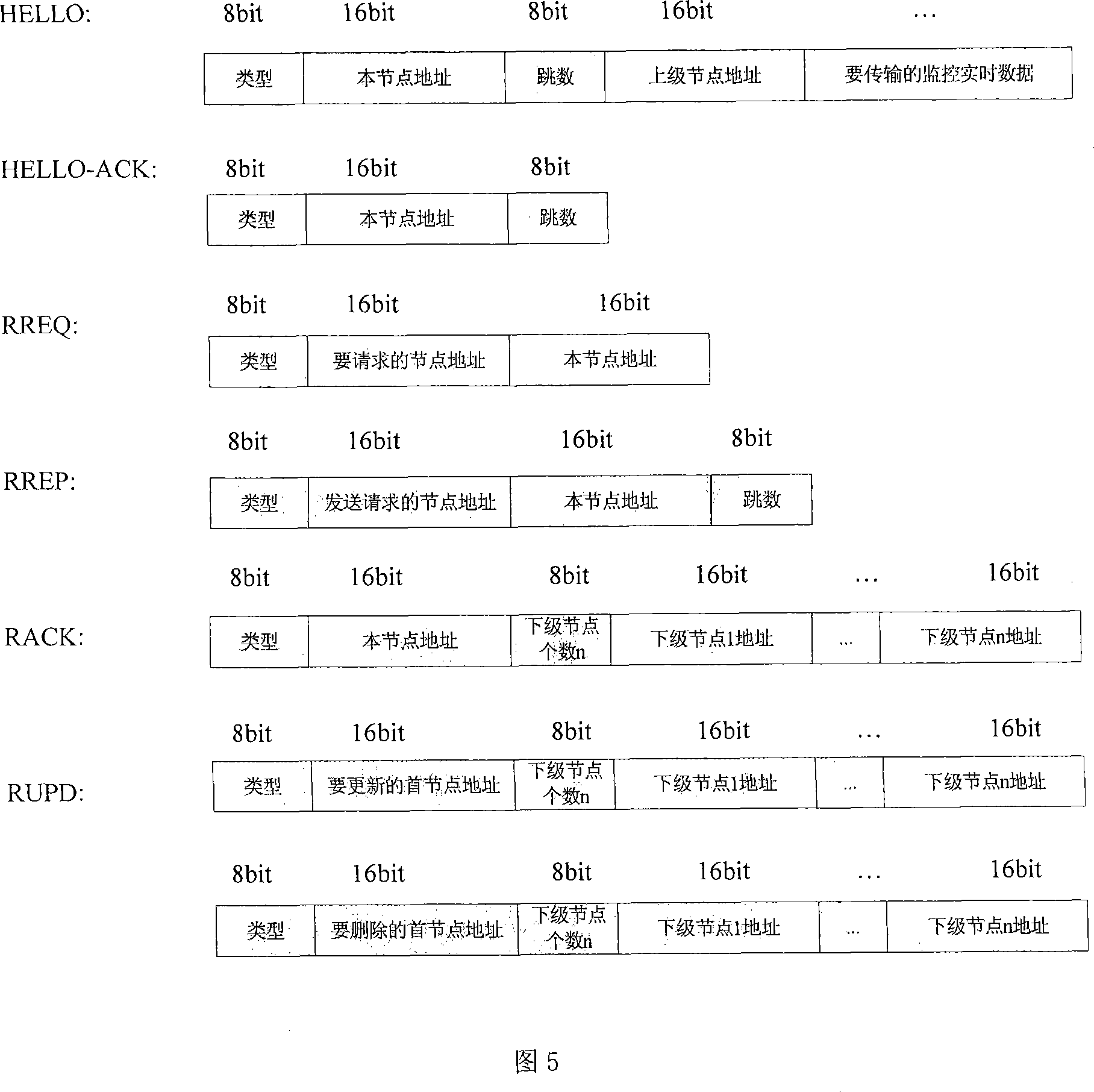Patents
Literature
1353 results about "Route" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
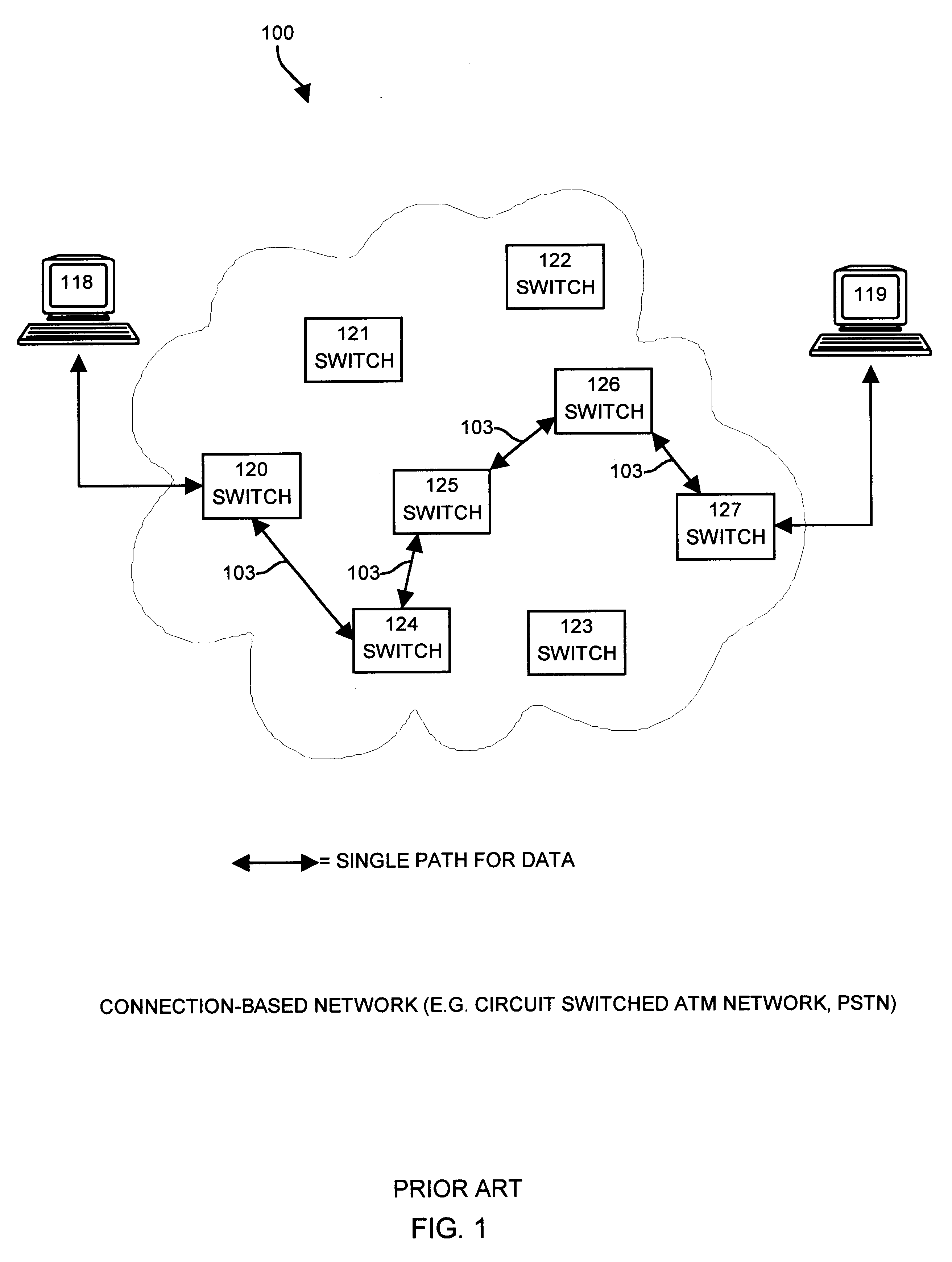
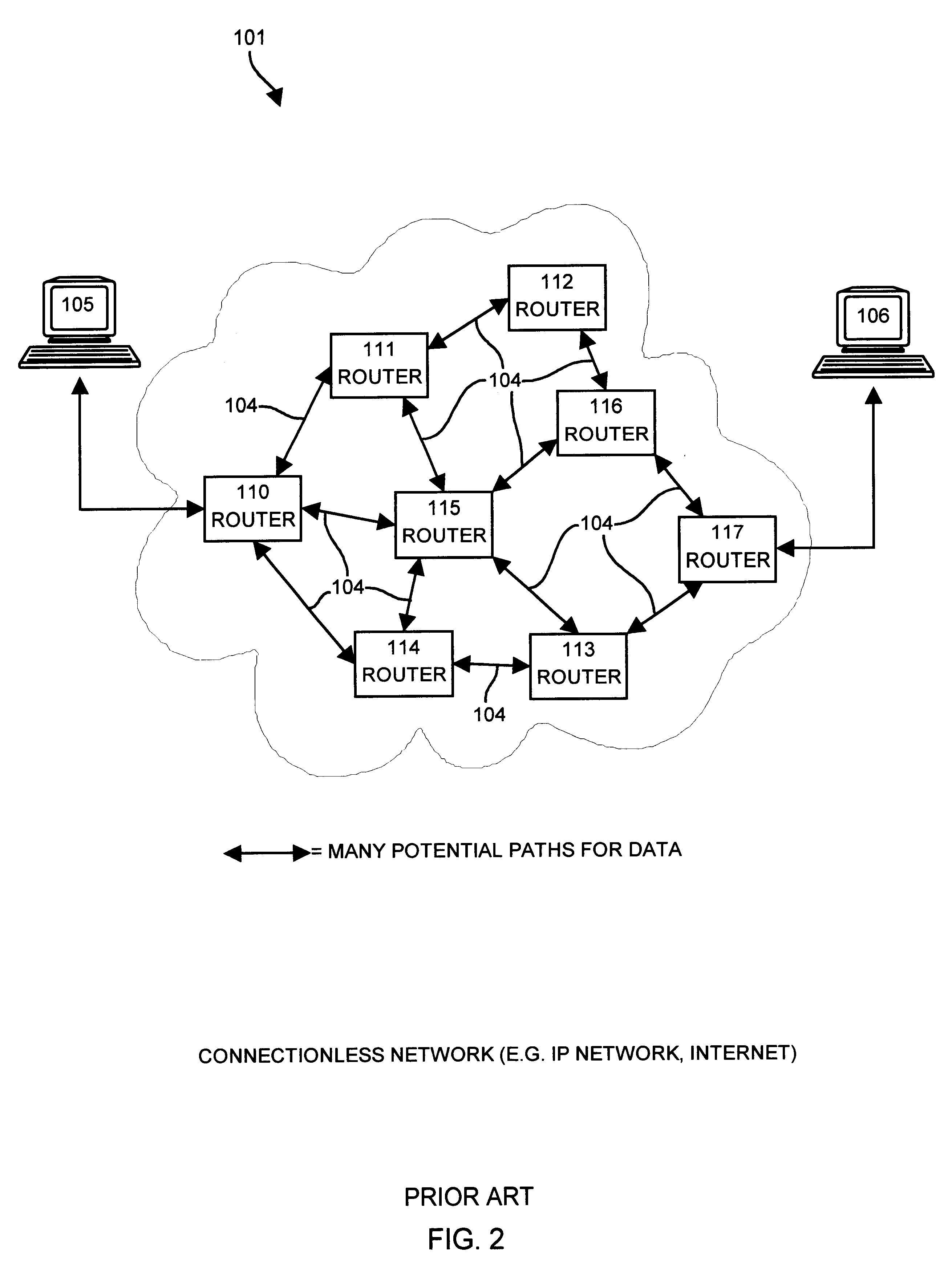
In computing, route is a command used to view and manipulate the IP routing table in Unix-like and Microsoft Windows operating systems and also in IBM OS/2 and ReactOS. Manual manipulation of the routing table is characteristic of static routing.
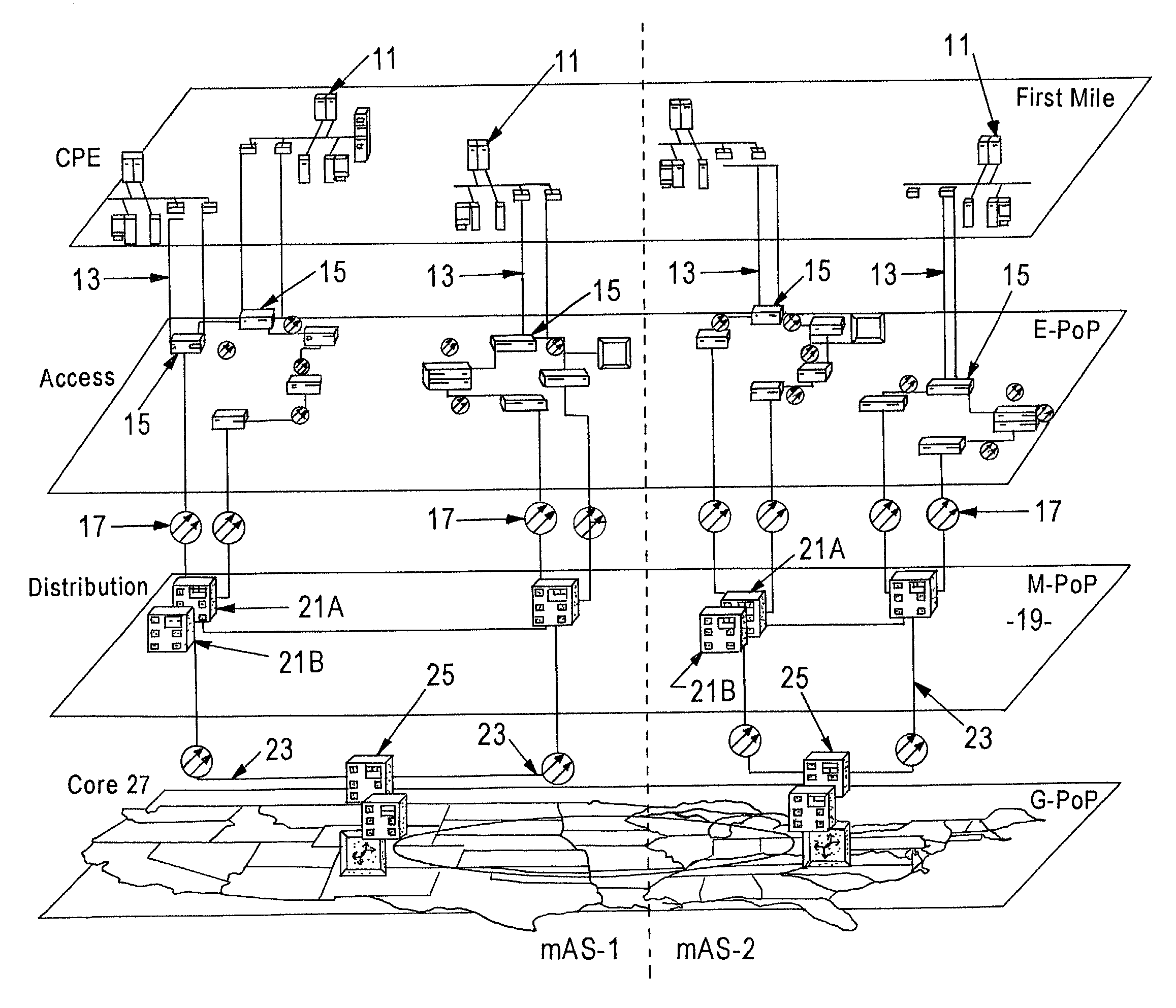
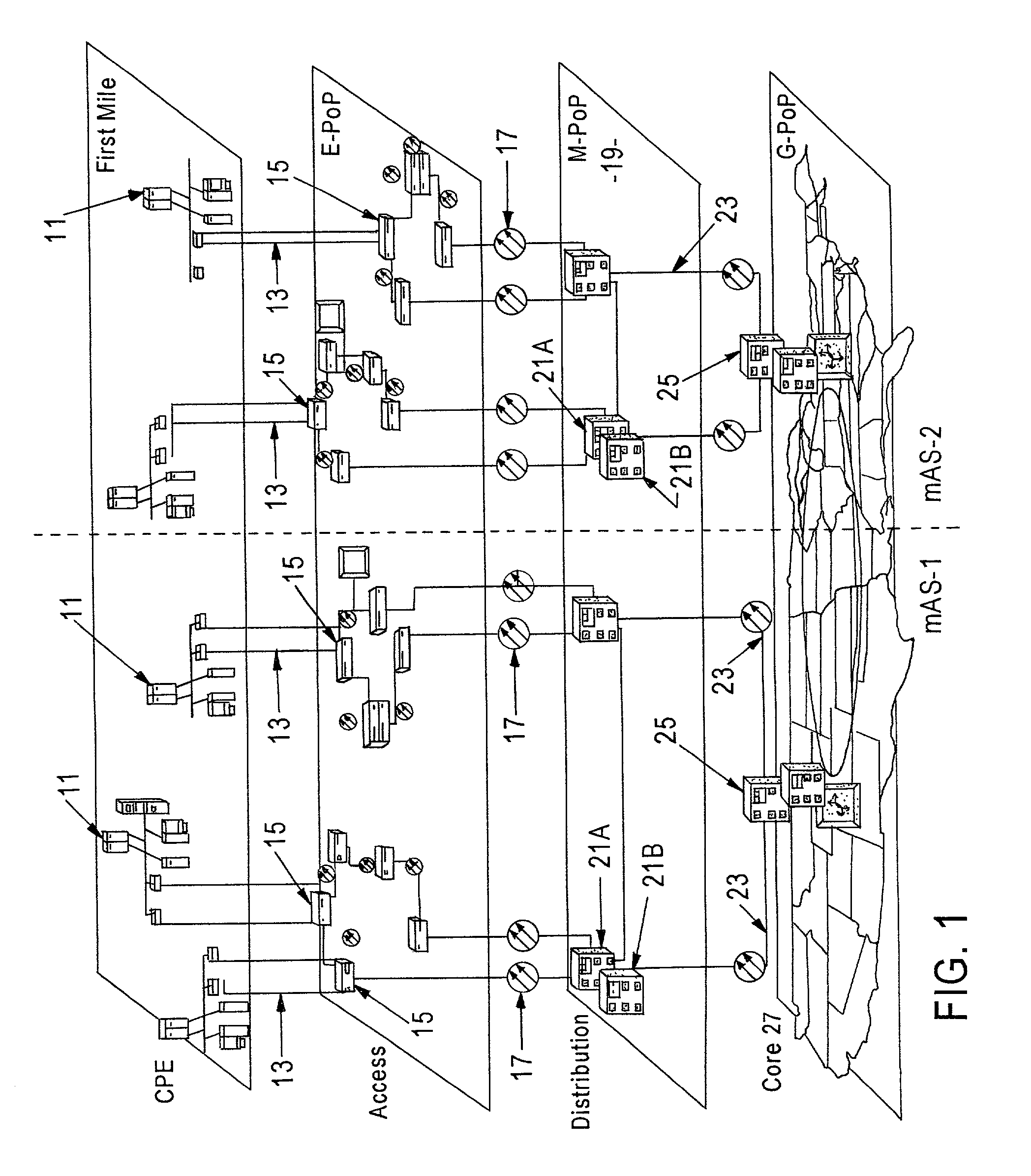
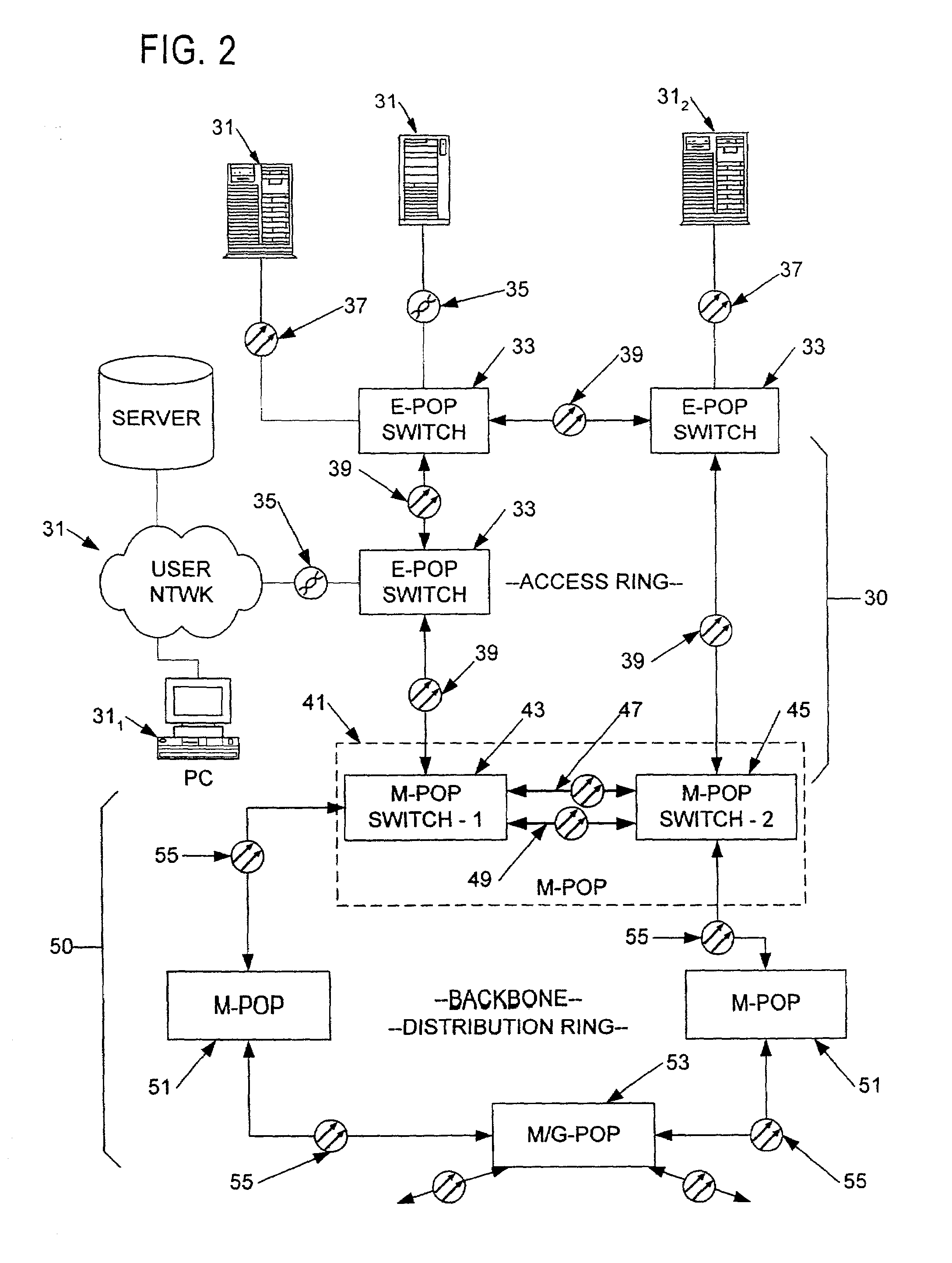
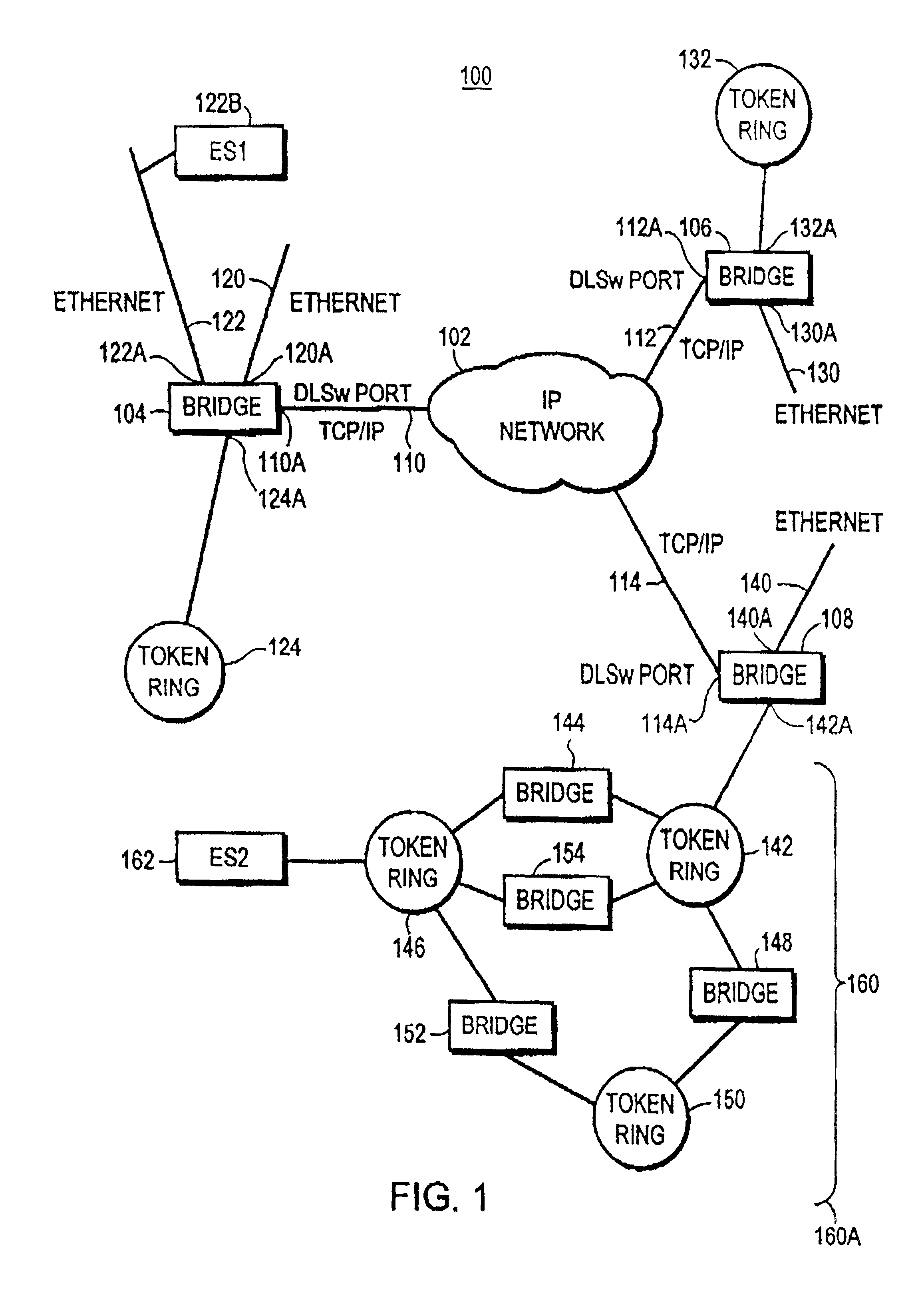
Enhanced data switching/routing for multi-regional IP over fiber network
InactiveUS6963575B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetworks interconnectionWide areaBorder Gateway Protocol
Wide-area data communications utilize regional networks transporting IP-over-Ethernet on fiber. For certain Layer 2 services, a regional implementation of the network makes limited use of spanning tree protocol on a backbone ring. Learning bridge operations in switches on associated access rings involve a short default for an aging timer. For use of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), the connection of each access ring to the backbone ring uses a pair of routers with dual links therebetween. One of these links is bonded to the backbone (OSPF Area 0), whereas the other link is bonded to the Area of the respective access ring. Also, certain routers within each regional network form a mini-autonomous system, for boundary gateway protocol (BGP). The mini-autonomous systems of the regional networks form a confederation. The network utilizes route reflectors in the mini-autonomous systems. The Internet carries confederation commands to and from a designated hub.
Owner:YIPES ENTERPRISE SERVICES
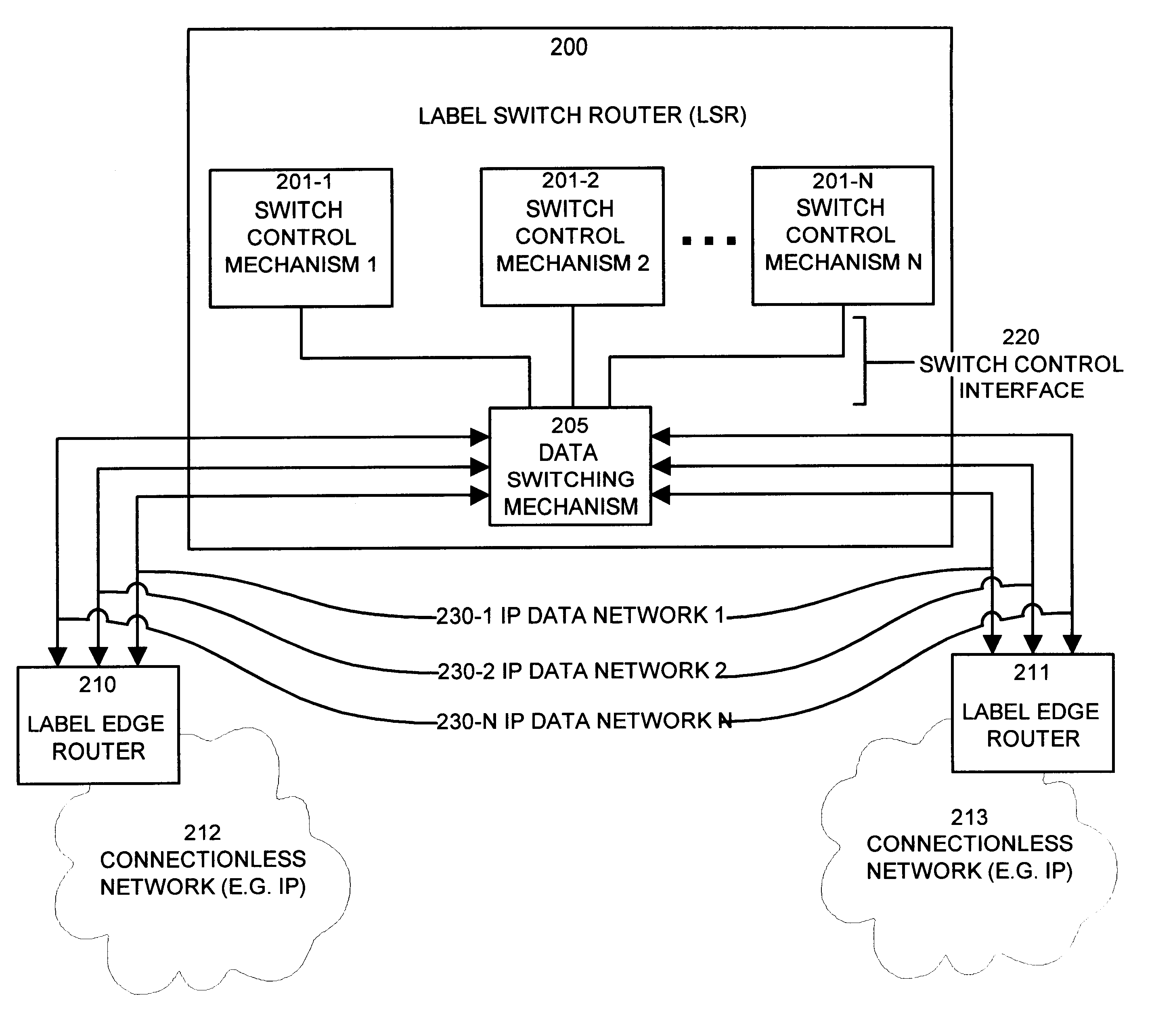
Apparatus and methods providing redundant routing in a switched network device
InactiveUS6628649B1Improve fault toleranceHigh degreeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationData transmissionData loss
The invention provides unique architectures and techniques for routing redundancy in a data switch configured to use label switching. Multiple label switch controllers (LSCs) each operate concurrently but independently of each other to provide routes through a data switching mechanism. Preferred embodiments provide a plurality of LSCs offering MPLS capabilities coupled to a single switch, such as an ATM switch. The similarly configured LSCs each can concurrently support a route for data (e.g., labeled ATM cells) within the data switching mechanism in parallel, thereby providing the ability to support redundant and multiple parallel data networks. The configuration is called a label switch router (LSR). A fully-meshed embodiment allows selected routes to share bandwidth on ports, while a fully parallel embodiment provides separate ports for selected routes. Since each LSC provides parallel routes with the other LSCs in an LSR, a communications between an LSR and a label edge router (LER) can use multipath routing to concurrently distribute data equally across the parallel routes for each destination. Alternatively, unipath routing techniques can select one route for use for each destination from the available routes concurrently offered by each LSC. In the event of a failure of one of the LSCs, multipath routing implementations can exclude transmission of data onto the failed network, while continuing to use the other parallel networks supported by non-failed LSCs in a concurrent manner. Alternatively, if a failure occurs with unipath routing, a new route offered by another LSC can be selected for data transfers. In either case, the LSC that fails does not need to provide state or connection information to the LSCs that operate subsequently to the failure, since they are already configured in parallel to support the same route. Upon an LSC failure, switch resources such as bandwidth that were used by the failed LSC are made available to the remaining non-failed LSCs. The design allows failures are handled gracefully without diminished network capacity or data loss resulting in a highly reliable routing capability provided within connection-based or circuit-switched networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
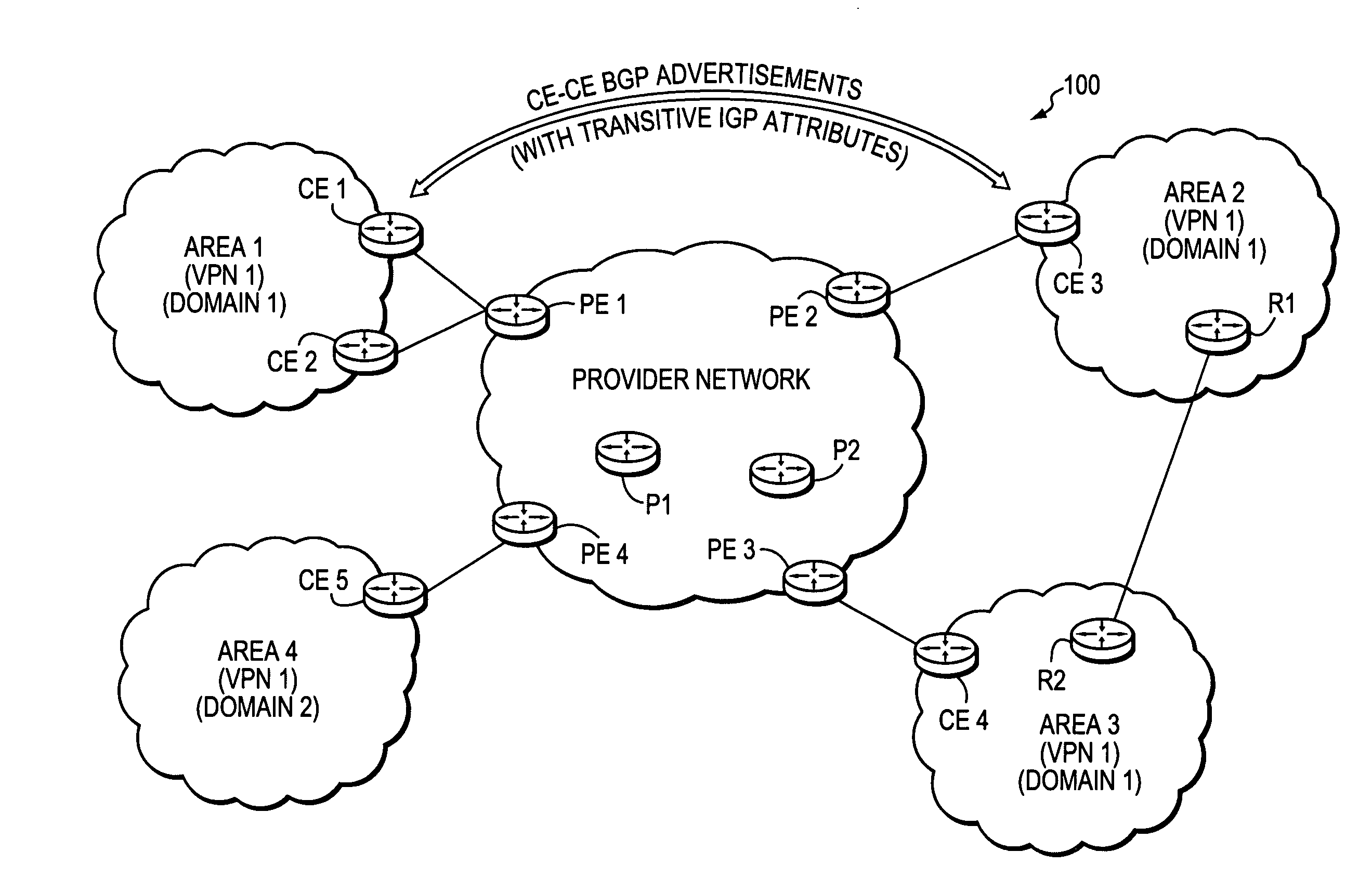
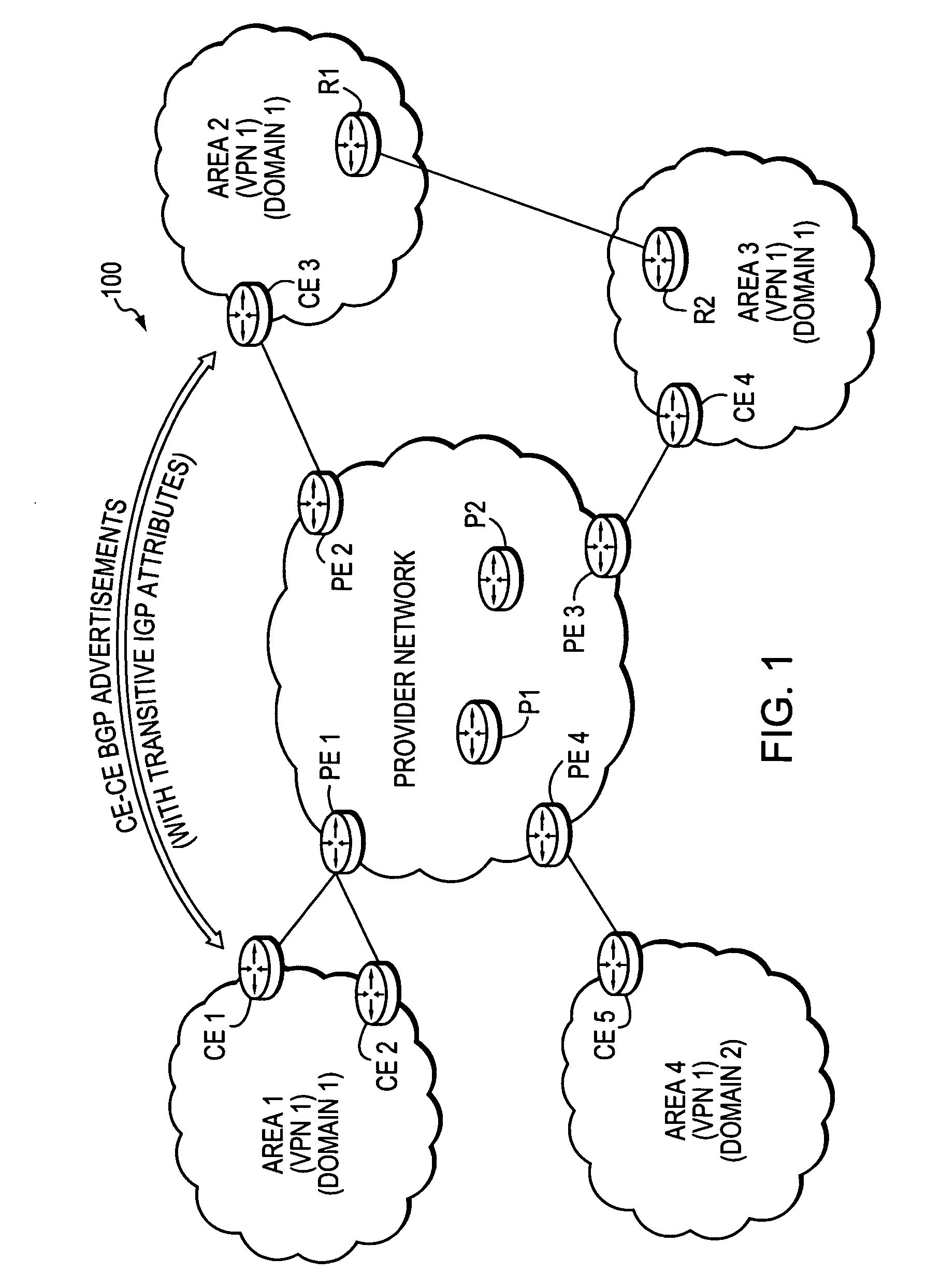
Maintaining IGP transparency of VPN routes when BGP is used as a PE-CE protocol
InactiveUS20070260746A1Maintains IGP transparencyReduce needDigital computer detailsNetwork connectionsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessNovel technique
A technique maintains Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) transparency of Virtual Private Network (VPN) routes when Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is used as a Provider Edge Device (PE) to Customer Edge Device (CE) protocol in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a first CE generates a BGP advertisement to advertise one or more VPN routes of its customer network, the BGP advertisement having one or more transitive IGP attributes for the advertised routes. The first CE sends the BGP advertisement to a first PE, which then propagates the BGP advertisement among devices of a provider network maintaining the transitive IGP attributes. A second PE sends the BGP advertisement to a second CE, along with the transitive IGP attributes. Upon receiving the BGP advertisement, the second CE converts the BGP advertisement and transitive IGP attributes into corresponding IGP advertisements. The second CE may then propagate the IGP advertisements into its customer network as either internal VPN routes or as external routes accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
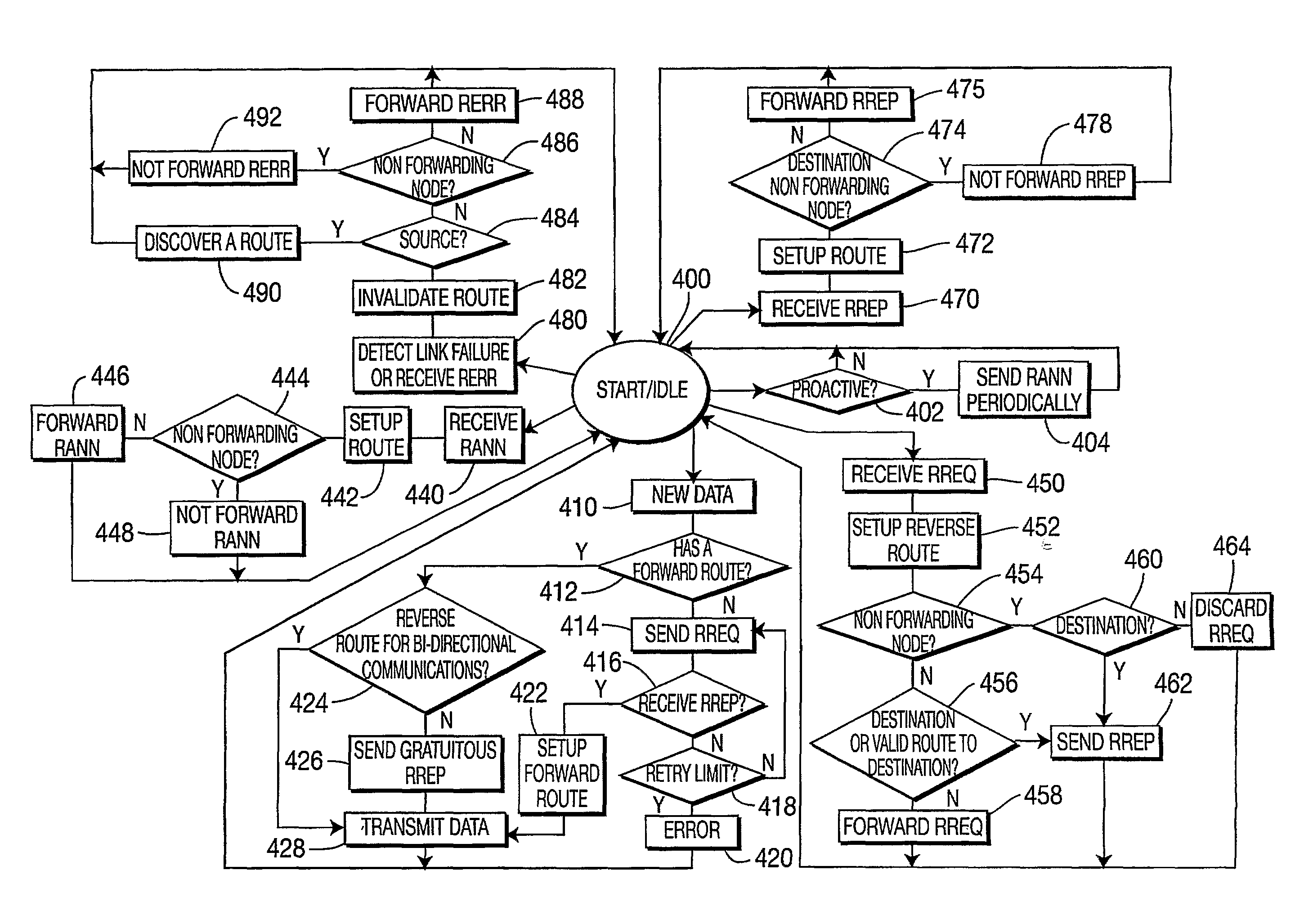
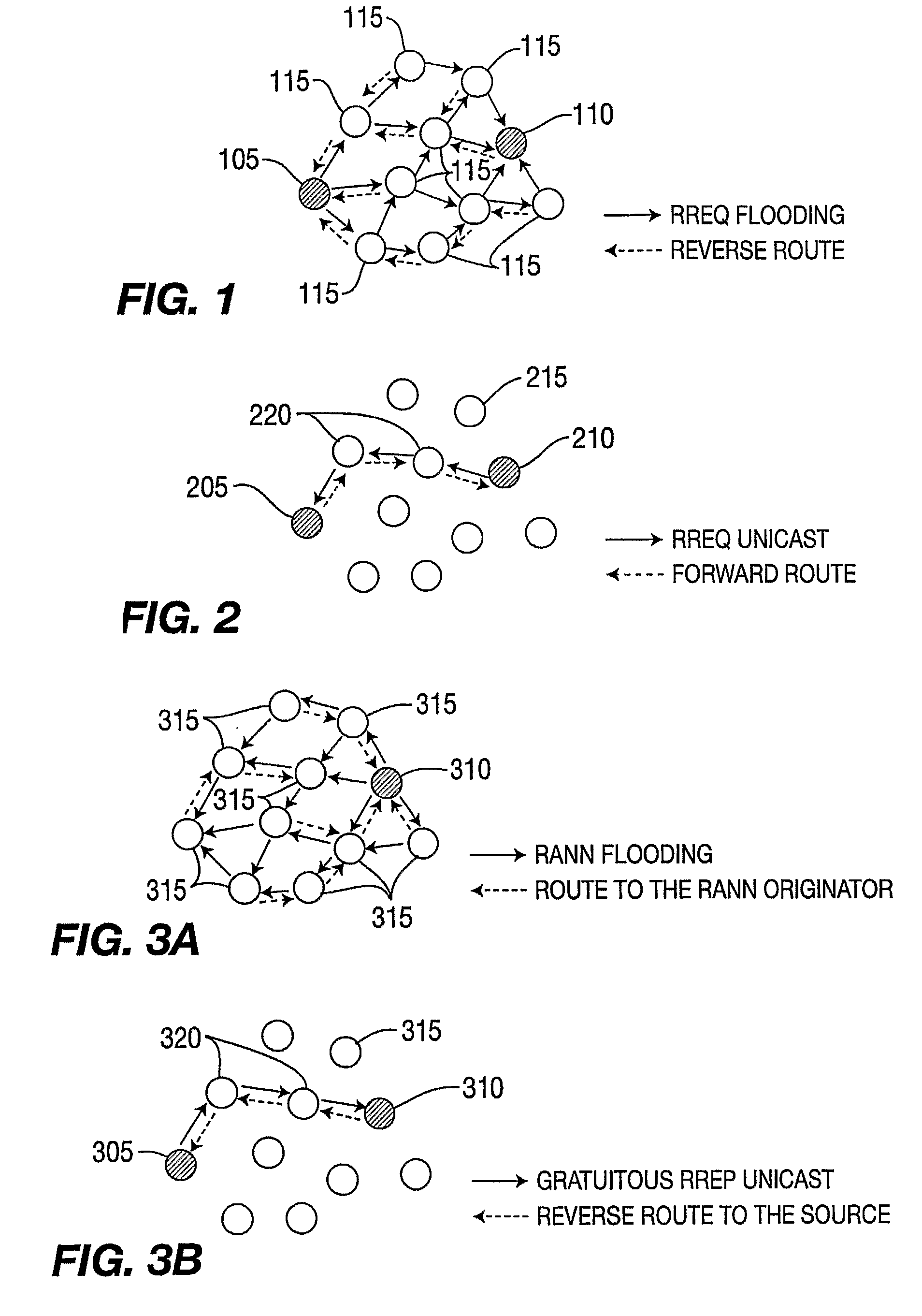
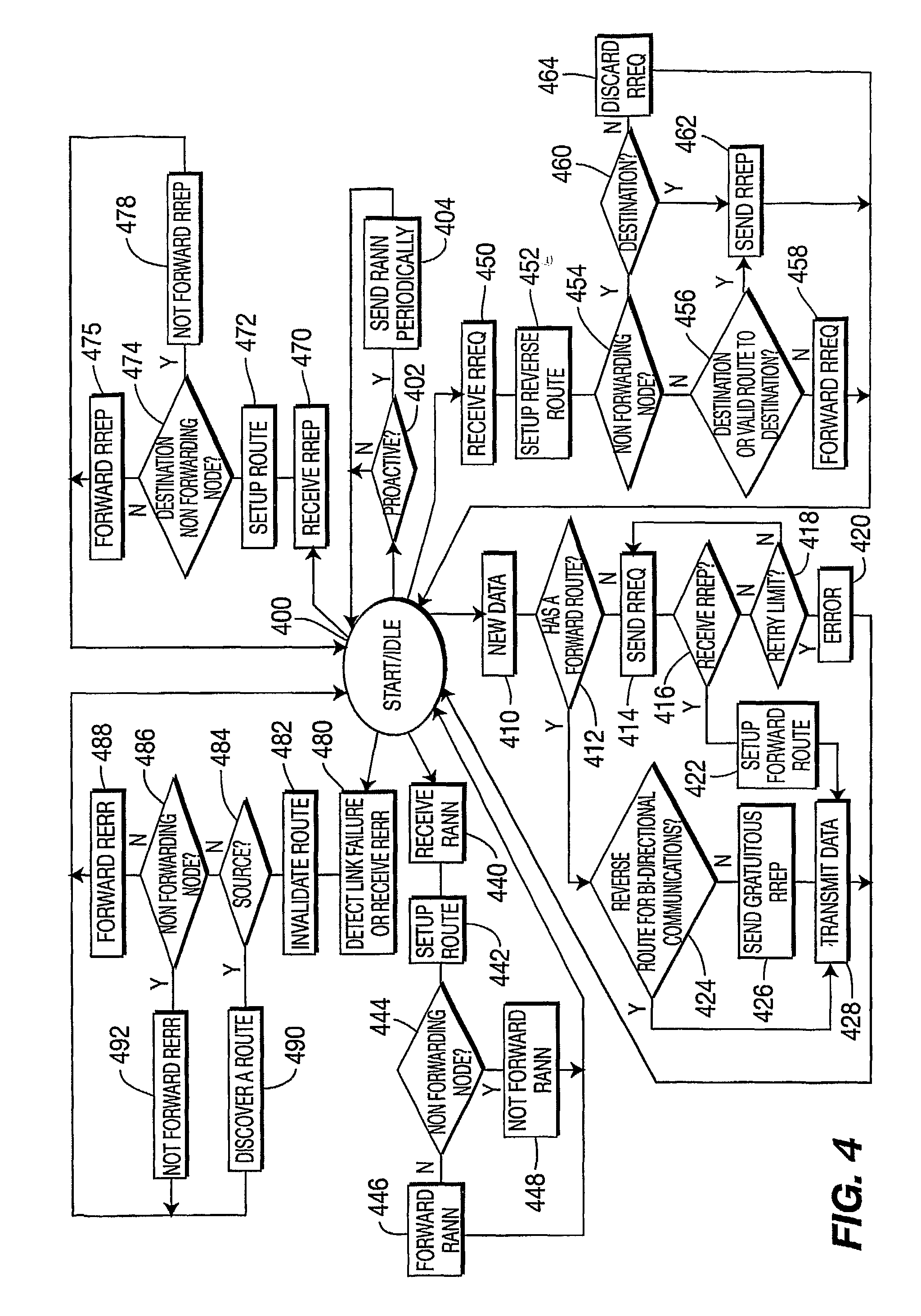
Hybrid mesh routing protocol
ActiveUS8467297B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless mesh networkEngineering
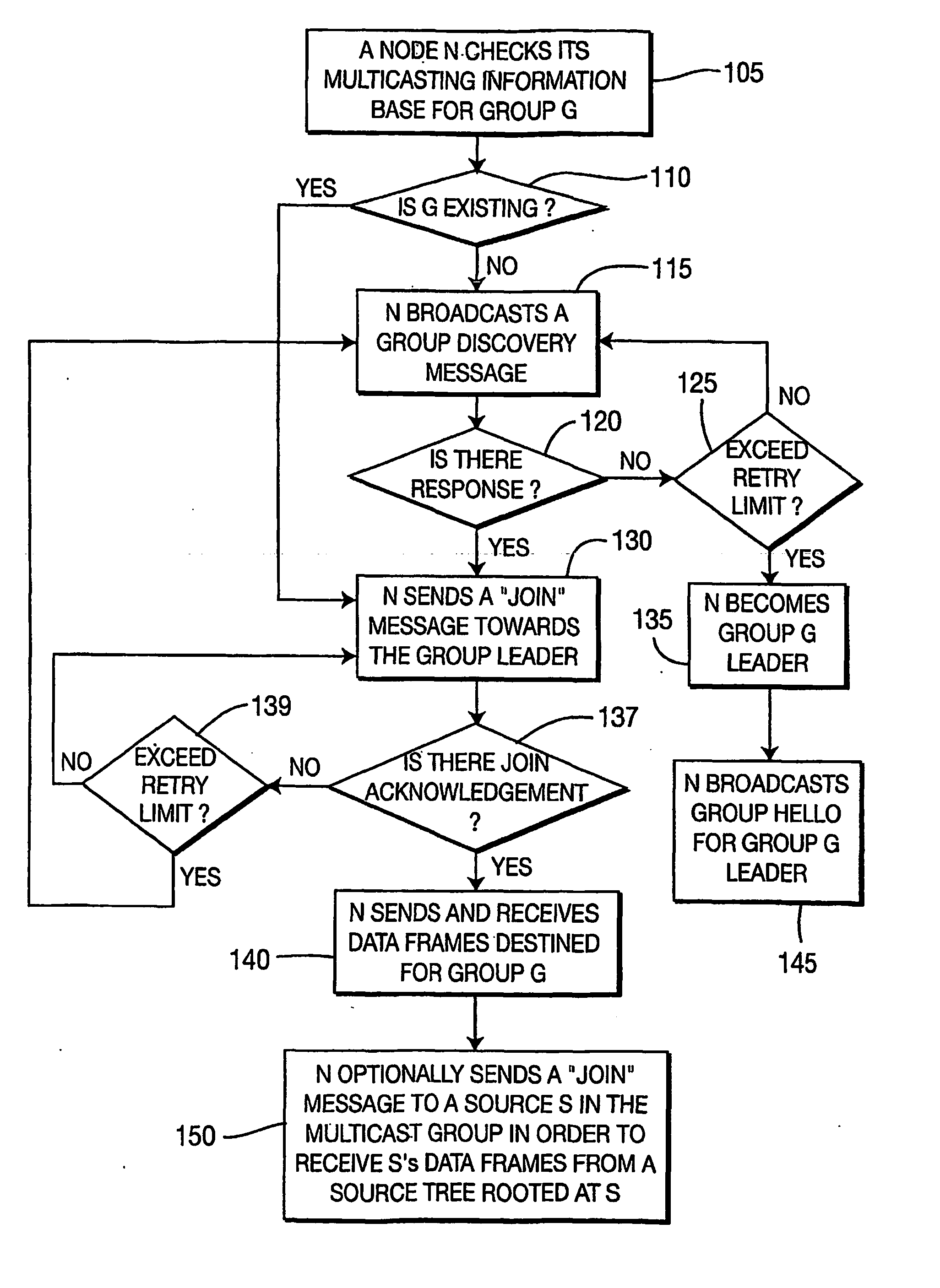
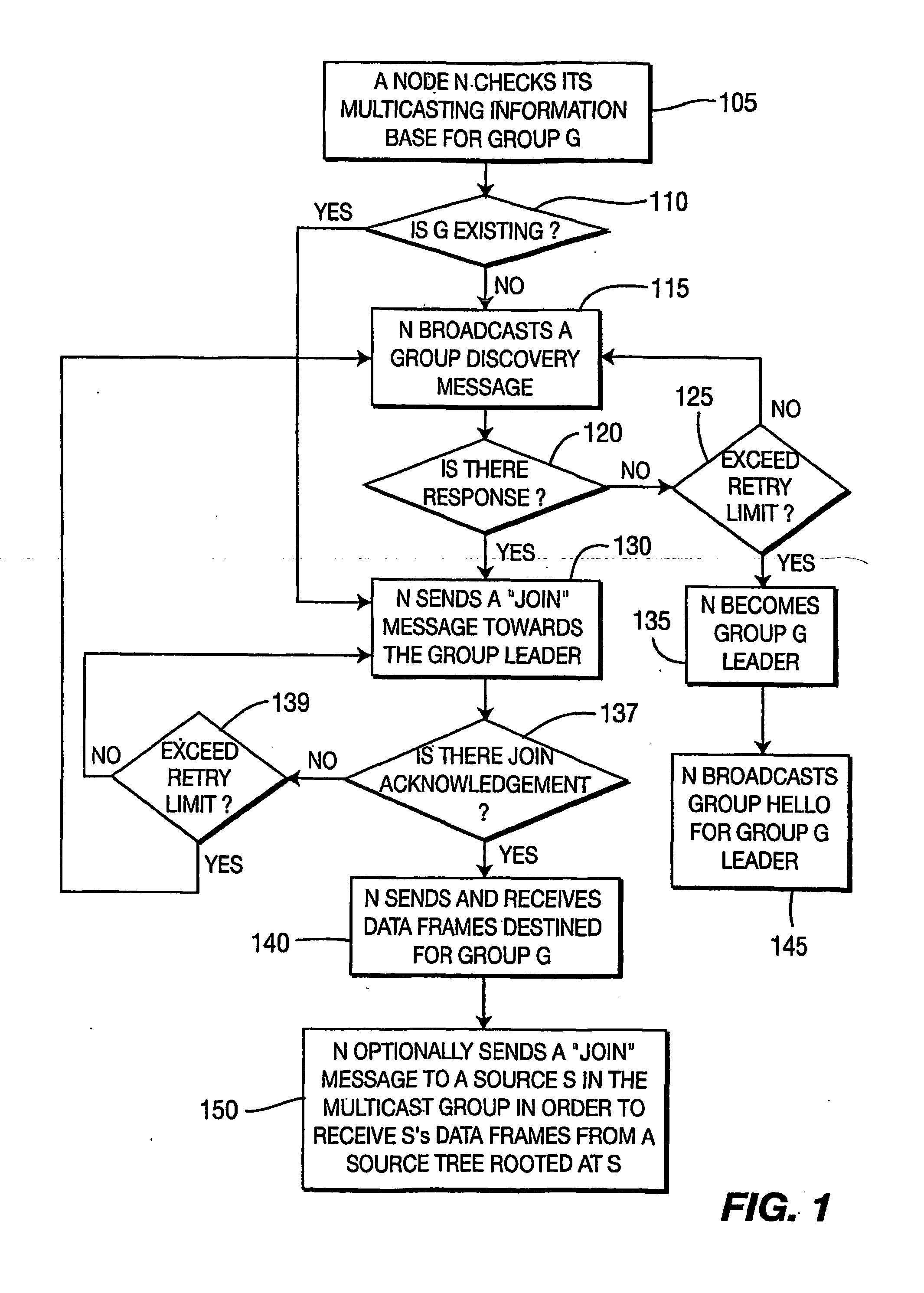
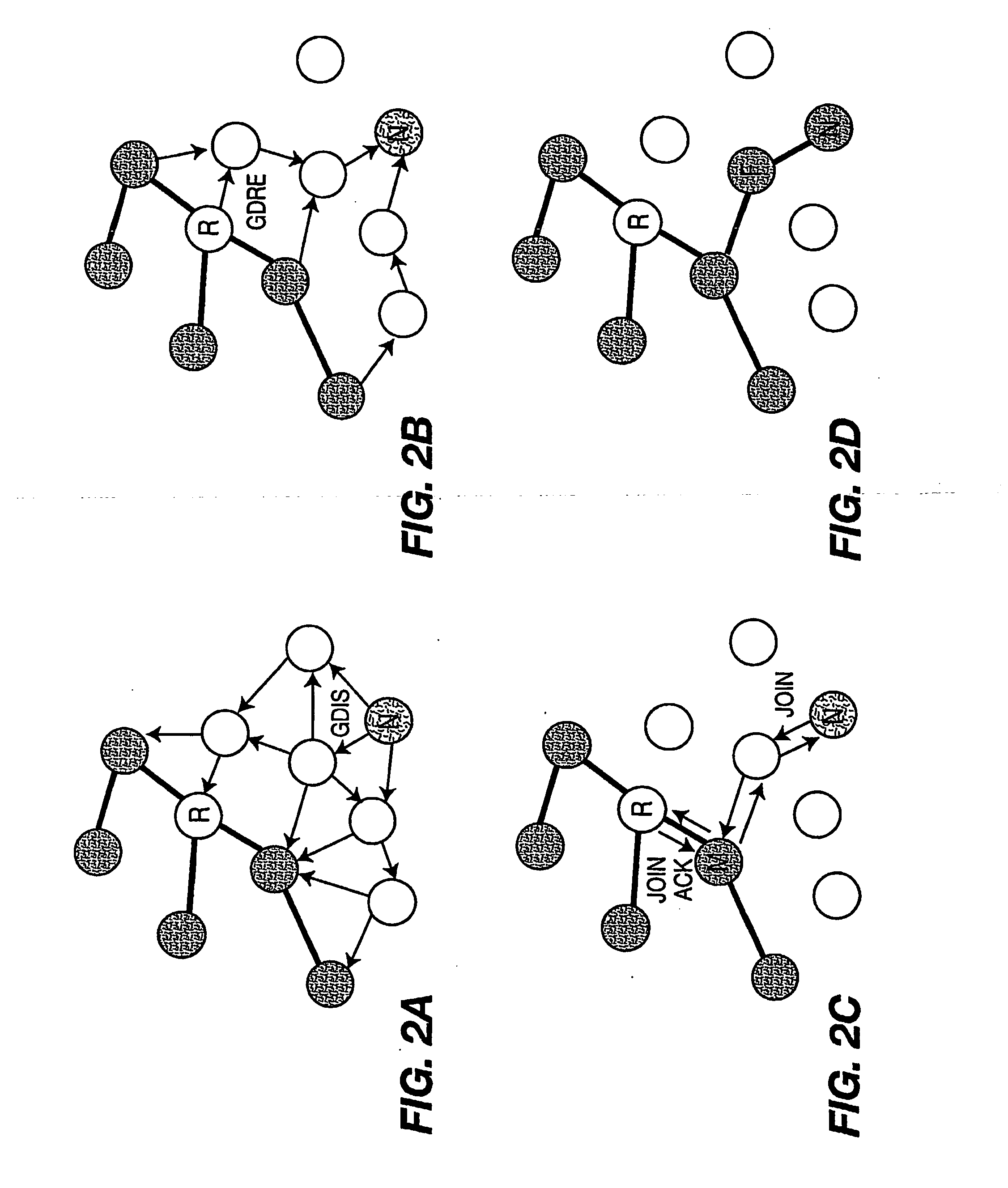
A method for selecting a route by a node between a source node and a destination node in a wireless mesh network by establishing the route between the source node and the destination node using media access control addresses is described. A method for a node to selecting a route to join a multicast group in a wireless mesh network using media access control addresses, is also described.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
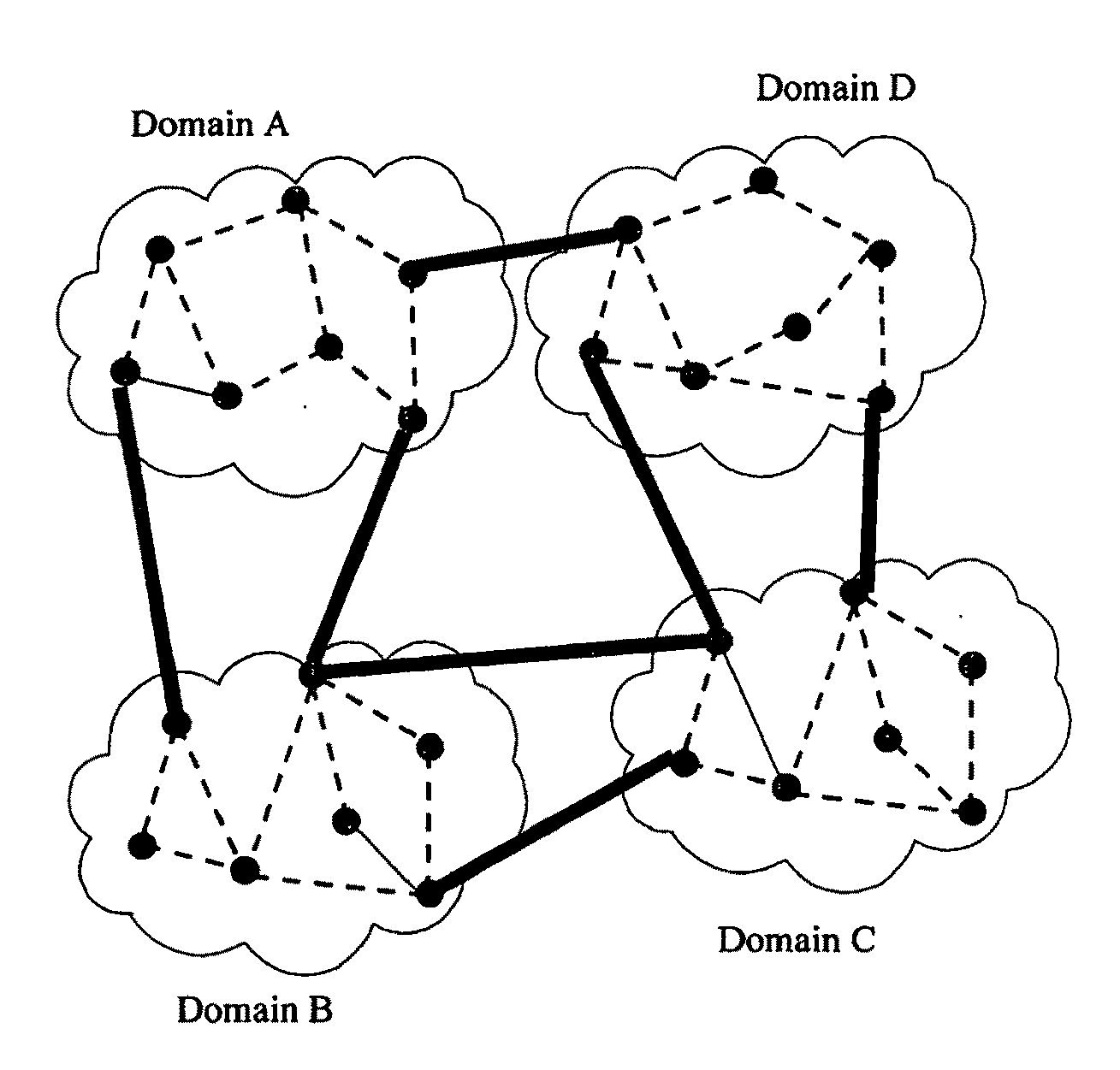
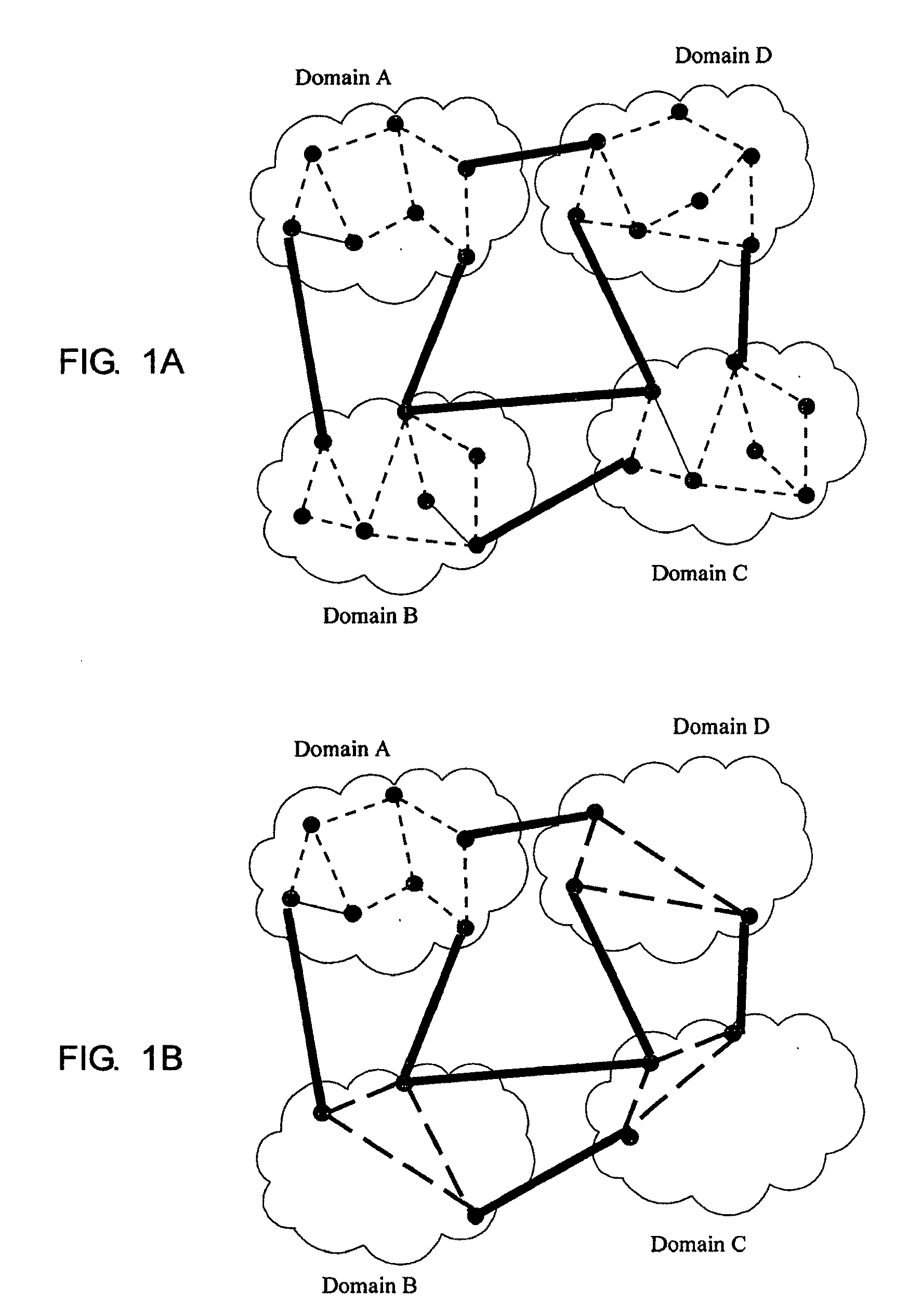
Multi-domain network and method for multi-domain network
Each domain of a multi-domain network collects intra-domain routing information relating to that domain and makes a reduced view of that information available to other domains of the network, and in which each domain of the network uses its own intra-domain routing information together with the reduced-view routing information from the other domains to form a logical view of the network so as to enable that domain to make an end-to-end route selection decision.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
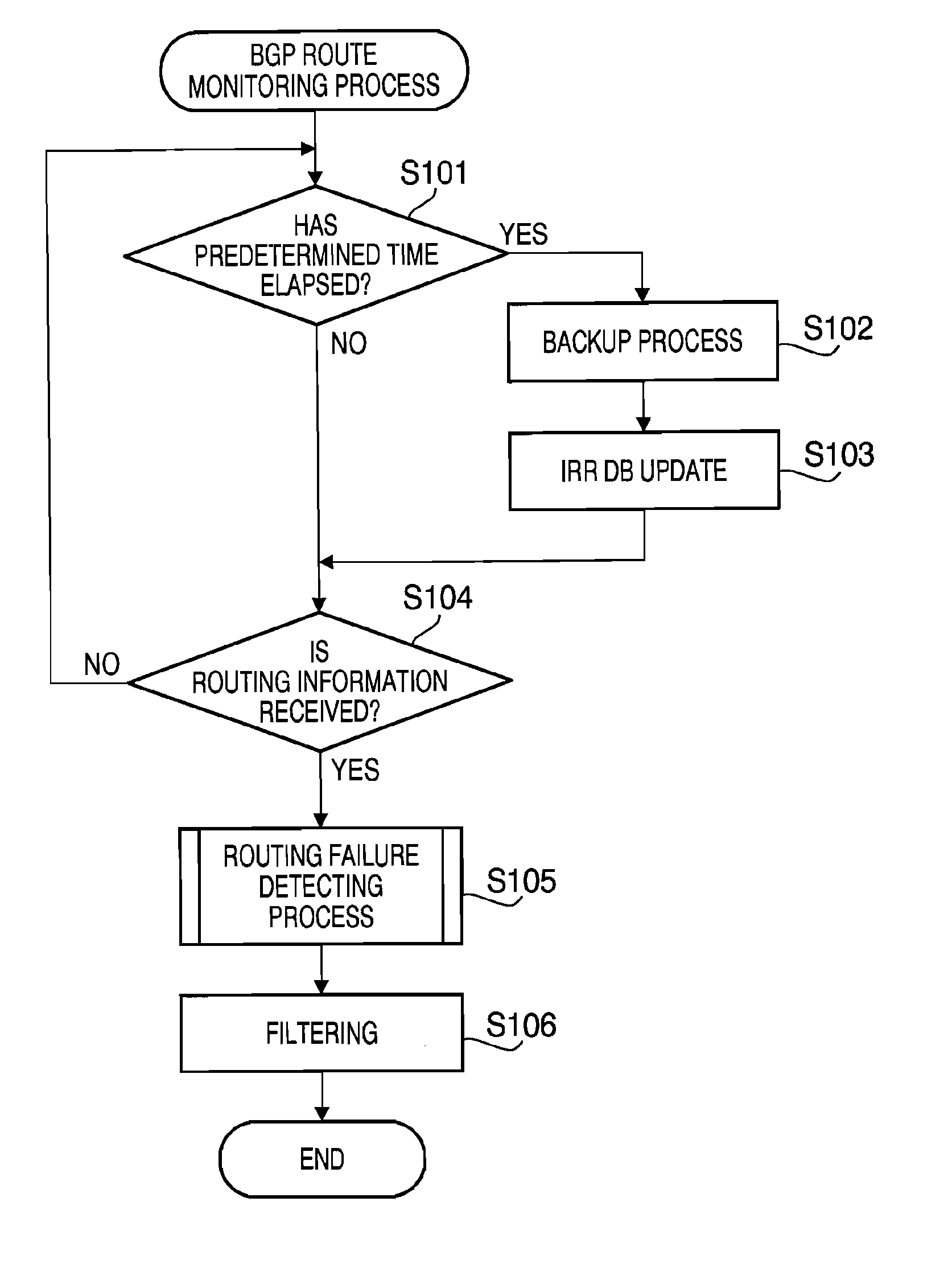
Device, method and computer readable medium for bgp route monitoring
InactiveUS20110093612A1Invalid informationDigital computer detailsTransmissionMonitor equipmentDistributed computing
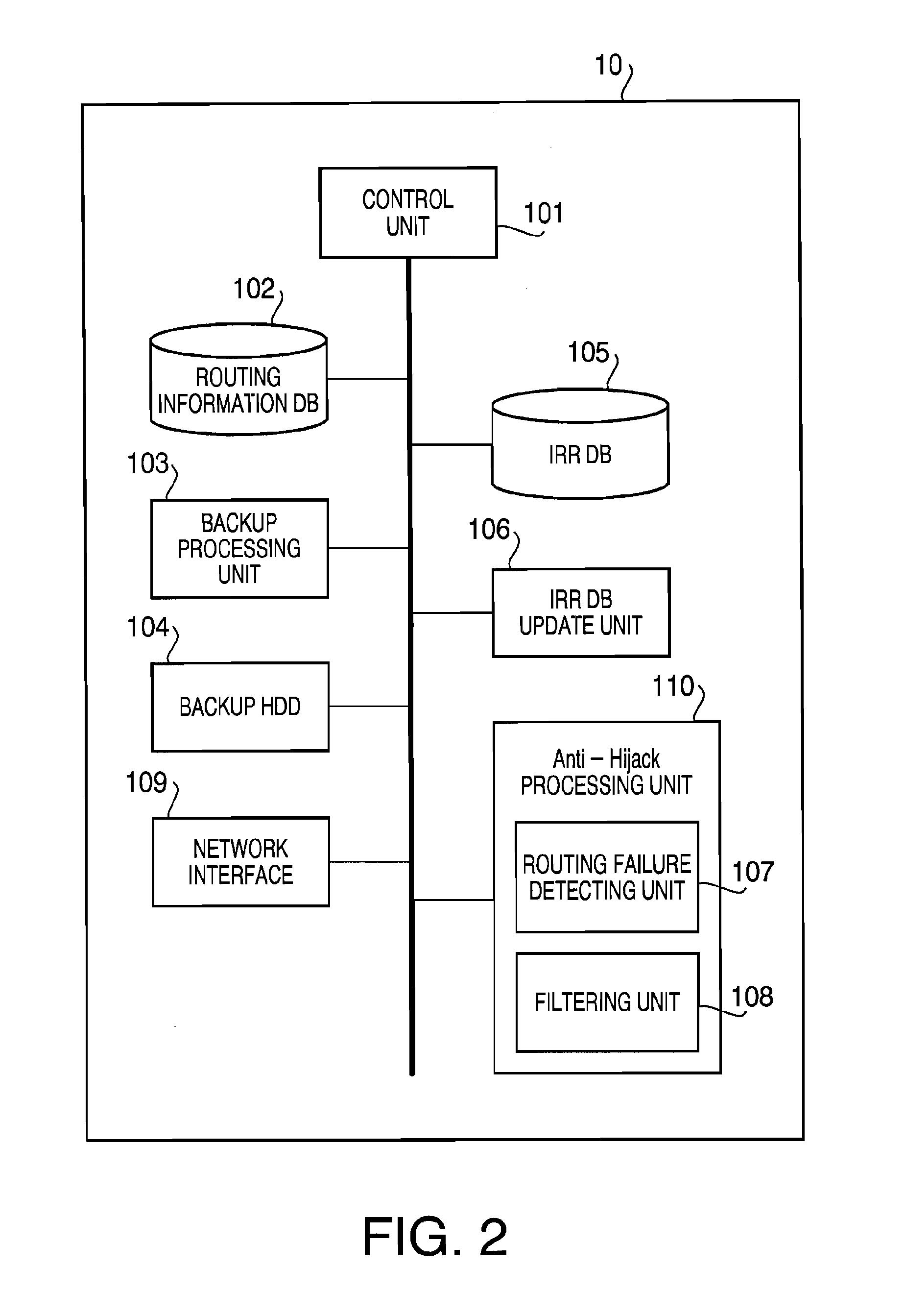
A BGP route monitoring device includes a routing information receiving unit configured to receive BGP routing information. The device also includes a first database storing a plurality of pieces of BGP routing information registered in an IRR server. The server also includes a routing failure detecting unit to classify the received BGP information into states by comparing the received BGP information with the first database and to determine whether the received BGP routing information is an invalid path based on the classified states. In this configuration, the plurality of states include a state where Prefix of the received BGP information matches Prefix of BGP routing information in the first database, the PrefixLength of the received BGP information is shorter than PrefixLength of the BGP routing information in the first database, and Origin AS number of the received BGP routing information matches Origin AS number of the BGP routing information in the first database.
Owner:IP INFUSION INC
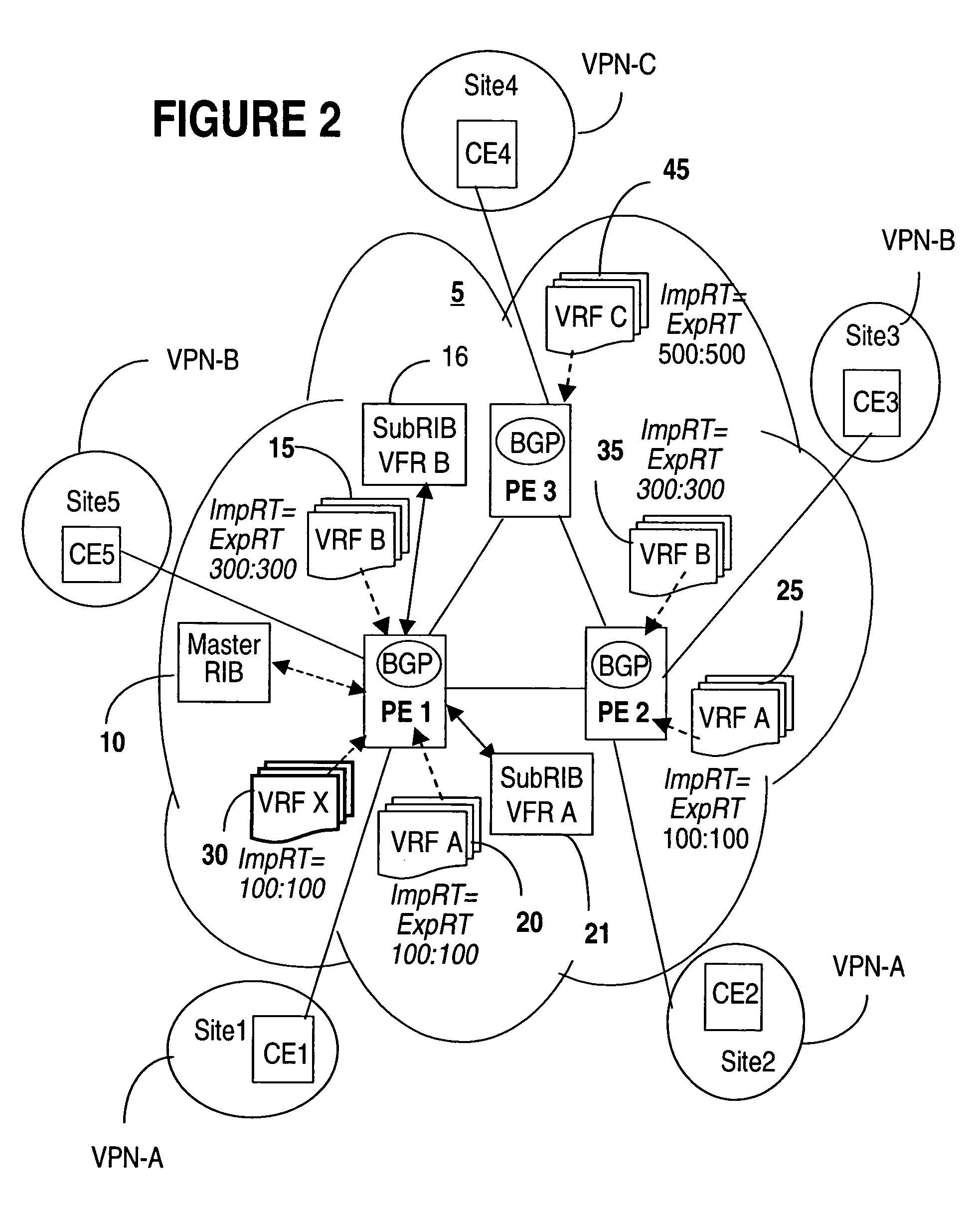
Managing L3 VPN virtual routing tables
InactiveUS20050188106A1Efficiently setupEffective maintenanceDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionRouting tablePrivate network
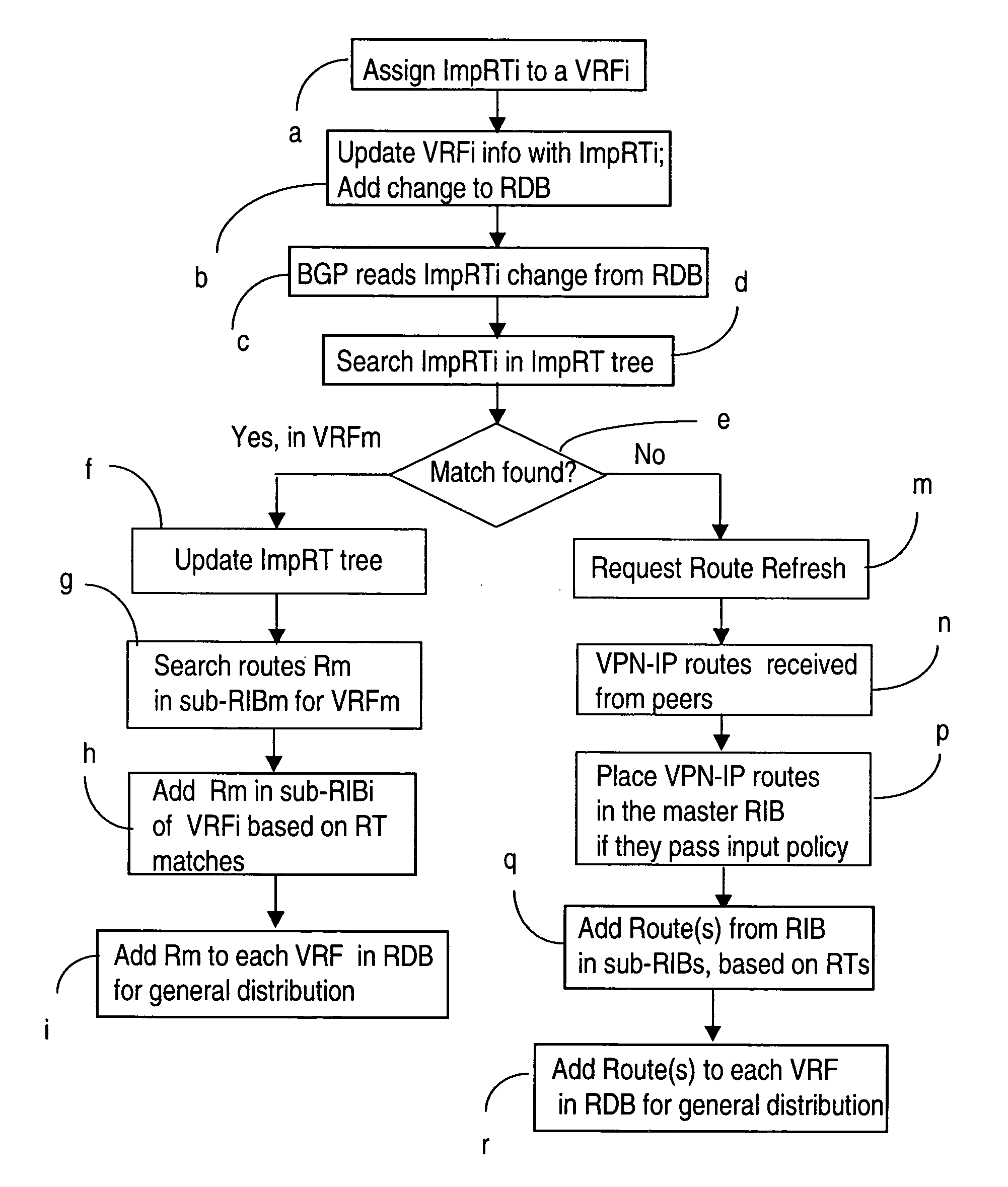
A method of managing virtual routing forwarding (VRF) tables at a provider edge PE router of a L3 virtual private network (VPN) is provided. An import route target (ImpRT) tree is maintained at the PE router, which keeps the association between all ImpRT attributes currently configured on said PE router and the virtual routing table VRF at that router. When an ImpRT attribute is configured on a VRF table, the PE router first searches the tree to identify a local VRF table that contains a route(s) with that ImpRT attribute. If this information is available locally, the VRF is updated by copying the route information, and there is no need to do a route refresh. When an ImpRT is deleted from a VRF, a route refresh is avoided by parsing all the routes in the VRF and removing the routes that no longer have a matching route target. In an alternative implementation, the local source is the master RIB (routing information base) which includes all routes in all VRFs at the router, and optionally even rejected routes that were filtered out using ImpRTs. In this variant, even routes associated with ImpRTs that are new to the router would be available to update the VRF without requiring a route refresh.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
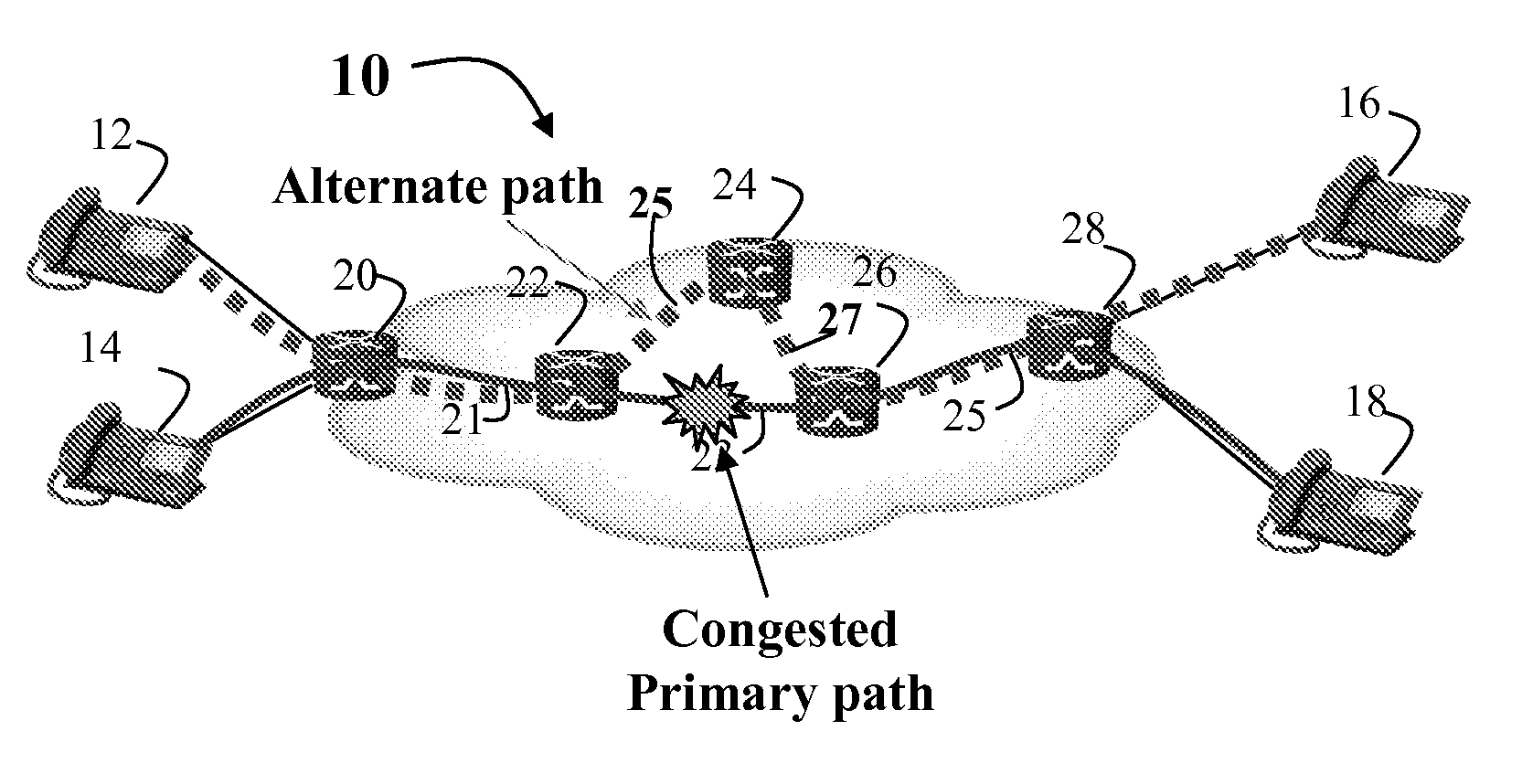
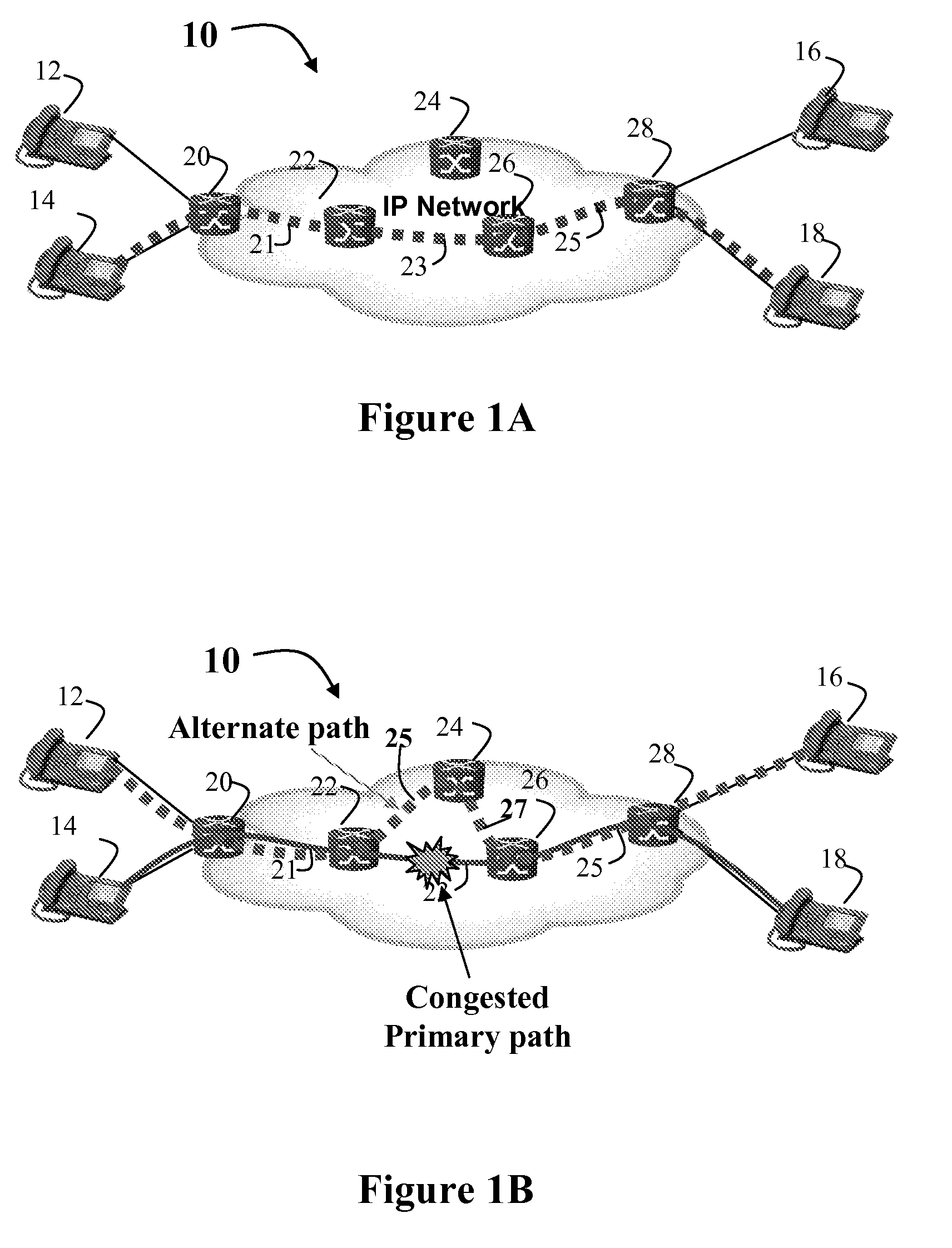
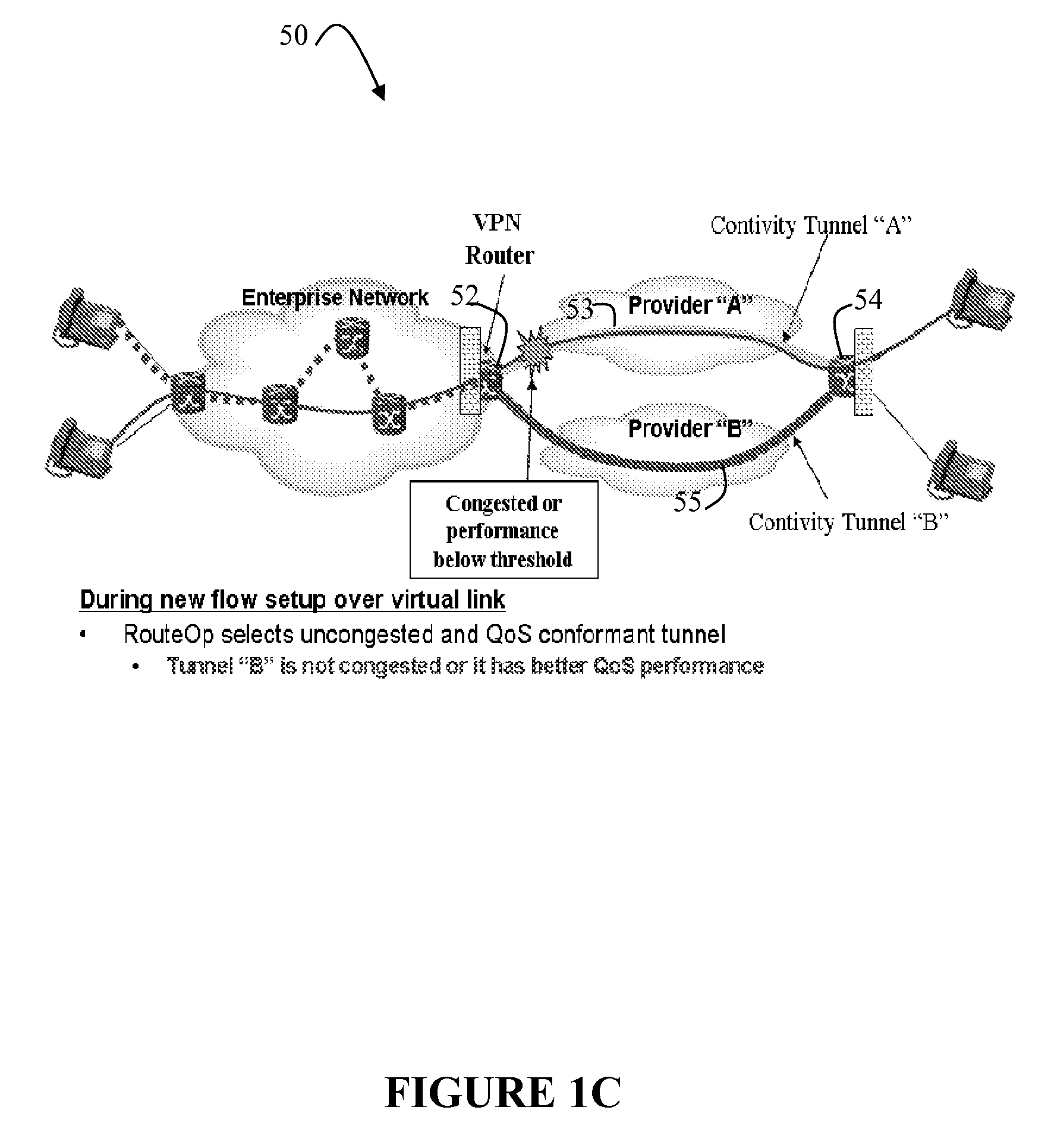
Route Optimization Using Measured Congestion
A flow based routing method and apparatus selects a path from a plurality of different paths for assignment to a flow. The path is selected based on a traffic performance measurements which identify relative congestion and performance of the different paths, so that traffic flows can be diverted away from network congestion points, thereby allowing network resources to be load balanced at a flow granularity. The present invention may be configured on physical or virtual links on an NE to enhance the forwarding of packets using the primary link and one or more alternate links to any given destination.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Multicast mesh routing protocol
ActiveUS20090303902A1Reduce delaysData efficientSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast transmission systemsMesh routingMedia access control
A method for a node to select a route to join a multicast group in a wireless mesh network, including establishing the route between the node and the multicast group using media access control addresses is described. A method for determining a multicast group leader of the multicast group of a wireless mesh network using media access control addresses is also described.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Dynamic retrieval of routing information for inter-AS TE-LSPs
A technique dynamically triggers an exchange of reachability information between a tail-end (remote) domain target node (e.g., a tail-end node) of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) and a local domain head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The inter-domain information retrieval technique is illustratively based on triggering a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session whereby at least a portion of the reachability, i.e., routing, information of the tail-end node is transmitted to the head-end node of the TE-LSP in accordance with BGP. Specifically, once a TE-LSP is established between the head-end node and the tail-end node, the head-end node triggers the tail-end node, e.g., through extensions to a request / response signaling exchange, to establish the BGP session. Establishment of the BGP session enables transmission of the routing information from the tail-end node to the head-end node. The head-end node uses the routing information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for fast computation of routes under multiple network states with communication continuation
A system and method for network routing is provided where significant (those that impact optimal network routes) state changes of network components are considered. A set of optimal communication paths are generated for a number of actual and potential component failure scenarios. An optimal communication path is generated for each failure scenario. In addition, a method that enables continued communication using intermediate routing points and routing update propagation during periods of network non-convergence or congestion is disclosed.
Owner:OPCOAST
Link grouping for route optimization
A technique manages route optimization for one or more groups of links in a computer network. According to the novel technique, each group or “subgroup” of links comprises one or more links, wherein the group may be configured based on various measures, such as, e.g., connectivity (physical or virtual), policies to be applied, per-prefix, per-application (e.g., Internet traffic or voice over IP, VoIP), geographic location, and / or quality-based (e.g., primary links and secondary / backup links). One or more policies may be defined for the groups of links (i.e., where these group policies are to be applied to the group as a whole), in addition to policies that may be defined for individual to links and / or prefixes. Once the link groups are established, traffic over the groups of links (e.g., routes to reachable address prefixes) may be managed and optimized according to the group policies, such as in accordance with Optimized Edge Routing (OER) techniques.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
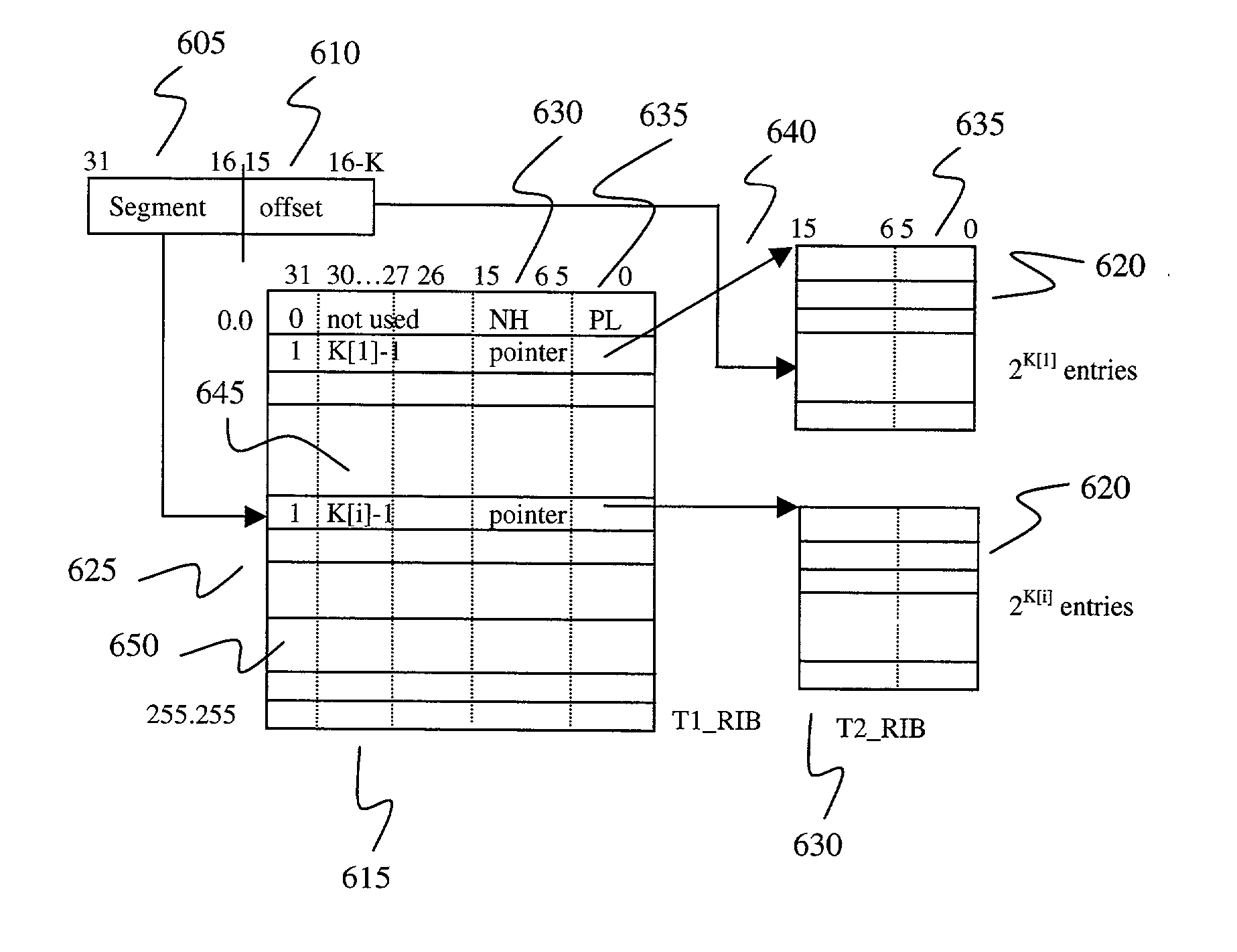
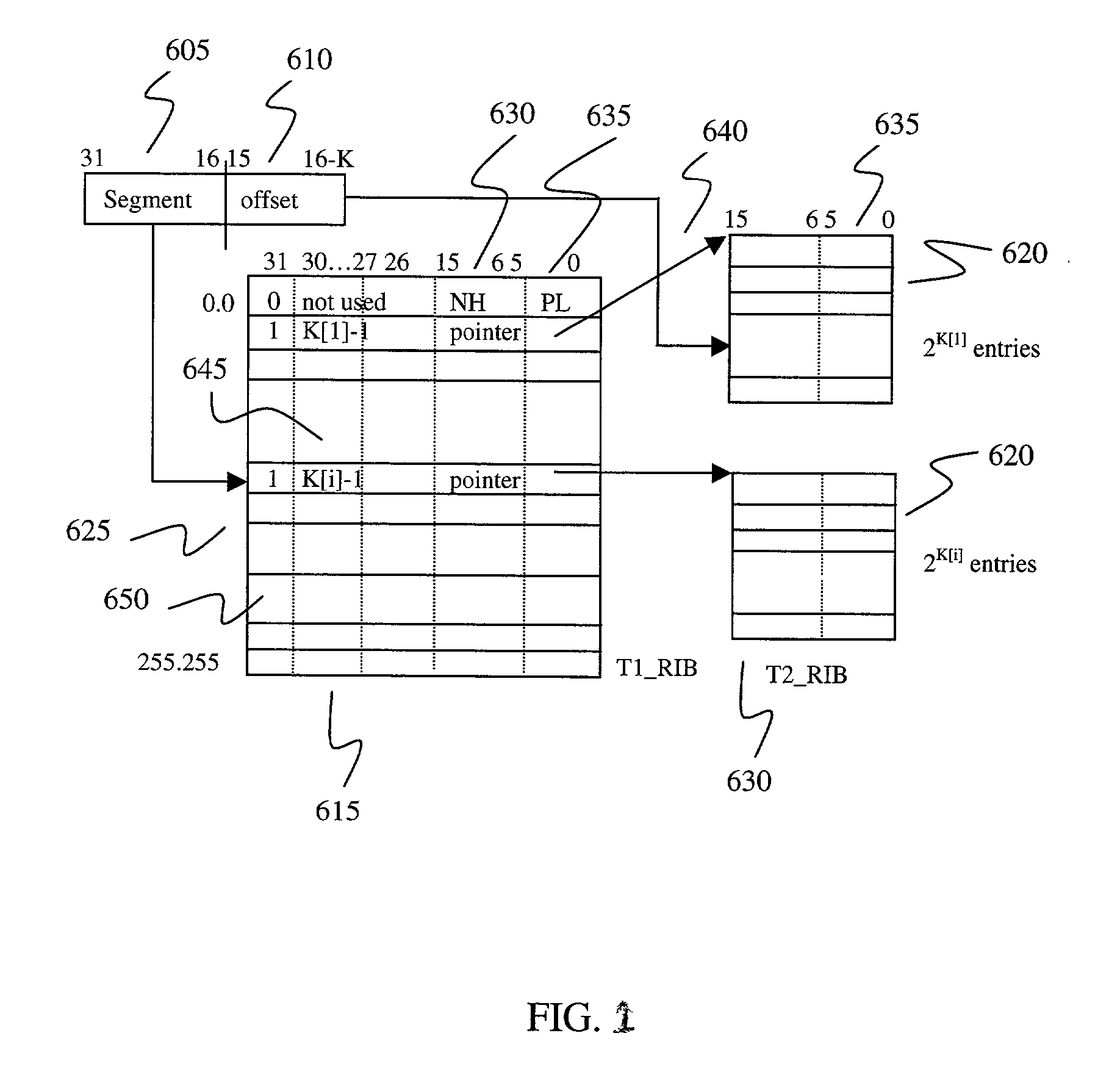
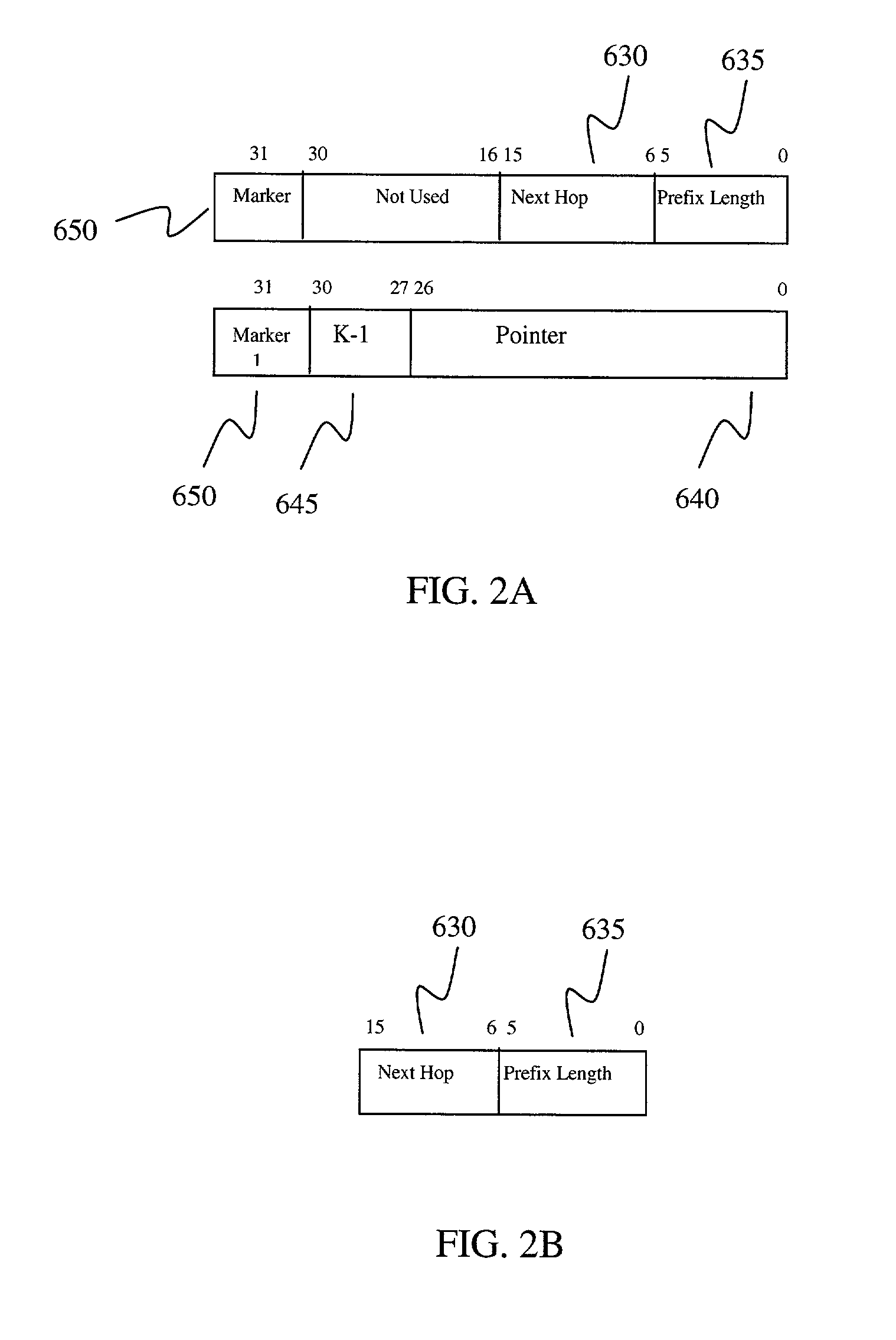
Fast IP route lookup with 16/K and 16/Kc compressed data structures
InactiveUS20020172203A1Data switching by path configurationOther databases indexingPresent dayArray data structure
An advanced data structure allows lookup based upon the most significant 16 bits and the following variable number of K bits of the IP destination address. This 16 / K scheme requires less than 2 MB memory to store the whole routing tables of present day backbone routers. A 16 / Kc version utilizes bitmaps to compress the table to less than 0.5 MB. For the 16 / K data structure each route lookup requires at most 2 memory accesses while the 16 / Kc requires at most 3 memory accesses. By configuring the processor properly and developing a few customized instructions to accelerate route lookup, one can achieve 85 million lookups per second (MLPS) in the typical case with the processor running at 200 MHz. Further, the lookup method can be implemented using pipelining techniques to perform three lookups for three incoming packets simultaneously. Using such techniques, 100 MLPS performance can be achieved.
Owner:TESILICA
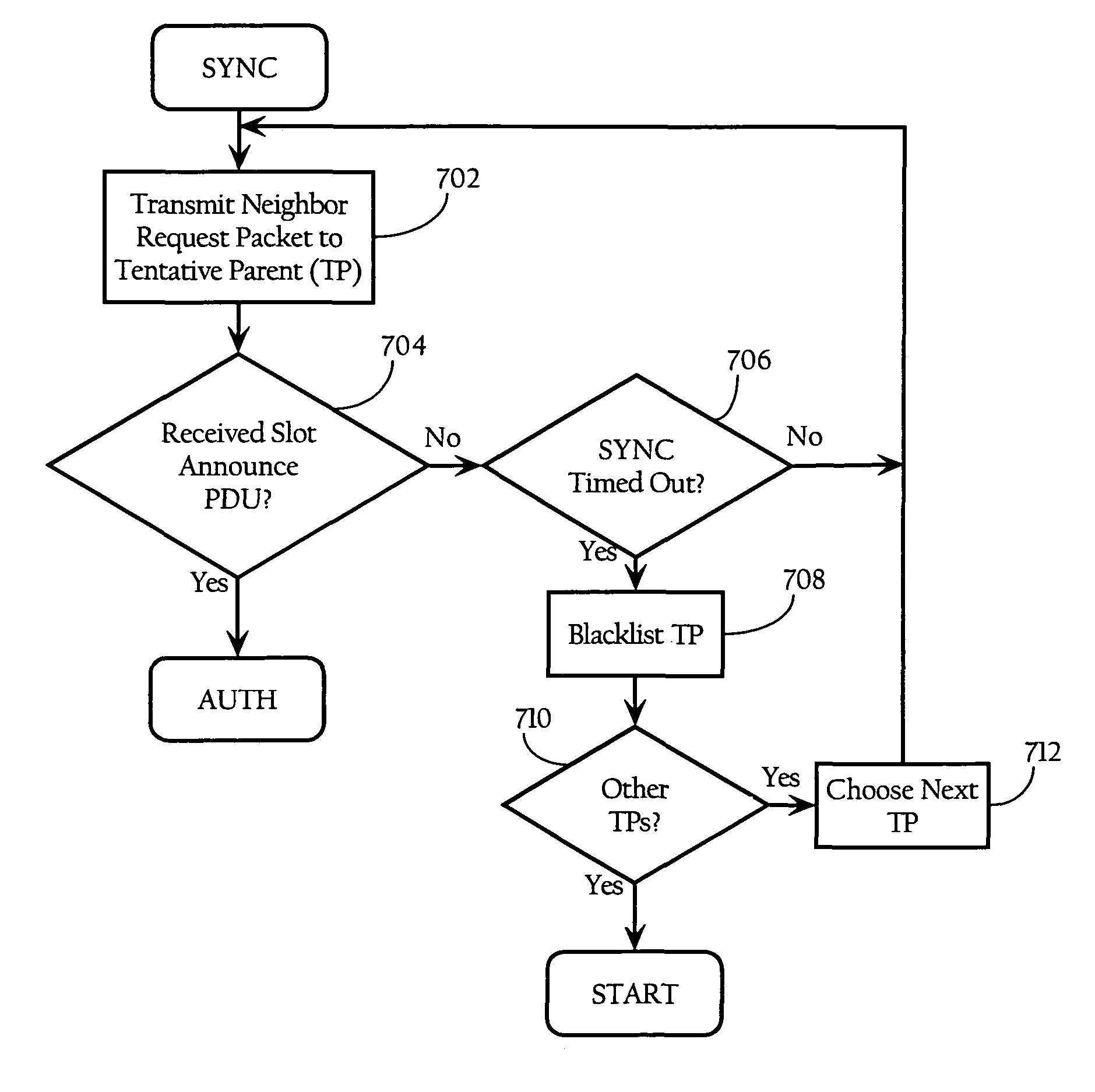
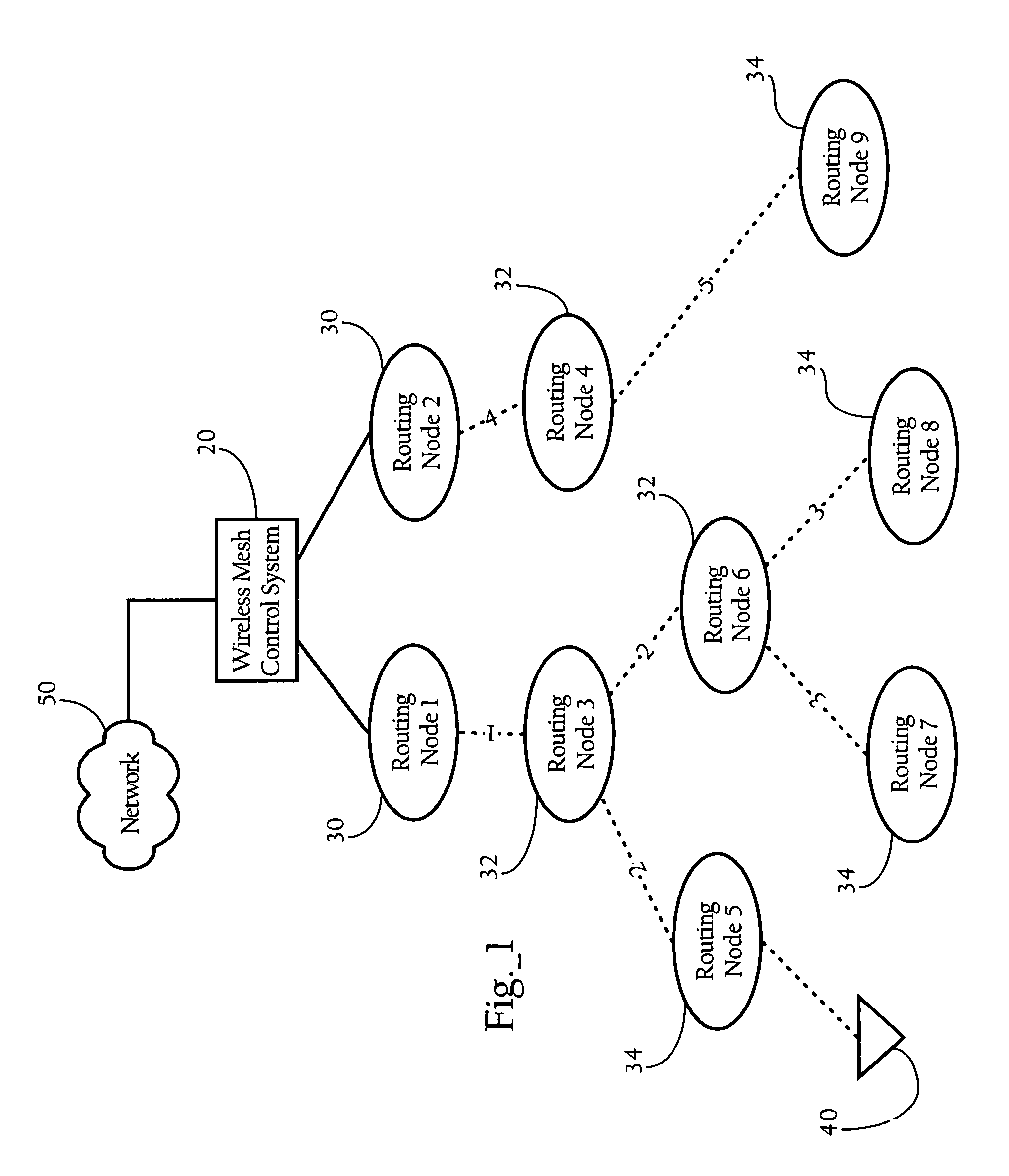
Automatic route configuration in hierarchical wireless mesh networks
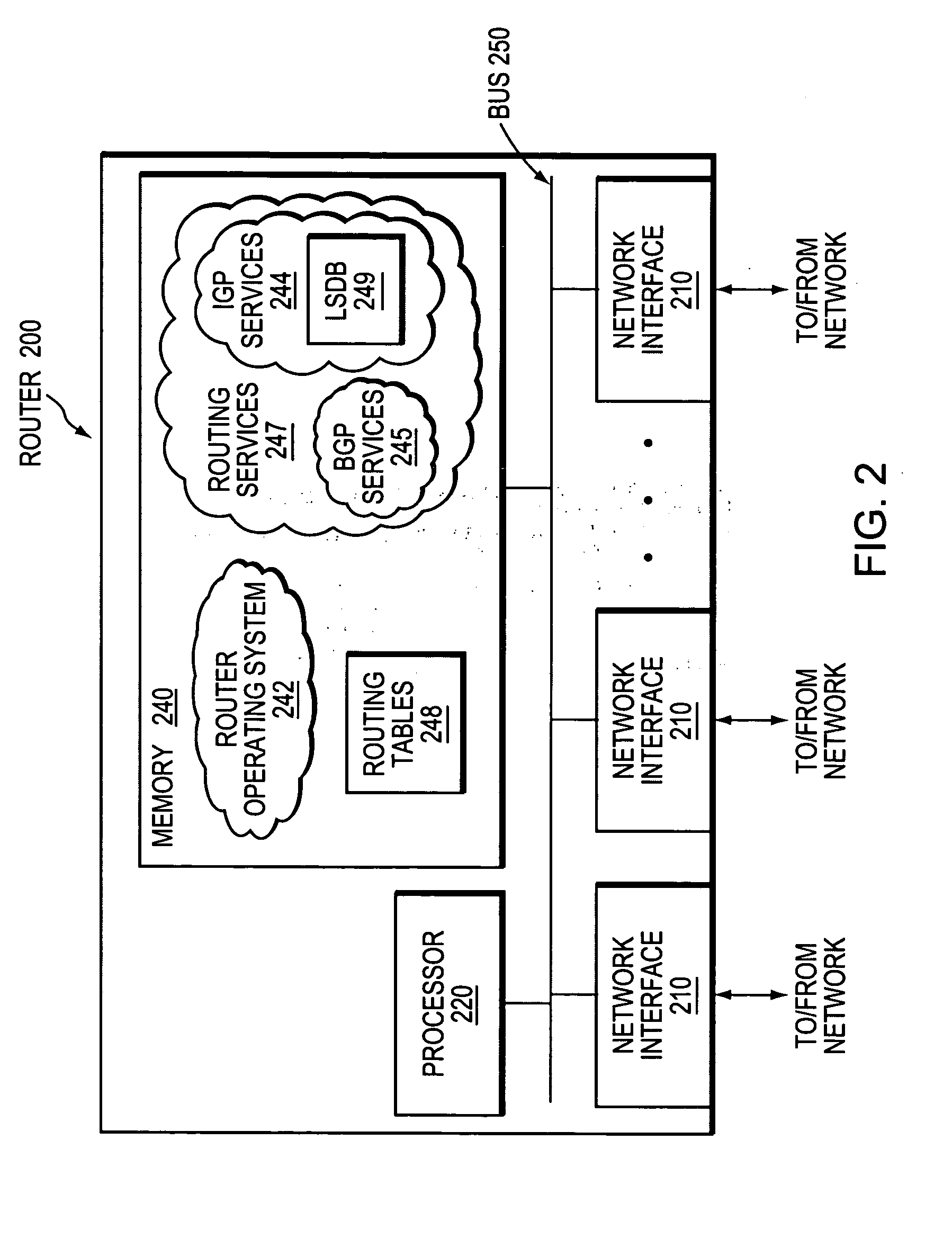
ActiveUS7899027B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless mesh networkProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to routing configuration in a hierarchical wireless mesh network. In one implementation, the present invention uses neighbor messages to allow routing nodes to discover one another and configure a hierarchical routing configuration. In one implementation, the present invention provides a neighbor and adjacency protocol that provides for automatic mesh configuration and loop-free mesh topologies.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
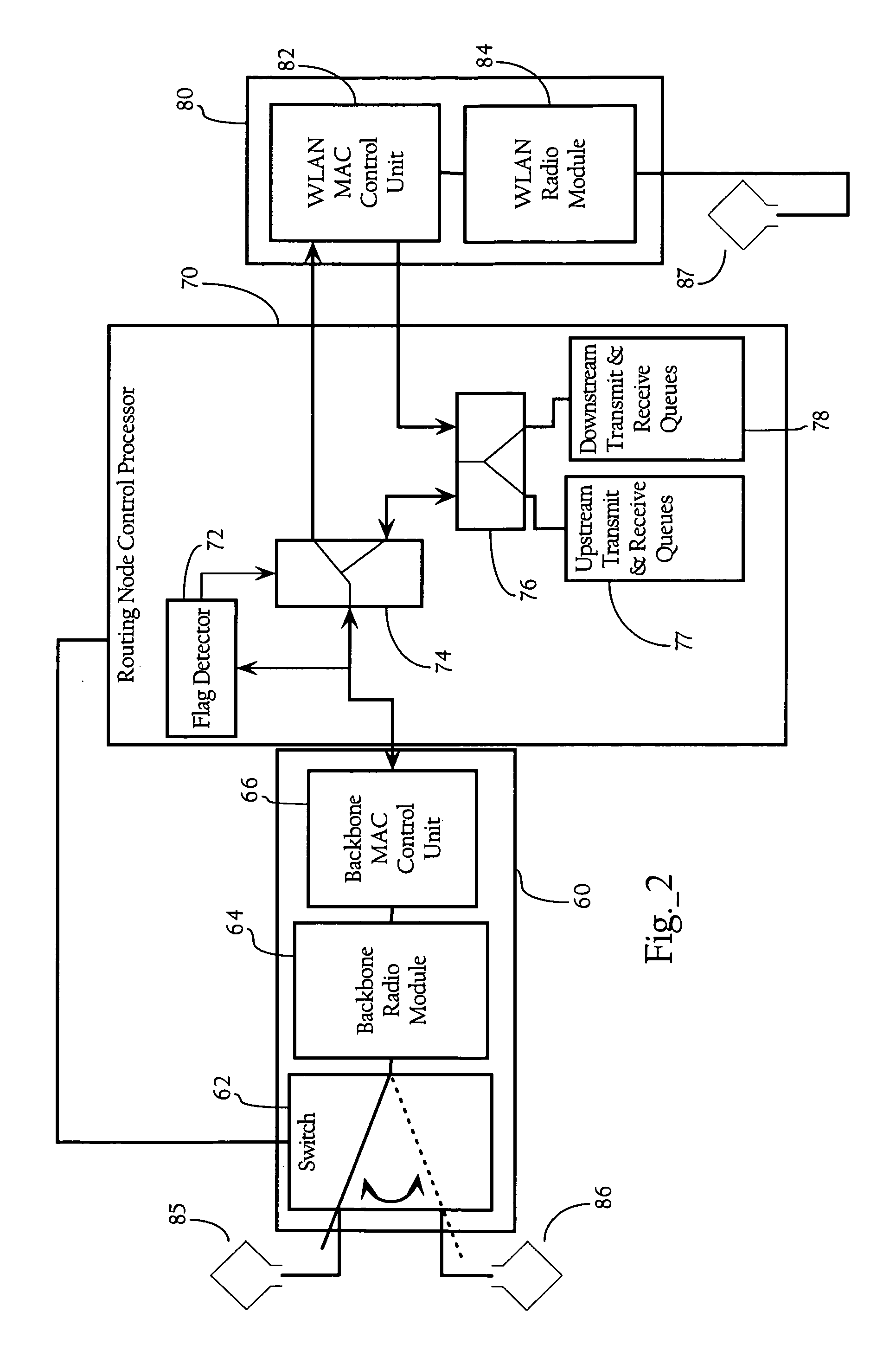
System and method for enhancing the availability of routing systems through equal cost multipath
In a networking environment including one or more network processing (NP) devices and implementing a routing protocol for routing data packets from a source NP devices to destination NP devices via a switch fabric, with each network processing device supporting a number of interface ports, a system and method for enabling a routing system to recover more quickly that the routing protocol so as to significantly reduce the occurrence of lost data packets to a failed target interface / blade. The routing system is enabled to track the operational status of each network processor device and operational status of destination ports supported by each network processor device in the system, and maintains the operational status as a data structure at each network processing device. Prior to routing packets, an expedient logical determination is made as to the operational status of a target network processing device and target interface port of a current packet to be routed as represented in the data structure maintained at the source NP device. If the target blade / interface is not operations, an alternative route may be provided by ECMP. In this manner, correct routing of packets is ensured with reduced occurrence of lost data packets due to failed target NP devices / ports.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Data routing in a communication network
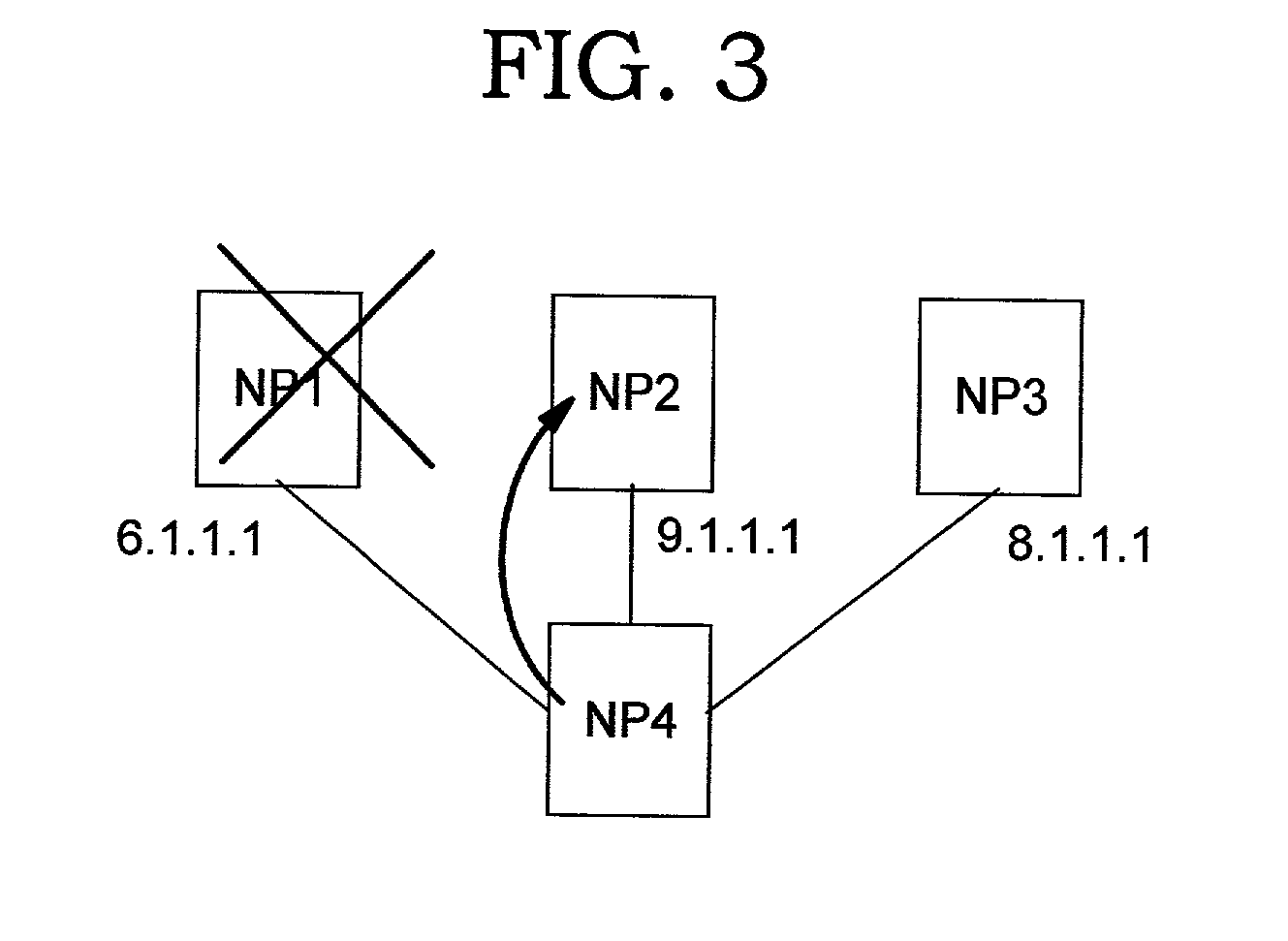
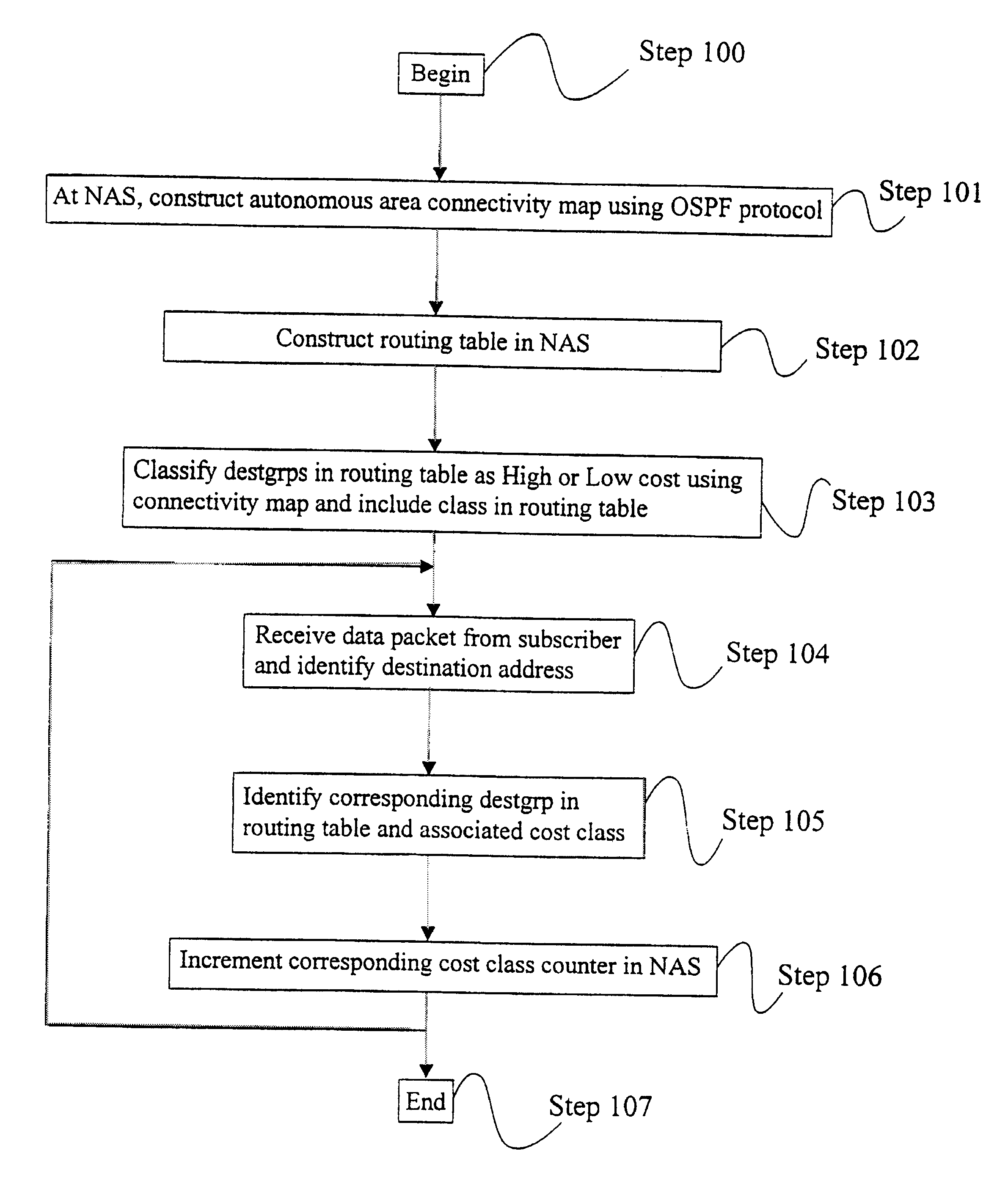
InactiveUS6584500B1Classification is relatively shortMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsData switching by path configurationRouting tableInternet users
A method of collecting charging information relating to usage of the Internet by an Internet user. The method comprises constructing in a router of the Internet a routing table containing a set of destination address ranges and a set of respective next hop network nodes. Each address range in the routing table is assigned a cost class in dependence upon the route via which a packet must travel to an address within the range. Upon receiving a data packet from the network user, the destination address of the packet is identified by the router. The router then determines from the routing table the associated cost class. A corresponding cost class counter in the router is then incremented.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
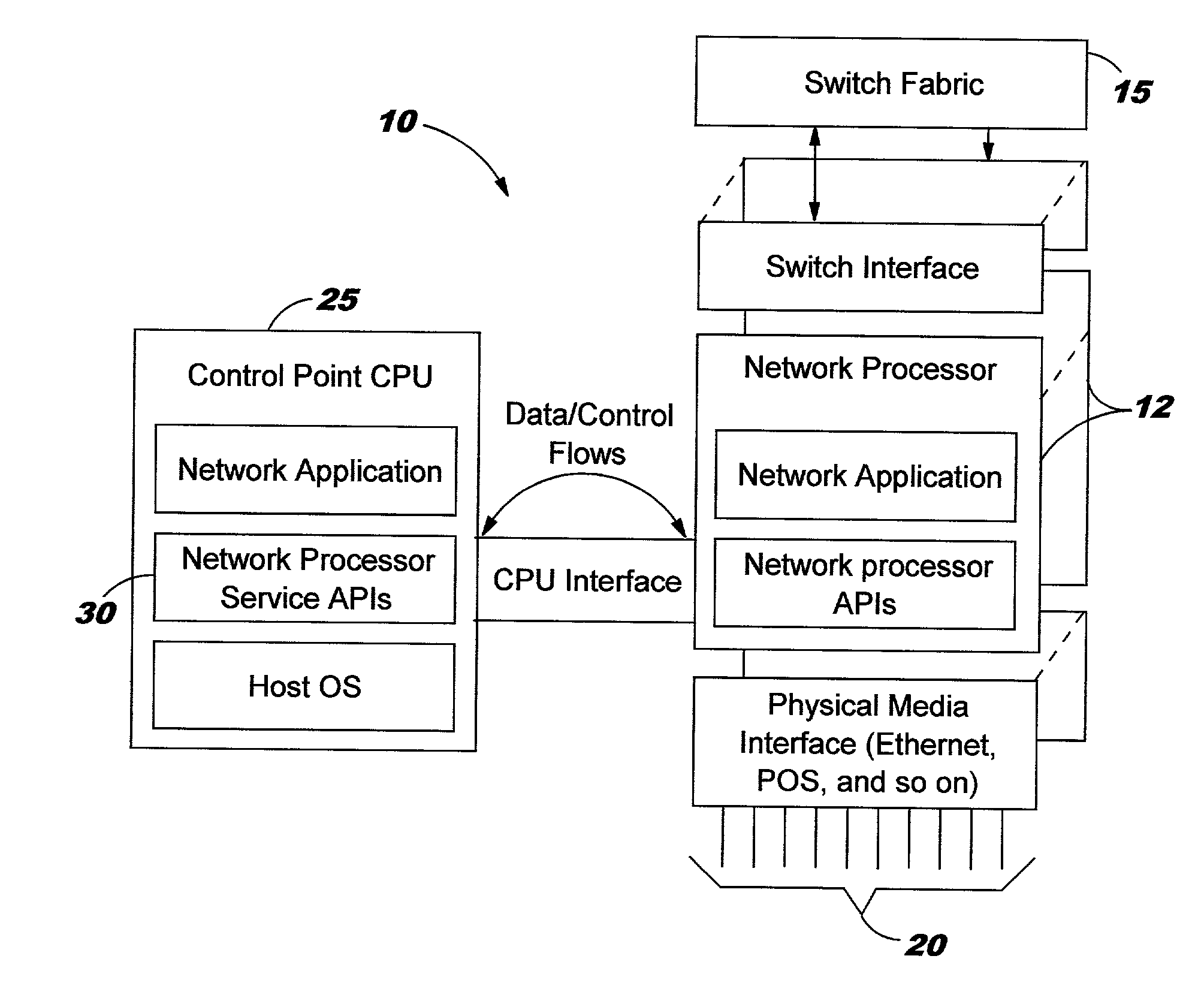
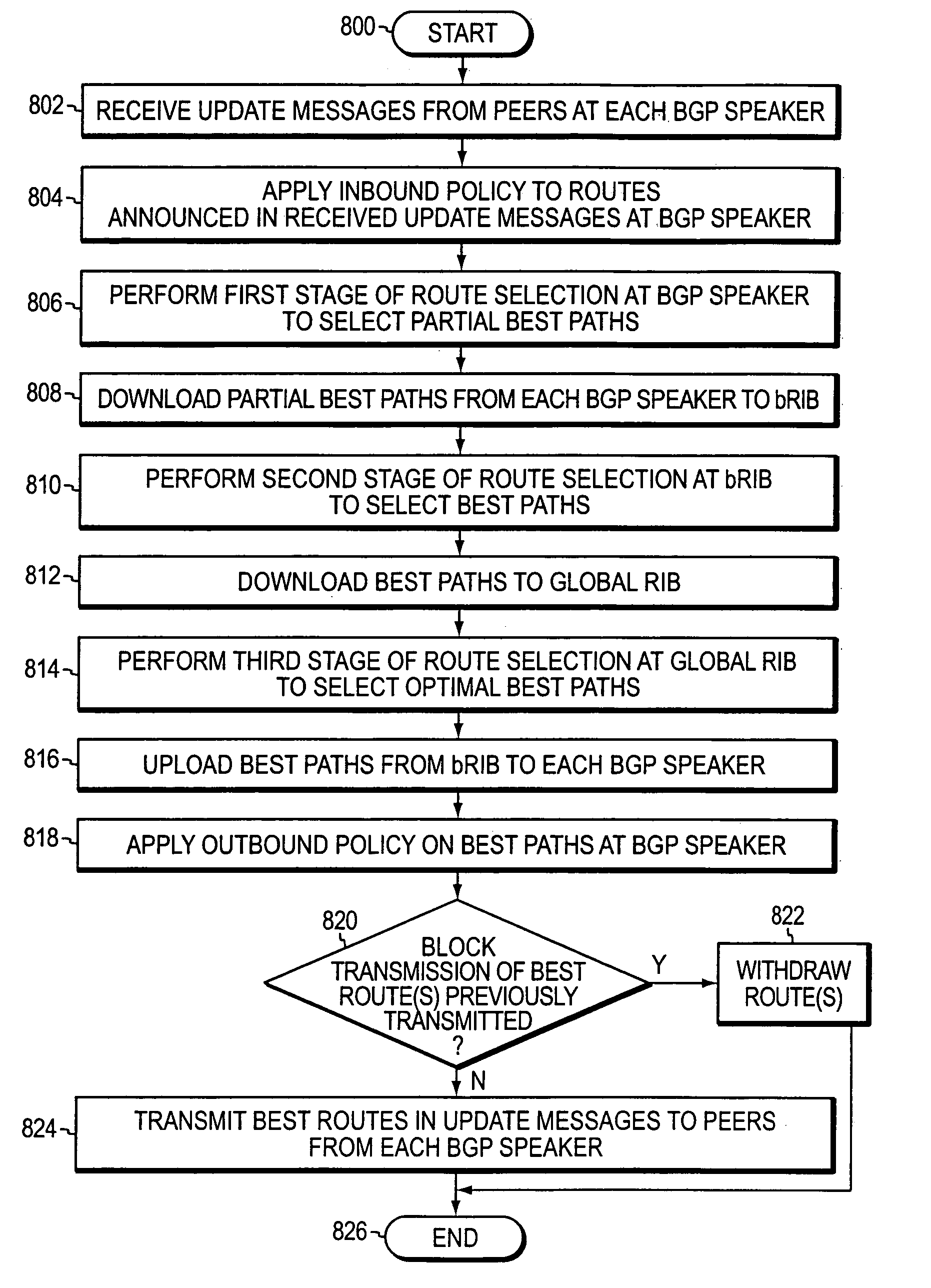
System and method for distributing route selection in an implementation of a routing protocol
ActiveUS7023808B2Reduce memory usageOvercome disadvantagesError preventionTransmission systemsPathPingData pack
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
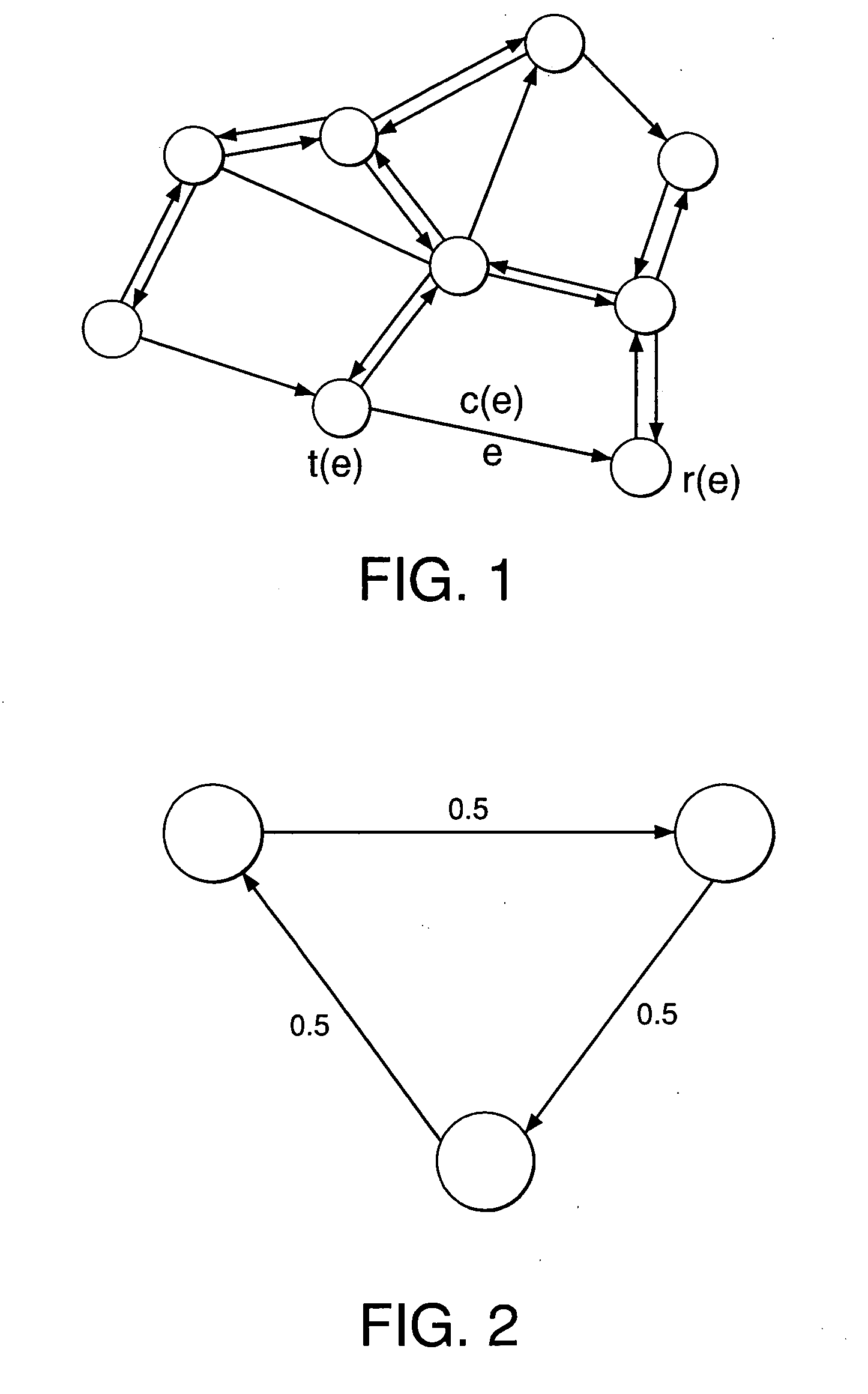
Characterizing achievable flow rates in multi-hop mesh networks with orthogonal channels
InactiveUS20070025364A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiple edgesEdge coloring
A method of routing data from a source node to a destination node in a multi-hop network of nodes interconnected by links comprises: (a) determining that a link-flow vector satisfies one or more necessary scheduling conditions for achievability, wherein the link-flow vector represents a set of flows to be routed on one or more links from the source node to the destination node; (b) generating a scheduling multi-graph for the network, wherein the scheduling multi-graph comprises a graph having at least one pair of nodes with multiple edges therebetween; (c) deriving one or more sufficient scheduling conditions for achievability of the link-flow vector by edge-coloring the scheduling multi-graph; (d) solving a linear optimization problem over the one or more necessary scheduling conditions to obtain an upper bound on the achievability of the link-flow vector; (e) generating, based on the scheduling multi-graph, a solution comprising a set of routes and an associated schedule for achieving the link-flow vector, the solution being a lower bound on the achievability of the link-flow vector; and (f) implementing a routing method using the set of routes and the associated schedule to route the link-flow vector from the source node to the destination node. At least one node v of the network is adapted to receive transmissions from a specified plurality Ω(v) of other nodes, and at least one of the scheduling conditions depends on Ω(v).
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
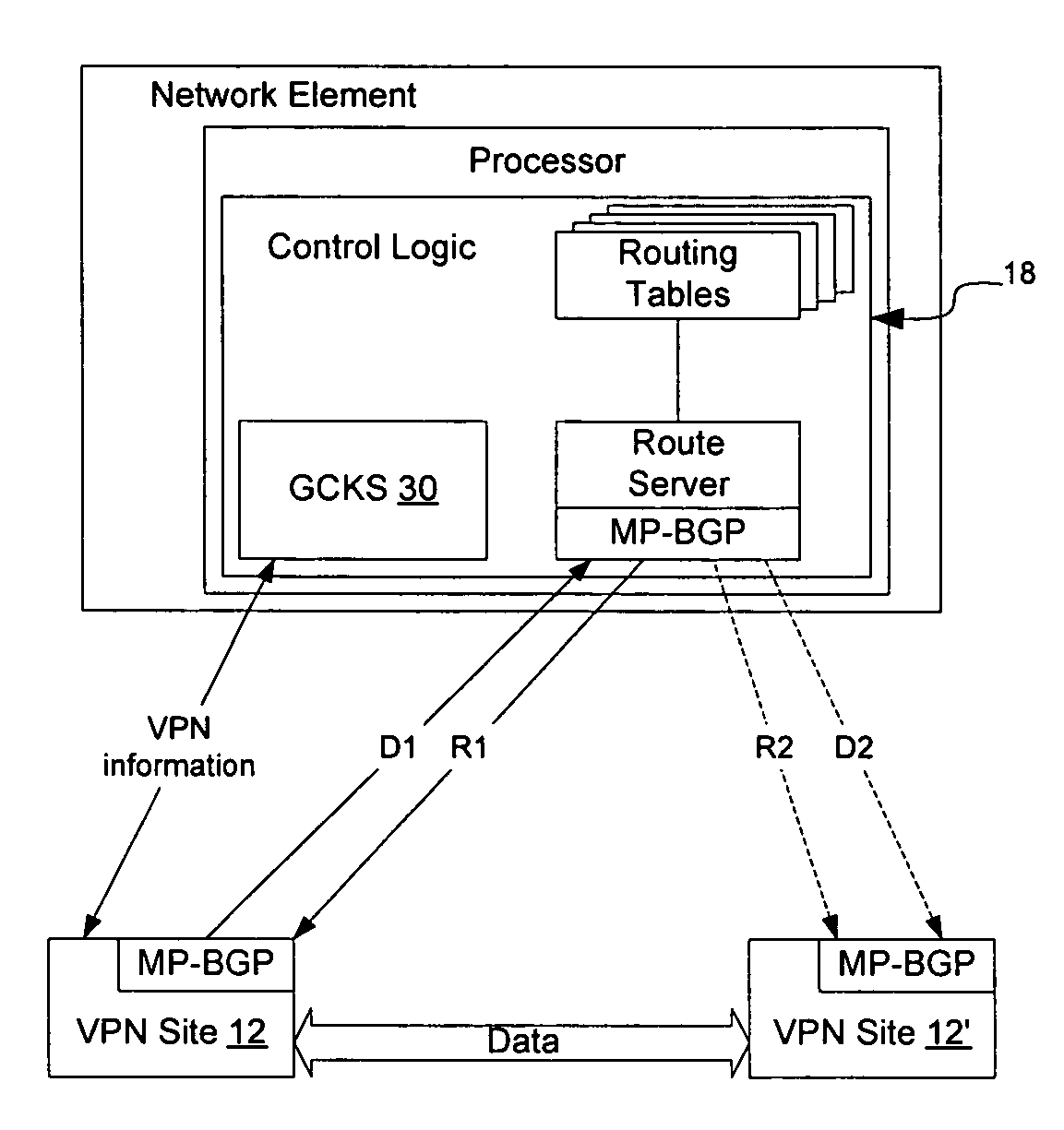
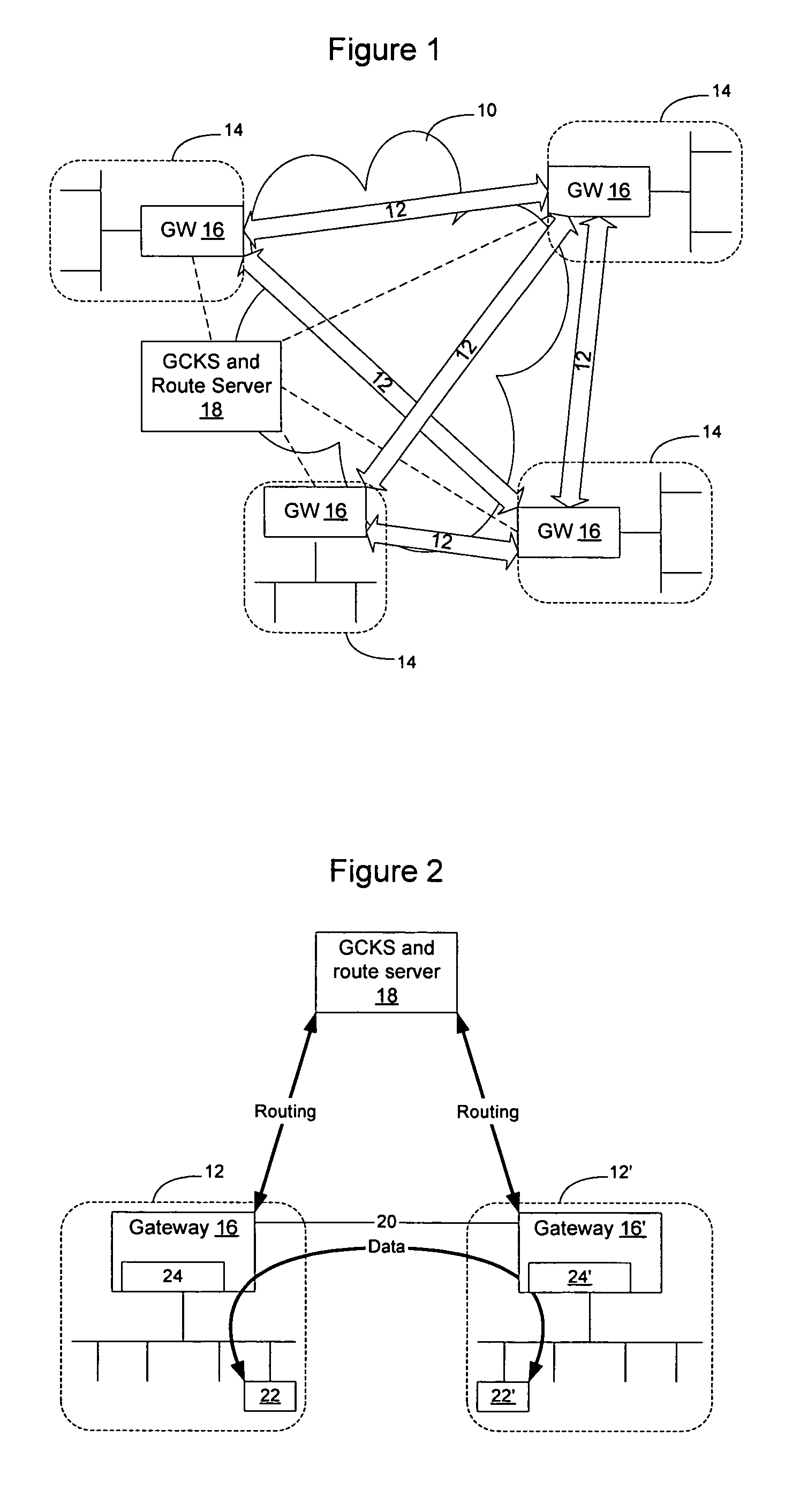
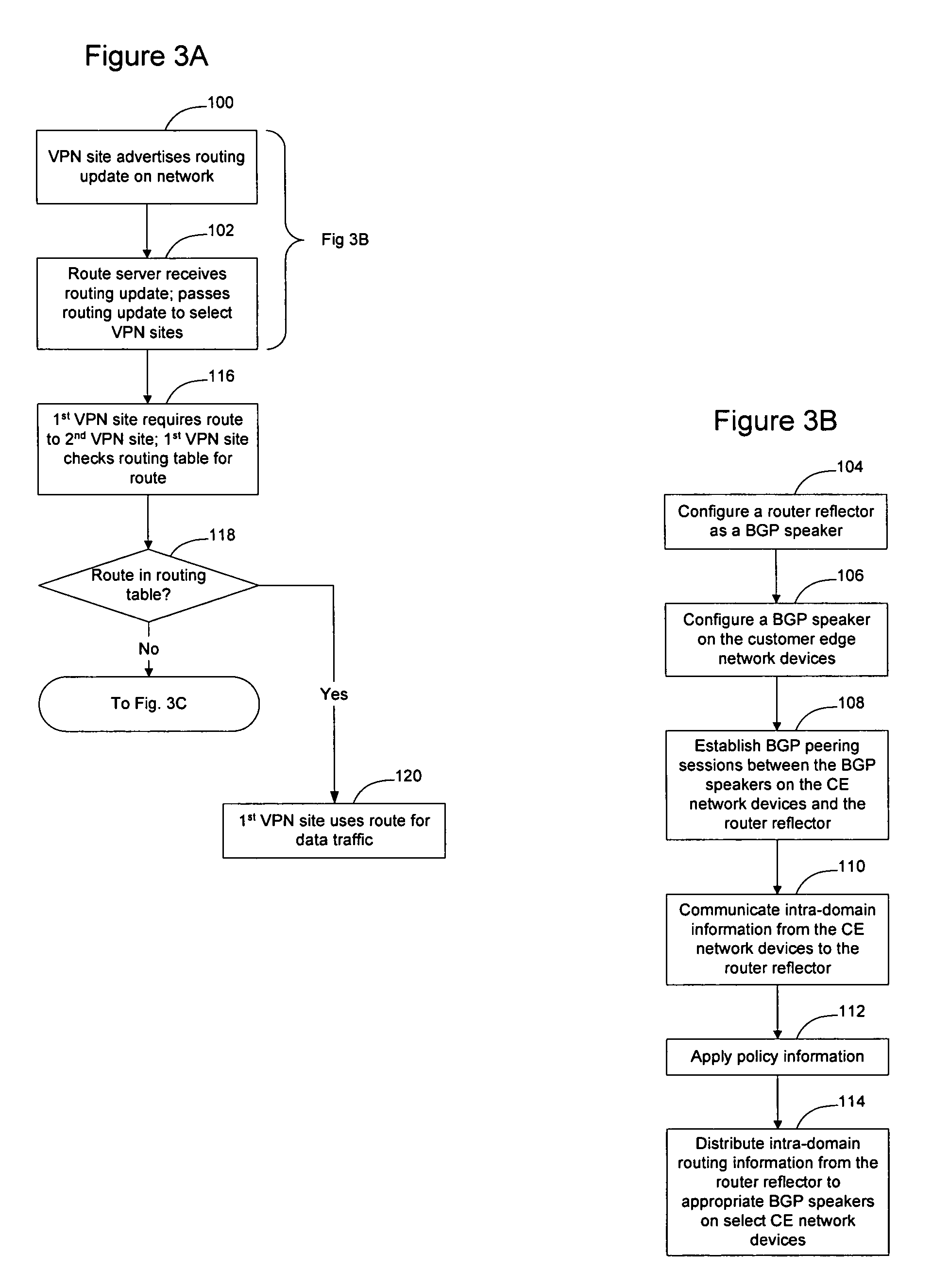
Method and apparatus for obtaining routing information on demand in a virtual private network
InactiveUS7590074B1Overcomes drawbackData switching by path configurationGroup controllerRouting table
Routing information may be provided to VPN sites on demand to allow smaller VPN sites with smaller routing tables to communicate directly with other VPN sites. This allows the meshed VPN architecture to scale to a size larger than where each VPN site is required to store routing information for all other VPN sites. A route server is instantiated on the network, optionally in connection with a Group Controller Key Server, to manage distribution of routes on the network and to provide routes to VPN sites on demand. As routes are learned by the VPN sites they are advertised to the route server, which selectively advertises the routes to other VPN sites depending on the per-site preferences. When a VPN site needs routing information to communicate with another VPN site, the network element will check its routing table for the route, and if the route is not available, will obtain the route on-demand from the route server.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method for wireless self-organizing of monitoring system to form tree-shaped routing
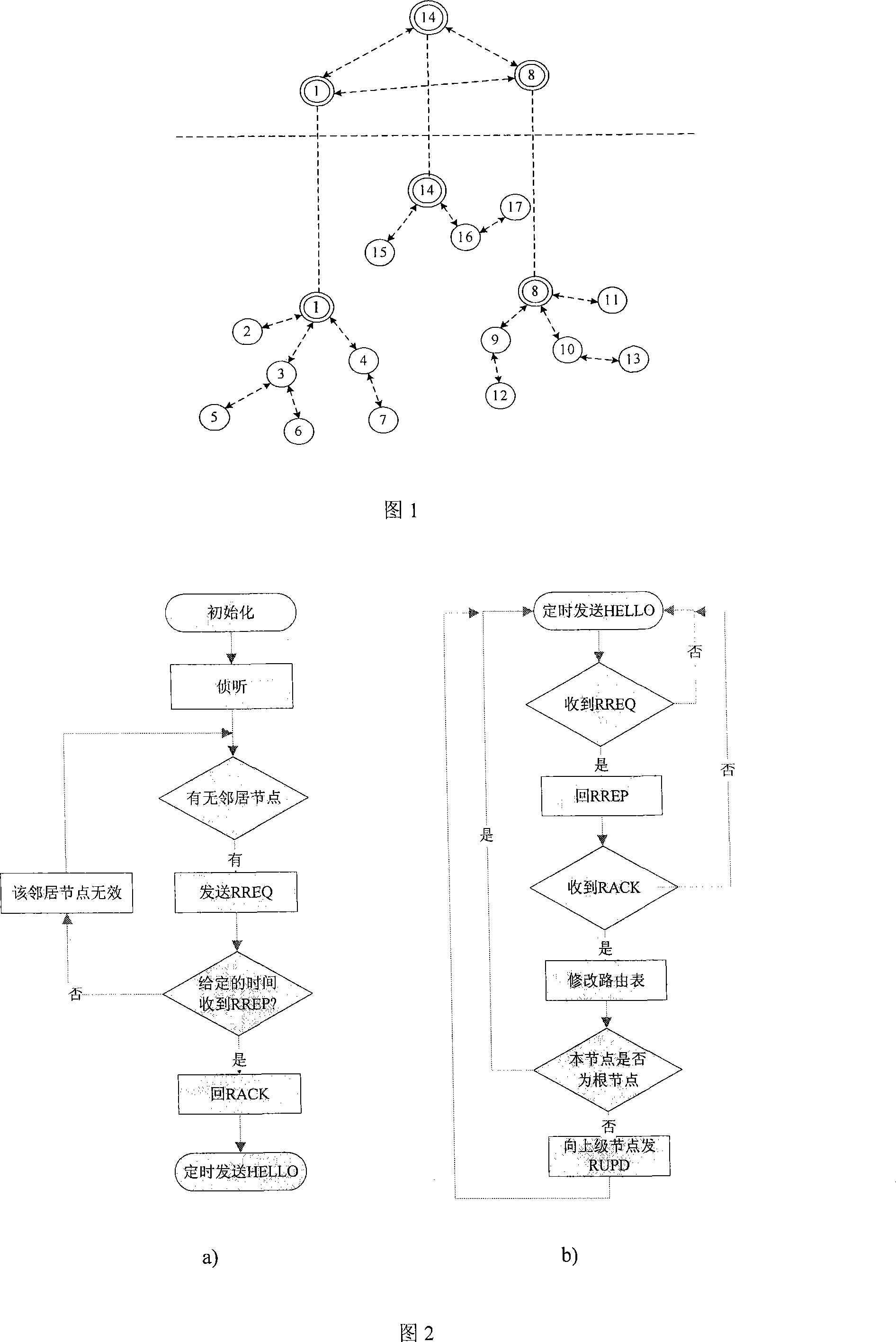
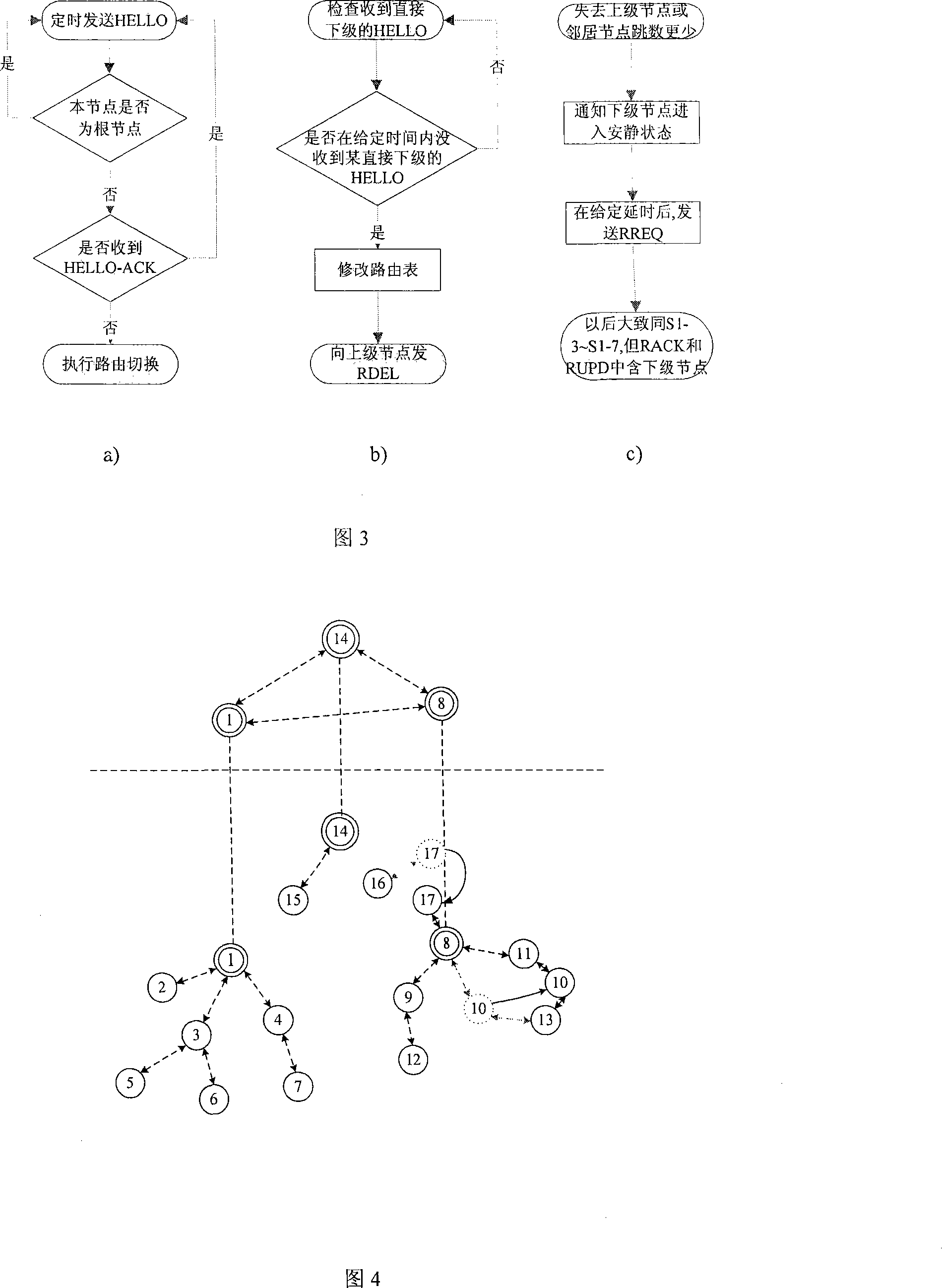
InactiveCN101179499AAdaptableReduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationStructure of Management InformationNetwork communication
The invention relates to a method for routing a queue tree in a wireless self-organization network applicable to a monitoring system. The invention includes a routing generation process, a dynamic maintenance of the routing and a monitoring data amalgamation transmission based on routing arithmetic. A network node selects the neighboring node with a small hot count to send a routing establishment request, and according to a handshaking mechanism, a routing relationship between an upper level and a lower level is established, and the whole network is formed a plurality of tree routing structures; according to ways of a connection detection, a past-due detection and upper node switching, a dynamic maintenance of the routing is realized, changes in network communication topology caused by factors such as the motion of the node and power change are adapted; by using the network structure of the tree routing, the node is able to inosculate the a communication desire to monitor the data in due time at the same time of maintaining the route. The method of the invention has the advantages of low spending on the communication, small delay of transmission and steady and reliable network.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
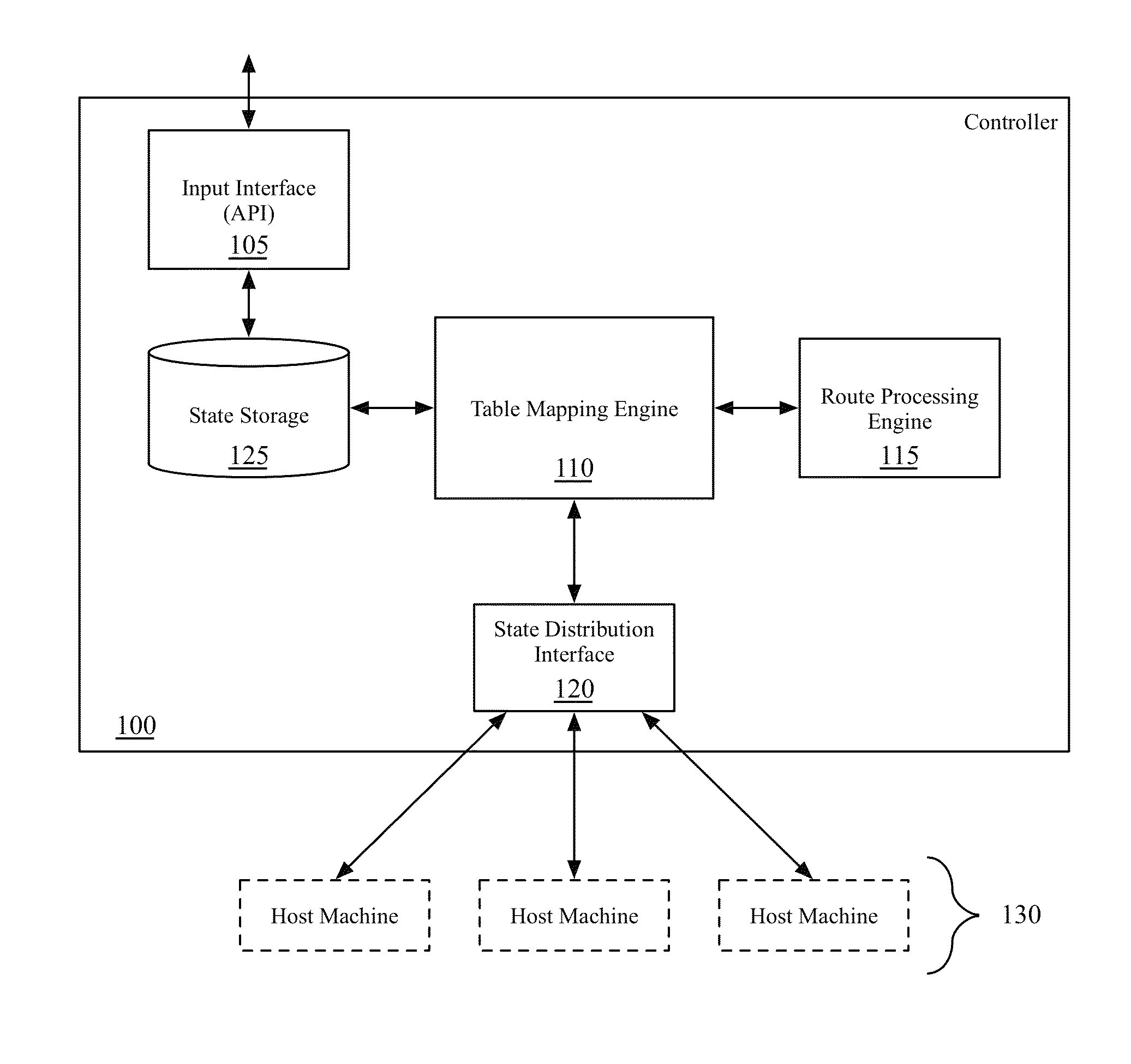
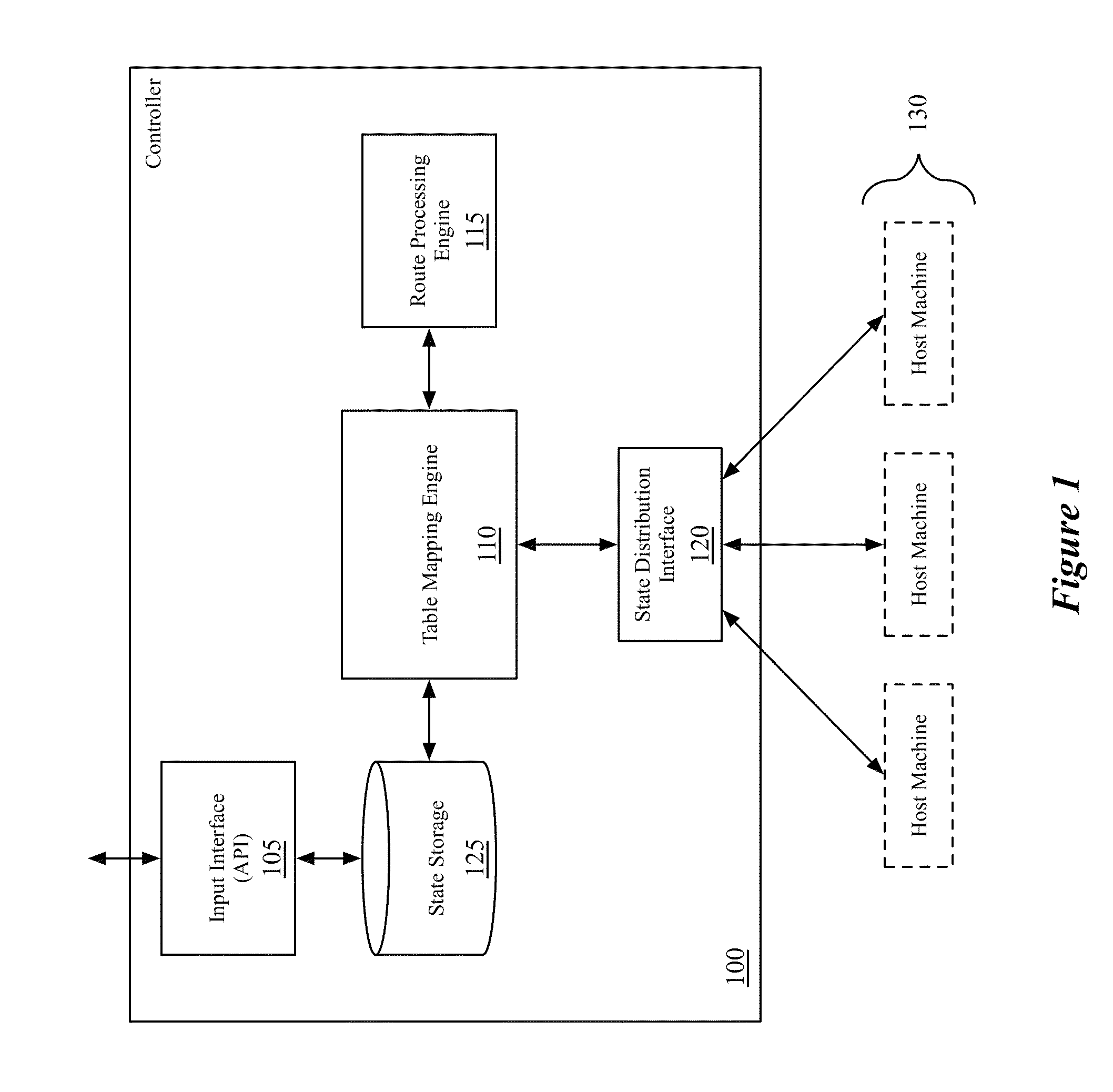
Static routes for logical routers
Some embodiments provide a method for a network controller. The method receives configuration data, for a logical router managed by the network controller, that specifies at least one logical port for the logical router. The method automatically generates connected routes for the logical router based on network address ranges specified for the logical ports of the logical router. The method receives a manually input static route for the logical router. The method generates data tuples, for distribution to several managed network elements, based on the connected and static routes for the logical router in order for the several managed network elements to implement the logical router.
Owner:NICIRA
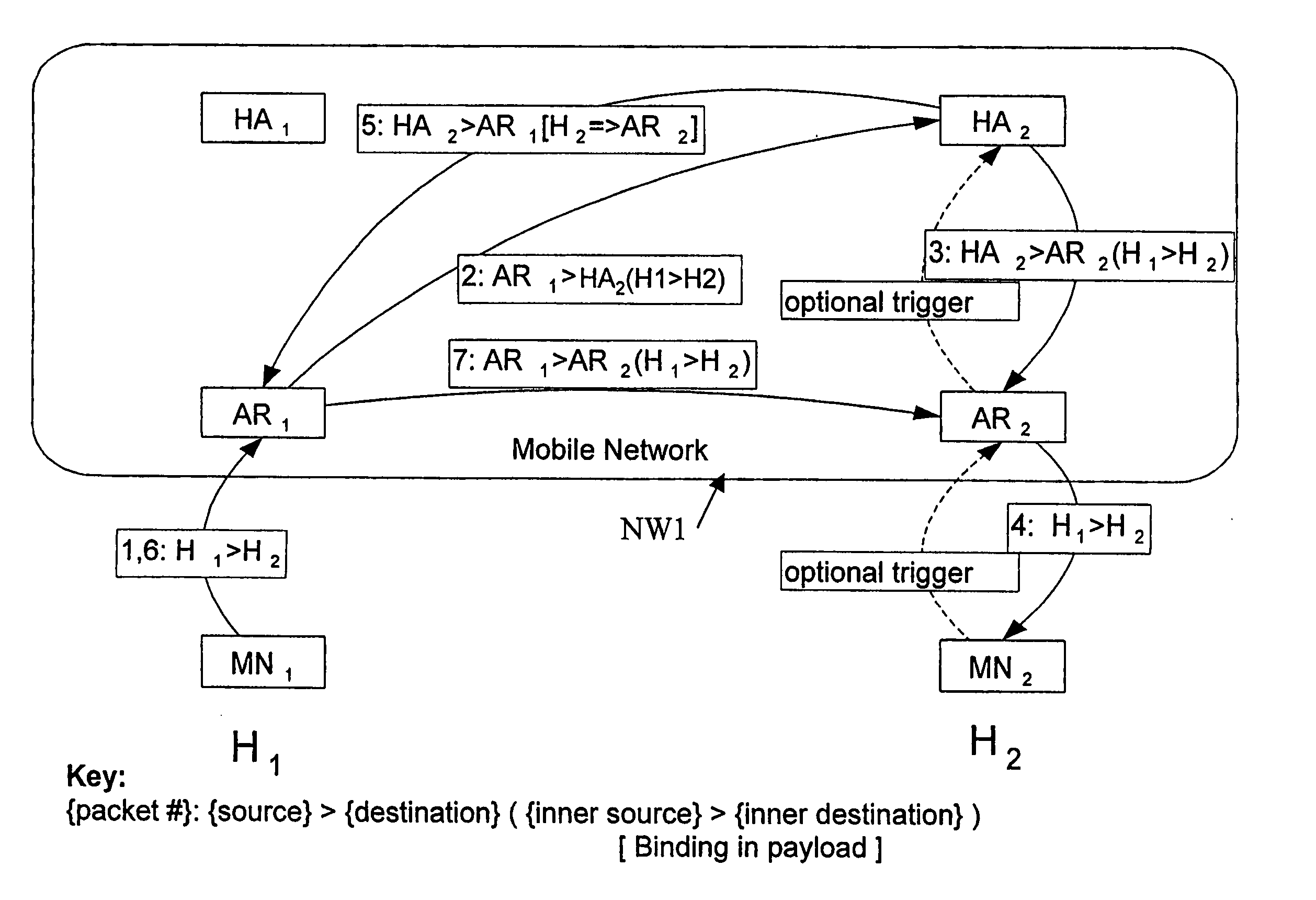
Route optiminzing in mobile ip providing location privacy
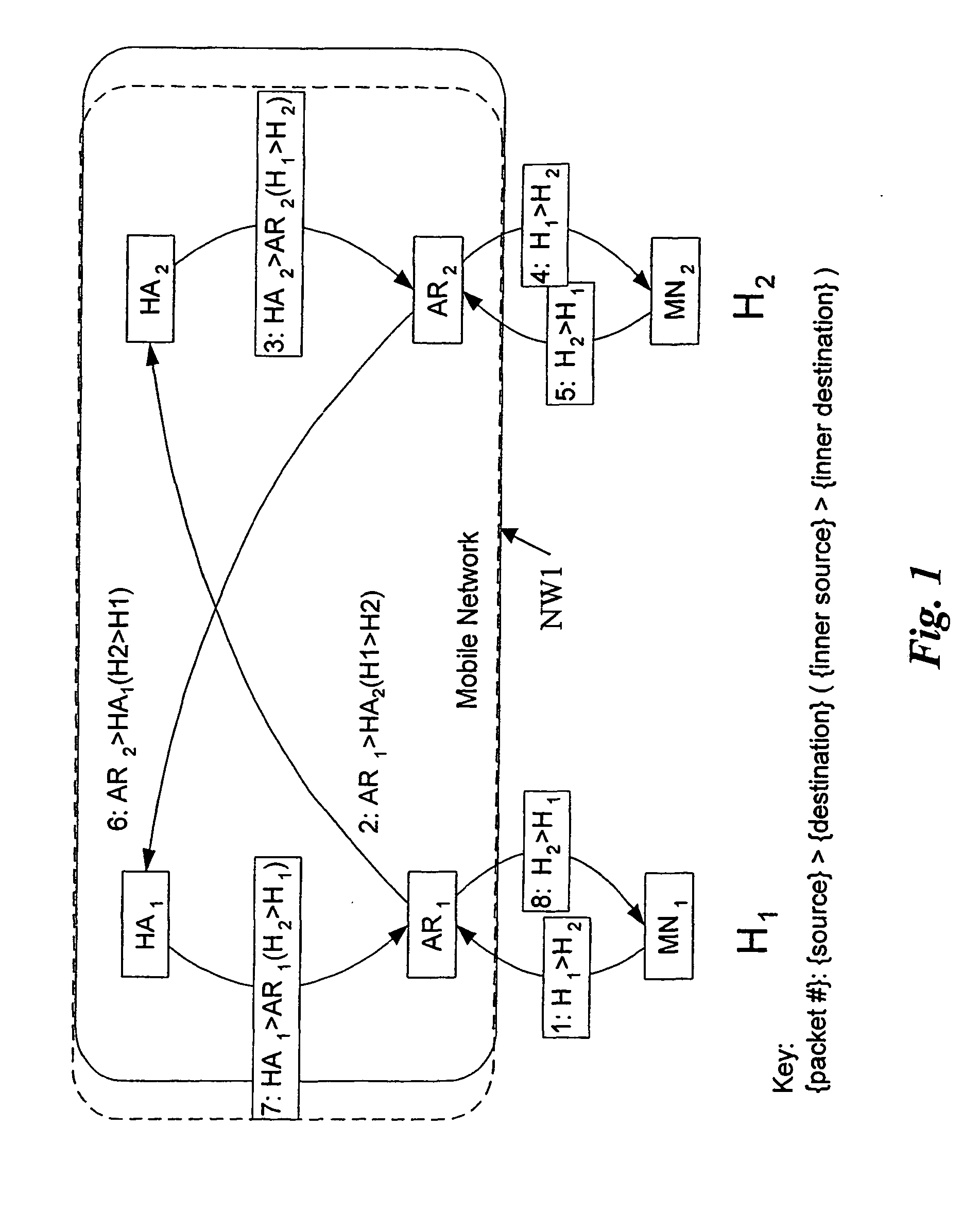
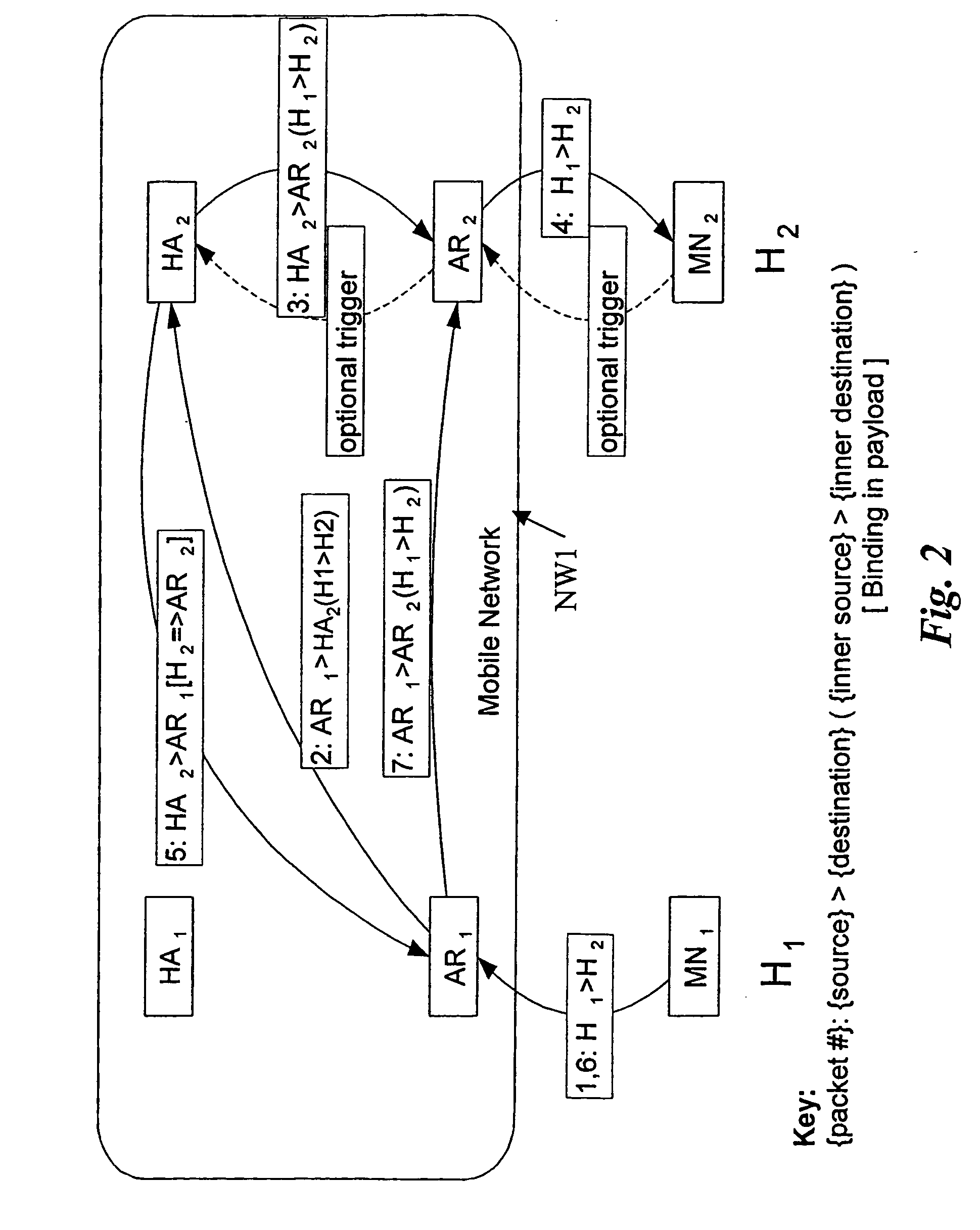
A routing method for routing data packets from a source terminal to a destination terminal via at least one communication network, said at least one communication network comprising at least one mobility agent entity for each of said terminals, the method comprising the steps of: establishing a route from the source via at least one first mobility agent, at least two consecutively arranged second mobility agents, to said destination, deciding that said route is to be optimized, rerouting said route from one of said at least one first mobility agents directly to one of the at least two consecutively arranged second mobility agents such that at least one intermediate mobility agent in said route is bypassed in the resulting rerouted route.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Edge routing node and method for prefetching content from multisource by edge routing node
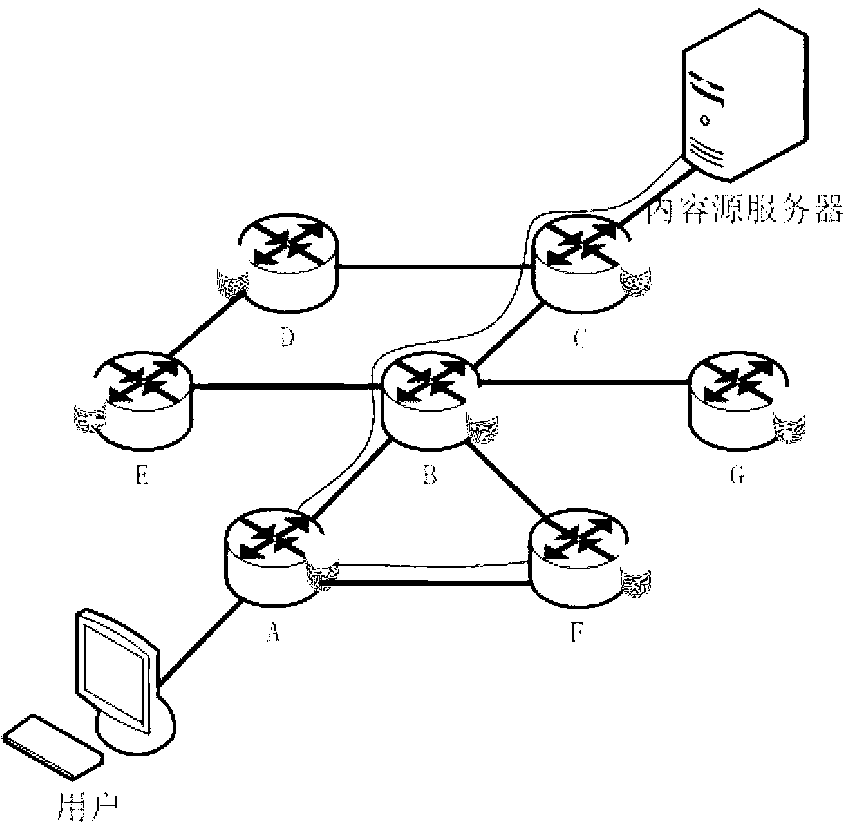
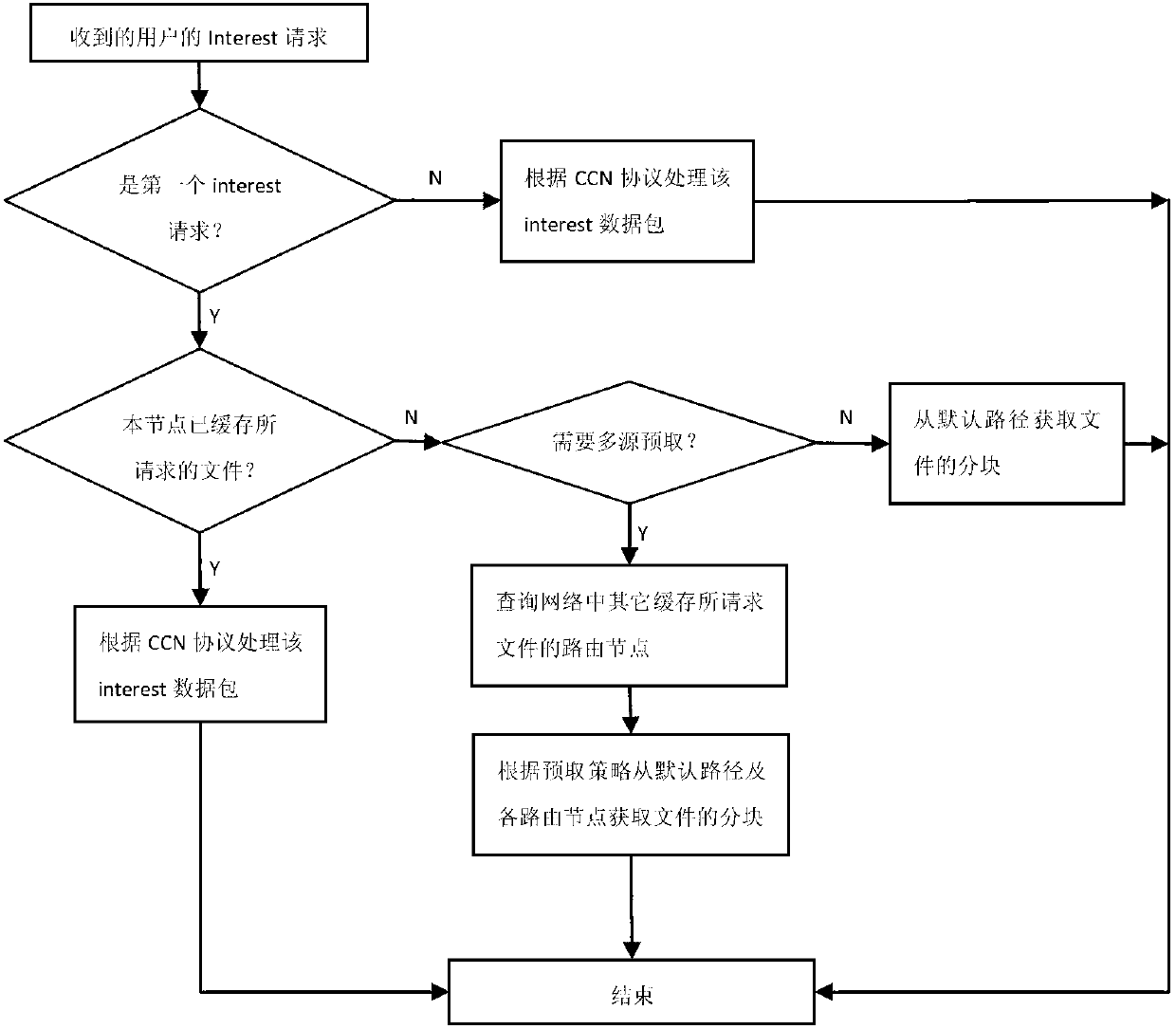
InactiveCN103023768AImprove distribution efficiencyImprove acquisition efficiencyData switching networksWeb resourceNetwork packet
The invention relates to method for prefetching content from multisource by an edge routing node of a content central network and the edge routing node. The method includes: judging whether a data packet arrives the first time or not; if so, inquiring whether the node caches corresponding contents or not; and if not, judging whether the contents satisfy conditions for starting multisource prefetching or not, and if so, performing multisource prefetching. The multisource prefetching includes: inquiring which routing nodes caches the contents, by the edge routing node, parallelly acquiring different blocks of the contents from a content source server of the content central network and routing nodes cached with the contents. Multisource prefetching is started on the basis of size of contents, parallel prefetching proportion is set on the basis of available link bandwidth, route path of newly increased routes fields can be appointed, utilization efficiency of network resources is improved, and distribution and acquisition efficiency of contents are improved.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
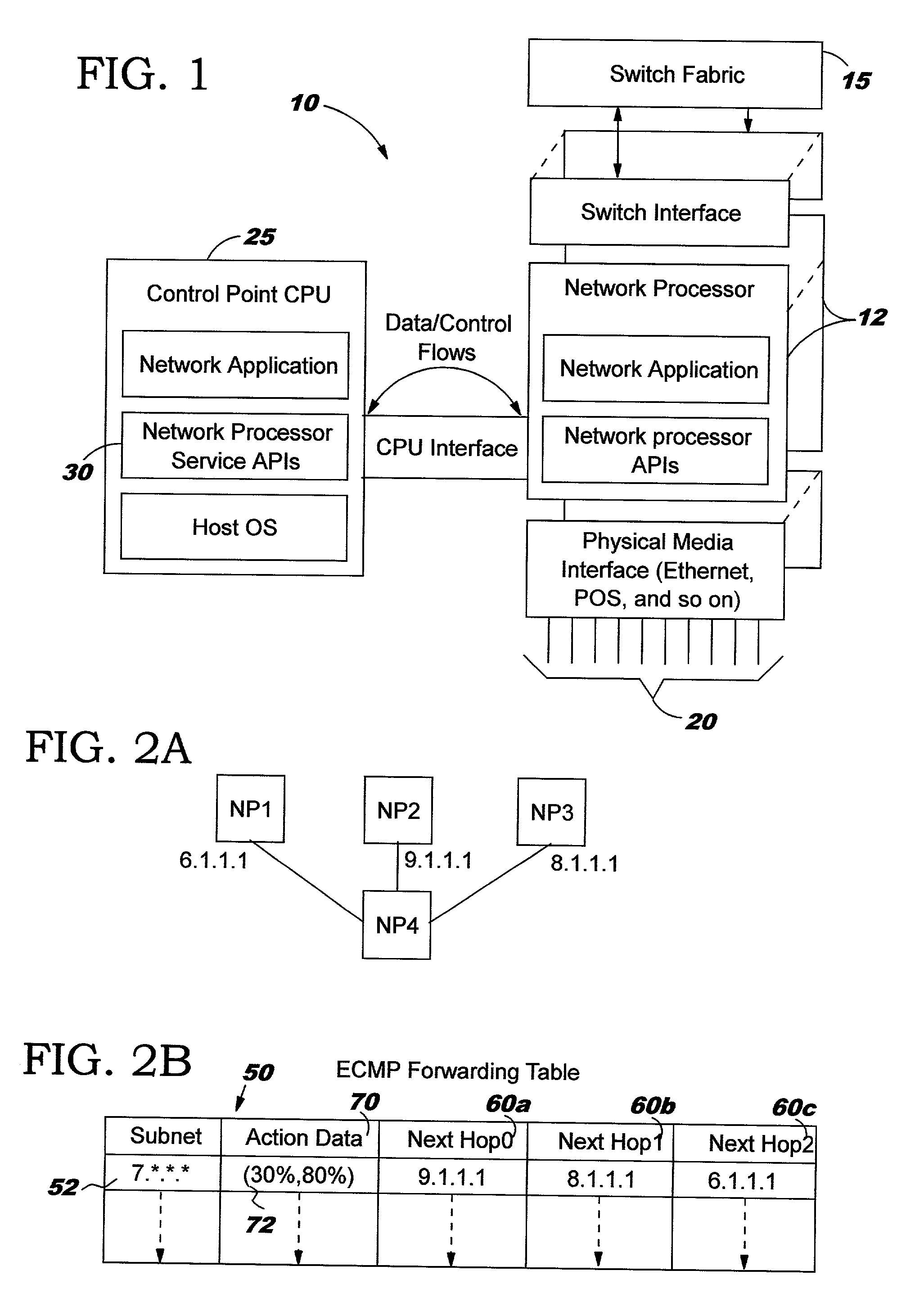
System and method for distributing route selection in an implementation of a routing protocol
ActiveUS20050135256A1Easy accessReduce memory usageError preventionTransmission systemsRouting protocolManet routing
A partial best path technique distributes route selection in a routing protocol implementation on a router. The technique also ensures that announced paths received from peers of the router (i.e., a “load”) are compared in a correct order to select best paths that are then used by the router to forward packets and to advertise to the peers. When employed in a distributed architecture, the technique further reduces memory usage. To that end, the partial best path technique enhances a best path selection algorithm executed by the router to enable dispersion of the received path load among processing nodes or elements of the router, while maintaining the ordering requirement of the algorithm. The partial best path technique essentially provides an enhancement to the best path selection algorithm that selects a subset of paths from a plurality of paths, with that subset being the minimal subset needed to select the best paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multi-path load balancing using route controller
ActiveUS20110134769A1Low costRaise the ratioError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic load balancingService control
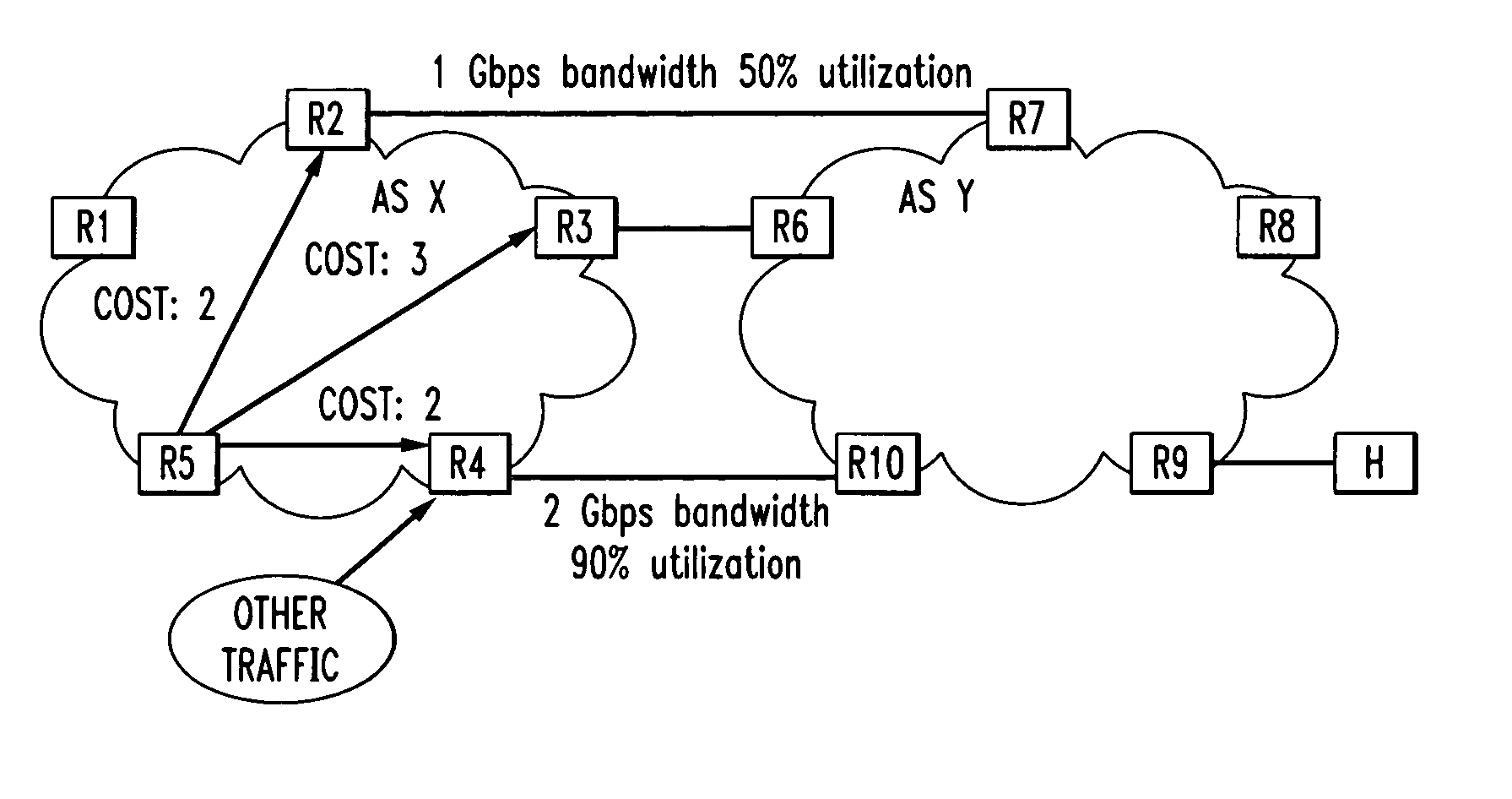
Systems and methods are described that employ multi-path BGP to realize dynamic multi-path load balancing based on an Intelligent Route Service Control Point (IRSCP) router control architecture that uses dynamic traffic flow information to perform dynamic load balancing to enable precise and effective load balancing.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
MAC address population protocol
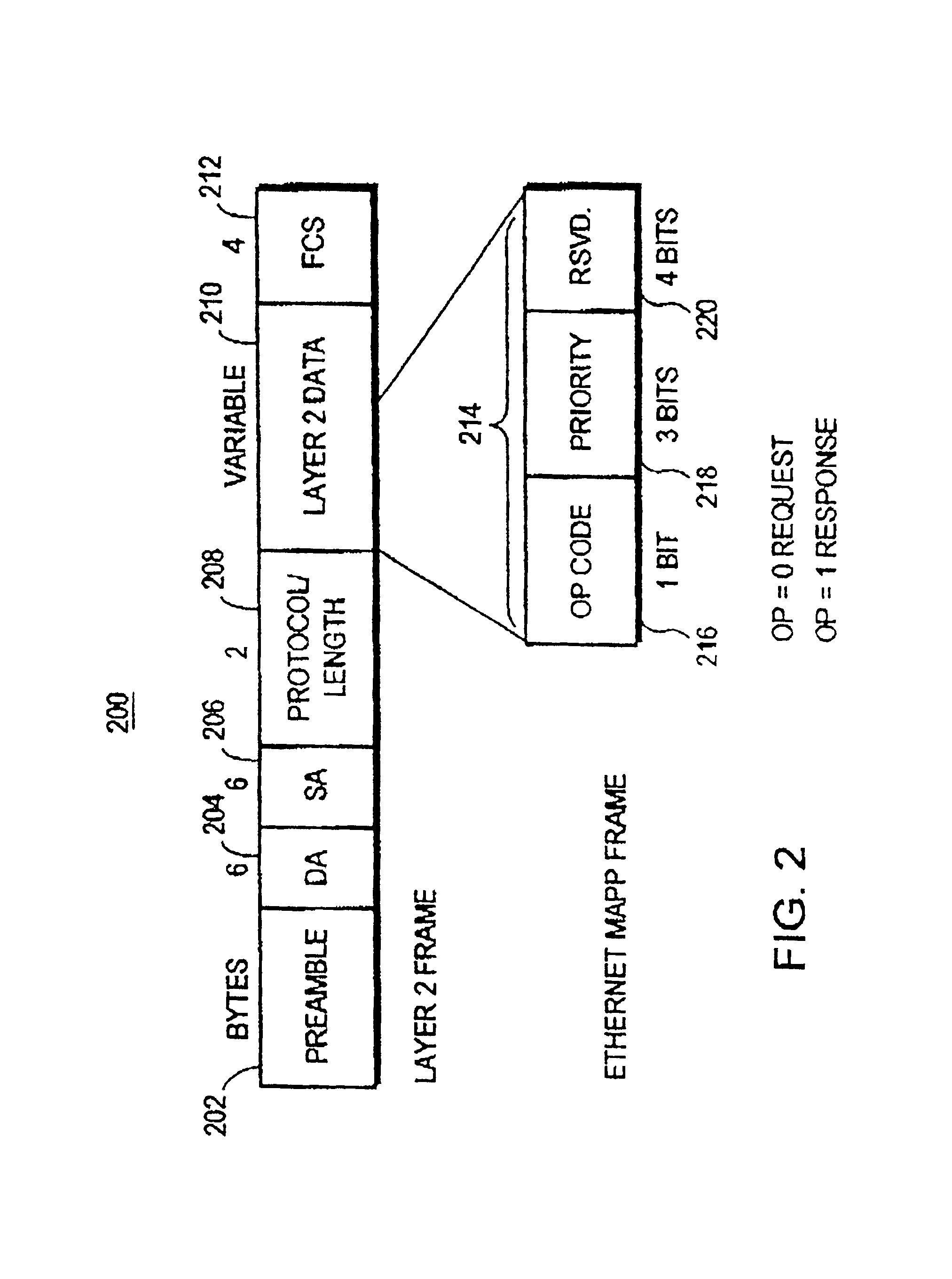
InactiveUS6873603B1Reduce network bandwidth consumptionNo need to waste bandwidthTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionPopulation protocolEthernet lan
A new search protocol uses a message which a router periodically transmits onto the local LANs connected to its ports, and in response to the new protocol, all end stations receiving the message transmit their addresses to the router. The addresses transmitted to the router comprise the addresses and any other information needed by the router to reach the end station. For example, for an Ethernet LAN the layer 2 or MAC layer address of the end station is transmitted to the router. In the event that the protocol of the LAN uses source routing, the information transmitted to the router includes both the MAC address and the Route Information Field of the end station. In any event, the router uses the information received from the end stations to build its routing table. Then, upon receipt of the next CANUREACH message from a peer router, the desired destination end station will appear in the router's routing table, and there will be no need to waste bandwidth by transmitting search messages looking for the end station. The new protocol messages are transmitted periodically in order to keep the routing tables current is as the network changes dynamically.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for multi-layer network routing
ActiveUS20070058607A1Facilitate multi-layer routingEliminate and greatly reduce disadvantageData switching by path configurationConnection typeTelecommunications network
Each node of a telecommunications network determines interface point connection type attributes available for each signal type supported by the node. Each signal type represents a different connection routing layer within the telecommunications network. Adaptation costs involved in traversing from one connection routing layer to another connection routing layer in the node are calculated. The connection type attributes and adaptation costs are included in a link state advertisement broadcasted by each node in the telecommunications network. A route calculation is performed for a desired signal to determine a route through the telecommunications network for the signal. The route calculation takes into account the various connection type attributes, availability, and adaptation costs in determining the shortest route for the signal through the telecommunications network.
Owner:DR REDDYS LAB LTD +1
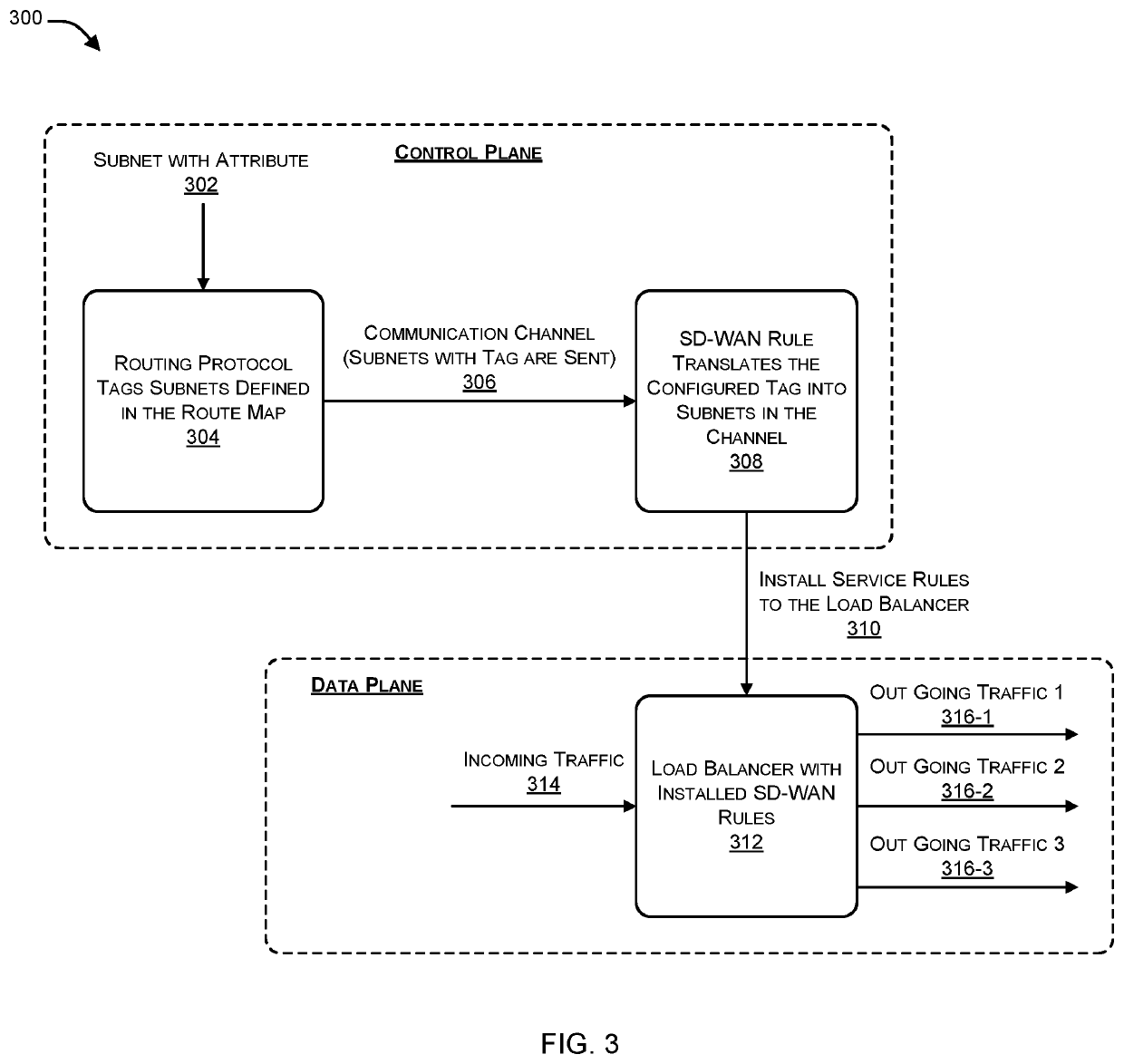
Dynamic service-based load balancing in a software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN)
Systems and methods for dynamic service-based load balancing in an SD-WAN are provided. According to one embodiment, a routing protocol daemon of an SDN controller within a spoke network receives a dynamically assigned subnet and associated attributes for a client device newly registered with the hub network. The routing protocol daemon tags the subnet with a route tag using a route map based on the received attributes meeting network administrator-defined match criteria for corresponding attributes associated with the route tag in the route map. The tagged subnet is communicated to an SD-WAN daemon of the SDN controller, which translates an SD-WAN service rule defined with reference to the route tag to an SD-WAN service rule defined with reference to the subnet. A load balancer associated with the spoke network is caused to perform load balancing of incoming network traffic in accordance with the translated SD-WAN service rule.
Owner:FORTINET
Central authority for service and topology exchange
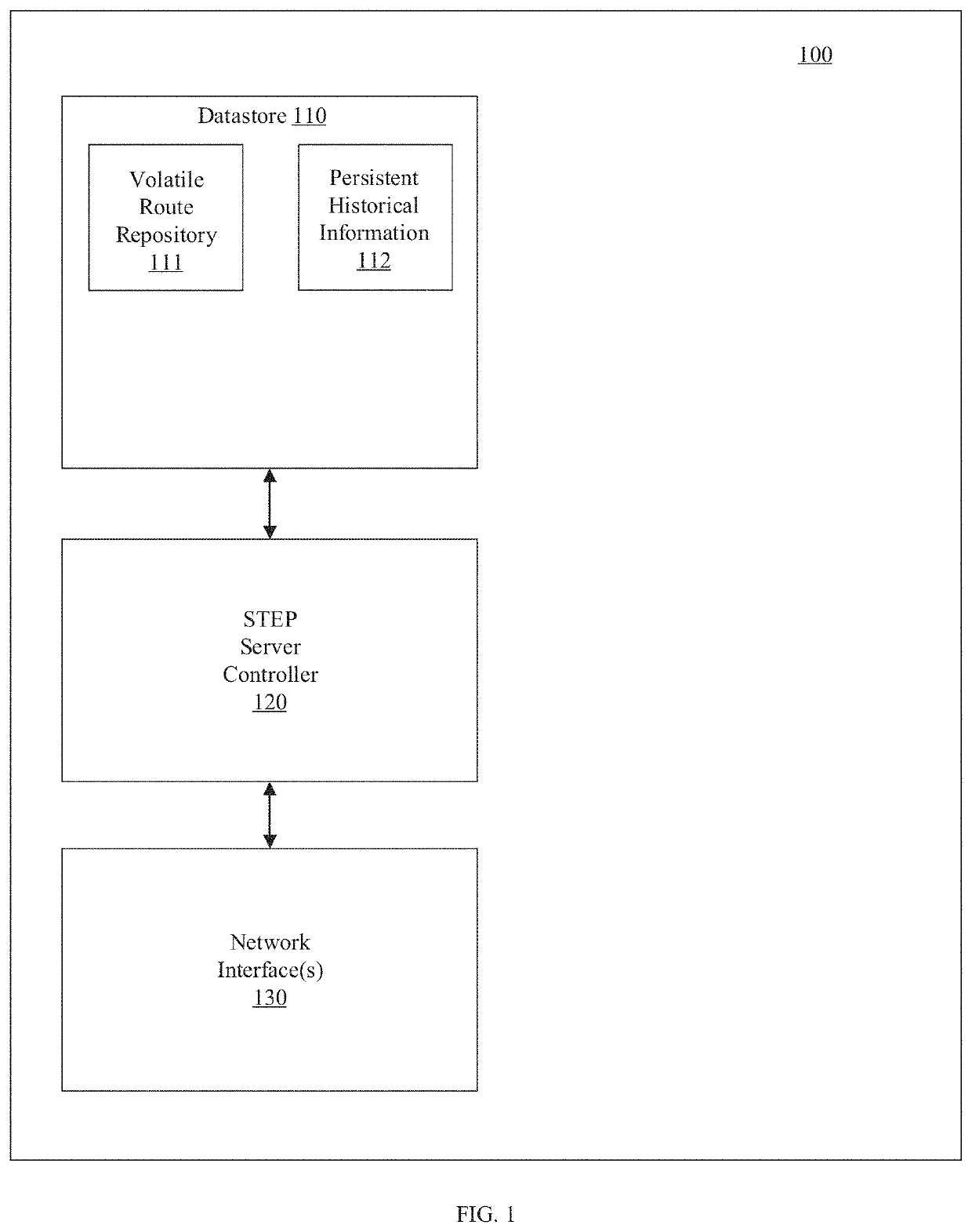
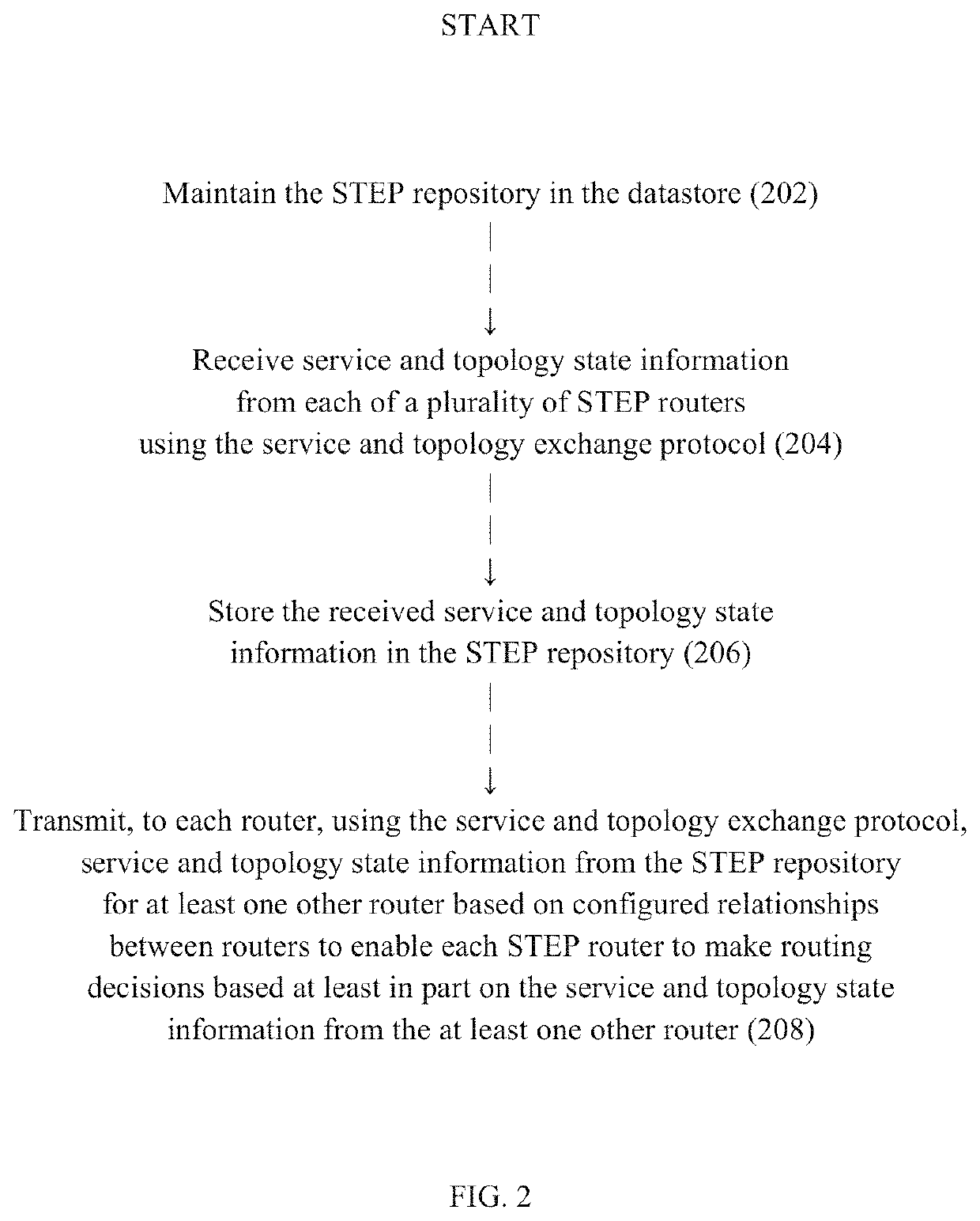
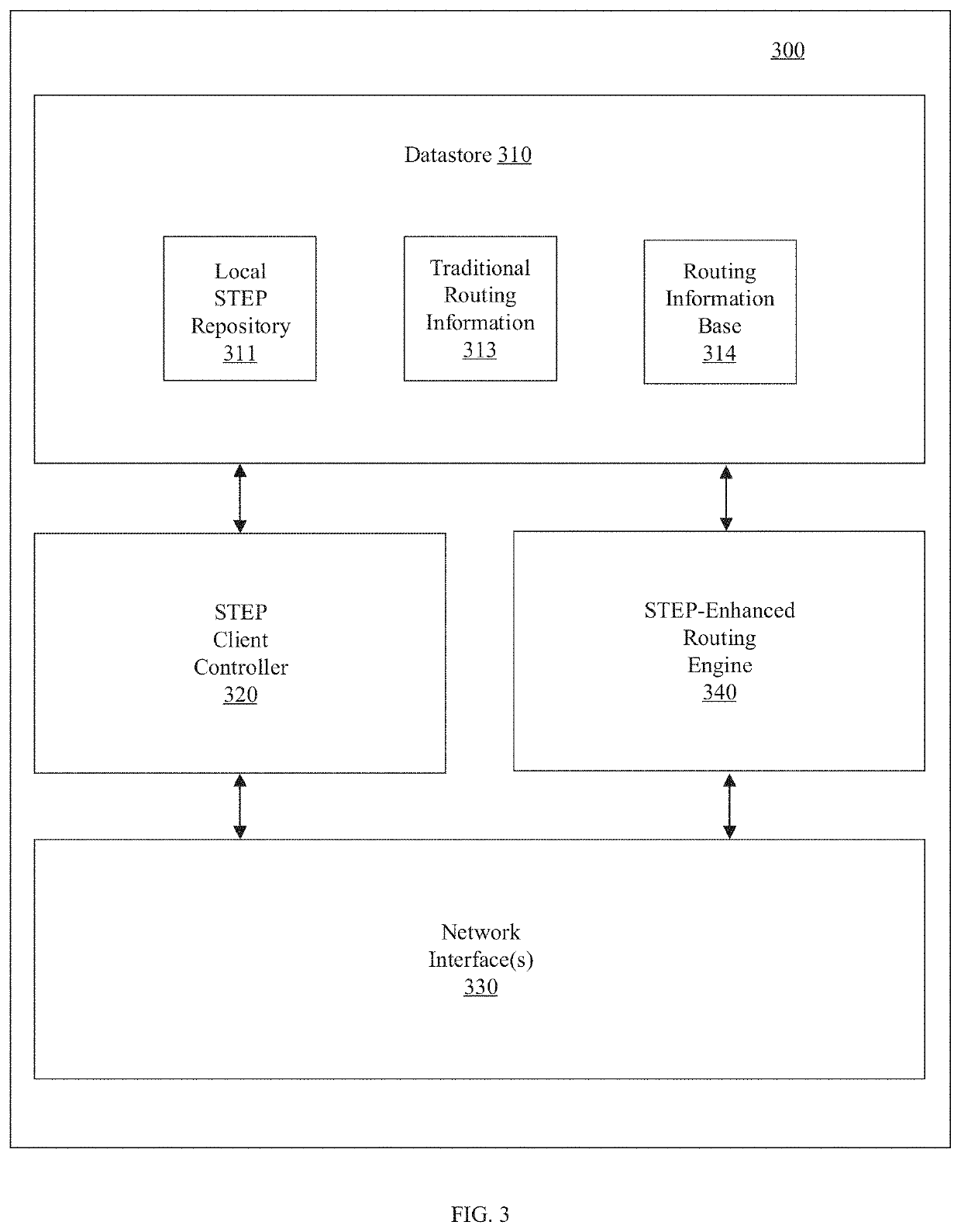
A routing system for implementing a service and topology exchange protocol (STEP) comprises a primary STEP server configured to maintain a STEP repository and a plurality of routers, each router including a STEP client in communication with the primary STEP server. The STEP client of each router is configured to transmit, using the service and topology exchange protocol, service and topology state information for at least one route or service available through the router to the primary STEP server for storage in the STEP repository. The primary STEP server is configured to determine, for each router, whether the STEP repository includes any service and topology state information changes for the router based at least in part on the service and topology state information received from the routers and to transmit to the STEP client of each router for which there are service and topology state information changes, using the service and topology exchange protocol, only the service and topology state information changes.
Owner:128 TECH
Scalable unidirectional routing with zone routing protocol extensions for mobile AD-HOC networks
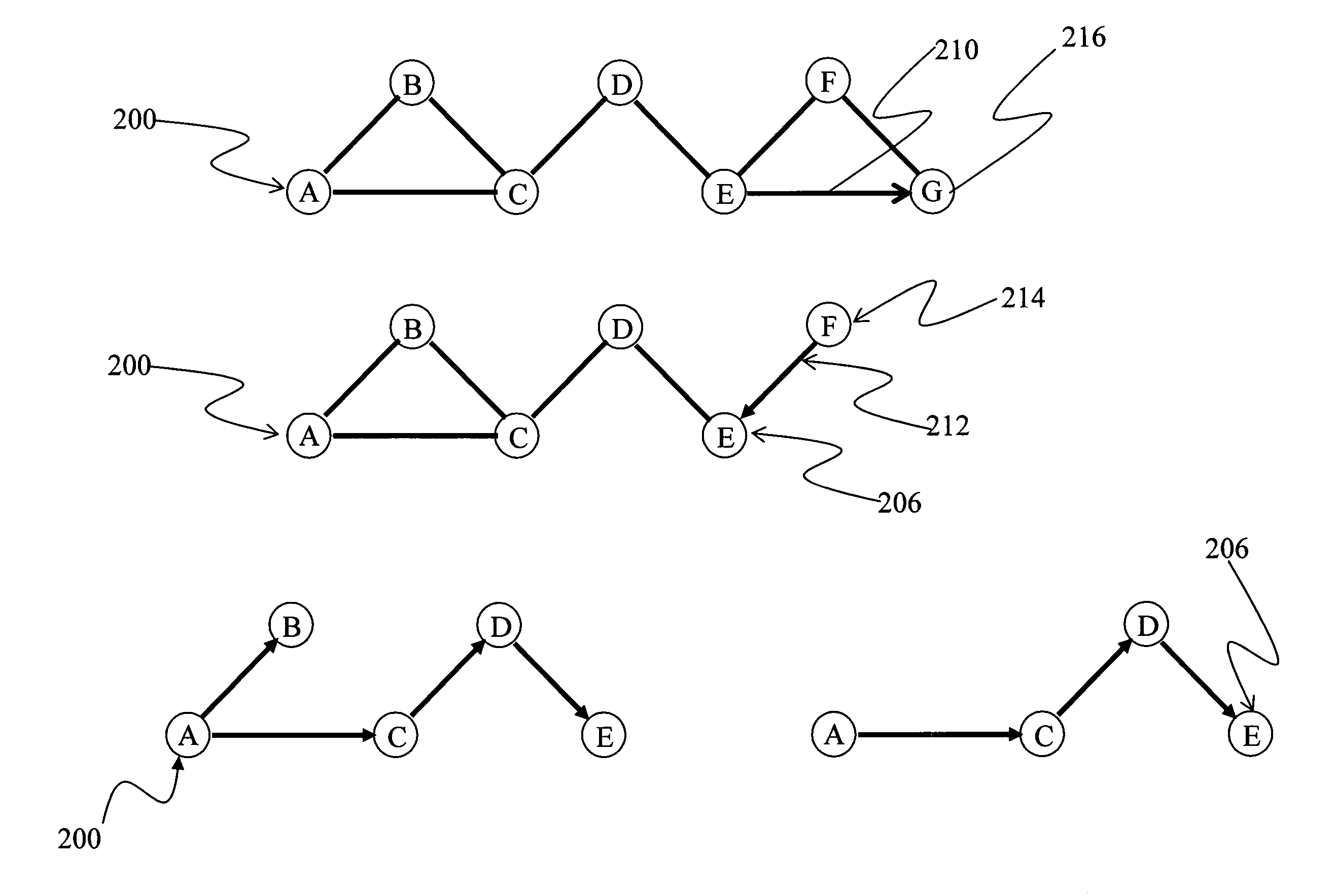
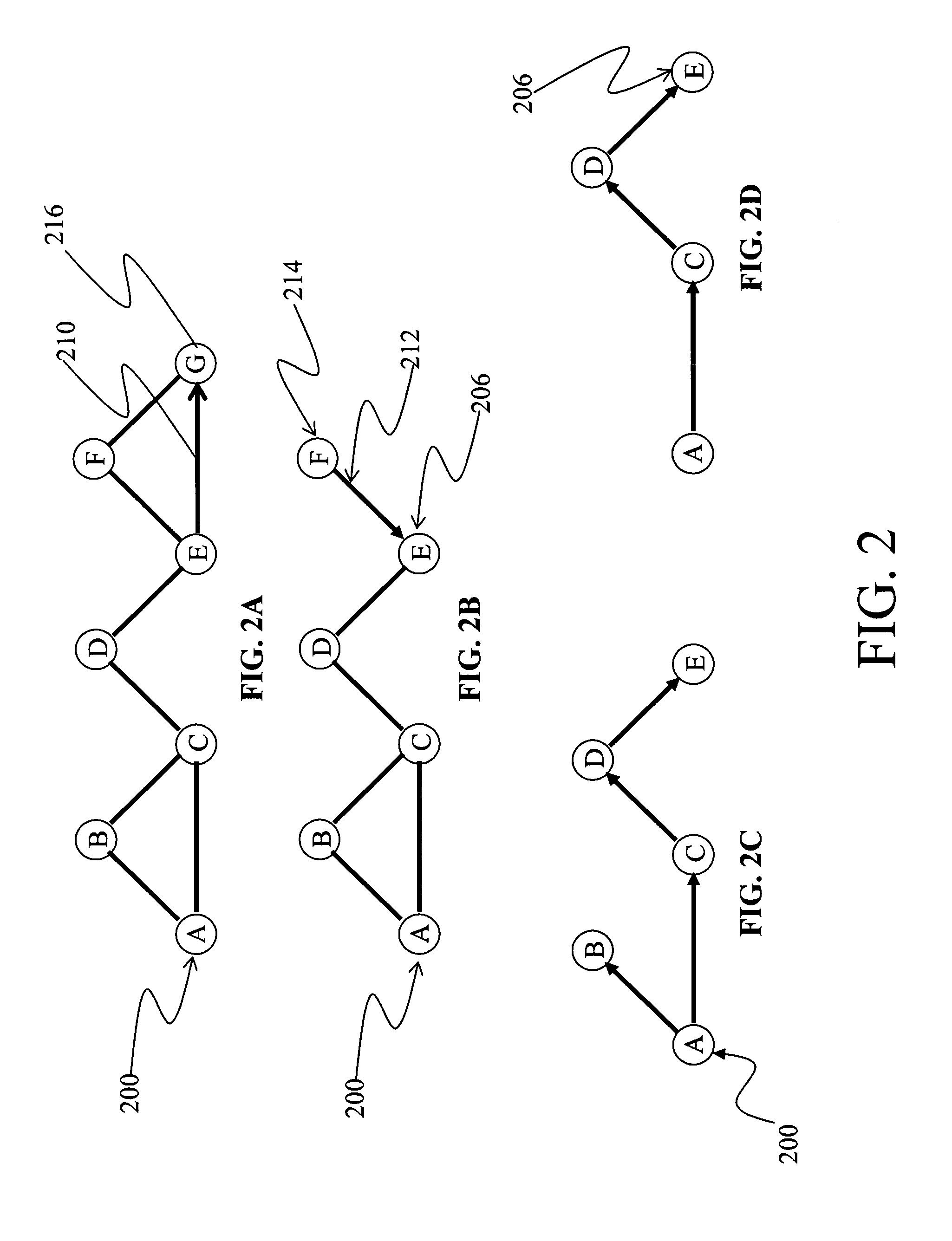
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for extending a zone routing protocol. The invention is configured to provide a robust scalable framework for routing data in wireless ad-hoc networks when unidirectional links 210 are present. When the reverse path from a destination node (the tail) of a unidirectional link 210 to the originating node (the head) of the link is beyond a designated length, the invention is configured to revert to an on-demand search mechanism. The on-demand search mechanism recursively attempts to build a path to the destination 206 by recognizing nodes that have a route to the destination.
Owner:HRL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com