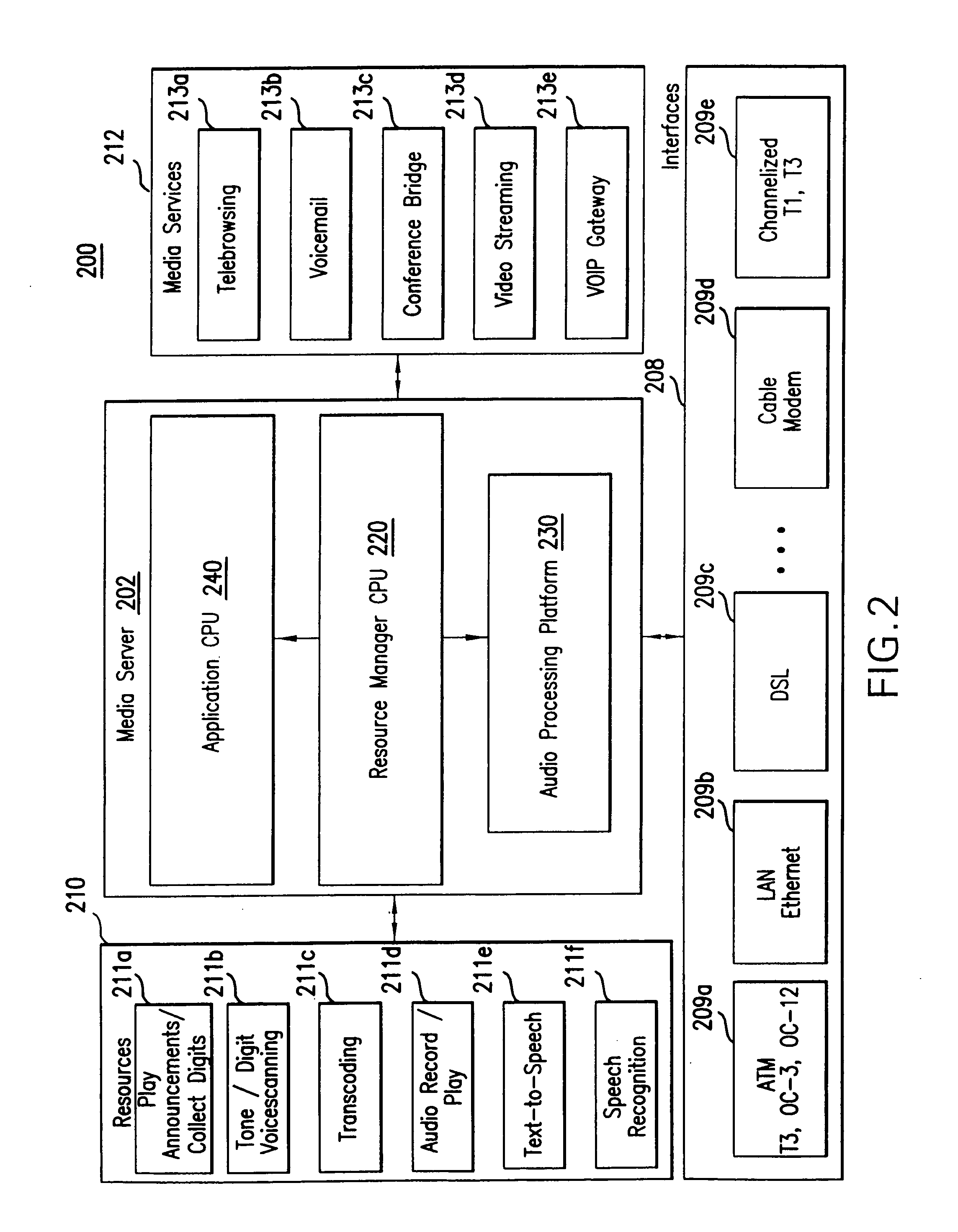
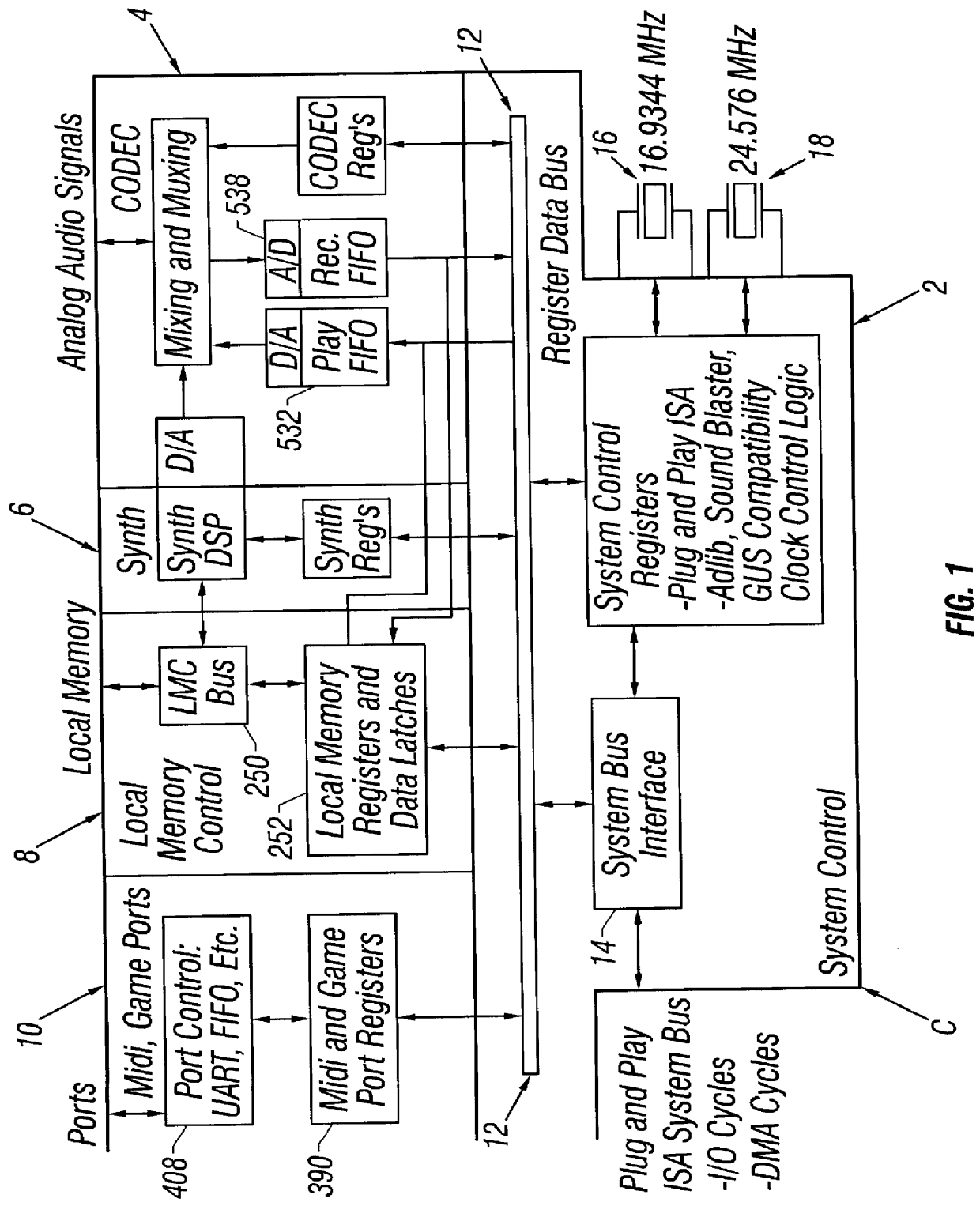
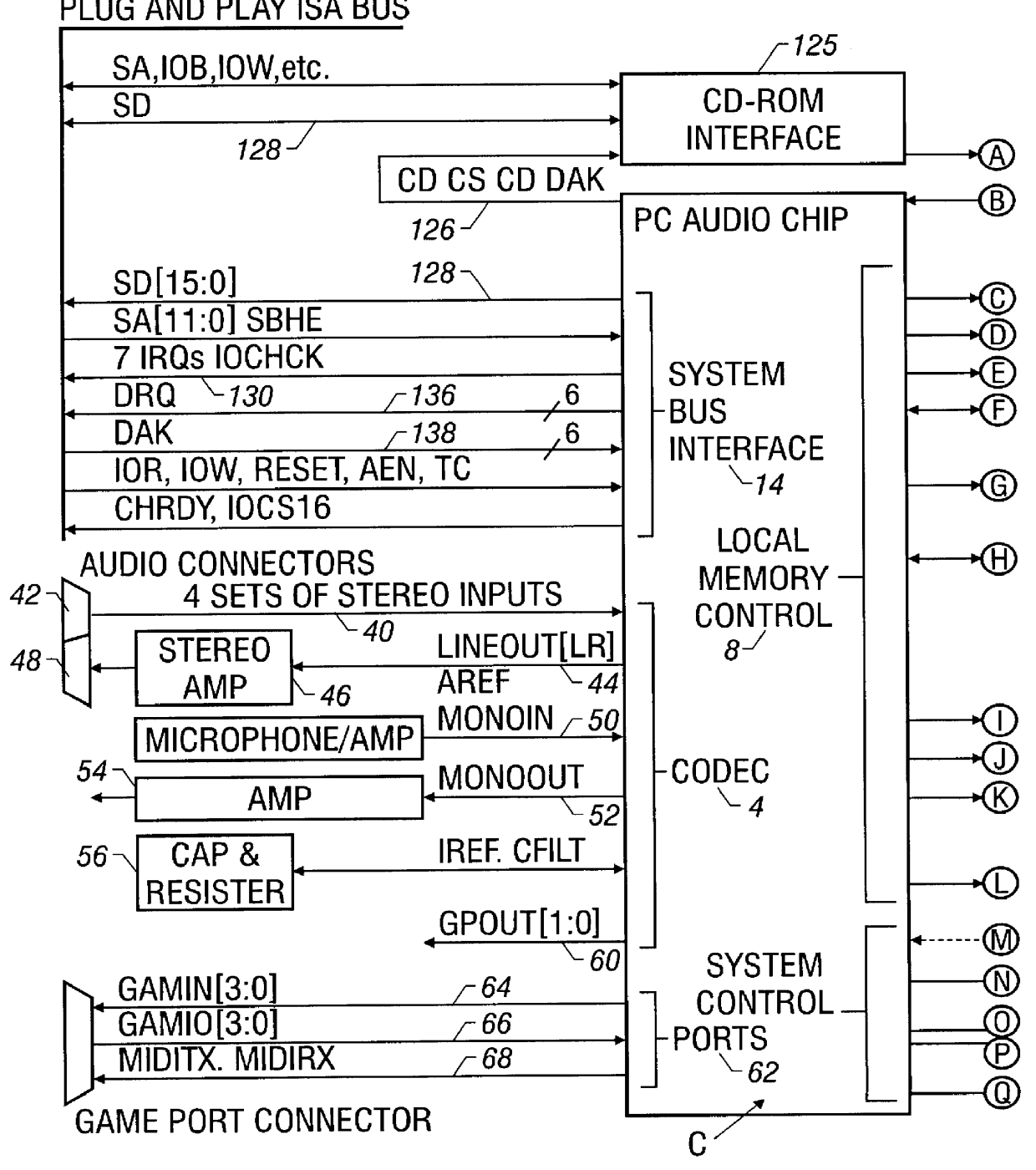
Patents
Literature
9941 results about "Noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acoustic noise is any sound in the acoustic domain, either deliberate or unintended. It is important to recognise that the term "noise" is also used to refer to other, non-audible forms, especially in electronics and in the radio/radar spectrum.
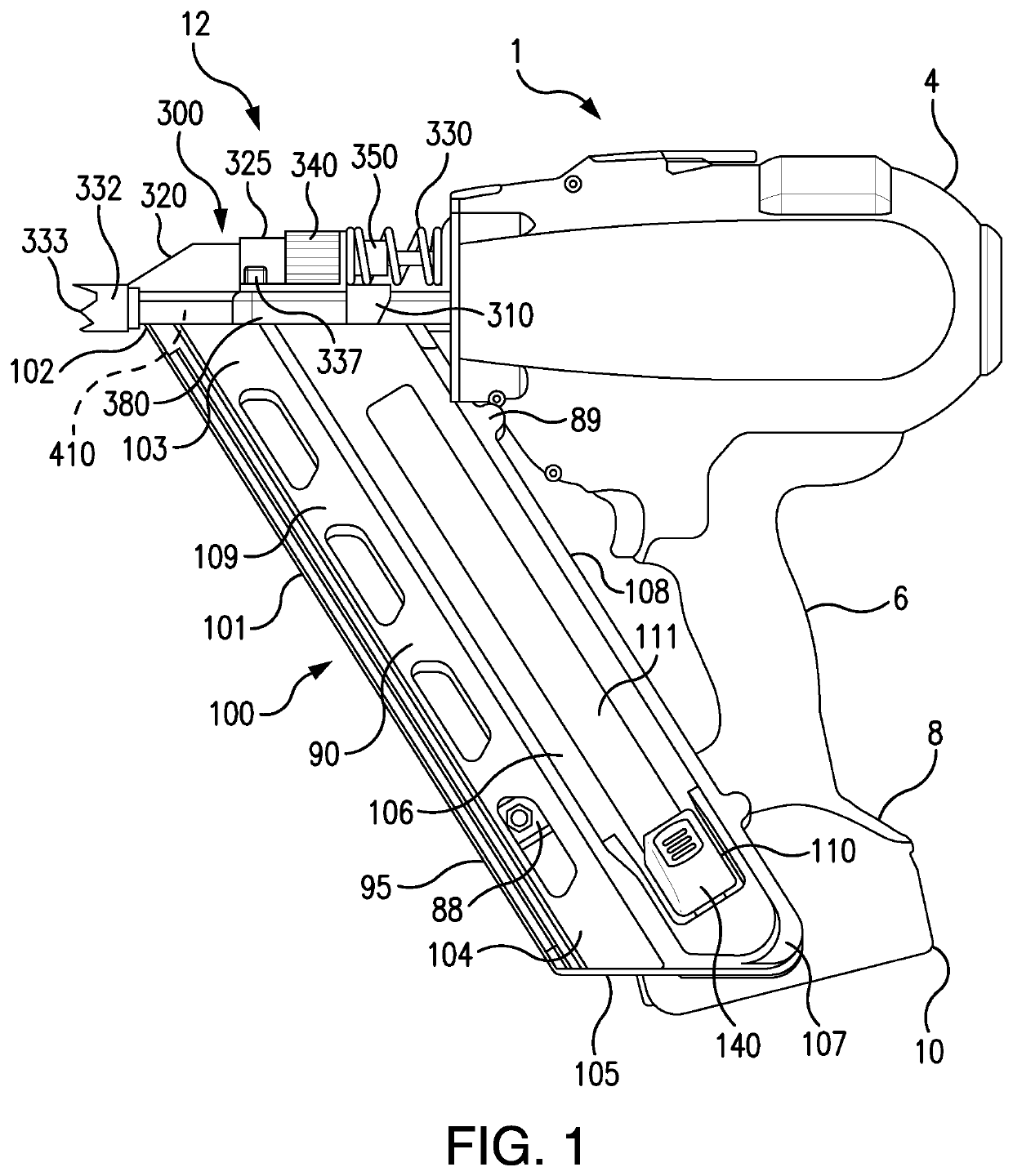
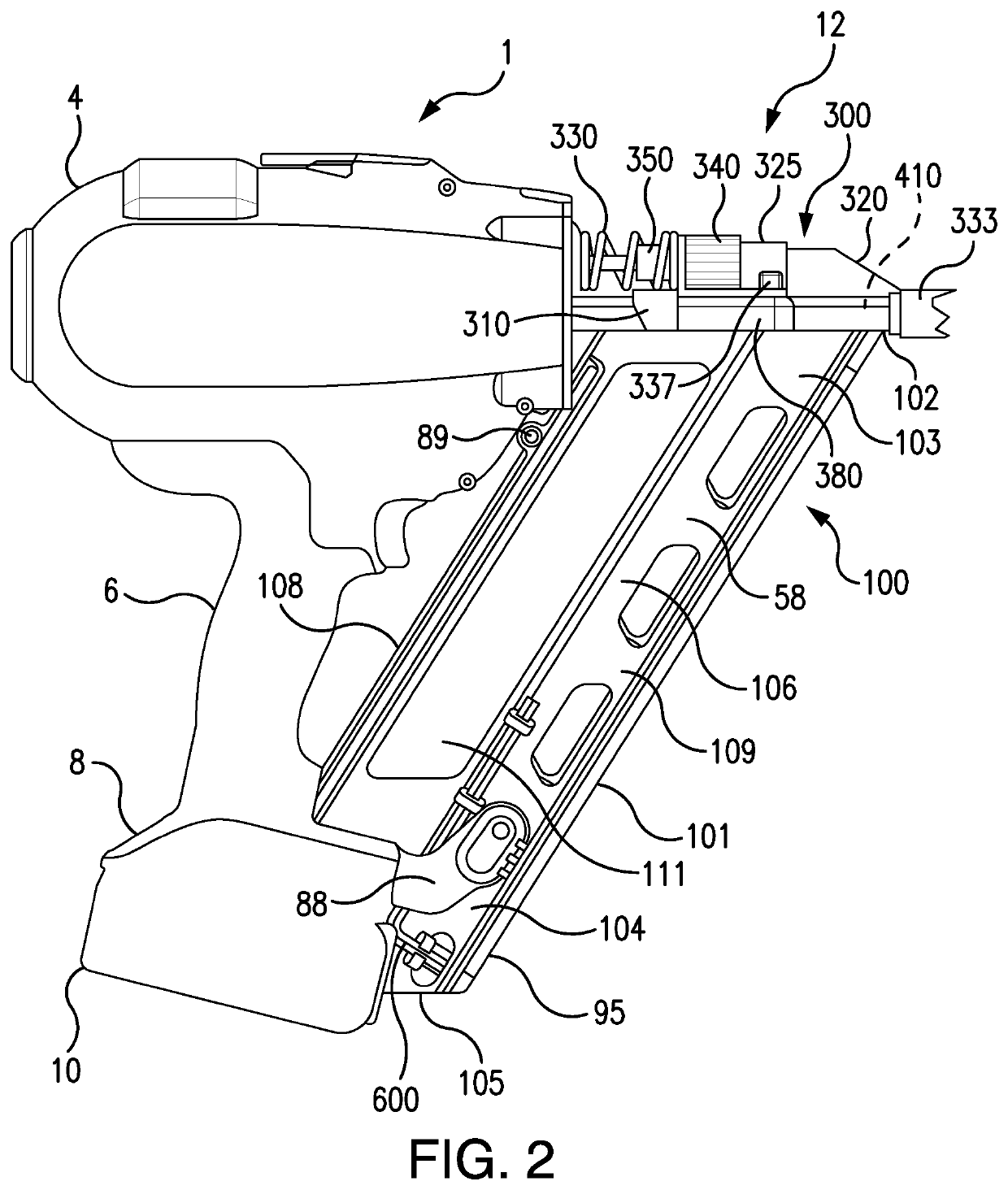
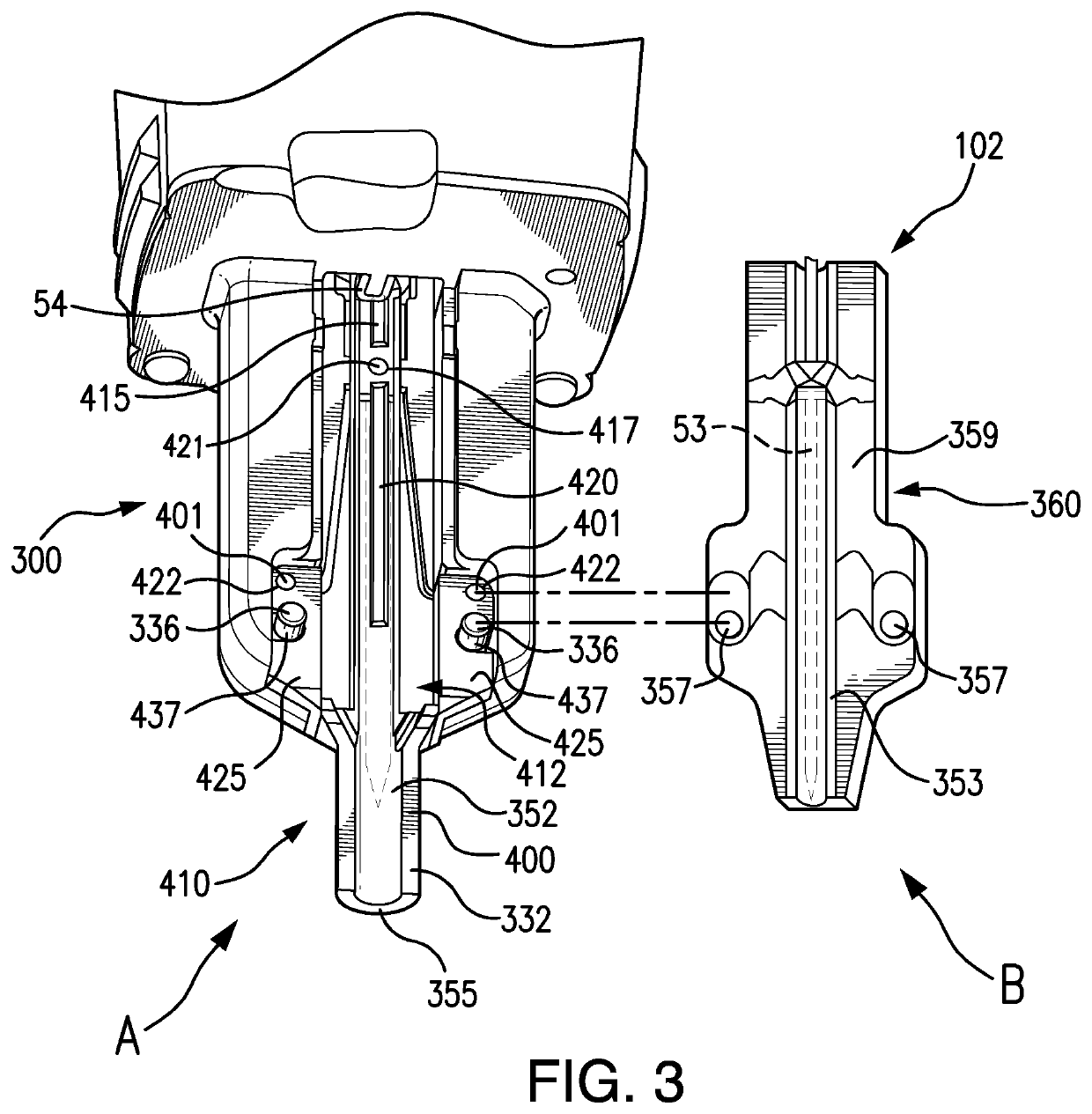
Sound damping for power tools
ActiveUS10717179B2Reduce noiseUndesired noisePortable power-driven toolsNailing toolsControl systemNoise
A power tool having one or more sound damping members which reduce sound and / or vibration from one or more parts of a power tool. The sound damping member can reduce sound and / or vibration from static or dynamic parts of a power tool. The sound damping member can reduce noise and / or vibration from one or more rotating or moving parts of a power tool and its housing or internal structure. Methods, means, controls, systems and practices for reducing or eliminating undesired sound from a power tool are disclosed.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
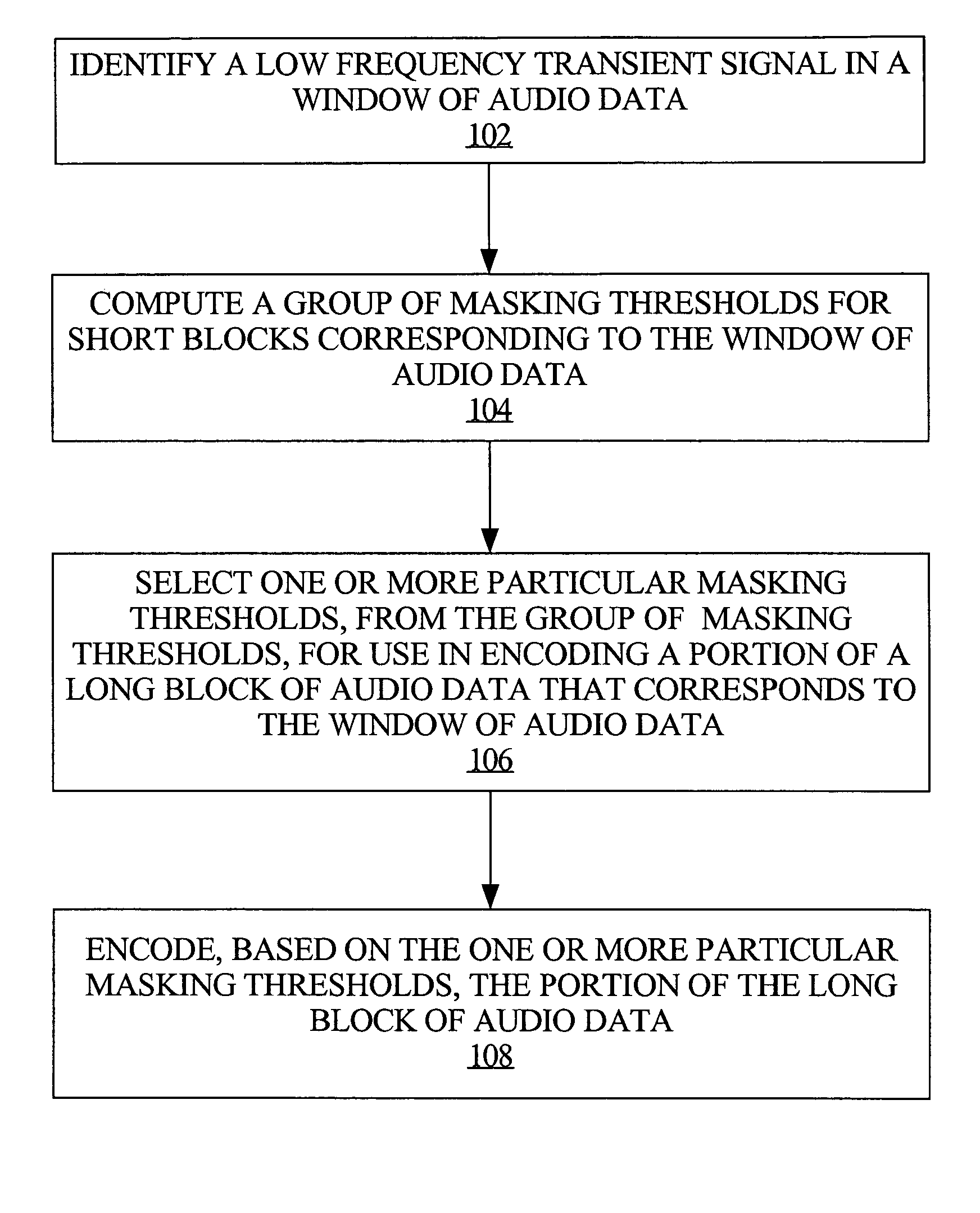
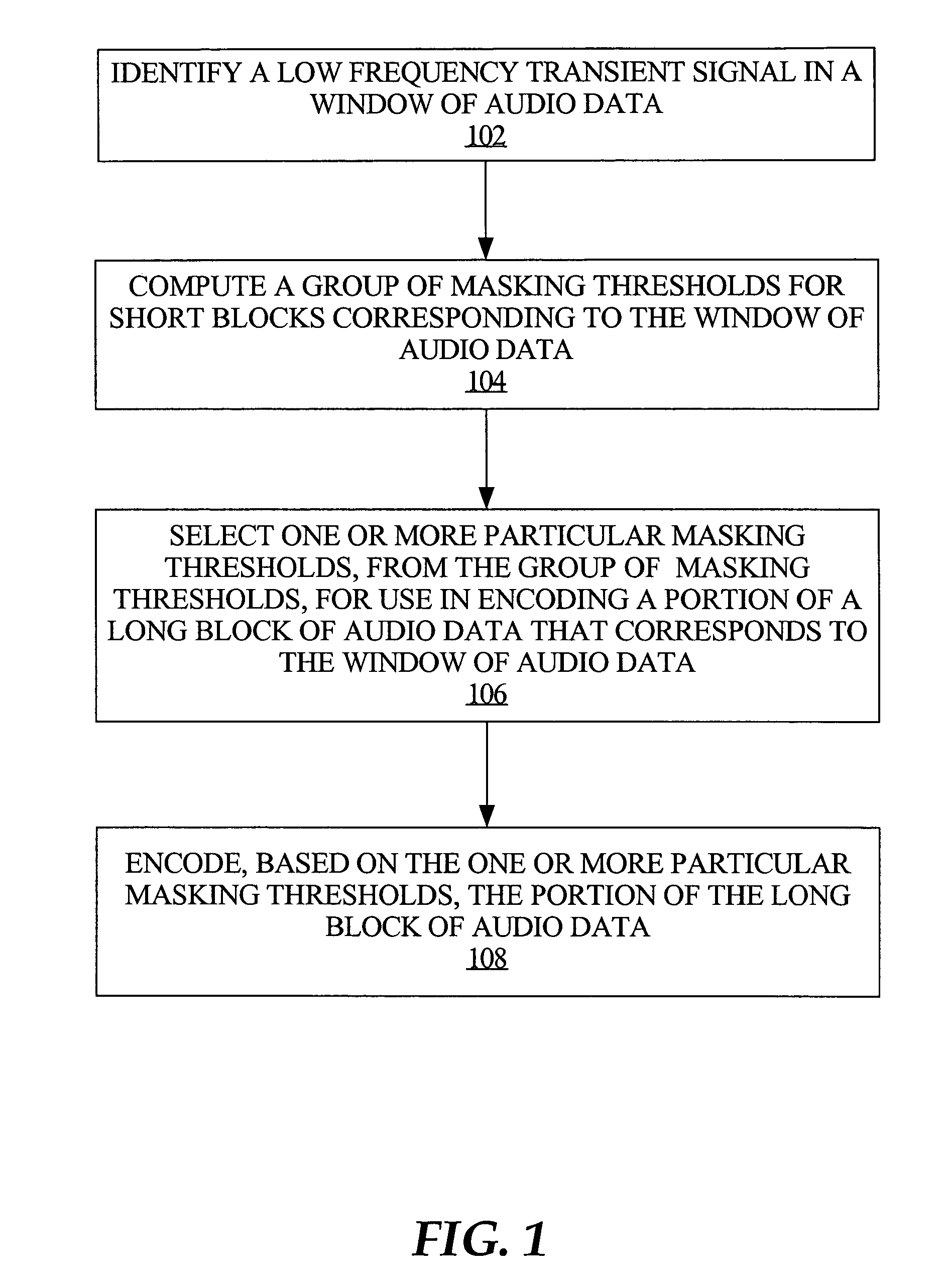
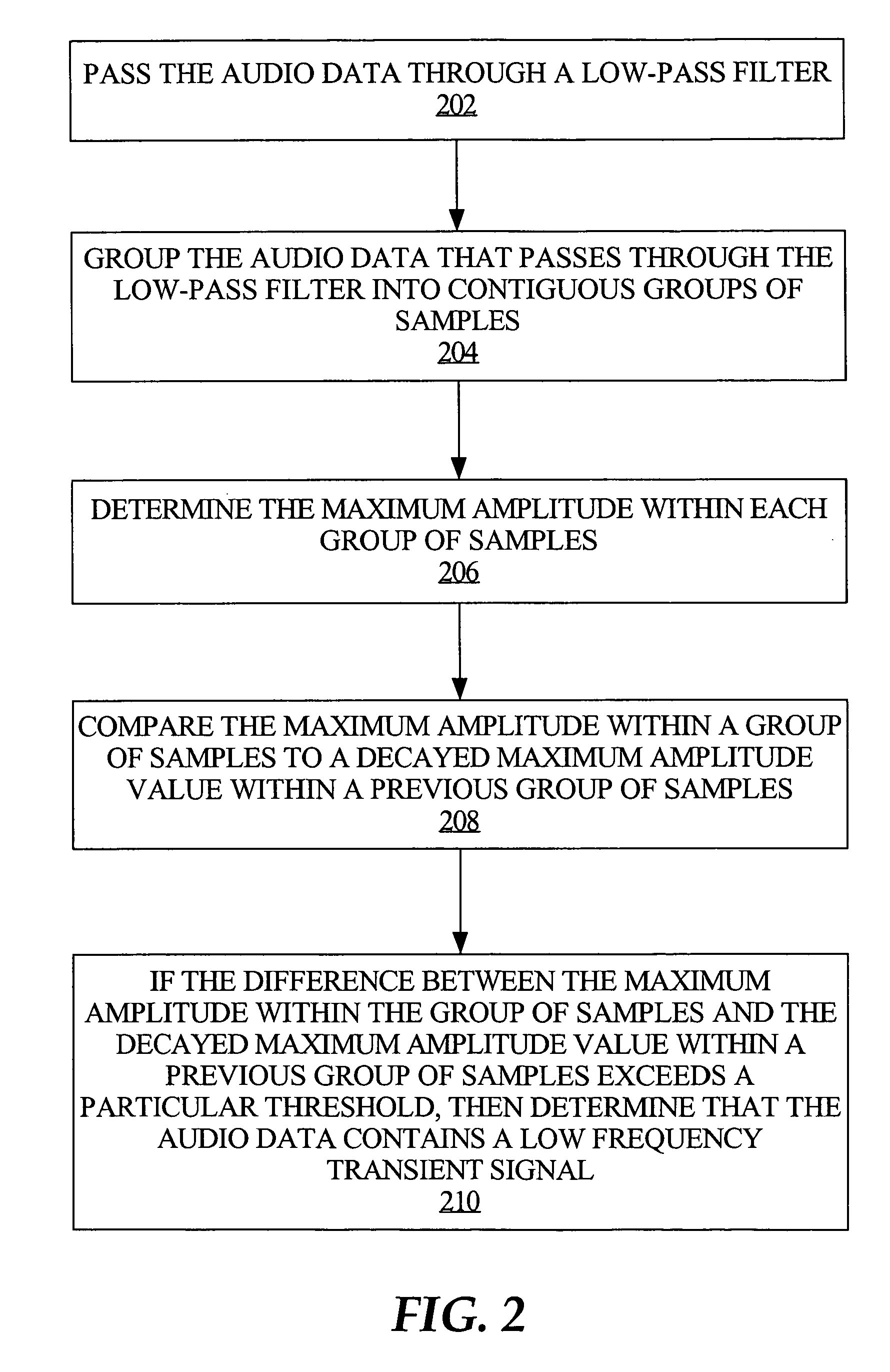
Adapting masking thresholds for encoding a low frequency transient signal in audio data
An improved audio coding technique encodes audio having a low frequency transient signal, using a long block, but with a set of adapted masking thresholds. Upon identifying an audio window that contains a low frequency transient signal, masking thresholds for the long block may be calculated as usual. A set of masking thresholds calculated for the 8 short blocks corresponding to the long block are calculated. The masking thresholds for low frequency critical bands are adapted based on the thresholds calculated for the short blocks, and the resulting adapted masking thresholds are used to encode the long block of audio data. The result is encoded audio with rich harmonic content and negligible coder noise resulting from the low frequency transient signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
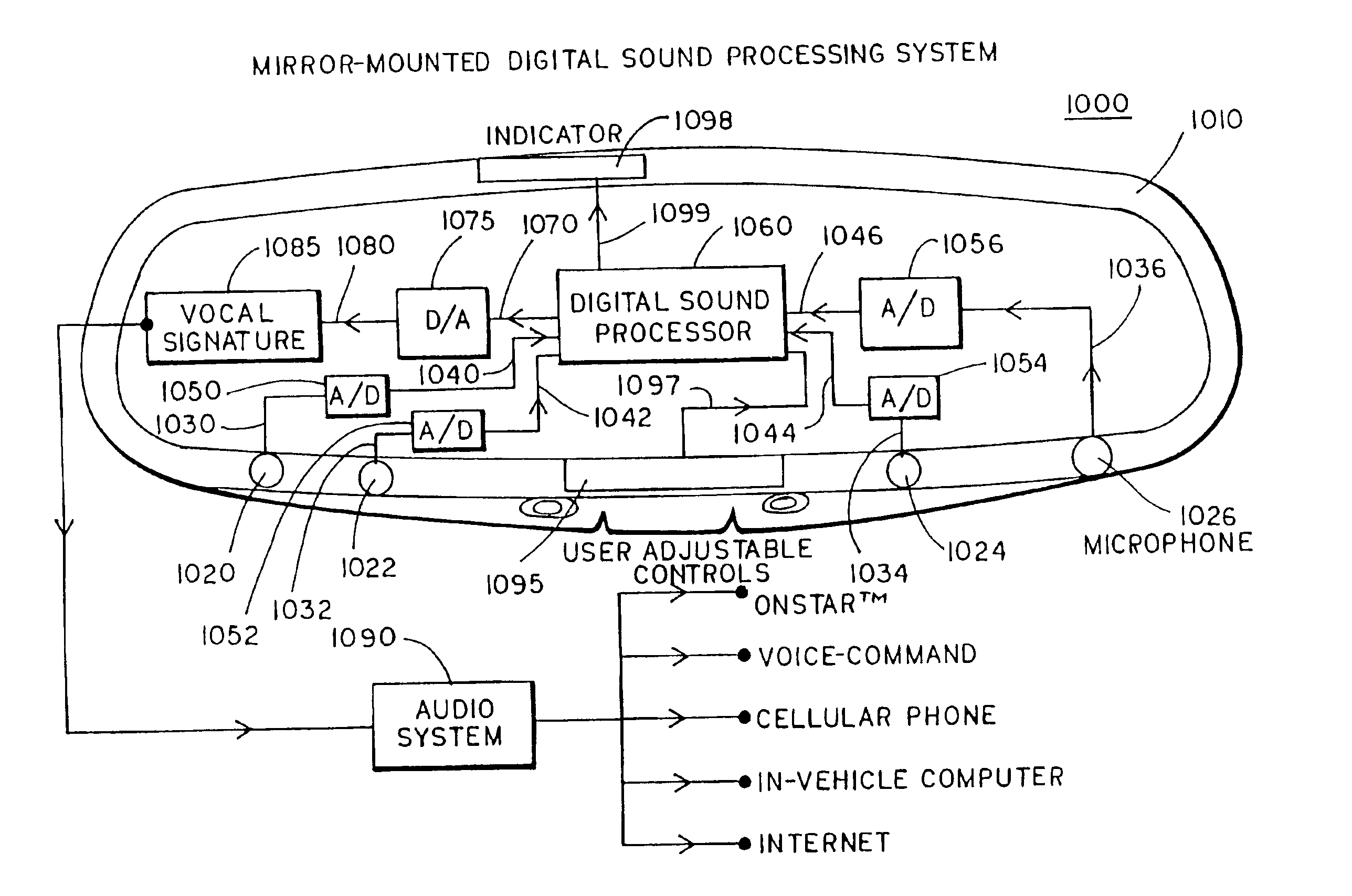
Vehicular sound-processing system incorporating an interior mirror user-interaction site for a restricted-range wireless communication system
InactiveUS6906632B2Facilitates few partEasy to installPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesOrganic chemistryCommunications systemEngineering
The interior cabin of a vehicle is provided with a vehicular sound-processing system that comprises an interior rearview mirror assembly, the mirror assembly including a mirror housing and a reflective element. An accessory is located in the interior cabin. The interior rearview mirror assembly comprises a user-interaction site for a wireless communication system, the wireless communication system communicating with the accessory. The user-interaction site comprises at least one microphone for producing an audio output in response to detection of vocal input of a human speaker in the interior cabin with the vehicle cabin noise superimposed thereon. Preferably, the user-interaction site further comprises at least one manually operated control input. The restricted-range wireless communication system preferably comprises one of a radio frequency restricted-range wireless communication system and an infrared restricted-range wireless communication system. Signals indicative of the vocal input detected at the user-interaction site of the interior mirror assembly are wirelessly broadcast to the accessory located in the interior cabin of the vehicle.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Noise protection verification device
InactiveUS6567524B1Hearing protectionFacilitate communicationVibration measurement in fluidIntra aural earpiecesVocal tractEngineering
Ear protecting device with a sealing section for acoustically sealing the meatus of a human, includes a sound generator with a sound outlet for being directed toward the user meatus; an inner microphone with a sound inlet from the meatus, arranged for measuring the resulting sound field in the meatus; connected to an electronics unit including a sound analyser coupled to the inner microphone, for analyzing sound characteristics of the resulting sound field in the meatus, producing analyzed sound characteristics; storing part in the electronics unit for storing measured predetermined sound characteristics of a properly functioning ear protecting device; a comparing part in the electronics unit for comparing the inner microphone analyzed sound characteristics with the stored measured predetermined sound characteristics; indicating part coupled to the comparing part for being activated if the analyzed sound characteristics differ significantly from the predetermined sound characteristics.
Owner:HONEYWELL HEARING TECH
Dual-Microphone Spatial Noise Suppression
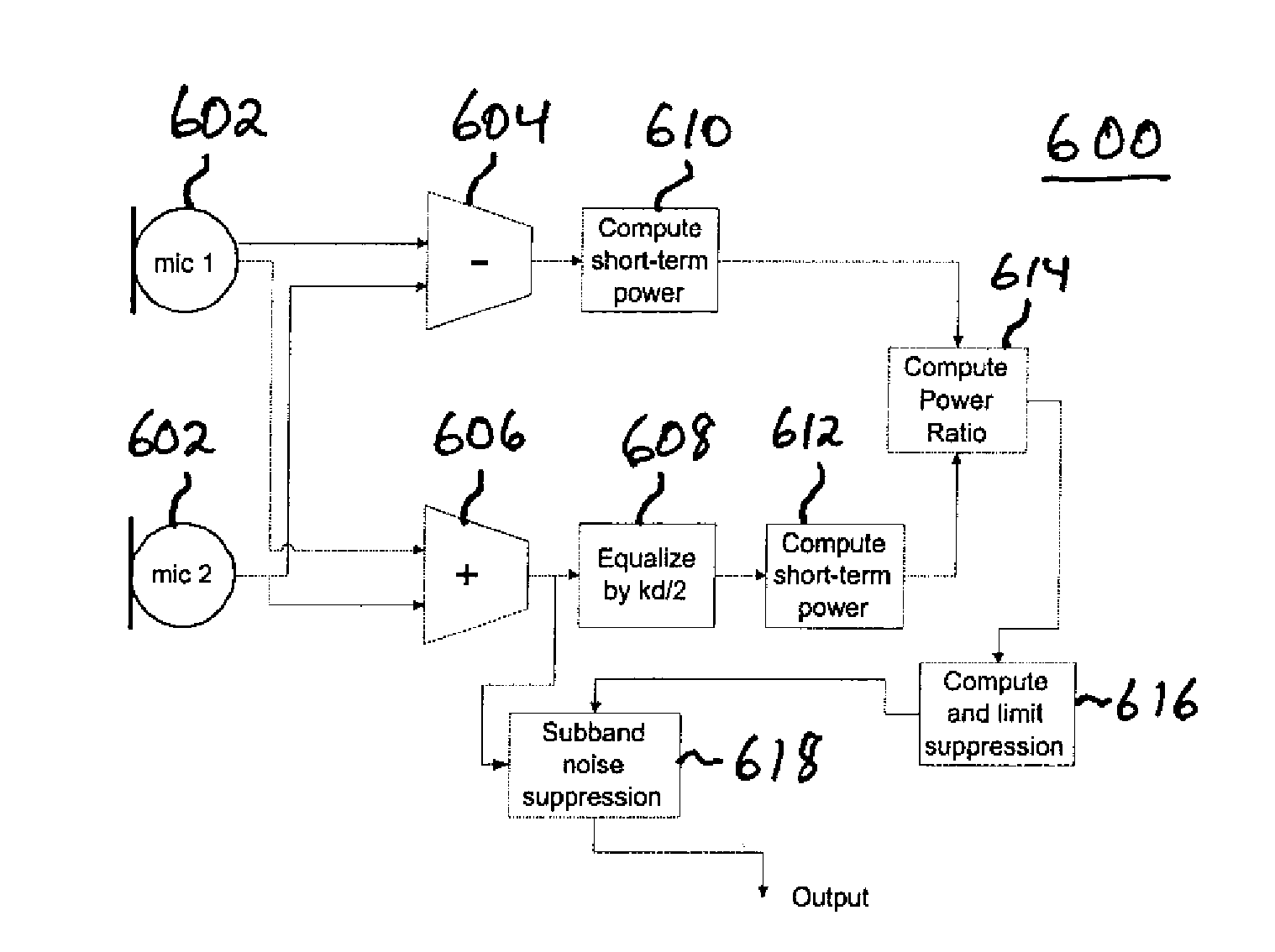
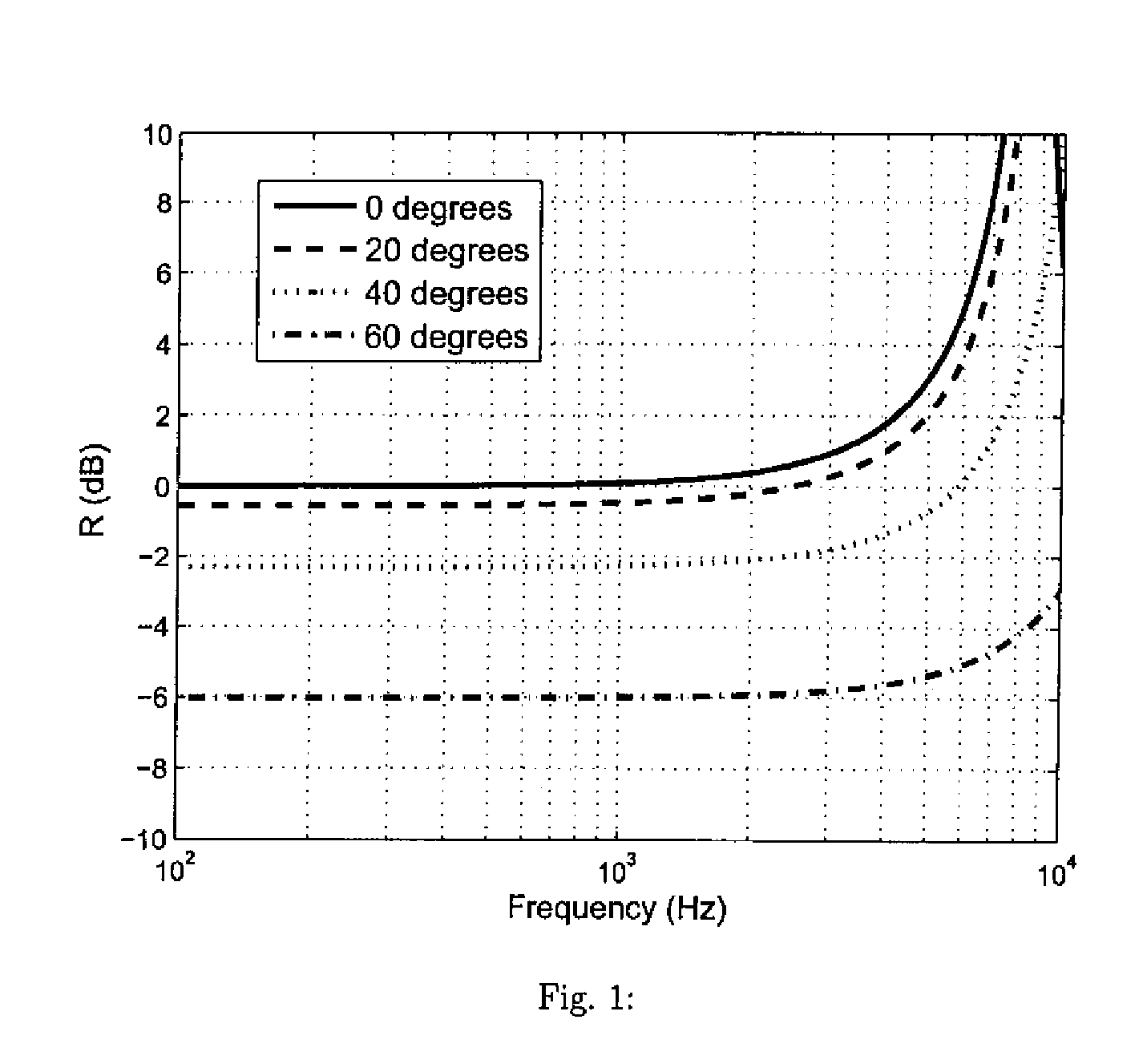
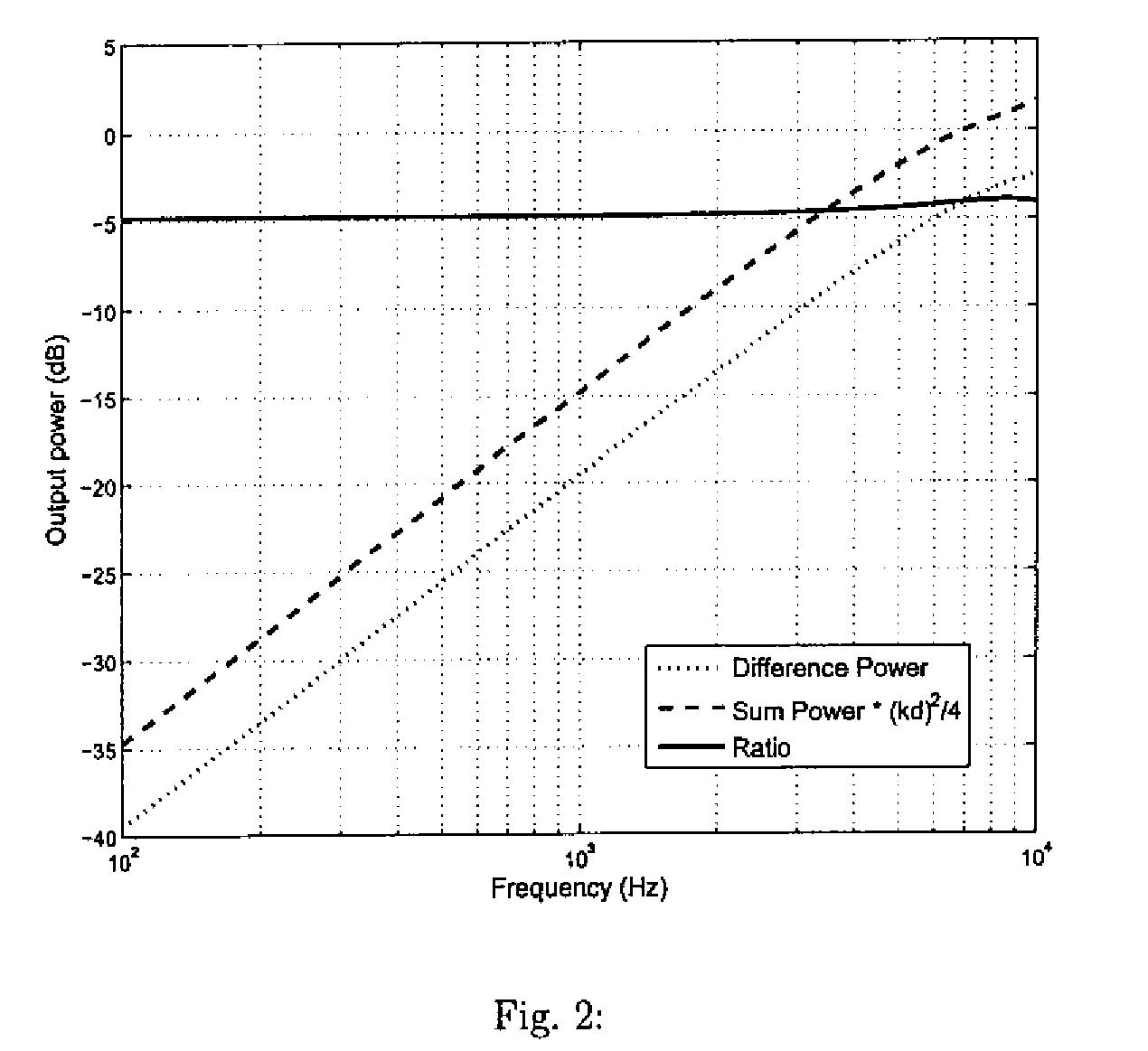
Spatial noise suppression for audio signals involves generating a ratio of powers of difference and sum signals of audio signals from two microphones and then performing noise suppression processing, e.g., on the sum signal where the suppression is limited based on the power ratio. In certain embodiments, at least one of the signal powers is filtered (e.g., the sum signal power is equalized) prior to generating the power ratio. In a subband implementation, sum and difference signal powers and corresponding the power ratio are generated for different audio signal subbands, and the noise suppression processing is performed independently for each different subband based on the corresponding subband power ratio, where the amount of suppression is derived independently for each subband from the corresponding subband power ratio. In an adaptive filtering implementation, at least one of the audio signals can be adaptively filtered to allow for array self-calibration and modal-angle variability.
Owner:MH ACOUSTICS
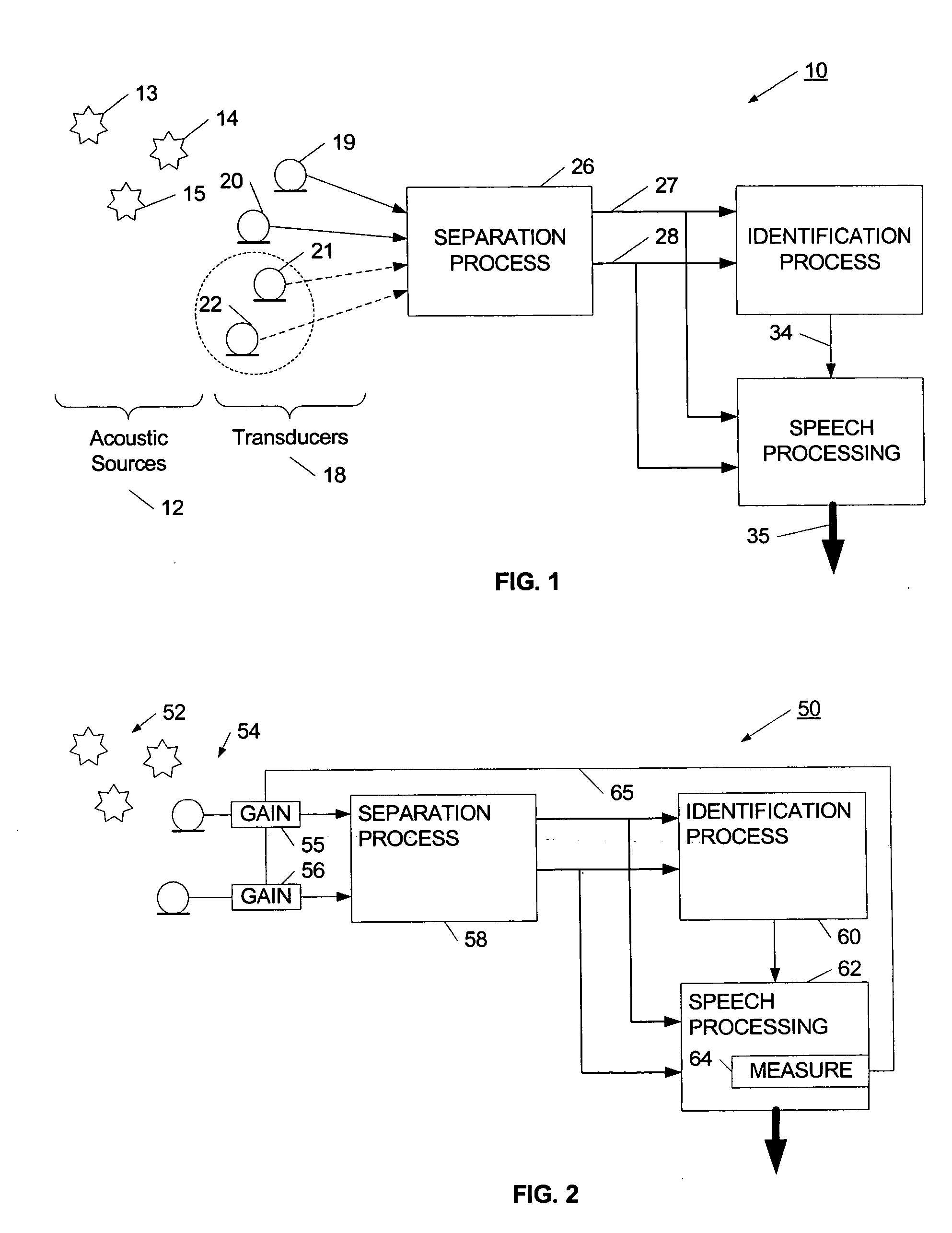
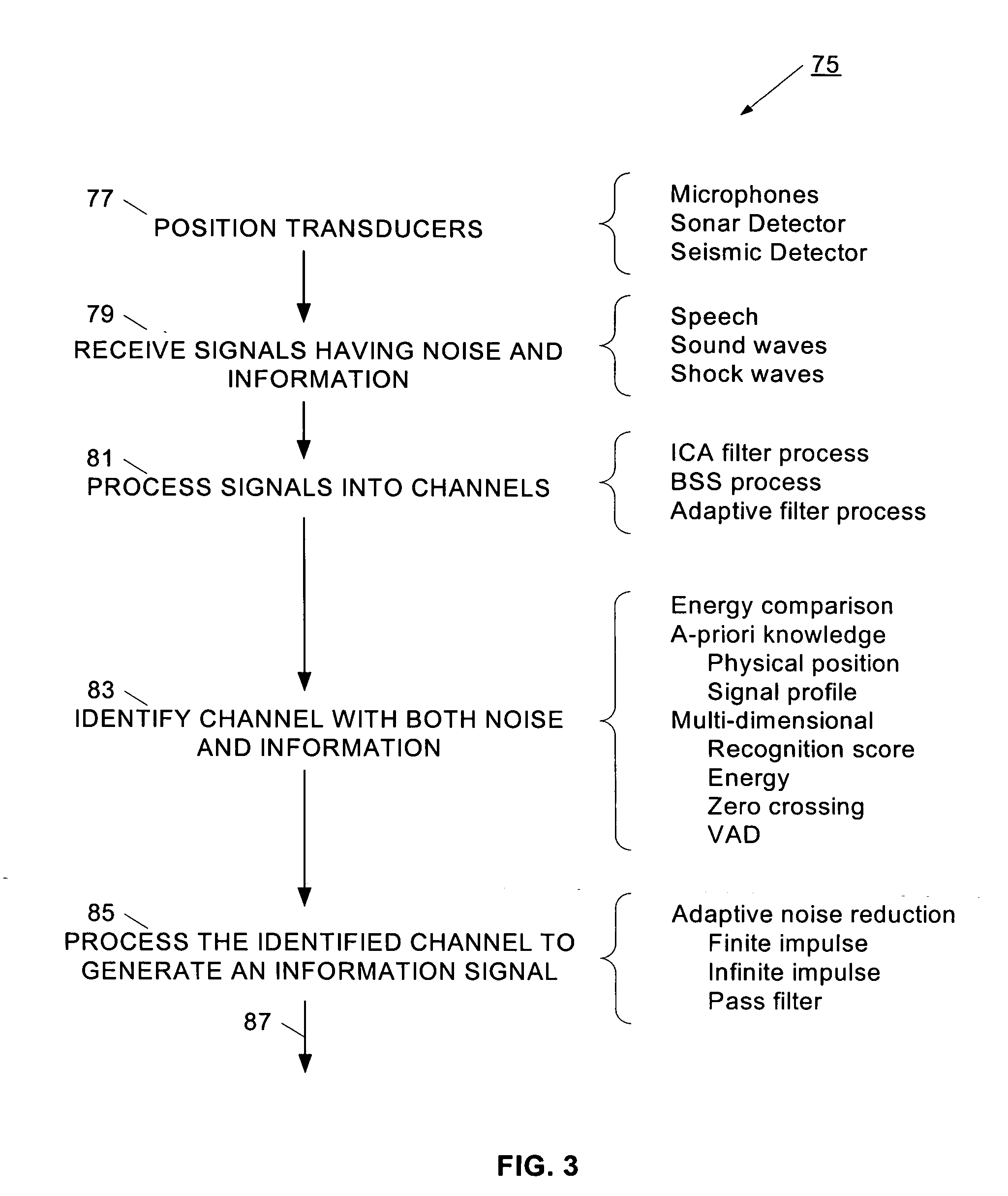
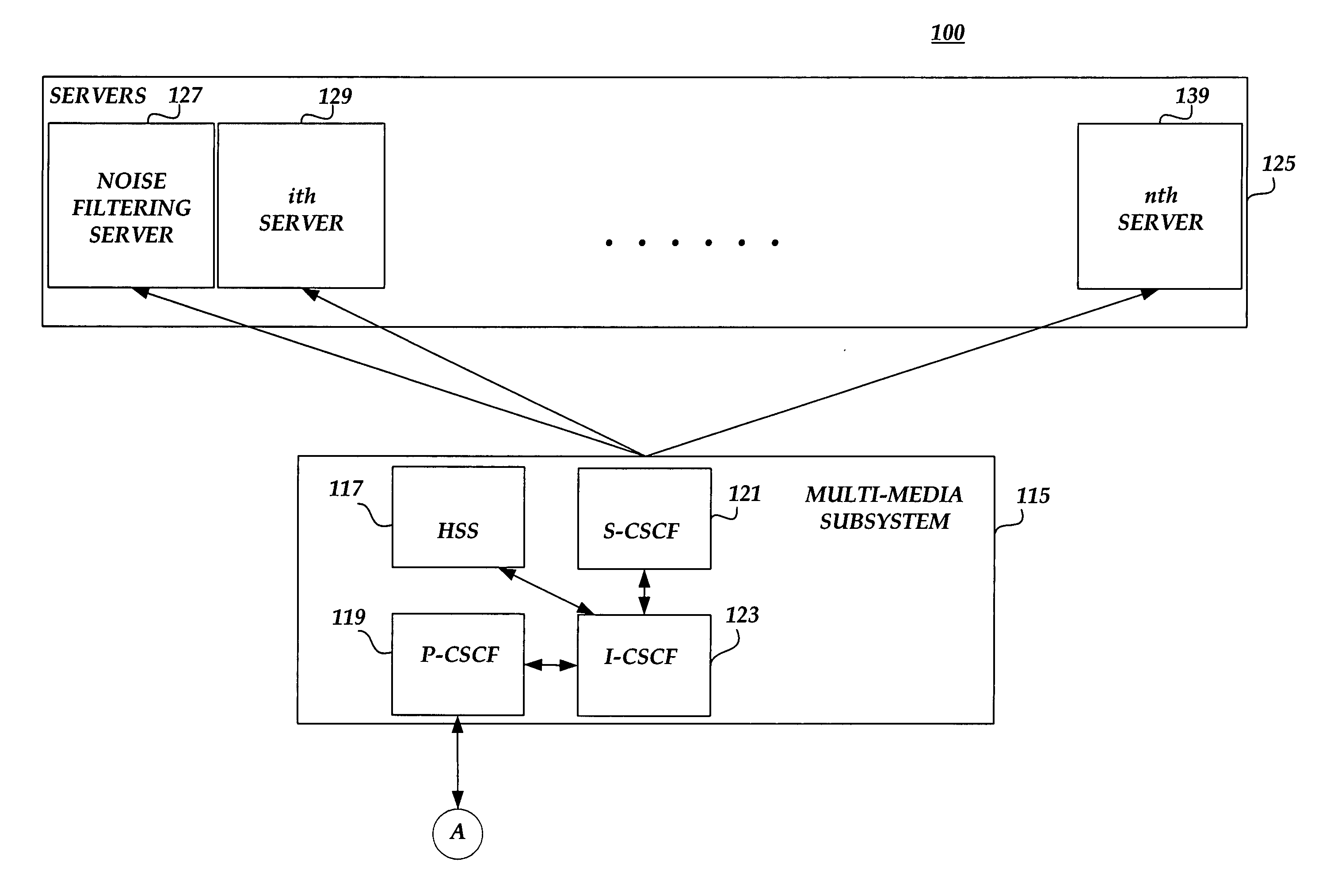
Separation of target acoustic signals in a multi-transducer arrangement
ActiveUS20050060142A1Efficient removalQuality improvementSignal processingEarpiece/earphone attachmentsSeparation processEngineering
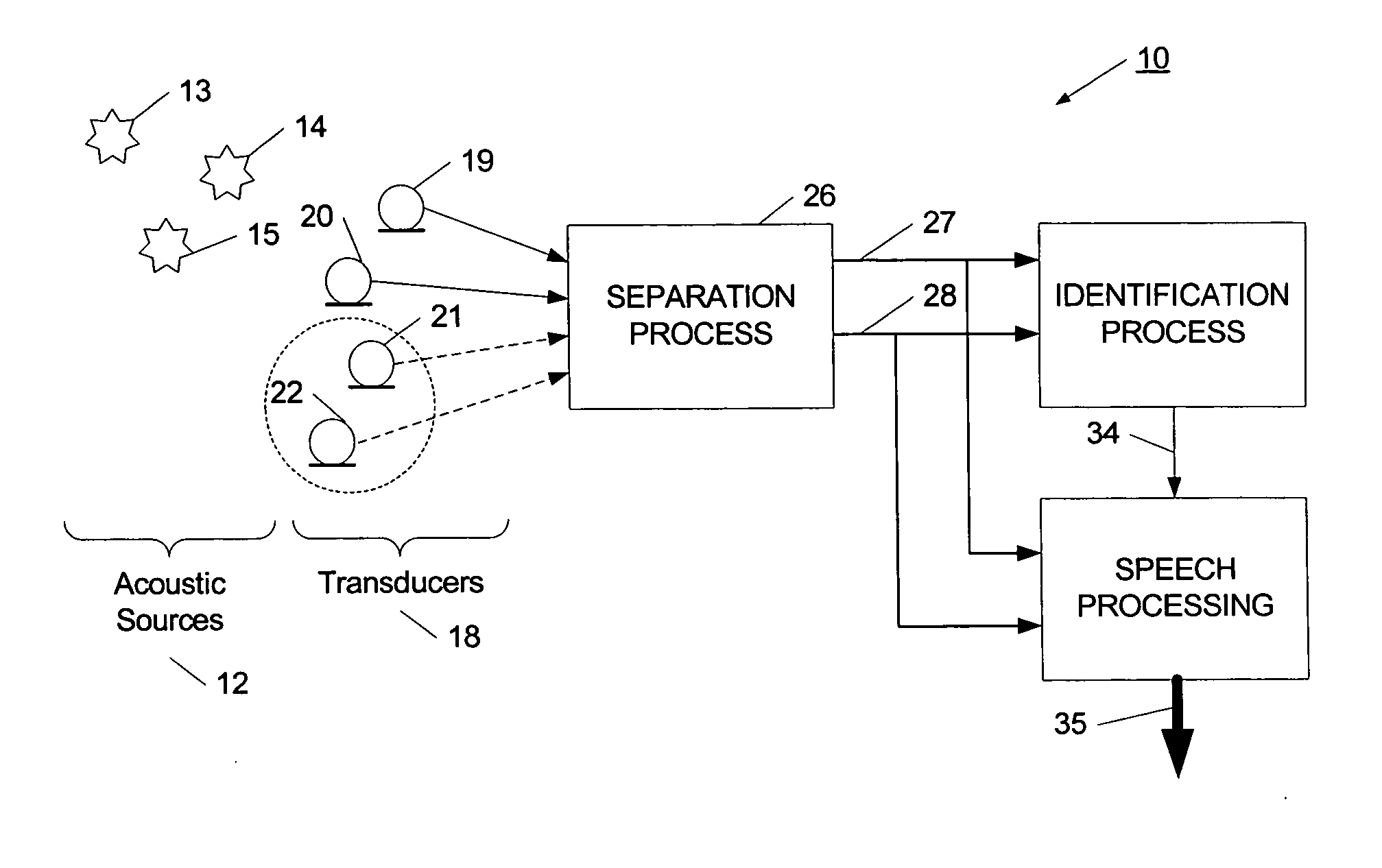
The present invention provides a process for separating a good quality information signal from a noisy acoustic environment. The separation process uses a set of a least two spaced-apart transducers to capture noise and information components. The transducer signals, which have both a noise and information component, are received into a separation process. The separation process generates one channel that is substantially only noise, and another channel that is a combination of noise and information. An identification process is used to identify which channel has the information component. The noise signal is then used to set process characteristics that are applied to the combination signal to efficiently reduce or eliminate the noise component. In this way, the noise is effectively removed from the combination signal to generate a good qualify information signal. The information signal may be, for example, a speech signal, a seismic signal, a sonar signal, or other acoustic signal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Methods and systems for providing noise filtering using speech recognition
Systems and methods are disclosed for providing noise filtering using speech recognition. The disclosed systems and methods may include performing a speech recognition process on a signal. Furthermore, the disclosed systems and methods may include determining a first frequency range based on the performed speech recognition process, the first frequency range corresponding to an expected voice associated with the signal. In addition, the disclosed systems and methods may include attenuating a second frequency range in the signal, the second frequency range being outside the first frequency range and the extemporaneous noise in the first frequency.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Low power activation of voice activated device
In a mobile device, a bone conduction or vibration sensor is used to detect the user's speech and the resulting output is used as the source for a low power Voice Trigger (VT) circuit that can activate the Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) of the host device. This invention is applicable to mobile devices such as wearable computers with head mounted display, mobile phones and wireless headsets and headphones which use speech recognition for the entering of input commands and control. The speech sensor can be a bone conduction microphone used to detect sound vibrations in the skull, or a vibration sensor, used to detect sound pressure vibrations from the user's speech. This VT circuit can be independent of any audio components of the host device and can therefore be designed to consume ultra-low power. Hence, this VT circuit can be active when the host device is in a sleeping state and can be used to wake the host device on detection of speech from the user. This VT circuit will be resistant to outside noise and react solely to the user's voice.
Owner:DSP GROUP
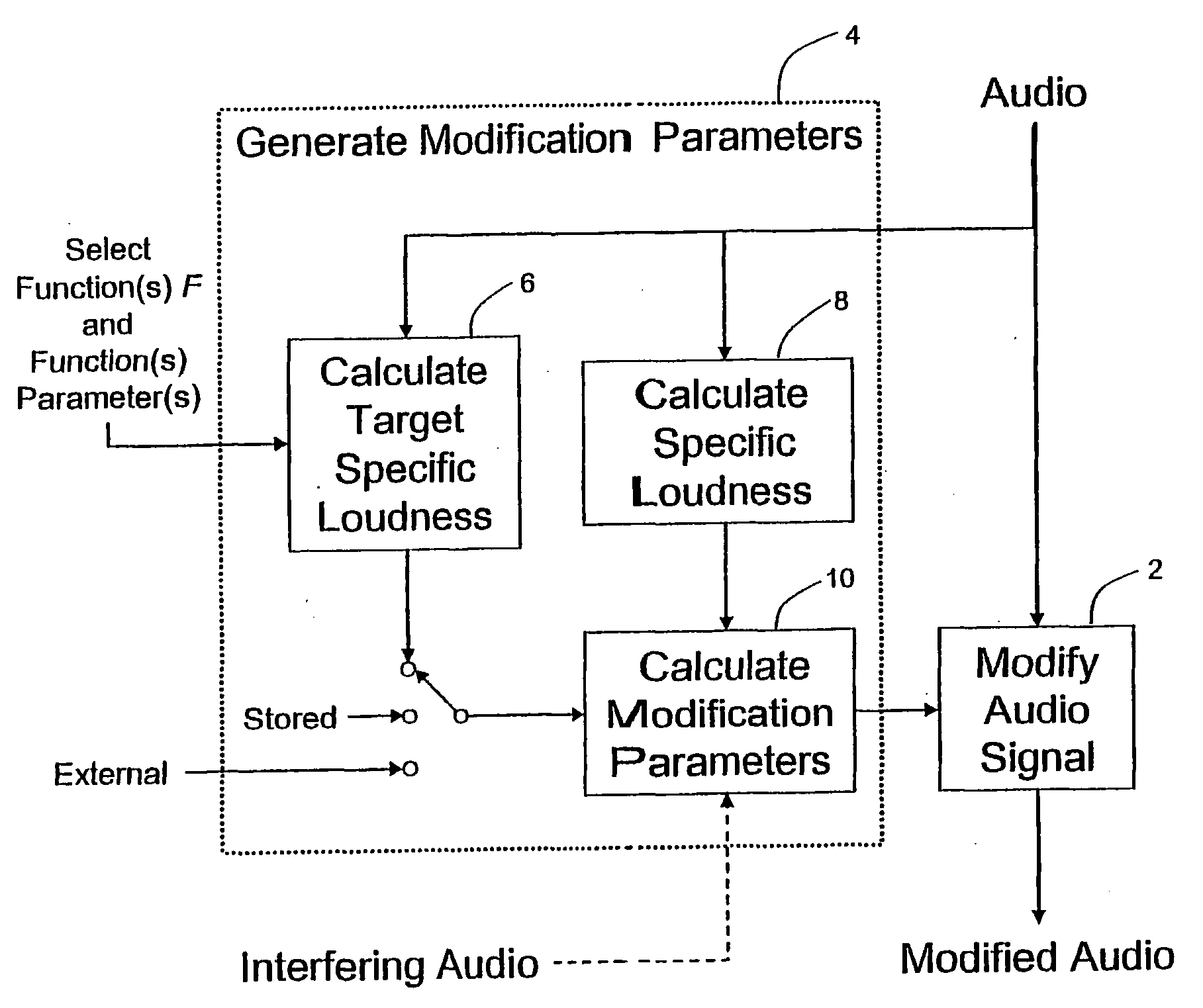
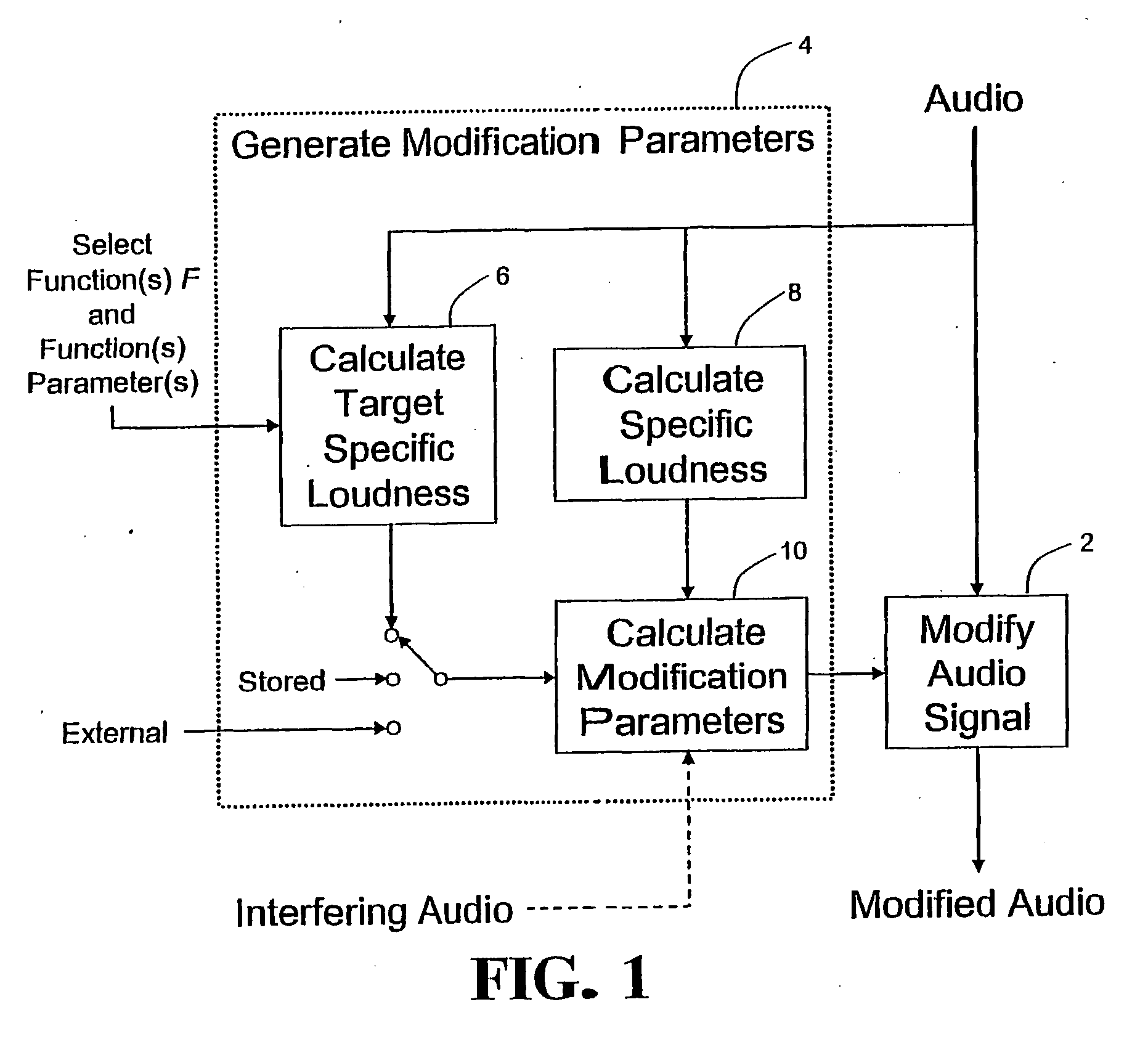
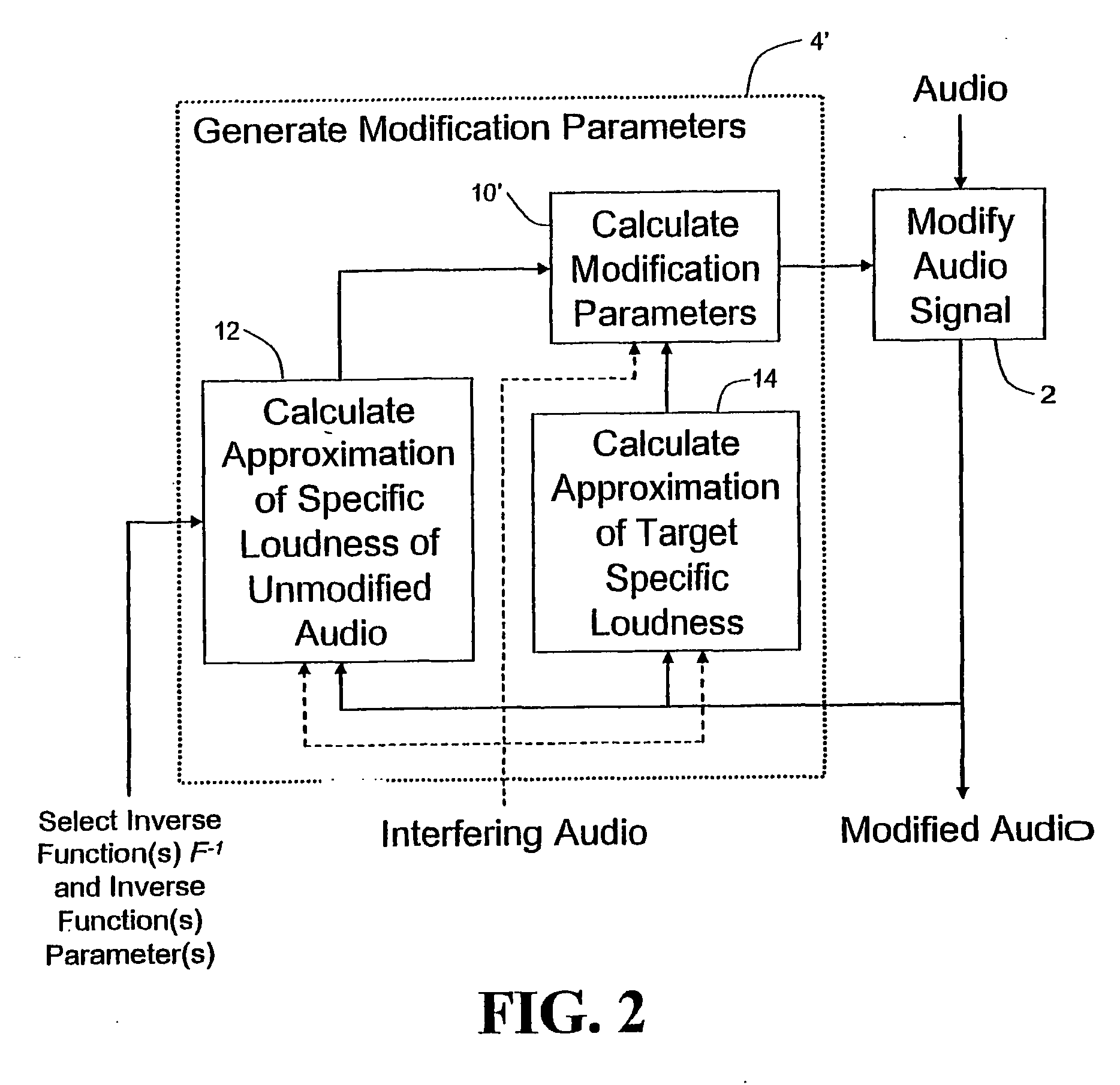
Calculating and Adjusting the Perceived Loudness and/or the Perceived Spectral Balance of an Audio Signal
ActiveUS20070291959A1Mitigate effectReduce differenceGain controlSpeech analysisLimiterAudio frequency
The invention relates to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal. An audio signal is modified in response to calculations performed at least in part in the perceptual (psychoacoustic) loudness domain. The invention is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. The invention includes not only methods but also corresponding computer programs and apparatus.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
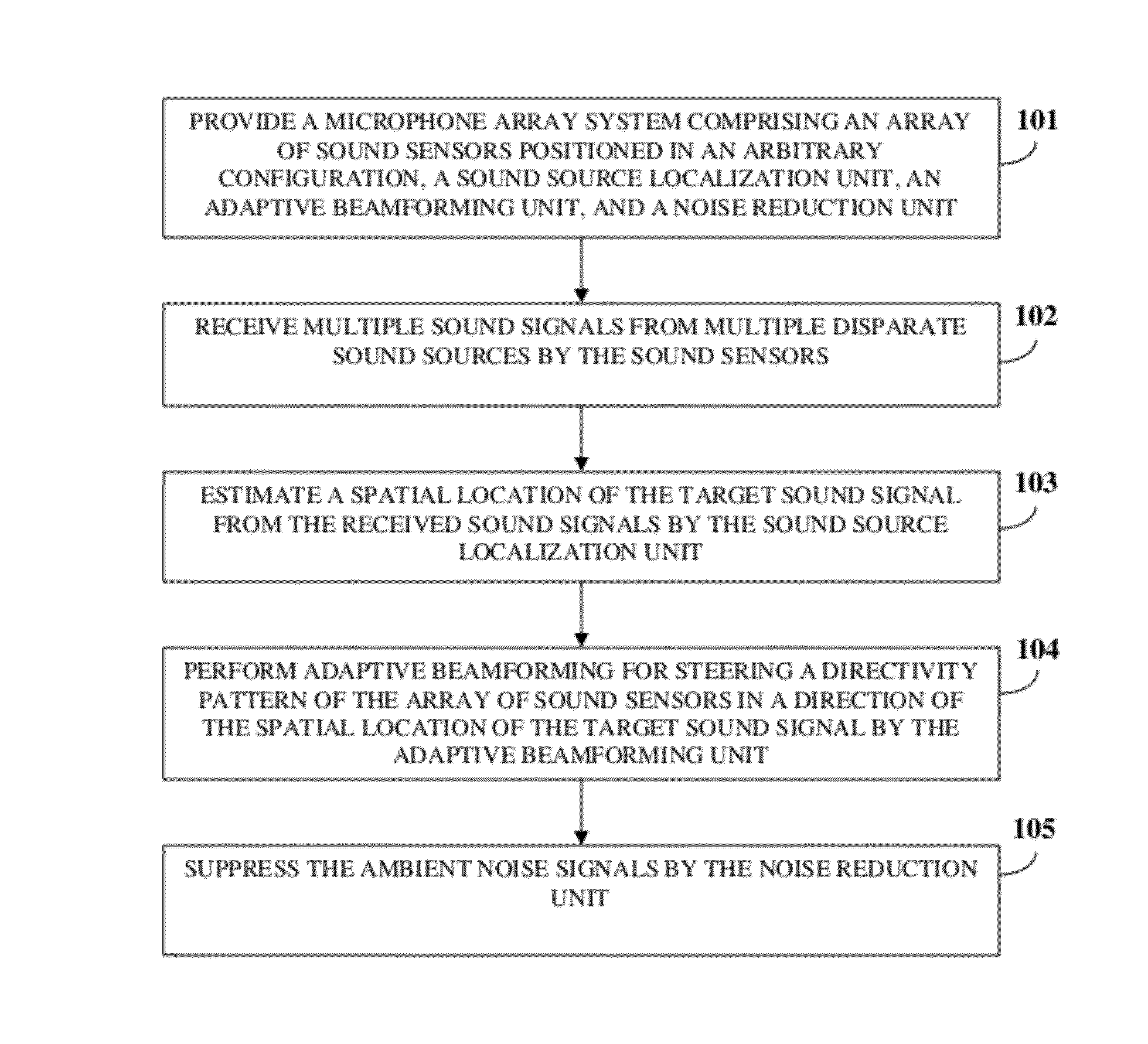
Microphone Array System
ActiveUS20120076316A1Increase heightPartially suppresses ambient noise signalMicrophonesEar treatmentSensor arrayEnvironmental noise
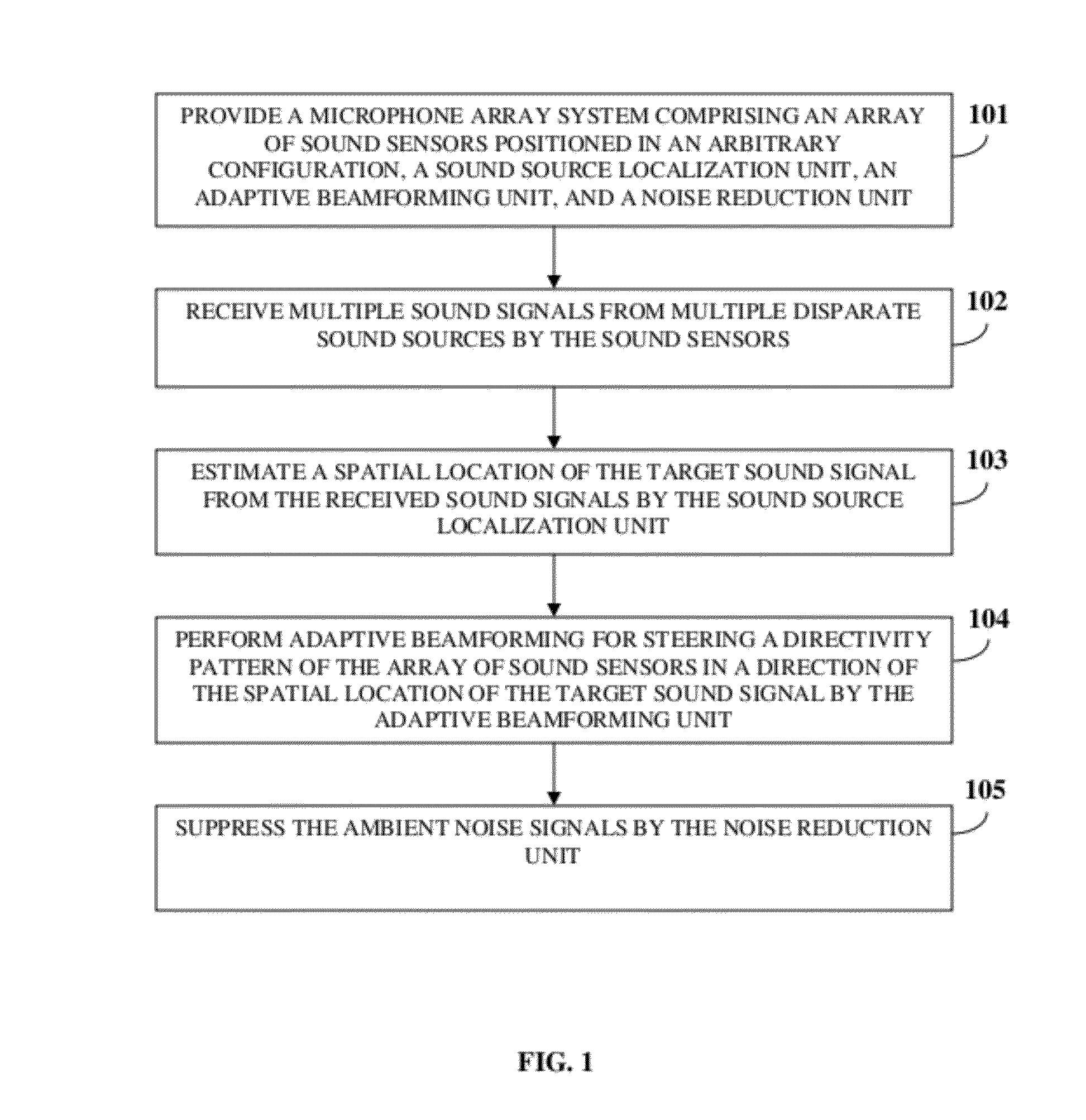
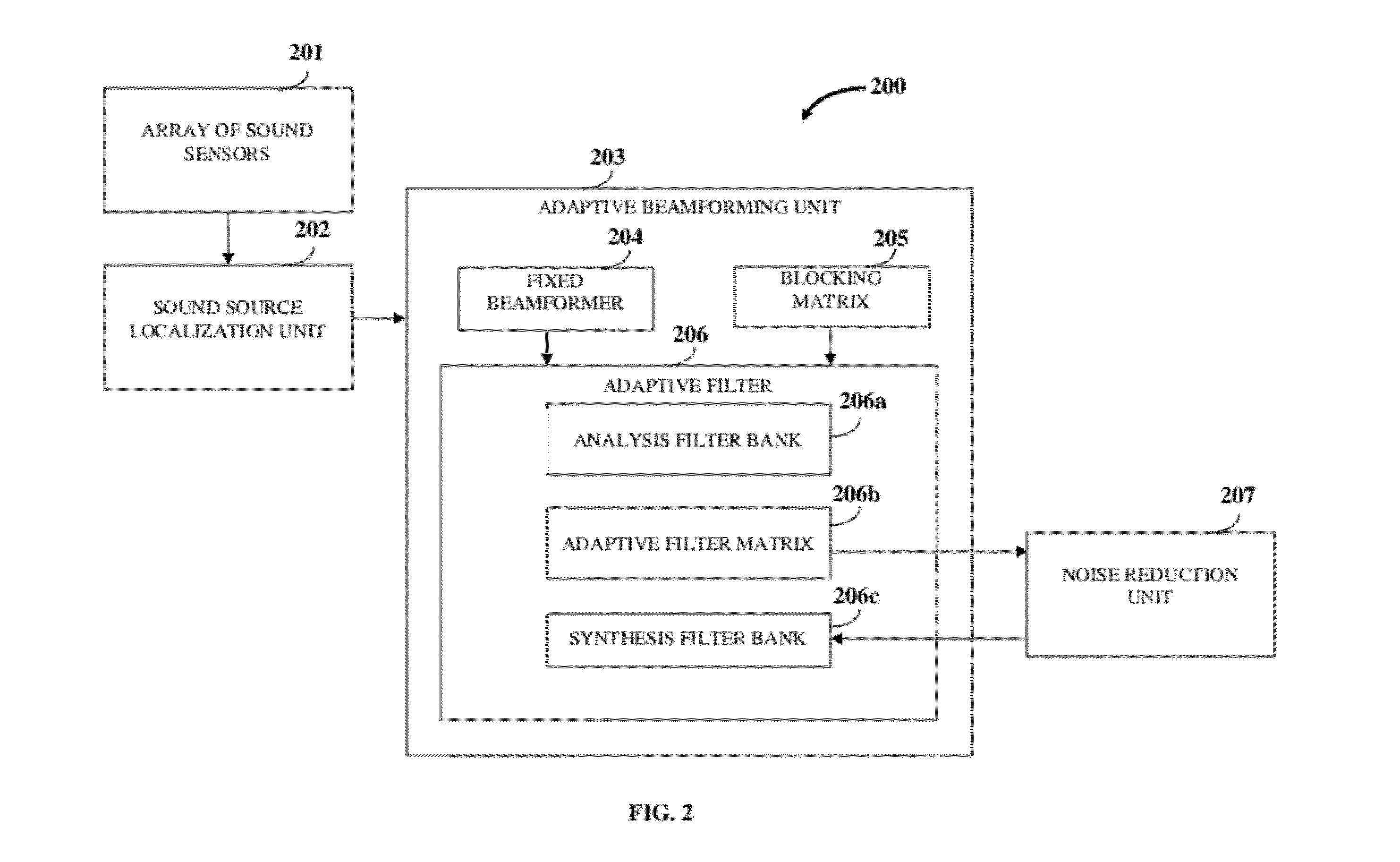
A method and system for enhancing a target sound signal from multiple sound signals is provided. An array of an arbitrary number of sound sensors positioned in an arbitrary configuration receives the sound signals from multiple disparate sources. The sound signals comprise the target sound signal from a target sound source, and ambient noise signals. A sound source localization unit, an adaptive beamforming unit, and a noise reduction unit are in operative communication with the array of sound sensors. The sound source localization unit estimates a spatial location of the target sound signal from the received sound signals. The adaptive beamforming unit performs adaptive beamforming by steering a directivity pattern of the array of sound sensors in a direction of the spatial location of the target sound signal, thereby enhancing the target sound signal and partially suppressing the ambient noise signals, which are further suppressed by the noise reduction unit.
Owner:VOCALIFE LLC +1
Method and system for switching among independent packetized audio streams
InactiveUS7161939B2Broaden applicationIncrease the number ofSpecial service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersComputer scienceAudio frequency
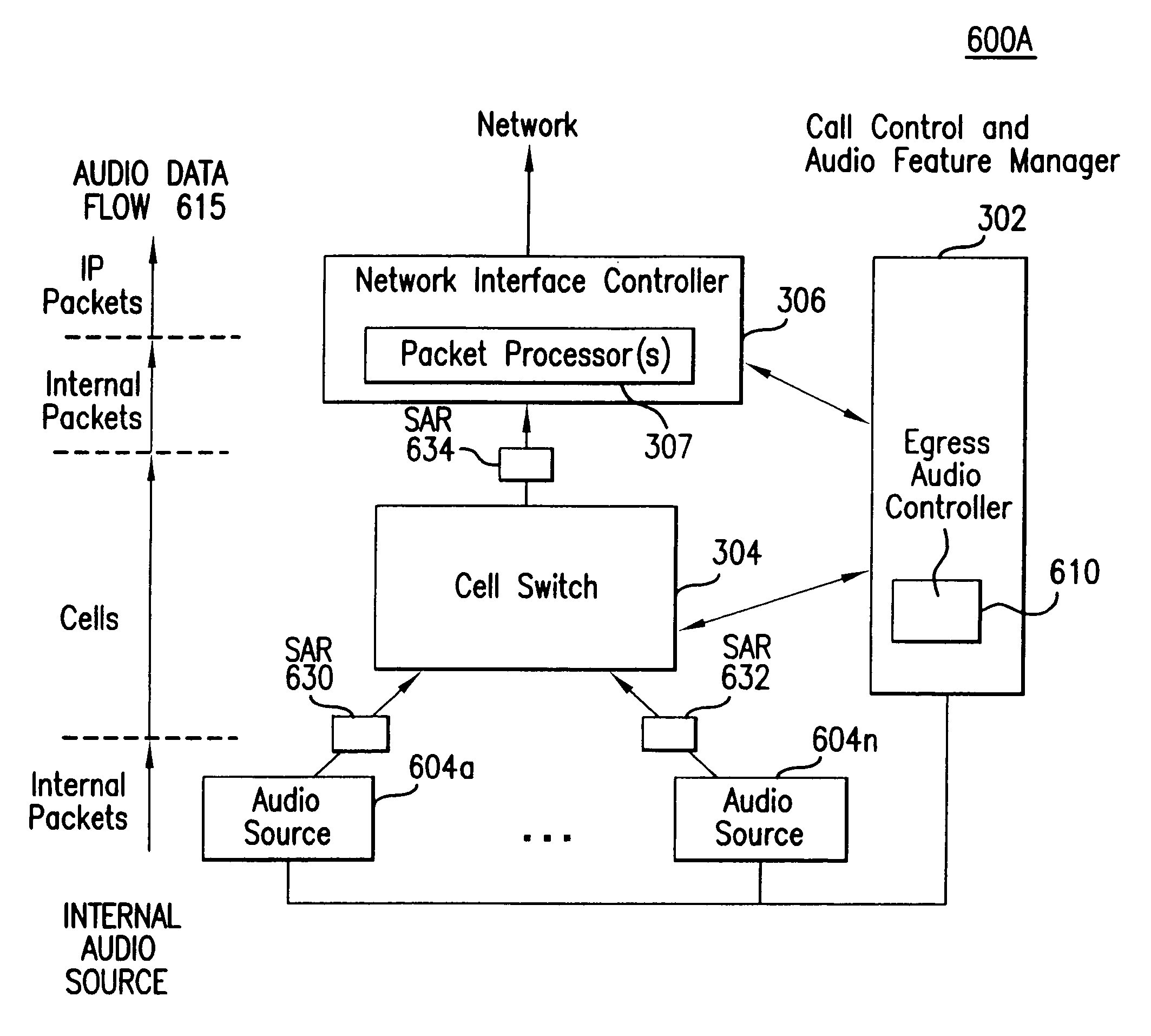
The present invention provides a method and system for noiselessly switching between independent audio streams. Such noiseless switching preserves valid RTP information at the time of switch over. For established VOIP calls, the present invention can noiselessly switch audio from one audio source to another. A switch directs audio data from multiple audio sources to a network interface controller. The switch can be a cell switch or a packet switch. The audio sources can be internal audio sources and / or external audio sources. An egress audio controller controls the operation of internal audio sources, the switch and the network interface controller to carry out noiseless switching according to the present invention. Certain call events which involve additional audio trigger a noiseless switch over.
Owner:MOVIUS INTERACTIVE CORP
Digital wavetable audio synthesizer with delay-based effects processing
InactiveUS6047073AElectrophonic musical instrumentsCounting chain pulse countersAudio synthesisNoise
A digital wavetable audio synthesizer is described. The synthesizer can generate up to 32 high-quality audio digital signals or voices, including delay-based effects, at either a 44.1 KHz sample rate or at sample rates compatible with a prior art wavetable synthesizer. The synthesizer includes an address generator which has several modes of addressing wavetable data. The address generator's addressing rate controls the pitch of the synthesizer's output signal. The synthesizer performs a 10-bit interpolation, using the wavetable data addressed by the address generator, to interpolate additional data samples. When the address generator loops through a block of data, the signal path interpolates between the data at the end and start addresses of the block of data to prevent discontinuities in the generated signal. A synthesizer volume generator, which has several modes of controlling the volume, adds envelope, right offset, left offset, and effects volume to the data. The data can be placed in one of sixteen fixed stereo pan positions, or left and right offsets can be programmed to place the data anywhere in the stereo field. The left and right offset values can also be programmed to control the overall volume. Zipper noise is prevented by controlling the volume increment. A synthesizer LFO generator can add LFO variation to: (i) the wavetable data addressing rate, for creating a vibrato effect; and (ii) a voice's volume, for creating a tremolo effect. Generated data to be output from the synthesizer is stored in left and right accumulators. However, when creating delay-based effects, data is stored in one of several effects accumulators. This data is then written to a wavetable. The difference between the wavetable write and read addresses for this data provides a delay for echo and reverb effects. LFO variations added to the read address create chorus and flange effects. The volume of the delay-based effects data can be attenuated to provide volume decay for an echo effect. After the delay-based effects processing, the data can be provided with left and right offset volume components which determine how much of the effect is heard and its stereo position. The data is then stored in the left and right accumulators.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
High sensitivity noise immune stethoscope
ActiveUS20070165872A1Efficient couplingHigh elastic modulusTransducer detailsStethoscopeEngineeringActive systems
A physiological sensing stethoscope suitable for use in high-noise environments is disclosed. The stethoscope is designed to be substantially matched to the mechanical impedance of monitored physiological activity and substantially mismatched to the mechanical impedance of air-coupled acoustic activity. One embodiment of the stethoscope utilizes a passive acoustic system. Another embodiment utilizes an active Doppler system. The passive and active systems can be combined in one stethoscope enabling switching from a passive mode to an active mode suitable for use in very high-noise environments. The stethoscope is suitable for use in environments having an ambient background noise of 100 dBA and higher. The passive includes a head having a housing, a flexural disc mounted with the housing, and an electromechanical stack positioned between the housing and the flexural disc in contact with the skin of a patient. The active system detects Doppler shifts using a high-frequency transmitter and receiver.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
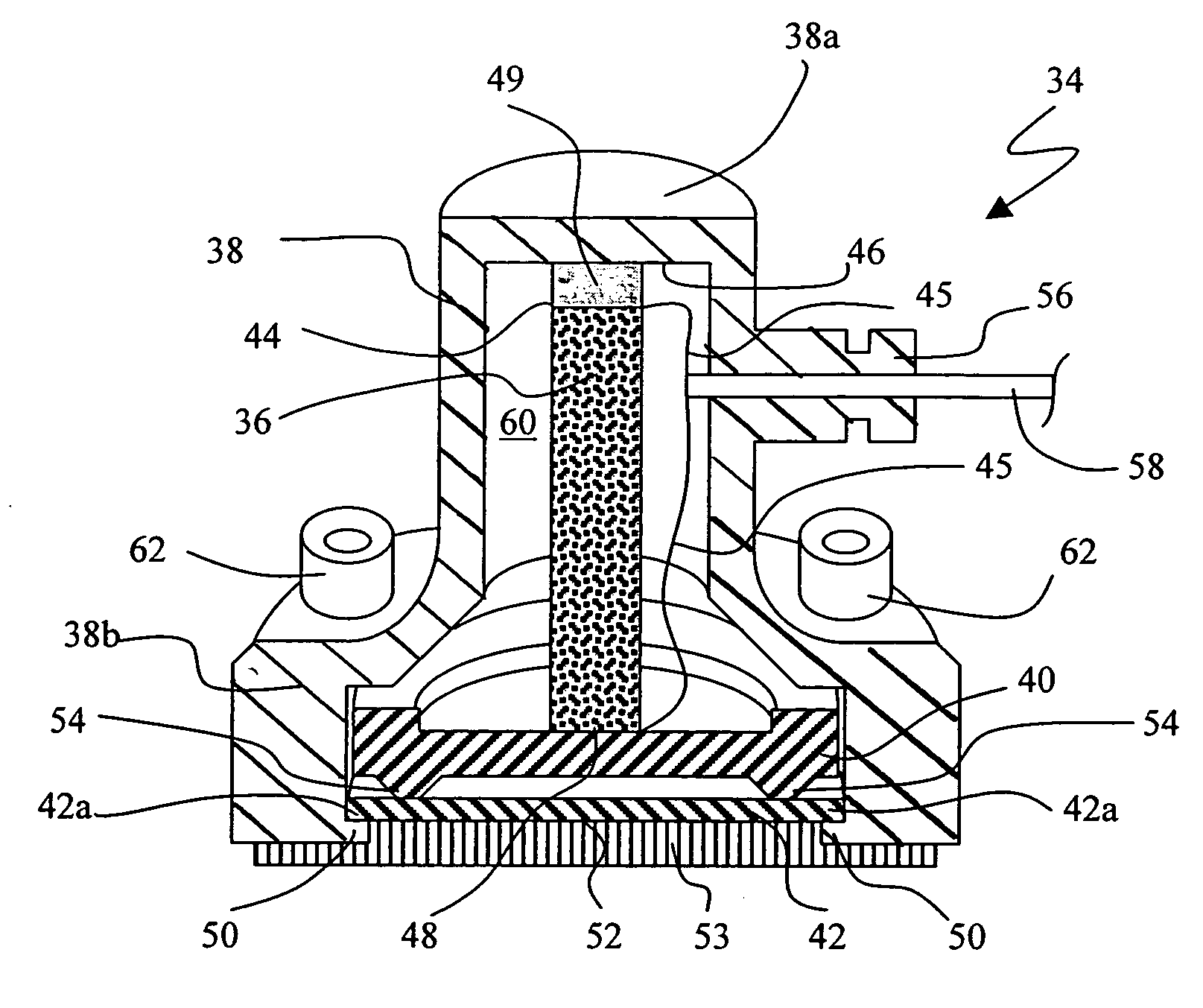
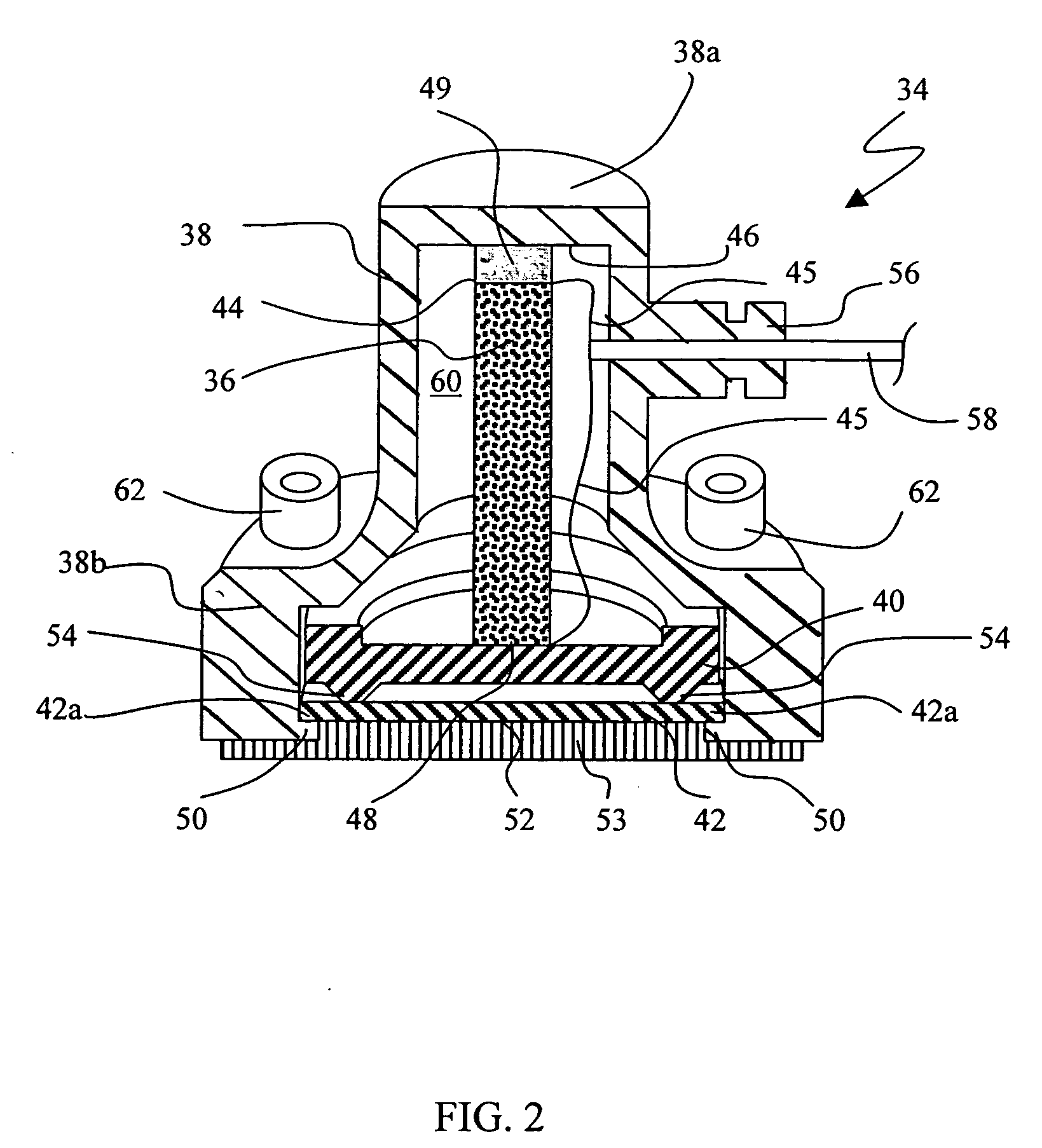
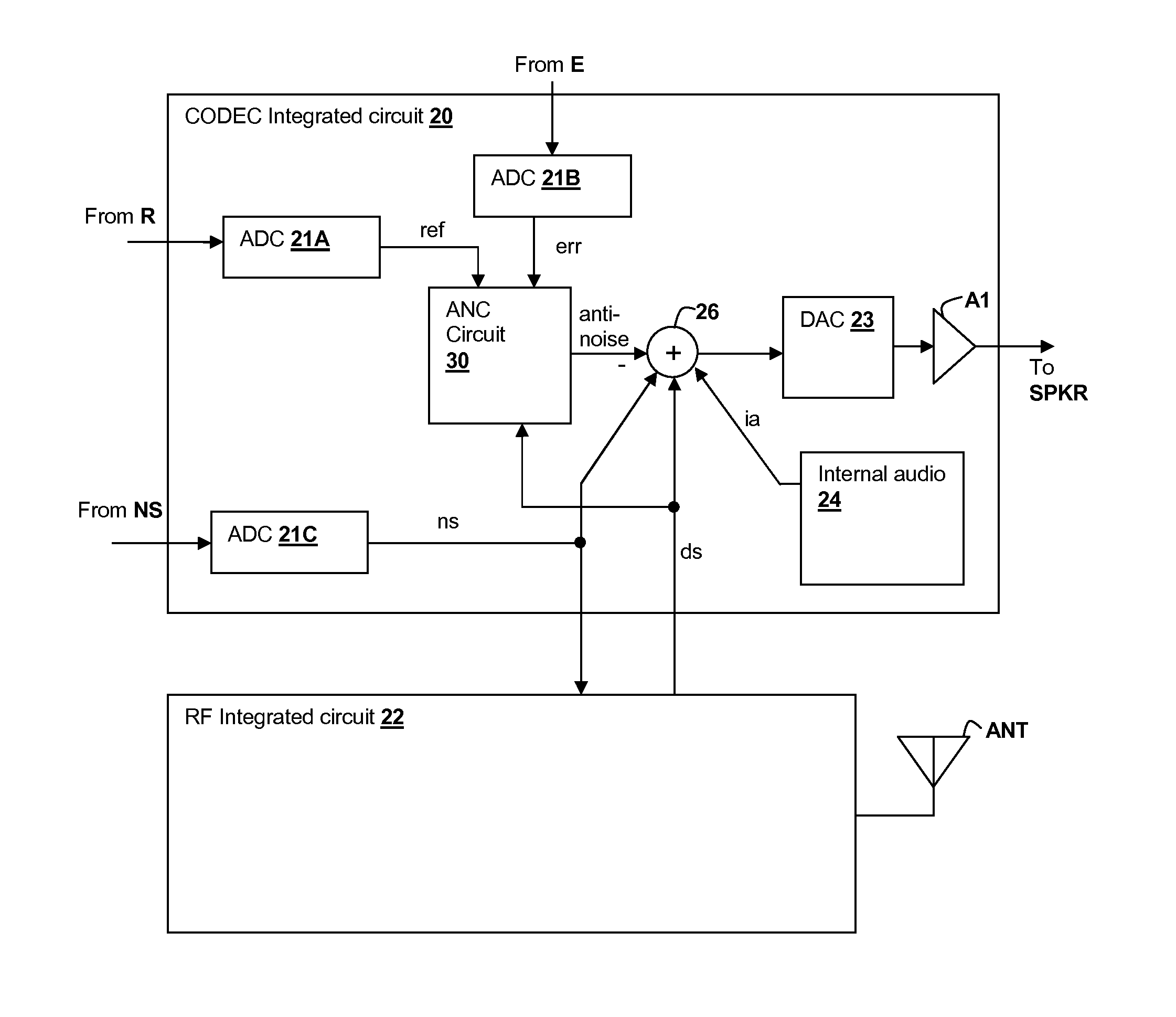
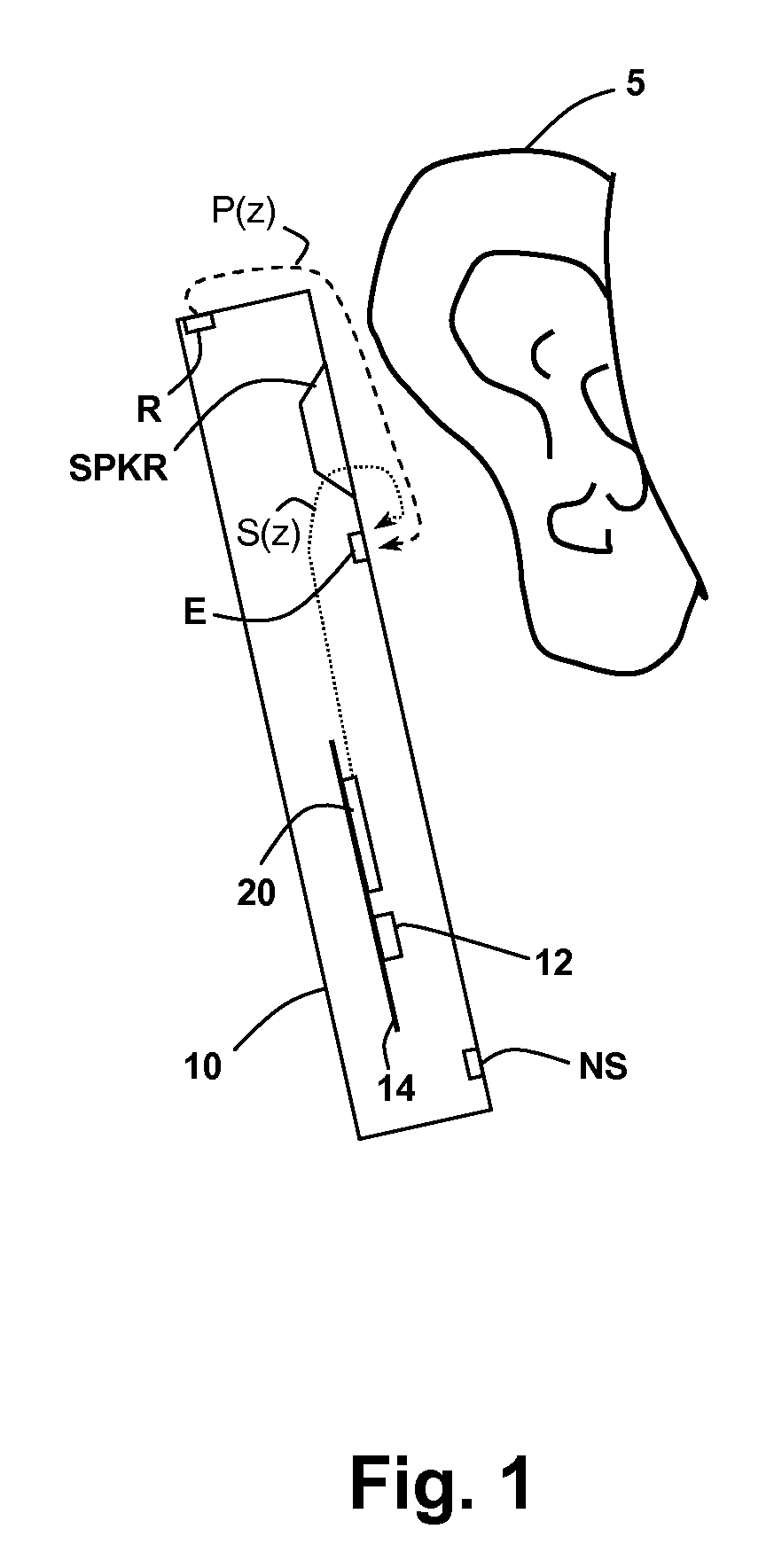
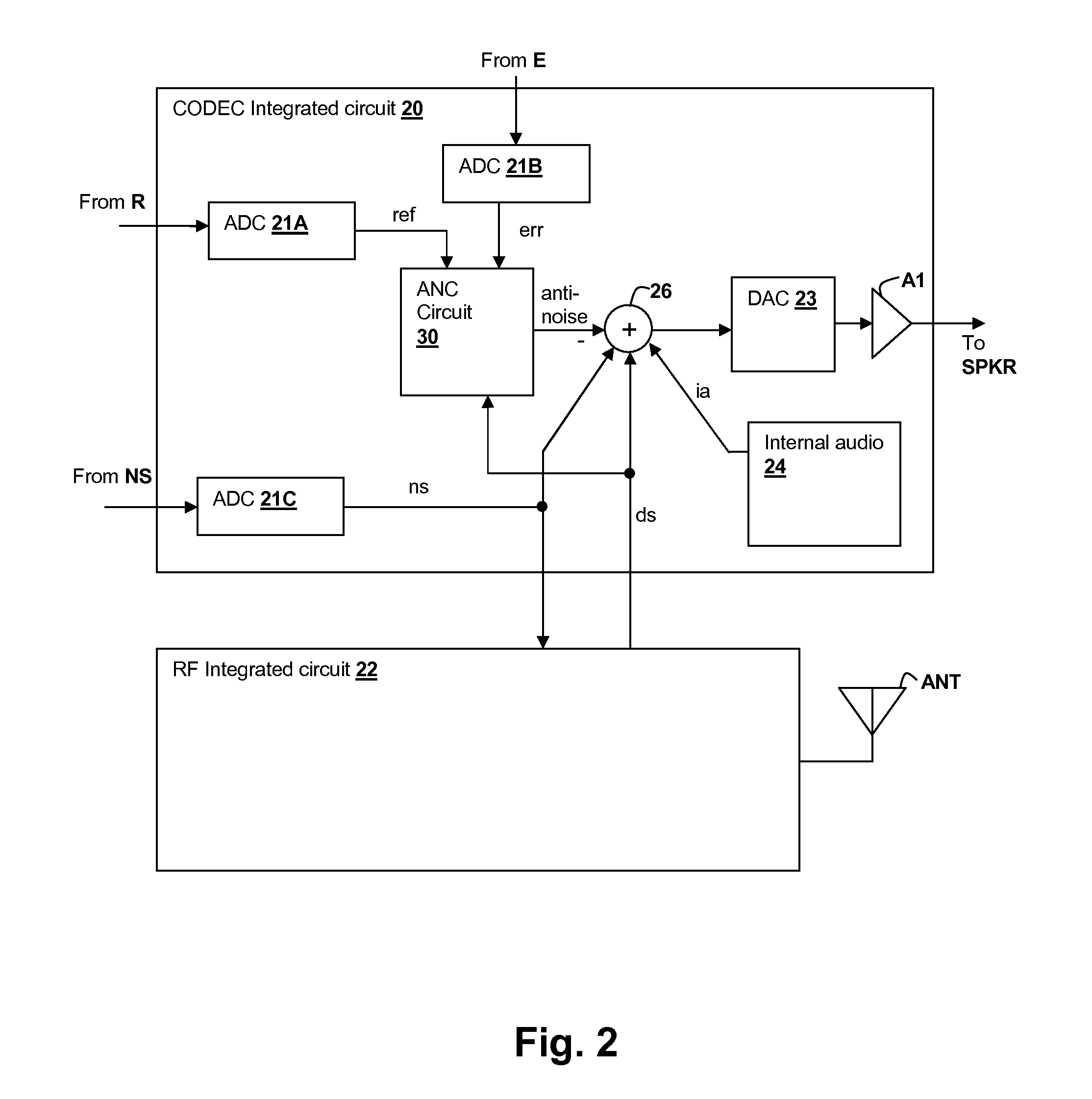
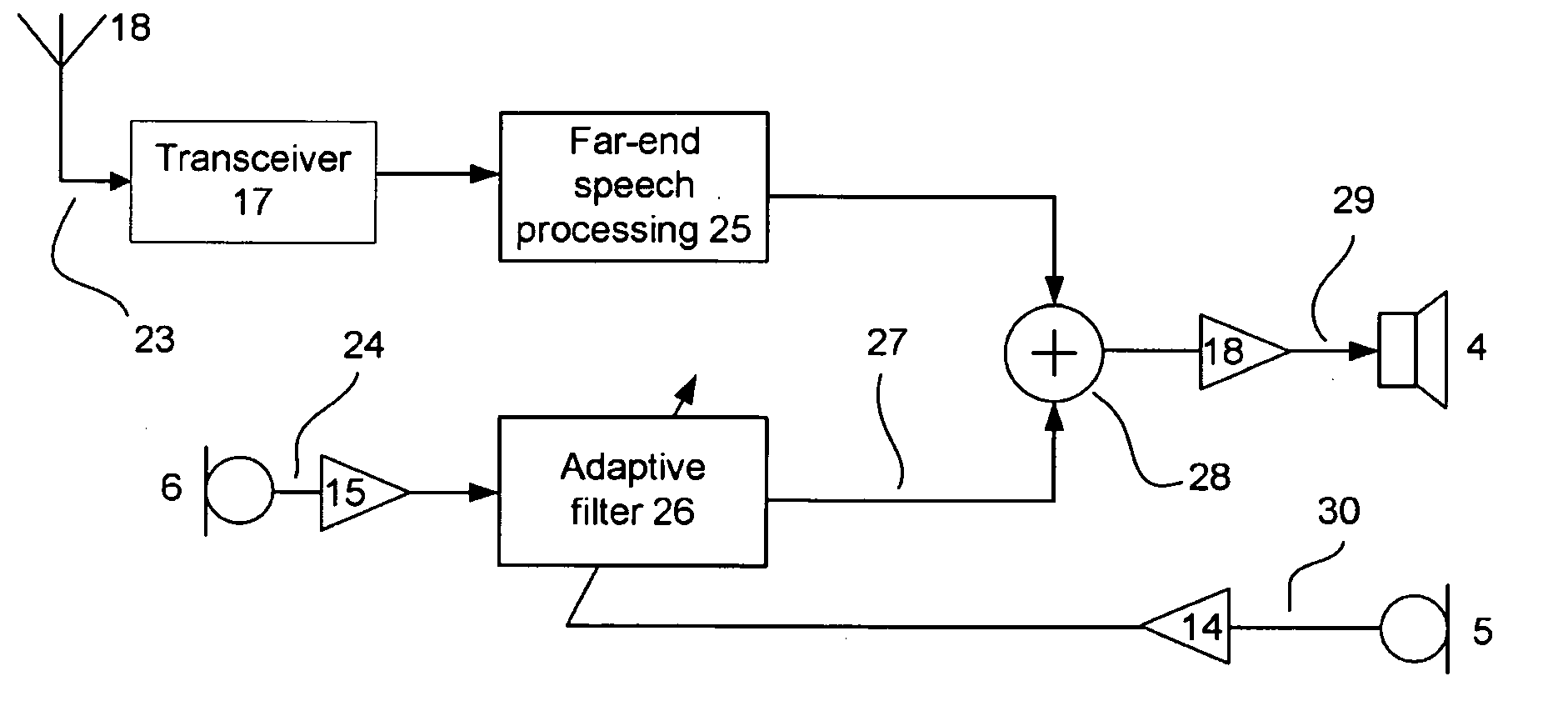
Oversight control of an adaptive noise canceler in a personal audio device
ActiveUS20120140943A1Reduce impactAvoid signalingEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationTransducerMicrophone signal
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes an adaptive noise canceling (ANC) circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. An error microphone is also provided proximate the speaker to measure the ambient sounds and transducer output near the transducer, thus providing an indication of the effectiveness of the noise canceling. A processing circuit uses the reference and / or error microphone, optionally along with a microphone provided for capturing near-end speech, to determine whether the ANC circuit is incorrectly adapting or may incorrectly adapt to the instant acoustic environment and / or whether the anti-noise signal may be incorrect and / or disruptive and then take action in the processing circuit to prevent or remedy such conditions.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
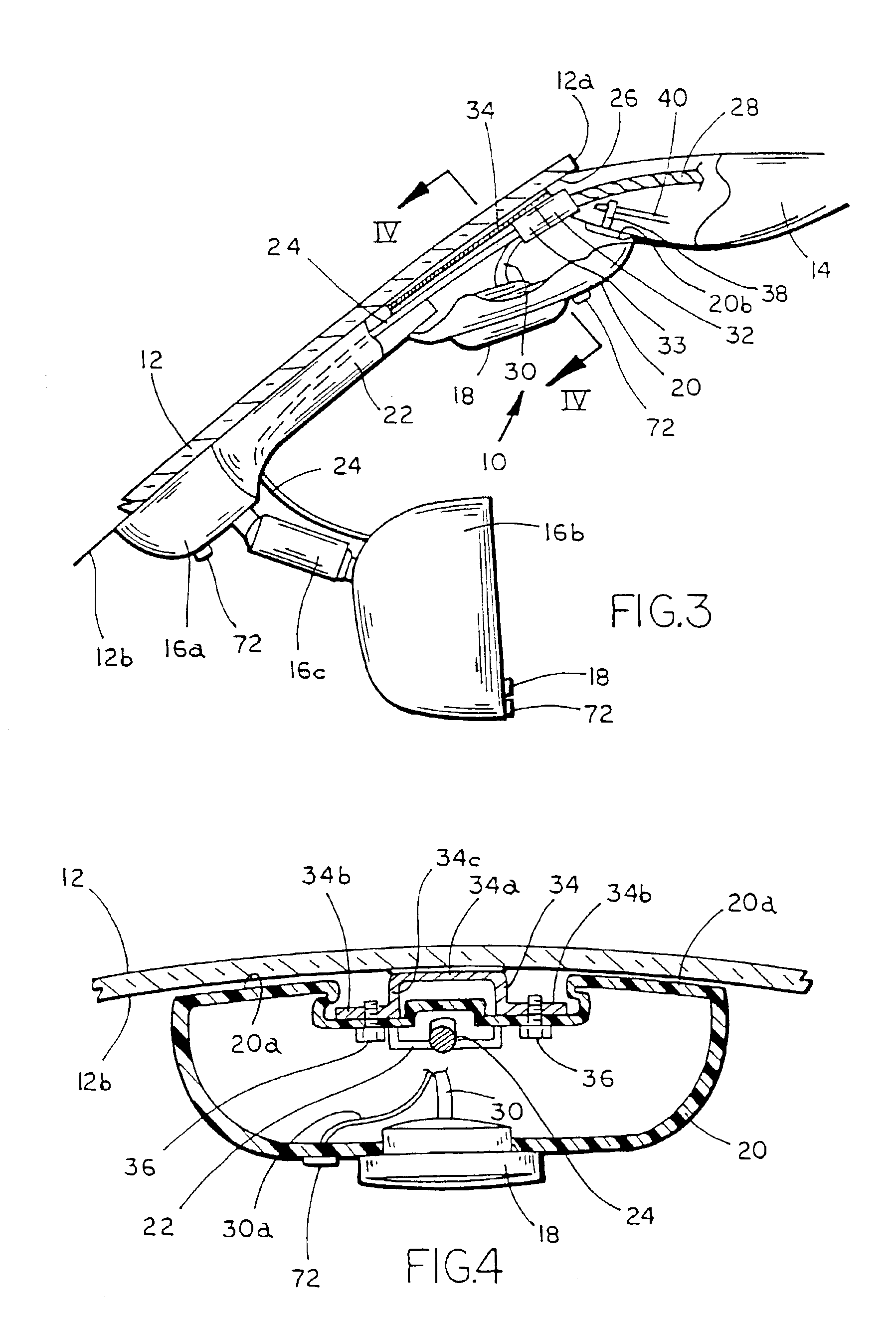
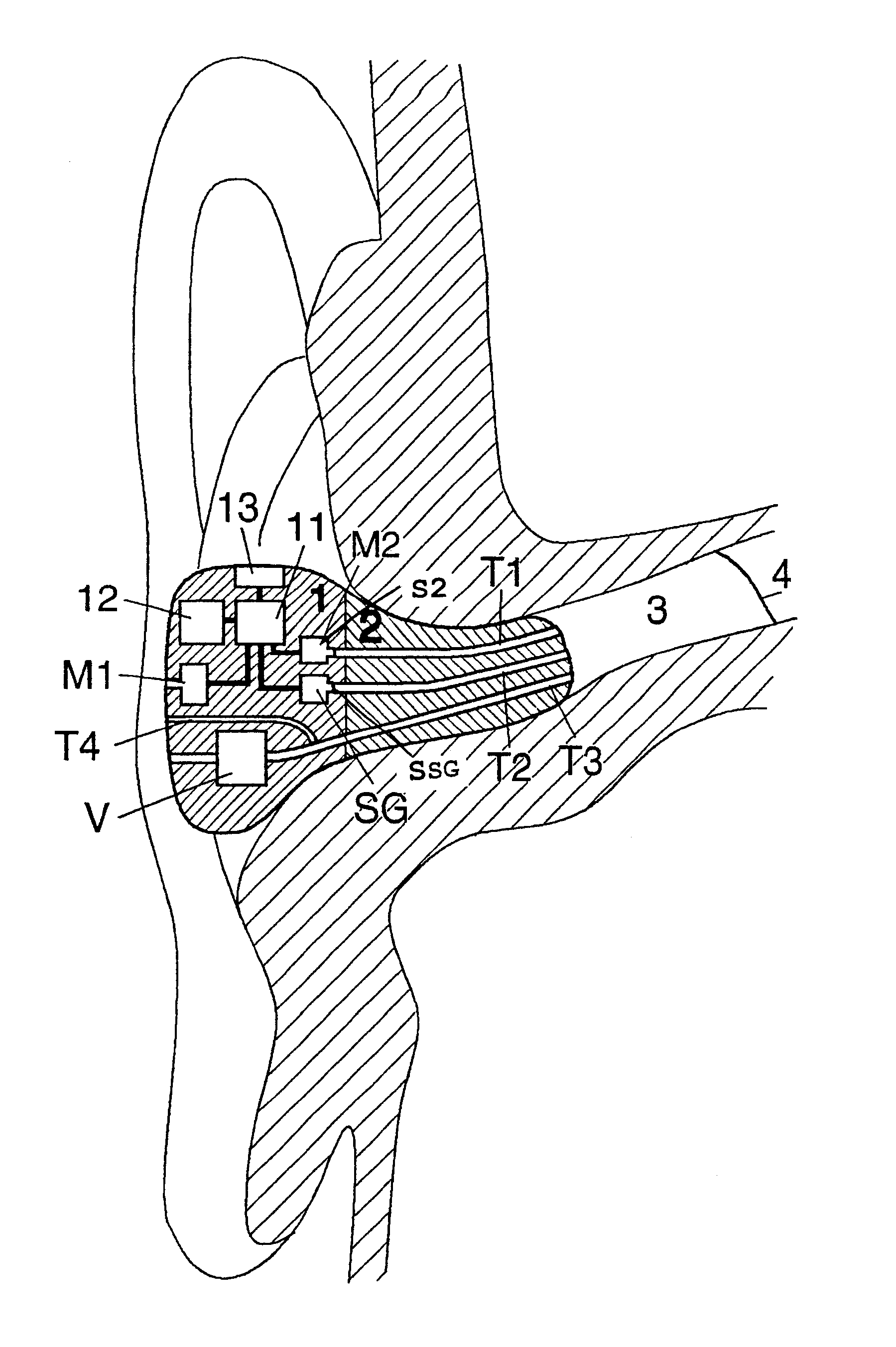
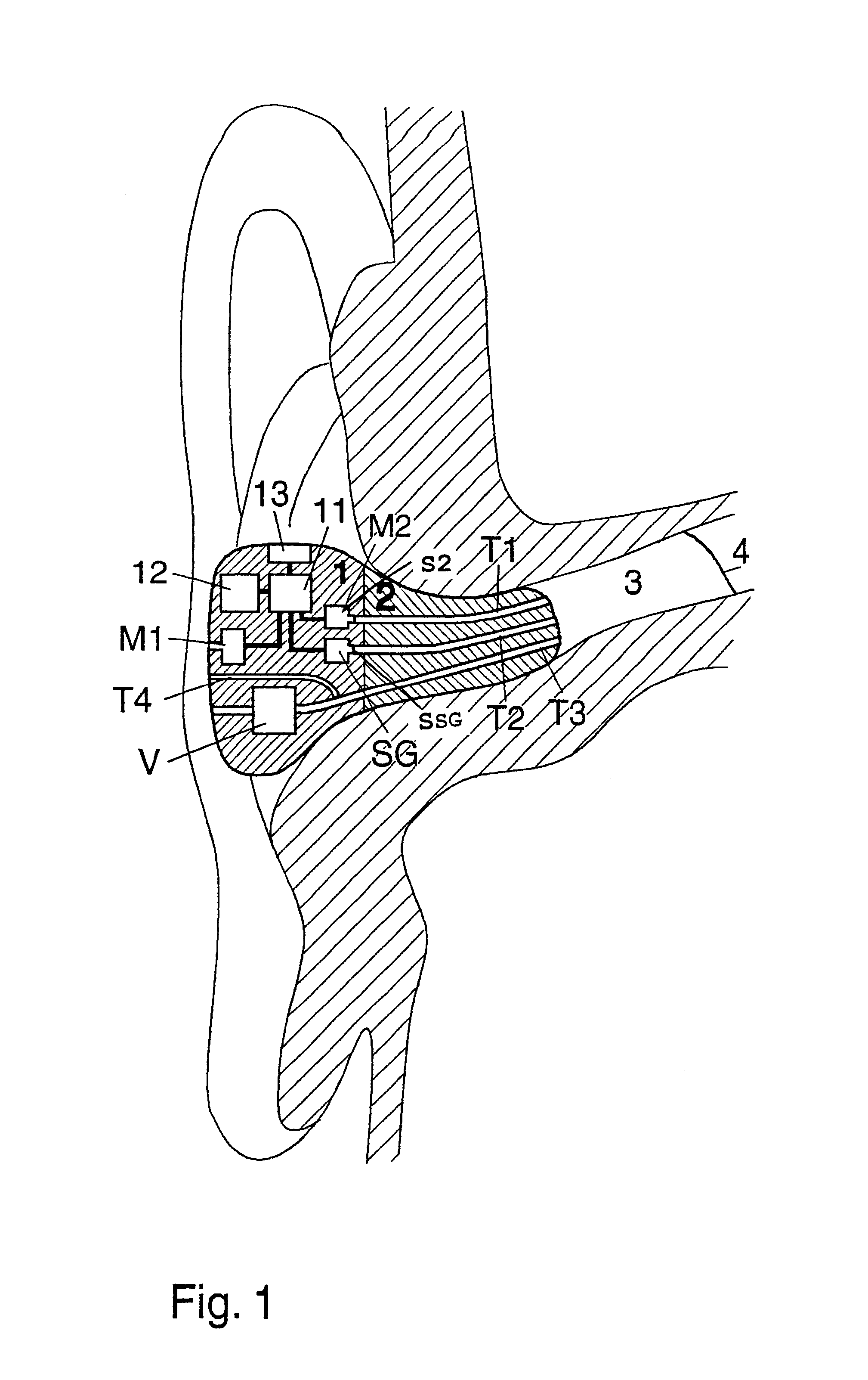
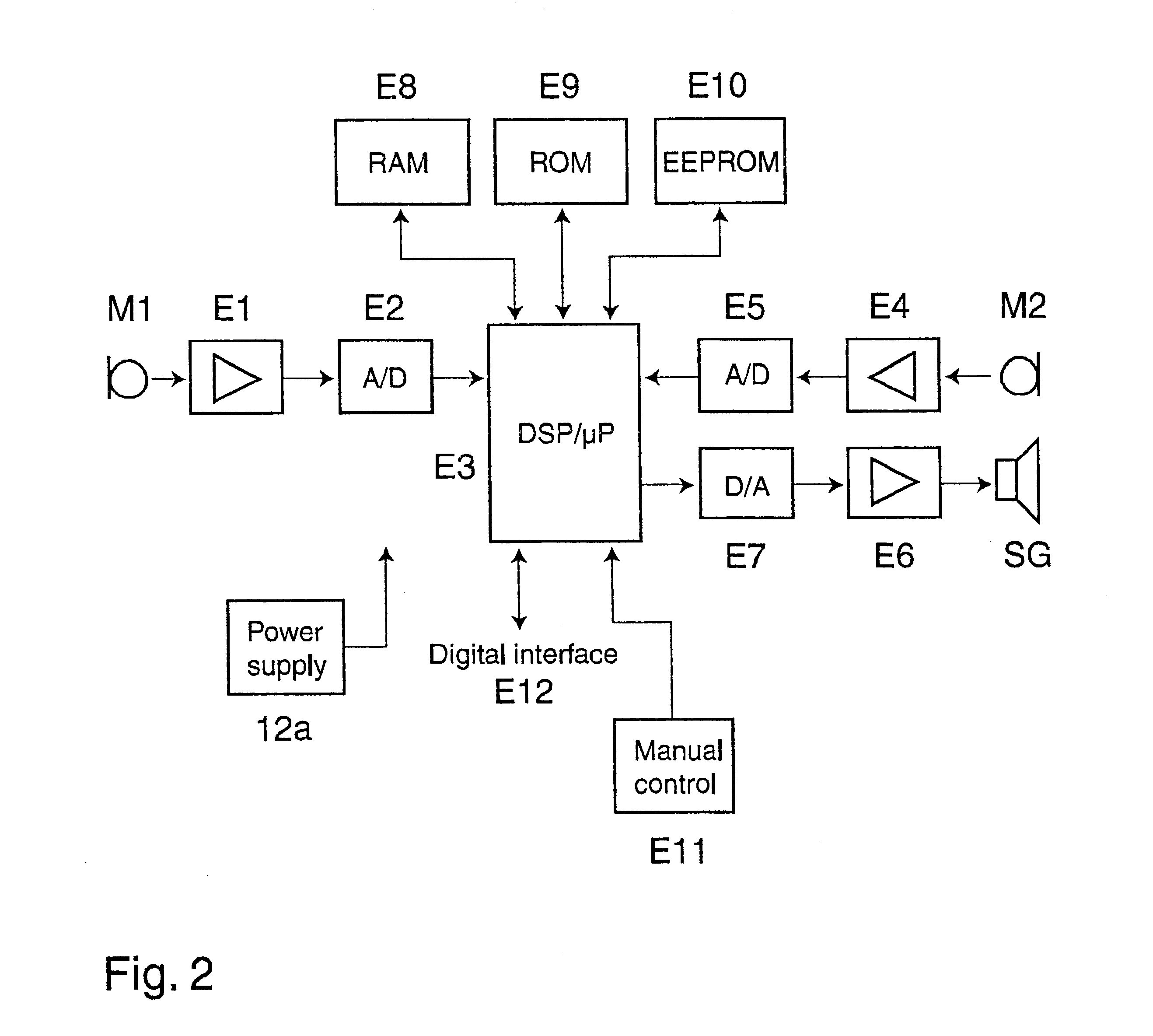
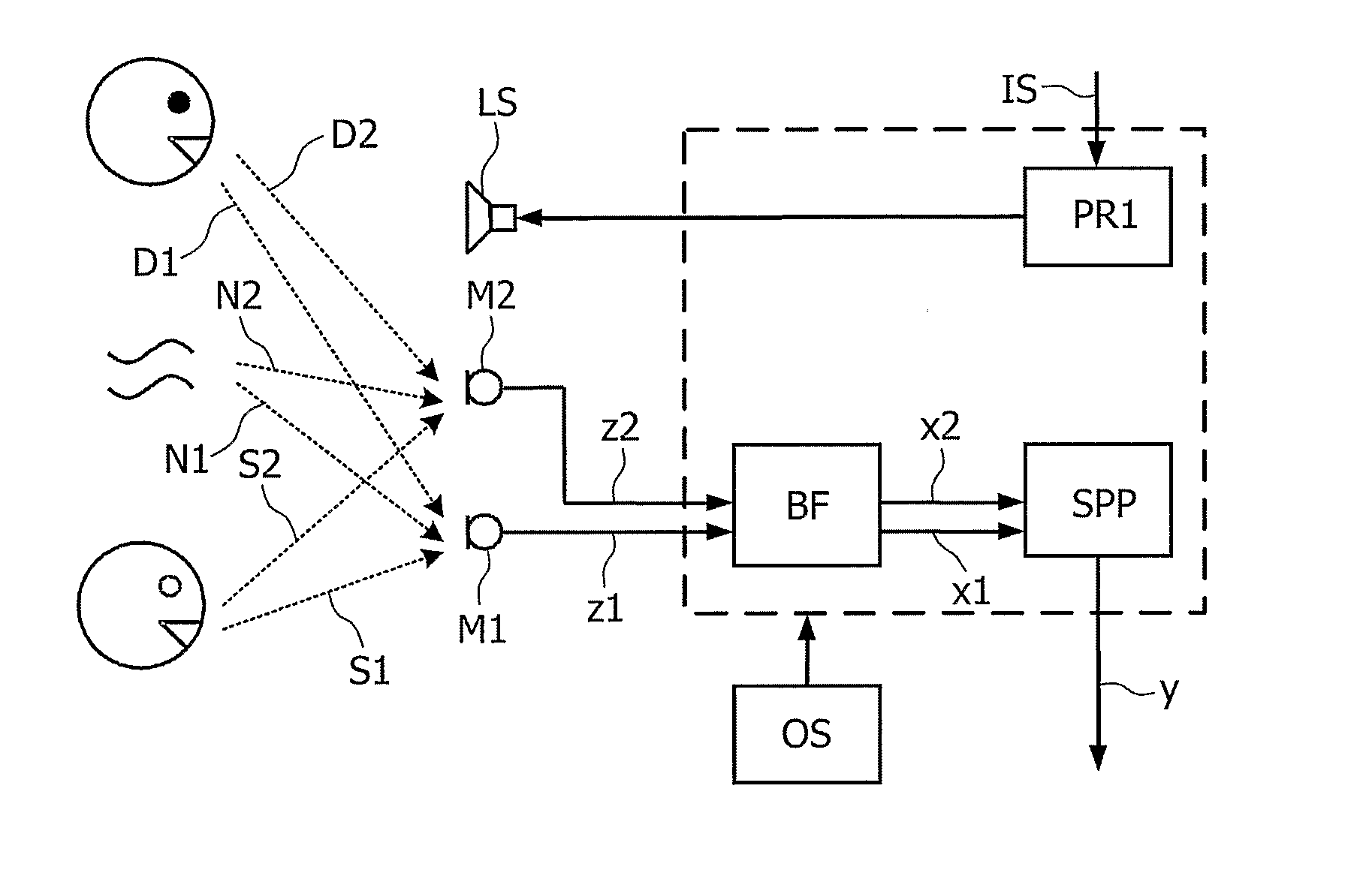
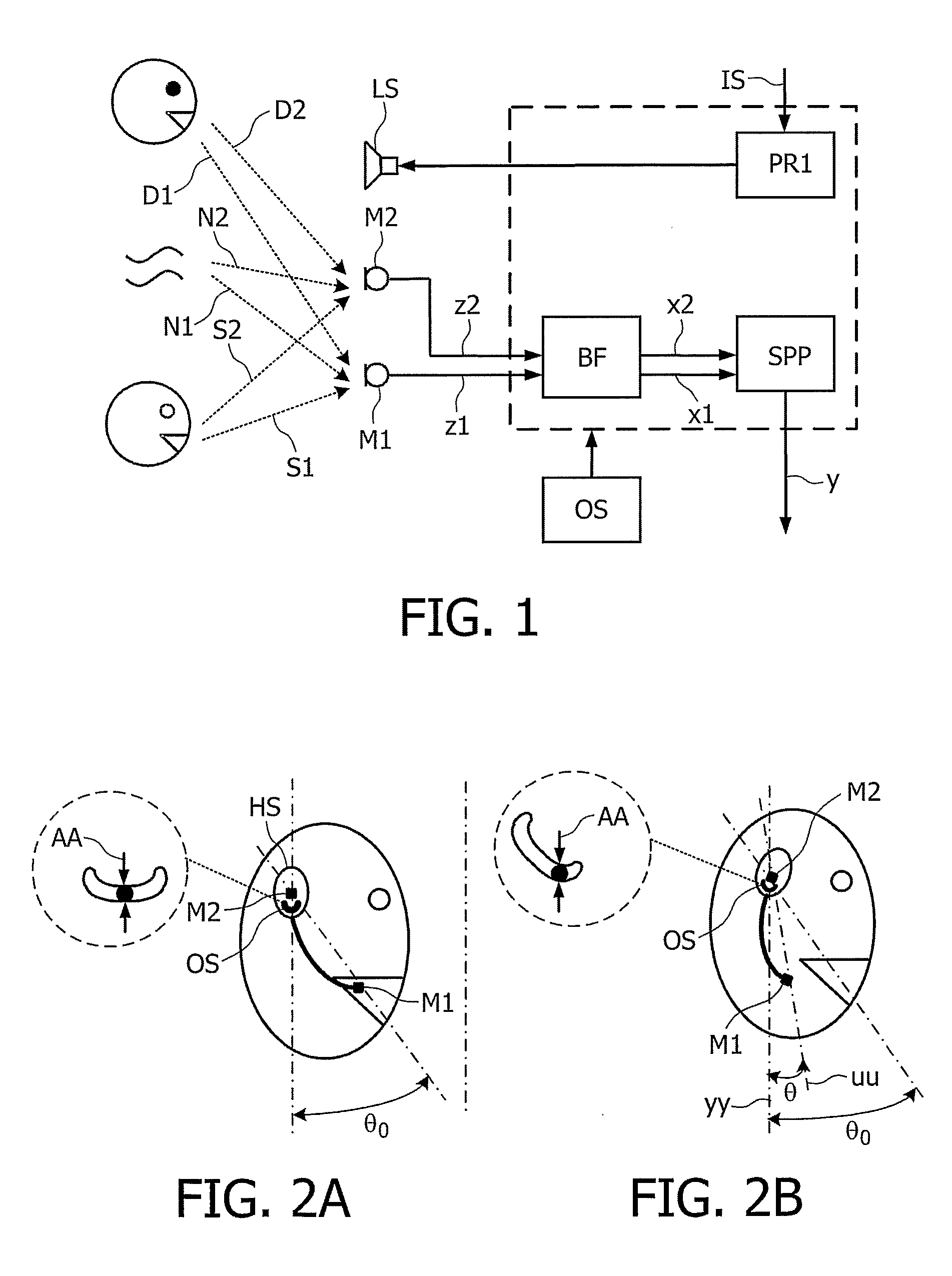
Telephony Device with Improved Noise Suppression
InactiveUS20070230712A1Unwanted noise signalMaximize qualityEar treatmentMicrophone structural associationFrequency spectrumPost processor
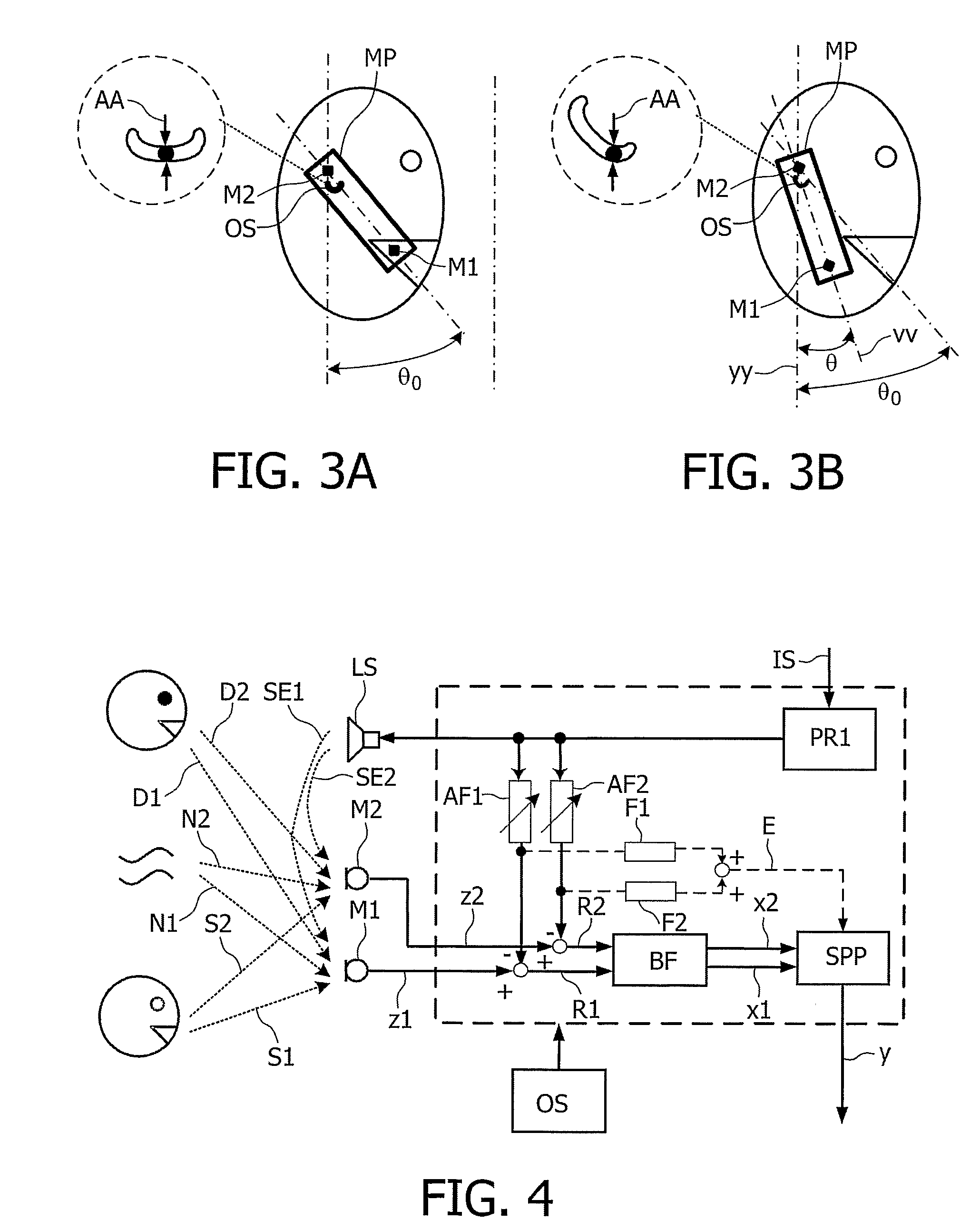
The present invention relates to a telephony device comprising a near-mouth microphone (M1) for picking up an input acoustic signal including the speaker's voice signal (S1) and an unwanted noise signal (N1,D1), a far-mouth microphone (M2) for picking up an unwanted noise signal (N2,D2) in addition to the near-end speaker's voice signal (S2), said speaker's voice signal being at a lower level than the near-mouth microphone, and an orientation sensor for measuring an orientation indication of said mobile device. The telephony device further comprises an audio processing unit comprising an adaptive beamformer (BF) coupled to the near-mouth and far-mouth microphones, including spatial filters for spatially filtering the input signals (z1,z2) delivered by the two microphones, and a spectral post-processor (SPP) for post-processing the signal delivered by the beam-former so as to separate the desired voice signal from the unwanted noise signal so as to deliver the output signal (y).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus and method to classify sound to detect speech
Audio frames are classified as either speech, non-transient background noise, or transient noise events. Probabilities of speech or transient noise event, or other metrics may be calculated to indicate confidence in classification. Frames classified as speech or noise events are not used in updating models (e.g., spectral subtraction noise estimates, silence model, background energy estimates, signal-to-noise ratio) of non-transient background noise. Frame classification affects acceptance / rejection of recognition hypothesis. Classifications and other audio related information may be determined by circuitry in a headset, and sent (e.g., wirelessly) to a separate processor-based recognition device.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
Sand monitoring within wells using acoustic arrays
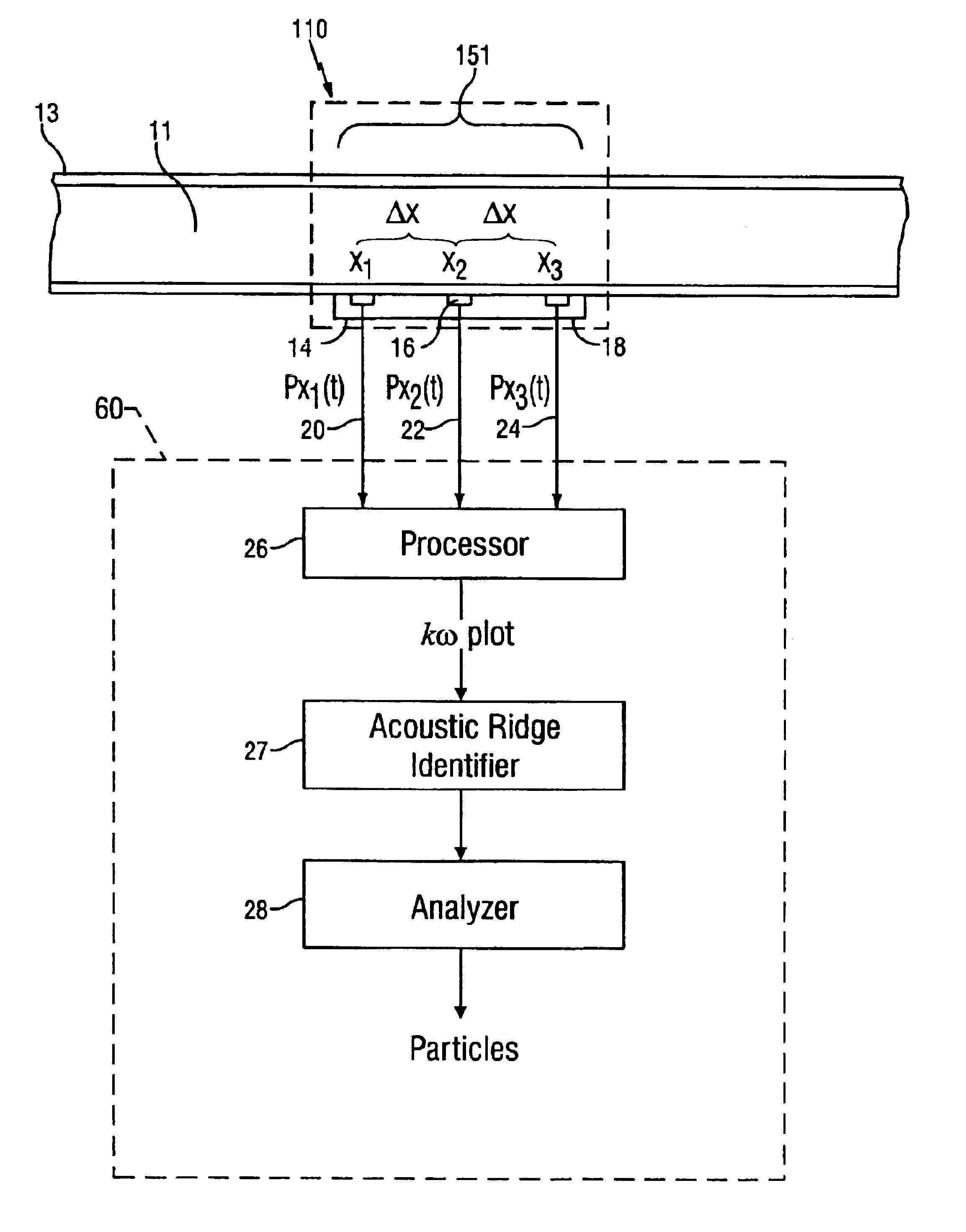
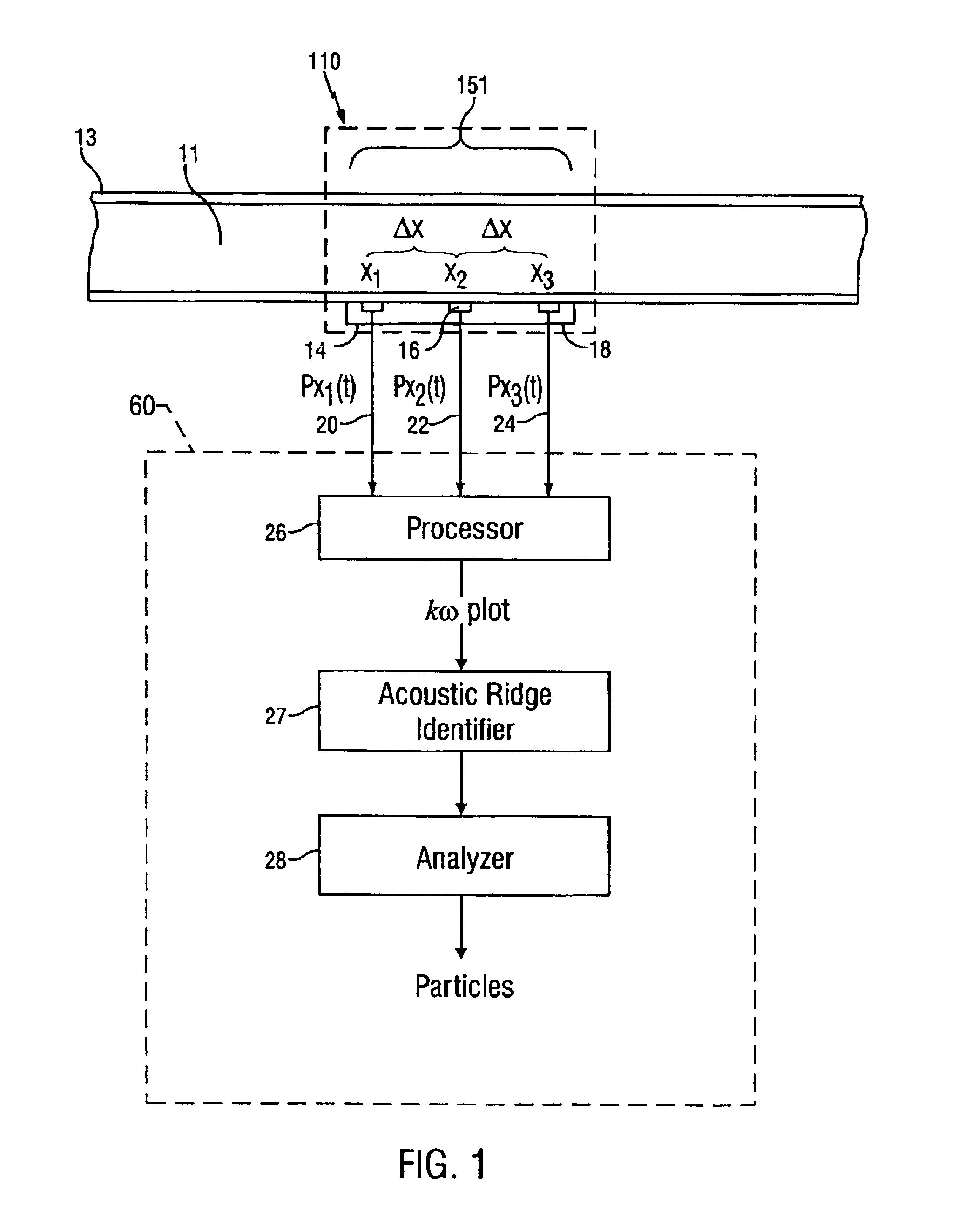
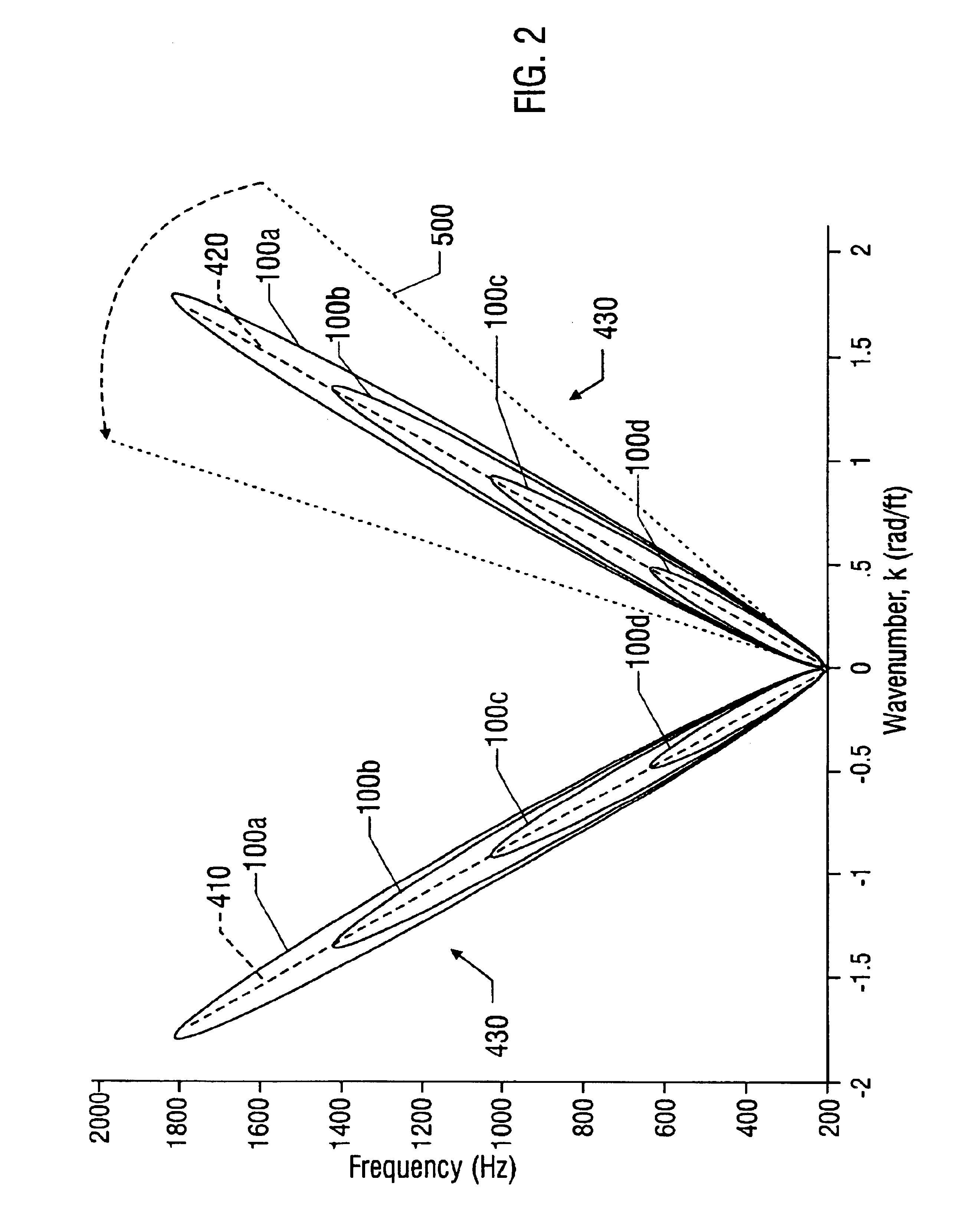
ActiveUS6837098B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic arrayData point
A method for detecting the presence of particles, such as sand, flowing within a fluid in a conduit is disclosed. At least two optical sensors measure pressure variations propagating through the fluid. These pressure variations are caused by acoustic noise generated by typical background noises of the well production environment and from sand particles flowing within the fluid. If the acoustics are sufficiently energetic with respect to other disturbances, the signals provided by the sensors will form an acoustic ridge on a kω plot, where each data point represents the power of the acoustic wave corresponding to that particular wave number and temporal frequency. A sand metric then compares the average power of the data points forming the acoustic ridge to the average power of the data points falling outside of the acoustic ridge. The result of this comparison allows one to determine whether particles are present within the fluid. Furthermore, the present invention can also determine whether the generated acoustic noise is occurring upstream or downstream of the sensors, thus giving an indication of the location of the particles in the fluid relative to the sensors.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
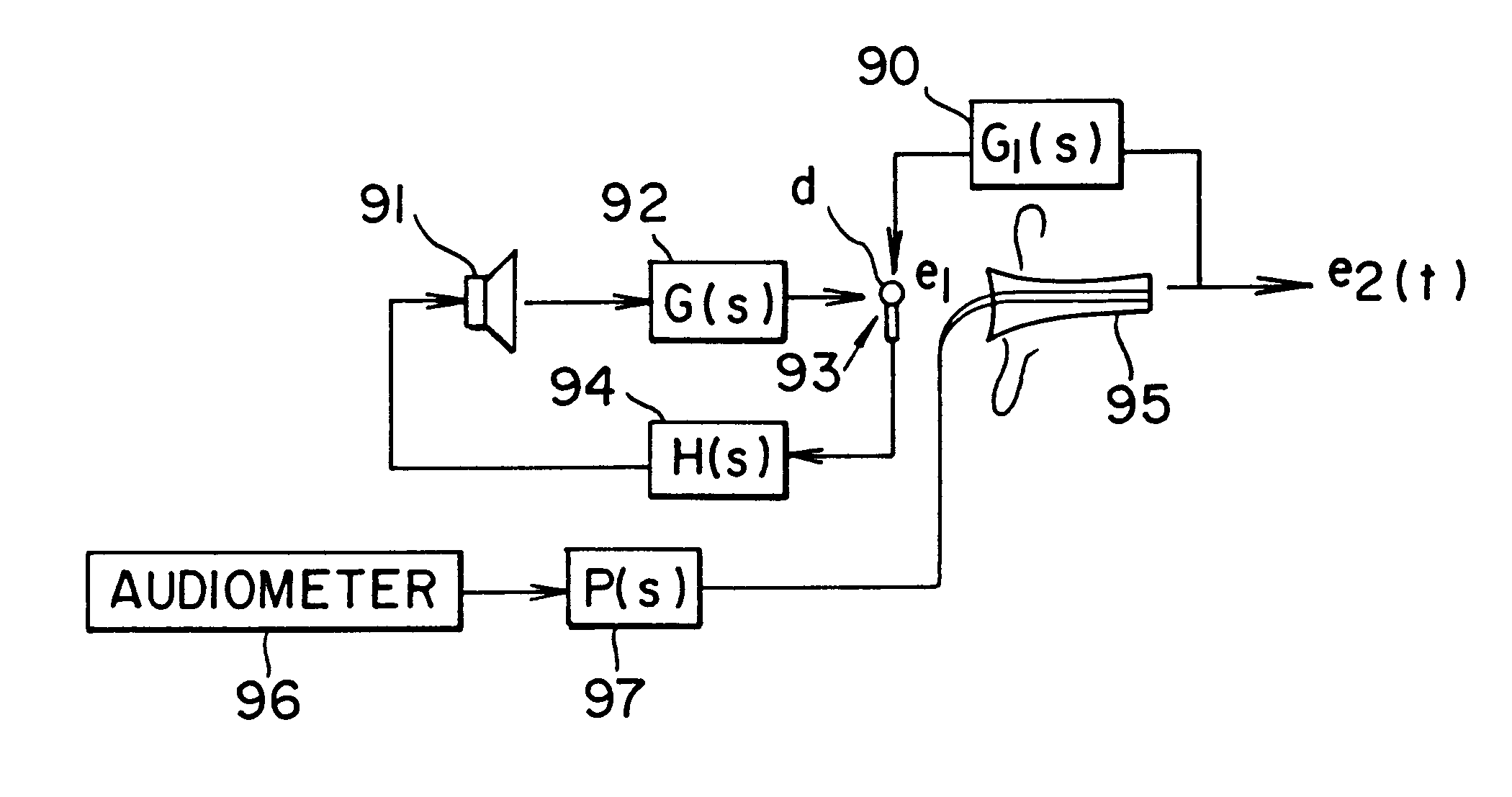
Active noise reduction for audiometry
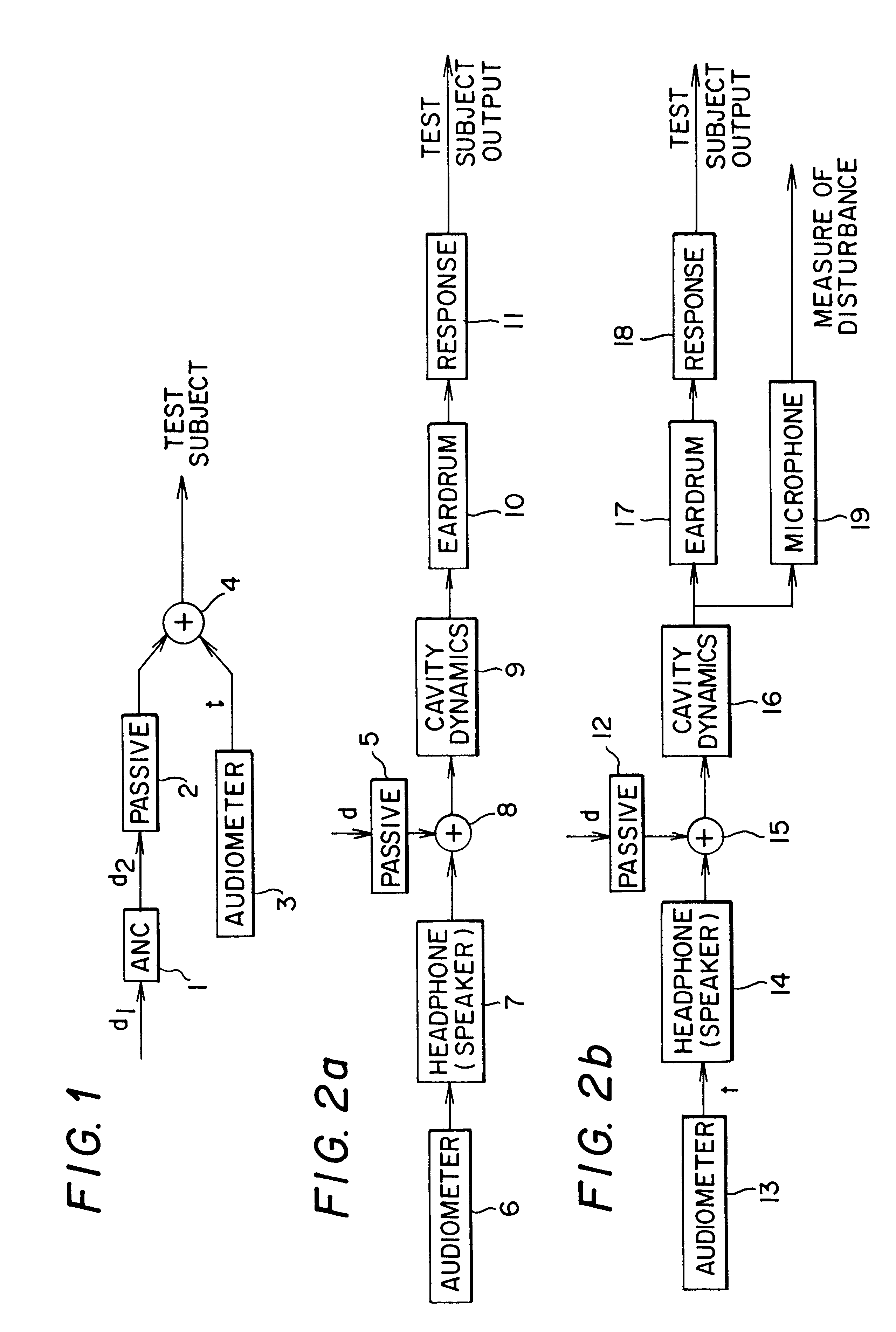
InactiveUS6396930B1Maximize noise control performanceAccurate comparisonEar treatmentAudiometeringNoise controlNoise field
The technology of active noise reduction (ANR) is incorporated into audiometry testing in a variety of formats. Analog feedback, digital feedback, adaptive feedforward, and adaptive feedback noise control schemes are presented for use in audiometry to reduce the ambient noise heard by the test subject, allowing subject testing in higher ambient noise fields. Audiometer test signals are appropriately compensated so the test results are accurate and comply with existing calibration standards for audiometers. Existing audiometry headphone technologies are modified so that ANR can be accomplished while satisfying existing standards for audiometric testing. Embodiments are also defined for alternate headphone arrangements that may not conform to current (1997) audiometric testing standards but provide sufficient performance advantages to warrant new standards for audiometry testing in the future.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Method for dynamic suppression of surrounding acoustic noise when listening to electrical inputs
ActiveUS20110137649A1Improved listening comfortAccurate monitoringHearing device active noise cancellationHearing aids signal processingElectricityEngineering
A listening instrument includes a) a microphone unit for picking up an input sound from the current acoustic environment of the user and converting it to an electric microphone signal; b) a microphone gain unit for applying a specific microphone gain to the microphone signal and providing a modified microphone signal; c) a direct electric input signal representing an audio signal; d) a direct gain unit for applying a specific direct gain to the direct electric input signal and providing a modified direct electric input signal; e) a detector unit for classifying the current acoustic environment and providing one or more classification parameters; f) a control unit for controlling the specific microphone gain applied to the electric microphone signal and / or the specific direct gain applied to the direct electric input signal based on the one or more classification parameters.
Owner:OTICON
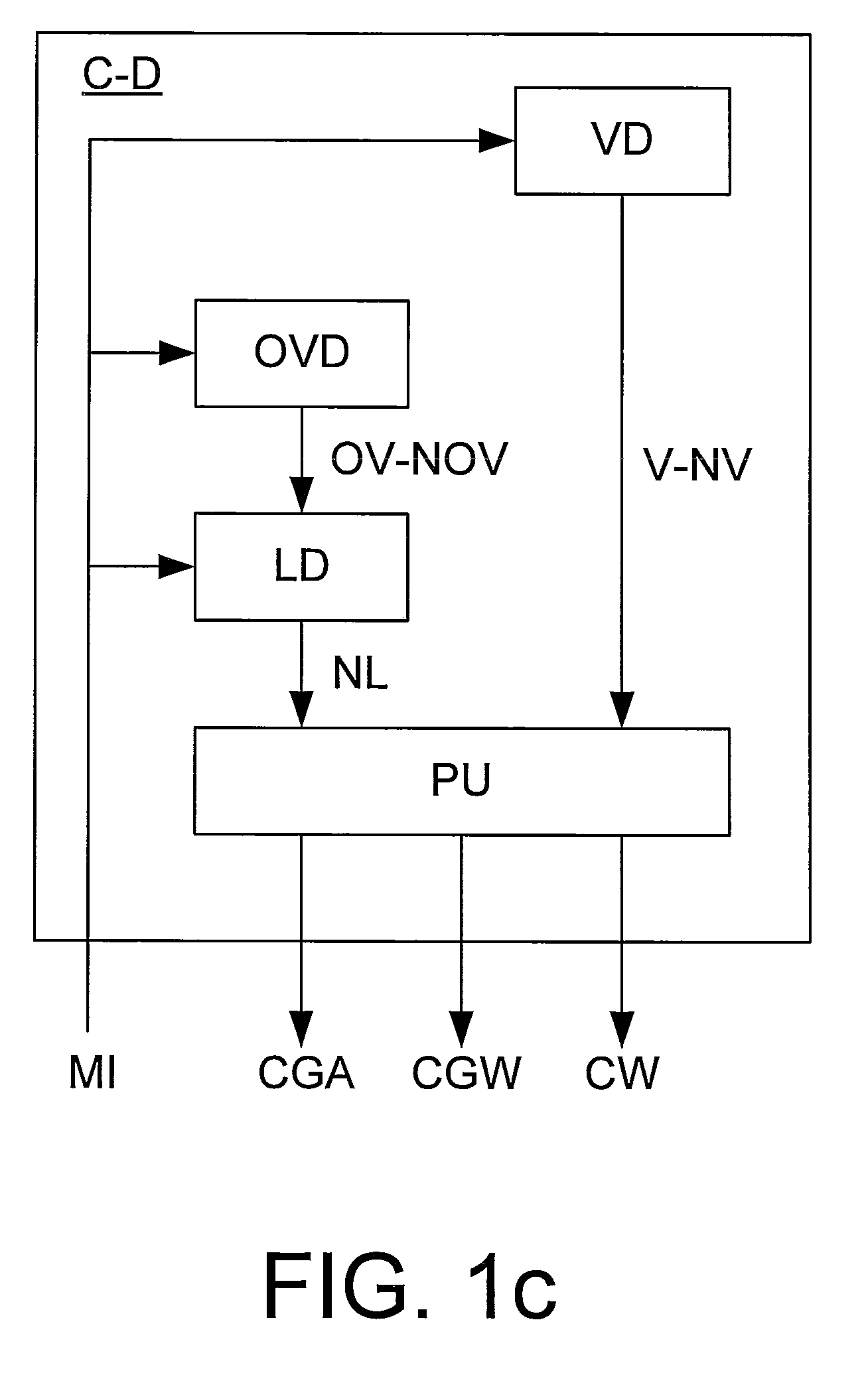
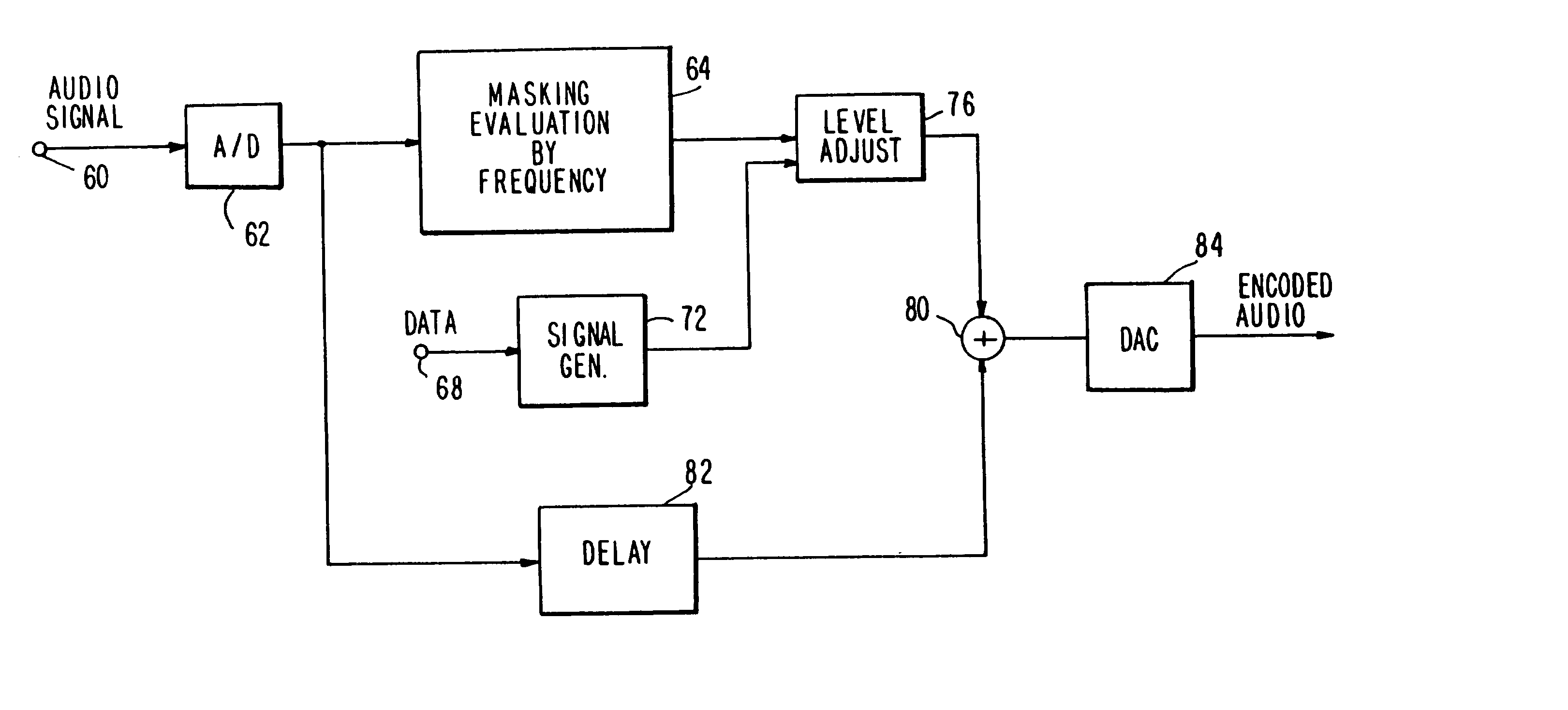
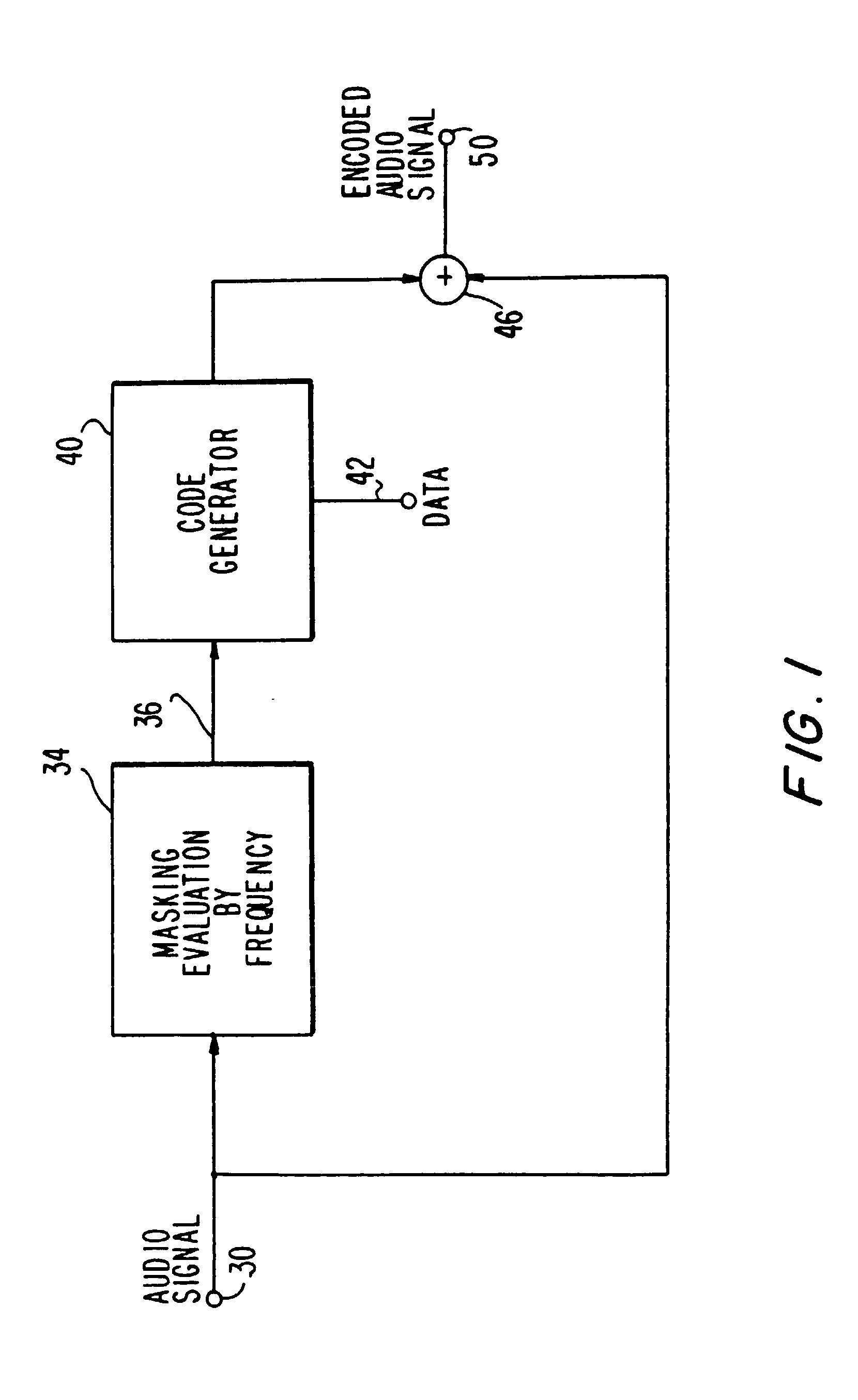
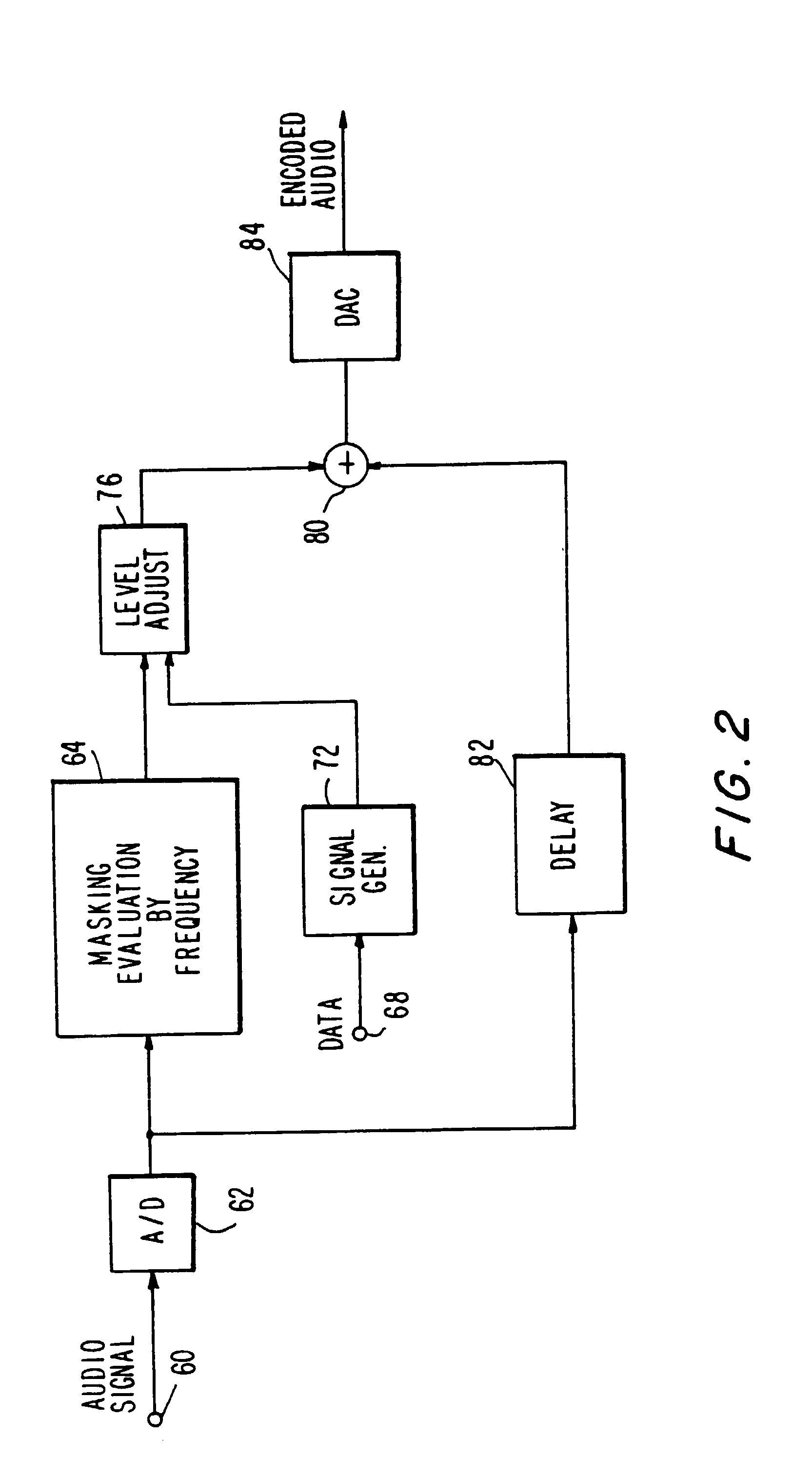
Apparatus and methods for including codes in audio signals
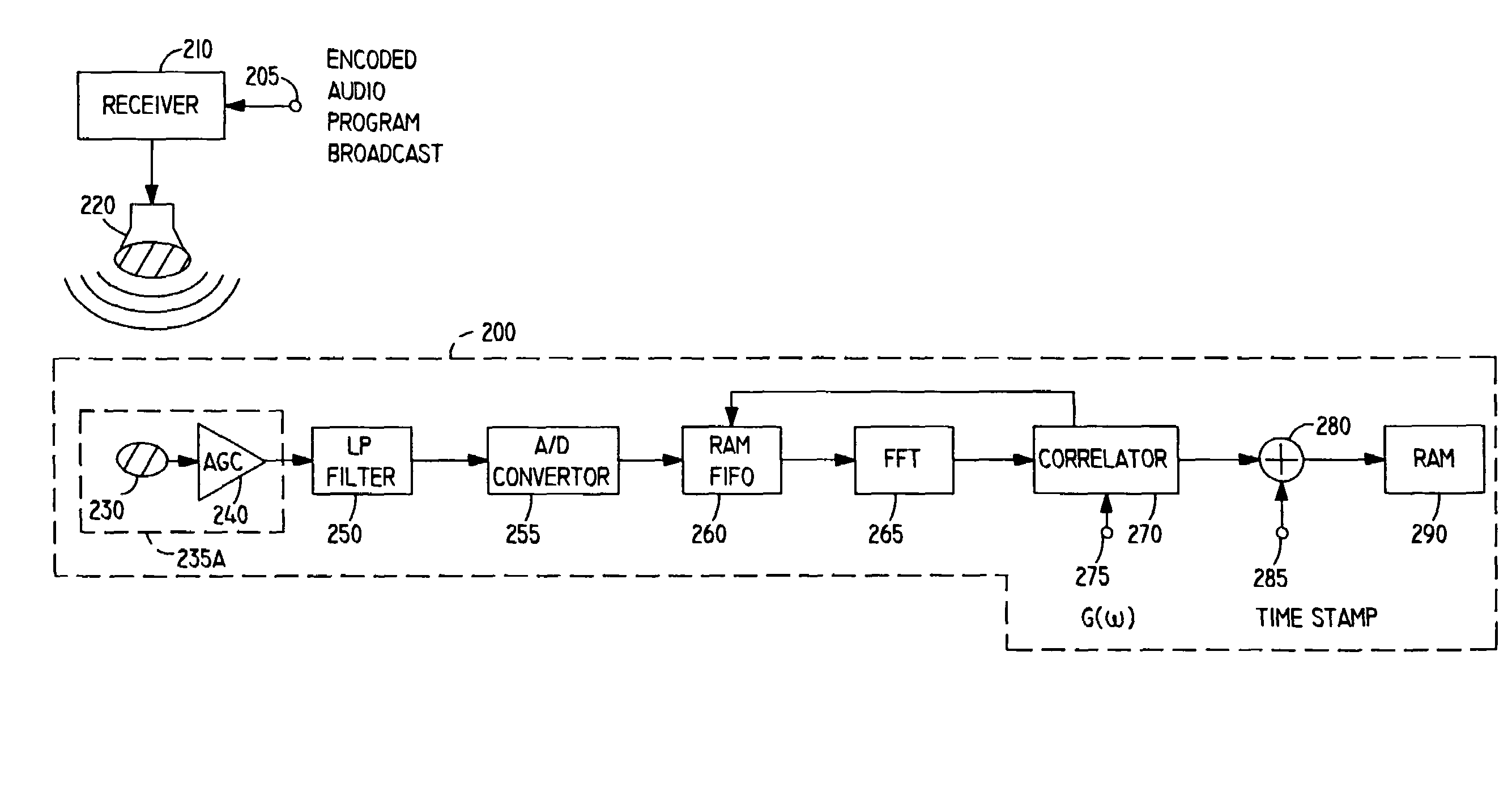
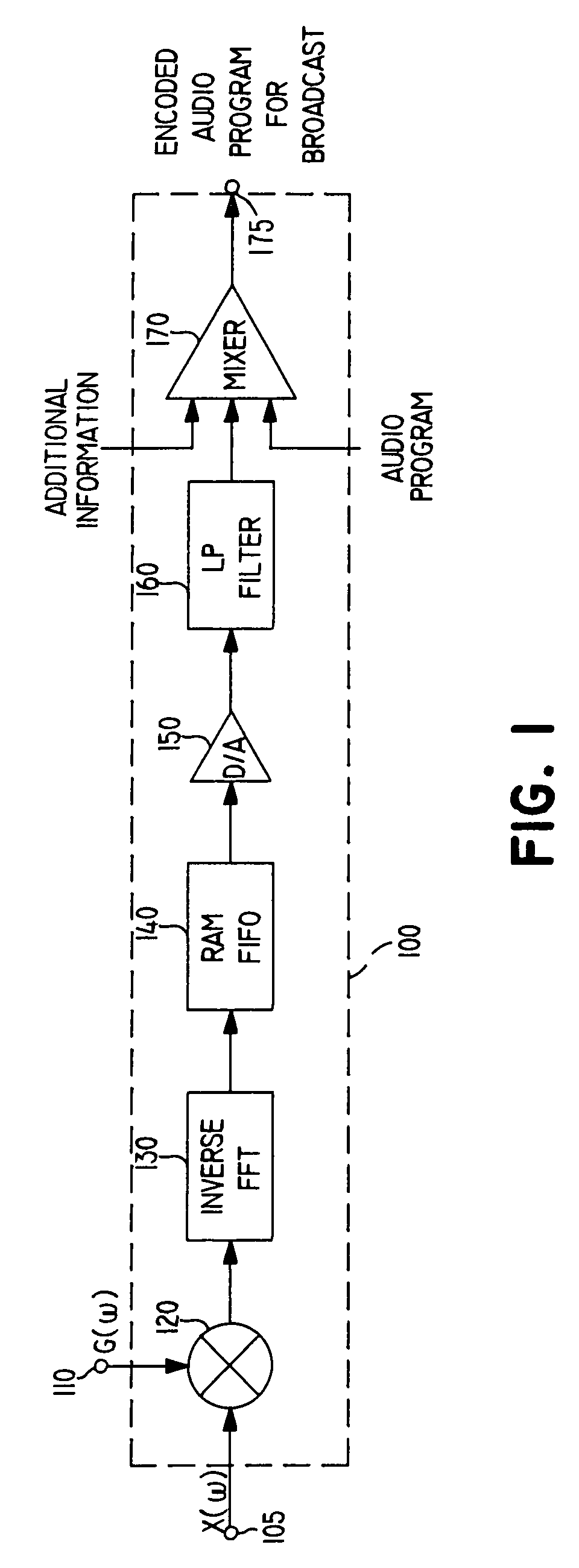
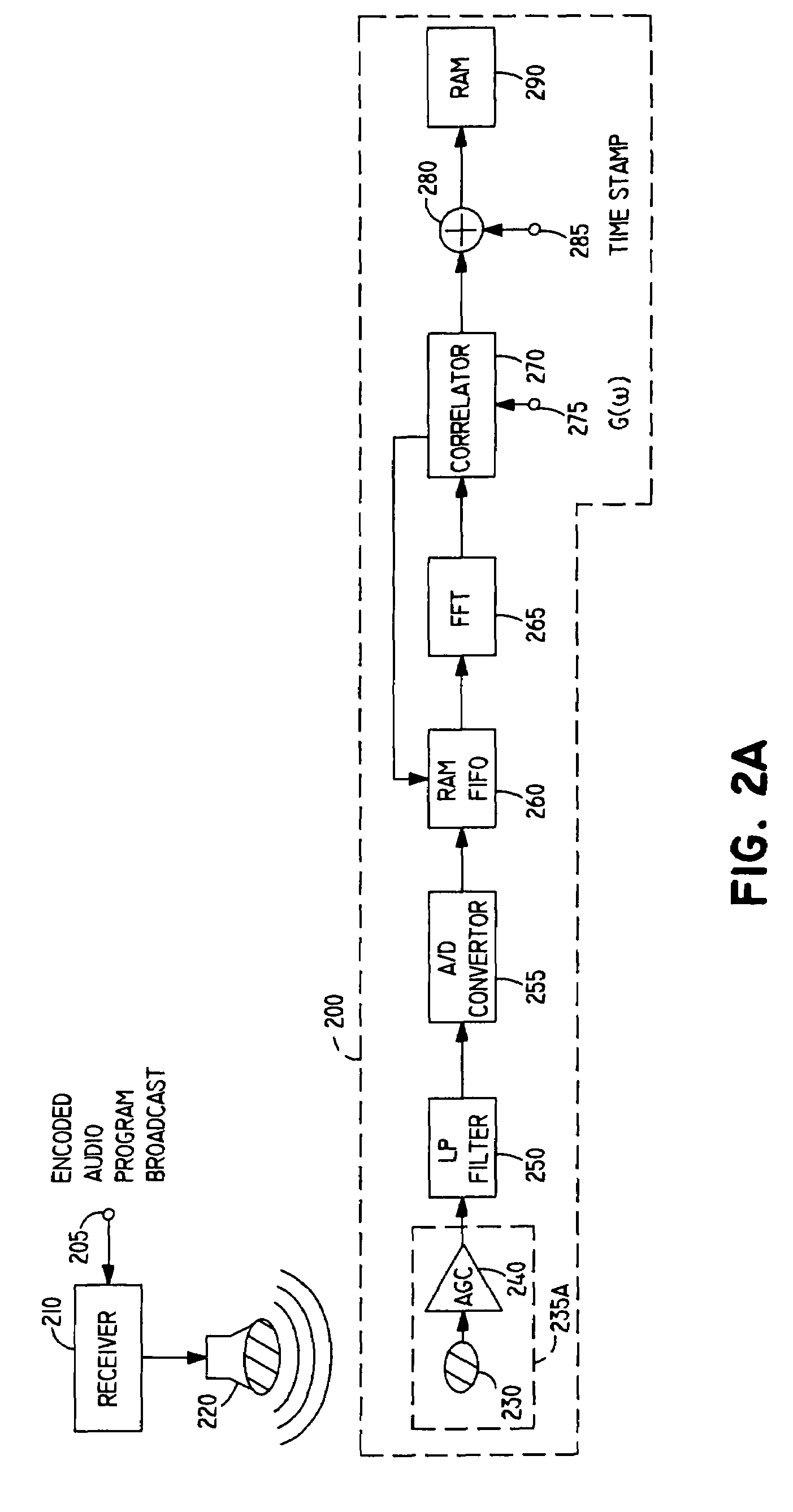
InactiveUS20030081781A1Reliable recoveryTelevision system detailsBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionAudio signal flowAudio frequency
Apparatus and methods for including a code having at least one code frequency component in an audio signal are provided. The abilities of various frequency components in the audio signal to mask the code frequency component to human hearing are evaluated and based on these evaluations an amplitude is assigned to the code frequency component. Methods and apparatus for detecting a code in an encoded audio signal are also provided. A code frequency component in the encoded audio signal is detected based on an expected code amplitude or on a noise amplitude within a range of audio frequencies including the frequency of the code component.
Owner:NIELSEN HLDG NV +1
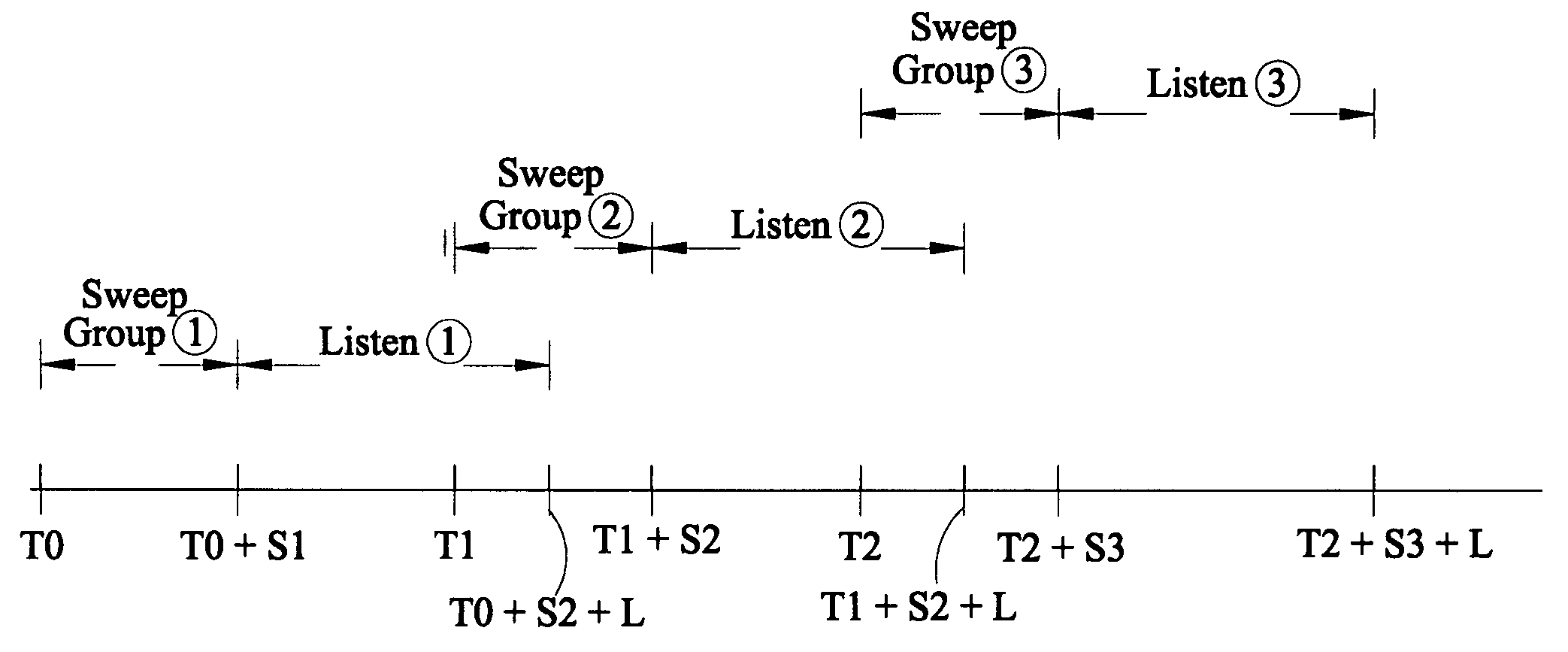
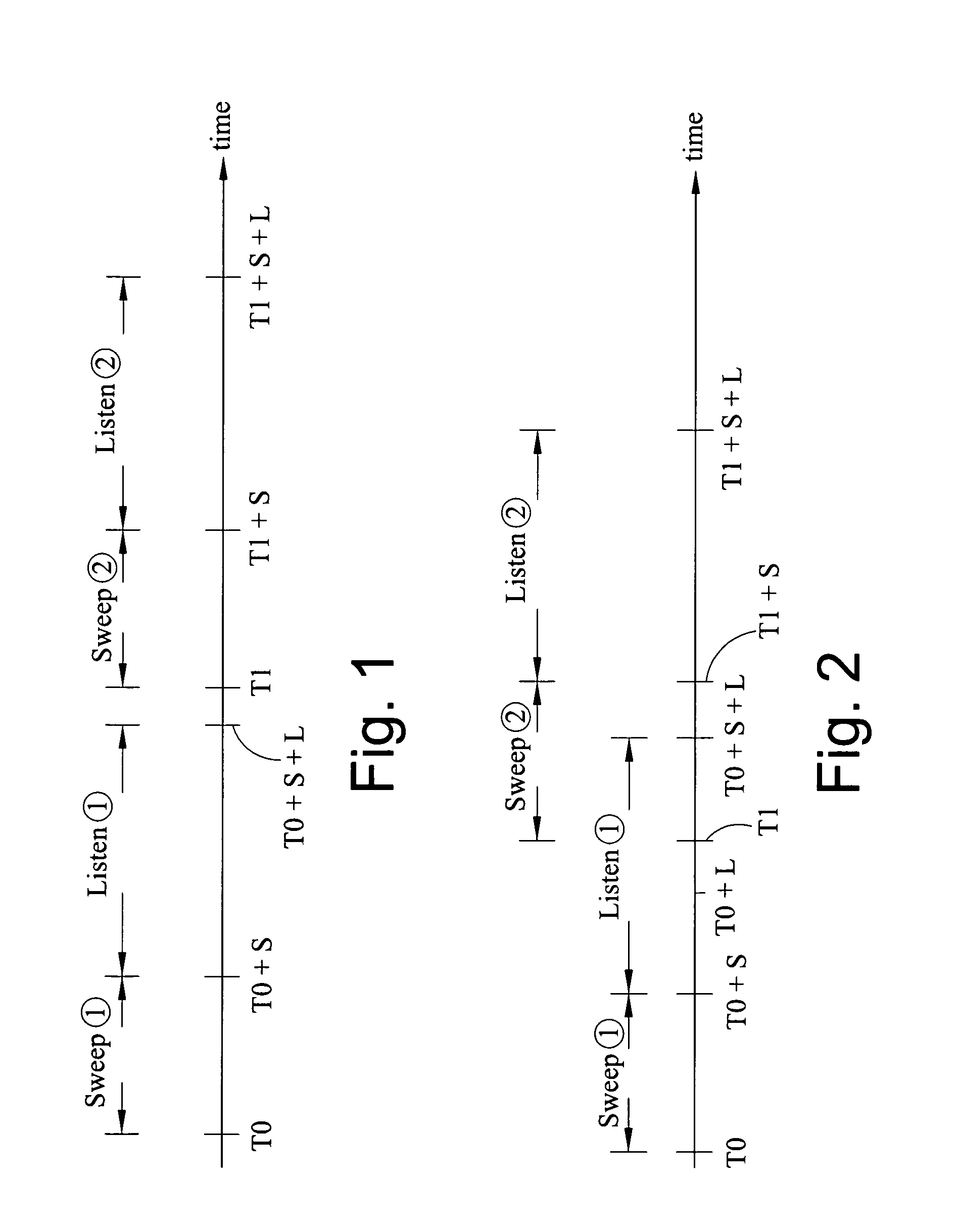
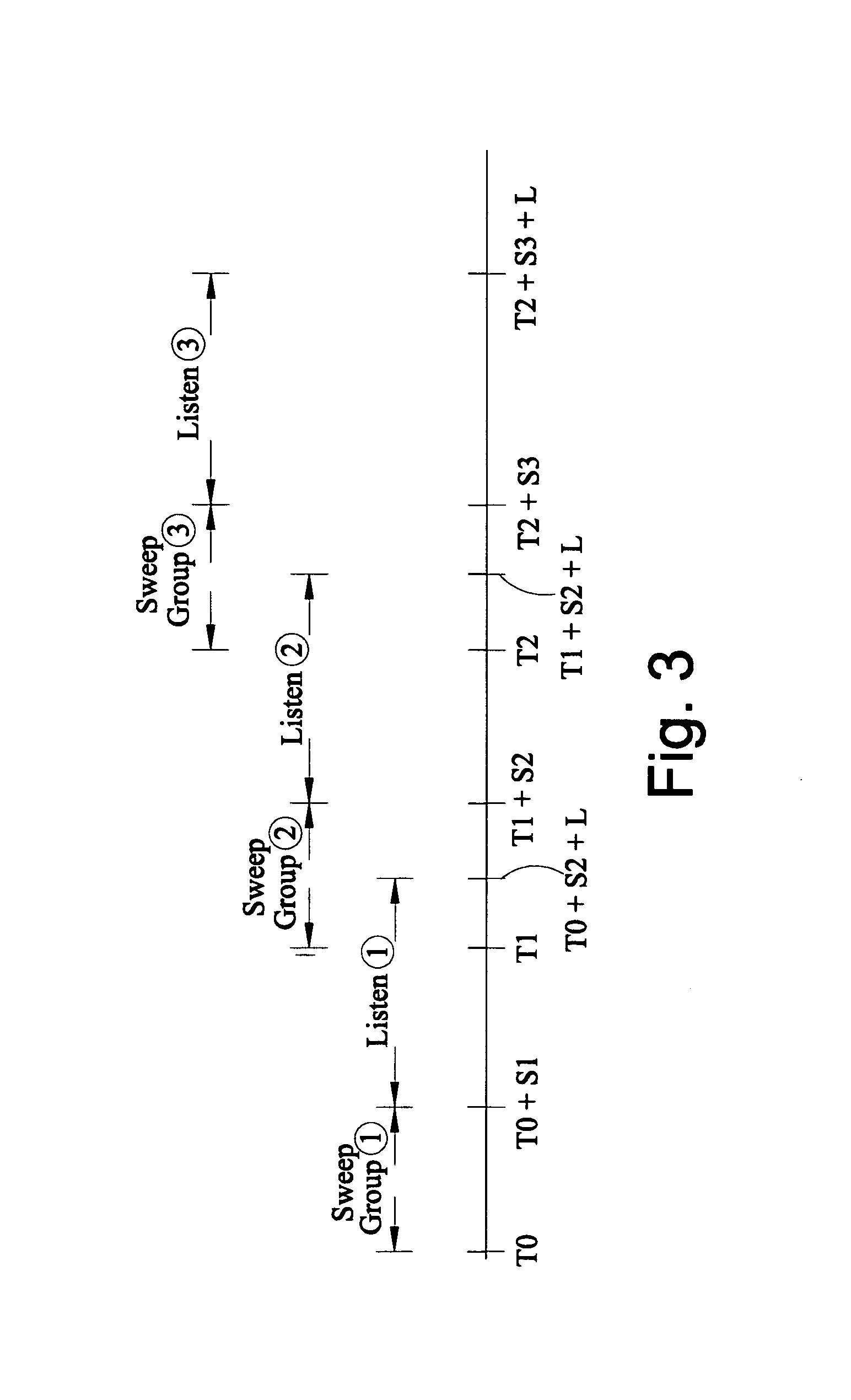
Method of seismic surveying
A method of seismic surveying comprising the steps of actuating the or each vibrator in a first vibrator group at time T0, and subsequently actuating the or each vibrator in a second vibrator group at time T1 that satisfies T0<T1<T0+S1+L where S1 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group and L is the listening time. At least one of the first vibrator group and the second vibrator group comprises at least two vibrators. The first group and the second group of vibrators may be the same group, or they may be different groups. This method enables the time required to complete a seismic survey to be reduced compared to the prior art “simultaneous shooting” and “slip-sweep shooting” techniques.In a case where the first group and the second group of vibrators are different, the method may further comprise actuating the or each vibrator in the first vibrator group at time T2, where T1<T2<T1+S2+L and S2 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group, and then actuating the or each vibrator in the second vibrator group at time T3 where T2<T3<T2+S1+L and where T3−T2≠T1−T0. The varying time delay between a shot of the first vibrator group and the corresponding shot of the second vibrator group means that harmonic noise will occur at different times in the shot records so that the noise may be eliminated by appropriately combining the shot records.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
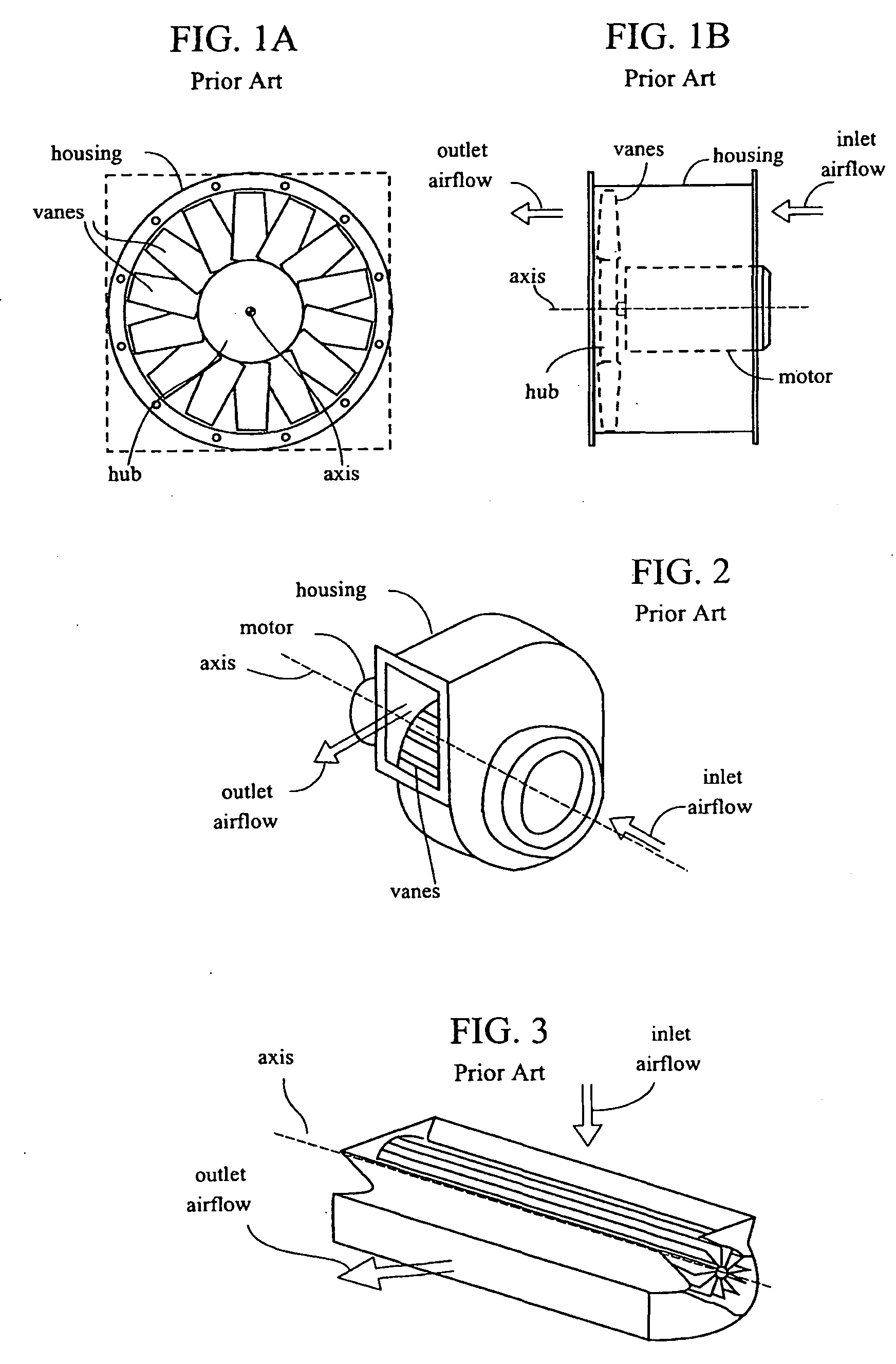
Quiet fan incorporating active noise control (ANC)
ActiveUS20100028134A1Reduce cross echoEar treatmentPump componentsUltrasound attenuationNoise control
An active noise control (ANC) system may be implemented to both sides of a fan, such that both directions of the noise emitting are treated to reduce the overall noise. The impact on airflow is minimal, and the technique is very effective in a broad range of low frequencies. Passive sound-absorbing materials may be included for attenuation of high frequencies. The resulting quiet fan produces a low level of noise compared to any other device based on fan, which produces the same capacity of airflow. The quiet fan may be incorporated in any mechanical system which requires airflow induction such as: computers, air conditioners, machines, and more.
Owner:SILENTIUM LTD
Apparatus including microphone arrangements
ActiveUS20100195838A1Reduce the impactReduce impactPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesGain controlEngineeringVideo recording
An apparatus includes first and second microphone arrangements, arranged to output first and second signals respectively and is operable in a first mode and a second mode. In the first mode, an output signal is generated based on the second signal and a third signal, where the second signal and, optionally, the first signal, can be used to compensate for ambient noise, for example, for noise cancellation when a telephone call is relayed through a speaker. In the second mode, an output signal is generated based on the first and second signals. In this manner, the combination of the first and second microphone arrangements provides a directional sensitivity that can pick up sound from a remote source, for example, in an audio or video recording session. The apparatus may include a sensor to allow automatic switching between one or more of modes, directional sensitivity patterns and types of recording session.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
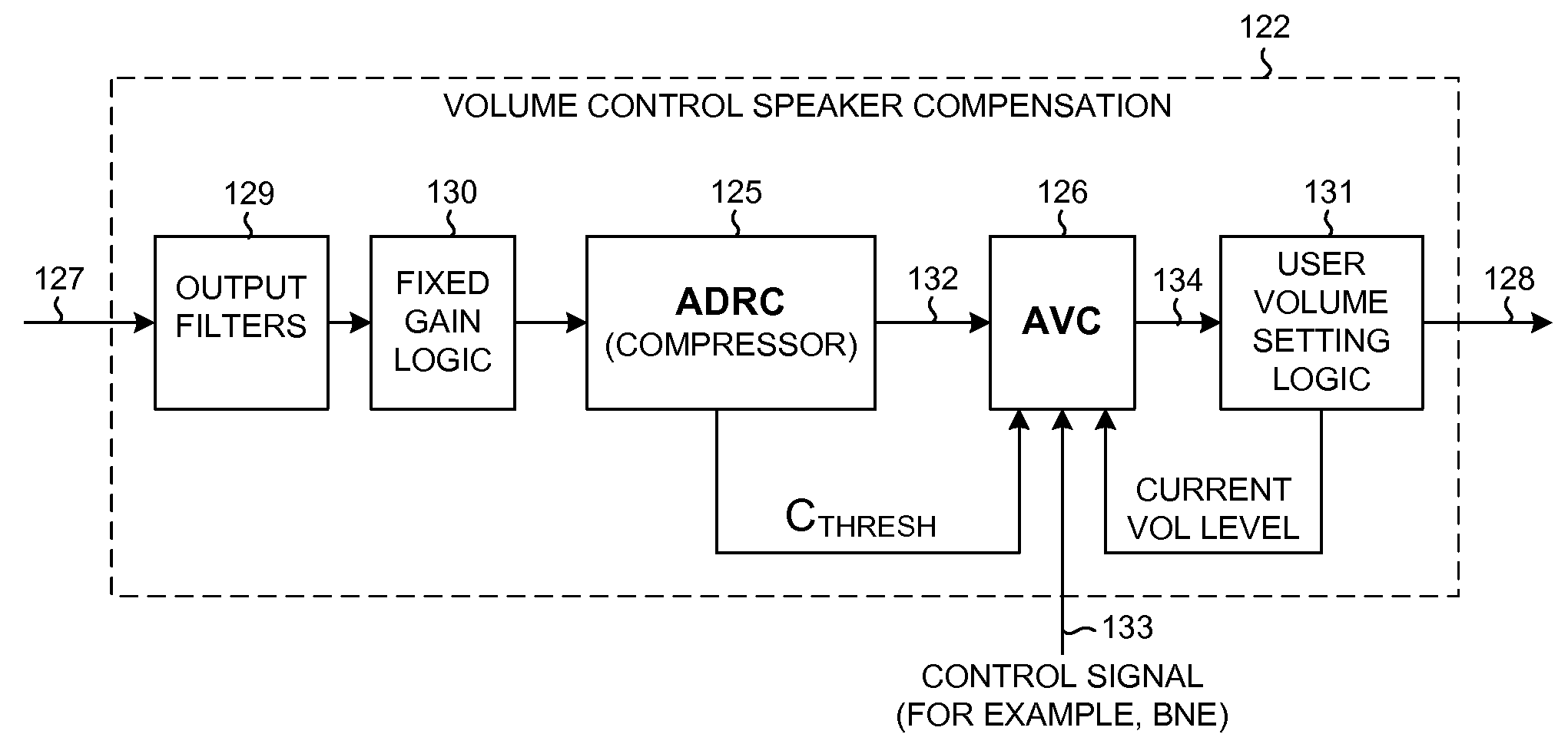
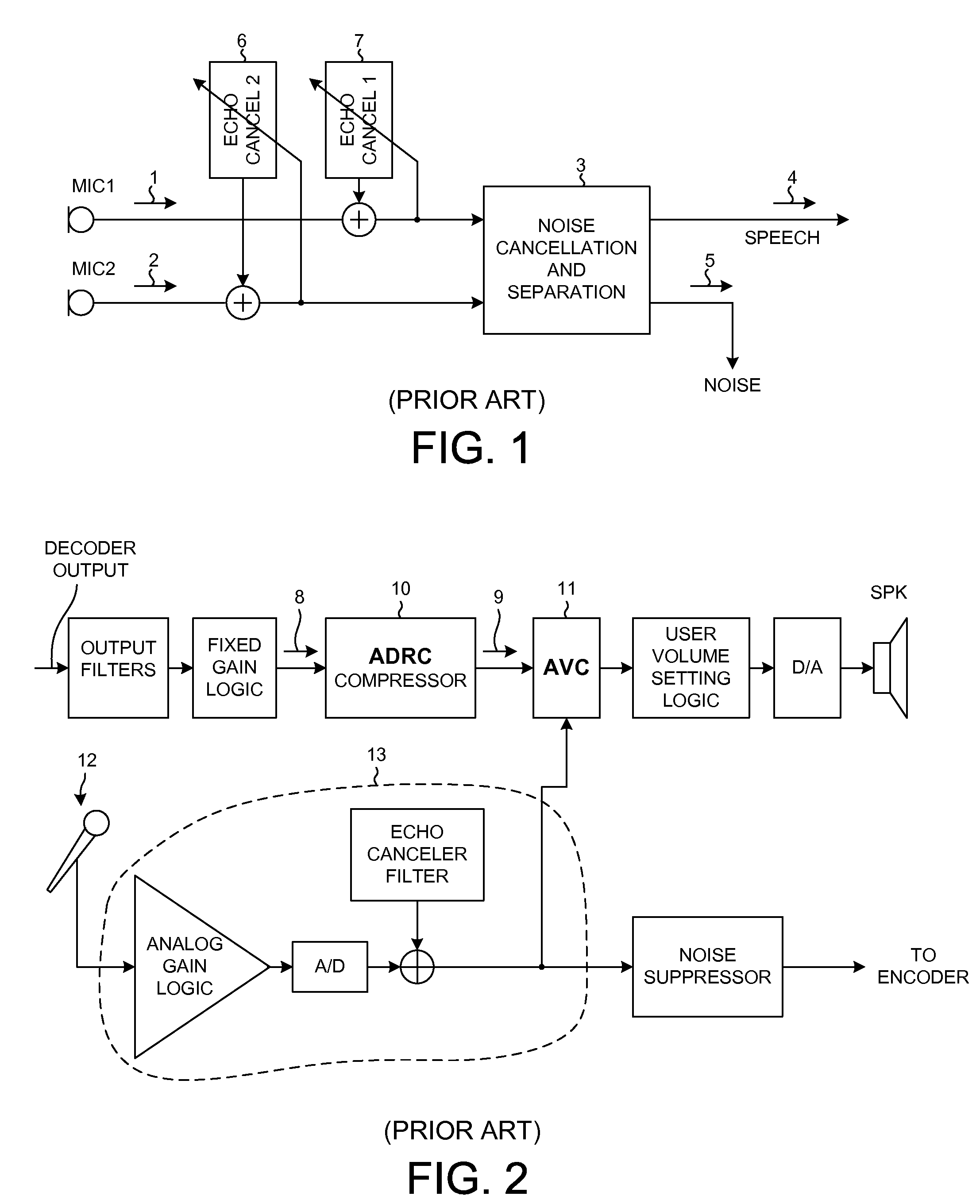
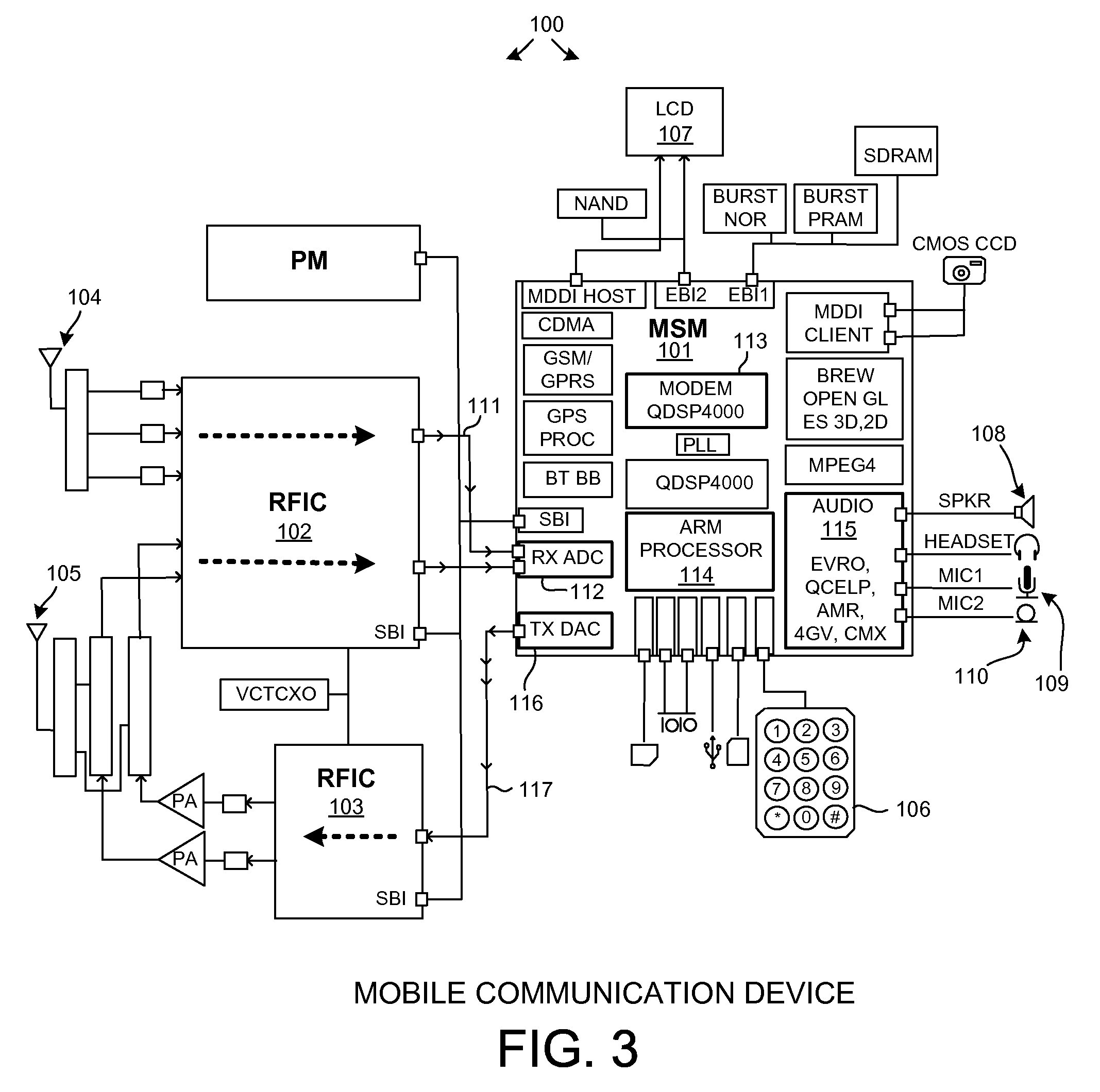
Automatic volume and dynamic range adjustment for mobile audio devices
ActiveUS20080269926A1Limited dynamic rangeBoosting amplitudeGain controlSubstation speech amplifiersNoiseEngineering
A mobile audio device (for example, a cellular telephone, personal digital audio player, or MP3 player) performs Audio Dynamic Range Control (ADRC) and Automatic Volume Control (AVC) to increase the volume of sound emitted from a speaker of the mobile audio device so that faint passages of the audio will be more audible. This amplification of faint passages occurs without overly amplifying other louder passages, and without substantial distortion due to clipping. Multi-Microphone Active Noise Cancellation (MMANC) functionality is, for example, used to remove background noise from audio information picked up on microphones of the mobile audio device. The noise-canceled audio may then be communicated from the device. The MMANC functionality generates a noise reference signal as an intermediate signal. The intermediate signal is conditioned and then used as a reference by the AVC process. The gain applied during the AVC process is a function of the noise reference signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for encoding/decoding broadcast or recorded segments and monitoring audience exposure thereto
InactiveUS7316025B1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionThird partyNoise
Methods and apparatus for encoding and decoding information in broadcast or recorded segment signals are described. In certain embodiments, an audience monitoring system encodes identification information in the audio signal portion of a broadcast or recorded segment using spread spectrum encoding. A personal monitoring device receives an acoustically reproduced version of the broadcast or recorded signal via a microphone, decodes the identification information from the audio signal portion despite significant ambient noise, and stores this information, automatically providing a diary for the audience member which is later uploaded to a centralized facility. A separate monitoring device decodes additional information from the broadcast signal, which is matched with the audience diary information at the central facility. This monitor may simultaneously send data to the centralized facility using a dial-up telephone line, and receive data from the centralized facility through a signal encoded using a spread spectrum technique and modulated with a broadcast signal from a third-party.
Owner:THE ARBITRON A DIV OF CERIDIAN CORP +1
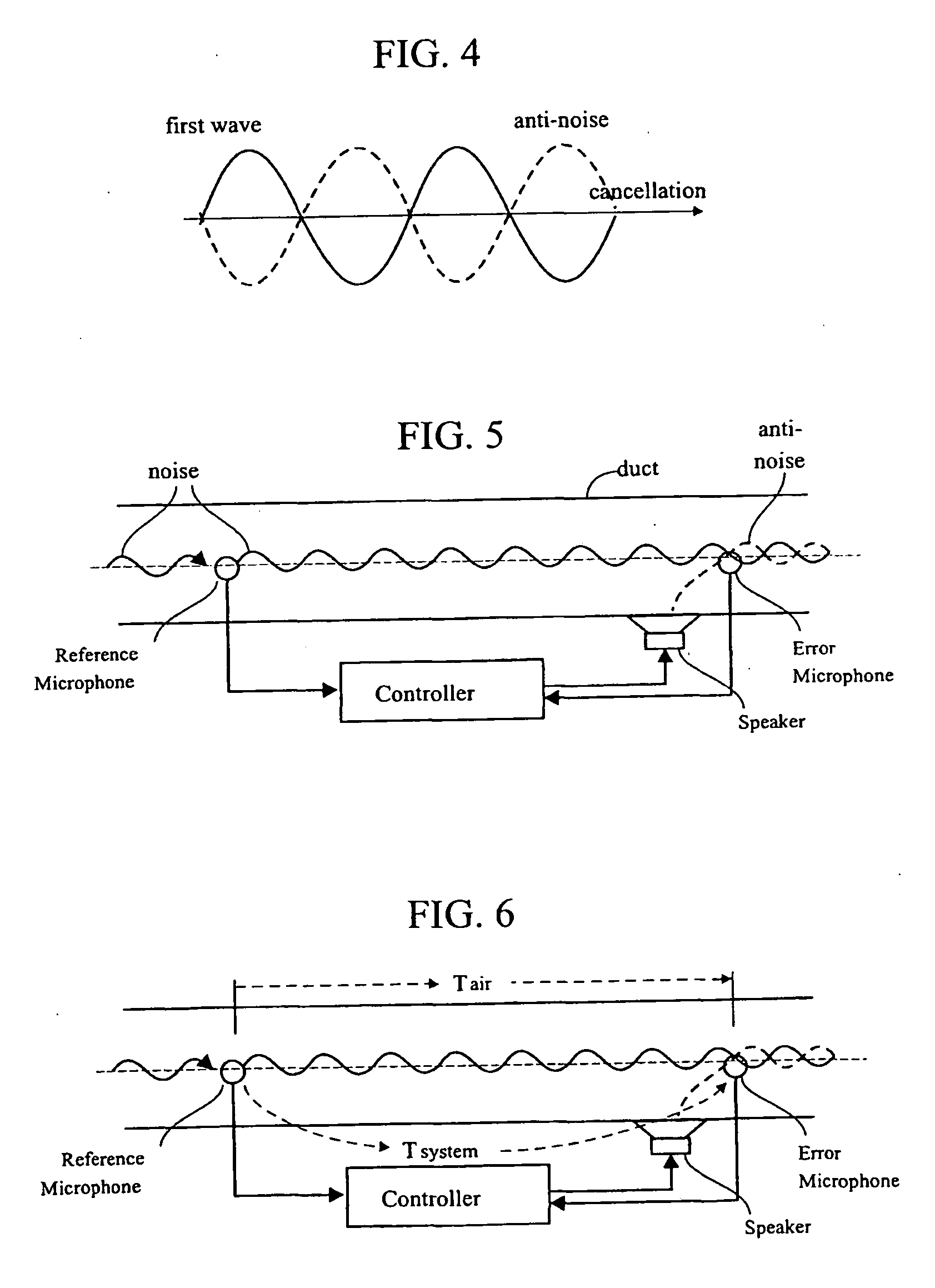
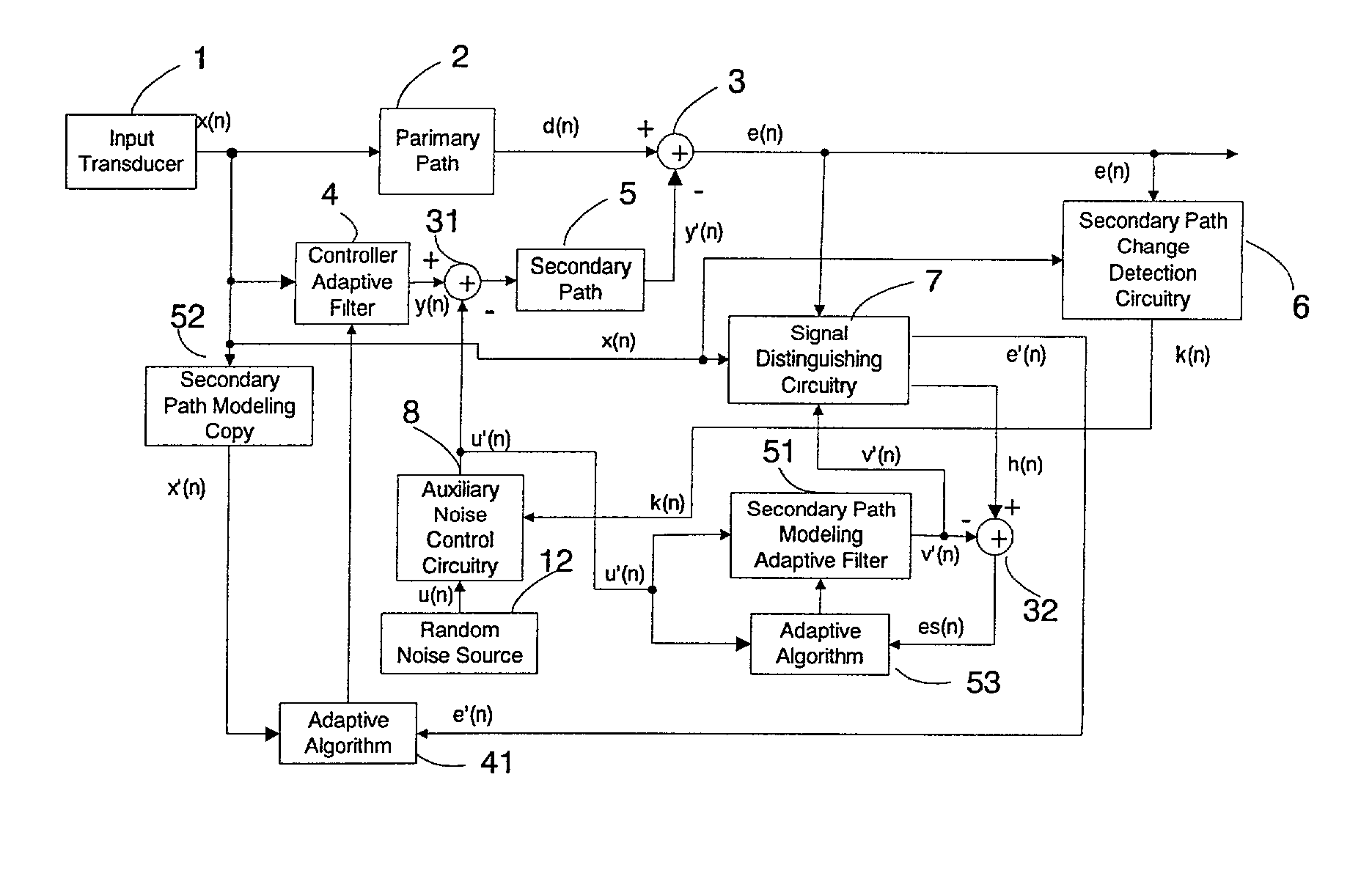
Active noise control system with on-line secondary path modeling
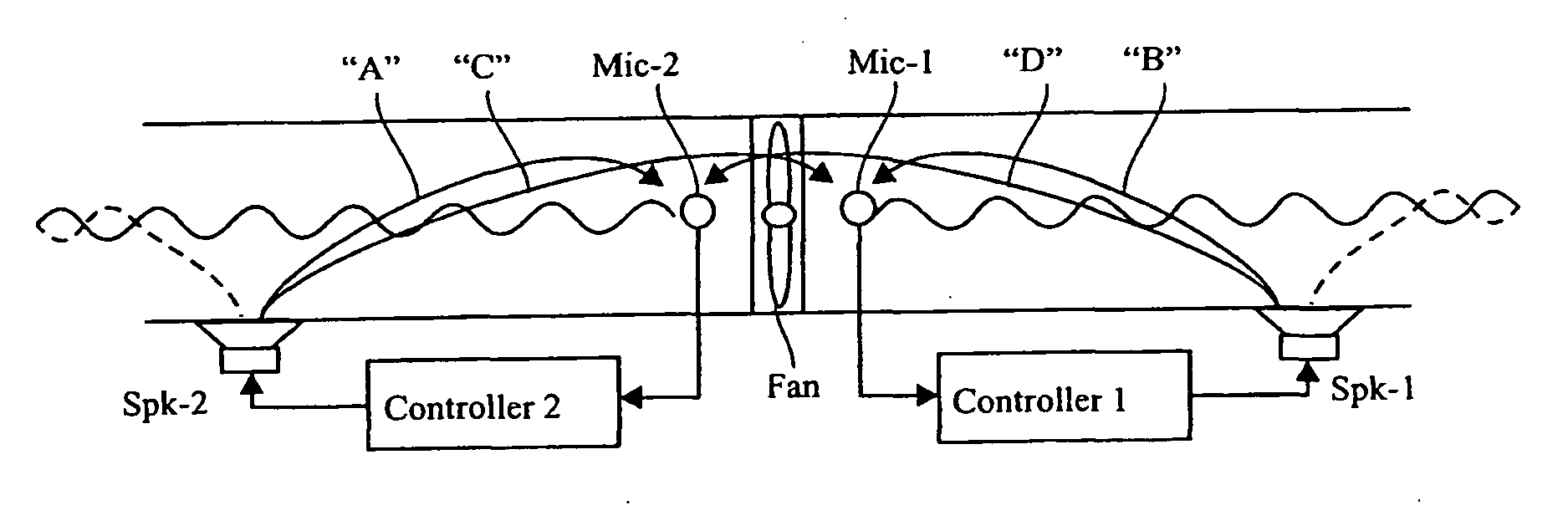
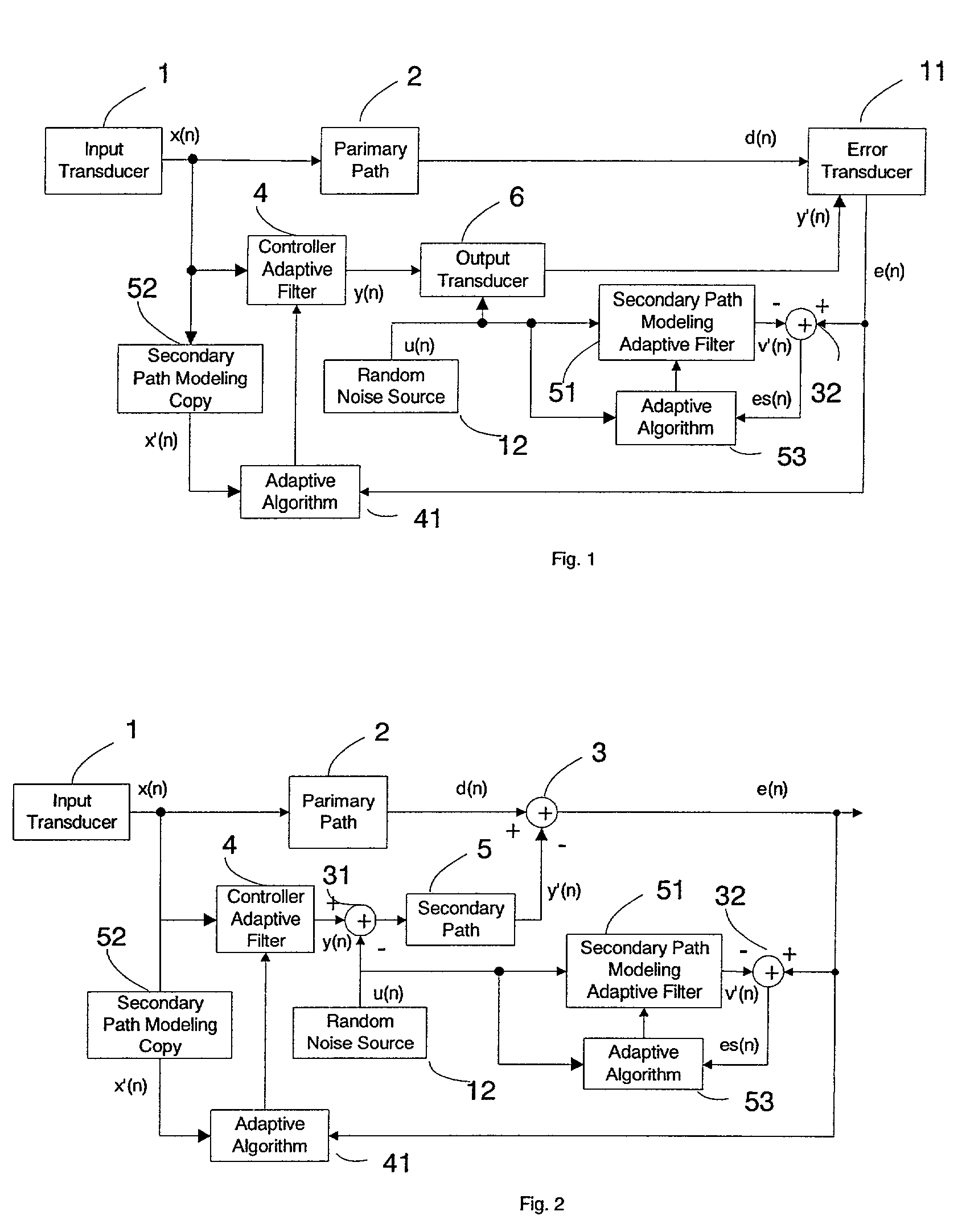
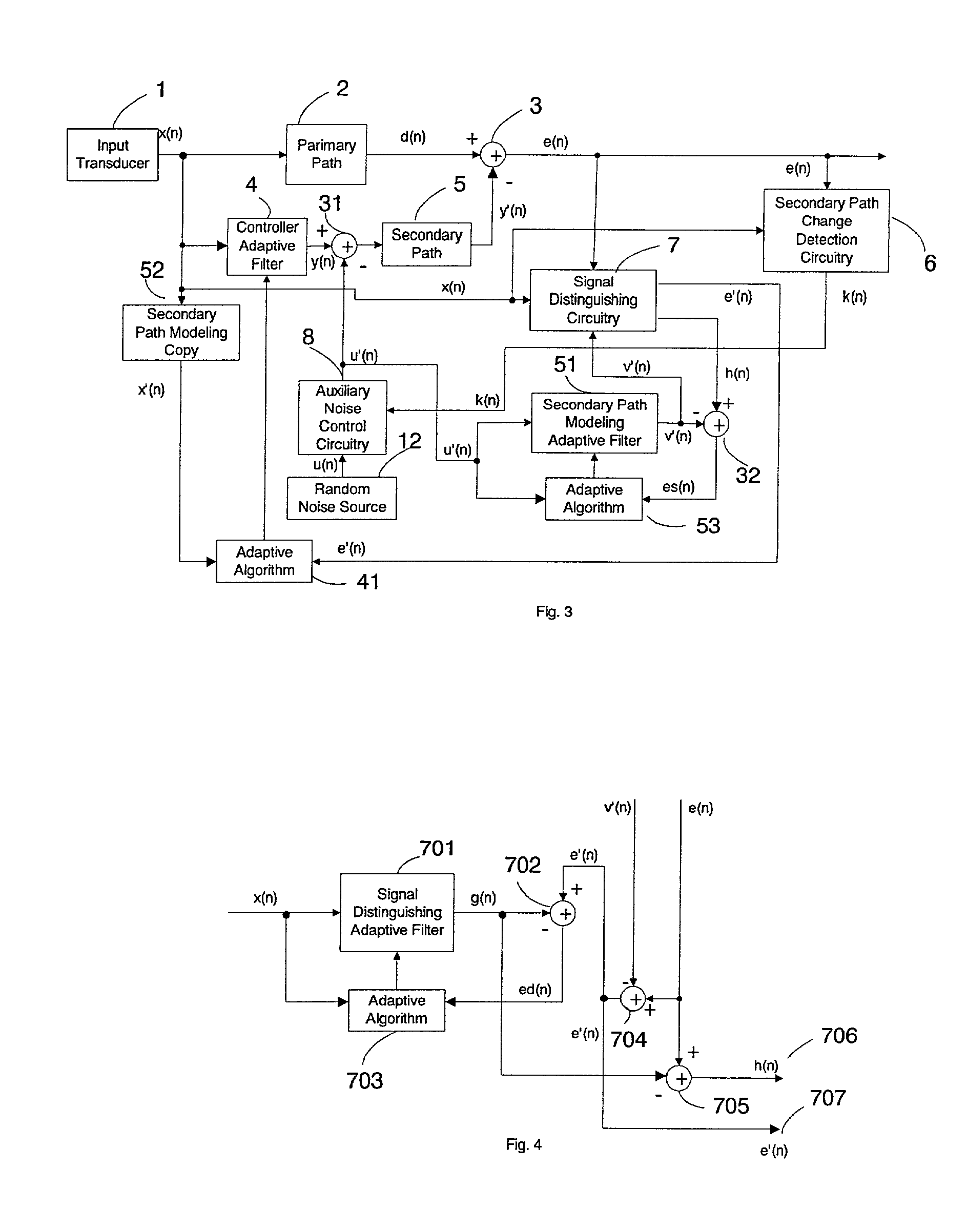
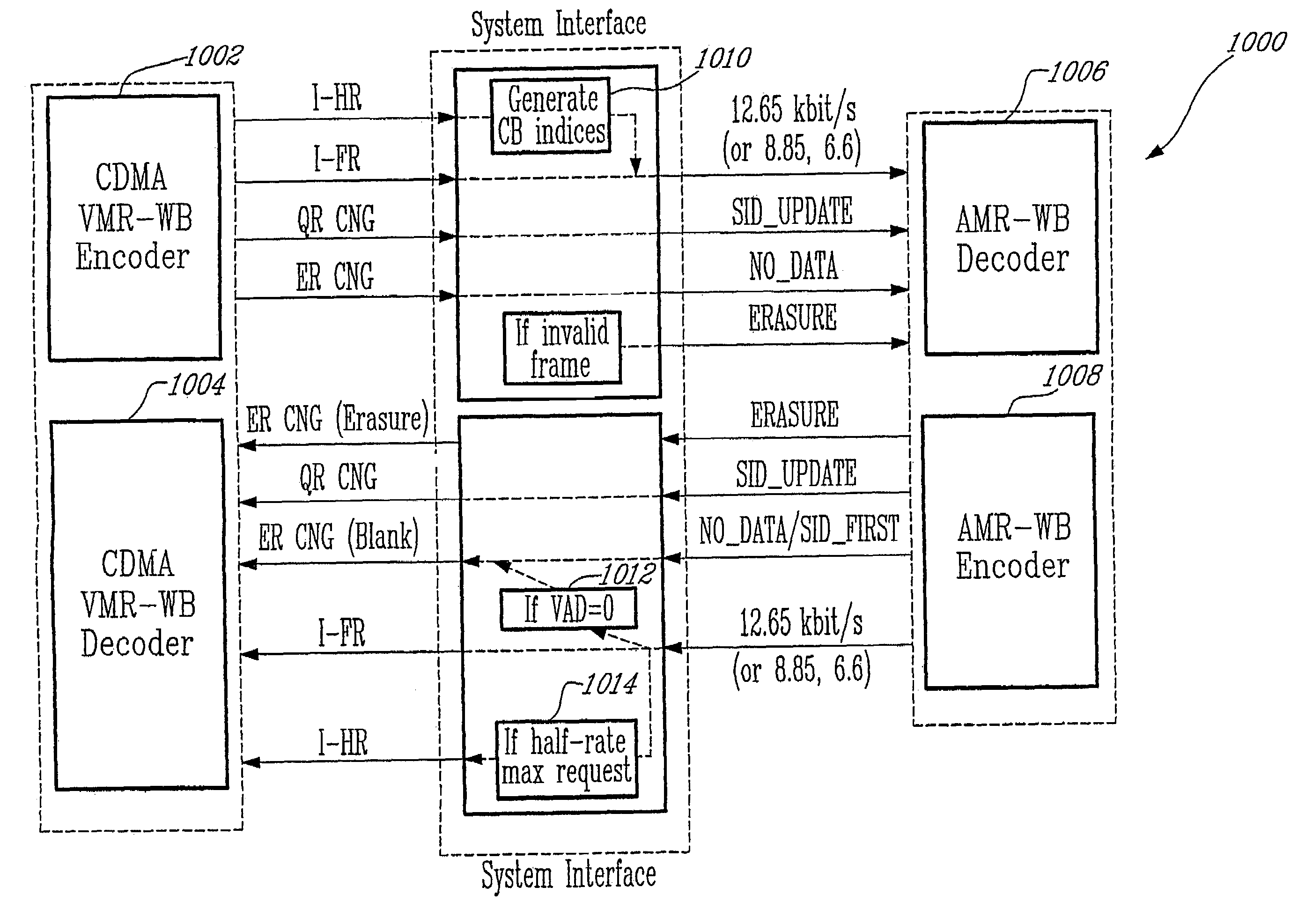
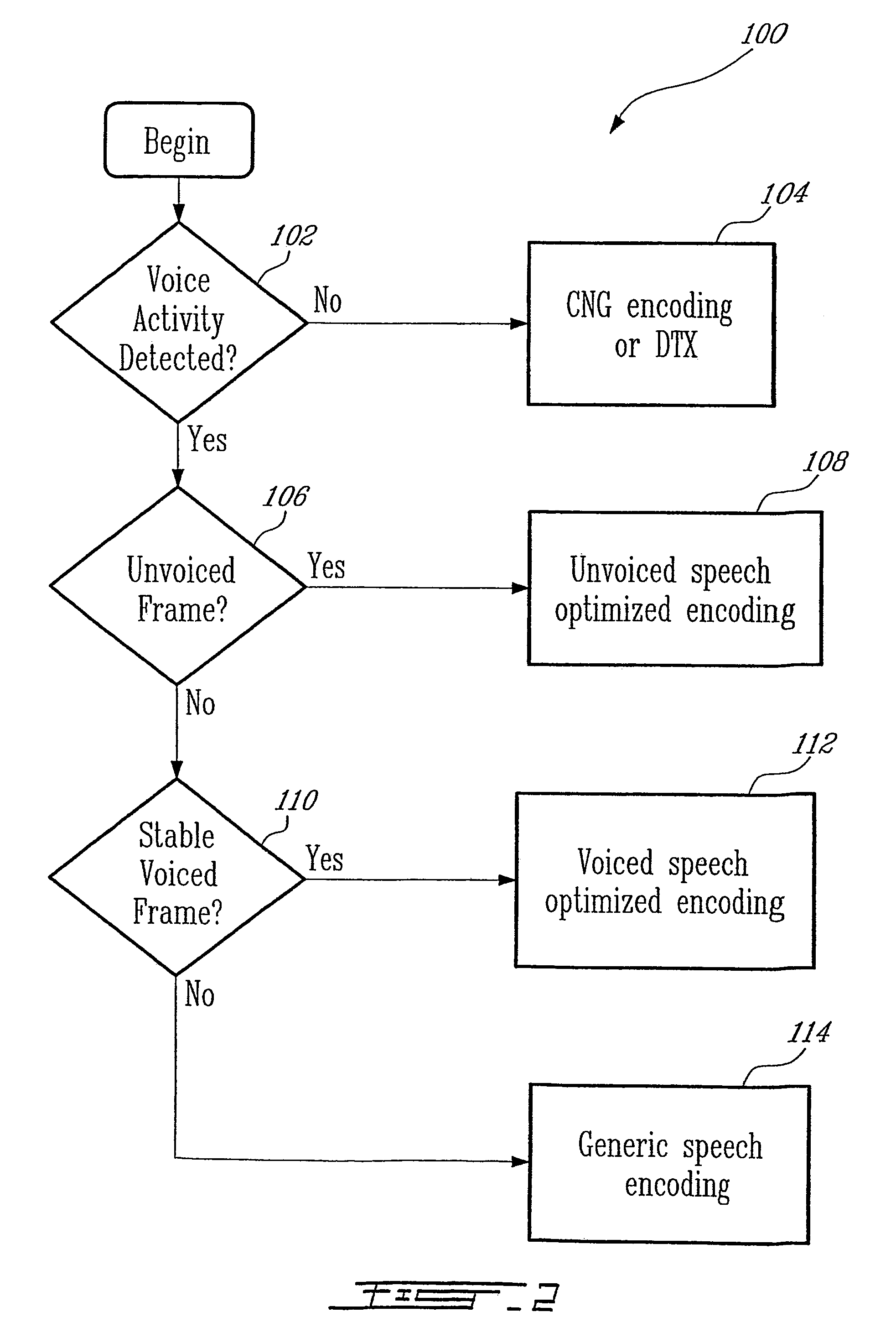
An active noise control system is provided to specify an input transducer, an error transducer, an output transducer and an active noise controller for generating an anti-phase canceling acoustic signal to attenuate an input noise and to output a reduced noise. The active noise control system also performs on-line secondary path modeling. For this purpose the active noise control system comprises, in addition to known systems, a secondary path change detection circuitry (6), a signal distinguishing circuitry (7) and an auxiliary noise control circuitry (8), all of them being used to model said secondary path. FIG. 3
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
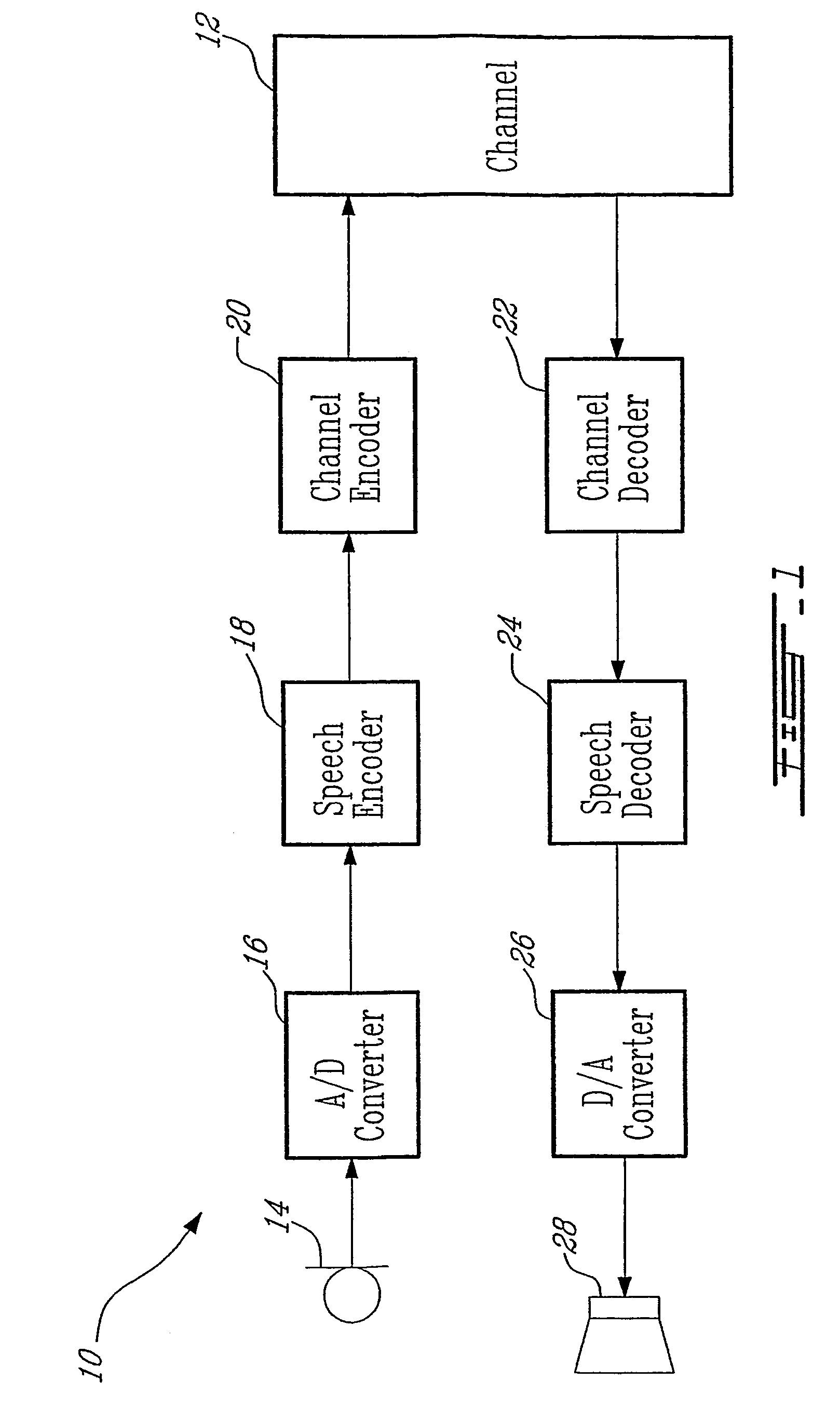
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
InactiveUS7203638B2Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementUltra-widebandBit allocation
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Method and apparatus for objective assessment of in-ear device acoustical performance
ActiveUS20050123146A1Simple reliability (stability) checkEasy to checkEar moulds/tips acoustic sealsHearing aids testing/monitoringSubject specificEvaluation testing
A method and apparatus for objectively assessing acoustical performance of an in-ear device having a passageway extending there through use a dual microphone probe that removably engages the passageway. The acoustical performance of the in-ear device is performed with the in-ear device inserted into the ear canal of the user and a reference sound source. A clip holding the probe in an acoustic near field of the sound source permits real time calibration thereof. The method and apparatus allow on-site and in-situ measurement of a predicted personal attenuation rating of the device, a subject-fit re-insertion test, an acoustic seal test, a rating test, a stability and reliability test, as well as a protection test of the device with an assessment of a filtered predicted exposure level at the ear for a specific noise exposure level. The apparatus may be simply housed along with the sound source for in-field evaluation tests.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
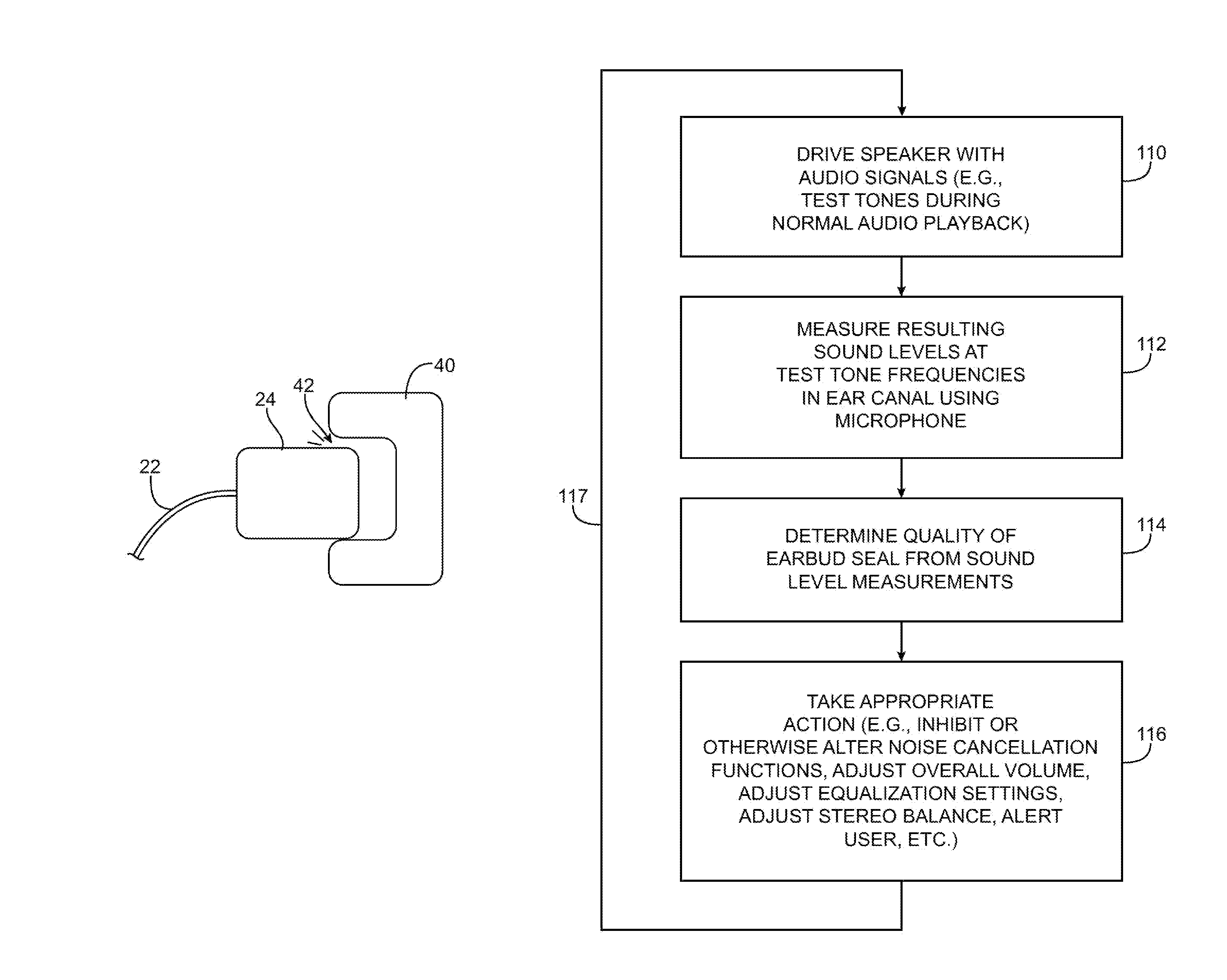
Electronic device and headset with speaker seal evaluation capabilities
Electronic devices and accessories for electronic devices such as headsets are provided. The electronic devices may produce audio output. The headsets may include earbuds with speakers that play the audio output for a user while the earbuds are located in the user's ears. Circuitry in an electronic device and a headset may be used in evaluating how well the earbuds are sealed to the user's ears. In response to seal quality measurements, informative messages can be generated for the user, overall earbud volume may be increased, balance adjustments may be made to correct for mismatched balance between left and right earbuds, equalization settings may be adjusted, and noise cancellation circuitry settings can be changed. Electrical impedance measurements and acoustic measurements can be used in evaluating seal quality.
Owner:APPLE INC
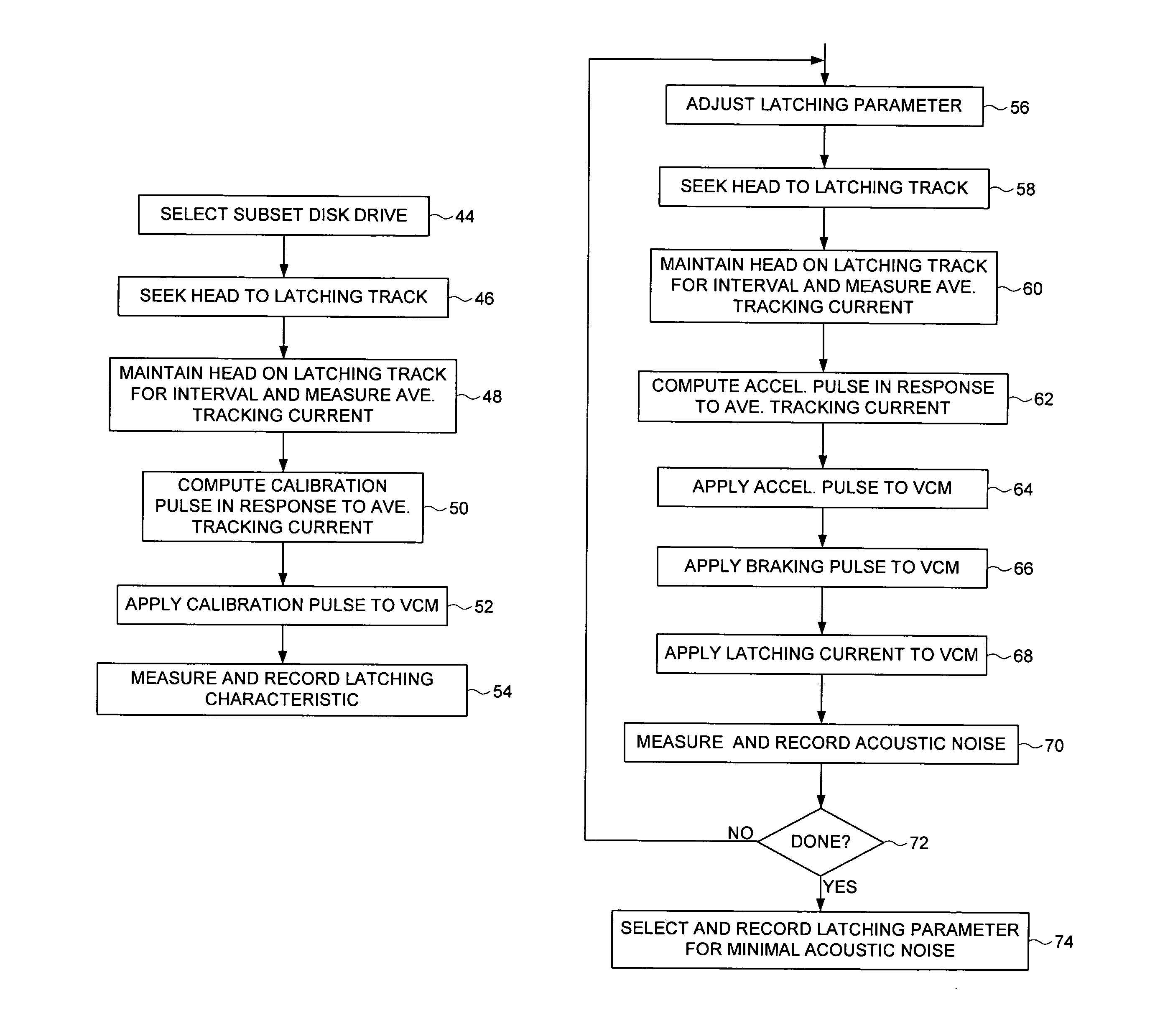
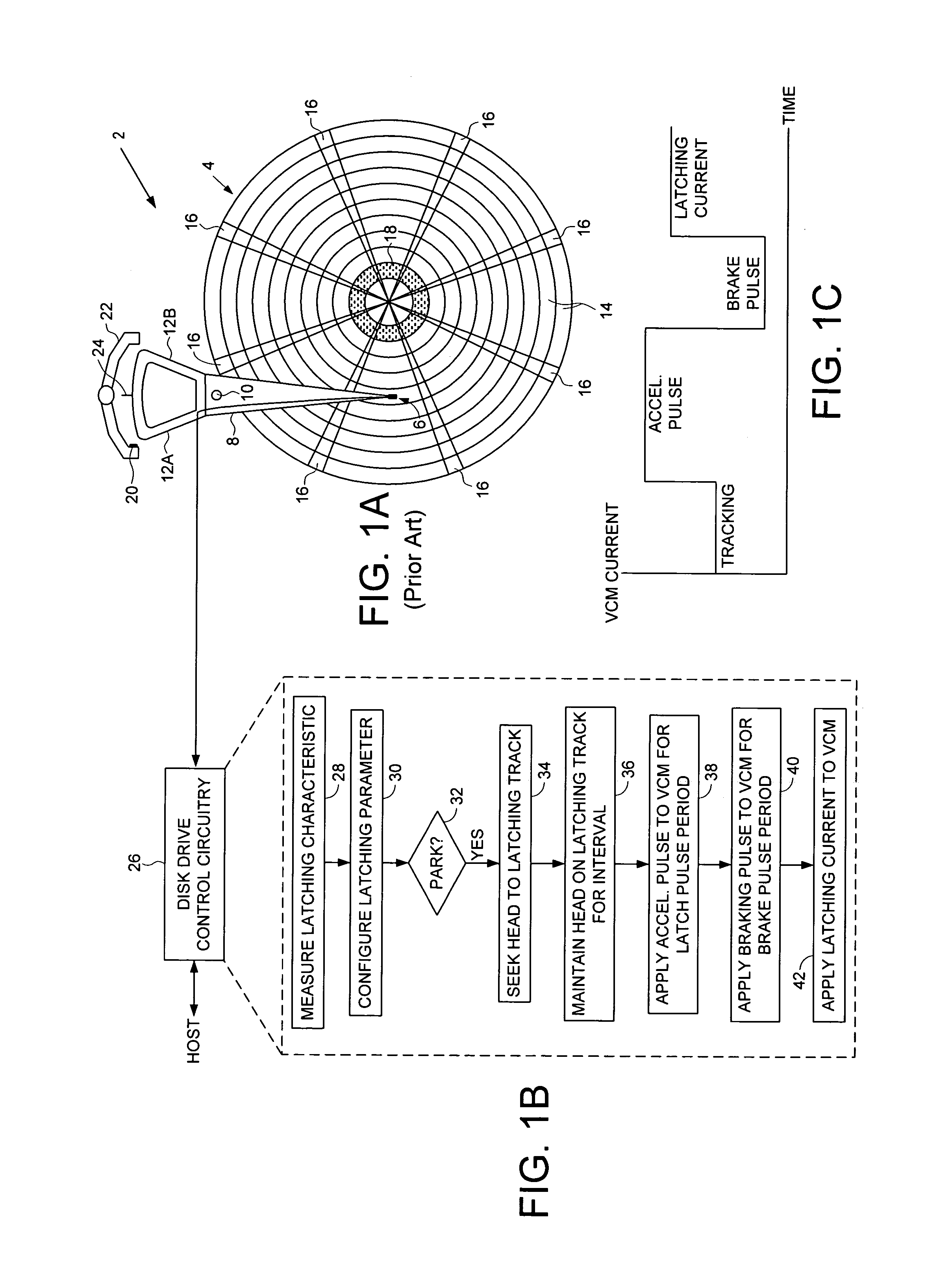
Disk drive employing a calibrated brake pulse to reduce acoustic noise when latching an actuator arm
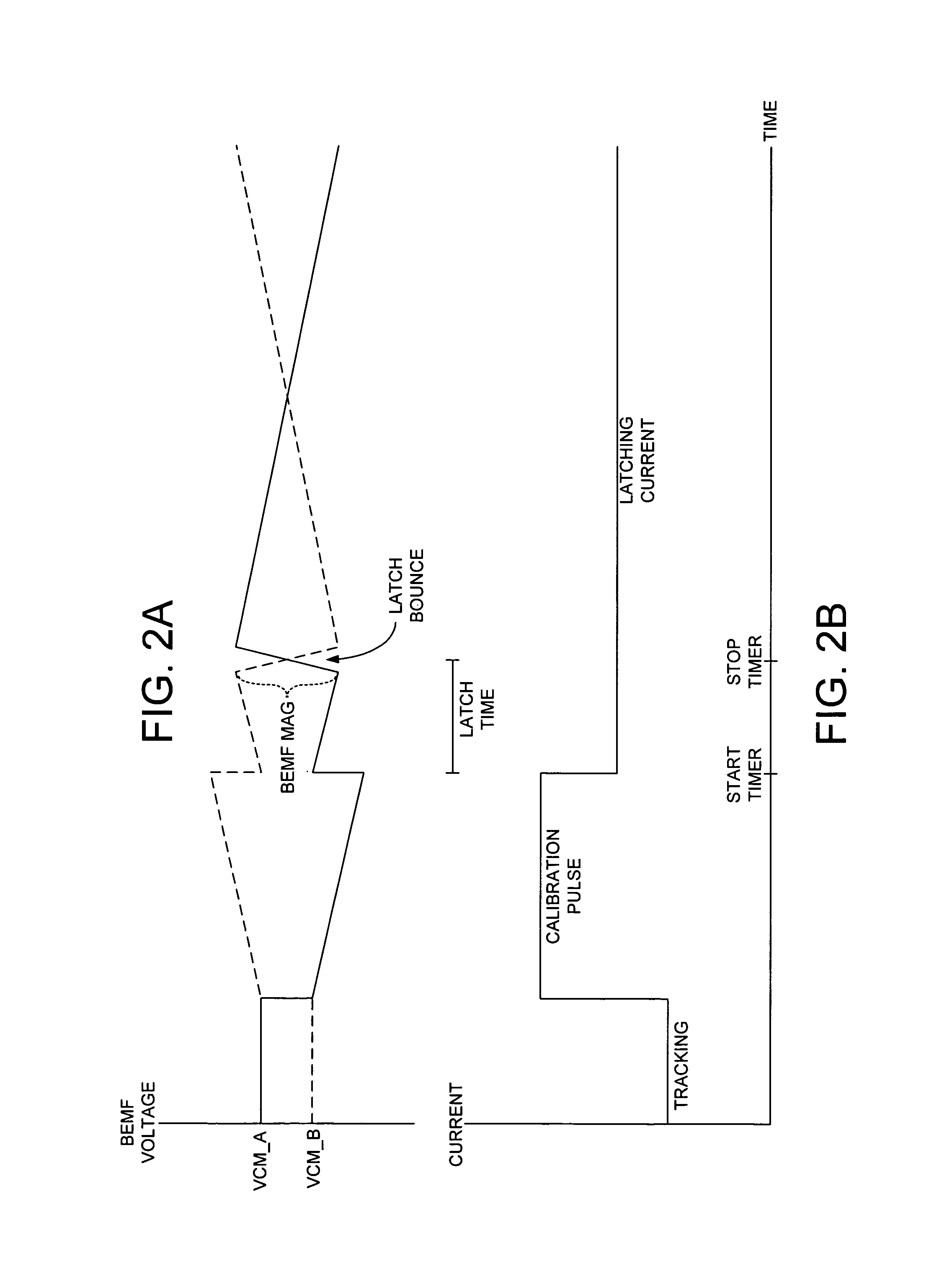
InactiveUS7224546B1Reduce noiseMinimize acoustic noiseDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringControl theory
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating an actuator arm about a pivot in order to actuate a head over the disk. During a park operation, a latching characteristic associated with latching the actuator arm is measured and used to configure a latching parameter that reduces acoustic noise. The latching parameter is used to latch the actuator arm by seeking the head to a latching track, maintaining the head over the latching track for a predetermined interval, applying an acceleration pulse to the VCM for an acceleration pulse period, applying a braking pulse to the VCM for a brake pulse period, and applying a latching current to the VCM.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com