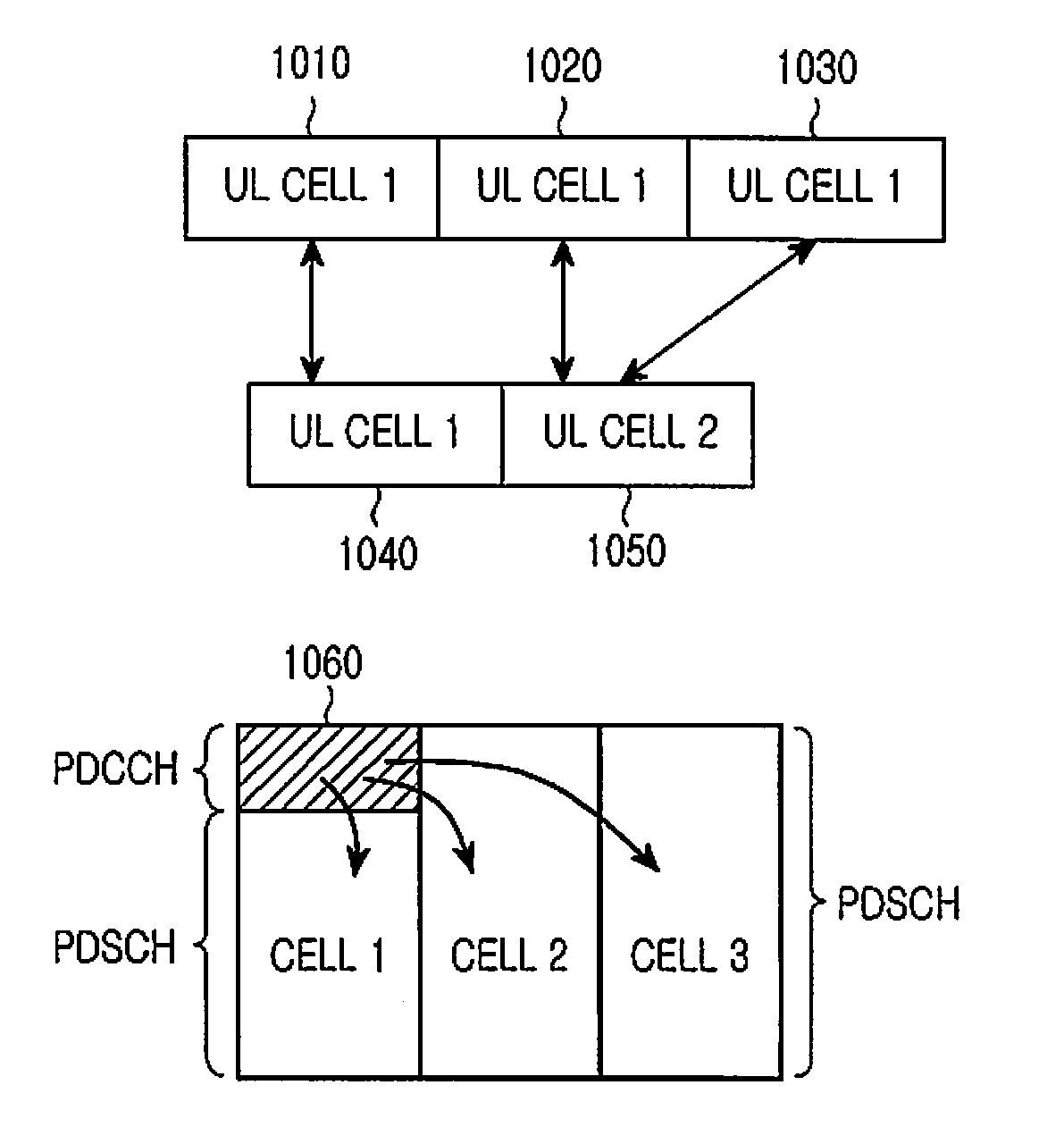
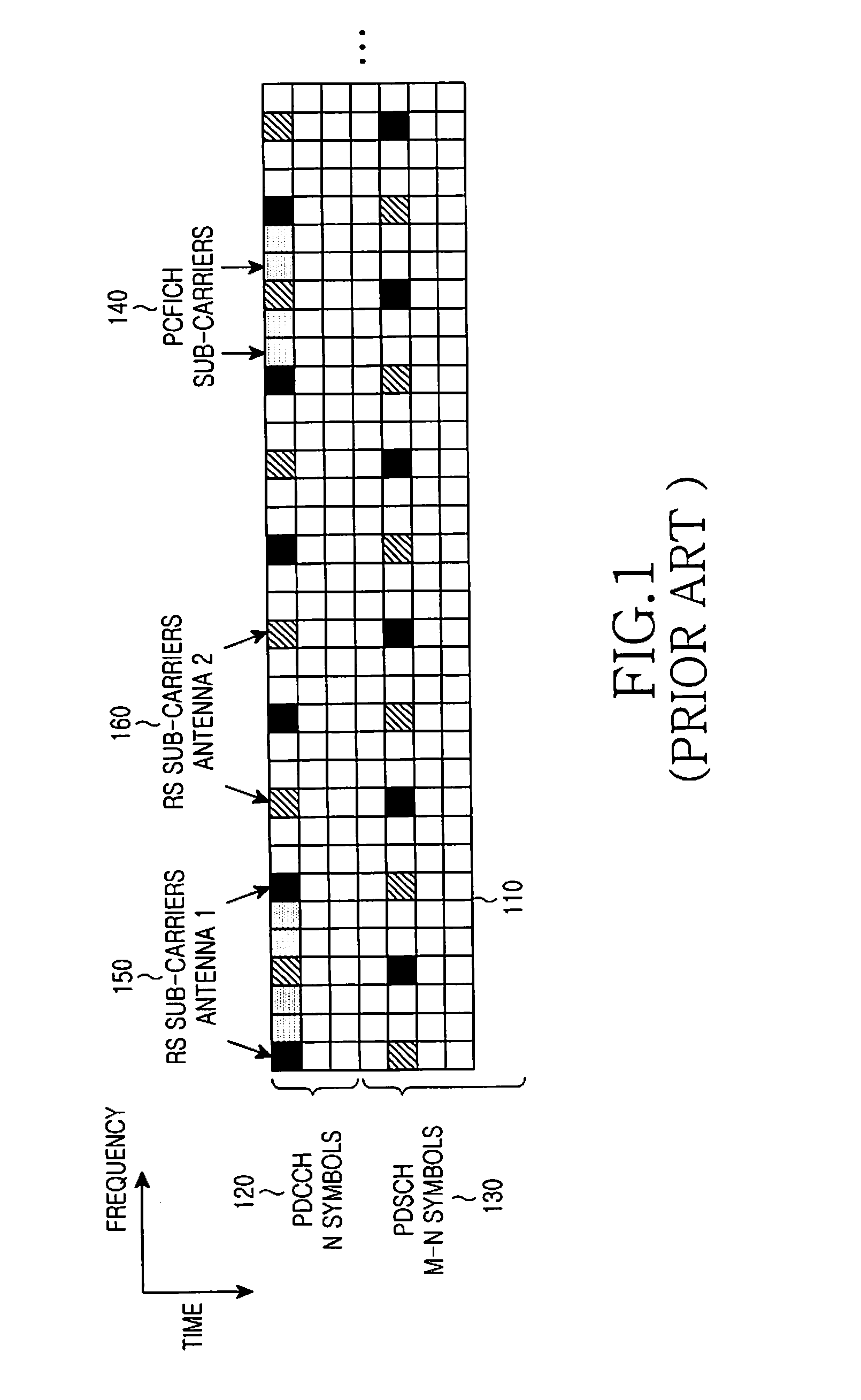
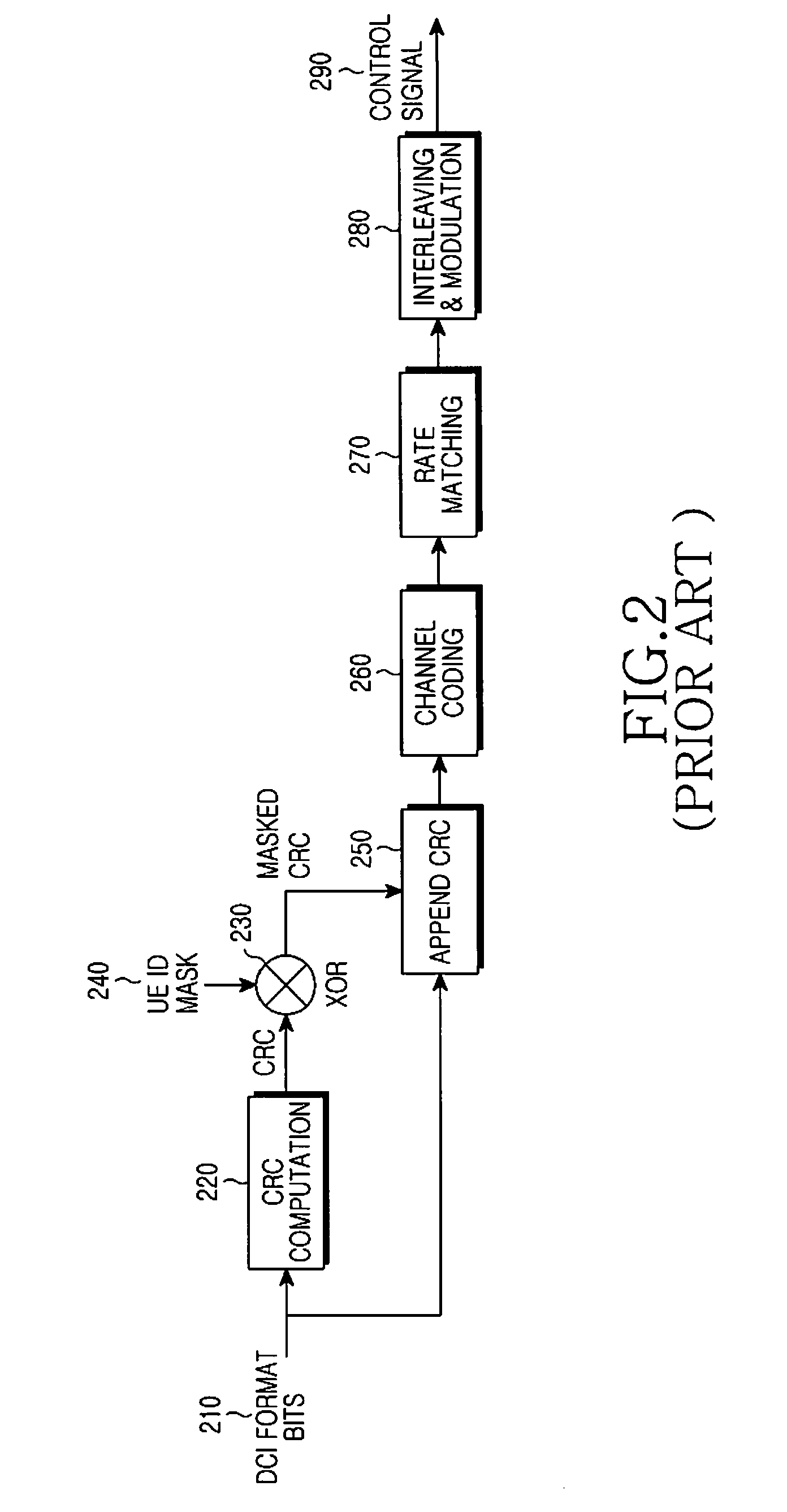
Patents
Literature
11760 results about "Control channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
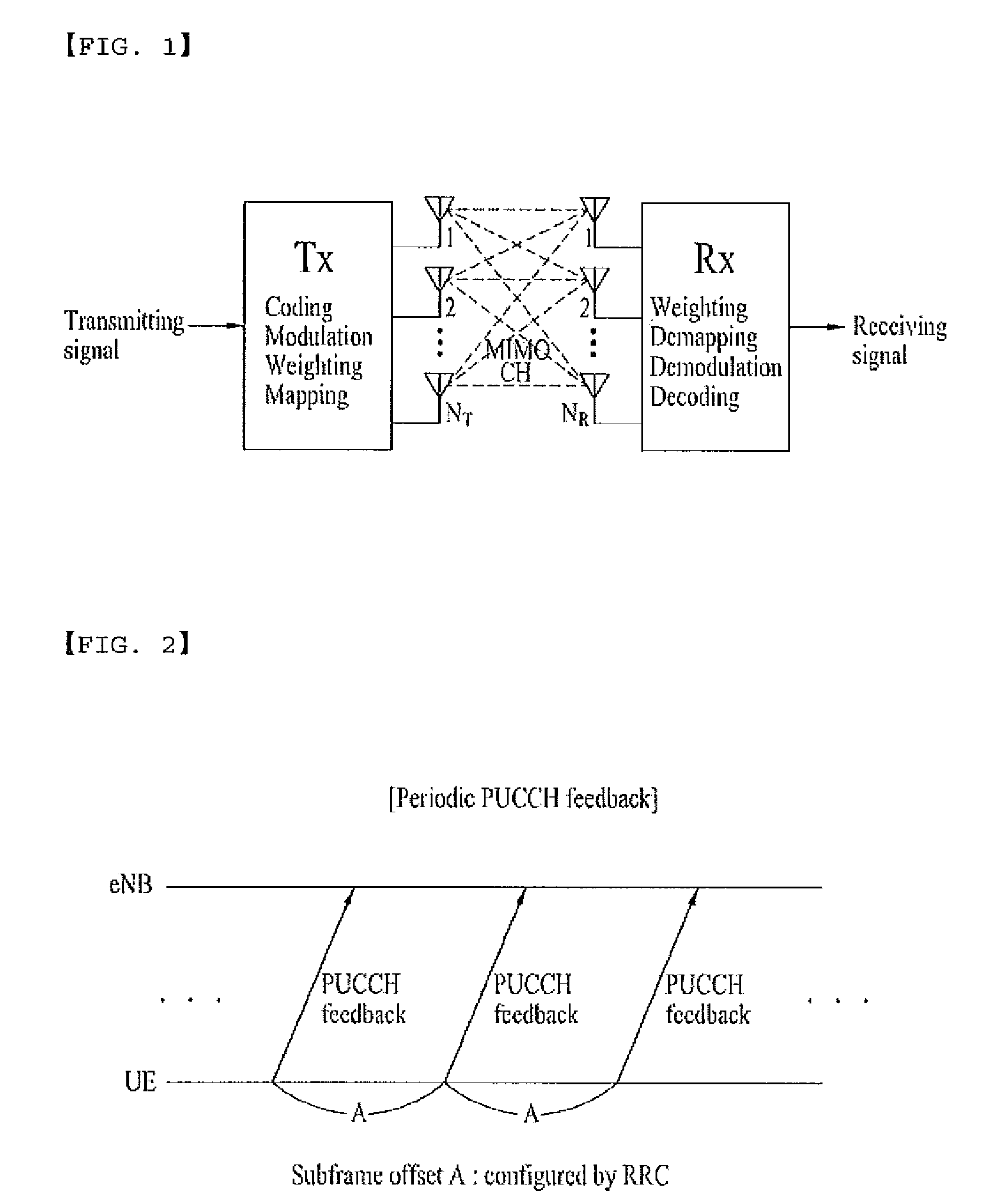
In radio communication, a control channel is a central channel that controls other constituent radios by handling data streams. It is most often used in the context of a trunked radio system, where the control channel sends various data which coordinates users in talkgroups.
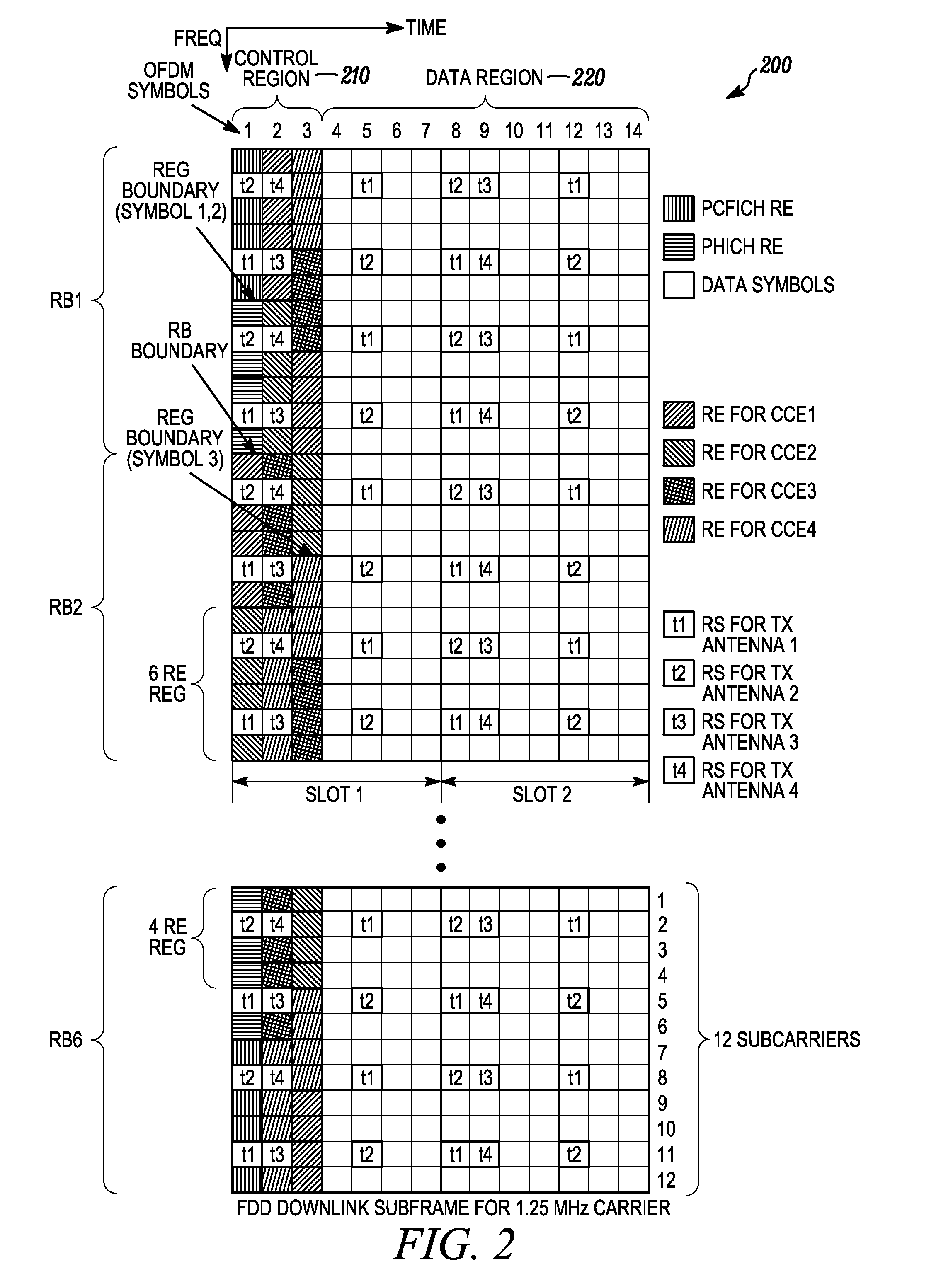
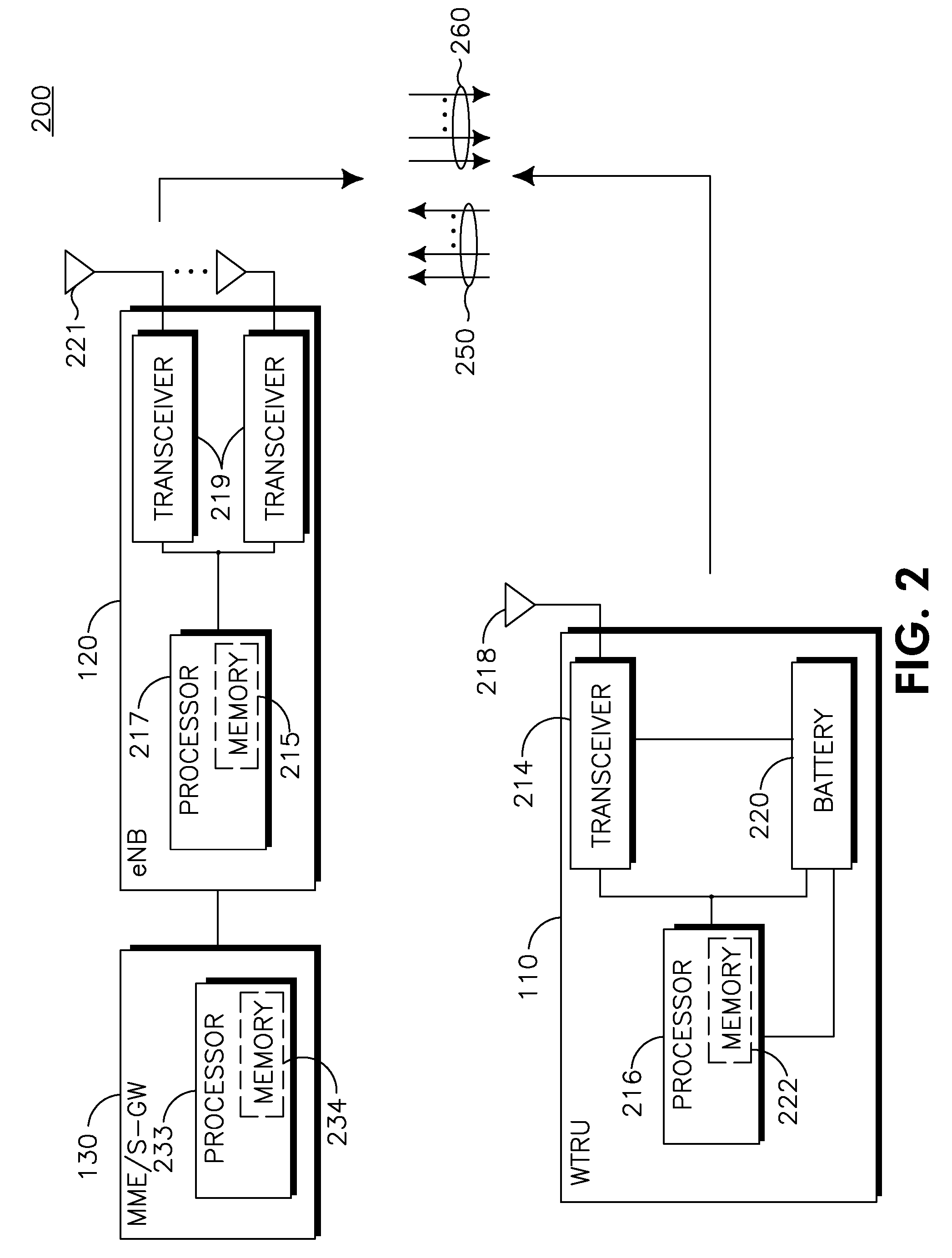
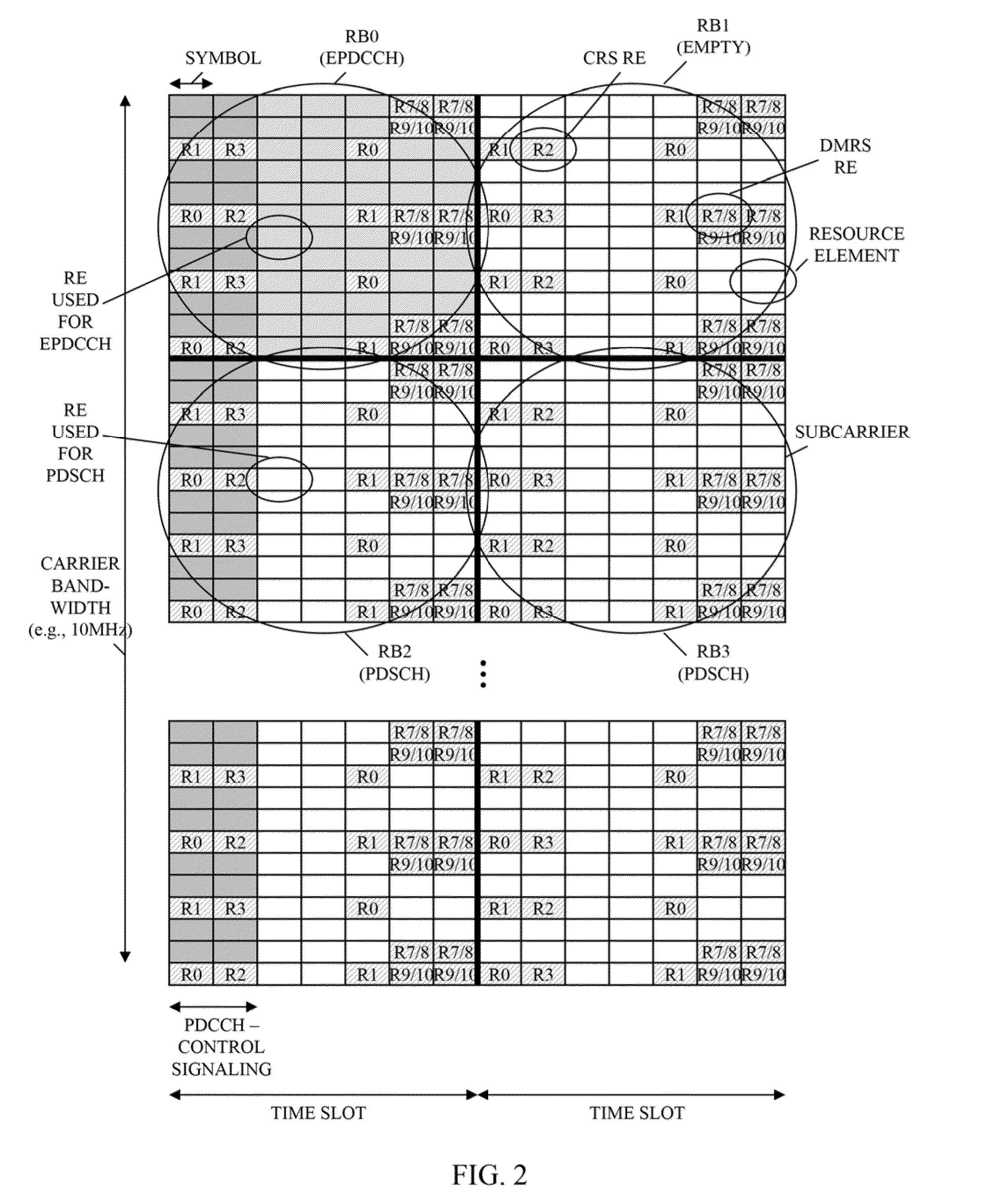
Wireless communication system for monitoring physical downlink control channel
ActiveUS20090088148A1Reduce in quantityTransmission path divisionAssess restrictionCommunications systemTelecommunications
A method of monitoring a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) in a wireless communication system is provided. A user equipment monitors a set of PDCCH candidates for a search space in a subframe. The search space includes a common search space monitored by all user equipments in a cell and a UE-specific search space monitored by at least one UE in the cell.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
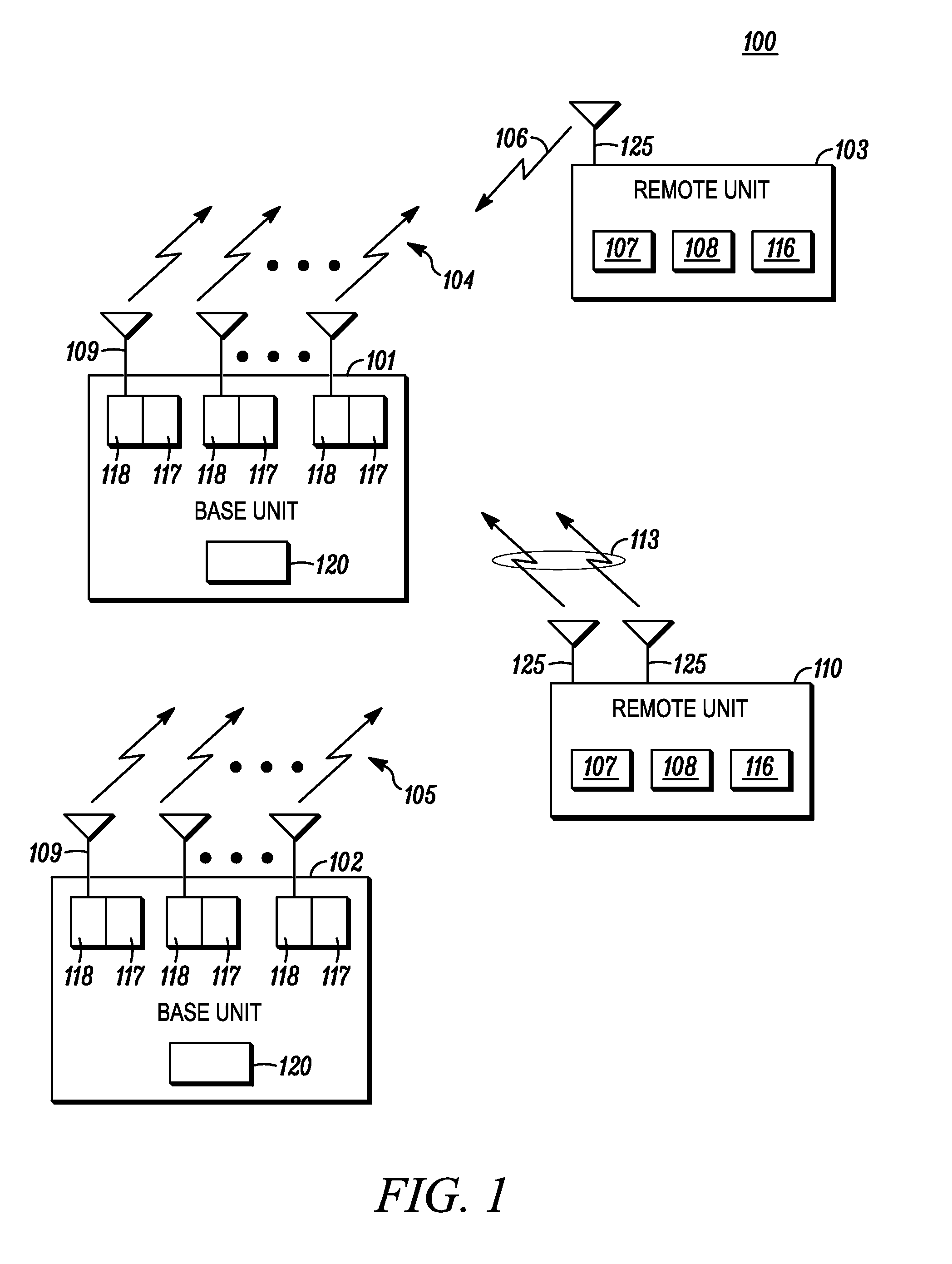
Control Channel Provisioning and Signaling
There is provided a communication device and a base unit, and methods thereof, for determining control information. The communication device receives a control channel message associated with the communication device in a control region on a first carrier from a base unit. The communication device also determines a set of resources in a search space within the control region, attempts to decode the set of resources in the search space for the control channel message, and determines control information from the decoded control channel message. The base unit generates a control channel message comprising control information associated with the communication device, determines a set of resources in a search space within a control region, selects a subset of resources within the determined set of resources for transmitting the control channel message, and transmits the control channel message on the selected resources in the control region on a first carrier.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information for carrier aggregated spectrums
InactiveUS20100271970A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
Methods and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information (UCI) in carrier aggregated spectrums are disclosed. UCI may include, but is not limited to, Precoding Matrix Indicator (PMI), Rank Indication (RI), Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), Acknowledge / Not Acknowledge (ACK / NACK) and Scheduling Request (SR). For symmetric carrier aggregation, uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) component carriers may be paired and use physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) in each UL component carrier to send UCI for the corresponding DL component carrier. For asymmetric carrier aggregation, methods are provided for UCI transmission and resource allocation depending on component carrier configuration or assignment. Methods are provided for multiple and single component carrier configurations that may further provide backward compatibility.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
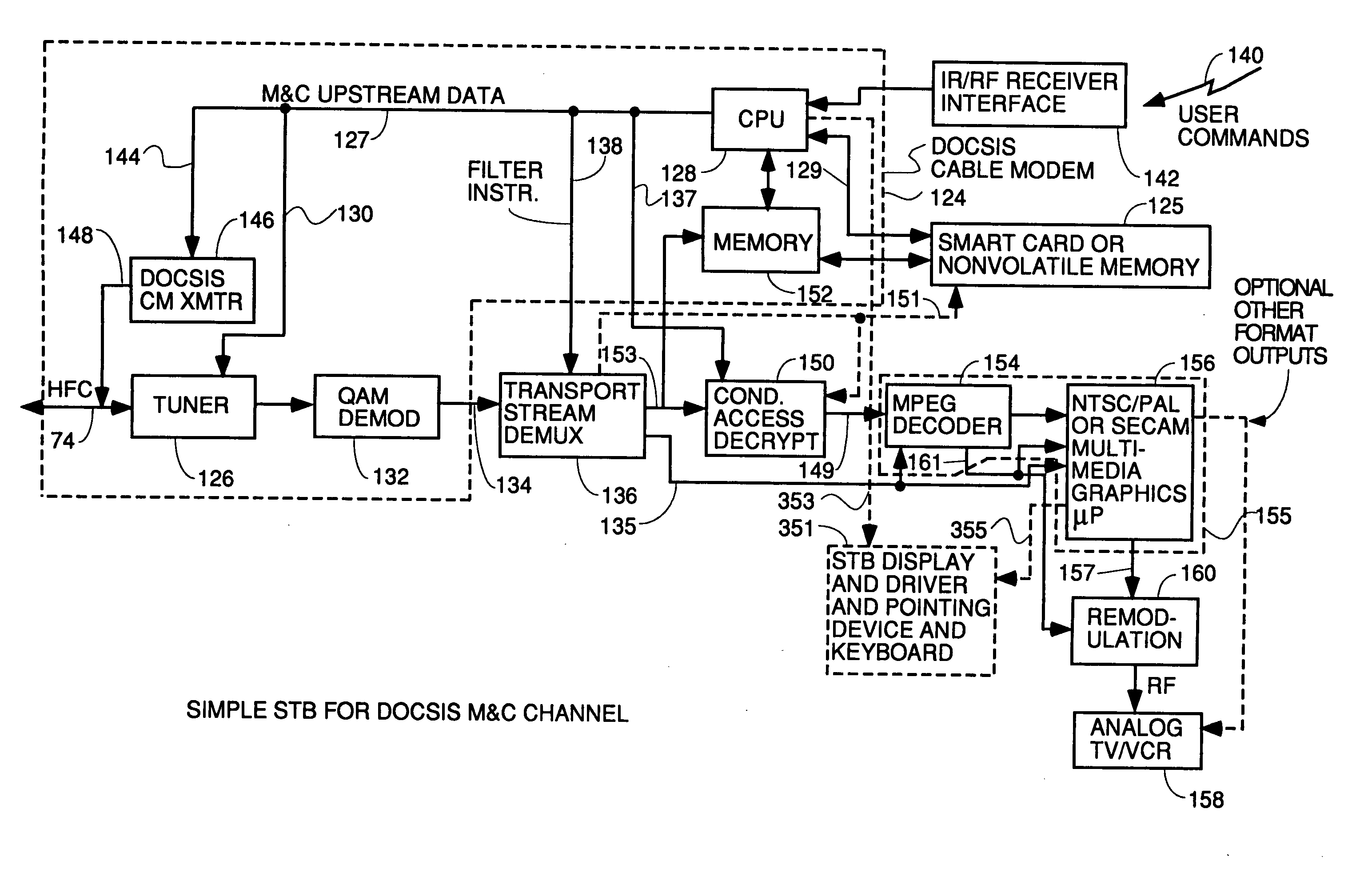
Thin DOCSIS in-band management for interactive HFC service delivery
InactiveUS20040181800A1Simple processLess-expensive to buildAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsModem deviceConditional access
Circuitry and processes carried out thereby are disclosed for implementing simple single tuner set top box decoders which do not require a separate tuner for an out of band management and control channel. Removable smart card conditional access circuitry and replaceable modules having decoding circuitry for different compression schemes and encoding circuitry for different format television circuits is disclosed. An embodiment with a single tuner and a full DOCSIS compatible modem which can interface to personal computers, etc. is also disclosed to make the set top box a simple, inexpensive home gateway is also disclosed.
Owner:TERAYON COMM SYST
Extending physical downlink control channels
ActiveUS20110075624A1Limit regionSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsControl channel
Methods and apparatus for transmitting and receiving Downlink Control Information (DCI) in a single cell in order to support communication over multiple cells. The DCI is conveyed by DCI formats transmitted through Physical Downlink Control CHannels (PDCCHs) in a UE-Common Search Space (UE-CSS) and in a UE-Dedicated Search Space (UE-DSS). A distinct UE-DSS is defined in the single cell for each of the multiple cells. Each distinct UE-DSS has the same structure as a conventional UE-DSS and a location that is determined by the same parameters as the location of the conventional UE-DSS and by the respective cell identity (Cell_ID).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
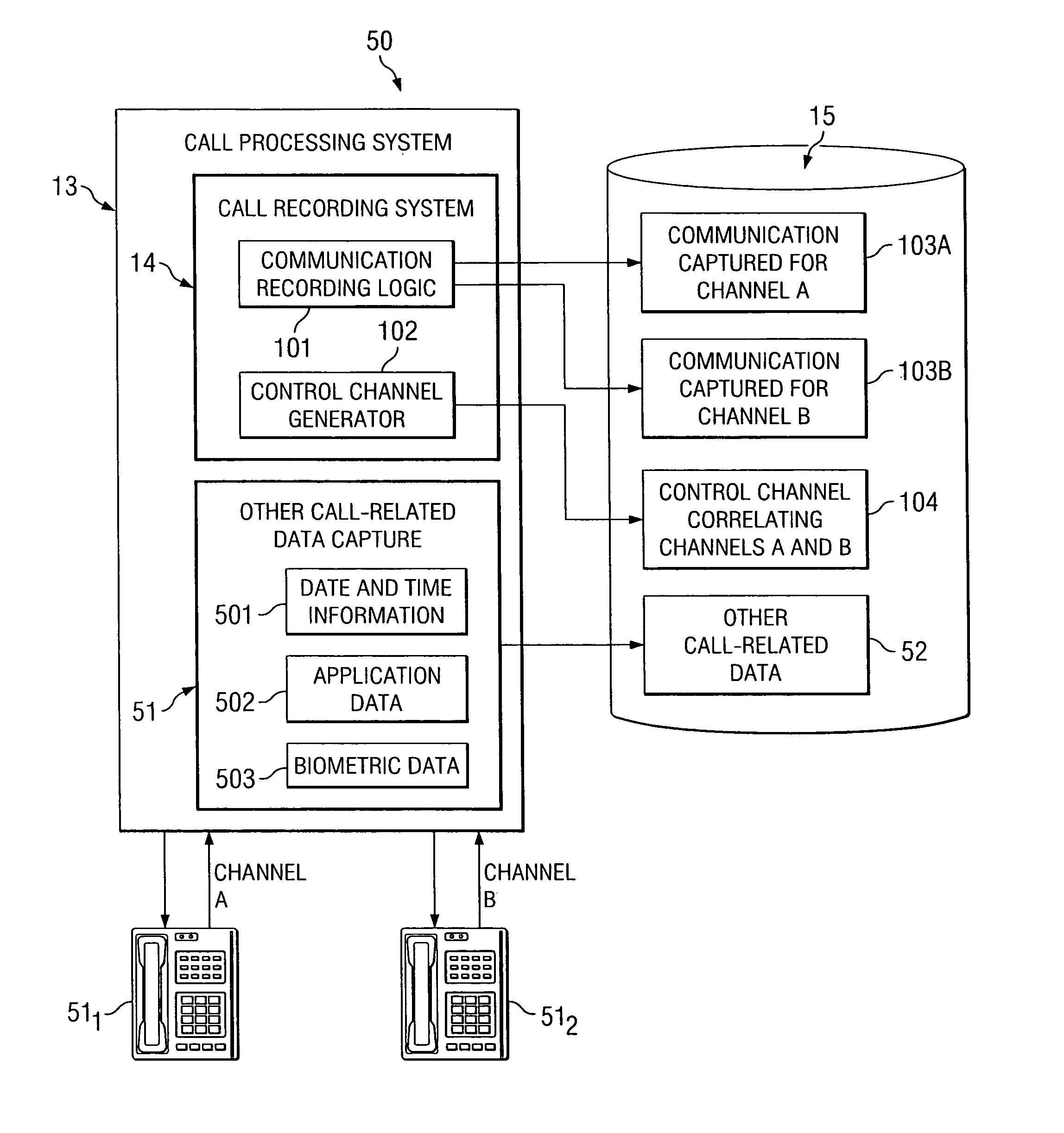
System and method for multi-channel recording
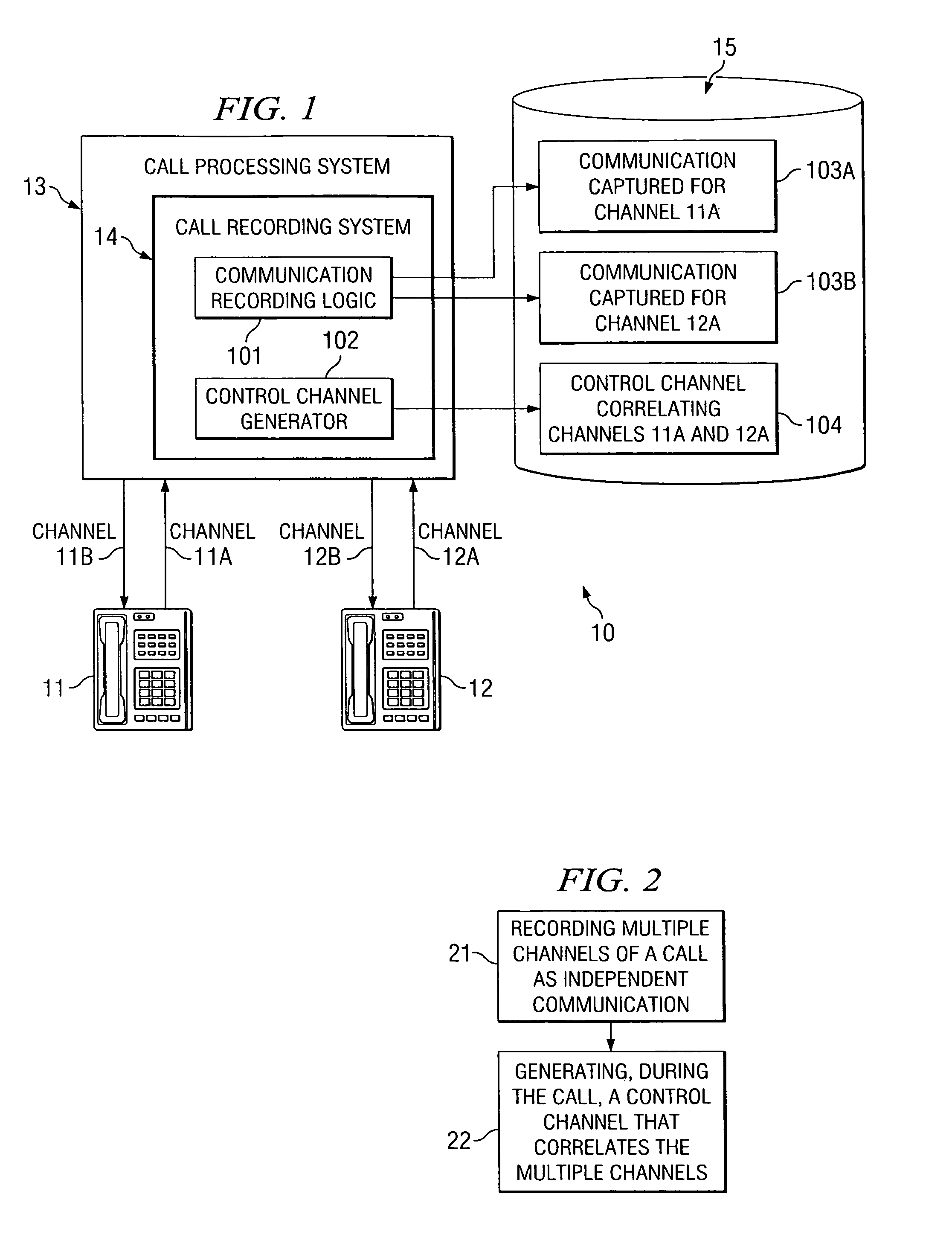
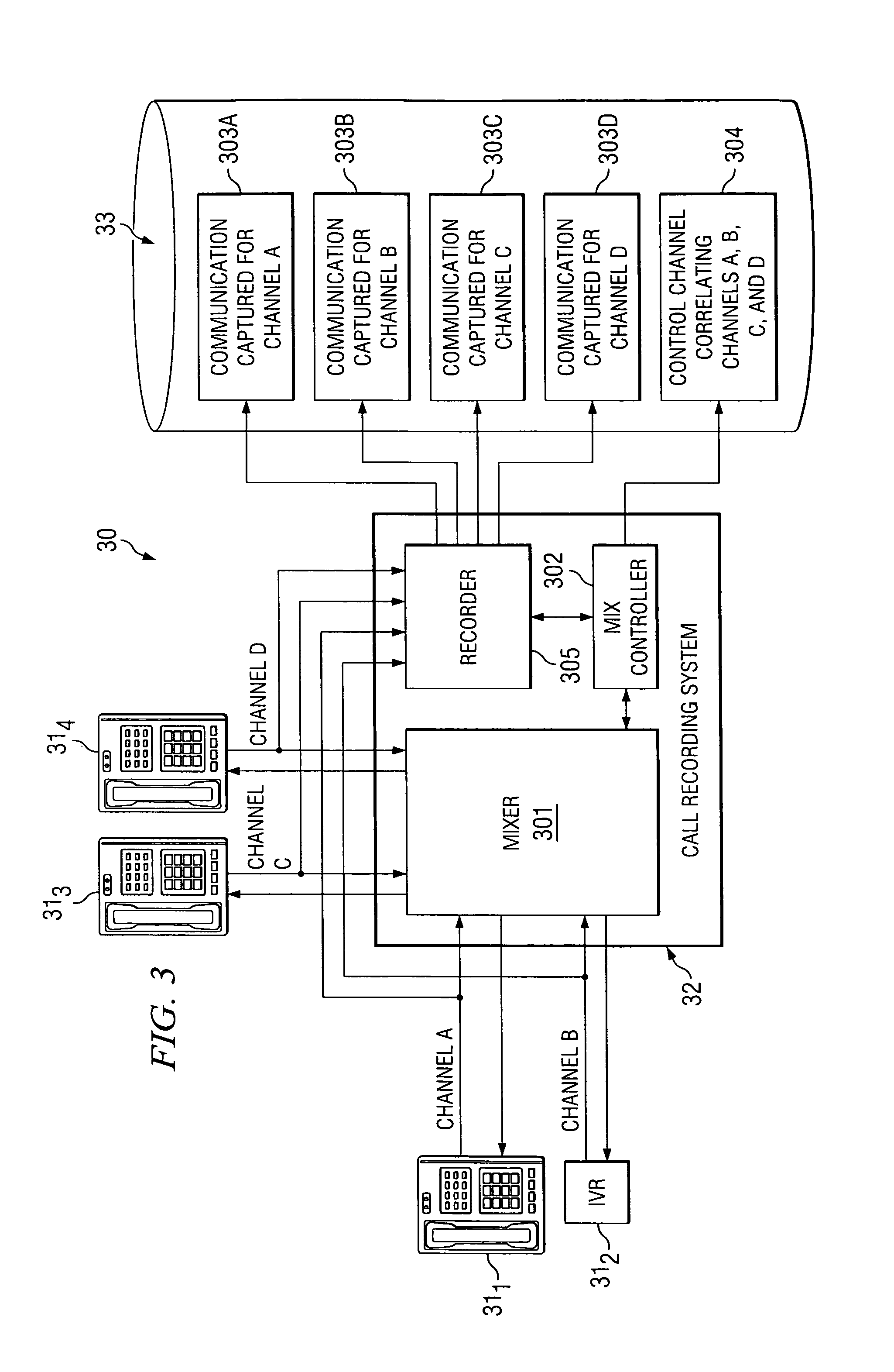
InactiveUS8135115B1Good flexibilityAccurately re-creatingSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsInbound communicationControl channel
Embodiments of the present invention are directed generally to recording communication of a call utilizing a multi-channel recording technique. According to one exemplary embodiment, inbound communication from each party to a call (e.g., from each communication device that is party to a call) to a recording system is assigned to a separate channel, and communication on each channel is independently recorded. Further, during the call, a control channel is generated that correlates the multiple communication channels. The independently recorded communication channels and control channel may be used to analyze a recorded call from any desired perspective. For instance, communication from a given party may be analyzed in isolation. Further, the control channel enables the recorded multiple communication channels to be correlated such that the communication received (e.g., heard) by any selected party may be accurately re-created for analysis thereof.
Owner:SECURUS TECH
Time division multiple access downlink personal communications system voice and data debit billing method
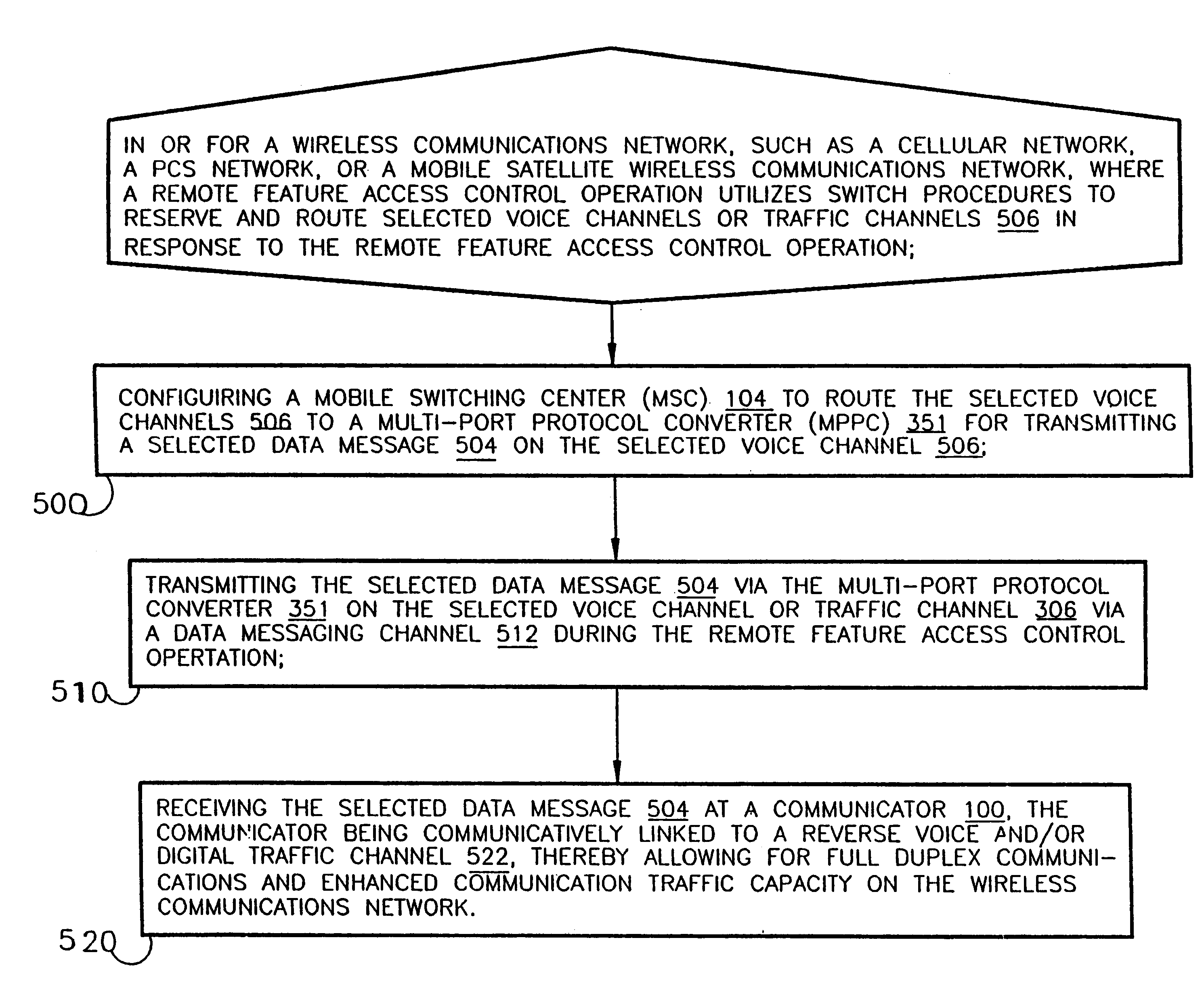
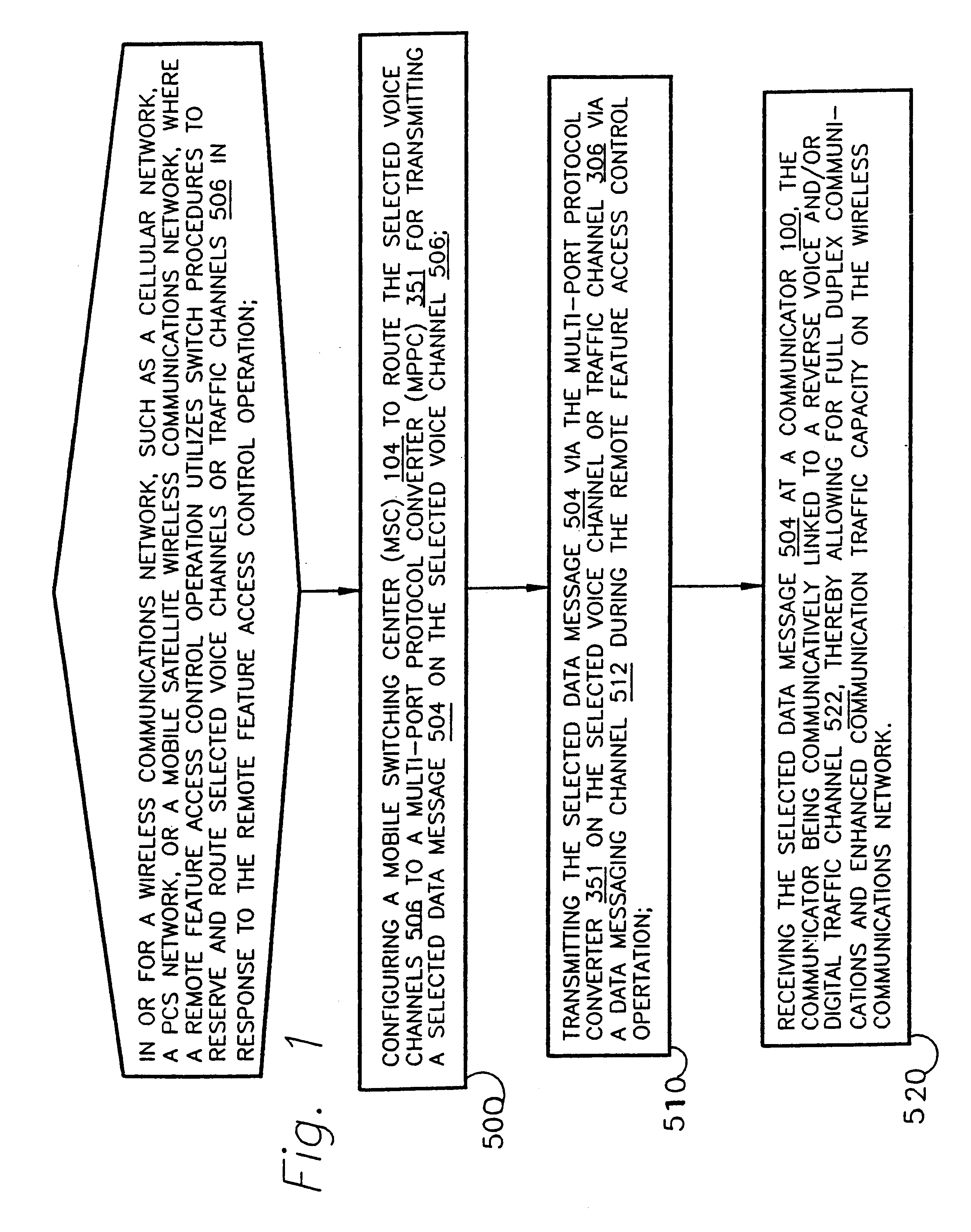
InactiveUS6185198B1Increase capacityFunction increaseTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCode division multiple accessControl channel
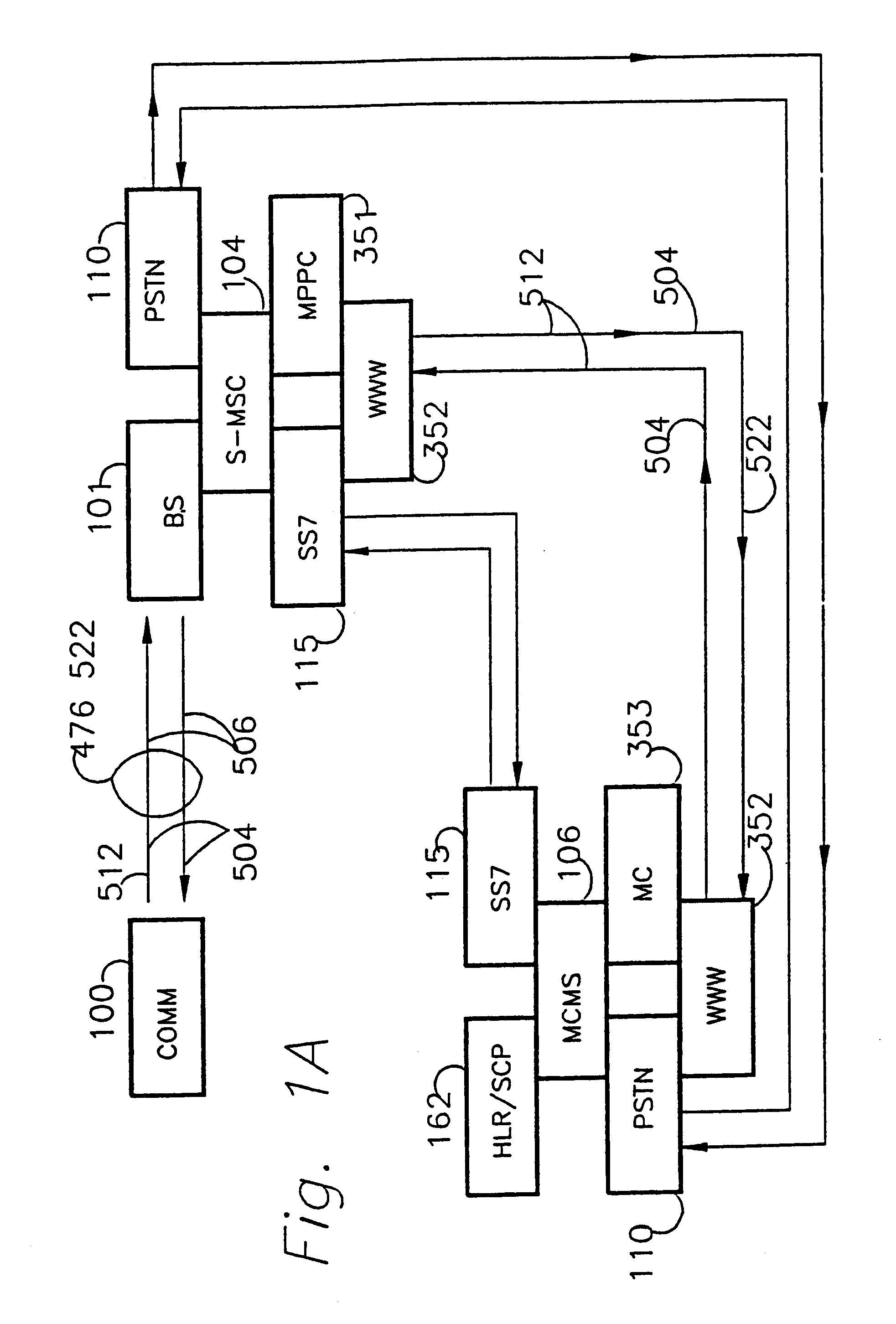
A method and apparatus for full-duplex data communication in or for a wireless communications network, such as a cellular network, PCS network, or mobile satellite network, where a remote feature access control operation utilizes a switch to reserve and route selected voice channels or traffic channels in response to the remote feature access control operation. The method comprising the steps of: configuring a mobile switching center (MSC) to route the selected voice channels to a multi-port protocol converter (MPPC) for transmitting a selected data message on the selected voice channel. Transmitting the selected data message via the multi-port protocol converter on the selected voice channel via a data messaging channel during the remote feature access control operation. Then the selected data message is received at a communicator, which is communicatively linked to a reverse voice and / or digital traffic channel of the wireless network, thereby providing for both forward and reverse messaging on the wireless communications network. An apparatus is disclosed for data communication in or for a wireless communications network for transmitting and receiving both forward and reverse voice, traffic, and control channel messages utilizing the disclosed methodology.
Owner:AERIS COMM
Low latency cacheable media streaming
ActiveUS20110080940A1Lower latencyRaise the possibilityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningGroup of picturesCache server
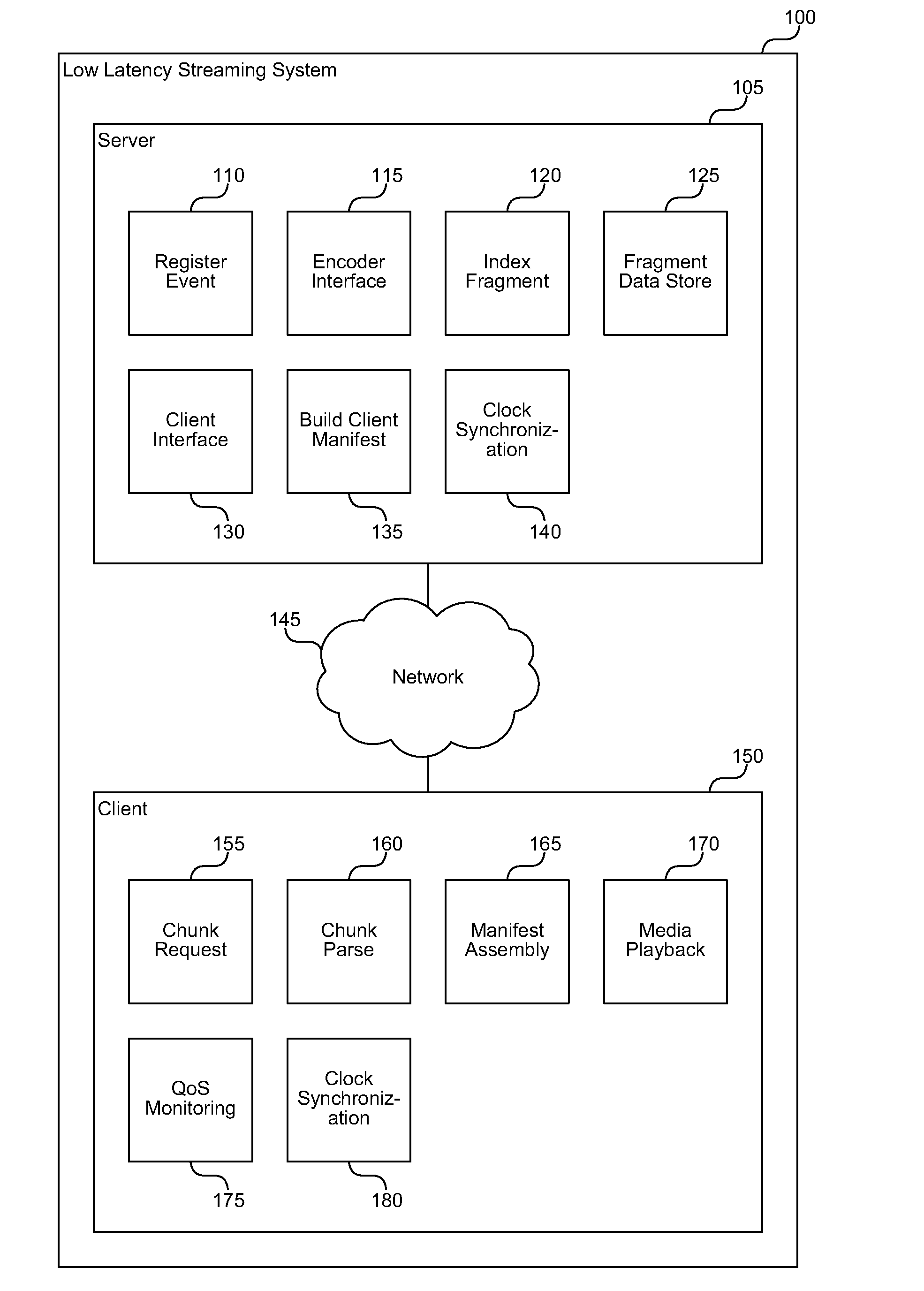
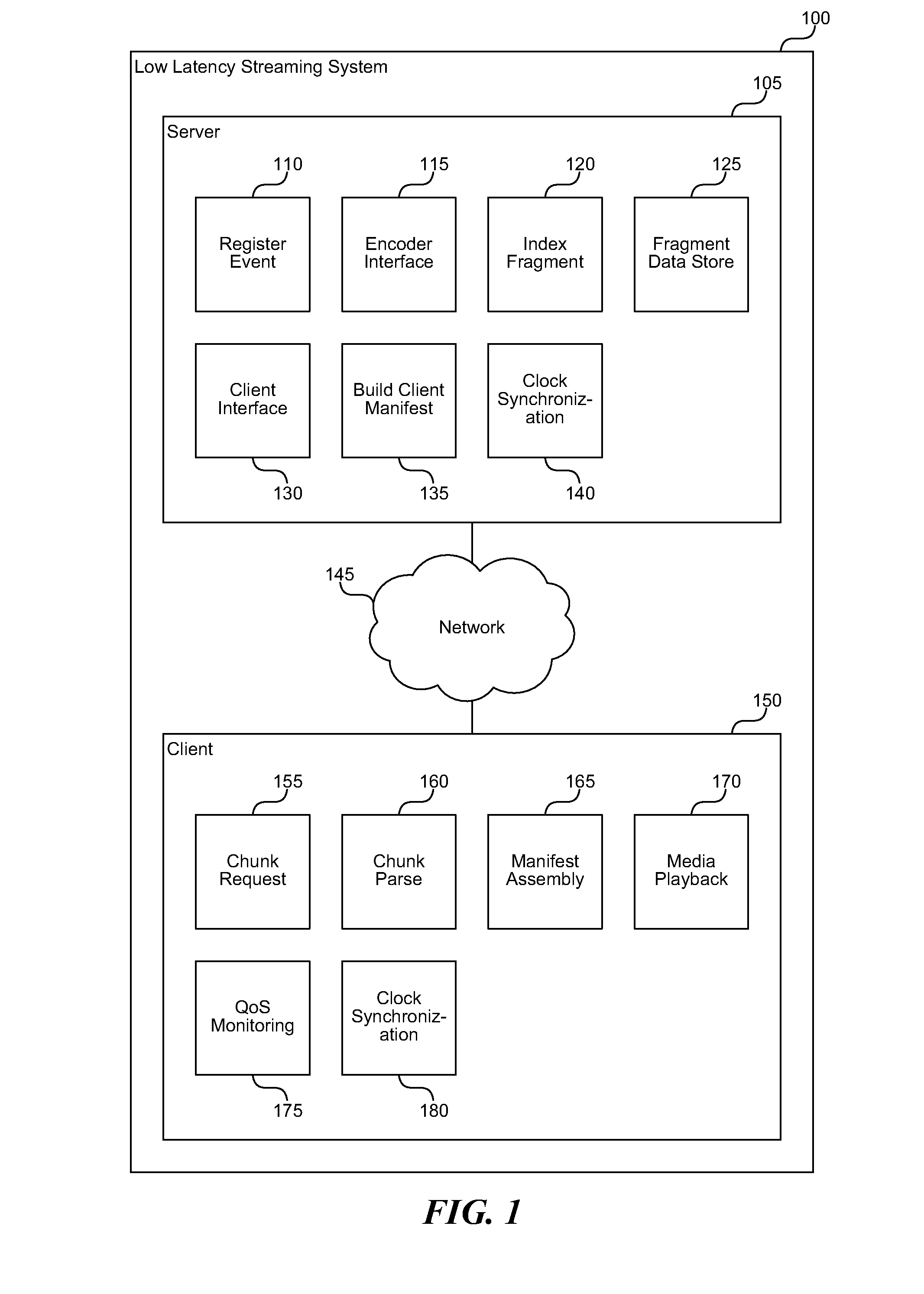
A low latency streaming system provides a stateless protocol between a client and server with reduced latency. The server embeds incremental information in media fragments that eliminates the usage of a typical control channel. In addition, the server provides uniform media fragment responses to media fragment requests, thereby allowing existing Internet cache infrastructure to cache streaming media data. Each fragment has a distinguished Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that allows the fragment to be identified and cached by both Internet cache servers and the client's browser cache. The system reduces latency using various techniques, such as sending fragments that contain less than a full group of pictures (GOP), encoding media without dependencies on subsequent frames, and by allowing clients to request subsequent frames with only information about previous frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
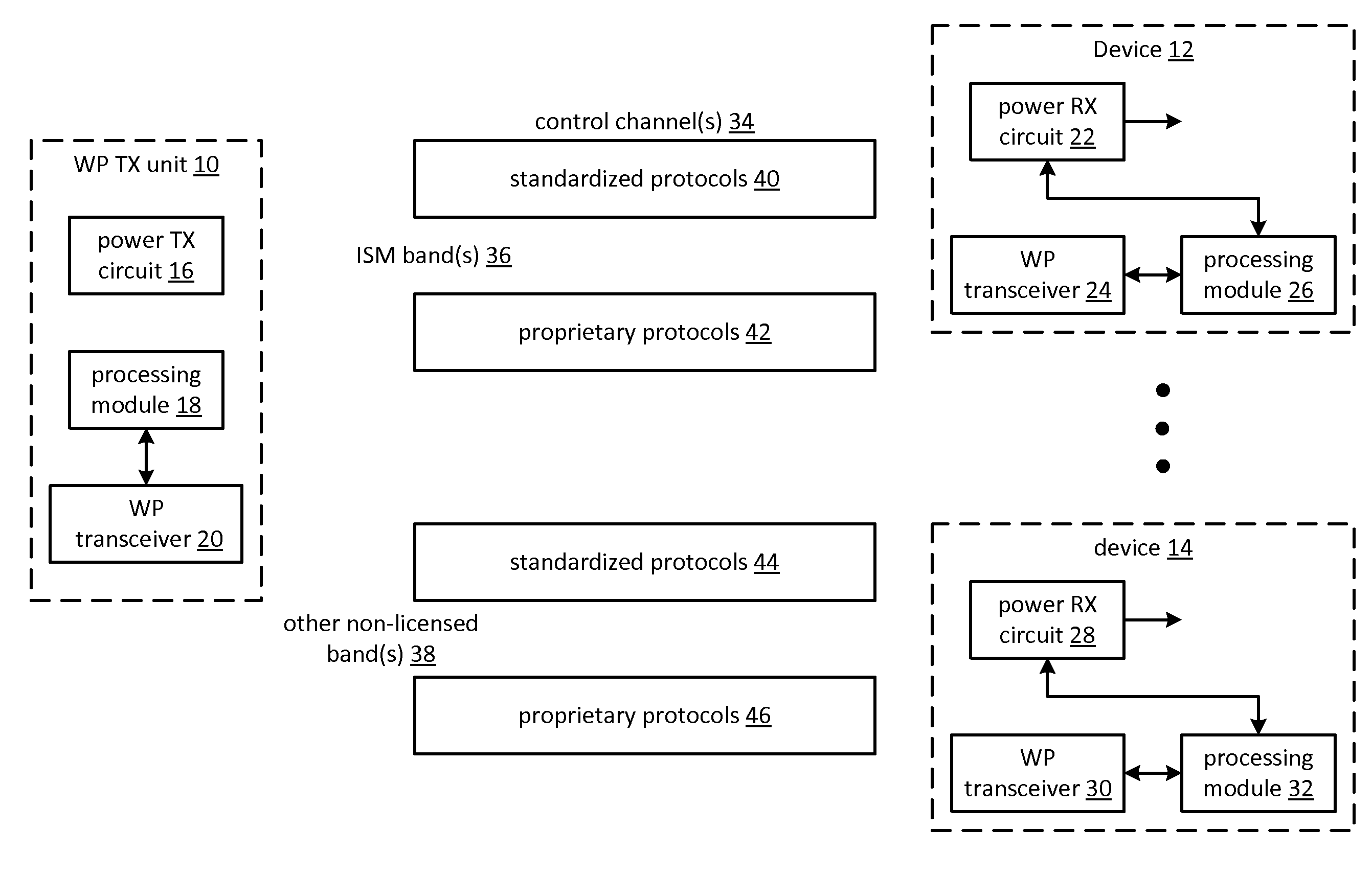
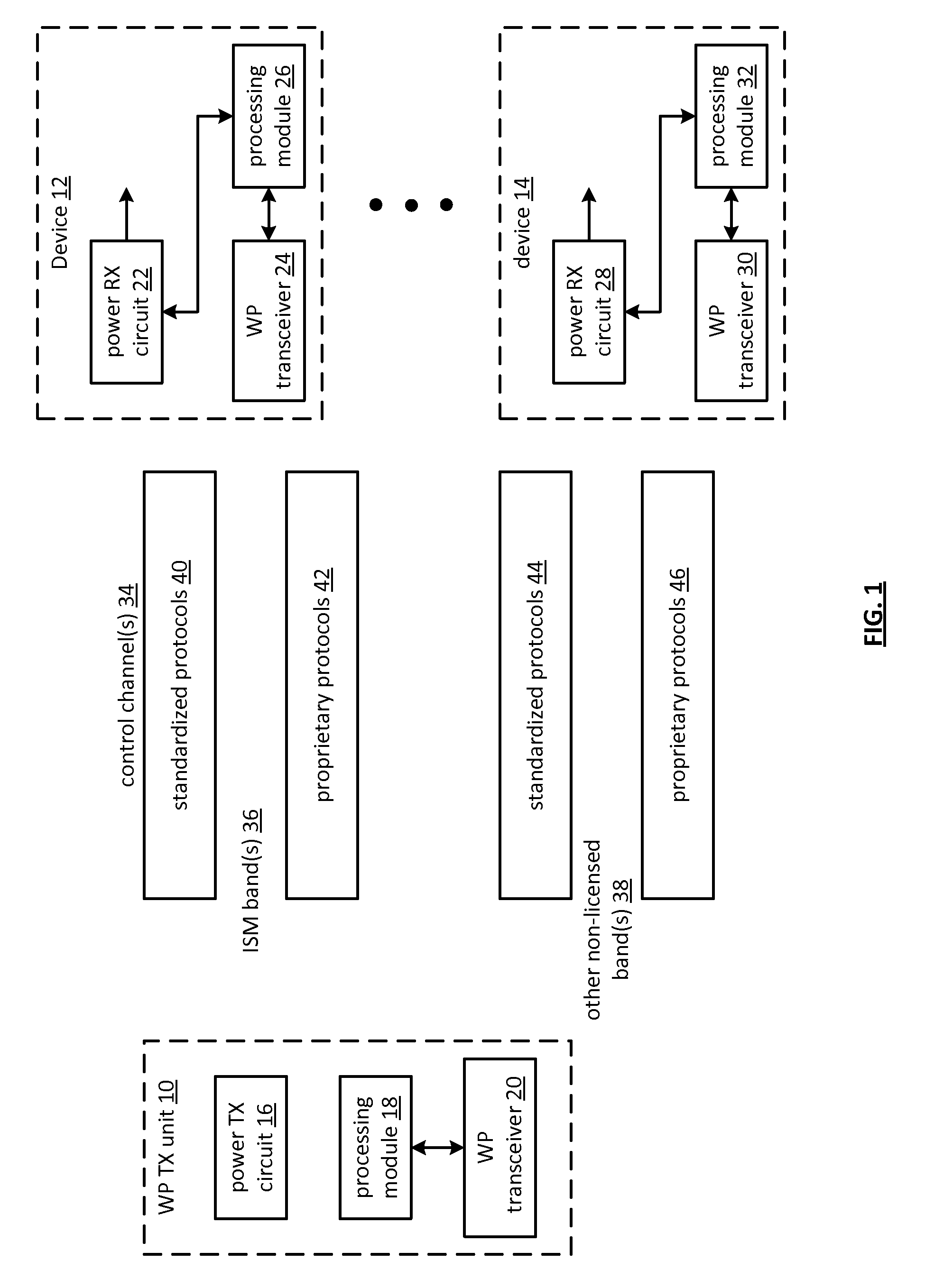
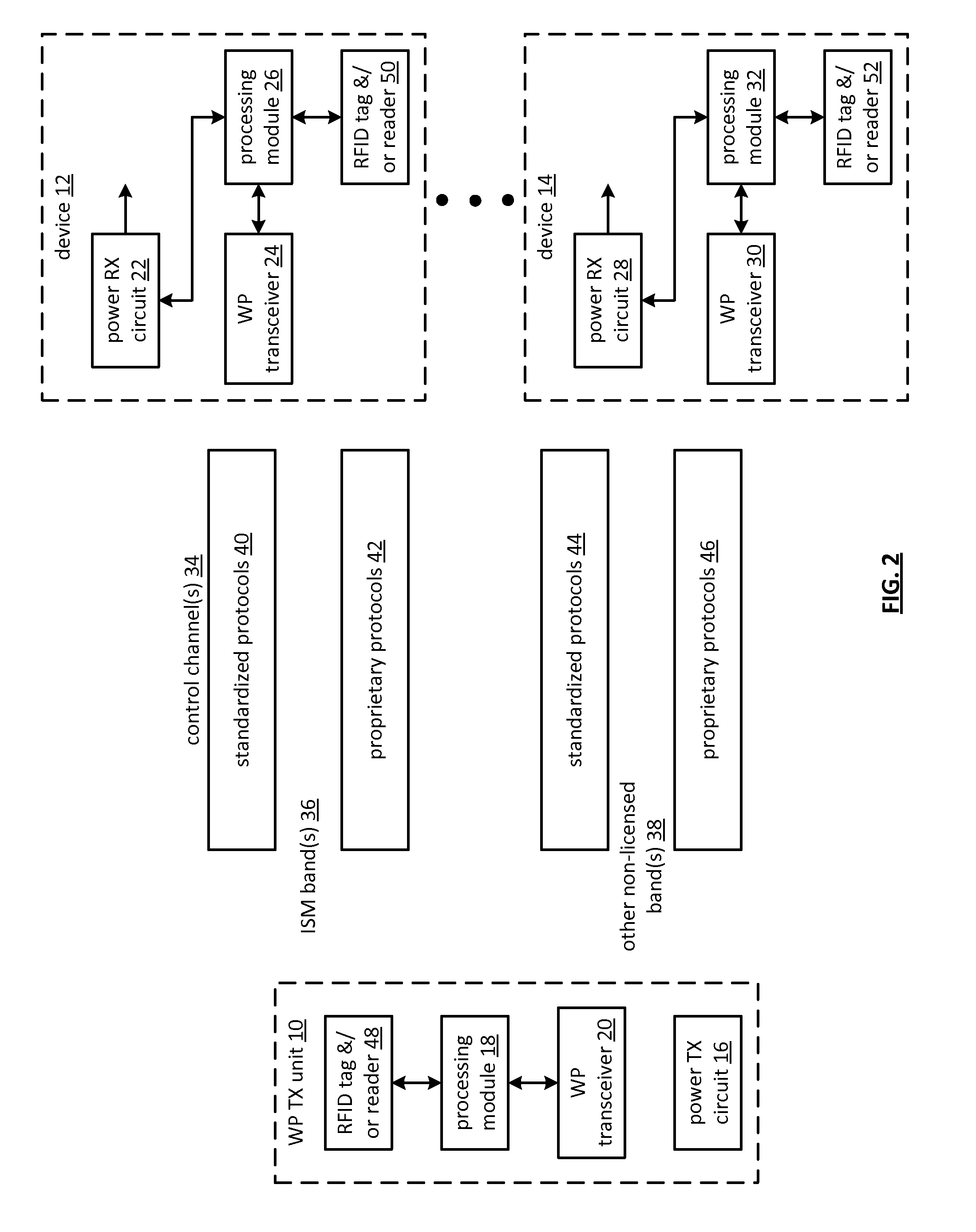
IC controlled wireless power operation and applications thereof
ActiveUS20110127952A1Near-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionTransceiver
An integrated circuit (IC) for use in a device includes a wireless power receiver circuit, a transceiver, and a processing module. The wireless power receiver circuit is operable to convert an electromagnetic signal into a voltage. The transceiver, when operable, transceives a control channel communication. The processing module is operable to: transition the device from an idle state to a charge state when a wireless power transmitter unit is detected; transition the device from the idle state to a wireless power operated state when a wireless power transmit circuit is detected and the device is enabled; and transition the device from the idle state to a battery operated state when the device is enabled and the wireless power transmit circuit is not detected.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
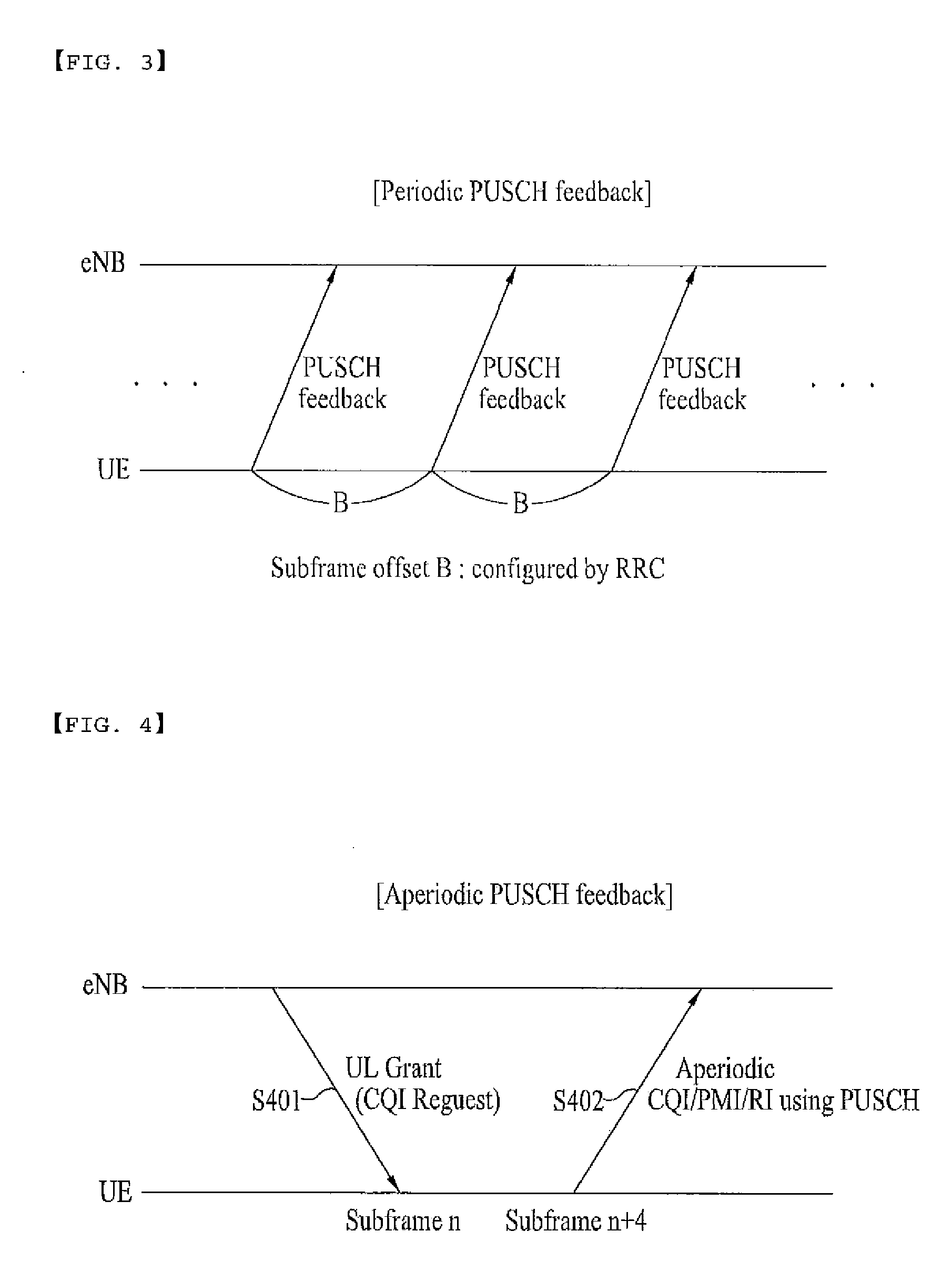
Method for transmitting and receiving channel state information periodically or aperiodically
ActiveUS20090190528A1Effectively transmit channel state informationEfficient solutionError preventionTransmission systemsChannel state informationControl channel
A method for transmitting and receiving channel state information (CSI) periodically and aperiodically is disclosed. The method for aperiodically transmitting channel state information (CSI) by a terminal includes receiving an indicator requesting a channel state information report of a downlink channel from a base station over a downlink control channel, and aperiodically transmitting the channel state information (CSI) to the base station over a physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) upon receiving the indicator from the base station.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
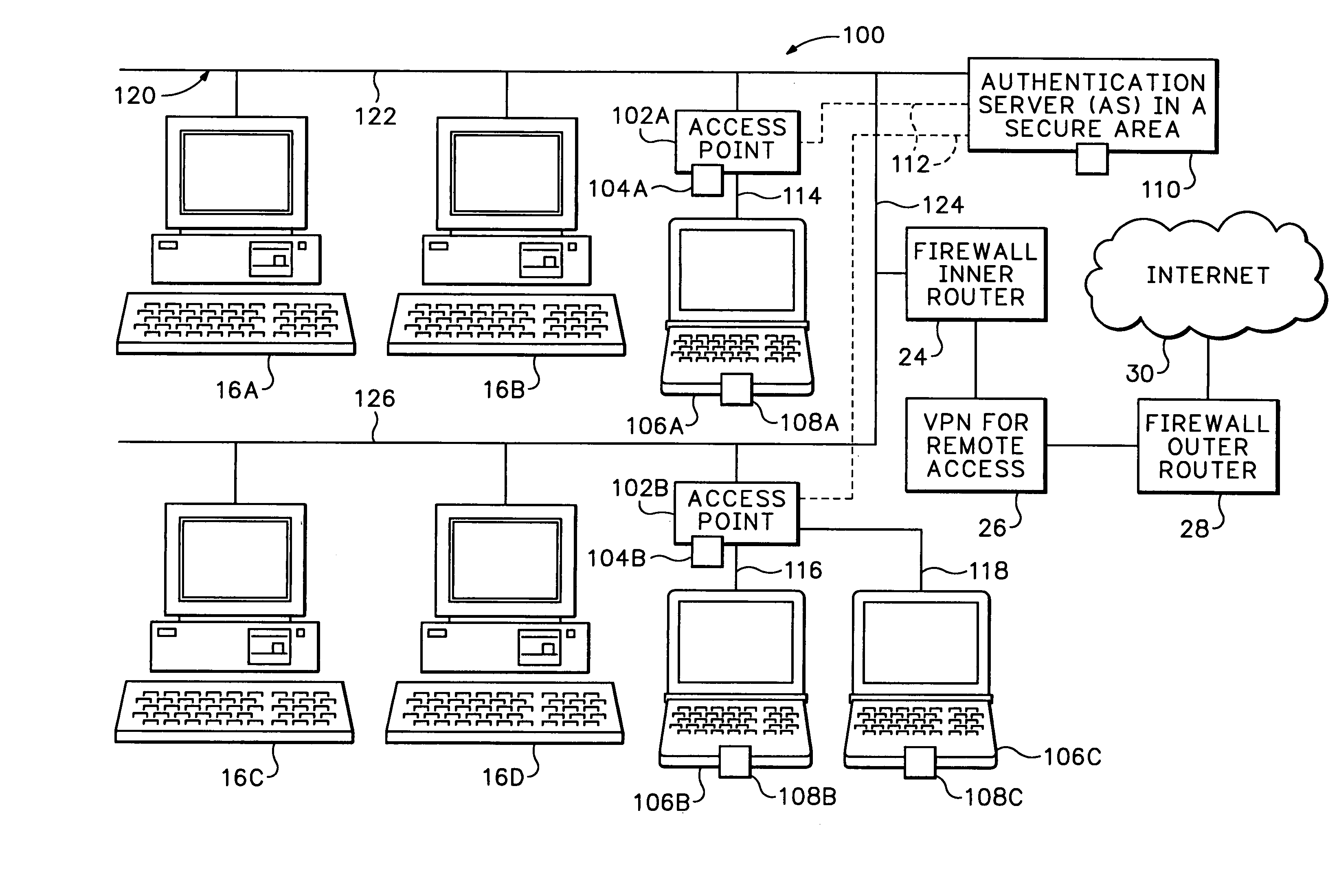
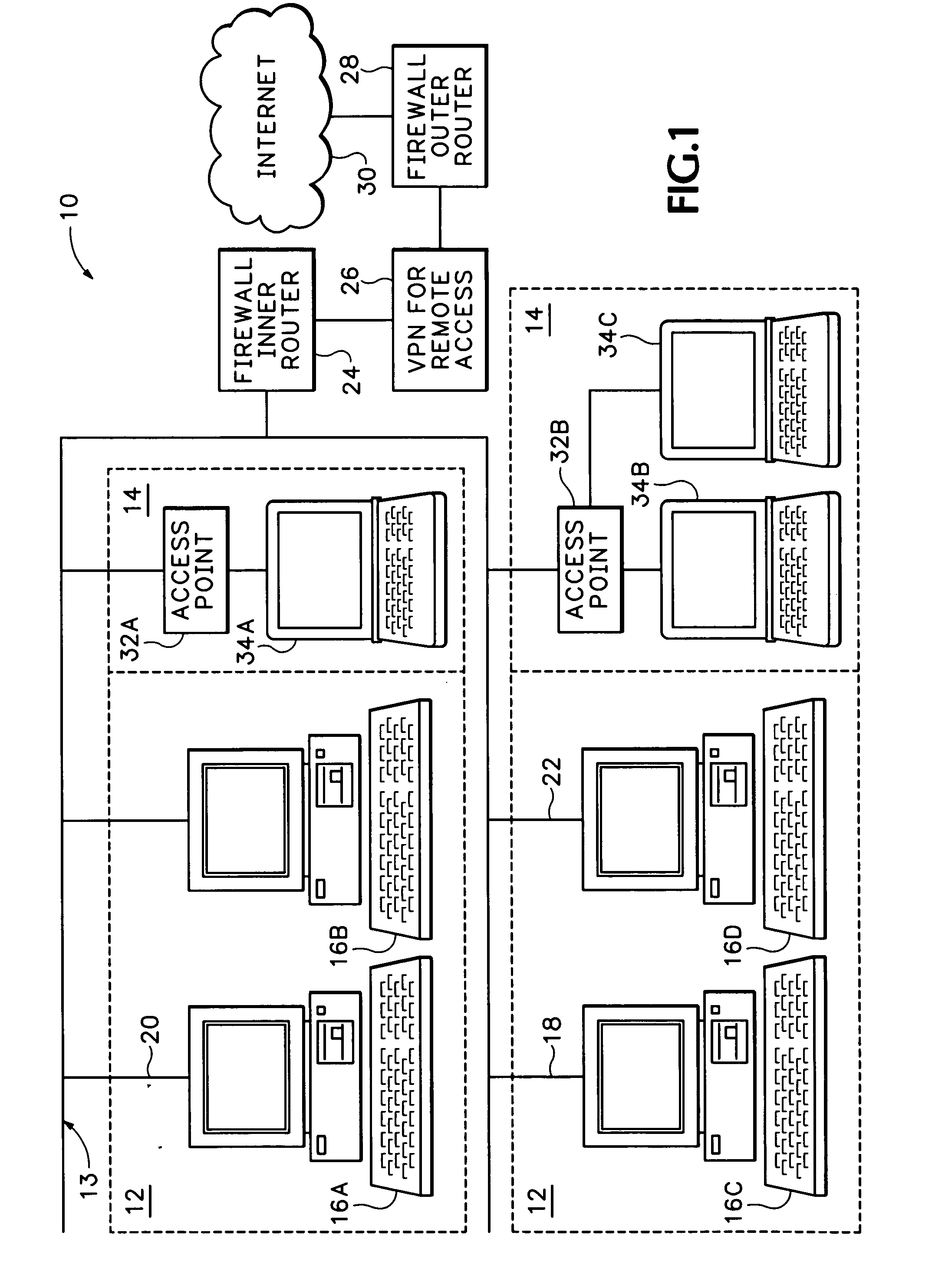
Secure wireless local area network
InactiveUS7174564B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordNetwork addressing
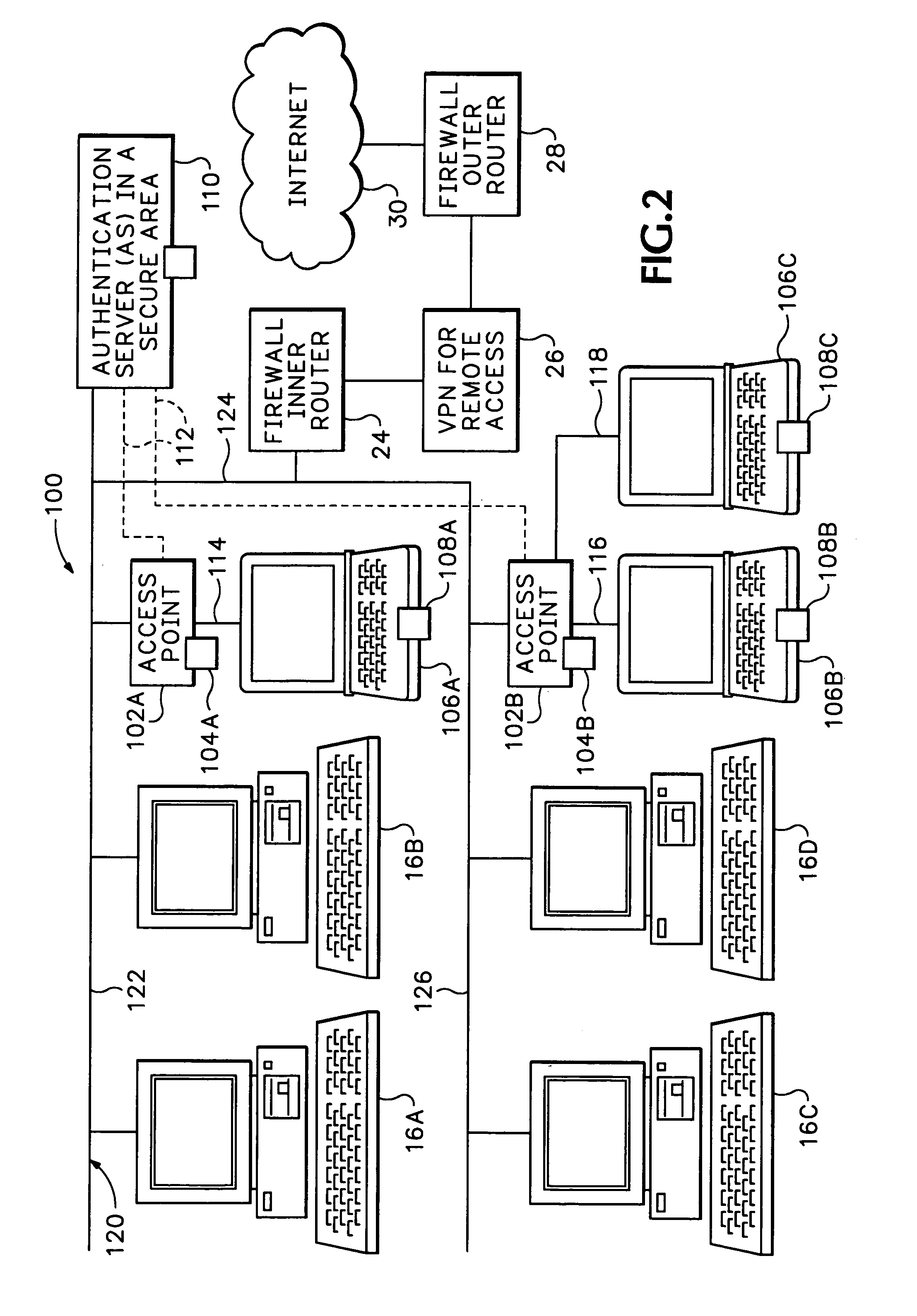
The secure wireless local area network of the present invention includes a single wired network that supports both wired and wireless devices. The network addresses security concerns by including an authentication server that services a plurality of access points. Each access point includes a first authentication device that generates and transmits a first authentication message to the corresponding wireless device over an air channel. The first authentication message includes encrypted validating information about the access point including an access point key that uniquely identifies the access point. Each wireless device includes a second authentication device. The wireless device receives the first authentication message and determines whether the access point is authorized to connect to the wired network. If the access point is valid, the second authentication device responds to the first authentication message by generating and transmitting a second authentication message to the access point. The second authentication message includes encrypted validating information about the wireless device and operator, e.g., a device key and the operator's logon name and password. The access point determines the authenticity of the wireless device by decrypting the portion of the second authentication message that includes the device key. If the wireless device is valid, the AP opens a control channel with the authentication server. The AP transmits the first and second authentication messages to the authentication server. If the authentication server validates the access point and the operator's logon name and password, it will authorize access to the wired network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Personalized multimedia services using a mobile service platform
ActiveUS20030050062A1Minimize congestionEffective controlData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPersonalizationMultimedia servers
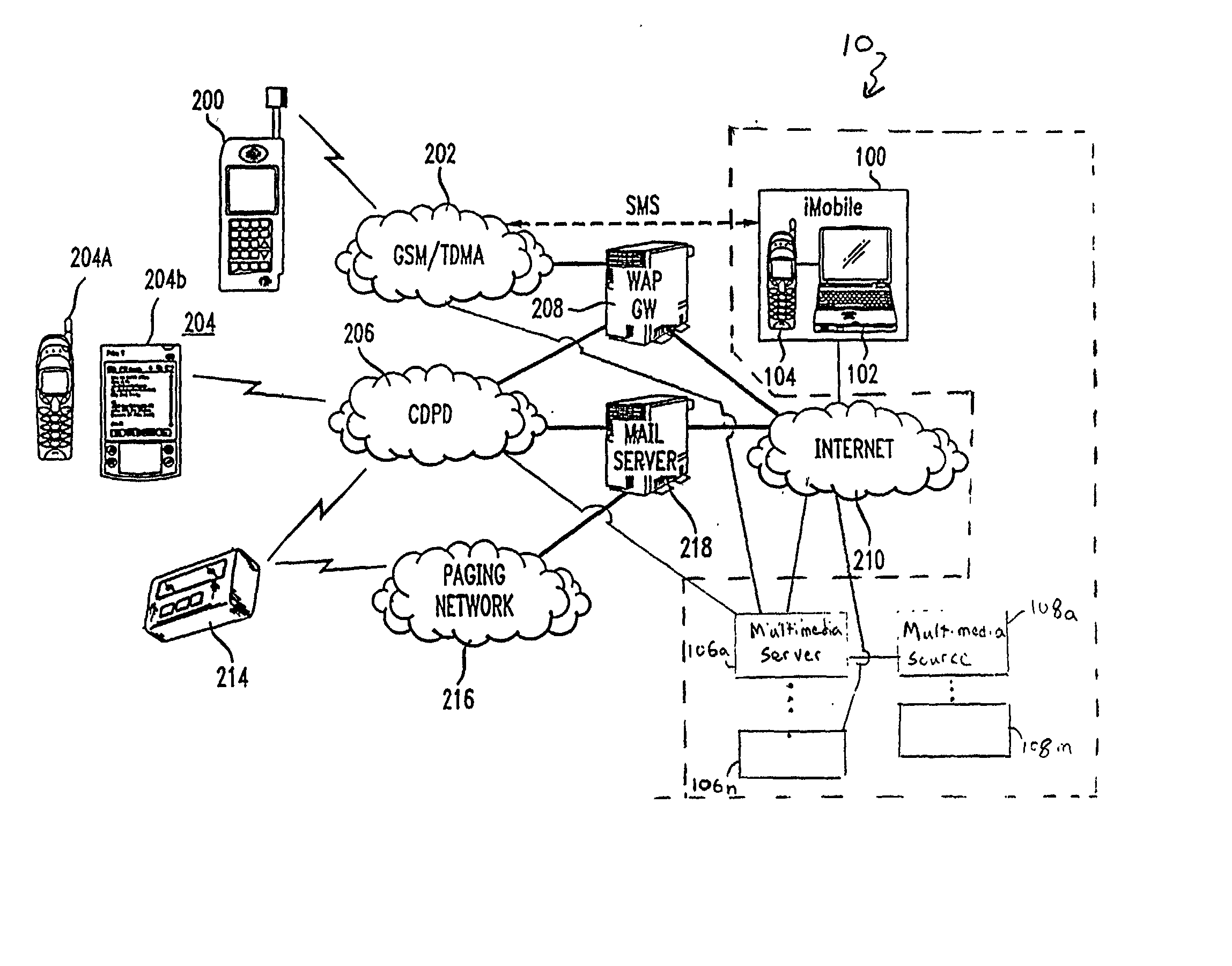
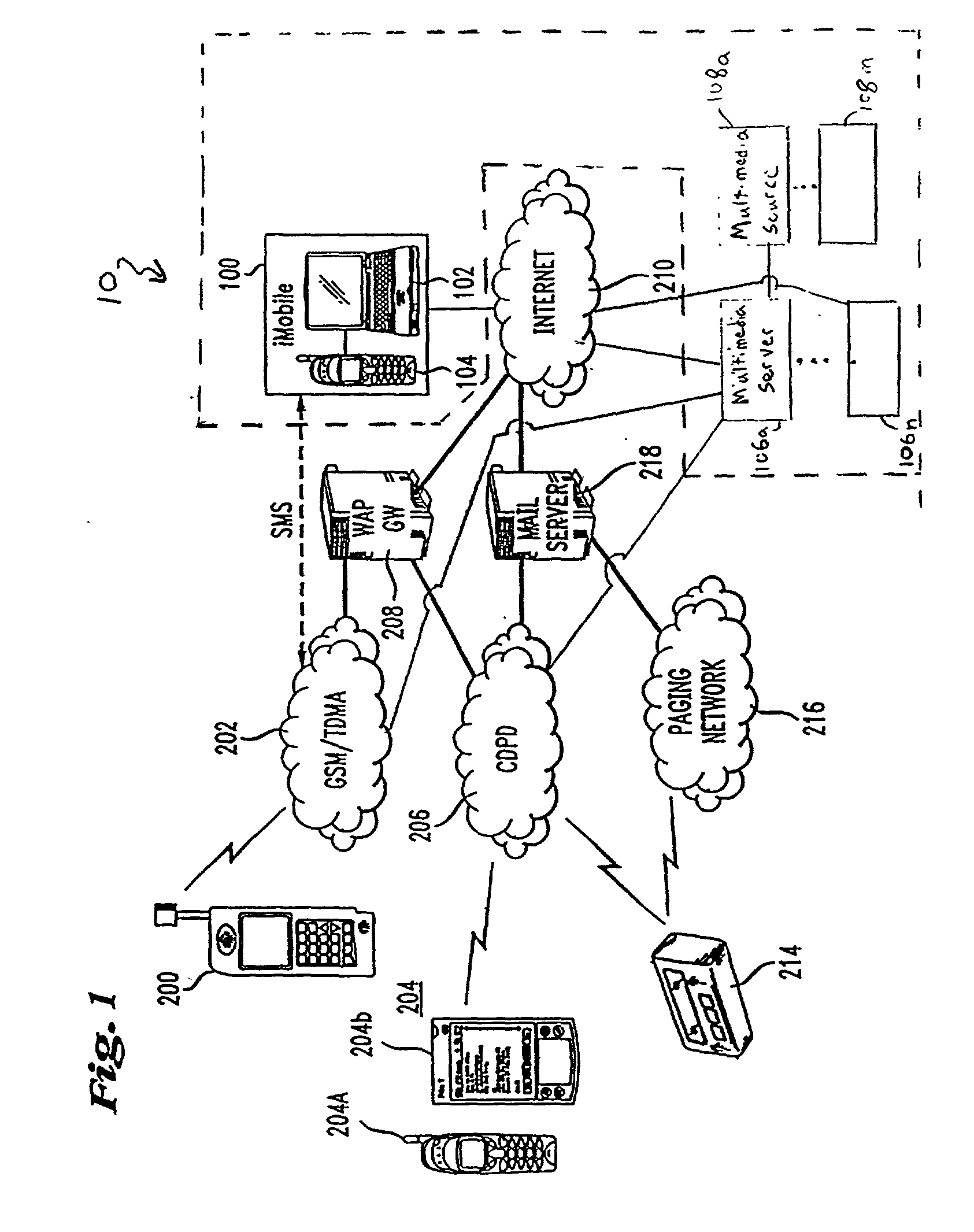
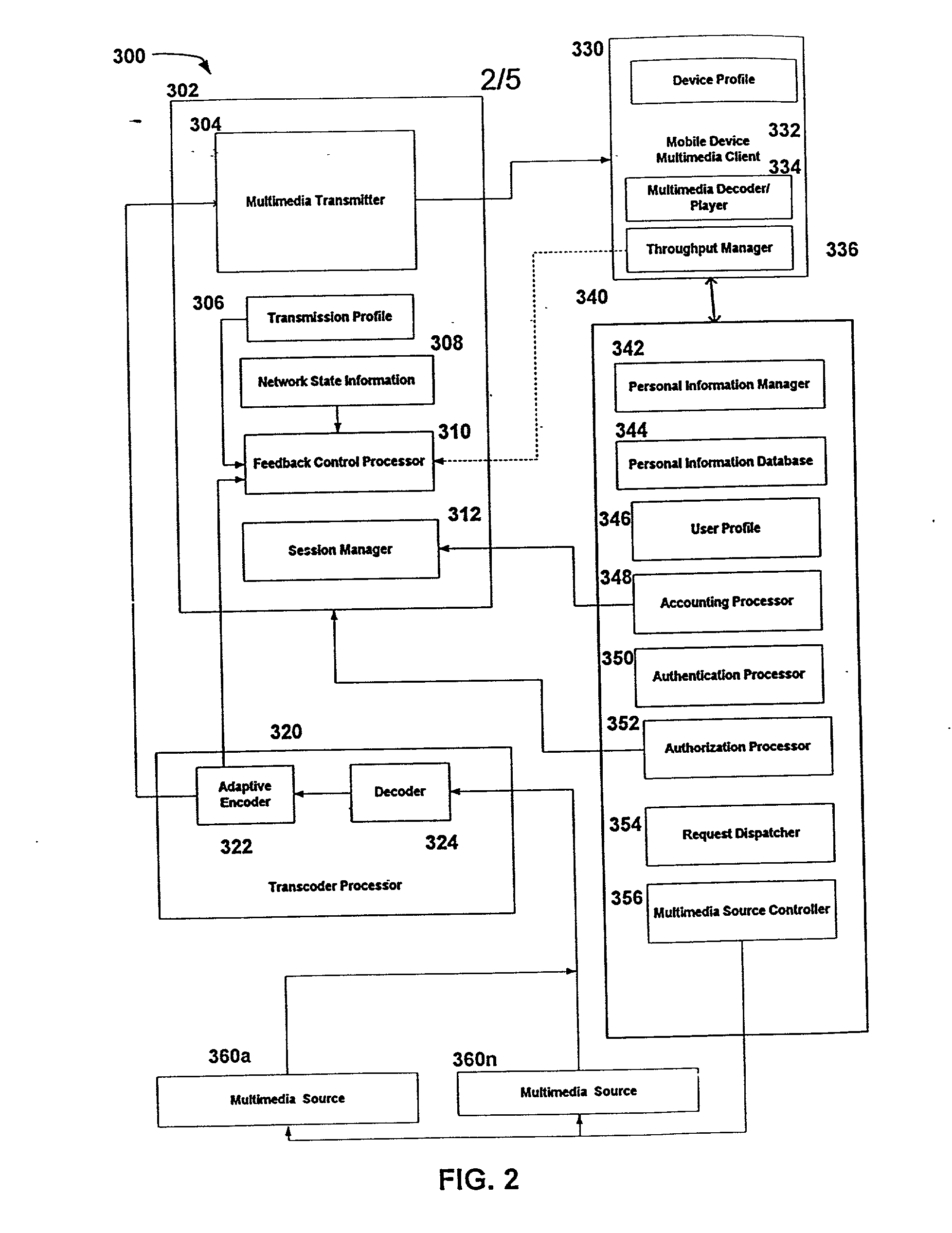
A method for providing multimedia data from at least one controllable multimedia source to a mobile device includes providing a request path from the mobile device to a mobile service platform, receiving a request from the mobile device, obtaining a device profile from the mobile device, authenticating the identity of a user of the mobile device, and determining a user profile in response to the user identity. The method further includes authorizing control and access to the at least one multimedia source, providing a control channel from the mobile service platform to at least one multimedia server, providing multimedia data delivery information to the at least one multimedia server, and providing multimedia data to the mobile device in response to the request via the at least one multimedia server.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
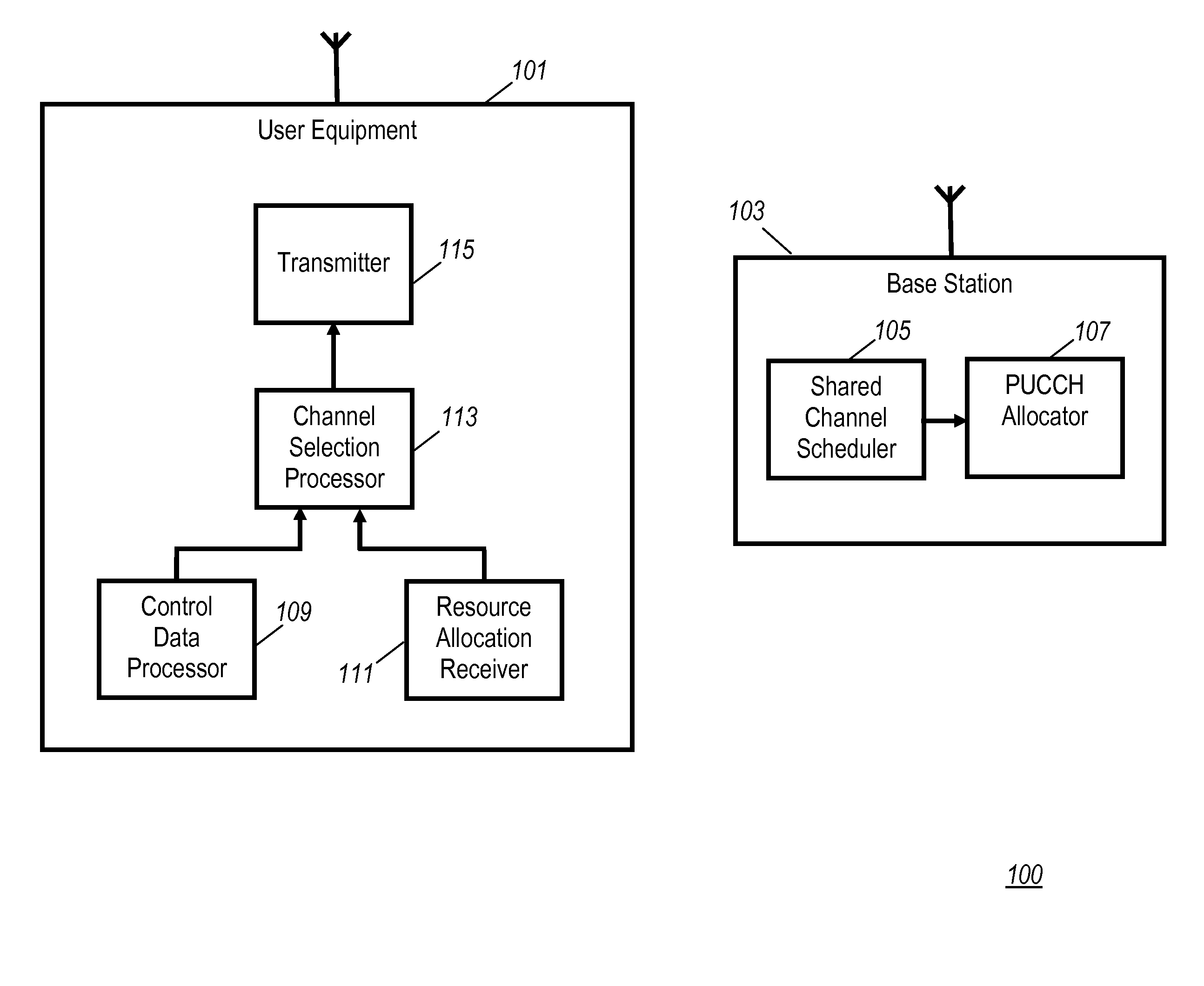
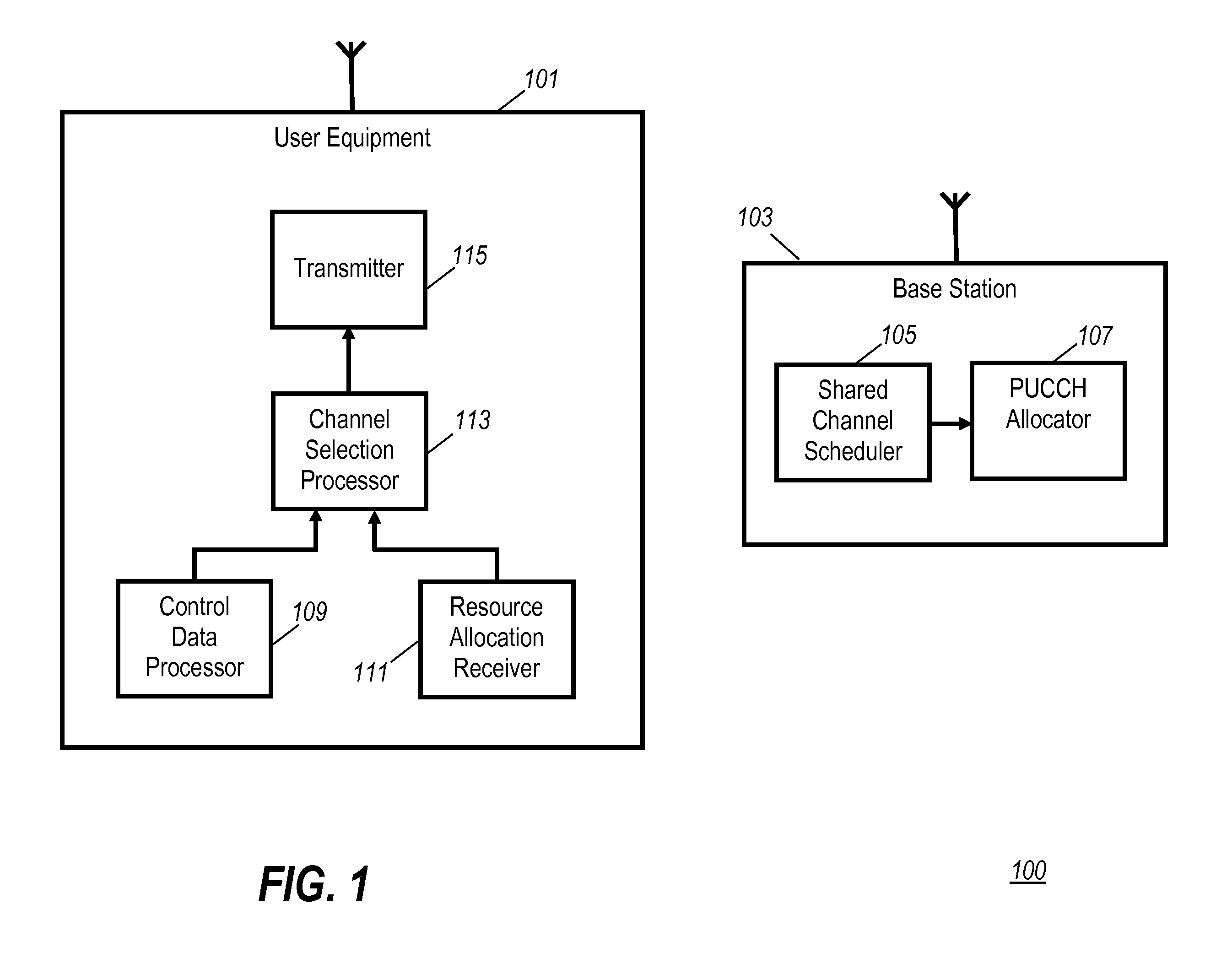
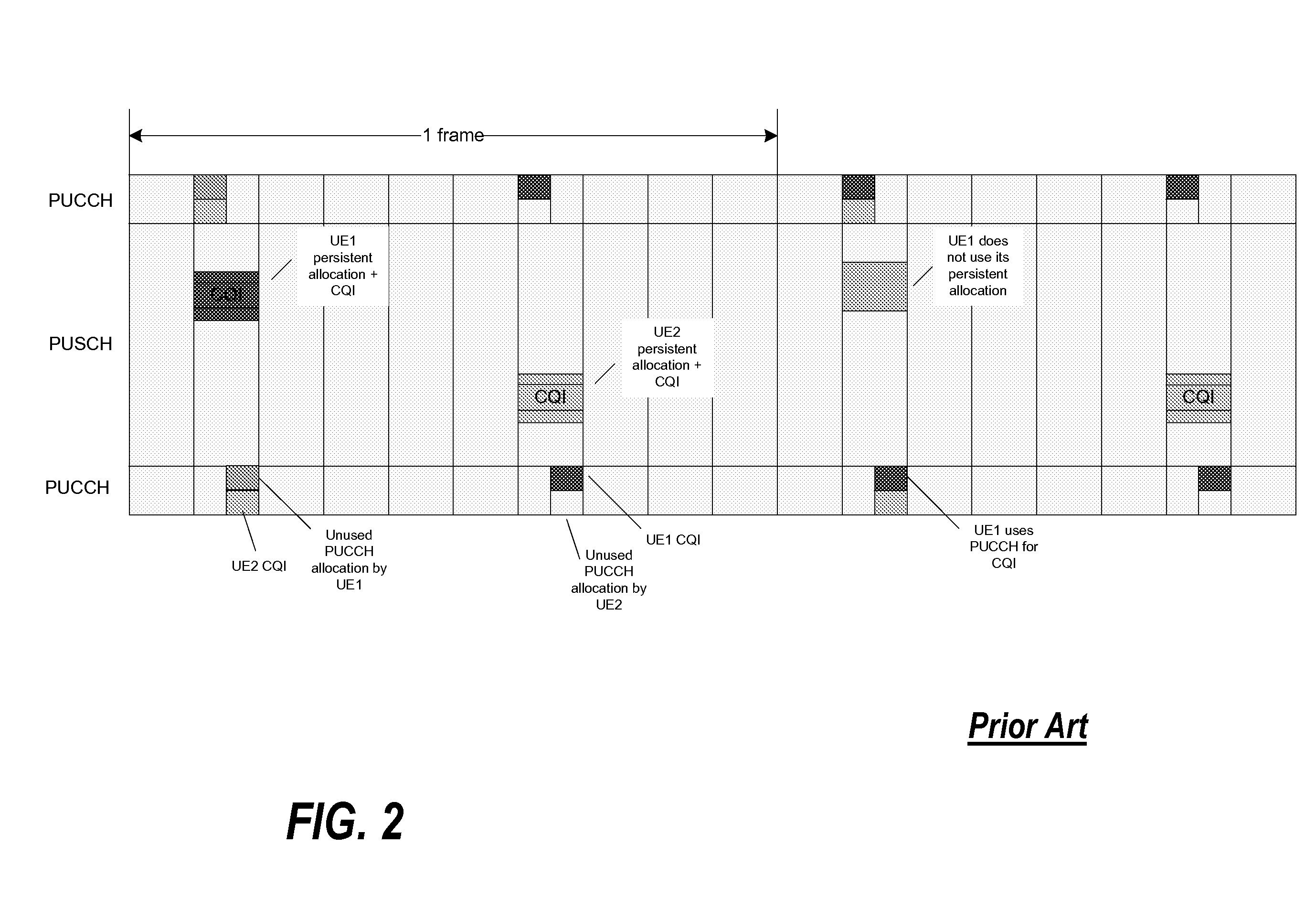
Use of the physical uplink control channel in a 3rd generation partnership project communication system
ActiveUS20080311919A1Easy to optimizeEfficient use of resourcesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignalling characterisationCommunications systemControl channel
In a 3rd Generation Partnership Project, 3GPP, communication system a base station comprises a scheduler allocating communication resource of at least one of a Physical Uplink Shared CHannel, PUSCH, and a Physical Downlink Shared CHannel, PDSCH to a User Equipment (UE). The scheduling may either be a dynamic scheduling wherein a resource allocation for a single frame is provided to the UE or a persistent scheduling wherein a resource allocation for a plurality of frames is provided to the UE. A resource allocator assigns resource of a Physical Uplink Control CHannel, PUCCH, to the UE dependent on whether dynamic scheduling or persistent scheduling is performed by the scheduler for the UE. The UE transmits uplink control data on a physical uplink channel which is selected as the PUCCH or the PUSCH in response to whether persistent scheduling is used for the UE. The invention allows e.g. reduced PUCCH loading.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for machine-to-machine communication registration
ActiveUS20110128911A1Network traffic/resource managementBroadcast service distributionControl channelComputer science
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for Machine to Machine (M2M) communication registration. The methods provide single and periodic registration and may be device or network based. The devices in the system may be divided into groups. A single device member may perform the basic access steps for the group. Other devices may receive related access information on a control channel and use the information to access the system. The devices may send data, get updates, and then go to sleep. Internet addresses may be released or maintained. During a control cycle, the devices may wake up and listen to the control channel for any paging messages. Individual devices or the entire group may access the system. During a reporting cycle, all the devices may wake up and access the system to connect to the M2M system to upload data.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Method and apparatus for increasing performance of HTTP over long-latency links
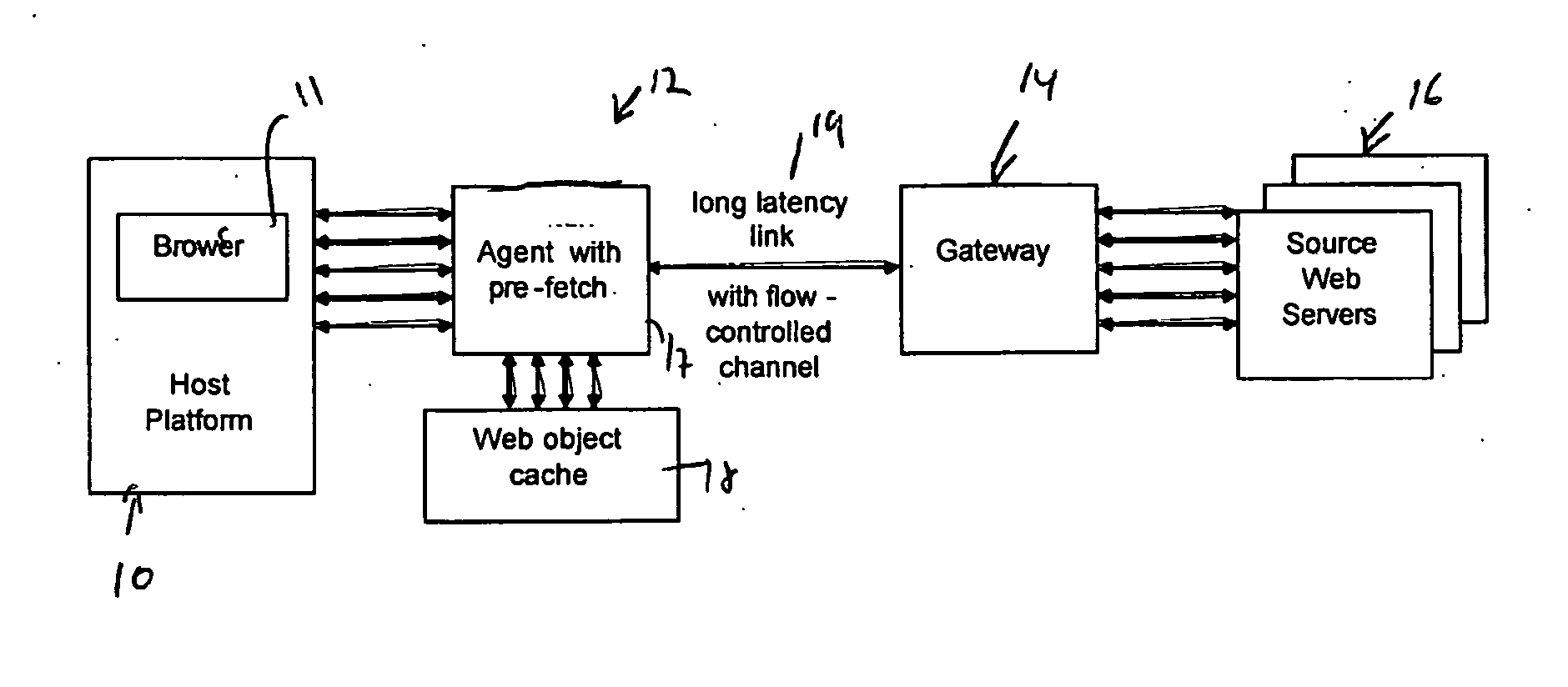
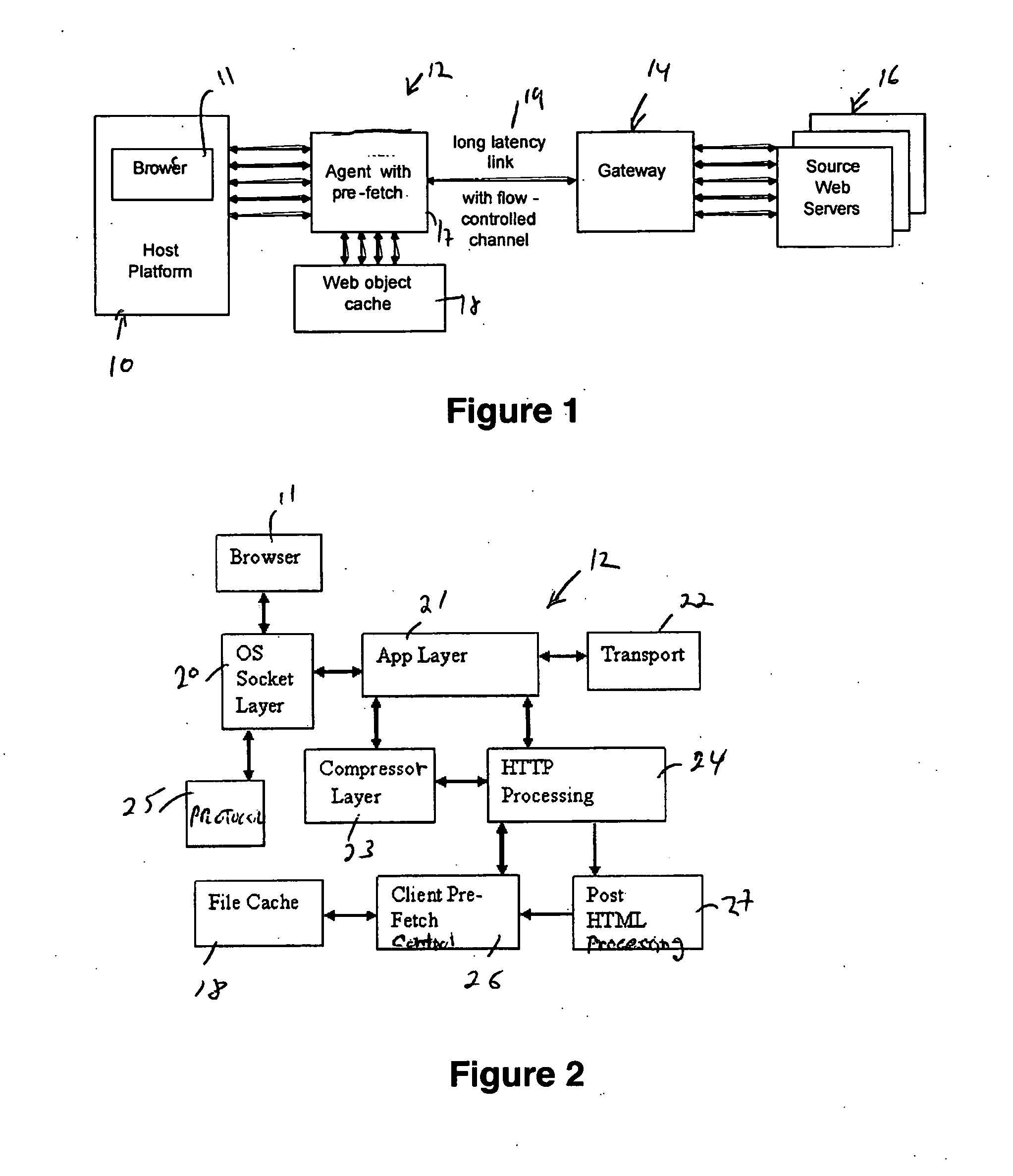
ActiveUS20060253546A1Reduce negative impactImprove parallelismDigital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsWeb siteWeb browser
The invention increases performance of HTTP over long-latency links by pre-fetching objects concurrently via aggregated and flow-controlled channels. An agent and gateway together assist a Web browser in fetching HTTP contents faster from Internet Web sites over long-latency data links. The gateway and the agent coordinate the fetching of selective embedded objects in such a way that an object is ready and available on a host platform before the resident browser requires it. The seemingly instantaneous availability of objects to a browser enables it to complete processing the object to request the next object without much wait. Without this instantaneous availability of an embedded object, a browser waits for its request and the corresponding response to traverse a long delay link.
Owner:VENTURI WIRELESS
Method for efficiently transmitting physical channel in multi-carrier aggregation state to support broadband
ActiveUS20110268032A1Efficient communicationReduce blind decoding overheadError preventionTransmission path divisionCarrier signalControl channel
The present invention relates to a wireless connection system, and more specifically to a method for efficiently transmitting a control channel in a multi-carrier aggregation state. According to one aspect of the invention, a method for enabling a terminal to transmit data in a broadband wireless connection system that supports multiband comprises the steps of: receiving uplink acknowledgement information from a base station through a first downlink component carrier among plural downlink component carriers available in the terminal; transmitting data to the base station through an uplink resource indicated by the uplink acknowledge information; and receiving feedback information from the base station through the first control channel of the first downlink component carrier, wherein the feedback information indicates whether there is an error in the reception of the transmitted data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
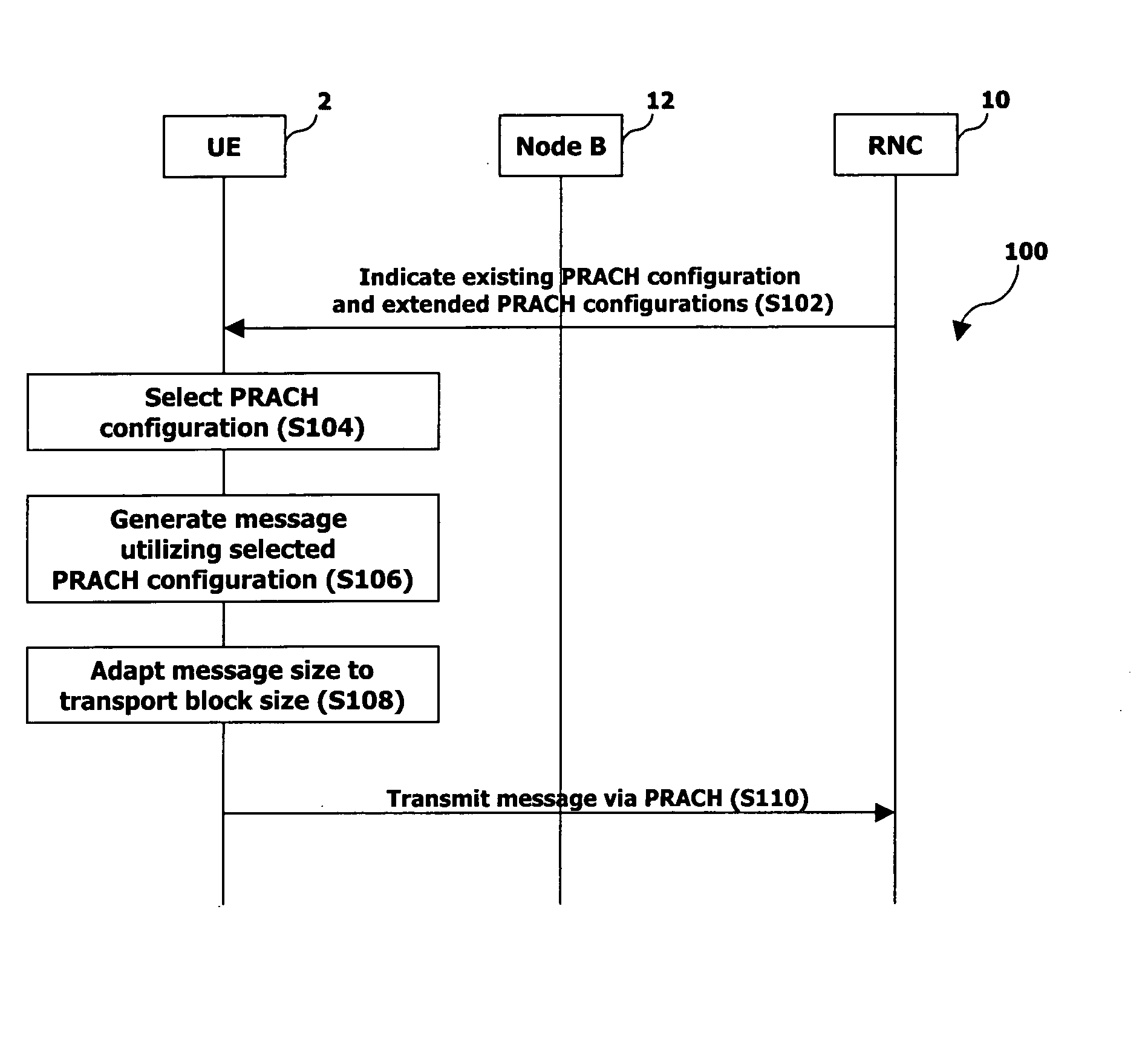
Method and apparatus for providing enhanced messages on common control channel in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20050266846A1Enhanced signalNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemControl channel
A method and apparatus for providing new configurations for transmitting control information between a mobile terminal and a network using a common control channel (CCCH) logical channel / transport channel. The new configurations enable messages to be sent that are larger than currently allowed and the availability of the new configurations is indicated such that mobile terminals that do not support the new configurations are not impacted.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
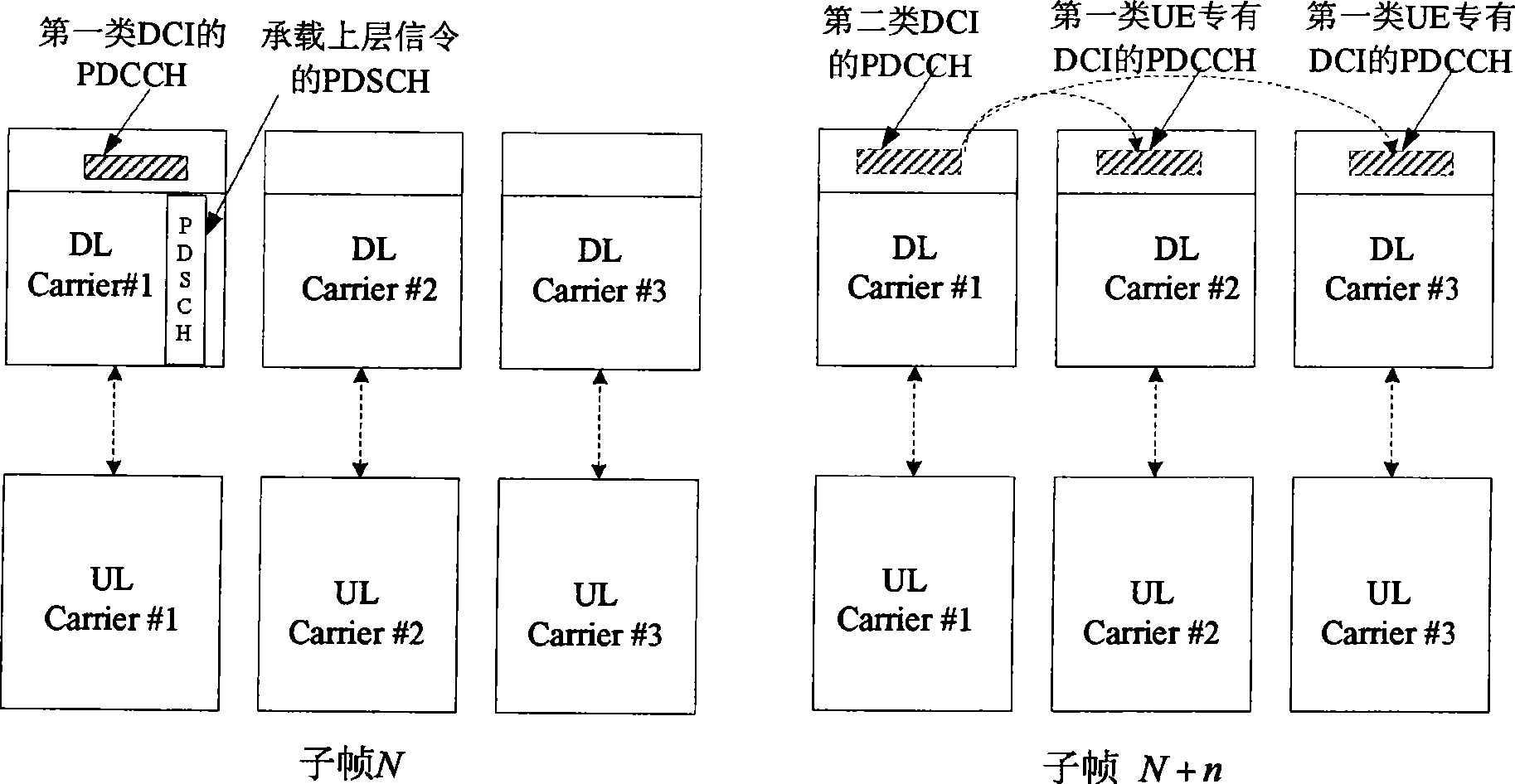
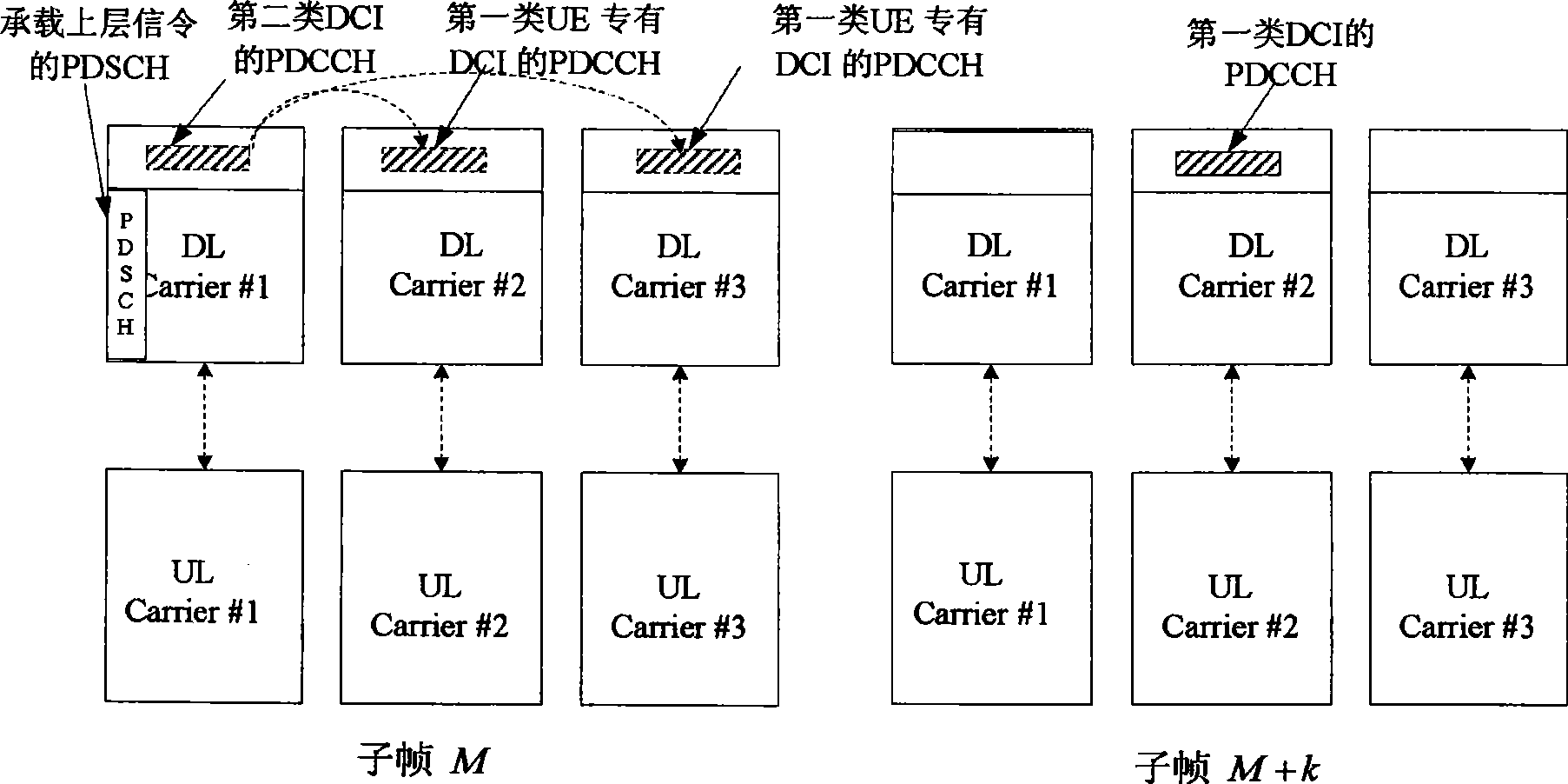
Downlink control information sending and detecting method
ActiveCN101478808AImprove compatibilityEasy to implementError preventionAssess restrictionCarrier signalControl channel
The invention provides a method for sending downlink control information. A base station carries the downlink control information in the physical downlink control channel, sends the channel by component carrier and indicates the component carrier by high-level signal. The information is the first and / or the second category downlink control information. The first category information includes public downlink control information and terminal proprietary downlink control information; the second category information carries the indicating information related to the terminal propriety downlink control information. The invention also provides the detection method of the downlink control information. The terminal is used for receiving the high-level signal, indicating the component carrier according to the high-level signal, detecting the physical channel on the carrier and obtaining the downlink control information.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Communication system with a beamformed control channel and method of system control
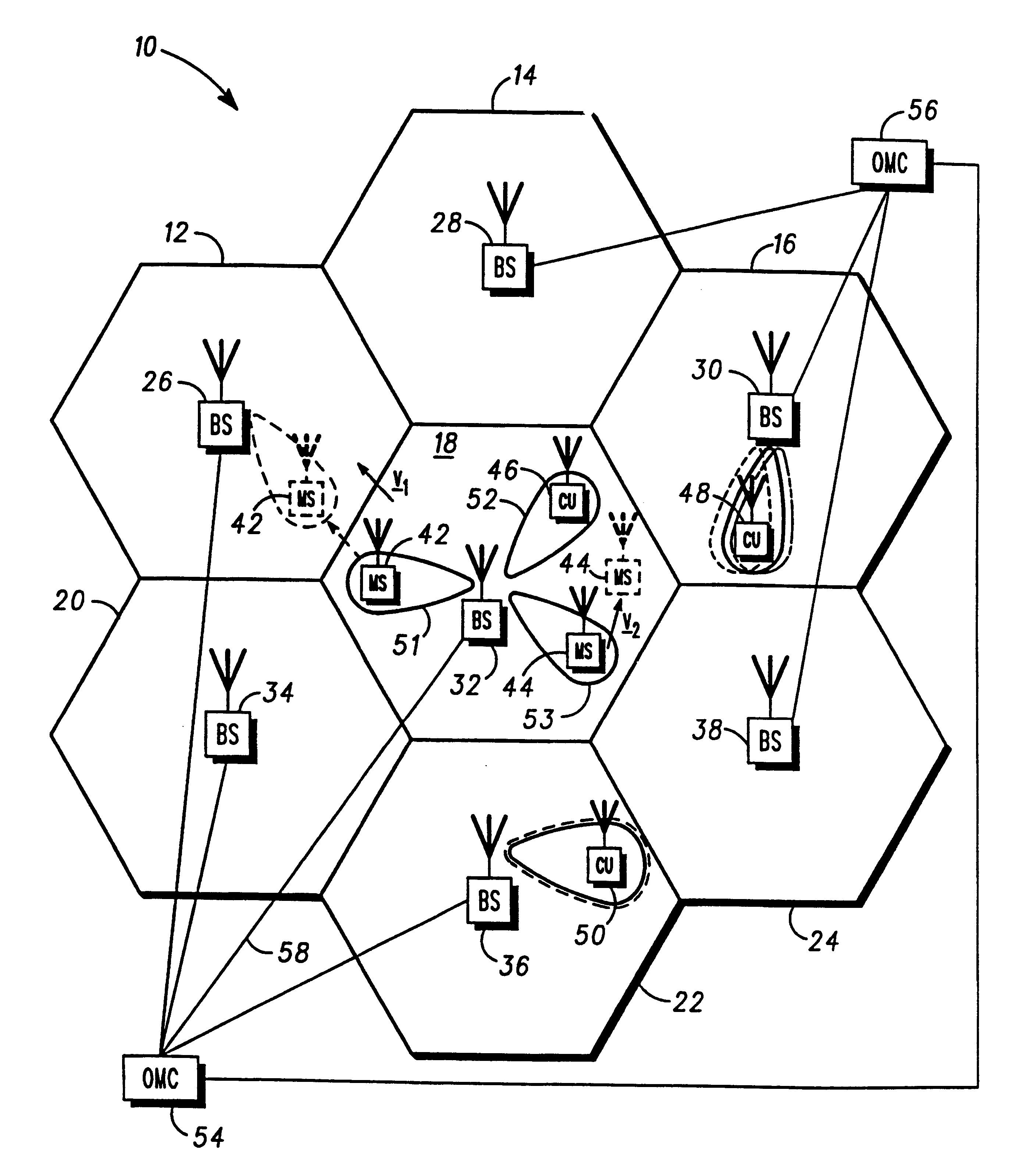
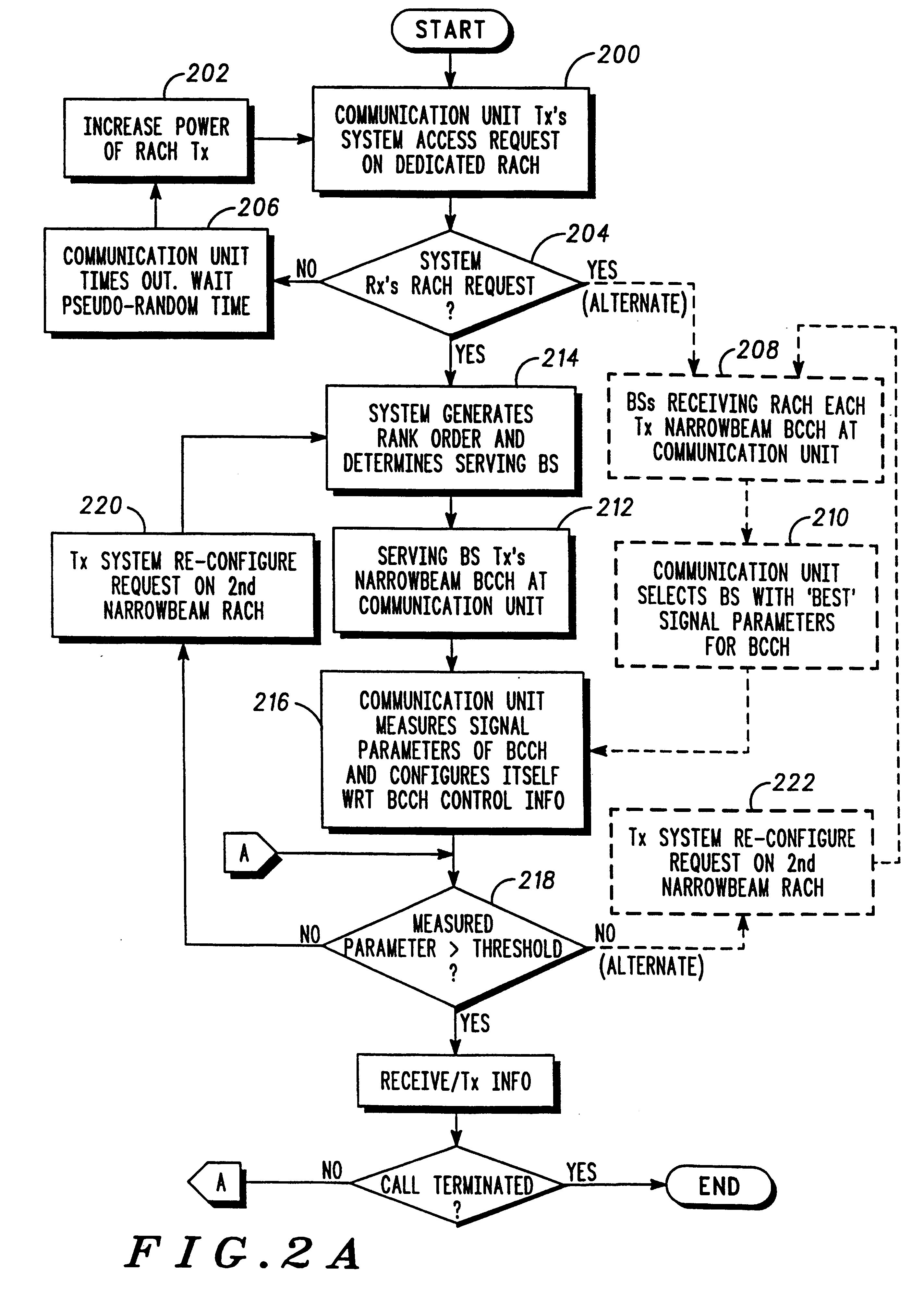
InactiveUS6330459B1Reduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementPolarisation/directional diversityWide areaCommunications system
To reduce interference in a communication system (10), a communication unit (42-50) is arranged to initiate establishment of a radio frequency communication with a base station (26-38) by transmitting a system access request on a dedicated, wide area control channel. Upon receipt of the system access request, a base station (32) of the communication system of FIG. 1 responds by forming a narrowbeam control channel to the communication unit and transmitting system control information to the communication unit on the narrowbeam control channel, the system control information transmitted from the array of antenna elements and arranged to identify a narrowbeam communication resource for use in the radio communication. The communication unit (42-50), upon receiving the system control information, then configures itself to utilise the narrowbeam communication resource for the radio communication.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Resource allocation apparatus and method in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
InactiveUS20080233966A1Reduce Inter-Cell InterferenceMechanism suitableTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCommunications systemControl channel
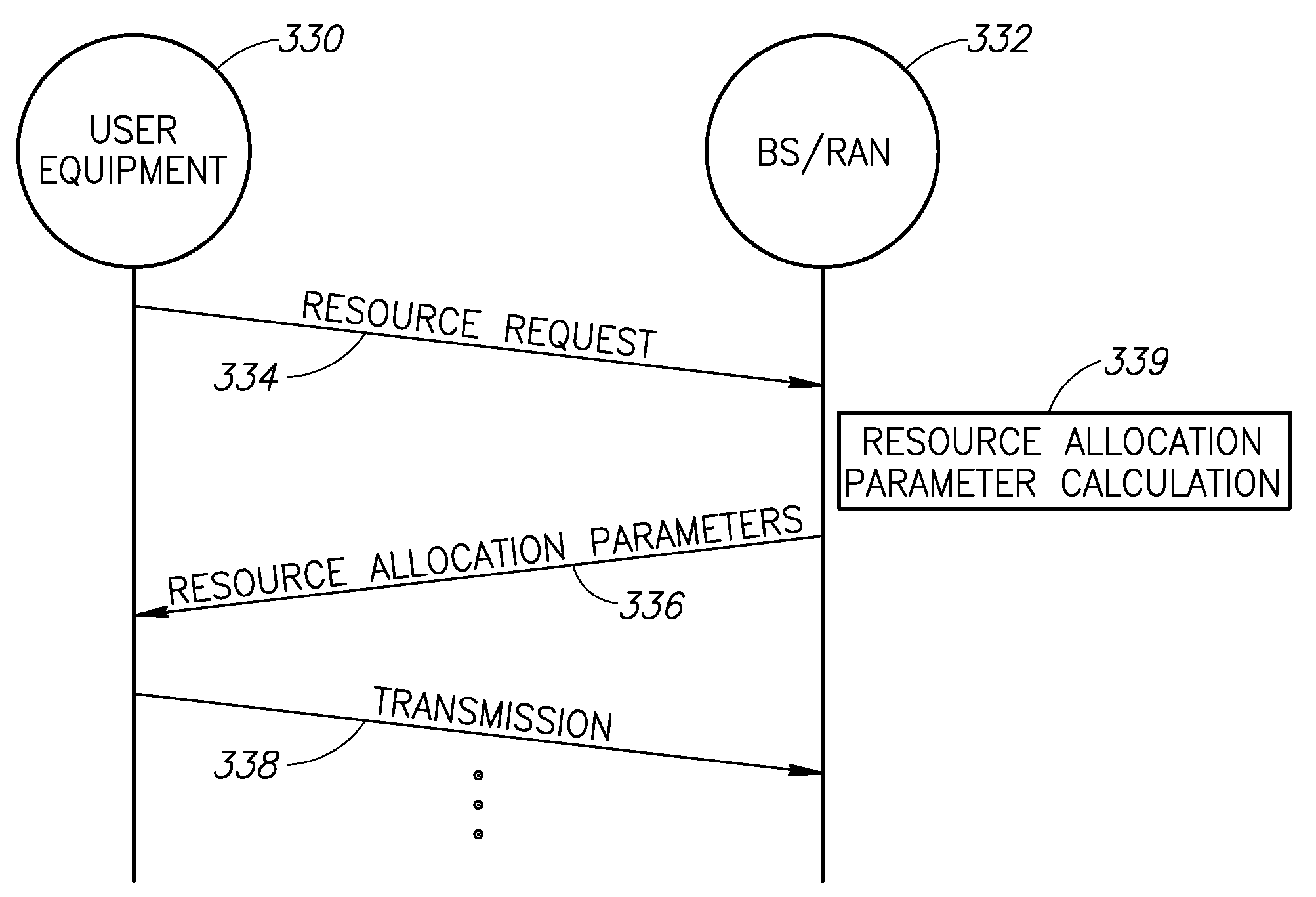
A novel and useful method and system for resource allocation in OFDM communication systems. The mechanism reduces inter-cell interference by randomizing the inter-cell interference experienced in each cell. The mechanism effectively spreads the resource allocation in each cell in a random manner resulting in statistical-like inter-cell interference behavior. In many cases, use of the mechanism is sufficient to obviate the need for frequency planning between cells. A formula or hardware permutation machine is used to generate a random list of indices. The indices are then used to assign user data to the system resources. One or more parameters defining the random index generator at the transmitter are forwarded to the receiver to enable the local generation of an exact copy of the list of indices generated at the transmitter, thus enabling the DL and UL at the receiver while minimizing the required control channel signaling.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
System and method for dynamic frequency assignment
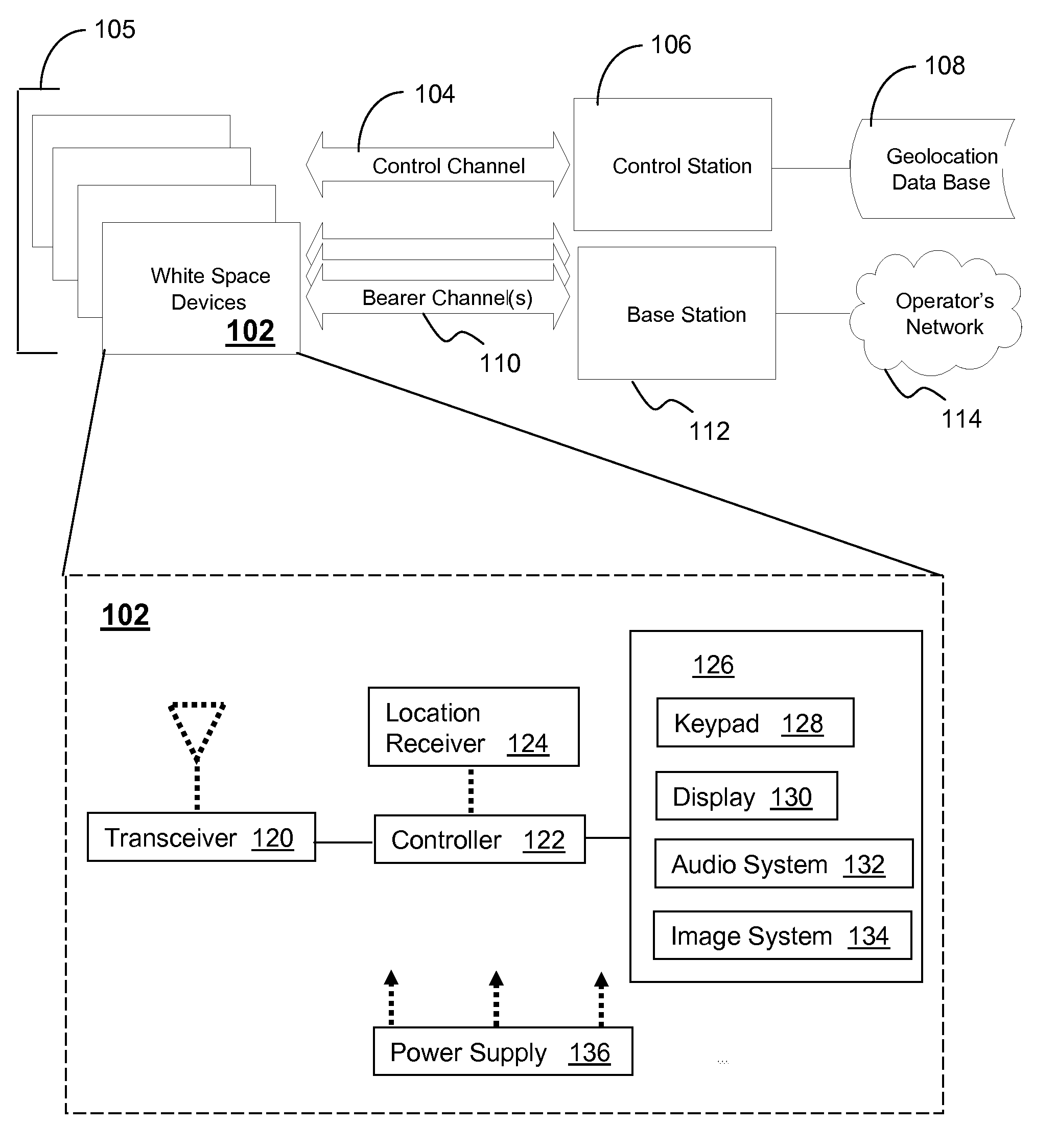
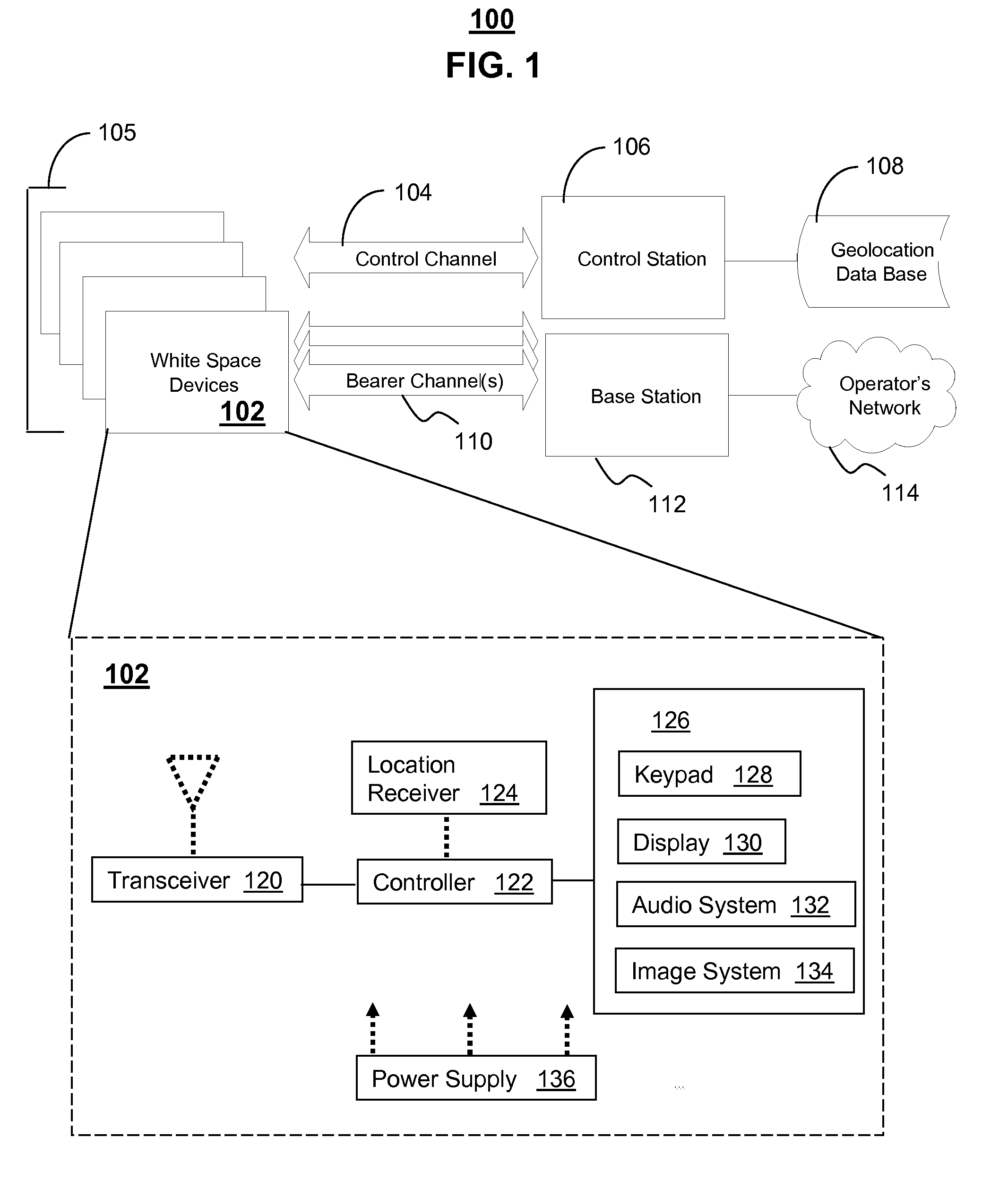
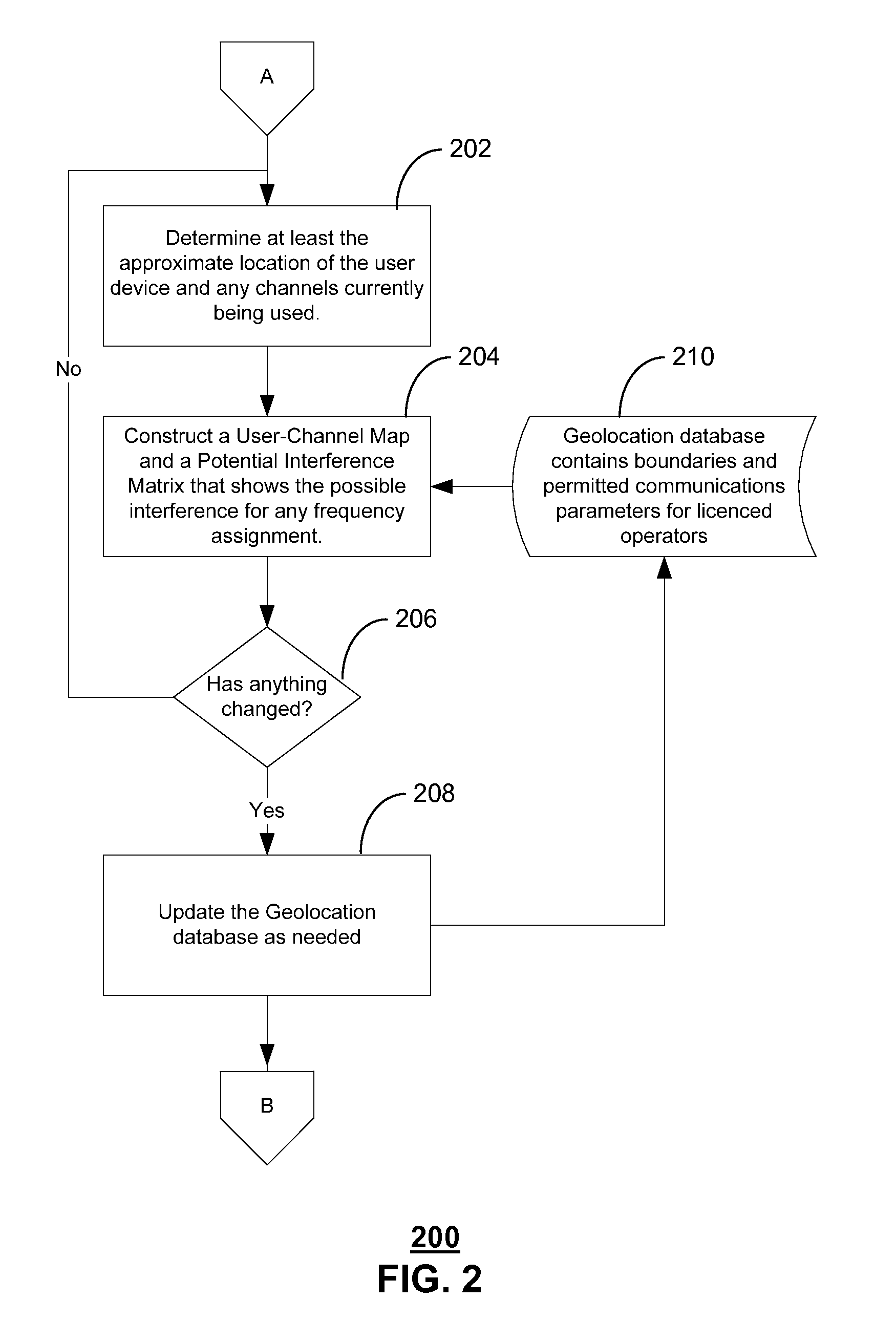
White space devices (102) are unlicensed radiofrequency devices that must have certain capabilities in order to avoid harmful interference to licensed operations. In general, they must be location-aware, must be able to contact a geolocation database (108) and may not operate without receiving a positive control signal. A number of white space devices can use a control channel (104) to communicate with a control station (106). In addition to meeting the geolocation and positive control requirements given above, the control station coordinates the channels used by the white space devices so as to minimize (308) their aggregate interference. In one embodiment, a control channel uses a separate frequency band with high availability and reliability but low throughput. Embodiments optimize channel assignments where the potential interference depends on the mutual distances between the white space devices. Potential interference reductions of 20-30 dB have been found in simulations. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:PROGENY LMS
Multi-channel digital wireless audio system
ActiveUS8050203B2Improve service qualityReduce dataError preventionStereophonic circuit arrangementsComputer hardwareDigital radio
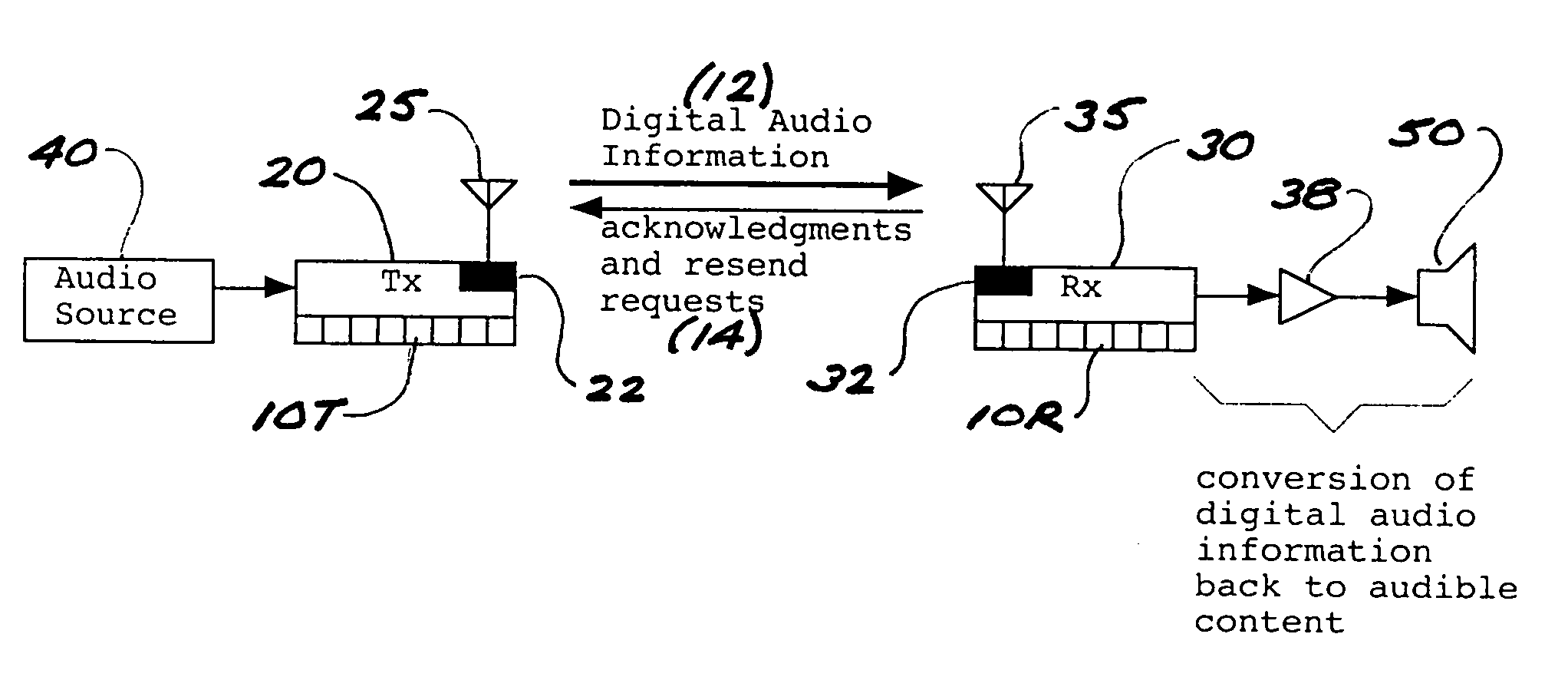
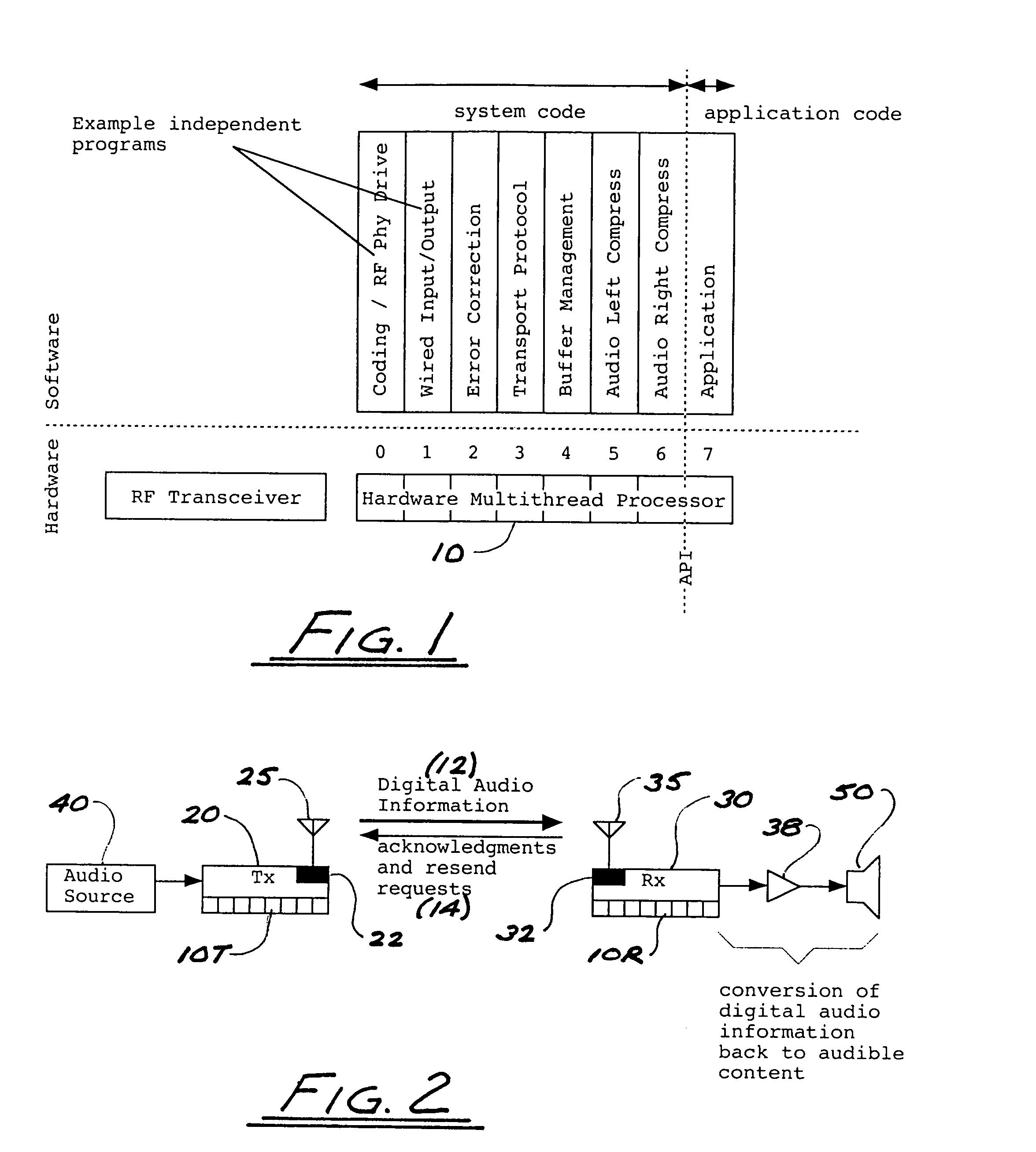
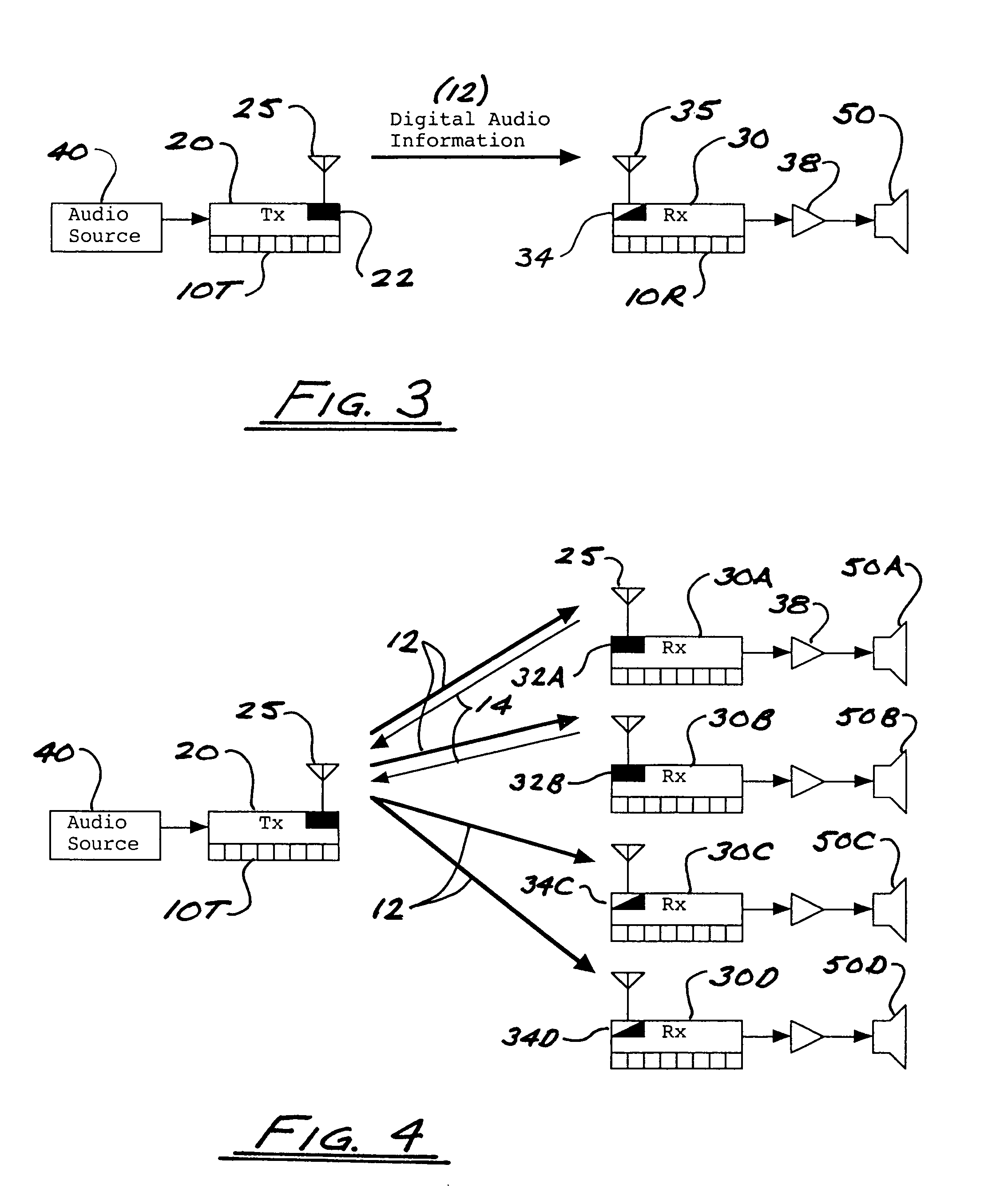
In a multi-channel digital wireless audio system with at least one transmit node and at least one receive node, each node can both receive and transmit digital audio signals. Signals sent from a receive node to a transmit node may acknowledge satisfactory signal receipt, or may requesting retransmission of data packets received in a corrupted state. Original and retransmitted signals may be sent in compressed form to enable use of narrow-band digital radios. The system preferably incorporates a dual control channel to enable transmission of meta data. Each system node preferably incorporates a hardware-multithreaded processor adapted to implement various functions such as baseband functions, RF protocol functions, error correction functions, and audio processing functions, with each independent thread being adapted to implement a different functional block.
Owner:ELEVEN ENG
Ad-hoc control protocol governing use of an unlicensed or shared radio frequency band
InactiveUS6882851B2Spectrum efficiency is improvedMore reliable and enjoyableNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumOrganizational control
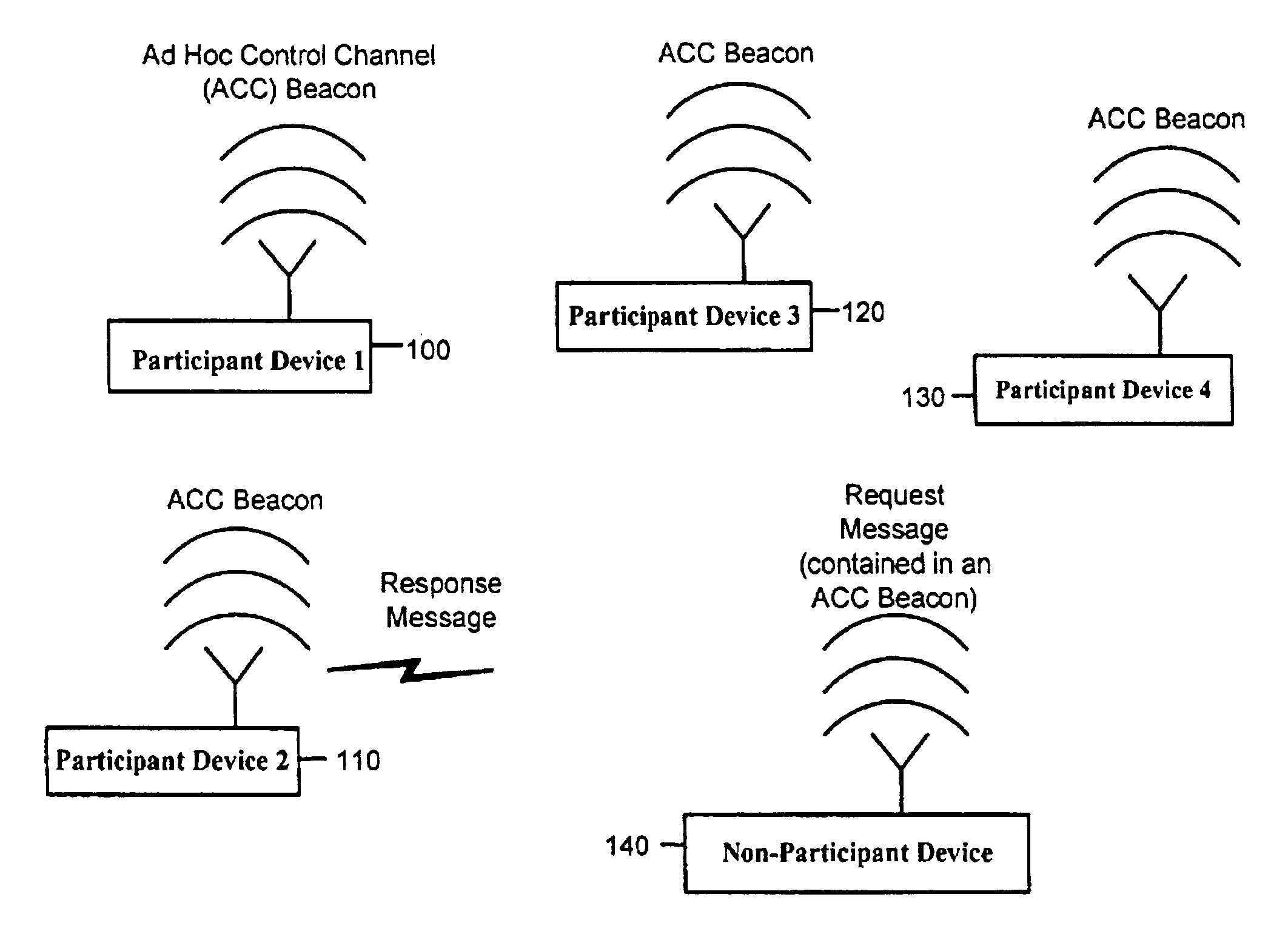
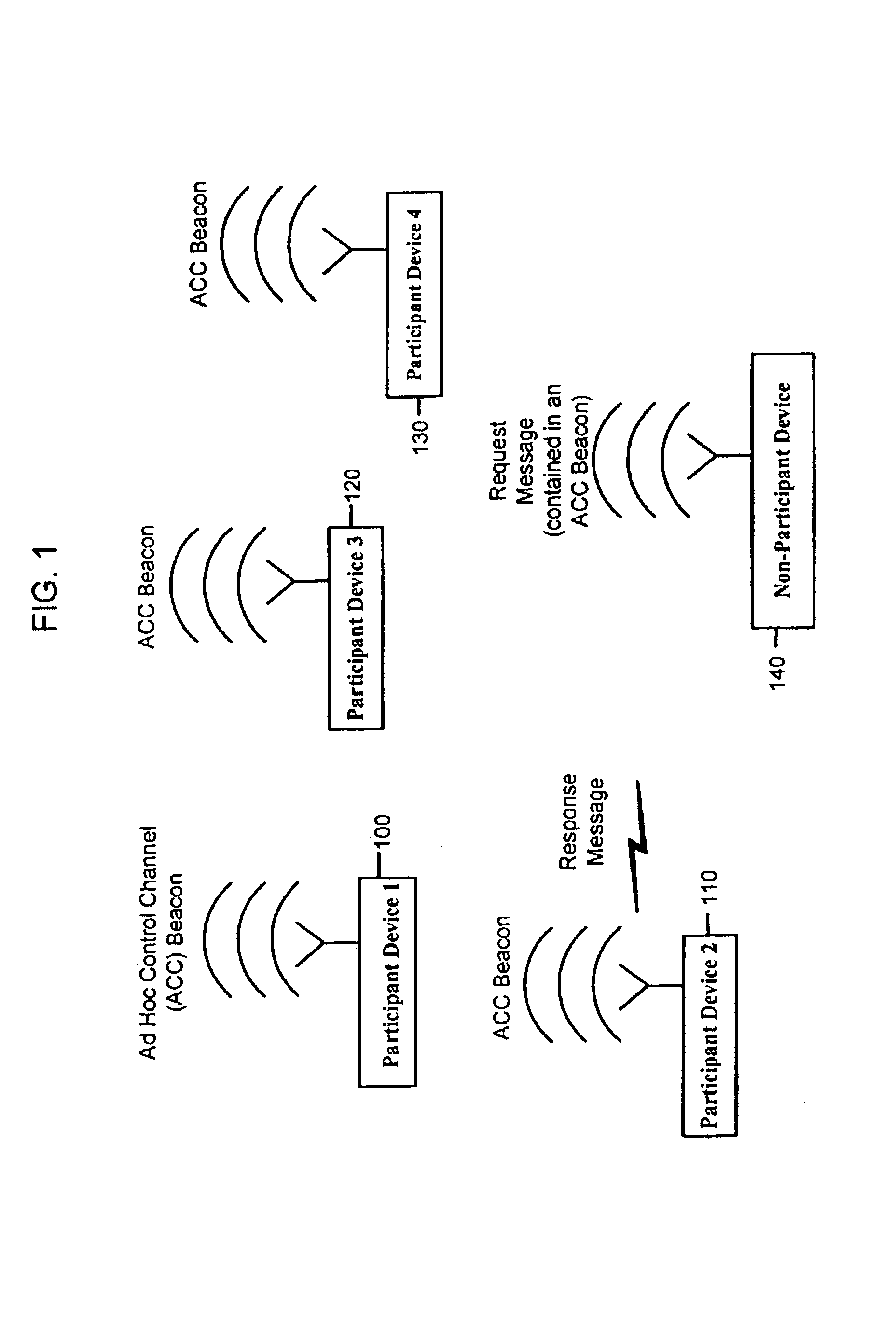
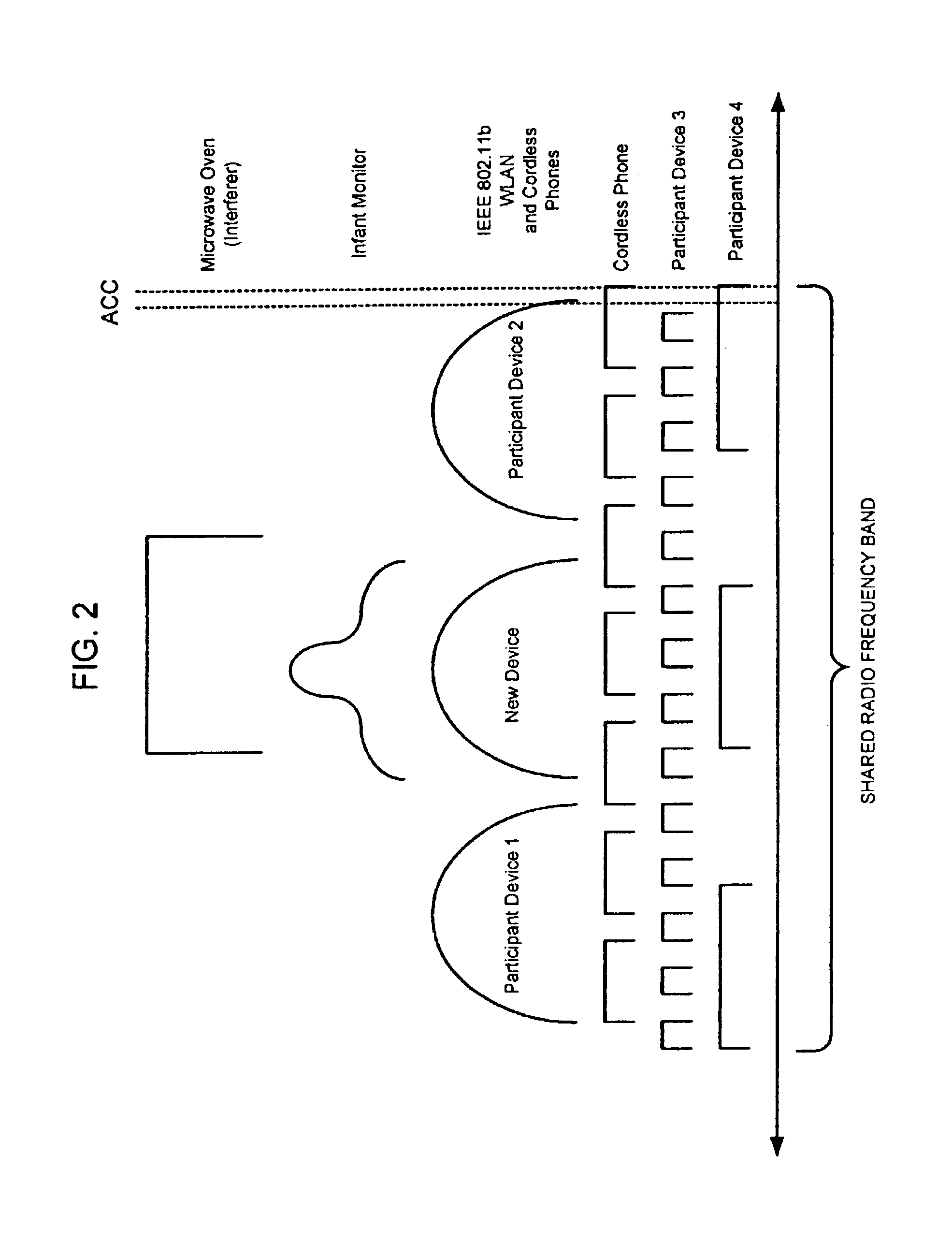
Systems and methods to enable different types of radio communication devices to communicate using a common language in order to enable the devices to regulate their use of the spectrum. Each device participating in the ad hoc control channel (ACC) protocol transmits information using a common signal format that each of the other participant devices is capable of recognizing, in order to share information about how it uses the radio frequency band. Each device receives the information transmitted by other participant devices and based on that information, controls one or more of its operational parameters that impact usage of the radio frequency band. The ACC protocol enables devices of the same or different type to harmonize (instead of alienate) themselves with each other by allowing them to communicate about their usage of the radio frequency band using a common signaling framework. Improvement can be achieved in spectrum efficiency and ultimately provide a more reliable and enjoyable experience for the end user of a device that operates in that radio frequency band.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for securing quality of communication service to mobile terminal
InactiveUS20050042987A1Minimum quality of serviceNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadcast service distributionQuality of serviceCommunications system
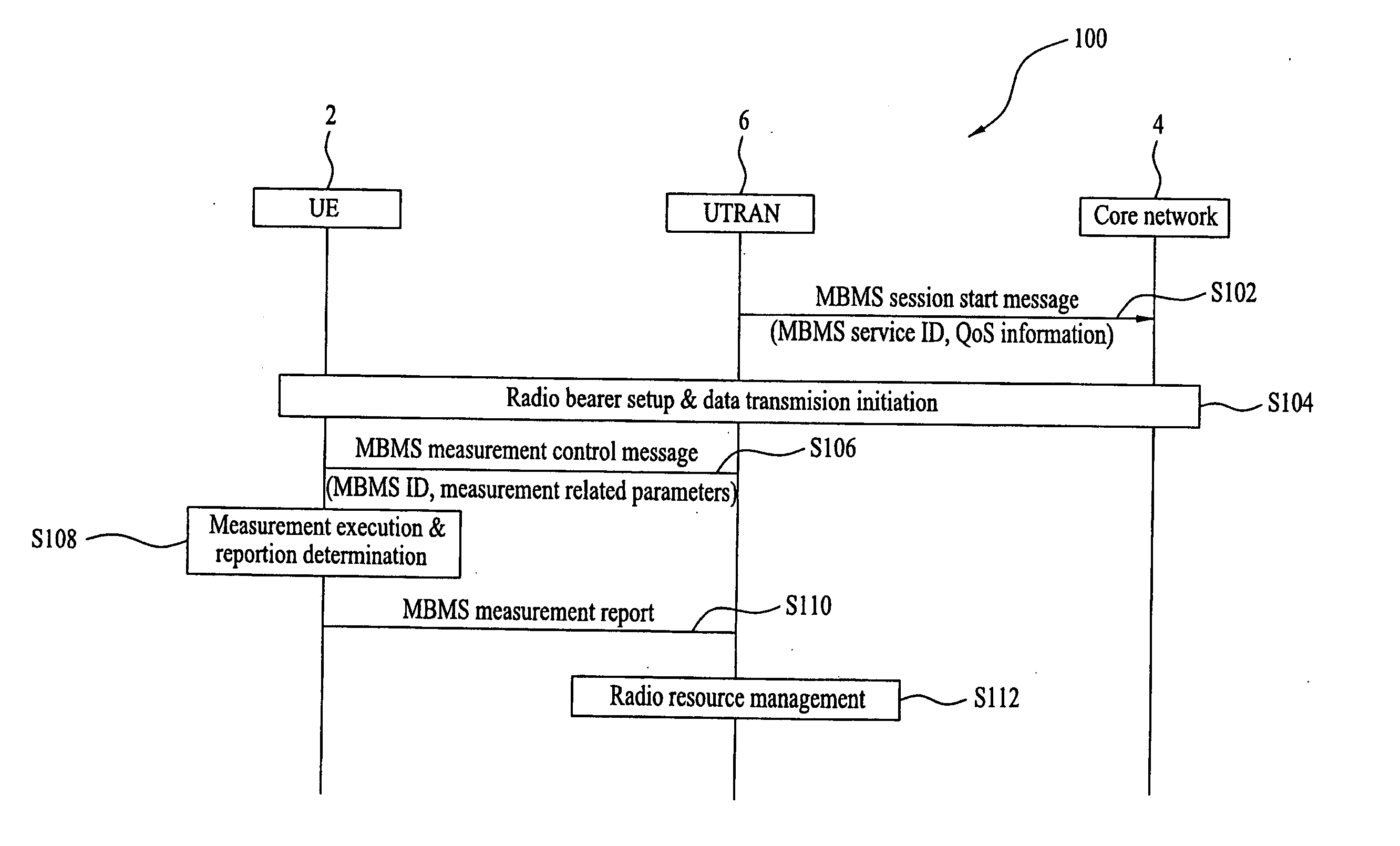
A method and apparatus is provided for securing a quality of service of packet data service provided in a communication system by enabling mobile terminals that receive the packet data service in the RRC-idle mode to provide information to the network regarding the quality of the received service. A mobile receiving a specific service, for example MBMS, may provide information related to the quality of the received service or the results of measurements performed to determine the quality of the received service to a network via a common control channel either in response to a measurement request from the network or if the mobile terminal determines that the quality of the received service is below a minimum quality of service to be secured.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
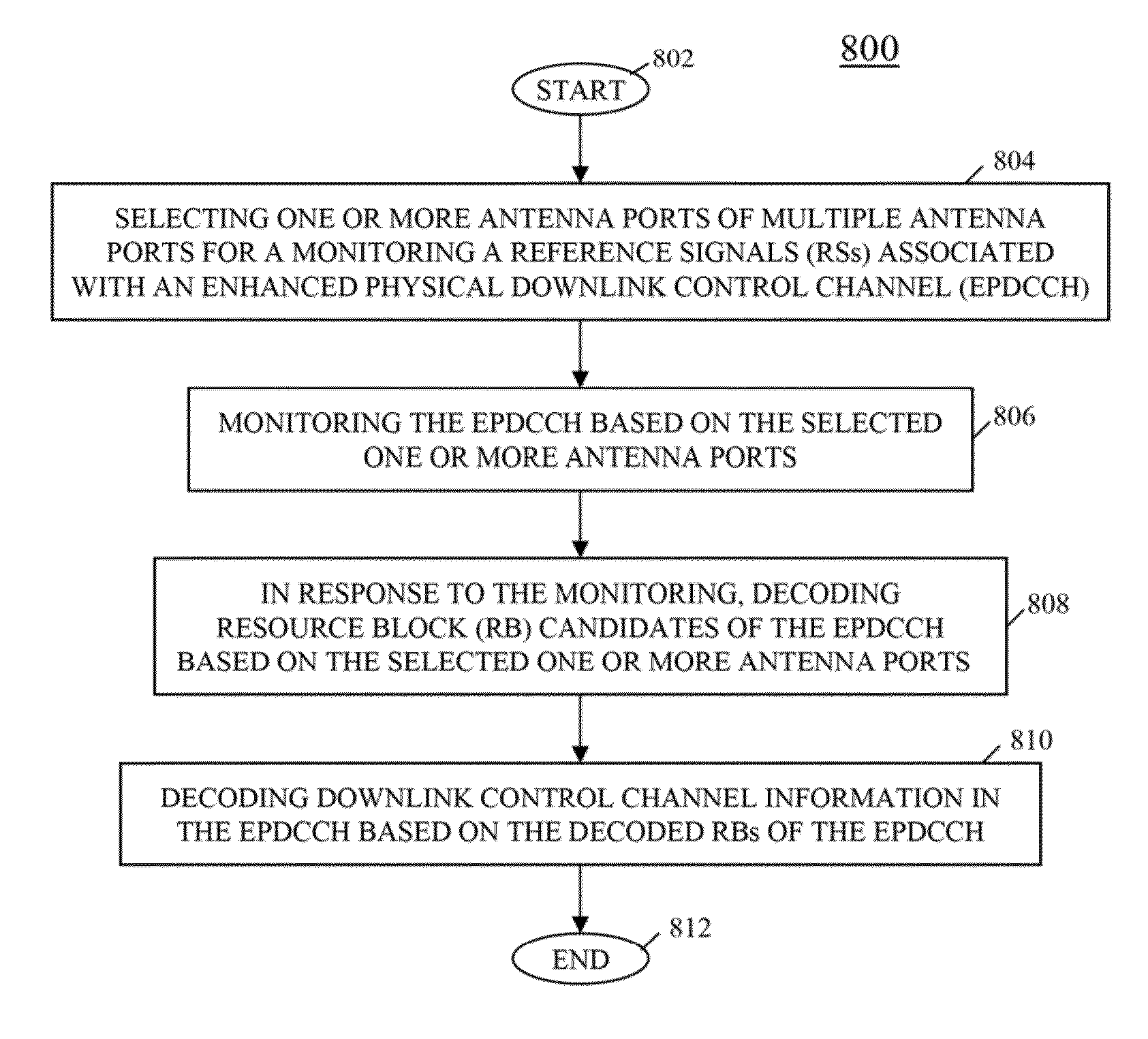
Method and apparatus for control channel transmission and reception
A user equipment (UE) receives a signal comprising multiple resource blocks and configured for receiving a subframe comprising multiple time-frequency resources, the time-frequency resources comprising at least two control channel candidates. The UE determines a first control channel candidate of the at least two control channel candidates in the subframe, determines a first antenna port (AP) associated with the first control channel candidate, decodes the first control channel candidate based on the first AP, determines a second control channel candidate of the at least two control channel candidates in the subframe, determines a second AP associated with the second control channel candidate, and decodes the second control channel candidate based on the second AP, wherein the AP used for decoding the first control channel candidate is distinct from the AP used for decoding the second control channel candidate.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
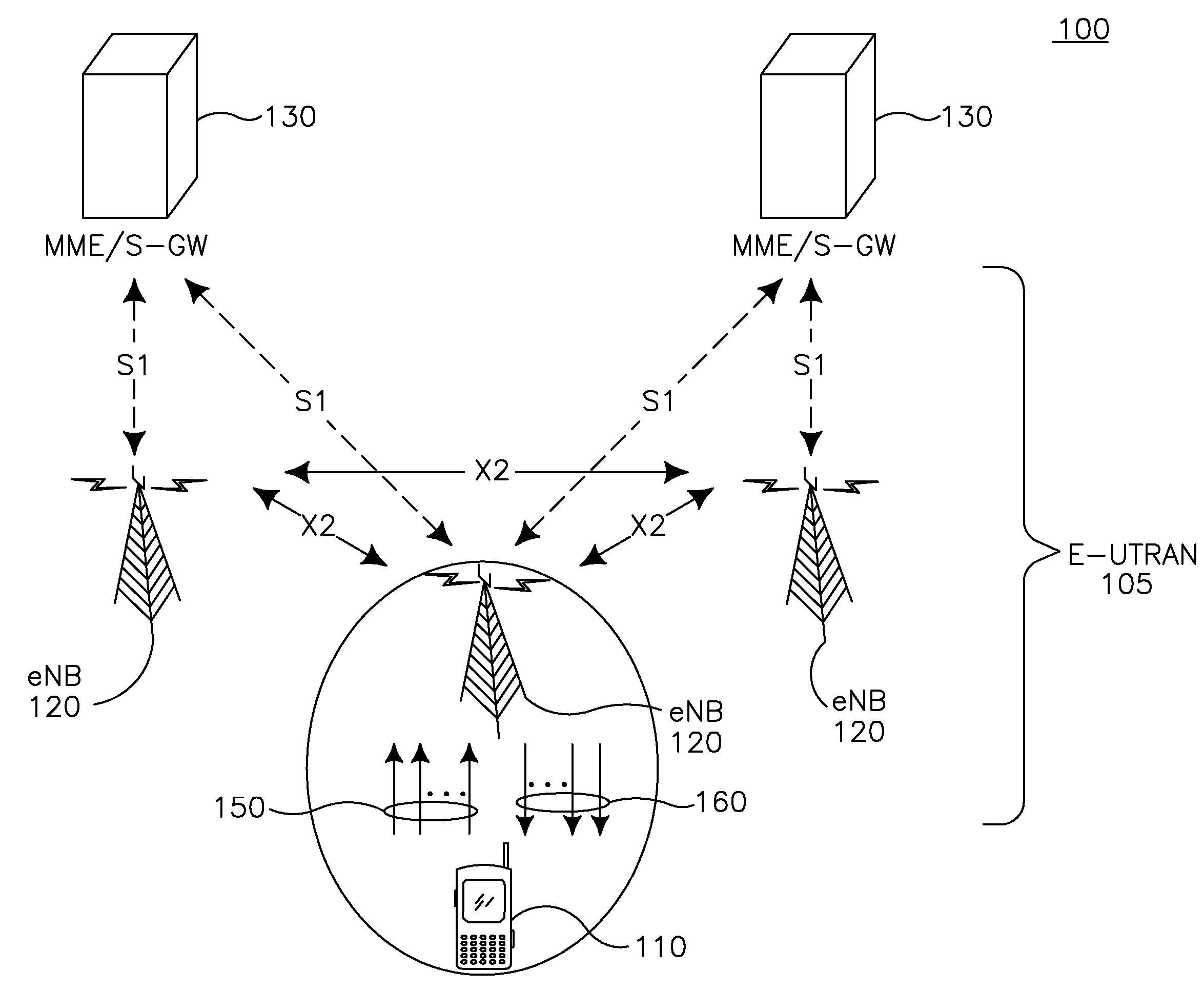
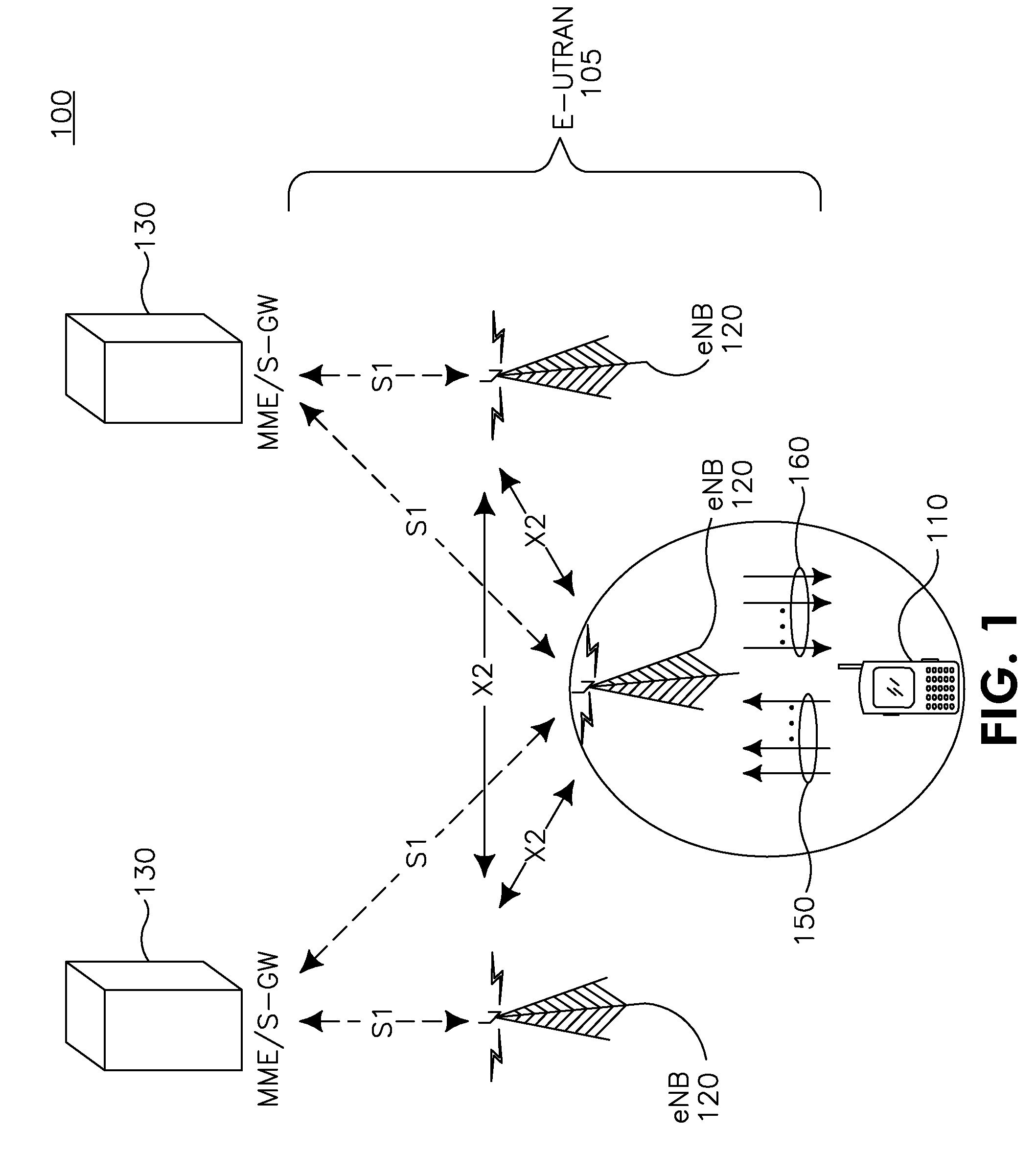
Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power
InactiveUS8918135B2Accurate powerReduce calculationPower managementSite diversityUplink transmissionControl channel
The present description relates to a method for controlling uplink power in a distributed multi-node system, comprising the following steps: receiving reference signals from a plurality of antenna nodes containing at least one antenna; estimating average propagation loss on the basis of the receiving power of the reference signals received from the plurality of antenna nodes; receiving, via a downlink control channel, noise and interference (NI) information from a base station which contains the plurality of antenna nodes; and determining uplink transmission power using the estimated average propagation loss and the received noise and interference information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Dynamic resource allocating method and apparatus, base station, terminal
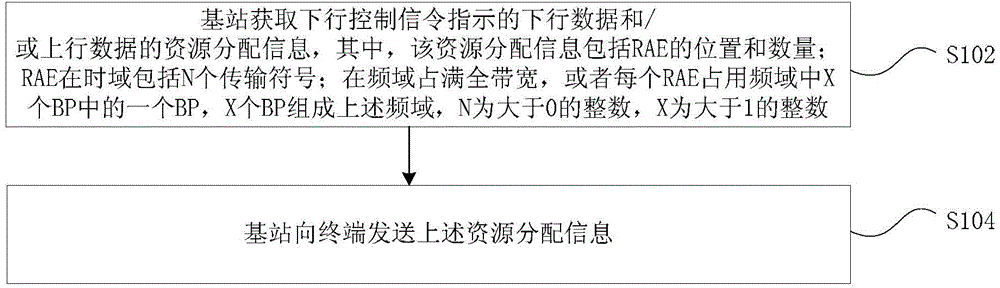
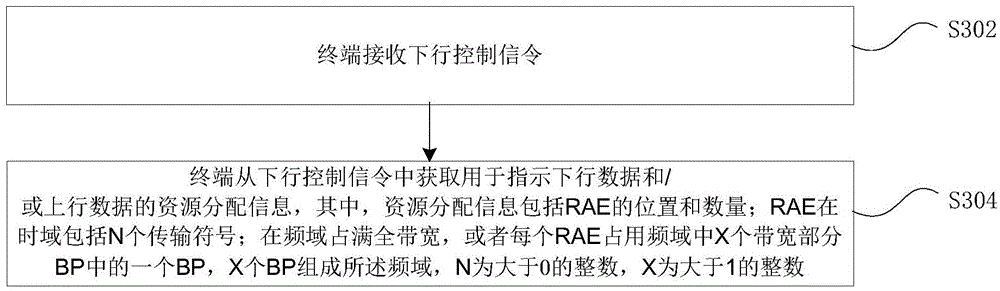
ActiveCN105099634ASolve problems such as high costReduce overheadTransmission path divisionSignal allocationTime domainDynamic resource
Provided are a dynamic resource allocation method and device, a base station and a terminal. The method comprises: a base station acquiring resource allocation information about downlink data and / or uplink data indicated by downlink control signalling, wherein the resource allocation information comprises the location and number of resource allocation elements (RAEs); the RAEs comprise N transmission symbols in a time domain; and the RAEs completely occupy the full bandwidth in a frequency domain, or each RAE occupies one BP among X bandwidth parts (BPs) in the frequency domain, the X BPs forming the frequency domain, where N is an integer greater than 0, and X is an integer greater than 1; and the base station sending the resource allocation information to a terminal. By means of the technical solution provided in the present invention, the problems in the related art that it is not possible to use an LTE control channel to schedule uplink and downlink services of a plurality of transmission symbols on a high-frequency carrier and the transmission of uplink services, and that the overhead of control signalling is relatively high in a network independently networked by an LTE carrier and the high-frequency carrier and the like are solved, thus achieving that the LTE carrier schedules the high-frequency carrier across carriers.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Reuse of a physical control channel in a distributed cellular radio communication system
InactiveUS6108550AReduce generationIncrease capacityTransmission control/equalisingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular radioCommunications system
The present invention relates to the reuse of a control channel in a distributed cellular radio communication system. At least one physical channel, the so called physical control channel, in the radio communication system is used for transferring logical control channels. According to the present invention the physical uplink control channel can be reused with respect to logical control channels comprising an access request. The physical downlink control channel can be reused with respect to logical control channels comprising a message that access is granted to a mobile station or a message that someone requests contact with a mobile station. According to the invention the physical uplink control channel and / or the physical downlink control channel is reused. This means that more connections per time unit may be established in the radio communication system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Spanning tree root selection in a hierarchical network
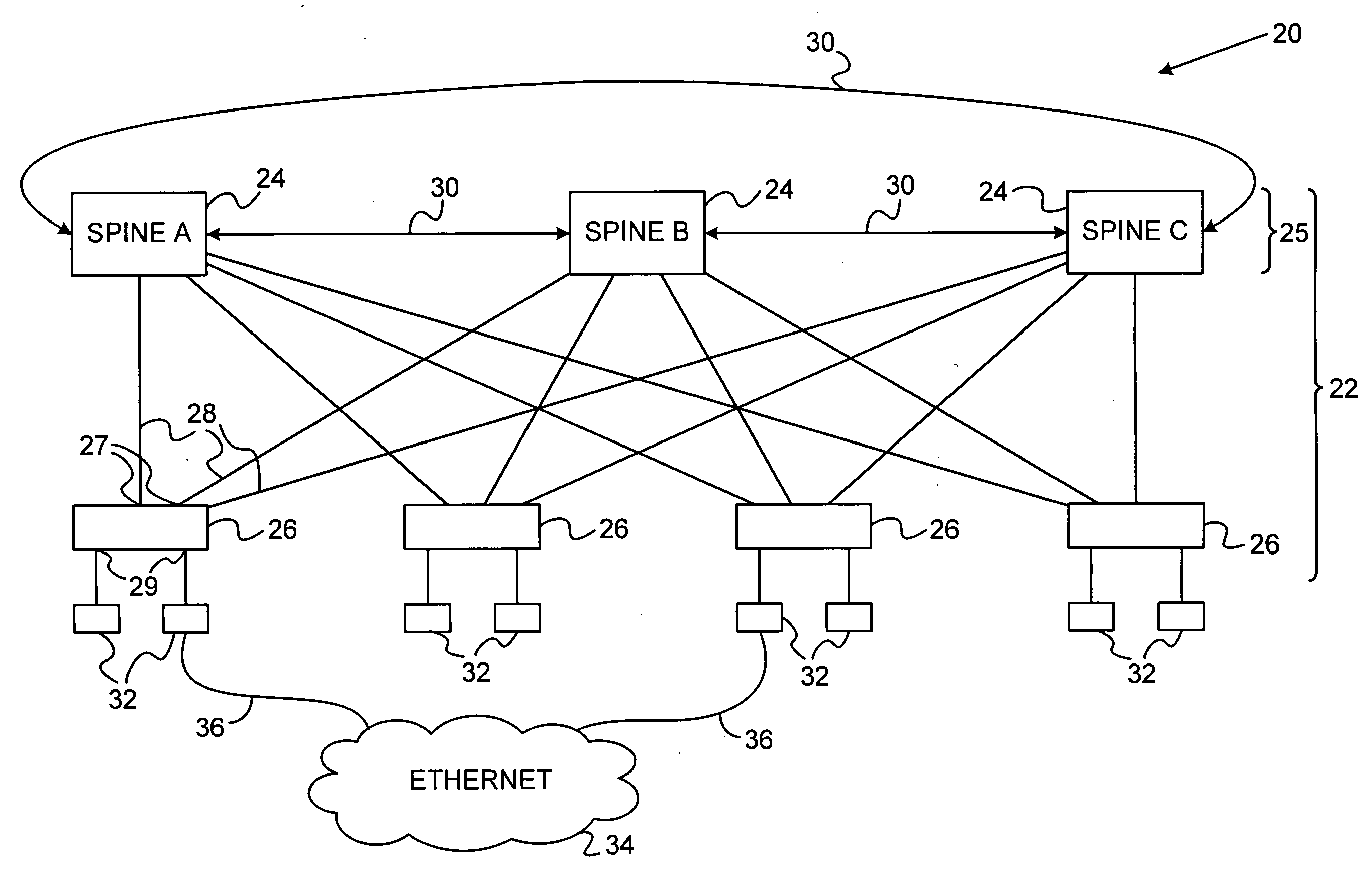
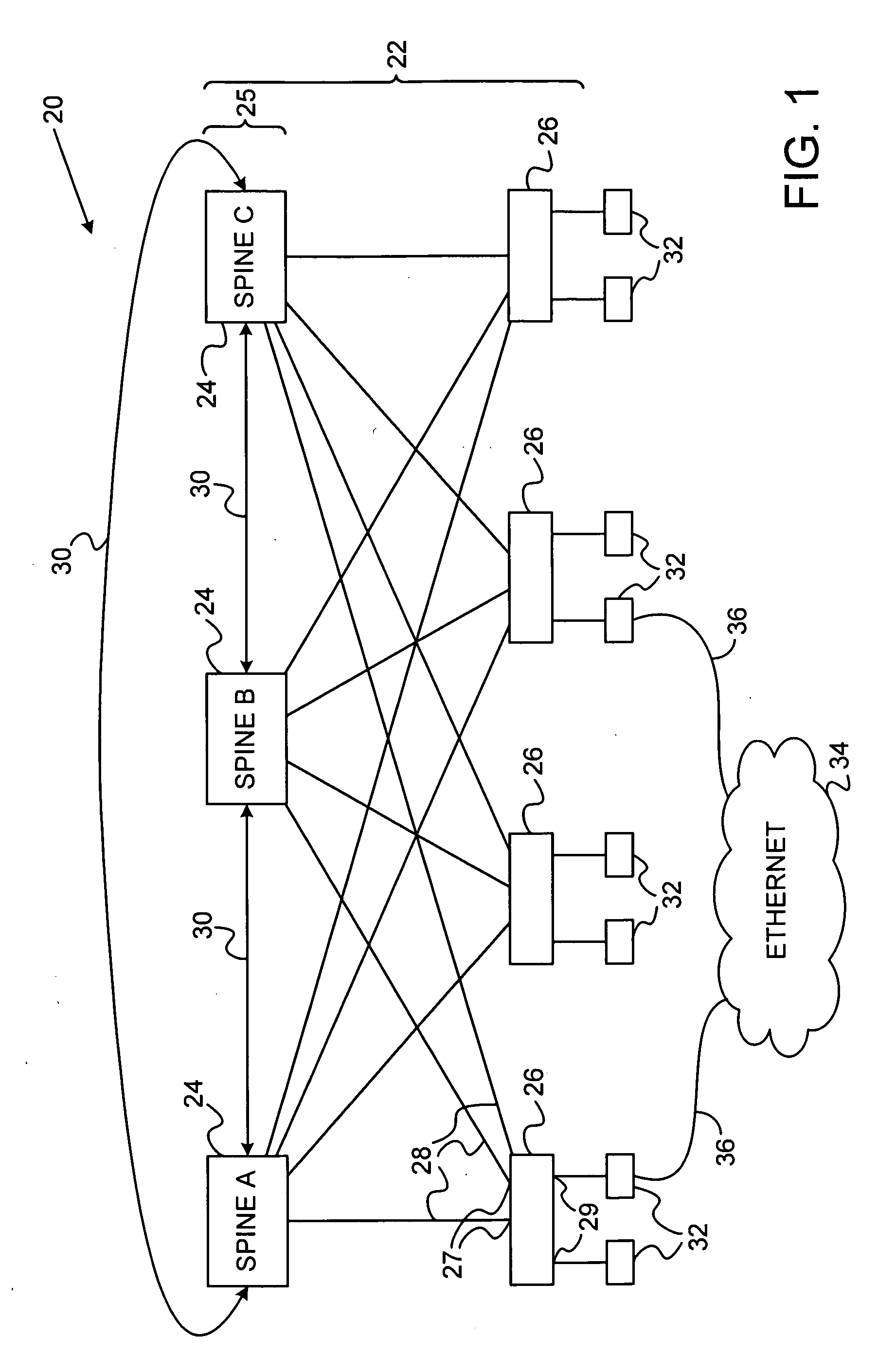
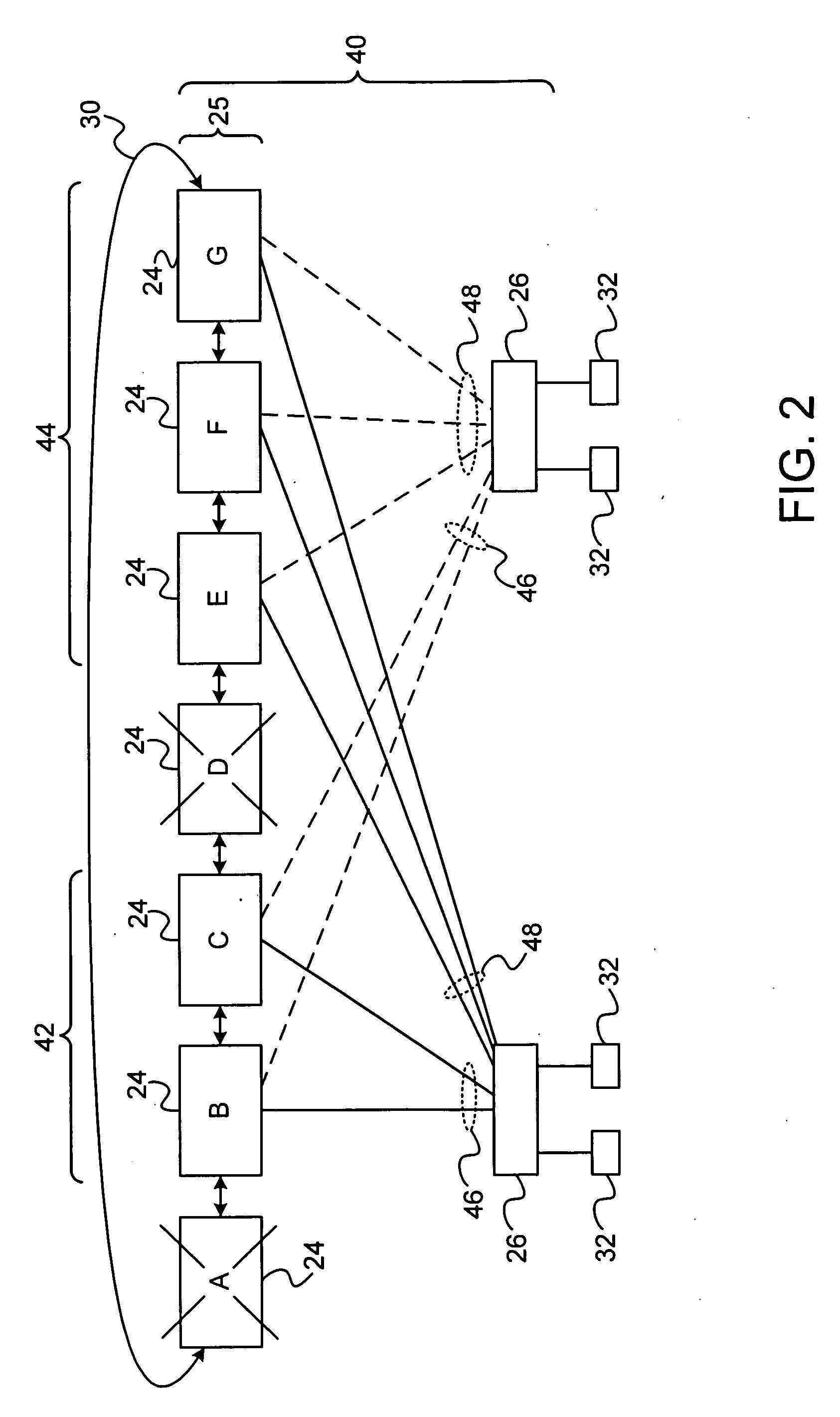
Communication apparatus includes a hierarchical network of switches, which includes at least a first plurality of spine switches, interconnected by a control channel, and a second plurality of edge switches having internal ports coupled to communicate via respective links with the spine switches and external ports for connecting to client devices. The spine switches are configured to detect, via the control channel, a partitioning of the hierarchical network into first and second partitions, including respective first and second numbers of the spine switches, wherein the first number is greater than the second number, and to assign respective priorities to the spine switches responsively to the first and second numbers so as to cause the larger of the partitions to be elected as a spanning tree root.
Owner:MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Method and control channel for uplink signaling in a communication system
InactiveUS20050047393A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCommunications systemUplink transmission
In a method of transmitting control signals for uplink transmission of packet data in a communication network, control signal data related to scheduling a user for uplink transmission of packet data is transmitted over a single control channel. The single control channel may be configured based on the transmission mode the user is in for scheduling an uplink transmission from the user to the network, so that only one control channel is used, regardless of the transmission mode the user is in for scheduling the user for the uplink transmission. The control channel may be embodied as a sub-frame adapted to carry control information that is dependent based on the transmission mode the user is in for scheduling an uplink transmission from the user to the network.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com