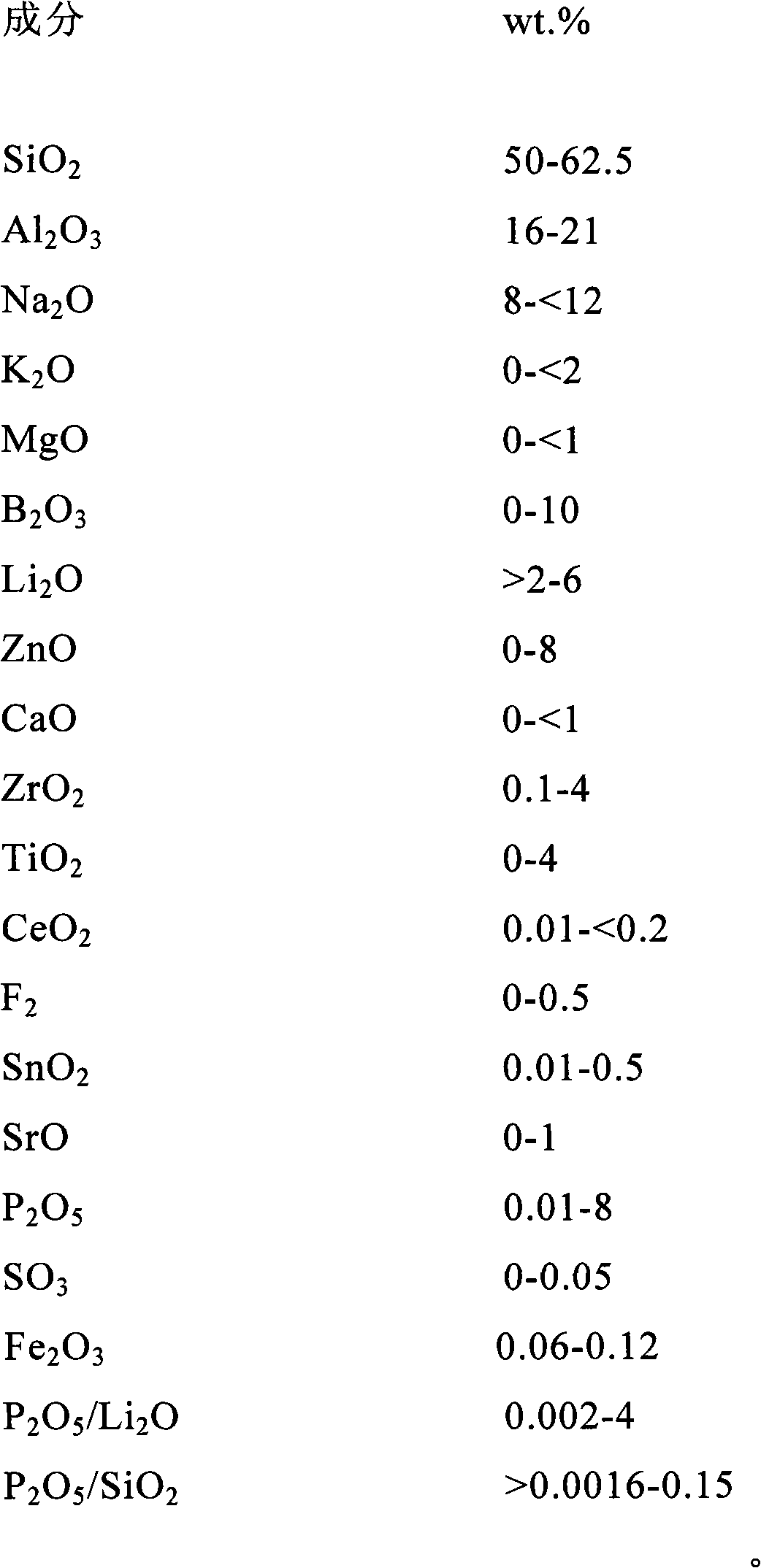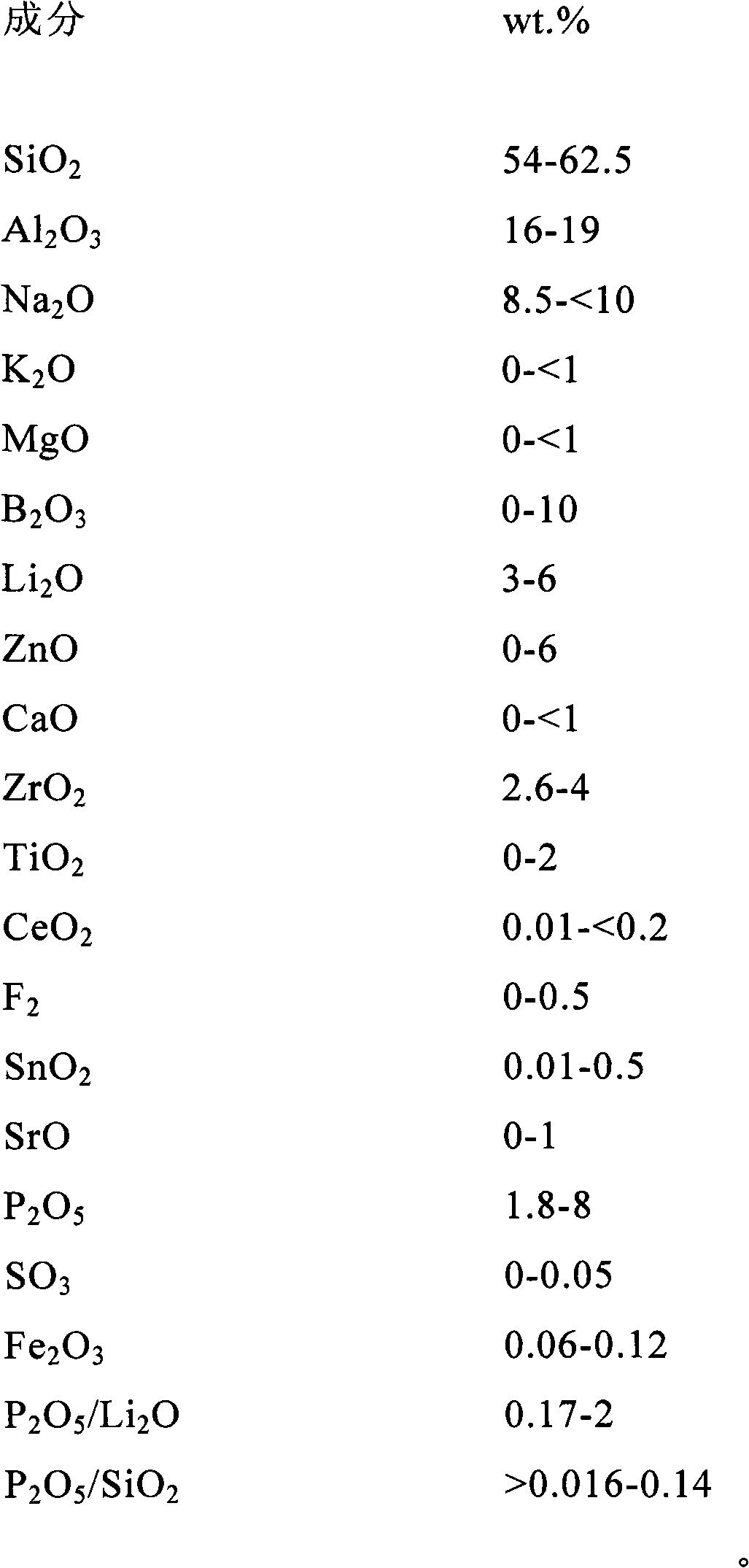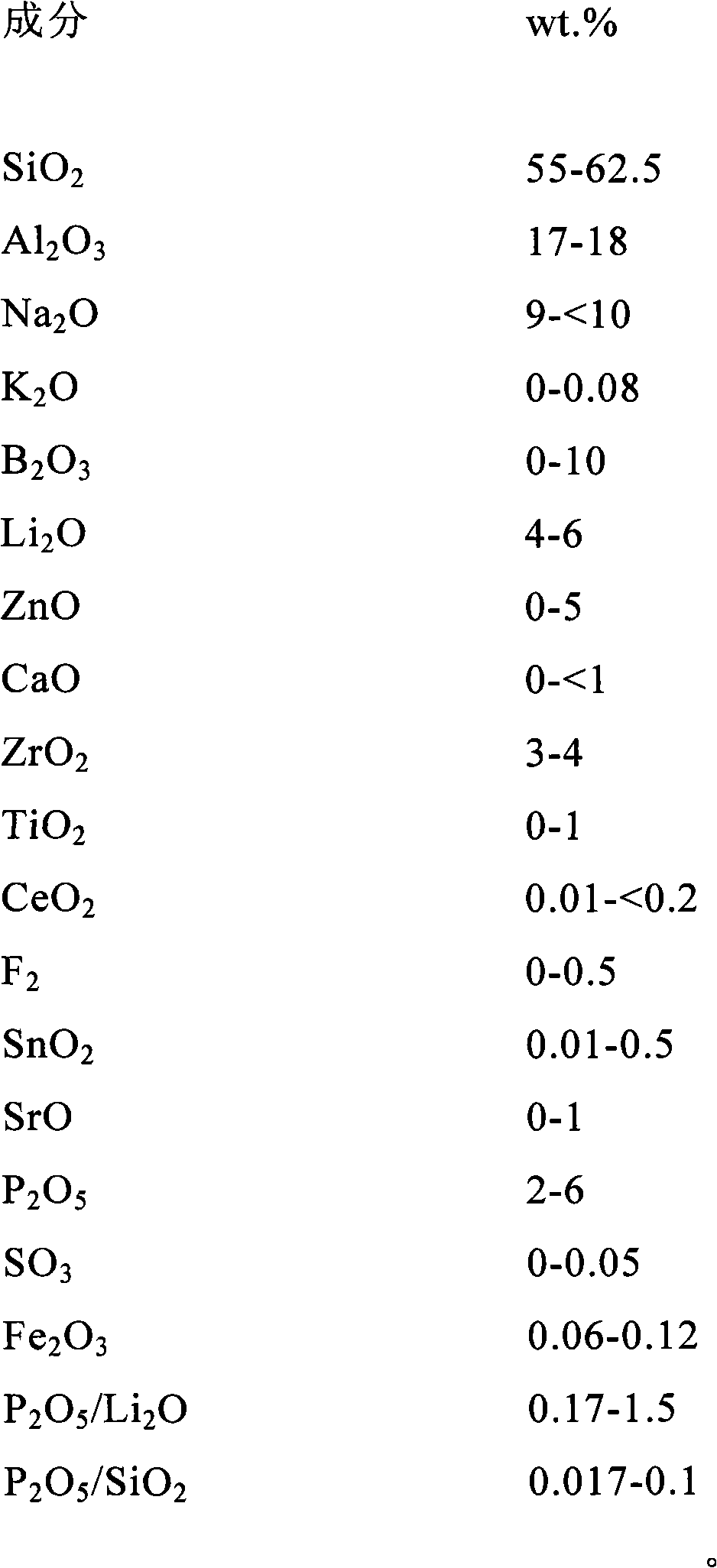Patents
Literature
17878 results about "Ion exchange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ion exchange is an exchange of ions between two electrolytes or between an electrolyte solution and a complex. In most cases the term is used to denote the processes of purification, separation, and decontamination of aqueous and other ion-containing solutions with solid polymeric or mineralic "ion exchangers".
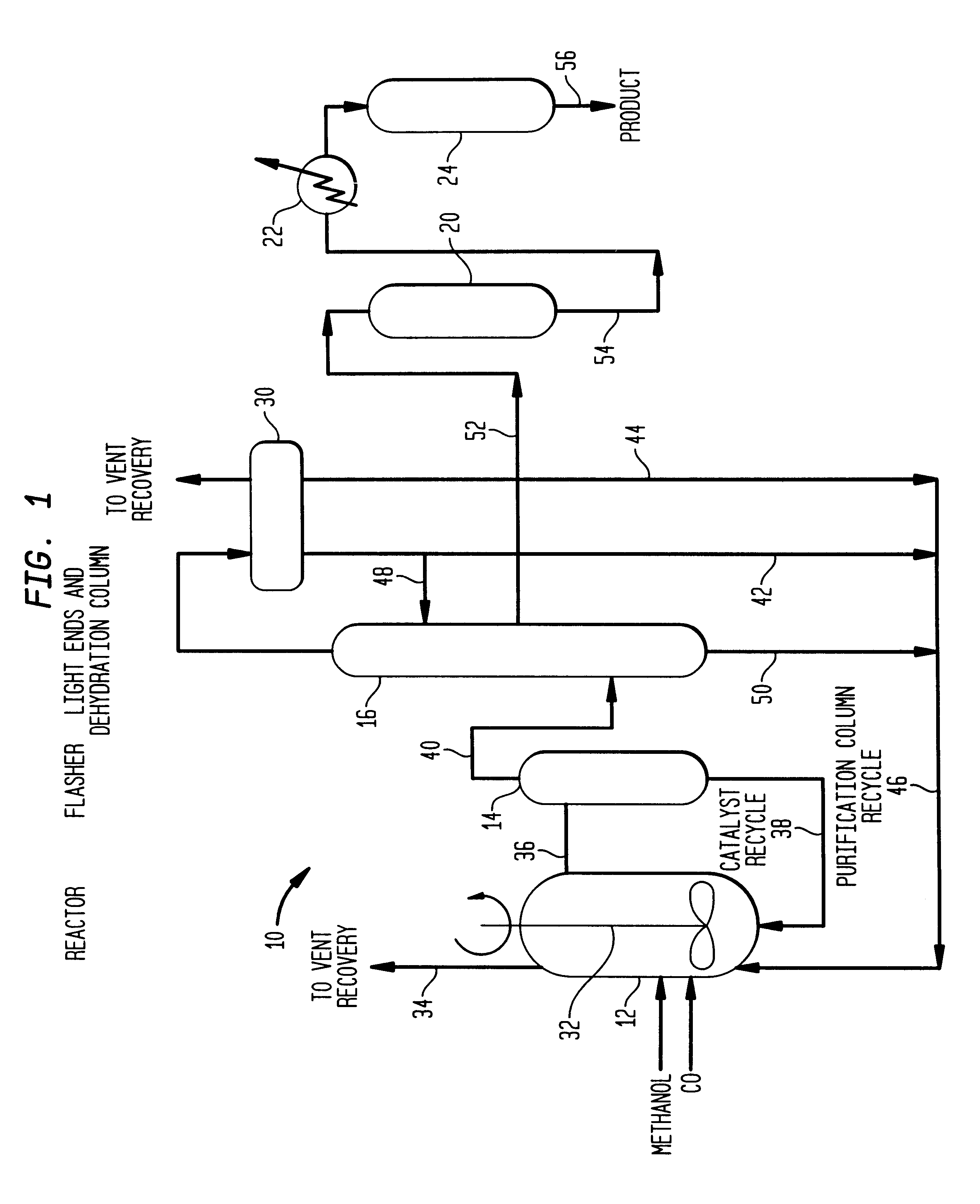
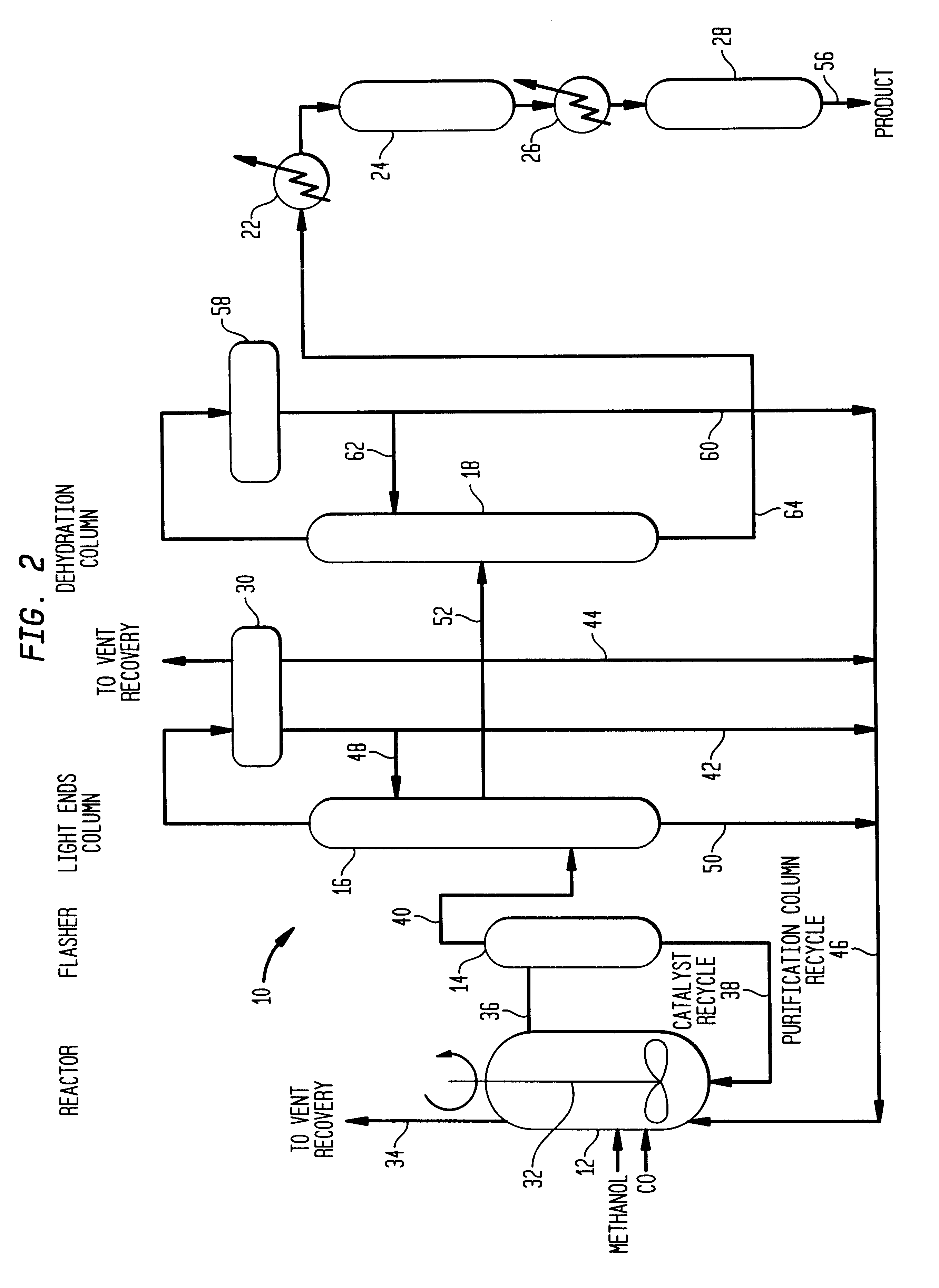
Low energy carbonylation process
InactiveUS6657078B2Weaken energyHigh purityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPropanoic acidIodide
A low energy process for producing acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol is disclosed. The process involves a rhodium-catalyzed system operated at less than about 14% water utilizing up to 2 distillation columns. The process is preferably controlled such that the product stream has a low level of propionic acid impurity and the level of aldehyde impurities is minimized by way of aldehyde removal or minimizing aldehyde generation. The level of iodides is controlled by contacting the product, at elevated temperatures, with ion exchange resins. In preferred embodiments, at least one silver or mercury exchanged macroreticular strong acid ion exchange resin is used to purify the product. The high temperature treatment provides the added benefit of controlling the Color Value (Pt-Co units) of the product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Support for high performance affinity chromatography and other uses
Multilayered particulate materials are formed by coating a particulate substrate with a metal and adsorbing an organic layer comprising a recognition moiety onto the metal film. The recognition moiety interacts with an analyte of interest allowing for its detection, purification, etc. Suitable recognition moieties can be selected from a range of species including, small molecules, polymers and biomolecules and the like. The novel particulate materials of the invention can be utilized in an array of methods including, ion-exchange, ion-selective ion-exchange, assays, affinity dialysis, size exclusion dialysis, as supports in solid phase synthesis, combinatorial synthesis and screening of compound libraries and the like.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Down-drawable, chemically strengthened glass for cover plate
An alkali aluminosilicate glass that is chemically strengthened and has a down-drawable composition. The glass has a melting temperature less than about 1650° C. and a liquidus viscosity of at least 130 kpoise and, in one embodiment, greater than 250 kpoise. The glass undergoes ion exchange at relatively low temperatures to a depth of at least 30 μm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Catalytic dewaxing with trivalent rare earth metal ion exchanged ferrierite
InactiveUS6013171AMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonCation-exchange capacityIon exchange
A process for dewaxing waxy hydrocarbonaceous materials, such as hydrocarbon fuel and lubricating oil fractions to reduce their cloud and pour points comprises reacting the material with hydrogen in the presence of a dewaxing catalyst comprising at least one metal catalytic component and ferrierite in which at least a portion of its cation exchange positions are occupied by one or more trivalent rare earth metal cations. The rare earth ion exchanged ferrierite catalyst has good selectivity for lubricating oil production, particularly when dewaxing a Fischer-Tropsch wax hydroisomerate. Preferably at least 10% and more preferably at least 15% of the ferreirite cation exchange capacity is occupied by one or more trivalent rare earth metal cations.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Purification of biologically-produced 1,3-propanediol
InactiveUS20050069997A1Reduce the amount of waterFermented solutions distillation/rectificationMembranesEscherichia coliDistillation
A process for purifying 1,3-propanediol from the fermentation broth of a cultured E. coli that has been bioengineered to synthesize 1,3-propanediol from sugar is provided. The basic process entails filtration, ion exchange and distillation of the fermentation broth product stream, preferably including chemical reduction of the product during the distillation procedure. Also provided are highly purified compositions of 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC +1
Electrode materials with high surface conductivity
InactiveUS6855273B2Electrode manufacturing processesDouble layer capacitorsSurface conductivityIon exchange
The present invention concerns electrode materials capable of redox reactions by electrons and alkaline ions exchange with an electrolyte. The applications are in the field of primary (batteries) or secondary electrochemical generators, super capacitors and light modulating system of the super capacitor type.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
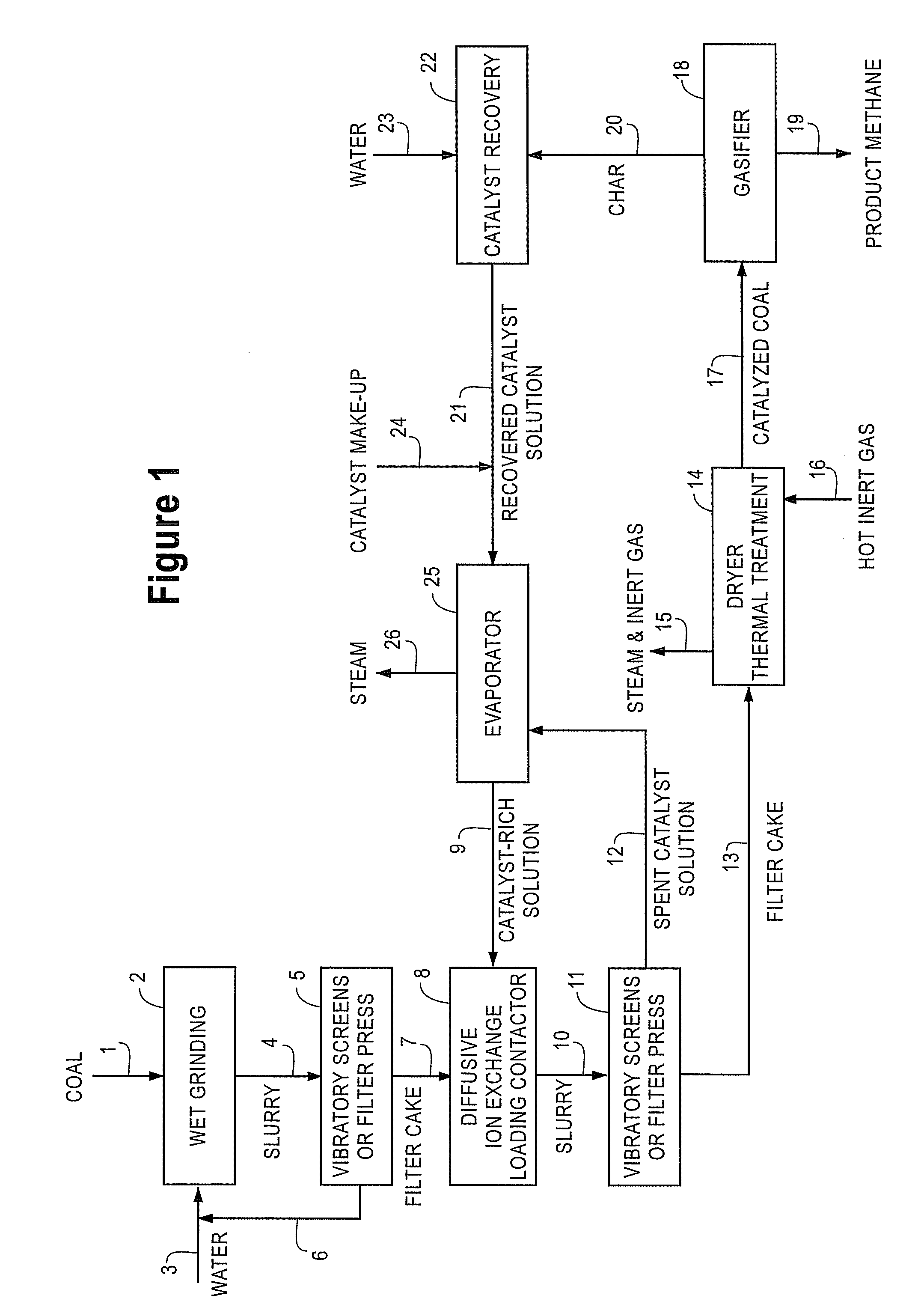
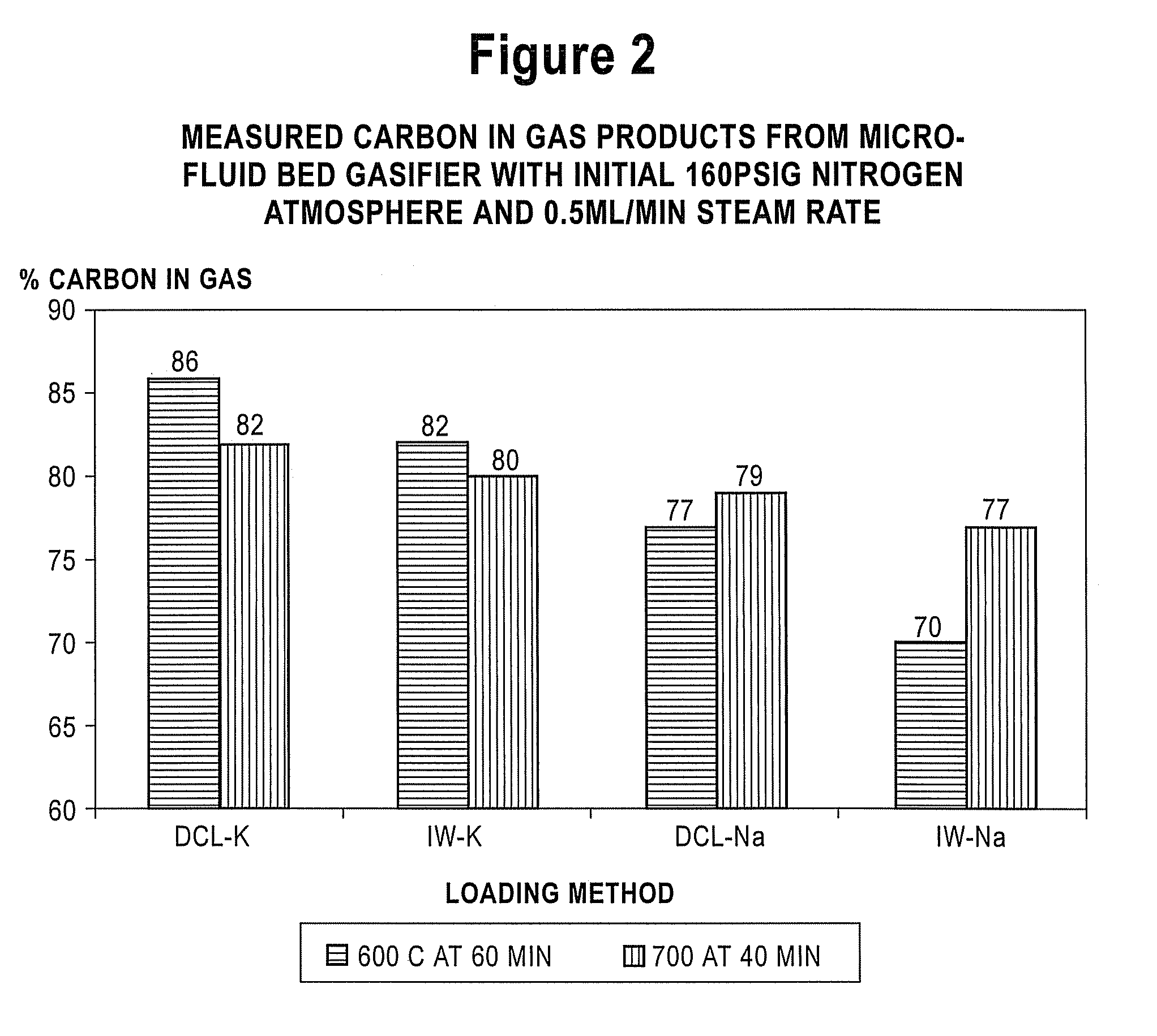
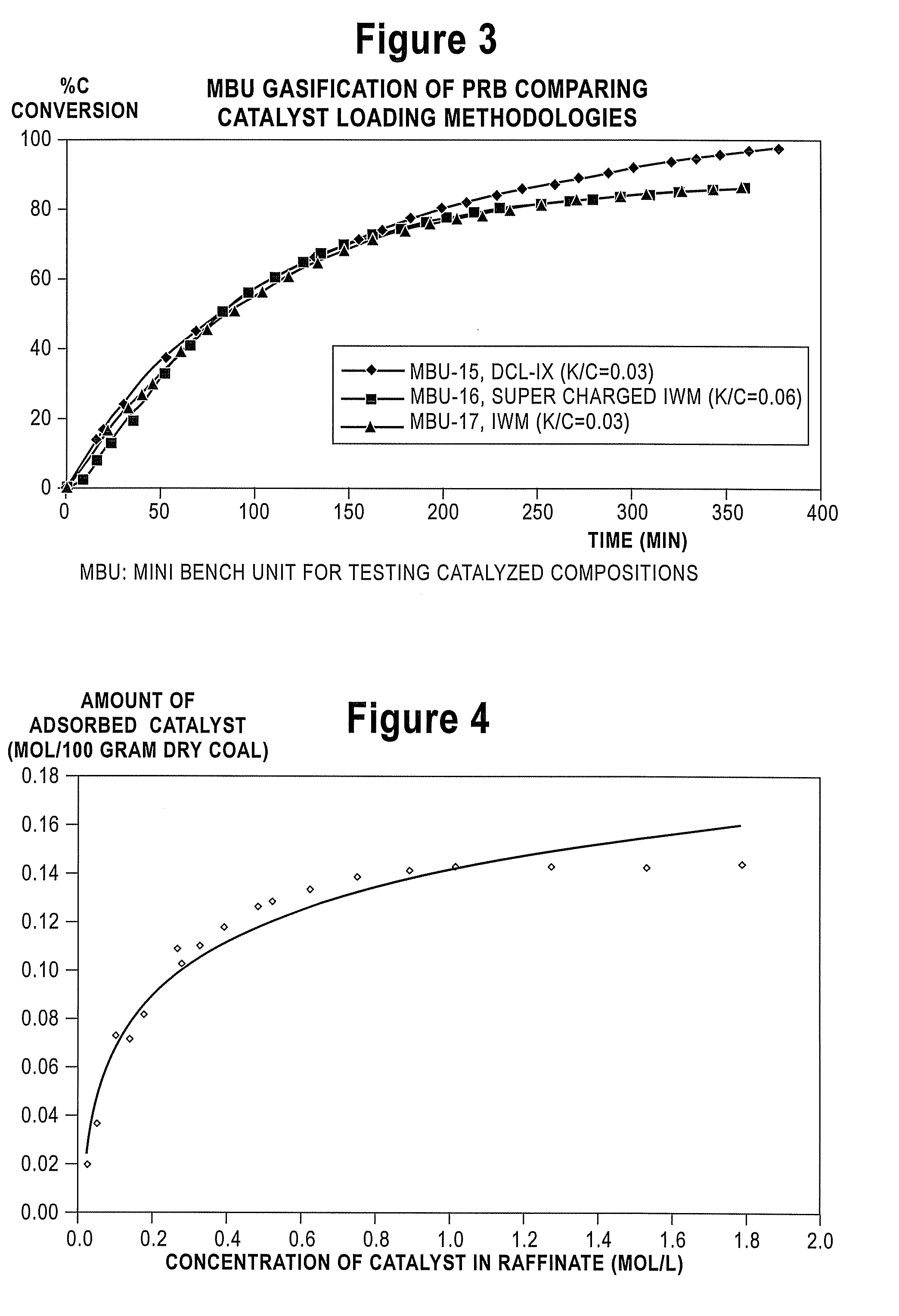
Catalyst-Loaded Coal Compositions, Methods of Making and Use
ActiveUS20090048476A1Efficient and high-yielding gasificationHigh yield productionCatalyst regeneration/reactivationSolid fuelsPtru catalystCoal matrix
The present invention relates to catalyst-loaded coal compositions having a moisture content of less than about 6 wt %, a process for the preparation of catalyst-loaded coal compositions, and an integrated process for the gasification of the catalyst-loaded coal compositions. The catalyst-loaded coal compositions can be prepared by a diffusive catalyst loading process that provides for a highly dispersed catalyst that is predominantly associated with the coal matrix, such as by ion-exchange.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
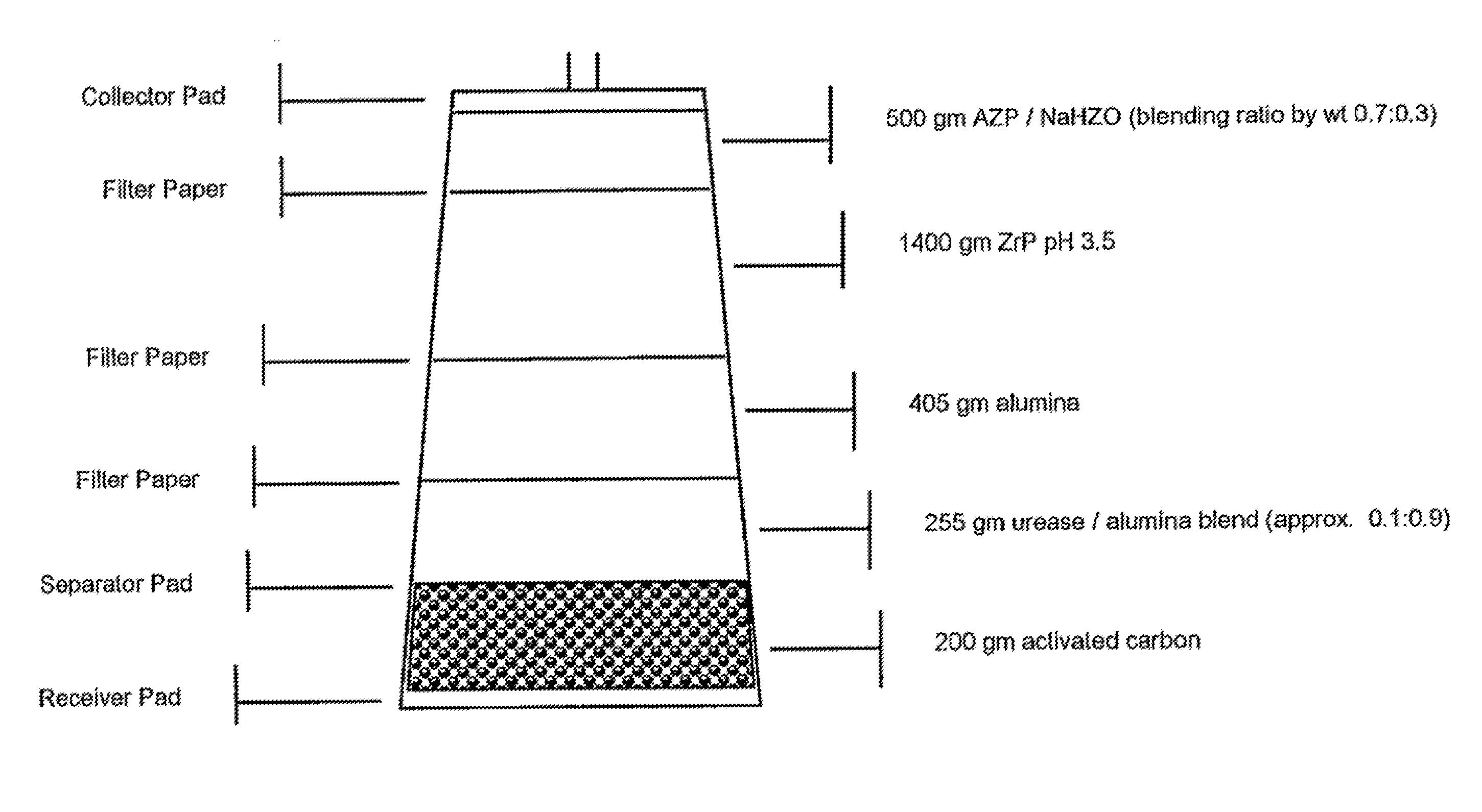
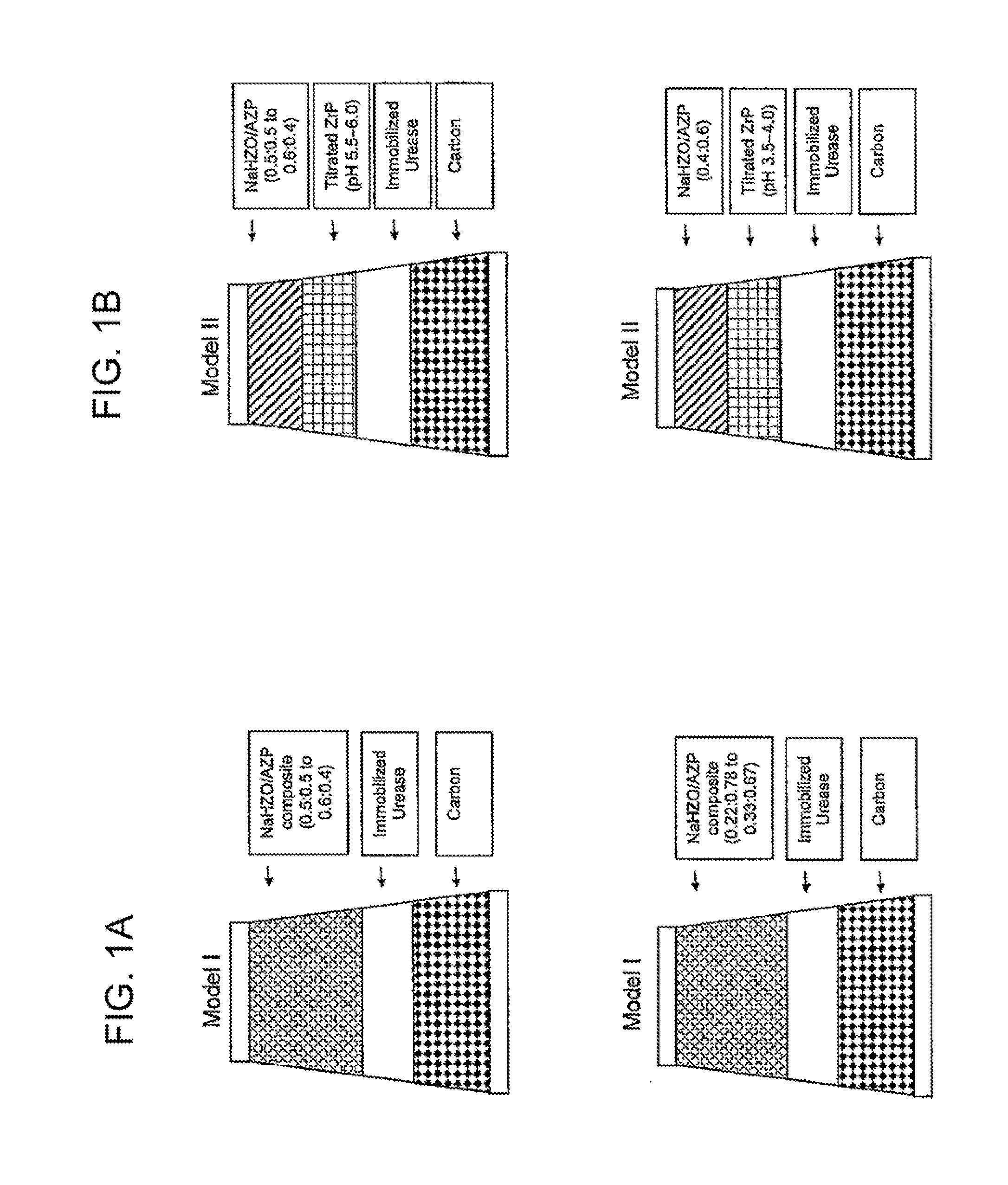
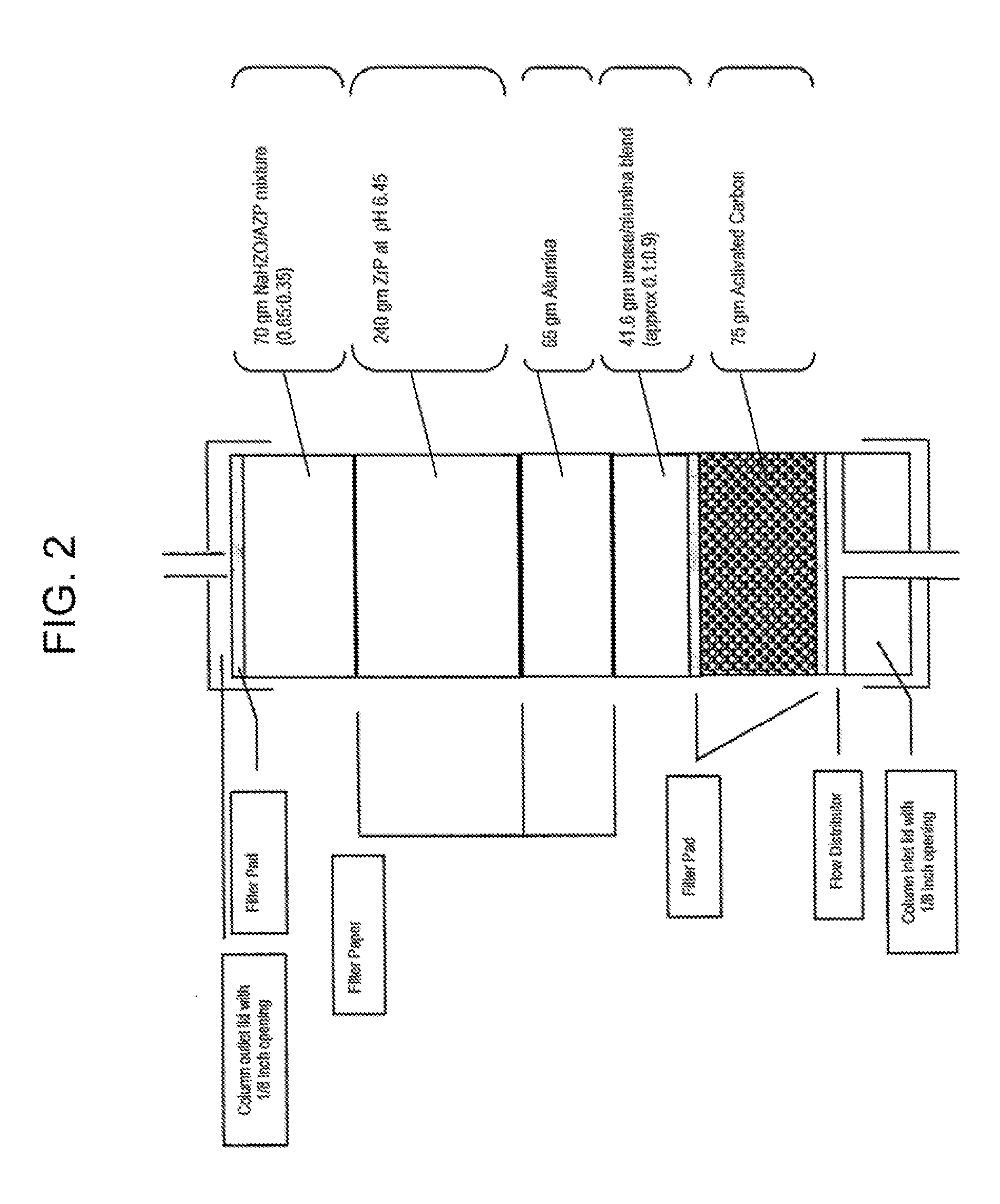
Acid Zirconium Phosphate and Alkaline Hydrous Zirconium Oxide Materials For Sorbent Dialysis
ActiveUS20100078387A1Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Antibody purification
The invention provides a method for producing a host cell protein-(HCP) reduced antibody preparation from a mixture comprising an antibody and at least one HCP, comprising an ion exchange separation step wherein the mixture is subjected to a first ion exchange material, such that the HCP-reduced antibody preparation is obtained.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Dosage forms using drug-loaded ion exchange resins
InactiveUS20050181050A1Avoid breakingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPill deliveryOral medicationImmediate release
A multiparticulate, modified release composition for oral administration has been developed. The formulation is made by complexing a drug with an ion-exchange resin in the form of small particles, typically less than 150 microns. The present invention provides novel extended release coated ion exchange particles comprising drug-resin complexes, produced by binding the salt form of the drug, that do not require impregnating agents to insure the integrity of the extended release coat. To prepare a modified release formulation, one or more of the following types of particles are formulated into a final dosage form: (a) Immediate release particles, (b) Enteric coated particles, (c) Extended release particles, (d) Enteric coated-extended release particles; and (e) Delayed release particles. The various drug-containing particles described above can be further formulated into a number of different easy-to-swallow final dosage forms including, but not limited to, a liquid suspension, gel, chewable tablet, crushable tablet, rapidly dissolving tablet, or unit of use sachet or capsule for reconstitution
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
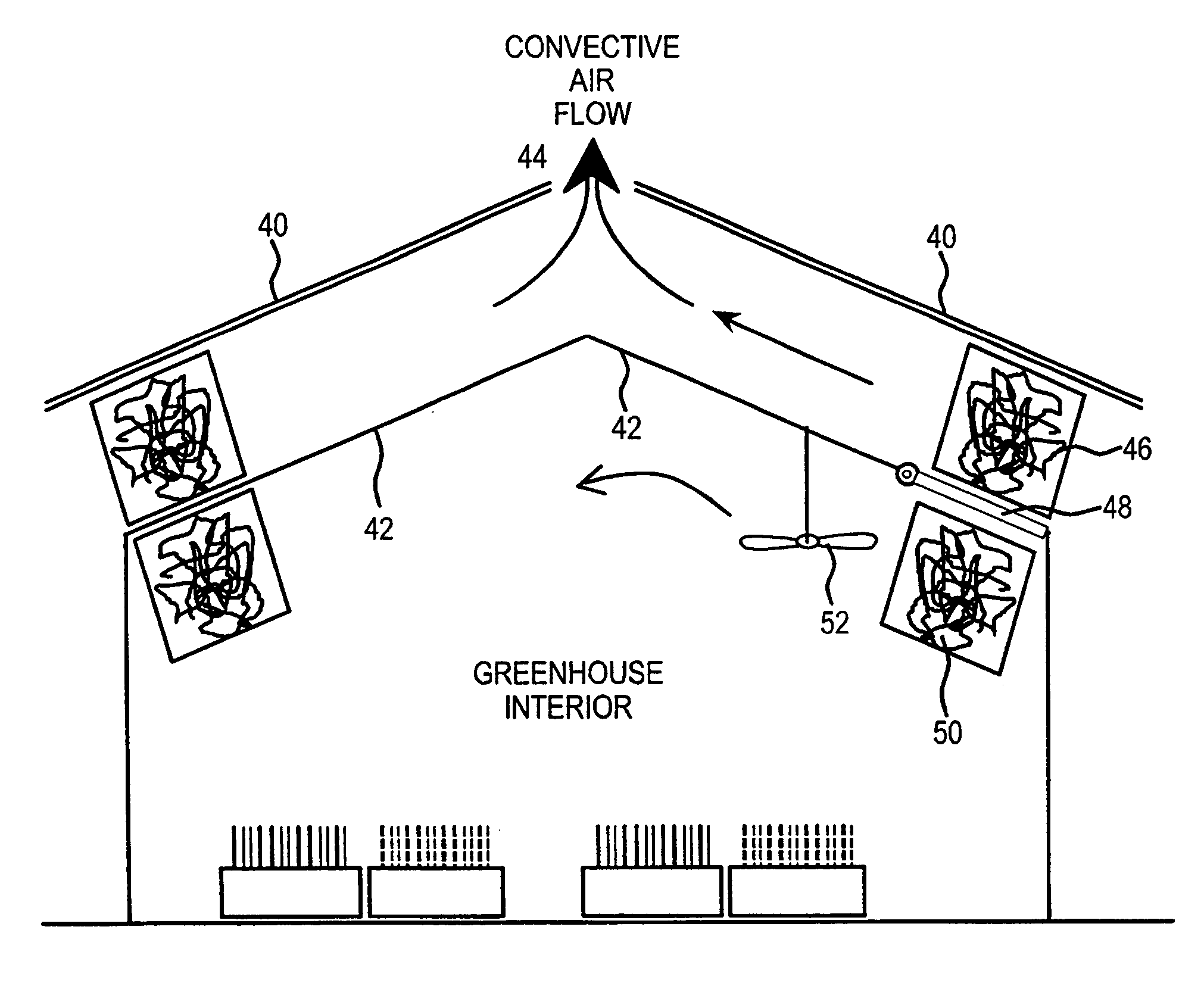
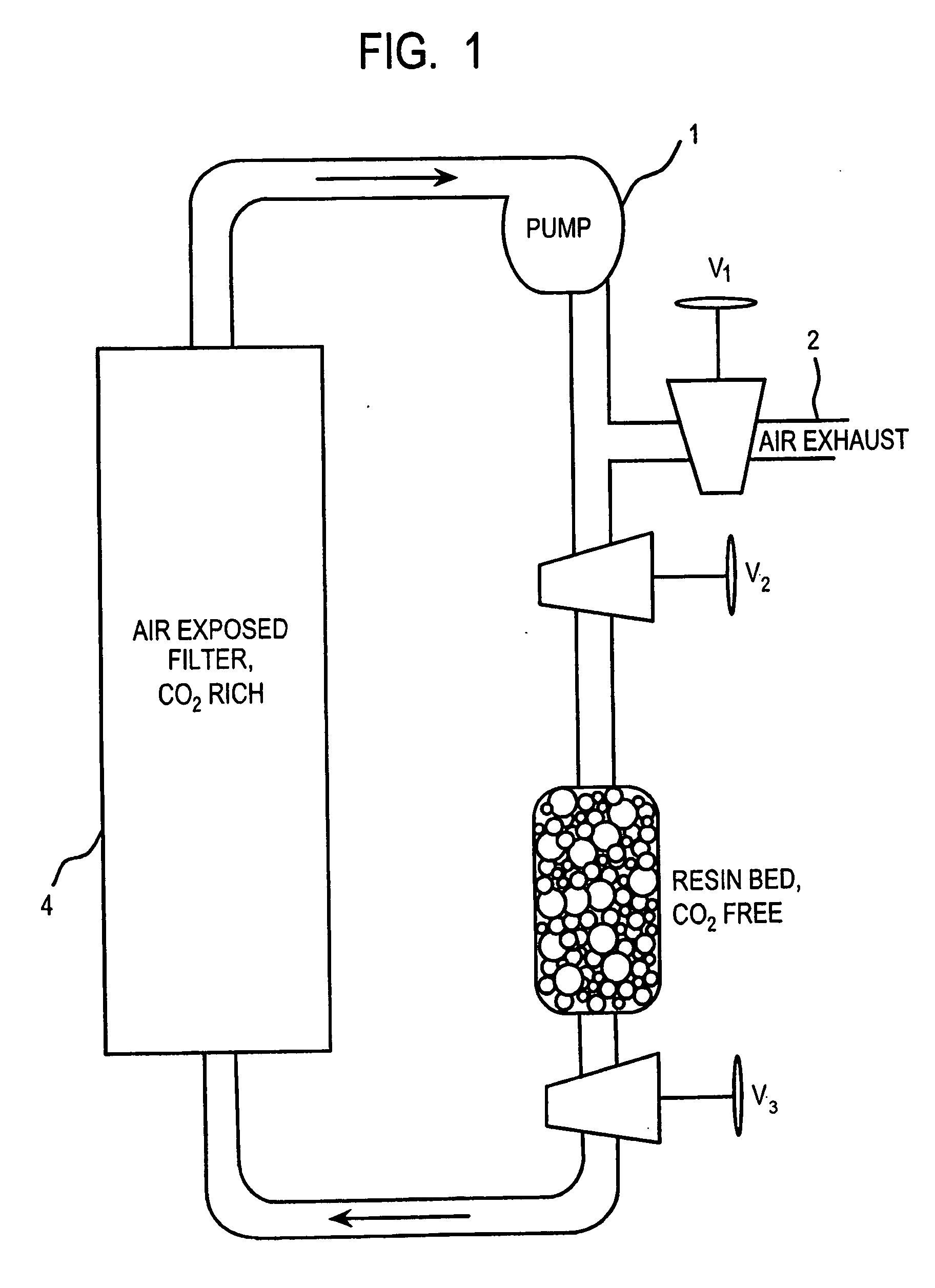
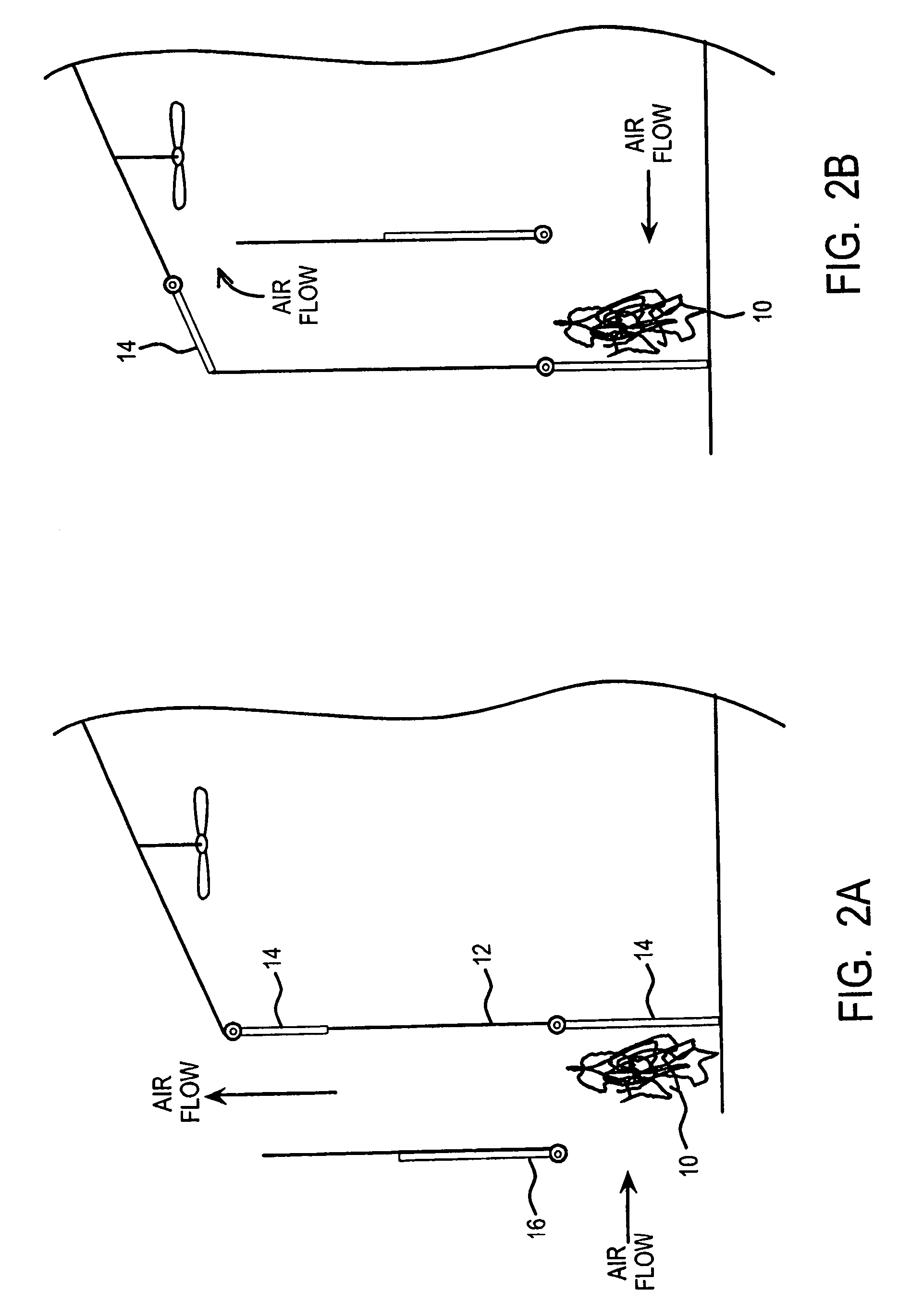
Method and apparatus for extracting carbon dioxide from air
A method and apparatus for extracting CO2 from air comprising an anion exchange material formed in a matrix exposed to a flow of the air, and for delivering that extracted CO2 to controlled environments. The present invention contemplates the extraction of CO2 from air using conventional extraction methods or by using one of the extraction methods disclosed; e.g., humidity swing or electro dialysis. The present invention also provides delivery of the CO2 to greenhouses where increased levels of CO2 will improve conditions for growth. Alternatively, the CO2 is fed to an algae culture.
Owner:CARBON SINK
Antibody purification
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
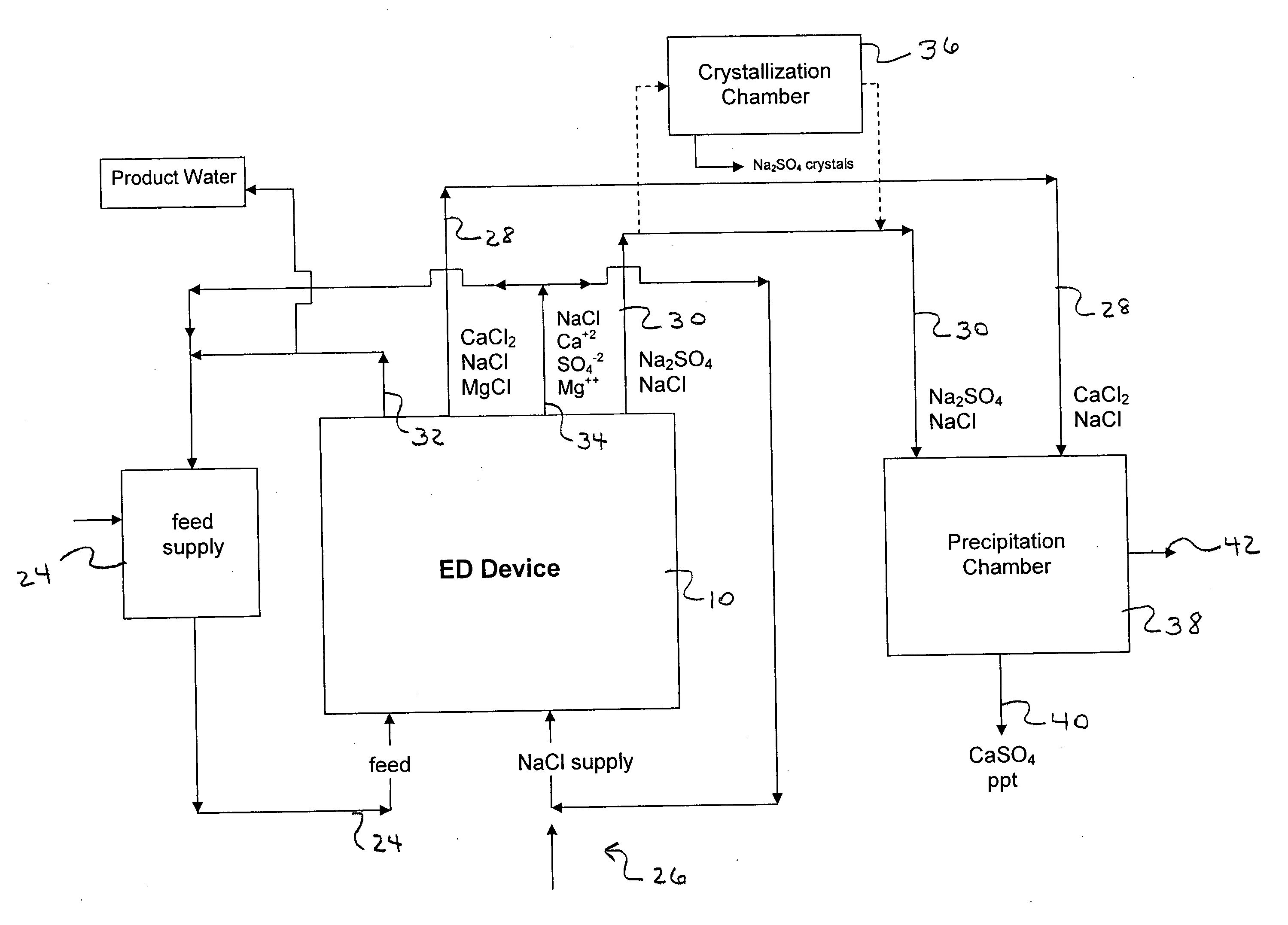
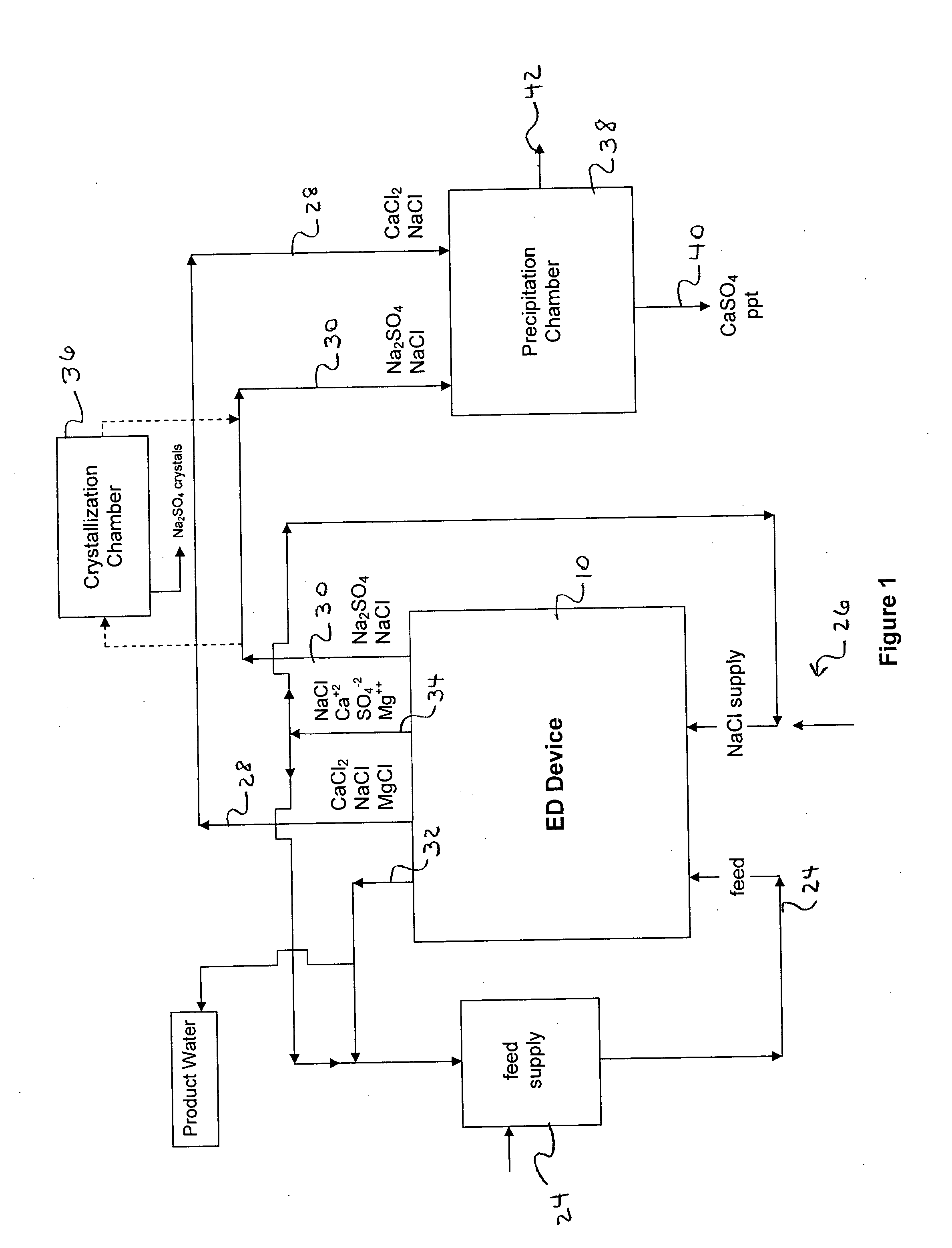
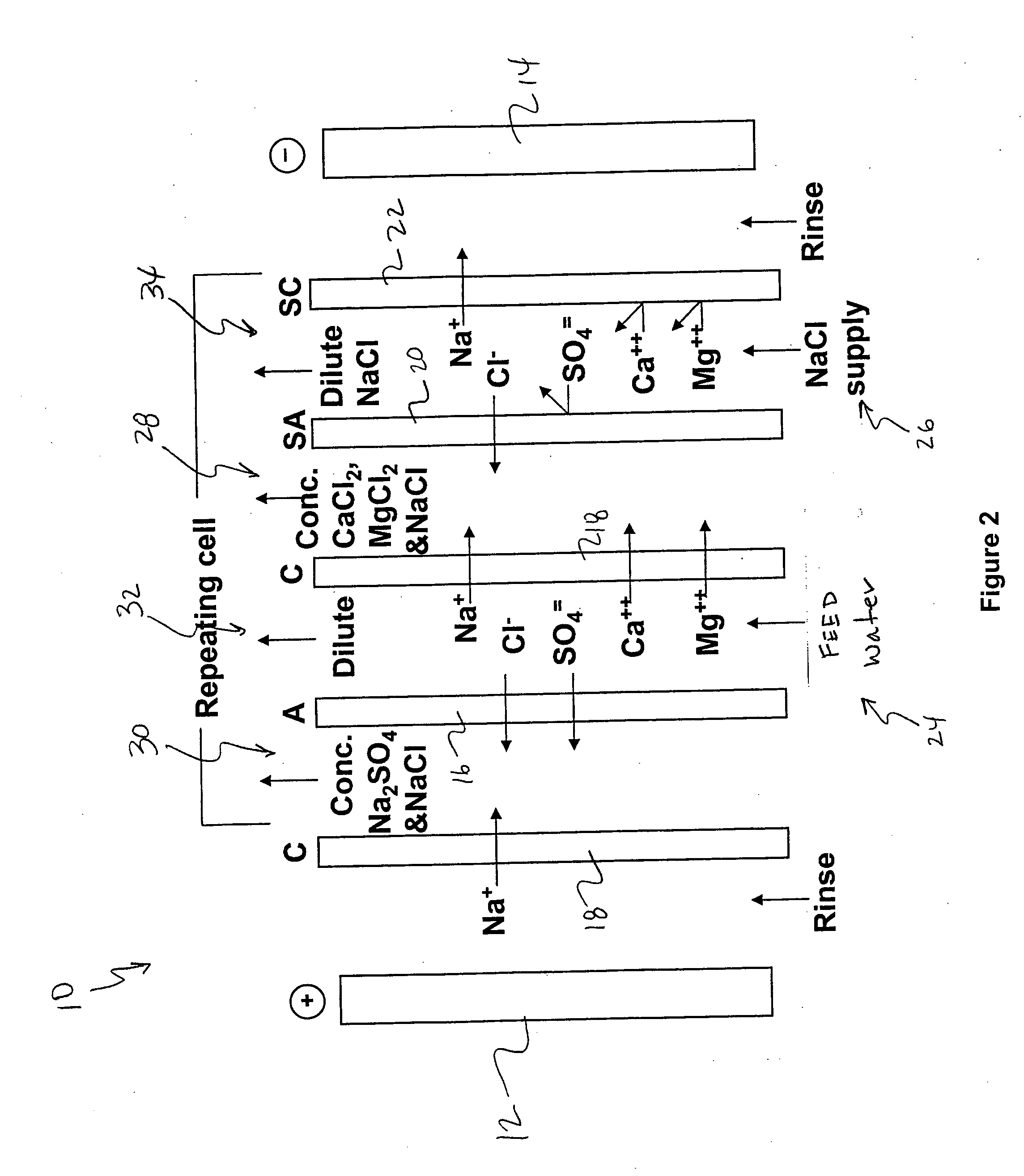
Water desalination process and apparatus
ActiveUS20060060532A1Electrolysis componentsGeneral water supply conservationSolubilityWater desalination
A process and system for purifying water is disclosed. For example, in one embodiment, the process may be used to remove a divalent salt, such as calcium sulfate, from a water source in order to prevent the divalent salt from precipitating during the process. The water source, for instance, may be fed to an ion separating device, such as an electrodialysis device. In the electrodialysis device, an ion exchange takes place between the divalent salt and another salt, such as a monovalent salt to produce two concentrated salt streams that contain salts having greater solubility in water than the divalent salt. In one embodiment, the two salt streams that are produced may then be combined to precipitate the divalent salt in a controlled manner. During the process, various other components contained within the water feed stream may also be removed from the stream and converted into useful products. In one particular embodiment, the process is configured to receive a byproduct stream from a reverse osmosis process.
Owner:SOUTH CAROLINA THE UNIV OF
Modified release formulations containing drug-ion exchange resin complexes
ActiveUS20070215511A1Reduction of undesirable tasteConvenient coatingPowder deliverySmall article dispensingDrugPlasticizer
A coated drug-ion exchange resin complex comprising a core composed of a drug complexed with a pharmaceutically acceptable ion-exchange resin is provided. The drug-ion exchange resin complex is in admixture with a release retardant. The coating is a polyvinyl acetate polymer and a plasticizer. Methods of making and products containing this coated complex are described.
Owner:TRIS PHARMA
Strengthened glass substrate and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20100087307A1Excellent devitrification proofHigh mechanical strengthGlass/slag layered productsThin material handlingDevitrificationMetallurgy
An object of the invention is to obtain a glass substrate having high mechanical strength by reconciling suitability for ion exchange and devitrification proof in a glass. The strengthened glass substrate of the invention is a strengthened glass substrate having a compression stress layer in the surface thereof, the glass substrate having a glass composition including, in terms of % by mass, 40-70% of SiO2, 12-25% of Al2O3, 0-10% of B2O3, 0-8% of Li2O, 6-15% of Na2O, 0-10% of K2O, 13-20% of Li2O+Na2O+K2O, 0-3.9% of MgO, 0-5% of CaO, 0-5% of ZnO, 0-6% of ZrO2, and 0-5% of SrO+BaO, the value of (MgO+ZrO2+ZnO) / (MgO+ZrO2+ZnO+Al2O3) in terms of mass proportion being from 0.25 to 0.45. The above-mentioned strengthened glass can be produced by melting raw glass materials mixed together so as to result in the given glass composition, forming the melt into a sheet by an overflow downdraw process, and then conducting an ion exchange treatment to form a compression stress layer in the glass sheet surface.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Point-of-use water purification system with a cascade ion exchange option
InactiveUS6080313AHigh purityEasy to install and replaceSolid sorbent liquid separationLoose filtering material filtersFiltrationIon exchange
A modular water treatment and purification system, suitable for home use, is connected to a water supply and contains a closed fluid treatment circuit extending to a water outlet. The closed fluid circuit flows through a plurality of replaceable water treatment modules each having a specific water treatment function, such as the removal of a particular material from the water by the use of filtration, carbon adsorption, ion exchange or the addition of a chemical to balance the desired water conditions. Preferably the circuit also includes traversing a radiation device, for example an ultra violet light, for the purpose of sanitizing the water.
Owner:KELADA MAHER I
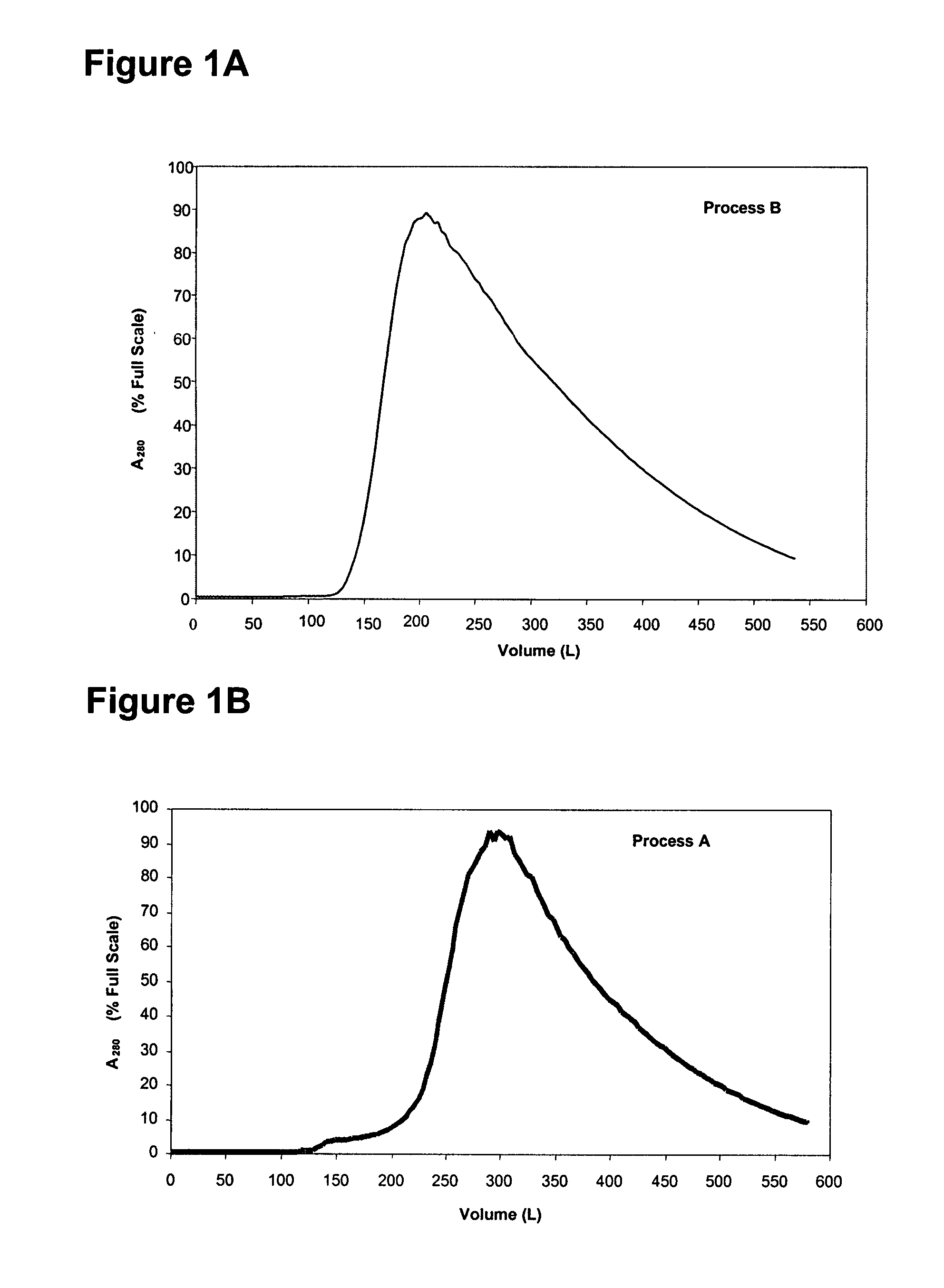
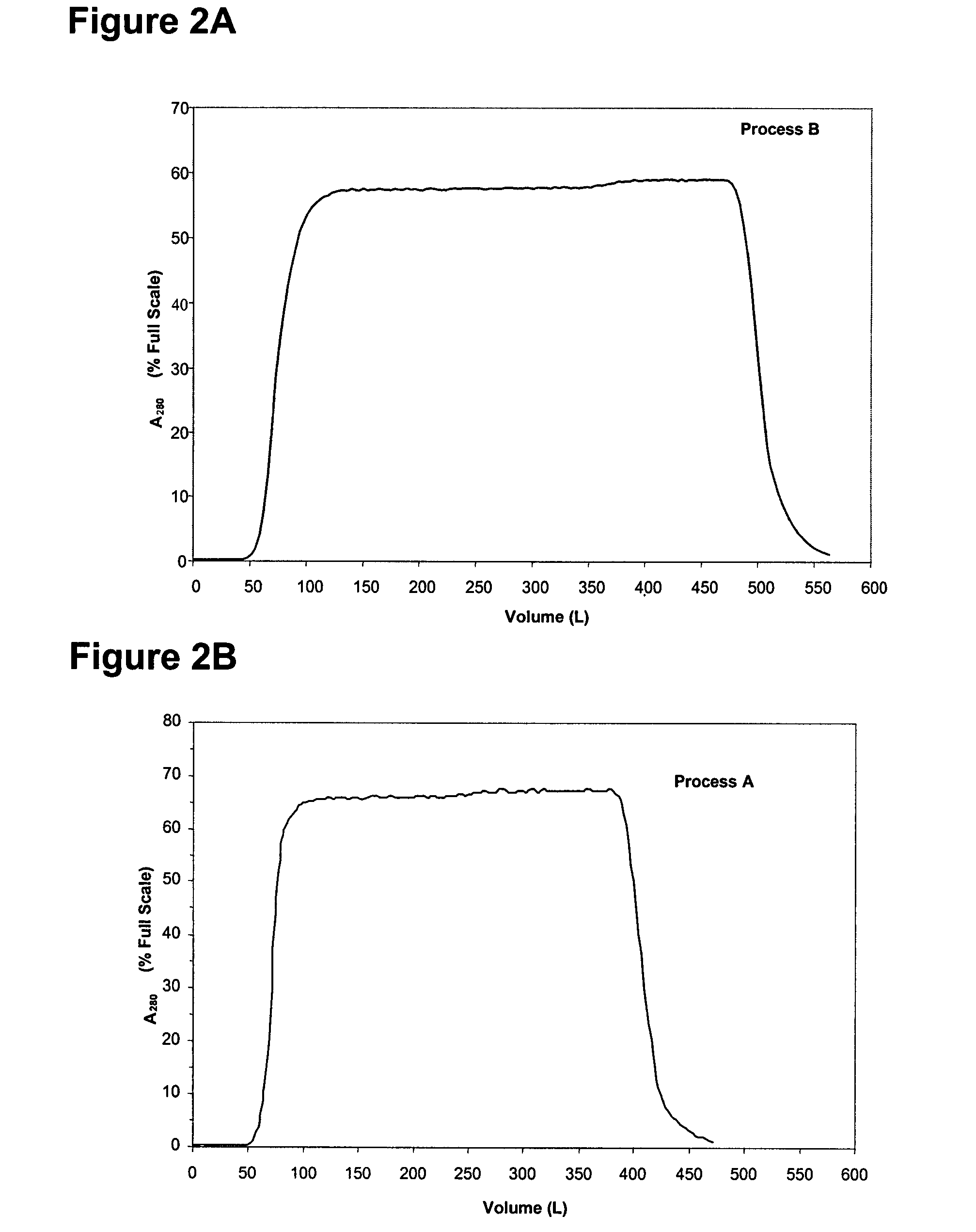
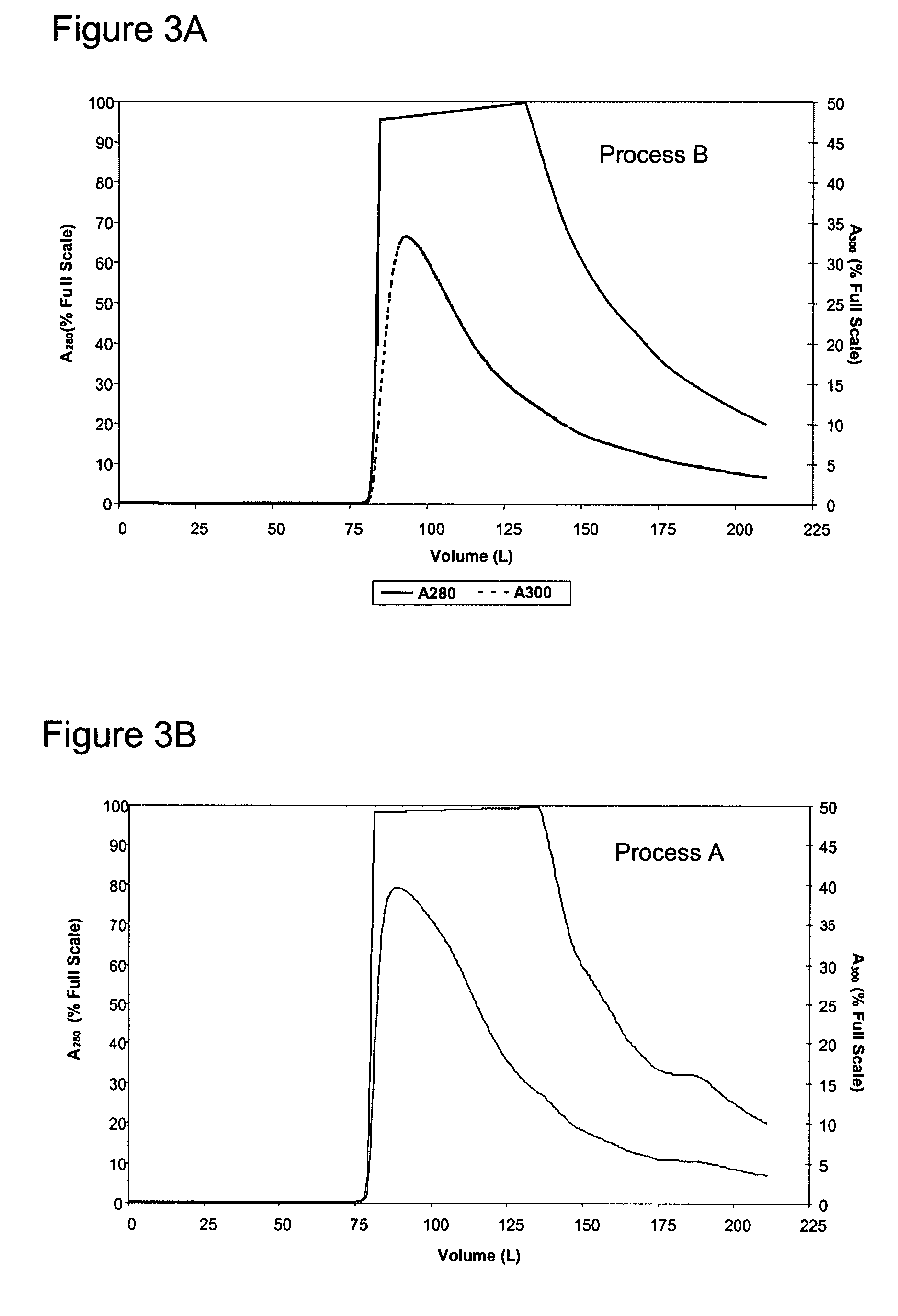
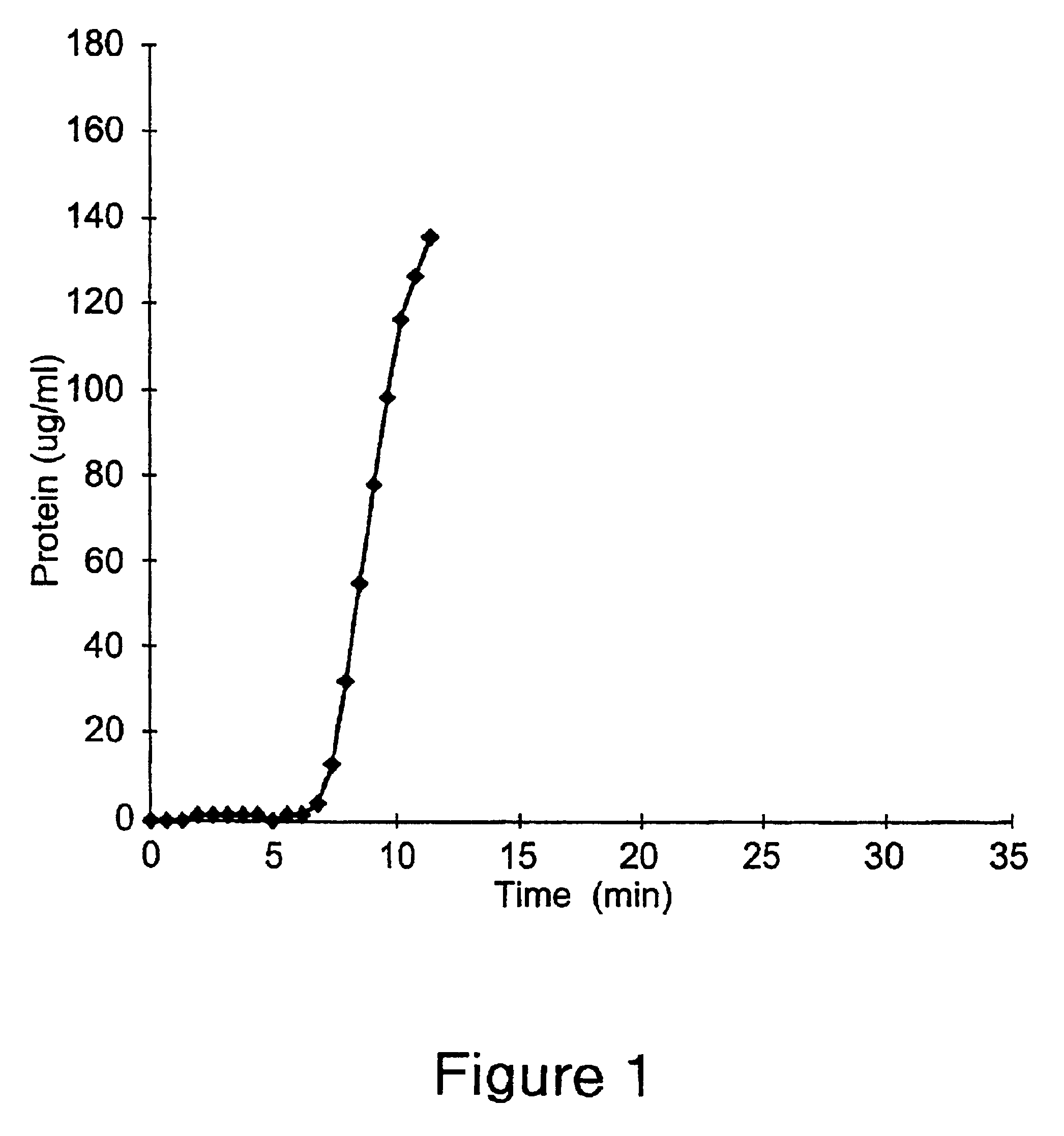
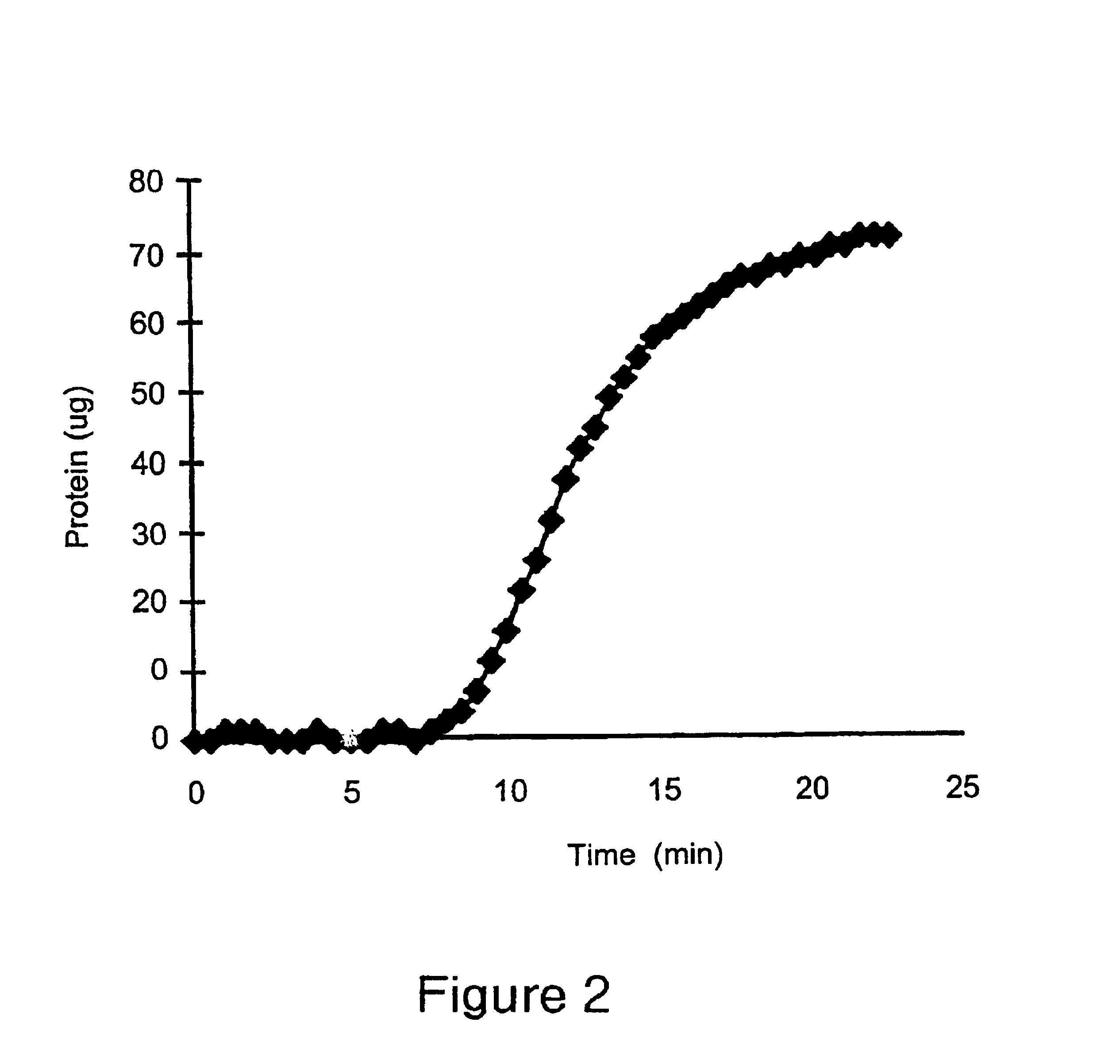
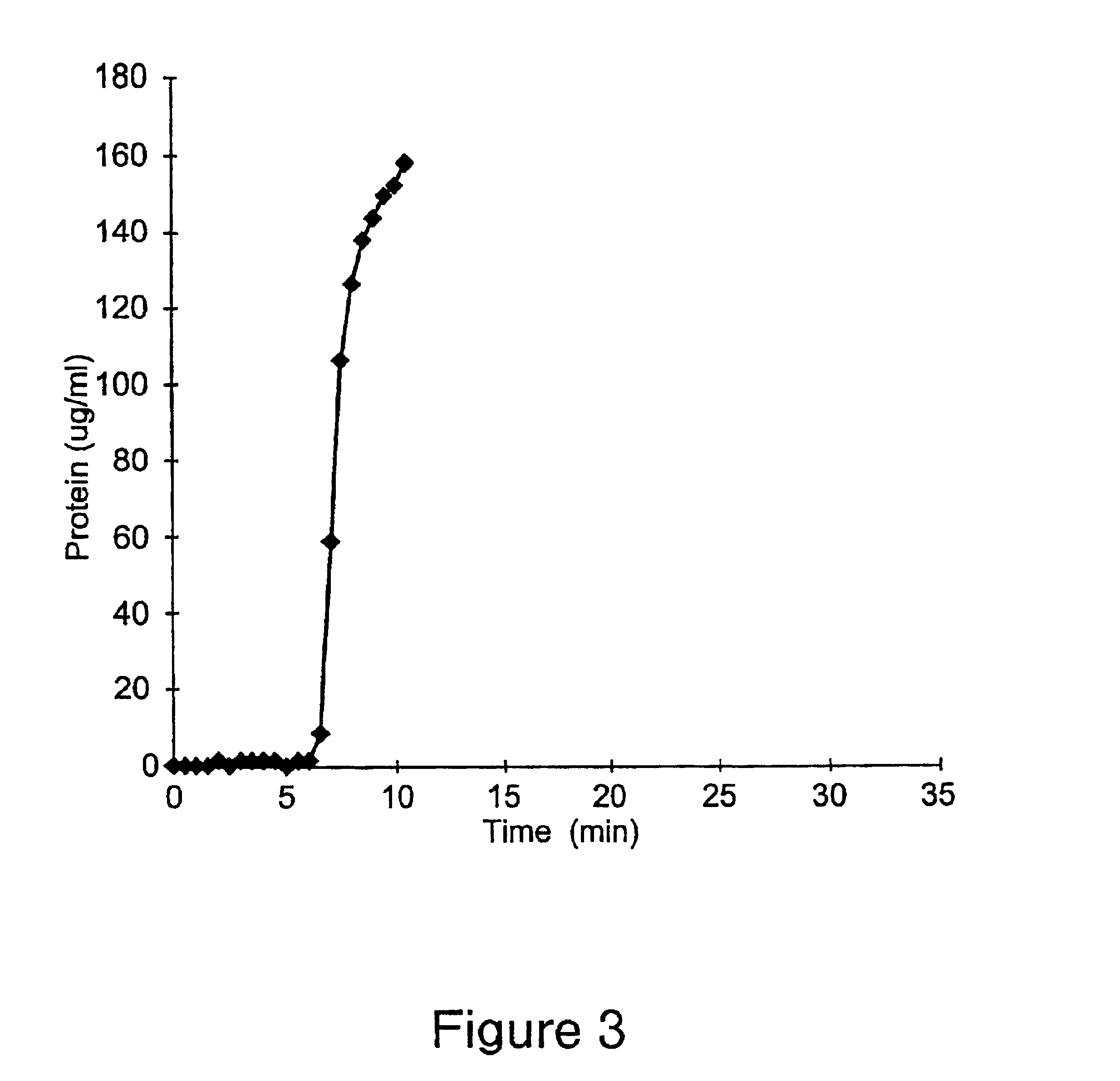
Protein purification
InactiveUS7074404B2High recovery ratePeptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsIon chromatographyMulti pollutant
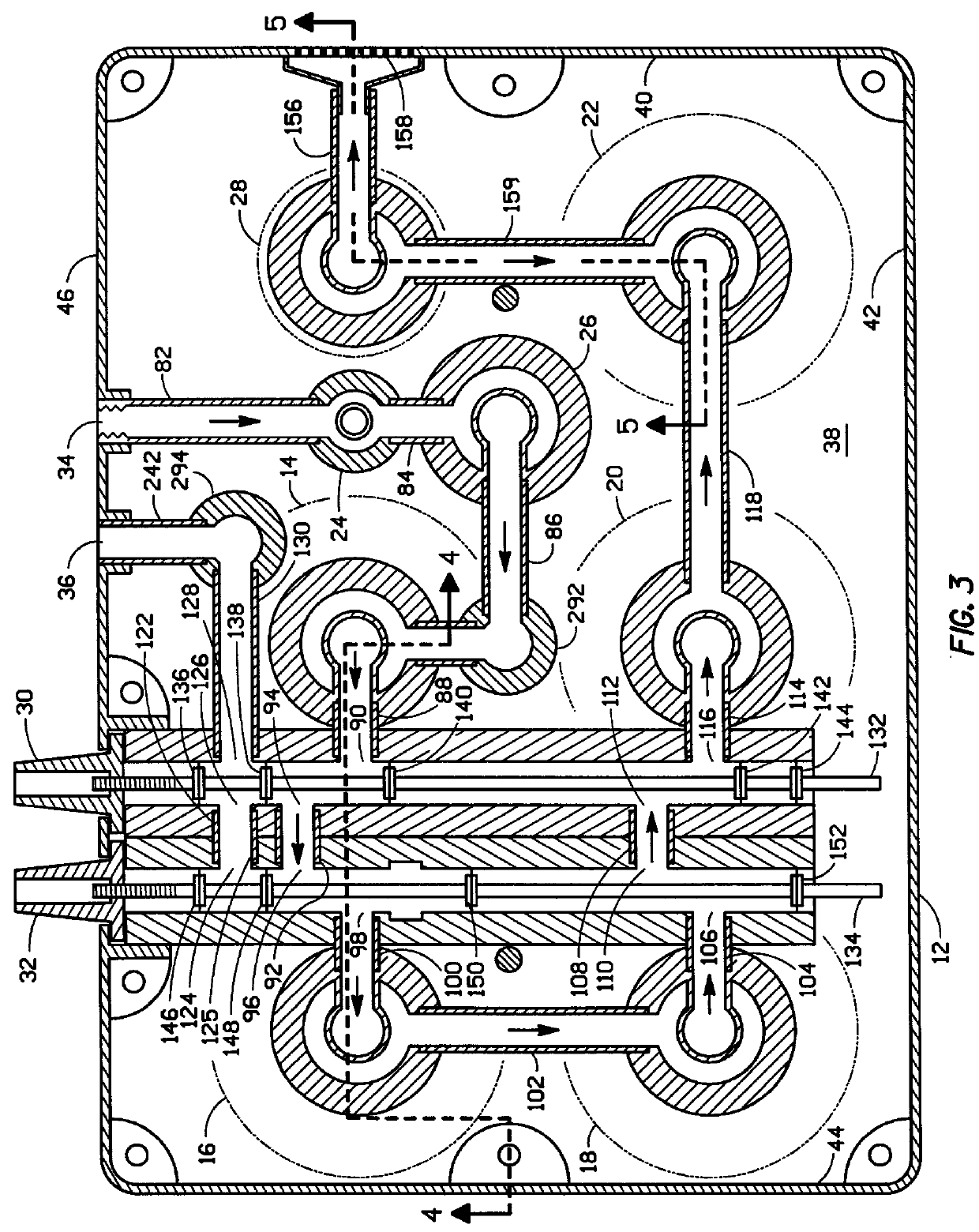
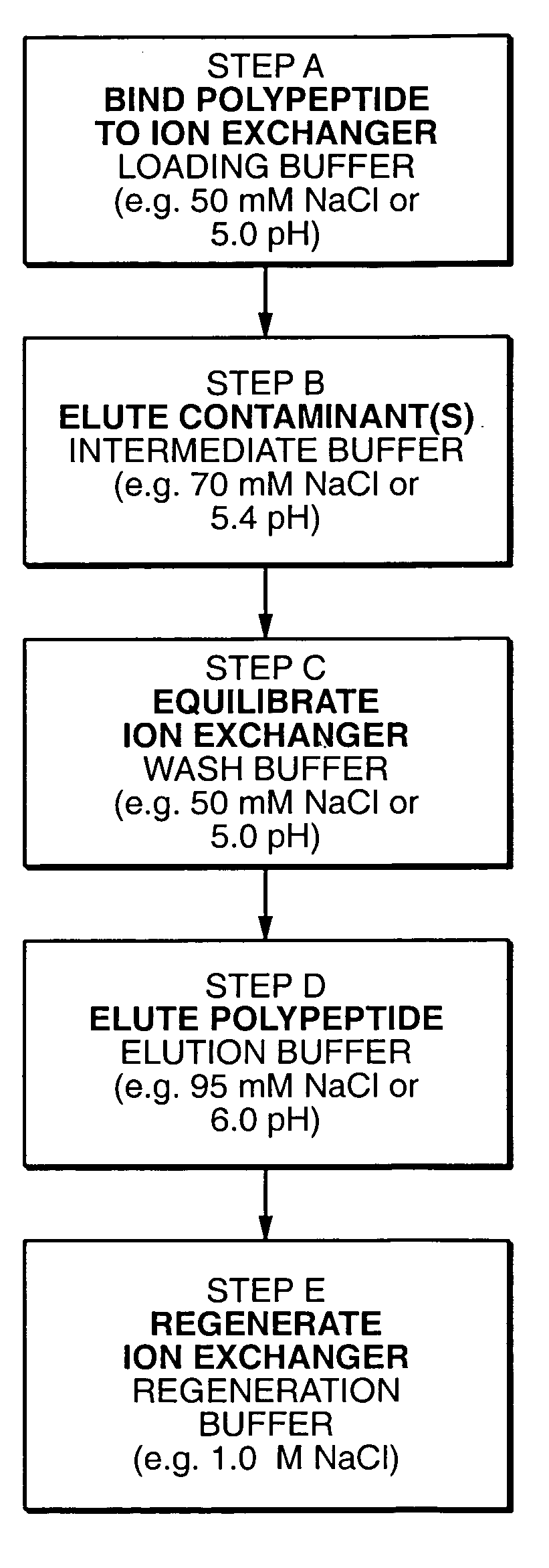
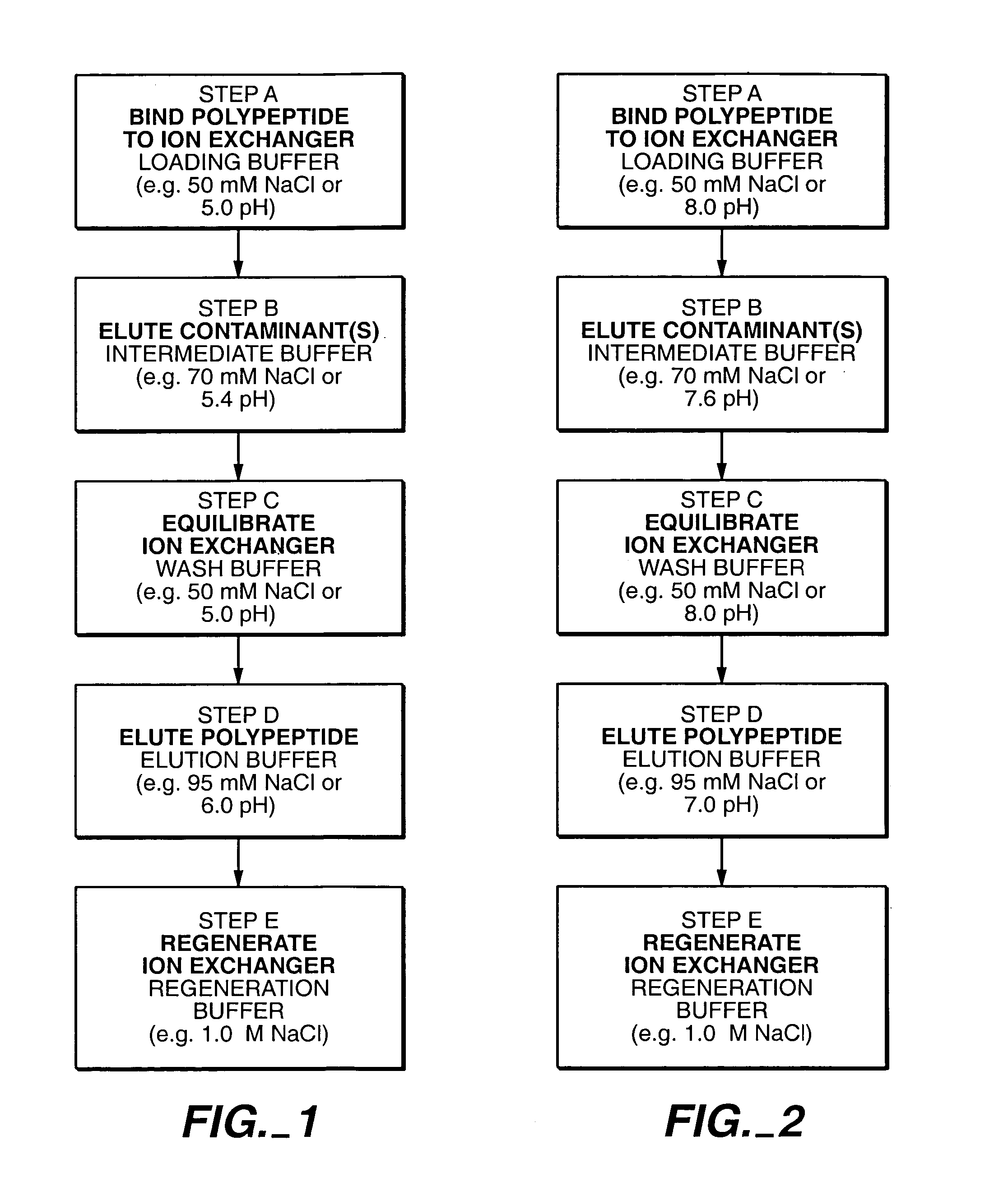
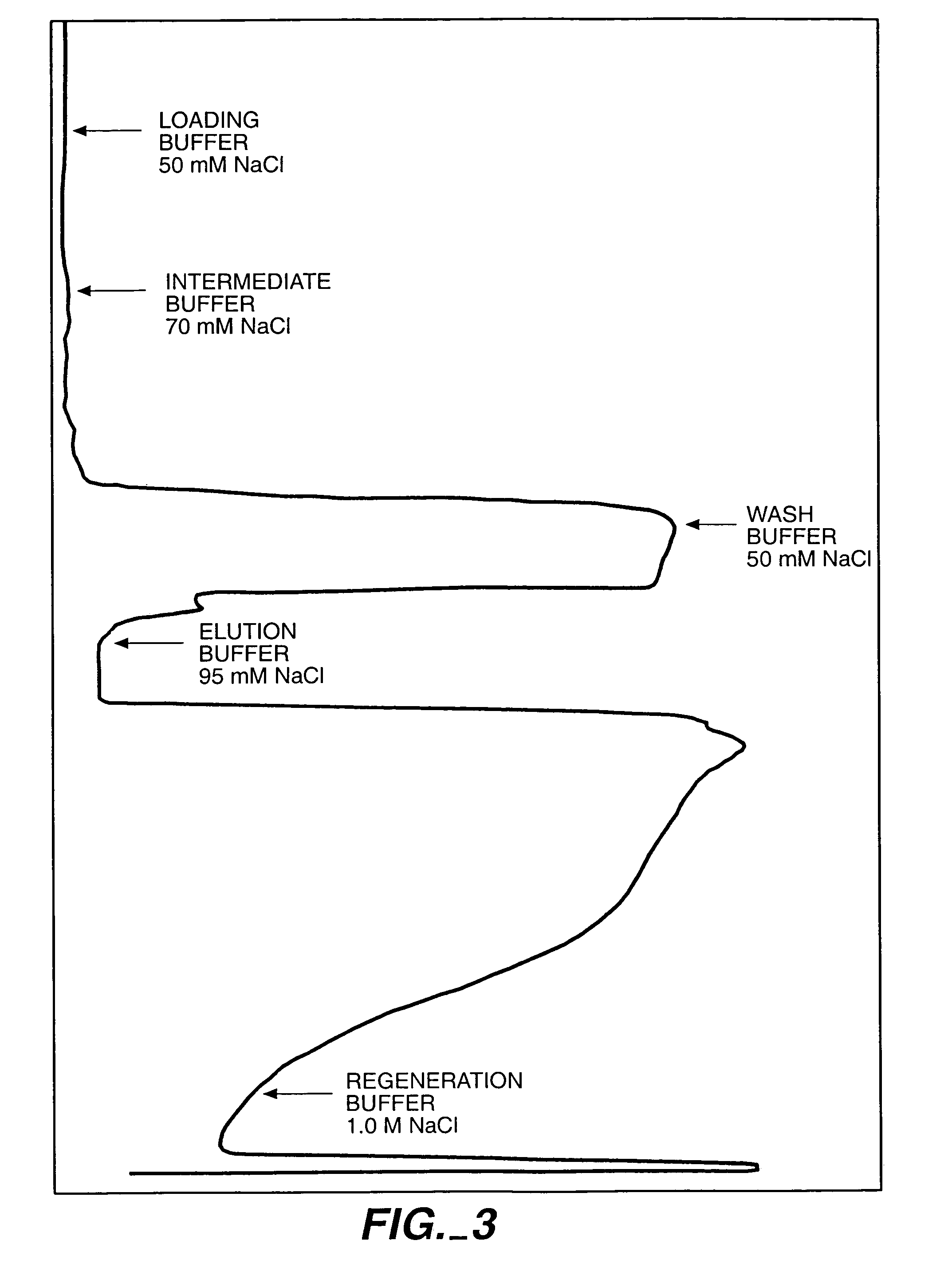
A method for purifying a polypeptide by ion exchange chromatography is described which involves changing the conductivity and / or pH of buffers in order to resolve a polypeptide of interest from one or more contaminants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Sprayable formulations for the treatment of acute inflammatory skin conditions
A topical spray or foam, methods of making the formulation, and methods of use thereof, has been developed. In one preferred embodiment, the composition includes one or more active agents and exhibits both antibacterial activity and antifungal activity. Excipients such as chemical disinfectants, anti-pruritic agents to minimize itching, and skin protective compounds may be added. The composition may be formulated to be dispensed as a spray or foam and the spray or foam may be administered either by a hand pump or by an aerosolizing propellant. A second single phase formulation has also been developed. The formulation comprises a first drug which is water soluble or hydrophilic and a second drug which is lipid soluble or hydrophobic, wherein at least one of the drugs is bound to an ion-exchange resin. The use of binding resins, such as ion-exchange resins, allows drugs with incompatible solvent requirements to be prepared in a single-phase formulation.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Positively charged membrane
InactiveUS6780327B1High rateHigh charge densityCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPorous substrateFiltration
The present invention provides a positively charged microporous membrane having a protein binding capacity about 25 mg / ml or greater comprising a hydrophilic porous substrate and a crosslinked coating that provides a fixed positive charge to the membrane. The present invention further provides a positively charged microporous membrane comprising a porous substrate and a crosslinked coating comprising pendant cationic groups. The membranes of the present invention find use in a variety of applications including ion-exchange chromatography, macromolecular transfer, as well as detection, filtration and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, endotoxins, and the like.
Owner:PALL CORP
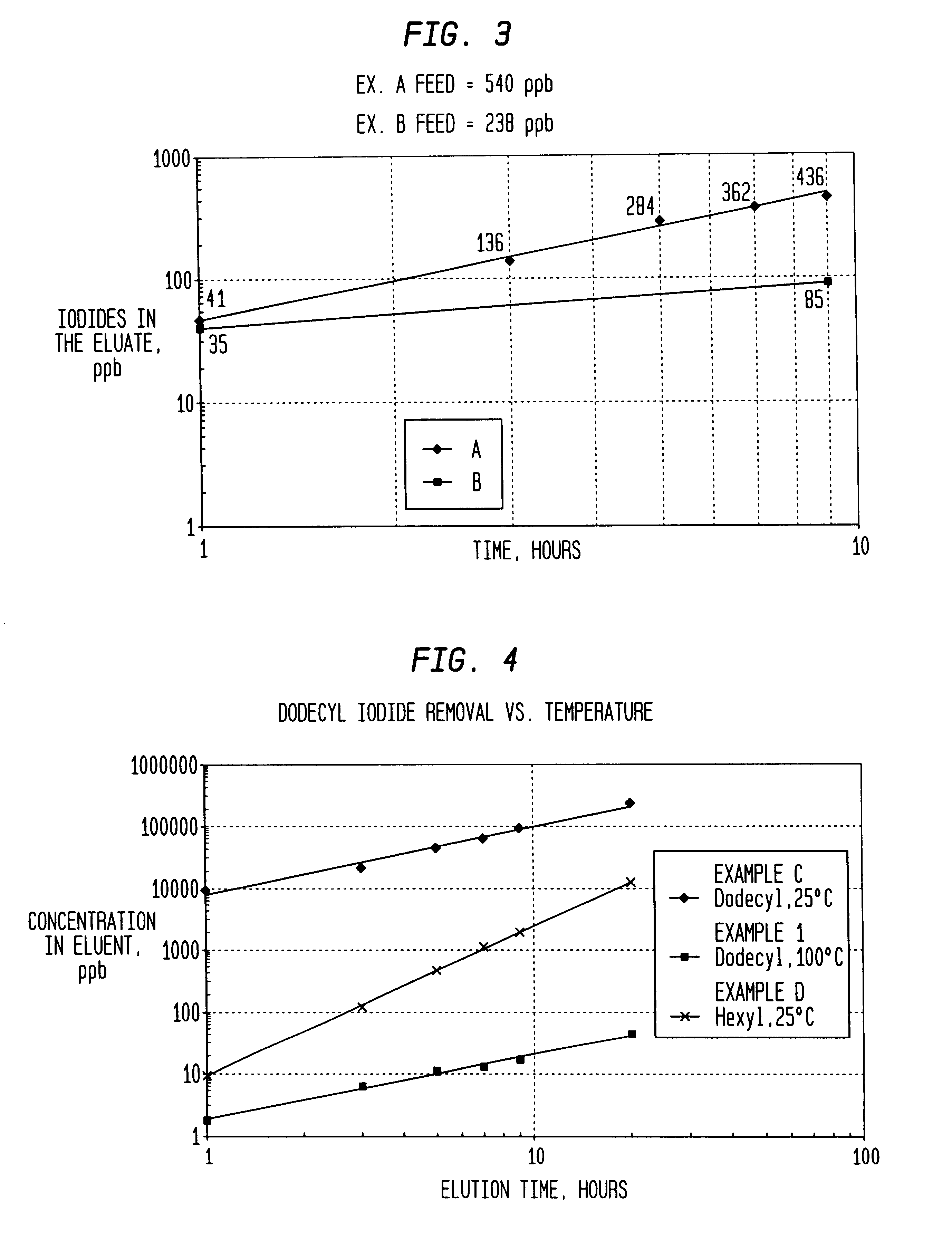
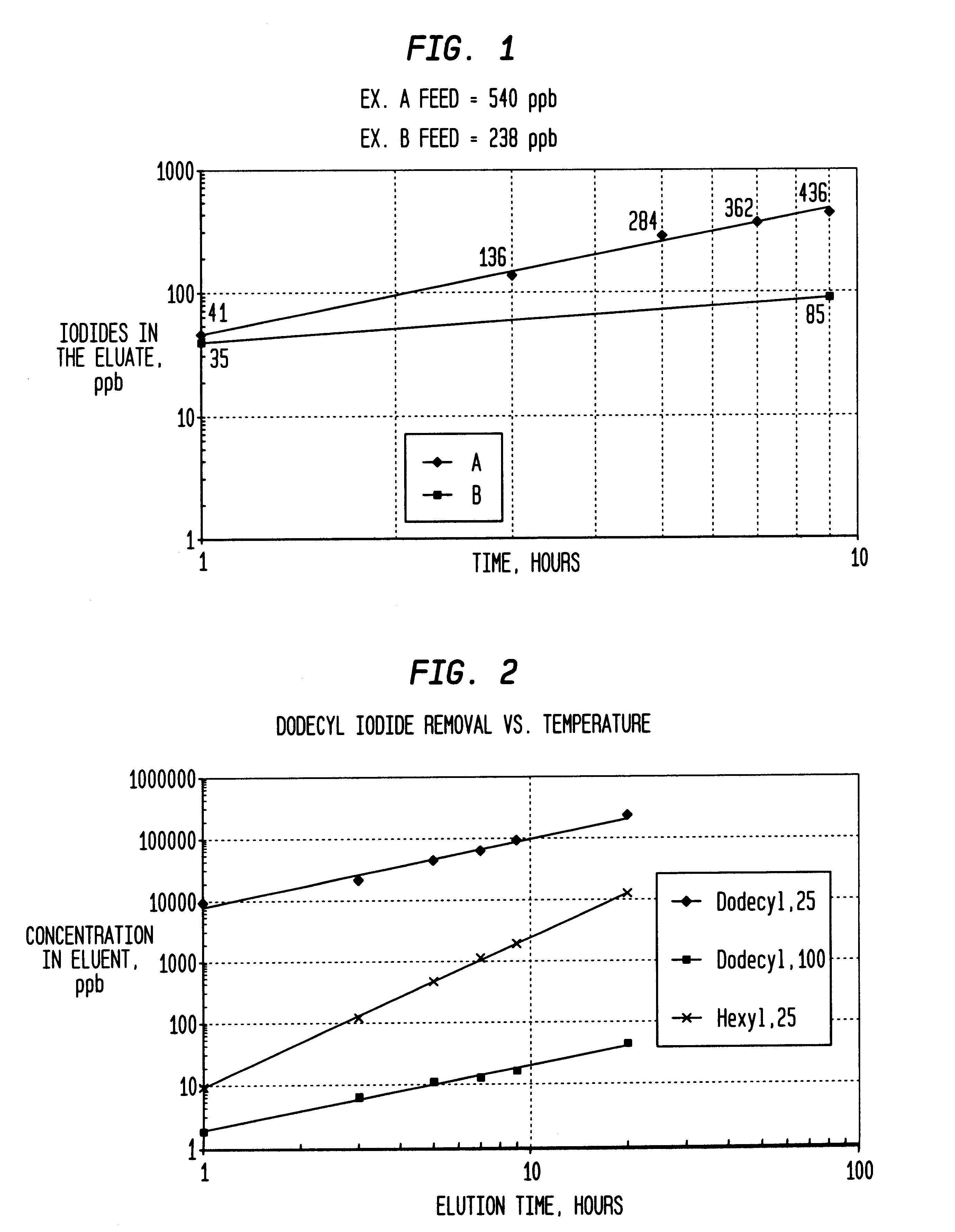
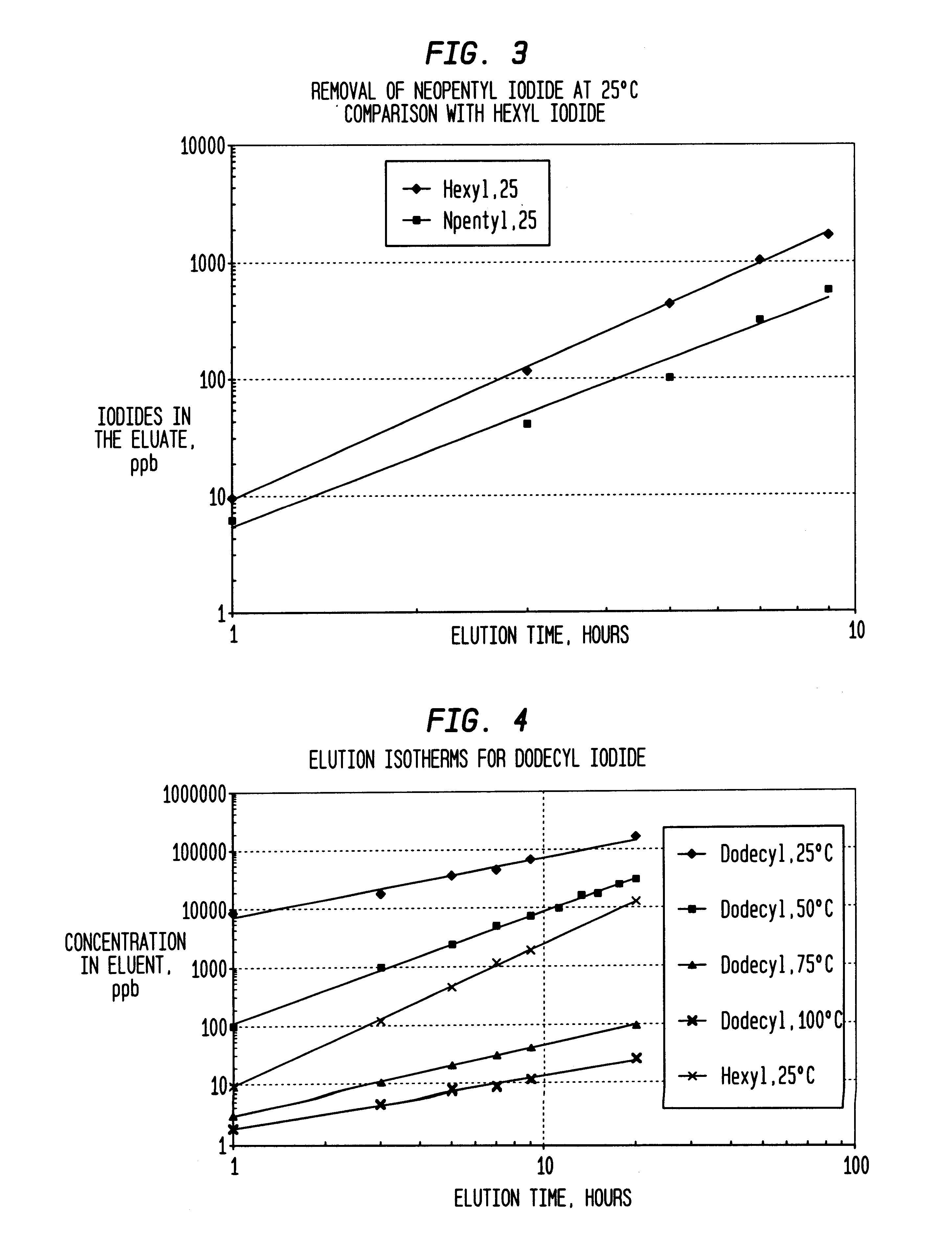
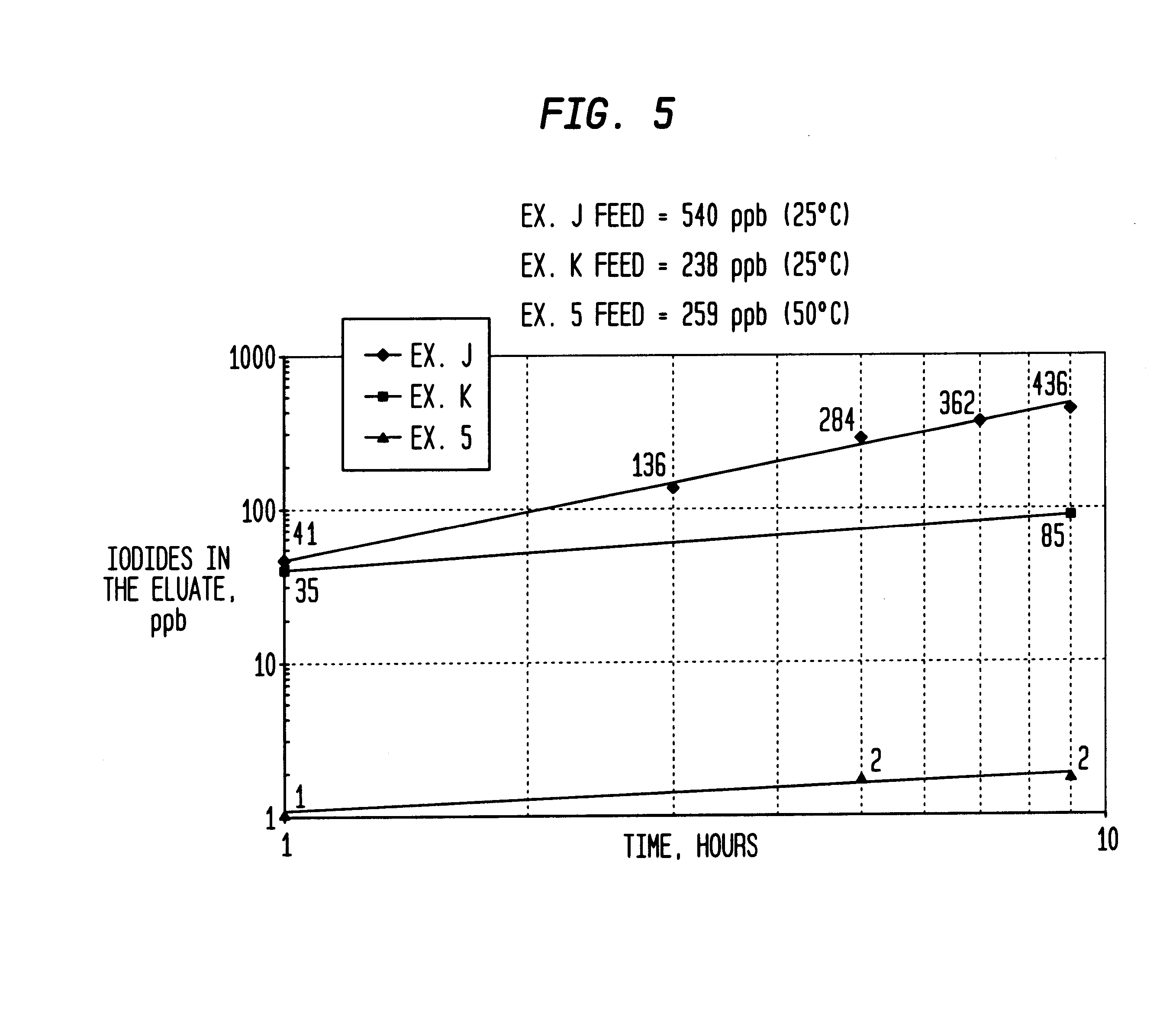
Method of removing organic iodides from organic media
InactiveUS6225498B1Efficient removalCation exchanger materialsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidAcetic anhydride
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method for producing chemically tempered glass
To provide a method for producing chemically tempered glass, whereby frequency of replacement of the molten salt can be reduced. A method for producing chemically tempered glass, which comprises repeating ion exchange treatment of immersing glass in a molten salt, wherein the glass comprises, as represented by mole percentage, from 61 to 77% of SiO2, from 1 to 18% of Al2O3, from 3 to 15% of MgO, from 0 to 5% of CaO, from 0 to 4% of ZrO2, from 8 to 18% of Na2O and from 0 to 6% of K2O; SiO2+Al2O3 is from 65 to 85%; MgO+CaO is from 3 to 15%; and R calculated by the following formula by using contents of the respective components, is at least 0.66:R=0.029×SiO2+0.021×Al2O3+0.016×MgO−0.004×CaO+0.016×ZrO2+0.029×Na2O+0×K2O−2.002
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Methods of Fabricating Glass Articles by Laser Damage and Etching
Methods of forming a glass article are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of forming a glass article includes translating a pulsed laser beam on a glass substrate sheet to form a laser damage region between a first surface and a second surface of the glass substrate sheet. The method further includes applying an etchant solution to the glass substrate sheet to remove a portion of the glass substrate sheet about the laser damage region. The method may further include strengthening the glass substrate sheet by an ion-exchange strengthening process, and coating the glass substrate sheet with an acid-resistant coating. Also disclosed are methods where the laser damage region has an initial geometry that changes to a desired geometry following the reforming of the glass substrate sheet such that the initial geometry of the laser damage region compensates for the bending of the glass substrate sheet.
Owner:CORNING INC
Aqueous dispersions of polythienothiophenes with fluorinated ion exchange polymers as dopants
ActiveUS20060076557A1Solve problemsMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensCarbon nanotubeIon exchange
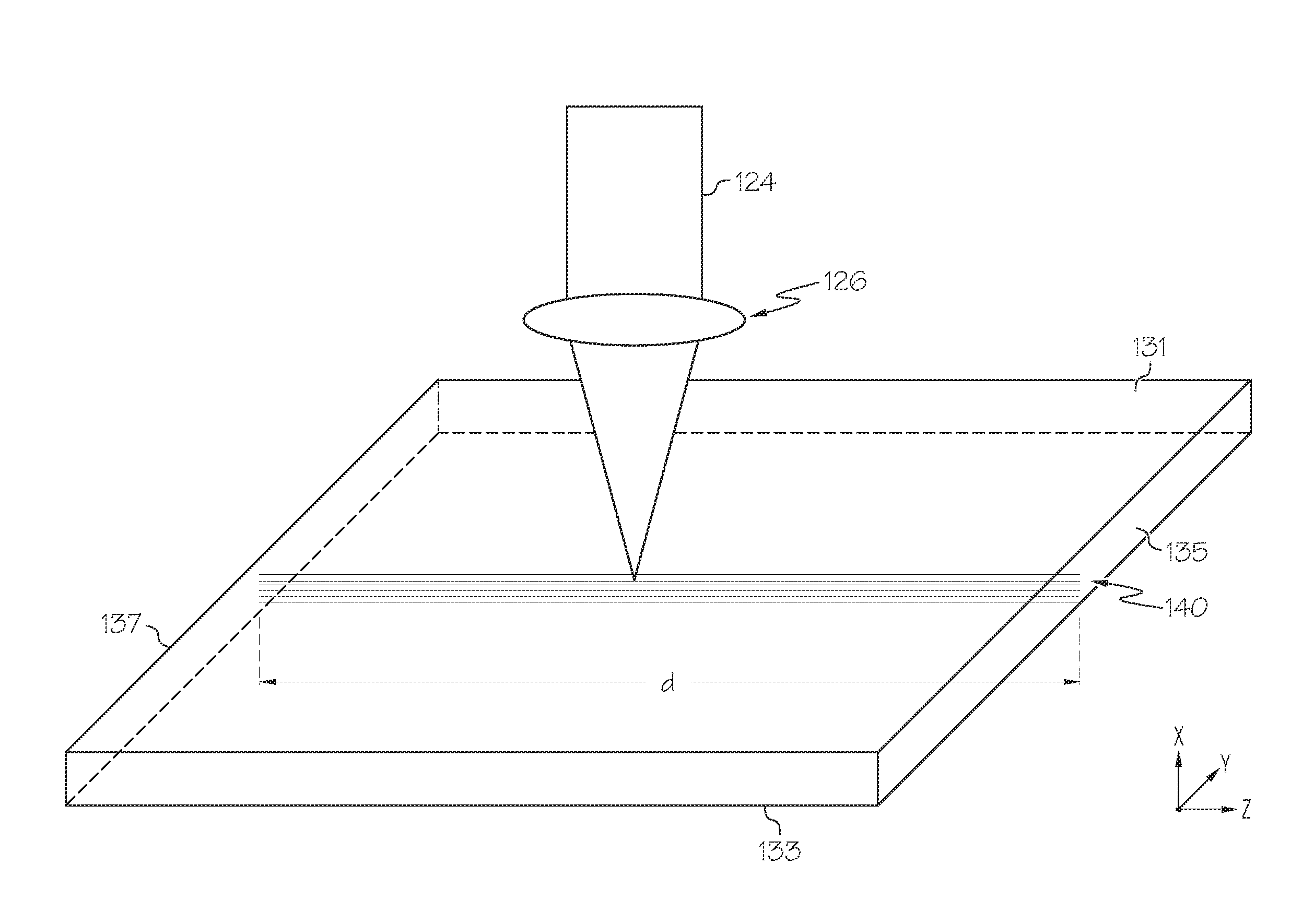
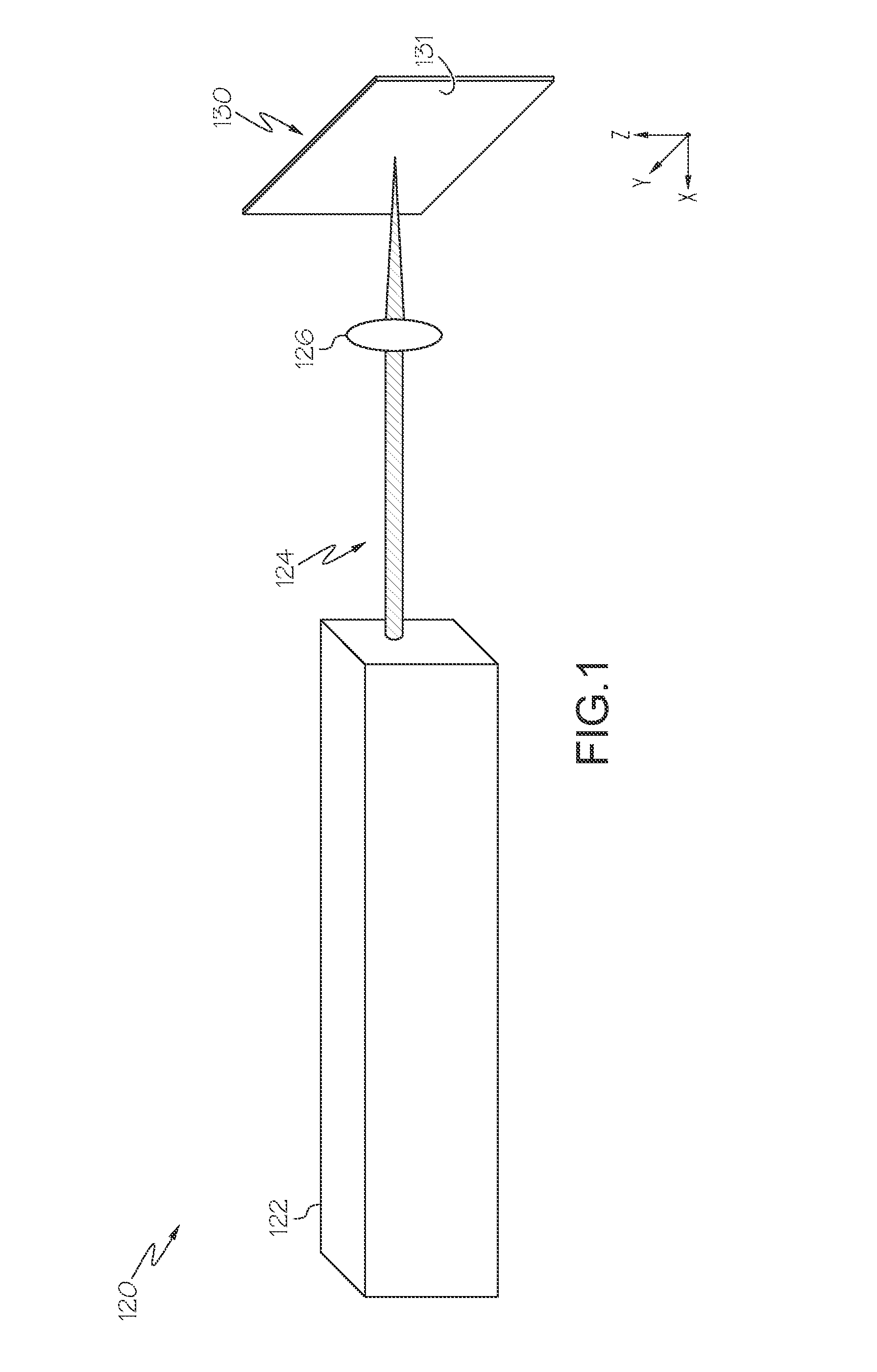
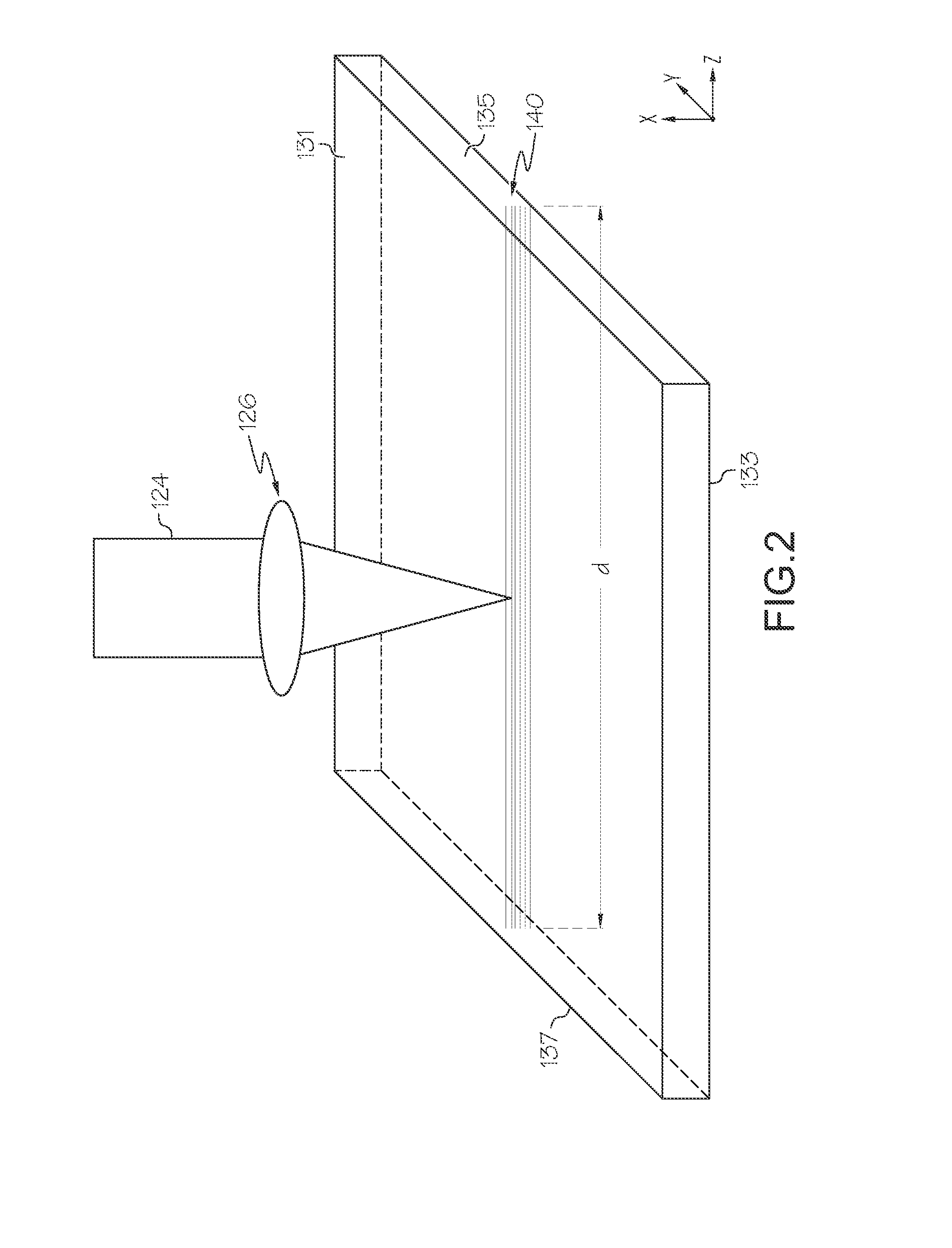
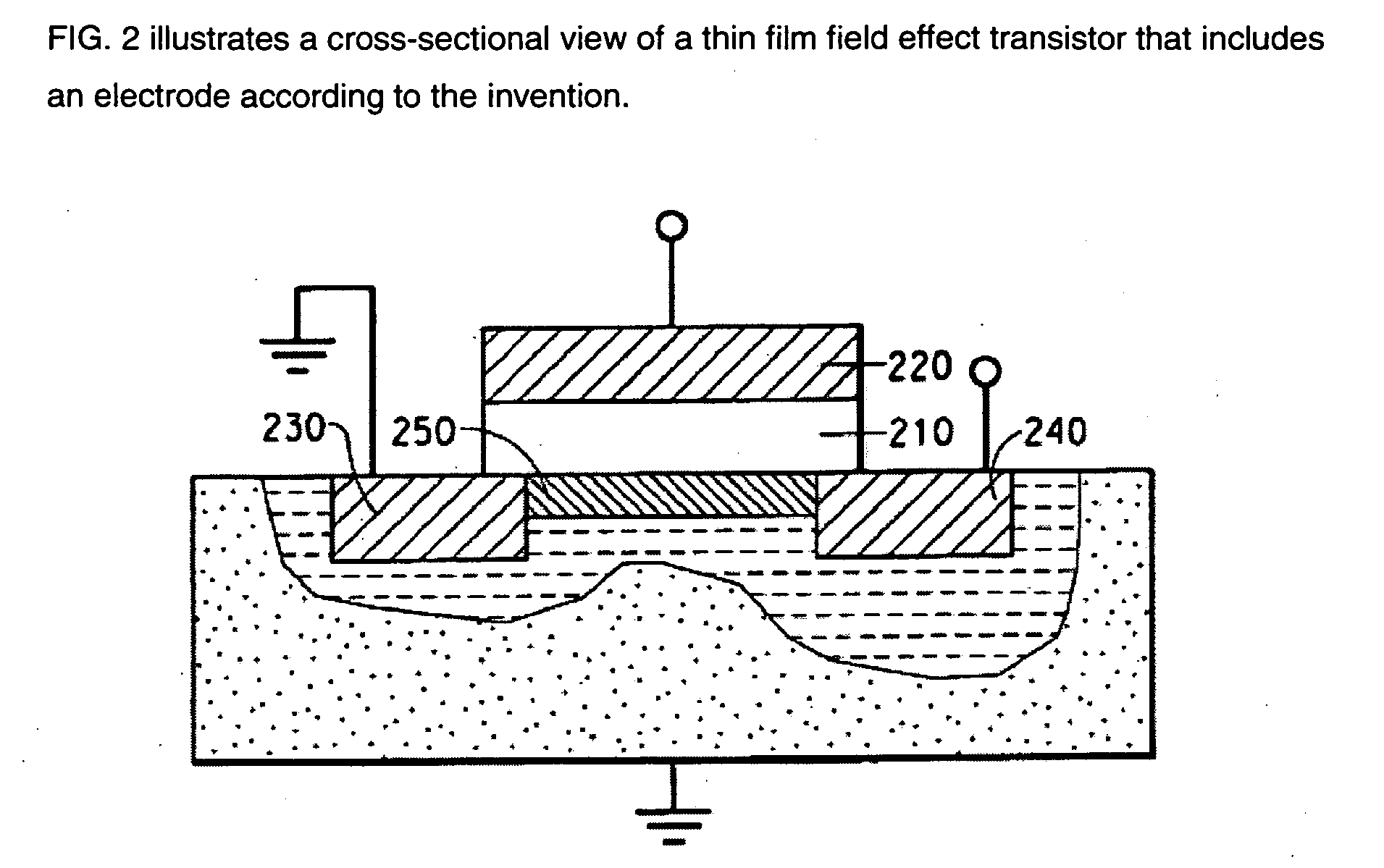
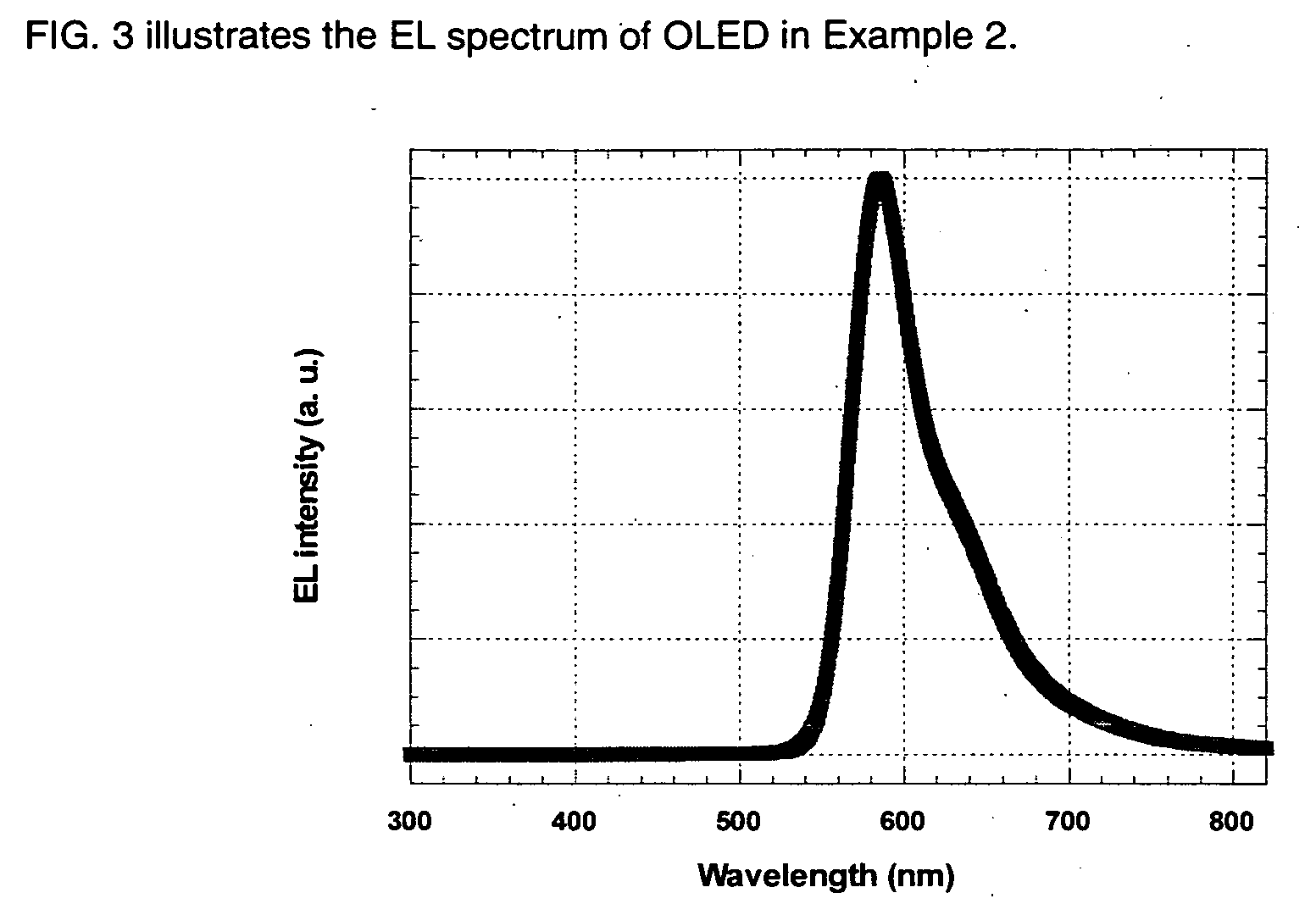
Compositions are provided comprising aqueous dispersions of polythienothiophenes and colloid-forming polymeric acids. Films from invention compositions are useful as hole injection layers in organic electronic devices, including electroluminescent devices, such as, for example, organic light emitting diodes (OLED) displays, as hole extraction layers in organic optoelectronic devices, such as organic photovoltaic devices, and in combination with metal nanowires or carbon nanotubes in applications such as drain, source, or gate electrodes in thin film field effect transistors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Aluminosilicate glass for chemical tempering and glass ceramics
The invention discloses aluminosilicate glass for chemical tempering and glass ceramics, and particularly discloses aluminosilicate glass which contains Li2O and P2O5 and can be chemically tempered. The glass of the invention can realize high ion exchange speed by the addition of 0.01-8 wt% of P2O5. The glass of the invention contains 2-6 wt% of Li2O, which can reduce the glass melting temperature and the glass-transition temperature. The glass of the invention has a low glass-transition temperature (Tg) of 480-590 DEG C, and the glass hardness is at least 600 Kg / mm2. After chemical tempering, the glass of the invention has a large surface stress layer depth (DoL) and a high surface crushing stress (CS). After tempering in pure KNO3, a potassium ion stress layer is formed, which has a DoL of at least 20 microns and a CS of at least 600 MPa. After tempering in a mixed salt of KNO3 and NaNO3 or two-step tempering in KNO3 and NaNO3, a potassium and sodium ion stress layers can be formed simultaneously, which have a DoL of at least 50 microns and a CS of at least 600 MPa. In addition, the aluminosilicate glass of the invention can be converted into glass ceramics through further heat treatment.
Owner:SCHOTT GLASS TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
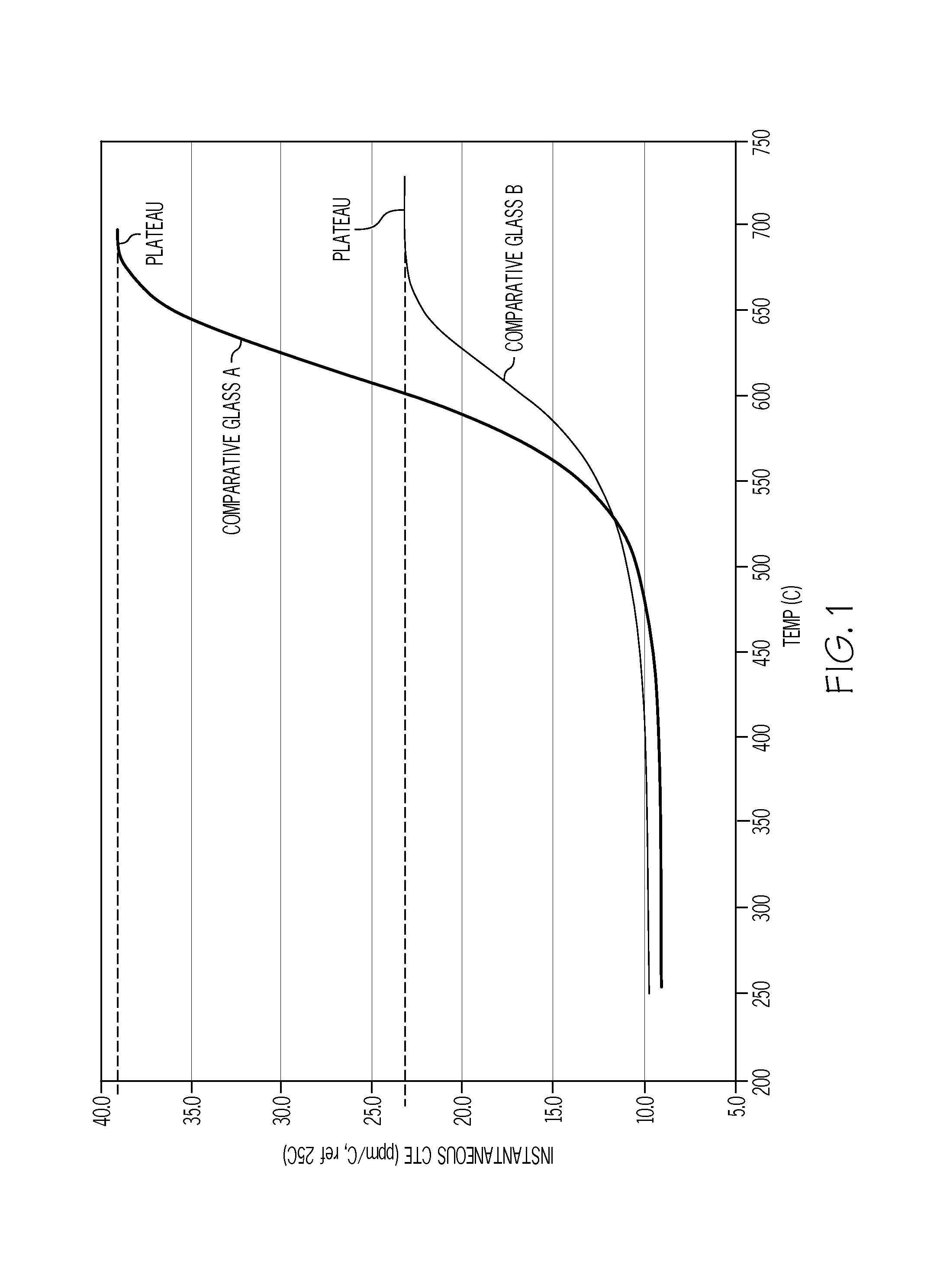
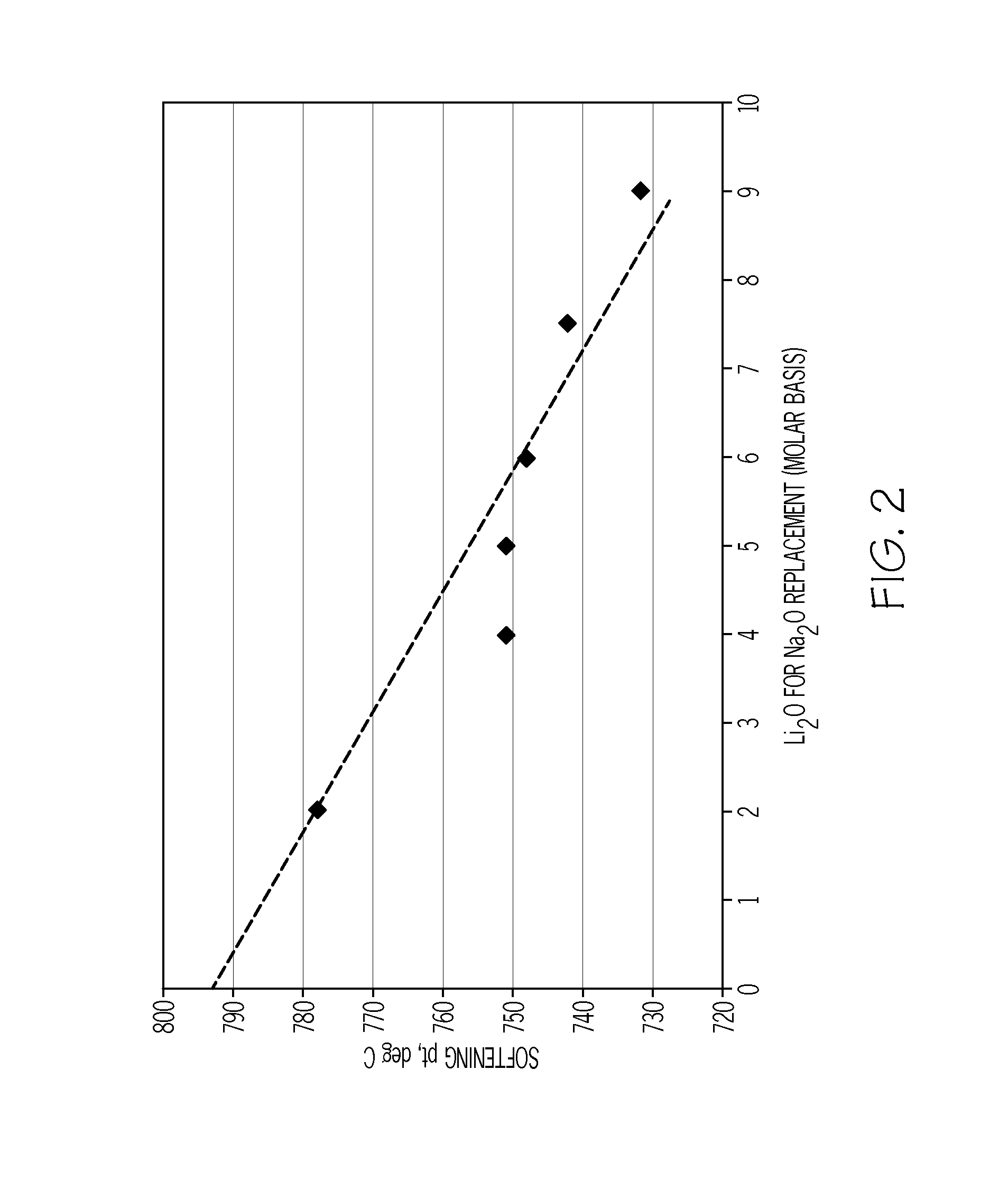
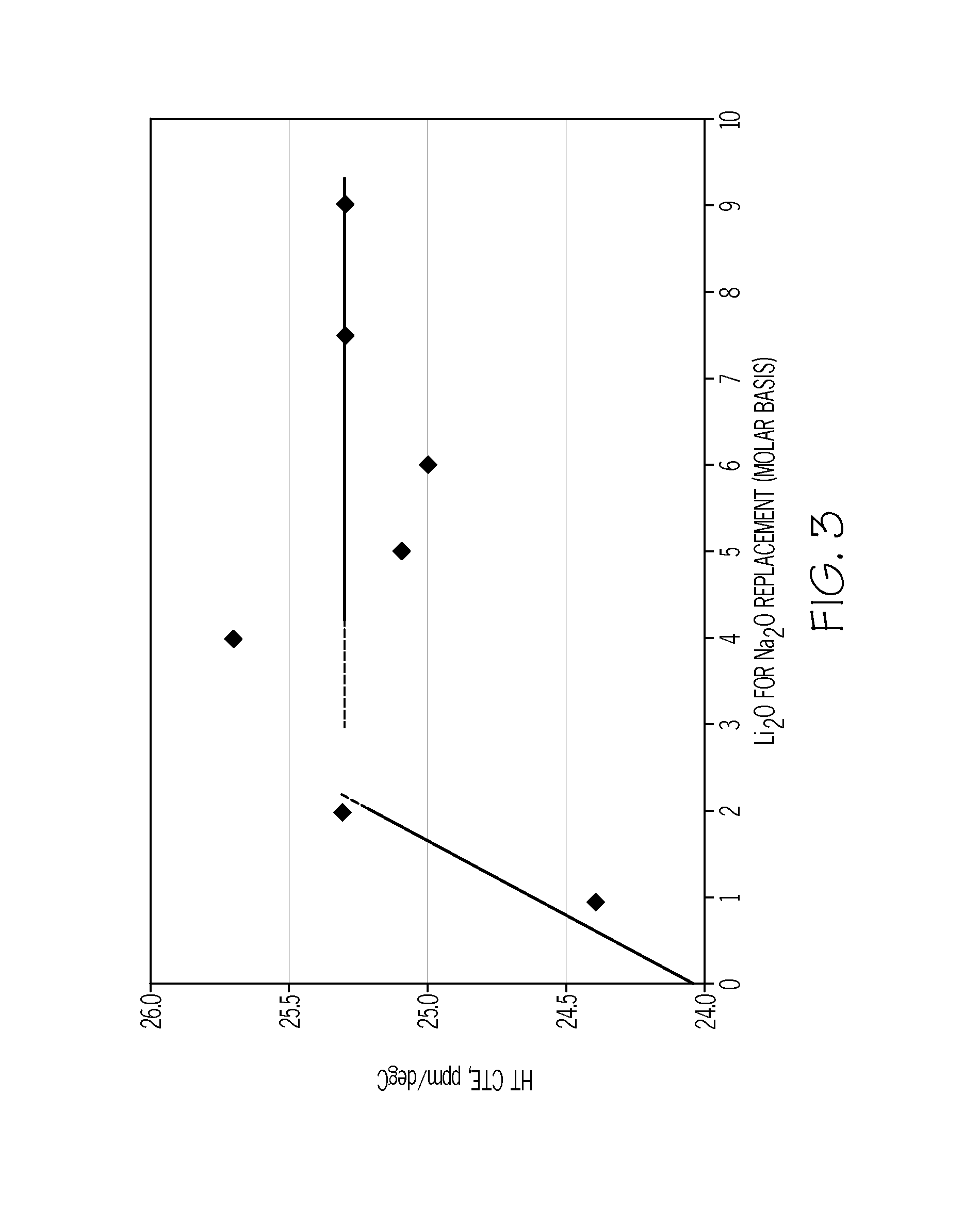
Ion exchangeable li-containing glass compositions for 3-d forming
According to one embodiment, a glass article may include SiO2, Al2O3, Li2O and Na2O. The glass article may have a softening point less than or equal to about 810° C. The glass article may also have a high temperature CTE less than or equal to about 27×10−6 / ° C. The glass article may also be ion exchangeable such that the glass has a compressive stress greater than or equal to about 600 MPa and a depth of layer greater than or equal to about 25 μm after ion exchange in a salt bath comprising KNO3 at a temperature in a range from about 390° C. to about 450° C. for less than or equal to approximately 15 hours.
Owner:CORNING INC
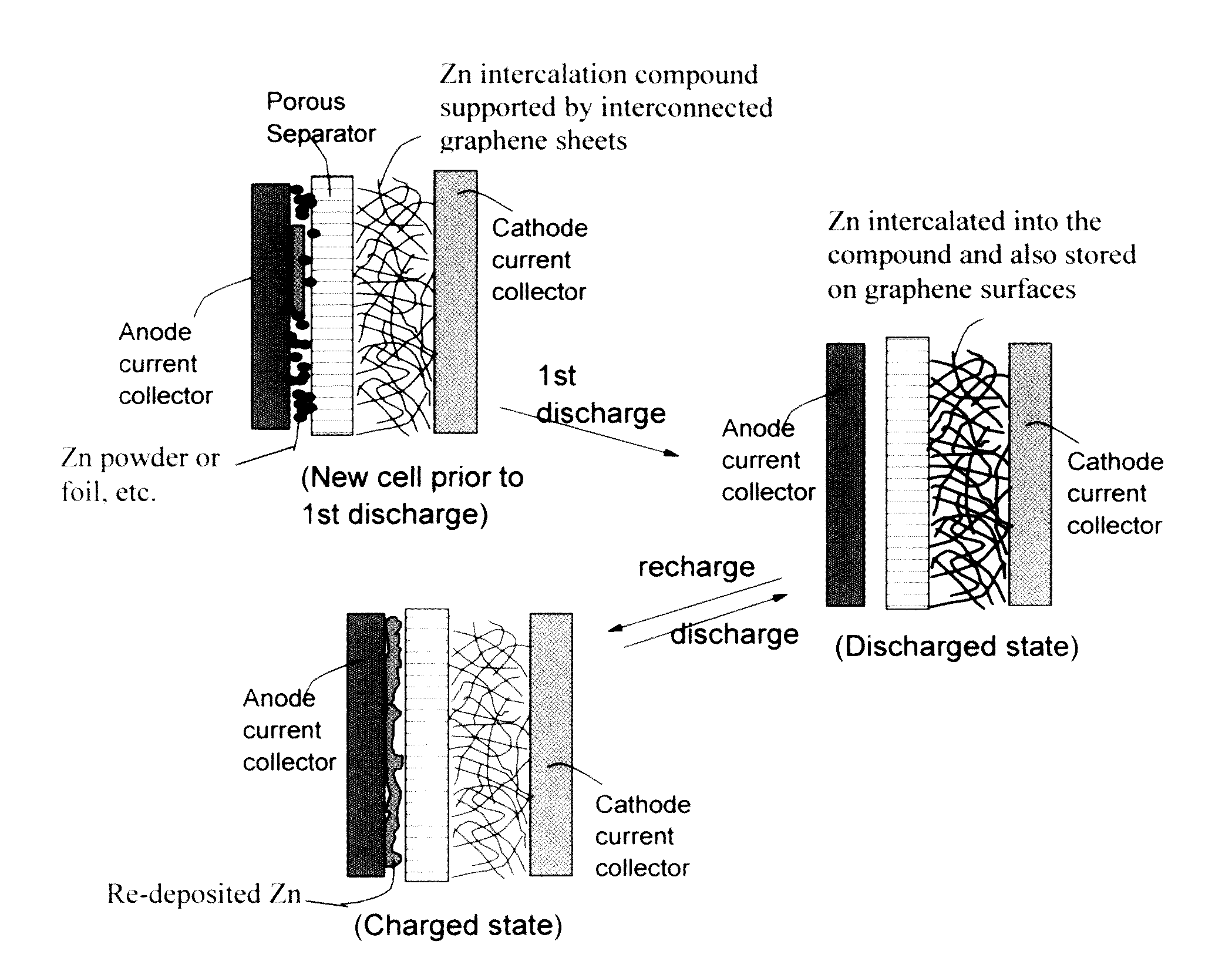
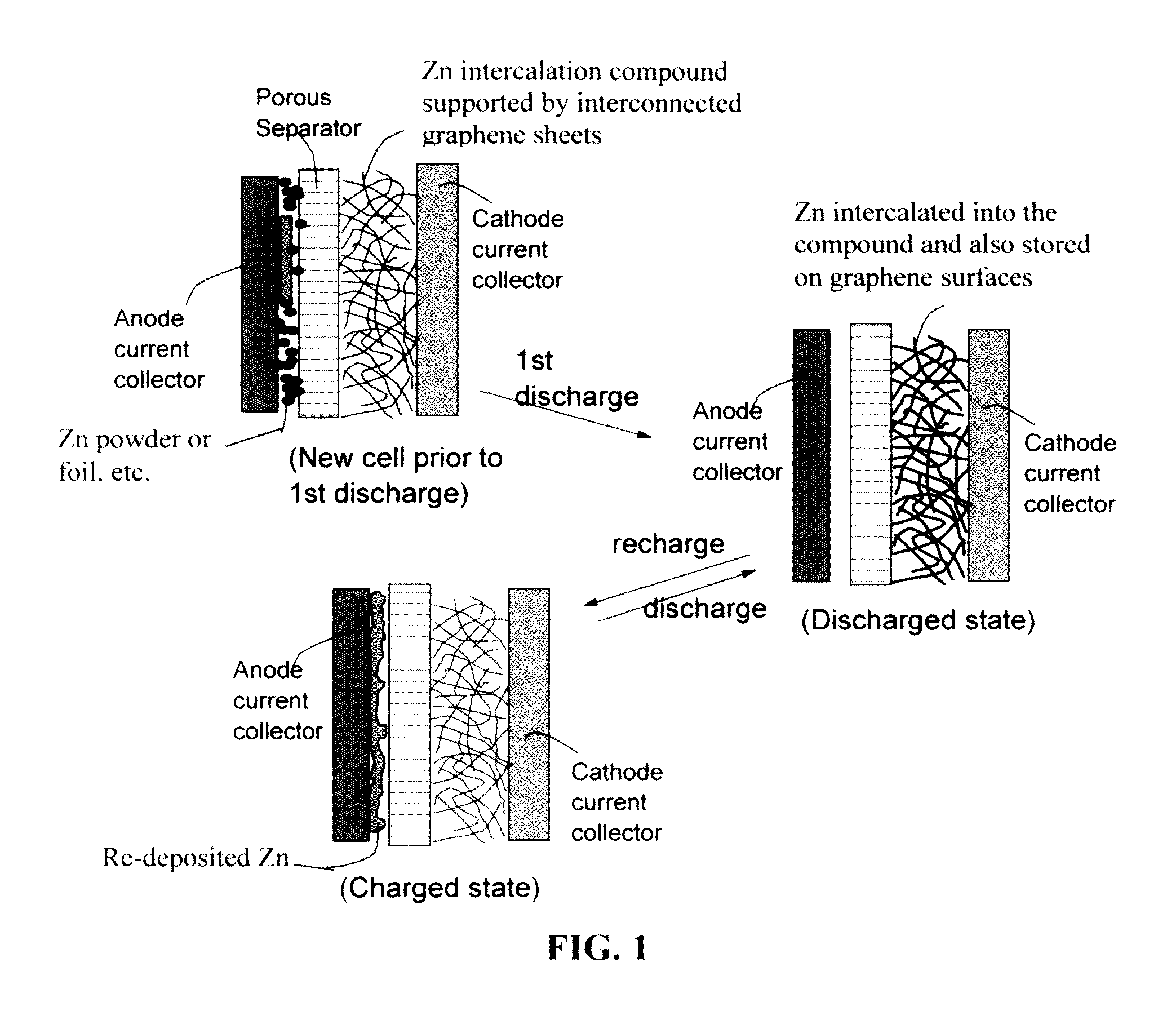
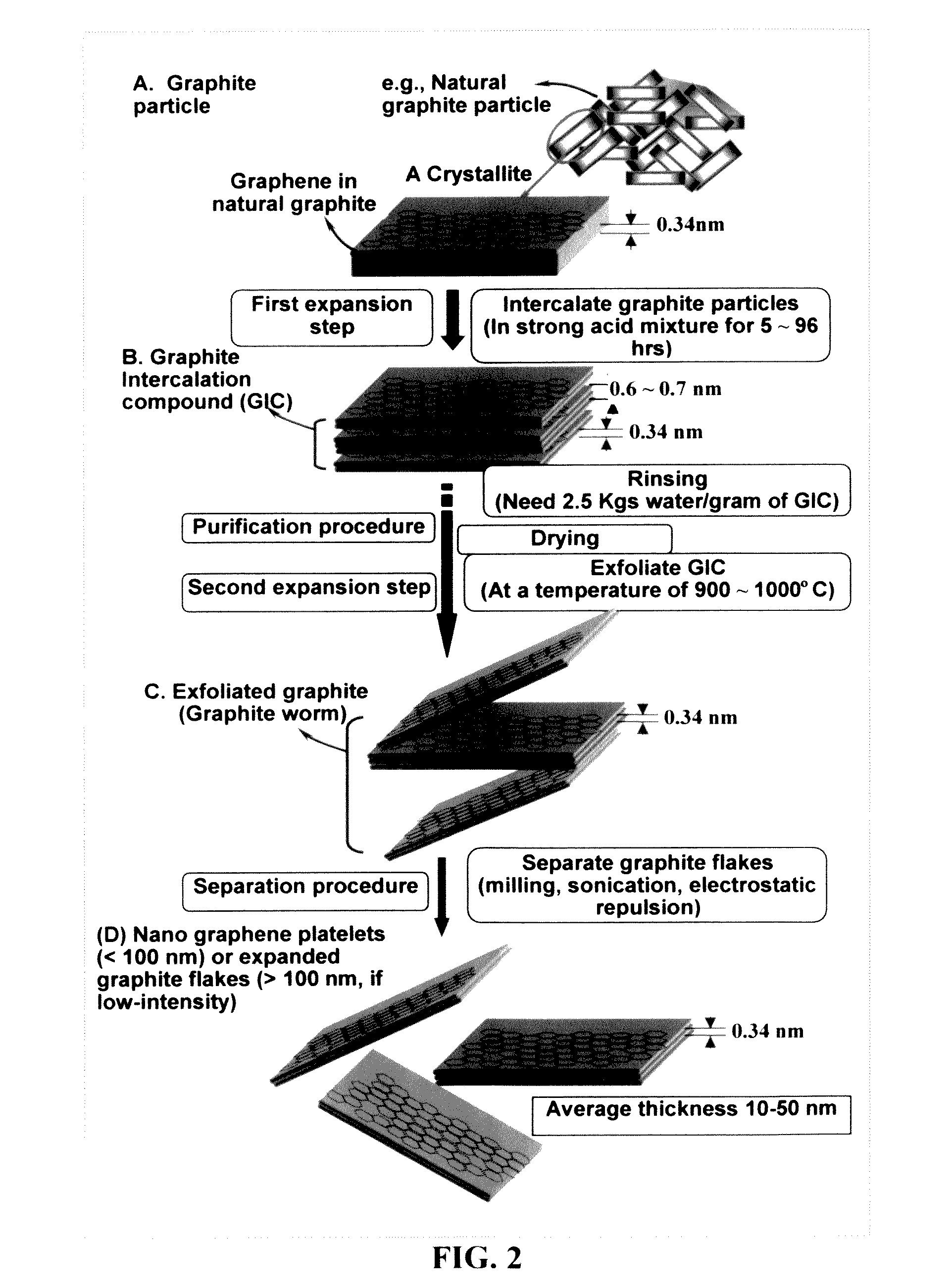
Zinc Ion-Exchanging Energy Storage Device
ActiveUS20160301096A1Quick releaseRapid depositionHybrid capacitor electrolytesAlkaline accumulatorsChemical treatmentZinc metal
A zinc ion-exchanging battery device comprising: (A) a cathode comprising two cathode active materials (a zinc ion intercalation compound and a surface-mediating material); (B) an anode containing zinc metal or zinc alloy; (C) a porous separator disposed between the cathode and the anode; and (D) an electrolyte containing zinc ions that are exchanged between the cathode and the anode during battery charge / discharge. The zinc ion intercalation compound is selected from chemically treated carbon or graphite material having an expanded inter-graphene spacing d002 of at least 0.5 nm, or an oxide, carbide, dichalcogenide, trichalcogenide, sulfide, selenide, or telluride of niobium, zirconium, molybdenum, hafnium, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, vanadium, chromium, cobalt, manganese, iron, nickel, or a combination thereof. The surface-mediating material contains exfoliated graphite or multiple single-layer sheets or multi-layer platelets of a graphene material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Compositions, methods, and kits for isolating and analyzing nucleic acids using an anion exchange material
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG +1
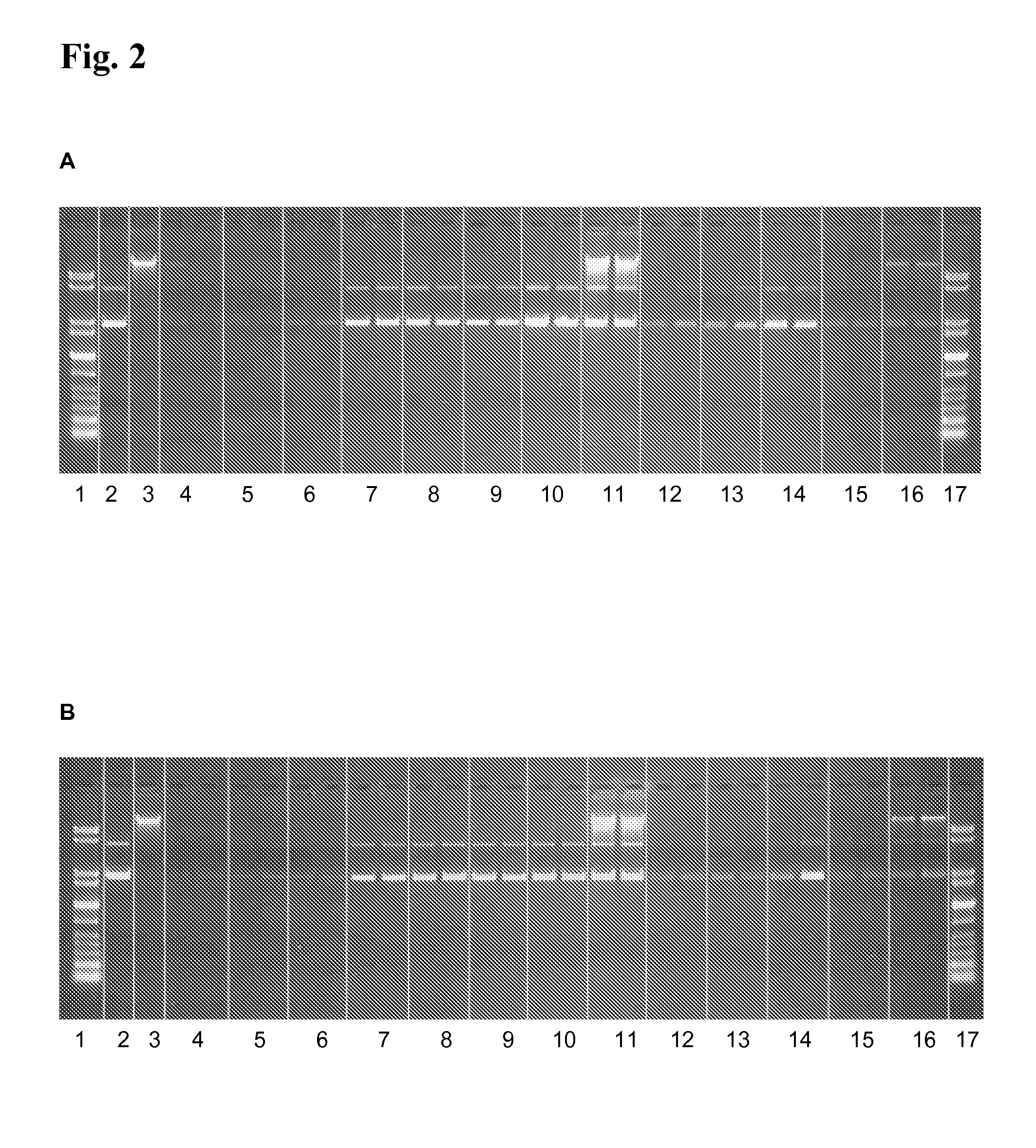
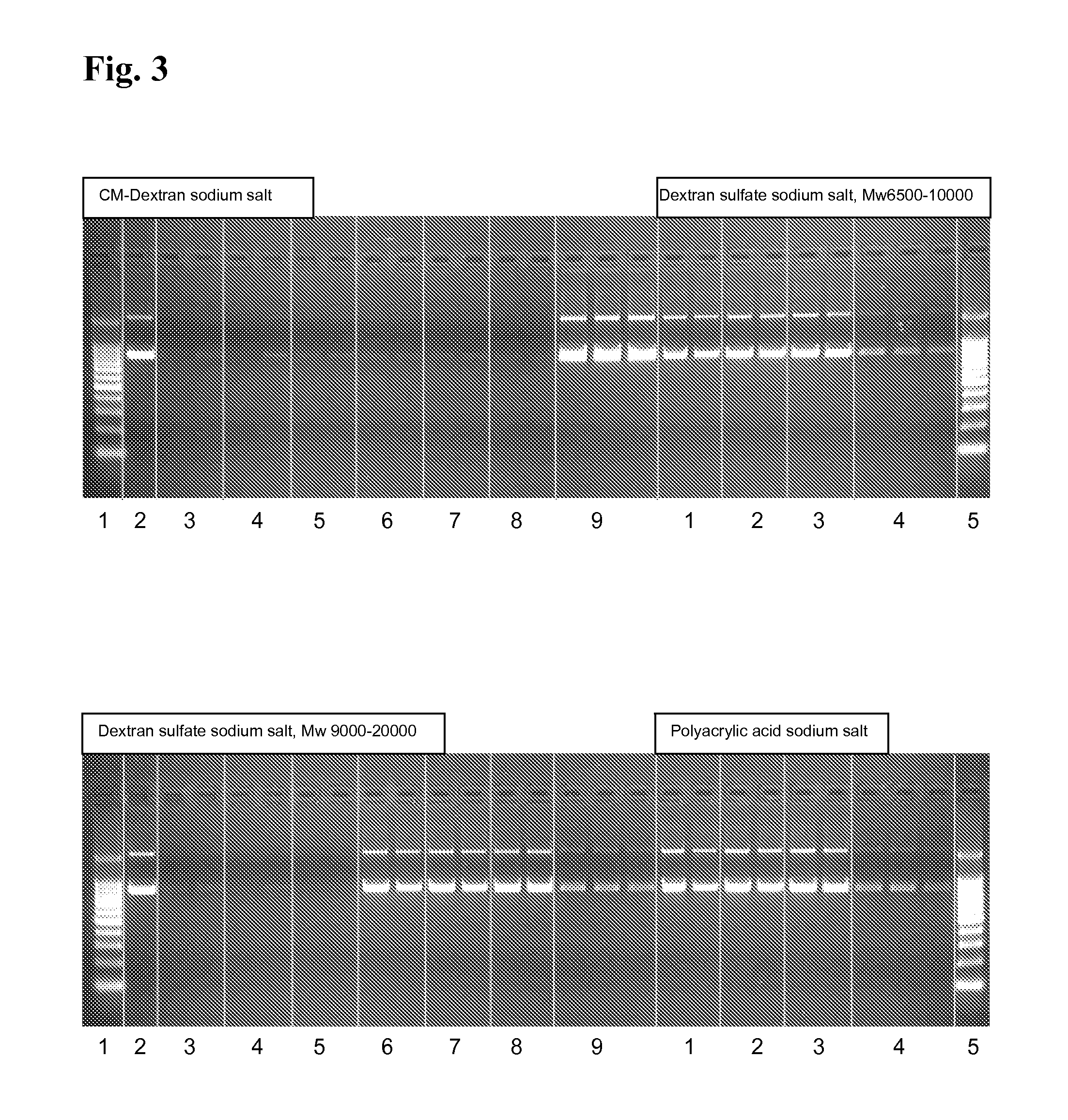
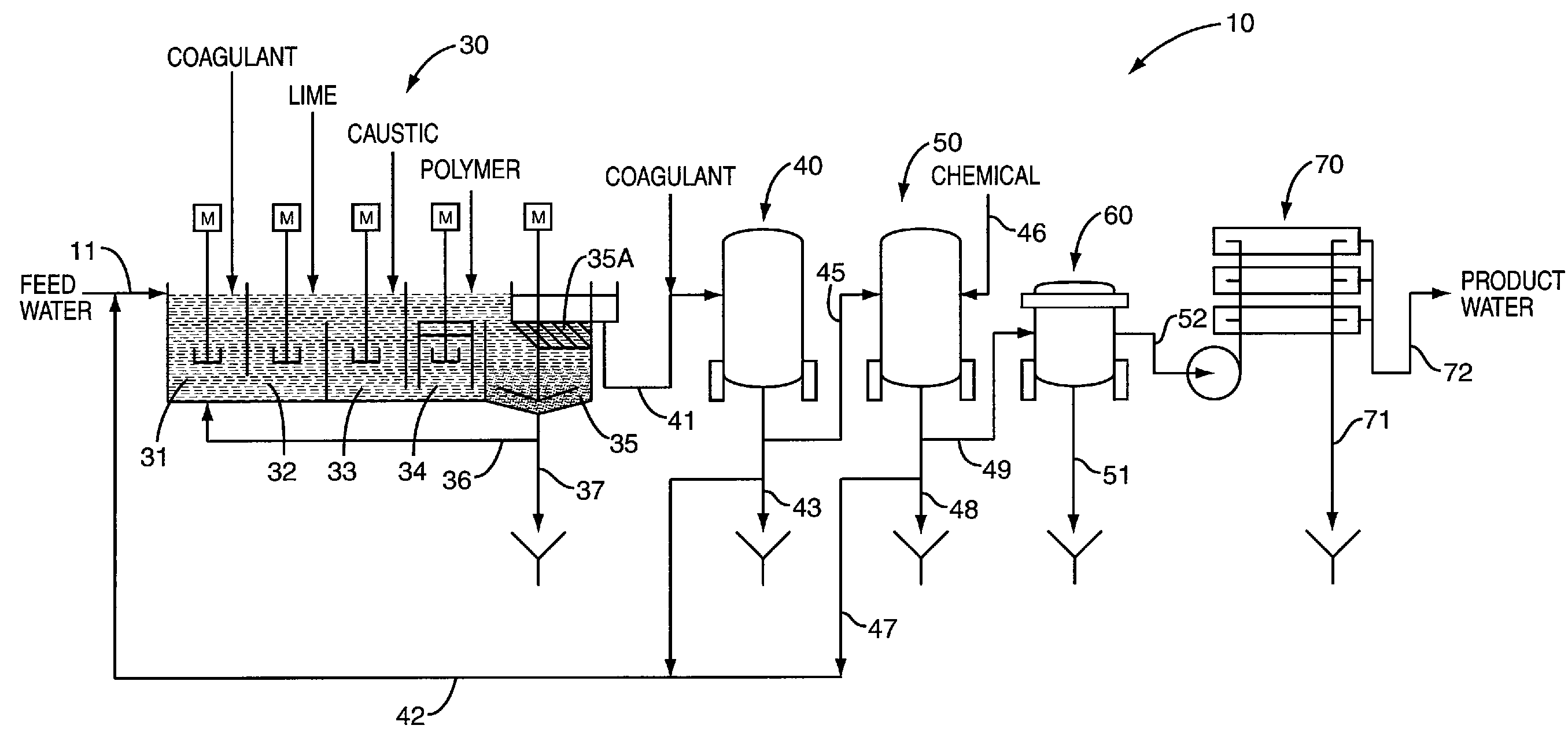
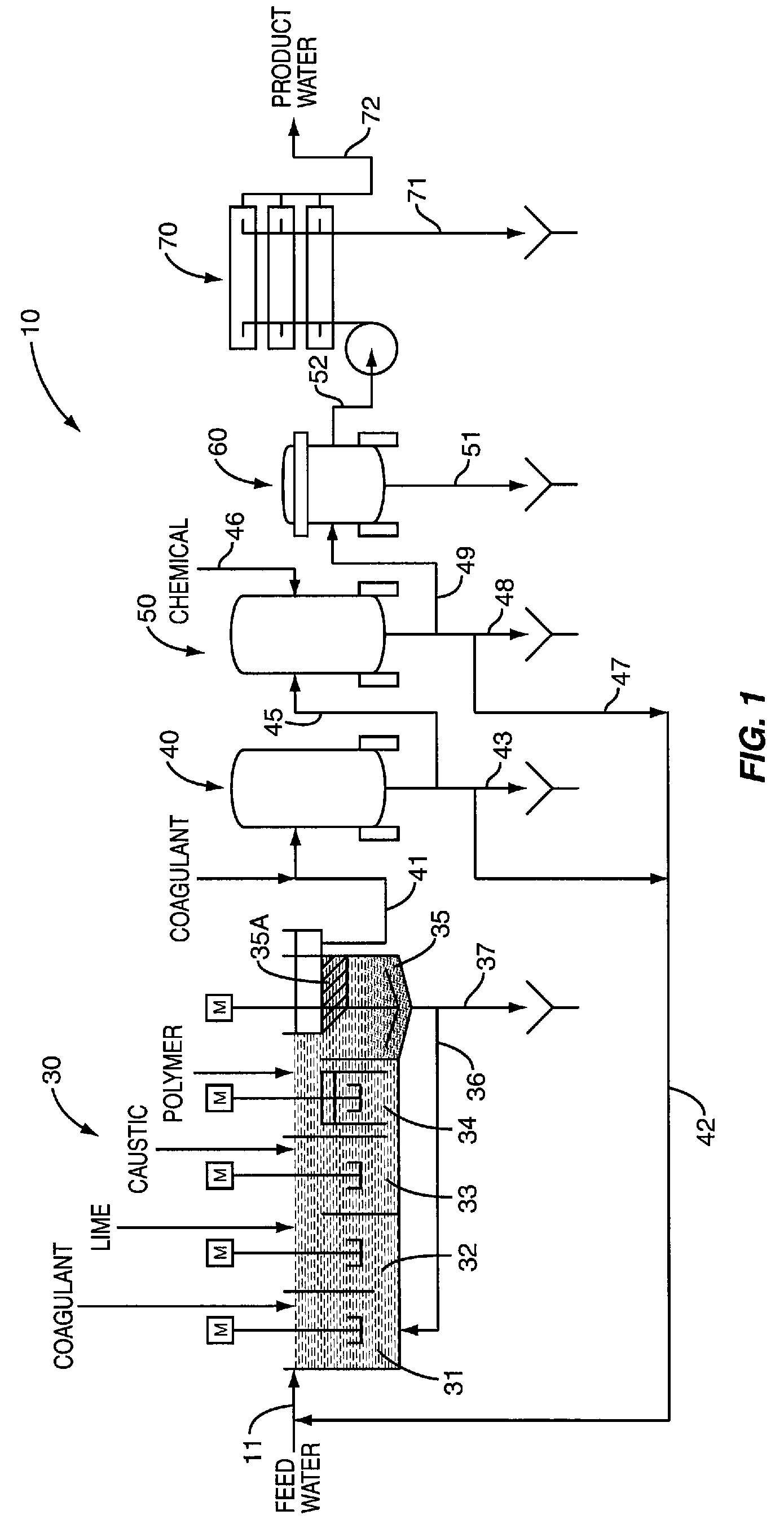
Method for treating wastewater or produced water
ActiveUS7815804B2Reduce hardnessReduce dissolved solidWaste water treatment from quariesGeneral water supply conservationWastewaterIon exchange
A method or process for treating wastewater containing high organics, silica, boron, hardness, and suspended and dissolved solids. The method includes degasifying the wastewater for the removal of dissolved gases and thereafter chemically softening the wastewater. After the chemical softening step, the wastewater is directed through a media filter or membrane which removes additional solids and precipitants. Thereafter the wastewater is directed through a sodium ion exchange that further softens the wastewater. The effluent from the ion exchange is directed through a cartridge filter and the effluent from the cartridge filter is directed through one or more reverse osmosis units. At a selected phase of the process, prior to the wastewater reaching the reverse osmosis unit or units, the pH of the wastewater is raised and maintained such that the pH of the wastewater reaching a reverse osmosis unit is at a pH greater than 10.5.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Electrical current generation system
InactiveUS6921597B2Facilitate pressureFacilitate ion exchangeFuel cell auxillariesHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHydrogenFuel cells
An electrical generating system consists of a fuel cell, and an oxygen gas delivery. The fuel cell includes and anode channel having an anode gas inlet for receiving a supply of hydrogen gas, a cathode channel having a cathode gas inlet and a cathode gas outlet, and an electrolyte in communication with the anode and cathode channel for facilitating ion exchange between the anode and cathode channel. The oxygen gas delivery system is coupled to the cathode gas inlet and delivers oxygen gas to the cathode channel. The electrical current generating system also includes gas recirculation means couple to the cathode gas outlet for recirculating a portion of cathode exhaust gas exhausted from the cathode gas outlet to the cathode gas inlet.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com