Patents
Literature
41 results about "Start site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Here's how to start a Web based business: Choose a domain name for your site. Set up a merchant account with your bank, and make the necessary provisions to receive payments from various credit cards. Design your Web site, keeping your target audience in mind. Choose a company with a Web hosting package.
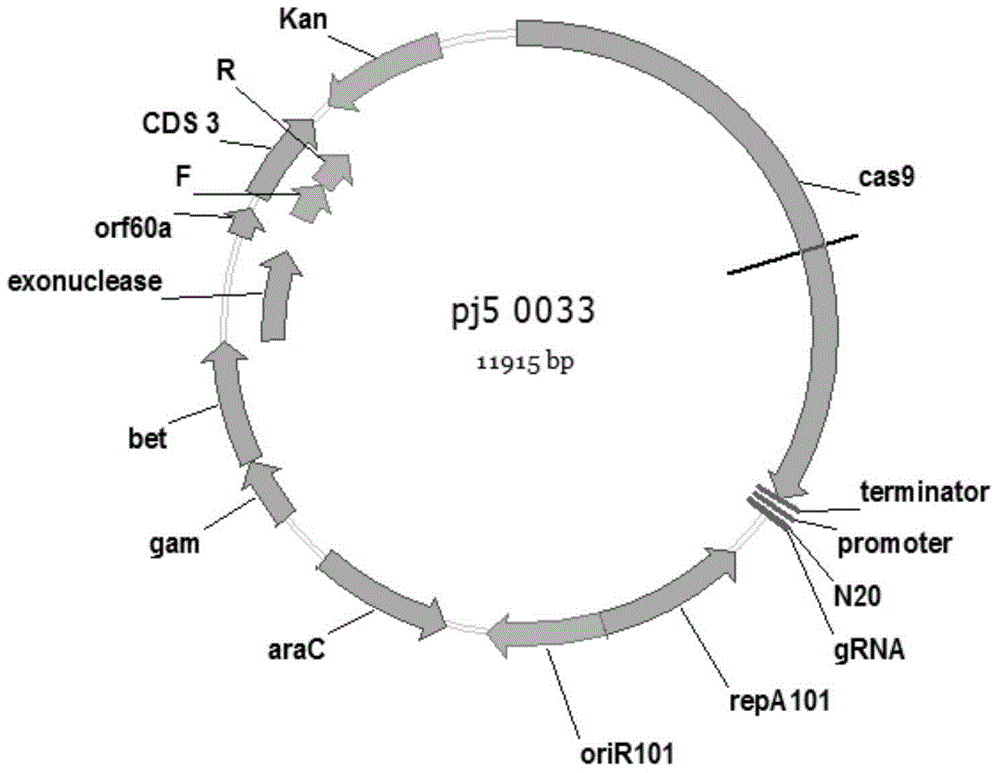
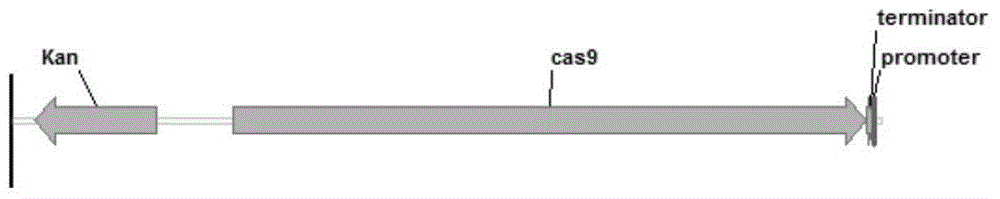
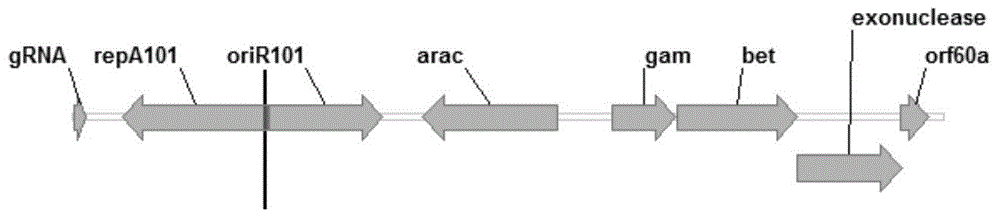
Construction and application of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing vector for microorganisms
ActiveCN105238806AQuick editShort test cycleVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses construction and application of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vector for microorganisms. The constructed CRISPR / Cas9 gene vector consists of a replication start site, a selection marker gene, a Cas9 protein gene, gRNA coding DNA, a homologous recombinant element and an operon. The CRISPR / Cas9 gene vector constructed by the invention is capable of editing (including performing such operations as knocking out, replacing, interpolating and the like on gene or DNA sequence) escherichia coli or corynebacterium glutamicum genome; and the gene vector has the advantages of being short in test cycle, time-saving and cost-saving, high in efficiency and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for identification and quantification of nucleic acid expression, splice variant, translocation, copy number, or methylation changes
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for manipulating translation of protein isoforms from alternative initiation of start sites
InactiveUS20140296321A1High sensitivityImprove translationSugar derivativesPolymorphism usesStart codonStart site
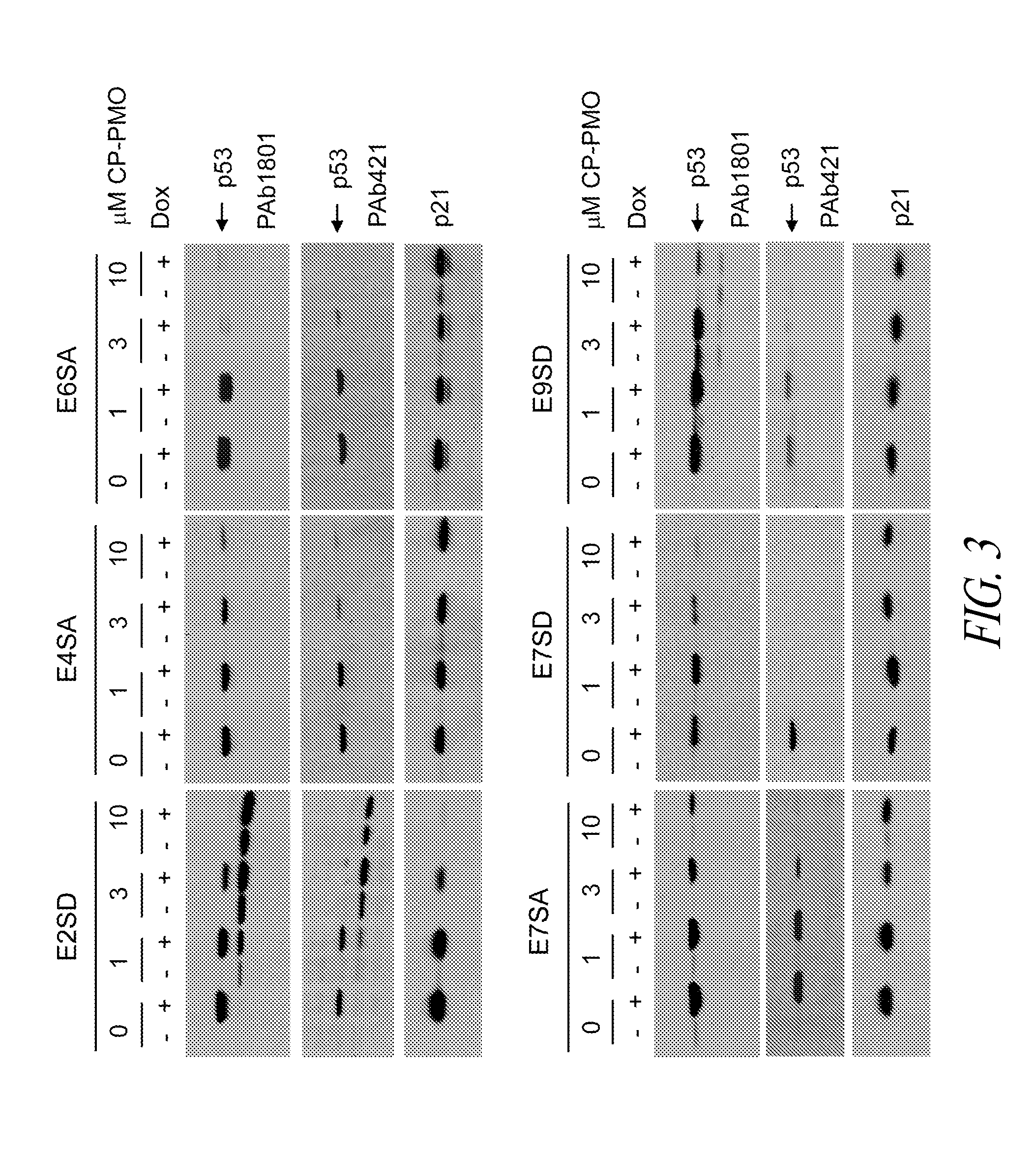
Provided herein are antisense oligonucleotides, compositions comprising antisense oligonucleotides, and methods for the use of antisense oligonucleotides in manipulating translation. Expression of isoforms of proteins expressed from different start codons of the same transcript are inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which may also enhance expression of non-target isoforms.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
MSMB-gene based diagnosis, staging and prognosis of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20090203010A1Loss of gene functionHigh degreeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAndrogen sensitivityRegulatory region
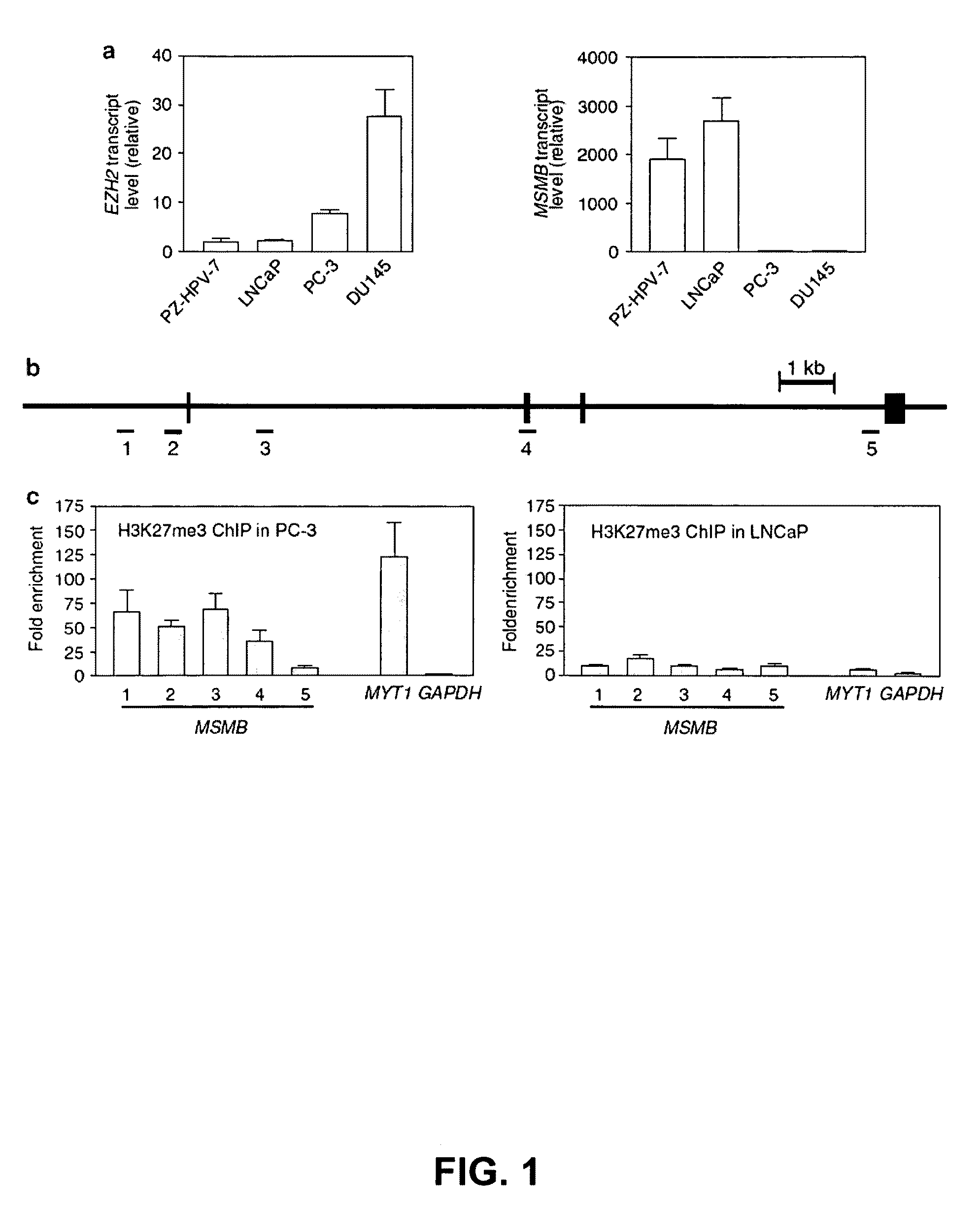
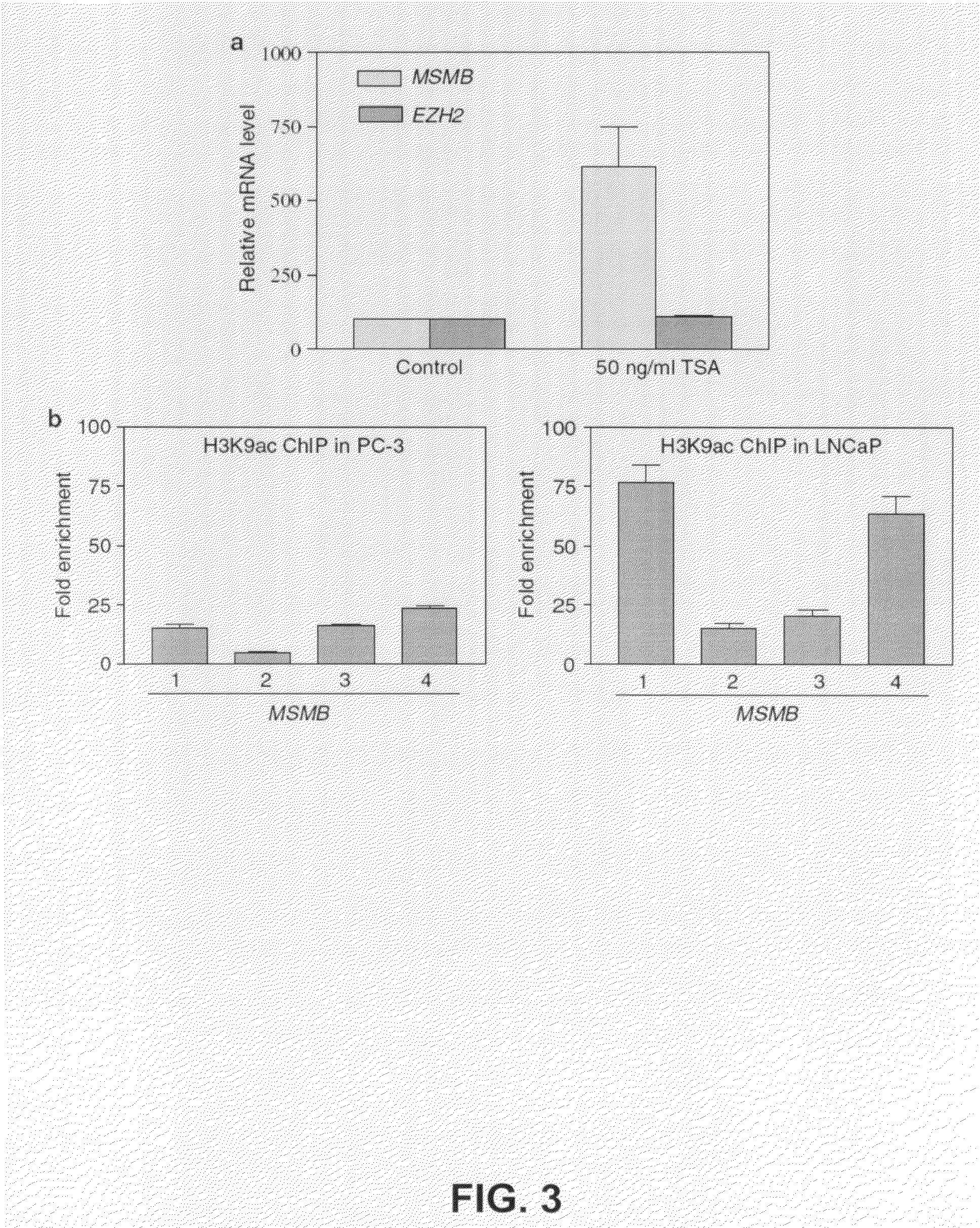
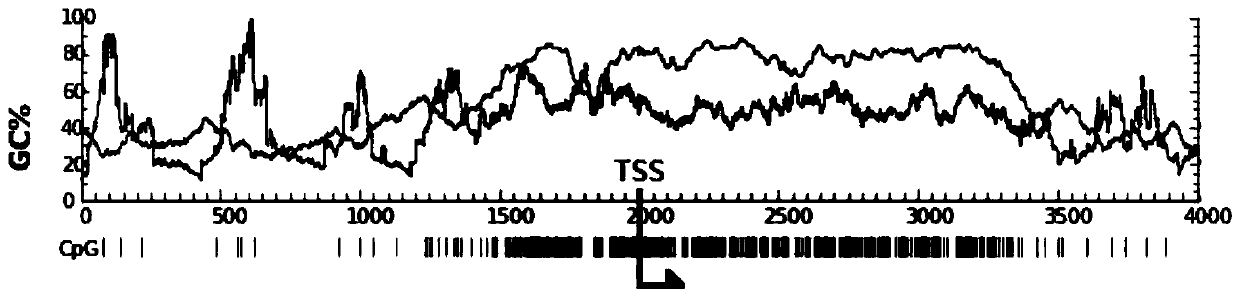
This invention relates generally to a method of diagnosis for distinguishing between a benign prostate hyperplasia and a prostate cancer and between a hormone-sensitive and a hormone-refractory prostate cancer condition and specifically to identification of a hypermethylated (on CpG and non-CpG dinucleotides) CpG island in the beta-microseminoprotein (MSMB) regulatory regions surrounding the transcriptional start site of the MSMB gene as a diagnostic indicator of prostate cancer (PrCa) and for distinguishing androgen-refractory from androgen-sensitive prostate cancer.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Antisense antiviral compounds and methods for treating a filovirus infection
Owner:UNITED STATES ARMY U S ARMY MEDICAL RES & MATERIAL COMMAND +2
Antisense antiviral compounds and methods for treating a filovirus infection
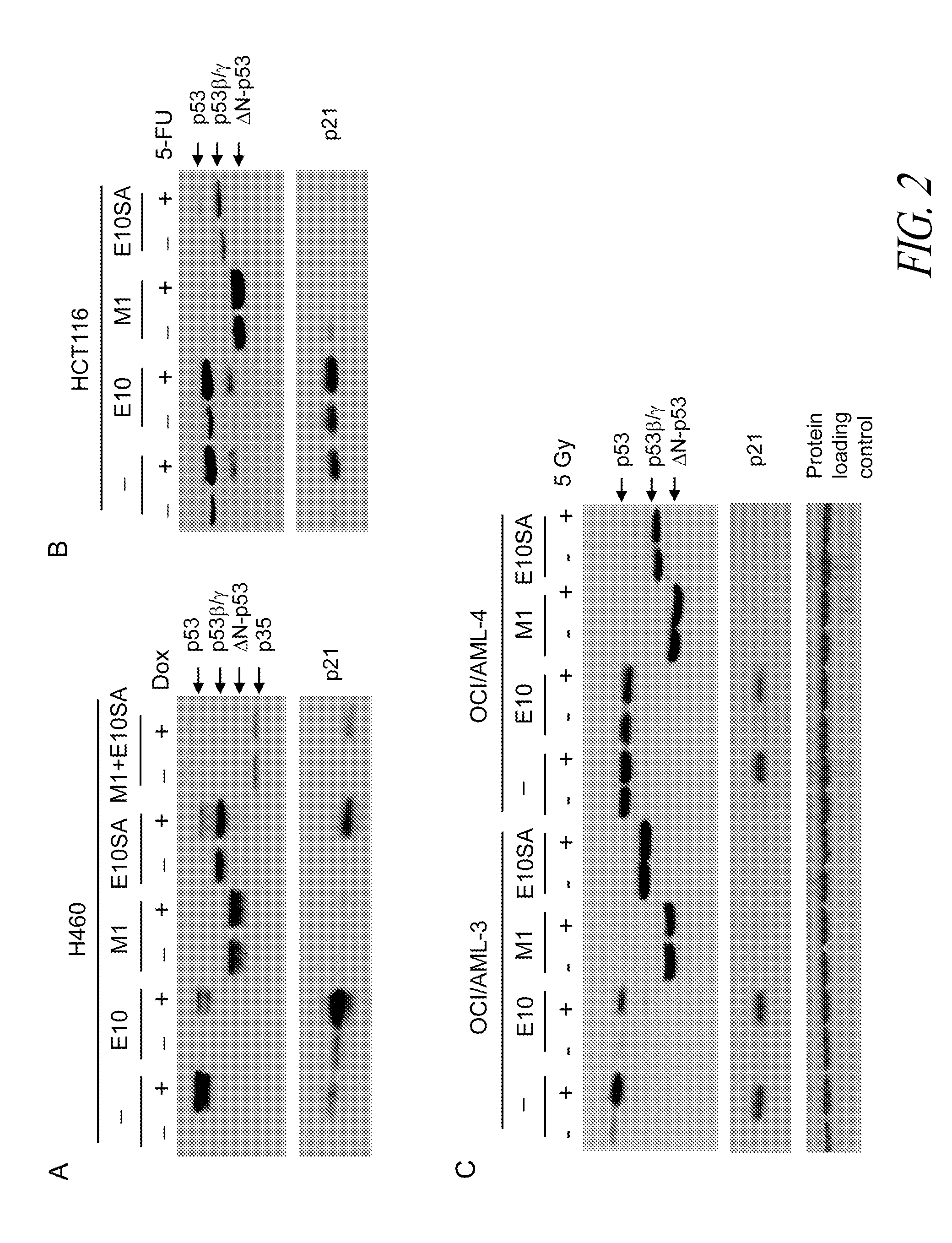
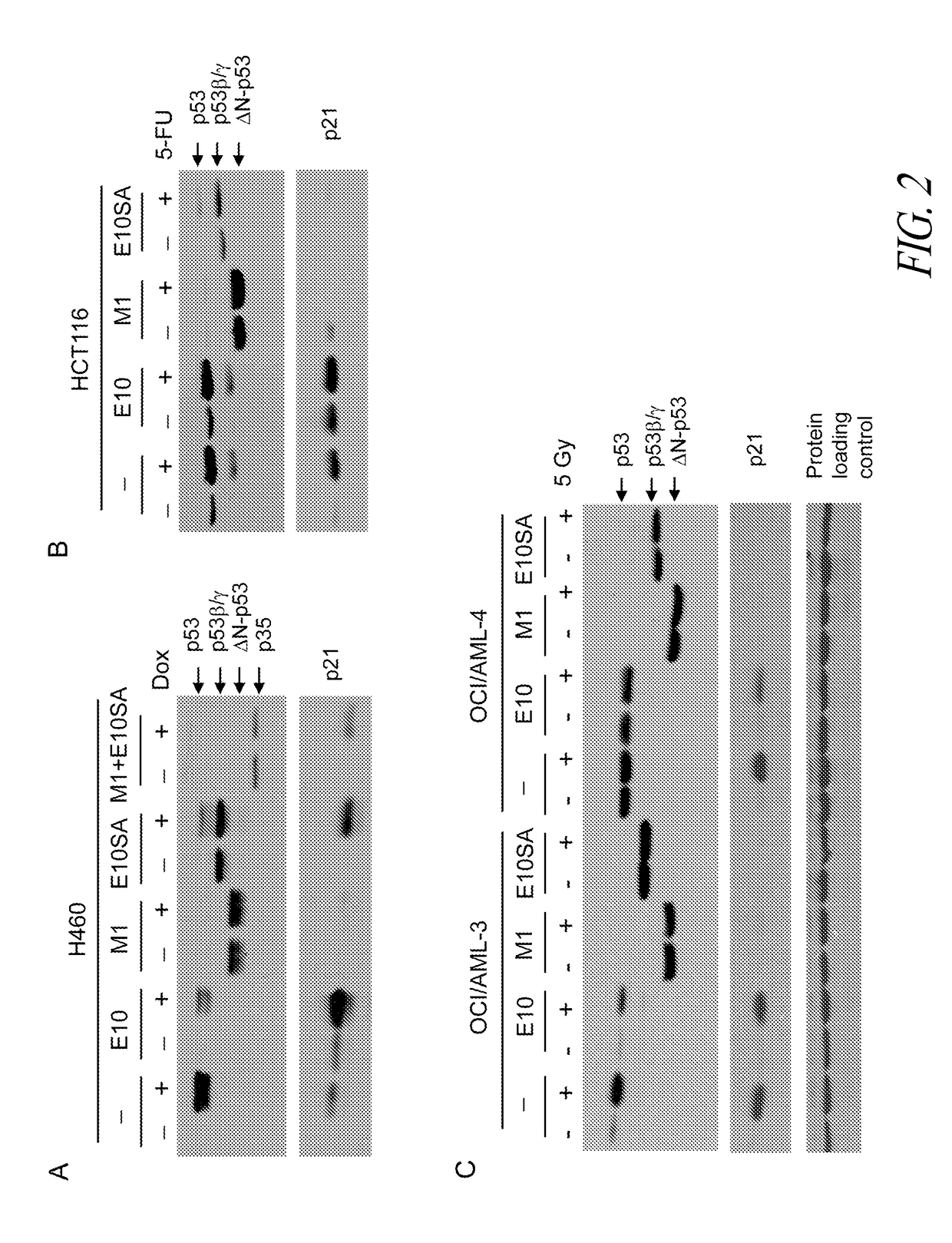
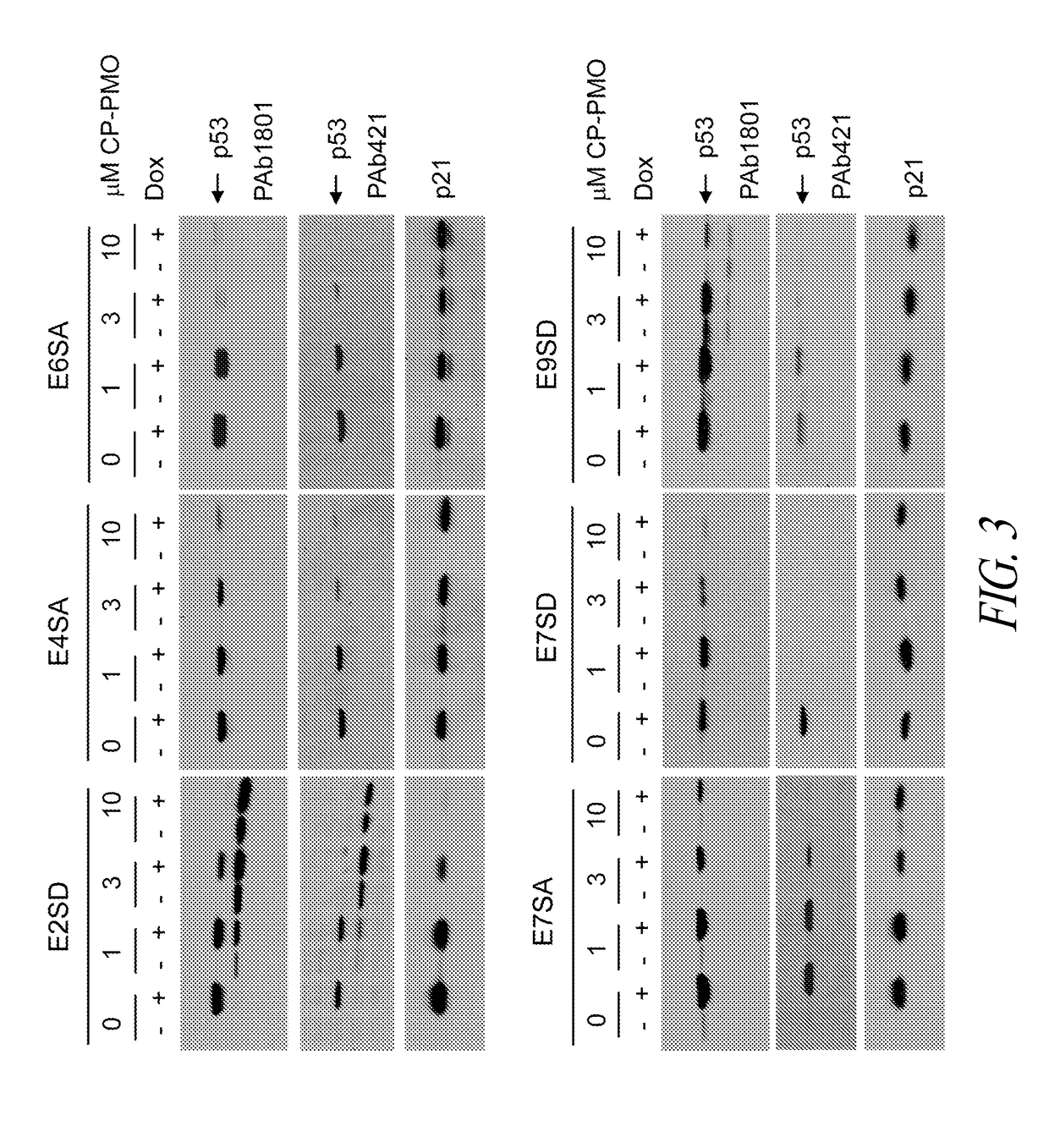
The present invention provides antisense antiviral compounds, compositions, and methods of their use and production, mainly for inhibiting the replication of viruses of the Filoviridae family, including Ebola and Marburg viruses. The compounds, compositions, and methods also relate to the treatment of viral infections in mammals including primates by Ebola and Marburg viruses. The antisense antiviral compounds include phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligonucleotides (PMOplus) having a nuclease resistant backbone, about 15-40 nucleotide bases, at least two but typically no more than half piperazine-containing intersubunit linkages, and a targeting sequence that is targeted against the AUG start site region of Ebola virus VP35, Ebola virus VP24, Marburg virus VP24, or Marburg virus NP, including combinations and mixtures thereof.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
System for matching carpool users, and method thereof
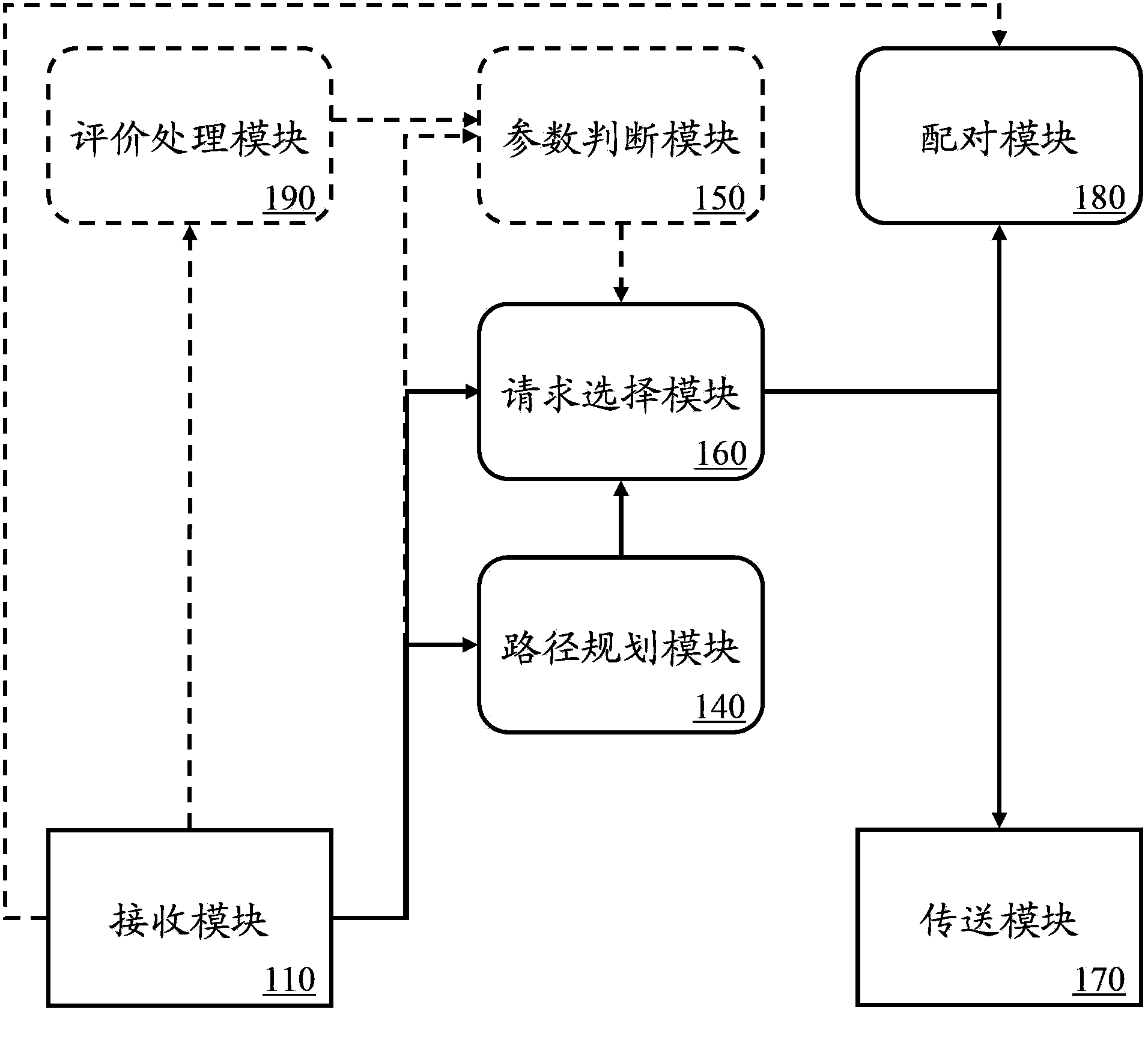
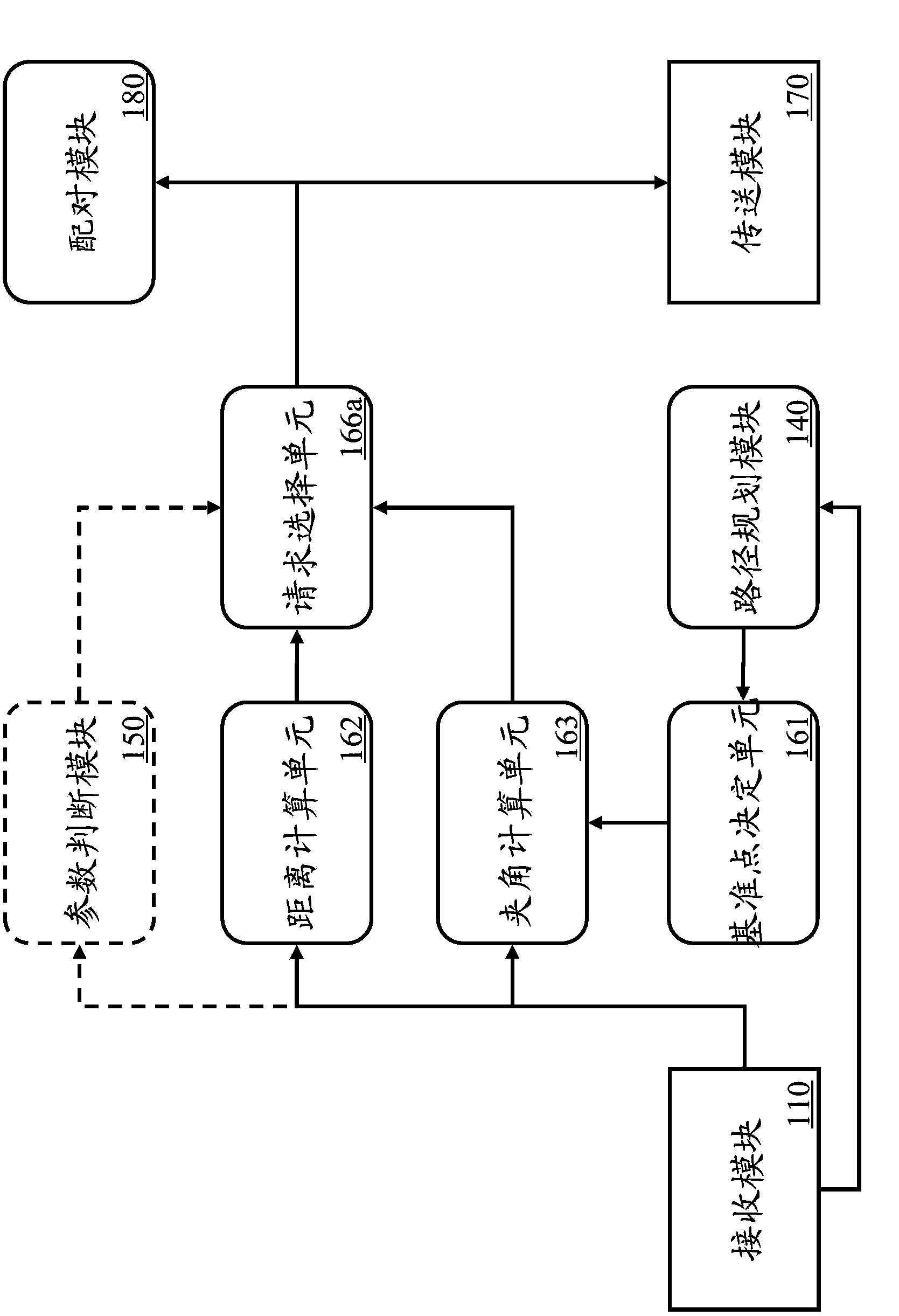
InactiveCN103426139AAchieve the technical effect of ride sharingData processing applicationsStart siteOverlap ratio
The invention provides a system for matching carpool users, and a method thereof. The method comprises the steps of receiving a first carpool request containing start site information and destination site information; receiving a second carpool request containing carpool information and get off sit information; calculating a start distance between the start site and the carpool site according to the start site information, each carpool information, the target site information and each get off site information; calculating a terminal site included angle formed from a reference site to the target site and from the reference site to the get off site; and / or calculating an overlapping ratio of driving routes from the start site to the target site and from the carpool site to the get off site, so as to match technical means of the first carpool request and the second carpool request, so that carpool matching service can be provided and technical functions suitable for matching the carpool users can be achieved.
Owner:张凯杰
Antisense antiviral compounds and methods for treating a filovirus infection
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Filoviridae family, and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds and methods relate to the treatment of viral infections in mammals including primates by Ebola and Marburg viruses. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged morpholino oligonucleotides having: a) a nuclease resistant backbone, b) 15-40 nucleotide bases, and c) a targeting sequence of at least 15 bases in length that hybridizes to a target region selected from the following: i) the AUG start site region of VP35, as exemplified by antisense compounds SEQ ID NO:21-26, ii) the AUG start site region of VP24, as exemplified by antisense compound SEQ ID NO:34, iii) the region 85 to 65 base pairs upstream of the AUG start site of VP24, as exemplified by SEQ ID NO:39, iv) the AUG start site region of polymerase L, as exemplified by antisense compound SEQ ID NO: 17, and v) combinations of (i), (ii), (iii), and / or (iv).
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
PCR primer capable of reducing non-specific amplification and PCR method using the PCR primer
ActiveUS20090258353A1Low costStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceTriplex PCR
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Methods for Obtaining Gene Tags
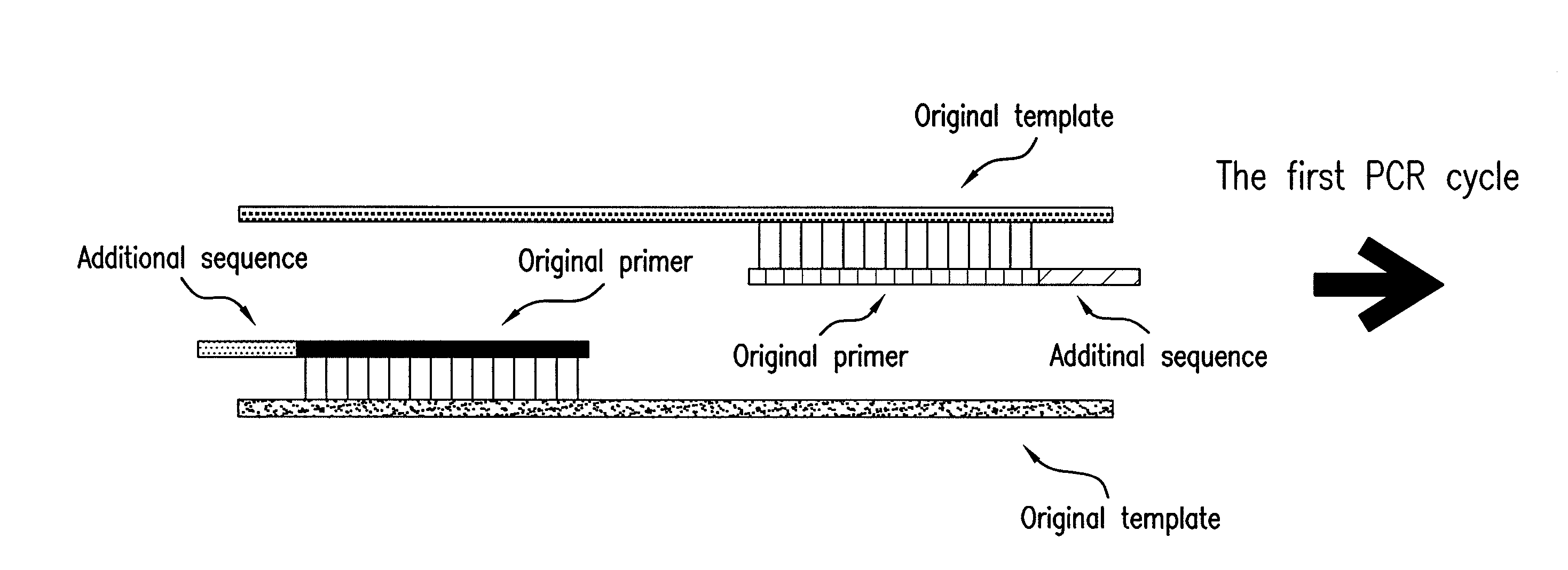
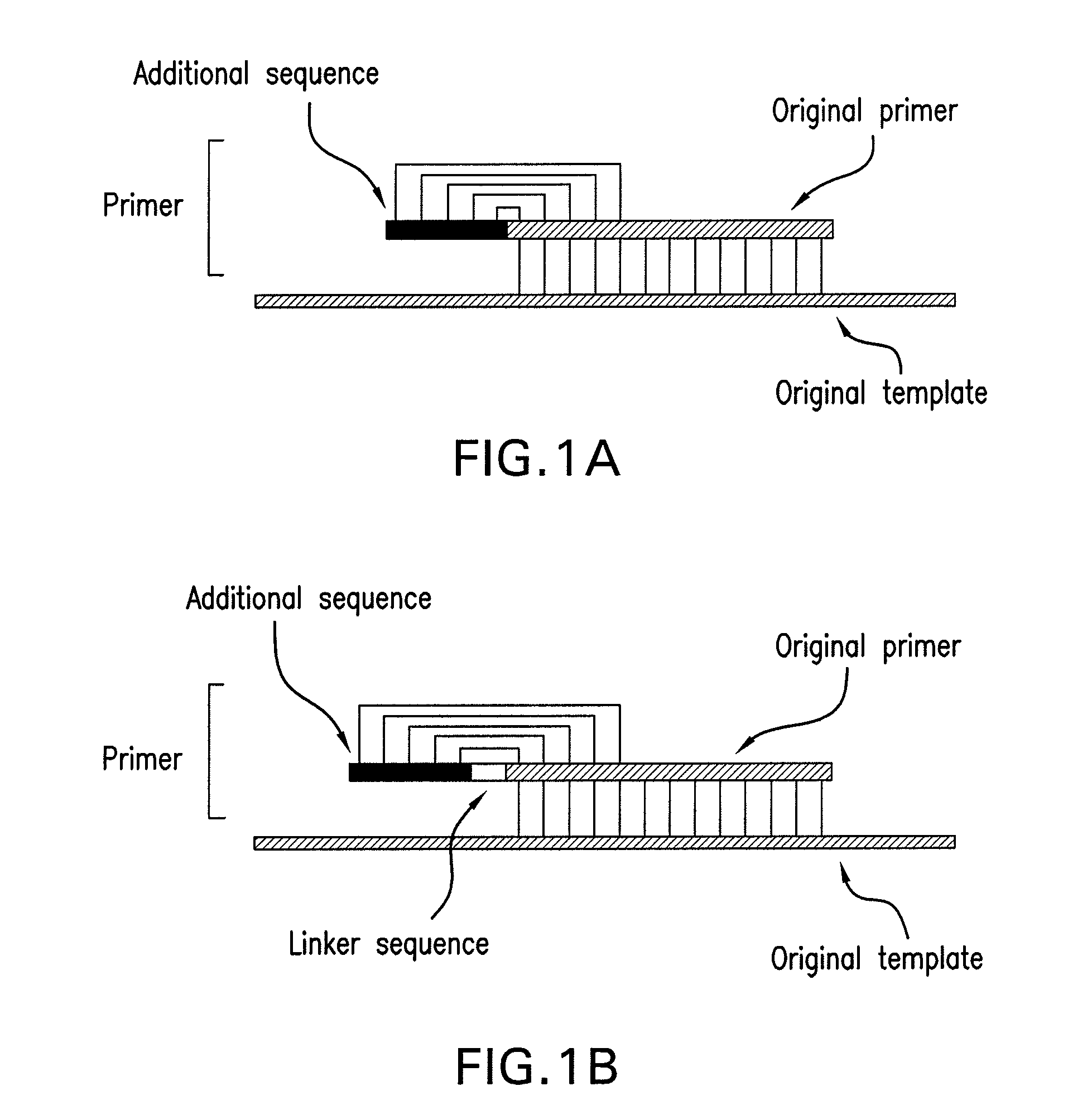
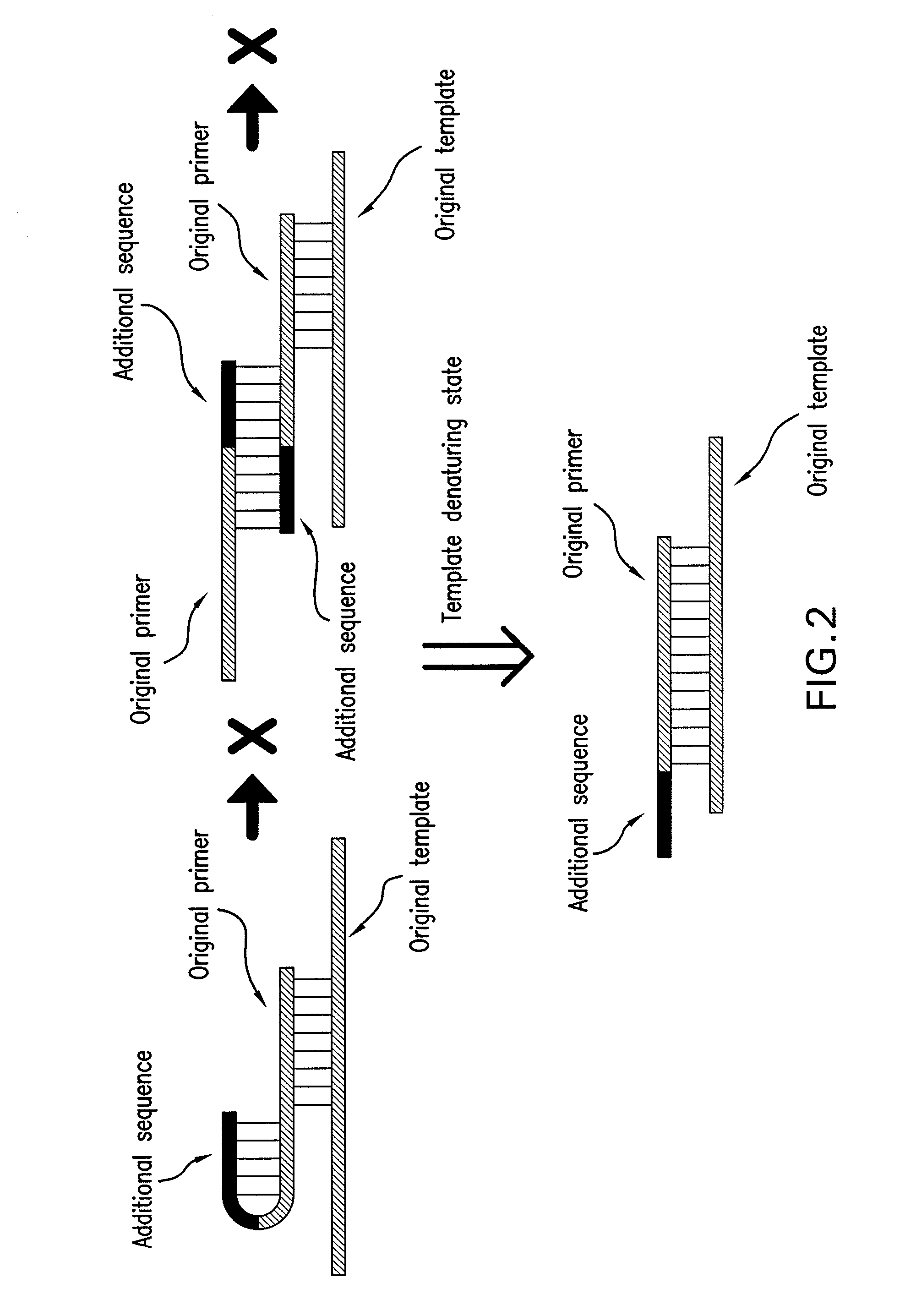
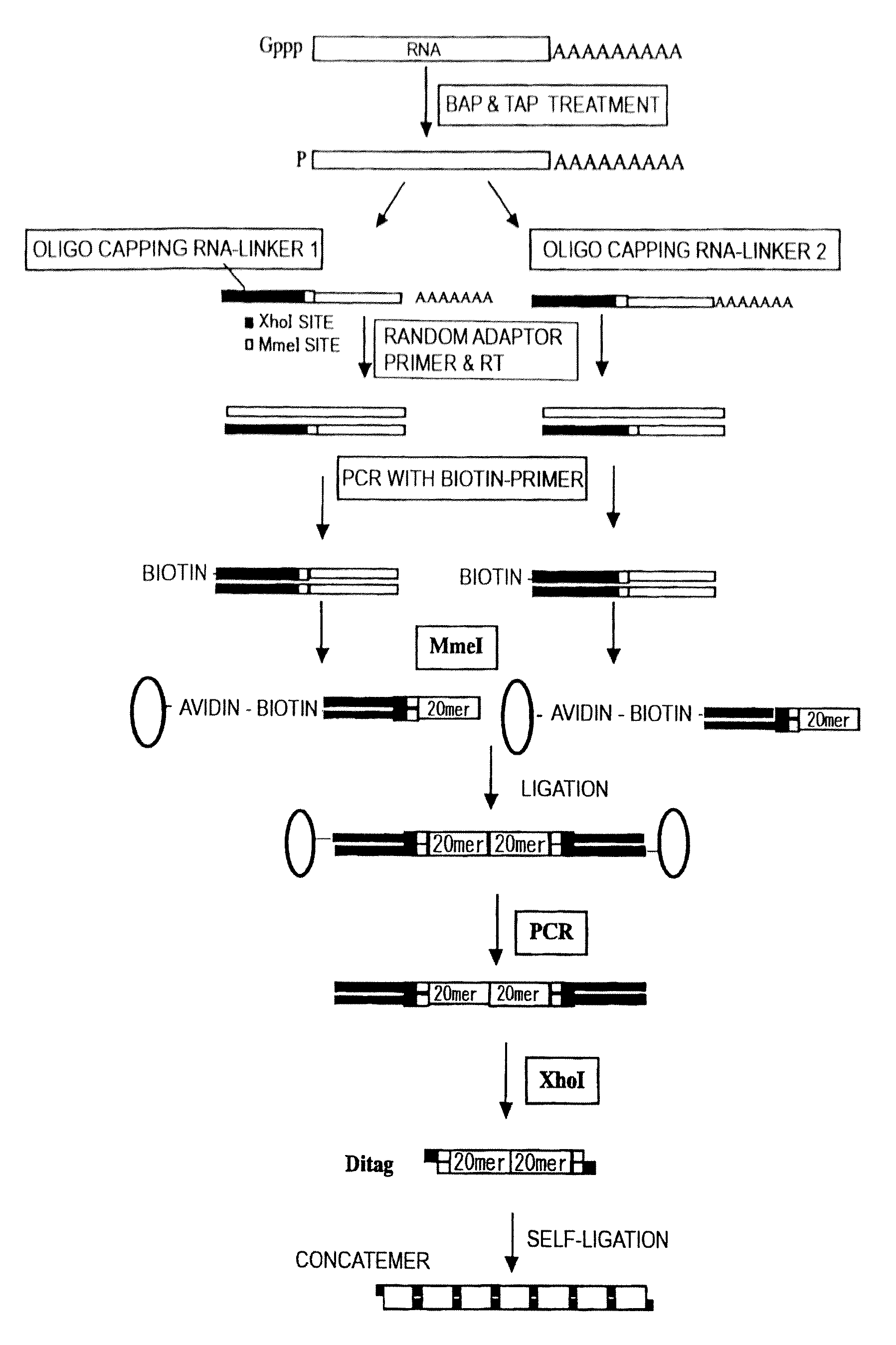
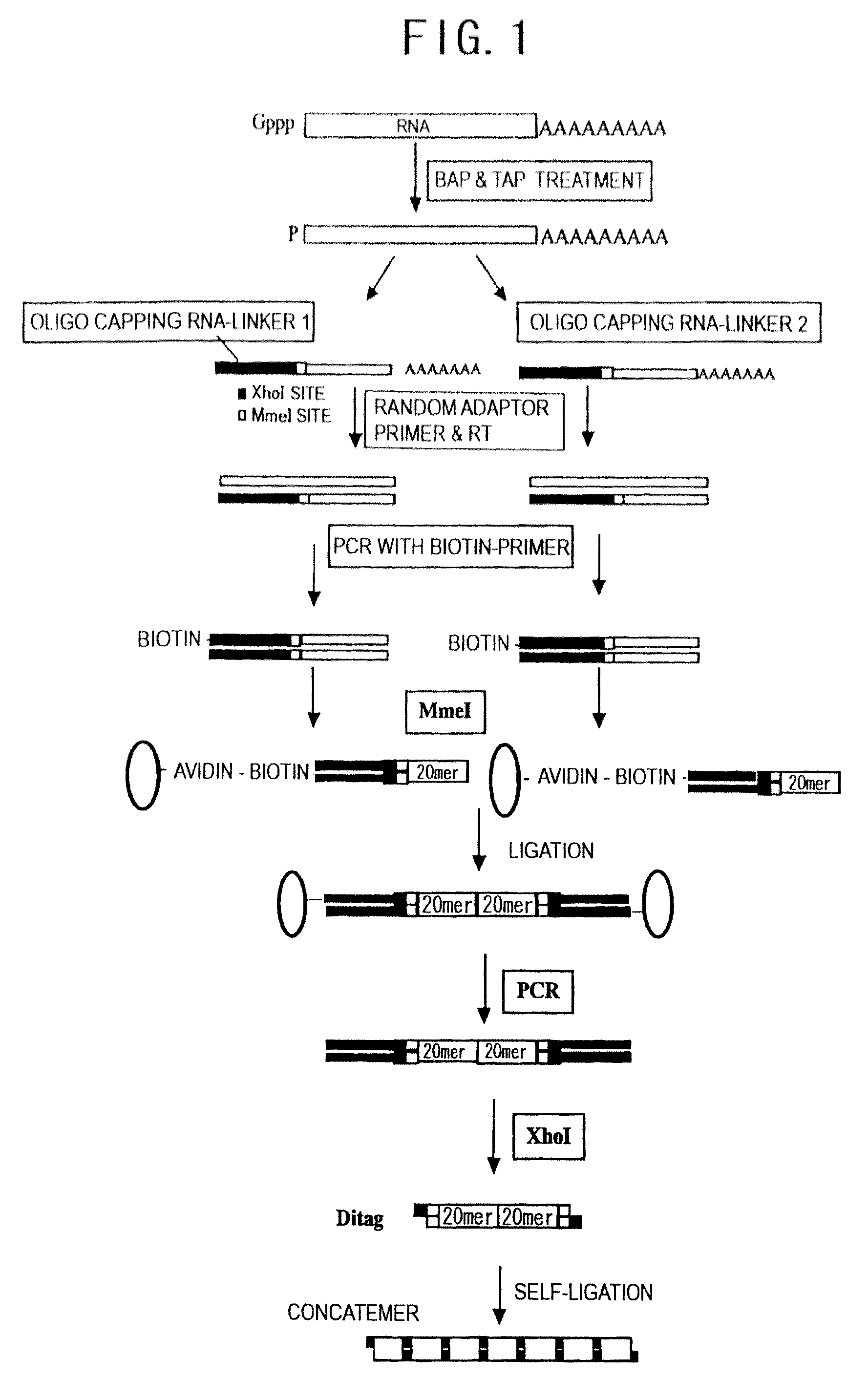
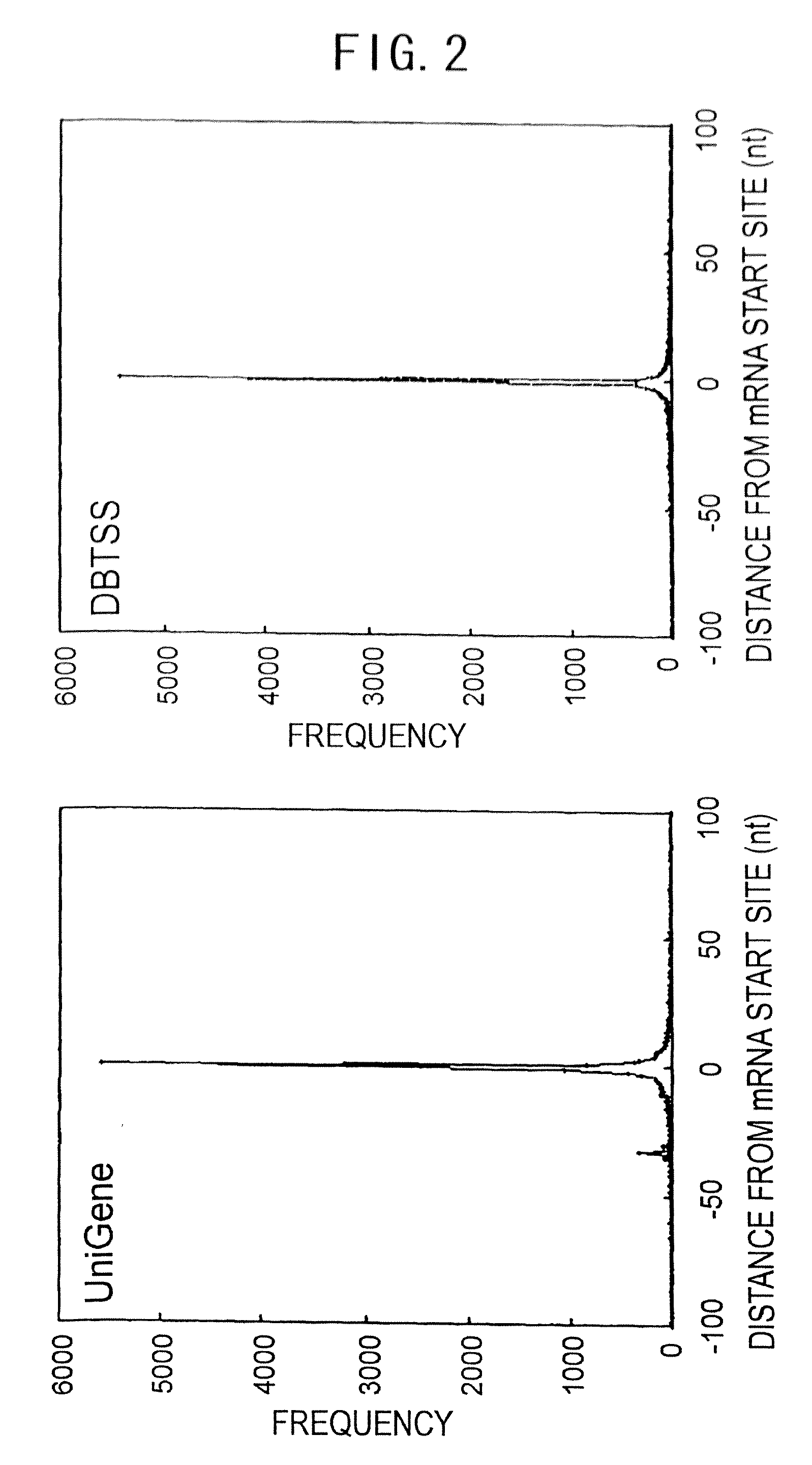
The present invention provides methods for providing as tags the nucleotide sequences at the 5′ end of mRNA. The method of the present invention comprises the step of synthesizing cDNA using, as a template, mRNA whose CAP structure is linked with a IIs linker having a type IIs endonuclease recognition sequence. Tags including the nucleotide sequence from the 5′ end of mRNA are generated by reacting the type IIs endonuclease to cDNA. Tags can be generated from all mRNA, independently of their nucleotide sequences. Methods for identifying transcriptional start sites and primers for full-length cDNA synthesis are provided based on the nucleotide sequence information of tags of the present invention.
Owner:POST GENOME INST CO LTD
Method for constructing mRNA 5'-termnal information library
ActiveCN105734052APromote enrichmentShorten the lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomicsStart site
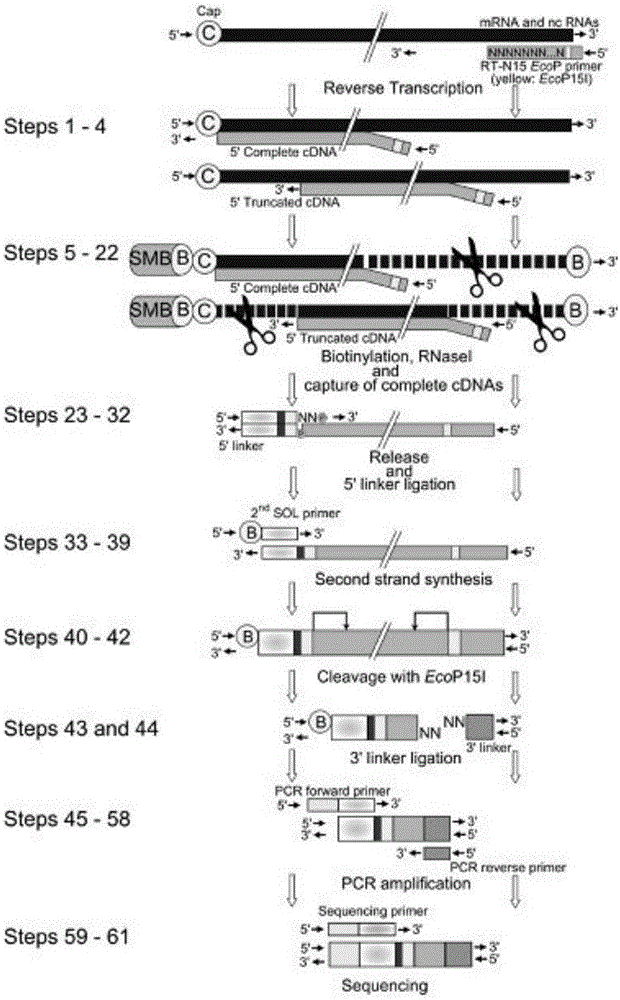
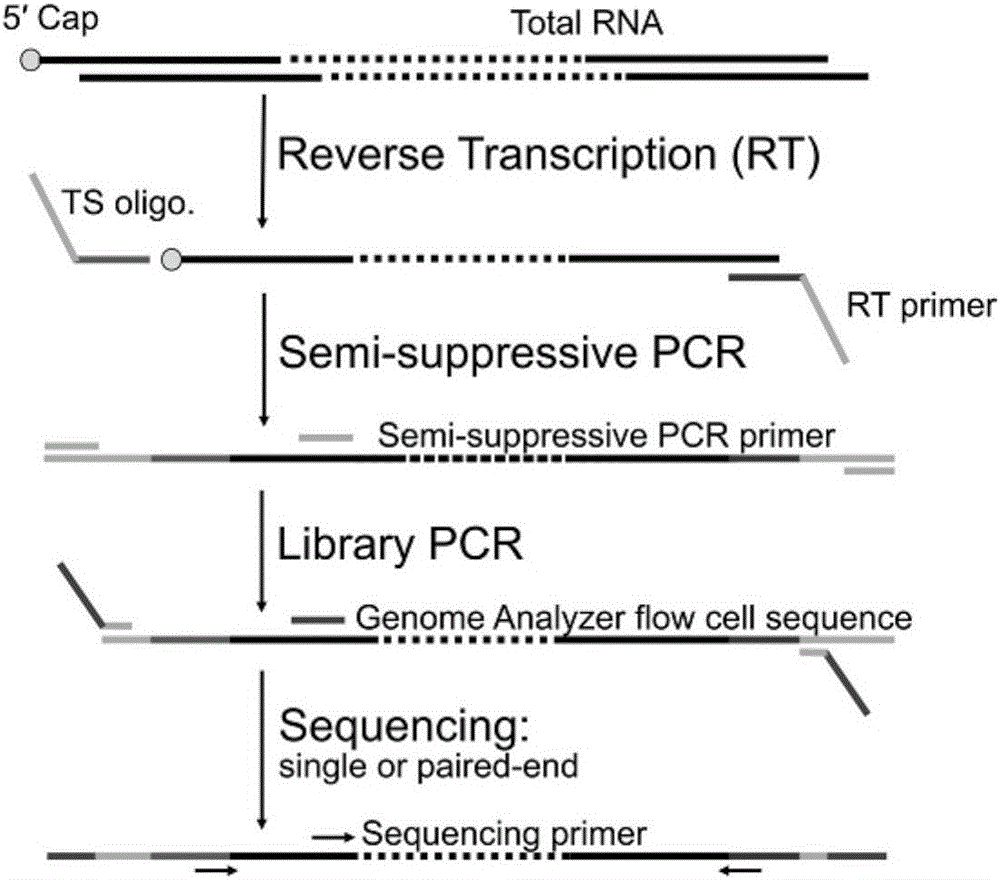
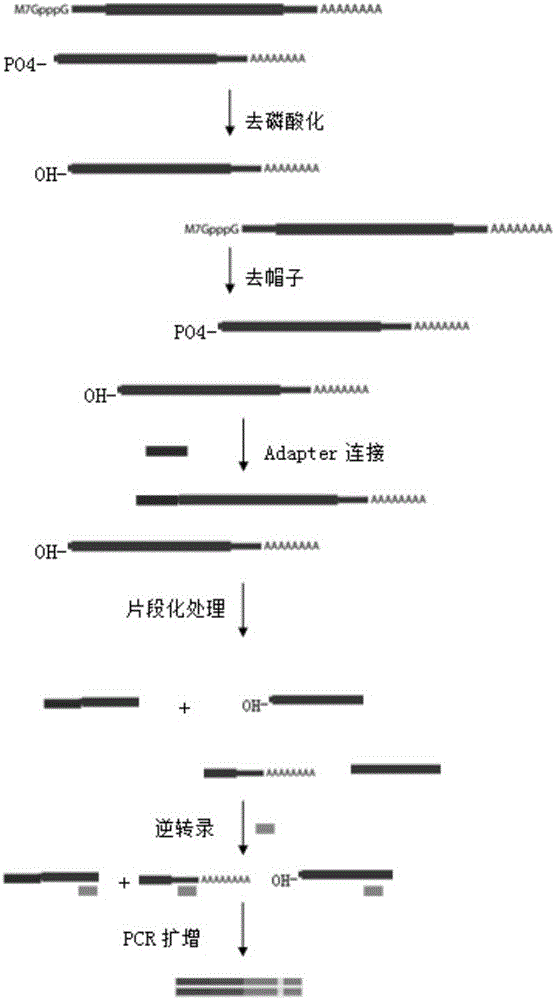
The invention belongs to the technical field of genomics, and particularly relate to a method for simplifying CAGE-seq library establishing.The method comprises the steps that mRNA and lncRNA containing cap structures are enriched, a 5'-termnal connector is specifically added, after fragmentation processing, reverse transcription is carried out, and 5'-terminal information is further enriched.According to the whole method, an existing mature RNA-seq kit of the gnomegen company is mixed.The method is easier to operate and high in success rate, the 5'-terminal information can be specifically enriched, the method is more helpful for verifying the transcriptional start site of mRNA in a whole cell, and thus acquiring accurate promoter information and 5'UTR information.The method is a powerful mode for studying gene expressions and is suitable for gene regulatory network studies.
Owner:武汉生命之美科技有限公司
saRNA molecules of TPO genes and application of saRNA molecules
ActiveCN106480028APromote biological efficacyRadioactive preparation carriersAntineoplastic agentsStart siteGene technology
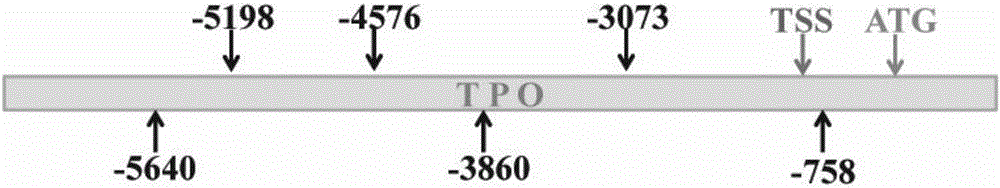
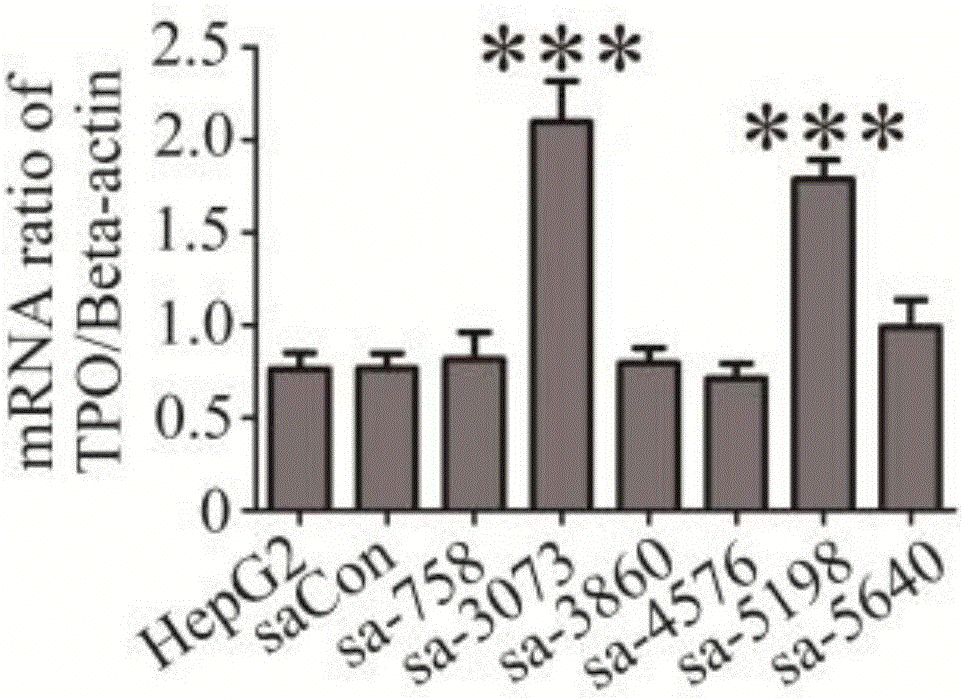
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology medicine. saRNA molecules of TPO genes are synthesized, the sequence of the saRNA molecules and the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 of the upstream 6,000bp and downstream 1,000bp areas of a TPO gene transcriptional start site are complementary, and low-expression or non-expression TPO genes in tumor cells can be effectively activated. A biological effect of promoting the tumor cells to hold radionuclide 131I is achieved, a novel method and novel molecular targets are provided for combining the gene technology with the radionuclide therapy for targeted therapy of tumors.
Owner:SHANGHAI SEVENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method and equipment for replaying of binary-system log of relation-type database
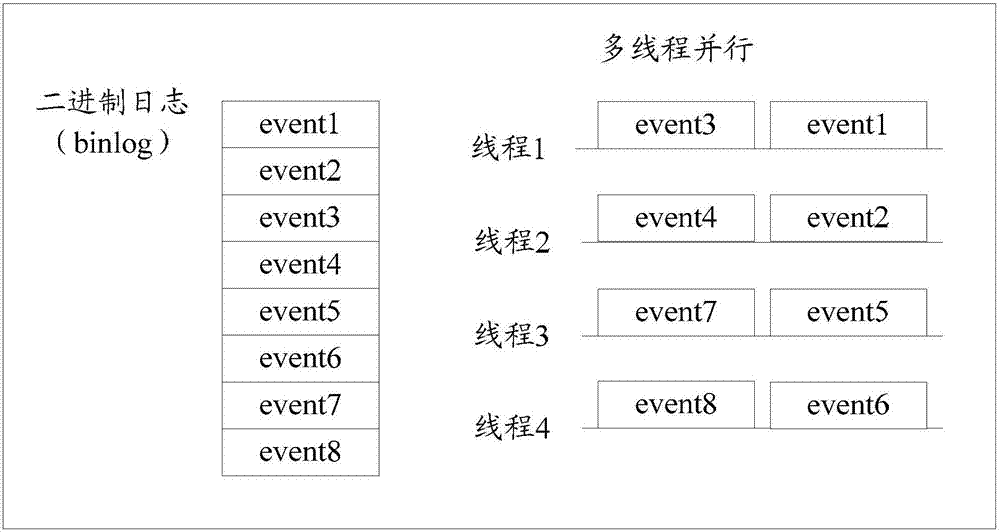
ActiveCN107102934AImprove playback efficiencyAvoid replay failuresRelational databasesHardware monitoringStart siteDatabase services
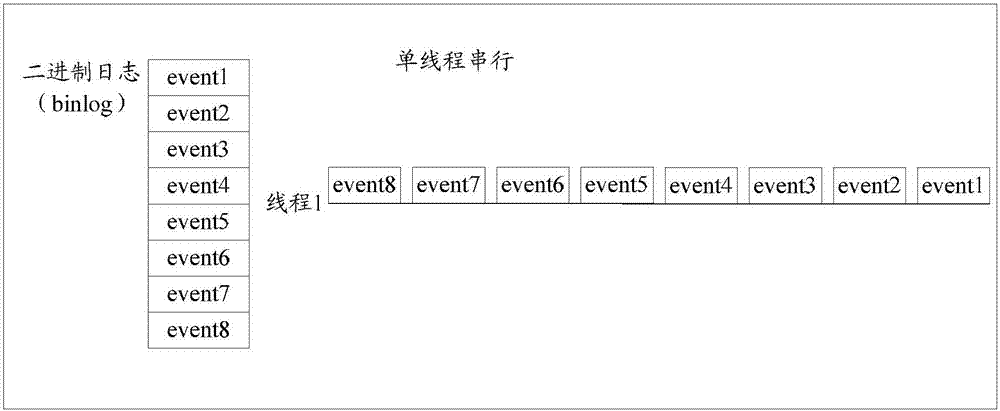
The application aims to provide a method and equipment for replaying of a binary-system log of a relation-type database. Replaying related data to be recovered is acquired from a backup set of service equipment of the relation-type database to be replayed; a replaying starting site of the replaying related data is acquired, and the binary-system log to be replayed from the replaying starting site to a replaying target site is acquired; based on a relay log rule, the binary-system needing to be replayed is stored in a catalog corresponding to a relay log, and an information document of a corresponding relay log site and a relay log index document are updated; and a replication application thread is started and the relay log is analyzed and executed, so that the binary-system log can be replayed, replaying failure appearing during replaying of the binary-system log to be replayed can be avoided, and replaying efficiency of the binary-system log to be replayed is effectively increased.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
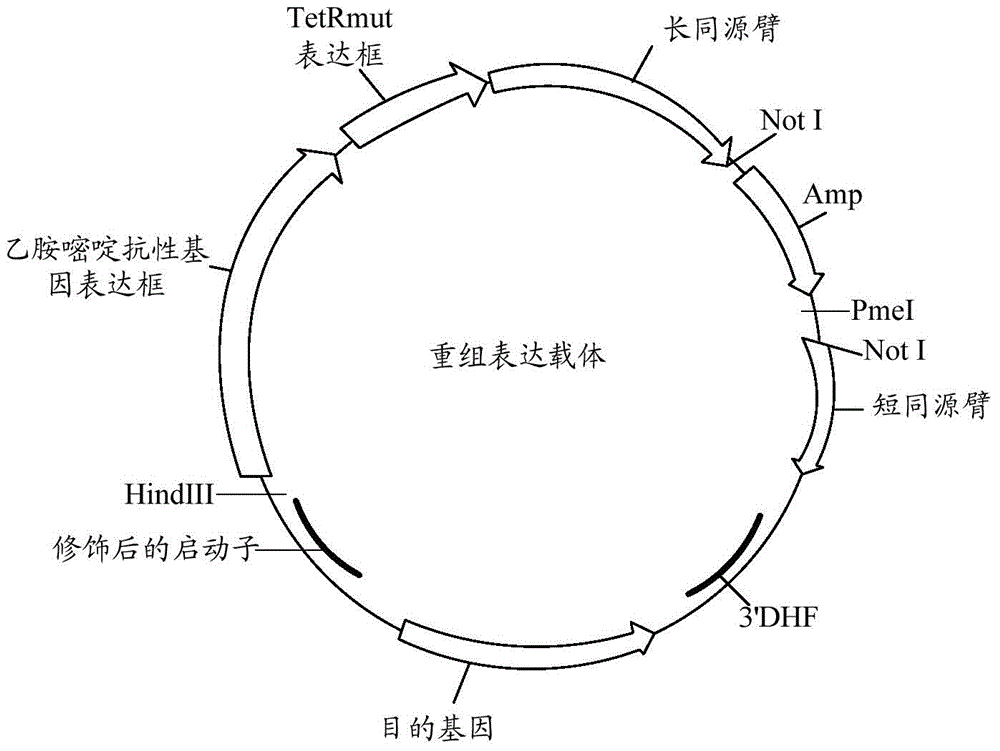
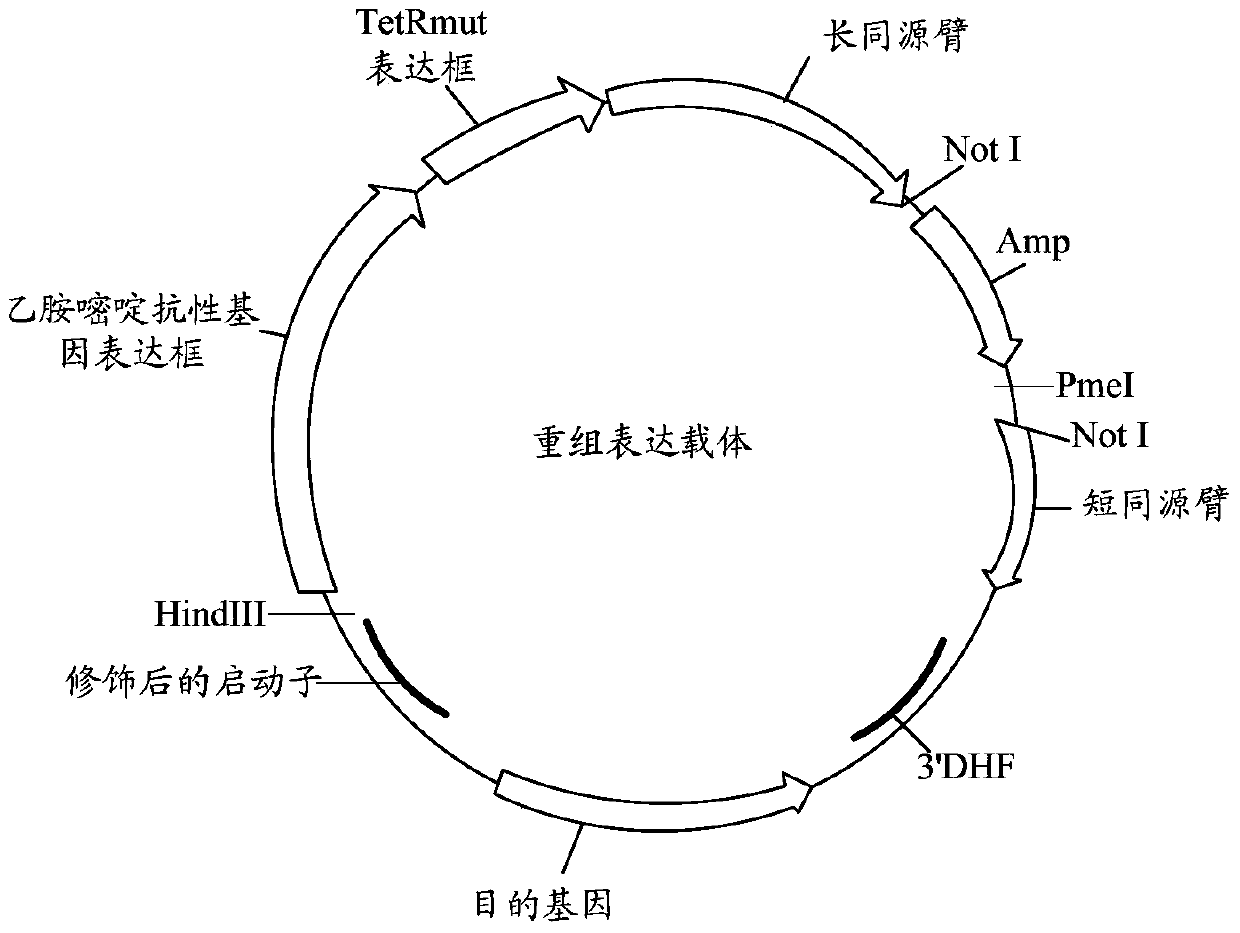
Controllable genome-modified plasmodium, recombinant expression vector and construction method and application of controllable genome-modified plasmodium and recombinant expression vector
The invention relates to a controllable genome-modified plasmodium, a recombinant expression vector and the construction method and application of the controllable genome-modified plasmodium and the recombinant expression vector. The recombinant expression vector comprises a gene targeting long homologous arm, a gene targeting short homologous arm, a tetracycline repression protein gene expression cassette, a pyrimethamine resistance gene expression cassette and a target gene expression cassette, wherein the tetracycline repression protein gene expression cassette, the pyrimethamine resistance gene expression cassette and the target gene expression cassette are located between the gene targeting long homologous arm and the gene targeting short homologous arm, and tetracycline operator gene sequences are inserted in multiple transcriptional start sites of a target gene promoter, so that the recombinant expression vector can be used for conditional research of the functions of a certain functional gene in a plasmodium genome. Furthermore, a functional gene expression sequence, corresponding to a target gene, in the plasmodium genome is knocked out by means of the gene knockout technique; meanwhile, the recombinant expression vector is transfected into a plasmodium with genes knocked out, so that the controllable genome-modified plasmodium is obtained; a new technical scheme is provided for further research of the functions of all functional genes in the plasmodium genome, and application prospects are broad.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Colorectal cancer diagnosis kit
InactiveCN110387418AHigh detection specificityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStart siteNon-coding RNA
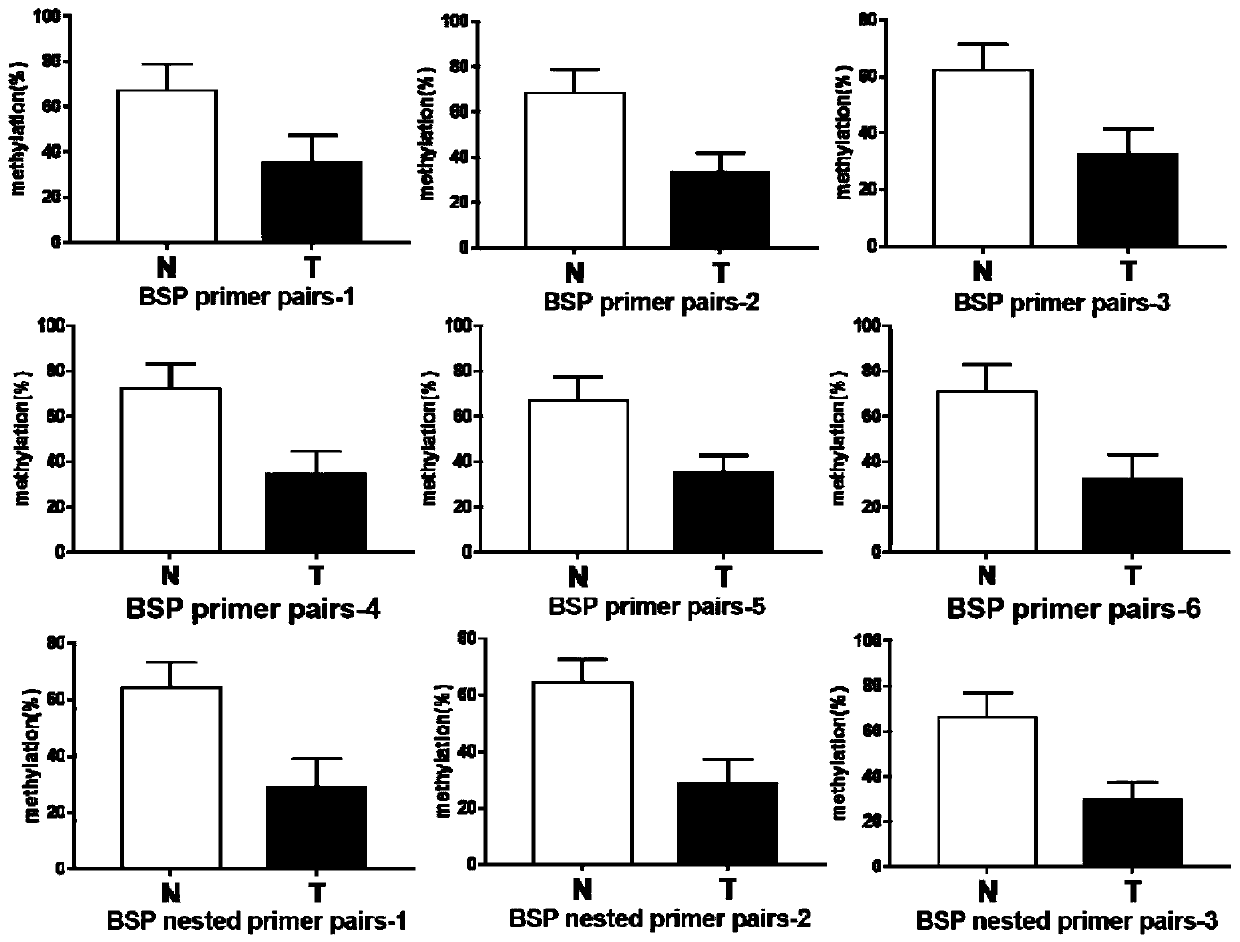
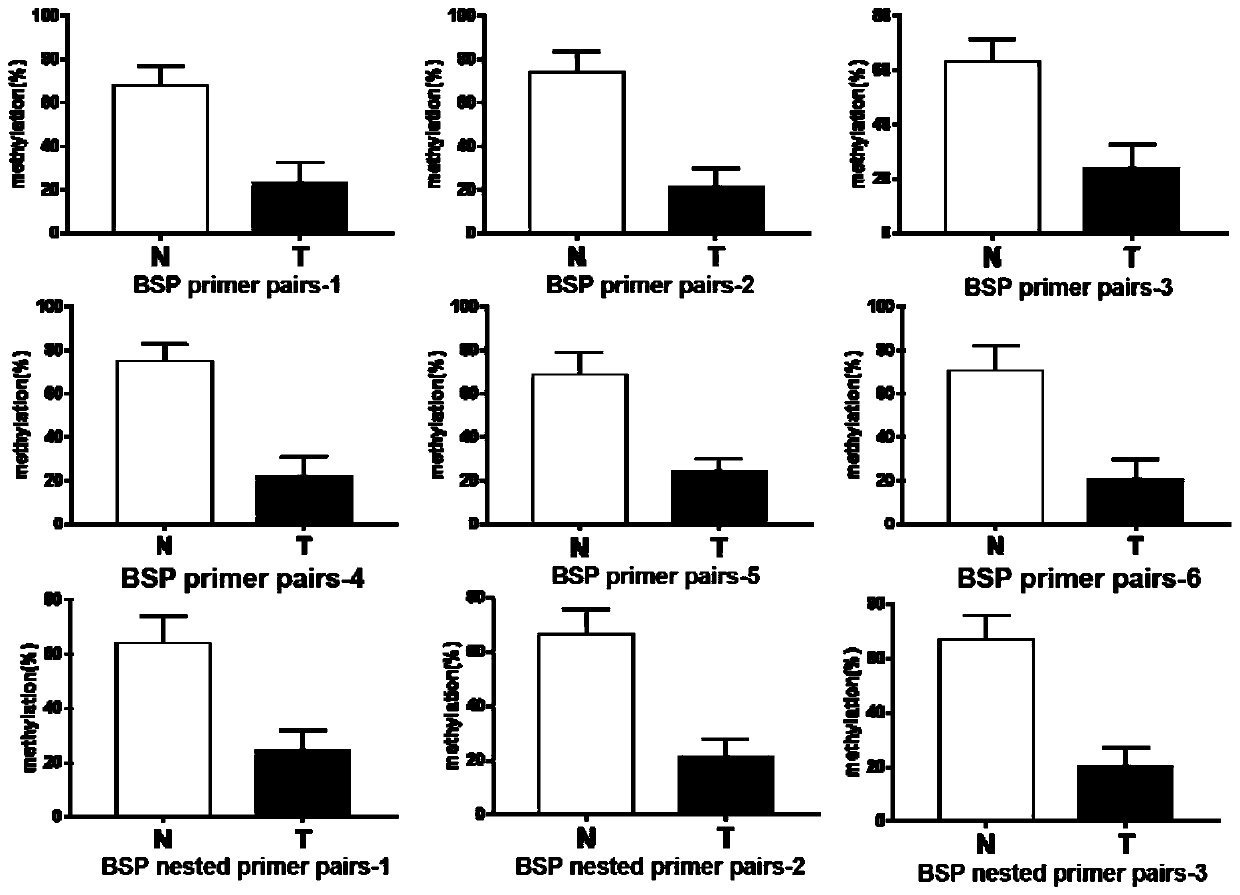
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a colorectal cancer diagnosis kit. The kit contains a reagent for detecting the methylation level of a to-be-detected sequence in a to-be-detected sample, and the to-be-detected sequence is located between an upstream 3.5kb sequence and a downstream 2kb sequence of an miR-17-92 cluster transcriptional start site. It is found for the first time that the low methylation level of an original cancer non-coding RNA miR-17-02 cluster in colorectal cancer is relevant to the generation and development of the colorectal cancer. The methylation level of the miR-17-92 cluster can be used as a biological indicator for tumor detection to assist diagnosis of the colorectal cancer, so that detection specificity and sensitivity are improved, the error rate is lowered, and the quite important clinic guidance significance to the tumor pathogenesis and diagnosis is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHONGYU BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Methods and compositions for manipulating translation of protein isoforms from alternative initiation start sites
InactiveUS20190241890A1High sensitivityImprove translationPolymorphism usesScreening processStart codonStart site
Provided herein are antisense oligonucleotides, compositions comprising antisense oligonucleotides, and methods for the use of antisense oligonucleotides in manipulating translation. Expression of isoforms of proteins expressed from different start codons of the same transcript are inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which may also enhance expression of non-target isoforms.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Flow-type safe work starting management and control method and system
InactiveCN107993014APrevent safety liability accidentsSafety Responsibility GuaranteeOffice automationResourcesStart siteTerminal equipment
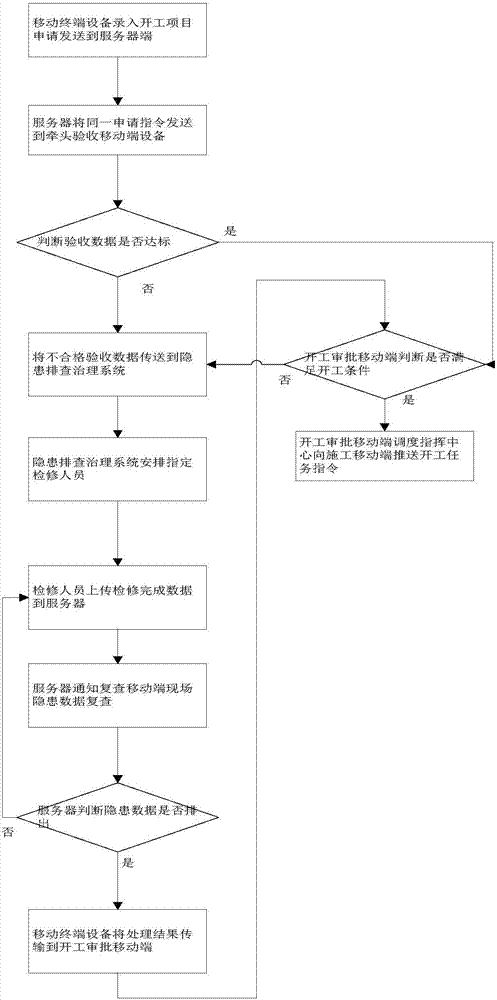
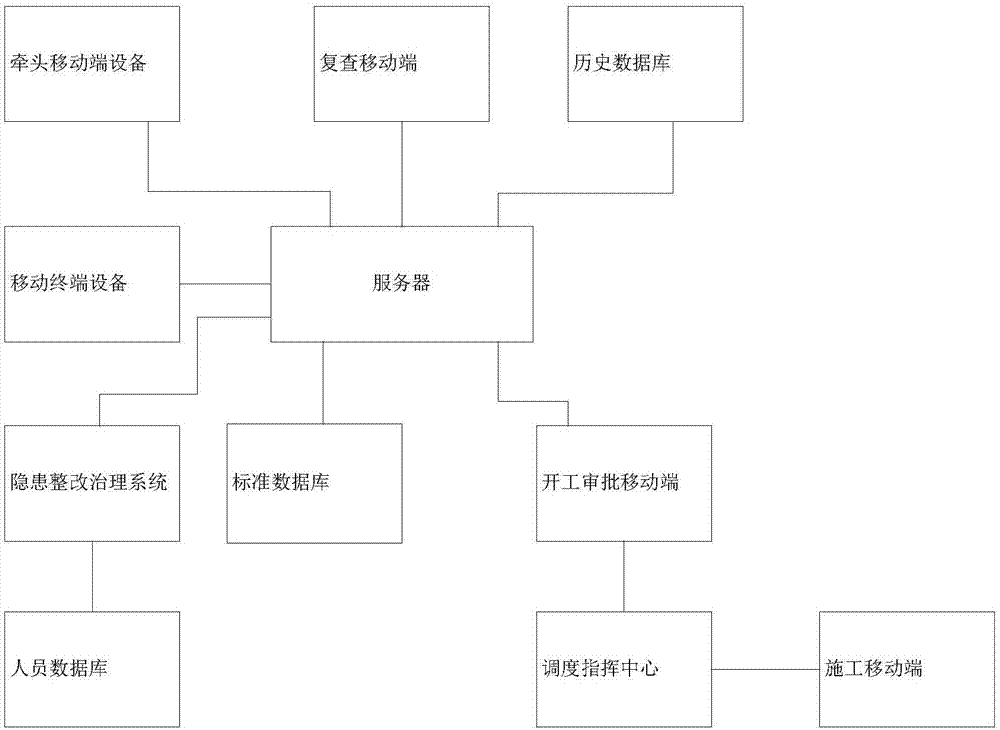
The invention discloses a flow-type safe work starting management and control method and system. The method includes the following steps that a mobile terminal device inputs an application for projects to be started, and sends the application to a server; the server pushes an application agreement instruction to an assigned leading mobile terminal device for acceptance inspection; the leading mobile terminal device swipes an address card of a work starting site, the server automatically matches and pushes on-site acceptance standard items to the leading mobile terminal device, and a mobile terminal gradually uploads collected information into the server one by one; centralized management of electronically computerized log data is convenient and fast, the problem that potential hazards aredifficult to search for on the basis of experience is solved, and the system stability is improved.
Owner:重庆天府矿业有限责任公司
Method and device for quickly querying bus line, terminal equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN108763549AQuick searchReduce waiting timeSpecial data processing applicationsStart siteUser input
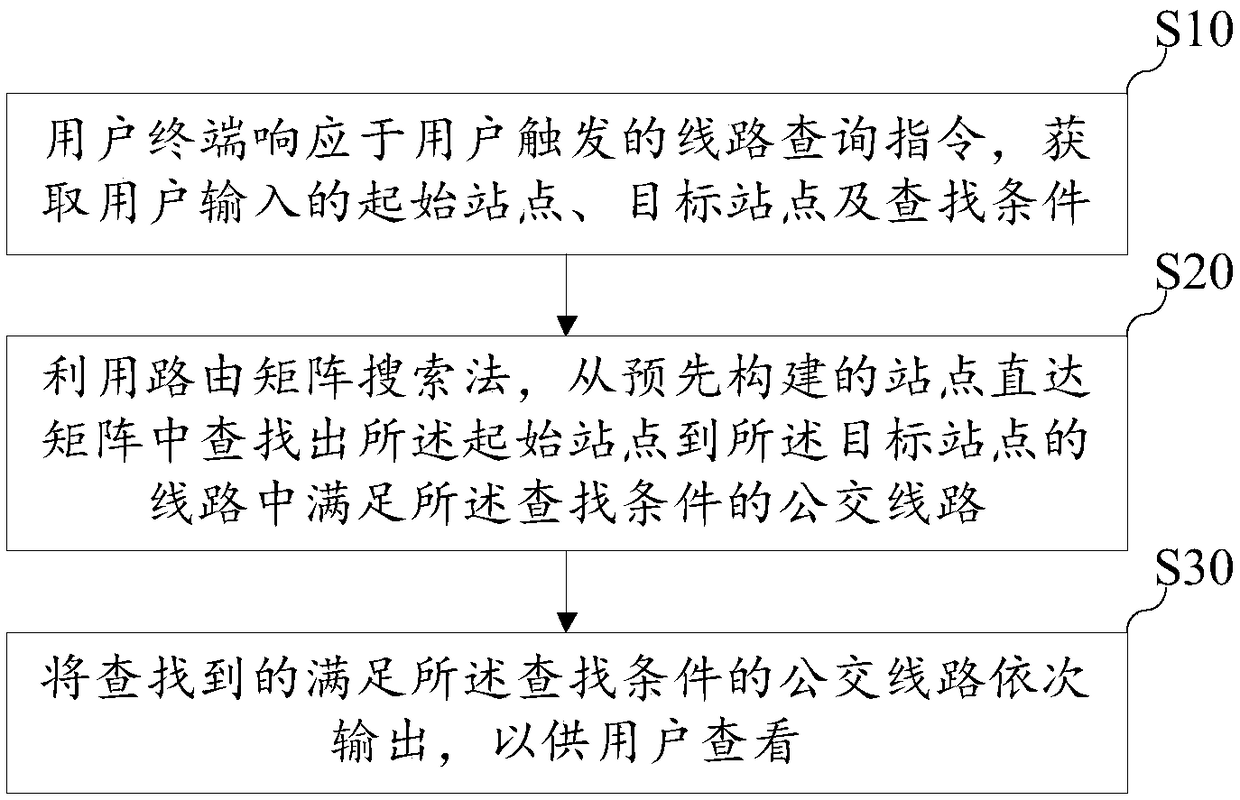
The invention discloses a method and device for quickly querying a bus line, terminal equipment and a storage medium. The method includes the following steps: pre-building a site direct-arrival matrixin the form of a routing matrix to store all bus lines that can be directly arrived from a starting site to a target site, after receiving a line query instruction triggered by a user, adopting a routing matrix searching method to search the bus lines that meet the searching conditions required by the user among the lines from the starting site to the target site input by the user from the site direct-arrival matrix in the form of the routing matrix, and sequentially outputting the searched bus lines that meet the searching conditions for the user to view. According to the above searching method, the bus lines that meet the requirements of the user can be quickly queried in a network environment, and the bus lines are recommended to the user for viewing, and thus the waiting time of the user can be greatly reduced, and the user experience can be improved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
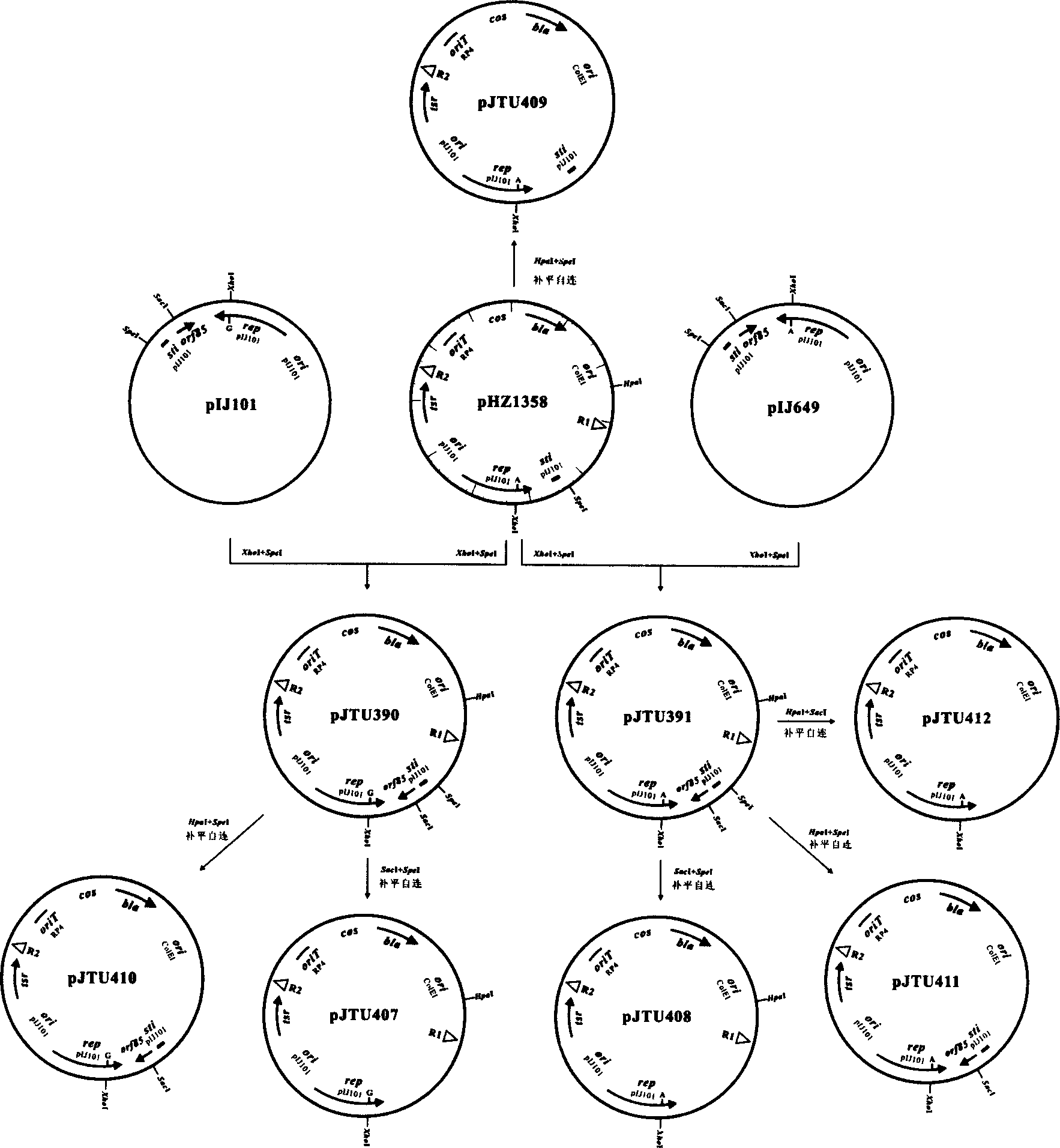
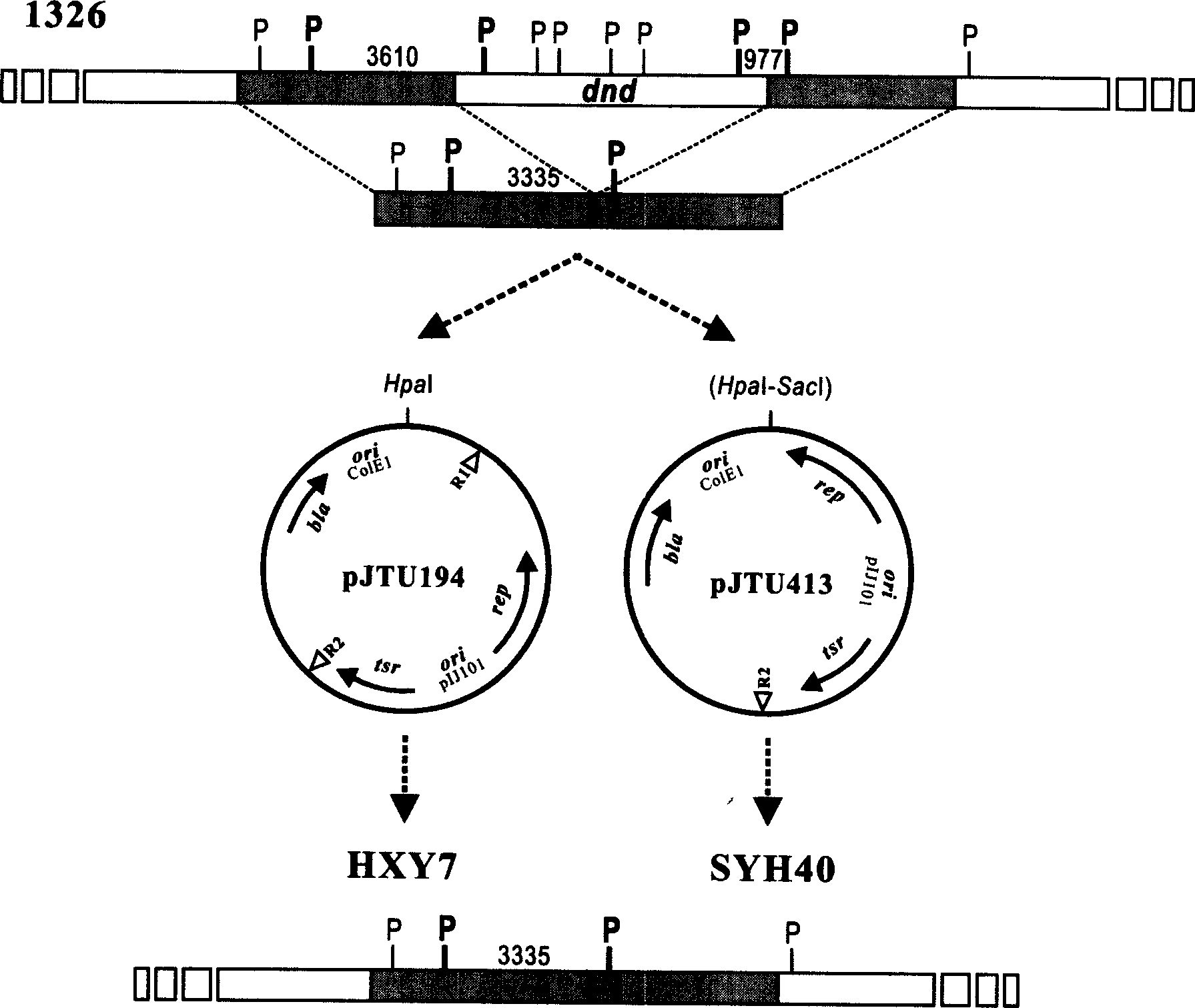
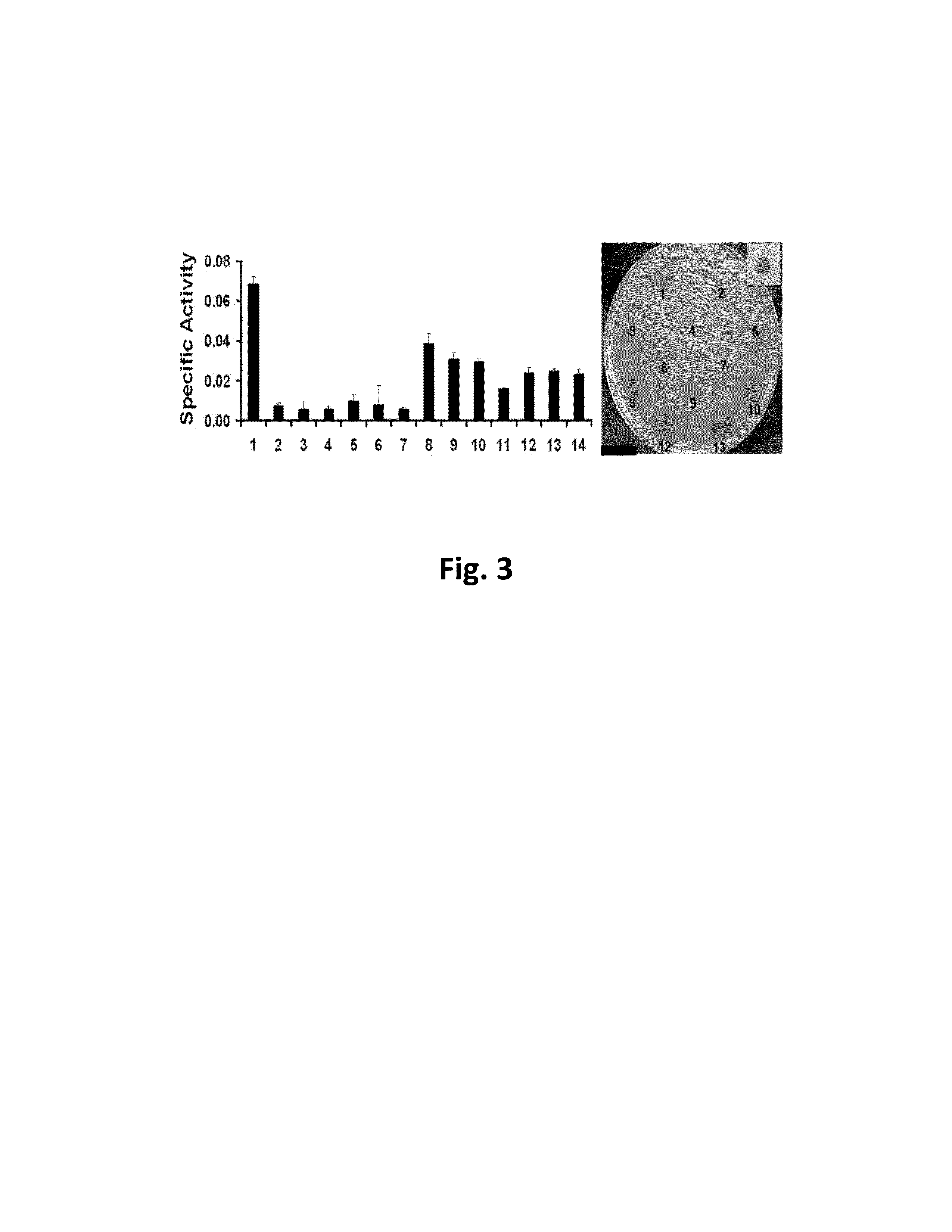
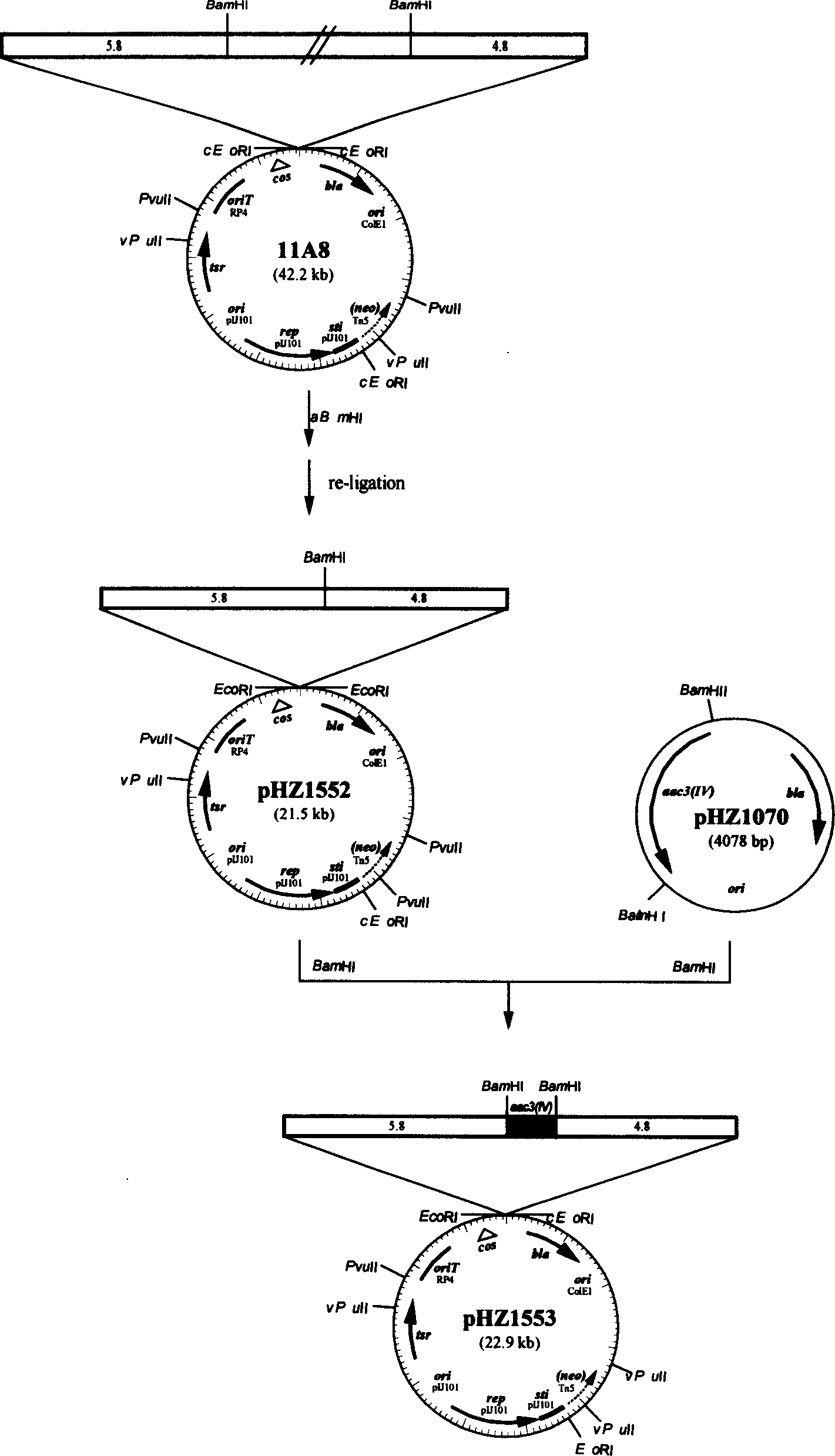
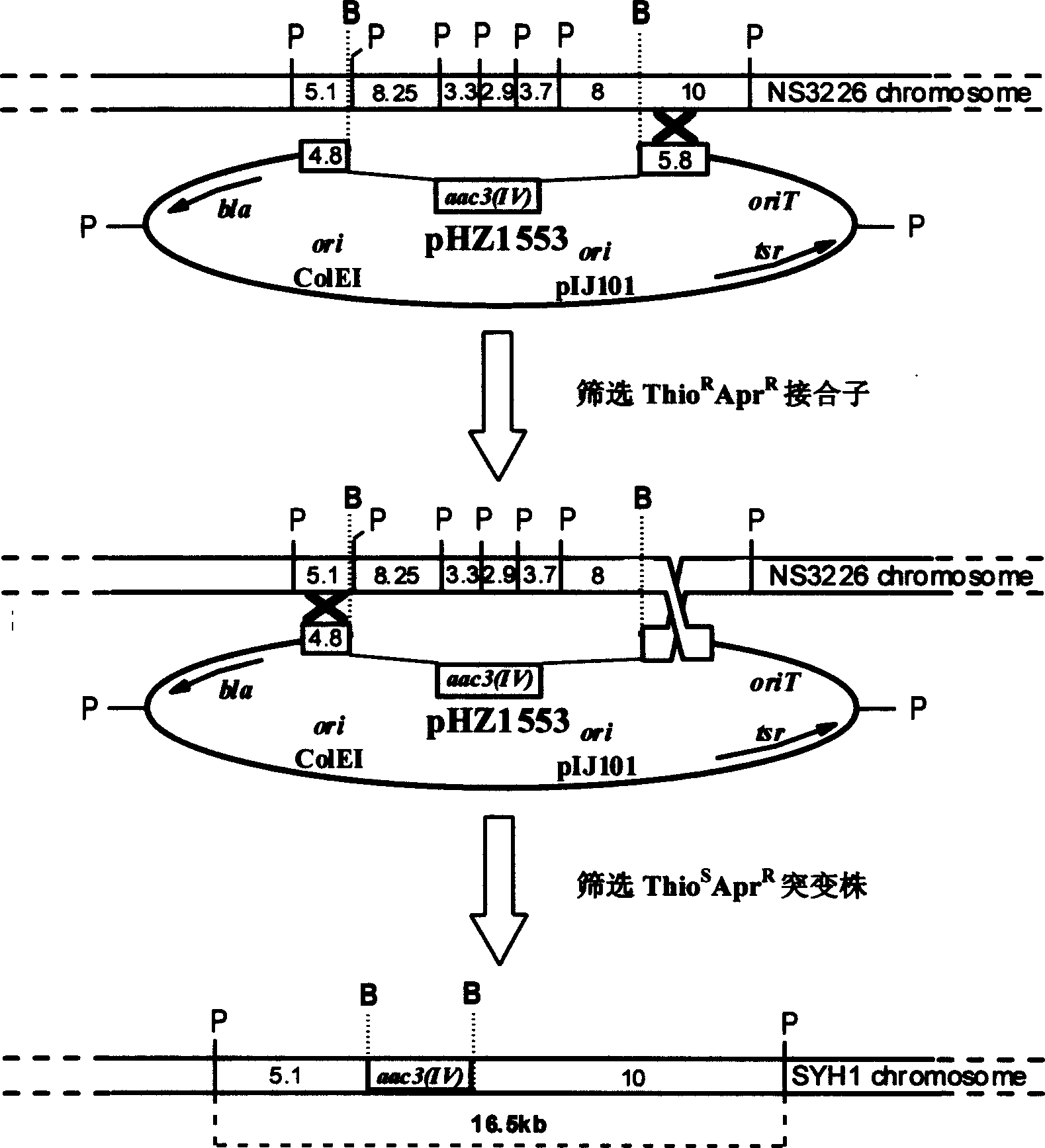
Serial duoble function kes carrier suitable for streptomycete chromosome gene knock-out
InactiveCN1587417AEasy to filterEfficient screeningVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliStart site
The serial double function cos carriers, including pJTU390, pJTU391, pJTU407, pJTU408, pJTU409, pJTU410, pJTU411 and pJTU412, suitable for streptomycede chromosome gene knock-out feature that each of them consists of following DNA elements: colibacillus plasmid Coie1 duplicating initiation site ori, ampicilin resistance gene bla, streptomycete plasmid pIJ101 duplicating initiation site and duplicon, thiactin resistance gene tsr, lambda bacteriophage cos site, RP4 conjugal transfer start site oriT, promoter capable of being identified specifically by T3 and T7 bacteriophage RNA polymerase, and neomycin resistance gene neo from Tn5 and containing no promoter. The present invention contains colibacillus plasmid, streptomycete plasmid duplicon and resistance screening mark simultaneously, has functions of autonomous duplicating and inheriting simultaneously in two kinds of hosts, and facilitates in vitro genetic operation and gene function analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
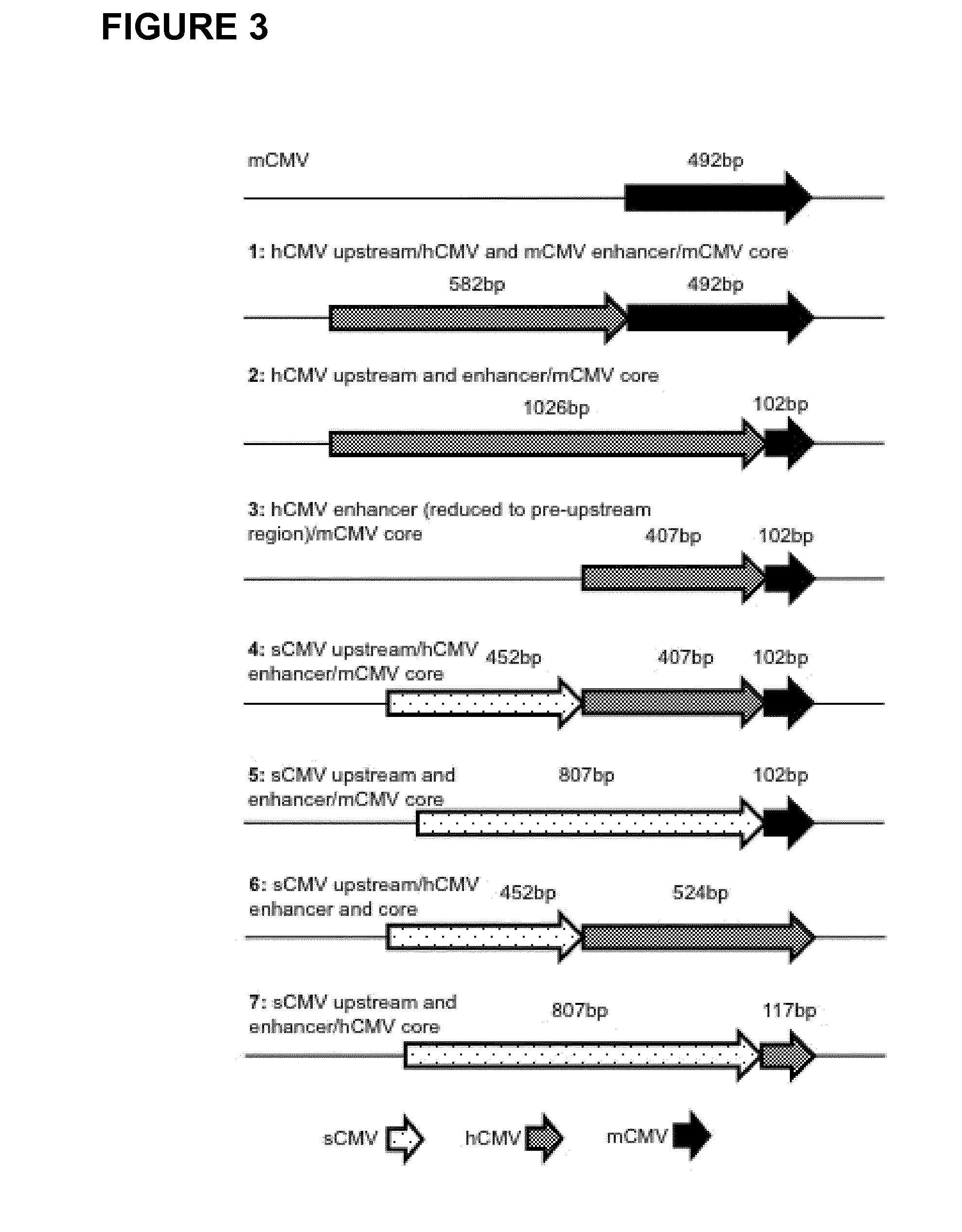
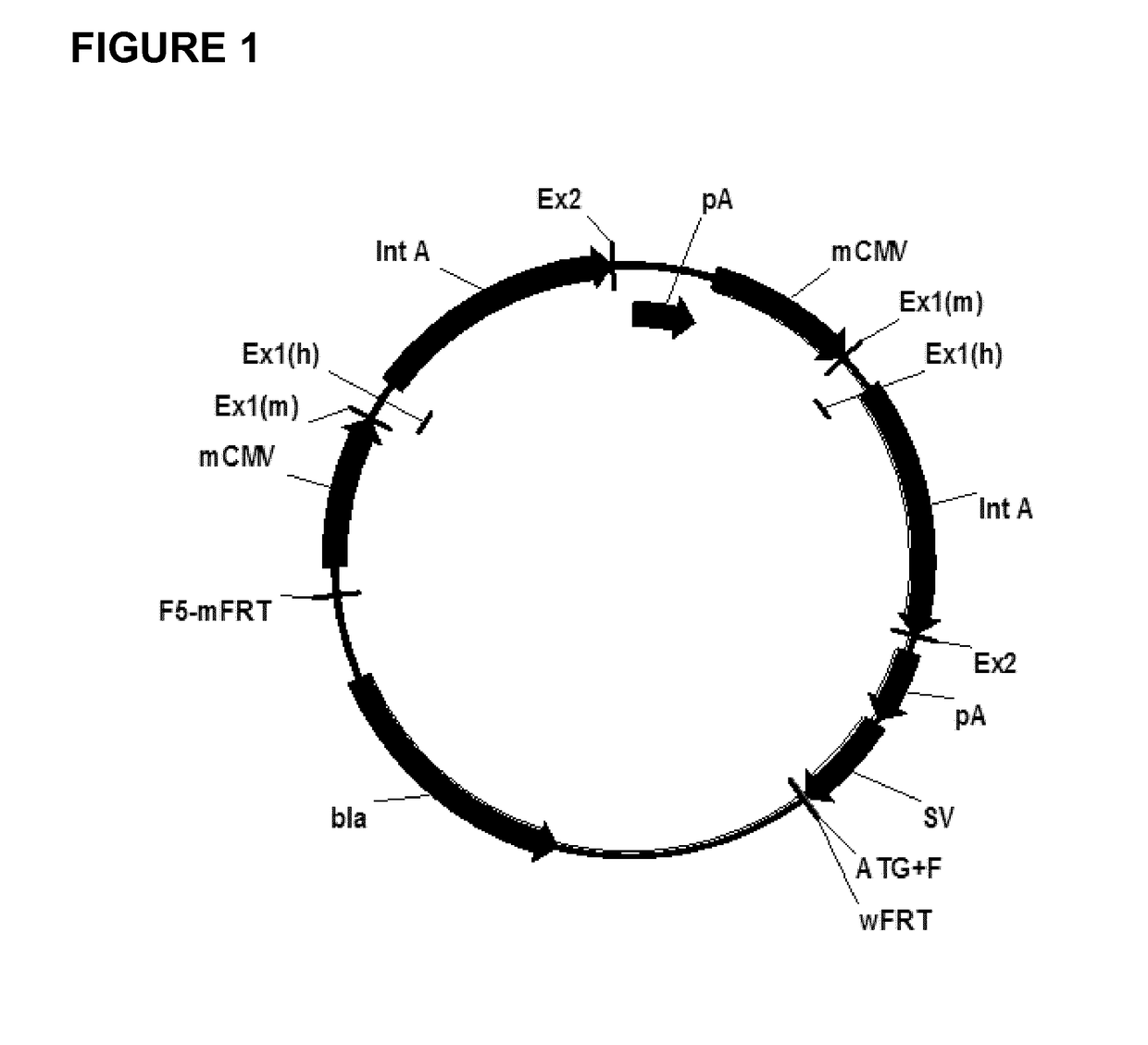
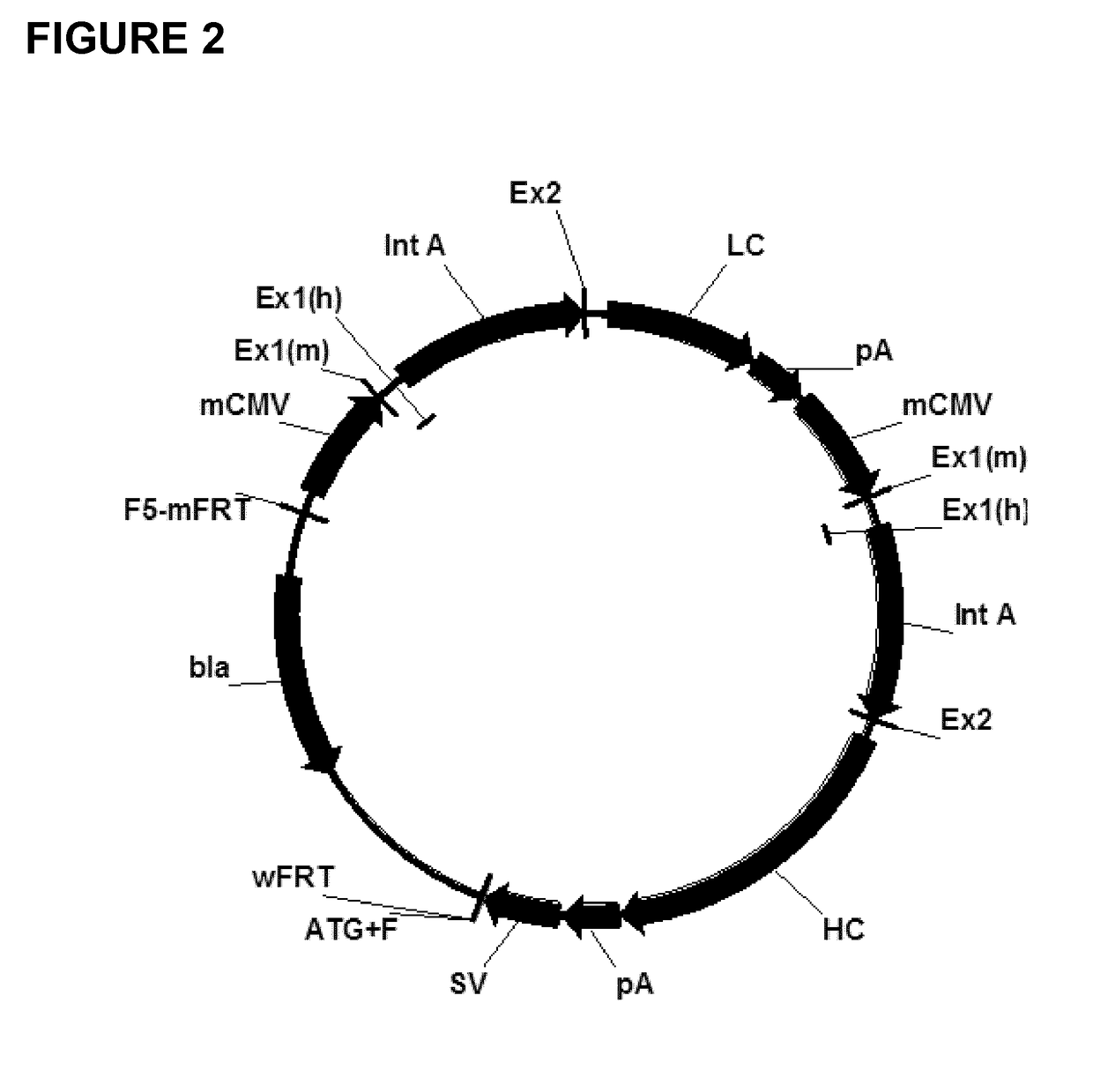
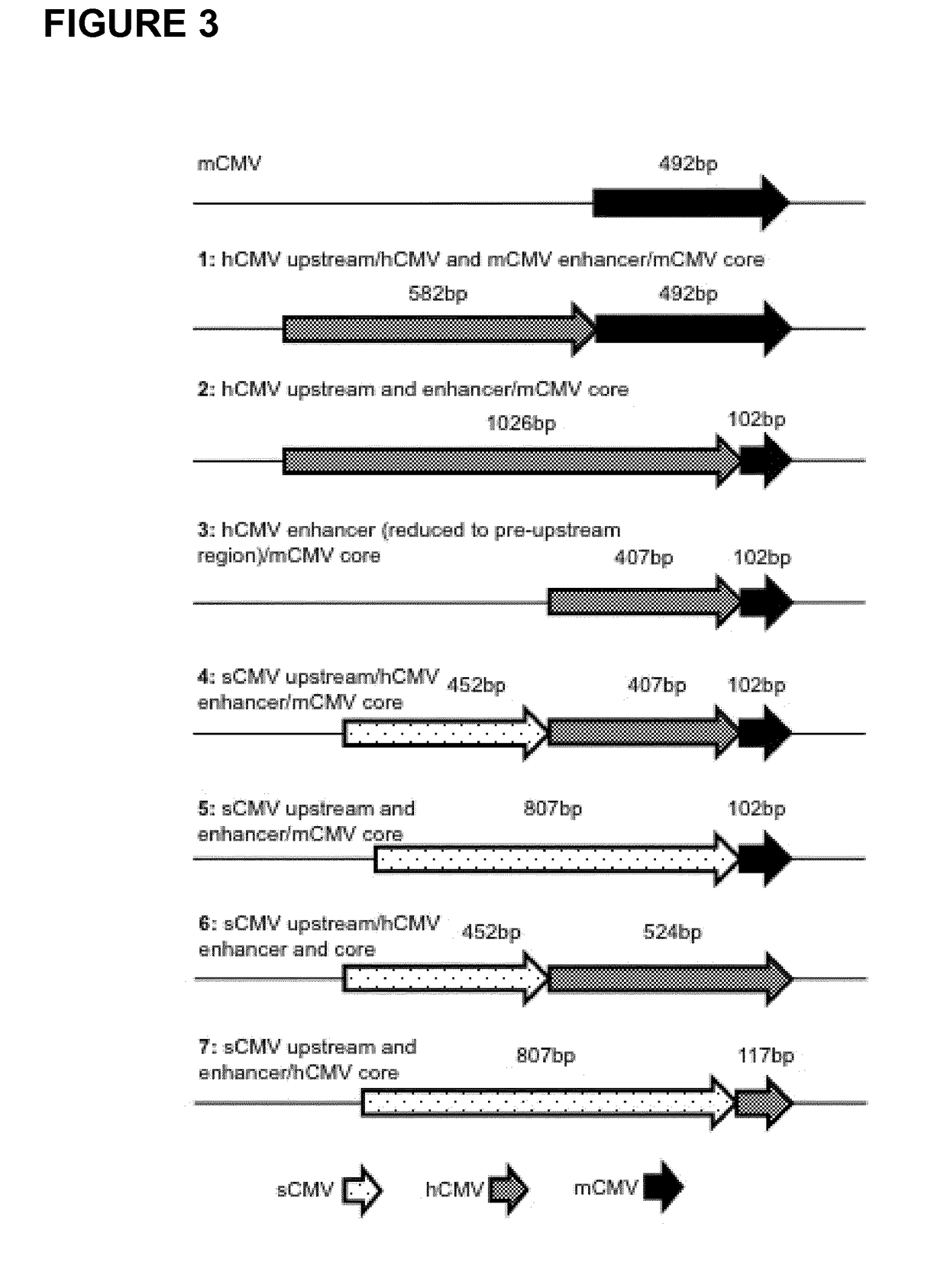
Expression vectors comprising chimeric cytomegalovirus promoter and enhancer sequences
The present invention relates to expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence of interest in mammalian cells, the vectors comprising a chimeric promoter regulatory sequence being operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence to be expressed, wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises a cytomegalovirus promoter sequence derived from murine cytomegalovirus or from human cytomegalovirus and being operably linked to the transcriptional start site of the nucleic acid sequence to be expressed; and a cytomegalovirus upstream region and / or enhancer sequence derived from human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus, wherein the upstream region and / or enhancer sequence is located 5′ of and operably linked to the murine or the human promoter sequence, and wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements being derived from at least two of the group consisting of murine cytomegalovirus, human cytomegalovirus and simian cytomegalovirus. In particular embodiments, the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements derived from the murine or the human cytomegalovirus IE1 promoter and from the human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus IE1 region. The invention also relates to mammalian host cells transfected with such expression vectors, a method for heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence in a mammalian host cell by employing such expression vectors, and the use of such expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
Expression vectors comprising chimeric cytomegalovirus promoter and enhancer sequences
The present invention relates to expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence of interest in mammalian cells, the vectors comprising a chimeric promoter regulatory sequence being operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence to be expressed, wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises a cytomegalovirus promoter sequence derived from murine cytomegalovirus or from human cytomegalovirus and being operably linked to the transcriptional start site of the nucleic acid sequence to be expressed; and a cytomegalovirus upstream region and / or enhancer sequence derived from human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus, wherein the upstream region and / or enhancer sequence is located 5′ of and operably linked to the murine or the human promoter sequence, and wherein the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements being derived from at least two of the group consisting of murine cytomegalovirus, human cytomegalovirus and simian cytomegalovirus. In particular embodiments, the chimeric promoter regulatory sequence comprises sequence elements derived from the murine or the human cytomegalovirus IE1 promoter and from the human and / or the simian cytomegalovirus IE1 region. The invention also relates to mammalian host cells transfected with such expression vectors, a method for heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence in a mammalian host cell by employing such expression vectors, and the use of such expression vectors for the heterologous expression of a nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
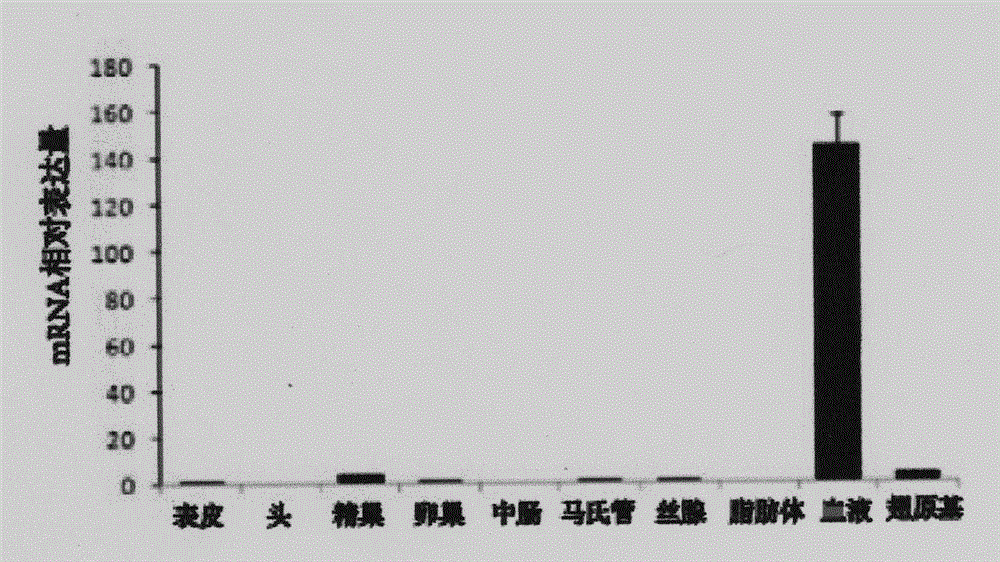
Identification of silkworm hemocyte specific expressed gene cathepsin O regulation element
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
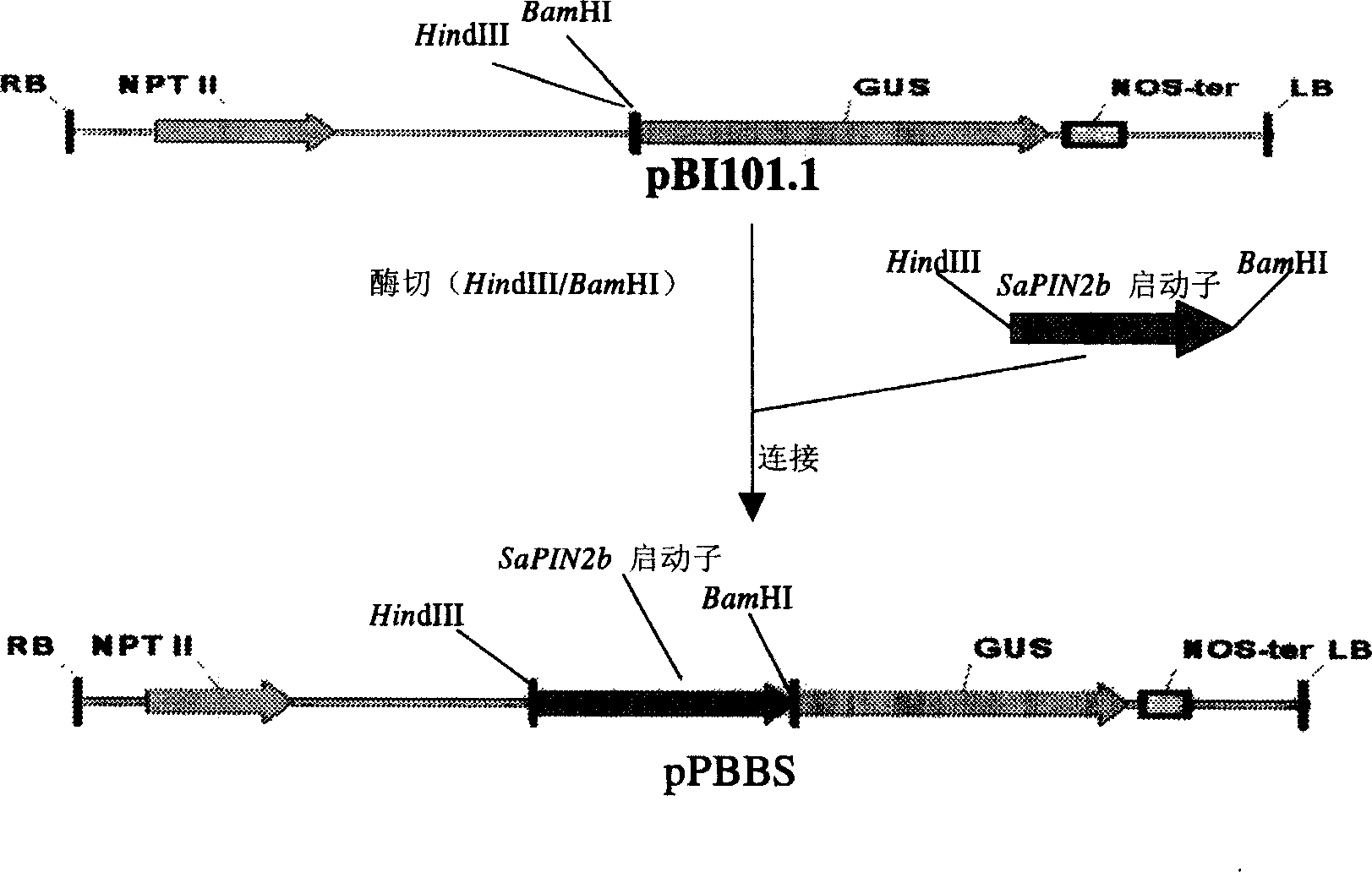
Gene promoter for specific expression of plant trichome
InactiveCN1657621AReduce physical space constraintsGood for high level expressionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionStart siteNicotiana tabacum
A genetic promoter with specific expression to vegetative trichome is disclosed. The sequence of the trichome-specific hydratropic proteinase inhibitor (SaPIN2b) gene promoter is cloned. The start site of SaPIN2b transcription is determined. Its plant expression carrier is configured. The test to its transgenic plant shows its specific expression in trichome.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods and compositions for manipulating translation of protein isoforms from alternative initiation of start sites
InactiveUS10100305B2High sensitivityImprove translationPolymorphism usesScreening processStart codonStart site
Provided herein are antisense oligonucleotides, compositions comprising antisense oligonucleotides, and methods for the use of antisense oligonucleotides in manipulating translation. Expression of isoforms of proteins expressed from different start codons of the same transcript are inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which may also enhance expression of non-target isoforms.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
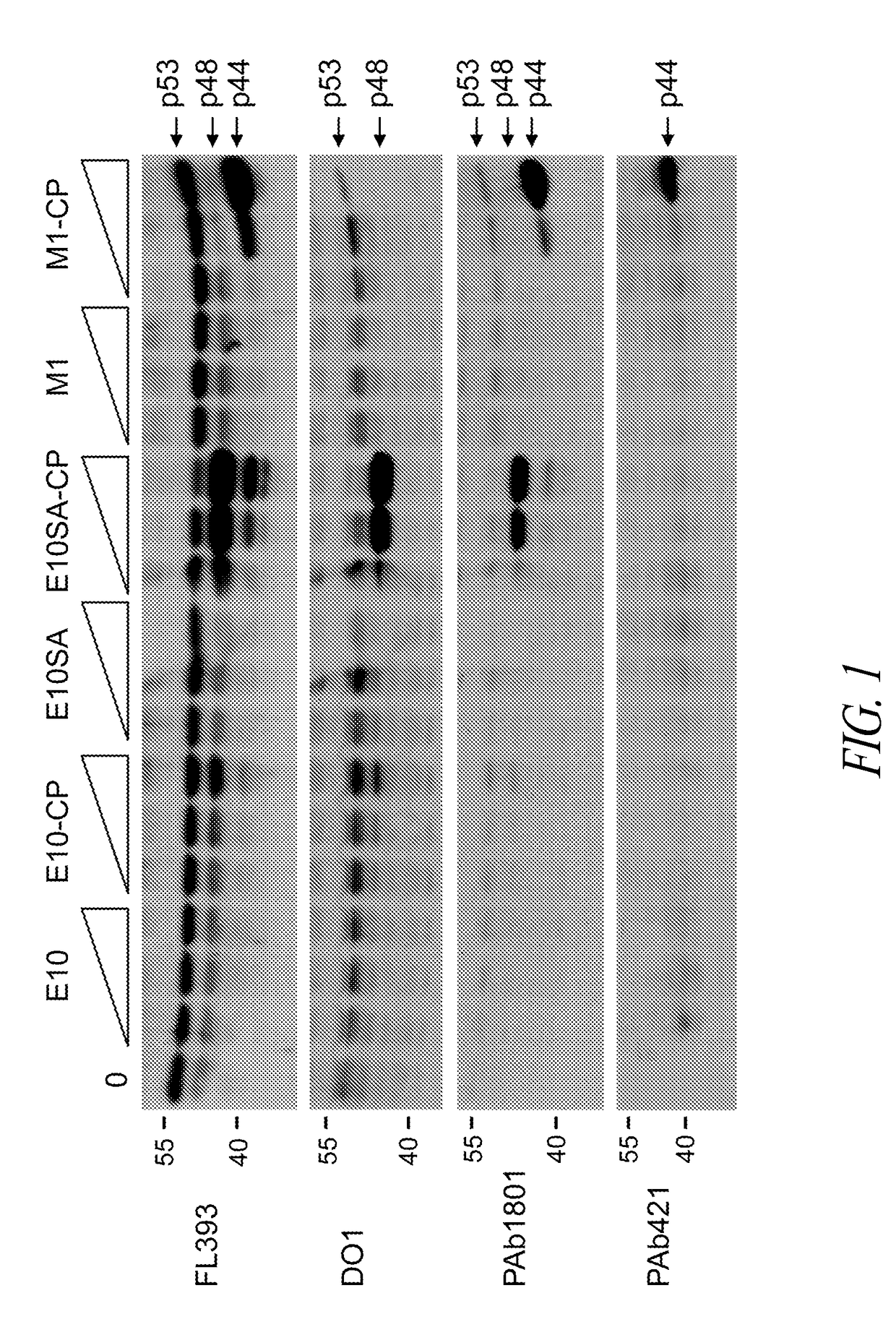
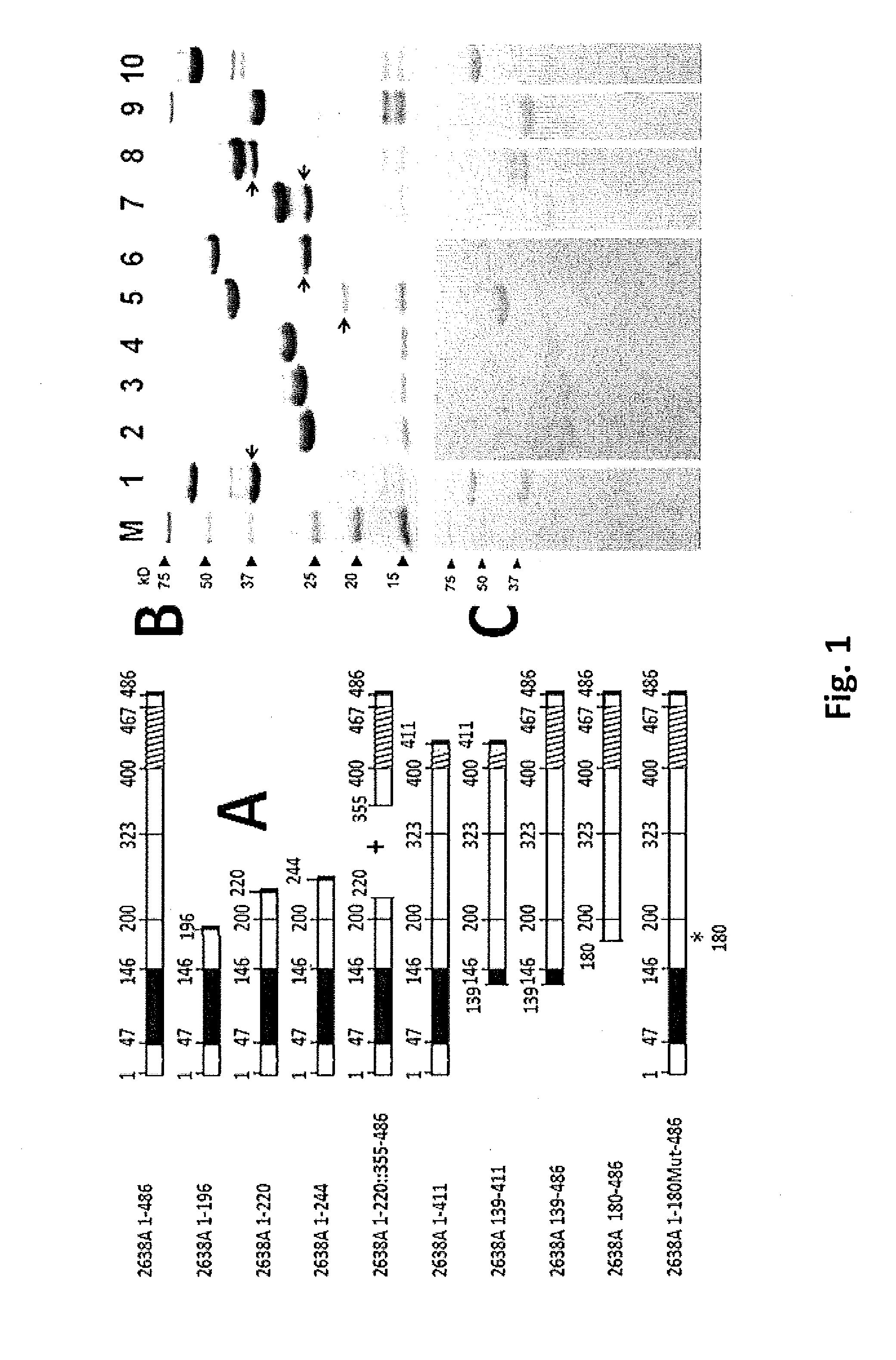
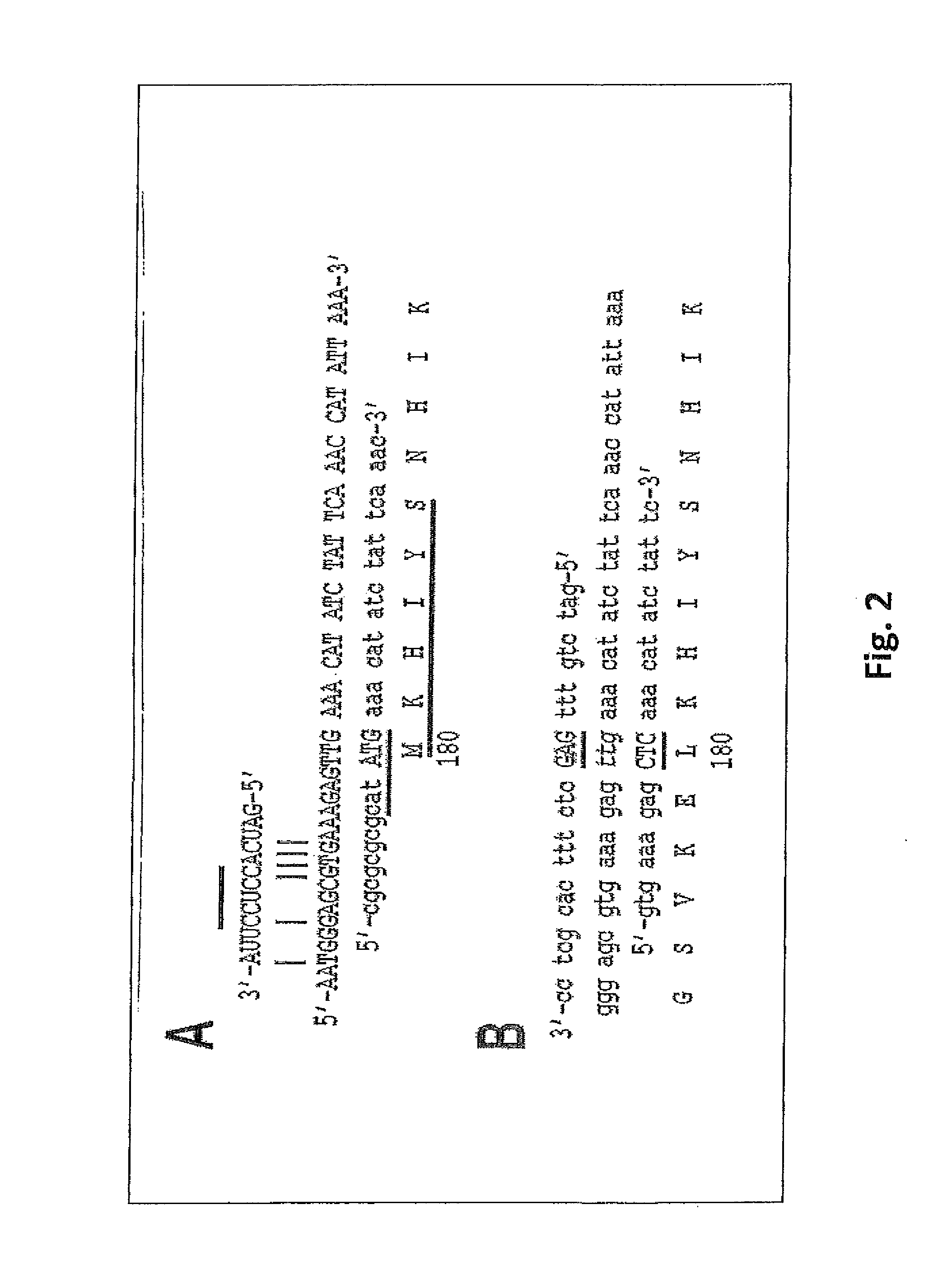
Staphylococcal Phage2638A endolysin amidase domain is lytic for Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS9206411B2Enhanced, specific antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaStaphylococcus cohniiPeptidoglycan Hydrolase
Staphylococcus aureus is notorious for developing resistance to virtually all antibiotics to which it is exposed. Staphylococcal phage 2638A endolysin is a peptidoglycan hydrolase that is lytic for S. aureus when exposed externally, making it a new antimicrobial candidate. It shares a common protein organization with over 40 other staphylococcal peptidoglycan hydrolases: a CHAP endopeptidase domain, a mid-protein amidase 2 domain and a C-terminal SH3b cell wall binding domain. It is the first phage endolysin reported with a cryptic translational start site between the CHAP and amidase domains. Deletion analysis indicates that the amidase domain confers most of the lytic activity and requires the full SH3b domain for maximal activity. It is common for one domain to demonstrate dominant activity over another; however, the phage 2638A endolysin is the first to show high amidase domain activity dominant over the N-terminal CHAP domain, an important finding for targeting novel peptidoglycan bonds.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Board game, apparatus, and method of play
A board game preferably for two players involving the movement of a single game piece along a plurality of three types of lanes differentiated on the basis of color, with the lanes having arrowheads showing allowable directions of movement to a plurality of sites including a start site for each player and a score site for each player. Players alternately toss a pair of cubic dice with each die having three sides of one color and three sides of another color corresponding to the colors of the lanes. The single game piece is moved from one site to an adjacent site along one of the lanes corresponding to the uppermost faces shown by the dice. Players win one point when the game piece moves into their score site; and when a player reaches a predetermined winning score, that player wins the game. The game can be played by a single player against an imaginary opponent.
Owner:VANLIER KENNETH E
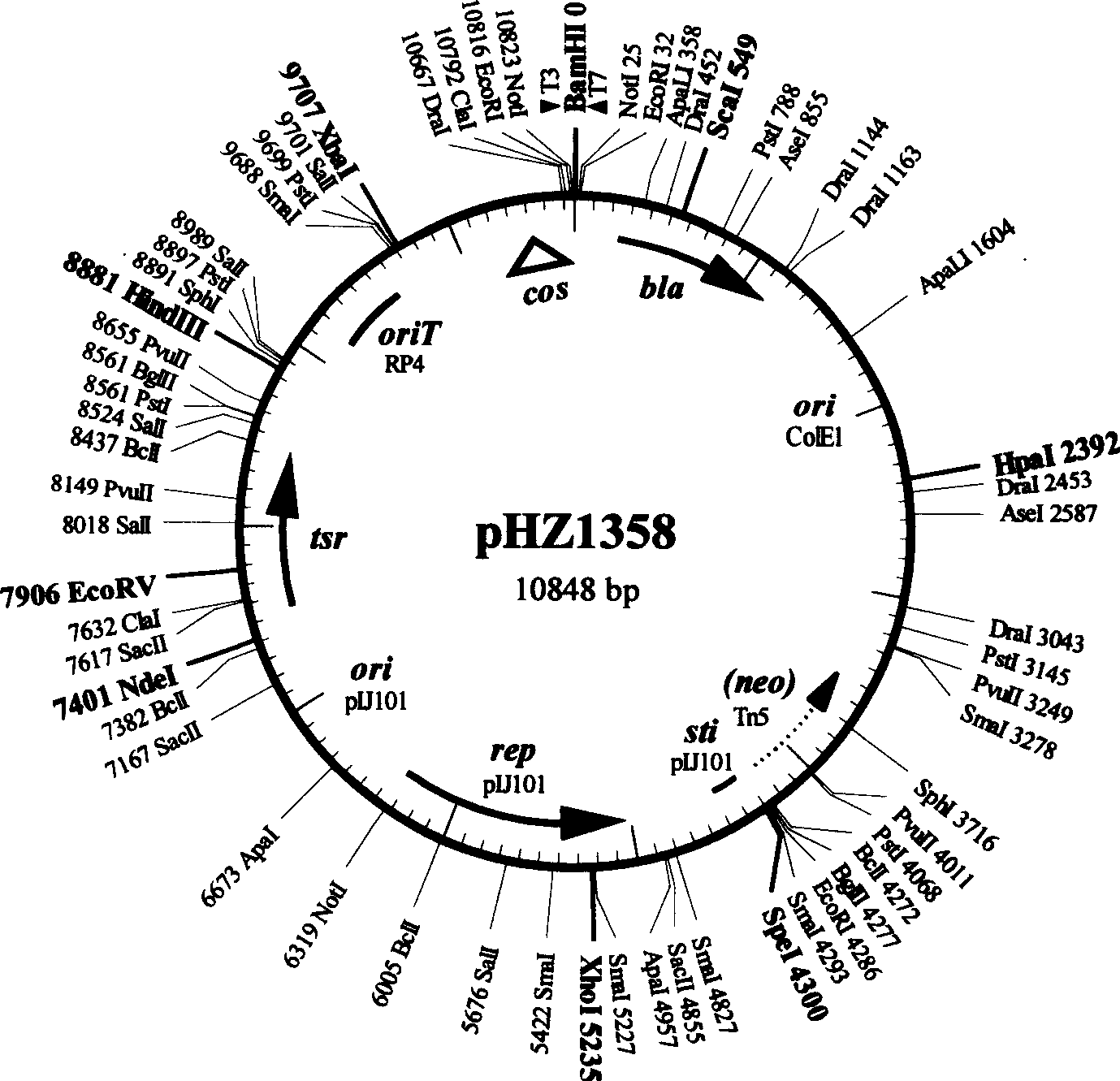
Double function kes carrier suitable for streptomycete chromosome gene knock-out
InactiveCN1587416AGenetic stabilityConvenient in vitro genetic manipulationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliStart site
The double function cos carrier suitable for streptomycede chromosome gene knock-out features that it consists of following DNA elements: colibacillus plasmid Coie1 duplicating initiation site ori, ampicilin resistance gene bla, streptomycete plasmid pIJ101 duplicating initiation site and duplicon, thiactin resistance gene tsr, strong streptomycete plasmid pIJ101 incompatibility area sti, lambda bacteriophage cos site, RP4 conjugal transfer start site oriT, promoter capable of being identified specifically by T3 and T7 bacteriophage RNA polymerase, and neomycin resistance gene neo from Tn5 and containing no promoter. The present invention may be used easily in knocking out streptomycede chromosome gene, contains colibacillus plasmid, streptomycete plasmid duplicon and resistance screening mark simultaneously and has functions of autonomous duplicating and inheriting simultaneously in two kinds of hosts.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
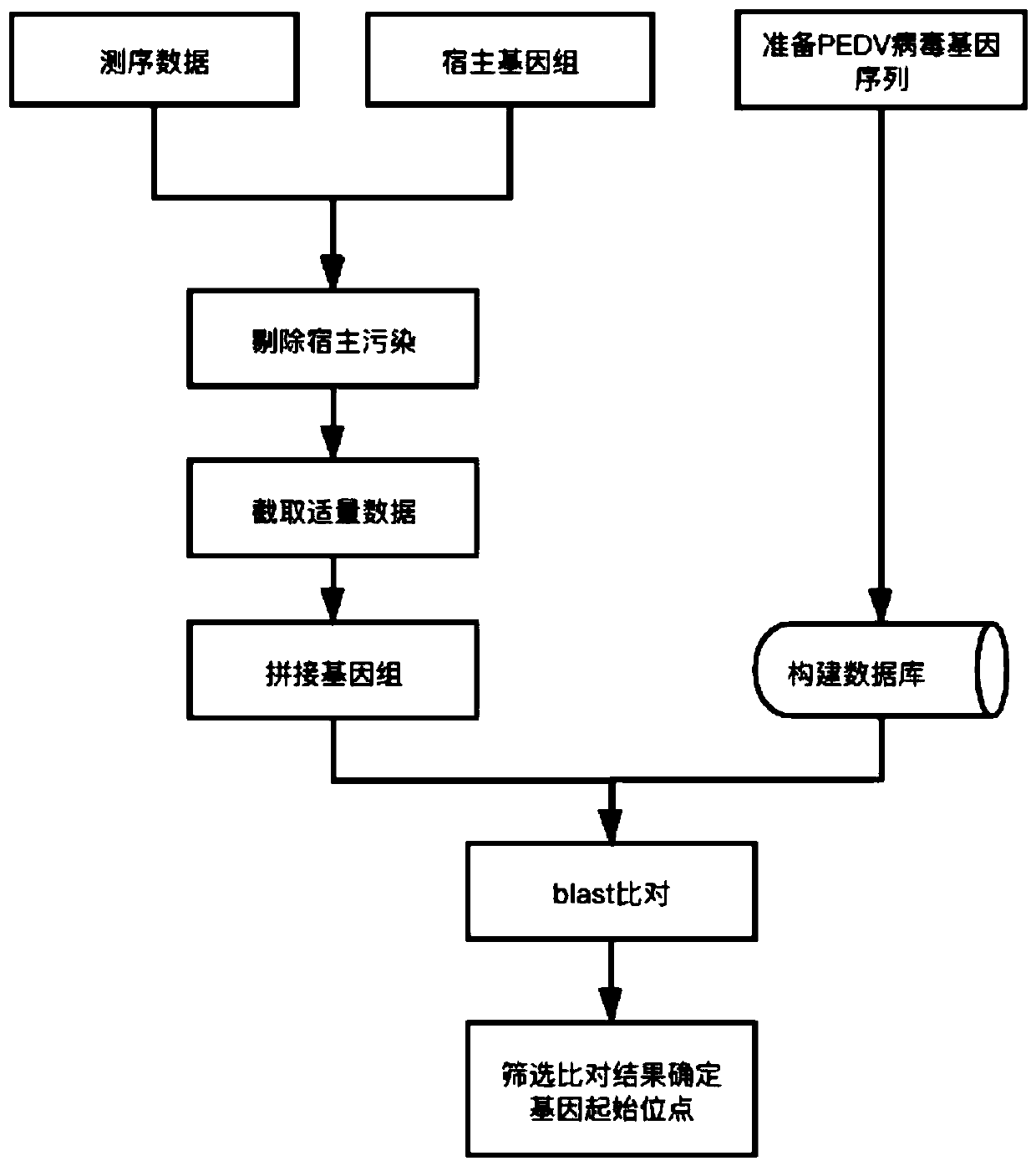
PEDV genome analysis method based on next-generation sequencing
The invention discloses a PEDV genome analysis method based on next-generation sequencing. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: downloading a genome sequence and a transcriptsequence of a host pig as a host reference sequence; acquiring a sequencing sequence for removing host pollution; splicing the genome; carrying out homologous comparison on the genome; selecting a comparison result; and taking the compared starting site as a starting site of the gene. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that gene structure can be accurately predicted, and omission is avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Controllable Genome Modification Plasmodium, Recombinant Expression Vector and Construction Method, Application
The invention relates to a controllable genome-modified plasmodium, a recombinant expression vector and the construction method and application of the controllable genome-modified plasmodium and the recombinant expression vector. The recombinant expression vector comprises a gene targeting long homologous arm, a gene targeting short homologous arm, a tetracycline repression protein gene expression cassette, a pyrimethamine resistance gene expression cassette and a target gene expression cassette, wherein the tetracycline repression protein gene expression cassette, the pyrimethamine resistance gene expression cassette and the target gene expression cassette are located between the gene targeting long homologous arm and the gene targeting short homologous arm, and tetracycline operator gene sequences are inserted in multiple transcriptional start sites of a target gene promoter, so that the recombinant expression vector can be used for conditional research of the functions of a certain functional gene in a plasmodium genome. Furthermore, a functional gene expression sequence, corresponding to a target gene, in the plasmodium genome is knocked out by means of the gene knockout technique; meanwhile, the recombinant expression vector is transfected into a plasmodium with genes knocked out, so that the controllable genome-modified plasmodium is obtained; a new technical scheme is provided for further research of the functions of all functional genes in the plasmodium genome, and application prospects are broad.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of design method of primer set and its application
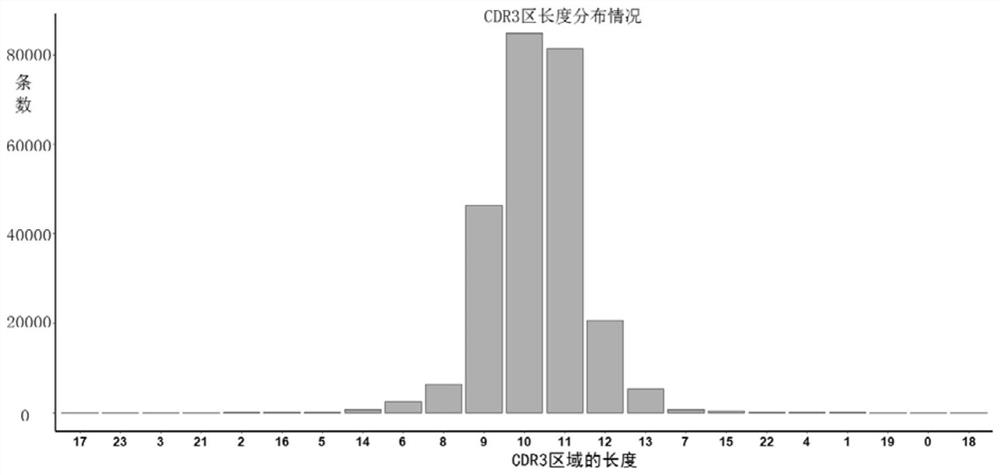
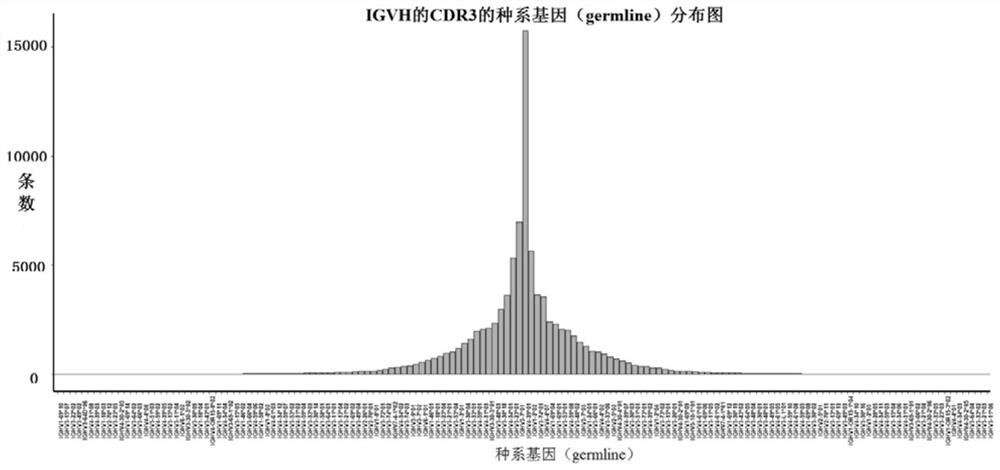
ActiveCN109411011BImprove integrityImprove reaction efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionHybridisationMultiplexStart site
The invention provides a design method and application of a primer set. According to the needs of amplification length, the sequence before the FR1 start site of the antibody is subtly extracted from the upstream of the FR1 start site of the antibody, and the sequence is extracted from the 5' end of the primer set. Starting from the first base, the fixed-length primer sequences are sequentially shifted and cut to form a candidate primer library. After cluster analysis, the primer set of the immune group library is screened. The primer set obtained by this method can significantly improve the immune group of the multiplex PCR method. The coverage and experimental efficiency of library amplification, reducing the amplification mismatch rate, the method is simple, and the cost is saved.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com