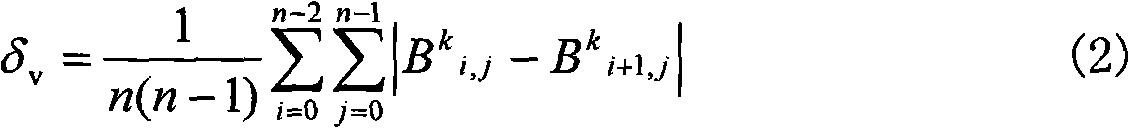Patents
Literature
464 results about "Bit allocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
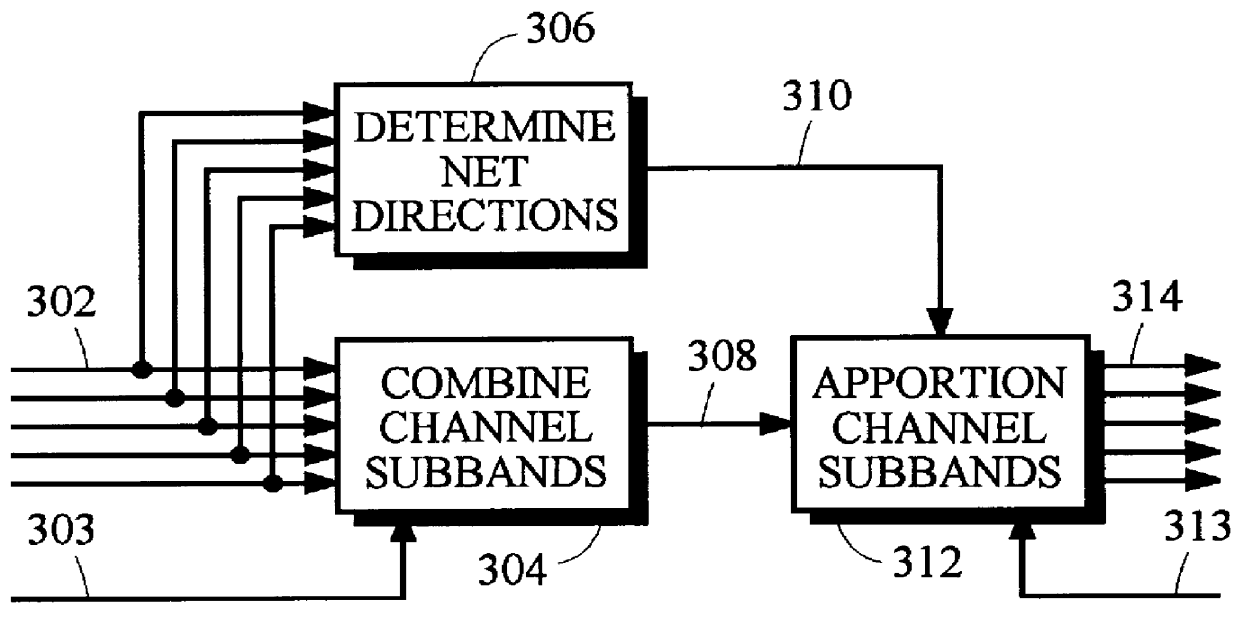
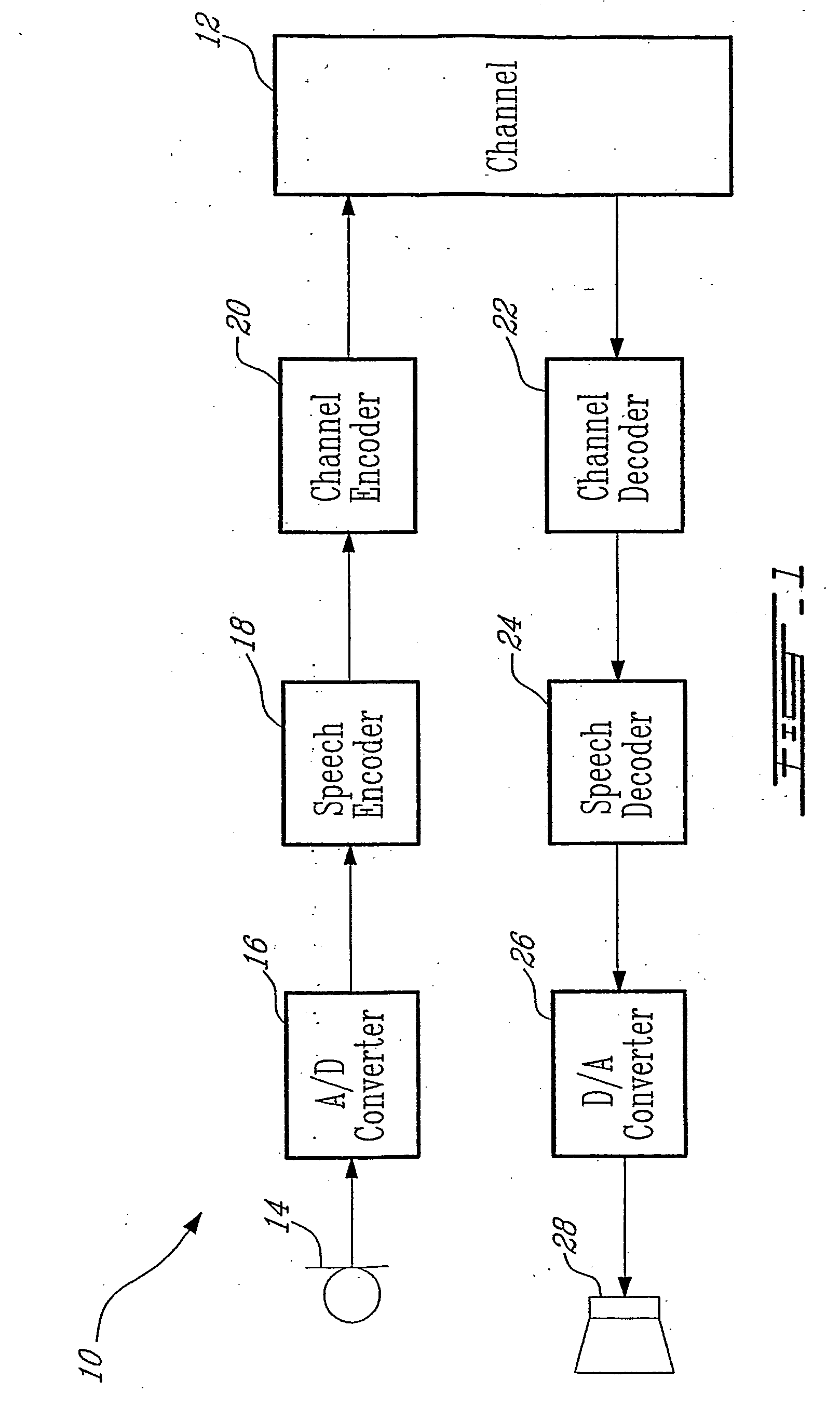
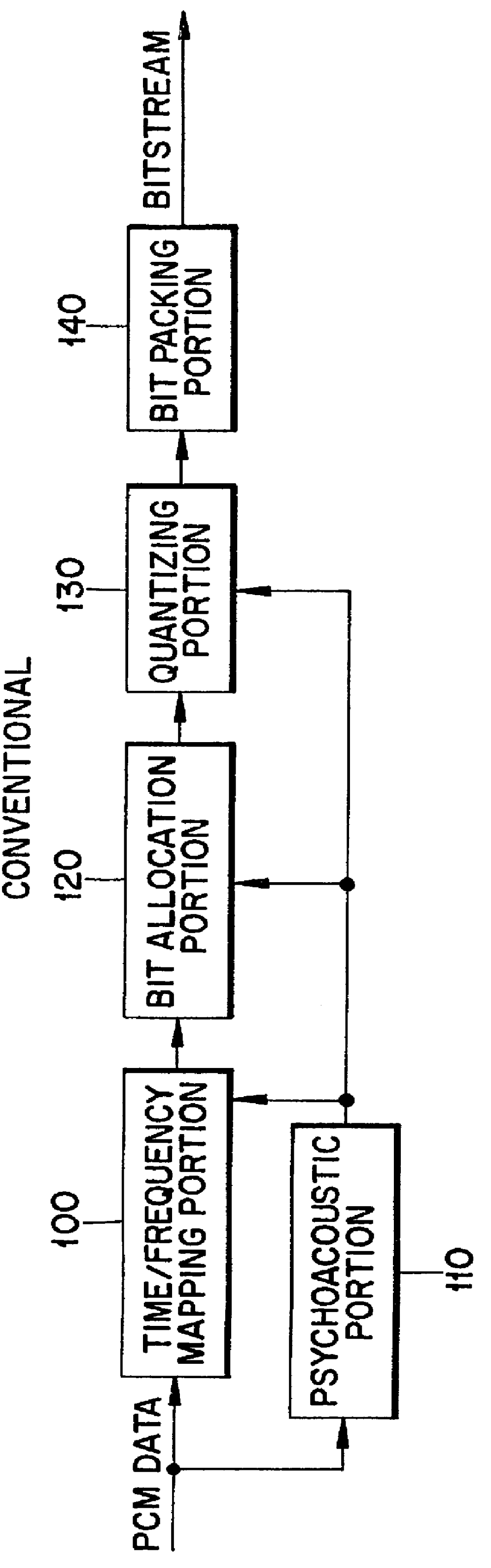
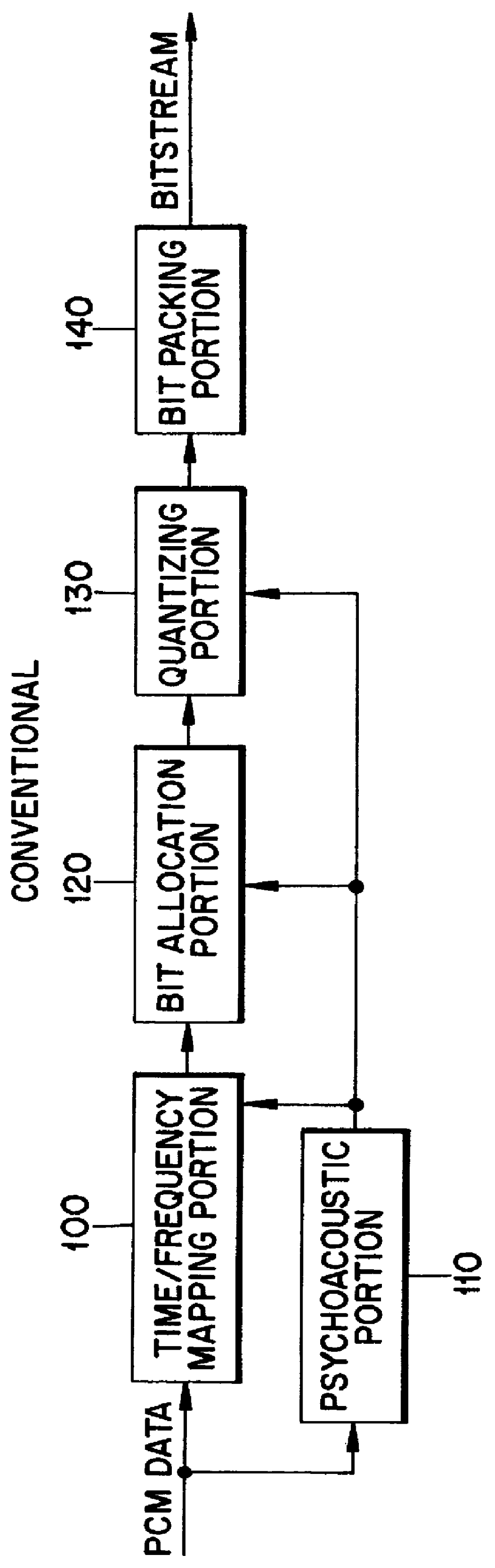
Bit Allocation. Through an iterative algorithm, the bit allocation uses information from the psychoacoustic model to determine the number of code bits to be allocated to each subband.
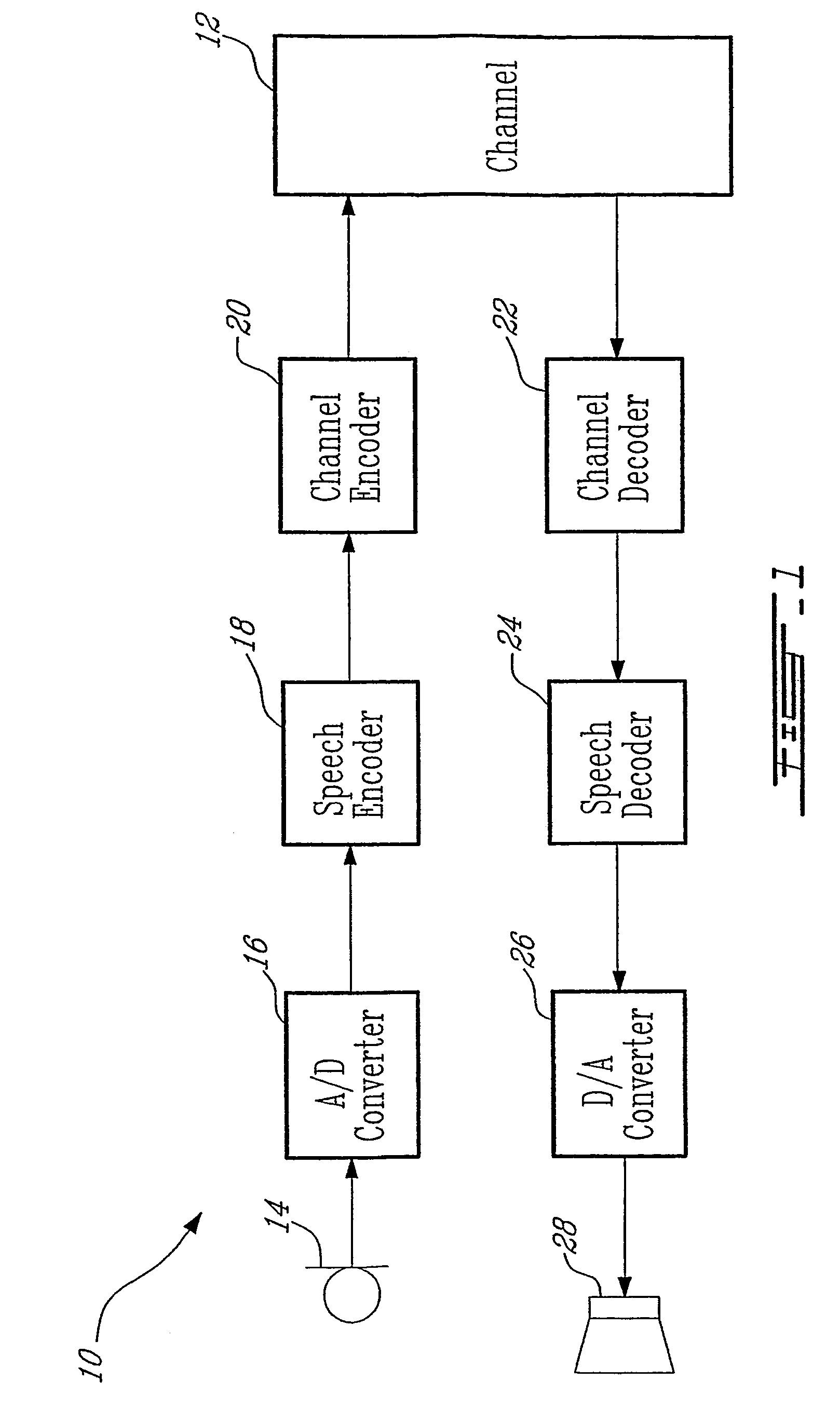
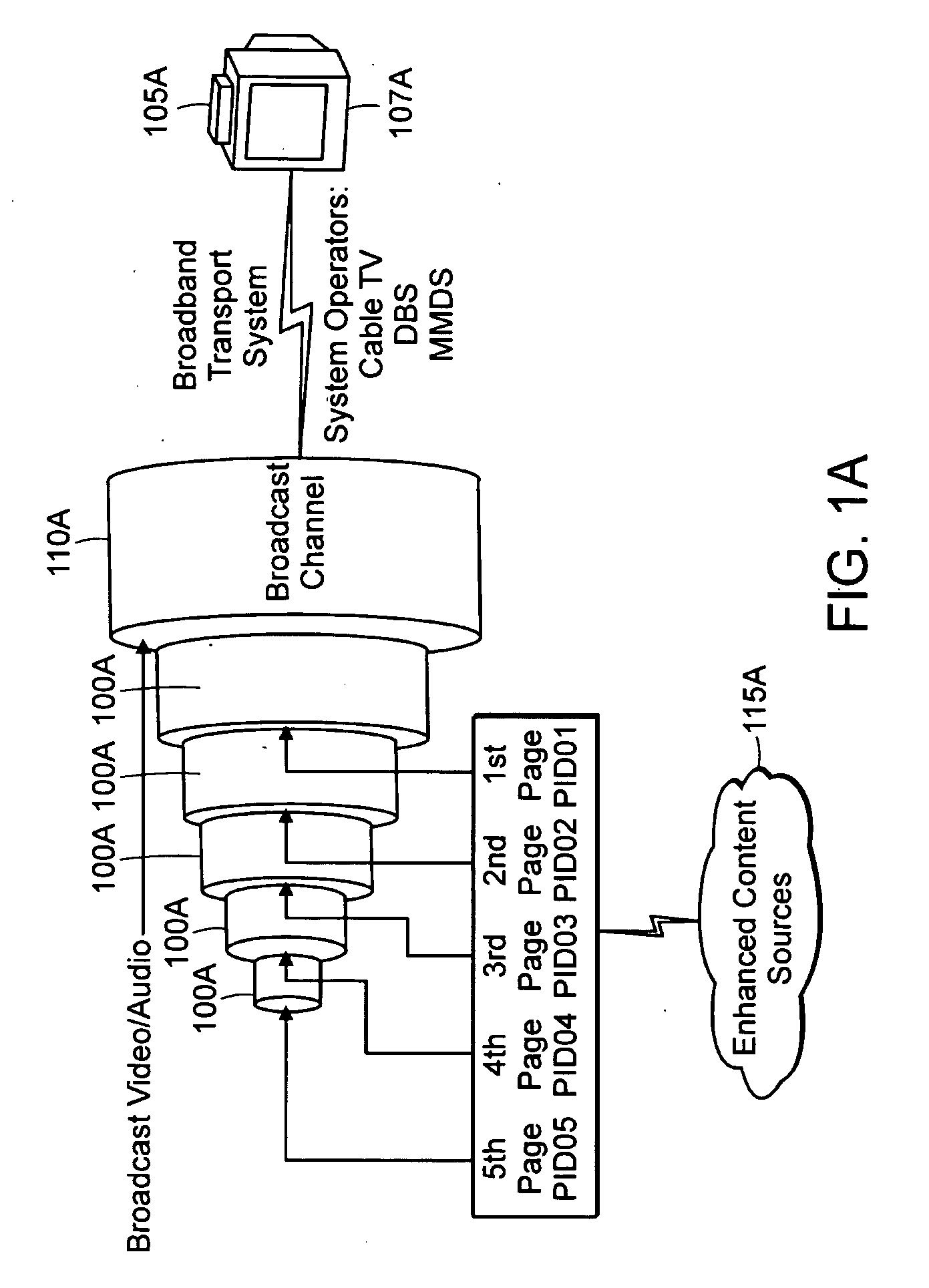
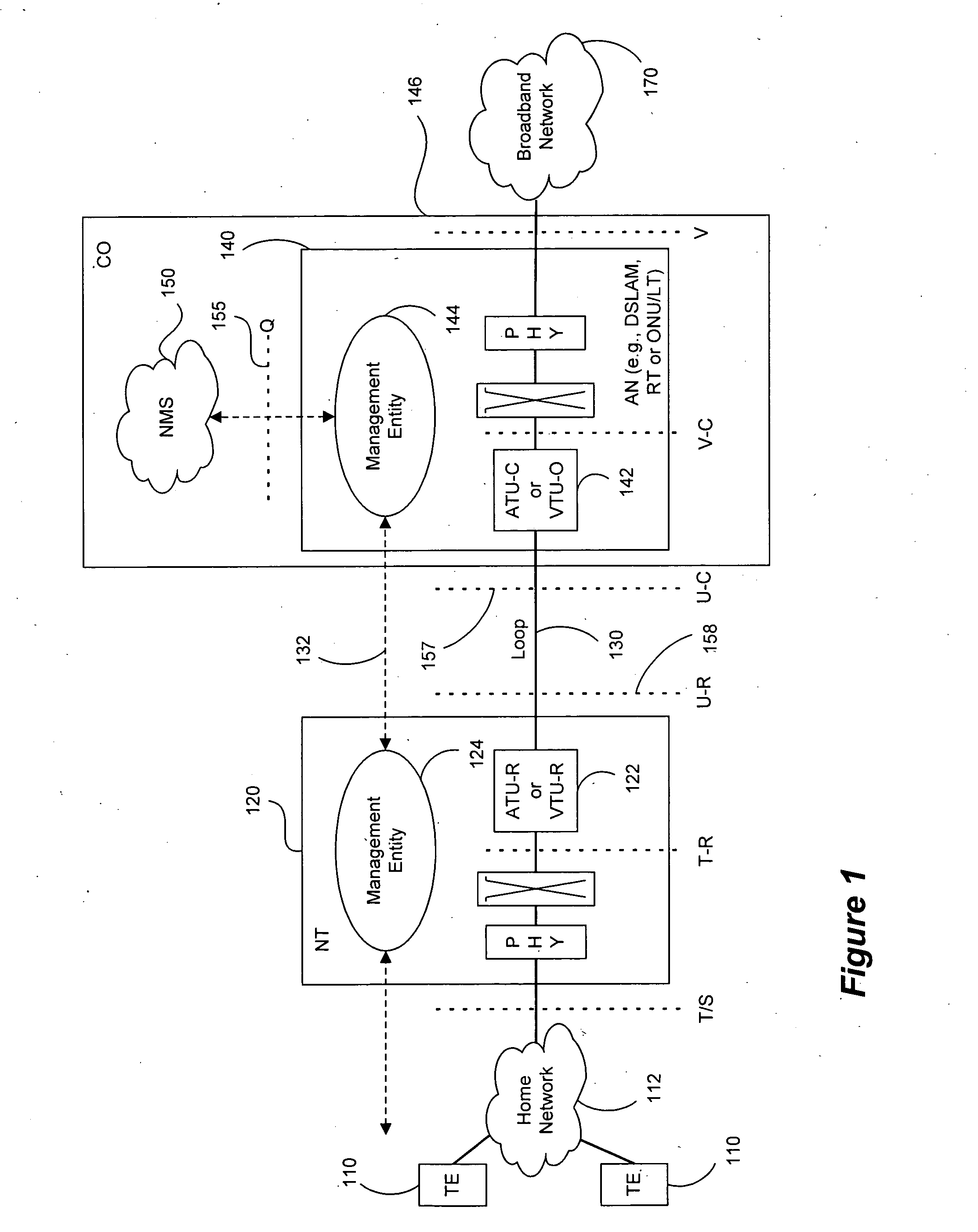
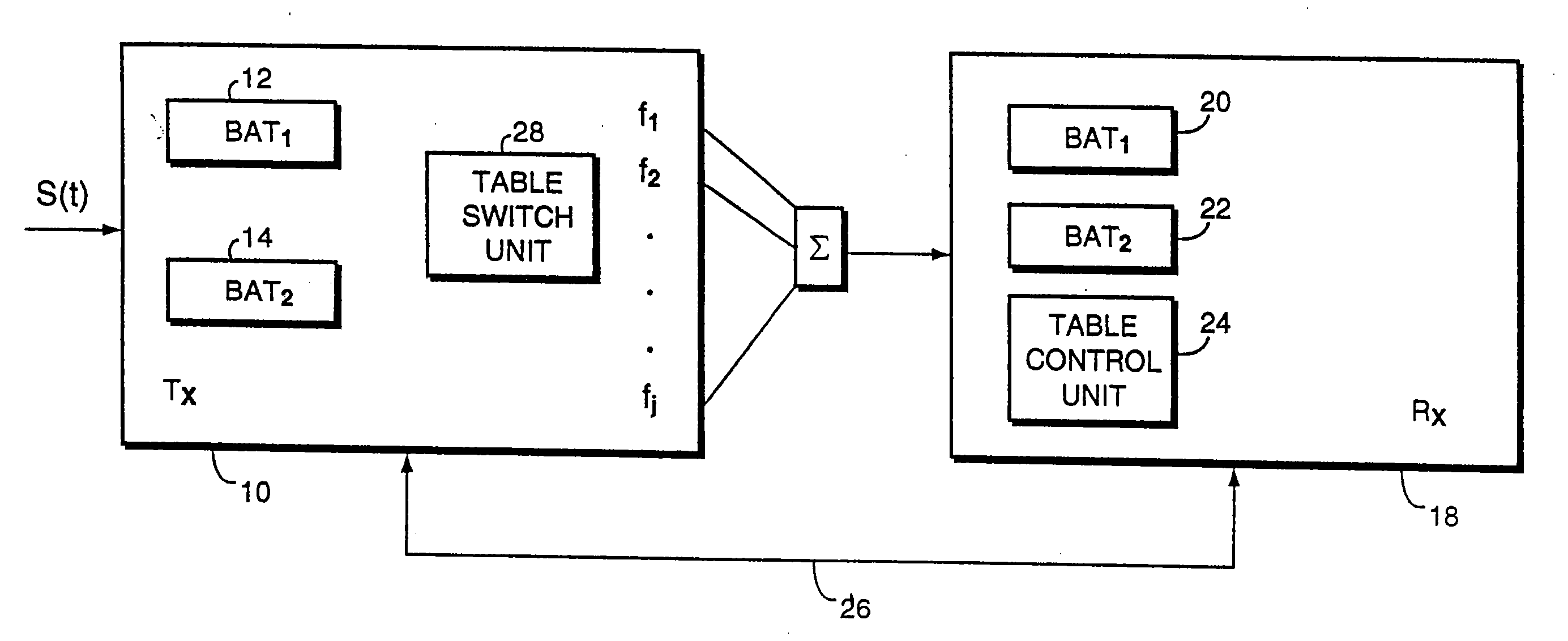
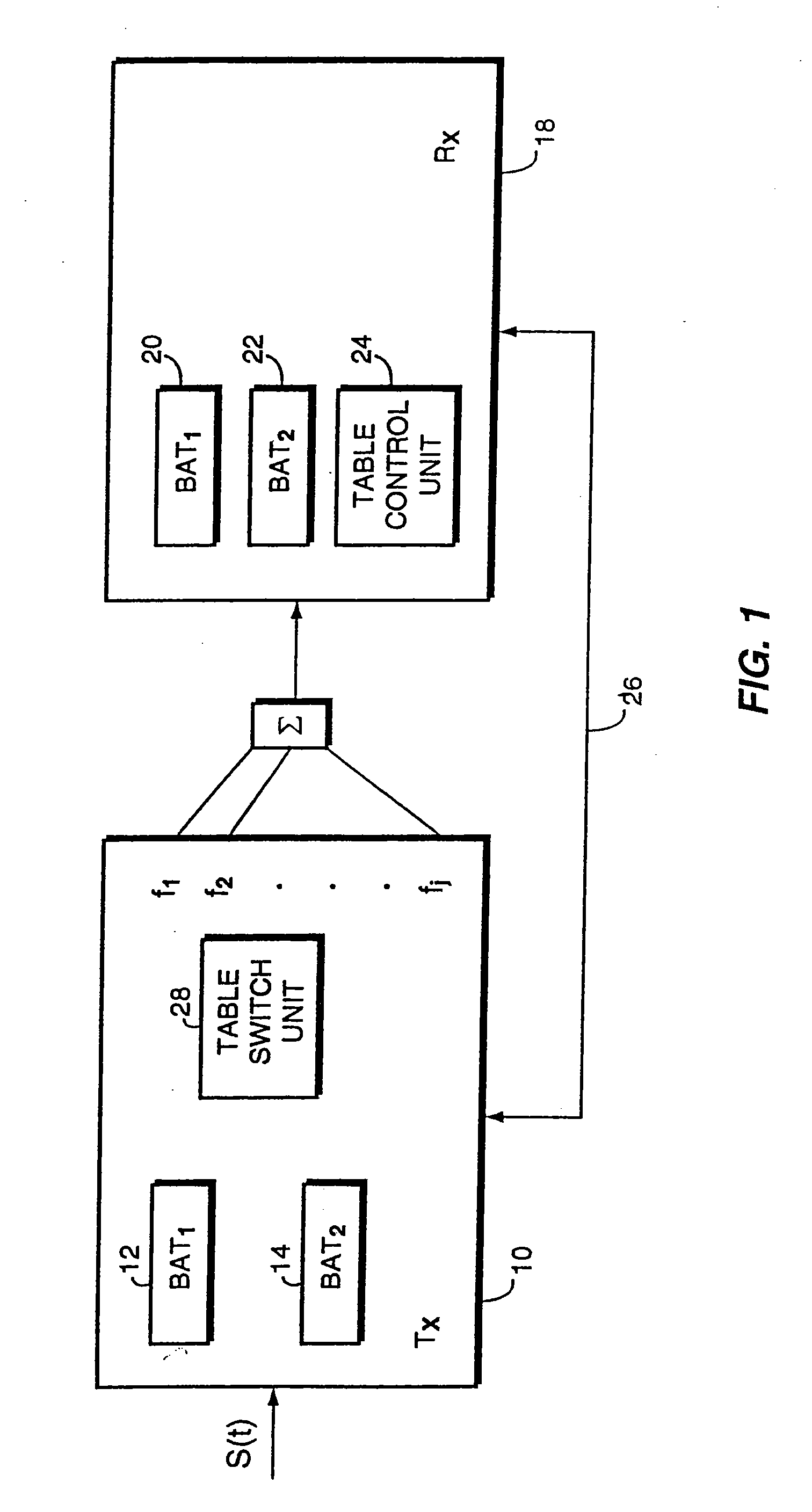
Coding method and apparatus for multiple channels of audio information representing three-dimensional sound fields
InactiveUS6021386AConserve substantial bandwidthConveniently implementedBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumBit allocation
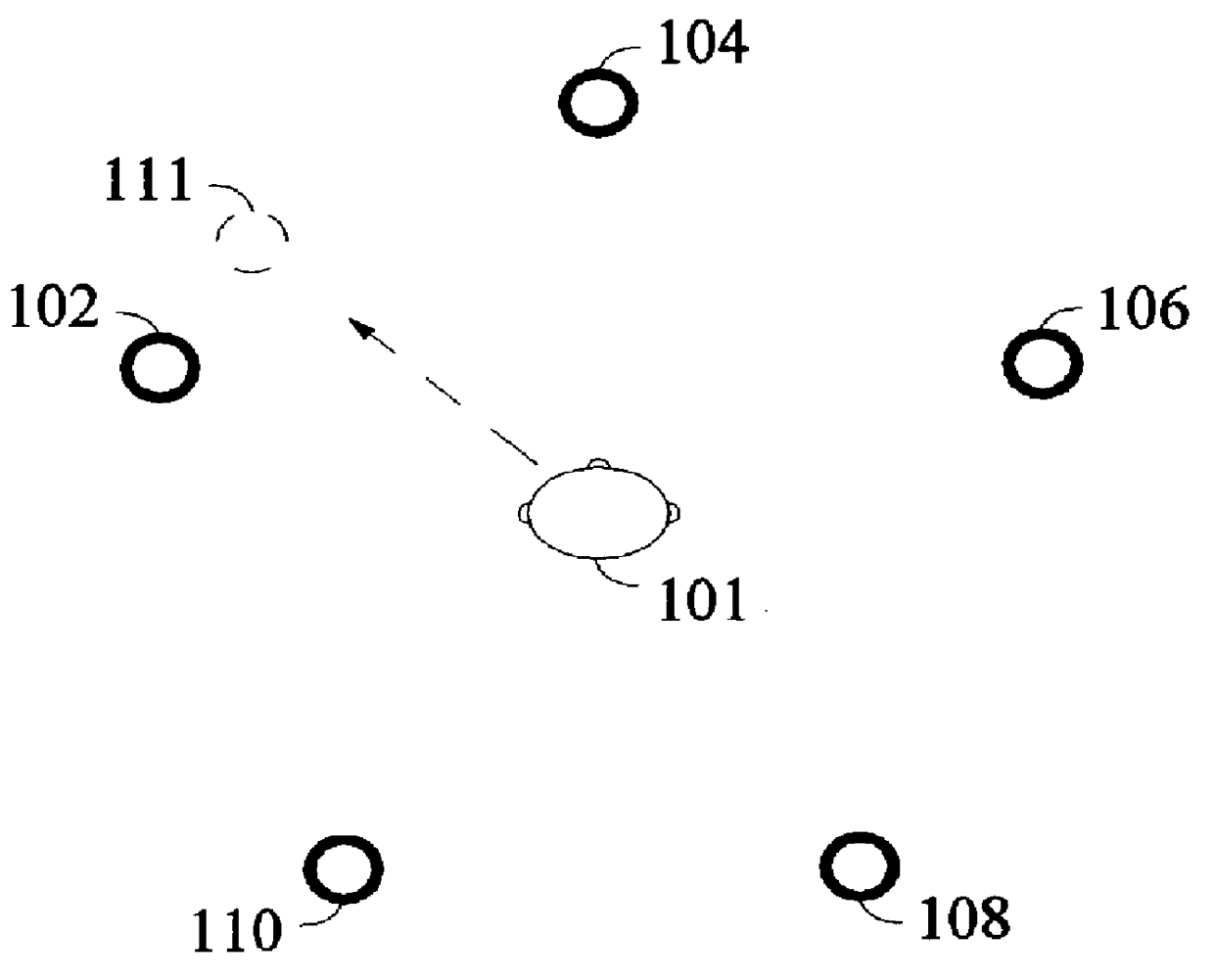
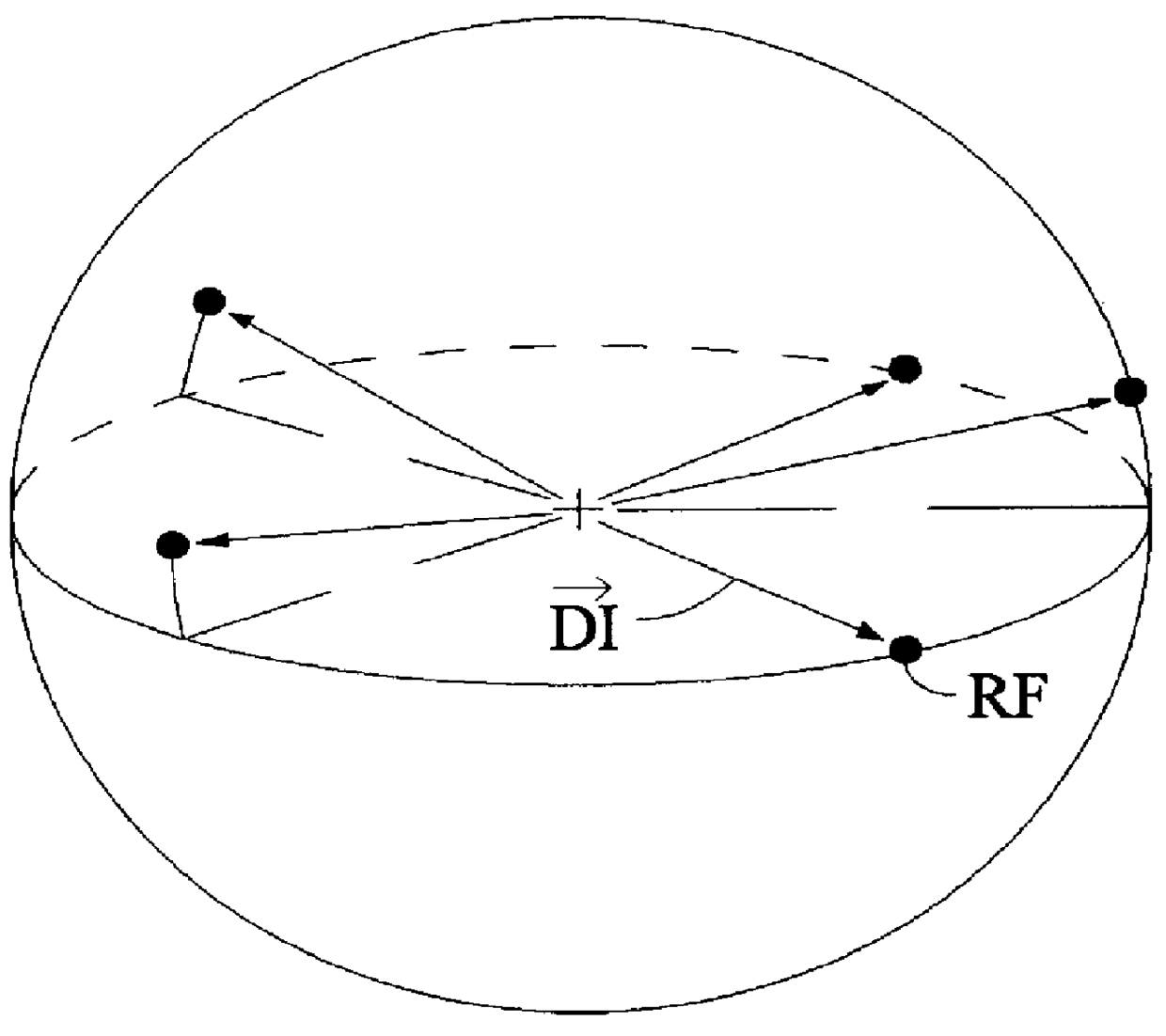
In an encoder, multiple channels of audio information representing multidimensional sound fields are split into subband signals and the subband signals in one or more subbands are combined to form composite signals. The composite signals, the subband signals not combined into a composite signal and information describing the spectral levels of subband signals combined into composite signals are assembled into an encoded output signal. The spectral level information conveys either the amplitude or power of the combined subband signals or the apparent direction of the sound field represented by the combined subband signals. In digital implementations, adaptive bit allocation may be used to reduce the informational requirements of the encoded signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
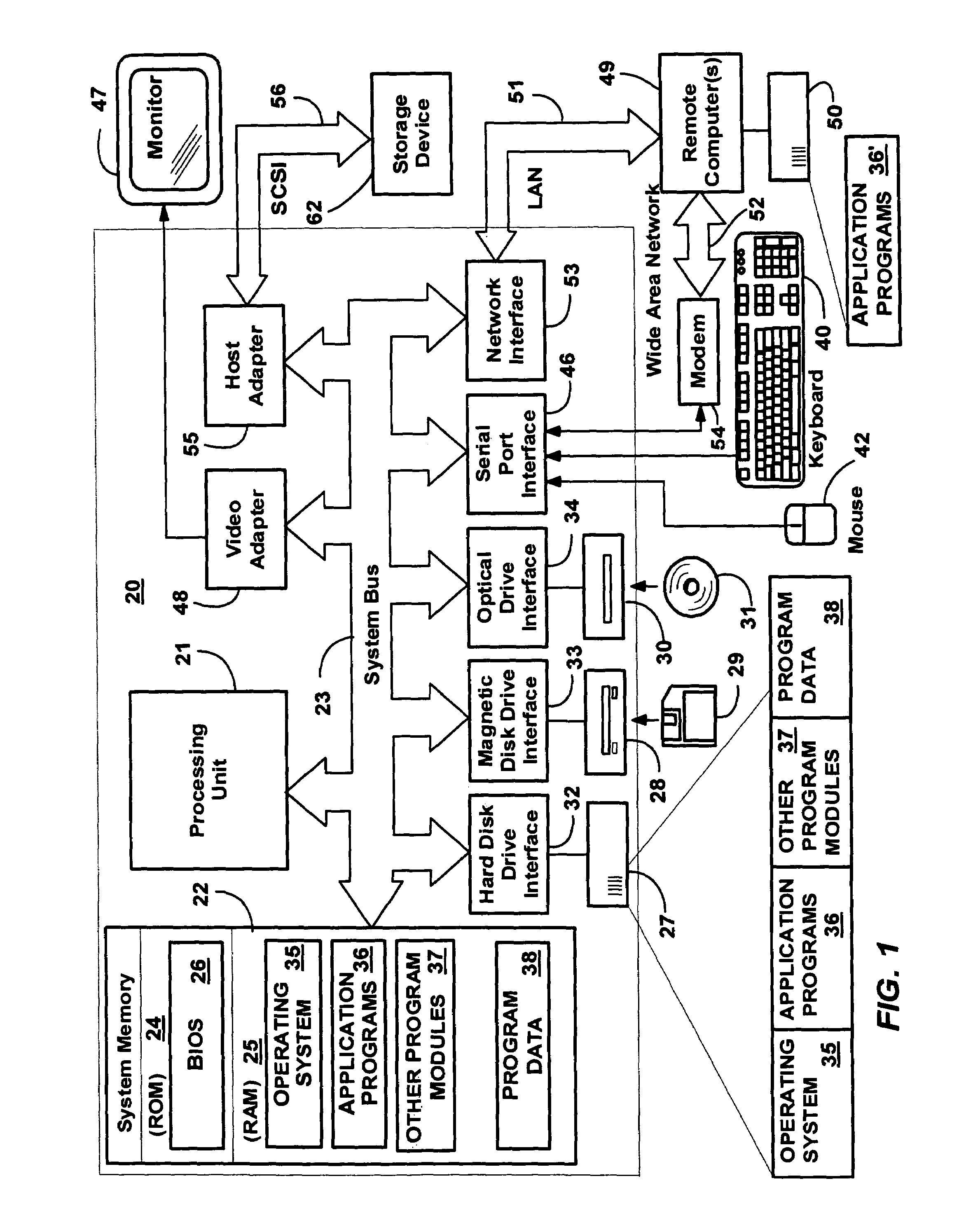
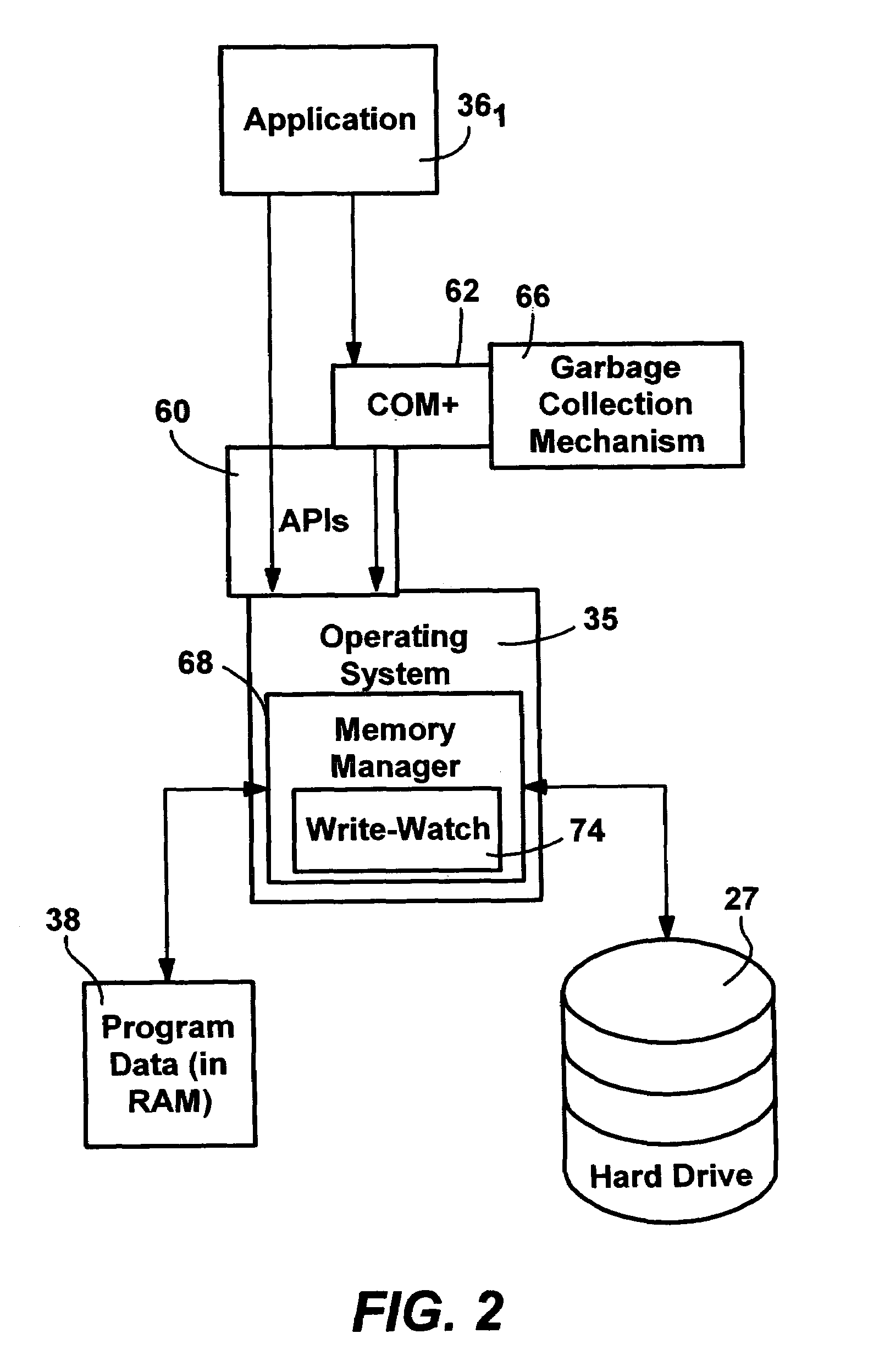
Efficient write-watch mechanism useful for garbage collection in a computer system
InactiveUS7065617B2Efficient write-watchReduce performanceData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputerized systemWaste collection
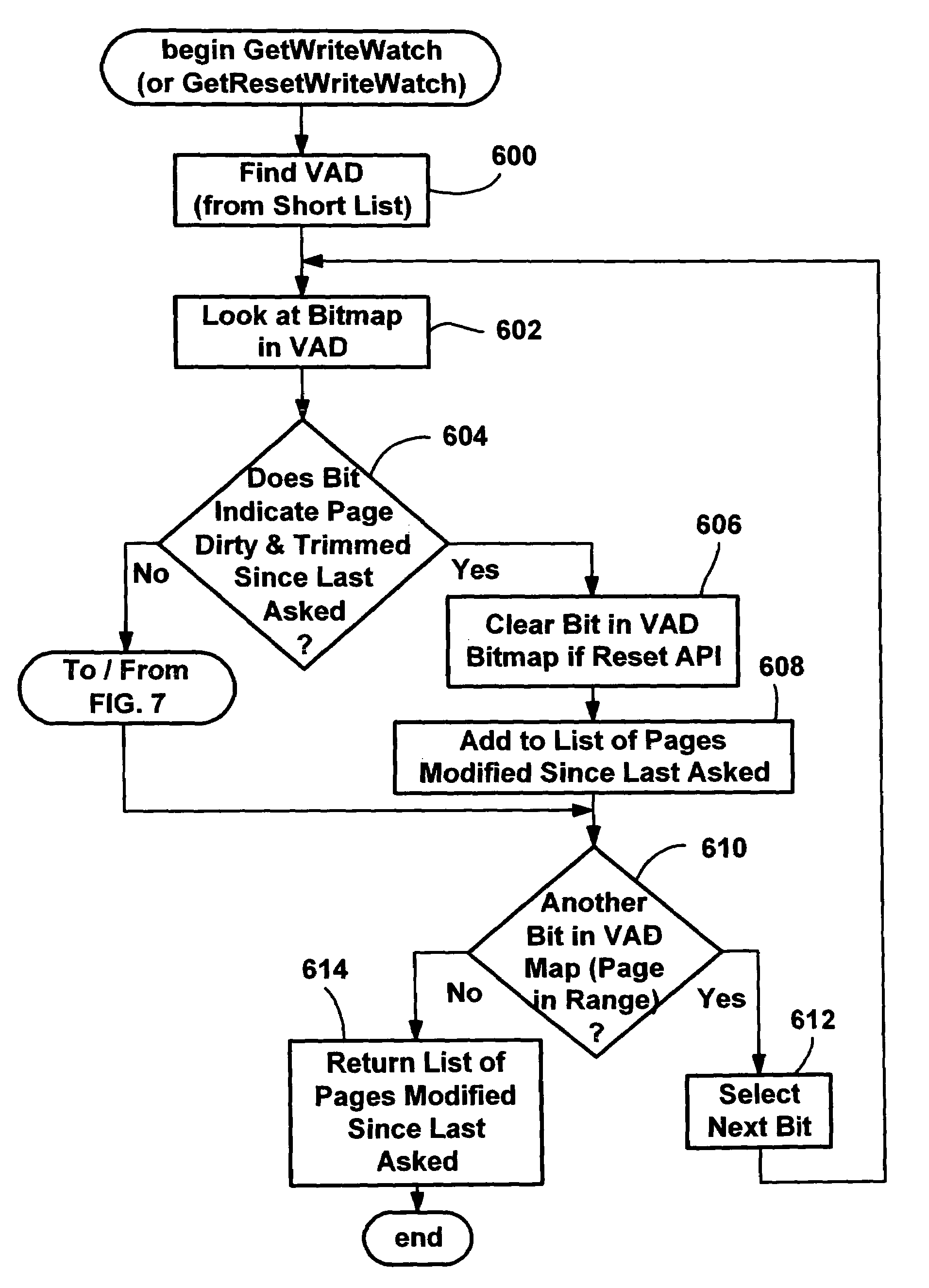
An efficient write-watch mechanism and process. A bitmap is associated with the virtual address descriptor (VAD) for a process, one bit for each virtual page address allocated to a process having write-watch enabled. As part of the write-watch mechanism, if a virtual address is trimmed to disk and that virtual address page is marked as modified, then the corresponding bit in the VAD is set for that virtual address page. In response to an API call (e.g., from a garbage collection mechanism) seeking to know which virtual addresses in a process have been modified since last checked, the memory manager walks the bitmap in the relevant VAD for the specified virtual address range for the requested process. If a bit is set, then the page corresponding to that bit is known to have been modified since last asked. If specified by the API, the bit is cleared in the VAD bitmap so that it will reflect the state since this time of asking. If the bit is not set, to determine if the page was modified, the page table entry (PTE) is checked for that page, and if the PTE indicates the page was modified, the page is known to be modified, otherwise that page is known to be unmodified since the last call. One enhancement uses page directory tables to locate a series of trimmed pages, sometimes avoiding the need to access the PTE.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
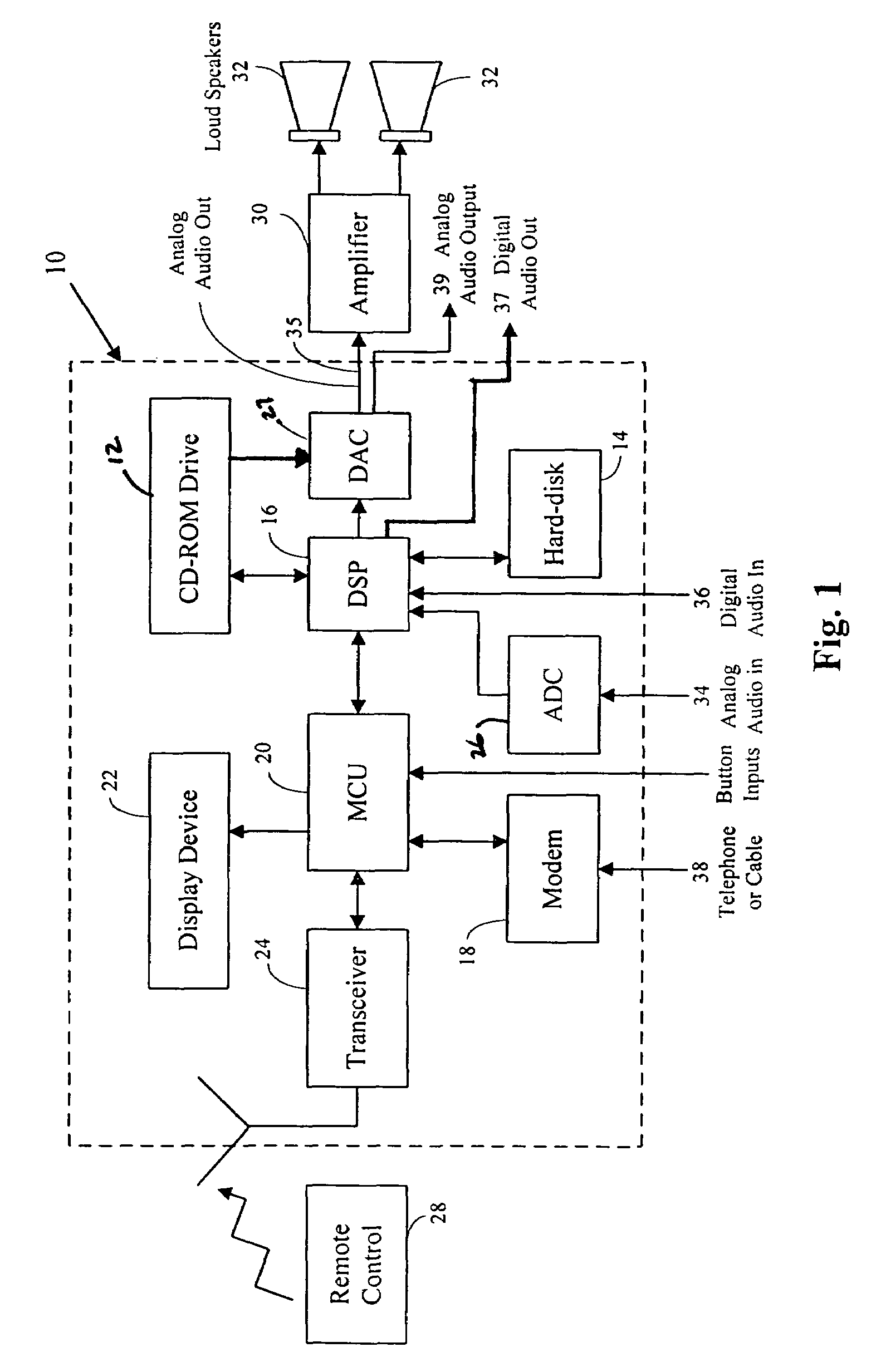
Digital multimedia jukebox
InactiveUS7548851B1Fast archivingEasy and convenient entryFlat record carrier combinationsSpeech analysisData setRemote control
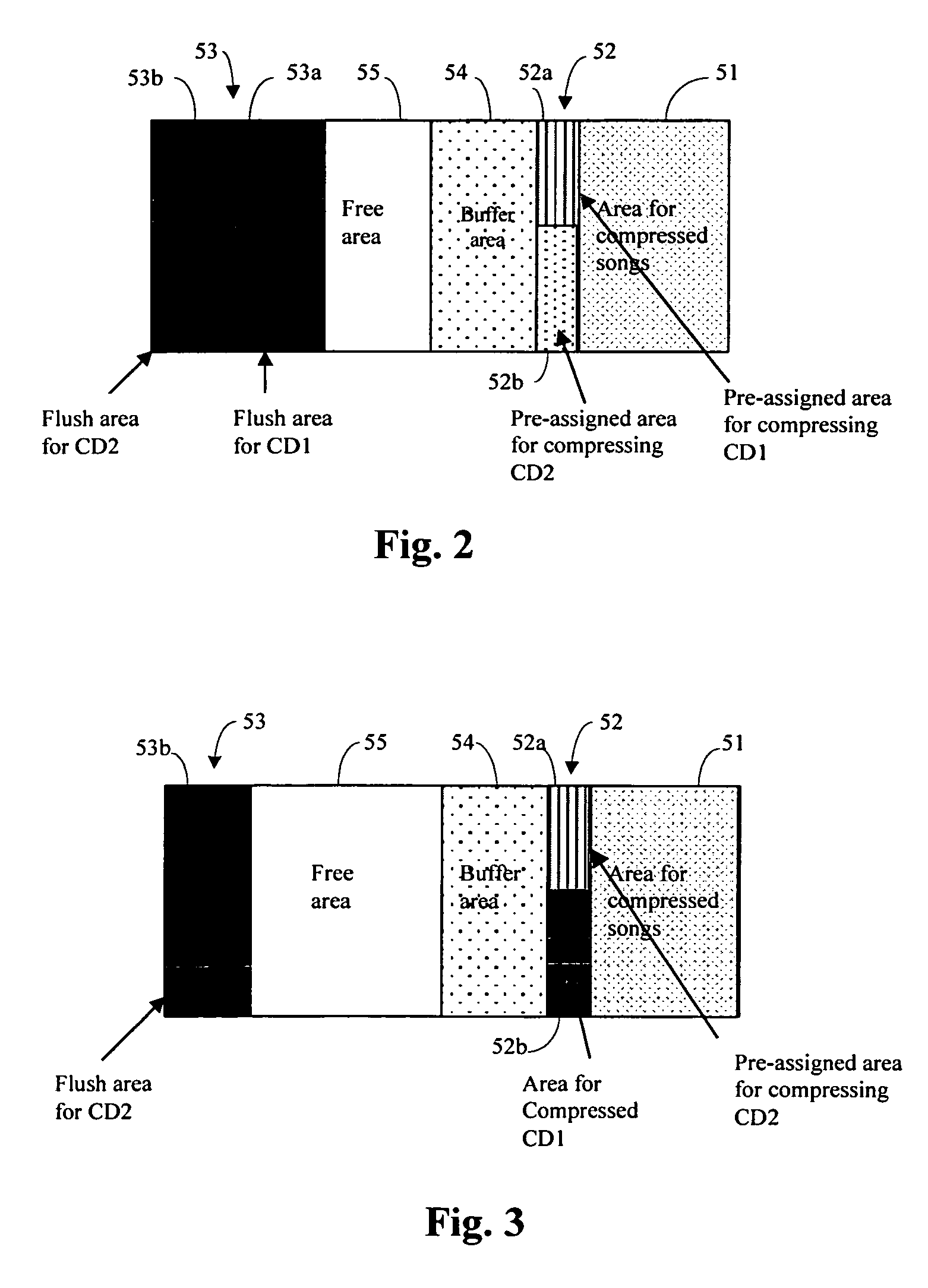
A musical jukebox is disclosed which provides for: fast archiving of songs; a flexible user interface; easy and convenient entry of, access to and / or display of data relating to songs archived by the jukebox; easy and convenient search and locate capabilities for locating, reviewing, retrieving and / or playing songs stored in the jukebox; and low cost relative to the functionality, features, conveniences and user-friendliness provided by the jukebox. Fast of flush archiving of songs (as well as other data and signals) is accomplished by first saving sets of data without compression, which allows the data to be entered quickly, and then, compressing later at an appropriate time. A unique MP3 bit allocation encoding scheme is used to compress data. A unique memory allocation supports fast data archiving. The user interface employs two-way communication between a remote control and the jukebox. A searchable song database is structured to enable very fast searching by music category, and also by title and artist. The jukebox is provided with an on-board song track database to automatically identify new songs input to the jukebox.
Owner:PERCEPTION DIGITAL TECH BVI
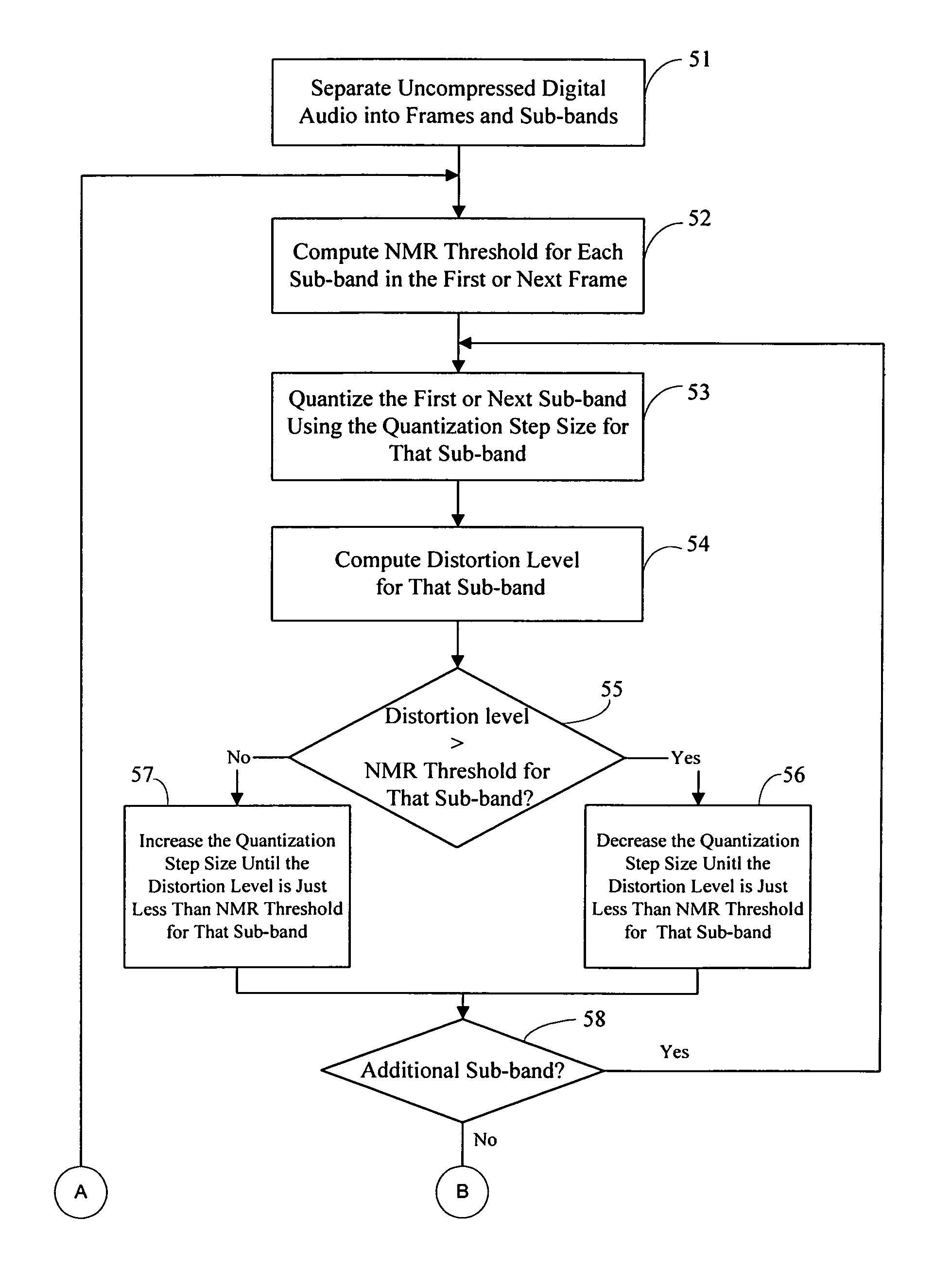
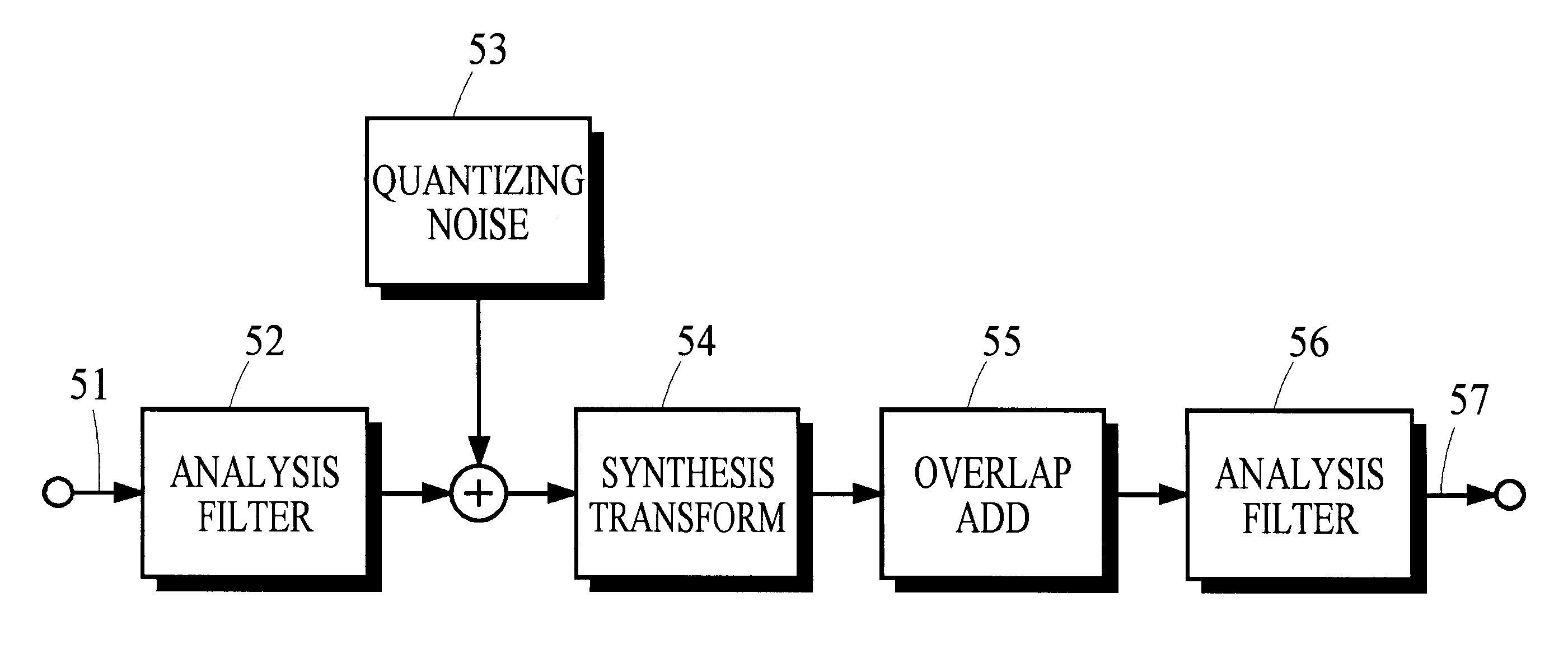
Quantization in perceptual audio coders with compensation for synthesis filter noise spreading and the overlap-add process
InactiveUS6363338B1Improve performanceAccurate noiseSpeech analysisCode conversionBit allocationAlgorithm
Many perceptual split-band coding systems that use analysis and synthesis filters assume the quantization noise introduced by quantizing split-band signals is substantially the same as the noise that results in the output signal obtained by applying the synthesis filters to the quantized split-band signals. In general, this assumption is not true because the synthesis filters modify or spread the quantization noise. A theoretical framework for deriving an optimum bit allocation that accounts for synthesis-filter noise spreading and the overlap-add process is disclosed. In concept, the problem of finding an optimal bit allocation can be expressed as a linear optimization problem in a multidimensional coordinate space. Simplified processes derived from this theoretical framework are disclosed that can obtain near-optimal solutions using modest computational resources.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
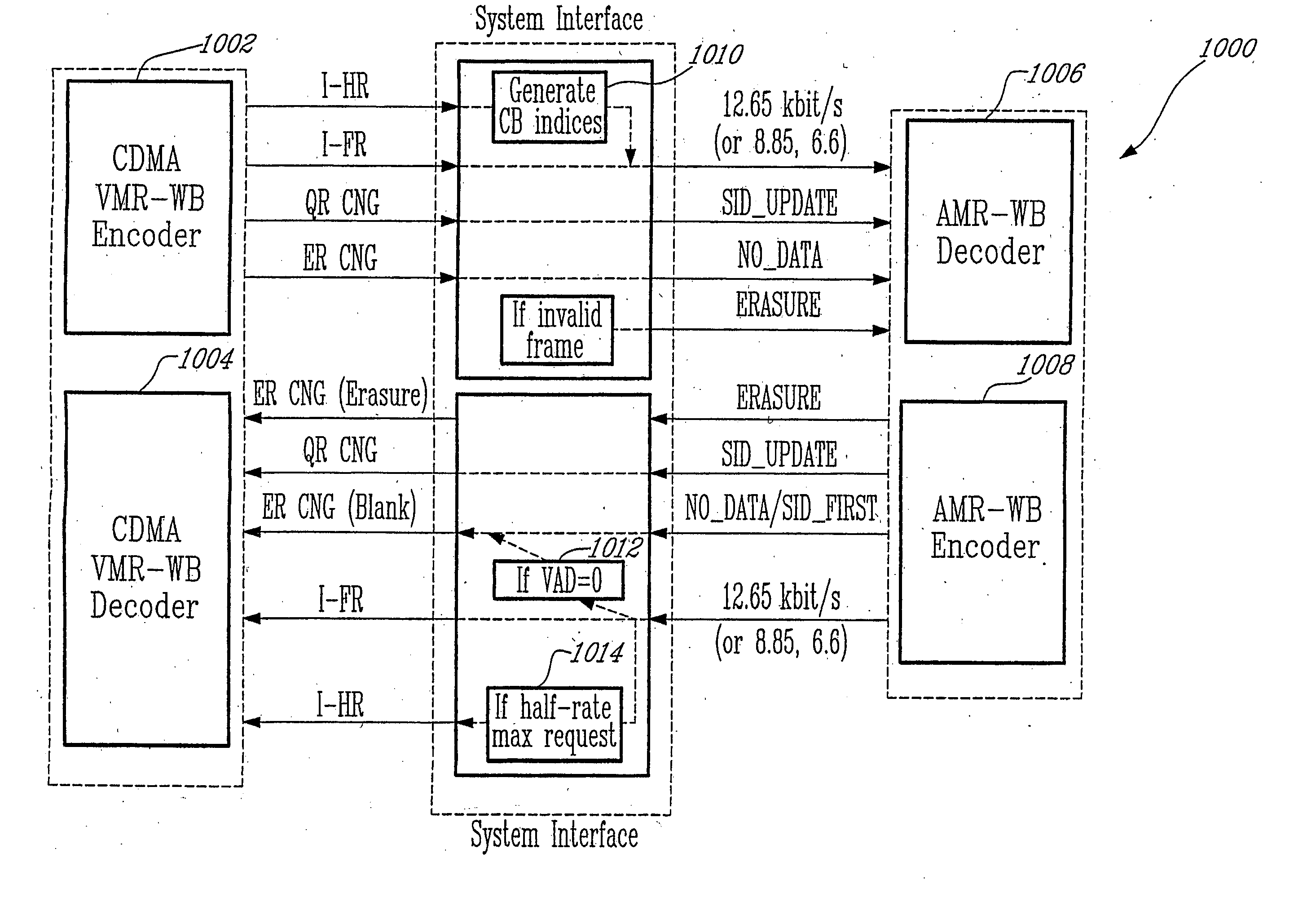
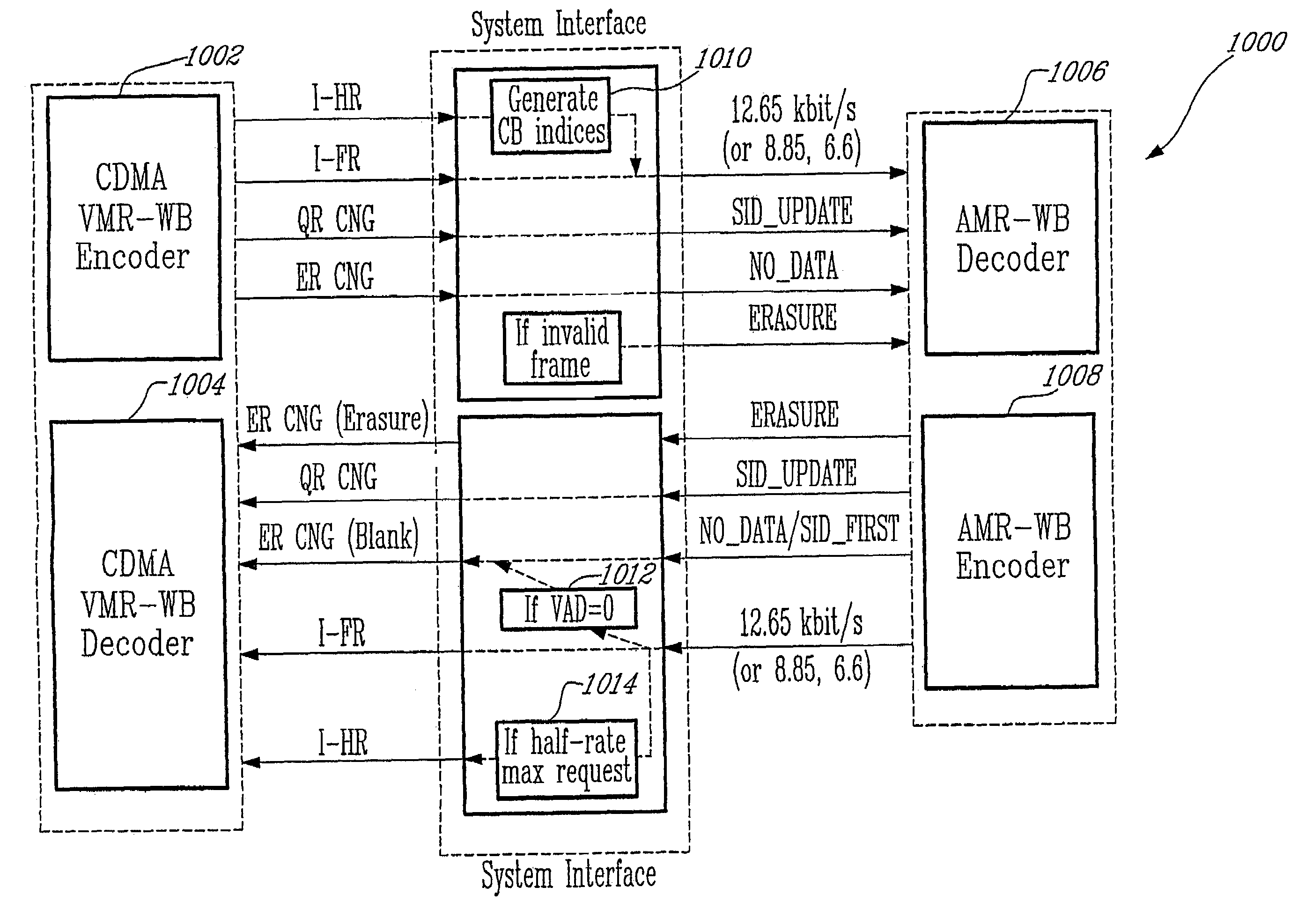
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
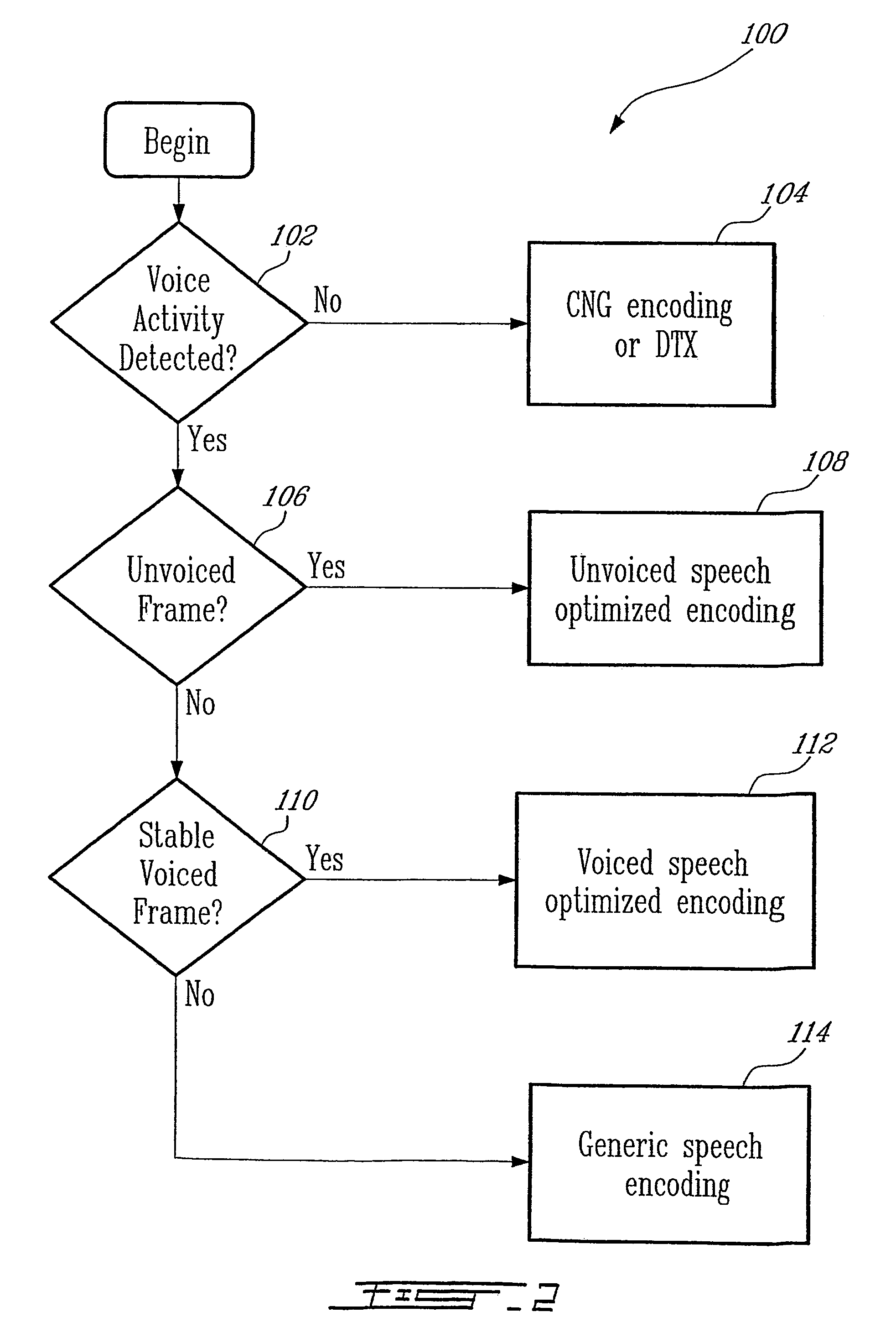
ActiveUS20050267746A1Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementBit allocationFull Rate
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
InactiveUS7203638B2Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementUltra-widebandBit allocation
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Scalable audio coding/decoding method and apparatus without overlap of information between various layers
InactiveUS6108625AEasy to useImprove sound qualityError detection/correctionSpeech analysisComputer architectureGamut
A scalable audio coding / decoding method and apparatus are provided. The coding method includes the steps of (a) signal-processing input audio signals and quantizing the same for each predetermined coding band; (b) coding the quantized data corresponding to the base layer within a predetermined layer size; (c) coding the quantized data corresponding to the next enhancement layer of the coded base layer and the remaining quantized data uncoded and belonging to the enhancement layer, within a predetermined layer size; and (d) sequentially performing the layer coding steps for all layers, wherein the steps (b), (c) and (d) each comprise the steps of: (i) obtaining gamut bit allocation information representing the number of bits of the quantized data corresponding to the respective subbands belonging to a layer to be coded; (ii) obtaining the number of bits allocated to the respective subbands within each subband size of the layers; (iii) generating an index representing the presence of quantized data for predetermined frequency components forming the subbands for the quantized data corresponding to the number of allocated bits; and (iv) generating bitstreams by coding the quantized data corresponding to the gamut bit allocation information, quantization step size, index and number of bits allocated to the respective subbands, by a predetermined coding method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scalable audio coding/decoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS6094636AEasy to useImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisTelevision systemsComputer architectureGamut
A scalable audio coding / decoding method and apparatus are provided. The coding method includes the steps of (a) signal-processing input audio signals and quantizing the same for each predetermined coding band; (b) coding the quantized data corresponding to the base layer within a predetermined layer size; (c) coding the quantized data corresponding to the next enhancement layer of the coded base layer and the remaining quantized data uncoded and belonging to the enhancement layer, within a predetermined layer size; and (d) sequentially performing the layer coding steps for all layers, wherein the steps (b), (c) and (d) each comprise the steps of: (i) obtaining gamut bit allocation information representing the number of bits of the quantized data corresponding to the respective subbands belonging to a layer to be coded; (ii) obtaining the number of bits allocated to the respective subbands within each subband size of the layers; (iii) generating an index representing the presence of quantized data for predetermined frequency components forming the subbands for the quantized data corresponding to the number of allocated bits; and (iv) generating bitstreams by coding the quantized data corresponding to the gamut bit allocation information, quantization step size, index and number of bits allocated to the respective subbands, by a predetermined coding method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
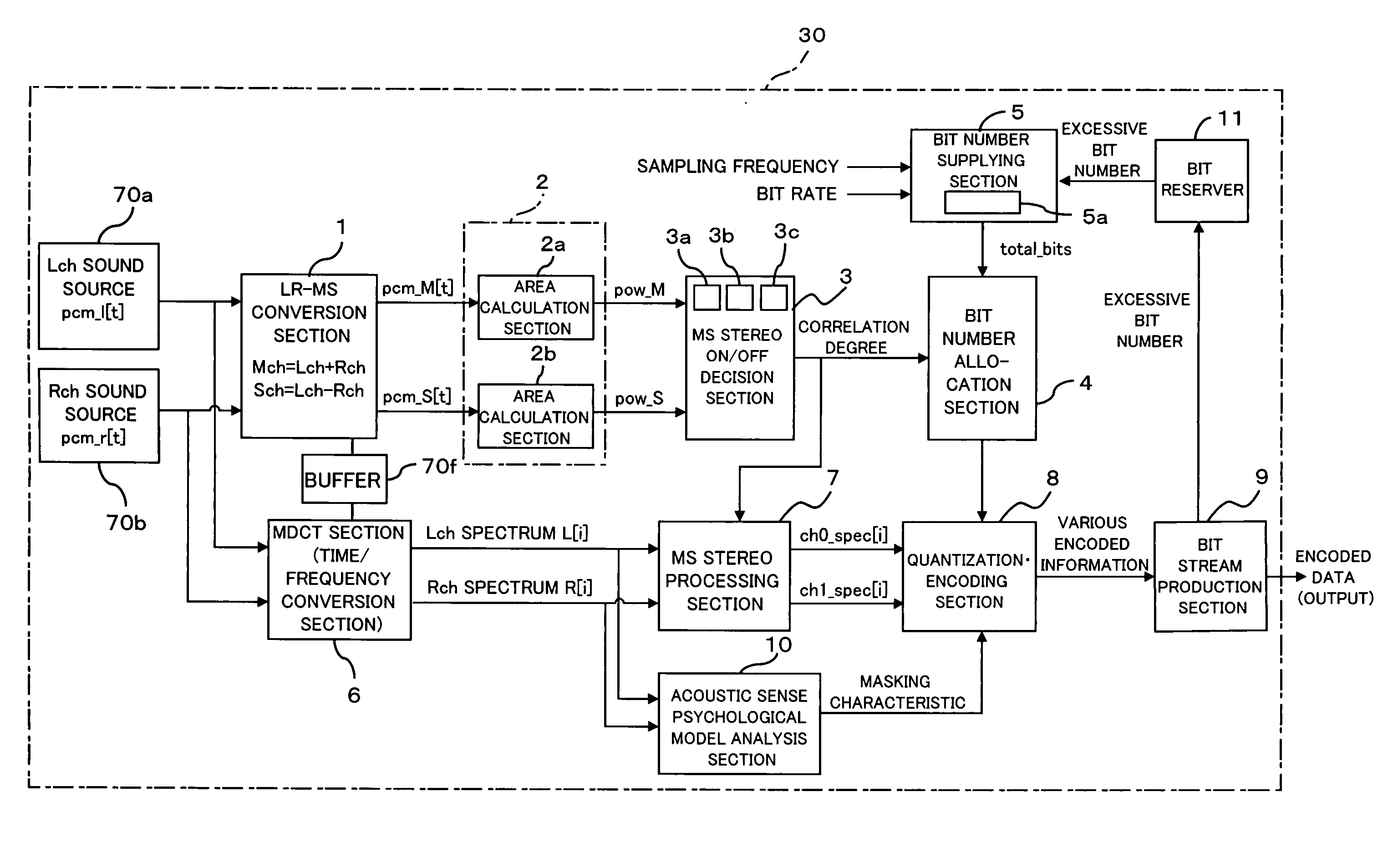
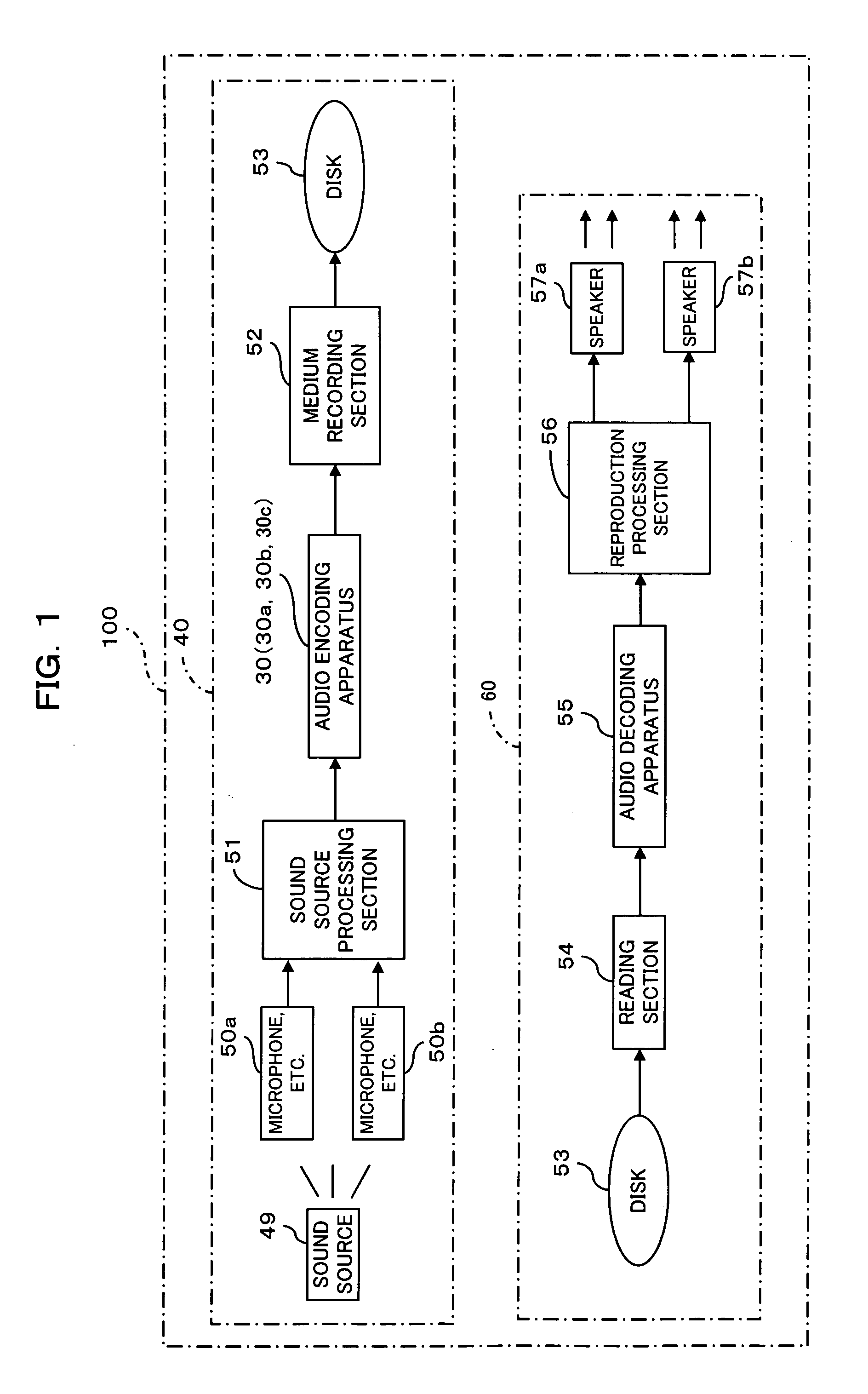
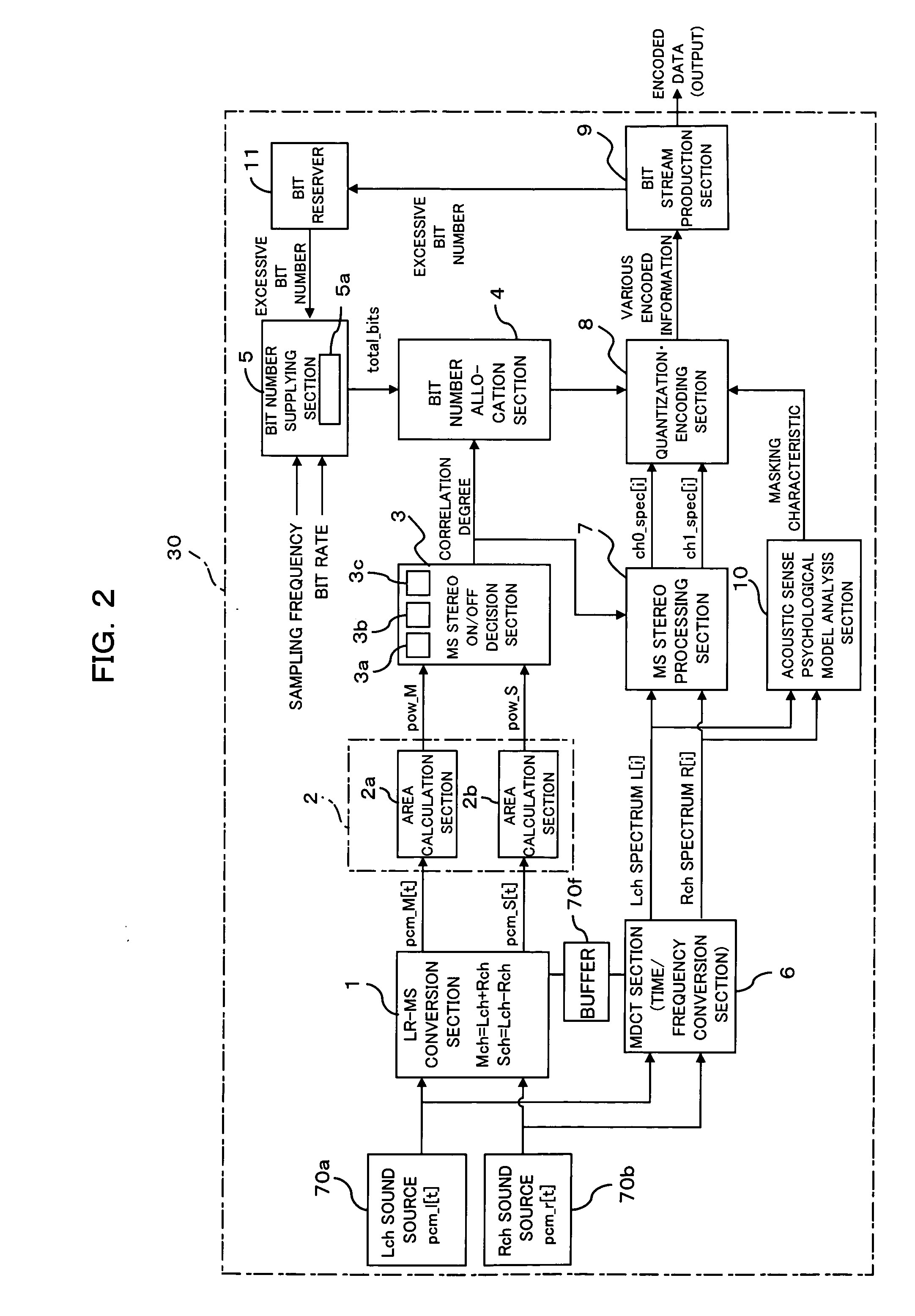
Audio encoding apparatus and frame region allocation circuit for audio encoding apparatus
InactiveUS20050157884A1Effective distributionAdjustable sizeSpeech analysisCode conversionBit allocationMiniaturization
An audio encoding apparatus for stereo audio encoding an L-channel PCM signal and an R-channel PCM signal efficiently allocates encoded data of the L-channel and the R-channel without varying an existing format and performs MS stereo on / off control and controls of a bit allocation amount or a frame region for the inputted PCM signals while miniaturization of the apparatus can be anticipated. A correlation degree calculation section calculates, based on the PCM signals of the L-channel and the R-channel, a correlation degree between the PCM signals, and decision section decides whether or not a stereo encoding process should be performed based on the calculated correlation degree. An allocation section allocates regions for individually storing a difference signal and a sum signal between the PCM signals based on a result of the decision, and an audio encoding section encodes the difference signal and the sum signal based on the allocated regions.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
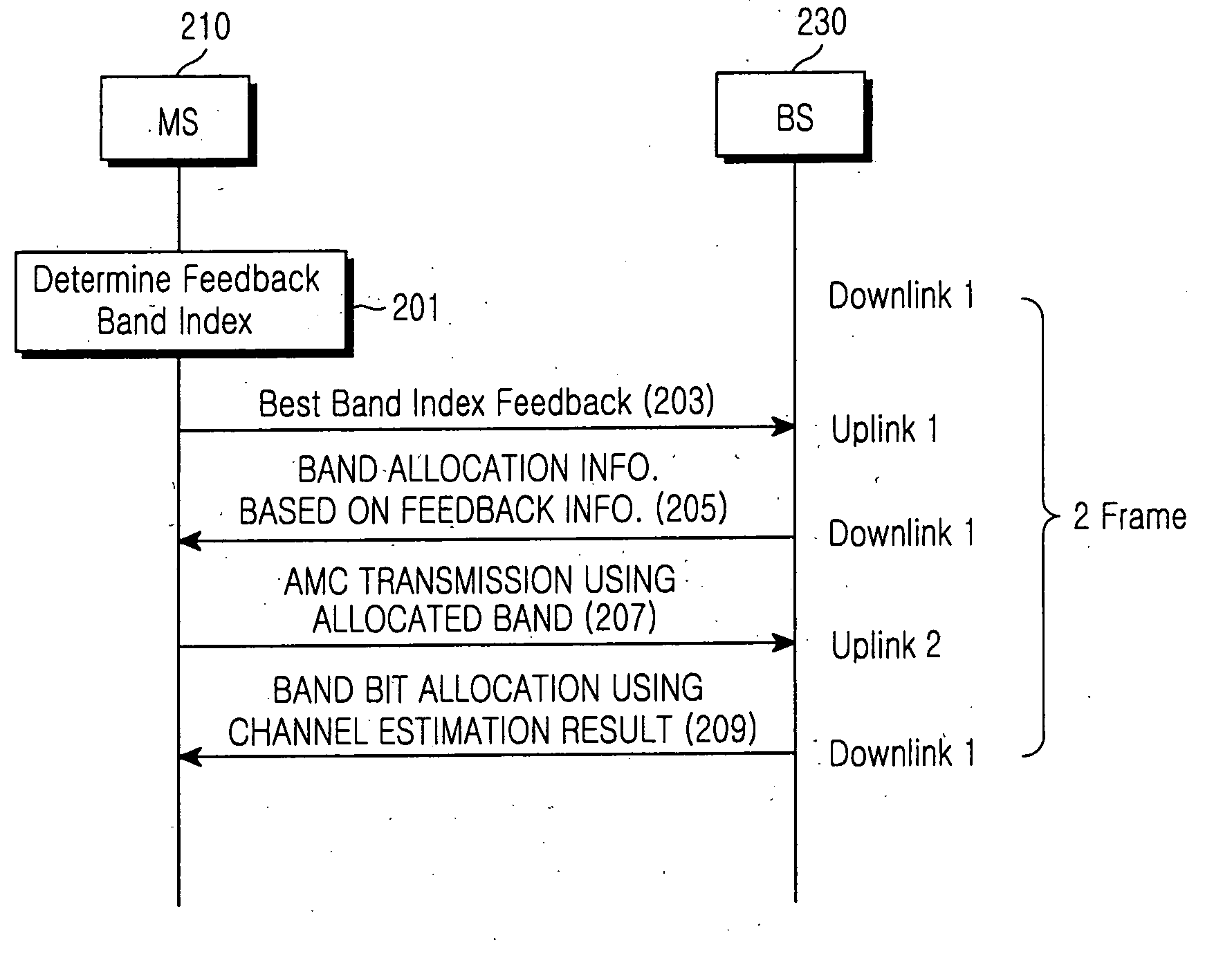
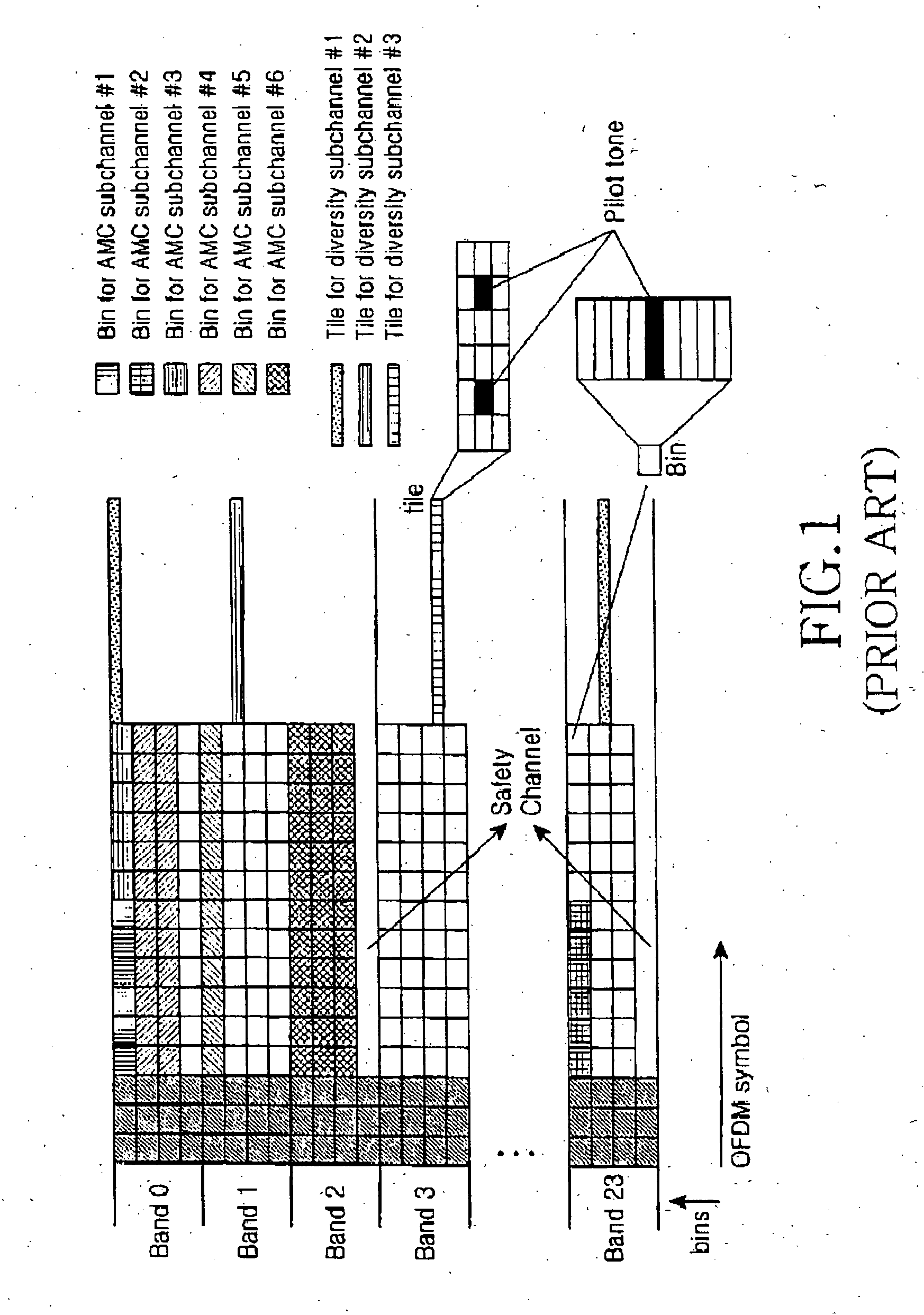
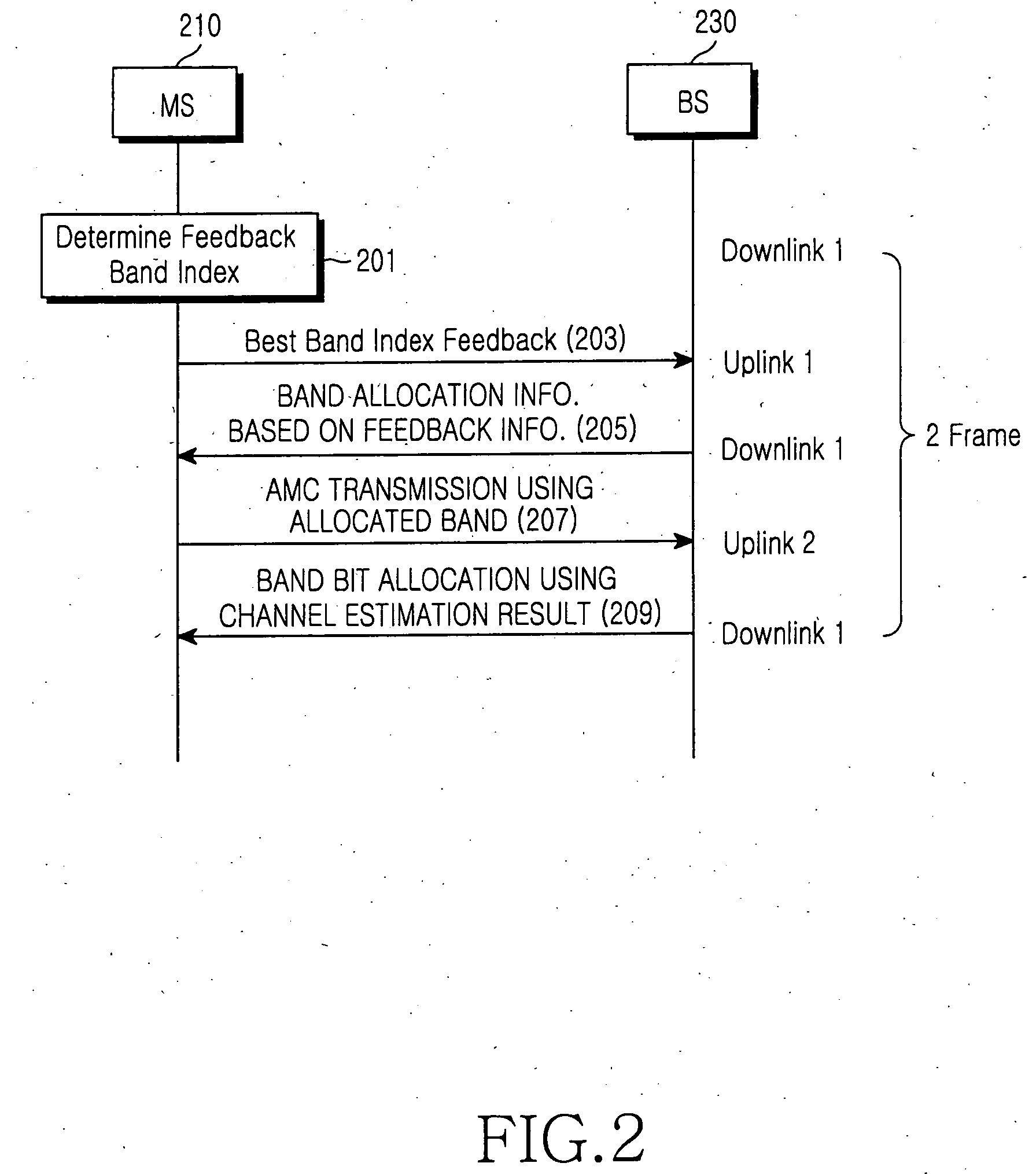
Adaptive subchannel and bit allocation method using partial channel information feedback in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
ActiveUS20060146856A1Improve transmission efficiencyHigh data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemBit allocation
An adaptive subchannel and bit allocation method in a wireless communication system. A mobile station analyzes channel quality information of a subchannel at a predetermined period and determines a feedback band index with a maximum decision criterion. The mobile station feeds back the determined feedback band index with the maximum decision criterion to a base station. The base station generates band allocation information using the feedback information from the mobile station, and transmits the band allocation information to the mobile station. The mobile station transmits AMC information using the band allocation information received from the base station. The base station estimates a channel using the AMC information transmitted from the mobile station and allocates bits to the allocated band according to the channel estimation result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
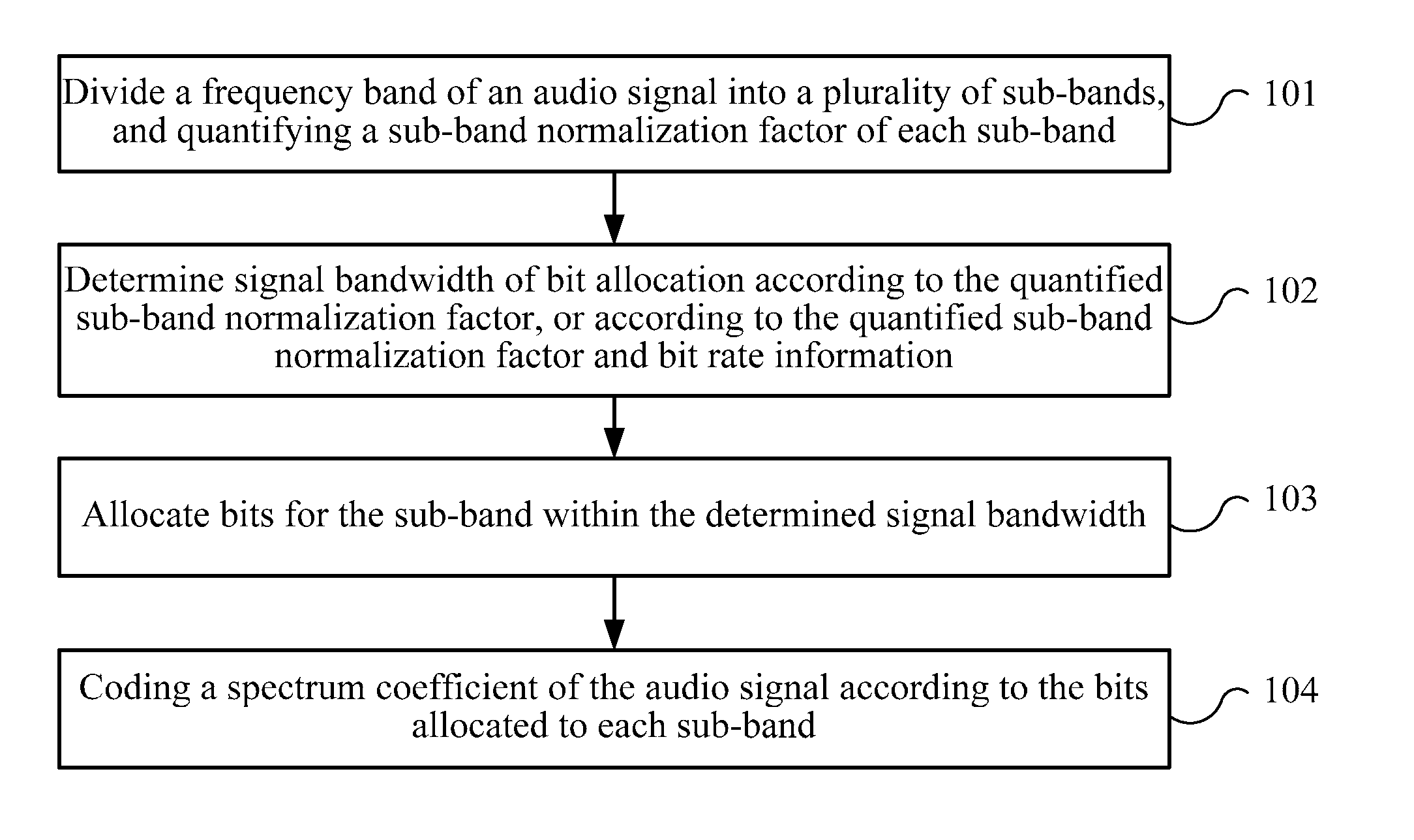
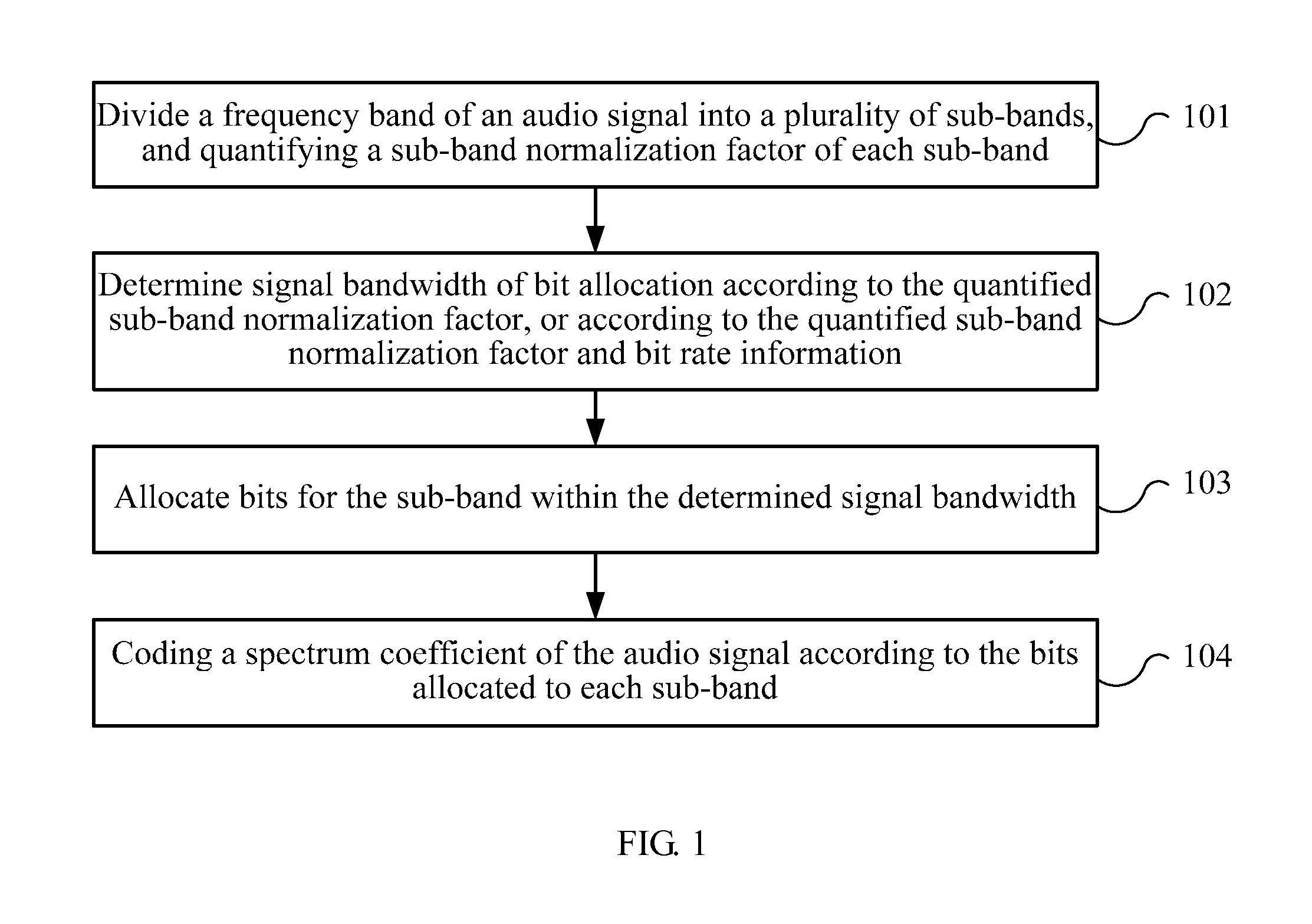
Audio signal coding and decoding method and device
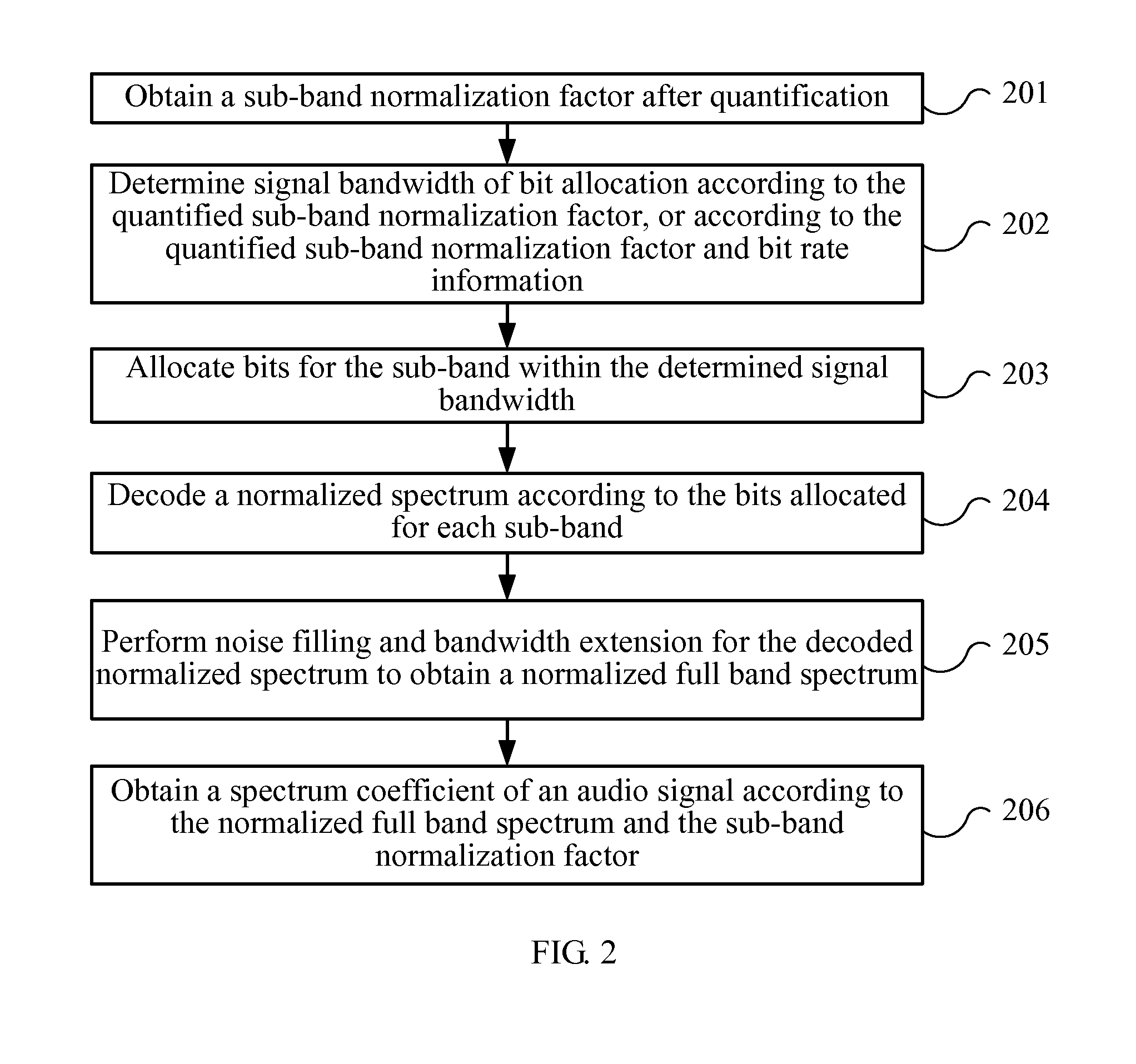
Embodiments of the present invention provide an audio signal coding and decoding method and device. The coding method includes: dividing a frequency band of an audio signal into a plurality of sub-bands, and quantifying a sub-band normalization factor of each sub-band; determining signal bandwidth of bit allocation according to the quantified sub-band normalization factor, or according to the quantified sub-band normalization factor and bit rate information; allocating bits for a sub-band within the determined signal bandwidth; and coding a spectrum coefficient of the audio signal according to the bits allocated for each sub-band. According to embodiments of the present invention, during coding and decoding, signal bandwidth of bit allocation is determined according to the quantified sub-band normalization factor and bit rate information. In this manner, the determined signal bandwidth is effectively coded and decoded by centralizing the bits, and audio quality is improved.
Owner:TOP QUALITY TELEPHONY LLC
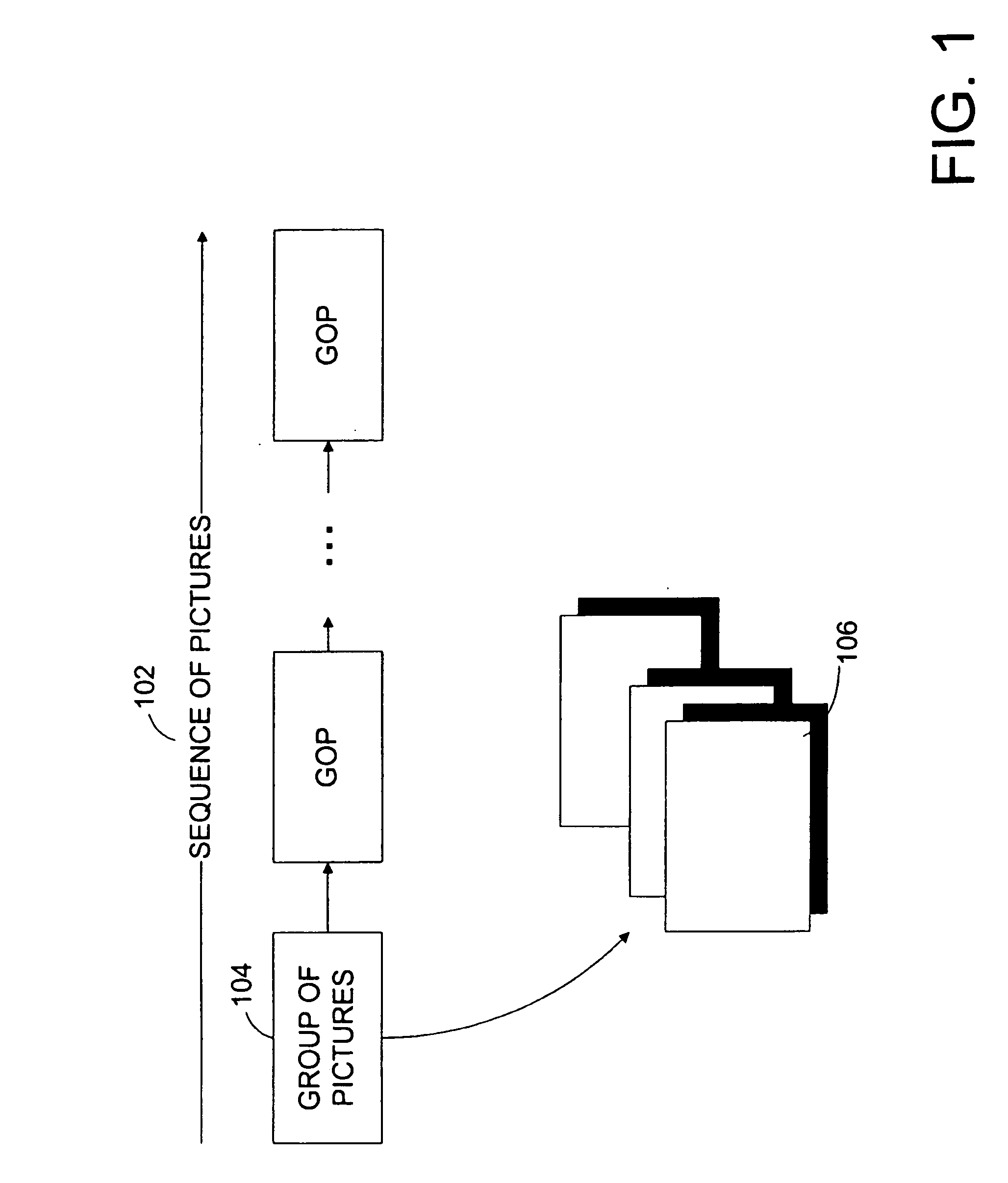
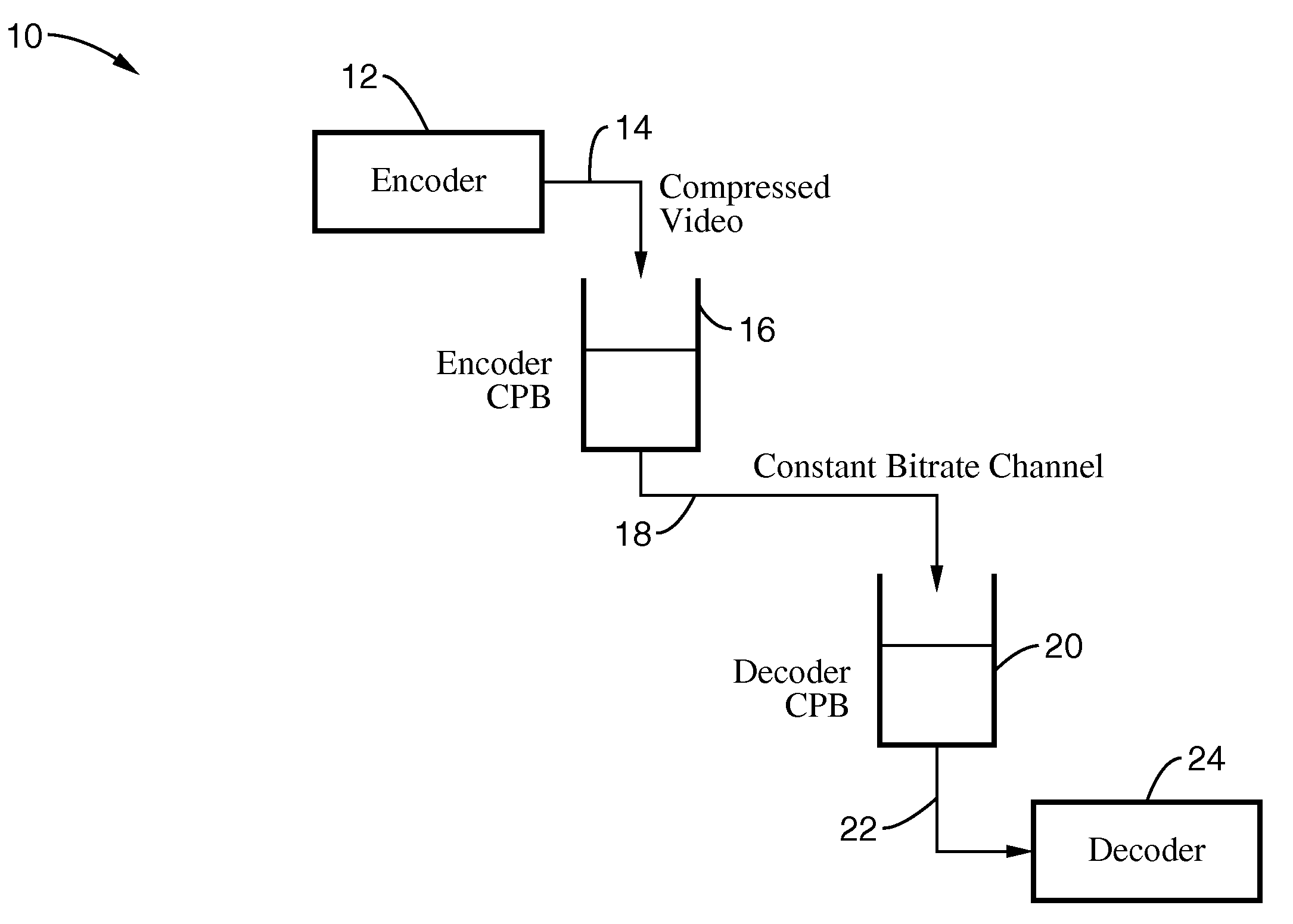
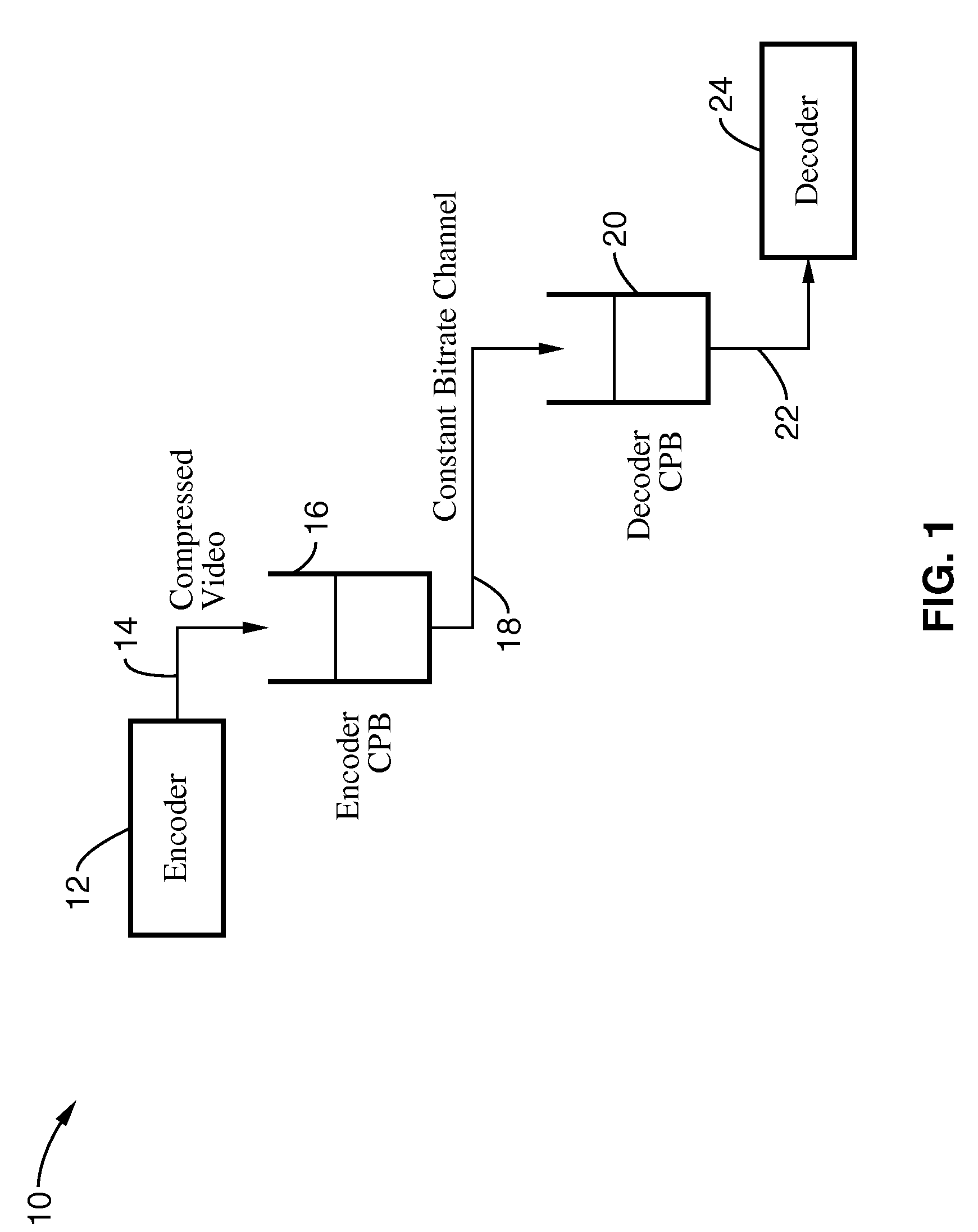
Rate control method with frame-layer bit allocation and video encoder
ActiveUS20080063051A1Improve video qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareBit allocation
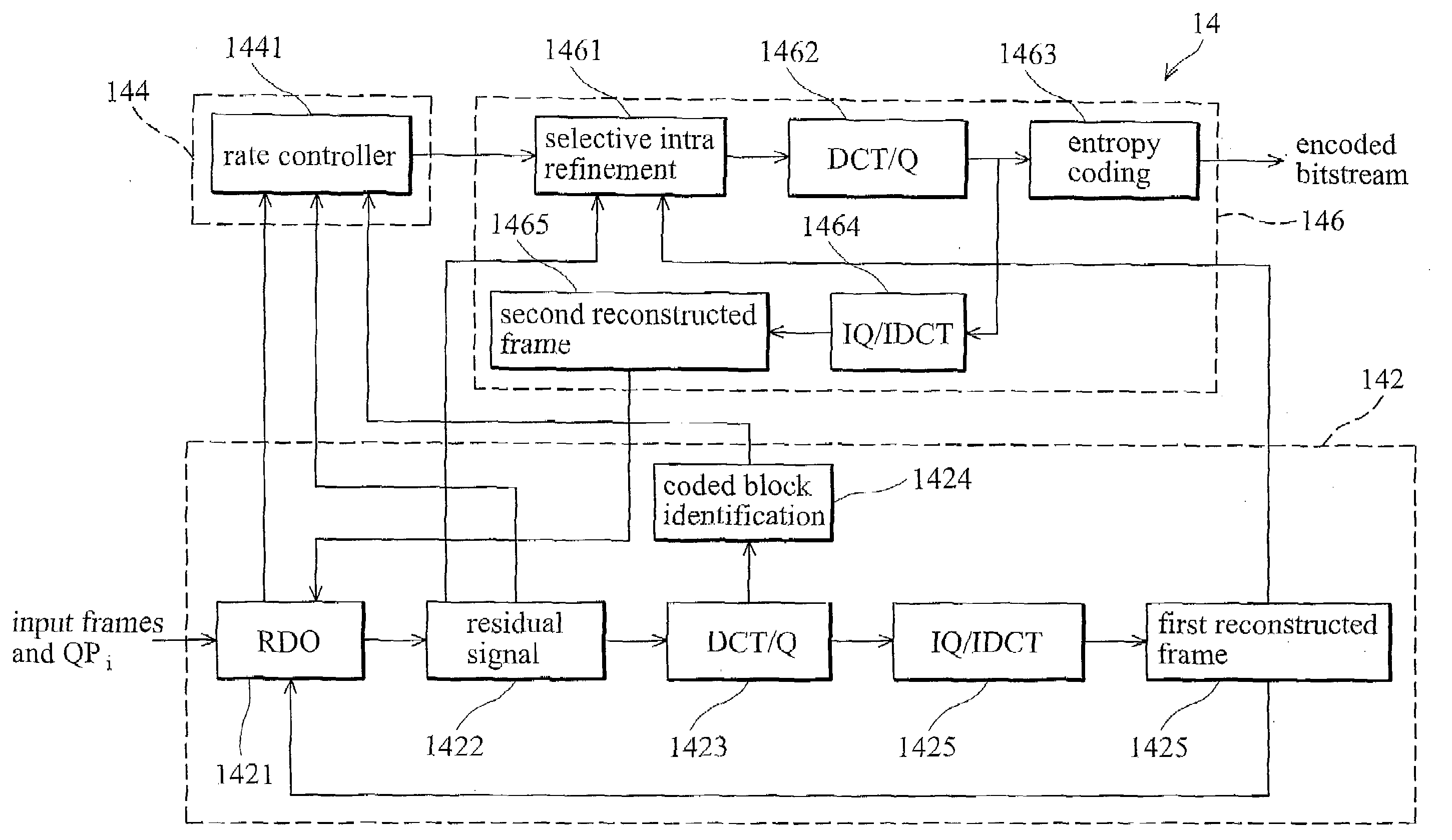
A video encoder controlling rate of each frame in a current frame set (Group of Picture, GOP), and method thereof. The video encoder comprises a frame grouping device, a GOP initialization device, and a GOP encoding device. The frame grouping device allocates a target bit budget RGOP to the current frame set. The GOP initialization device is coupled to the frame grouping device, and estimates a first quantization parameter QP1 based on the target bit budget RGOP and complexity of the current frame set. The GOP encoding device is coupled to the GOP initialization device, and encoding a frame in the current frame set with the second quantization parameter QP2 to generate output data.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
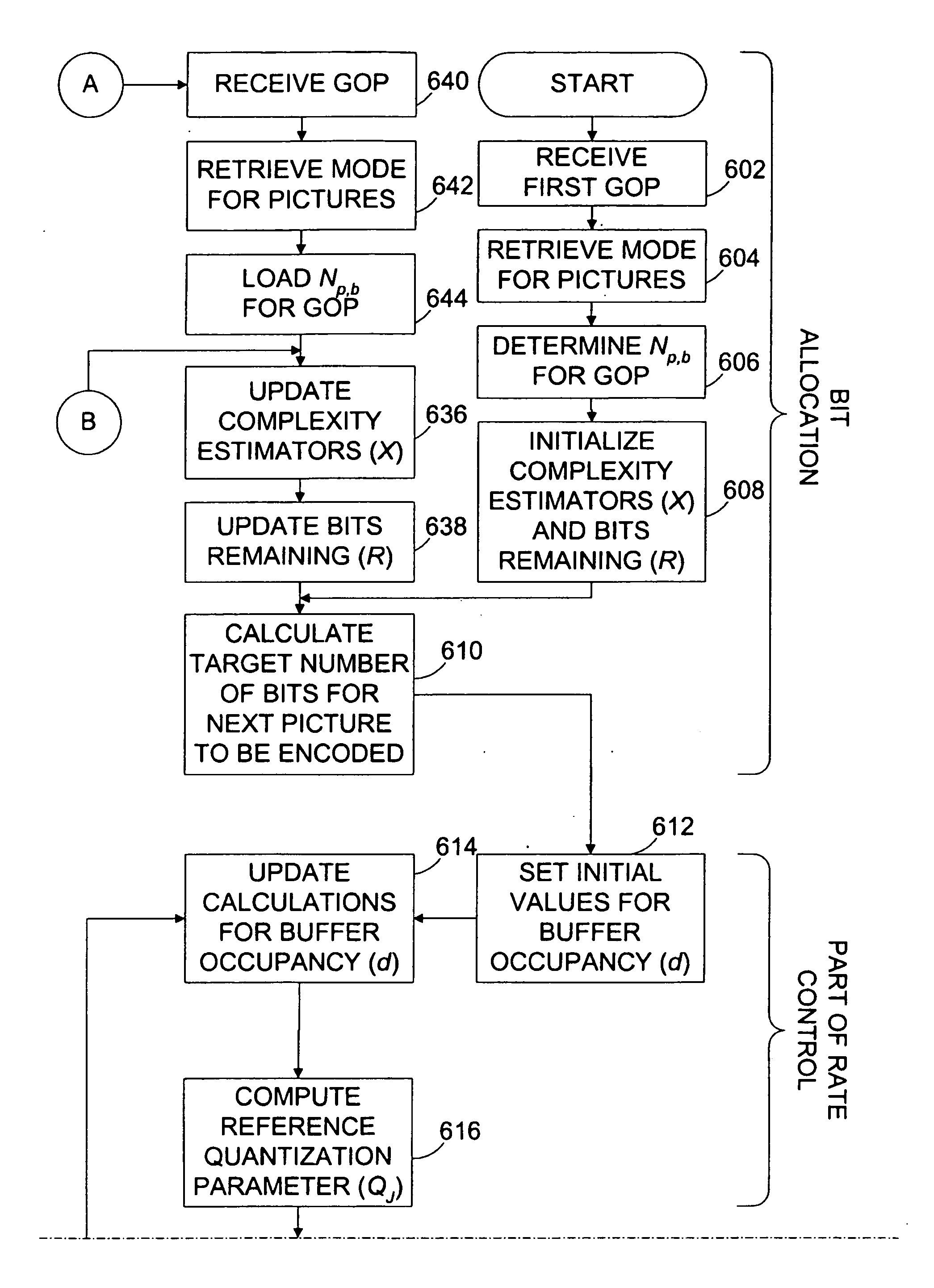
Single pass target allocation for video encoding
InactiveUS6181742B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingBit allocation
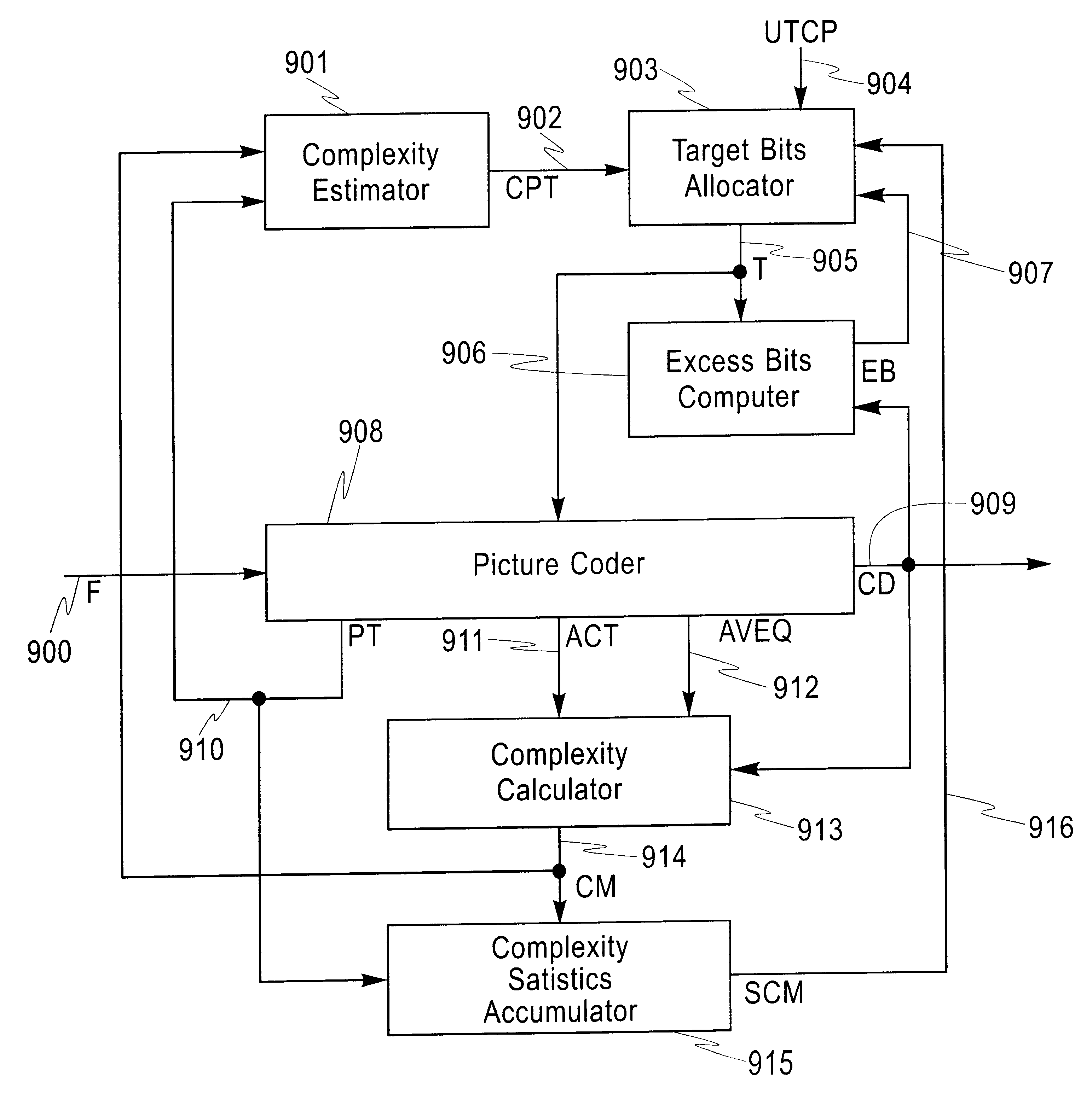
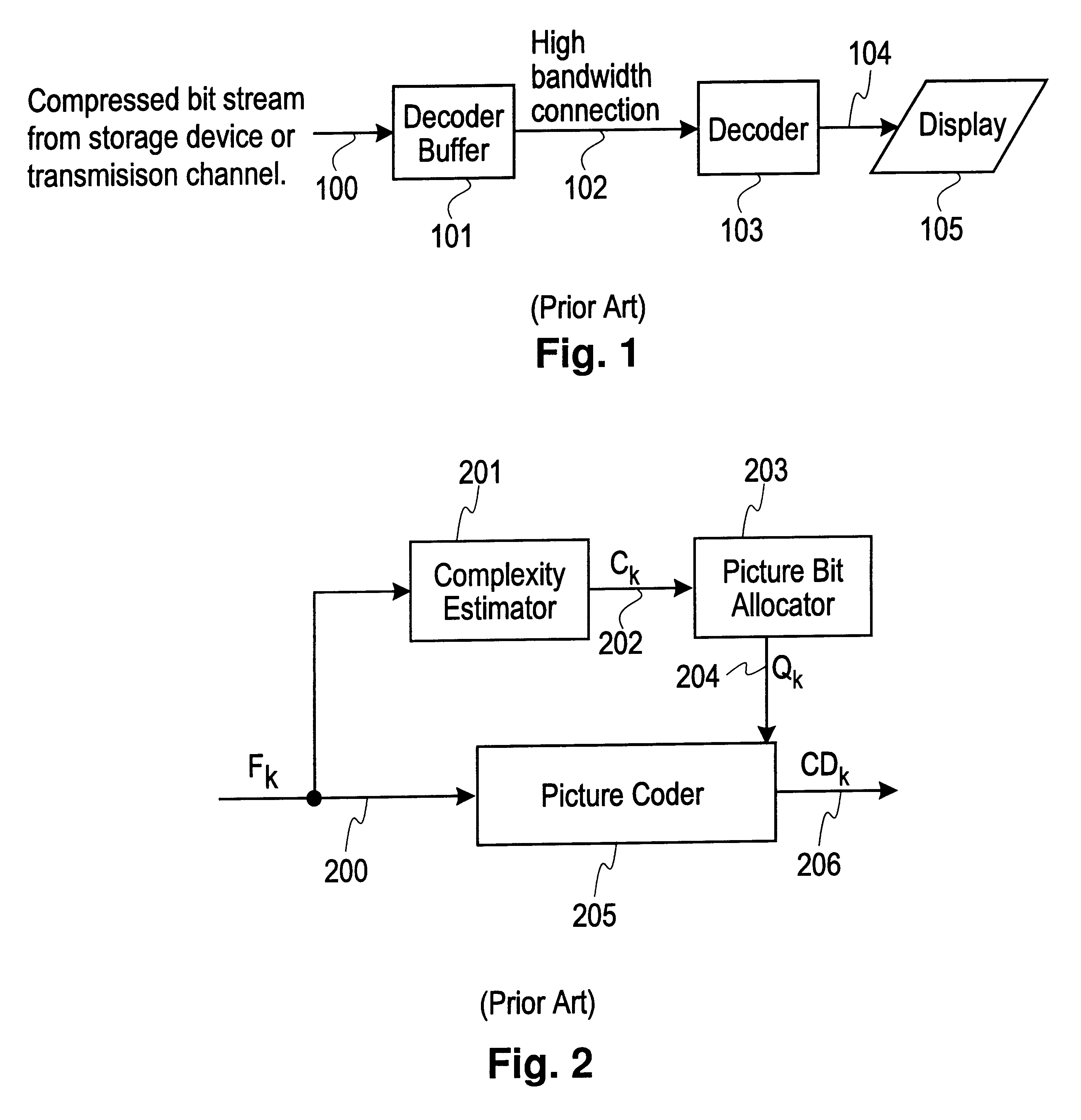
Systems and methods are provided for allocating bits to pictures in accordance with the bit allocation constraints for operation at both constant and variable bit rates. A statistical complexity measure which is an estimate of the average encoding complexity of the entire data is updated after encoding each picture. This set of parameters, along with an estimate of the encoding complexity of the current picture and the desired average coding rate is used to allocate target bits for encoding the current picture. One method of allocating bits to a picture is to used the statistical complexity measure to vary the instantaneous rate of encoding and allocate bits for this picture so as to generate encoded data at this rate. Another method is to modulate the target generated by a conventional encoder using the current level of the Virtual Buffer Verifier and the deviation of the estimated encoding complexity of the current picture from the statistical complexity measures.
Owner:IBM CORP
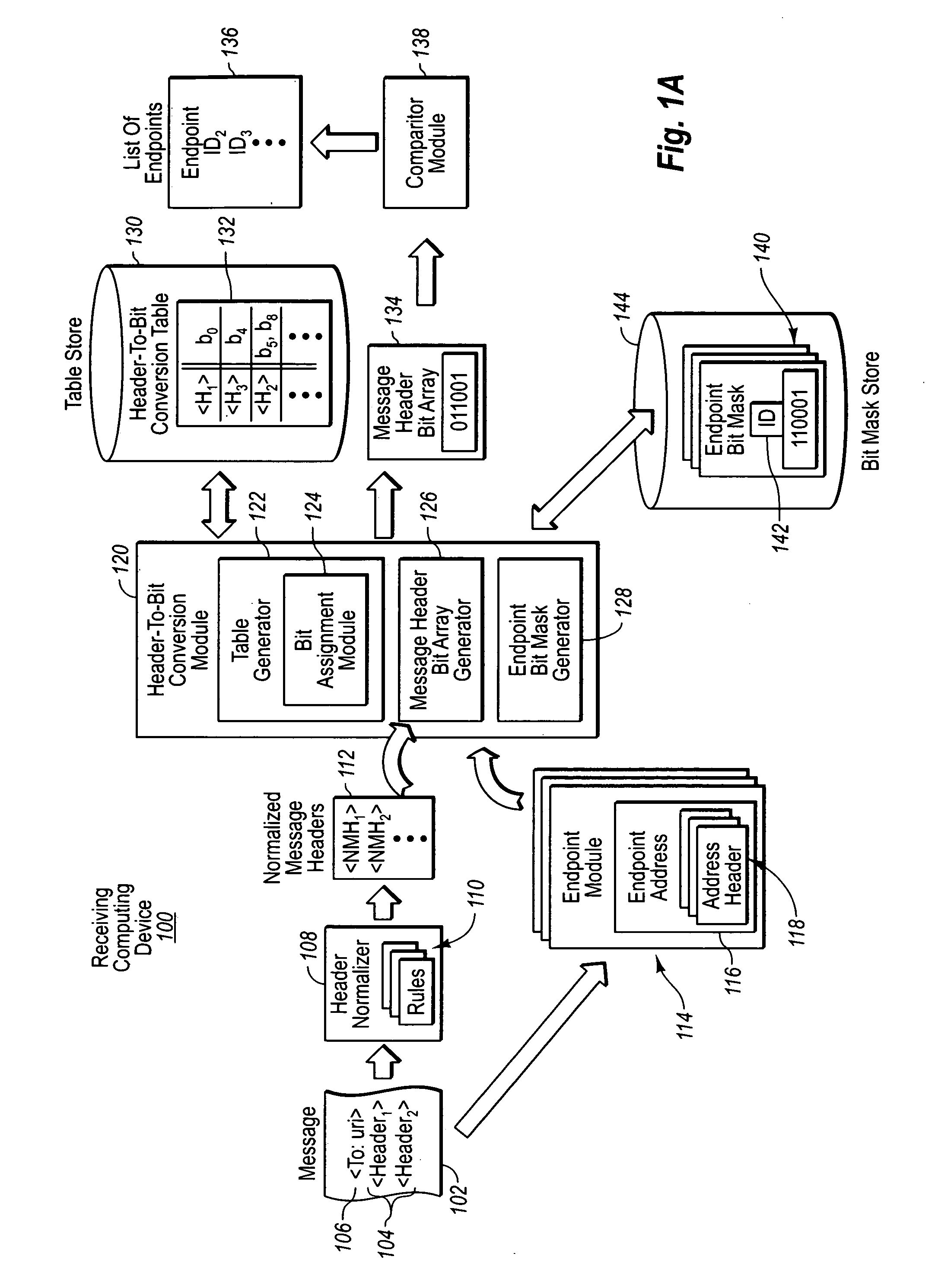
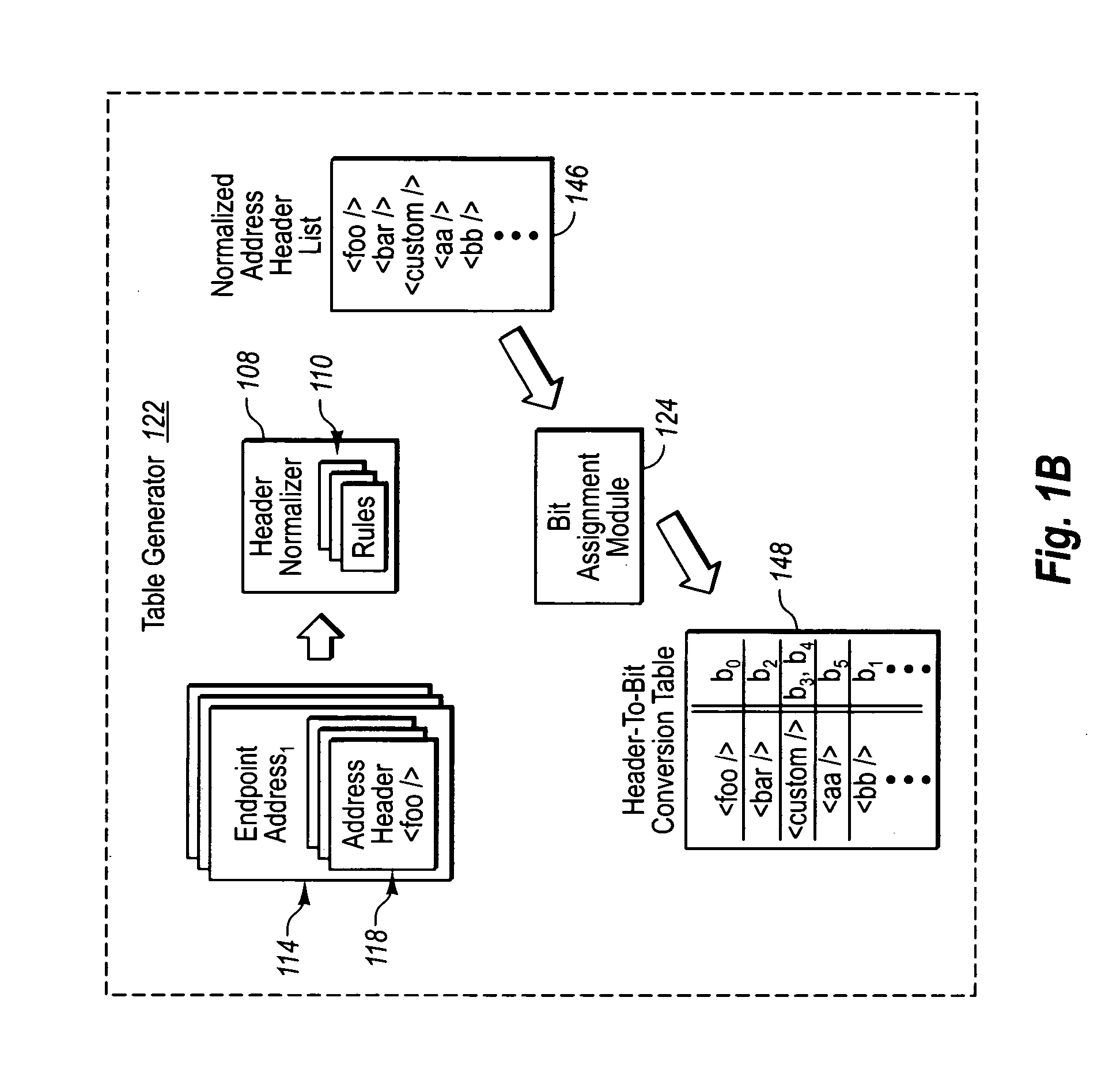
Efficient endpoint matching using a header-to-bit conversion table
ActiveUS20070078997A1Efficiently determinedEliminate duplicationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionBit arrayComputer network
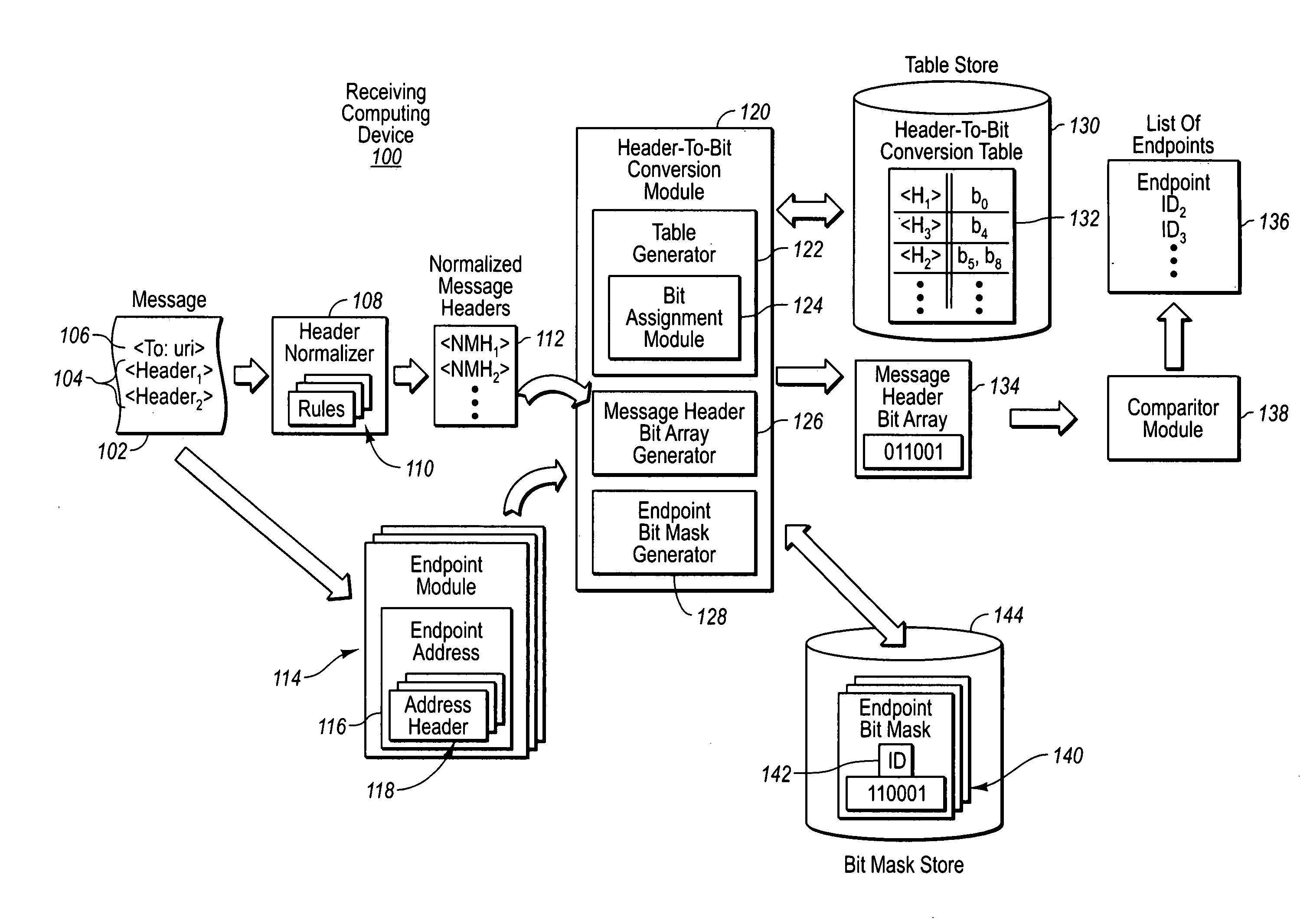
A header-to-bit conversion table is provided that includes a list of address headers for registered endpoints. Assigned to each address header within the list is a bit placement within a string of bits. As messages are received, select headers within a message are compared with the address headers within the list. Each intersection or match for headers sets a bit true within a bit array for the message corresponding to the bit assignment for the header within the header-to-bit conversion table. Such array may then be compared with bit masks for each endpoint, wherein those bits set true within the bit masks represent those headers needed to satisfy the criteria for a particular endpoint. If a match is found, the message (or portion(s) thereof) may be sent to the particular endpoint for processing.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
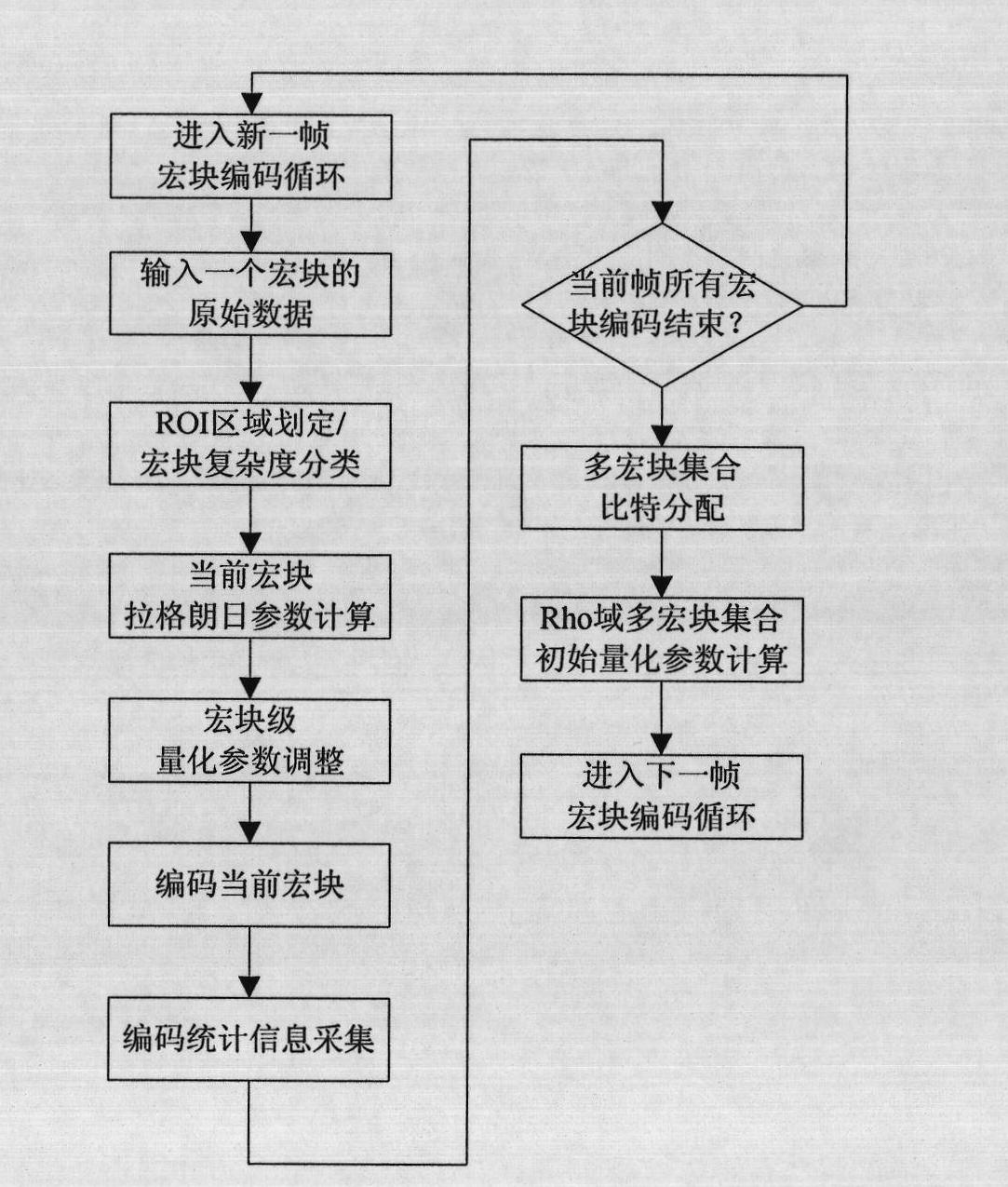
Video coding method based on region of interest (ROI)
InactiveCN101945275AEffective distributionAdd code bitsTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionBit allocation
The invention relates to a video coding method based on a region of interest (ROI). A video coder receives the original video data of a macroblock; an ROI preprocessing module divides the macroblocks in a frame image into ROI macroblocks and non-ROI macroblocks according to the ROI predefined by a user; if the user does not define the ROI, the macroblocks in the frame are categorized by adopting an image content analyzing method; the ROI preprocessing module calculates a Lagrangian multiplier; a quantification parameter adjusting module adjusts the sensitive degree of the current macroblock and the macroblock set initial quantification parameters according to the human vision; the video coder codes the current macroblocks according to the adjusted quantification parameters; and a multiple macroblock set bit allocation module distributes the target bits for each macroblock according to the macroblock set coding statistic information after the macroblocks in the frame are completely coded, and finally calculates the initial quantification parameter of each macroblock set.
Owner:ZHENJIANG TANGQIAO MICROELECTRONICS
Apparatus and method for dynamic resource allocation in broadband wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090154418A1Reduce overheadRadio transmissionSignalling characterisationCommunications systemBit allocation
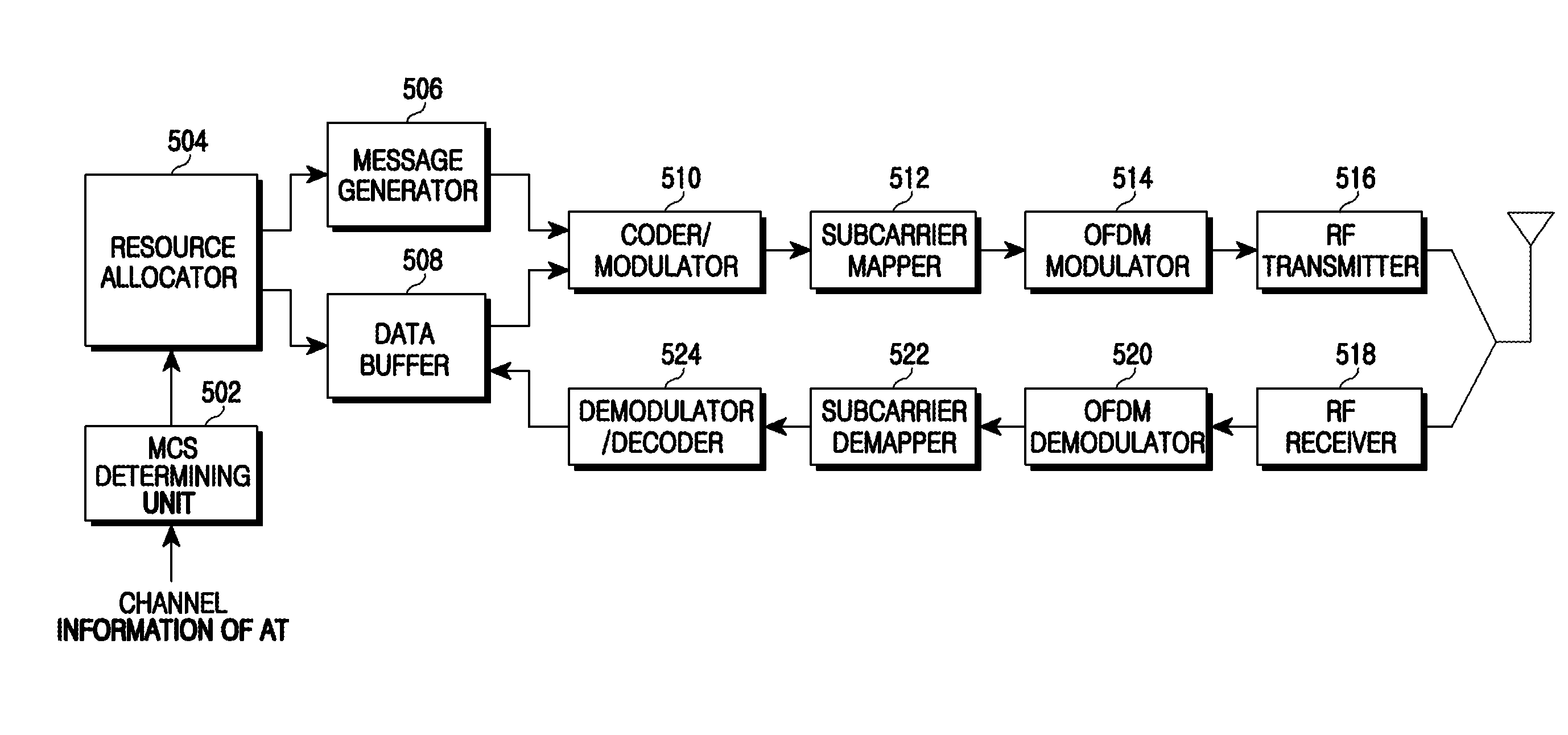
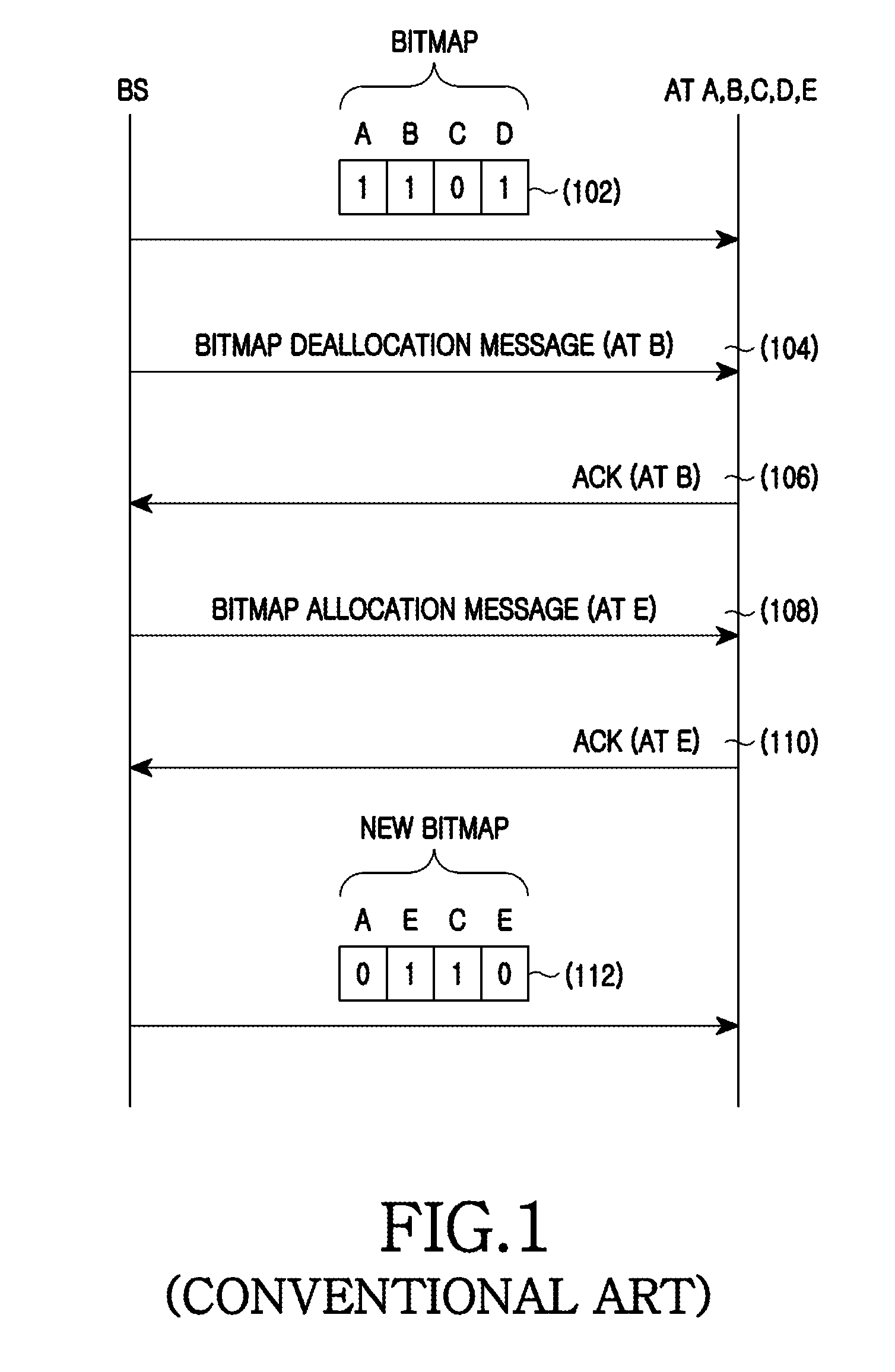
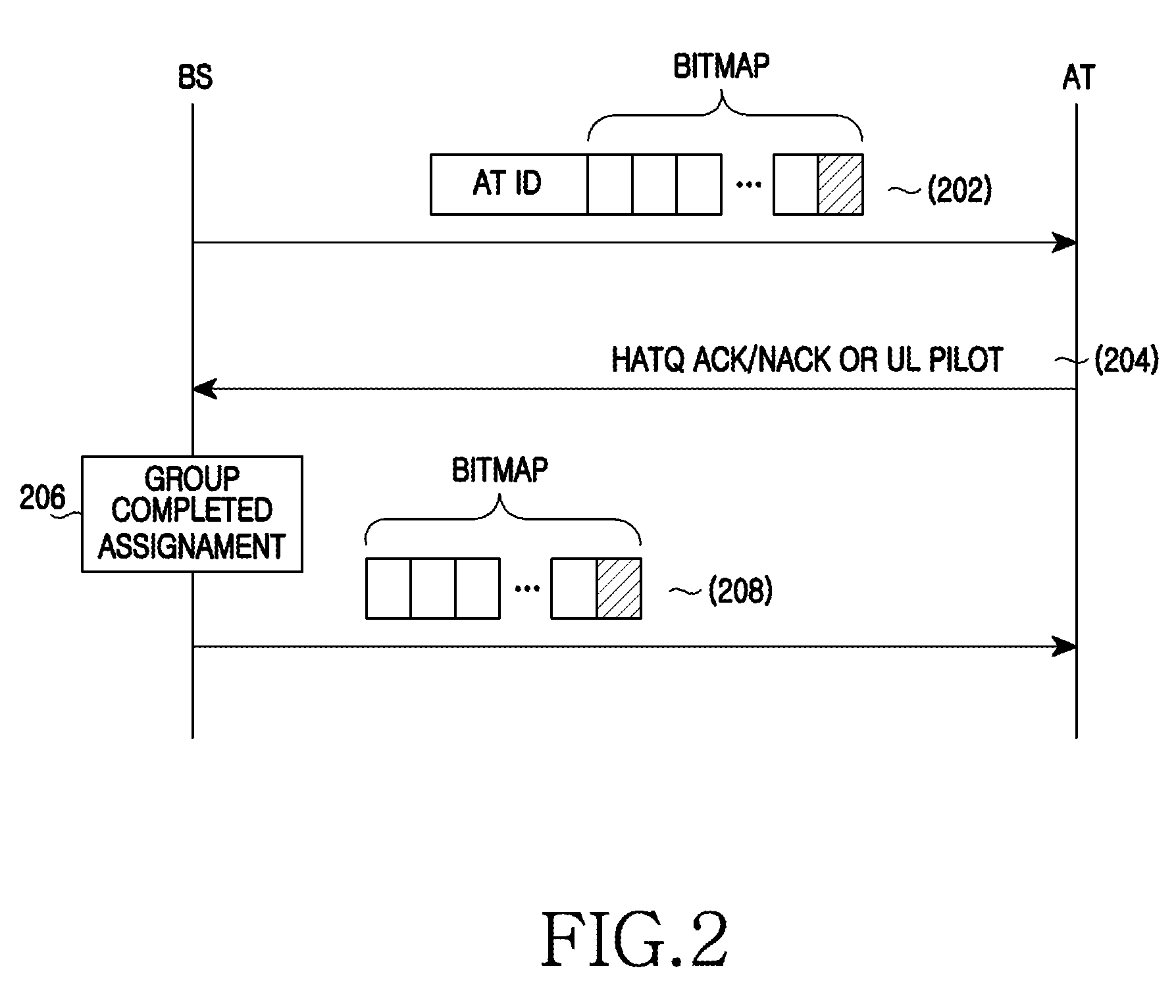
An apparatus and method for dynamic resource allocation in a wireless communication system are provided. A method of operating a Base Station (BS) includes configuring a bitmap to indicate whether radio resources are allocated to respective Access Terminals (ATs) according to resource scheduling, generating a resource allocation message including at least one of the configured bitmap, bit allocation information of the bitmap, and bit deallocation information of the bitmap, and transmitting the resource allocation message.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
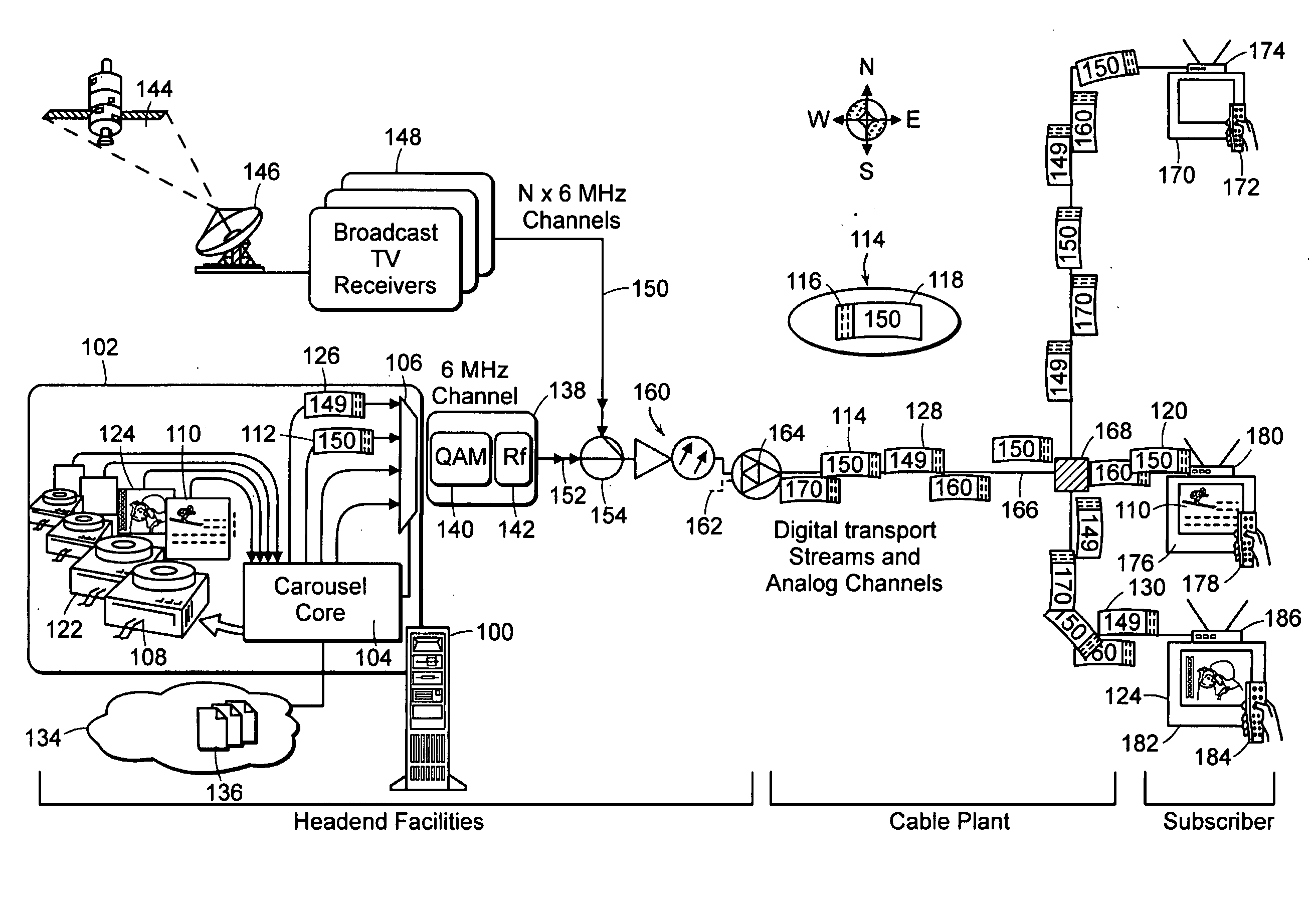
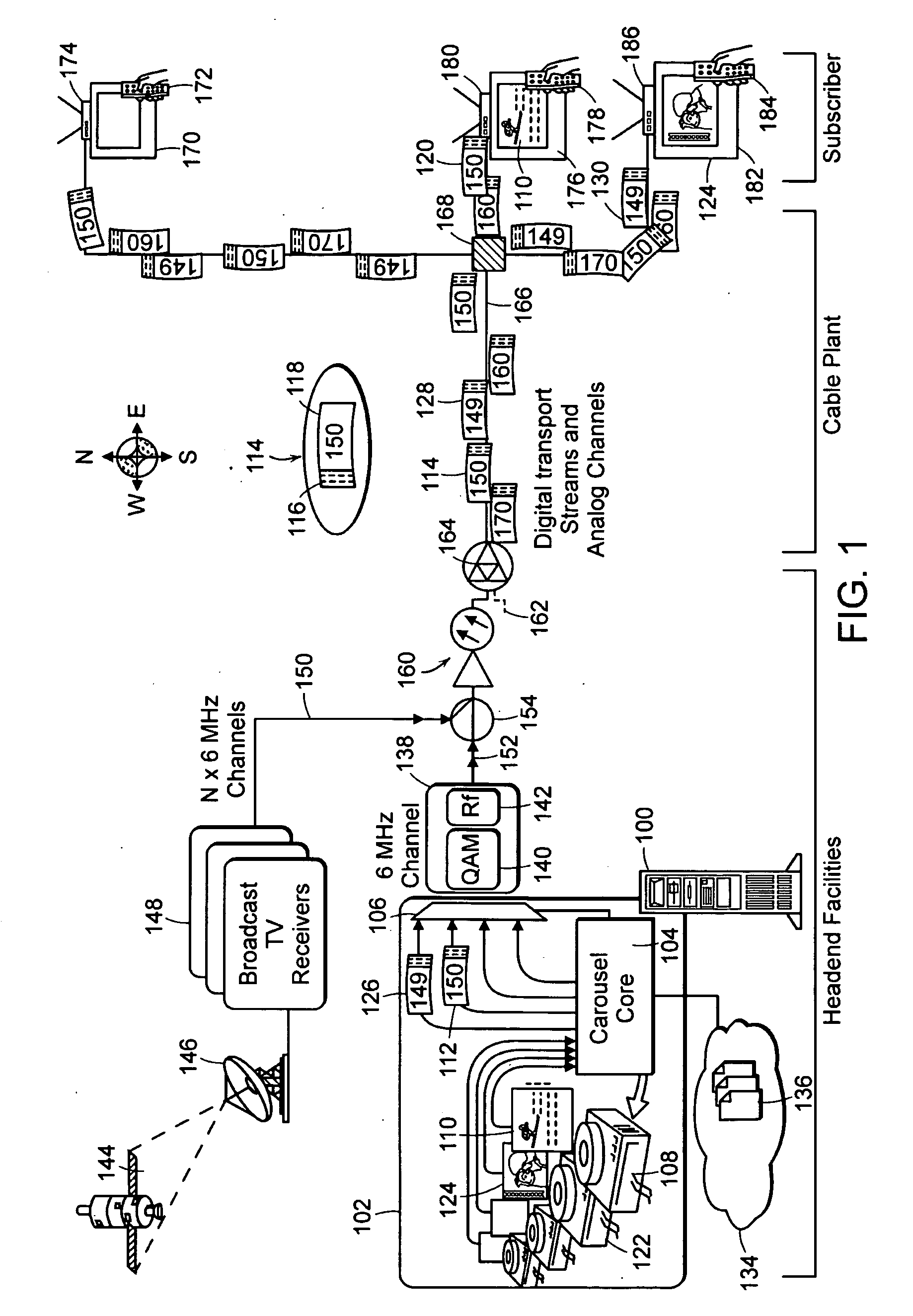
Method for Bandwidth Regulation on a Cable Television System Channel
InactiveUS20090041118A1Low bandwidthQuick provisioning and configuringTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesTelevision systemDigital data
A method for regulating bandwidth usage in an output data stream transmitted on an analog channel from a cable head end. The output data stream comprises a plurality of input information content signals. For each input information content signal, a series of images are captured, compressed and formed into an input digital data stream. The bandwidth of each input digital data stream is regulated by associating the stream with a current bit allocation total. During each frame time: a bit allocation increment is added to the current bit allocation total for each input digital data stream. When a data packet to be transmitted for an input digital data stream is received by the multiplexer, the data packet is stored. When the number of bits in the stored data packet is not more than the current bit allocation total for the input digital data stream, the multiplexer forwards the stored data packet for transmission in the output data stream on the analog channel and decrements the current bit allocation total for the given input digital data stream by the number of bits in the stored data packet. In this way, no individual input channel takes more than its share of the bandwidth on the output stream on the analog channel.
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
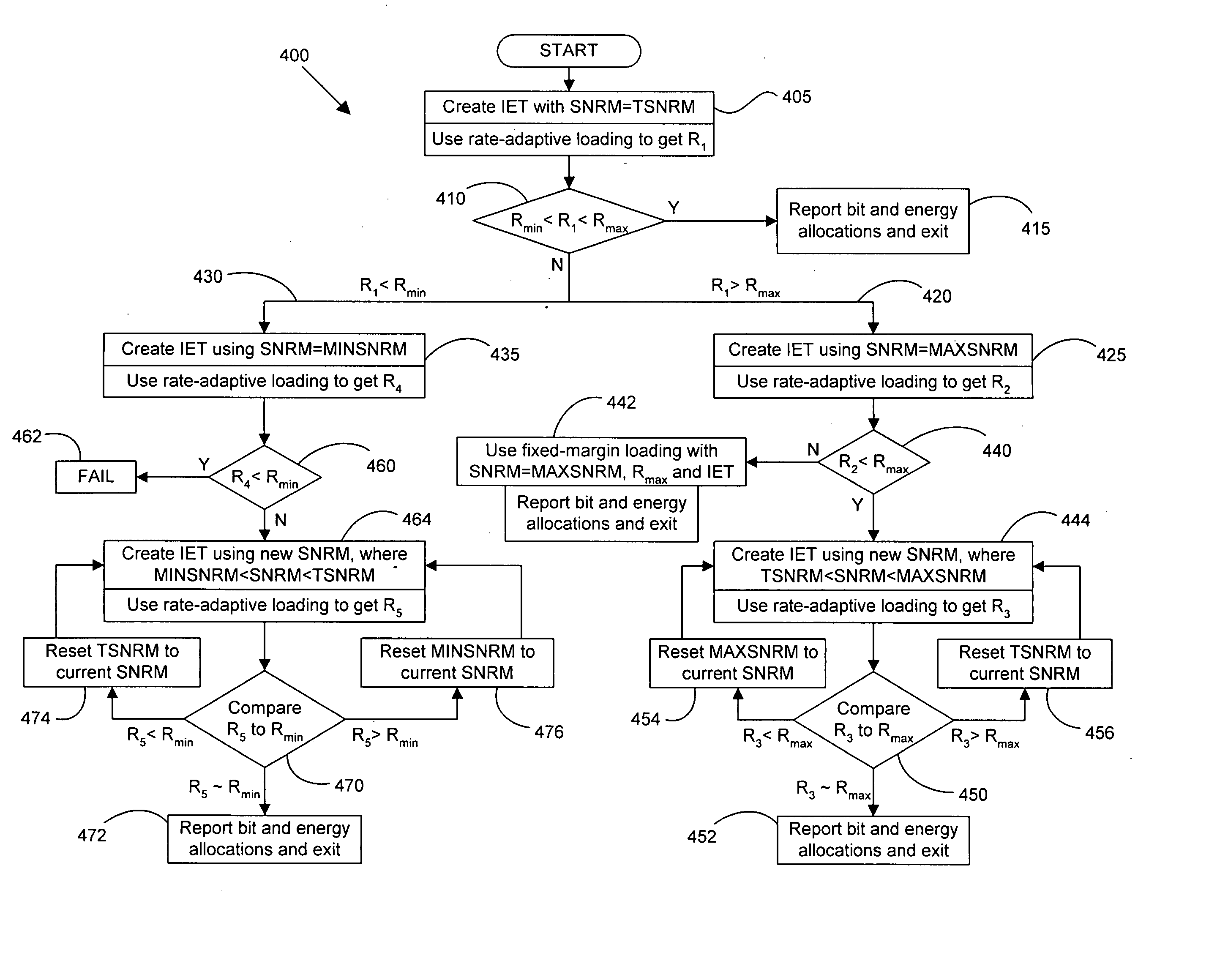
DSL system loading and ordering
ActiveUS20060280237A1Favorable vector of rateReduce complexityTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationBit allocationEngineering
Loading and ordering techniques are provided for one-sided and two-sided vectored line groups, as well as loading methodologies that also can be used on a single line, in communication systems such as DSL binders. For single-user lines, bits and energy are optimally allocated for a given set of parameters, which may include maximum rate, minimum rate, maximum margin, target margin, minimum margin and PSD mask of any shape. Iterations, bit-swapping during loading or adaptive margin update during loading can be used in single-user loading, which has low complexity and can be used for a variety of loading objectives and / or goals, such as rate-adaptive, margin-adaptive and fixed-margin objectives. For multi-user vectoring systems, ordering as well as loading is provided for a supplied rate-tuple within a rate region, determining acceptable user loadings and orderings so that the rate-tuple can be implemented. For one-sided vectored DSL, some loading and ordering determines acceptable allocations of bits, energy and decoding / precoding ordering(s) for each tone of each user for a specified set of rates on the vectored lines. PSD determination, ordering and bit allocation can be iteratively used in multi-user loading and ordering and can augment and alter the criteria used for bit swapping procedures used in single lines (or in bonded multiple lines for a single user) so that a favorable vector of rates is achieved for all users. Order swapping can adjust a bit vector and / or rate vector within a constant-rate-sum convex subset of a hyperplane towards the desired vector of user rates for each of the lines.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
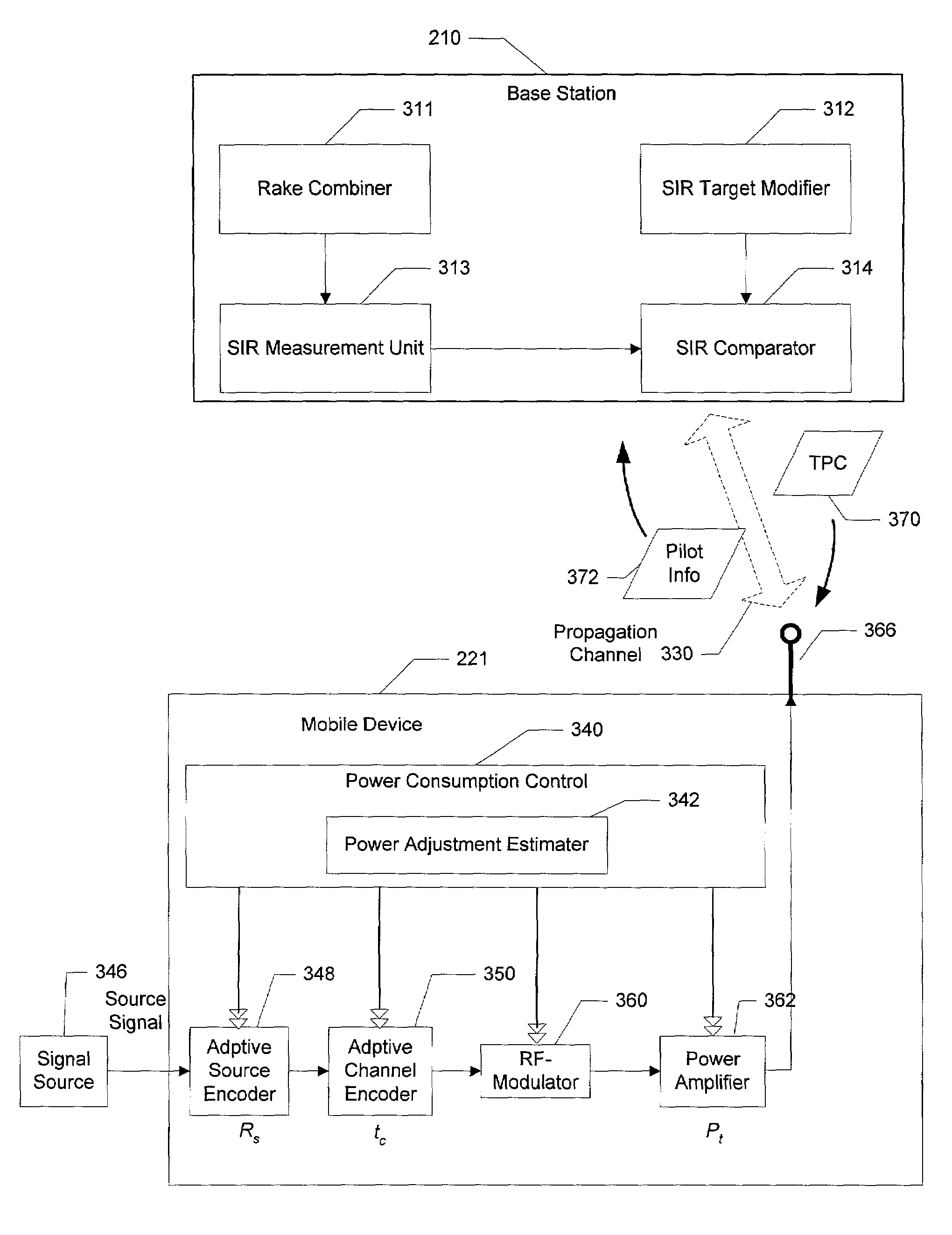
System and method for reducing power consumption for wireless communications by mobile devices
InactiveUS7096034B2Maximize system capacityReduce transmit powerPower managementEnergy efficient ICTSignal qualitySystem capacity
A power control scheme for a wireless network communication system that includes a base station and multiple wireless mobile device dynamically adjusts transmission power of a mobile device in conjunction with adjusting its bit allocation in source coding and channel coding to minimize its total power consumption while maximizing the system capacity in terms of the total effective transmission rates received by the base station. The base station sets a target signal quality value for each mobile station, and the target values are determined by the base station such that the total effective data rate from all the mobile devices is maximized under constraints of the total received power and the error protection level requirements for the mobile devices. The base station periodically measures a signal quality value, such as a signal-to-interference ratio (SIR), from transmissions received by the base from each mobile device, compares it with the measured signal quality value for that mobile device, and sends a control signal instructing the mobile device to increase or decrease its transmission power based on the result of the comparison. When the mobile device receives the control signal, it determines an amount of adjustment to its transmission power by performing a minimum calculation under constraints on the total data distortion and the maximum transmission rate to adjust the parameters for source coding, channel coding, and transmission under the constraints to result in a redistribution of power between the components that provides the minimized total power consumption.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
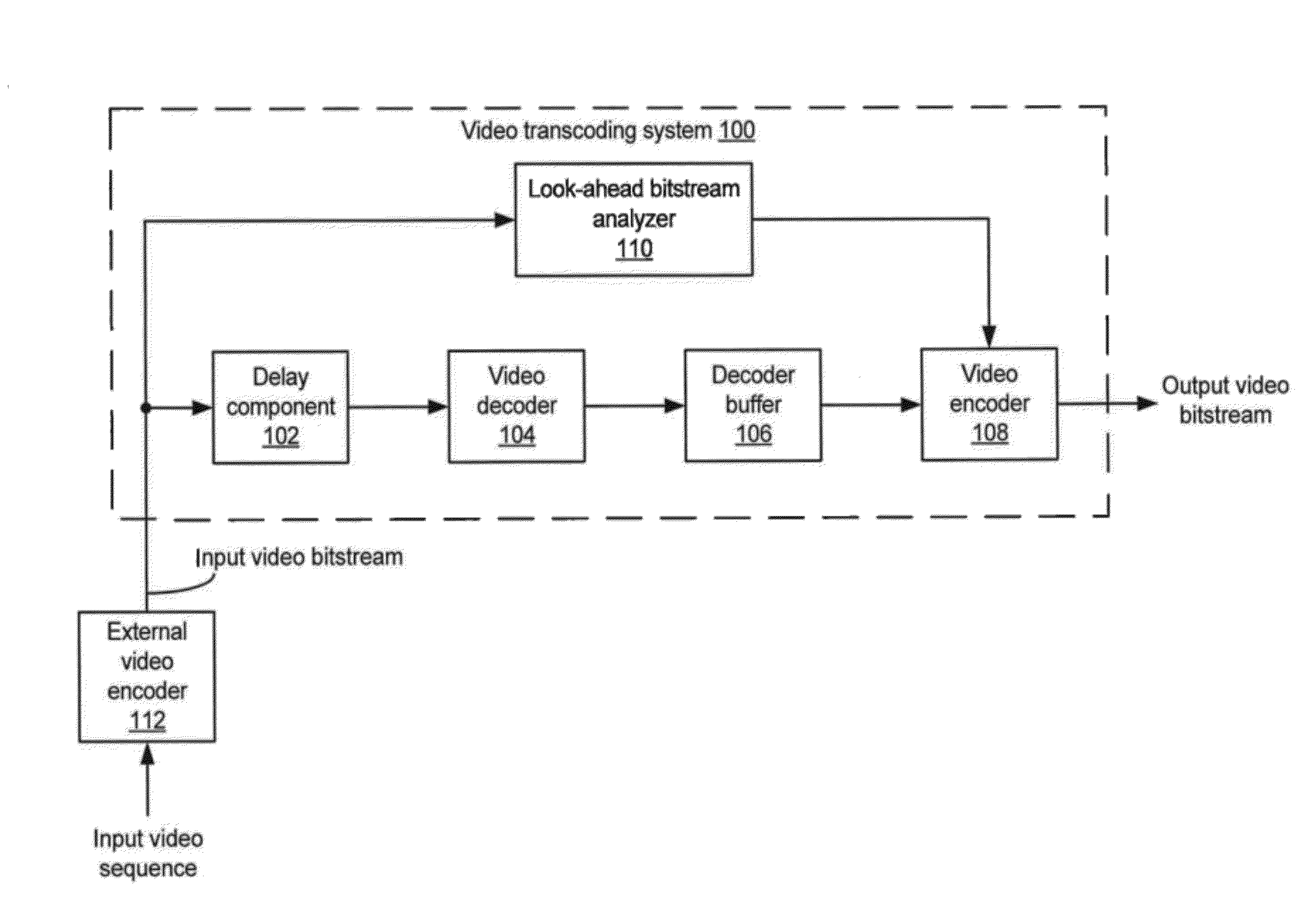
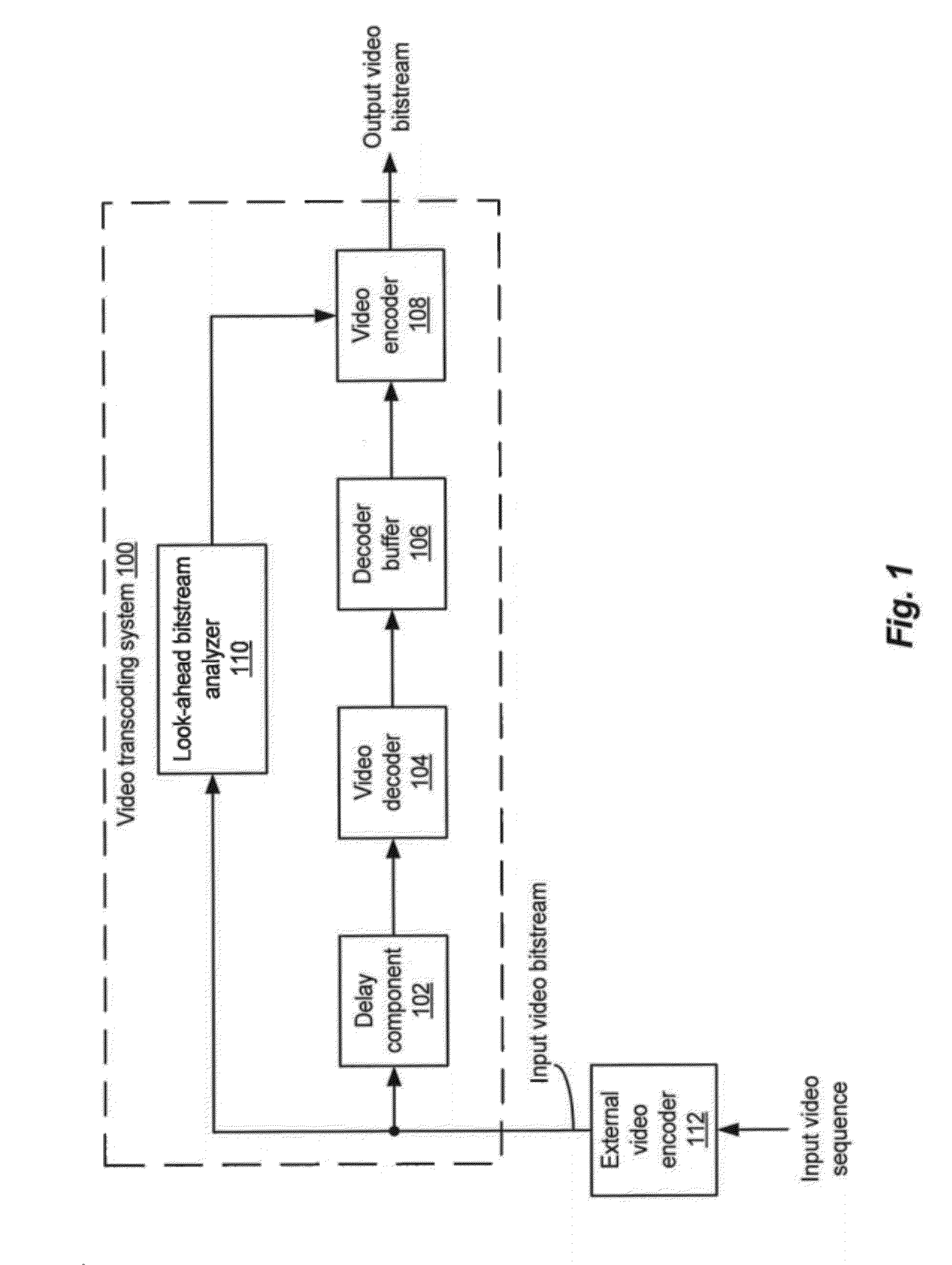
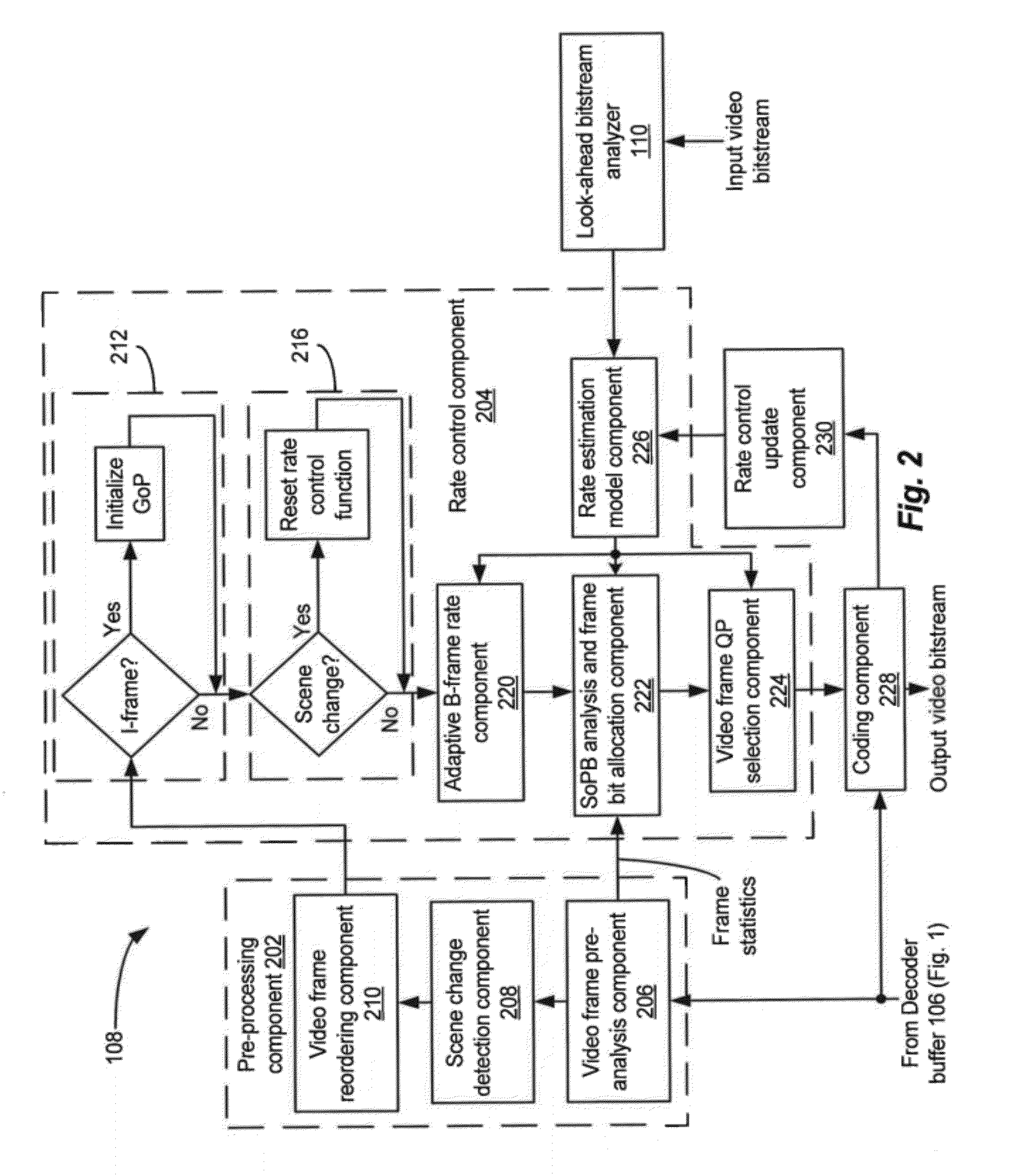
Rate control with look-ahead for video transcoding
ActiveUS20120269258A1Improve QoEImprove perceived qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamComputer graphics (images)
Systems and methods of transcoding video bitstreams that employ look-ahead approaches to enhance the overall perceptual quality of transcoded video information, communications, and entertainment delivered to an end user. The disclosed systems and methods of transcoding video bitstreams take into account the scene characteristics and the local coding complexity of video frames in a video sequence before performing bit allocations for the video frames, thereby significantly improving the perceptual quality of transcoded video delivered to the end user.
Owner:DIALOGIC INC
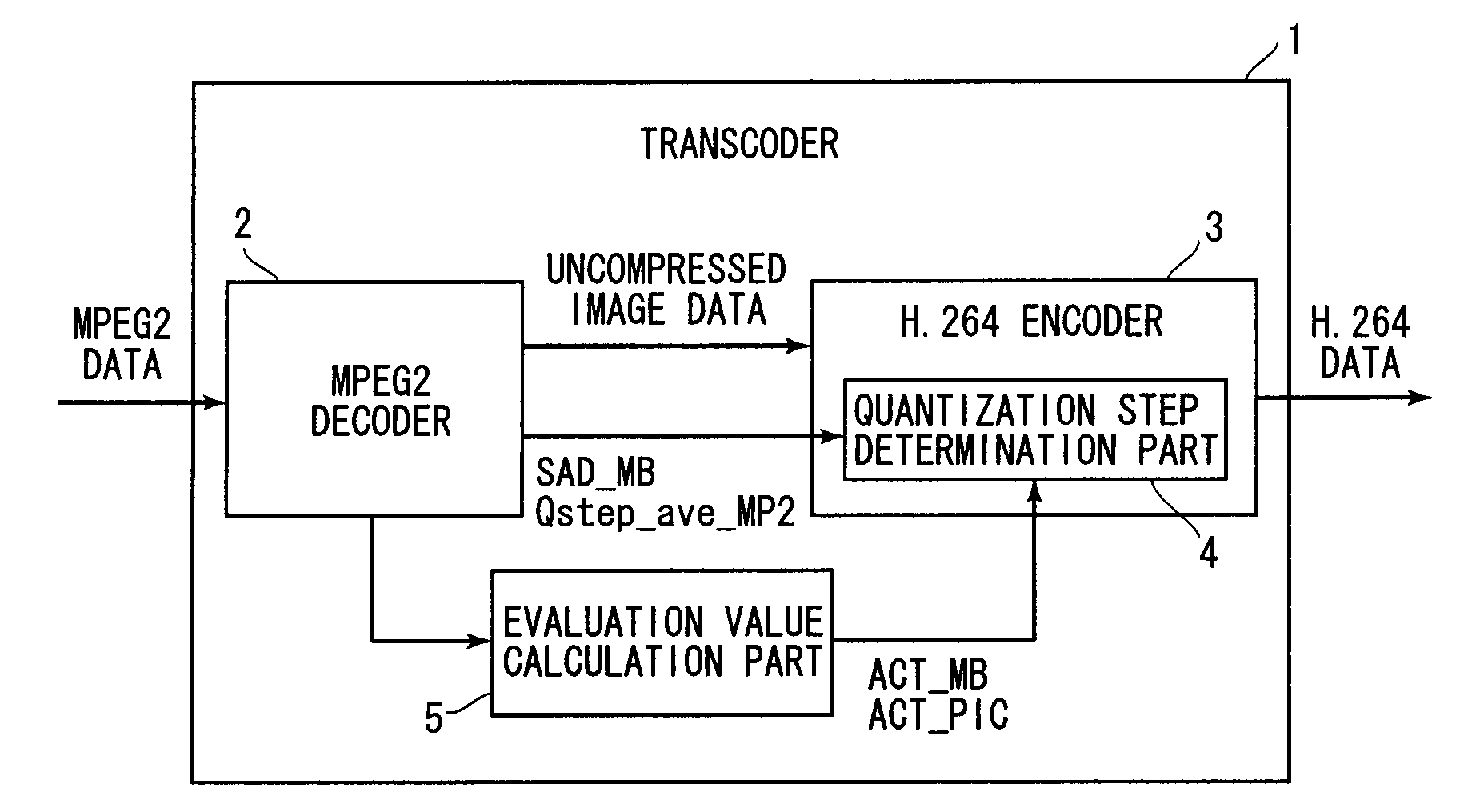
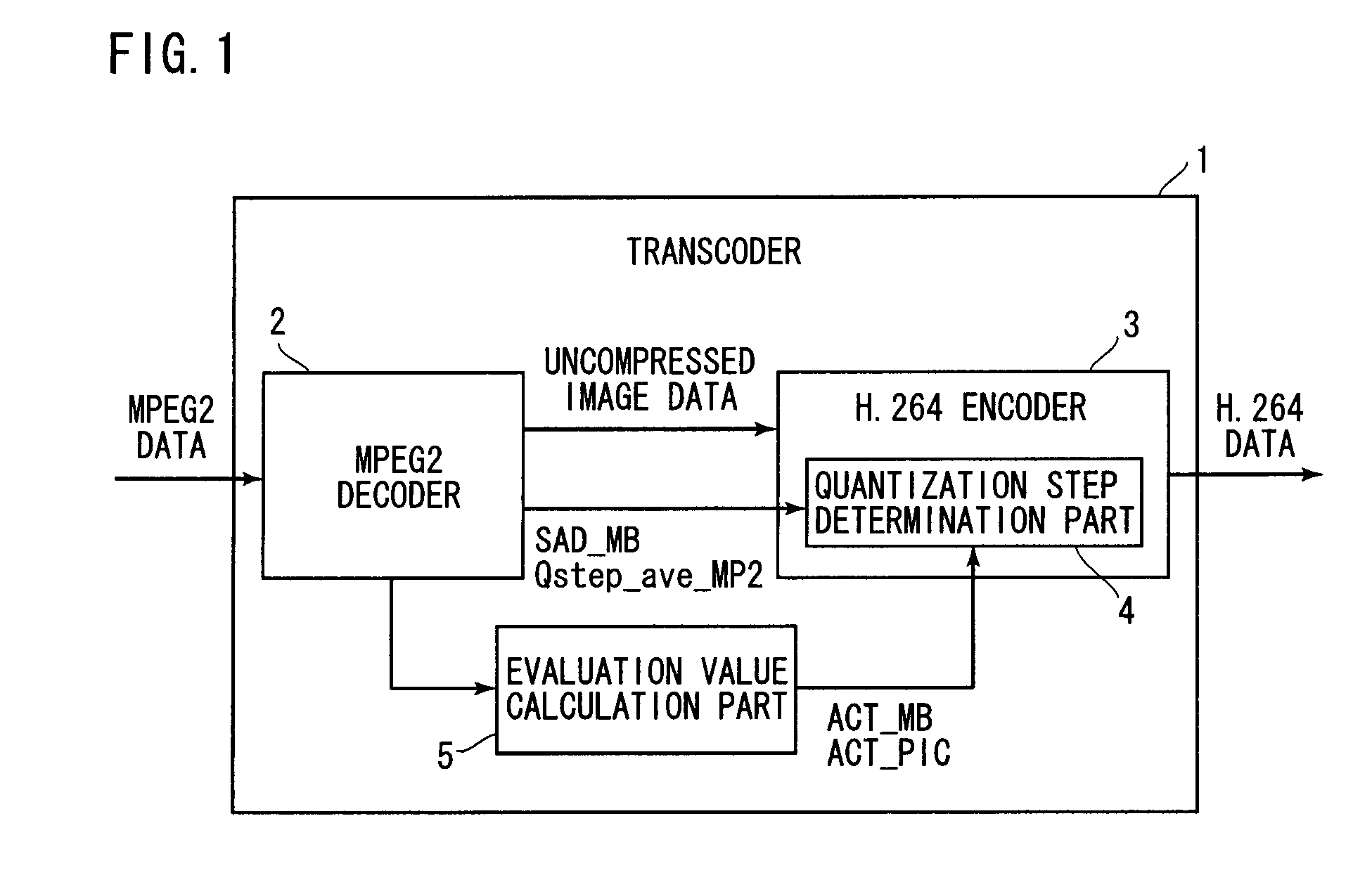
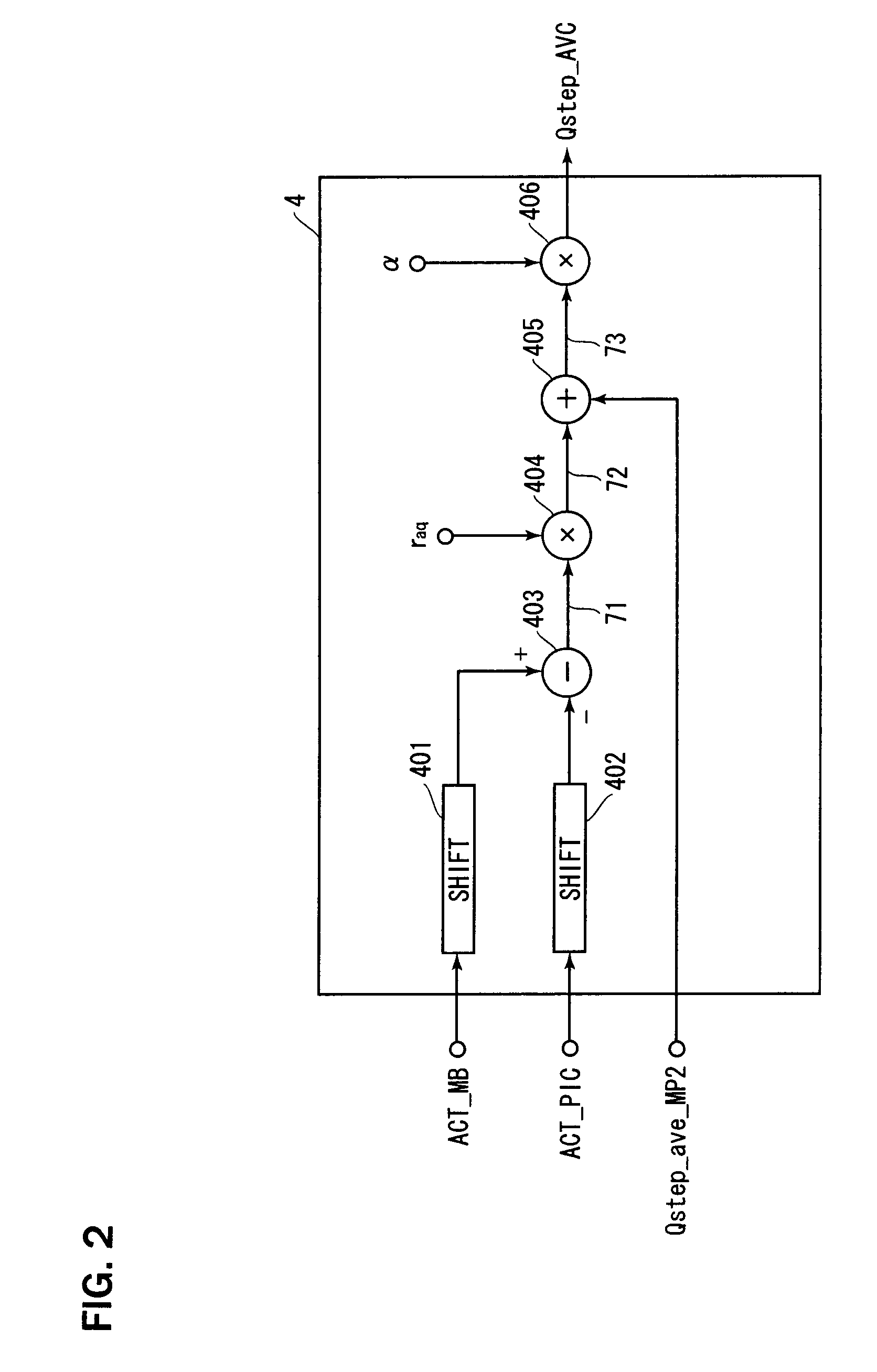
Transcoder and coded image conversion method
ActiveUS20080031337A1Quality improvementReduce the amount requiredColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmBit allocation
A quantization step determination part inputs an evaluation value (ACT_MB) indicating the dispersion in a macroblock and its average value (ACT_PIC). A subtracter obtains the difference between these values, and a multiplier multiplies the difference by raq (<1) to obtain a weighting value. Next, an adder adds the weighting value to an average quantization step value of source data, and finally a multiplier multiplies the sum by a step value adjustment factor α (>1) to obtain a converted quantization step value (Qstep_AVC). This optimizes a bit allocation in accordance with an Activity value of the macroblock, to thereby improve the quality of image.
Owner:MEGACHIPS +1
Systems methods for adjusting targeted bit allocation based on an occupancy level of a VBV buffer model
InactiveUS20080123738A1Improve bit rate controlColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBit allocationParallel computing
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that advantageously improve bit rate control in a video encoder, such as an MPEG video encoder. One embodiment of the invention advantageously varies the targeted bit allocation for a picture to be encoded based on an occupancy level of a buffer model, such as a video buffer verifier (VBV) buffer model.
Owner:COREL CORP
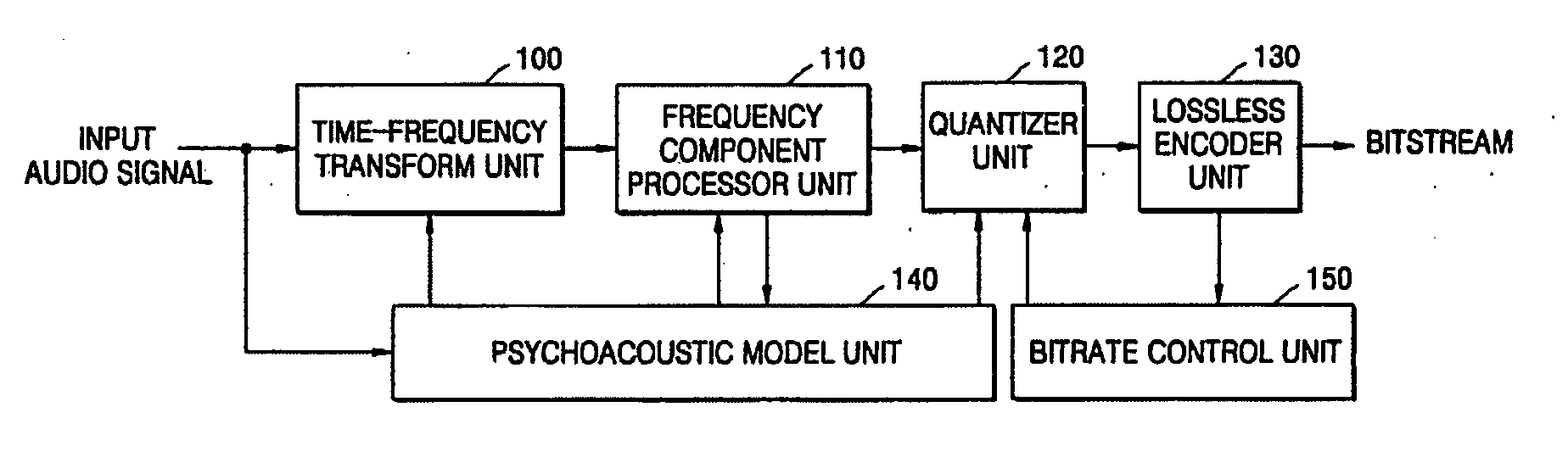
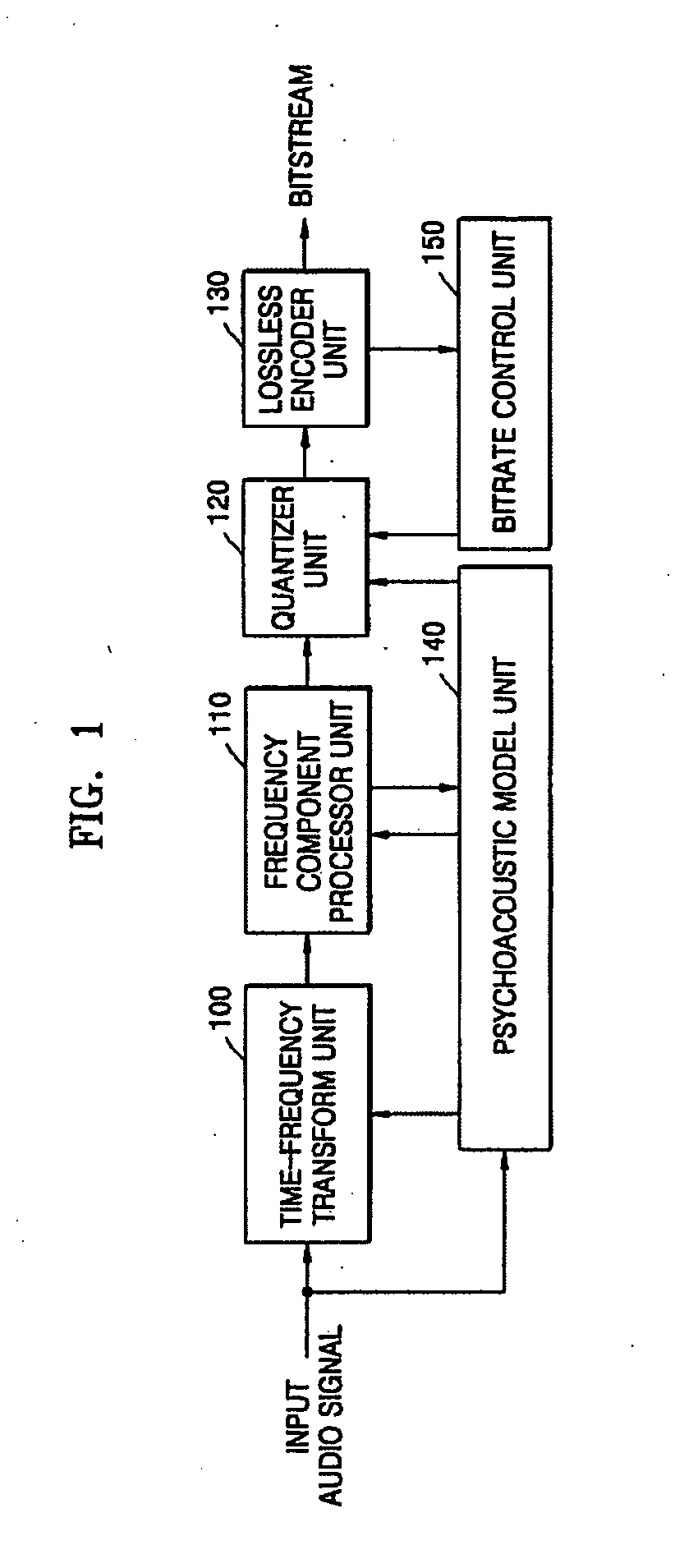
Low-bitrate encoding/decoding method and system
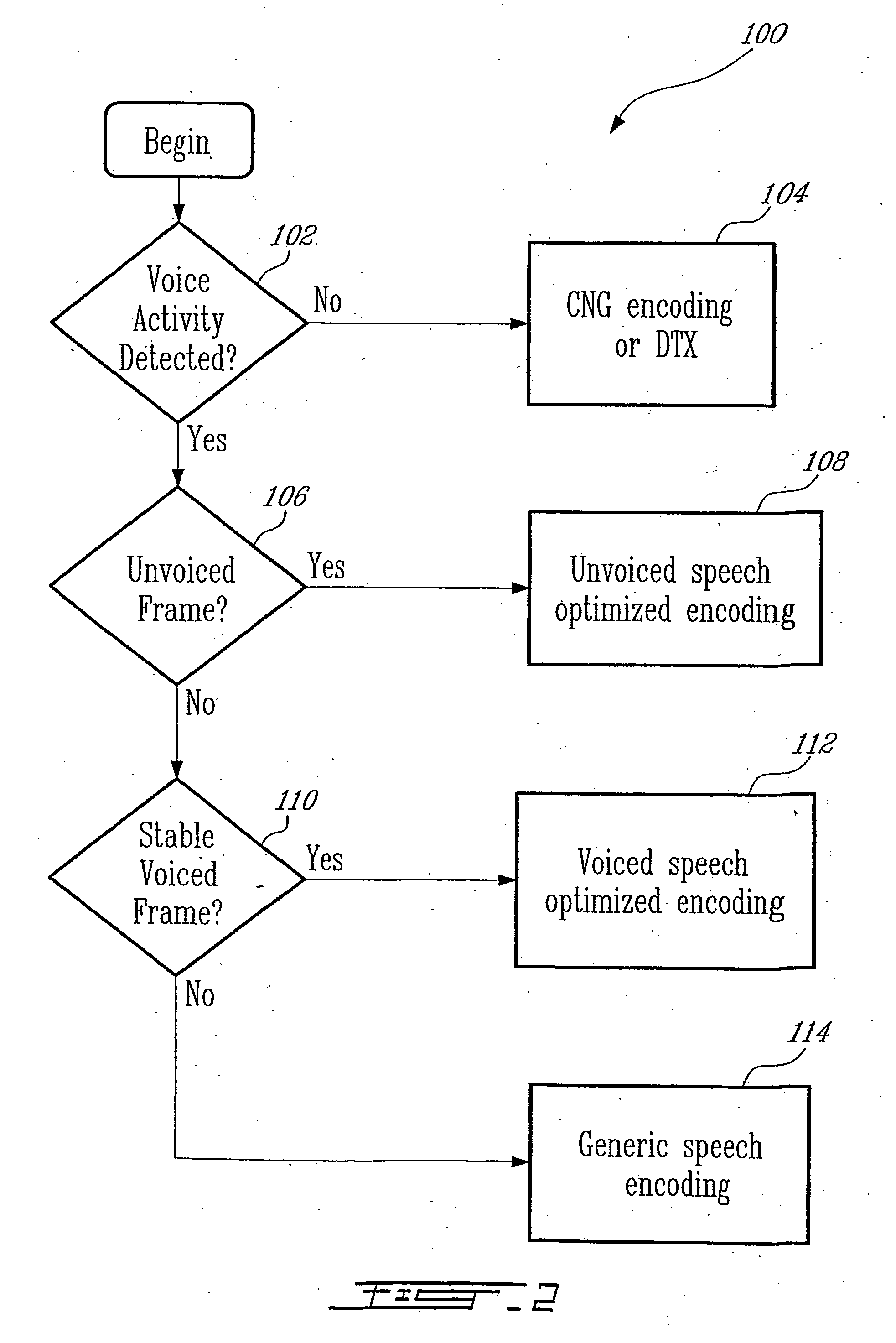
InactiveUS20060004566A1Efficient compressionHigh-quality audio signalSpeech analysisCode conversionBit allocationAudio signal
A low-bitrate encoding system includes: a time-frequency transform unit transforming an input time-domain audio signal into a frequency-domain audio signal; a frequency component processor unit decimating frequency components in the frequency-domain audio signal; a psychoacoustic model unit modeling the received time-domain audio signal on the basis of human auditory characteristics, and calculating encoding bit allocation information; a quantizer unit quantizing the frequency-domain audio signal input from the frequency component processor unit to have a bitrate based on the encoding bit allocation information input from the psychoacoustic model unit; and a lossless encoder unit encoding the quantized audio signal losslessly, and outputting the encoded audio signal in a bitstream format. Using the low-bitrate encoding system, it is possible to effectively compress data at a low bitrate, and thus to provide a high quality audio signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
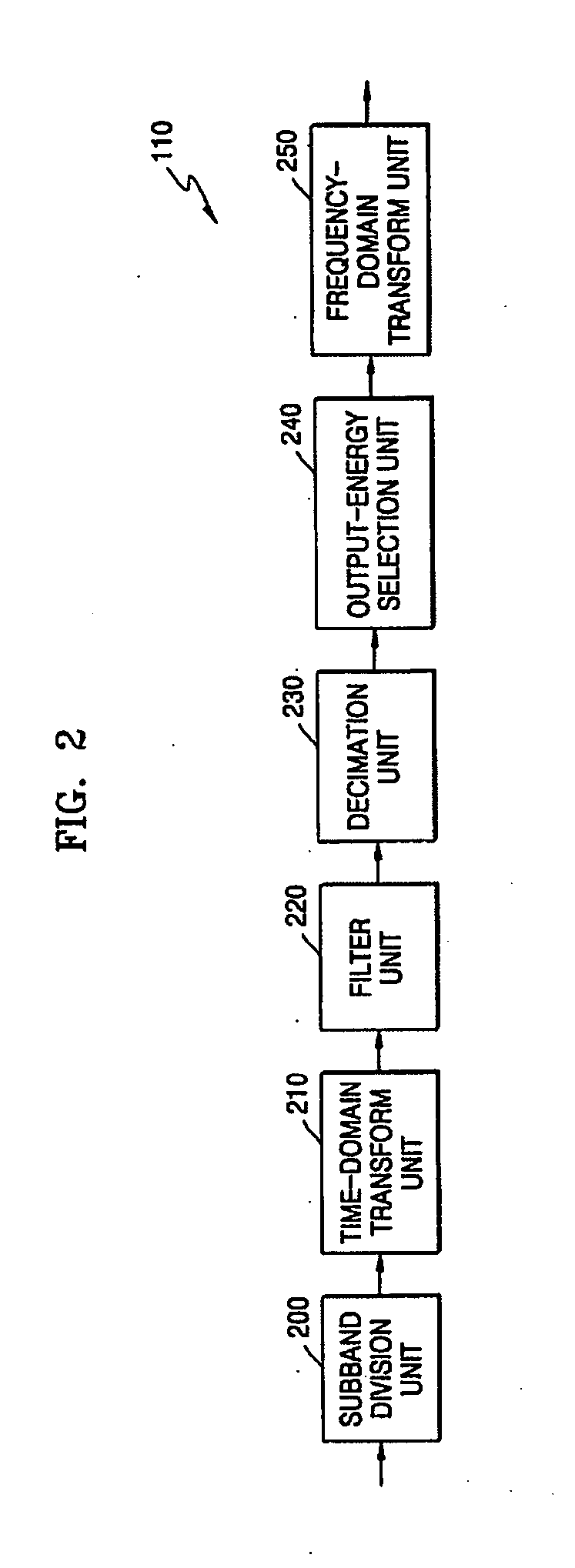
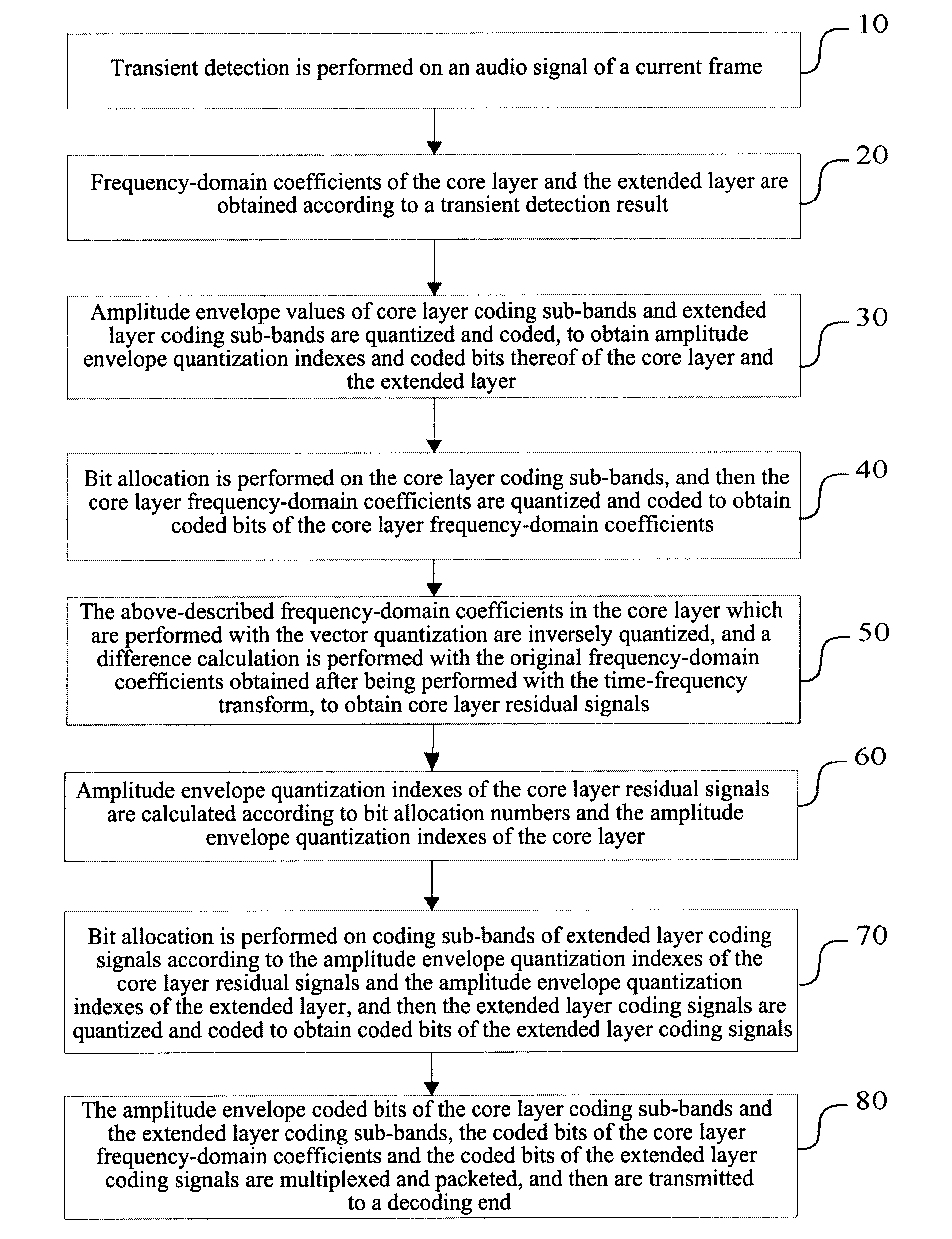
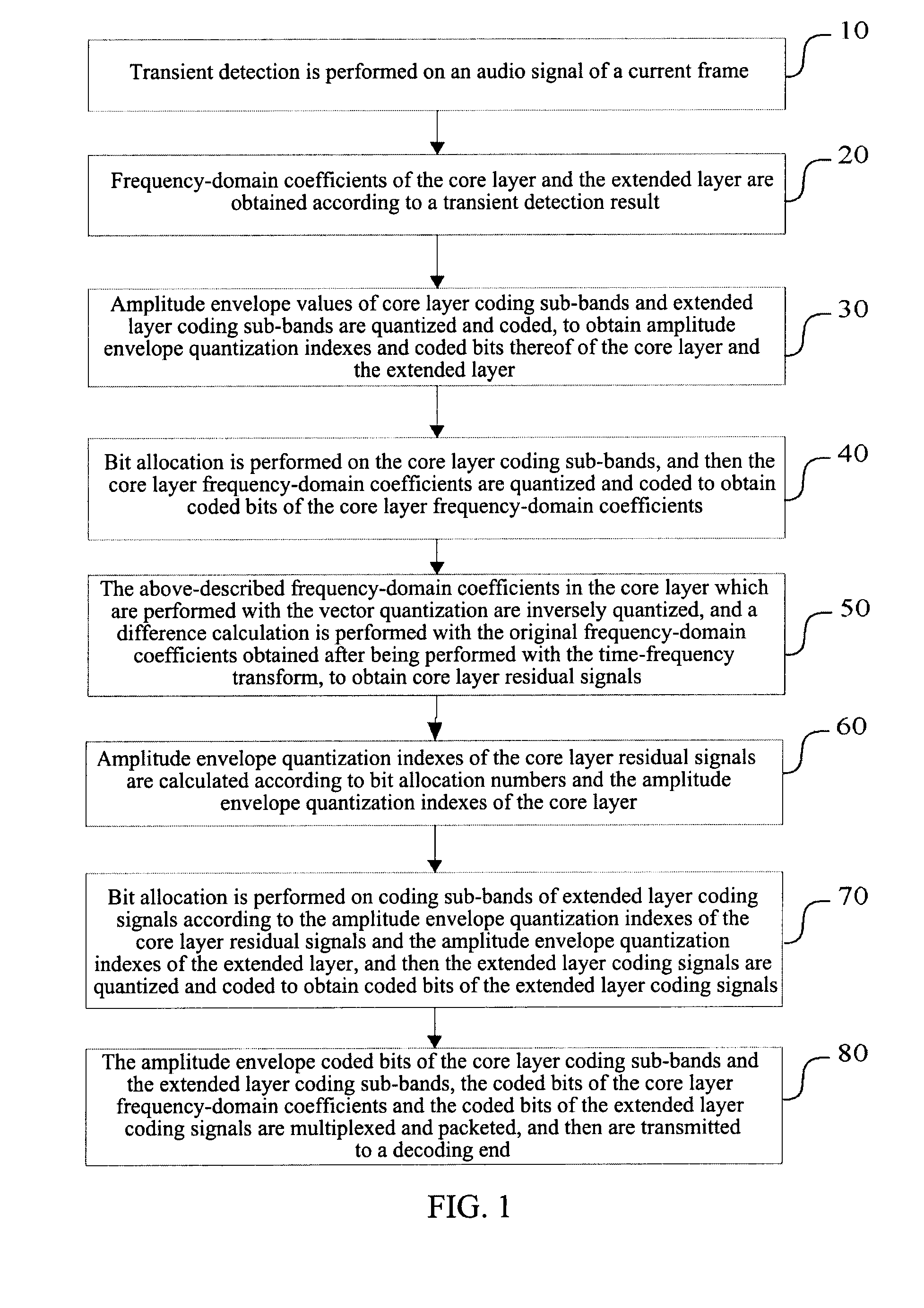
Hierarchical Audio Frequency Encoding and Decoding Method and System, Hierarchical Frequency Encoding and Decoding Method for Transient Signal
ActiveUS20120323582A1Improve coding efficiencyQuality improvementSpeech analysisDecoding methodsComputer architecture
Hierarchical audio coding and decoding method and system and hierarchical audio coding and decoding method for transient signals are provided. In the present invention, by introducing a processing method for transient signal frames in the hierarchical audio coding and decoding methods, a segmented time-frequency transform is performed on the transient signal frames, and then the frequency-domain coefficients obtained by transformation are rearranged respectively within the core layer and within the extended layer, so as to perform the same subsequent coding processes, such as bit allocation, frequency-domain coefficient coding, etc., as those on the steady-state signal frames, thus enhancing the coding efficiency of the transient signal frames and improving the quality of the hierarchical audio coding and decoding.
Owner:ZTE CORP
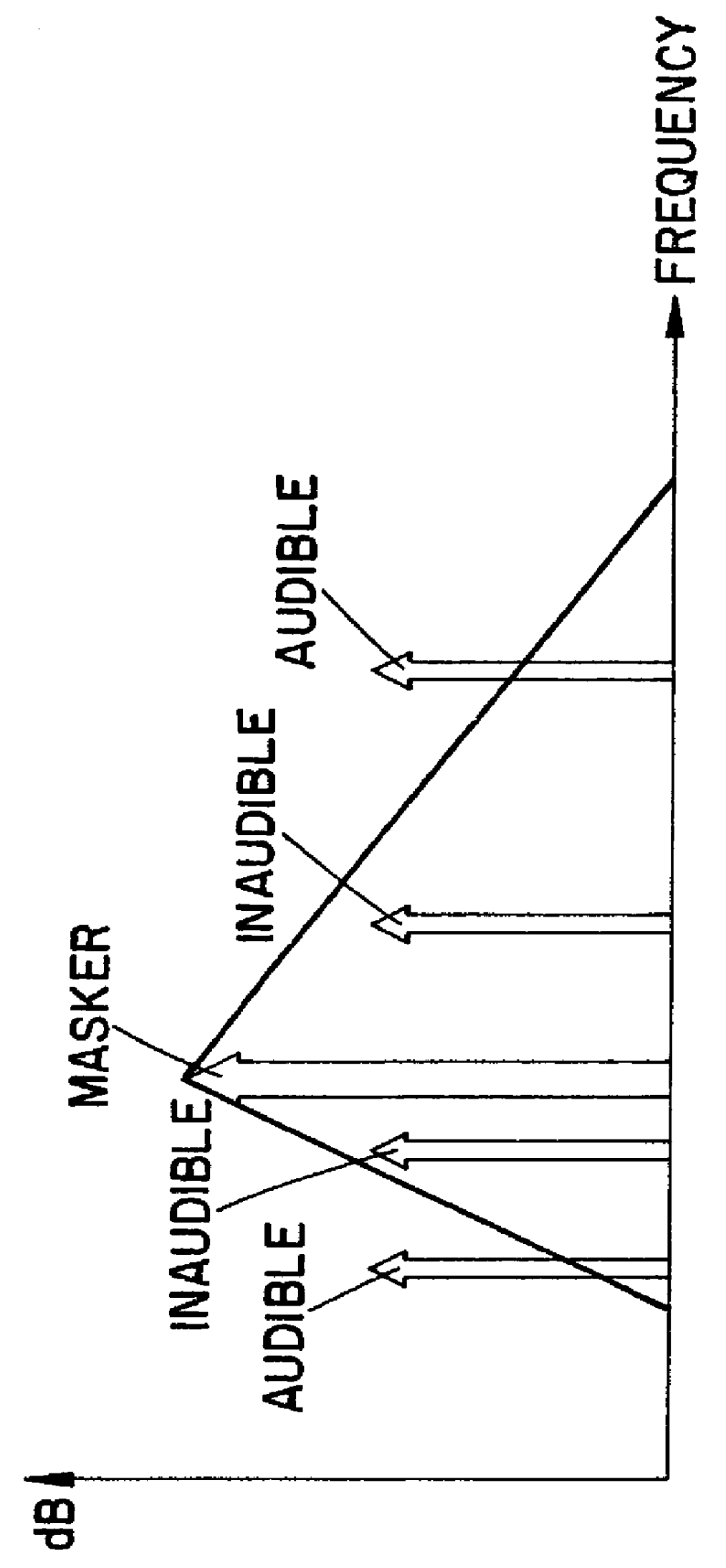
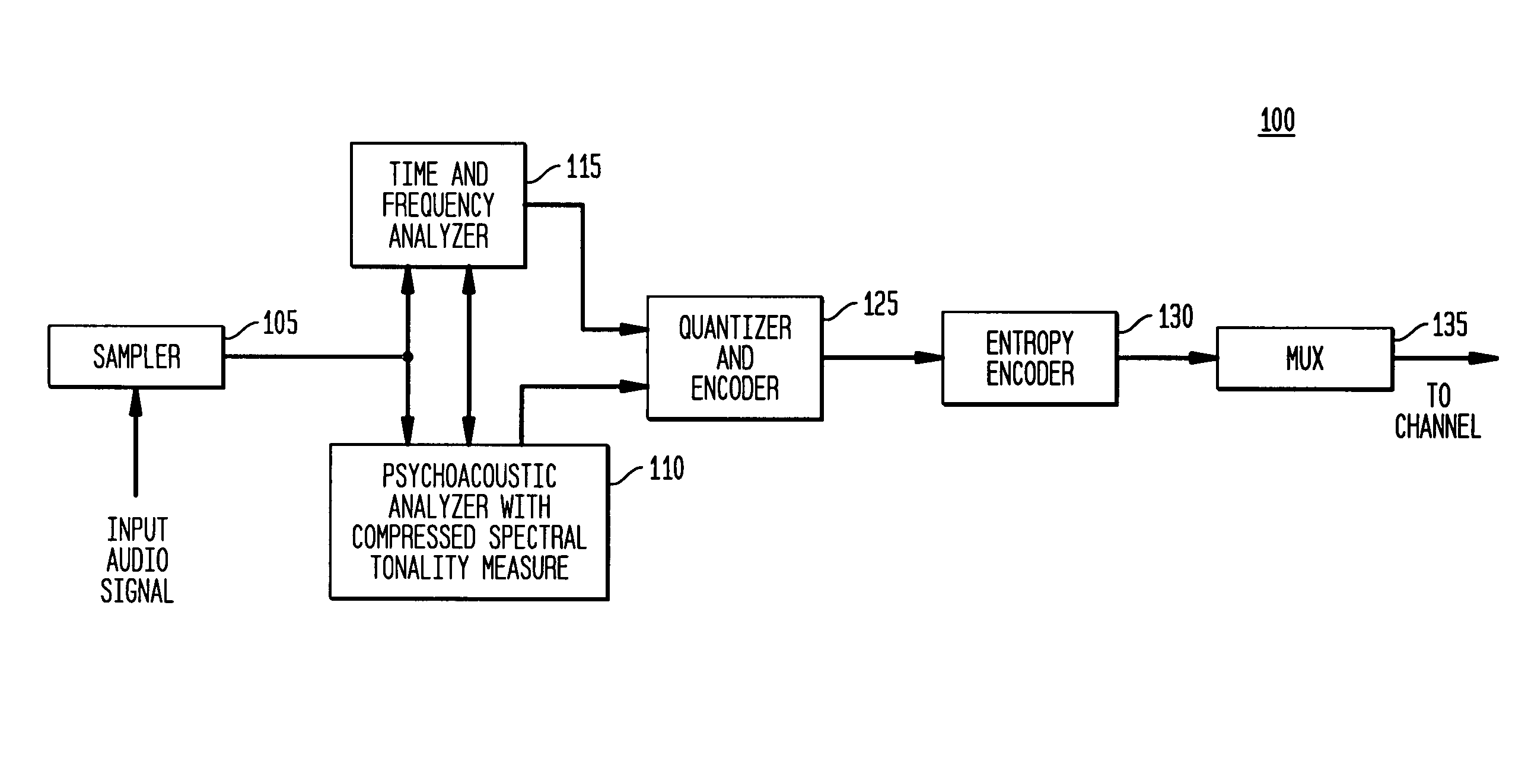
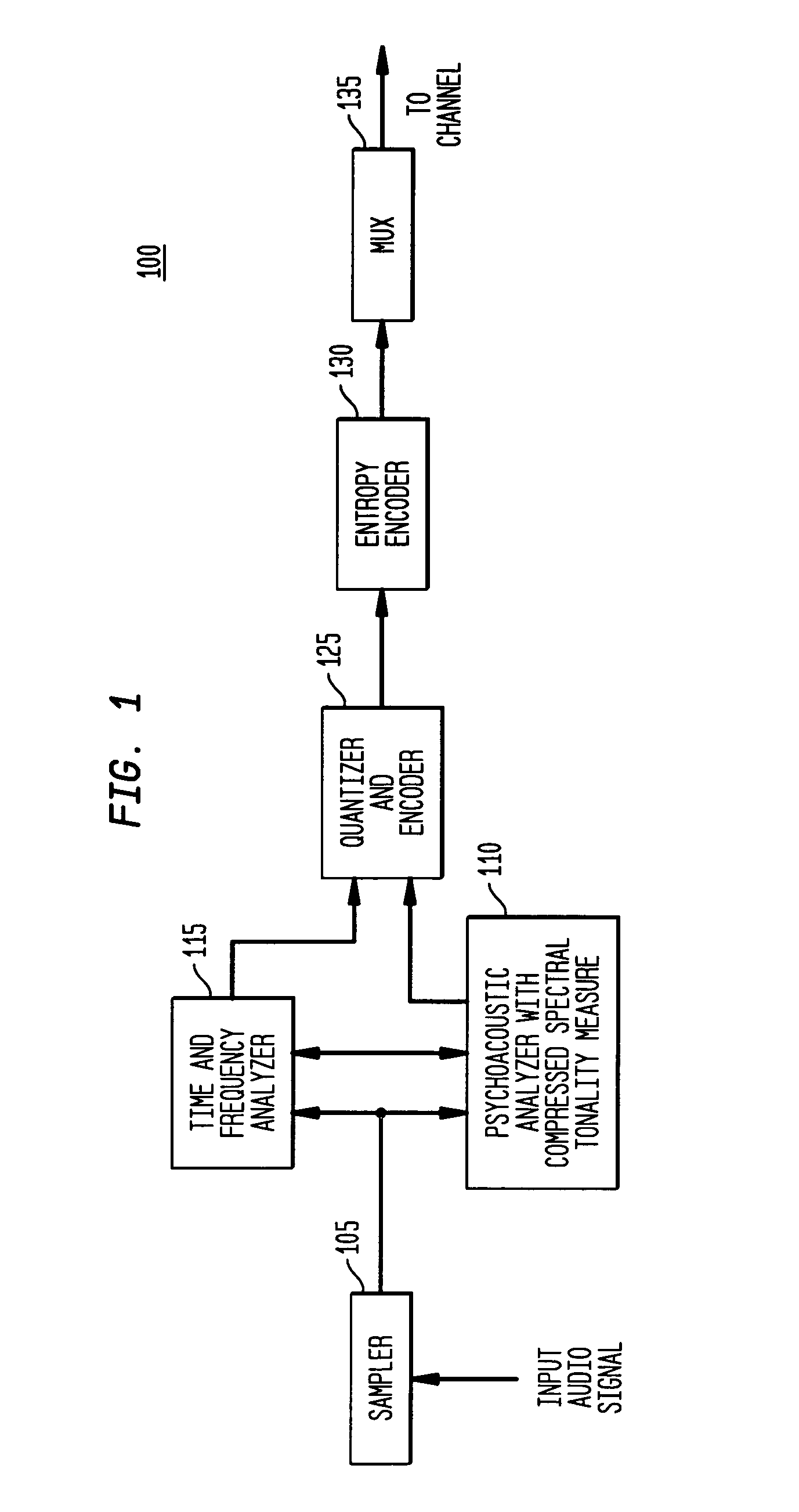
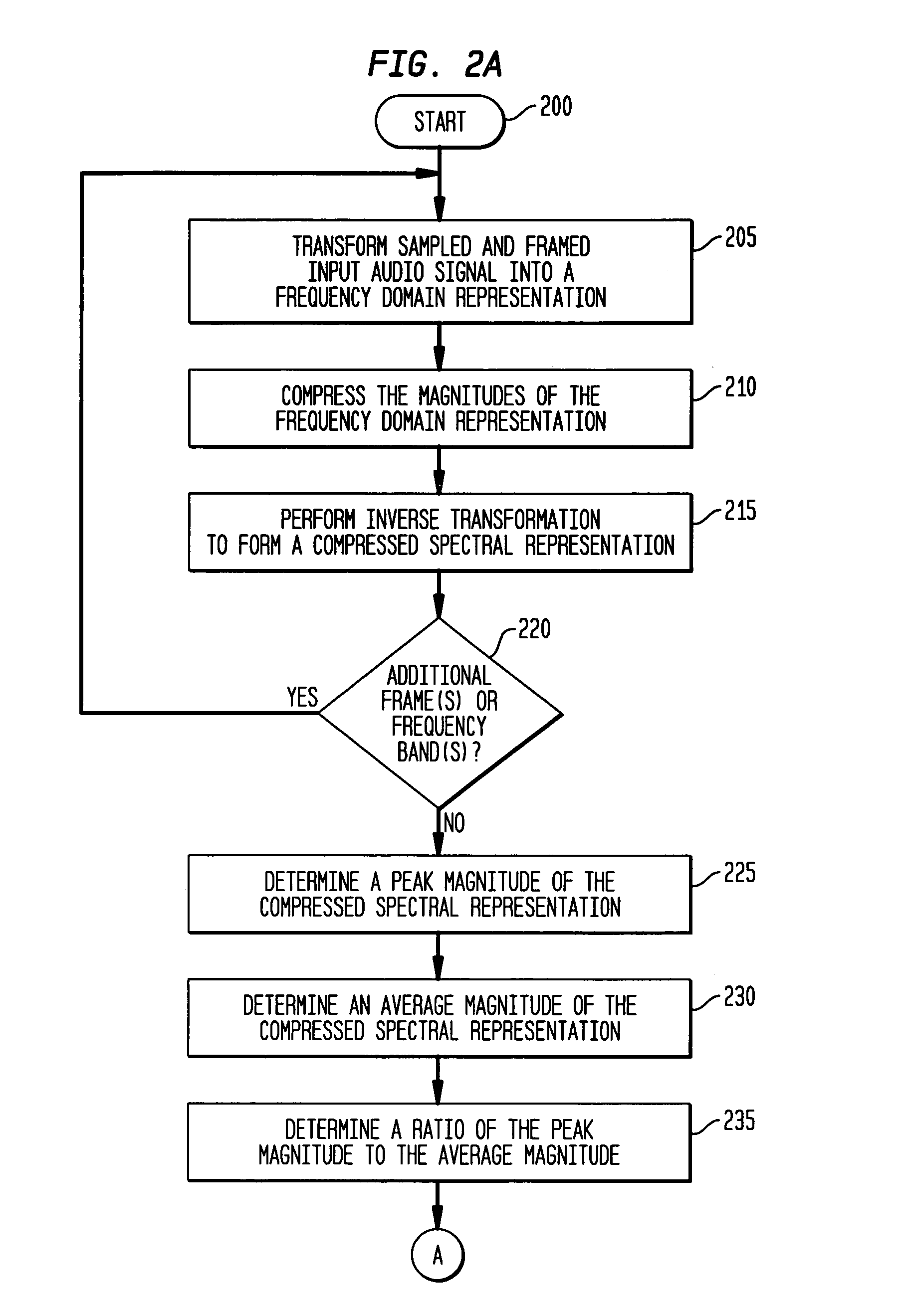
Tonal analysis for perceptual audio coding using a compressed spectral representation
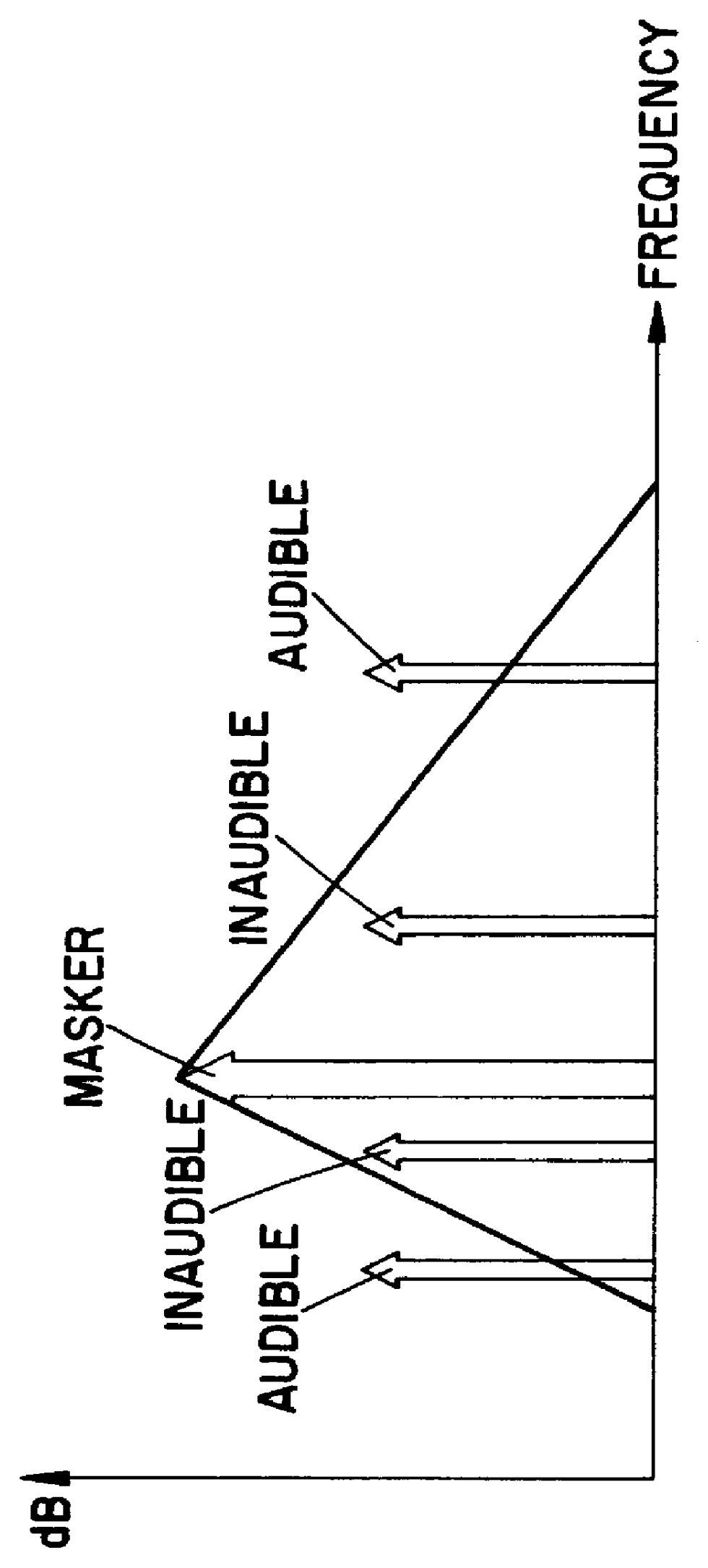
The present invention provides an apparatus, method and tangible medium storing instructions for determining tonality of an input audio signal, for selection of corresponding masked thresholds for use in perceptual audio coding. In the various embodiments, the input audio signal is sampled and transformed using a compressed spectral operation to form a compressed spectral representation, such as a cepstral representation. A peak magnitude and an average magnitude of the compressed spectral representation are determined. Depending upon the ratio of peak-to-average magnitudes, a masked threshold is selected having a corresponding degree of tonality, and is used to determine a plurality of quantization levels and a plurality of bit allocations to perceptually encode the input audio signal with a distortion spectrum beneath a level of just noticeable distortion (JND). The invention also includes other methods and variations for selecting substantially tone-like or substantially noise-like masked thresholds for perceptual encoding of the input audio signal.
Owner:MUCH SHELIST FREED DENENBERG ARNENT & RUBENSTEIN P C +1
System and method to control compressed video picture quality for a given average bit rate
InactiveUS20080232459A1Limit bit rateAvoid adjustmentColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBit allocationGroup of pictures
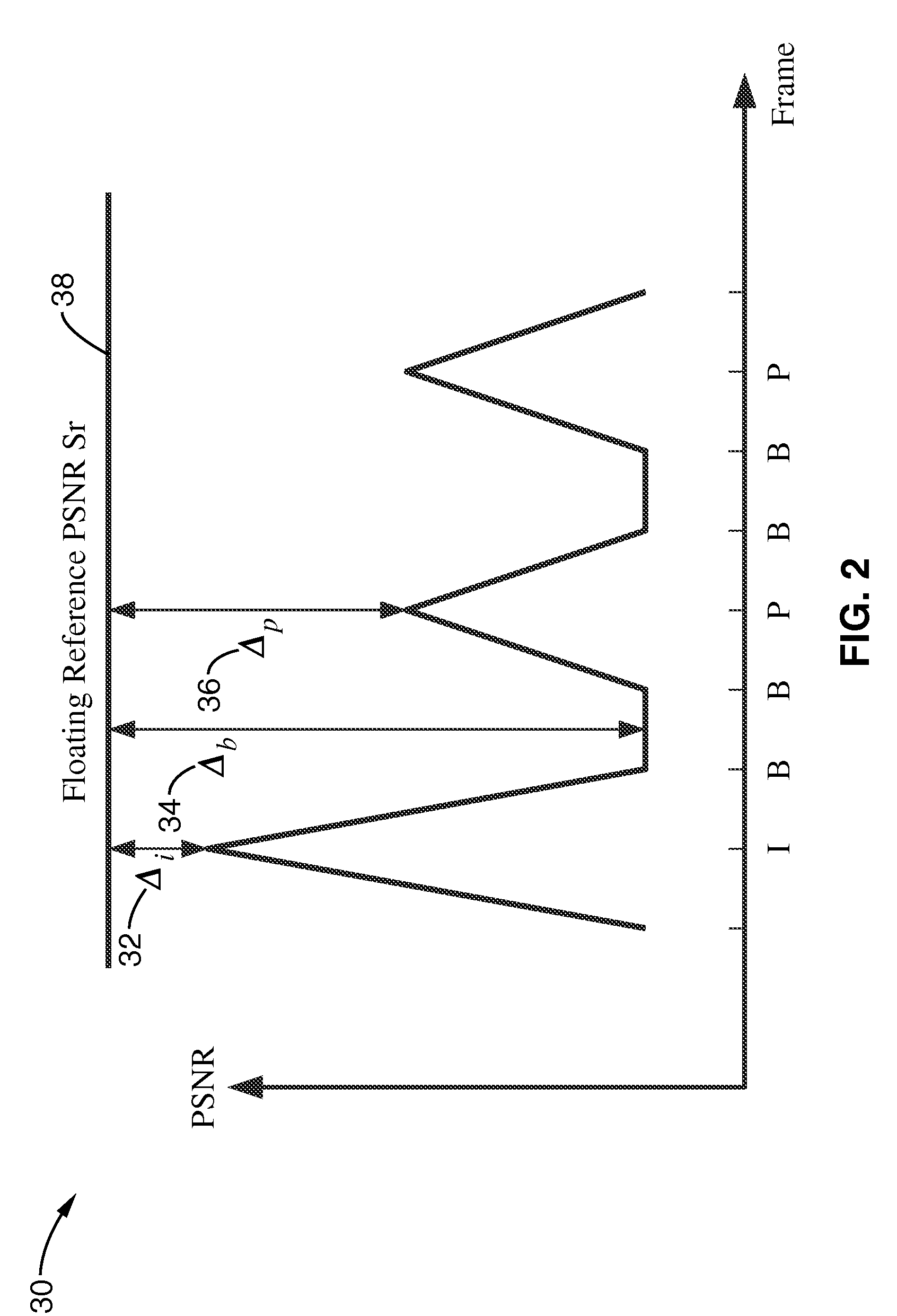
Picture level rate control systems, apparatuses and methods are described which indirectly control bit rate through peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), thereby providing a stable PSNR while maintaining a given target average bit rate. In a preferred implementation, encoding is performed in conjunction with macroblock QP modulation. In this way, the picture level rate control provides stable temporal quality and the macroblock QP modulation provides stable spatial quality. By way of example, the number of bits generated in a group of pictures (GOP) is controlled by modulating the target bit allocation for a group of pictures (GOP) based on coded picture buffer (CPB) fullness. Macroblocks are encoded for each picture based on a rate-distortion model, which is modified in response to the relative fluctuation of PSNR of pictures within a group of pictures.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Adaptive Allocation For Variable Bandwidth Multicarrier Communication
InactiveUS20060209894A1Time-division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsControl communicationsBit allocation
Data is distributed among the channels of an asynchronous data subscriber loop (ADSL) communications system in accordance with an adaptive algorithm which from time to time measures the signal to noise ratio of the various channels and finds a margin for each channel dependent on achievement (where possible) of a given bit error rate and a desired data transmission rate. The margin distribution is achieved by augmenting the constellation signal to noise ratio to enhance computational efficiency and allow redetermination of bit allocation tables during transmission as necessary. Pairs of bit allocation tables are maintained at the transmitter and receiver and one table of each pair at the transmitter and receiver is updated while the other pair is in use for controlling communication.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Scalable and perceptually ranked signal coding and decoding
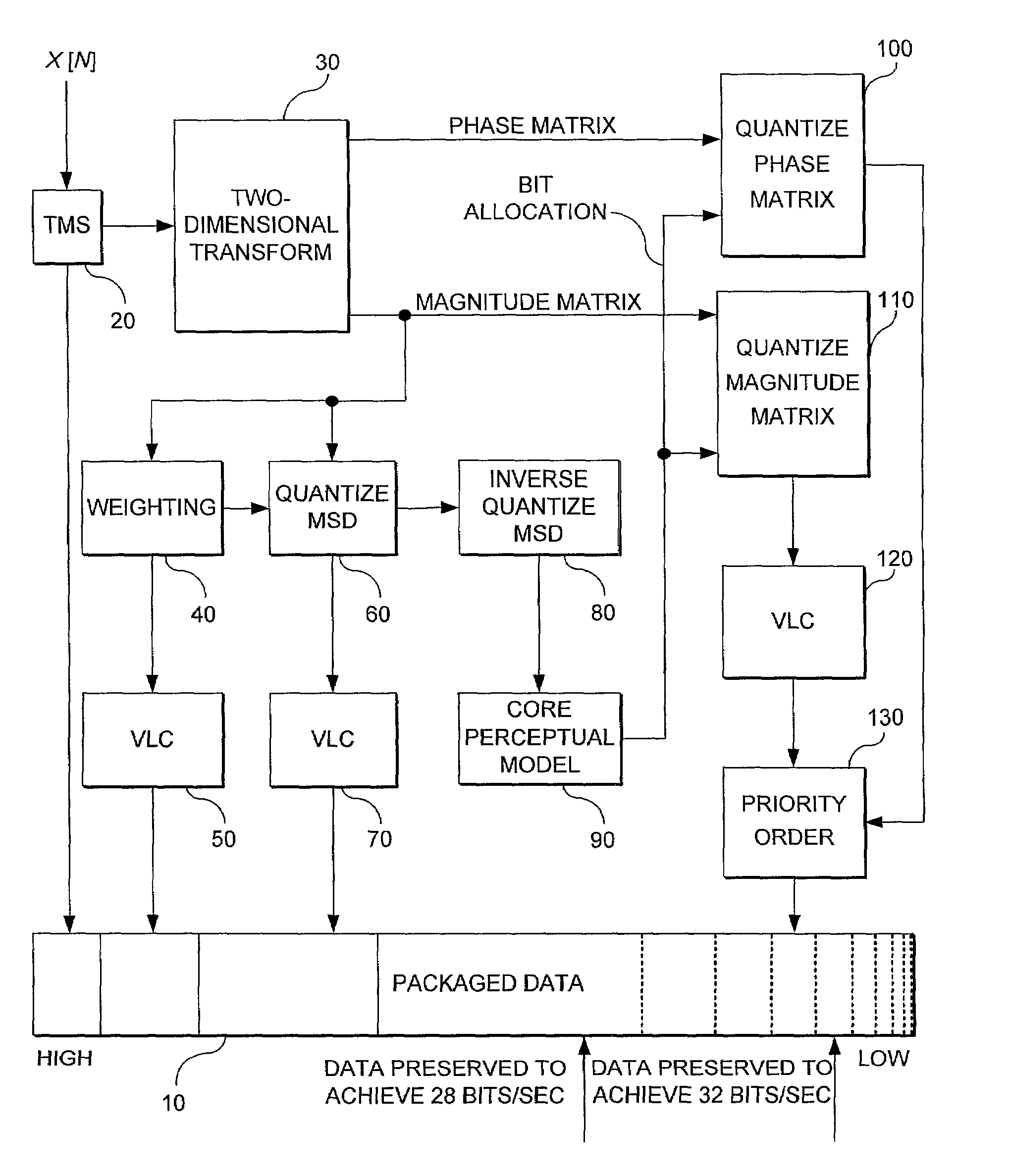
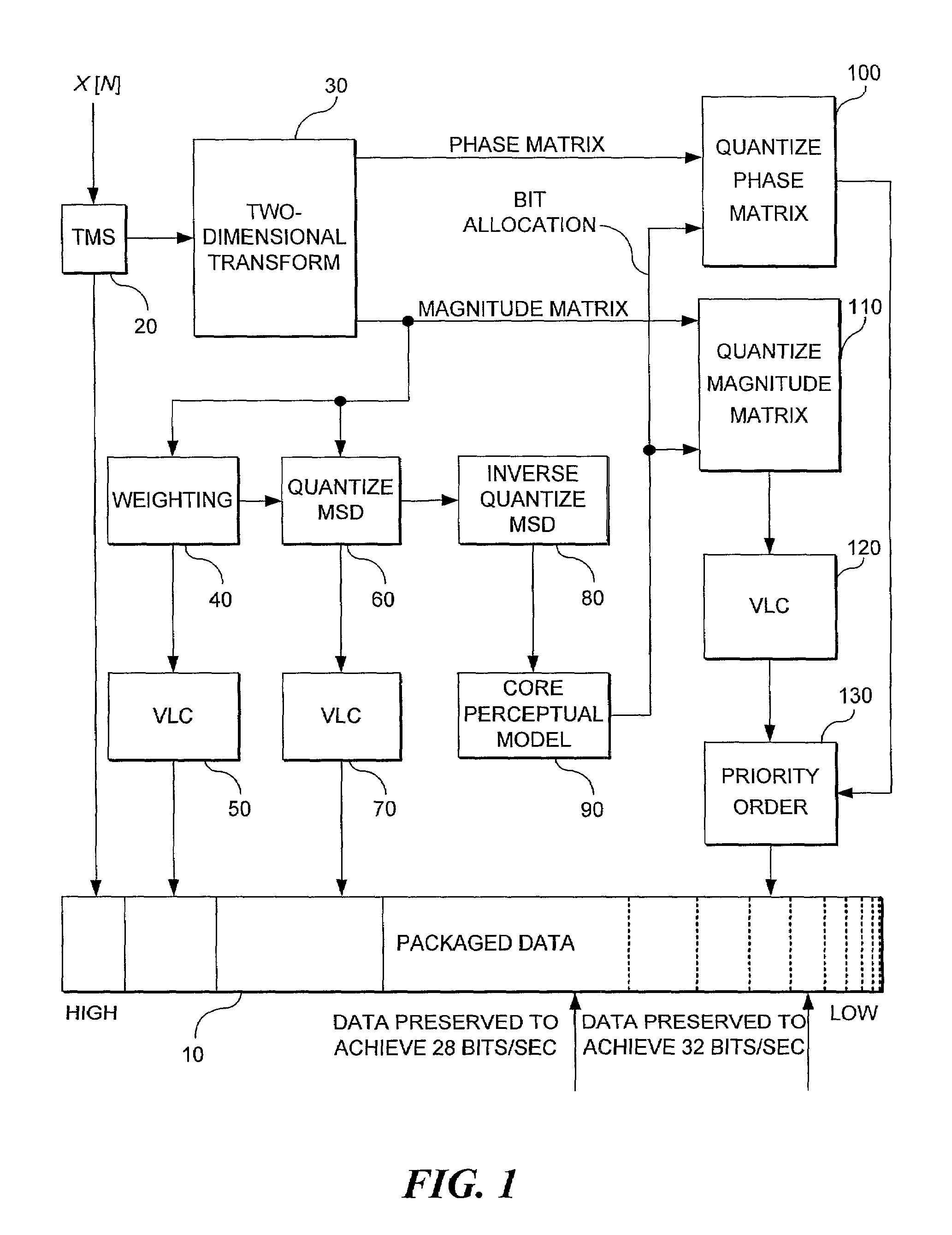
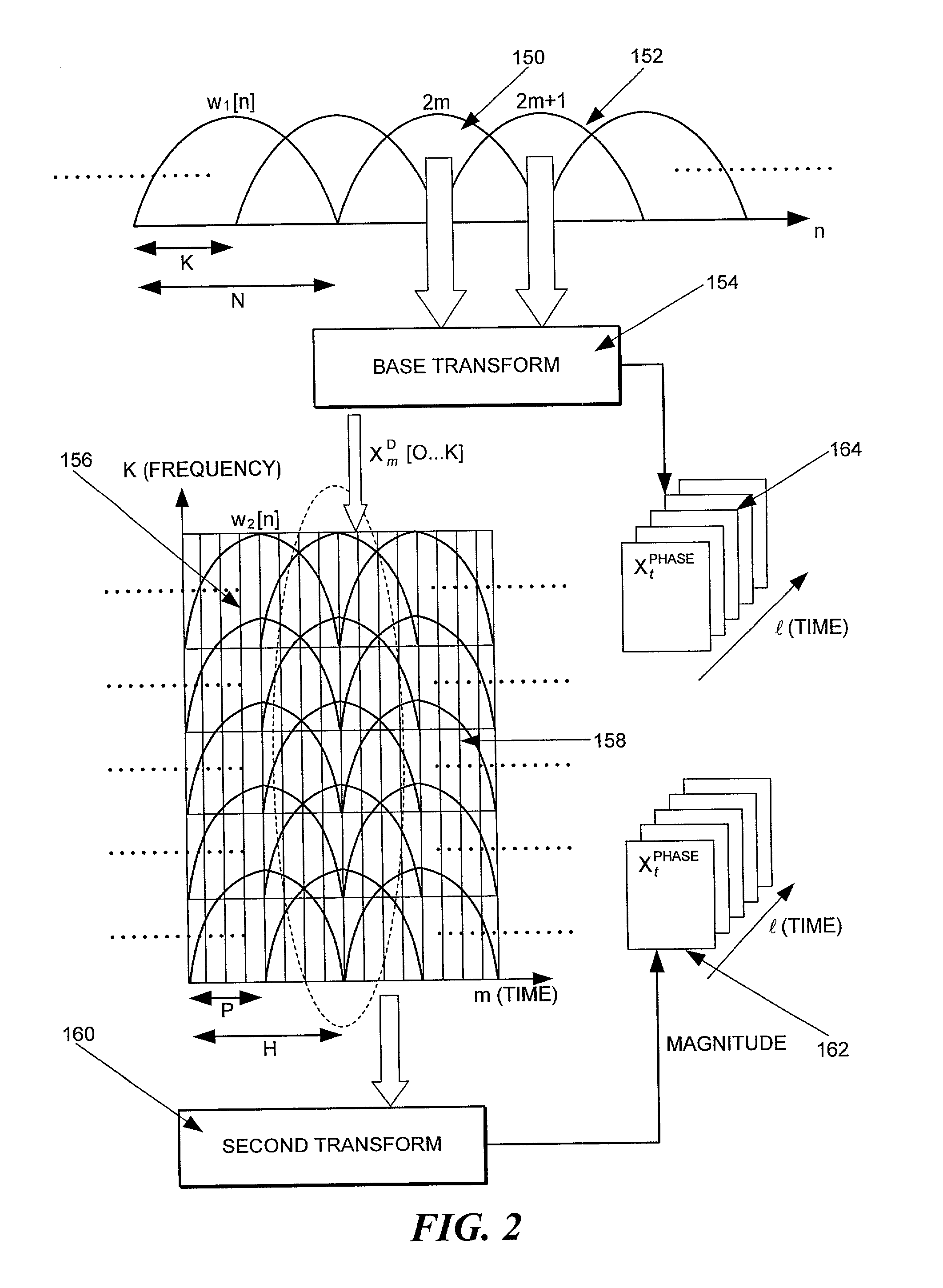
A method and system for encoding and decoding an input signal in relation to the most perceptually relevant aspects of the input signal. A two-dimensional (2D) transform is applied to the input signal to produce a magnitude matrix and a phase matrix that can be inverse quantized by a decoder. A first column of coefficients of the magnitude matrix represents a mean spectral density (MSD) function of the input signal. Relevant aspects of the MSD function are encoded at a beginning of a data packet. The MSD function is also processed through a core perception model to determine bit allocation. The matrices are then quantized and priority ordered into a data packet, with the least perceptually relevant information at the end of the packet so that it may be ignored or truncated for scalability to the channel data rate capacity.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Bit-loading method and system for a DMT transceiver
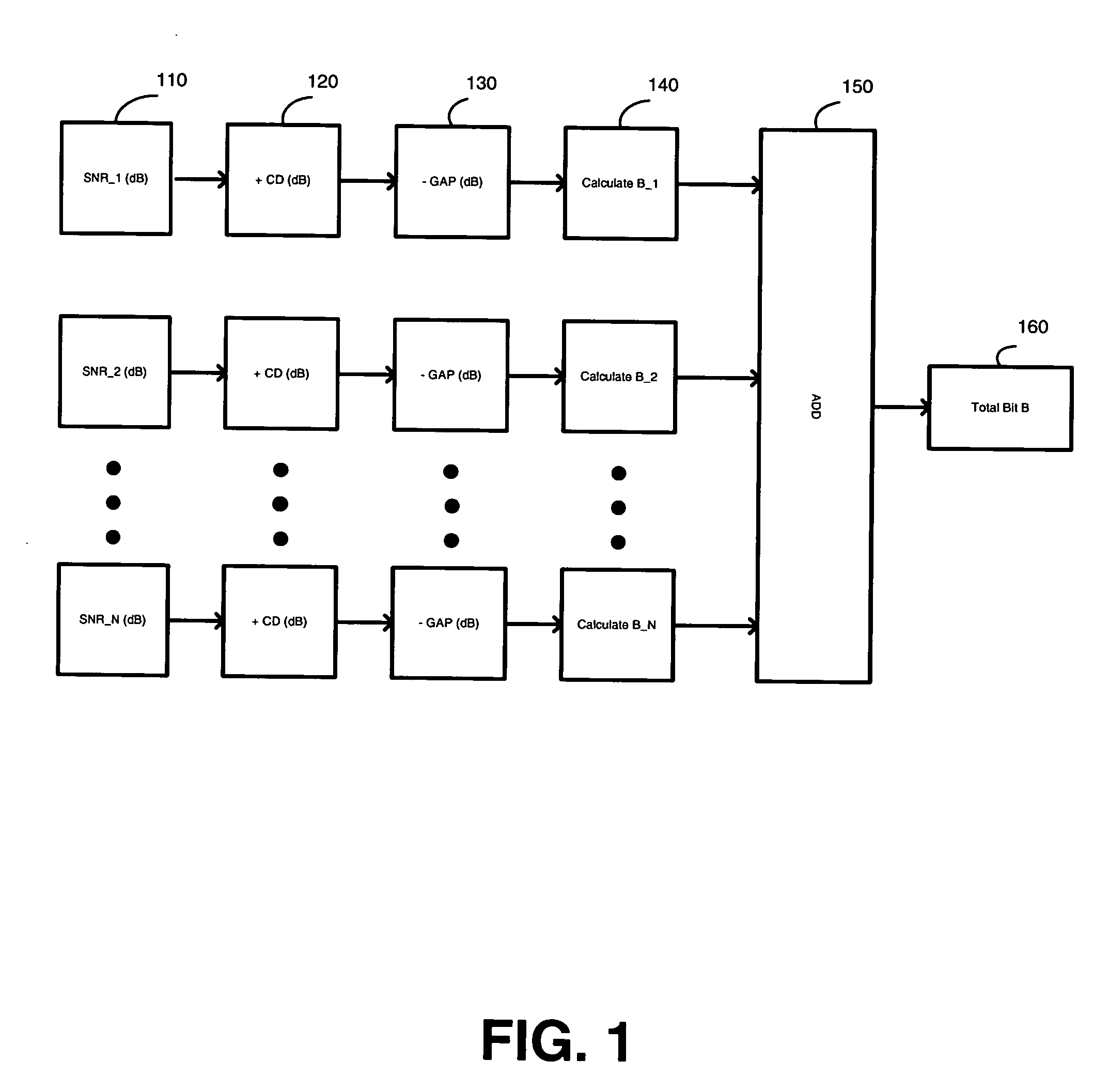
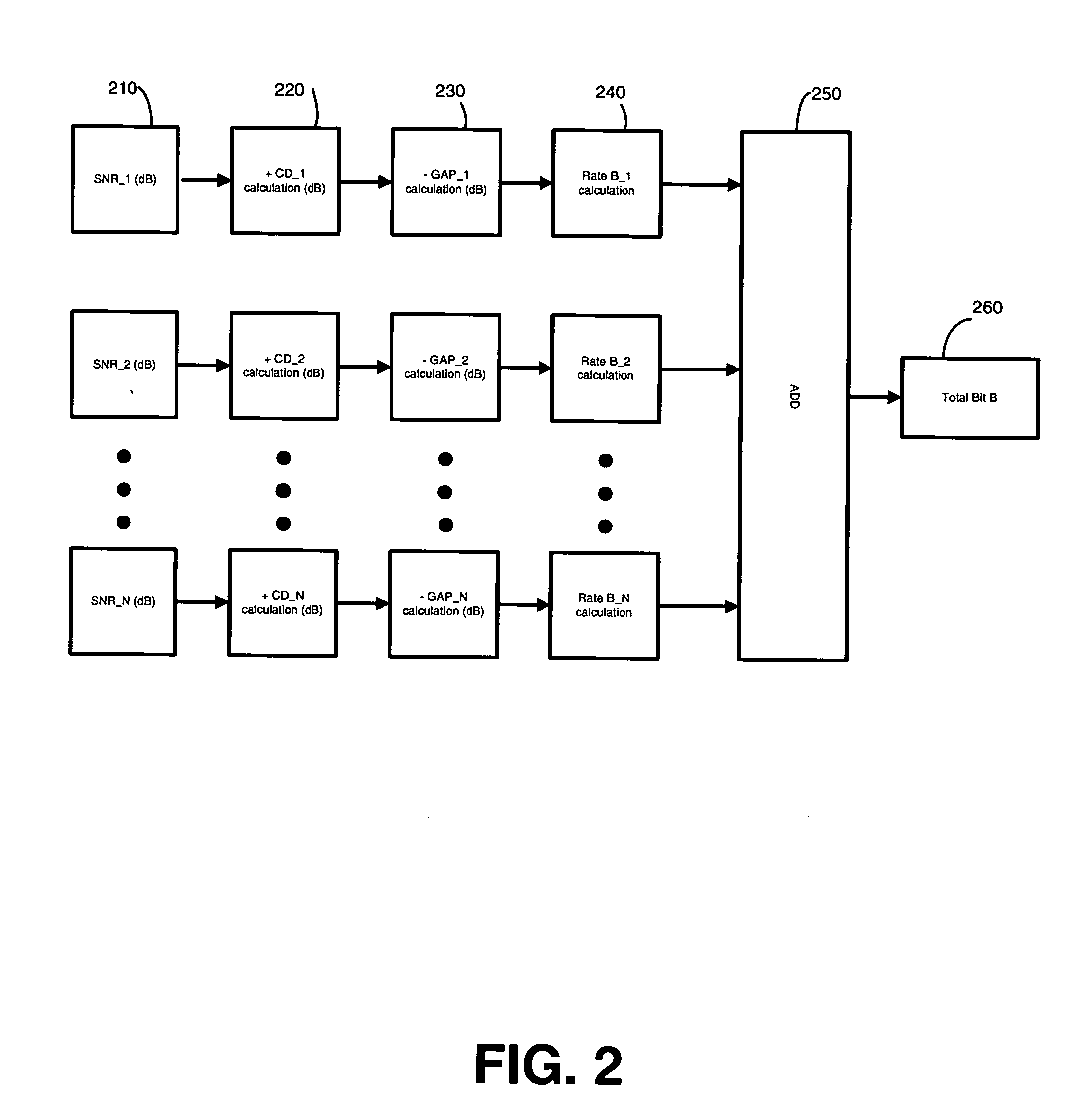
InactiveUS20070147530A1Inhibition effectAvoid large gapsPower managementSecret communicationBit allocationComputer science
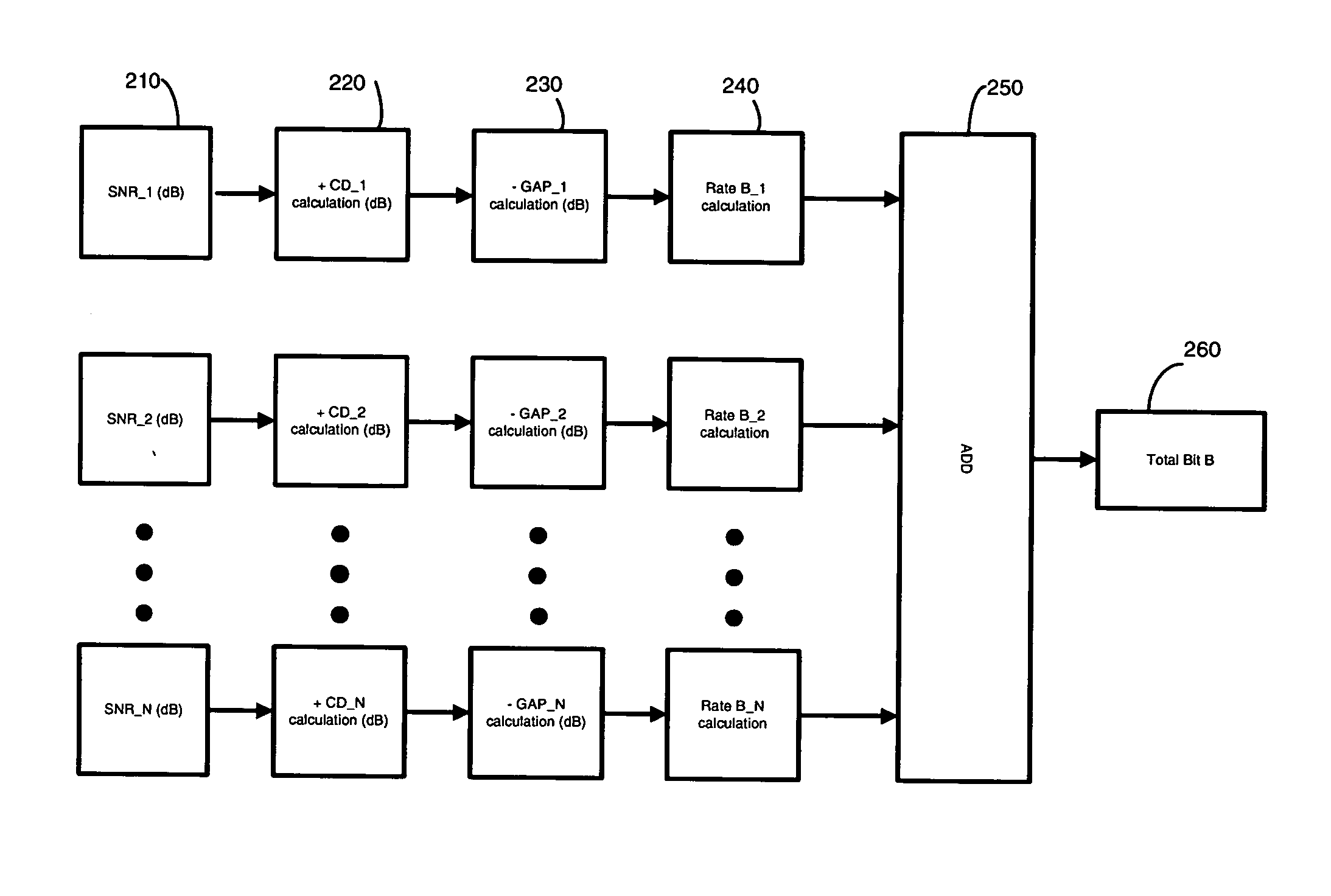
A system and method for a bit-loading algorithm based on an equal error rate principle for each sub-channel (bin) used in a discrete multi-tone modulation (DMT) system. The system and method of the present invention provides a bit-loading algorithm that provides long reach, high data rate and good error performance at a given condition. The bit-loading method and system depends on the Shannon channel capacity formula to allocate bits to different sub-channels. For DMT, the system and method tabulates different SNR GAP for different sub-channels (bins), and constructs a look-up table for the SNR GAP with different bits to achieve a better performance for the DMT system. In addition, Trellis coding across all the sub-channels are optionally supported in DMT, and likewise, the system and method creates another look-up table for variable coding gain provided for the Trellis coding gain in the bit-loading algorithm to further improve the system performance, knowing that the Trellis coding gain is different for different sub-channels with different bit allocation.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
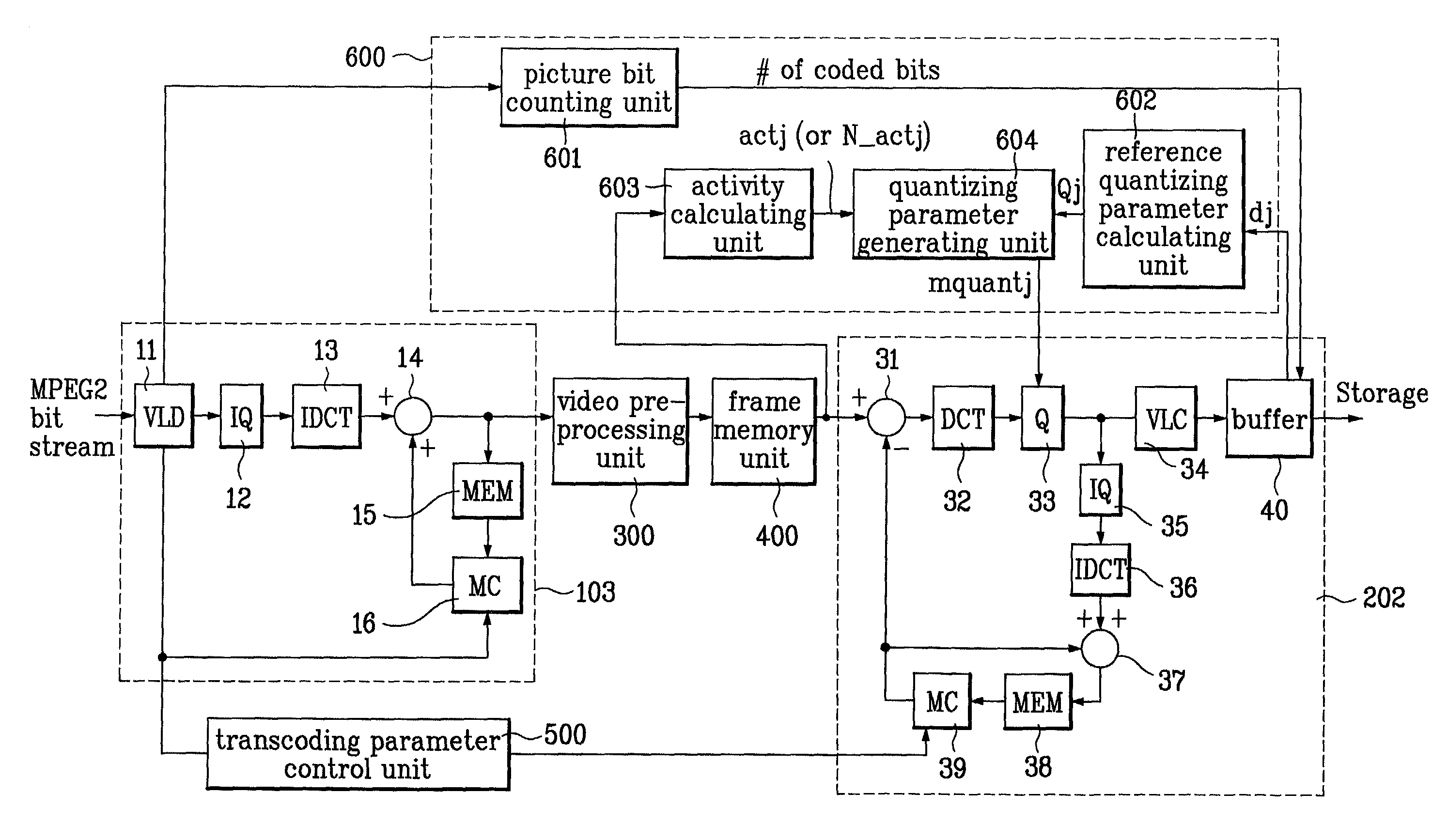
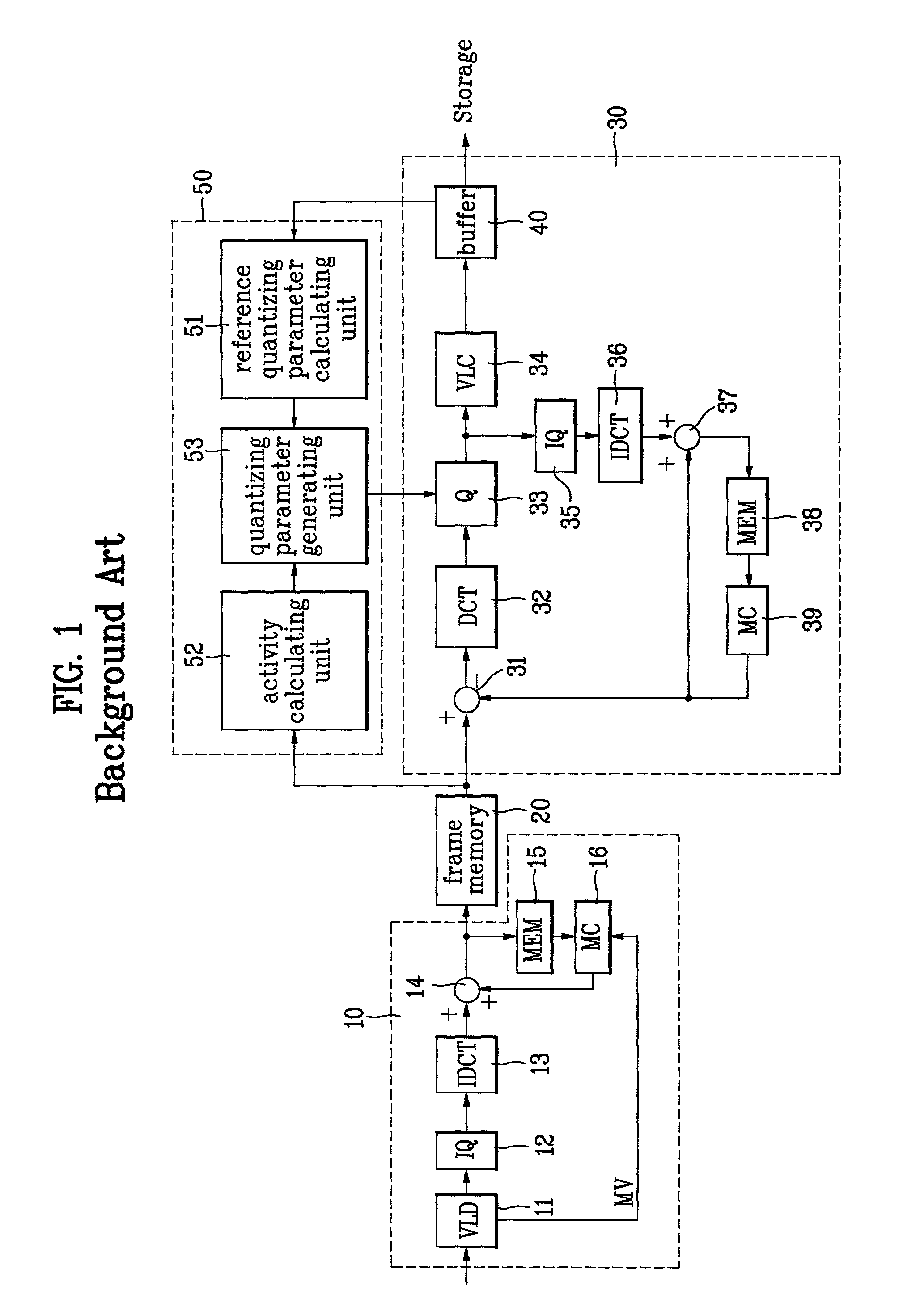
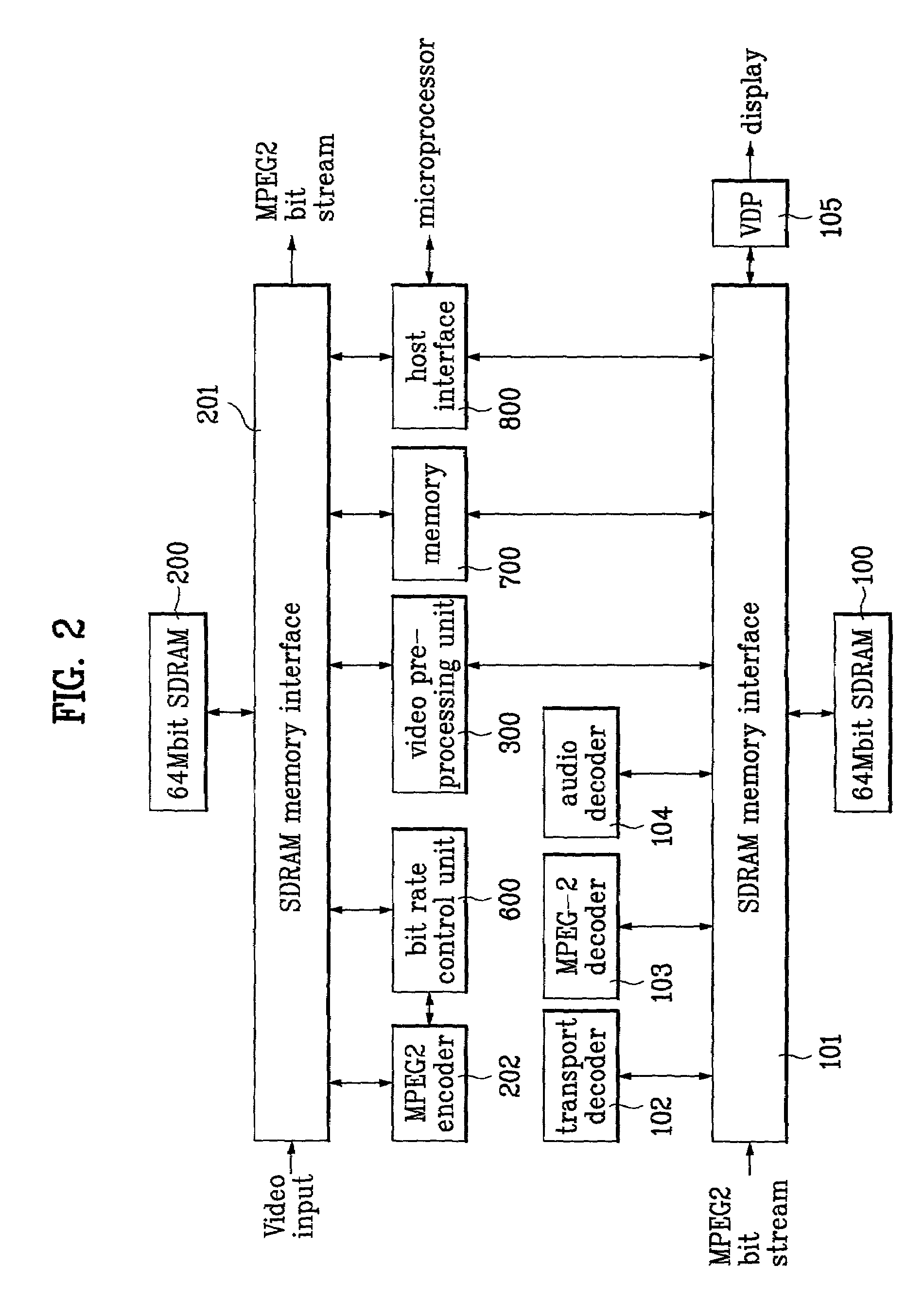
Video transcoding apparatus
InactiveUS7266148B2Reduce lossesReduce resolutionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningBit allocationTranscoding
Disclosed is a video transcoding apparatus converting a specific bit rate of an MPEG (moving pictures experts group) bit stream into a different rate thereof for transportation. The present invention includes a video pre-processing unit having a predetermined matrix structure and down-sampling a macro block decoded by the video decoder by transforming the macro block into a corresponding picture structure to the compressed video bit stream, a transcoding parameter control unit detecting information about a picture from a previous bit stream variable-length-decoded by the video decoder and setting up an encoding mode for a transcoding in accordance with the detected information, etc. Therefore, the present invention does not need the motion estimation unit of encoder and reduce the complexity of the bit allocation unit. When changing HD-rated MPEG sequence over 10 Mbps into NTSC-rated MPEG sequence below 6 Mbps, the present invention reduces calculation time and complexity of hardware.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com