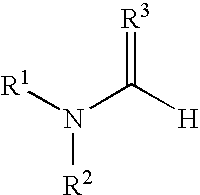
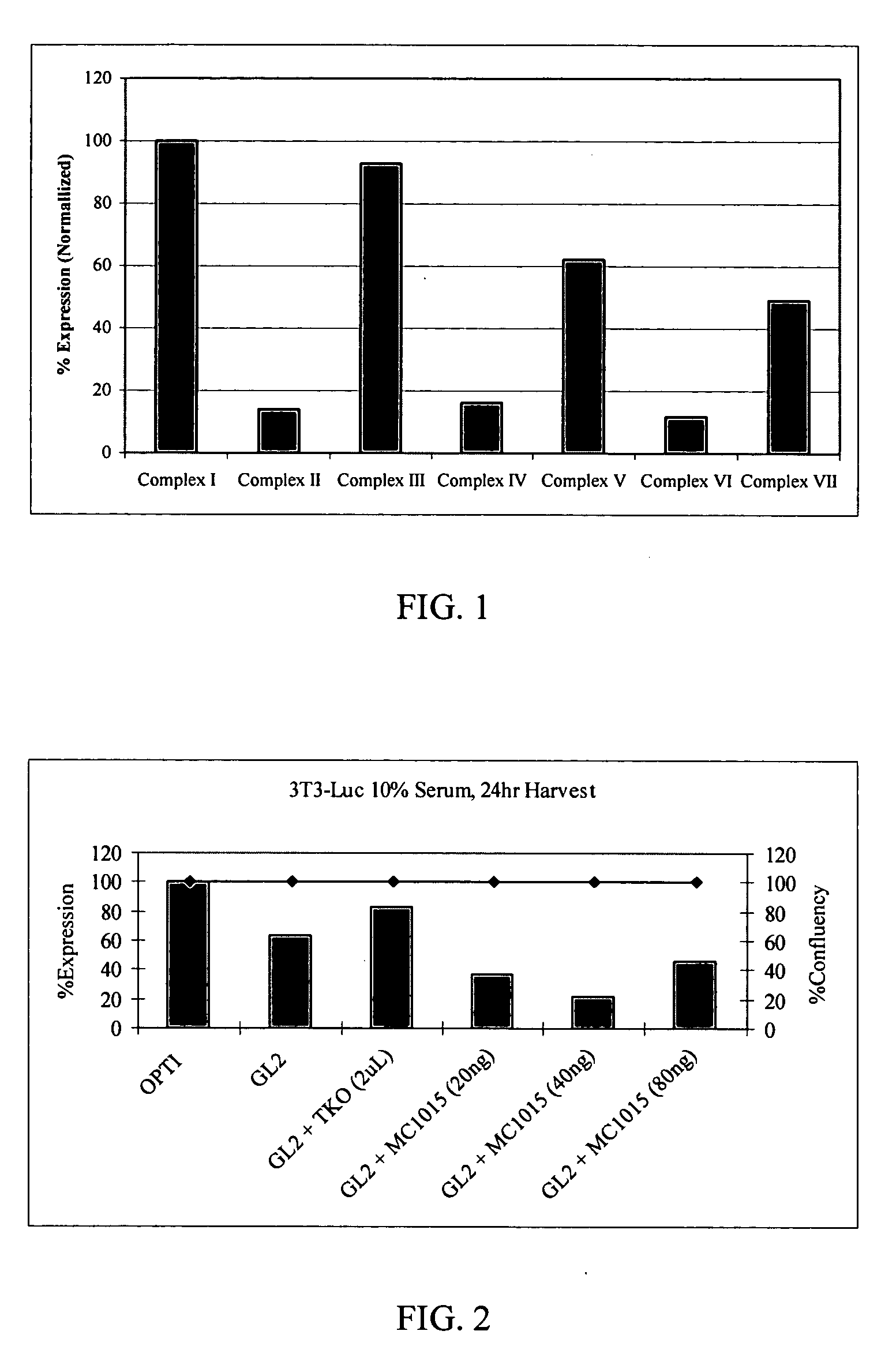
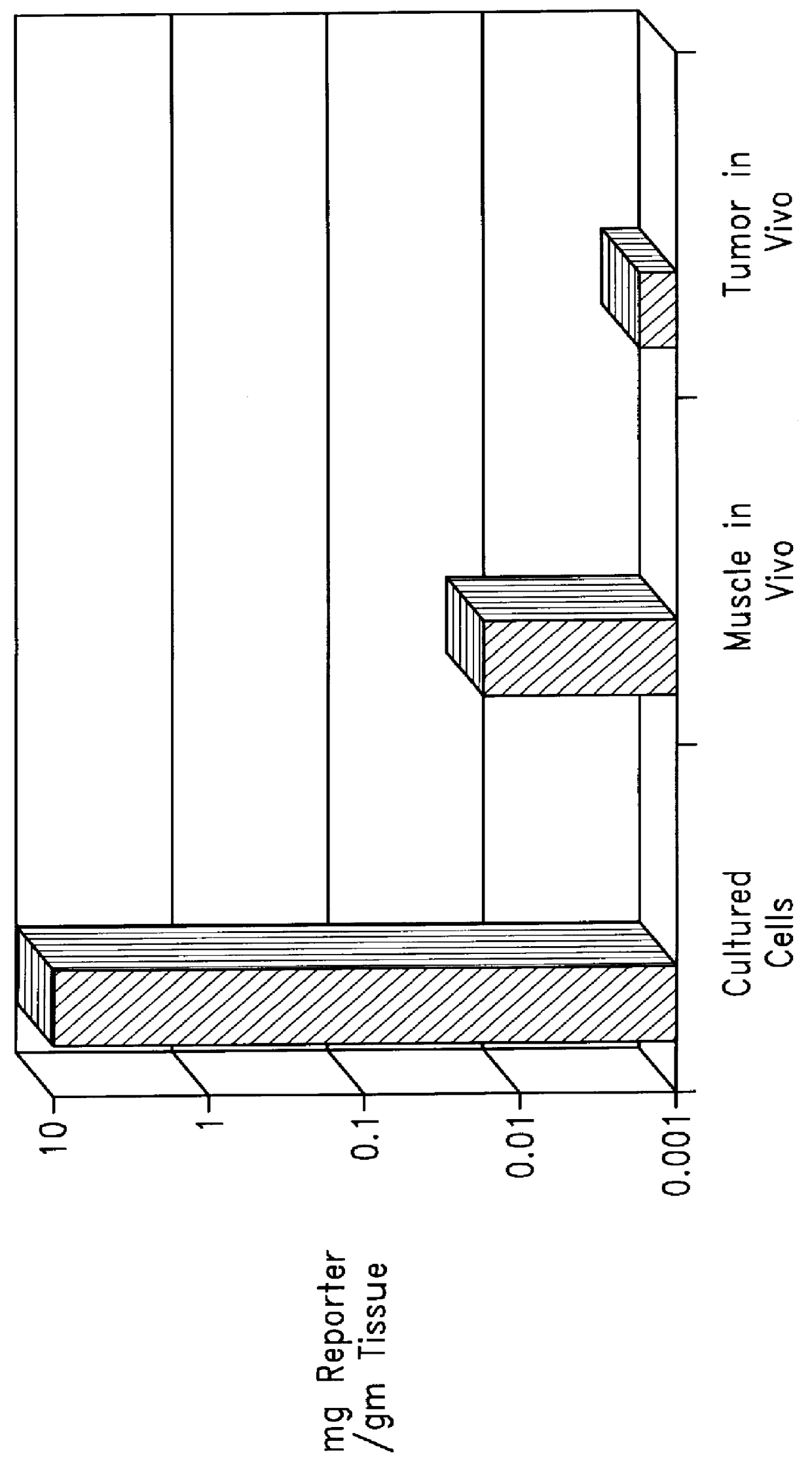
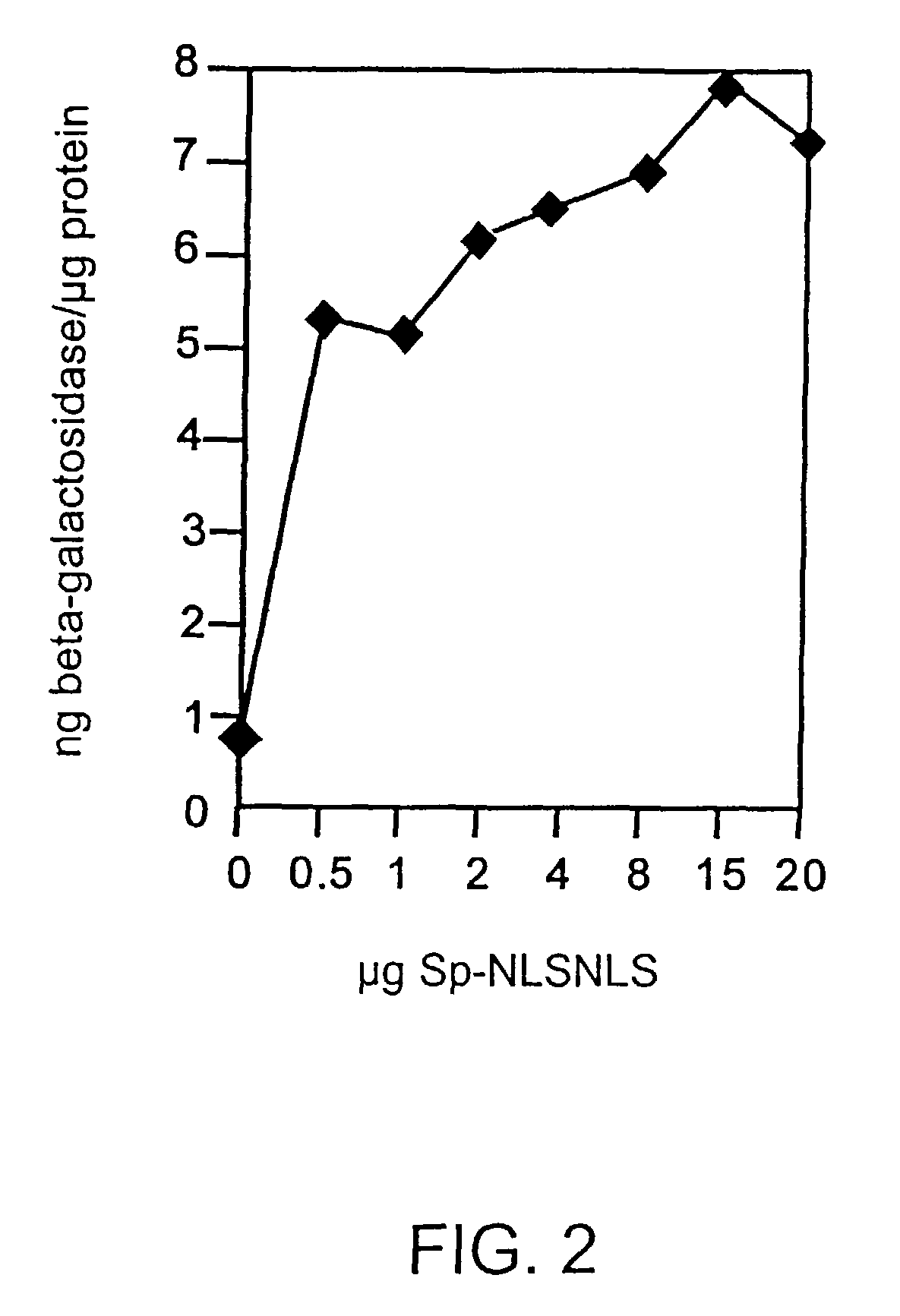
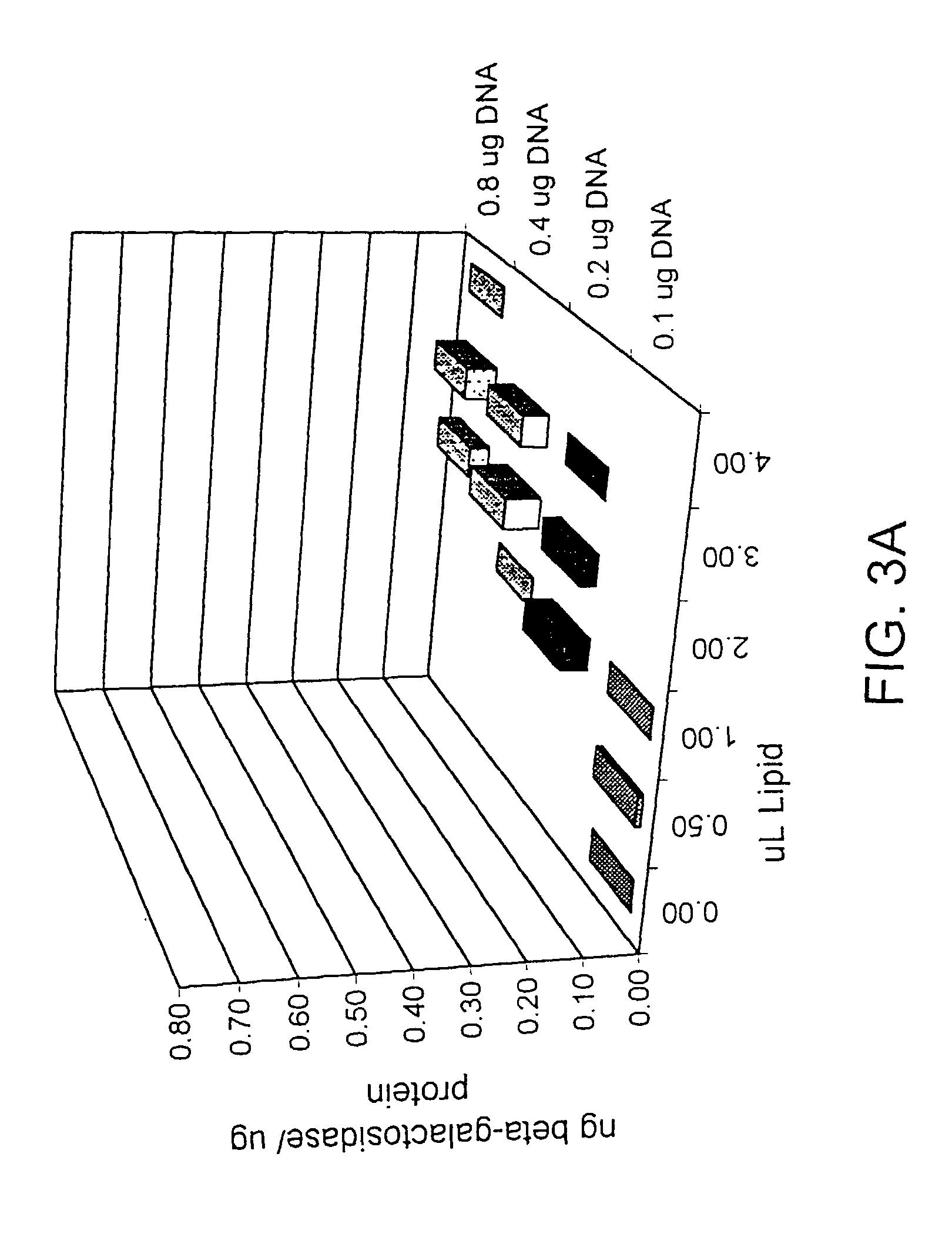
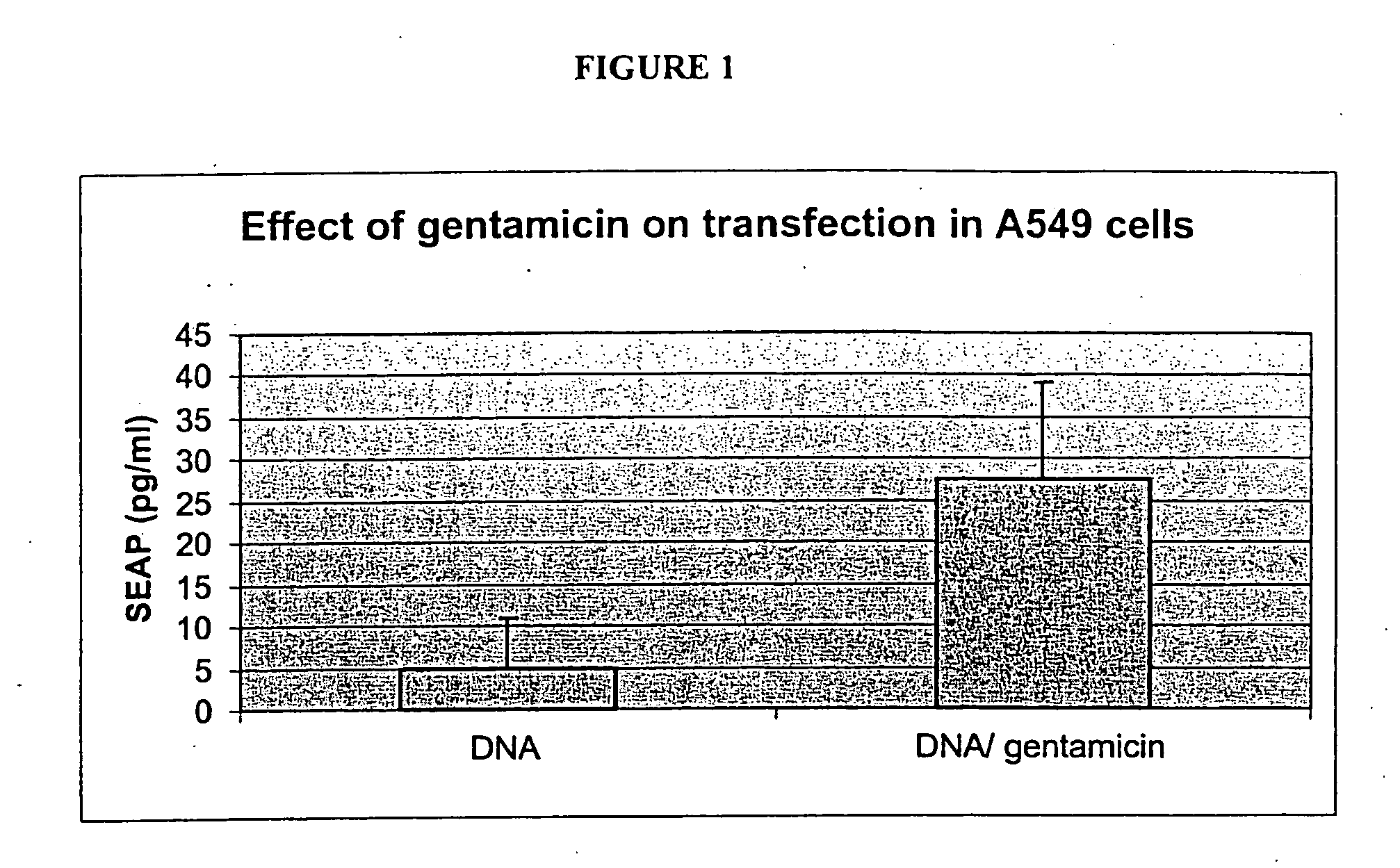
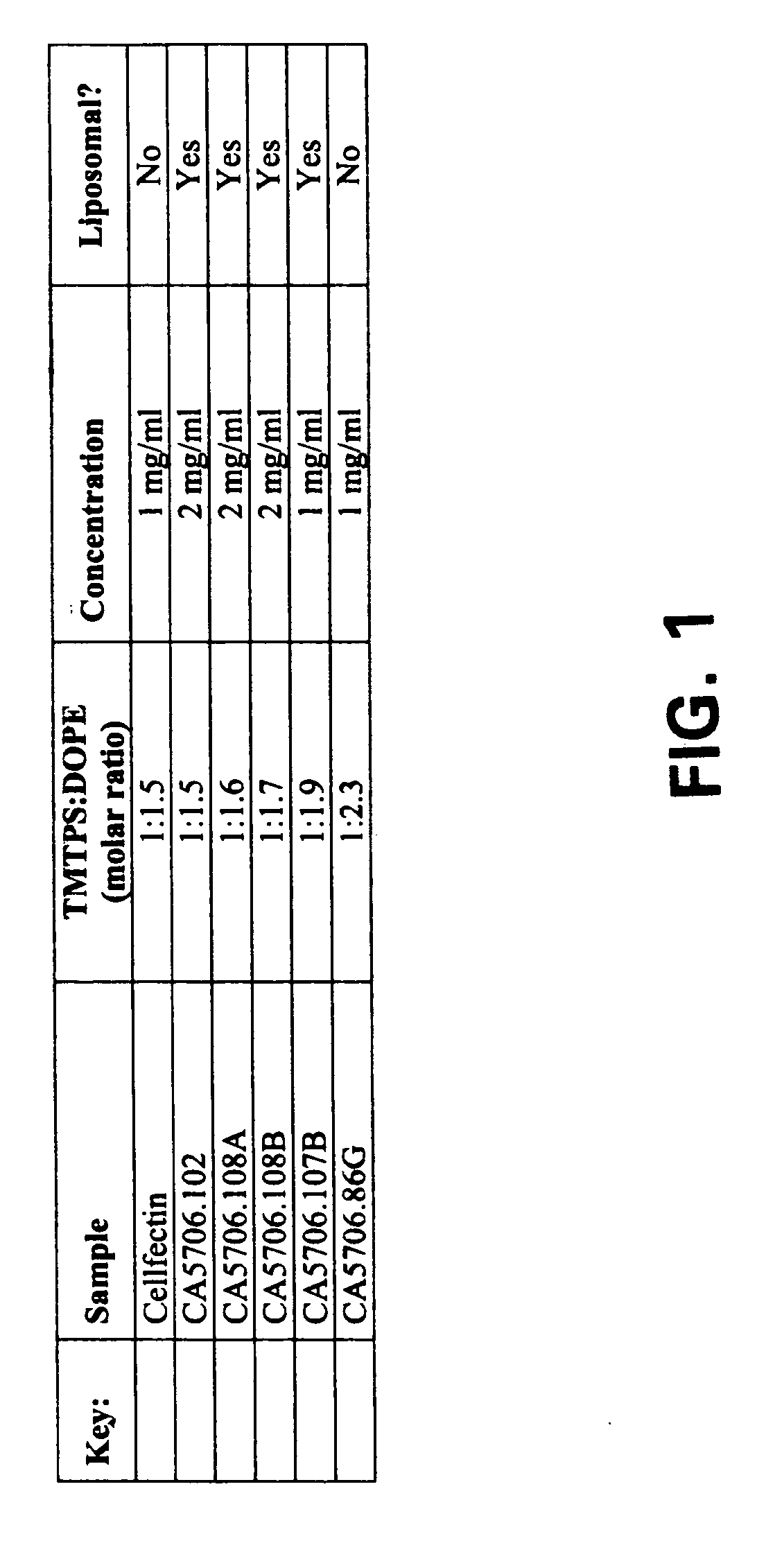
Patents
Literature
942results about How to "High transfection efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
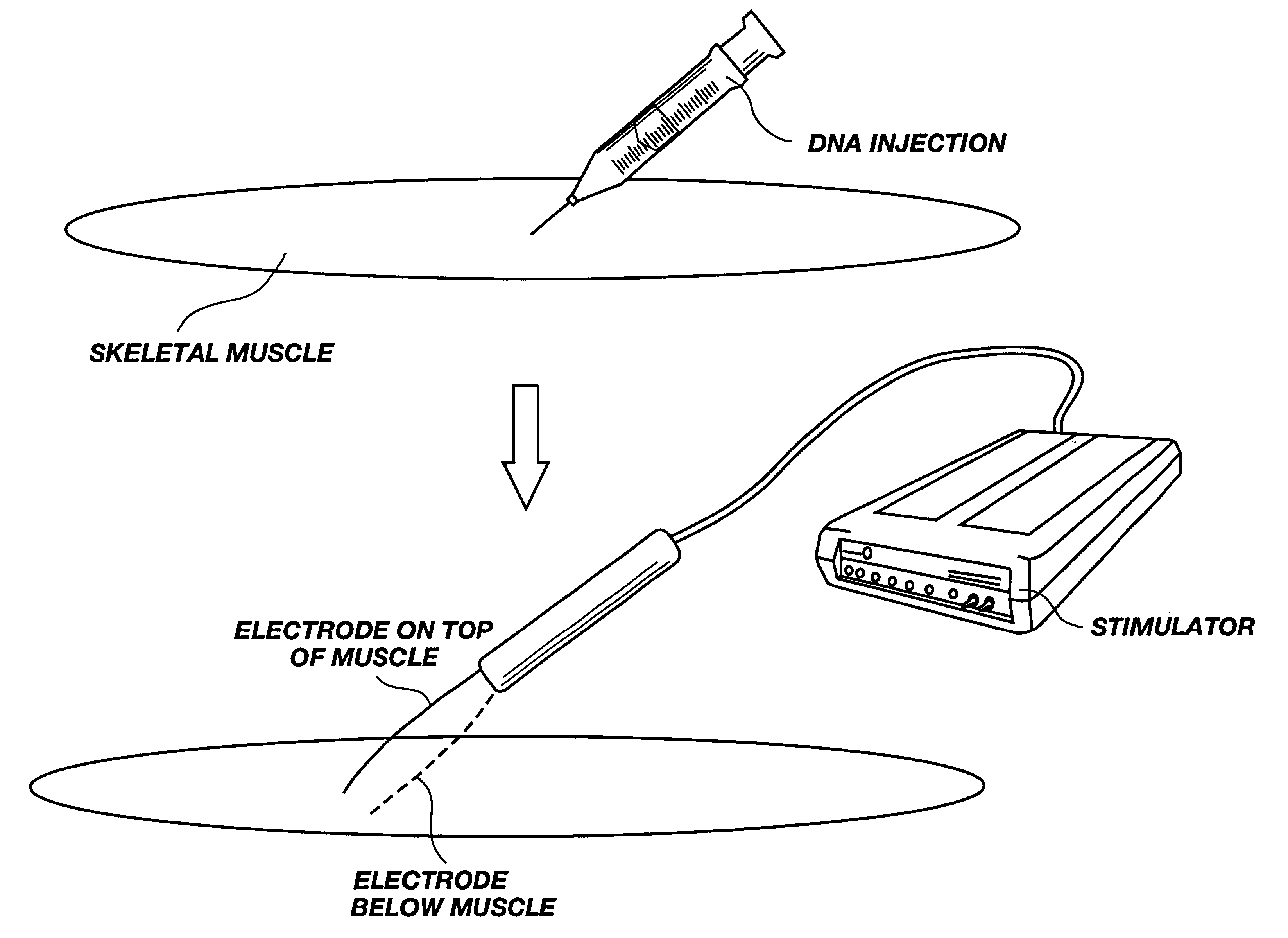
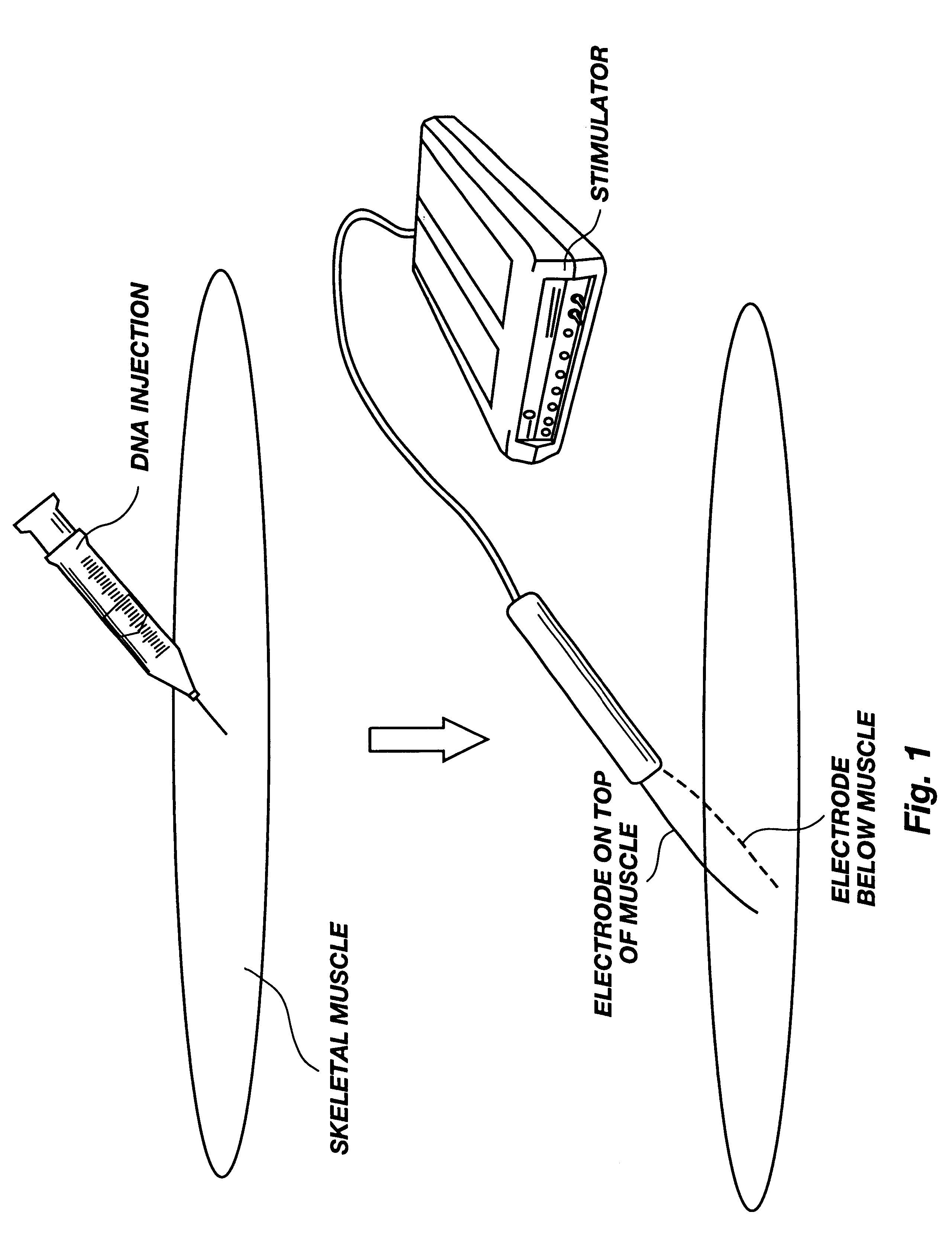
Method for genetic immunization and introduction of molecules into skeletal muscle and immune cells
InactiveUS6261281B1High transfection efficiencyGreat luciferace activityBacterial antigen ingredientsElectrotherapyVaccinationWhole body
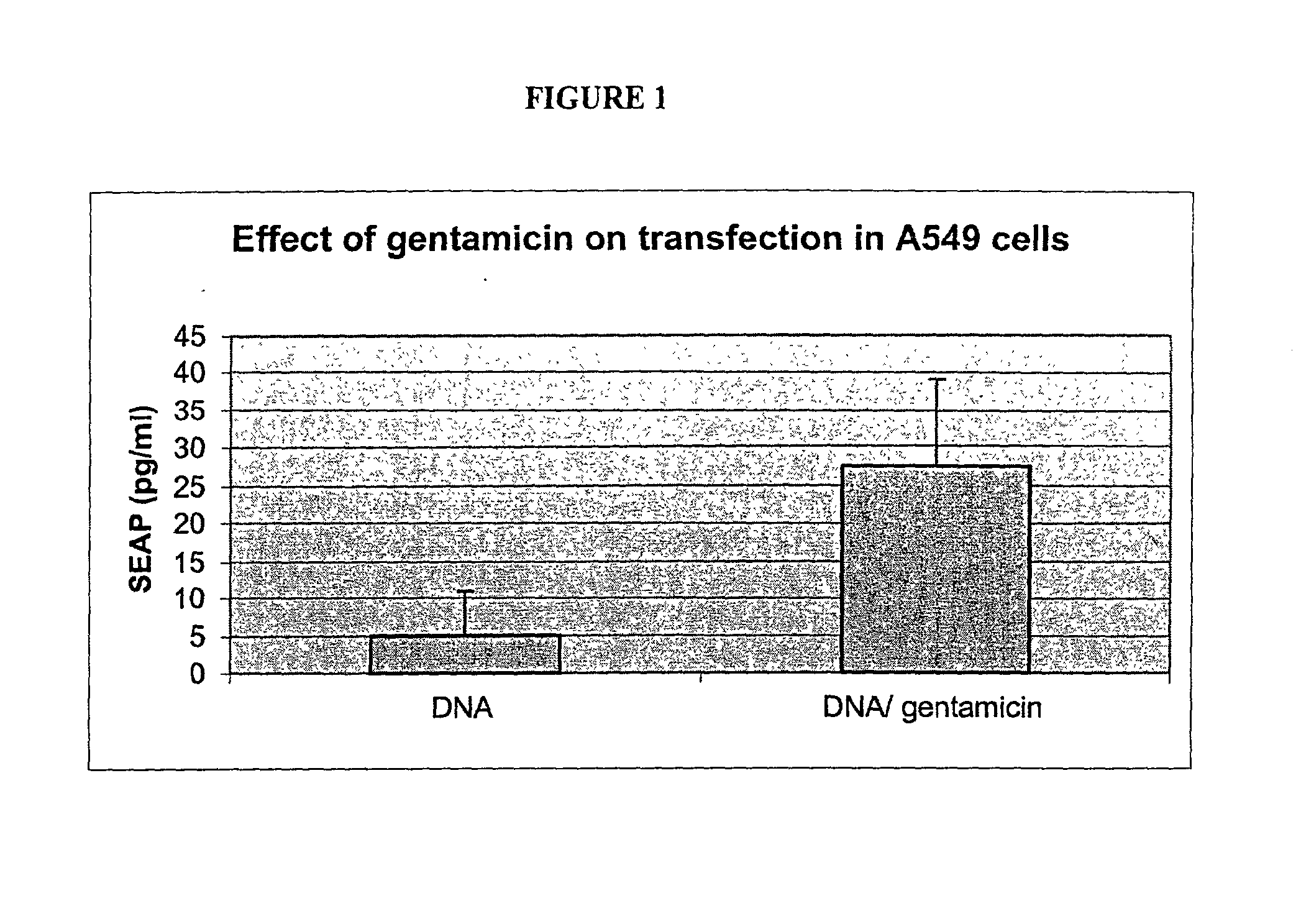
A method is disclosed for enhanced vaccination and genetic vaccination of mammals. The vaccination is accomplished by delivering molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids into skeletal muscle and other cells residing in the skeletal muscle in vivo. The protein or nucleic acid is first injected into the muscle at one or multiple sites. Immediately or shortly after injection, electrodes are placed flanking the injection site and a specific amount of electrical current is passed through the muscle. The electrical current makes the muscle permeable, thus allowing the pharmaceutical drug or nucleic acid to enter the cell. The efficiency of transfer permits robust immune responses using DNA vaccines and produces sufficient secreted proteins for systemic biological activity to be observed.
Owner:INOVIO
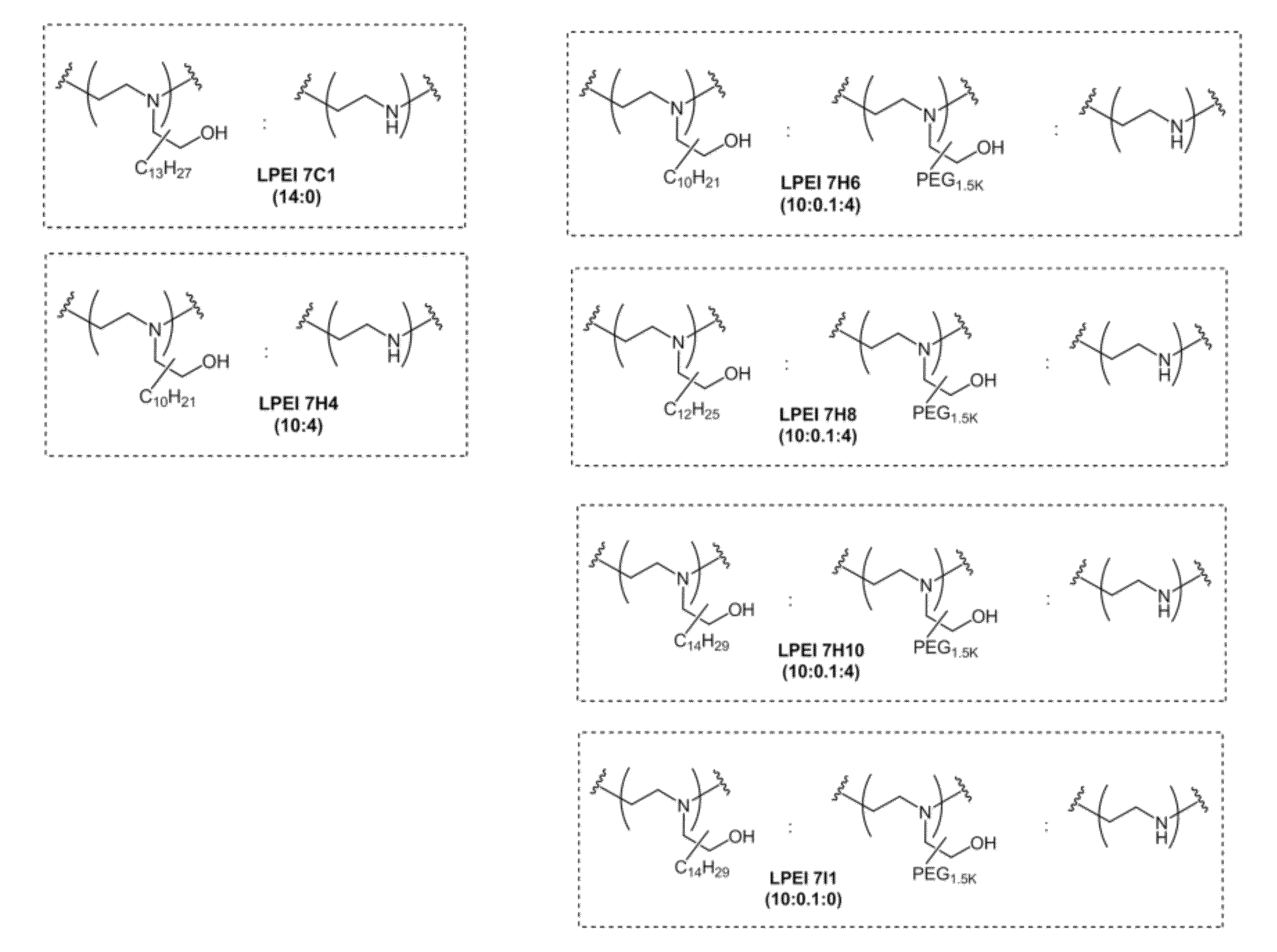
Conjugated lipomers and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120251560A1Reduce polydispersityHigh transfection efficiencyBiocideCosmetic preparationsAza CompoundsPolymer
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions for the delivery of therapeutic agents and uses thereof
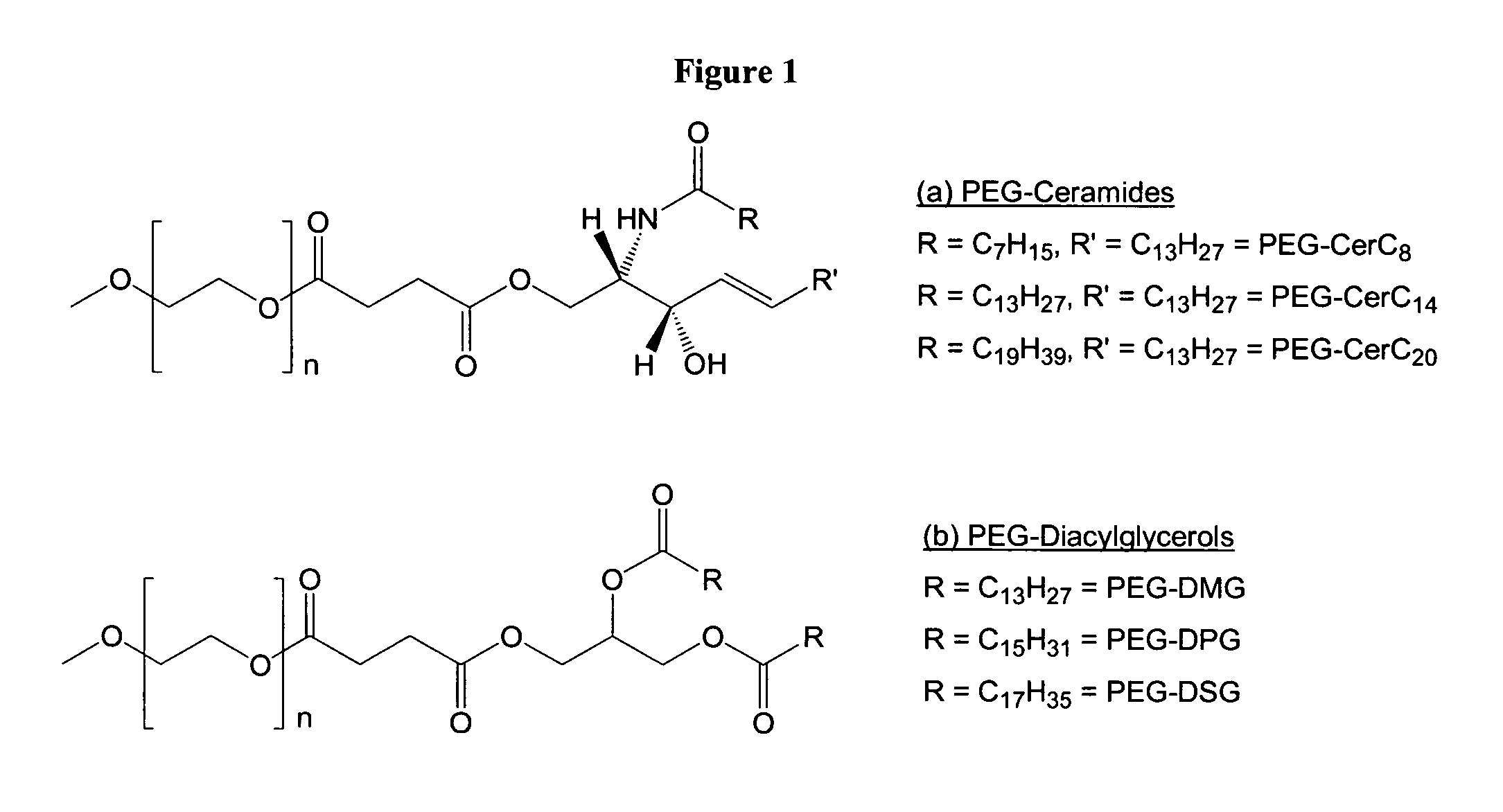
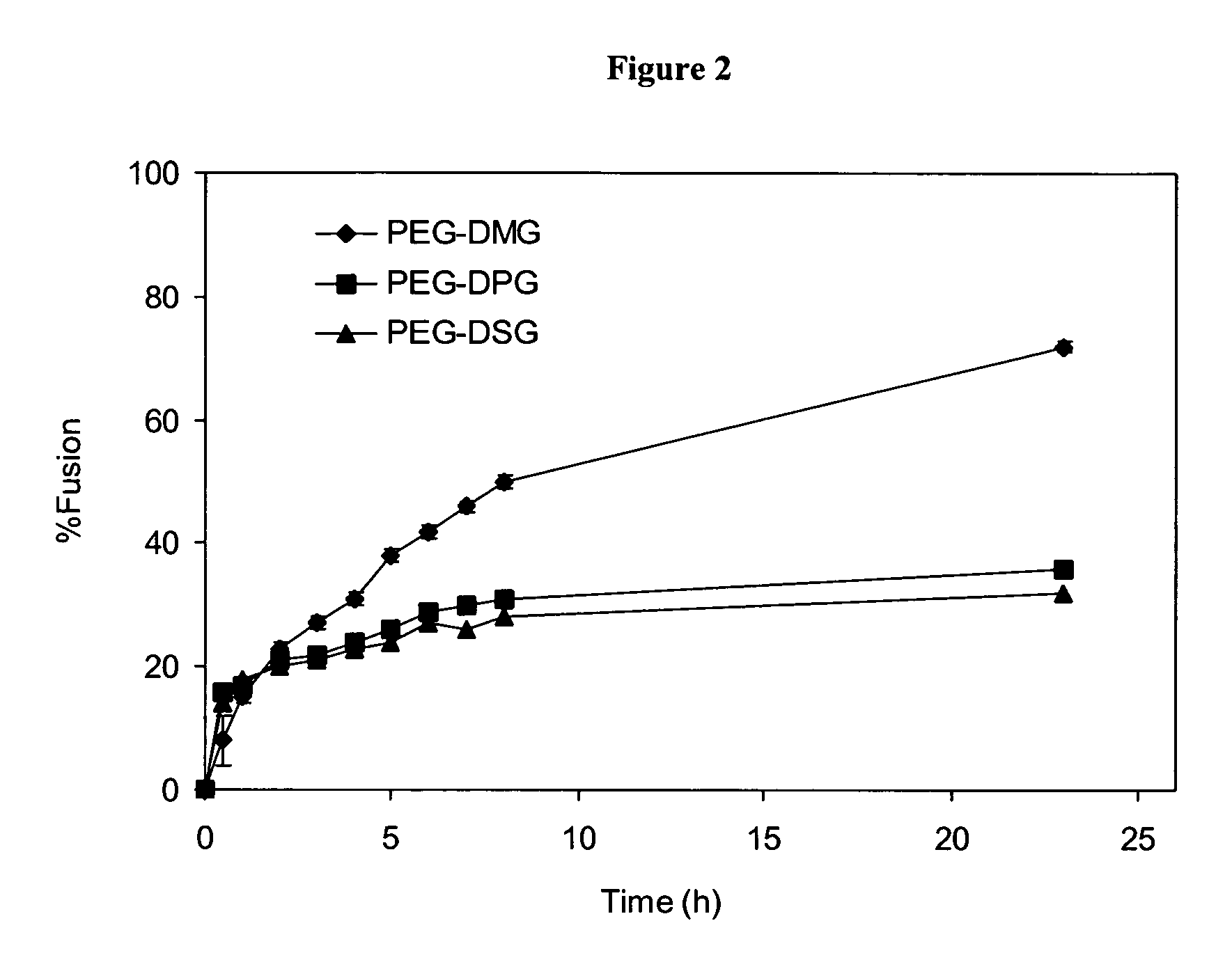
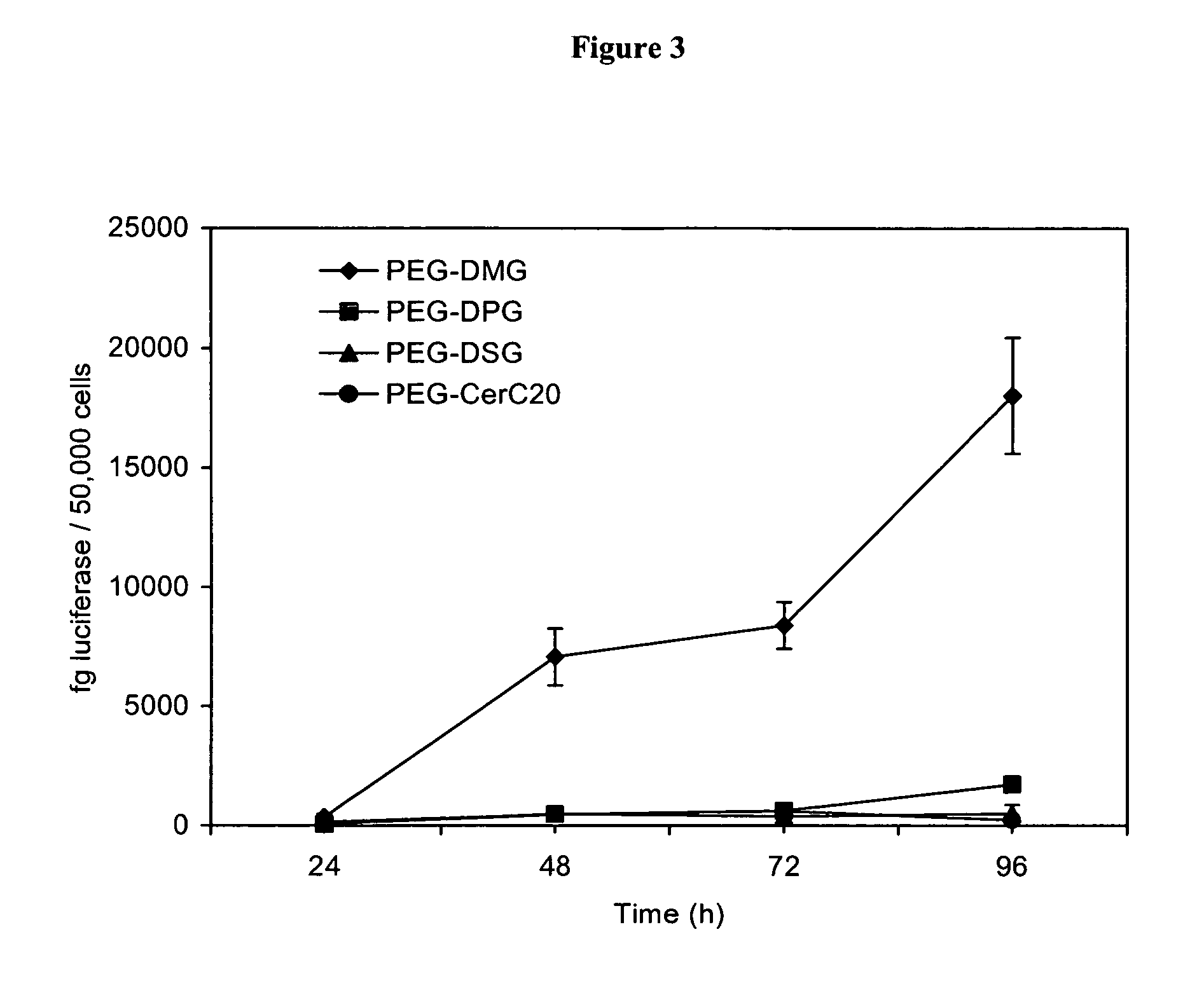
InactiveUS20060051405A1Improve stabilityPromote accumulationSpecial deliveryMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationMedicine
The present invention provides drug delivery vehicles comprising polytheylyene-lipid conjugates (PEG-lipid), wherein the circulation lifetime and biodistribution of the drug delivery vehicles are regulated by the PEG-lipid. More particularly, the present invention provides liposomes, SNALP and SPLP comprising such PEG-lipid conjugates, and methods of using such compositions to selectively target a tumor site or other tissue of interest (e.g., liver, lung, spleen, etc.).
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Biodegradable poly(beta-amino esters) and uses thereof
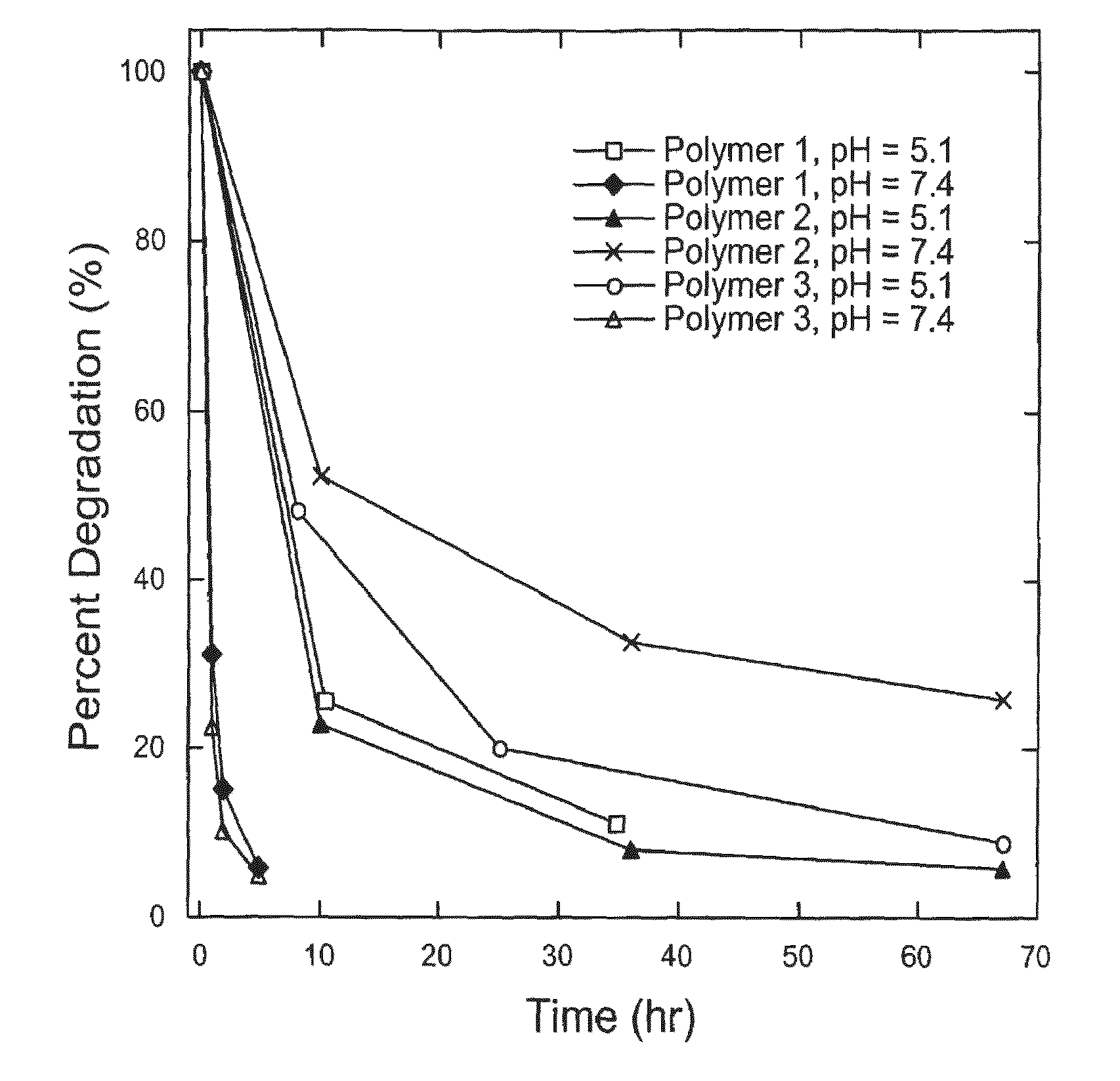
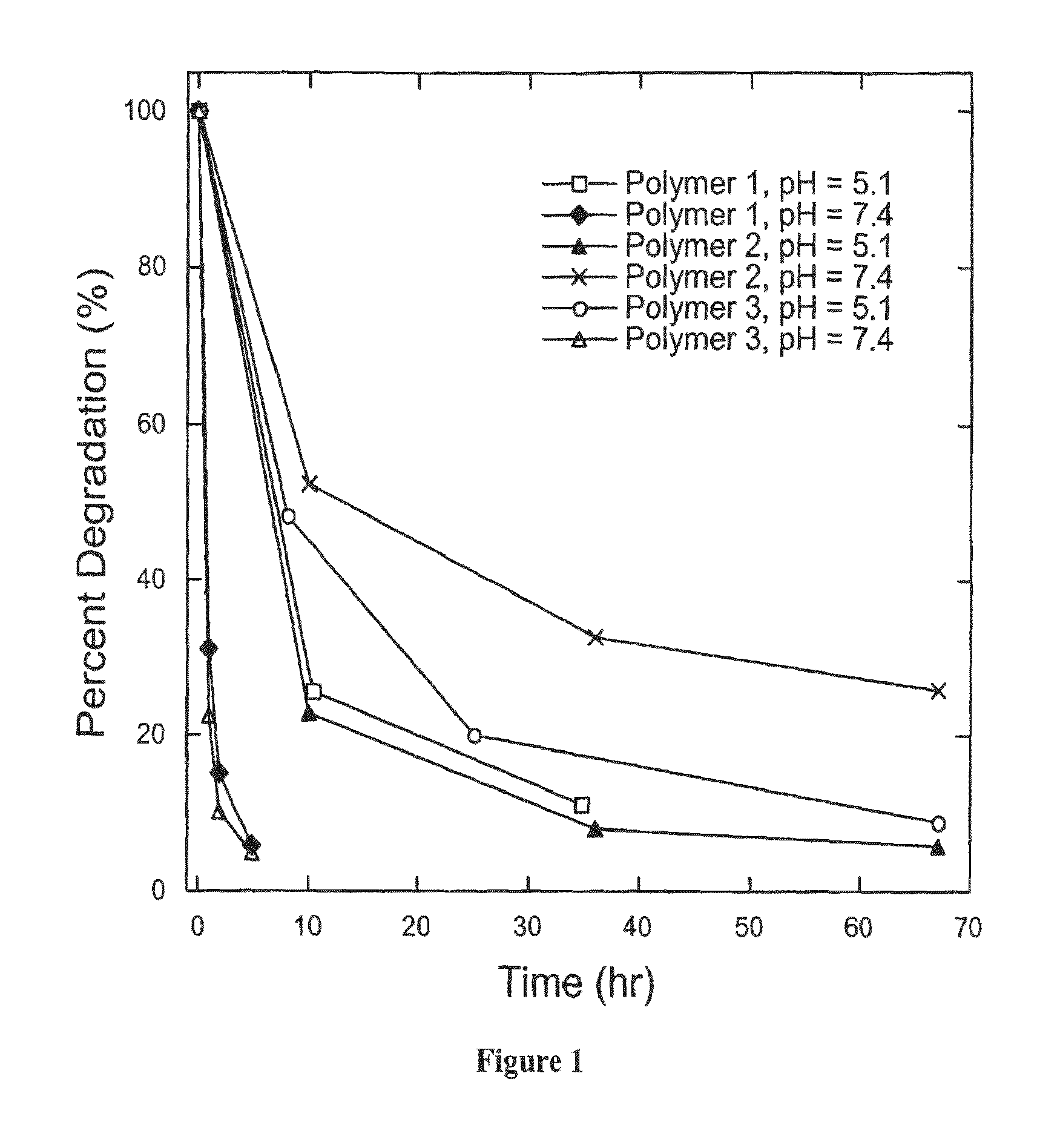
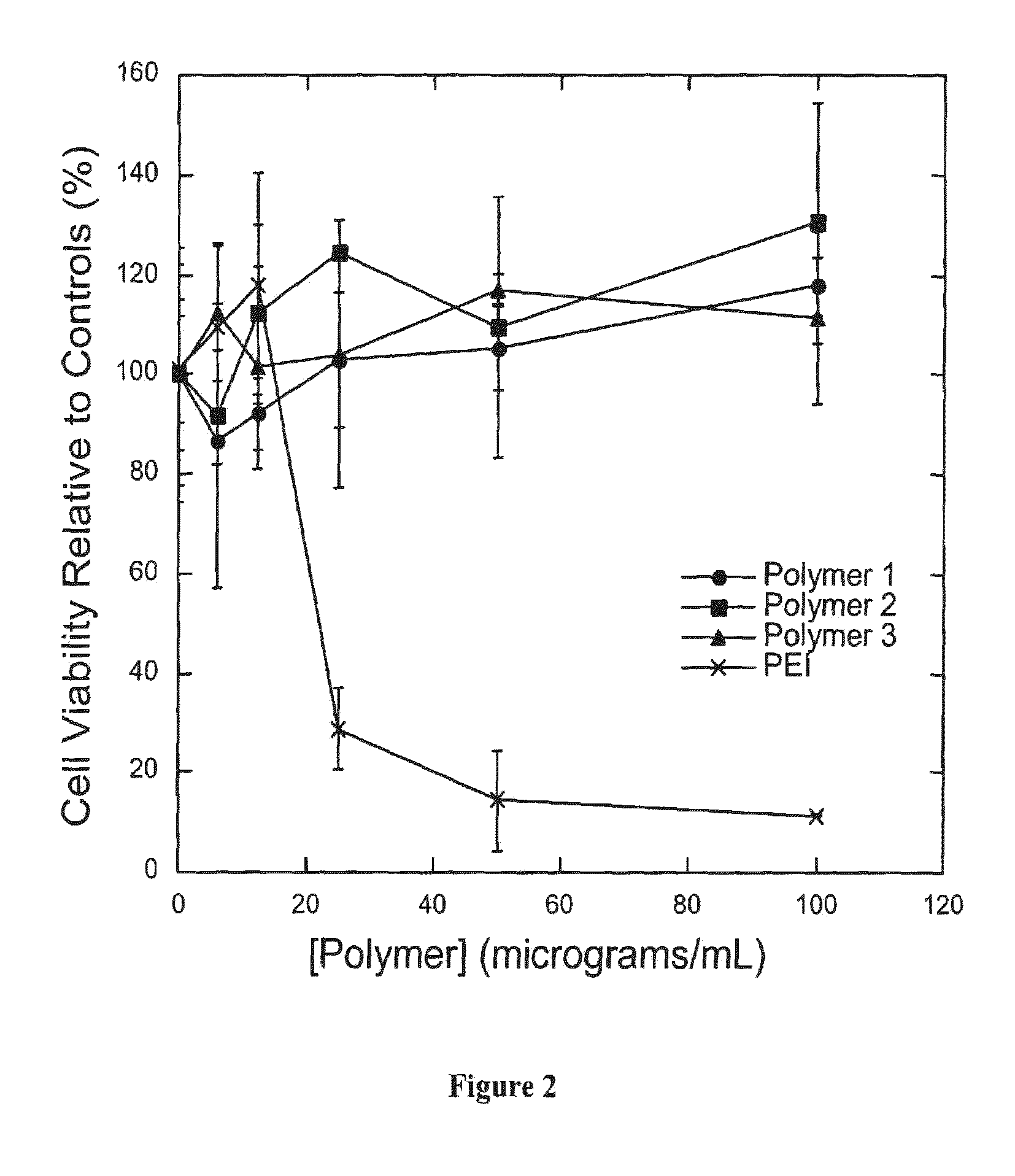
InactiveUS7427394B2High molecular weightHigh transfection efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAmino estersNucleotide
Poly(β-amino esters) prepared from the conjugate addition of bis(secondary amines) or primary amines to a bis(acrylate ester) are described. Methods of preparing these polymers from commercially available starting materials are also provided. These tertiary amine-containing polymers are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the poly(amine) nature of these polymers, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Nanoparticles containing polymer / polynucleotide complexes have been prepared. The inventive polymers may also be used to encapsulate other agents to be delivered. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings. A system for preparing and screening polymers in parallel using semi-automated robotic fluid delivery systems is also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Amino acid-, peptide-and polypeptide-lipids, isomers, compositions, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130158021A1Improved nucleotide deliveryHigh transfection efficiencyUrea derivatives preparationOrganic active ingredientsCyclic peptideNucleotide
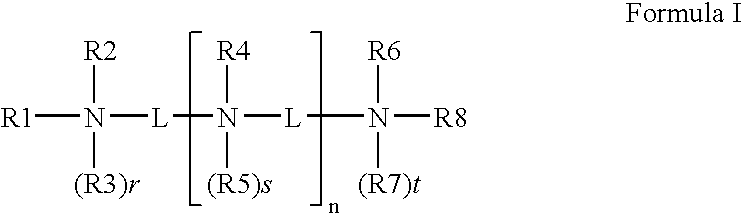
Described herein are compounds and compositions characterized, in certain embodiments, by conjugation of various groups, such as lipophilic groups, to an amino or amide group of an amino acid, a linear or cyclic peptide, a linear or cyclic polypeptide, or structural isomer thereof, to provide compounds of the present invention, collectively referred to herein as “APPLs”. Such APPLs are deemed useful for a variety of applications, such as, for example, improved nucleotide delivery. Exemplary APPLs include, but are not limited to, compounds of Formula (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V), and (VI), and salts thereof, as described herein:wherein m, n, p, R′, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R8, Z, W, Y, and Z are as defined herein.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
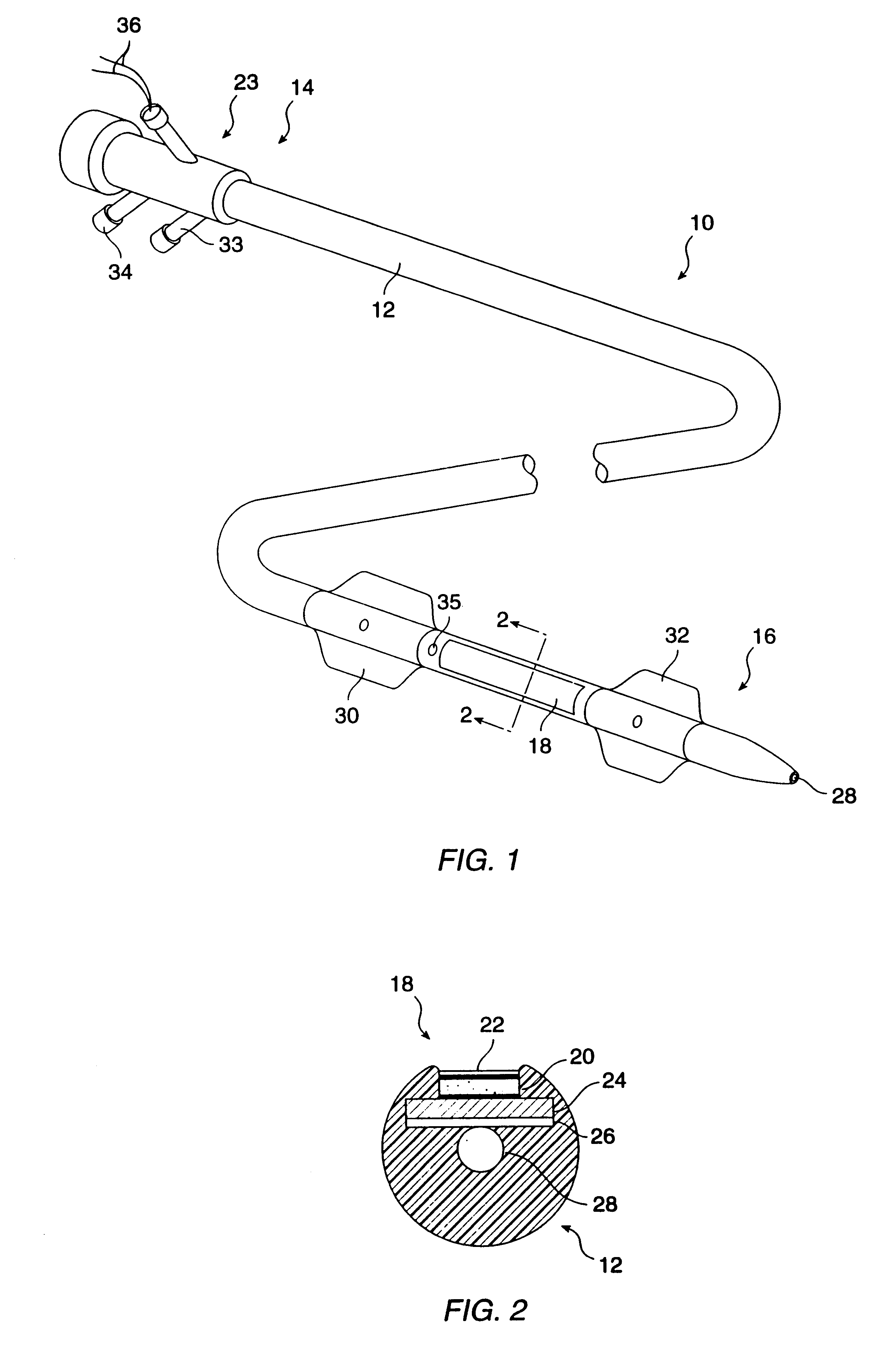
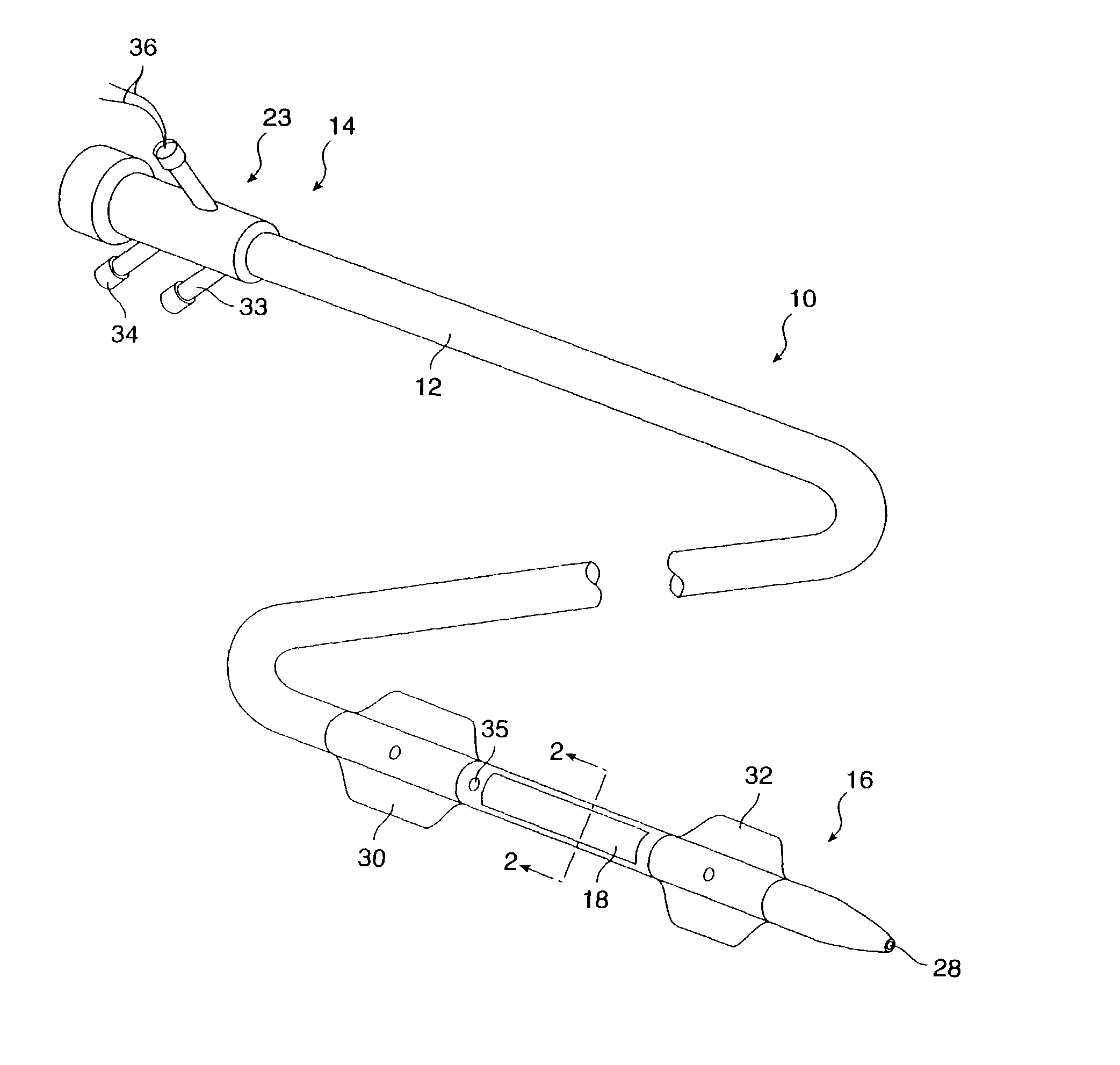
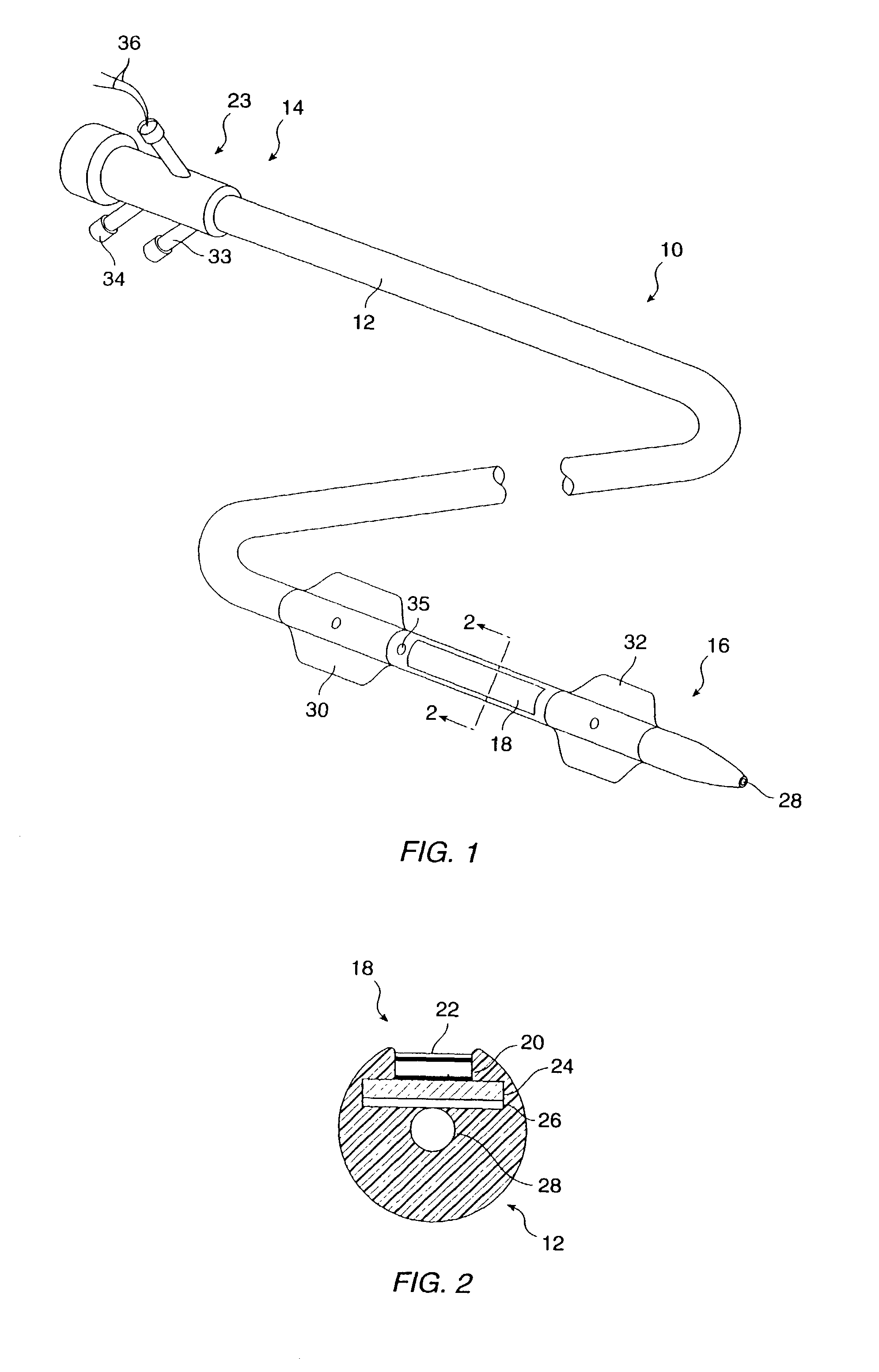
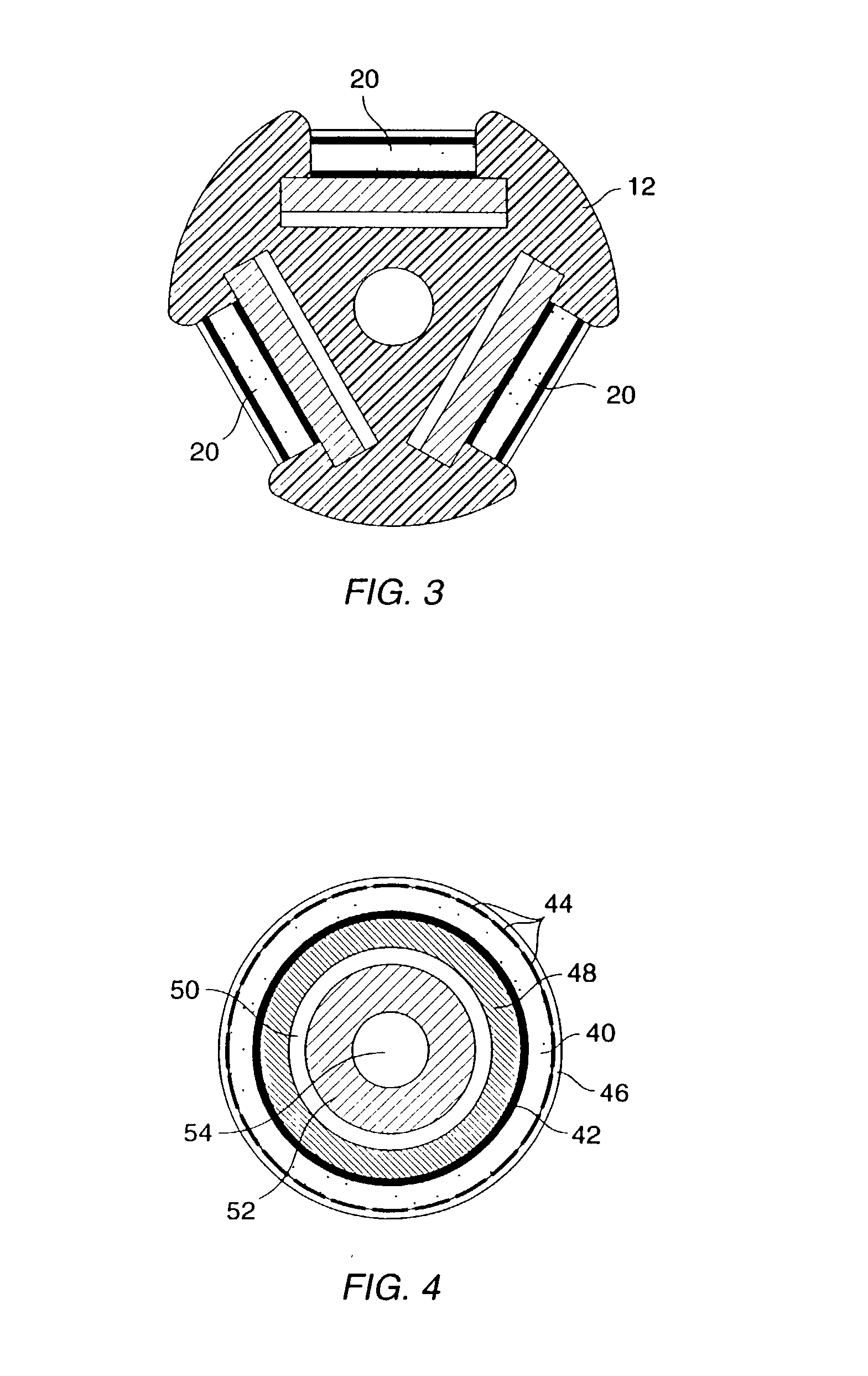
Medicament injection kit and medicament injection method
ActiveUS7297475B2Safely and efficiently in vivoSafely and efficiency in vivoBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedication injectionVein
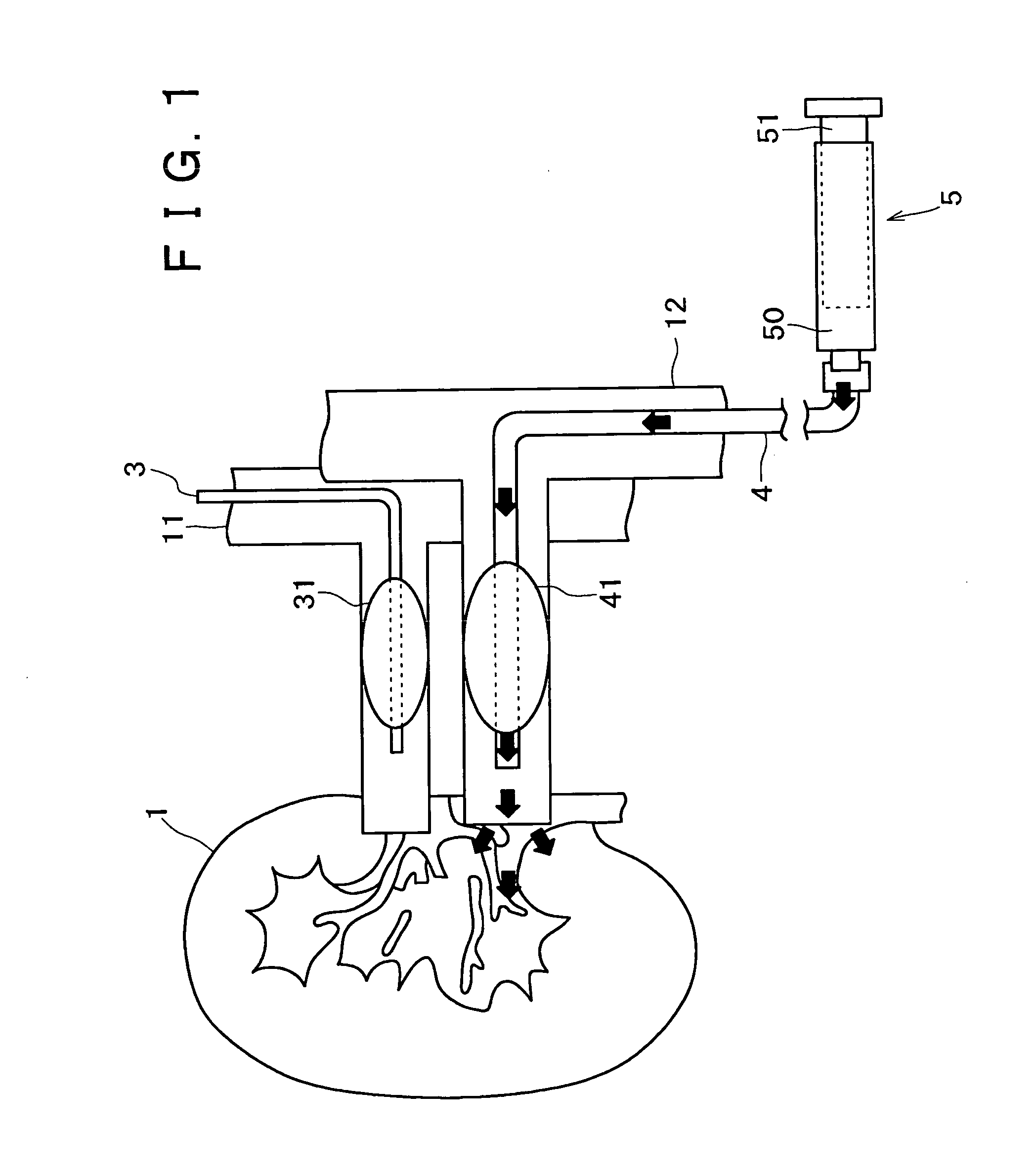
A medicament injection kit, for use in occluding a renal artery and a renal vein in a kidney and injecting a therapeutic medicament into the kidney so as to pressurize the kidney, includes: an artery catheter which includes a first balloon capable of occluding the renal artery; a vein catheter which includes a second balloon capable of occluding the renal vein; a syringe for injecting the therapeutic medicament, the syringe being capable of being connected to at least one of the artery catheter and the vein catheter; and a syringe for pressurizing the inside of the kidney by injecting a liquid, the syringe being capable of being connected to at least one of the artery catheter and the vein catheter.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Cationic peg-lipids and methods of use
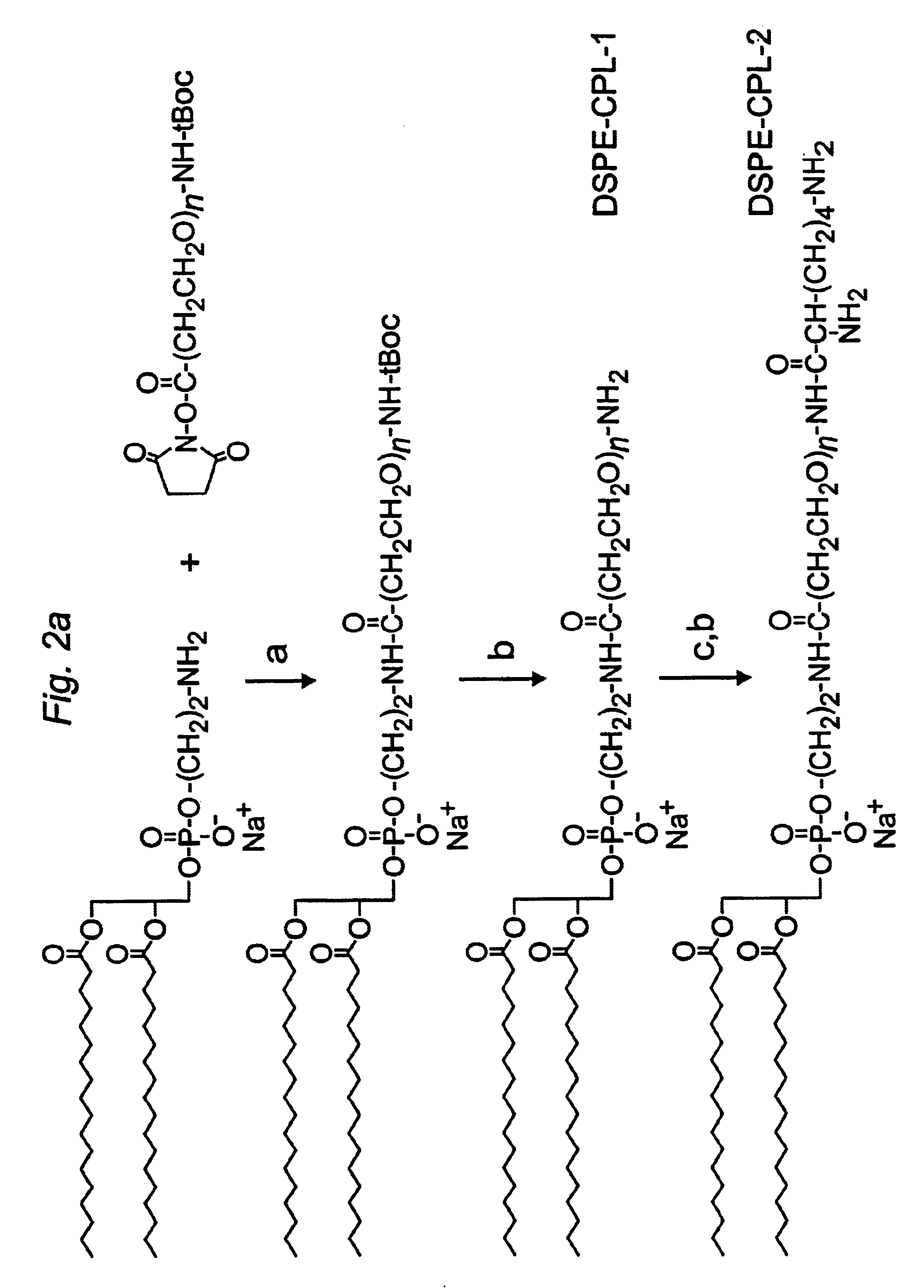
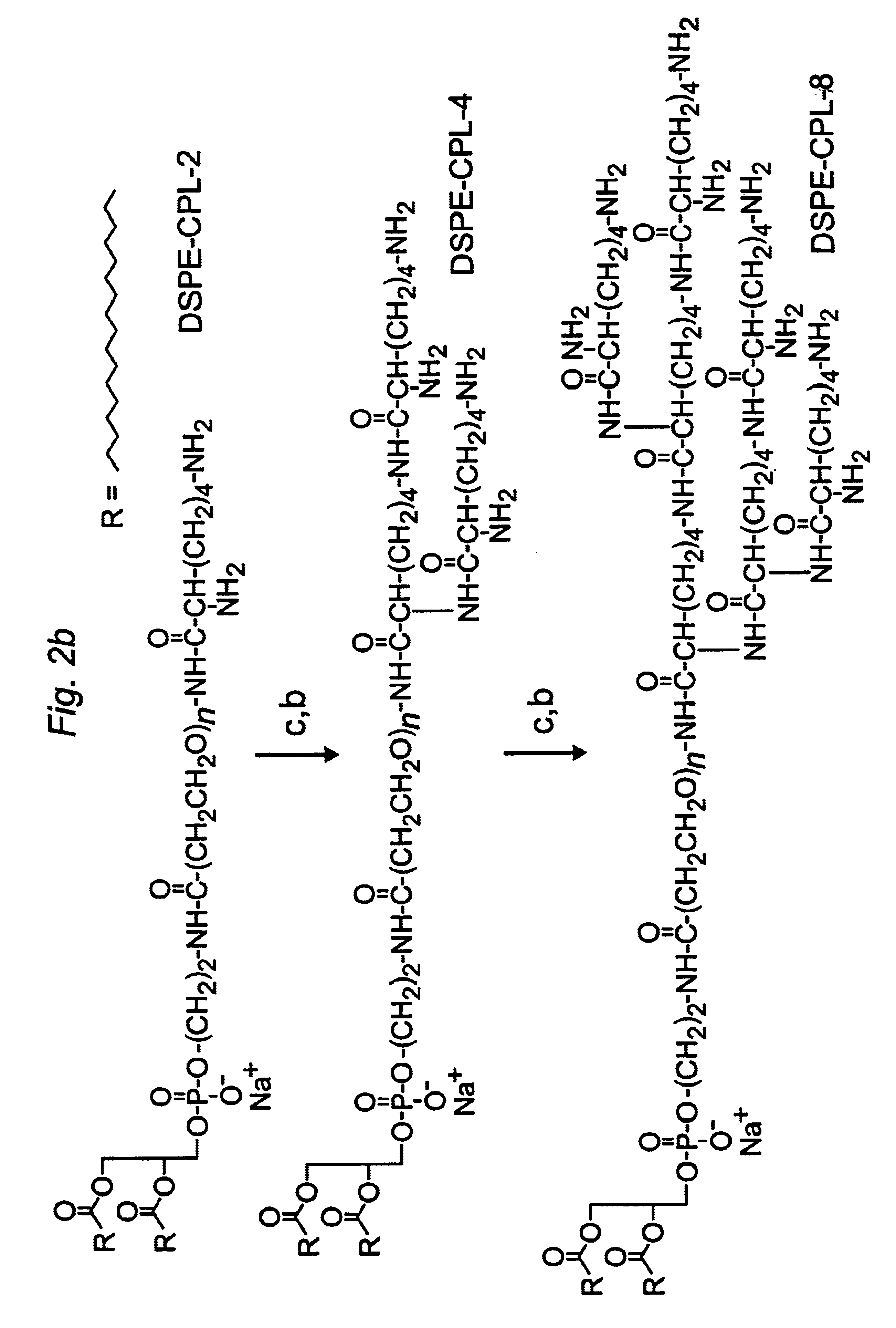
InactiveUS6852334B1High transfection efficiencyMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsLipid formationHydrophilic polymers
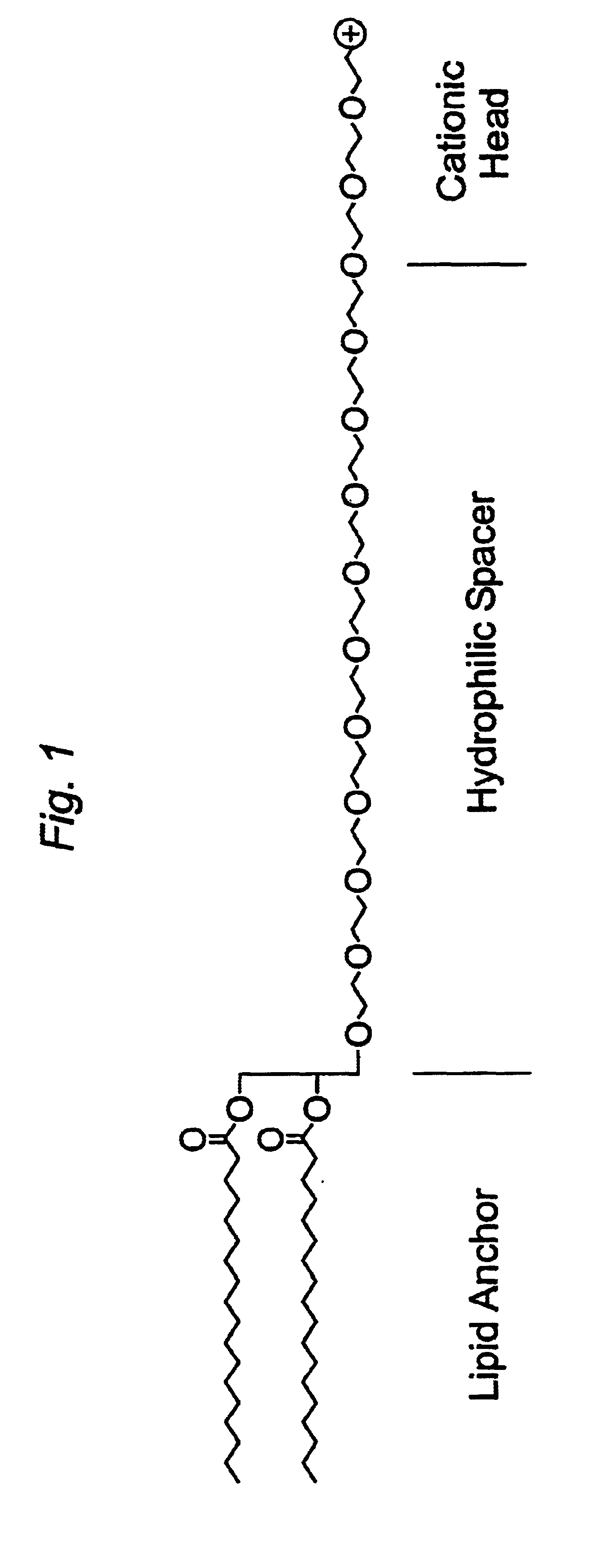
The present invention provides cationic-polymer-lipid conjugates (CPLs) such as distal cationic-poly(ethylene glycol)-lipid conjugates which can be incorporated into conventional and stealth liposomes or other lipid-based formulation for enhancing cellular uptake. The CPLs of the present invention comprise a lipid moiety; a hydrophilic polymer; and a polycationic moiety. Method of increasing intracellular delivery of nucleic acids are also provided.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Buffer solution for electroporation and a method comprising the use of the same
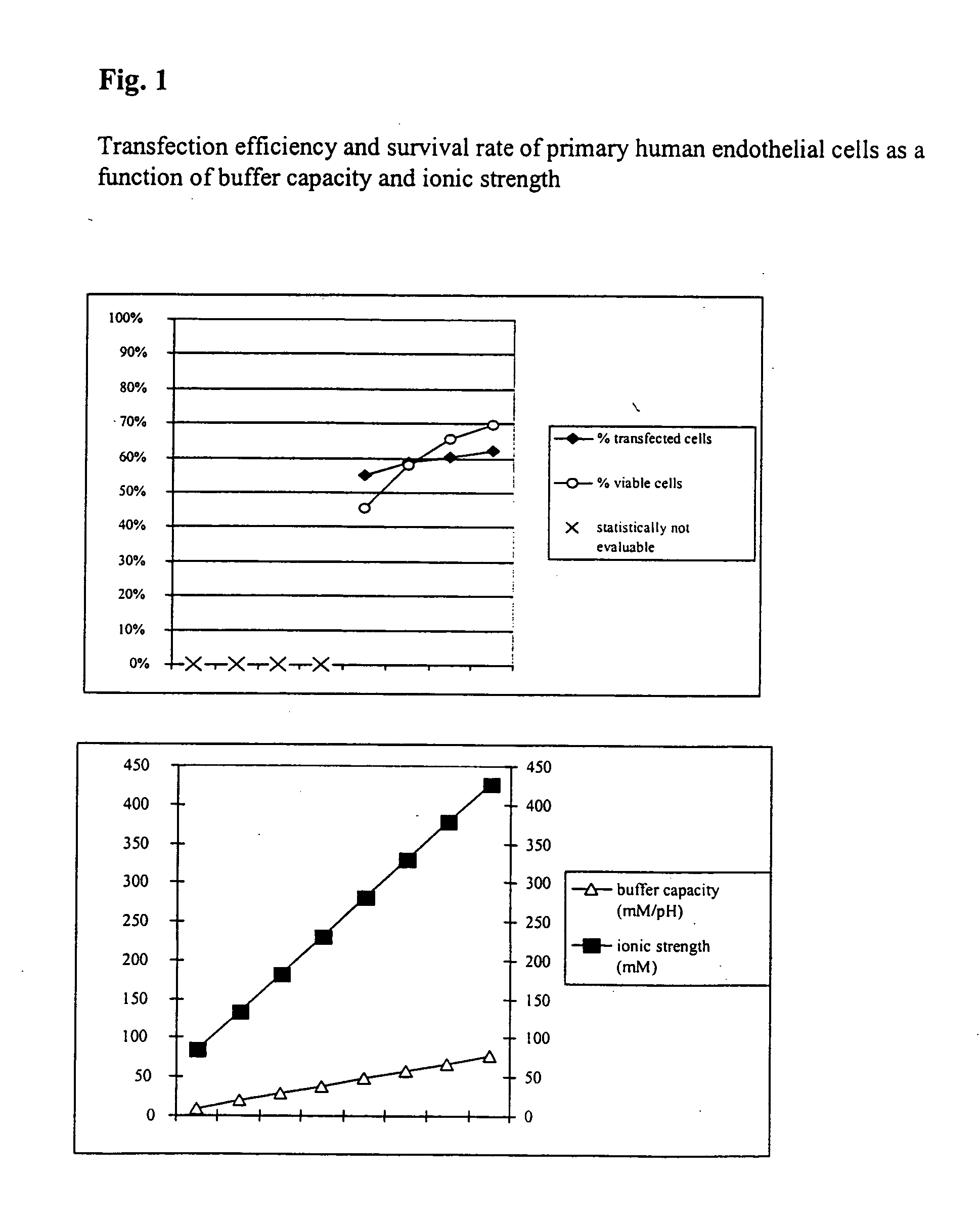
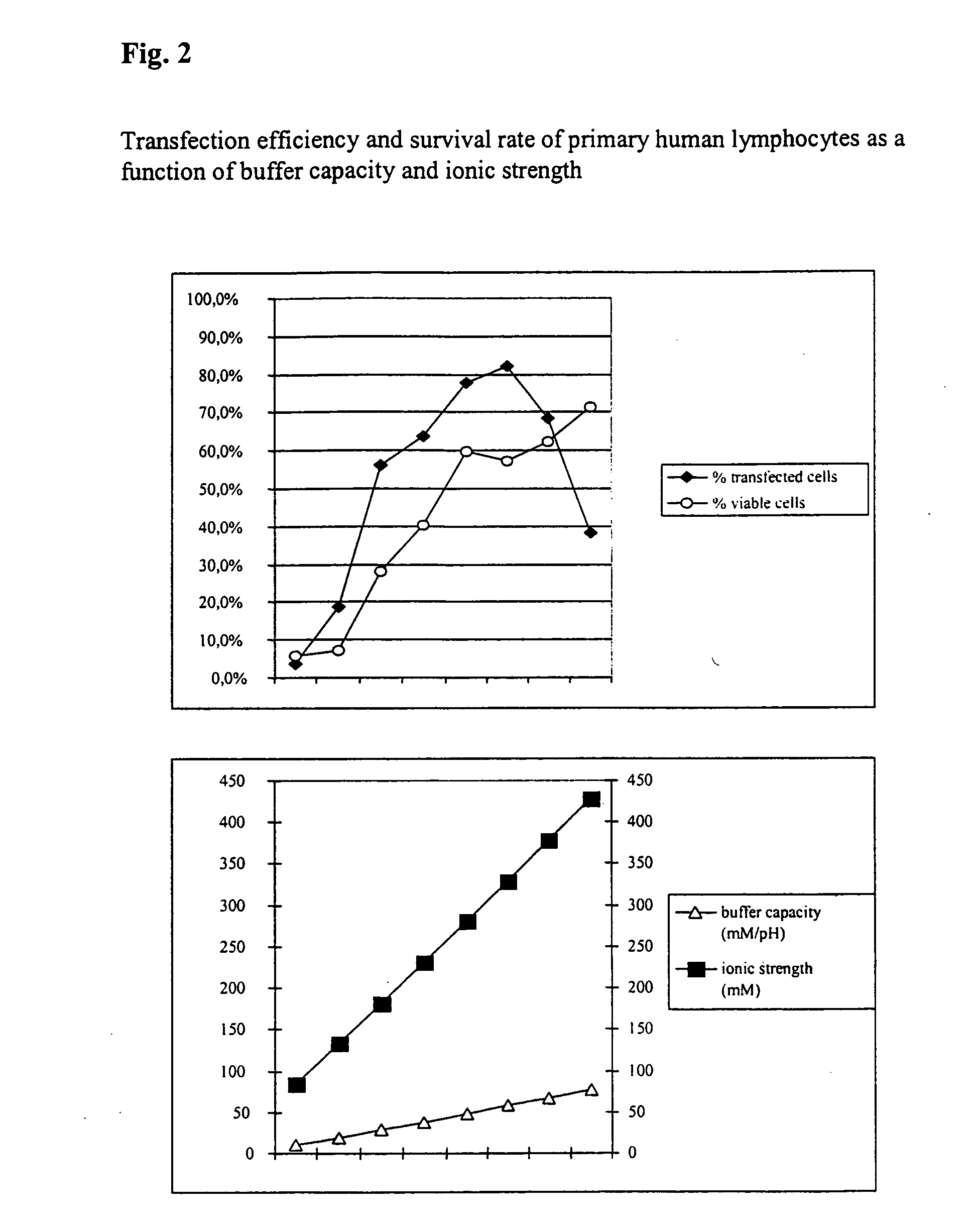
InactiveUS20050064596A1High transfection efficiencyReduce cell deathPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsElectroporationIon
The invention relates to a buffer solution for suspending animal or human cells and for dissolving biologically active molecules in order to introduce said biologically active molecules into the cells using an electric current and to a method for introducing biologically active molecules into animal or human cells using an electric current and a buffer solution. The inventive buffer solution has a buffering capacity of at least 20 mmol*I−1*pH−1 and an ionic strength of at least 200 mmol*I−1 during a change to the pH value from pH 7 to pH 8 and at a temperature of 25° C. The use of a buffer solution of this type in the corresponding method allows biologically active molecules to be introduced into animal and human cells with a high degree of transfection efficiency and at the same time a low cell mortality. Different cell types, in particular dormant and actively dividing cells of low activity, can be successfully transfected in said buffer solution.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE
Supercharged proteins for cell penetration
InactiveUS20110112040A1Improved cell penetrationReduce biological activityMicrobiological testing/measurementSaccharide peptide ingredientsInfective disorderDisease cause
Compositions, systems and related methods for delivering a supercharged protein or a complex of a supercharged protein and therapeutic agent (e g, nucleic acid, peptide, small molecule) to cells are disclosed. Superpositively charged proteins may be associated with nucleic acids (which typically have a net negative charge) via electrostatic interactions. The systems and methods may involve altering the primary sequence of a protein in order to “supercharge” the protein (e g, to generate a superpositively-charged protein). The compositions may be used to treat proliferative diseases, infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, inborn errors in metabolism, genetic diseases, etc.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
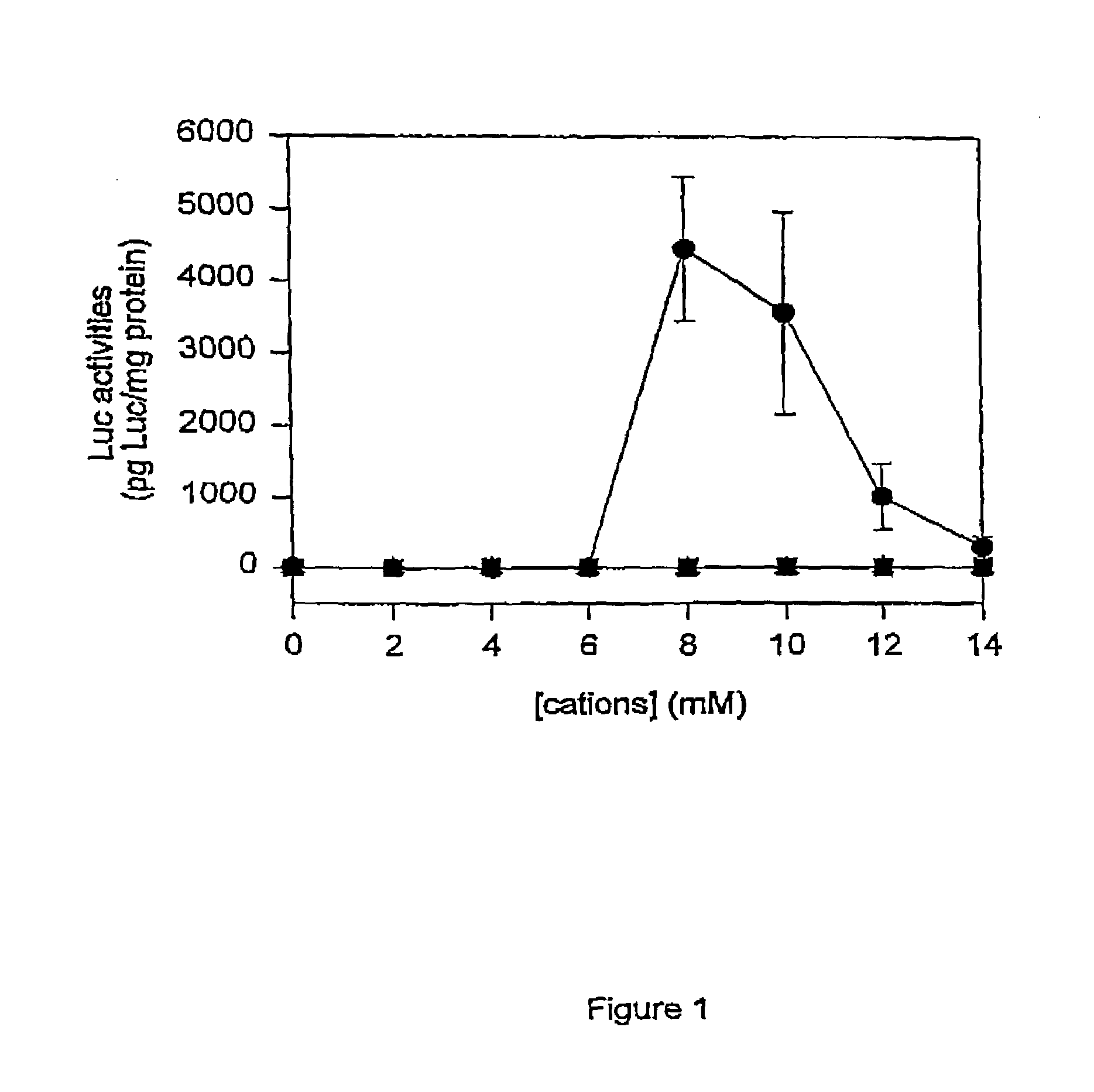
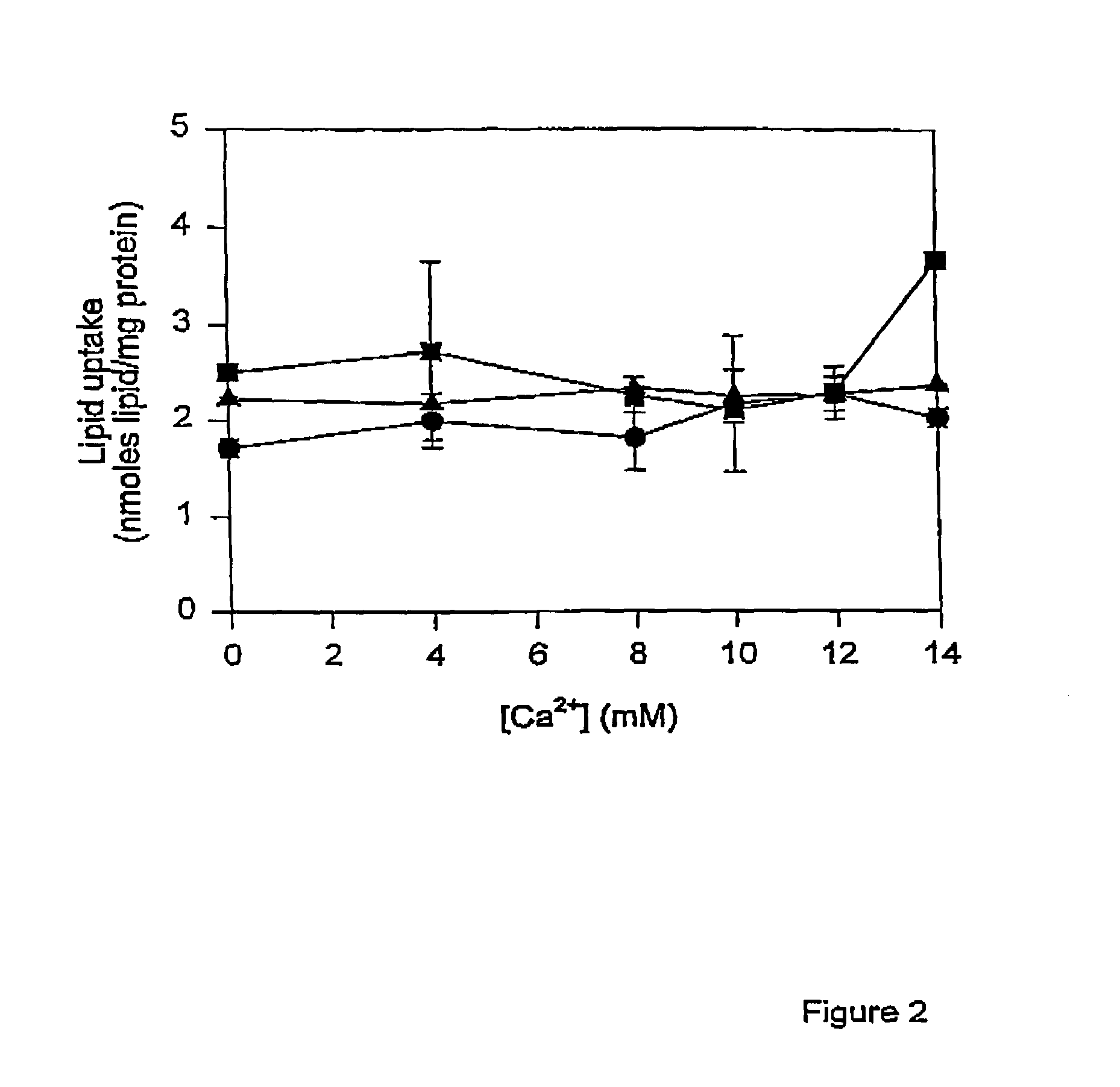
Methods of enhancing SPLP-mediated transfection using endosomal membrane destabilizers
InactiveUS7189705B2Increase in transfection efficiencyIncrease transfection efficiencySugar derivativesMicroencapsulation basedBiophysicsPlasmid
The present invention provides novel and surprisingly effective methods for delivering nucleic acids to cells. These methods are based upon the discovery that the presence of endosomal membrane destabilizers (e.g., calcium) leads to a dramatic increase in the transfection efficiency of plasmids formulated as SPLP, or “stabilized plasmid-lipid particles.”
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
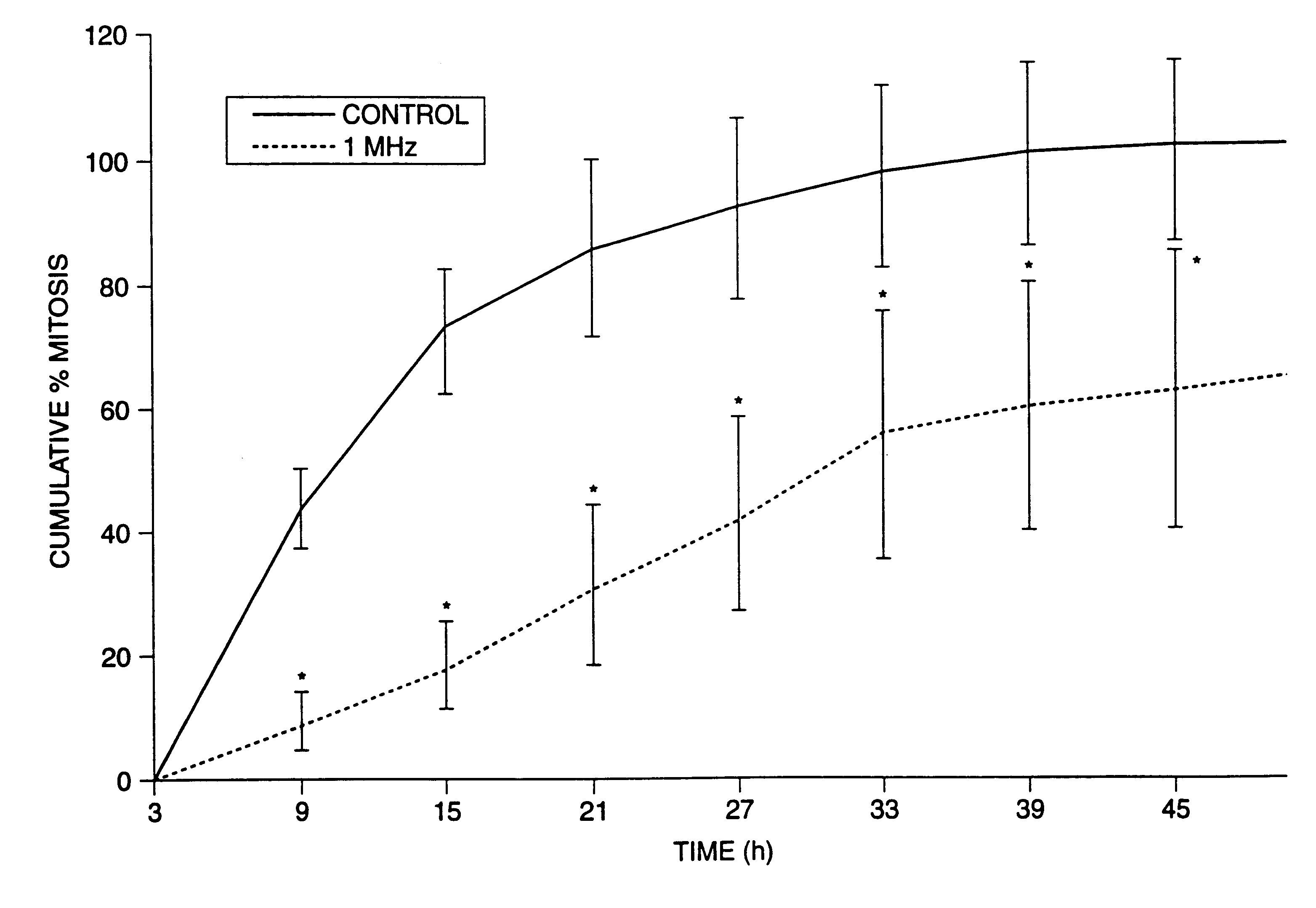
Methods, systems, and kits for intravascular nucleic acid delivery
InactiveUS6372498B2High transfection efficiencyMaximum efficiencyBiocideElectrotherapyTransfectionVascular smooth muscle
Nucleic acid transfection of vascular smooth muscle cells is enhanced by the application of vibrational energy to the cells. By applying vibrational energy at frequency in the range from 1 kHz to 10 MHz and at an intensity in the range from 0.01 W / cm2 to 100 W / cm2, significant enhancement of the uptake of nucleic acids into vascular smooth muscle cells can be achieved.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
Method and apparatus for treating materials with electrical fields having varying orientations
InactiveUS6117660AMany timesImprove cell survivalElectrolysis componentsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringPulse sequence
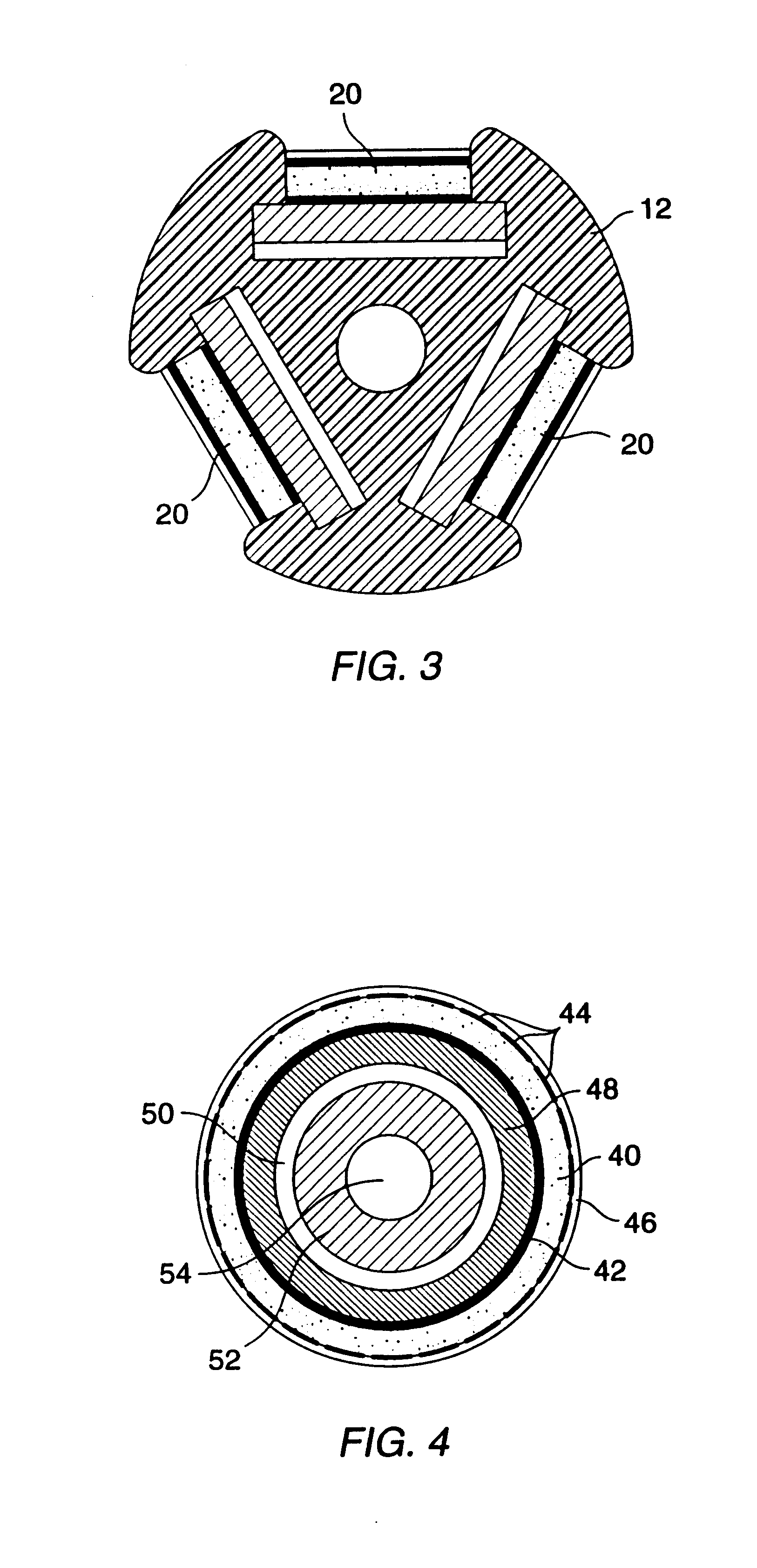
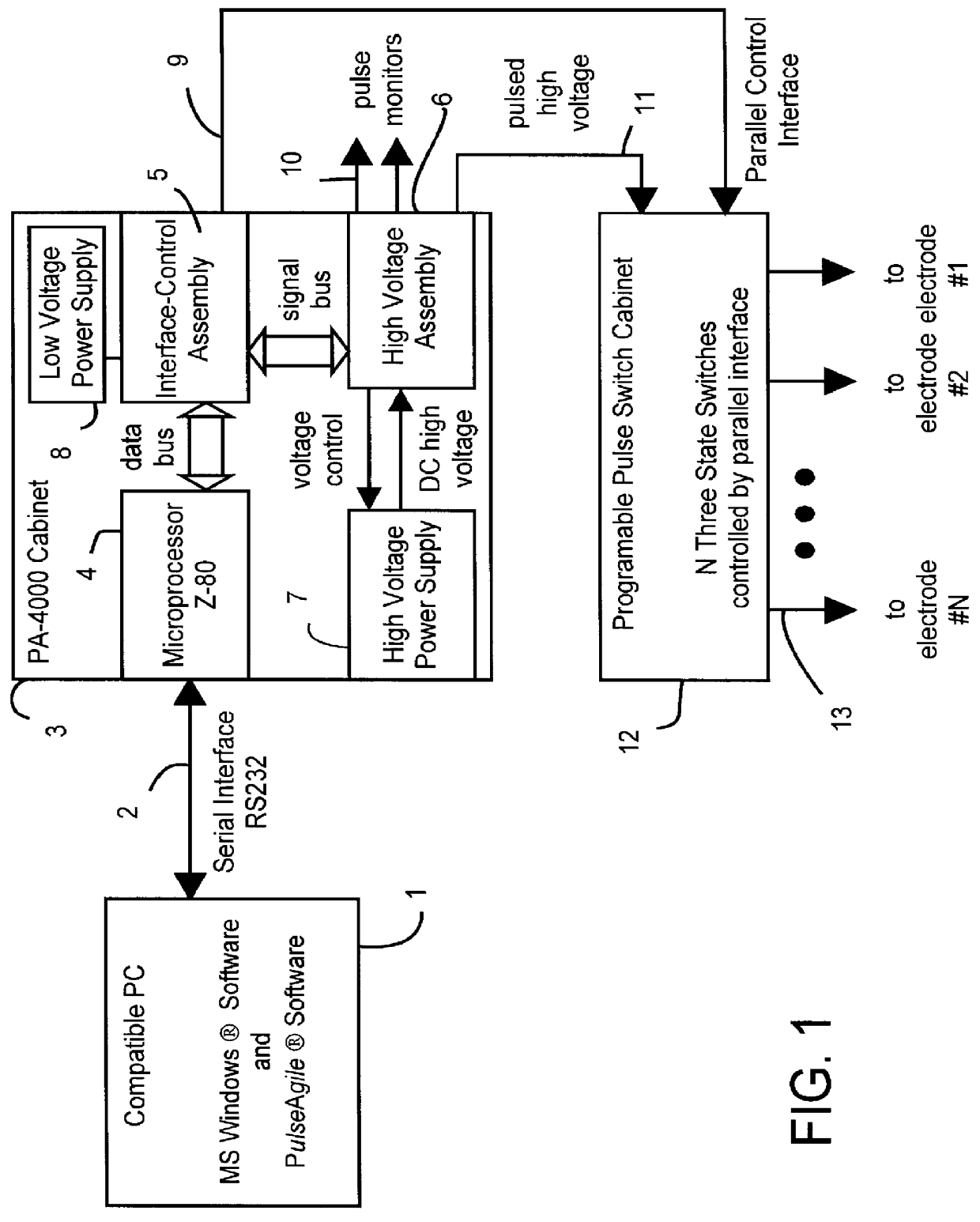
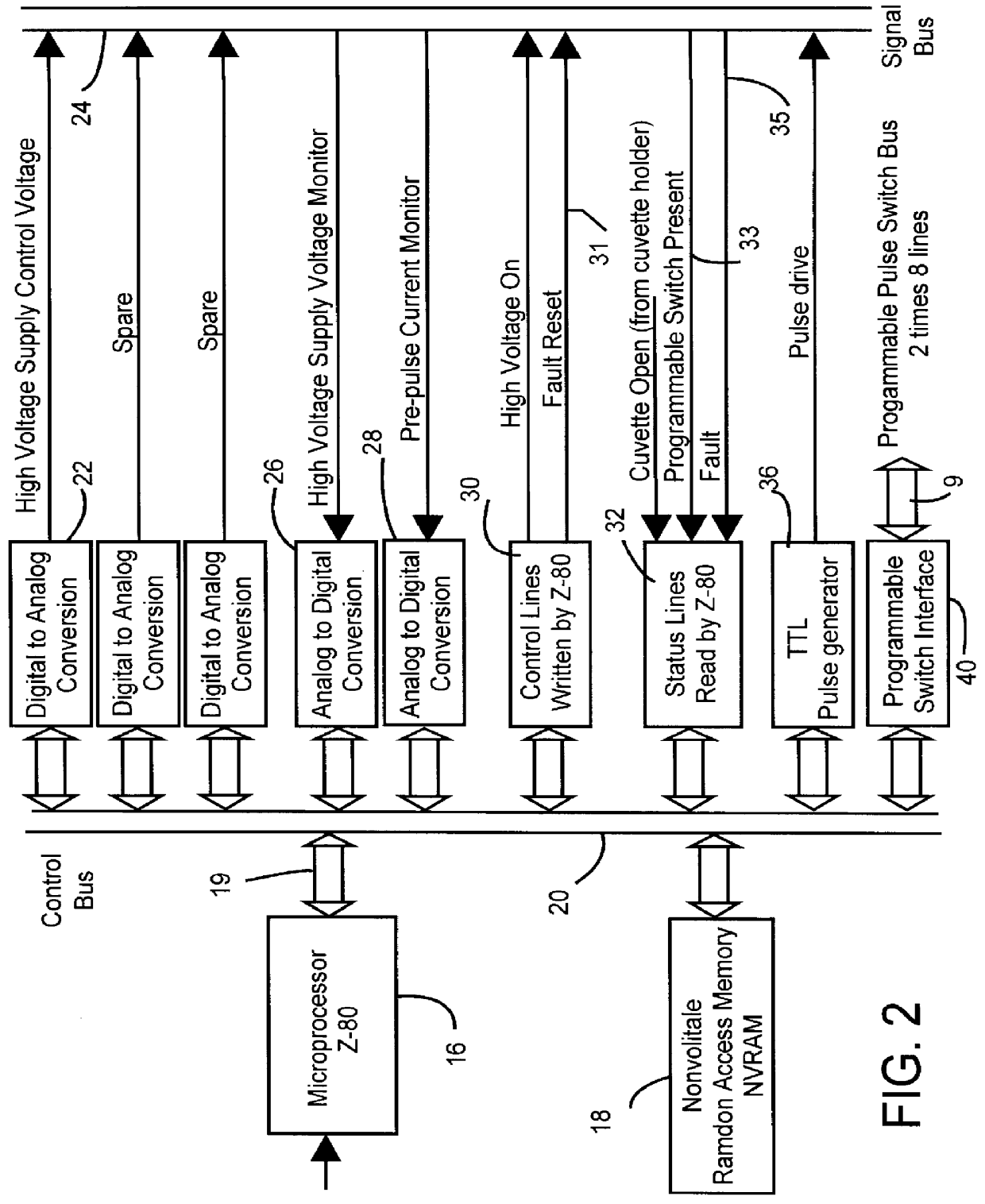
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 09300 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 10, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 10, 1999 PCT Filed Jun. 10, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 56893 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 17, 1998The object of the invention is to provide a method and apparatus for treating membrane containing material with electrical fields and with an added treating substance. With the method, a plurality of electrodes (121-128) are arrayed around the material to be treated and are connected to outputs of an electrode selection apparatus (110). Inputs of the electrode selection apparatus are connected to outputs of an agile pulse sequence generator. A treating substance is added to the membrane-containing material. Electrical pulses are applied to the electrode selection apparatus and are routed through the electrode selection apparatus in a predetermined, computer-controlled sequence to selected electrodes in the array of electrodes, whereby the membrane containing material is treated with the added treating substance and with electrical fields of sequentially varying directions. The routing of applied pulses through the electrode selection apparatus (110) to selected electrodes (121-128) can be done in an enormous number of ways.
Owner:ICHOR MEDICAL SYST
Biodegradable poly(β-amino esters) and uses thereof
InactiveUSRE43612E1High molecular weightHigh transfection efficiencyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAmino estersNanoparticle
Poly(β-amino esters) prepared from the conjugate addition of bis(secondary amines) or primary amines to a bis(acrylate ester) are described. Methods of preparing these polymers from commercially available starting materials are also provided. These tertiary amine-containing polymers are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the poly(amine) nature of these polymers, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Nanoparticles containing polymer / polynucleotide complexes have been prepared. The inventive polymers may also be used to encapsulate other agents to be delivered. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings. A system for preparing and screening polymers in parallel using semi-automated robotic fluid delivery systems is also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
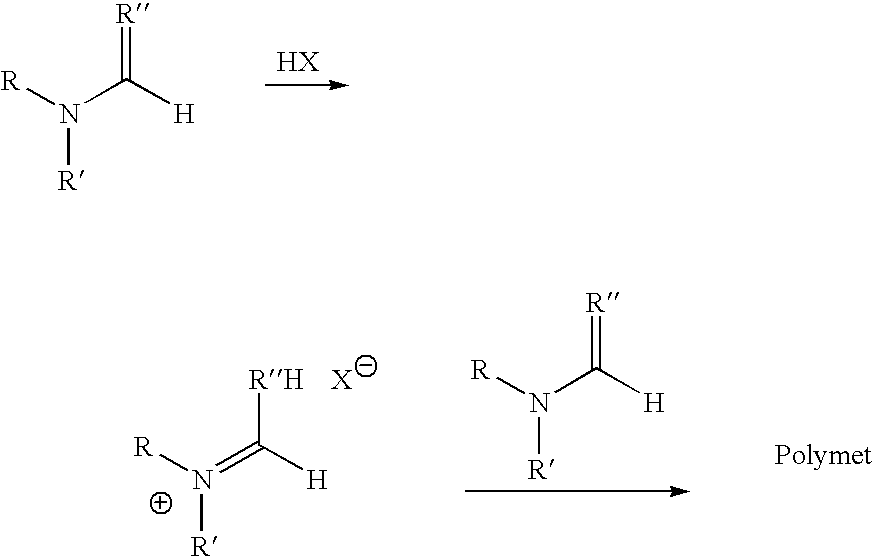
Polymerized formamides for use in delivery of compounds to cells
InactiveUS20050265957A1Increase transfection efficiencyHigh transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCompound (substance)Formamide
The invention provides for polycations for condensation and delivery of polynucleotides to cells. Processes for forming the polycations by the polymerization of formamide monomers is also described.
Owner:ROCHE MADISON
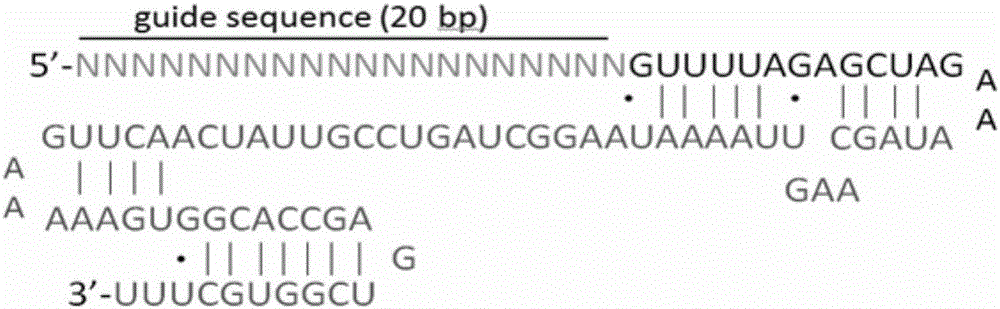
Method for knocking off animal FGF5 gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
ActiveCN104531704AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNAExon
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal FGF5 gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second FGF5 exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second FGF5 exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal FGF5 gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for knocking off animal myostatin gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN104531705AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal myostatin gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second myostatin exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second myostatin exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal myostatin gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
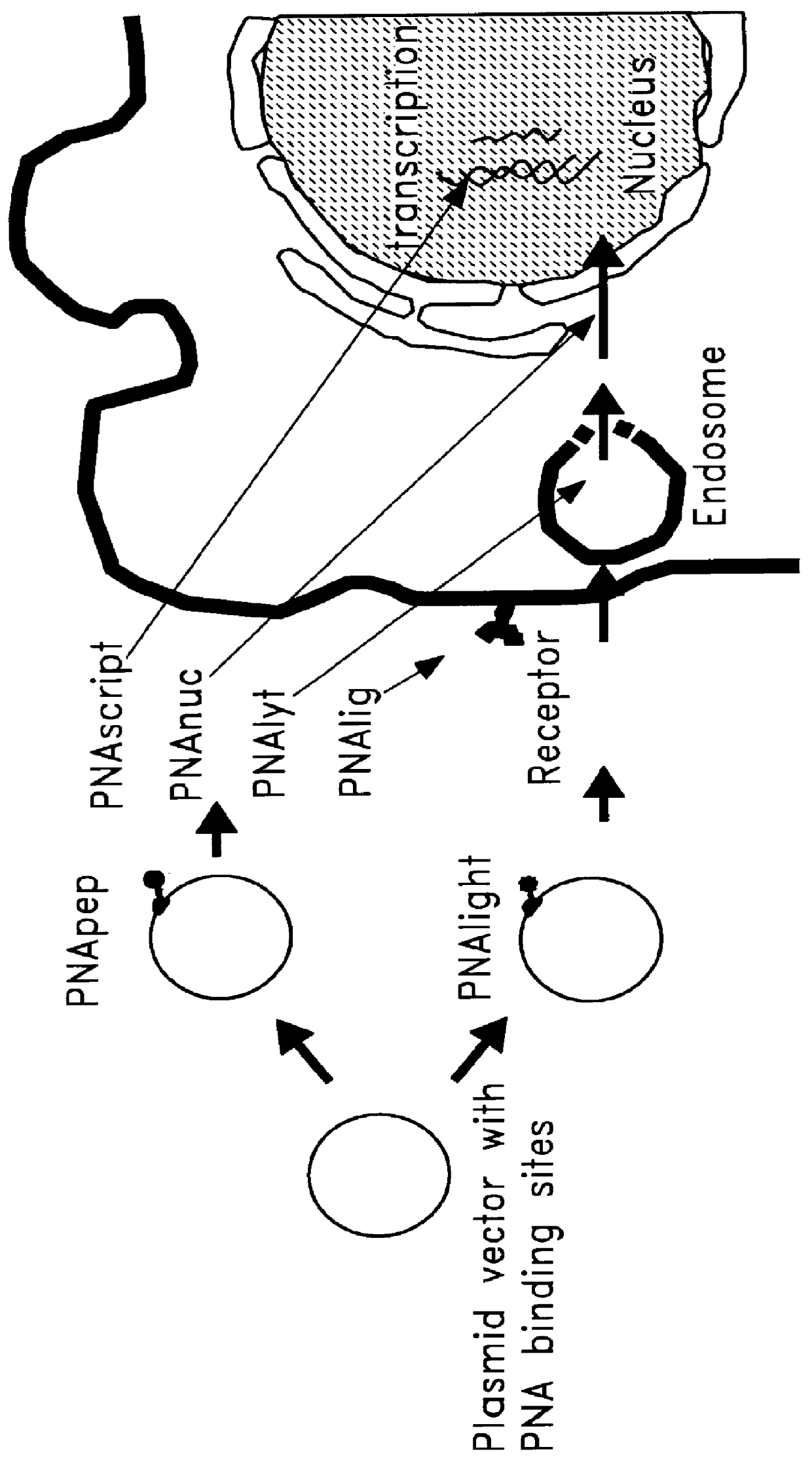
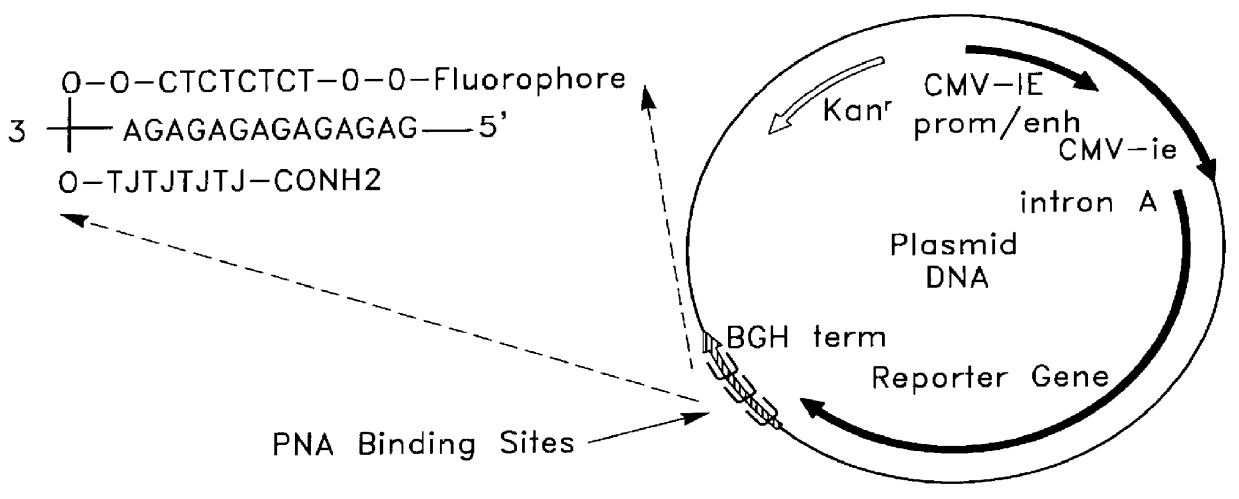
Chemical modification of DNA using peptide nucleic acid conjugates
InactiveUS6165720AReduce deliveryHigh transfection efficiencyFungiBacteriaEukaryotic plasmidsBiological activation
Complexes comprising a nucleic acid molecule and a conjugated peptide nucleic acid (PNA). The PNA may be labeled or conjugated to a protein, peptide, carbohydrate moiety or receptor ligand. These complexes are used to transfect cells to monitoring plasmid biodistribution, promote nuclear localization, induce transcriptional activation, lyse the endosomal compartment and facilitate transfection. These complexes increase the efficiency of expression of a particular gene.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST +1
Process for transfecting plants
InactiveUS20130212739A1Increase probabilityHigh transfection efficiencyBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyA-DNA
A process of transfecting a plant, comprising spraying parts of said plant with an aqueous suspension containing cells of an Agrobacterium strain and at least one abrasive suspended in said suspension, said Agrobacterium strain comprising a DNA molecule comprising a nucleic acid construct containing a DNA sequence of interest to be transfected into the plant.
Owner:NOMAD BIOSCI
Methods, systems, and kits for intravascular nucleic acid delivery
InactiveUS20030040501A1High transfection efficiencyMaximum efficiencyElectrotherapyBalloon catheterTransfectionVibrational energy
Nucleic acid transfection of vascular smooth muscle cells is enhanced by the application of vibrational energy to the cells. By applying vibrational energy at frequency in the range from 1 kHz to 10 MHz and at an intensity in the range from 0.01 W / cm2 to 100 W / cm2, significant enhancement of the uptake of nucleic acids into vascular smooth muscle cells can be achieved.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
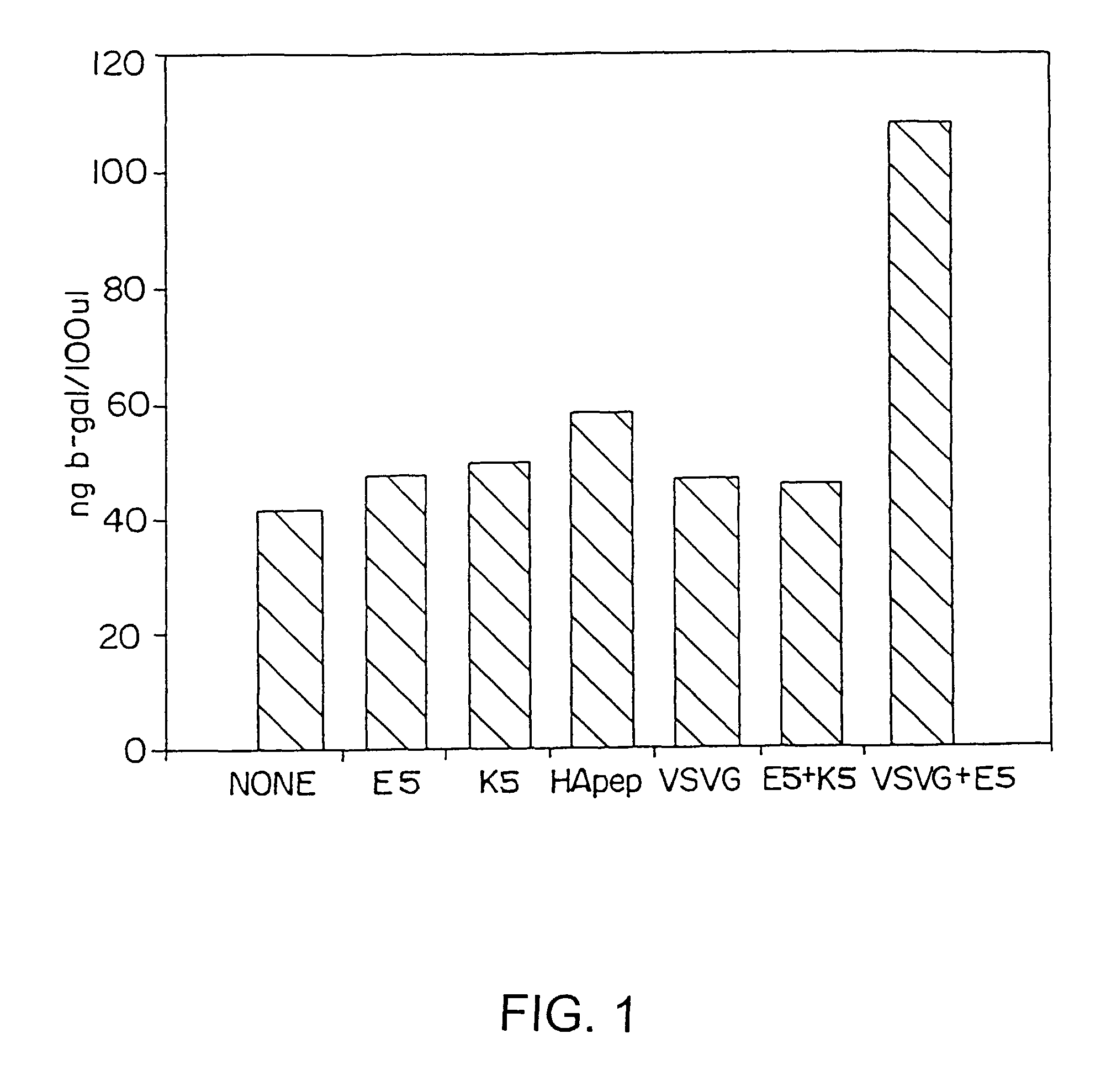
Peptide-enhanced transfections
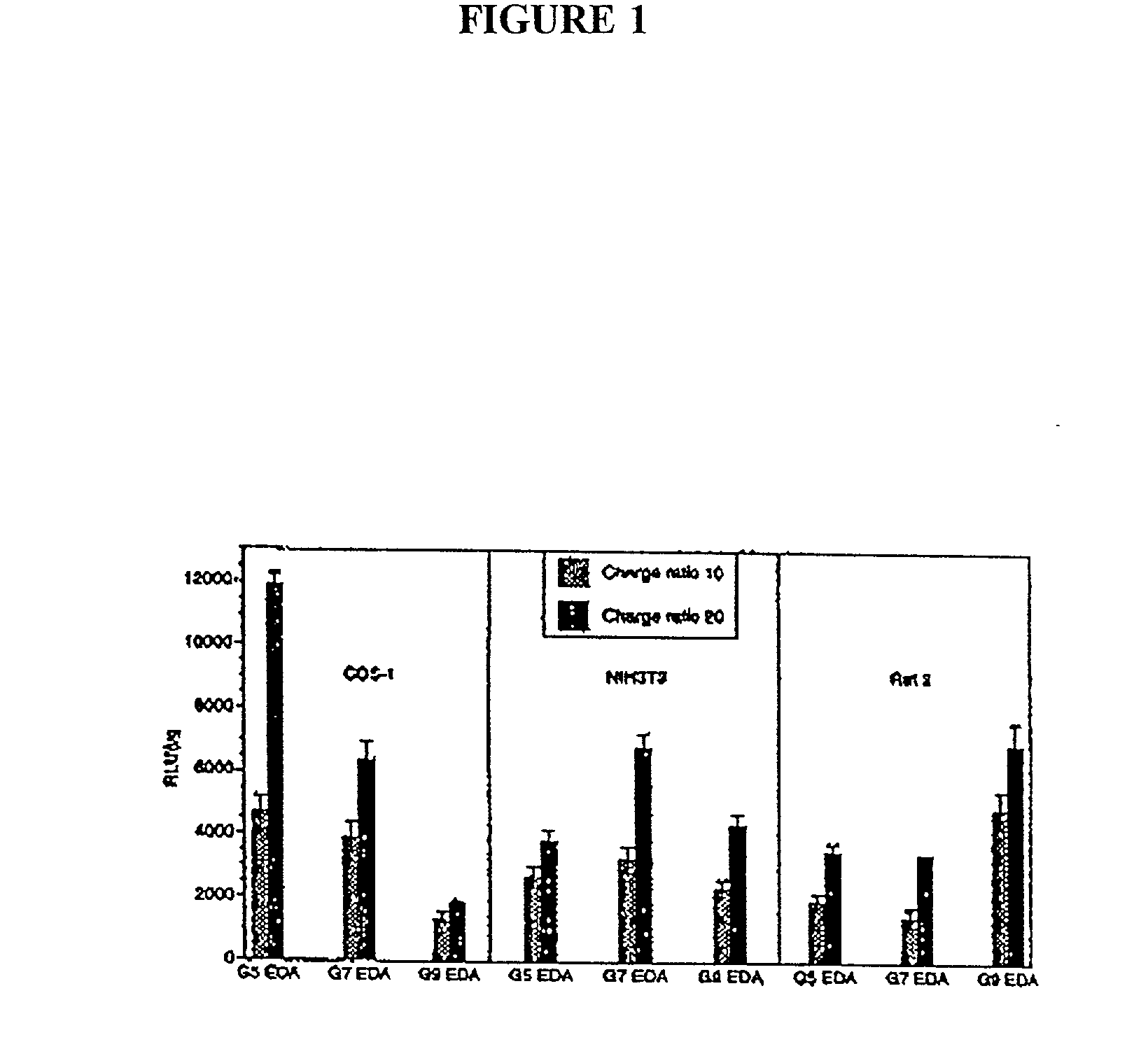
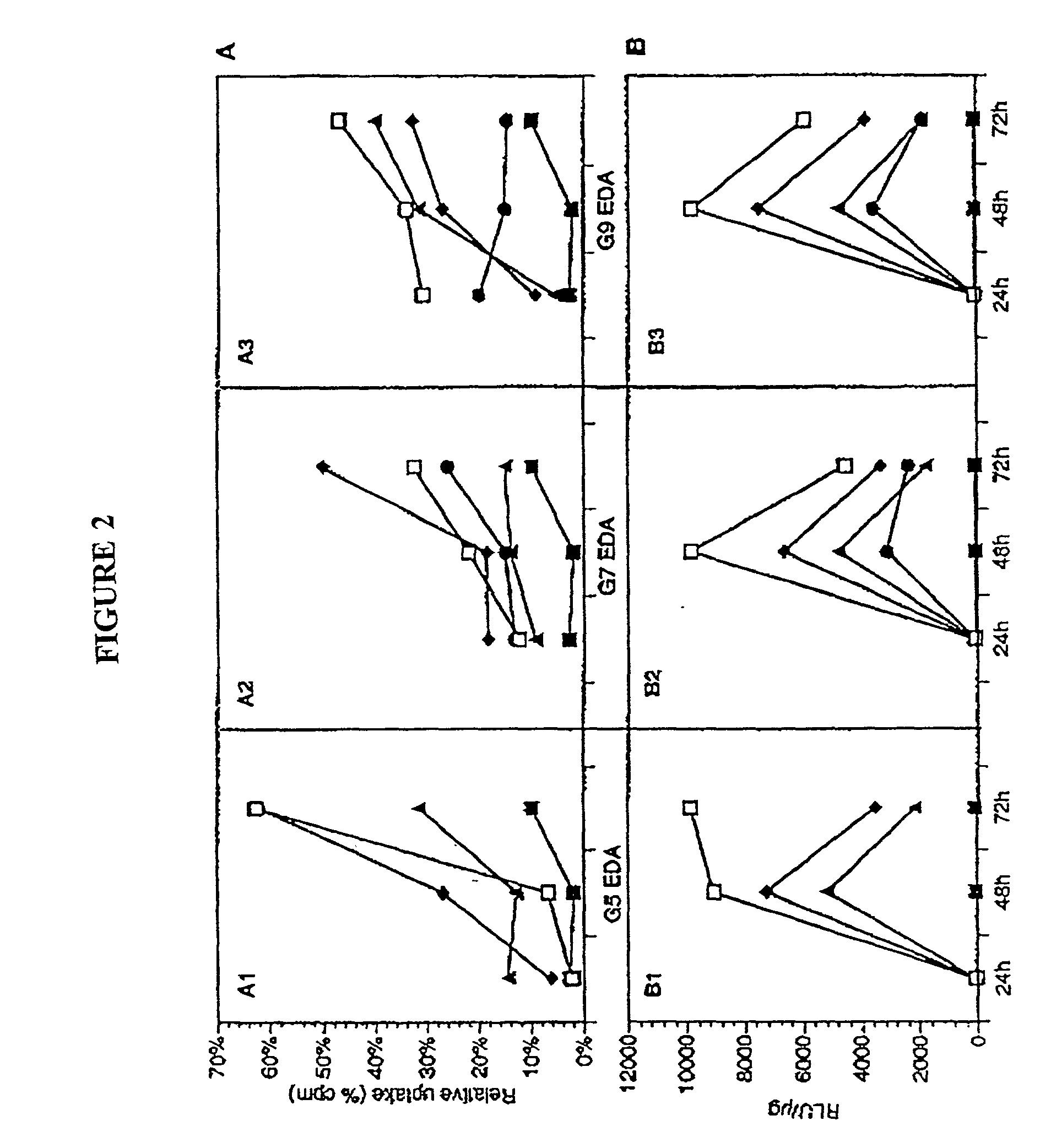
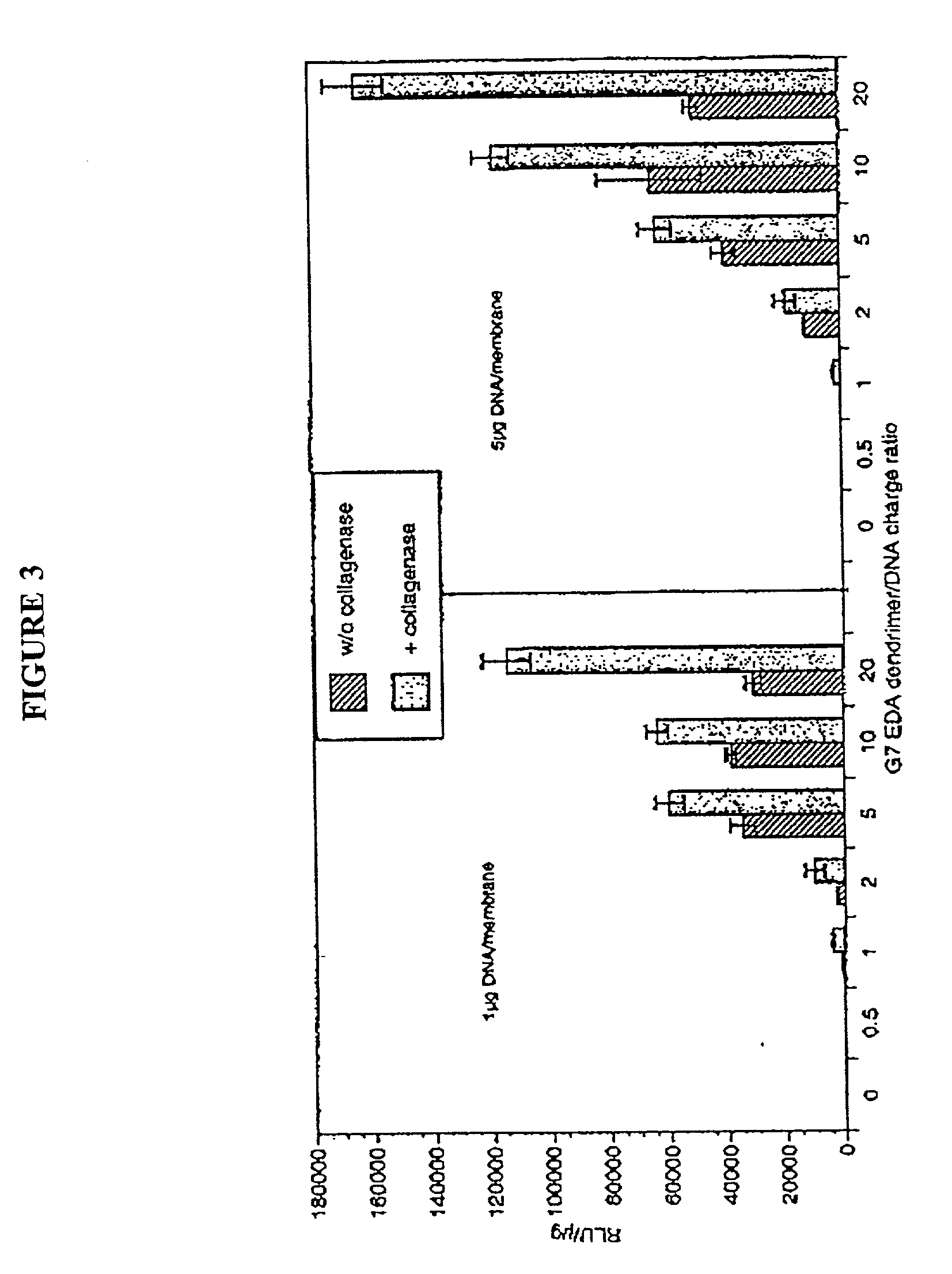
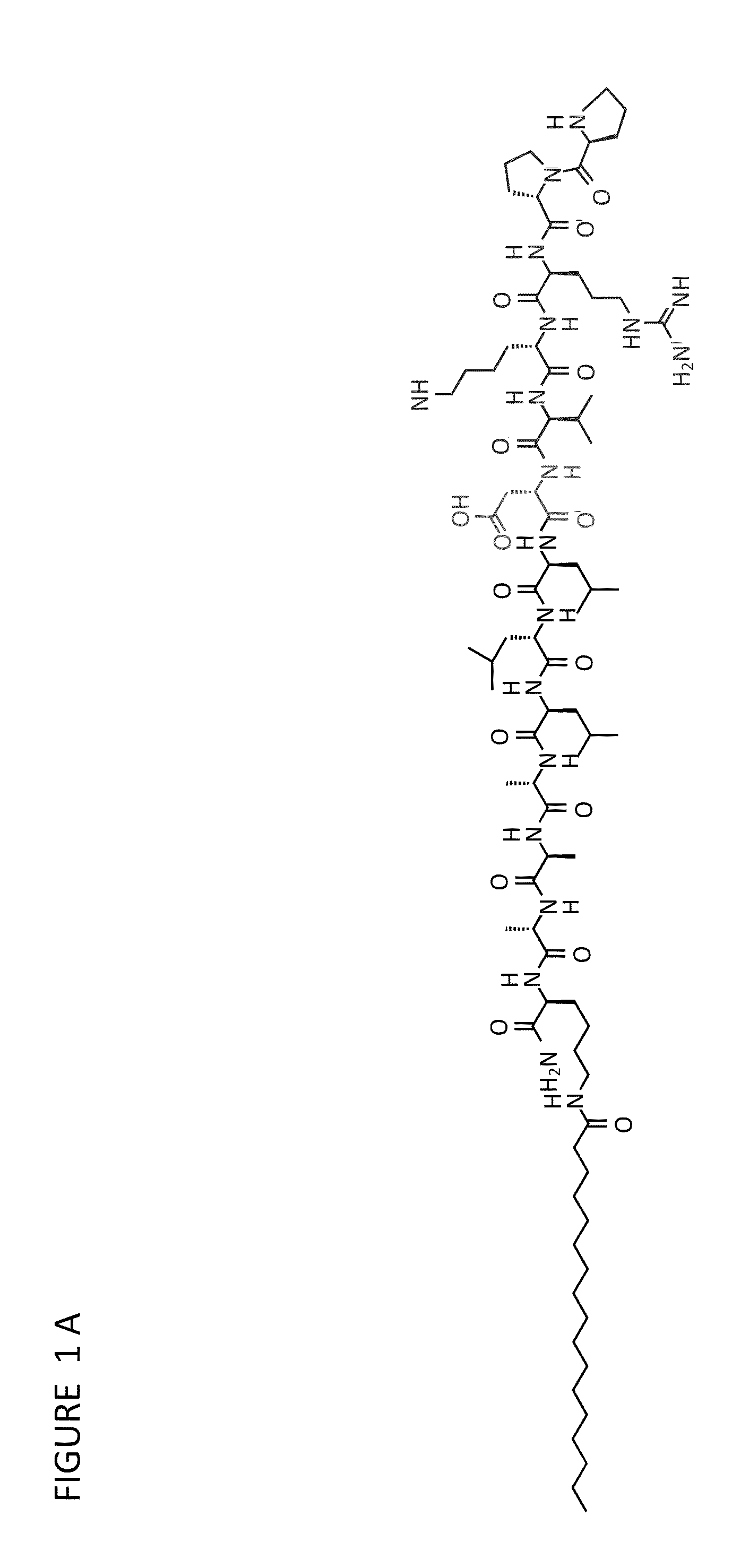
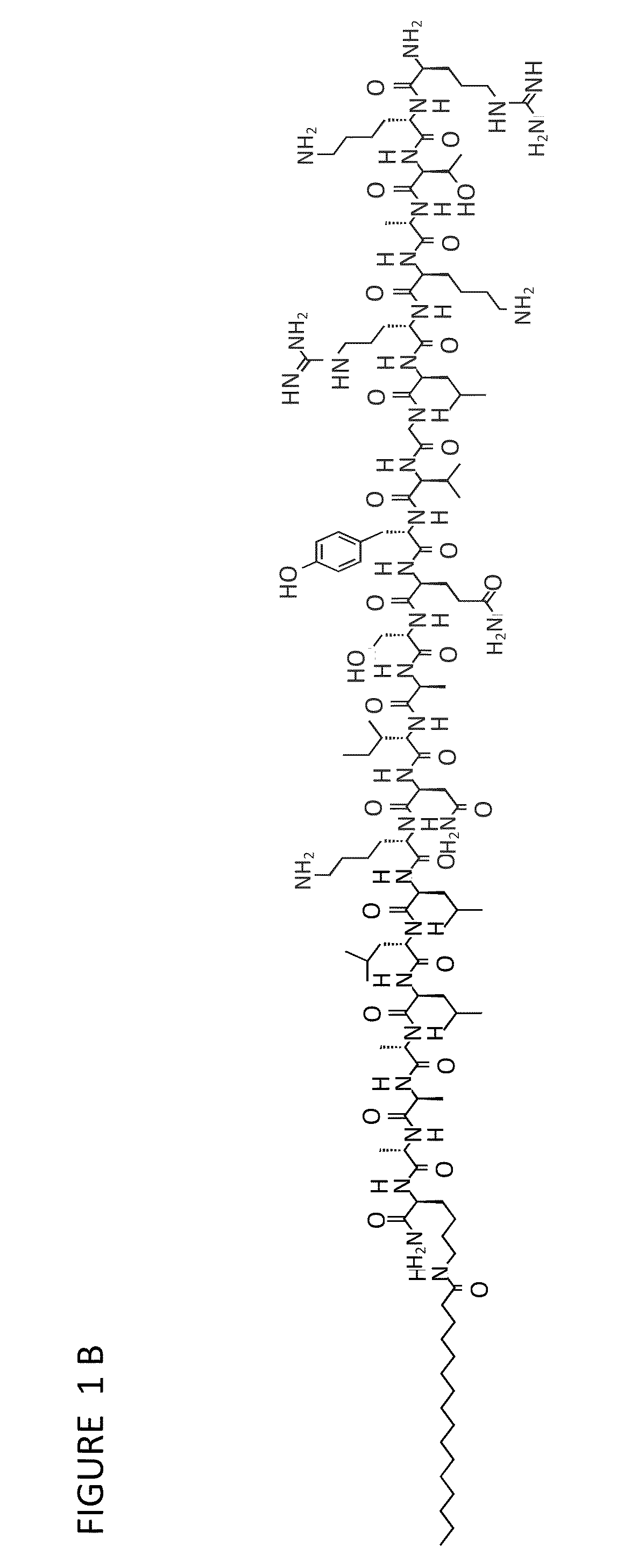
InactiveUS8058068B2High transfection efficiencyImprove bindingVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDendrimerLipid formation
The present invention provides compositions useful for transfecting eukaryotic cells comprising nucleic acid complexes with peptides, wherein the peptide is optionally covalently coupled to a nucleic acid-binding group, and cationic lipids or dendrimers as transfection agents. The invention also provides transfection compositions in which a peptide is covalently linked to the transfection agent (lipid, cationic lipid or dendrimer). Inclusion of peptides or modified-peptides in transfection compositions or covalent attachment of peptides to transfection agents results in enhanced transfection efficiency. Methods for the preparation of transfection compositions and methods of using these transfection compositions as intracellular delivery agents and extracellular targeting agents are also disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Compositions of nucleic acids and cationic aminoglycosides and methods of using and preparing the same
InactiveUS20050019926A1High transfection efficiencyAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryPolymerAminoglycoside Agents
Compositions that include nucleic acid and cationic aminoglycosides and methods for their use are provided. The subject compositions are characterized by having nucleic acid complexed with a cationic aminoglycoside, where the nucleic acid is condensed. In certain embodiments, the cationic aminoglycoside is a cationic aminoglycoside antibiotic. The composition may further include one or more of: functional groups such as targeting moieties, nuclear localization or targeting peptides, endosomolytic peptides and / or one or more lipids and / or polymers, where the lipids may be provided in a manner to encapsulate the nucleic acid. The present invention also provides methods of using and preparing the nucleic acid-aminoglycoside compositions.
Owner:ARADIGM
Transfection reagent for non-adherent suspension cells
InactiveUS20060228406A1High transfection efficiencyToxic reductionMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsCompound (substance)Transfection
The present invention discloses liposomal transfection reagents for delivery of macromolecules and other compounds into cells, particularly non-adherent suspension cells. They are especially useful for the DNA-dependent transformation of cells. Methods for their preparation and use as intracellular delivery agents are also disclosed.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
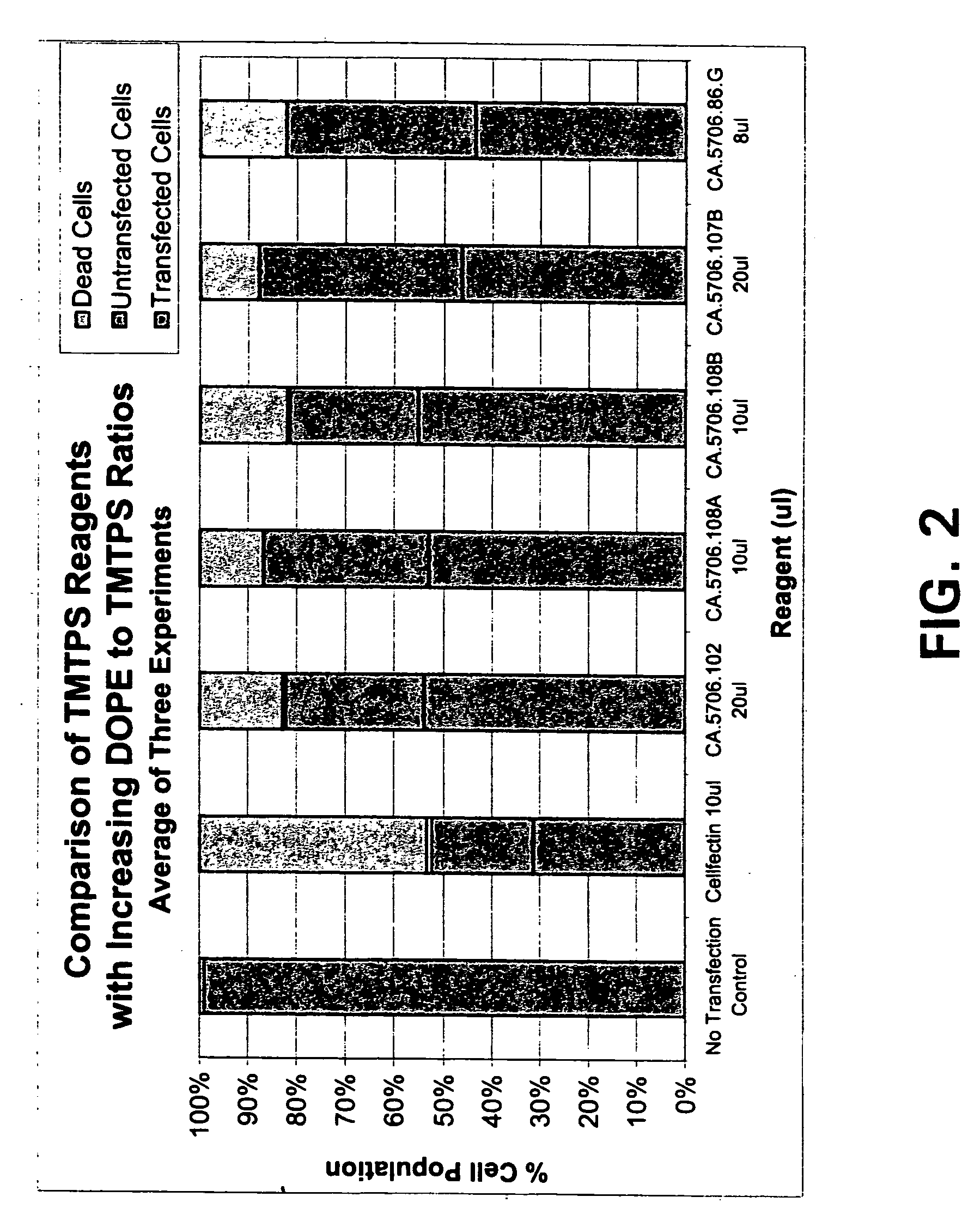
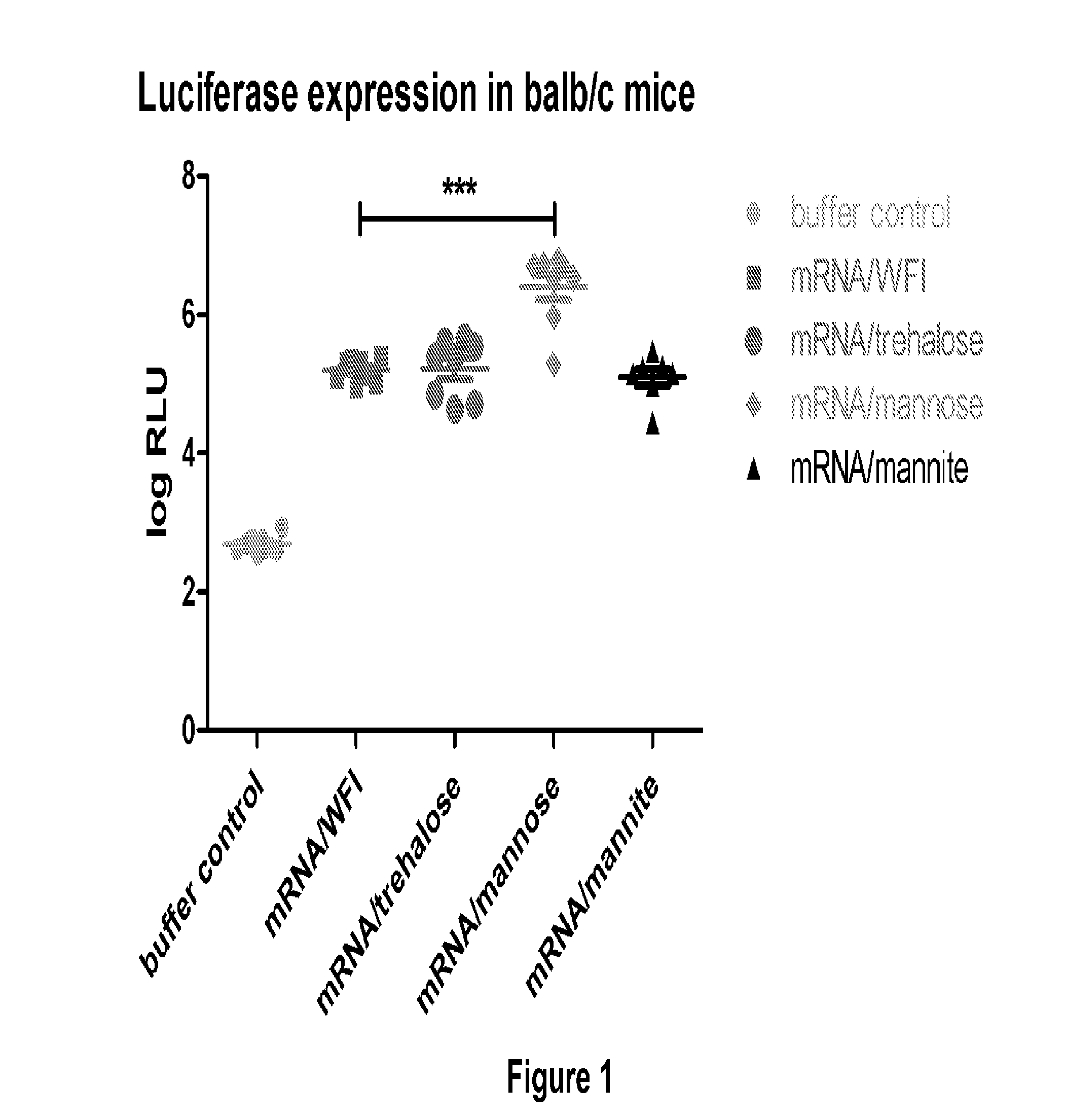
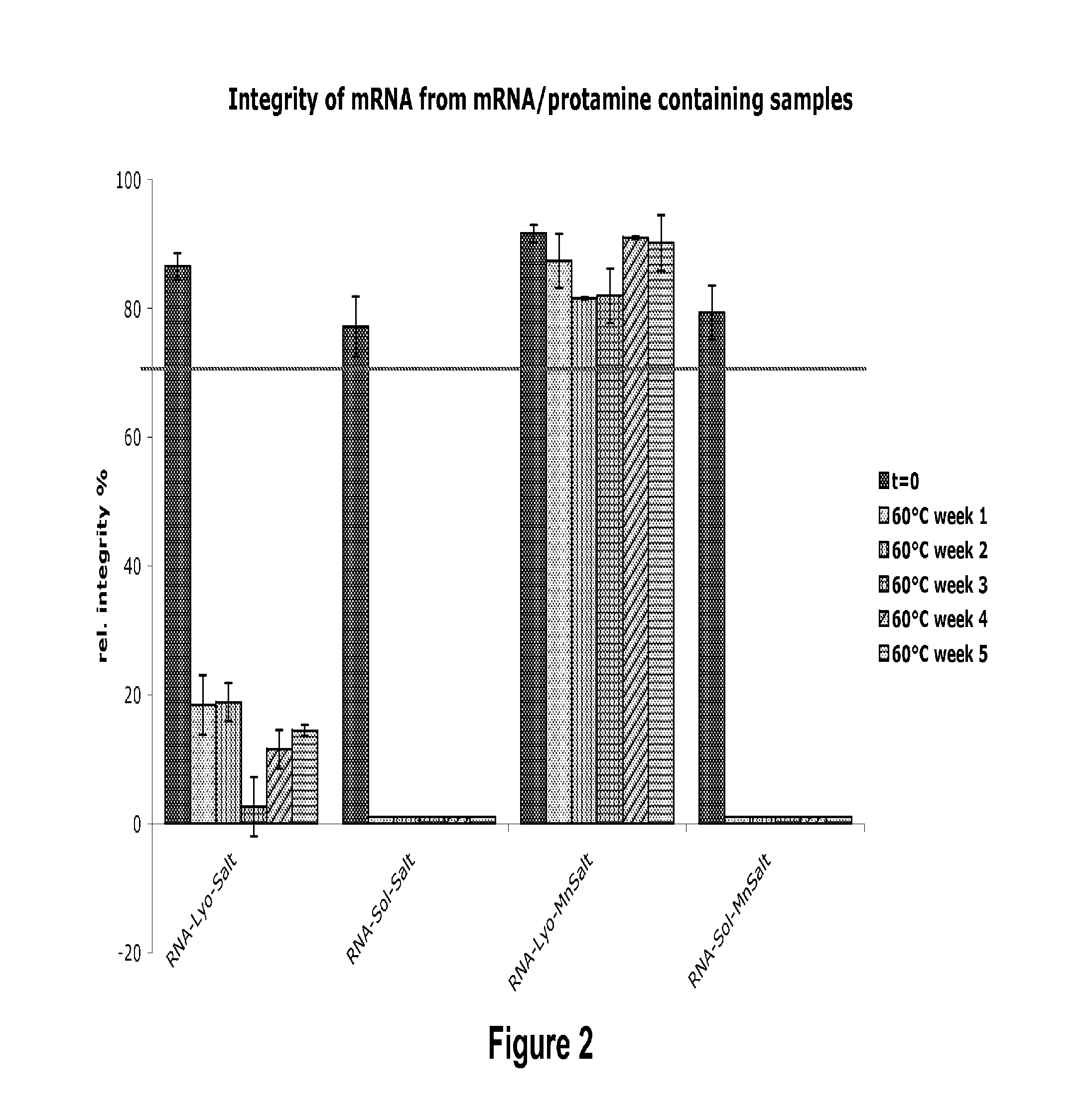
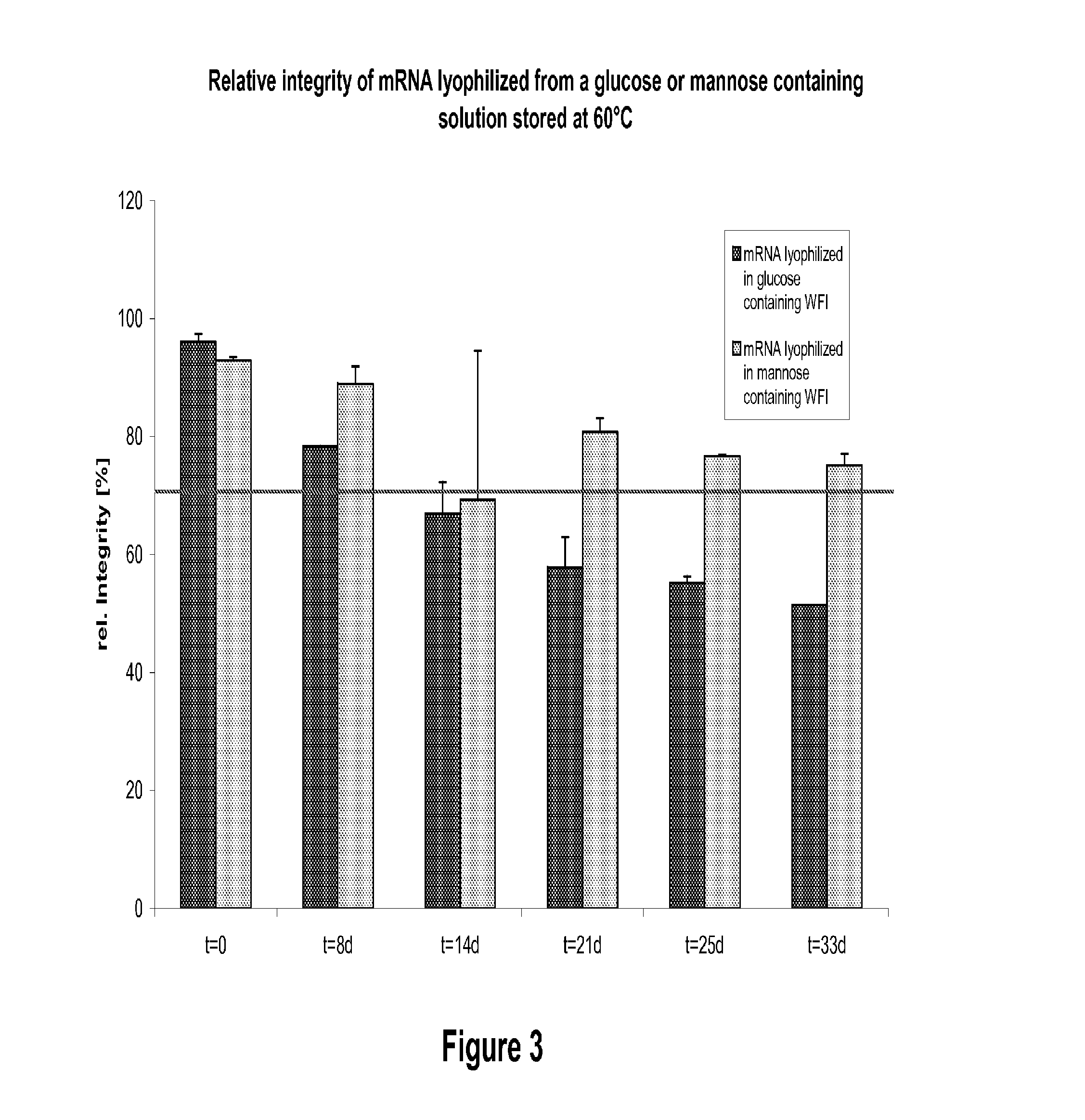
Mannose-containing solution for lyophilization, transfection and/or injection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20150141498A1Positive effect on stabilization of the nucleic acid (sequence)High transfection efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoTransfection
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Safe and efficient CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated protein 9) gene editing technology
InactiveCN108795902AImprove editing targetingImprove editing efficiencyHydrolasesDNA preparationA-DNASite-directed mutagenesis
The invention aims at the technical defects of off-target effects of an existing CRISPR / Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated protein 9) gene editing technology to carry out site-directed mutation of an amino acid site on a site combined with a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of Cas9 protein to obtain the Cas9 protein with low off-target efficiency,so as to realize a gene editing unction with higher targeting performance and higher efficiency. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a method for carrying out HEK293T cell gene editing by adopting a gene editing method.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHANGENE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Delivery systems comprising biocompatible and bioerodable membranes
InactiveUS20040120979A1Reduce deliveryHigh expressionGenetic material ingredientsNanomedicineDendrimerIn vivo
The present invention relates to novel compositions and methods for delivering substances to target tissues and cells by contacting the targets with delivery systems associated with membranes (e.g., biocompatible or bioerodable membranes). More particularly, the present invention is directed to dendrimer-based methods and compositions for use in disease therapies, wound healing, and generally, improved gene transfection and compound delivery to target cells and tissues in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:ROESSLER BLAKE J +2
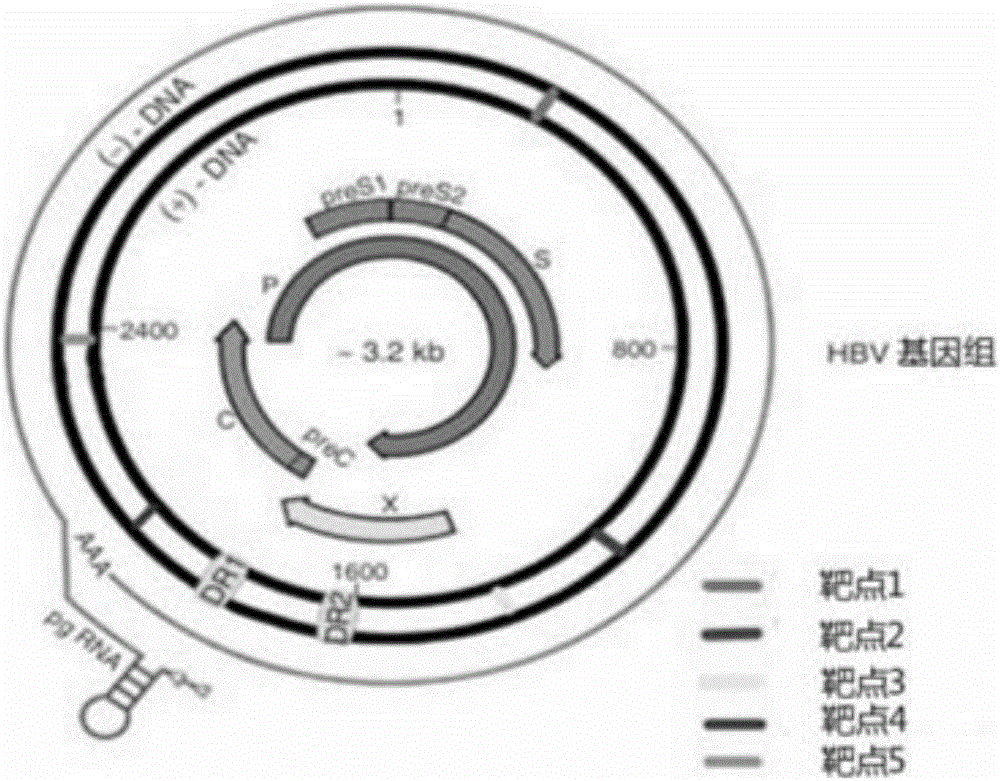
DNA, plasmid and preparation capable of directionally clearing HBV (Hepatitis B virus) ccc in hepatocyte
ActiveCN106754912AReduce inhibition of replicationInhibition of replicationMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsLipid formationAntigen
The invention belongs to the technical field of bio-macromolecular pharmaceutical preparations, and specifically relates to a DNA, a plasmid and a preparation capable of directionally clearing HBV (Hepatitis B virus) ccc in hepatocyte. According to the invention, five brand-new CRISPR / Cas systems are discovered through wide and in-depth studies, and can effectively clear HBV ccc DNA in cells, inhibit reproduction of HBVs, and reduce expression of proteins related to the HBVs. A pH-sensitive and PEG-modified cationic lipid carrier is further prepared, and has the advantages of good stability and high transfection efficiency; and internal instability of multiple cationic lipid carriers is overcome. The CRISPR / Cas systems are combined with the pH-sensitive and PEG-modified cationic lipid carrier to prepare a CRISPR / Cas9 cationic lipid carrier preparation which can effectively inhibit virus reproduction in a murine model suffering from acute HBV infection and reduce antigen expression level.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for applying functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and nanometer compound thereof in gene transfection
InactiveCN103435815AImprove transfection abilityGood gene transfection effectGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCompound sBiology
The invention relates to a method for applying a functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and a nanometer compound thereof in gene transfection. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and the nanometer compound thereof, surface functional modification and characterization; preparation of functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-nanometer compound / pDNA; and research on gene transfection efficiency of the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-nanometer compound / pDNA. The advantages of easy operation, simple transfection conditions, high transfection efficiency, strong specificity and the like are obtained in application of the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and the nanometer compound thereof in gene transfection, and the functionalized poly(amidoamine) dendrimer and the nanometer compound thereof have good application prospects in aspects like gene therapy of cancers.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Compositions of nucleic acids and cationic aminoglycosides and methods of using and preparing the same
InactiveUS20030096774A1Effectively tranfect complexesHigh transfection efficiencyAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryOrganic chemistryAntibiotic drug
Compositions that include nucleic acid and cationic aminoglycosides and methods for their use are provided. The subject compositions are characterized by having nucleic acid complexed with a cationic aminoglycoside, where the nucleic acid is condensed. In certain embodiments, the cationic aminoglycoside is a cationic aminoglycoside antibiotic. The composition may further include one or more of: functional groups such as targeting moieties, nuclear localization or targeting peptides, endosomolytic peptides and / or one or more lipids and / or polymers, where the lipids may be provided in a manner to encapsulate the nucleic acid. The present invention also provides methods of using and preparing the nucleic acid-aminoglycoside compositions.
Owner:ARADIGM
Bone-targeted delivery system for osteogenesis treatment based on small nucleic acid medicine, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102824647AAvoid degradationSilent efficiency is highGenetic material ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsLiposomeOsteoblast like cell
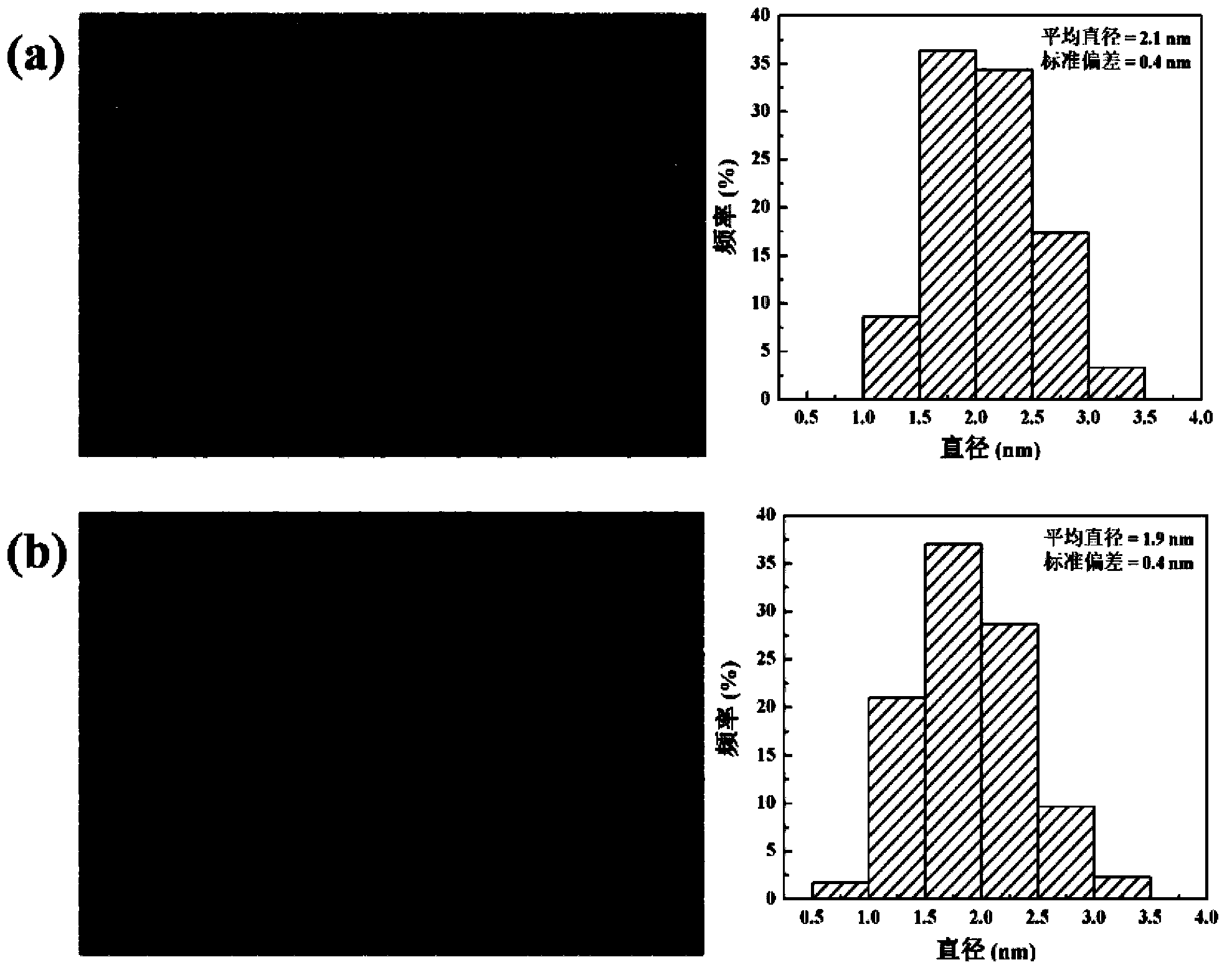
The invention provides a bone-targeted delivery system for osteogenesis treatment based on small nucleic acid medicine, and a preparation method thereof. The bone-targeted delivery system comprises liposome, bone-targeted molecules and small nucleic acid medicine, wherein the bone-targeted molecules are one or more selected from bisphosphonate, eight aspartic acid polypeptide repeat sequences, six aspartic acid-serine-serine polypeptide repetitive sequences and screened out aptamer aiming at osteoblastlike cells; and the small nucleic acid medicine is one or more selected from blocking agents of small interfering ribonucleic acid, micro ribonucleic acid mimics and micro ribonucleic acid which have the function of promoting bone formation. Compared with conventional bone-targeted delivery systems, the bone-targeted delivery system has stronger specificity and high transfection efficiency for the small nucleic acid, and can reach relatively high silencing efficiency.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
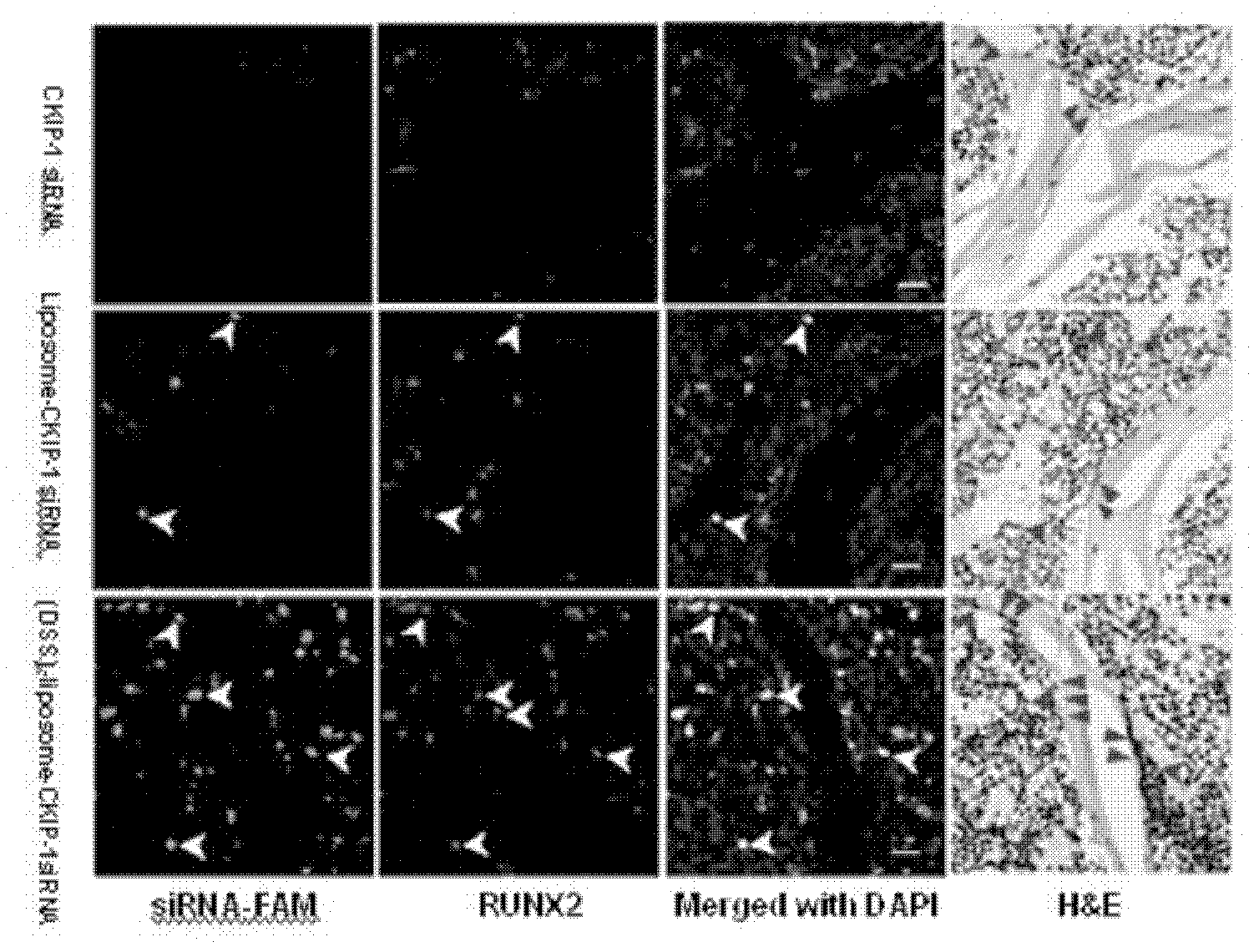
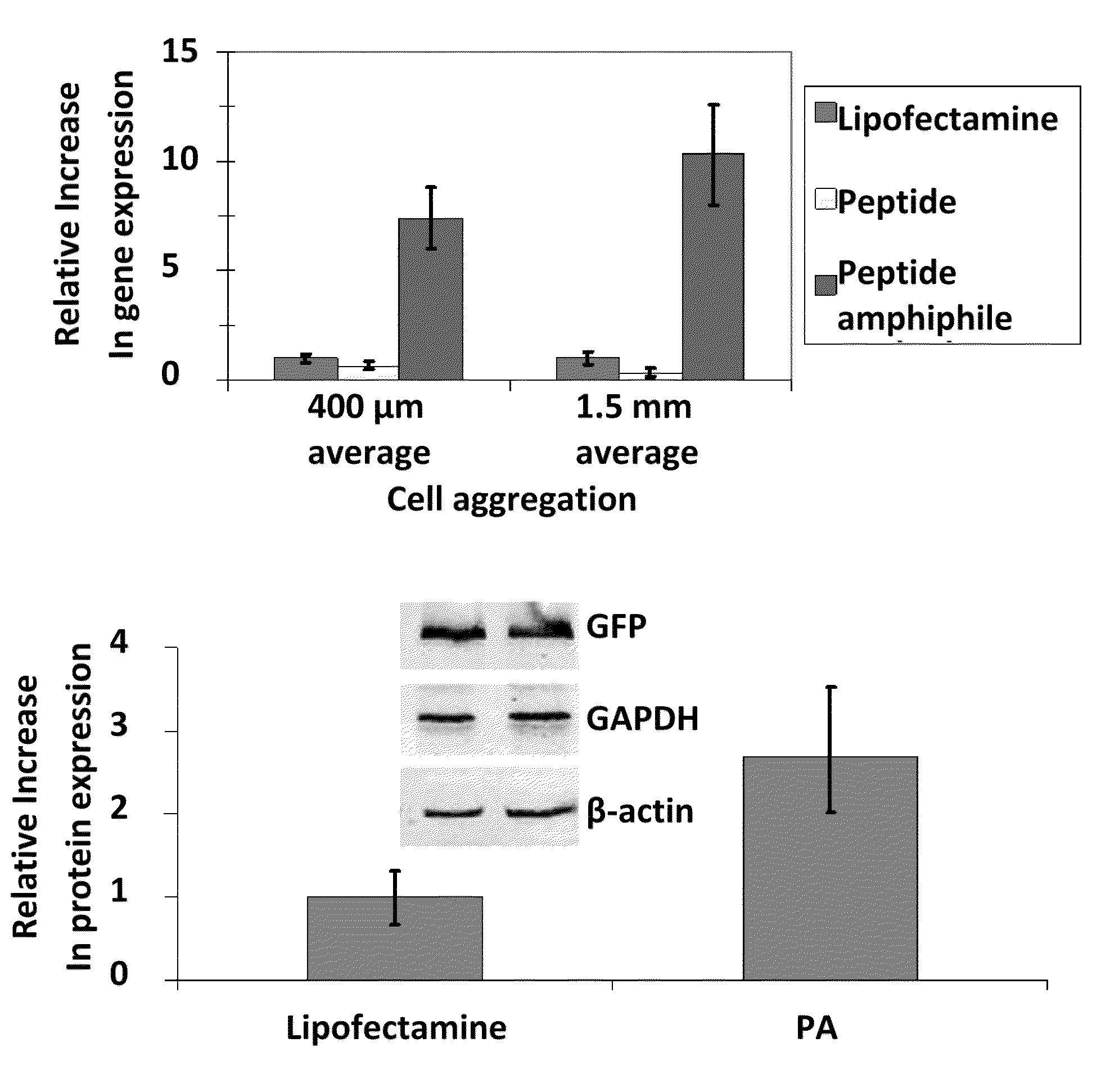
Self assembling peptide systems and methods
InactiveUS20090098652A1Improve transfection efficiencyHigh efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide-nucleic acidsBiophysicsBiological activity
The present invention provides a self-assembling peptide system which utilizes a bioactive sequence which enhances transfection efficiency. In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods for transfecting aggregates of cells at a higher efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com