Patents
Literature
2403 results about "System capacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of System capacity System capacity means the system's operational, technical, managerial and financial capability to achieve and maintain compliance with all relevant local, state, and federal plans and regulations.
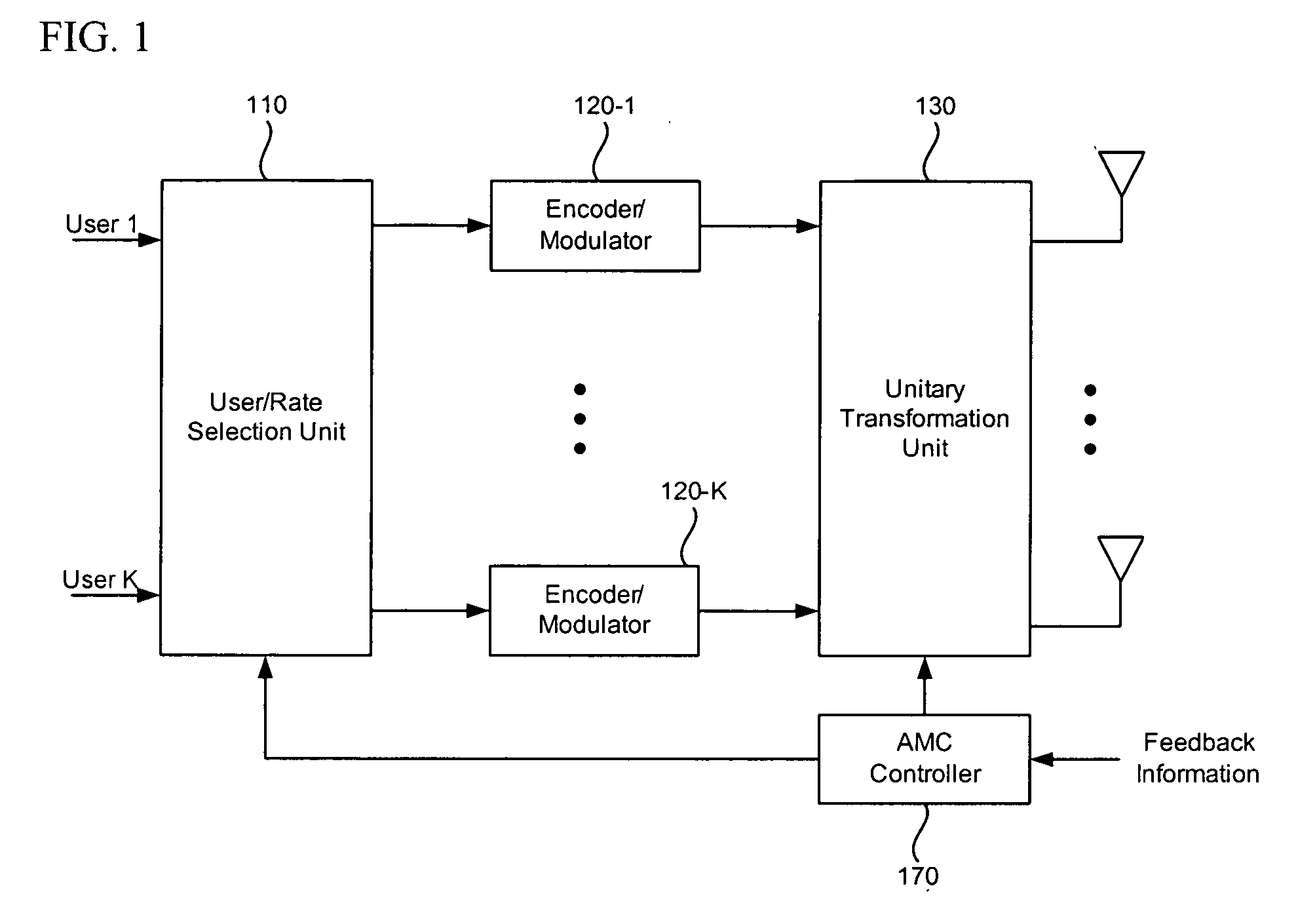
Capacity enhancement for multi-code CDMA with integrated services through quality of service and admission control
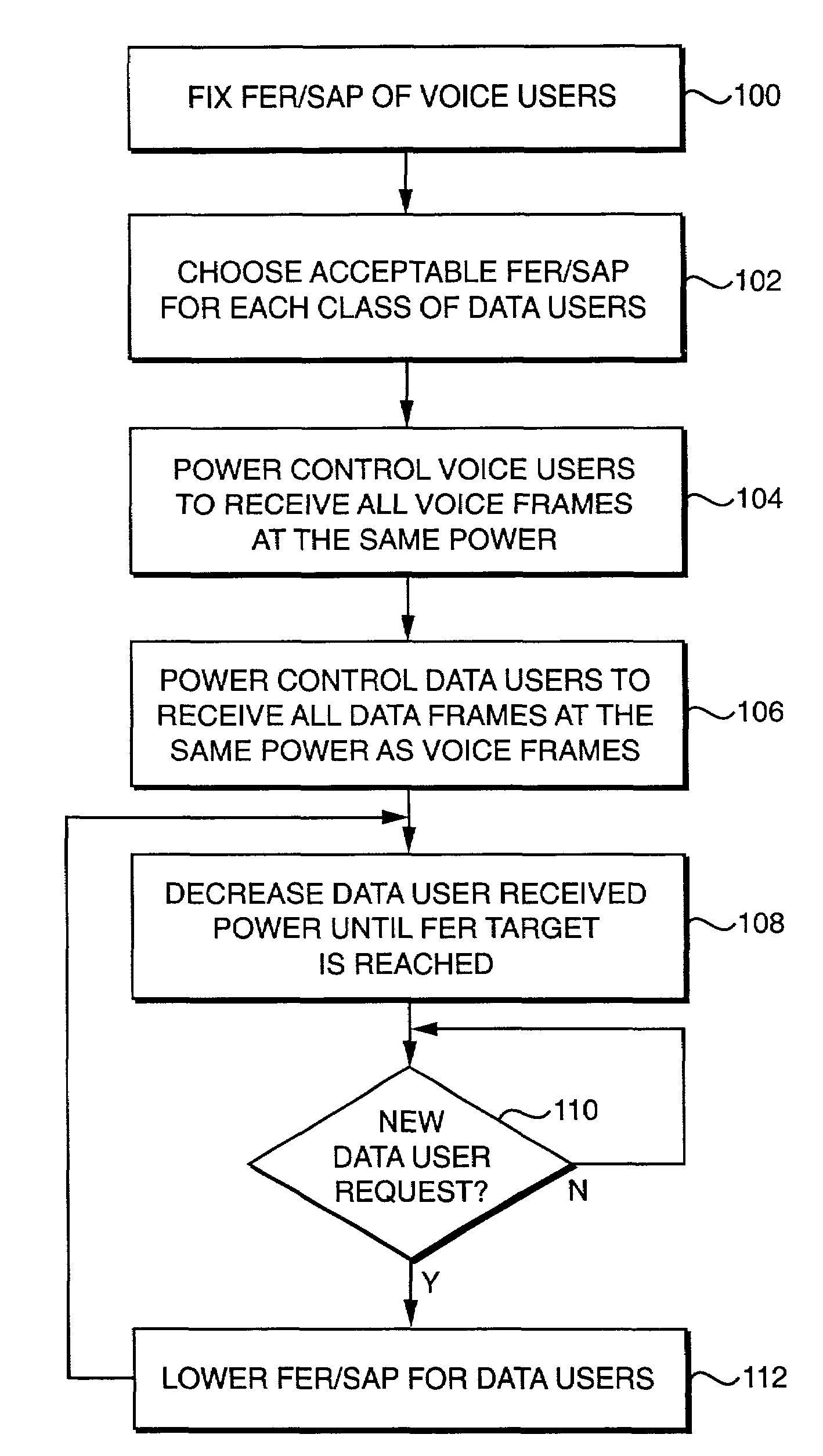
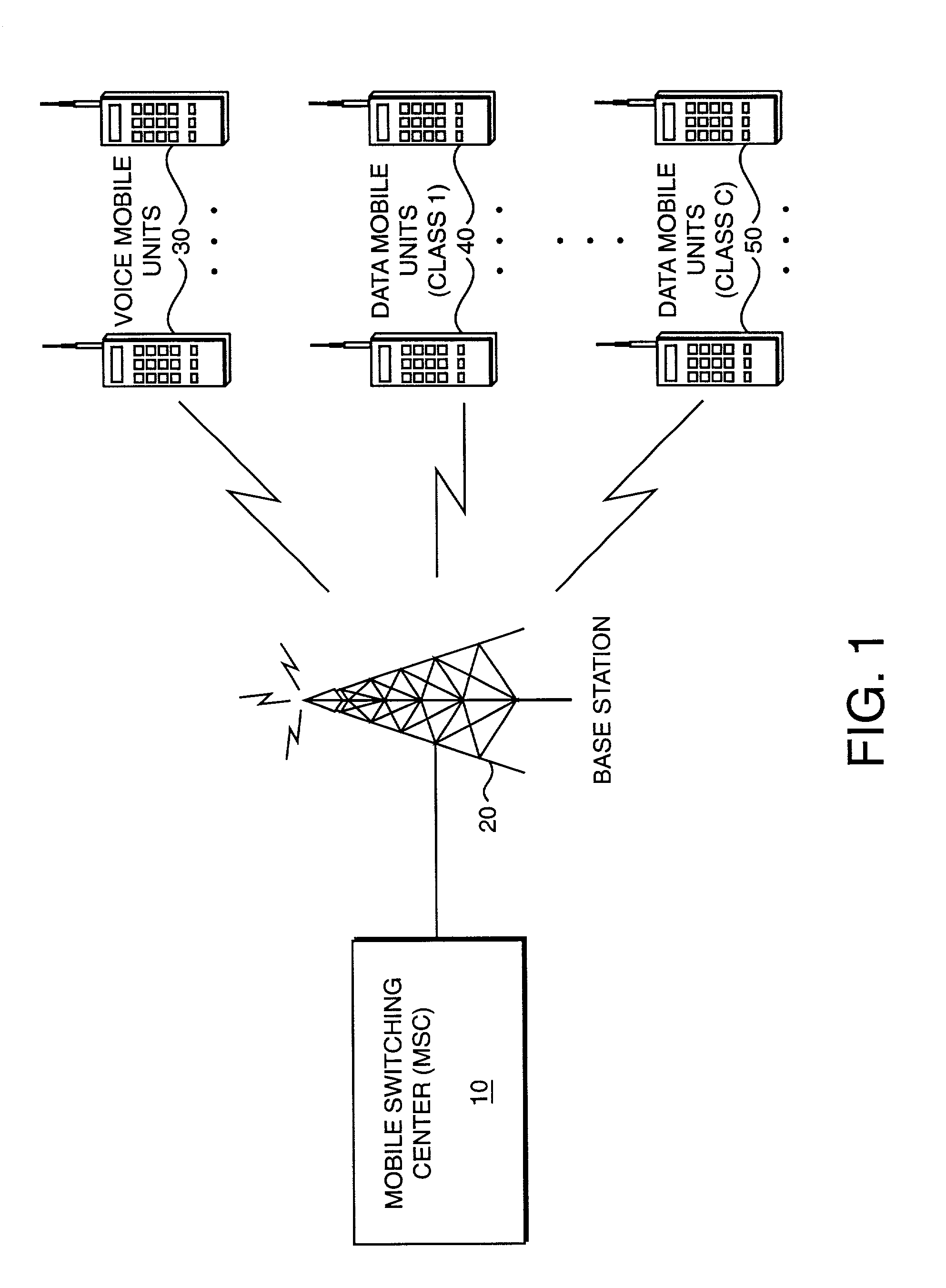
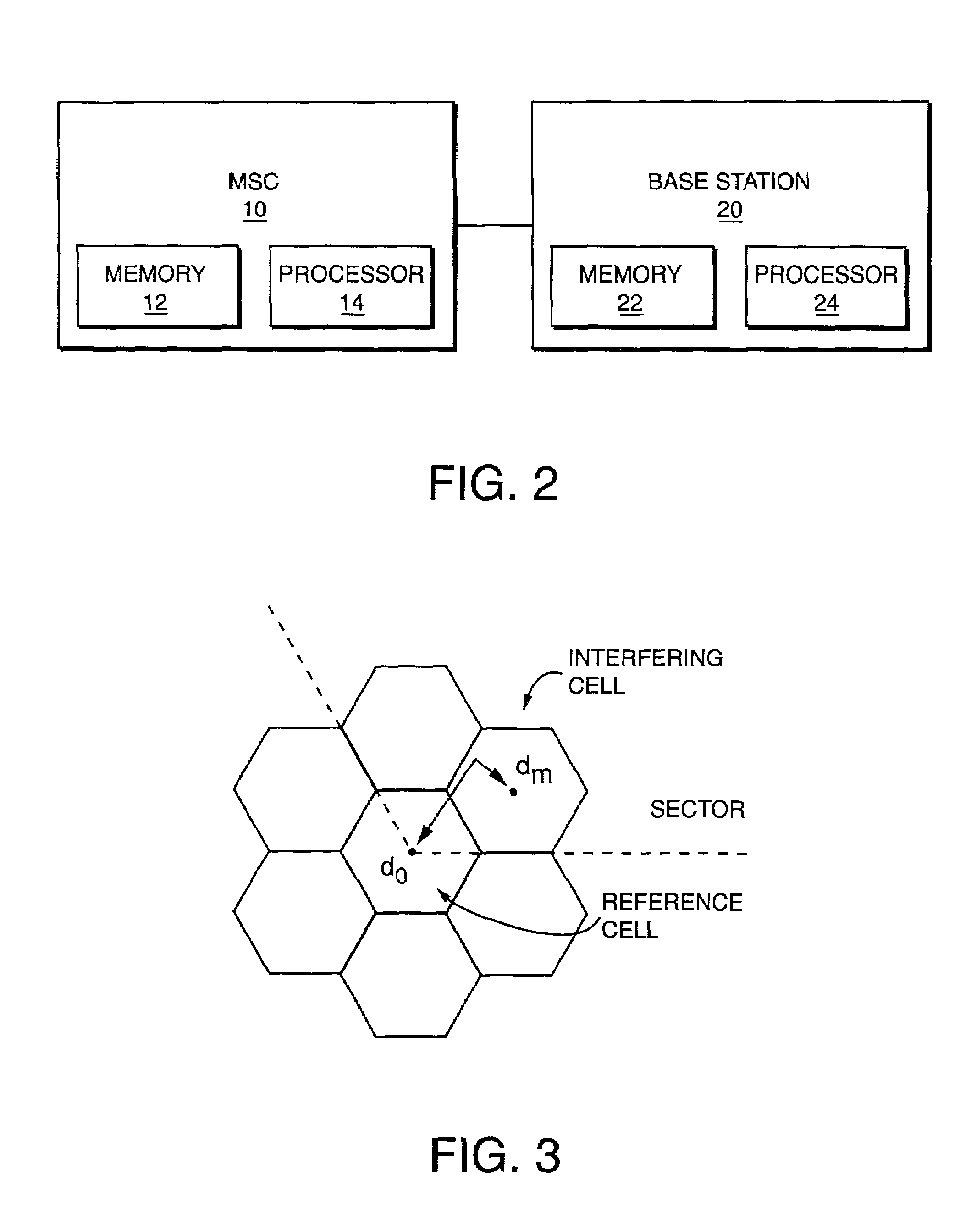
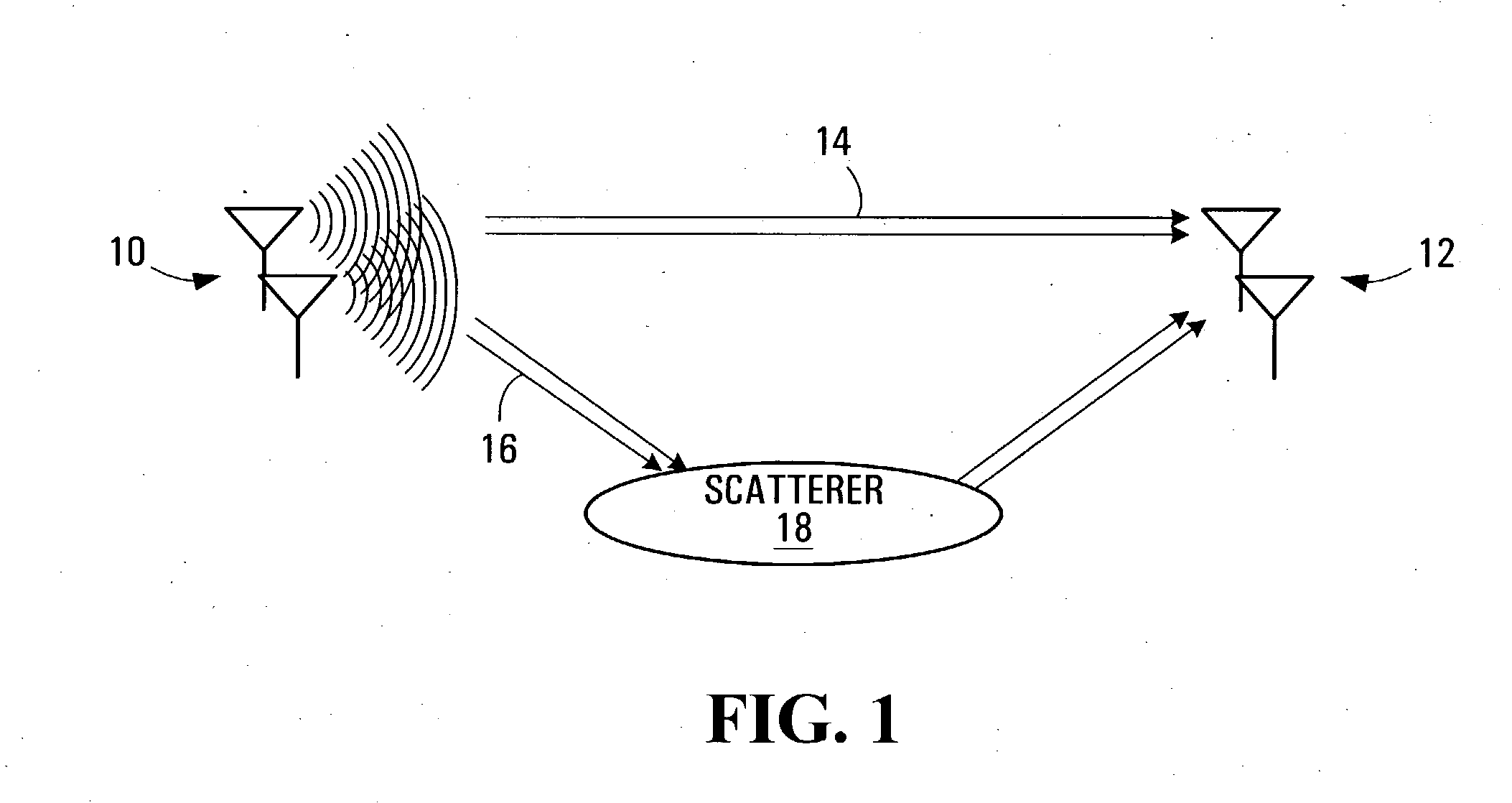
With the addition of high-speed data traffic to traditional CDMA cellular networks, there is a need to efficiently utilize system capacity so that the quality of service of existing voice and low-speed data users is maintained while new high-speed data users are added to the network. Methods and systems are presented that control allocation of power to users, quality of service requirements, and / or user activity levels to enhance capacity utilization. These methods and systems are based on a method for estimating the capacity of a CDMA carrier with both voice and data users using an interference-based analysis of the reverse link. In particular, the methods enhance capacity utilization in a multi-code CDMA network architecture, in which several codes are allocated to a single high-speed data user for parallel transmission.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
Subscriber based smart antenna
InactiveUS6229486B1Cost effectiveReduce distractionsSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsSystem capacitySignal quality
Owner:KRILE DAVID JAMES
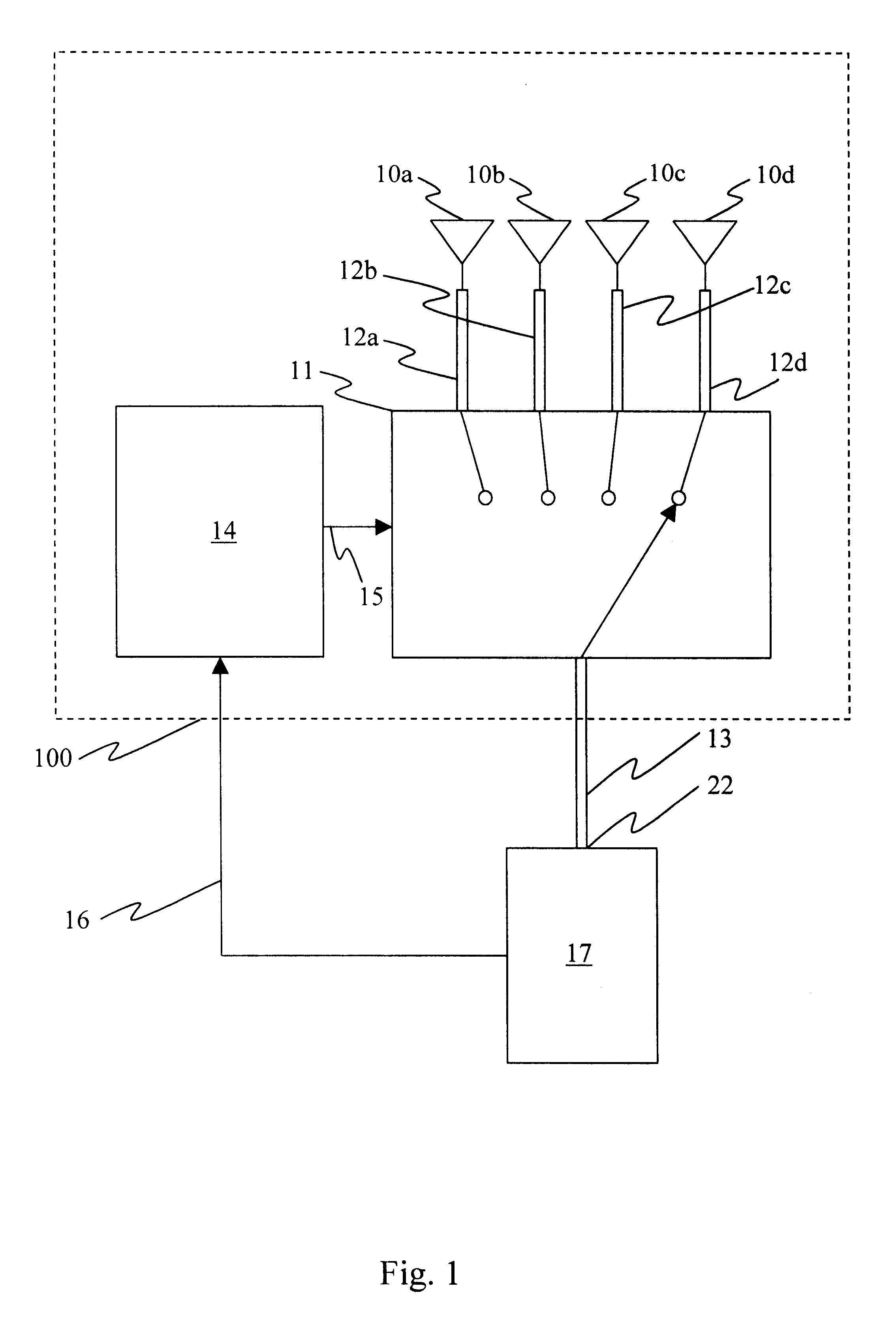
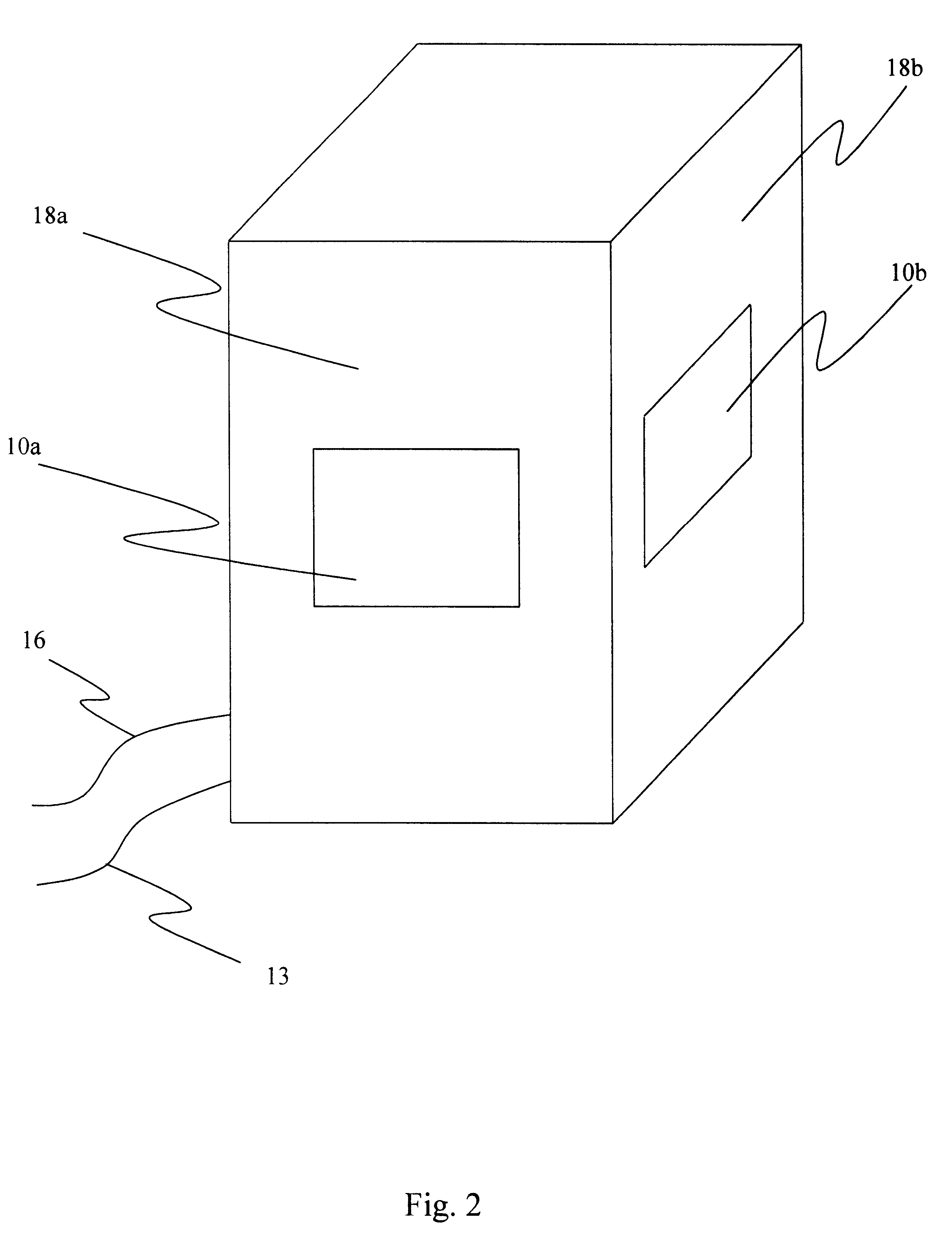
Method of band multiplexing to improve system capacity for a multi-band communication system
ActiveUS20070054680A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMulti bandCommunications system
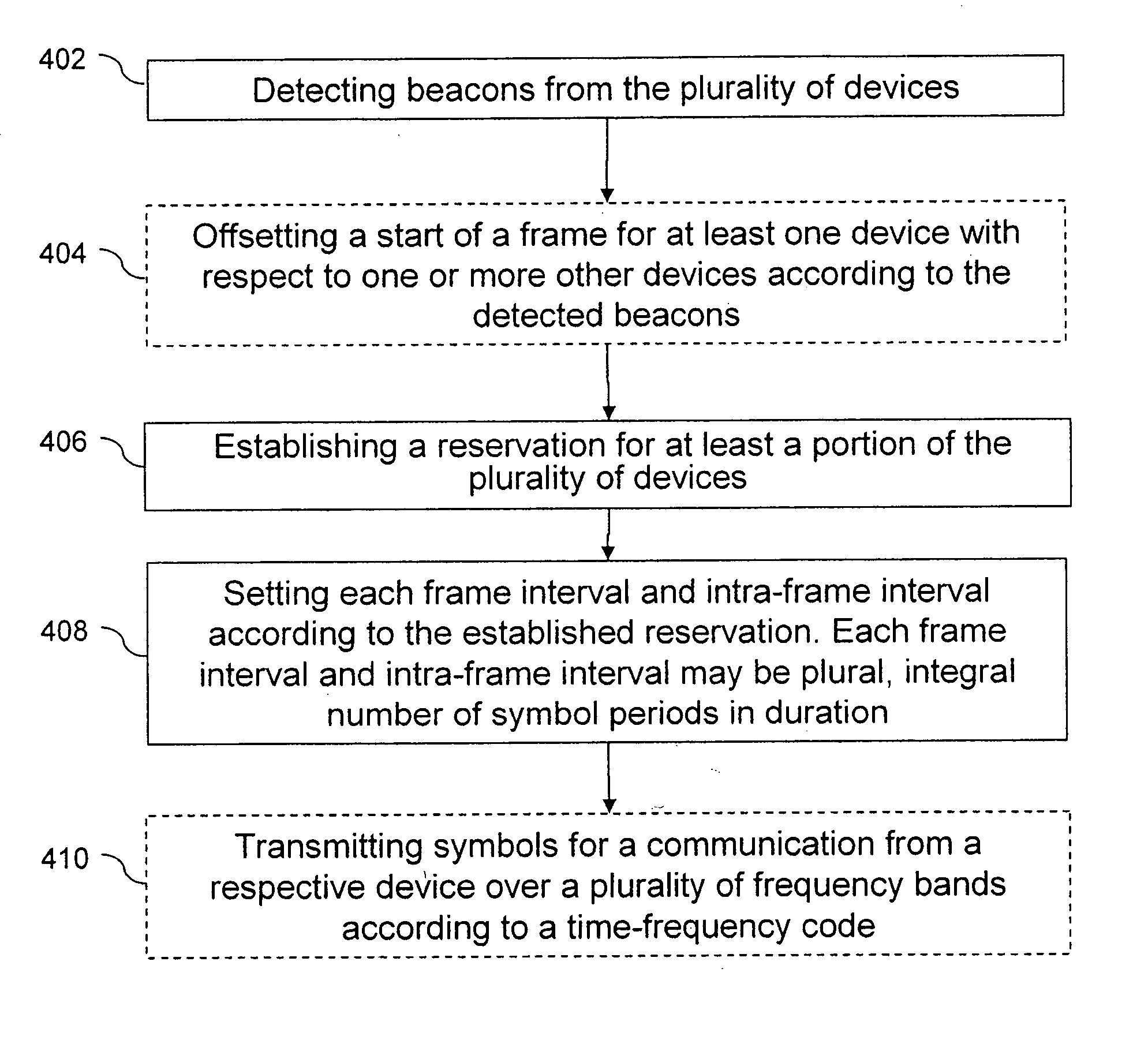
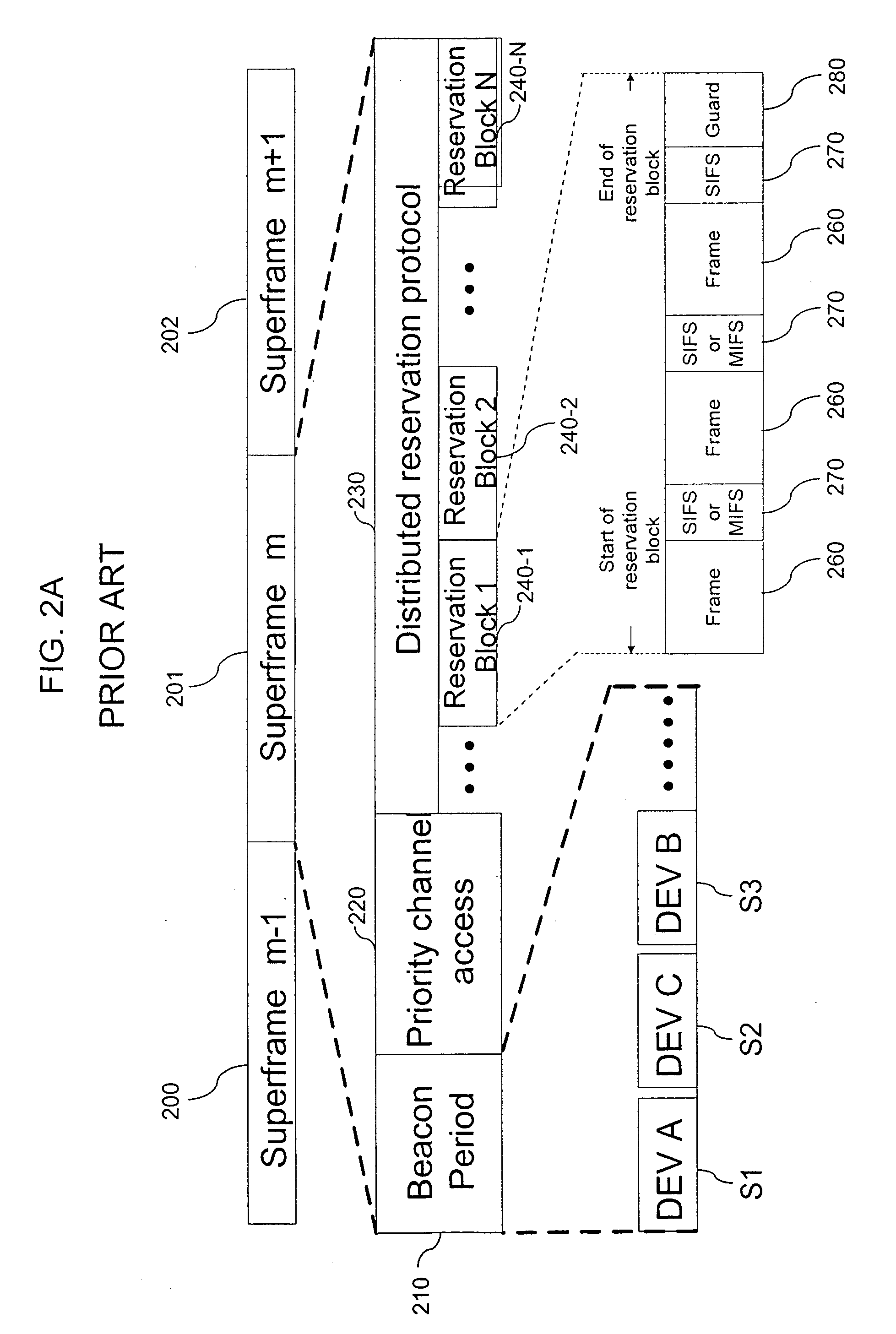
A control method of synchronizing communications between or among a plurality of devices in a communication system includes detecting beacons from the plurality of devices in the communication system, and establishing a reservation for at least a portion of the plurality of devices in the communication system. Each reservation is a frame interval in which to transmit symbols from one device to one or more of the other devices in the communications system. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is set according to the established reservation. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is a plural, integral number of symbol periods in duration.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
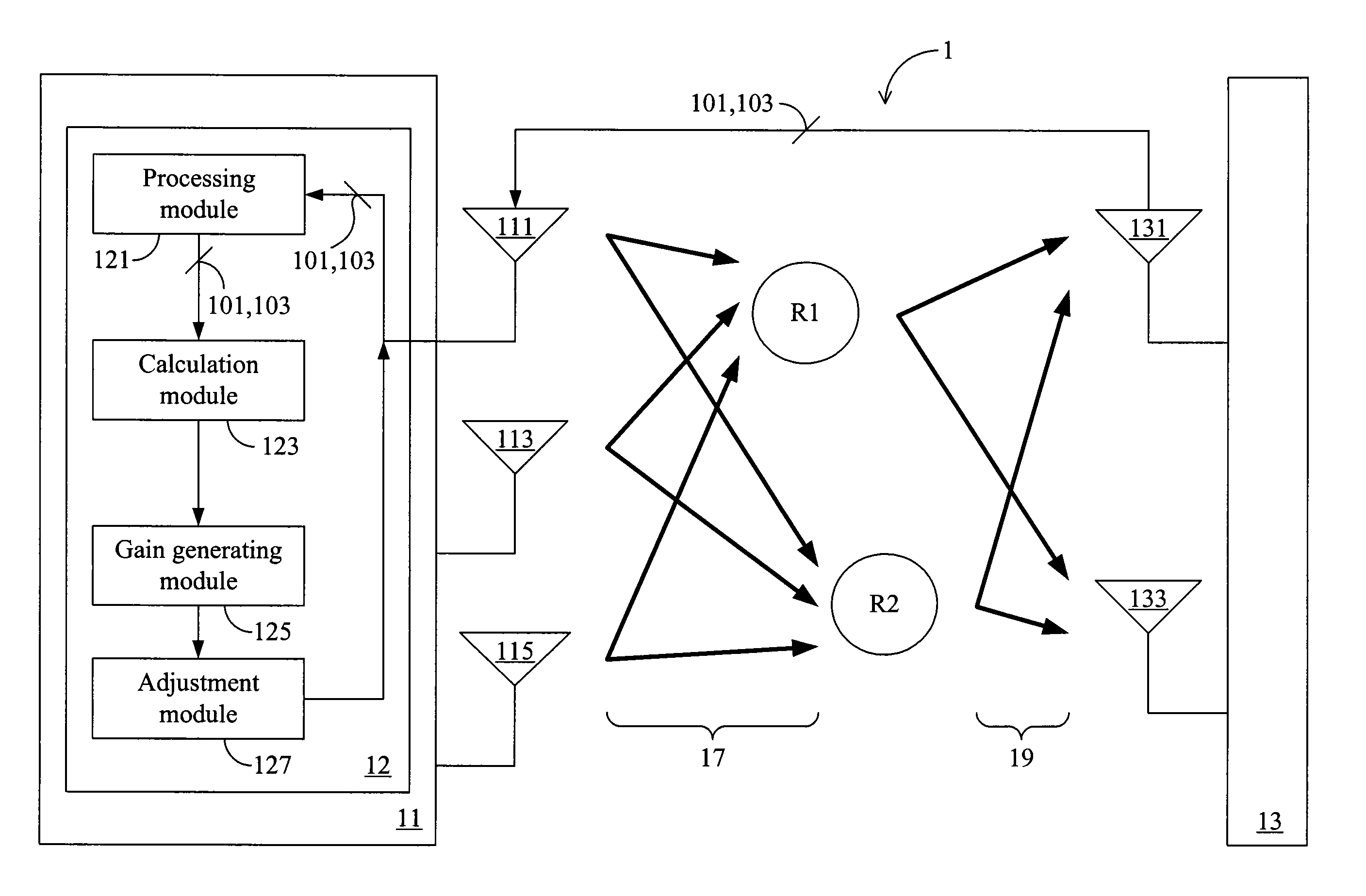
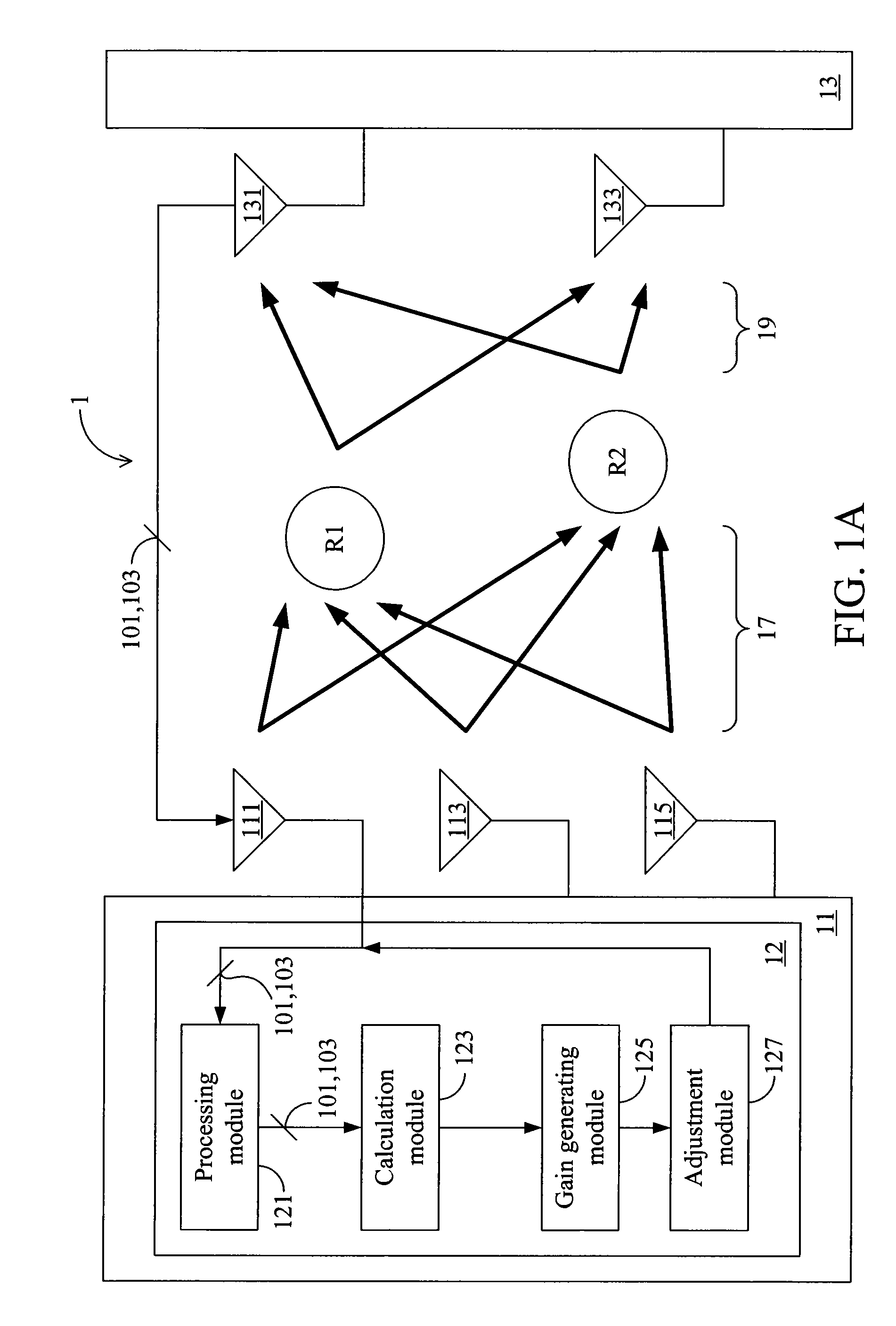
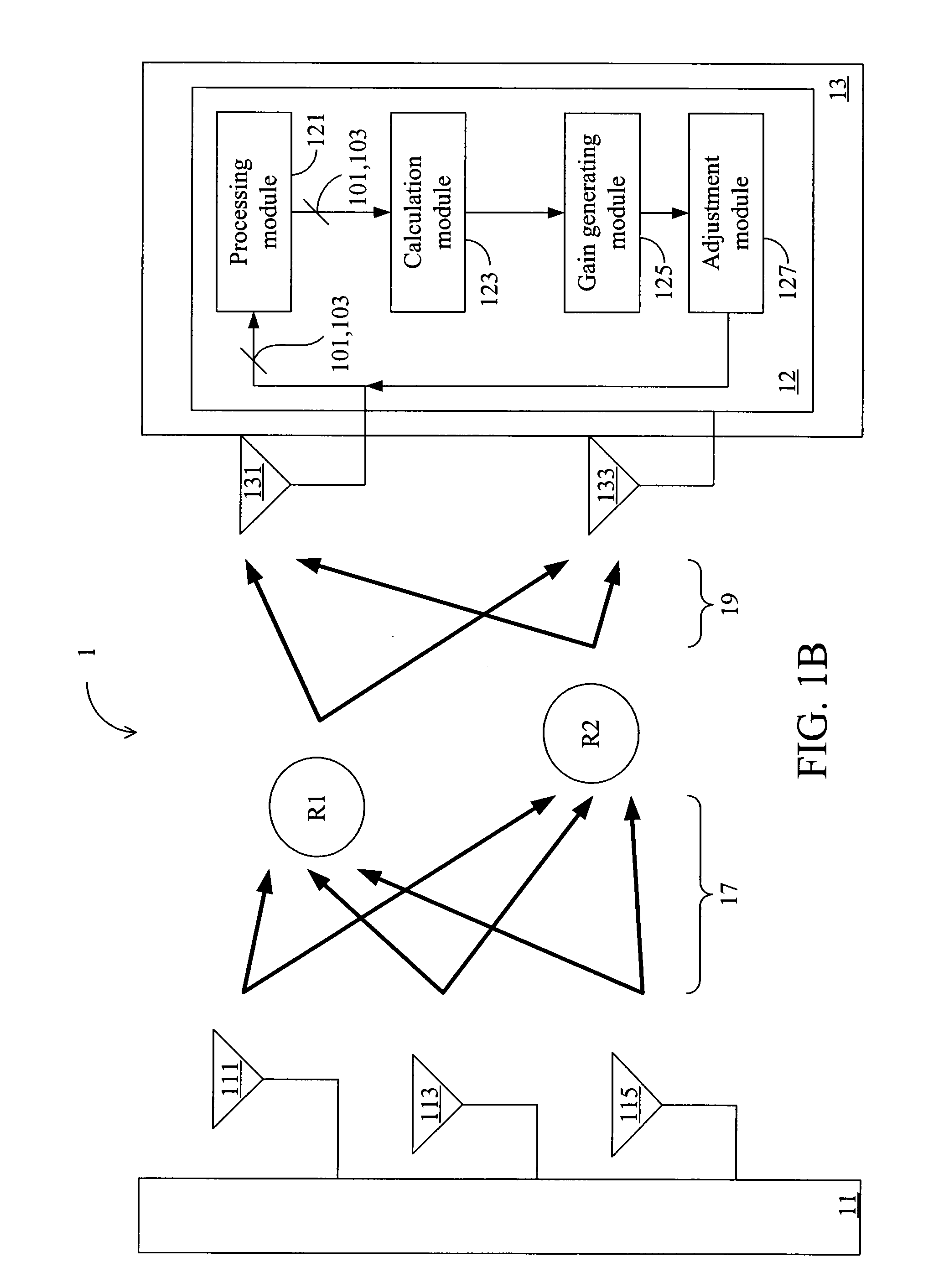
Gain adjustment apparatus, method, and tangible machine-readable medium thereof for a multiple input multiple output wireless communication system
InactiveUS8126393B2High gainImprove signal transmission qualityPower managementRepeater circuitsSystem capacityCommunications system
A gain adjustment apparatus, a gain adjustment method, and a tangible machine-readable medium thereof for a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communication system are provided. The MIMO wireless communication system comprises source antennas, destination antennas, relay stations (RSs) and a relay transmission power limit value. The gain adjustment method comprises the following steps: adjusting the gain of one single RS according to a gain calculation; multiplying the gains of other relay stations by a scaling value for adjustment. According to aforesaid method, the present invention can increase the system capacity of the MIMO wireless communication system.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
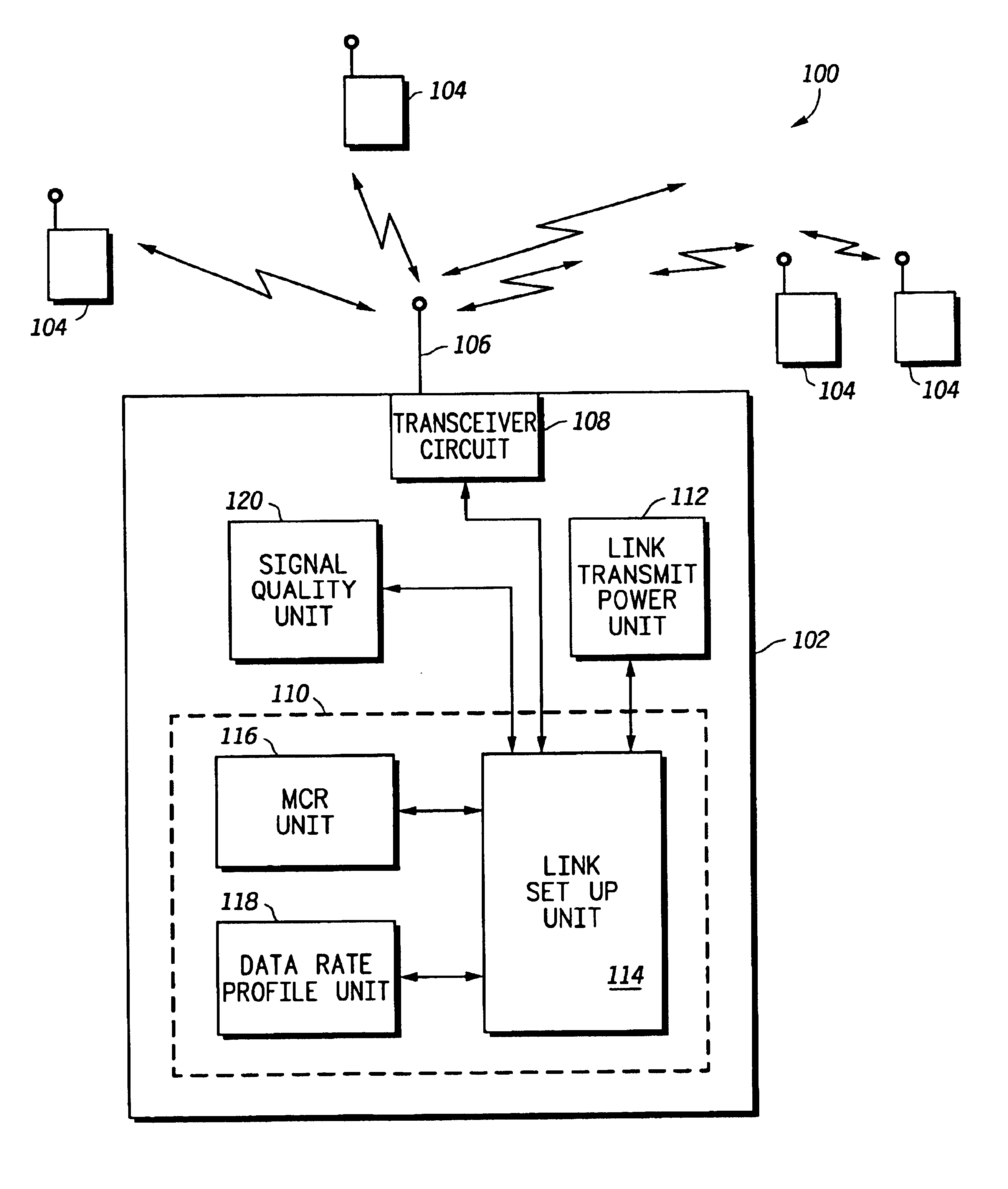
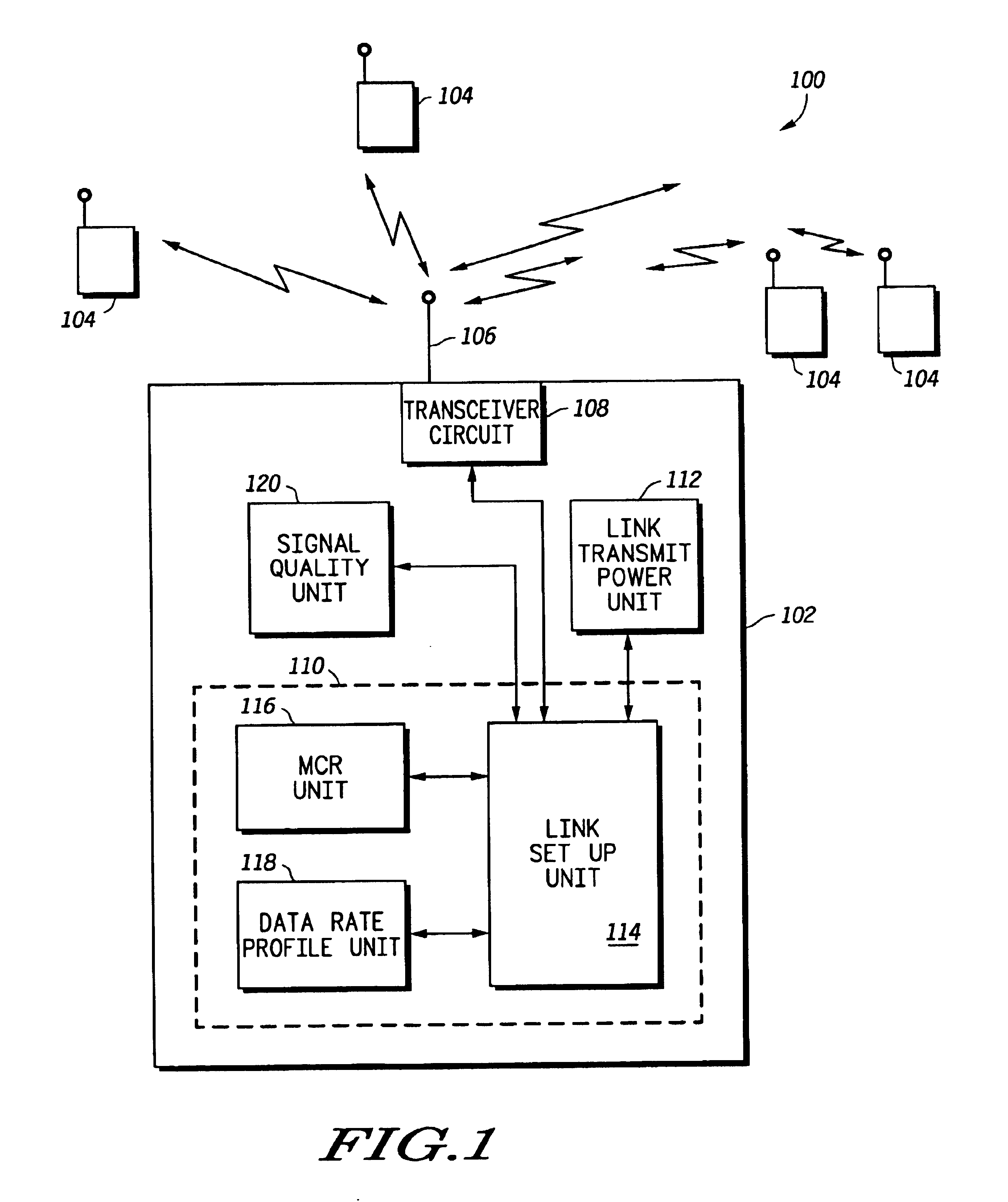
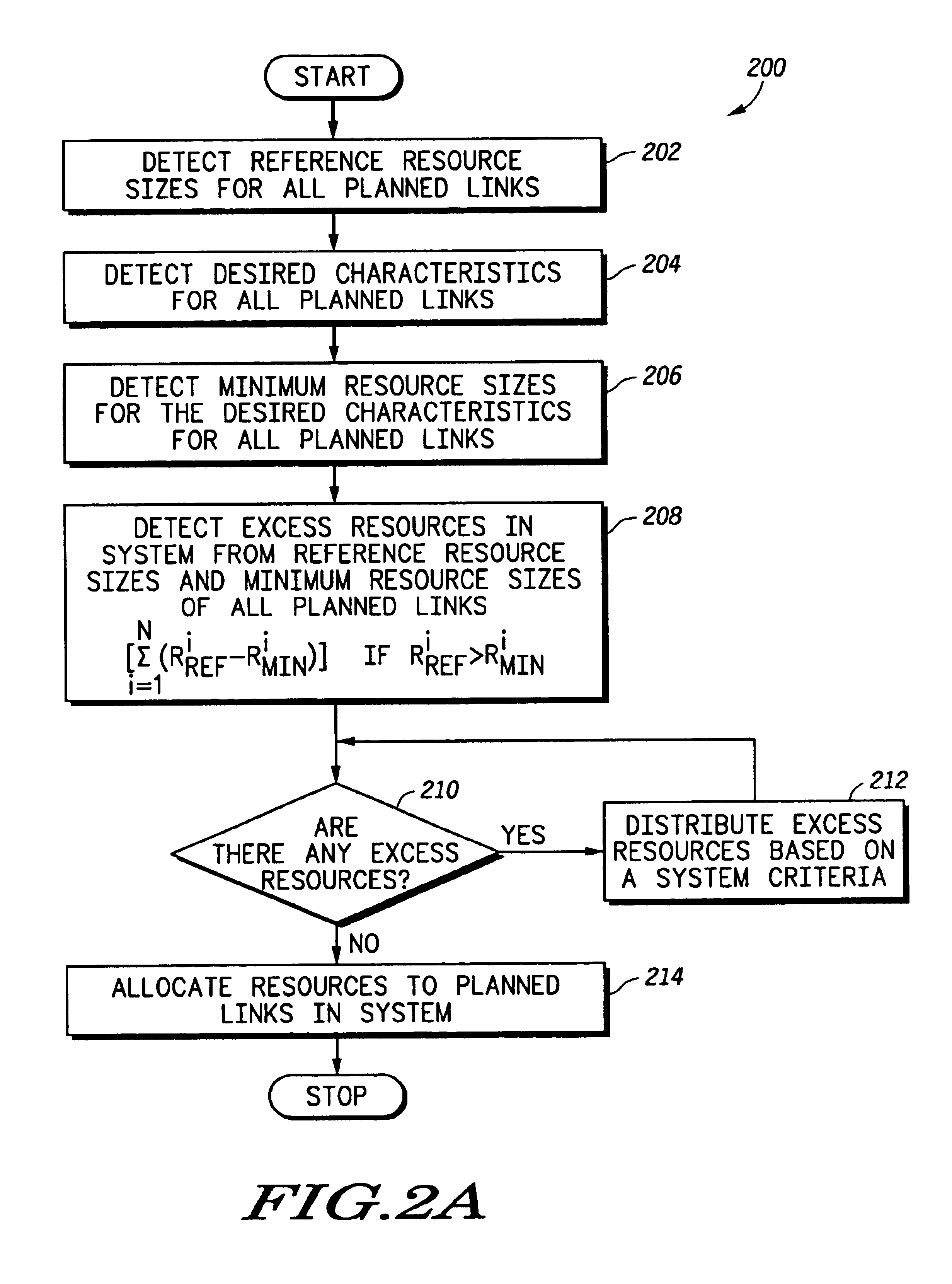
Method and system for excess resource distribution in a communication system
InactiveUS6865393B1Network traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSystem capacityCommunications system
A method and system (102) provide adaptive modulation / coding with distribution of excess resources based on one or more system criteria. The system (102) may be any system with more than one modulation rate or more than one coding rate and may be a wireless communication system using CDMA, TDMA, OFDM or any other signal formats. Generally, the method determines excess resources of the system based on desired characteristics of links supported by the system. The excess resources may be any number of system resources, such as transmit power. These excess resources are then distributed to the links based on various system criteria, such as to increase system coverage, to increase system capacity, to modify a data rate profile of the system or to reduce interference in the system. Methods for providing such distribution of the excess resources are also provided for equal data rate systems.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
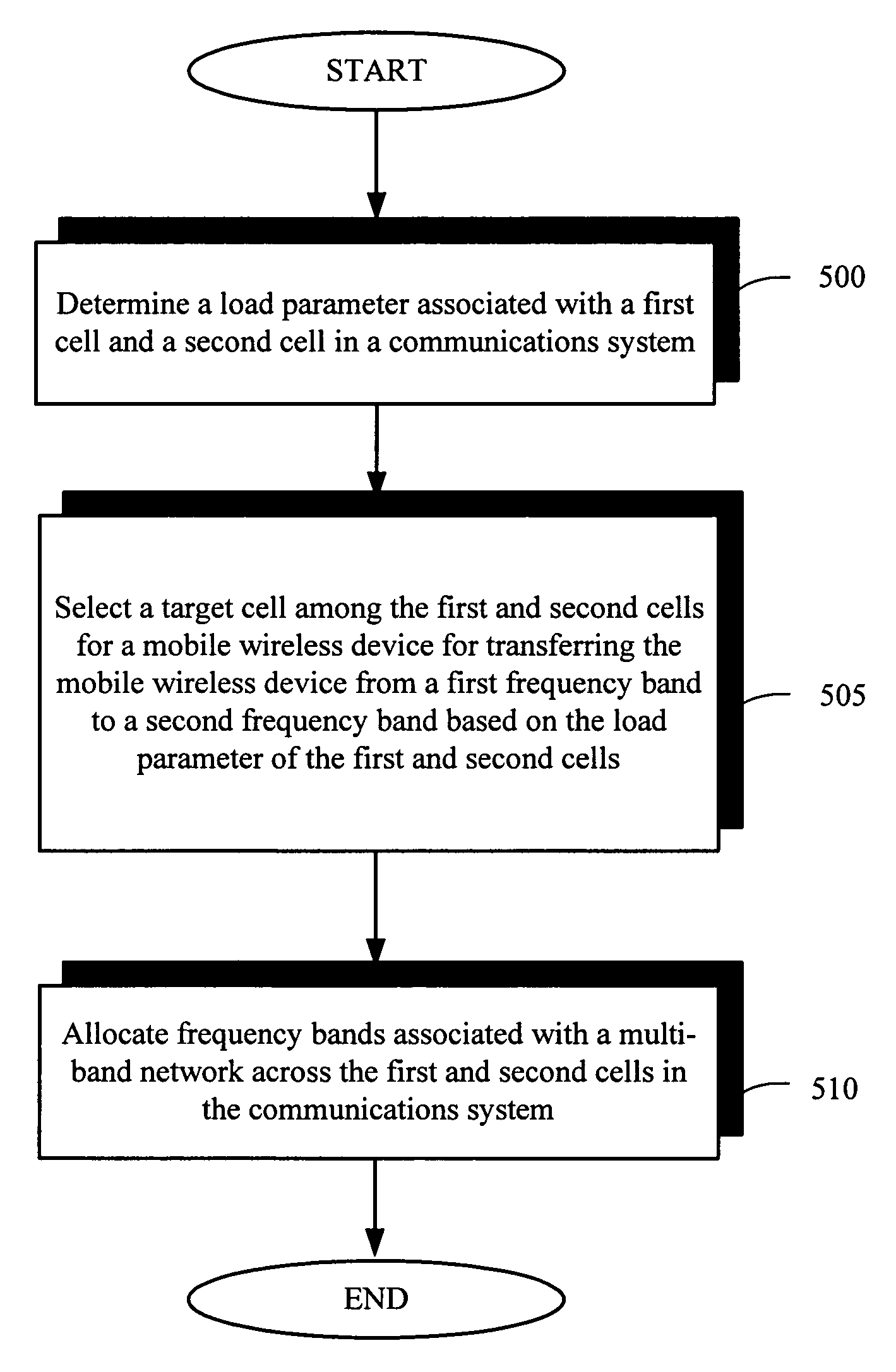
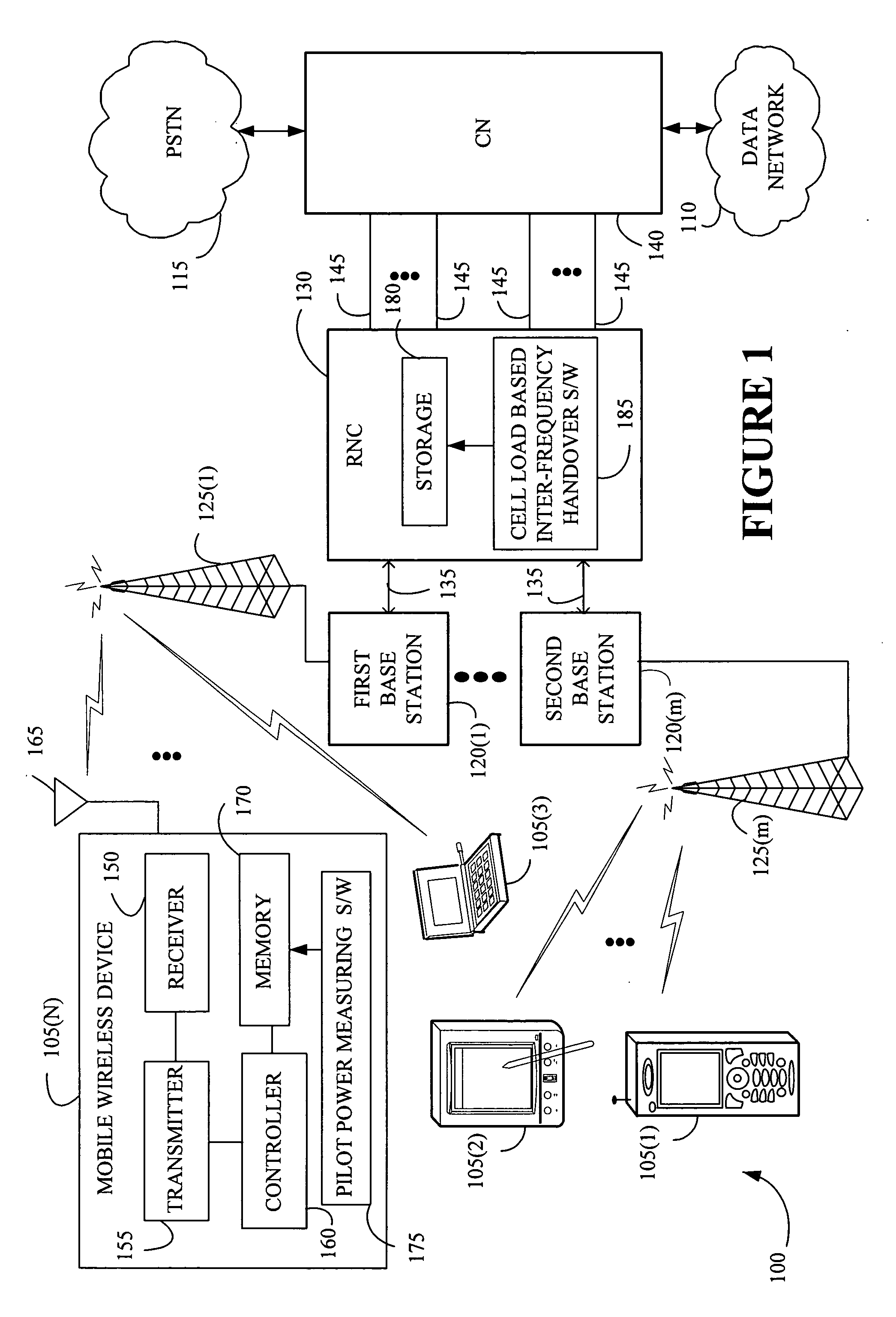
Balancing load of cells in inter-frequency handover of wireless communications
InactiveUS20060166677A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationMulti bandQuality of service
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for allocating frequency bands associated with a multi-band network across a first and a second cell in a communications system. The method comprises determining a load parameter associated with the first and second cells in the communications system, selecting a target cell among the first and second cells for a mobile wireless device for transferring the mobile wireless device from a first frequency band to a second frequency band based on the load parameter of the first and second cells. In one embodiment, selection of an appropriate frequency band may be realized for a mobile wireless device in a multi-band network based on measurements of pilot channel properties and a load parameter to take into account a cell load of a target set of cells for an inter-frequency handover. This integration of the cell load for ranking, selection and transfer of user to a target cell from an overloaded cell may prevent unnecessary inter-frequency handover of users to cells with a relatively higher load, resulting in an increase in overall system capacity as well as quality of service.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
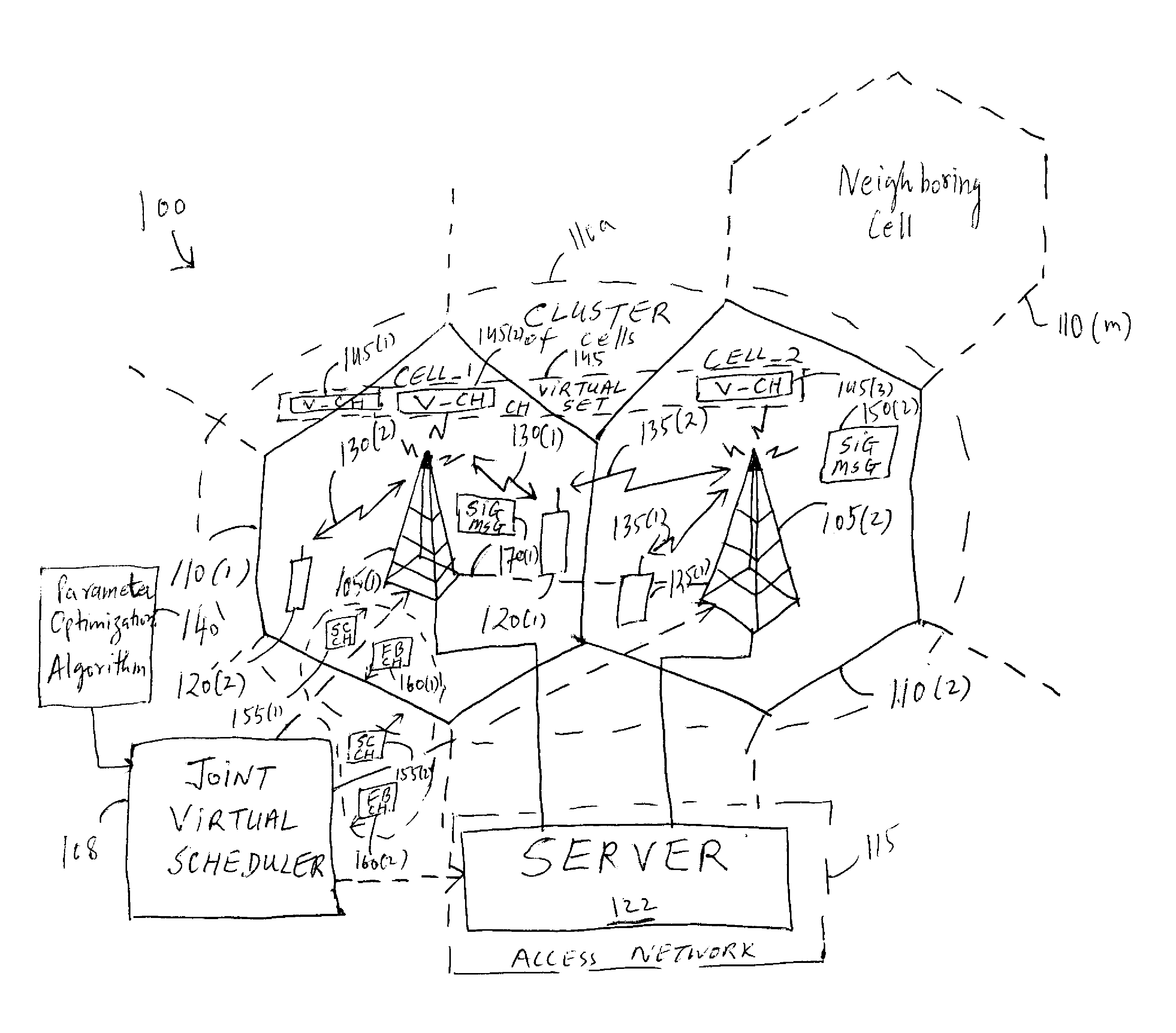
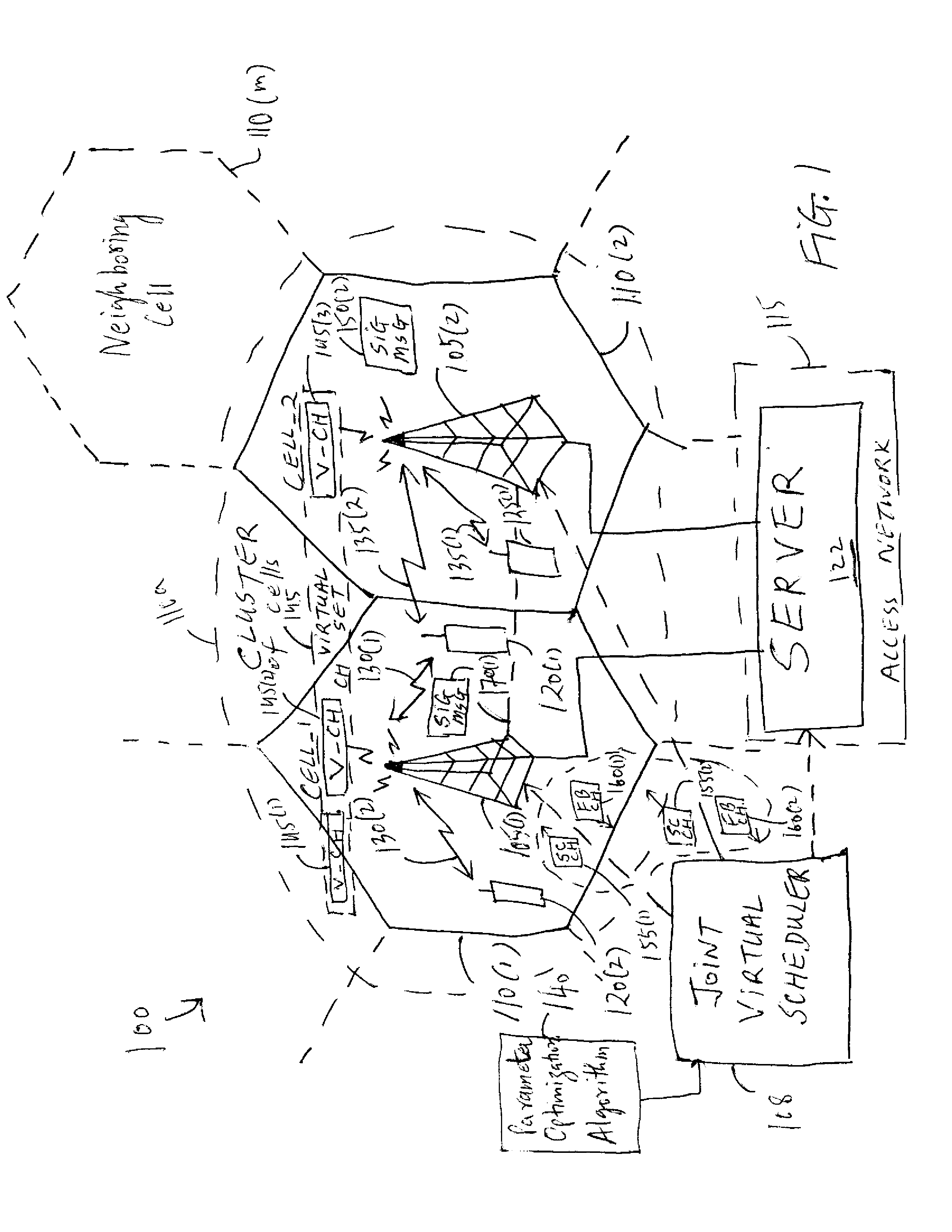
Coordinating transmission scheduling among multiple base stations
InactiveUS20070280175A1Well formedMaximize of capacity of wirelessSite diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemSystem capacity
A method and an apparatus for scheduling transmissions of a plurality of cells in a wireless communications system including one or more base stations is provided. The method comprises providing a set of virtual channels to enable an intra-cell transmission orthogonal to another transmission within each cell of the plurality of cells and inter-cell transmissions orthogonal to other transmissions across a cluster of cells associated with the one or more base stations. The method further comprises exchanging signaling messages between two or more base stations to coordinate scheduling of the intra-cell transmission with the inter-cell transmissions for the cluster of cells. For optimizing a parameter associated with scheduling of a plurality of users from a cluster of cells in a wireless communication system, an optimal power level for the parameter of each active user may be searched to maximize an indication of system capacity of the wireless communication system. This enables a coordinated jointly scheduling of the users active in the cluster of cells based on the optimal power levels such that the total interference within the cluster may be minimized to maximize the system throughput / capacity.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Spatial division multiple access for wireless networks
ActiveUS7352718B1Doubling and of network throughputIncrease system capacityPower managementPolarisation/directional diversityWireless mesh networkSystem capacity
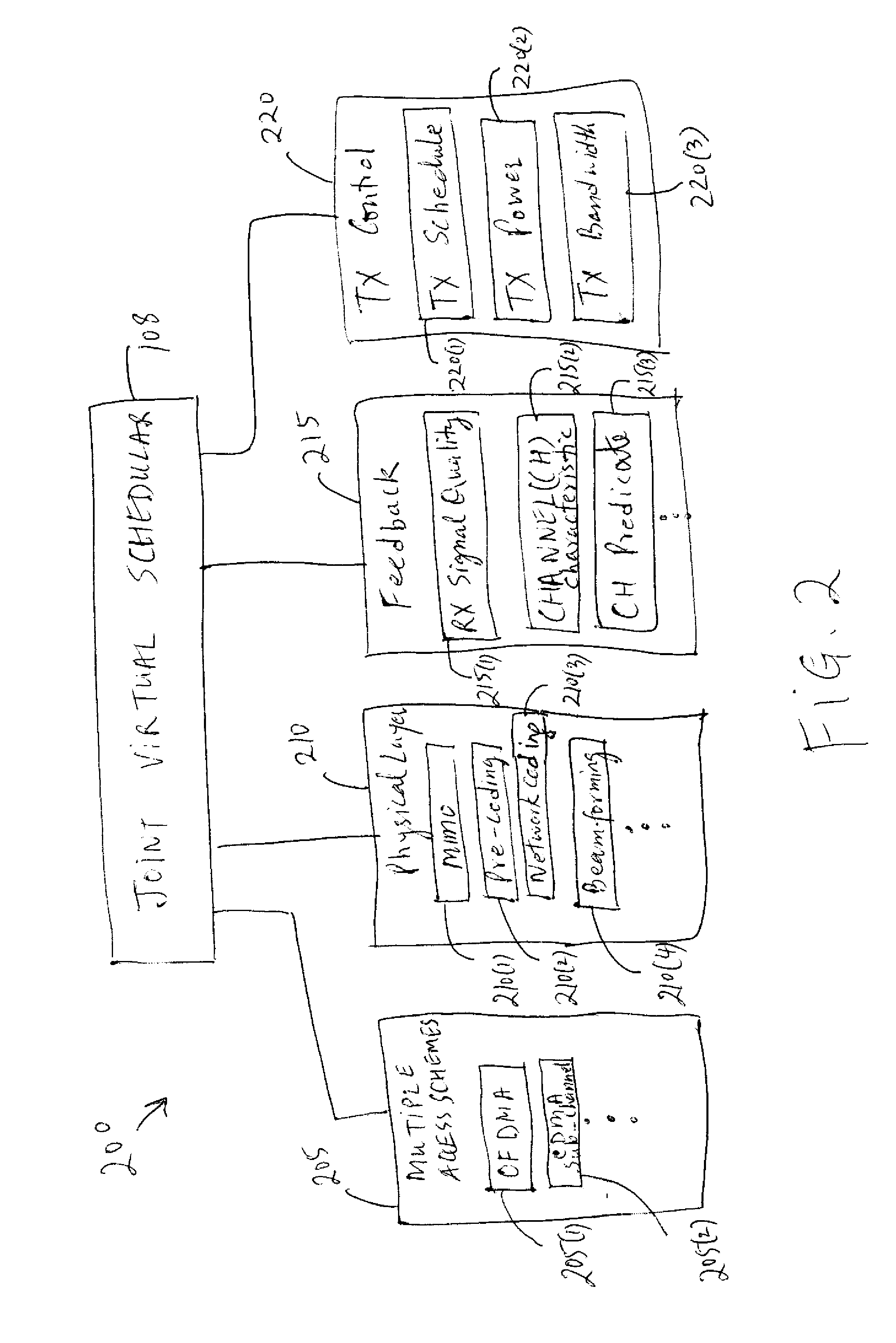
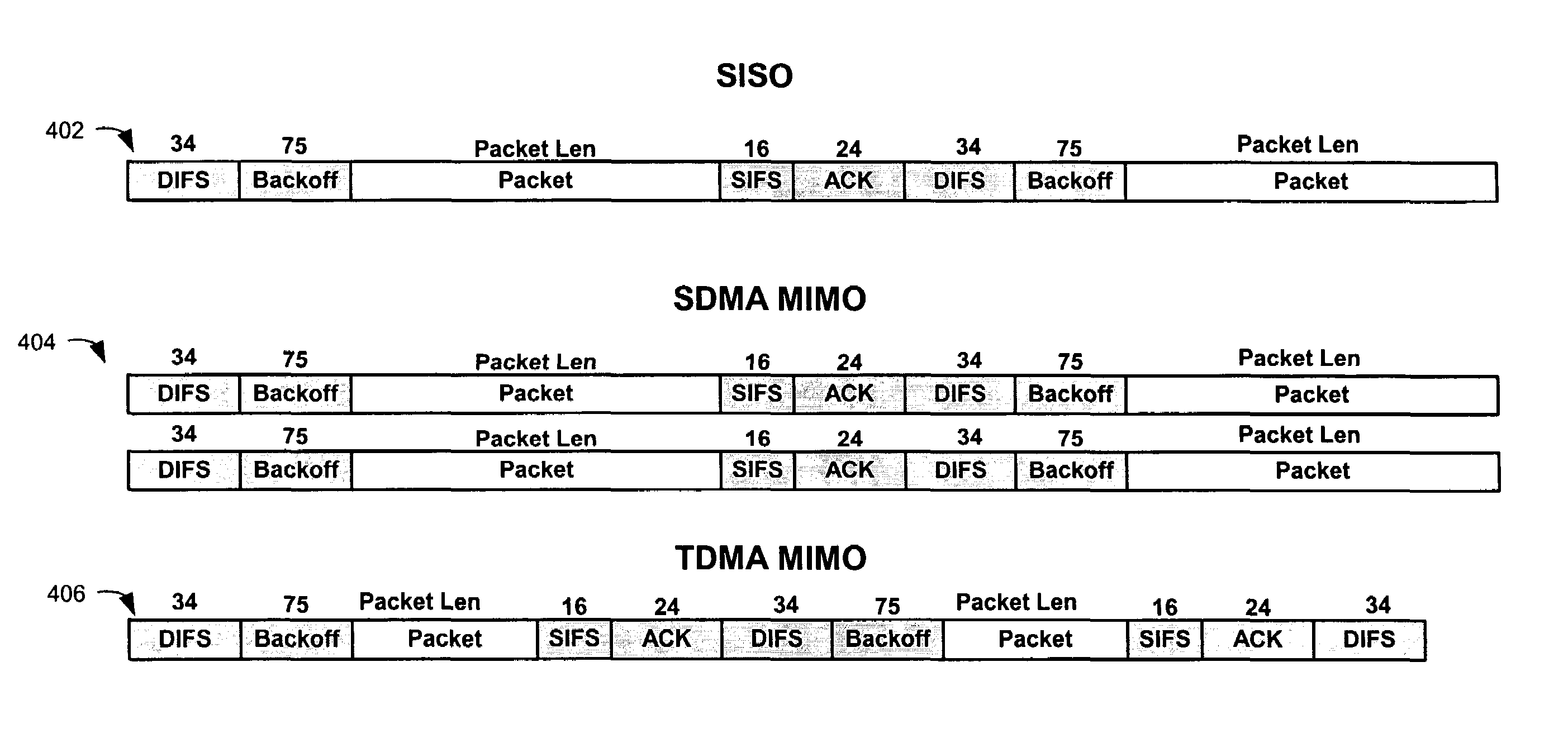
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology in conjunction with the IEEE 802.11 standard enables simultaneous communication of data packets to or from multiple users in the same frequency. Spatial divisional multiple access (SDMA) is thus provided. In this way, system capacity can be increased to an extent that depends on available antenna resources and the multipath characteristics of the communication channel. Doubling or quadrupling of network throughput can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20020051434A1Easy to liftReduce capacityRadio transmission for post communicationSystem capacityModem device
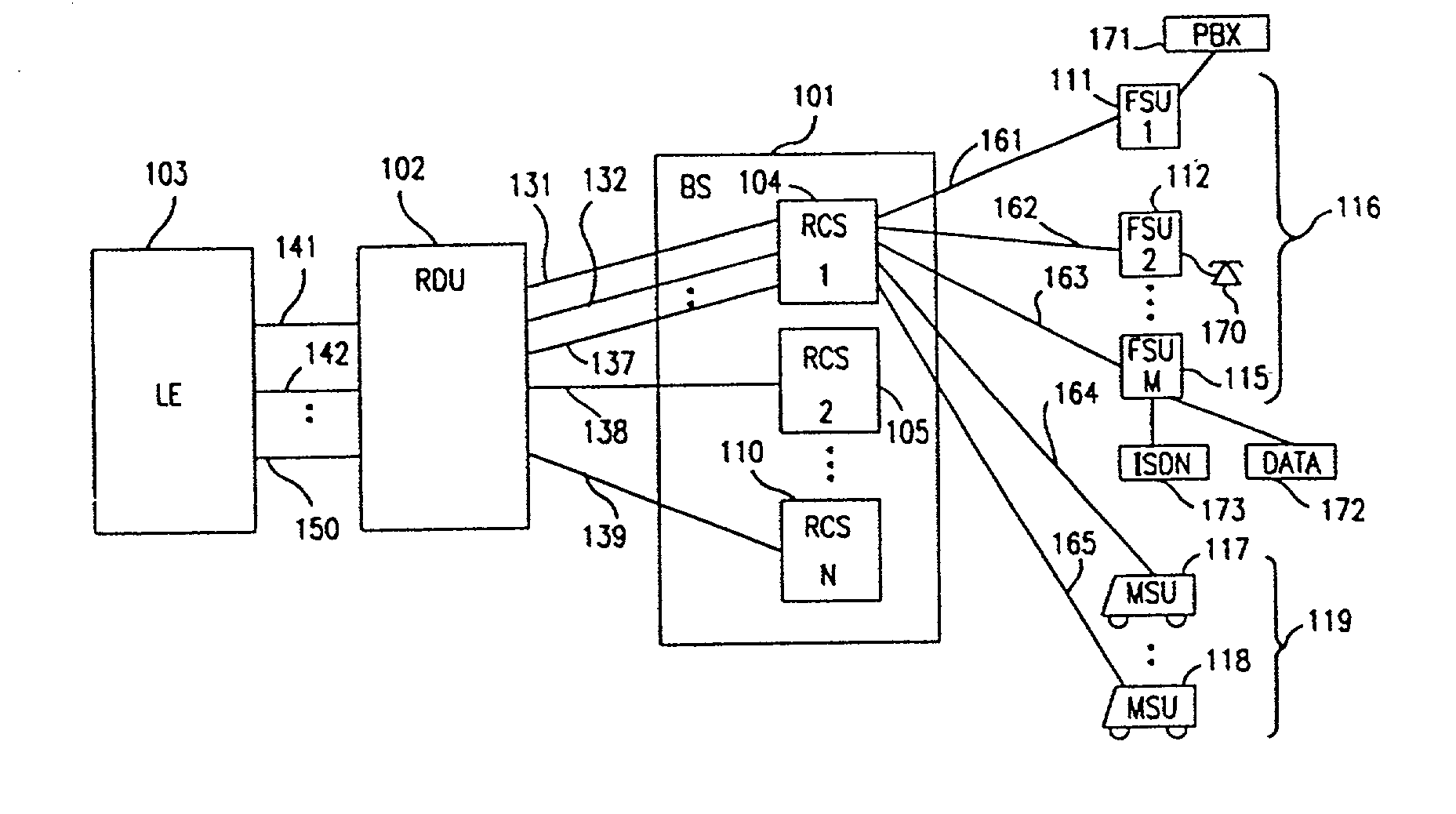
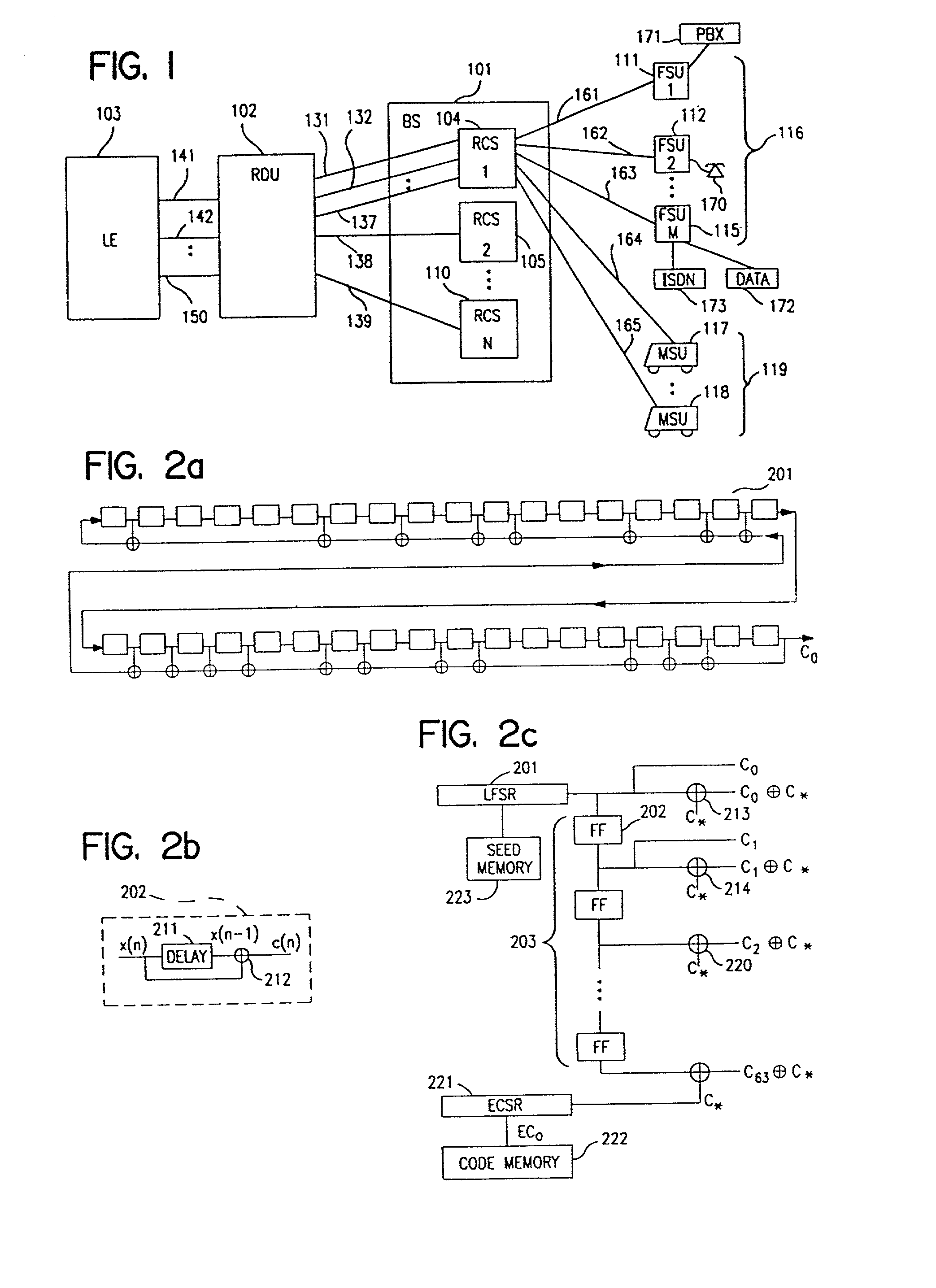
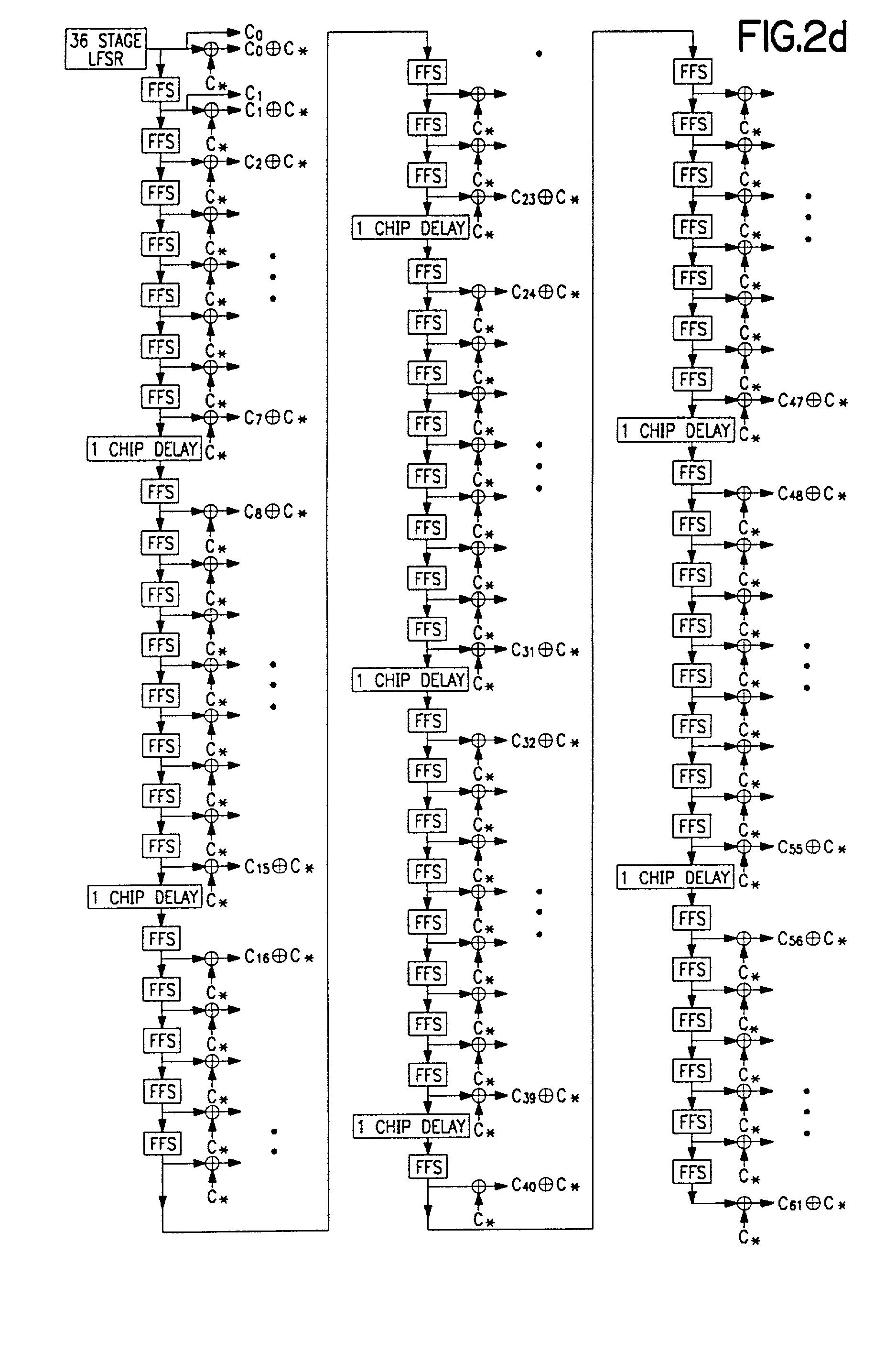
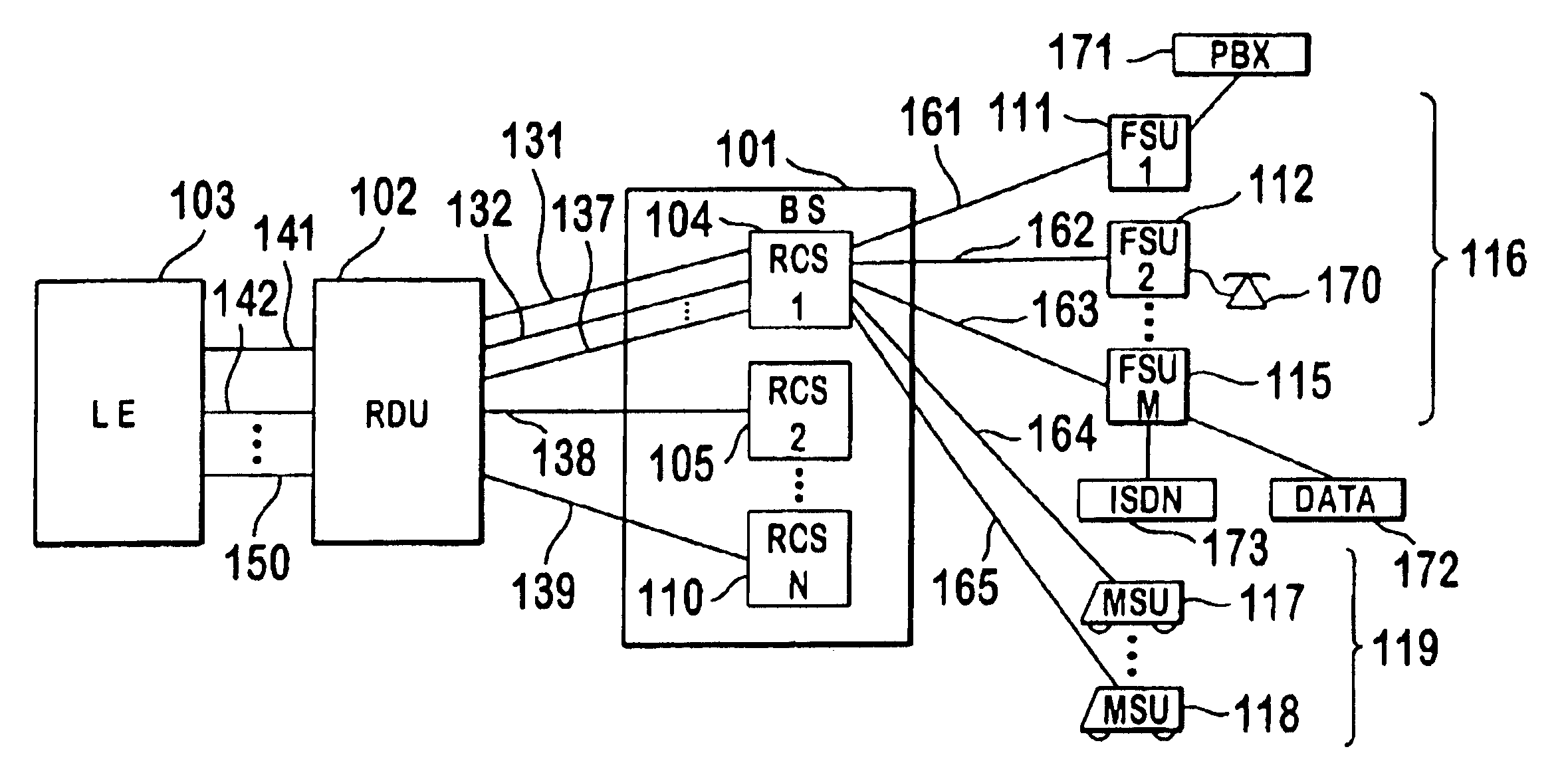
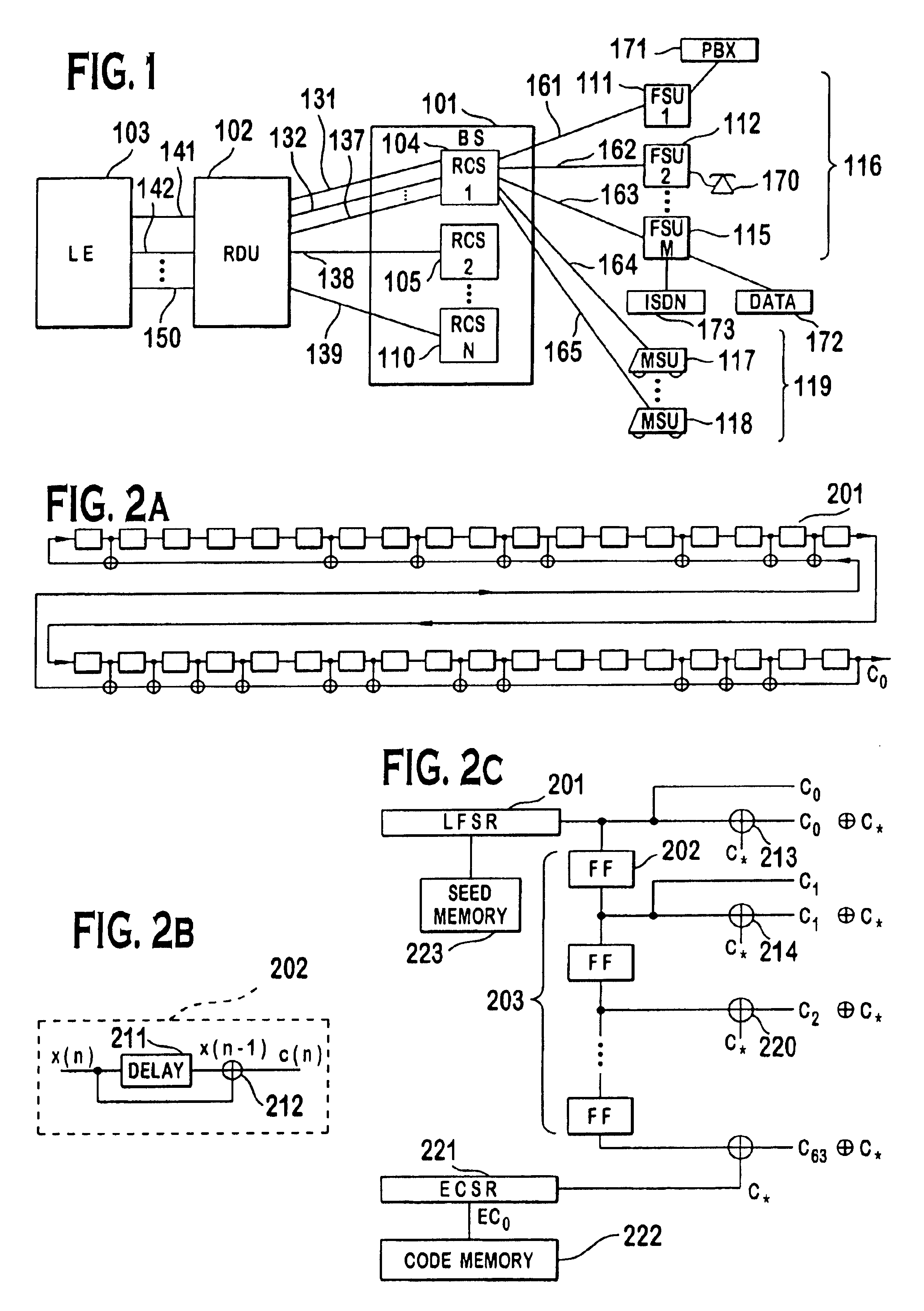
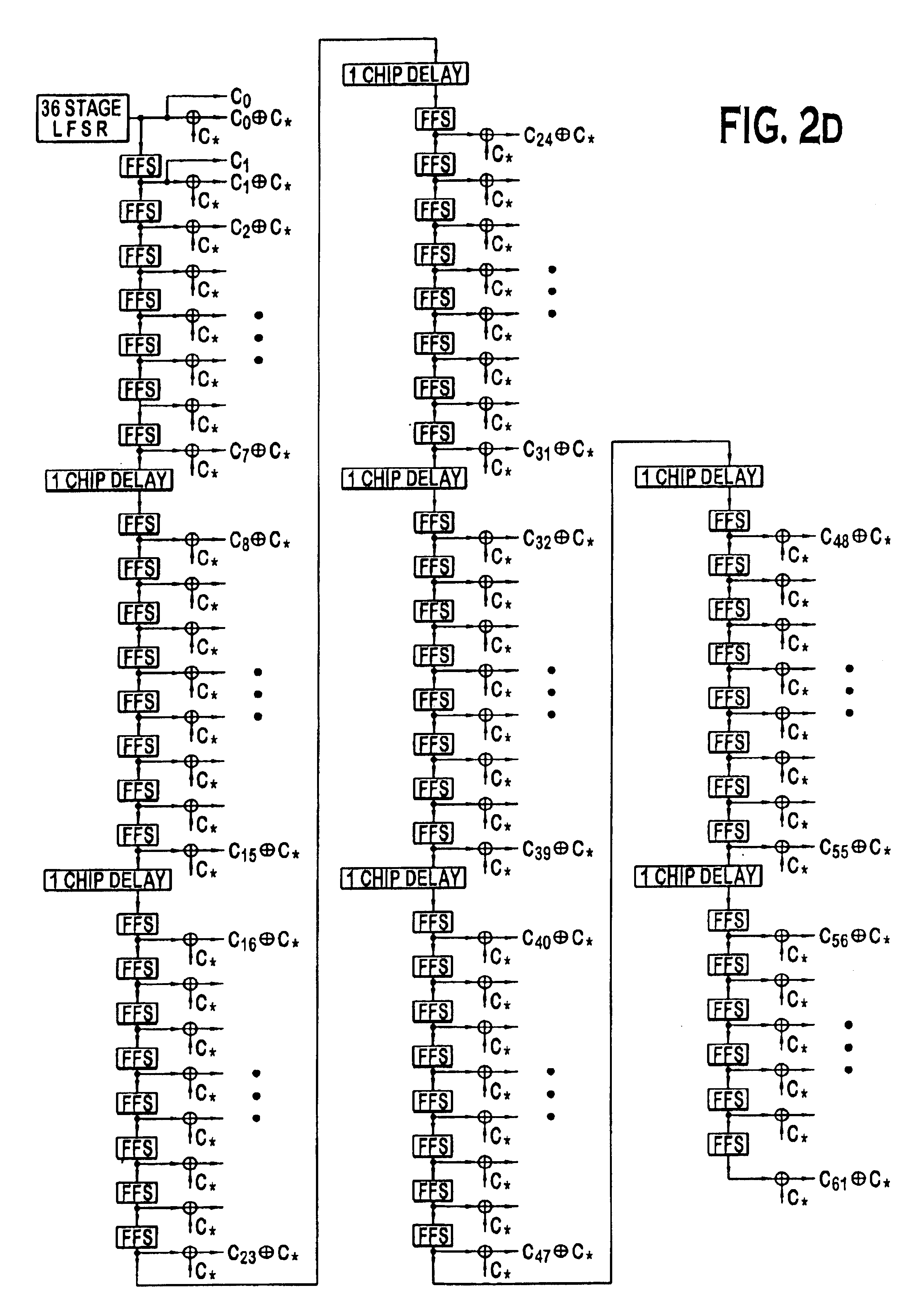
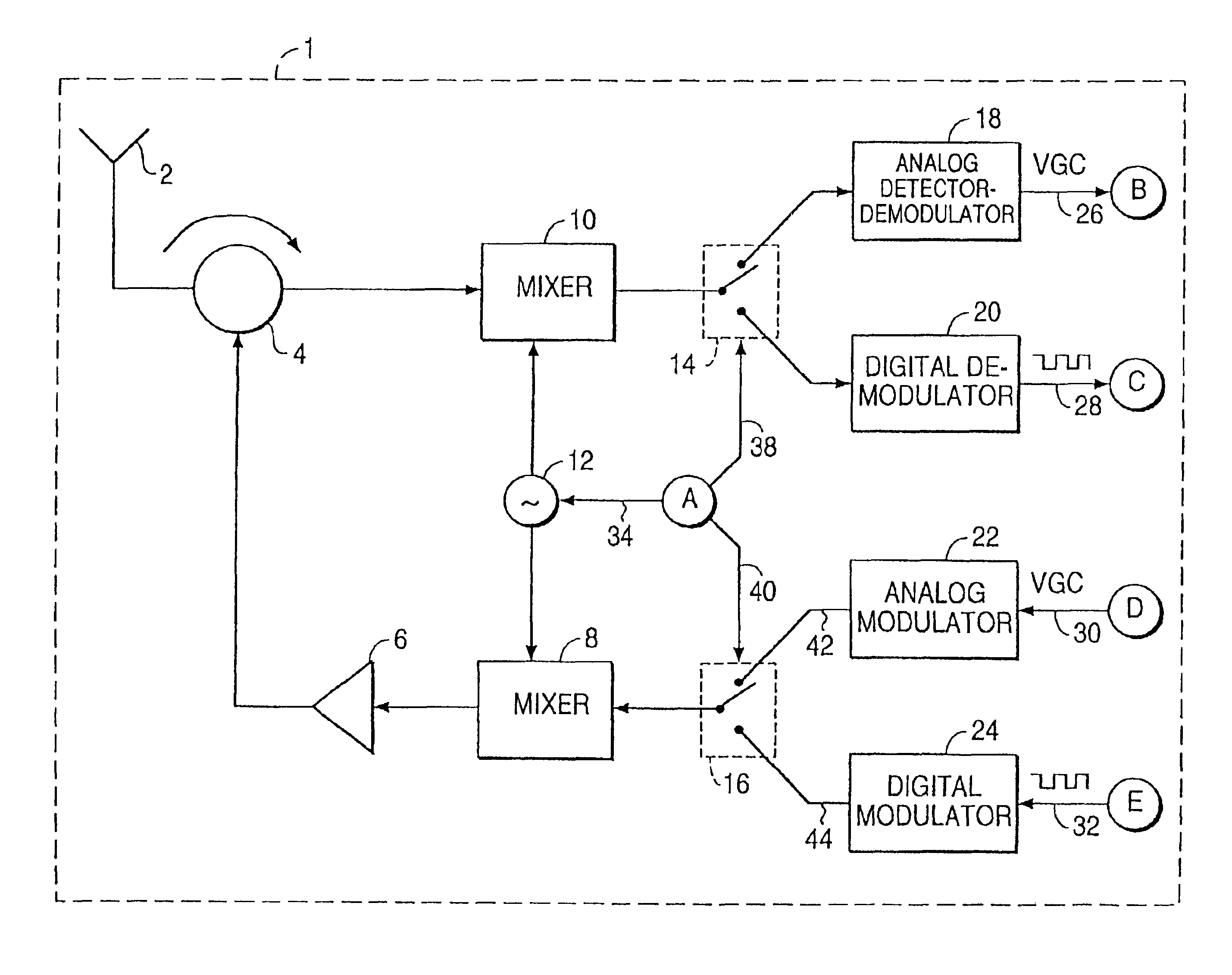
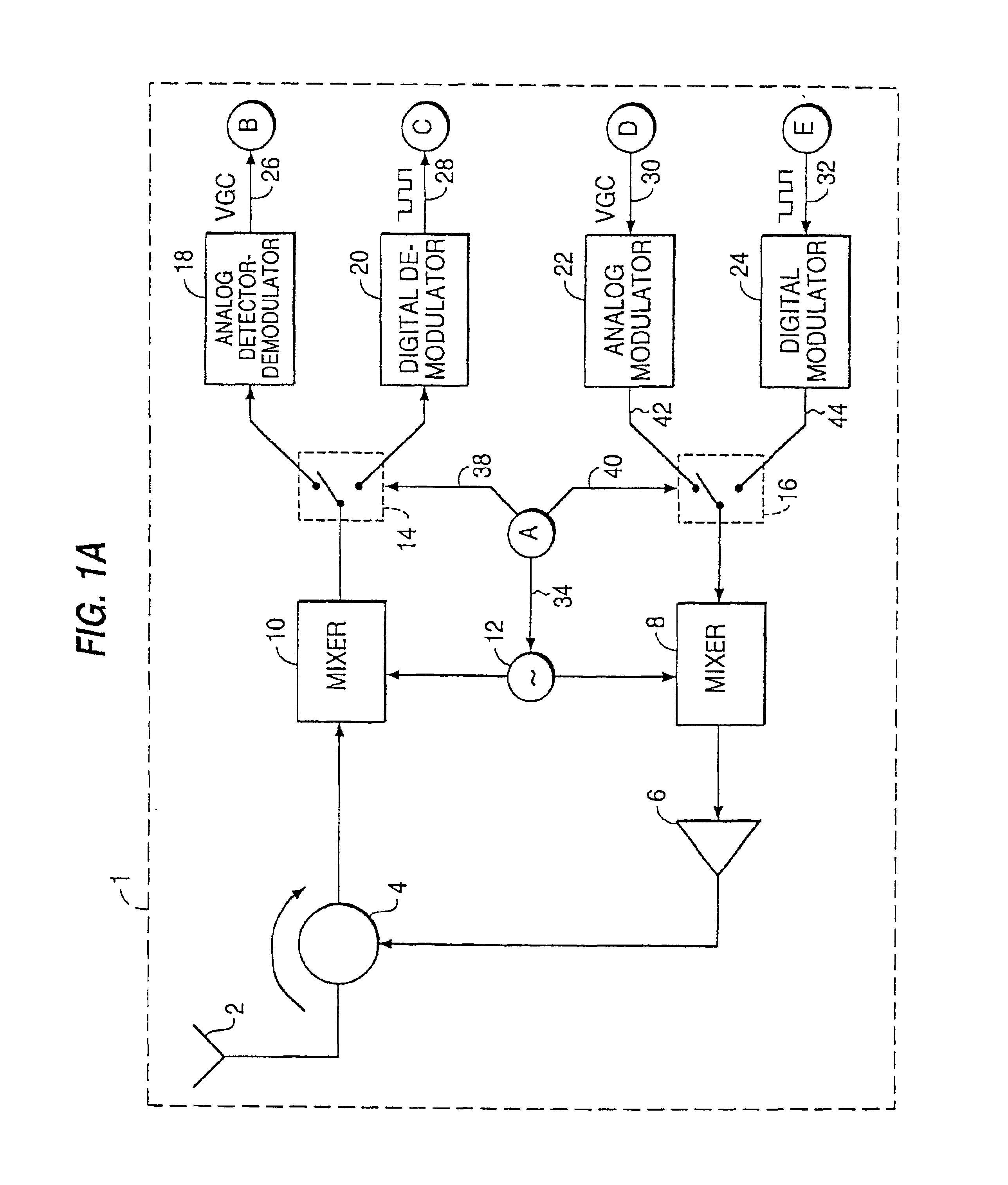
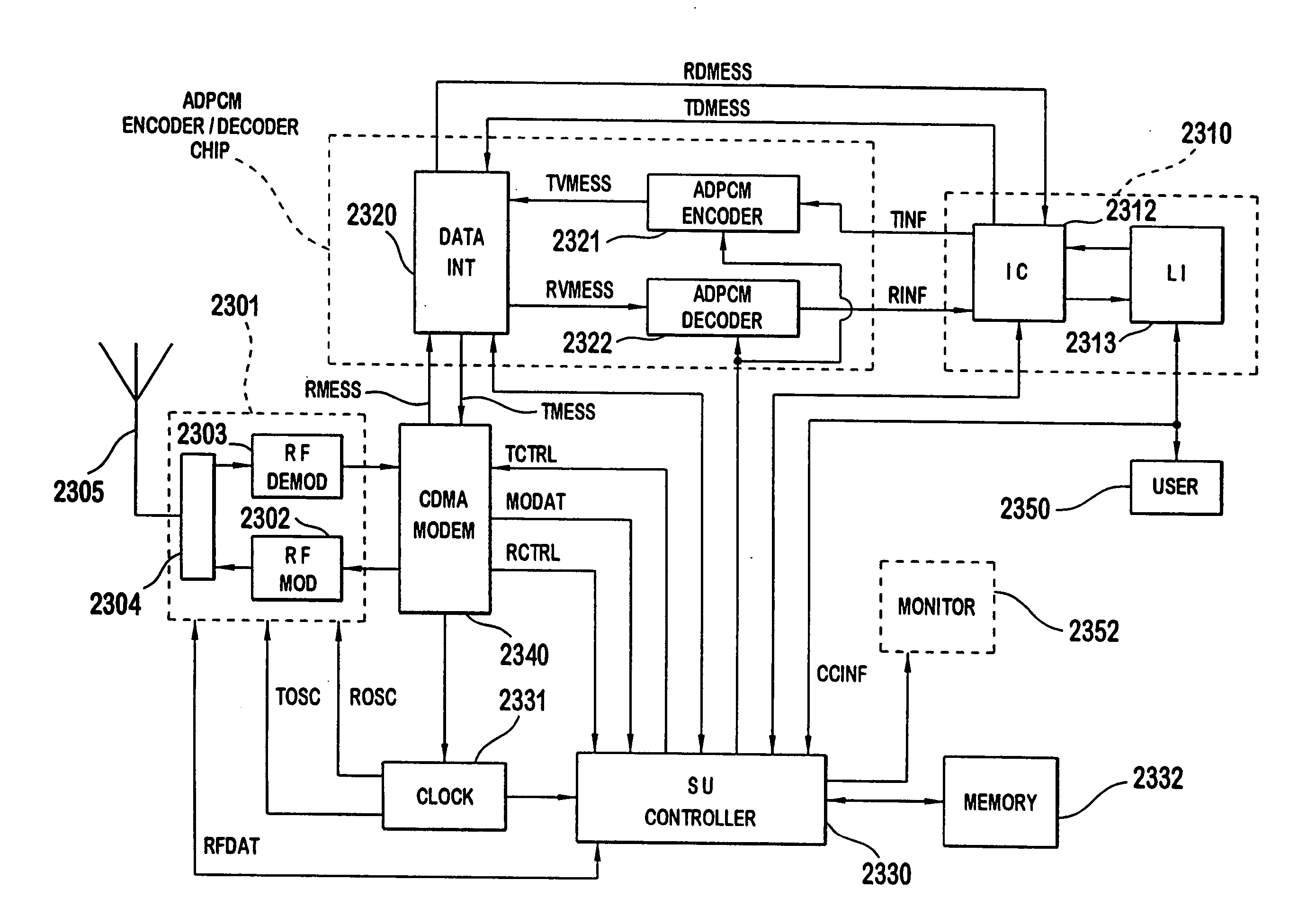
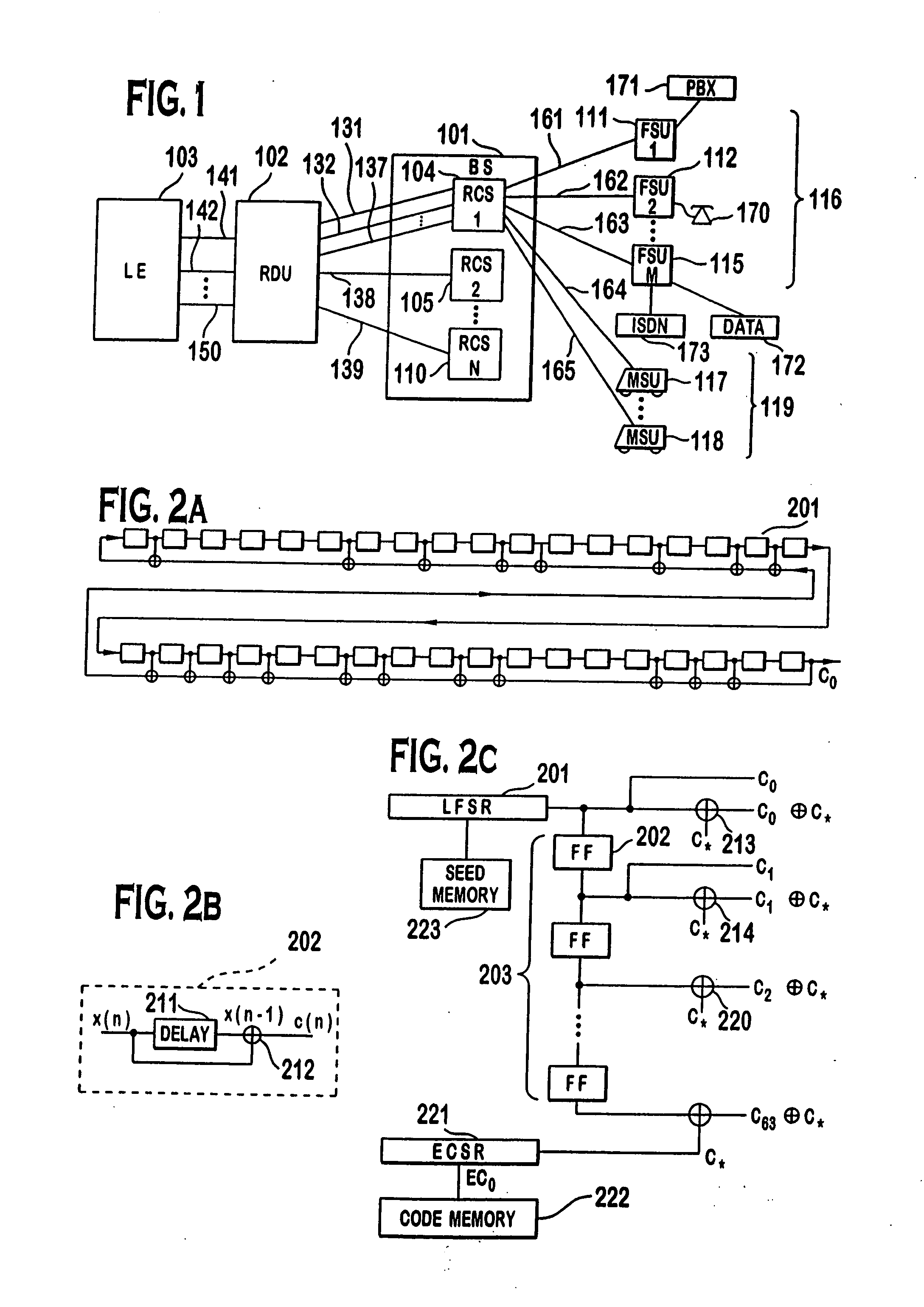
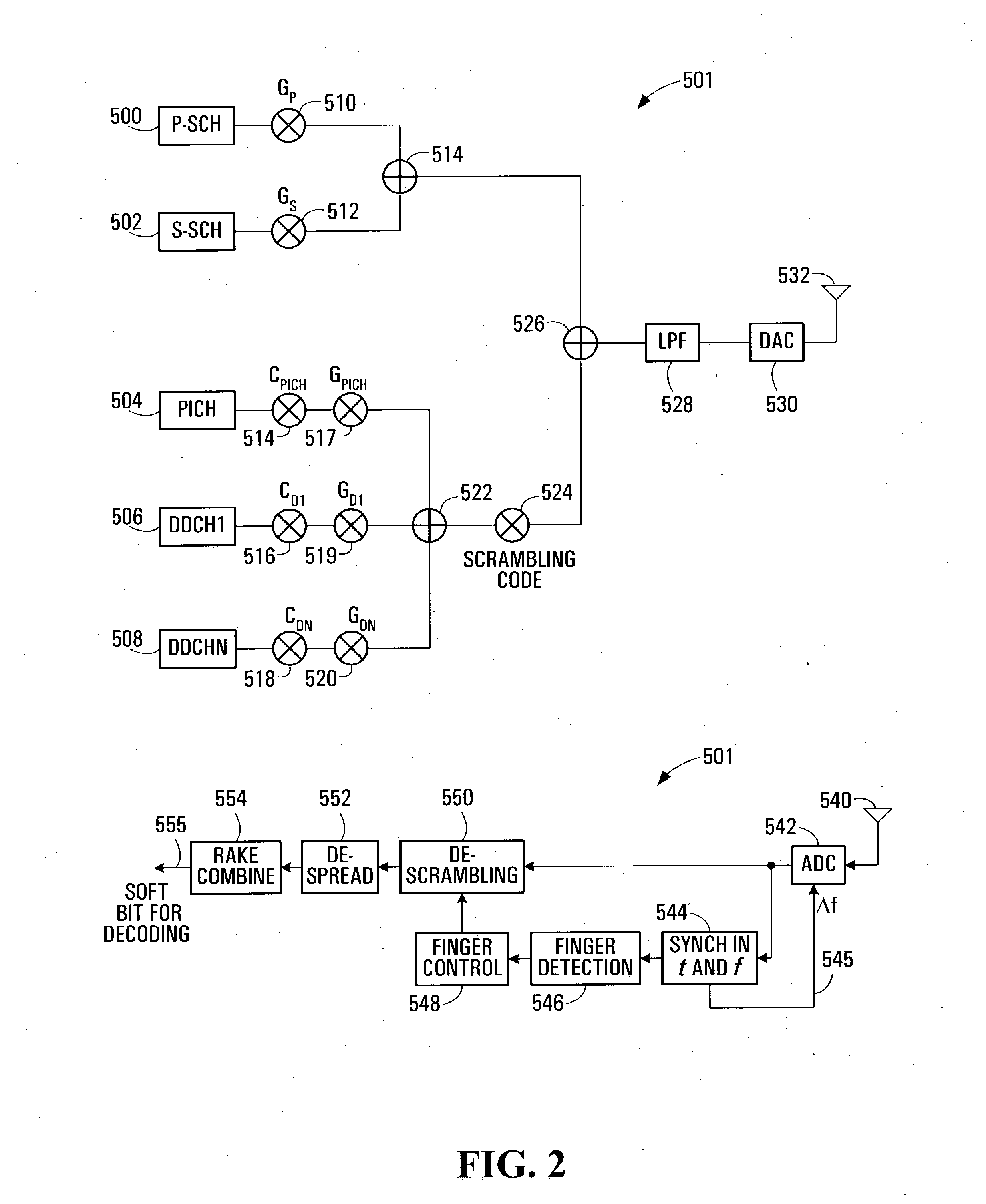
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a radio carrier station over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency channel as a code-division-multiplexed signal to a group of subscriber units. The radio carrier station receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The radio carrier station includes a plurality of CDMA modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a code division multiplexed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. A radio frequency transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the code division multiplexed processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a code division multiplexed signal. The transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the code division multiplexed signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through a radio frequency communication channel to the subscriber units. Each subscriber unit includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the code division multiplexed signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS6885652B1Increase profitPower managementBaseband system detailsModem deviceSystem capacity
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Adaptive omni-modal radio apparatus and methods
InactiveUS6934558B1Easily and conveniently identifyIntense competitionMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesTransmission protocolTransceiver
A frequency and protocol agile wireless communication product, and chipset for forming the same, including a frequency agile transceiver, a digital interface circuit for interconnecting the radio transceiver with external devices, protocol agile operating circuit for operating the radio transceiver in accordance with one of the transmission protocols as determined by a protocol signal and an adaptive control circuit for accessing a selected wireless communication network and for generating the frequency control signal and the protocol control signal in response to a user defined criteria Among the possible user defined criteria would be (1) the cost of sending a data message, (2) the quality of transmission link (signal strength, interference actual or potential), (3) the potential for being bumped off of the system (is service provider at near full capacity), (4) the security of transmnission, (5) any special criteria which the user could variably program into his omni-modal wireless product based on the user's desires or (6) any one or more combinations of the above features that are preprogrammed, changed or overridden by the user. The disclosed invention allows wireless service providers to broadcast electronically as part of any “handshaking” procedure with a omni-modal wireless product information such as (1) rate information and (2) information regarding system operating characteristics such as percent of system capacity in use and / or likelihood of being dropped. The disclosed invention creates a user oriented source enrollment and billing service in the wireless data market by establishing uniform standard for “handshakes” to occur between cell service providers and omni-modal wireless products. In addition, the disclosed invention can be implemented on a standard chip or chipset including a radio transceiver specifically designed to be used in all types of omni-modal wireless products.
Owner:ANTON INNOVATIONS INC
Base-station (BS)-combined direct-through terminal optimized resource allocation method in direct-through cellular system
ActiveCN102638893AImprove resource utilizationImprove effectivenessWireless communicationMultiplexingQuality of service
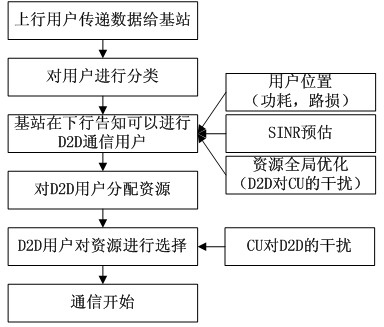
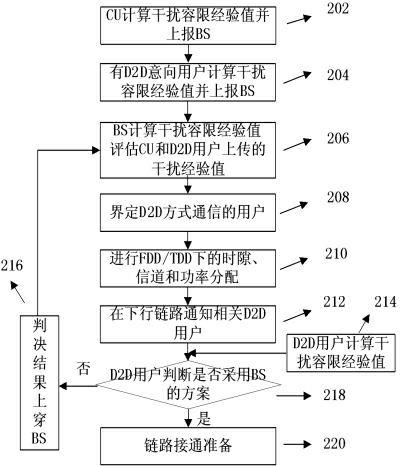
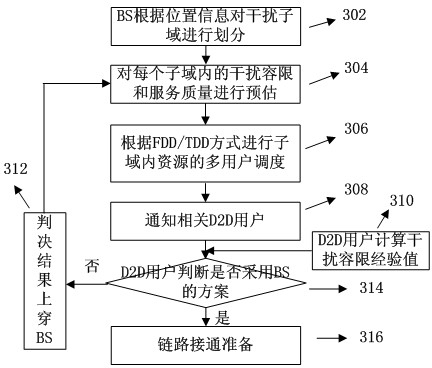
The invention provides a base-station (BS)-combined direct-through terminal optimized resource allocation method in a direct-through cellular system. In order not to interrupt the normal communication of traditional cellular subscriber links and obtain effective gain brought by device-to-device (D2D) direct-through technology, D2D subscribers are allowed to adopt a resource allocation manner that resources are selected by a D2D subscriber end when uplink and downlink resources of the cellular system are shared; at this time, the D2D subscribers only need to consider the interference to other cellular subscribers (CUs) arising from signals of the D2D subscribers; and meanwhile, a BS centralized-control manner is adopted to carry out resource allocation, the centralized-control advantage of a BS is exerted, a BS and D2D terminal combined optimization manner is fully utilized, and the advantages of the two allocation manners are exerted. The BS-combined direct-through terminal optimized resource allocation method in the direct-through cellular system has the advantages that the resource utilization ratio and availability of a coexistent system which is provided with the D2D direct-through technology are sufficiently improved, the multiplexing gain of the resources are maximally developed, the system capacity is increased, the service types are increased, and the quality of service is ensured; and many chances for resource multiplexing are developed under the condition of limited resources from a novel resource allocation viewing angle.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Indication method and apparatus for large bandwidth system physical ascending control channel
ActiveCN101442818ALarge frequency selective gainGuaranteed CompatibilityError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsSystem capacity
The invention provides a PUCCH indication method for large bandwidth system. Physical uplink control channel PUCCH resource transmits uplink mixed automatic retransmission request confirmation and corresponds to dynamically dispatched physical downlink sharing channel; index number of uplink component carrier frequency of physical uplink control channel PUCCH resource is mapped by downlink component carrier frequency index of physical downlink control channel PDCCH for dispatching the PDSCH to acquire, or a fixed value, or notified by high level signaling or physical signaling. Index number of uplink component carrier frequency of PUCCH resource for uplinkly transmitting HARQ-ACK corresponding to semi-static scheduled PDSCH is mapped and acquired by downlink component carrier frequency index number of PDSCH or notified by high level signaling. The invention guarantees compatibility of LTE-Advanced system and LTE Release-8 system, facilitates to increase system capacity and scheduling agility of LTE-Advanced system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
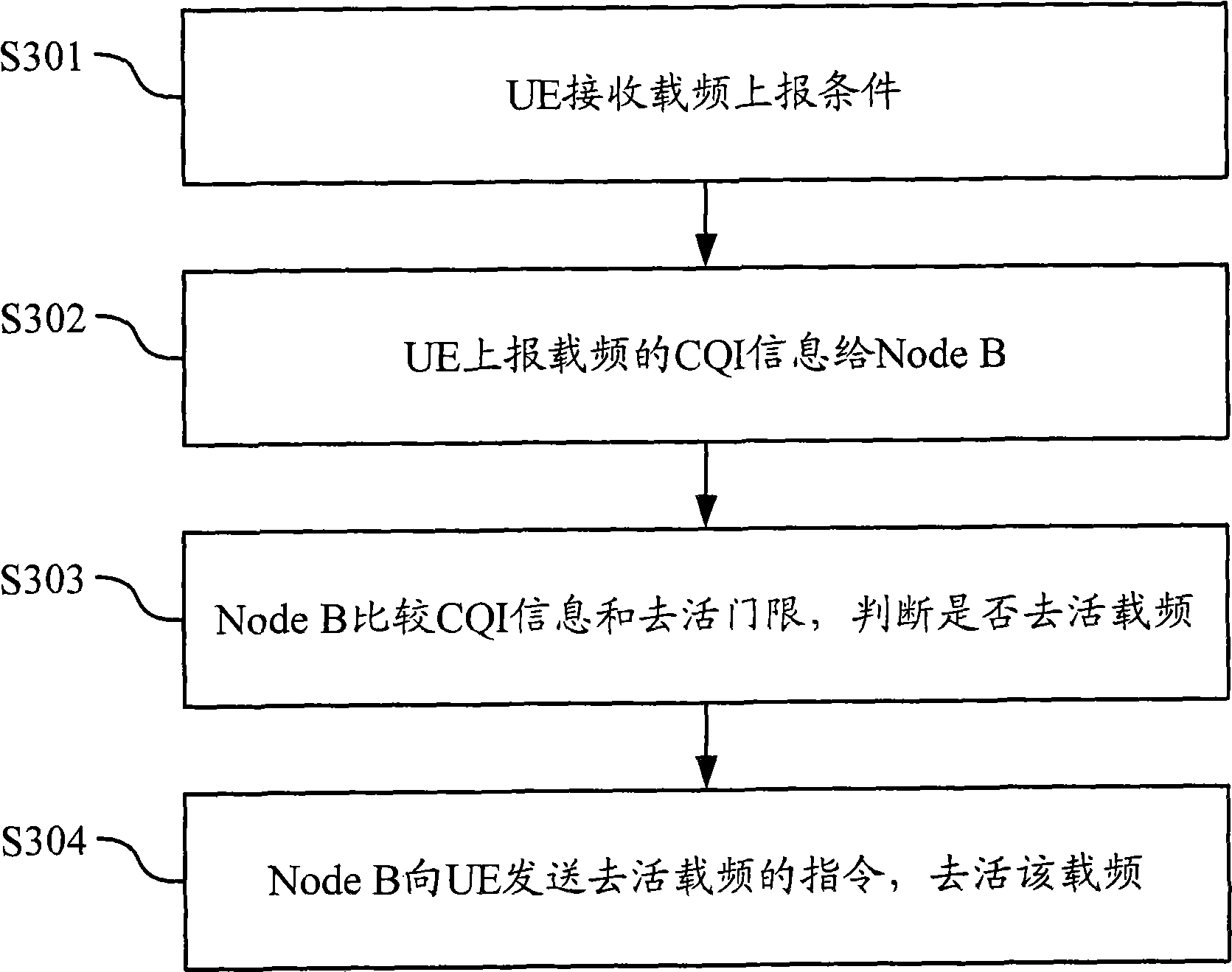
Method and device for controlling carrier frequency of multi-carrier/subdistrict system
ActiveCN101547477AQuality improvementImprove experienceNetwork traffic/resource managementSignal allocationSystem capacityEngineering
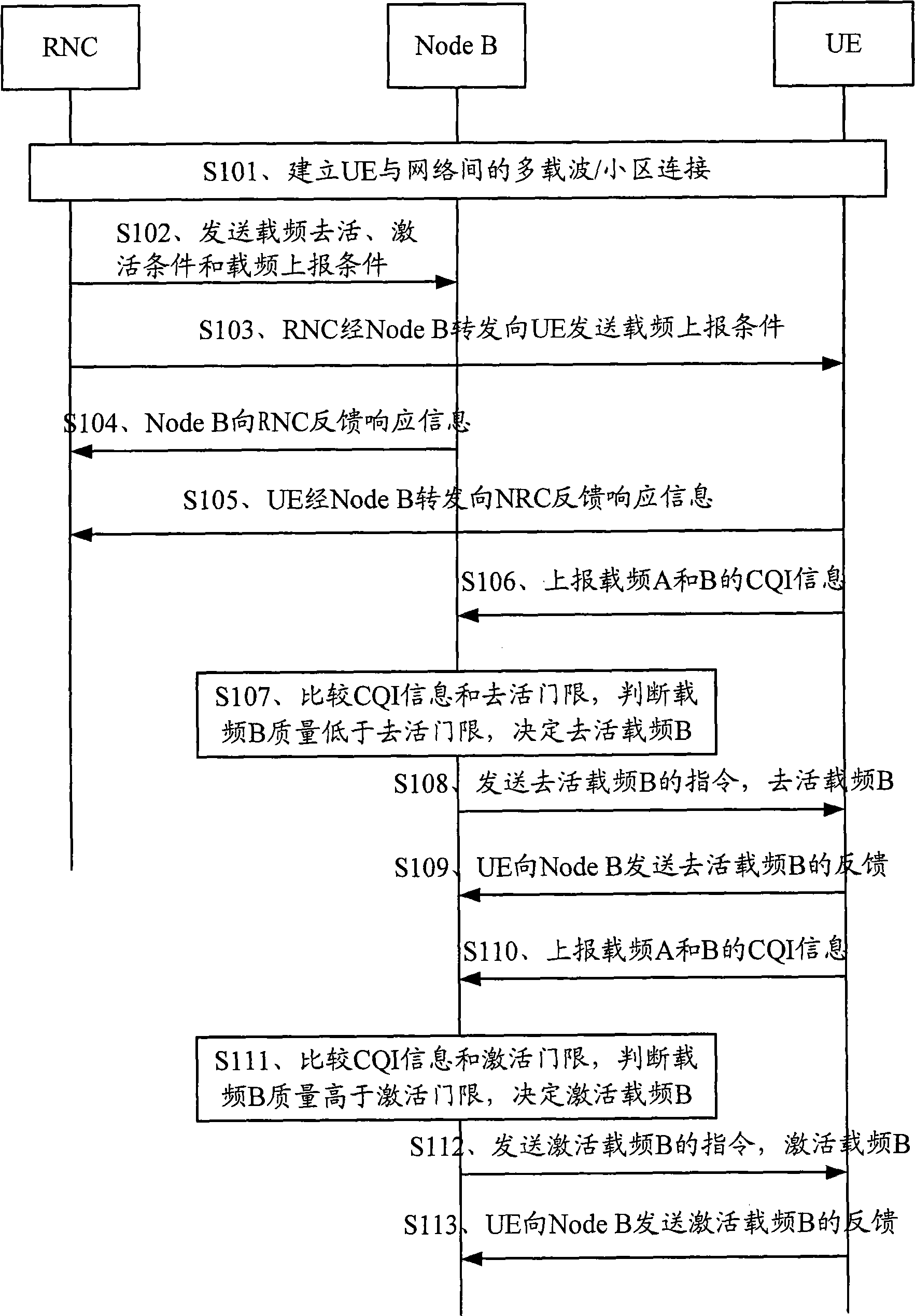
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for controlling the carrier frequency of a multi-carrier / subdistrict system. The method comprises the following steps: receiving the signal path quality indicating CQI information of the carrier frequency, which is reported by a terminal; carrying out deactivation or activation judgment for the carrier frequency according to the signal path quality indicating CQI information; and ordering the terminal to deactivate or activate the carrier frequency according to the judgment result. The method flexibly activates and deactivates a certain carrier frequency according to carrier frequency quality reporting and threshold comparison in the multi-carrier / subdistrict system, thereby enhancing the system capacity and having better load balancing effect.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
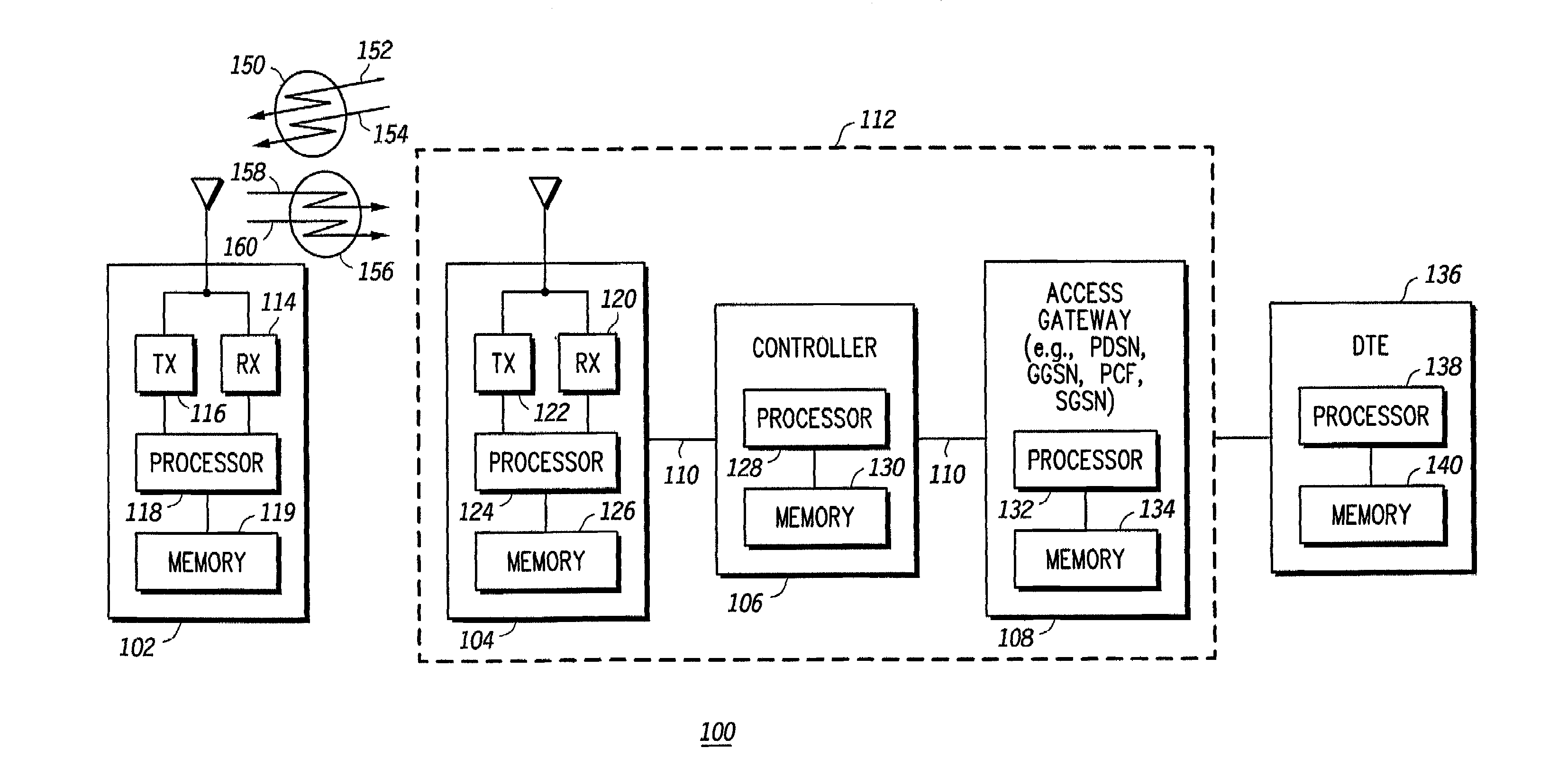
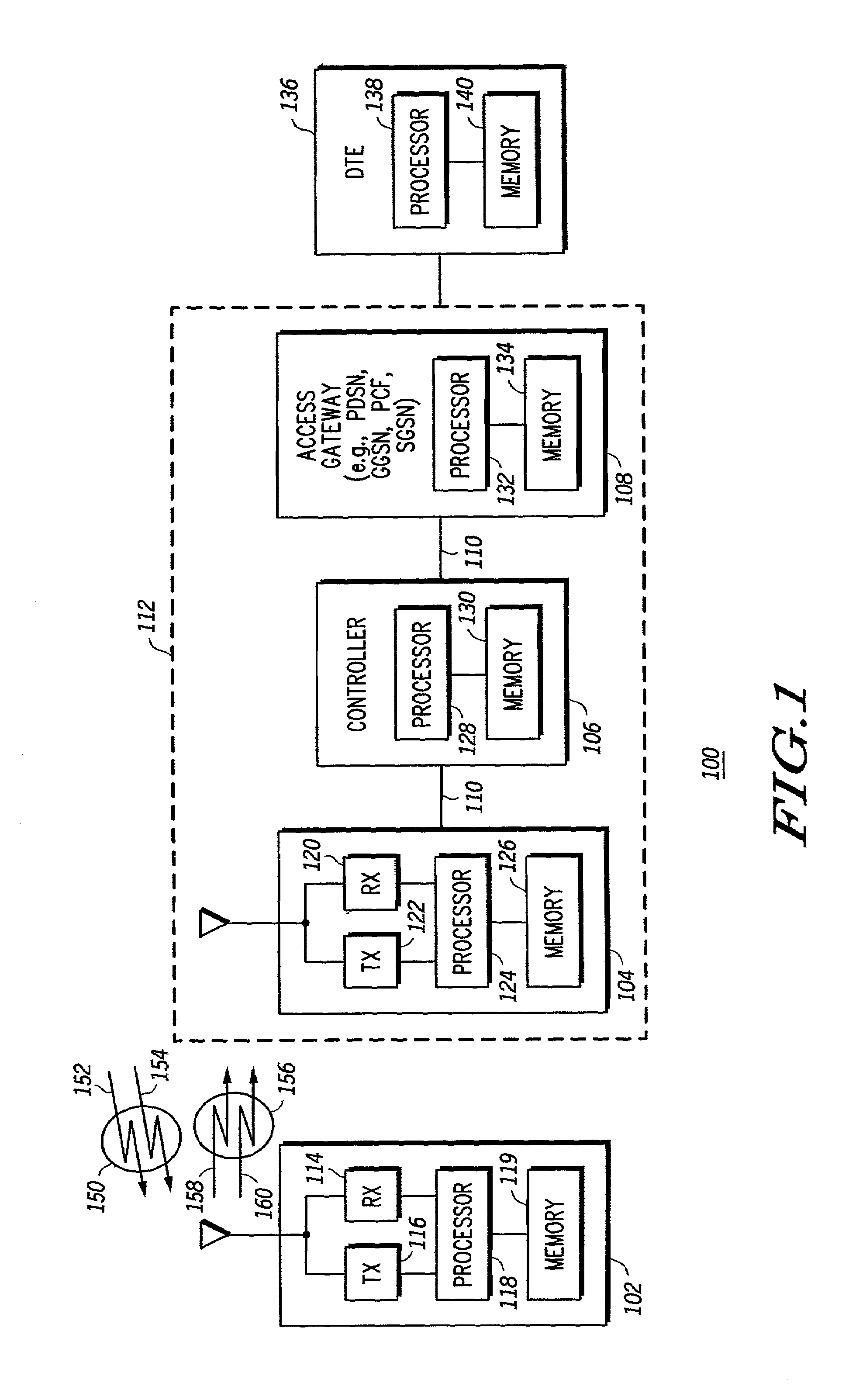
Method and apparatus for transmitting data in a communication system
ActiveUS7165112B2Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsAbstraction layerSystem capacity
A communication system distributes the functions of a socket abstraction layer of the prior art between a socket abstraction layer included in an client communication device, such as a mobile subscriber, and a socket abstraction layer in a an agent communication device, such as an infrastructure serving the mobile subscriber. By so distributing the functions of the socket abstraction layer, headers may be reduced in signaling between the client communication device and the corresponding agent communication device as part of call set ups and tear downs and in the exchange of payloads between the client and agent communication devices. By reducing the required headers, overhead is reduced and bandwidth is conserved in communications between the client and agent communication devices, such as in over-the-air communications between a mobile subscriber and an infrastructure serving the mobile subscriber, with resulting increases in system capacity and improvements in system efficiency.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS20040252668A1Easy to liftMaximize signal to noisePower managementBaseband system detailsSystem capacityCode division multiple access
A subscriber unit for use in a multiple access spread-spectrum communication system includes a spread spectrum radio interface, responsive to a rate function signal from a base station, and first and second despreaders. The base station assigns the rate function spread-spectrum message channels and the first despreader recovers and modifies an information signal one of the spread spectrum message channels. The information channel mode is then modified for processing by the second despreader, with the second despreader supporting a different information signal rate. The subscriber unit has a capability of communicating with a dynamically changing a transmission rate of an information signal which includes multiple spread spectrum message channels. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for a radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Virtual MIMO transmitters, receivers, systems and methods
A system for doing BLAST with fewer receive antennas or even only one receiving antenna is provided. A system implementation architecture is provided together with a detailed analysis on its principle and theory behind this engineering solution to reduce the MIMO technology cost by using fewer antennas whilst achieving high spectrum efficiency. Examples are provided on how to implement this idea in a CDMA platform and in a OFDM platform. For the CDMA system, the code space is automatically doubled or tripled and therefore a significant system capacity increase is realized. For OFDM systems, the throughput is doubled similar as 2×2 blasting. The system complexity is minimum and full standards backward compatibility can be achieved.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
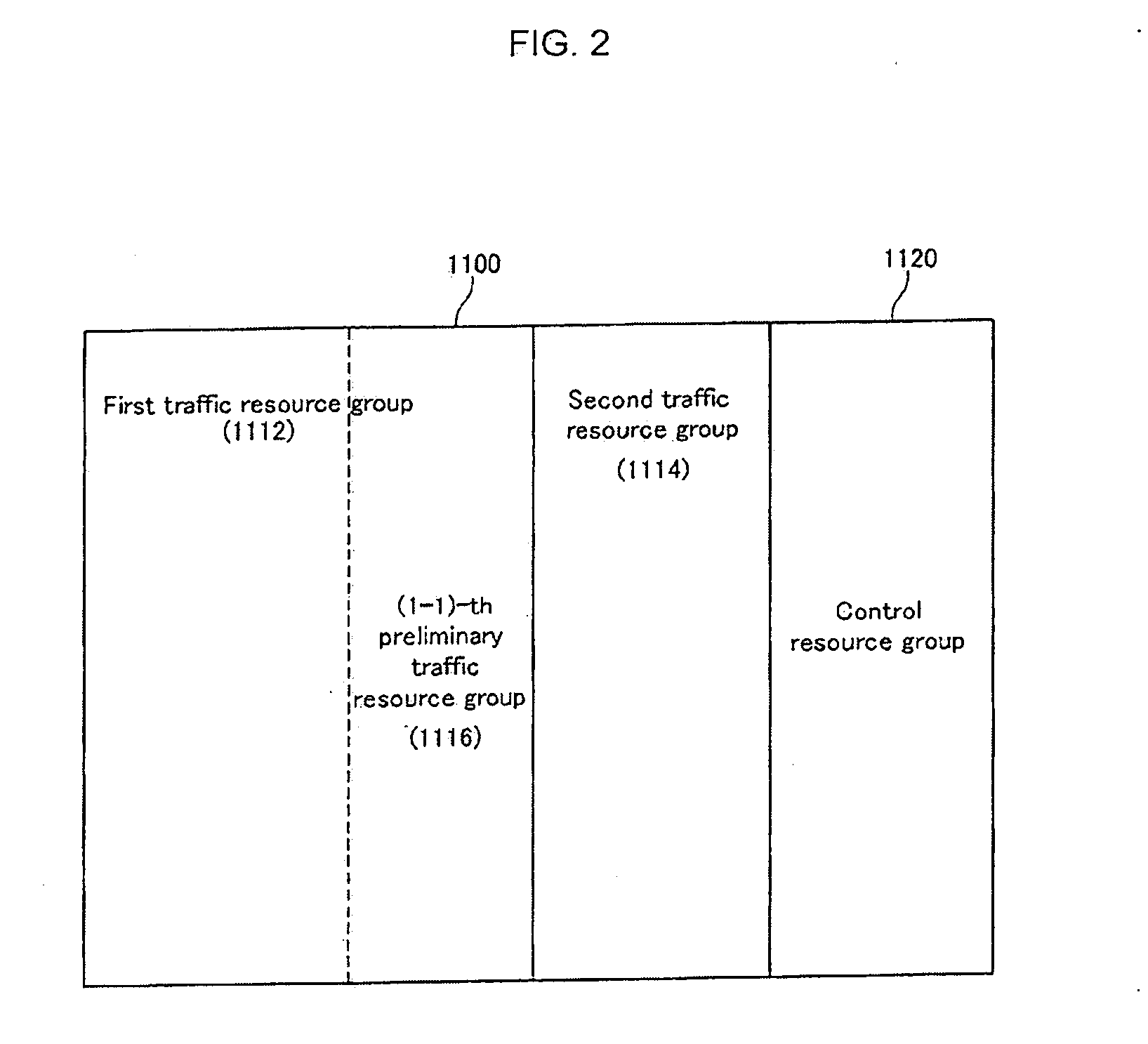
Method for resource partition, assignment, transmission and reception for inter-cell interference migration in downlink of OFDM cellular systems
InactiveUS20090069023A1EasilyReduce Inter-Cell InterferenceTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationTelecommunicationsSystem capacity
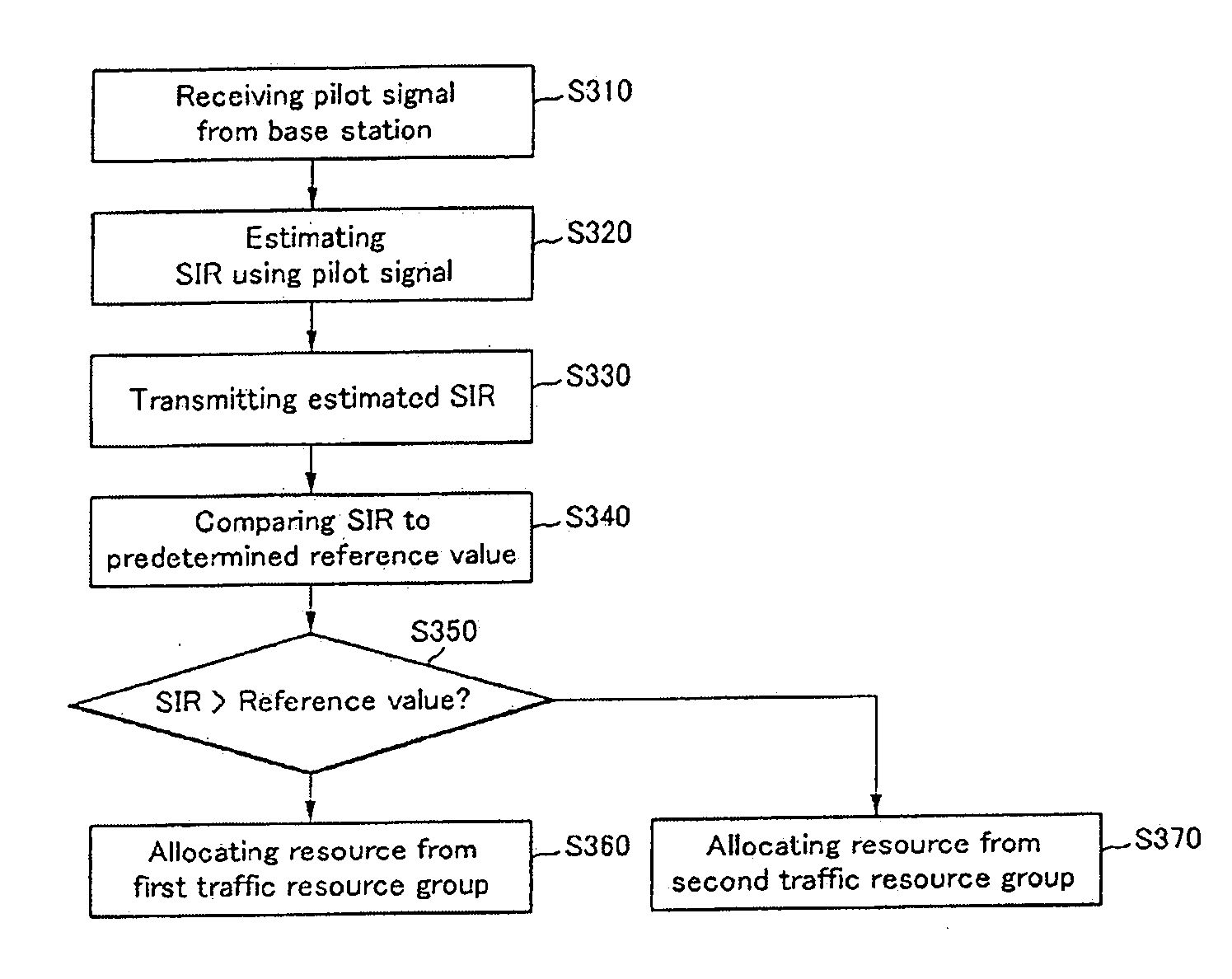
A resource division, allocation, and transmitting / receiving method of downlink for reducing inter-cell interference in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system are provided. Entire downlink radio resources are divided into a traffic resource group for a traffic channel and a control resource group for a control channel, the traffic resource group is divided into a first traffic resource group for the intra-cell mobile terminals and a second traffic resource group for a cell-boundary mobile terminal, and a part of the first traffic resource group is imaginarily divided into a (1−1)-th preliminary traffic resource group, the (1−1)-th preliminary traffic resource group being a preliminary resource group for the cell-boundary mobile terminal. The control resource group is allocated to a control channel for the intra-cell mobile terminal; and a resource of the first traffic resource group or the second traffic resource group is allocated to a traffic channel for the mobile terminal according to inter-cell interference affected to the mobile terminal. Radio resources may be reused in each downlink cell of the OFDM system, the traffic may be rapidly transmitted to the cell boundary mobile terminal, a system capacity may be increased, the cell plane may be easily performed, and the system capacity may not be decreased although the mobile terminal number, locations, and traffic density is not uniform.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
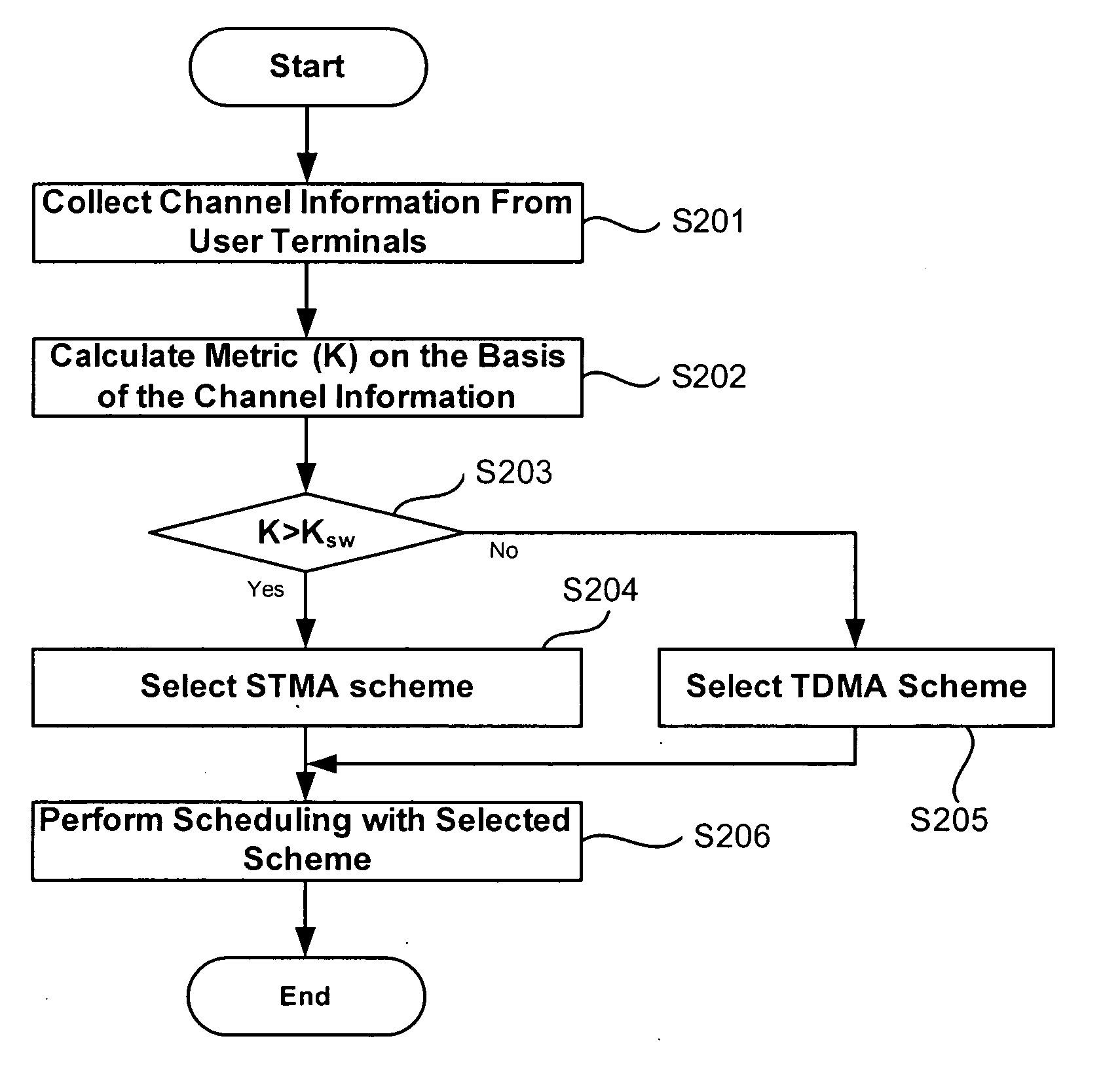
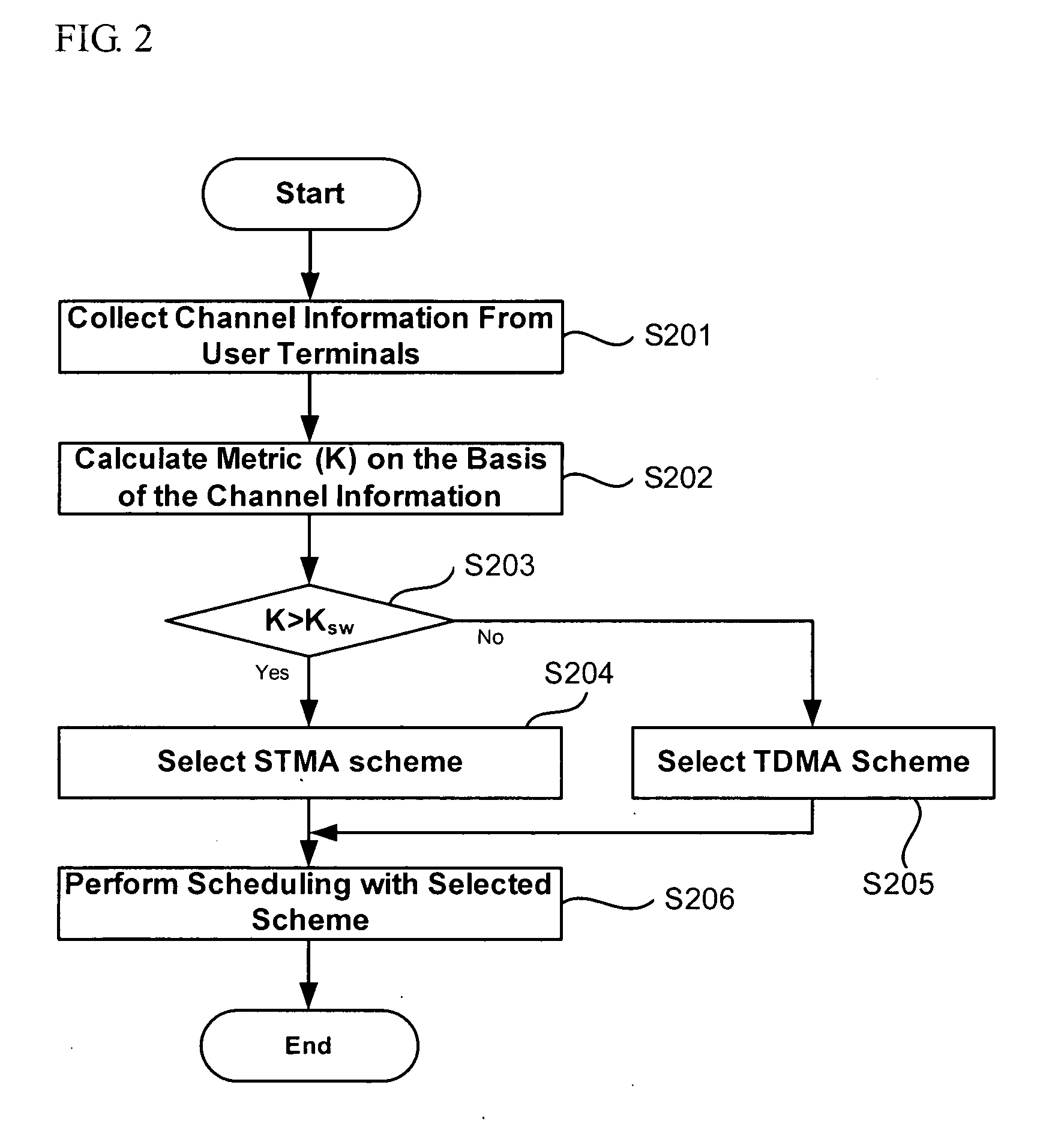
User scheduling method for multiuser MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20060209764A1Improve system performanceReducing receiver complexity and amount feedbackNetwork traffic/resource managementDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSystem capacityMultiple input
In multiuser Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems in which a base station performs scheduling on the basis of channel information fed back from a plurality of terminals, the user scheduling method of the present invention includes calculating a metric for scheduling the users using the channel information, selecting one of at least two preinstalled scheduling schemes according to the metric, and performing the scheduling with the selected scheduling scheme. The user scheduling method of the present invention performs scheduling with one of TDMA- and STMA-based scheduling schemes which show maximum capacity in different channel environments, such that the system capacity can be optimally maintained even when the channel environment is changed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Apparatus for transmitting data on contention based resource in radio communication system and method thereof
InactiveUS20090092086A1Transmission path divisionCriteria allocationSystem capacityCommunications system
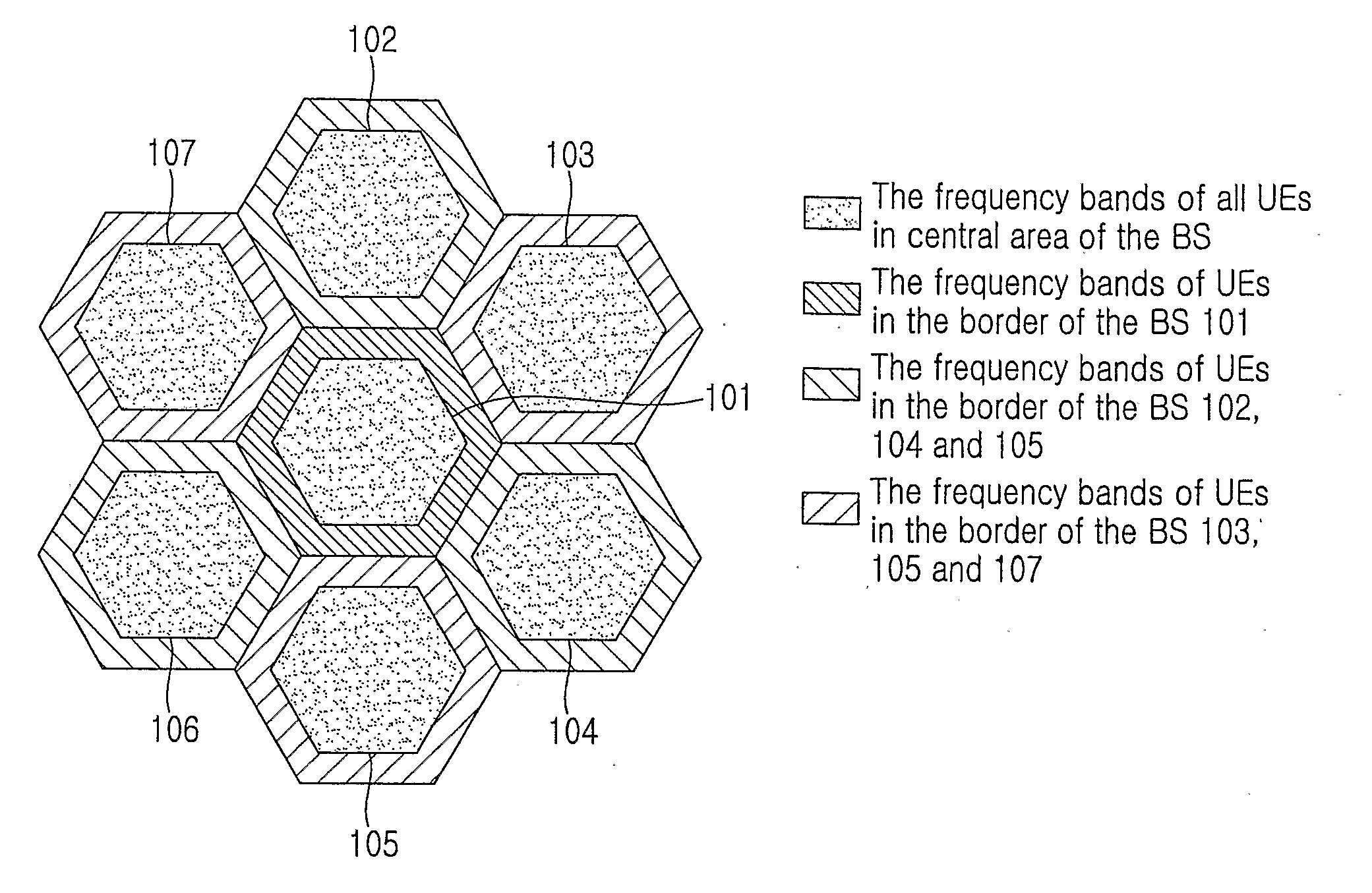
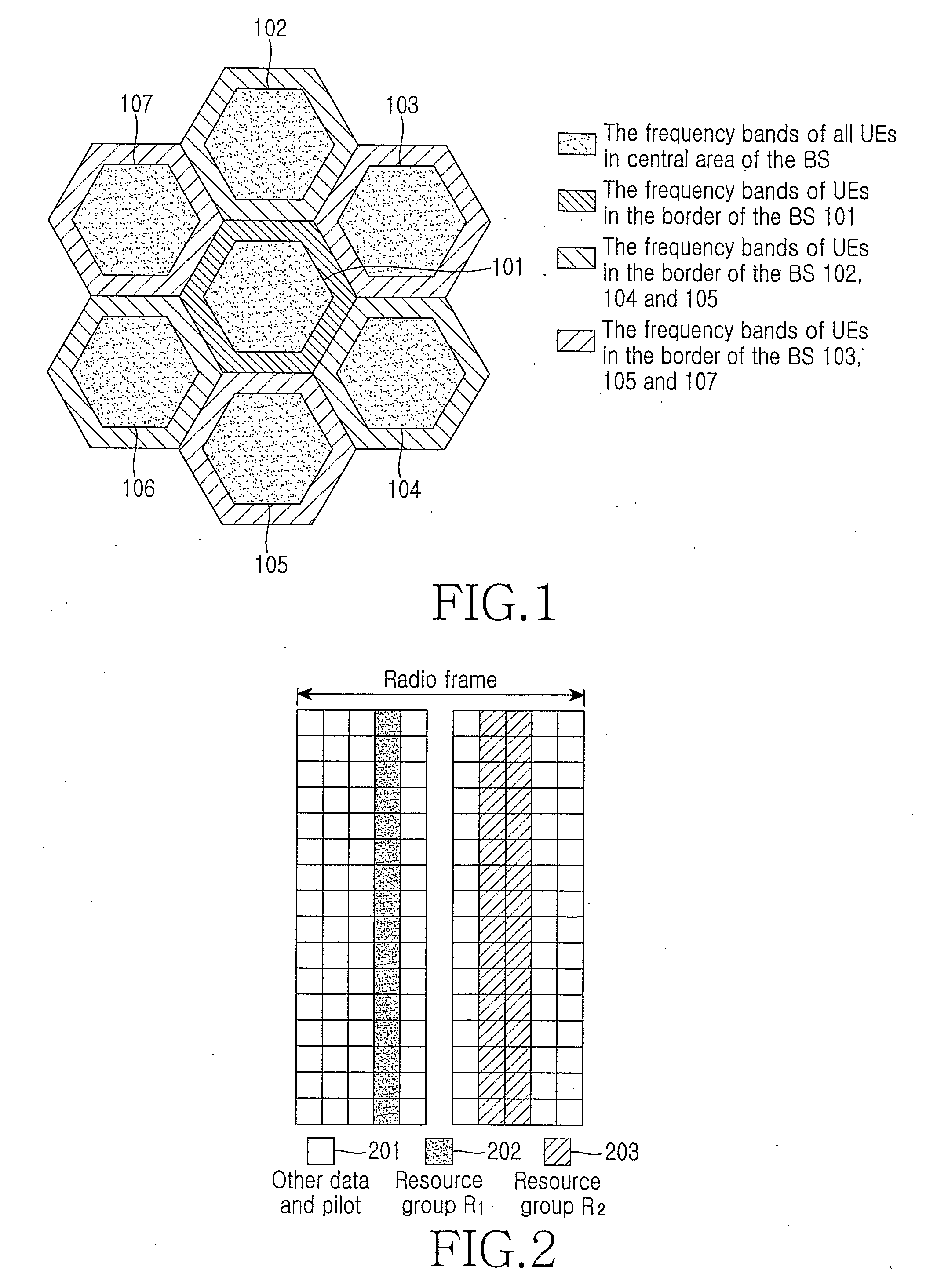
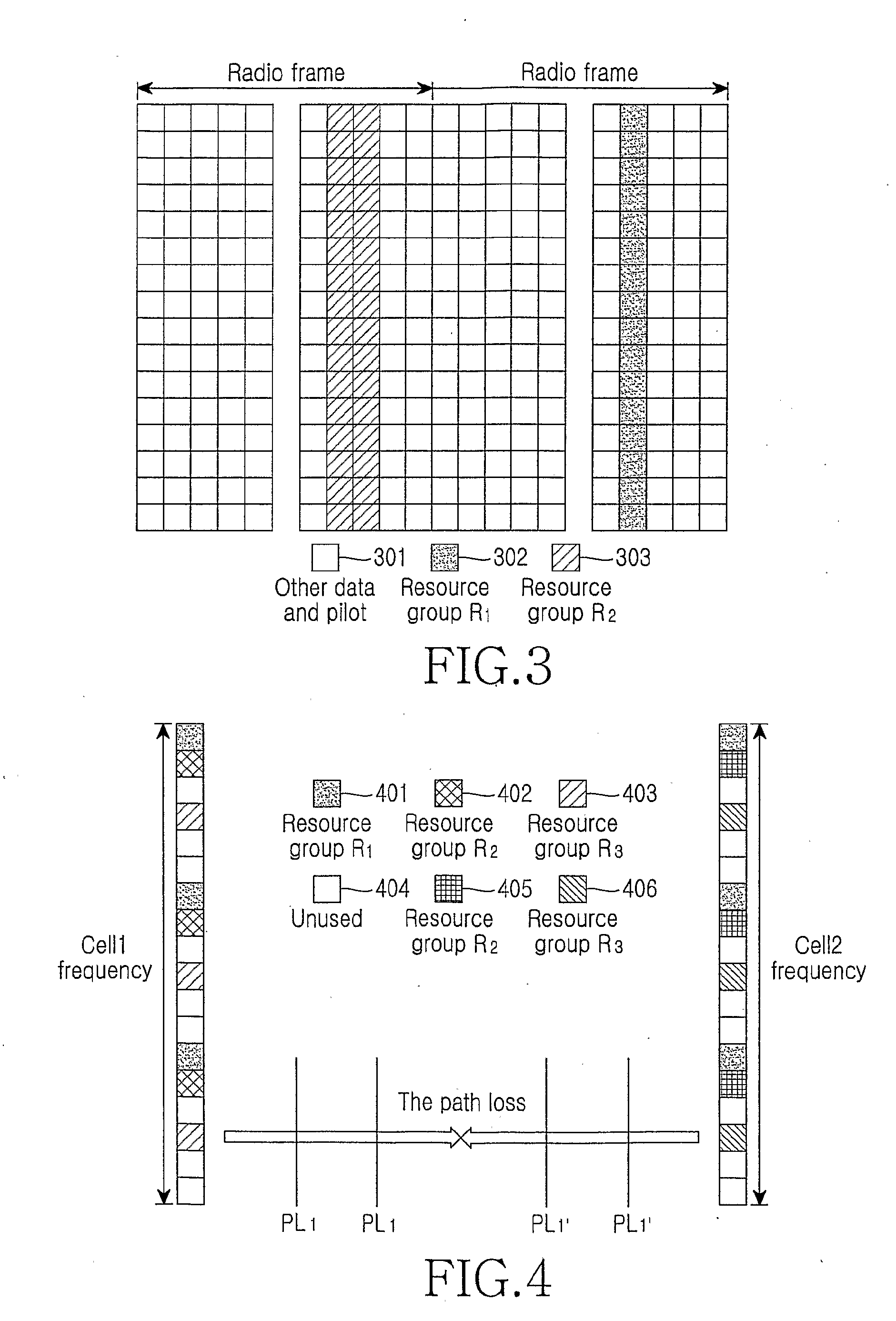
An apparatus and method for transmitting data on a contention based resource in a radio communication system. A base station broadcasts a definition of uplink contention based resource groups and a criterion for a User Equipment (UE) to use for selecting a group. The UE selects an uplink contention based resource to transmit data according to the criterion for selecting the group. The apparatus and method improve data transmission service quality of a UE in a border area of a cell may by providing an effective scheme, thereby improving uplink system capacity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method to provide unequal error protection and unequal error detection for internet protocol applications
InactiveUS20060245417A1Function increaseIncrease system capacityEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemSystem capacity
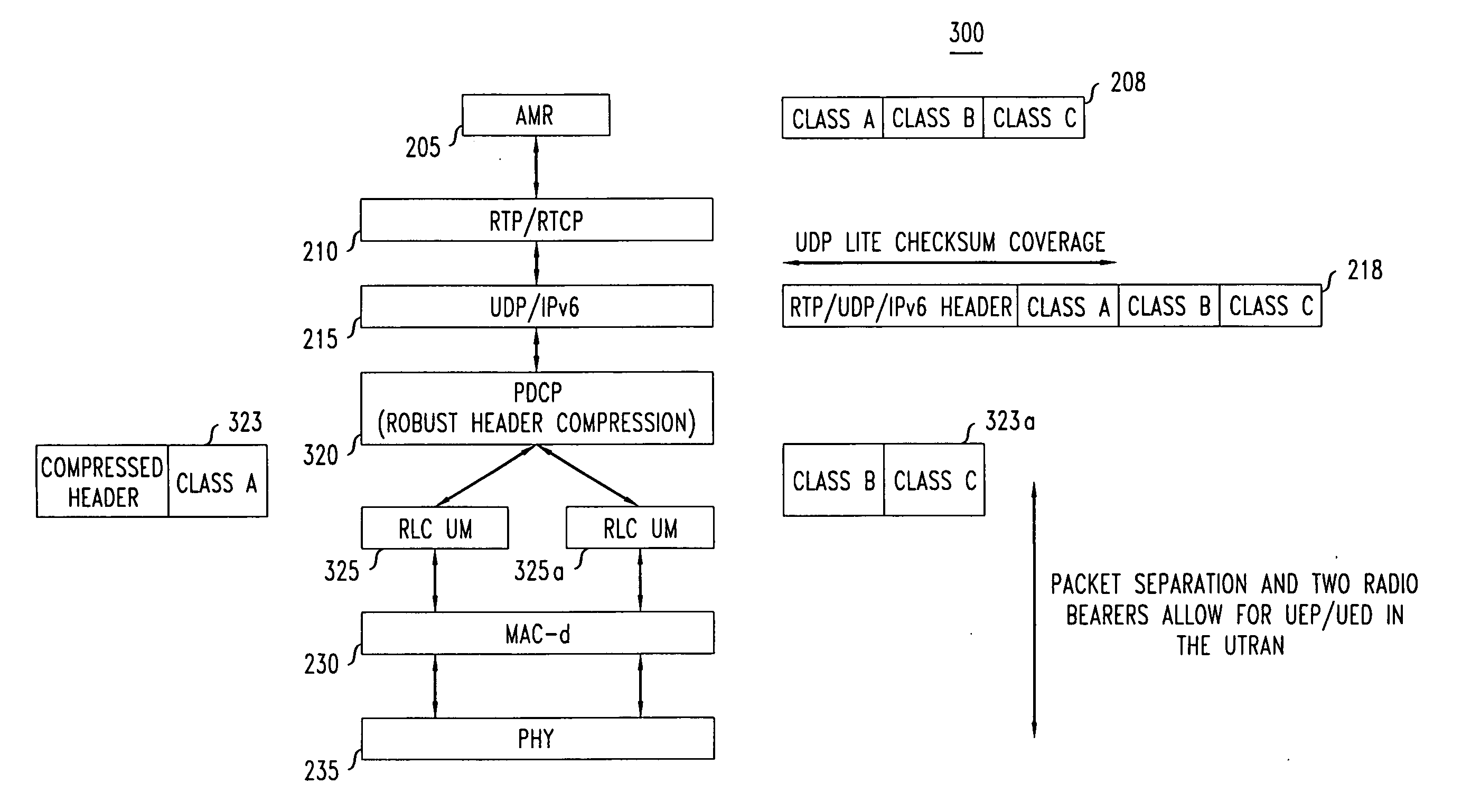
A method and system for providing Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) in a wireless communications system using a Packet Data Conversion Protocol (PDCP) with enhanced functionality that allows sub-packets to be processed for transmission over different Radio Bearers (RB) with unequal or different levels of error protection and / or error detection based on perceptual importance of the bits in the sub-packets. The enhanced PDCP being operable to partition a packet into a plurality of sub-packets such that different levels of error protection and / or error detection may be applied to the packet. An overall gain in system capacity can be expected due to transmit power savings provided via unequal error detection and error protection.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
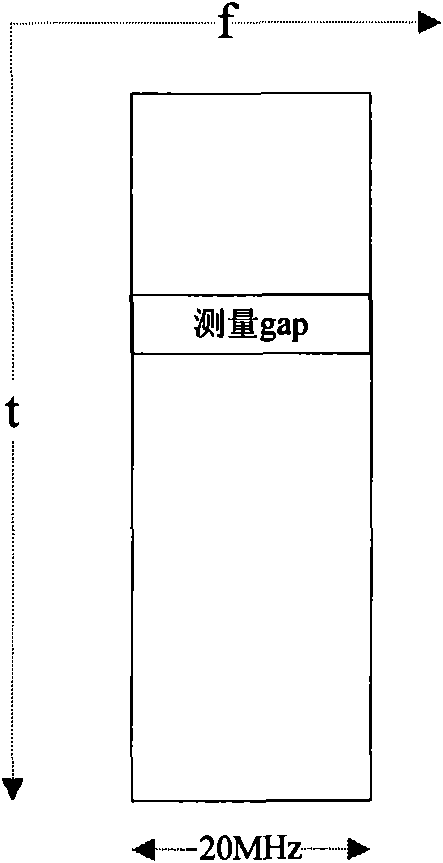
Measurement gap configuration method and device of multi-carrier polymerization system
ActiveCN101873646ARealize measurementImprove data transmission qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementSystem capacityCarrier signal
The invention discloses a measurement gap configuration method and a device of a multi-carrier polymerization system. The method comprises the following steps that: according to the measurement capability of a user terminal reported by the user terminal and the frequency points of a different frequency or a different system to be measured, the measurement gap configuration information of the userterminal is determined, and the measurement gap configuration information instructs to measure the different frequency or the different system to partial or all working member carriers of the user terminal; and the measurement gap configuration information is sent to the user terminal, and the measurement gap configuration information is used for providing the measurement of the different frequency or the different system to the user terminal when in multi-carrier polymerization transmission. The embodiment of the invention respectively configures measurement gaps to partial or all member carriers of the user terminal in a multi-carrier polymerization system, so that the user terminal does not need to stop CA transmission when entering the measurement gaps, thereby improving the data transmission quality and enhancing the transmission performance of the system and the system capacity.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
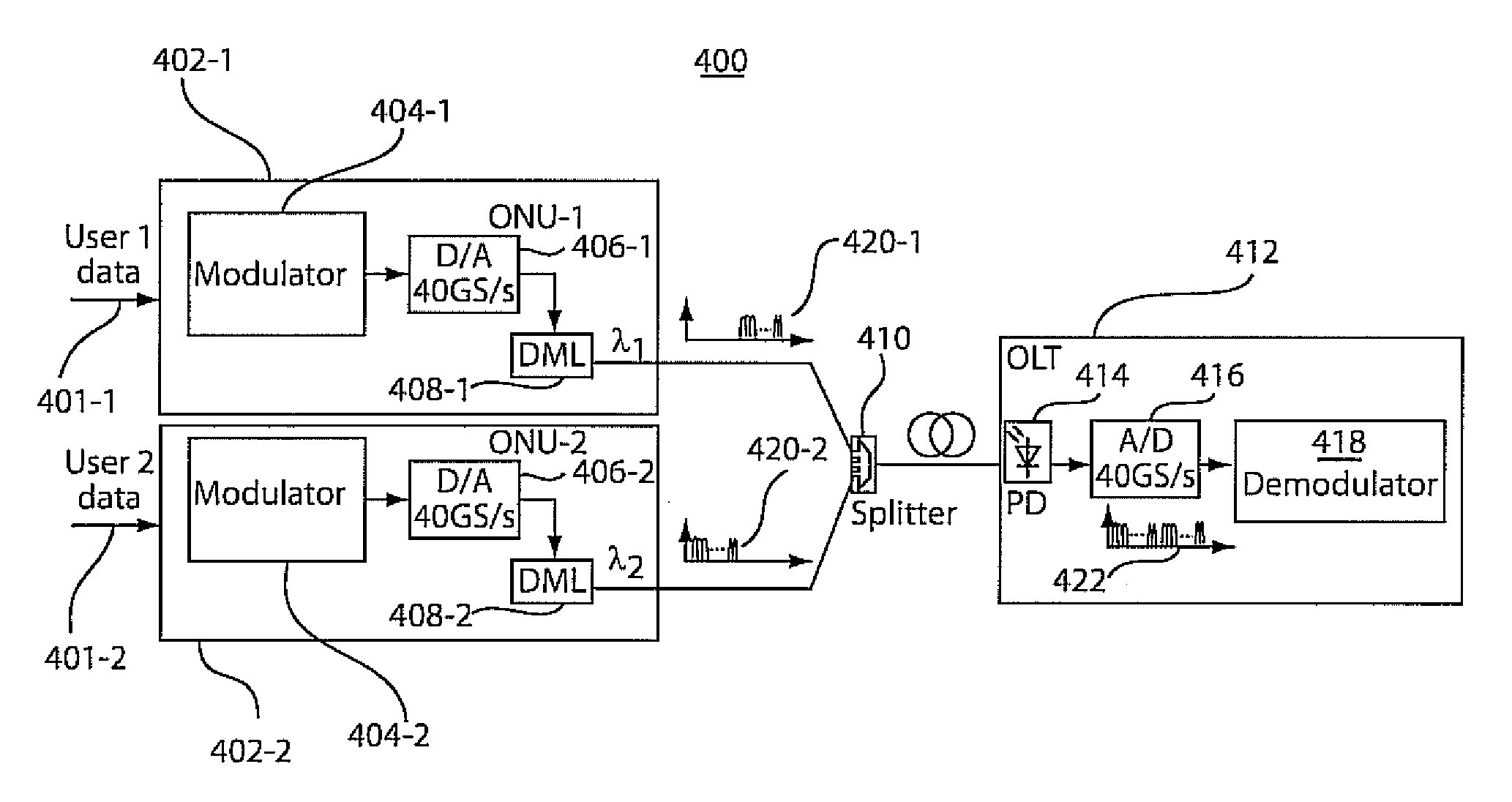
Passive optical network system employing sub-carrier multiplexing and orthogonal frequency division multiple access modulation schemes
InactiveUS20100028002A1Dynamic bandwidth allocationReduced sampling rate requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission path divisionSystem capacityEngineering
Implementations of the present principles include methods, systems and apparatuses for transmitting data through a sub-carrier multiplexing and orthogonal frequency-division multiple access passive optical network. In accordance with aspects of the present principles, a plurality of optical network units are assigned electrical carrier frequency bandwidths that are narrower than a system capacity bandwidth. Modulation of optical waves transmitted between an optical line terminal and each optical network unit is conducted on different orthogonal sub-carrier frequencies within the assigned bandwidths such that sampling of said orthogonal sub-carrier frequencies is limited to the assigned electrical carrier frequency bandwidths. The waves are thereafter received and demodulated for the extraction of data.
Owner:NEC CORP
System and method for a time-scalable priority-based scheduler
ActiveUS20050004970A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementSystem capacityFlexible scheduling
A system and method for a time-scalable priority-based scheduler. A flexible scheduling algorithm utilizing variable scheduling durations enables better system capacity utilization. A rate request is transmitted if data arrives in a buffer, data in the buffer exceeds a buffer depth, and sufficient power exists to transmit at the rate requested. A rate assignment responsive to the rate request indicates a scheduled duration and a scheduled rate applicable for the scheduled duration. The scheduled duration is less than or equal to a scheduling period. The scheduling period is an interval of time and after which a scheduler makes a scheduling decision. The scheduling period is variable and the scheduled duration is variable.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
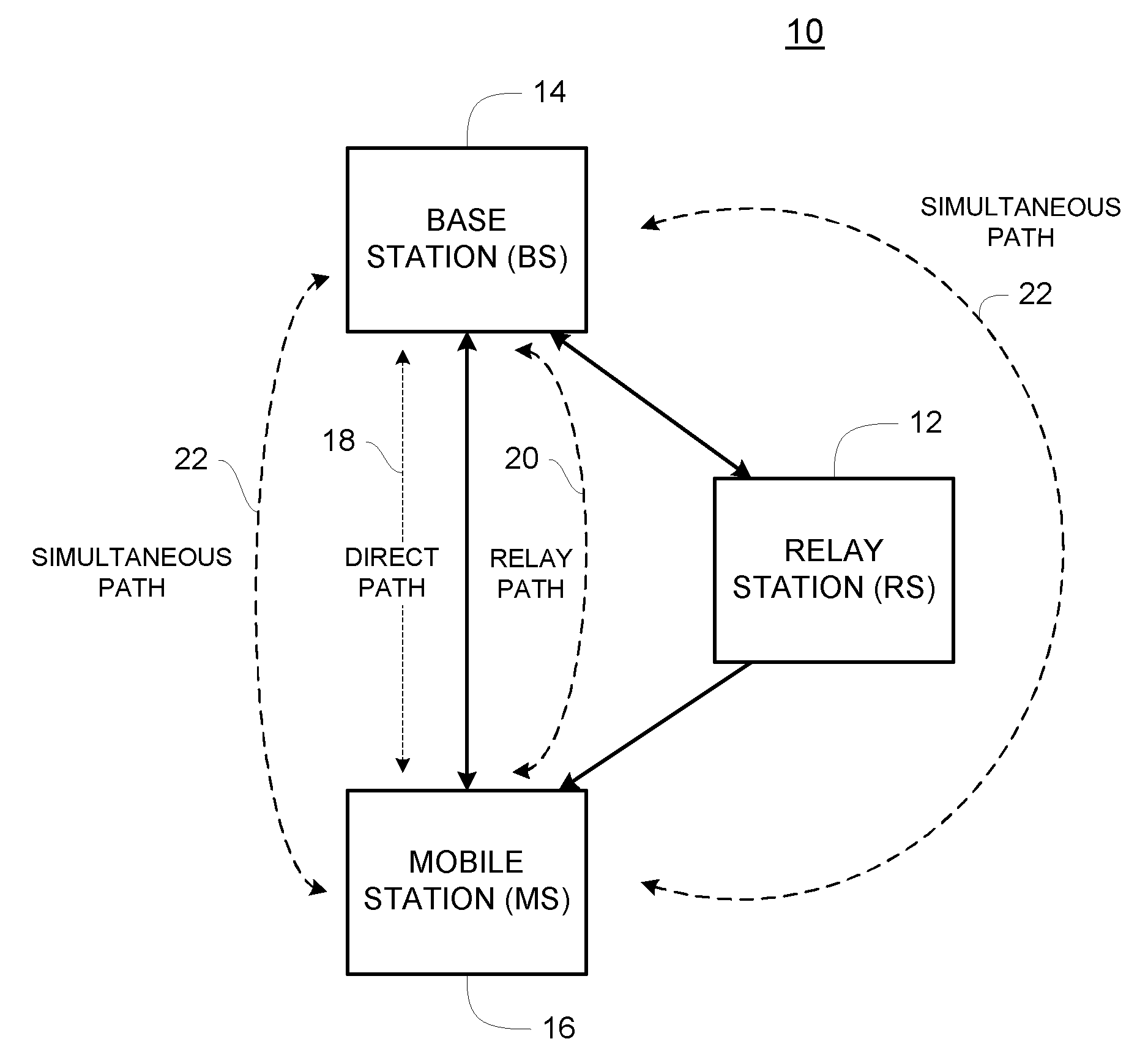
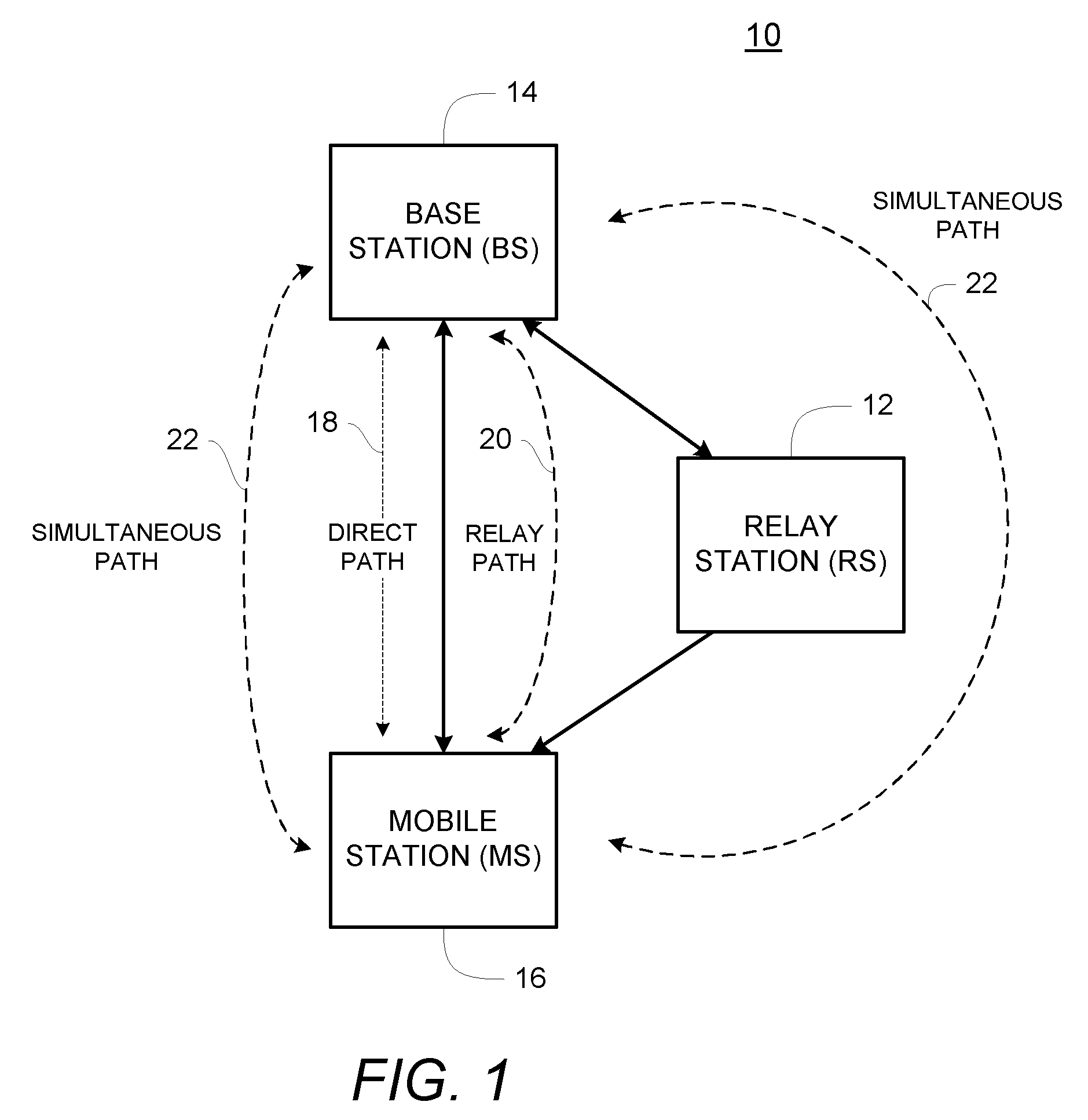
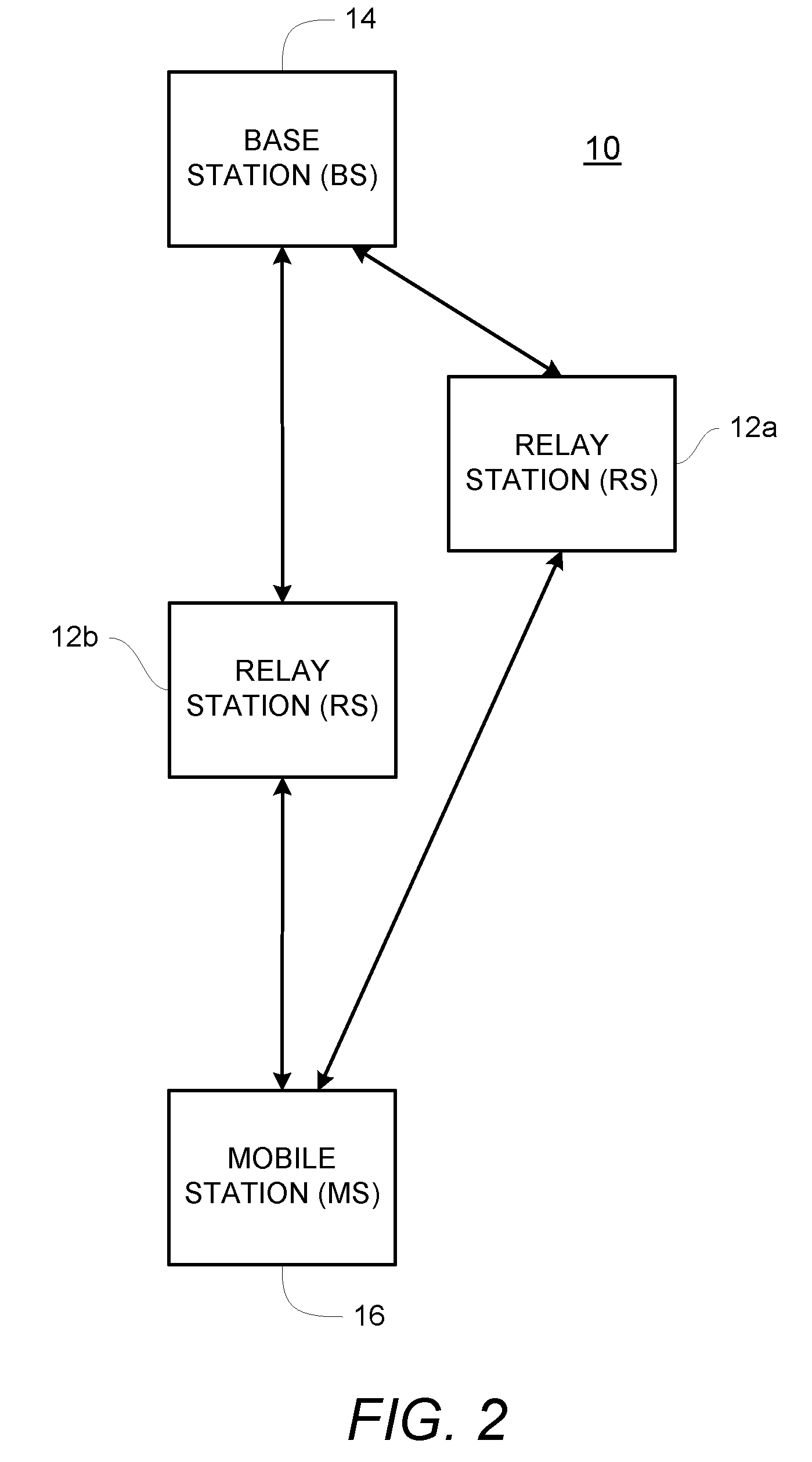
Path selection for a wireless system with relays
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
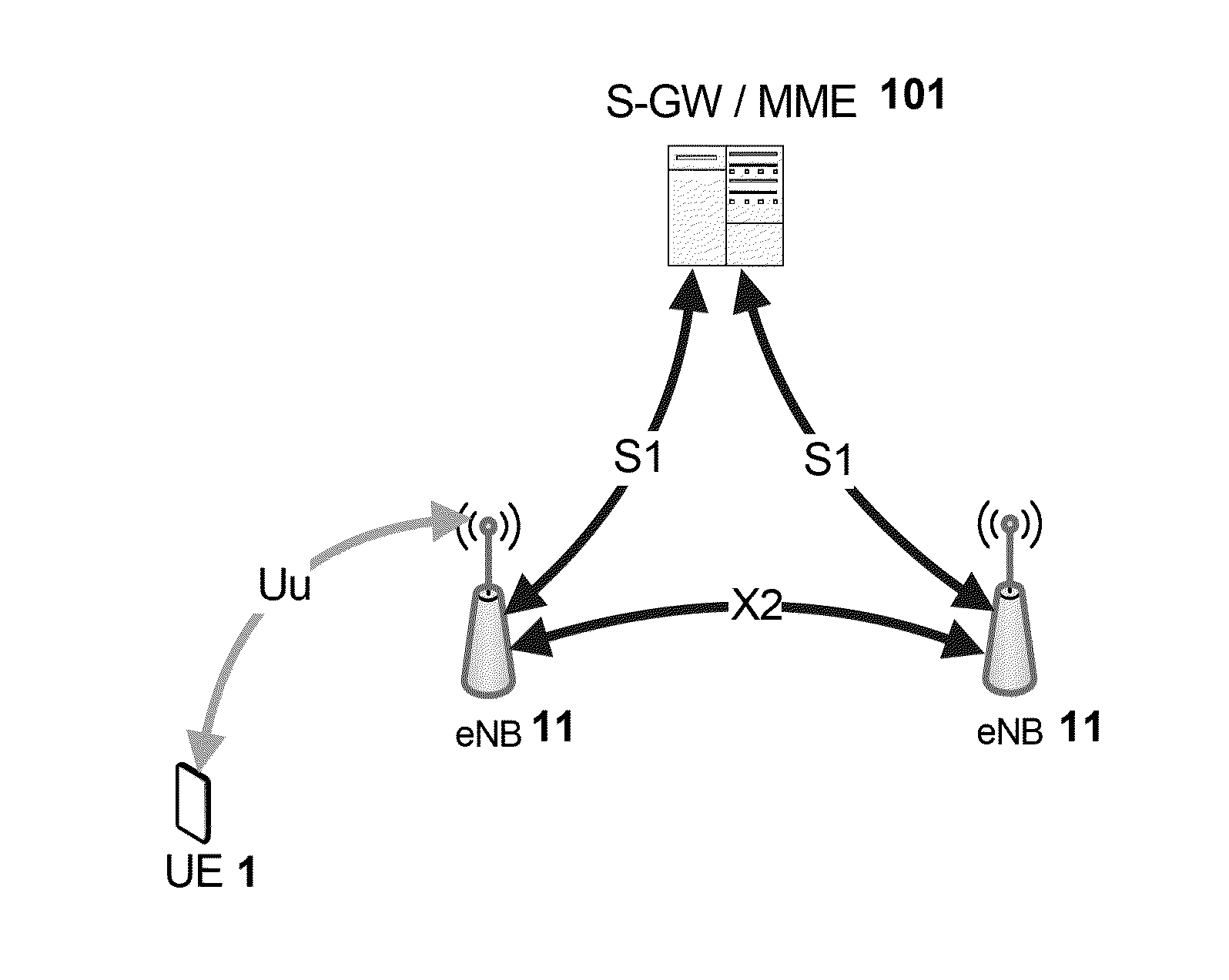
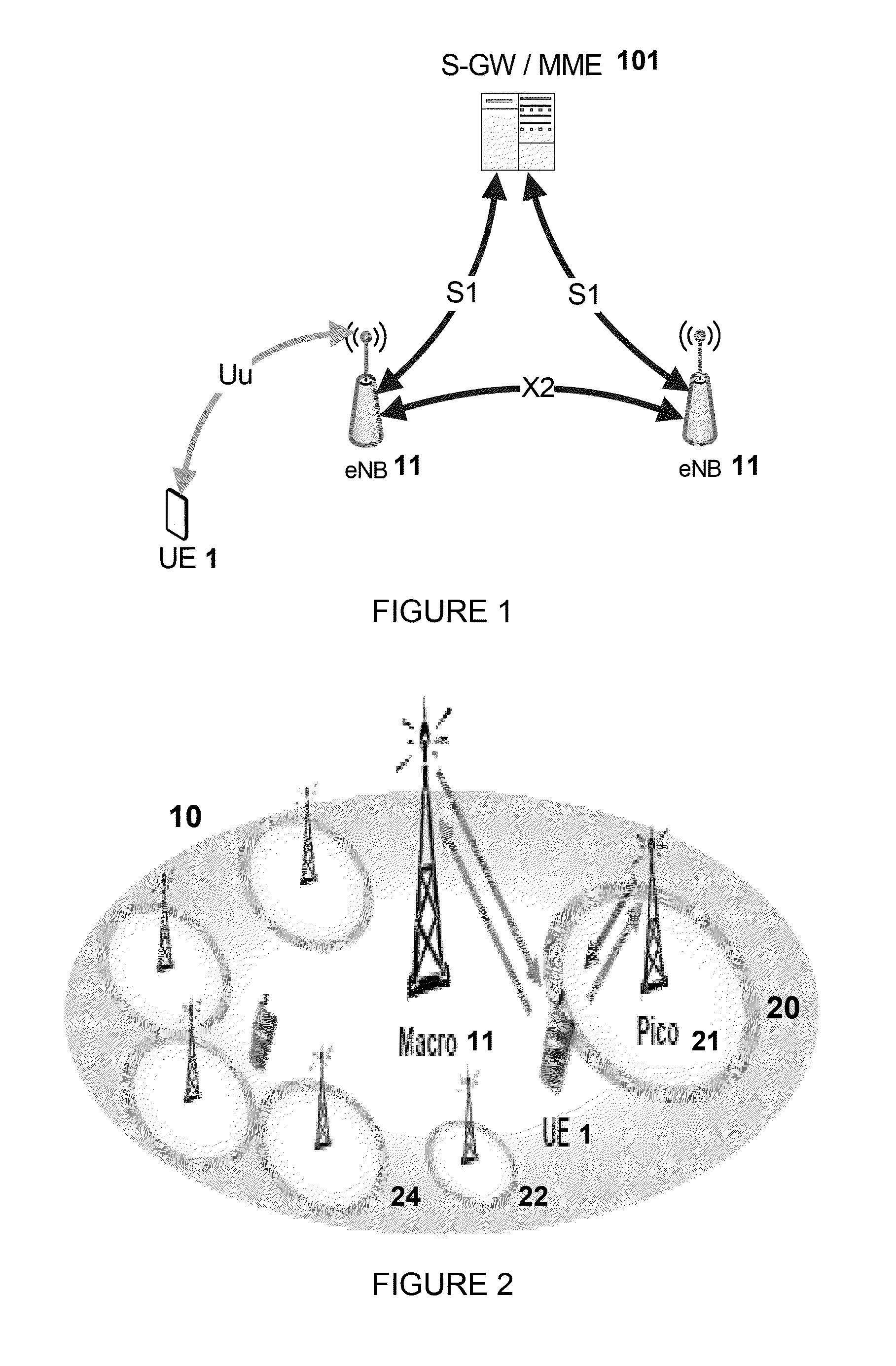
Resource requests in small cell networks
InactiveUS20150016350A1Improve achievable data rateIncreased rate capacityAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesSystem capacityRandom access
A Small Cell Network in which a terminal (1) is simultaneously served by a macro cell (10) and one or more small cells (20, 22, 24). When suitable uplink resources are not provided for data (PUSCH), the terminal (1) selects a cell and / or resource on which to transmit a scheduling request, or if no resource is allocated for scheduling requests (SR) the invention allows the terminal to select a suitable uplink cell and / or signature for a random access transmission (PRACH), and / or characteristic of a signal used to request such resources. A RACH transmission may also take place if SR has been transmitted more than a defined number of times without PUSCH resources being granted. Use of the most appropriate cell / resource for the request will improve the achievable data rate and system capacity.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
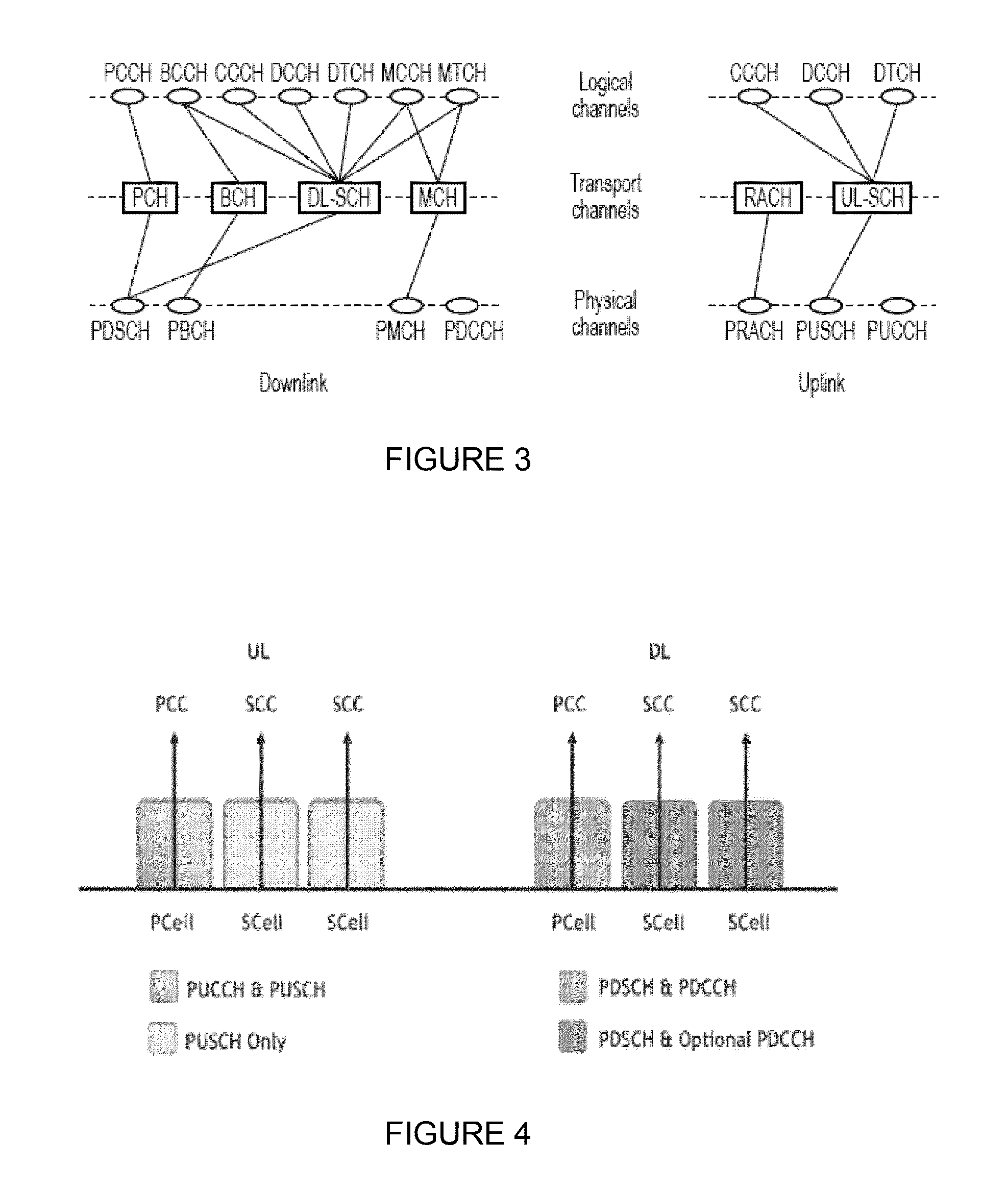
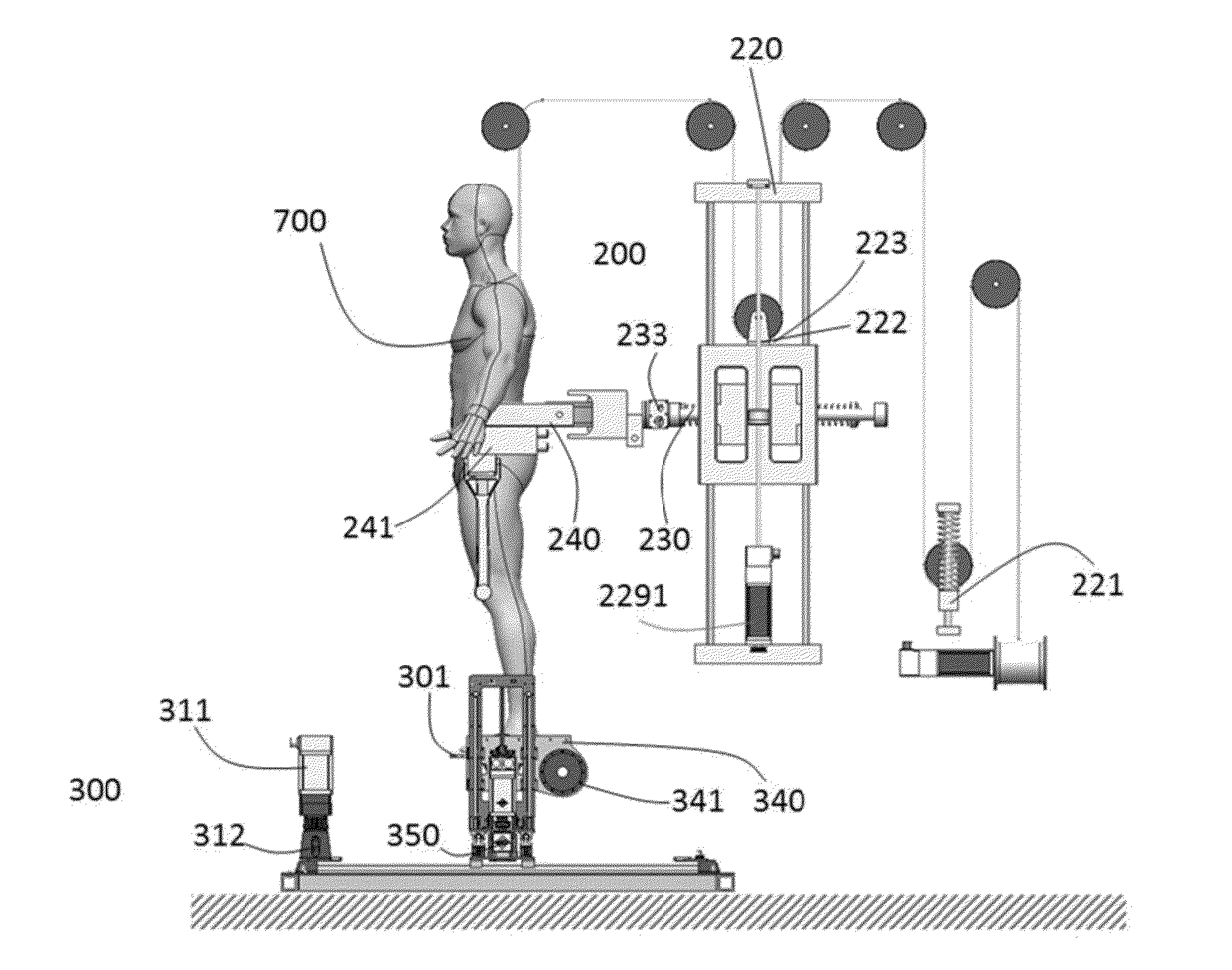
Lower Extremity Robotic Rehabilitation System
To achieve “ecological” robotic rehabilitation therapy, the present invention provides the system capacity of training of patients in different ambulatory tasks utilizing motorized footplates that guide the lower limbs according to human gait trajectories generated for different ambulatory tasks of interest. A lower extremity robotic rehabilitation system comprises an active pelvic / hip device which applies series elastic actuation to achieve an intrinsically safe and desirable impedance control. A robotic unit features the telepresence operation control that allows a patient stay at home or nursing home to continue his or her rehabilitation training under a physician's remote supervision and monitoring. The robot unit utilizes an affective patient-robot interface to capture emotional information of the patient, to allow for real-time adaptation of the robotic system and adjustments of treatment protocol, and to enhance the quality and effectiveness of rehabilitation
Owner:HU JIANJUEN +3
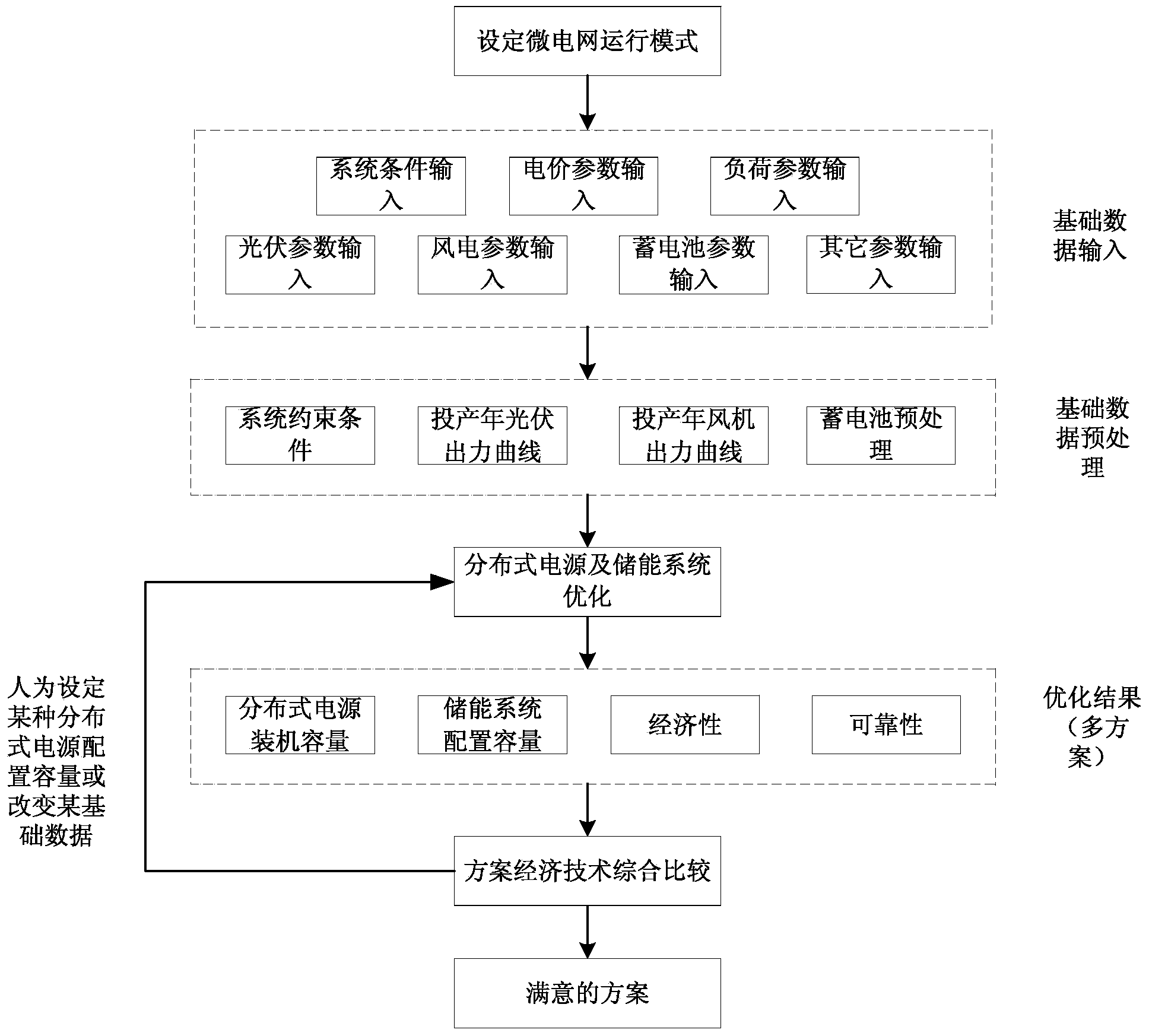
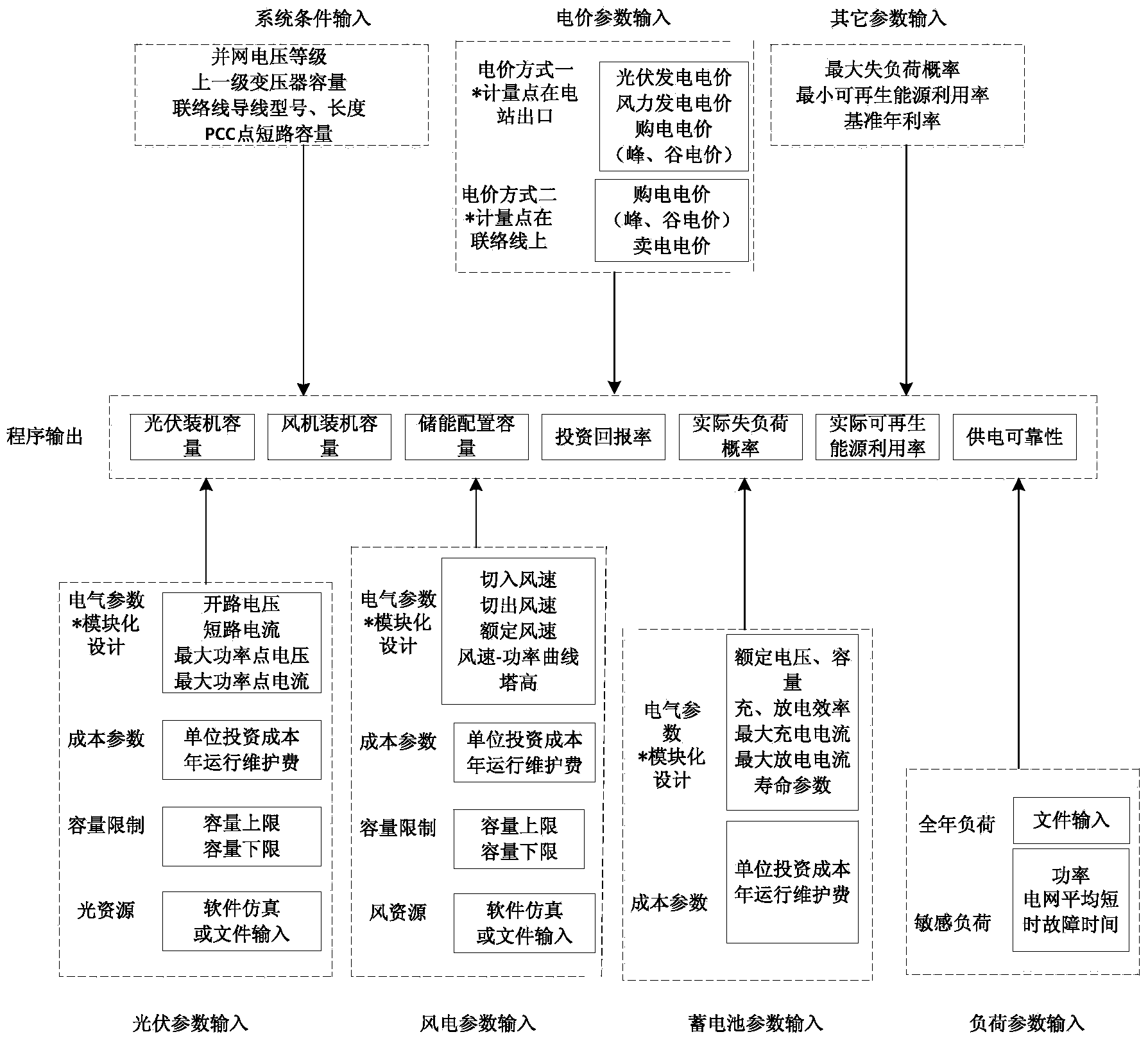
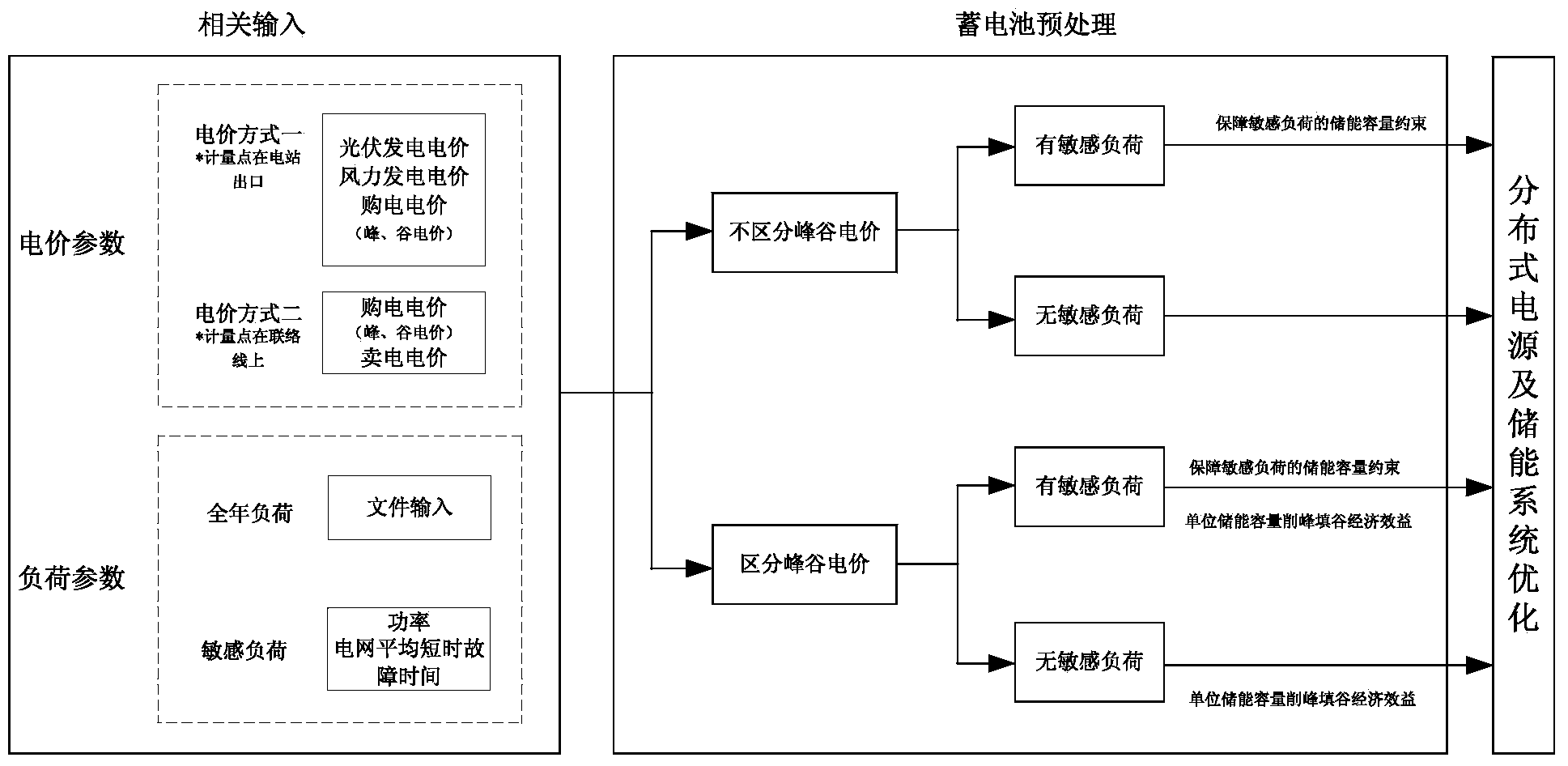
Micro-grid planning and capacity allocation method based on multi-objective optimization
ActiveCN103490410ASolve planning problemsSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsElectricitySystem capacity
The invention discloses a micro-grid planning and capacity allocation method based on multi-objective optimization. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of (1) setting the operation mode of a micro-grid, wherein the operation mode of the micro-grid comprises an independent mode and a grid-connected mode; (2) inputting basic data which comprise the system condition, electrovalence parameters, load parameters, photovoltaic parameters, wind electricity parameters and storage battery parameters; (3) pre-processing the basic data; (4) optimizing a distributed power supply and an energy storage system. According to the micro-grid planning and capacity allocation method, distributed power supply capacity and energy storage system capacity in micro-grid planning can be solved jointly, and optimizing allocation can be carried out at the same time.
Owner:CEEC JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST +1
Communication system and operating method thereof
InactiveUS6122291AMaximize Spectral EfficiencyImprove efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSystem capacity
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 00945 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 22, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 22, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 27, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 33393 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 12, 1997A communication system (28), comprises a master device (44) and slave device (30). Consequential to negotiations within the system (28) and having regard to system capacity and a relative hierarchy that exists between on-going communications, a bandwidth used for an on-going communication between the master device (44) and the slave device (30) is modified in proportion to a substantially instantaneous data rate requirement of the communication. As such, the system allows fluctuations in the amount of information, transmitted in a fixed time through an optimization of an available and dynamically varying bandwidth, while biasing the communication resource in relation to the relative hierarchy.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
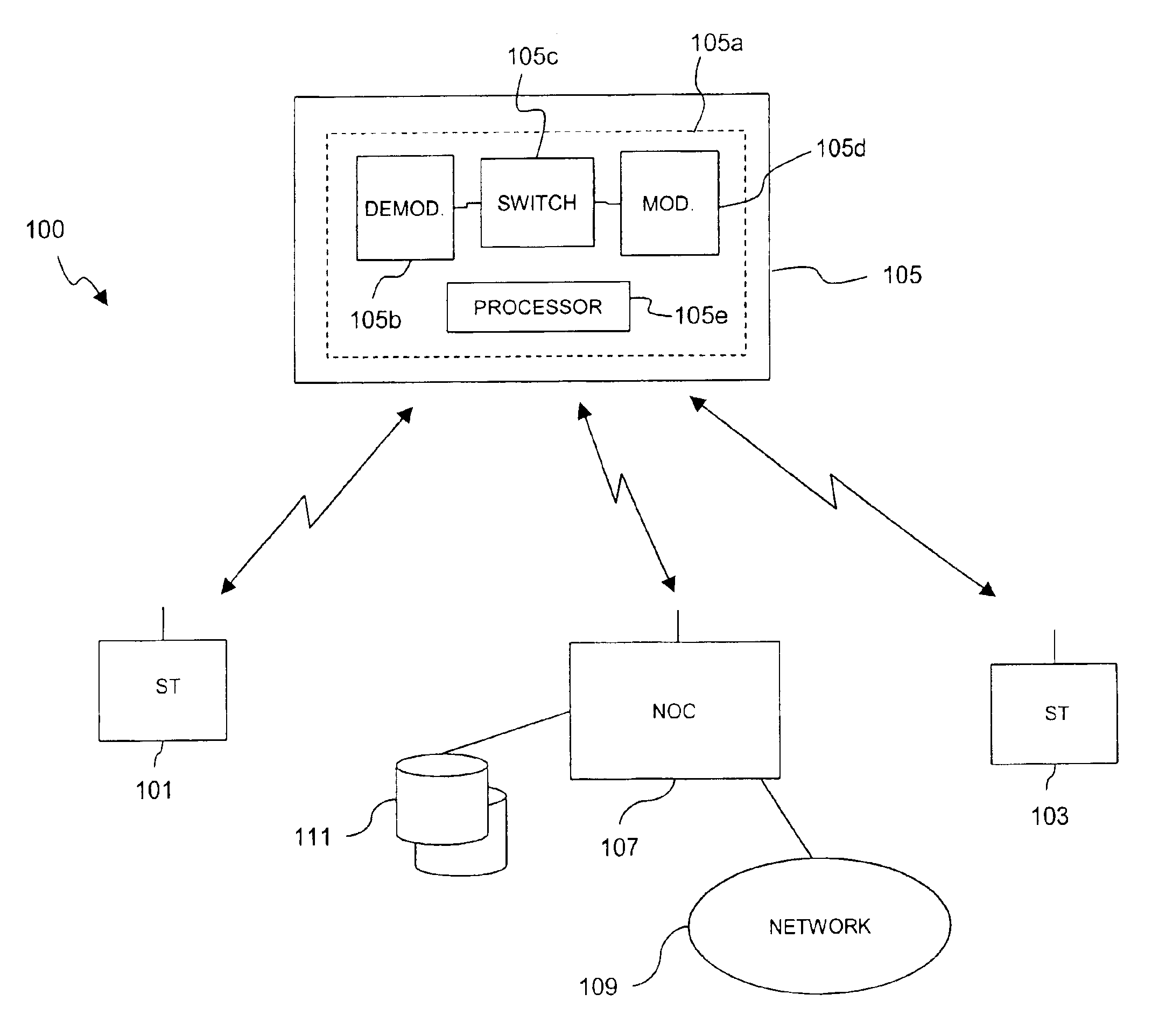
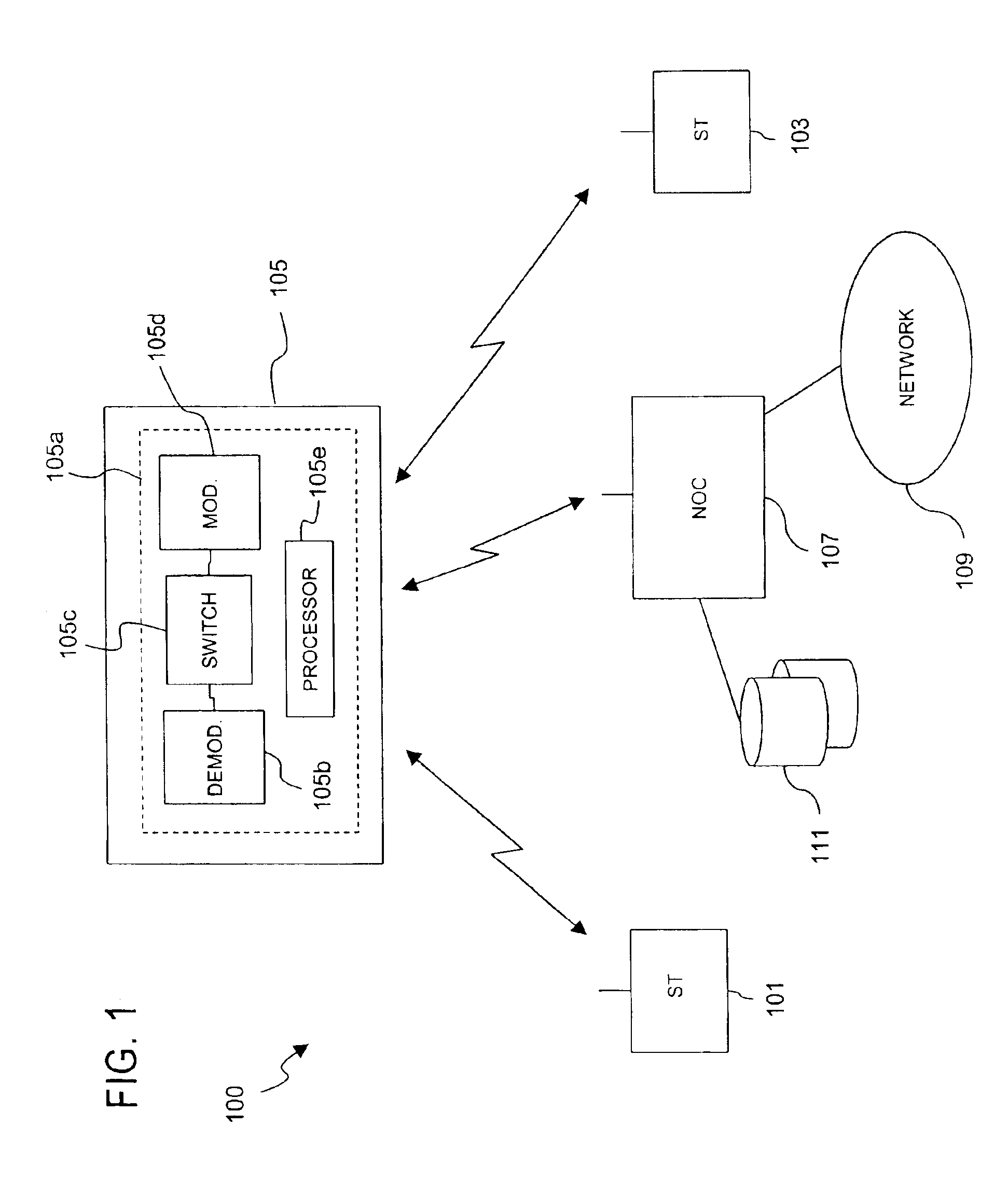
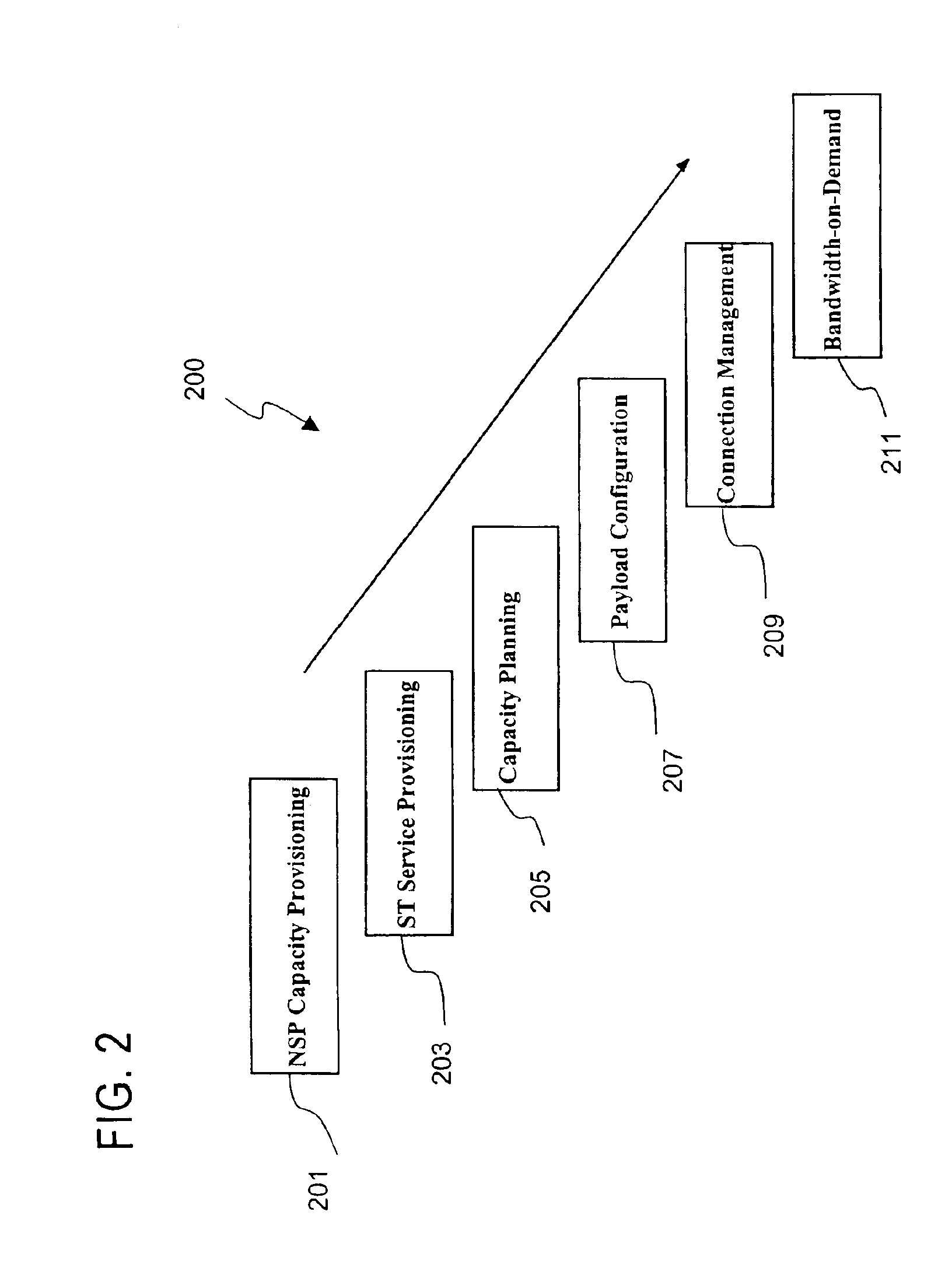
Capacity management in a broadband satellite communications system
InactiveUS6904265B1Partly effectiveMeet efficiency requirementsRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemSystem capacity
An approach for managing system capacity of a satellite communications system is disclosed. A satellite communications system provides communication services to a region. A terminal (101, 103) is located within the region and is configured to transmit and receive signals over a satellite (105) having a payload that processes the signals. The terminal (101, 103) has a predetermined profile that includes service class information and rate information. A hub (107) is configured to receive system capacity resource configuration data that reflect capacity requirements of a service provider and to determine partitioning of system capacity over the region based upon the system capacity resource configuration data. The hub (107) transmits configuration information to the payload of the satellite (105) according to the determined partitions. The terminal (101, 103) is configured to transmit a bandwidth request message to the payload. The payload selectively allocates bandwidth in response to the request message based upon the configuration information.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com