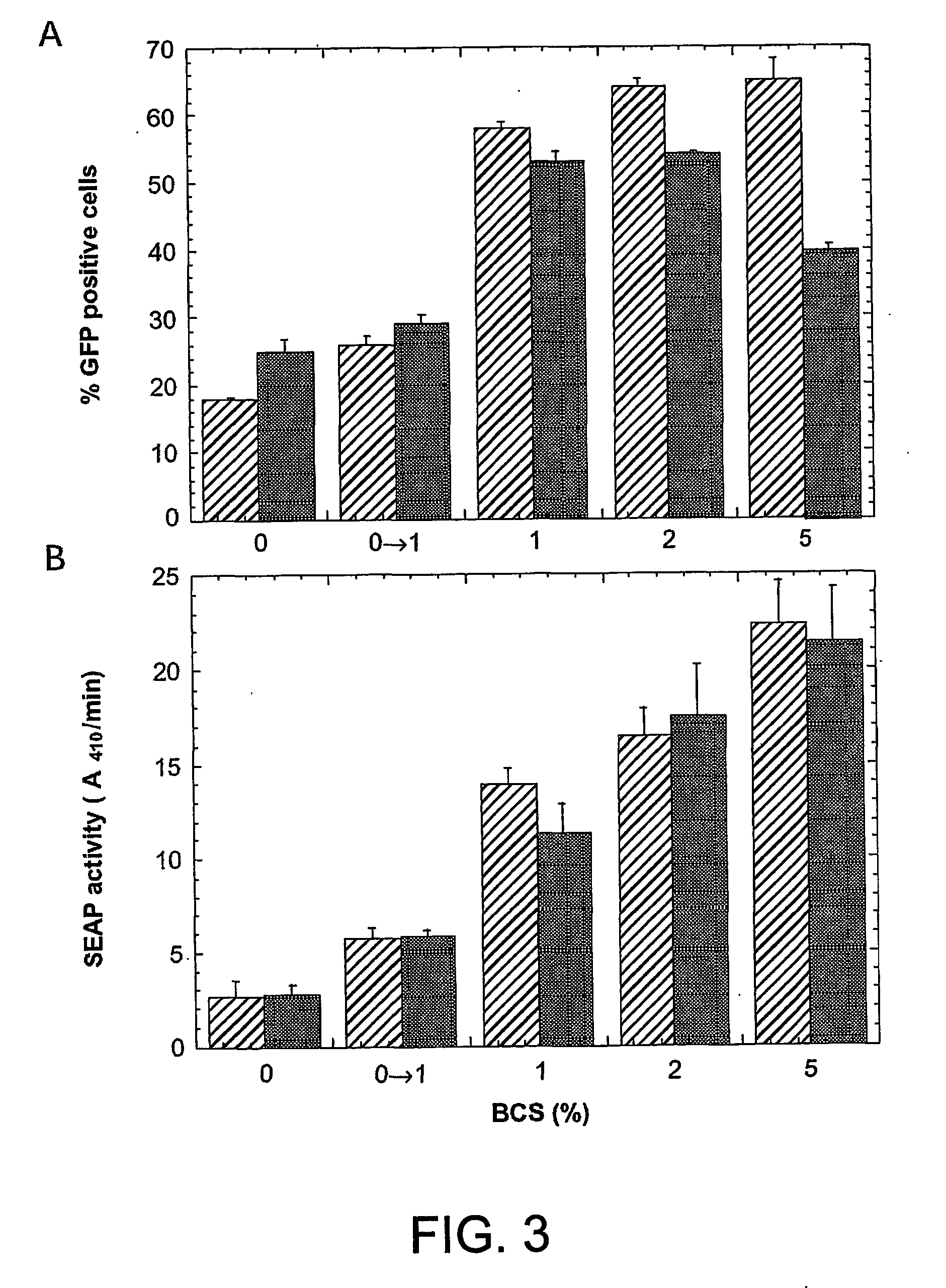
Disclosed is a new process for the production of recombinant proteins, by transient transfection of suspension-grown human embryonic kidney cells (293 cell line and its genetic variants) with an expression vector, using polyethylenimine (PEI) as a transfection reagent. In a preferred embodiment, the process uses 293E cells expressing the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) EBNA 1 protein, in combination with an oriP-based episomal expression vector having an improved cytomegalovirus expression cassette comprising the CMV5 promoter. The process combines in a single step the cell growth, transfection and protein expression, is carried out without changing the culture medium, and allows to achieve high expression levels in a short period of time. The process may be carried out in a serum-free, low-protein culture medium, is easily scalable, compatible with continuous production processes, and fully adapted to high-throughput production of milligram quantities of recombinant proteins.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Cells prepared by transient transfection and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20160151491A1Good metabolic stabilityConducive to survivalBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsDiseaseWhole body
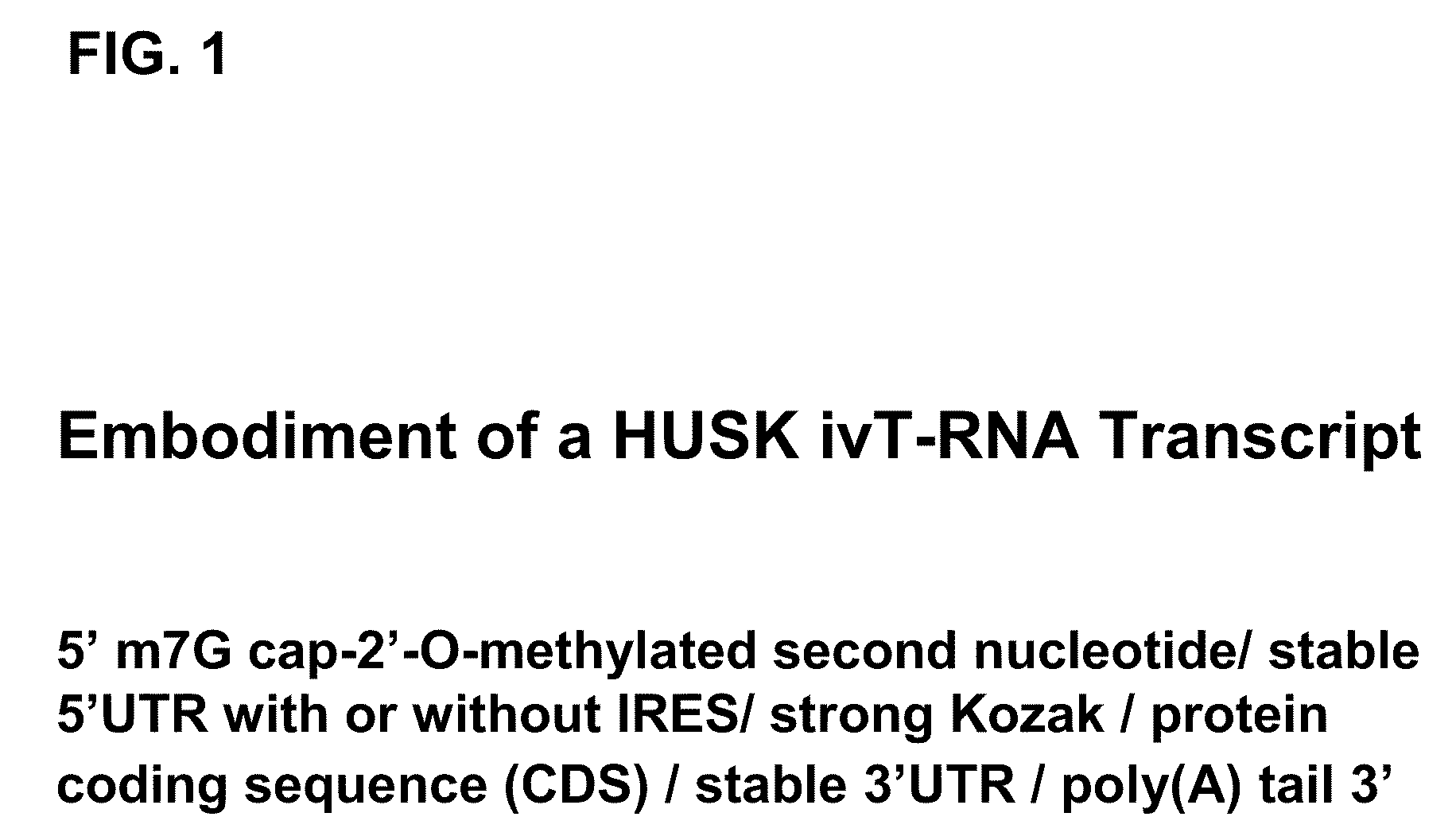
Compositions and methods of making cells using RNA, and cells made using the disclosed compositions and methods are also provided. In exemplary embodiments, RNA is transfected into cells to effect a molecular, biological, physiological, or histological change in the cells. In preferred embodiments, the RNA is prepared in vitro, more preferably using a DNA template according to the provided compositions and methods. Methods for treating or inhibiting a disorder or disease such cancer are also provided. The methods can include, for example, locally or systemically administering to the host an effective amount of one or more RNAs; or an effective amount of population of cells isolated from the subject or a syngeneic or histocompatible subject, contacted ex vivo with one or RNAs, and optionally expanded. The cells can be, for example, immune cells or stem cells.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Methods for generating antigen-specific effector T cells
InactiveCN101415827AImmunoglobulin superfamilyMicroinjection basedAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
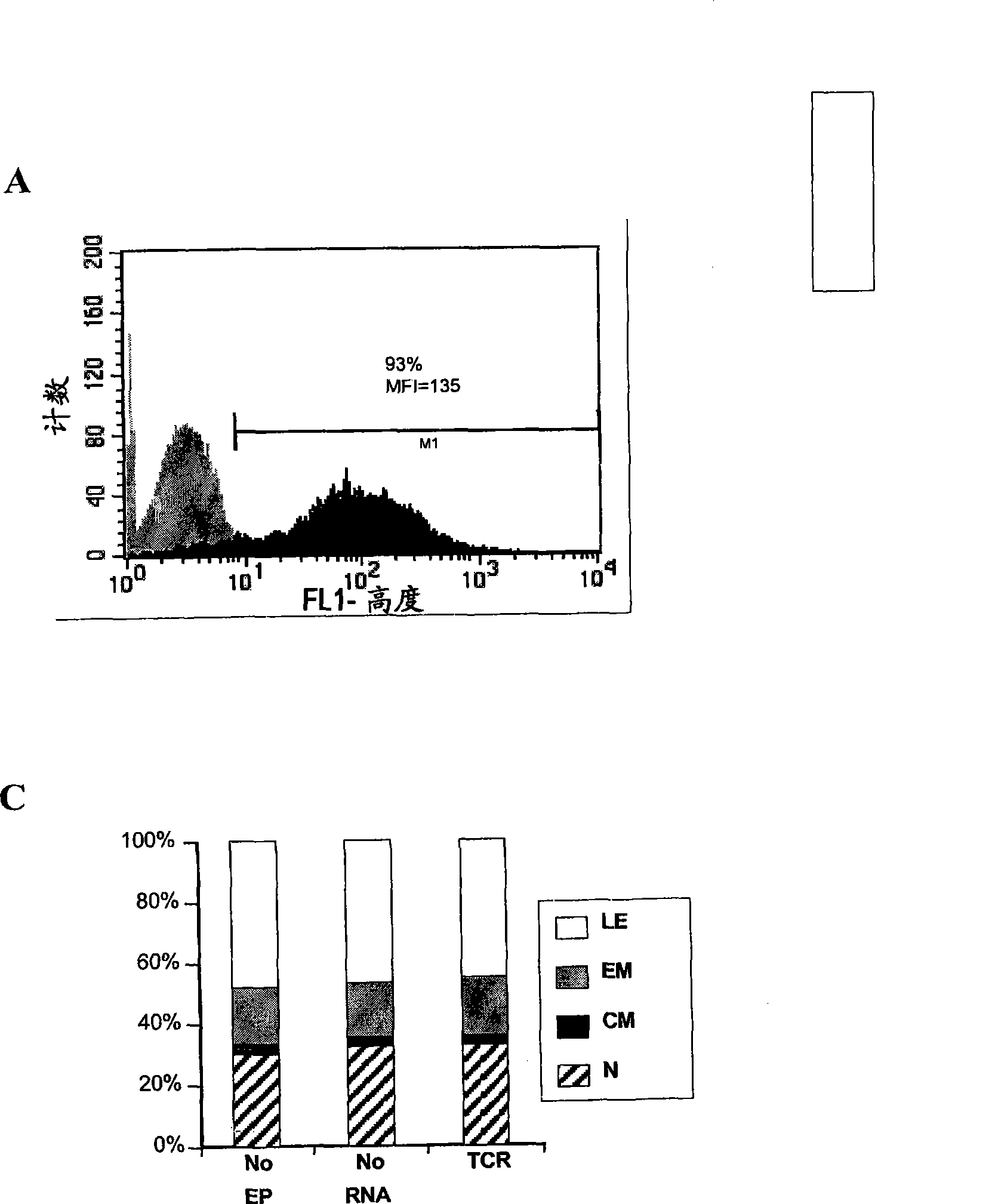
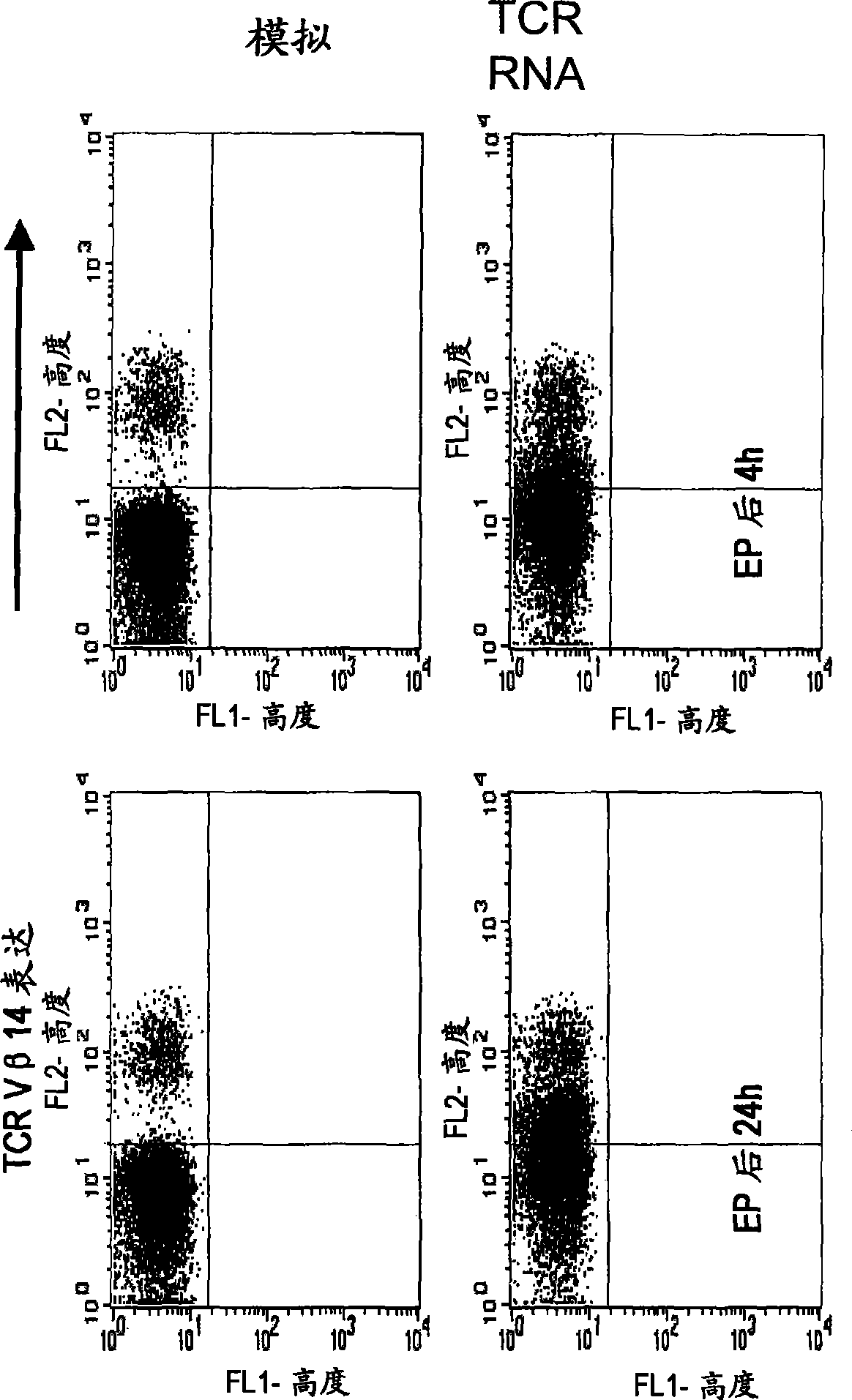
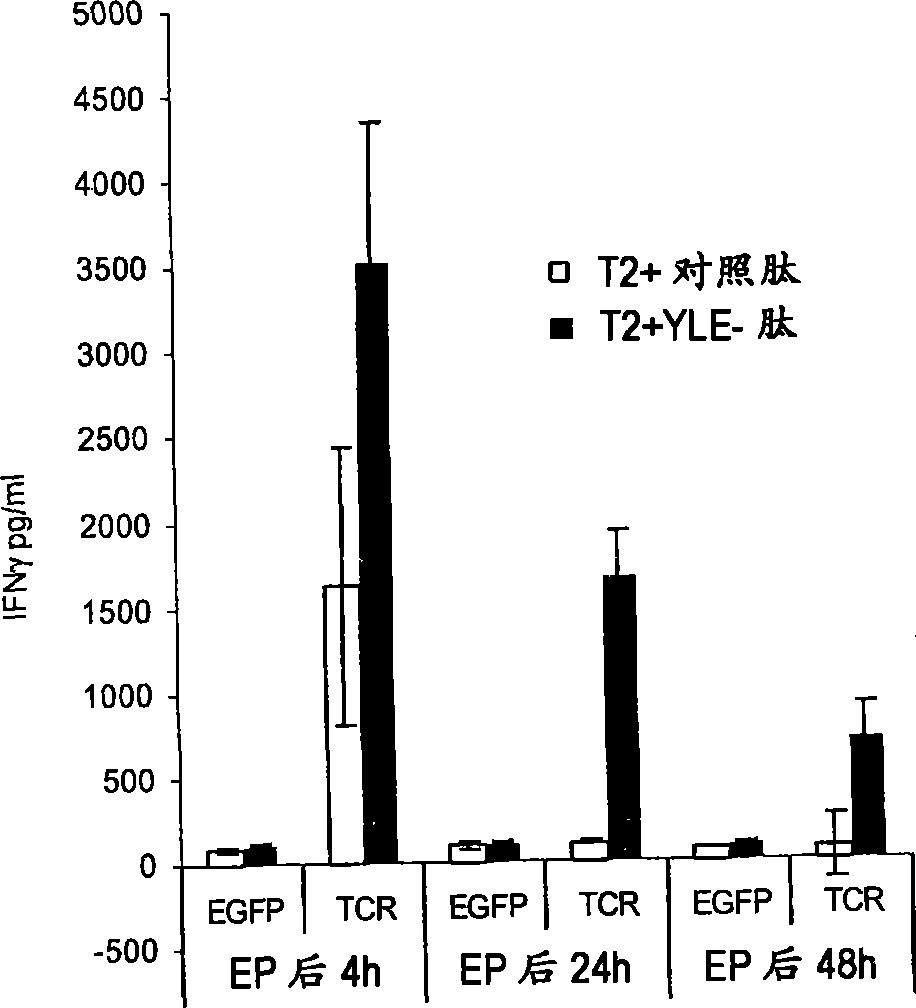
The invention relates to T cells transiently transfected with RNA, especially RNA encoding a T cell receptor and / or FoxP3, and methods of transfecting T cells with RNA by electroporation. Compositions of the invention include an effector T cell transiently transfected with RNA encoding a T cell receptor (TCR) specific for an antigen, wherein the T cell demonstrates effector function specific for cells presenting the antigen in complex with an MHC molecule. Treg cells comprising an exogenous RNA encoding FoxP3 are also provided. The transfected T cells are useful for immunotherapy, particularly in the treatment of tumors, pathogen infection, autoimmune disease, transplant rejection and graft versus host disease.
Owner:ARGOS THERAPEUTICS INC
Inducible alphaviral/orip based gene expression system
InactiveUS20060251620A1Rapid productionRapid and high level productionBiocideSugar derivativesTransient transfectionUntranslated RNA
The present invention relates to compositions and methods that allow the production of polypeptides and untranslated RNA molecules in host cells. More specifically, the invention provides nucleic acid molecules, expression systems, recombinant host cells, methods and kits, which enable the production and / or isolation and / or purification of polypeptides and untranslated RNA molecules. The compositions and methods of the invention can be applied in a regulatable expression system that is transiently transfected into mammalian host cells.
Owner:IVANOVA LIDIA +2
Methods of labeling transiently expressed proteins in large-scale eukaryotic cell cultures
InactiveUS20070161047A1Rapid productionSufficient quantityFungiTransferasesChemical compositionProtein structure
The present invention is based on observations that transiently transfecting large-scale eukaryotic cell cultures with a polynucleotide encoding a protein of interest can be used to rapidly produce the large quantities of labeled proteins required for various biochemical techniques such as spectroscopy, microscopy, and crystallography, and applications including protein structure determination, protein tracing and / or localization, diagnostic and therapeutic applications, and affinity experiments. Thus, the present invention provides methods for rapidly producing large quantities of labeled proteins by using transient transfection of large-scale eukaryotic cell cultures, which are then grown in a chemically defined labeling medium that includes labeled amino acids. The present invention is also directed to methods of using the labeled proteins produced by the novel labeling methods for use in various techniques.
Owner:WYETH LLC
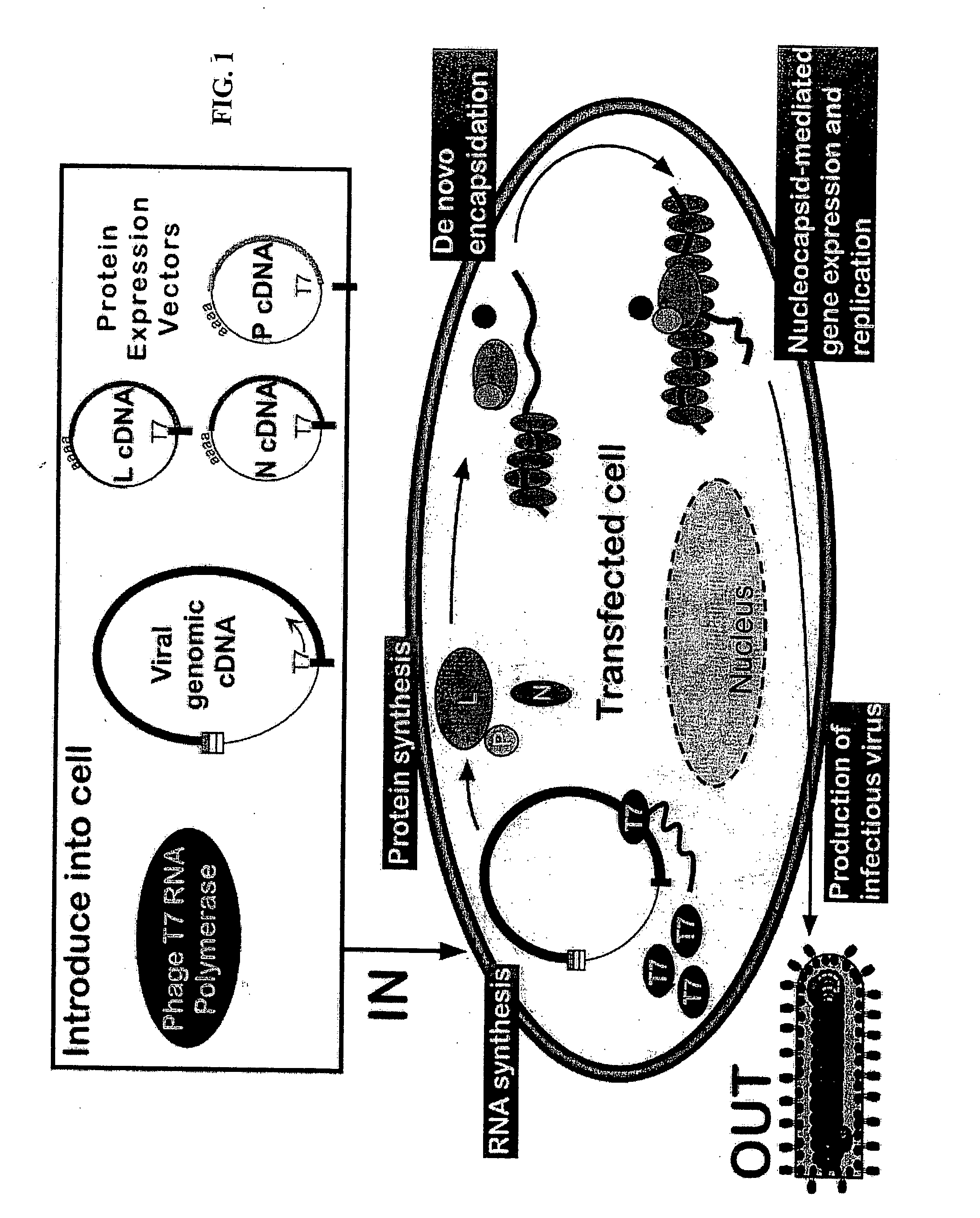
Method for the recovery of non-segmented, nagative-stranded RNA viruses from cDNA
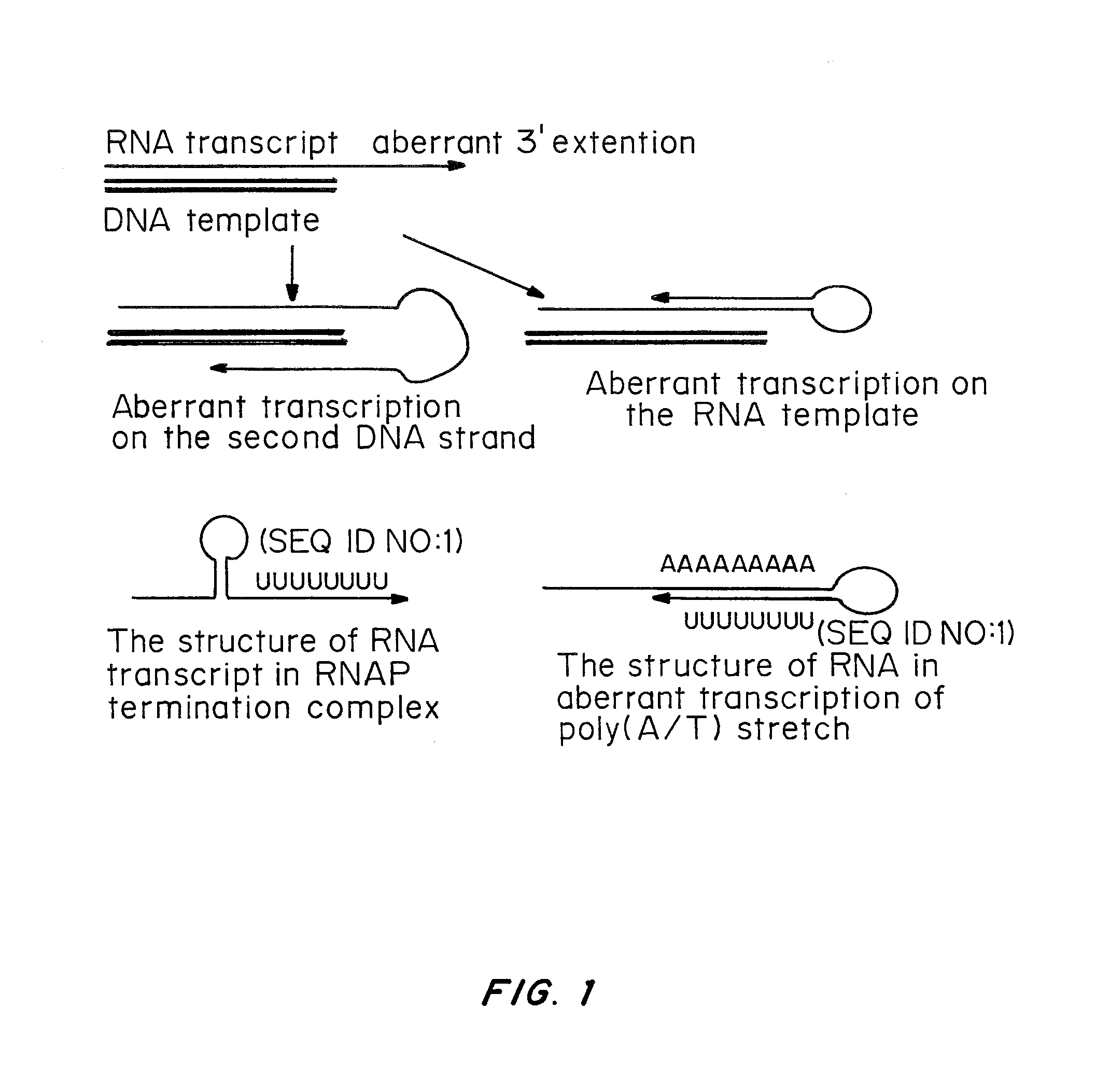
InactiveUS20060153870A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsNegative strandSubviral particle
Methods for producing infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA viruses of the Order Mononegavirales are provided that involve coexpression of a viral cDNA along with essential viral proteins, N, P, and L in a host cell transiently transfected with an expression vector encoding an RNA polymerase. In alternate methods, after the host cell is transfected with a viral cDNA expression vector and one or more vectors encoding the RNA polymerase, N protein, P protein, and L protein, the host cell is exposed to an effective heat shock under conditions sufficient to increase recovery of the recombinant virus. In other alternate embodiments, the host cells are transferred after viral rescue begins into co-culture with a plaque expansion cell, typically a monolayer of expansion cells, and the assembled infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA virus is recovered from the co-culture. Also provided within the invention are compositions for producing infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA virus of the Order Mononegavirales, recombinant viruses produced using the foregoing methods and compositions, and immunogenic compositions and methods employing the recombinant viruses. In additional embodiments, the methods and compositions of the invention are employed to produce growth- or replication-defective non-segmented negative-stranded RNA viruses and subviral particles.
Owner:WYETH LLC
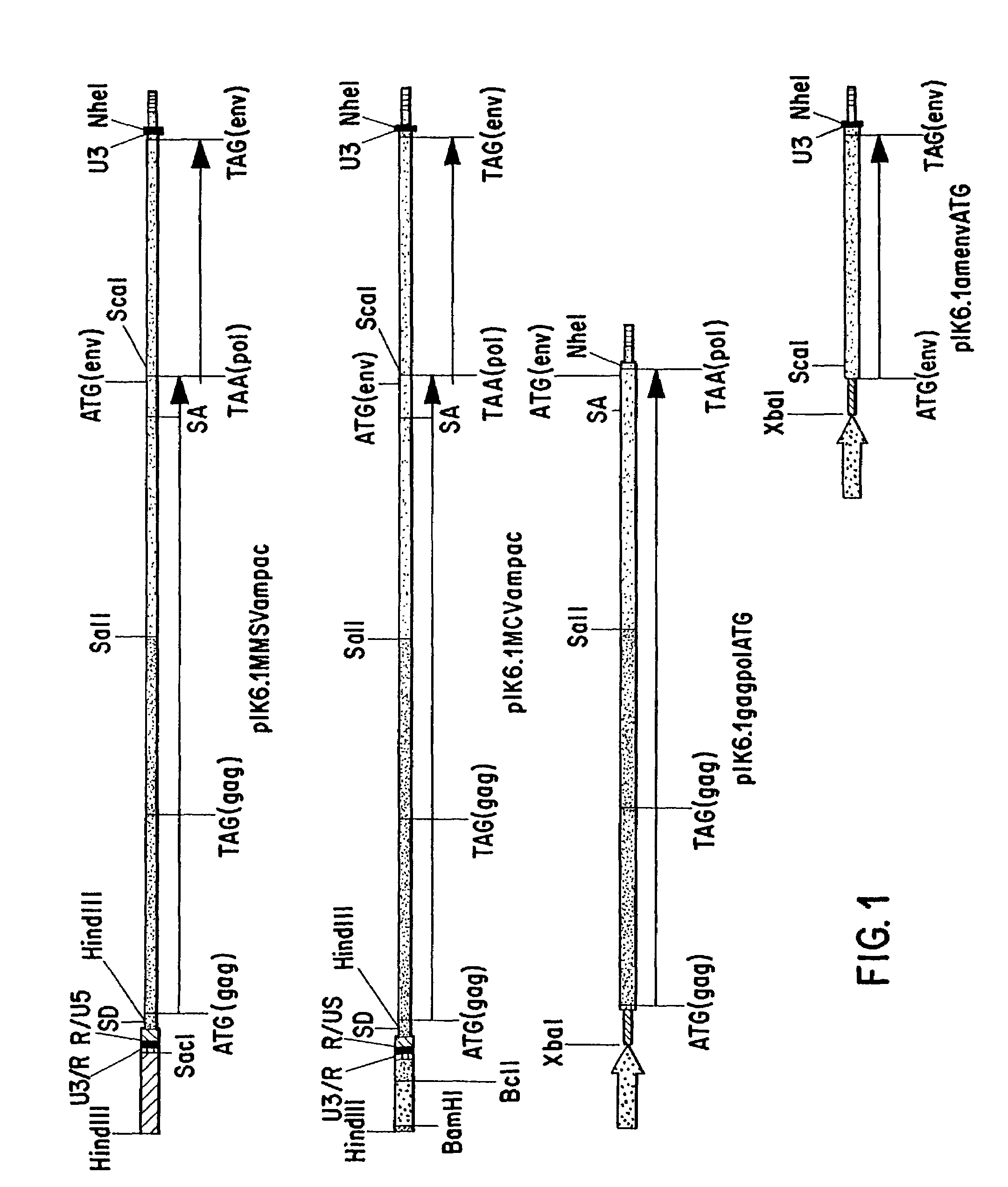
Method for production of high titer virus and high efficiency retroviral mediated transduction of mammalian cells
InactiveUS7252991B2Rapid productionHighly efficient transductionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsMammalHuman cell
The invention provides a novel retroviral packaging system, in which retroviral packaging plasmids and packagable vector transcripts are produced from high expression plasmids after stable or transient transfection in mammalian cells. High titers of recombinant retrovirus are produced in these transfected mammalian cells and can then transduce a mammalian target cell by cocultivation or supernatant infection. The methods of the invention include the use of the novel retroviral packaging plasmids and vectors to transduce primary human cells, including T cells and human hematopoietic stem cells, with foreign genes by cocultivation or supernatant infection at high efficiencies. The invention is useful for the rapid production of high titer viral supernatants, and to transduce with high efficiency cells that are refractory to transduction by conventional means.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC TECH
Cell line screened by anti-oxidant or chemical preventive agent, construction and application
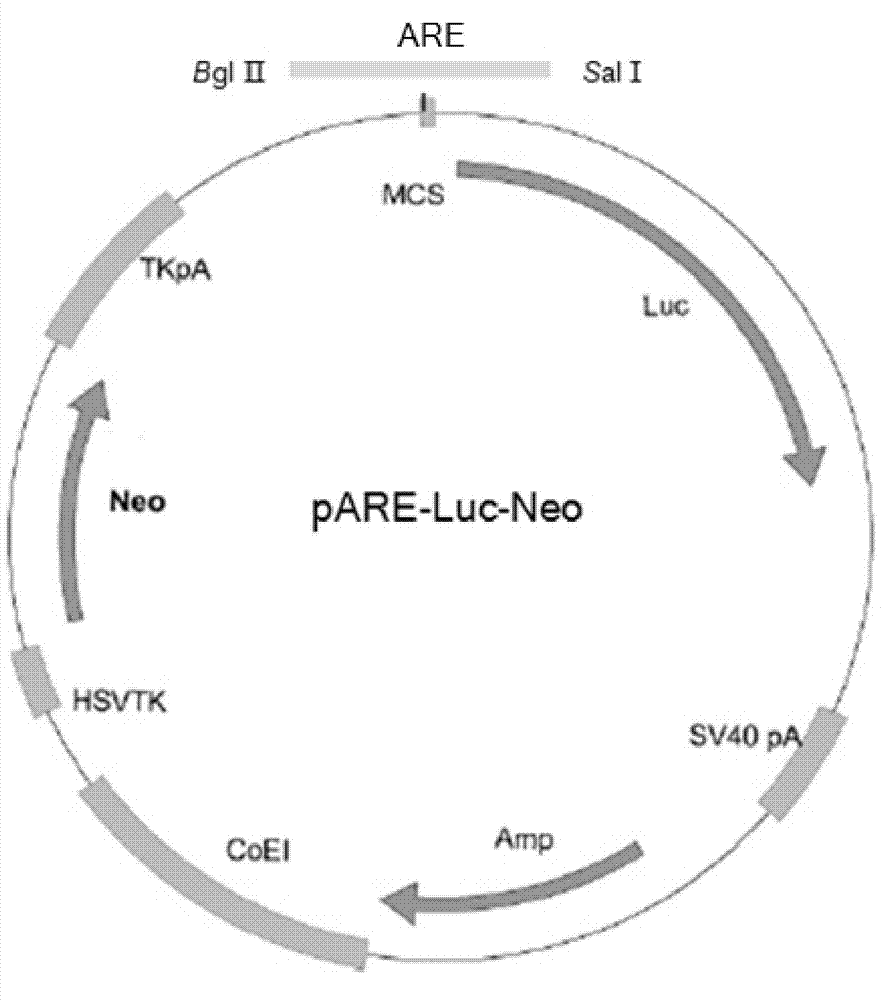
InactiveCN102899351AIncrease vitalityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAntioxidative responseNeomycin
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid and a construction method, the recombinant plasmid contains an antioxidation reaction element, luciferase gene and neomycin resistant gene. The invention also discloses a cell line screened by an anti-oxidant or a chemical preventive agent, a construction and an application, and the cell line is the cell integrated with the above recombinant plasmid. The provided cell line integrates the ARE gene in a recombinant plasmid carrier pARE-Luc-Neo, luciferase gene and neomycin resistant gene to a genome of a host cell Hek293, by following with subcultring of cell (more than 10 generation), the detection of a luciferase expression is stable, compared with a transient transfection method, and the construction provided by the invention is more convenient, sensitive and reliable.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for producing a recombinant protein at high specific productivity, high batch yield and high volumetric yield by means of transient transfection
InactiveUS20080145893A1Increase speedImprove versatilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetically modified cellsBiotechnologyEngineering
Recombinant proteins are of great commercial interest. Yet, most current production methods in mammalian cells involve the time- and labor-consuming step of creating stable cell lines. Production methods based on transient gene expression are advantageous in terms of speed and versatility, yet, thus far, those methods have not shown the specific productivity, batch yield and volumetric yield to be an economic alternative to stable cell lines. The inventors improved on the methodology of transient transfection and achieved commercially relevant yields in terms of specific productivity (exceeding 35 pg per cell per day), batch yield (exceeding 700 mg / l) and volumetric yield.
Owner:HILDINGER MARKUS
Novel double promoter structural unit
InactiveCN104278032AStrong transcription efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionStructural unitNucleic acid sequence
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and particularly relates to a novel double promoter structural unit. The novel double promoter structural unit disclosed by the invention comprises two CMV promoters shown in a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO. 2 and a sequence shown in a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO. 1. The double promoter structural unit is integrated by chromosomes, so that transcription or expression of a target gene in an expression system is increased. The promoter structural unit provided by the invention can be used for constructing expression vectors of cells of mammals and the constructed plasmid can be used for transient transfection for cells of mammals and construction of a stable expression cell strain. Compared with the conventional CMV promoter, the promoter unit provided by the invention is stronger in transcription efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI MBR BIOMEDICAL TECH
Androgen receptor coactivators
Disclosed are androgen receptor-associated proteins, designated ARA24, ARA54, ARA55, and Rb, that have been demonstrated to interact with the androgen receptor to alter levels of androgen receptor-mediated transcriptional activation. Certain of these proteins interact with the androgen receptor in an androgen-dependent manner, whereas certain proteins may induce transcriptional activation in the presence of other ligands, such as E2 or HF. Also disclosed is a method of detecting androgenic or antiandrogenic activity using these proteins in a mammalian two-hybrid transient transfection assay.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Exosome coupled with coronavirus S protein on surface and preparation method for exosome and application of exosome
InactiveCN111647557AImprove securityAvoid the risk of infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsCD63Receptor
The invention provides an exosome coupled with coronavirus S protein on the surface and a preparation method for the exosome and application of the exosome, and belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy. A stable cell line is obtained through transient transfection of human cells or infection with a recombinant lentivirus to achieve recombinant expression of aptamer CP05-S protein, andthe aptamer CP05-S protein is mixed with human plasma for incubation, and the exosome is bound to an aptamer CP05 through surface CD63 membrane molecules to form the exosome coupled with the S protein on the surface. The exosome provided by the invention is employed to present antigen S protein, so that a prepared vaccine avoids the toxicity of an immunologic adjuvant and the risk of virus vaccine infection, and loading the S protein to the surface of the exosome to prepare the vaccine is an ideal vaccine development strategy, and is also an ideal strategy for blocking a virus invasion route;and meanwhile, the S protein is delivered through the exosome, and thus, competitive inhibition can be performed on binding of the S protein of the novel coronavirus to a receptor, the blocking action is exerted, and invasion of the novel coronavirus is effectively blocked, and accordingly, as an inhibitor for novel coronavirus infection, the exosome coupled with the S protein can be used for treatment of acute novel coronavirus pneumonia.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Autoimmune encephalitis antibody transient transfection and stable transfection detection method and application thereof
PendingCN113755443ABiological material analysisMicroorganism based processesImmunofluorescenceTransient transfection
The invention provides an autoimmune encephalitis antibody transient transfection and stable transfection detection method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a recombinant cell for expressing mutant NMDAR, the recombinant cell expresses fusion protein of exogenous mutant NMDAR and fluorescent protein, and the transfection survival rate is high. The recombinant cell provided by the invention can be used for detecting antibodies related to autoimmune encephalitis, including NMDAR, AMPAR1, AMPAR2, LGI1, Caspr2 and GABABR. The invention also provides a method for detecting anti-autoimmune encephalitis by using the transfected cell line through an indirect immunofluorescence method based on the recombinant transfected cell line provided by the invention. The method disclosed by the invention has high sensitivity and specificity, and can be used for accurately detecting the types of pathogenic antibodies so as to help a patient to carry out targeted immunotherapy and recover health.
Owner:陈向军
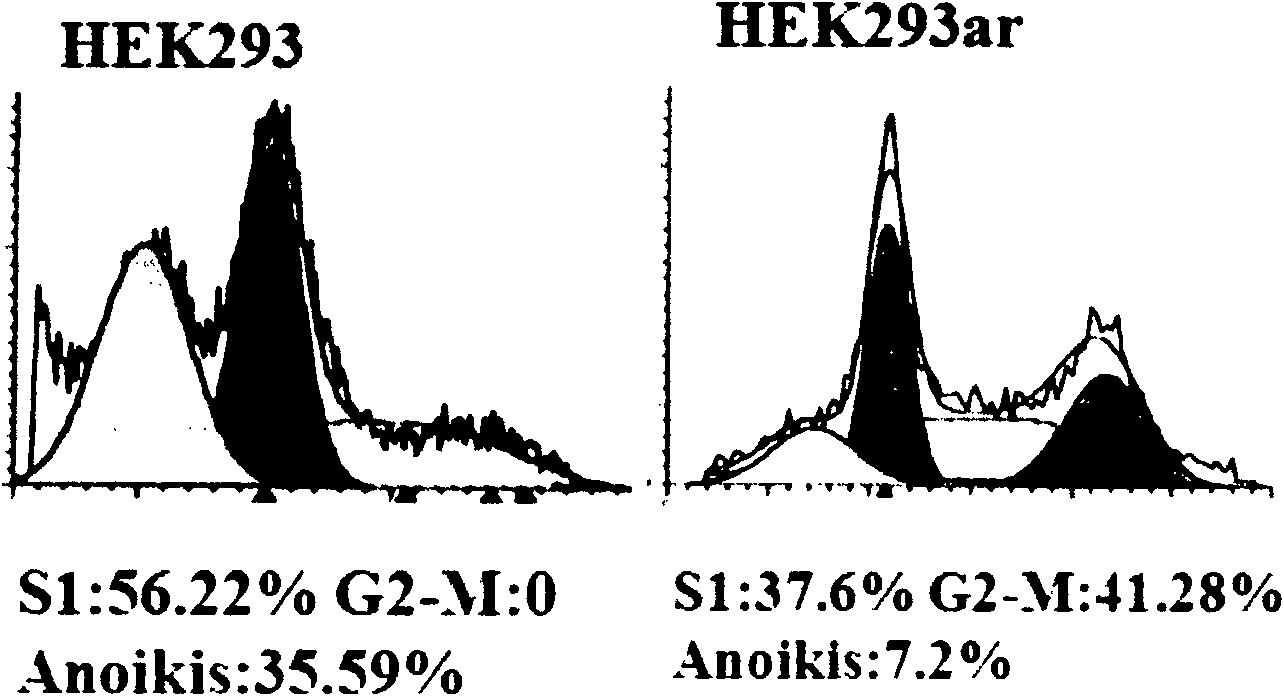
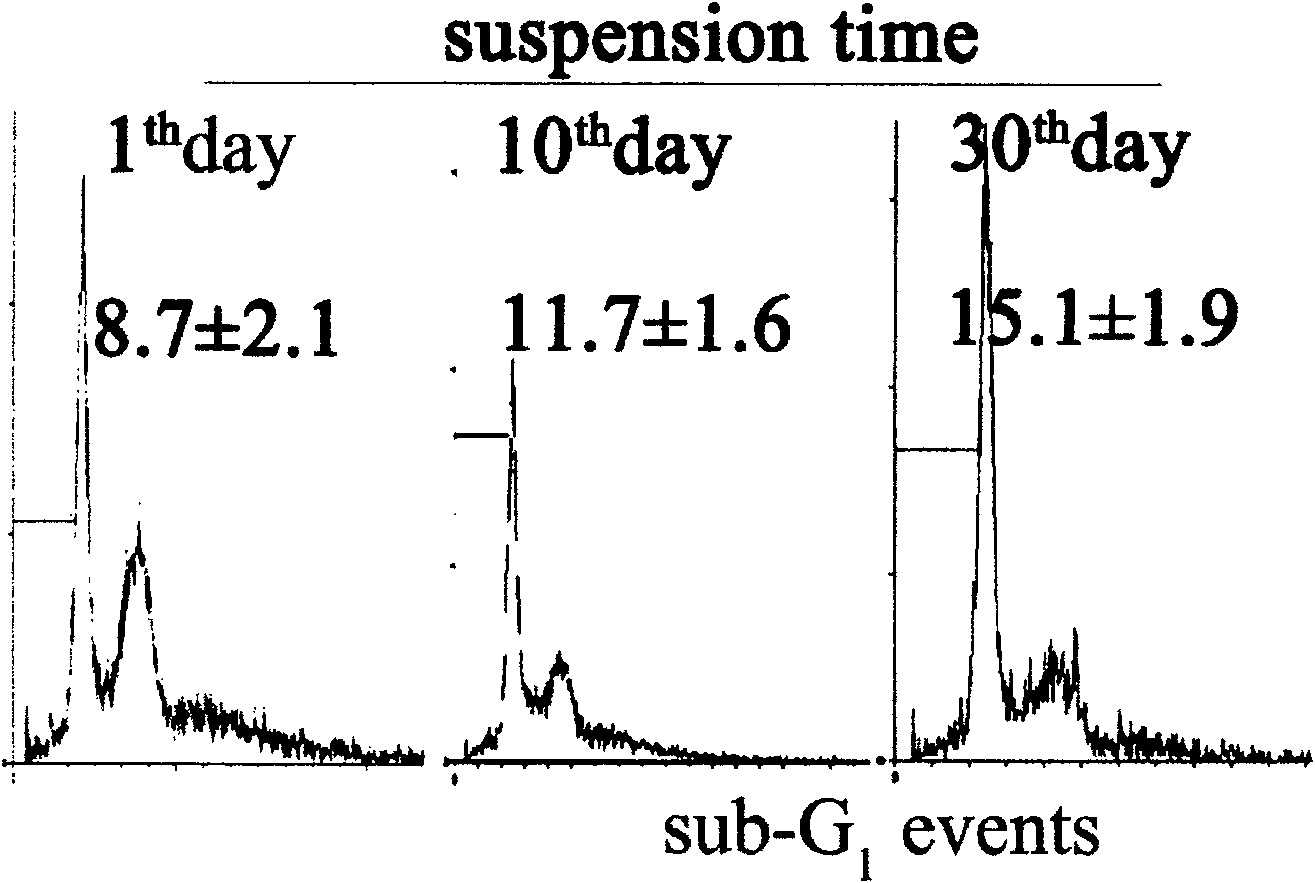
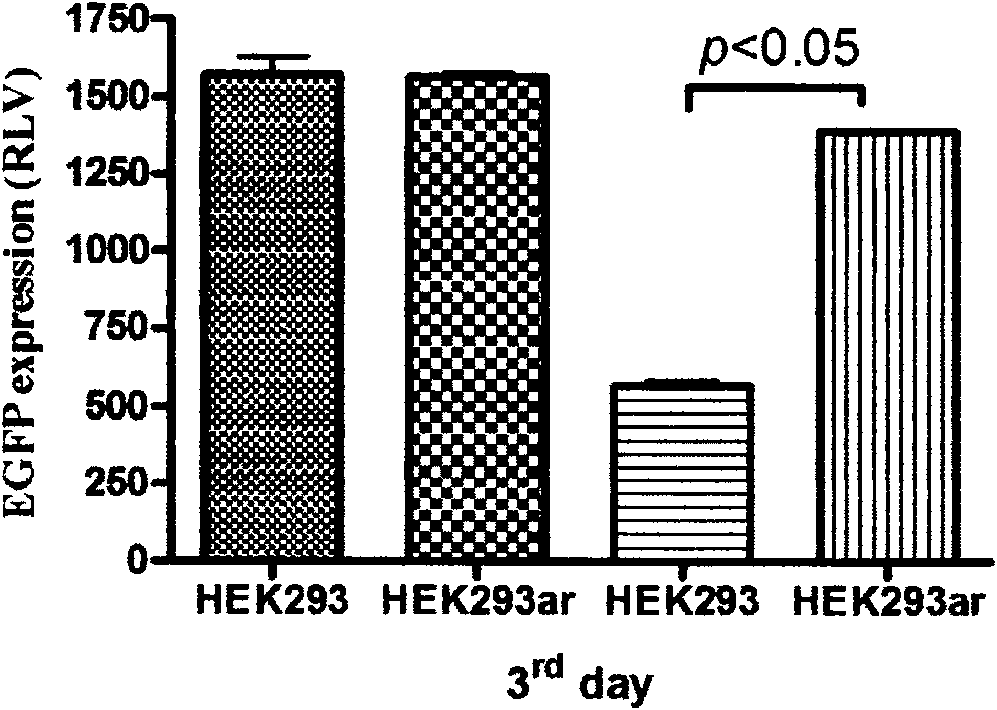
Novel human embryo kidney 293 cell HEK293ar of mammal engineering cell subset
ActiveCN101570740AReduce lossWithout destroying the basic production characteristicsTissue cultureFermentationMammalCell mass
The invention provides a novel human embryo kidney 293 cell HEK293ar of a mammal engineering cell subset and application thereof. The novel human embryo kidney 293 cell HEK293ar of the mammal engineering cell subset is preserved by the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: C200927. The novel human embryo kidney 293 cell HEK293ar of the mammal engineering cell subset can be used for high-efficiency transient transfection exogenous genes and can grow in the form of a cell mass. A cell subset provided by the invention has the characteristics of suspension adaptable growth and adherent growth at the same time. The novel human embryo kidney 293 cell HEK293ar of the mammal engineering cell subset can overcome the defects that a gene expression product has short period and low yield when mammal engineering adherent cells are used for culturing and producing medicaments at present, and the efficiency for a suspension cell to perform transient transfection of exogenous genes is low. The novel human embryo kidney 293 cell HEK293ar of the mammal engineering cell subset can be used for establishing a novel scale transient high-efficiency transfection system for producing pharmaceutical proteins in an adherent transfection-suspension culture mode, and establishing an economic vector-free immobilized culture production mode by using the cell mass as a growth pattern.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
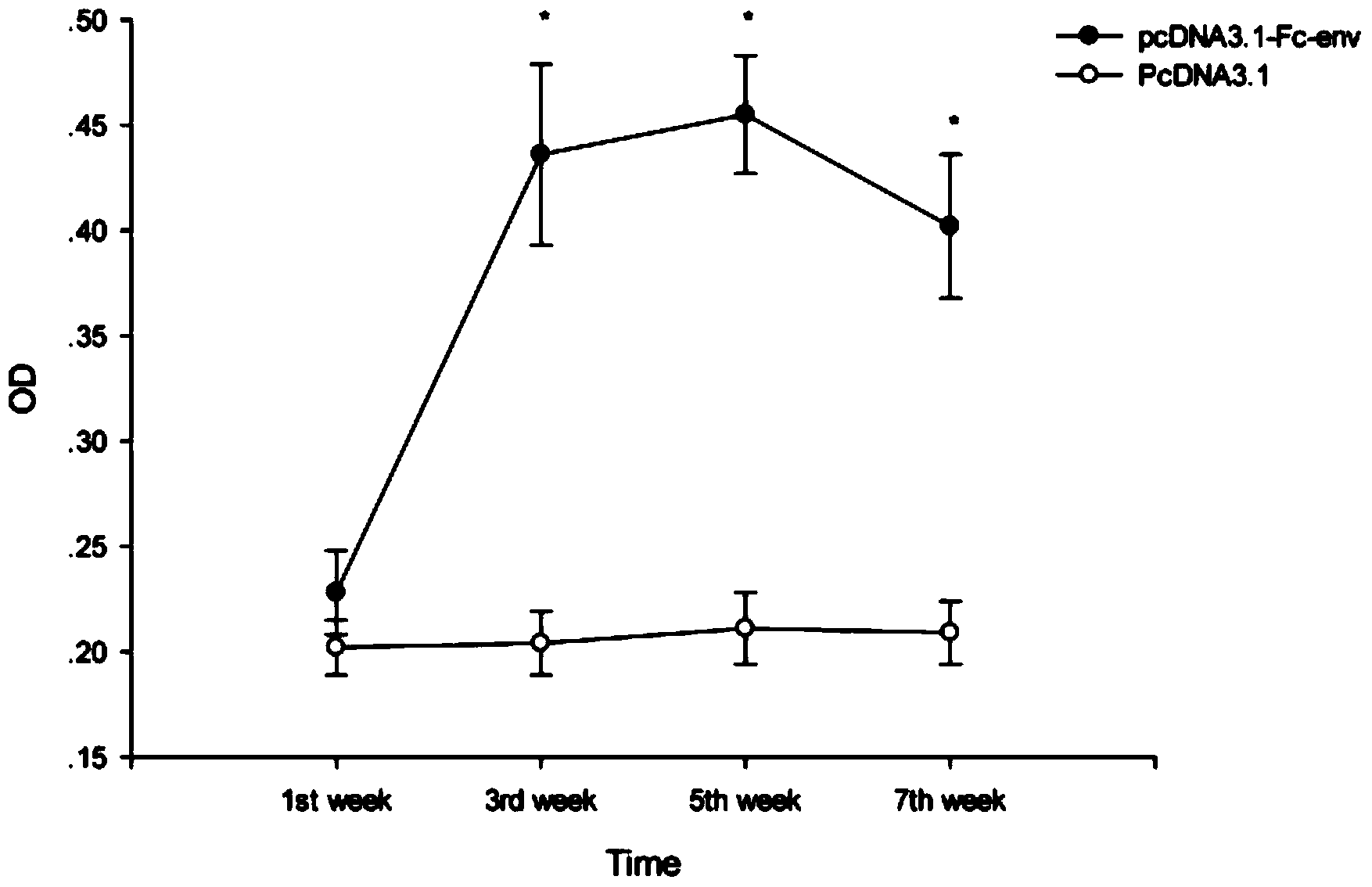
Construction method and application of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) vaccine for avian leukosis virus subgroup J
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) vaccine for avian leukosis virus subgroup J. A recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA3.1-Fc-env of an Fc fragment gene for expressing chicken immunoglobulin G and an envelope protein (env protein) gene of the avian leukosis virus subgroup J is constructed; transient transfection and indirect immunofluorescence assay prove that the pcDNA3.1-Fc-env can be accurately expressed in a 293T cell; a great number of plasmids are extracted, purified and quantified to 1mg / ml, then, the recombinant plasmids are used for immunizing mice, each mouse is immunized three times, 100mu g of recombinant plasmids are used in each immunization, and one immunization is carried out every two weeks; the level of an ALV-J env protein-specific antibody in serum is detected to show that the pcDNA3.1-Fc-env has the effect of preventing the avian leukosis virus subgroup J.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
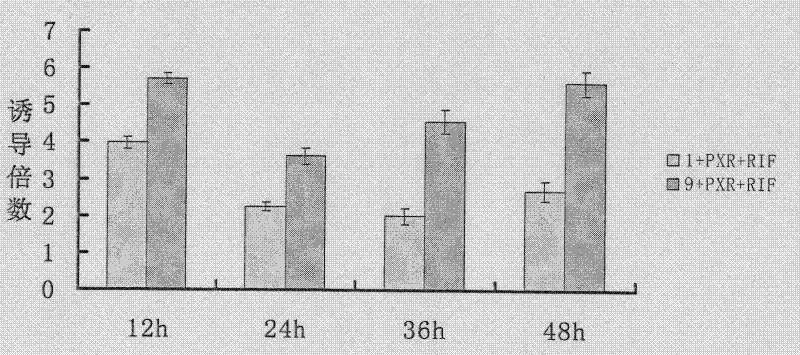
Method for in-vitro screening of PXR activation characteristics
InactiveCN102533925AGuide developmentGuide its clinical applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionCYP3AHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a method for in-vitro screening inducers, particularly to a method for in-vitro screening of PXR (pregnane X receptor) activation characteristics, which comprises the following steps: constructing a reporter gene vector; culturing cells, and screening G418 working concentration; carrying out transient transfection of cells; screening stably transfected cell clones; inducing and identifying stably transfected cell strain with a tested drug (ligand drug); and screening the PXR activation characteristics. When the PXR is activated by the ligand drug, the PXR can regulate the expression CYP3A gene. PXR gene-deficient mice lose drug inductivity of CYP3A. Contrarily, hPXR (human pregnane X receptor) receptor in activation state expressed in liver of a transgenic mouse can lead to continuous high expression of CYP3A enzyme. The method of the invention establishes critical technology for high-throughput screening based on the passway and carries out screening of PXR activation characteristics from mass compounds in a compound library at the early stage of drug development, and can reduce the risk of adverse drug interactions after the new drug comes into the market, and greatly reduce development cost.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Cells prepared by transient transfection and methods of use thereof
Compositions and methods of making cells using RNA, and cells made using the disclosed compositions and methods are also provided. In exemplary embodiments, RNA is transfected into cells to effect a molecular, biological, physiological, or histological change in the cells. In preferred embodiments, the RNA is prepared in vitro, more preferably using a DNA template according to the provided compositions and methods. Methods for treating or inhibiting a disorder or disease such cancer are also provided. The methods can include, for example, locally or systemically administering to the host an effective amount of one or more RNAs; or an effective amount of population of cells isolated from the subject or a syngeneic or histocompatible subject, contacted ex vivo with one or RNAs, and optionally expanded. The cells can be, for example, immune cells or stem cells.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Cationic transfection agent and preparation and application methods thereof
ActiveCN110129367AOptimizing componentsLow cytotoxicityVector-based foreign material introductionAmmonium sulfateGenetic engineering
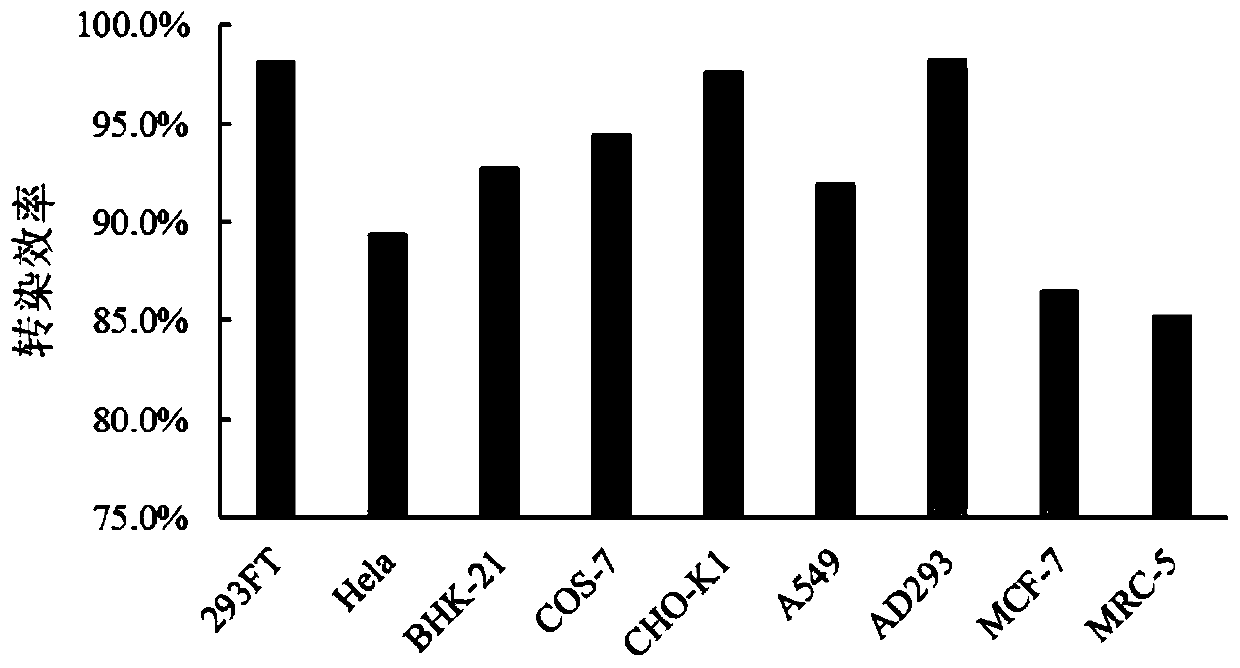
The invention provides a cationic transfection agent and preparation and application methods thereof and relates to the field of genetic engineering. The cationic transfection agent is composed of polyethyleneimine, cationic polyacrylamide, cationic liposome, fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether ammonium sulfate and vitamin D. By optimizing the components, the cationic transfection agent can significantly improve the transfection efficiency and achieve a 293FT cell transfection rate up to 95%. Besides, the cationic transfection agent can achieve transfection instantly when adherent cells are not adhered after passage, thereby achieving instant passage and transfection; transfection operation is simple and rapid and can be applied within one minute. Therefore, the cationic transfection agentcan be widely applied to rapid, large-scale and instant transfection of various mammalian cells.
Owner:苏州博特龙免疫技术有限公司
Method for improving transient expression of recombinant proteins in mammalian cells through temperature jump
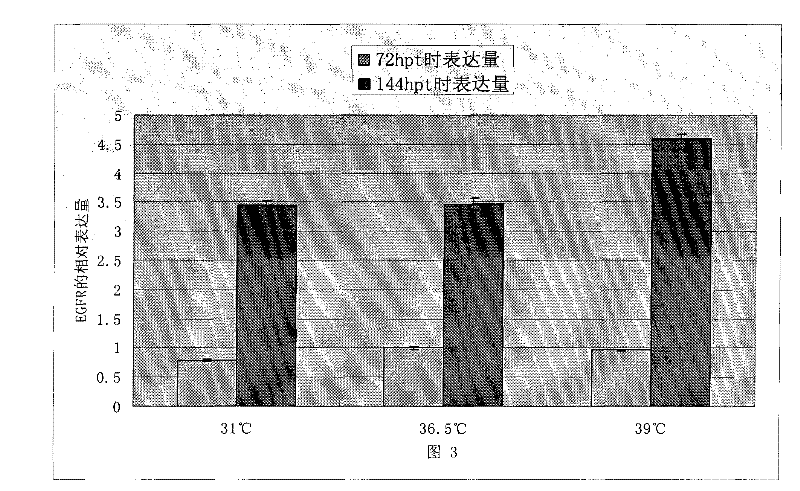
ActiveCN102533722AHigh expressionHigh transfection efficiencyRecombinant DNA-technologyForeign genetic material cellsTransient transfectionMammalian cell
Provided is a method for improving transient expression of recombinant proteins through improvement of transfection efficiency, wherein the transfection efficiency is improved through changing of environment of cells before and after transfection. The method enables expression index of the transient transfection recombinant proteins to be improved by 37% to 56%.
Owner:北京义翘神州科技股份有限公司
Serotype 8 recombinant adeno-associated virus preparation method
ActiveCN108179137AAddress process complexitySolve the process conditionsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSerum free mediaSerotype
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering, and more specifically relates to a method for preparing serotype 8 recombinant adeno-associated virus, The method comprises the following steps: 1) using a serum-free medium for culturing 293T cell in a sheet carrier; 2) performing transient transfection on the cultured 293T cell by adeno-associated viral vector system plasmid to obtain the transfected cell; and the adeno-associated viral vector system plasmid comprises AAV expression vector plasmid, auxiliary plasmid pHelper and AAV capsid plasmid pRC8; and 3) continuously culturing the transfected cell, collecting and replacing the serum-free medium on time to obtain a medium containing the recombinant adeno-associated virus. The preparation method can guarantee production stability,preparation and purifying steps are saved, downstream virus purifying difficulty is obliviously reduced, and the preparation method is especially suitable for industrial scale-production of the serotype 8 recombinant adeno-associated virus.
Owner:BRAINVTA (WUHAN) CO LTD
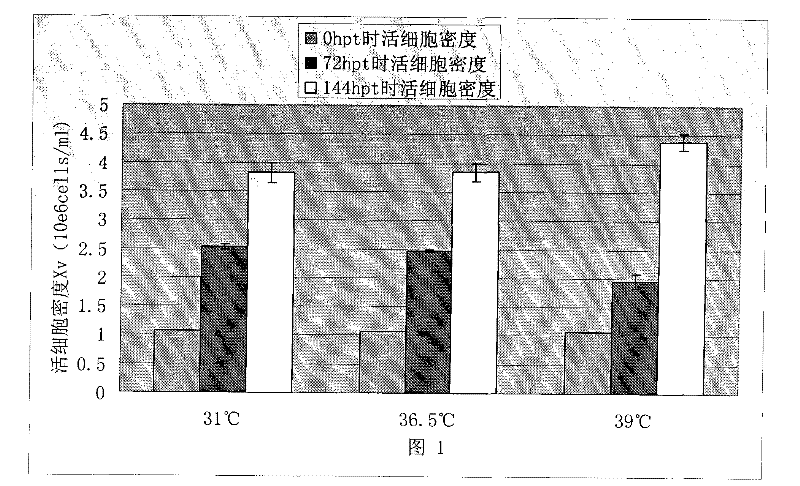
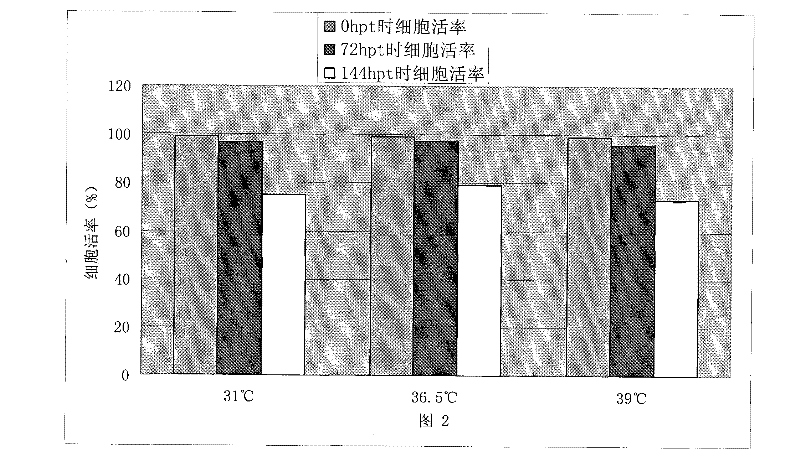
Method for improving transient transfection of insect cell and stably expressing protein expression quantity
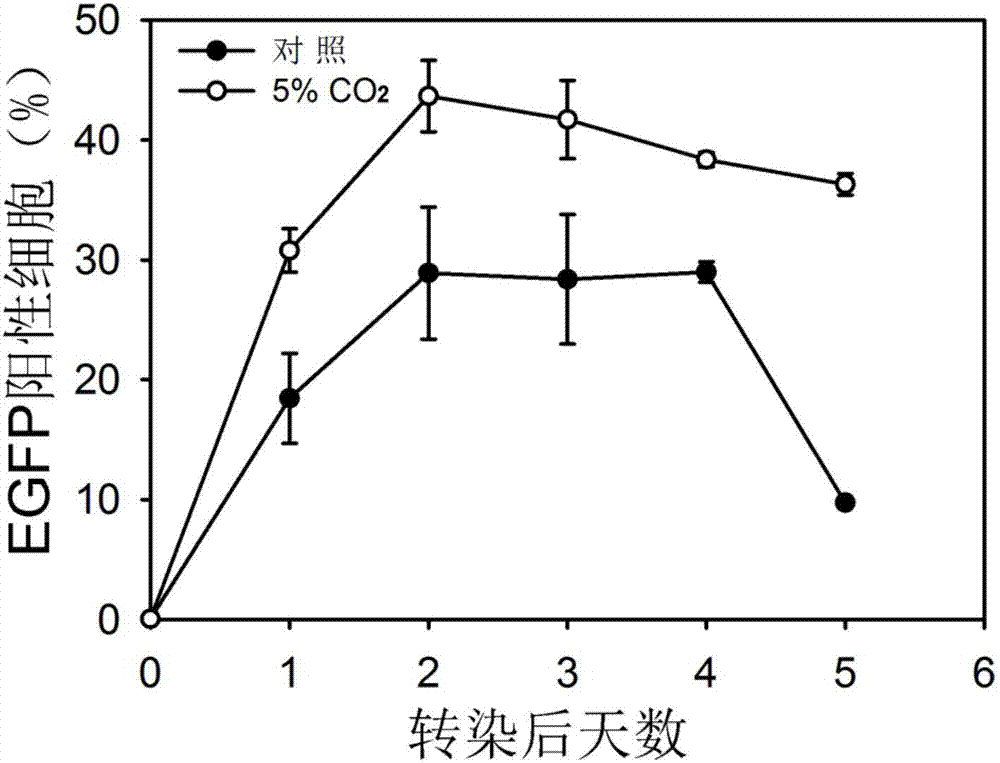
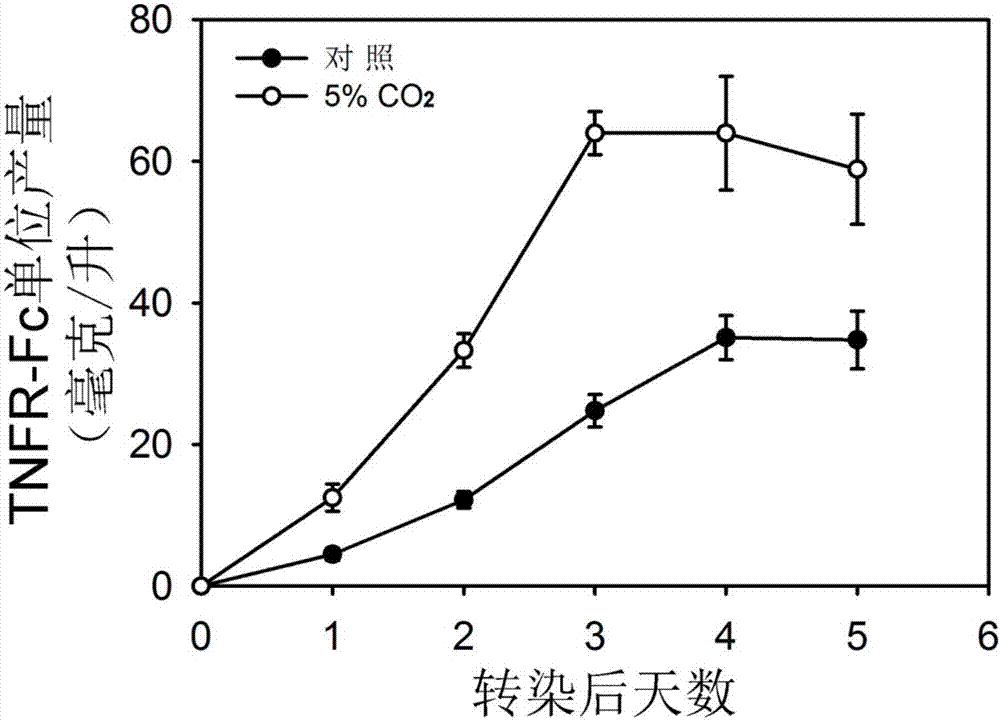
ActiveCN107236761AHigh expressionGood lifting effectVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryCellular respirationProtein target
The invention discloses a method for improving transient transfection of insect cell and stably expressing protein expression quantity. A traditional insect cell cultivation method adopts a phosphate buffer system mostly, CO2 is not required to add during the cultivation process, and the expression quantity of a target protein is relatively low. The method creatively finds that the protein expression quantity can be improved by adding CO2 in a cultivating box or changing an air permeable cover to be a sealing cover after transfection to increase CO2 concentration in a bottle upon the self-breathing effect of insect cells regardless of transient transfection or protein expression and production process of a stable cell pond when the insect cell is cultivated; moreover, the lifting effect is significant. The CO2 is added in the cultivation box during the insect cell cultivation process, or the cultivation bottle cover is changed to be a sealing cover, the method is simple and easy to practice, and the cost is low; the method is extensive in use and capable of significantly improving the protein expression quantity of the insect cells.
Owner:FOSHAN CANTON BIOLOGICS CO LTD +1
Genomic DNA fragments containing regulatory and coding sequence for the beta2-subunit of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and transgenic animals made using these fragments or mutated fragments
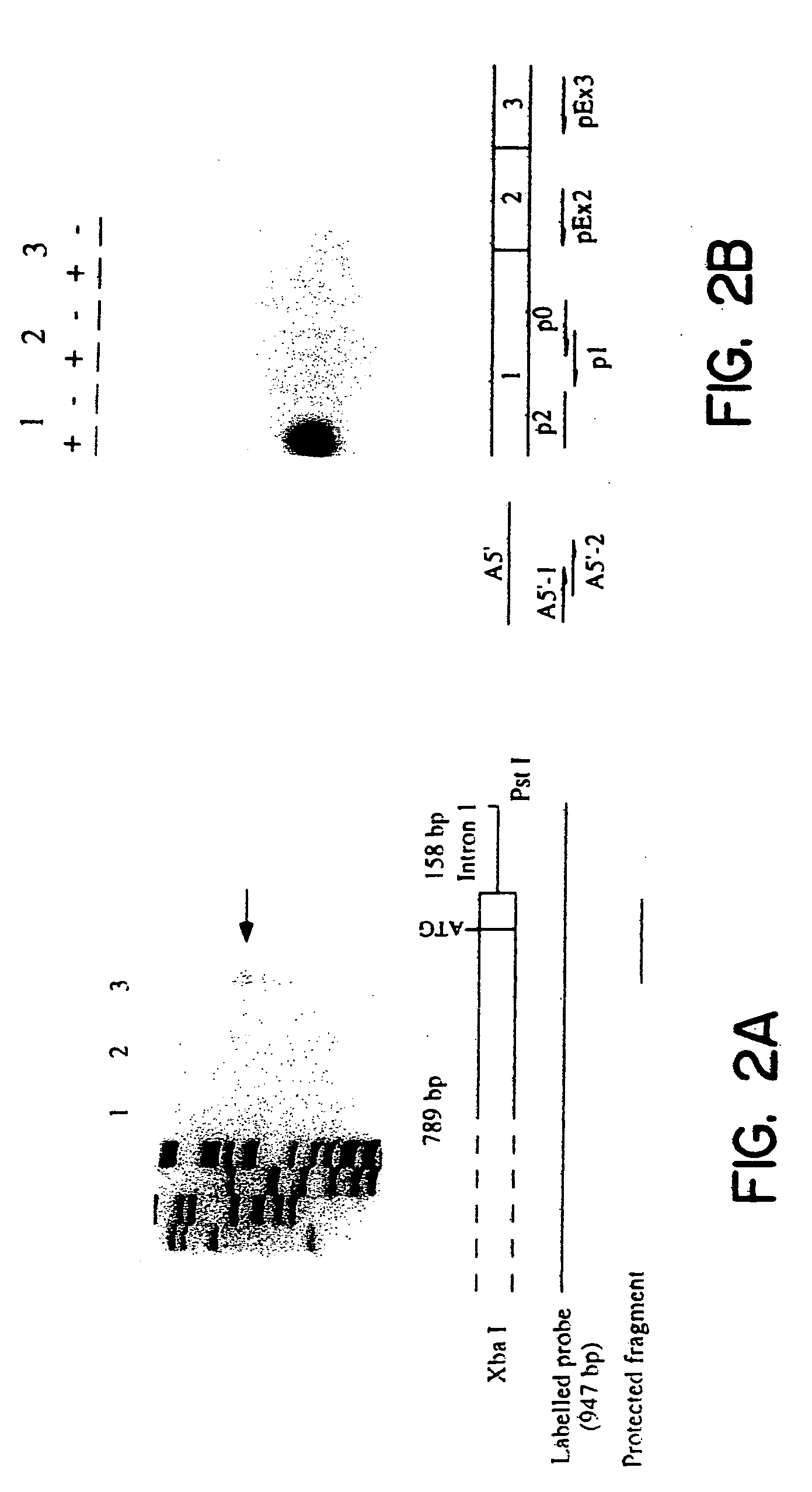
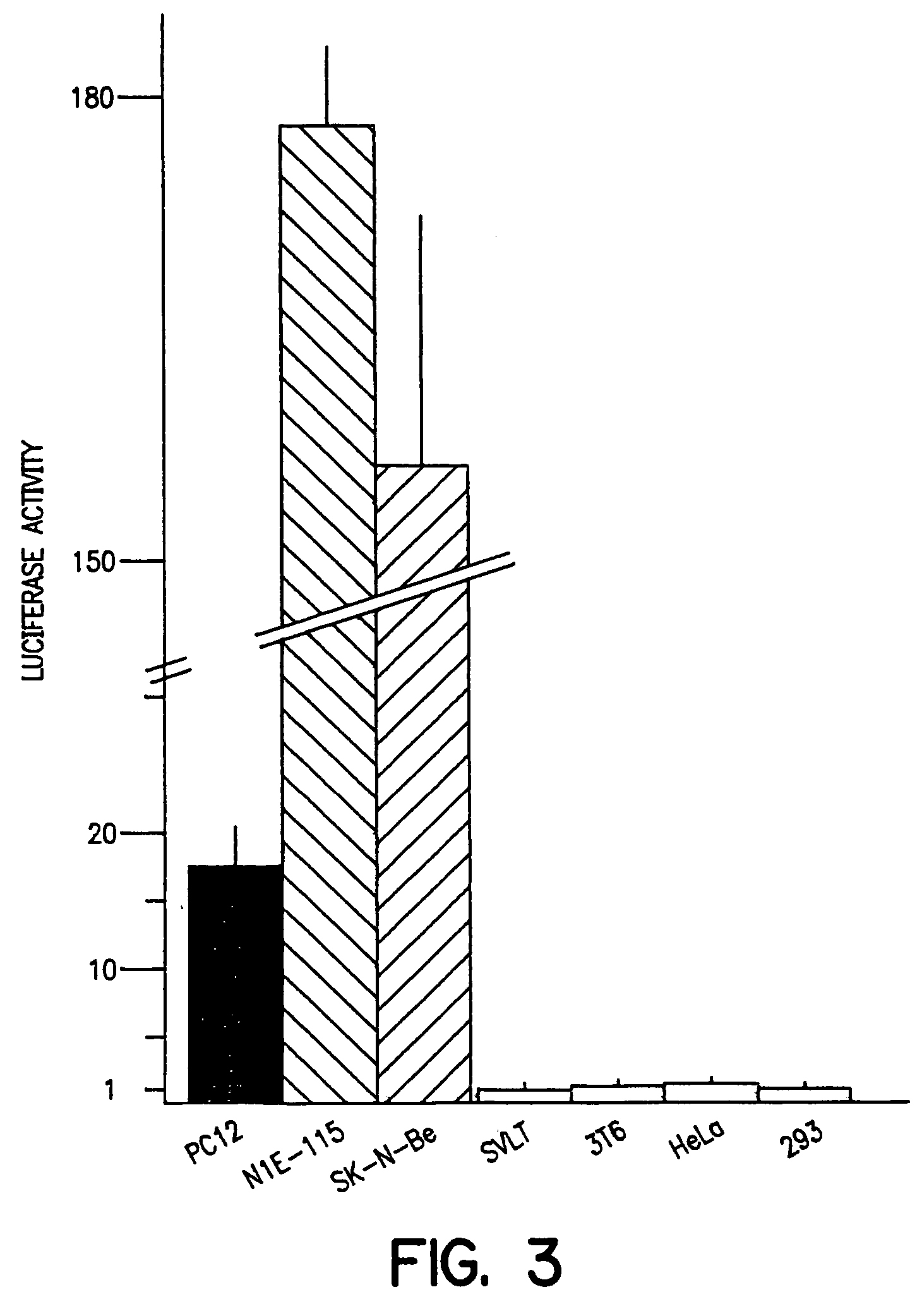
Several genes encoding subunits of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors have been cloned and regulatory elements involved in the transcription of the ∝:2 and ∝:7-subunit genes have been described. Yet, the detailed mechanisms governing the neuron-specific transcription and the spatio-temporal expression pattern of these genes remain largely uninvestigated. The β2-subunit is the most widely expressed neuronal nicotinic receptors subunit in the nervous system. We have studied the structural and regulatory properties of the 5′ sequence of this gene. A fragment of 1163 bp of upstream sequence is sufficient to drive the cell-specific transcription of a reporter gene in both transient transfection assays and in transgenic mice. Deletion analysis and site-directed mutagenesis of this promoter reveal two negative and one positive element. The positively acting sequence includes one functional E-box. One of the repressor elements is located in the transcribed region and is the NRSE / RE1 sequence already described in promoters of neuronal genes.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Method for establishing stable transgenic flounder embryo cell strain
ActiveCN106399370ASolve efficiency problemsSolve functionVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMolecular levelActin beta
The invention provides a method for establishing a stable transgenic flounder embryo cell strain. The method for establishing stable transgenic flounder embryo cell strain comprises the following steps: transfecting flounder embryo cells by using plasmids which can widely express enhanced green fluorescent protein promoted by a beta-actin promoter in flounders and can express G418 resistant protein; after 24h, observing expression of the EGFP (express enhanced green fluorescent protein) under a fluorescent microscope, and through G418 screening, obtaining the embryo cells with stable genetic expression. By the method, an exogenous gene widely expressed in the flounders and promoted by the beta-actin can be effectively transfected into the flounder embryo cells, and can be genetically expressed in the flounder embryo cells stably, so that a novel method is provided for researching for flounder genes, the problem that difficult cellular-level gene function analysis and research caused by low transient transfection efficiency of the flounder cells is solved, and a novel technical means is provided for a molecular-level genetic breeding work of the flounders, and a transgenic method for stably inheriting a marine fish cell line is provided.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
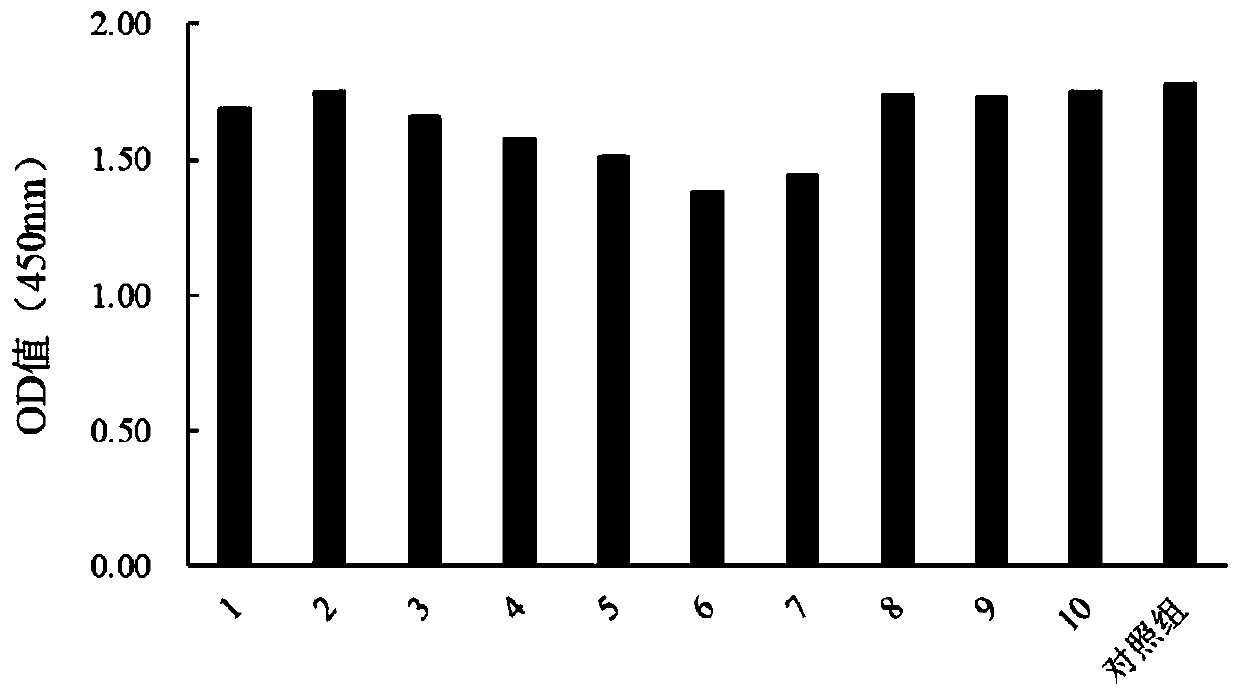
Transient transfection reagent and use thereof
InactiveCN106591339AImprove stabilityLow toxicityNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionLipofectamineCytotoxicity
The invention provides a transient transfection reagent and a use thereof. The transfection efficiency of the transfection reagent is high and stable and is equivalent to the transfection efficiency of Lipofectamine 3000 (hereinafter referred to as lipo3000). The transient transfection reagent has high transfection efficiency both in plasmid single transfection and co-transfection and has very small cytotoxicity. The transient transfection reagent can be simply operated. Compared with lipo3000, the transient transfection reagent is free of plasmid dilution and reagent transfection, realizes transfection in 10min, has high solution stability, can be stored at a temperature of 4 DEG C for a long time, has a low cost, very high transfection efficiency and high stability, can be operated easily, is suitable for a wide range of host cells, is not influenced by antibiotics of the culture medium in transfection efficiency and is an excellent choice for a lab where a lot of transient transfection experiments are carried out.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cell membrane particle expressing parafusin and preparation and application of particle
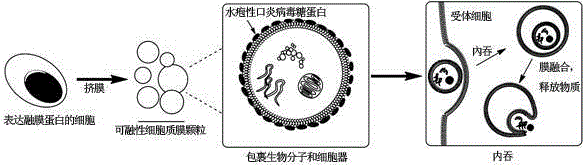
ActiveCN105255835AImproves the efficiency of releasing mitochondriaImprove transfer efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCell membraneVirus Protein
The invention relates to a cell membrane particle expressing parafusin and preparation and application of the particle. VSVG is expressed on the cell membrane particle. Biomacromolecules and organelles are wrapped in the cell membrane particle. The cell membrane particle does not have a cell nucleus. The preparation method includes the steps that transient transfection is conducted on Ad293 cells through expression vesicular stomatits virus protein plasmids; the cells are digested through pancreatic enzymes 48 hours after transfection is carried out, and then centrifugation is carried out for 3 min; an obtained cell suspension is placed in a syringe, the syringe is installed in a syringe filter provided with a polycarbonate membrane, the syringe is pushed so that the cell suspension can be pushed from one side of the filter to the other side of the filter, and the cell membrane particle expressing VSVG is obtained. The cell membrane particle expressing parafusin is applied to biomacromolecule and organelle transfer. The membrane particle is larger, can wrap biomacromolecules and mitochondria, and transfers protein and the mitochondria in the aspect of function. Extra chemical reagents are not added, activity of VSVG is effectively maintained, mitochondrion release efficiency of the membrane particle is improved after the membrane particle enters a body, and accordingly mitochondrion transfer efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
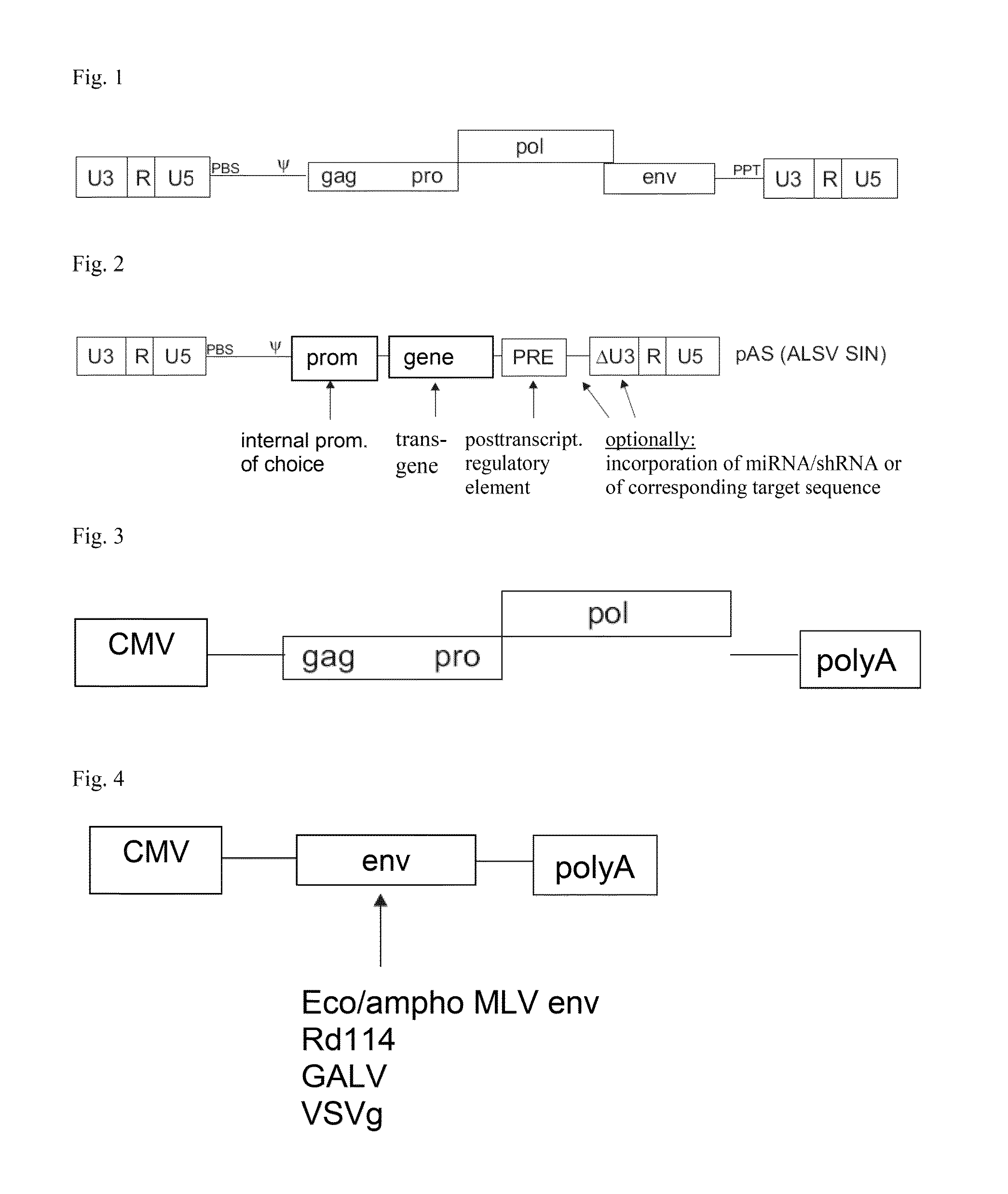
ASLV vector system
ActiveUS8642570B2Risk minimizationEfficiently translatedSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsVector systemAvian leukosis viruses
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com