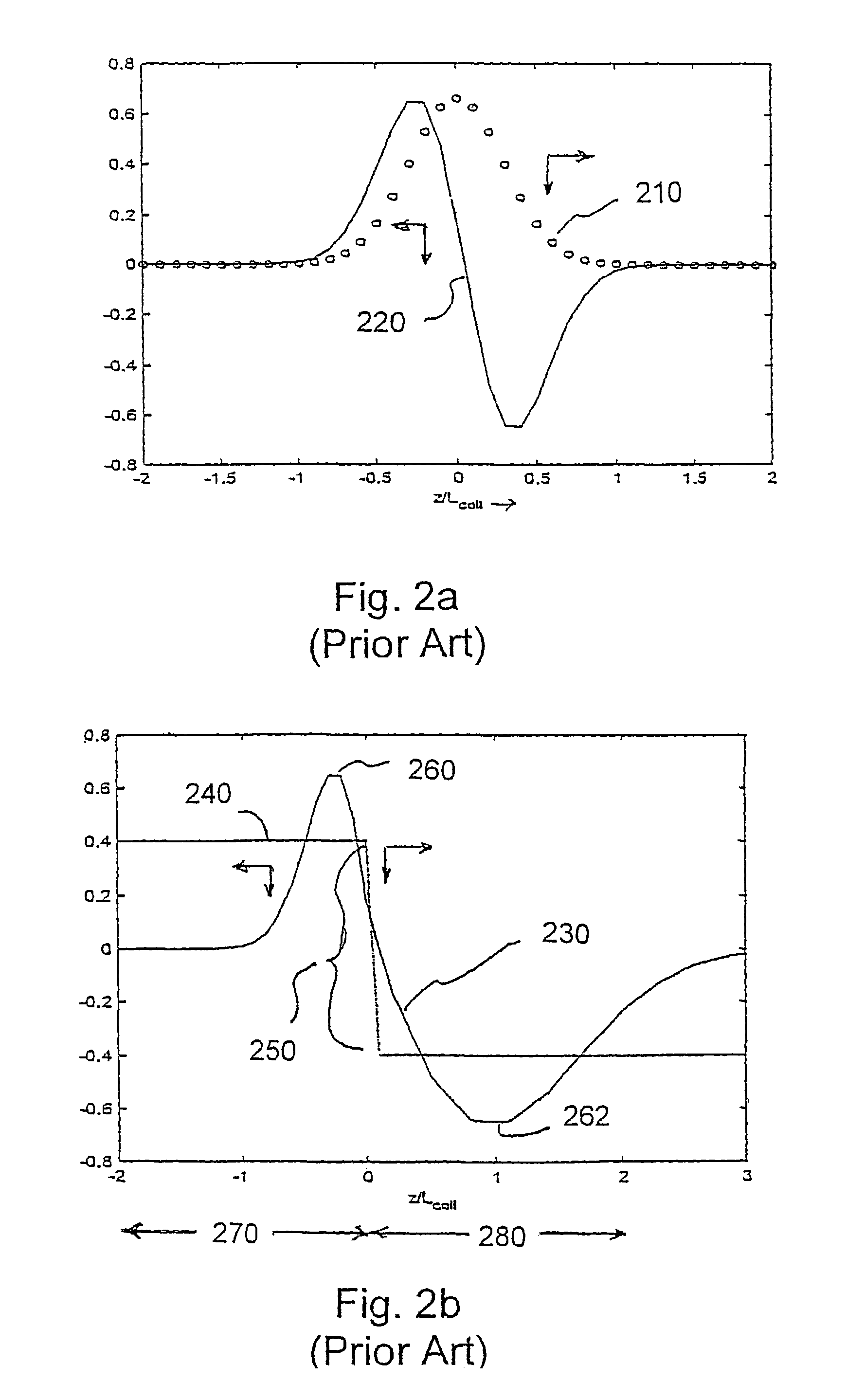
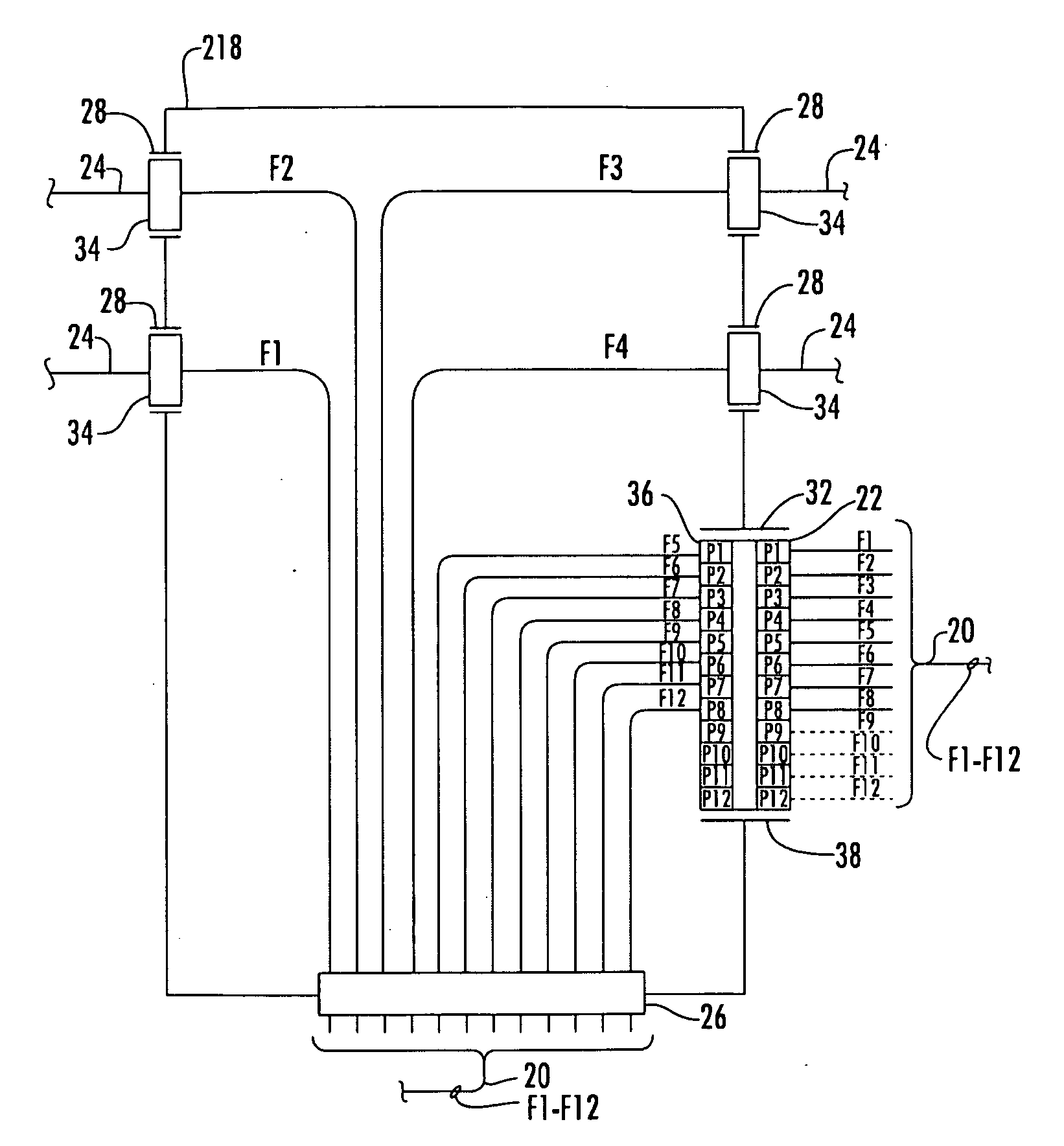
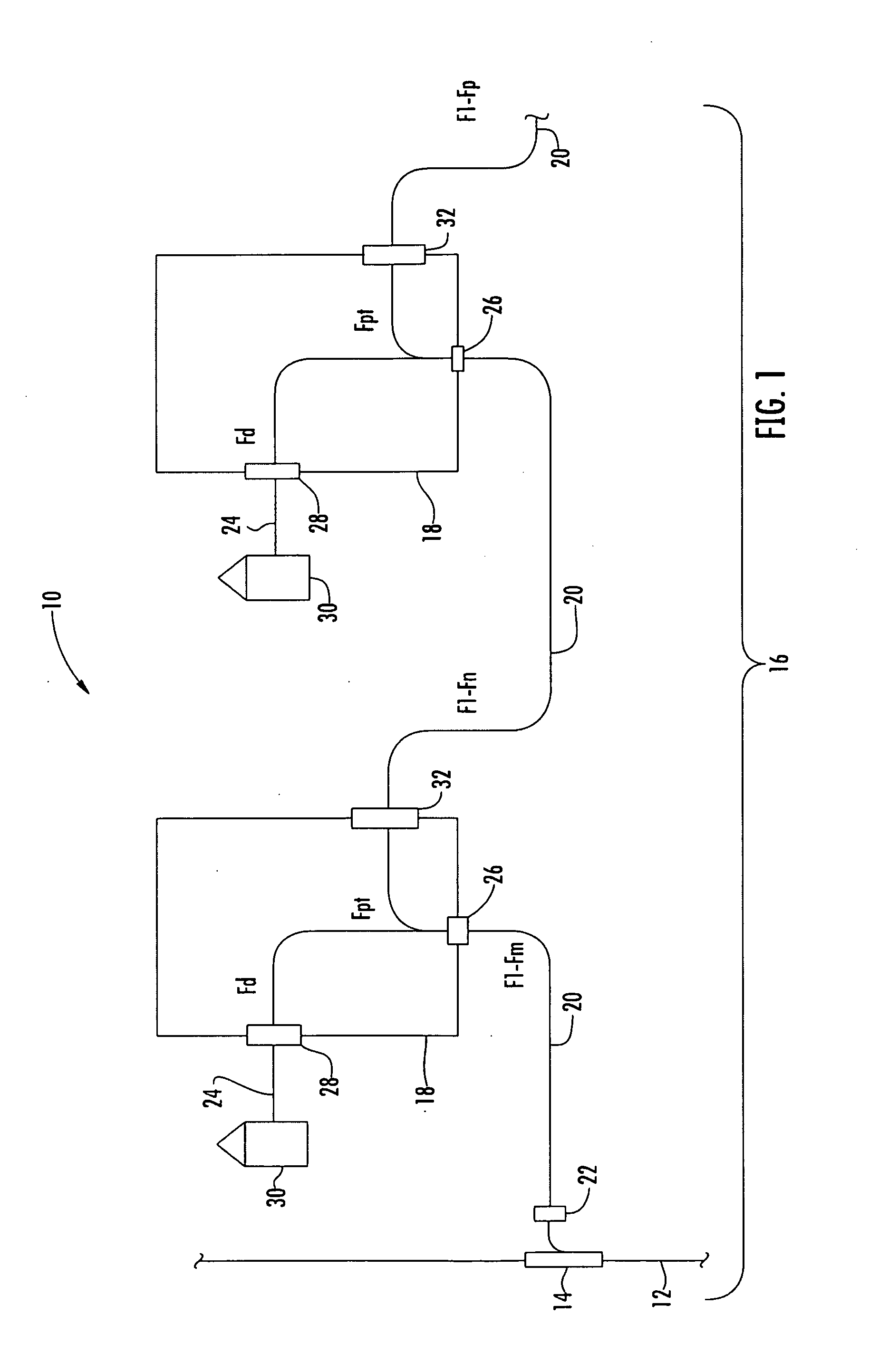
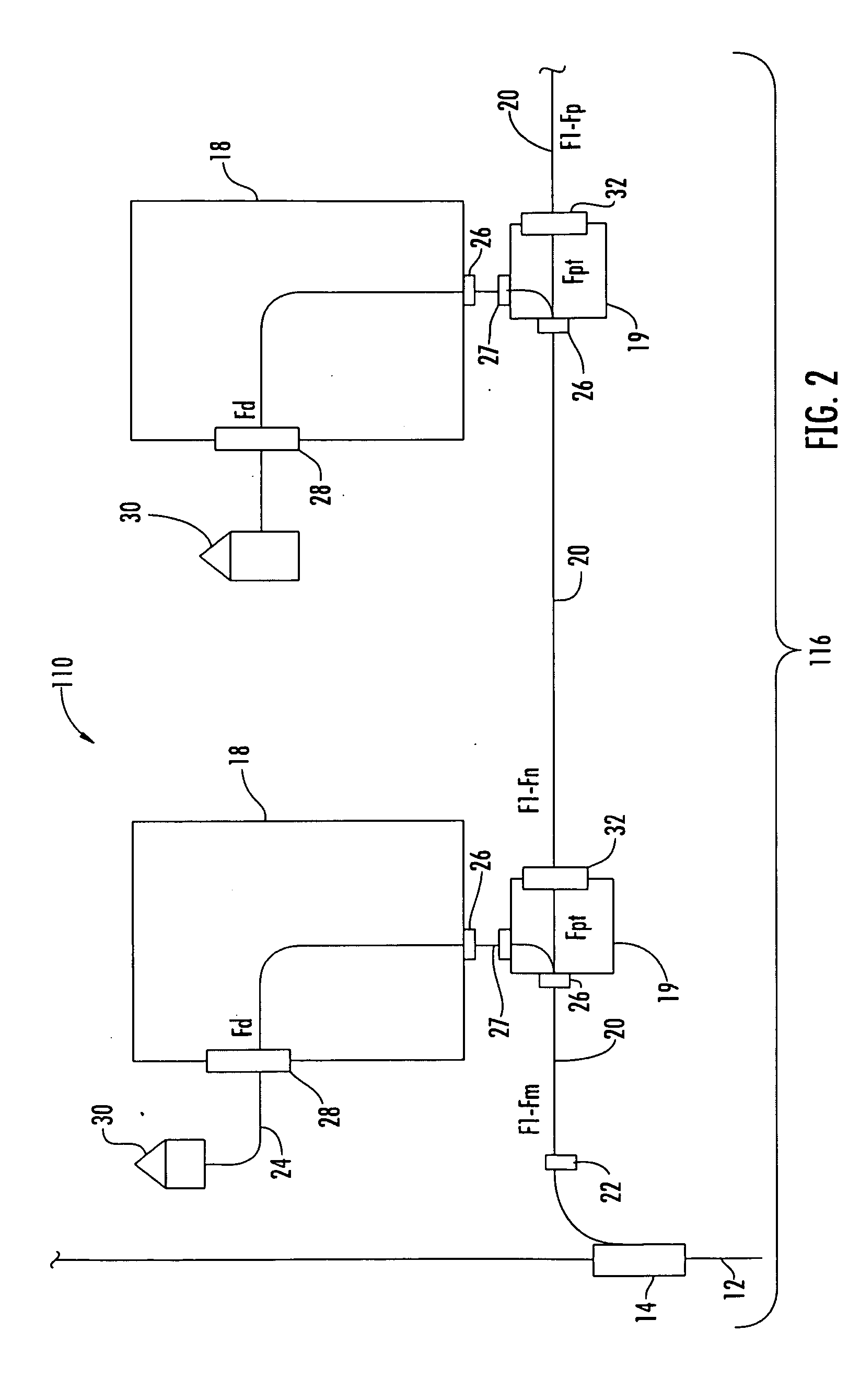
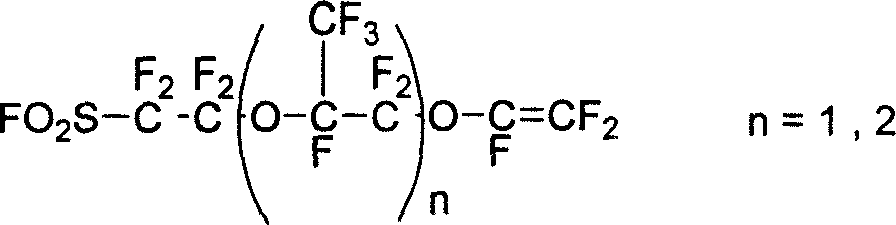Patents
Literature
1091 results about "Fiber network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
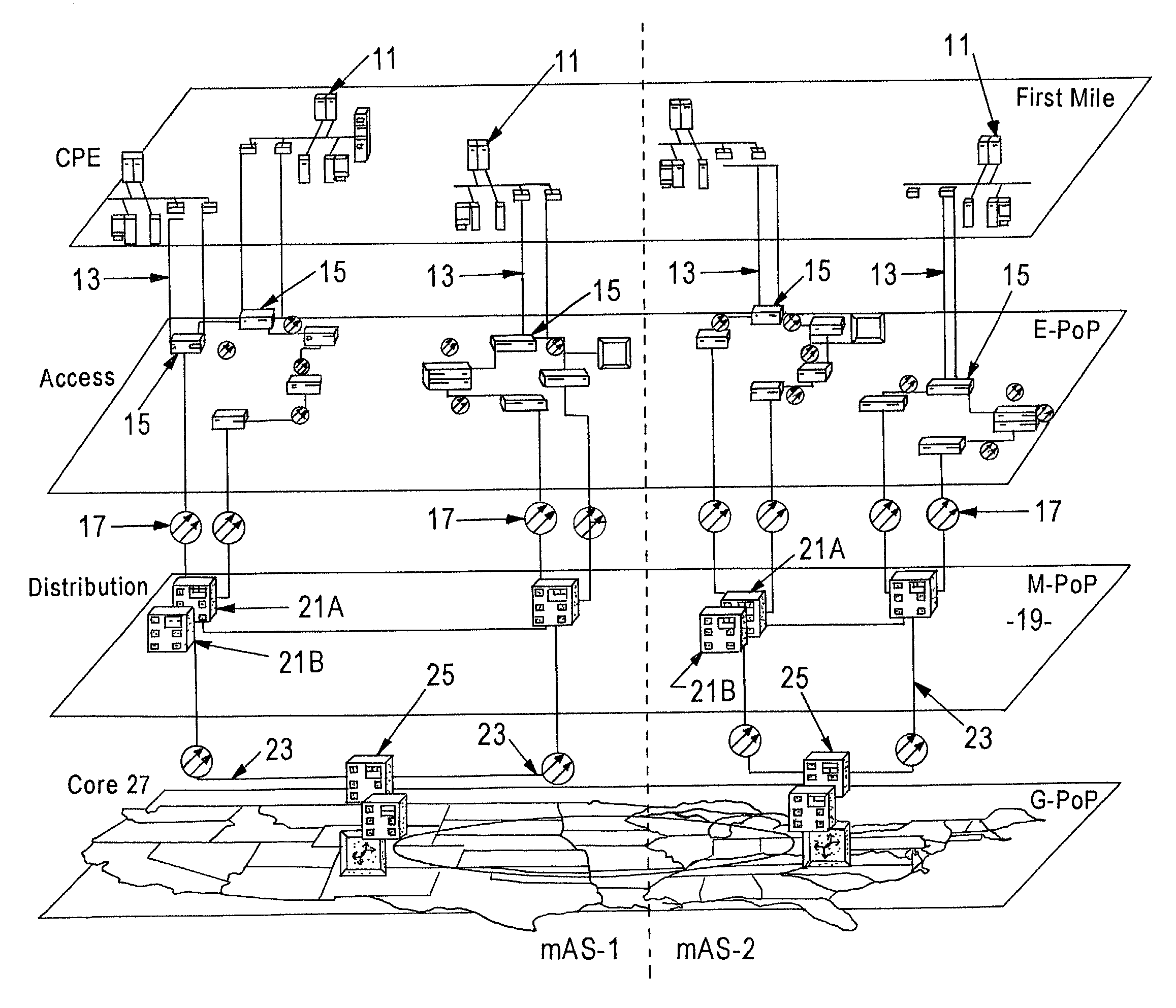
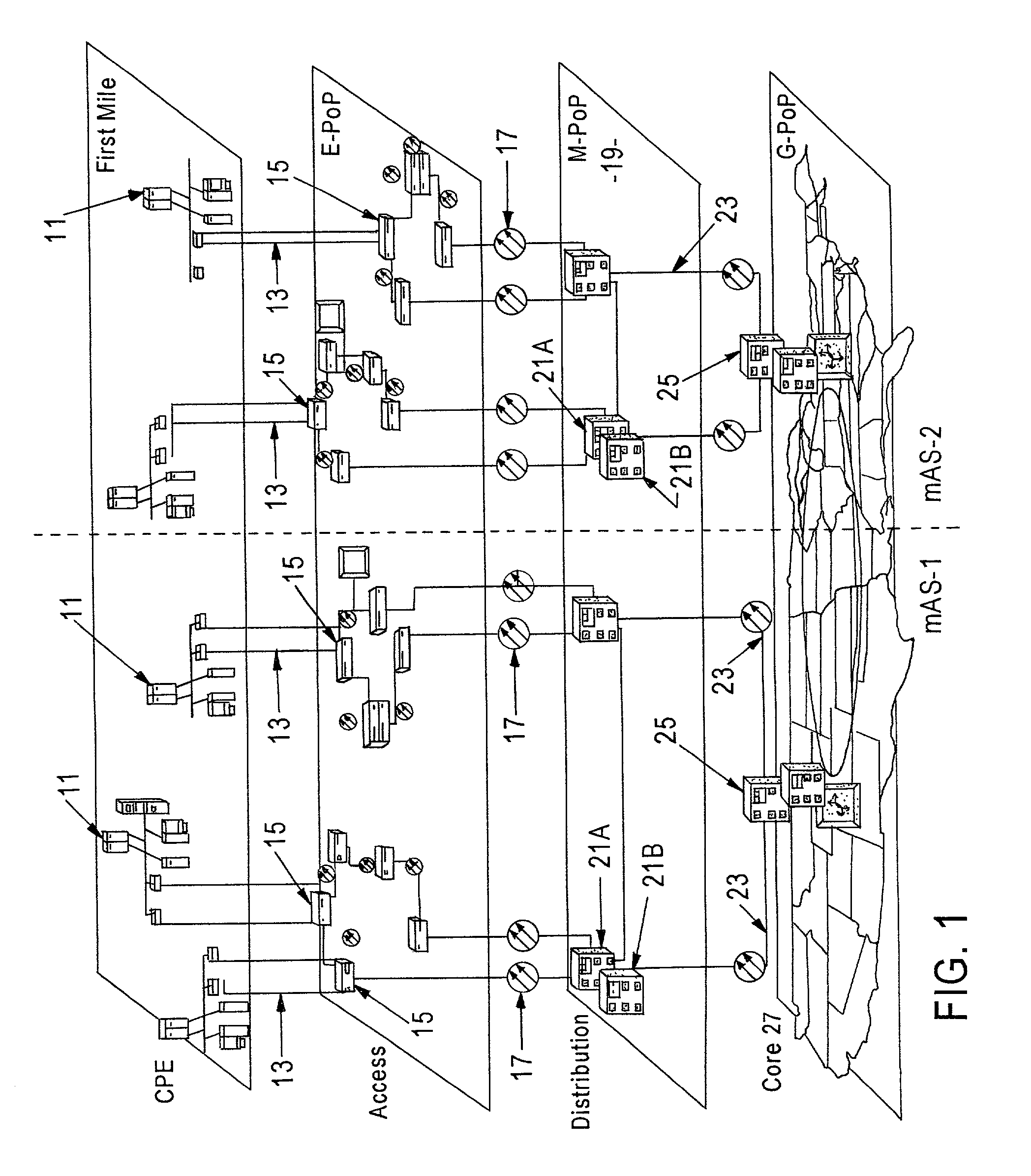
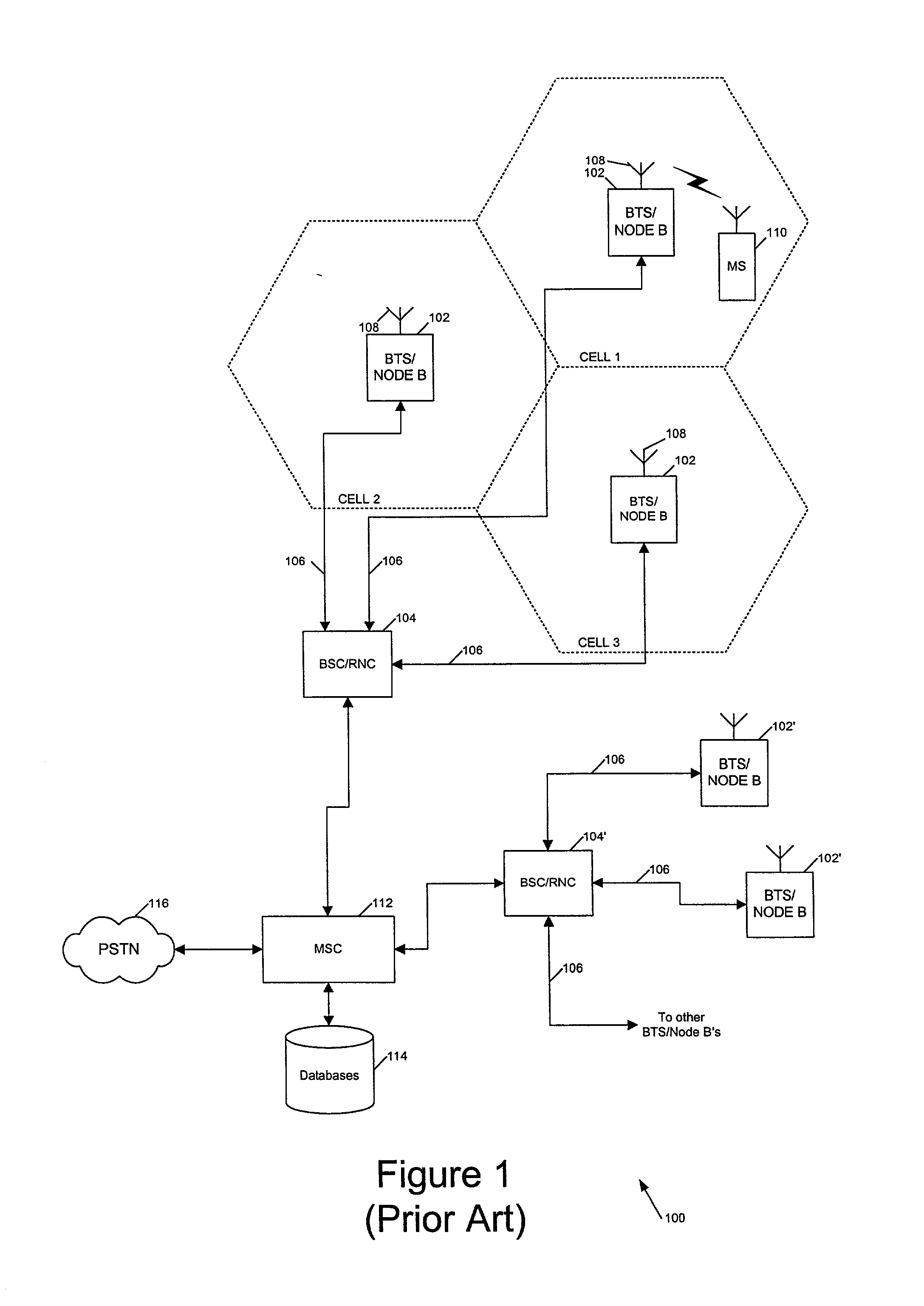
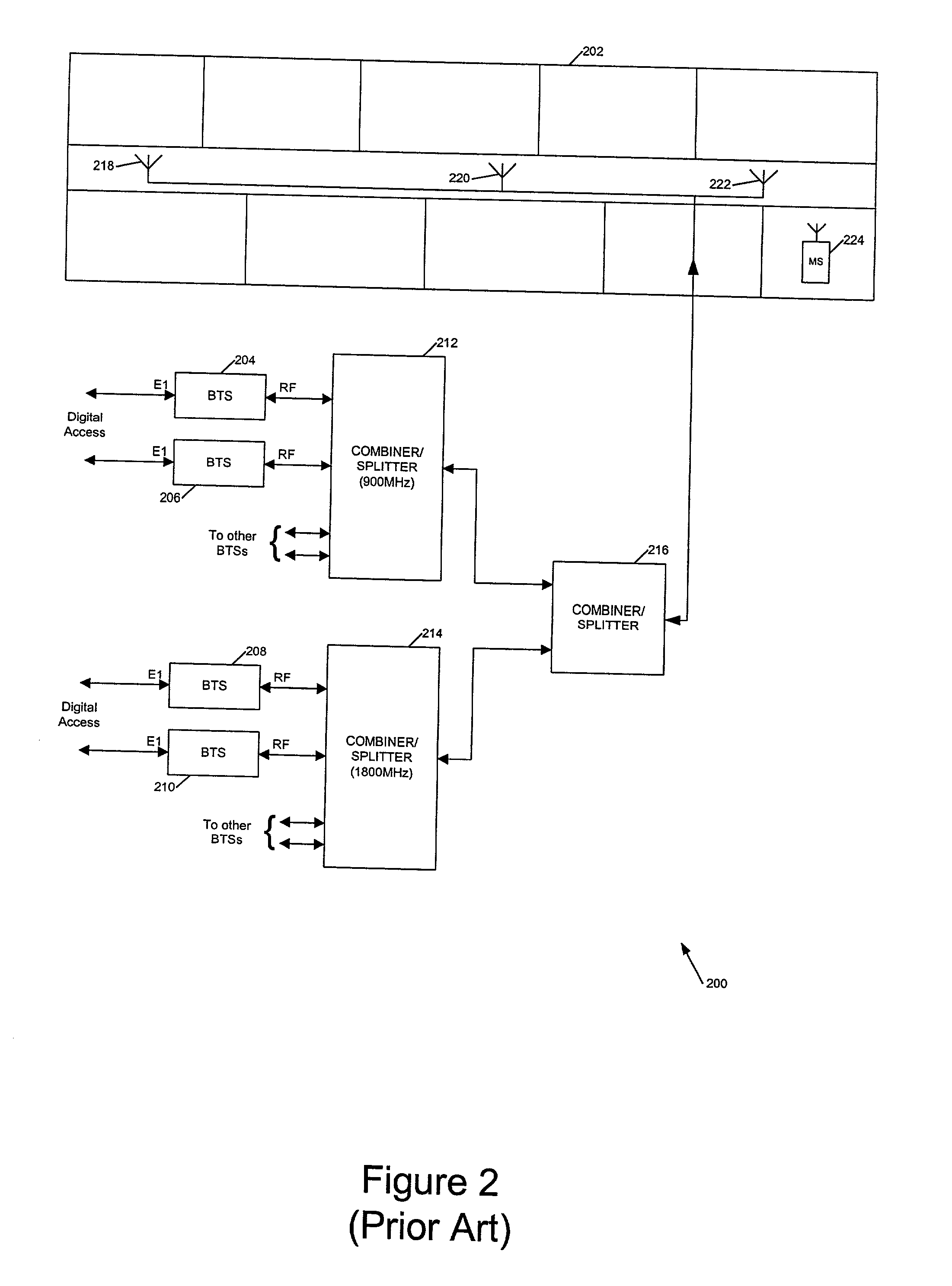
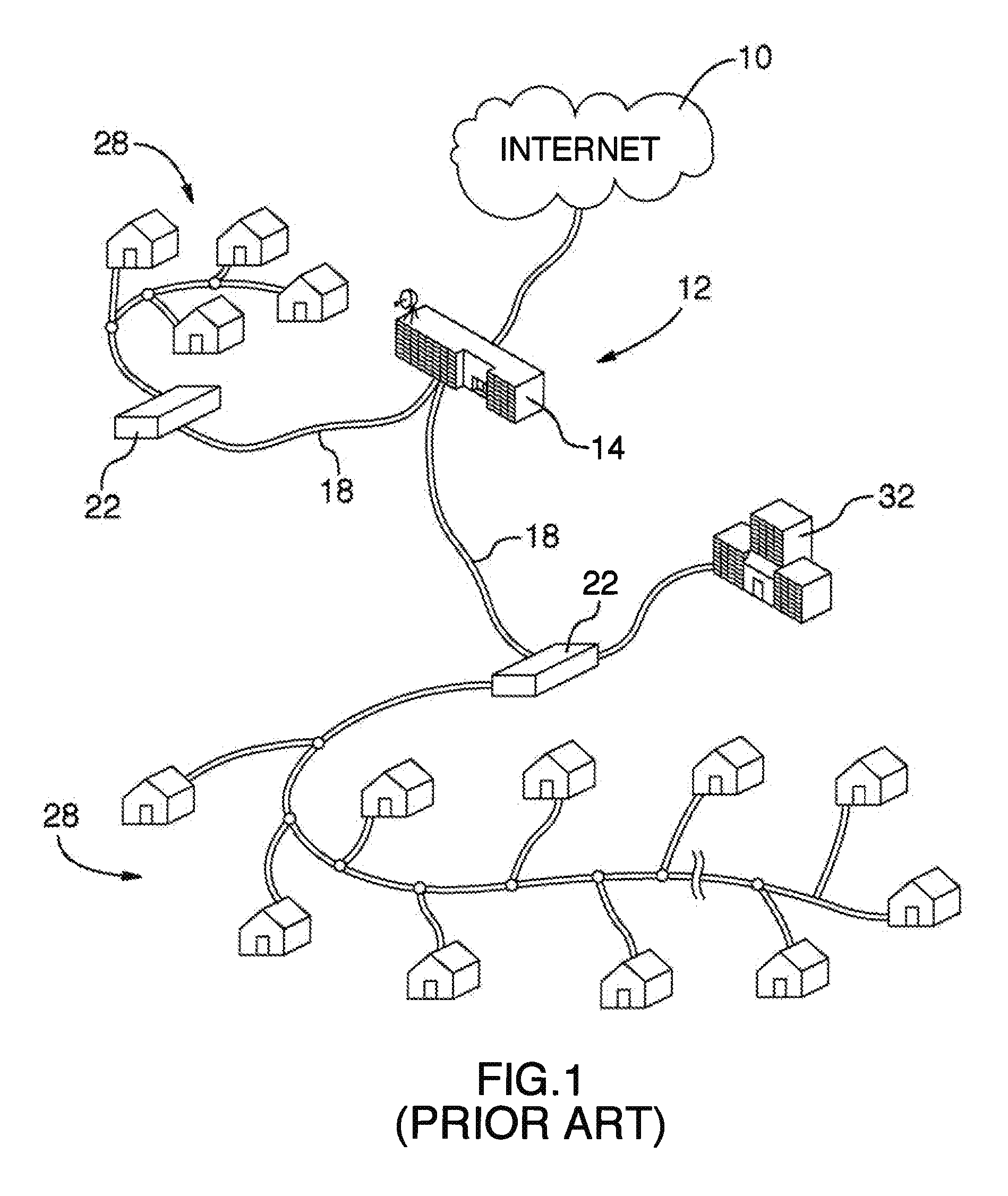
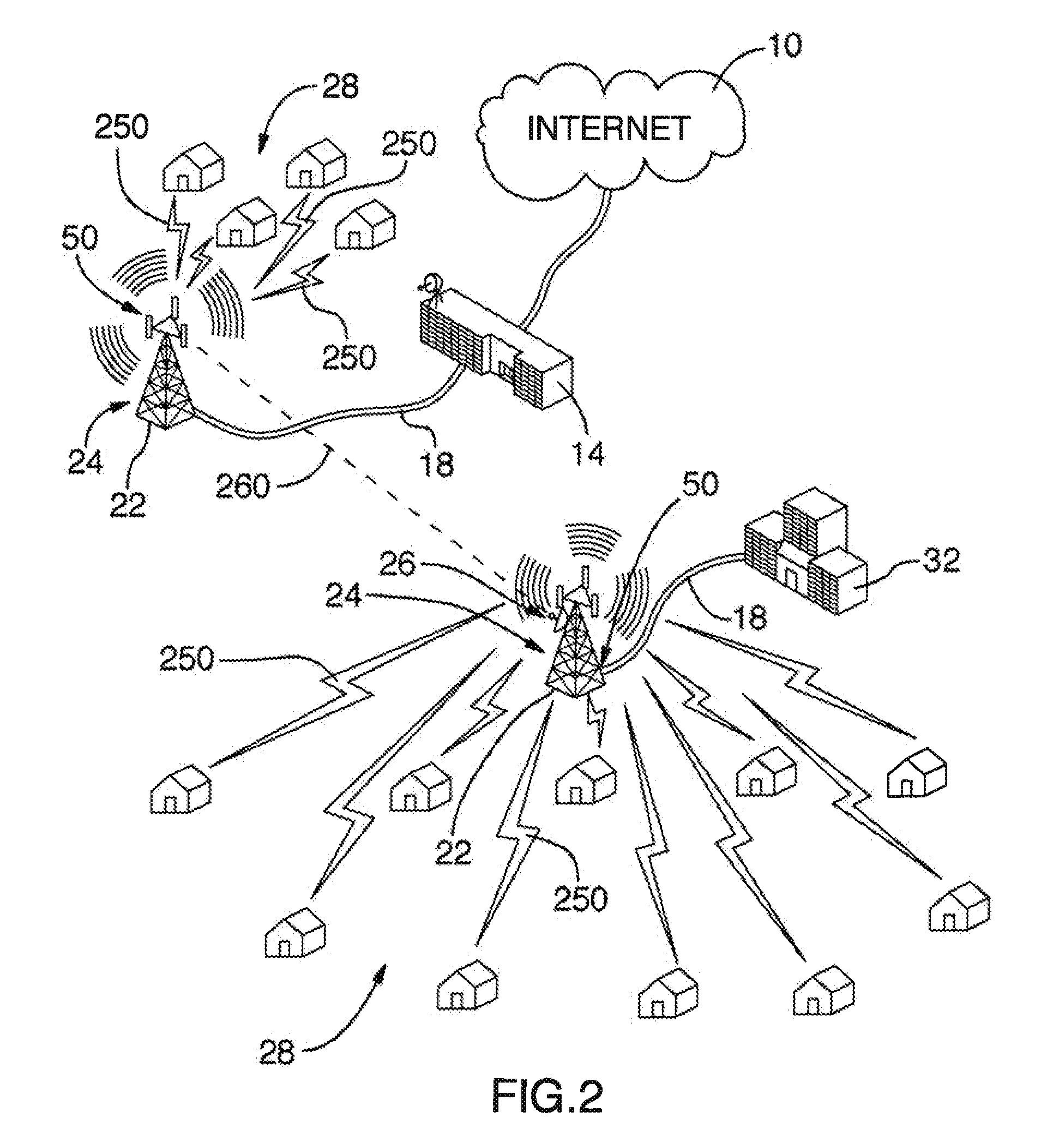
A fiber-optic network is a computer-to-computer or computer-to-Internet network created using fiber-optic cables. These cables are made of thin strands of glass that transmit light. Computer information is converted into light pulses to send across the cables and is converted back into regular data when it reaches its destination.
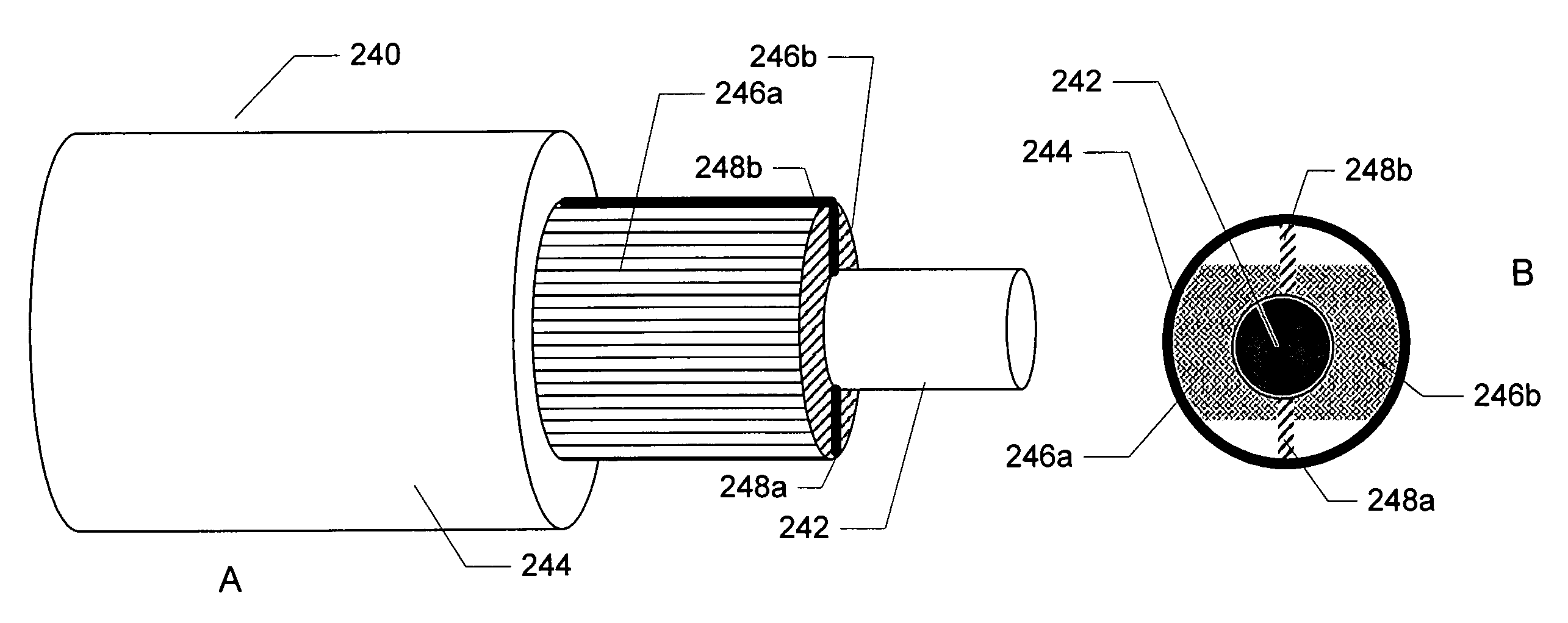
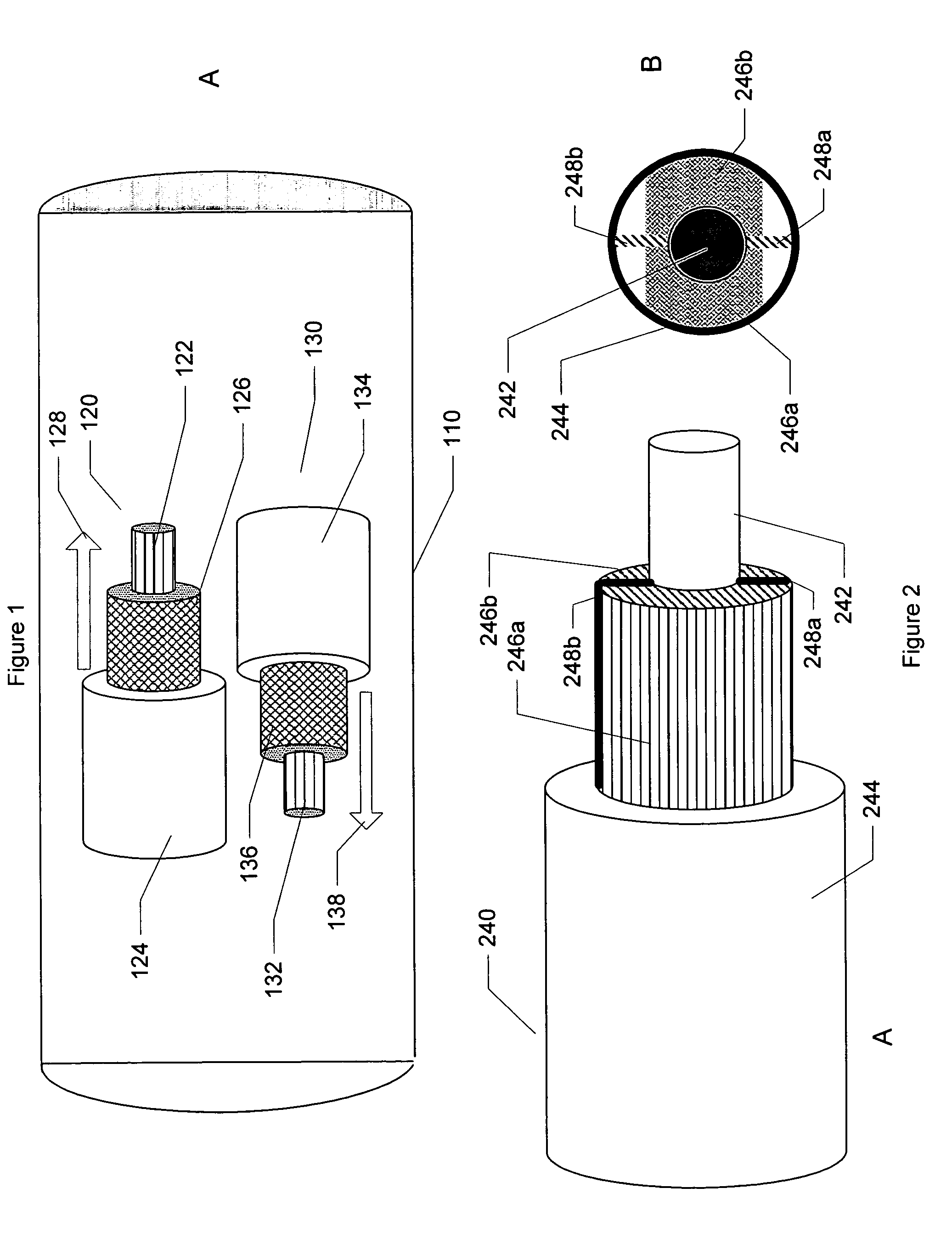
Powered fiber cable
InactiveUS7272281B2Communication cablesFibre mechanical structuresInformation transmissionTransmitted power
An optical fiber for information transmission contains a glass tube core wrapped in a sheath of conductive material attachable to a power source such as a battery or generator to transmit power via the conductive sheath of the fiber. Methods to transmit power via an optical fiber, together with fiber optic networks are described.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
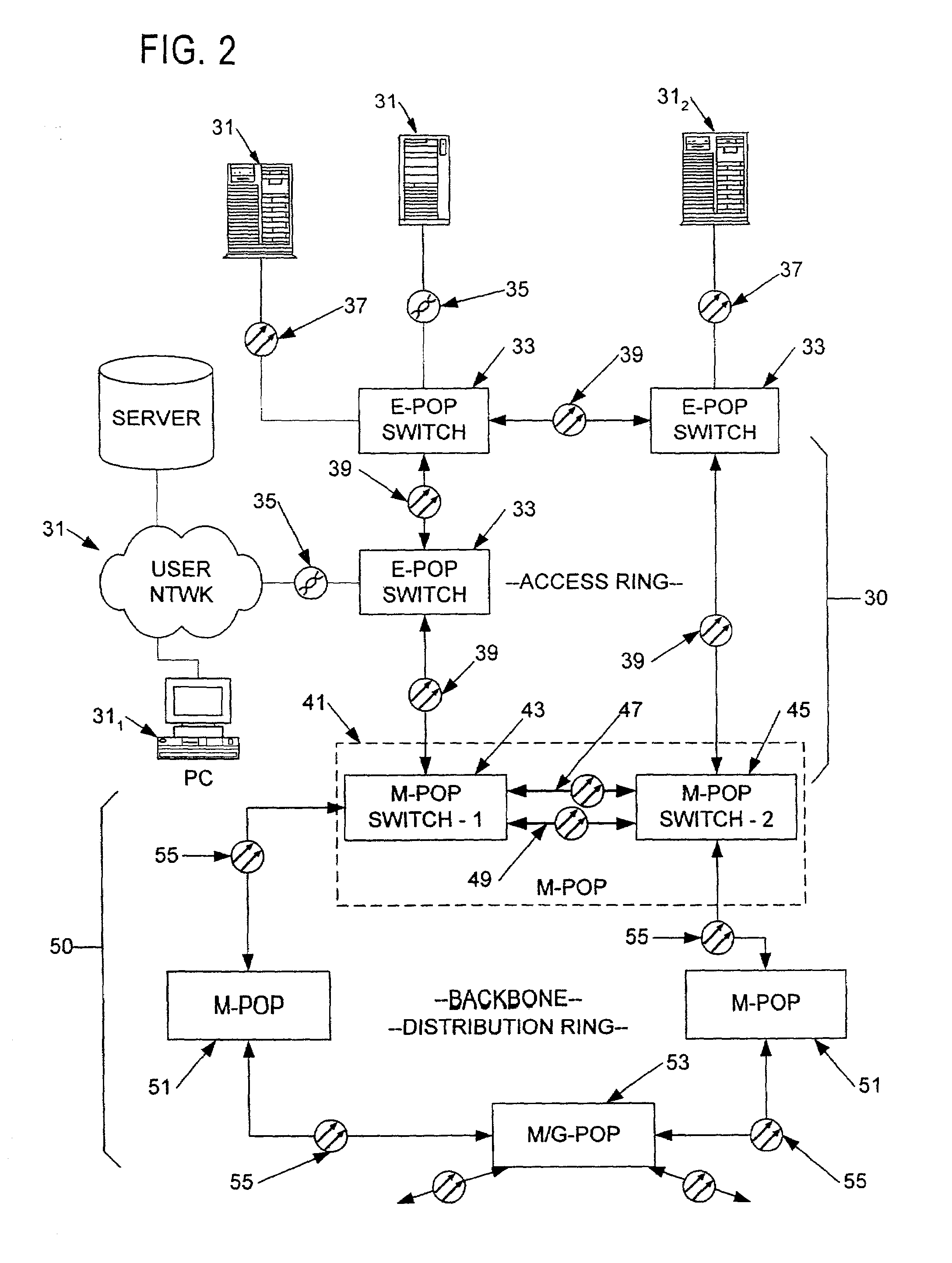
Enhanced data switching/routing for multi-regional IP over fiber network
InactiveUS6963575B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetworks interconnectionWide areaBorder Gateway Protocol
Wide-area data communications utilize regional networks transporting IP-over-Ethernet on fiber. For certain Layer 2 services, a regional implementation of the network makes limited use of spanning tree protocol on a backbone ring. Learning bridge operations in switches on associated access rings involve a short default for an aging timer. For use of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), the connection of each access ring to the backbone ring uses a pair of routers with dual links therebetween. One of these links is bonded to the backbone (OSPF Area 0), whereas the other link is bonded to the Area of the respective access ring. Also, certain routers within each regional network form a mini-autonomous system, for boundary gateway protocol (BGP). The mini-autonomous systems of the regional networks form a confederation. The network utilizes route reflectors in the mini-autonomous systems. The Internet carries confederation commands to and from a designated hub.
Owner:YIPES ENTERPRISE SERVICES
Electrically optimized hybird "last mile" telecommunications cable system
InactiveUS6091025AEqual performanceEquivalent signal performanceCoaxial cables/analogue cablesQuad constructionsElectrical conductorTelecommunications cable
A cable system is provided which can accomodate electrical and optical cabling. The conductors of the system employ a layer which is impedance-matched to space, decreasing their cross-section to electromagnetic interference. The conductors of the system also employ a layer which symmetrizes electromagnetic interference signals, reducing the effect of interference and crosstalk on the signals carried by the conductors. The system also includes a node interface device for connection to a global electrical and fiber network. The node interface device connects to a user interface device through the cable.
Owner:KHAMSIN TECH LLC
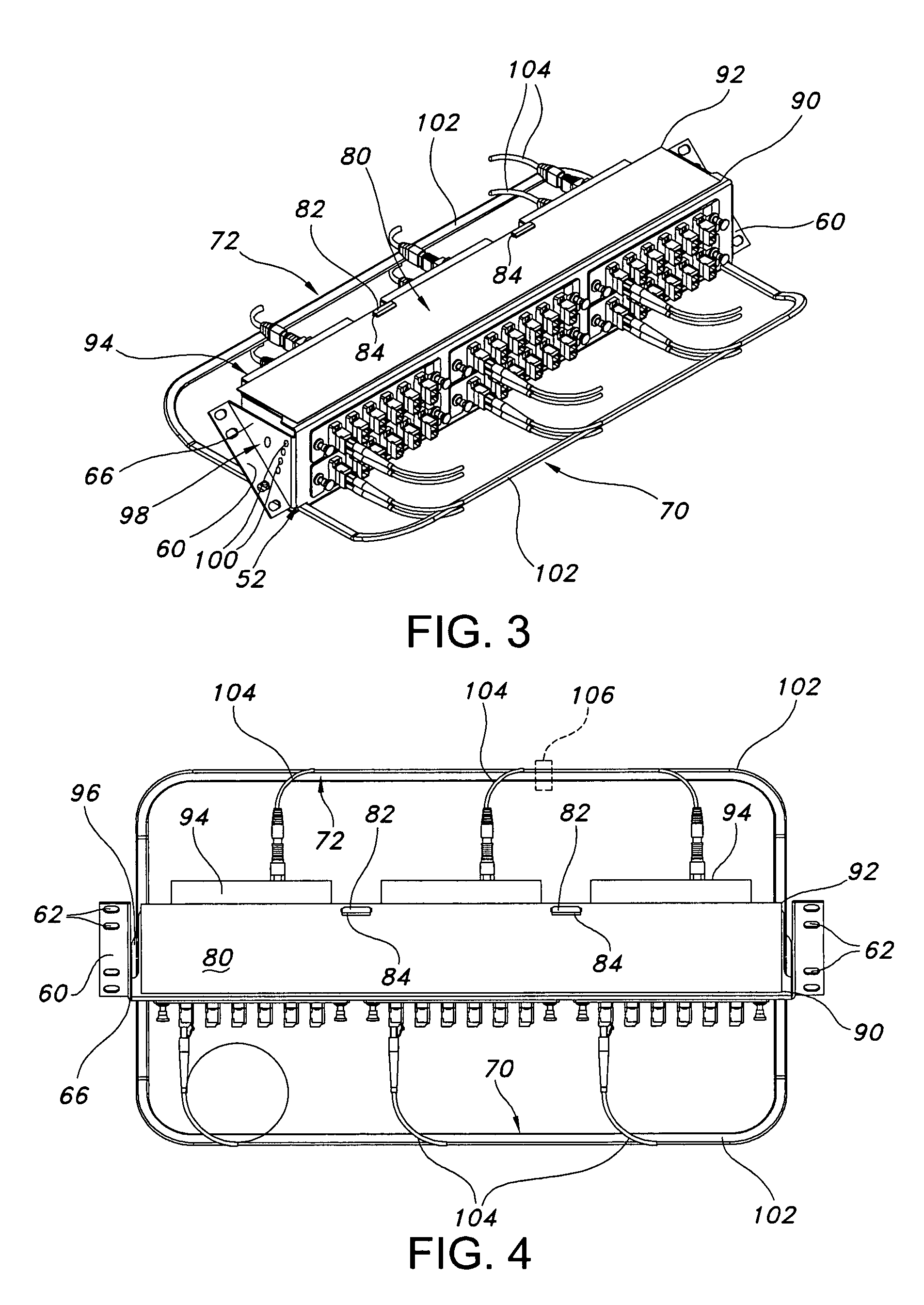
Variably configurable and modular local convergence point
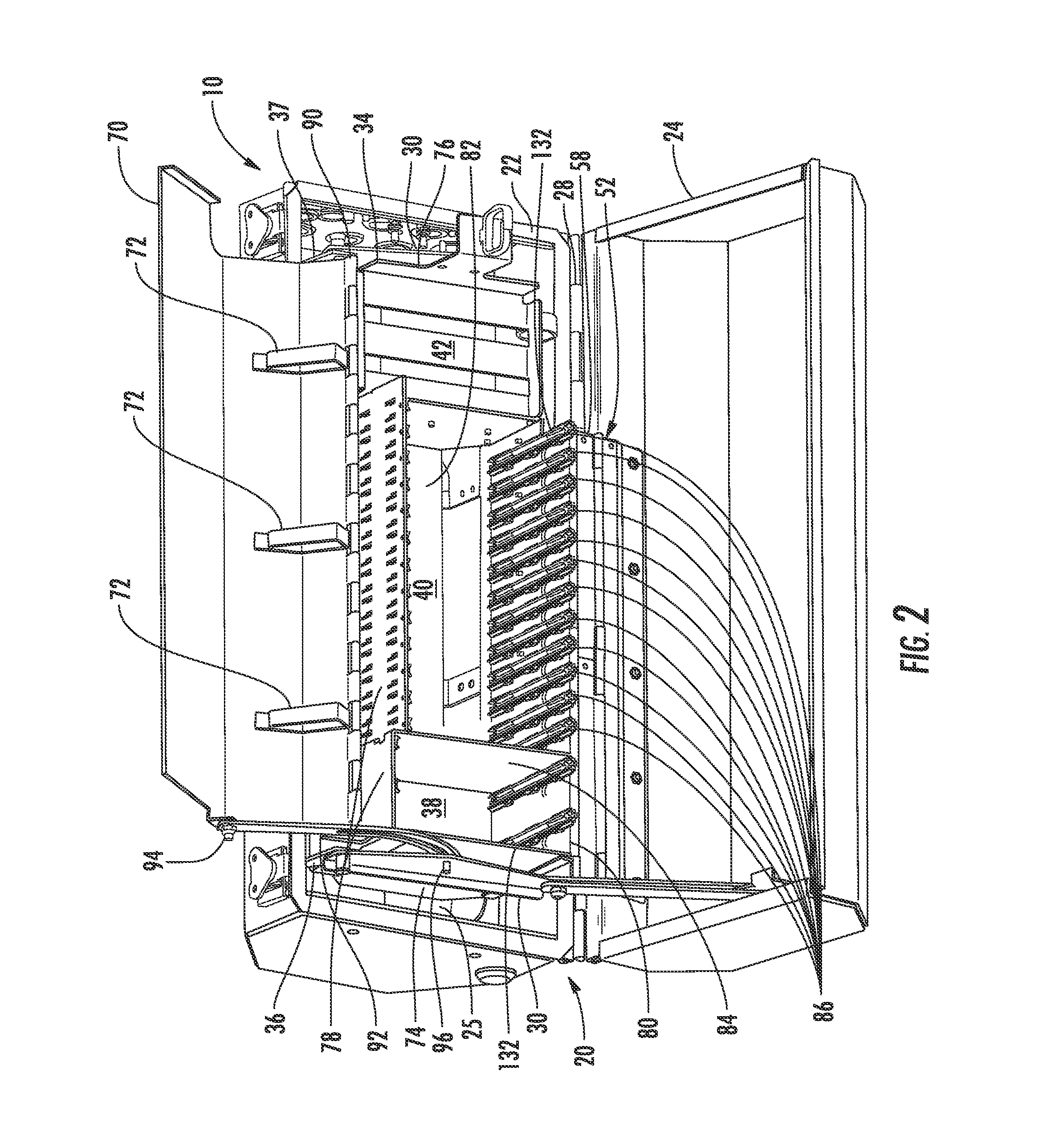
ActiveUS20110211799A1Easy accessOptical fibre/cable installationMetal working apparatusInterior spaceParking area
A variably configurable fiber optic terminal as a local convergence point in a fiber optic network is disclosed. The fiber optic terminal has an enclosure having a base and a cover which define an interior space. A feeder cable having at least one optical fiber and a distribution cable having at least one optical fiber are received into the interior space through a feeder cable port and a distribution cable port, respectively. A movable chassis positions in the interior space and is movable between a first position, a second position and third position. The movable chassis has a splitter holder area, a cassette area and a parking area. A cassette movably positions in the cassette area. A splitter module holder having a splitter module movably positioned therein movably positions in the splitter holder area. The optical fiber of the feeder cable and the optical fiber of the distribution cable are optically connected through the cassette, which also may be through the splitter module. In such case, the optical fiber of the feeder cable optically connects to an input optical fiber to the slitter module, where the optical signal is split into a plurality of output optical fibers. One of the plurality of output optical fibers connects to the optical fiber of the distribution cable for distribution towards a subscriber premises. The interior space is variably configurable by changeably positioning the cassette and splitter modules in the movable chassis.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
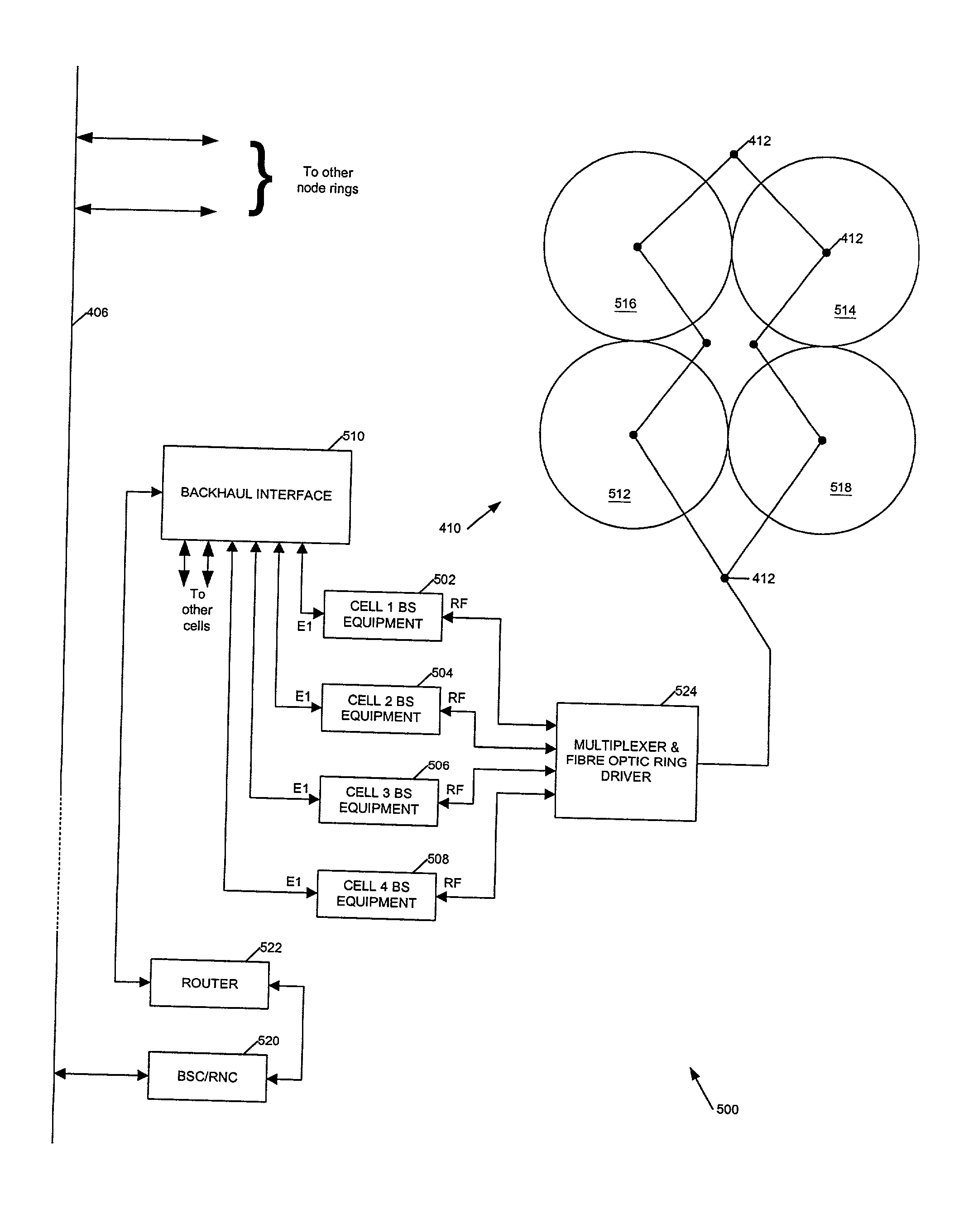
Signal transmission systems
Signal transmission systems for second and third generation mobile communications networks are described. A signal distribution system comprises a plurality of rf transmitters for serving a plurality of network cells. The system is characterised by a multiplexer coupled to the transmitters for multiplexing the transmitter outputs, a signal transporter for transporting the multiplexed signals to each of the network cells, and a multiplexed signal receiver at each cell for selecting and receiving a signal from a transmitter serving the cell. The invention also provides a complementary signal reception system, and corresponding methods. Preferably, the multiplexed signals are transported over a fibre optic network such as an existing cable TV network. The system simplifies the deployment of network infrastructure for third generation mobile communications systems.
Owner:NTL GROUP
System and method for providing wireless over a passive optical network (PON)
ActiveUS20080063397A1Maximize utilizationConvenient supplementMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsService provisionNetworked system
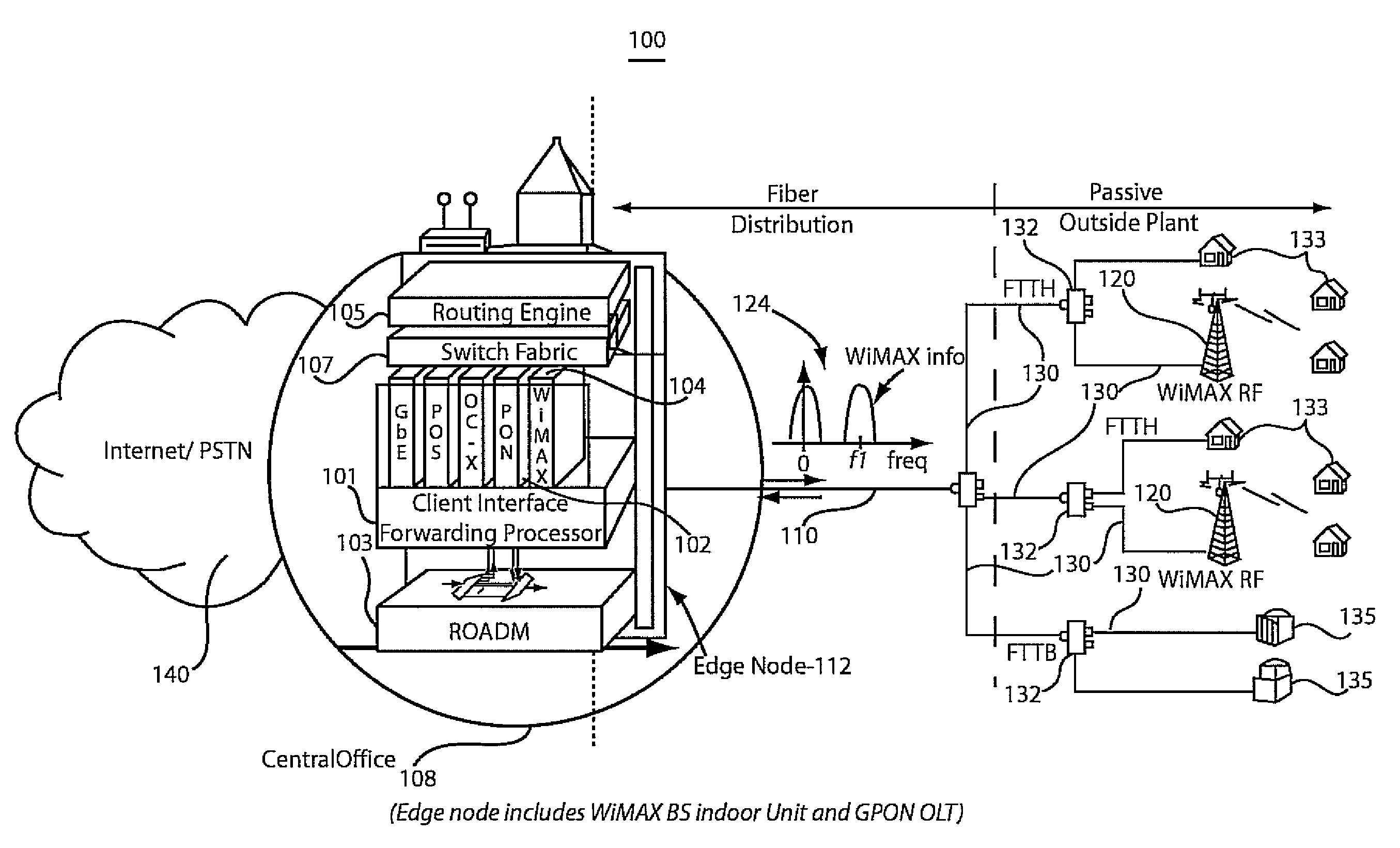
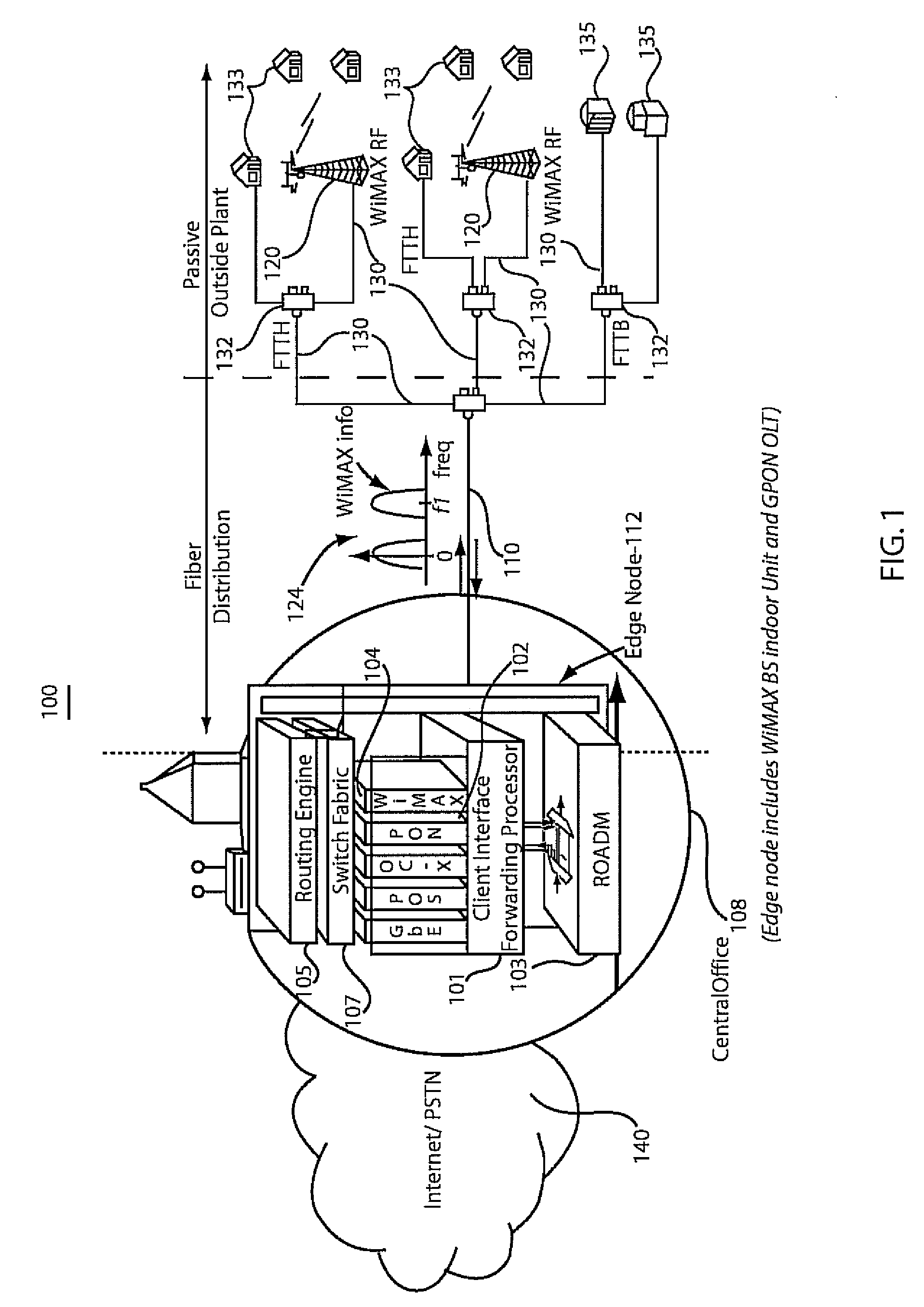
A network system and method include a wireless base station integrated at a central office of a service provider. The wireless base station is configured to provide portable and fixed services to customers. A passive optical network is coupled to the wireless base station at the central office to provide a link to extend an antenna for wireless operations of the wireless base station to a remote site such that a wireless signal from the wireless base station is transmitted in parallel with a passive fiber network signal through the link.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multi-ply paper towel with absorbent core
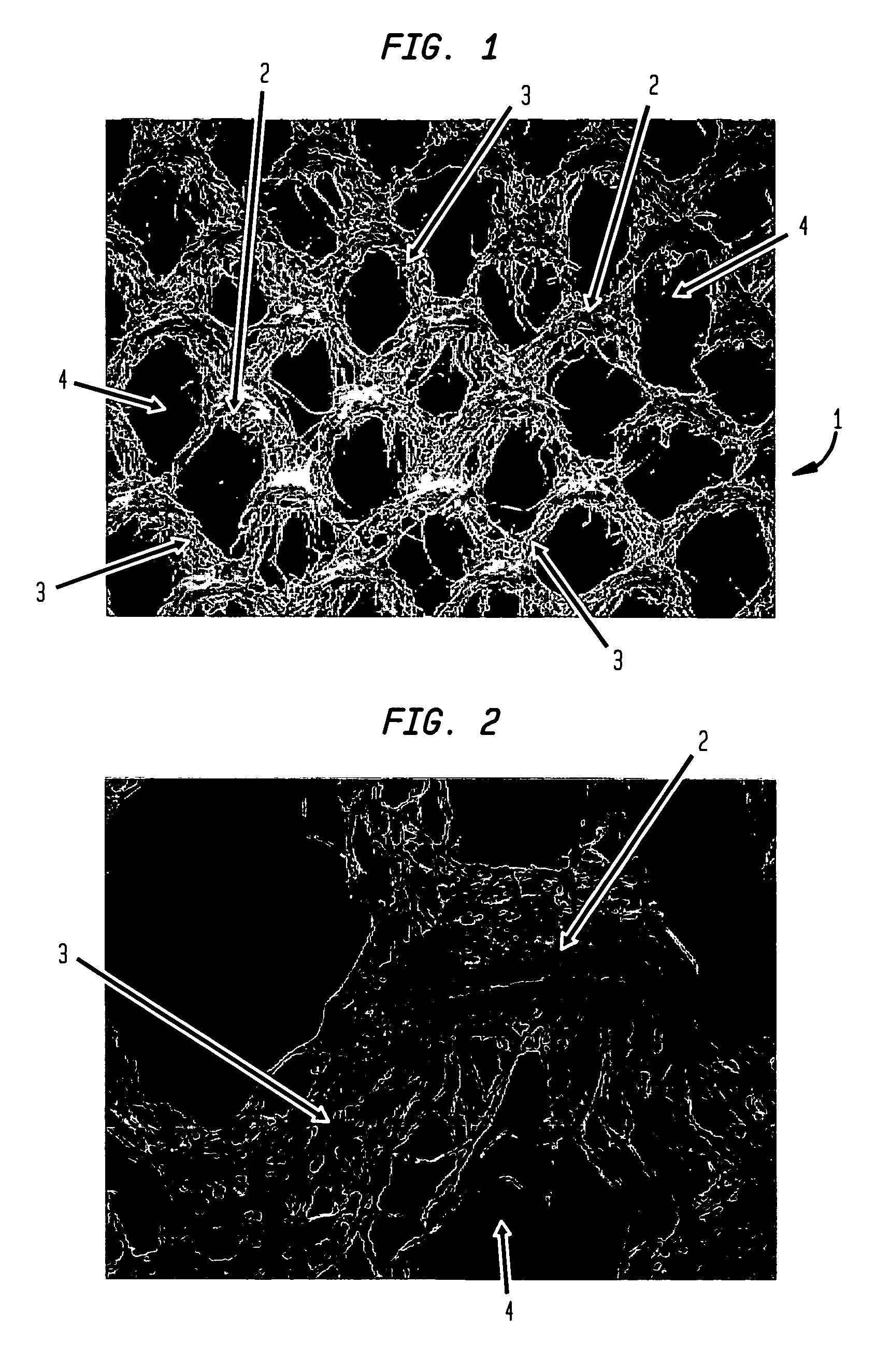
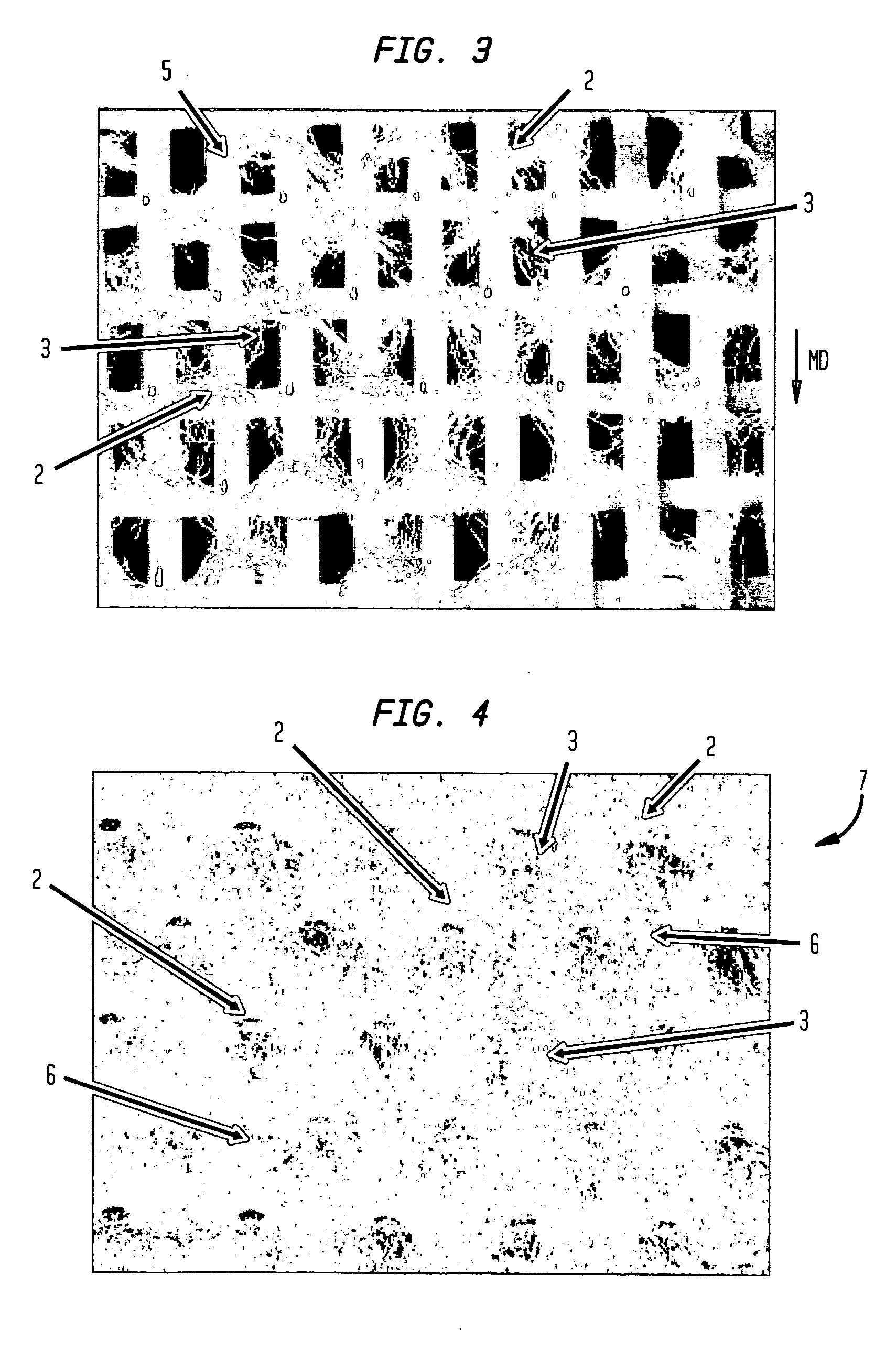
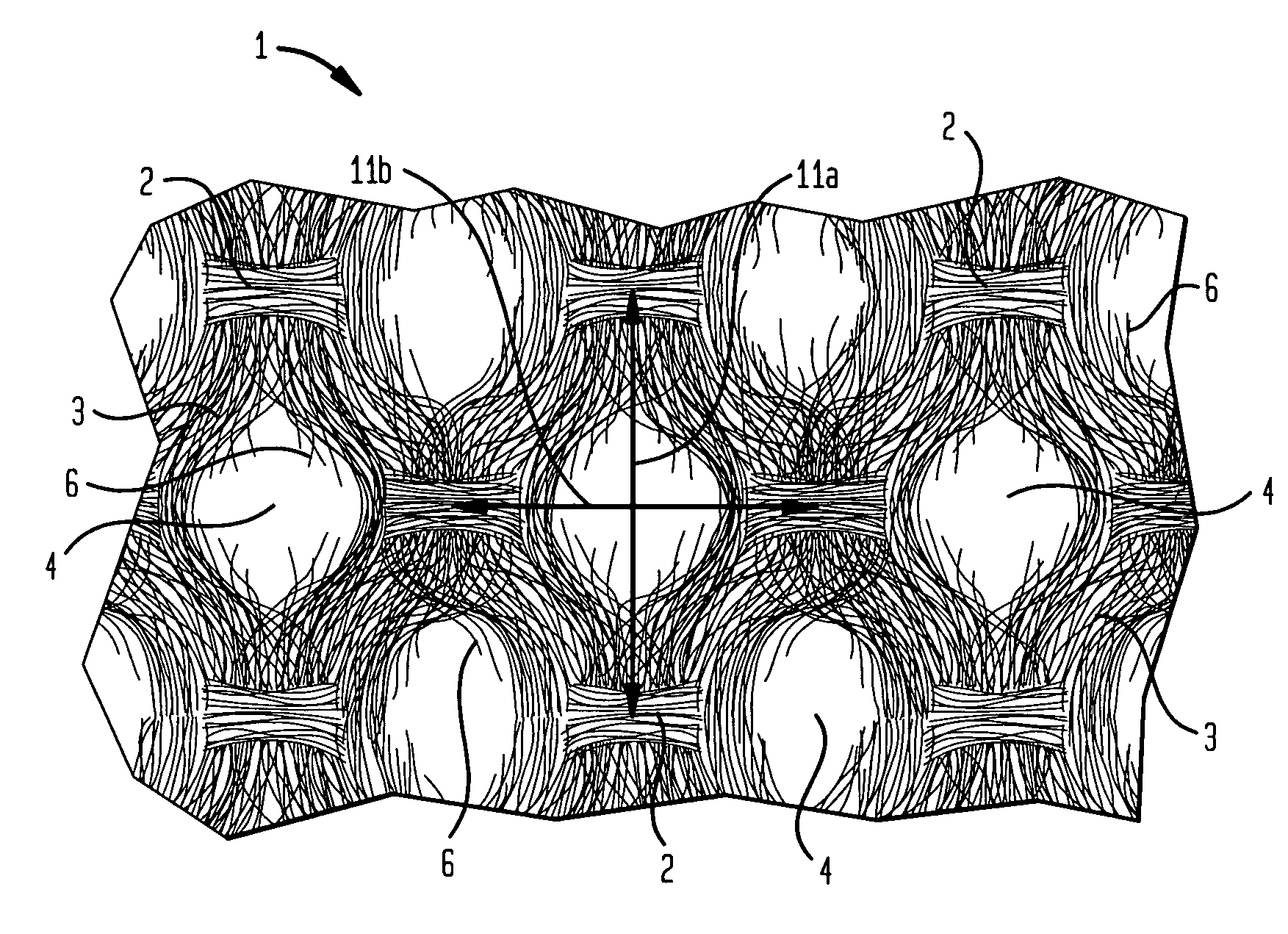
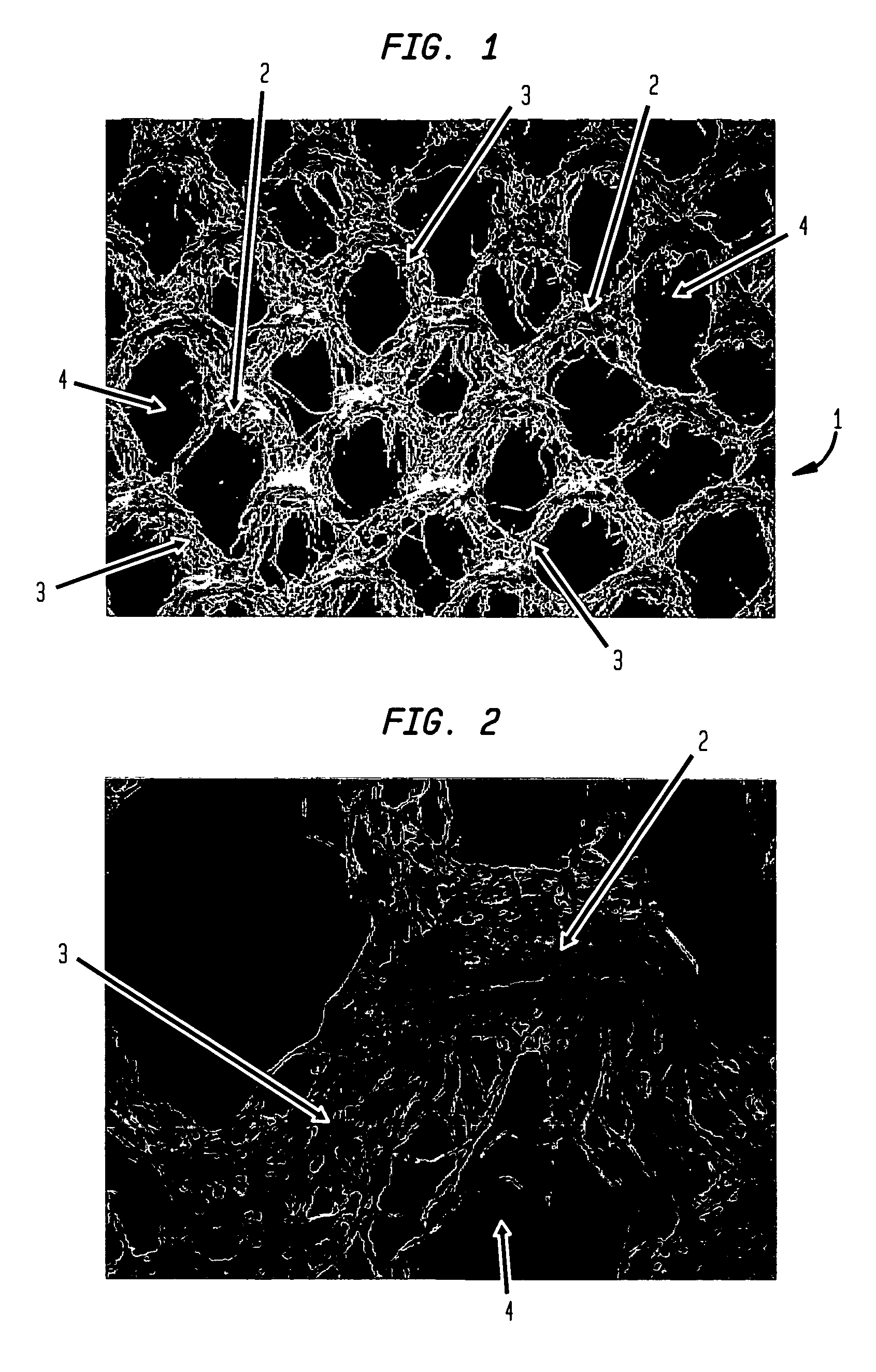
ActiveUS20060237154A1High performance absorbencyVariationNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiber networkEngineering
A multi-ply absorbent sheet of cellulosic fiber with continuous outer surfaces is provided an absorbent core between the outer surfaces. The absorbent core includes a non-woven fiber network having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking regions whose fiber orientation is biased along the direction between pileated regions interconnected thereby, and (iii) a plurality of fiber-deprived cellules between the fiber enriched and linking regions, also being characterized by a local basis weight lower than the fiber enriched regions. The cellules provide a sponge-like internal structure of low fiber density regions.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Multi-ply paper towel with absorbent core
ActiveUS7662257B2VariationImprove performanceNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulosePaper towel
A multi-ply absorbent sheet of cellulosic fiber with continuous outer surfaces is provided an absorbent core between the outer surfaces. The absorbent core includes a non-woven fiber network having: (i) a plurality of pileated fiber enriched of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by way of (ii) a plurality of lower local basis weight linking whose fiber orientation is biased along the direction between pileated interconnected thereby, and (iii) a plurality of fiber-deprived cellules between the fiber enriched and linking regions, also being characterized by a local basis weight lower than the fiber enriched regions. The cellules provide a sponge-like internal structure of low fiber density regions.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
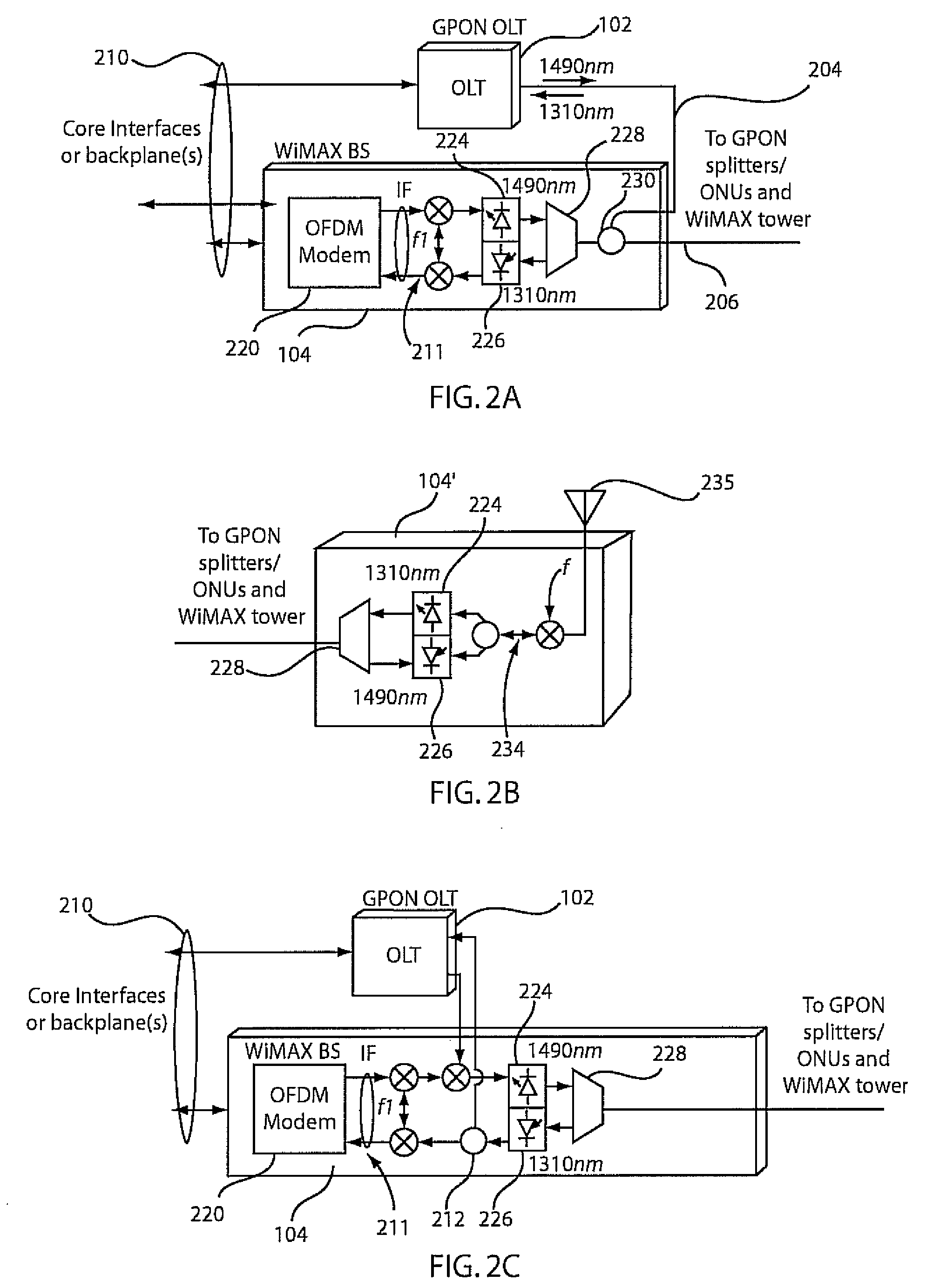
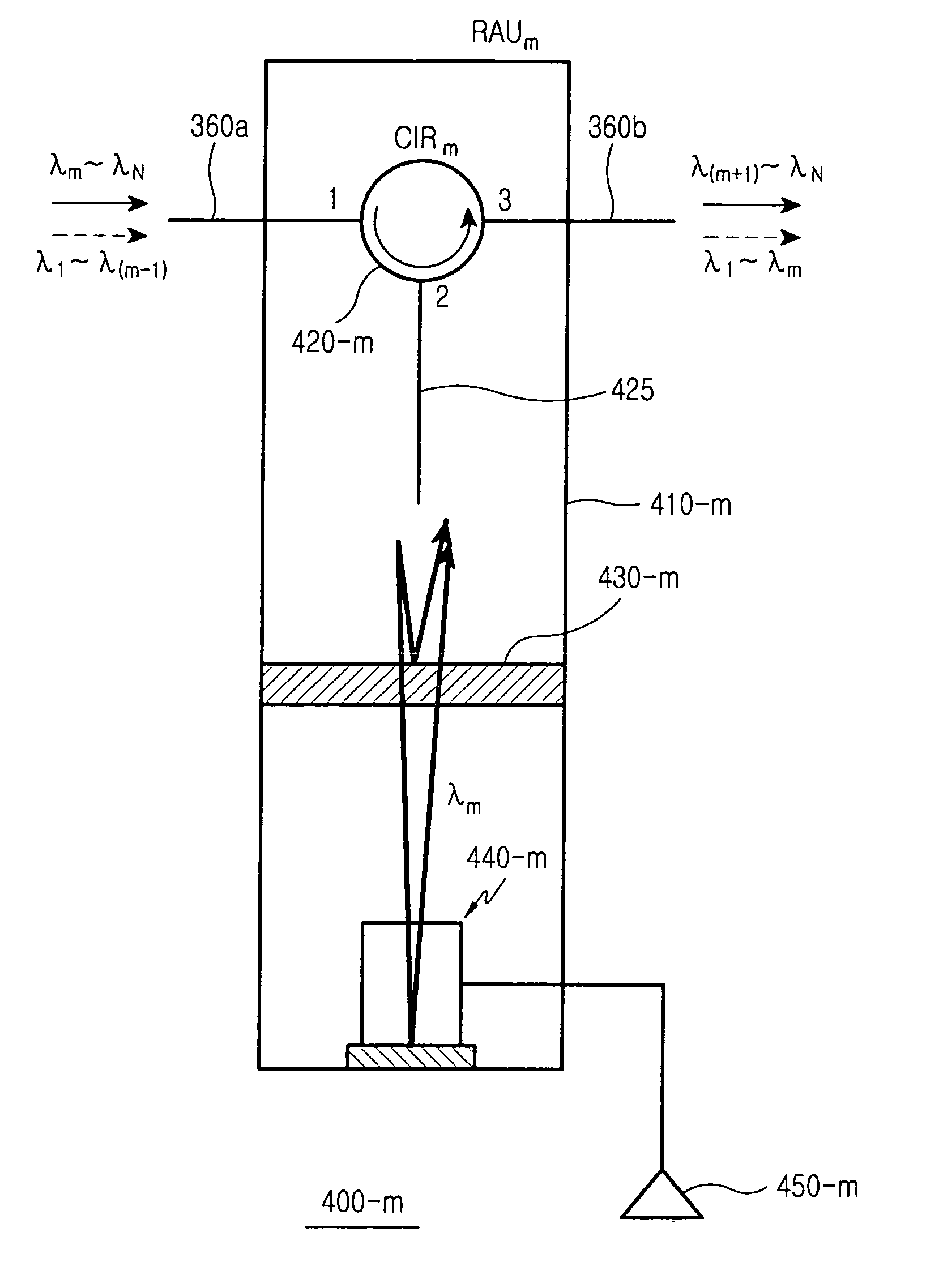
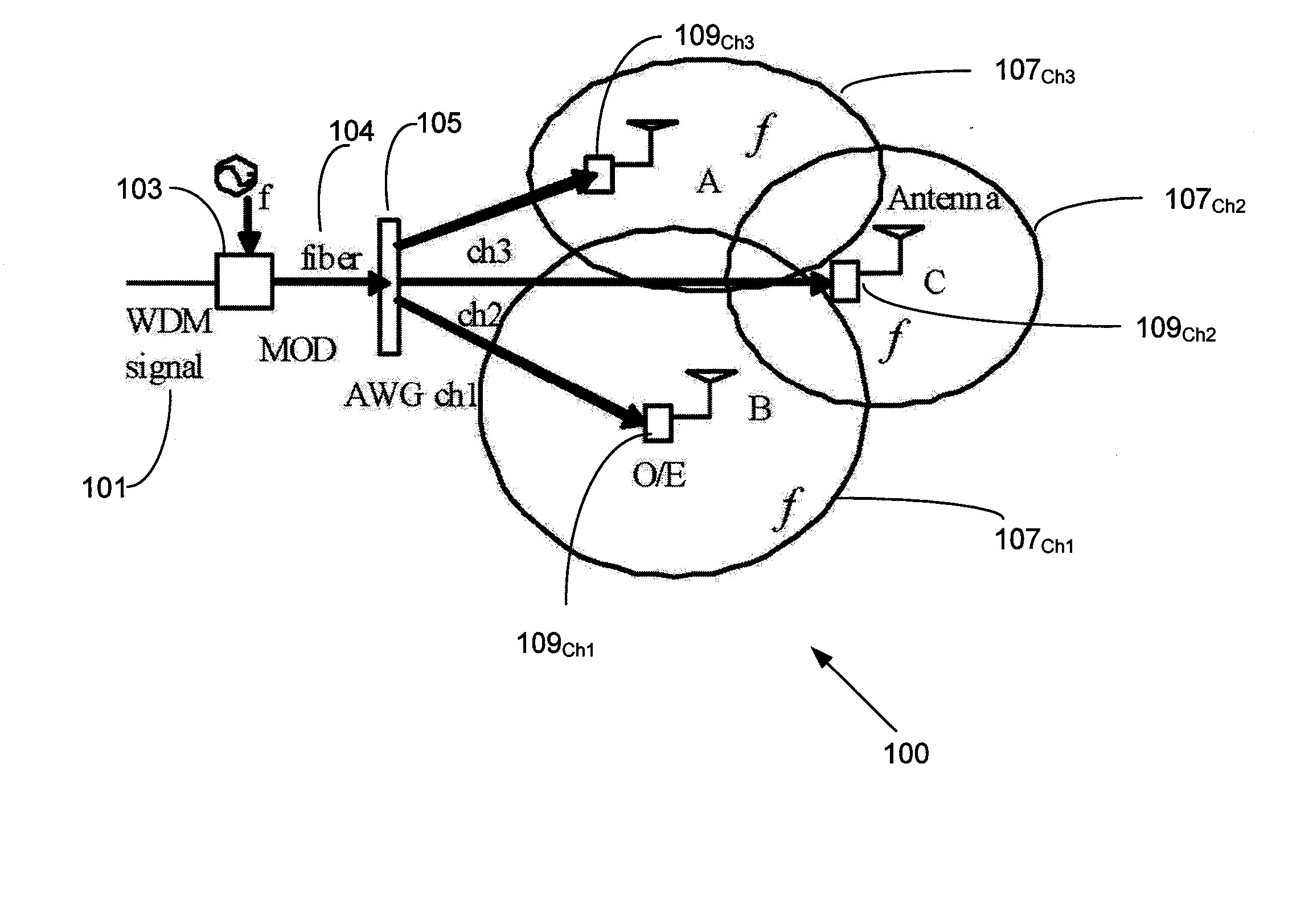
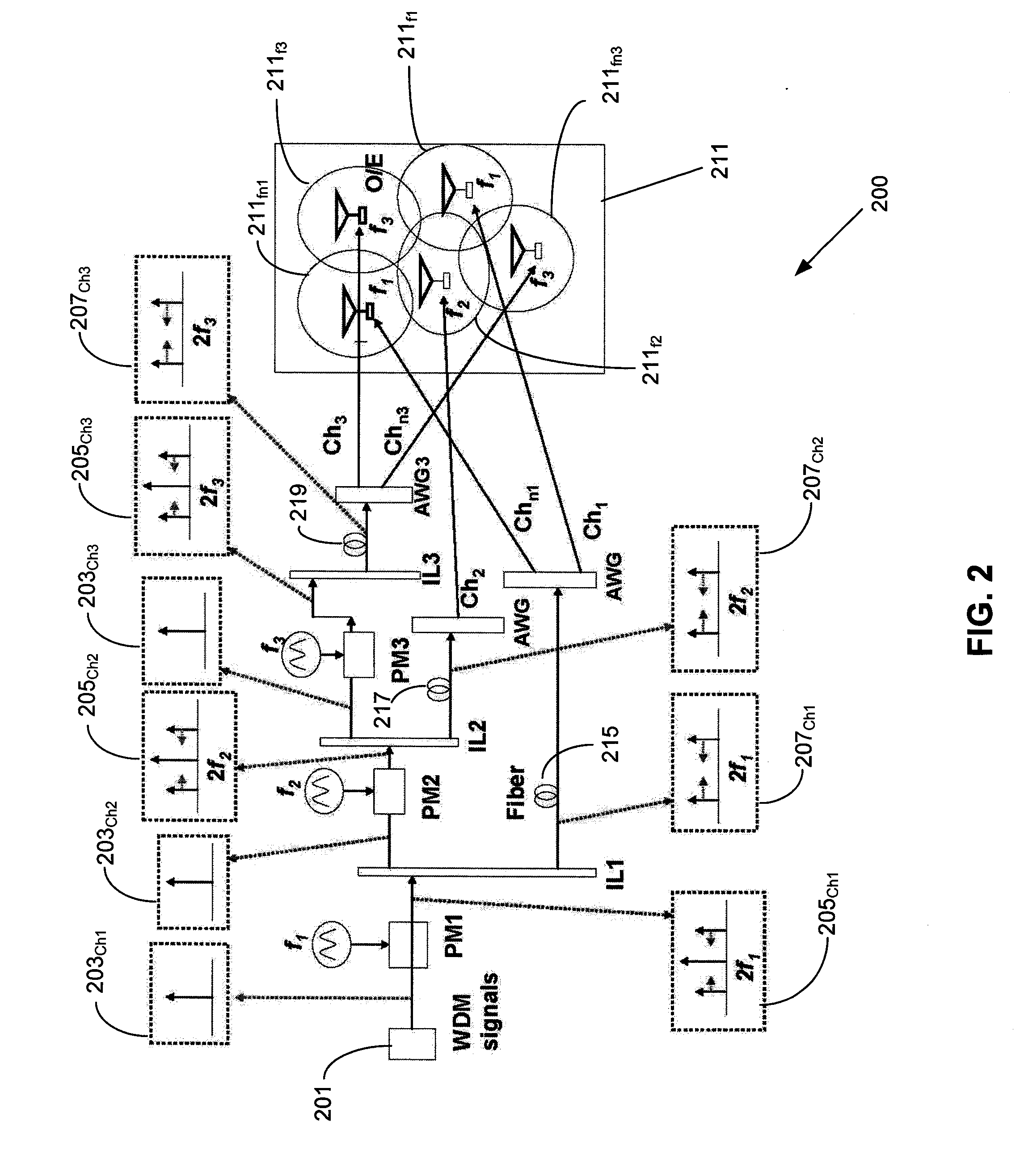
Remote antenna unit and wavelength division multiplexing radio-over-fiber network
InactiveUS7269311B2Simple structureLow costCoupling light guidesRadio-over-fibreElectricityRadio over fiber
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
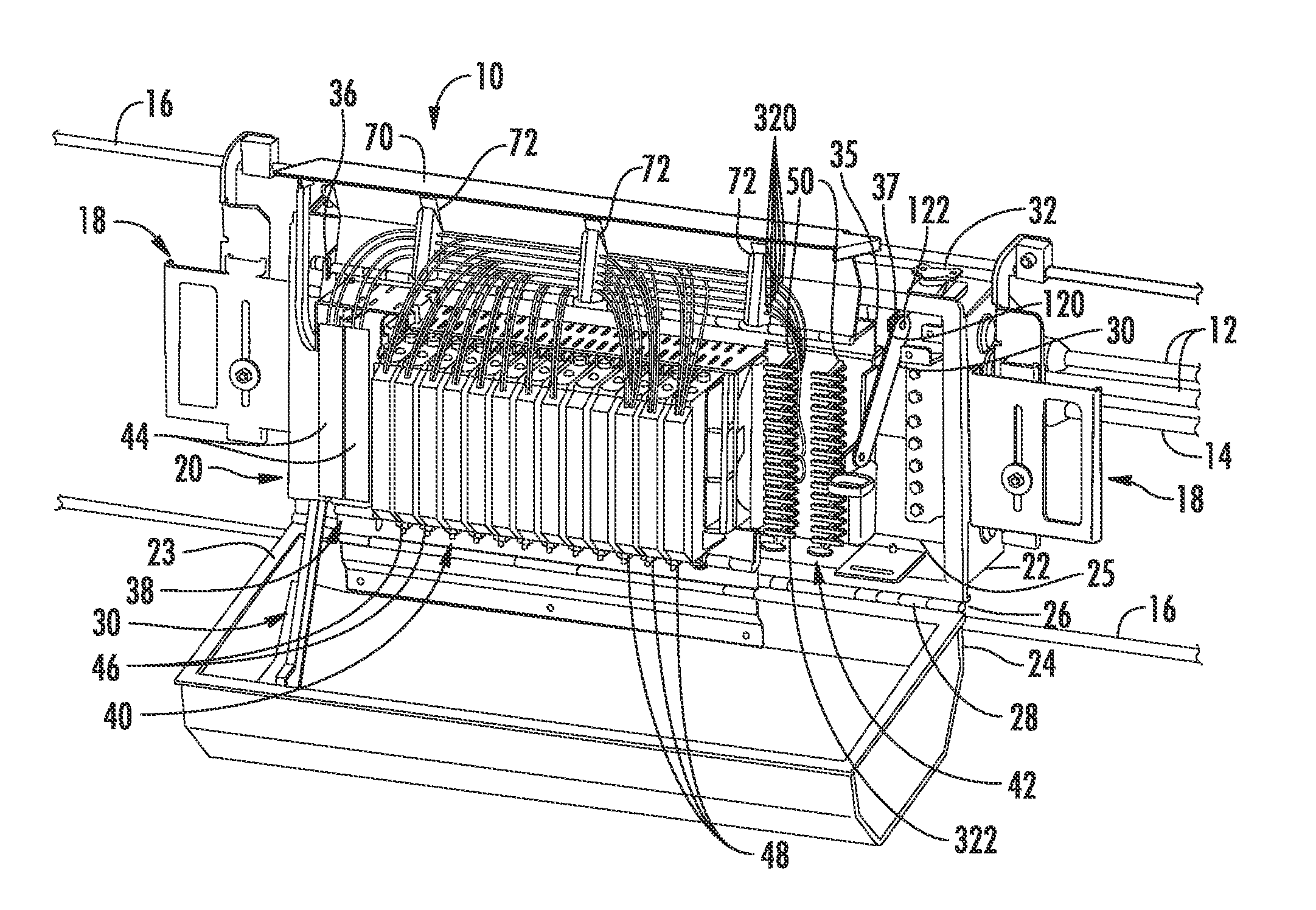
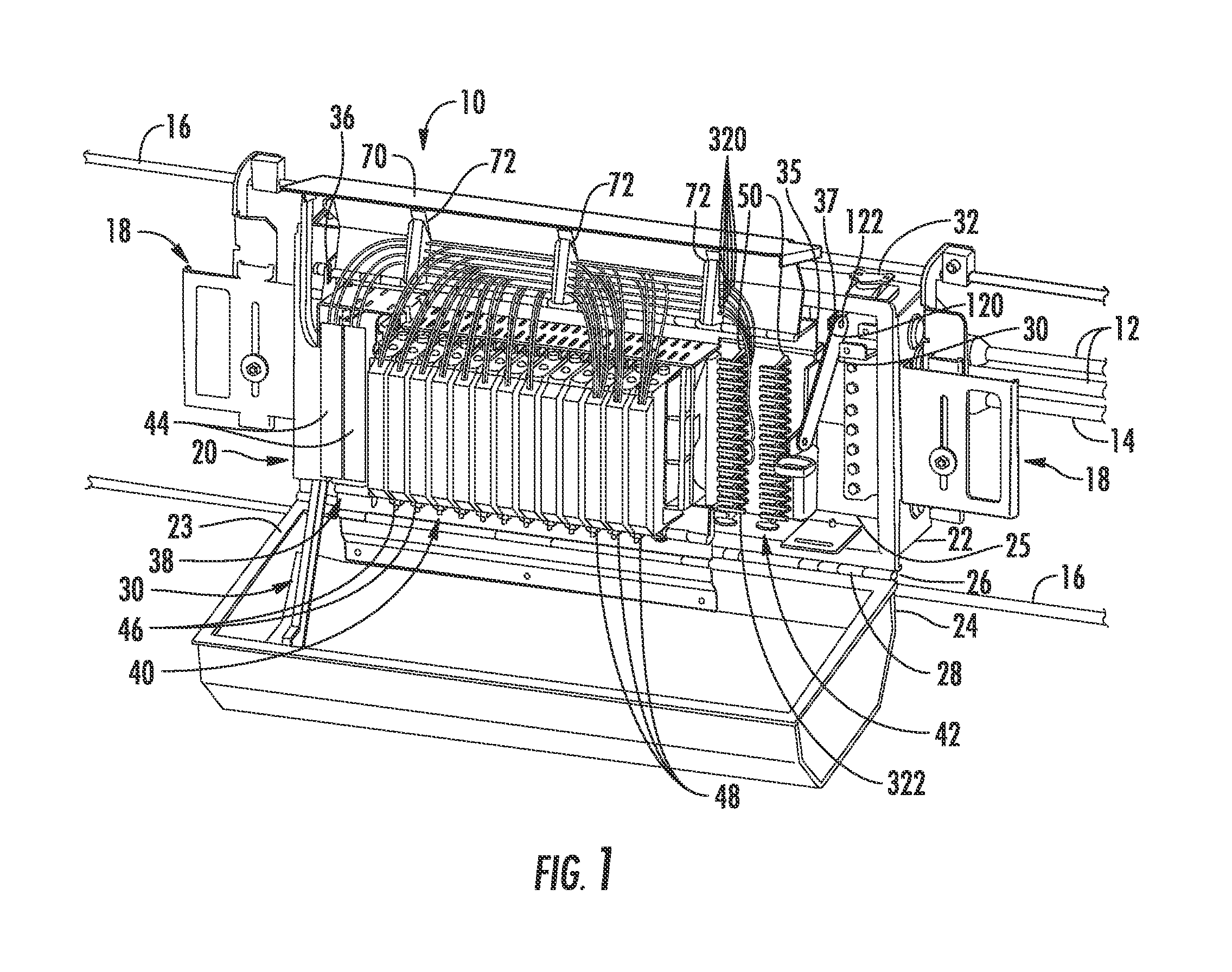
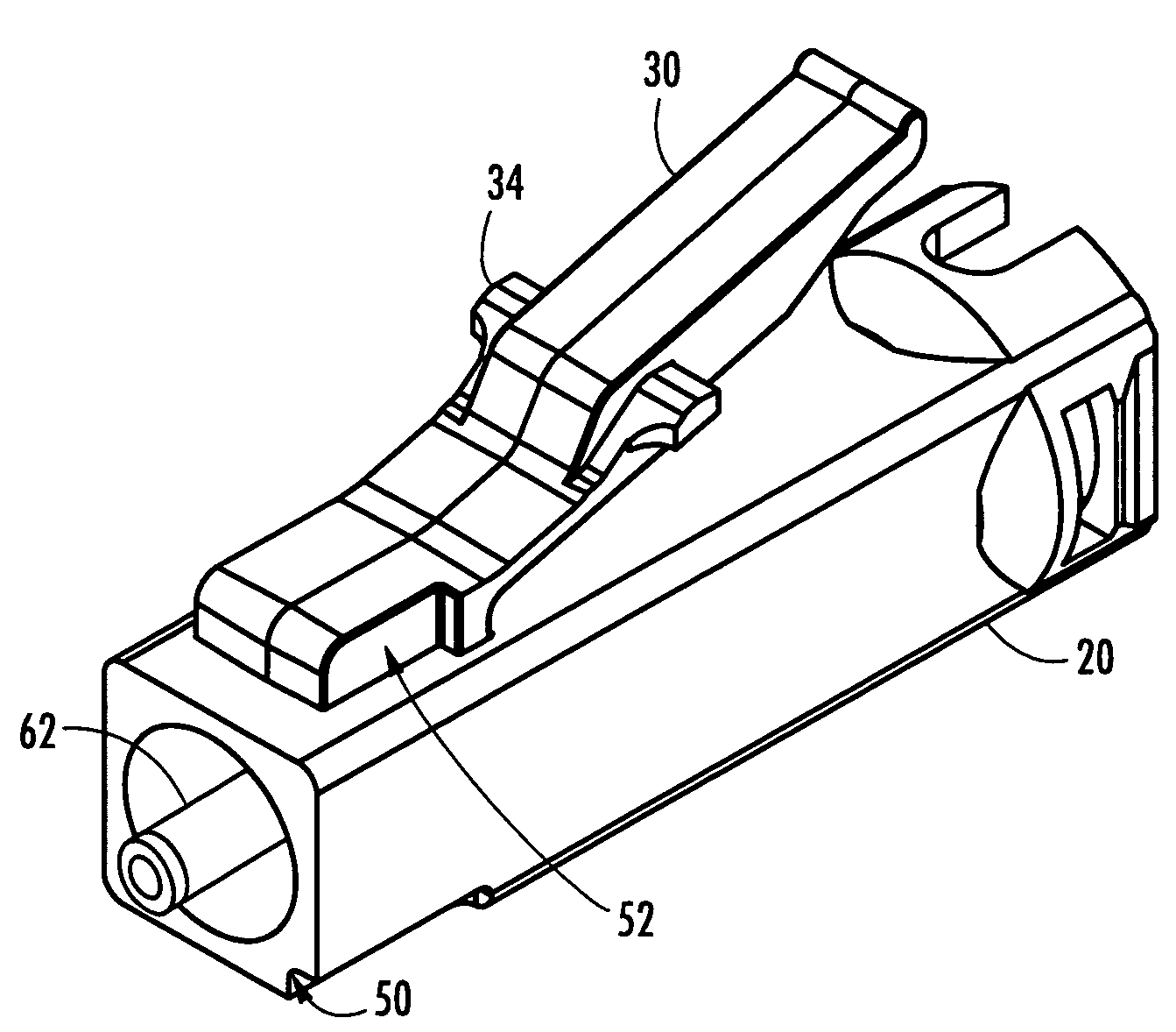
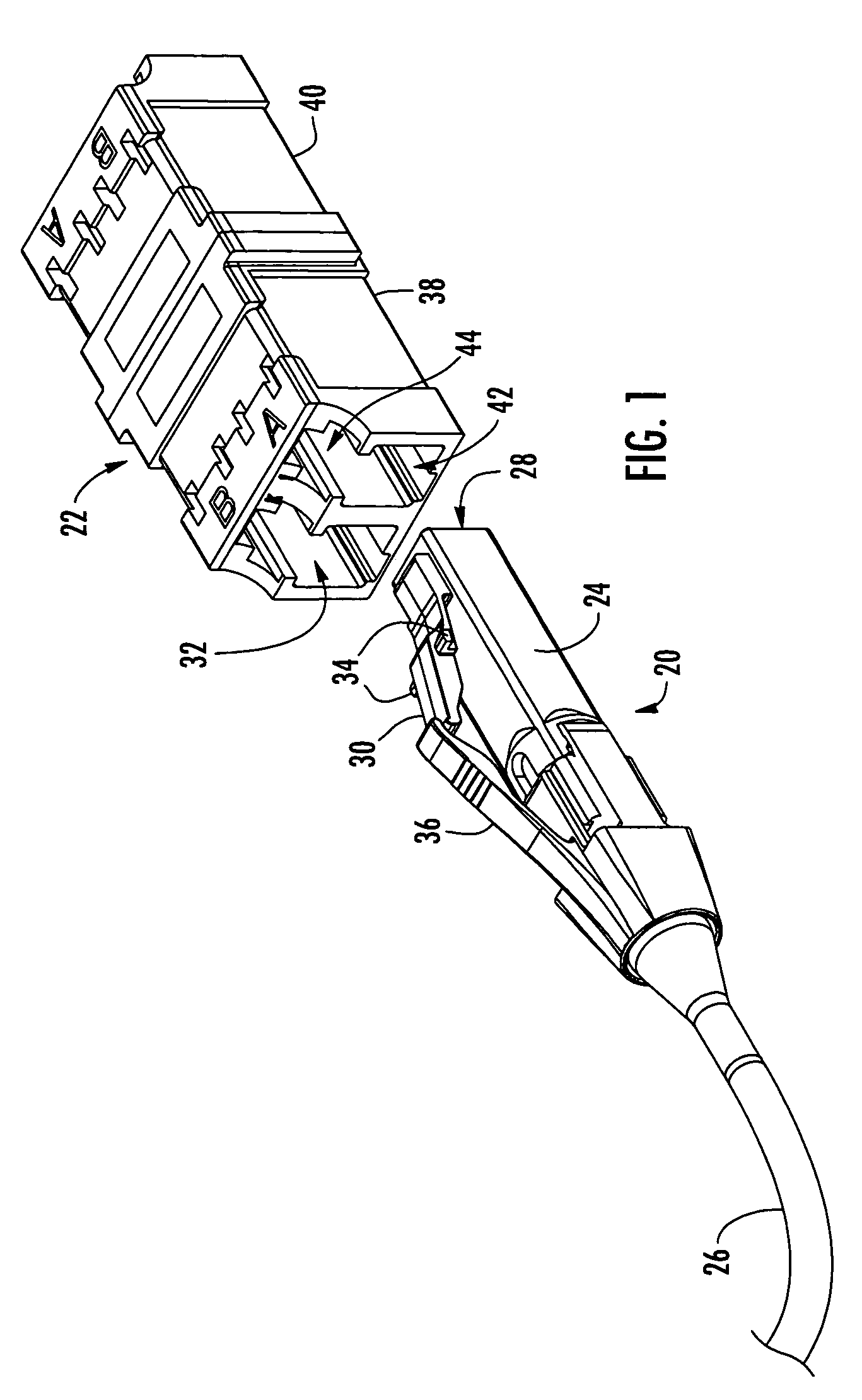
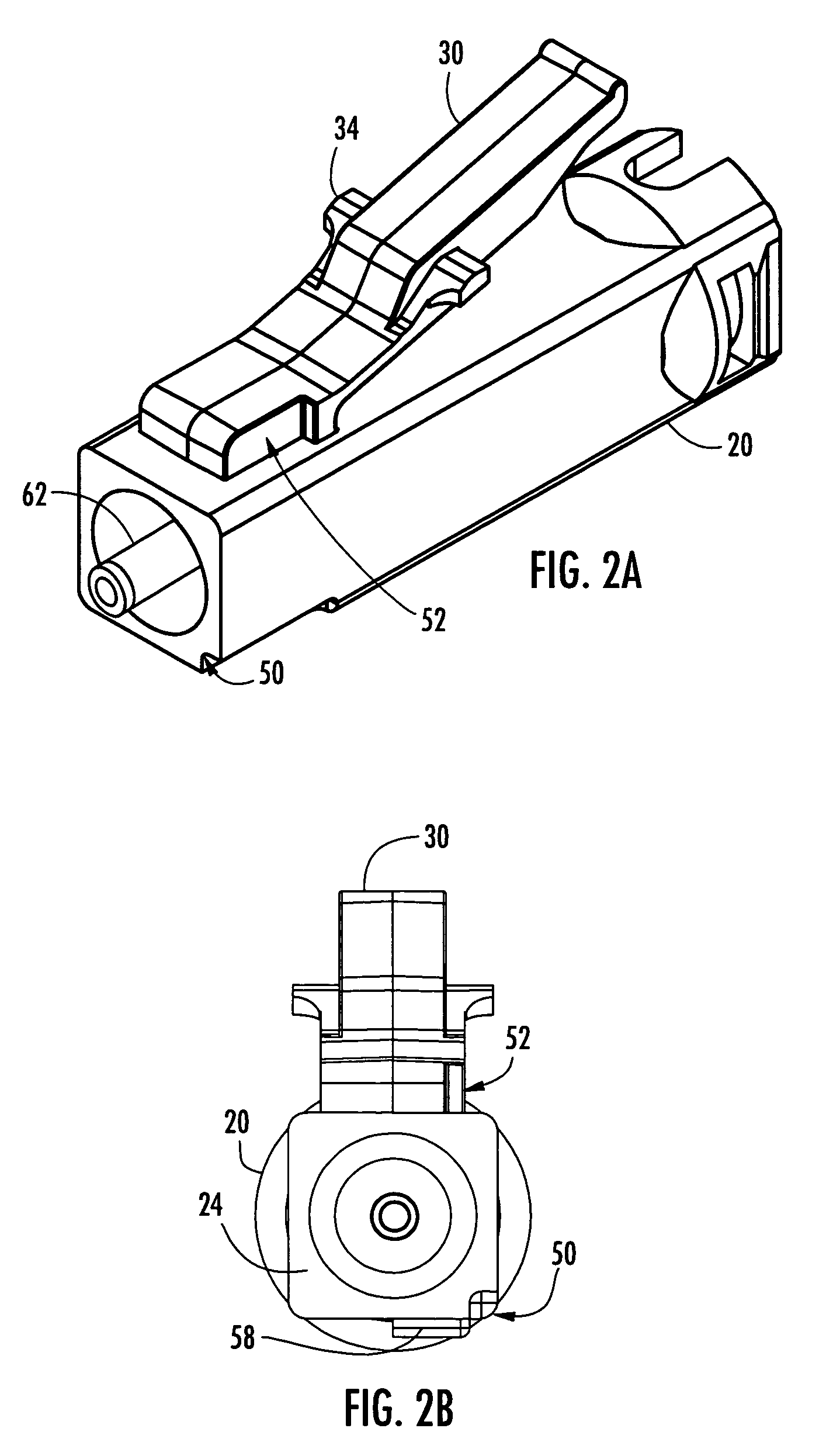
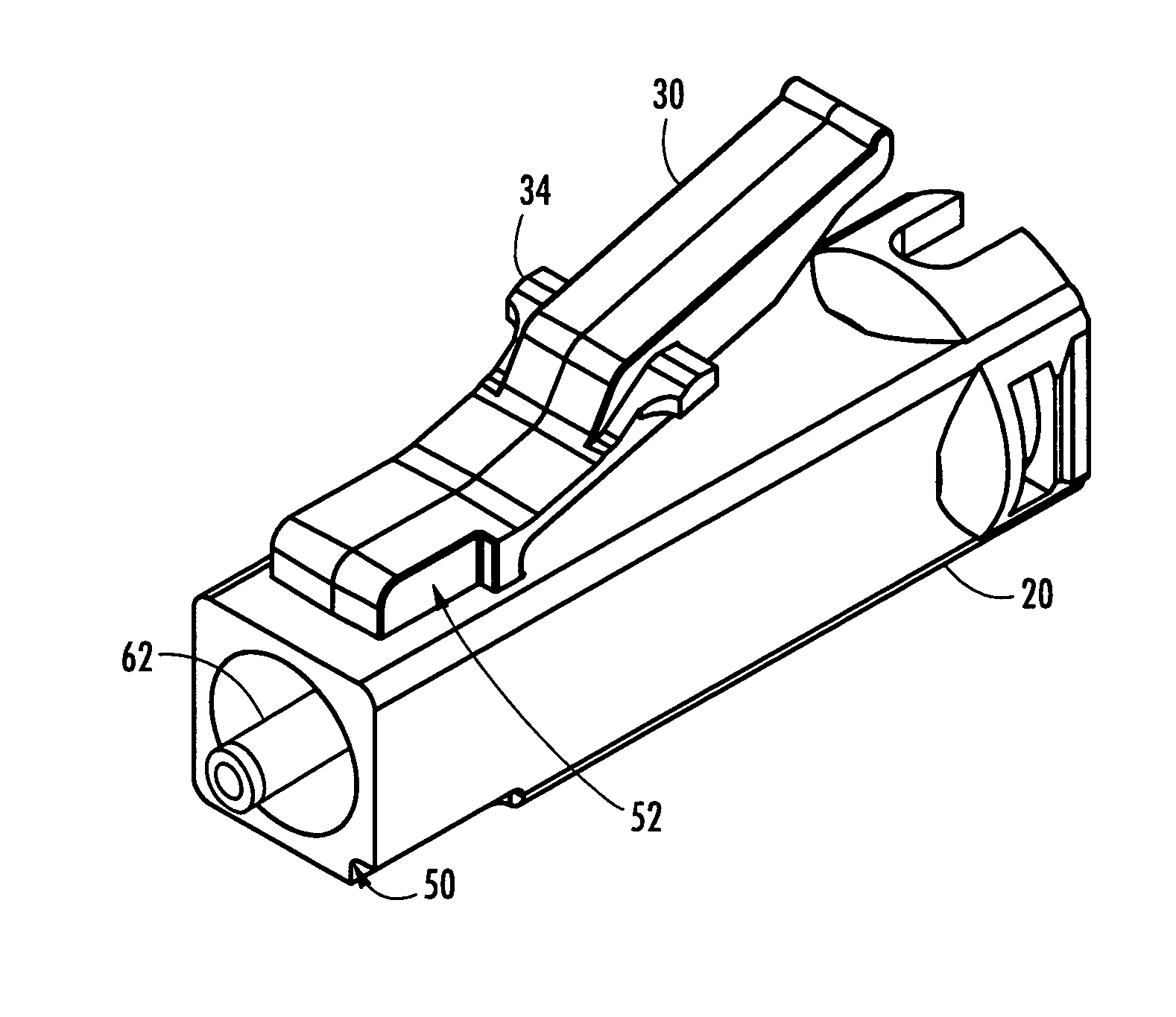
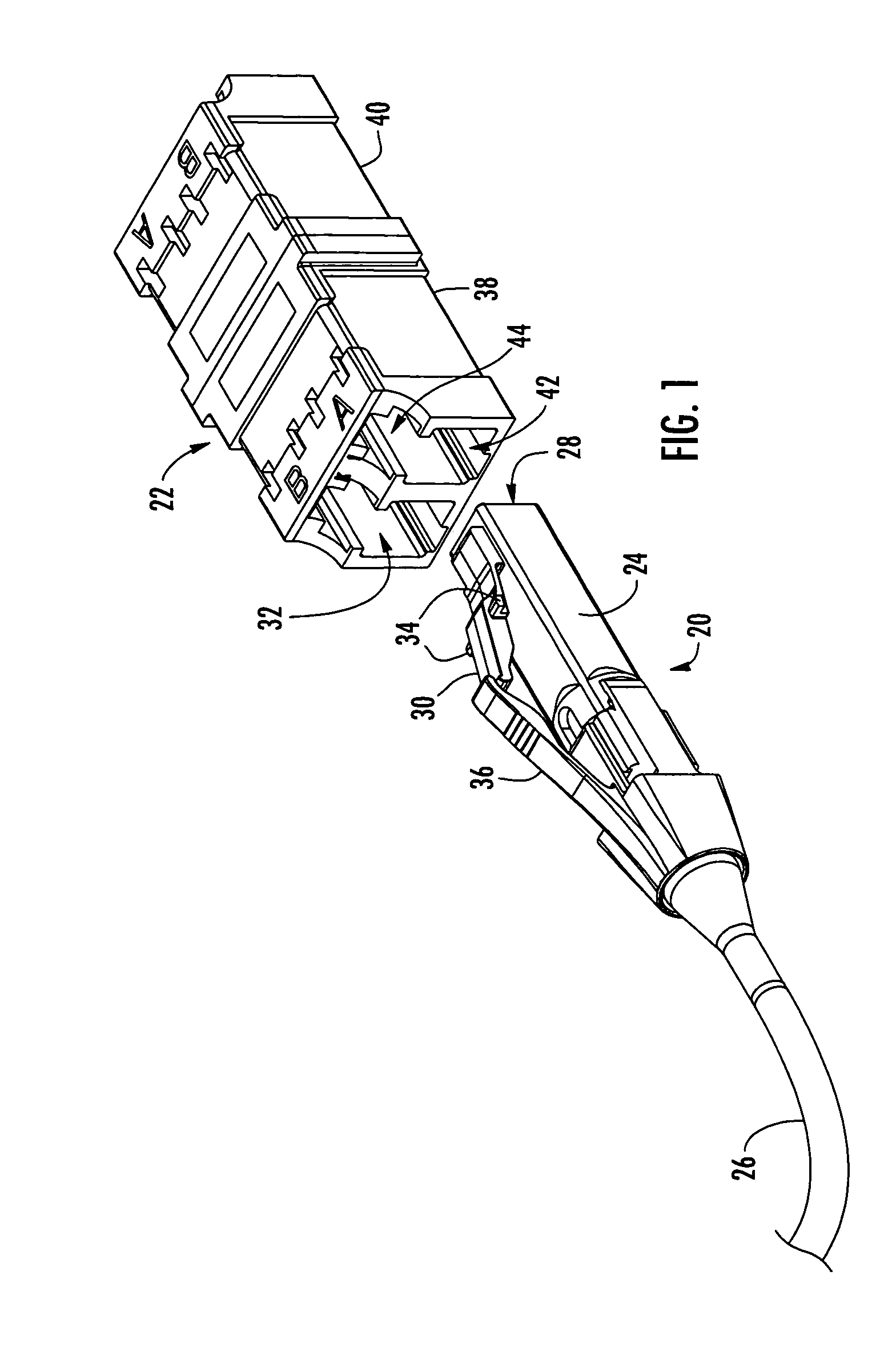
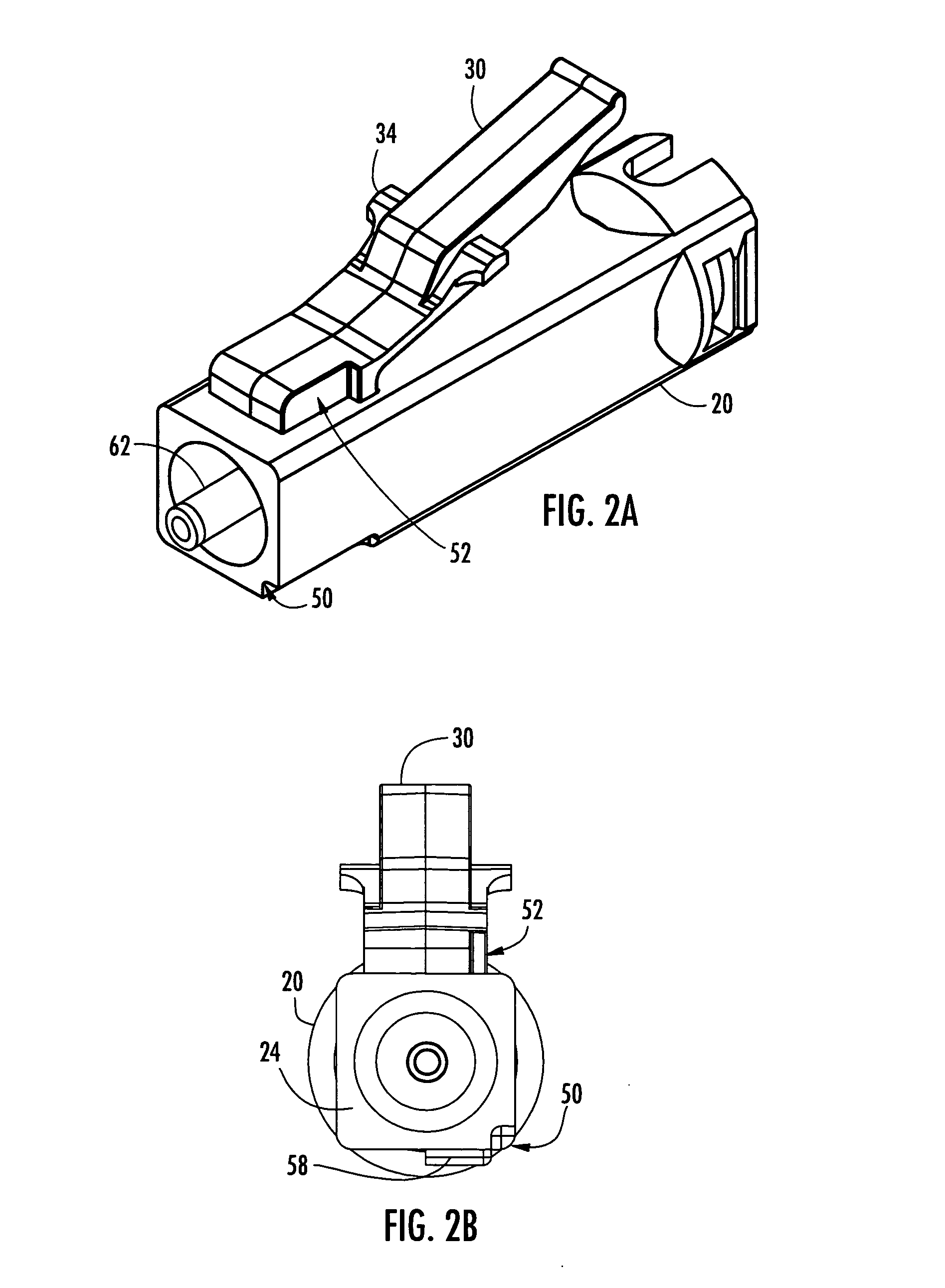
Secure fiber optic connector and adapter systems
A secure fiber optic connector and adapter system including at least one connector including a first housing portion defining a first key slot and a second housing portion defining a second key slot independent of the first key slot, and at least one adapter including a first cavity for receiving the first housing portion and defining a first key therein for engaging with the first key slot, and a second cavity for receiving the second housing portion and defining a second key therein for engaging with the second key slot, wherein only a connector and an adapter having corresponding key slots and keys may mate. A secure fiber optic connector and adapter system for providing a level of secure access within a fiber optic network.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Secure fiber optic network keyed connector assembly
InactiveUS7390203B2Prevent rotationAvoid damageLive contact access preventionOptical light guidesFiberEngineering
Owner:ORTRONICS INC +1
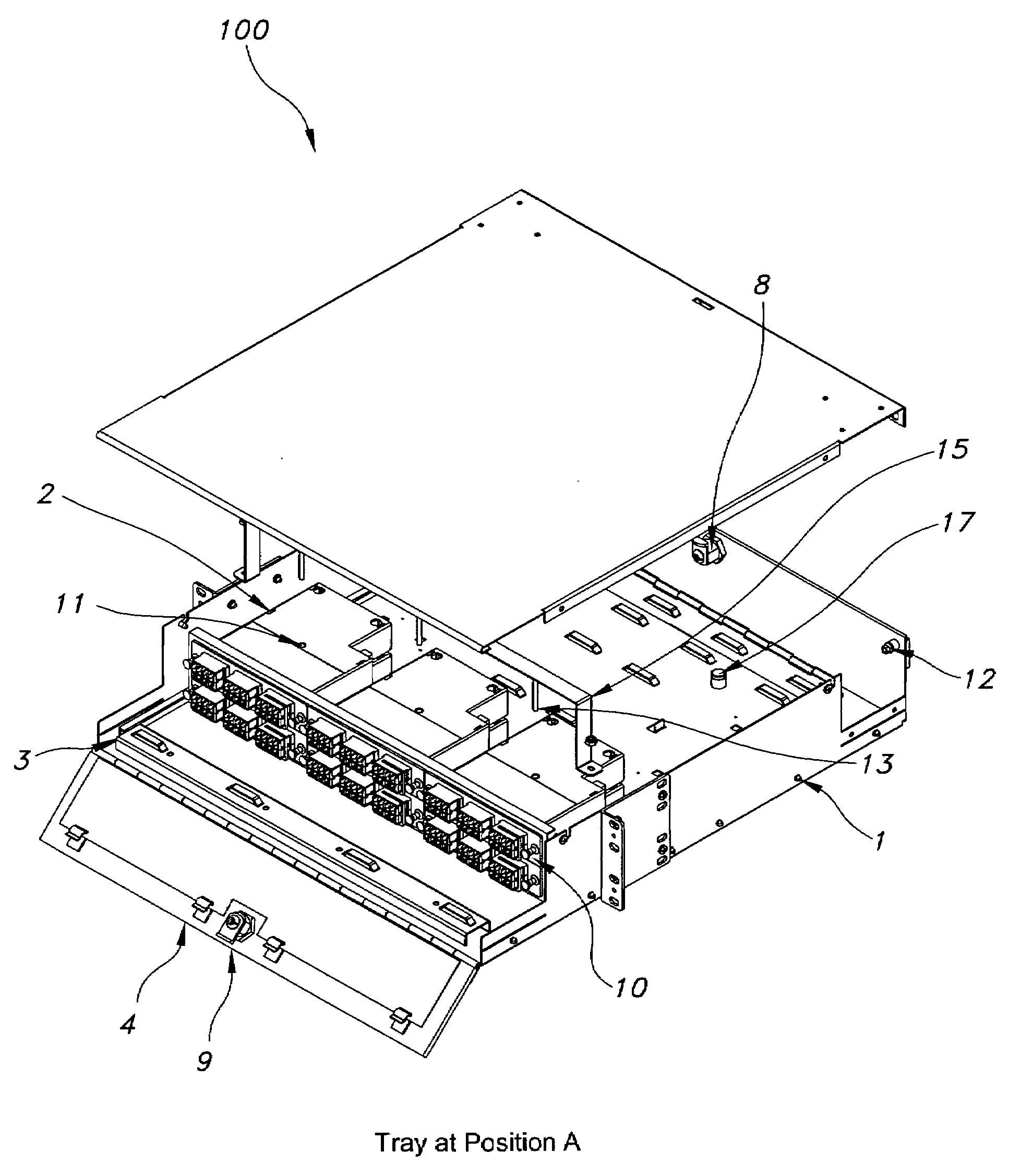
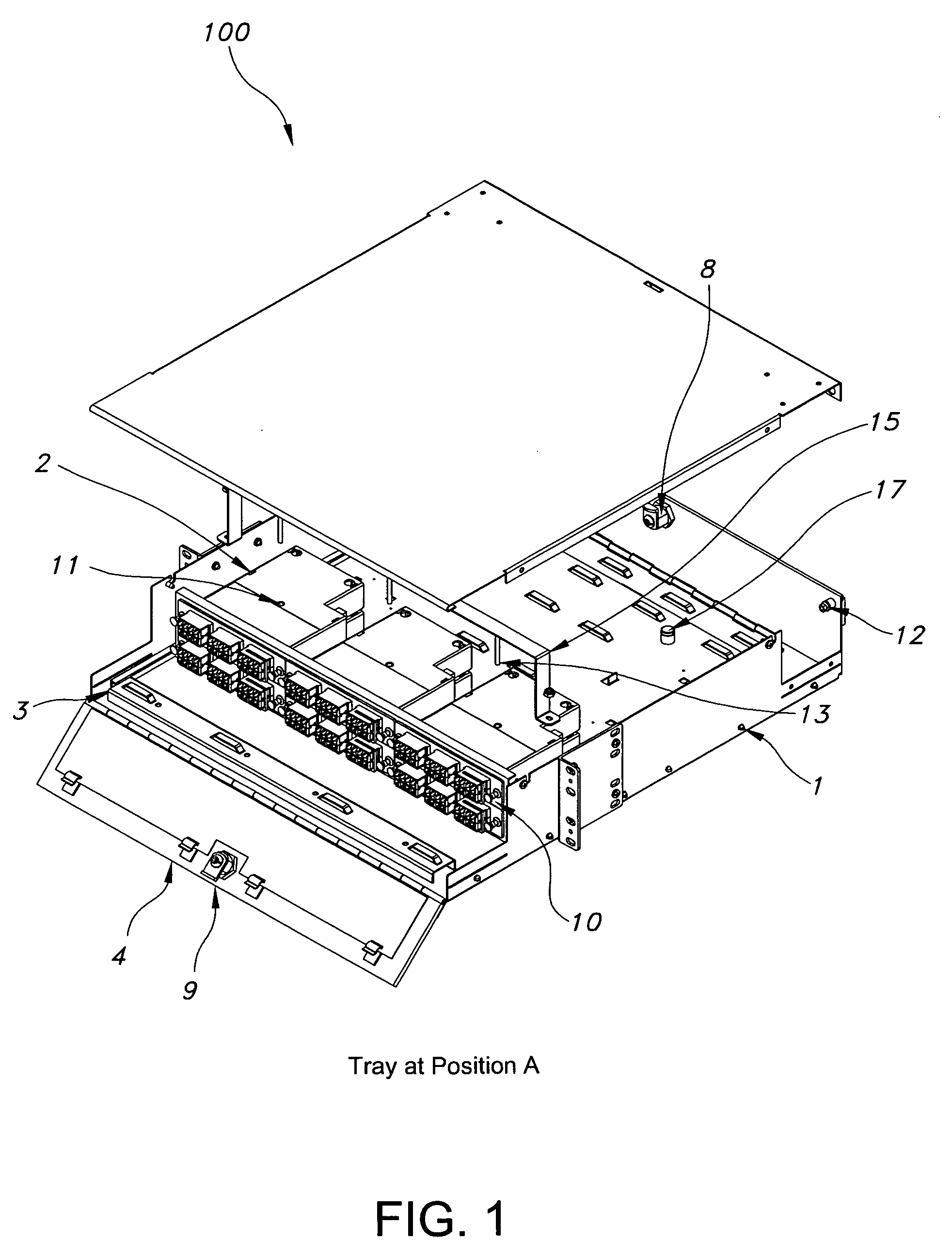
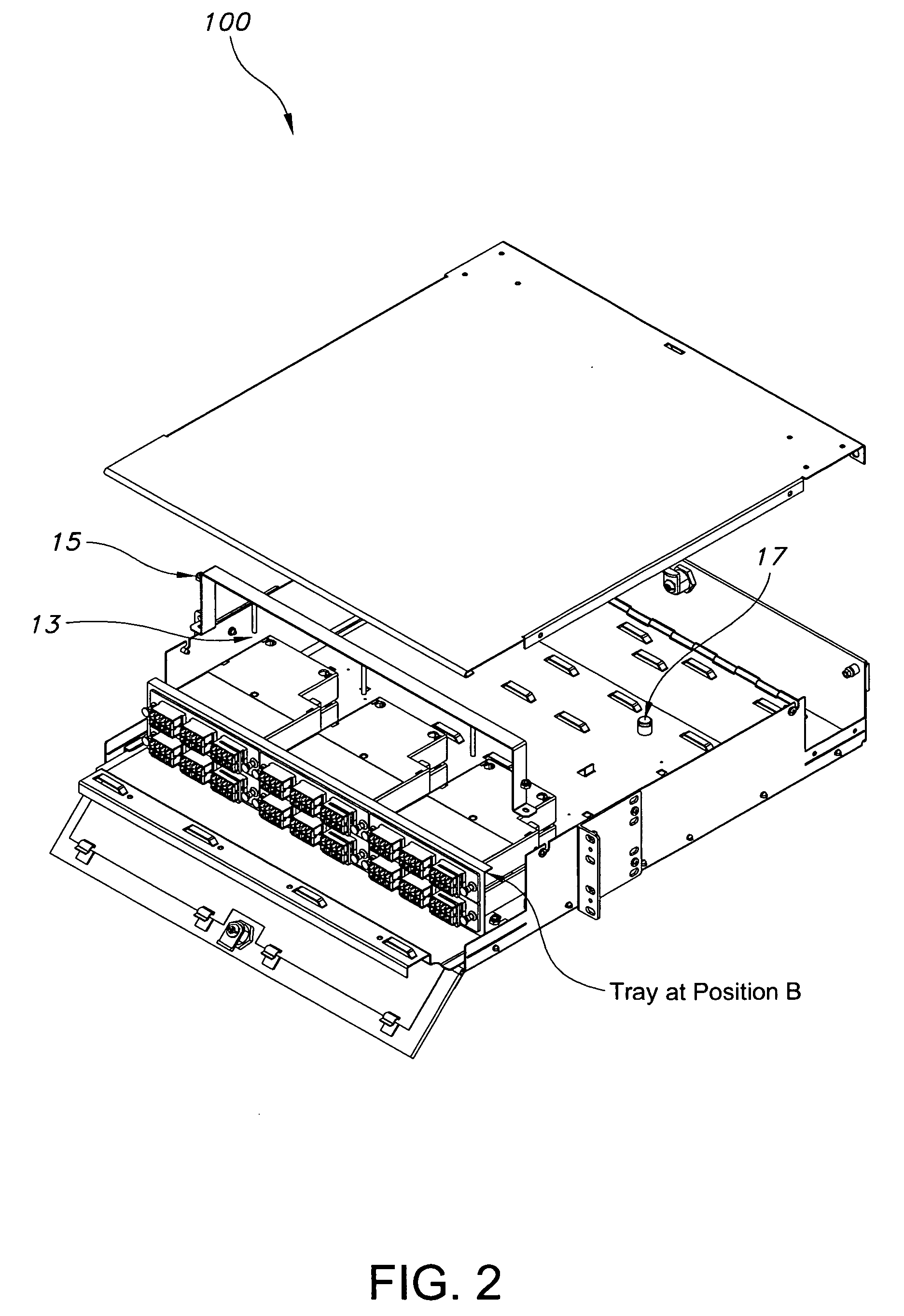
Patch panel for fiber optic network
The present disclosure is related to an apparatus and method that enables fiber optic network installers to mount fiber optic connections in raised floor locations that would otherwise be unsuited to the task. The method and apparatus permit using a de facto standard raised floor enclosures to accommodate fiber optic connections while maintaining bend radius considerations. In an exemplary embodiment, a patch panel includes a panel face defined by a bottom edge, a top edge and opposing side edges each joined to the bottom and top edges; a cable management bar operably coupled to the panel face, spaced apart from at least one surface side defining the panel face and extending a substantial length defining a length of the panel face; and a pair of mounting brackets extending from the opposing side edges. Each mounting bracket includes a mounting plane aligned with a plane of a corresponding angled mounted rail for mounting thereto such that the panel face is perpendicular to a bottom wall defining the enclosure in which it is mounted.
Owner:ORTRONICS INC
Secure fiber optic connector and adapter systems
A secure fiber optic connector and adapter system including at least one connector including a first housing portion defining a first key slot and a second housing portion defining a second key slot independent of the first key slot, and at least one adapter including a first cavity for receiving the first housing portion and defining a first key therein for engaging with the first key slot, and a second cavity for receiving the second housing portion and defining a second key therein for engaging with the second key slot, wherein only a connector and an adapter having corresponding key slots and keys may mate. A secure fiber optic connector and adapter system for providing a level of secure access within a fiber optic network.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
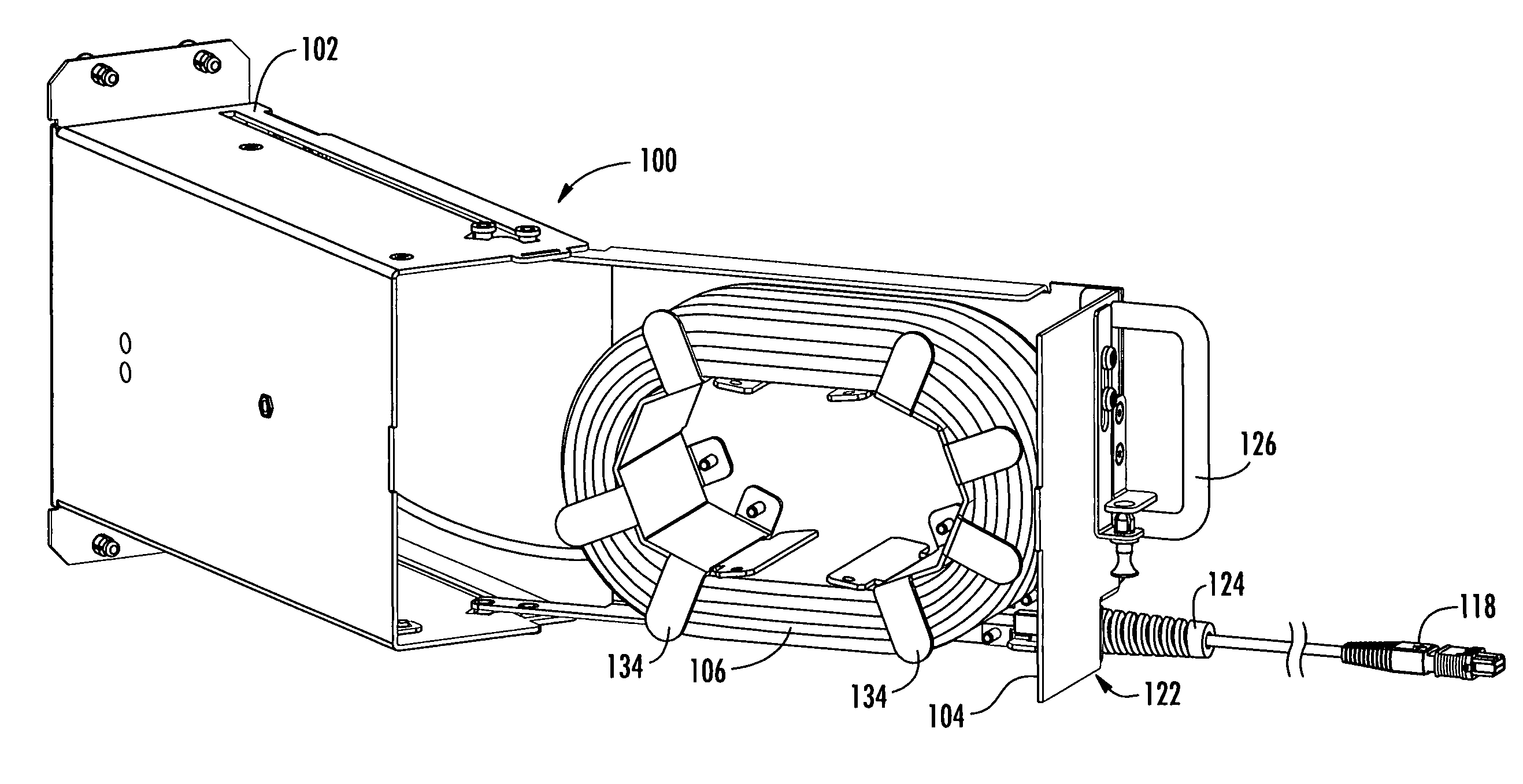
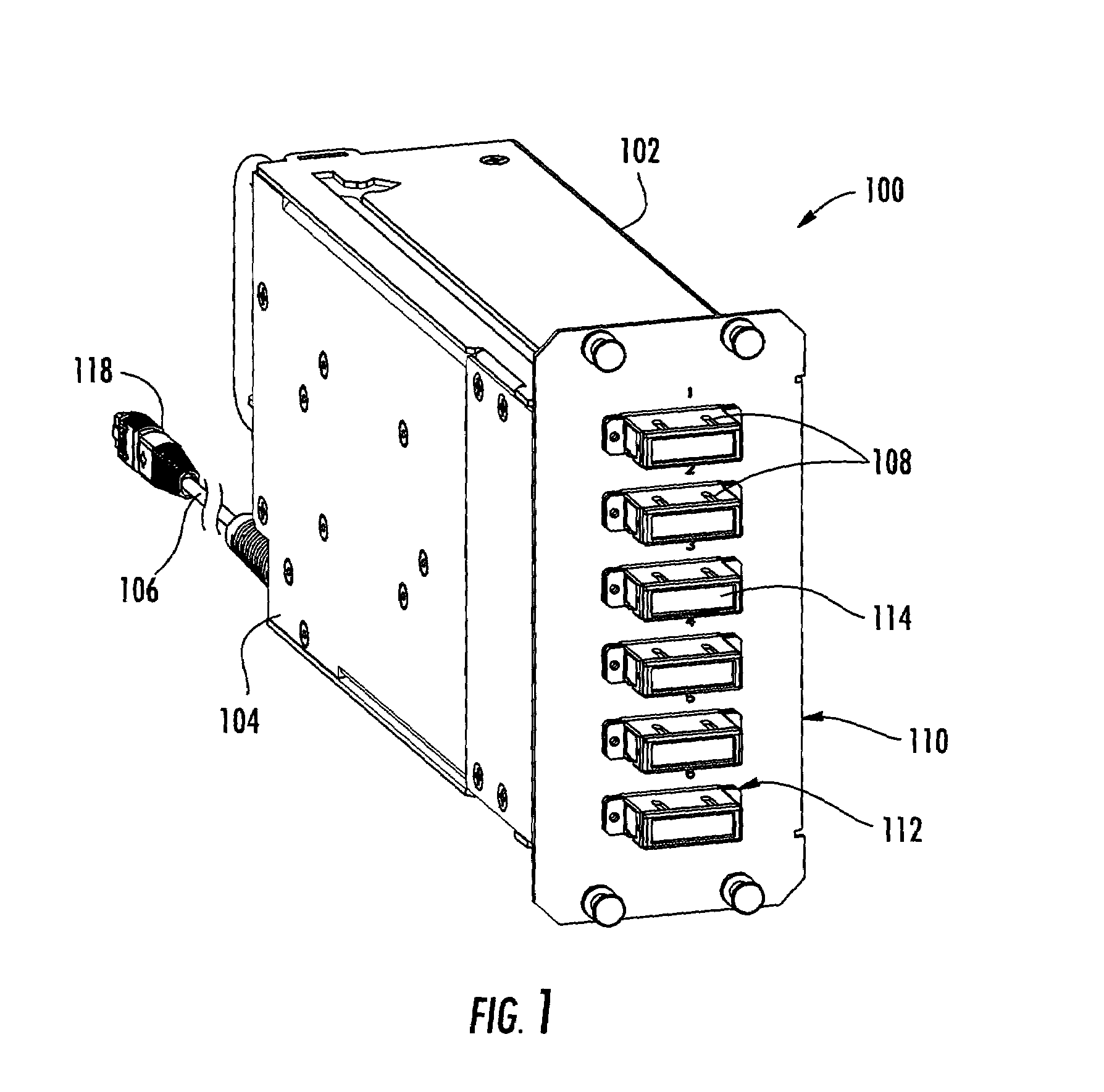
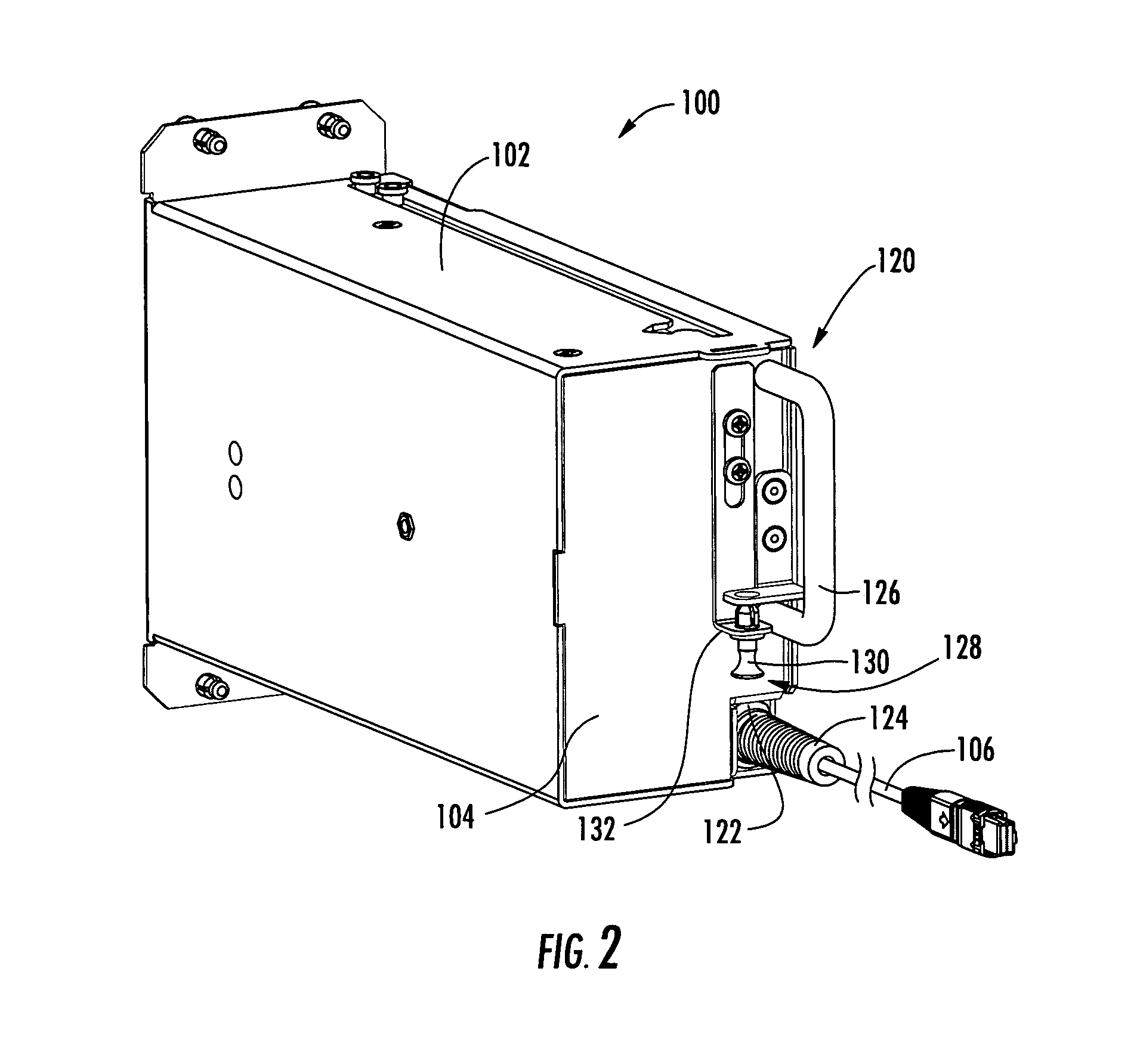
Pre-connectorized fiber optic cable network interconnection apparatus
ActiveUS7391952B1Avoid damagePrevents kinking or sharp bendingOptical light guidesData centerEngineering
A pre-connectorized network interconnection apparatus including a housing defining at least one opening for mounting at least one adapter therein, a cable storage tray movably attached to the housing movable between an opened position and a closed position for cable access, and a predetermined length of pre-connectorized fiber optic cable maintained on the storage tray, wherein a first end of the fiber optic cable terminates in at least one connector routed to the at least one connector adapter within the apparatus and a second end of the fiber optic cable terminates in at least one connector that is routed to a predetermined location within a fiber optic network. A data center network apparatus for linking separated fiber optic connection points using a length of pre-connectorized fiber optic cable.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Optical Re-Modulation in DWDM Radio-Over-Fiber Network
InactiveUS20070292143A1Reduce distractionsElectromagnetic transmittersRadio over fiberWireless transmission
An apparatus includes multiple signal paths for optically converting an optical signal to multiples of the optical signal at different respective carrier frequencies for reducing interference between wireless transmissions of the multiples of the optical signal. Preferably, the converting includes a first modulator for modulating the optical signal into a first optical carrier and an initial first-order sideband signal with a frequency spacing twice that of the first optical carrier and a first interleaver for separating the first optical carrier and the initial first-order sideband signal. The converting also includes a second phase modulator for modulating the first optical carrier into a second optical carrier and a second first-order sideband signal with a frequency spacing twice that of the second optical carrier.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Secure fiber optic network cassette assembly
InactiveUS7509015B2Avoid damageEffective protectionTents/canopiesOptical light guidesMagnetic tapeEngineering
Owner:ORTRONICS INC
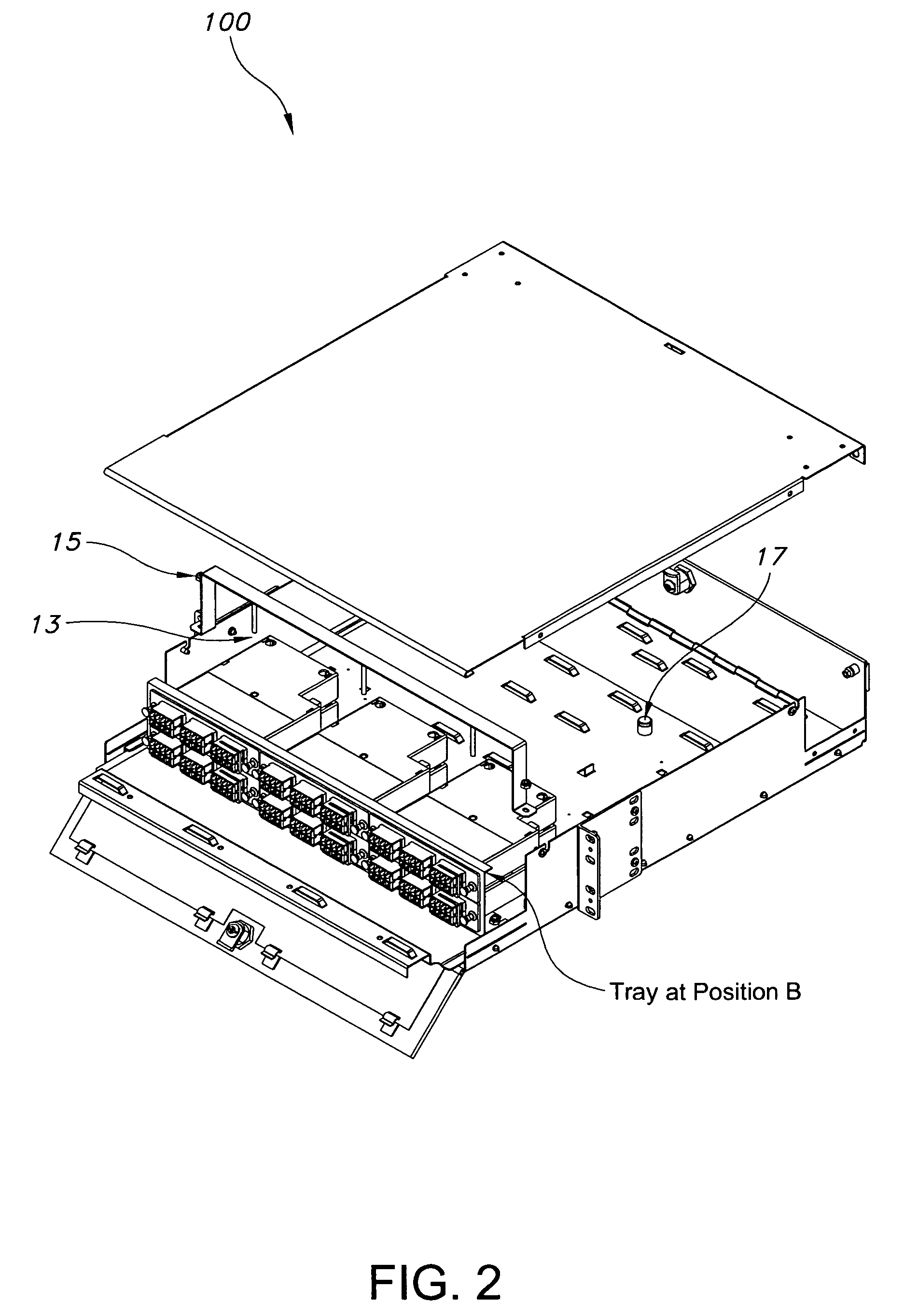
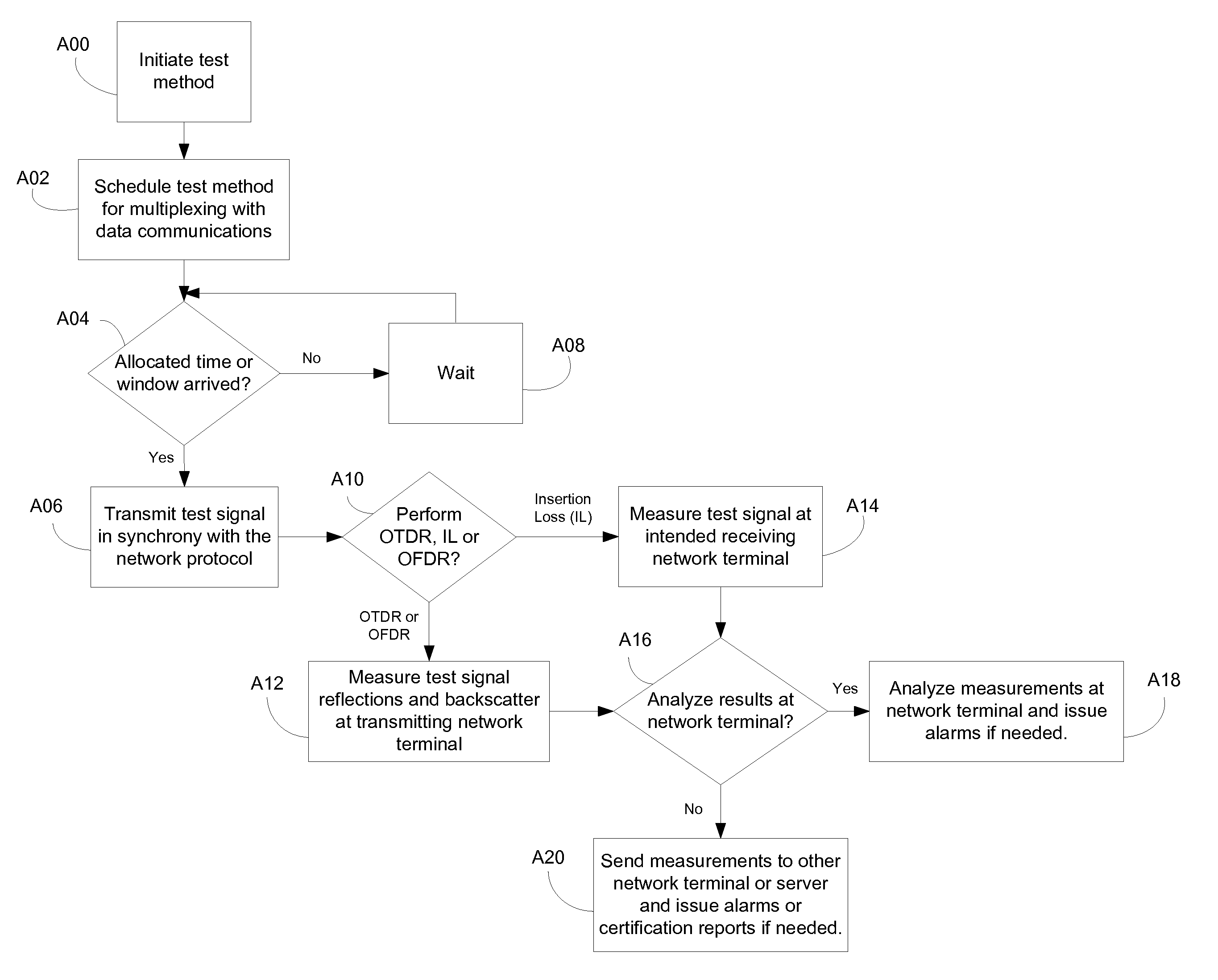
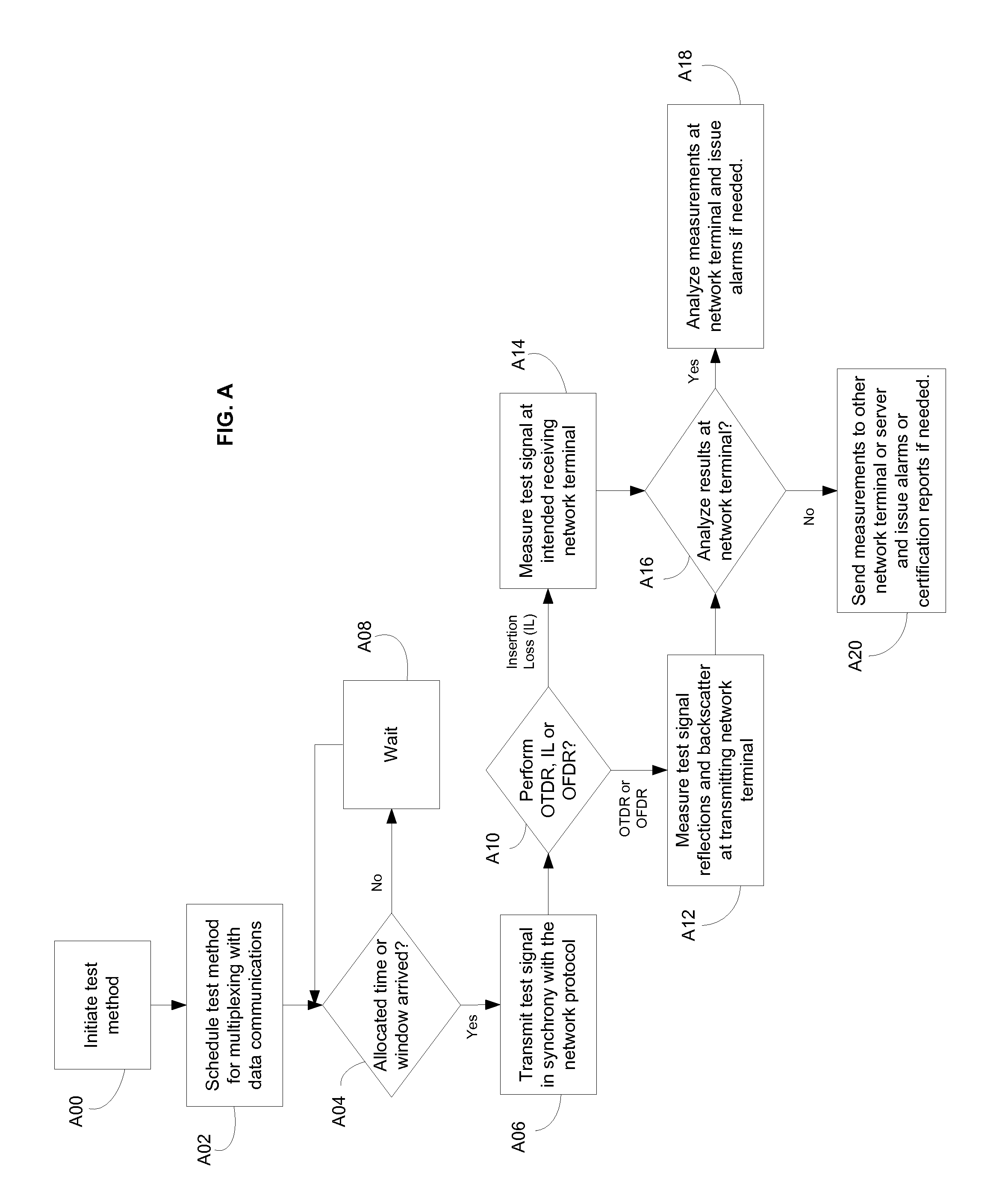
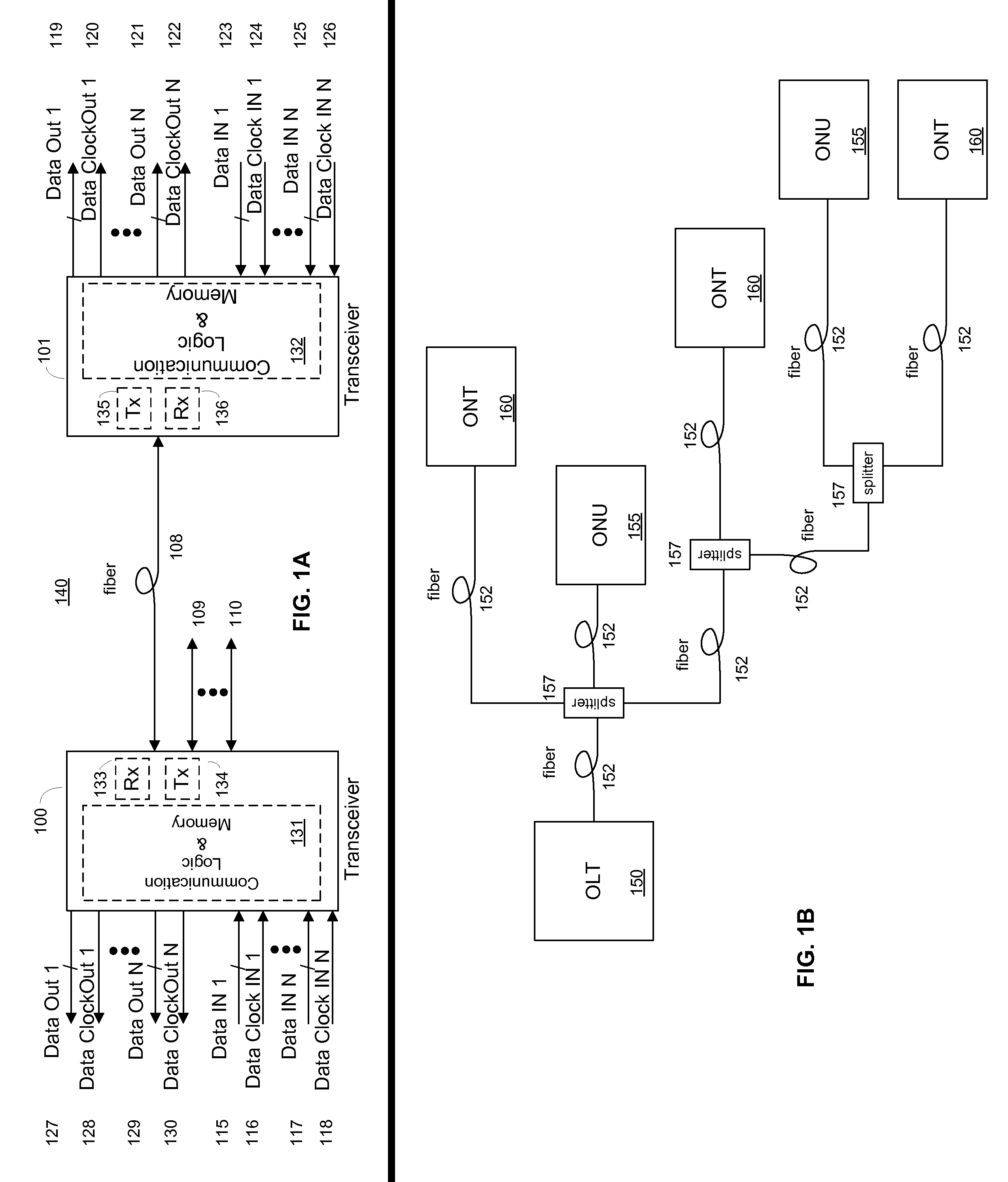
System and method for performing in-service optical fiber network certification
ActiveUS20110211827A1Timely controlWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringTime-domain reflectometryFiber network
A system and method for performing an in-service optical time domain reflectometry test, an in-service insertion loss test, and an in-service optical frequency domain reflectometry test using a same wavelength as the network communications for point-to-point or point-to-multipoint optical fiber networks while maintaining continuity of network communications are disclosed.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
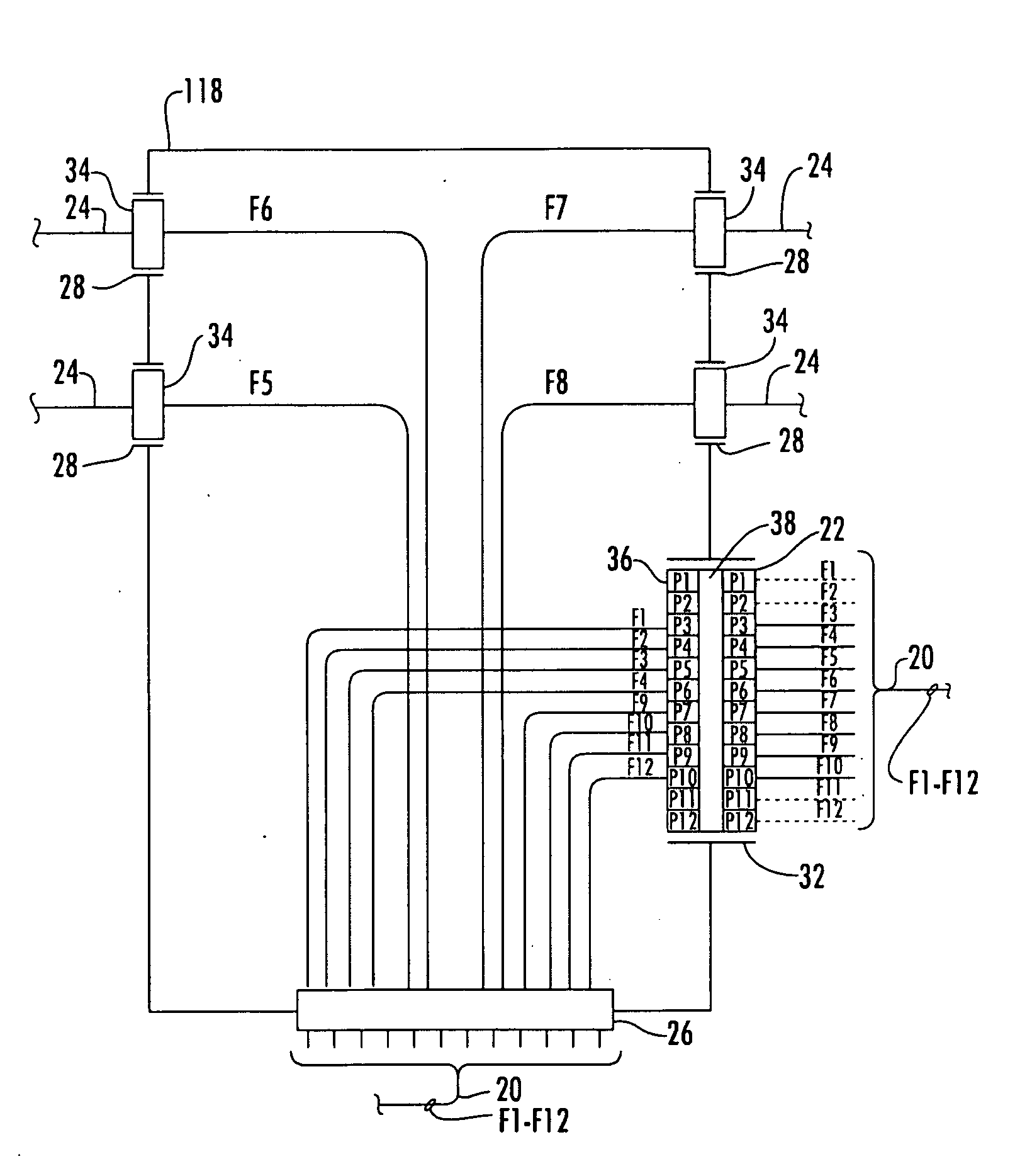
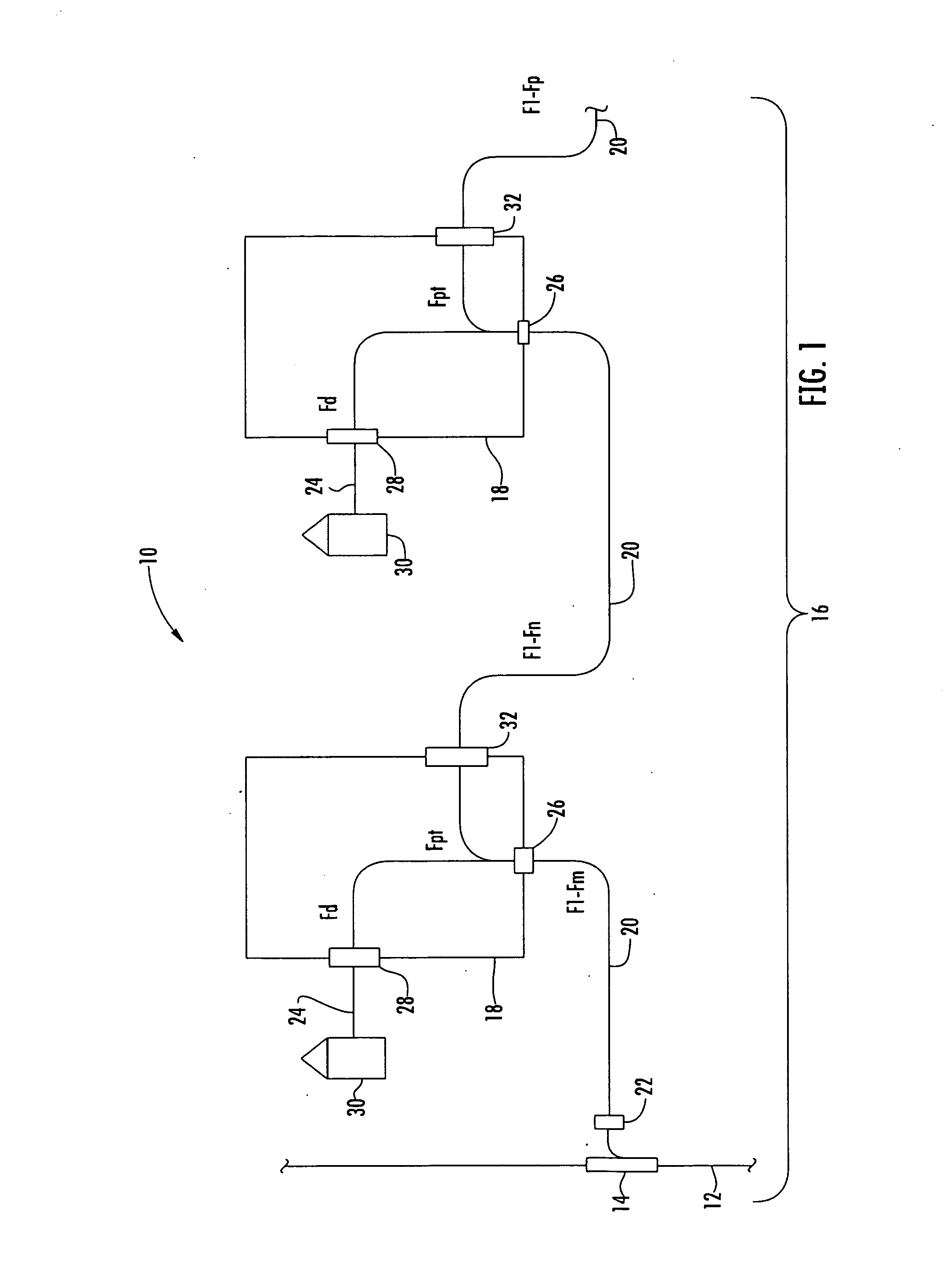
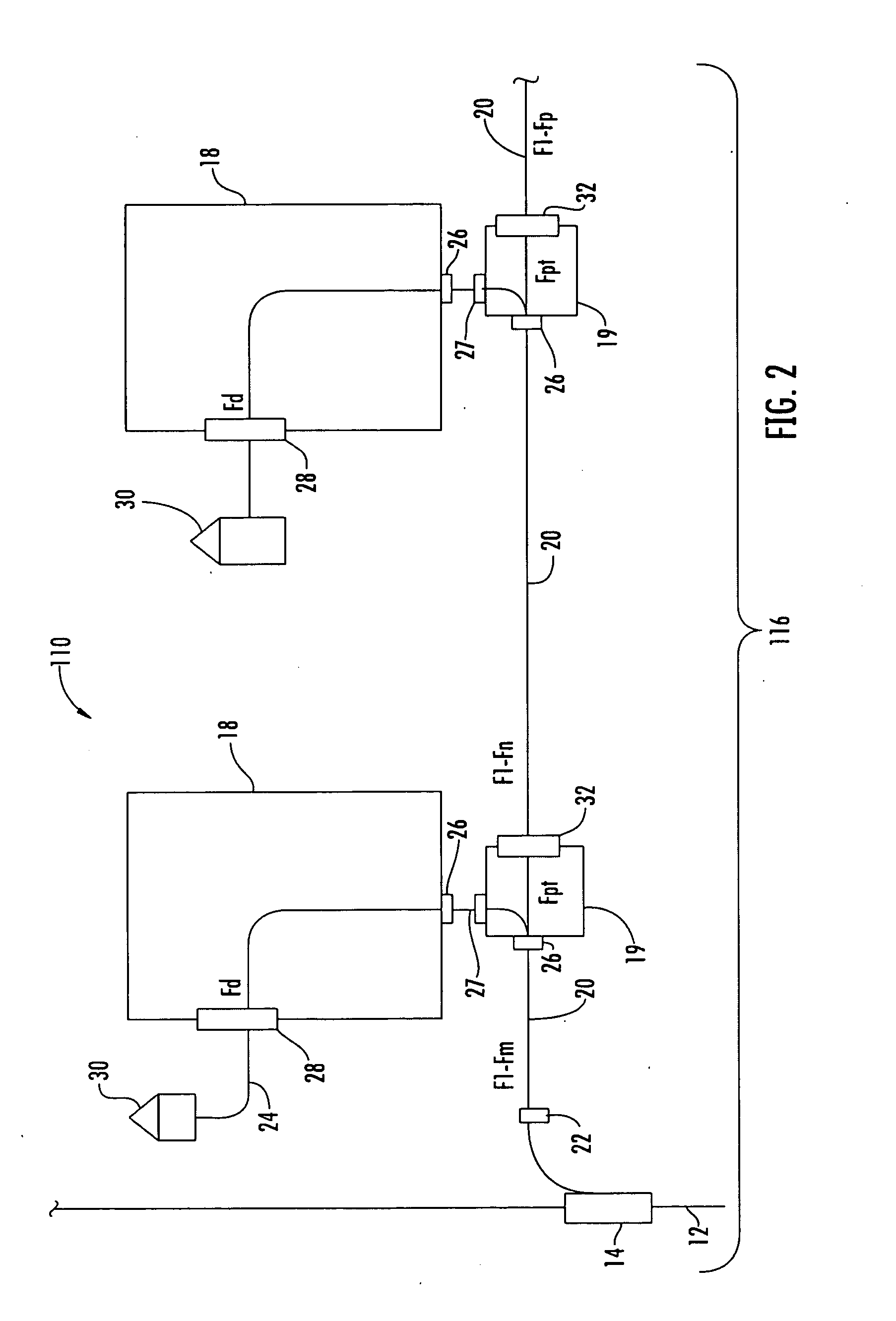
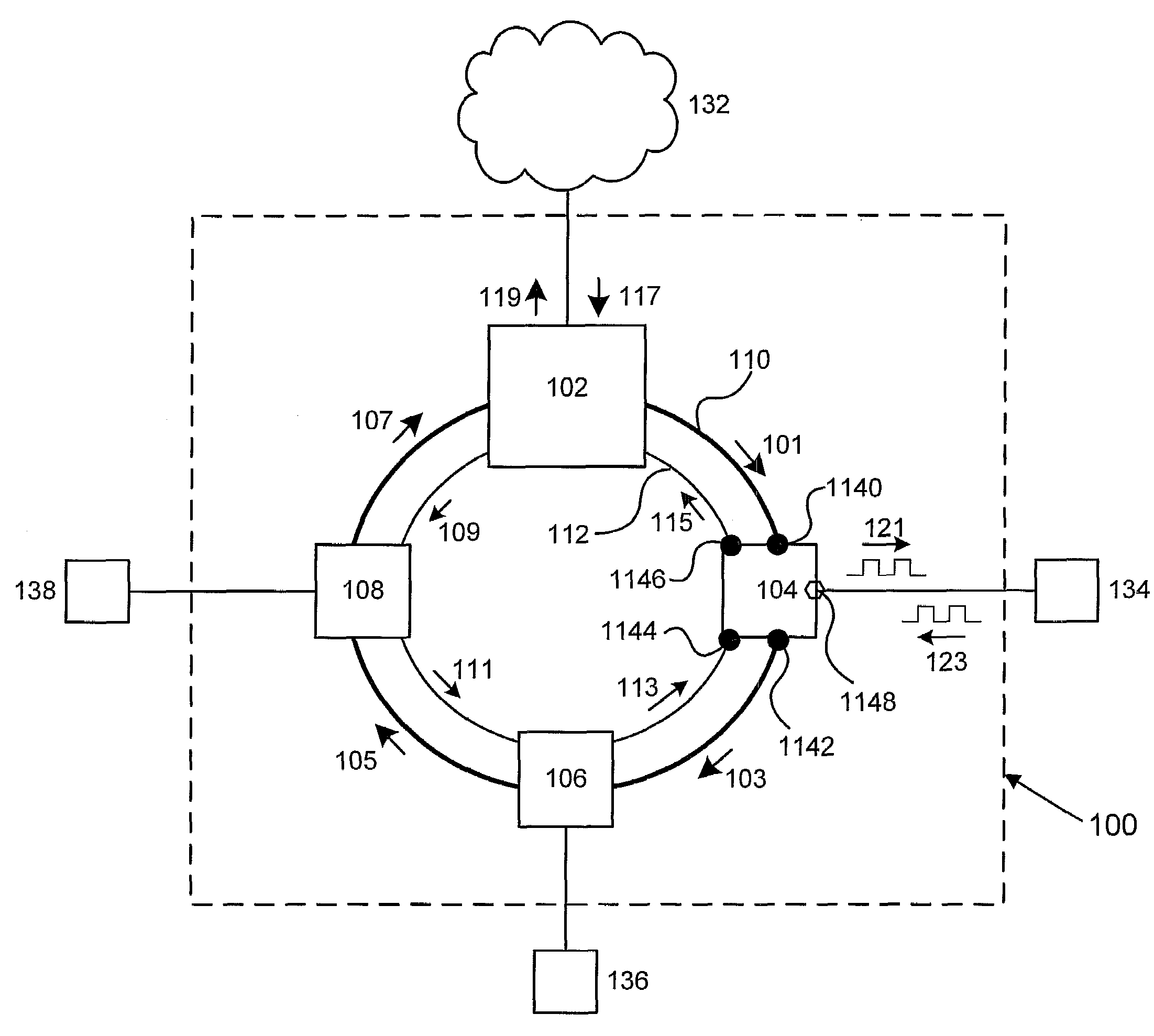
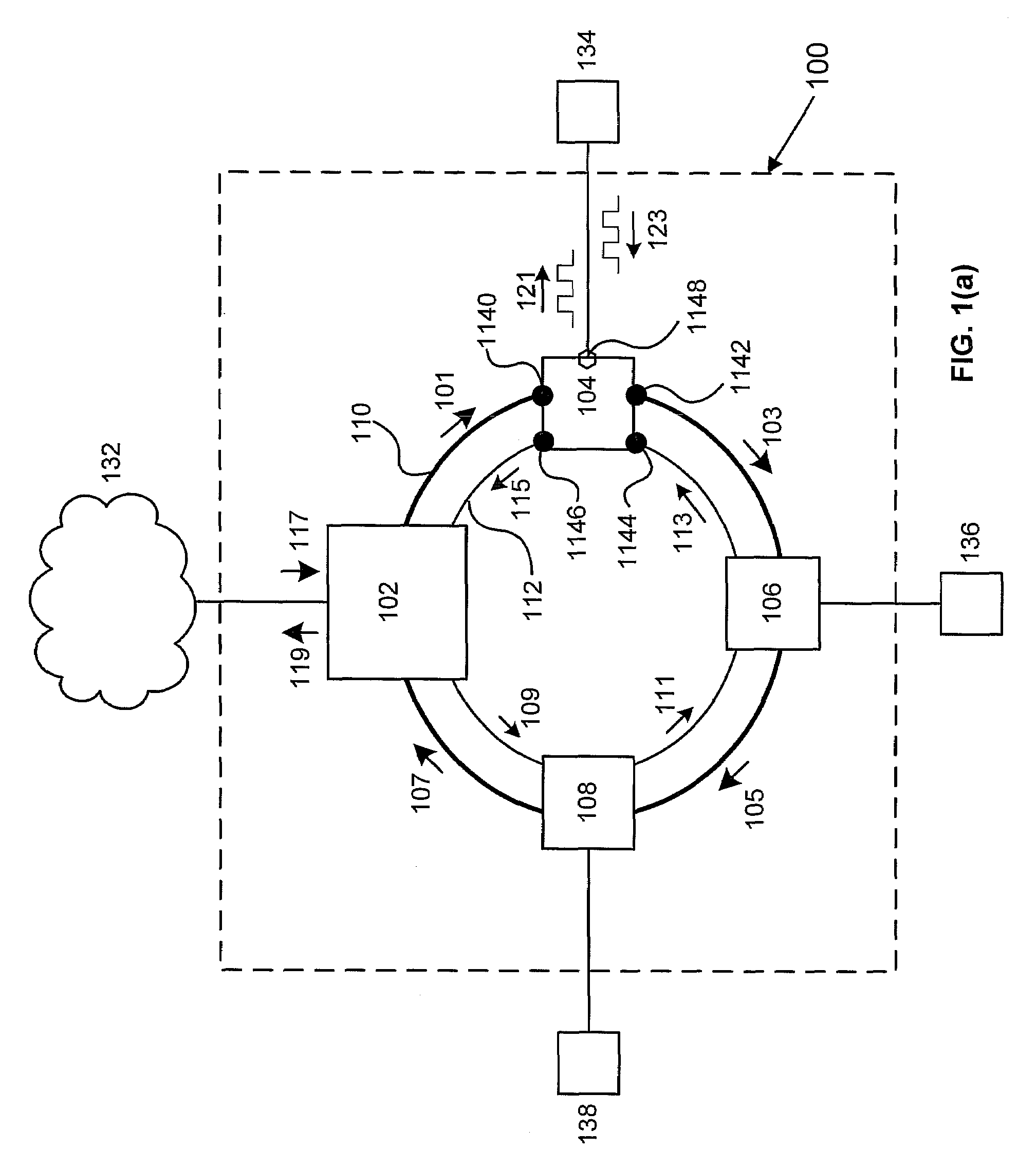
Fiber Optic Network Architecture Having Optical Connection Terminals in Series Arrangement
A fiber optic network having a branch cable with a plurality of optical fibers optically coupled to a distribution cable, and first and second optical connection terminals connected in series is disclosed. The first optical connection terminal is adapted to receive a first segment of the branch cable. The first optical connection terminal is configured such that predetermined ones of a first plurality of ports comprise one or more of a first drop port and a first pass-through port. The first drop port is operable for optically coupling a first respective predetermined one of the plurality of optical fibers to a first drop cable. The first pass-through port is operable for optically coupling a second respective predetermined one of the plurality of optical fibers to a second segment of the branch cable extending externally from the first optical connection terminal. The second optical connection terminal is adapted to receive the second segment of the branch cable. The second optical connection terminal is configured such that a predetermined one of a second plurality of ports comprises a second drop port operable for optically coupling the second respective predetermined one of the plurality of optical fibers to a second drop cable.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
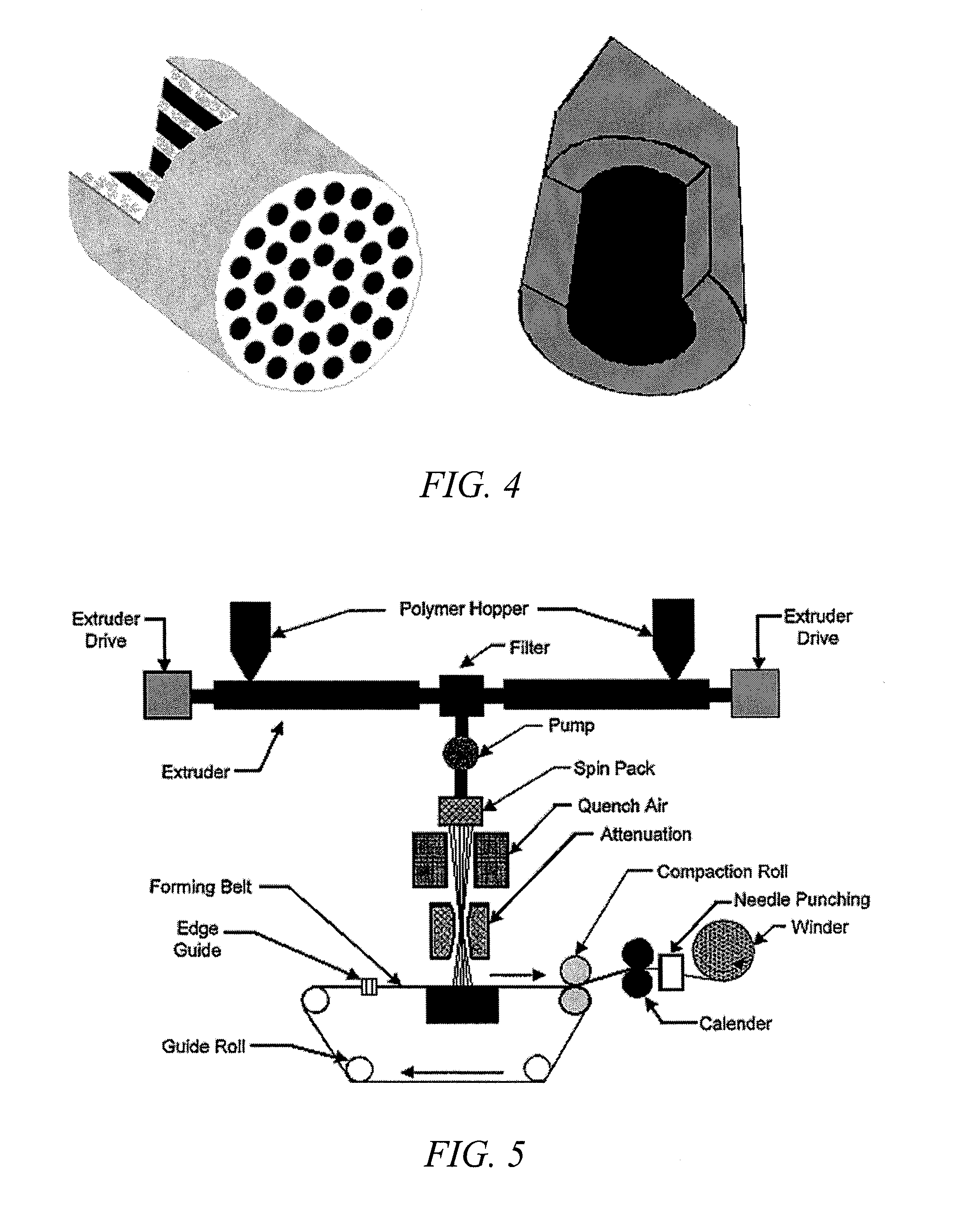
Mixed fibers and nonwoven fabrics made from the same
ActiveUS20090042475A1Improve breathabilityIncrease flexibilityLaminationLamination apparatusFiltrationSubject matter
The subject matter disclosed herein relates generally to the production of a predetermined ratio of multicomponent fibers in combination with monocomponent fibers or other multicomponent fibers, preferably through a spunbonding process. After extrusion, these fibers can produce a fiber network that is subsequently bonded to produce a nonwoven fabric comprising multiple types of fibers. The multicomponent fibers within the network may be processed to remove one component by dissolution or to split the individual components into separate fibers. As a result, the fabric will be comprised of fibers with a range of diameters (micro- or nano-denier fibers as well as higher denier fibers) such that the fibers will not pack as tightly as in a homogeneous nonwoven fabric produced from one type of monocomponent or multicomponent fiber. The present invention additionally relates to methods for producing nonwoven fabrics with increased loft, breathability, strength, compressive properties, and filtration efficiency.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Secure fiber optic network cassette assembly
InactiveUS20080025683A1Avoid damageEffective protectionTents/canopiesOptical light guidesComputer hardwareEngineering
Assemblies and methods for securing a fiber optic network cassette assembly are provided. A typical secure cassette assembly includes a cabinet adapted to be locked on both a front and rear side of the cabinet. Internally, a plurality of cassettes are placed on a cassette tray adapted to slide back and forth within the cabinet. Insert pins are placed into holes on the cassettes locking into the cassette tray. A limiter is placed inside the cabinet that prevents the cassette tray from sliding when engaged. If one of the cassettes is forcibly removed, the insert pin will shear the fiber internal to the cassette and destroy the cassette, thereby disabling the network and typically alerting a network administrator or designated individual.
Owner:ORTRONICS INC
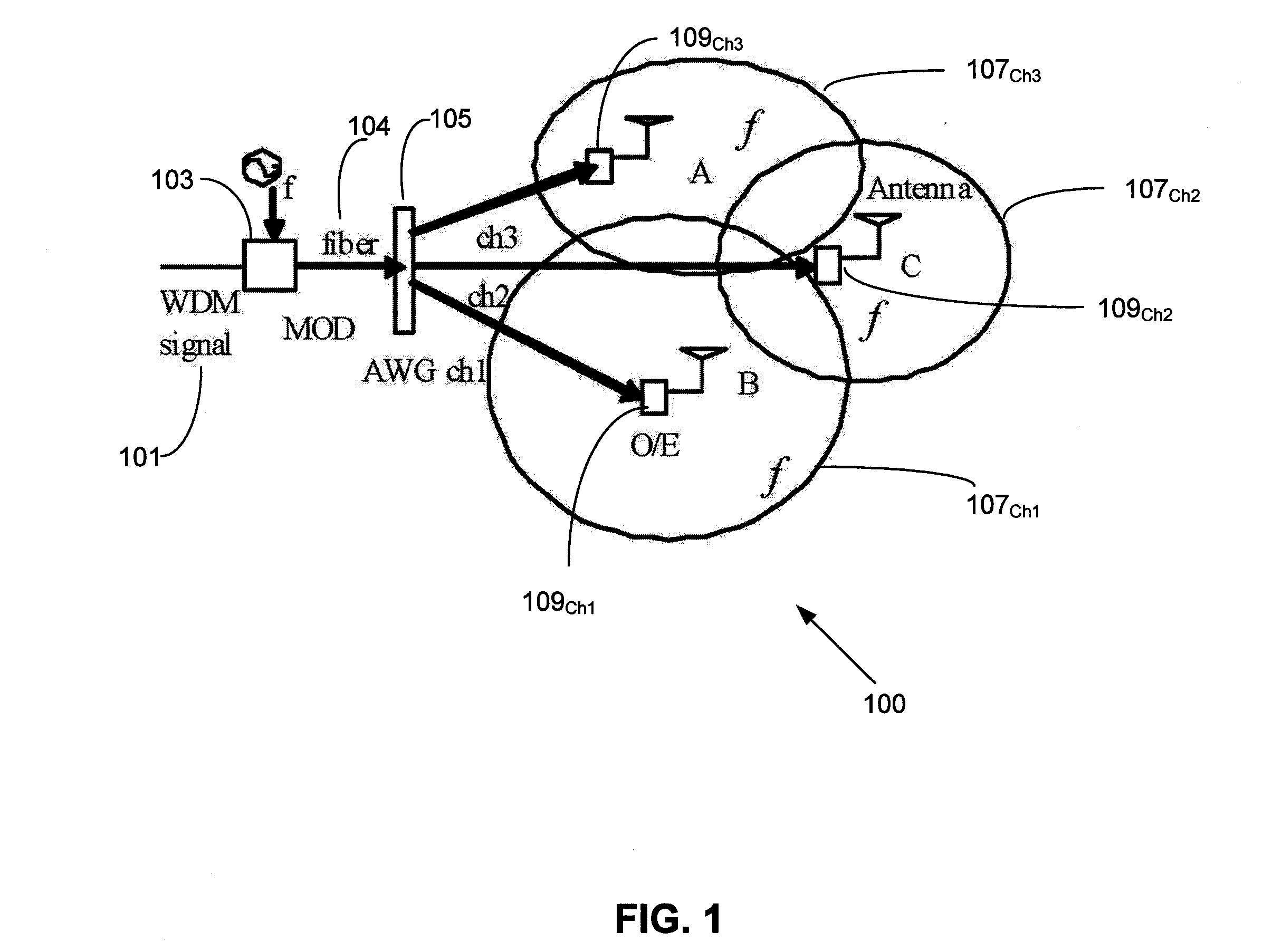
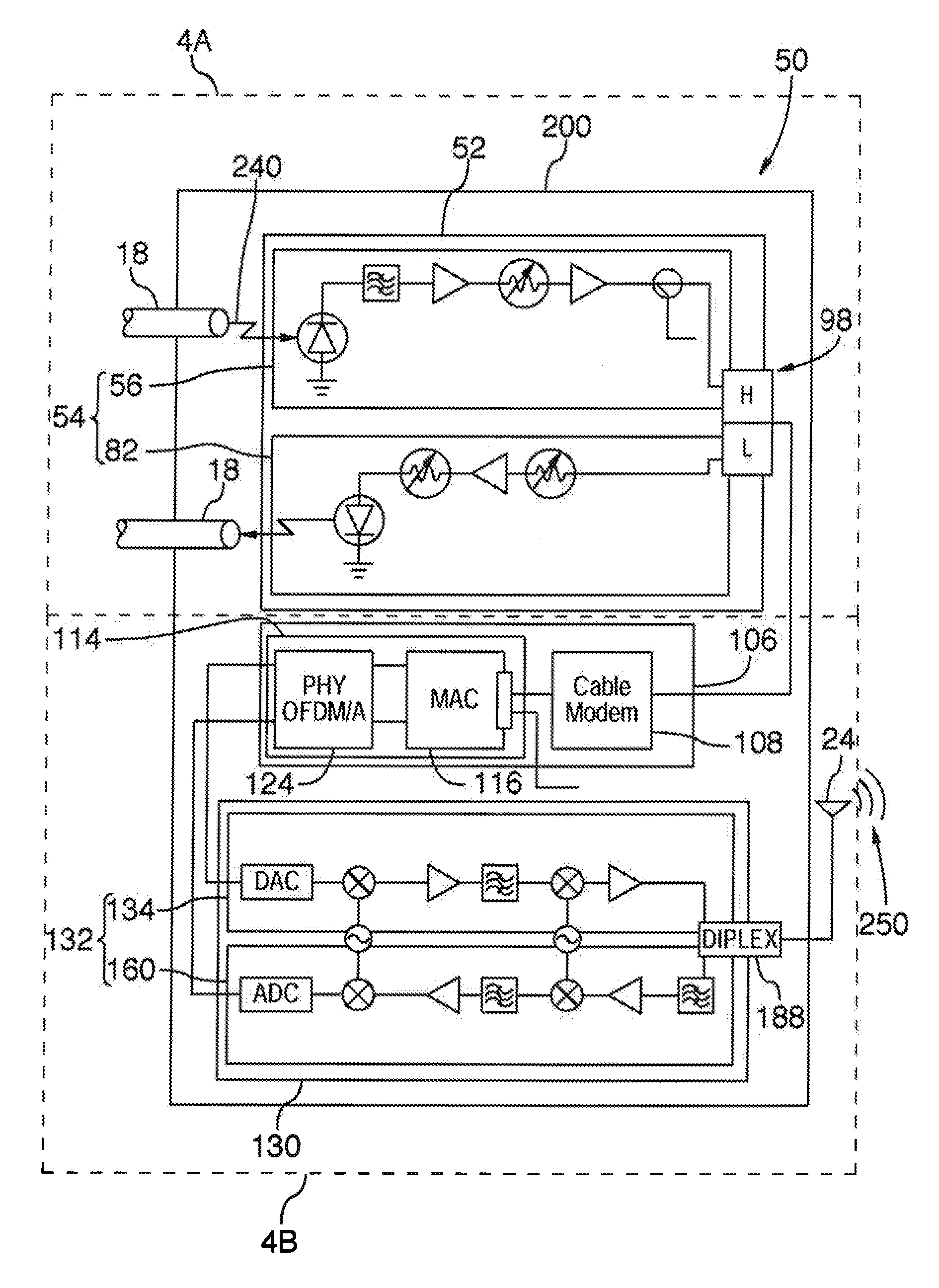
Apparatus and method for transferring signals between a fiber network and a wireless network antenna
An apparatus and method transfers signals between a fiber network and a wireless network antenna. In a fiber to wireless stage, fiber signals are optically transferred from the fiber network and converted into RF signals compatible with the DOCSIS interface standard. The RF signals are electronically converted into data packets, the data packets are electronically converted into baseband digital signals, and the digital signals are converted into analog signals, before being transferred to the network antenna for wireless transmission. The data packets, digital signals, and analog signals are compatible with the IEEE 802.l6 wireless networking standard. Conversely, in a wireless to fiber stage, the analog signals are transferred from the antenna, and converted into digital signals, which are then electronically converted into data packets. The data packets are electronically converted into RF signals, which are next converted into fiber signals, before being optically transferred to the fiber network.
Owner:LOGUS BROADBAND WIRELESS SOLUTIONS
Polymer of containing fluorin, and application as material of ion exchange fiber
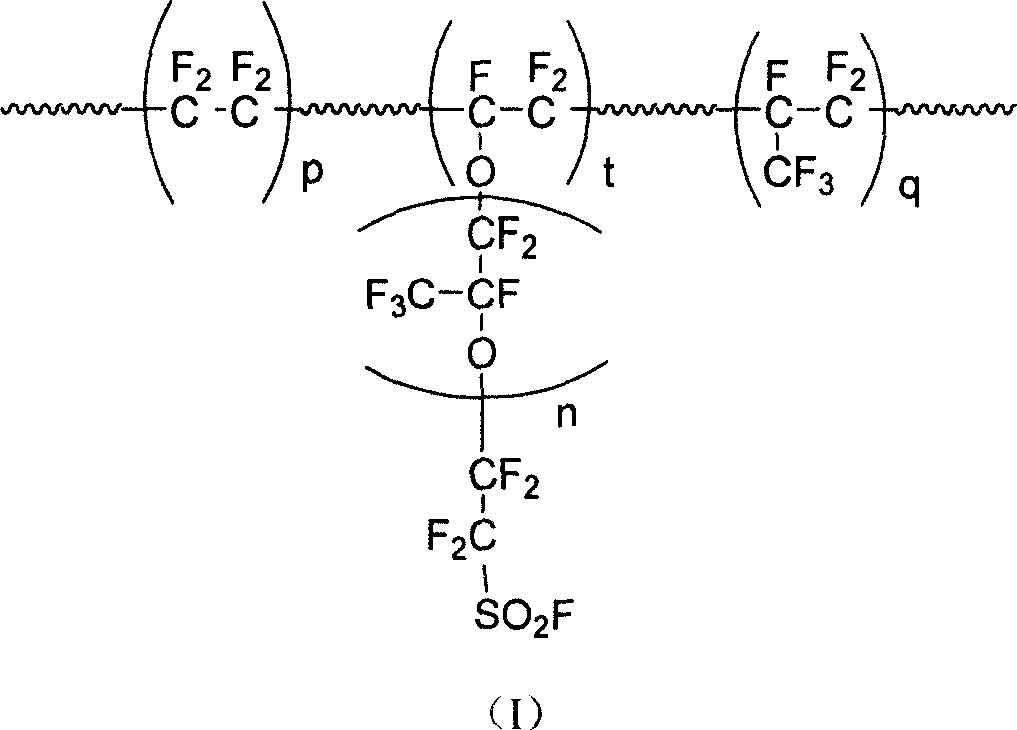
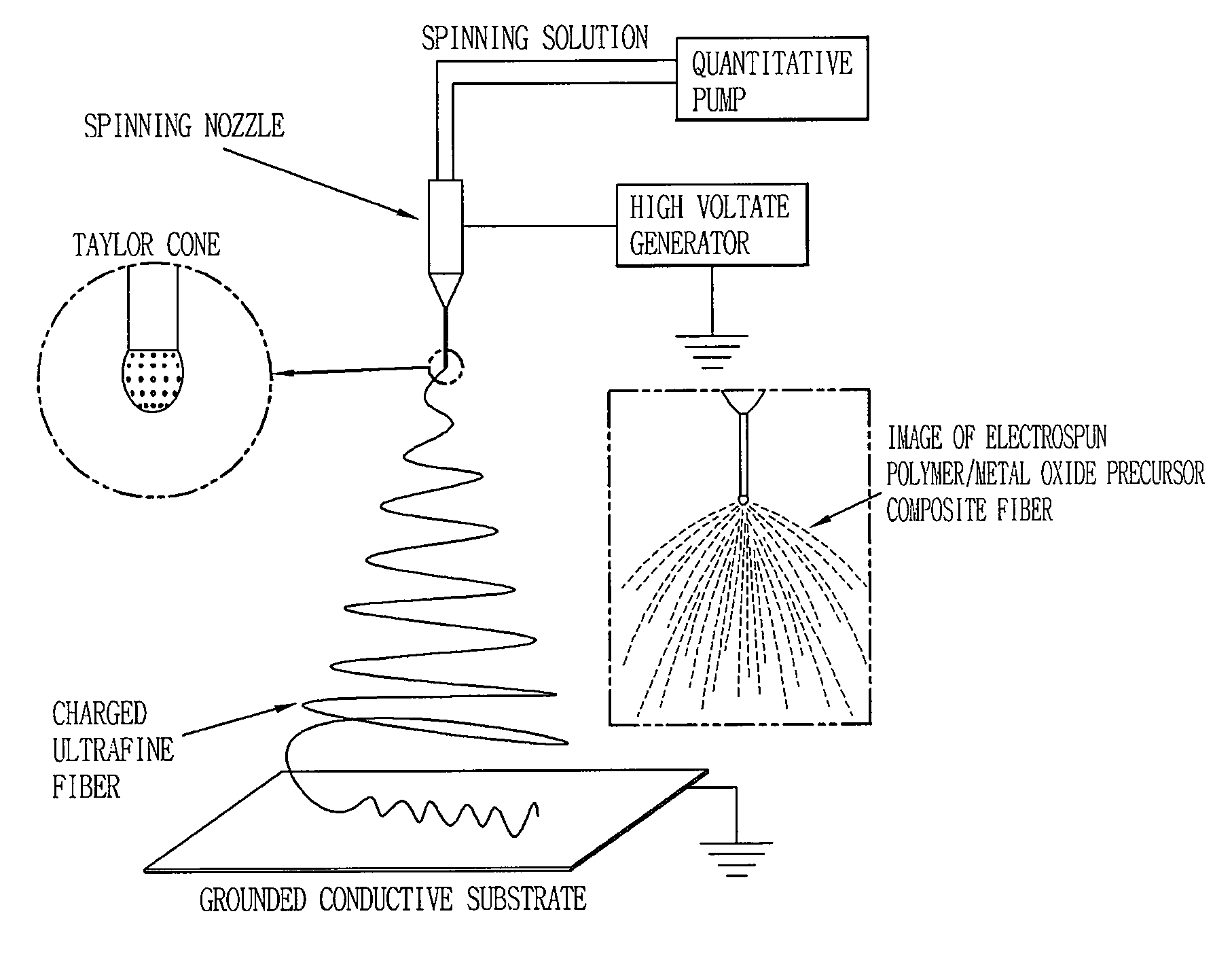
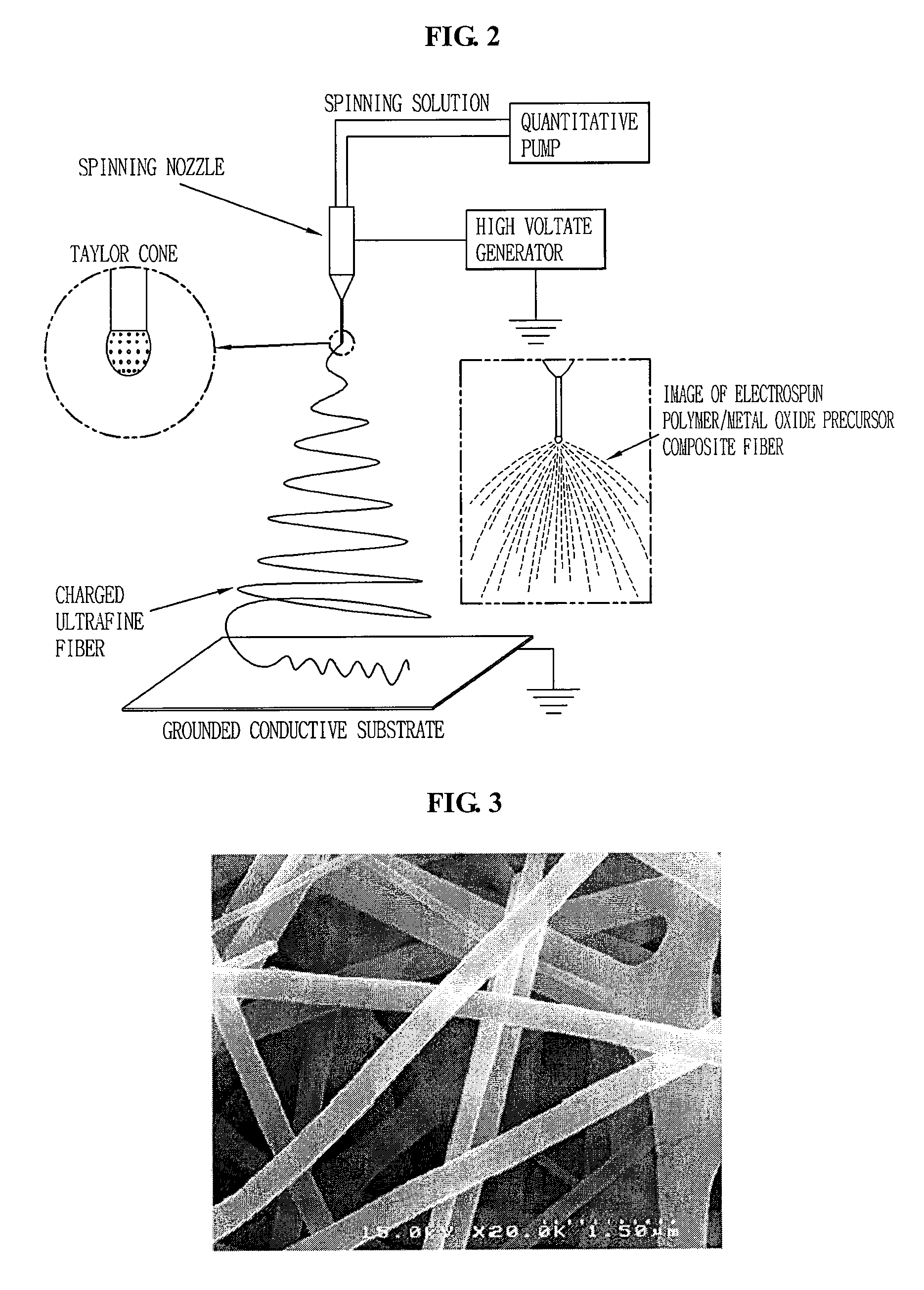
InactiveCN101003588AIncrease the effective areaLower resistanceMelt spinning methodsVinyl etherAlkali ions
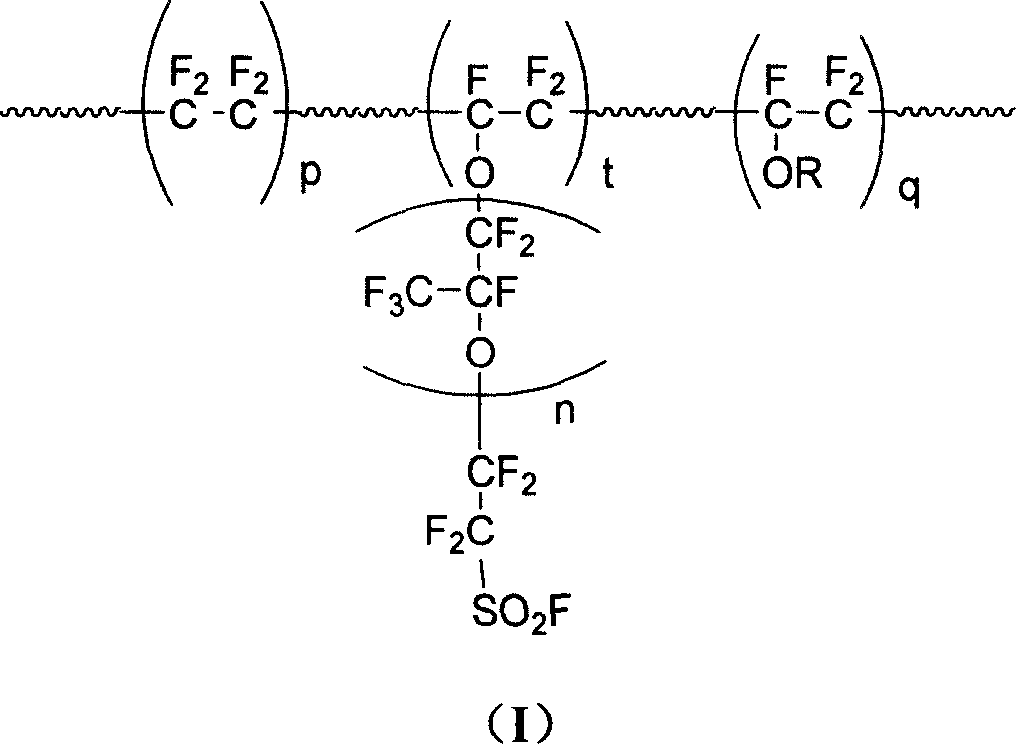
This invention discloses a fluorine-containing polymer and its application as ion exchange fiber material. The fluorine-containing polymer is a perfluoro resin containing sulfonylfluoride groups, and is shown in formula 1. The fluorine-containing polymer has ion exchange function, and is prepared by free radical copolymerization of perfluorosulfonyl vinyl ether, tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene in the presence of dispersant, solvent and initiator. The dispersant / solvent is mixed solution of melamine derivative containing linear perfluoro hydrocarbon and water. The fluorine-containing polymer can be melt-spun into polymer fibers, which can be woven into fiber network that can be used as the reinforcing network material for ion exchange membranes and chlor-alkali ion membrane to reinforce and improve the ion exchange ability.
Owner:SHANDONG HUAXIA SHENZHOU NEW MATERIAL
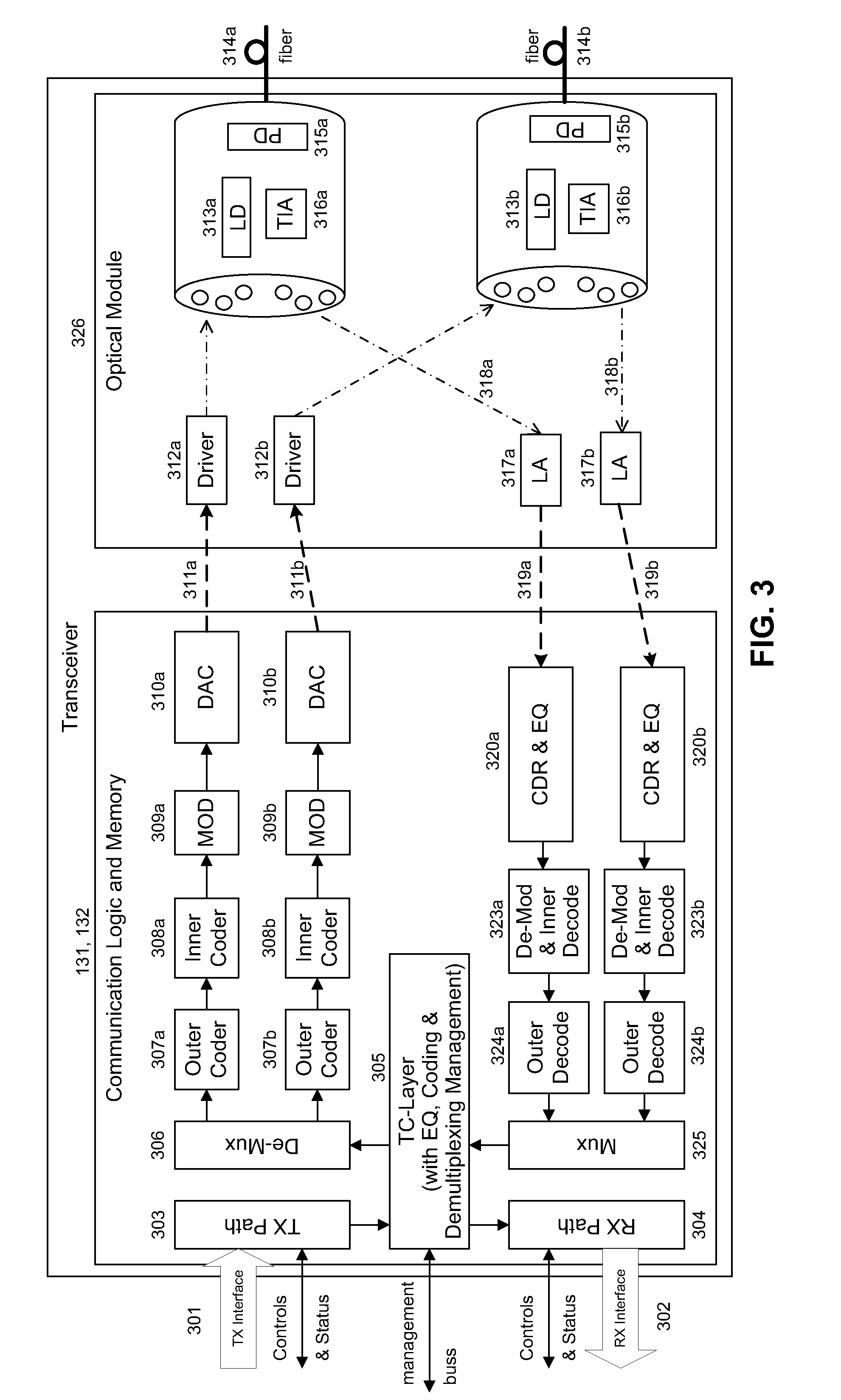
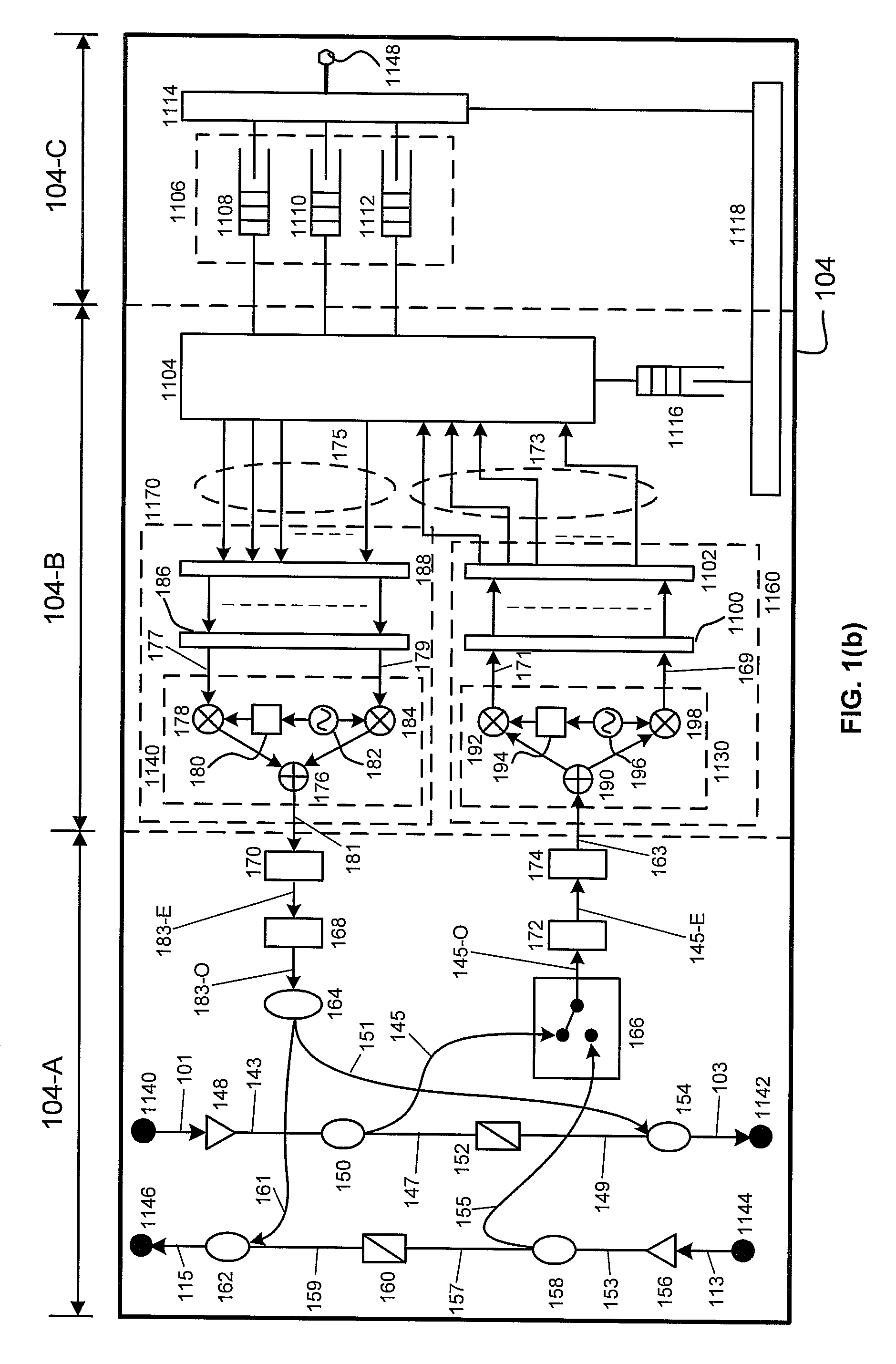
System and method for performing high-speed communications over fiber optical networks
ActiveUS20100158530A1Low line rateIncrease data throughputWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationFiberWaiting period
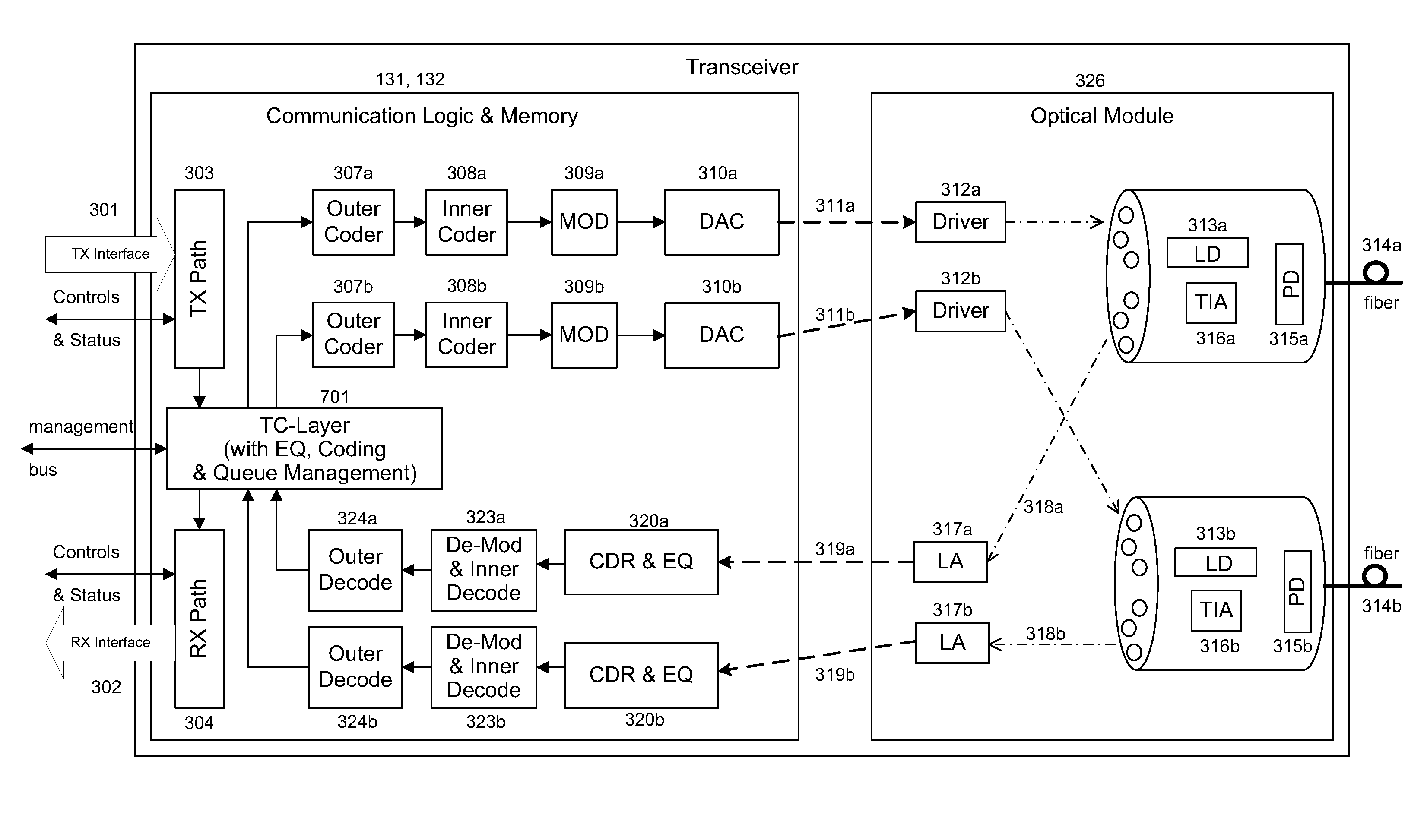
Processing a received optical signal in an optical communication network includes equalizing a received optical signal to provide an equalized signal, demodulating the equalized signal according to an m-ary modulation format to provide a demodulated signal, decoding the demodulated signal according to an inner code to provide an inner-decoded signal, and decoding the inner-decoded signal according to an outer code. Other aspects include other features such as equalizing an optical channel including storing channel characteristics for the optical channel associated with a client, loading the stored channel characteristics during a waiting period between bursts on the channel, and equalizing a received burst from the client using the loaded channel characteristics.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
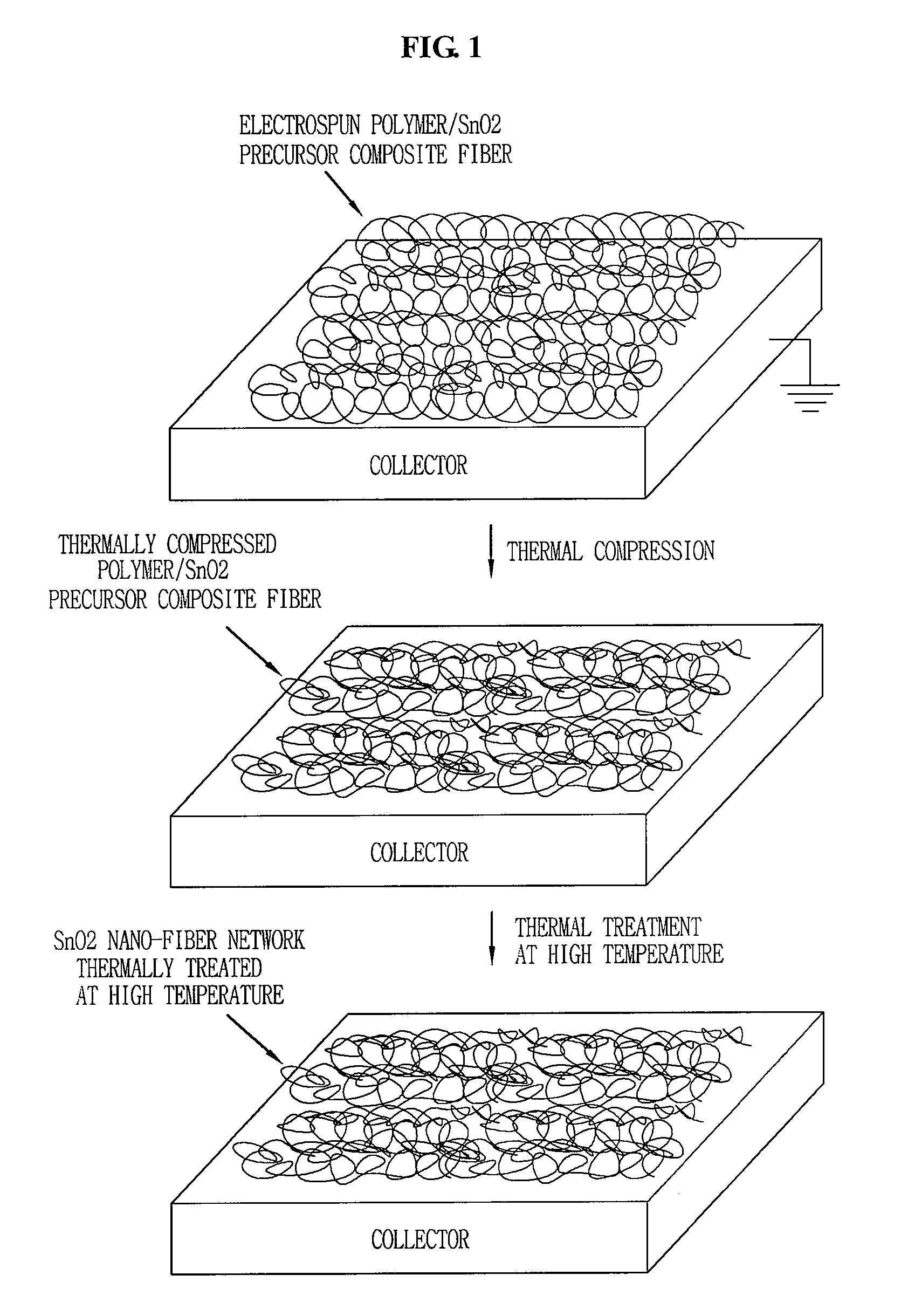
Anode for secondary battery having negative active material with nano-fiber network structure and secondary battery using the same, and fabrication method of negative active material for secondary battery
InactiveUS20080274403A1Maximize cycling characteristicIncrease speedElectrode rolling/calenderingMaterial nanotechnologyCurrent collectorFiber network
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access Based Optical Ring Network
ActiveUS20090092389A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission path divisionData streamCarrier signal
A fiber optic network transmits data between a hub node and a plurality of local nodes connected by at least one unidirectional fiber ring. Downstream data streams are carried on wavelength-division-multiplexed optical carriers from the hub node to the local nodes. An optical carrier corresponding to a specific wavelength carries downstream data streams to a specific local node. Downstream data streams are multiplexed onto an optical carrier via orthogonal frequency division multiplexing. A parallel signal detector in each local node detects all downstream optical carriers. A signal processing module demultiplexes the data stream from the optical carrier having the specific wavelength corresponding to the local node. An upstream data stream is multiplexed via orthogonal frequency division multiplexing onto an upstream optical carrier having the same specific wavelength and transmitted from the local node to the hub node. Upstream data awaiting transmission is allocated to specific subcarriers and time slots.
Owner:NEC CORP
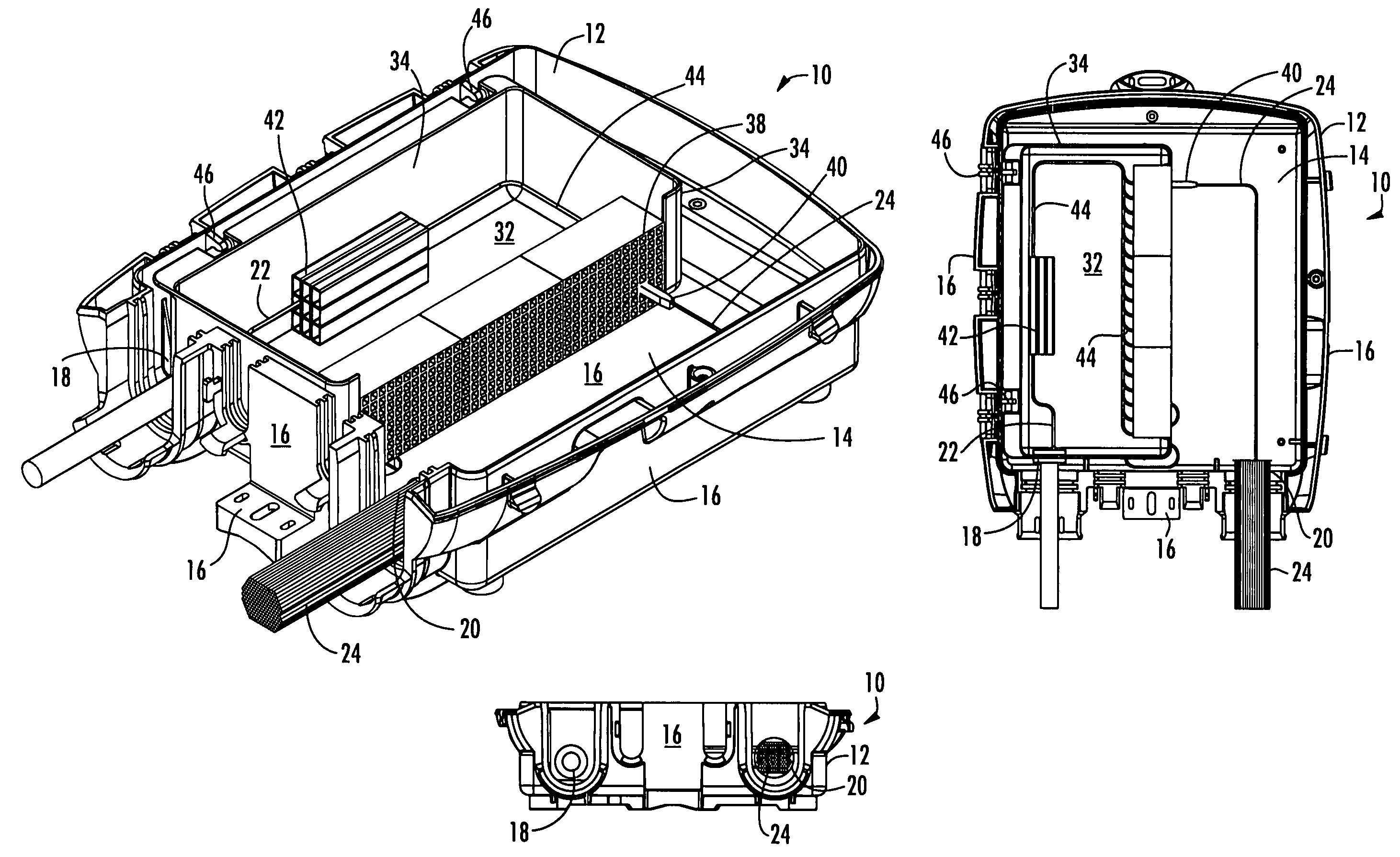
Fiber optic local convergence points for multiple dwelling units
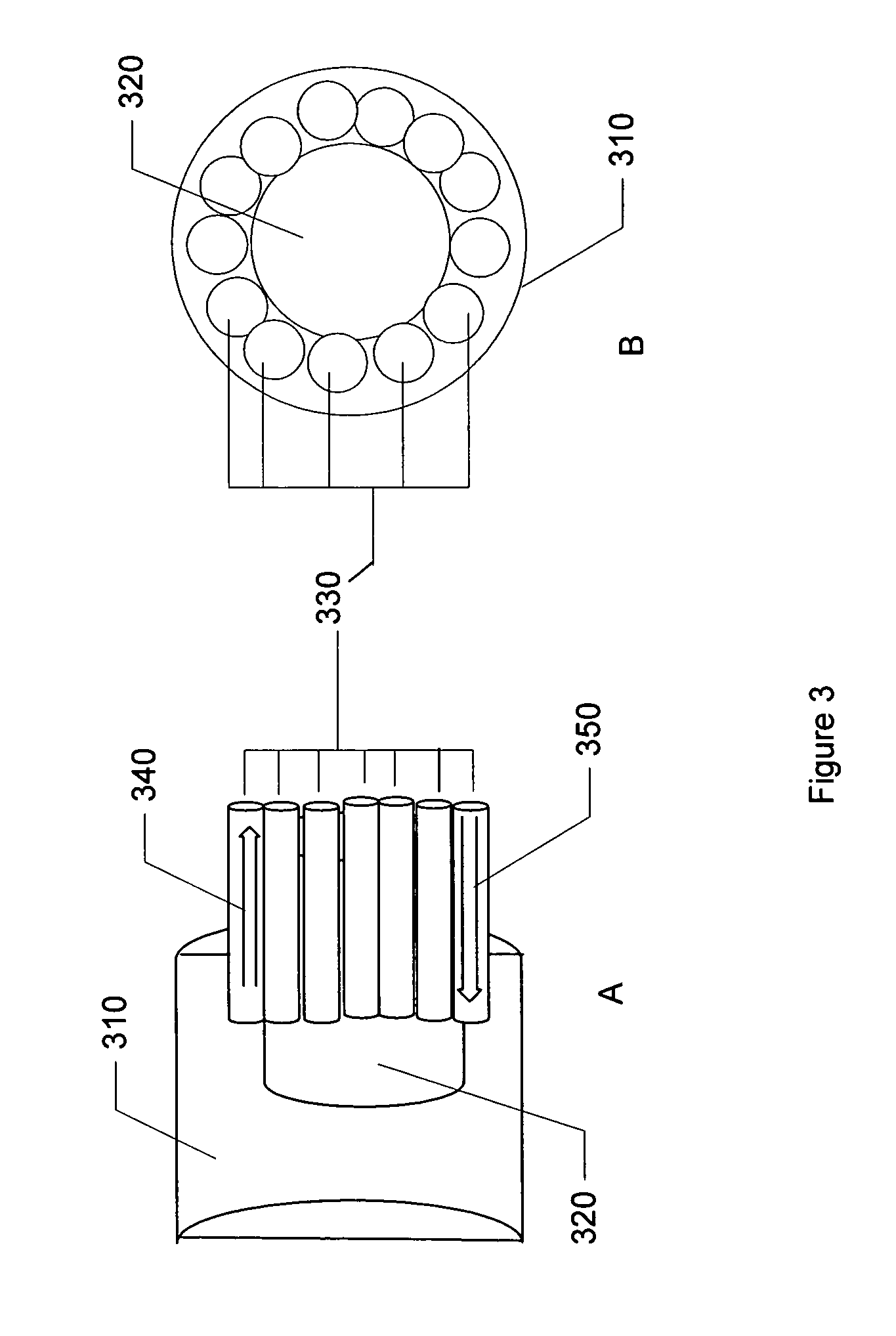
ActiveUS7349616B1Small minimum bend radiusMore versatilityCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesEngineeringFiber network
There are provided fiber optic local convergence points (“LCPs”) adapted for use with multiple dwelling units (“MDUs”) that facilitate relatively easy installation and / or optical connectivity to a relatively large number of subscribers. The LCP includes a housing mounted to a surface, such as a wall, and a cable assembly with a connector end to be optically connected to a distribution cable and a splitter end to be located within the housing. The splitter end includes at least one splitter and a plurality of subscriber receptacles to which subscriber cables may be optically connected. The splitter end of the cable assembly of the LCP may also include a splice tray assembly and / or a fiber optic routing guide. Furthermore, a fiber distribution terminal (“FDT”) may be provided along the subscriber cable to facilitate installation of the fiber optic network within the MDU.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Error mitigation system using line coding for optical WDM communications
InactiveUS7016606B2Error detection/correctionWavelength-division multiplex systemsData streamEngineering
An apparatus and method of line coding to mitigate collision induced errors in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) optical communications systems is disclosed. The apparatus and method prevents Soliton-Soliton-Collision induced errors by reducing a variance in a number of possible collisions between solitons in multiple channels in a WDM fiber optic communication system using a sliding window criterion. The sliding window criterion defines a set of parametric values based on physical properties of the transmission network, a transmission frequency and a defined data block size. N-bit codes are iteratively selected and sequentially assigned to segments of a mapping table indexed by all possible unique combinations of “1”s and “0”s in a block of data. Input data blocks are mapped to corresponding code words having a reduced number of transitions for transmission on the fiber optic network. Received code words are converted back to a data stream corresponding to the input data stream.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Optical Connection Terminal Having Port Mapping Scheme
A fiber optic network device for optically coupling a fiber optic distribution cable with a fiber optic drop cables is disclosed. Disposed within the fiber optic network device is a plurality of optical fibers optically coupled to the distribution cable. A plurality of ports opens into the fiber optic network device. Predetermined ones of the plurality of ports are operable for optically coupling respective predetermined ones of the plurality of optical fibers each to at least one drop cable external to the fiber optic network device. At least one of the predetermined ones of the plurality of ports is a pass-through port operable for optically coupling at least one of the respective pre-determined ones of the plurality of optical fibers to the at least one drop cable through another fiber optic network device. A pass-through connector comprising a plurality of connection ports adapted for receiving in a predetermined alignment the respective pre-determined ones of the plurality of optical fibers may be seated within the pass-through port. The fiber optic network device may be an optical connection terminal and / or a distribution closure. The fiber optic network device may further include one or more splitters. The predetermined ones of a plurality of ports may be operable for optically coupling at least one of the respective predetermined ones of the plurality of optical fibers to a drop cable through one or more splitters.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
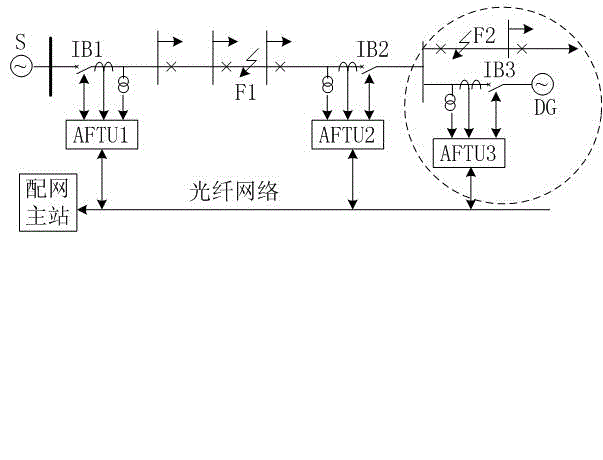
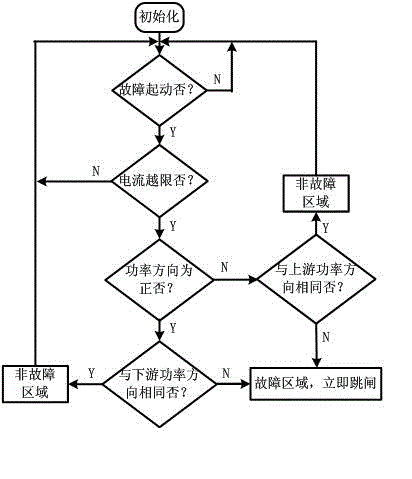
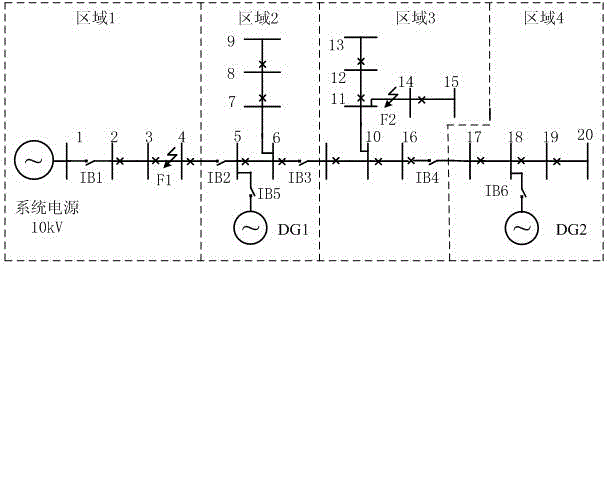
DG (distributed generation)-containing power distribution network distributed protection and control method
InactiveCN102882197ARapid positioningAchieve isolationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsIslandingComputer terminal
The invention discloses a DG (distributed generation)-containing power distribution network distributed protection and control method, and provides a protection and control technical method based on an AFTU (advanced feeder terminal unit) for the phenomenon that the high-permeability distributed power access power distribution network causes great difficulties in traditional power distribution protection and control. The method disclosed by the invention divides the DG-containing power distribution network into multiple areas capable of running as islands in advance according to the DG capacity and load. Circuit breakers and AFTUs are arranged at the feeder outlet, the DG access position and the area boundary, and the AFTUs are connected through an optical network. Each AFTU detects local electric quantity information in real time and performs information interaction with other AFTUs. The method disclosed by the invention quickly positions the fault section according to the local and neighbor electric quantity information, and realizes the fault isolation and island running. A reclosing and island network re-connection control strategy is designed by use of the related AFTU information.
Owner:YANTAI POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +2
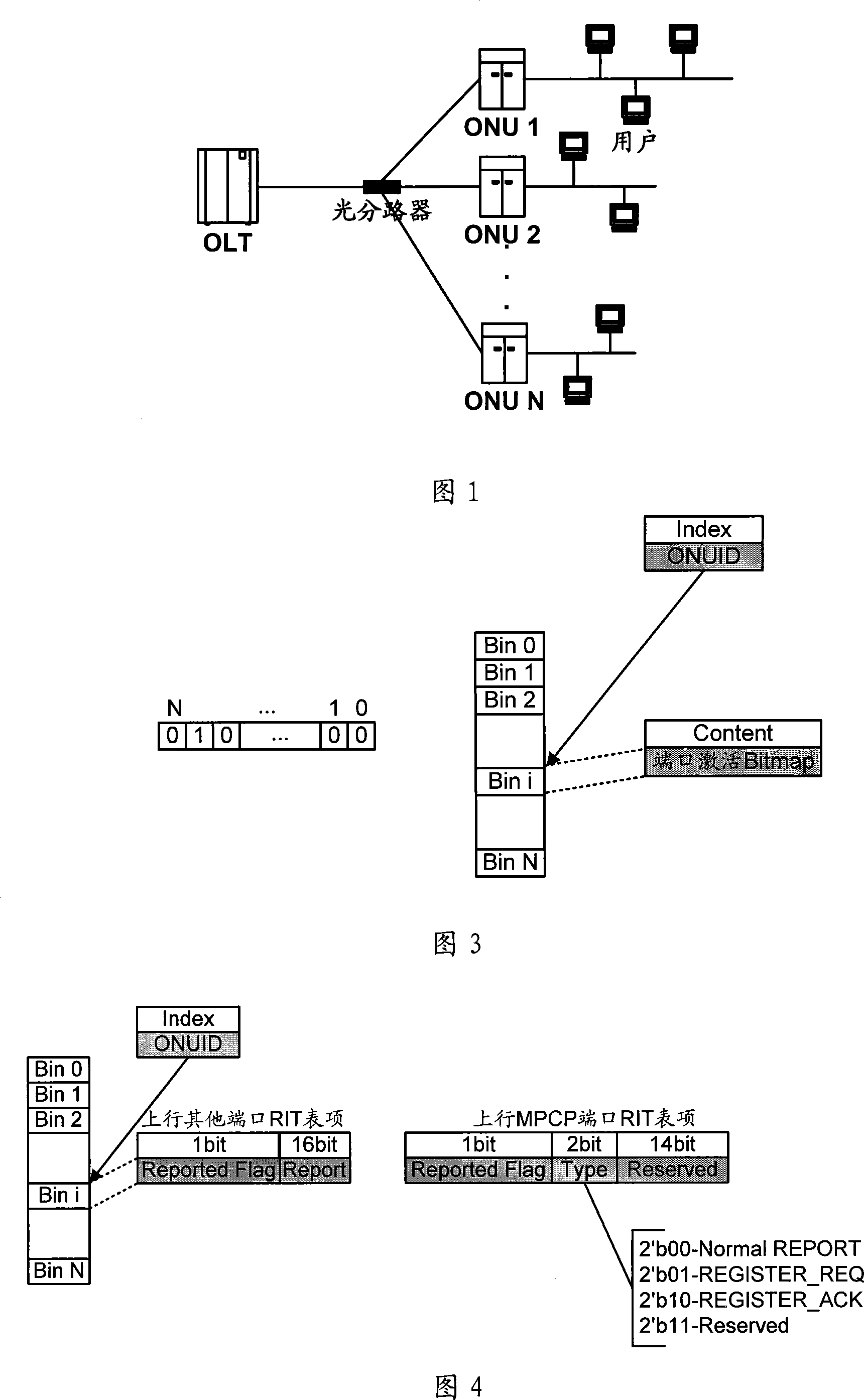
Dynamic bandwidth allocation device and method of passive optical network
ActiveCN101087238AIncrease profitEfficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsStore-and-forward switching systemsService flowOptical communication
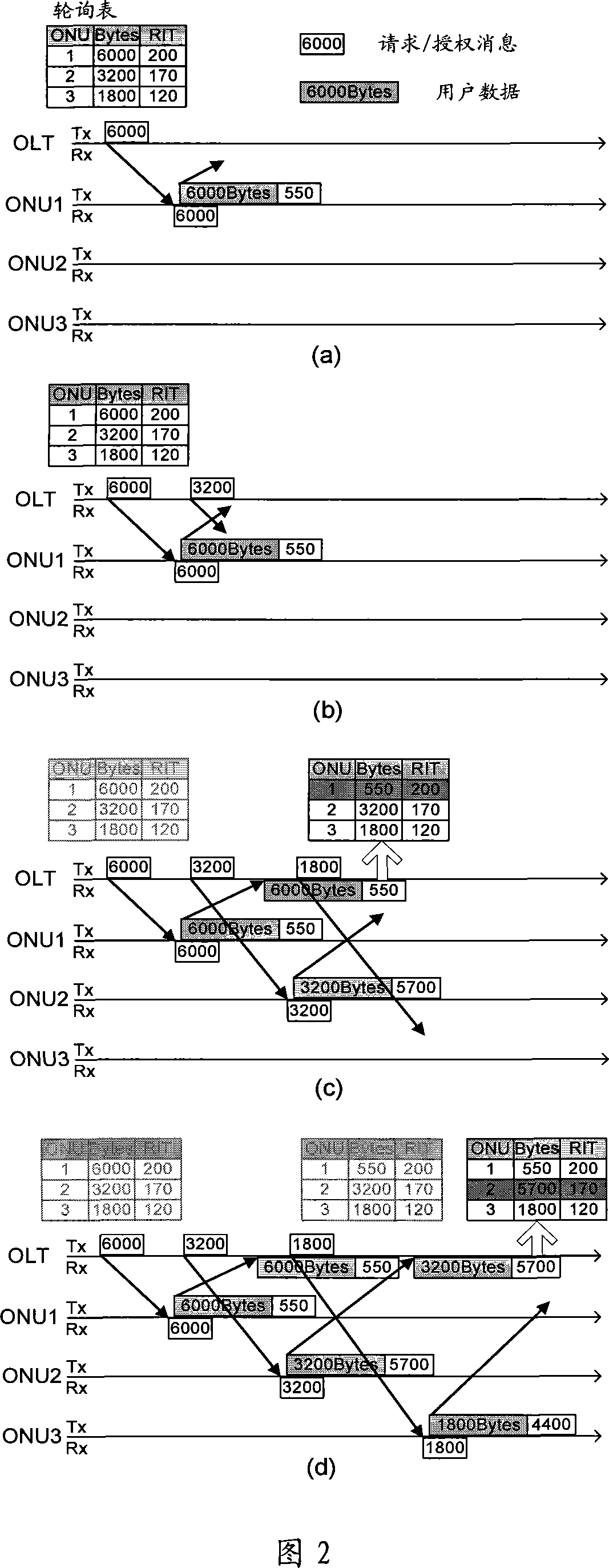
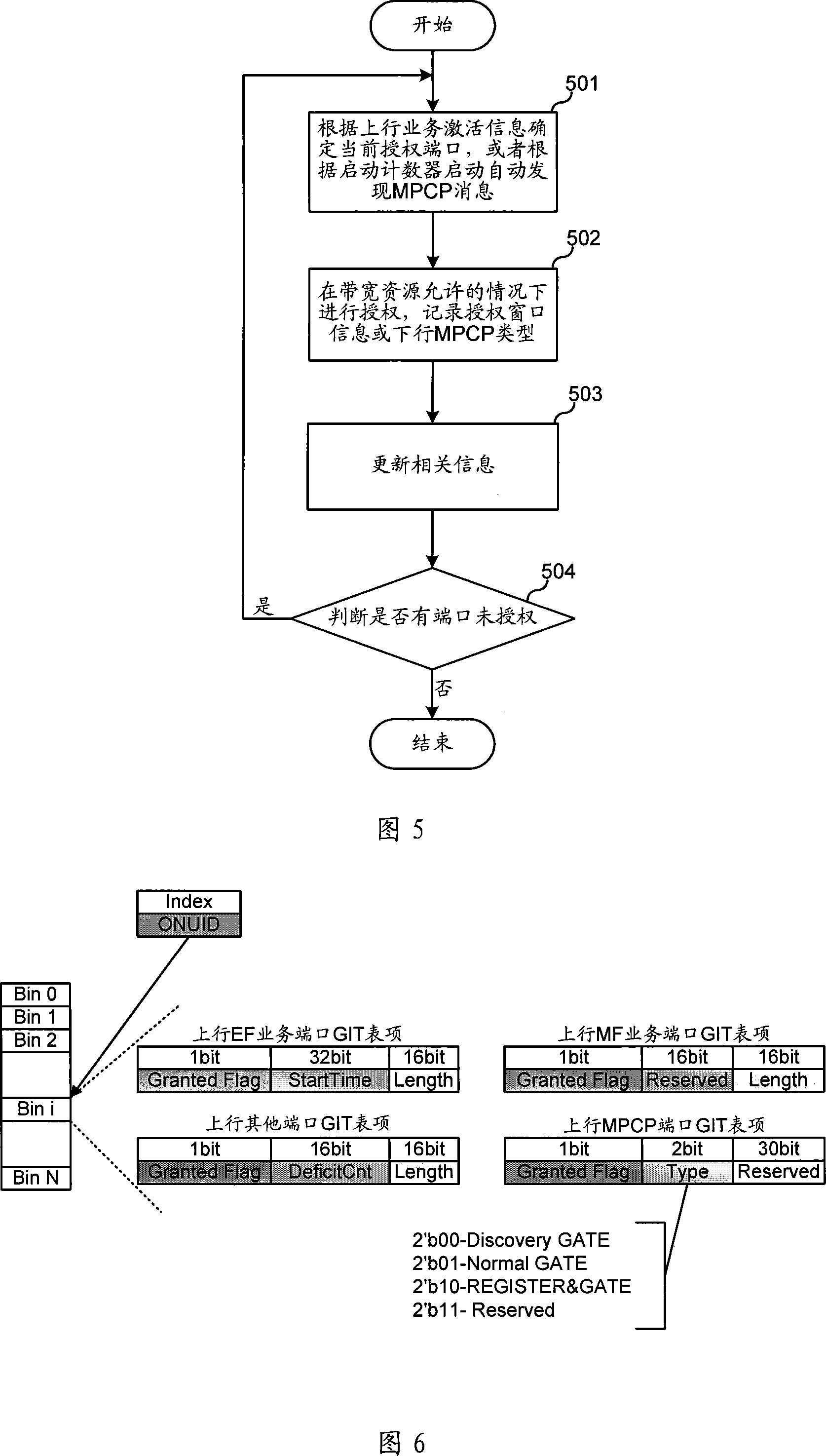
The invention relates to optical communication field, discloses a collating device and method for dynamic bandwidth in source-free optical network, and the distribution method for dynamic bandwidth is transparent, which can satisfy the requirement for different service, improve the utilization rate of bandwidth, realize the fair distribution for bandwidth, good haleness, real time, and can distribute bandwidth for different port, and support to release offline bandwidth of ONU. The distributing device for dynamic bandwidth in source-free optical network includes ascending service active fiber network unit bit-mapping register, ascending service active port bit-mapping table, ascending virtual media accessing control sub-layer information table, descending virtual media accessing control sub-layer authorization information table; said distributing device for dynamic bandwidth, consults said fiber network unit active information, port active information and length information of sending data, according to preset priority of different service, process the service flow according to priority according to preset priority, and distributes the dynamic bandwidth for ports.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com