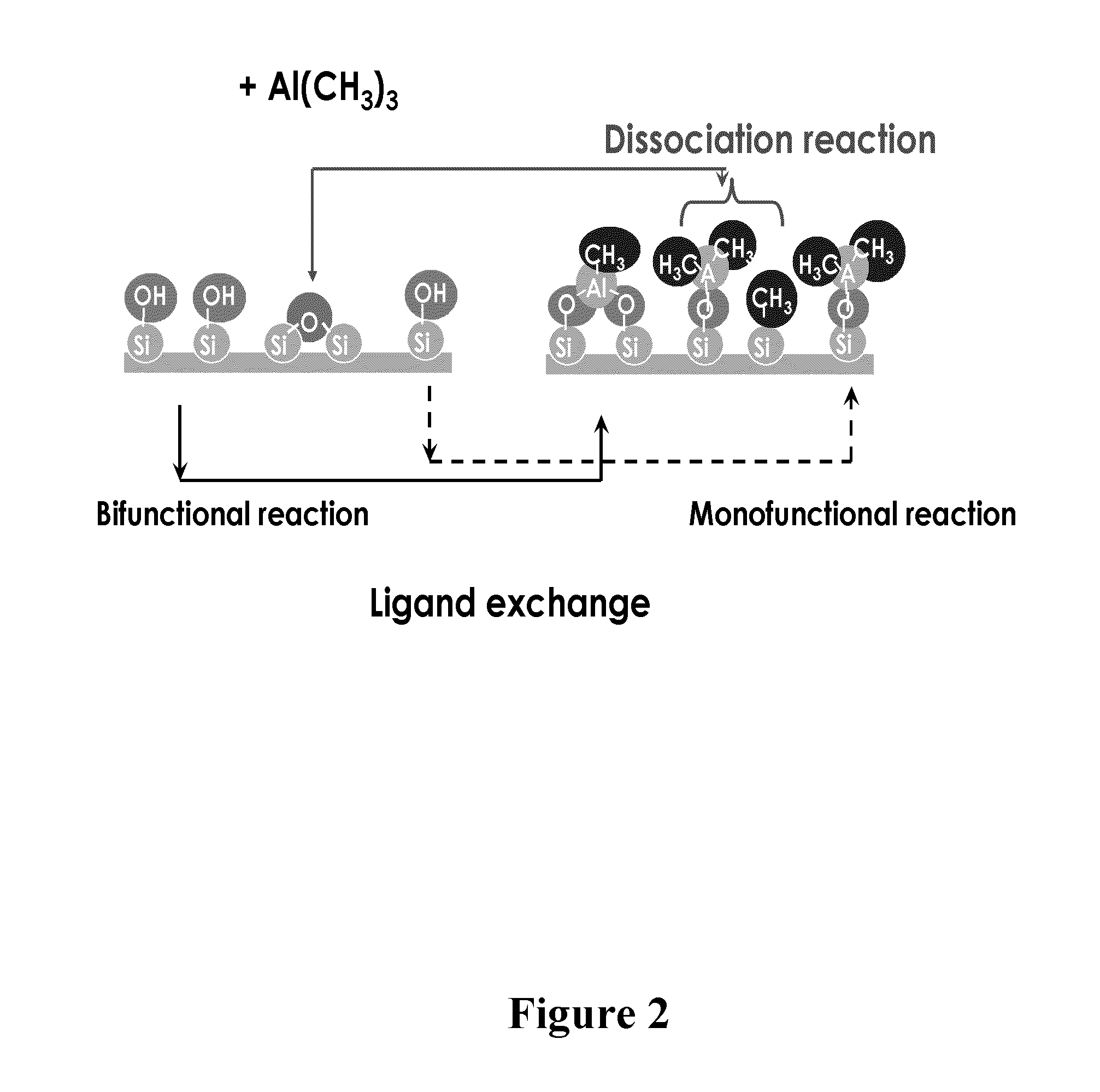
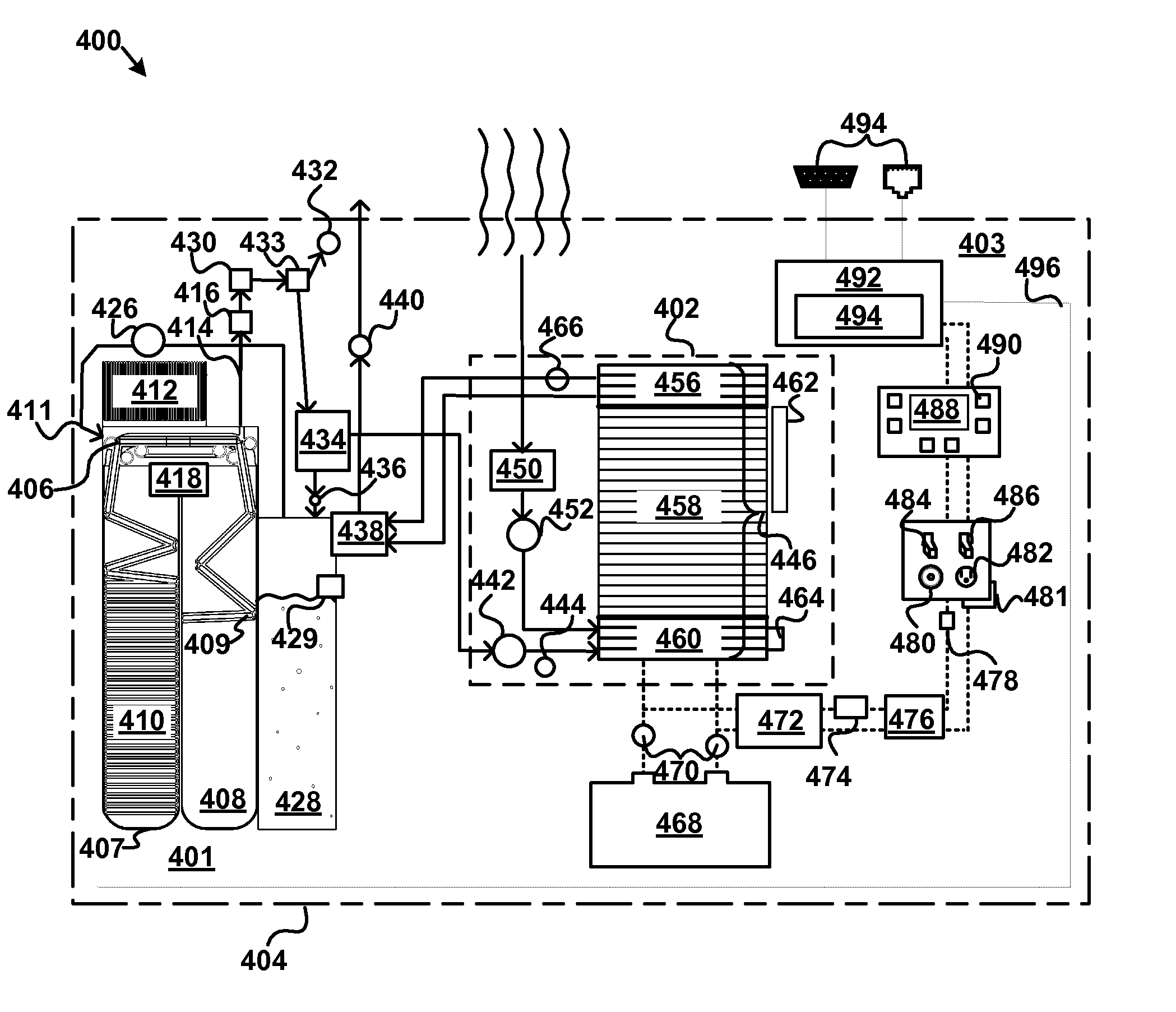
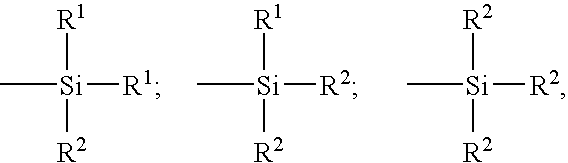Patents
Literature
75107 results about "Reagent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A reagent /riˈeɪdʒənt/ is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or added to test if a reaction occurs. The terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably—however, a reactant is more specifically a substance consumed in the course of a chemical reaction. Solvents, though involved in the reaction, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, catalysts are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates.
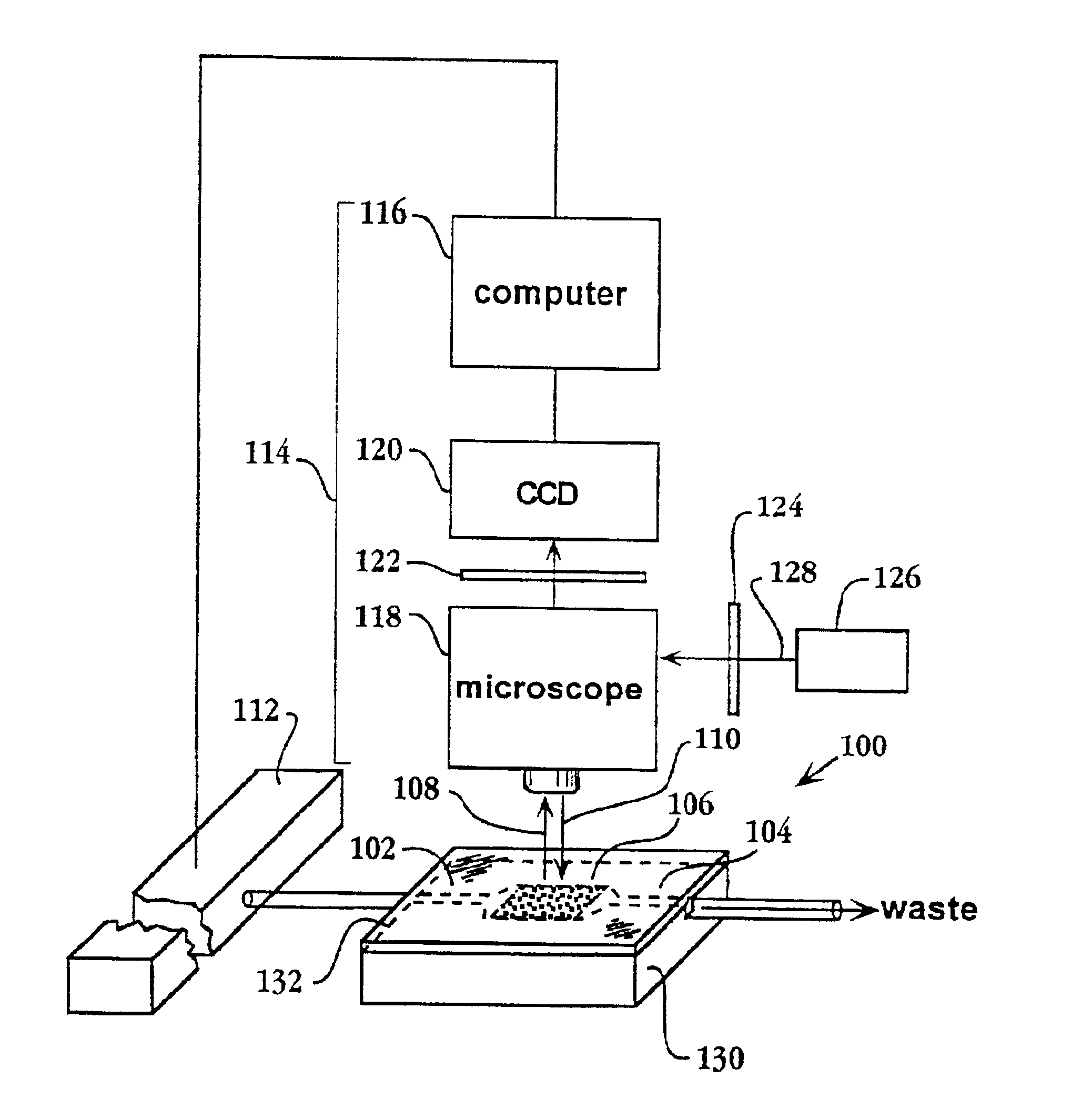
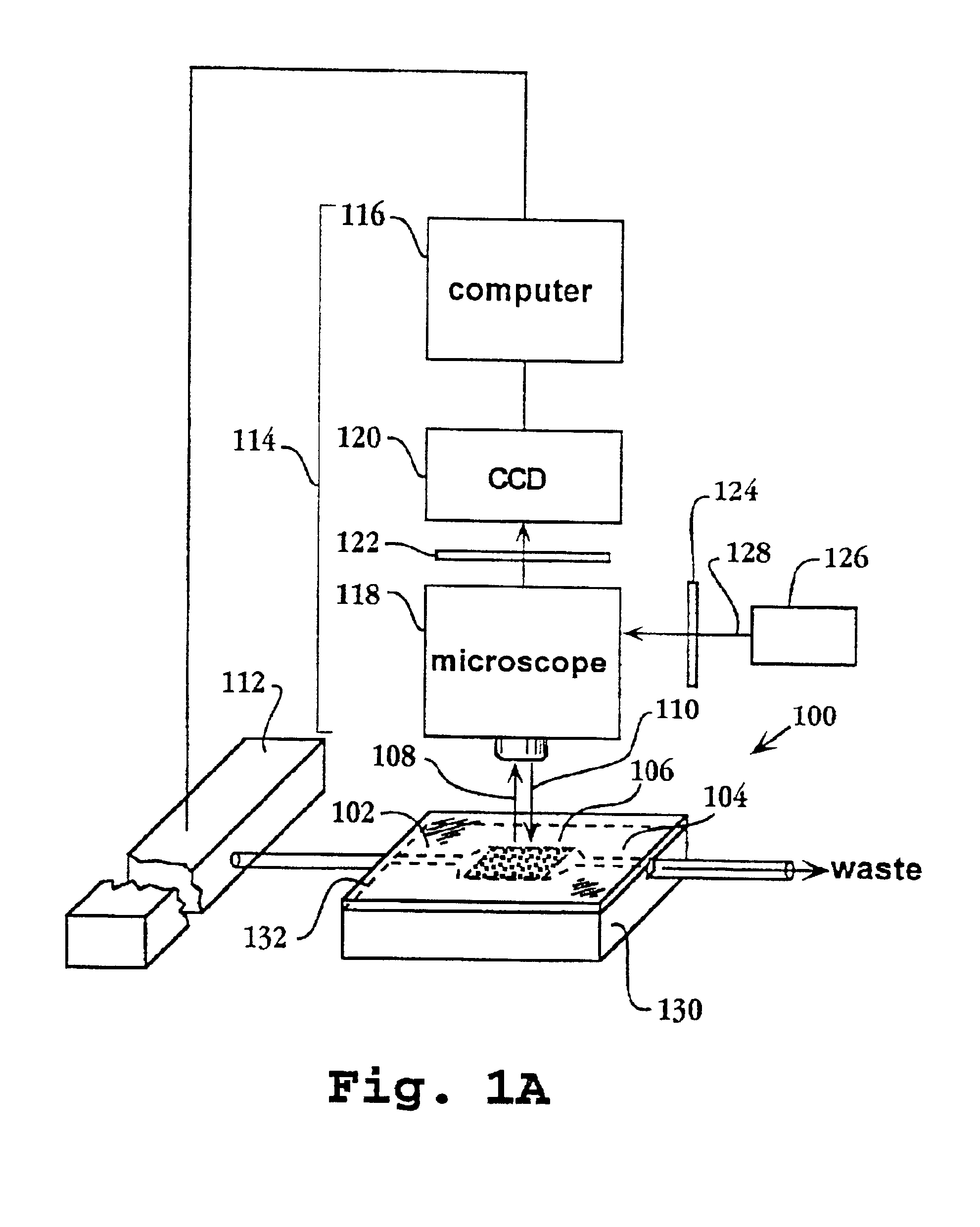
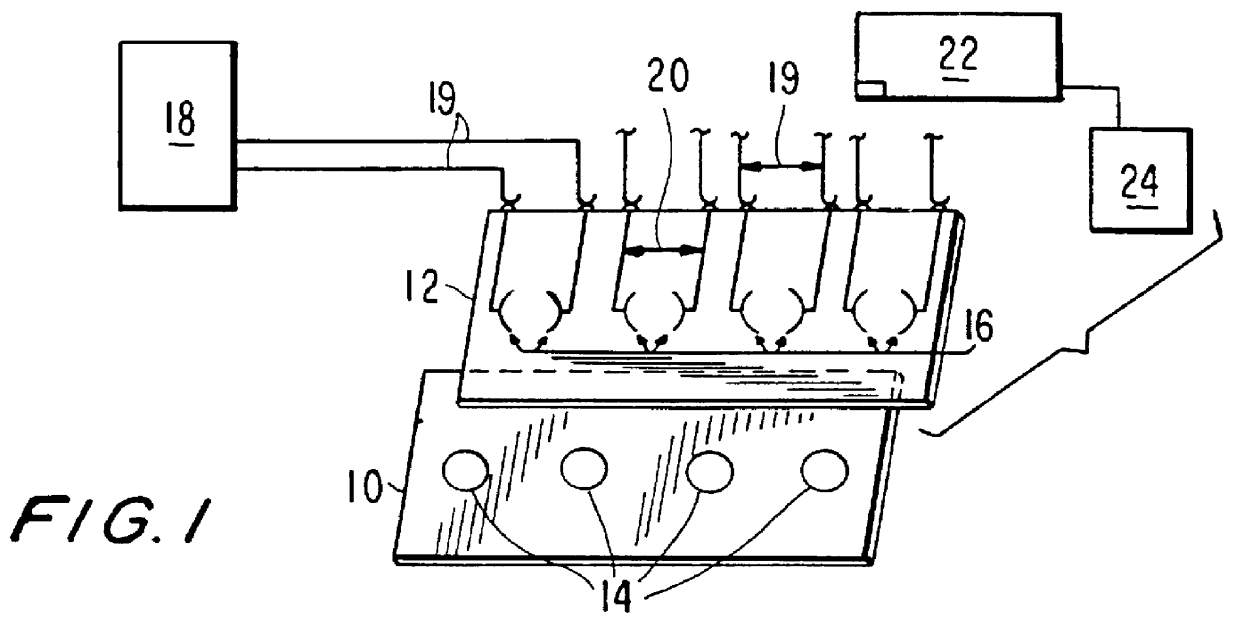
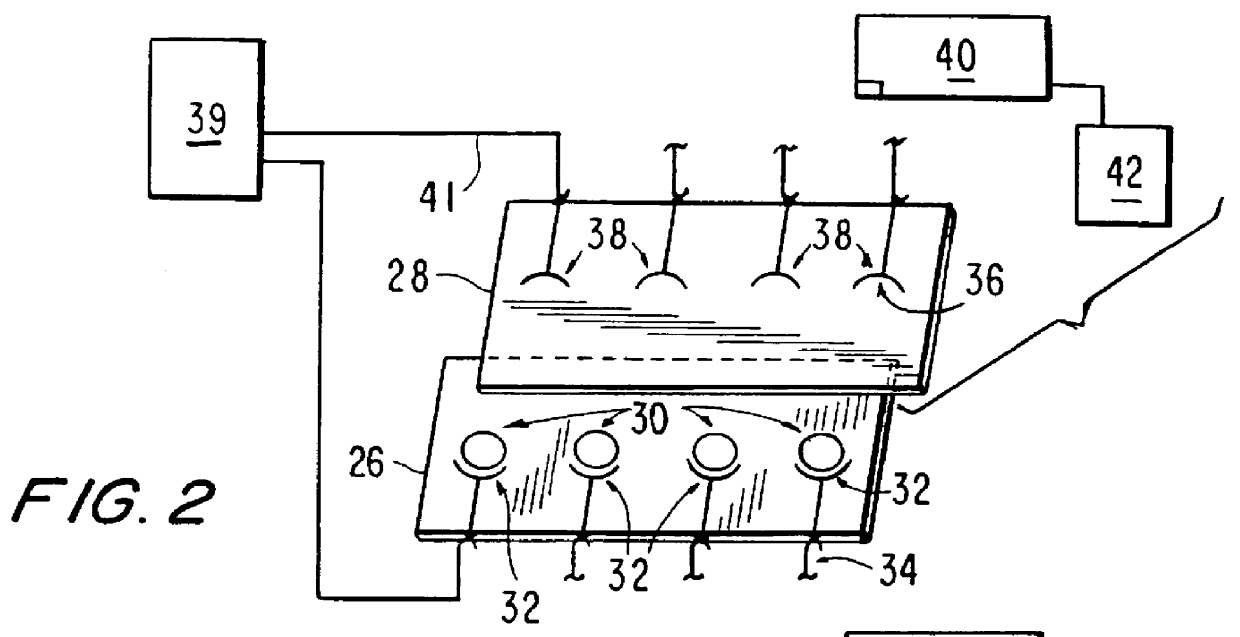
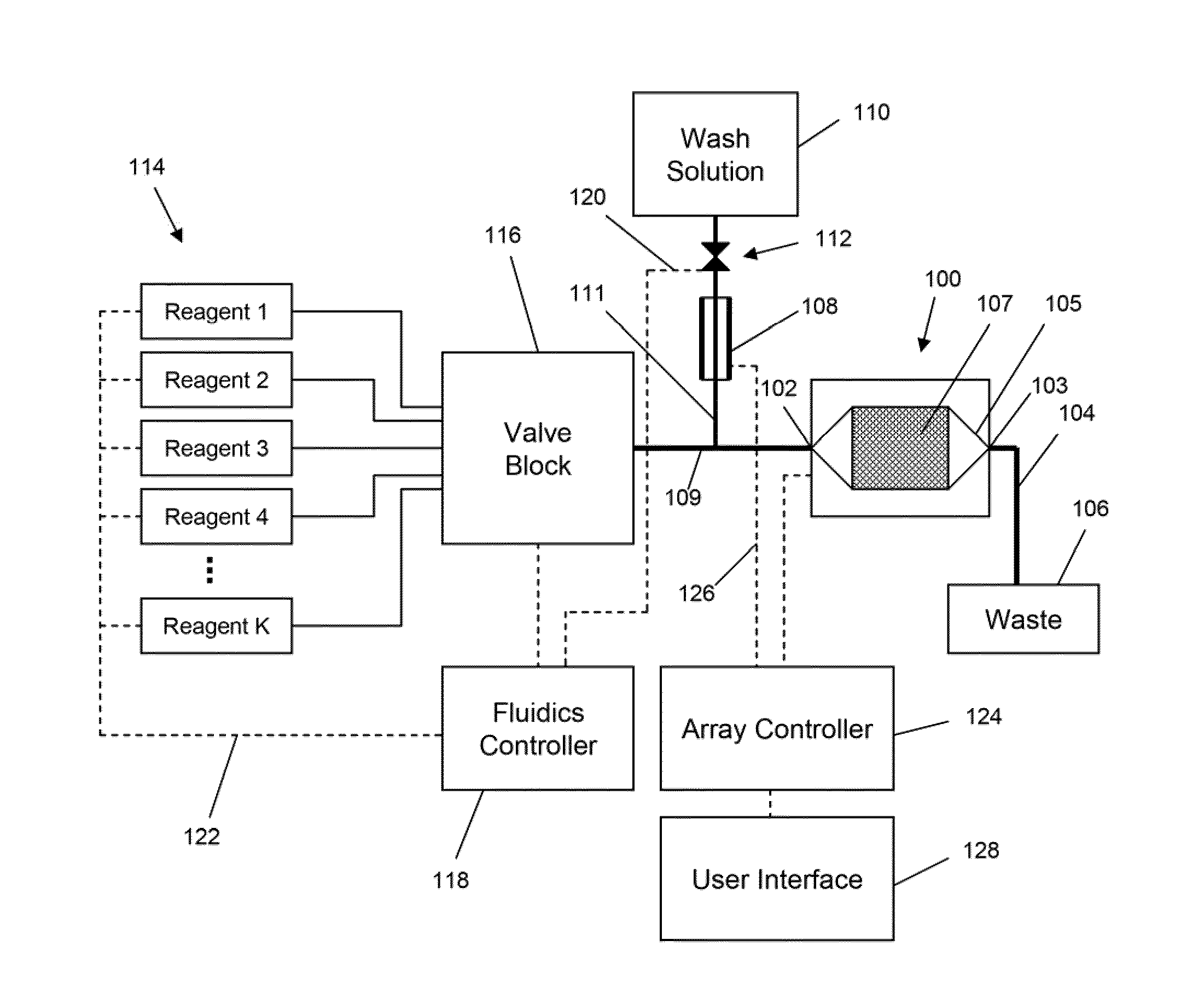
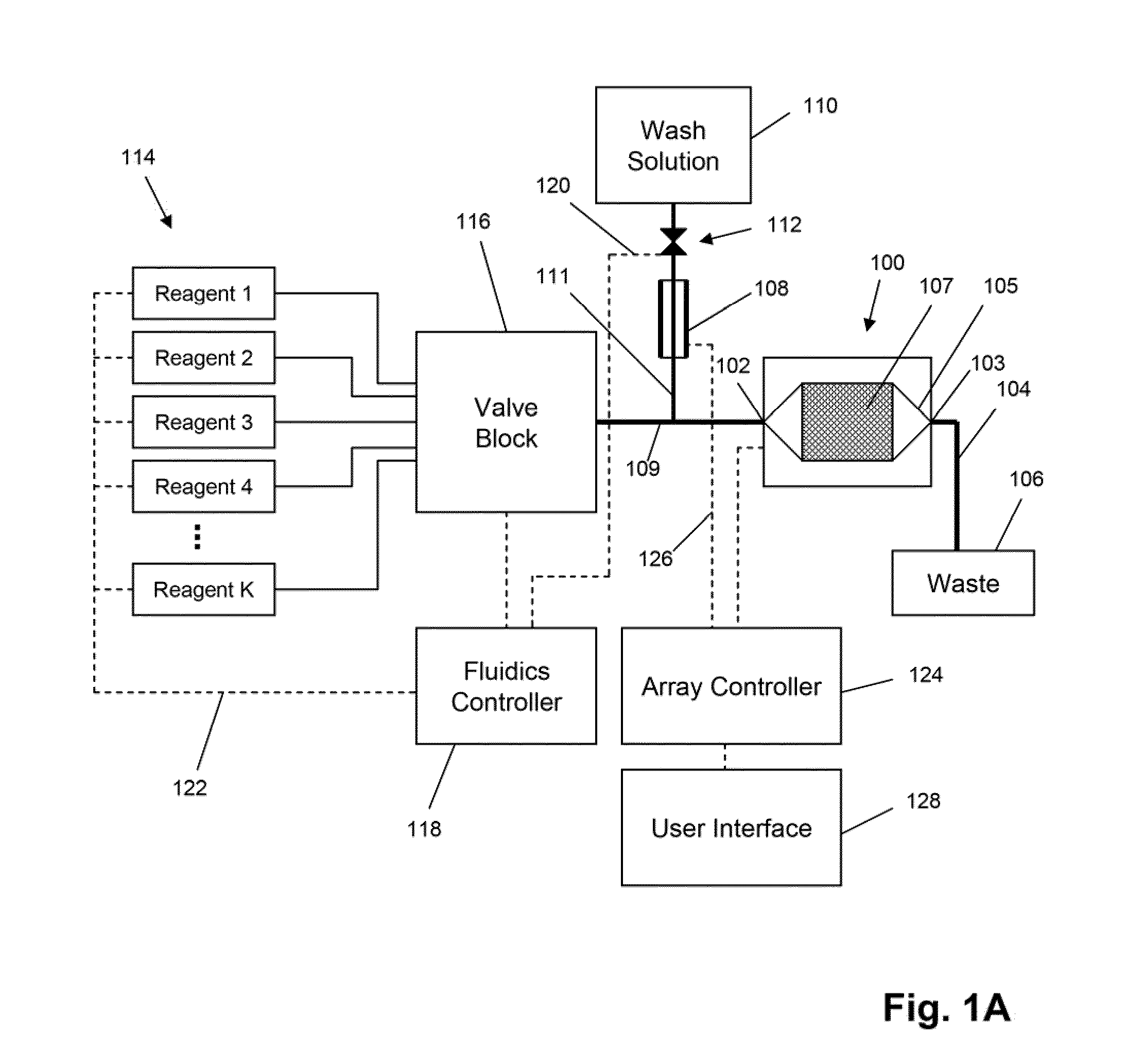
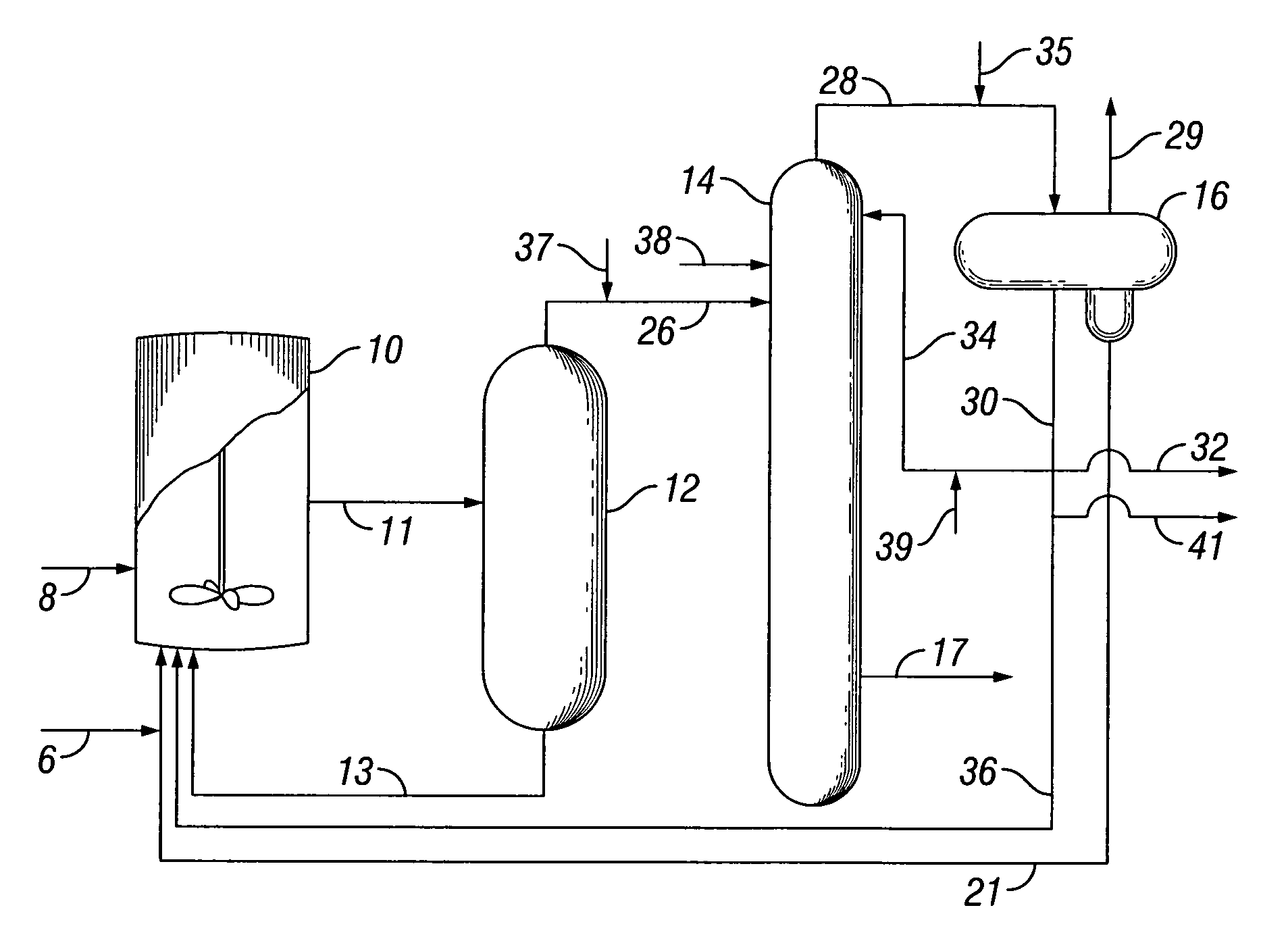
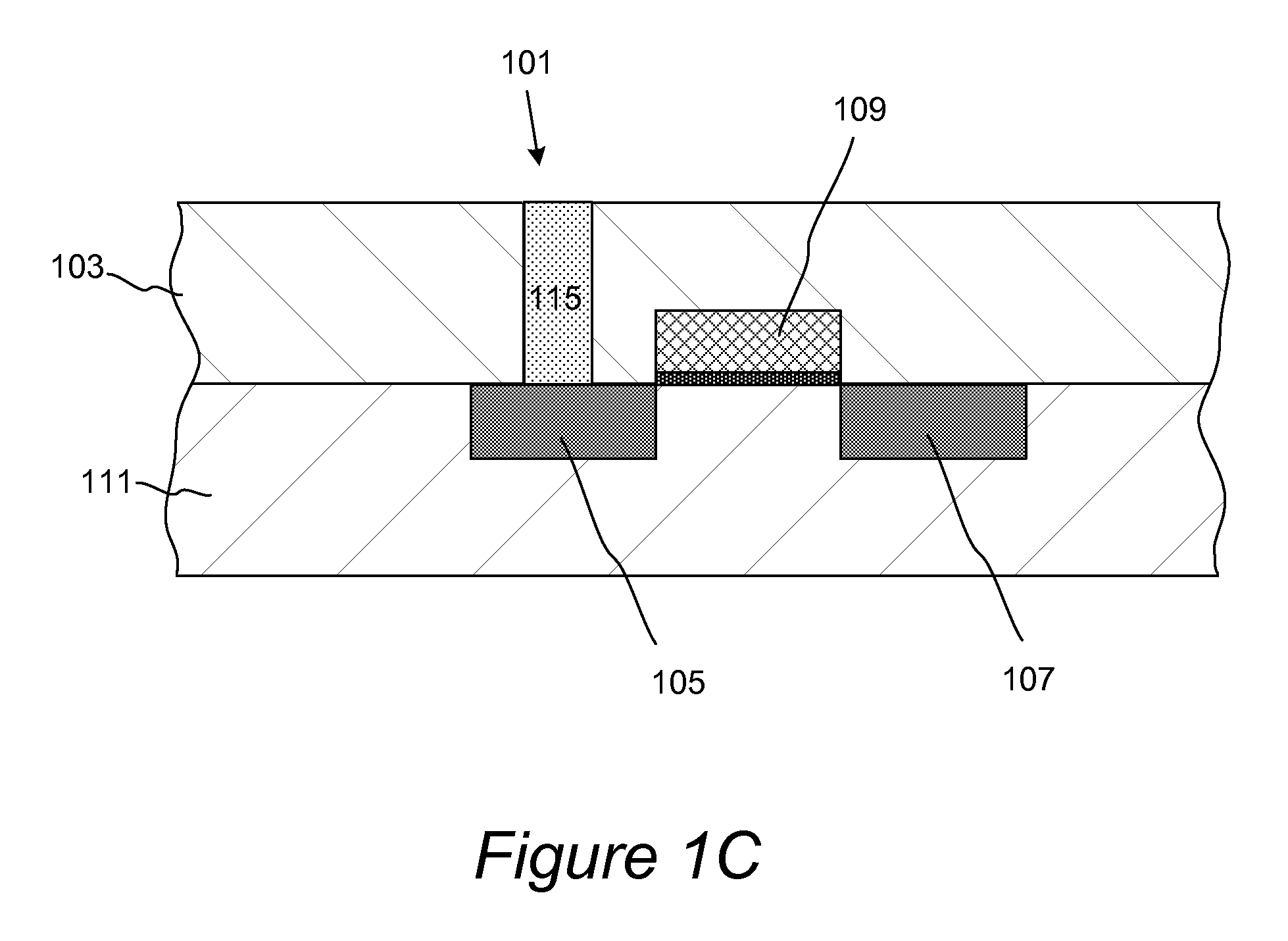
System and apparatus for sequential processing of analytes
InactiveUS6969488B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMicroparticle
An apparatus and system are provided for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of analytes anchored to microparticles. Microparticles each having a uniform population of a single kind of analyte attached are disposed as a substantially immobilized planar array inside of a flow chamber where steps of an analytical process are carried out by delivering a sequence of processing reagents to the microparticles by a fluidic system under microprocessor control. In response to such process steps, an optical signal is generated at the surface of each microparticle which is characteristic of the interaction between the analyte carried by the microparticle and the delivered processing reagent. The plurality of analytes are simultaneously analyzed by collecting and recording images of the optical signals generated by all the microparticles in the planar array. A key feature of the invention is the correlation of the sequence of optical signals generated by each microparticle in the planar array during the analytical process.
Owner:SOLEXA
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6066448AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Process for obtaining a grafted elastomer having functional groups along the chain and a rubber composition
A process for obtaining a grafted diene elastomer having functional groups along the chain, a rubber composition containing this grafted elastomer and having in particular improved hysteresis properties in the cross-linked state, a preparation process for this composition, a tire tread made from this composition and a tire of reduced rolling resistance which incorporates this tread. A process for obtaining this grafted elastomer includes a radical grafting reaction carried out in solution or without a solvent by means of a reagent of the mercaptan type to graft functional groups on to the chain of a starting elastomer. The starting elastomer is treated with an antioxidant having at least one aromatic amine function before the grafting reaction, so that the grafted elastomer has a macrostructure which is practically identical to that of the starting elastomer. A rubber composition containing the grafted diene elastomer includes a reinforcing inorganic filler, and the grafted elastomer preferably has a molar ratio of units originating from conjugated dienes greater than 30%.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
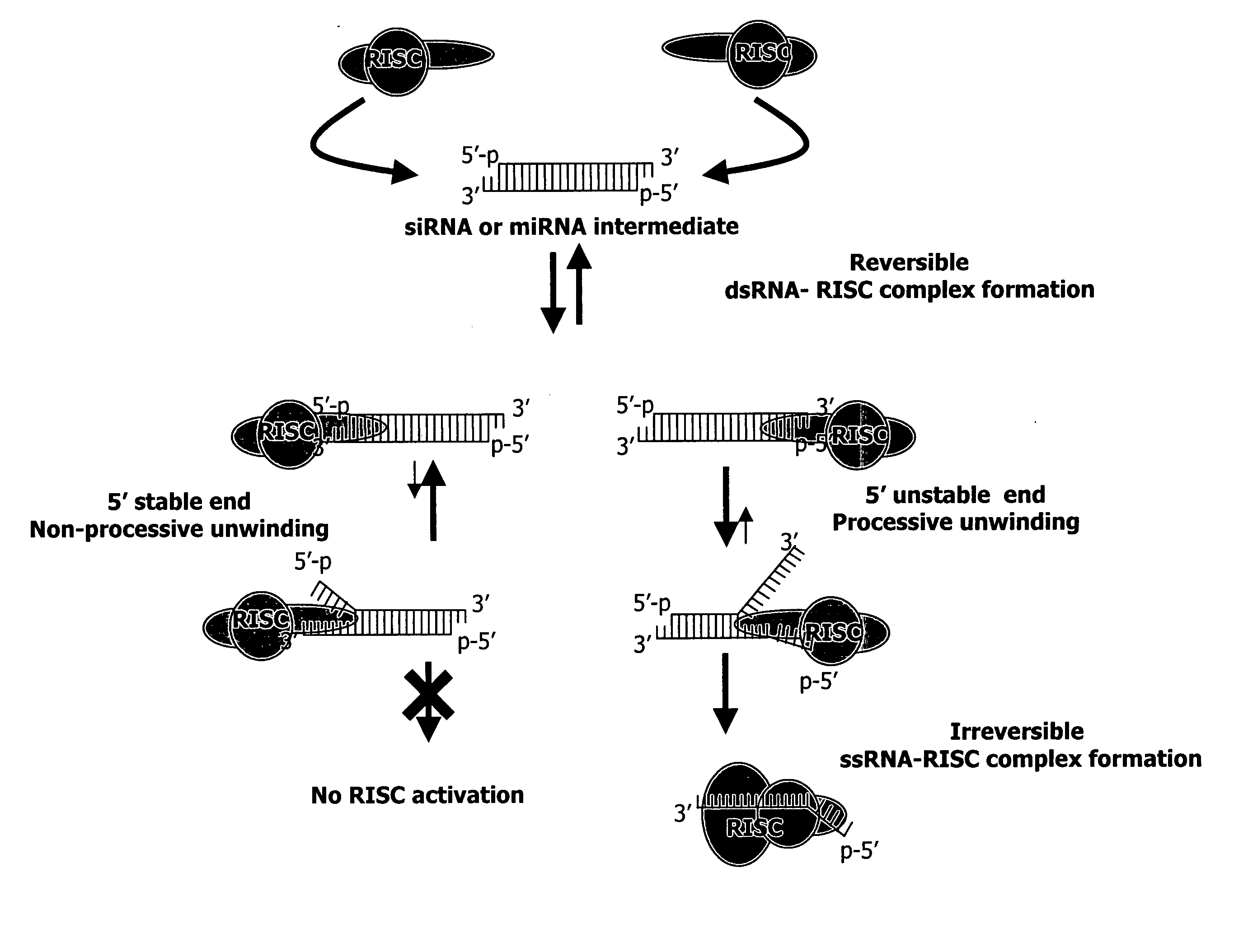
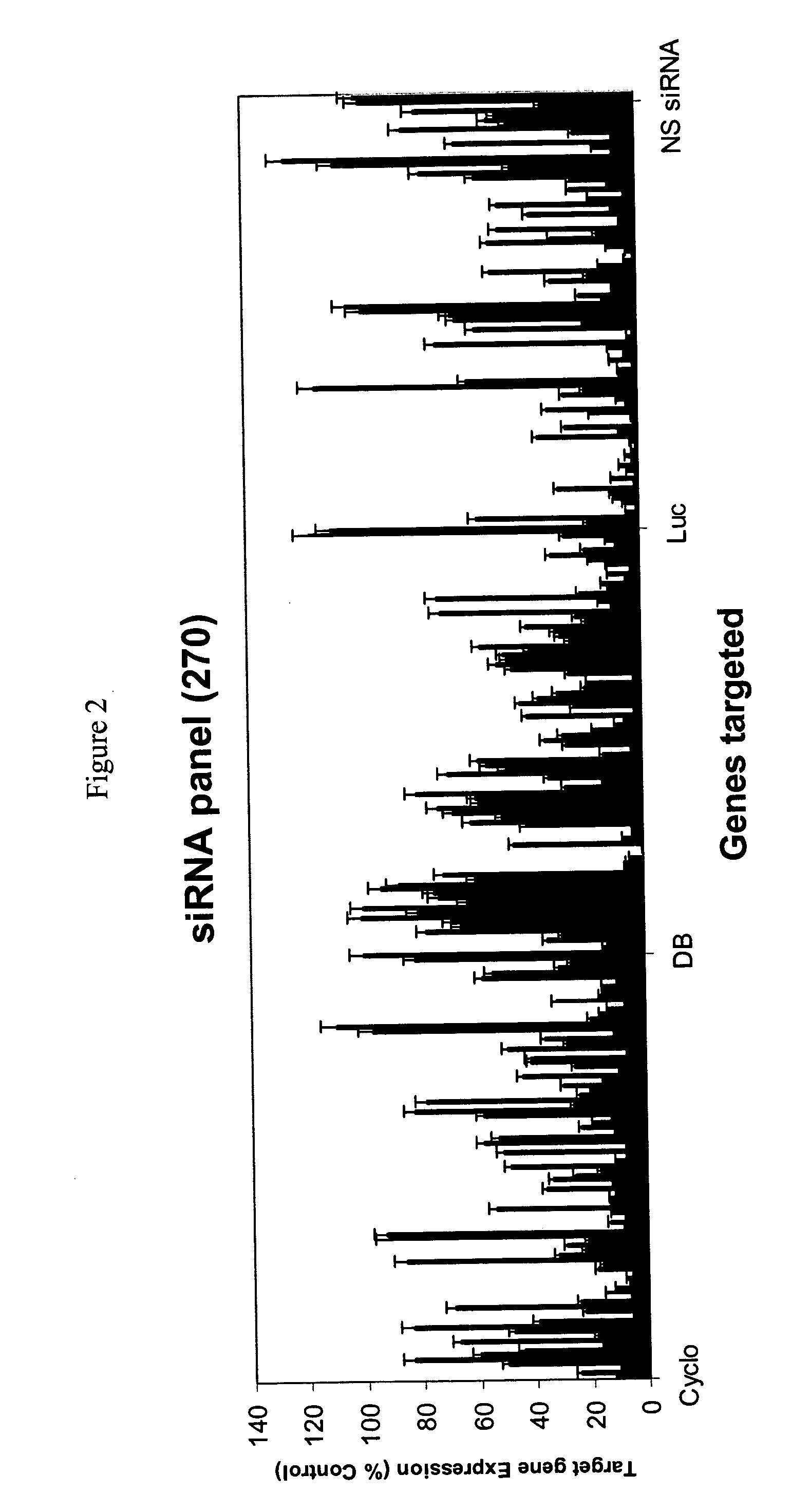
Methods and compositions for selecting siRNA of improved functionality
InactiveUS20050255487A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene silencingSilencing gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
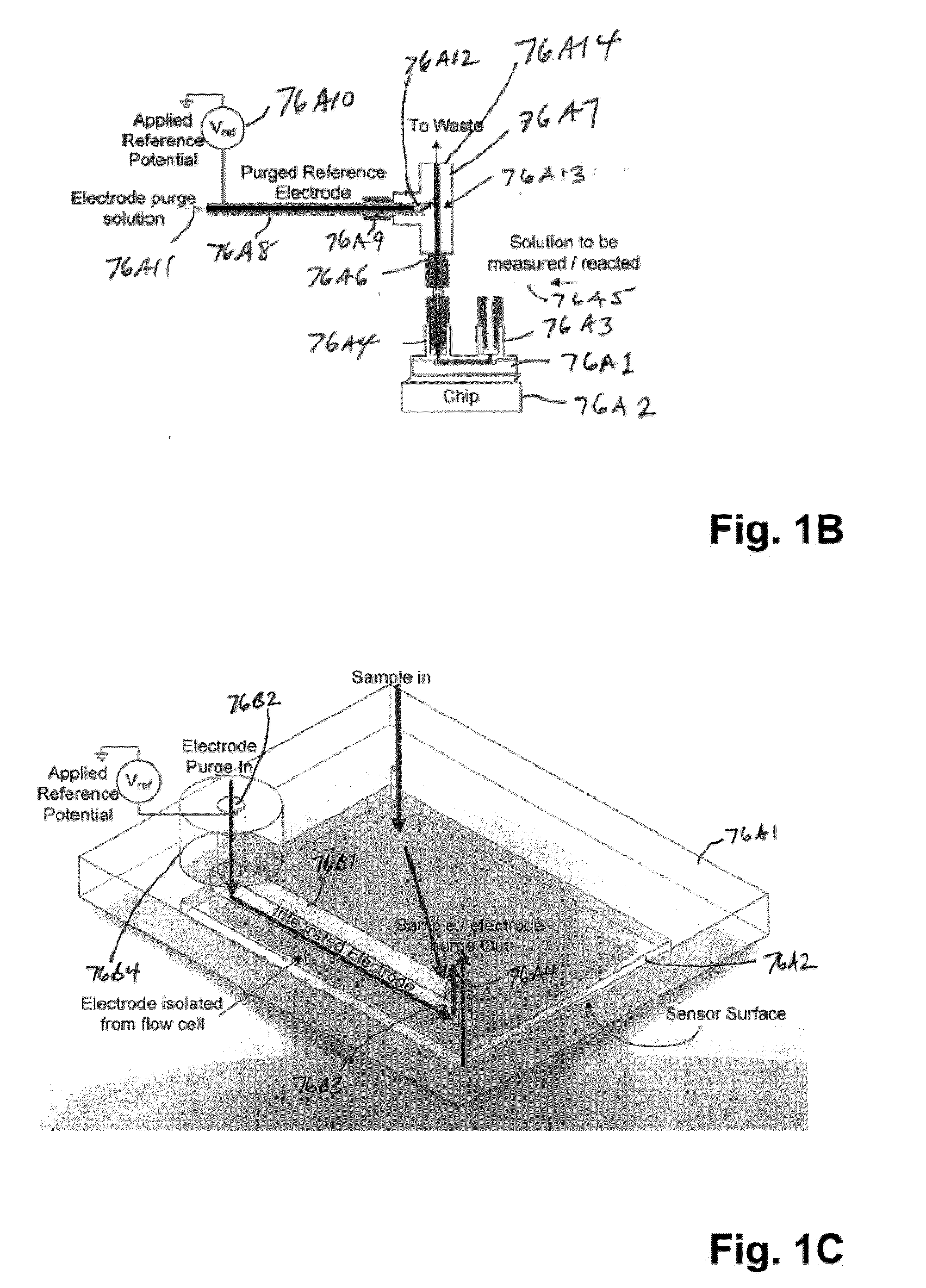
Apparatus and methods for performing electrochemical reactions
ActiveUS20100300895A1Reduce noiseWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectrochemical responseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention is directed to apparatus and methods for delivering multiple reagents to, and monitoring, a plurality of analytical reactions carried out on a large-scale array of electronic sensors underminimal noise conditions. In one aspect, the invention provides method of improving signal-to-noise ratios of output signals from the electronic sensors sensing analytes or reaction byproducts by subtracting an average of output signals measured from neighboring sensors where analyte or reaction byproducts are absent. In other aspects, the invention provides an array of electronic sensors integrated with a microwell array for confining analytes and / or particles for analytical reactions and a method for identifying microwells containing analytes and / or particles by passing a sensor-active reagent over the array and correlating sensor response times to the presence or absence of analytes or particles. Such detection of analyte- or particle-containing microwells may be used as a step in additional noise reduction methods.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Thermoplastic starch compositions incorporating a particulate filler component
InactiveUS6231970B1Reduce molecular weightAvoid hydrolysisProtein adhesivesPaper coatingParticulatesCross-link
Thermoplastic starch compositions that include a particulate filler, e.g. an inorganic filler component, and optional fibrous component The compositions include a thermoplastic phase comprising a thermoplastic starch melt that contains, at a minimum, starch blended with an appropriate plasticizing agent under conditions in order for the starch to form a thermoplastic melt. The thermoplastic phase may also include one or more additional thermoplastic polymers and other optional reactants, liquids or cross-linking agents to improve the water-resistance, strength, and / or other mechanical properties of the thermoplastic melt, particularly upon solidification. The inorganic filler component may affect the mechanical properties but will mainly be added to reduce the cost of the thermoplastic starch compositions by displacing a significant portion of the more expensive starch or starch / polymer melt. Fibers may optionally be included in order to improve the mechanical properties of the thermoplastic starch compositions. The thermoplastic starch compositions may be shaped into a wide variety of useful articles, such as sheets, films, containers, and packaging materials. Because the thermoplastic starch compositions will typically include a thermoplastic phase that is biodegradable, and because the other components will either constitute a naturally occurring mineral and optionally a natural fiber, the overall composition will typically be more environmentally friendly compared to conventional thermoplastic materials.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Capillary immunoassay and device therefor comprising mobilizable particulate labelled reagents
InactiveUS6228660B1Improve completenessAnalysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationParticulatesAnalyte
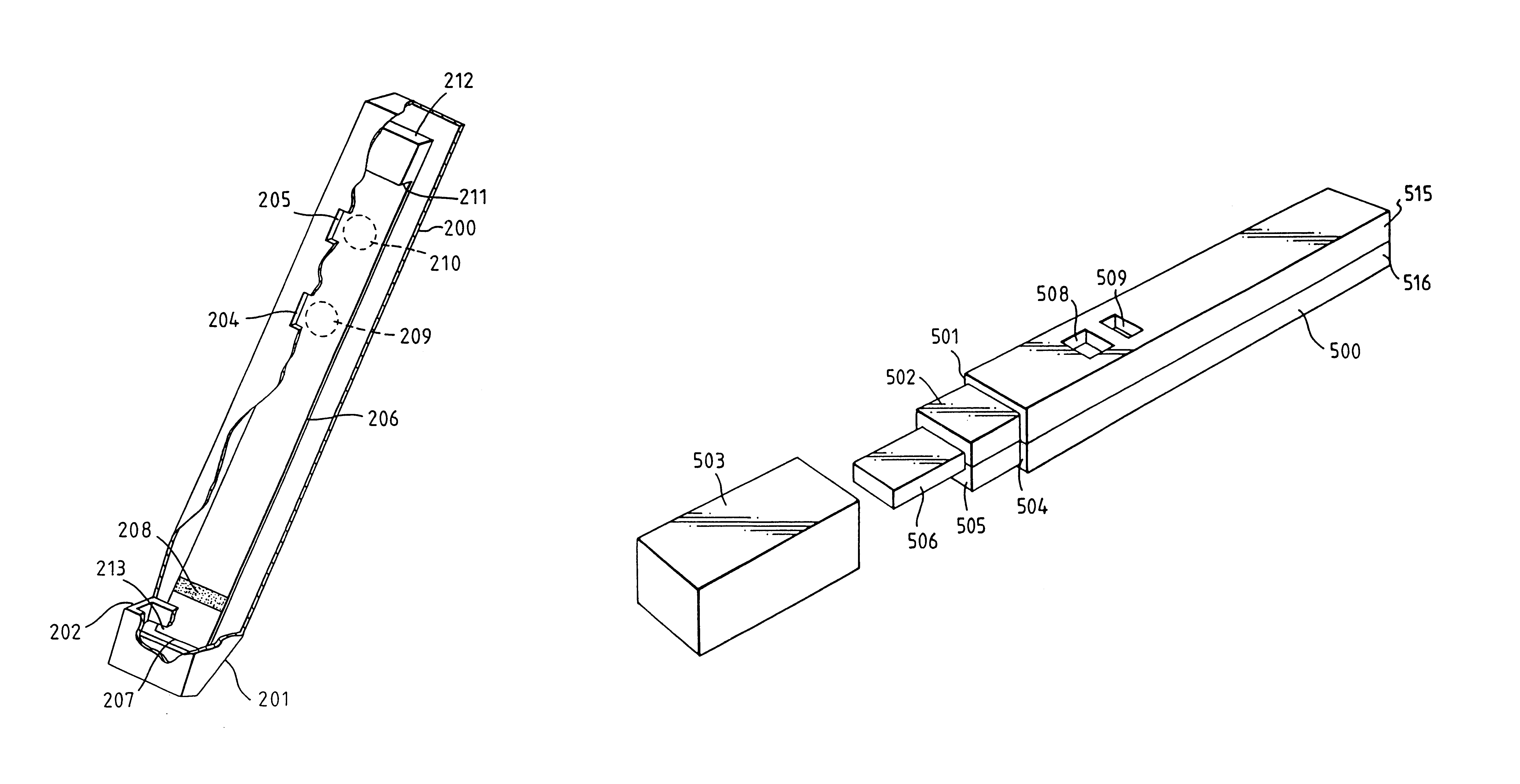
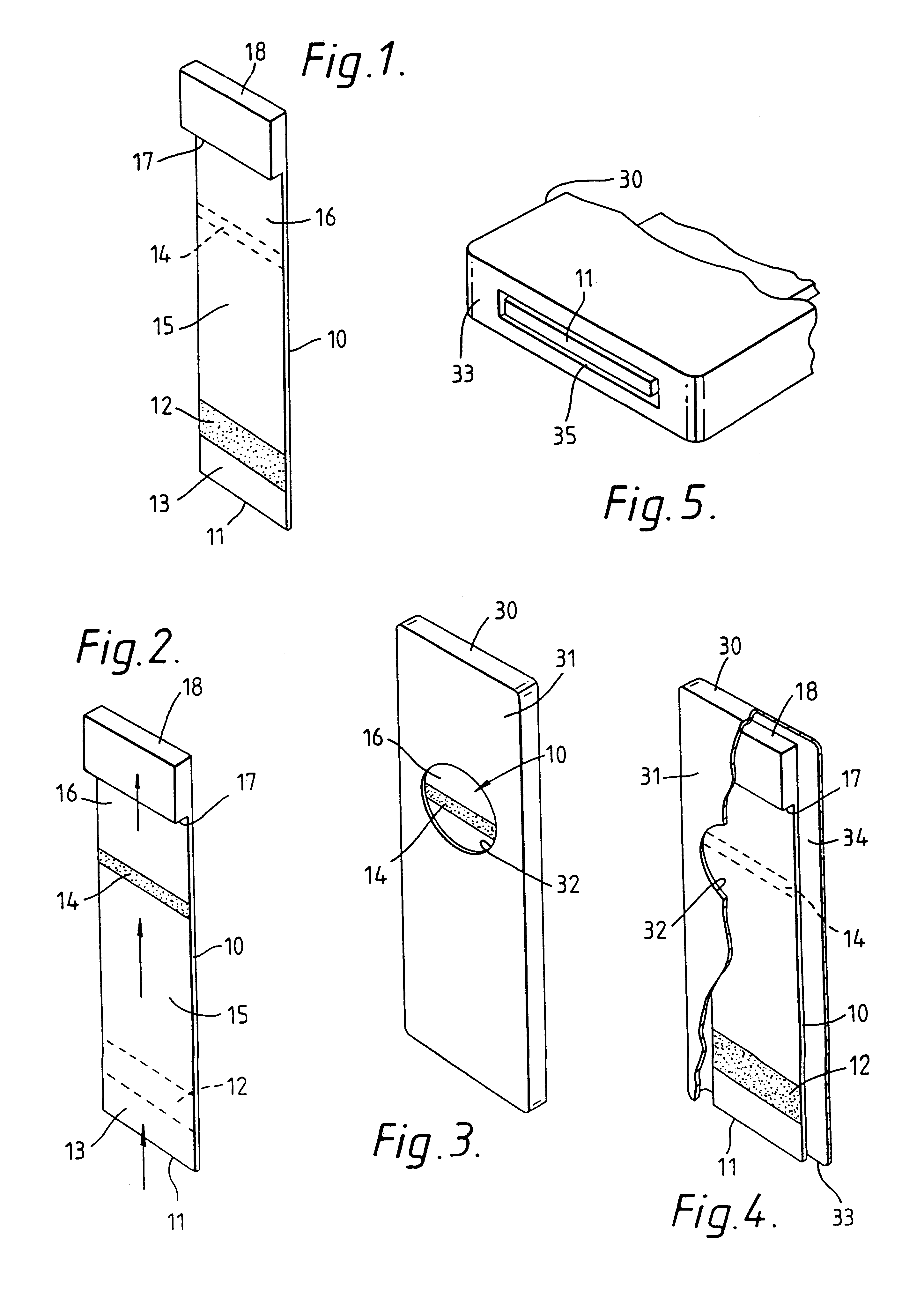
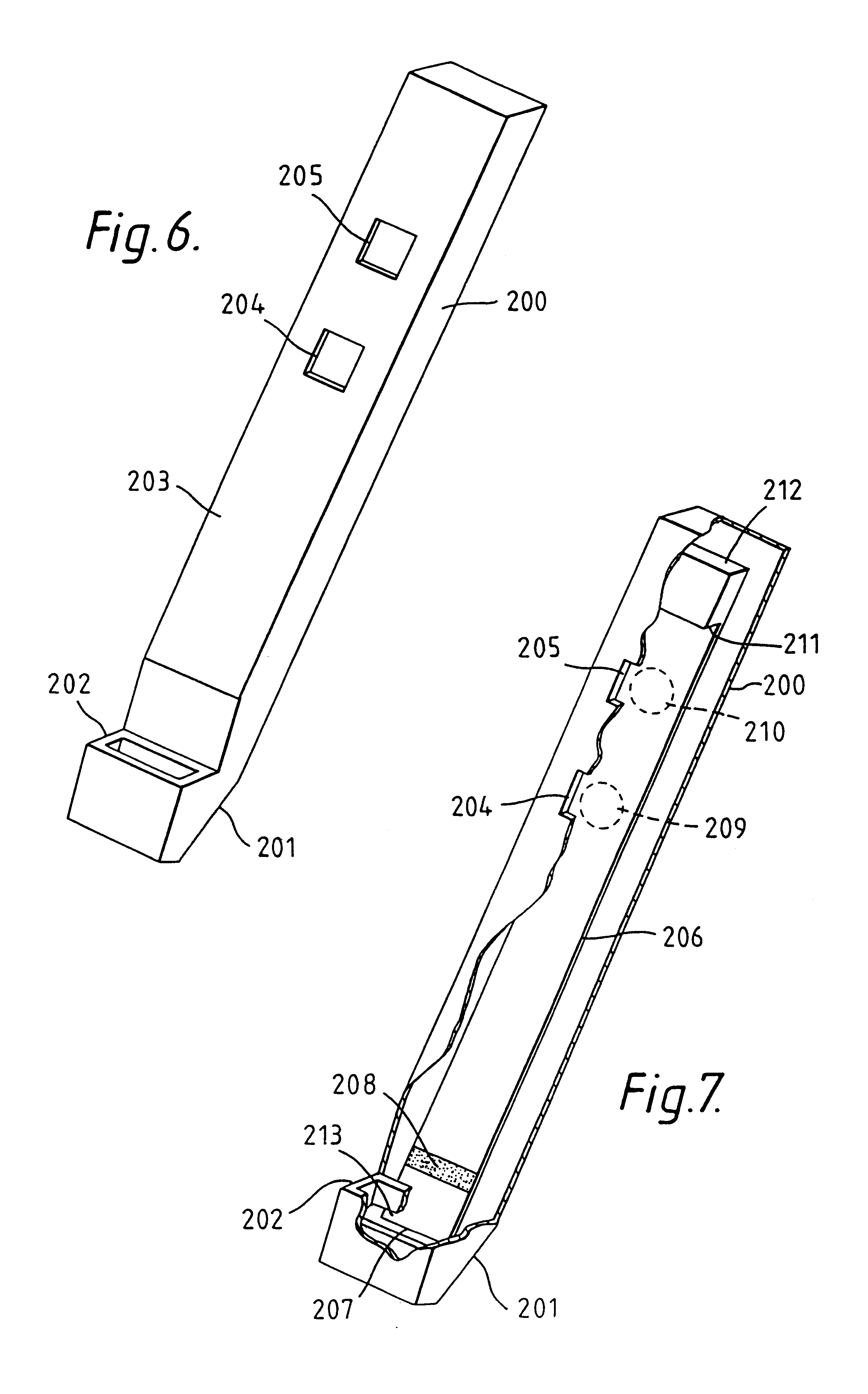
An analytical test device useful for example in pregnancy testing, comprises a hollow casing (500) constructed of moisture-impervious solid material, such as plastics materials, containing a dry porous carrier (510) which communicates indirectly with the exterior of the casing via a bibulous sample receiving member (506) which protrudes from the casing such that a liquid test sample can be applied to the receiving member and permeate therefrom to the porous carrier, the carrier containing in a first zone a labelled specific binding reagent is freely mobile within the porous carrier when in the moist state, and in a second zone spatially distinct from the first zone unlabelled specific binding reagent for the same analyte which unlabelled reagent is permanently immobilized on the carrier material and is therefore not mobile in the moist state, the two zones being arranged such that liquid sample applied to the porous carrier can permeate via the first zone into the second zone, and the device incorporating means, such as an aperture (508) in the casing, enabling the extent (if any) to which the labelled reagent becomes bound in the second zone to be observed. Preferably the device includes a removable cap for the protruding bibulous member.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7208624B2Easy to separateFacilitate phase separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateFormate Esters
An improved process is disclosed for producing acetic acid, including the following steps: reacting a carbonylatable reactant such as methanol, methyl acetate, methyl formate or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in a reaction medium containing water, methyl iodide, and a catalyst to produce a reaction product that contains acetic acid; separating the reaction product to provide a volatile phase containing acetic acid, water, and methyl iodide and a less volatile phase; distilling the volatile phase to produce a purified acetic acid product and a first overhead containing water, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide; phase separating the first overhead to provide a first liquid phase containing water and a second liquid phase containing methyl iodide; and adding dimethyl ether to the process in an amount effective to enhance separation of the first overhead to form the first and second liquid phases.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Solid precursor-based delivery of fluid utilizing controlled solids morphology
ActiveUS20100255198A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMetal halidesAtomic layer deposition
Apparatus and method for volatilizing a source reagent susceptible to particle generation or presence of particles in the corresponding source reagent vapor, in which such particle generation or presence is suppressed by structural or processing features of the vapor generation system. Such apparatus and method are applicable to liquid and solid source reagents, particularly solid source reagents such as metal halides, e.g., hafnium chloride. The source reagent in one specific implementation is constituted by a porous monolithic bulk form of the source reagent material. The apparatus and method of the invention are usefully employed to provide source reagent vapor for applications such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) and ion implantation.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Reaction system for growing a thin film
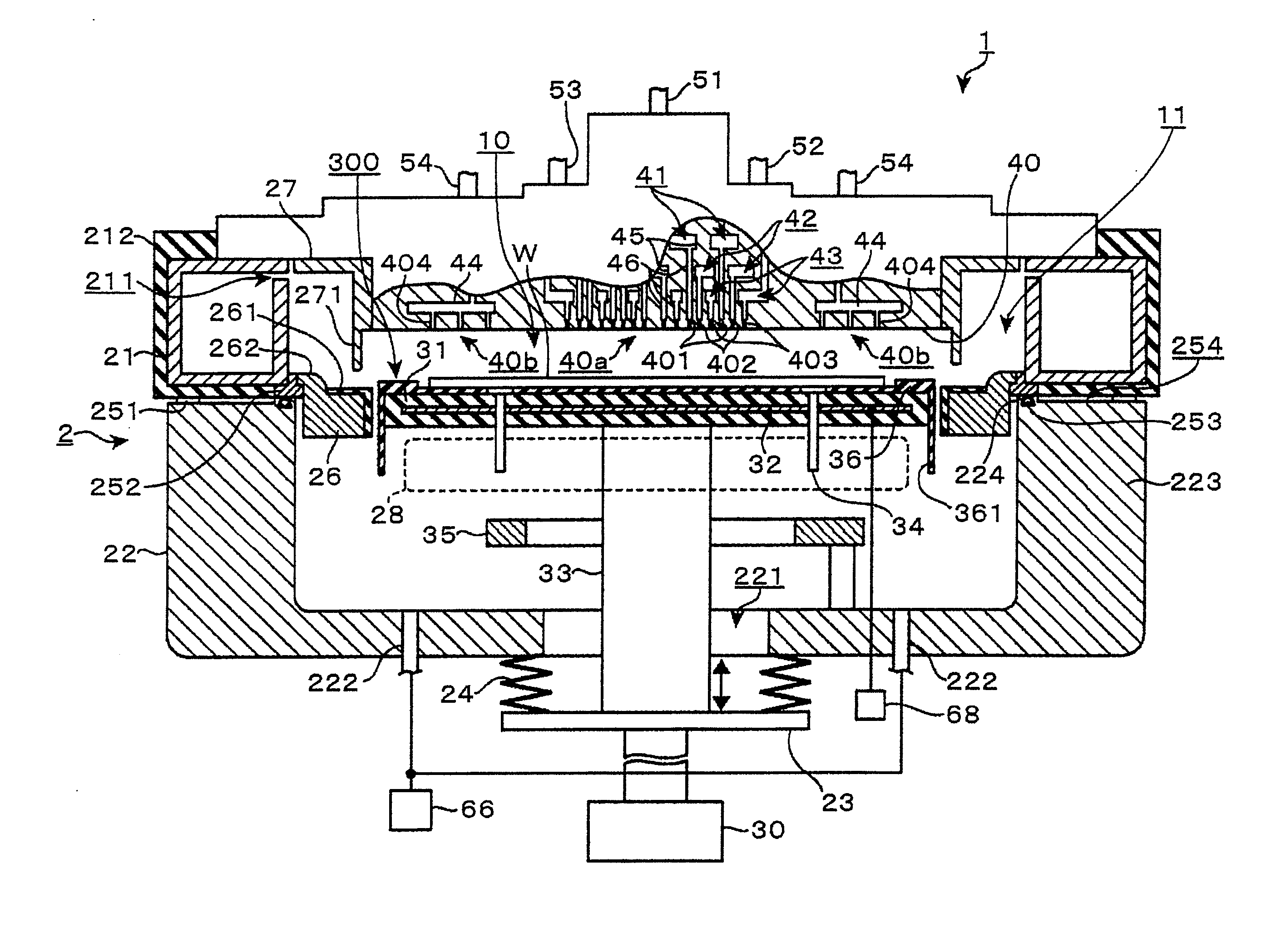
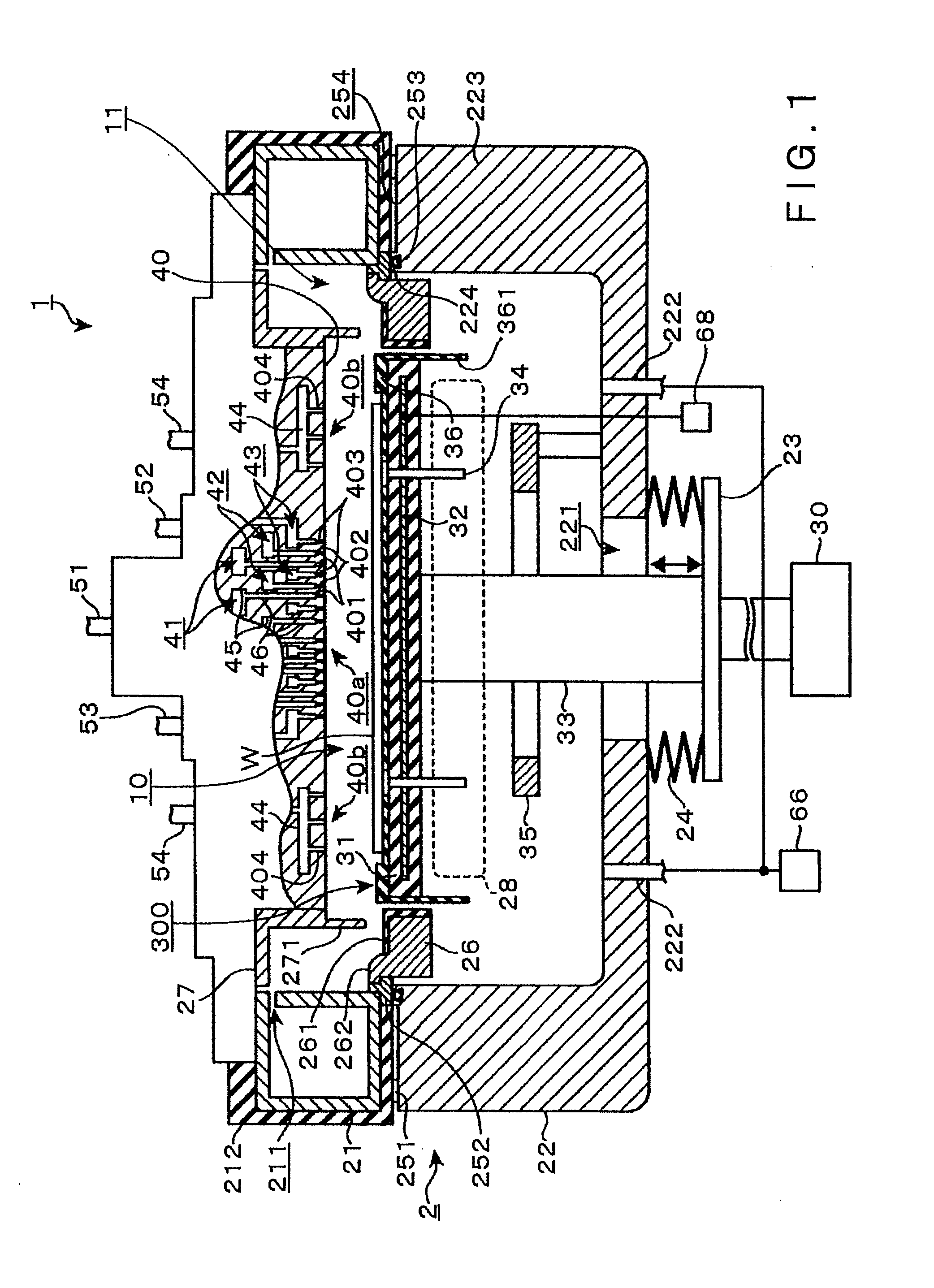
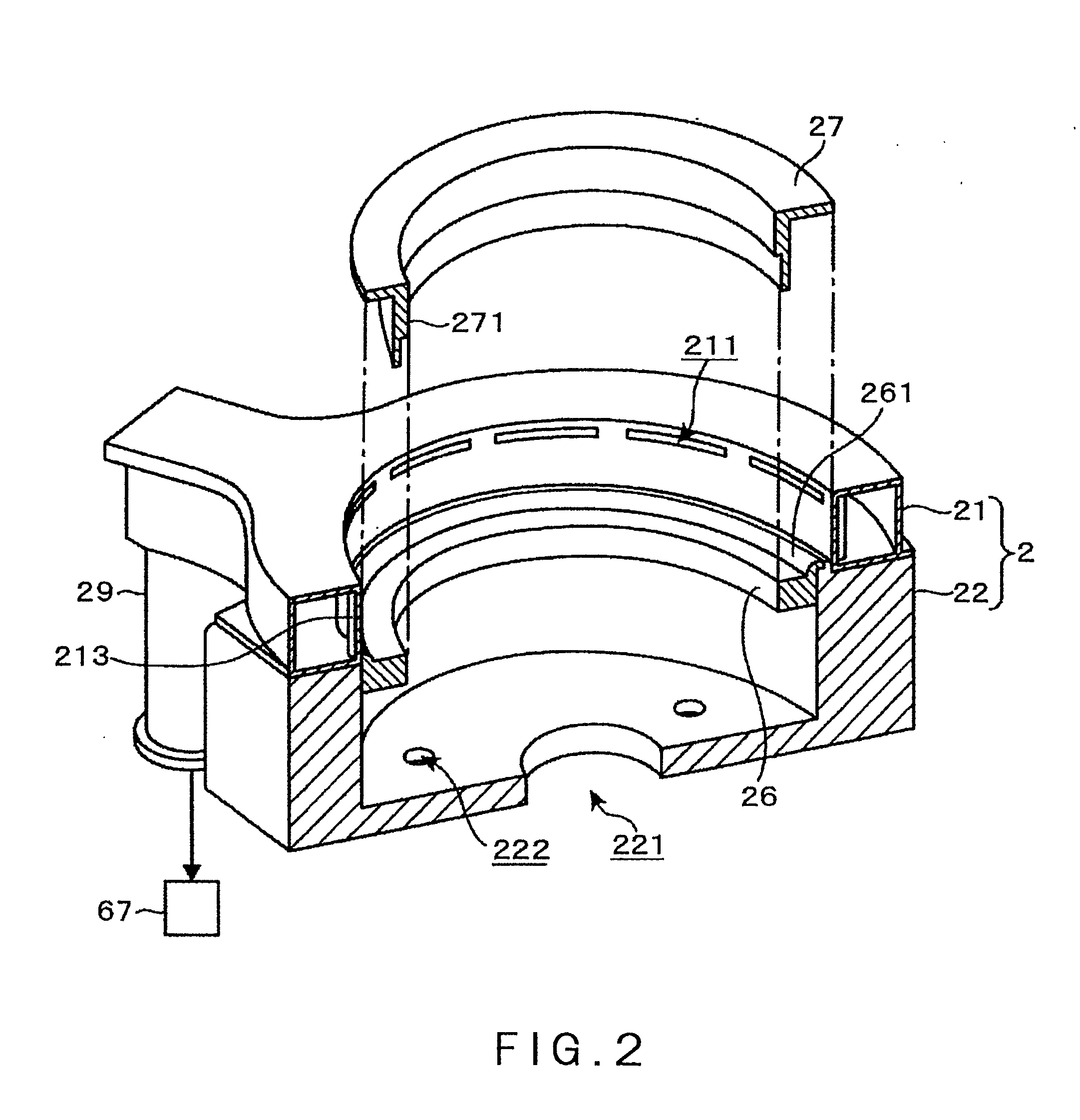
ActiveUS20050241176A1Extension of timeLong stepDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatControl systemDiffusion barrier
A reactor defines a reaction chamber for processing a substrate. The reactor comprises a first inlet for providing a first reactant and to the reaction chamber and a second inlet for a second reactant to the reaction chamber. A first exhaust outlet removes gases from the reaction chamber. A second exhaust outlet removes gases from the reaction chamber. A flow control system is configured to alternately constrict flow through the first and second exhaust outlets. The reactor chamber is configured to for a diffusion barrier within the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Methods of Analyzing Nucleic Acids from Individual Cells or Cell Populations
InactiveUS20150376609A1Facilitate hybridizationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationReagentNucleic acid
Methods, compositions and systems for analyzing individual cells or cell populations through the partitioned analysis of contents of individual cells or cell populations. Individual cells or cell populations are co-partitioned with processing reagents for accessing cellular contents, and for uniquely identifying the contents of a given cell or cell population, and subsequently analyzing the cell's contents and characterizing it as having derived from an individual cell or cell population, including analysis and characterization of the cell's nucleic acids through sequencing.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
InactiveUS6801041B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsTarget analysisAnalyte
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
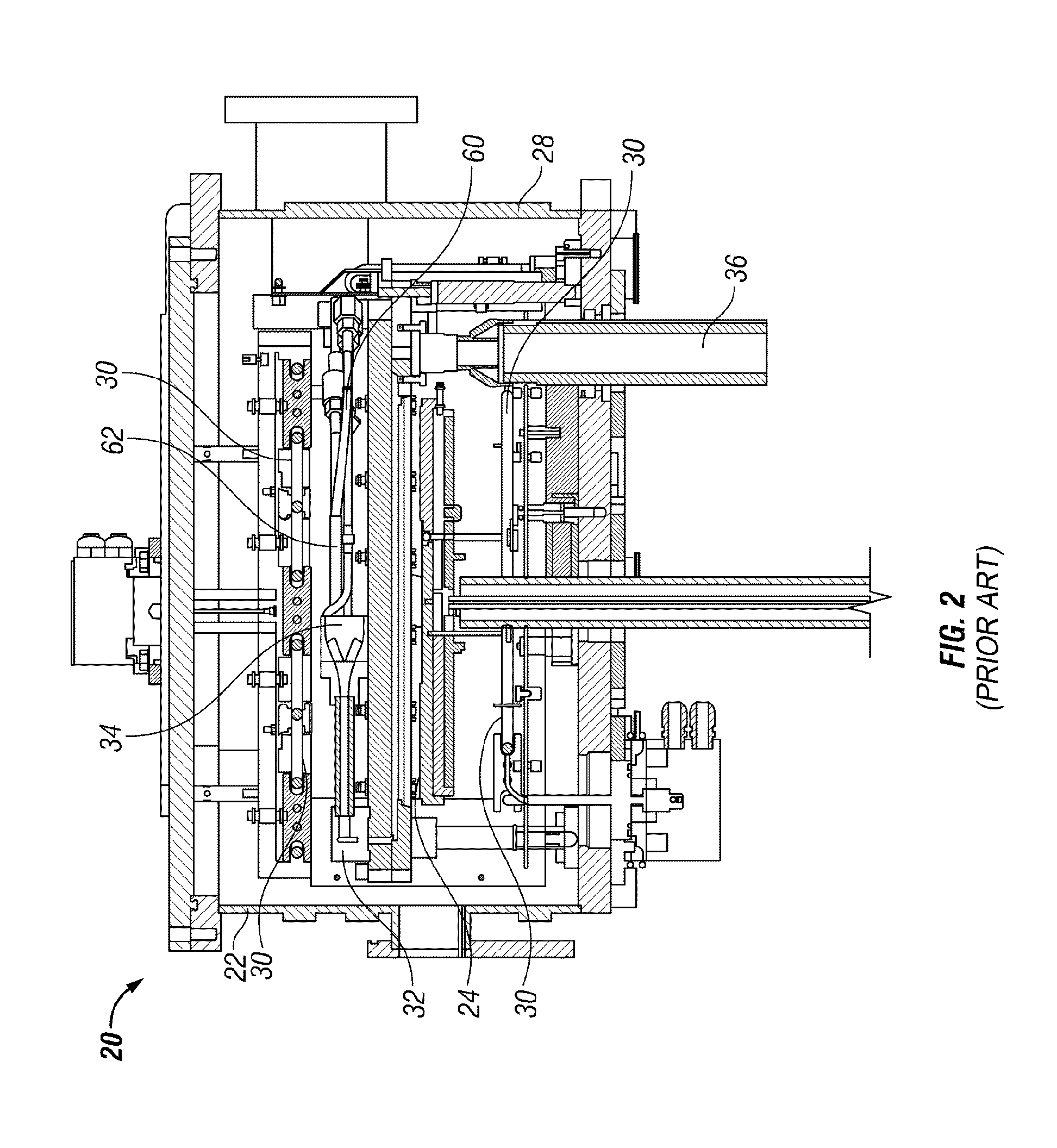
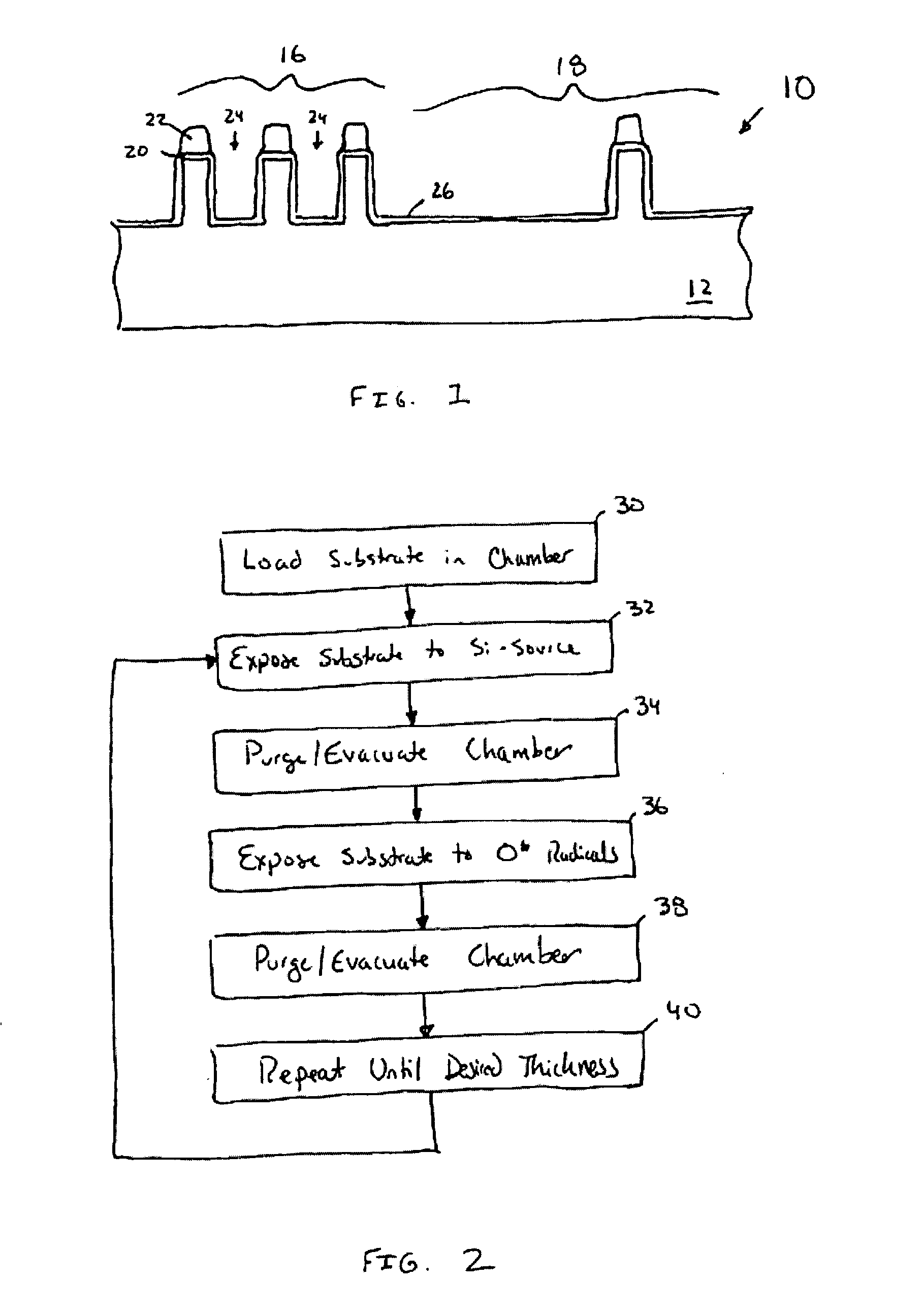
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
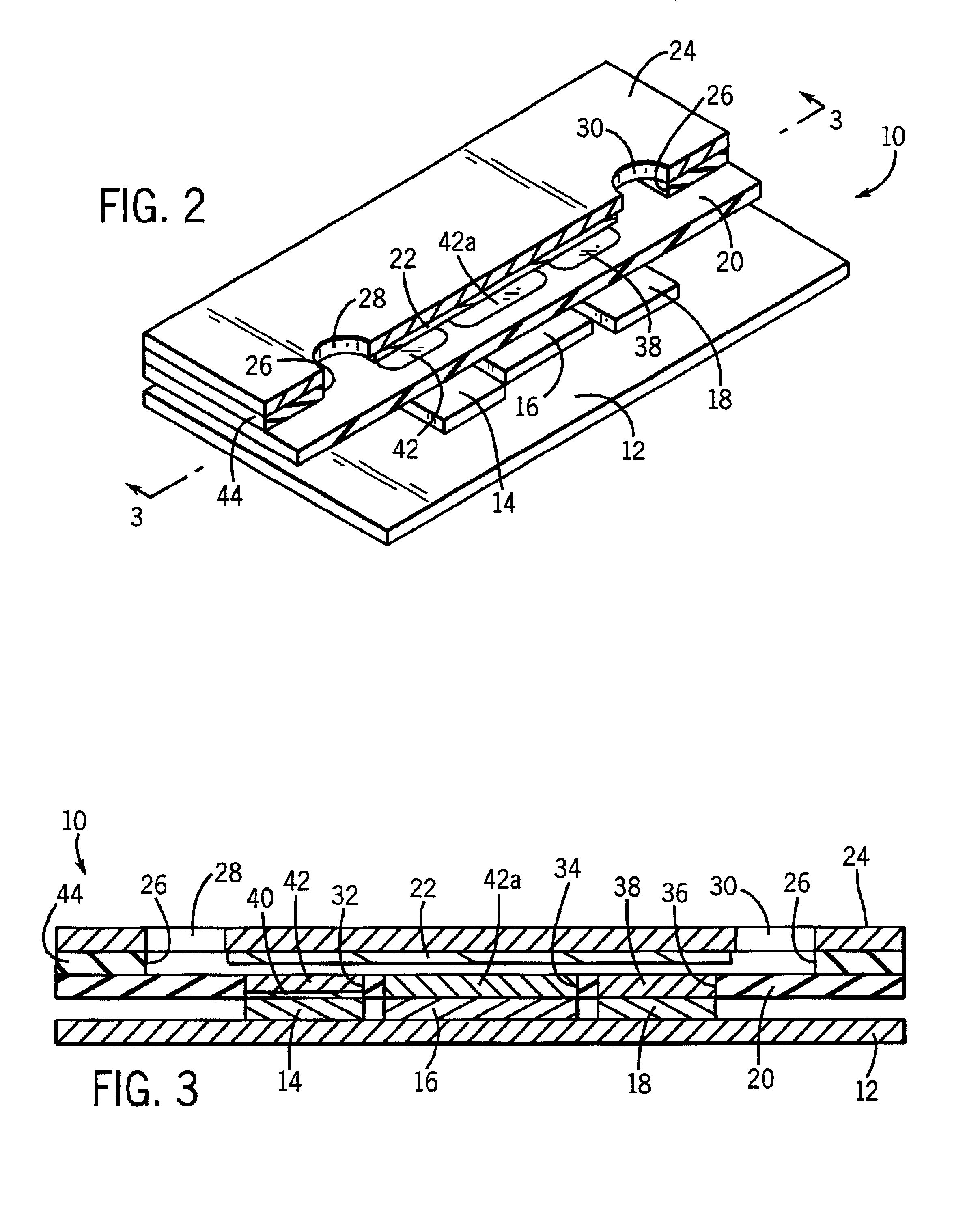
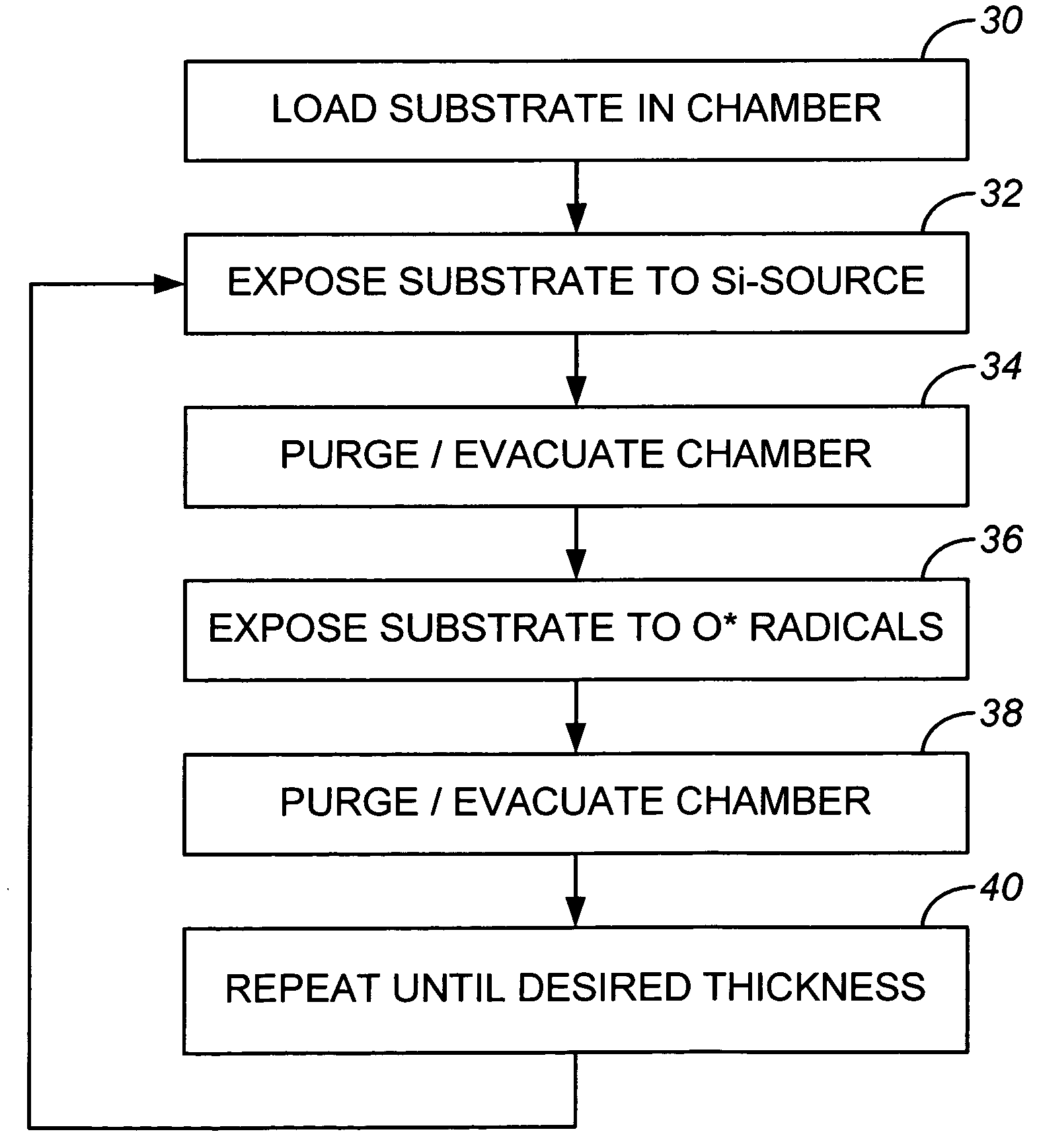
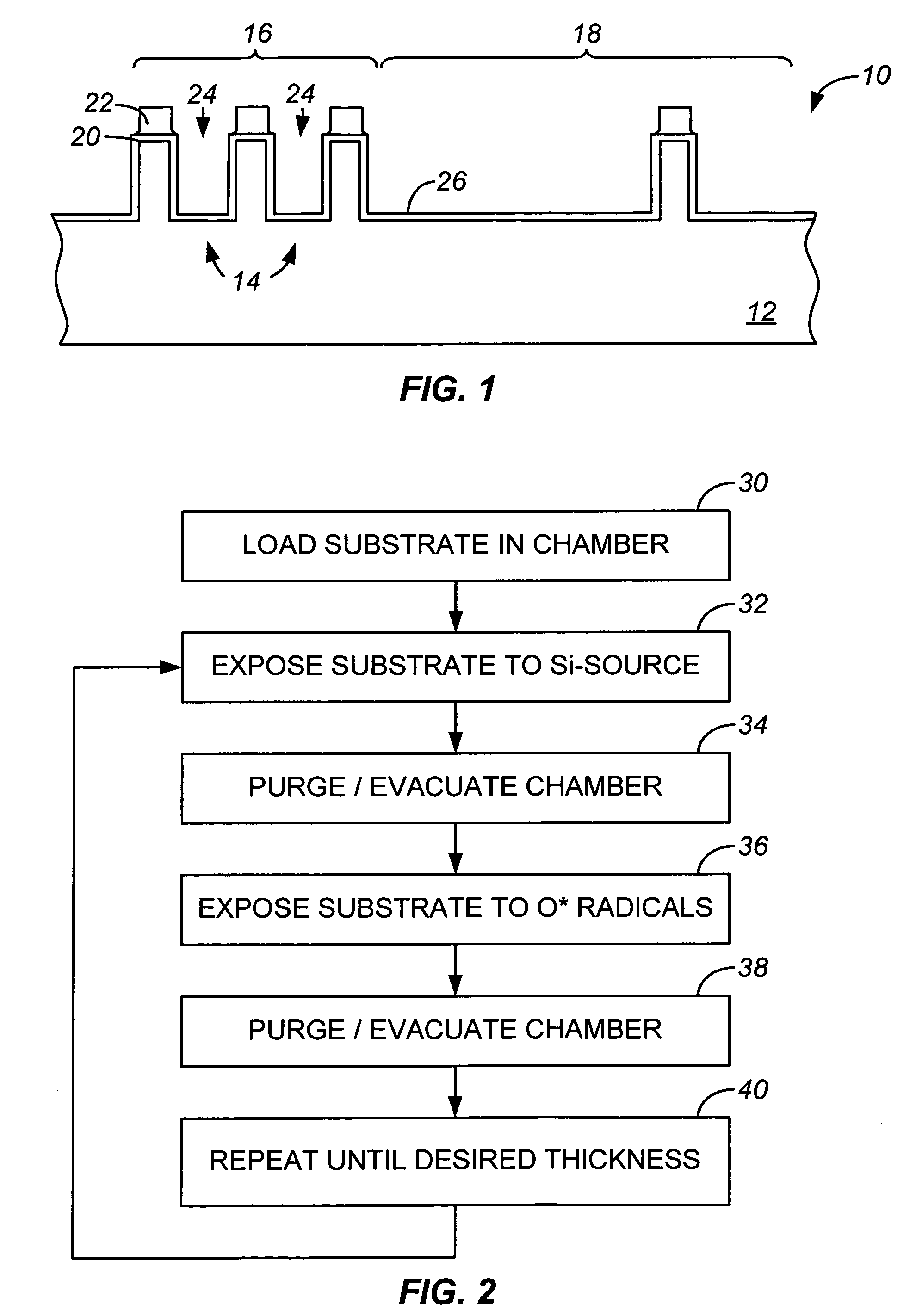
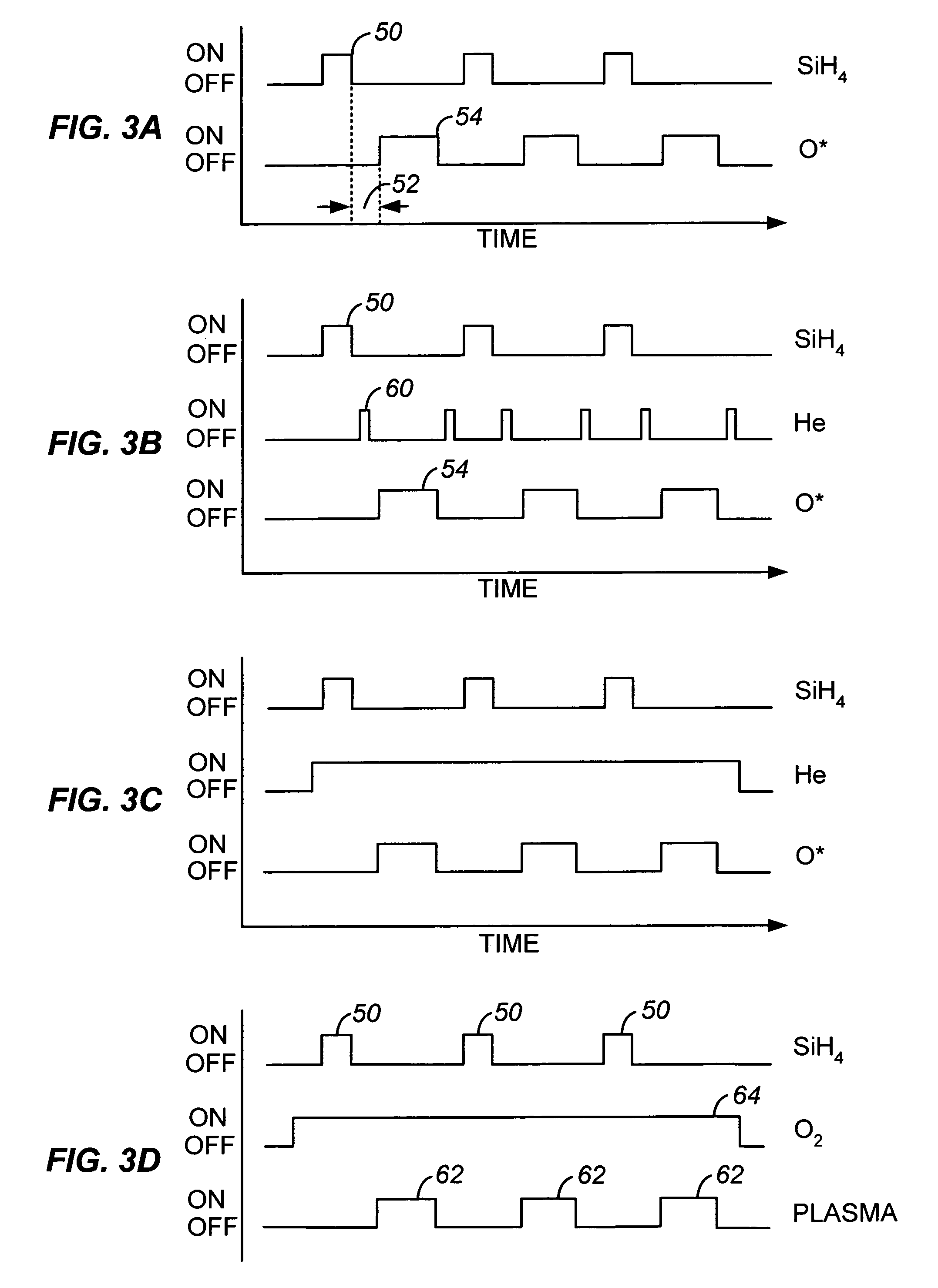
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Mammalian cell surface antigens; related reagents
InactiveUS7025962B1Abnormal immune responseFacilitated DiffusionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammalT cell
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Compositions for targeting the vasculature of solid tumors
InactiveUS6051230AEffectively compete for bindingReduce TEC-4 or TEC-11 bindingHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCell Surface Antigens
The present invention relates generally to methods and compositions for targeting the vasculature of solid tumors using immunological- and growth factor-based reagents. In particular aspects, antibodies carrying diagnostic or therapeutic agents are targeted to the vasculature of solid tumor masses through recognition of tumor vasculature-associated antigens, such as, for example, through endoglin binding, or through the specific induction of endothelial cell surface antigens on vascular endothelial cells in solid tumors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS6541266B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such as glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Vapor flow control apparatus for atomic layer deposition
A device for performing ALD includes a housing having a vacuum chamber that surrounds a horizontal flow reactor. The device further includes a gas distribution system for delivering gases to the reactor. The gas distribution system includes at least one of a high temperature valve and a high temperature filter disposed inside the vacuum chamber. The high temperature valve (and / or filter) controls (and / or filters) a supply of a precursor / reactant gas, inert gas, or precursor / reactant and inert gas mixture before it enters the horizontal flow reactor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
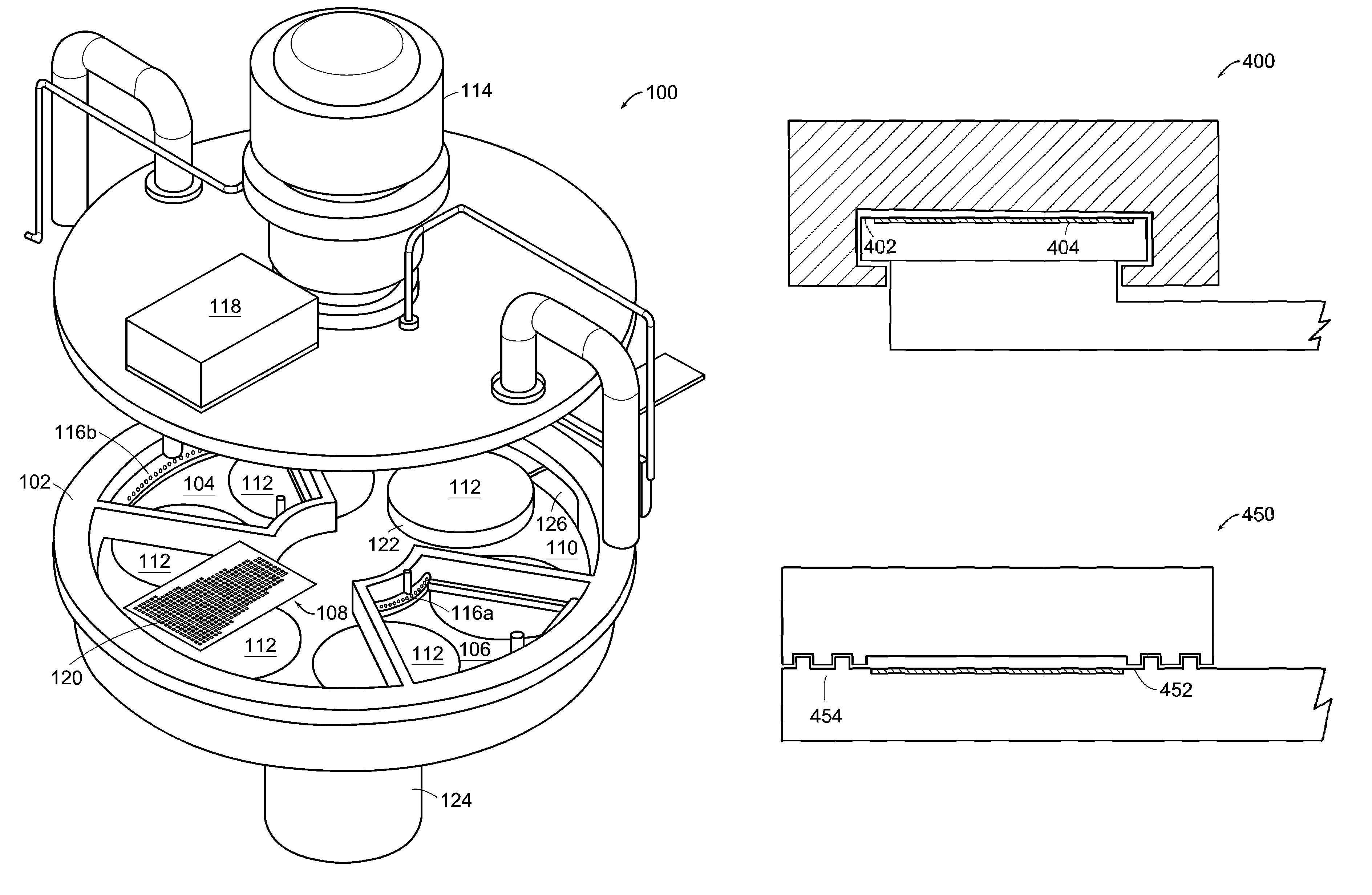
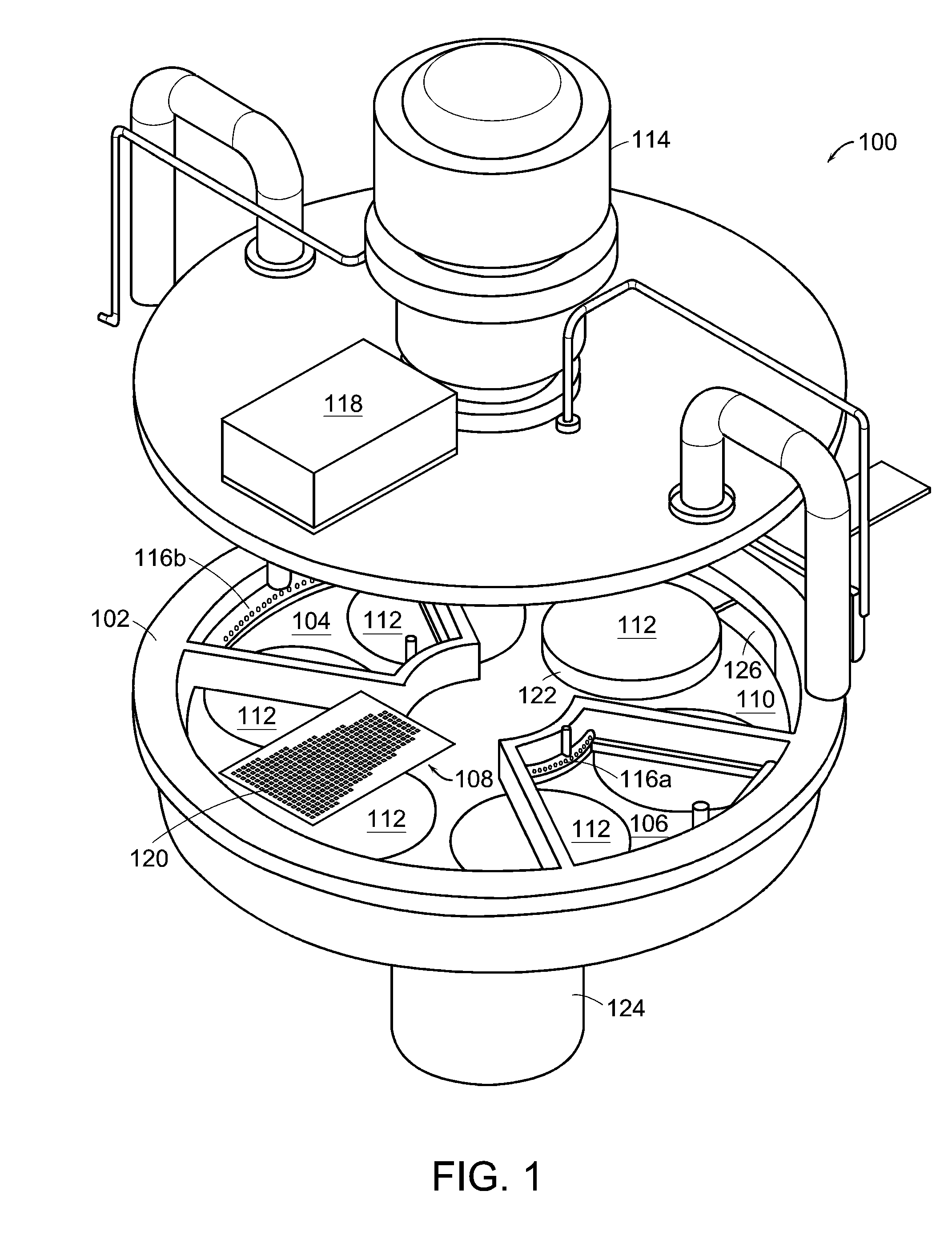
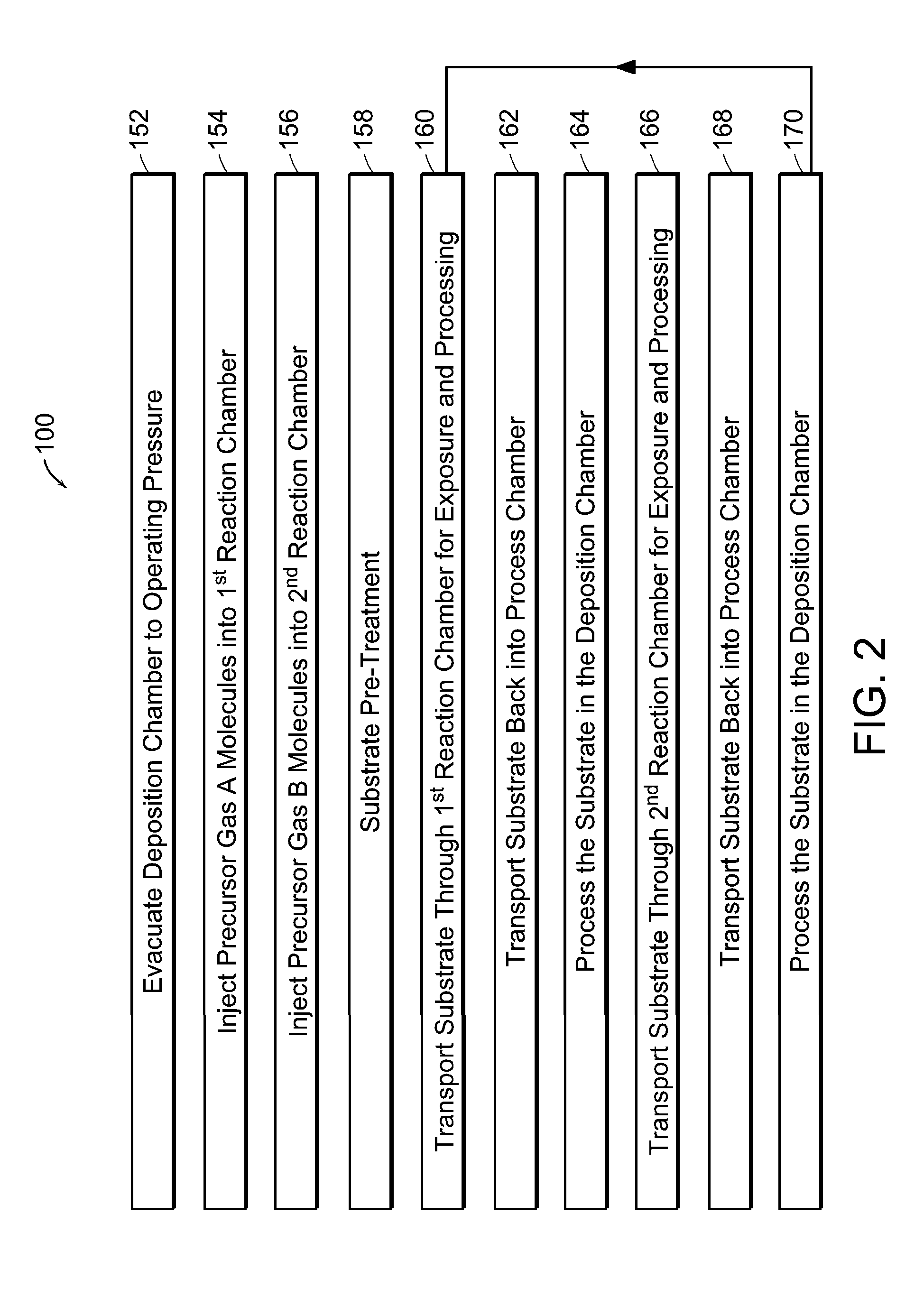
Continuous flow deposition system
An atomic layer deposition system is described that includes a deposition chamber. A first and second reaction chamber are positioned in the deposition chamber and contain a first and a second reactant species, respectively. A monolayer of the first reactant species is deposited on a substrate passing through the first reaction chamber. A monolayer of the second reactant species is deposited on a substrate passing through the second reaction chamber. A transport mechanism transports a substrate in a path through the first reaction chamber and through the second reaction chamber, thereby depositing a film on the substrate by atomic layer deposition. The shape of the first and the second reaction chambers are chosen to achieve a constant exposure of the substrate to reactant species when the transport mechanism transports the substrate in the path through the respective reaction chambers at the constant transport rate.
Owner:VEECON INSTR
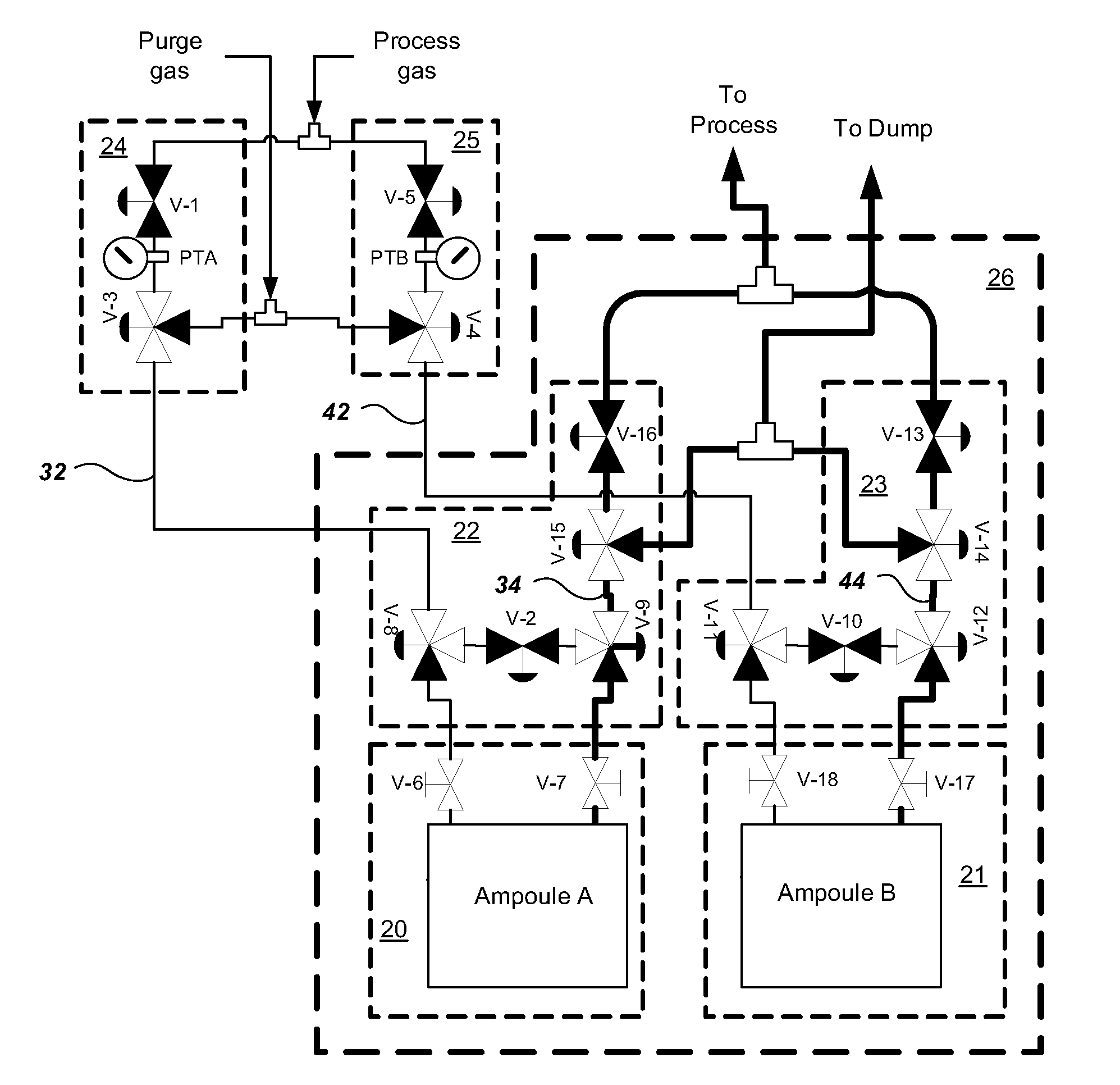
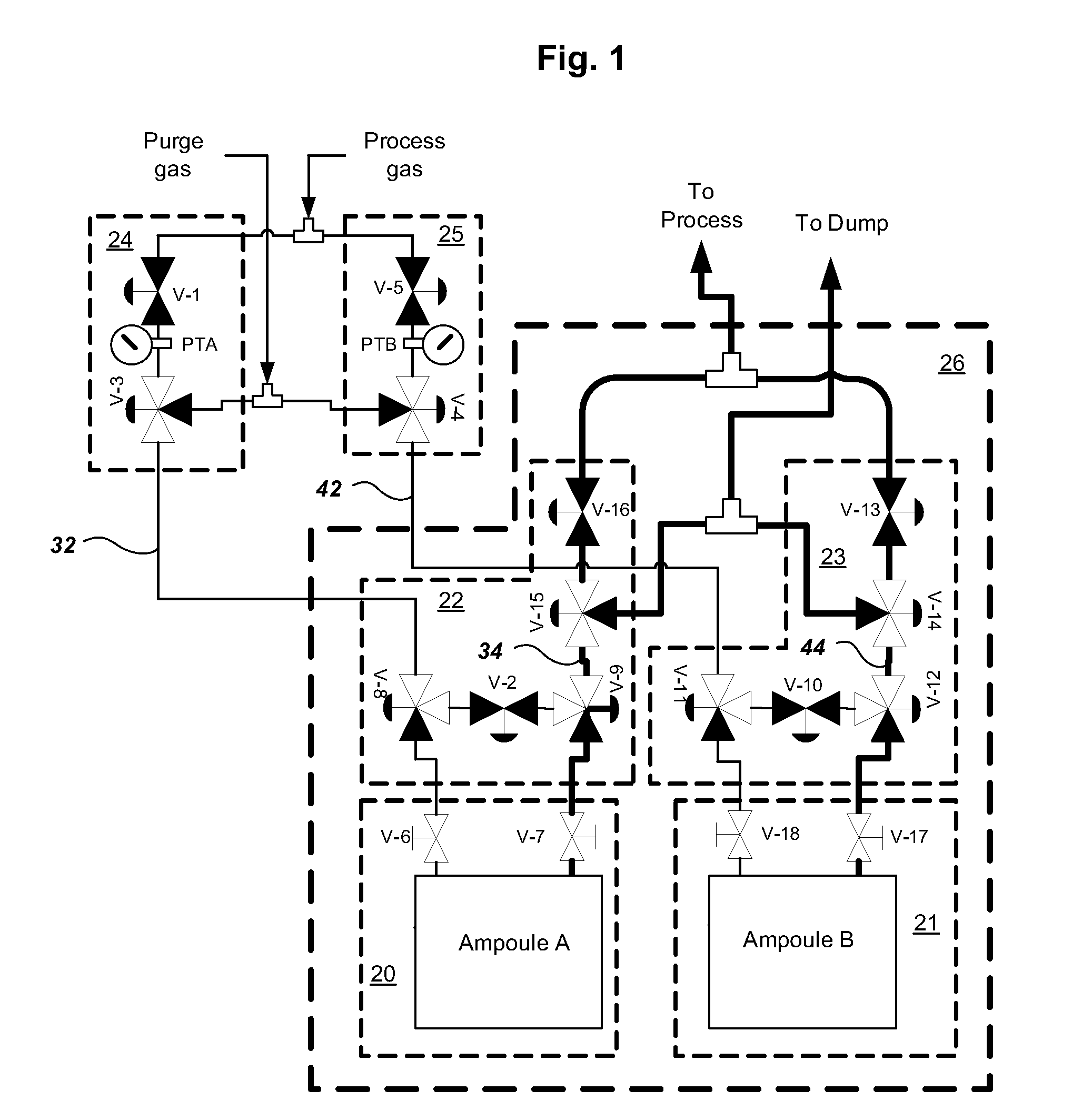
Multiple ampoule delivery systems
InactiveUS20090211525A1Easy to useReduce wasteLiquid surface applicatorsPipeline systemsSemiconductor materialsDelivery system
This invention relates to an integrated vapor or liquid phase reagent dispensing apparatus having a plurality of vessels and a plurality of carrier or inert gas feed / vapor or liquid phase reagent delivery manifolds, that may be used for continuously dispensing vapor or liquid phase reagents such as precursors for deposition of materials in the manufacture of semiconductor materials and devices.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Method for forming thin film
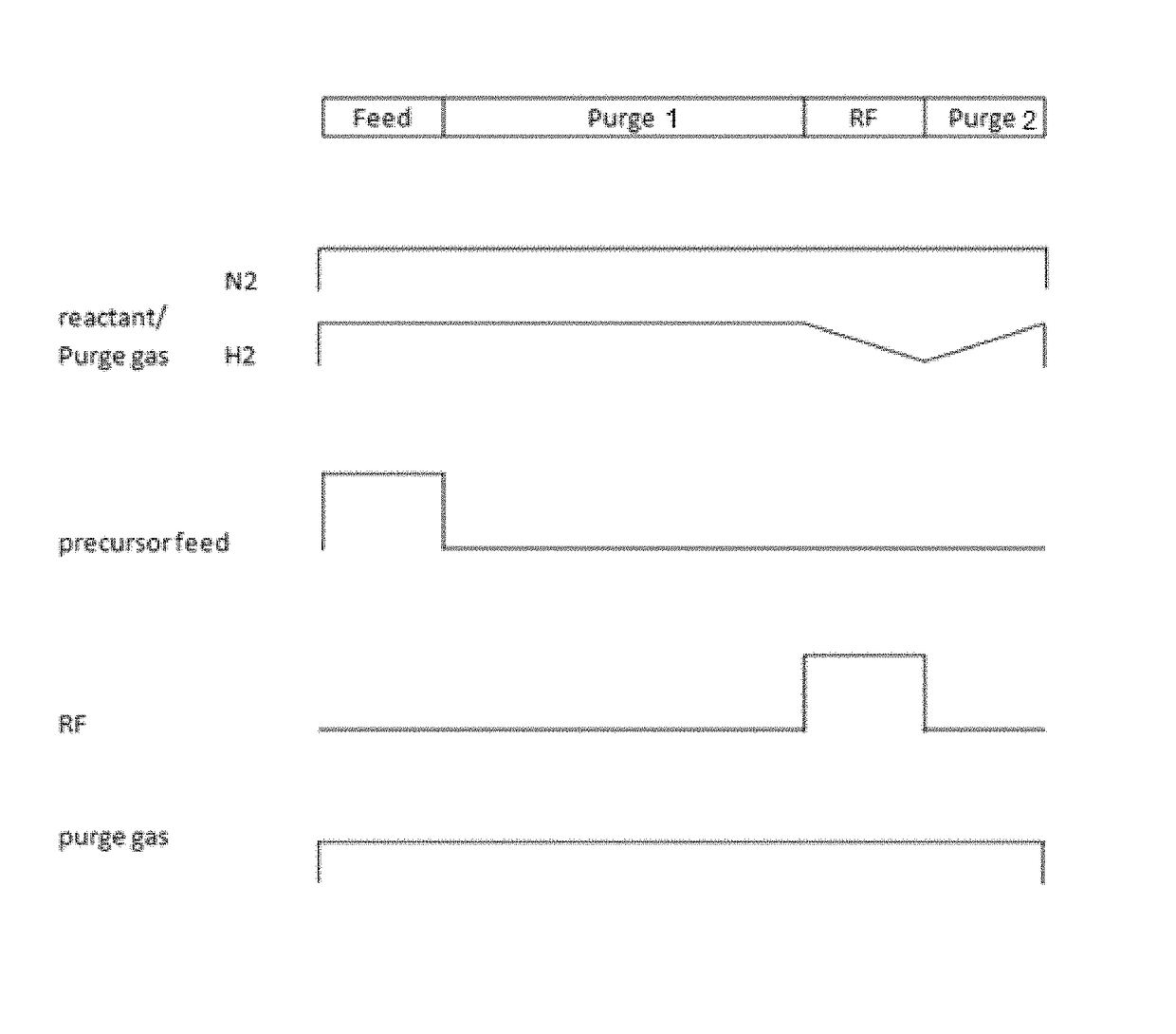
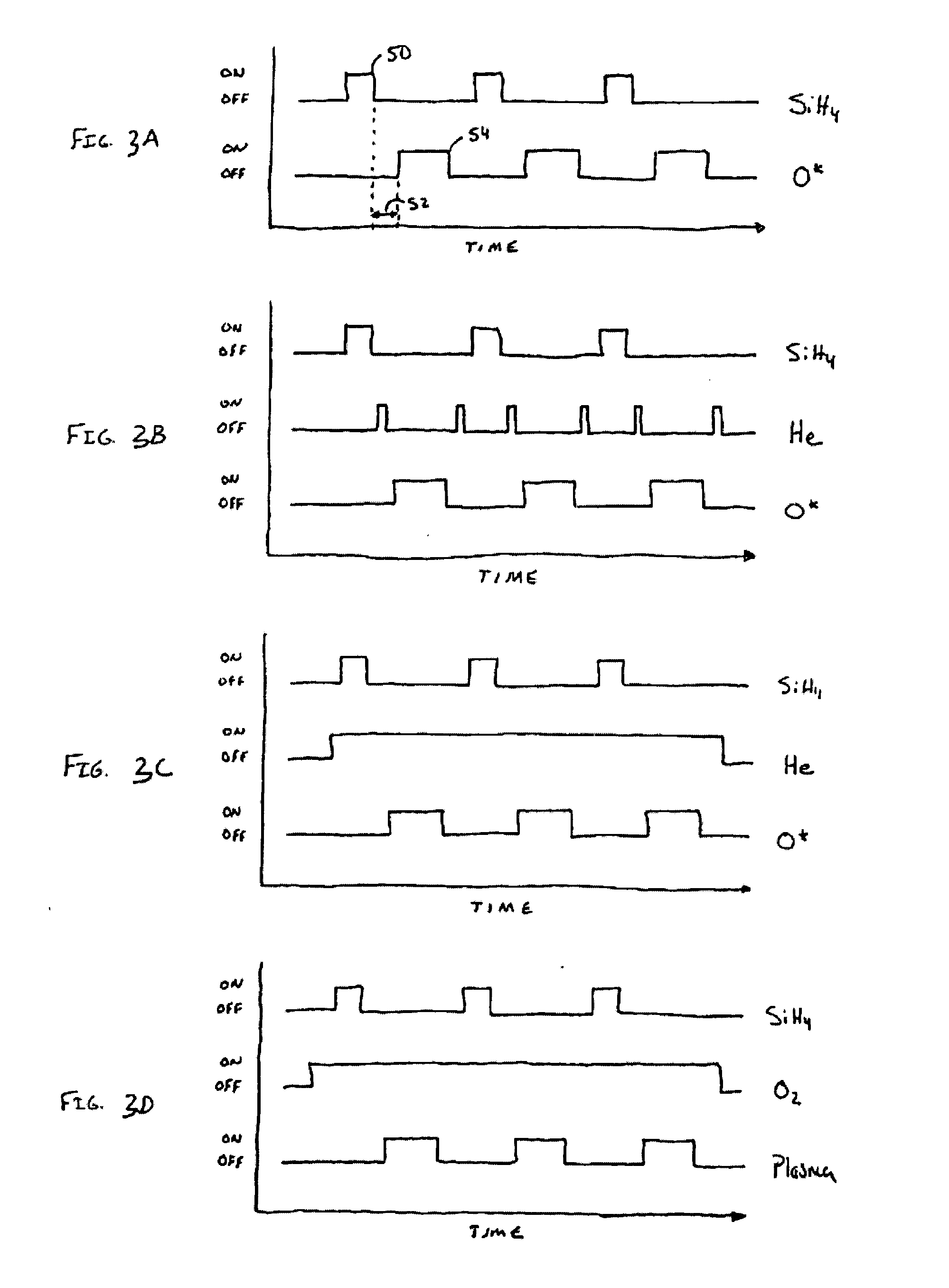
InactiveUS20050037154A1Prolonged durationIncrease ratingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingThin layerProduct gas
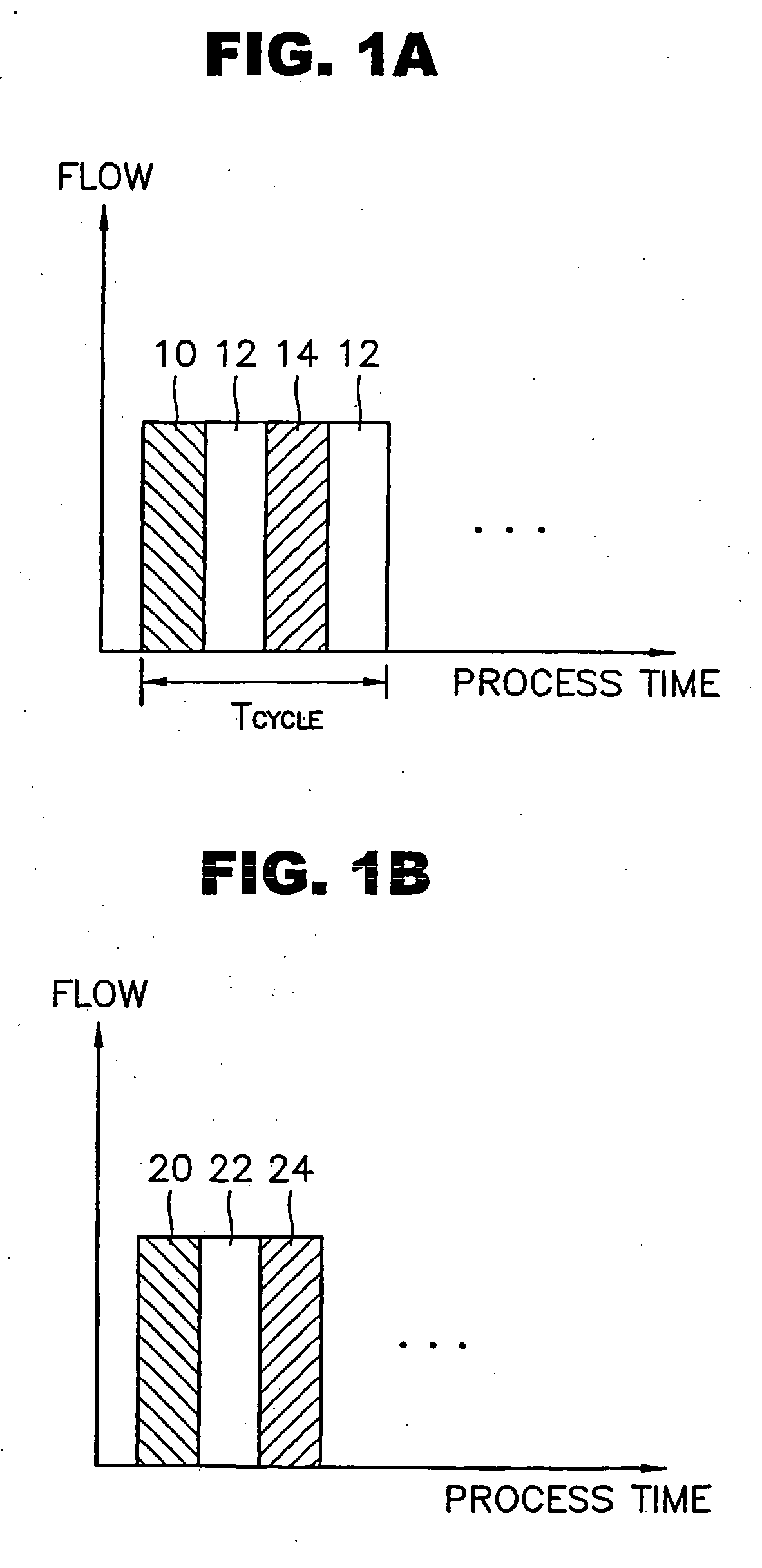
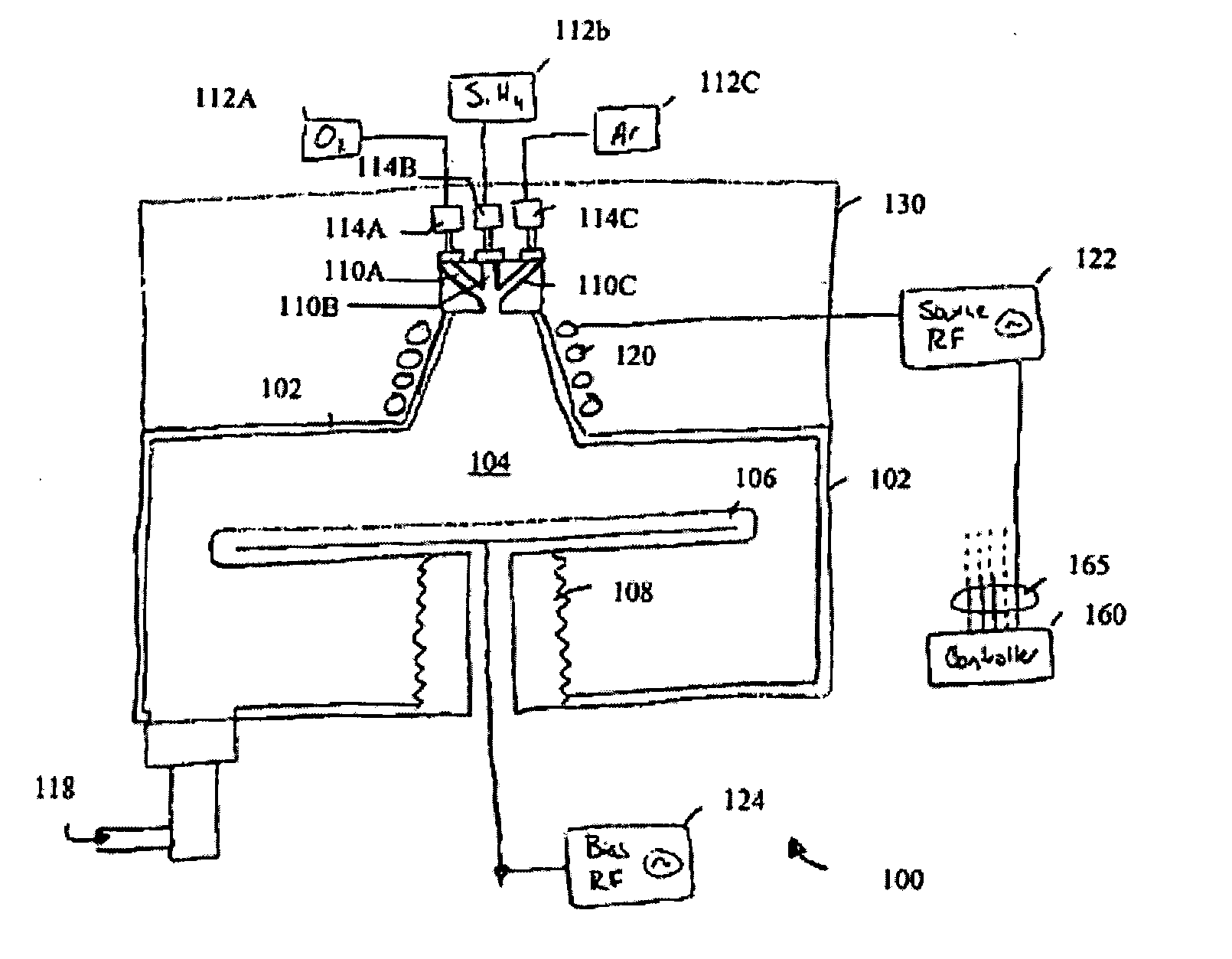
Method for forming a thin film at low temperature by using plasma pulses is disclosed. While a purge gas or a reactant purge gas activated by plasma is continuously supplied into a reactor, a source gas is supplied intermittently into the reactor during which period plasma is generated in the reactor so that the source gas and the purge gas activated by plasma reacts, so that a thin film is formed according to the method. Also, a method for forming a thin layer of film containing a plural of metallic elements, a method for forming a thin metallic film containing varied contents by amount of the metallic elements by using a supercycle Tsupercycle comprising a combination of simple gas supply cycles Tcycle, . . . , and a method for forming a thin film containing continuously varying compositions of the constituent elements by using a supercycle Tsupercycle comprising a combination of simple gas supply cycles Tcycle, . . . , are disclosed. The methods for forming thin films disclosed here allows to shorten the purge cycle duration even if the reactivity between the source gases is high, to reduce the contaminants caused by the gas remaining in the reactor, to form a thin film at low temperature even if the reactivity between the source gases is low, and also to increase the rate of thin film formation.
Owner:ASM GENITECH KOREA
Adsorption based material removal process
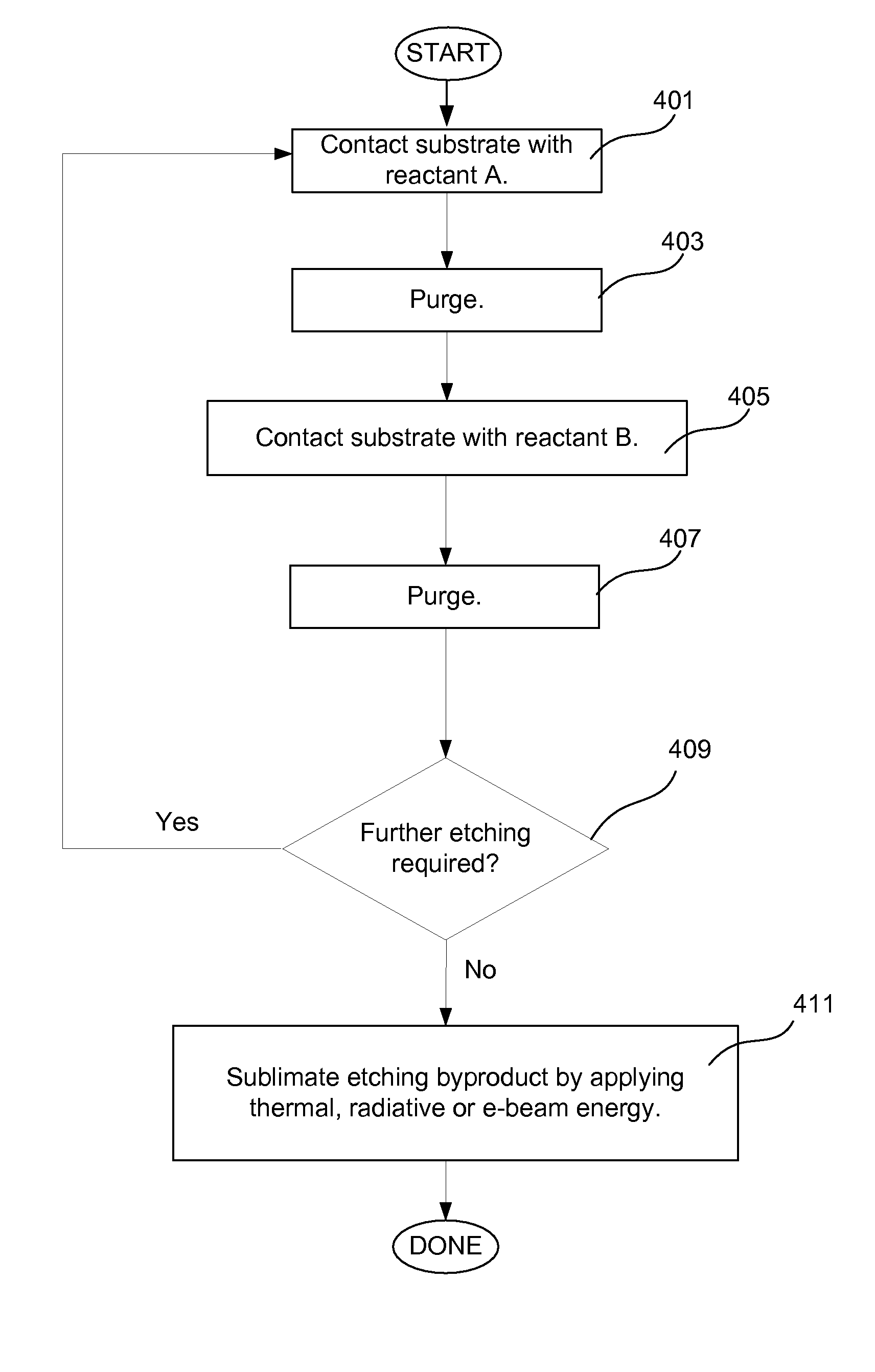
InactiveUS8043972B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingEtching
Methods for accurate and conformal removal of atomic layers of materials make use of the self-limiting nature of adsorption of at least one reactant on the substrate surface. In certain embodiments, a first reactant is introduced to the substrate in step (a) and is adsorbed on the substrate surface until the surface is partially or fully saturated. A second reactant is then added in step (b), reacting with the adsorbed layer of the first reactant to form an etchant. The amount of an etchant, and, consequently, the amount of etched material is limited by the amount of adsorbed first reactant. By repeating steps (a) and (b), controlled atomic-scale etching of material is achieved. These methods may be used in interconnect pre-clean applications, gate dielectric processing, manufacturing of memory devices, or any other applications where removal of one or multiple atomic layers of material is desired.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
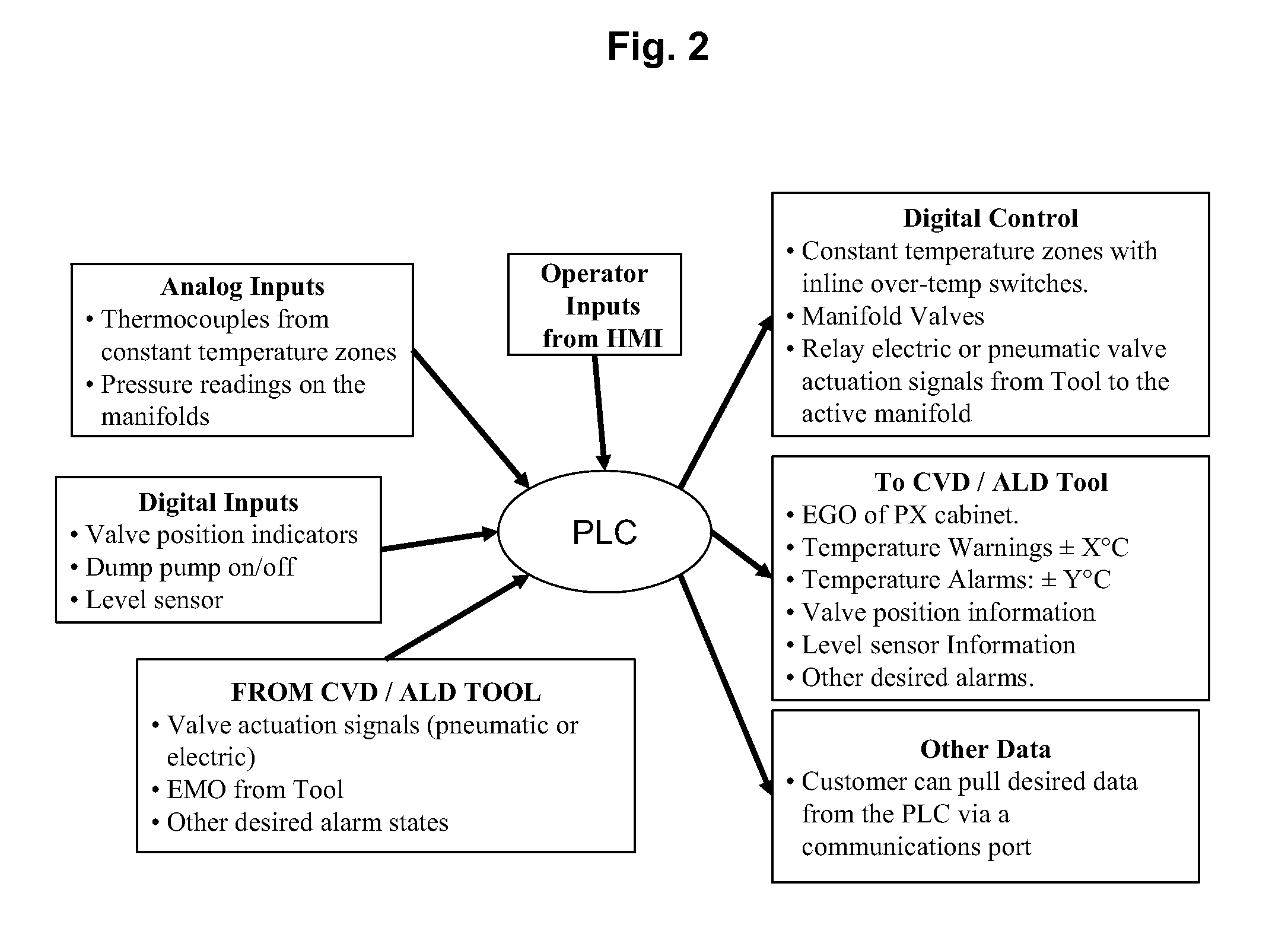
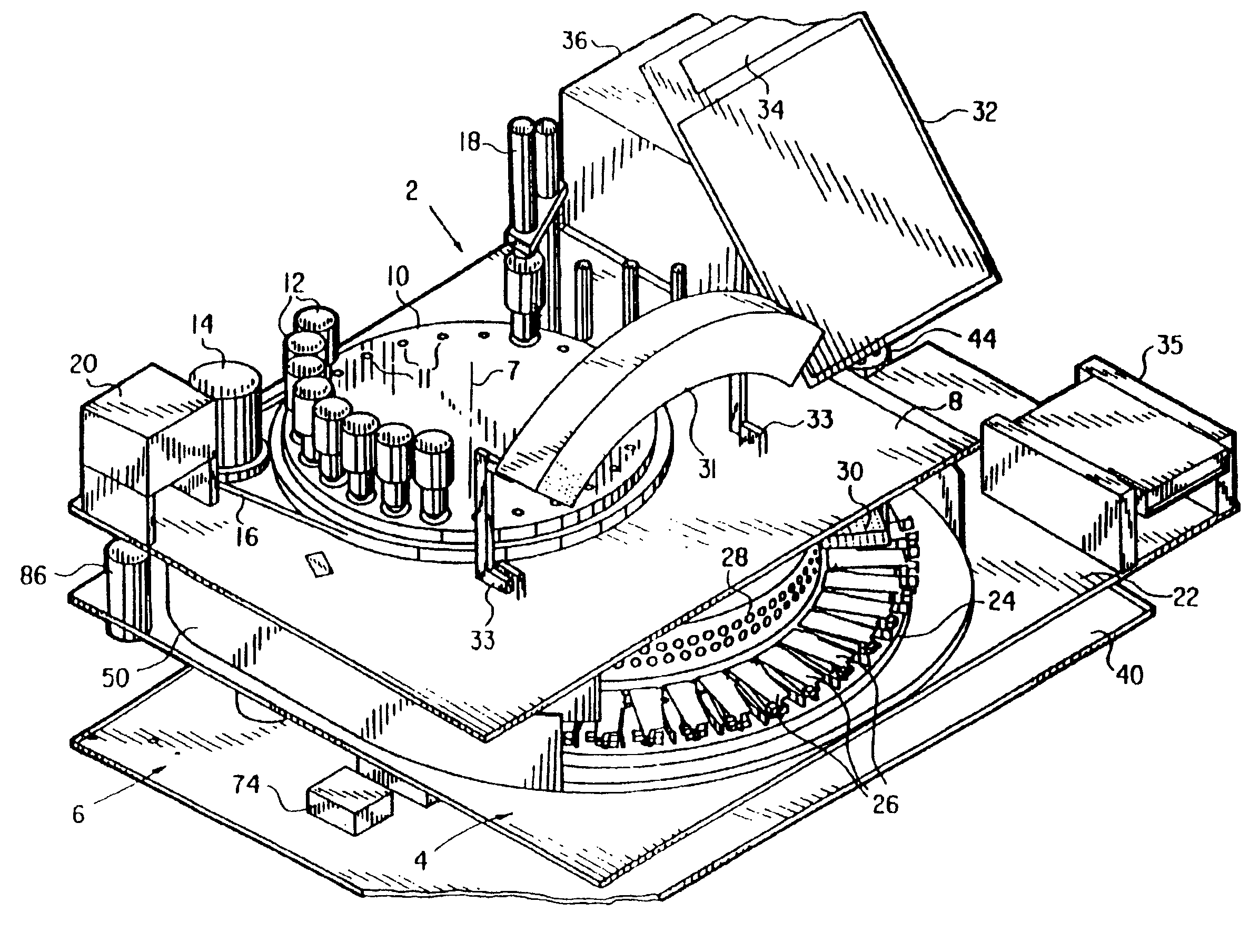
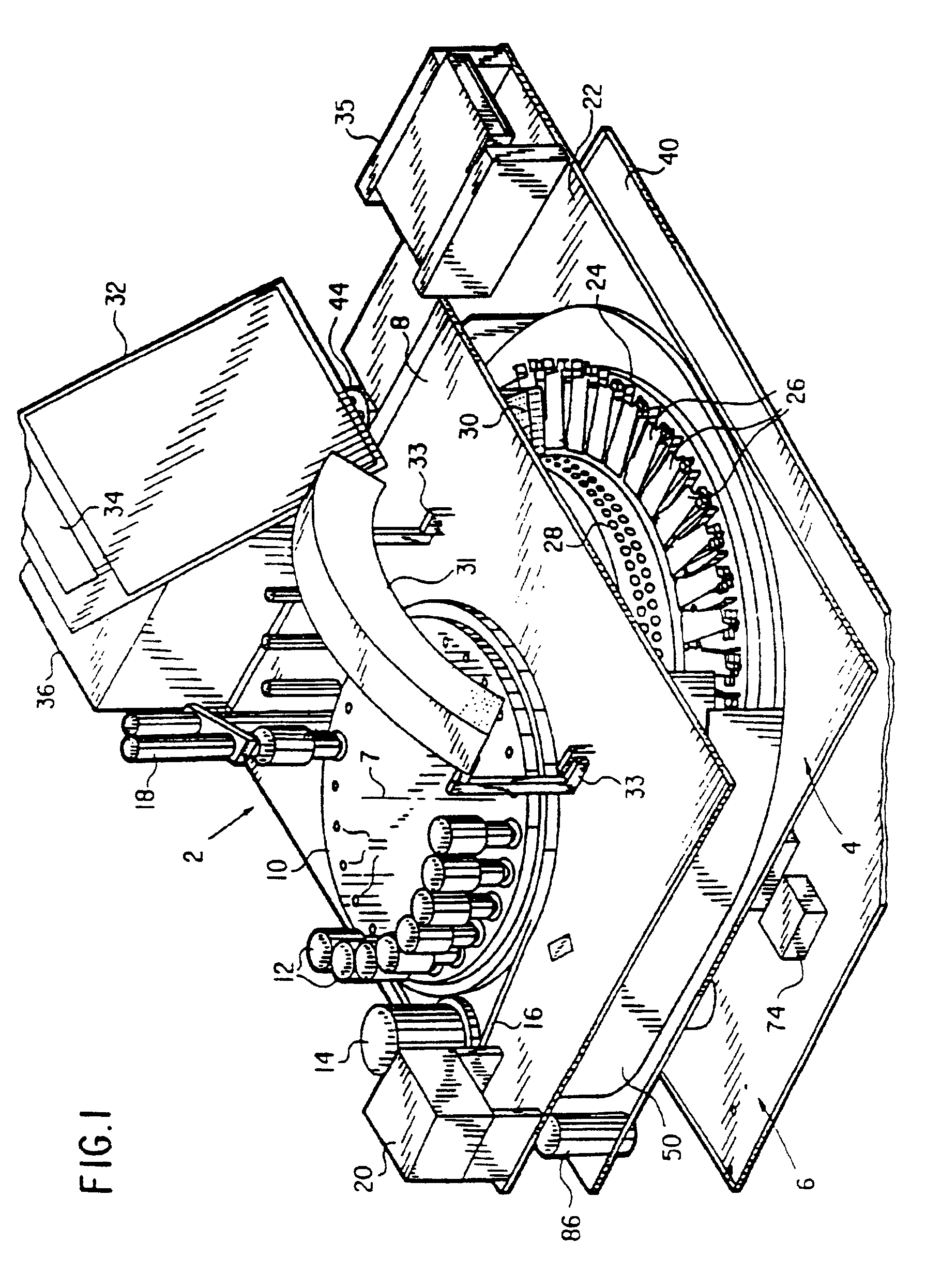
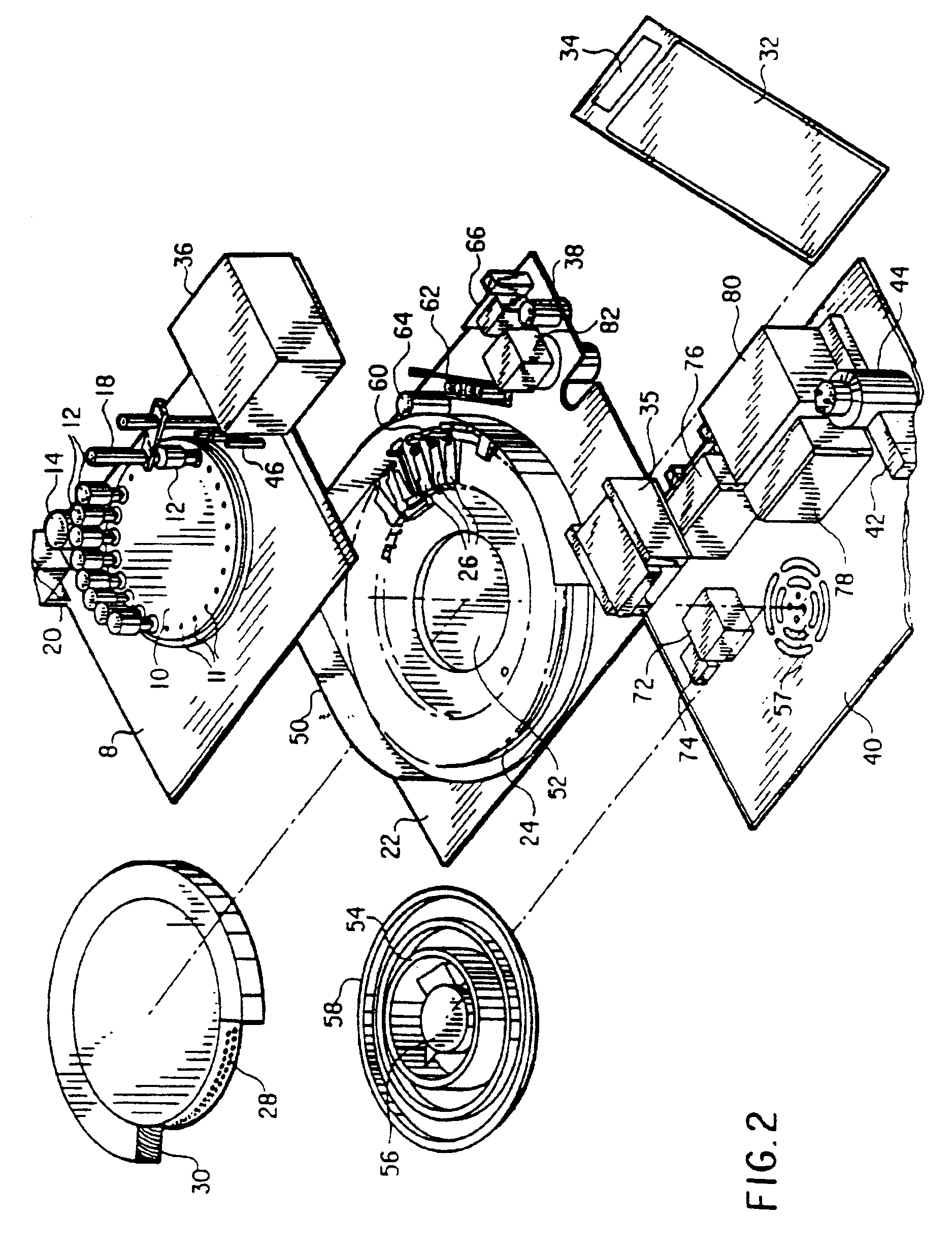
Automated biological reaction apparatus
An automated immunostaining apparatus having a reagent application zone and a reagent supply zone. The apparatus has a carousel slide support supporting a plurality of slide supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel slide support for consecutively positioning each of a plurality of slide supports in the reagent application zone. The apparatus also has a carousel reagent support having a plurality of reagent container supports thereon, and drive means engaging the carousel for rotating the carousel and positioning a preselected reagent container support in the reagent supply zone. The apparatus also has a reagent delivery actuator means positioned for engaging a reagent container positioned on a container support in the reagent delivery zone and initiating reagent delivery from the reagent container to a slide supported on a slide support in the reagent receiving zone.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Film deposition apparatus and film deposition method
ActiveUS20100279008A1Efficient solutionHigh in-plane uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringTransfer mechanism
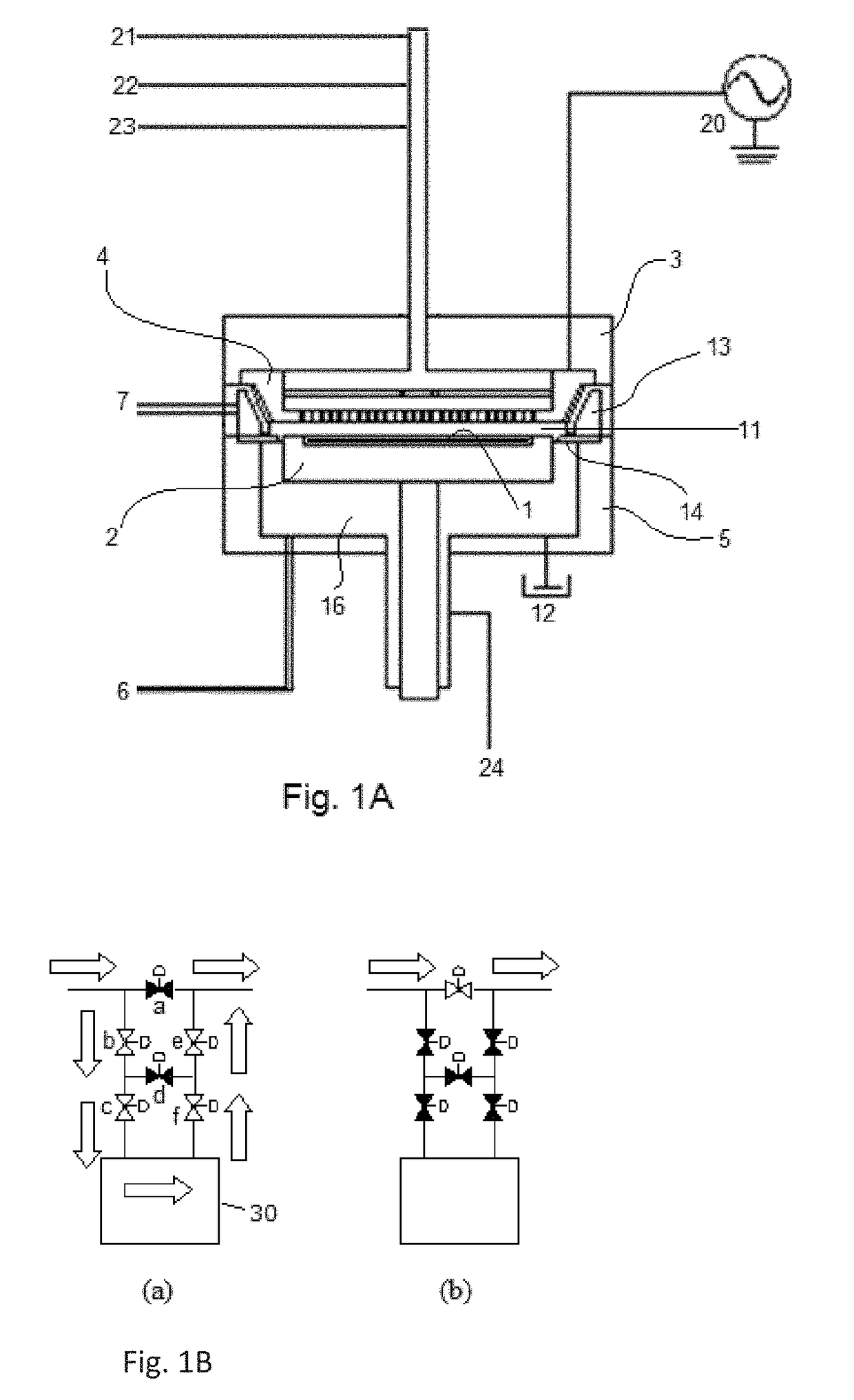
The present invention is a film deposition apparatus configured to deposit a film on a substrate that has been loaded into a vacuum container via a transfer opening and placed on a table in the vacuum container, by supplying a process gas to the substrate from a process-gas supply part opposed to the table under a vacuum atmosphere, while heating a table surface of the table, the film deposition apparatus comprising: an elevating mechanism configured to vertically move the table between a process position at which the substrate is subjected to a film deposition process, and a transfer position at which the substrate is transferred to and from an external transfer mechanism that has entered from the transfer opening; a surrounding part configured to surround the table with a gap therebetween, when the table is located at the process position, so that the surrounding part and the table divide an inside of the vacuum container into an upper space, which is located above the table, and a lower space, which is located below the table; a vacuum exhaust conduit in communication with the upper space, through which a process atmosphere in the upper space is discharged to create a vacuum in the upper space; a heating unit configured to heat a gas contact region ranging from the upper space to the vacuum exhaust conduit, to a temperature higher than a temperature allowing adhesion of reactant; and a heat insulation part disposed between the heating unit and a lower part of the vacuum container surrounding the lower space.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
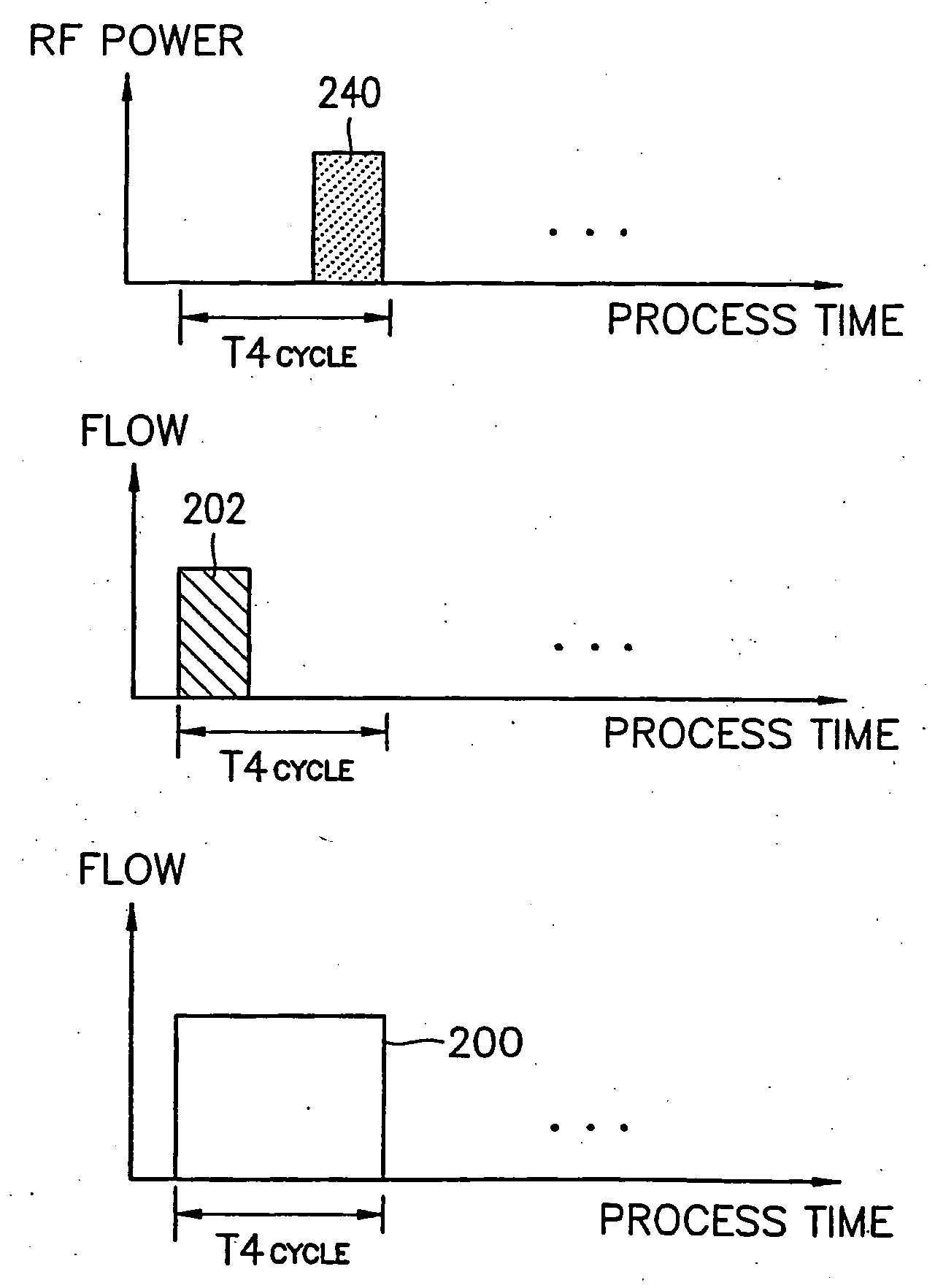
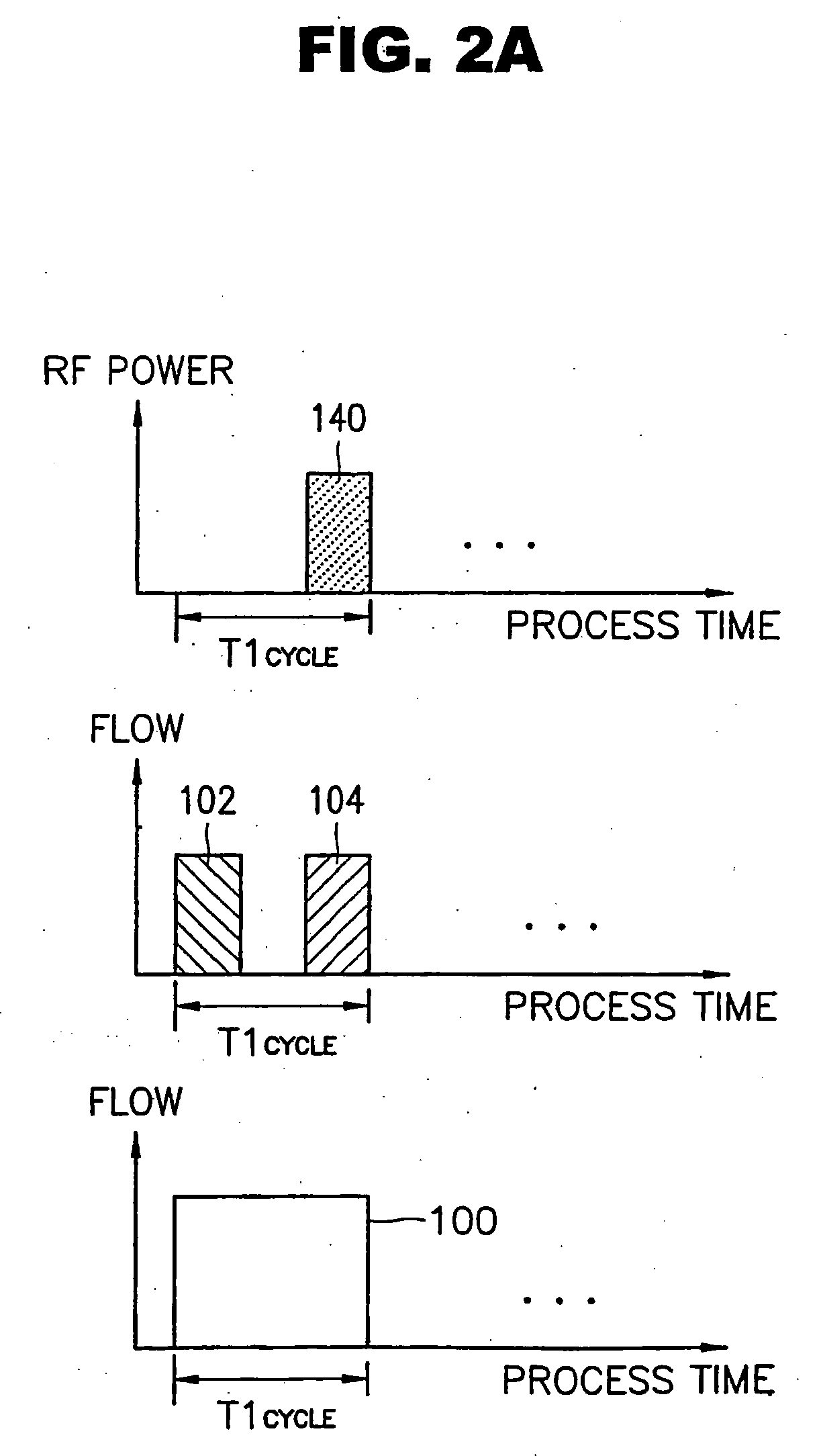
Method of plasma-assisted cyclic deposition using ramp-down flow of reactant gas
ActiveUS9984869B1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenOxygen
A method is for forming a nitride or oxide film by plasma-assisted cyclic deposition, one cycle of which includes: feeding a first reactant, a second reactant, and a precursor to a reaction space where a substrate is placed, wherein the second reactant flows at a first flow ratio wherein a flow ratio is defined as a ratio of a flow rate of the second reactant to a total flow rate of gases flowing in the reaction space; and stopping feeding the precursor while continuously feeding the first and second reactants at a flow ratio which is gradually reduced from the first flow ratio to a second flow ratio while applying RF power to the reaction space to expose the substrate to a plasma. The second reactant is constituted by a hydrogen-containing compound or oxygen-containing compound.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
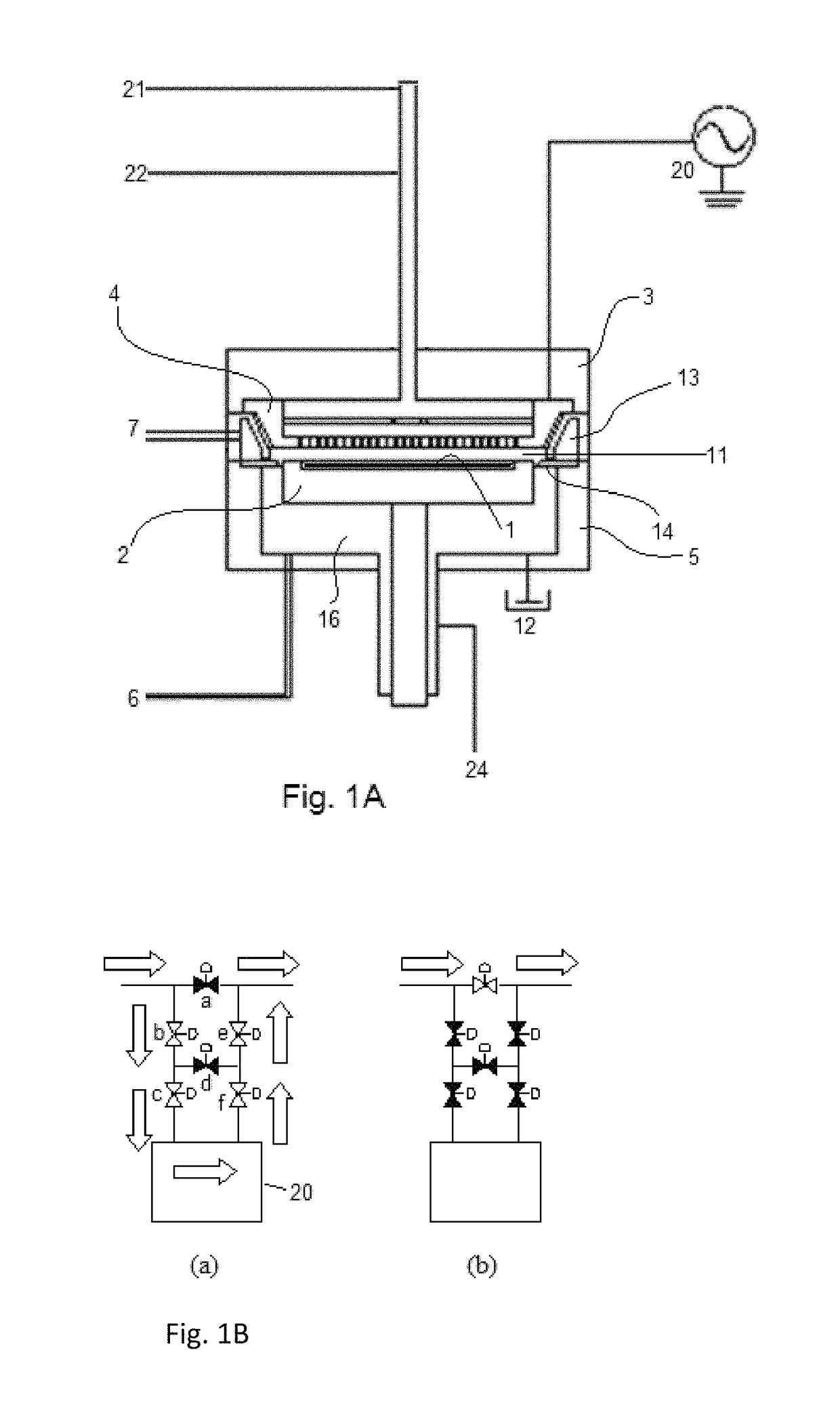
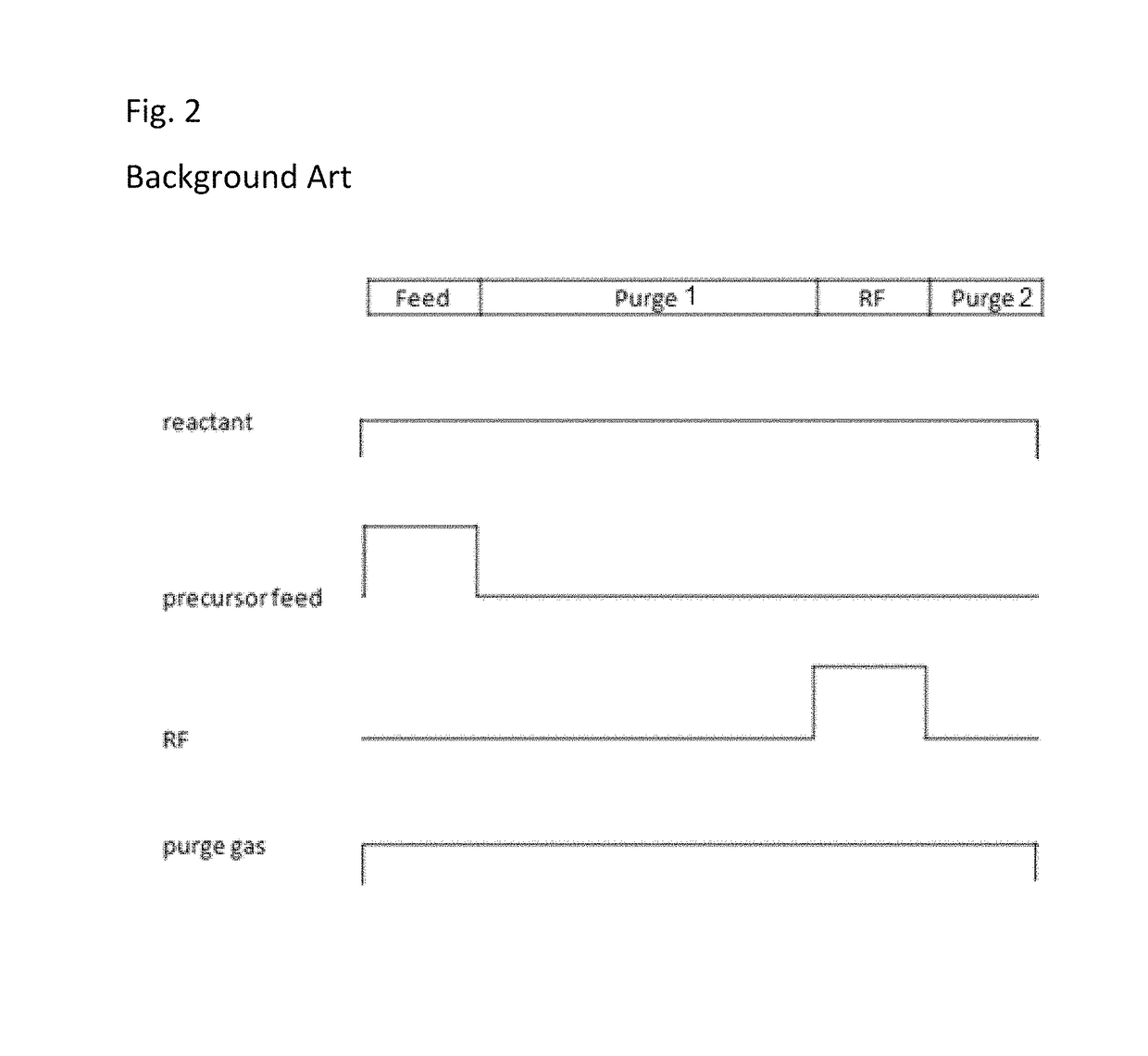
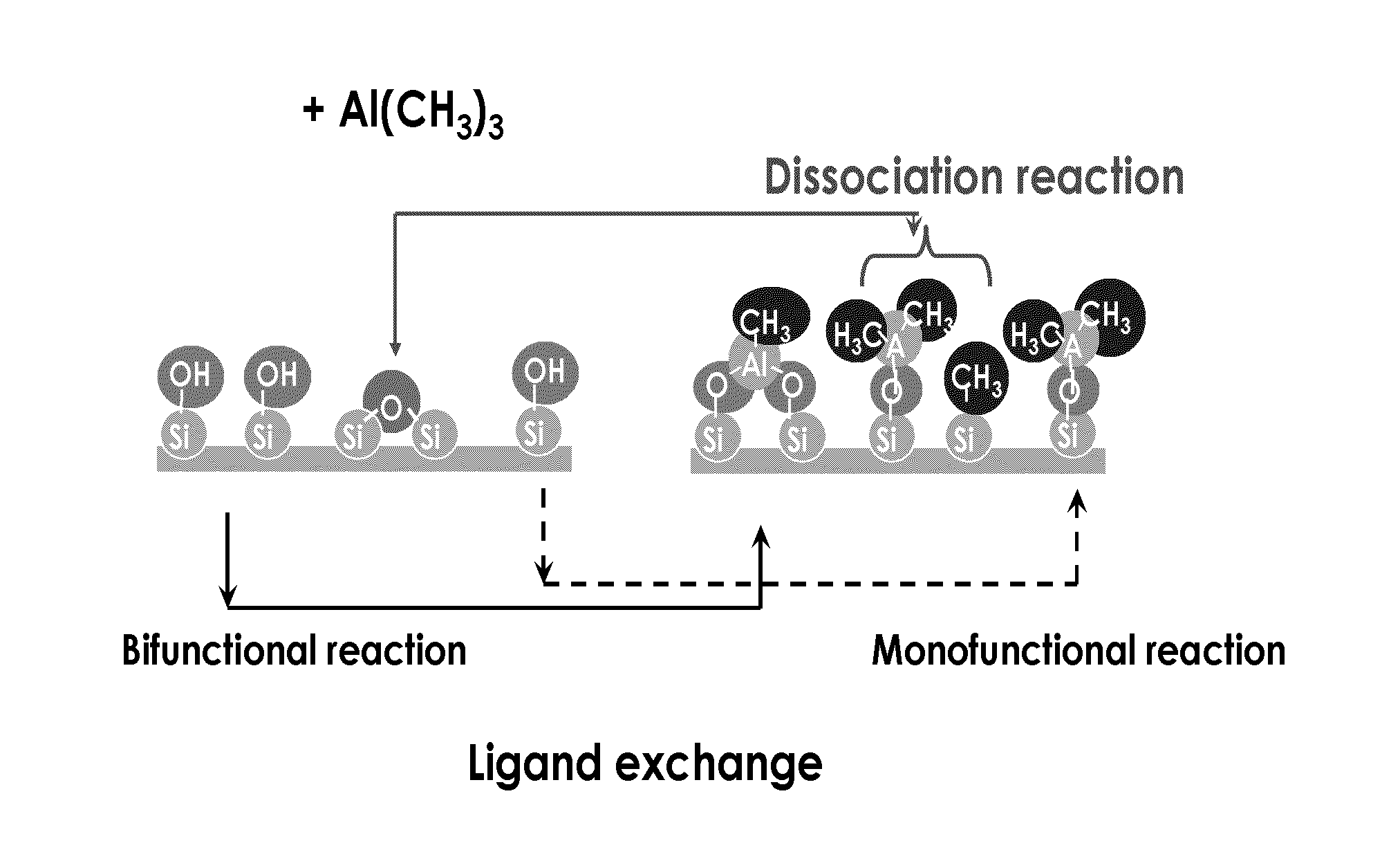
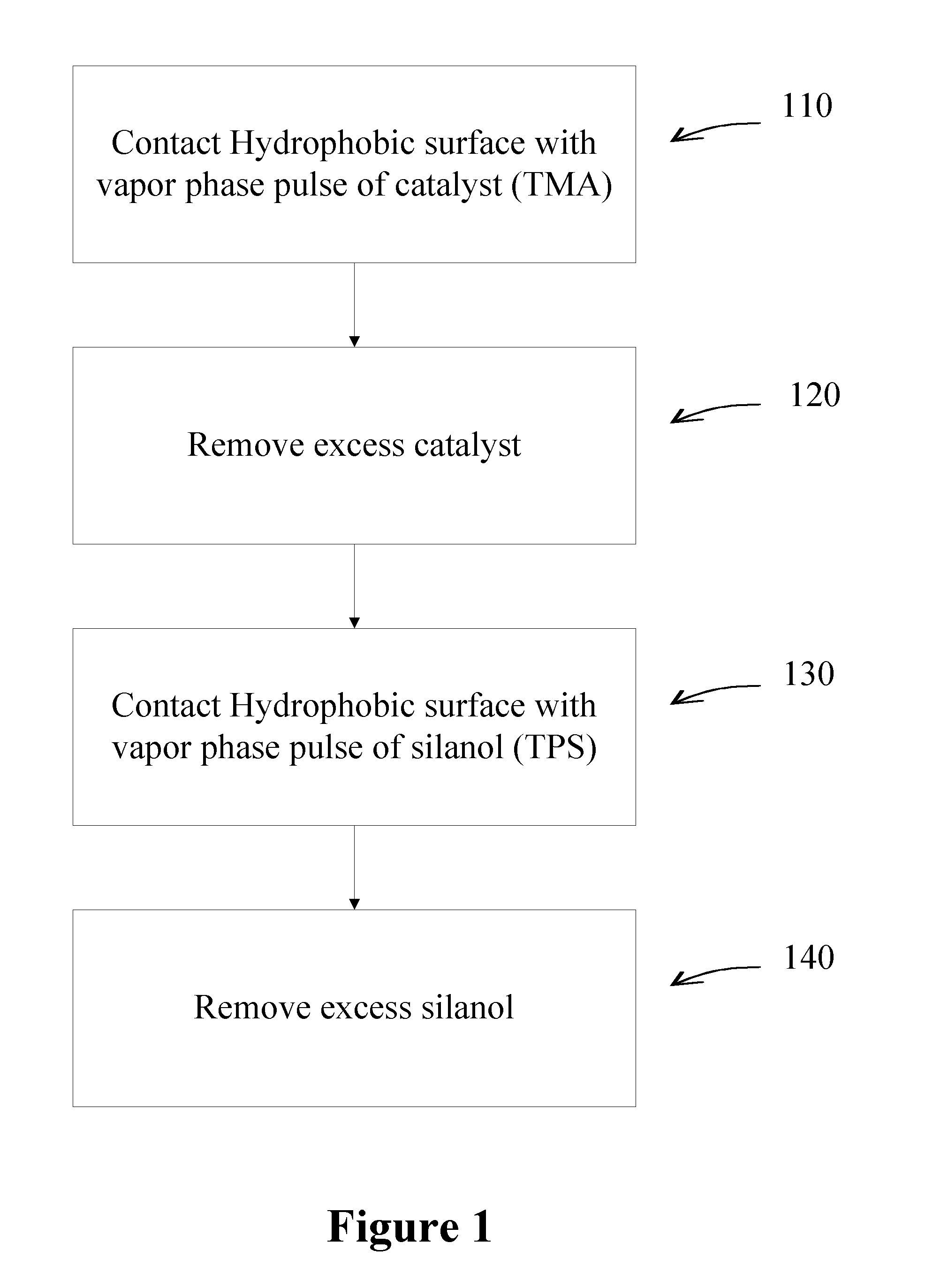
Deposition of silicon dioxide on hydrophobic surfaces
InactiveUS20120263876A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilanolSilicon dioxide
Methods for forming silicon dioxide thin films on hydrophobic surfaces are provided. For example, in some embodiments, silicon dioxide films are deposited on porous, low-k materials. The silicon dioxide films can be deposited using a catalyst and a silanol. In some embodiments, an undersaturated dose of one or more of the reactants can be used in forming a pore-sealing layer over a porous material.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
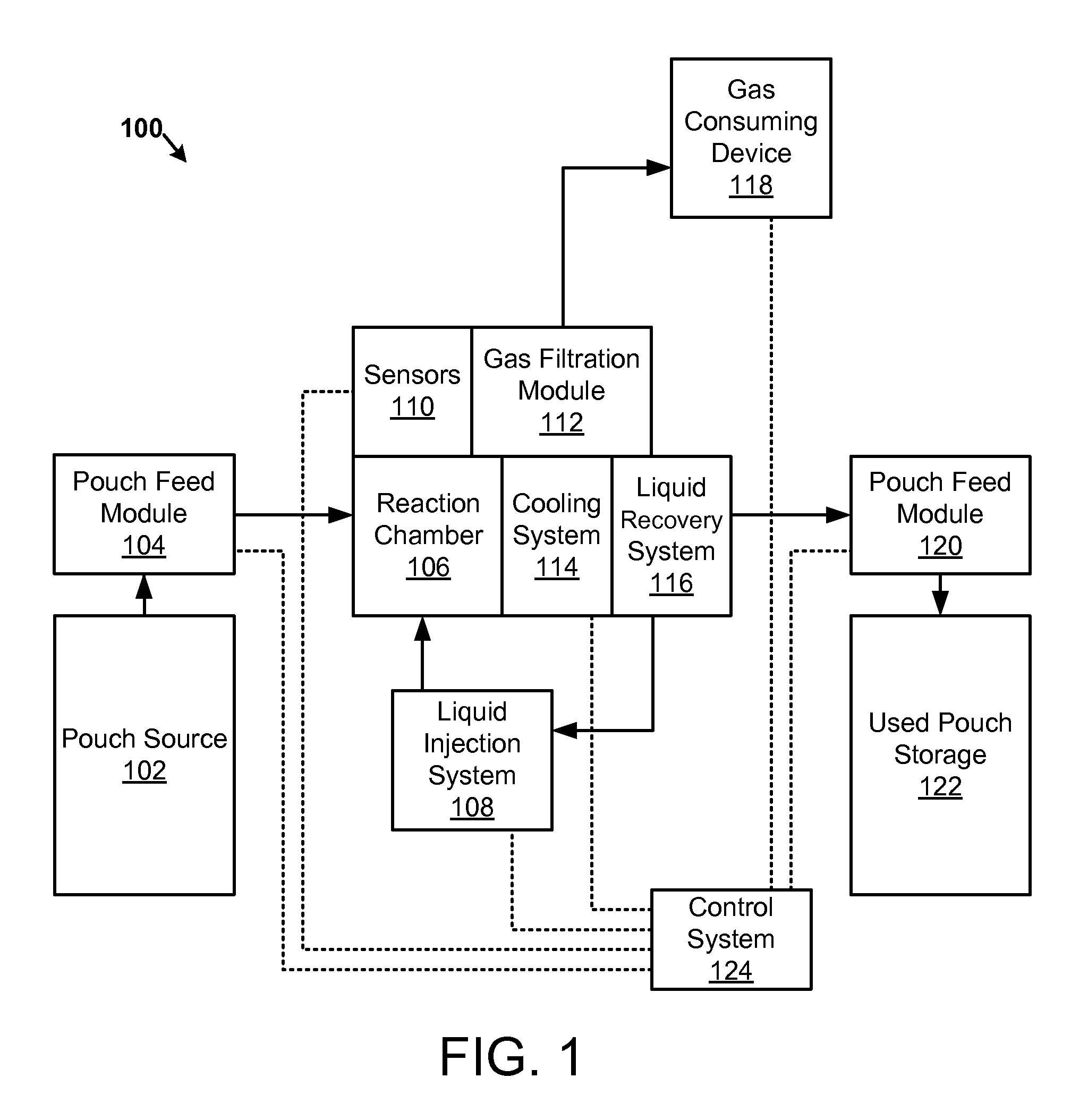
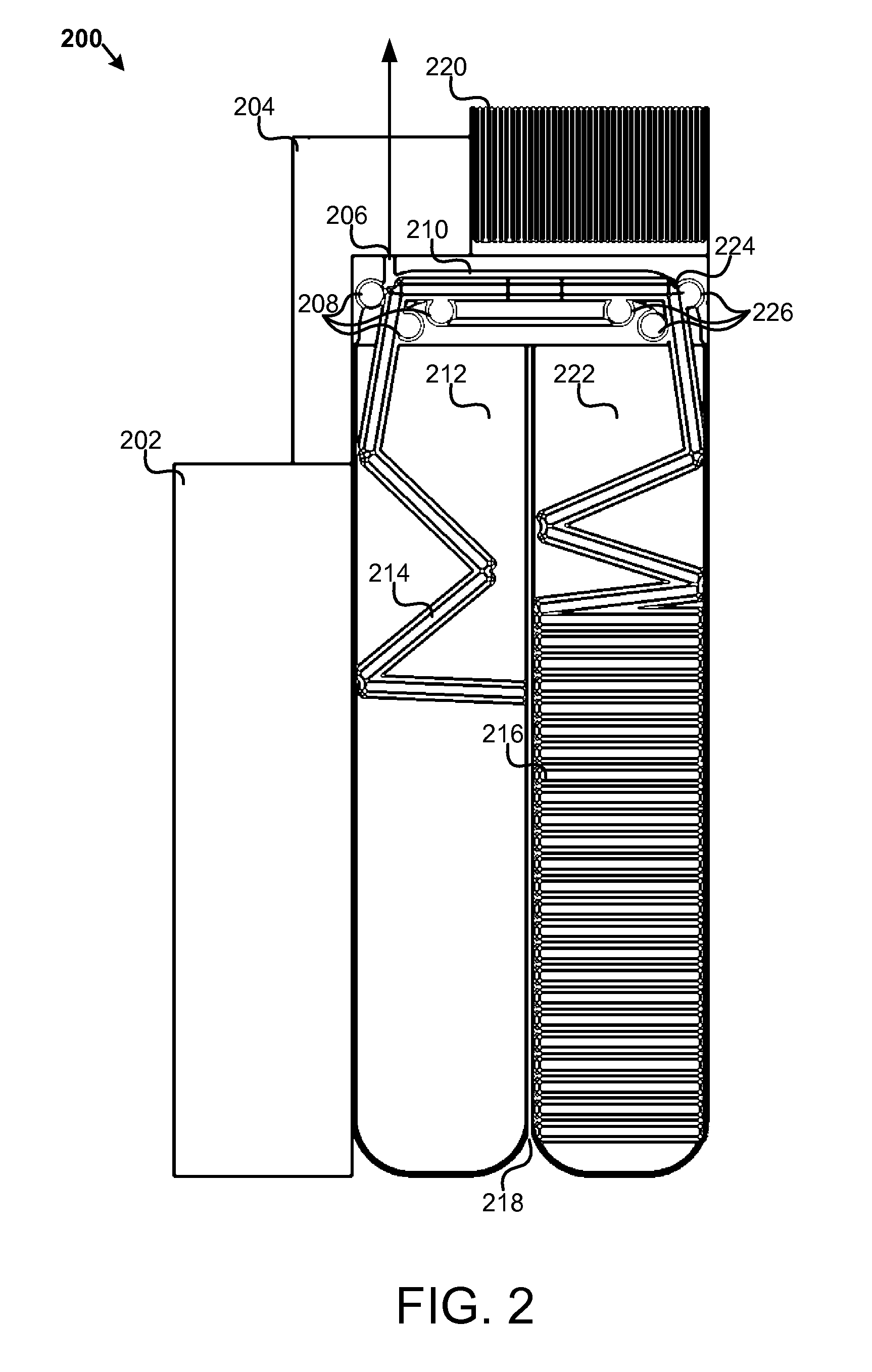
Apparatus, system, and method for generating a gas from solid reactant pouches
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for generating a gas. One or more liquid permeable pouches each define a cavity that contains a solid anhydrous reactant, such as a chemical hydride. A reaction chamber made of a heat, chemical and / or pressure resistant material receives the one or more pouches from a pouch feeder that transfers the one or more pouches into the reaction chamber successively at a feed rate. One or more liquid sources inject a liquid reactant into the reaction chamber so that the liquid reactant contacts a portion of the one or more pouches. The one or more liquid sources inject the liquid reactant at an injection rate that corresponds to the feed rate. A gas outlet releases a gas, such as hydrogen, oxygen, ammonia, borazine, nitrogen, or a hydrocarbon, that is produced by a reaction between the solid reactant and the liquid reactant.
Owner:TRULITE INC
Method for forming spacers using silicon nitride film for spacer-defined multiple patterning
ActiveUS20170316940A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSurface patternSilanes
A method of forming spacers for spacer-defined multiple pattering (SDMP), includes: depositing a pattern transfer film by PEALD on the entire patterned surface of a template using halogenated silane as a precursor and nitrogen as a reactant at a temperature of 200° C. or less, which pattern transfer film is a silicon nitride film; dry-etching the template using a fluorocarbon as an etchant, and thereby selectively removing a portion of the pattern transfer film formed on a top of a core material and a horizontal portion of the pattern transfer film while leaving the core material and a vertical portion of the pattern transfer film as a vertical spacer, wherein a top of the vertical spacer is substantially flat; and dry-etching the core material, whereby the template has a surface patterned by the vertical spacer on a underlying layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Sequential gas flow oxide deposition technique
InactiveUS20050019494A1High aspect ratioGood effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOxygenSilicon dioxide
A method of depositing a silica glass insulating film over a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises exposing the substrate to a silicon-containing reactant introduced into a chamber in which the substrate is disposed such that one or more layers of the silicon-containing reactant are adsorbed onto the substrate; purging or evacuating the chamber of the silicon-containing reactant; converting the silicon-containing reactant into a silica glass insulating compound by exposing the substrate to oxygen radicals formed from a second reactant while biasing the substrate to promote a sputtering effect, wherein an average atomic mass of all atomic constituents in the second reactant is less than or equal to an average atomic mass of oxygen; and repeating the exposing, purging / evacuating and exposing sequence a plurality of times until a desired film thickness is reached.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
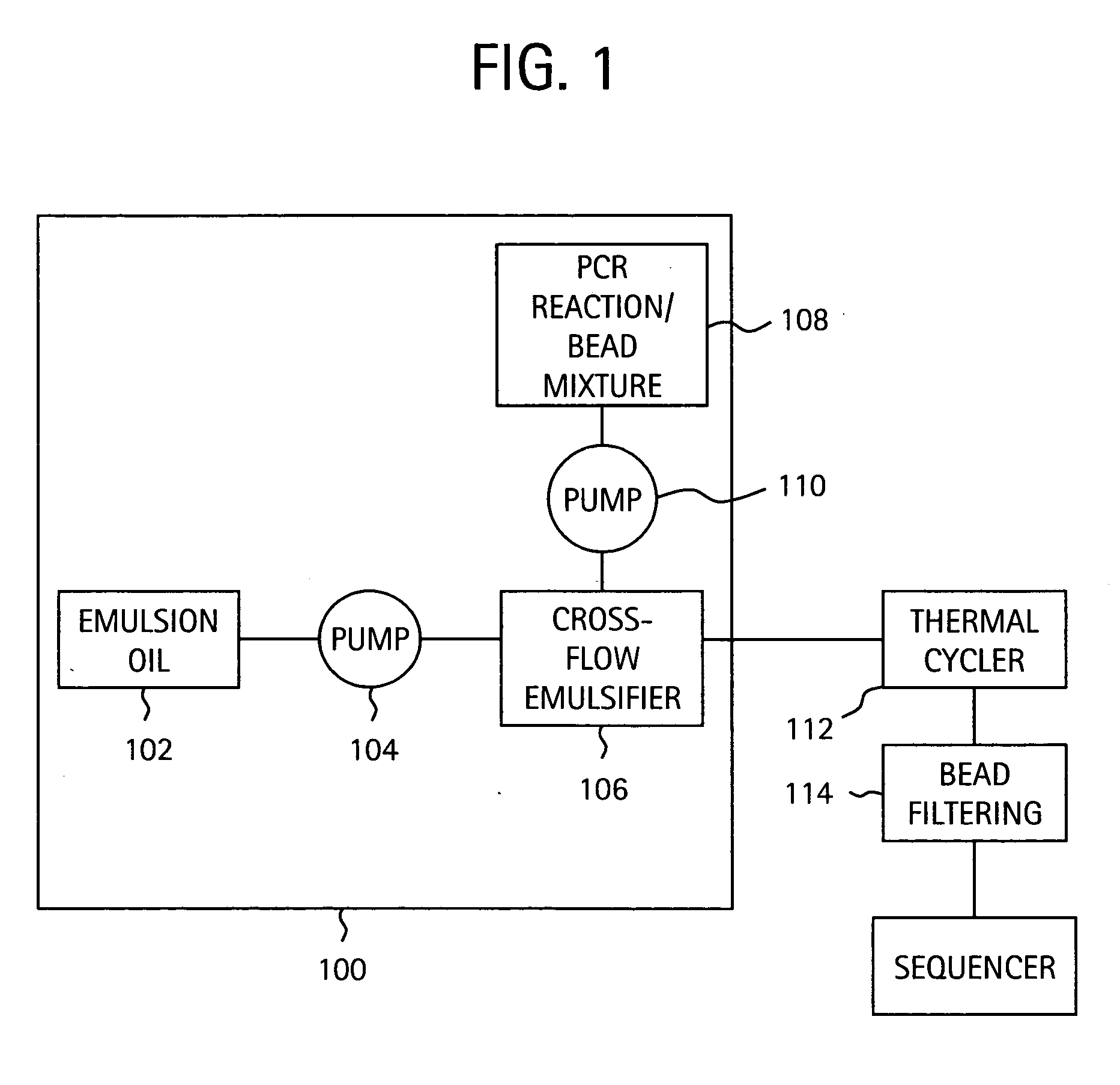
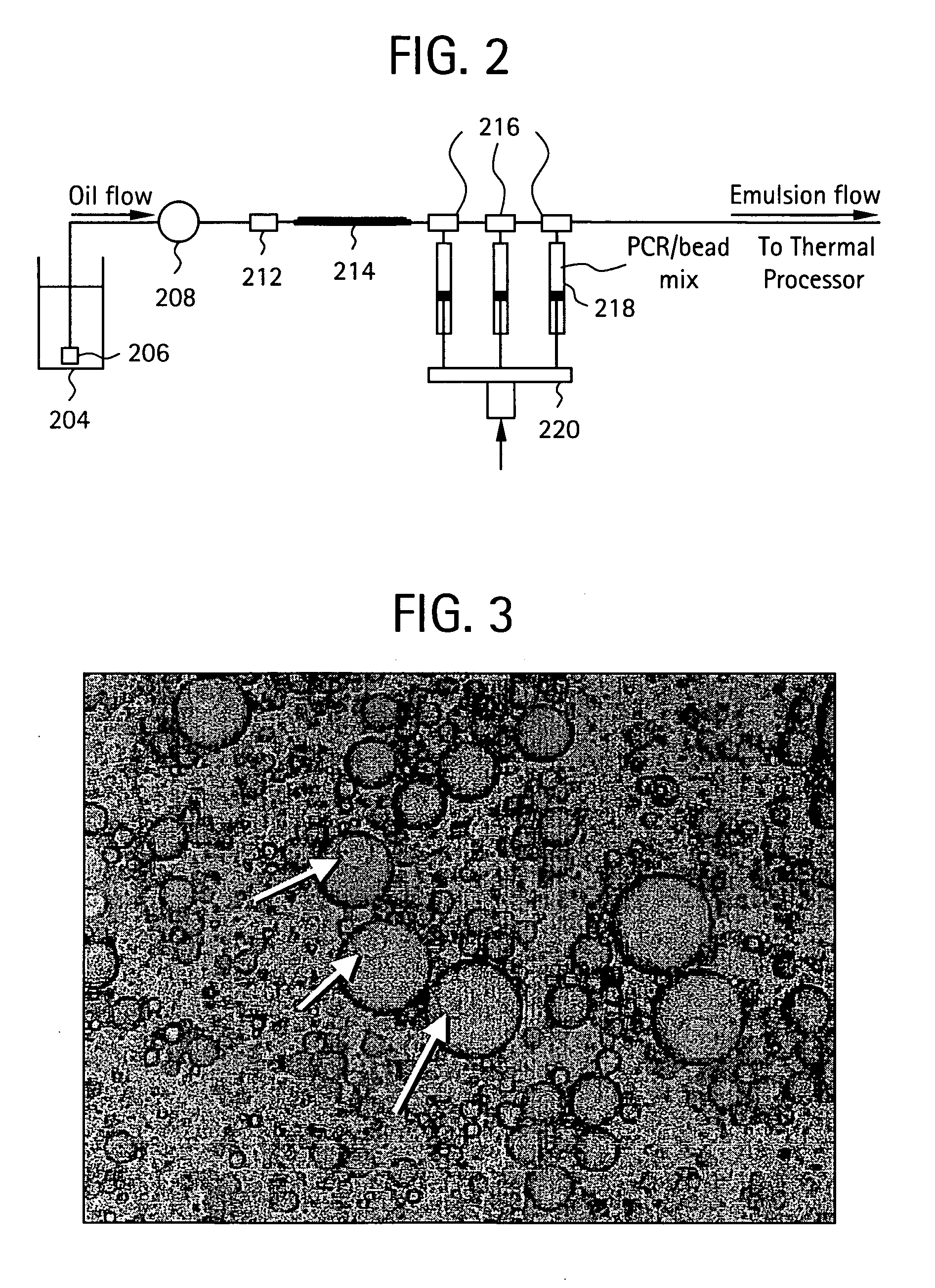
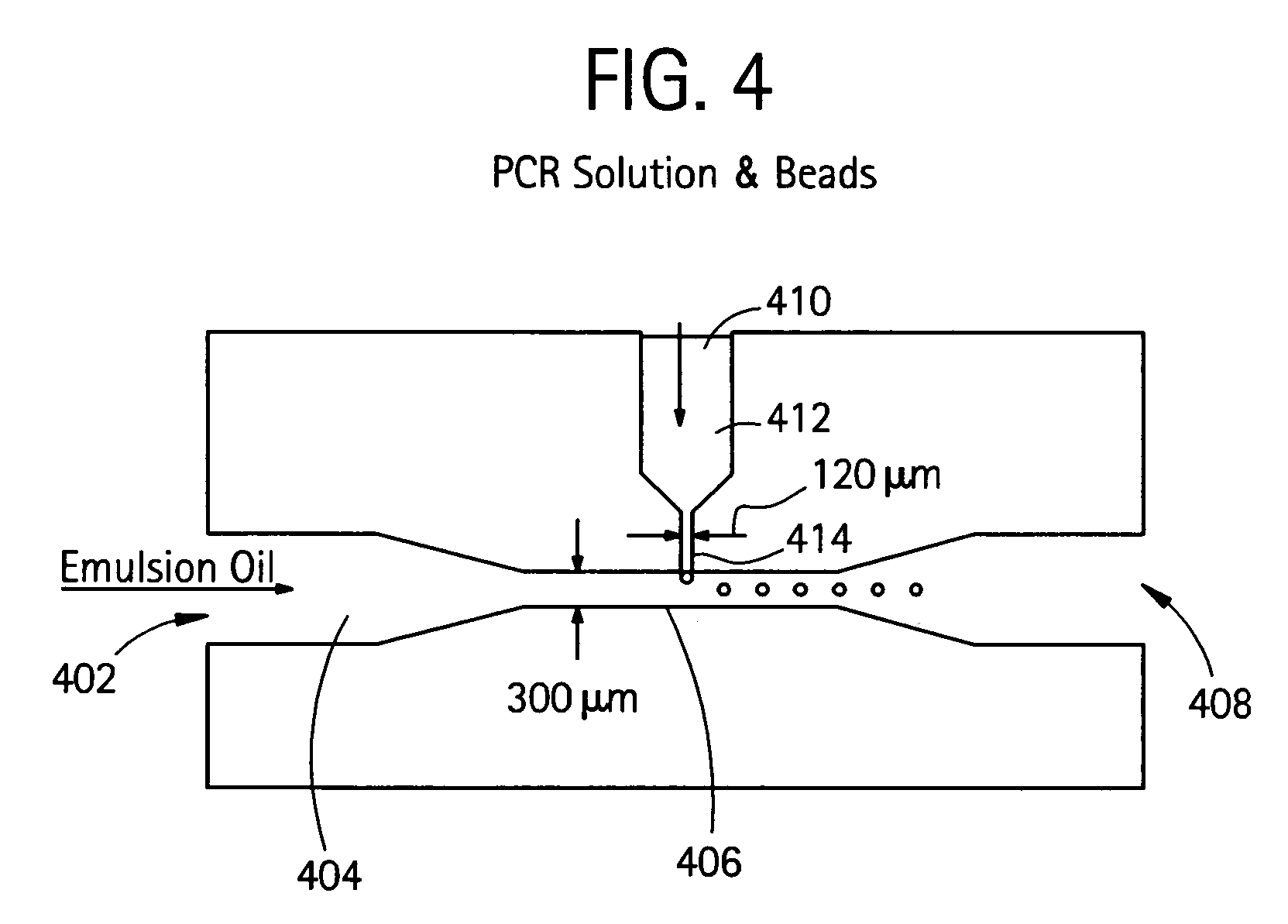
Nucleic acid amplification with continuous flow emulsion
InactiveUS20050227264A1Rapid and economical mannerReduce nozzle cloggingHeating or cooling apparatusFlow mixersMicroreactorGenetic Materials
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and devices / systems for amplifying genetic material and may include providing a water-in-oil emulsion in a continuous flow. The emulsion may include a plurality of water droplets comprising microreactors. Each of the plurality of microreactors may include a single bead capable of capturing a nucleic acid template, a single species nucleic acid template and sufficient reagents to amplify the copy number of the nucleic acid template. The method also includes flowing the emulsion across a first temperature zone and a second lower temperature zone to thermally process the microreactors to amplify the nucleic acid template by polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Method of forming a layer and method of forming a capacitor of a semiconductor device having the same
InactiveUS20060063346A1Improve reliabilityLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsKryptonDevice material
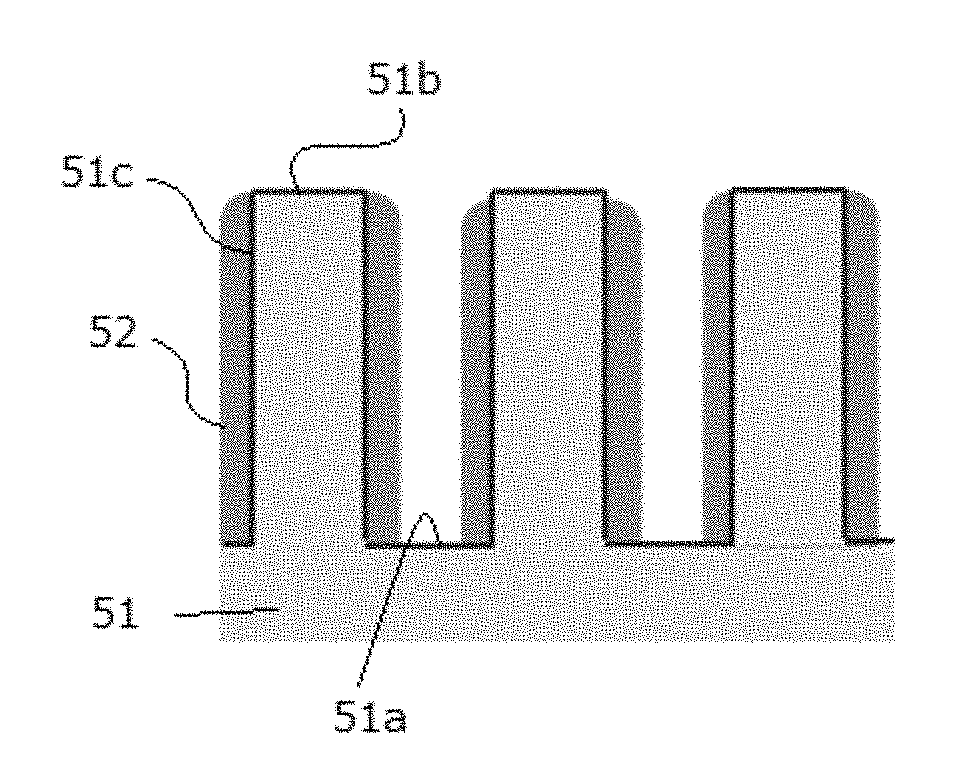
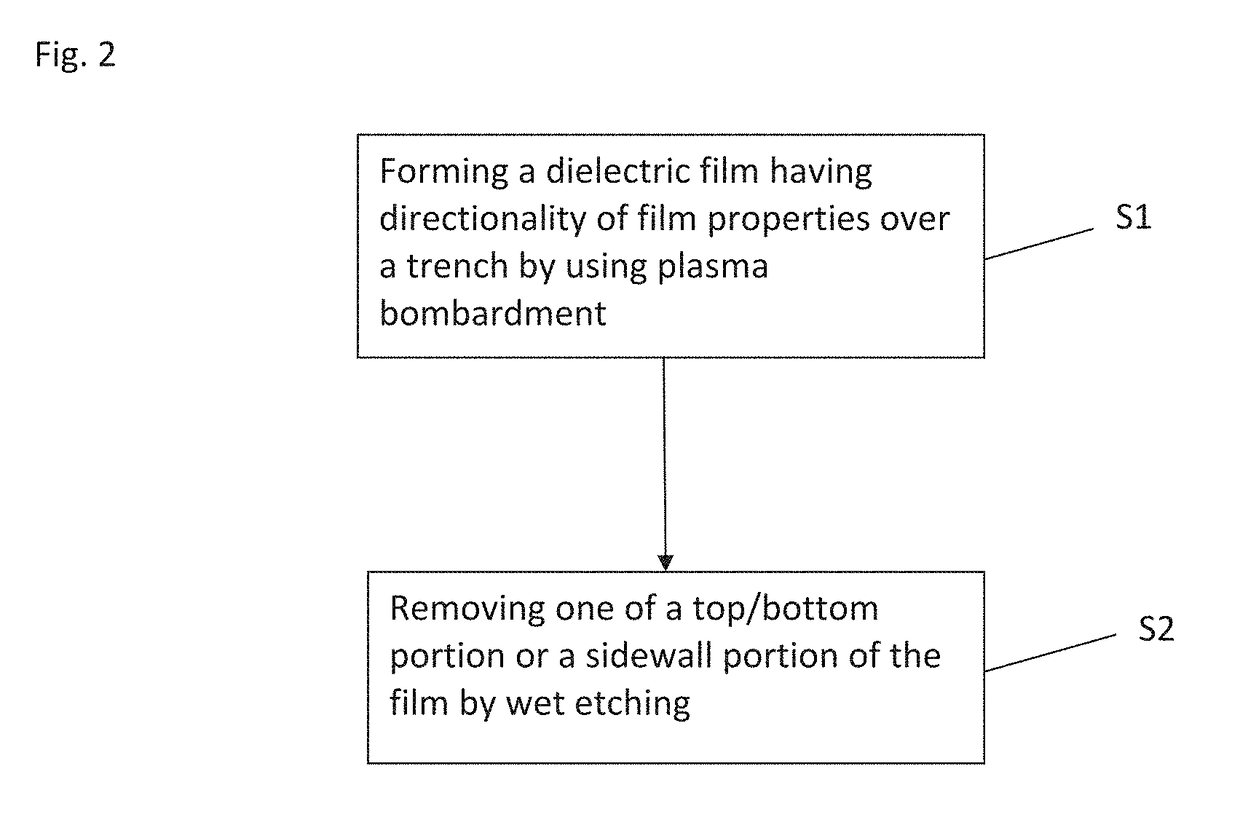
In a method of forming a layer using an atomic layer deposition process, after a substrate is loaded into a chamber, a reactant is provided onto the substrate to form a preliminary layer. Atoms in the preliminary layer are partially removed from the preliminary layer using plasma formed from an inert gas such as an argon gas, a xenon gas or a krypton gas, or an inactive gas such as an oxygen gas, a nitrogen gas or a nitrous oxide gas to form a desired layer. Processes for forming the desired layer may be simplified. A highly integrated semiconductor device having improved reliability may be economically manufactured so that time and costs required for the manufacturing of the semiconductor device may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com